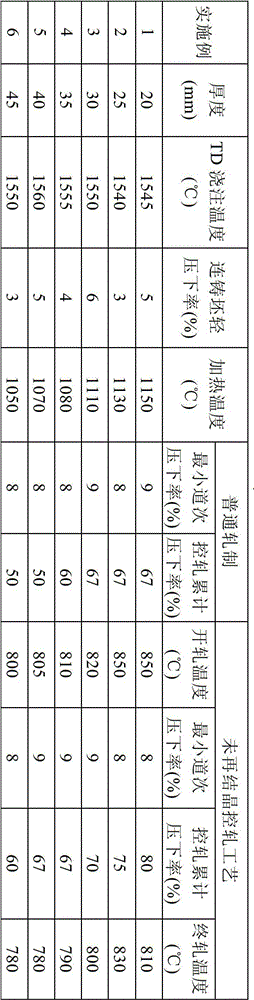
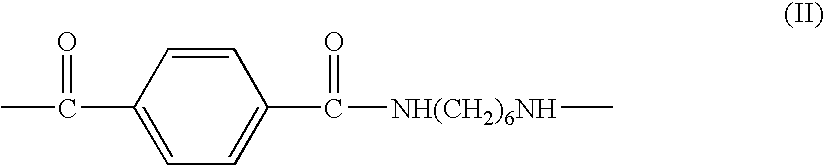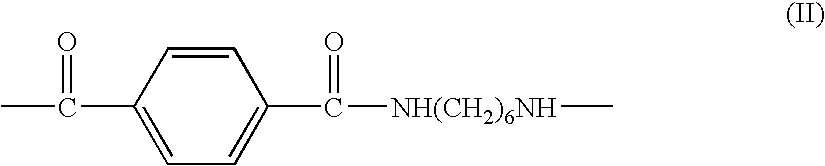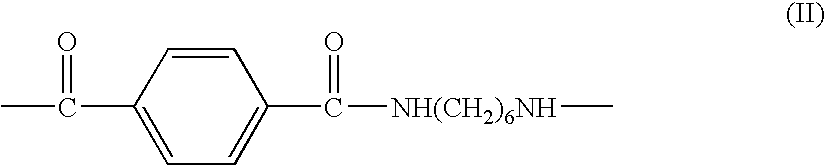Patents
Literature
536 results about "Stress corrosion cracking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
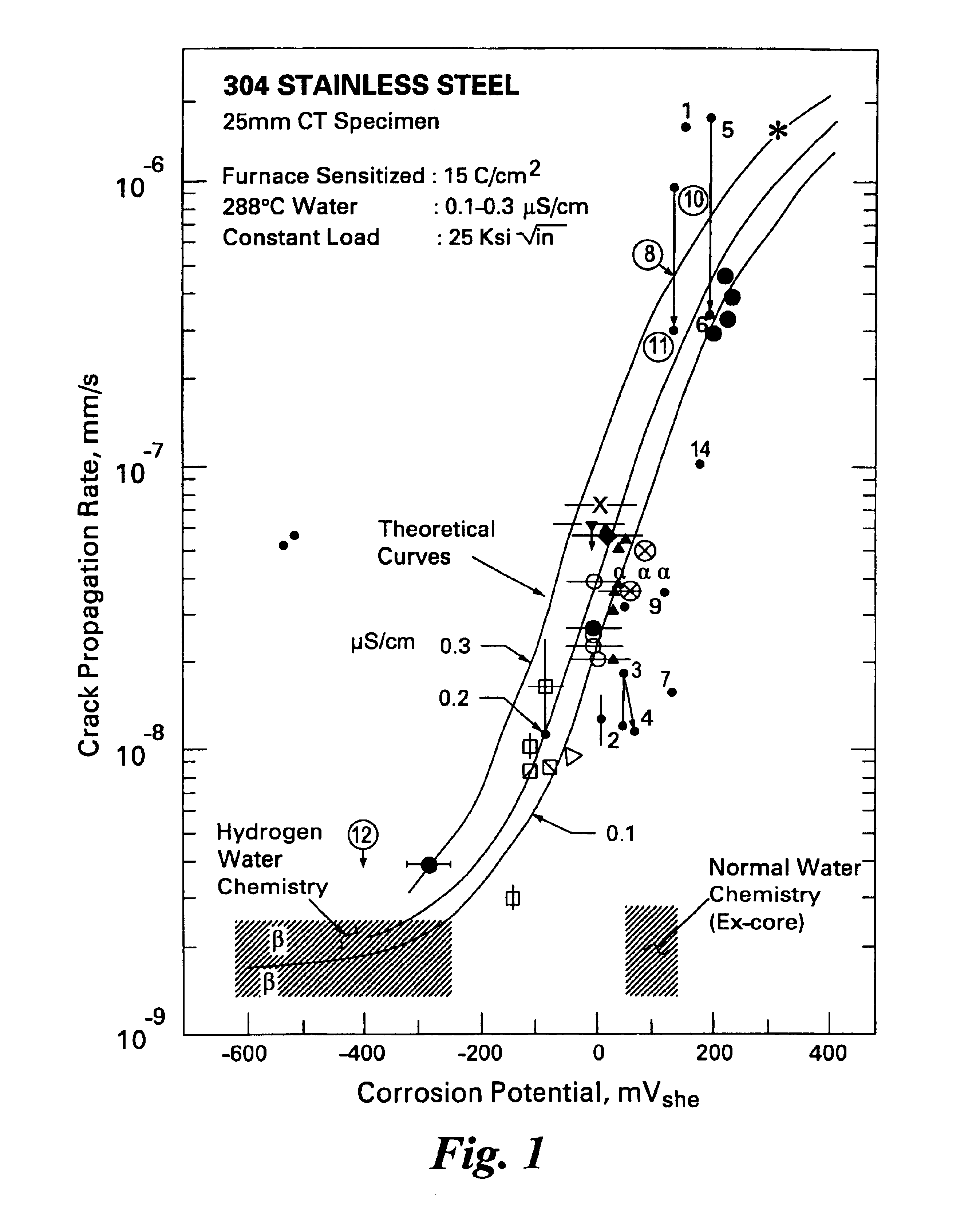
Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) is the growth of crack formation in a corrosive environment. It can lead to unexpected sudden failure of normally ductile metal alloys subjected to a tensile stress, especially at elevated temperature. SCC is highly chemically specific in that certain alloys are likely to undergo SCC only when exposed to a small number of chemical environments. The chemical environment that causes SCC for a given alloy is often one which is only mildly corrosive to the metal. Hence, metal parts with severe SCC can appear bright and shiny, while being filled with microscopic cracks. This factor makes it common for SCC to go undetected prior to failure. SCC often progresses rapidly, and is more common among alloys than pure metals. The specific environment is of crucial importance, and only very small concentrations of certain highly active chemicals are needed to produce catastrophic cracking, often leading to devastating and unexpected failure.
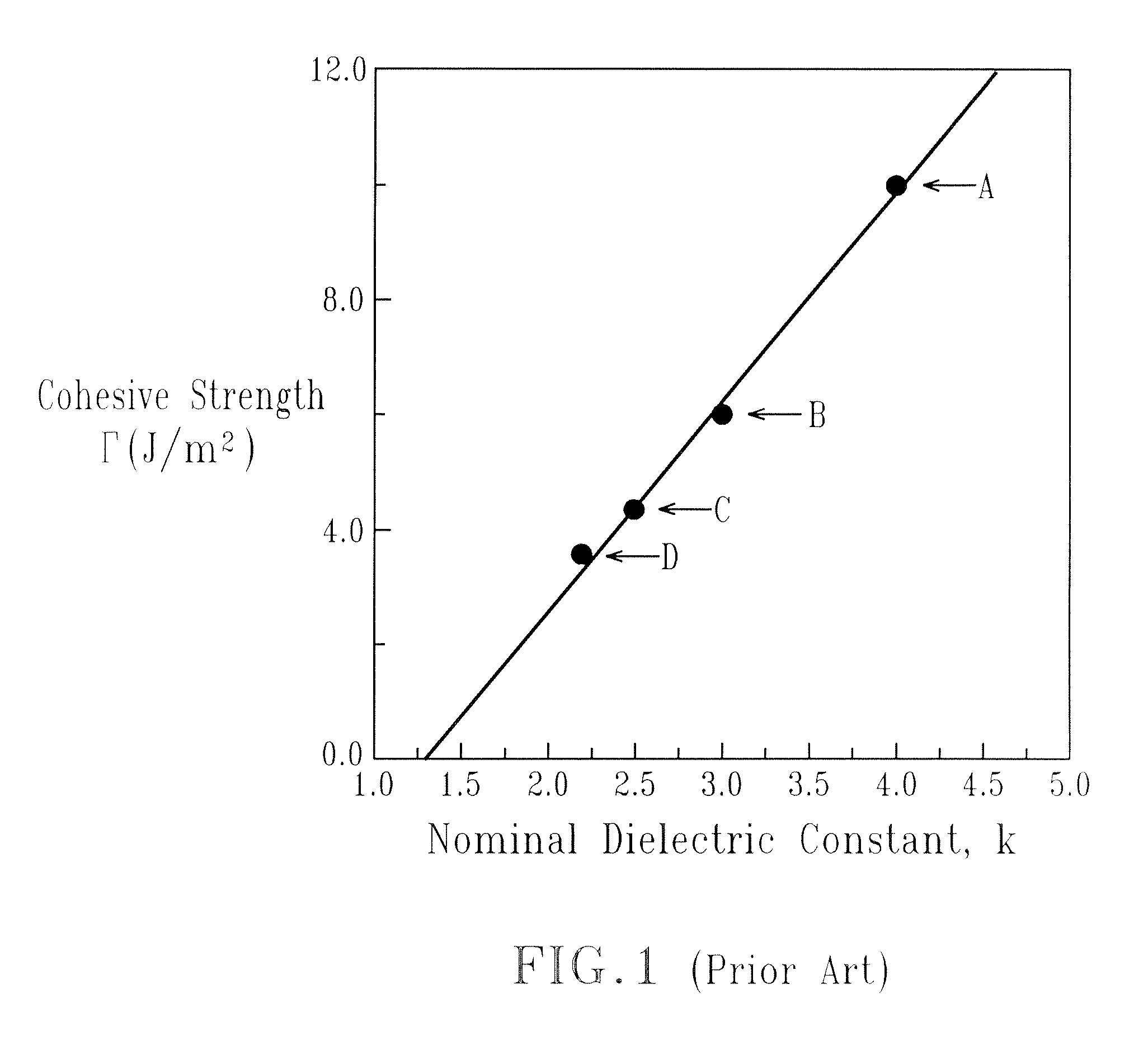
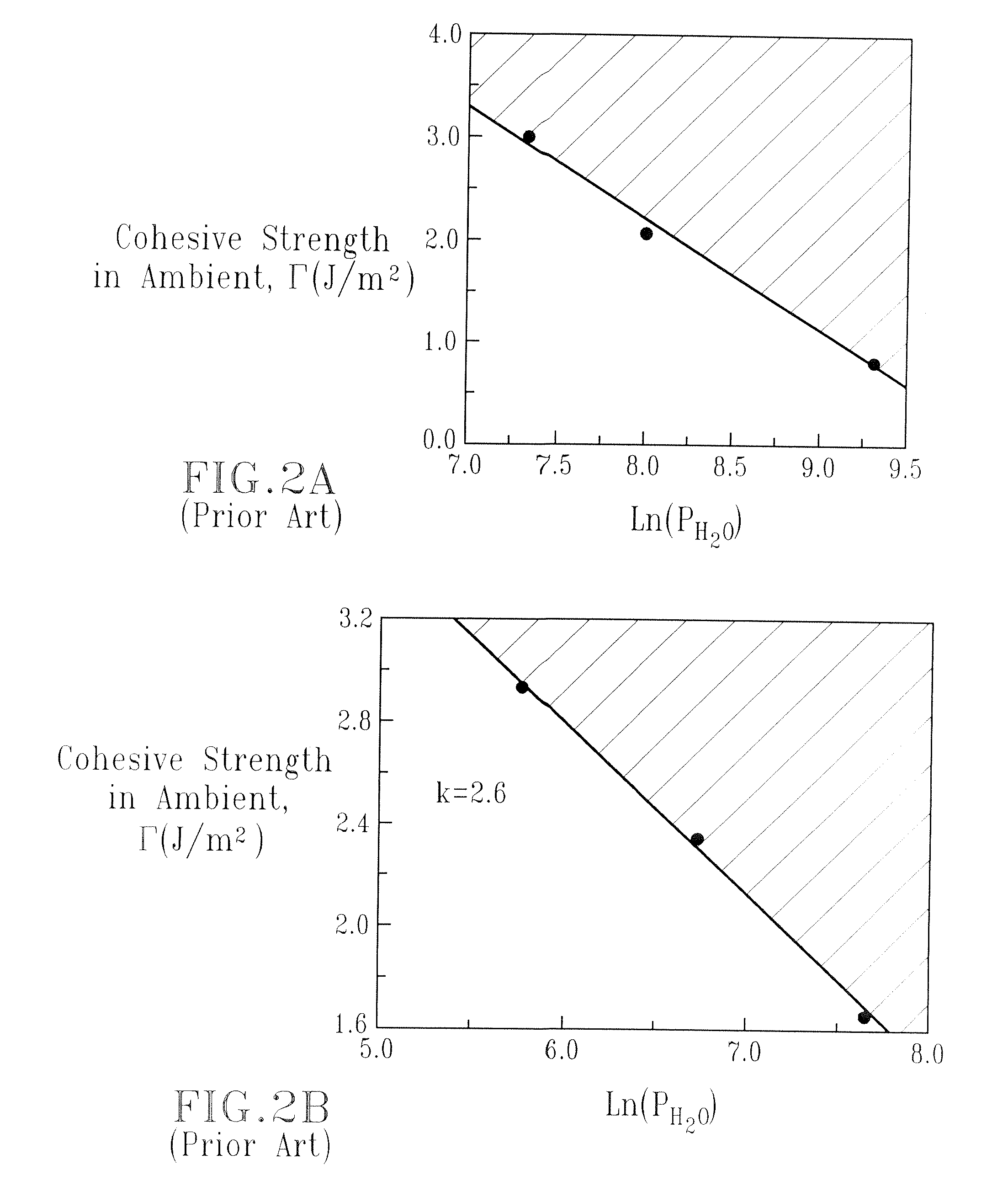
SiCOH dielectric
InactiveUS20070173071A1Improve cohesive strengthReduce brittlenessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricDevice material
A porous composite material useful in semiconductor device manufacturing, in which the diameter (or characteristic dimension) of the pores and the pore size distribution (PSD) is controlled in a nanoscale manner and which exhibits improved cohesive strength (or equivalently, improved fracture toughness or reduced brittleness), and increased resistance to water degradation of properties such as stress-corrosion cracking, Cu ingress, and other critical properties is provided. The porous composite material is fabricating utilizing at least one bifunctional organic porogen as a precursor compound
Owner:INTEL CORP
Methods to form SiCOH or SiCNH dielectrics and structures including the same
InactiveUS20080009141A1Low costSimple methodSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDielectricElectronic structure
Methods of forming dielectric films comprising Si, C, O and H atoms (SiCOH) or Si, C, N and H atoms (SiCHN) that have improved cohesive strength (or equivalently, improved fracture toughness or reduced brittleness), and increased resistance to water degradation of properties such as stress-corrosion cracking, Cu ingress, and other critical properties are provided. Electronic structures including the above materials are also included herein.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
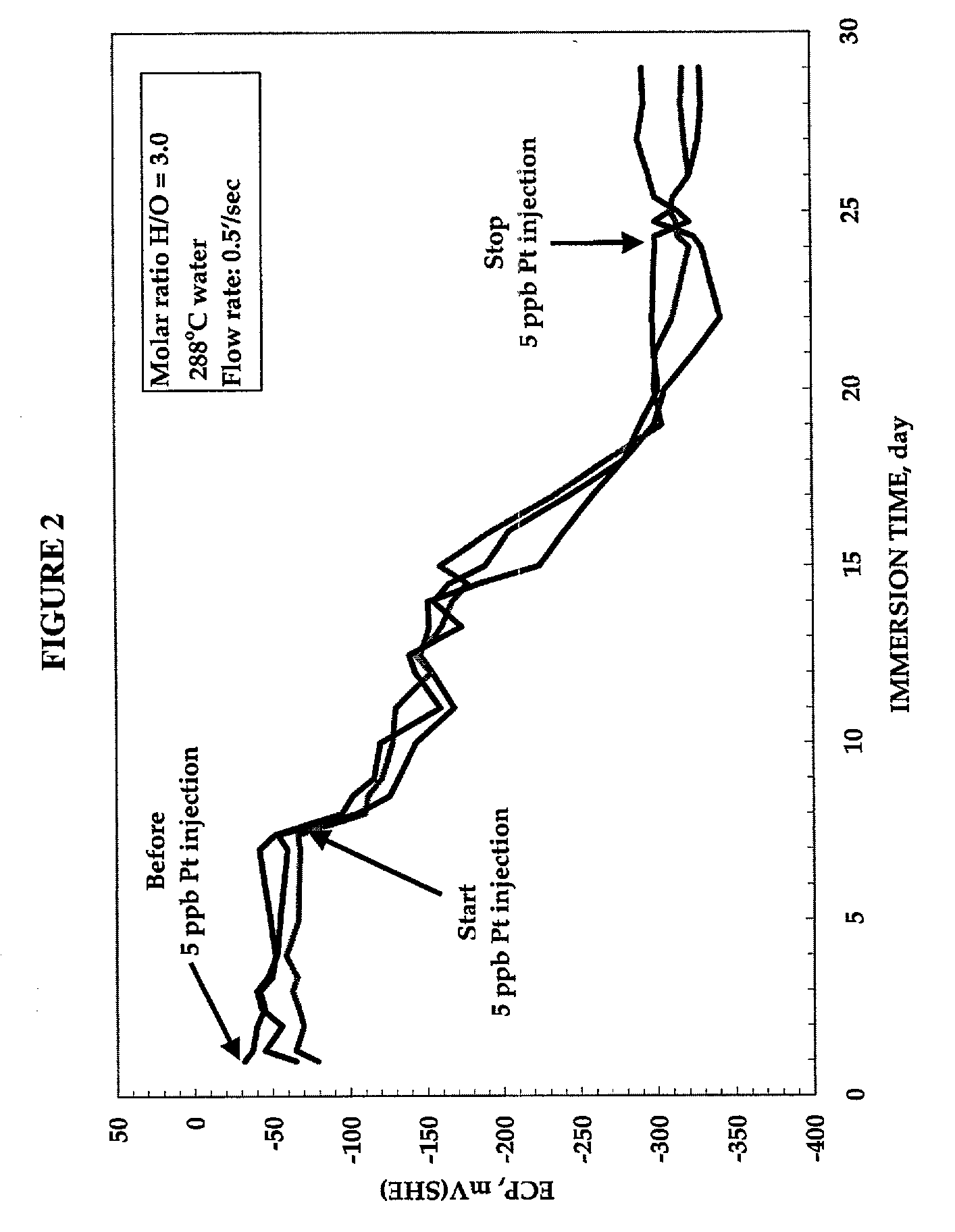
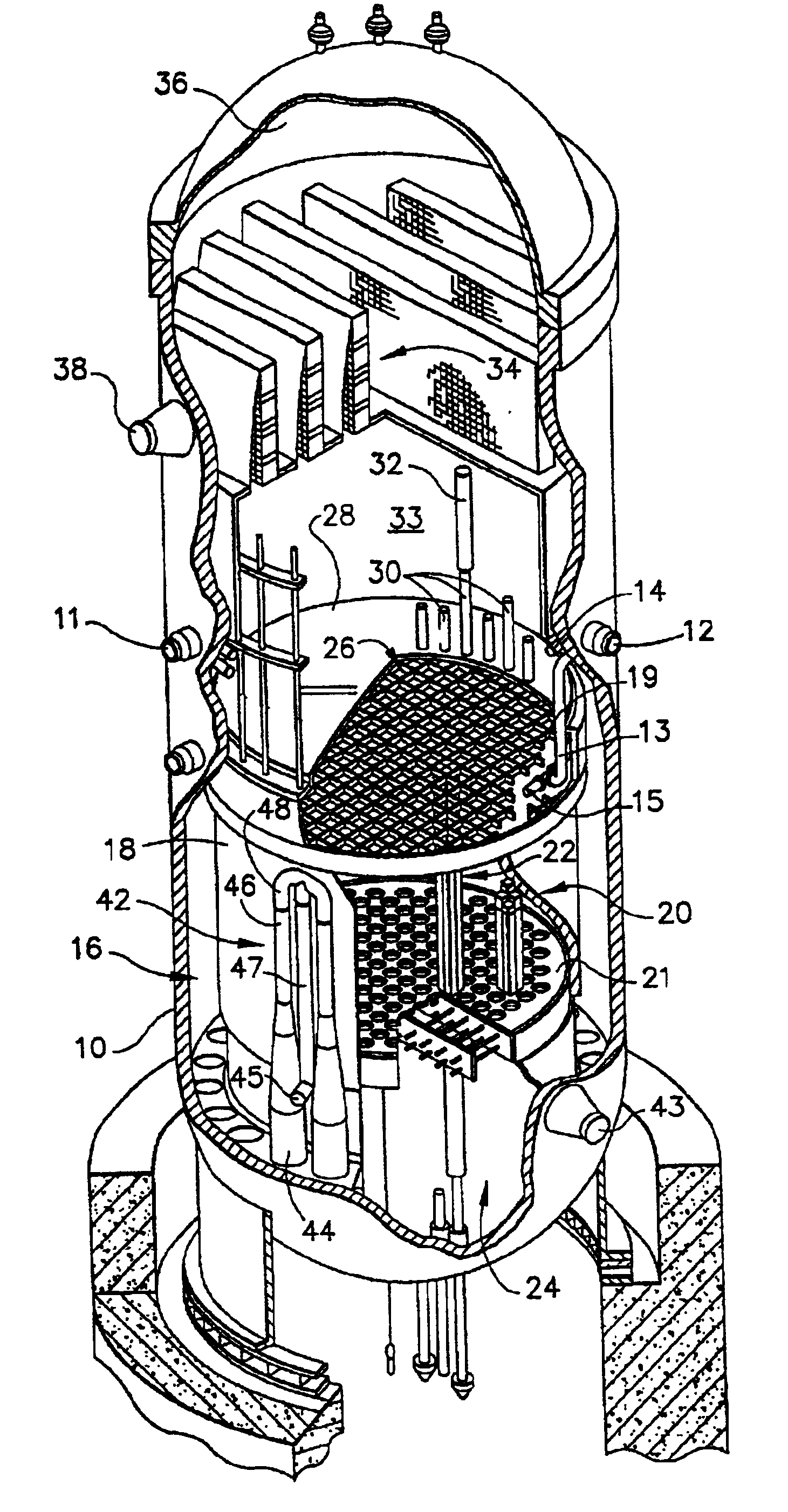
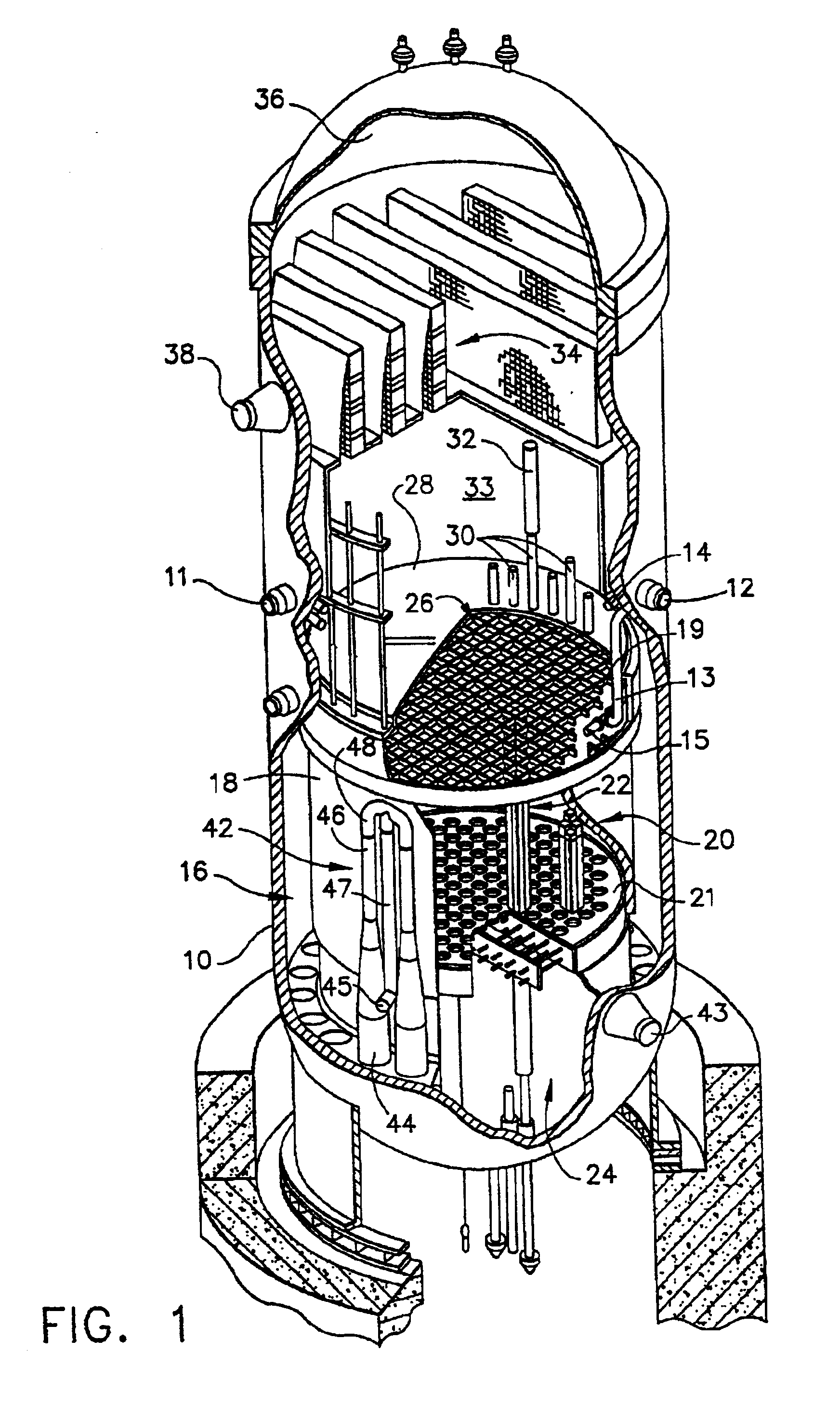
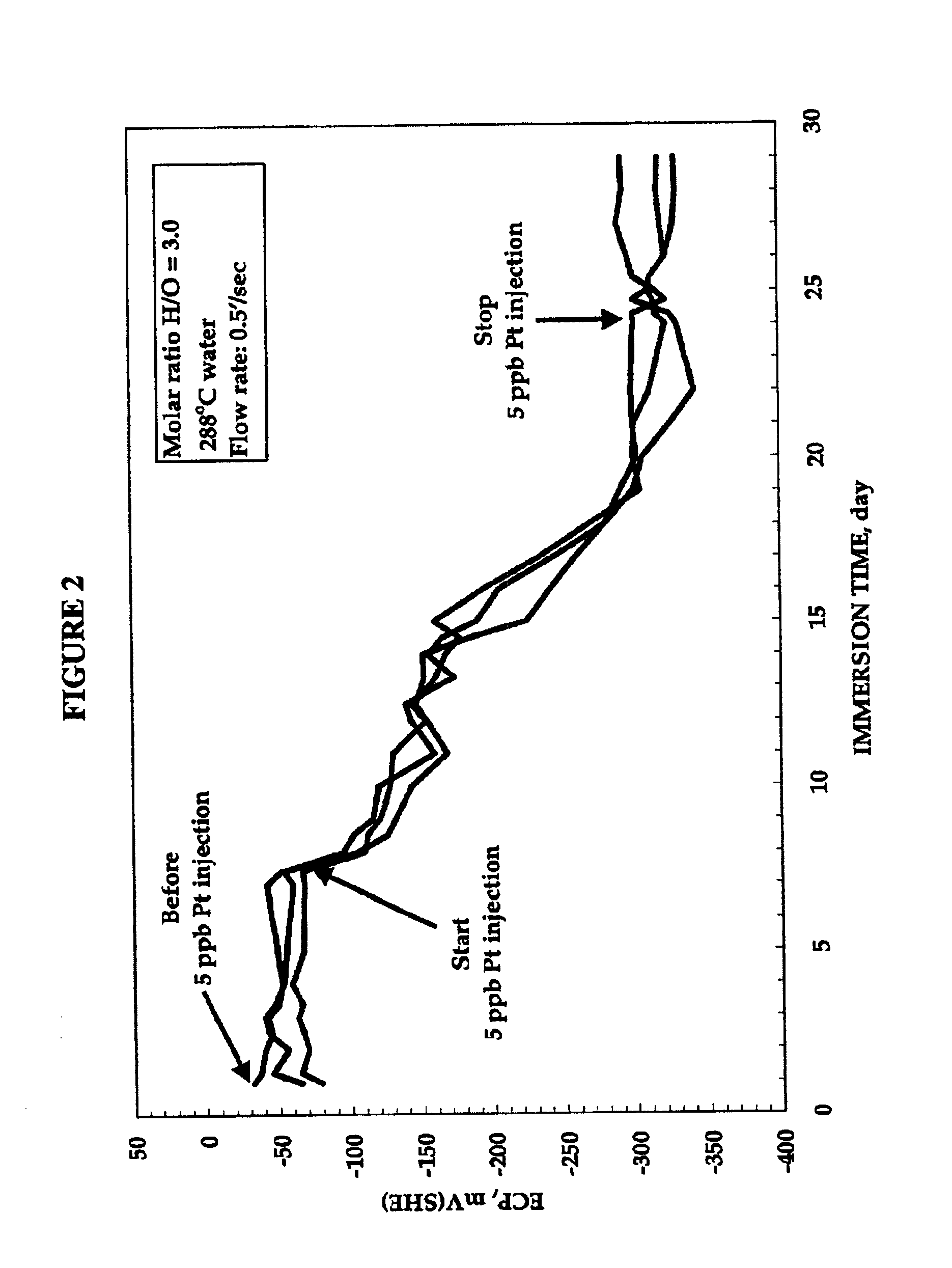
Process to mitigate stress corrosion cracking of structural materials in high temperature water
InactiveUS6724854B1Reduce crackingReducing the electrochemical corrosion potentialPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationNanoparticleStress corrosion cracking
A method for mitigating stress corrosion cracking in high temperature water includes introducing catalytic nanoparticles and dielectric nanoparticles to the high temperature water in an amount effective to reduce a electrochemical corrosion potential of the high temperature water.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
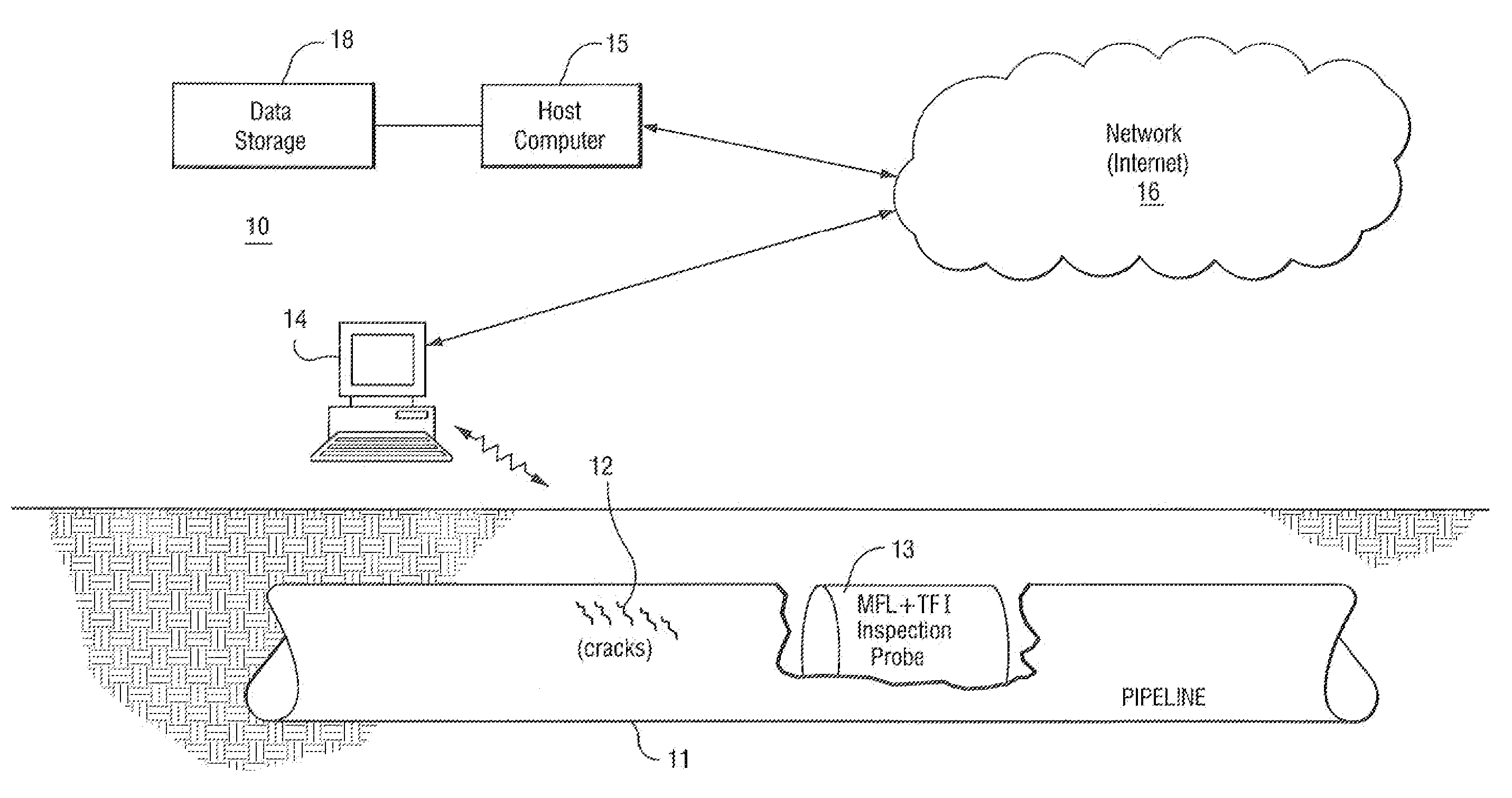
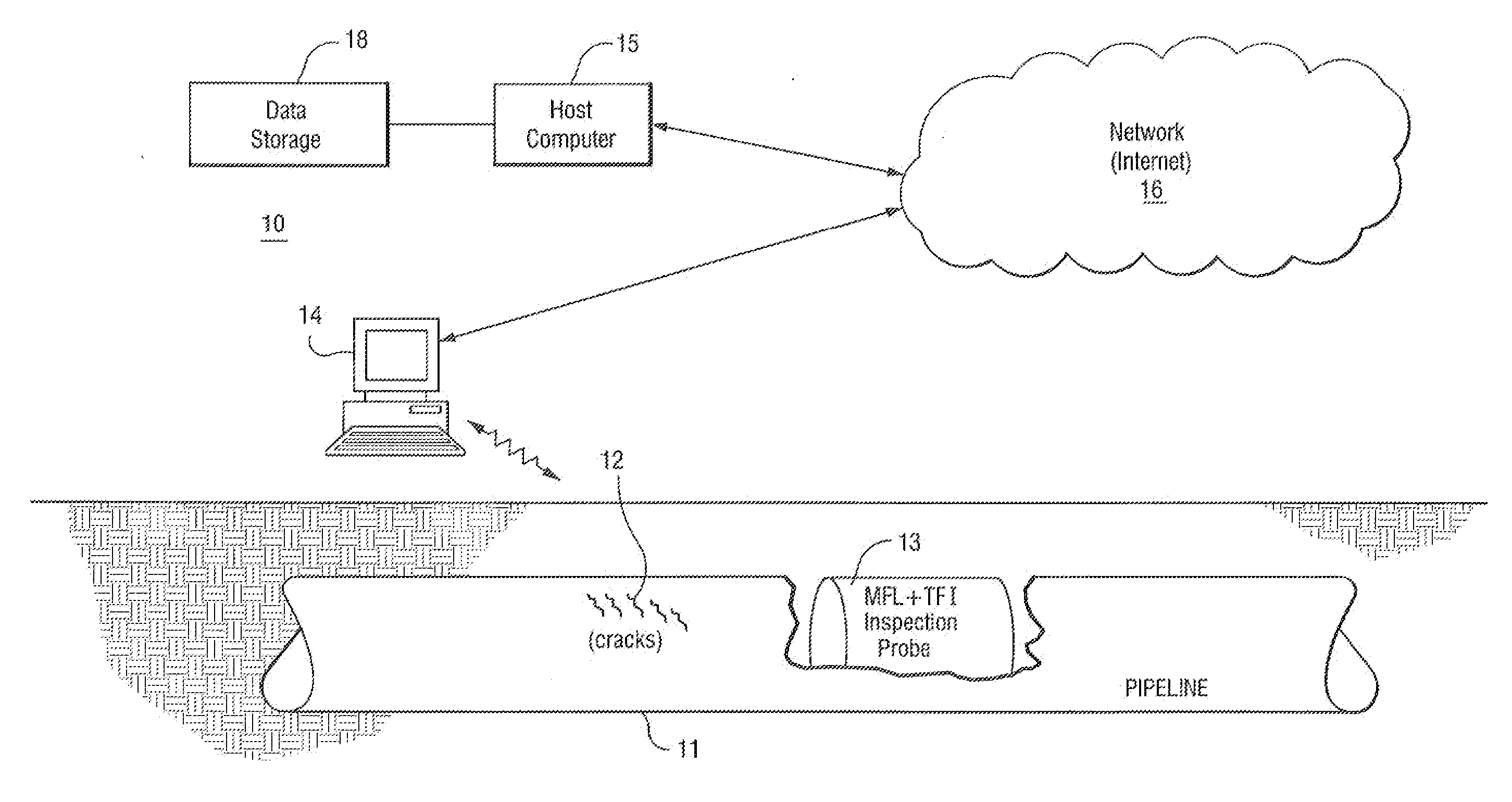
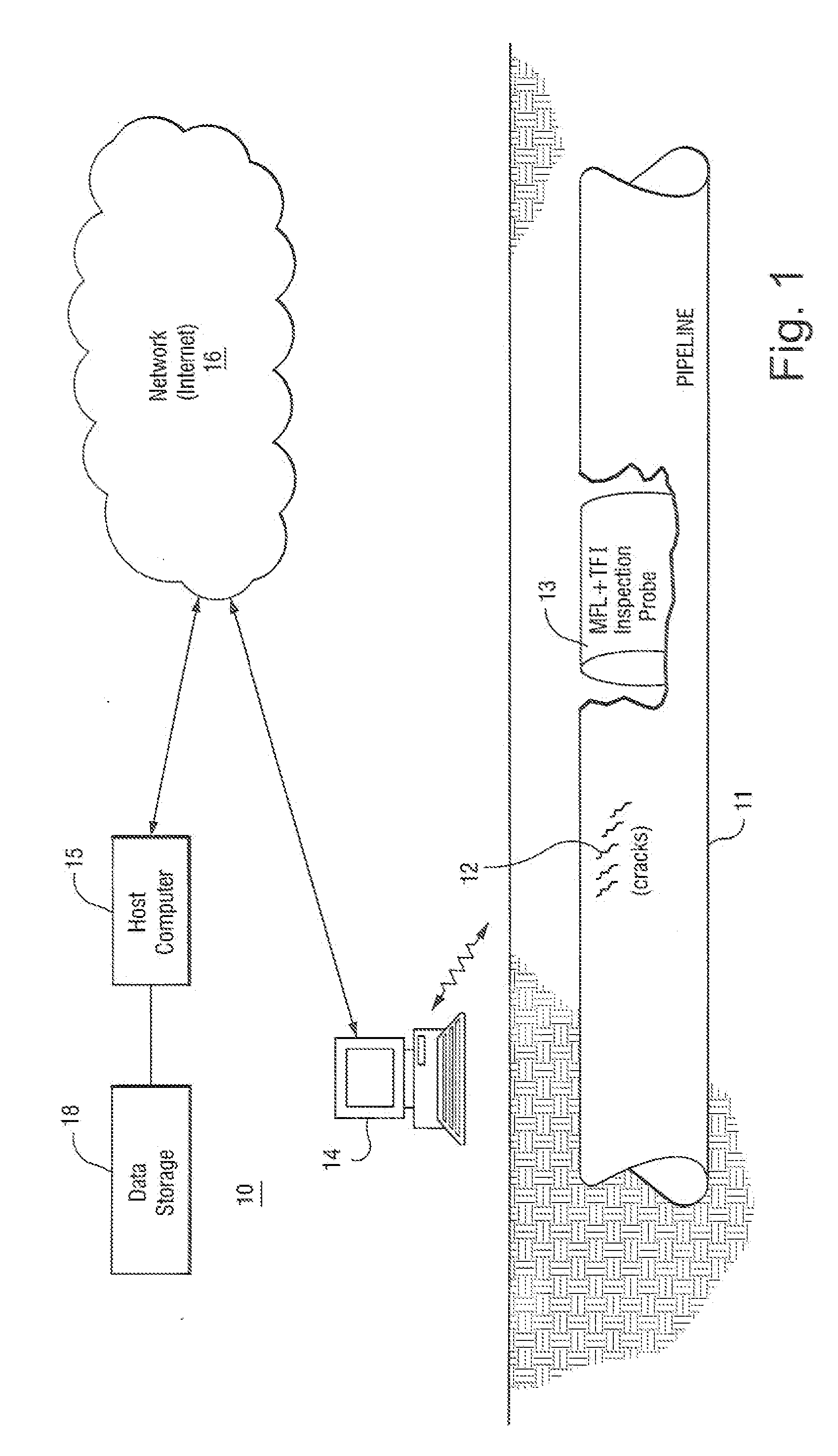
Method and apparatus inspecting pipelines using magnetic flux sensors
InactiveUS7414395B2Improve trustMagnetic property measurementsMaterial magnetic variablesEngineeringStress corrosion cracking
The method for detecting stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of pipelines, comprising the steps of: identifying pipeline locations and pipeline conditions that are amenable to inspection by a magnetic flux inline tool and by a TFI tool; performing two inspections on the pipeline, one inspection performed using the magnetic flux inline (MFL) tool and an other inspection performed using the TFI tool; aligning signal features resulting from the two inspections; identifying TFI signals occurring above a specified threshold; identifying MFL signals for a section of pipeline corresponding to the identified TFI signals; for the identified TFI signals, determining whether the MFL signals are below a second threshold level; designating the sections of the pipeline corresponding to identified TFI signals above the threshold and below the second threshold as a potential corrosion feature; identifying TFI signals that exceed a defined metal loss percentage; measuring a width and length of the signal features, and if the width and length of the signal feature exceed threshold crack width and length values, designating as a potential corrosion feature section of pipeline corresponding to the identified TFI signals.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
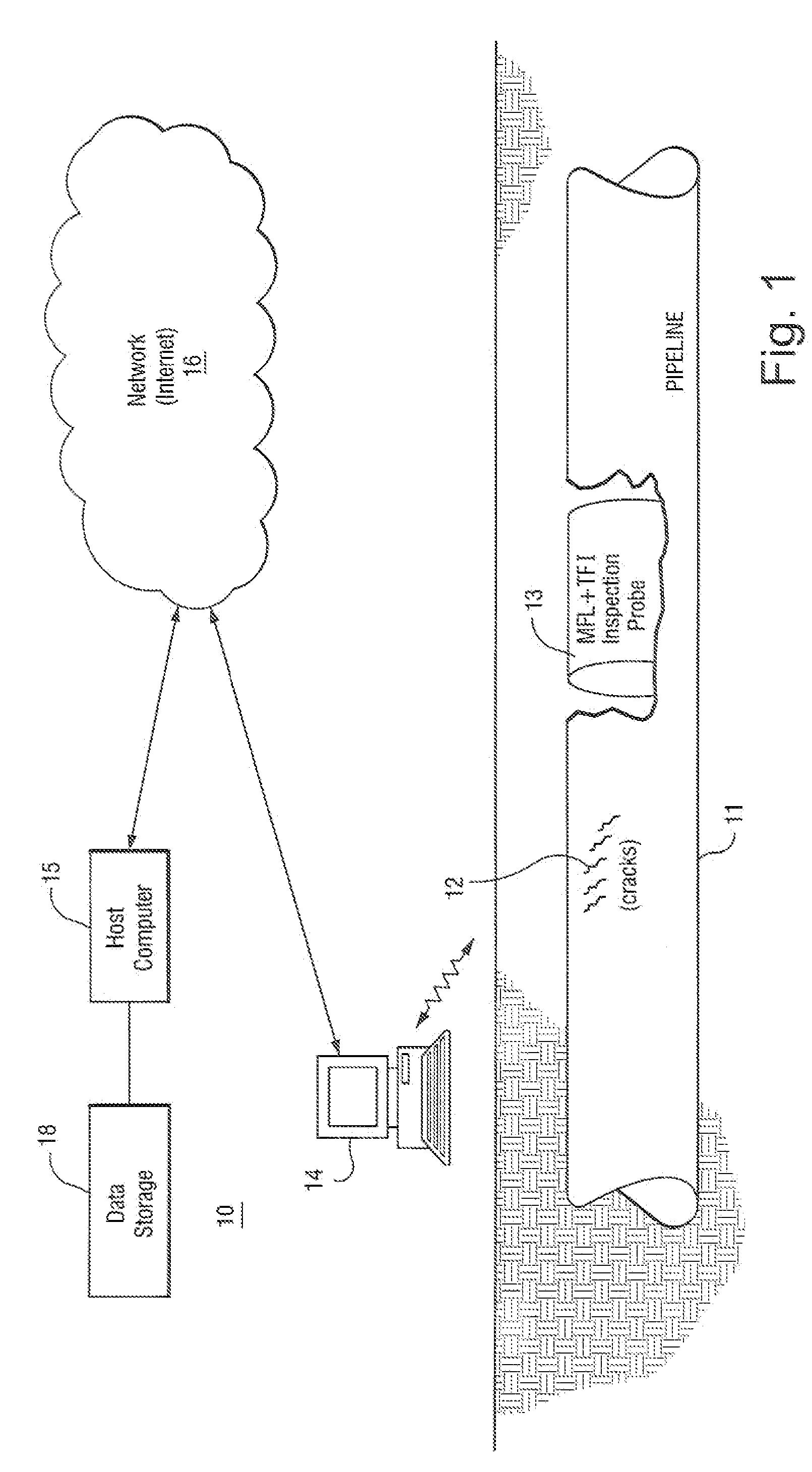
Method and apparatus inspecting pipelines using magnetic flux sensors
InactiveUS20070222436A1Improve trustReliable detectionMagnetic property measurementsMaterial magnetic variablesEngineeringStress corrosion cracking
The method for detecting stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of pipelines, comprising the steps of: identifying pipeline locations and pipeline conditions that are amenable to inspection by a magnetic flux inline tool and by a TFI tool; performing two inspections on the pipeline, one inspection performed using the magnetic flux inline (MFL) tool and an other inspection performed using the TFI tool; aligning signal features resulting from the two inspections; identifying TFI signals occurring above a specified threshold; identifying MFL signals for a section of pipeline corresponding to the identified TFI signals; for the identified TFI signals, determining whether the MFL signals are below a second threshold level; designating the sections of the pipeline corresponding to identified TFI signals above the threshold and below the second threshold as a potential corrosion feature; identifying TFI signals that exceed a defined metal loss percentage; measuring a width and length of the signal features, and if the width and length of the signal feature exceed threshold crack width and length values, designating as a potential corrosion feature section of pipeline corresponding to the identified TFI signals.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
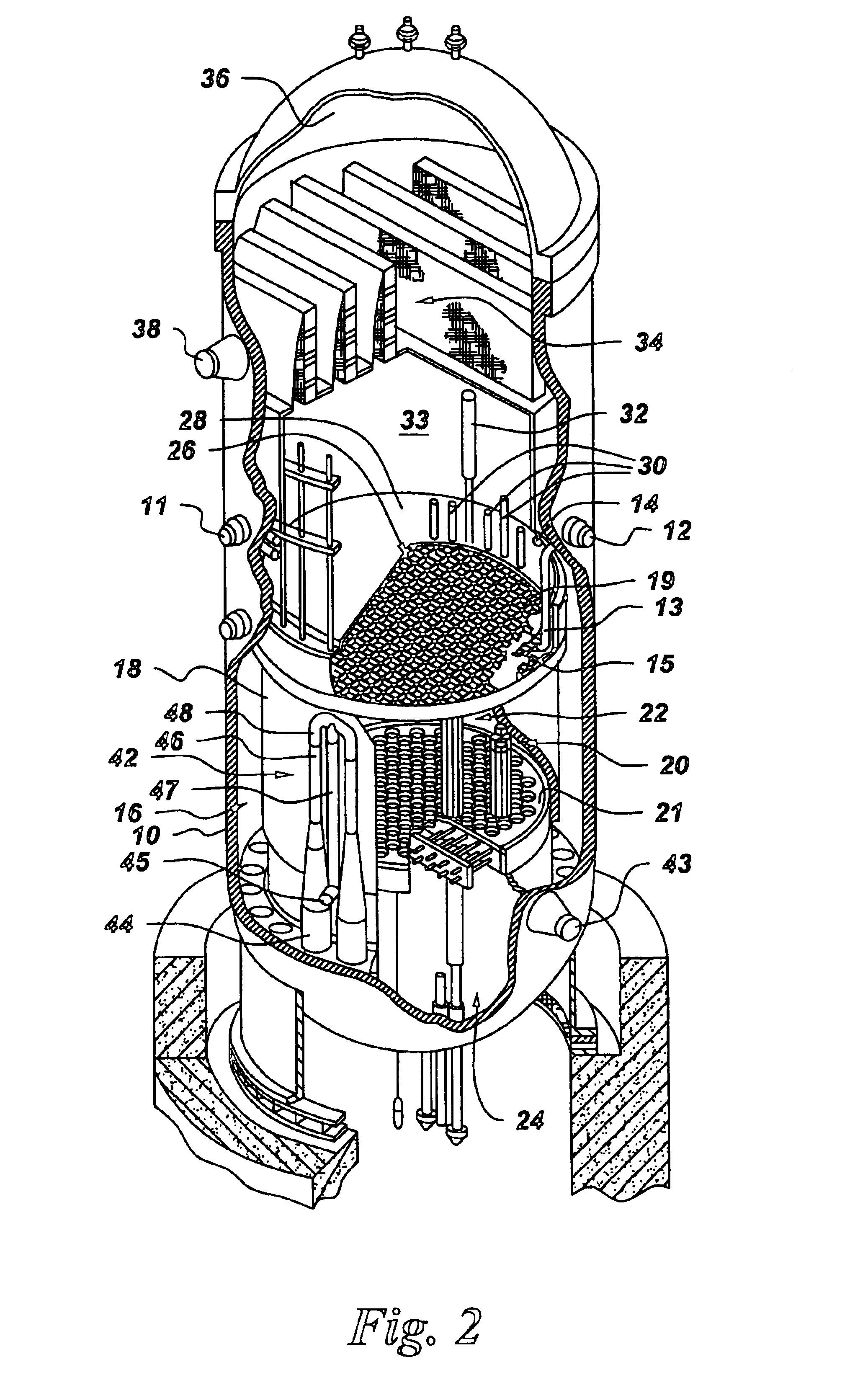
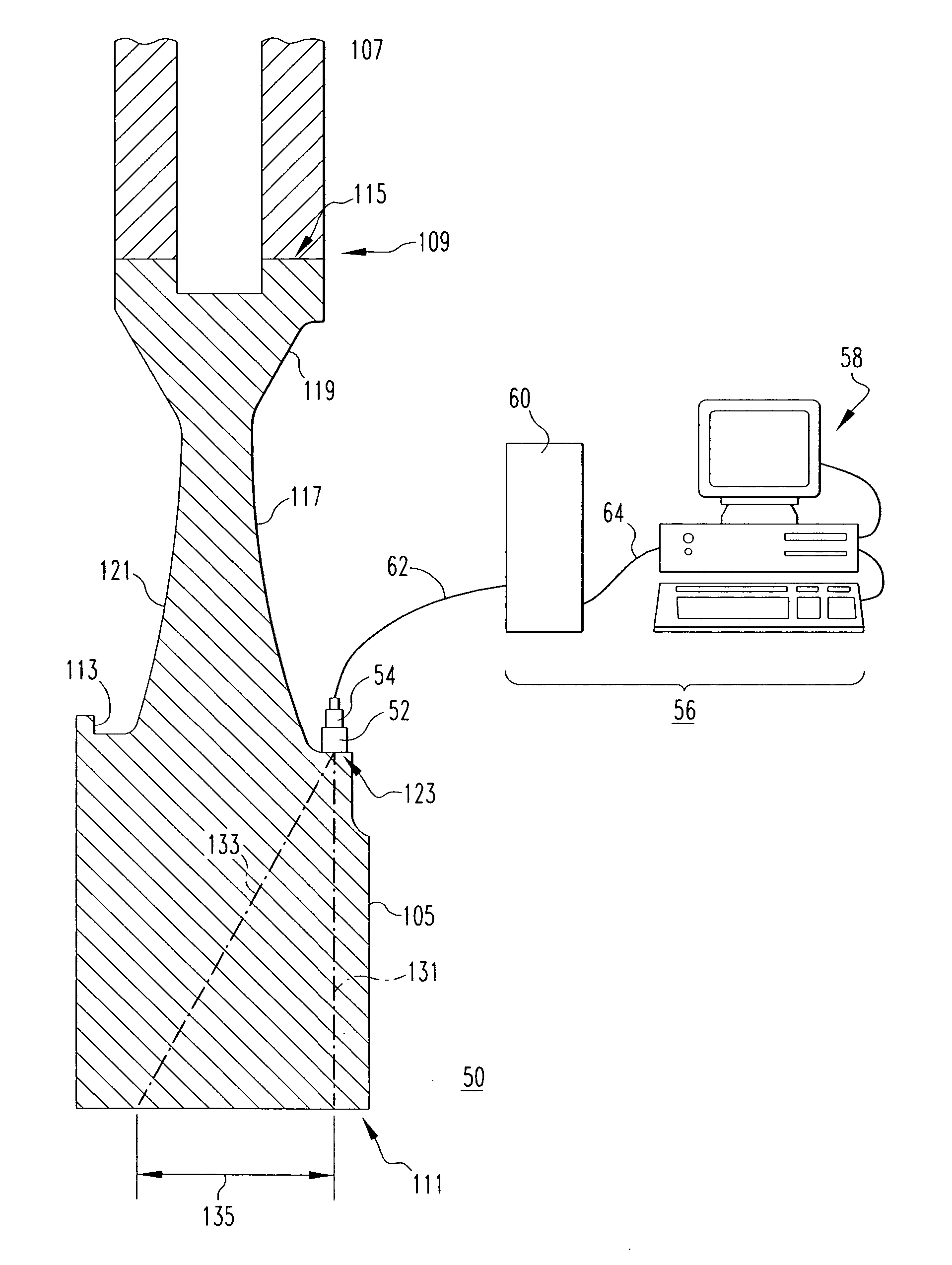
Phased array ultrasonic testing system and methods of examination and modeling employing the same
ActiveUS20060283250A1Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesCircular discSonification
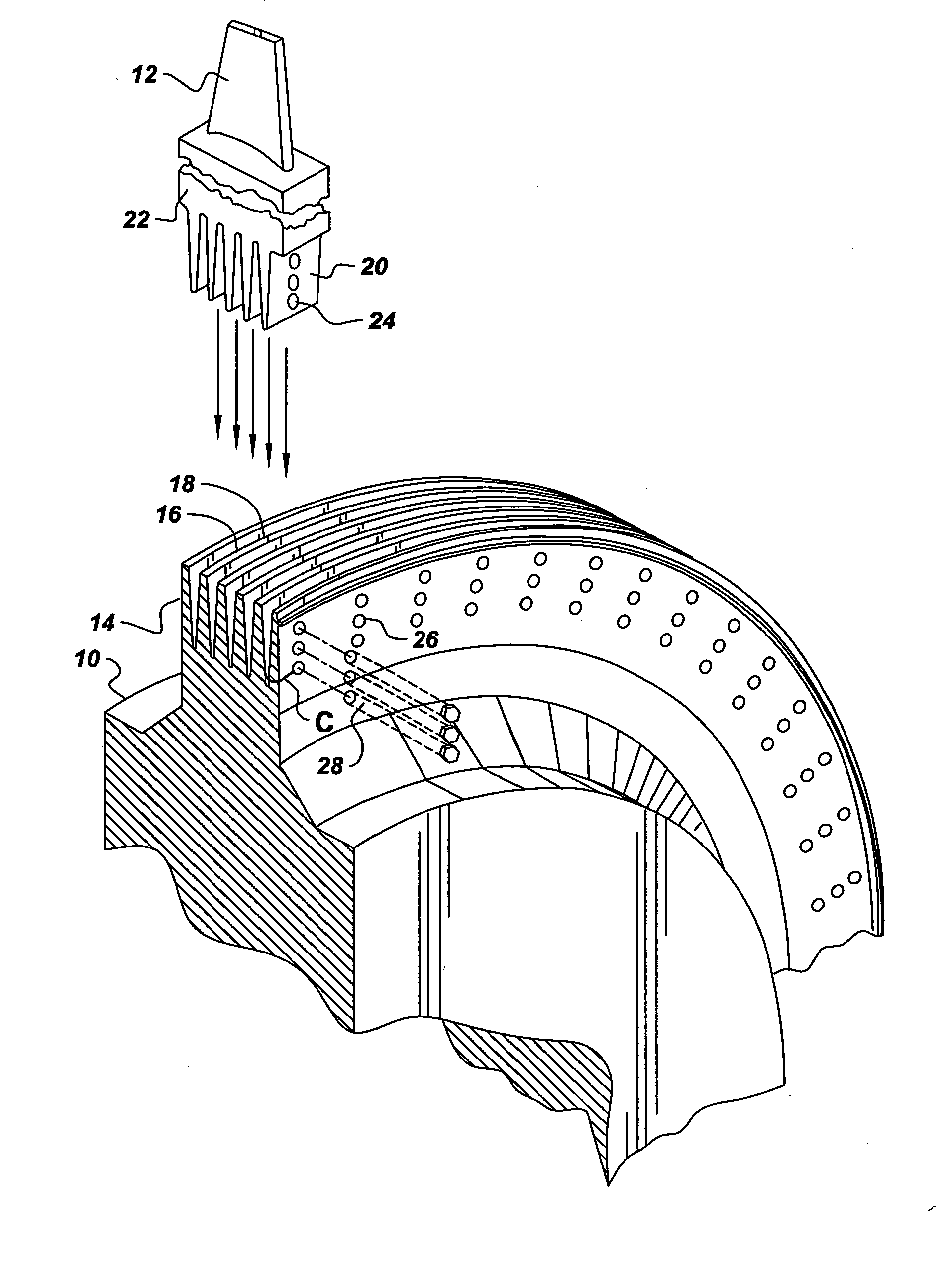
A phased array ultrasonic testing system is for examining turbine disc bores and blade attachments for discontinuities, such as stress corrosion cracking. The system is particularly suited to perform an accurate and efficient inspection of components despite their having a relatively complex geometry, such as axial entry blade attachments and bores of associated discs. The system includes a control system with a computer and a controller for programming, emitting, and steering an ultrasonic beam via at least one two-dimensional phased array probe, thereby precisely inspecting the area of interest while simultaneously accommodating the aforementioned complex geometry of the disc or blade attachment. Computer control of the beam permits the number of inspection locations and the number of different probe wedges to be reduced providing for an efficient, timely inspection. Methods of profiling and examining turbine components of known and unknown geometries, are also disclosed.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Application of catalytic nanoparticles to high temperature water systems to reduce stress corrosion cracking
InactiveUS20030012686A1Reducing electrochemical corrosion potentialReduce componentsNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear reactorNanoparticle
A method and system for reducing stress corrosion cracking in a hot water system, such as a nuclear reactor, by reducing the electrochemical corrosion potential of components exposed to high temperature water within the structure. The method comprises the steps of: providing a reducing species to the high temperature water; and providing a plurality of noble metal nanoparticles having a mean particle size of up to about 100 nm to the high temperature water during operation of the hot water system. The catalytic nanoparticles, which may comprise at least one noble metal, form a colloidal suspension in the high temperature water and provide a catalytic surface on which a reducing species reacts with least one oxidizing species present in the high temperature water. The concentration of the oxidizing species is reduced by reaction with the reducing species on the catalytic surface, thereby reducing the electrochemical corrosion potential of the component.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Application of catalytic nanoparticles to high temperature water systems to reduce stress corrosion cracking
InactiveUS6793883B2Reducing electrochemical corrosion potentialReduced dose rateNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear reactorNanoparticle
A method and system for reducing stress corrosion cracking in a hot water system, such as a nuclear reactor, by reducing the electrochemical corrosion potential of components exposed to high temperature water within the structure. The method includes the steps of: providing a reducing species to the high temperature water; and providing a plurality of noble metal nanoparticles having a mean particle size of up to about 100 nm to the high temperature water during operation of the hot water system. The catalytic nanoparticles, which may contain at least one noble metal, form a colloidal suspension in the high temperature water and provide a catalytic surface on which a reducing species reacts with least one oxidizing species present in the high temperature water. The concentration of the oxidizing species is reduced by reaction with the reducing species on the catalytic surface, thereby reducing the electrochemical corrosion potential of the component.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
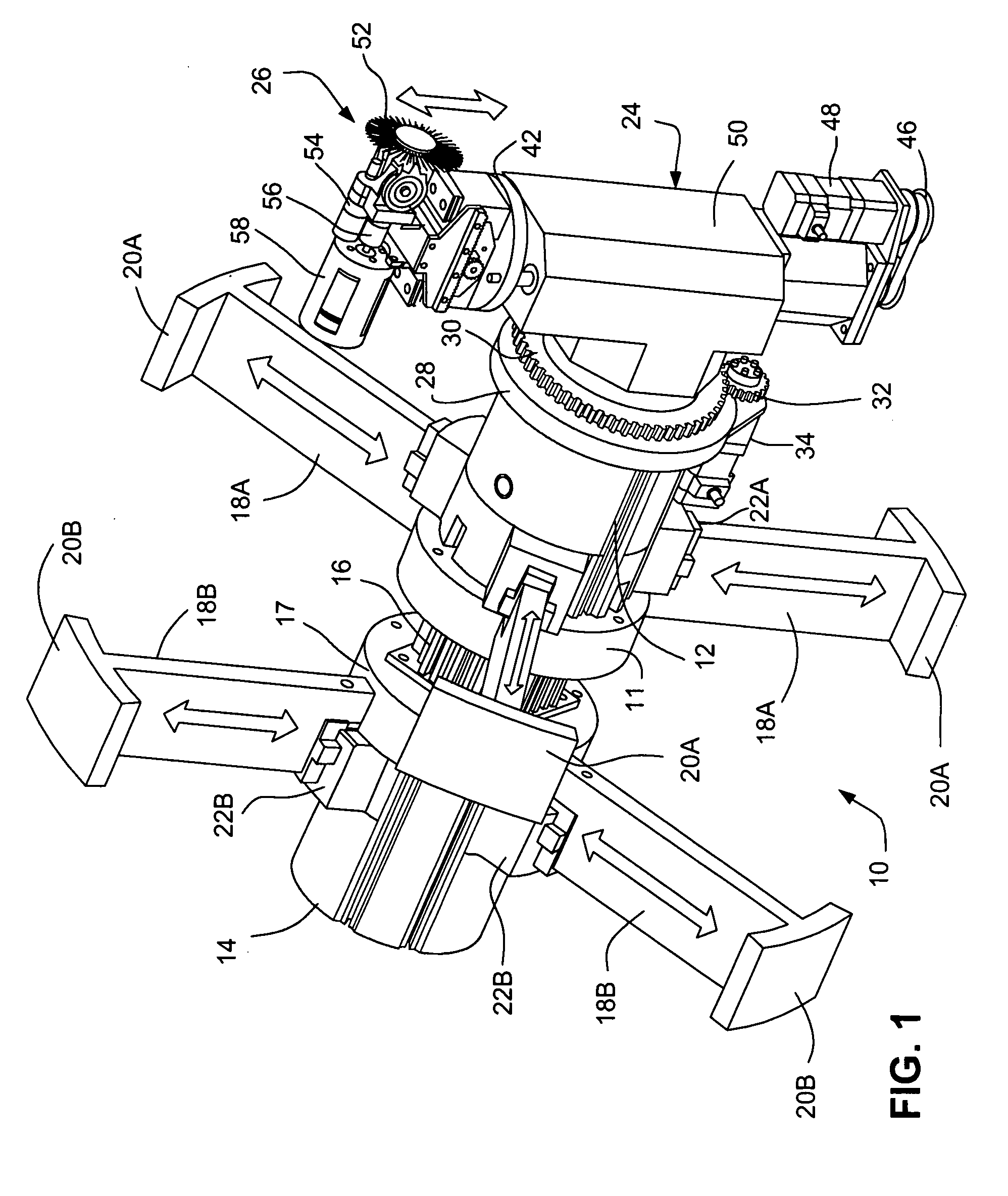
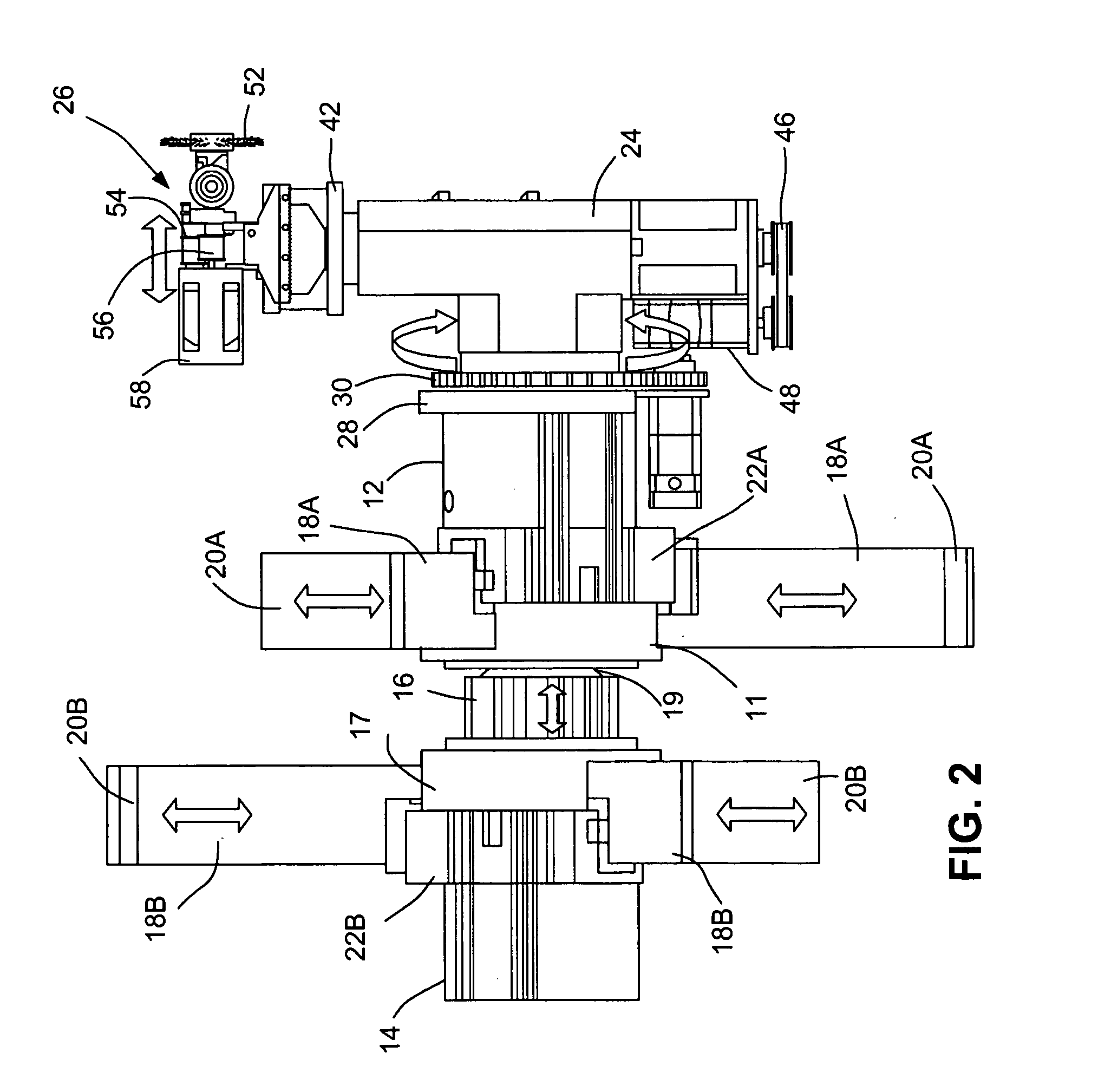
Method and compression apparatus for introducing residual compression into a component having a regular or an irregular shaped surface
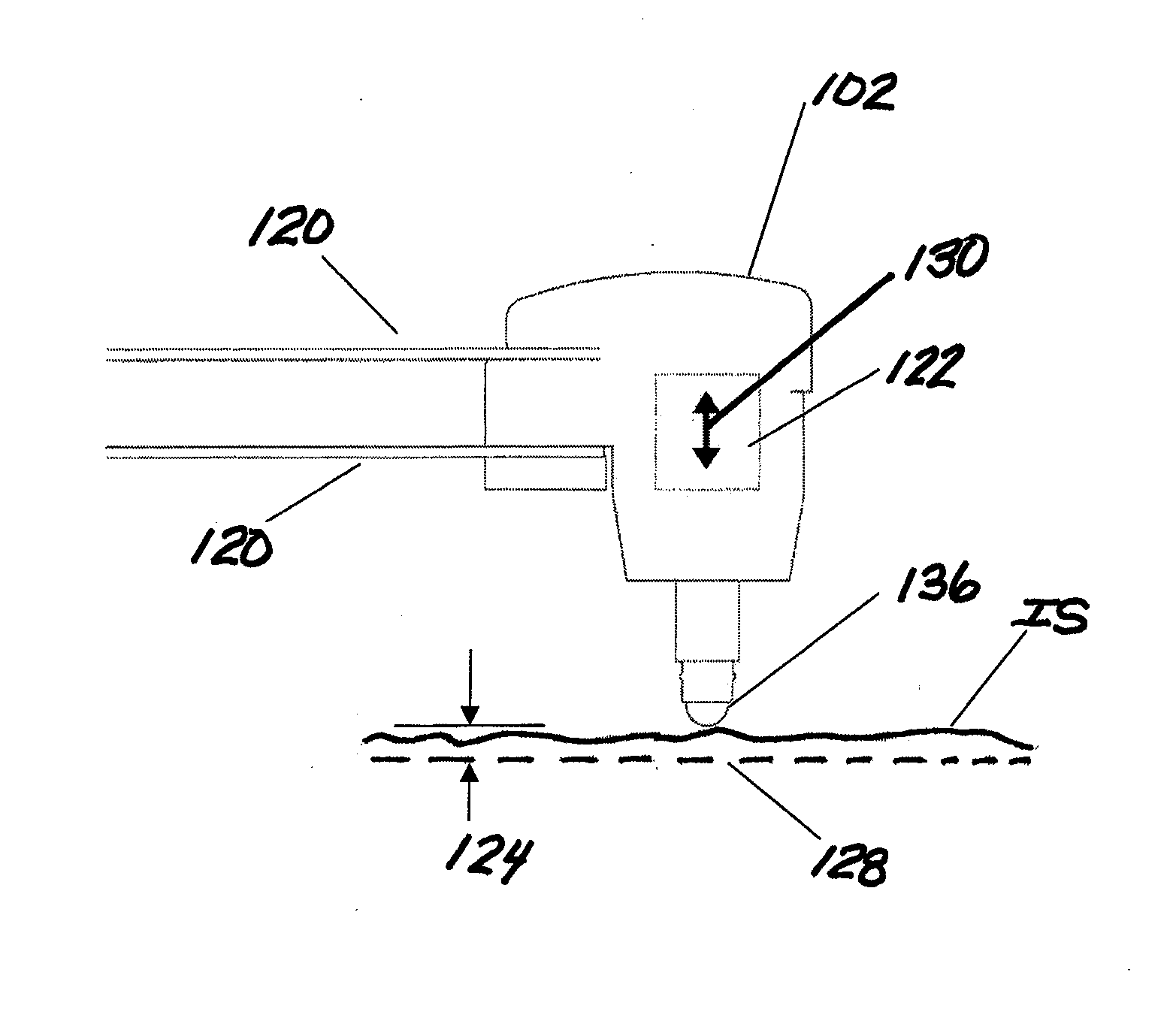
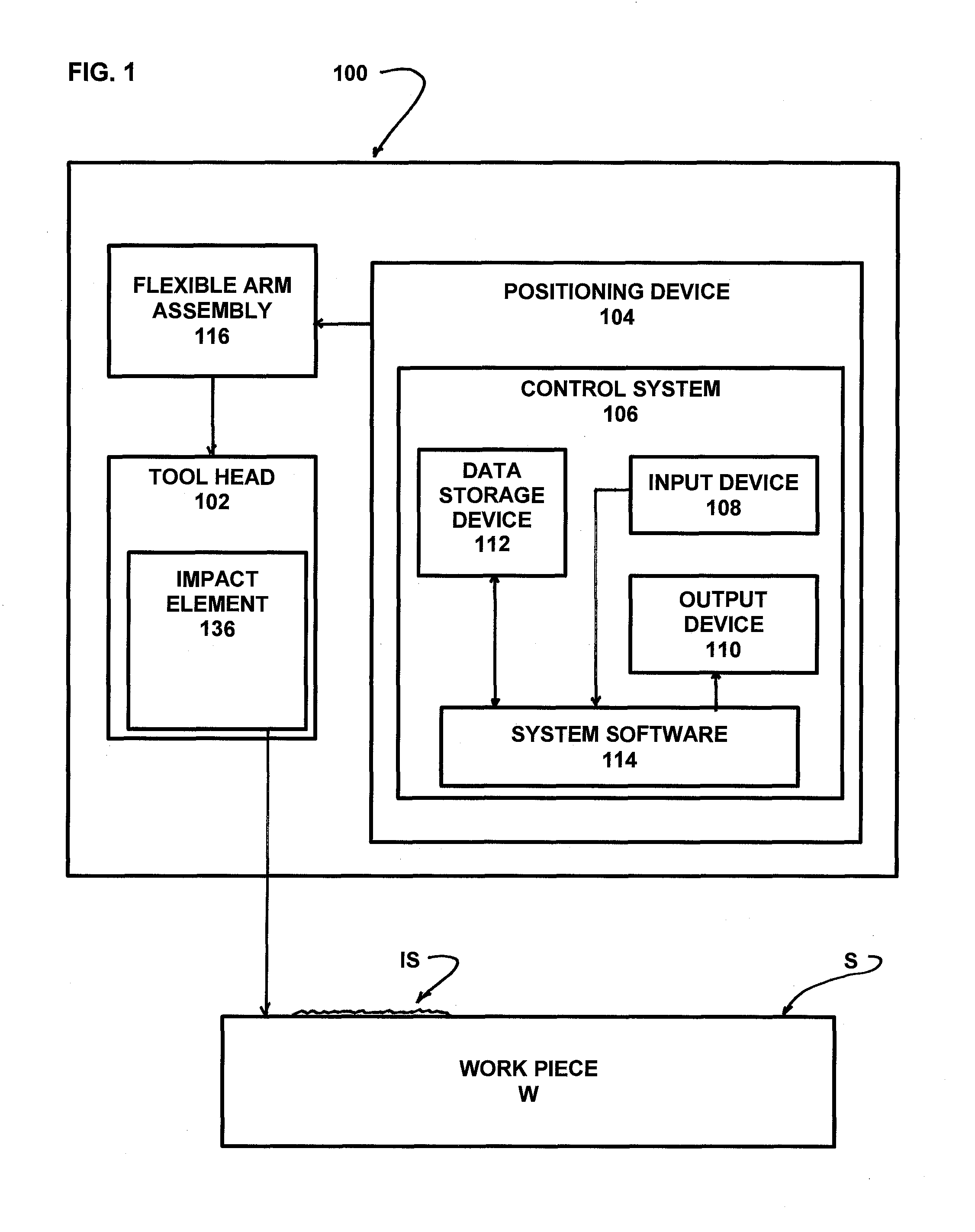
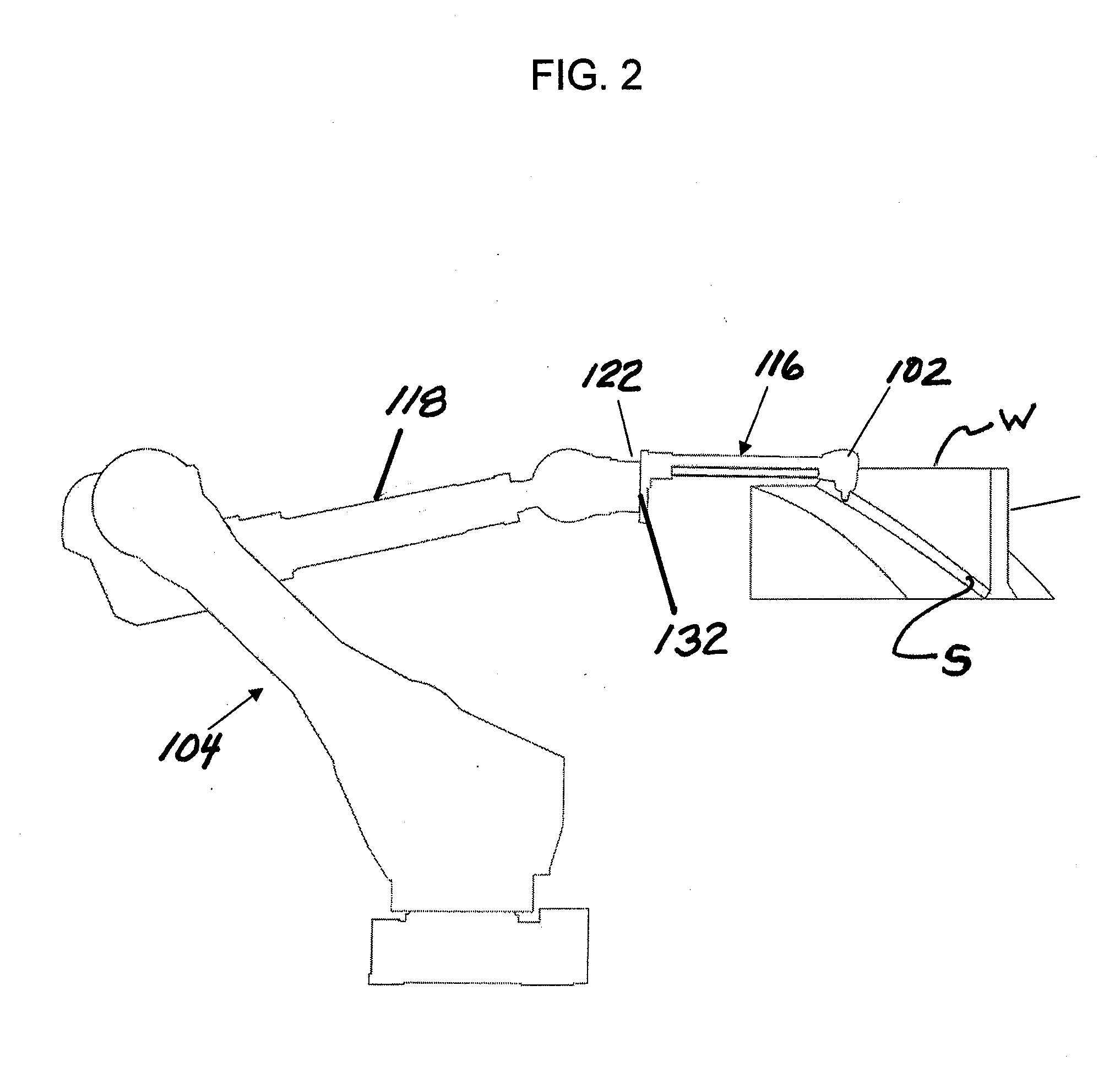
ActiveUS20140007394A1Freedom of movementDeformation MinimizationBurnishing machinesGrinding machinesCompression deviceClosed loop
A method and apparatus for improving the fatigue and stress corrosion cracking performance of irregular surfaces, such as welds assemblies of components, using a positioning system, such as a robotic or CNC machine, to position a tool head for inducing compression along and into the surface of a workpiece to automatically follow the surface irregularities. The method and apparatus operates to follow a virtual control surface located below the actual surface of the workpiece thereby allowing the irregular topography surface to be uniformly processed with closed loop process control.
Owner:SURFACE TECH HLDG
Indicators for early detection of potential failures due to water exposure of polymer-clad fiberglass
A composite insulator containing means for providing early warning of impending failure due to stress corrosion cracking, flashunder, or destruction of the rod by discharge activity conditions is described. A composite insulator comprising a fiberglass rod surrounded by a polymer housing and connected with metal end fittings on either end of the rod is doped with a dye-based chemical dopant. The dopant is located around the vicinity of the outer surface of the fiberglass rod. The dopant is formulated to possess migration and diffusion characteristics, and to be inert in dry conditions and compatible with the insulator components. The dopant is positioned within the insulator such that upon the penetration of moisture through the housing to the rod through a permeation pathway in the outer surface of the insulator, the dopant will become activated and will leach out of the same permeation pathway or diffuse through the housing. The activated dopant then creates a deposit or stain on the outer surface of the insulator housing. The dopant comprises an oil-soluble dye, an indicator, or a stain compound that can either be visually identified, or is sensitive to radiation at one or more specific wavelengths. The dopant could also be formulated by a nanoparticle enabled material. Deposits of activated dopant on the outer surface of the insulator can be detected upon imaging of the outer surface of the insulator by appropriate imaging instruments or the naked eye.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST INC
Phased array ultrasonic testing system and methods of examination and modeling employing the same
ActiveUS7428842B2Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationEngineering
A phased array ultrasonic testing system is for examining turbine disc bores and blade attachments for discontinuities, such as stress corrosion cracking. The system is particularly suited to perform an accurate and efficient inspection of components despite their having a relatively complex geometry, such as axial entry blade attachments and bores of associated discs. The system includes a control system with a computer and a controller for programming, emitting, and steering an ultrasonic beam via at least one two-dimensional phased array probe, thereby precisely inspecting the area of interest while simultaneously accommodating the aforementioned complex geometry of the disc or blade attachment. Computer control of the beam permits the number of inspection locations and the number of different probe wedges to be reduced providing for an efficient, timely inspection. Methods of profiling and examining turbine components of known and unknown geometries, are also disclosed.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
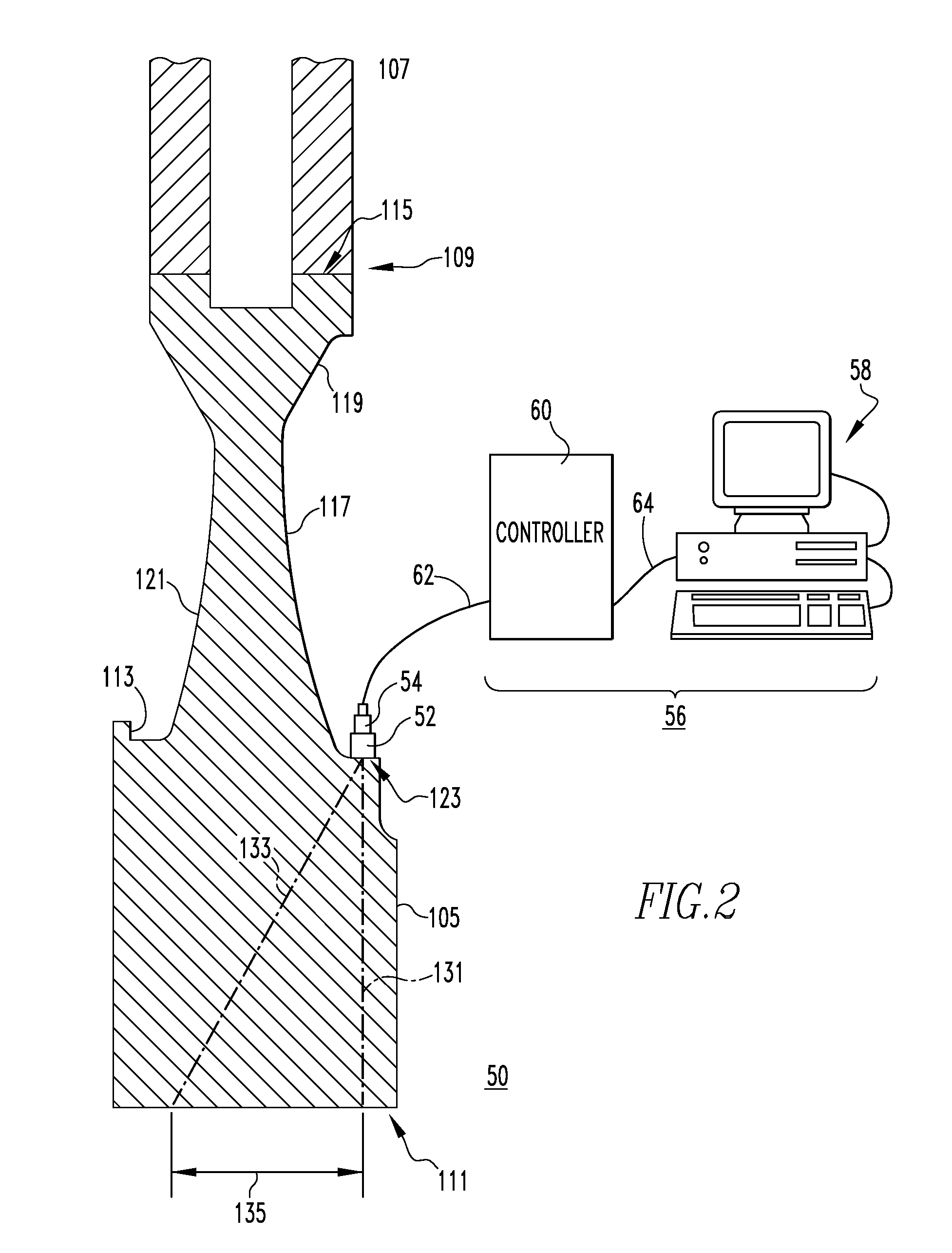
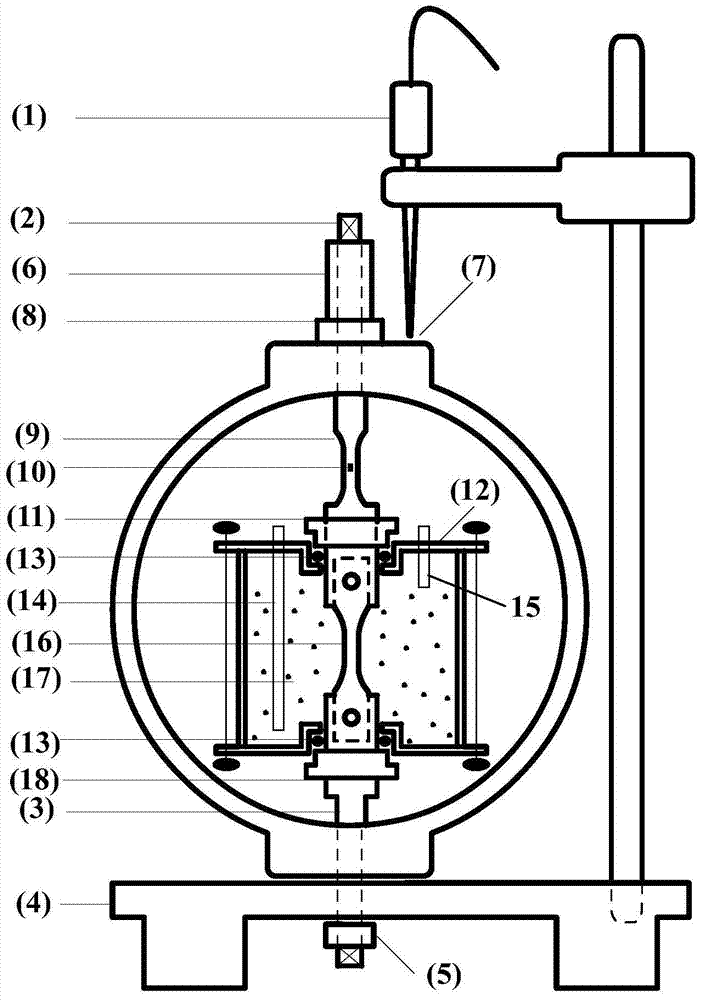
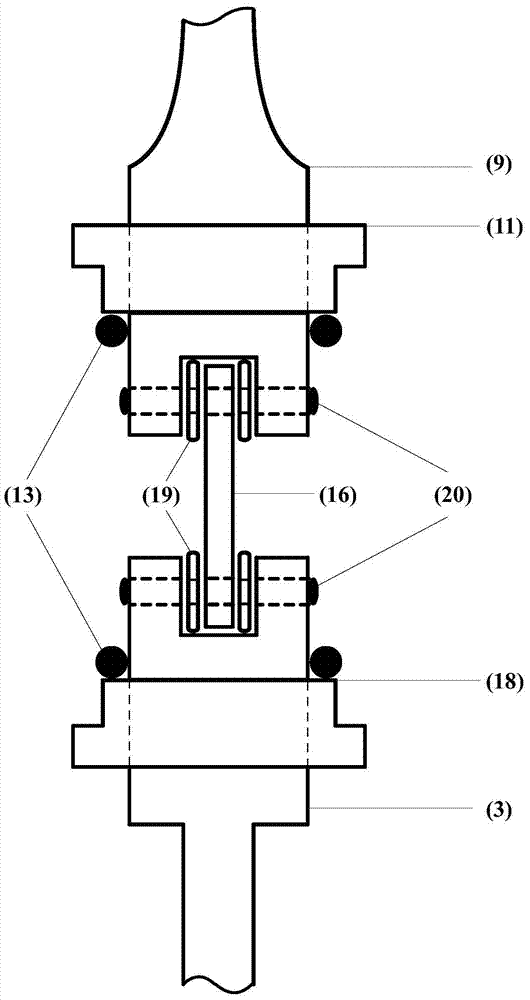
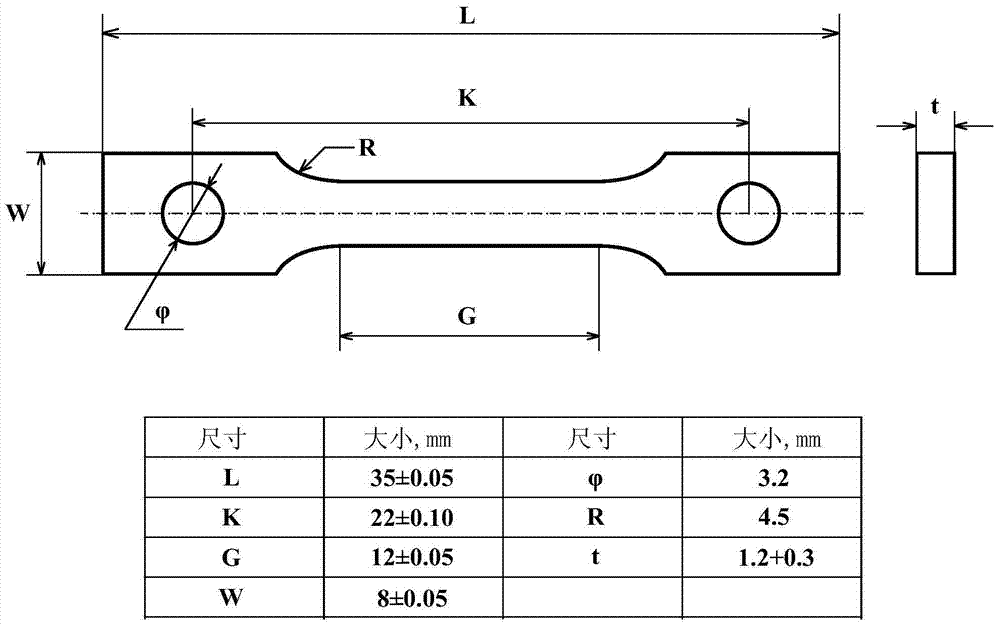
Constant-load stress corrosion testing device of small test sample and testing method thereof
InactiveCN103926146ASmall sizeEasy to processWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesConstant loadAnti stress
The invention relates to a constant-load stress corrosion evaluation method and a constant-load stress corrosion evaluation device of a small test sample. The essentials are as follows: the constant-load stress corrosion testing method and device can be used for testing an anti-stress corrosion cracking property of a thin-wall pipe and a small-size member; the small-size test sample is designed and processed and the level of the loaded stretching stress is accurately controlled; a stress corrosion experiment is carried out in an acidic environment; an anti-sulfide stress corrosion performance and an acting mechanism of the thin-wall pipe and the small-size member in the acidic corrosion environment are evaluated and researched according to an experiment result. With the adoption of the evaluation method and device, the anti-stress corrosion cracking property of the thin-wall pipe and the small-size member, which can not be used for processing a standard test sample, can be determined; the applicability of the material of the member can be obtained according to a testing result, so that the material selection and the applicability evaluation of the thin-wall pipe and the small-size member are carried out.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
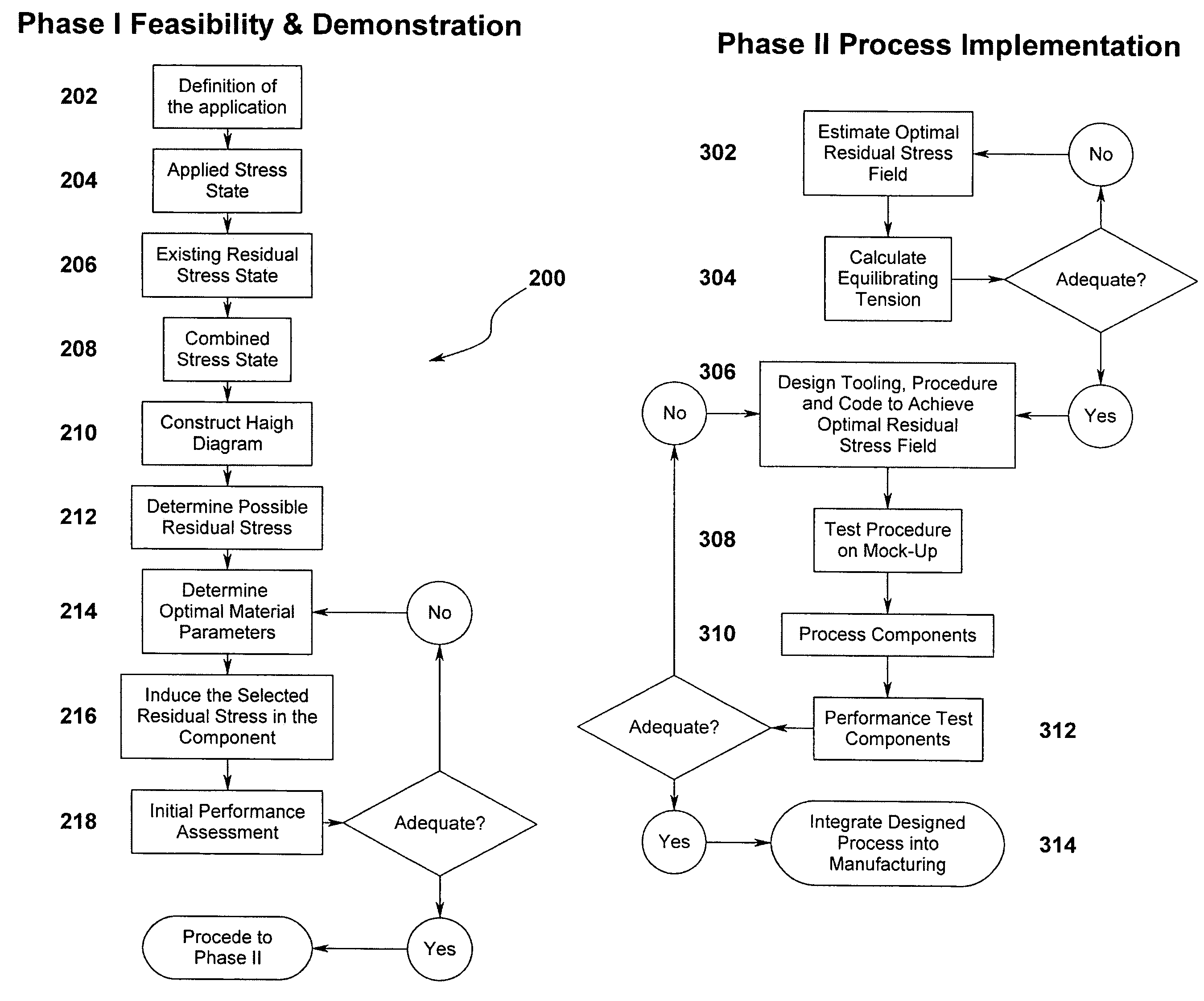
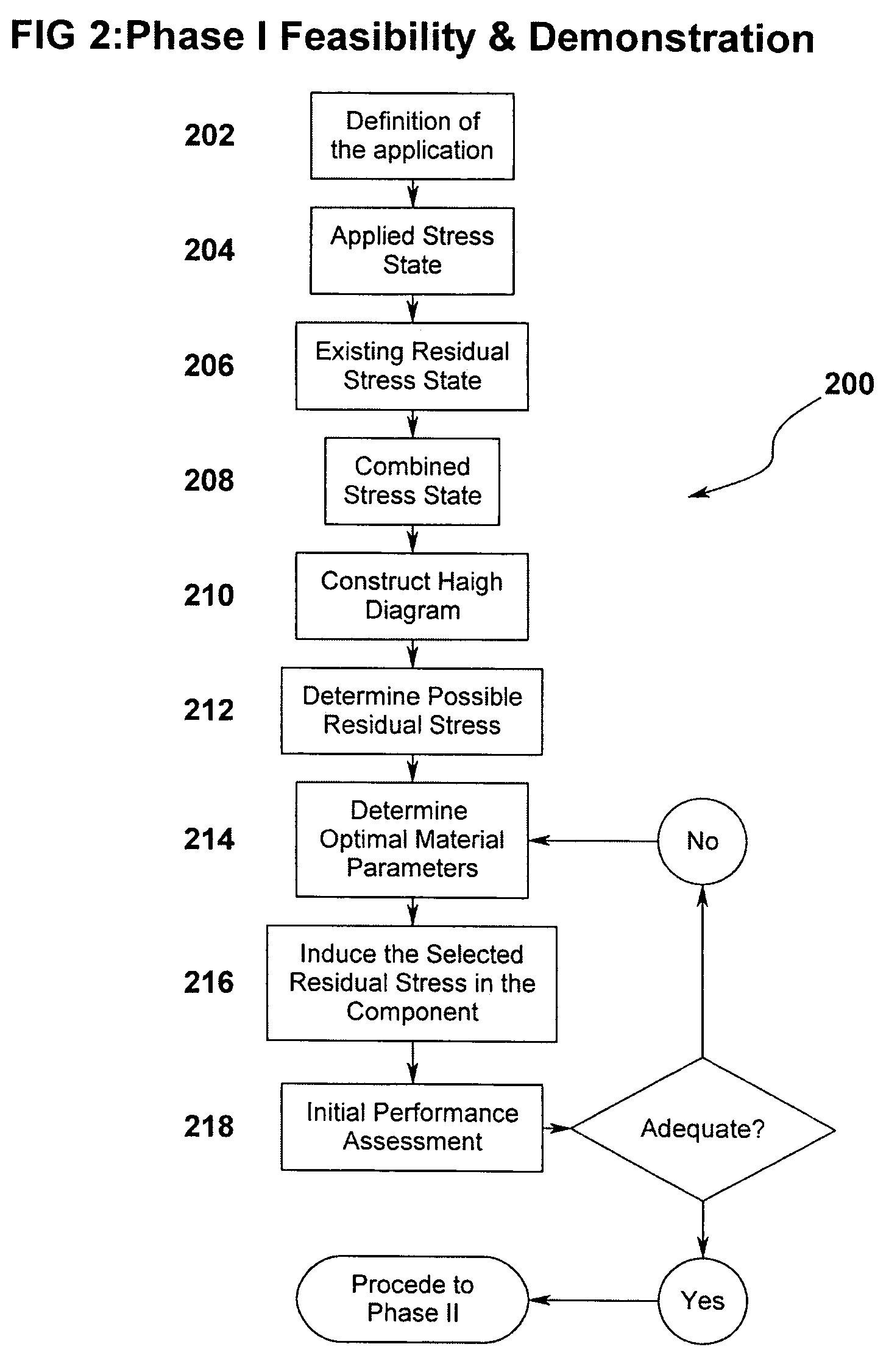
Method and system for improving a part's resistance to stress induced failure
ActiveUS7219044B1Offsetting effectUsing mechanical meansComputer aided designStress inducedStressed state
A method and system for designing a part with improved fatigue life and resistance to stress corrosion cracking in which residual stresses existing in the part are accounted for. The performance criteria and operating conditions of the part are assessed and a total stress state is determined from the sum of the residual stresses and applied stresses acting on the part. Unified Fatigue Performance Model or Smith-Topper-Neuber parameters are used to determine fatigue life functions which, in turn, are used in conjunction with a fatigue design diagram to determine the appropriate residual stress to introduce in order to optimize the part's resistance to stress induced failure mechanisms. A residual stress distribution is then designed to avoid distortion of the part while still imparting the beneficial effects of compressive residual stress.
Owner:SURFACE TECH HLDG
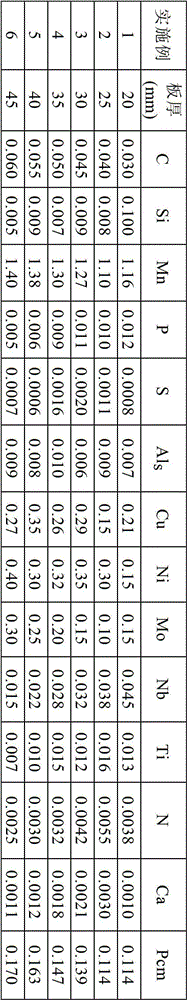
High-strength low-temperature steel with high hydrogen induced cracking (HIC) and sulfide stress corrosion cracking (SSC) resistance and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102719745AReduce consumptionReduce difficultyHeat treatment process controlStress corrosion crackingSteel tube
The invention relates to high-strength low-temperature steel with high hydrogen induced cracking (HIC) and sulfide stress corrosion cracking (SSC) resistance and a manufacturing method thereof. A low alloy steel component system with ultra-low C content, low Si content, medium Mn content, low Als content, low N content, a little alloyed Ni and Mo and trace Ti and Nb is adopted, Mn / C is more than or equal to 22, the segregation index 1.32 (percent C)*[(1.53 (percent Mn)+1.37 (percent Si)+1.15 (percent Mo)+1.06 (percent Cr)+(percent Cu)+0.86 (percent Ni)]*[(30 (percent P)+10 (percent S)] is less than or equal to 0.060, [(percent Si)+(percent Als)]*(percent C) is less than or equal to 0.0035, Pcm is less than or equal to 0.018 percent, Nib / Ti is 1.5 to 3.5, Ca treatment is performed, Ca / S is 0.80 to 3.00, the microstructure of a finished steel plate product consists of uniform and fine acicular ferrites and a few upper bainites by optimizing a thermal mechanical control processing (TMCP) technology, and the average particle size is less than 10mu m; and the characteristics of high strength, toughness and HIC and SSC resistance are achieved, high heat input welding can be performed, and the steel is particularly suitable for manufacturing a low temperature storage tank, a low temperature pressure steel pipe, an ocean platform in an ice sea area, and the like.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Method for protecting new/used engine parts
InactiveUS20050158460A1Reduce erosionLower requirementLayered productsBlade accessoriesProcess engineeringStress corrosion cracking
New and used parts of gas and steam turbine engines are protected by imparting a controlled residual compressive stress to given portions of the part and then coated by a CVD or PVD process at low temperatures with layers of TiN or alloys thereof at alternate selective hard and less hardened levels. The protective treatment is particularly efficacious for airfoils of compressor blades / vanes of gas turbine engines and airfoils of airfoils and certain components of steam turbine engines. This method is targeted to reduce erosion, corrosion and stress-corrosion cracking in these parts.
Owner:PERFORMANCE TURBINE COMPONENTS T AMOR
Pipeline steel excellent in acid corrosion resistance on seabed and production method
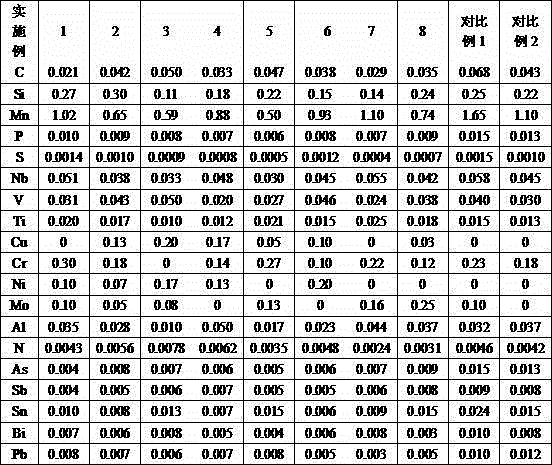
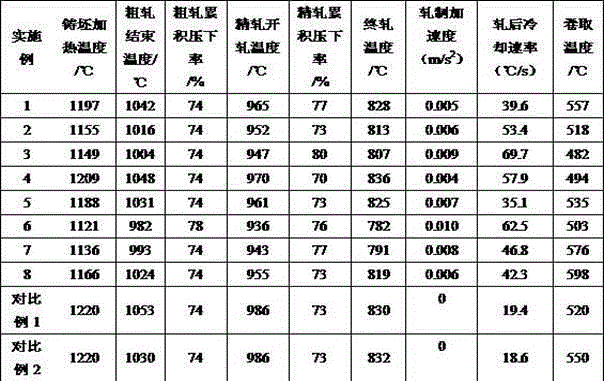
The invention discloses pipeline steel excellent in acid corrosion resistance on the seabed. The pipeline steel comprises, by weight, 0.020-0.050% of C, 0.10-0.30% of Si, 0.50-1.10% of Mn, 0.012% of P or less, 0.0015% of S or less, 0-0.20% of Cu, 0-0.30% of Cr, 0-0.20% of Ni, 0-0.25% of Mo, 0.030-0.055% of Nb, 0.020-0.050% of V, 0.010-0.025% of Ti, 0.010-0.050% of Al and 0.008% of N or less. A production method comprises the steps of heating after continuous casting and blank forming, rough rolling, precise rolling, cooling, reeling and cooling to indoor temperature. By means of the pipeline steel and the production method, an ideal complex-phase structure containing ultra-fine grain polygonal ferrite and a small number of methyl acrylate (MA) components which are distributed dispersively can be obtained, the Rt0.5 is equal to or higher than 485 MPa, the Rm is equal to or higher than 570 MPa, -20 DEG C KV2 is equal to or higher than 250 J, and -15 DEG C DWTT SA is equal to or higher than 85%. A hydrogen induced crack j (HICj) test and a sulfide stress corrosion cracking (SSCC) test indicate that no fracture or crack occurs.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Smelting method of HIC (Hydrogen Induced Crack)/SSCC (Sulfide Stress Corrosion Cracking)-preventing steel
ActiveCN103540833AImprove dynamic conditionsAchieve transformationManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementOxygenStress corrosion cracking
The invention discloses a converter smelting and external refining control method of HIC (Hydrogen Induced Crack) / SSCC (Sulfide Stress Corrosion Cracking)-preventing steel. A smelting process route of converter-CAS (Control Automatic System) station-LF (Low Frequency) refining-VD (Vacuum Distillation) / RH (Relative Humidity) vacuum-calcium treatment-soft blowing-continuous casting is adopted. Low-phosphor requirements of the HIC / SSCC-preventing steel are obtained through controlling the converter smelting process route; and meanwhile, part of deoxidation type inclusions are removed by carrying out strong deoxidation, alloying as well as residue washing in a converter steel-tapping process, and over 60% of sulfur in molten steel is removed by sufficient stirring of the residue washing. In the LF refining process, refining furnace slag which is high in alkalinity, high in Al2O3 and strong in reducibility is obtained by regulating components of the refining furnace slag, and the inclusions are transformed and removed towards a low melting point by virtue of balance of the furnace slag-molten steel-inclusions. Proper vacuum treatment time and vacuum degree are kept at a vacuum treatment furnace so as to remove part of gas and inclusions, excessive calcium line is fed into the molten steel after being broken in air, and then the molten steel is softly blown and stirred for over 20 minutes to obtain the molten steel with ultralow oxygen and ultralow sulfur.
Owner:HUNAN VALIN XIANGTAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
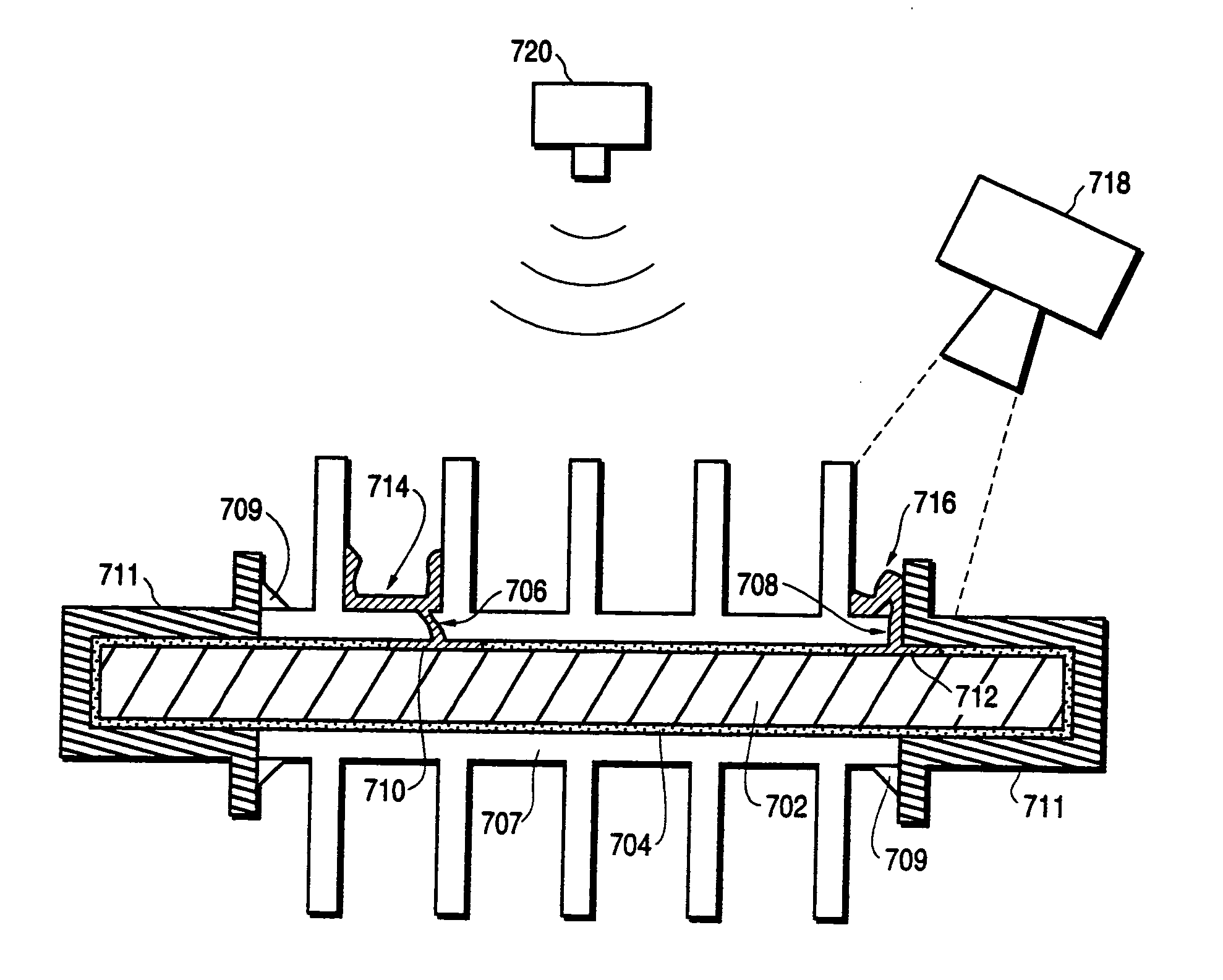
Dry-coupled permanently installed ultrasonic sensor linear array
InactiveUS20100236330A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMagnetic property measurementsProcess equipmentCoupling
This invention relates to permanent, ultrasonic, flexible, dry-coupled, linear arrays for the inspection of pipelines, process equipment, and the like. The permanent, ultrasonic, flexible, dry-coupled, linear arrays detect and / or measure corrosion wall loss, stress corrosion cracking, and / or internal initiated pipeline cracking. The apparatus for ultrasonically testing materials includes a linear array of ultrasonic sensors, and a flexible, acoustically transmissive, dry-coupling surrounding at least a portion of each of the ultrasonic sensors.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
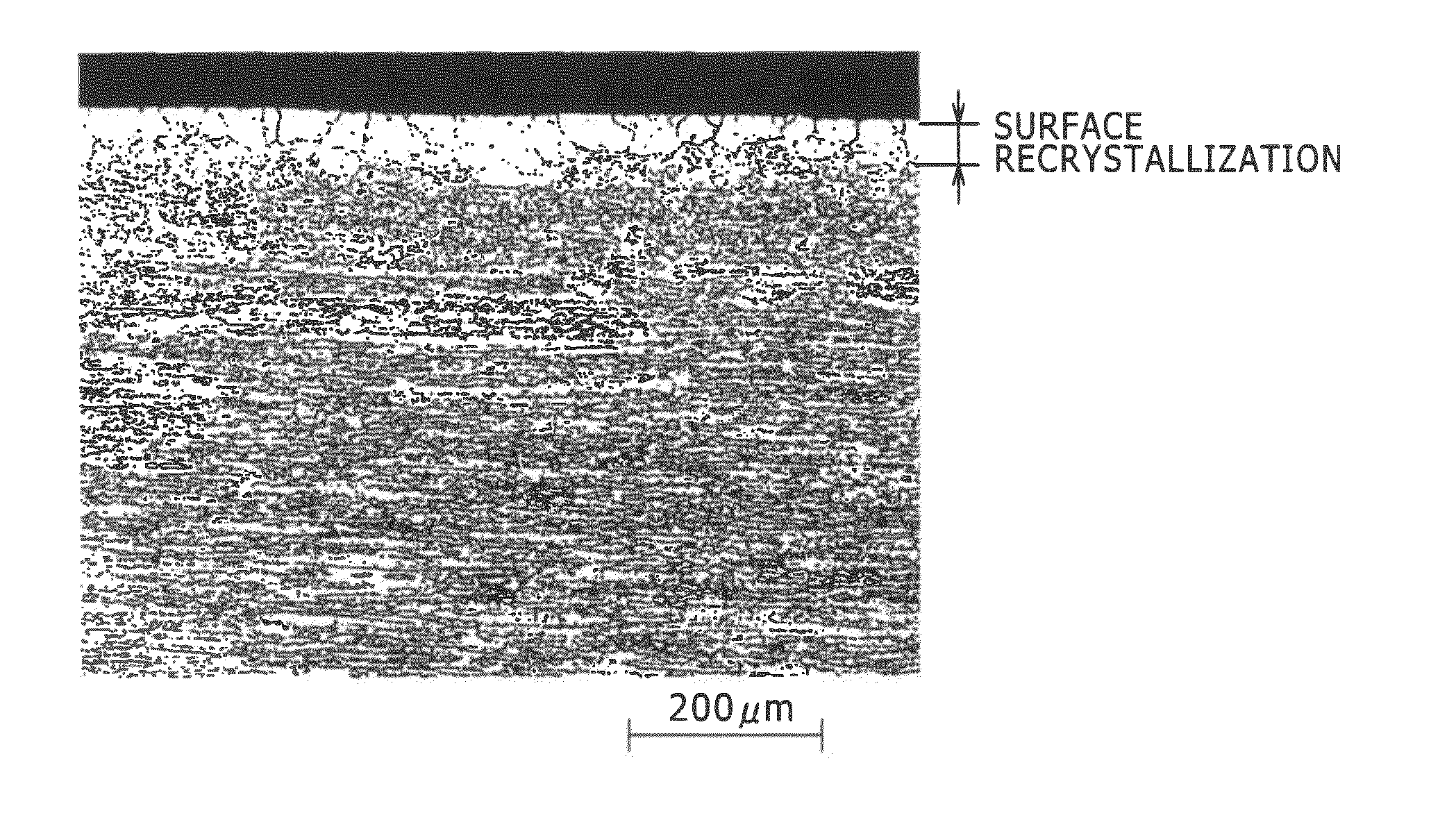
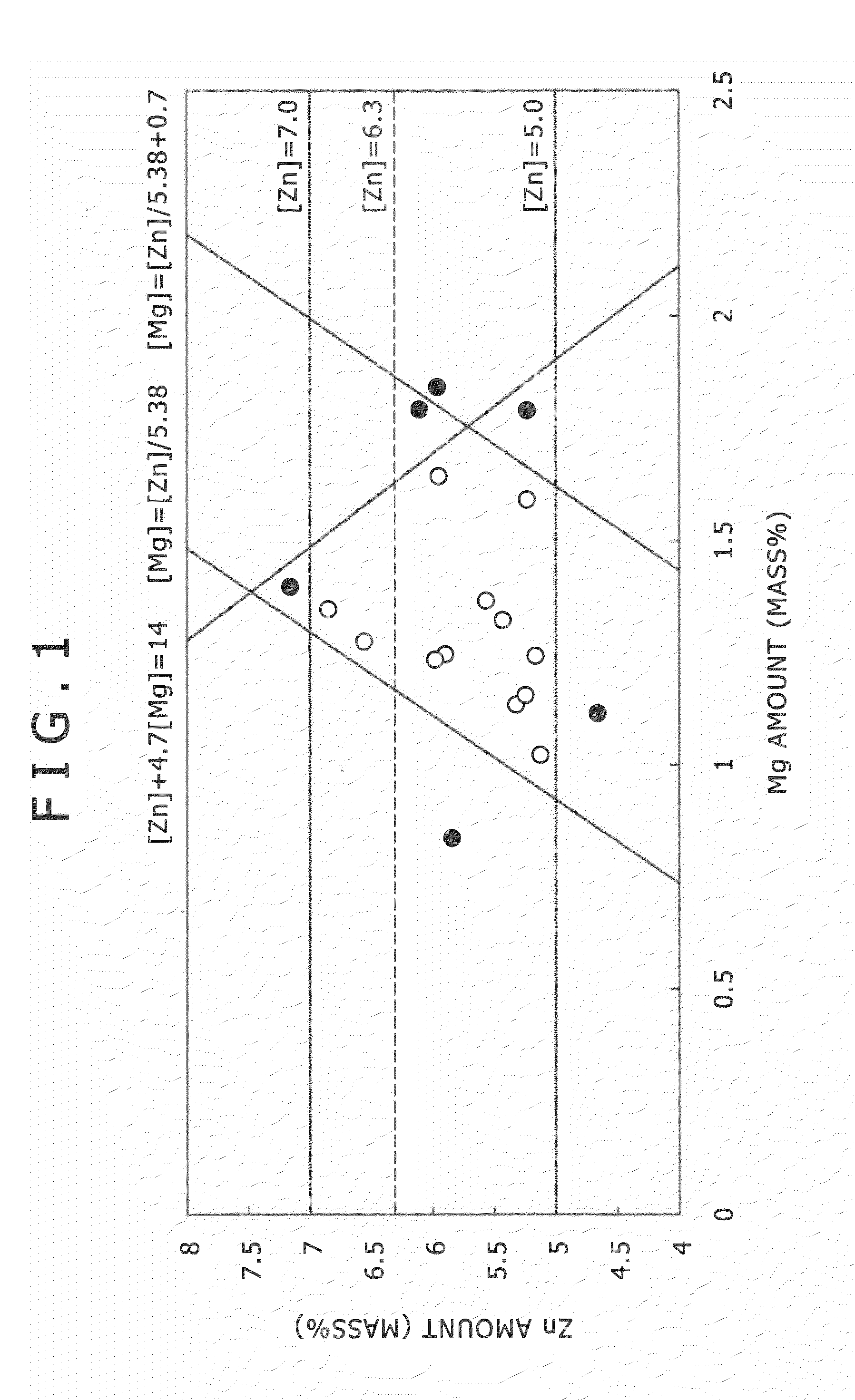
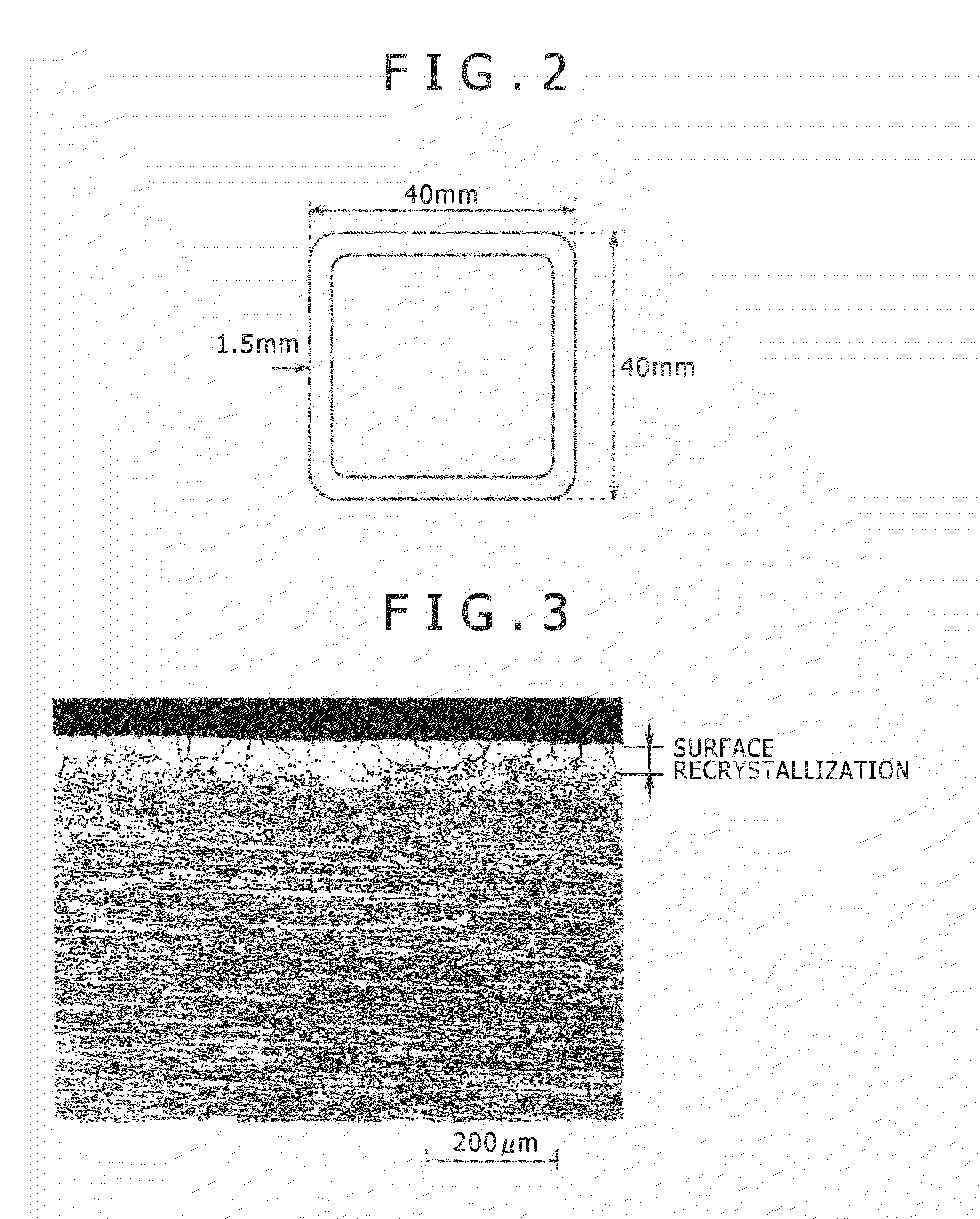
High strength aluminum alloy extruded material excellent in stress corrosion cracking resistance
An aluminum alloy extruded material in relation with the present invention is with high strength by die quench air cooling and excellent in SCC resistance. The aluminum alloy extruded material is an Al—Zn—Mg-based aluminum alloy extruded material for structural member for automobiles such as a bumper reinforce, a door guard bar and the like which satisfies three expressions of 5.0≦[Zn]7.0, [Zn] / 5.38<[Mg]≦[Zn] / 5.38+0.7, and [Zn]+4.7[Mg]≦14, where [Mg] represents mass % of Mg and [Zn] represents mass % of Zn, and contains at least either one element of Cu: 0.1-0.6 mass % and Ag: 0.01-0.15 mass %, Ti: 0.005-0.05 mass %, and at least one element out of Mn: 0.1-0.3 mass %, Cr: 0.05-0.2 mass %, Zr: 0.05-0.2 mass %.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
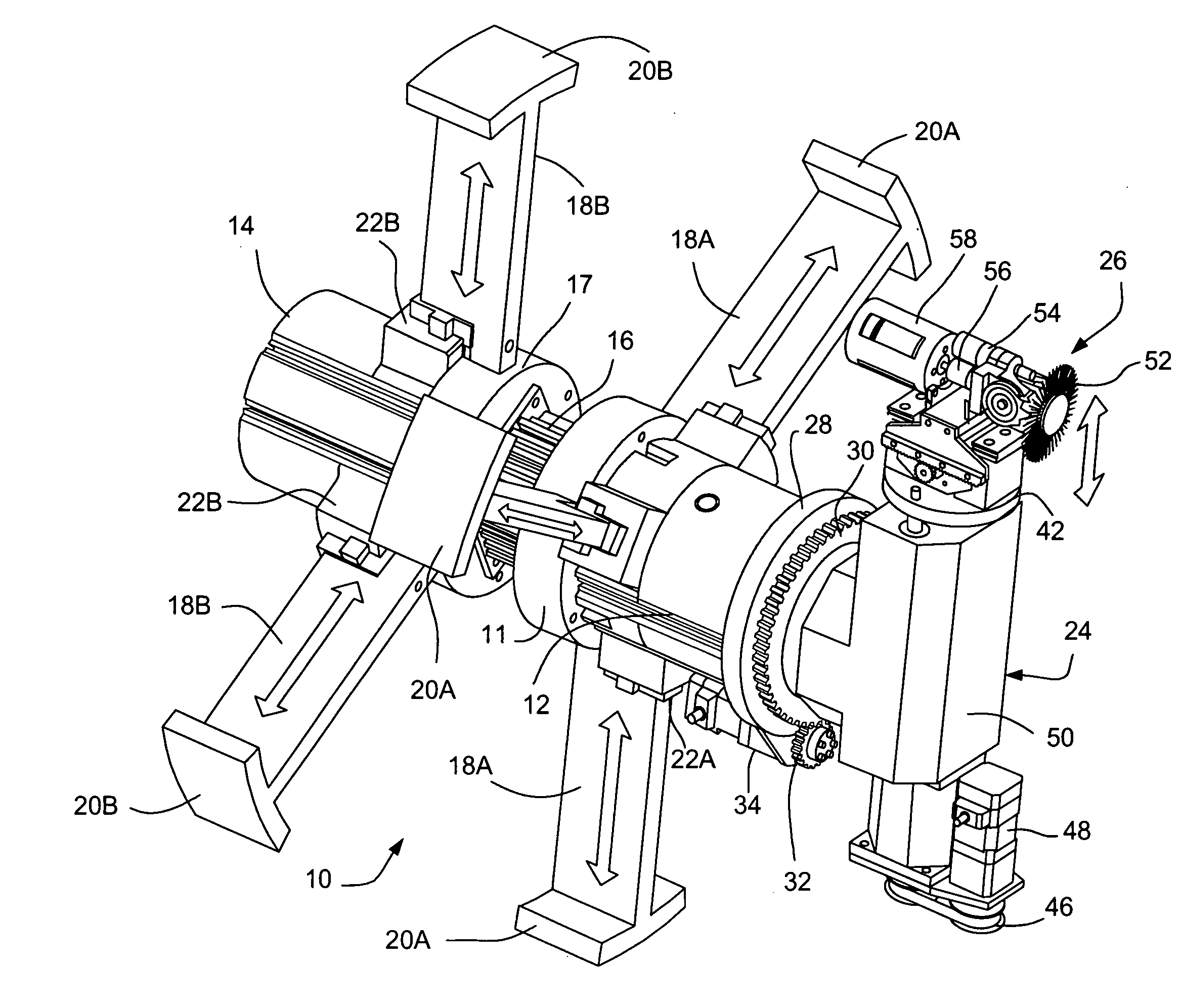
Method and apparatus for remotely inspecting and/or treating welds, pipes, vessels and/or other components used in reactor coolant systems or other process applications
InactiveUS20090307891A1Reduce crackingAutomatic control devicesNuclear energy generationMarine engineeringActuator
A tool is disclosed for remotely inspecting and / or treating welds, pipes, vessels and / or other components used in reactor coolant systems or other process applications to, among other things, mitigate stress corrosion cracking in the welds, pipes, vessels and / or other components. The tool is placed at the entrance to a pipe or vessel and walks into the pipe or vessel to a pre-selected weld, pipe or vessel location or other component. Upon reaching the pre-selected weld, pipe or vessel location or other component, the tool anchors itself, then advances an end effector to inspect and / or treat the pre-selected weld, pipe or vessel location or other component.
Owner:GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY AMERICAS
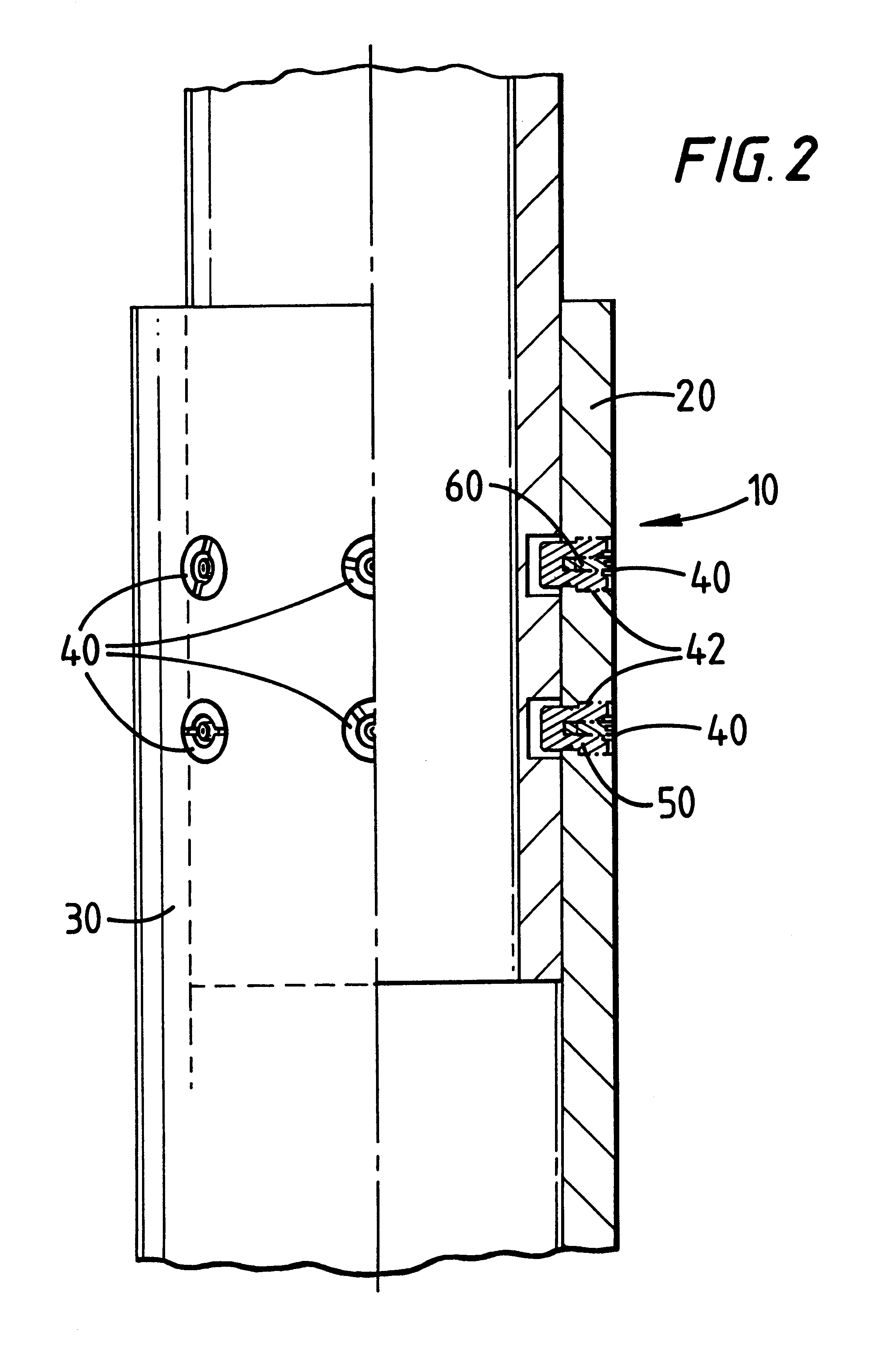
Casing slip joint
A casing slip joint has been invented that has a first tubular casing member disposed around and releasably connected to a second casing member, the second casing member within and surrounded by the first casing member. Self-destructive shear screws according to the present invention releasably hold the first casing member to the second casing member. In one aspect, a shear screw according to this invention has an outer shear screw with a central recess and an inner member therein. In one aspect the outer shear screw is made of one metal and the inner screw is made of another so that contact by a well fluid sets up a galvanic cell that produces stress corrosion cracking in the outer shear screw that weakens it and / or destroys it. The propagation of such cracks is facilitated by placing one or more notches or recesses in the body of the components.
Owner:WEATHERFORDLAMB
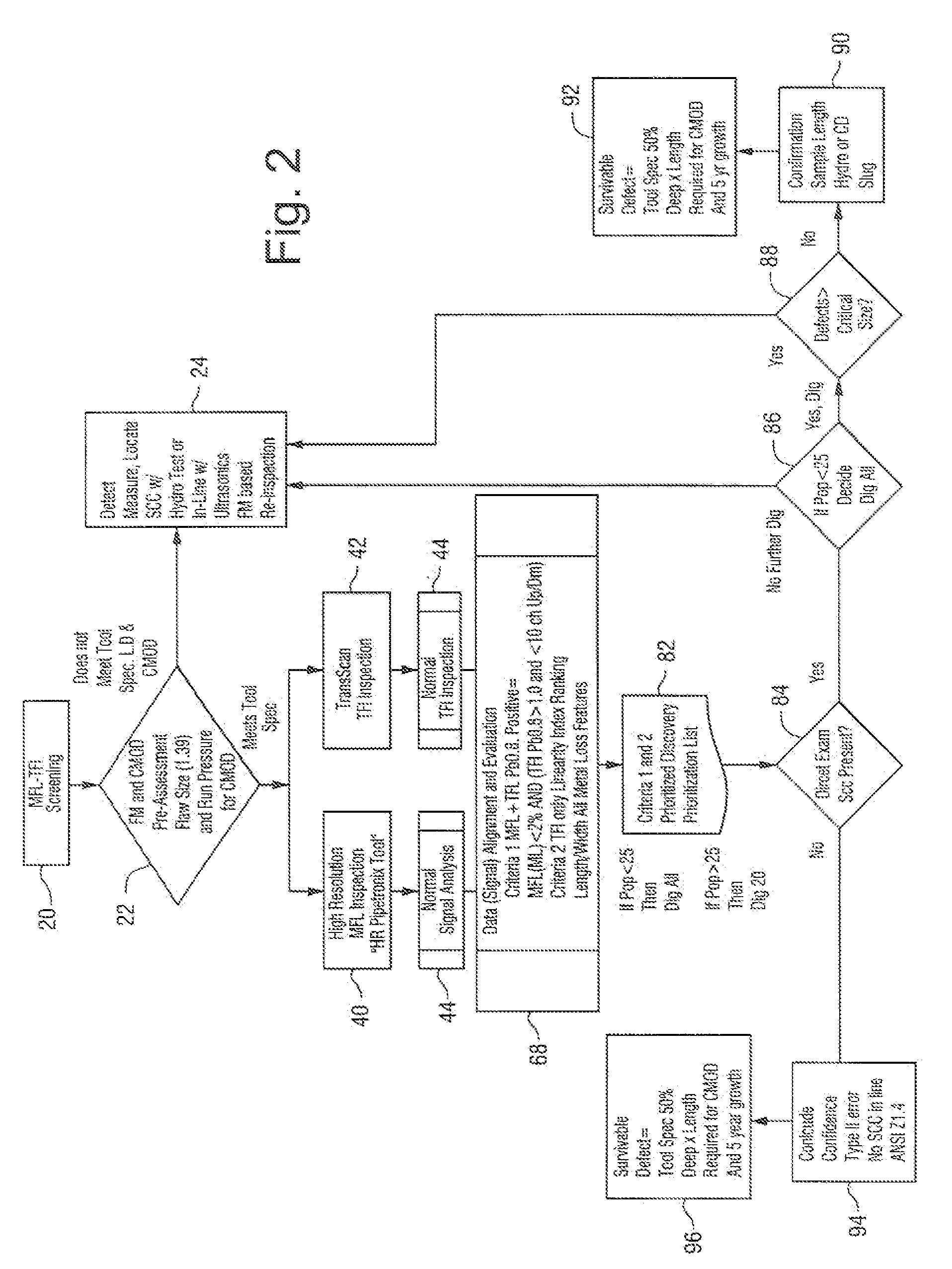
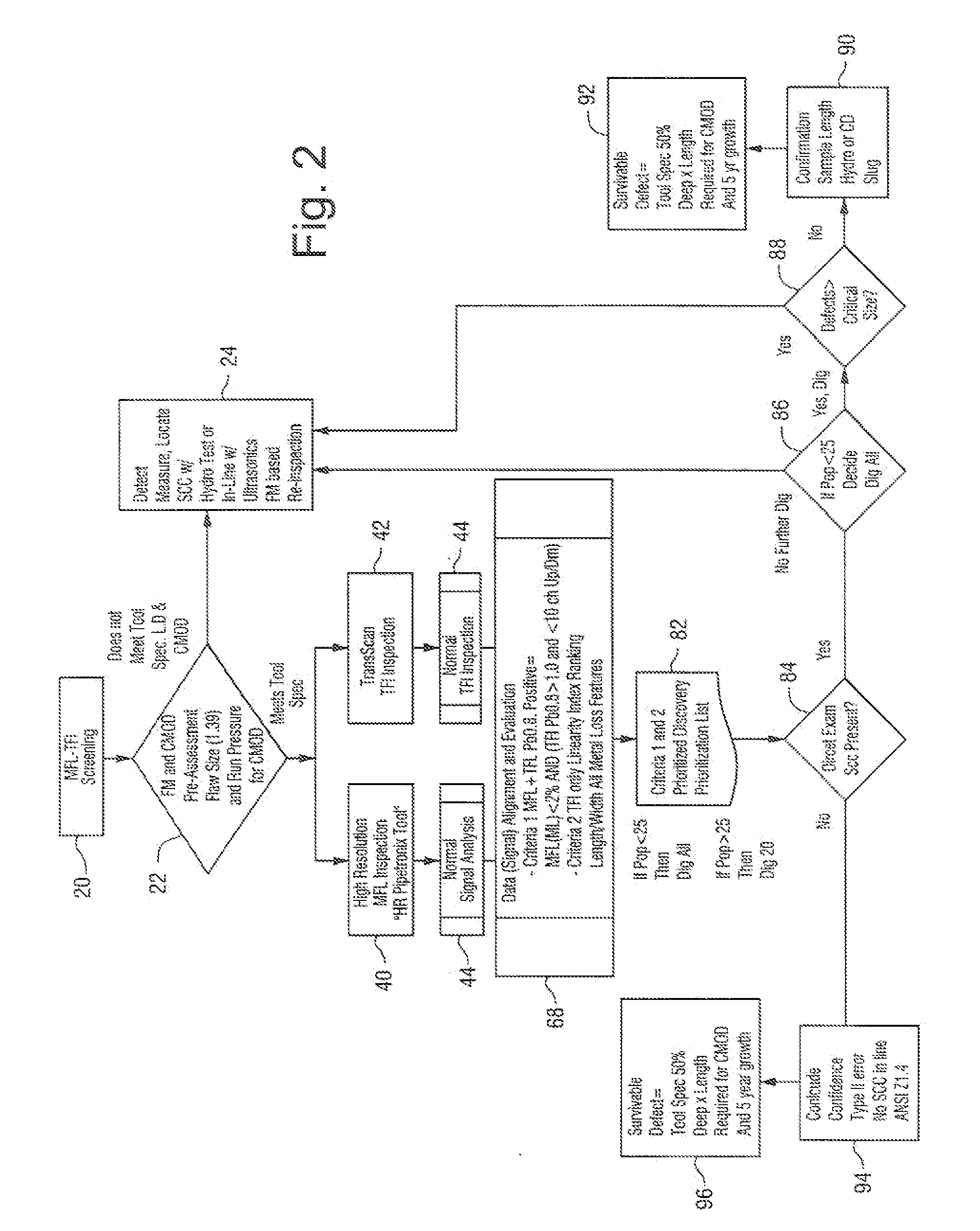
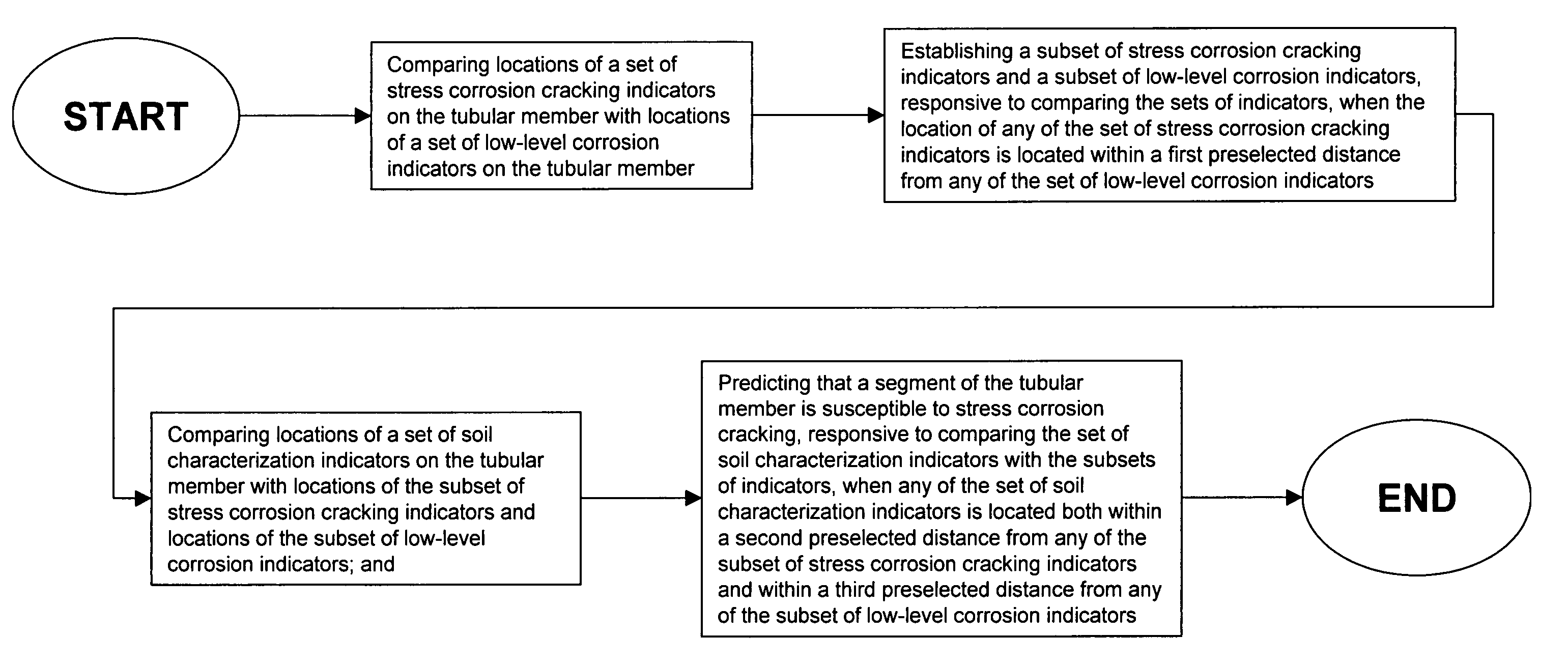
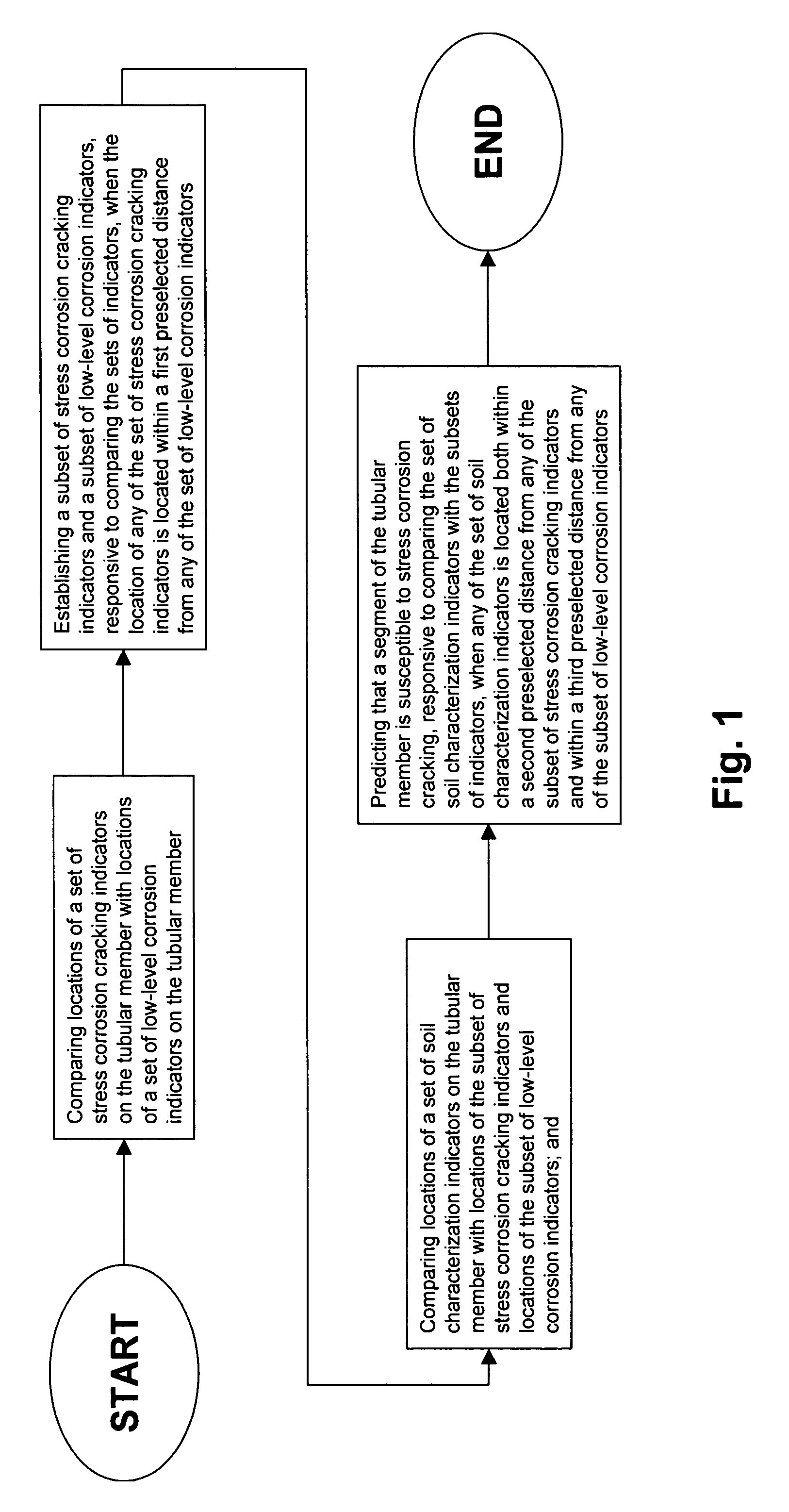
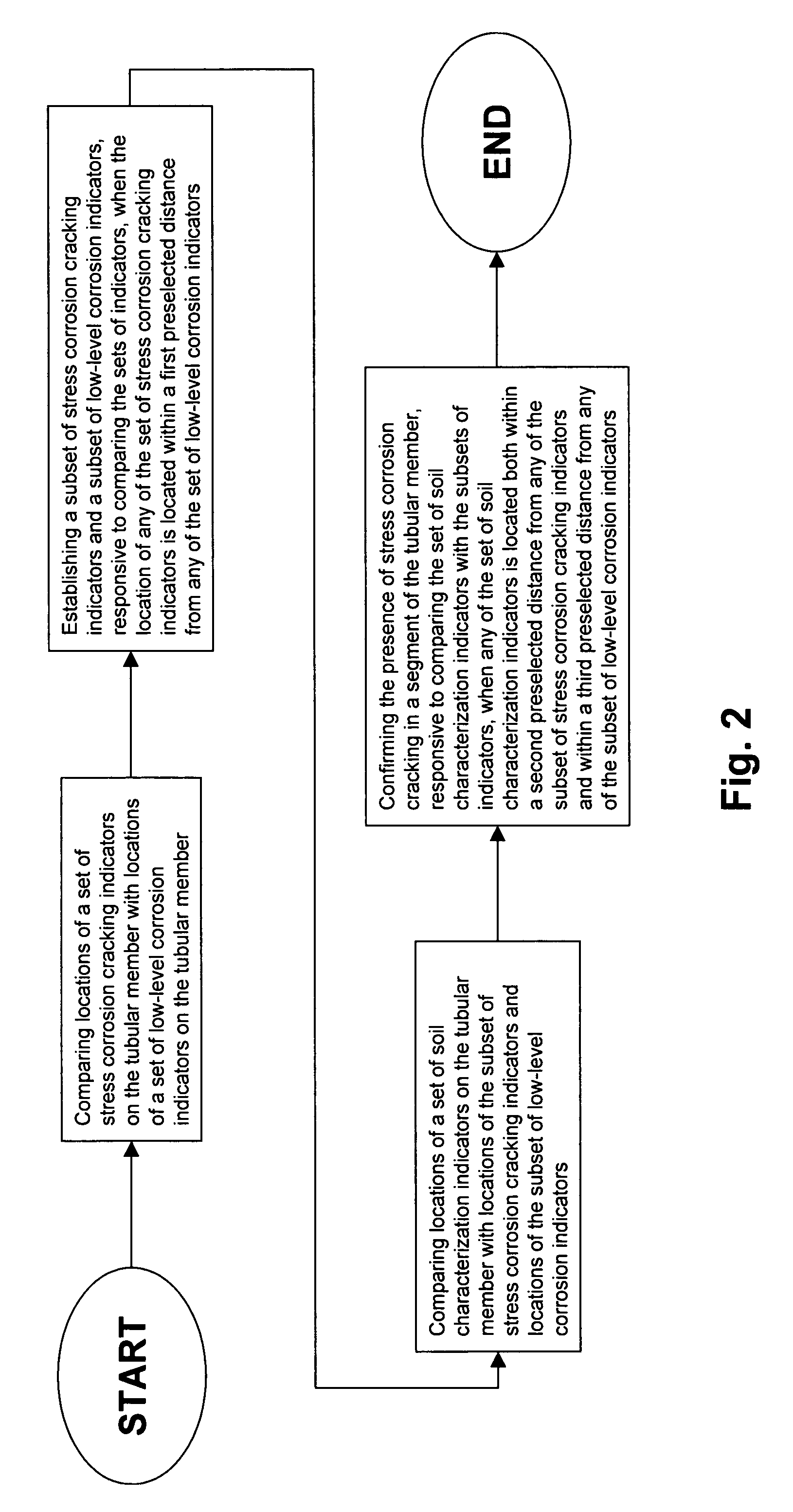
Method for detecting near neutral/low pH stress corrosion cracking in steel gas pipeline systems
InactiveUS7013249B1High precisionSurveyNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementStress corrosion crackingMetal
A method for predicting the location of stress corrosion cracking in a steel gas pipeline in which in-line stress corrosion cracking smart tool data, external low level metal loss data and soil characterization data are compiled to predict the location of stress corrosion cracking in a steel gas pipeline segment.
Owner:KINDER MORGAN
Martensitic stainless steel
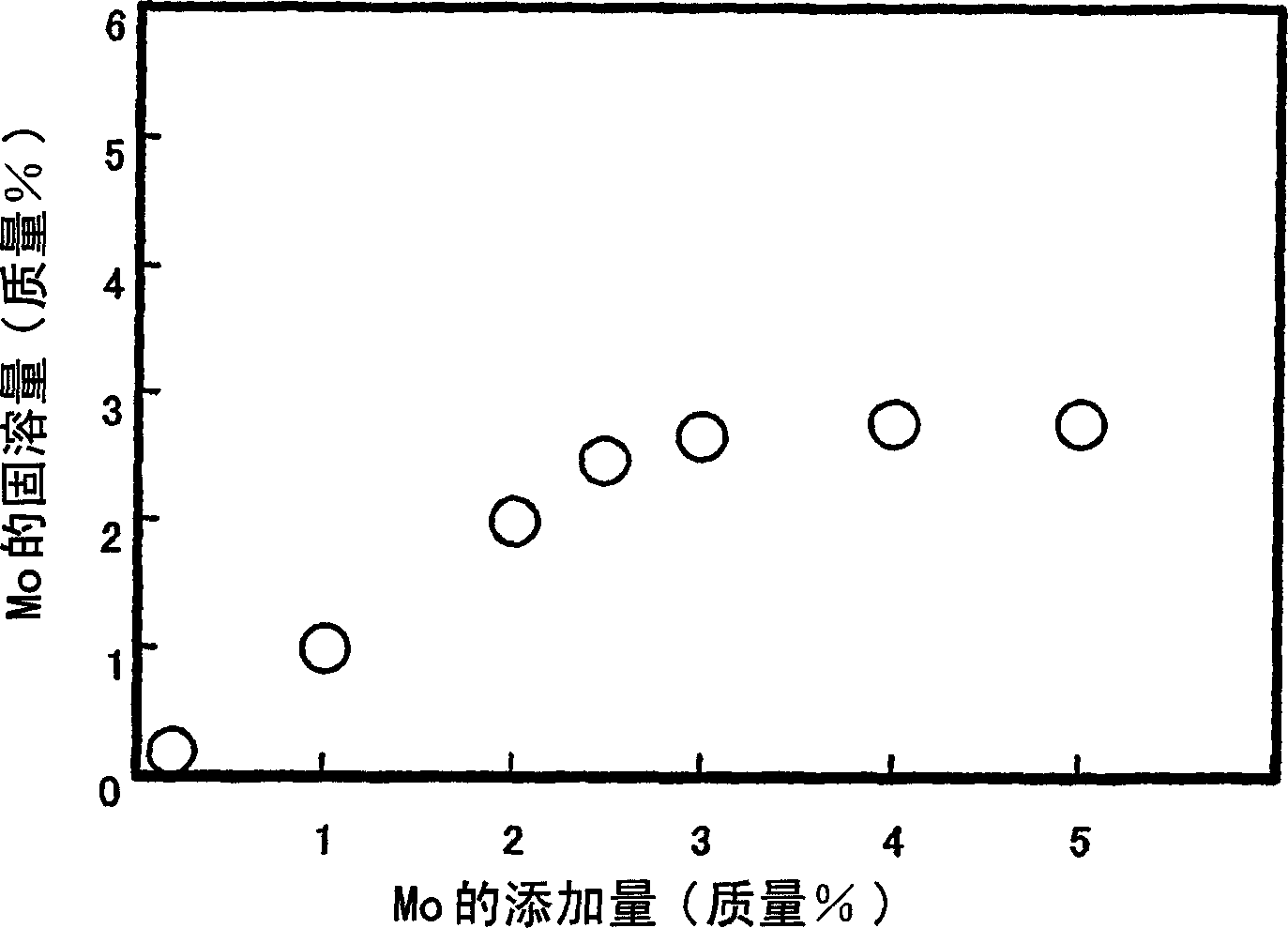
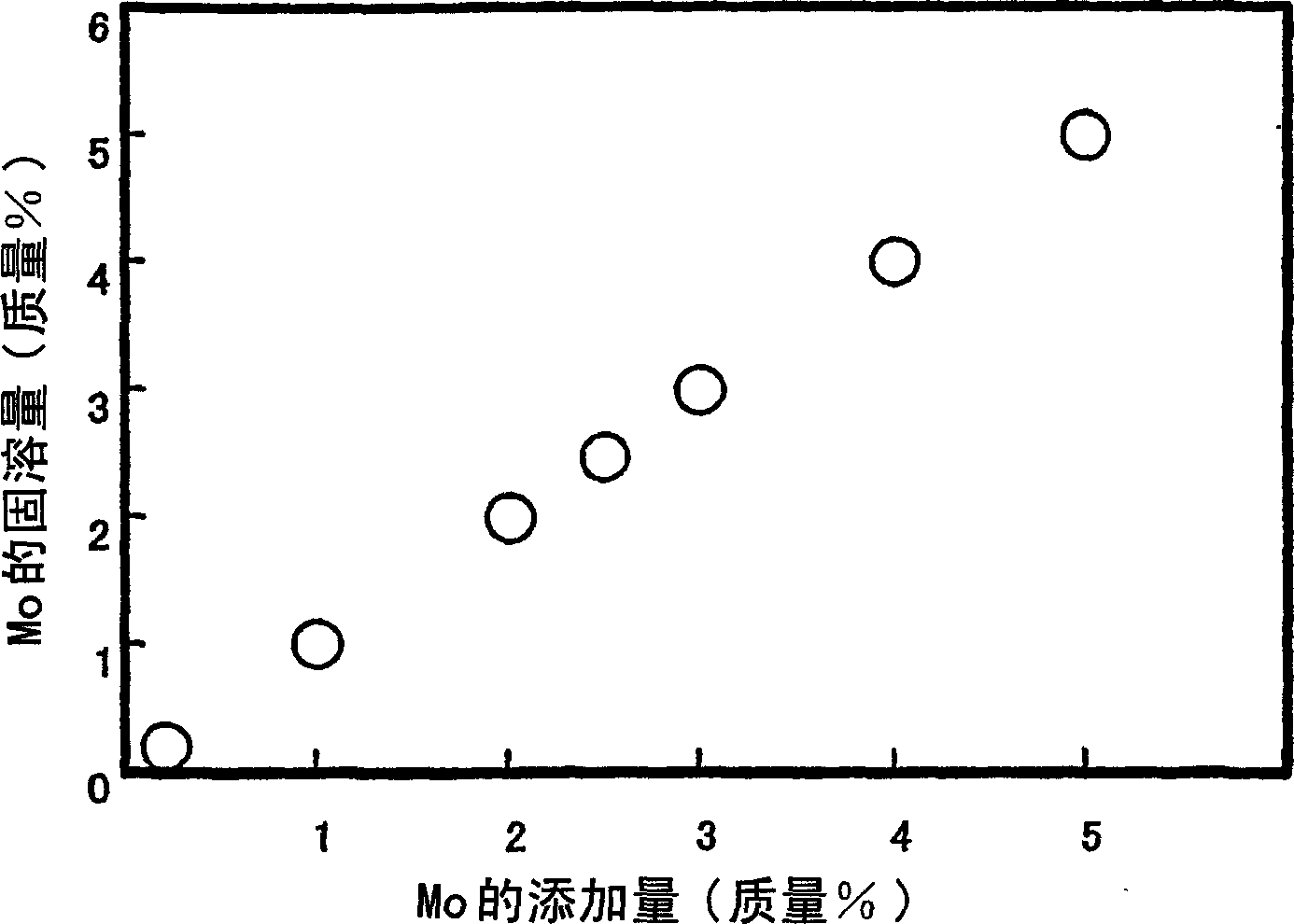
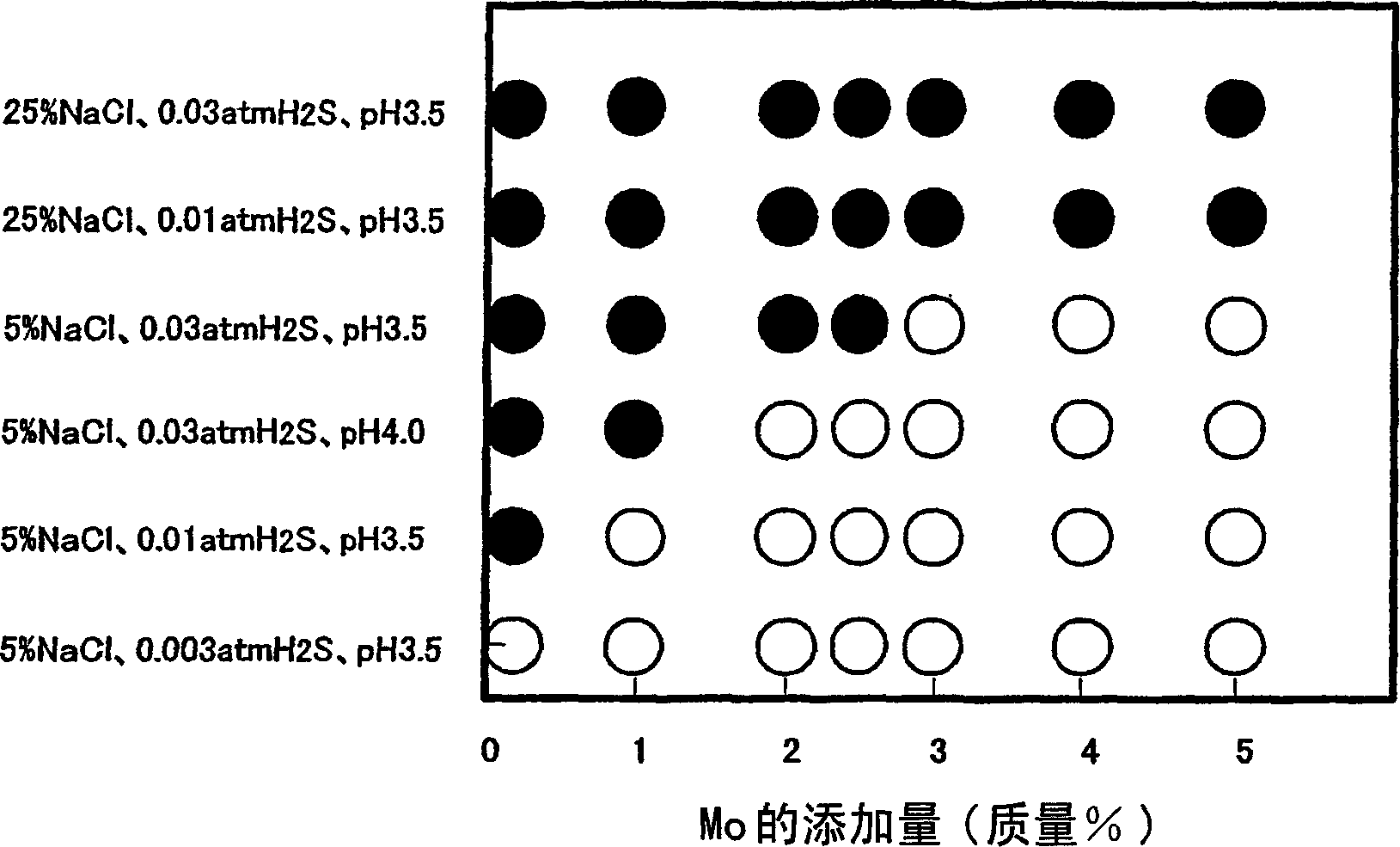
A martensitic stainless steel which has a essential chemical composition, in mass %, wherein C: 0.001 to 0.1 %, Si: 0.05 to 1.0 %, Mn: 0.05 to 2.0 %, P: 0.025 % or less, S: 0.010 % or less, Cr: 11 to 18 %, Ni: 1.5 to 10 %, sol.Al: 0.001 to 0.1 %, N: 0.1 % or less, O: 0.01 % or less, Cu: 0 to 5 %, and Mo forming a solid 3.5 to 7 %, wherein the following formula (1) is satisfied and optionally one or more elements selected from at least one group of the following A to C groups are further contained, and wherein the balance is composed of Fe, Mo forming no solid solution, if any, and impurities, formula (1): Ni-bal.= 30(C+N)+0.5(Mn+Cu)+Ni+8.2 -1.1(Cr+Mo+1.5Si) >= -4.5; A group - W: 0.2 to 5 %, B group - V: 0.001 to 0.50 %, Nb: 0.001 to 0.50 %, Ti: 0.001 to 0.50 % and Zr: 0.001 to 0.50 %, C group - Ca: 0.0005 to 0.05 %, Mg: 0.0005 to 0.05 %, REM: 0.0005 to 0.05 % and B: 0.0001 to 0.01 %. The martensitic stainless steel has the resistance to sulfide stress corrosion cracking being superior to that of super 13 Cr steel and exhibits the strength and corrosion resistance comparable to those of duplex stainless steel.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
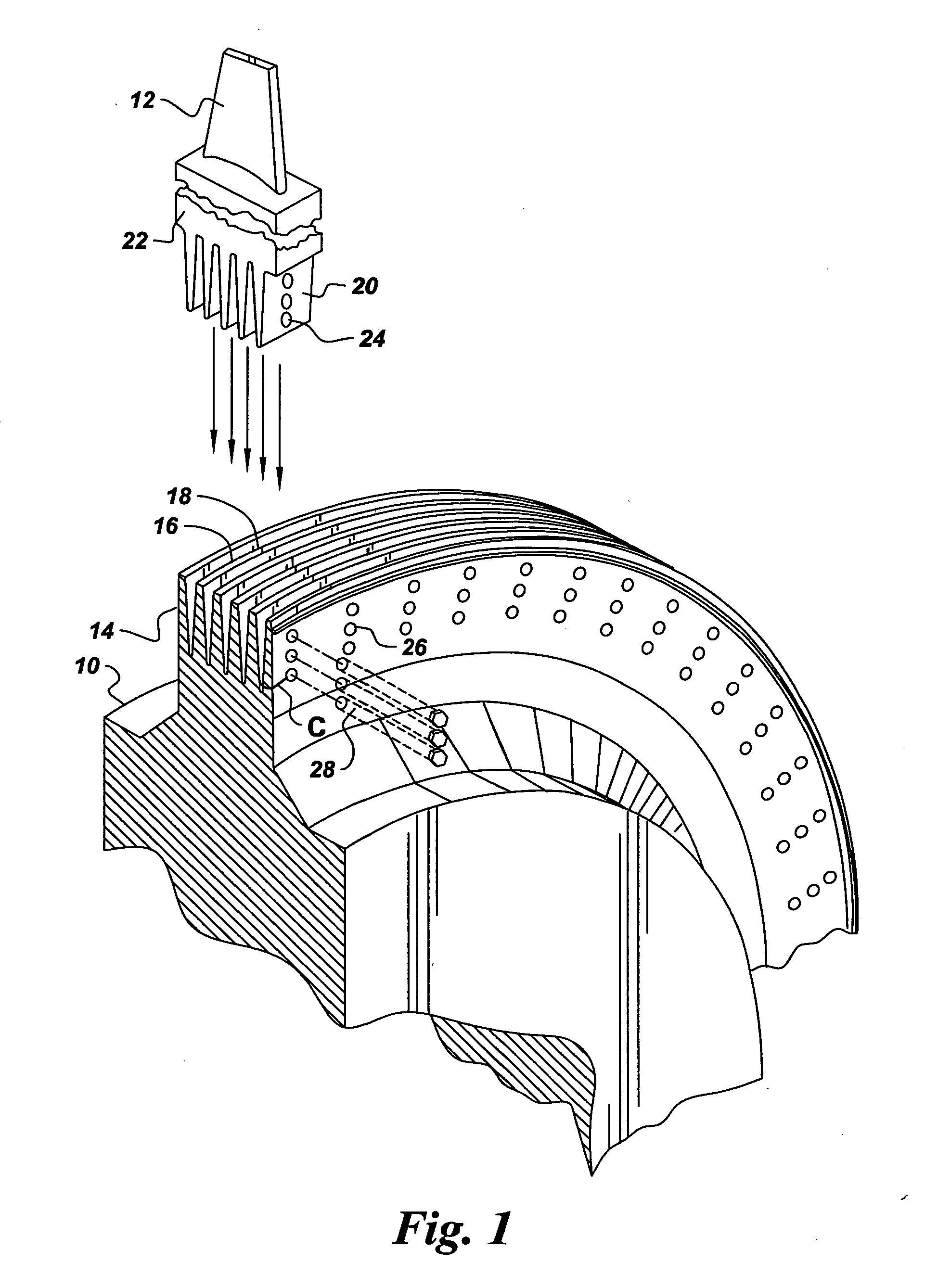
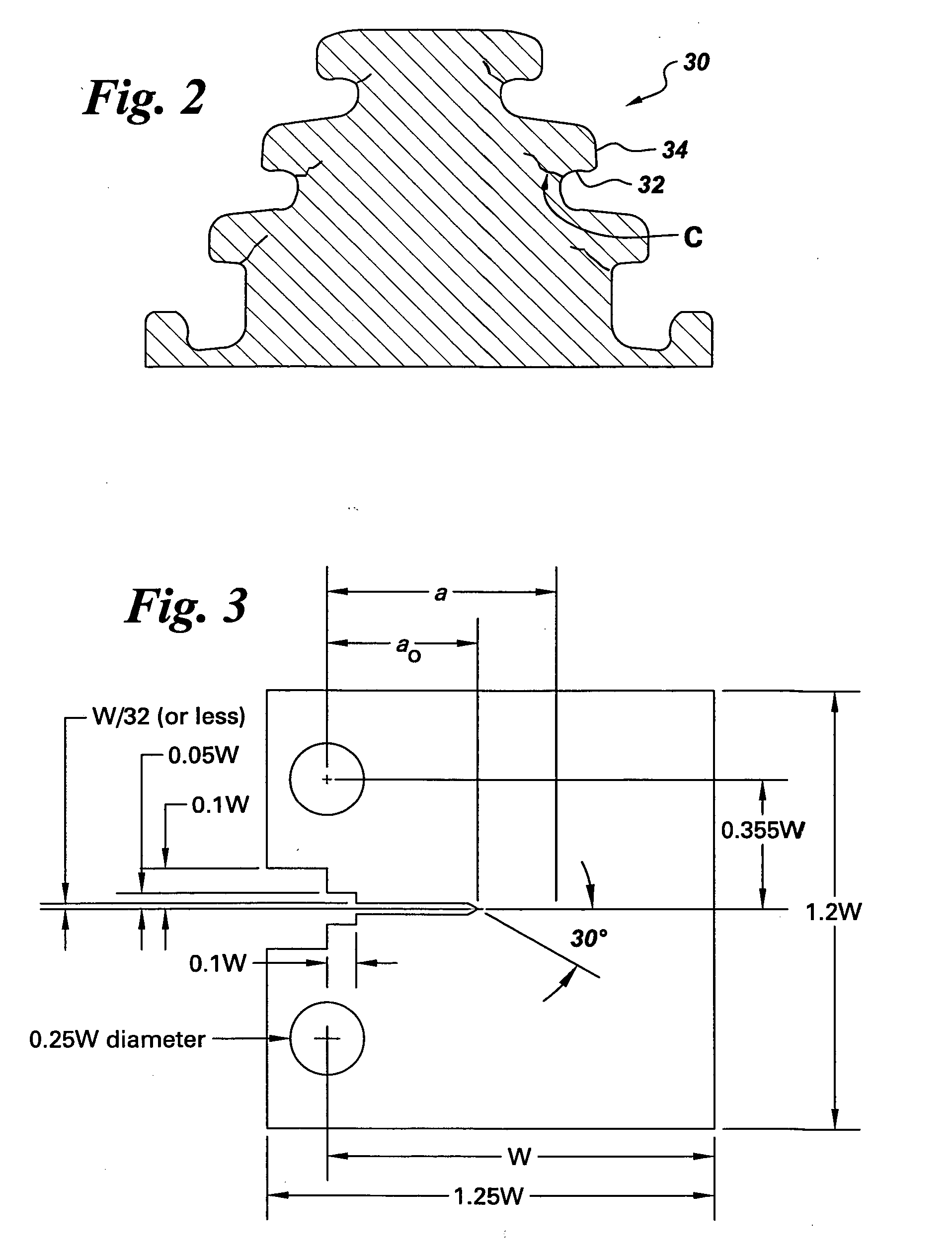
Mitigation of steam turbine stress corrosion cracking
InactiveUS20040258192A1Reduce crackingReduce concentrationMaterial nanotechnologyBlade accessoriesIridiumStress corrosion cracking
A process for mitigating stress corrosion cracking of steam turbine components in a steam environment, includes coating the metal components of the steam turbine with a noble metal. The noble metal is preferably a platinum group metal selected from the group consisting of platinum, palladium, osmium, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium, and combinations comprising at least one of the foregoing platinum group metals. In another embodiment, the process comprises coating the metal components with a platinum group metal and introducing a reductant into the steam to mitigate the stress corrosion cracking. Also disclosed herein is a steam turbine comprising a metal component having a surface coated with a platinum group metal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Salt resistant polyamide compositions
Polyamides made from 1,6-hexanediamine, and the dicarboxylic acids 1,10-decandioic acid and / or 1,12-dodecanedioic acid, and terephthalic acid in specified proportions are particularly resistant to salt stressed (induced) corrosion cracking. This makes them particularly useful as vehicular parts which may be exposed to salts. Particularly when these polyamides contain tougheners and / or plasticizers they are especially useful for hoses and tubes.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
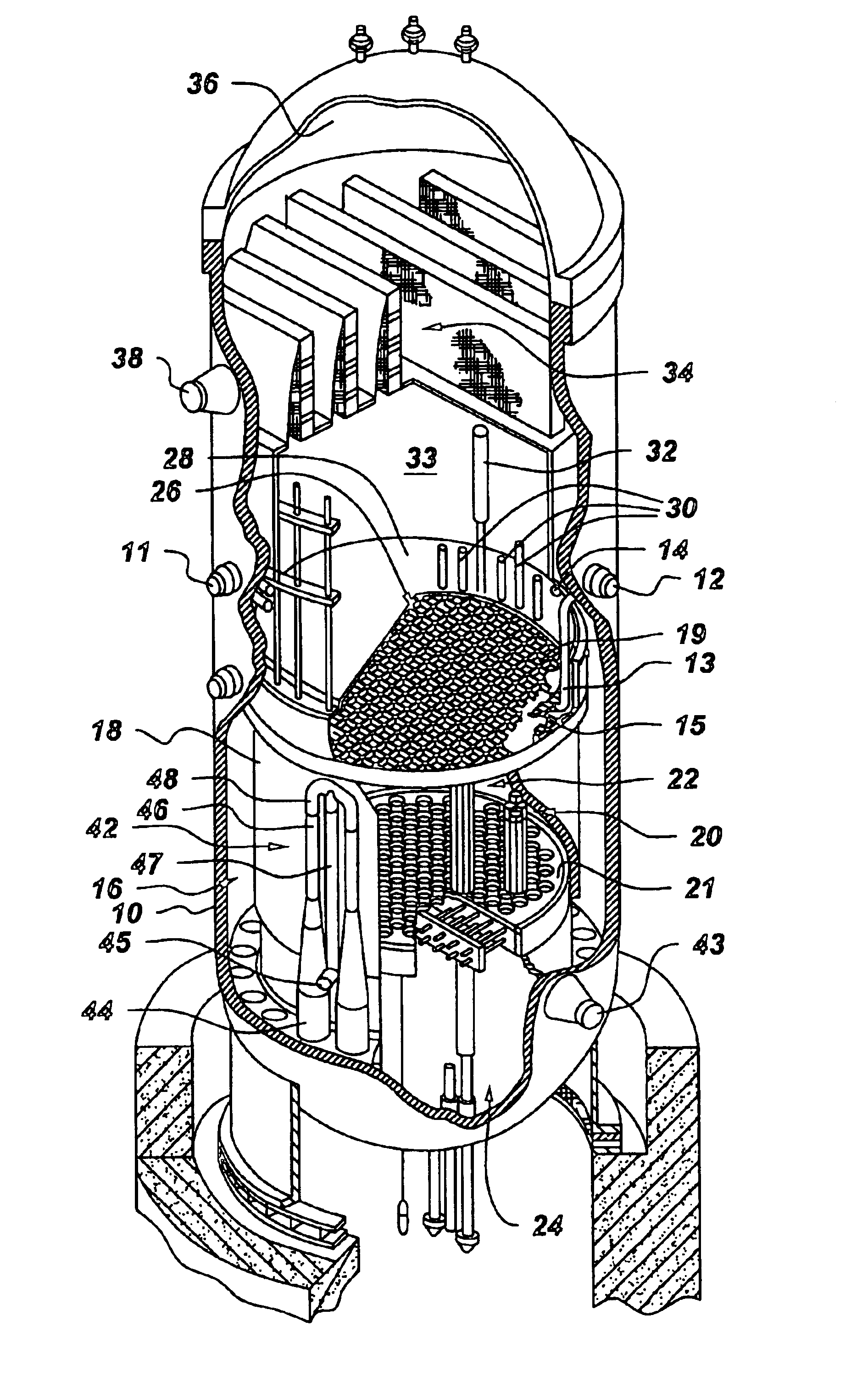
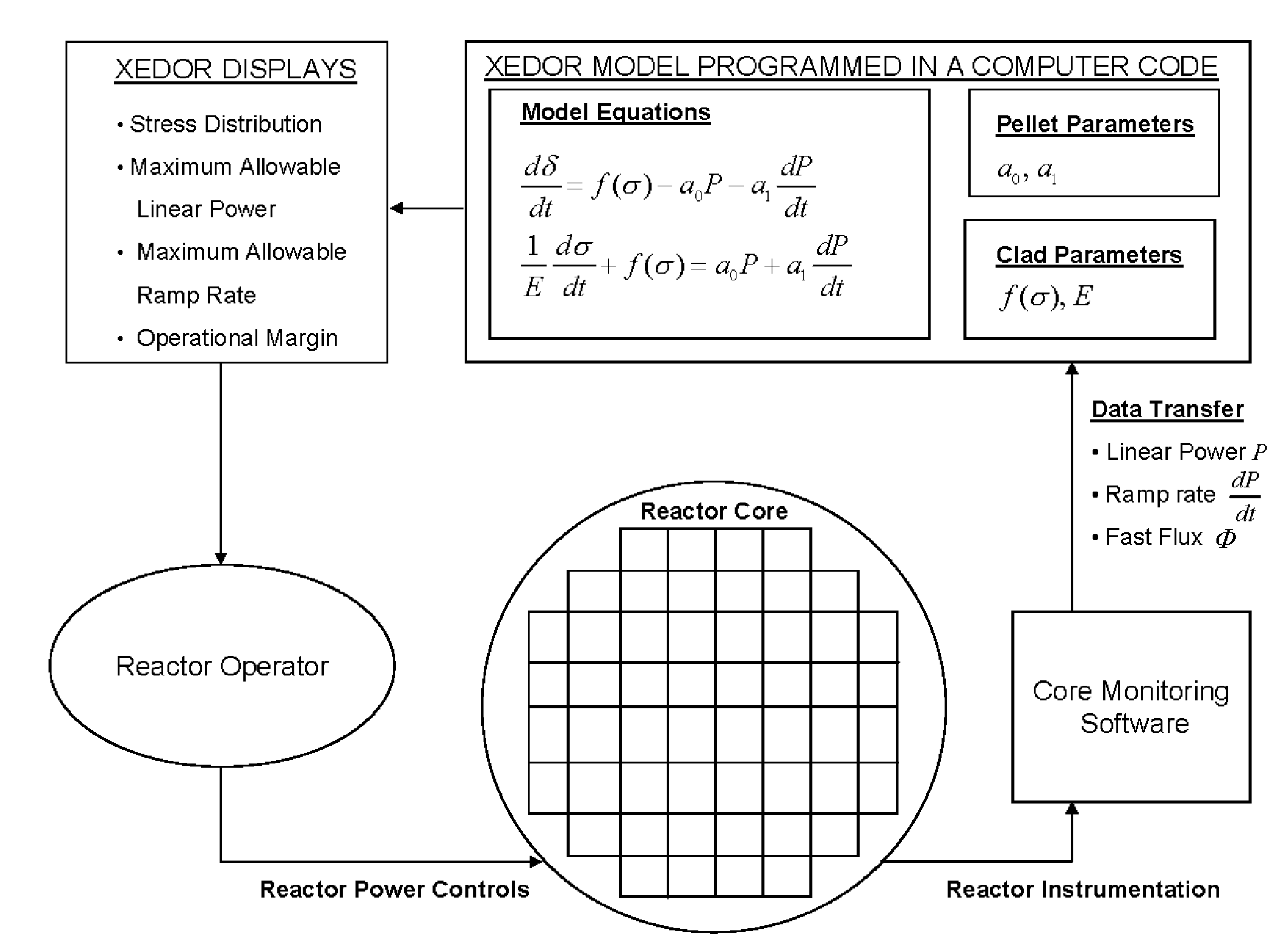
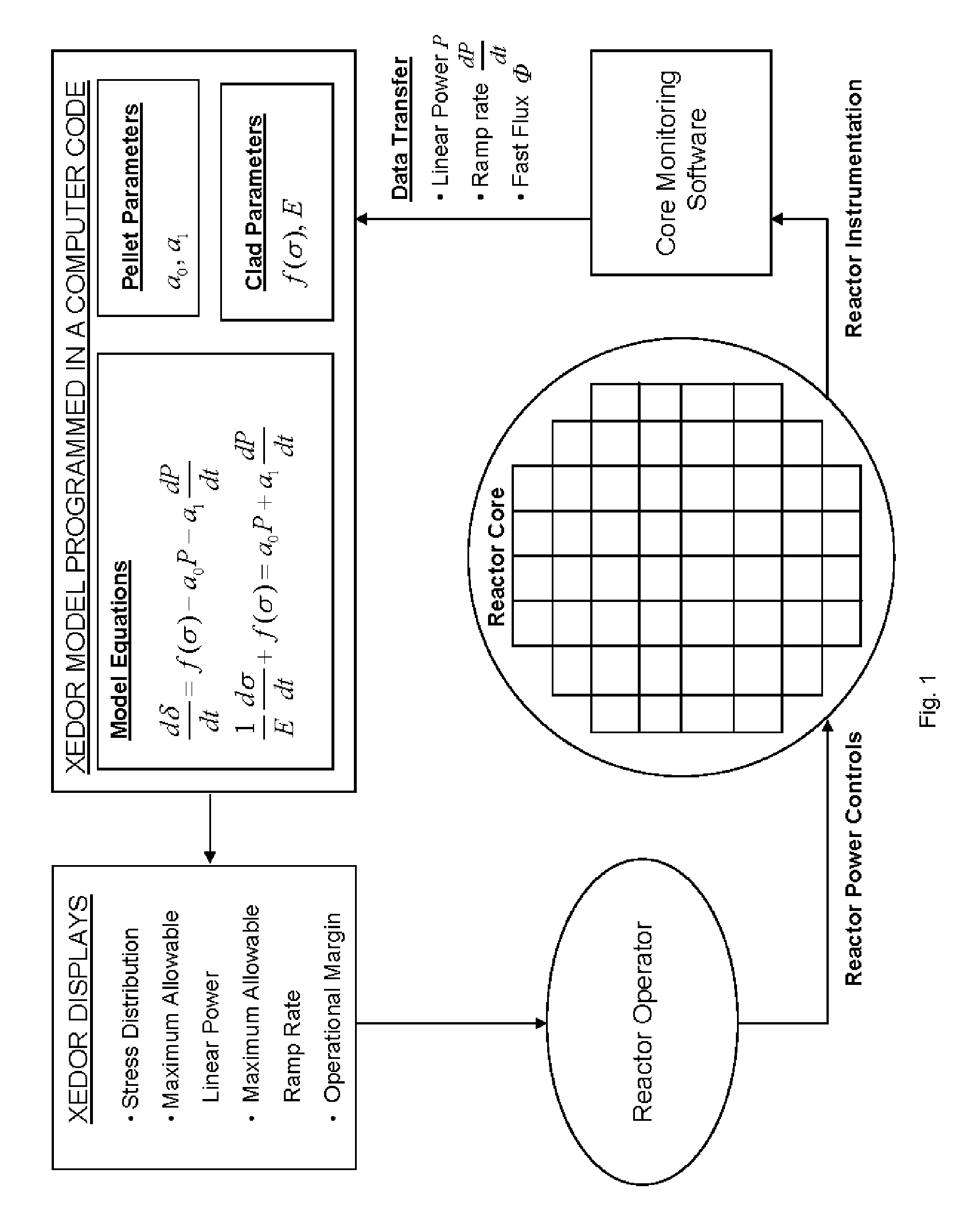
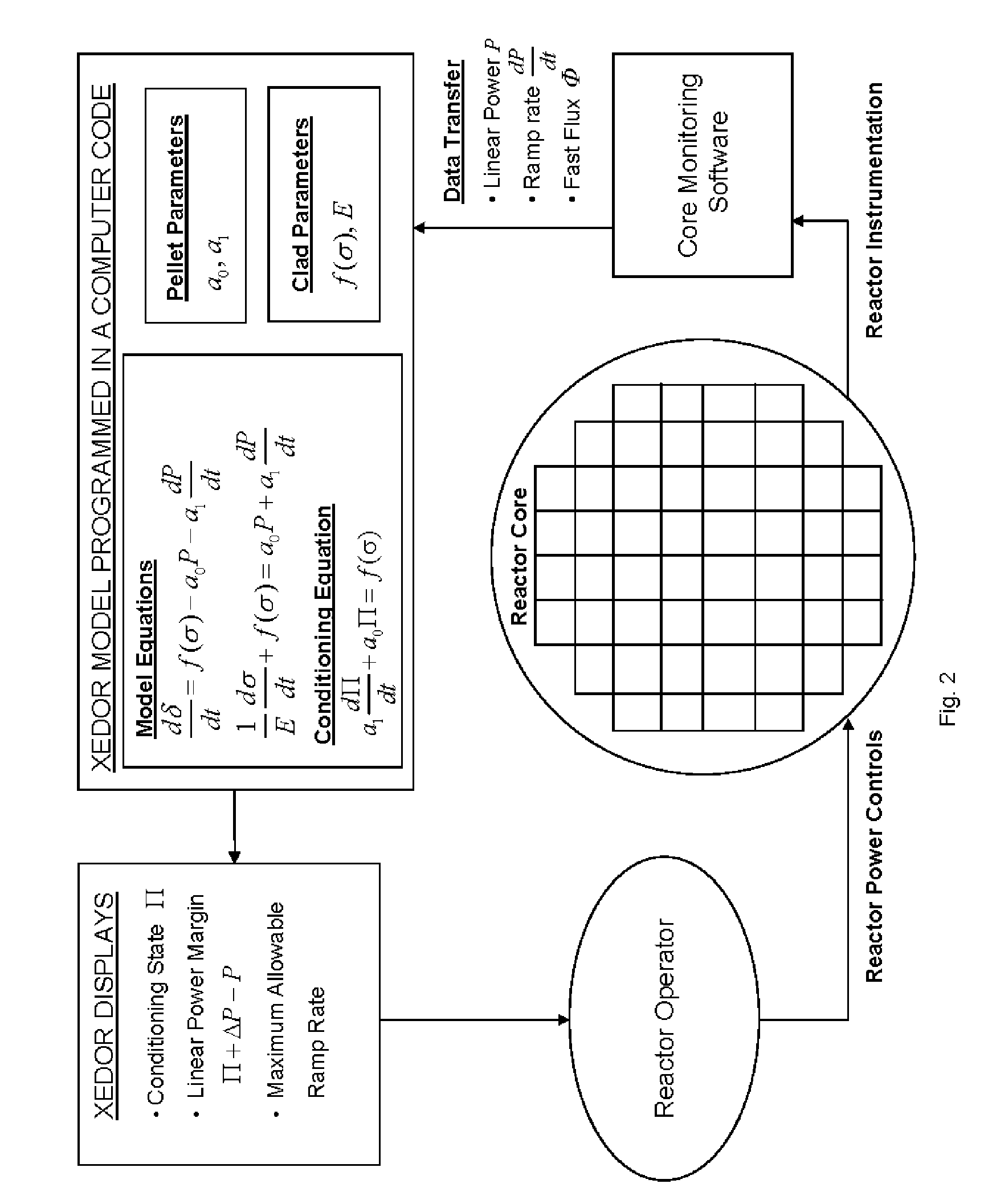
Reduced Order Stress Model for Online Maneuvering, Diagnostics of Fuel Failure and Design of Core Loading Patterns of Light Water Reactors
ActiveUS20090080585A1Nuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringStress corrosion crackingReduced order
The invention is principally directed to a reduced order model, XEDOR, facilitating the prediction of and the diagnostics of pellet-clad interaction stress-corrosion-cracking failure of nuclear fuel rods. The invention more particularly relates to assessment of susceptibility to PCI failure for guidance in the design of fuel loading in nuclear reactors. The invention additionally relates to the protection against PCI failure by providing operational information to operators of a nuclear reactor during power maneuvering, including predictive calculations prior to executing power maneuvers. Additionally, the invention relates to the diagnostics of an event suggesting a possible PCI cladding failure.
Owner:AREVA NP SAS
High strength steel pipes with excellent toughness at low temperature and sulfide stress corrosion cracking resistance
ActiveUS20120199255A1Improve low temperature toughnessImprove corrosion resistanceFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesAustenite grainStress corrosion cracking
Low-alloy steels and methods of manufacturing pipes having a wall thickness greater than or equal to about 8 mm and less than or equal to about 35 mm therefrom are provided. In one embodiment, a steel composition is processed that yields an average prior austenite grain size greater than about 15 or 20 μm and smaller than about 100 μm. A quenching sequence has been determined that yields a microstructure of greater than or equal to about 60% martensite by volume, and less than or equal to about 40% by volume lower bainite, without substantial formation of ferrite, upper bainite, or granular bainite. The yield strength of the quenched and tempered pipes may be greater than about 70 ksi, 80 ksi, or 90 ksi. The quenched and tempered pipes are suitable for 70 ksi, 80 ksi, and 90 ksi grades and resistant to sulfide stress corrosion cracking.
Owner:DALMINE SPA
Method of stress corrosion cracking mitigation for nuclear power plant structural materials
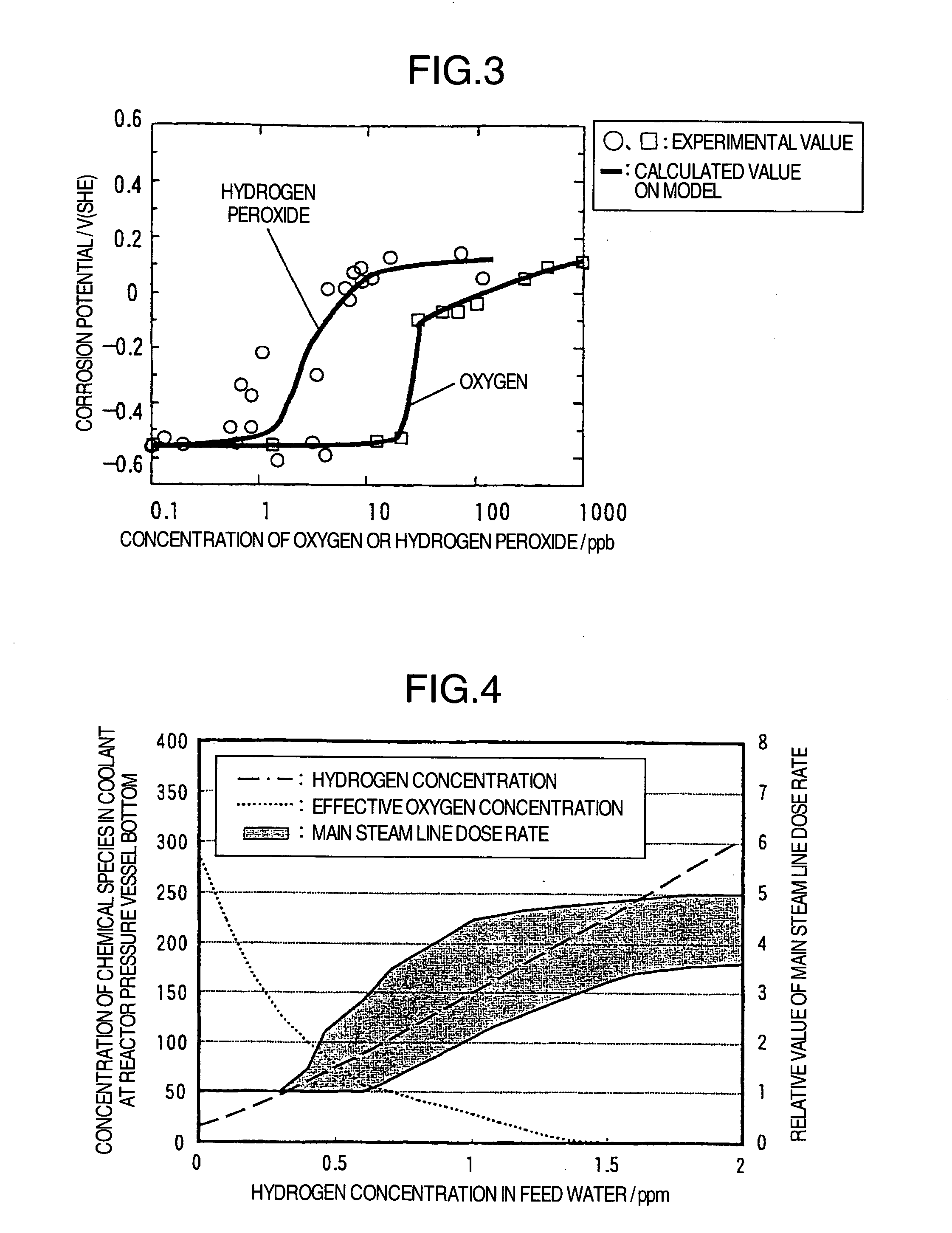
InactiveUS20050018805A1Reduce stress corrosion crackingReduce stressPlant parameters regulationNuclear energy generationDose rateHydrazine compound
The object of this invention is to provide a method for mitigating a stress corrosion cracking of reactor structural material which makes it possible to suppress the rise in the main steam line dose rate without secondary effects such as a rise in the concentration of radioactive cobalt-60, etc. in the reactor water. Hydrogen and a reductive nitrogen compound containing nitrogen having a negative oxidation number (for example, hydrazine) are injected into the core water of boiling water nuclear power plant. By injecting the reductive nitrogen compound containing nitrogen having a negative oxidation number into the core water, the stress corrosion cracking of structural material of reactor can be mitigated without side reactions such as a rise in the concentration of cobalt-60, etc.
Owner:HITACHI-GE NUCLEAR ENERGY LTD
Steel plate for 500MPa-level pressure container for resisting sulfide stress corrosion cracking and production method thereof
The invention relates to the field of manufacturing of a steel plate for a pressure container, and particularly relates to a steel plate for a 500MPa-level pressure container for resisting sulfide stress corrosion cracking and a production method thereof. The steel plate is prepared from the following components by mass percent: no more than 0.20% of C, 0.15-0.50% of Si, no more than 1.35% of Mn, no more than 0.012% of P, no more than 0.002% of S, no more than 0.10% of Nb, V and Ti, 0.020-0.050% of Alt, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The steel plate has the beneficial effects that each component is accurately controlled in the smelting process, the content of harmful elements such as P, S and the like in steel is strictly controlled, the cleanliness of molten steel is improved, a continuous casting blank is heated after being slowly cooled by a burial pit or a slow cooling cover, and the steel plate for the pressure container having the advantages of resisting sulfide stress corrosion cracking, hydrogen-induced cracking and lamellar tearing, high temperature resistance, being easy to weld, and the like is obtained by reasonably controlling slowly cooling and normalizing heat treatment processes of rolled and steel plates.
Owner:JIGANG GRP
Method For Protecting New/Used Engine Parts
InactiveUS20090004364A1Reduce the temperatureReduce erosionSpark gapsBlade accessoriesEngineeringStress corrosion cracking
New and used parts of gas and steam turbine engines are protected by imparting a controlled residual compressive stress to given portions of the part and then coated by a CVD or PVD process at low temperatures with layers of TiN or alloys thereof at alternate selective hard and less hardened levels. The protective treatment is particularly efficacious for airfoils of compressor blades / vanes of gas turbine engines and airfoils of airfoils and certain components of steam turbine engines. This method is targeted to reduce erosion, corrosion and stress-corrosion cracking in these parts.
Owner:HOLLIS TERRY +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com