Patents
Literature
247 results about "Cold zone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
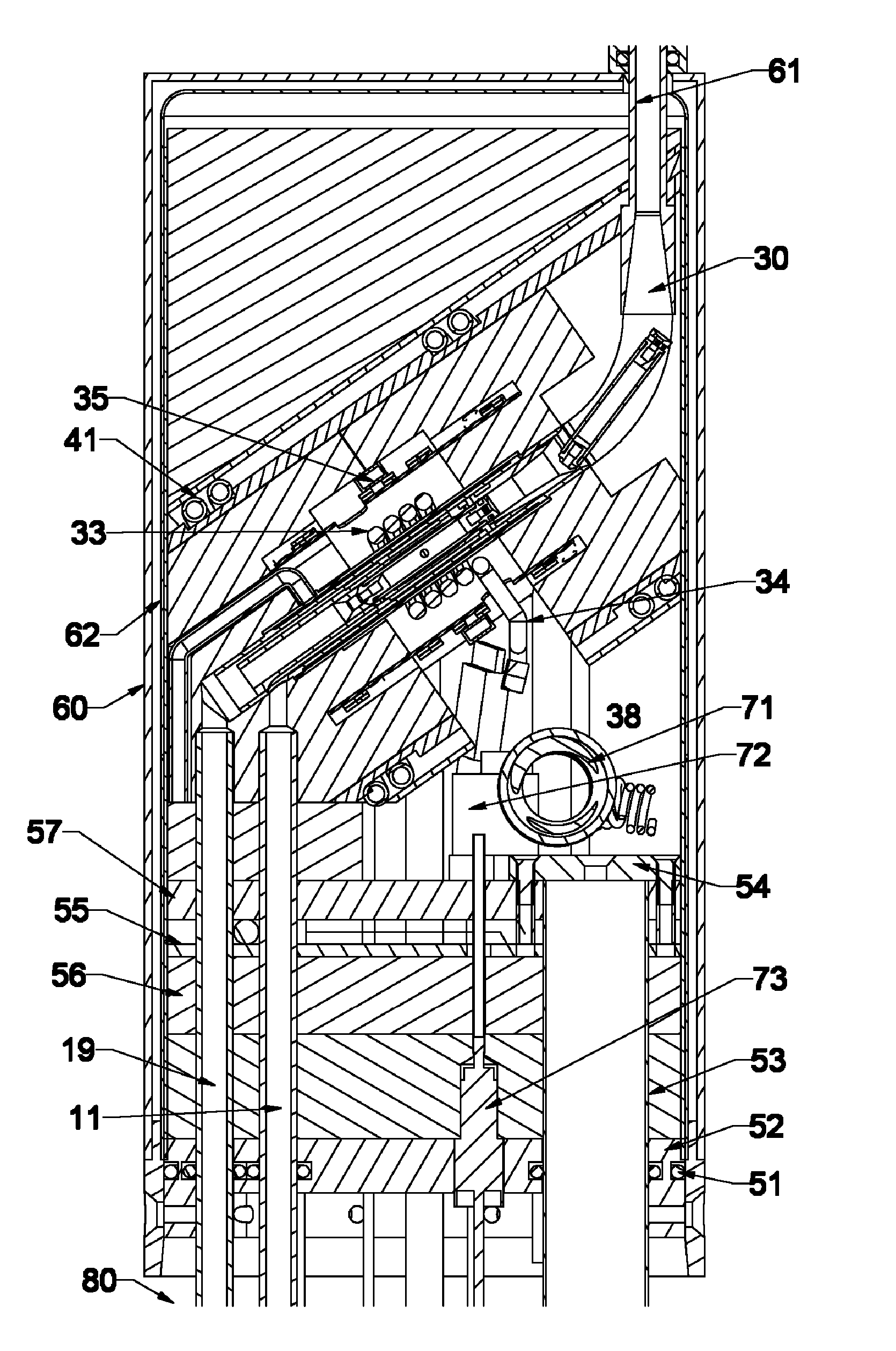
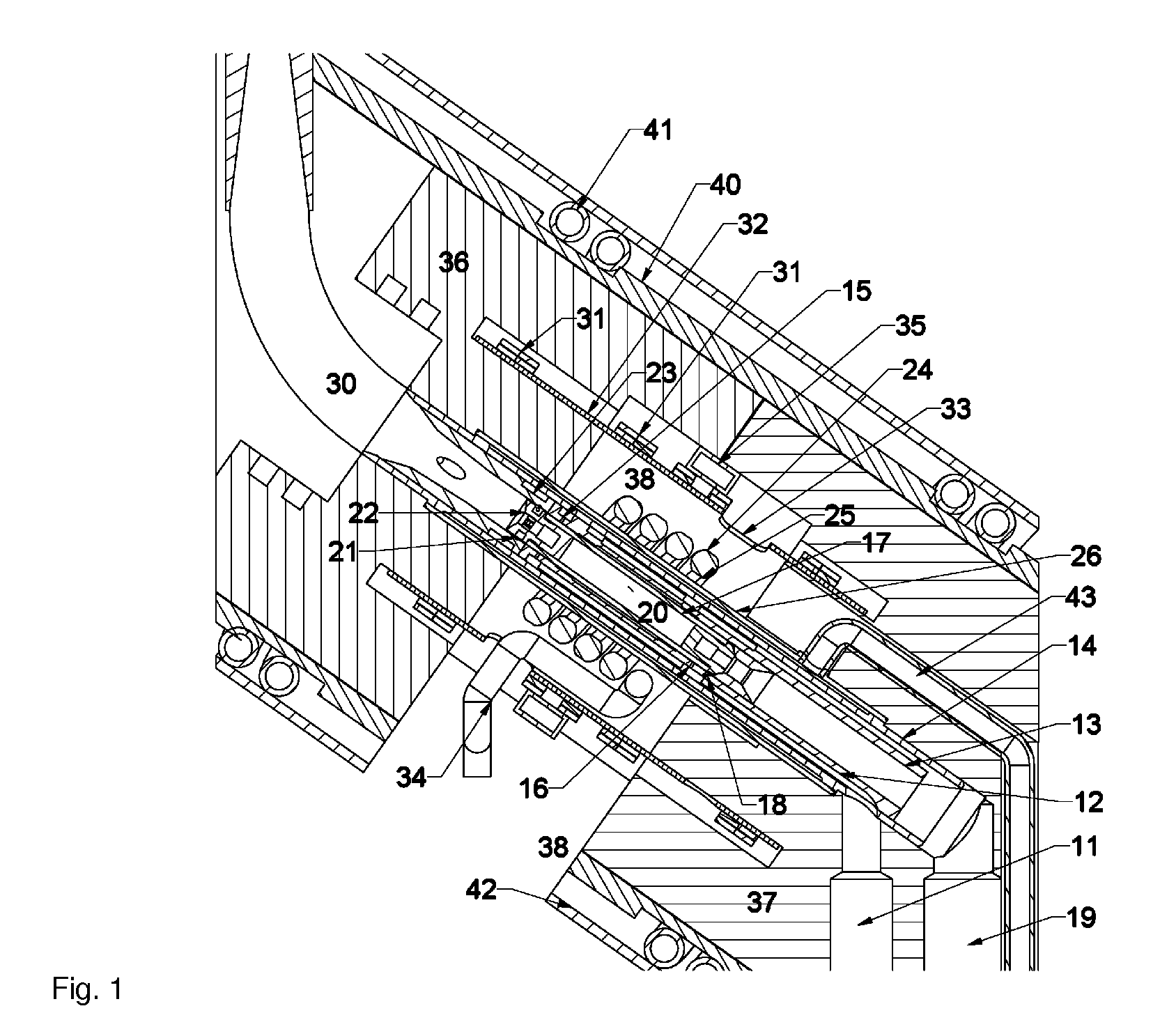
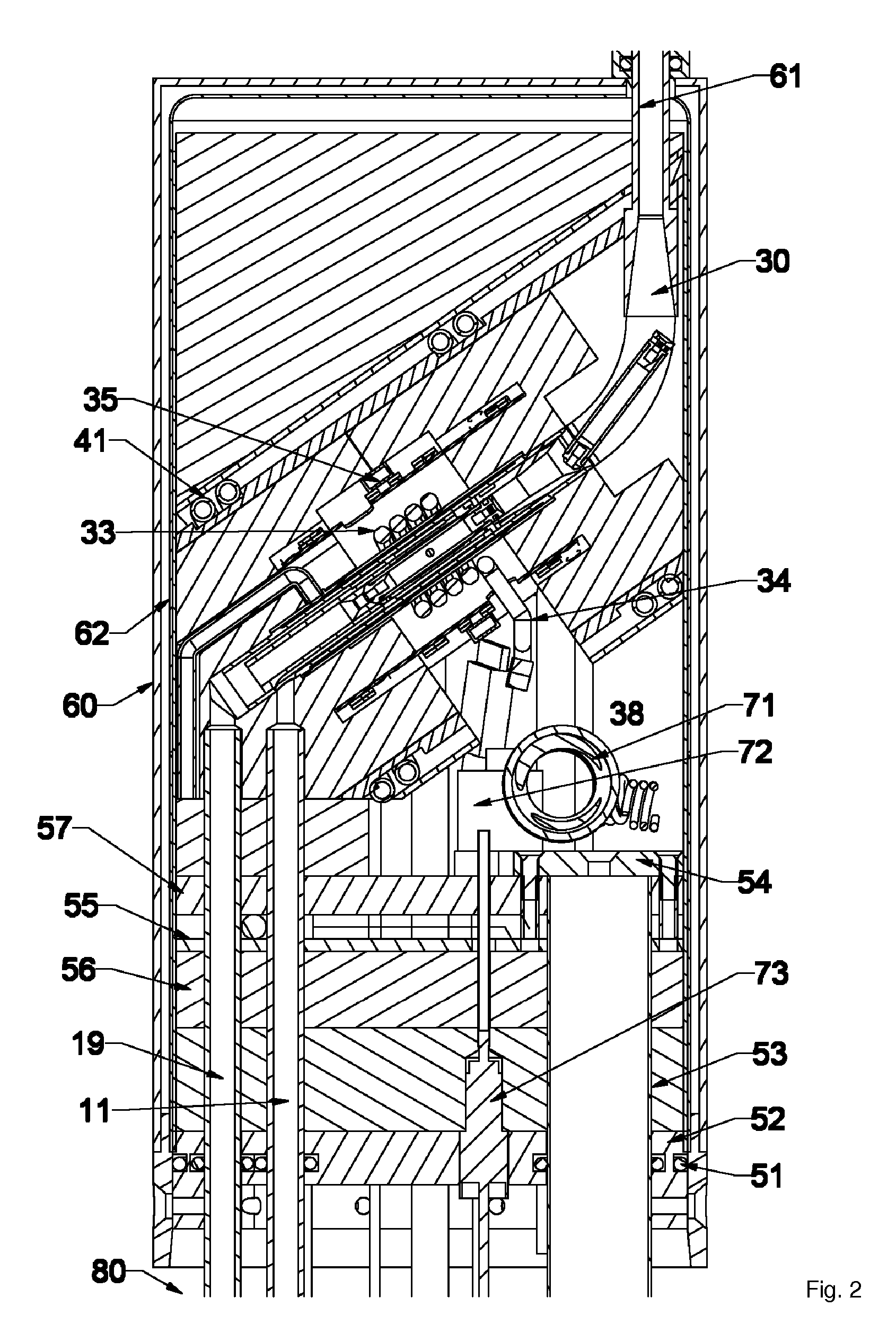
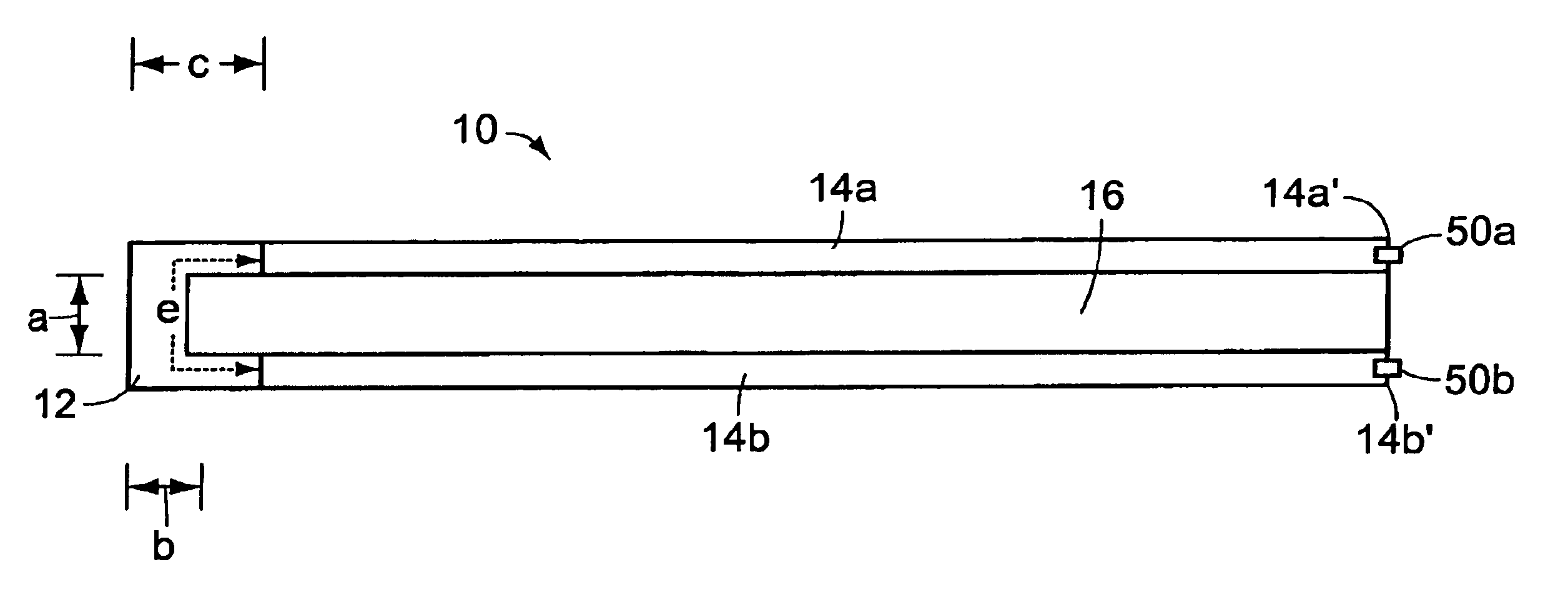
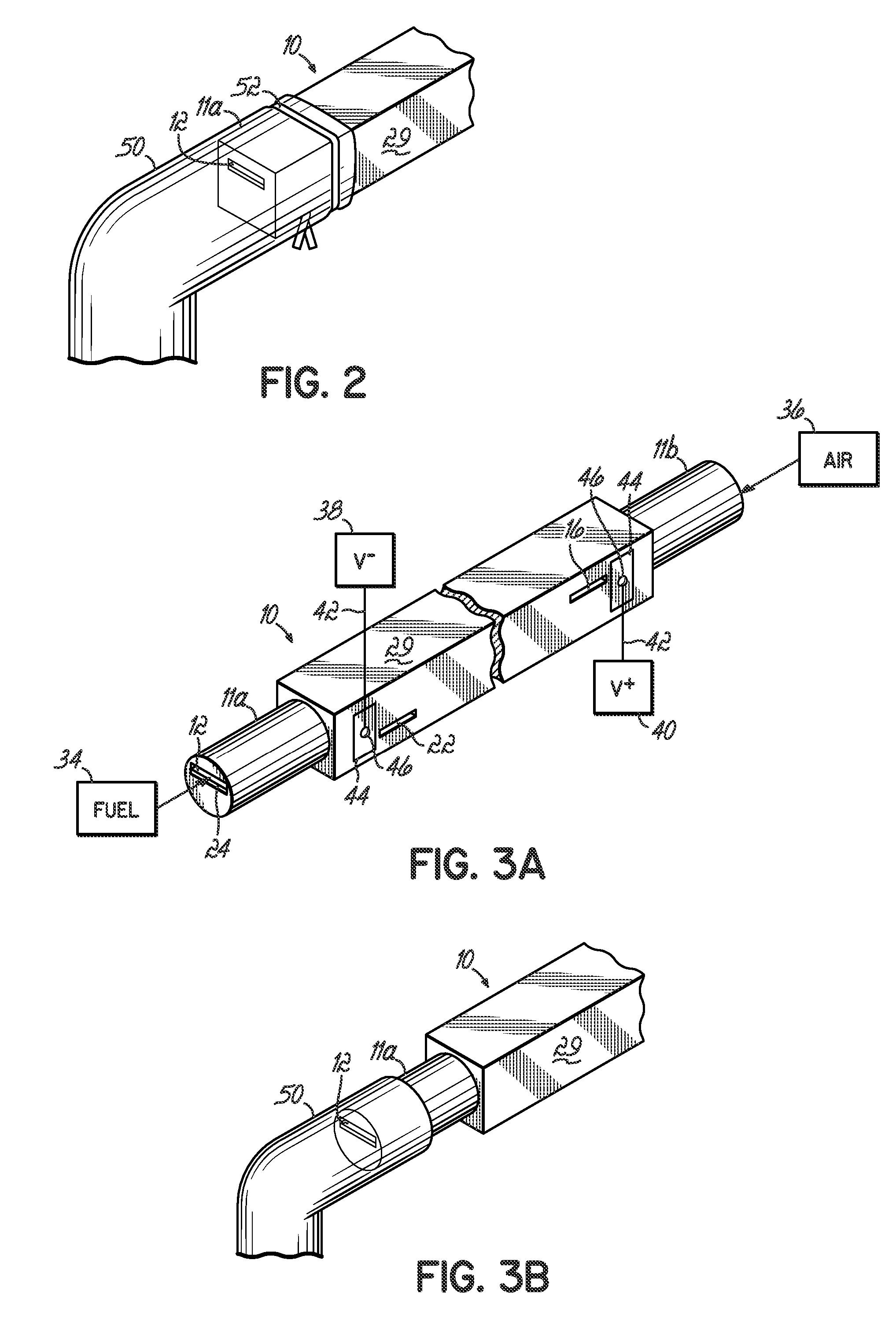
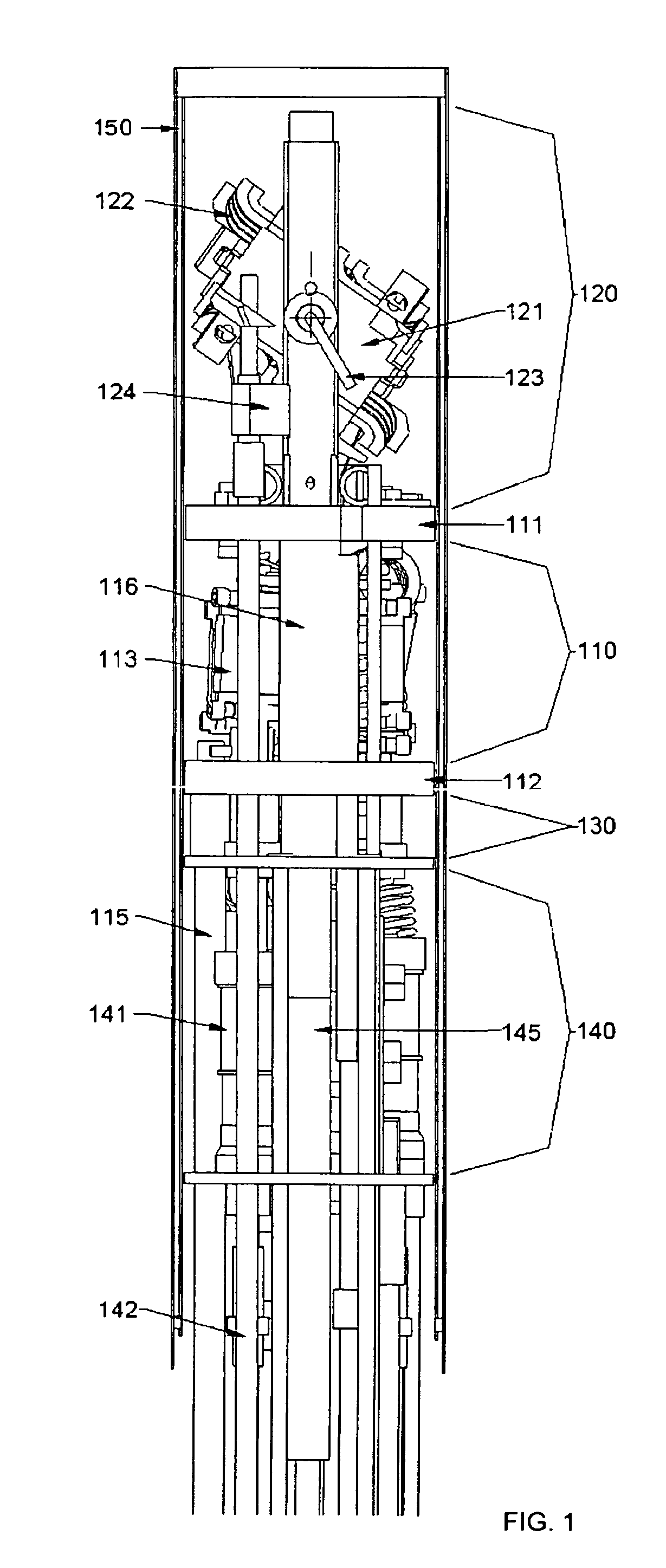
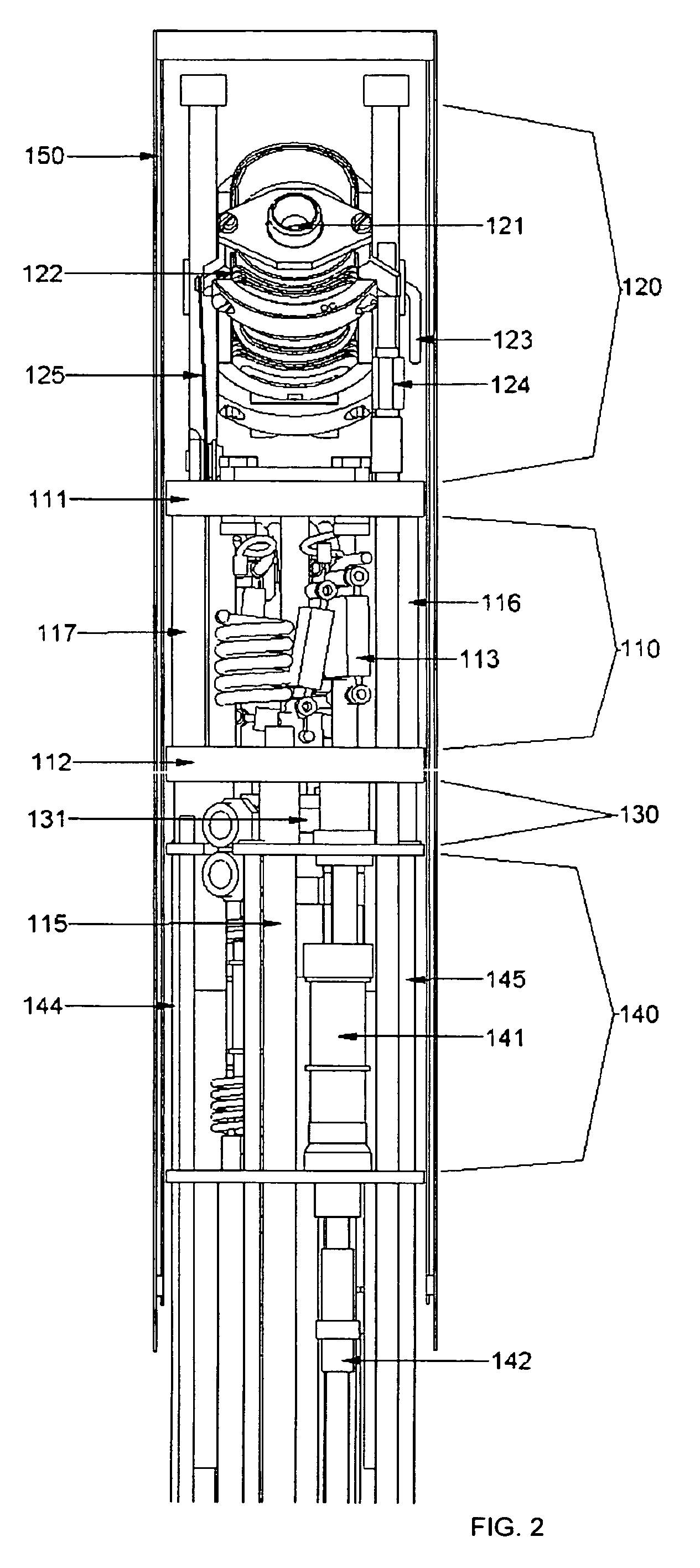
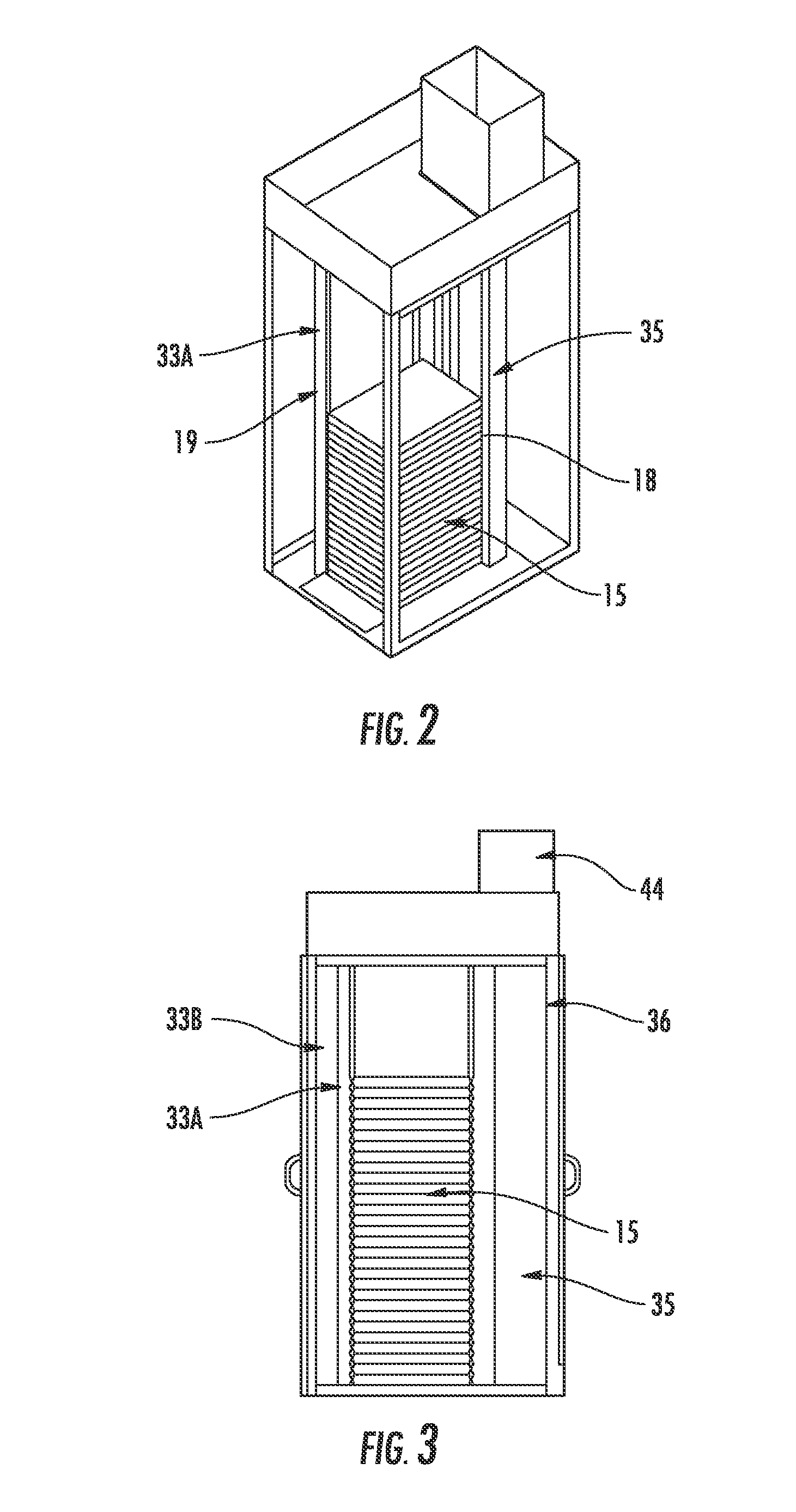
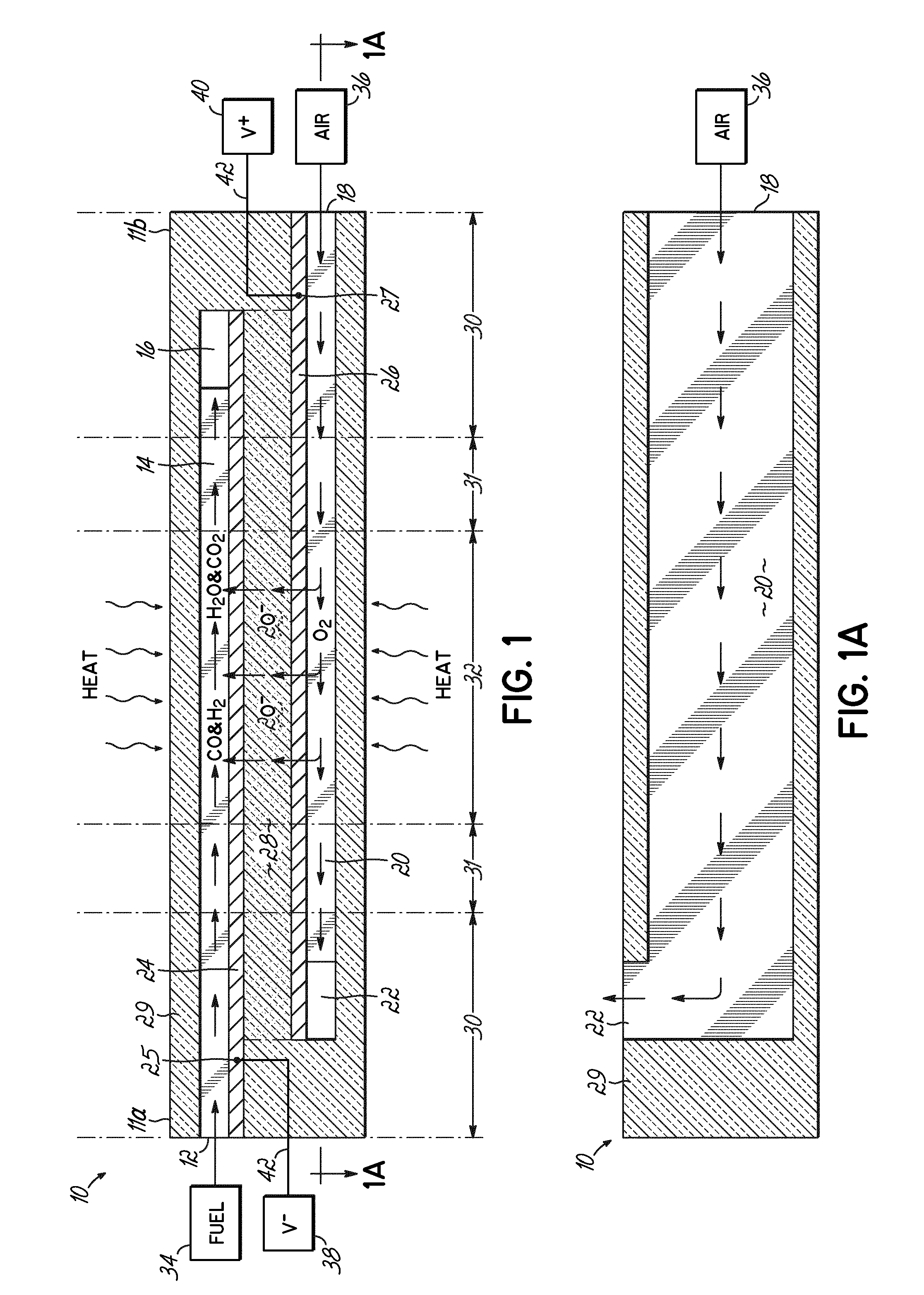
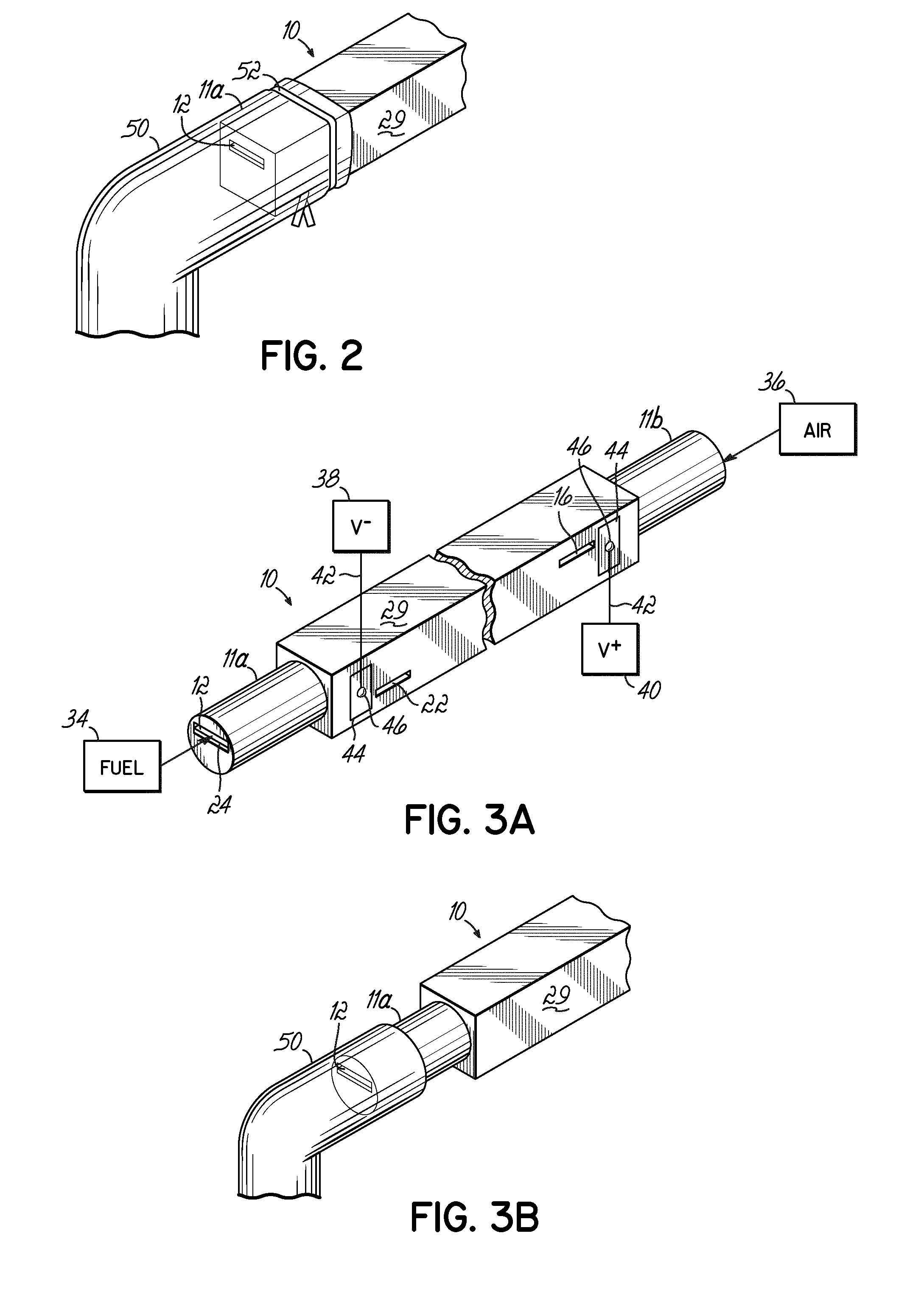
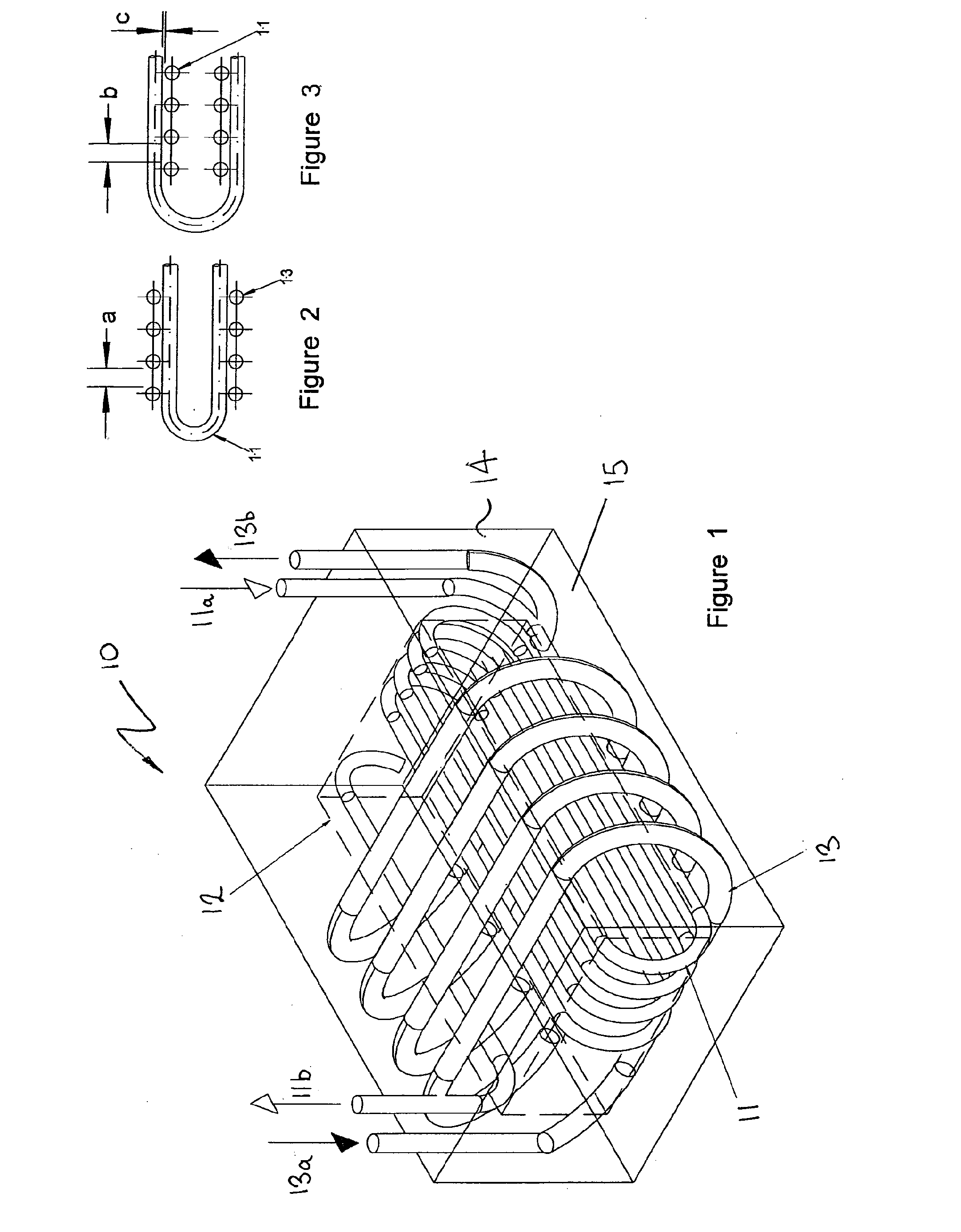
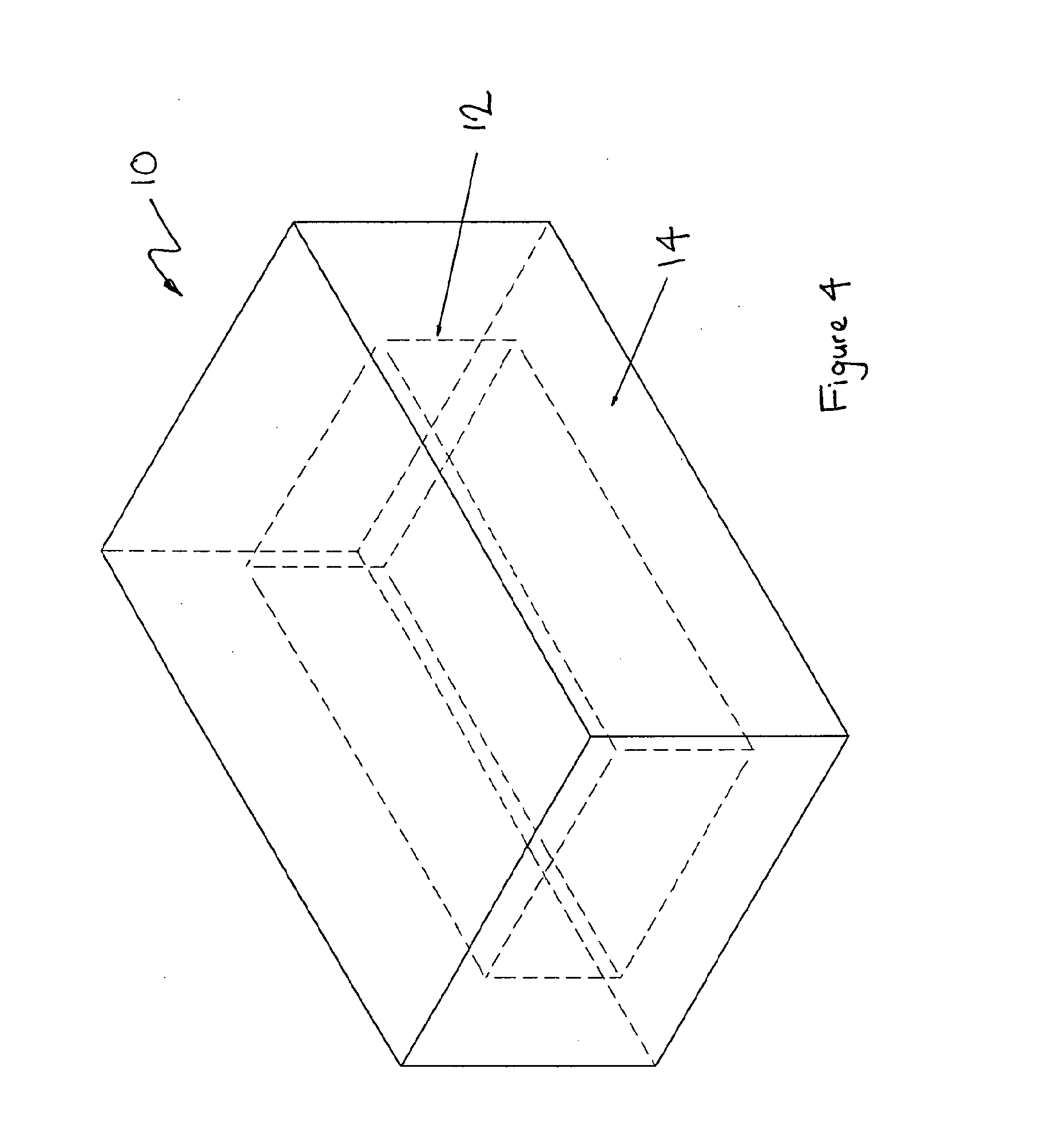
Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Device and System
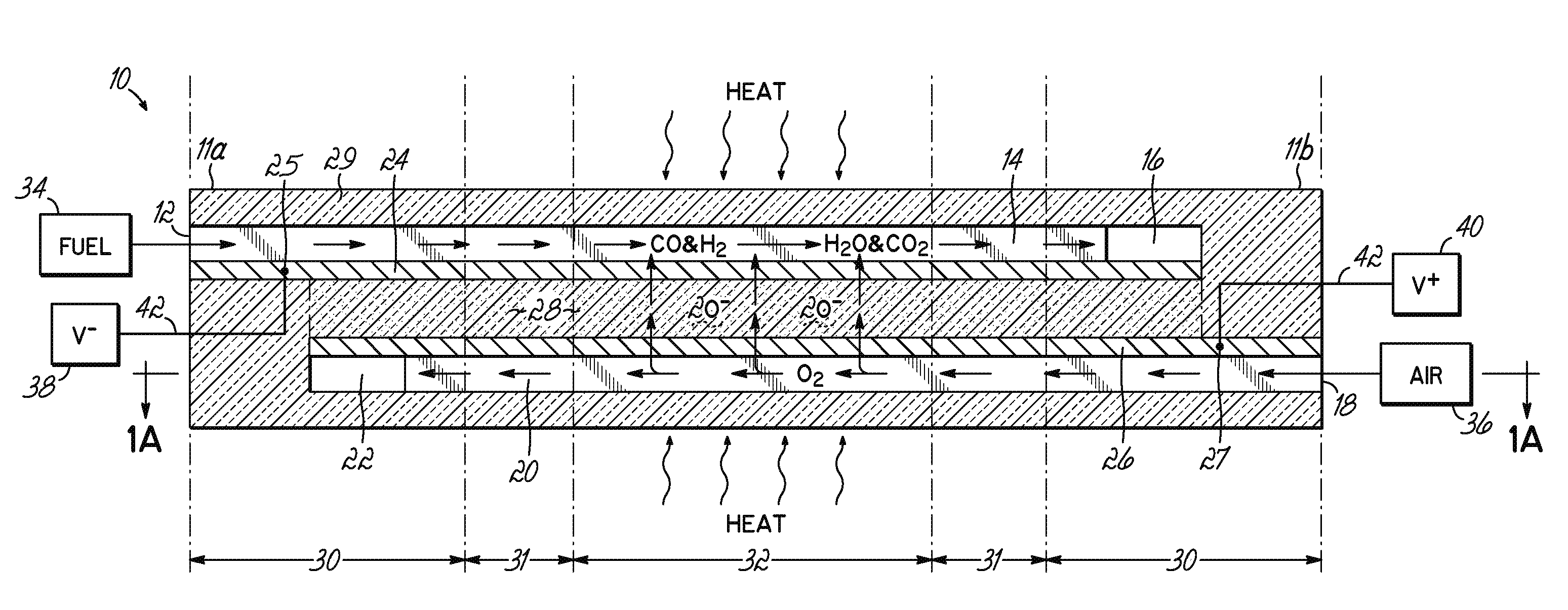
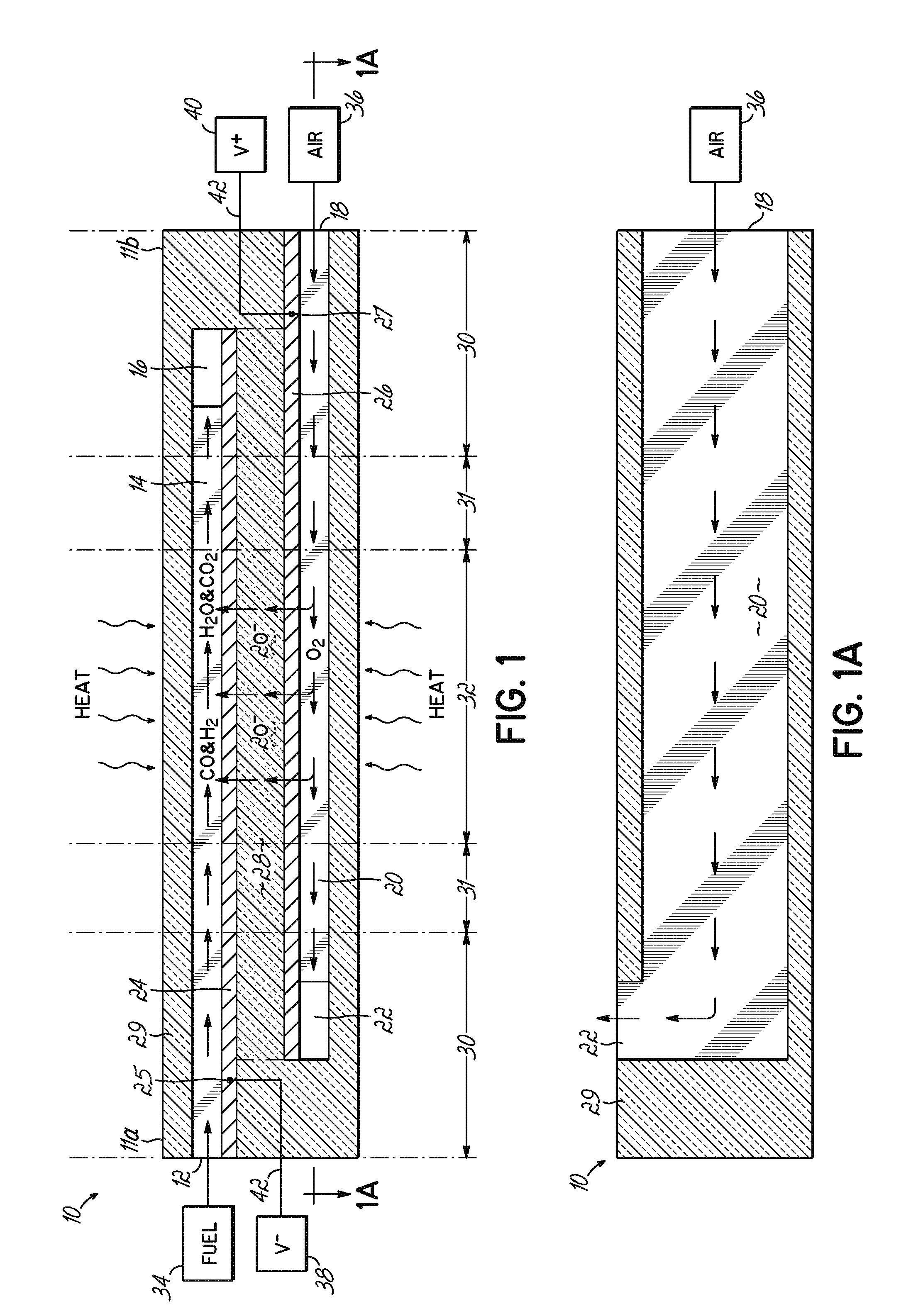
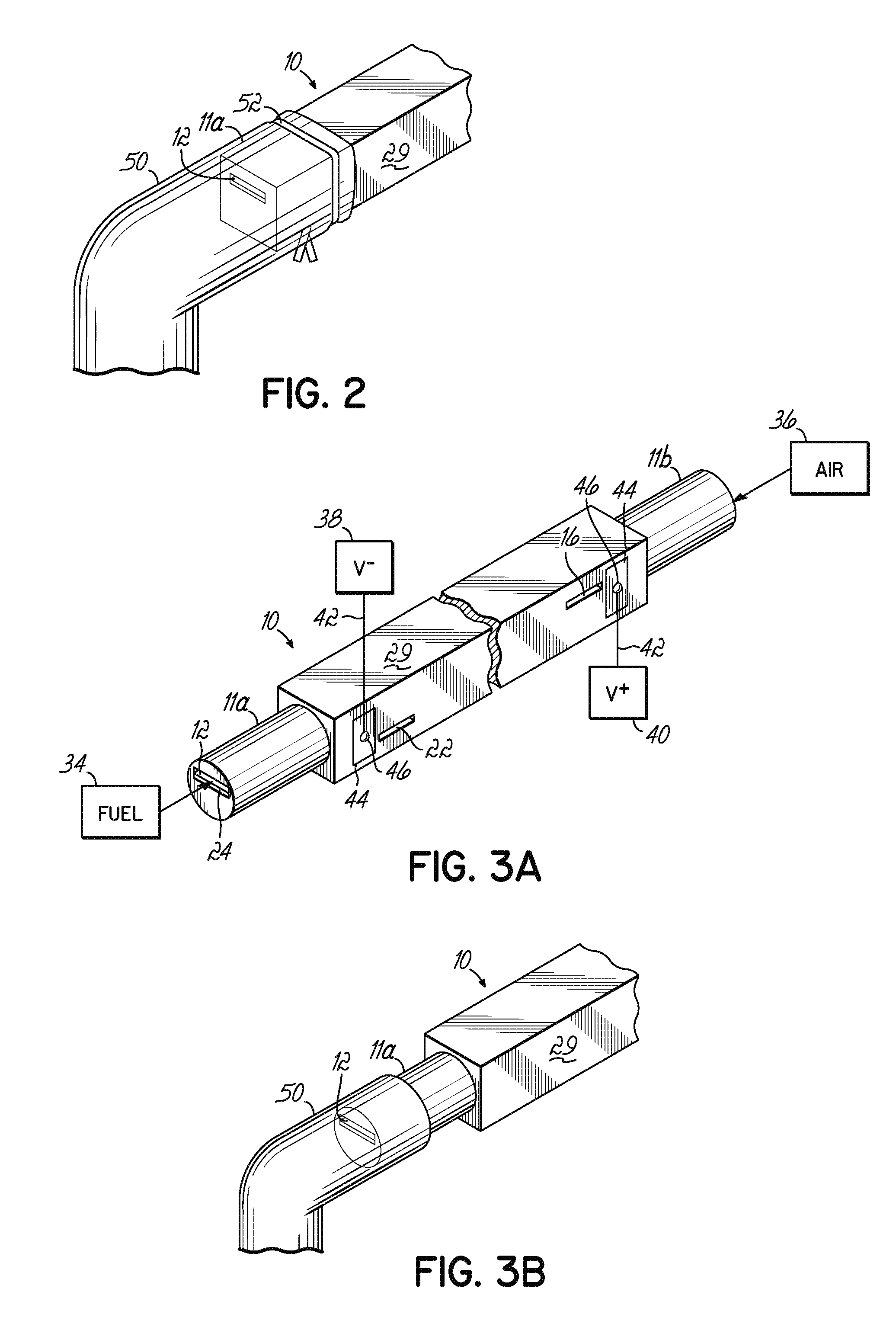
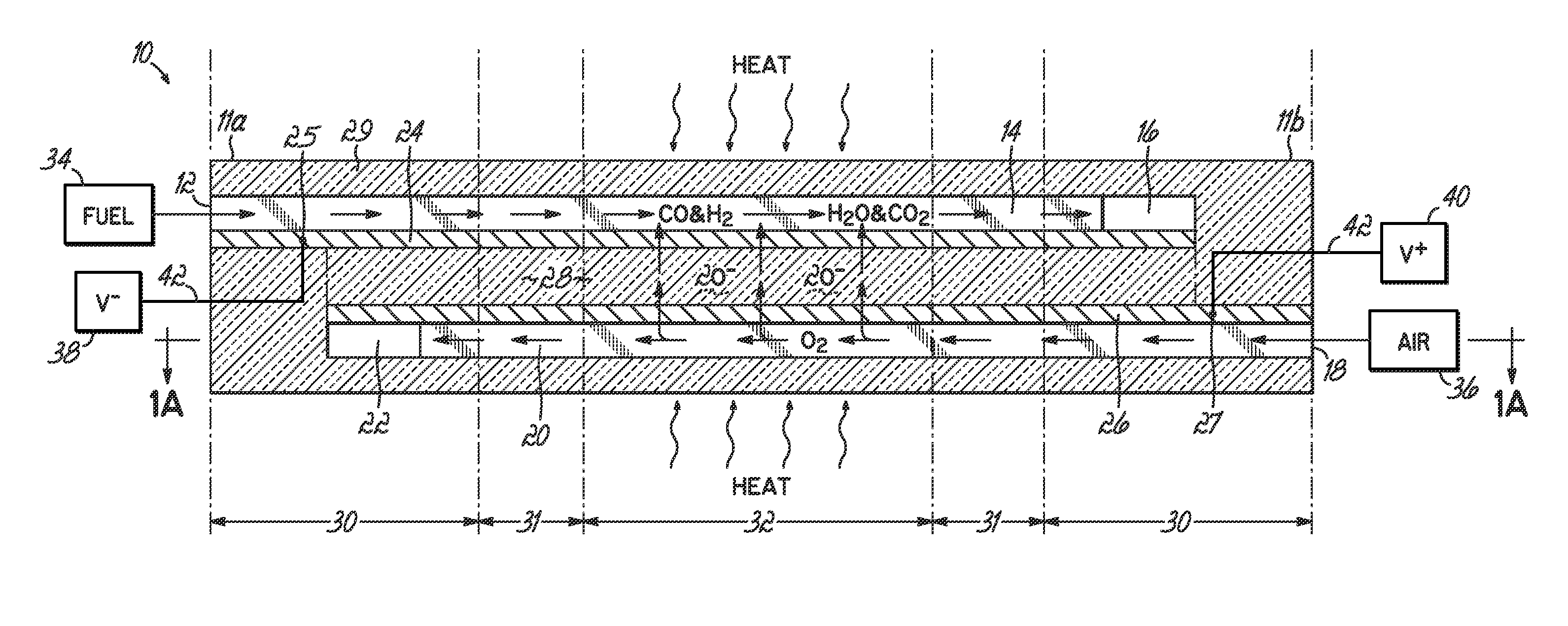
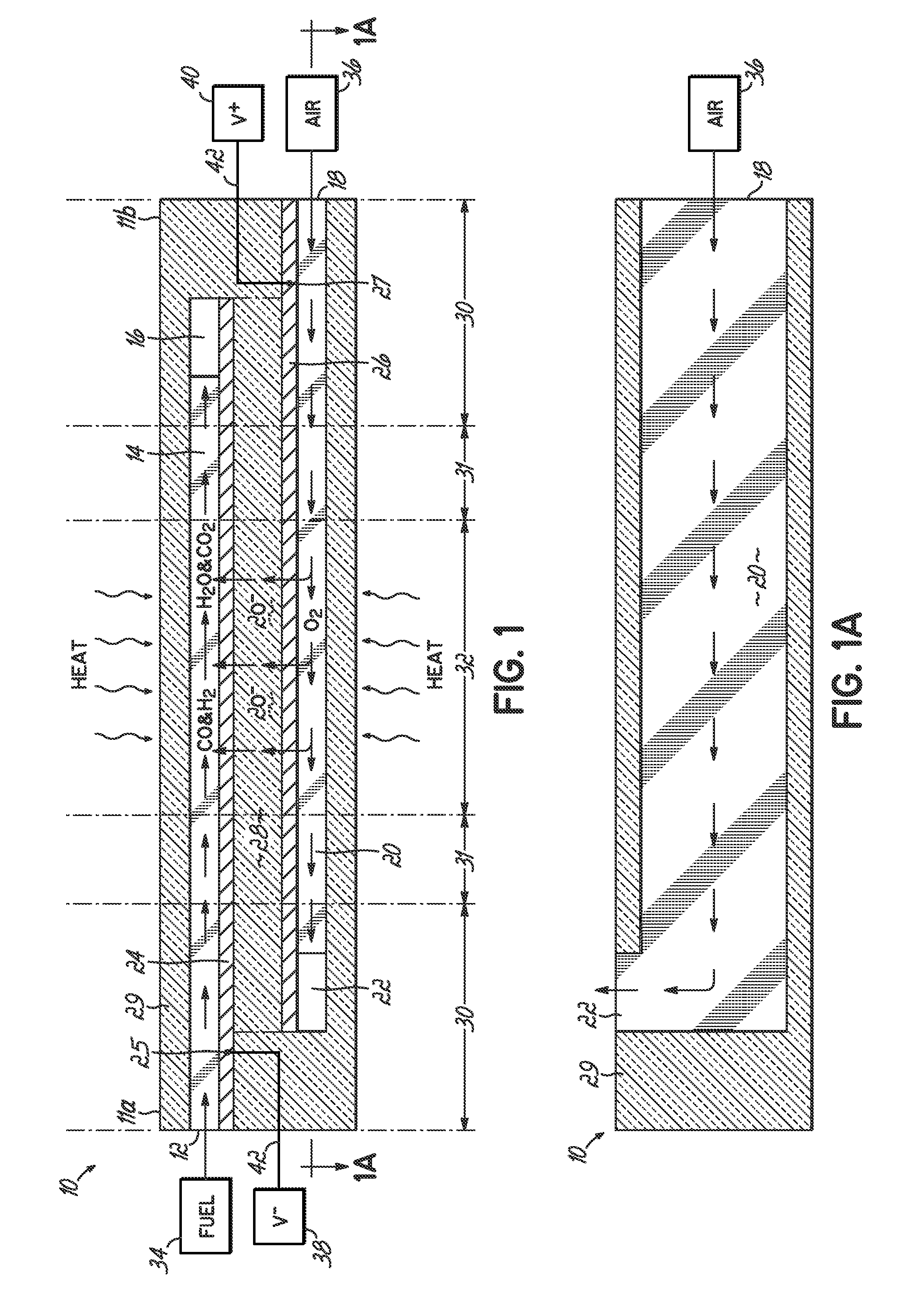
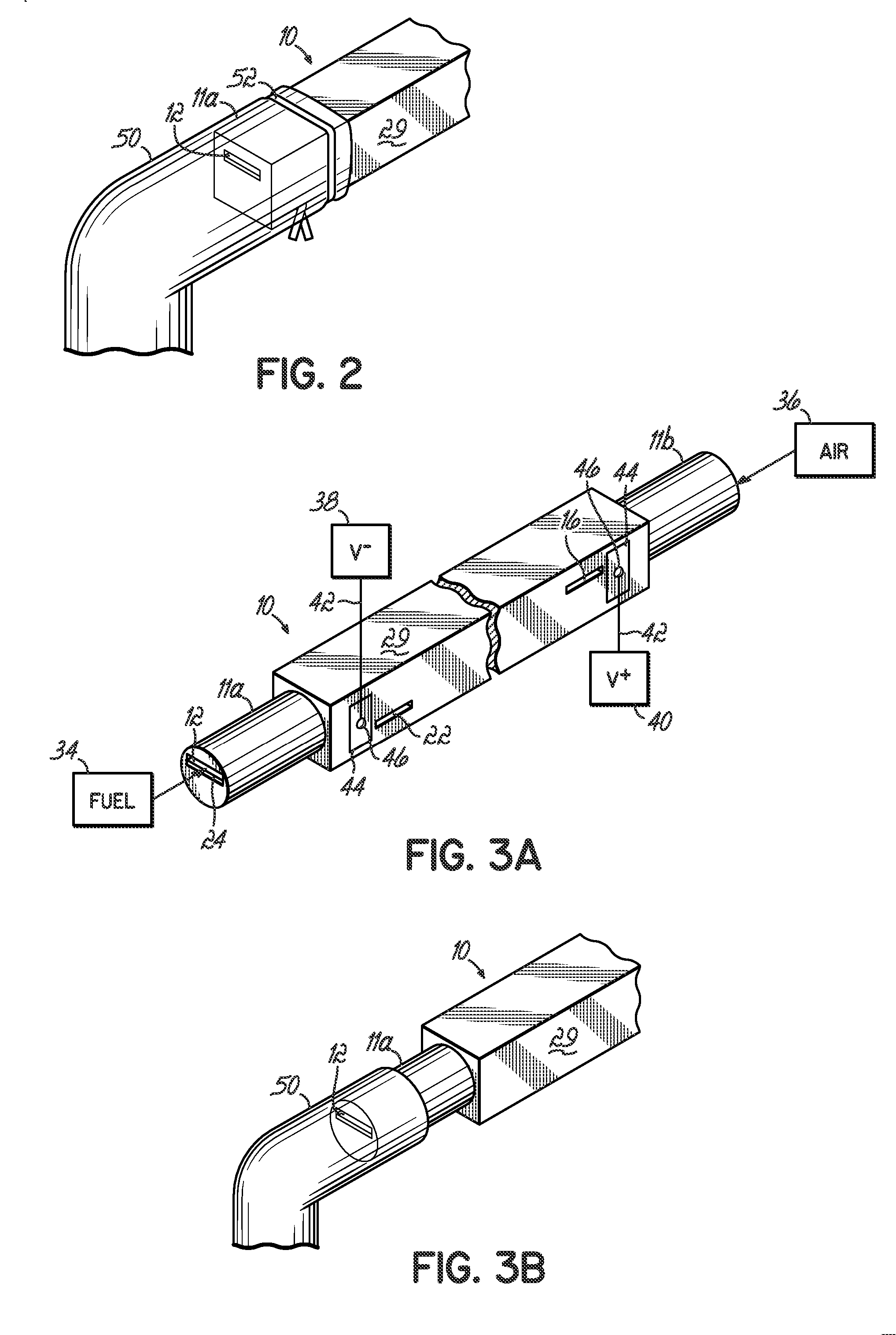
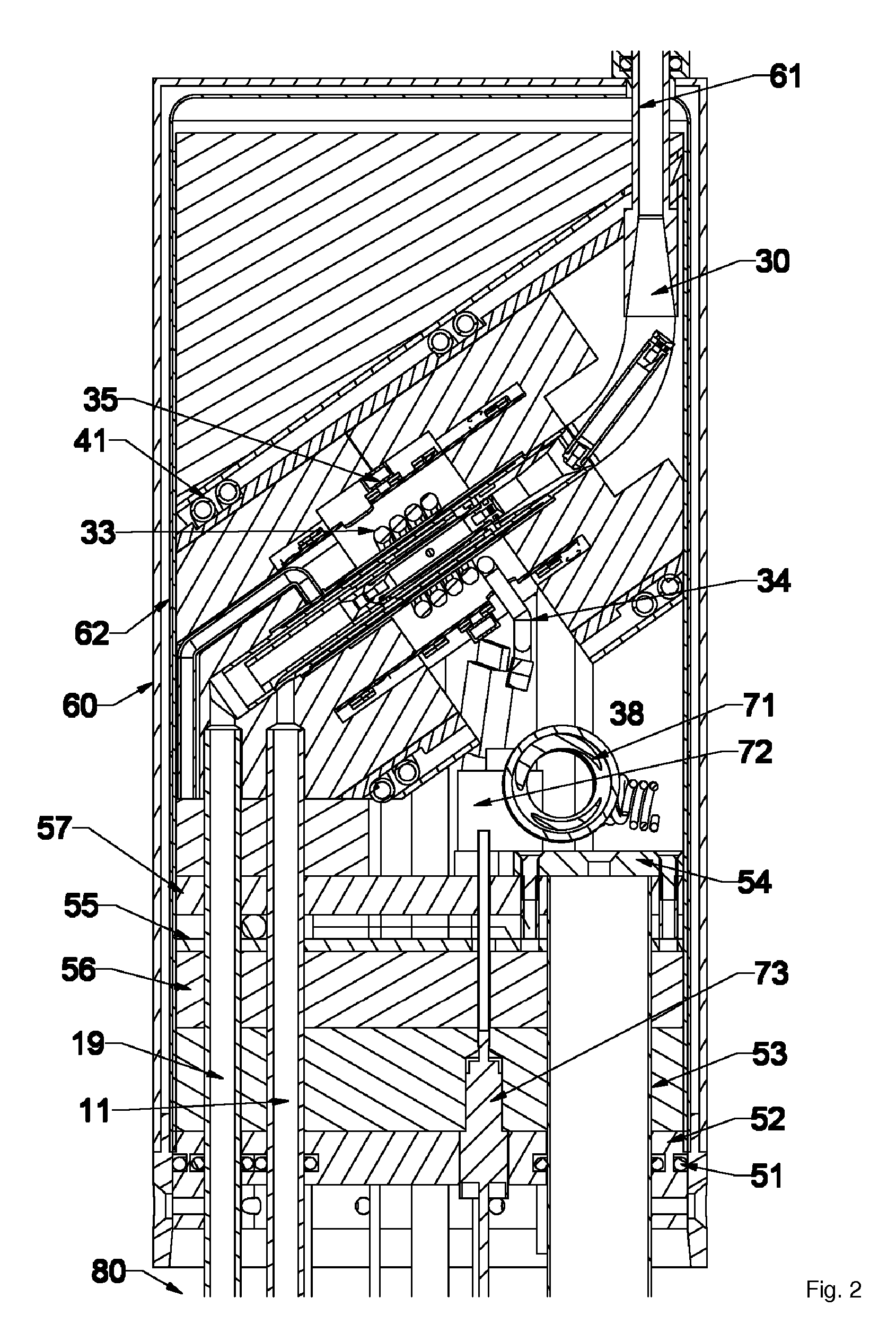
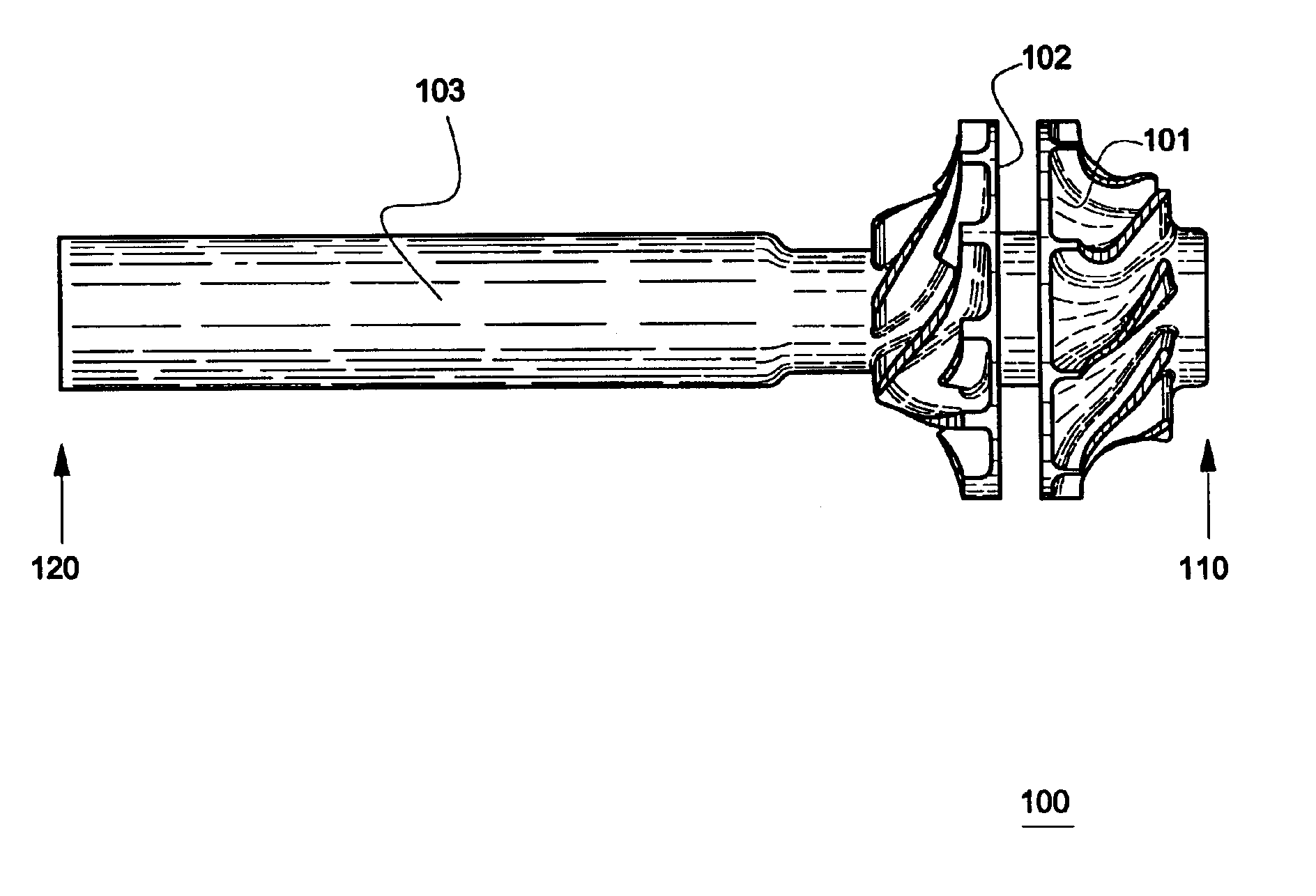
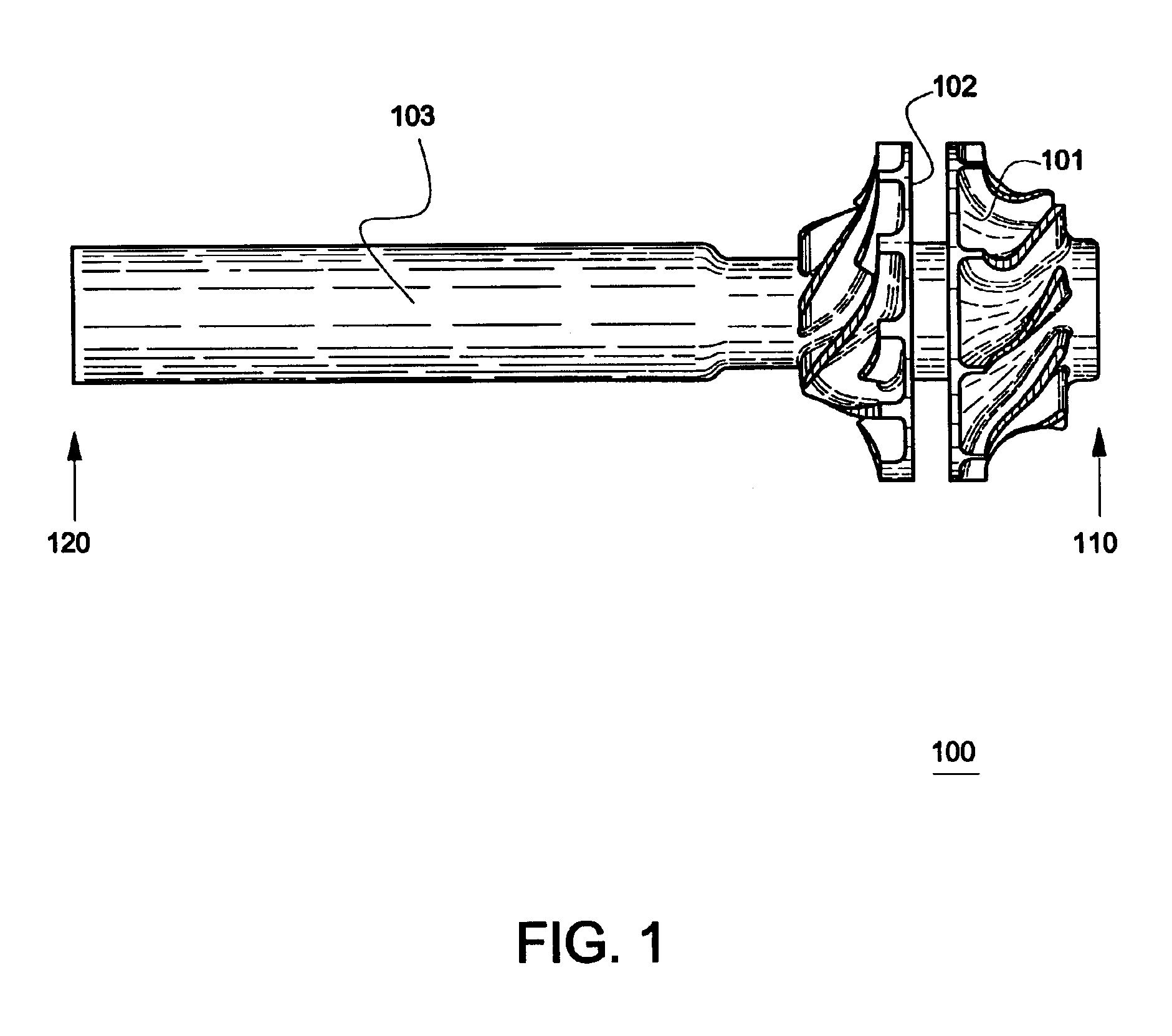
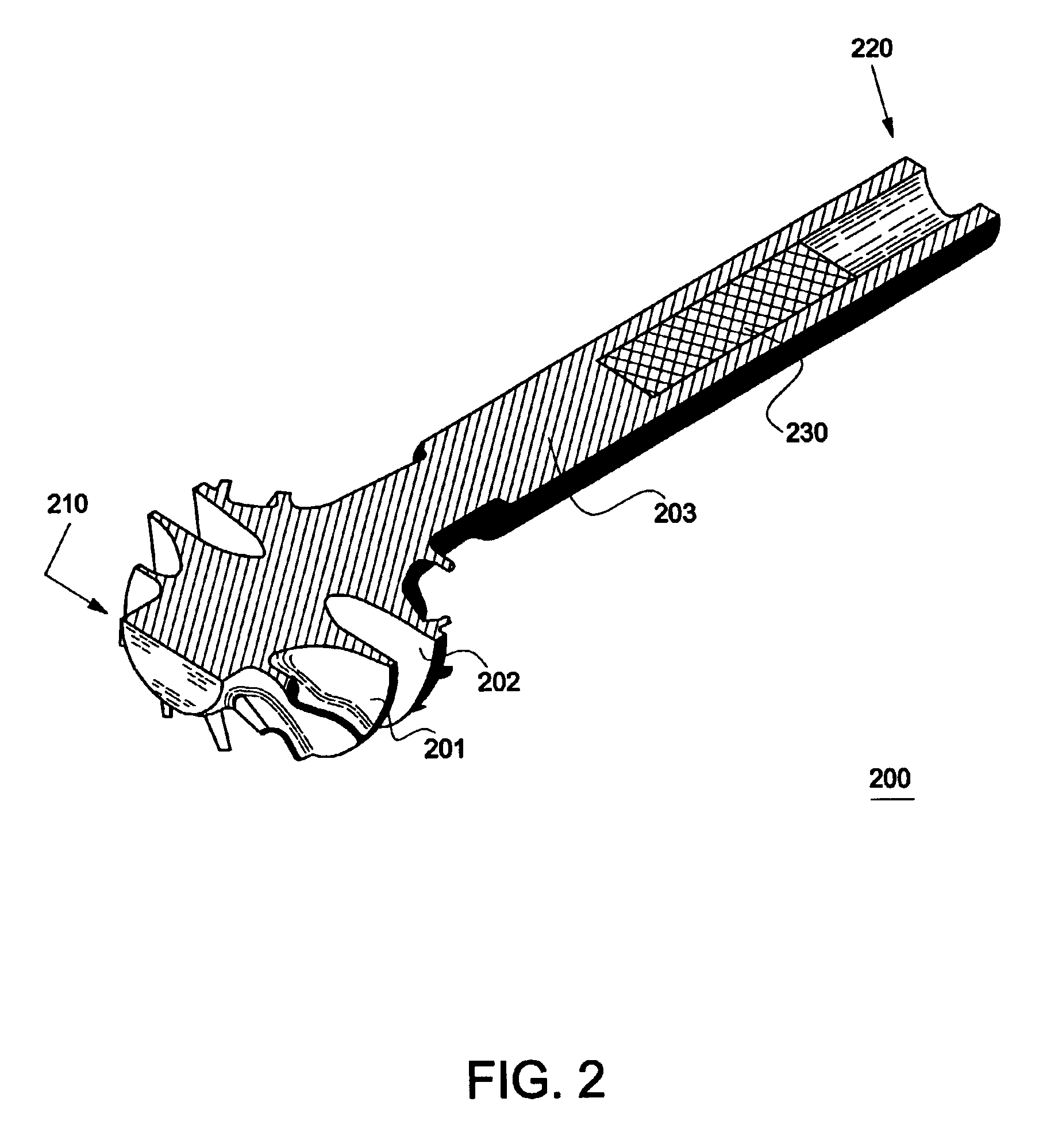
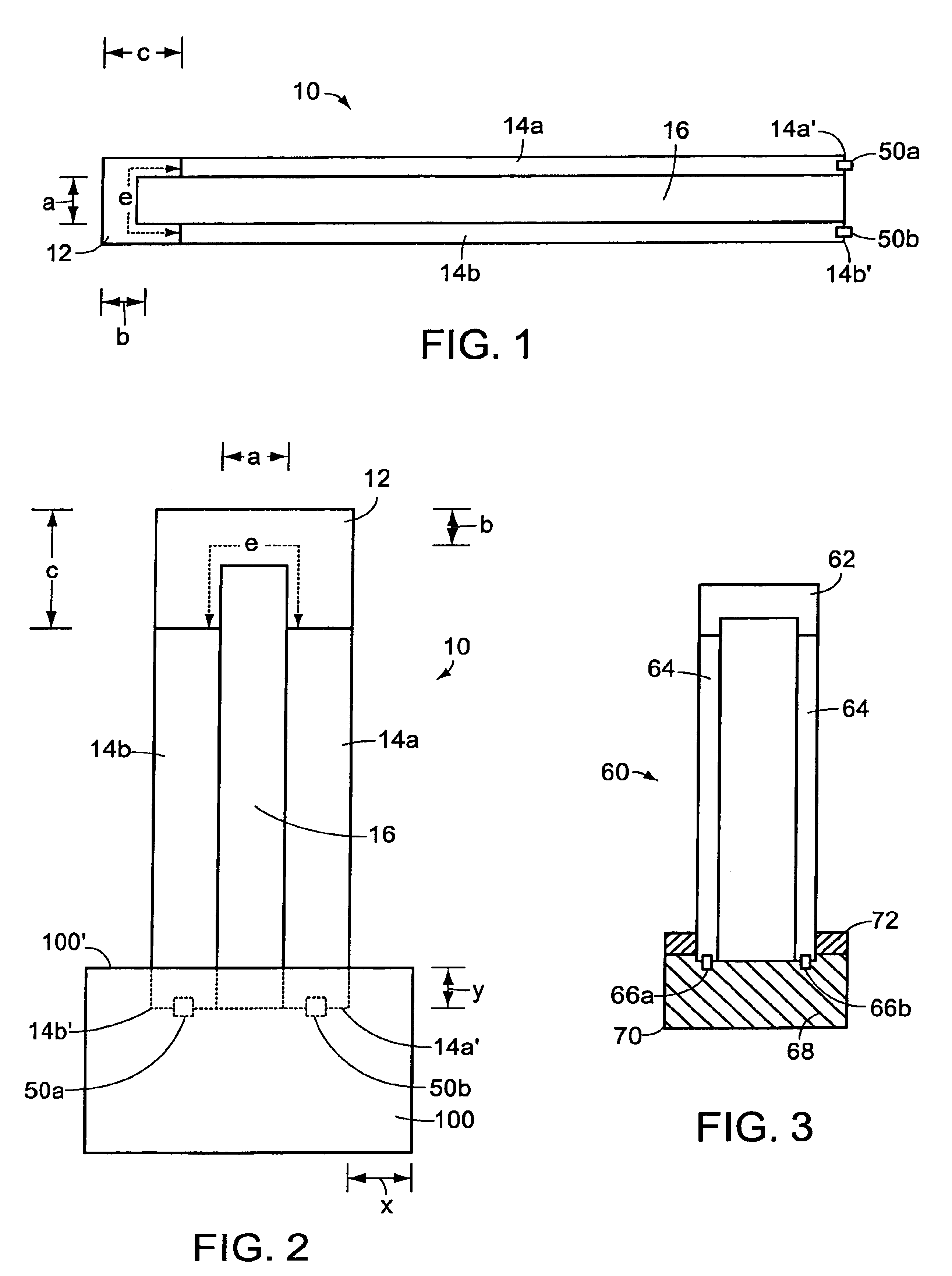
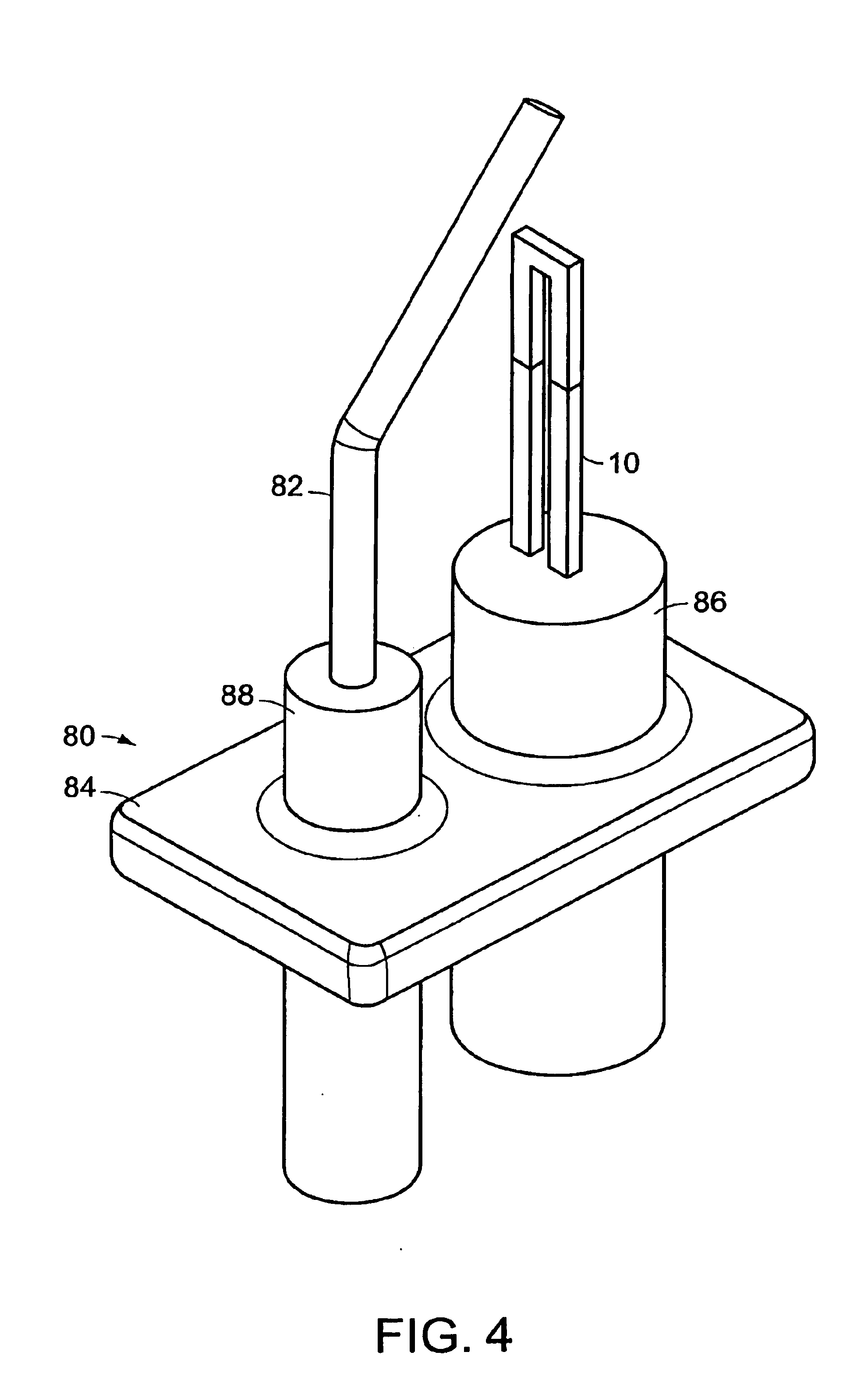
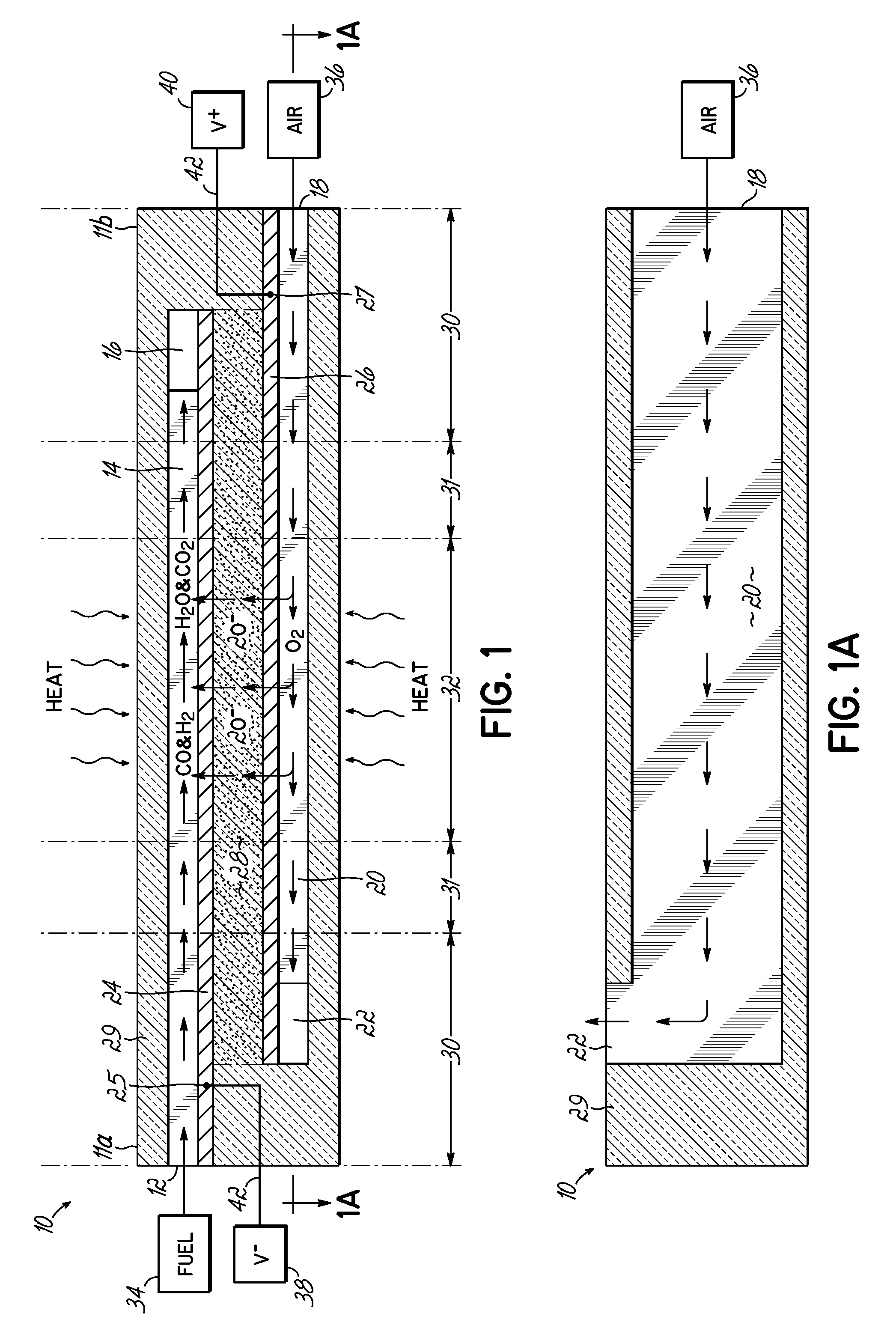
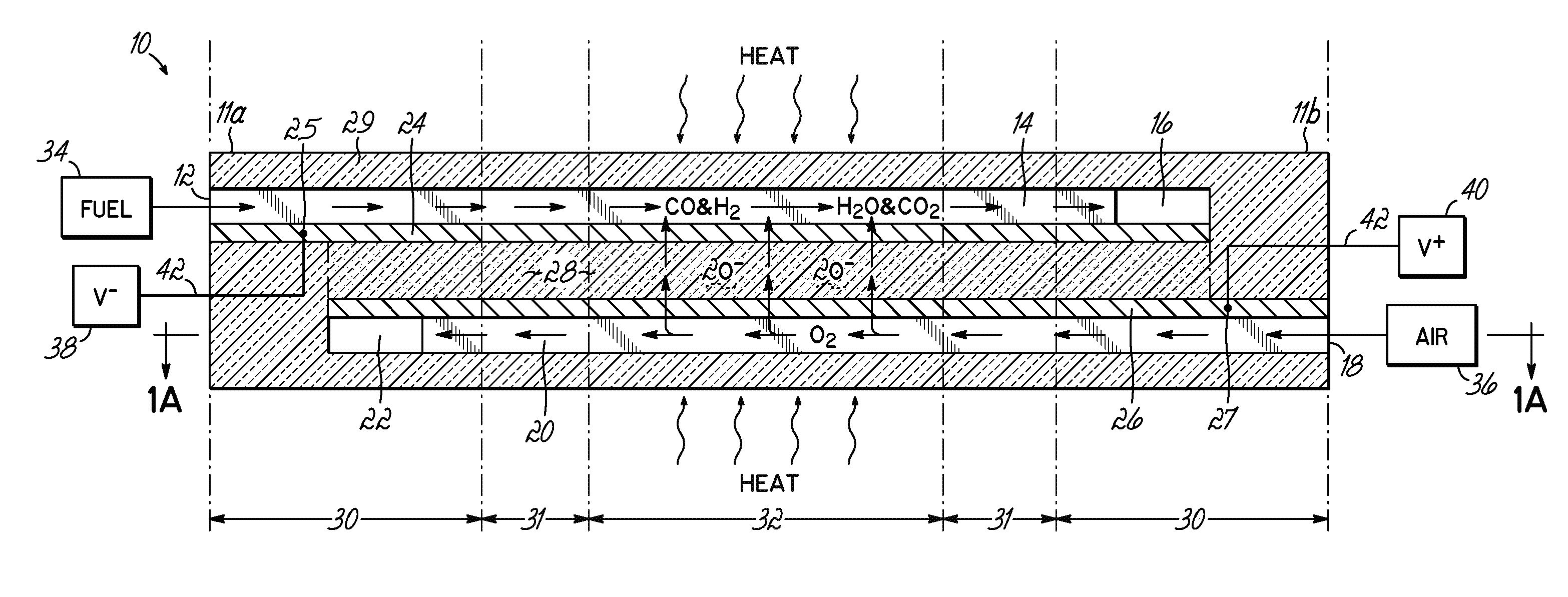
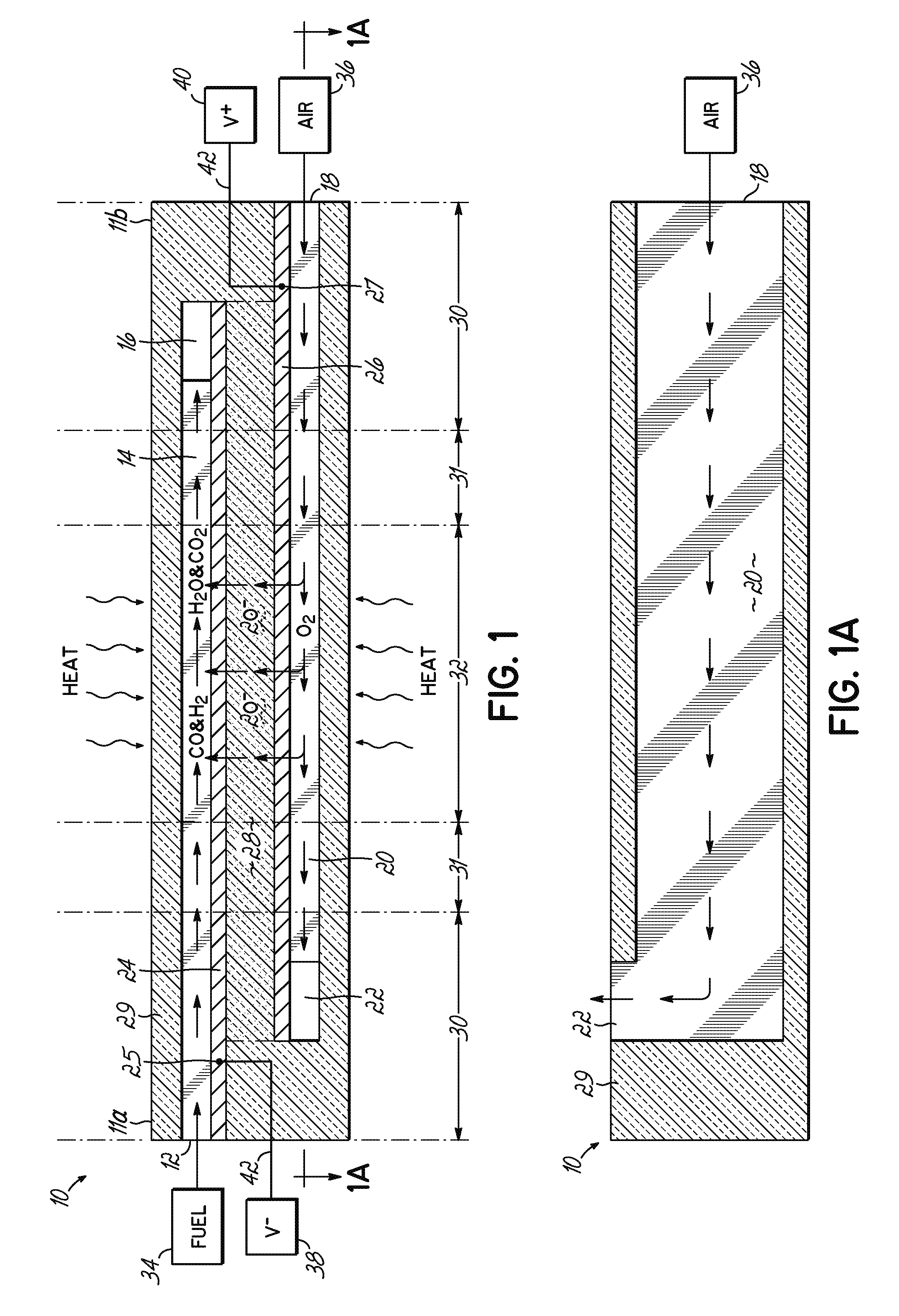
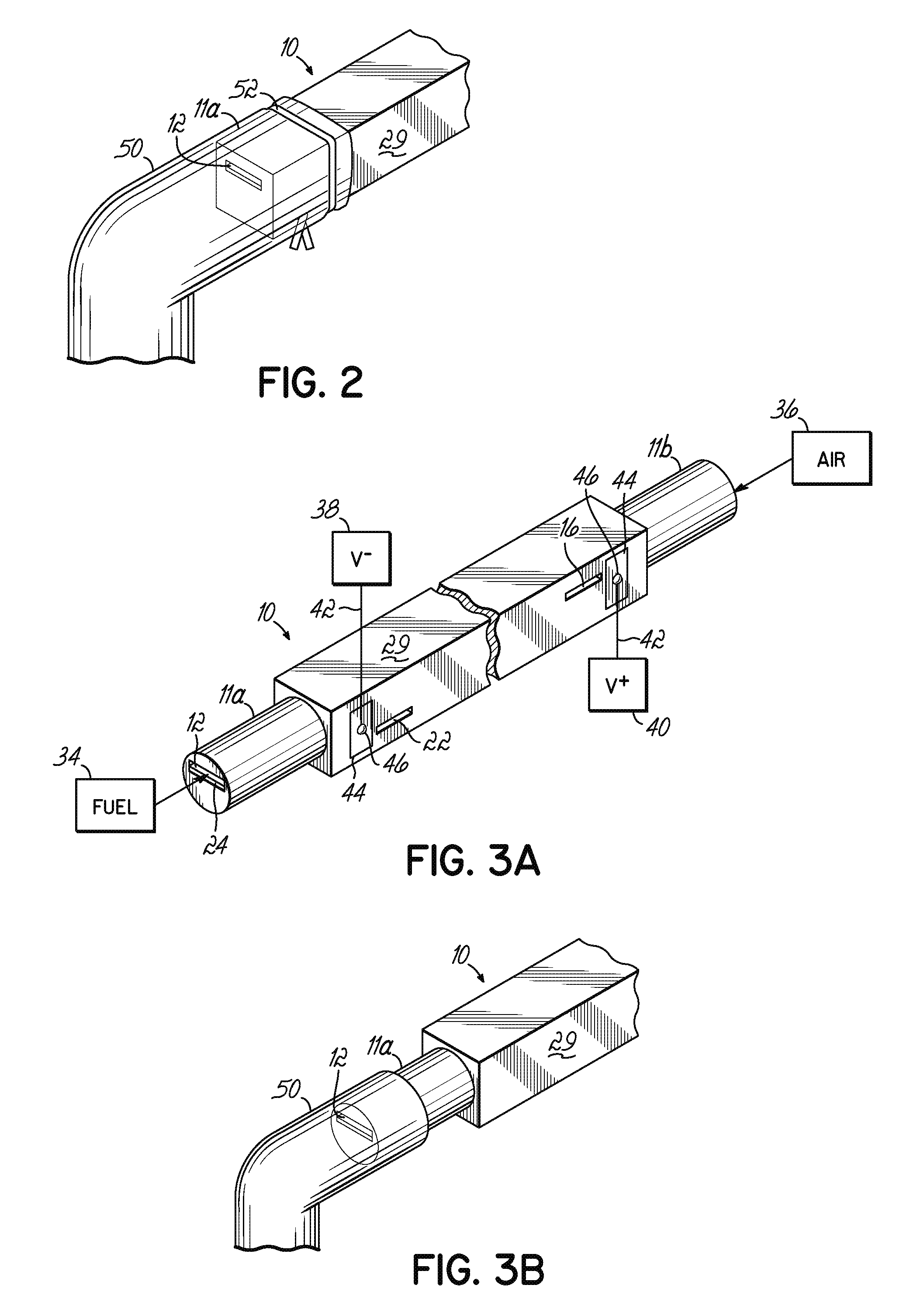
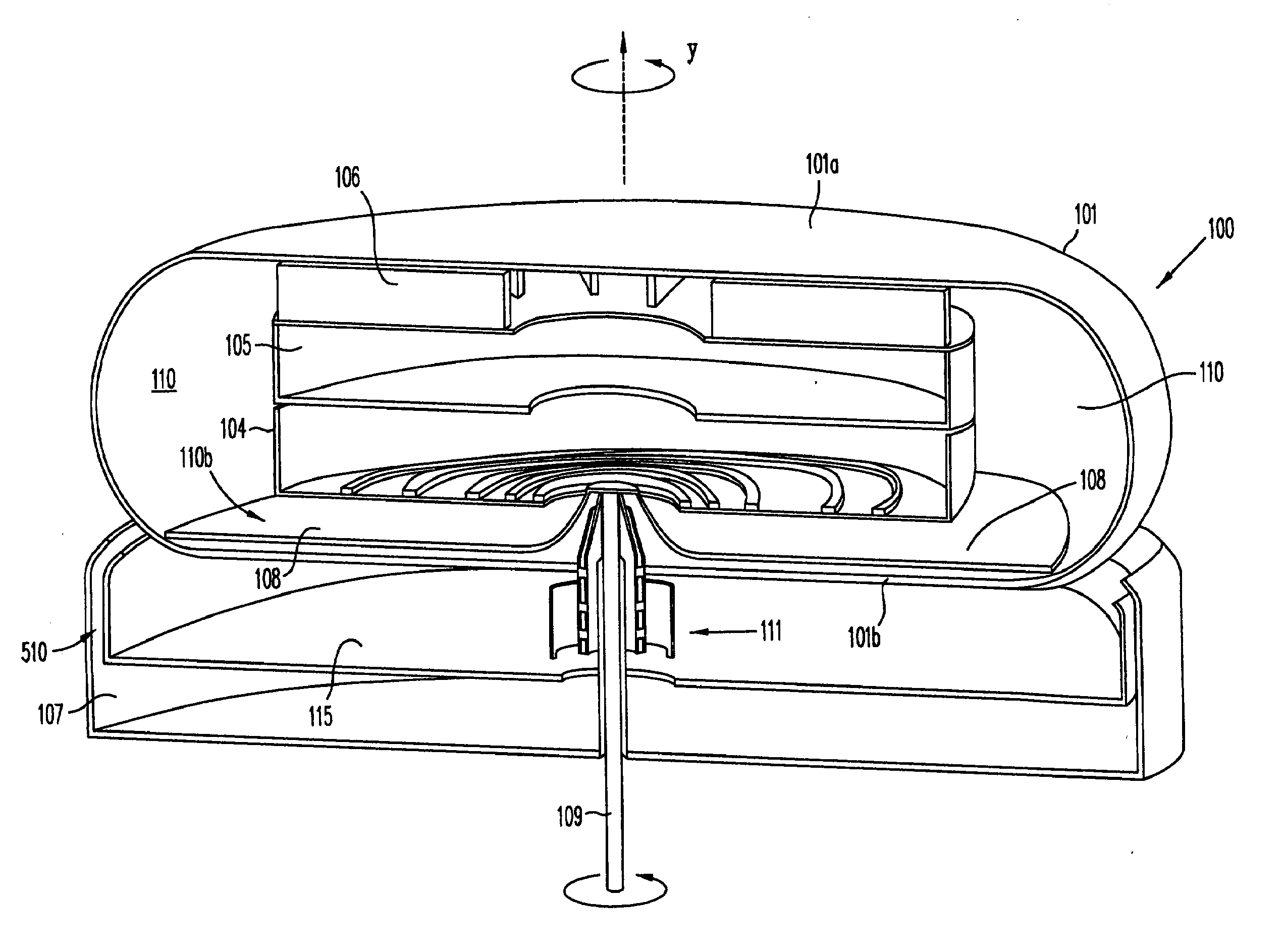
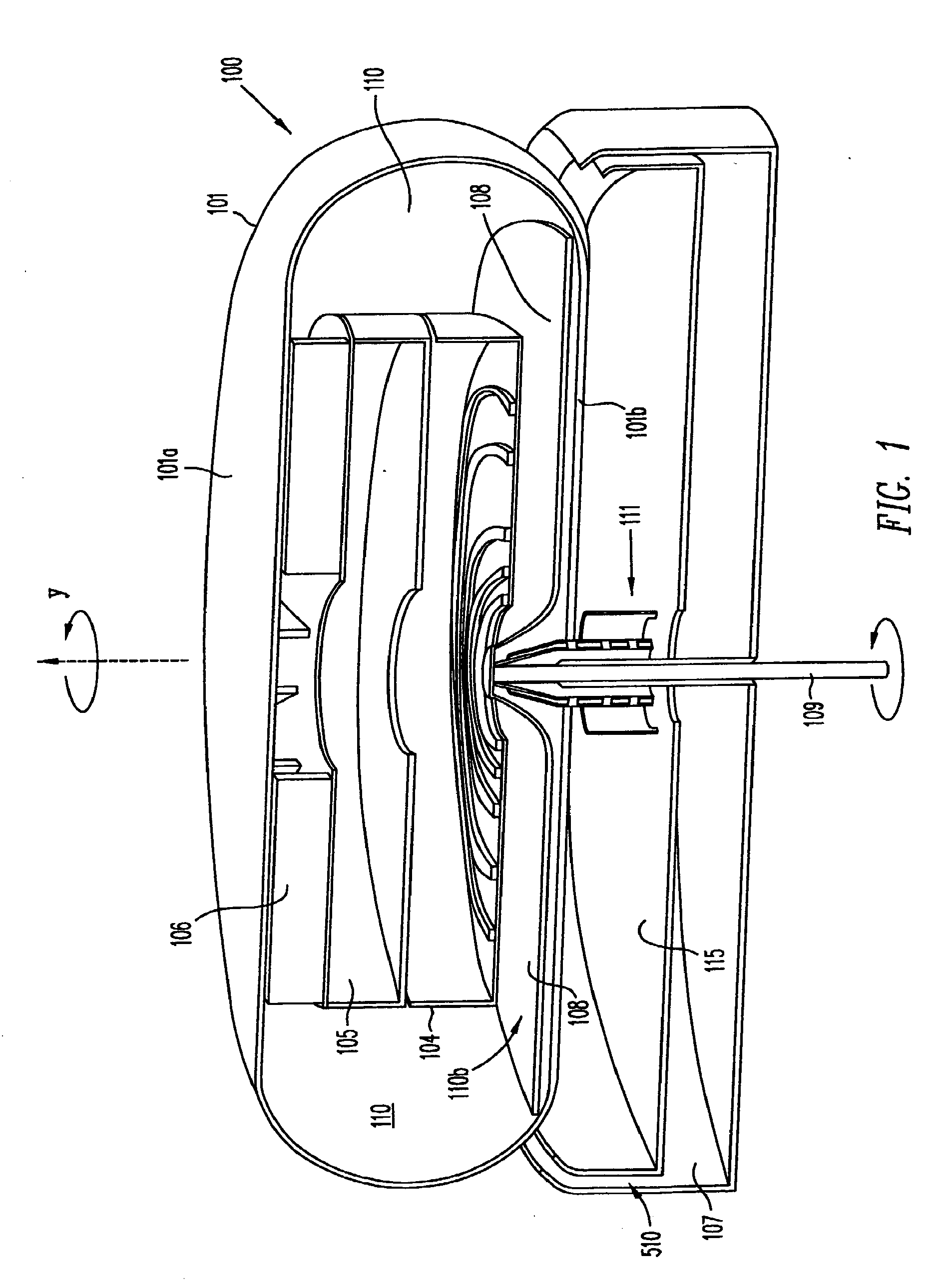
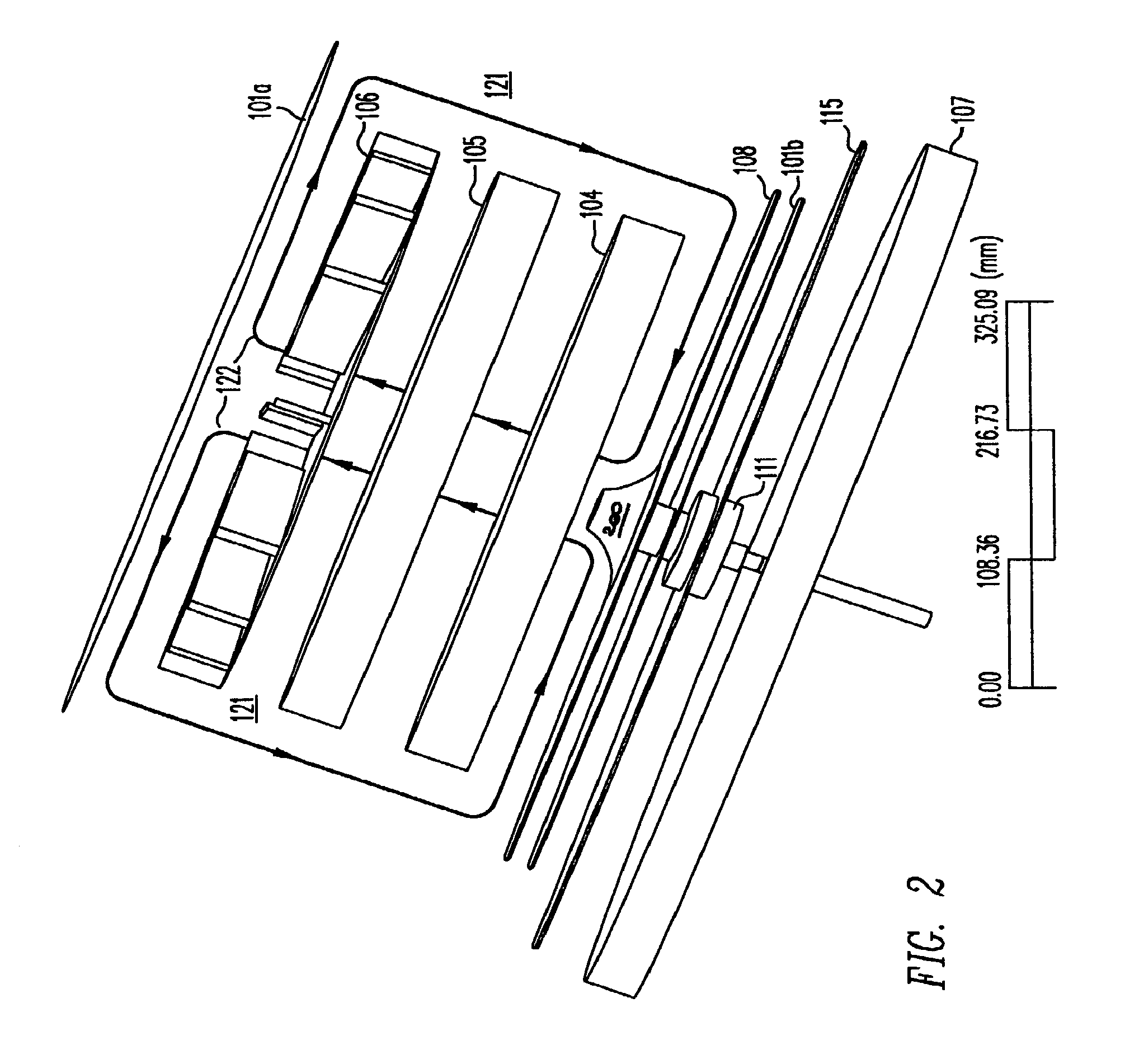
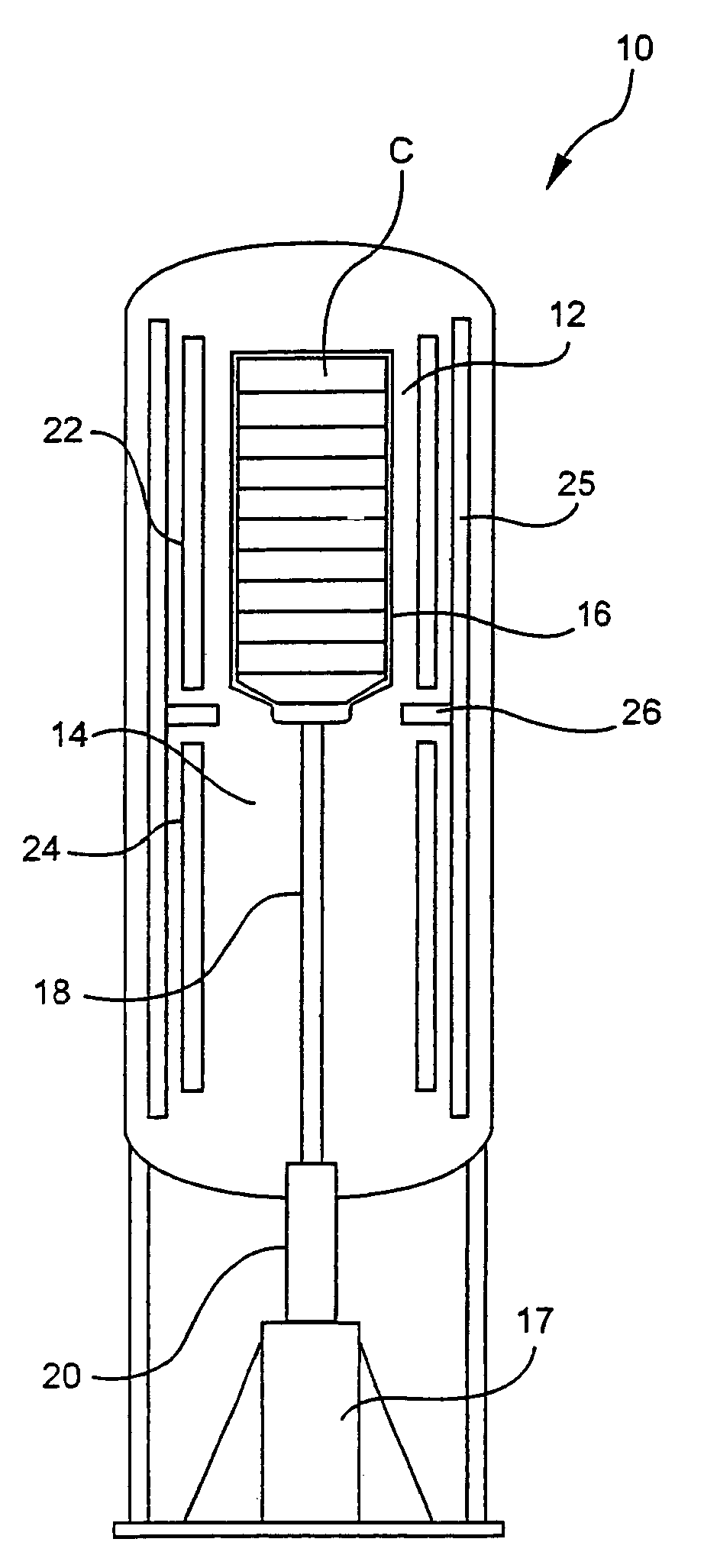
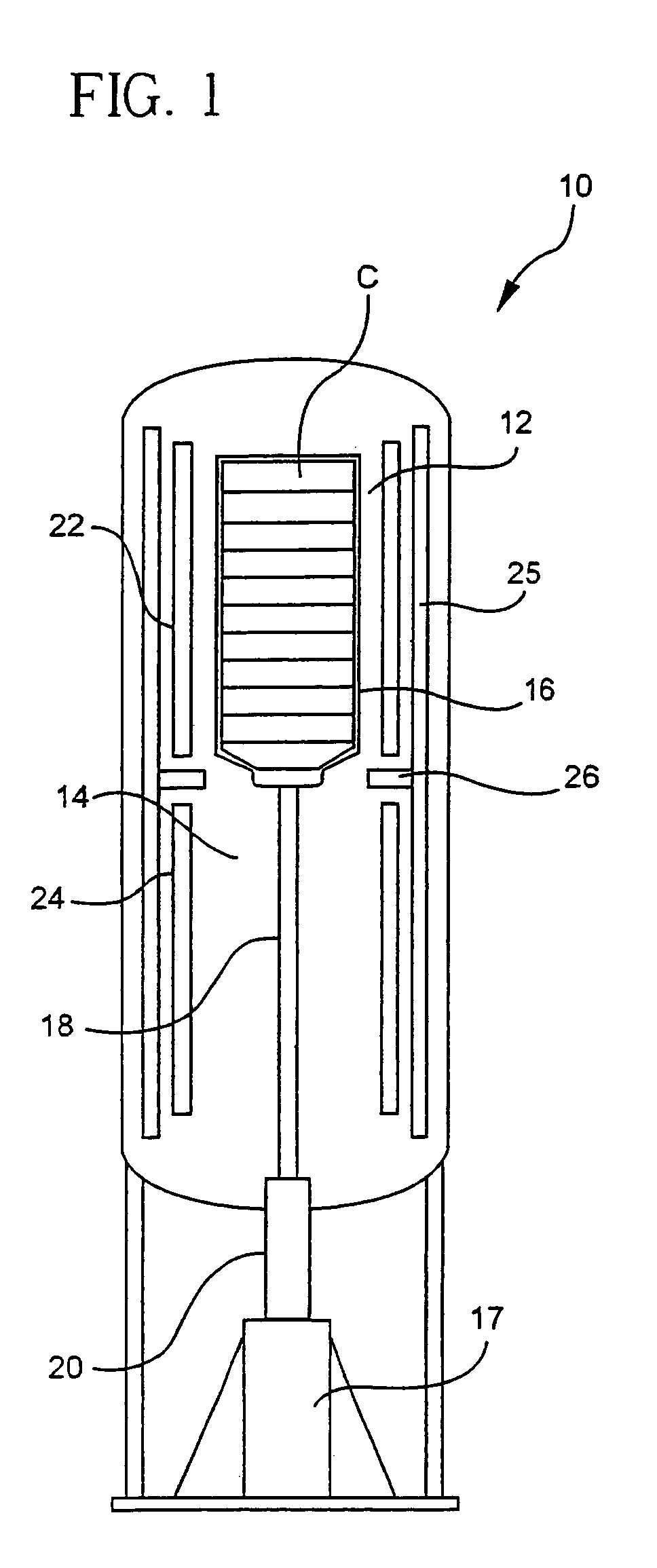
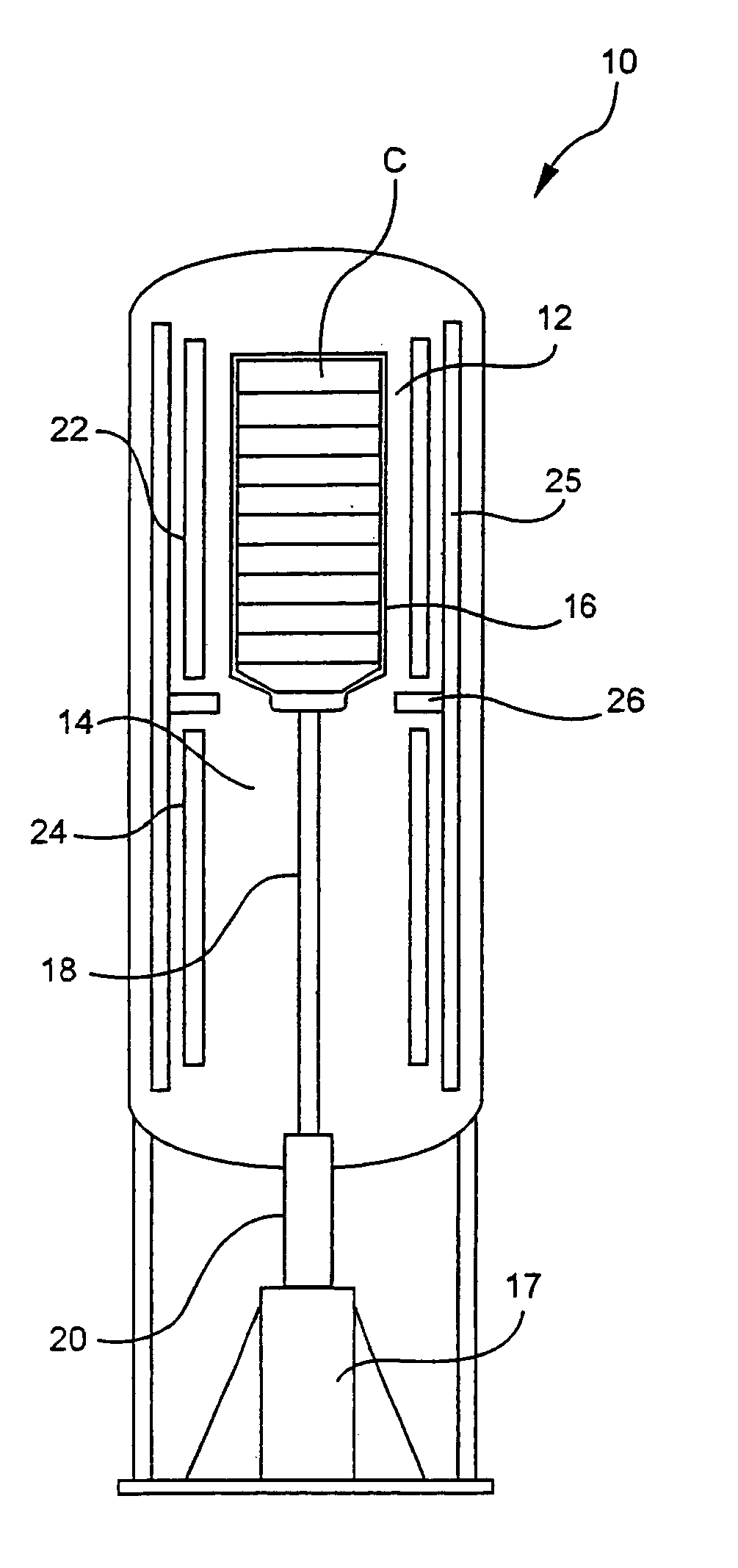
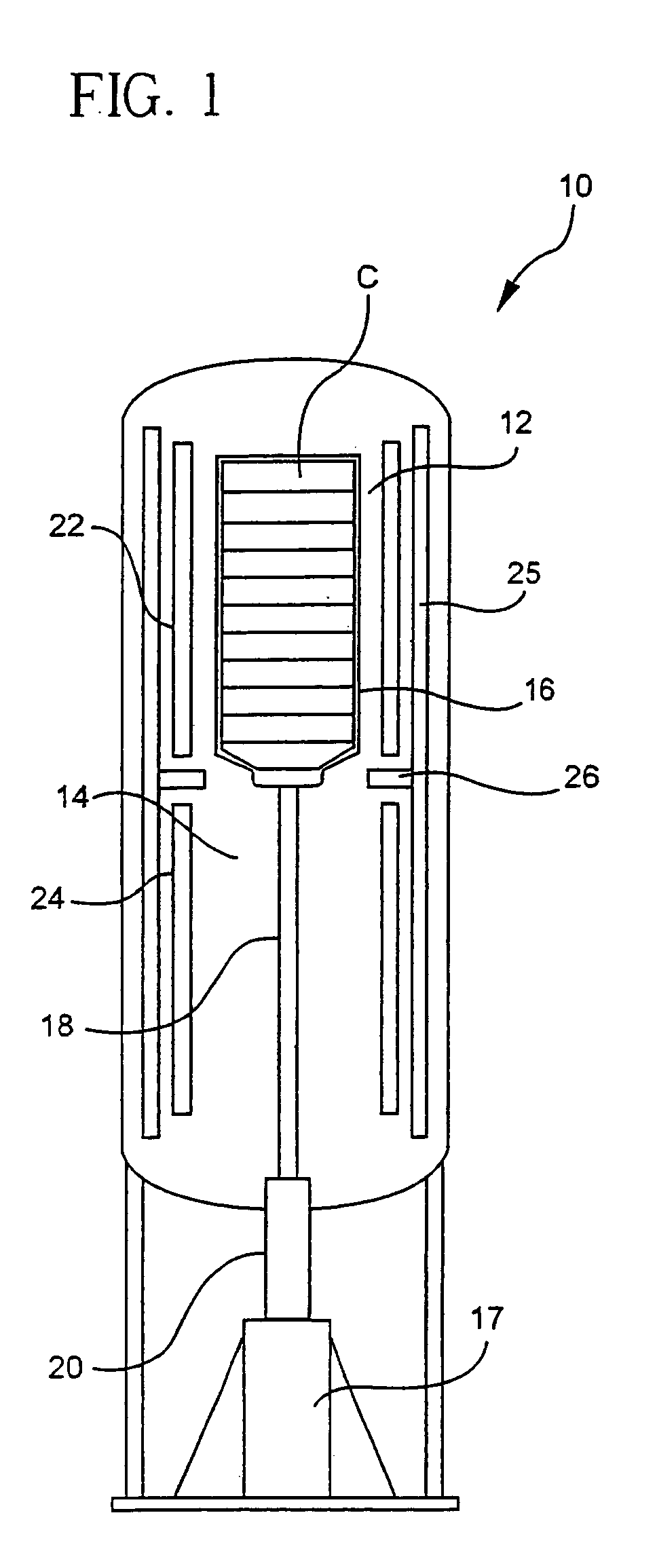
The invention provides solid oxide fuel cell devices and a fuel cell system incorporating a plurality of the fuel devices, each device including an elongate substrate having a reaction zone for heating to an operating reaction temperature, and at least one cold zone that remains at a low temperature below the operating reaction temperature when the reaction zone is heated. An electrolyte is disposed between anodes and cathodes in the reaction zone, and the anode and cathode each have an electrical pathway extending to an exterior surface in a cold zone for electrical connection at low temperature. In one embodiment, the device is a multi-layer anode-cathode structure, and in another embodiment, the device is an electrode-supported device. The system further includes the devices positioned with their reaction zones in a hot zone chamber and their cold zones extending outside the hot zone chamber. A heat source is coupled to the hot zone chamber to heat the reaction zones to the operating reaction temperature, and fuel and air supplies are coupled to the substrates in the cold zones.
Owner:DEVOE ALAN +1
Superimposed Computer Room Building and Process for Cooling this Building
InactiveUS20110138708A1Easy temperature controlLower overall pressure dropTemperature control without auxillary powerRoof covering using slabs/sheetsHot zoneEngineering
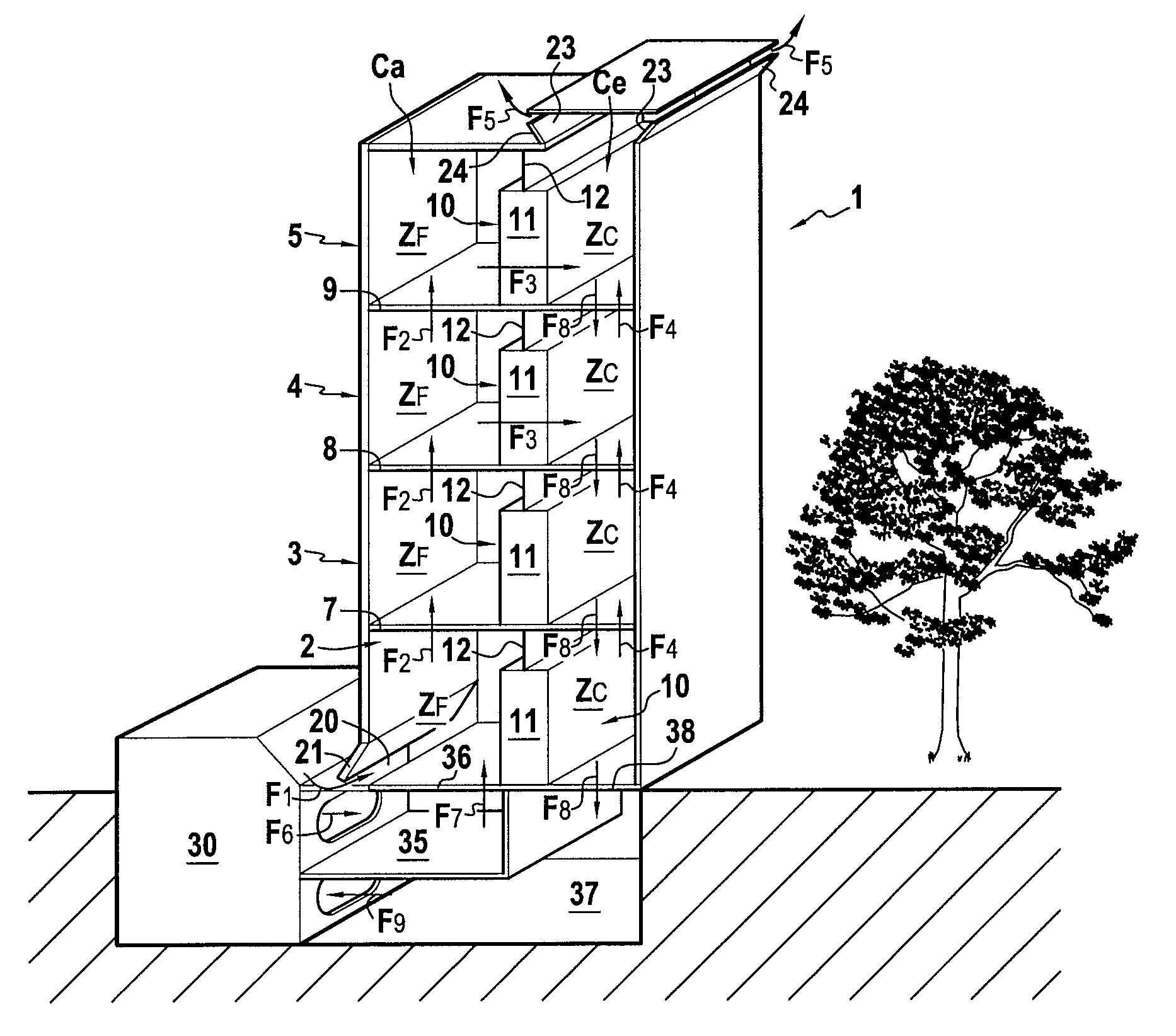
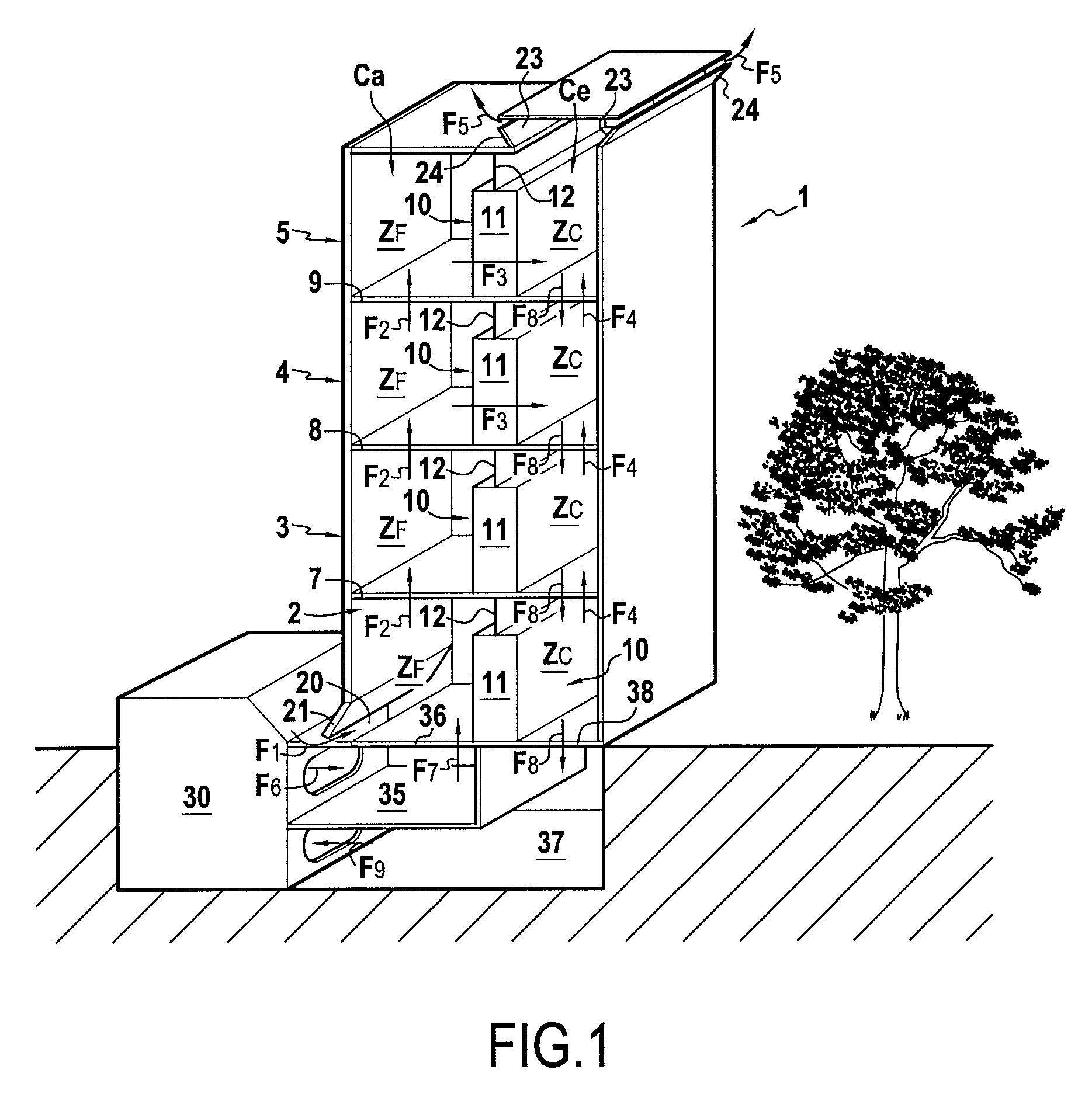
Building comprising at least two vertically superimposed computer rooms 2, 3, 4, 5 each limited by a peripheral wall 6 and separated from each other by an intermediate floor 7 and which each contain computer cabinets 11 for computer or electronic equipment 25. The building is characterised in that: each computer room 2, 3, 4, 5 comprises at least one interior wall 10 formed in part or less by the computer cabinets 11 and which separates the interior volume of each computer room into a hot zone Zc and a cold zone Zf, since the air cannot flow between the hot zone Zc and the cold zone Zf without passing through the computer cabinets 11; each intermediate floor 7, 8, 9 is perforated to allow free circulation of air, all cold zones Zf are superimposed and forming a supply column of fresh air Ca and all the hot spots are superimposed forming an exhaust column of hot air Ce; the floors 7, 8, 9, the perimeter walls 6 and interior walls 10 are adapted to prevent a direct flow of air between the supply column Ca and the exhaust column Ce, and the building comprises fresh air means 20, 30 in the supply column Ca and means for evacuating 23, 30 hot air from the exhaust column Ce.
Owner:ENIA ARCHITECTES +1
Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Device and System
InactiveUS20070105003A1Great dimensionAvoid layeringFuel cell heat exchangeReactant parameters controlFuel cellsHot zone
The invention provides a solid oxide fuel cell device and a fuel cell system incorporating a plurality of the fuel devices, each device including an elongate substrate the length of which is the greatest dimension such that the elongate substrate has a coefficient of thermal expansion having only one dominant axis that is coextensive with the length. A reaction zone is provided along a first portion of the length for heating to an operating reaction temperature, and at least one cold zone is provided along a second portion of the length that remains at a low temperature below the operating reaction temperature when the reaction zone is heated. A plurality of fuel passages and oxidizer passages are provided in the elongate substrate extending from the at least one cool zone to the reaction zone, each fuel passage having an associated anode in the reaction zone, and each oxidizer passage having an associated cathode in the reaction zone positioned in opposing relation to a respective one of the associated anodes. An electrolyte is disposed between each of the opposing anodes and cathodes in the reaction zone. The system further includes the devices positioned with their first portions in a hot zone chamber and their cold zones extending outside the hot zone chamber. A heat source is coupled to the hot zone chamber to heat the reaction zones to the operating reaction temperature. A fuel supply is coupled outside the hot zone chamber to the at least one cold zones in fluid communication with the fuel passages for supplying a fuel flow into the fuel passages.
Owner:DEVOE ALAN +1
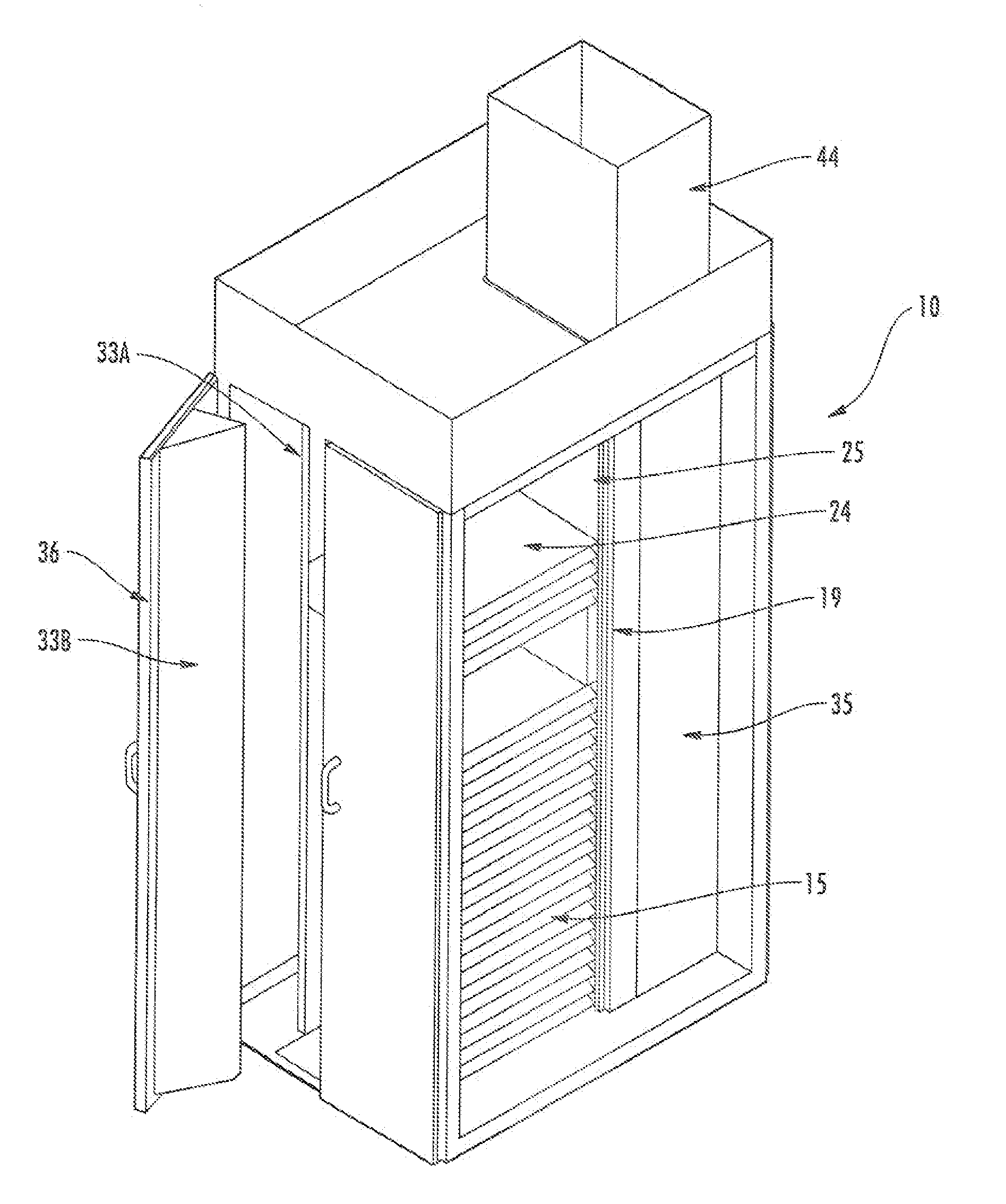
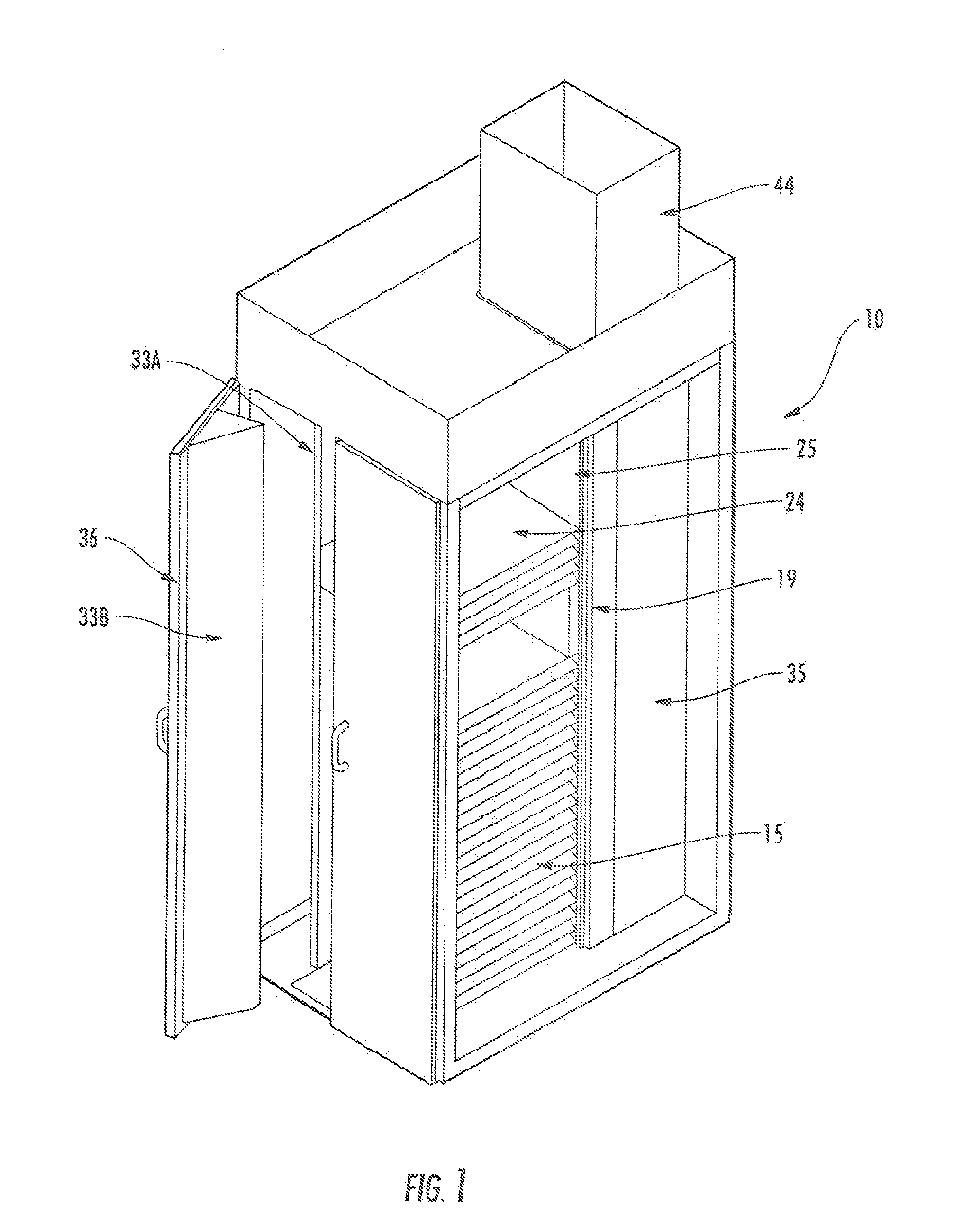
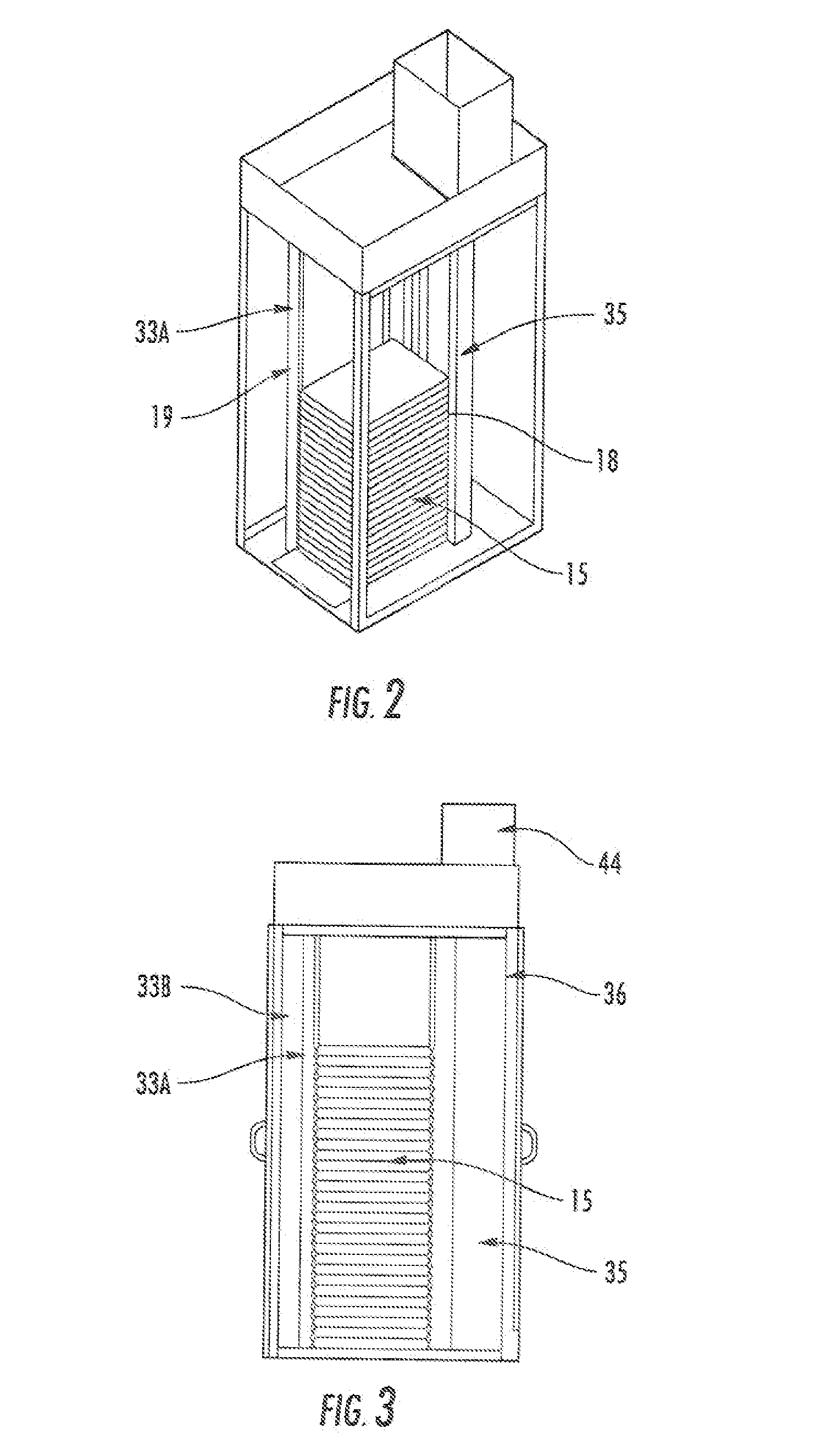
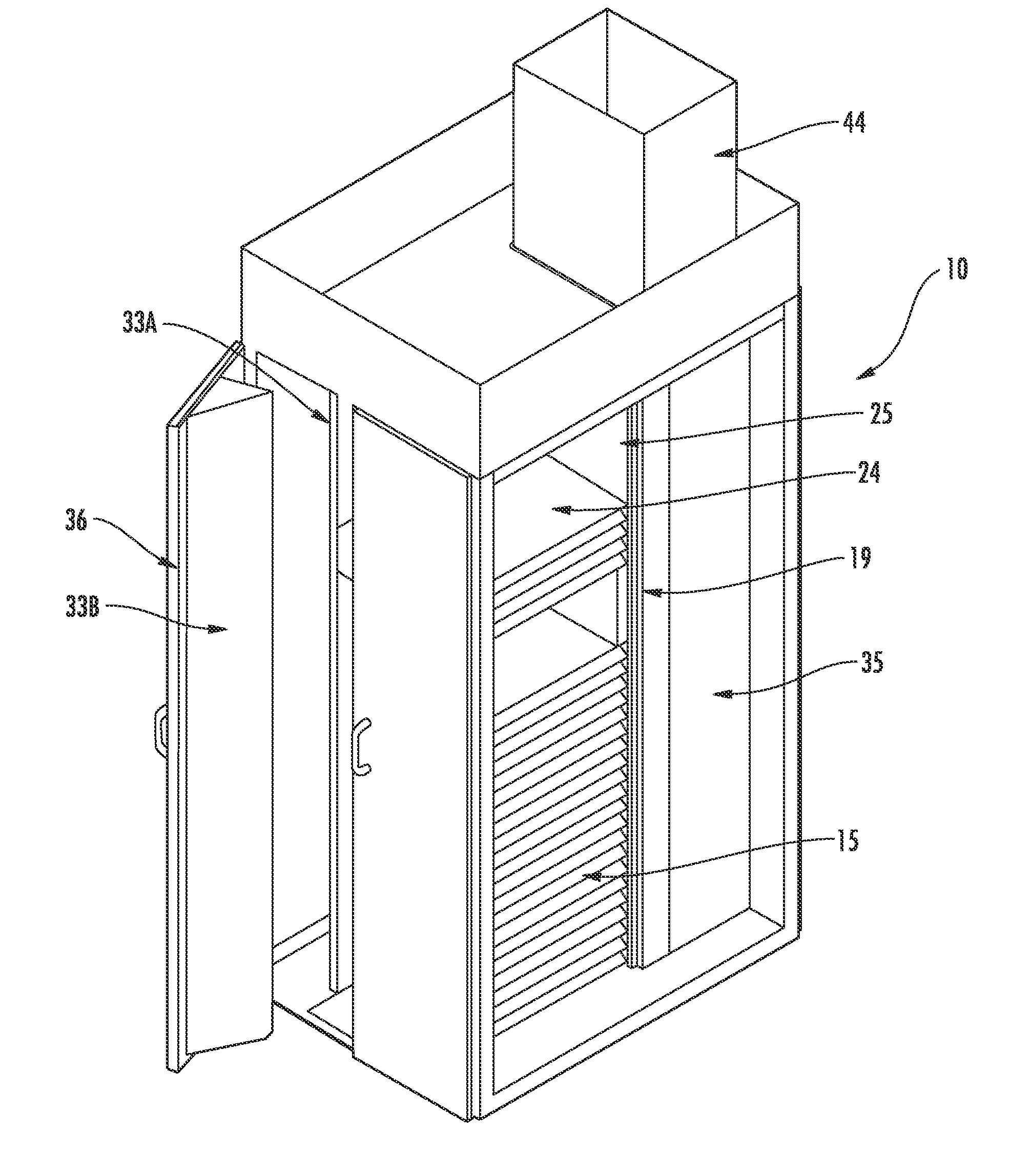
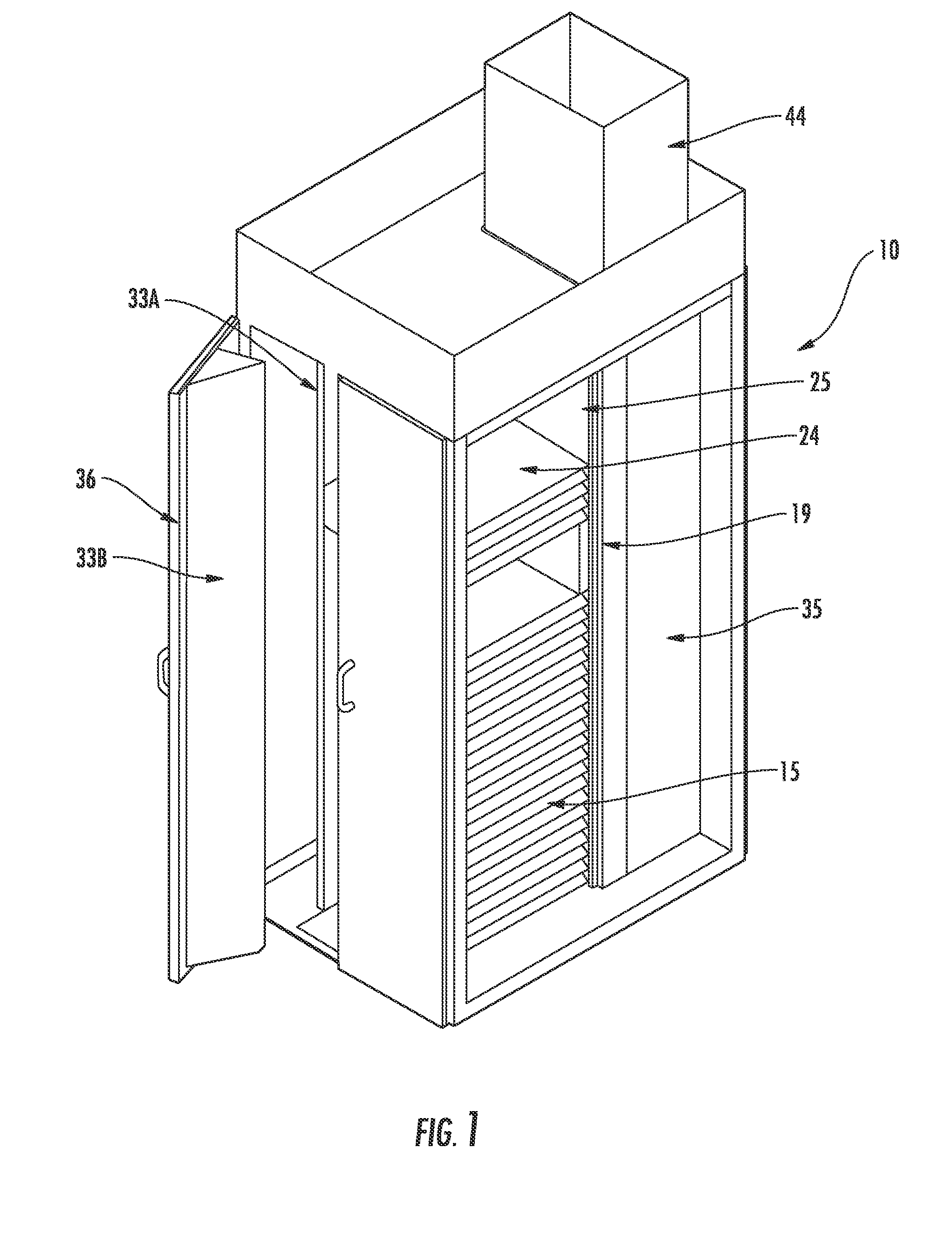
Thermal Management Cabinet for Electronic Equipment
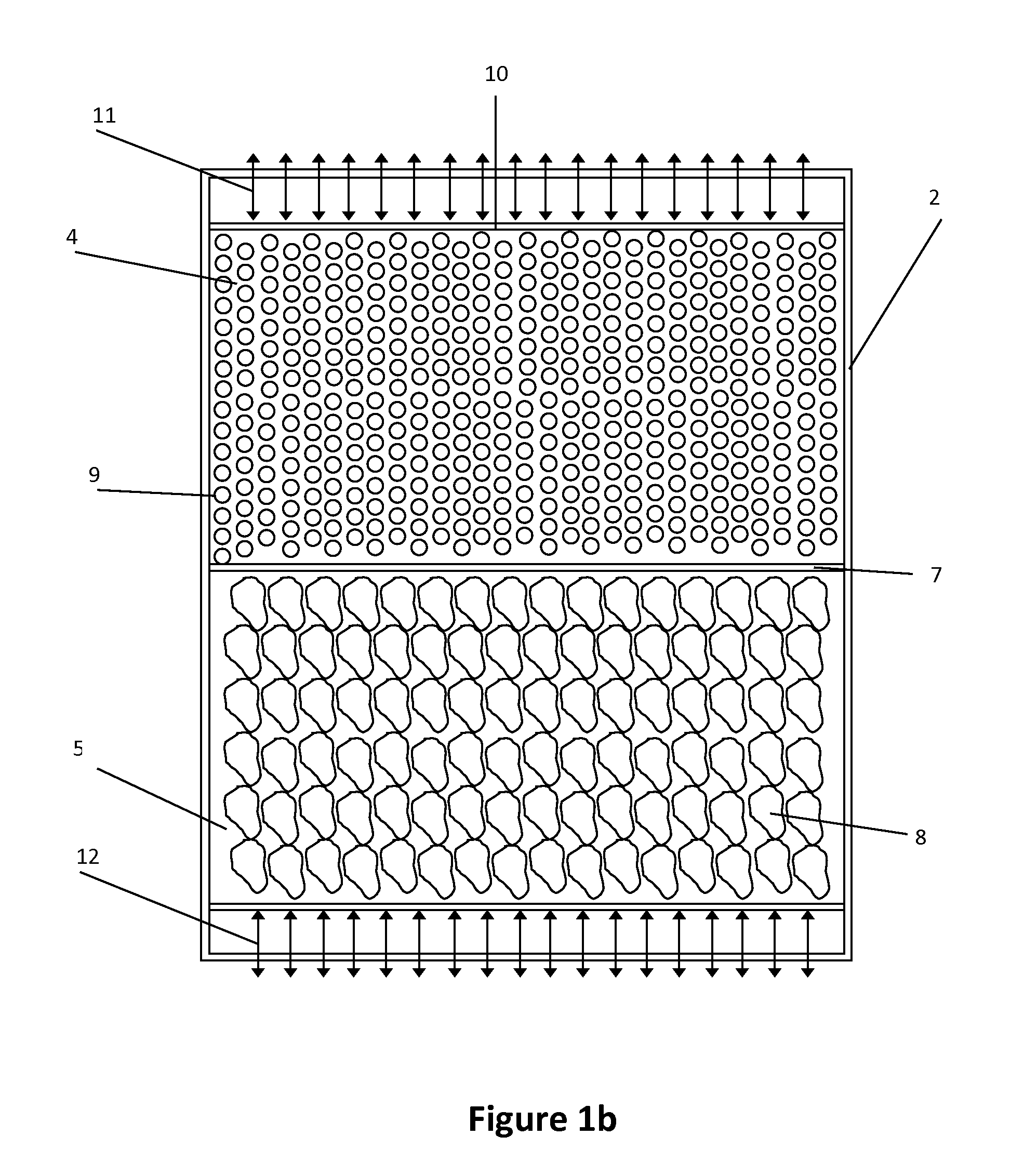
A thermal management cabinet for electronic equipment such as servers, having an opening in the top and bottom of the cabinet. The cabinet extends between a raised access floor of a building carrying cooled air and a drop ceiling for venting heated air. The bottom opening of the cabinet is alignable with an opening in the access floor such that cool air can pass into the cabinet and can flow through the electronic component storage area to the top opening, which is alignable with an opening in the drop ceiling. The cabinet interior is separated into temperature zones comprising at least a cold zone supplied with air from the access floor and a hot zone for venting through the top opening. At least one baffle creates the temperature zones such that air is directed to flow from the cold zone through the electronic component storage area to the hot zone.
Owner:BASELAYER TECH
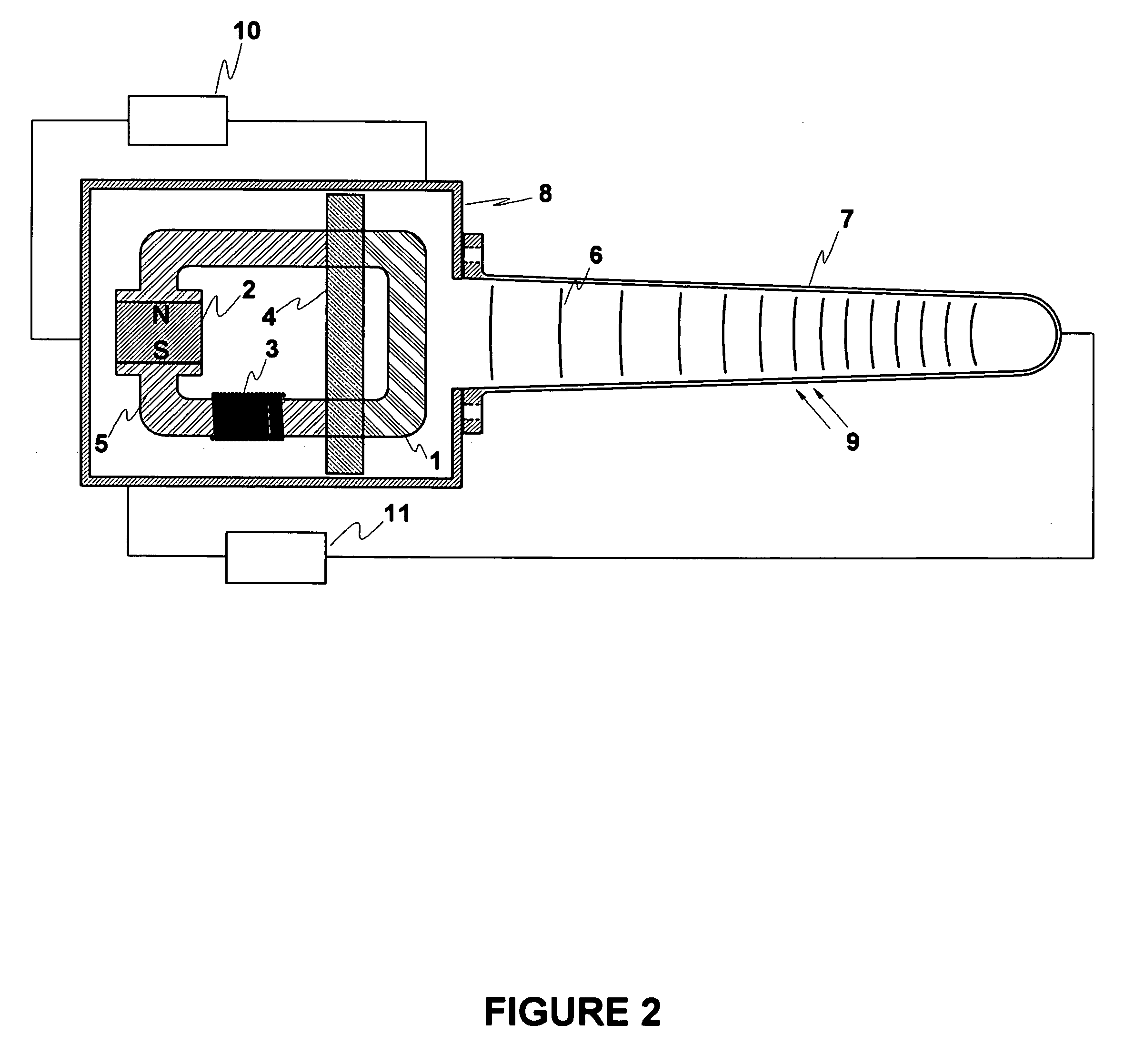
NMR CryoMAS probe for high-field wide-bore magnets
InactiveUS7282919B2Reduce riskAvoid flowElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagic angle spinningNitrogen gas
Owner:DOTY SCI
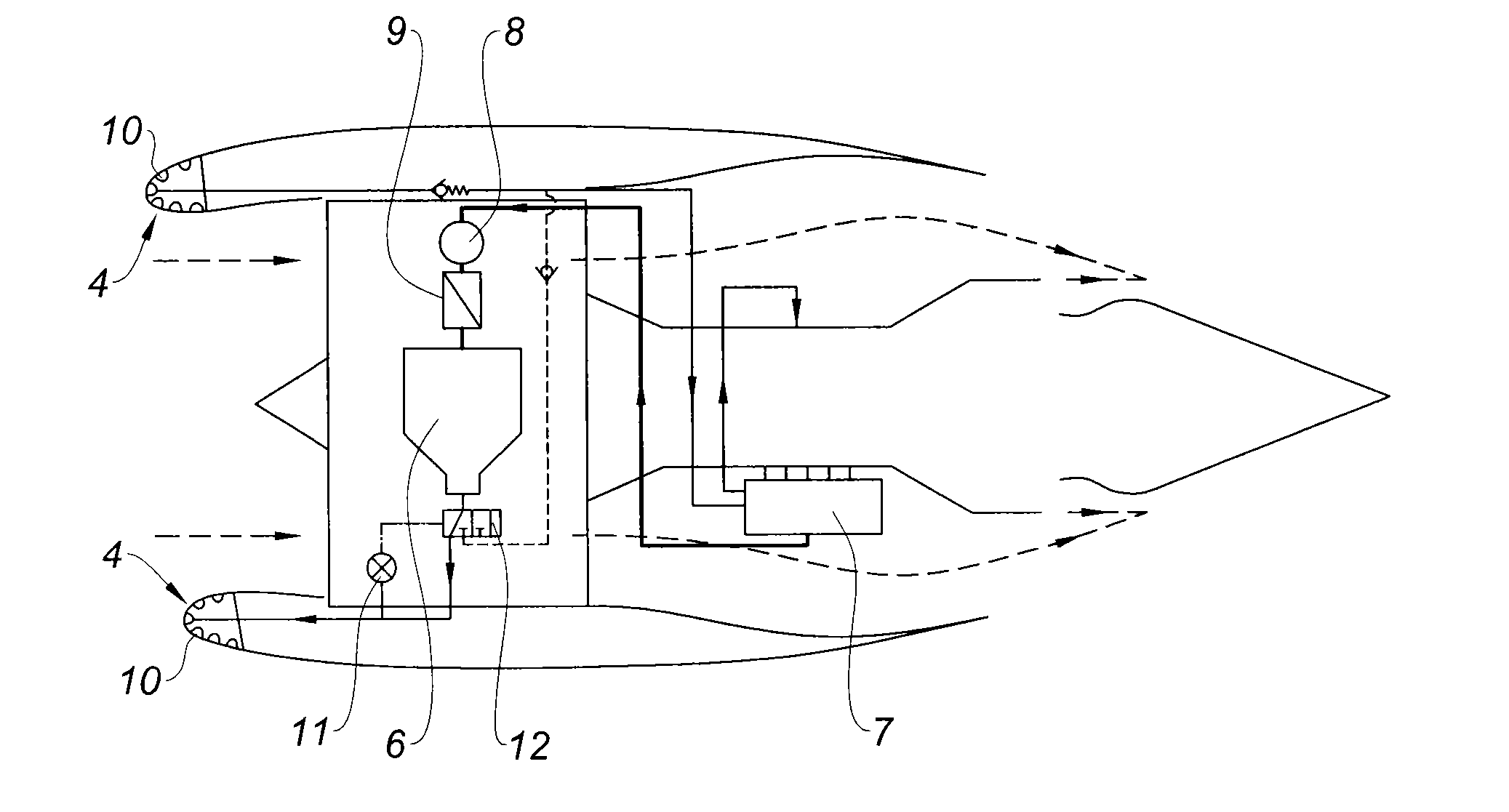
Regulated oil cooling system for a turbine engine with deicing of the nacelle
InactiveUS20140205446A1Many timesDischarging heatPump componentsGas turbine plantsNacelleCooling capacity
The invention relates to an oil cooling system of a turbine engine installed in an aircraft comprising a circuit suitable for circulating the oil between the engine and at least one external heat exchanger placing the oil in thermal communication with a part of the lip of the nacelle, wherein it also comprises at least one air / oil heat exchanger placing the oil in thermal communication with the air circulating in the cold zone of the turbine engine, equipped with a device suitable for varying its oil cooling capacity, and with a control means for said cooling capacity variation device.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
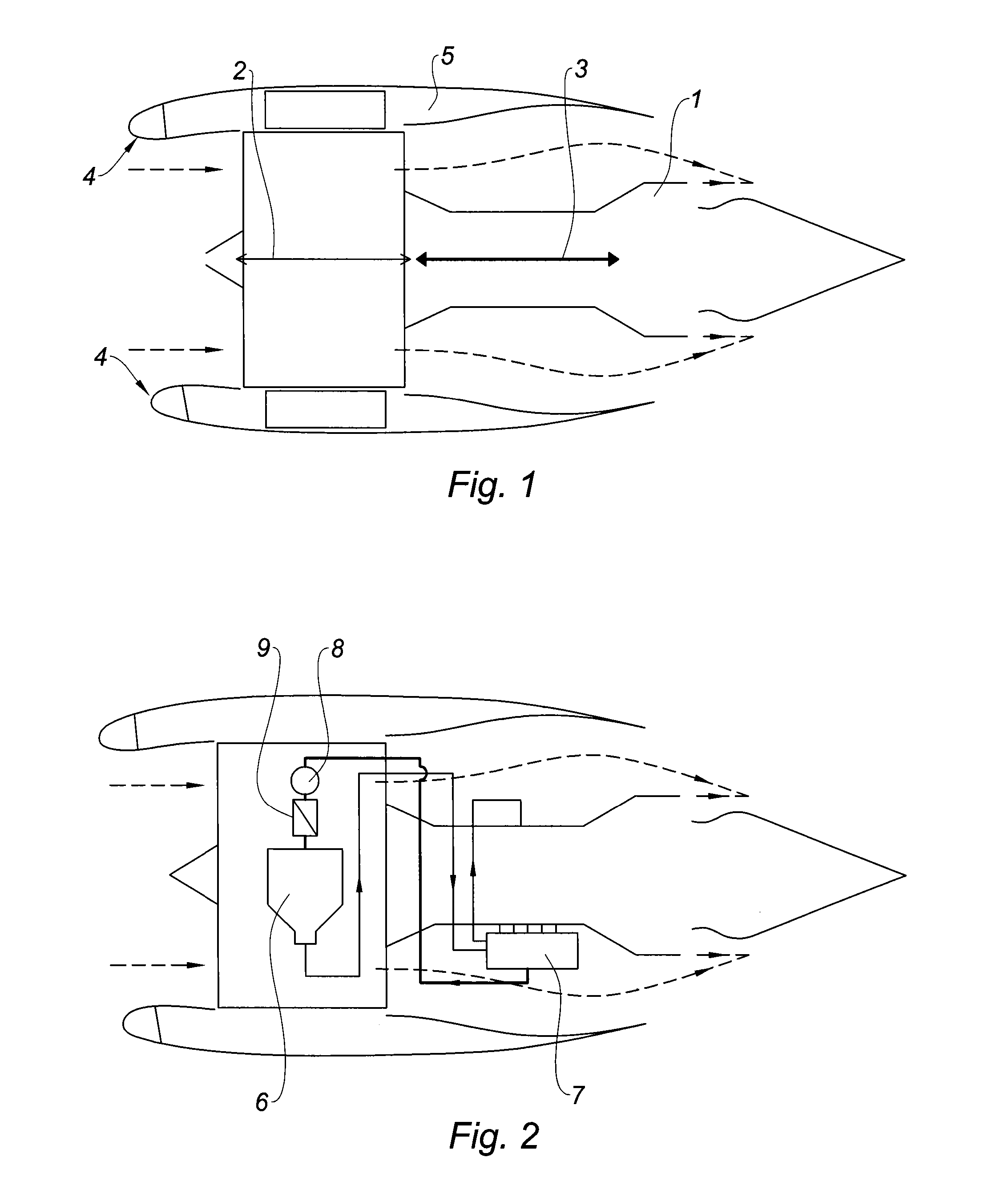
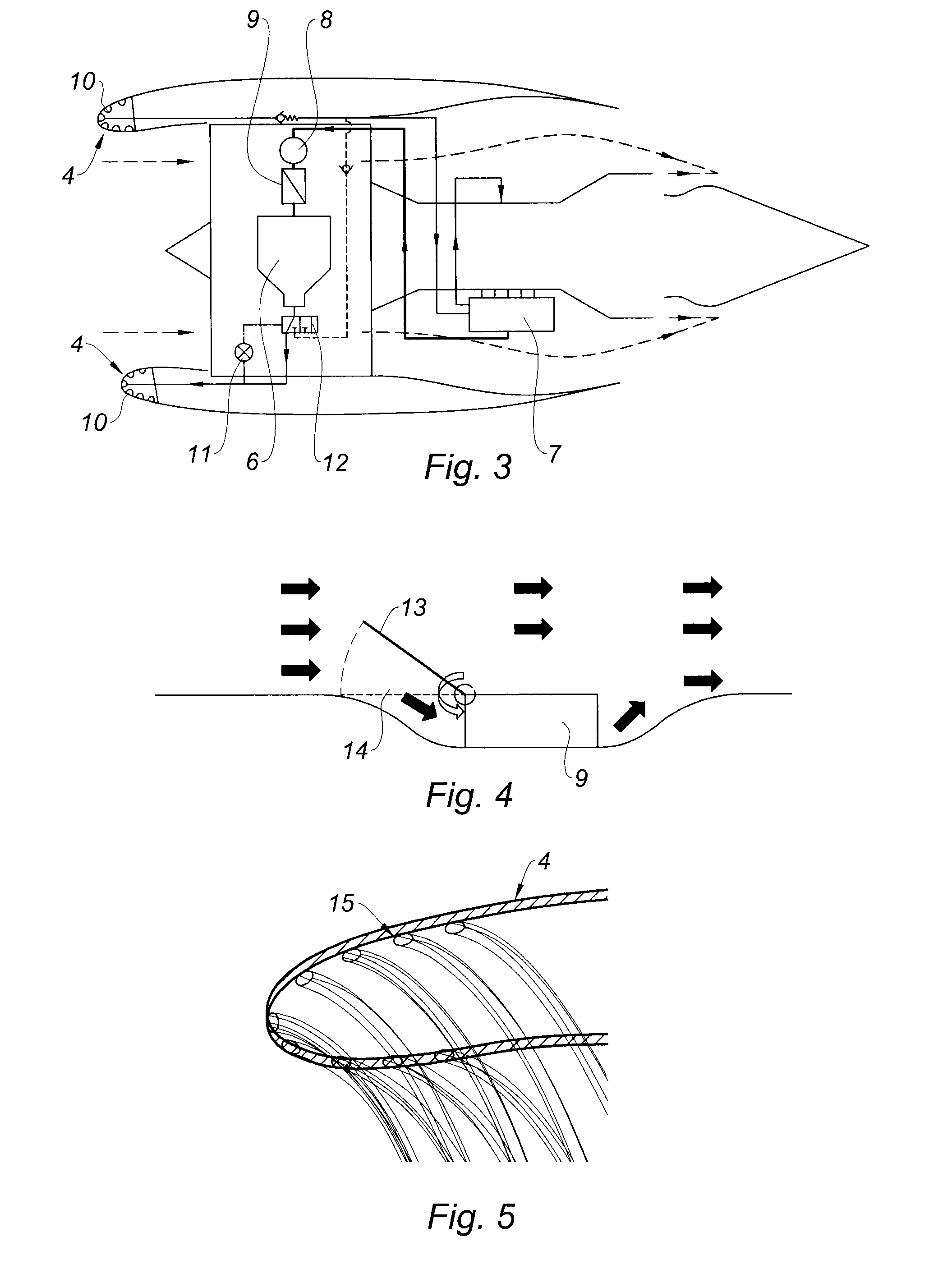
Method and a circuit for ventilating equipment of a turbojet by thermoelectricity
InactiveUS20160123185A1Limit overuseEffective supervisionPump componentsEngine fuctionsJet enginePotential difference
The invention provides a method of ventilating equipment of a turbojet, the turbojet (10) having a cold zone (ZF) including a fan (14) upstream from a hot zone (ZC), the turbojet equipment (32) for ventilating being arranged in a ventilation space (30) available around the hot zone between a primary air stream passage (26) and a secondary air stream passage (28) of the turbojet, the method comprising taking ventilation air from one of the air stream passages in order to convey it to the ventilation space, and providing forced flow of the ventilation air by means of at least one electric fan (36) positioned inside the ventilation space and powered electrically by at least one thermoelectric generator (38) suitable for inducing a potential difference (ΔV) and positioned in a wall (40) between the ventilation space and the secondary air stream passage.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
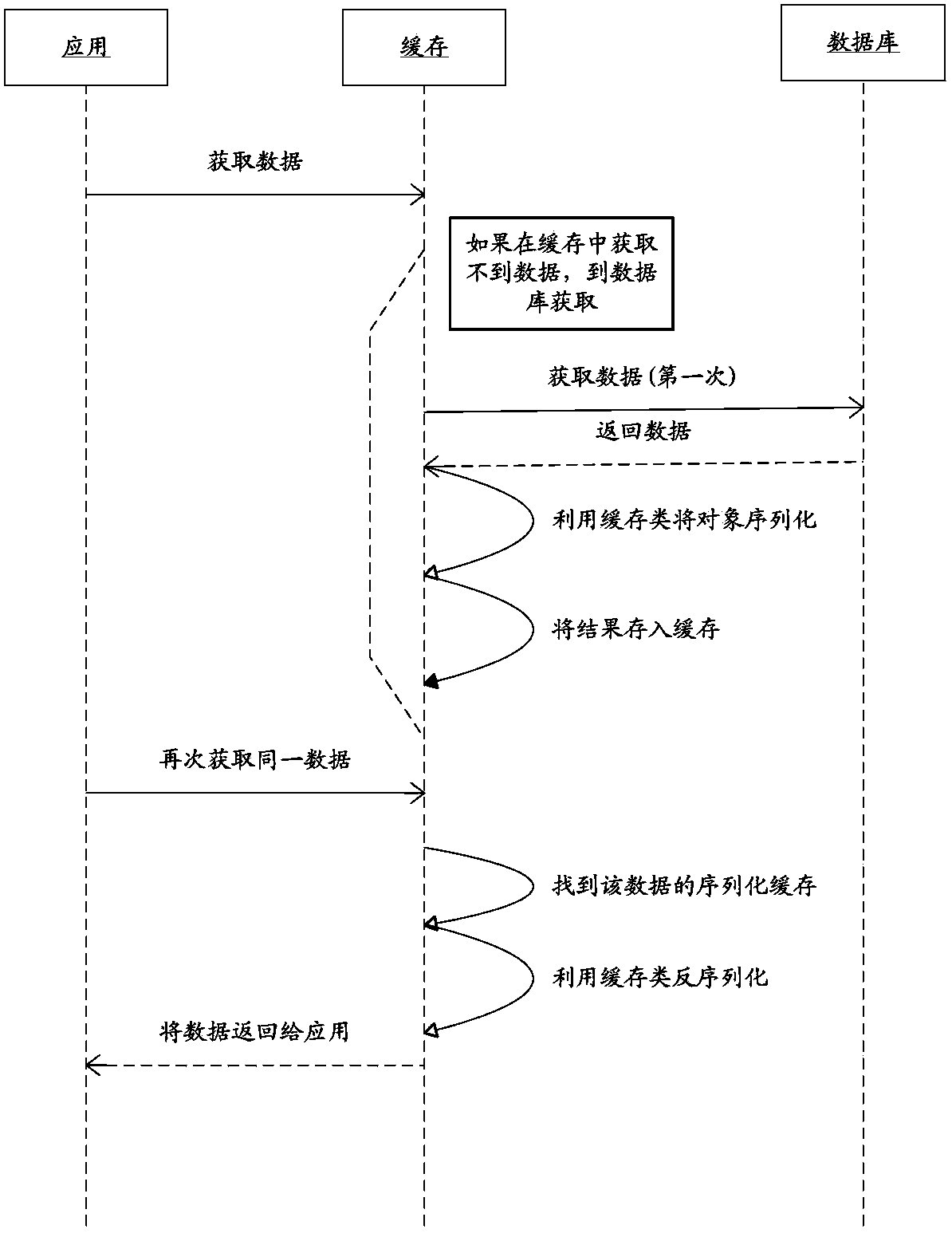
Method for caching data
ActiveCN103514106AReduce occupancyIncrease storage capacityInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationHot zoneSerialization
The invention discloses a method for caching data. The method includes the steps that serialization processing is conducted on data placed in a cache; the cache is divided into a cold zone and a hot zone, and both the cold zone and the hot zone are of a bi-directional linked list structure; when the data are inserted into the cache, the data are firstly placed in the cold zone; when the data in the cache are hit, if the hit data are in the cold zone, whether the data are hit by preset times or not is judged, if yes, the data are transferred to the tail of the hot zone, if not, the data are transferred to the head of a linked list of the cold zone; if the hit data are in the hot zone, the data are transferred into the head of a linked list of the hot zone. By the adoption of the technical scheme, caching efficiency of the hot data is effectively improved.
Owner:ULTRAPOWER SOFTWARE
NMR CryoMAS Probe for High-field Wide-bore Magnets
InactiveUS20060176056A1Reduce riskImprovement factorElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonancePartial solutionNitrogen gas
An MAS probe is disclosed for obtaining a substantial improvement in signal to noise (S / N) in triple-resonance high-resolution (HR) magic-angle-spinning (MAS) NMR of samples near room temperature (RT) in high-field magnets where the magnet's RT shim bore is greater than 60 mm. All critical circuit components, including the sample coils, are located along with the spinner assembly in a thermally insulated cold zone pressurized with helium gas. The spinner assembly attaches to a sealed, curved, rotor-loading tube to permit automatic sample change, and it is surrounded by a partially insulated jacket cooled with a cryogenic fluid, generally nitrogen gas. The MAS probe is also compatible with magic angle gradients, variable temperature operation, field locking, and commonly available closed-cycle cold fingers. One major challenge in implementing CryoMAS is solving the problem of gas leakage from the spinner bearing, drive, and exhaust nitrogen into the cold zone, as some components will necessarily be ceramic, some plastic, and some metal. It is not desirable to use helium for the spinner bearing and drive gases for cost reasons and to prevent risk of degradation of o-ring-sealed magnet cryostats. A pressurized helium atmosphere in the cold zone may be utilized to prevent nitrogen flow from the spinner exhaust streams or atmosphere into the cold zone. The drawback to a pressurized cold zone is that the heat transfer coefficient in dense helium at low temperatures is very high, making it challenging to cool the sample coils and all the large, critical, circuit components in a practical manner. Part of the solution here is to use a first-stage cooling-jacket around the major heat leaks near the spinner exhaust flows. The critical components may be insulated with fine glass wool or teflon foam and conduction cooled without cooling much of the cold zone below the temperature of the first-stage cooling. The use of coaxial sapphire capacitors allows the noise contributions from the most critical capacitors to be reduced to a minor fraction of the total.
Owner:DOTY SCI
Miniature gas turbine engine with unitary rotor shaft for power generation
InactiveUS6866478B2Quality improvementImprove performanceEngine manufacturePump componentsCantileverTurbine
The present invention provides a miniature gas turbine engine for power generation. The engine has a highly integrated unitary rotor shaft where turbine, compressor and shaft are made in one piece in one fabrication process. The turbine and compressor are positioned back to back on the shaft in an overhung configuration, allowing the front bearings to be located in the cold zone of the engine. Preferably, the Mold SDM fabrication technique is utilized to make the unitary rotor shaft in one monolithic part out of ceramics such as silicon nitride, eliminating the need for post process assembly while strengthening the integrity, reliability, and performance of the unitary rotor shaft. Integrated with a permanent magnet in the unitary rotor shaft, the miniature gas turbine engine can generate electric power of 1 kW or less. Additionally, the axial length of the miniature gas turbine engine is about 100 mm or less. The miniature gas turbine engine according to the present invention is therefore particularly useful for powering lightweight, self-sustaining mobile devices such as unmanned vehicles and-autonomous robots.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
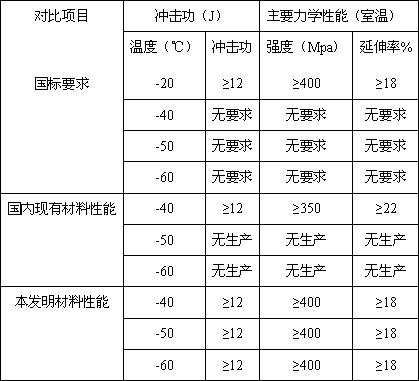
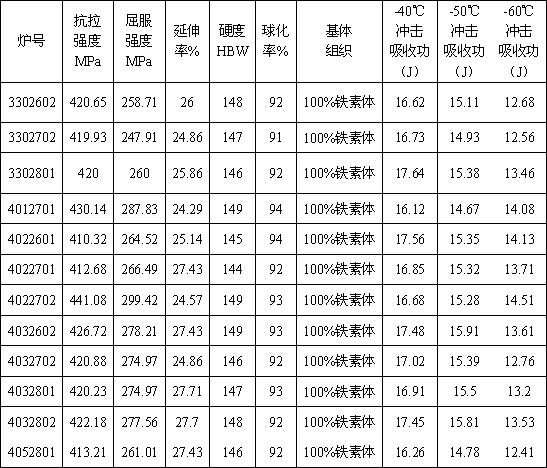
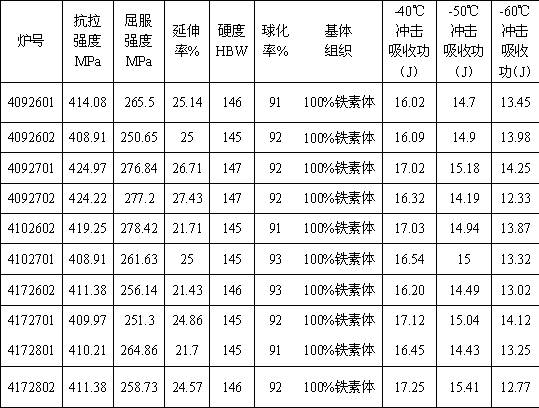
Manufacturing method of low-temperature ferrite nodular cast iron material
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a low-temperature ferrite nodular cast iron material. The material consists of the following chemical components: 3.5-3.9% of C, 1.9-2.3% of Si, not greater than 0.2% of Mn, not greater than 0.03% of P, not greater than 0.02% of S, 0.04-0.06% of Mg, and 0.25-0.95% of Ni. The performances of the material are as follows: at minus 40 DEG C, minus 50 DEG C and 60 DEG C, impact energies are not less than 12K, room-temperature tensile strength is not lower than 400MPa, ductility is not lower than 18%, and other major mechanical performance indexes are qualified. The nodular cast iron material can be widely applicable to cold zone as well as manufacturing of mechanical equipment products with requirements on low-temperature impact resistance and high ductility.
Owner:LAIZHOU XINZHONGYAO MACHINERY
Ceramic igniters with sealed electrical contact portion
InactiveUS6933471B2Improve permeabilityIncrease resistanceIncandescent ignitionHeater elementsElectricityHot zone
Robust ceramic igniters are provided that include an improved sealing system which can significantly enhance operational life of the igniter. Preferred igniters comprise a conductive cold zone and hot zone with higher resisitivity. A hermetic sealant material covers one or more electrical connections on the of each cold zone, thus shielding the electrical connections from environmental exposure, and thereby avoiding igniter failure resulting from electrical shorts and / or undesired oxidation.
Owner:COORSTEK INC
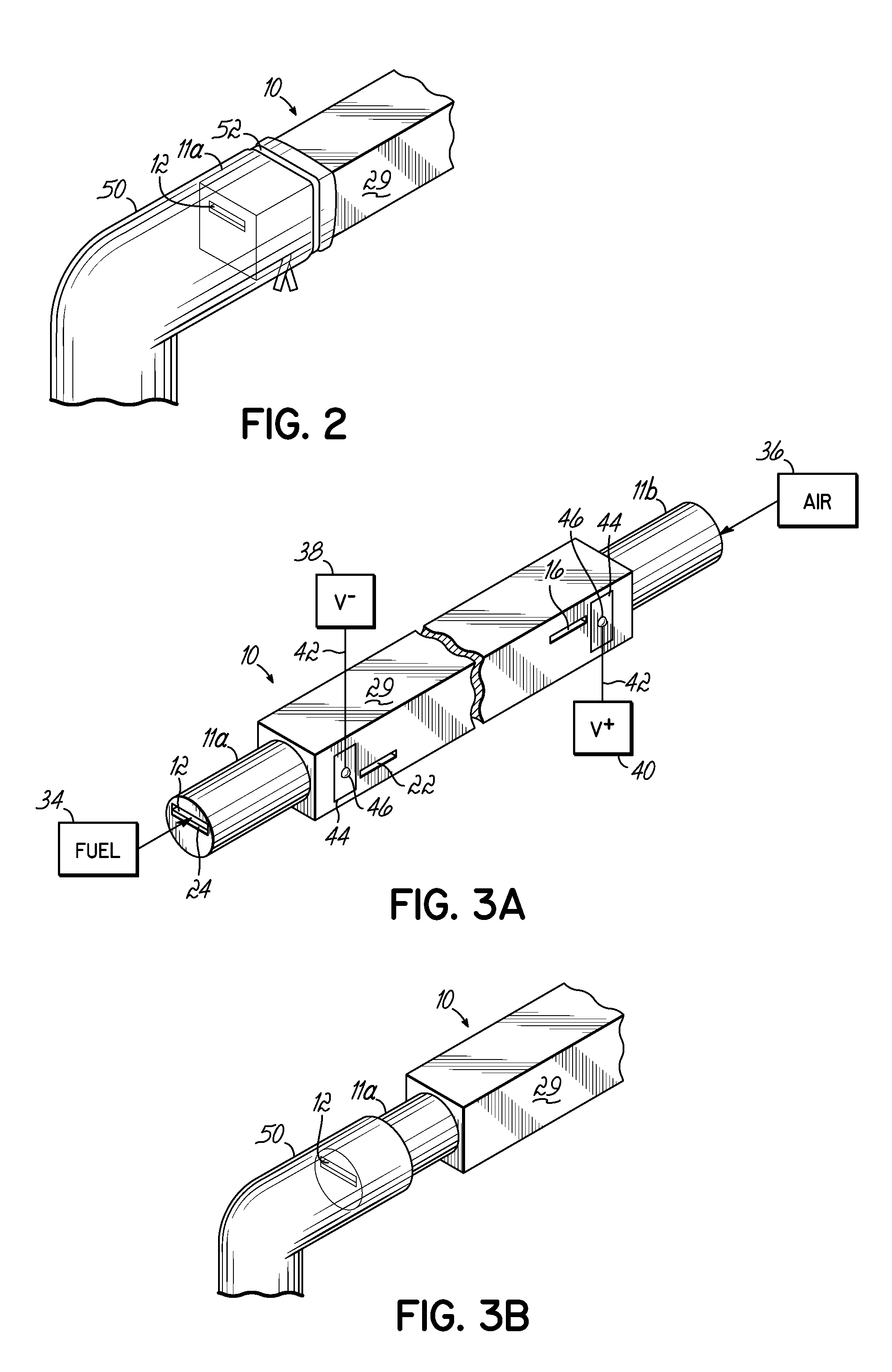
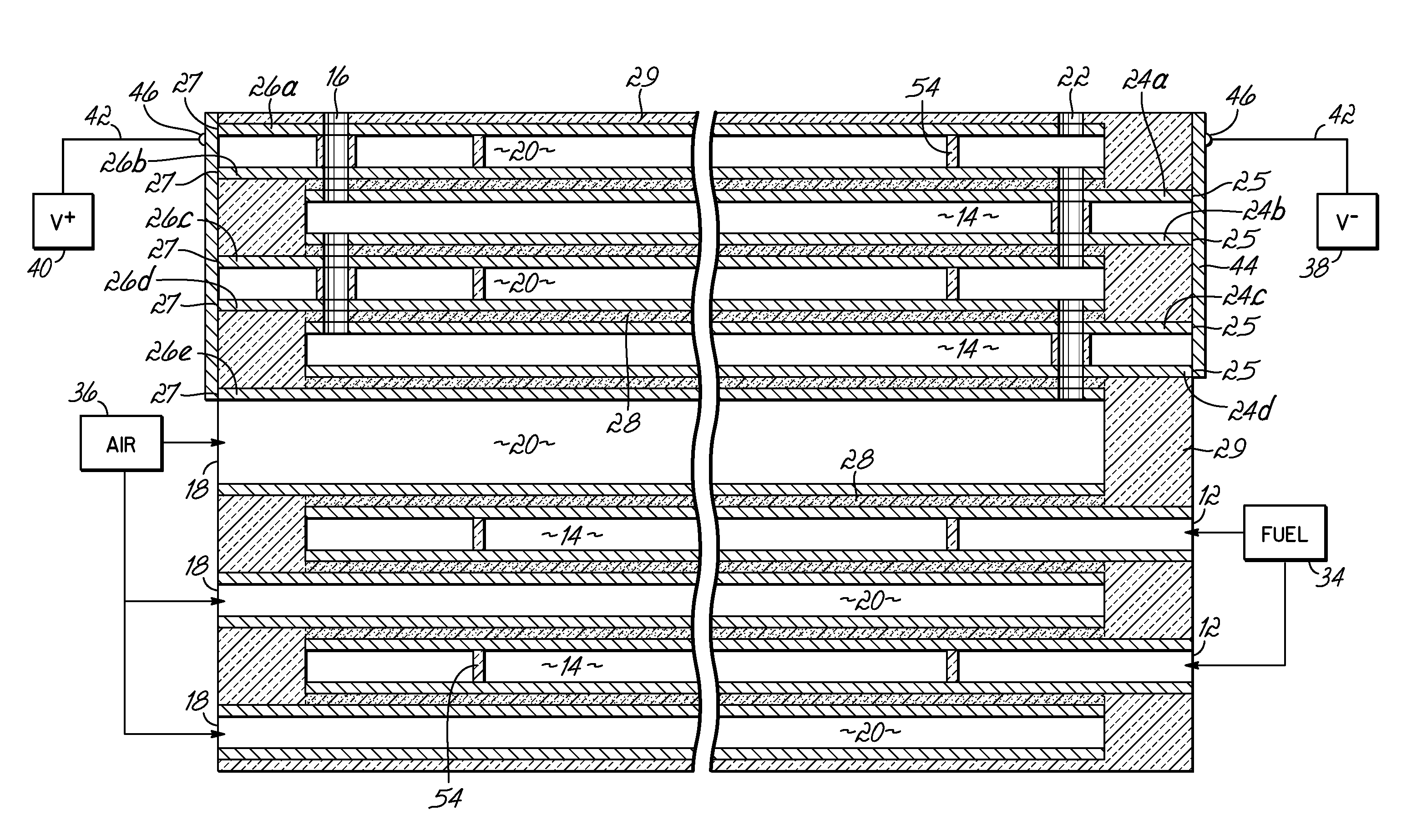
Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Device and System, Method of Using and Method of Making
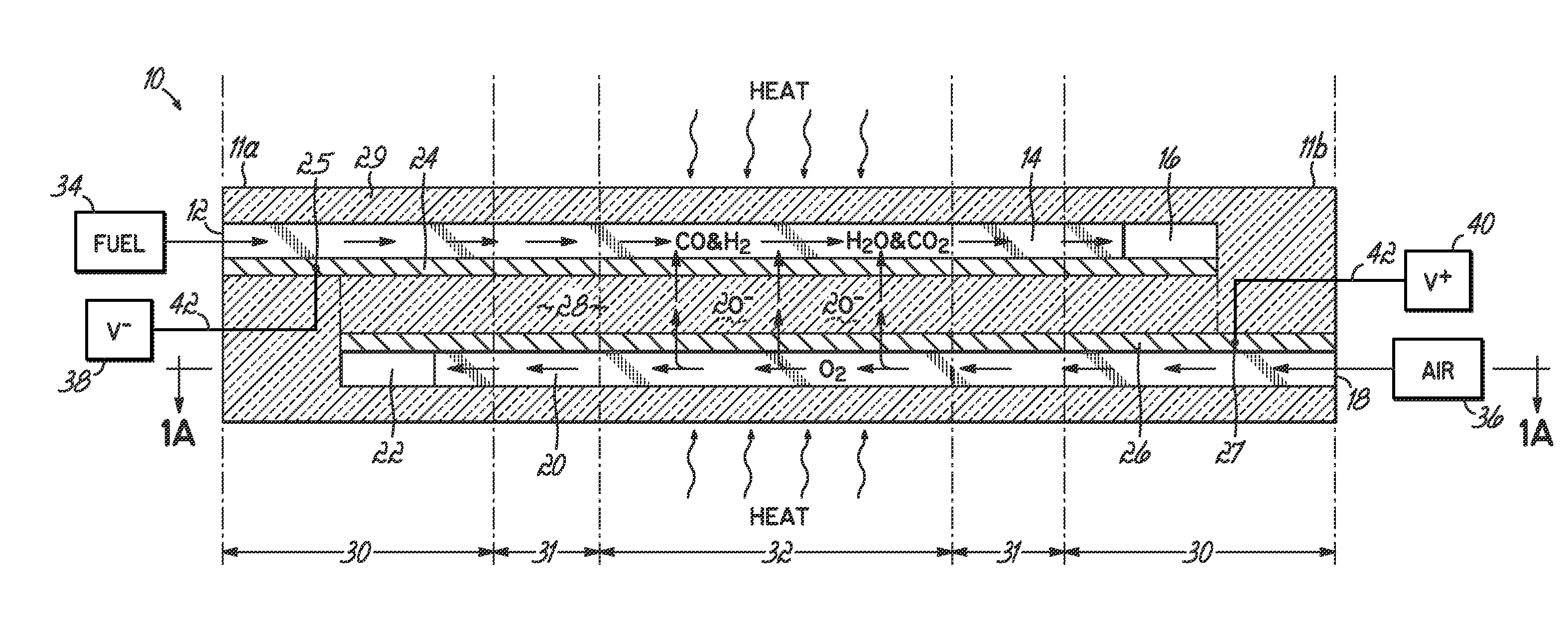
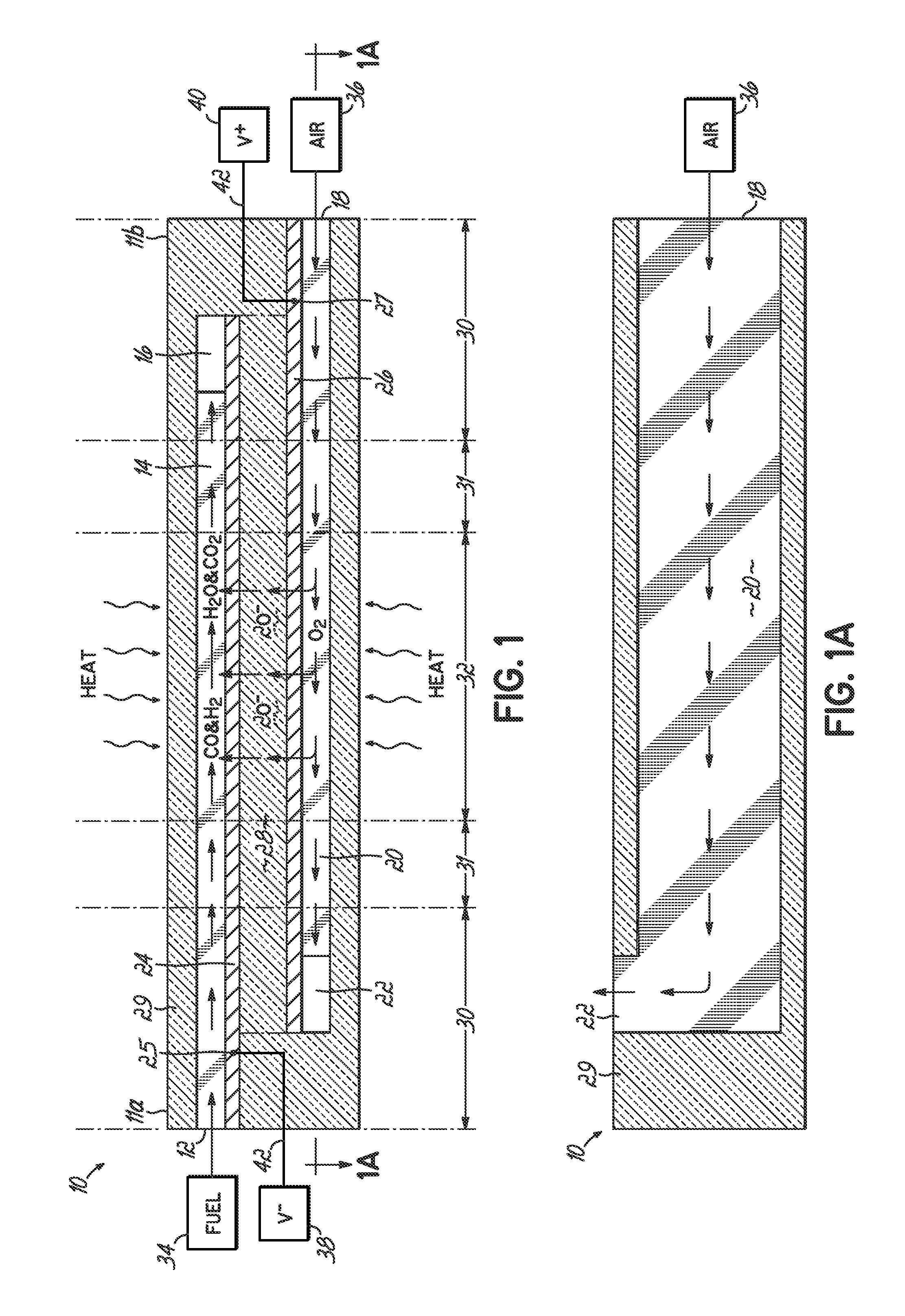
InactiveUS20070105012A1Avoid layeringAvoid obstructionFuel cell heat exchangeDeferred-action cellsReaction temperatureElectrical connection
A solid oxide fuel cell device that includes an elongate substrate having a first end and an opposing second end with a length therebetween, a cold zone along a first portion of the length adjacent the first end, and a hot reaction zone along a second portion of the length adjacent the second end. The hot reaction zone is configured to be heated to an operating reaction temperature, and the cold zone is configured to remain at a low temperature below the operating reaction temperature. A fuel inlet and air inlet are each positioned in the cold zone and coupled to respective elongate fuel and oxidizer passages that extend through the hot reaction zone within the elongate substrate in parallel and opposing relation to respective fuel and air outlets adjacent the first end. An anode and a cathode are each positioned adjacent a respective fuel and oxidizer passage in the hot reaction zone within the elongate substrate and each is electrically coupled to a respective first and second exterior contact surface on the elongate substrate in the cold zone. A solid electrolyte is positioned between the anode and cathode, and negative and positive electrical connections are made to the respective first and second exterior contact surfaces. A fuel cell system is also provided incorporating a plurality of the fuel devices with their hot reaction zones positioned in a hot zone chamber and their cold zones extending outside the hot zone chamber. A heat source is coupled to the hot zone chamber to heat the reaction zones to the operating reaction temperature. Fuel and air supplies are coupled outside the hot zone chamber to the cold zones for supplying fuel and air flows into the respective fuel and oxidizer passages. A method of making a solid oxide fuel cell device is also provided in which fluid anode and cathode materials are flowed into passages followed by liquid removal to thereby form anodes and cathodes in the passages.
Owner:DEVOE ALAN +1
Method and system for generation of power using stirling engine principles
InactiveUS7320218B2Reduce the temperaturePrevent backflowFrom solar energyGas turbine plantsEngineeringGuide tube
A heat engine enclosing a chamber in housing has two zones maintained at different temperatures. The first zone receives heat energy from an external power source. The second zone is connected to the hot zone by two conduits, such that a fluid (e.g., air, water, or any other gas or liquid) filling the chamber can circulate between the two zones. The expansion of the fluid in the hot zone and the compression of the fluid in the cold zone drive the rotation of the housing to provide a power output. The fluid may be pressurized to enhance efficiency. A cooling fluid provided in a stationary reservoir maintains a preferred operating temperature difference between the hot zone and the cold zone. A heat storage structure containing a fluid with a high heat capacity may be provided as a heat reservoir.
Owner:SILVER GUY +1
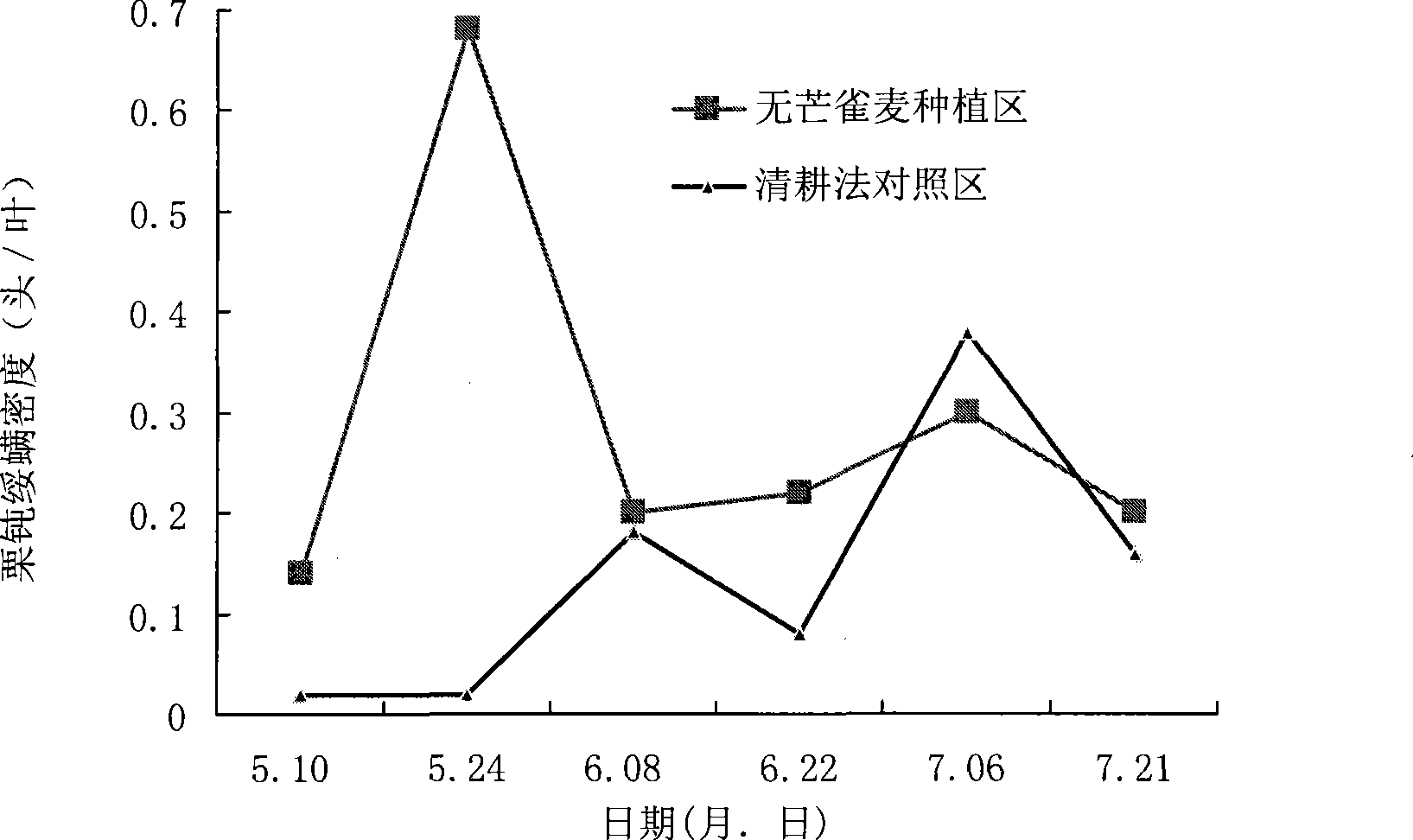
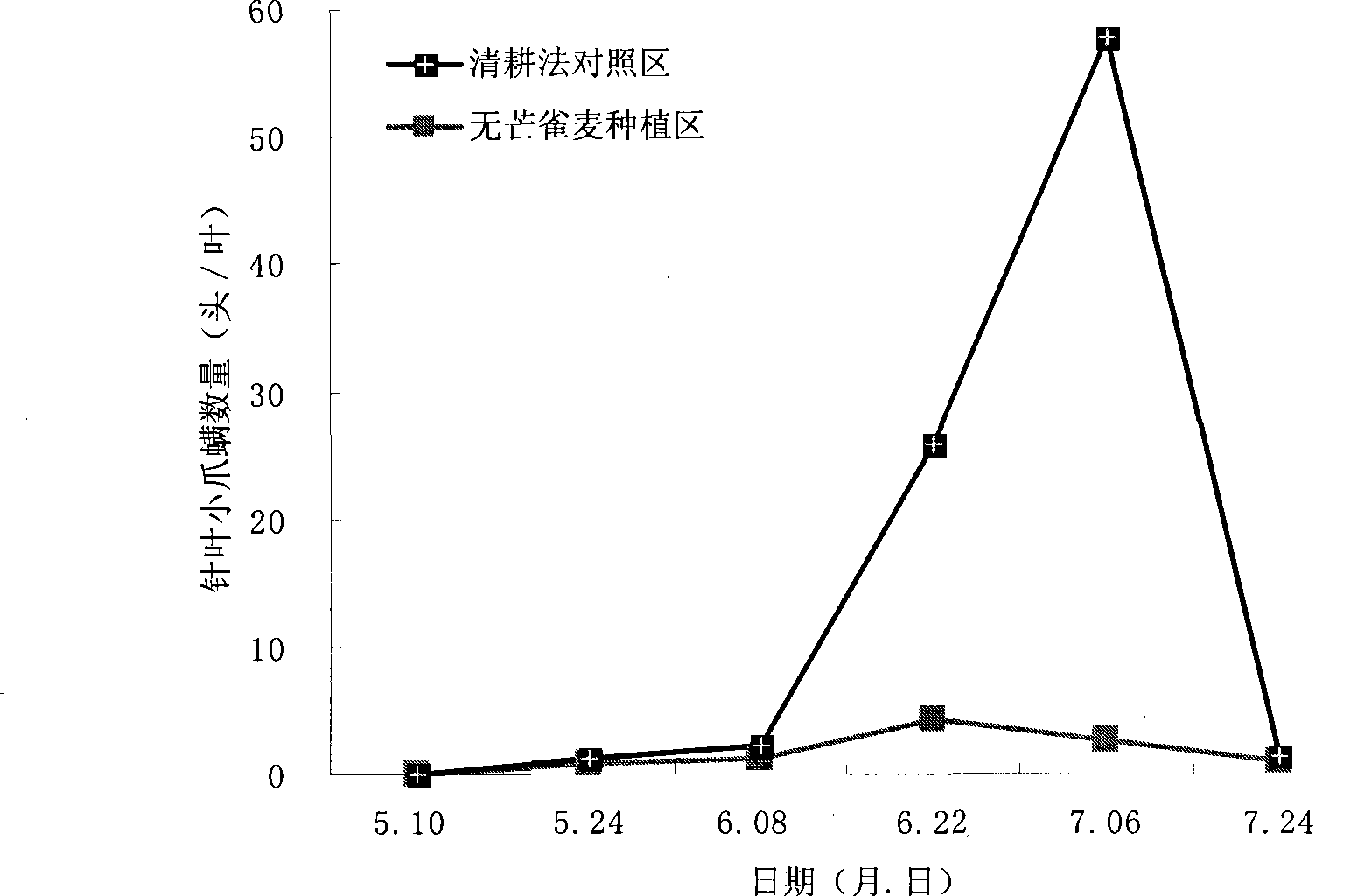
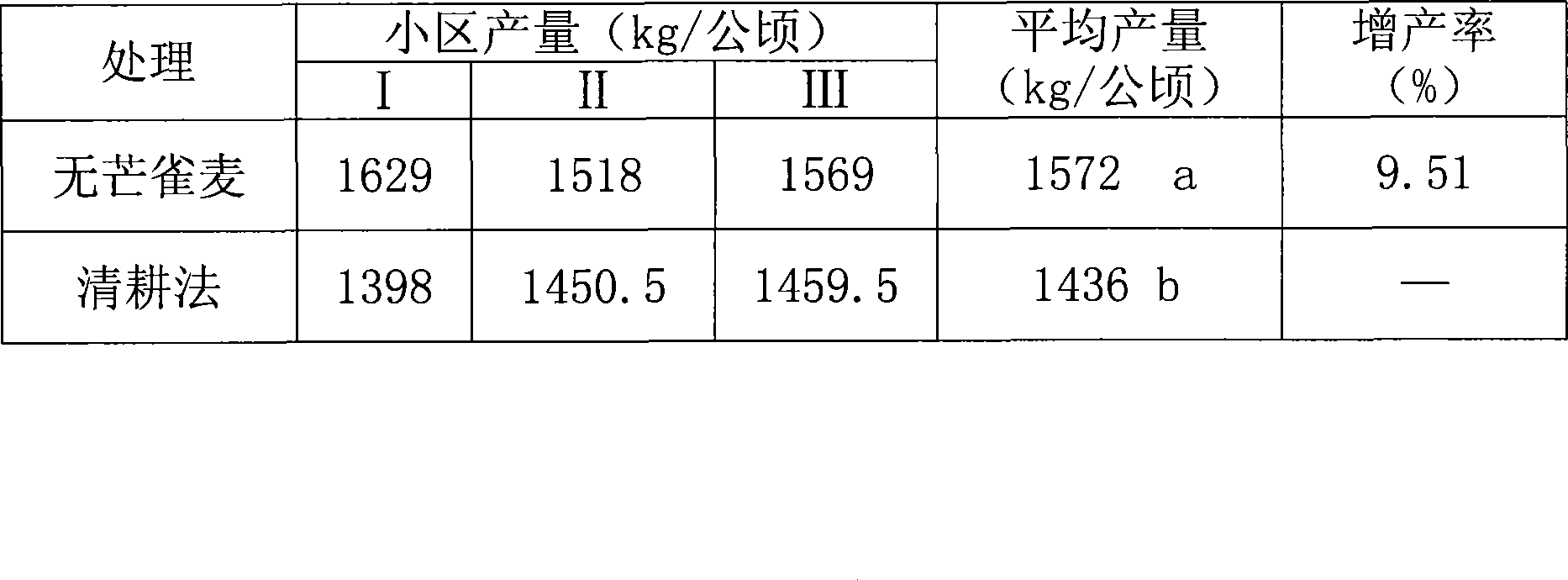
Method for intercropping cover plant in glade of cold temperate zone
InactiveCN101473752AStrong stress resistanceStrong shade toleranceFertilising methodsHorticultureWood pastureTree line
The invention discloses a method for intercropping a cover plant in glades of cold zones and temperate zones. In the method, smooth brome is mainly planted among tree lines with the crown density of 0.2-0.9, wherein, the distance of the smooth brome from tree stumps is 20-50cm; the specific planting method comprises seeding, weeding, applying fertilizers, cutting and the like. The smooth brome intercropped by the method has the advantages of good cold resistance and drought resistance, strong shade tolerance, perennation and the like, and is applicable to being taken as the cover plant in orchards and artificial woodlands. The smooth brome is taken as the cover plant, which can reduce water loss and soil erosion, improve the population number of natural enemies and reduce the number of pests to reduce damages of the pests to fruit trees or forest trees, and further reduce the consumption of herbicides and pesticides, lower the production cost and reduces the environmental pollution; and the harvested smooth brome is taken as pasture grass, which can also increase the income of farmers.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
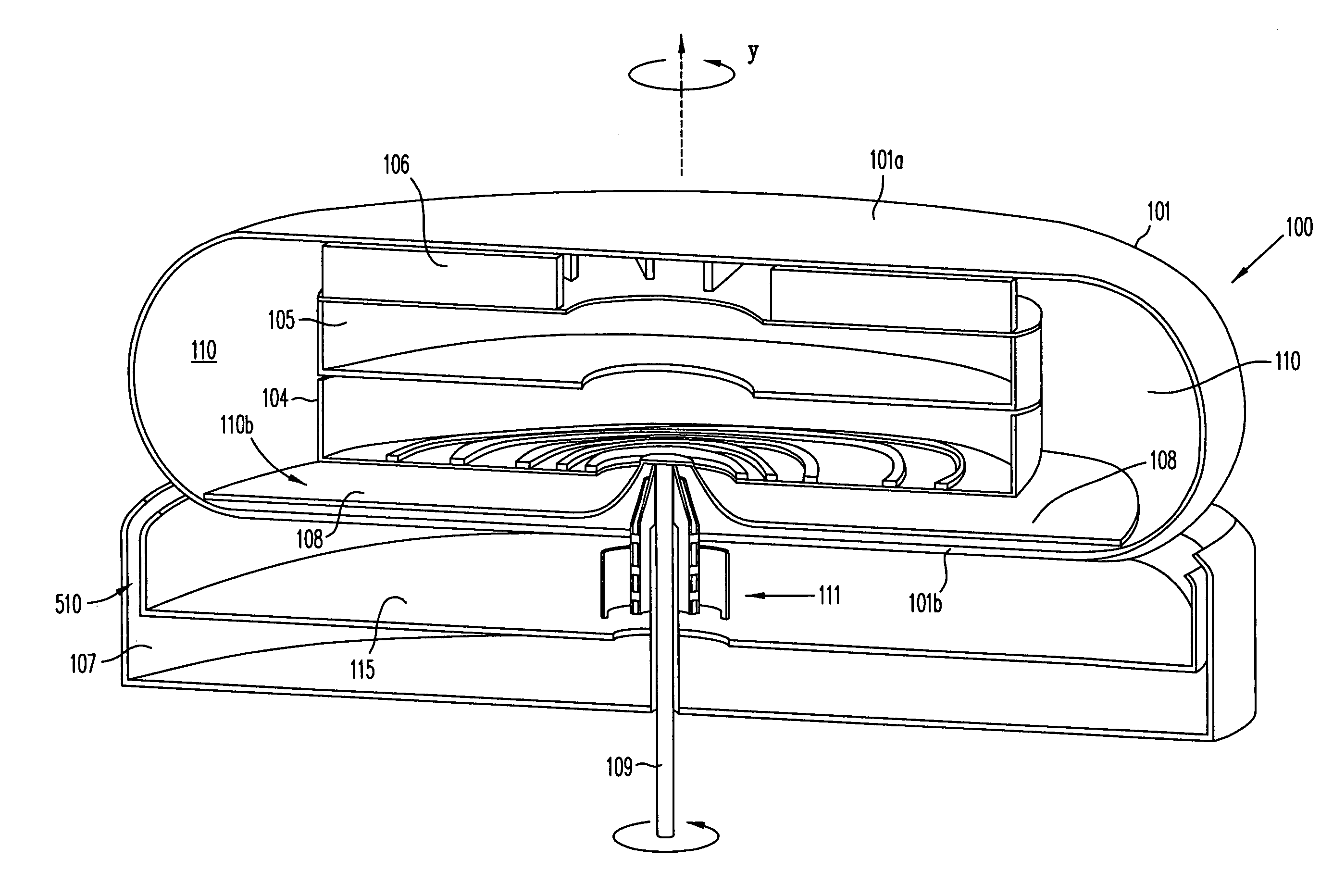
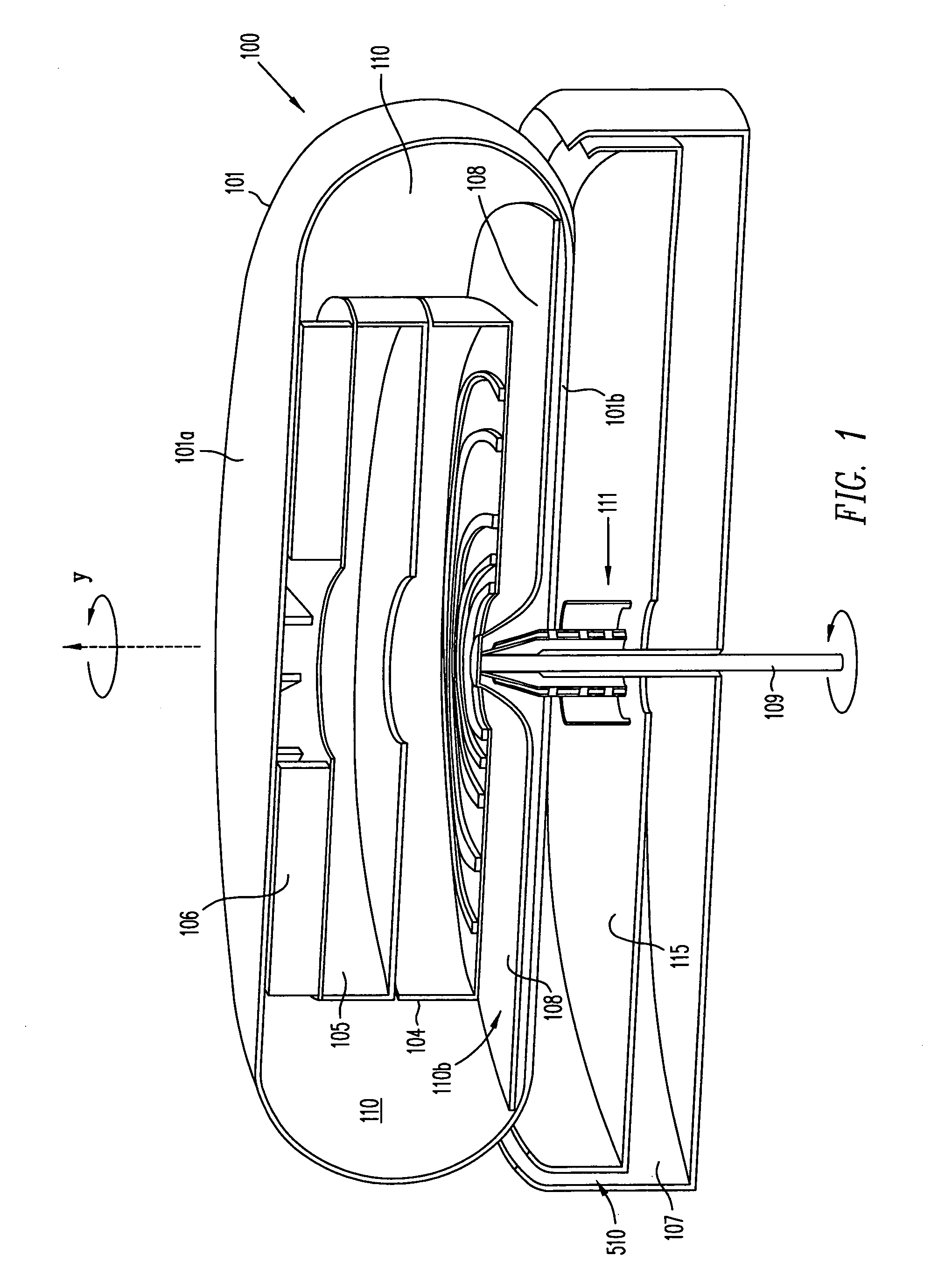
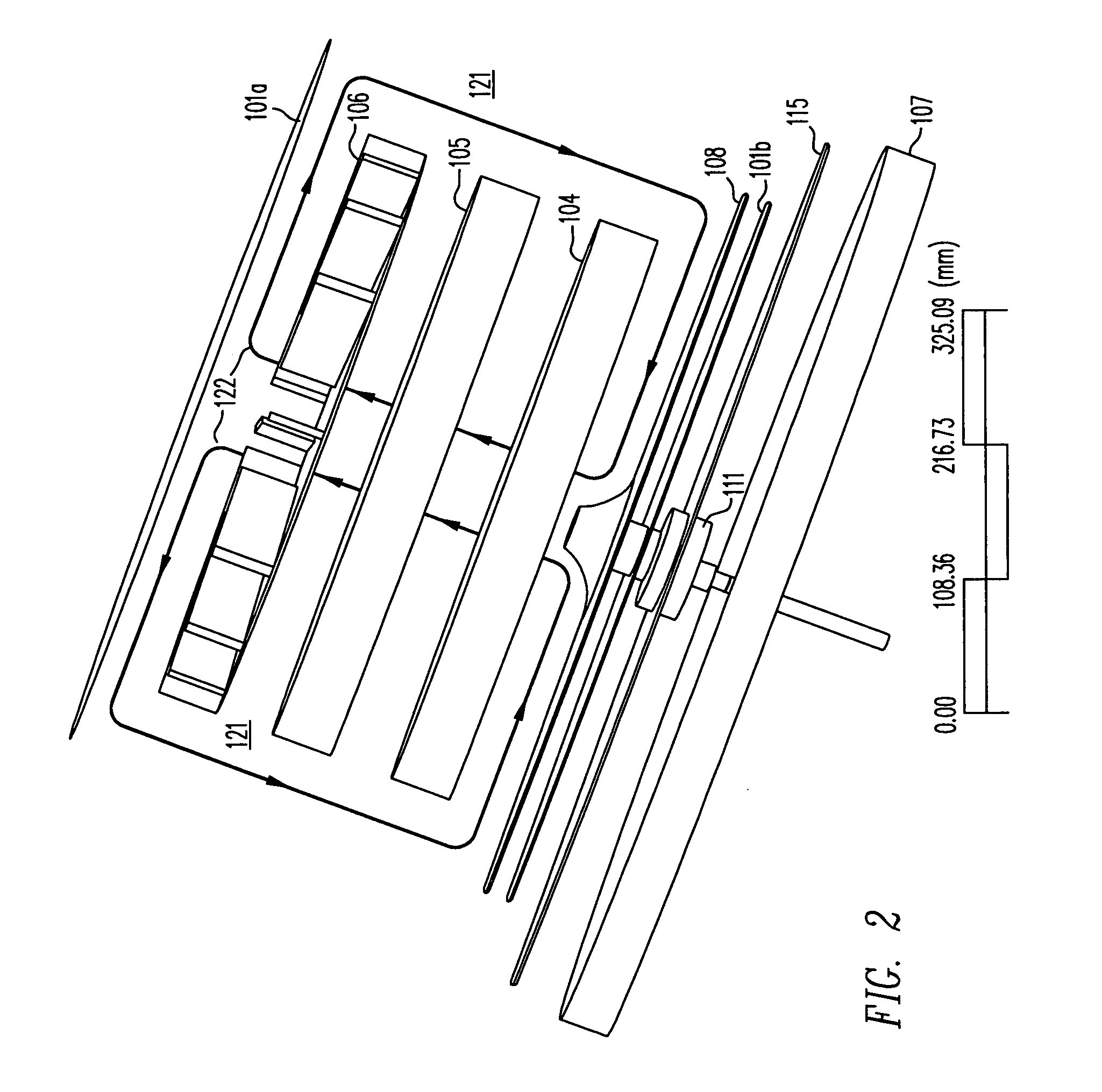
NMR MAS probe with cryogenically cooled critical circuit components
ActiveUS7151374B2Enhanced signalReduce noiseElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagic angle spinningHigh field
A MAS probe offers a substantial improvement in signal to noise (S / N) in triple-resonance high-resolution (HR) magic-angle-spinning (MAS) NMR of samples near room temperature (RT) in high field magnets, especially where the RT shim bore is less than 55 mm. Critical circuit components other than the sample coils, including both high-power capacitors and inductors for one or more channels are located in a small, thermally insulated, cold zone immediately below the sample spinner assembly. Cooling these components to 100 K allows their thermal noise power to be conveniently reduced by a factor of three or more. Variable capacitors for fine tuning are located in an RT tuning zone below the cold zone. The circuit is designed such that the currents, voltages, and standing wave ratio (SWR) in circuit tuning elements in the RT tuning zone are relatively low, so rf losses and noise contributions below the cold zone may be only a few percent. The MAS probe is also compatible with magic angle gradients, automatic sample change, multi-nuclear tuning, variable temperature operation, field locking, and optical spin rate detection.
Owner:DOTY SCI
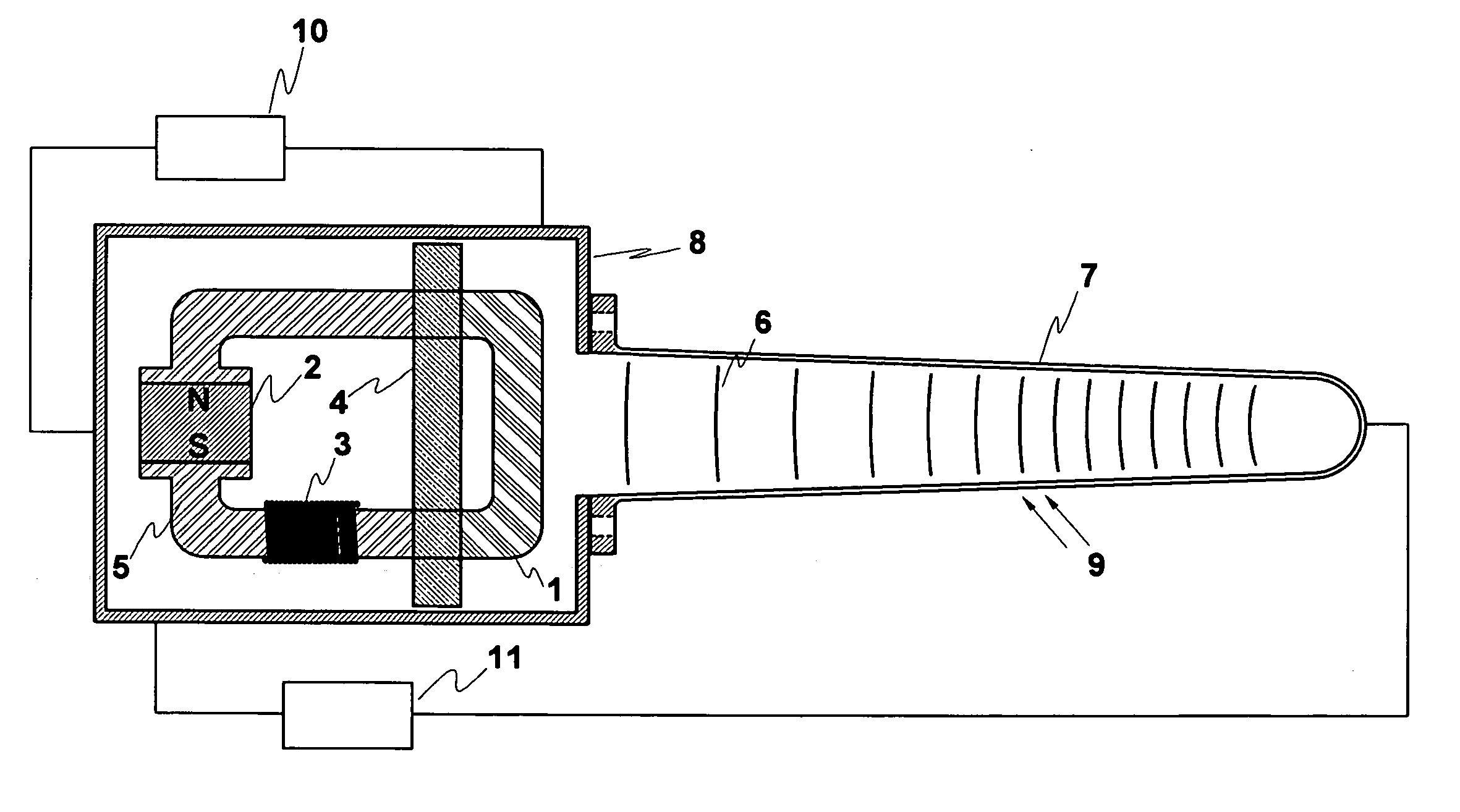
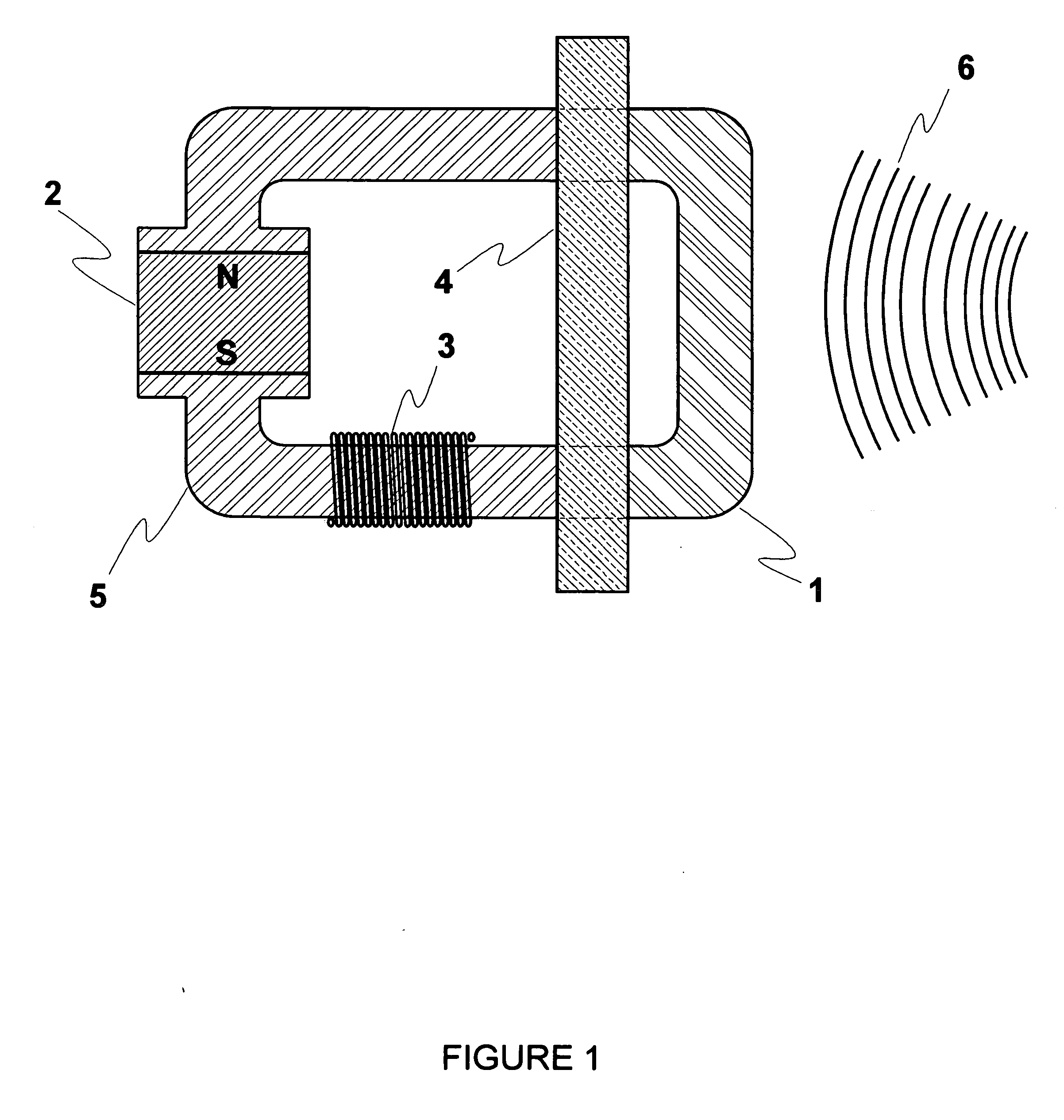
Thermoacoustic Thermomagnetic Generator
InactiveUS20060266041A1Thermoelectric deivce with magnetic permeability thermal changeSteam engine plantsWorking fluidAlternating current
This Thermoacoustic Thermomagnetic Generator uses the thermal gradient in thermoacoustic waves to periodically raise the temperature of a thermomagnetic material past its Curie point so that it alternates between magnetic and non-magnetic states. In conjunction with a stator, induction windings and magnet, the metal alloy forms a magnetic circuit that is periodically interrupted and re-established by the action of the thermoacoustic waves. The expanding and collapsing magnetic field induces an alternating current in the stator windings. The resultant generator has no moving parts. This Thermoacoustic Thermomagnetic Generator embodies hot and cold heat exchangers, a working fluid contained in a reservoir that is divided into hot and cold zones, a resonant waveguide means and an electrical generating means that are typical of the art of thermoacoustic engine-generators, but the thermal-to-electric conversion means and process are entirely unique. This basic arrangement of components can be scaled in size from the micro-miniature to the very large. The thermoacoustic thermomagnetic generators can also be arrayed in multiple units with common waveguide, housing and hot and cold heat exchanger means, such as in a panel array of multiple miniature units.
Owner:FELLOWS OSCAR L
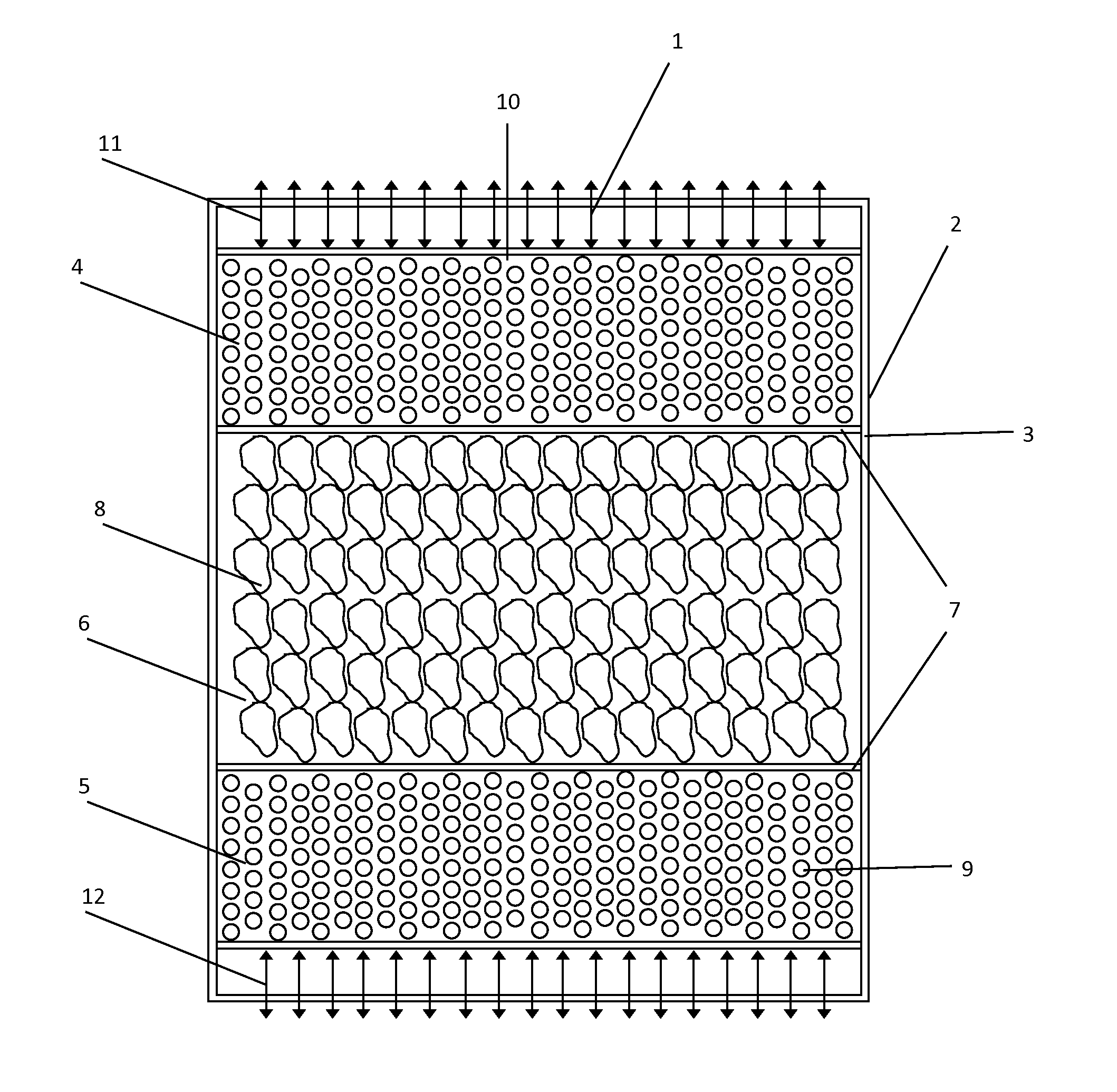
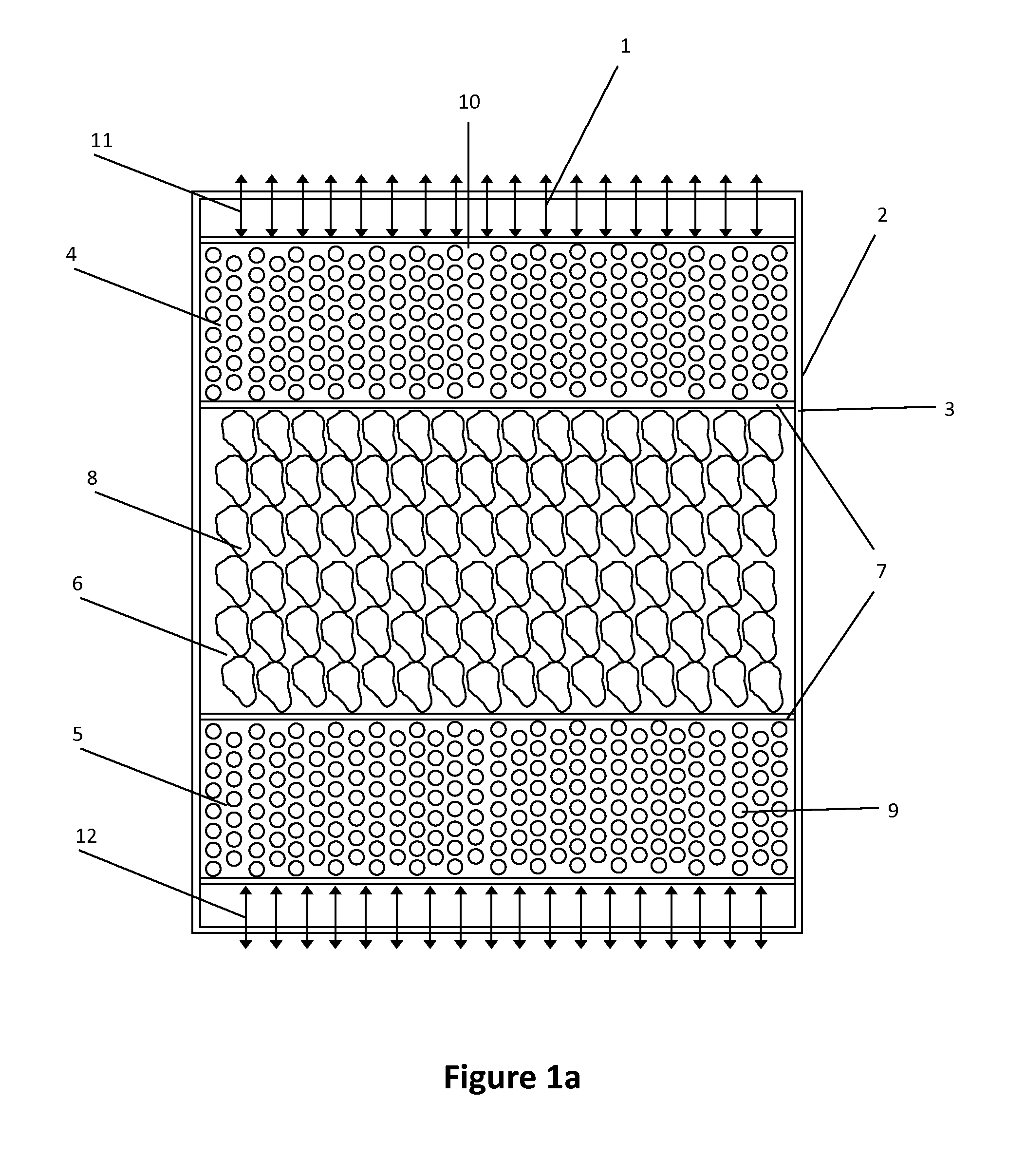
Thermal energy storage system combining sensible heat solid material and phase change material
The invention relates to a system for the storage and recovery of thermal energy, using, as its medium, at least one phase change material (solid-liquid) and a sensible heat solid material for storing / recovering the heat obtained from an external source in the form of phase change latent heat and sensible heat. The aforementioned materials are duly housed inside a single tank containing at least two zones which are differentiated by the range of temperatures to which they are subjected, each zone containing a different material. The most common configuration consists of three different zones located inside the tank, namely: a hot zone in the upper part of the tank, enclosing an encapsulated phase change material characterized by a high melting temperature; a cold zone housed in the lower part of the tank, containing a phase change material with a low melting temperature; and a middle zone containing a sensible heat solid material.
Owner:UNIV POLITECNICA DE CATALUNYA
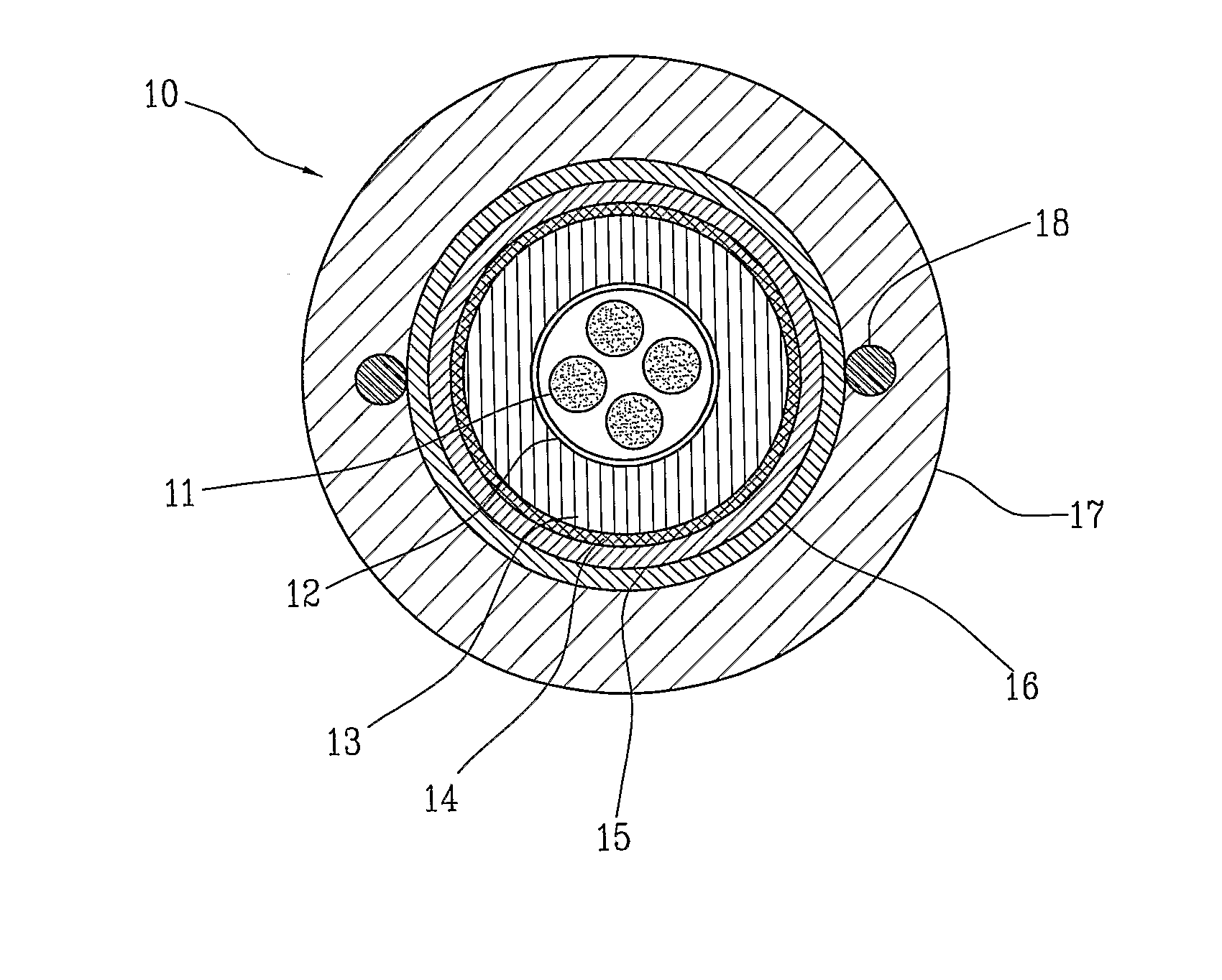
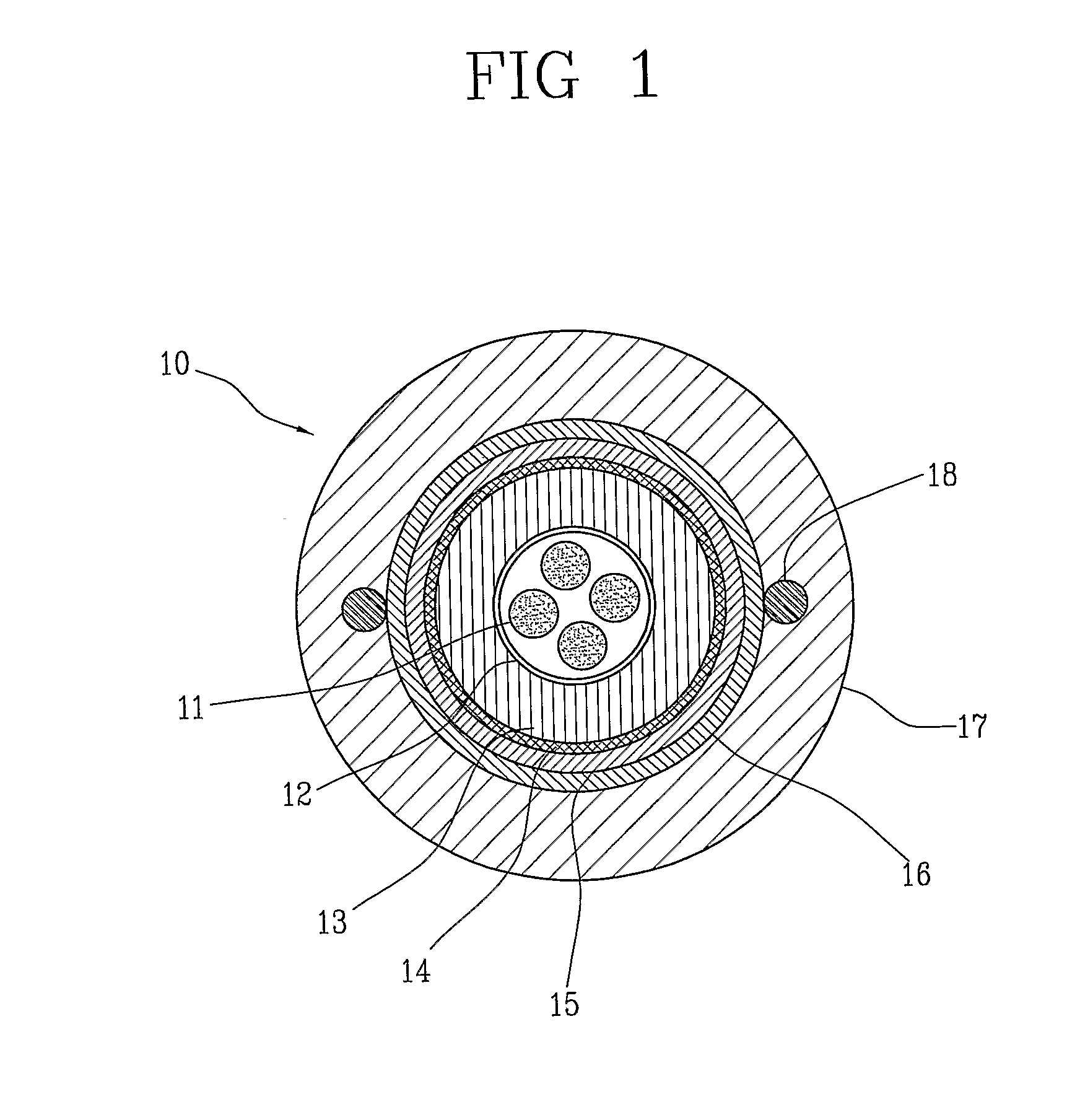
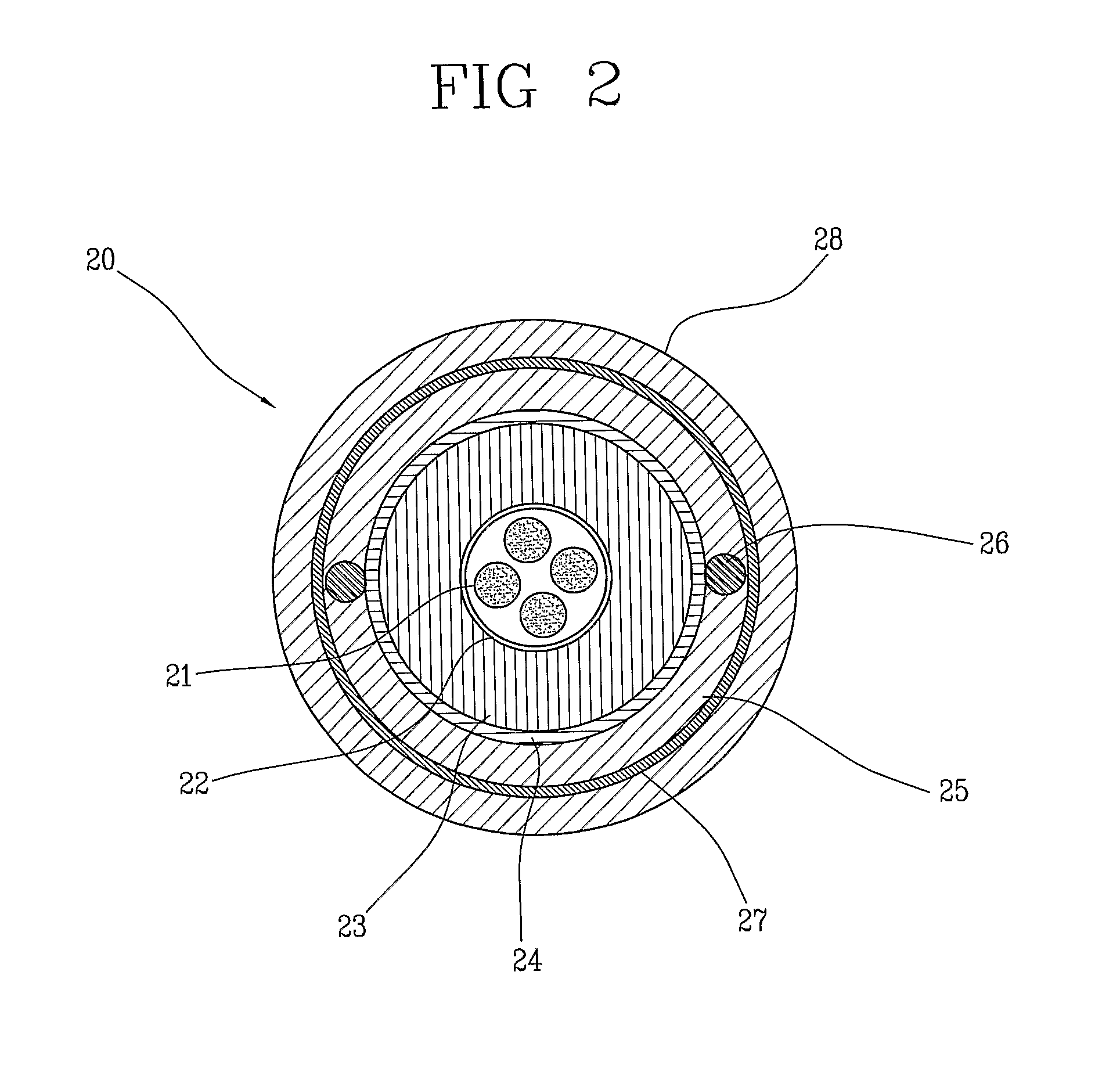
Fire resistant optical cable
ActiveUS20130170800A1Improve mechanical propertiesInsulated cablesFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringOptical fiber cable
A fire resistant optical cable includes: a plurality of optical fibers; at least one tubular layer of a ceramifiable material surrounding the plurality of optical fibers; and at least one flame shielding layer surrounding the tubular layer. The tubular layer of the ceramifiable material is able to mechanically protect the optical fibers not only during heating but also when the fire is extinguished, since it forms a sufficiently robust layer to withstand the mechanical stresses caused by the collapsing of the materials still surrounding the cable, especially in the transition portions between hot and cold zones. The tubular layer of the ceramifiable material is protected by means of at least one flame shielding layer which prevents the flames from directly acting on the ceramifiable material.
Owner:PRYSMIAN SPA
Fuel cell device and system
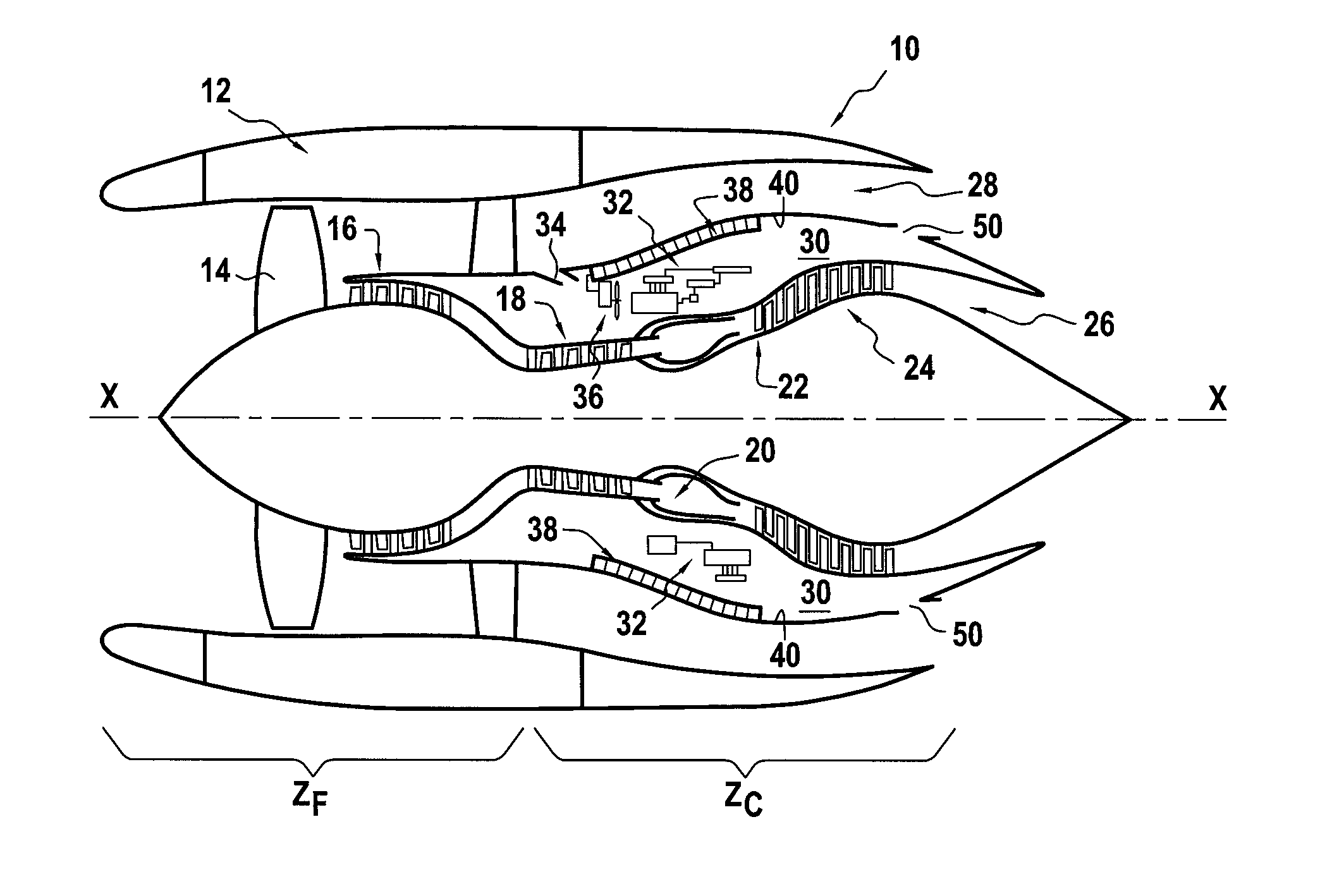
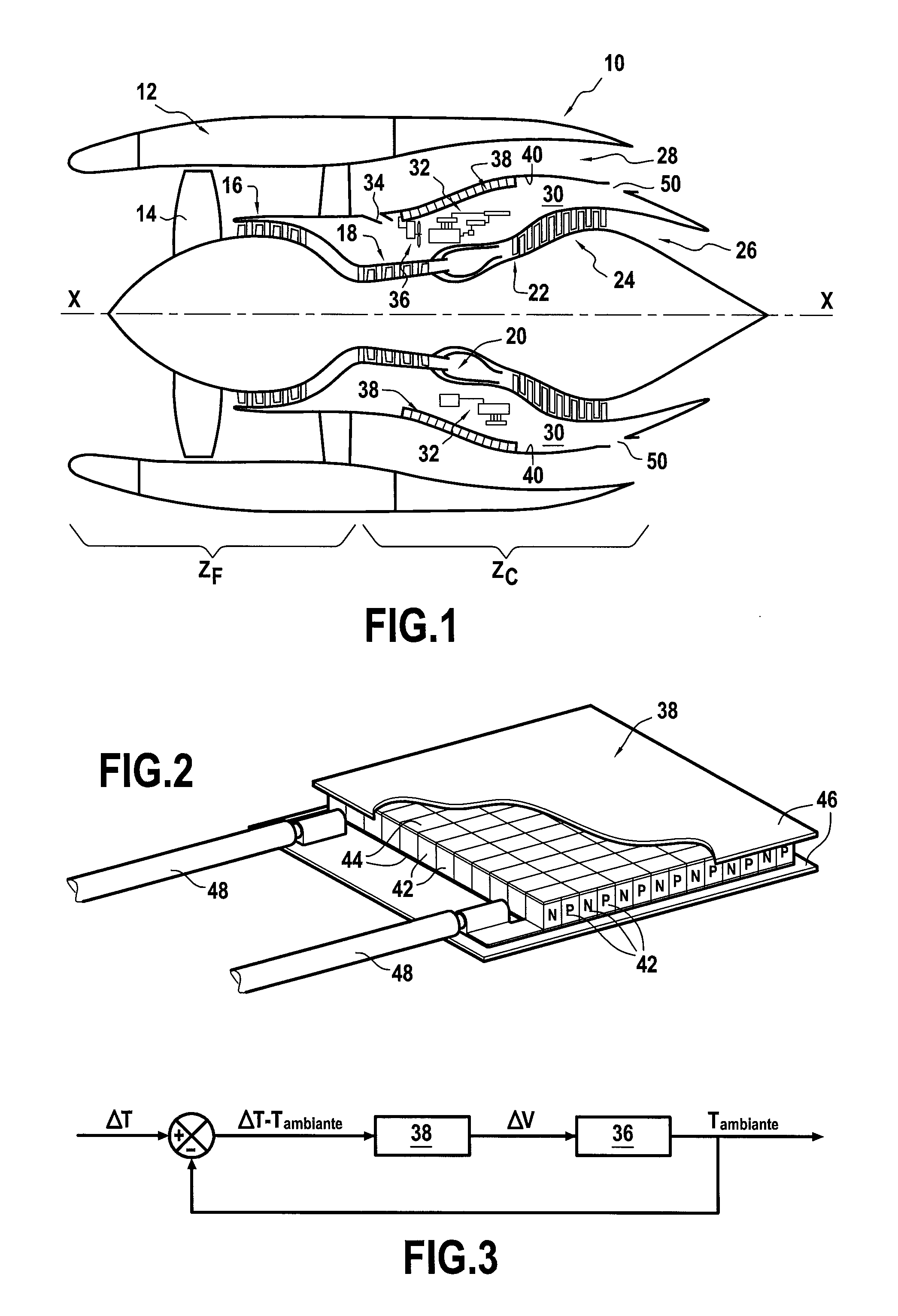
ActiveUS8343684B2Additive manufacturing apparatusFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cellsReaction temperature
Fuel cell devices and systems are provided. In certain embodiments, the devices include a ceramic support structure having a length, a width, and a thickness. A reaction zone positioned along a portion of the length is configured to be heated to an operating reaction temperature, and has at least one active layer therein comprising an electrolyte separating first and second opposing electrodes, and active first and second gas passages adjacent the respective first and second electrodes. At least one cold zone positioned from the first end along another portion of the length is configured to remain below the operating reaction temperature. An artery flow passage extends from the first end along the length through the cold zone and into the reaction zone and is fluidicly coupled to the active first gas passage, which extends from the artery flow passage toward at least one side. The thickness of the artery flow passage is greater than the thickness of the active first gas passage. In other embodiments, fuel cell devices include an electrolyte having at least a portion thereof comprising a ceramic material sintered from a nano-sized powder. In yet other embodiments, cold zones are provided at each end of the device with the reaction zone therebetween having at least two discrete power sections, each having one or more active layers, the power sections fed by discrete fuel passages to provide a device and system capable of operating at more than one power level.
Owner:DEVOE ALAN +1
Thermal Management Cabinet for Electronic Equipment
A thermal management cabinet for electronic equipment such as servers, having an opening in the top and bottom of the cabinet. The cabinet extends between a raised access floor of a building carrying cooled air and a drop ceiling for venting heated air. The bottom opening of the cabinet is alignable with an opening in the access floor such that cool air can pass into the cabinet and can flow through the electronic component storage area to the top opening, which is alignable with an opening in the drop ceiling. The cabinet interior is separated into temperature zones comprising at least a cold zone supplied with air from the access floor and a hot zone for venting through the top opening. At least one baffle creates the temperature zones such that air is directed to flow from the cold zone through the electronic component storage area to the hot zone.
Owner:BASELAYER TECH
Fuel cell device and system
The present invention relates to fuel cell devices and fuel cell systems, methods of using fuel cell devices and systems, and methods of making fuel cell devices. According to certain embodiments, the fuel cell devices may include an elongate substrate, such as a rectangular or tubular substrate, the length of which is the greatest dimension such that the coefficient of thermal expansion has only one dominant axis that is coextensive with the length. In addition, or in accordance with other certain embodiments, a reaction zone is positioned along a first portion of the length for heating to an operating reaction temperature, and at least one cold zone is positioned along a second portion of the length for operating at a temperature below the operating reaction temperature. There are one or more fuel passages in the elongate substrate, each having an associate anode, and one or more oxidizer passages in the elongate substrate, each having an associate cathode. In some embodiments, the passages are formed by sacrificial organic materials that are melted or baked out of the structure and / or by removable structures that are pulled out after lamination. Bake-out paths may also be used to facilitate removal of the sacrificial organic materials, which paths are later sealed. Embodiments of the invention further include methods and devices in which a current collector is recessed into the electrode.
Owner:DEVOE ALAN +1
Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Device and System
The invention provides tubular solid oxide fuel cell devices and a fuel cell system incorporating a plurality of the fuel devices, each device including an elongate tube having a reaction zone for heating to an operating reaction temperature, and at least one cold zone that remains at a low temperature below the operating reaction temperature when the reaction zone is heated. An electrolyte is disposed between anodes and cathodes in the reaction zone, and the anode and cathode each have an electrical pathway extending to an exterior surface in a cold zone for electrical connection at low temperature. In one embodiment, the tubular device is a spiral rolled structure, and in another embodiment, the tubular device is a concentrically arranged device. The system further includes the devices positioned with their reaction zones in a hot zone chamber and their cold zones extending outside the hot zone chamber. A heat source is coupled to the hot zone chamber to heat the reaction zones to the operating reaction temperature, and fuel and air supplies are coupled to the tubes in the cold zones.
Owner:DEVOE ALAN +1
Heat exchanges for dispensing sub-zero beer
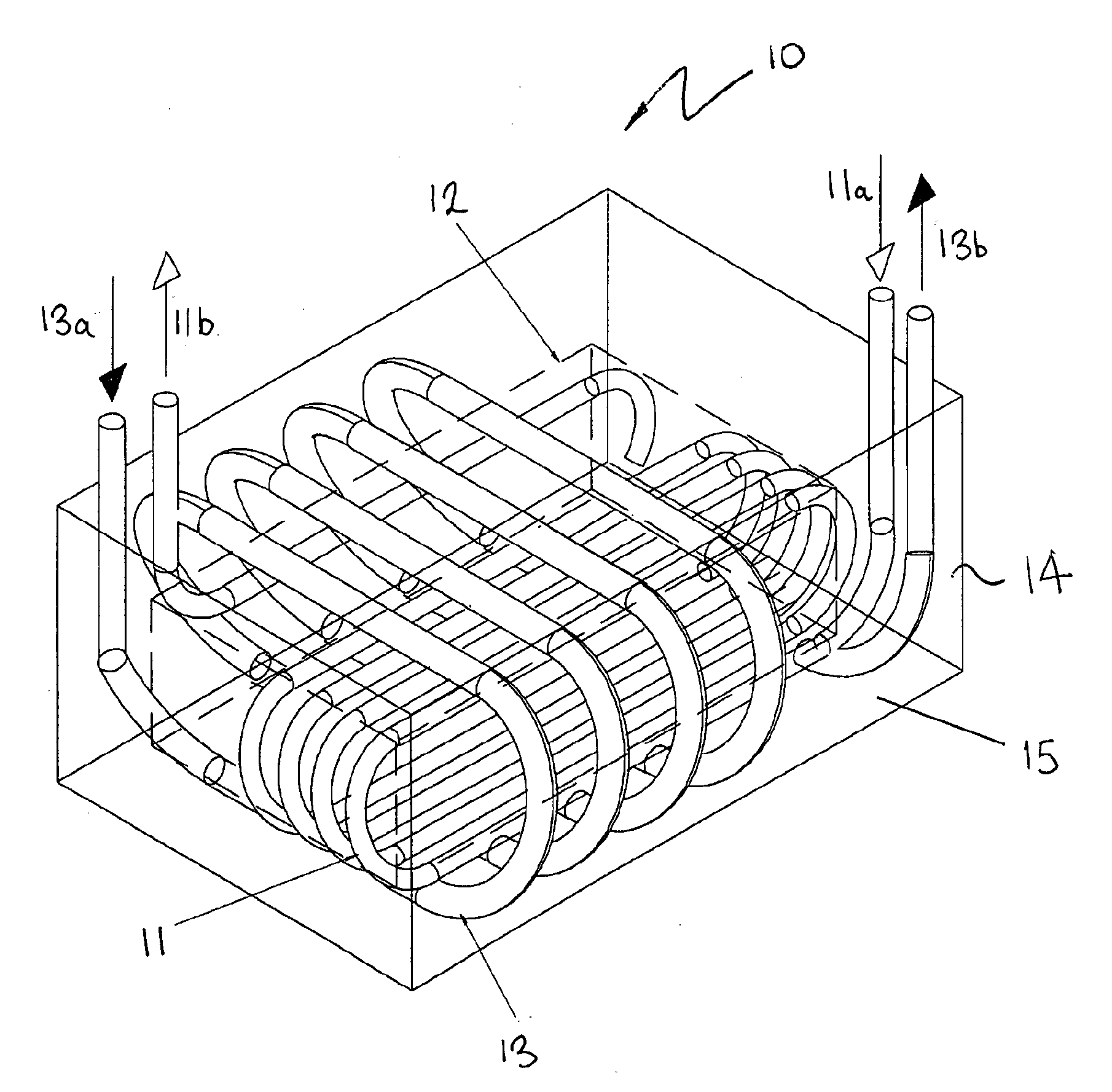
InactiveUS20110011569A1Maximising available transferAccurate temperatureStationary tubular conduit assembliesHelical coilEngineering
A heat exchanger (10) comprises a coolant line (11) and a beverage line (13), embedded in a solid block of Aluminium (15). The coolant line (11) is in the form of a first helical coil defining a plurality of turns typically located in the centre of the block. The beverage line (13) is in the form of a second helical coil defining a plurality of turns extending around the first coil. The coolant line defines a cold zone (12), typically in the centre of the block, with the volume outside the central zone carrying the beverage line ratio defining an designated beverage cooling zone (14). The volume ratio of the designated zone to the cold zone is about 150:100. The heat exchanger allows for cooling of beer to precise temperatures and even temperatures close to freezing point, using direct expanded Freon refrigeration methods. The complete system including the refrigeration equipment to be packaged into a small area, such as is available under bars and dispensing counters etc., which removes the need for large installations and the associated costs and maintenance of the same. In a variant an additional beverage cooling zone may be located inside the cold zone. The positions of the coolant and beverage lines may also be reversed in certain applications.
Owner:TEMPAK INT
Thermal energy storage system combining sensible heat solid material and phase change material
ActiveUS20160201995A1Low efficiencyLow melting pointHeat storage plantsHeat exchange apparatusSeasonal thermal energy storageHot zone
The invention relates to a system for the storage and recovery of thermal energy, using, as its medium, at least one phase change material (solid-liquid) and a sensible heat solid material for storing / recovering the heat obtained from an external source in the form of phase change latent heat and sensible heat. The aforementioned materials are duly housed inside a single tank containing at least two zones which are differentiated by the range of temperatures to which they are subjected, each zone containing a different material. The most common configuration consists of three different zones located inside the tank, namely: a hot zone in the upper part of the tank, enclosing an encapsulated phase change material characterised by a high melting temperature; a cold zone housed in the lower part of the tank, containing a phase change material with a low melting temperature; and a middle zone containing a sensible heat solid material.
Owner:UNIV POLITECNICA DE CATALUNYA
Method and system for generation of power using stirling engine principles
InactiveUS20090025388A1Reduce the temperaturePrevent backflowFrom solar energySteam accumulatorsThermal energyEngineering
A heat engine enclosing a chamber in housing has two zones maintained at different temperatures. The first zone receives heat energy from an external power source. The second zone is connected to the hot zone by two conduits, such that a fluid (e.g., air, water, or any other gas or liquid) filling the chamber can circulate between the two zones. The expansion of the fluid in the hot zone and the compression of the fluid in the cold zone drive the rotation of the housing to provide a power output. The fluid may be pressurized to enhance efficiency. A cooling fluid provided in a stationary reservoir maintains a preferred operating temperature difference between the hot zone and the cold zone. A heat storage structure containing a fluid with a high heat capacity may be provided as a heat reservoir.
Owner:SILVER GUY +1
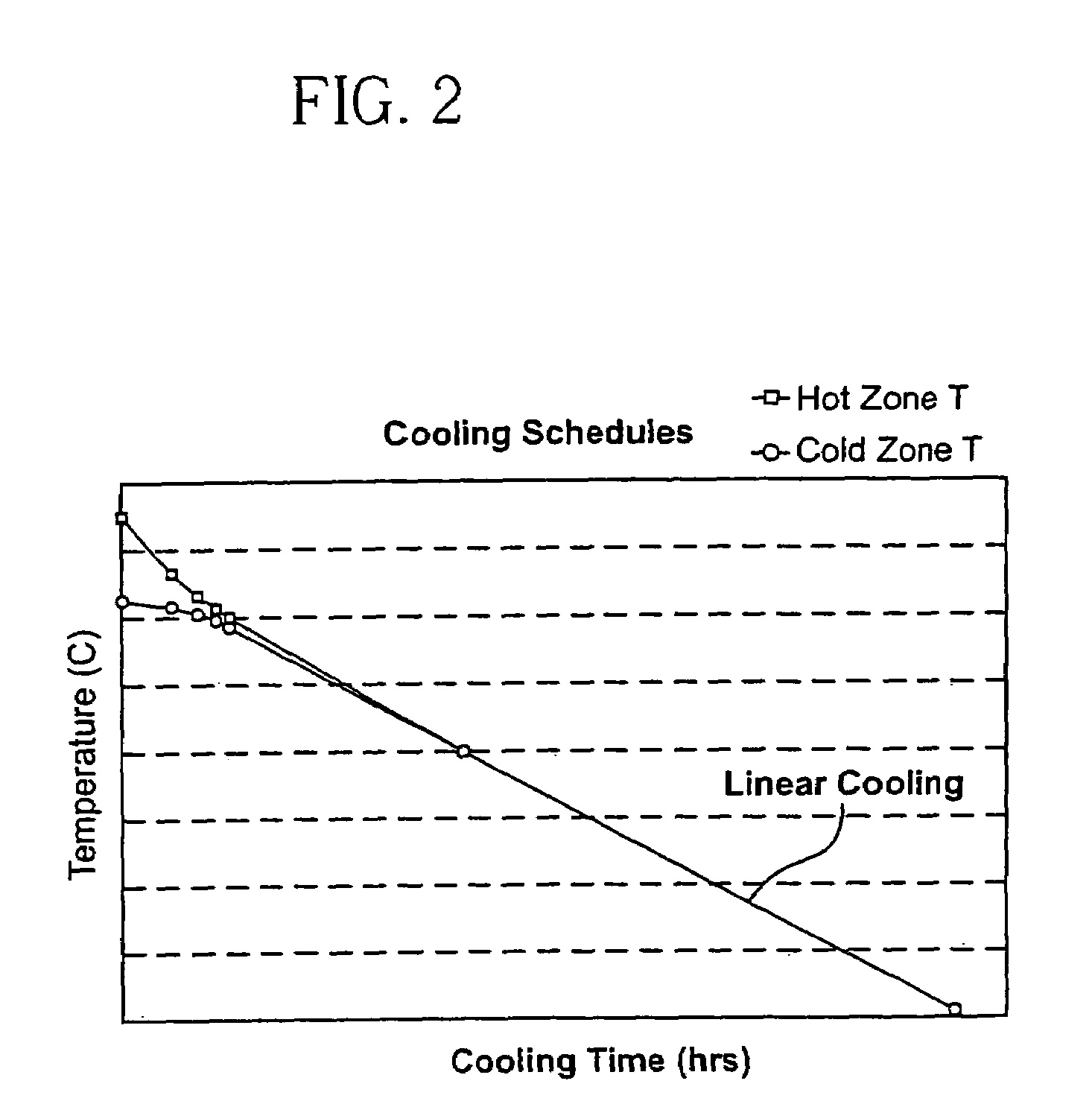
Crystal growth methods
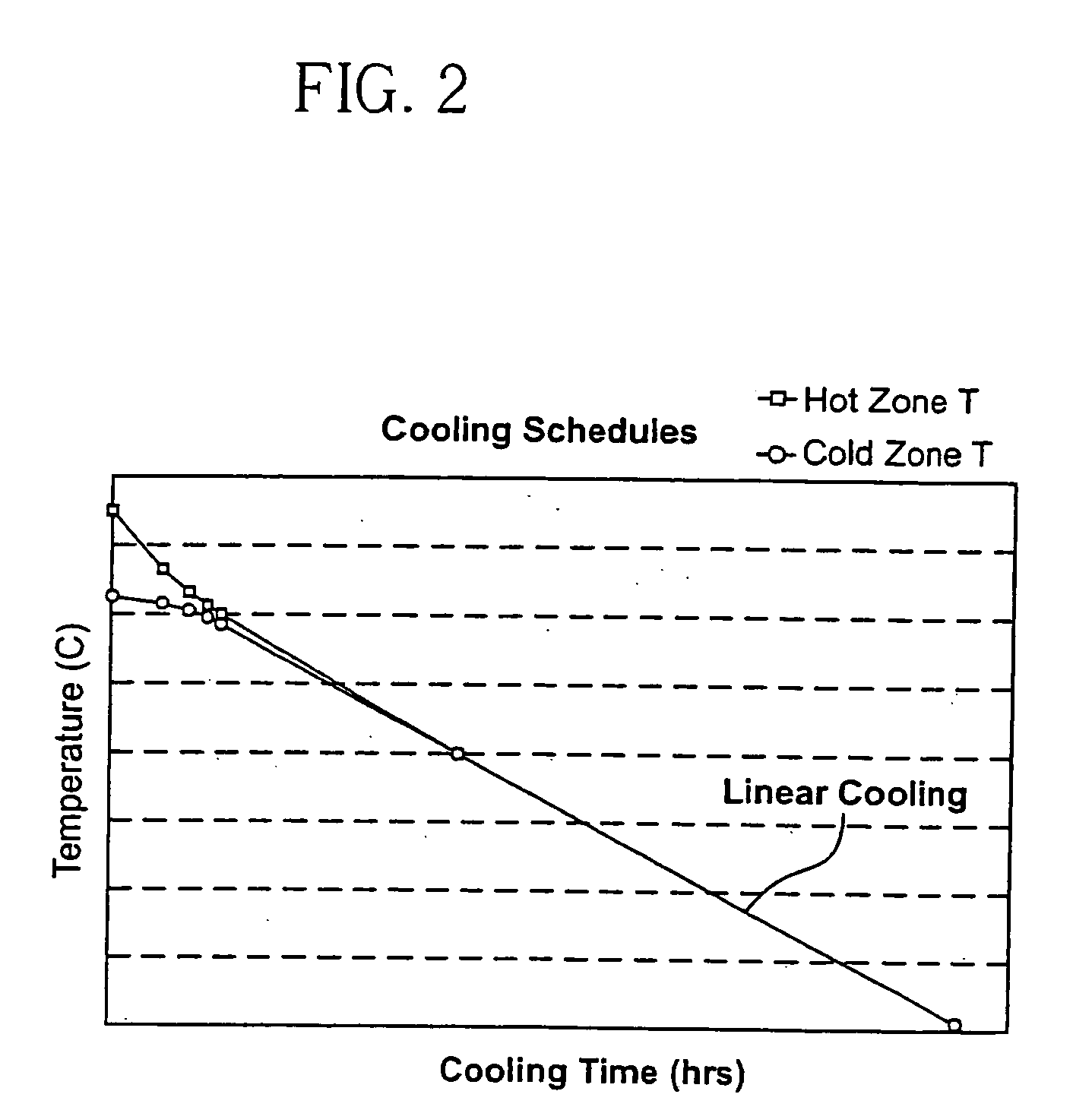
InactiveUS7033433B2Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle crystalSlow cooling
The invention is directed to method of preparing metal fluoride single crystals and particularly to crystals where the metal is calcium, barium, magnesium or strontium, or a mixture thereof. The invention uses a decreasing fast cooling profile and an increasing slow cooling profile for the hot zone and the cold zone, respectively, after crystal formation during cooling from melt temperatures to a first temperature. A substantially constant cooling rate is then applied to the both zones during cooling from the first temperature to a final temperature, usually room temperature. It has been found that the substantially constant cooling rate during the annealing process results in crystals having improved homogeneity and birefringence.
Owner:CORNING INC
L485M pipeline steel excellent in low-temperature toughness and manufacturing method of pipeline steel
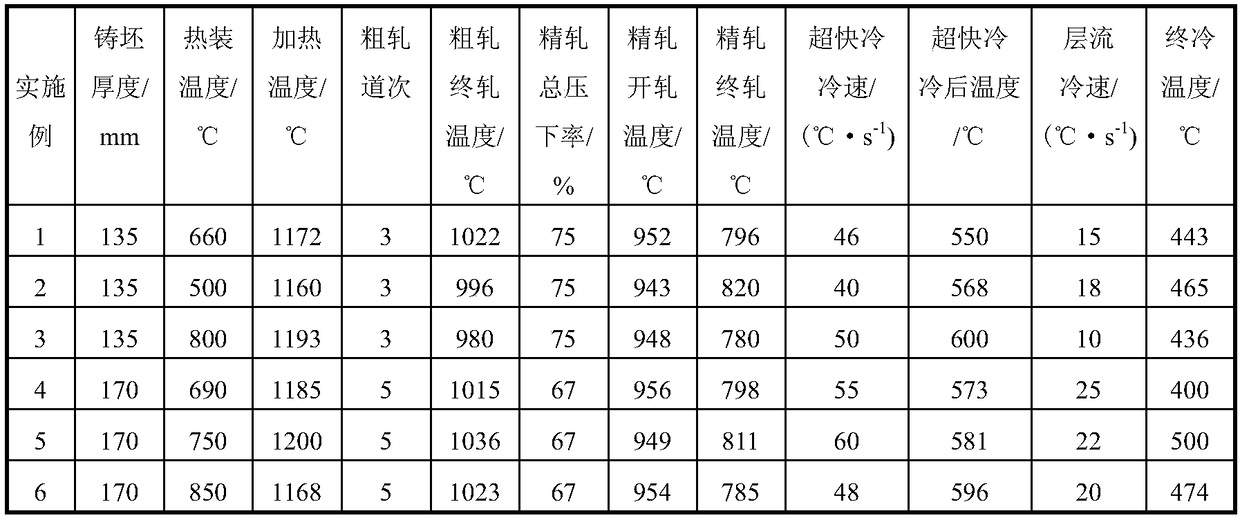
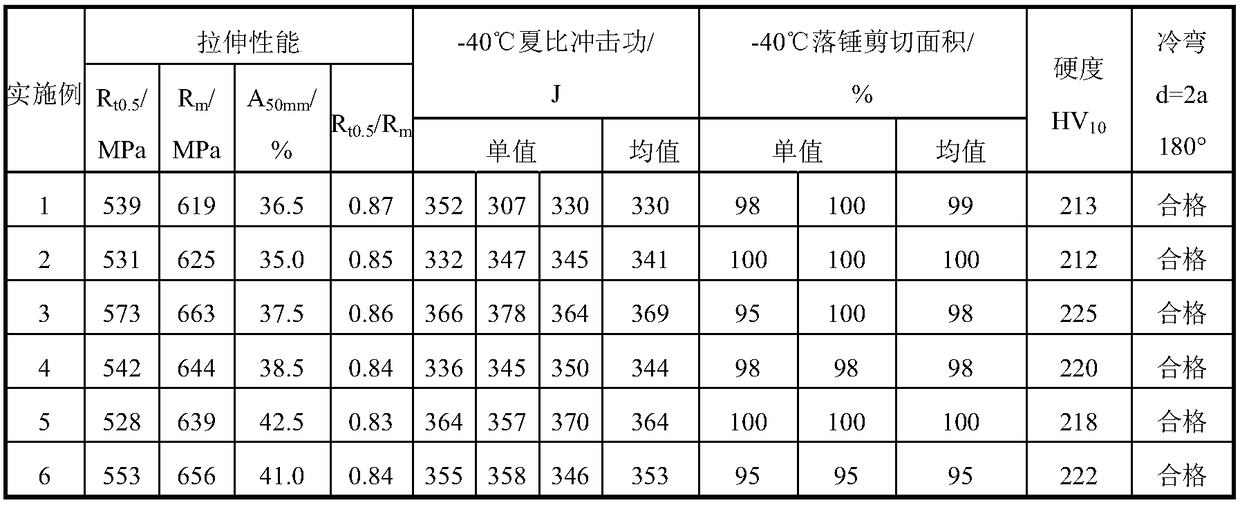
InactiveCN108950388AImprove performanceSimple designWork cooling devicesMetal rolling arrangementsToughnessCold zone
The invention discloses L485M pipeline steel excellent in low-temperature toughness and a manufacturing method of the pipeline steel. The steel comprises 0.045%-0.065% of C, 0.10%-0.25% of Si, 1.55%-1.65% of Mn, 0.055%-0.075% of Nb, 0.010%-0.025% of Ti, 0.10%-0.15% of Mo, 0.20%-0.30% of Cr, 0.015%-0.045% of Als, smaller than or equal to 0.015% of P, smaller than or equal to 0.003% of S, smaller than or equal to 0.006% of N, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities, and Pcm is smaller than or equal to 0.18%. The continuous cast blank thickness is smaller than or equal to 170 mm, hot charging is performed at 500-850 DEG C, heating is performed to 1160-1200 DEG C, the rough rolling final rolling temperature is larger than or equal to 980 DEG C, the finish rolling final rolling temperatureis 780-820 DEG C, the finish rolling total downward pressing rate is larger than or equal to 65%, then cooling is firstly performed at the speed of 40-60 DEG C / s till 550-600 DEG C is achieved, and then final cooling is performed at 10-25 DEG C / s till reeling is performed at 400-500 DEG C. A plate coil has excellent low temperature toughness, and using in extremely cold zones and regions harsh incondition is achieved.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Permanent and temporary combined anti-freezing drainage structure and method for high altitude severe cold rich water tunnel
The invention discloses a permanent and temporary combined anti-freezing drainage structure and method for a high altitude severe cold rich water tunnel. A parallel pilot pit is arranged on the side lower than a tunnel cavity body section and communicated with the tunnel through a transverse channel. Full section grouting is conducted on a tunnel cavity opening section full section to form a superfine cement full section grouting blocking solidification ring. Two inclined drainage holes are formed in the outside of the blocking solidification ring at the positions lower than two sides of a cavity opening. At least one end of the parallel pilot pit is communicated with the outer portion of the tunnel through a drainage cavity arranged in an inclined mode. According to the tunnel running wind flowing characteristic of high altitude severe cold zones, the parallel pilot pit which is excavated in advance in a construction period and lower than the main line tunnel position is utilized to achieve main line tunnel bottom embedded heat insulation transverse drainage, and a tunnel vertical reversed V-shaped drainage pipe is matched to improve drainage of tunnel surrounding rock water. Smooth drainage of the high altitude severe cold rich water tunnel is achieved by means of the small cavity diameter and the large-slope drainage hole which are formed through a directional drilling and hole expanding technology by water in the tunnel and matched with the middle parallel pilot pit, and safety and stability of the tunnel structure are ensured.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Crystal growth methods
InactiveUS20040154527A1Highly homogenous index of refractionLow stress birefringencePolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle crystalSlow cooling
The invention is directed to method of preparing metal fluoride single crystals and particularly to crystals where the metal is calcium, barium, magnesium or strontium, or a mixture thereof. The invention uses a decreasing fast cooling profile and an increasing slow cooling profile for the hot zone and the cold zone, respectively, after crystal formation during cooling from melt temperatures to a first temperature. A substantially constant cooling rate is then applied to the both zones during cooling from the first temperature to a final temperature, usually room temperature. It has been found that the substantially constant cooling rate during the annealing process results in crystals having improved homogeneity and birefringence.
Owner:CORNING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com