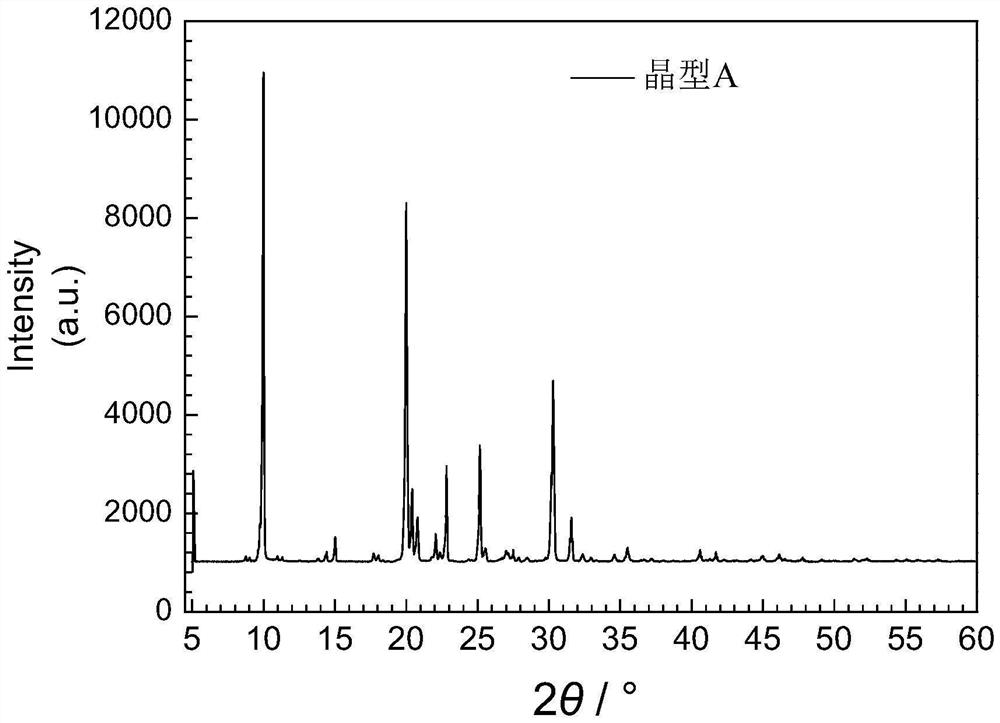
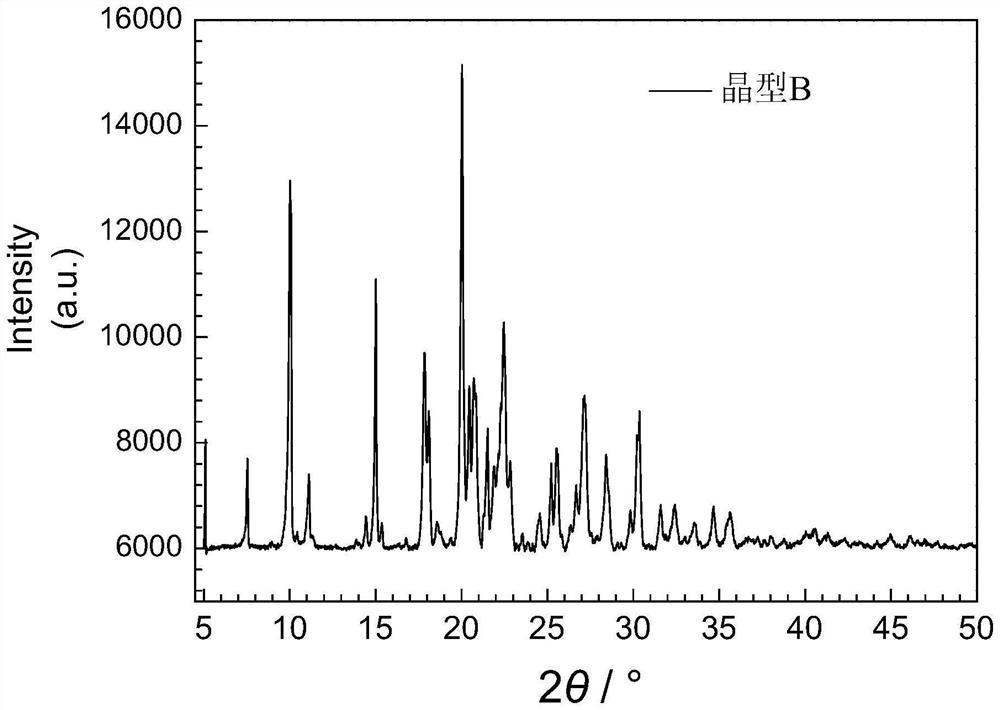
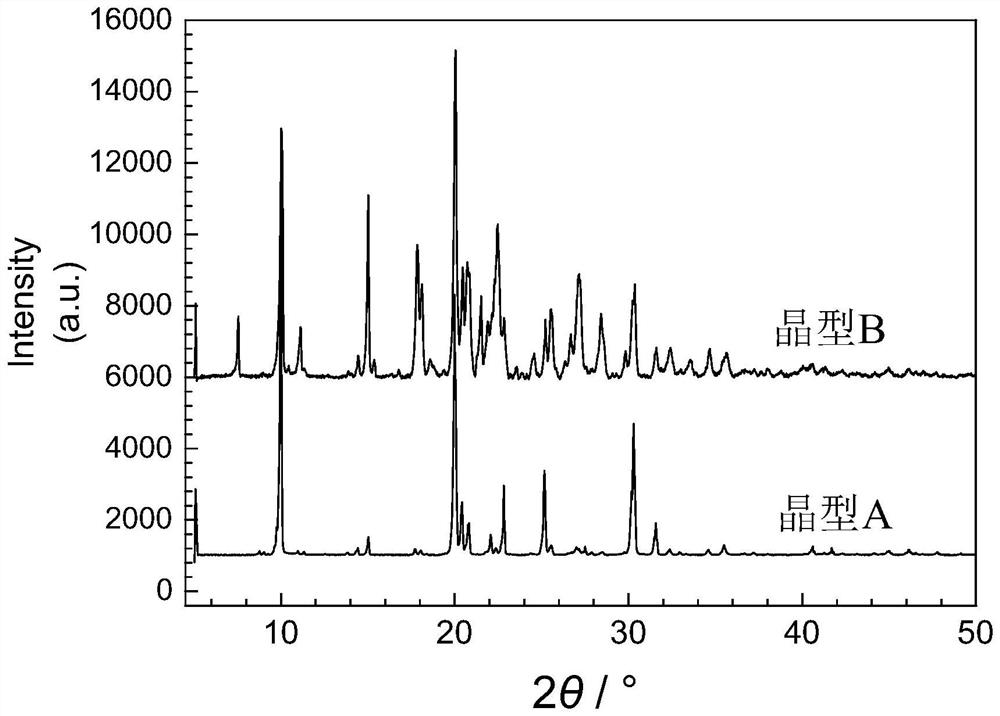
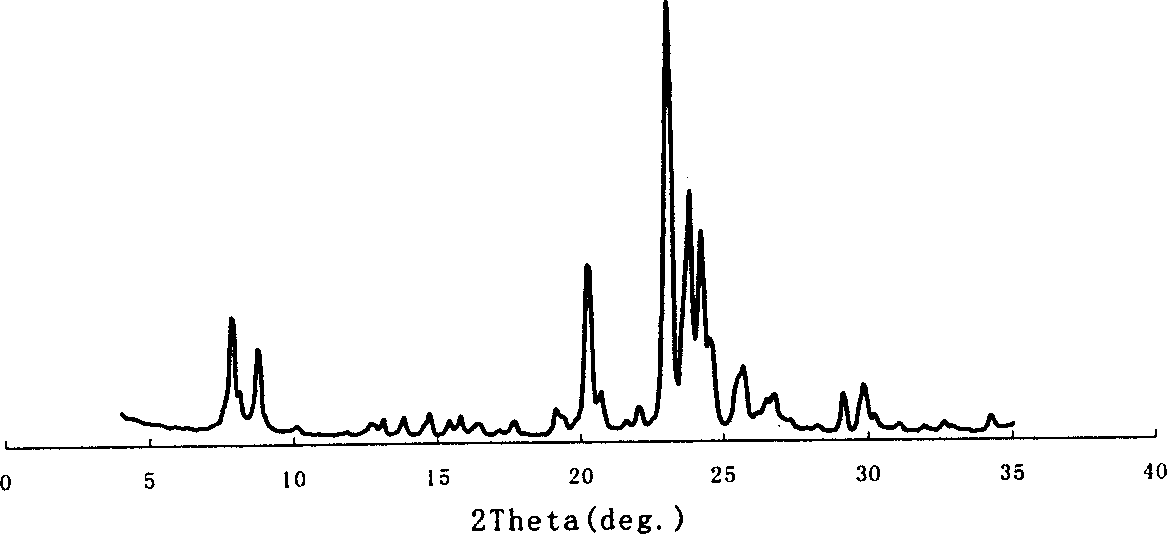
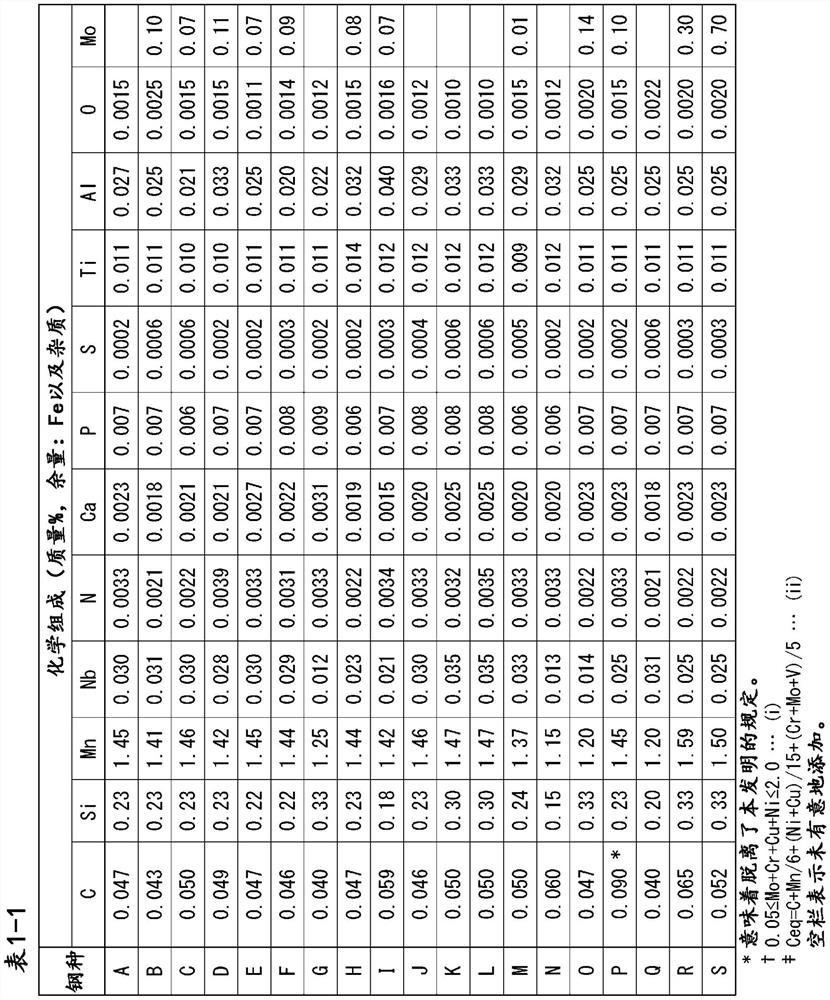
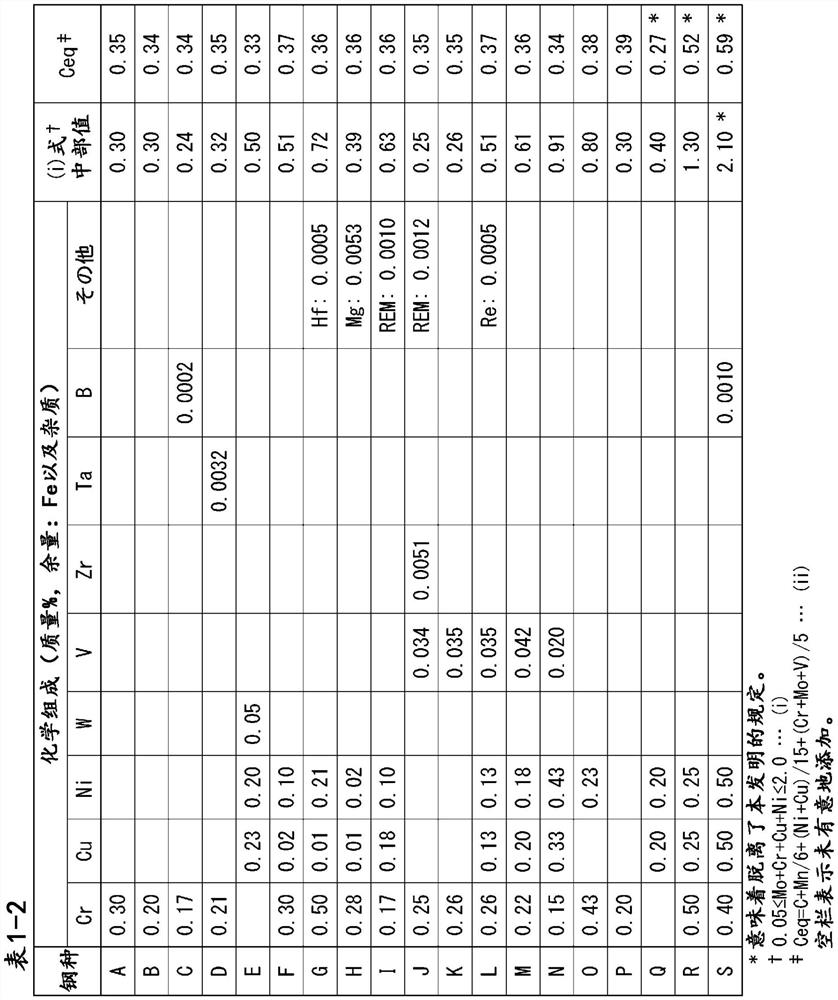
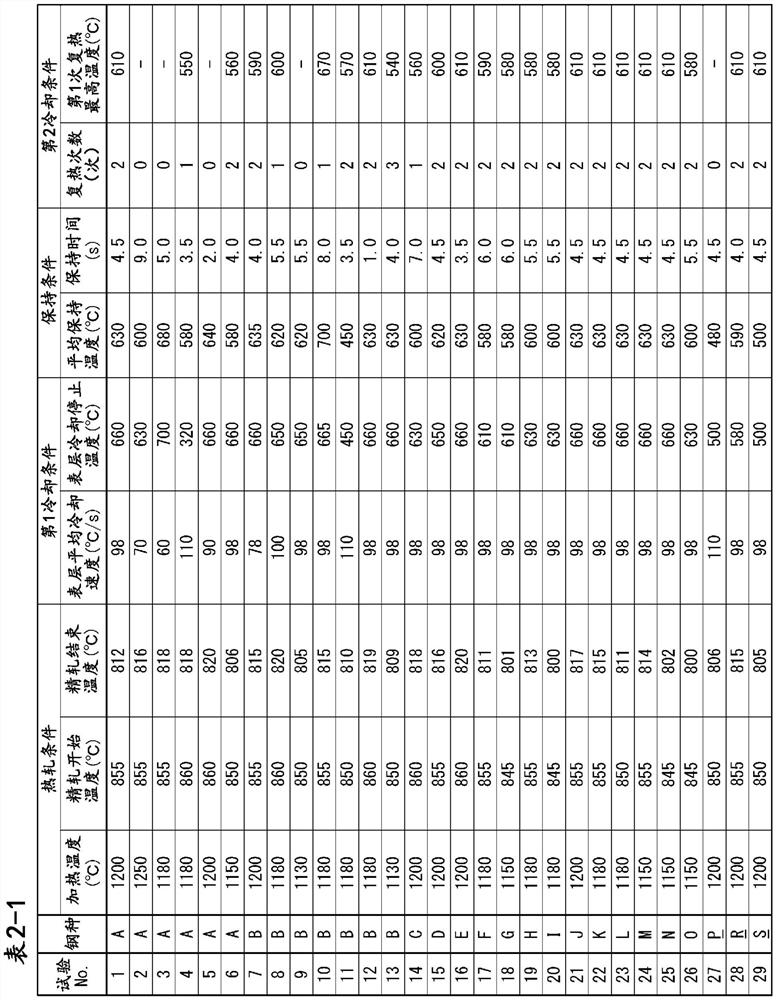
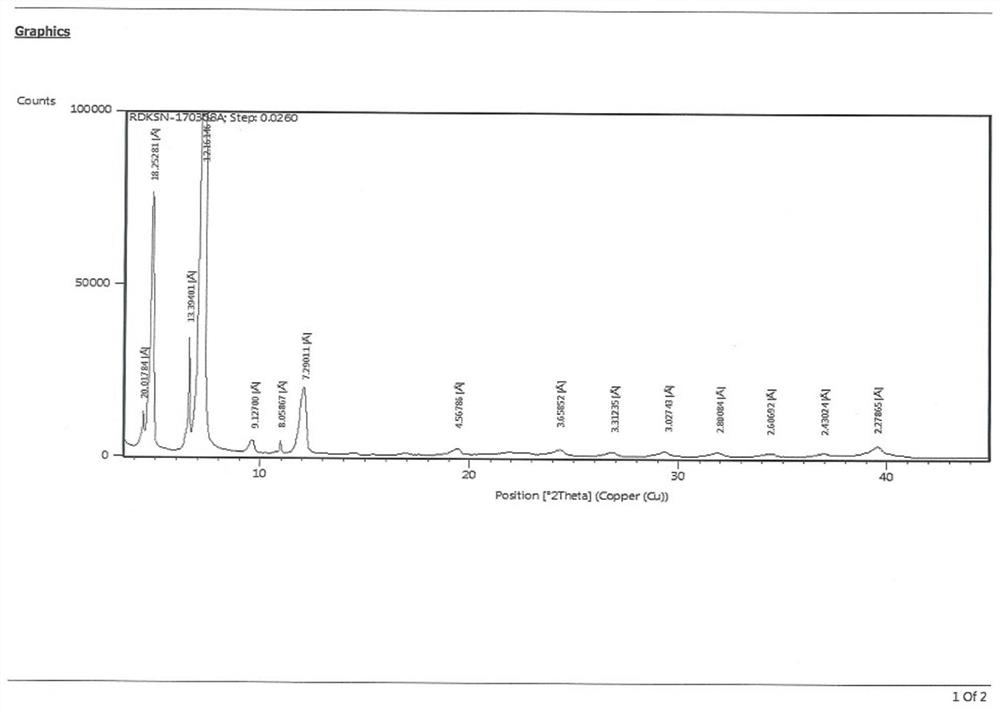
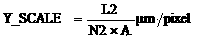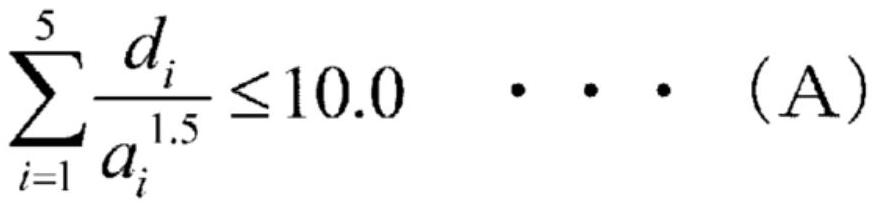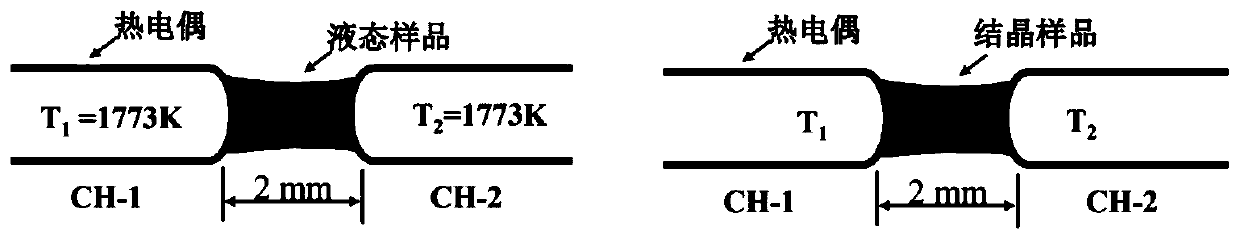Patents
Literature
36 results about "Acicular" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Acicular, in mineralogy, refers to a crystal habit composed of slender, needle-like crystals. Crystals with this habit tend to be fragile. Complete, undamaged acicular specimens are uncommon. The term "acicular" derives from the Late Latin "acicula" meaning "little needle". Strictly speaking, the word refers to a growth habit that is slender and tapering to a point. Prismatic crystals are not acicular; however, colloquial usage has altered the commonly understood meaning of the word. When writing for mineralogical publications, authors should restrict their usage of "acicular" to crystals with the tapering growth habit.
Quantitative measurement method for acicular ferrite of pipeline steel
InactiveCN101907585AAccurate measurementImprove correspondenceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationScanning probe techniquesScanning electron microscopeElectron microscope
The invention relates to a quantitative measurement method for acicular ferrite of pipeline steel, which utilizes an electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD) assembled on a scanning electron microscope (SEM) to carry out quantitative measurement on the acicular ferrite of the pipeline steel and comprises the following steps: grinding the cross section of a pipeline steel sample into a metallographical polished surface; etching the polished surface with natal, eliminating surface stress and showing an acicular texture; utilizing a conductive adhesive to fix the prepared sample on an EBSD sample stage; controlling the sample stage to rotate for 70 degrees by utilizing the SEM; vacuumizing an electron microscope sample chamber; when the vacuum degree reaches the electron microscope operating requirements, applying operational high pressure to acquiring an image, and finding a typical viewing field; stretching the probe of the EBSD into the sample chamber, and acquiring EBSD pattern data; and carrying out statistical treatment on the EBSD pattern data to obtain the effective crystallite dimension of the acicular ferrite texture. The invention is applied to the quantitative measurement of the acicular ferrite texture with unsharp boundaries in the pipeline steel.
Owner:WUHAN IRON & STEEL (GROUP) CORP
Method for rapidly measuring and finely classifying full-form crystal grains of steel material
InactiveCN103940708AHigh measurement accuracySatisfy the amount is very largeParticle size analysisBinary segmentationThresholding
The invention discloses a method for rapidly measuring and finely classifying full-form crystal grains of a steel material. The method comprises the following steps: performing the operations of filtering, denoising, gray level correcting and binary segmentation treatment on an original image in sequence, and reducing a target crystal grain binary image; setting a scale for the reduced image, performing area calibration on target crystal grains respectively, and respectively extracting form characteristic parameters of each target crystal grain, wherein the form characteristic parameters include the area, the circumference, the grain size, the length-width ratio, the circularity degree, the form coefficient and the transgranular polar angle; distinguishing equiaxial crystal grains from non-equiaxial crystal grains according to a primary threshold of the circularity degree and a primary threshold of the form coefficient; distinguishing circular-like and polygon crystal grains from the equiaxial crystal grains according to a secondary threshold of the circularity degree and a secondary threshold of the form coefficient; and identifying strip-like and strip crystal grains and thick needle and small needle shaped crystal grains from the non-equiaxial crystal grains according to the length-width ratio and primary and secondary thresholds of the transgranular polar angle. The method is high in measurement precision, and the efficient and precise method is provided for rapid and fine microanalysis on the full-form crystal grains of the steel material.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
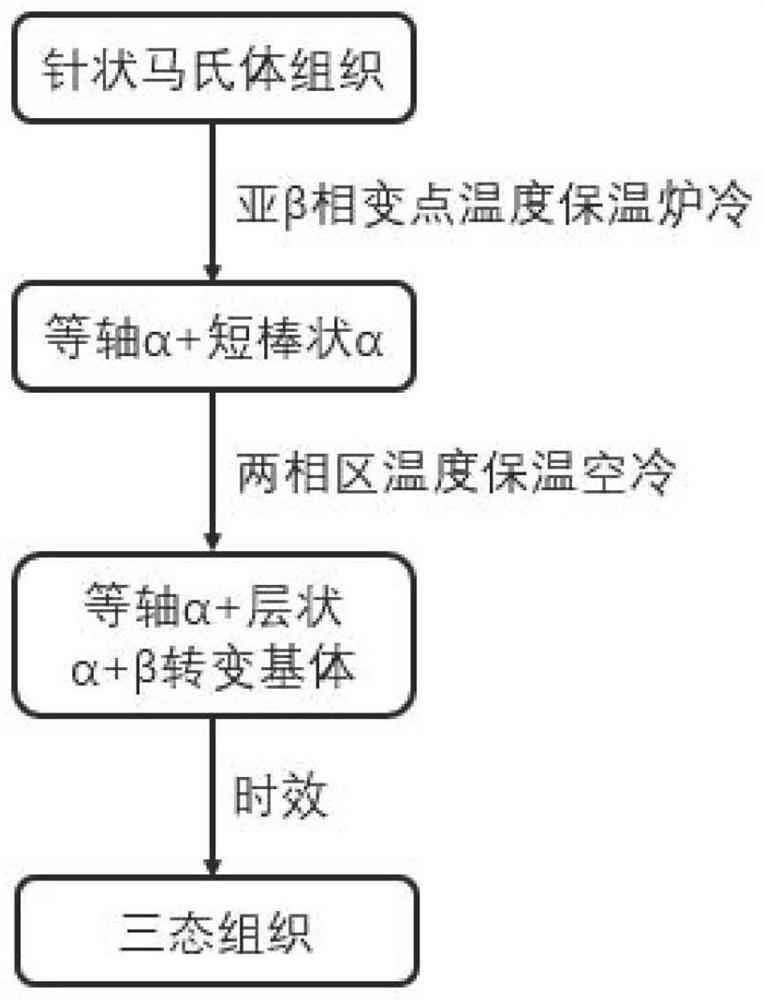
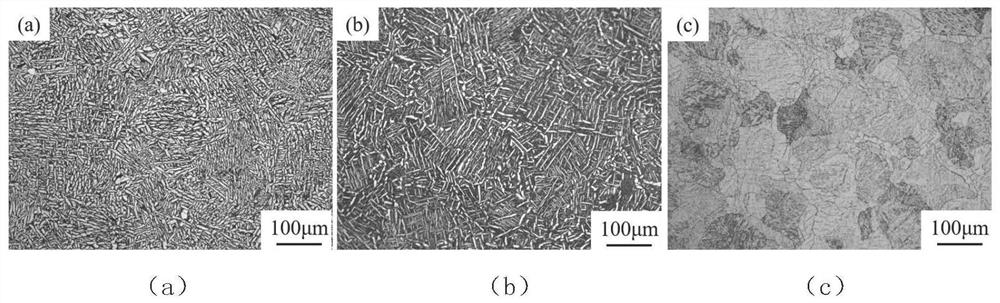
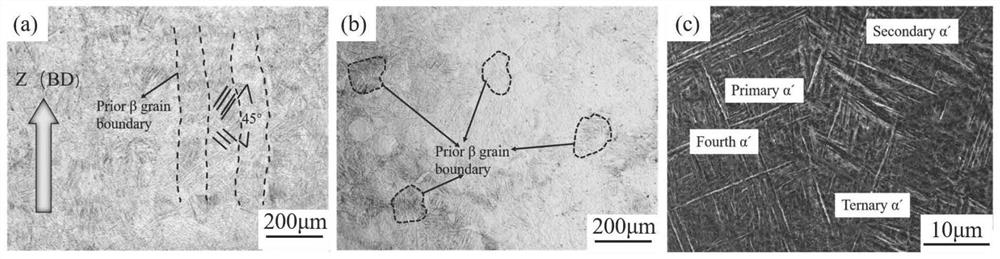
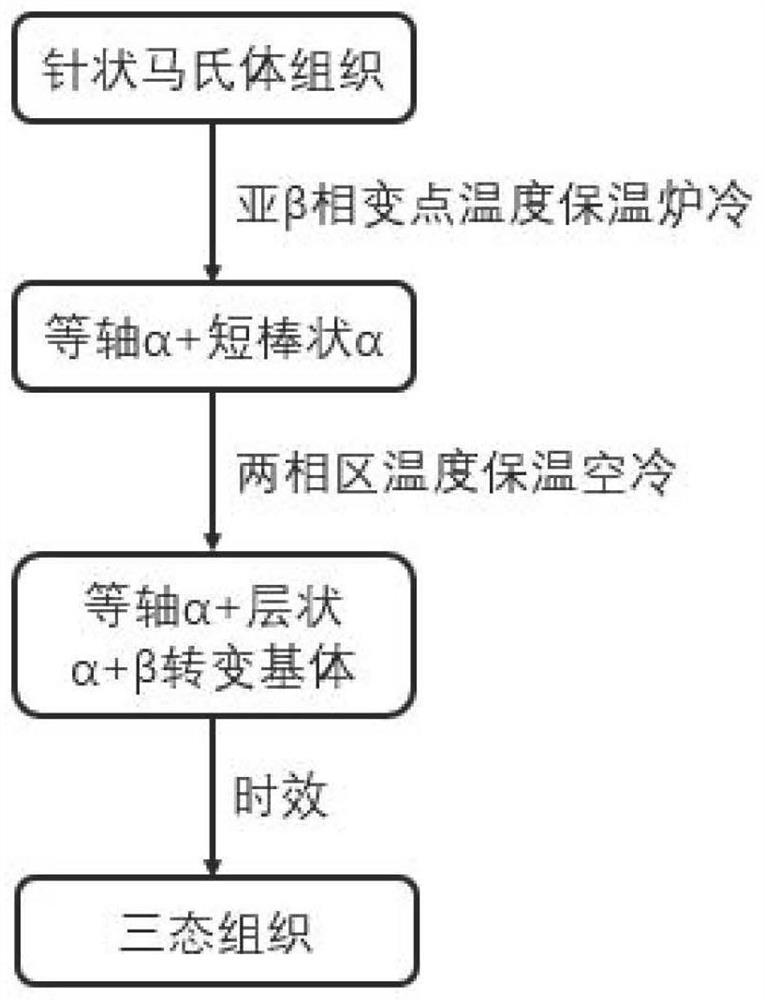
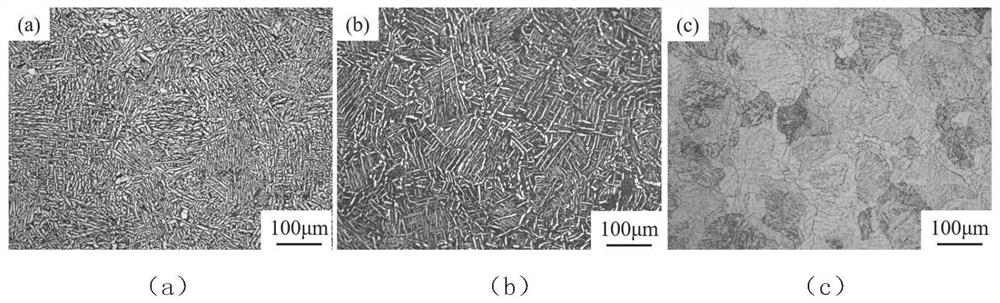
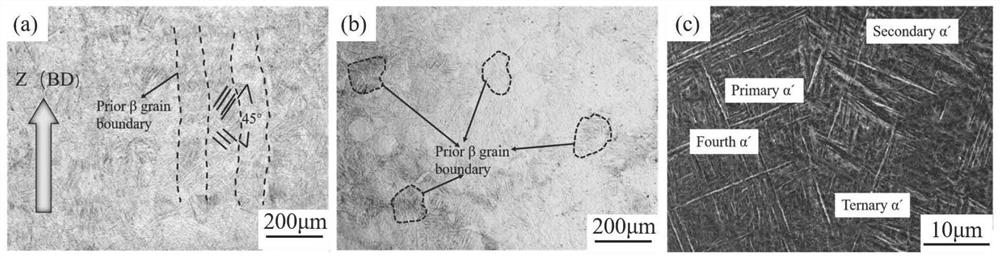
Heat treatment method for obtaining tri-state structure in SLM forming titanium alloy
ActiveCN113275600AImproved strength-plasticity mismatchExcellent strength-plasticity matchingAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencySelective laser meltingPhysical chemistry
The invention belongs to the field of selective laser melting forming, and particularly discloses a heat treatment method for obtaining a tri-state structure in an SLM forming titanium alloy. According to the heat treatment method, through multiple heat treatment of three stages of different temperature intervals, SLM forming near alpha and alpha + beta titanium alloy structures are adjusted, the original needle-like martensite structure (the forming direction is thick and large isometric crystals, the vertical forming direction is thick and large columnar crystals, the isometric crystals and the columnar crystals are internally provided with needle-like martensite, and a large number of twin crystals are included) is converted into the tri-state structure, the characteristic that the SLM forming near alpha and alpha + beta titanium alloy plasticity is poor is improved, and the tensile mechanical property with the strength and plasticity well matched is obtained.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Low-shrinkage, high-strength, and large ceramic plate and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20200361823A1High strengthImprove toughnessCeramic materials productionClaywaresSilicon oxideFumed silica
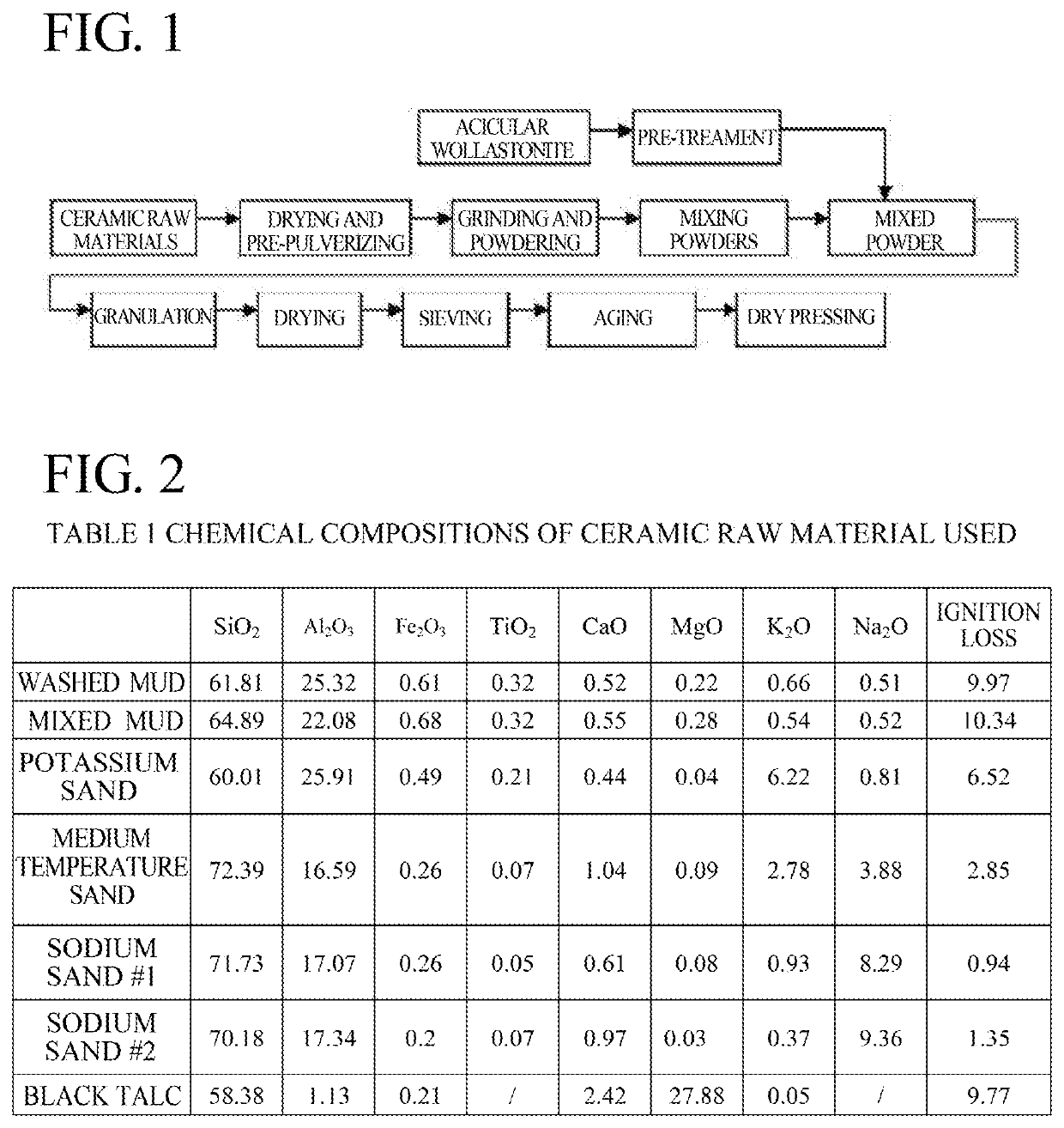
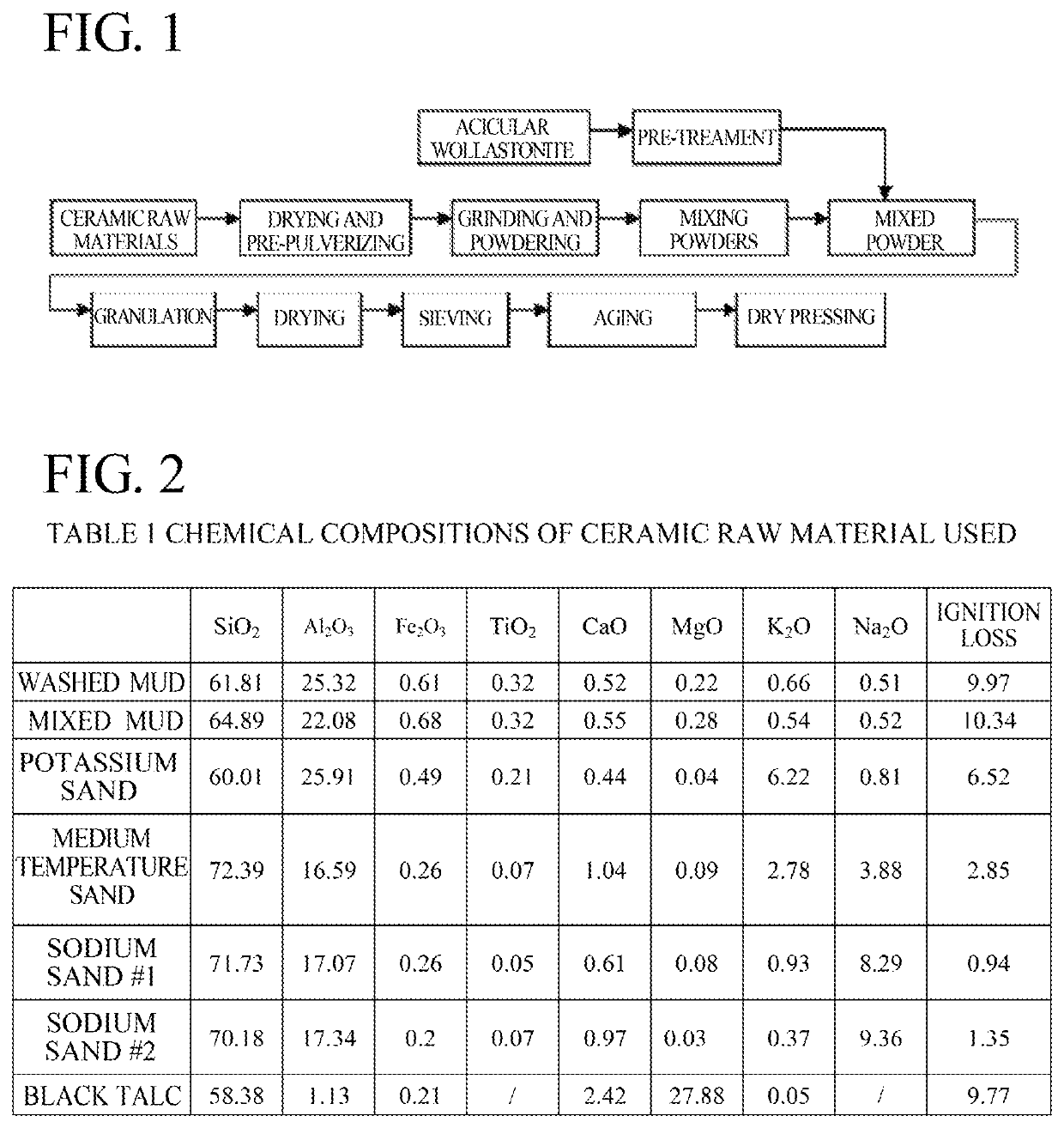
Disclosed are a low-shrinkage, high-strength, and large ceramic plate and a manufacturing method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a ceramic raw material powder; (2) subjecting an acicular wollastonite to surface coating with a silane coupling agent and to pre-dispersion with a fumed silica to obtain a pre-treated acicular wollastonite; and (3) thoroughly mixing the ceramic raw material powder and the pre-treated acicular wollastonite and granulating the resulting mixture, the amount of the pre-treated acicular wollastonite added being 10 wt % to 30 wt % of the ceramic raw material powder, and subjecting the resulting granules to dry pressing and sintering to obtain the large ceramic plate. The acicular wollastonite is incorporated into the manufacturing of the large ceramic plate to take full advantage of the reinforcing effect and low sintering shrinkage characteristics of the acicular wollastonite. The invention reduces sintering shrinkage and increases product strength.
Owner:MONALISA GRP CO LTD
High-strength steel plate having excellent formability, toughness and weldability, and production method of same
ActiveCN113166865AGood formabilityImprove toughnessHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesThick plateMartensite
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Methods of modifying crystal habit
InactiveUS20060078573A1Suitable for manufactureQuick mixPowder deliveryPreferential adsorptionCompound (substance)
The invention provides methods of modifying the crystal habit of a compound without altering the crystal structure of the compound through a controlled precipitation technique in the presence of a crystal growth inhibitor as well as the crystallized compounds formed by these methods. Using these methods, the crystal habit of the compound may be modified from acicular to bipyramidal. The modification in crystal habit is attributable to a preferential adsorption mechanism of the crystal growth inhibitor to a fast growing crystal face of the compound. Powder flow properties of the crystallized product are significantly enhanced with the habit modification. This selective crystal habit modification using a crystal growth inhibitor provides a strategy to circumvent the manufacturing difficulties associated with acicular crystal habits, and may increase the manufacturing capability of supercritical fluid based crystallization and precipitation technologies.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
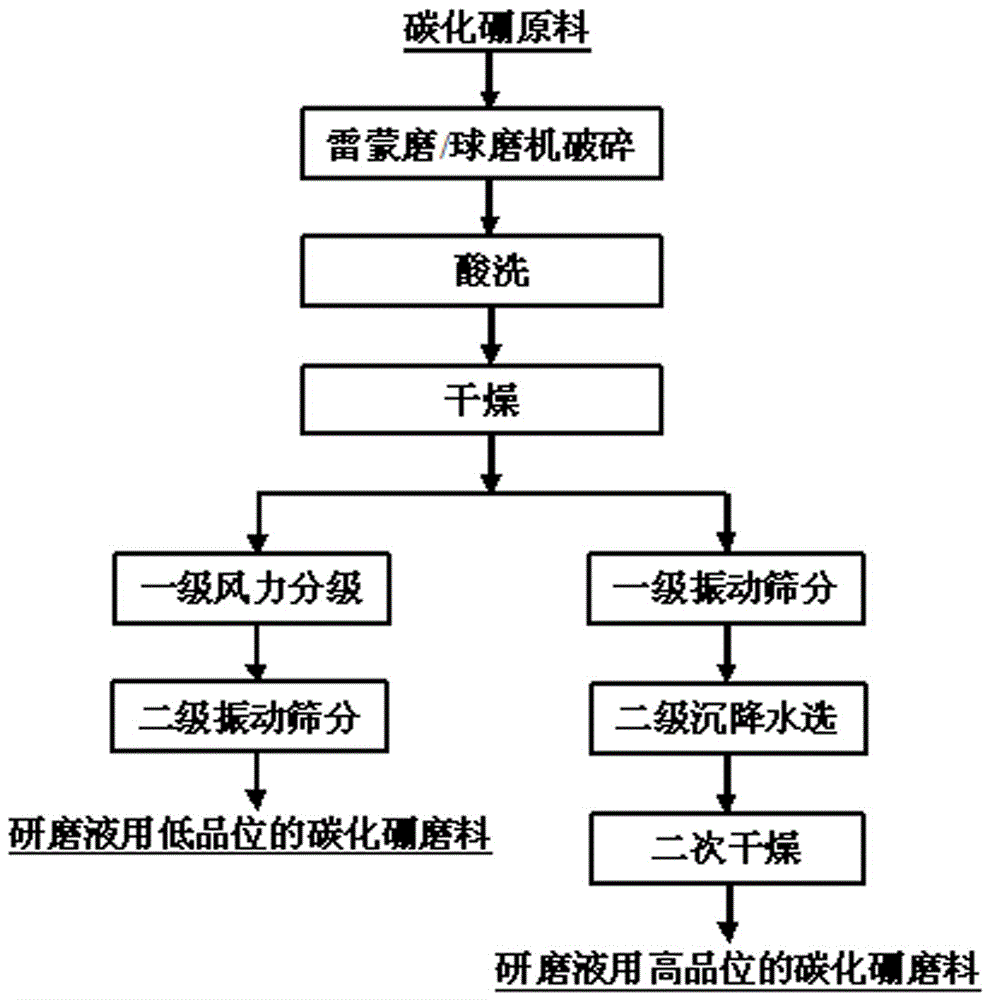
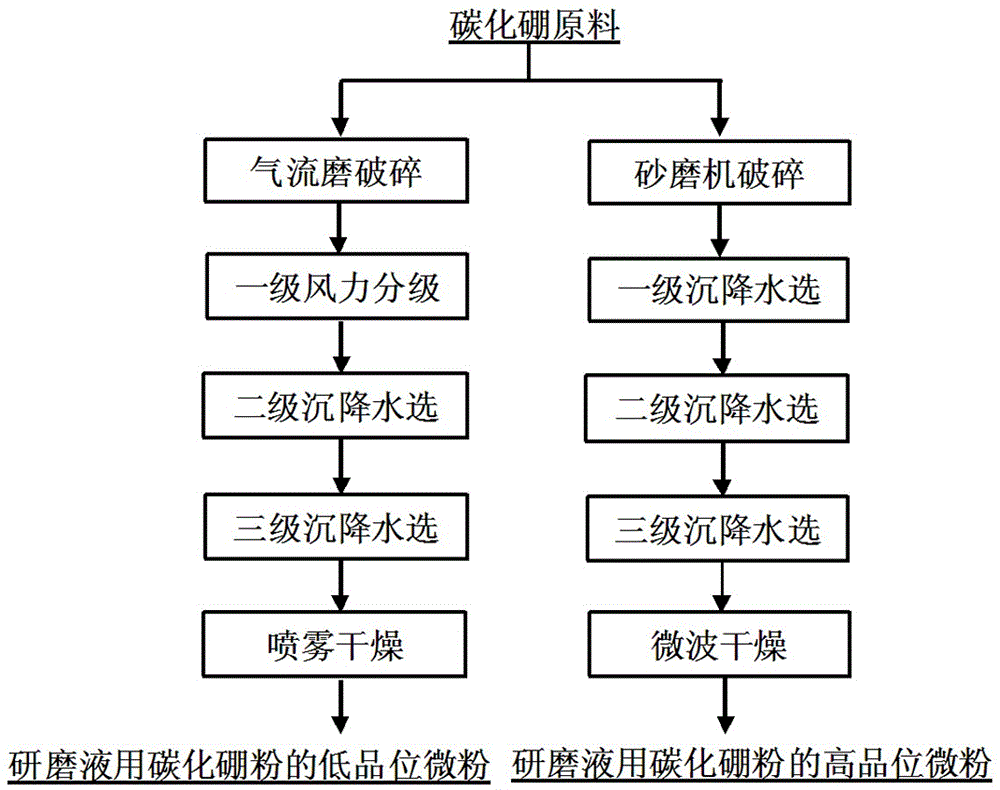
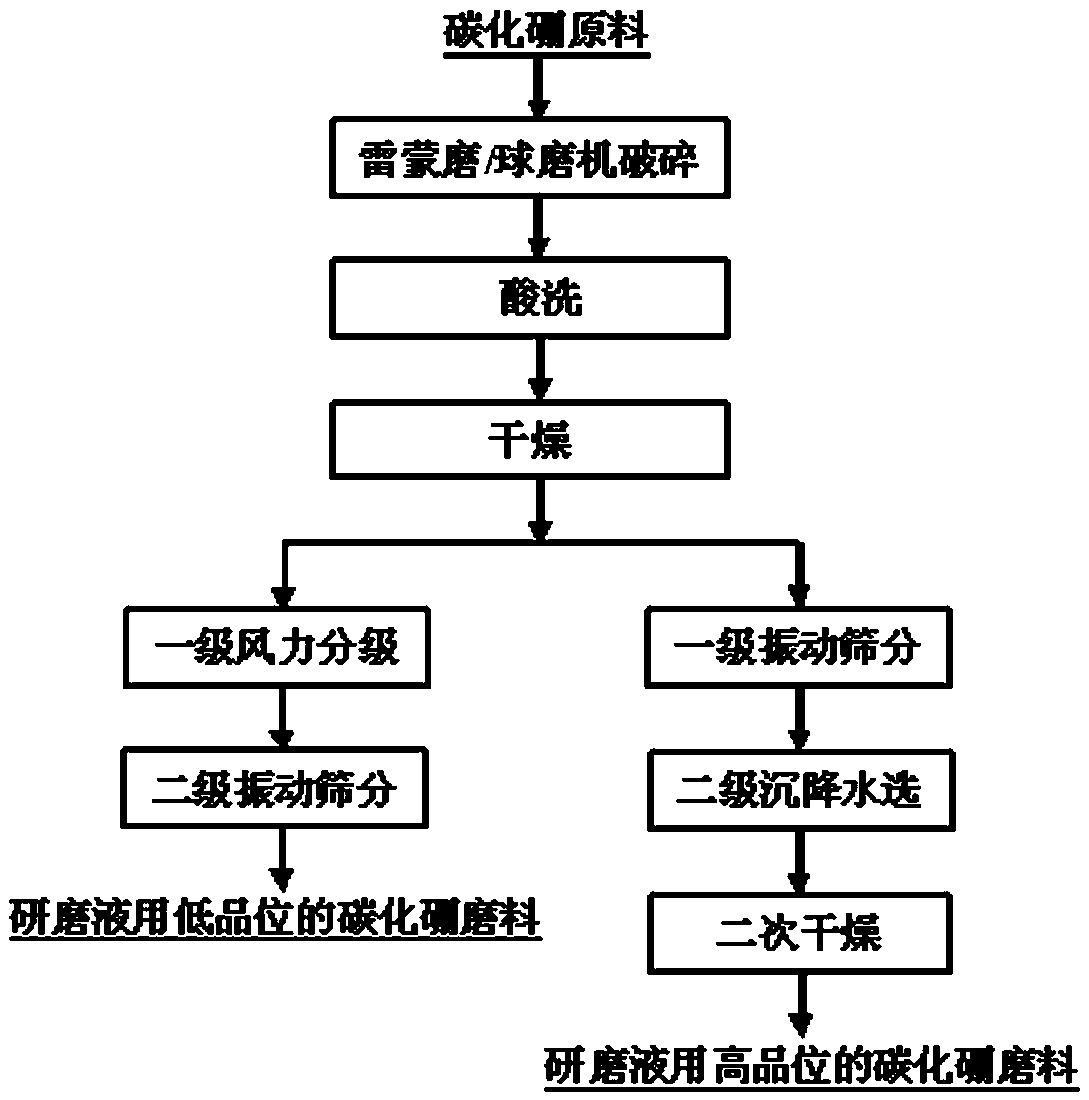
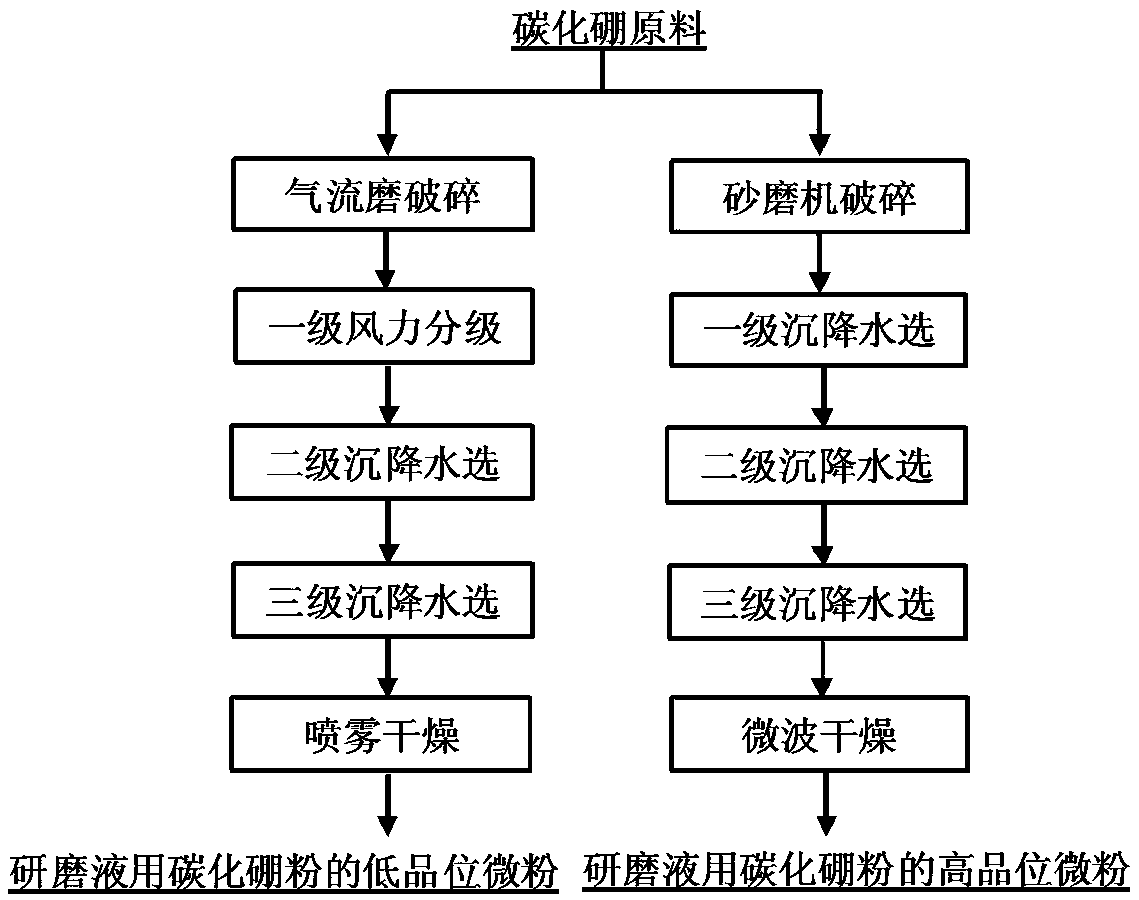
Preparation method of boron carbide powder for grinding liquid
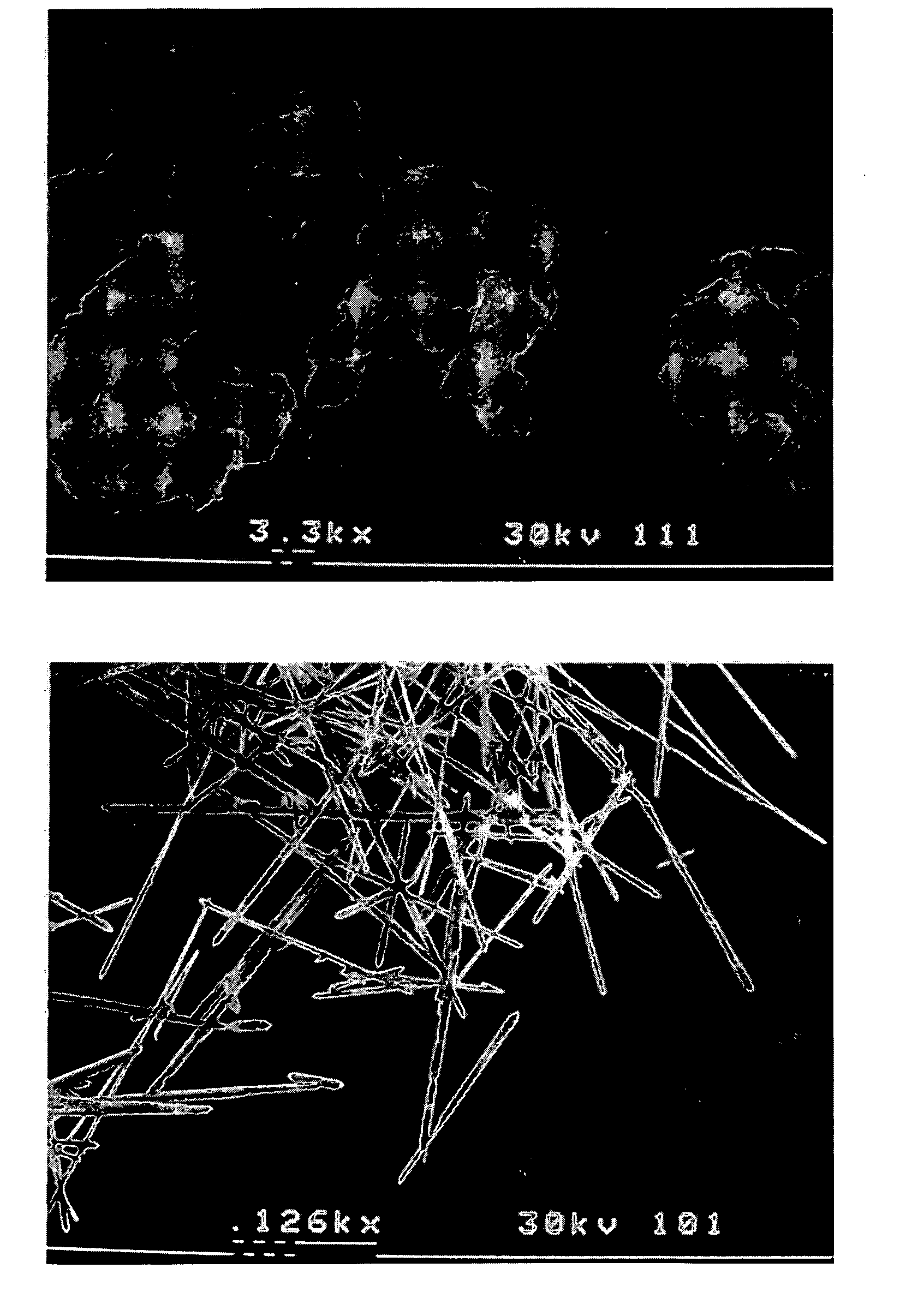
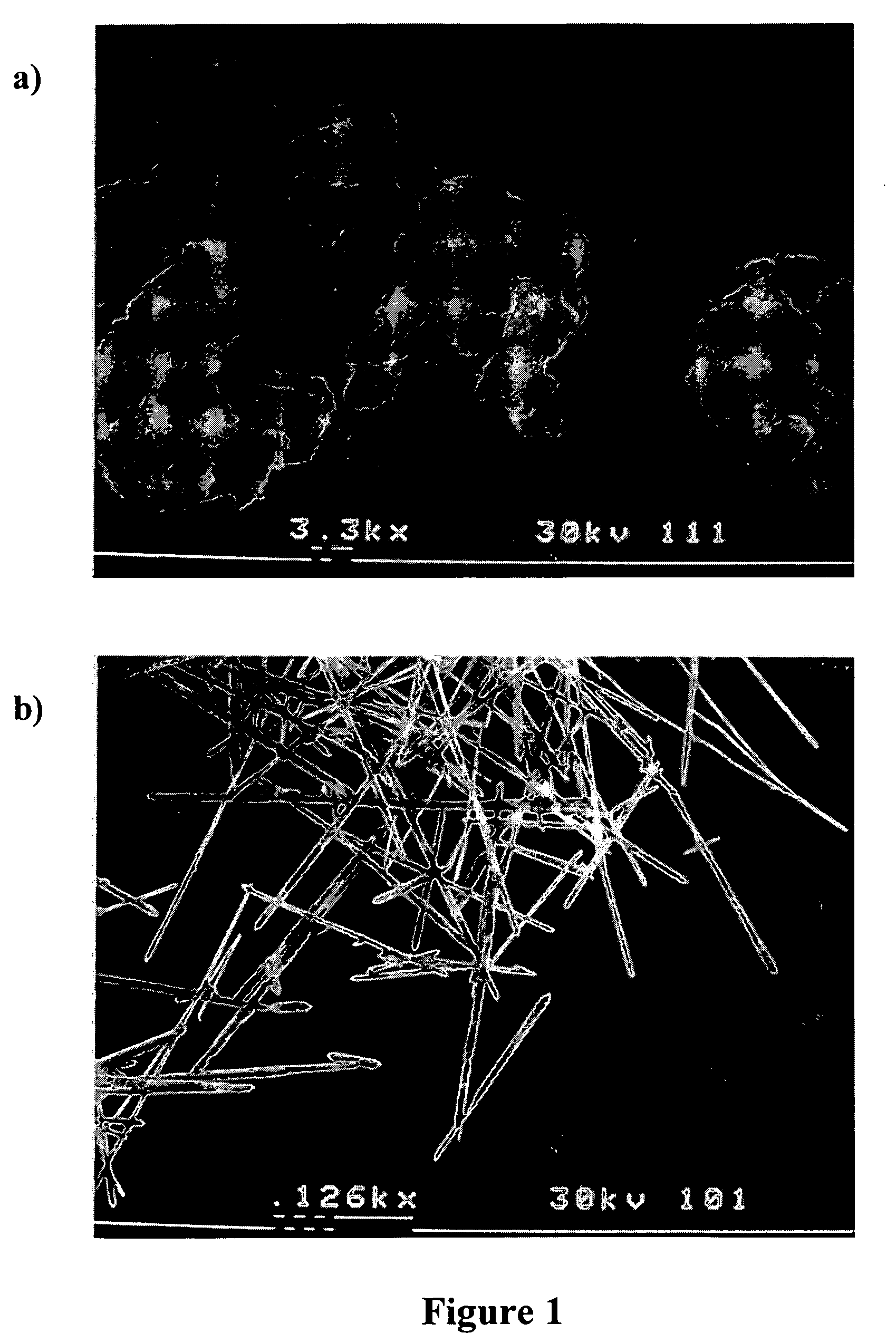
ActiveCN105776220AQuality improvementUniform particle sizeOther chemical processesAcicularBoron carbides
The invention provides a preparation method of boron carbide powder for grinding liquid. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a boron carbide raw material with the weight purity of 95 percent to 99 percent, wherein the volume percent ratio of needle-shaped crystals to flat crystals is smaller than or equal to 1 percent; (2) crushing the boron carbide raw material to obtain crushed boron carbide materials; (3) carrying out first-grade wind power grading and second-grade vibration sieving or carrying out primary vibration sieving, second-grade sedimentation and water selection, and second-grade drying to obtain a low-grade grinding material of the boron carbide powder for the grinding liquid; or carrying out multi-grade sieving and water selection to obtain high-grade micro-powder of the boron carbide powder for the grinding liquid. When the product prepared by the method is prepared into the grinding liquid for grinding, the grinding speed is rapid, and the flatness of a ground surface is high, so that the grinding cost of the product is greatly reduced.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
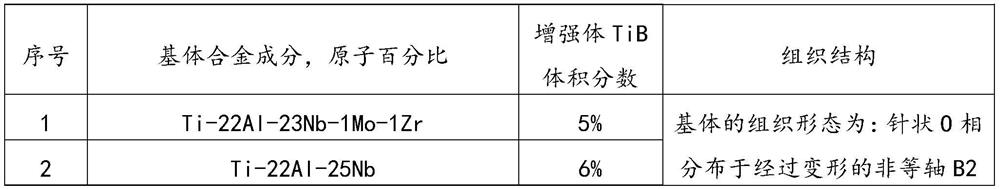
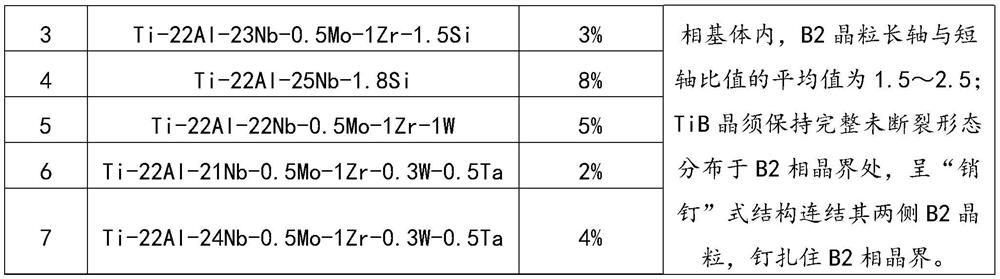
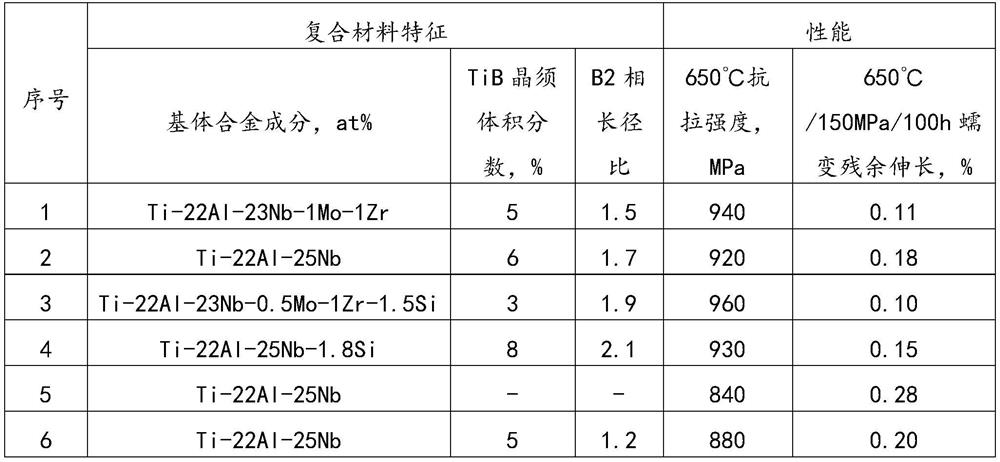
Ti-Al-Nb based composite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN114150238AImprove heat strengthEvenly distributedIncreasing energy efficiencyAlloyGrain boundary
The invention discloses a Ti-Al-Nb-based composite material and a preparation method thereof, the material comprises a Ti-Al-Nb alloy matrix and 1.5%-10% by volume of TiB whiskers, the matrix comprises 18-25 at% of Al, 12-27 at% of Nb and the balance Ti, the structure form of the matrix is that a needle-shaped O phase is distributed in a deformed non-equiaxial B2 phase matrix, and the average value of the ratio of the long axis to the short axis of B2 crystal grains is larger than or equal to 1.5; the TiB crystal whiskers are distributed at the B2 phase crystal boundary in a complete and unbroken form, are connected with B2 crystal grains on the two sides in a pin type structure, and pin the B2 phase crystal boundary. The matrix alloy of the composite material is deformed and has streamline characteristics; the reinforcement TiB whisker is complete, free of fracture and uniform in distribution; the TiB crystal whiskers with the high length-diameter ratio effectively pin a deformation matrix grain boundary, so that the grain boundary pinning strengthening effect and the intragranular deformation strengthening effect have a synergistic effect, and the thermal strength performance of the material is greatly improved.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Method for preparing acicular acetaminophen crystal by time domain shaping femtosecond laser
InactiveCN109867610ALow costComponents are pureCarboxylic acid amide separation/purificationEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesTime domainAcetaminophen crystals
The invention relates to a method for preparing acicular acetaminophen crystal by a time domain shaped femtosecond laser, and belongs to the field of preparation of pharmaceutical crystal materials. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a supersaturated solution of acetaminophen by using a heating device; (2) using a femtosecond laser irradiation method to enable the acetaminophen supersaturated solution to be ionized to generate cavitation bubbles and generate acicular acetaminophen crystal as the bubbles rupture; and (3) drying filtered acicular acetaminophen crystal by using a heating device. The method for preparing the acicular paracetamol crystal provided by the invention is carried out under normal temperature and normal pressure without any addition in the production, the manufacturing time is short, the ratio of the acetaminophen crystal is high, and the size is controllable.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Low-shrinkage, high-strength, and large ceramic plate and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS11084759B2High strengthImprove toughnessCeramic materials productionClaywaresSilicon oxideFumed silica
Disclosed are a low-shrinkage, high-strength, and large ceramic plate and a manufacturing method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a ceramic raw material powder; (2) subjecting an acicular wollastonite to surface coating with a silane coupling agent and to pre-dispersion with a fumed silica to obtain a pre-treated acicular wollastonite; and (3) thoroughly mixing the ceramic raw material powder and the pre-treated acicular wollastonite and granulating the resulting mixture, the amount of the pre-treated acicular wollastonite added being 10 wt % to 30 wt % of the ceramic raw material powder, and subjecting the resulting granules to dry pressing and sintering to obtain the large ceramic plate. The acicular wollastonite is incorporated into the manufacturing of the large ceramic plate to take full advantage of the reinforcing effect and low sintering shrinkage characteristics of the acicular wollastonite. The invention reduces sintering shrinkage and increases product strength.
Owner:MONALISA GRP CO LTD
Thermal treatment process for X12CrMoWVNbN10-1-1 grain refinement
The invention provides a thermal treatment process for X12CrMoWVNbN10-1-1 grain refinement. According to the thermal treatment process, the amount of acicular austenite is decreased as much as possible by increasing the heating speed, and the amount of spherical austenite is increased, so that grain refinement is achieved, the grain size can meet the technical requirement, and the using range of X12CrMoWVNbN10-1-1 is enlarged. Fed materials are forged into workpieces, the workpieces are sequentially subjected to high-temperature normalizing, high-temperature tempering, conventional normalizingand high-temperature tempering, and then the workpiece subjected to high-temperature tempering are subjected to subsequent processing treatment. In the high-temperature normalizing process, the temperature increasing speed of the workpieces in an alpha and gamma two-stage region is increased, the workpieces can pass through the two-stage region rapidly, and the spherical austenite can be obtainedas much as possible. On one hand, the orientation relationship of crystallography is broken through to a greater extent, namely, the K--S relationship; and on the other hand, the nucleation rate of the austenite can be increased by increasing the heating speed. The high-temperature tempering process particularly comprises the steps that heat preservation is conducted for 15-20 h at the environmental temperature of 700 DEG C to enable carbides to be dissolved as many as possible to further destroy the orientation relationship of metallography, and then air cooling is conducted.
Owner:WUXI HONGDA HEAVY IND
Fluxing agent for crystal growth and crystal growth method
InactiveCN111379014AReduce volatilityImprove stabilityPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsPhysical chemistryMetal halides
The invention discloses a fluxing agent for crystal growth and a crystal growth method. The crystal is Pb17O8Cl18, and a system of the fluxing agent comprises at least one of PbO, metal halide M'X, metal halide M''X2 and Bi2O3; wherein M' is Li, Na or K, M'' is Mg, Ca, Ba, Sr or Pb, and X is F or Cl. The crystal growth method comprises the following steps: mixing and melting a polycrystalline rawmaterial and the fluxing agent; starting seeding above a melt temperature saturation point, stabilizing the melt temperature at the saturation point, and starting crystal growth; and growing the crystal to a required size, lifting the seed rod crystal to be separated from the liquid level, and carrying out annealing treatment in a weak oxidizing atmosphere. According to the method, the crystal growth orientation is fully considered, the crystal growth stability is effectively improved, the solution volatilization and system viscosity in the growth process are reduced, the problems of needle-like growth of the crystal, easy cracking and color change of the grown crystal and the like are solved, and the grown crystal is large in size and high in optical quality.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Metastable and stable crystal forms of pyroxasulfone as well as preparation method and application of metastable and stable crystal forms of pyroxasulfone
PendingCN114213402AOvercome stabilityOvercome the disadvantages of poor crystal form uniformityBiocideOrganic chemistry methodsWater dispersiblePhysical chemistry
Owner:芮城华农生物化学有限公司
Small moleoule rare-earth atom containing composite molecular sieve and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN1242917CSmall grainShorten crystallization timeCrystalline aluminosilicate zeolitesRare-earth elementMolecular sieve
A RE atoms contained composite molecular sieve in the form of small crystal grains has the characteristics of the crystalline molecular sieve with TON and MFI structures, acicular crystal grains and RE elements contained on its skeleton. It is prepared in dynamic hydrothermal condition. In the procedure of preparing gel, RE metal salt and halide are added.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
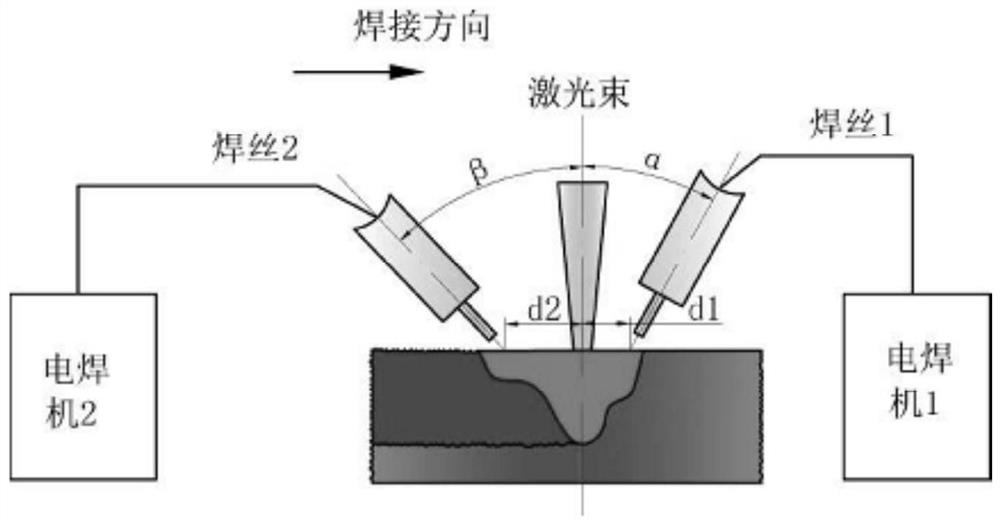
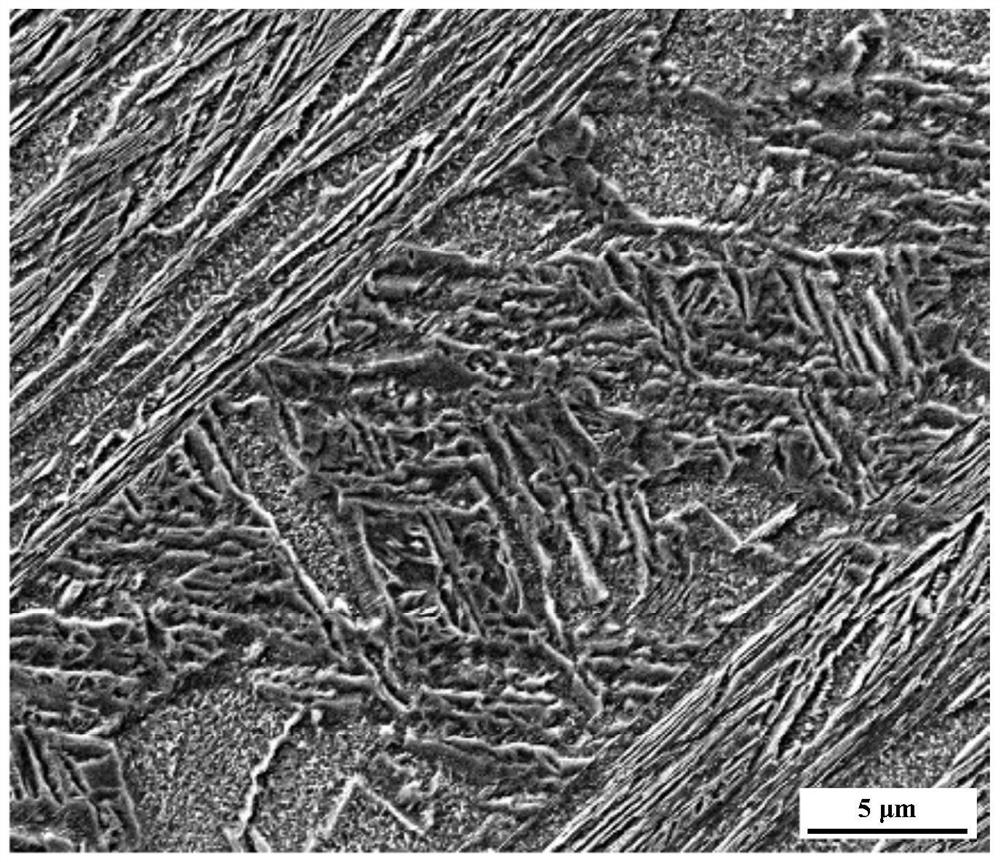
Welding joint of low-alloy and ultrahigh-strength steel and welding method
The invention discloses a welding joint of low-alloy and ultrahigh-strength steel. The welding joint is characterized in that the welding joint structure comprises acicular martensite and strip-shapedbainite, the volume percent of the acicular martensite is 70-80%, and the volume percent of the strip-shaped bainite is 20-30%. The invention further discloses a welding method forming the welding joint. Compared with the prior art, the complex-phase welding joint can meet the using requirements for high strength and high toughness of a welding joint piece of a low-alloy and ultrahigh-strength steel medium-thick plate, and meanwhile is easy to operate, high in welding efficiency and easy to apply and popularize.
Owner:CHINA WEAPON SCI ACADEMY NINGBO BRANCH
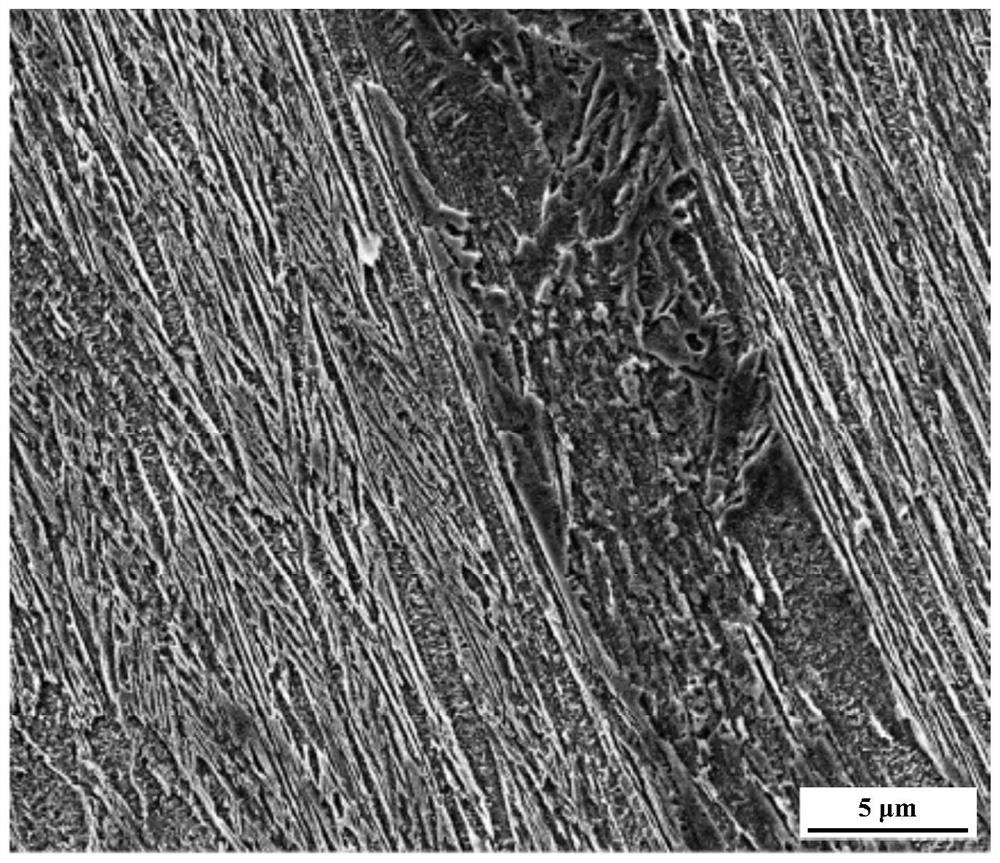
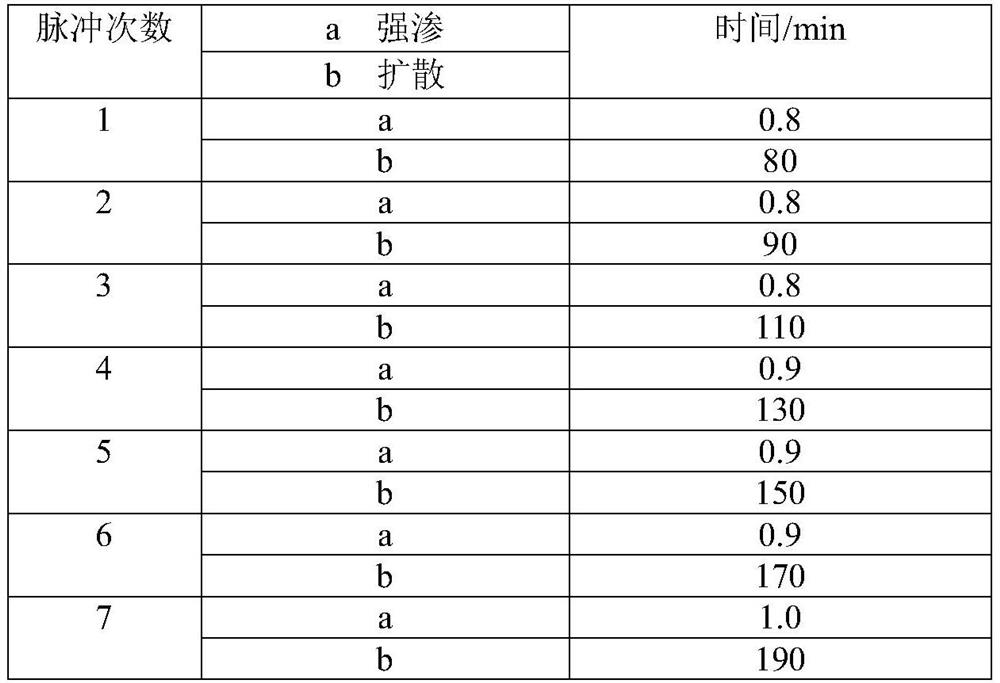
A method for controlling carburization of metallographic structure of bg801 material
ActiveCN109609891BGuaranteed depthMeet the design requirementsSolid state diffusion coatingSand blastingCarbide
The invention belongs to the technical field of metal heat treatment, and relates to a method for controlling carburization of metallographic structure of BG801 material. The metallographic structure carburization control method of the BG801 material of the present invention, after blasting the carburized surface, adopts the pulse strong infiltration method to carry out multiple cycle carburization on the carburized surface, wherein, each pulse process is to first vacuumize, and then pass through Acetylene, then, vacuum again, and then pass nitrogen, in each pulse, pulse diffusion time / pulse infiltration time ≥ 100. The carburizing control method of the BG801 material metallographic structure of the present invention optimizes the carburizing process parameters of the BG801 material, especially the strict control of the strong infiltration time, so as to ensure that the depth of the carburizing layer of BG801 meets the requirements, and can effectively avoid metallurgy. There is no Widmanstatten primary carbide acicular structure in the phase structure, so that the BG801 material meets the design requirements after carburizing.
Owner:HARBIN DONGAN ENGINE GRP
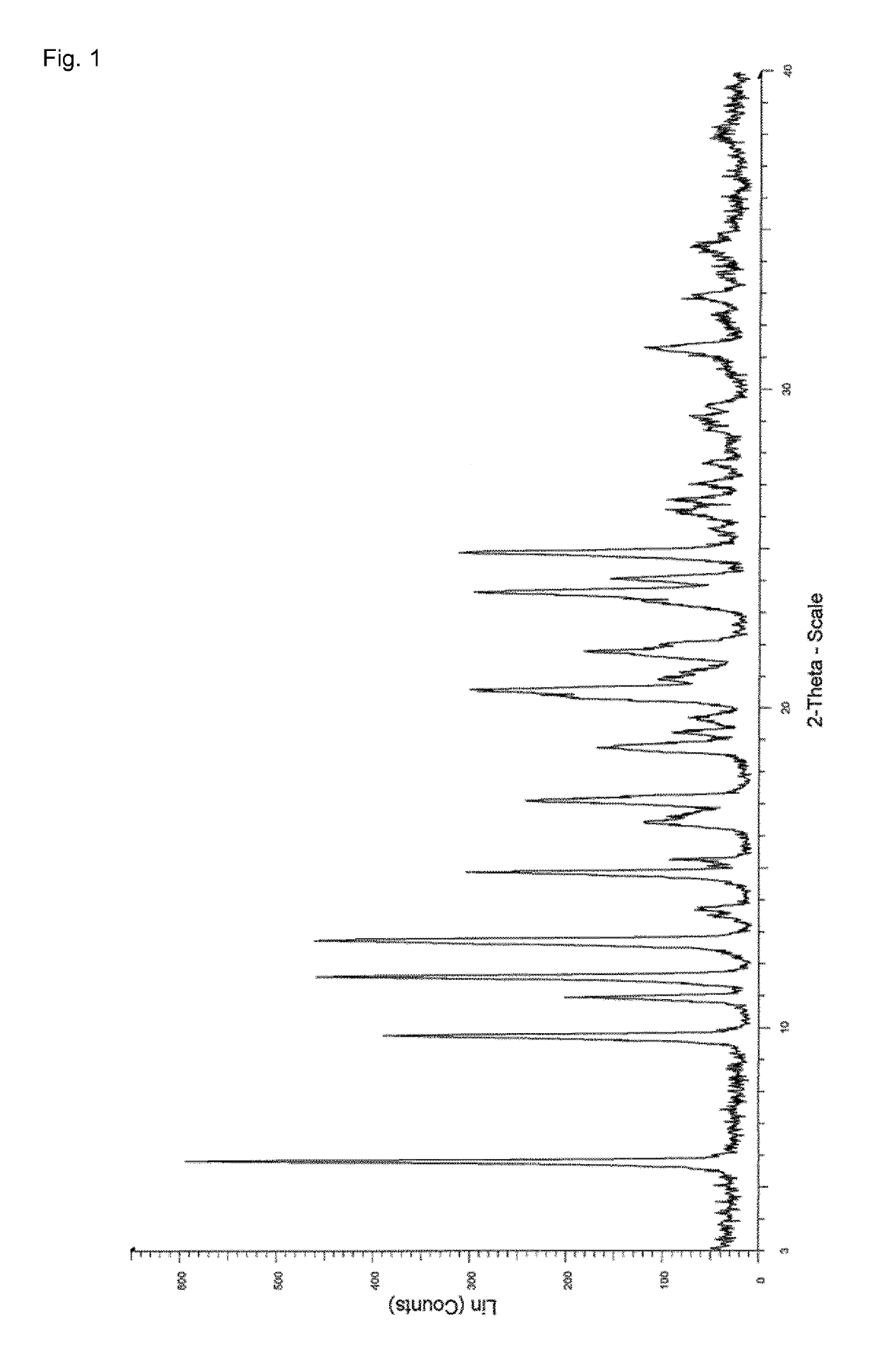
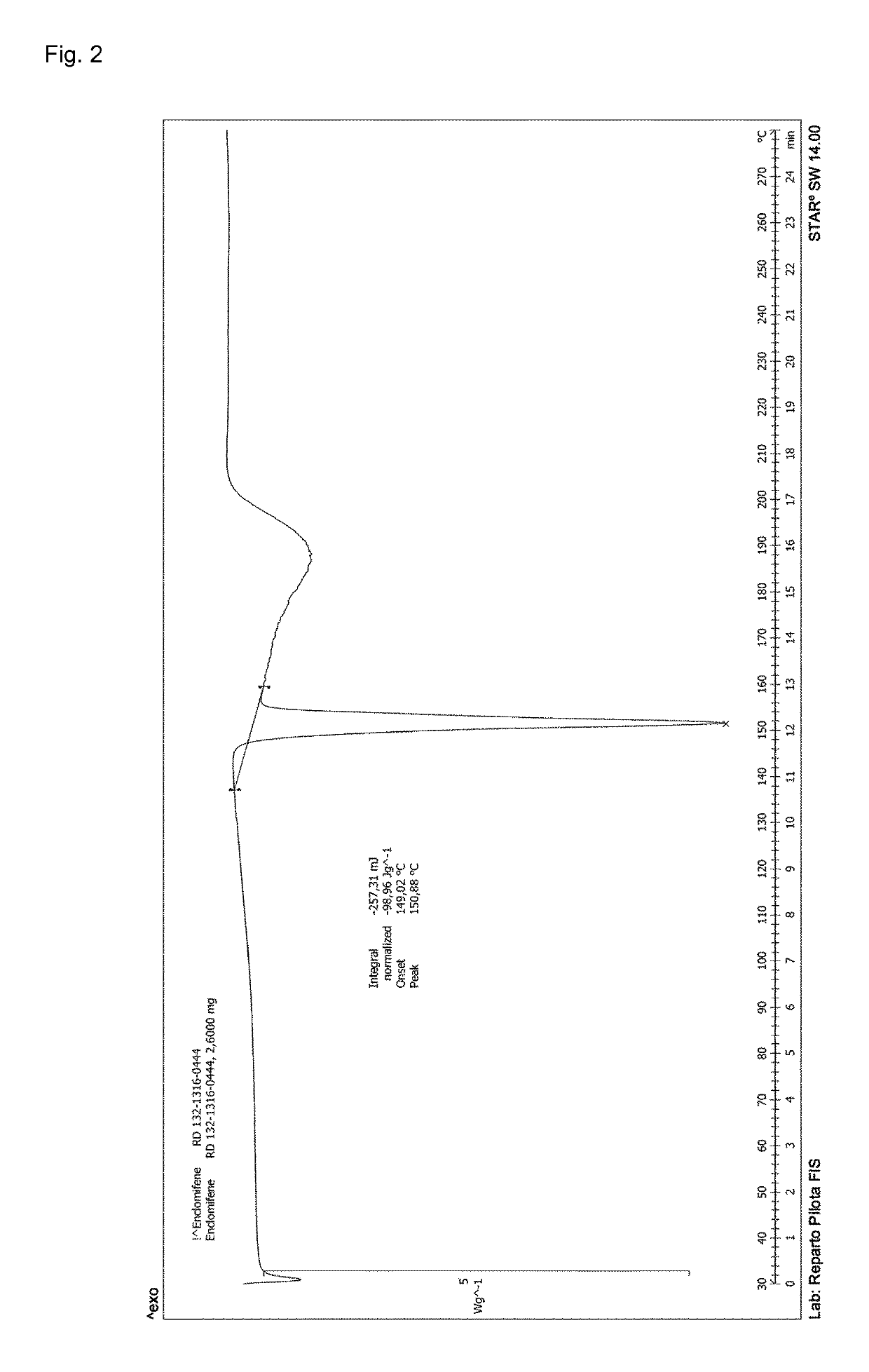
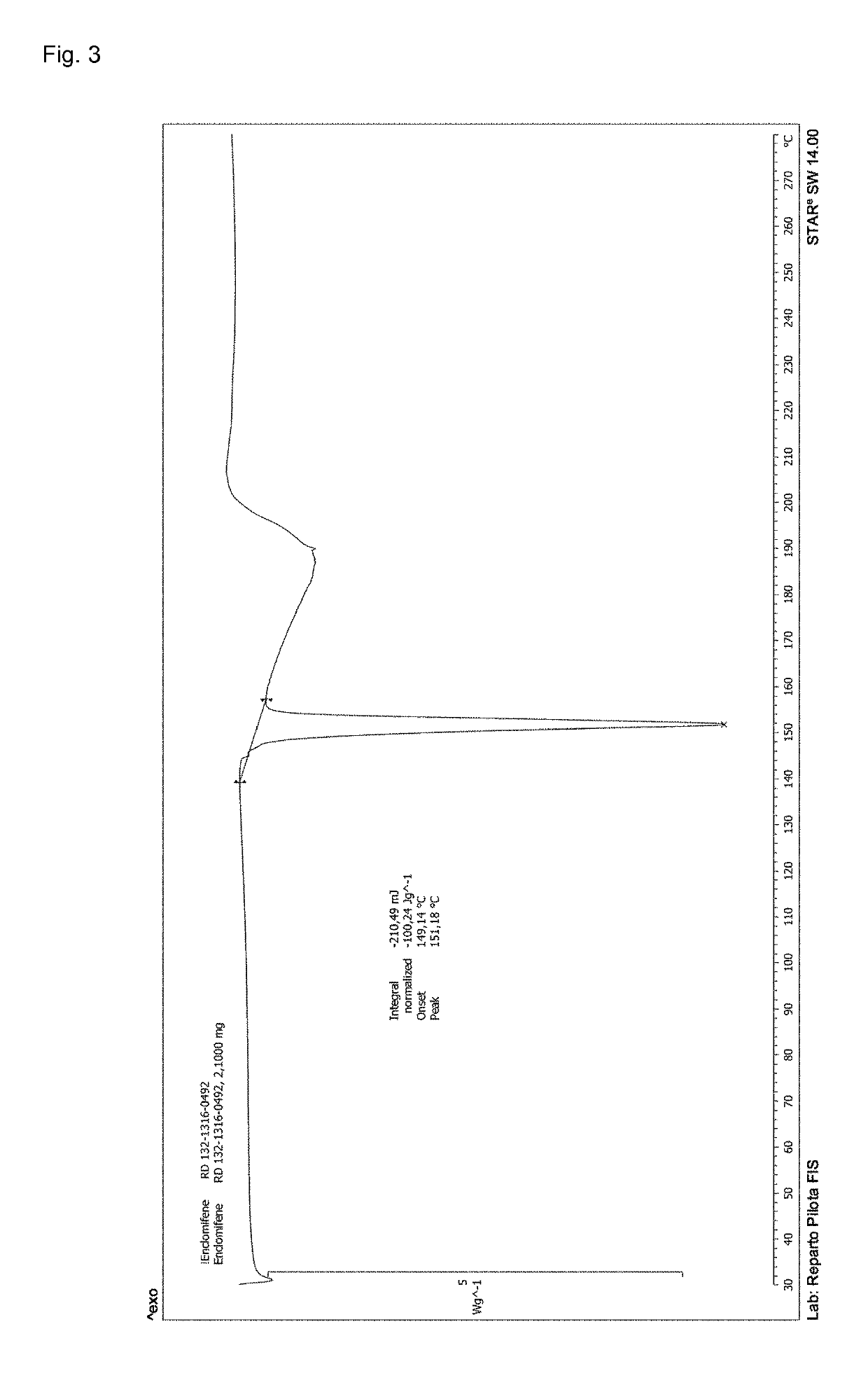
Process for the preparation of enclomiphene citrate having needle shaped crystal habit
Owner:F I S FAB ILTALIANA SINTETICI SPA
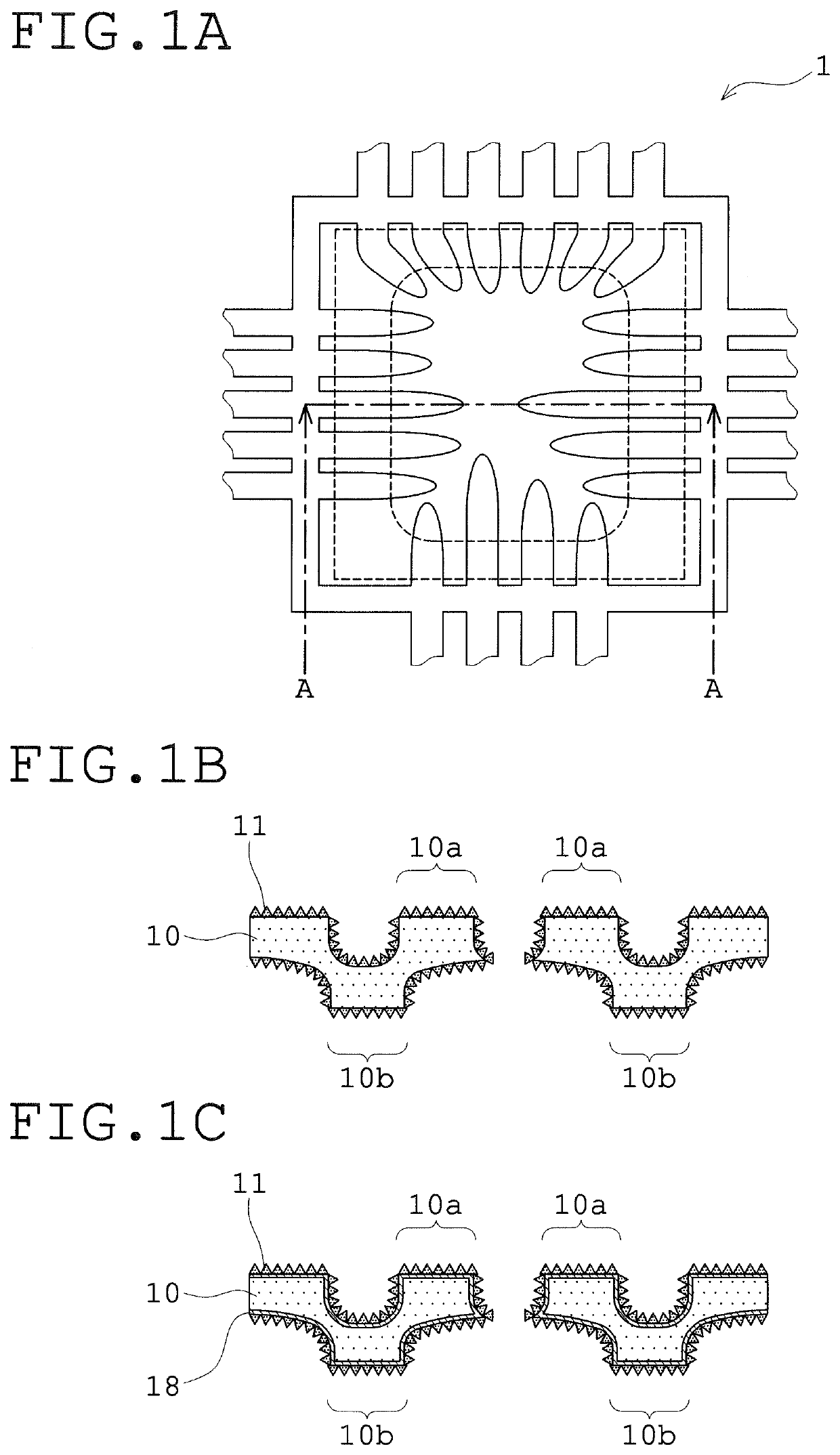
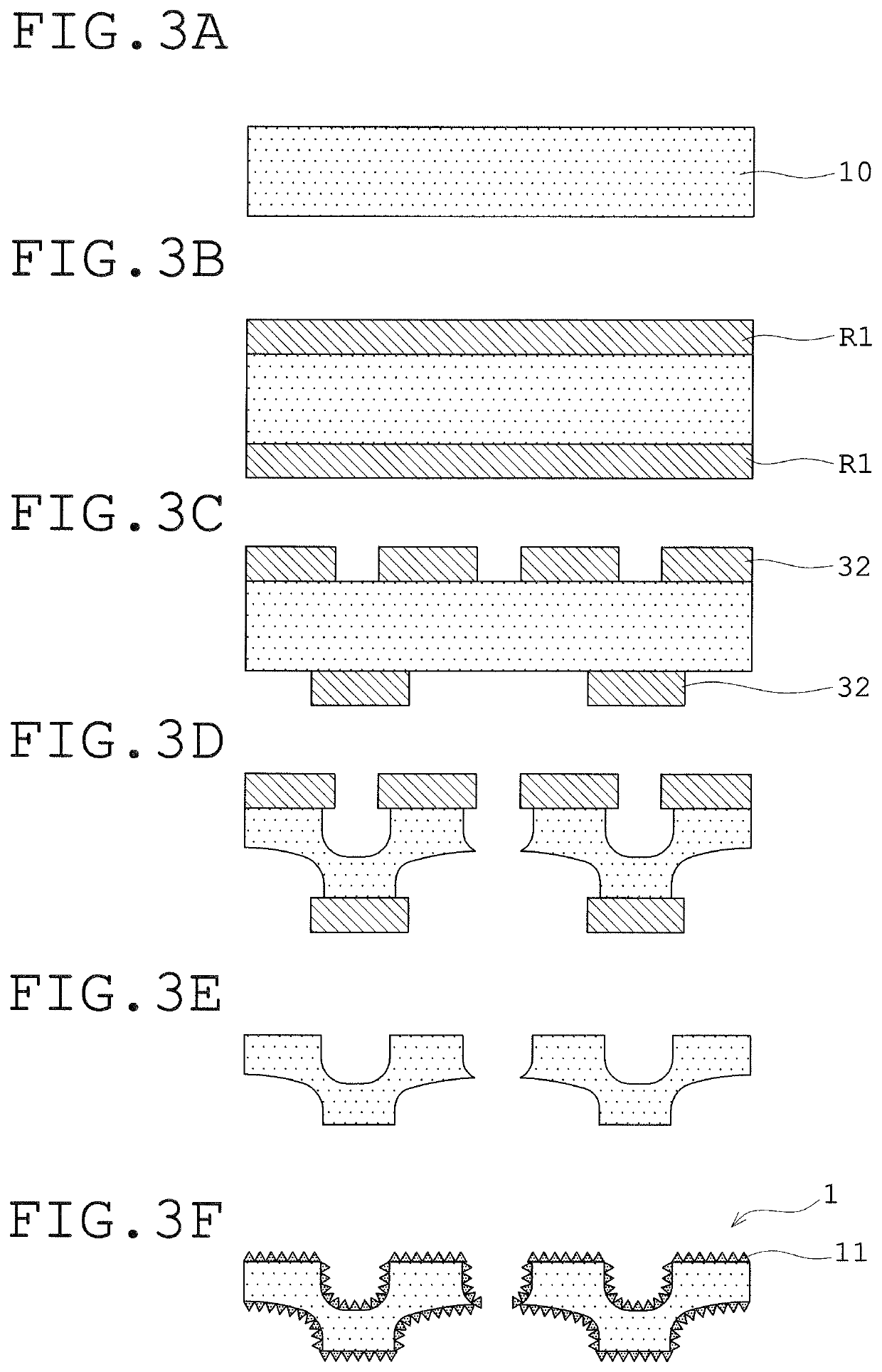
Lead frame
ActiveUS10763196B1Improve sealingLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCrystal structureLead frame
A lead frame includes, as an outermost plating layer, a roughened silver plating layer having acicular projections and covering the entire surface of a lead frame substrate made of a copper-based material. The roughened silver plating layer has a crystal structure in which the crystal direction <101> occupies a largest proportion among the crystal directions <001>, <111>, and <101>. The lead frame can be manufactured with improved productivity owing to reduction in cost and operation time, and achieves remarkably high adhesion to sealing resin while keeping the total thickness of plating layers including the silver plating layer to be thin.
Owner:CHANG WAH TECH
Steel sheet and steel pipe
PendingCN114846163AExcellent SSC resistanceExcellent resistance to HICFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesChemical compositionHardness
A steel sheet having a prescribed chemical composition, the steel sheet having a metallographic structure in the center of the sheet thickness comprising, in area%, 0-80% of polygonal ferrite; the present invention relates to a steel sheet having an effective crystal grain size of 15.0 [mu] m or less, and one or two elements selected from acicular ferrite and bainite, the remainder being an M-A phase, the steel sheet having an effective crystal grain size of 15.0 [mu] m or less, the metallographic structure in a surface layer, which is a range from the surface to 1.0 mm in the thickness direction, containing 95% or more in total in area% of one or two elements selected from acicular ferrite and bainite, and the remainder being an M-A phase, the steel sheet having an effective crystal grain size of 15.0 [mu] m or less, and the steel sheet having an effective crystal grain size of 15.0 [mu] m or less. The surface layer has a maximum hardness of 250 HV0.1 or less.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
A kind of sodium myristate crystal form and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109020807BGood chemical stabilitySolve the package problemOrganic chemistry methodsPlatinum organic compoundsEthyl acetateProtic solvent
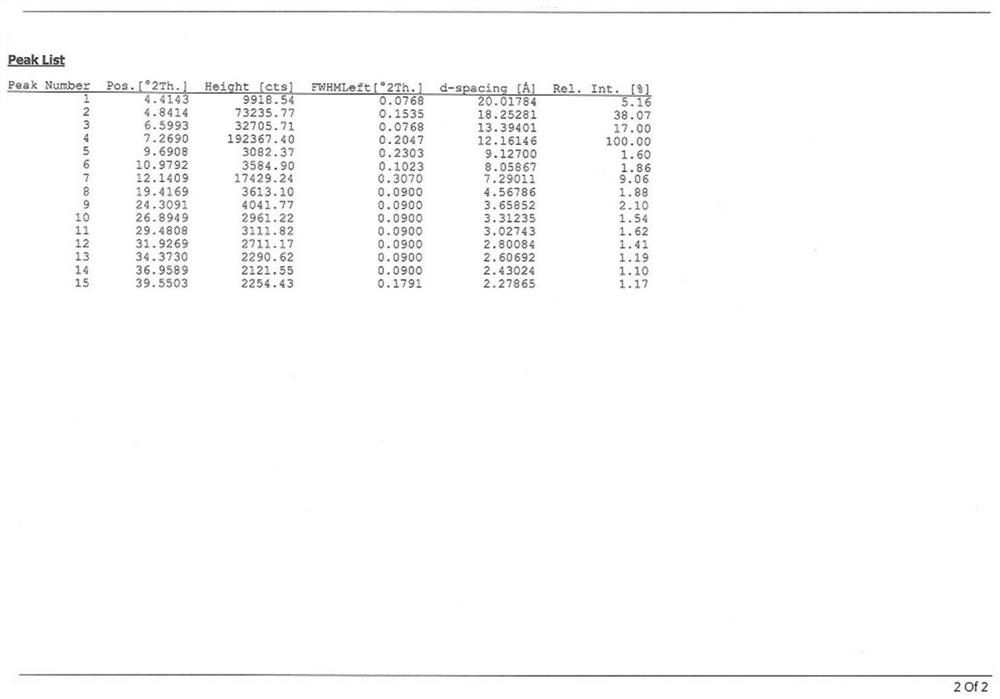
The invention belongs to the field of chemical industry and pharmacy, and specifically discloses a sodium myristate crystal form. The crystal form uses Cu-Kα radiation to represent X-ray powder diffraction (X-RPD) at 2θ angles at 2θ=4.8±0.2°, There are characteristic diffraction peaks at 6.6±0.2°, 7.3±0.2° and 12.1±0.2°. In addition, the present invention also discloses a preparation method of the sodium myristate crystal form, which comprises dissolving sodium myristate in a protic solvent, heating and dissolving, adding ethyl acetate, stirring and cooling down, and standing for crystallization to obtain the crystal form. The sodium myristate crystal form is needle-like crystal, has few impurities and high purity, and is not easy to be wrapped in the process of preparing rice platinum, so that the purity of rice platinum is higher, and the industrial production of rice platinum is convenient.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
Selection method for recovering needle-like wollastonite from mixed ores
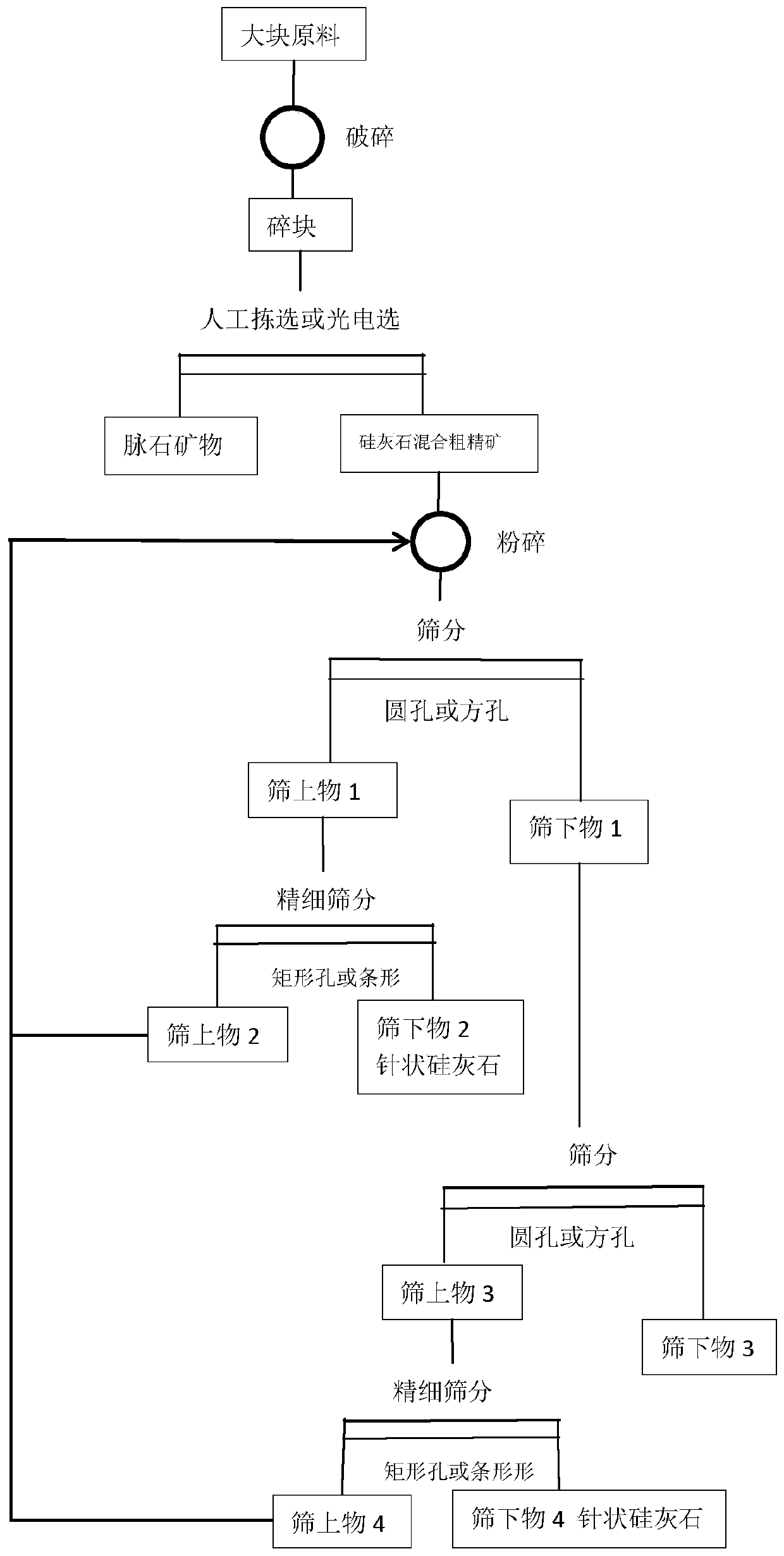
ActiveCN110743697AProtect unique structuresEnlarge the particle shape differenceSolid separationEngineeringWollastonite
The invention belongs to the technical field of non-metal mineral processing, and in particular relates to a selection method for recovering needle-like wollastonite from mixed ores. Mixed wollastonite ores are crushed by crushing equipment in a characteristic force applying mode by means of crushing characteristics and grain shape differences of the needle-like wollastonite and other polymorphicand gangue minerals, so that the grain shape differences are expanded while the needle-like structure is protected. A crushed product is then controlled and screened precisely, so that the needle-likewollastonite is separated effectively, and therefore, the recovery rate of the needle-like wollastonite can be improved effectively.
Owner:广东五岭硅灰石有限公司
A kind of preparation method of boron carbide powder for grinding liquid
ActiveCN105776220BQuality improvementUniform particle sizeCarbon compoundsOther chemical processesBoron carbideLower grade
A method for preparing boron carbide powder for grinding liquid, following the following steps: (1) Prepare boron carbide raw materials with a weight purity of 95~99%, in which the volume percentage of needle-shaped and flaky crystals is ≤1%; (2) Crush the boron carbide raw material to obtain boron carbide fragments; (3) After primary wind classification and secondary vibration screening, or through primary vibration screening, secondary sedimentation water separation and secondary drying; obtain boron carbide for grinding liquid Low-grade abrasive powder; or after multi-stage screening and water separation, high-grade micro-powder of boron carbide powder for grinding fluid can be obtained. When the product prepared by the method of the present invention is configured as a grinding fluid for grinding, it not only has a fast grinding rate, but also has a high grinding surface smoothness, which greatly reduces the grinding cost of the product.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
Lead frame
ActiveUS20200303210A1Improve adhesionReducing cost timeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCrystal structureLead frame
A lead frame includes, as an outermost plating layer, a roughened silver plating layer having acicular projections and covering only top faces on the upper surface side of a lead frame substrate made of a copper-based material. The roughened silver plating layer has a crystal structure in which the crystal direction <101> occupies a largest proportion among the crystal directions <001>, <111>, and <101>. The lead frame can be manufactured with improved productivity owing to reduction in cost and operation time, and achieves remarkably high adhesion to sealing resin while keeping the total thickness of plating layers including the silver plating layer to be thin.
Owner:OHKUCHI MATERIALS CO LTD
A kind of heat treatment method to obtain three-state structure in slm forming titanium alloy
ActiveCN113275600BImproved strength-plasticity mismatchExcellent strength-plasticity matchingAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyEquiaxed crystalsMartensite
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method capable of controlling uniform crystal and eliminating needle crystal
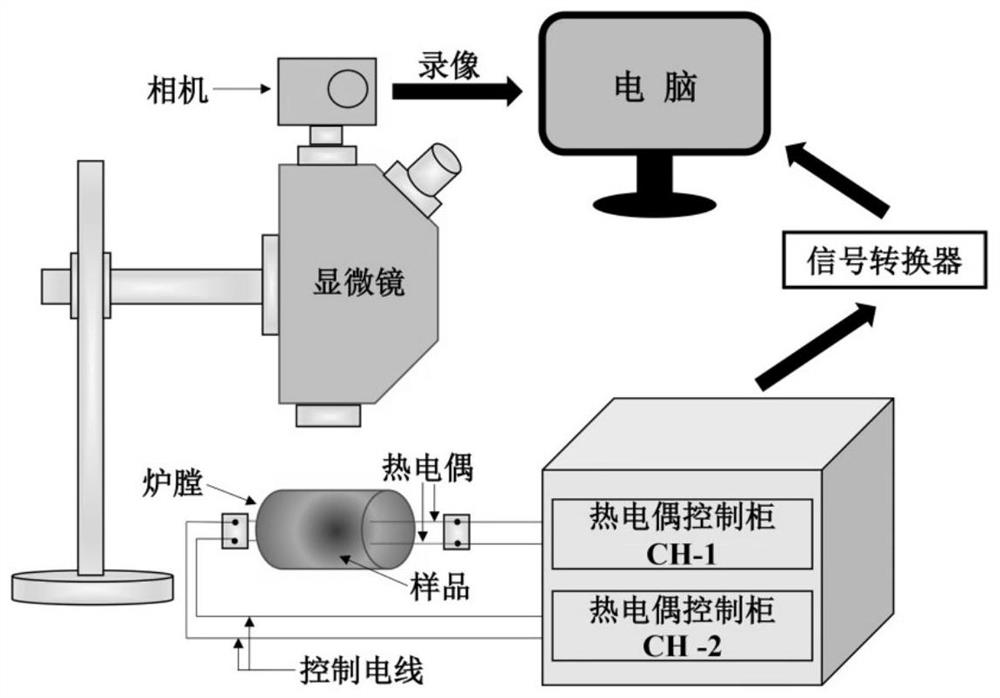
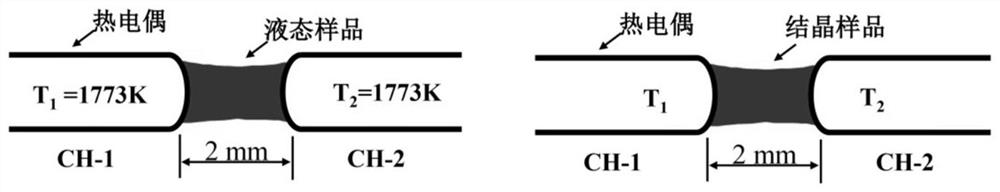
ActiveCN110918919AConducive to continuous casting experimental conditionsReduce stepsSlagLiquid state
The invention belongs to the field of steel smelting continuous casting, and relates to an experimental method capable of controlling uniform crystal phase and eliminating needle crystal. According tothe experimental method, after protective slag is directly melted at the two ends of thermocouples by means of a thermocouple double-wire technology, a uniform and consistent environment of the crystallization temperature of the protective slag is created by controlling the same temperature of the thermocouples at the two ends and setting the same hearth temperature so that in the crystal solidification process of the liquid protective slag, the uniform crystal phase can be obtained and needle crystal can be eliminated. According to the experimental method, the process of crystallizing the protective slag from high temperature to low temperature in the continuous casting process in a factory is simulated, and is more like the actual production process, the obtained experimental data is more convincing, compared with the method for obtaining the crystal phase by re-rising the temperature of the glass slag obtained by quenching the molten protective slag, the experimental method has theadvantages that the experimental operation time is short, the steps are simple and convenient, the workload is smaller, and the obtained product has no needle crystal and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A kind of single-crystal type high-nickel multi-component material precursor
ActiveCN109360948BImprove ionic conductanceReduce the maximum temperatureCell electrodesSecondary cellsCellulosePhysical chemistry
The present invention provides a kind of single-crystal high-nickel multi-component material precursor, which is characterized in that: the general chemical formula of the precursor is Ni (1‑a‑b) co a mn b (OH) 2 , where 1>1‑a‑b≥0.6, 0.4≥a≥0, 1≥b>0. The precursor of quasi-single-crystal type high-nickel multi-element material described in the present invention starts with the microstructure of the material, and controls the growth of the precursor in the early stage of the co-precipitation reaction by adding a dispersant in the bottom liquid of the reaction kettle, increases the amount of nucleation, and avoids the formation of common The needle-like or dot-like primary particle morphology precursor, at the same time, utilizes the cellulose thickener in the salt solution to form the radial growth of the primary particle at a low pH value at a high rotational speed, and finally forms a sheet-like morphology structure.
Owner:TIANJIN ENERGIES
High-strength steel material having enhanced resistance to brittle crack propagation and break initiation at low temperature and method for manufacturing same
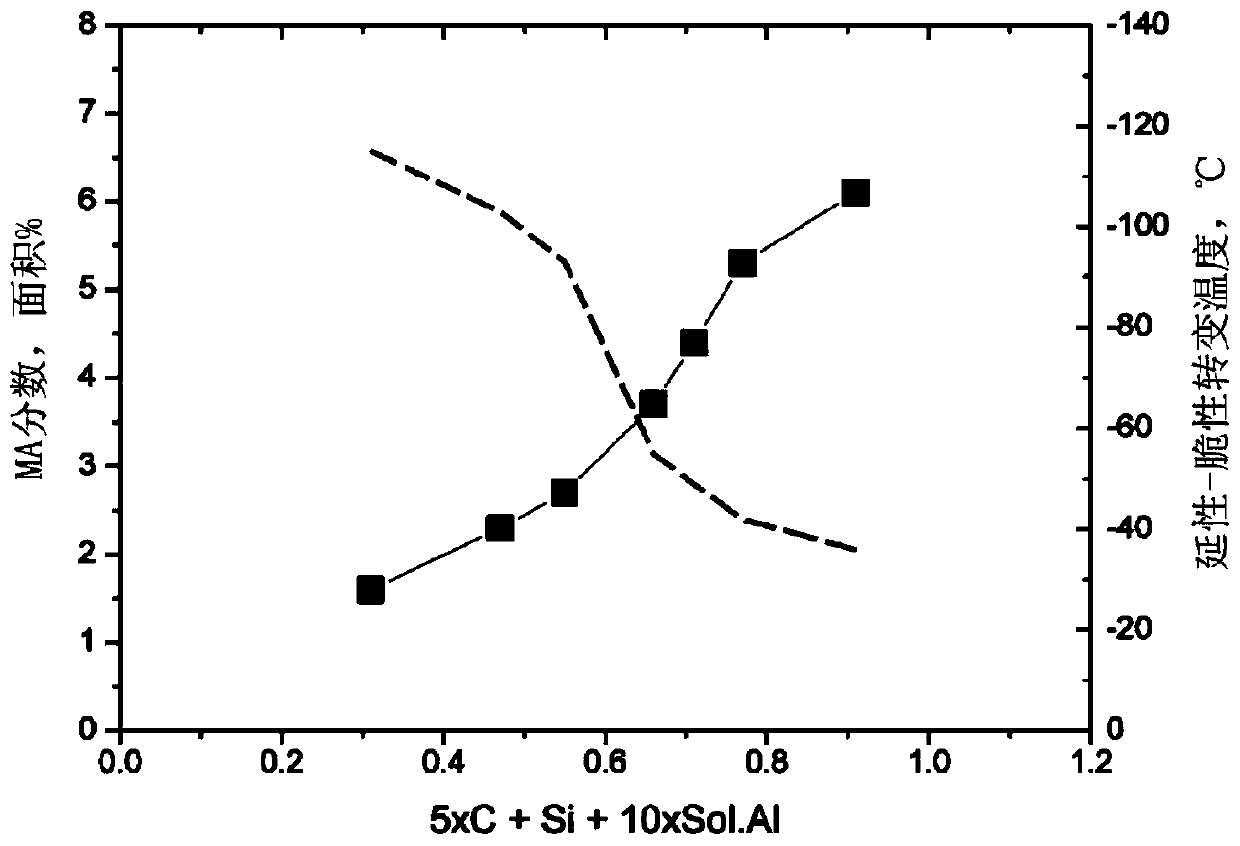
An aspect of the present invention relates to a high-strength steel material, having enhanced resistance to brittle crack propagation and break initiation at a low temperature, which comprises in weight % 0.02-0.09% of C, 0.005-0.3% of Si, 0.5-1.7% of Mn, 0.001-0.035% of Sol.Al, 0.03% or less of Nb (not including 0%), 0.01% or less of V (not including 0%), 0.001-0.02% of Ti, 0.01-1.0% of Cu, 0.01-2.0% of Ni, 0.01-0.5% of Cr, 0.001-0.5% of Mo, 0.0002-0.005% of Ca, 0.001-0.006% of N, 0.02% or less of P (not including 0%), 0.003% or less of S (not including 0%) and 0.002% or less of O (not including 0%) with a balance of Fe, and inevitable impurities, satisfies relational expression (1) below, has a microstructure comprising polygonal ferrite and needle-shaped ferrite of the total of 50 area% or greater, and comprises 3.5 area % or less of a martensite-austenite (MA) composite. Relational expression (1): 5*C + Si + 10*sol.Al <= 0.6 (In relational expression (1), each symbol for the element is a value indicating each element content in weight %).
Owner:浦项股份有限公司
Metal oxide film and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN108699718BImprove water repellencyImprove heat resistanceElectrolytic coatingsMetallurgyPhysical chemistry
A metal oxide film comprising a metal oxide represented by the following formula (1) or a metal oxide containing ZnO, and having a plurality of needle-shaped or plate-shaped crystals arranged in a mesh shape or a sword mountain shape. obtained porous structure. m x L 3‑x o 4 (1) (In the above formula, M≠L, M is selected from the group consisting of Mg, Fe, Zn, Mn, Cu, Co, Cr, Ni, L is selected from the group consisting of Co, Al, Fe, Cr , x satisfies 0≤x≤1).
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Lead frame
ActiveUS11404286B2Improve sealingLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCrystal structureLead frame
A lead frame includes, as an outermost plating layer, a roughened silver plating layer having acicular projections and covering only top faces on the upper surface side of a lead frame substrate made of a copper-based material. The roughened silver plating layer has a crystal structure in which the crystal direction <101> occupies a largest proportion among the crystal directions <001>, <111>, and <101>. The lead frame can be manufactured with improved productivity owing to reduction in cost and operation time, and achieves remarkably high adhesion to sealing resin while keeping the total thickness of plating layers including the silver plating layer to be thin.
Owner:CHANG WAH TECH
A method for controlling uniform crystallization of mold flux and eliminating needle crystallization
ActiveCN110918919BUniform crystallization temperatureHomogeneous crystalline phaseMaterial heat developmentFurnace temperatureSlag
The invention belongs to the field of iron and steel smelting and continuous casting, and relates to an experimental method capable of controlling the uniform crystal phase and eliminating needle crystals. The present invention directly melts the mold slag at the thermocouples at both ends through the thermocouple double wire technology, and creates an environment in which the crystallization temperature of the mold slag is uniform and consistent by controlling the same temperature of the thermocouples at both ends and setting the same furnace temperature. During the process of solidification and crystallization of the liquid mold powder, a uniform crystal phase can be obtained and needle crystals can be eliminated. The invention simulates the crystallization process of mold flux from high temperature to low temperature in the continuous casting process of the factory, which is more suitable for the actual production process, and the obtained experimental data is more convincing. Compared with the method of melting mold slag and quenching to obtain glass slag and then heating to obtain crystalline phase, the present invention has the advantages of short experimental operation, simple and convenient steps, less workload, and no needle crystals in the obtained product.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com