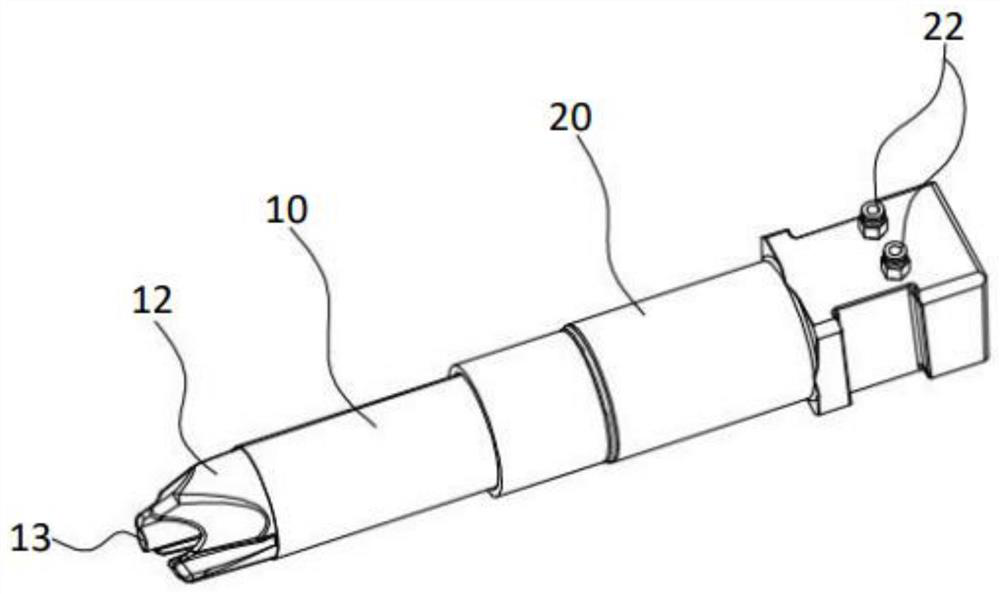
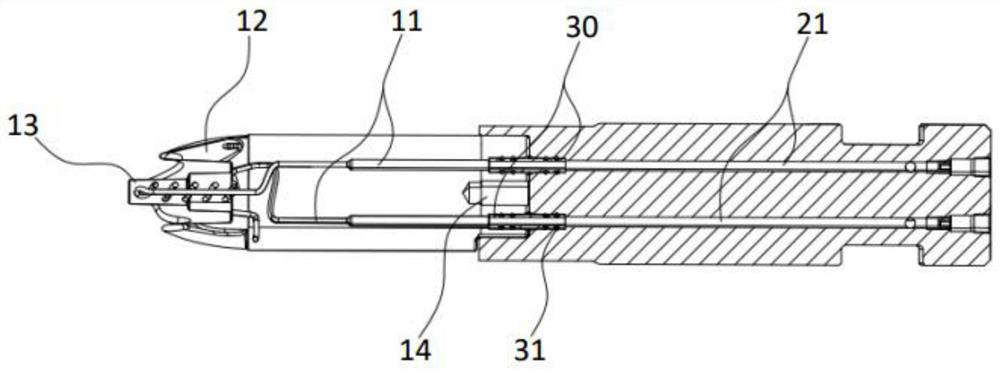
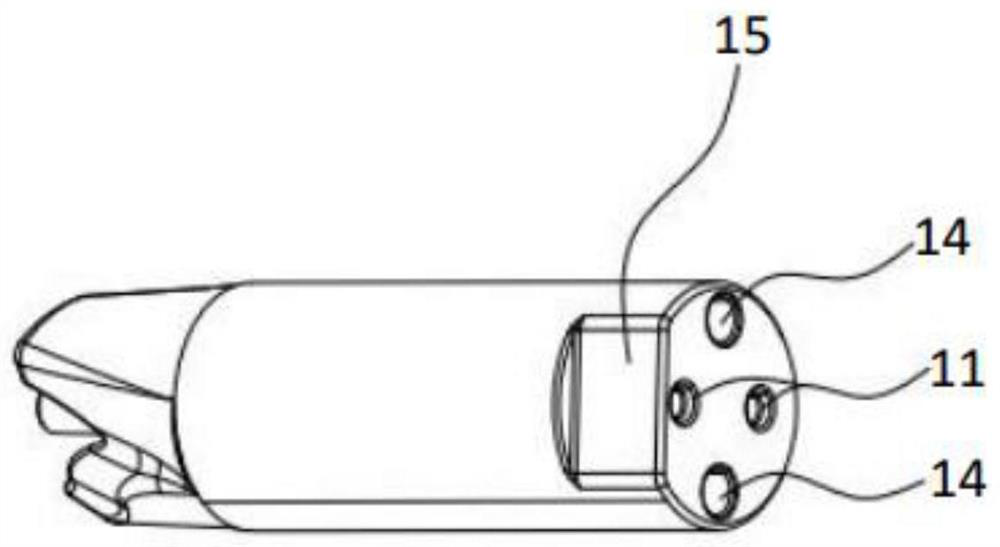
Patents
Literature
37results about How to "Excellent heat crack resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Insert
InactiveUS20070292671A1Improve wear resistanceExcellent heat crack resistancePigmenting treatmentMilling cuttersCompacted graphite ironAlloy
The present invention relates to a coated cemented carbide milling insert for either wet or dry machining of cast iron such as nodular cast iron (NCI), grey cast iron (GCI), austempered ductile iron (ADI) and compacted graphite iron (CGI) where a high wear resistance and an excellent resistance against thermo cracks are required comprising: a substrate comprising from about 5 to about 7 wt-% Co, from about 140 to about 250 ppm Ti+Ta and balance WC with a weight ratio Ti / Ta of from about 0.8 to about 1.3 and a PVD-layer consisting of AlxTi1-xN, with x=from about 0.50 to about 0.70 and with a thickness of from about 1 to about 10 μm. The invention also relates to a method for making cutting tool inserts and their use.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Insert
InactiveUS7767319B2Improve wear resistanceExcellent heat crack resistancePigmenting treatmentMilling cuttersHigh resistanceCompacted graphite iron
The present invention relates to a coated cemented carbide milling insert for either wet or dry machining of cast iron such as nodular cast iron (NCI), grey cast iron (GCI), austempered ductile iron (ADI) and compacted graphite iron (CGI) where a high wear resistance and an excellent resistance against thermo cracks are required comprising:a substrate comprising from about 5 to about 7 wt-% Co, from about 140 to about 250 ppm Ti+Ta and balance WC with a weight ratio Ti / Ta of from about 0.8 to about 1.3 anda PVD-layer consisting of AlxTi1−xN, with x=from about 0.50 to about 0.70 and with a thickness of from about 1 to about 10 μm. The invention also relates to a method for making cutting tool inserts and their use.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Welding material for ni-based heat-resistant alloy, and welded metal and welded joint each using same
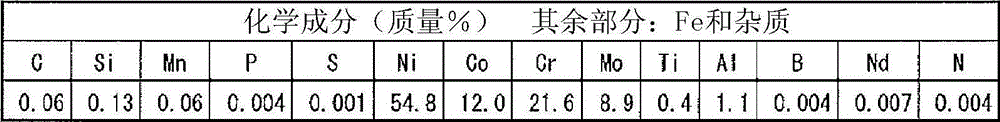
InactiveCN102947048AResistant to stress relaxation crackingExcellent heat crack resistanceWelding/cutting media/materialsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesCrack resistanceAlloy
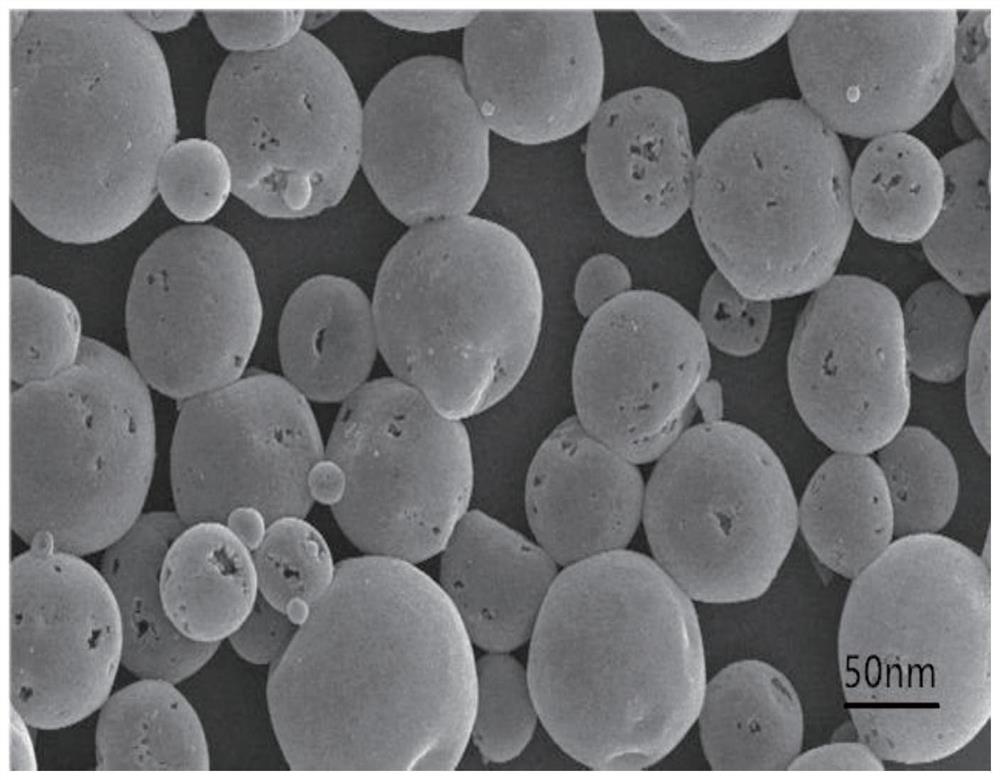
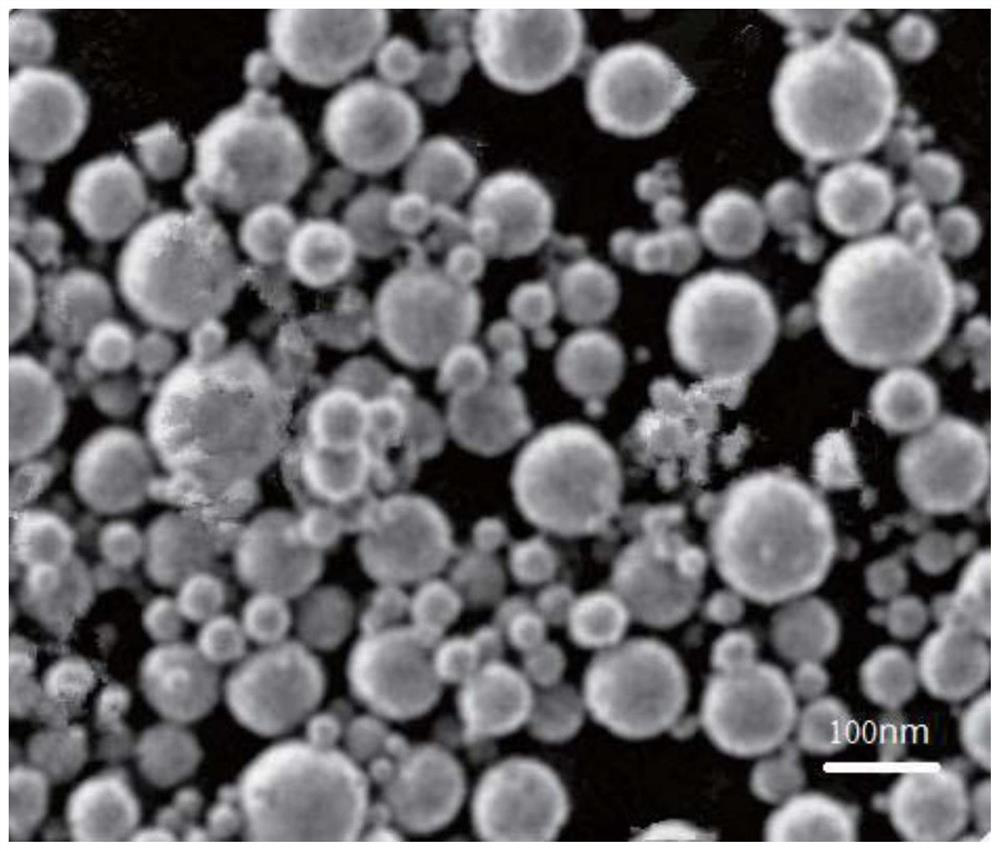
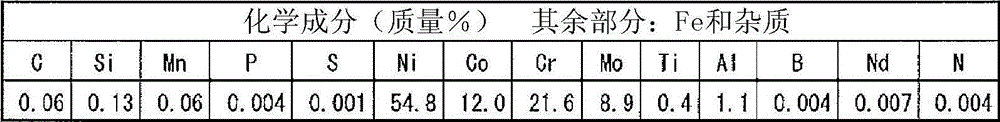
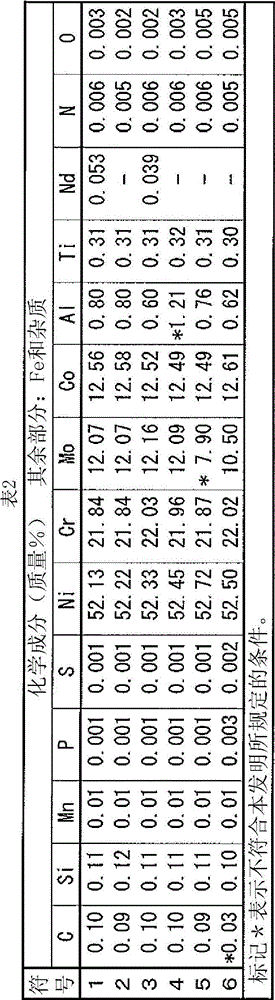
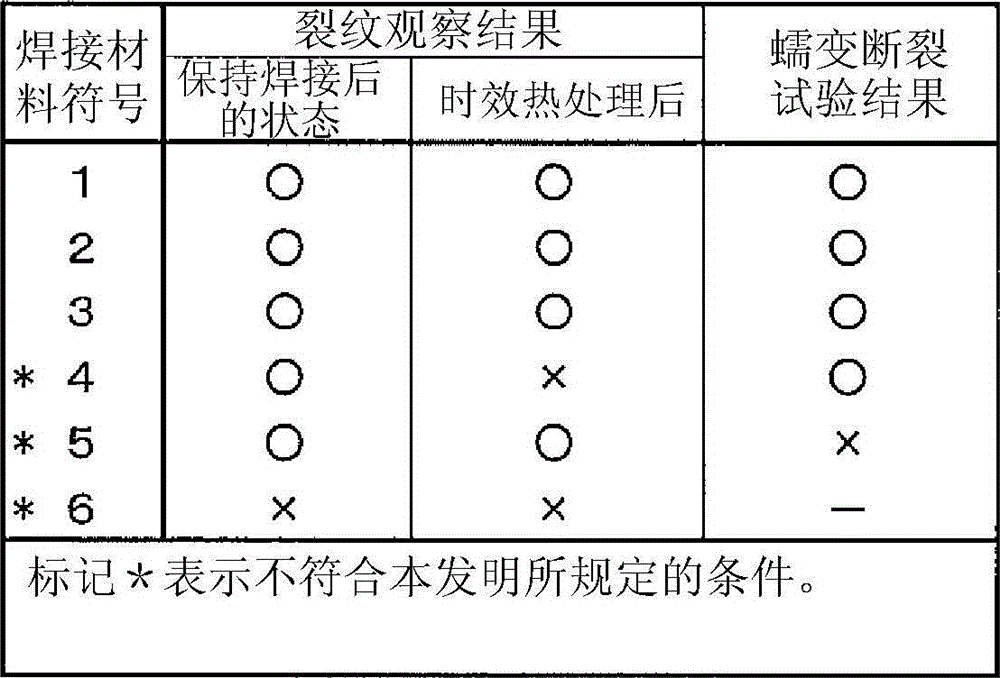
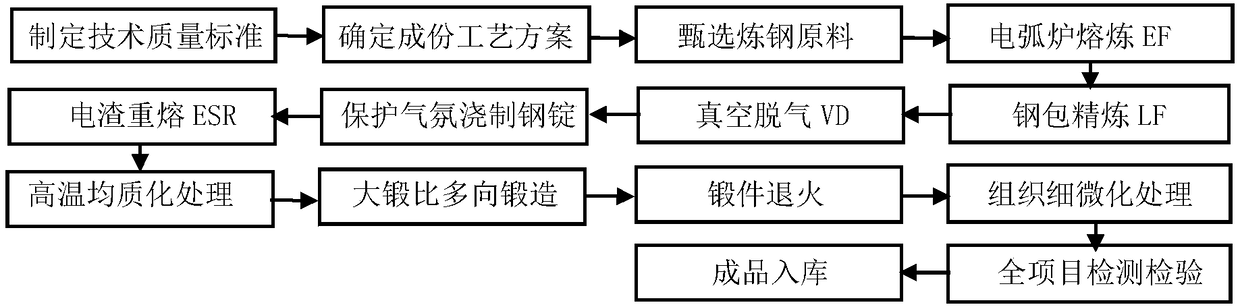
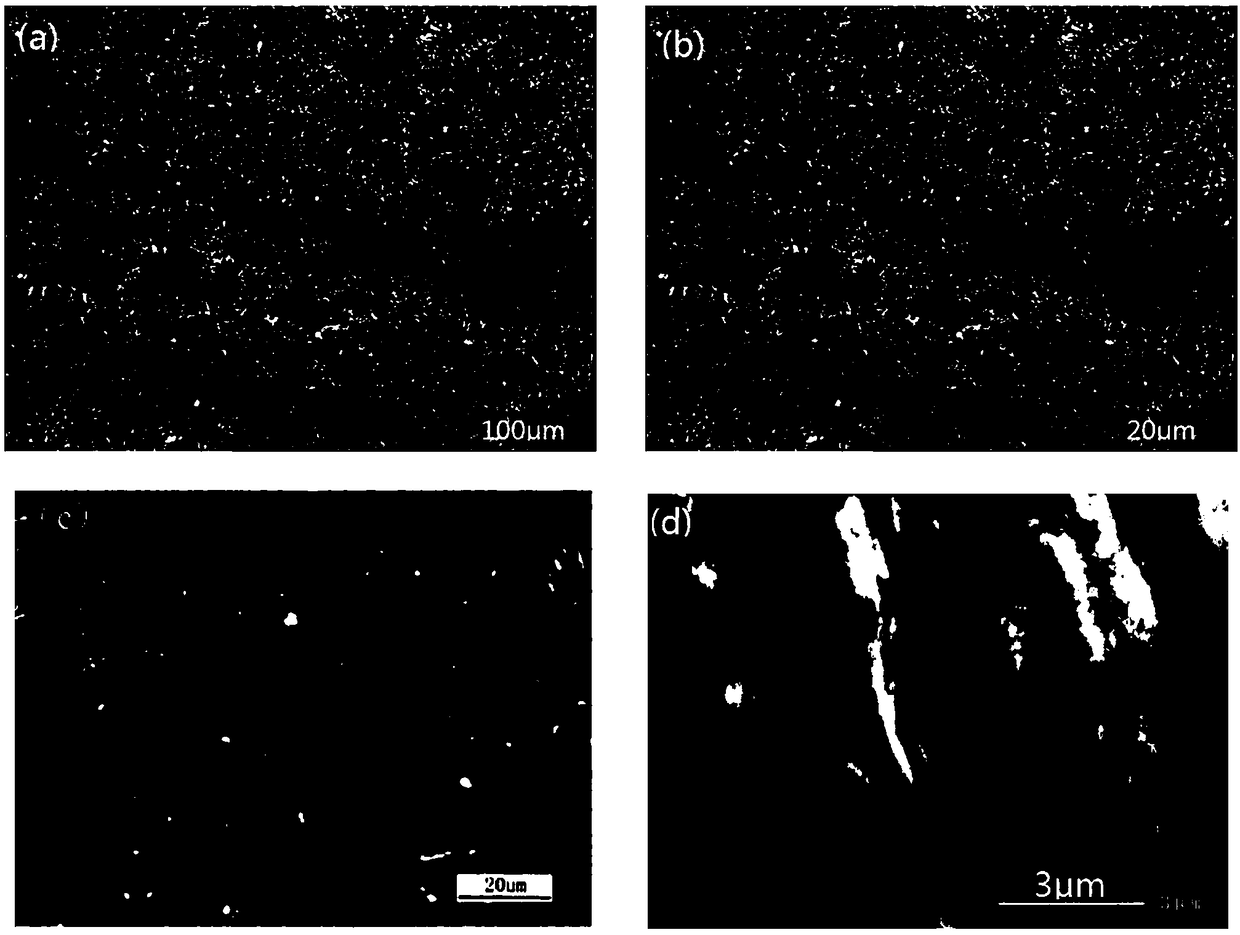
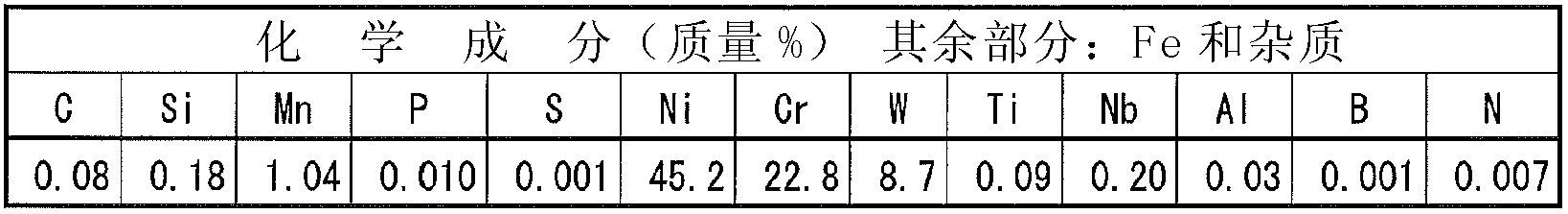
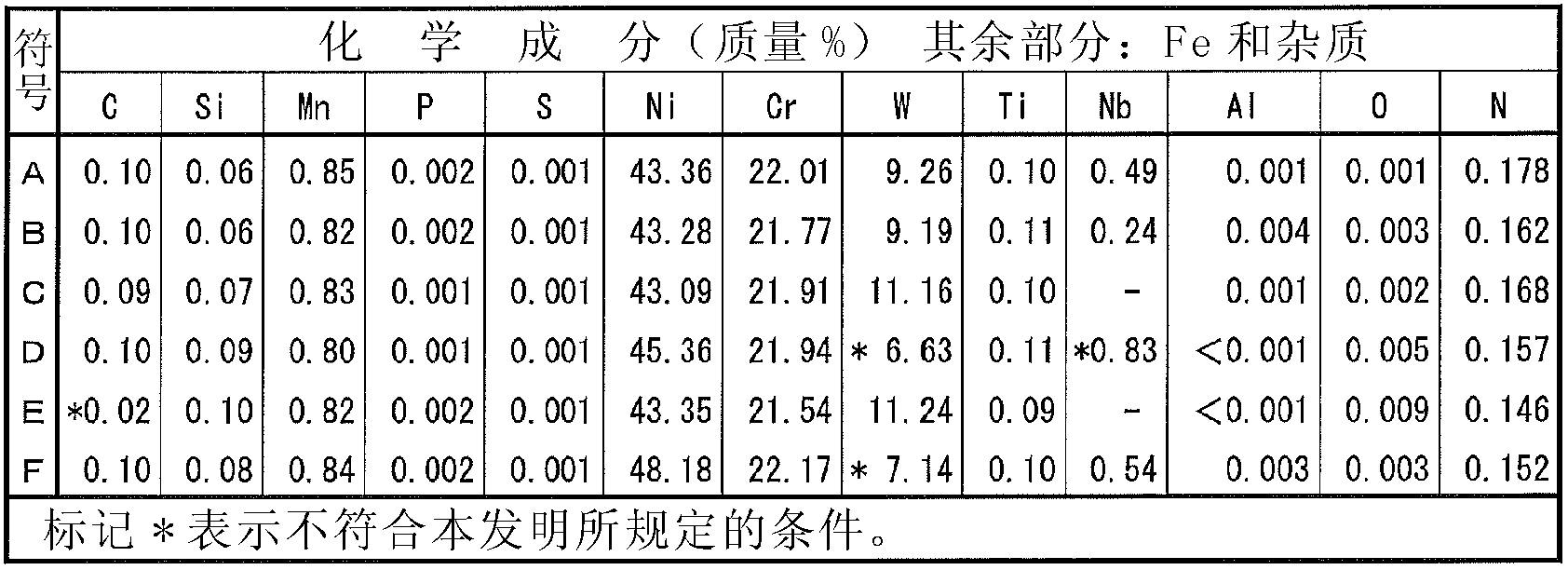
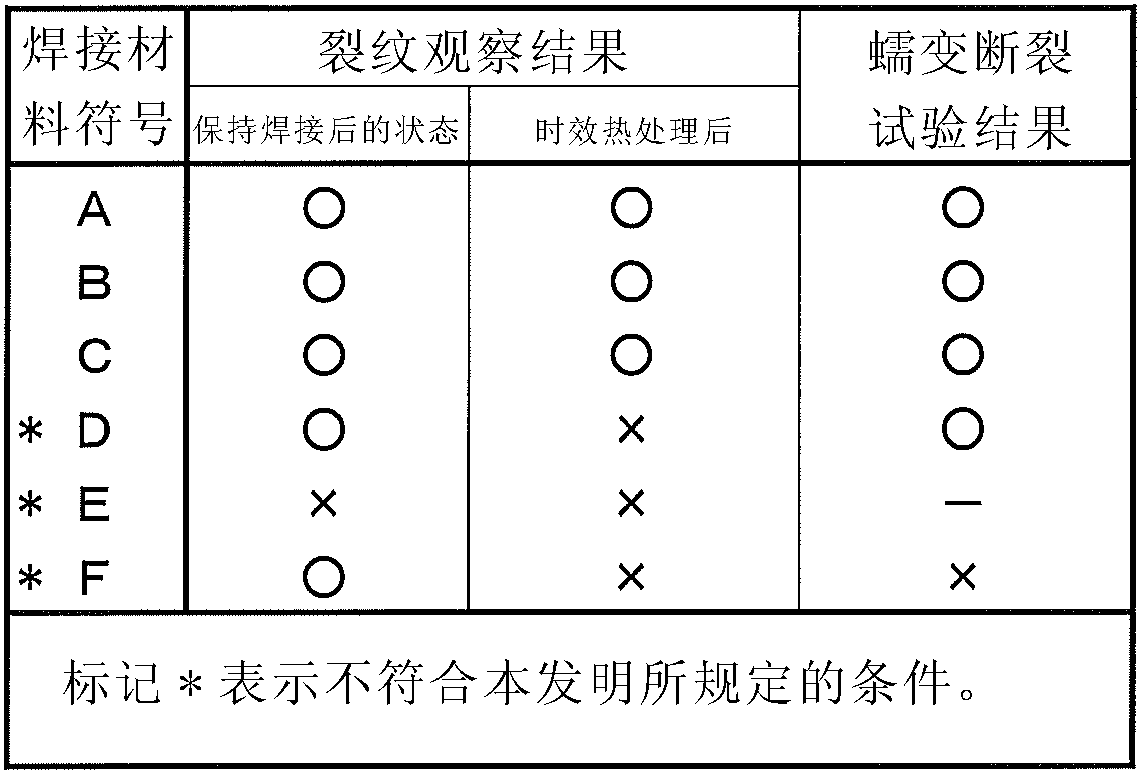
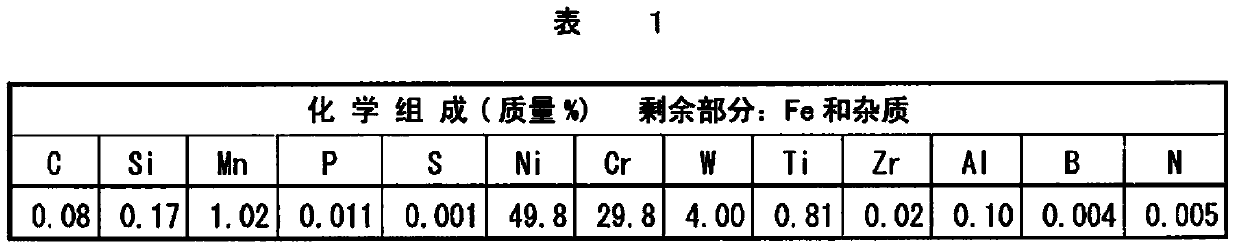
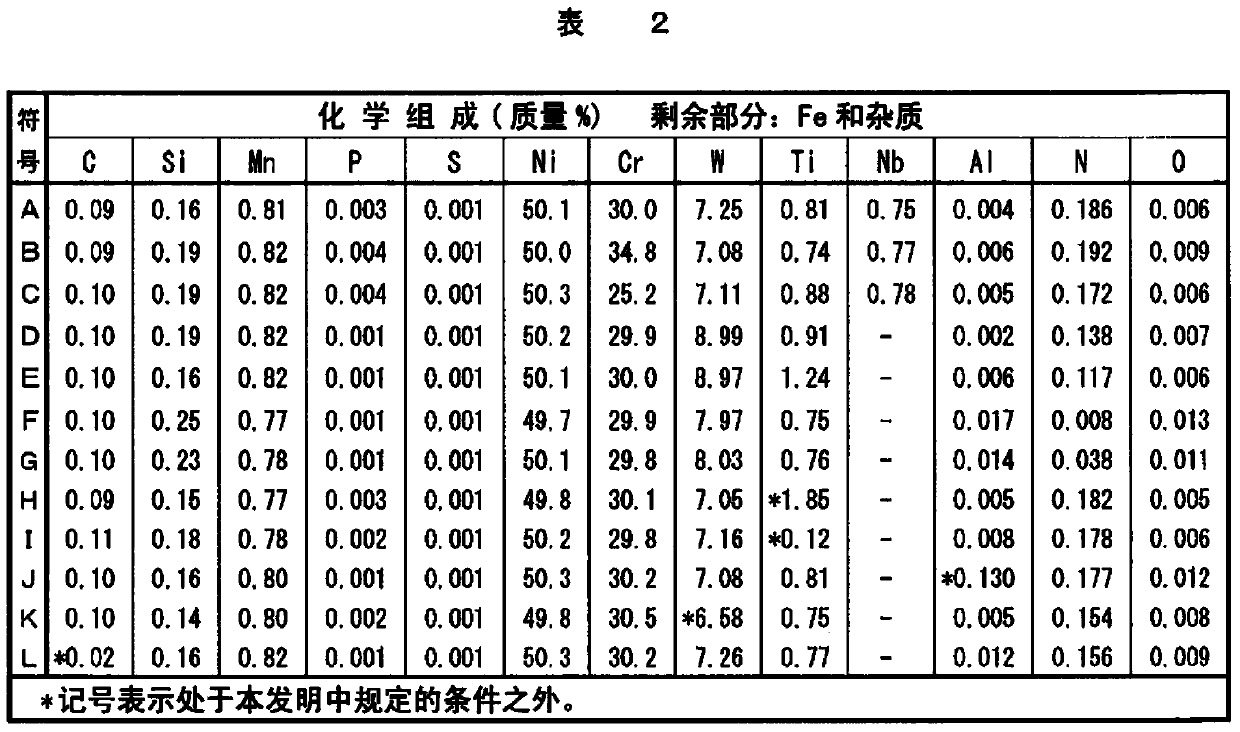
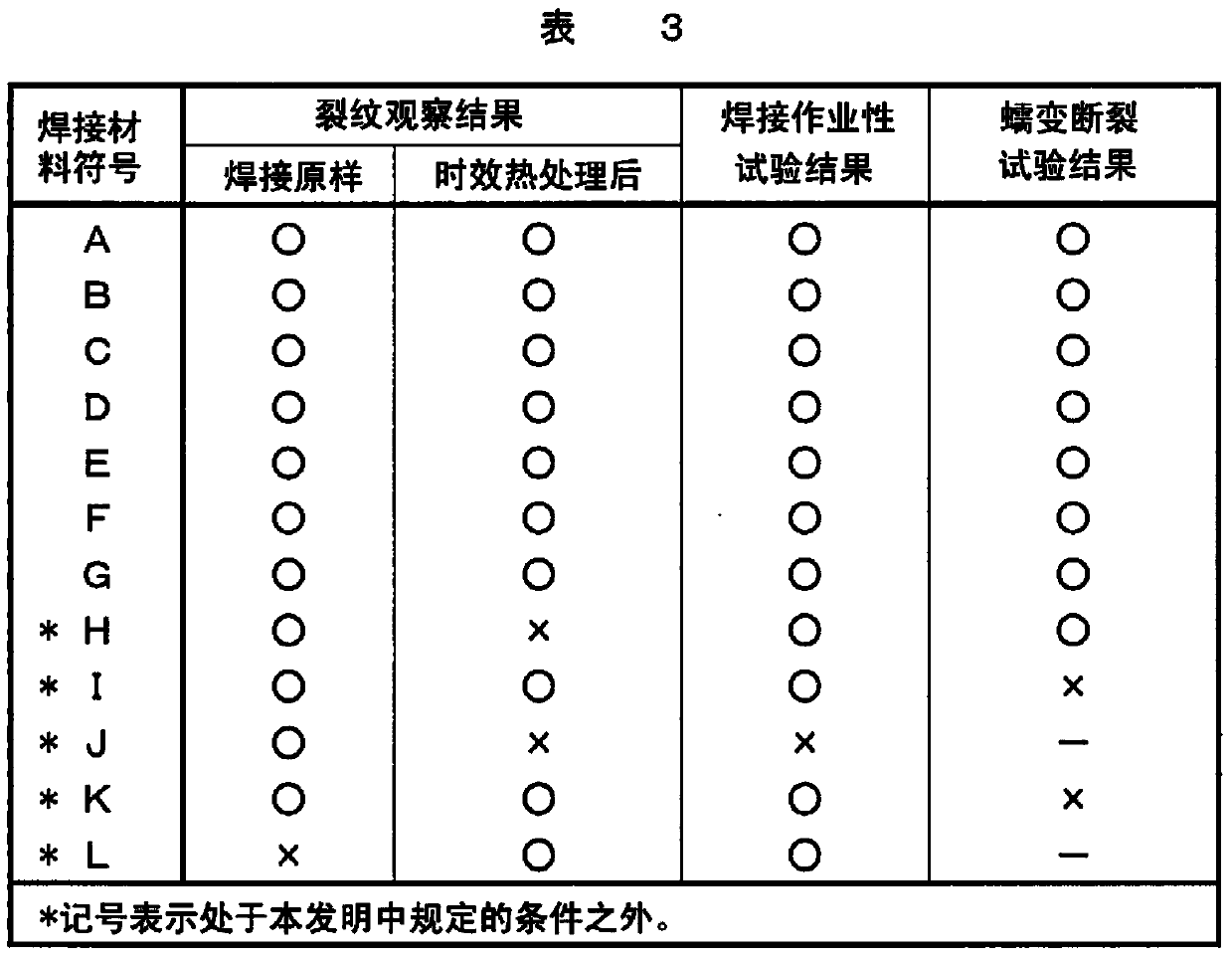
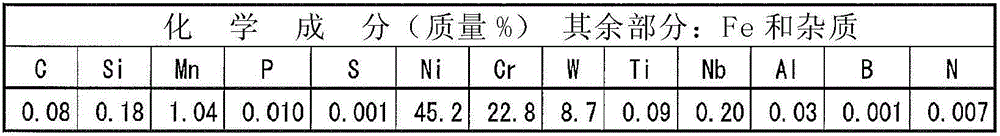
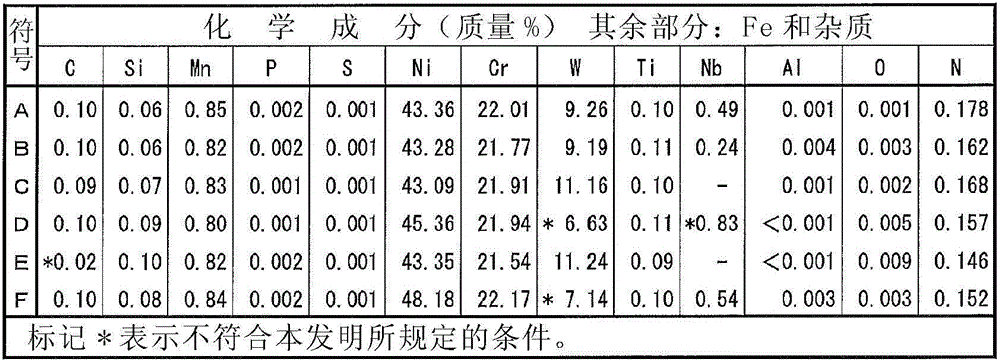
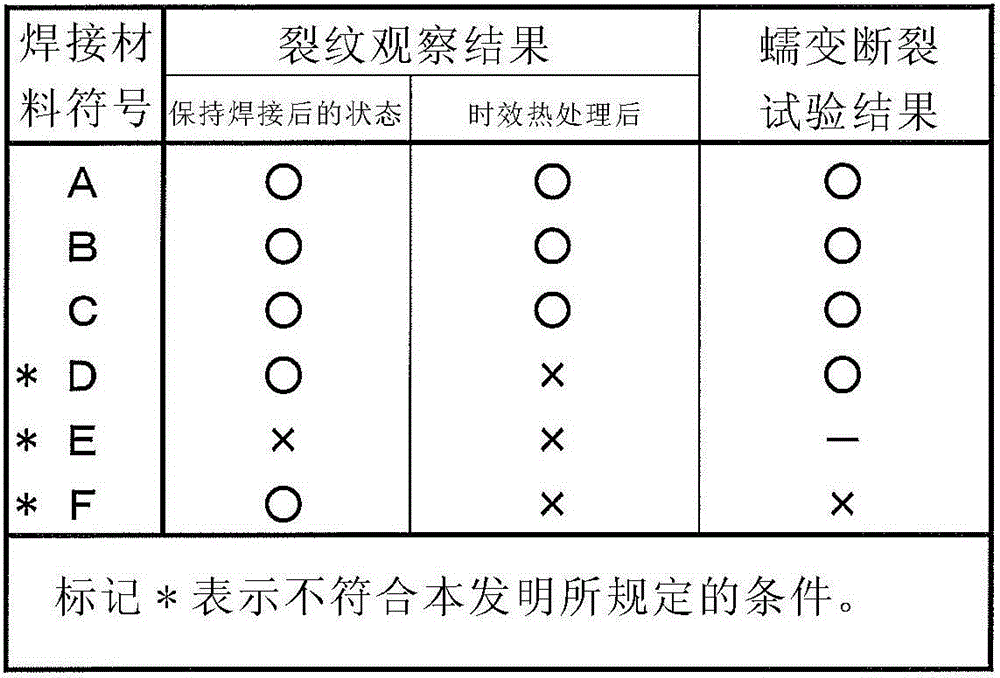
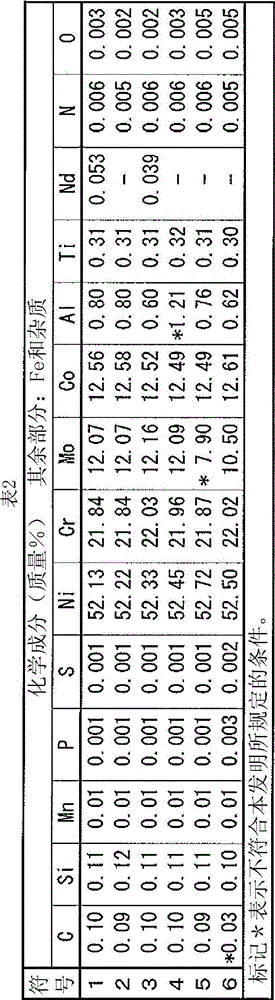
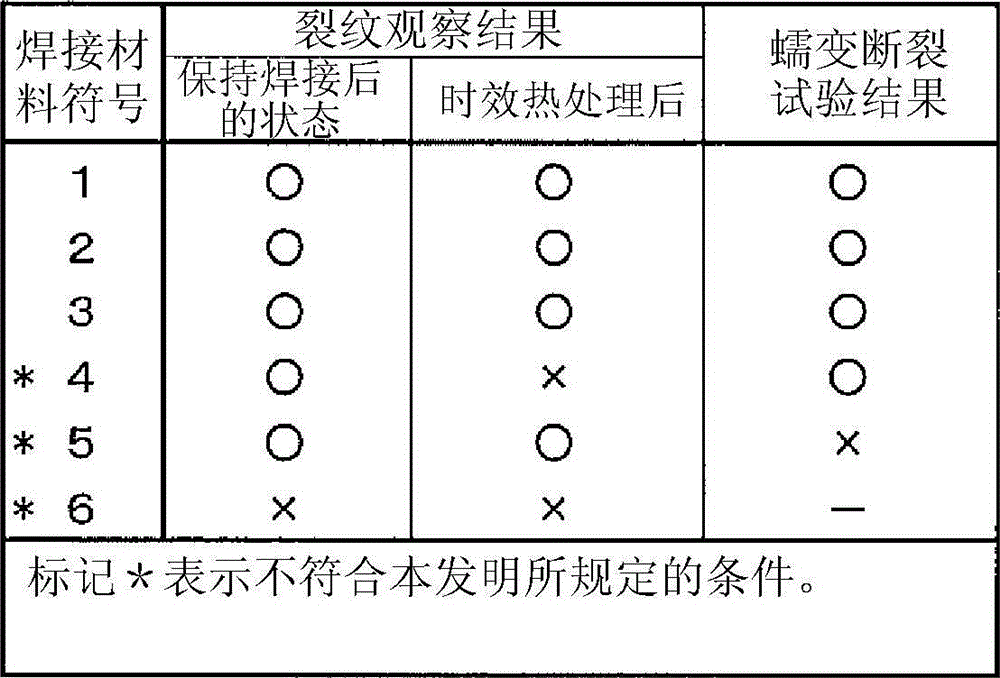
Disclosed is a welding material for an Ni-based heat-resistant alloy, which has a chemical composition that contains 0.06-0.18% of C, 0.5% or less of Si, 1.5% or less of Mn, 46-56% of Ni, 10-15% of Co, 20-25% of Cr, more than 10.0% but 14.0% or less of Mo, 0.01-0.5% of Ti, 0.1-1.0% of Al and 0.006% or less of N, and additionally if necessary, 0.1% or less of Nd with the balance made up of Fe and impurities, while controlling O, P and S contained as impurities to 0.02% or less, 0.008% or less, and 0.005% or less, respectively. The welding material for an Ni-based heat-resistant alloy exhibits excellent high-temperature cracking resistance during the welding. A welded metal that has high-temperature cracking resistance during the welding, stress relaxation cracking resistance when in use for a long period of time at high temperatures, and good creep strength can be provided using the above-described welding material. In addition, a welded joint can be provided using the above-described welding material, said welded joint being composed of a base of an Ni-based heat-resistant alloy that has excellent high-temperature strength and a welded metal that has high-temperature cracking resistance during the welding, stress relaxation cracking resistance when in use for a long period of time at high temperatures, and good creep strength.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Special hot-stamping die steel HS7 and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109402514AExcellent toughness and ductilityImprove performanceProcess efficiency improvementHot stampingCrack resistance
The invention discloses novel special hot-stamping die steel HS7 and relates to the technical field of die steel component formulas and manufacturing. The chemical components of the special hot-stamping die steel include, by weight, 0.41-0.45% of C, 0.45-0.55% of Si, 0.35-0.45% of Mn, 6.4-6.80% of Cr, 1.20-1.40% of Mo, 0.75-0.85% of V, 015% or below of P, 0.003% or below of S and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities and residual trace elements. The die steel adopts unique optimized alloy element proportion, the organization level of and purity degree of materials are greatly improved through refined smelting and multidirectional forging and combination with high temperature homogenizing, ultrafine processing and other processes, the key indicators of the hot-stamping die steel are obviously improved, including abrasion resistance, high temperature abrasion resistance, thermal fatigue cracking resistance, resistance to plastic deformation and the like. Therefore, improve the qualityof hot stamping dies can be obviously improved, the service life of the dies can be prolonged, and better economic benefits can be obtained.
Owner:上海合毓模具技术有限公司
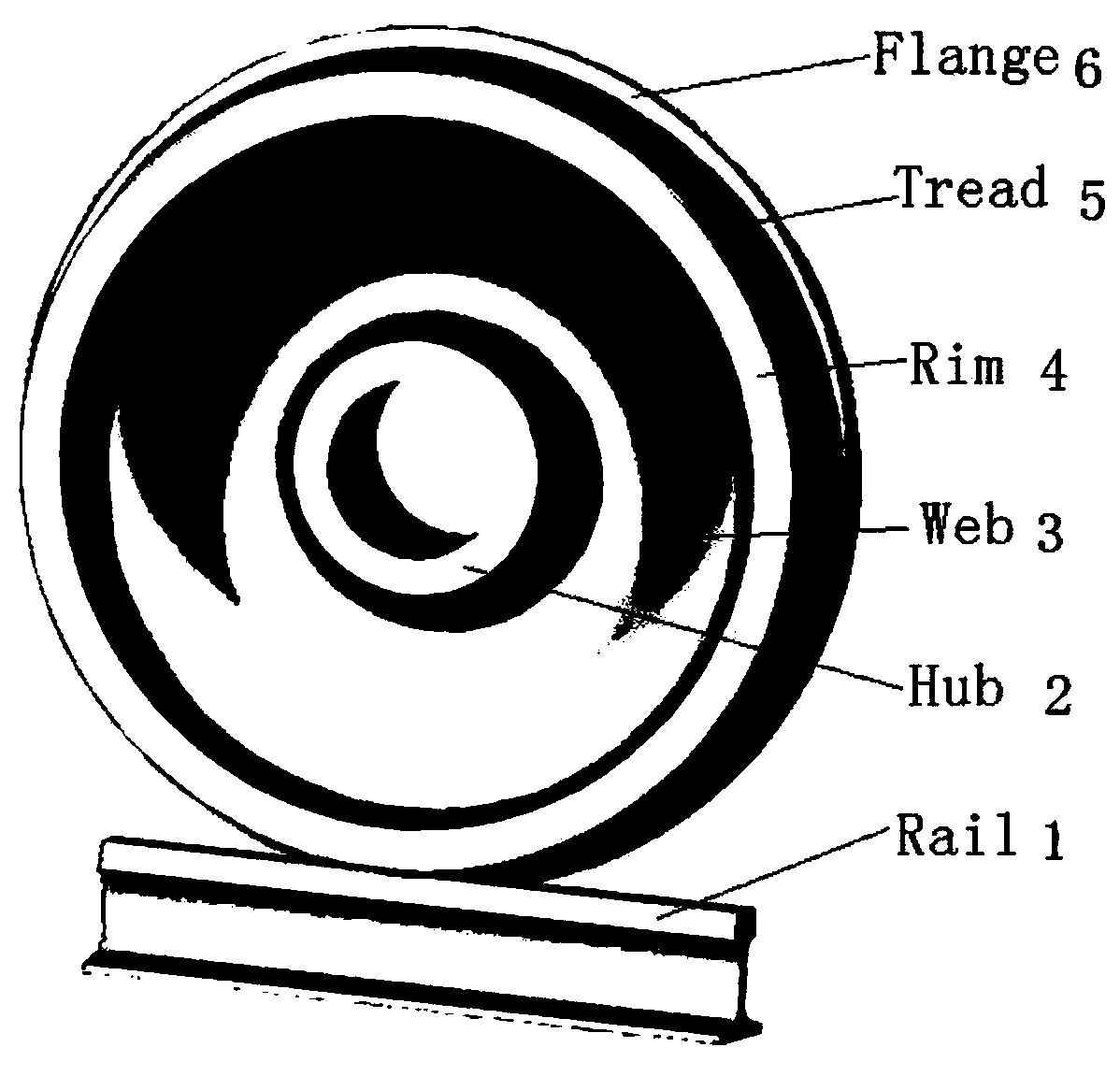
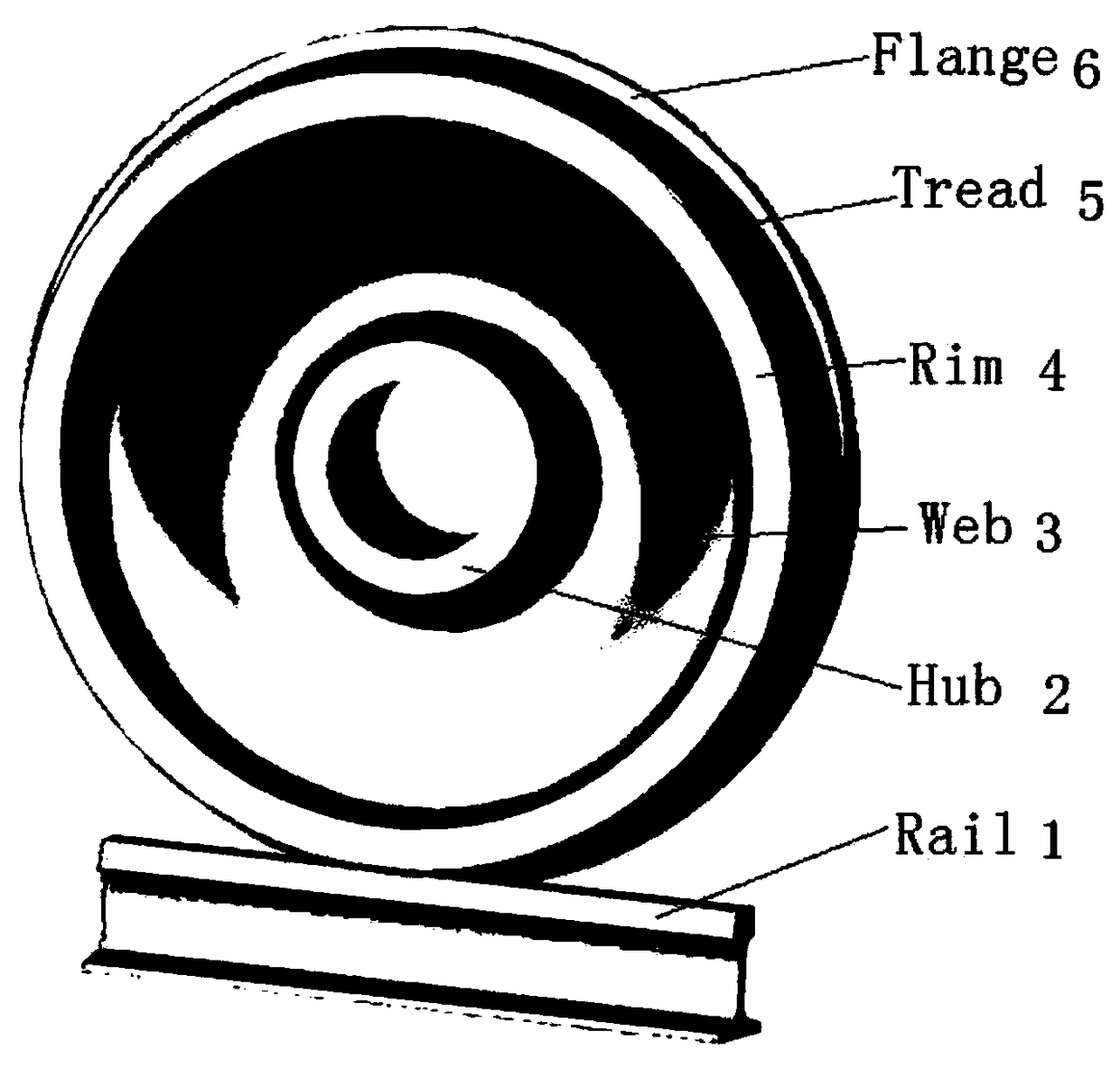
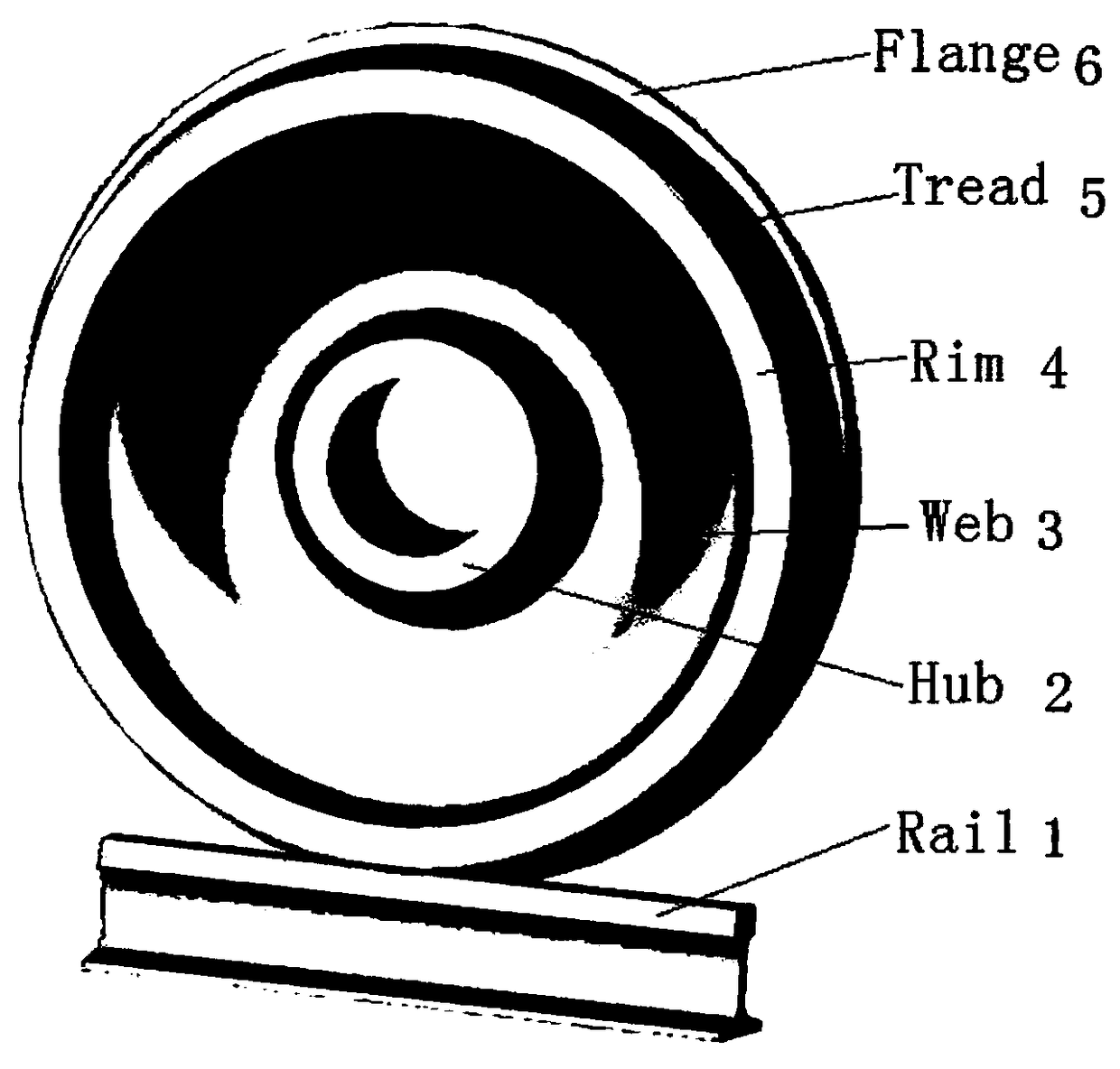
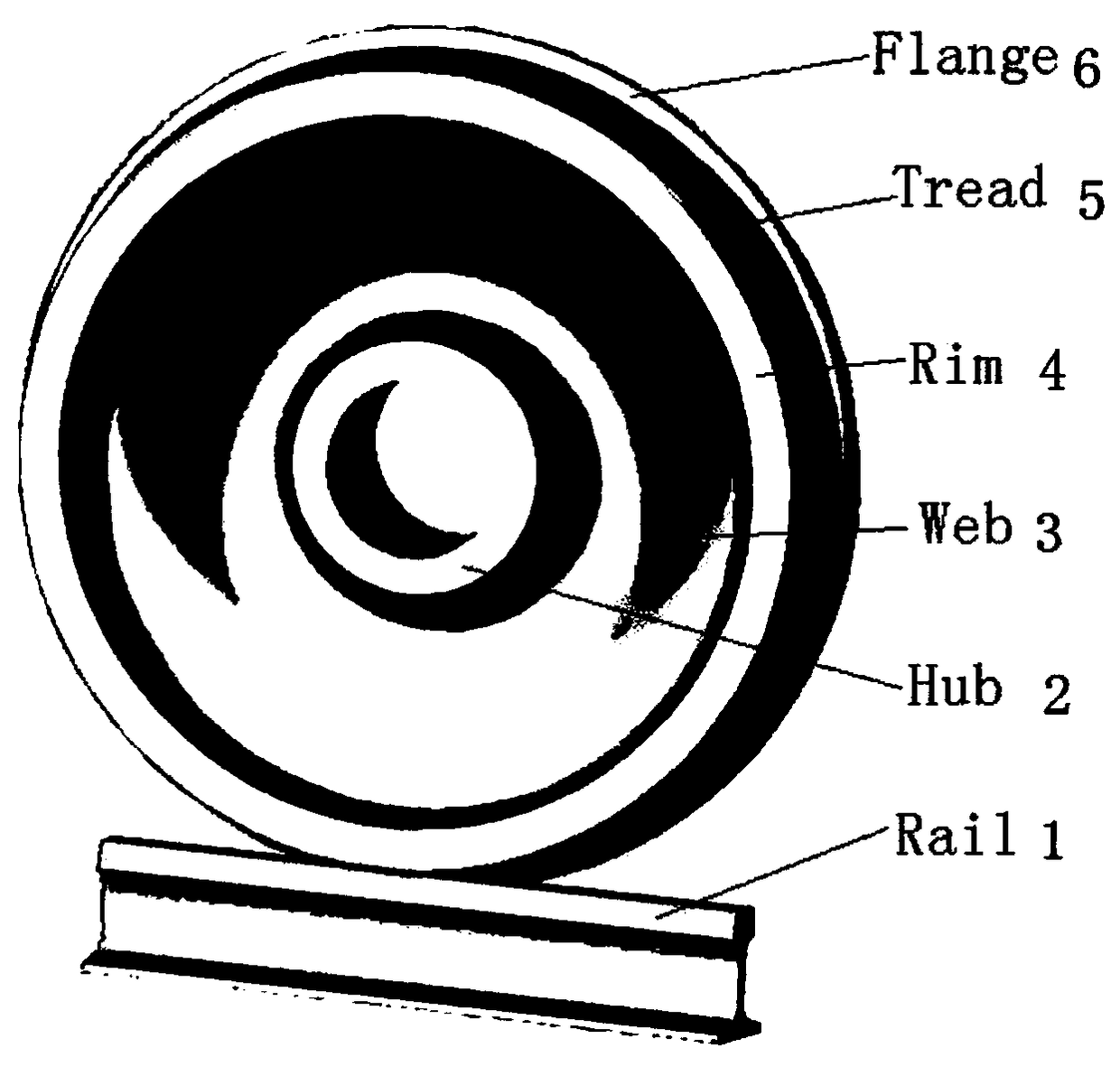
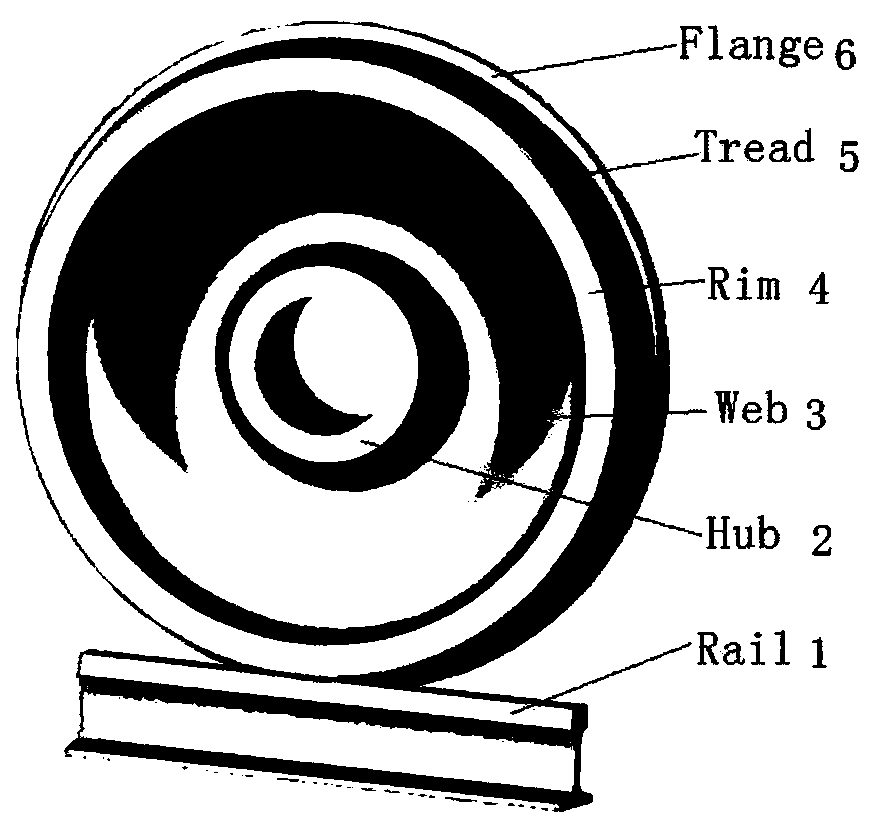
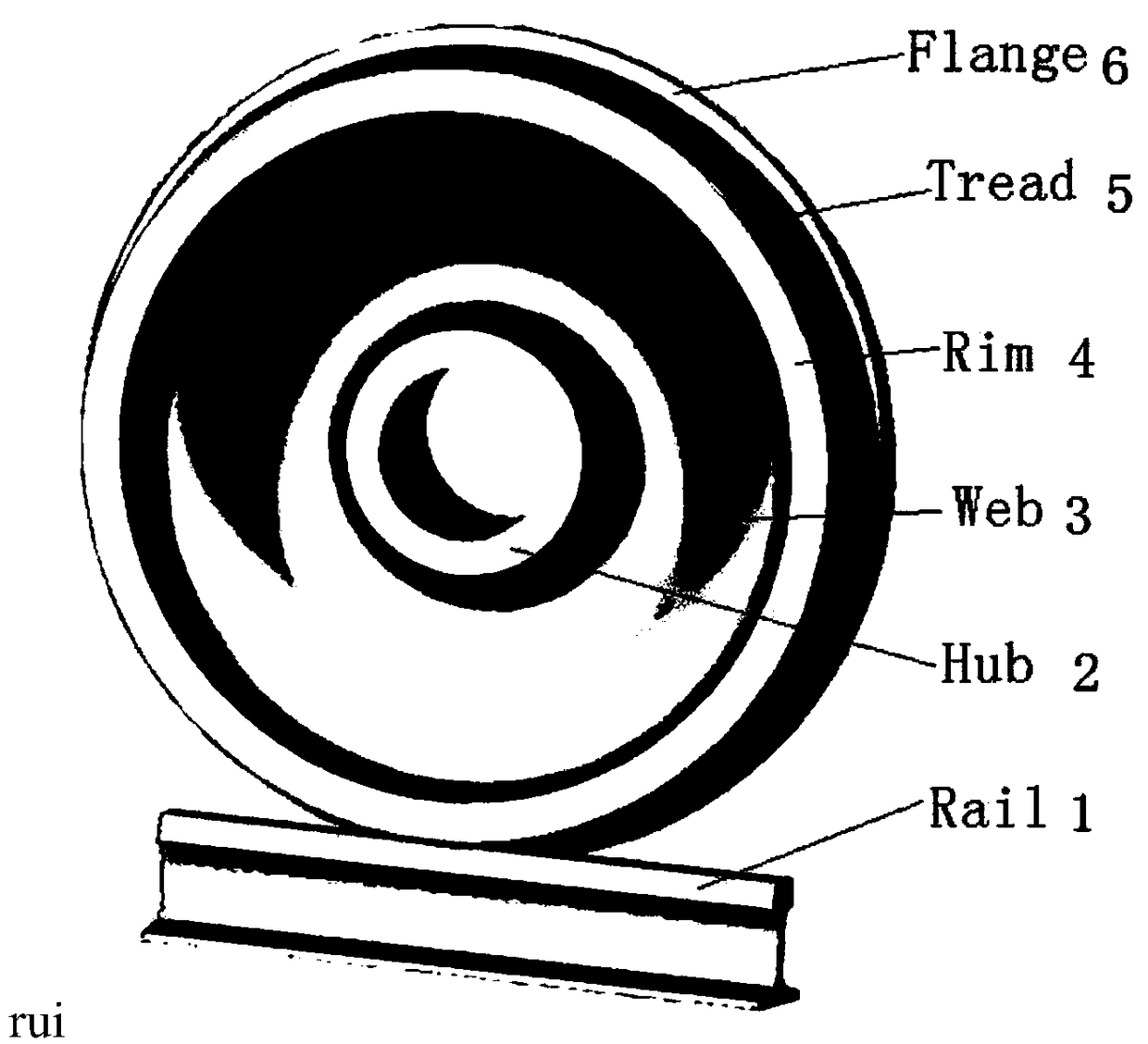
Common rail traffic bainite steel wheel used under cold and rigor service environment and manufacturing method of common rail traffic bainite steel wheel
InactiveCN108707831AHigh yield strengthHigh tensile strengthRail-engaging wheelsFurnace typesChemical compositionCommon rail
The invention discloses a common rail traffic bainite steel wheel used under the cold and rigor service environment and a manufacturing method of the common rail traffic bainite steel wheel. The common rail traffic bainite steel wheel comprises chemical components including 0.05%-0.30% of C, 0.50%-1.50% of Ni, 0.01%-1.20% of Cr, 0.70%-2.10% of Mn, 0.20%-1.00% of Si, 0.01%-1.00% of W, 0.05%-0.60% of Mo, 0.01%-0.80% of Cu, 0.01%-0.20% of V, 0.001%-0.20% of Nb, 0.0001%-0.0350% of B, 0.001%-0.040% of RE, not larger than 0.020% of P, not larger than 0.020% of S and the balance Fe and inevitable residual elements, wherein the sum of Mn and Cr is larger than or equal to 2.0% and smaller than or equal to 3.0%. By adopting a new alloy design system and alloying principle of C-Ni-Mn-Cr-Mo, after thewheel is molded, a rim obtained after advanced heat treatment obtains a carbide-free bainite organization structure, and the wheel has the excellent comprehensive mechanical property, decay resistance and service performance, in particular has the high low-temperature toughness and low-temperature breaking toughness, meets performance and service safety requirement under the low-temperature environment and is suitable for the cold zone under rigor conditions.
Owner:MAGANG (GROUP) HOLDING CO LTD +1
Welding material for austenitic heat-resistant steel, and welded metal and welded joint each using same
InactiveCN102947047AHeat crack resistanceResistant to stress relaxation crackingArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsChemical compositionCrack resistance
Disclosed is a welding material for austenitic heat-resistant steel, which has a chemical composition that contains more than 0.05% but 0.18% or less of C, 0.5% or less of Si, 1.5% or less of Mn, 40-50% of Ni, 20-25% of Cr, more than 8.0% but 13.0% or less of W, 0.01-0.2% of Ti, more than 0.03% but 0.20% or less of N and 0.01% or less of Al, and additionally if necessary, less than 0.60% of Nb, with the balance made up of Fe and impurities, while controlling O, P and S contained as impurities to 0.02% or less, 0.008% or less, and 0.005% or less, respectively. The welding material for austenitic heat-resistant steel exhibits excellent high-temperature cracking resistance during the welding. A welded metal that has high-temperature cracking resistance during the welding, stress relaxation cracking resistance when in use for a long period of time at high temperatures, and good creep strength can be provided using the above-described welding material. In addition, a welded joint can be provided, using the above-described welding material, from a base that has excellent creep strength at high temperatures and a welded metal that has high-temperature cracking resistance during the welding, stress relaxation cracking resistance when in use for a long period of time at high temperatures, and good creep strength.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Bainitic steel wheel for rail traffic with capability of resisting against damp, hot and corrosive environments and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN109182920AHigh yield strengthHigh tensile strengthRail-engaging wheelsFurnace typesCarbideAlloy
The invention discloses a bainitic steel wheel for rail traffic with capability of resisting against damp, hot and corrosive environments and a manufacturing method thereof. The bainitic steel wheel comprises the following chemical components: 0.05-0.40% of C, 0.40-1.50% of Ni, 0.25-1.50% of Cr, 0.70-2.10% of Mn, 0.20-1.00% of Si, 0.01-1.00% of W, 0.05-0.60% of Mo, 0.01-0.80% of Cu, 0.01-0.20% ofV, 0.001-0.20% of Nb, 0.0001-0.0350% of B, 0.001-0.040% of RE, less than or equal to 0.020% of P, less than or equal to 0.020% of S and the balance of Fe and inevitable residual elements, wherein Mn+Cr is more than or equal to 2.0% but less than or equal to 3.0%. The new alloy design system of C-Ni-Mn-Cr-Mo-Cu and alloying principle are adopted by the invention; after a wheel is formed, a rim after advanced thermal treatment is endowed with a carbide-free bainite structure; the wheel has excellent comprehensive mechanical property and service performance, especially, atmospheric corrosion resistance; the wheel is capable of resisting against damp, hot and corrosive environments and reducing the harmful influences of stress corrosion and medium corrosion; the service life and running safetyof the wheel can be further promoted.
Owner:MAGANG (GROUP) HOLDING CO LTD +1
Bainite steel wheel for rail traffic D-series high-speed train and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN108796372AHigh yield strengthHigh tensile strengthFoundry mouldsFurnace typesDesign systemsChemical composition
The invention discloses a bainite steel wheel for a rail traffic D-series high-speed train and a manufacturing method thereof. Chemical components of the bainite steel wheel comprise 0.05-0.30% of C,0.10-1.50% of Ni, 0.01-1.20% of Cr, 0.70-2.10% of Mn, 0.20-1.00% of Si, 0.01-1.00% of W, 0.05-0.60% of Mo, 0.01-0.80% of Cu, 0.01-0.20% of V, 0.001-0.20% of Nb, 0.0001-0.0350% of B, 0.001-0.040% of RE, smaller than or equal to 0.020% of P, smaller than or equal to 0.020% of S and the balance Fe and inevitable residual elements, and the sum of Mn and Cr is larger than or equal to 2.0% and smaller than or equal to 3.0%. According to the bainite steel wheel, the novel C-Ni-Mn-Cr-Mo alloy design system and the alloying principle are adopted, after the wheel is formed and subjected to advanced heattreatment, a rim obtains a no-carbide bainite structure, and the wheel has excellent comprehensive mechanical performance, anticorrosion performance and service performance, and especially has the beneficial effects of being high in strength, high in hardness, high in toughness, high in low-temperature toughness, high in wheeltrack rolling contact fatigue resisting performance (RCF), high in heatcrack resisting performance and the like.
Owner:MAGANG (GROUP) HOLDING CO LTD +1
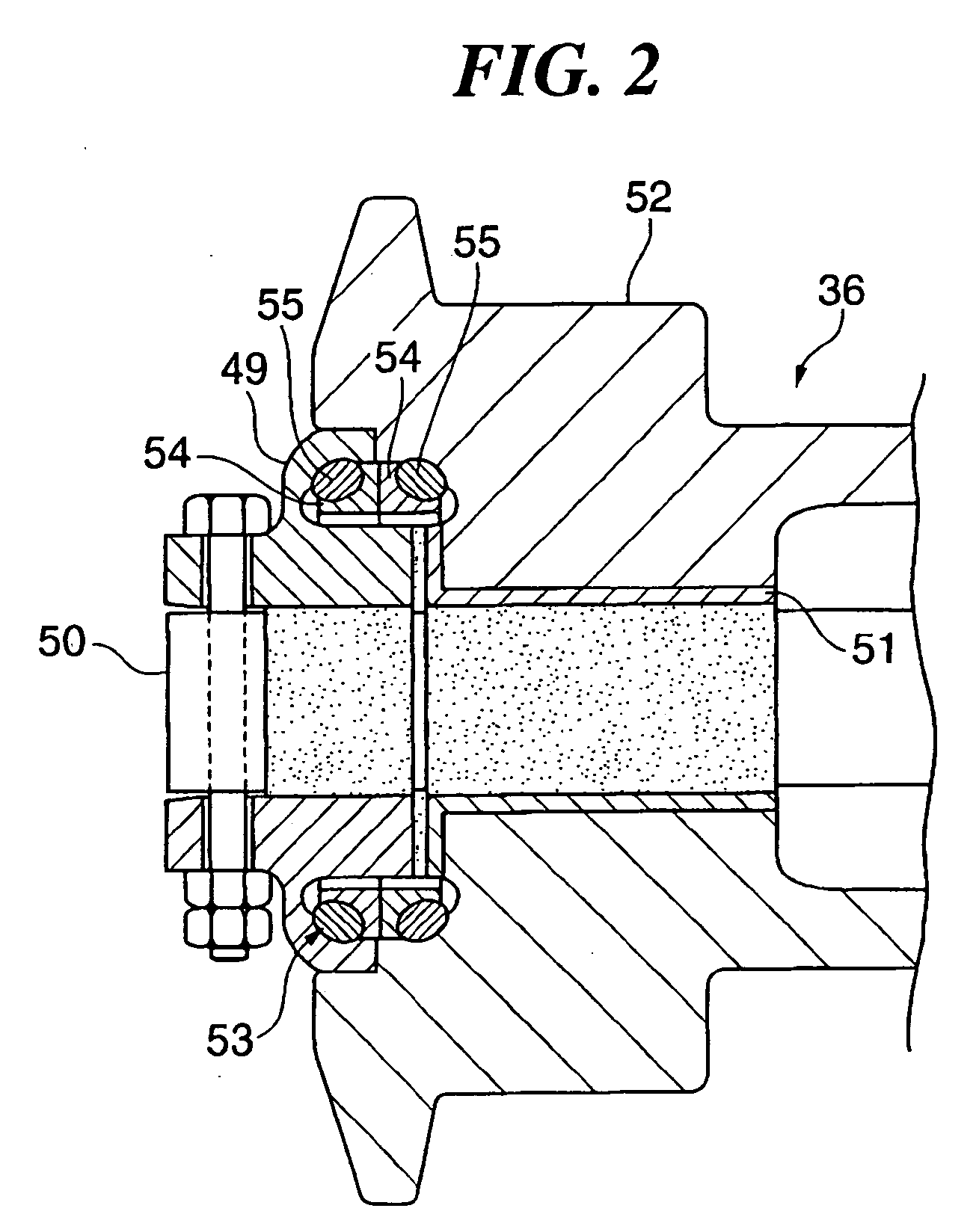
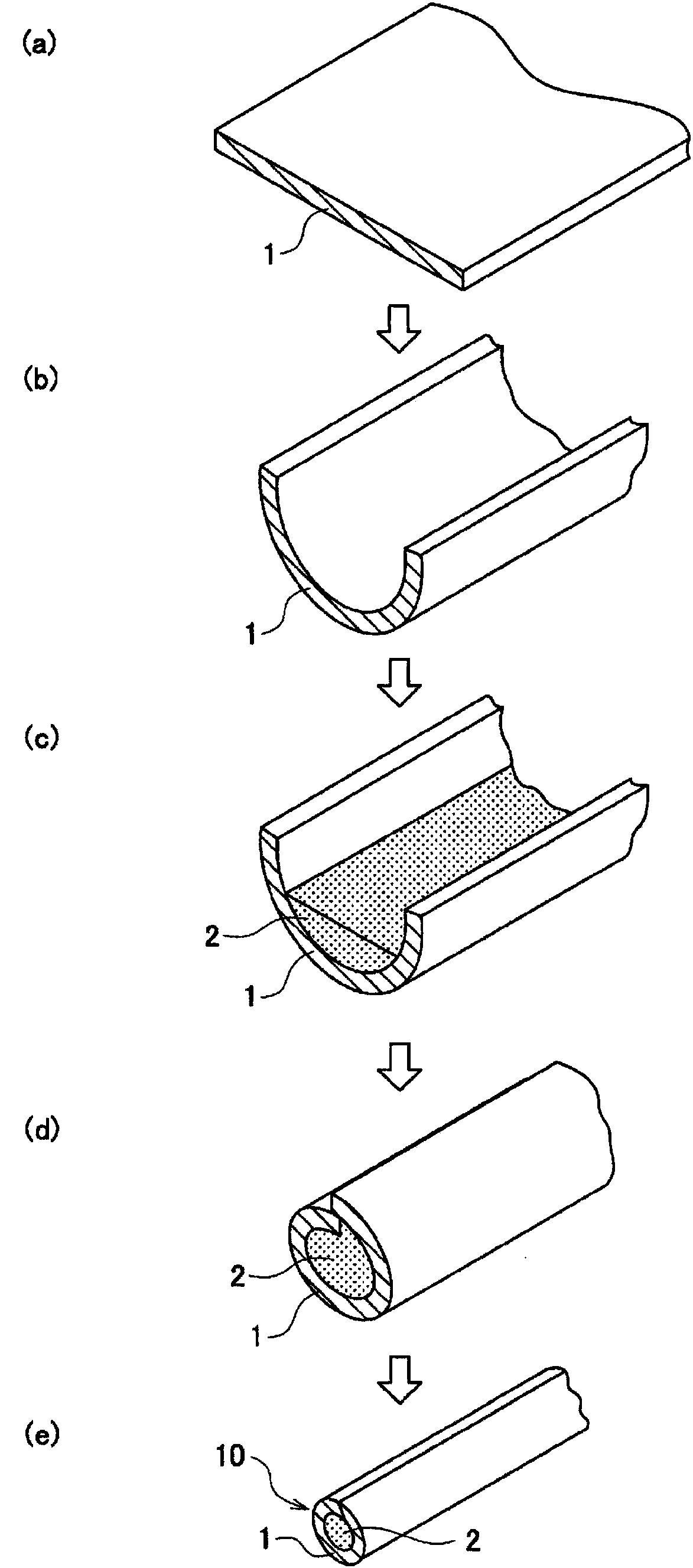
Ferrous seal sliding parts and producing method thereof
InactiveUS20070289714A1Excellent heat crack resistanceFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesCrack resistanceCarbide
A ferrous seal sliding part excellent in heat crack resistance, seizing resistance and abrasion resistance is provided. The ferrous seal sliding part having a seal sliding surface, wherein the seal sliding surface has a martensite parent phase which forms a solid solution with carbon of 0.15 to 0.6 wt % and contains a first dispersion material of at least either cementite of 5 to 70% by volume or MC-type carbide of 0.1 to 10% by volume and a second dispersion material of at least either graphite of 1 to 15% by volume or Cu alloy phase of 1 to 20% by volume dispersed therein, with a total content of the first dispersion material and the second dispersion material being 5 to 70% by volume.
Owner:TAKAYAMA TAKEMORI +2
Bainite steel wheel for rail traffic truck and manufacturing method of bainite steel wheel
InactiveCN108754329AReduce coefficient of frictionReduce wearFurnace typesProcess efficiency improvementCrack resistanceAlloy
The invention discloses a bainite steel wheel for a rail traffic truck and a manufacturing method of the bainite steel wheel. The bainite steel wheel for the rail traffic truck comprises the followingchemical components: 0.10-0.40% of C, 0.10-1.50% of Ni, 0.25-1.50% of Cr, 0.70-2.10% of Mn, 0.20-1.00% of Si, 0.01-1.00% of W, 0.05-0.60% of Mo, 0.01-0.80% of Cu, 0.01-0.20% of V, 0.001-0.20% of Nb,0.0001-0.0350% of B, 0.001-0.040% of RE, less than or equal to 0.020% of P, less than or equal to 0.020% of S and the balance of Fe and inevitable residual elements; and moreover, 2.0%< / = Mn+ Cr< / = 3.0%. A novel alloy design system of C-Ni-Mn-Cr-Mo and an alloying principle are adopted, after wheels are formed and subjected to advanced heat treatment, a carbide-free bainite organization structureis obtained, and the wheels have excellent integrated mechanical property, corrosion resistance and service performance, and particularly have the characteristics of high strength, hardness and toughness, high wheel track rolling contact fatigue (RCF) resistance, hot crack resistance and the like.
Owner:MAGANG (GROUP) HOLDING CO LTD +1
High cr cast iron having excellent heat resistance and its heat treatment
ActiveCN1746325AExcellent heat crack resistanceHeat treatment process controlCrack resistanceHeat resistance
The invention provides a high-Cr cast iron superior in heat-cracking resistance for an abrasion-resistant member receiving a heat cycle involving an impact, and to provide a heat treatment method therefor. The high-Cr cast iron comprises, by mass%, 2.5-3.5% C, 0.2-1.0% Si, 0.6-2.0% Mn, 11-22% Cr, 1.0-3.0% Mo, 0.01-0.15% N, and the balance Fe with unavoidable impurities, while controlling a ratio Cr / C of a Cr content to a C content into a range of 4.5 to 6.5, and a product Mn*Mo of a Mn content and a Mo content into a range of 1.8 to 2.5. The heat treatment method includes cooling the surface of the high-Cr cast iron at a cooling rate of 5[deg.]C / sec or lower in the step of quenching, to control a residual [gamma] phase in a structure to 30% or less by volume ratio. Thus, the high-Cr cast iron acquires improved heat-cracking resistance.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD +1
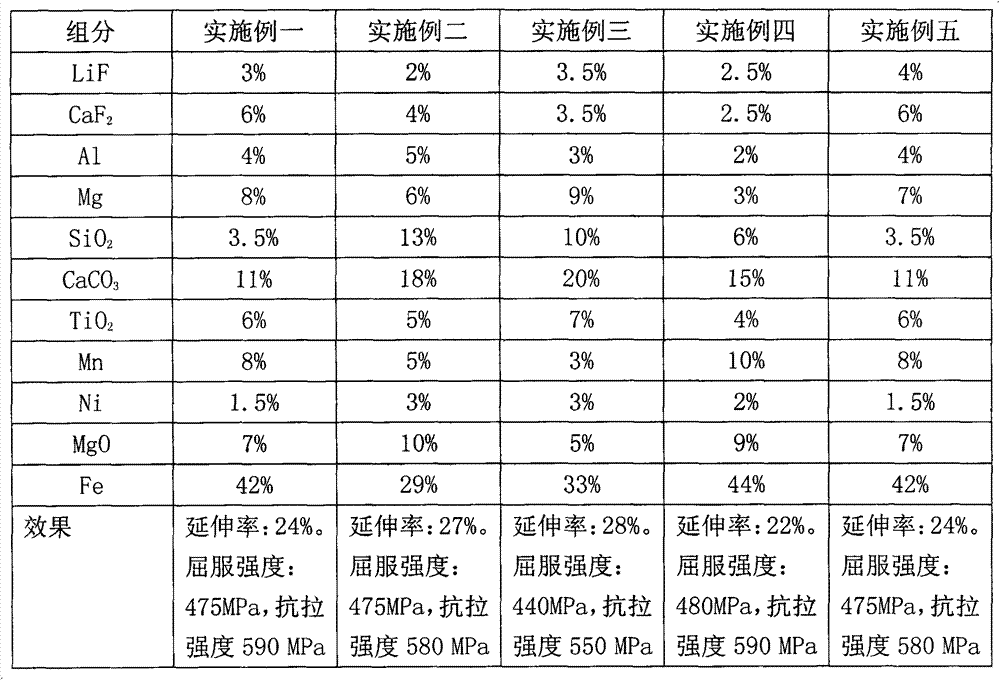
Self-protection flux-cored wire for downward welding and horizontal position welding
InactiveCN103170756AImprove plasticityHigh strengthWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaCrack resistanceSlag
The invention discloses a self-protection flux-cored wire for downward welding and horizontal position welding and provides a self-protection flux-cored wire through which the plasticity of welding line metal of the self-protection flux-cored wire can be improved, the splash degree is reduced, downward welding and horizontal position welding are facilitated and the slag removal performance and the weld molding are improved. According to the technical scheme, the flux core of the self-protection flux-cored wire comprises the following components by weight percent: 3-10 percent of manganese, 1-4 percent of nickel, 1-5 percent of aluminum, 1-9 percent of magnesium, 10-20 percent of carbonate, 1-10 percent of fluoride, 1-7 percent of titanium dioxide, 7-10 percent of magnesium oxide, 3-13 percent of silicon dioxide and 25-50 percent of iron powder. The self-protection flux-cored wire has the advantages that the plasticity and the strength are good, the splash is slight, only fine particles splash, the welding performances of downward welding and horizontal position welding are excellent, the slag removal performance and the weld molding property are obviously improved, the S element content of the deposited metal is extremely low, and the hot crack resistance is excellent.
Owner:HEBEI YICHEN INDAL GROUP
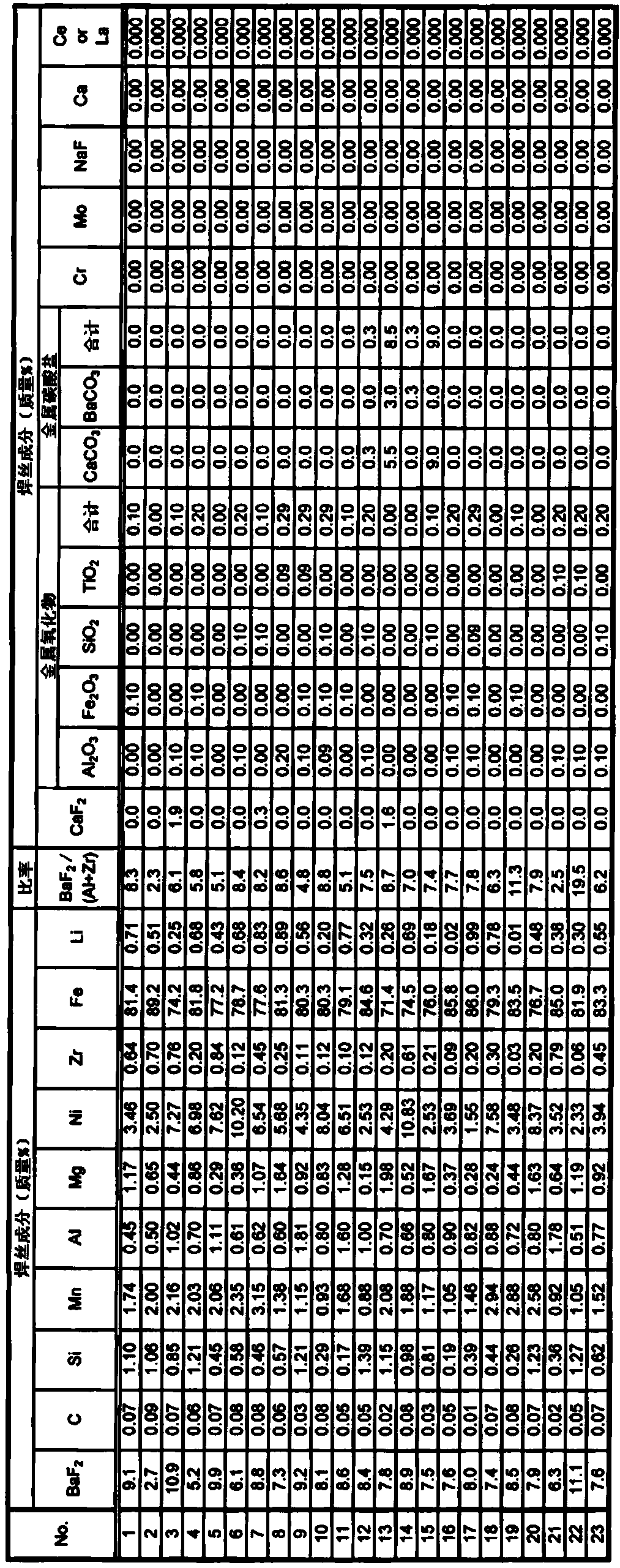
Wire containing flux for gas shield arc welding
ActiveCN107848082ALow amount of diffusible hydrogenExcellent welding workabilityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaMaterials scienceAl content
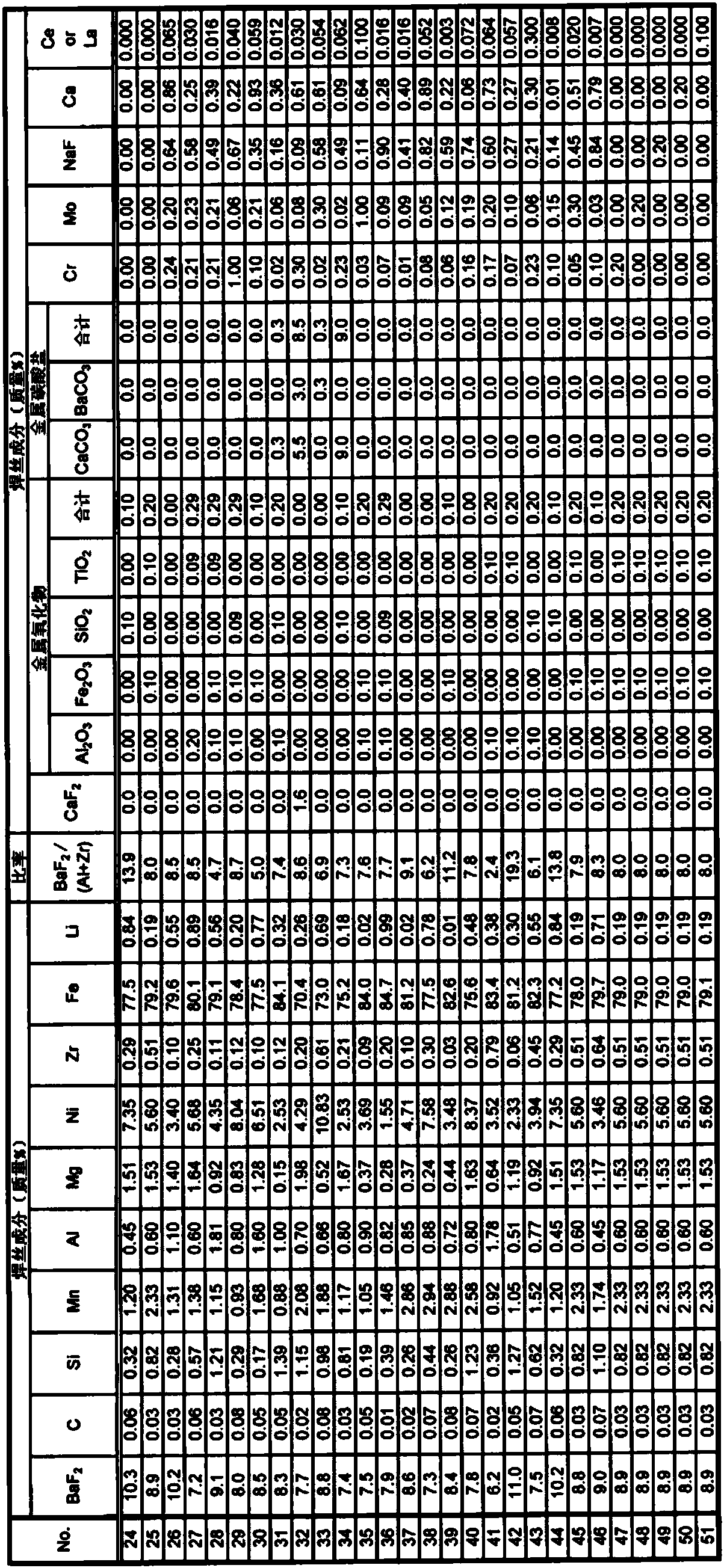
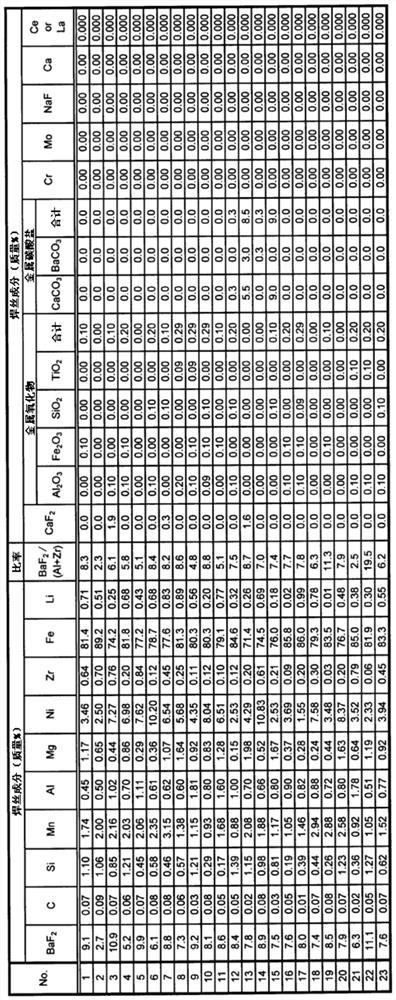
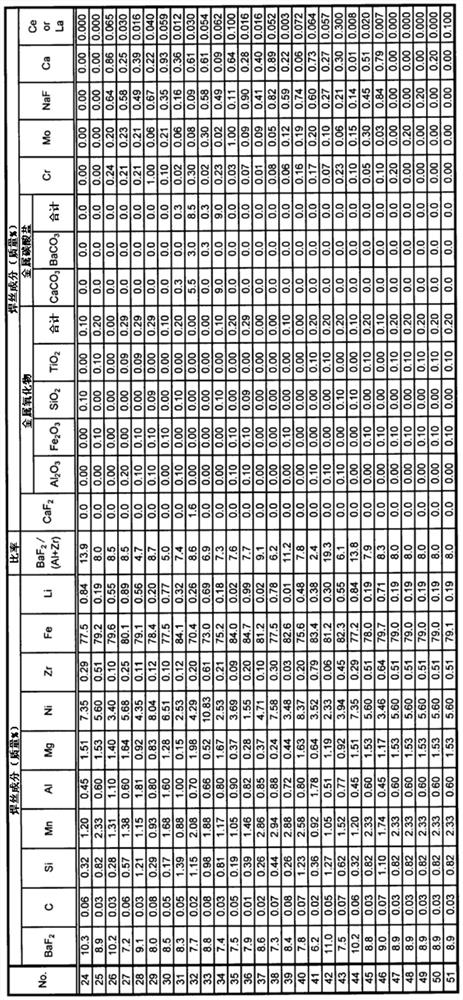
A wire containing flux for gas shield arc welding in which a steel casing is filled with flux, wherein: the wire contains BaF2, C, Si, Mn, Al, Mg, Ni, Zr, Fe, and Li in prescribed amounts per total mass of wire; and the value expressed by BaF2 content / (Al content+Zr content) is 2.1-20.0.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Bainite steel wheel for rail traffic passenger car and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN108728750AReduce coefficient of frictionImprove operational efficiencyRail-engaging wheelsFurnace typesDesign systemsCorrosion
The invention discloses a bainite steel wheel for a rail traffic passenger car and a manufacturing method thereof. The bainite steel wheel comprises the chemical components of 0.08-0.35% of C, 0.10-1.50% of Ni, 0.25-1.50% of Cr, 0.70-2.10% of Mn, 0.20-1.00% of Si, 0.01-1.00% of W, 0.05-0.60% of Mo, 0.01-0.80% of Cu, 0.01-0.20% of V, 0.001-0.20% of Nb, 0.0001-0.0350% of B, 0.001-0.040% of RE, 0-0.020% of P, 0-0.020% of S, and the balance Fe and inevitable residual elements, and in addition, the sum of Mn and Cr is larger than or equal to 2.0% and smaller than or equal to 3.0%. According to thebainite steel wheel for the rail traffic passenger car and the manufacturing method thereof, the novel C-Ni-Mn-Cr-Mo alloy design system and the alloying principle are adopted, after the wheel is formed, advanced heat treatment is conducted, then, the carbide-free bainite structure of a rim is obtained, and the wheel has the characteristics of being excellent in comprehensive mechanical property,corrosion resistance and service performance, high in strength, hardness, toughness, wheel rail rolling contact fatigue (RCF) resistance and hot crack resistance, and the like.
Owner:MAGANG (GROUP) HOLDING CO LTD +1
Welding material for ni-based heat-resistant alloys, and welded metal and melded joint each using same
ActiveCN104023903AExcellent welding workabilityImprove heat resistanceArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsChemical compositionCrack resistance
A welding material for Ni-based heat-resistant alloys, which has a chemical composition containing 0.06-0.18% of C, 0.5% or less of Si, 1.5% or less of Mn, 45-55% of Ni, 25-35% of Cr, 7.0-13.0% of W, more than 0.2% but 1.5% or less of Ti, less than 0.1% of Al, 0.002-0.20% of N, and if necessary, 1.0% or less of Nb, with the balance made up of Fe and impurities that include 0.02% or less of O, 0.008% or less of P and 0.005% or less of S. This welding material for Ni-based heat-resistant alloys exhibits excellent welding workability and high-temperature cracking resistance during welding.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Nickel-based welding electrode for welding nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloy
ActiveCN102430876BExcellent heat crack resistanceEasy to useWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaCrack resistanceNiobium
The invention relates to a nickel-based welding electrode which comprises the following component by weight percent (wt%): 50.0-68.0% of Ni, 18.0-23.0% of Cr, 6.0-11.0% of Mo, 3.0-6.0% of Nb, 2.50-9.00% of Fe, 0.01-0.1% of C, 0.10-1.00% of Mn, 0.010-0.10% of Si, 0.015% of S or less, 0.015% of P or less, 0.01-0.10% of Cu, 0.003-0.010% of Co and the balance of impurities. The coat of the nickel-based welding electrode comprises the following components by weight percent of the welding core: 12-18% of marble, 10-15% of fluorite, 12-18% of barium carbonate, 5.0-6.4% of rutile, 3.5-5.0% of ferroniobium, 3.3-4.5 of chromium metal powder, 0.45-0.65% of sodium carbonate, 0.45-0.65% of electrolytic manganese and 1.3-1.8% of zircon sand, and the adhesion agent is 10-20% of the total weight of the power. The nickel-based welding electrode is prepared by mixing, wrapping mixture on the welding core and baking at low and high temperature. The nickel-based welding electrode disclosed by the invention is used for nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloy steel welding, ensures that the excellent mechanical properties, the excellent corrosion resistance, the excellent thermal crack resistance and the hightensile strength of the welding seam match with those of the base material, has good welding process performance, guarantees attractive molding and can be used for the welding of the steel (with 9% of Ni) working at low temperature.
Owner:ATLANTIC CHINA WELDING CONSUMABLES
Bainite steel wheel for rail traffic heavy-duty freight car and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN108796371AHigh yield strengthHigh tensile strengthFoundry mouldsFurnace typesCrack resistanceAlloy
The invention discloses a Bainite steel wheel for rail traffic heavy-duty freight car and a manufacturing method thereof. The Bainite steel wheel comprises the chemical components of 0.10-0.40% of C,0.40-2.10% of Ni, 0.25-1.50% of Cr, 0.70-2.10% of Mn, 0.20-1.00% of Si, 0.01-1.00% of W, 0.05-0.60% of Mo, 0.01-0.80% of Cu, 0.01-0.20% of V, 0.001-0.20% of Nb, 0.0001-0.0350% of B, 0.001-0.040% of RE, less than or equal to 0.020% of P, less than or equal to 0.020% of S, and the balance Fe and inevitable residual elements, specifically, the sum of Mn and Cr is larger than or equal to 2.0% and smaller than or equal to 3.0%. By adoption of a novel alloy design system and alloying principle of C-Ni-Mn-Cr-Mo, after the wheel is formed, a rim is of a carbide-free Bainite tissue structure after advanced thermal treatment, and the wheel has excellent comprehensive mechanical properties, corrosion resistance and service performance, and particularly has the characteristics of high strength, hardness and toughness, high wheel track rolling contact fatigue (RCF) performance and hot crack resistance, and the like.
Owner:MAGANG (GROUP) HOLDING CO LTD +1
Self-shielded flux-cored wire used for downward welding and horizontal position welding
ActiveCN105149815AImprove plasticityHigh strengthWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSlagManganese
The invention belongs to the technical field of welding materials, and relates to a self-shielded flux-cored wire used for downward welding and horizontal position welding. A flux core of the self-shielded flux-cored wire is prepared from, by weight, 8-10% of manganese, 2-5% of chrome, 0.2-2% of zirconium, 3-8% of aluminum, 5-9% of carbonate, 11-20% of calcium fluoride, 7-10% of calcium oxide, 3-13% of zirconium oxide, 0.5-3% of ferric oxide and the balance iron powder. The manufactured self-shielded flux-cored wire has good plasticity and strength, splatter is little and is fine particle splatter, the welding performance of downward welding and horizontal position welding is excellent, slag detachability and weld seam formability are obviously improved, the content of the S element of deposited metal is very low, and excellent hot-crack-resisting performance is achieved. The self-shielded flux-cored wire is suitable for welding medium and thick steel plates at the same strength level, particularly suitable for welding butt-joint welding seams of a deep groove steel plate and capable of being widely applied to machine manufacturing, building and welding of structural parts with the low requirement for impact toughness.
Owner:HEBEI YICHEN INDAL GROUP
Welding material for austenitic heat-resistant steel, and welded metal and welded joint each using same
InactiveCN102947047BExcellent heat crack resistanceExcellent resistance to stress relaxation crackingArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsChemical compositionCrack resistance
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Stainless steel flux cored wire
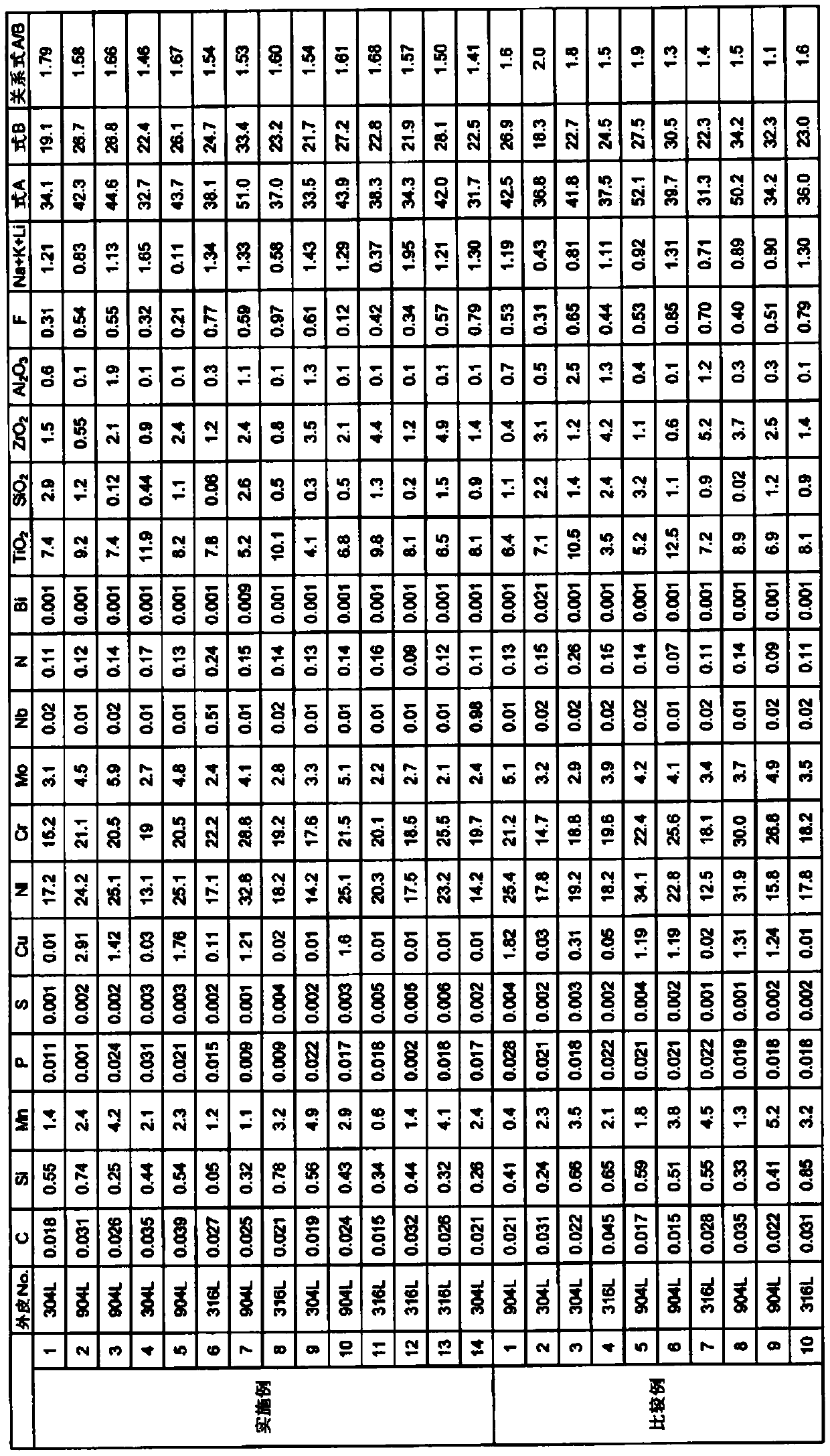
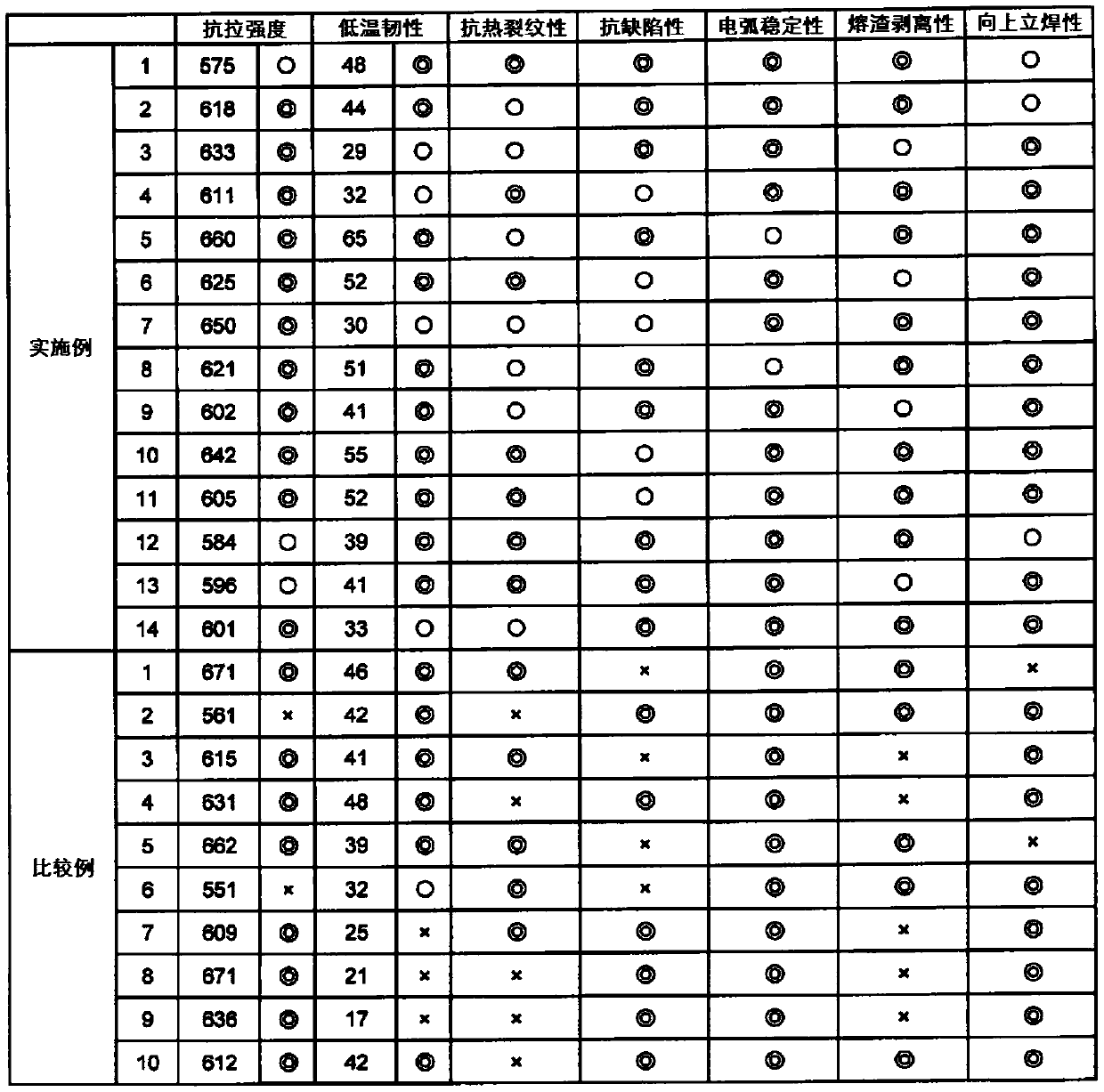
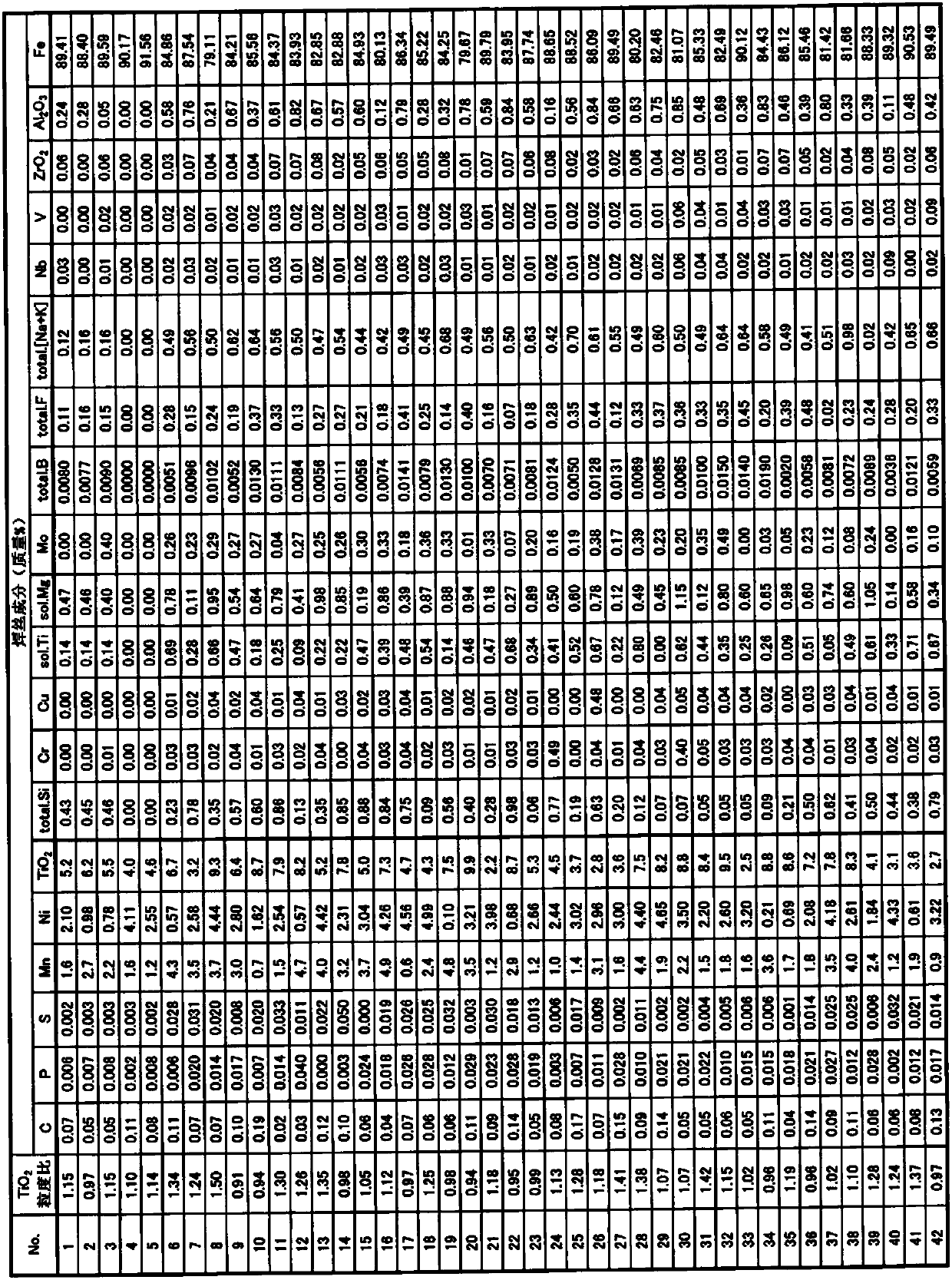
InactiveCN106994570BHigh tensile strengthImprove low temperature toughnessArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsNiobiumBismuth compound
THe invention provides a stainless steel flux cored wire, which is excellent in extension strength, low-temperature flexibility, anti-defection property and anti-hot-cracking property. The stainless steel flux cored wire inlcudes, by mass, lower than 0.04% of carbon, lower than 0.8% of silicon, 0.5-5.0% of manganese, lower than 3.0% of copper, 13-33% of nickel, 15-29% of chromium, 2.0-6.0% of molybdenum, lower than 1.0% of niobium, and 0.08-0.25% of nitrogen. In addition, the flux includes, by mass, 4.0-12.0% of TiO2, 0.05-3.0% of SiO2, 0.5-5.0% of ZrO2, lower than 2.0% of Al2O3, a bismuth compound with Bi equivalent value being lower than 0.01%, an alkali metal compound with alkali metal equivalent value being 0.1-2.0% and fluorides with fluorine equivalent value being 0.1-1.0%.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Flux-cored wire for gas-shielded arc welding
ActiveCN107921589AExcellent welding workabilityExcellent heat crack resistanceWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaMaterials scienceArc welding
Provided is a flux-cored wire for gas-shielded arc welding that contains specific amounts of C, Mn, TiO2, and Ni and specific amounts or less of P and S. The TiO2 has a ratio (Alpha 1 / Alpha 2) of 0.90-1.50 when Alpha 1 (mass%) is the content per wire total mass of particles having a size of 106 [mu]m or smaller and Alpha 2 (mass%) is the content per wire total mass of particles having a size exceeding 106 [mu]m.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Die-casting mold material and processing method for outer casing of auto parts
Owner:YANGZHOU KAIXIANG ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD
Cooling core puller
The invention discloses a cooling core puller. The cooling core puller comprises a core-pulling fixing base and a core pulling body which is detachably connected to the core-pulling fixing base, wherein one end, away from the core-pulling fixing base, of the core pulling body is a shaping end; the shaping end comprises an outer shaping part and an inner shaping part; the outer shaping part surrounds the inner shaping part, and a gap is formed between the outer shaping part and the inner shaping part; a first cooling water channel is arranged in the core pulling body; from the mounting end, away from the shaping end, of the core pulling body, the first cooling water channel sequentially passes through the inner shaping part and the outer shaping part, and finally returns to the mounting endof the core pulling body, so that a cooling water channel with inner and outer layers is formed in the core pulling body, and thus, cooling water uniformly cools the core pulling body by circulatinginside the core pulling body. The shaping end of the core pulling body is a structure with inner and outer layers, and the cooling water channel with inner and outer layers is arranged in the core pulling body, so that the cooling effect of a workpiece is improved, and the surface sintering and workpiece expanding and blocking problem is solved.
Owner:SUZHOU GUANGXING MOLD
High-speed train brake disc and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114318121AHigh and stable coefficient of frictionEasy to brakeBraking discsCrazingManganese
A cast steel disc body of the high-speed train brake disc comprises, by mass, 0.2%-0.32% of carbon, 0.5%-0.7% of silicon, 0.4%-0.8% of manganese, 0.01%-0.02% of tungsten, 0.1%-0.9% of vanadium, 0.7%-0.9% of molybdenum, 1.0%-1.5% of nickel, 0.9%-1.2% of chromium, 0.01%-0.02% of titanium, 0.020%-0.035% of aluminum, 0.1%-0.3% of copper, 0.035%-0.050% of zirconium, 0.001%-0.003% of boron, 0.1%-0.2% of cobalt, the sum of the content of phosphorus and the content of sulfur is smaller than or equal to 0.01%, and the balance iron. The cast steel disc body of the high-speed train brake disc is prepared through a remelting method, vacuum melting and aluminum insertion deoxidation tapping, a Re-Ti-Si creep modifier is poured into a steel ladle through an in-ladle pouring method, and impurities are removed through an in-ladle argon blowing purification process, so that the high-speed train brake disc has enough strength and a high and stable friction coefficient, and the service life of the high-speed train brake disc is prolonged. The wear resistance is higher; and the thermal crack resistance is better.
Owner:JIANGSU DINGTAI ENG MATERIAL
Welding material for ni-based heat-resistant alloy, and welded metal and welded joint each using same
InactiveCN102947048BResistant to stress relaxation crackingExcellent heat crack resistanceWelding/cutting media/materialsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesCrack resistanceStress relaxation
Disclosed is a welding material for an Ni-based heat-resistant alloy, which has a chemical composition that contains 0.06-0.18% of C, 0.5% or less of Si, 1.5% or less of Mn, 46-56% of Ni, 10-15% of Co, 20-25% of Cr, more than 10.0% but 14.0% or less of Mo, 0.01-0.5% of Ti, 0.1-1.0% of Al and 0.006% or less of N, and additionally if necessary, 0.1% or less of Nd with the balance made up of Fe and impurities, while controlling O, P and S contained as impurities to 0.02% or less, 0.008% or less, and 0.005% or less, respectively. The welding material for an Ni-based heat-resistant alloy exhibits excellent high-temperature cracking resistance during the welding. A welded metal that has high-temperature cracking resistance during the welding, stress relaxation cracking resistance when in use for a long period of time at high temperatures, and good creep strength can be provided using the above-described welding material. In addition, a welded joint can be provided using the above-described welding material, said welded joint being composed of a base of an Ni-based heat-resistant alloy that has excellent high-temperature strength and a welded metal that has high-temperature cracking resistance during the welding, stress relaxation cracking resistance when in use for a long period of time at high temperatures, and good creep strength.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
A kind of tungsten steel ceramic hard alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a tungsten steel ceramic hard alloy and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of hard alloys. Including: S1. get WC powder, Ni powder and Fe-Si-Al oxide nanopowder and inhibitor and mix uniformly in 97# gasoline to obtain the mixture; S2. add 97# gasoline to the mixture and carry out ball milling, and sieve to obtain Mix the slurry; S3. add carboxymethyl cellulose to the mixed slurry as a forming agent, perform ball milling, and dry to obtain a powder; 4. Put the powder into a mold for extrusion, and dry to obtain a green body; S5. The green body is subjected to discharge plasma sintering, cooled out of the furnace, and sandblasted to obtain tungsten steel ceramic cemented carbide. The tungsten steel ceramic cemented carbide prepared by the present invention has good corrosion resistance, heat resistance and high temperature oxidation resistance, excellent wear resistance, good toughness, strength and bending resistance, high hardness, high density, microstructure Small and uniform, it has broad application prospects.
Owner:HEYUAN YONGXING CEMENTED CARBIDE
Flux cored wire for gas shielded arc welding
ActiveCN107848082BLow amount of diffusible hydrogenExcellent welding workabilityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaMetallurgyEngineering
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Ultra-fine grain high-nickel-chromium molybdenum infinitely chilled ductile cast iron and composite roll thereof
ActiveCN101509095BImprove bindingExtended service lifeRollsMetal rolling arrangementsCrack resistanceCrazing
Ultra-fine grain high Ni-Cr-Mo indefinite chilled cast iron belongs to roll materials used for rolling large vessels. The component comprises the followings based on the weight percentage: 2.9-3.7% of C, 0.6-1.2% of Si, 0.4-1.2% of Mn, 3.01-5.00% of Ni, 1.00-2.00% of Cr, 0.20-0.60% of Mo and Fe being the balance. The component also comprises 1-3% of antimony, which substantially eliminates the network structure of the carbide, causes the structure to be more dispersed, changes the metallographic structure and property of the materials, effectively combines the wear resistance and hot crack resistance of the materials and comprehensively prolongs the service life of the materials.
Owner:JIANGSU GONGCHANG ROLL
High-temperature welding material
InactiveCN105436736AHigh strengthExcellent heat crack resistanceWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaCrack resistanceCobalt
The invention discloses a high-temperature welding material which consists of the following raw materials of , by weight, 2-3 parts of magnesium oxide, 3-6 parts of iron, 3-5 parts of aluminum, 5-7 parts of sodium carbonate, 3-5 parts of quartz, 1-3 parts of nickel, 0.5-1 part of carbon, 0.3-0.6 part of silicon, 2-4 parts of cobalt, 0.5-1 part of tungsten, and 0.01-0.05 part of chromium, wherein the grain size of the raw materials is 10-50 meshes. The high-temperature welding material is excellent in hot crack resistance, and has good anti-high-temperature-creep strength and ablation resistance; and a welded interface is high in strength.
Owner:青岛唐鹏钢结构工程有限公司
A high-nitrogen and low-nickel high-temperature flux-cored welding wire and its preparation process
ActiveCN110539100BSettle the priceSolve the scarcityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaPhysical chemistryTemperature resistance
The invention provides a high-nitrogen, low-nickel, high-temperature flux-cored welding wire and a preparation process. The high-nitrogen, low-nickel, high-temperature flux-cored welding wire is composed of the following elements by mass percentage: C: below 0.04wt%, Si: below 0.8wt%, Mn: 0.5~5.0wt%, Cu: 1.0wt% or less, Ni: 25~33wt%, Cr: 17~26wt%, Mo: 3.0~6.0wt%, Nb: 3.0~5.0wt%, N: 0.1~0.4 wt%, Ti: 0.4~1.1wt%, Al: 0.1~0.5wt%, Ti / Al: 1.8~2.3 and Ti+Al: 0.5~1.5wt%, (Ti+Al) / N: 1.5~4.0, V : 0.04 to 0.12 wt%, Fe: the remainder. The invention adopts low-cost N to replace part of Ni elements, and prepares a new type of welding material used for welding 316L and part of nickel-based superalloys and whose high-temperature performance is not lower than that of nickel-based flux-cored welding wires, and simultaneously solves the problem of high price and scarcity of Ni. question. The high-nitrogen, low-nickel, and high-temperature flux-cored welding wire prepared by the invention can be used under high temperature (600-700° C.) conditions, and has excellent high-temperature mechanical properties, thermal crack resistance and high-temperature corrosion resistance.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com