A high-nitrogen and low-nickel high-temperature flux-cored welding wire and its preparation process
A flux-cored wire, high-temperature technology, applied in welding equipment, manufacturing tools, welding media, etc., can solve the problems of poor high-temperature corrosion resistance of flux-cored wire, different strength requirements, and high-temperature tensile strength that cannot reach 700 MPa or more. Achieve excellent heat crack resistance, solve the problem of high price and scarcity, and excellent high temperature corrosion resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0092] Further, the preparation method of the high-nitrogen and low-nickel high-temperature flux-cored wire includes the following steps:
[0093] (1) Preparation of flux powder: mix the flux powder evenly according to the required mass percentage;
[0094] (2) Flux filling: after cleaning the outer skin of the nickel strip, roll it into a "U" shape, fill it with uniformly mixed flux powder, and then roll the outer skin of the nickel strip into an "O" sealed flux powder to obtain a semi-finished welding wire;
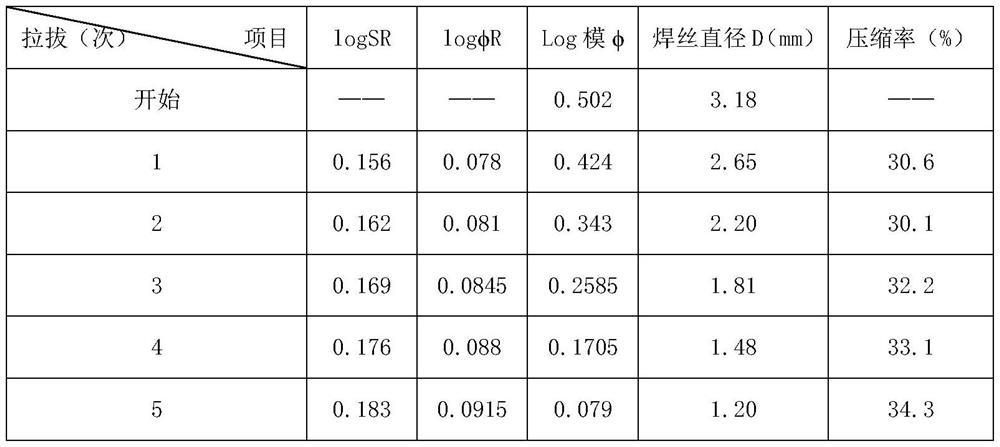
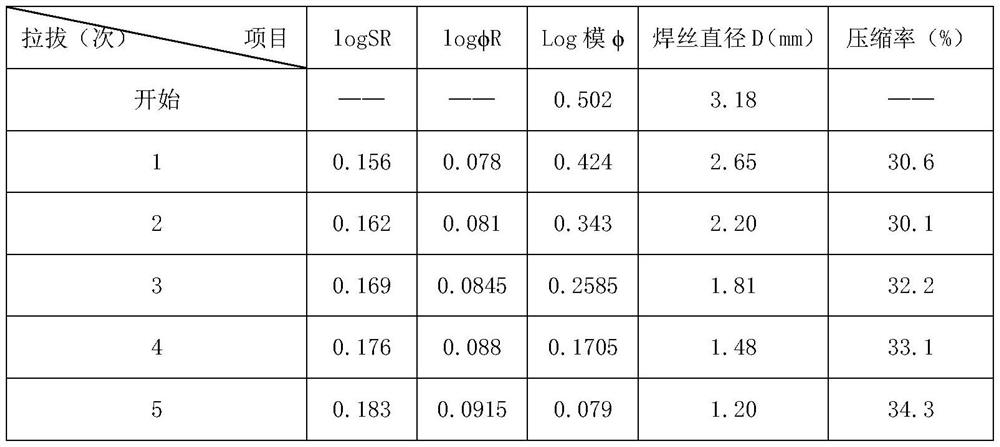
[0095] (3) Diameter-reducing wire drawing: the semi-finished welding wire is lubricated, and then drawn from a diameter of 3.18mm to 1.2mm through five passes, and finally a high-nitrogen, low-nickel high-temperature flux-cored wire is obtained.
[0096] Further, the calculation of the flux powder filling rate in the step (2) is realized by the following:
[0097] The flux powder is filled into the U-shaped nickel belt driven by the conveyor belt, and the mathematical ...
Embodiment 1-6 and comparative example 1-3
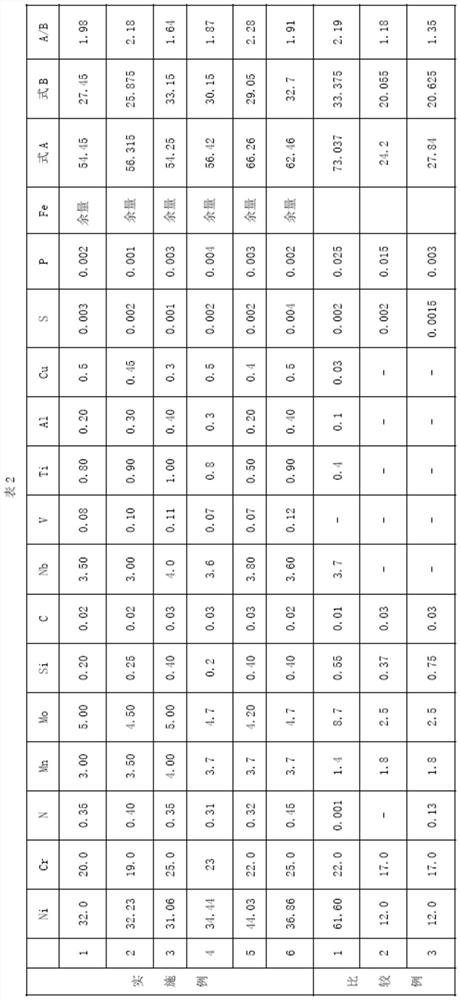
[0153] Flux-cored wires having the chemical compositions shown in Table 2 were produced.
[0154] Among them, Comparative Example 1 is an ENiCrMo3 nickel-based superalloy flux-cored welding wire. Comparative example 2 is a 316L stainless steel flux cored wire. Comparative example 3 is a 316LN stainless steel flux-cored welding wire.
[0155] The wire diameters of the obtained flux-cored wires were all 1.2 mm, and the filling rate was 25-30 wt%.
[0156] In addition, the chemical compositions in Table 2 are expressed in wt% relative to the total mass of the welding wire. In addition, among the contents of the various components contained in the so-called "Formula A" welding wire, the value represented by [Ni+30×C+28×N+0.5×Mn+0.3×Cu+10.4], the so-called "Formula B" formula The value represented by [Cr+Mo+1.5×Si+0.5×Nb+5×V] among the contents of each component included in the welding wire.
[0157]
[0158] Evaluation of the properties of the obtained flux-cored wire and w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com