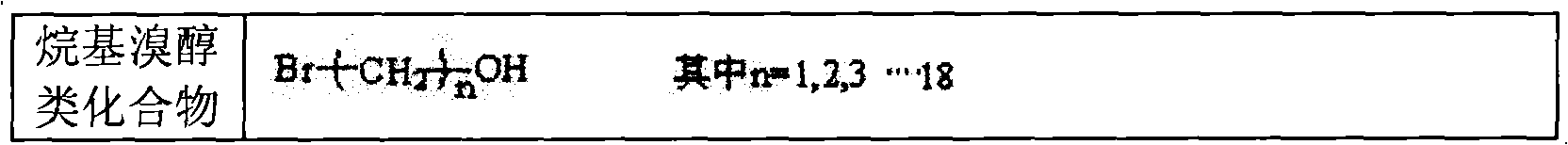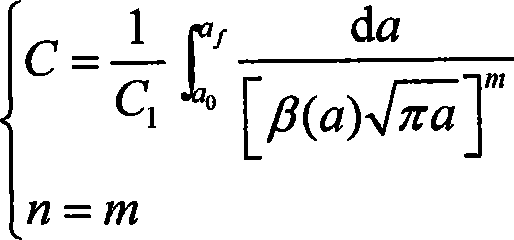Patents
Literature
3751 results about "Crazing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
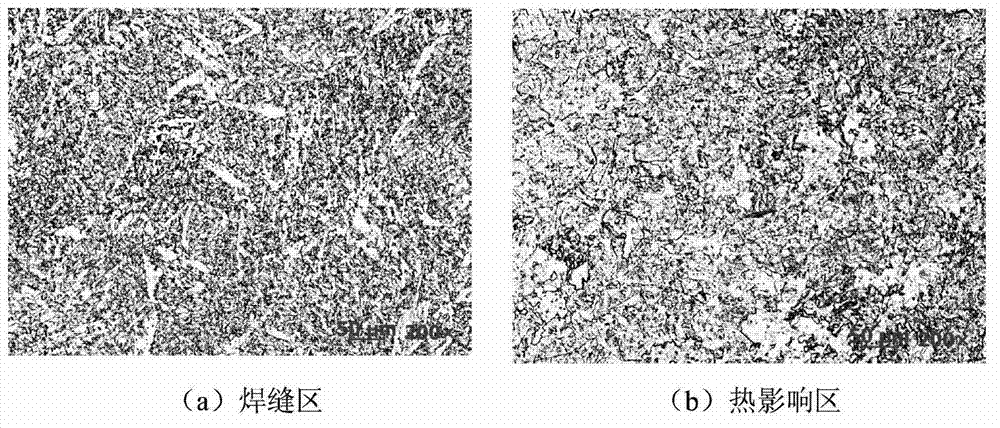
Crazing is the phenomenon that produces a network of fine cracks on the surface of a material, for example in a glaze layer. Crazing frequently precedes fracture in some glassy thermoplastic polymers. As it only takes place under tensile stress, the plane of the crazing corresponds to the stress direction. The effect is visibly distinguishable from other types of fine cracking because the crazing region has different refractive indices from surrounding material. Crazing occurs in regions of high hydrostatic tension, or in regions of very localized yielding, which leads to the formation of interpenetrating microvoids and small fibrils. If an applied tensile load is sufficient, these bridges elongate and break, causing the microvoids to grow and coalesce; as microvoids coalesce, cracks begin to form.
Semiconductor device
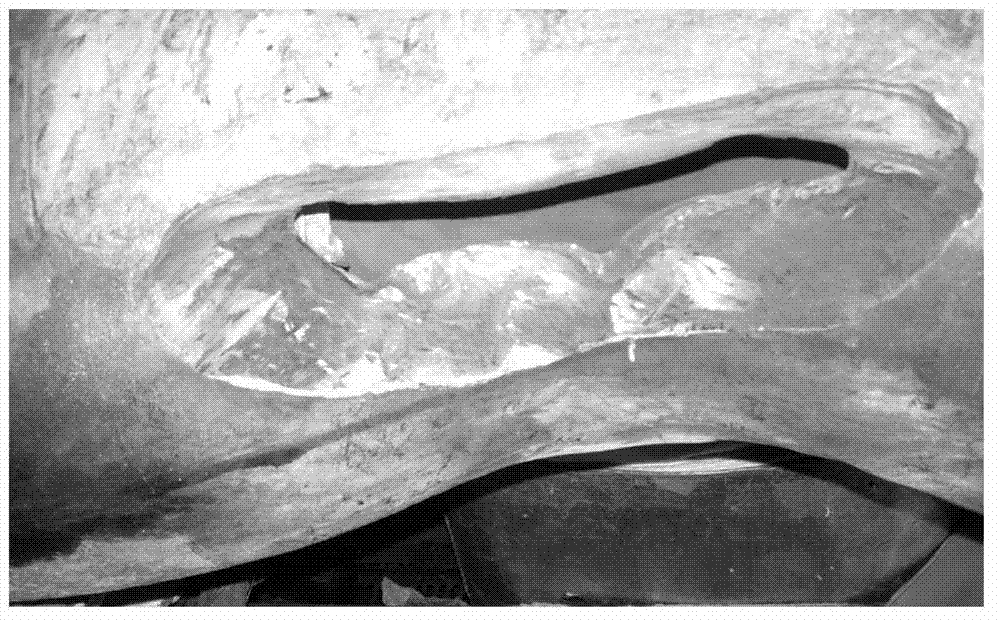
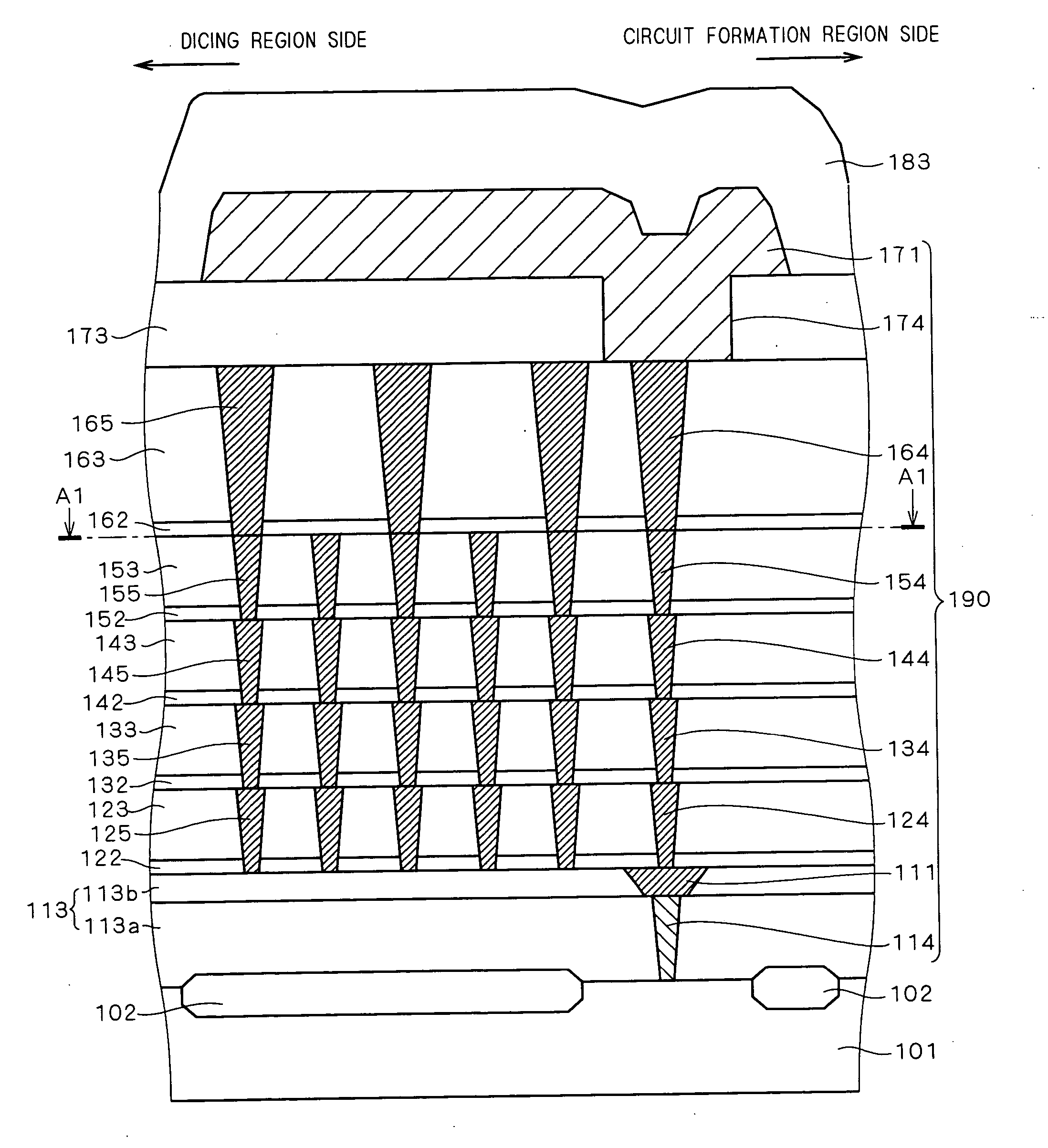
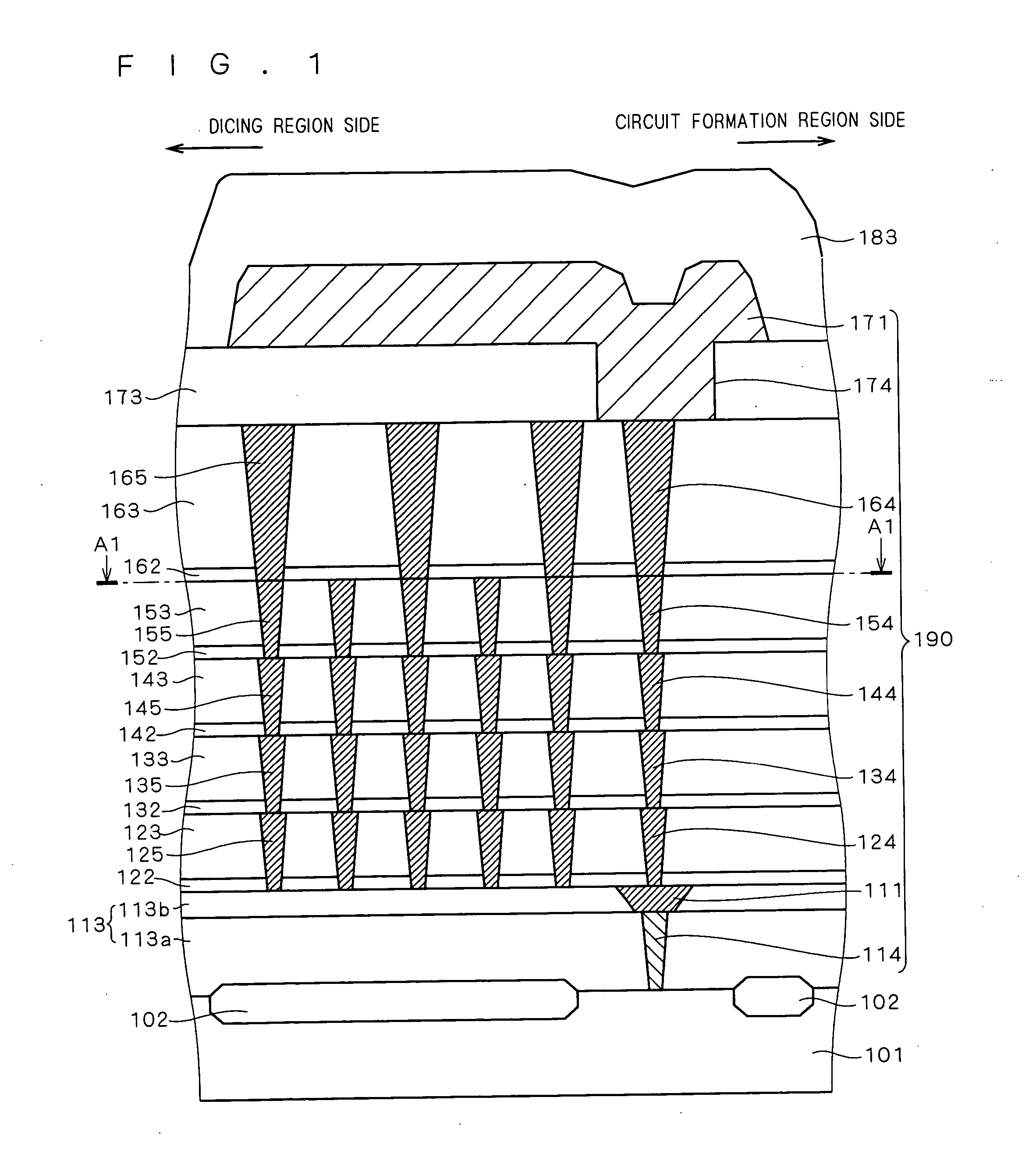
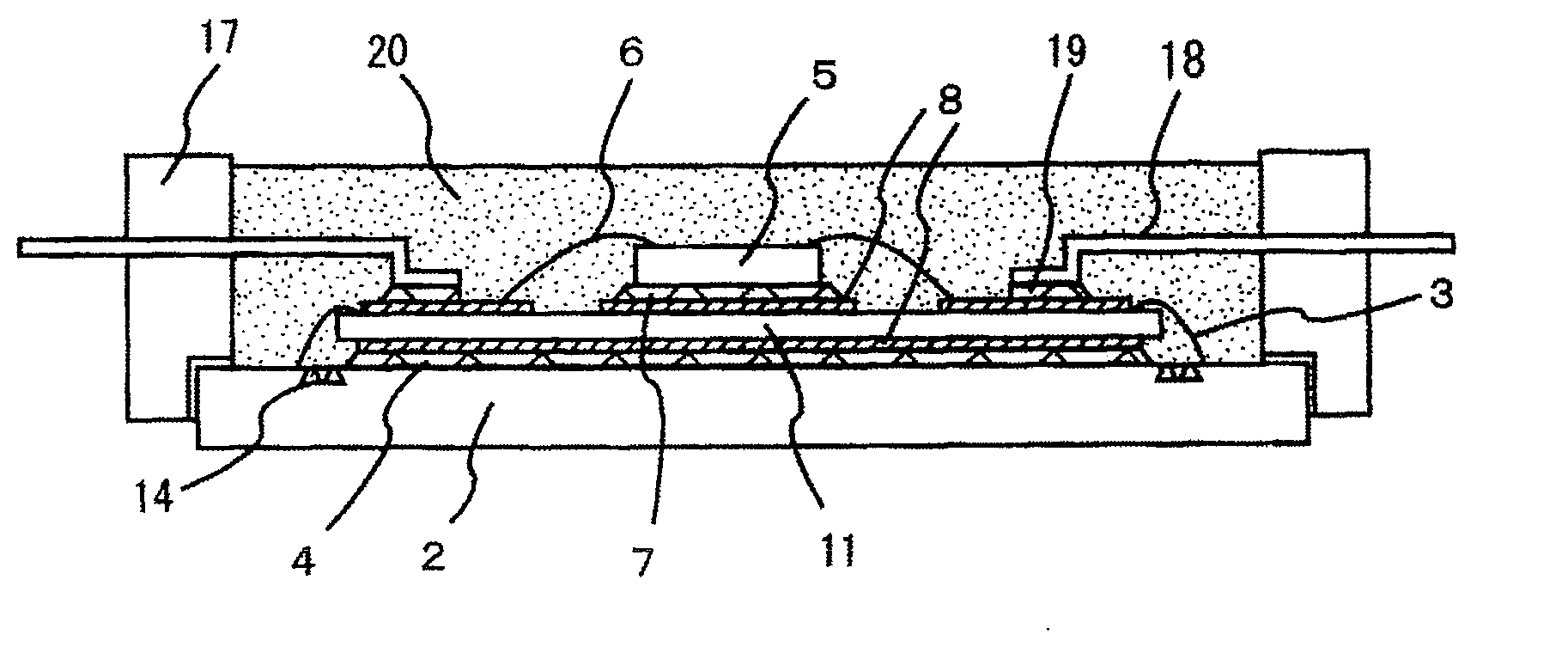
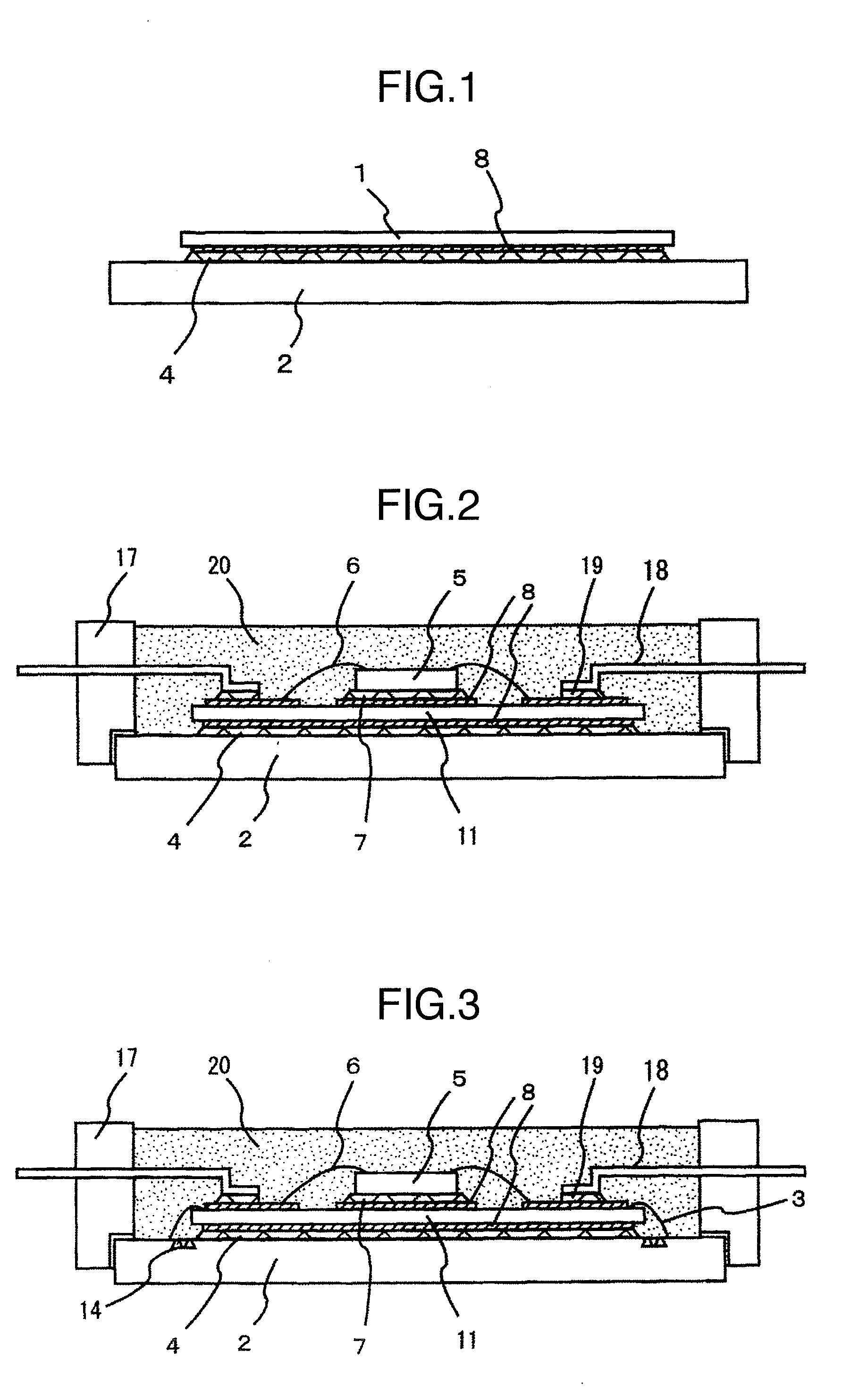
ActiveUS20050280120A1Improve reliabilityAvoid crackingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCrazingDevice material
The present invention provides a technique for improving the reliability of a semiconductor device where spreading of cracking that occurs at the time of dicing to a seal ring can be restricted even in a semiconductor device with a low-k film used as an interlayer insulating film. Dummy vias are formed in each layer on a dicing region side. The dummy vias are formed at the same intervals in a matrix as viewed in a top view. Even in the case where cracking occurs at the time of dicing, the cracking can be prevented from spreading to a seal ring by the dummy vias. As a result, resistance to moisture absorbed in a circuit formation region can be improved, and deterioration in reliability can be prevented.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
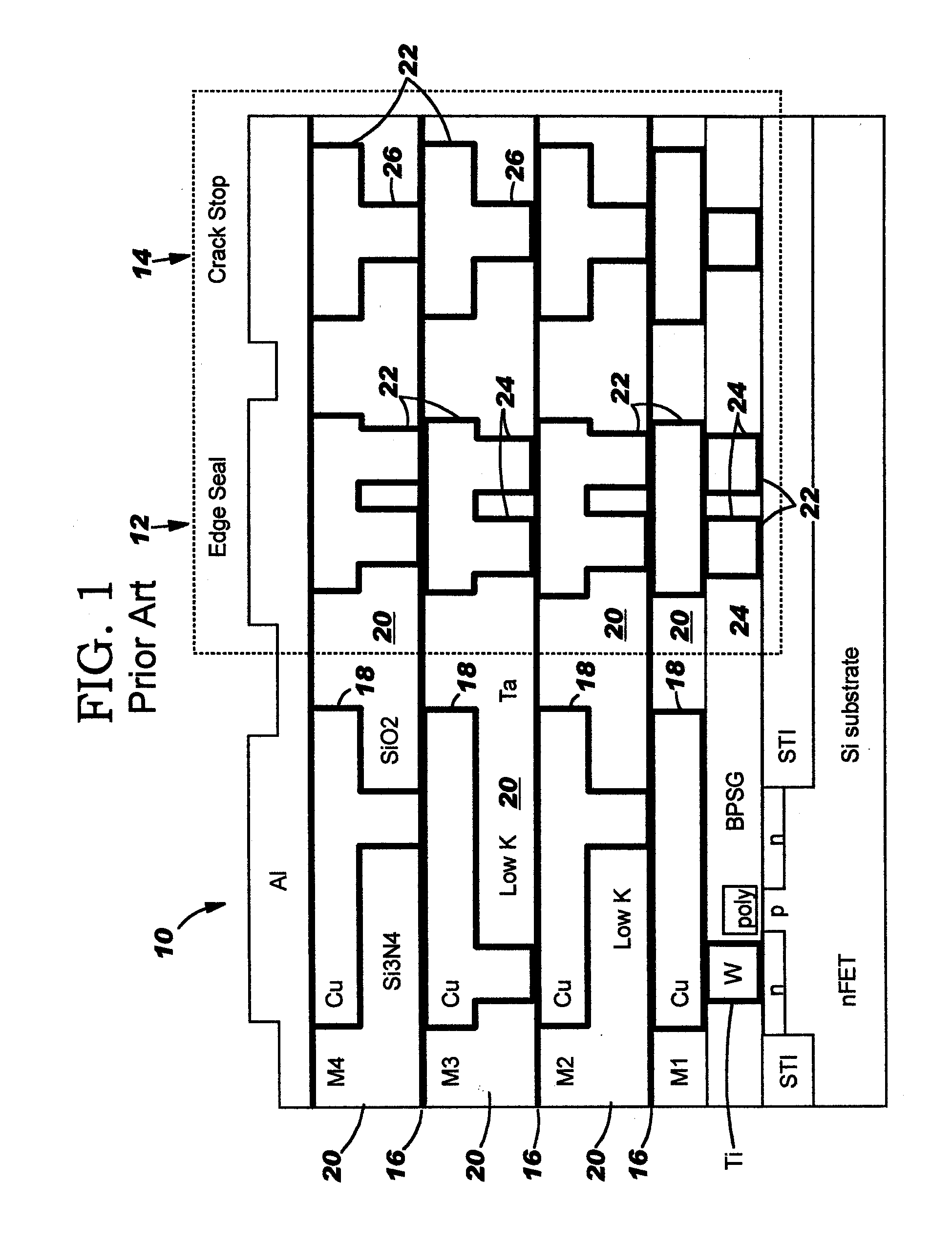
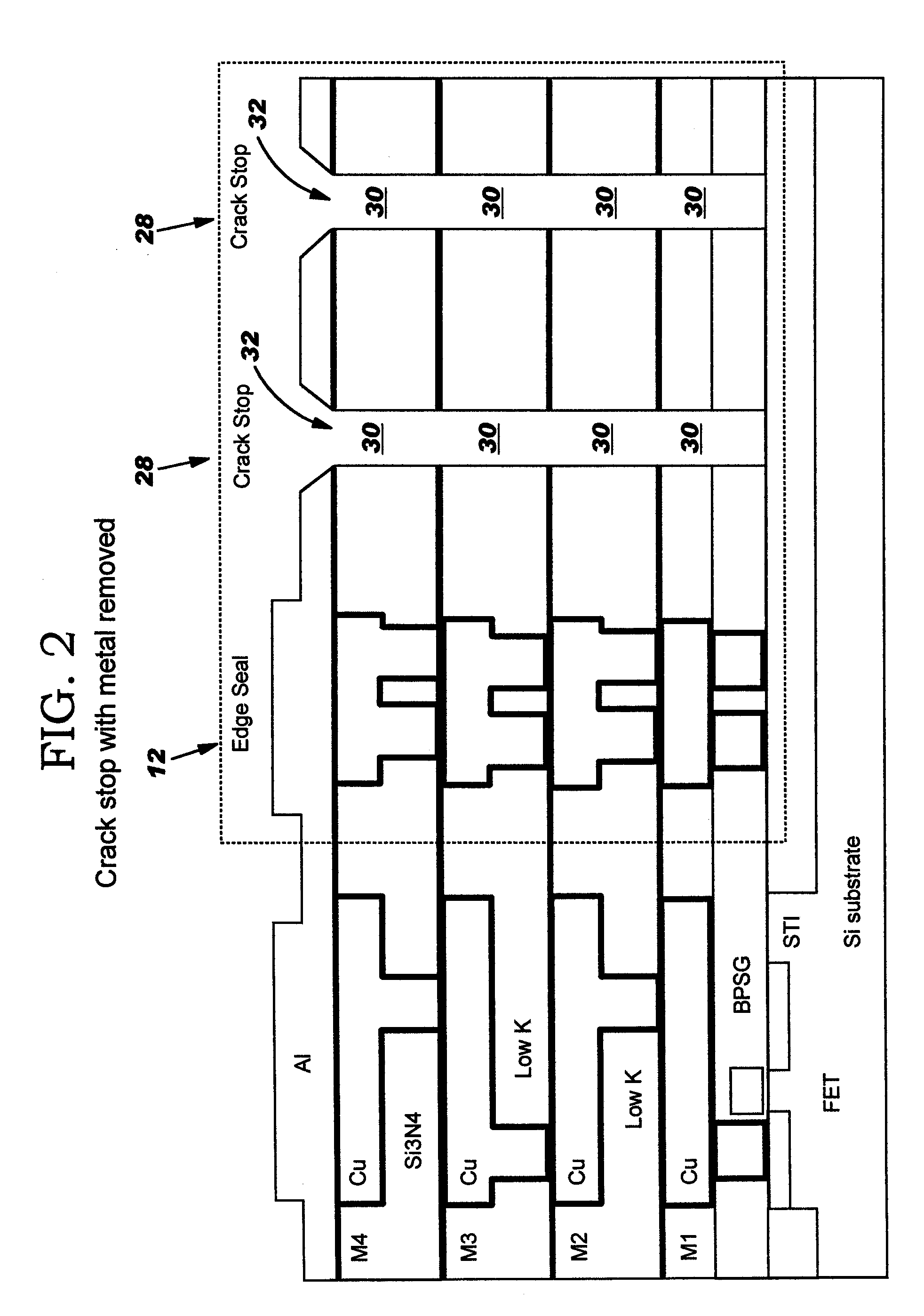
Crack stop for low k dielectrics
InactiveUS20050026397A1Hinders its propagationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetal interconnectCrazing
A crack stop for low K dielectric materials of an integrated circuit (IC) formed on an IC chip using metal interconnects which do not form a self-passivating oxide layer, such as copper or silver interconnects, in a low-K dielectric material to prevent damage to the active area of the IC chip caused by chipping and cracking formed along peripheral edges of the IC chip during a dicing operation. A moisture barrier or edge seal is formed as a metal stack positioned along the outer peripheral edges of the active area of the IC chip. The crack stop is formed by at least one trench or groove positioned outside of the moisture barrier / edge seal on the outer periphery of the IC chip.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Semiconductor device member, production method of semiconductor-device-member formation liquid and semiconductor device member, and semiconductor-device-member formation liquid, phosphor composition, semiconductor light-emitting device, lighting system and image display system using the same
ActiveUS20090309116A1Improve sealingMaintain performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCrazingDevice material
To provide a semiconductor device member that is superior in heat resistance, light resistance, film-formation capability and adhesion, and is capable of sealing a semiconductor device and holding a phosphor without causing cracks, peelings and colorings even after used for a long period of time, the weight loss at the time of heating, measured by a predetermined weight-loss at-the-time-of-heating measurement method, is 50 weight % or lower and the ratio of peeling, measured by a predetermined adhesion evaluation method, is 30% or lower, in the semiconductor device member.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Method and apparatus for determining and assessing a characteristic of a material
InactiveUS20050072236A1Low costImprove accuracyAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDifferential measurementCrazing
An acoustic energy-based, non-contact or contact testing approach provides low cost, highly accurate, and reliable information to (a) identify flaws and anomalies and (b) assess the integrity of a particular material. This approach is not hindered by surface conditions or impediments, and indeed, looks beneath the surface of the material by propagating an acoustic wave through the material using two differential transducers. A dynamic differential measurement is made of the material under a load condition and an unloaded condition that allows identification and assessment of various characteristics of the material. Multiple “windows” of information may be generated that permit (a) direct detection of flaws, defects, and anomalies using a scattering technique, (b) detection of crack closure and opening used to assess the stability of the material, (c) determination of strain on the material which relates to its performance, and (d) determination of defect dynamics linked to the defect size and stability.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
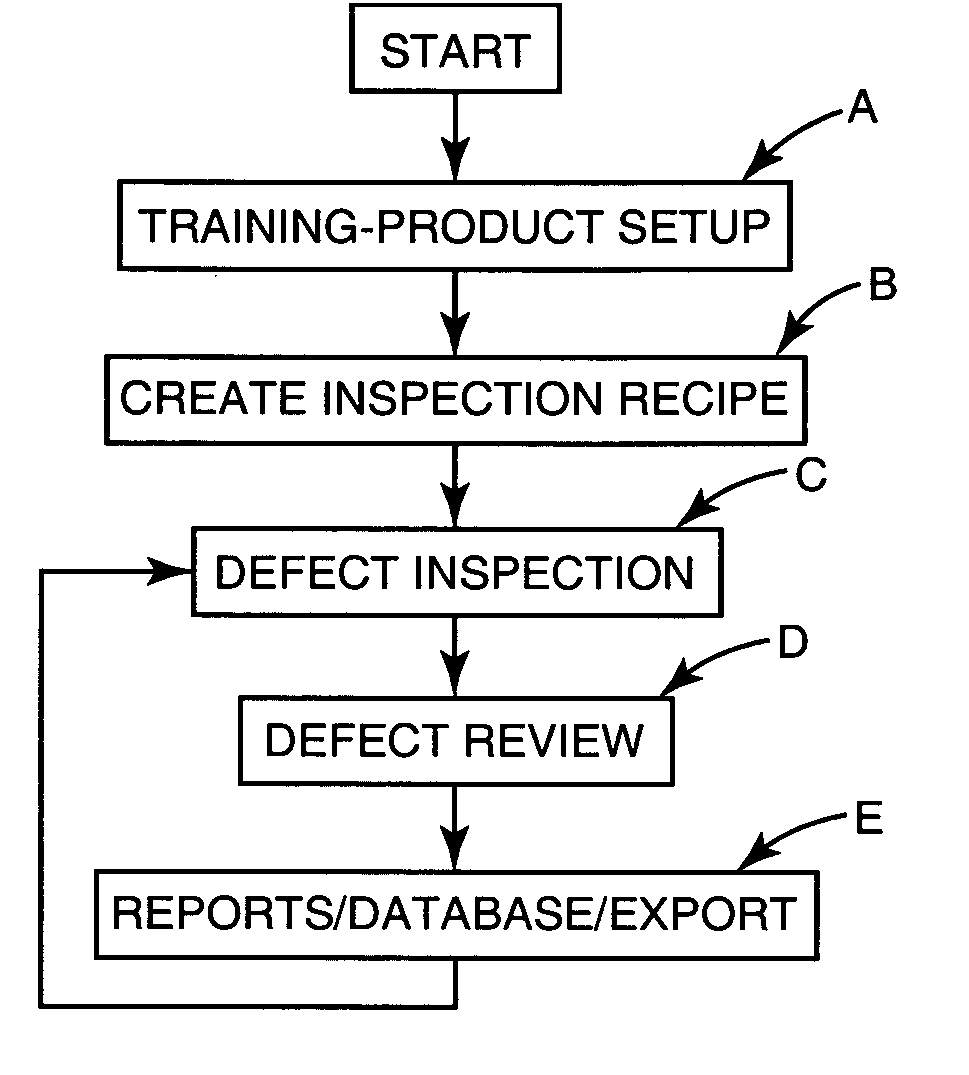
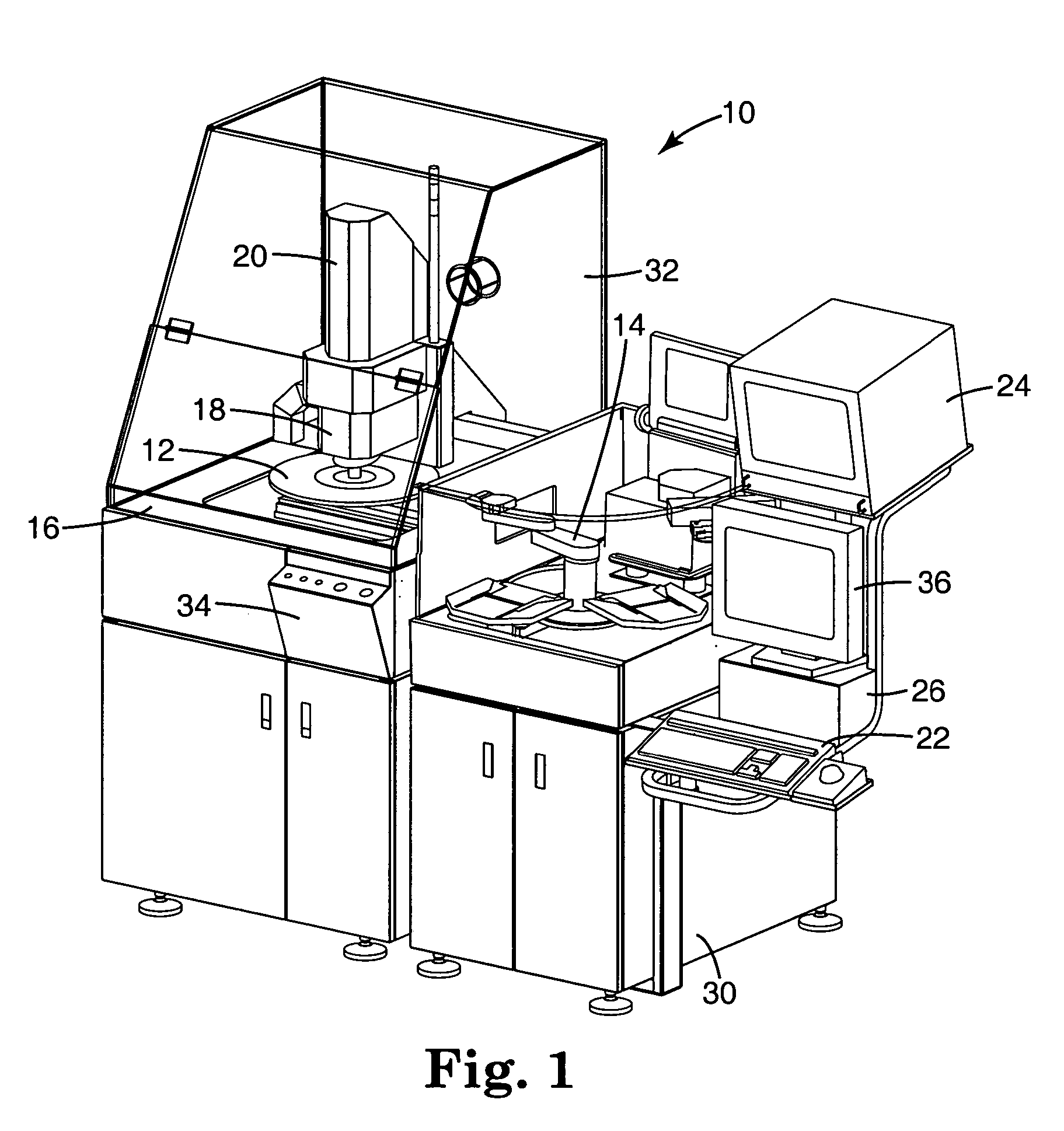
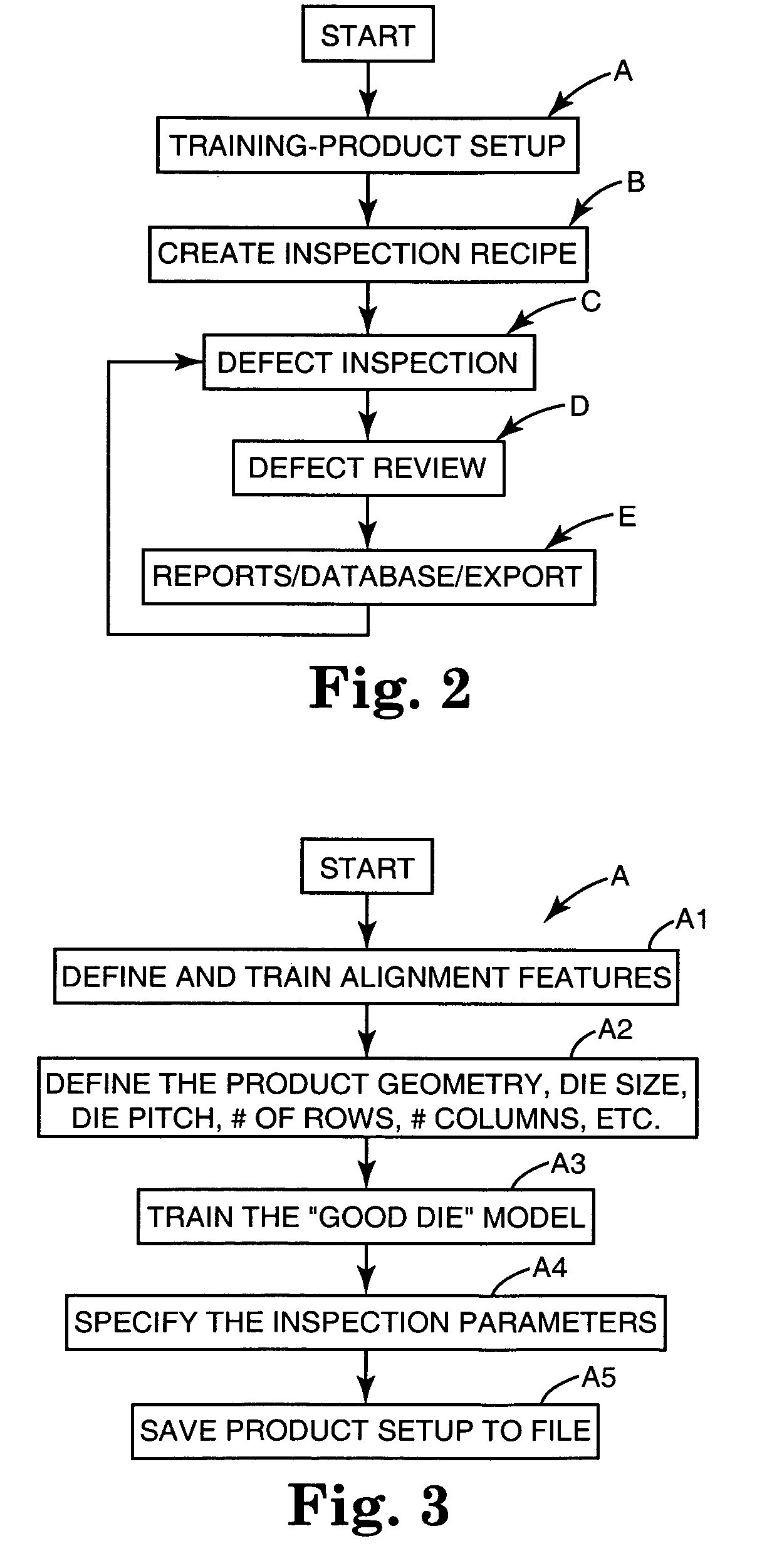
Automated wafer defect inspection system and a process of performing such inspection
InactiveUS20050008218A1Improve inspection qualityEasy to controlImage enhancementImage analysisCrazingEngineering
An automated defect inspection system has been invented and is used on patterned wafers, whole wafers, broken wafers, partial wafers, sawn wafers such as on film frames, JEDEC trays, Auer boats, die in gel or waffle packs, MCMs, etc. and is specifically intended and designed for second optical wafer inspection for such defects as metalization defects (such as scratches, voids, corrosion, and bridging), diffusion defects, passivation layer defects, scribing defects, glassivation defects, chips and cracks from sawing, solder bump defects, and bond pad area defects.
Owner:RUDOLPH TECHNOLOGIES INC
Crack repair method
InactiveUS20050067466A1Rapid and inexpensive mannerMinimize cracksTurbinesArc welding apparatusCrazingGas turbines
A method of repairing cracks on a surface of a component such as gas turbine components includes the steps of repairing the cracks of the component by brazing, detecting remaining cracks on the surface or below the surface, which were not properly filled with braze material during the repair brazing operation, and repairing the crack zones with a focussed low-heat input welding method using an appropriate weld filler materials.
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
Ceramic material for 3D light curing formation printing and preparation method of ceramic element
InactiveCN109400177AHigh ceramic contentEasy to printAdditive manufacturing apparatusOligomerAgent Combination
The invention relates to a ceramic material for 3D light curing formation printing and a preparation method of a ceramic element. The ceramic material is prepared from 30 to 70 vol percent of ceramicpowder and 30 to 70 vol percent of photosensitive resin premixed liquid, wherein the photosensitive resin premixed liquid is prepared from 37 to 50 weight percent of oligomers, 30 to 60 weight percentof reactive diluents, 0.1 to 5 weight percent of photoinitiators, 1 to 5 weight percent of dispersing agents, 0.1 to 0.6 weight percent of ultraviolet blocking agents, 0 to 0.05 weight percent of polymerization inhibitors, 1 to 4 weight percent of anti-foaming agents, 0.5 to 2.35 weight percent of anti-settling agents and 0.3 to 3 weight percent of leveling agents. In the degreasing and sinteringpost-treatment work procedures, specific parameters are used, so that a sintering element can reach good sintering density and mechanical performance. By optimizing the composition and the proportionof light curing ceramic resin, and selecting the excellent dispersing agent combination and the reasonable consumption, the ceramic powder can be better dispersed in the resin; the problems that theexisting light curing ceramic resin has poor flowability and low formation precision, and that a finally prepared ceramic product can easily generate cracks or deformation, and the like are solved.
Owner:西安点云生物科技有限公司
Single/multi-layer magnetic conductive sheet for wireless charging and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104900383AImprove permeabilityIncrease contact resistanceBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemCrazingEngineering
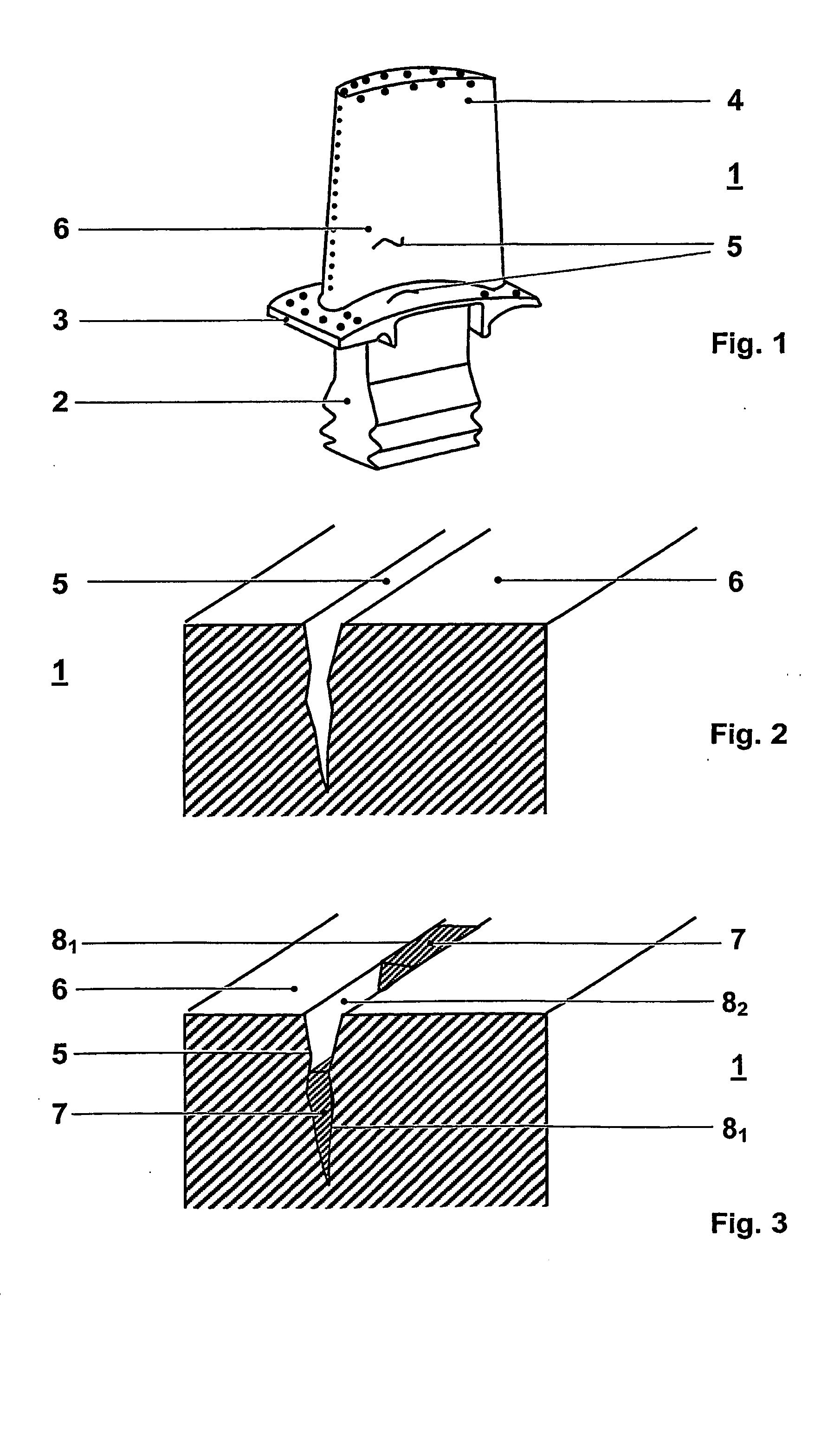
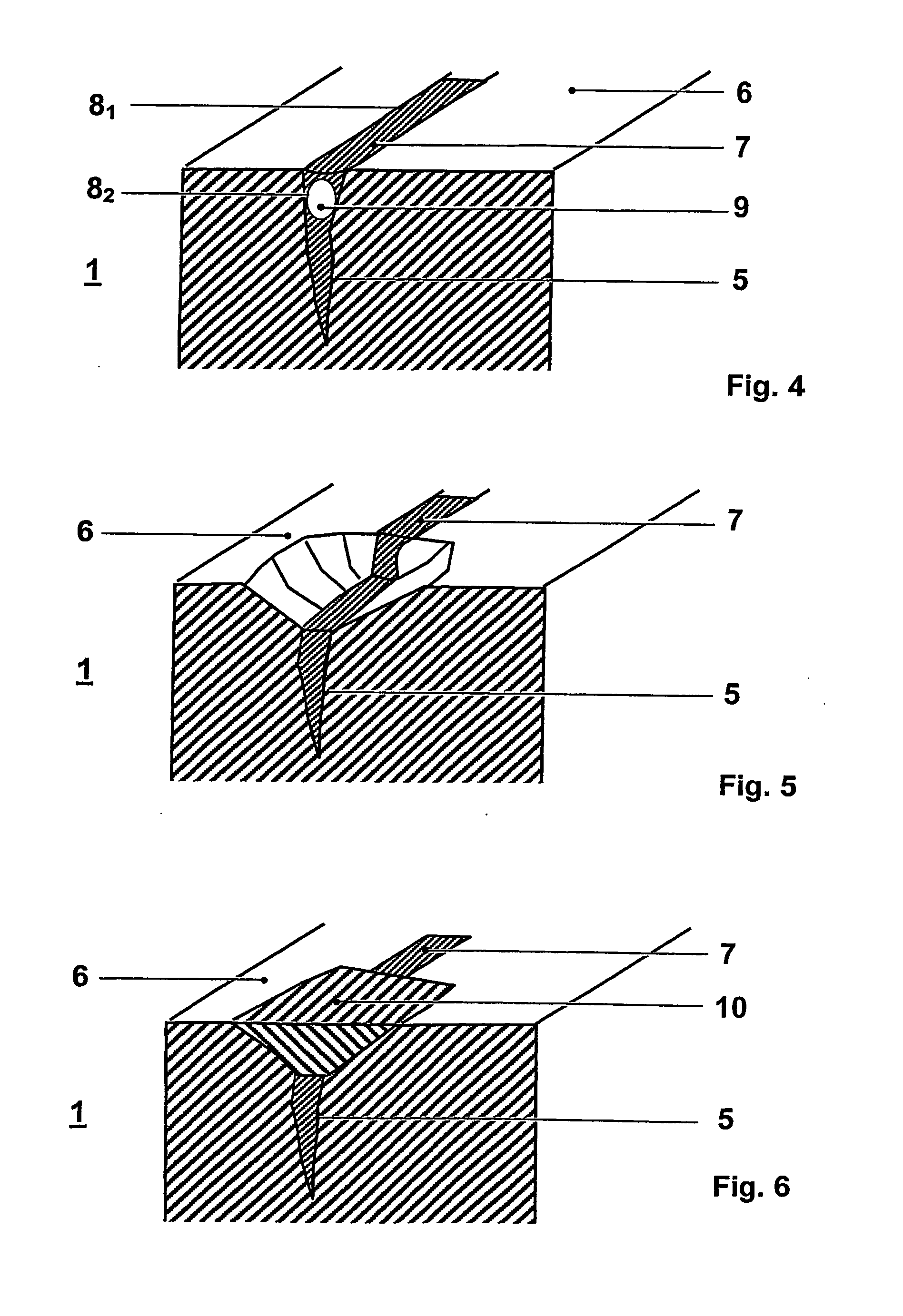
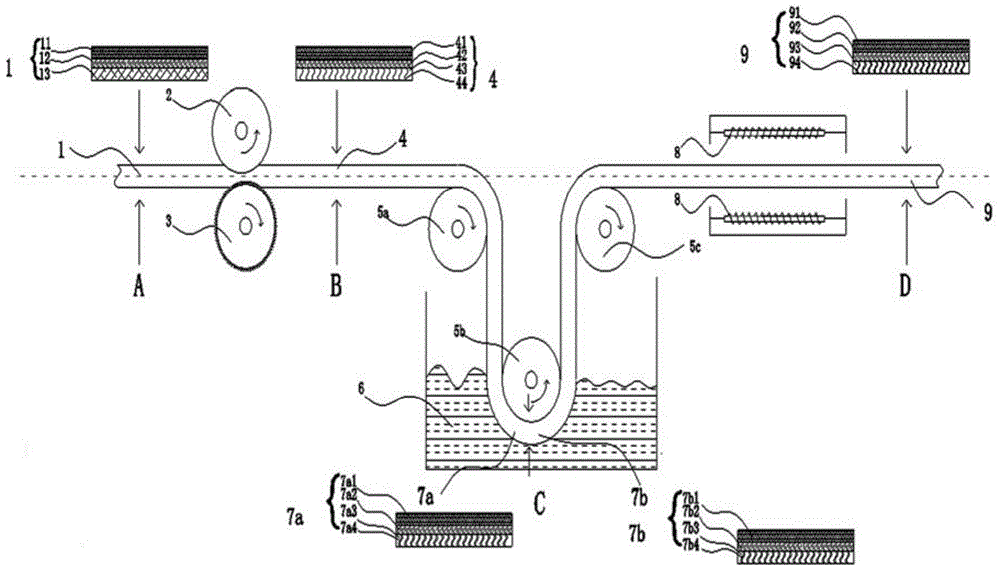
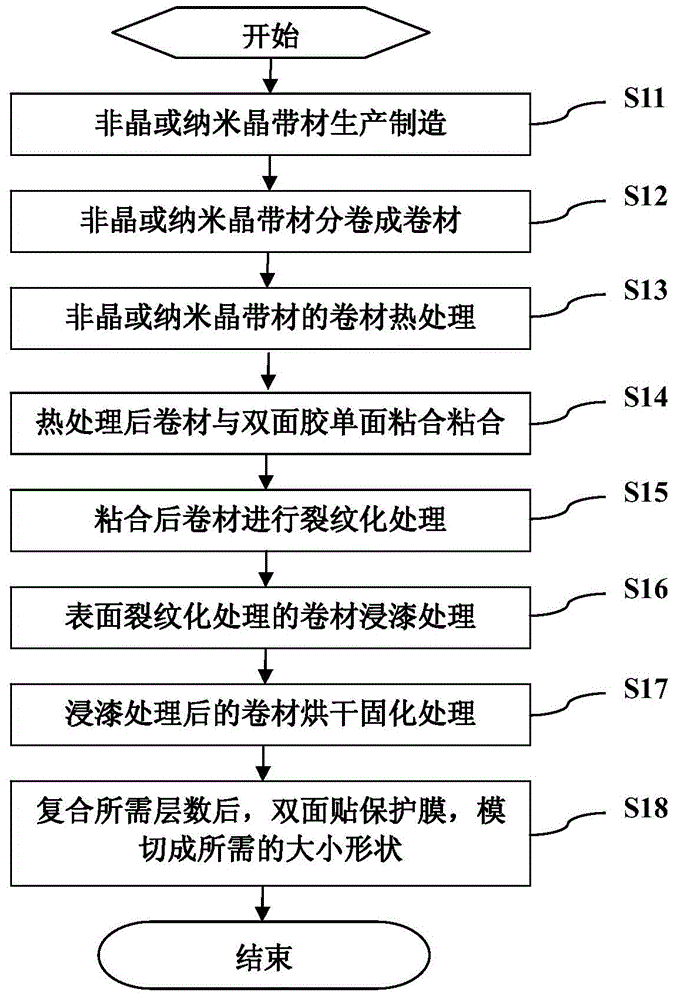
The invention discloses a single / multi-layer magnetic conductive sheet for wireless charging and a preparation method thereof. The single-layer magnetic conductive sheet comprises a layer of magnetic slice. Multiple strips of cracks are uniformly distributed on the slice and divide the slice into multiple fragment units. Gaps of the cracks are filled with insulation medium, so fragment units on two sides of the cracks are mutually insulated. The single-layer magnetic conductive sheet also comprises a double-faced adhesive tape which is adhered to one face of the magnetic slice. A protection film formed by the insulation medium is formed on the other face of the magnetic slice. The preparation method comprises steps of heat treatment, adhesion of the double-faced adhesive tape, crack processing, gum dipping processing and drying and curing processing. According to the invention, inductance value and quality factor of a charging coil are increased, charging efficiency is increased and loss is reduced. The continuously prepared magnetic conductive sheet is characterized by controllable magnetic conductivity, continuous production, convenient operation and simple insulation processing.
Owner:ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY & MATERIALS CO LTD
Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposited SIO2/SI3N4 multilayer passivation layer for semiconductor applications
InactiveUS6017614ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesResistCorrosive chemical
A method was achieved for forming a multilayer passivation layer comprised of a silicon oxide / silicon nitride / silicon oxide / silicon nitride by depositing the layers consecutively in a single PECVD system. The method consists of depositing a first SiO2 layer that serves as a stress-release layer, a thin Si3N4 layer that serves as a buffer layer that minimizes cracking and as a passivation layer that prevents mobile alkaline ion penetration, a thin second SiO2 layer to fill and seal any remaining cracks and pinholes in the first Si3N4 layer, and a main Si3N4 passivation layer that prevents water and / or other corrosive chemicals from attacking the metal. Since this multilayer passivation layer can be deposited essentially pinhole-free to a thickness that is less than the prior art's passivation layer of 8000 Angstroms needed to prevent pinholes, it can be used on 0.38 to 0.25 um DRAM technology, which eliminates voids that could otherwise trap photoresist which can later cause corrosion of the metal lines.
Owner:VANGUARD INTERNATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION
Semiconductor power module
ActiveUS20070246833A1Temperature cycle life is improvedImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsCrazingEngineering
Use of Pb-free solder has become essential due to the environmental problem. A power module is formed by soldering substrates with large areas. It is known that in Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu which hardly creeps and deforms with respect to large deformation followed by warpage of the substrate, life is significantly shortened with respect to the temperature cycle test, and the conventional module structure is in the situation having difficulty in securing high reliability. Thus, the present invention has an object to select compositions from which increase in life can be expected at a low strain rate. In Sn solder, by doping In by 3 to 7% and Ag by 2 to 4.5%, the effect of delaying crack development at a low strain rate is found out, and as a representative composition stable at a high temperature, Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu-5In is selected. Further, for enhancement of reliability, a method for partially coating a solder end portion with a resin is shown.
Owner:HITACHI POWER SEMICON DEVICE
Crack free metallic articles
InactiveUS6103402AReduce material stressReduce solidificationTurbinesBy zone-melting liquidsCrazingClosed loop
A containerless method of producing a crack free metallic article of near-net shape includes melting a filler material into a metallic substrate or seed under conditions chosen to preclude cracking. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, a laser beam is operated at a relatively low power density and at a relatively large beam diameter at the substrate surface for an extended length of time to produce a molten pool with a low aspect ratio. Near-net shape is achieved by applying the process in a closed-loop, multi-axis material deposition system.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Coated tool of cemented carbide
InactiveUS6187421B1Improve propertiesImprove tool lifePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesCoated membraneCarbide coating
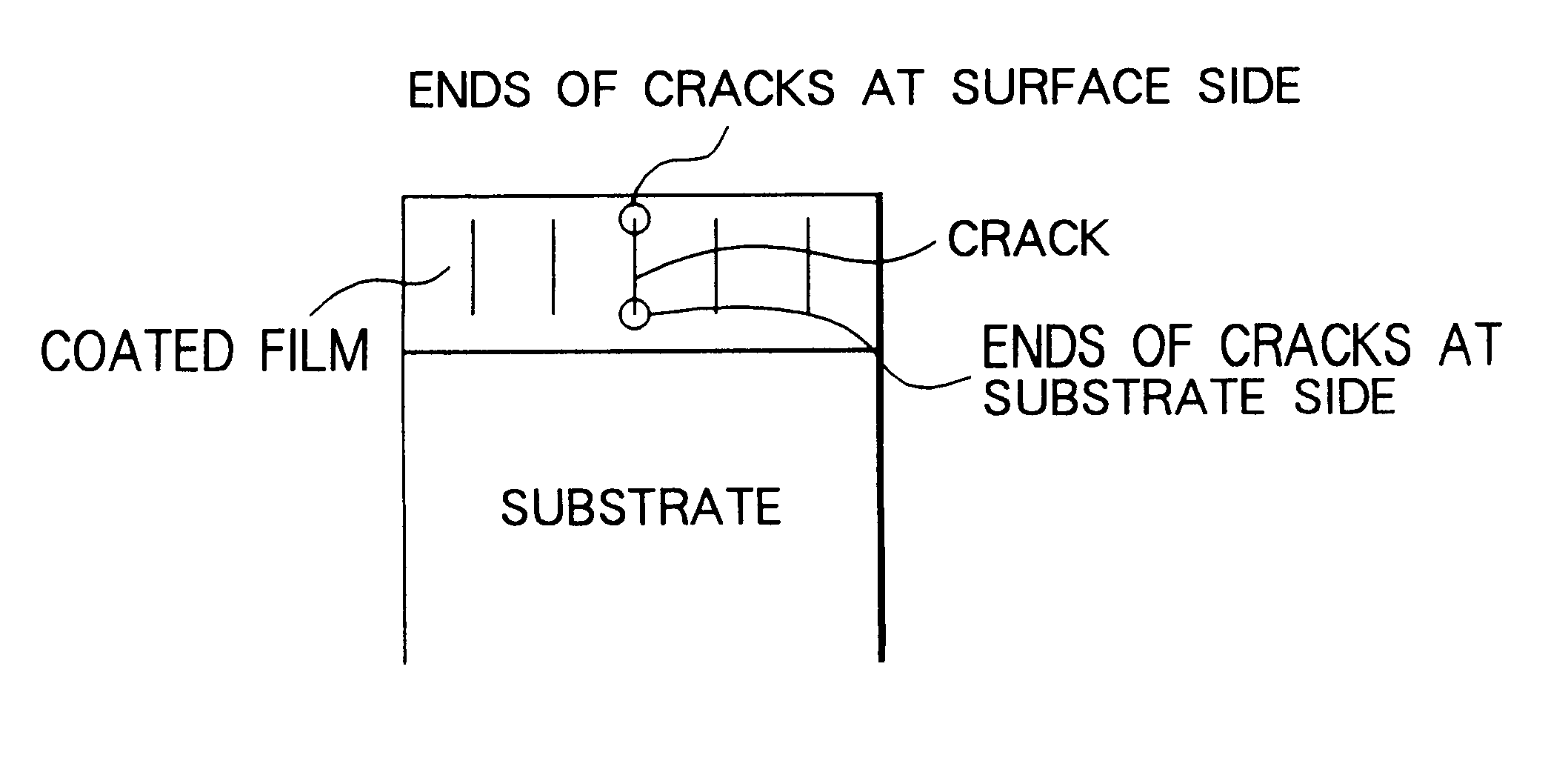
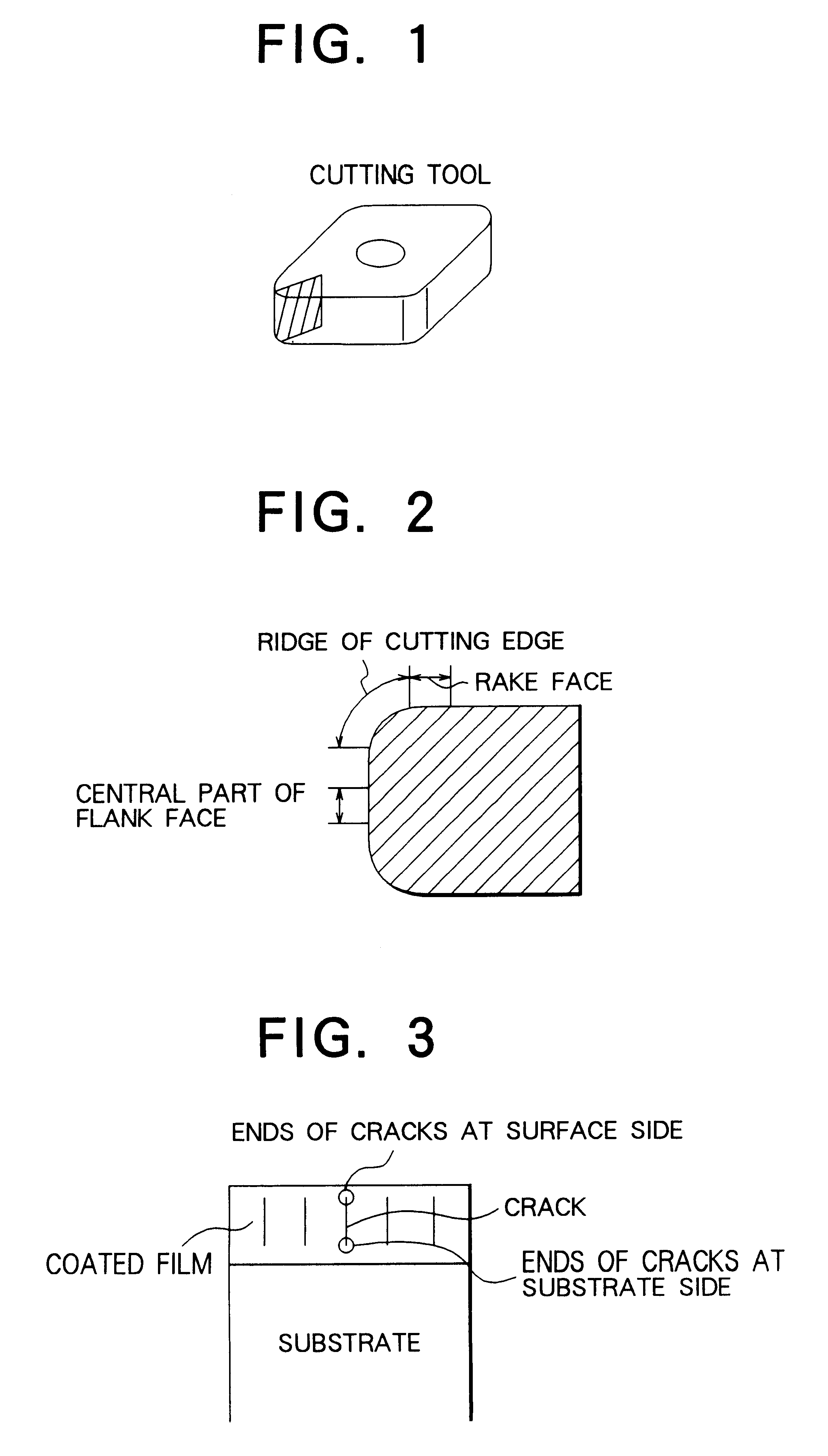
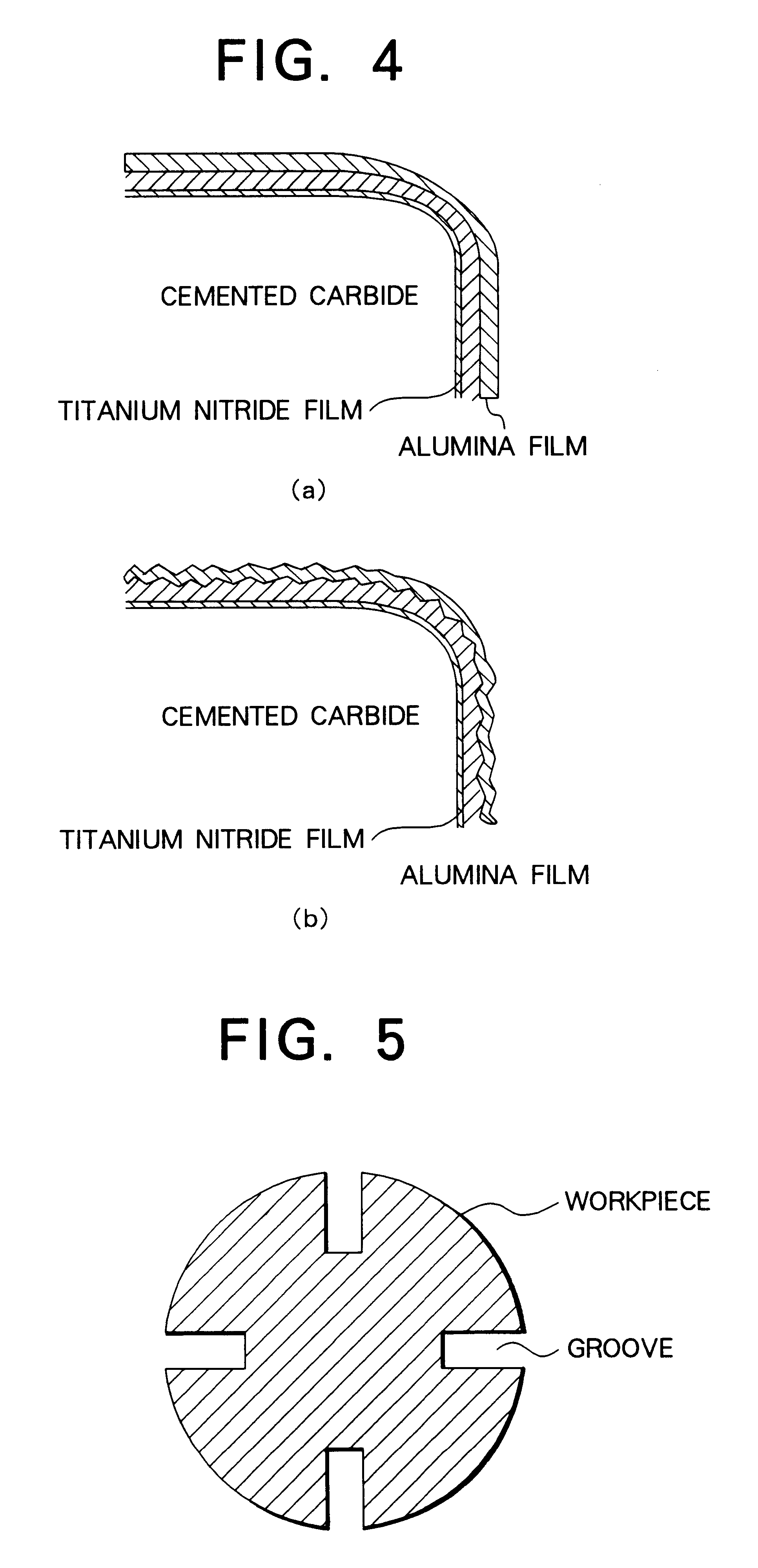
The principal object of the present invention is to provide a coated cemented carbide tool whose both properties of breakage resistance and wear resistance are improved and whose life is lengthened.The present invention has been made to achieve this object and is related with a coated cemented carbide cutting tool comprising a substrate consisting of a matrix of WC and a binder phase of an iron group metal and a plurality of coated layers provided on a surface of the substrate, in which (a) an innermost layer, adjacent to the substrate, of the coated layers consists essentially of titanium nitride having a thickness of 0.1 to 3 mum, (b) on a mirror-polished cross-sectional microstructure of the said tool, an average crack interval in the coated film on a ridge of a cutting edge and / or rake face is smaller than an average crack interval in the coated layer on a flank face, (c) at least 50% of the cracks in the coated film on the said ridge of the cutting edge and / or rake face have ends of the cracks in the said innermost titanium nitride layer, in a layer above the titanium nitride layer or in an interface between these layers and (d) an average crack length in the coated film on the said ridge of the cutting edge and / or rake face is shorter than an average film thickness on the flank face.According to the present invention, quantitatively specifying the crack intervals and positions of the ends of the cracks in the coated layer results in excellent breakage resistance as well as wear resistance.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Photo-induced reversible self-repair polyurethane film and repair method
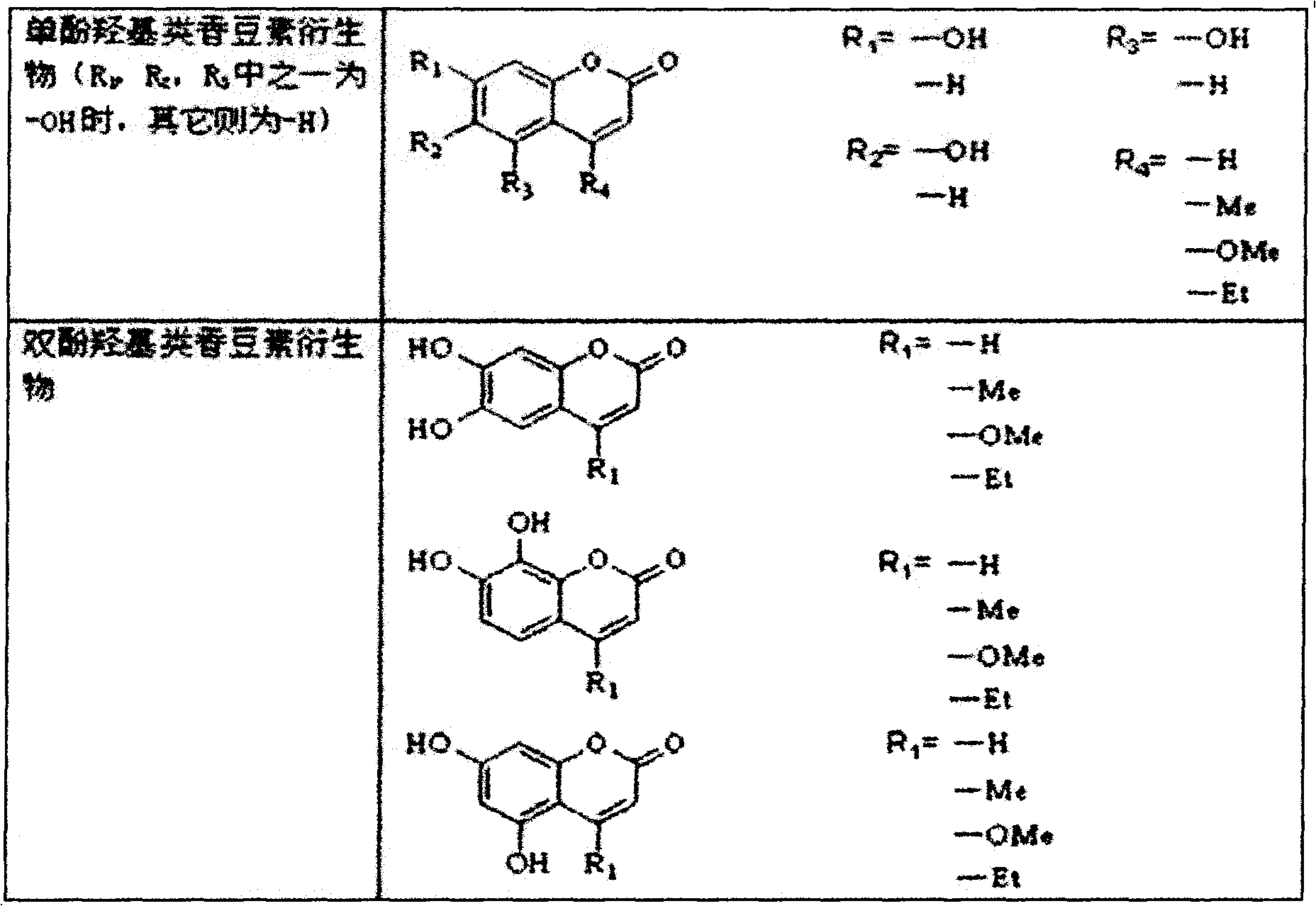
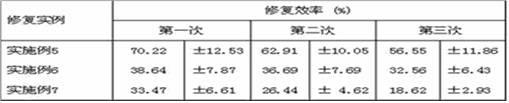
The invention relates to a photo-induced reversible self-repair polyurethane film and a preparation method and a repair method thereof. The polyurethane film mainly comprises 10 to 40 parts of phenolic hydroxyl coumarin derivative, 10 to 50 parts of alkyl bromal compound, 10 to 40 parts of polyisocyanate, and 10 to 30 parts of polyether polyol or polyester polyol. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: generating phenolic hydroxyl coumarin by using the phenolic hydroxyl coumarin derivative and the alkyl bromal compound under the action of absolute potassium carbonate; and reacting the phenolic hydroxyl coumarin, the polyisocyanate and the polyether polyol or the polyester polyol to obtain polyurethane solution, and performing cross linking under the irradiation of ultraviolet with wavelength of 350 nanometers after the film is formed to obtain the polyurethane film. The damaged surface is irradiated through the ultraviolet with wavelength of 254 to 350 nanometers, so that the reduced coumarin monomers are subjected to dimer cross linking reaction again and the purpose of repairing cracks is fulfilled. Compared with the prior art, the polyurethane film has the characteristics of good film forming property and high transparency; and the repair process is simple and has low cost.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
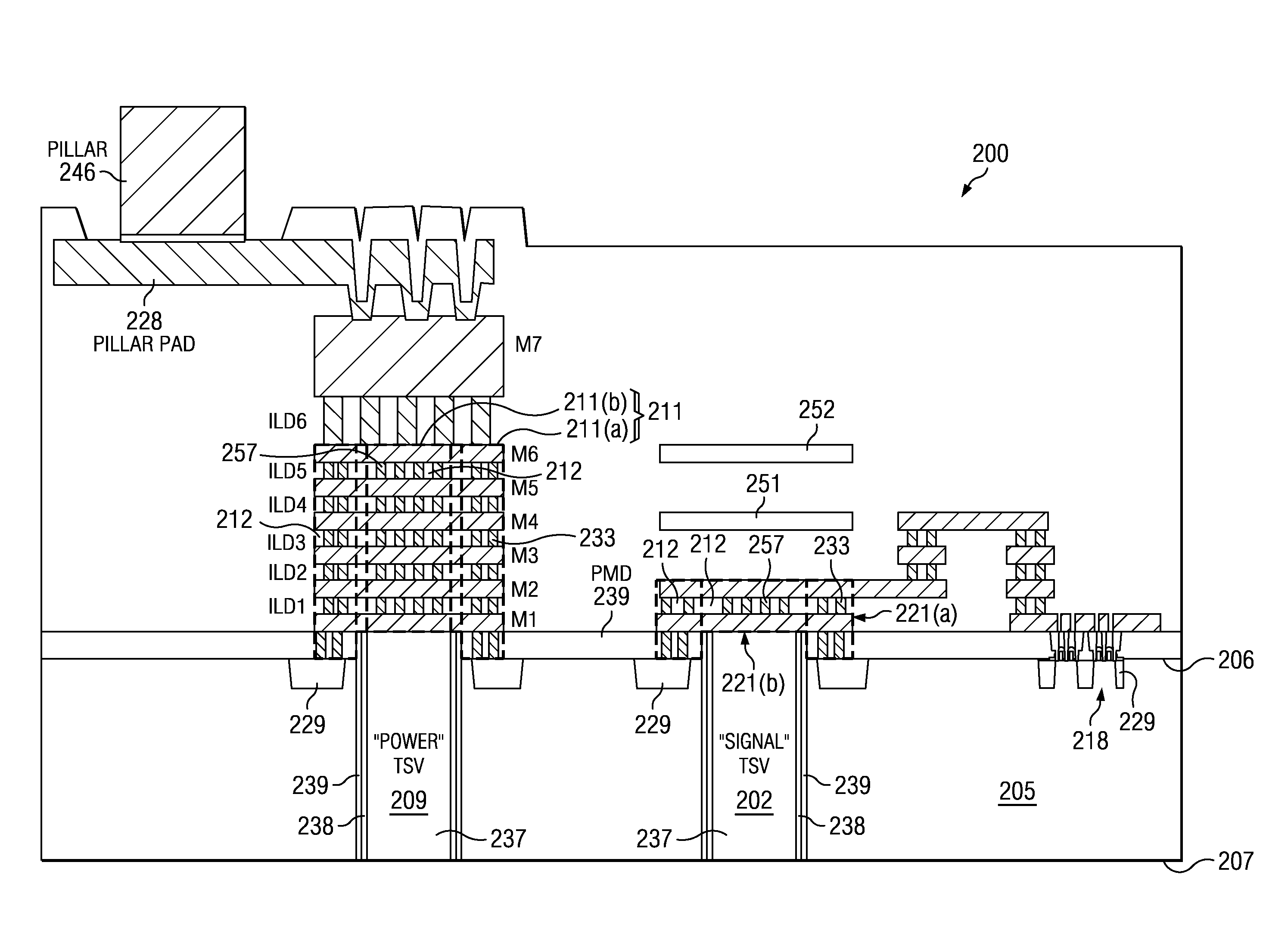
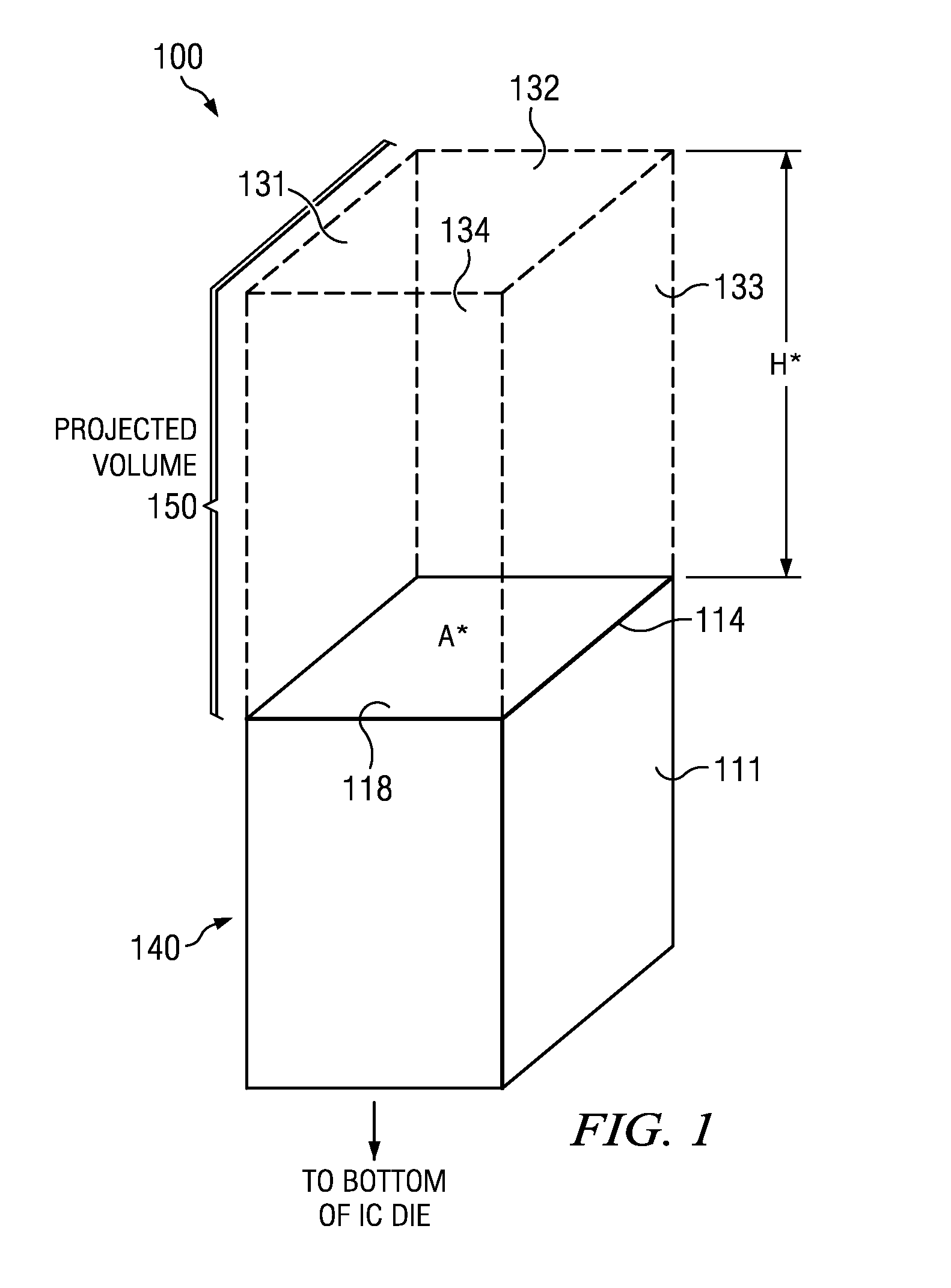
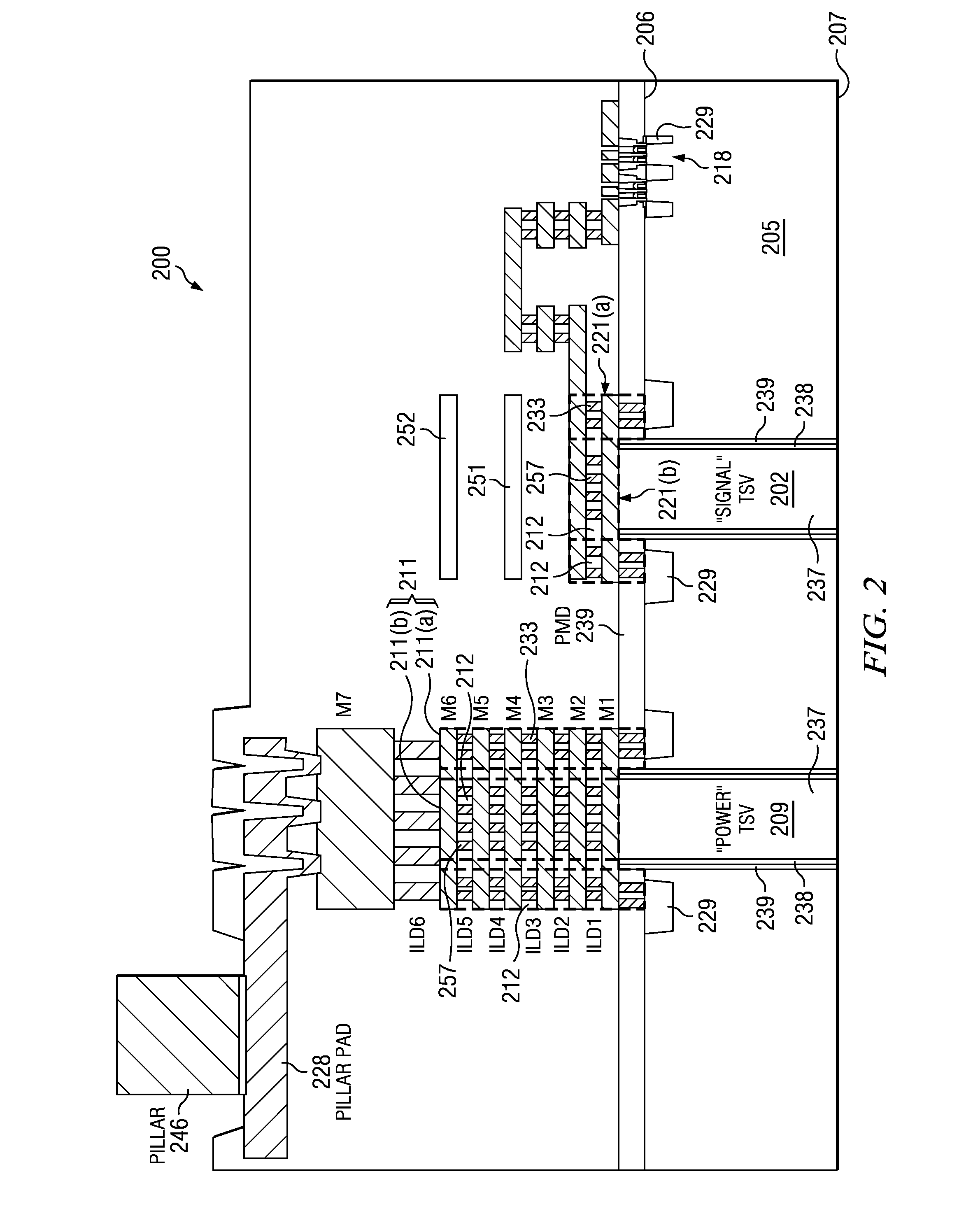
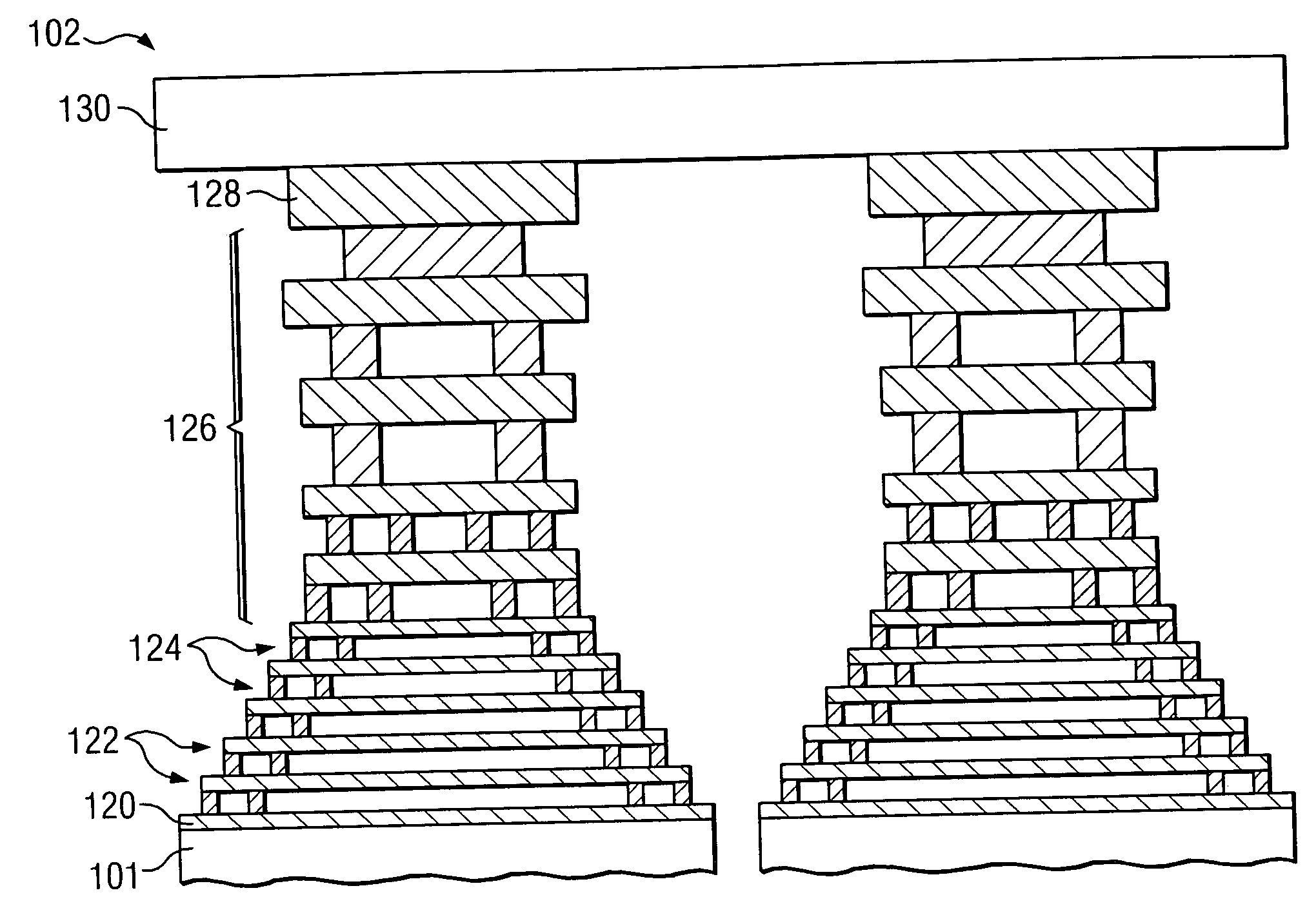
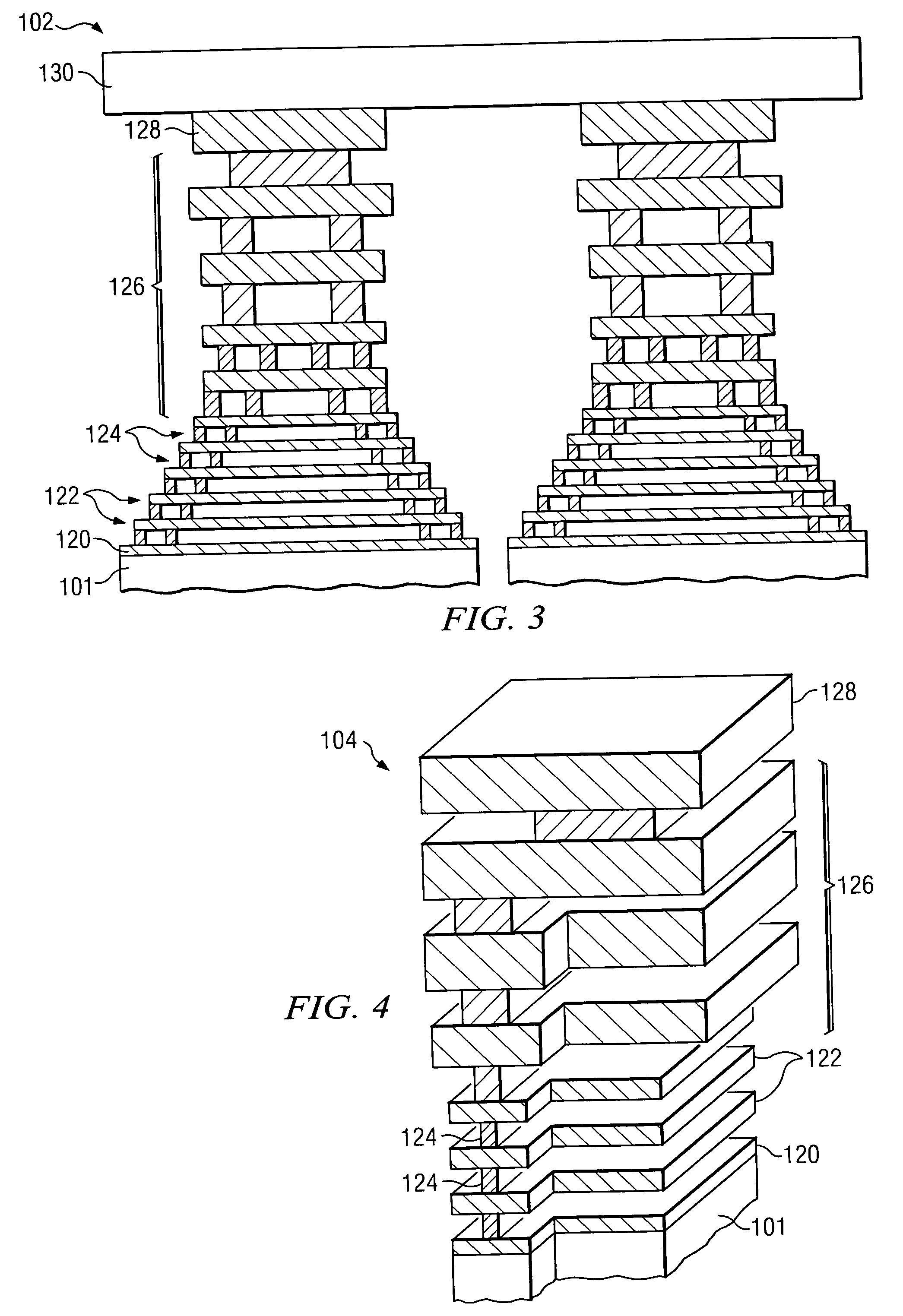
Integrated circuit (IC) having tsvs with dielectric crack suppression structures
ActiveUS20110031581A1Reduce the amount requiredTSV resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCrazingMetal interconnect
An IC includes a substrate having a semiconductor top surface, a plurality of metal interconnect levels having inter-level dielectric (ILD) layers therebetween on the top surface, and a bottom surface. A plurality of through substrate vias (TSVs) extend from a TSV terminating metal interconnect level downward to the bottom surface. The plurality of TSVs include an electrically conductive filler material surrounded by a dielectric liner that define a projected volume. The projected volume includes a projected area over the electrically conductive filler material and a projected height extending upwards from the TSV terminating metal interconnect level to a metal interconnect level above, and a projected sidewall surface along sidewalls of the projected volume. A crack suppression structure (CSS) protects TSVs and includes a lateral CSS portion that is positioned lateral to the projected volume and encloses at least 80% of the projected sidewall surface.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Field welding repair method especially for larger and penetrating defects in steel casting with heavy wall thickness
The invention relates to a field welding repair method especially for larger and penetrating defects in a steel casting with heavy wall thickness. The method comprises a pre-welding preparation process, a welding repair process and a post-welding quality inspection process, wherein the welding repair process comprises the steps of (1) preheating; (2) carrying out 1 to 2 layers of backing weld for all positions of a groove by adopting TIG weld, and filling the whole bottom of the groove with solid wire materials; (3) warming up to 220 to 330 DEG C, carrying out constant thermal insulation for 3 to 8 hours, adopting manual arc welding to implement the filler welding for the groove, hammering the welded bead immediately with an air hammer, and ensuring the dense and uniform traces of the hammer; (4) carrying out dehydrogenation heat treatment; (5) carrying out post-welding treatment: carrying out stress annealing at the temperature of 500 to 550 DEG C, then carrying out high tempering at the temperature of 700 to 750 DEG C, and finally, cooling at the speed of 65 to 150 DEG C / h to the room temperature. After welding repair, a welding seam is tested to be good in quality, and have low possibility of cracking again.
Owner:SUZHOU NUCLEAR POWER RES INST +4
Method of welding a gamma-prime precipitate strengthened material
A method for welding a gamma-prime precipitation strengthened alloy component. In one aspect the welding process includes preheating the alloy component to minimize the difference in contraction between the weld deposit and the substrate portion of the component during solidification and cooling. The component having a weld that is substantially free of solidification cracking.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE CORP
High intensity and high-toughness hot-rolled steel sheet and method for producing the same
ActiveCN101397626ALow costReduced Hot Brittle TendencyTemperature control deviceLiquid ironProduction control
The invention discloses a high strength and high toughness hot-rolled steel plate, the chemical components thereof and the weight percentages of the component are: 0.03 to 0.09 percent of C, 0.15 to 0.35 percent of Si, 1.40 to 2.0 percent of Mn, 0.02 to 0.05 percent of Al, 0.05 to 0.13 percent of Nb, 0.010 to 0.025 percent of Ti, being equal to or less than 0.30 percent of Cu, being equal to or less than 0.30 percent of Cr, being equal to or less than 0.012 percent of P, being equal to or less than 0.004 percent of S, being equal to or less than 0.004 percent of N and the rest are Fe; and Ceq can not be more than 0.44, crack sensitive index Pcm can not be more than 0.23, the production steps thereof are: liquid iron pre-desulphurization, bessemerizing, LF refining, RH(VD) processing, slab blank continuous casting, slab blank reheating, temperature controlling rolling, controlled cooling, hot straightening, cold bed cooling and cooling in heap; the advantages thereof are as follows: molybdenum can be omitted and nickel can be saved, thus reducing the cost; the steel plate has good weldability, high rolling efficiency and precise production control.
Owner:SHAGANG GROUP
Impact induced crack propagation in a brittle material
InactiveUS20070039990A1Easy to separateStable separationConveyorsFine working devicesCrazingEngineering
A sheet of brittle material, such as glass, flat or bowed, is separated along a score line by applying vibration energy through a probe into previously scored sheet material. The separation time is less than 1 second with smooth edge quality. The brittle material can be in the form of a moving ribbon of glass sheet, where a vibrational load is applied transverse to the score line to enhance crack propagation along the score line. A controller operates the probe at selected vibration frequencies, amplitudes, contact velocities, contact forces of impact, alignment with the score line, and the like, depending on material properties and structure, and depending on optimal process parameters.
Owner:CORNING INC
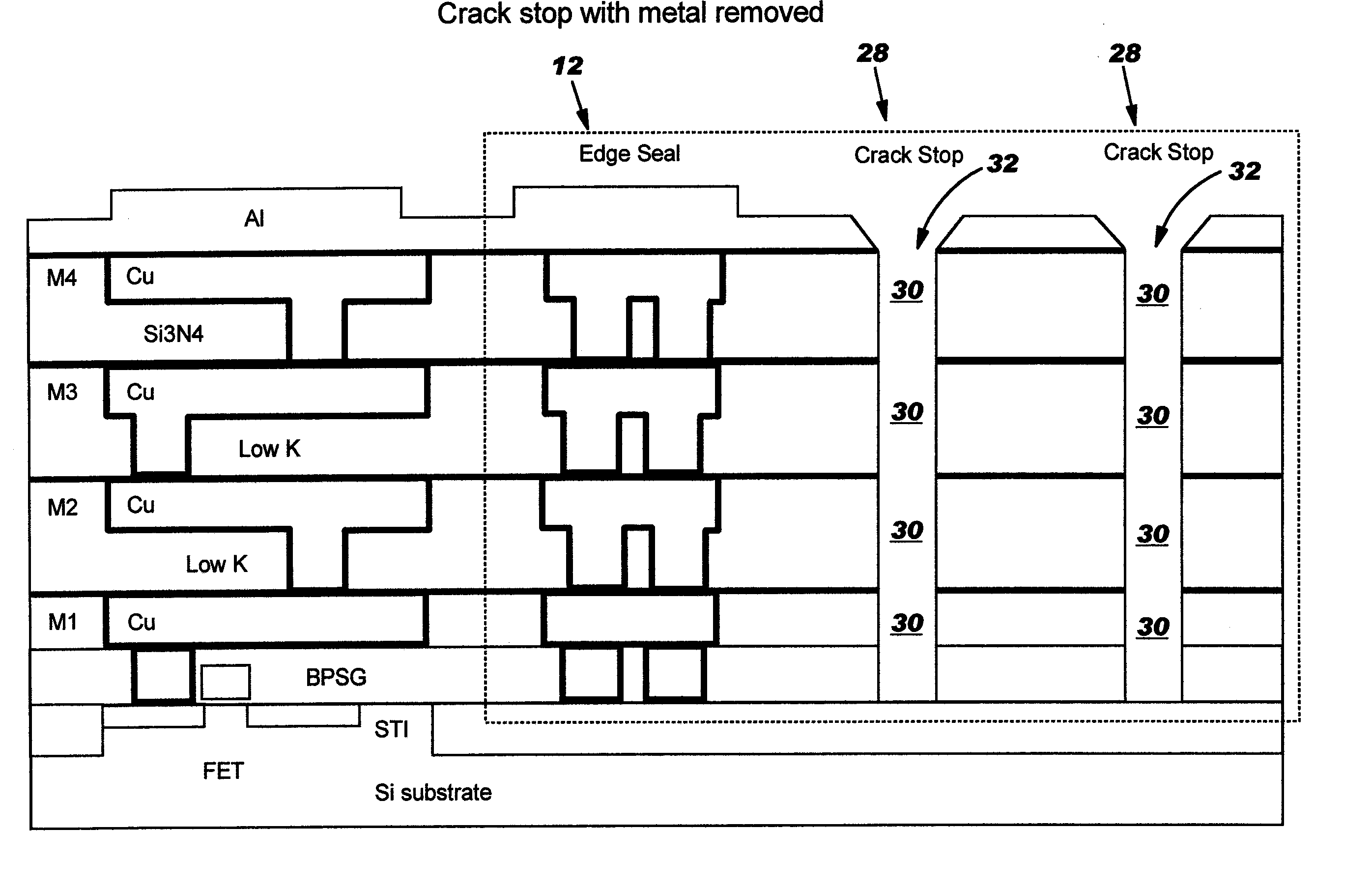
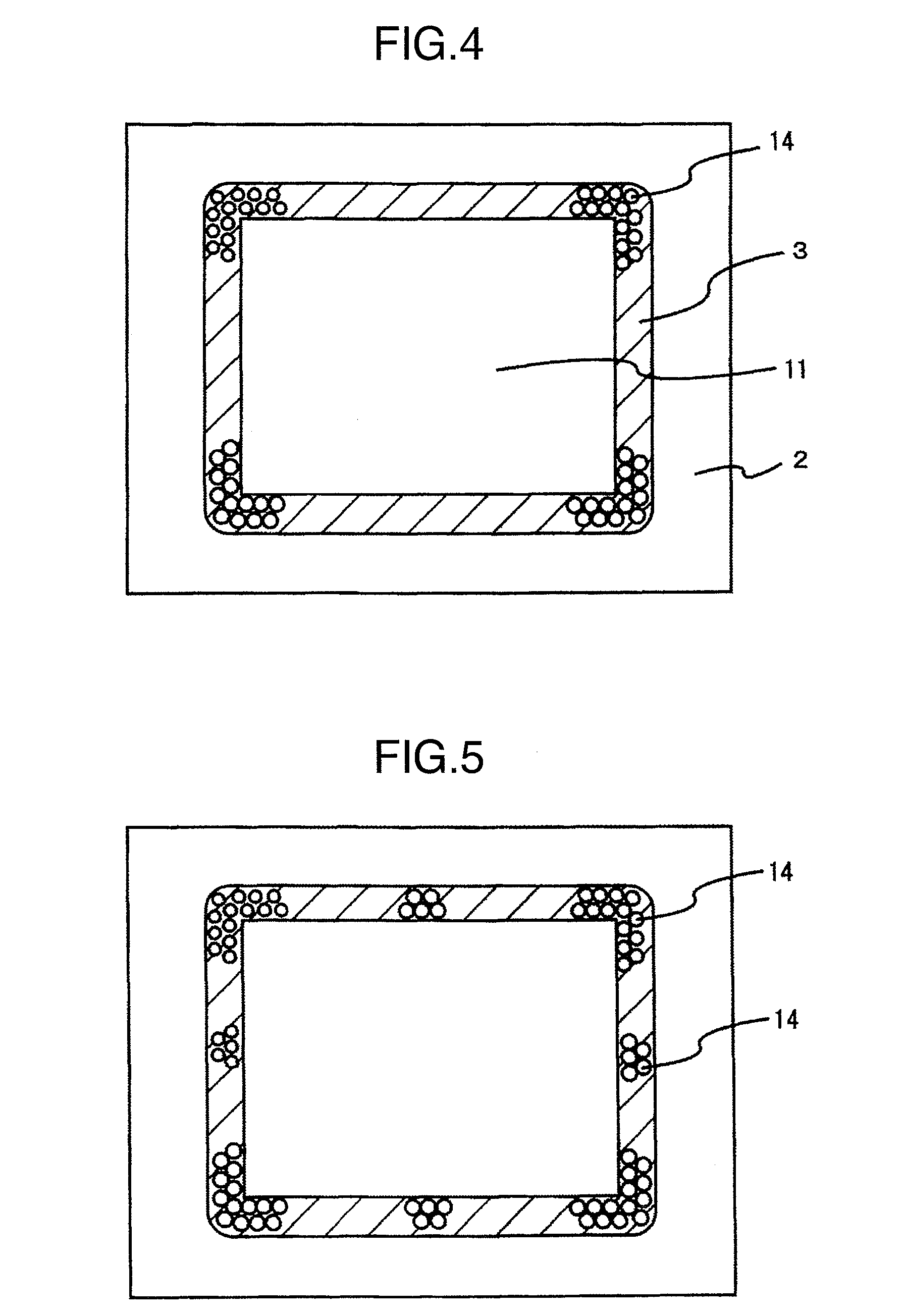
Crack stop and moisture barrier
ActiveUS20060220250A1Easily implemented into semiconductor designEasy to implementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCrazingDevice material
A design for a crack stop and moisture barrier for a semiconductor device includes a plurality of discrete conductive features formed at the edge of an integrated circuit proximate a scribe line. The discrete conductive features may comprise a plurality of staggered lines, a plurality of horseshoe-shaped lines, or a combination of both.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Crosslinkable rubber compositions and uses thereof
The crosslinkable rubber composition is crosslinkable at room temperature, has a gelation time at room temperature of 30 days or less, and can prepare a crosslinked rubber sheet by crosslinking the composition at room temperature, wherein the crosslinked rubber sheet has a tensile elongation of 20% or more, and is free of cracks after treatment at 40° C. in a 50 pphm ozone concentration for 96 hr. Specifically, it comprises an ethylene / alpha-olefin / non-conjugated polyene random copolymer rubber comprising a norbornene compound having a specific vinyl end group, an SiH group-containing compound, which has at least two SiH groups in one molecule, and optionally a platinum catalyst, a reaction inhibitor and / or a silane-coupling agent. The sealing, potting and coating materials and adhesives of the present invention comprise the above rubber composition. The rubber composition has a high crosslinking rate at room temperature and excellent productivity, and can prepare crosslinked rubber molded products (including foamed products) having excellent weathering resistance, ozone resistance, heat aging resistance and compression set at low cost. Further, it is suitable for use of electric and electronic parts, transportation machines, civil engineering and construction materials, medical appliances and goods for leisure activities.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
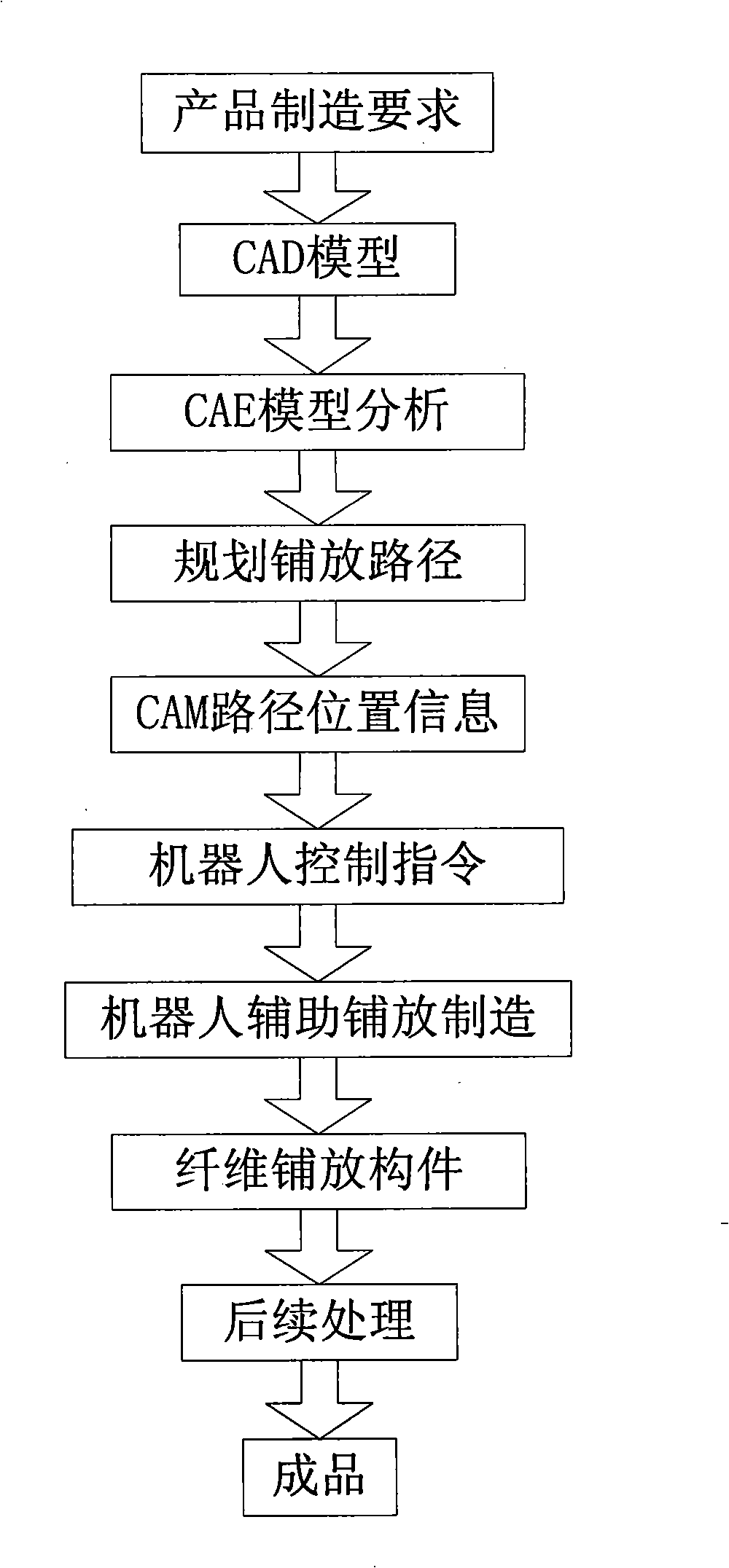
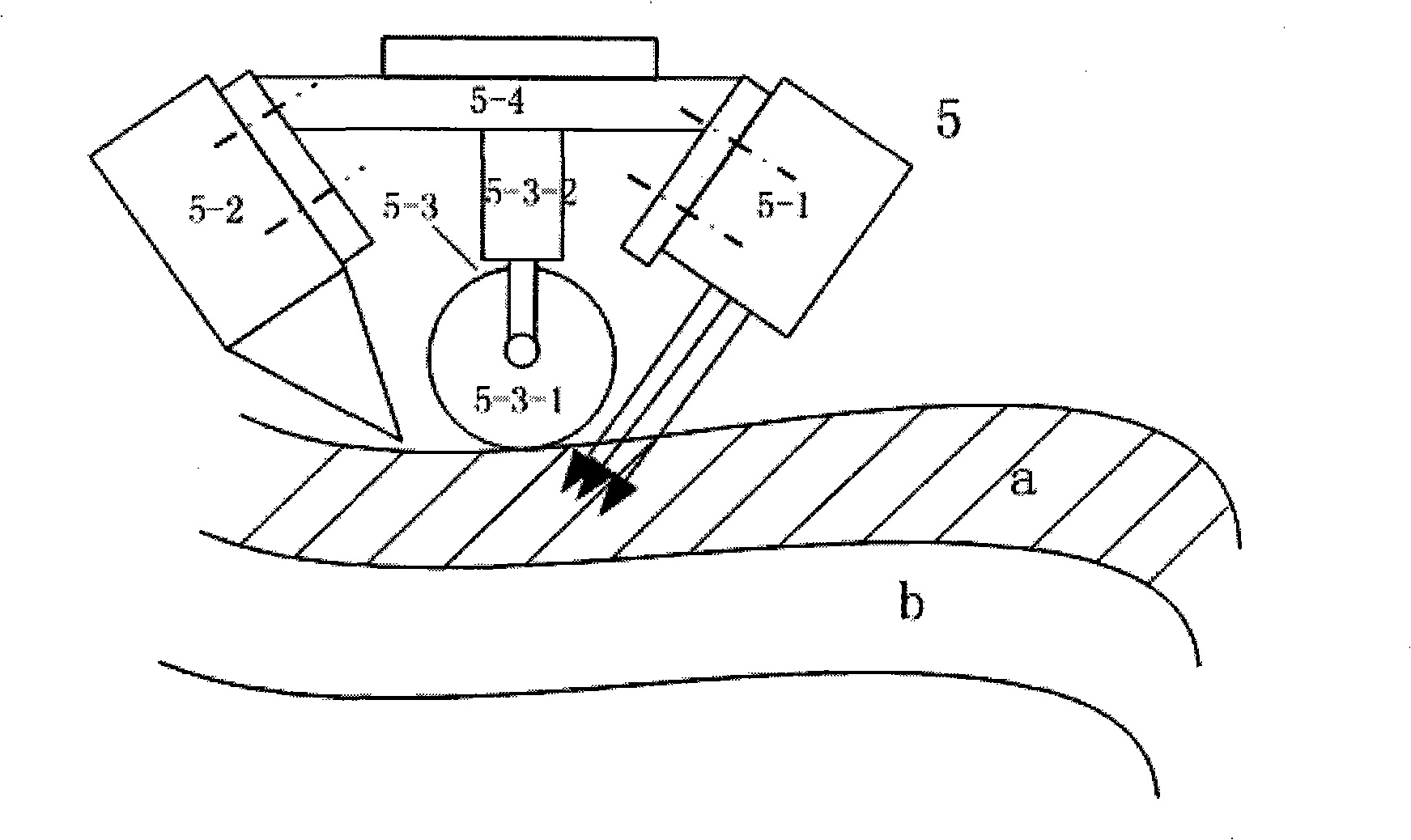
In-situ consolidation fibre laying method and device for producing resin-based compound material component
InactiveCN101254652ASimple manufacturing processShorten the manufacturing cycleCrazingThermal deformation
The invention discloses a method and a device for manufacturing resin-based composite material component by using fiber placement technology. By adopting fiber placement technology, the method and the device can place a fiber placement layer on the surface of a core die by a compaction mechanism to solve the problem of conventional winding equipment that is incapable of manufacturing surface component with negative curvature and non-gyrorotor component. Meanwhile, in-situ instantaneous stratified radiation curing is adopted to eliminate the influence of a tensile force in the fiber placement layer on the shape of the product and to solve the problems and disadvantages of large thermal deformation and easy generation of cracks due to autoclave curing treatment, the restriction of the autoclave volume on the component size, high production cost, and long production period. Based on industrial robot as the manufacture body, the device can improve the problems of prior placement equipment such as the deficiency of the flexibility in manufacturing more complex surface and complex structure.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for manufacturing semiconductor apparatus, and semiconductor apparatus and electric appliance
ActiveUS20060220211A1Thickness drasticallyLow costPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCrazingDevice material
According to the package and the method for manufacturing the package of the present invention, a chip can be formed extremely to be thin, and manufactured at lower cost and higher throughput, and the variations of a chip thickness can be reduced without back grind that causes cracks or polishing marks. In the present invention, a semiconductor film with a thickness of at most 500 μm deposited over a substrate serving as a support medium is crystallized with a CW laser light, and a chip having a semiconductor device is formed to have a total thickness of 5 μm, preferably at most 2 μm by using the crystallized semiconductor film. Consequently, the chip is mounted on an interposer after separating a substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for manufacturing soft magnetic material
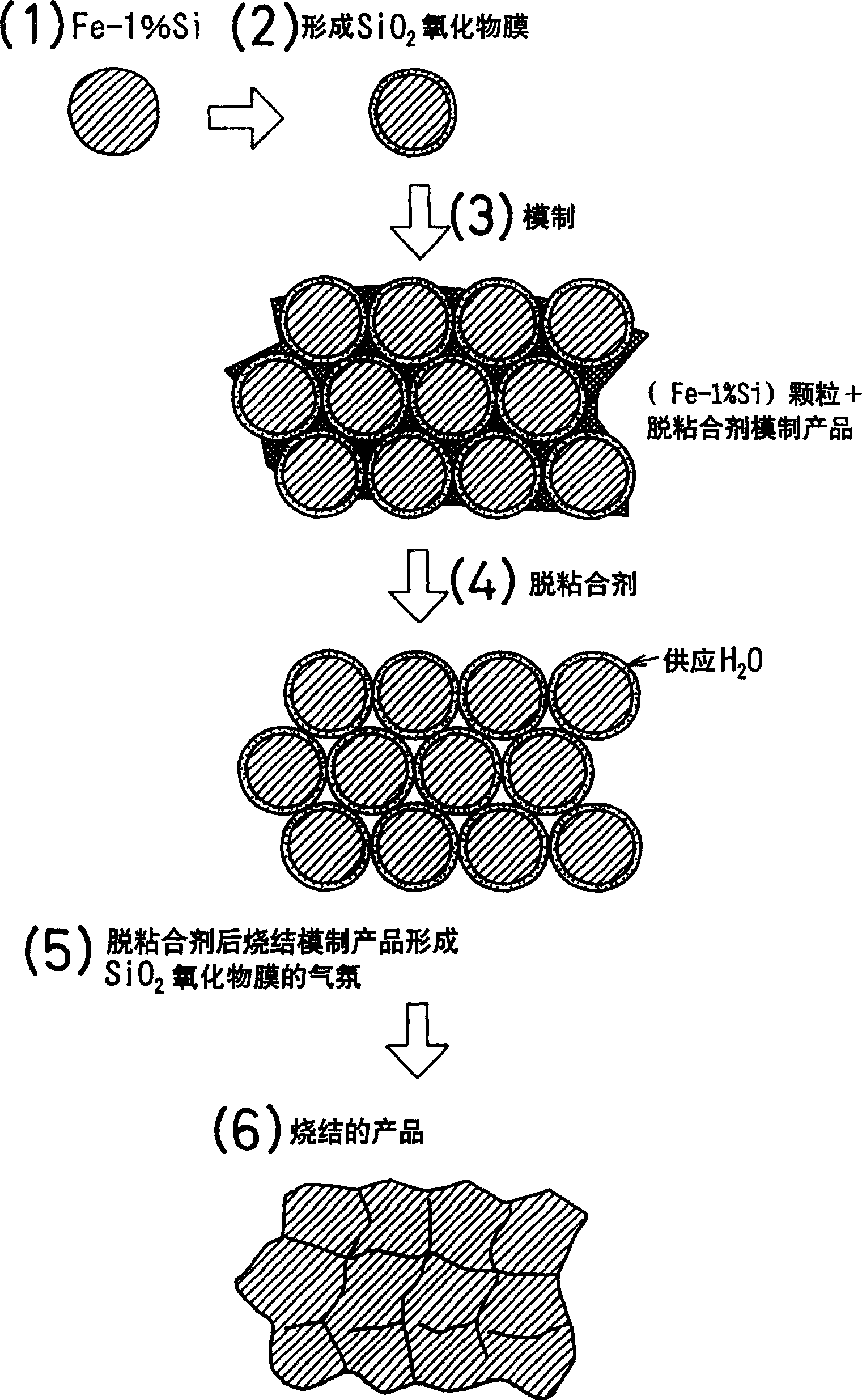
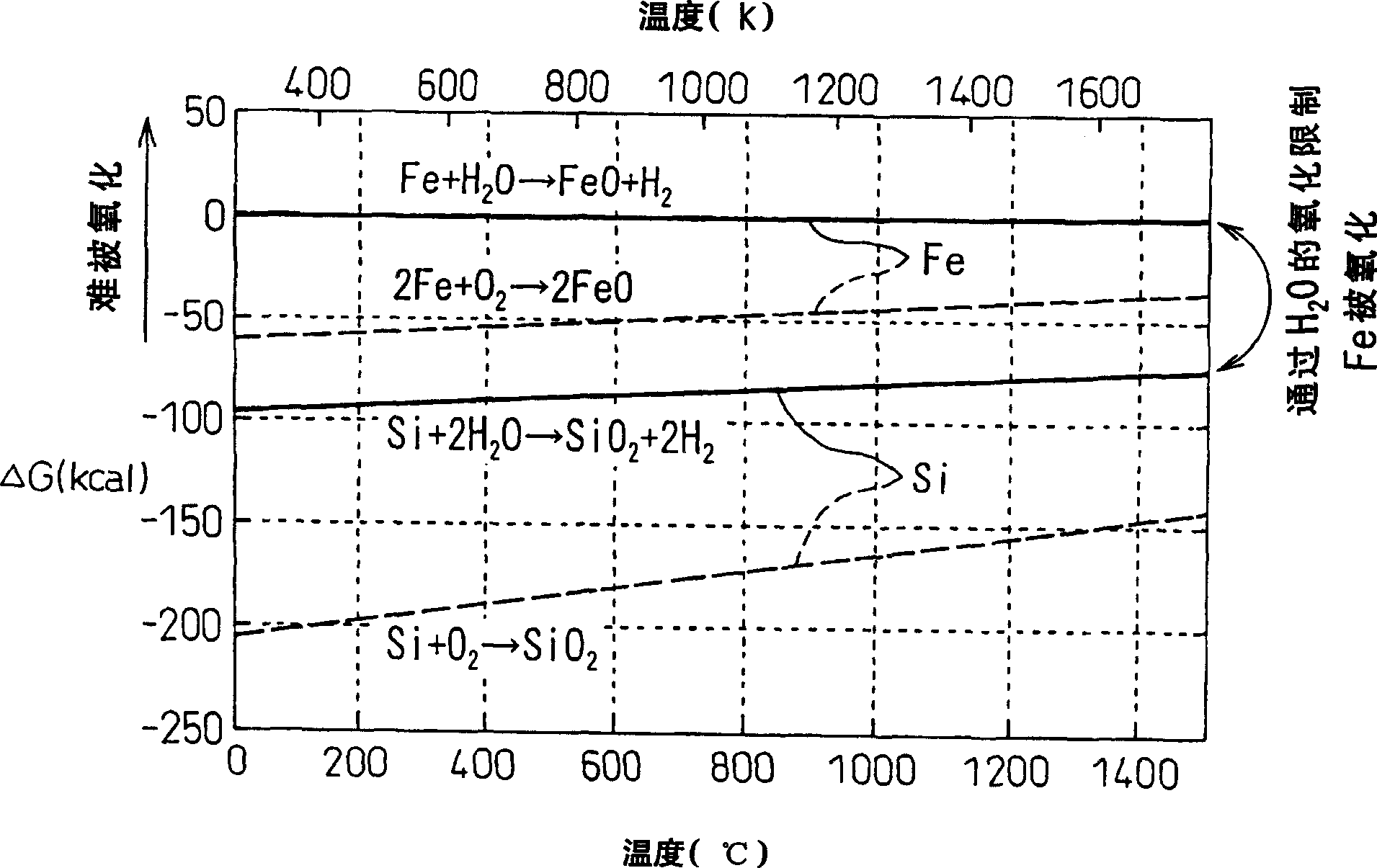
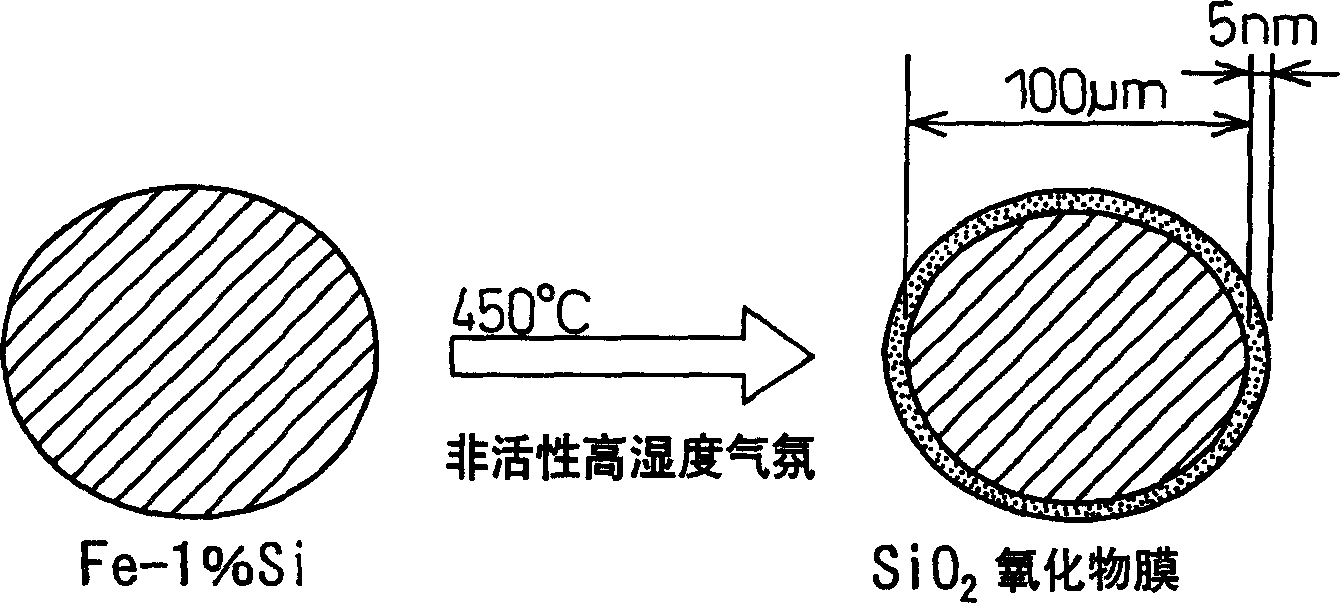
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a soft magnetic material, wherein an Fe-Si alloy powder is heated in a weakly oxidizing atmosphere to form a SiO2 oxide film on the surface, and the powder is then press-molded and fired in a weakly oxidizing atmosphere to obtain a sintered product. By performing the surface oxidizing step in a weakly oxidizing atmosphere such as water vapor, Si is selectively oxidized to form a thin oxide film with high electrical resistance. Furthermore, by firing the molded product in a weakly oxidizing atmosphere, the sintering can be performed while the oxide film, in which cracks and the like are generated at the press-molding, is repaired.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Nitride semiconductor device and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS20060094244A1Acceptable surface roughnessLong life-timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor lasersCrazingSource material
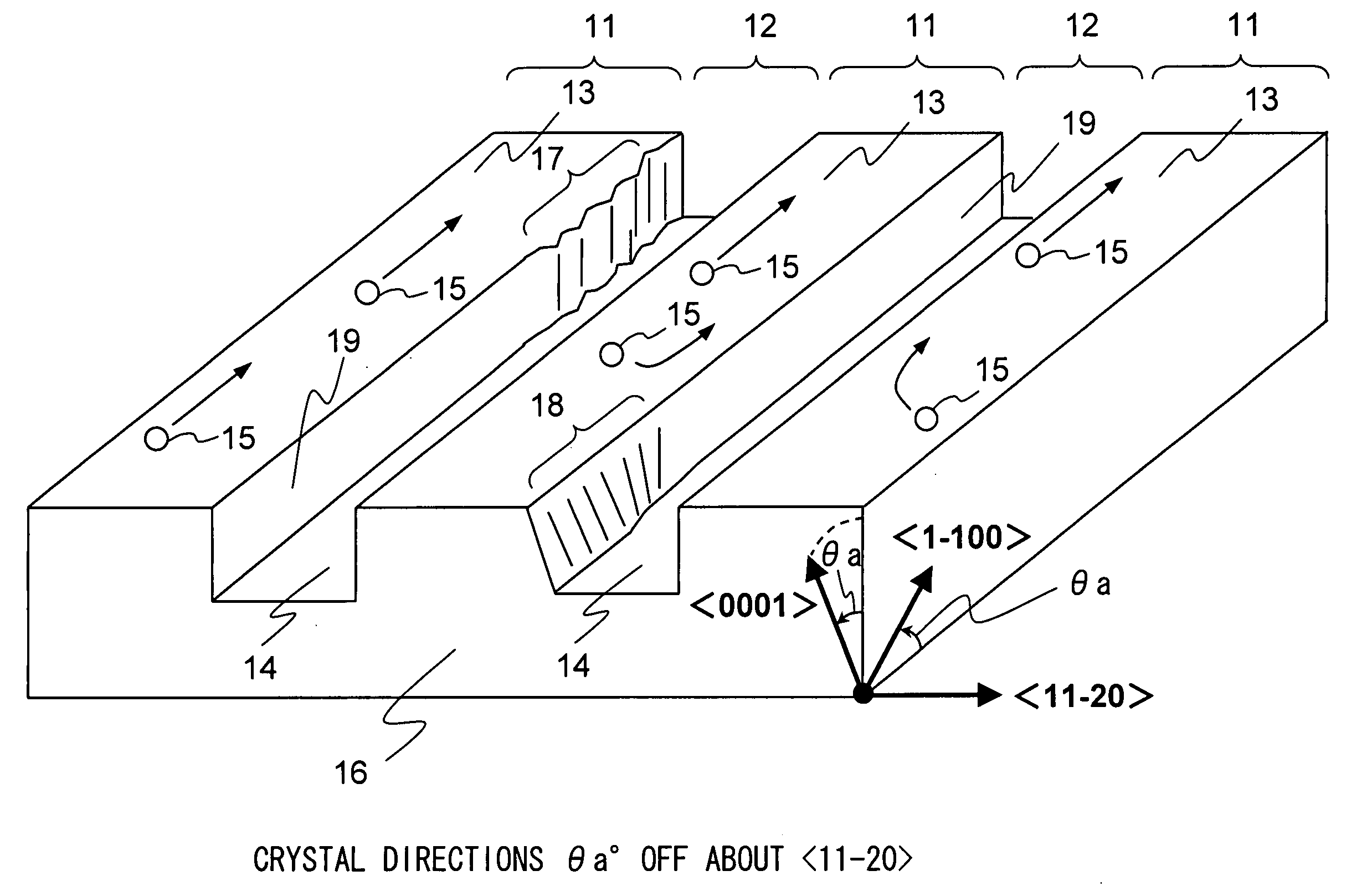
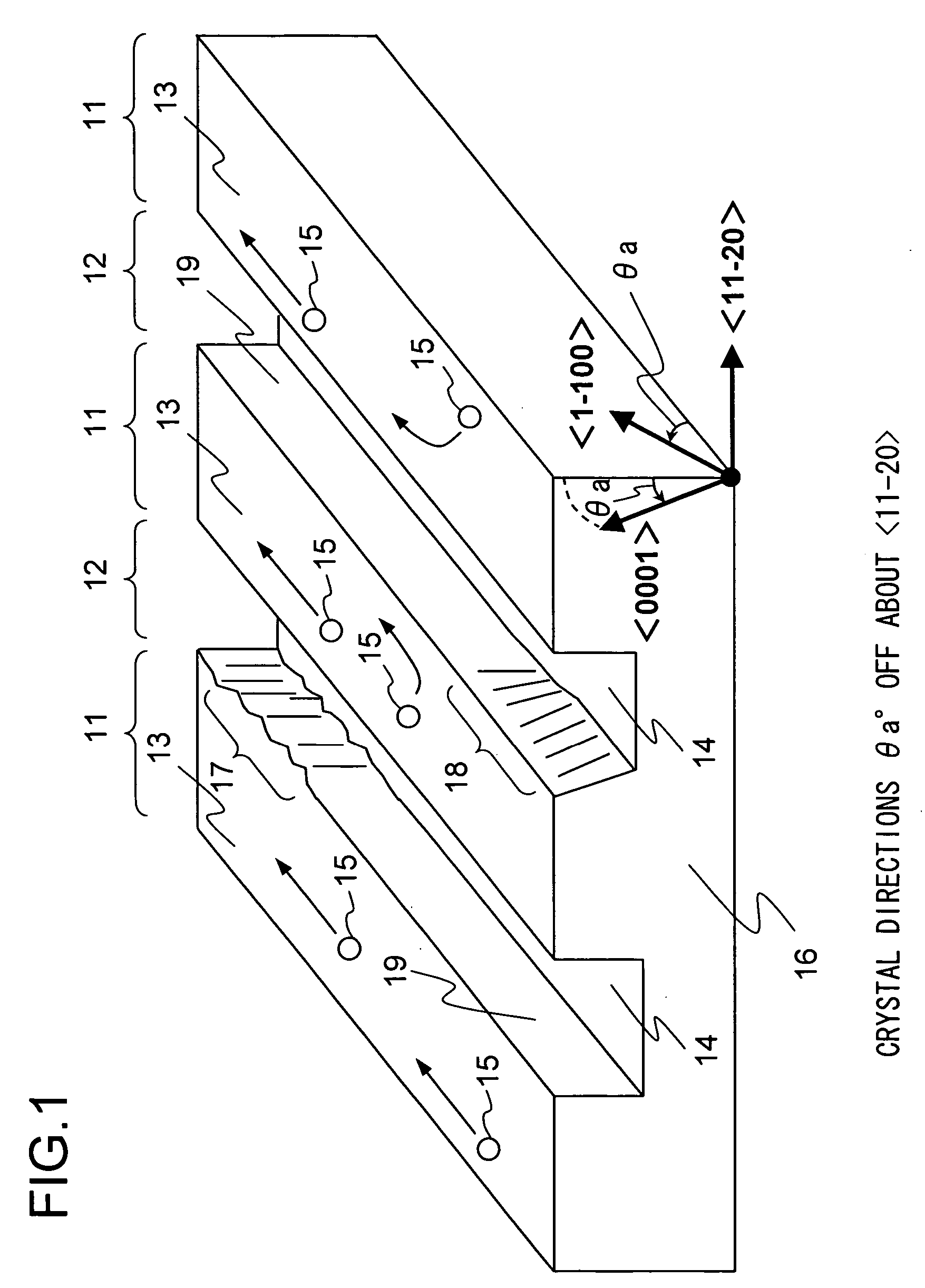
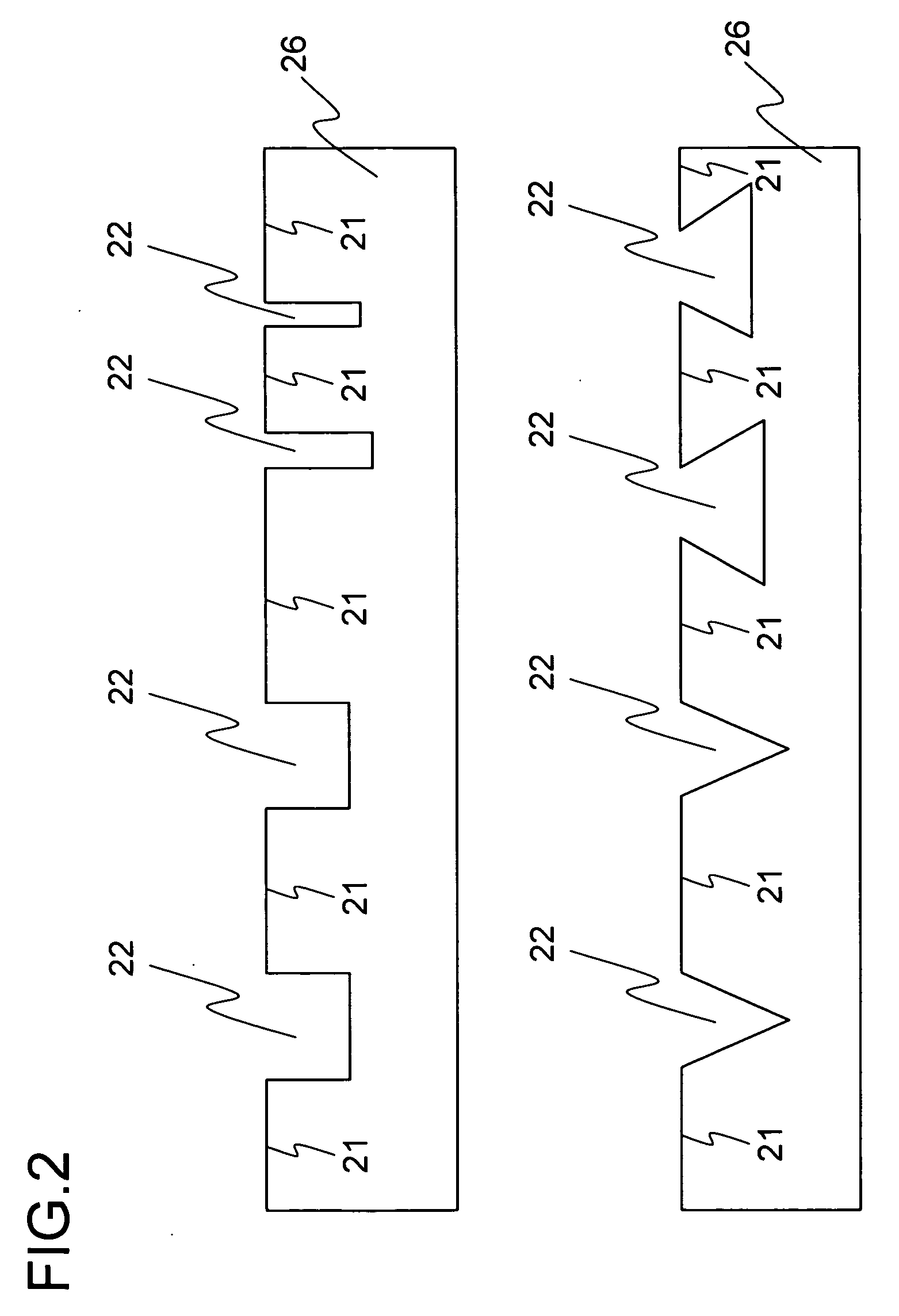
A nitride semiconductor device is provided that prevents development of cracks, that has nitride semiconductor thin films with uniform thicknesses and good growth surface flatness, and is thus consistent in characteristics, and that can be fabricated at a satisfactory yield. In this nitride semiconductor device, the nitride semiconductor thin films are grown on a substrate having an off-angle between a direction normal to the surface of ridges and the crystal direction <0001>. This helps either reduce or intentionally promote diffusion or movement of the atoms or molecules of a source material of the nitride semiconductor thin films through migration thereof. As a result, a nitride semiconductor growth layer with good surface flatness can be formed, and thus a nitride semiconductor device with satisfactory characteristics can be obtained.
Owner:SHARP FUKUYAMA LASER CO LTD
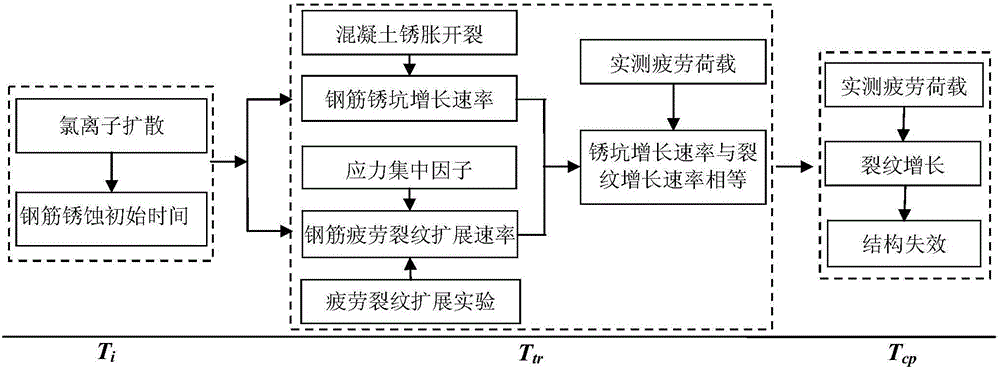
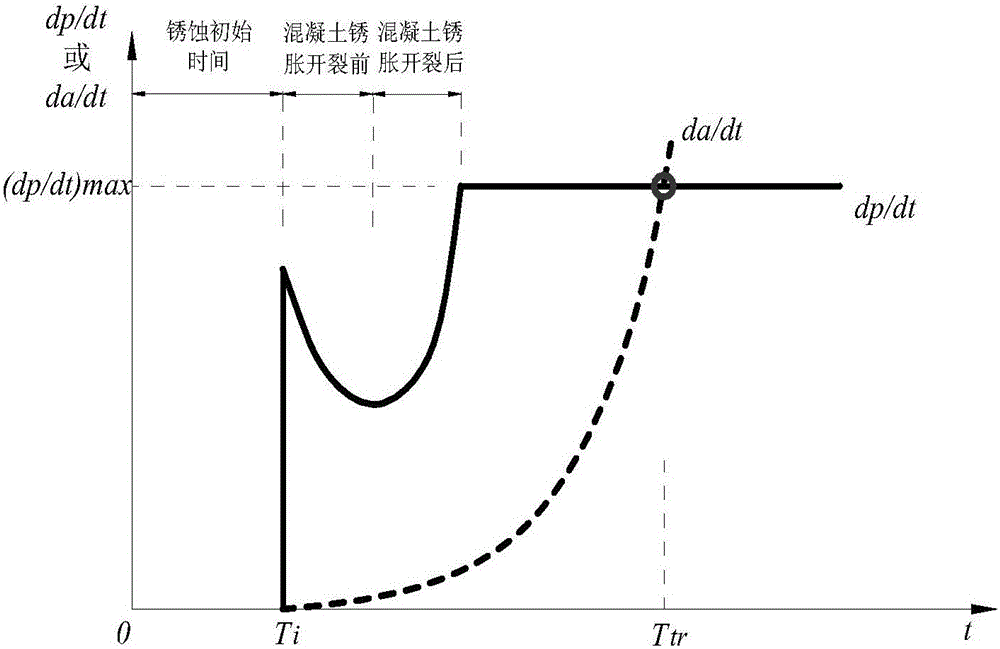
Method for evaluating fatigue life of aged reinforced concrete bridge
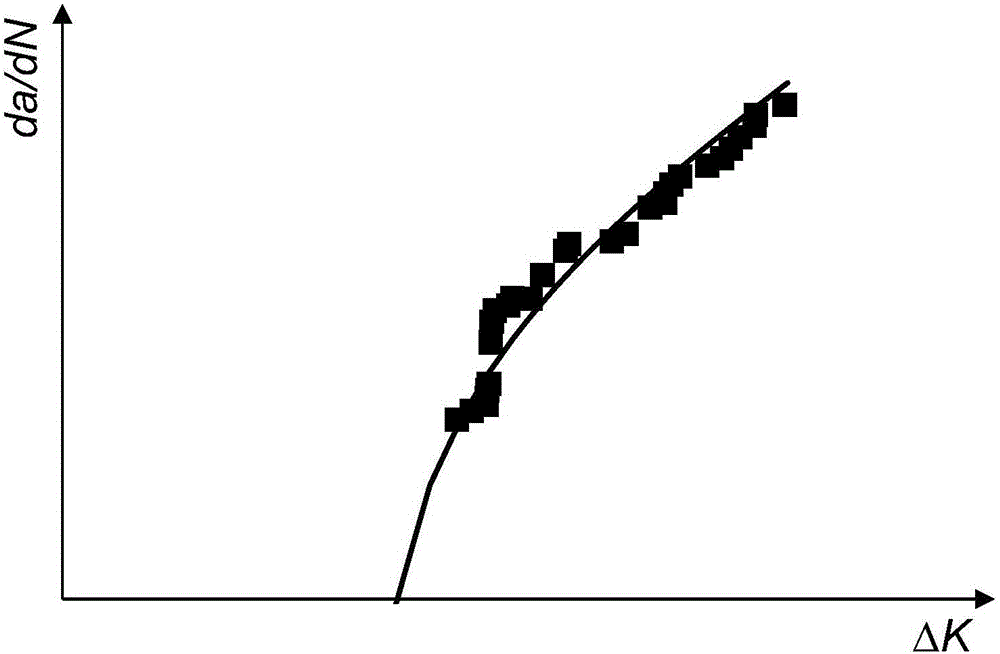
ActiveCN105825030AThe prediction method is reasonableGeometric CADForecastingStress concentrationCrazing
The invention discloses a method for evaluating the fatigue life of an aged reinforced concrete bridge. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining initial corrosion time of reinforcement in concrete based on the second diffusion law of Fick, and considering the influence of concrete cracking due to corrosion expansion in a corrosion rate model; adopting a small crack growth and near threshold growth analysis and determining relevant parameters of fatigue crack propagation rate of materials by developing a fatigue crack propagation test of reinforced concrete materials; performing a corrosion fatigue test or finite element analysis on corroded reinforcement to obtain stress concentration factors at different corrosion levels, and integrating into a stress intensity factor model to obtain the fatigue crack propagation rate of the reinforcement under the influence of corrosion; comparing the magnitude of a corrosion pit growth rate and the fatigue crack propagation rate and gradually converting into a single growth analysis on fatigue cracks of the reinforcement; meanwhile, combining with vehicle load observing information to realize life evaluation of a bridge at different service stages. The prediction method disclosed by the invention is reasonable and high in popularization, and can provide technical support for evaluating the life of the concrete bridges.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Structures for dense, crack free thin films
InactiveUS20070134532A1Reduce resistance lossHigh strengthFuel cells groupingFinal product manufactureHigh densityCrazing
The process described herein provides a simple and cost effective method for making crack free, high density thin ceramic film. The steps involve depositing a layer of a ceramic material on a porous or dense substrate. The deposited layer is compacted and then the resultant laminate is sintered to achieve a higher density than would have been possible without the pre-firing compaction step.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Centrifugal composite modified indefinite chilled cast iron roller and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101177759AFine structure of roll bodyEvenly distributedRollsMetal rolling arrangementsCrazingImpurity
The invention relates to a centrifugal combined indefinite chill cast-iron roller and a preparation method thereof, pertaining to steel rolling technical field. The chemical composition of a roll barrel is (weight percent): 3.2-3.8 C, 3.8-4.5 Ni, 1.2-1.8 Cr, 0.2-0.4 Mo, 0.2-0.5Cu, 1.0-1.8 Si, <0.8Mn, 0.10-0.30 Nb, 0.05-0.20 V, 0.05-0.20 Ti, 0.04-0.07Mg, 0.02-0.05 Y, 0.01-0.03 Sb, and the rest are Fe and unavoidable microimpurity. The invention employs a electric stove to produce a roller, and the roller is moulded with centrifugal casting method; the roller is characterized by high strength and hardness, good toughness, hardness uniformity and hardenability, excellent wear resistance and oxidation resistance and the anti-cold shock and heat shock properties are also good; no phenomena like breaking, peeling, crazing and steel sticking are in the operation process; the service performance is apparently better than high nickel-chrome indefinite chill cast-iron roller; the processing technique is simple, high-heat treatment is not needed and the production cost is low. The invented roll has the advantages that: the rolling mill operating rate is significantly improved, the production cost of mill bar is reduced, the surface quality of the mill bar is improved and the economic and social benefits are good.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Nickel-based welding electrode for welding nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloy
ActiveCN102430876AExcellent heat crack resistanceEasy to useWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaCrack resistanceNiobium
The invention relates to a nickel-based welding electrode which comprises the following component by weight percent (wt%): 50.0-68.0% of Ni, 18.0-23.0% of Cr, 6.0-11.0% of Mo, 3.0-6.0% of Nb, 2.50-9.00% of Fe, 0.01-0.1% of C, 0.10-1.00% of Mn, 0.010-0.10% of Si, 0.015% of S or less, 0.015% of P or less, 0.01-0.10% of Cu, 0.003-0.010% of Co and the balance of impurities. The coat of the nickel-based welding electrode comprises the following components by weight percent of the welding core: 12-18% of marble, 10-15% of fluorite, 12-18% of barium carbonate, 5.0-6.4% of rutile, 3.5-5.0% of ferroniobium, 3.3-4.5 of chromium metal powder, 0.45-0.65% of sodium carbonate, 0.45-0.65% of electrolytic manganese and 1.3-1.8% of zircon sand, and the adhesion agent is 10-20% of the total weight of the power. The nickel-based welding electrode is prepared by mixing, wrapping mixture on the welding core and baking at low and high temperature. The nickel-based welding electrode disclosed by the invention is used for nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloy steel welding, ensures that the excellent mechanical properties, the excellent corrosion resistance, the excellent thermal crack resistance and the hightensile strength of the welding seam match with those of the base material, has good welding process performance, guarantees attractive molding and can be used for the welding of the steel (with 9% of Ni) working at low temperature.
Owner:ATLANTIC CHINA WELDING CONSUMABLES
Mechanical structure crack expansion rate and crack expansion life span predication method
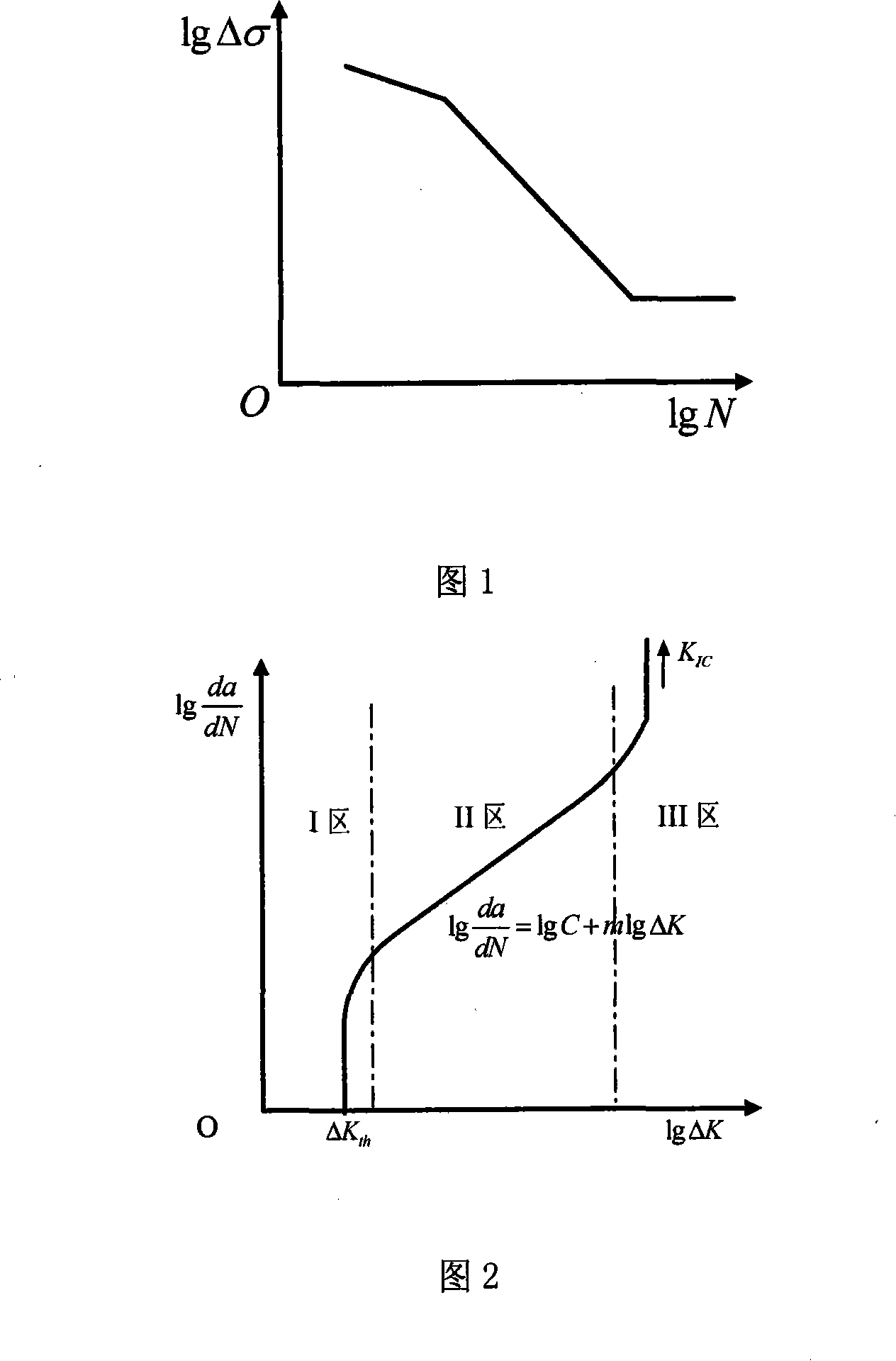
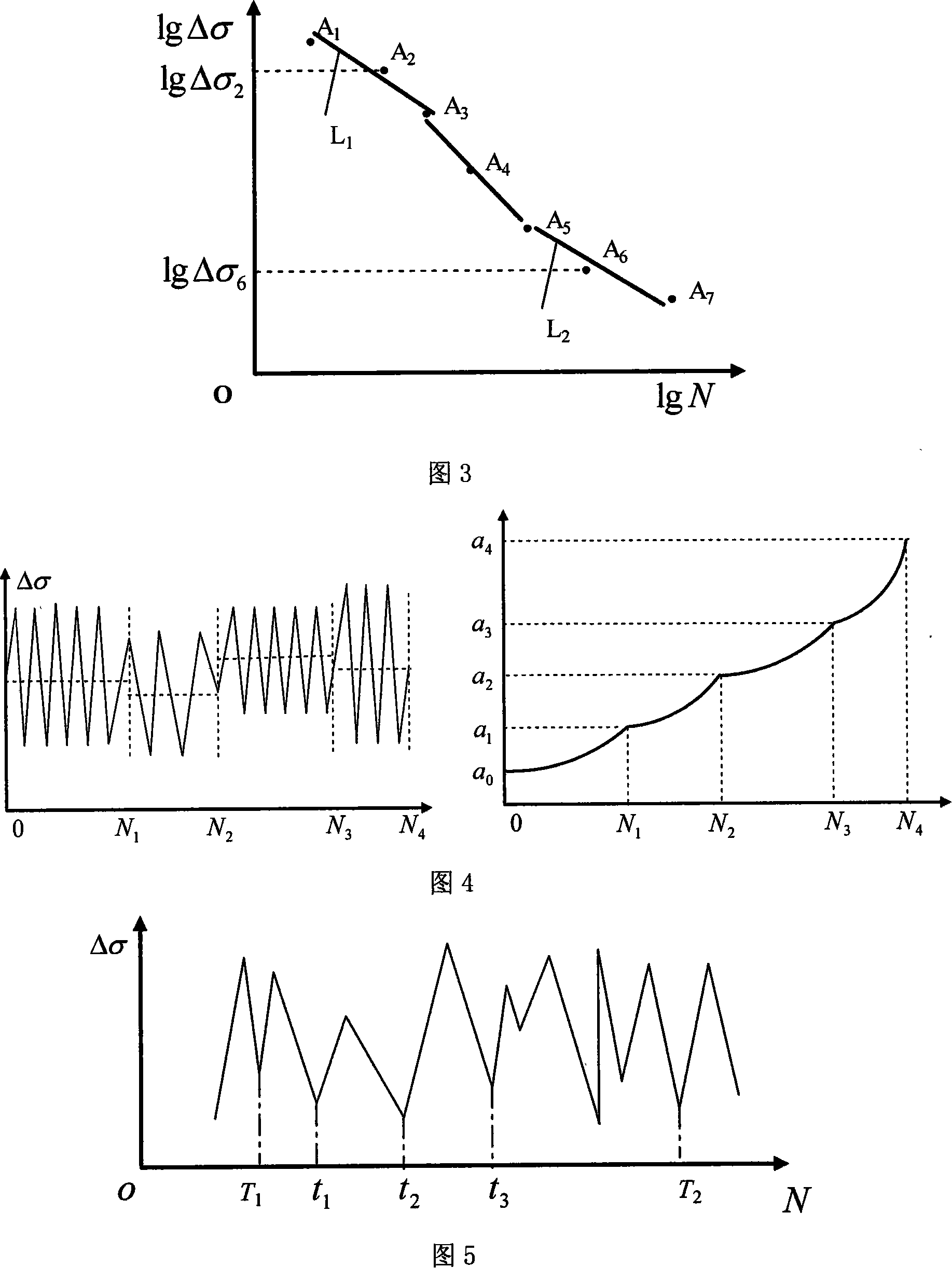
InactiveCN101122560ASave moneyShorten the development cycleUsing mechanical meansComplex mathematical operationsHysteresisCrazing
A crack growth rate and crack growth life prediction method for a mechanical structure belongs to a calculation method for fatigue crack growth rate and crack growth length of the mechanical structure. At first, a relationship between S-N and P-S-N curve expressions (power function form) and a crack growth rate curve expression (Paris formula) is built up in the method. A determination method of the crack growth rate under the conditions of block spectrum load, overload hysteresis load and random load is proposed. And a determination method of Paris curve parameters is provided when the S-N and P-S-N curves cannot be expressed in power function form. And a method for improving the prediction precision of the crack growth rate and the crack growth life is proposed. The S-N and P-S-N curves are used by the method to predict the crack growth rate and the crack growth life. Therefore, the method has the advantages of little dependence on tests and high precision and can shorten the product development period and save much manpower, material resources and financial resources.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Welding repair method for large-sized heat-resistant steel castings
ActiveCN103962791AEliminate Large Area DefectsRelieve welding stressArc welding apparatusShielded metal arc weldingCrazing
The invention relates to a welding repair method for large-sized heat-resistant steel castings, and solves the problems that the welding stress is difficultly removed, the defects of incomplete fusion, incomplete penetration, delayed crack and slag inclusion are easily caused in a repair process and the repair quality is difficultly guaranteed as the heat-resistant steel castings are poorer in welding performance, complicated in defect position and large in workpiece in an existing manual arc welding type surfacing welding mode for repairing large-sized castings. The method mainly comprises the following steps: 1, removing the defects; 2, performing heat treatment; 3, performing dye check; 4, performing statistics on the repair welding quantity; 5, preheating before welding; 6, performing repair welding on defect parts; 7, cleaning and repairing; 8, performing post-welding heat treatment; 9, performing nondestructive inspection. According to the method, the large-area defects of the castings can be effectively repaired, the repair quality is guaranteed, the processing and use requirements of the castings can be met after repair, and the economic loss of scrapped important or major castings is reduced. The method is used for repairing the large-area defects of the large-sized heat-resistant steel castings.
Owner:HARBIN JIANCHENG GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com