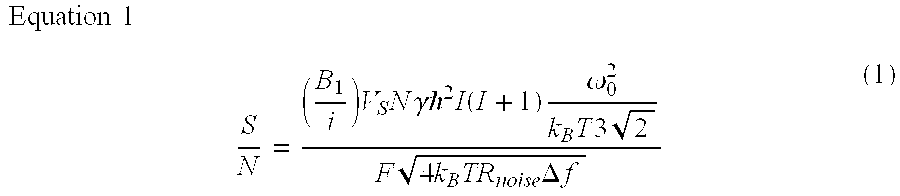Patents
Literature
42 results about "Magic angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The magic angle is a precisely defined angle, the value of which is approximately 54.7356°. The magic angle is a root of a second-order Legendre polynomial, P₂(cos θ) = 0, and so any interaction which depends on this second-order Legendre polynomial vanishes at the magic angle. This property makes the magic angle of particular importance in magic angle spinning solid-state NMR spectroscopy. In magnetic resonance imaging, structures with ordered collagen, such as tendons and ligaments, oriented at the magic angle may appear hyperintense in some sequences; this is called the magic angle artifact or effect.
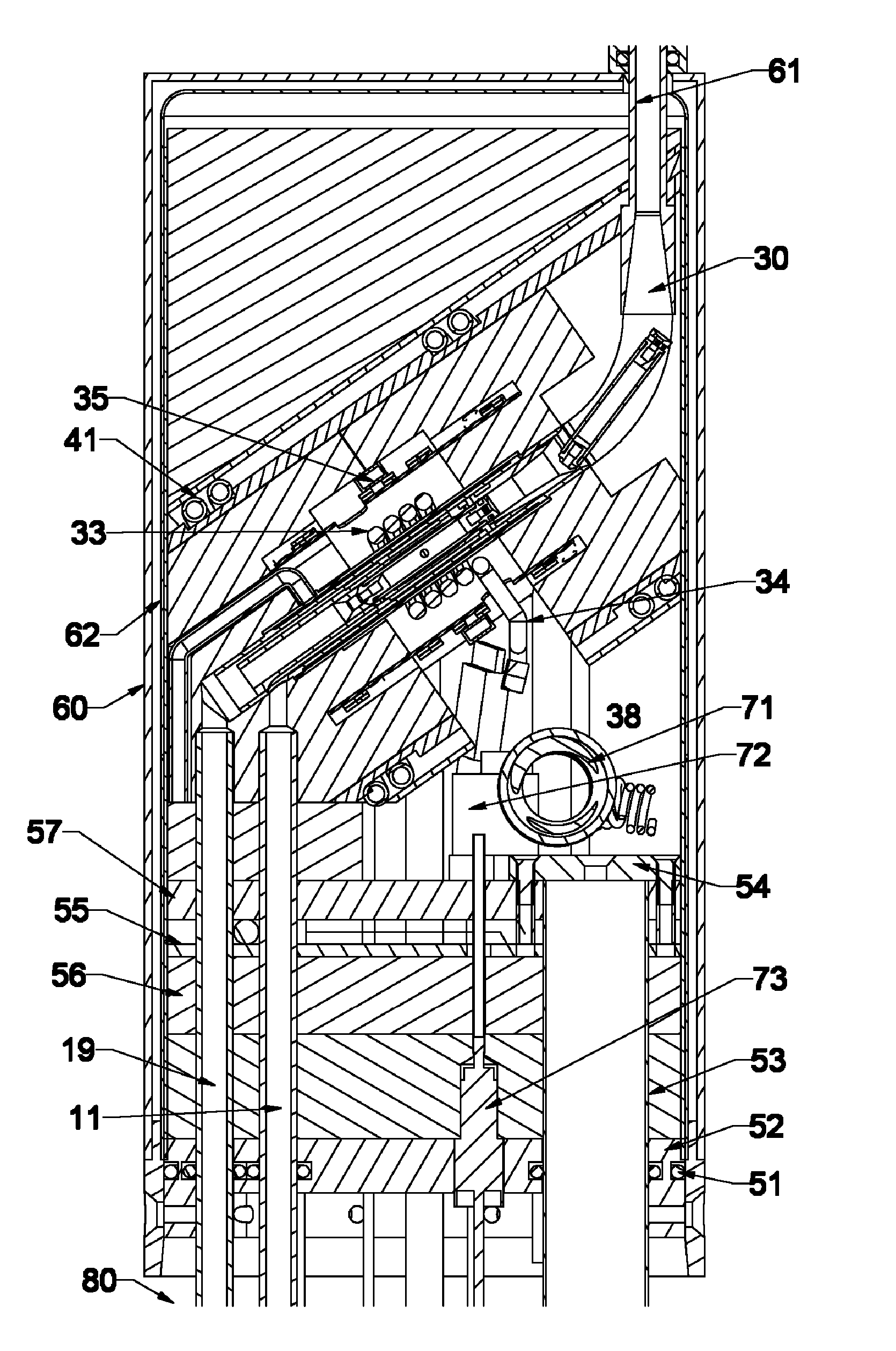
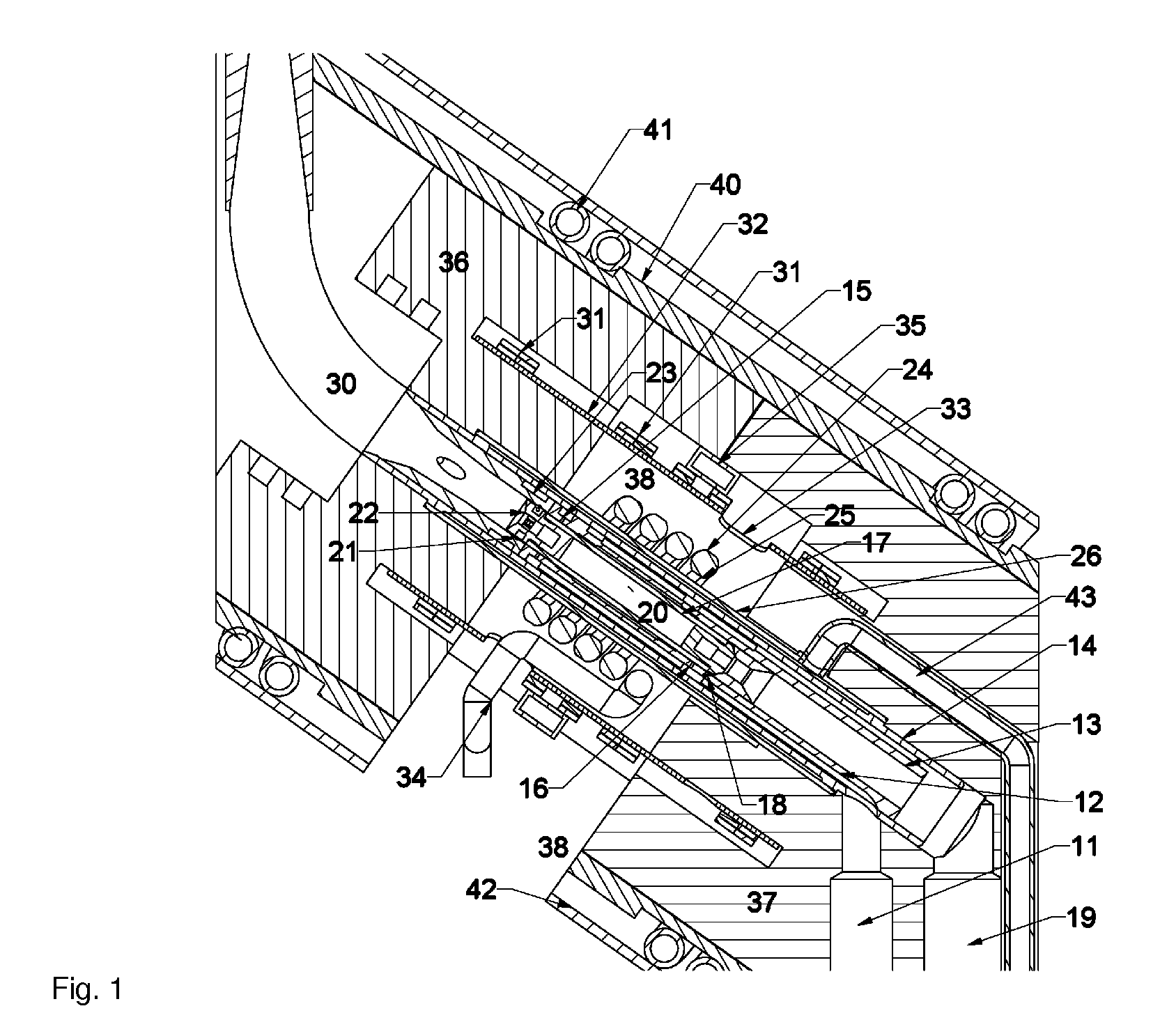
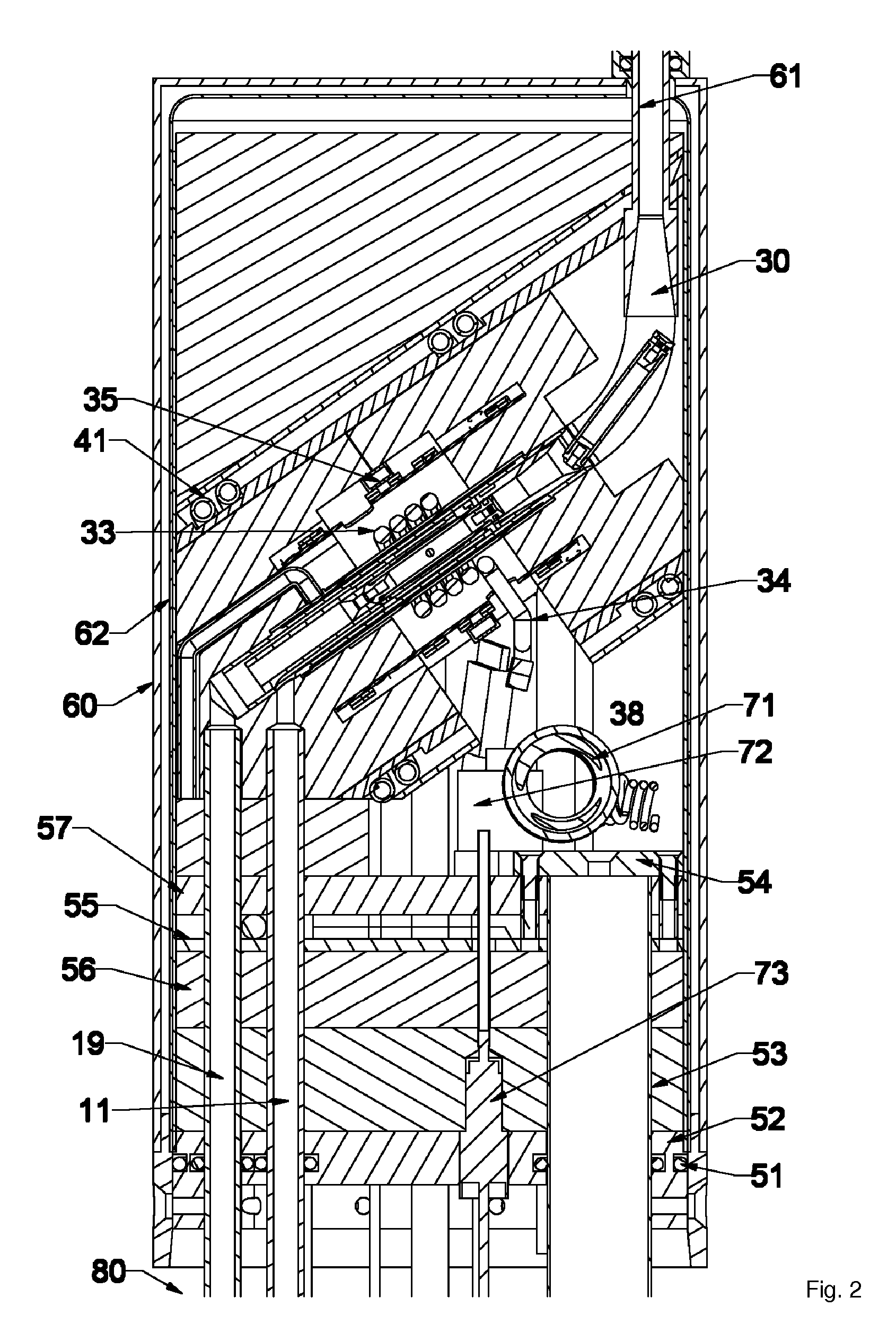
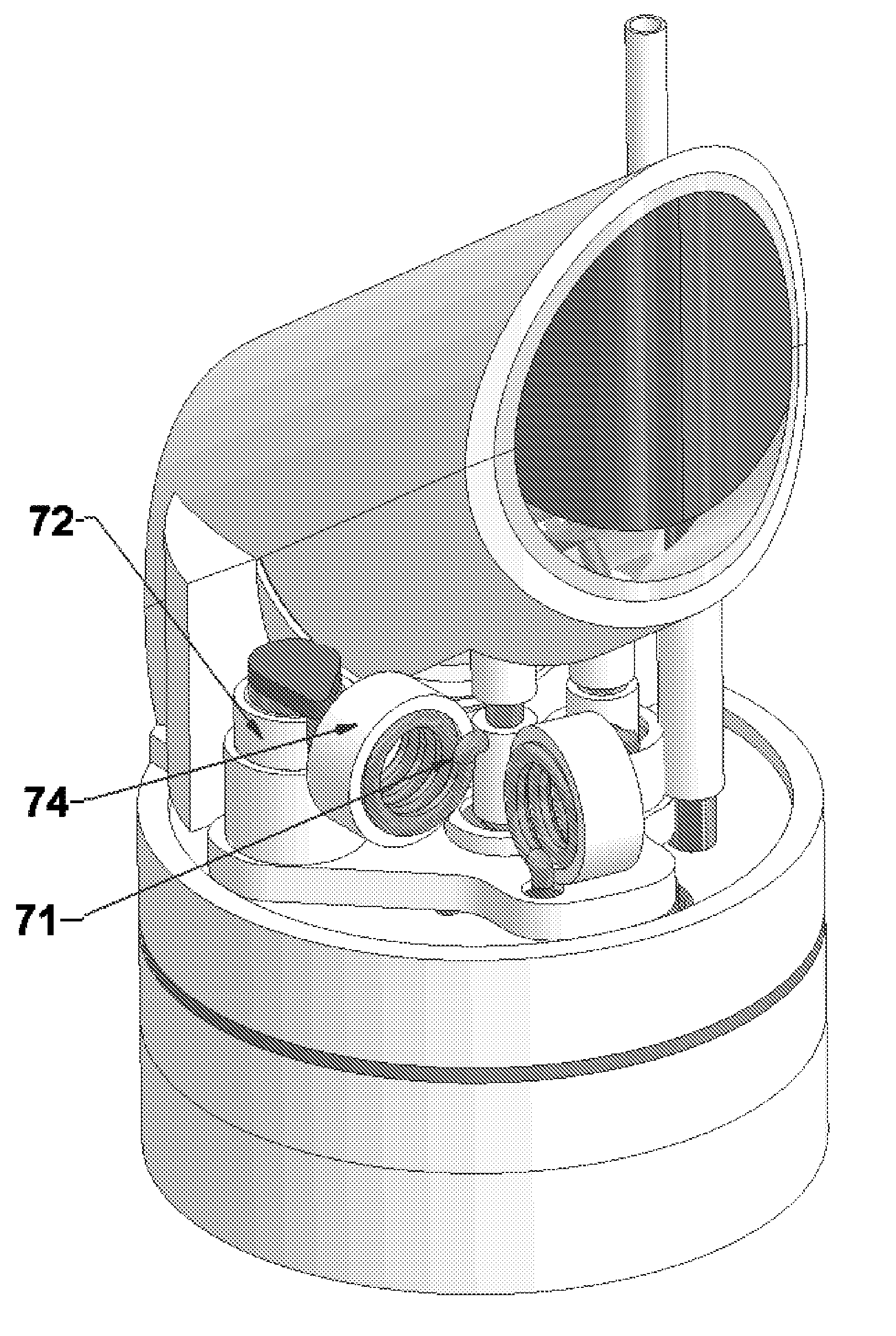
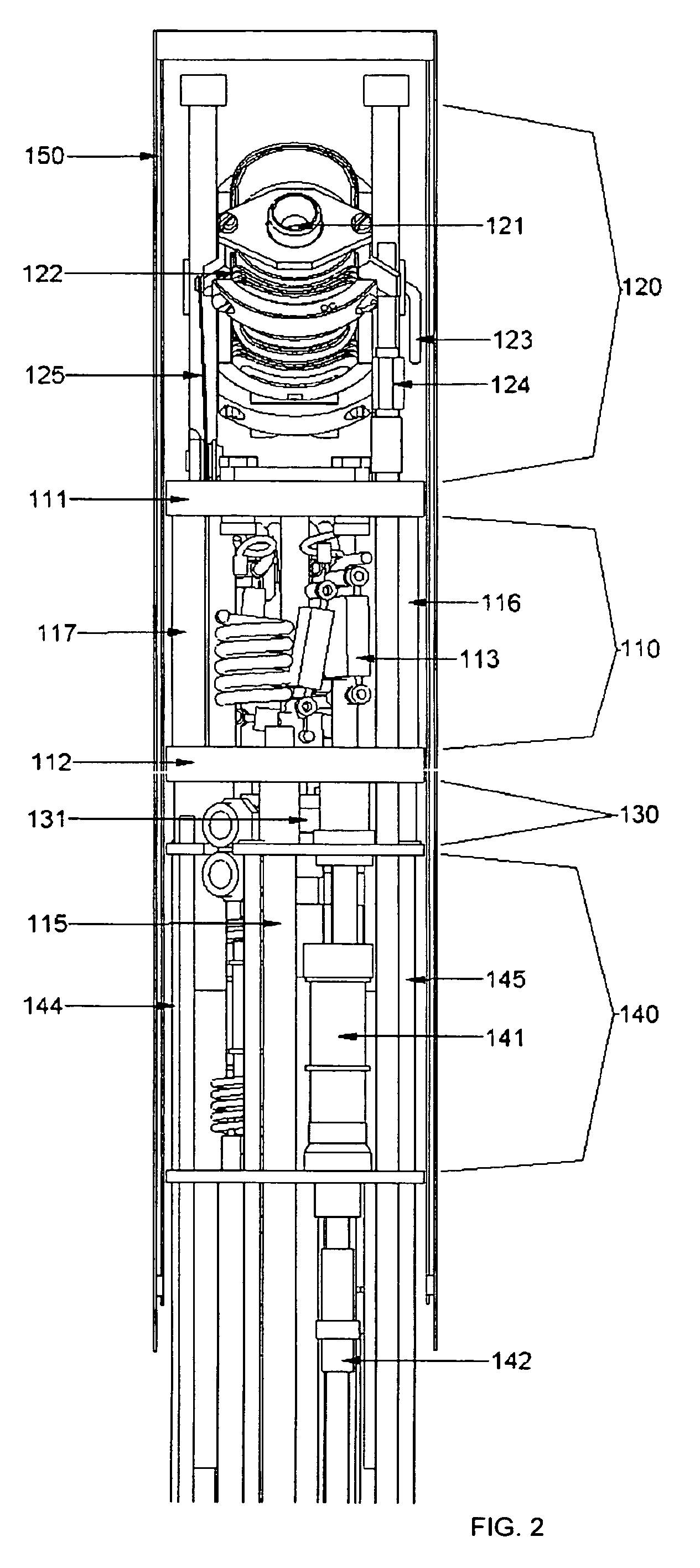
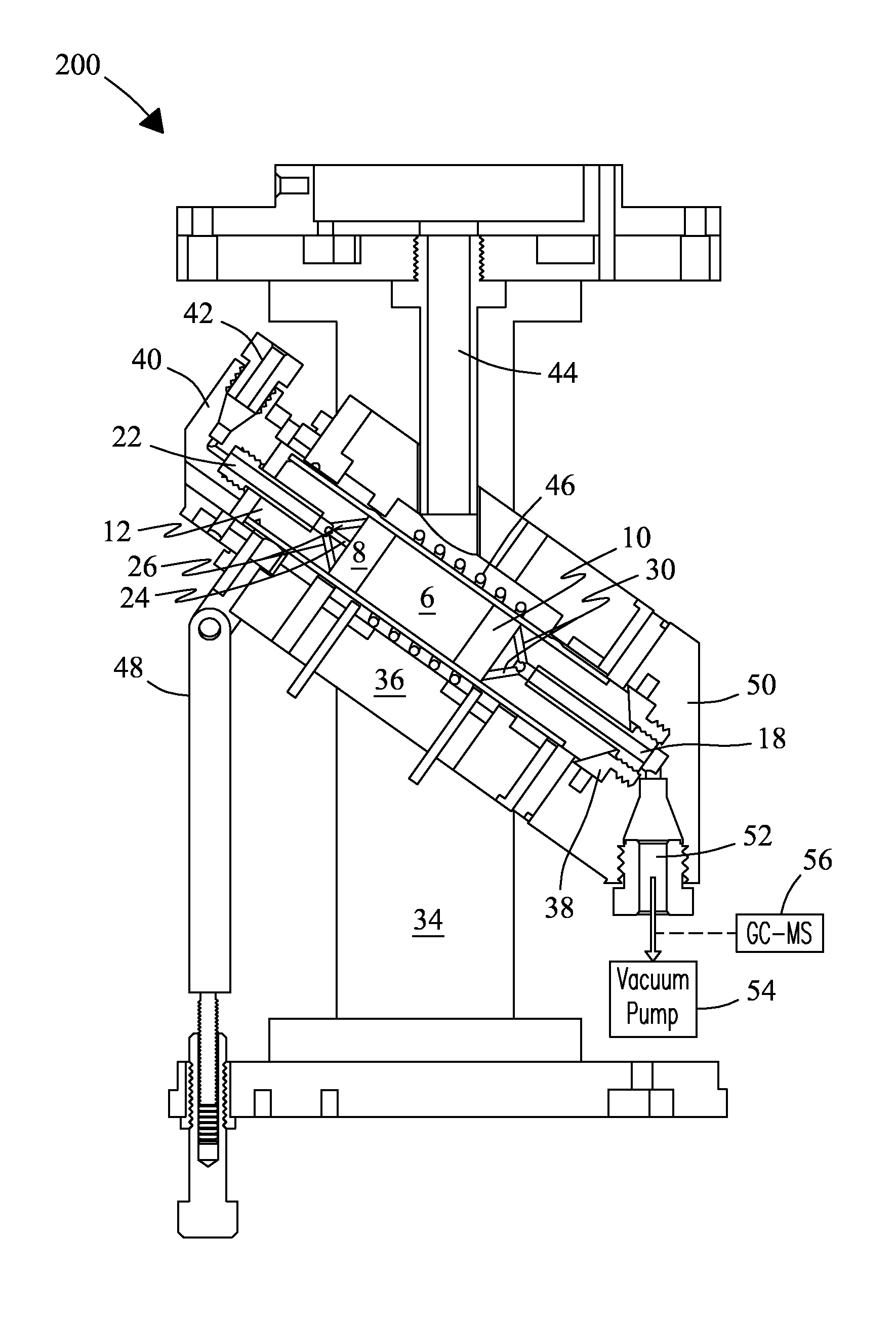
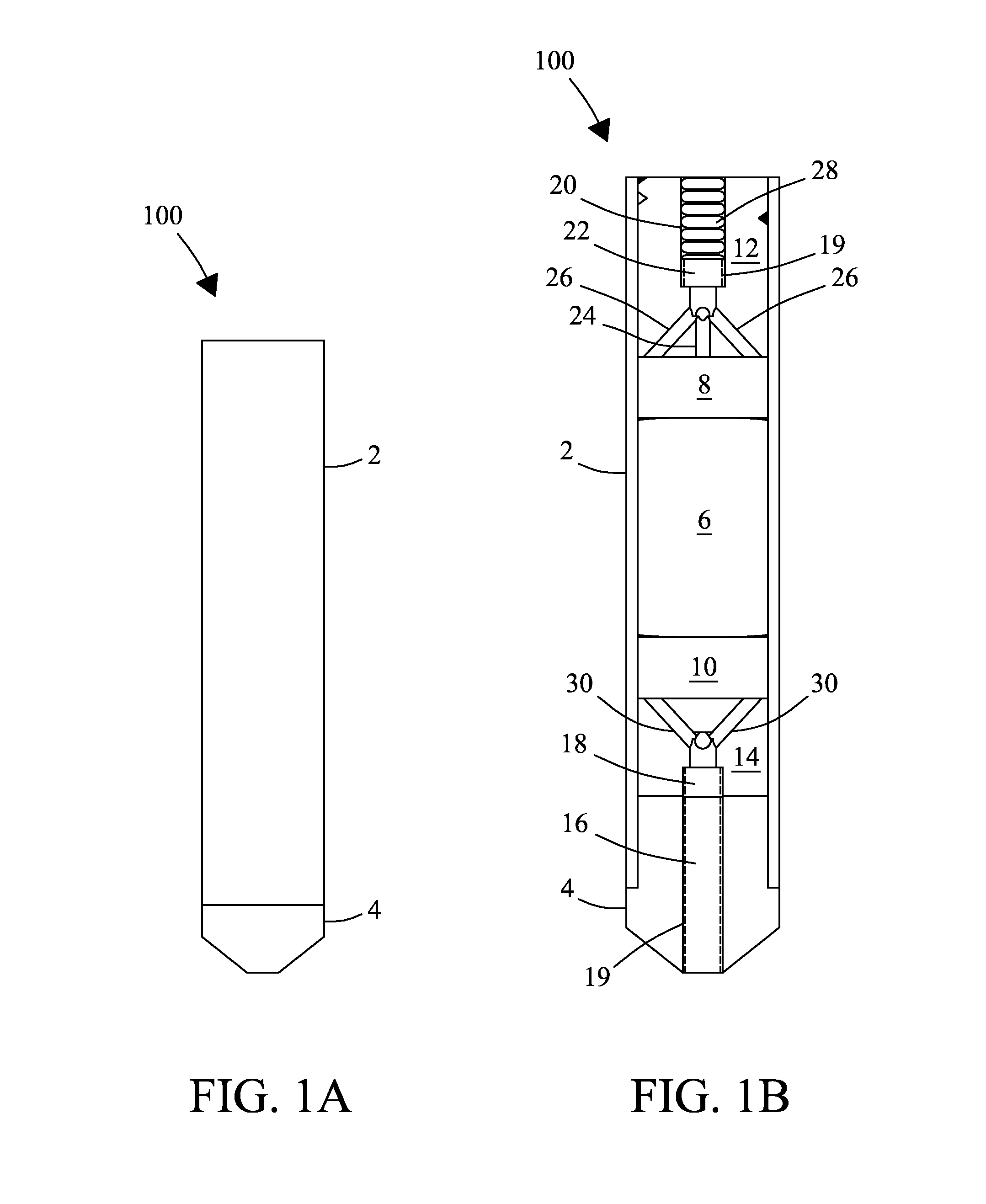
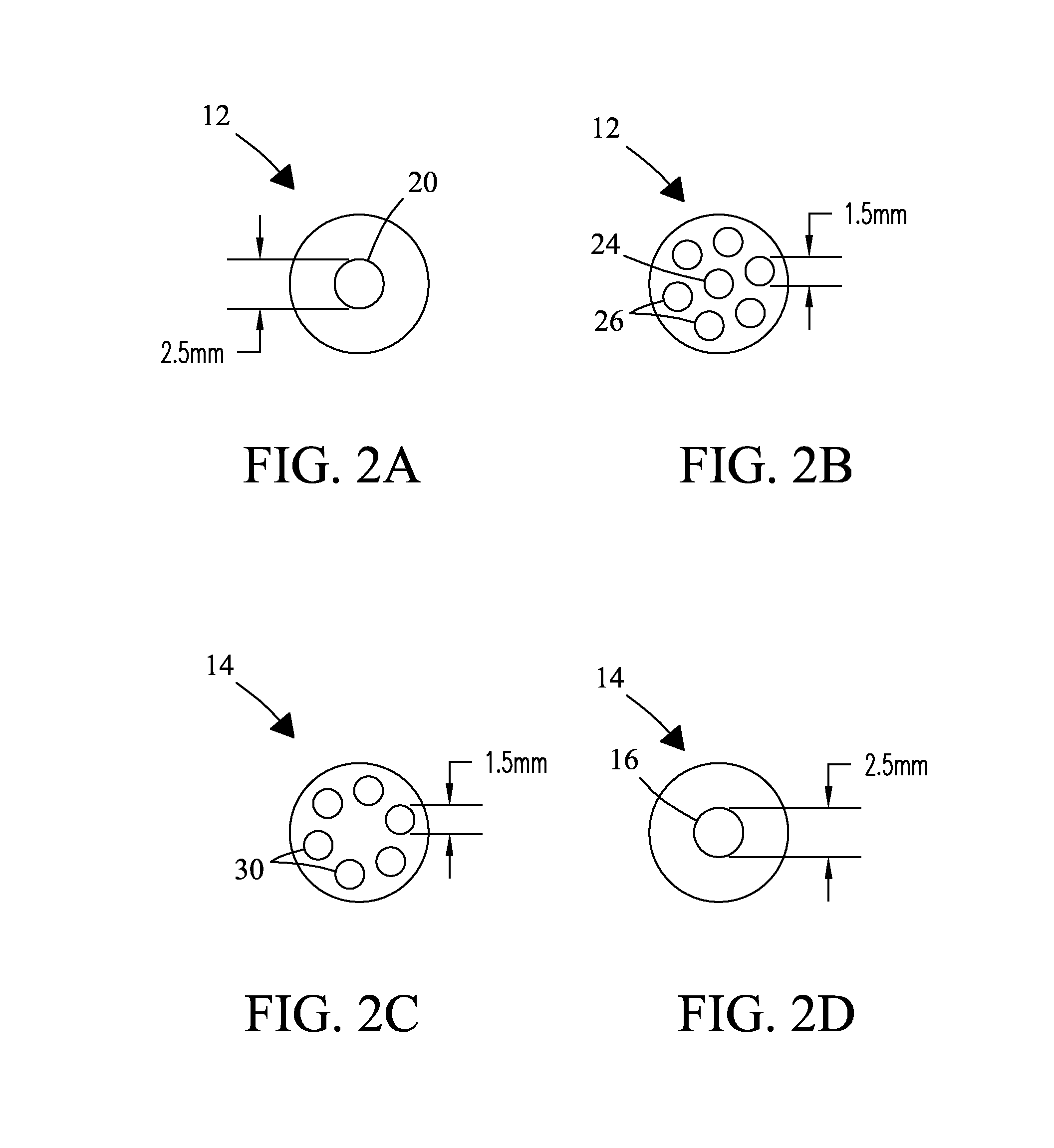
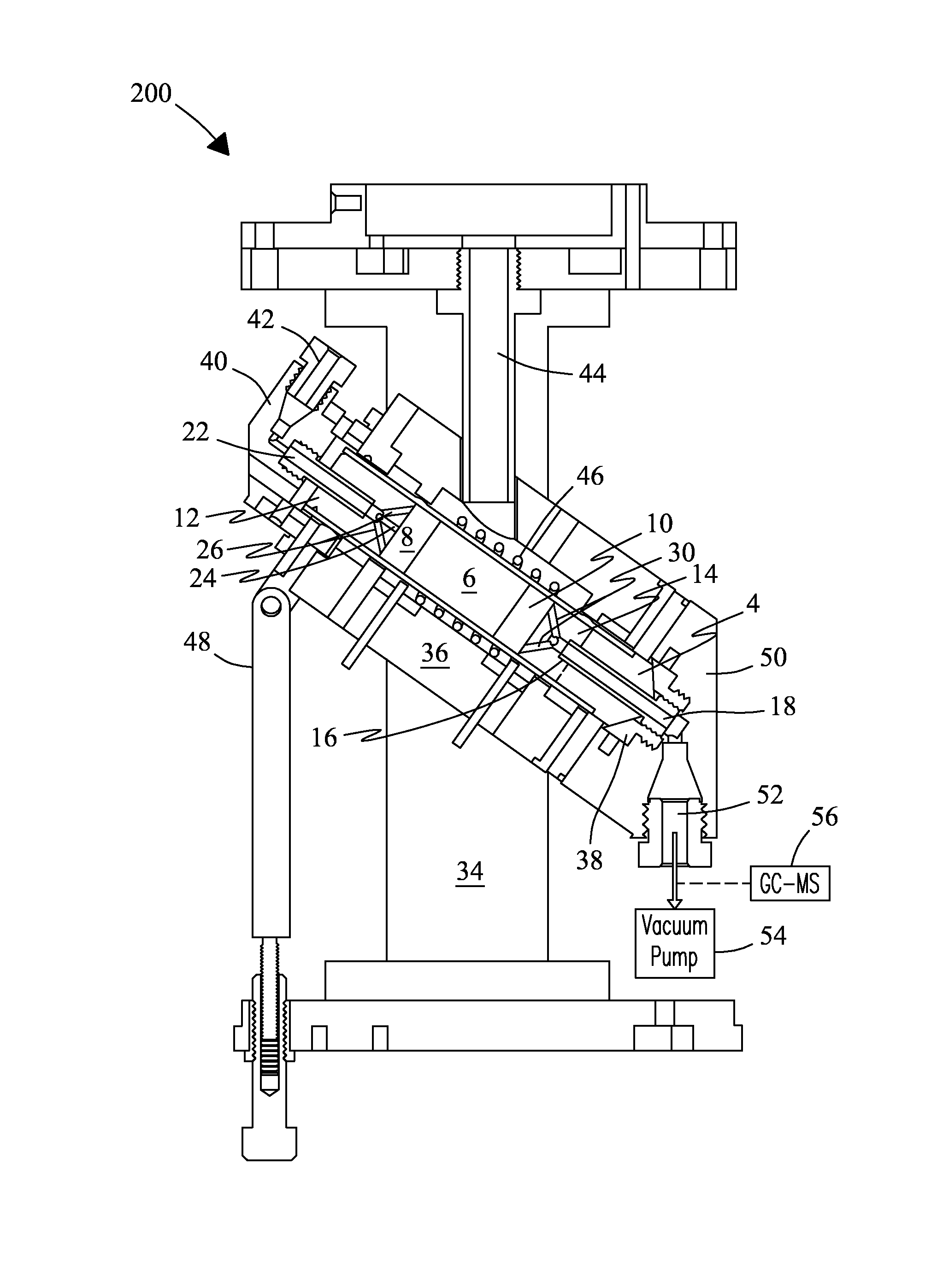
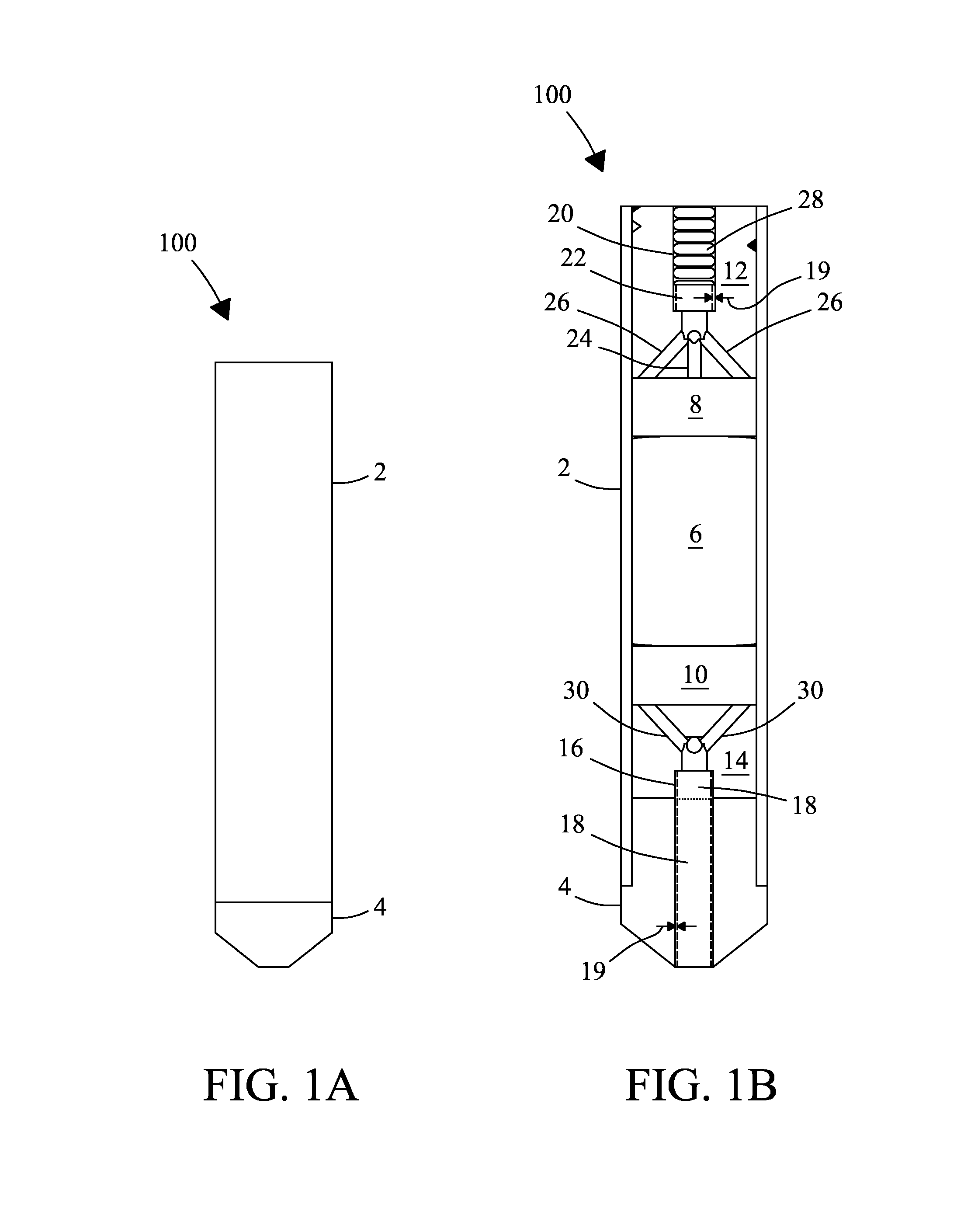
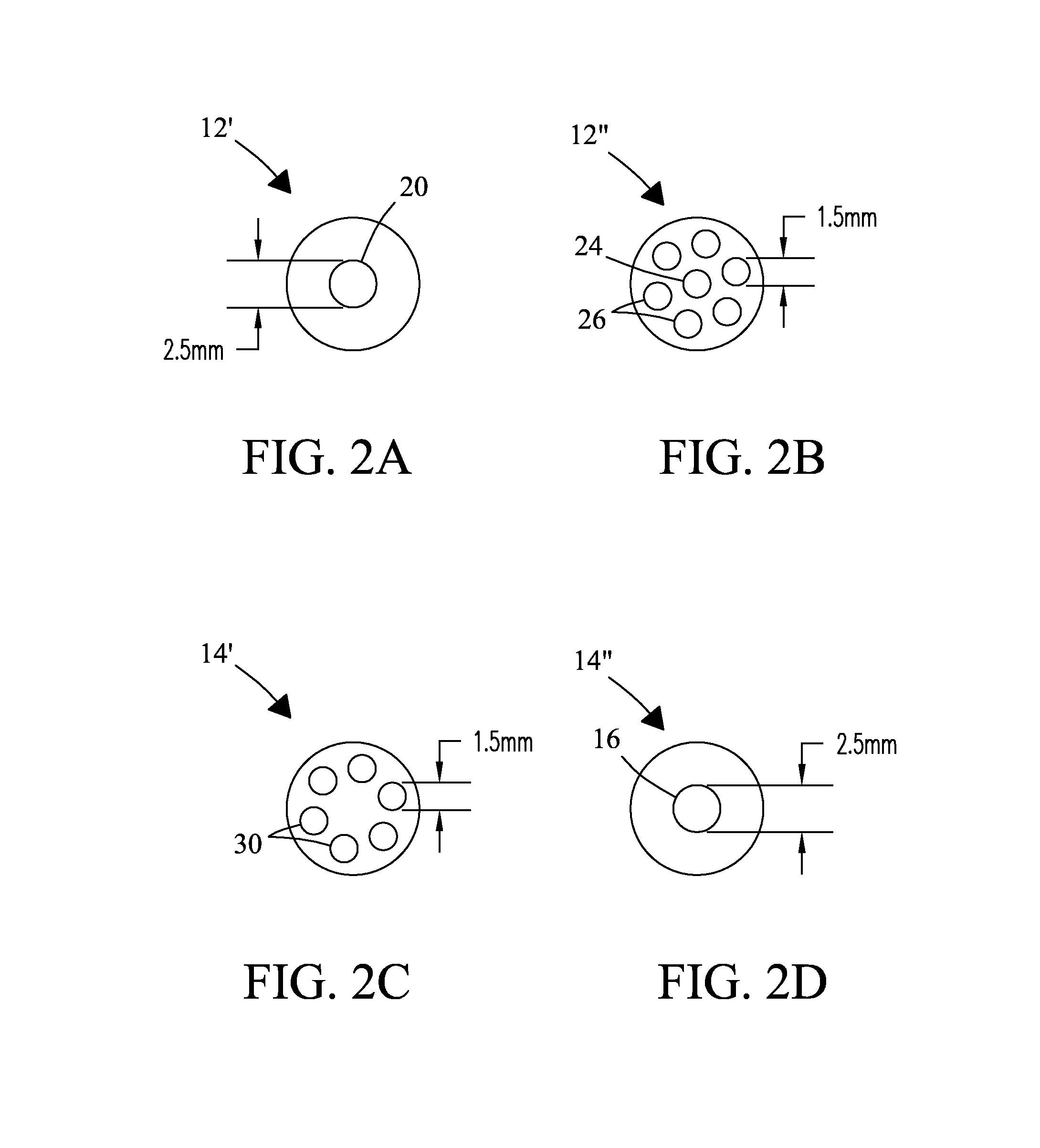
NMR CryoMAS probe for high-field wide-bore magnets
InactiveUS7282919B2Reduce riskAvoid flowElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagic angle spinningNitrogen gas
Owner:DOTY SCI
NMR CryoMAS Probe for High-field Wide-bore Magnets
InactiveUS20060176056A1Reduce riskImprovement factorElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonancePartial solutionNitrogen gas
An MAS probe is disclosed for obtaining a substantial improvement in signal to noise (S / N) in triple-resonance high-resolution (HR) magic-angle-spinning (MAS) NMR of samples near room temperature (RT) in high-field magnets where the magnet's RT shim bore is greater than 60 mm. All critical circuit components, including the sample coils, are located along with the spinner assembly in a thermally insulated cold zone pressurized with helium gas. The spinner assembly attaches to a sealed, curved, rotor-loading tube to permit automatic sample change, and it is surrounded by a partially insulated jacket cooled with a cryogenic fluid, generally nitrogen gas. The MAS probe is also compatible with magic angle gradients, variable temperature operation, field locking, and commonly available closed-cycle cold fingers. One major challenge in implementing CryoMAS is solving the problem of gas leakage from the spinner bearing, drive, and exhaust nitrogen into the cold zone, as some components will necessarily be ceramic, some plastic, and some metal. It is not desirable to use helium for the spinner bearing and drive gases for cost reasons and to prevent risk of degradation of o-ring-sealed magnet cryostats. A pressurized helium atmosphere in the cold zone may be utilized to prevent nitrogen flow from the spinner exhaust streams or atmosphere into the cold zone. The drawback to a pressurized cold zone is that the heat transfer coefficient in dense helium at low temperatures is very high, making it challenging to cool the sample coils and all the large, critical, circuit components in a practical manner. Part of the solution here is to use a first-stage cooling-jacket around the major heat leaks near the spinner exhaust flows. The critical components may be insulated with fine glass wool or teflon foam and conduction cooled without cooling much of the cold zone below the temperature of the first-stage cooling. The use of coaxial sapphire capacitors allows the noise contributions from the most critical capacitors to be reduced to a minor fraction of the total.
Owner:DOTY SCI
NMR MAS probe with cryogenically cooled critical circuit components
ActiveUS7151374B2Enhanced signalReduce noiseElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagic angle spinningHigh field
A MAS probe offers a substantial improvement in signal to noise (S / N) in triple-resonance high-resolution (HR) magic-angle-spinning (MAS) NMR of samples near room temperature (RT) in high field magnets, especially where the RT shim bore is less than 55 mm. Critical circuit components other than the sample coils, including both high-power capacitors and inductors for one or more channels are located in a small, thermally insulated, cold zone immediately below the sample spinner assembly. Cooling these components to 100 K allows their thermal noise power to be conveniently reduced by a factor of three or more. Variable capacitors for fine tuning are located in an RT tuning zone below the cold zone. The circuit is designed such that the currents, voltages, and standing wave ratio (SWR) in circuit tuning elements in the RT tuning zone are relatively low, so rf losses and noise contributions below the cold zone may be only a few percent. The MAS probe is also compatible with magic angle gradients, automatic sample change, multi-nuclear tuning, variable temperature operation, field locking, and optical spin rate detection.
Owner:DOTY SCI
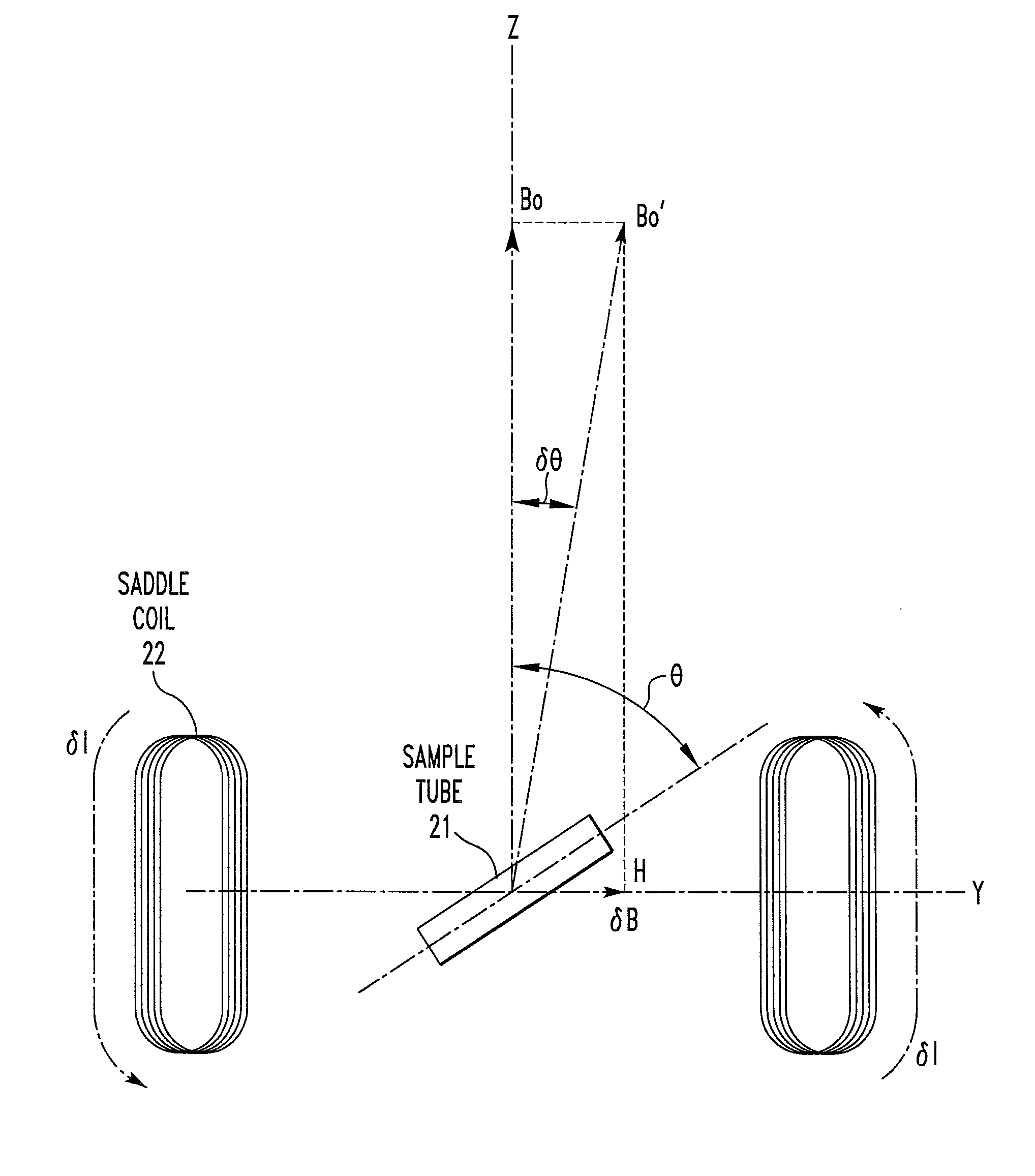
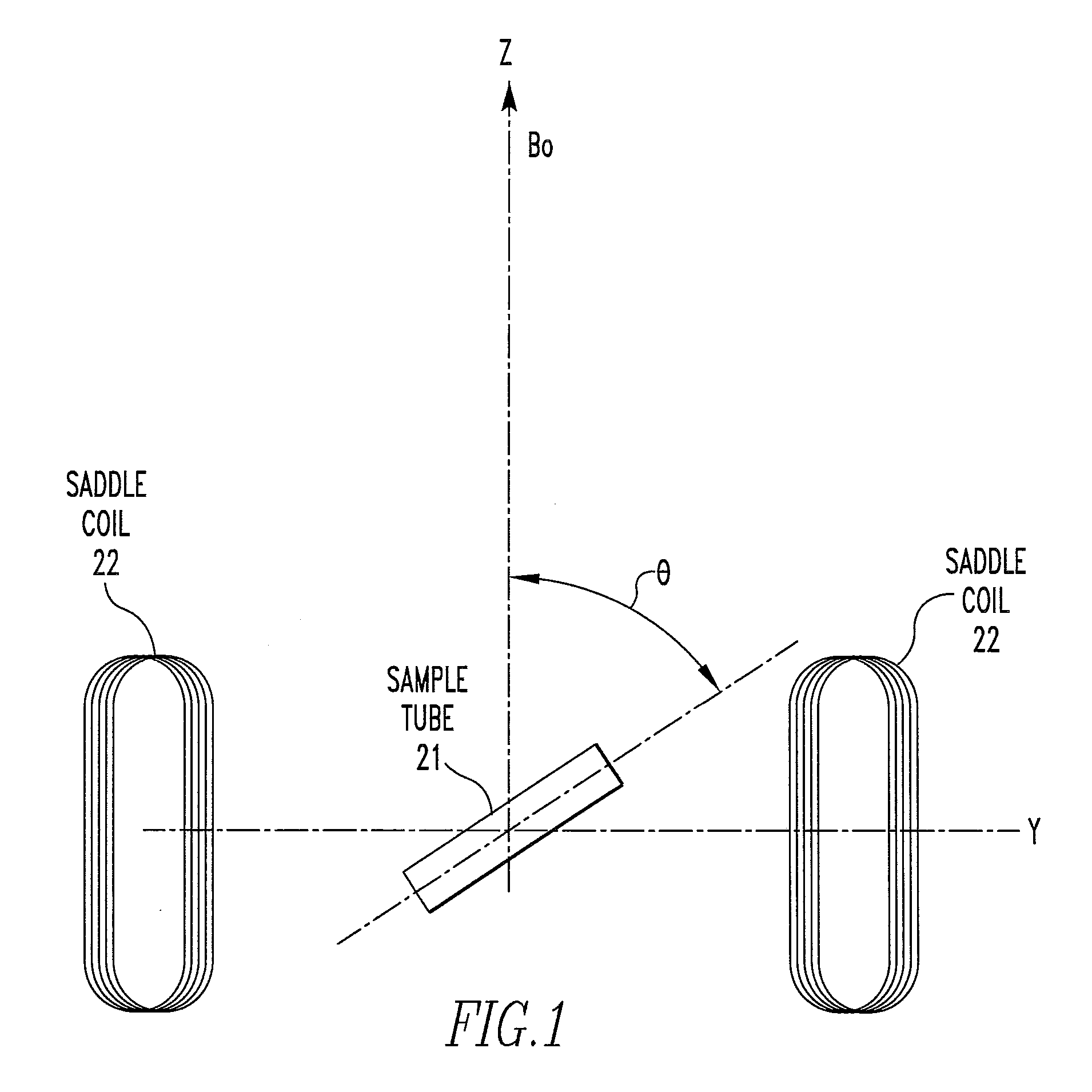
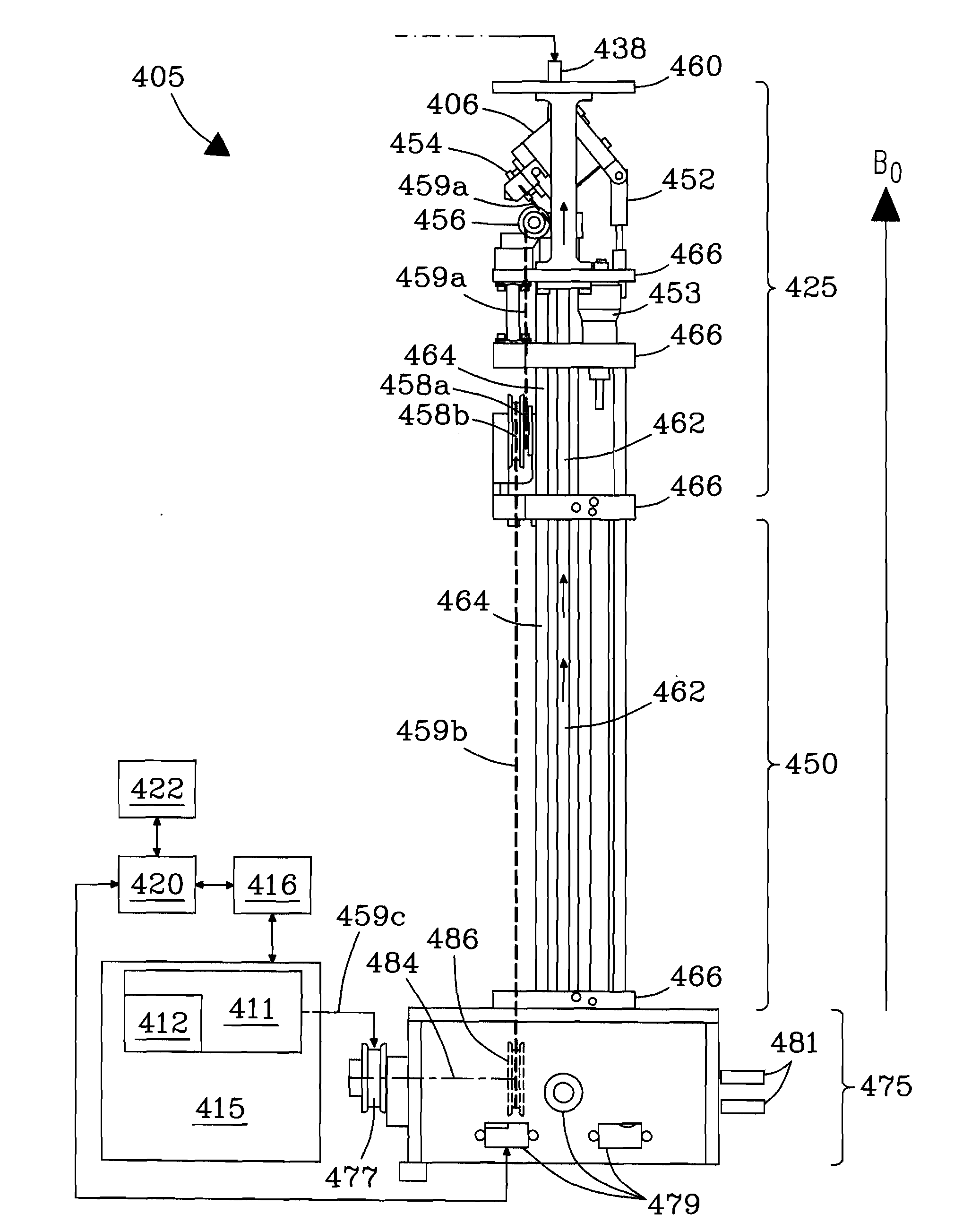
Method and apparatus for accurately adjusting magic angle in NMR
ActiveUS8547099B2Easy to adjustSuppression of distortionMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionUniform fieldMagic angle
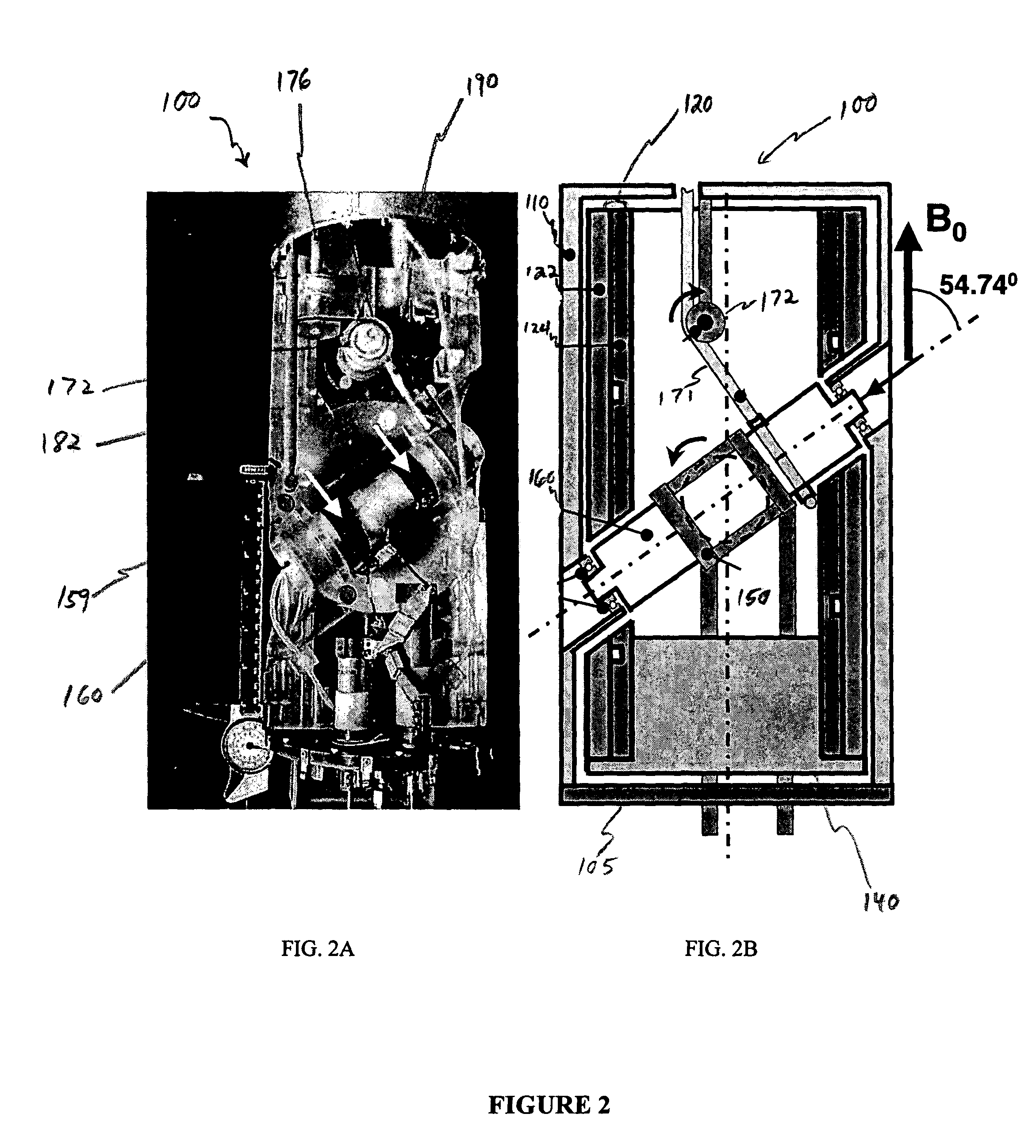
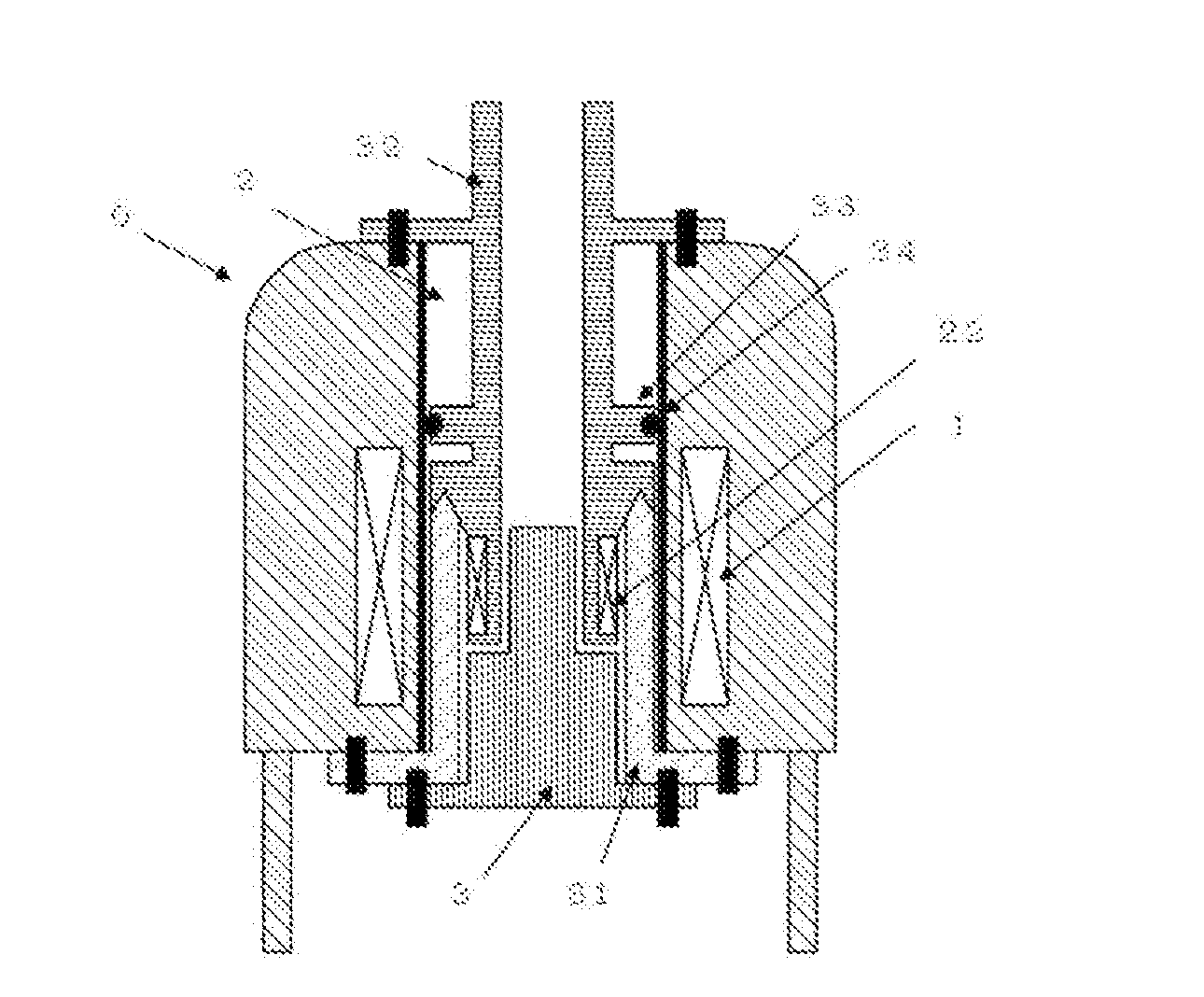
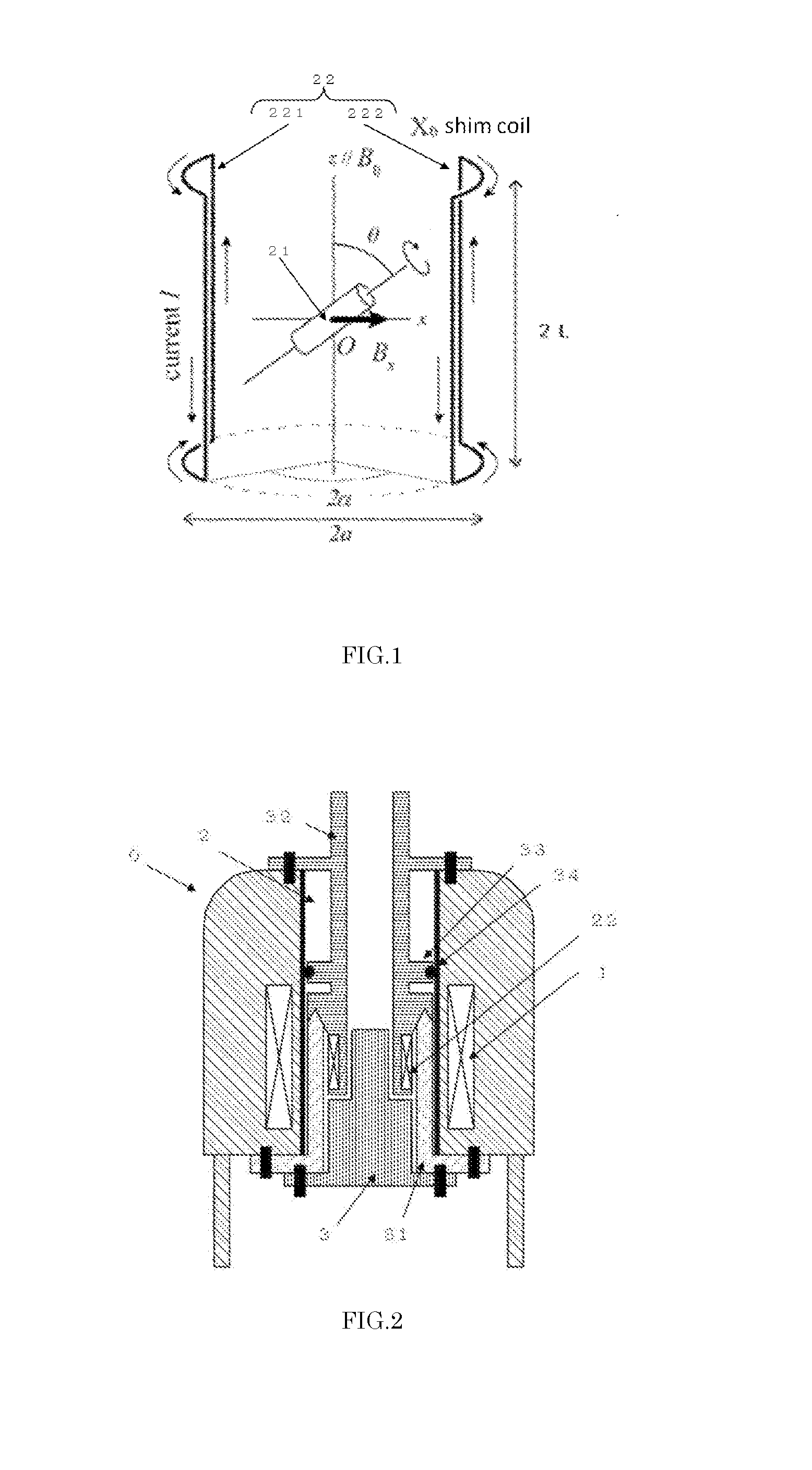
Method and apparatus for accurately adjusting the magic angle in NMR. The NMR probe has a uniform magnetic field coil assembly disposed to produce a uniform magnetic field H. The uniform magnetic field H is produced by controlling the currents flowing through the uniform magnetic field coil assembly. The vector sum of the external field B0 and the uniform field H is used to determine a new external magnetic field B0′.
Owner:JEOL LTD
Magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus and process for high-resolution in situ investigations
ActiveUS20140099730A1Short timeRaise the ratioMeasurements using NMR spectroscopySupporting apparatusMagic angle spinningContinuous flow
A continuous-flow (CF) magic angle sample spinning (CF-MAS) NMR rotor and probe are described for investigating reaction dynamics, stable intermediates / transition states, and mechanisms of catalytic reactions in situ. The rotor includes a sample chamber of a flow-through design with a large sample volume that delivers a flow of reactants through a catalyst bed contained within the sample cell allowing in-situ investigations of reactants and products. Flow through the sample chamber improves diffusion of reactants and products through the catalyst. The large volume of the sample chamber enhances sensitivity permitting in situ 13C CF-MAS studies at natural abundance.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Discrete magic angle turning system, apparatus, and process for in situ magnetic resonance spectroscopy and imaging
InactiveUS20080297157A1High resolutionElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingMagic anglePulse sequence
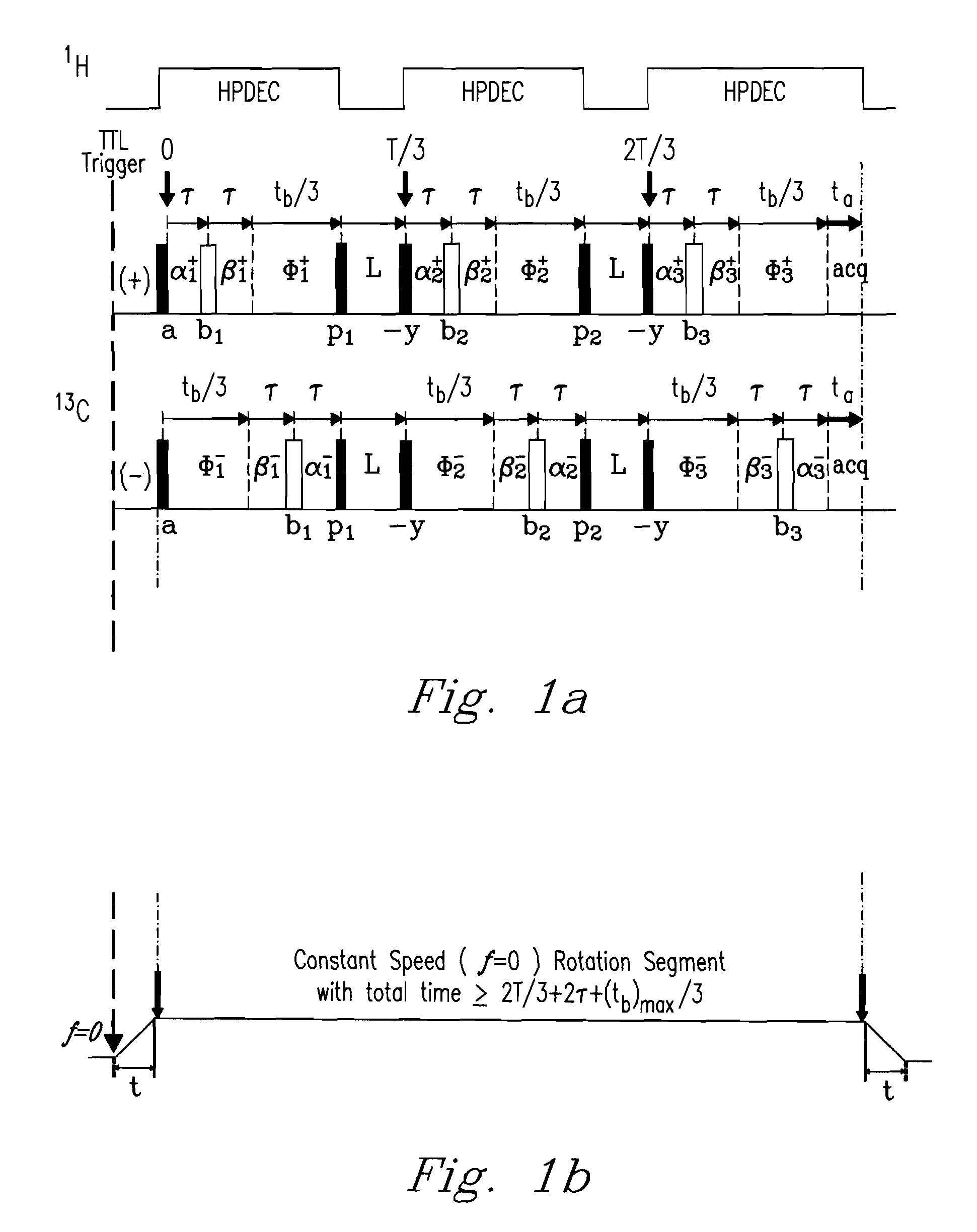
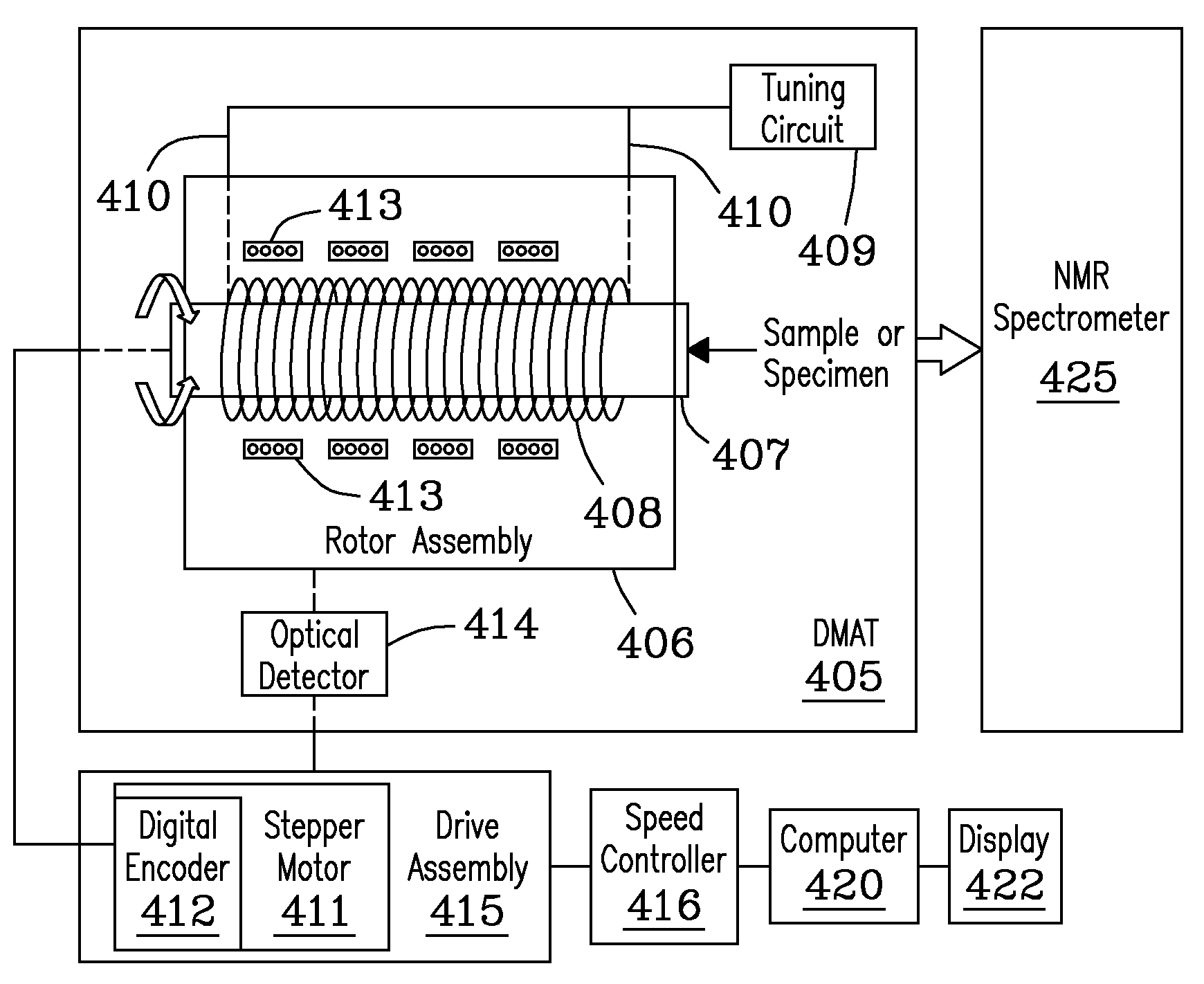
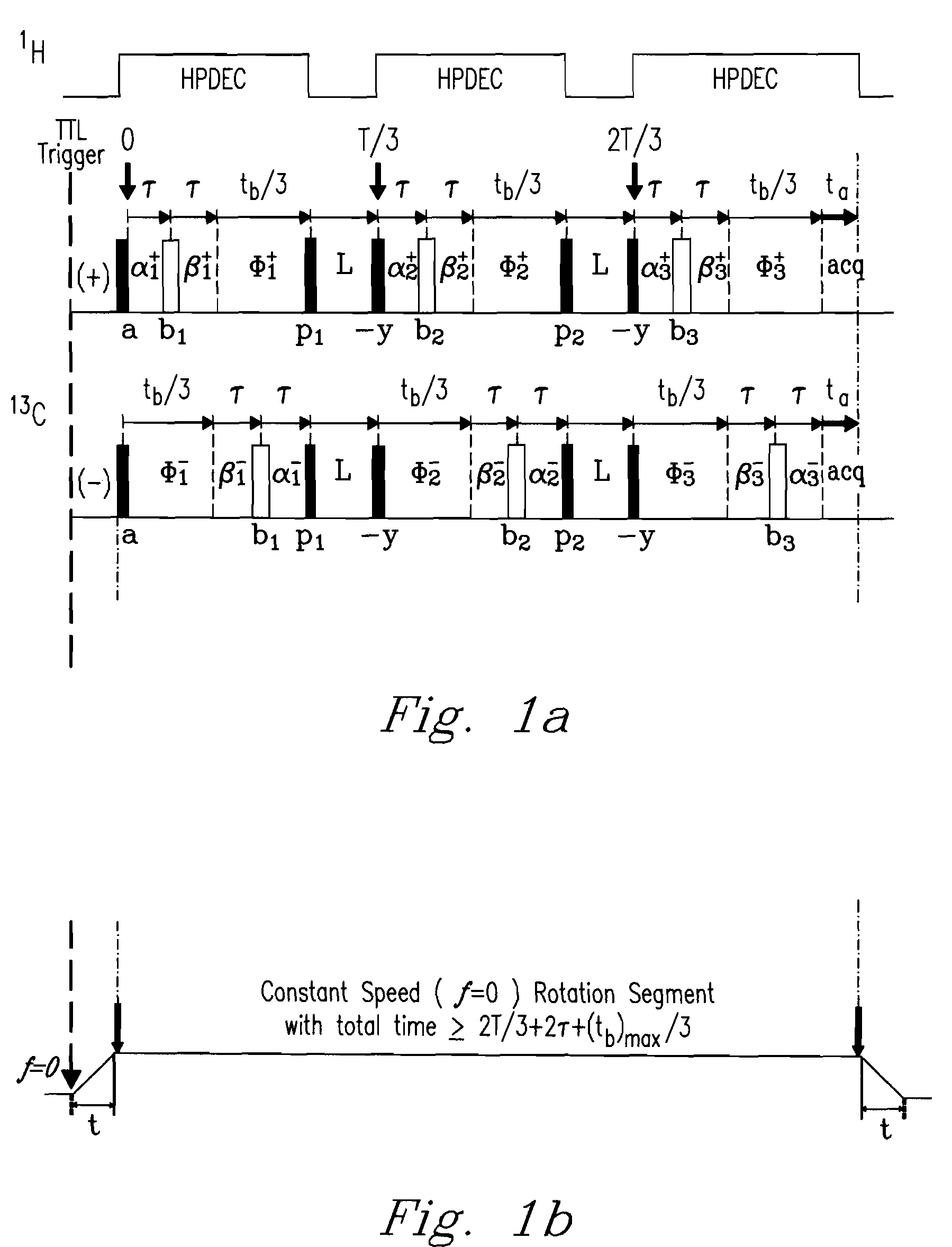
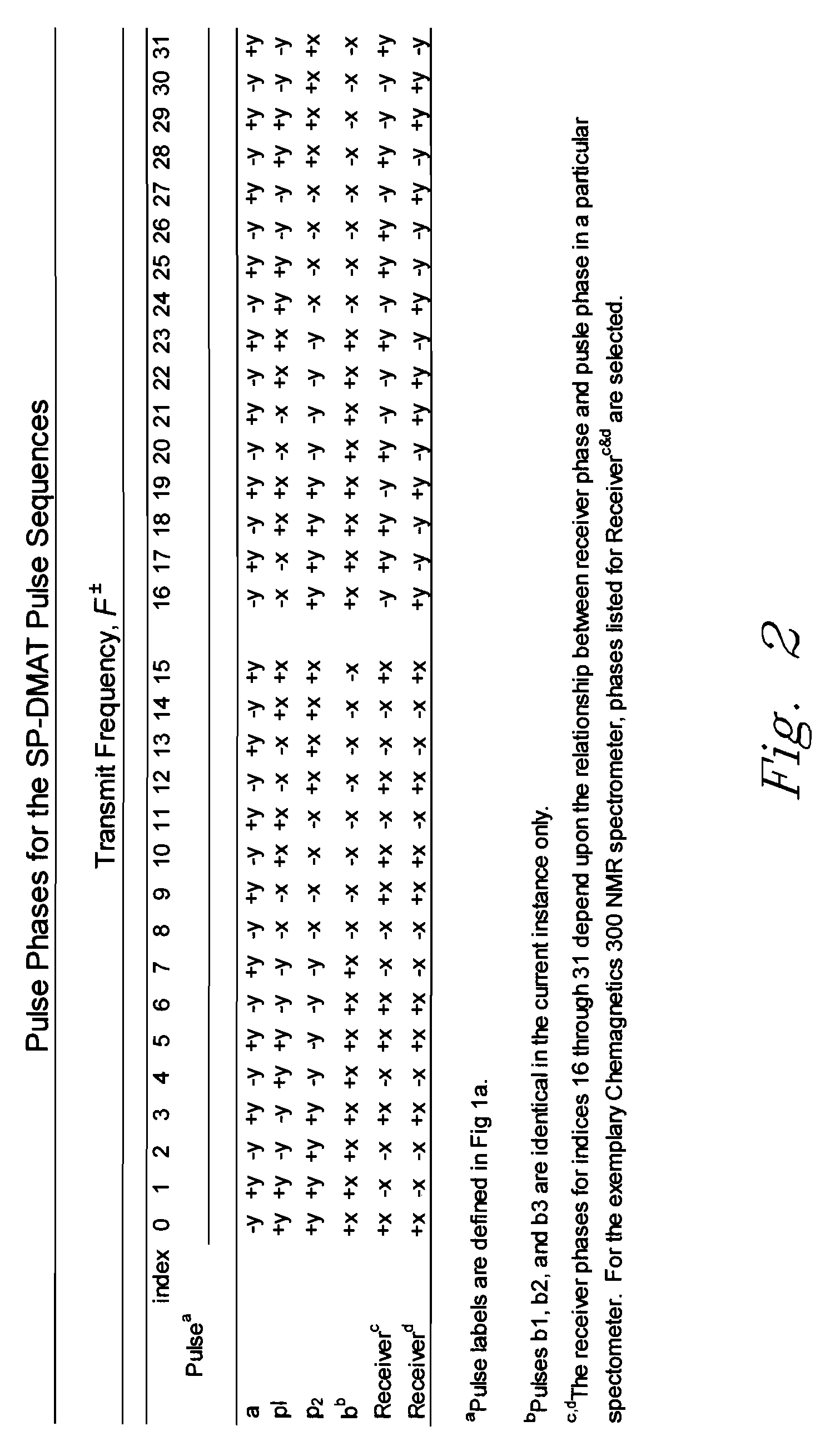
Described are a “Discrete Magic Angle Turning” (DMAT) system, devices, and processes that combine advantages of both magic angle turning (MAT) and magic angle hopping (MAH) suitable, e.g., for in situ magnetic resonance spectroscopy and / or imaging. In an exemplary system, device, and process, samples are rotated in a clockwise direction followed by an anticlockwise direction of exactly the same amount. Rotation proceeds through an angle that is typically greater than about 240 degrees but less than or equal to about 360 degrees at constant speed for a time applicable to the evolution dimension. Back and forth rotation can be synchronized and repeated with a special radio frequency (RF) pulse sequence to produce an isotropic-anisotropic shift 2D correlation spectrum. The design permits tubes to be inserted into the sample container without introducing plumbing interferences, further allowing control over such conditions as temperature, pressure, flow conditions, and feed compositions, thus permitting true in-situ investigations to be carried out.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Discrete magic angle turning system, apparatus, and process for in situ magnetic resonance spectroscopy and imaging
InactiveUS7535224B2High resolutionMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMagic anglePulse sequence
Described are a “Discrete Magic Angle Turning” (DMAT) system, devices, and processes that combine advantages of both magic angle turning (MAT) and magic angle hopping (MAH) suitable, e.g., for in situ magnetic resonance spectroscopy and / or imaging. In an exemplary system, device, and process, samples are rotated in a clockwise direction followed by an anticlockwise direction of exactly the same amount. Rotation proceeds through an angle that is typically greater than about 240 degrees but less than or equal to about 360 degrees at constant speed for a time applicable to the evolution dimension. Back and forth rotation can be synchronized and repeated with a special radio frequency (RF) pulse sequence to produce an isotropic-anisotropic shift 2D correlation spectrum. The design permits tubes to be inserted into the sample container without introducing plumbing interferences, further allowing control over such conditions as temperature, pressure, flow conditions, and feed compositions, thus permitting true in-situ investigations to be carried out.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Method for high resolution magnetic resonance analysis using magic angle technique
InactiveUS20020125887A1Eliminates spinning sideband peakHigh resolutionMagnetic property measurementsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPhase correctionMagic angle
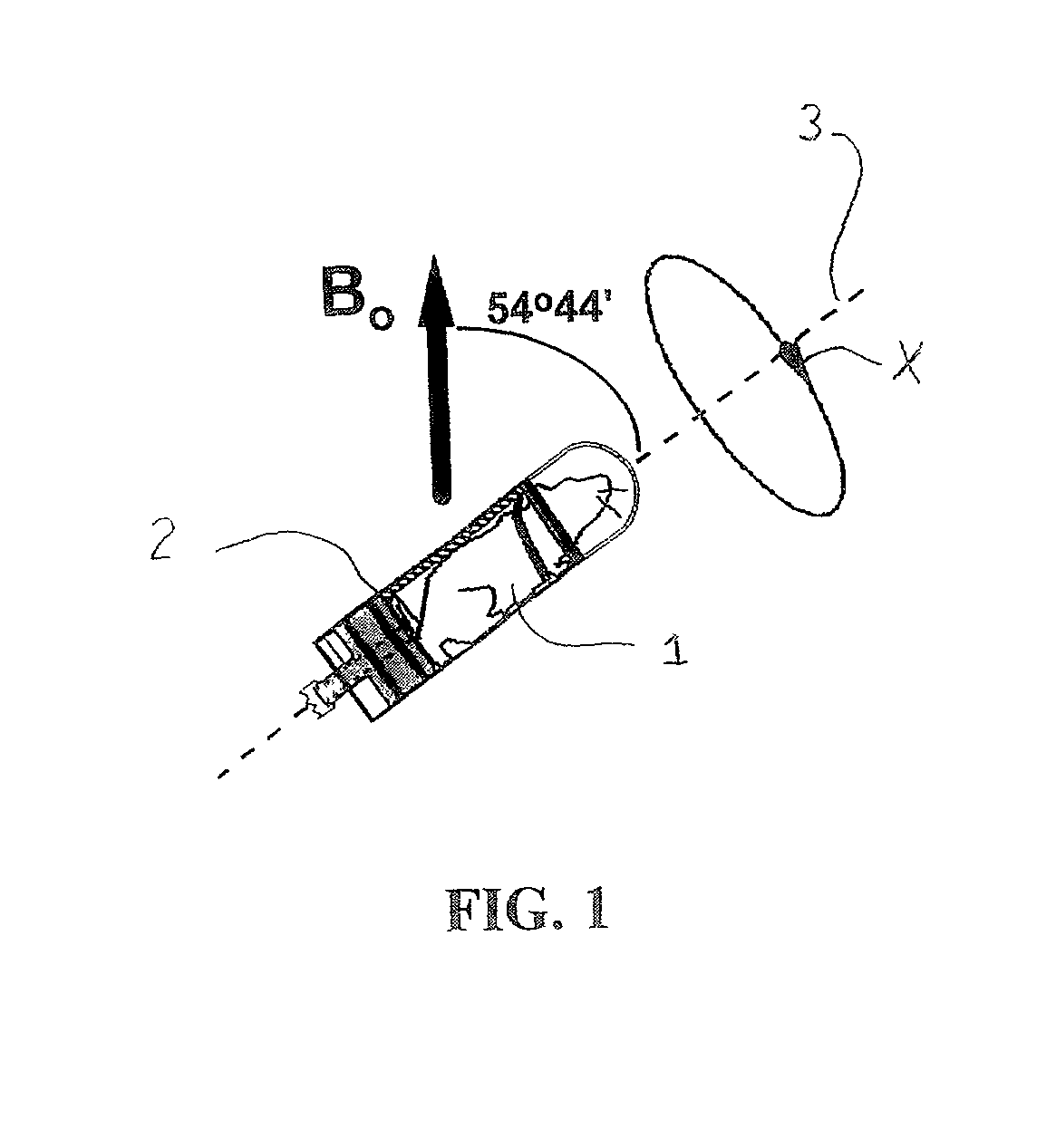
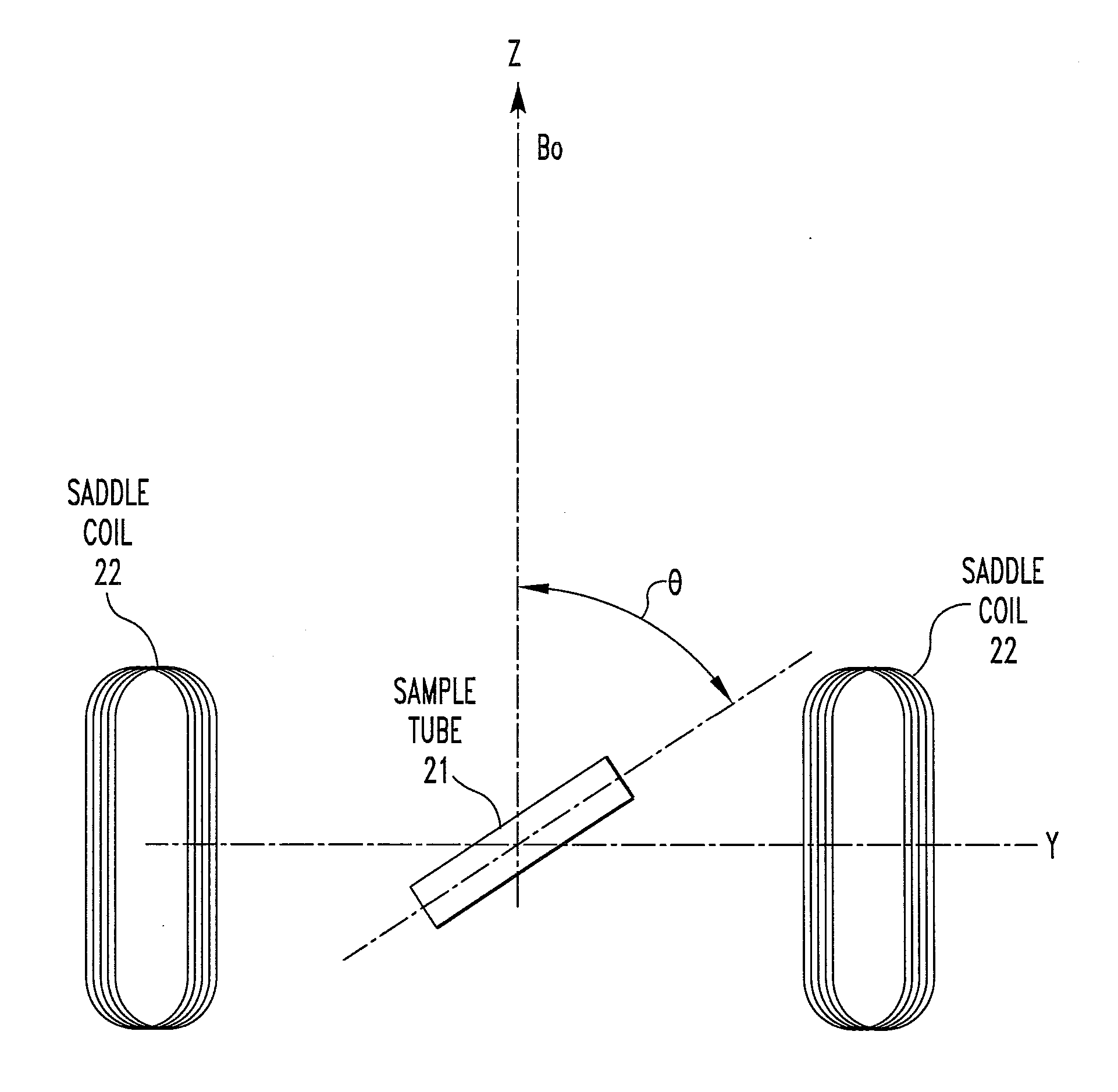
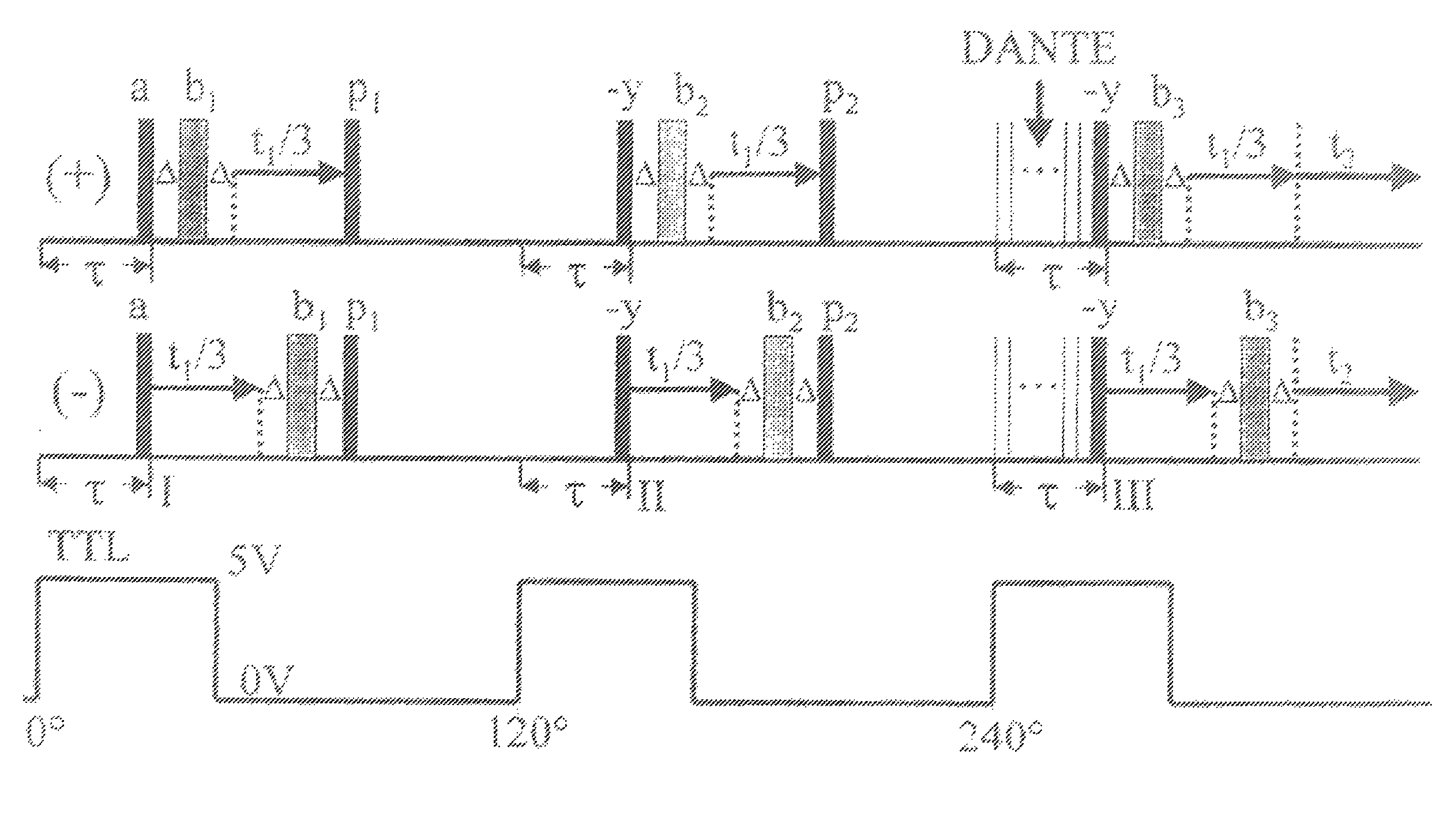
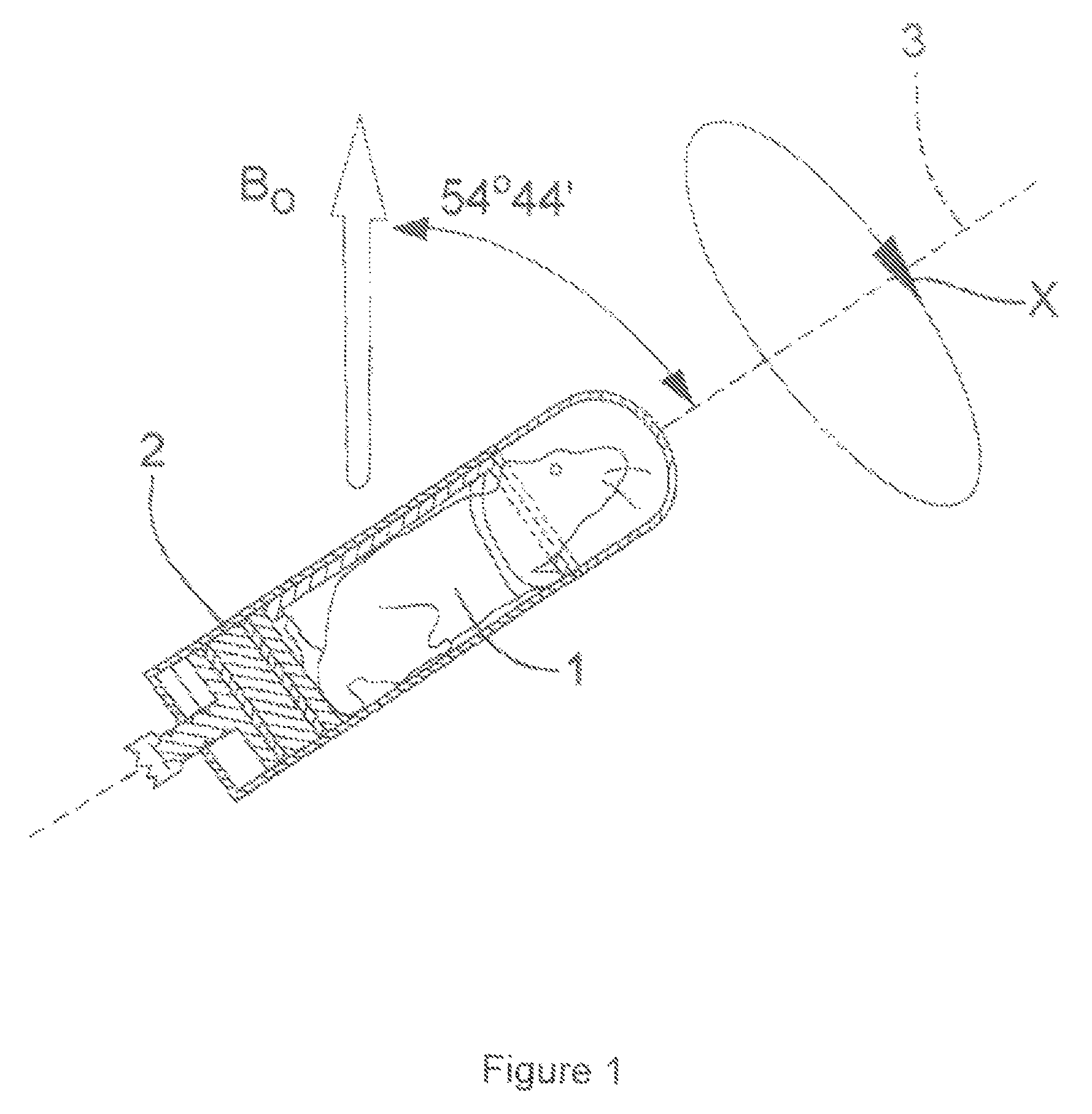
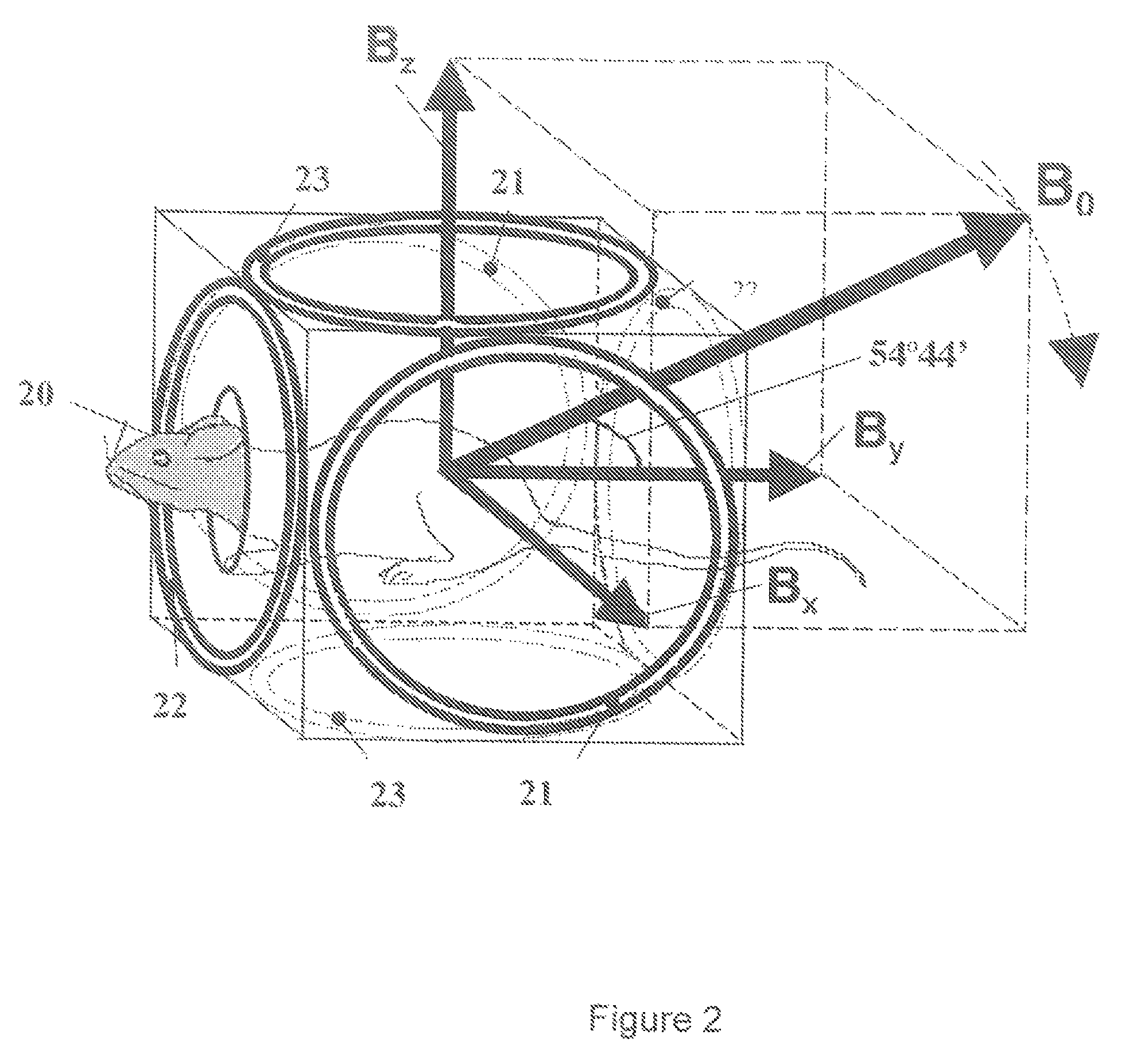
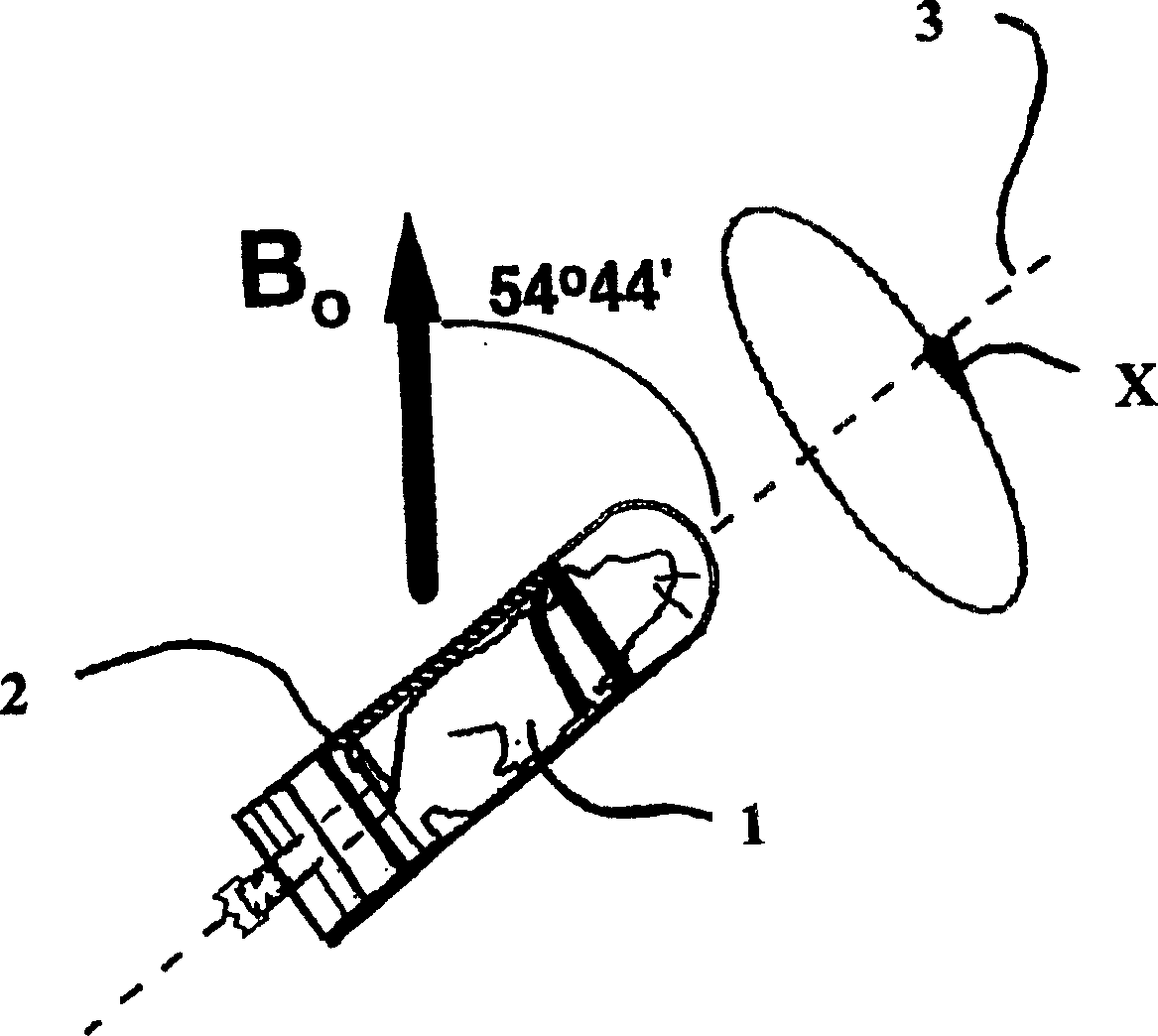
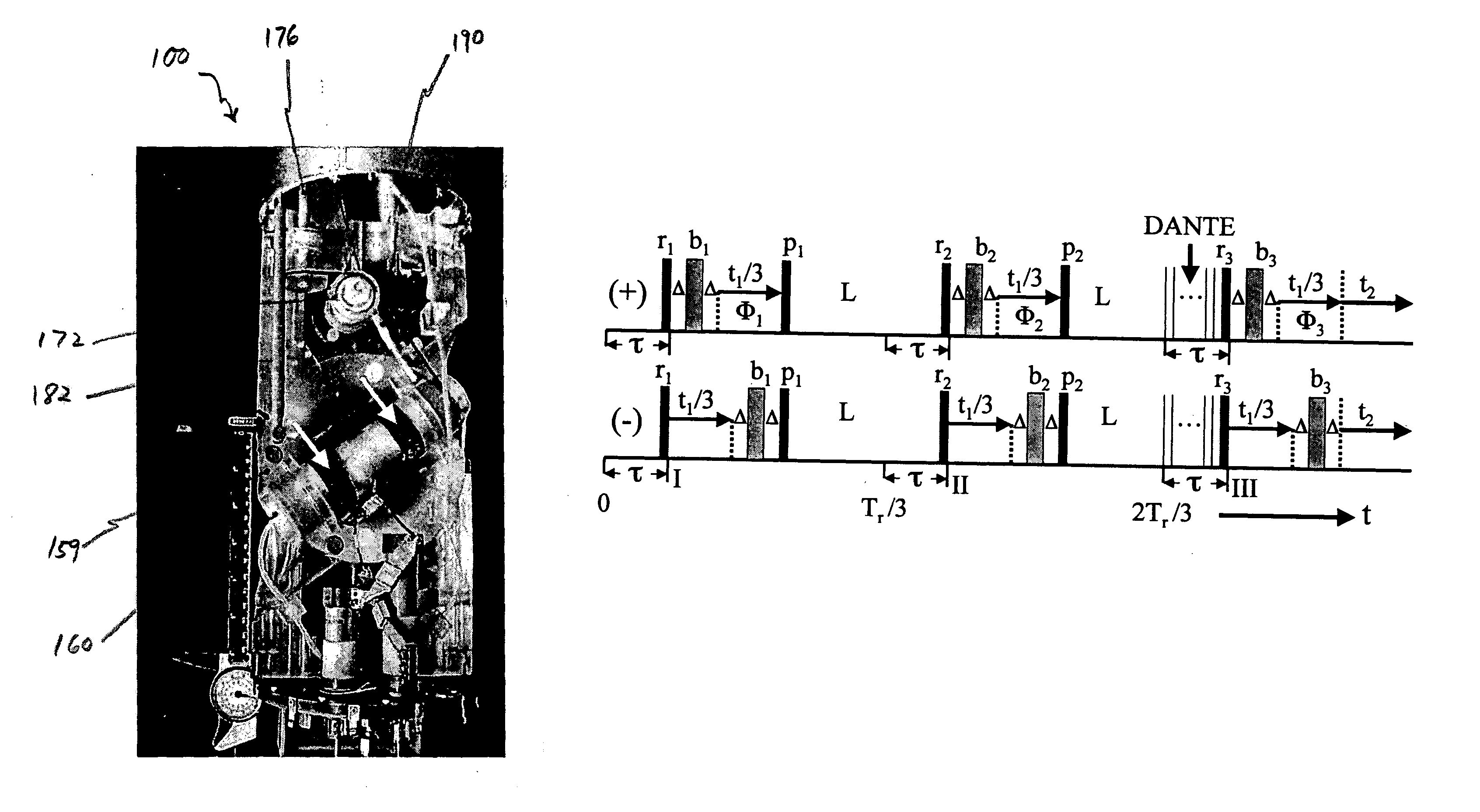
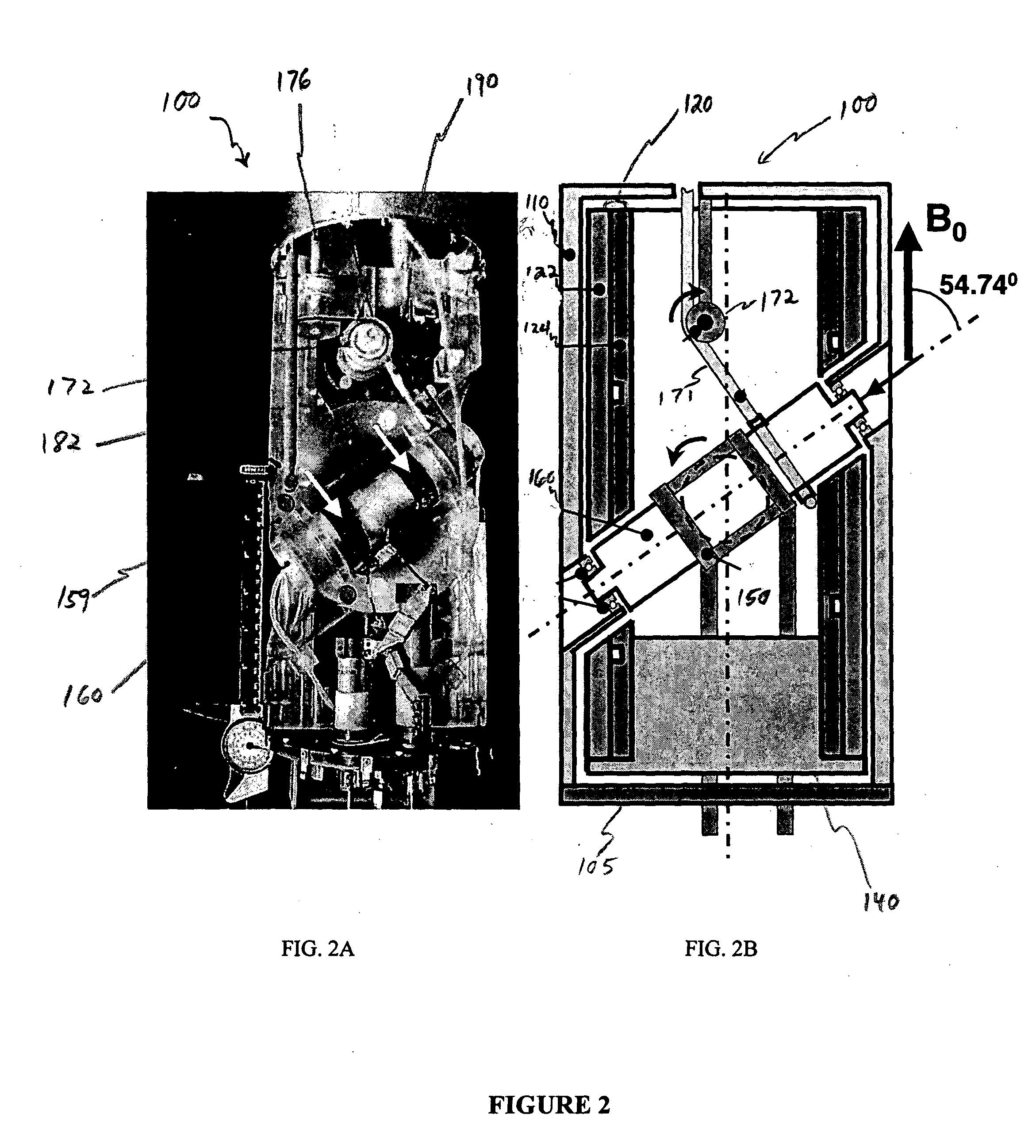
A method of performing a magnetic resonance analysis of a biological object that includes placing the object in a main magnetic field (that has a static field direction) and in a radio frequency field; rotating the object at a frequency of less than about 100 Hz around an axis positioned at an angle of about 54.degree.44' relative to the main magnetic static field direction; pulsing the radio frequency to provide a sequence that includes a phase-corrected magic angle turning pulse segment; and collecting data generated by the pulsed radio frequency. The object may be reoriented about the magic angle axis between three predetermined positions that are related to each other by 120.degree.. The main magnetic field may be rotated mechanically or electronically. Methods for magnetic resonance imaging of the object are also described.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Method and Apparatus for Accurately Adjusting Magic Angle in NMR
ActiveUS20110080171A1Easy to adjustSuppression of distortionElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRUniform fieldMagic angle
Method and apparatus for accurately adjusting the magic angle in NMR. The NMR probe has a uniform magnetic field coil assembly disposed to produce a uniform magnetic field H. The uniform magnetic field H is produced by controlling the currents flowing through the uniform magnetic field coil assembly. The vector sum of the external field B0 and the uniform field H is used to determine a new external magnetic field B0′.
Owner:JEOL LTD
Advanced slow-magic angle spinning probe for magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy
InactiveUS6989674B2Additive manufacturing apparatusMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyMagic angle spinningMetabolite
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
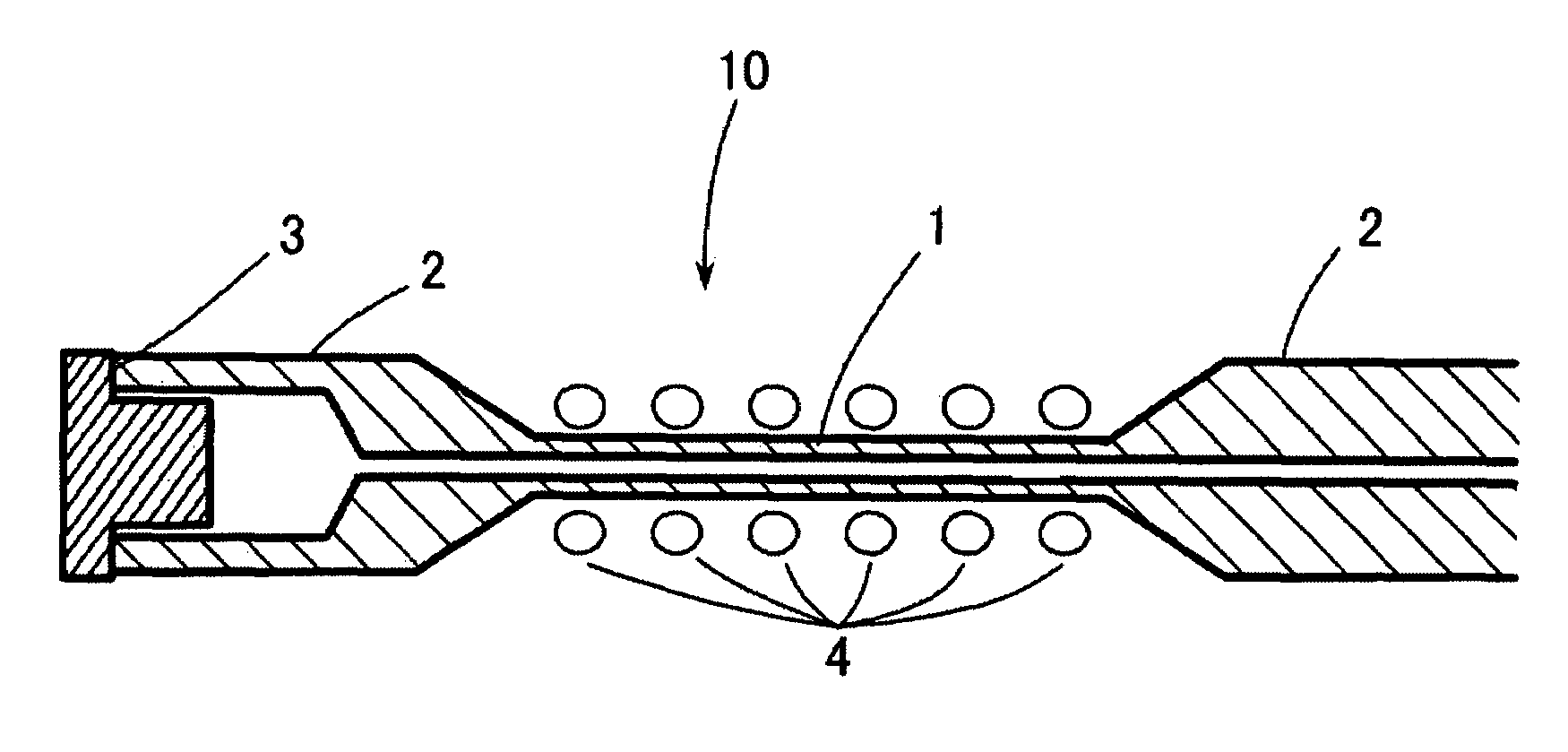
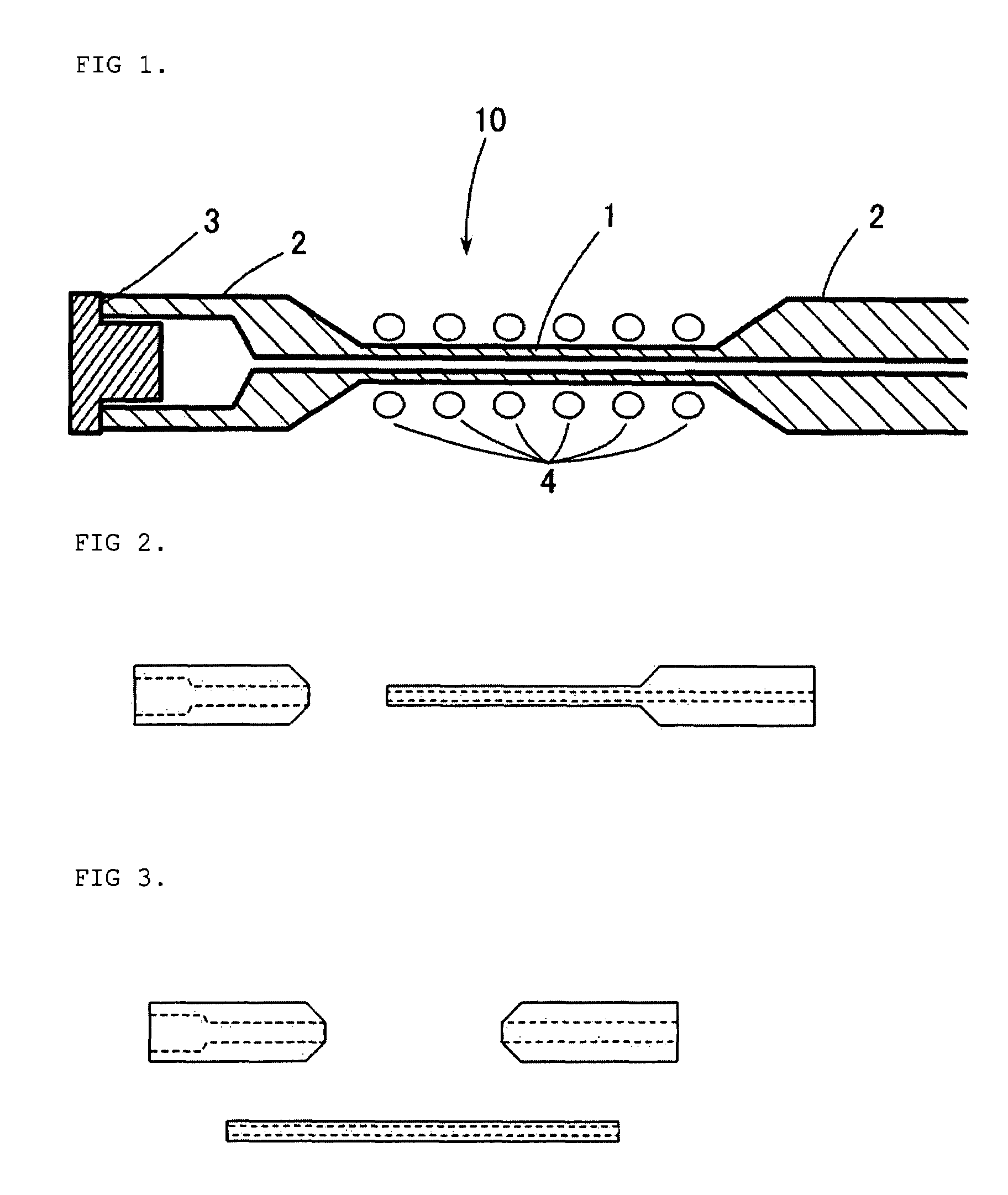
Sample Tube for Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Apparatus Magic Angle High-Speed Rotation Method and Method for Measuring Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Absorption Spectrum Employing It
InactiveUS20080007262A1Smooth rotationHigh sensitivityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
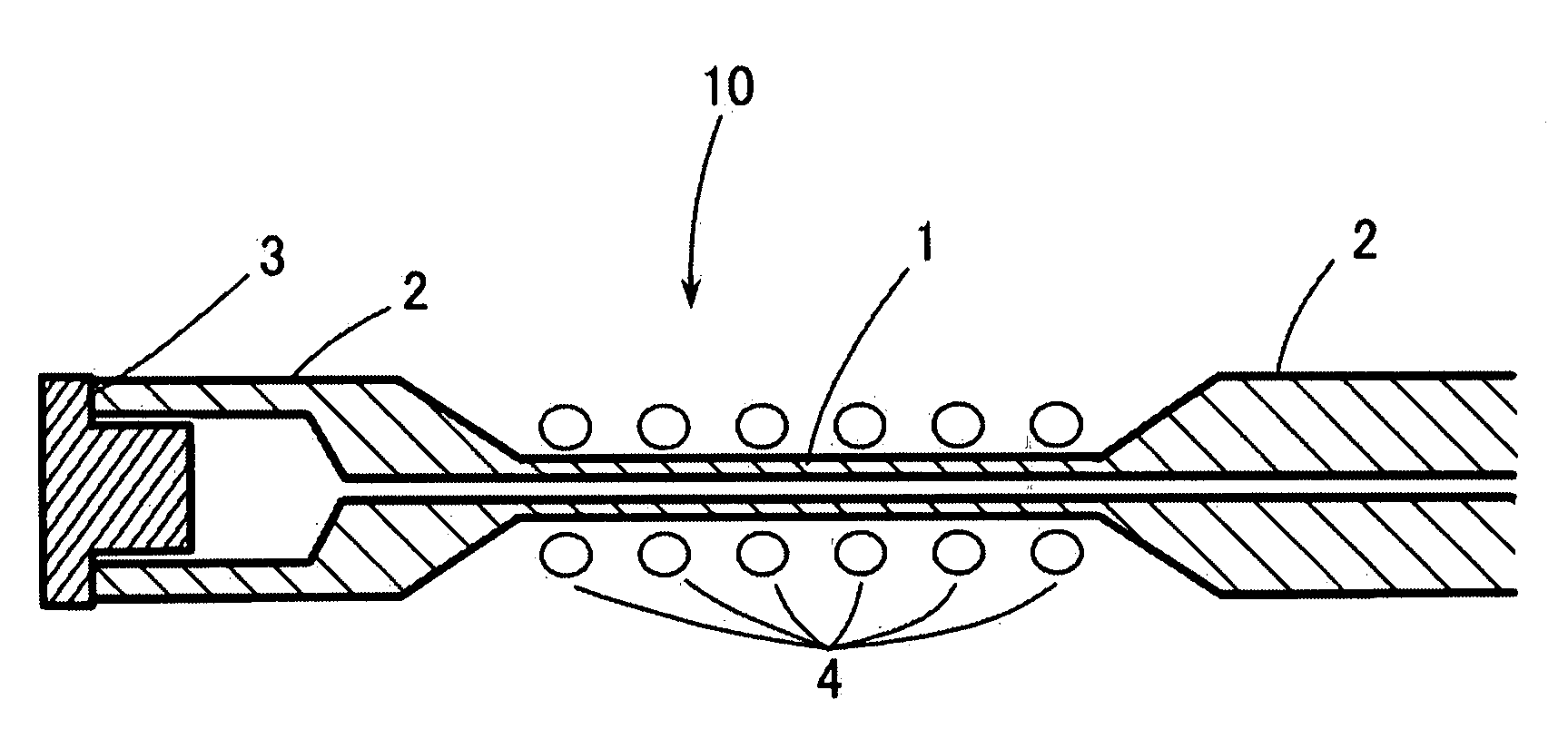
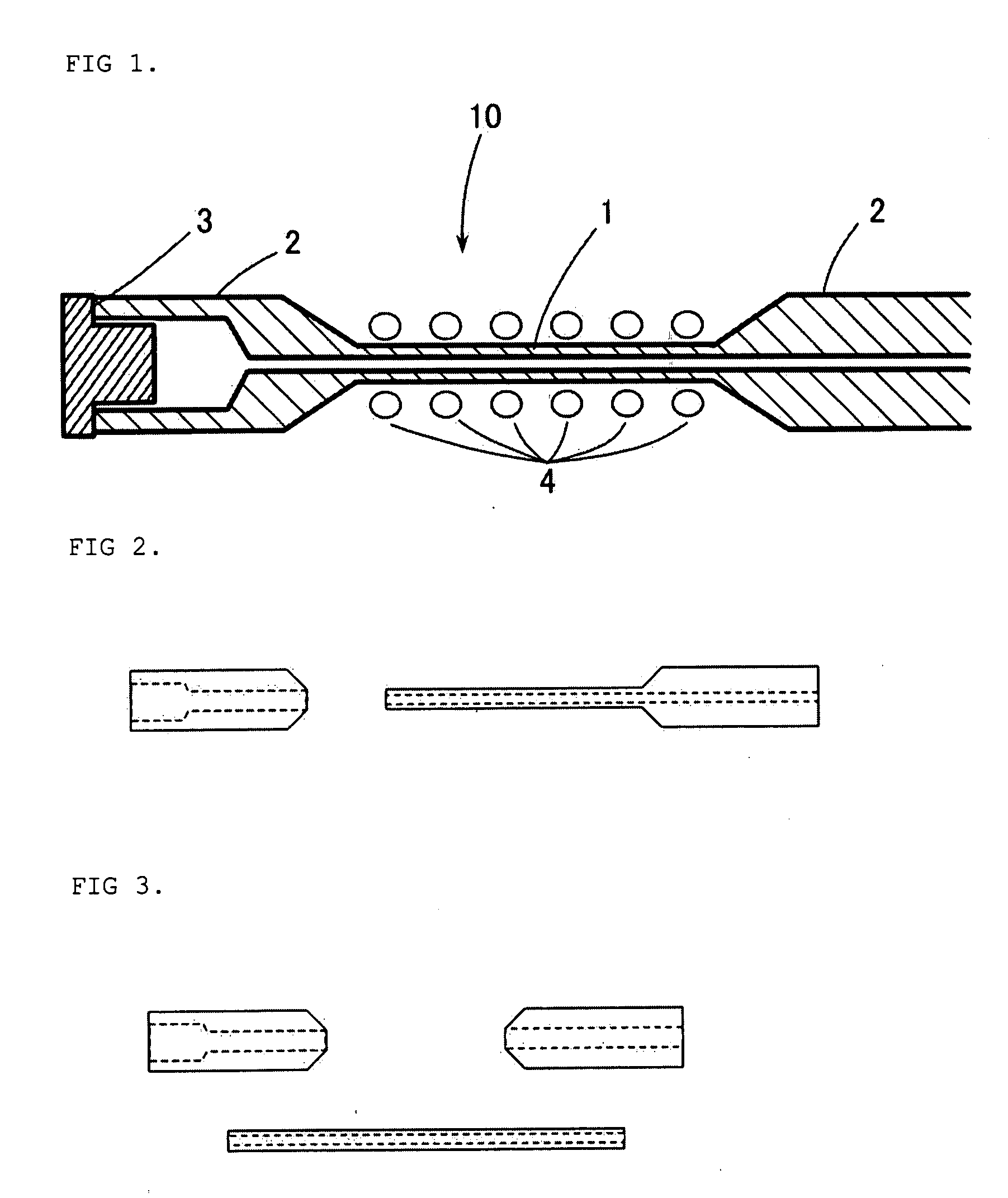
The present invention discloses a sample tube for the magic angle high-speed rotation method used in a solid nuclear magnetic resonance device probe wherein a radio wave irradiation / detection coil is disposed close to a sample and a method of measuring a high resolution nuclear magnetic resonance absorption spectrum using the same. This tube is suitable for solid nuclear magnetic resonance (solid NMR) measurements of minute amounts of sample. The sample tube has a capillary part filled with a sample and non-capillary parts situated at its two ends, and a spinner which can be detachably inserted into at least one of the outer ends of the non-capillary parts. The capillary part and non-capillary parts are made of a ceramic and / or polymer material.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP TOKYO UNIV OF AGRI & TECH
Methods for magnetic resonance analysis using magic angle technique
ActiveUS8064982B2Reduce unwanted signalReduce signalingMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringBiological bodyVoxel
Methods of performing a magnetic resonance analysis of a biological object are disclosed that include placing the object in a main magnetic field (that has a static field direction) and in a radio frequency field; rotating the object at a frequency of less than about 100 Hz around an axis positioned at an angle of about 54°44′ relative to the main magnetic static field direction; pulsing the radio frequency to provide a sequence that includes a phase-corrected magic angle turning pulse segment; and collecting data generated by the pulsed radio frequency. In particular embodiments the method includes pulsing the radio frequency to provide at least two of a spatially selective read pulse, a spatially selective phase pulse, and a spatially selective storage pulse. Further disclosed methods provide pulse sequences that provide extended imaging capabilities, such as chemical shift imaging or multiple-voxel data acquisition.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Method for high resolution magnetic resonance analysis using magic angle technique
InactiveCN1524187AMagnetic property measurementsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceBiological bodyMagic angle
A method of performing a magnetic resonance analysis of a biological object that includes placing the object in a main magnetic field (that has a static field direction) and in a radio frequency field; rotating the object at a frequency of less than about 100 Hz around an axis positioned at an angle of about 54 DEG 44' relative to the main magnetic static field direction; pulsing the radio frequency to provide a sequence that includes a phase-corrected magic angle turning pulse segment; and collecting data generated by the pulsed radio frequency. The object may be reoriented about the magic angle axis between three predetermined positions that are related to each other by 120 DEG. The main magnetic field may be rotated mechanically or electronically. Methods for magnetic resonance imaging of the object are also described.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
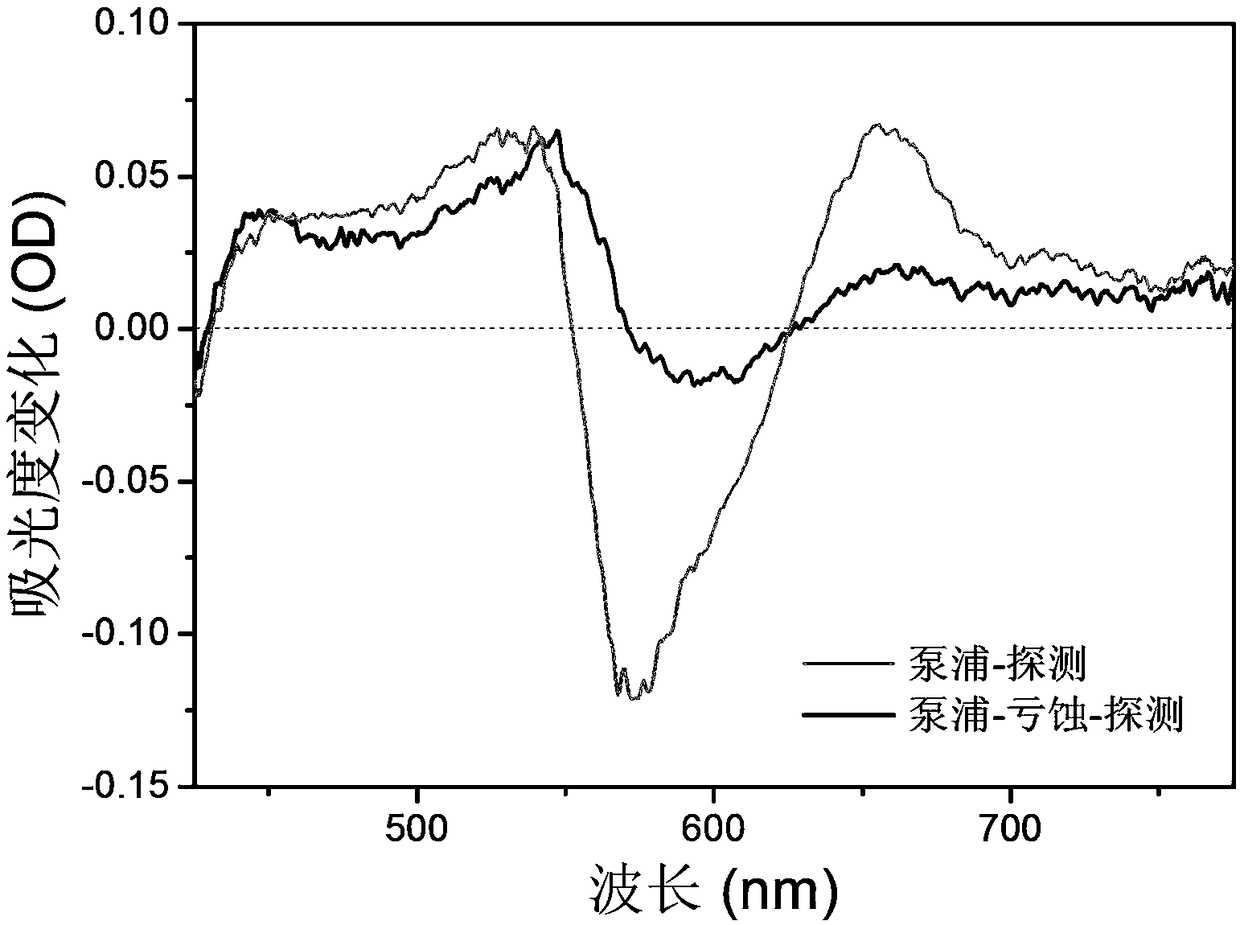
Femtosecond broadband pumping-excitation/eclipse-detection spectrometer
ActiveCN108872073ARealize measurementAccurate measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical reactionOptoelectronics
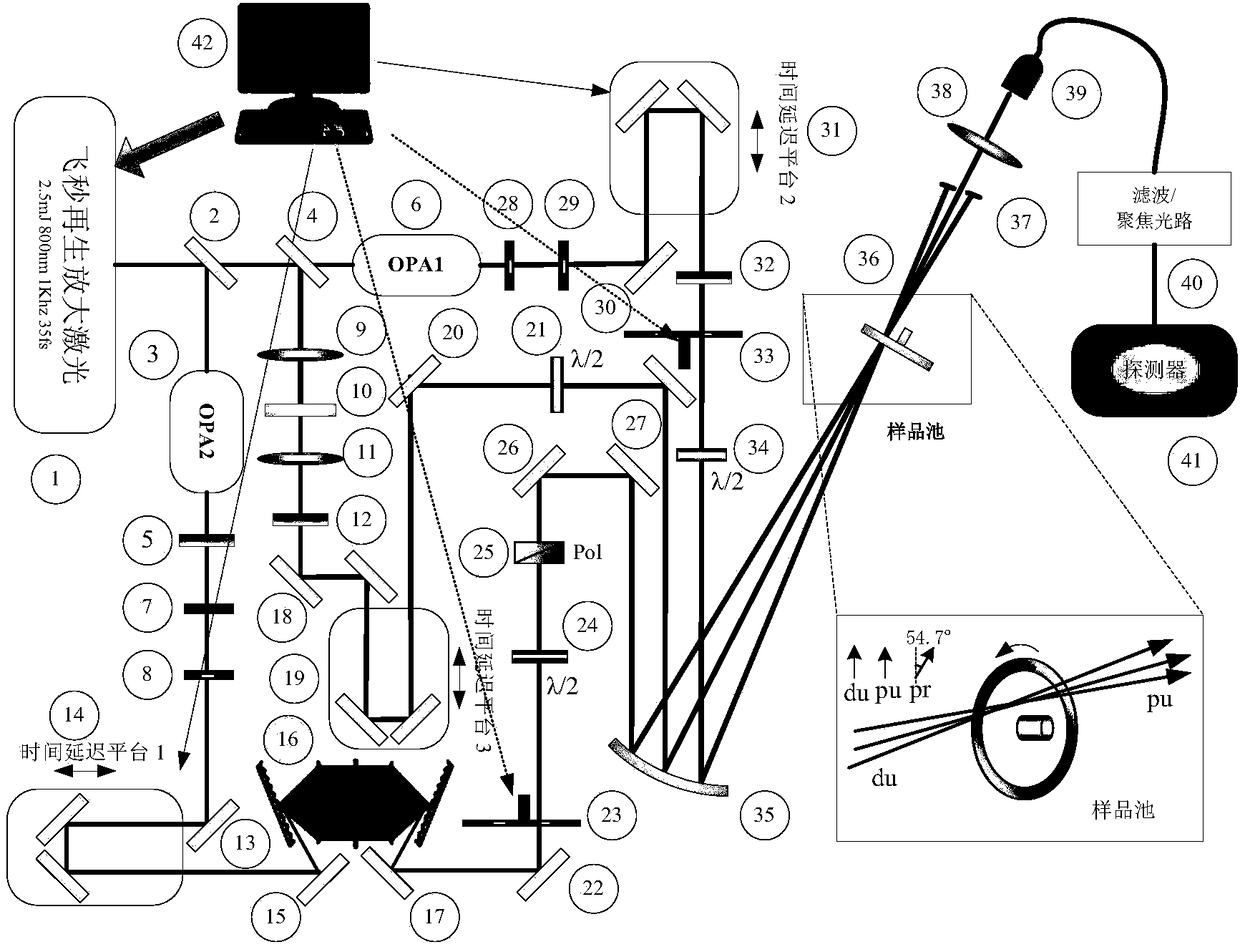
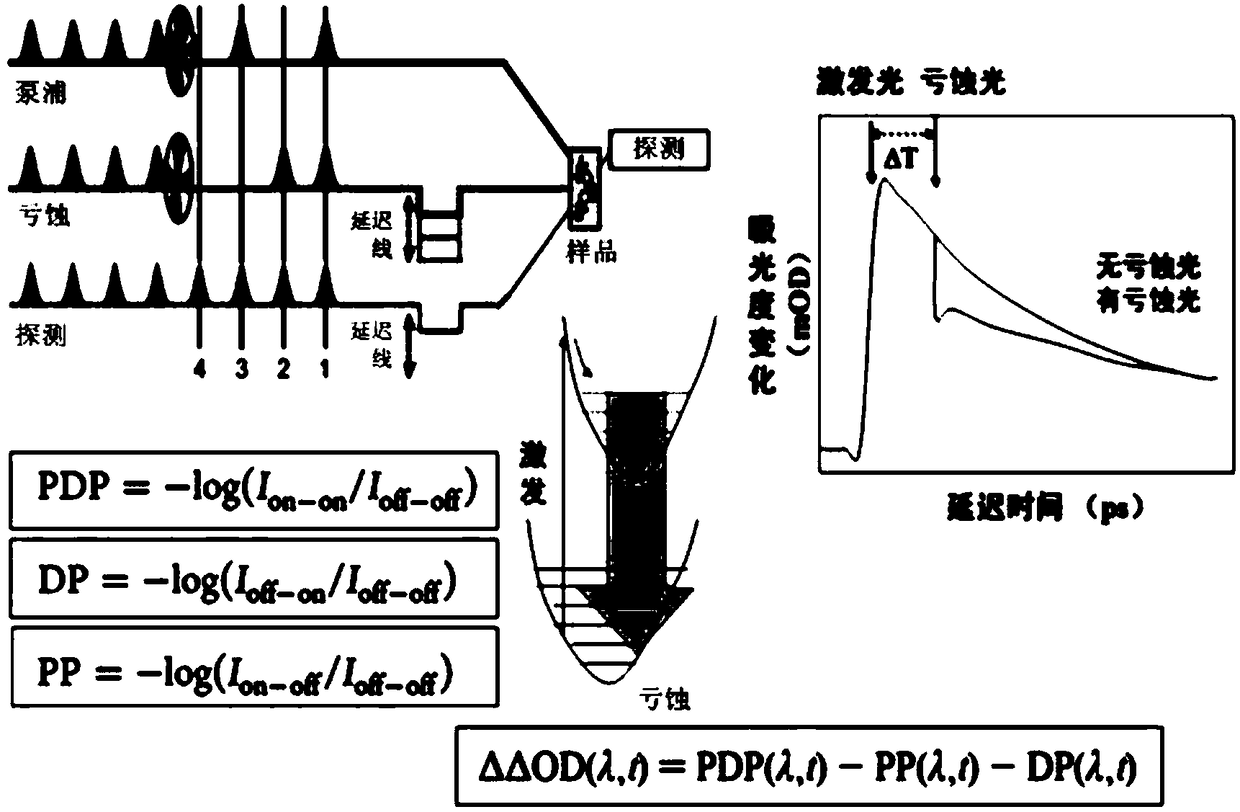
The invention relates to a femtosecond broadband pumping-excitation / eclipse-detection spectrometer. The spectrometer generates pumping light, detection light and excitation / eclipse light, the spectrometer can perform double chopping modulation on the pumping light, and the excitation / eclipse light, and can control the time sequence of the excitation / eclipse light and the detection light reaching asample, wherein the detection light is ultra-continuous detection pulse forming a magic angle with the polarization direction of the pumping light. In addition, the polarization directions of the pumping light, and the excitation / eclipse light are consistent. The spectrometer can be used for detecting and acquiring the spectrum signals of the broadband detection light under each corresponding time sequence for further studying the ultra-fast dynamic behaviors of sample molecules in different excitation state processes. Compared with the existing relevant study methods, the spectrometer provided by the invention has the characteristics that the time resolution is high; the functions are strong; the processes capable of being studies are wider, and the like. The physical and chemical reaction artificial quantum regulation and control can be realized; the technology belongs to one of the novel and effective detection technologies in the modern ultra-fast spectrum technology.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
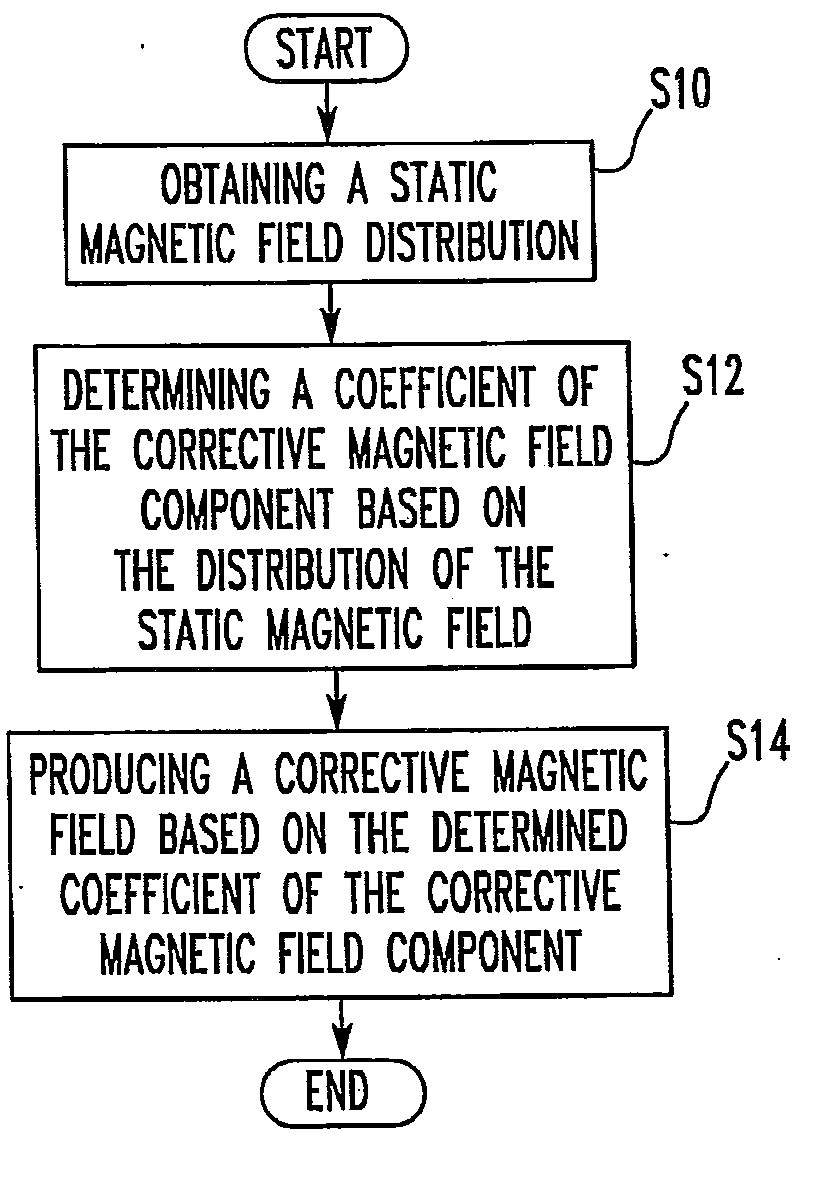
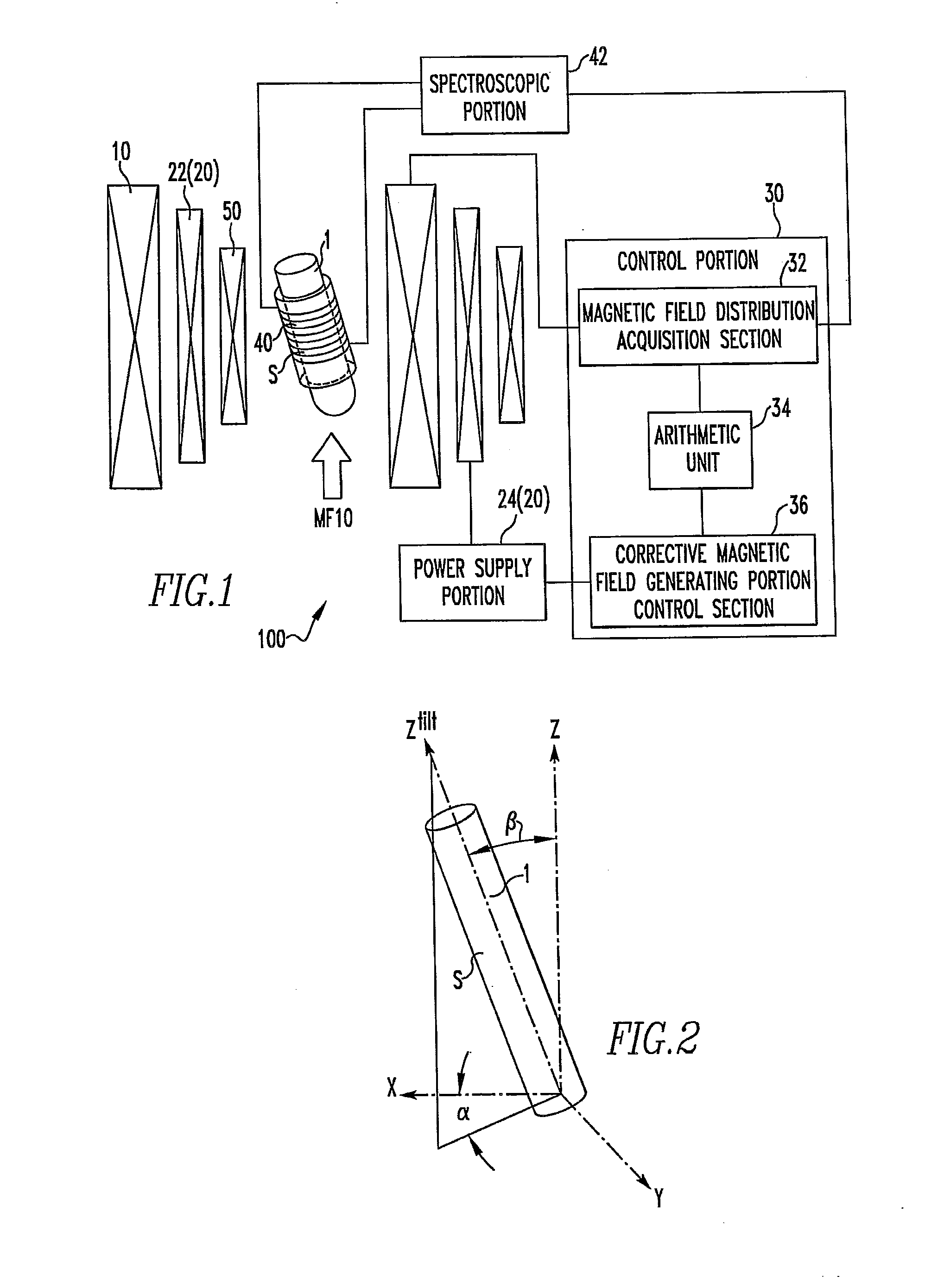
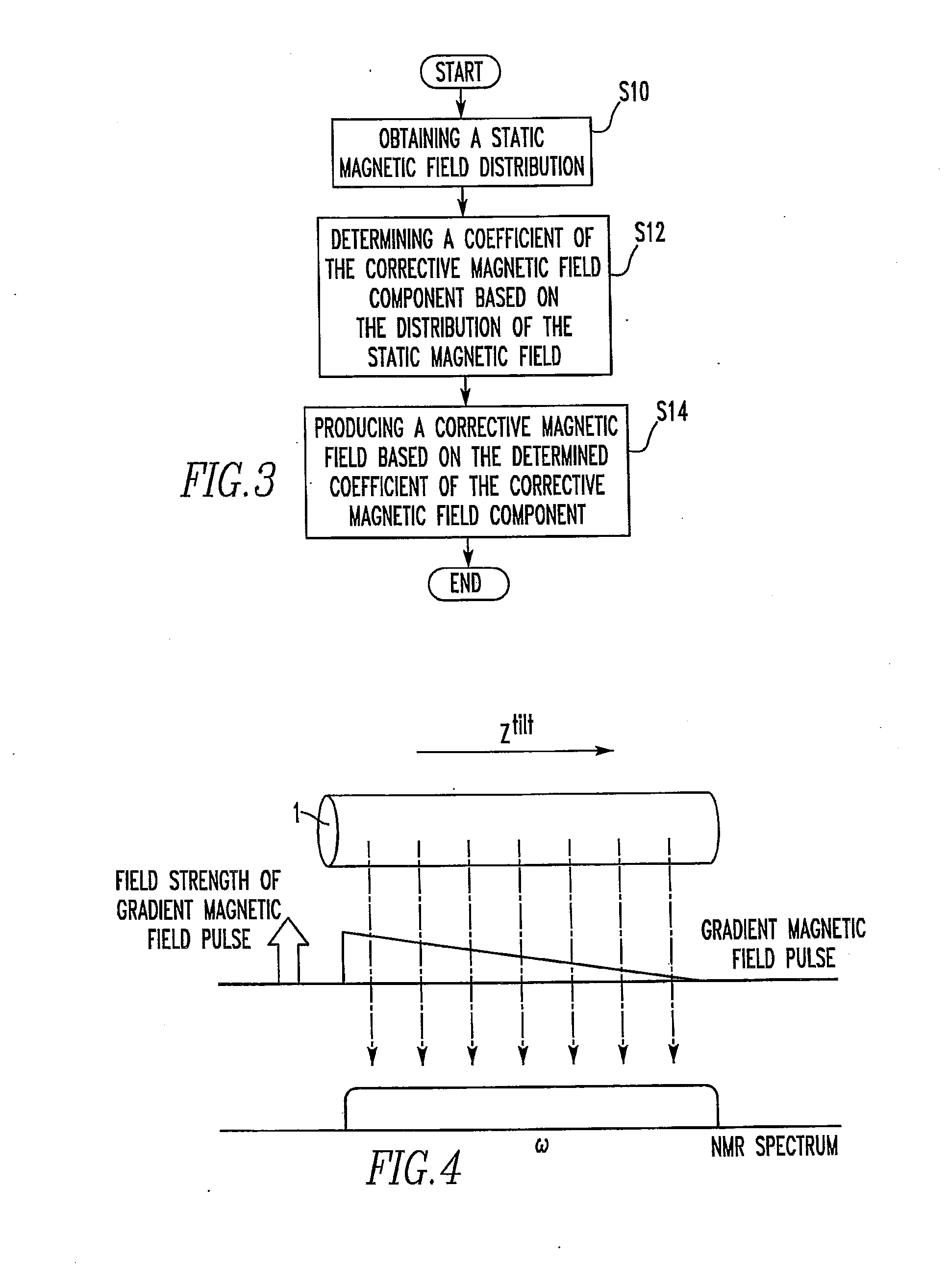
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer and Method of Magnetic Field Correction
ActiveUS20130030749A1Effective correctionTesting/calibration apparatusMagnetic measurementsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMagic angle
In a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrometer, a sample spins about an axis tilted at a magic angle, a corrective magnetic field generating portion produces a corrective magnetic field, and a control portion controls the operation of the corrective magnetic field generating portion. An arithmetic unit included in the control portion uses at least one of BZ(1), B1(1)e, and B1(1)o or the linear sum of at least two of them as the first-order magnetic field component of the corrective magnetic field, uses at least one of B2(2)e, B2(2)o, B2(1)e, and B2(1)o or the linear sum of at least two of them as the second-order magnetic field component of the corrective magnetic field, and uses at least one of BZ(3), B3(1)e, B3(1)o, B3(2)e, B3(2)o, B3(3)e, and B3(3)o or the linear sum of at least two of them as the third-order magnetic field component of the corrective magnetic field.
Owner:JEOL LTD
Advanced slow-magic angle spinning probe for magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy
InactiveUS20050035766A1Additive manufacturing apparatusMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyMagic angle spinningMetabolite
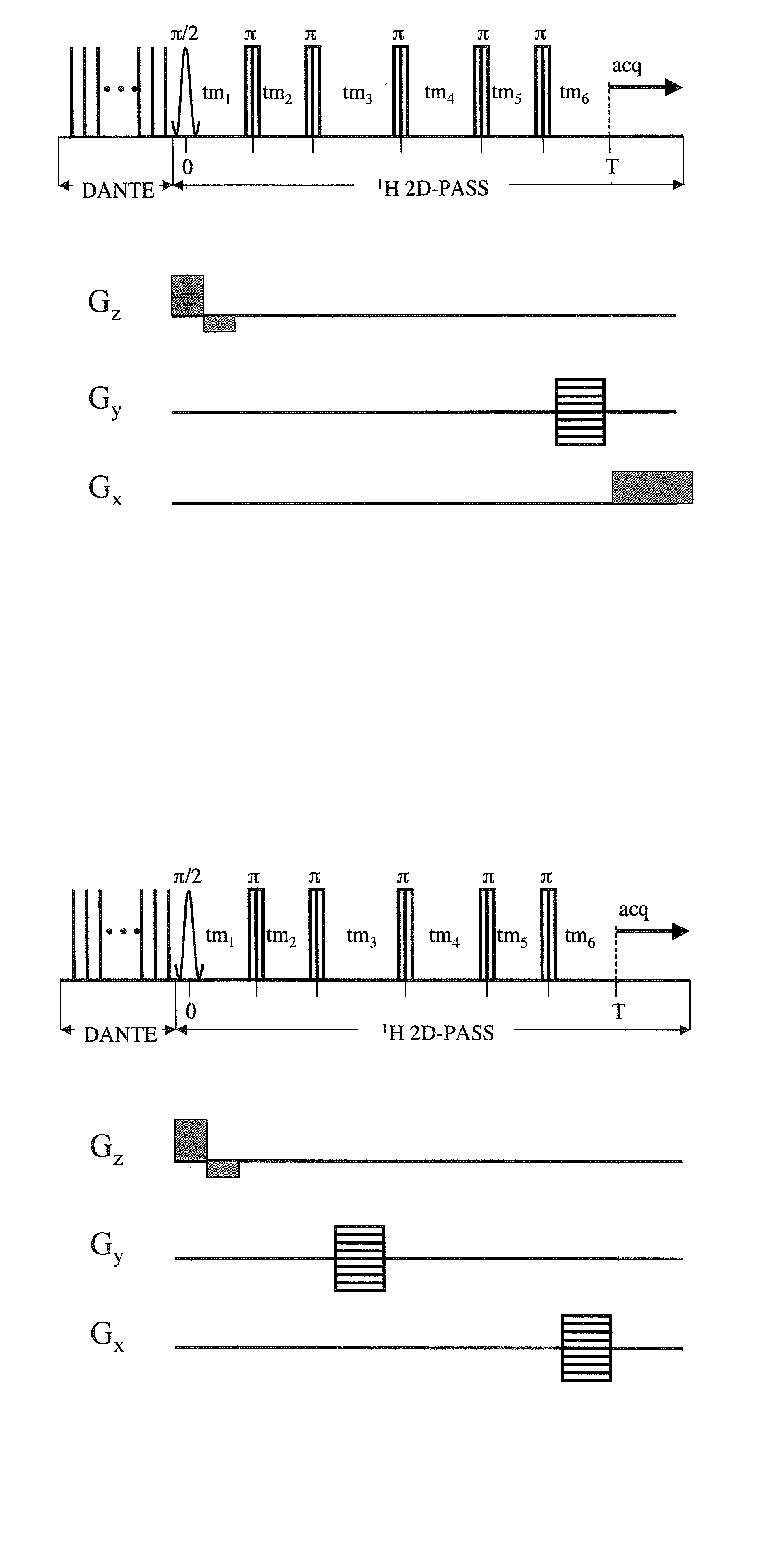
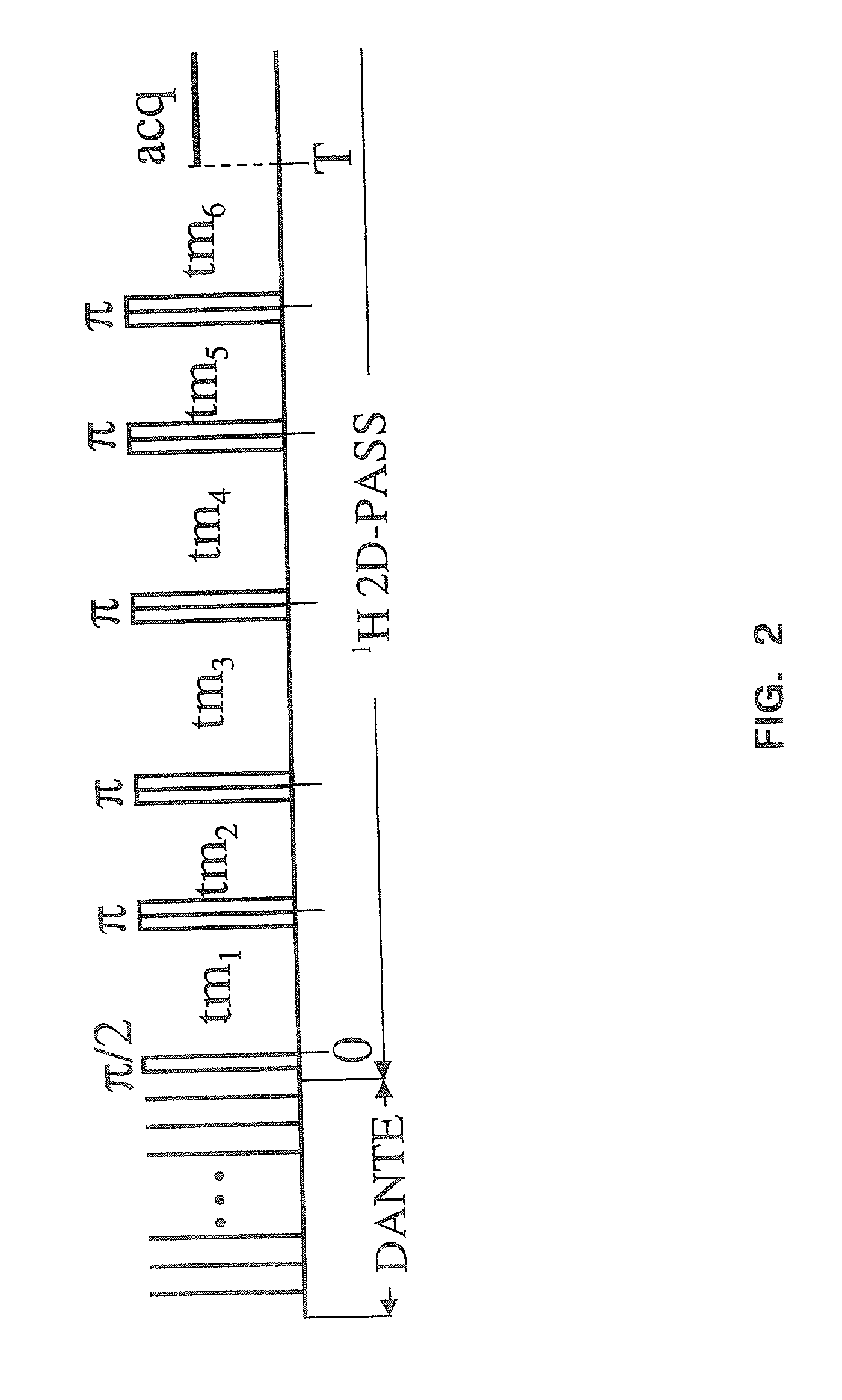
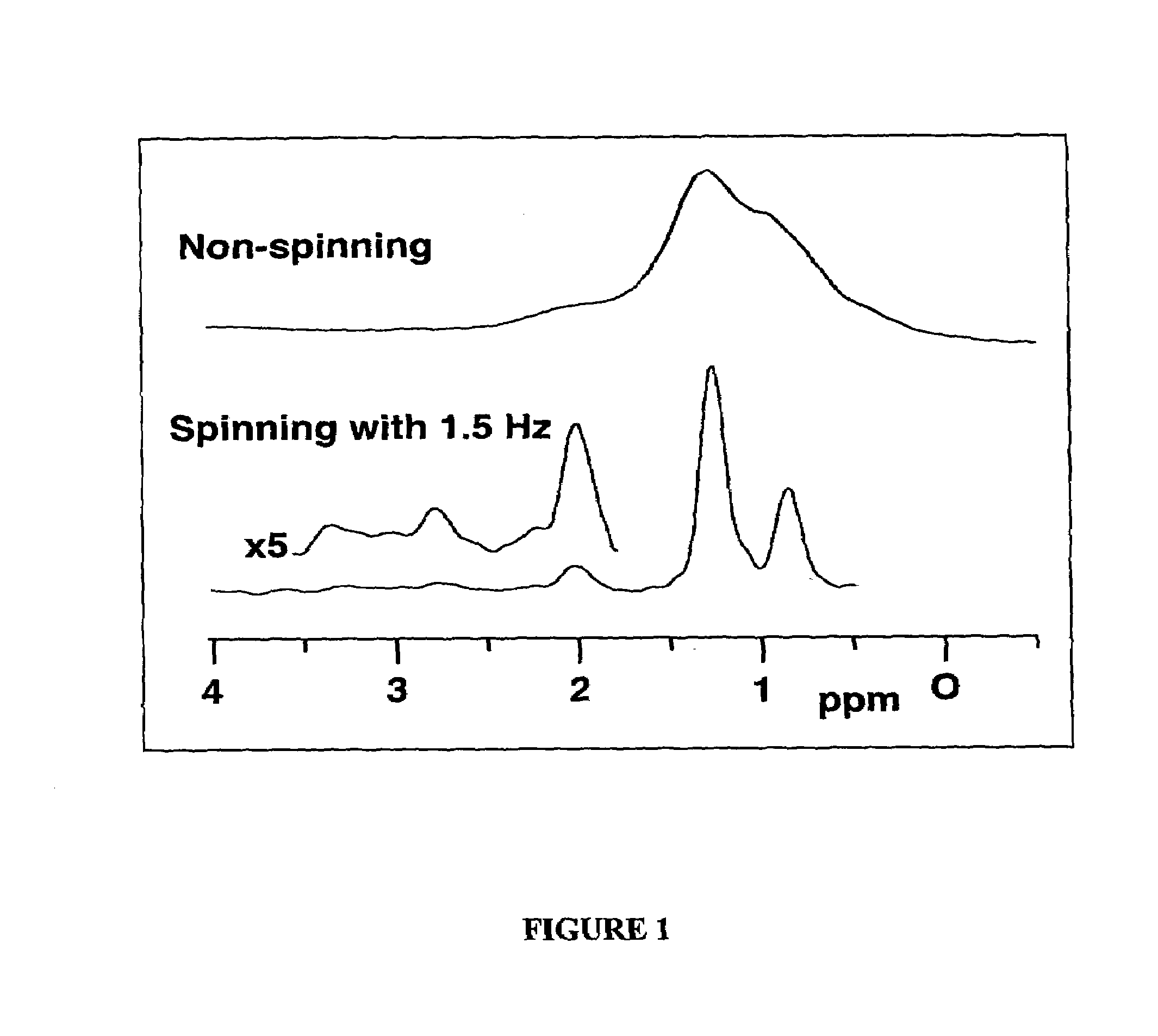
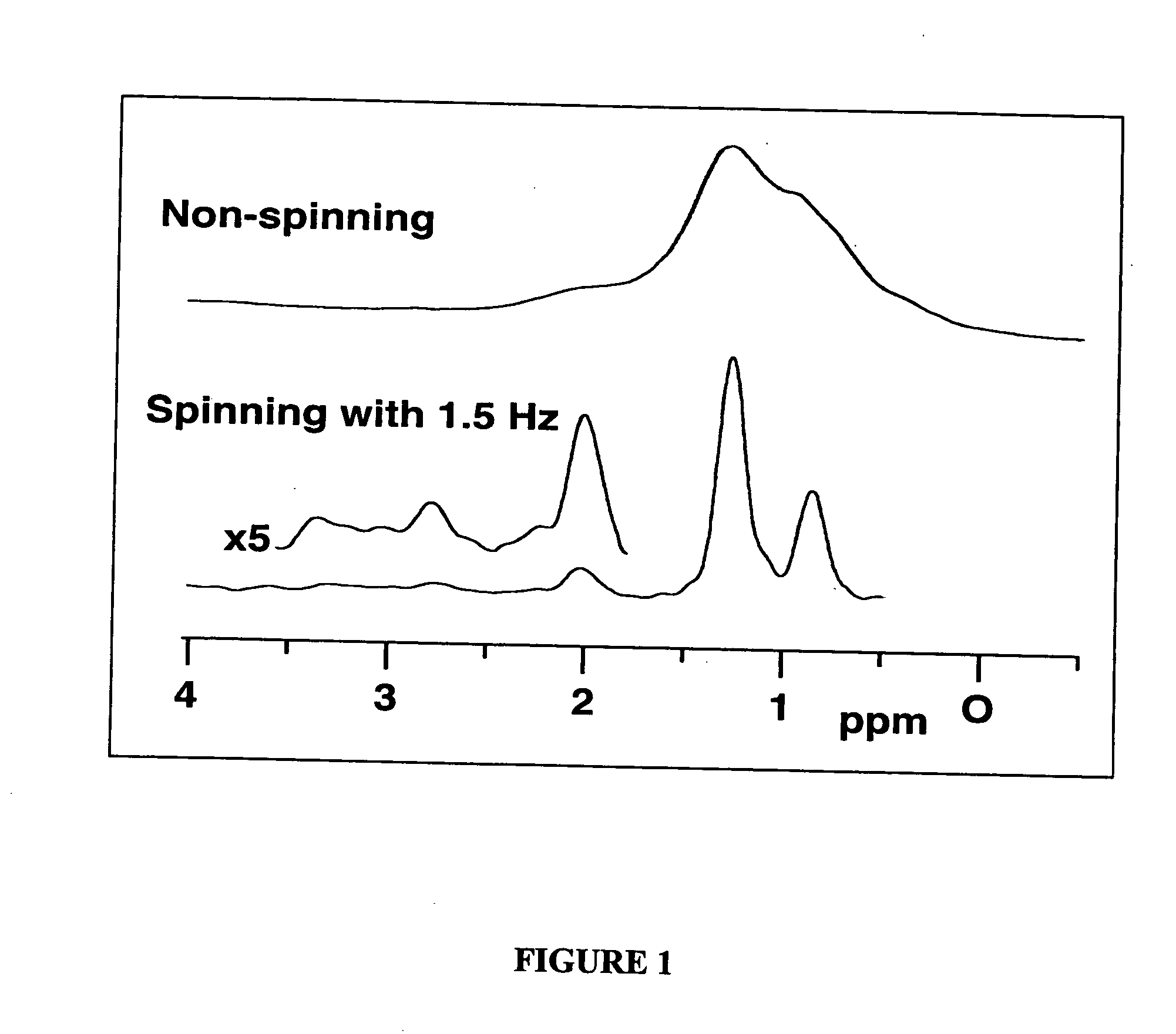
The present invention relates to a probe and processes useful for magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy instruments. More particularly, the invention relates to a MR probe and processes for obtaining resolution enhancements of fluid objects, including live specimens, using an ultra-slow (magic angle) spinning (MAS) of the specimen combined with a modified phase-corrected magic angle turning (PHORMAT) pulse sequence. Proton NMR spectra were measured of the torso and the top part of the belly of a female BALBc mouse in a 2 T field, while spinning the animal at a speed of 1.5 Hz. Results show that even in this relatively low field with PHORMAT, an isotropic spectrum is obtained with line widths that are a factor 4.6 smaller than those obtained in a stationary mouse. Resolution of 1H NMR metabolite spectra are thus significantly enhanced. Results indicate that PHORMAT has the potential to significantly increase the utility of 1H NMR spectroscopy for in vivo biochemical, biomedical and / or medical applications involving large-sized biological objects such as mice, rats and even humans within a hospital setting. For small-sized objects, including biological objects, such as excised tissues, organs, live bacterial cells, and biofilms, use of PASS at a spinning rate of 30 Hz and above is preferred.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Magnetic resonance imaging device and quantitative susceptibility mapping method
ActiveUS9766316B2Magnetic susceptibility of tissue can be calculatedImprove accuracyMedical imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic susceptibilityQuantitative susceptibility mapping
The estimation accuracy of a magnetic susceptibility value of tissue is improved by computing an edge image which represents the edge of the tissue on a magnetic susceptibility distribution and to reduce background noise without lowering the magnetic susceptibility value of the tissue. The present invention computes an absolute value image and a phase image from a complex image obtained by MRI, from the phase image, computes a low frequency region magnetic susceptibility image in which background noise is greater than a desired value, computes an edge information magnetic susceptibility image and computes a high frequency region magnetic susceptibility image, computes an edge mask from the edge information magnetic susceptibility image, smooths a magic angle region from the edge mask and the low frequency region magnetic susceptibility image and finally smooths a high frequency region using the high frequency region magnetic susceptibility image.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
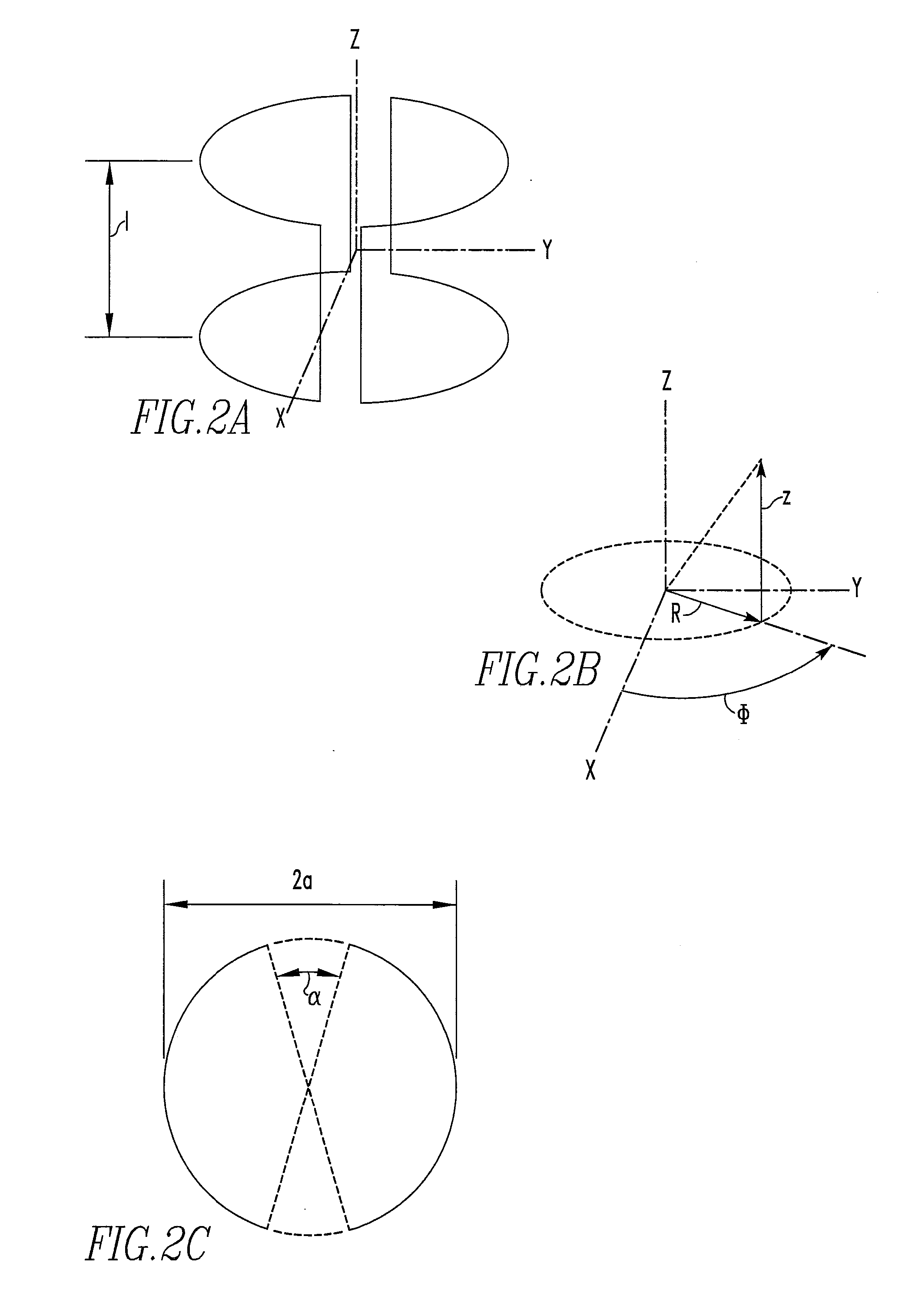
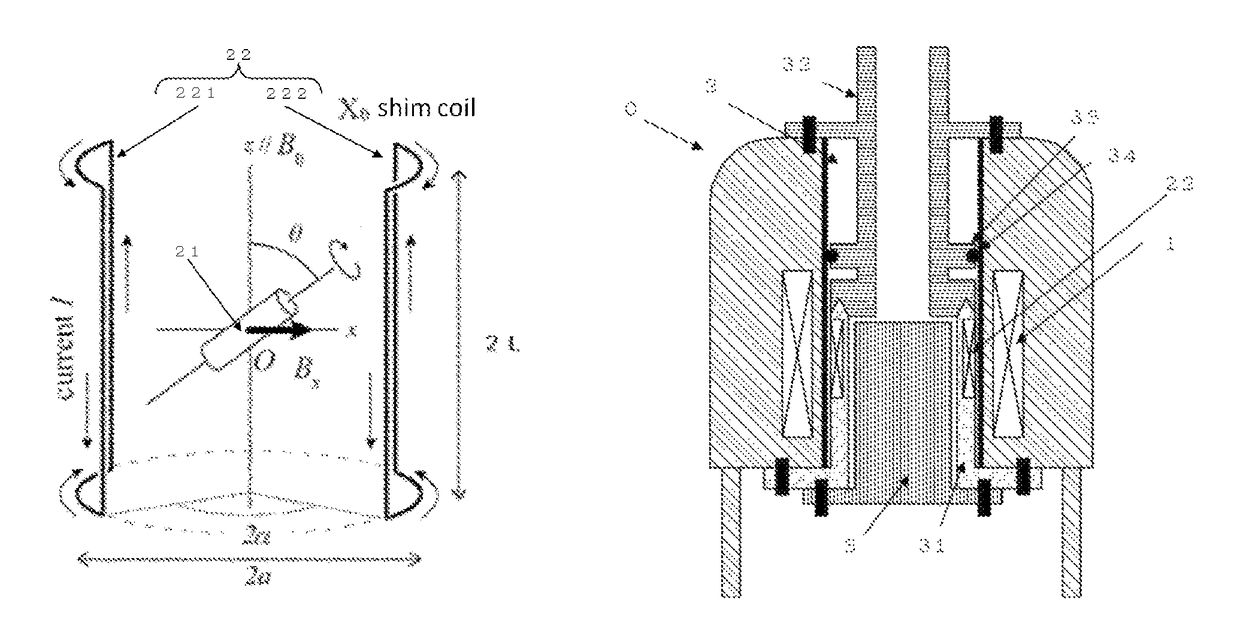
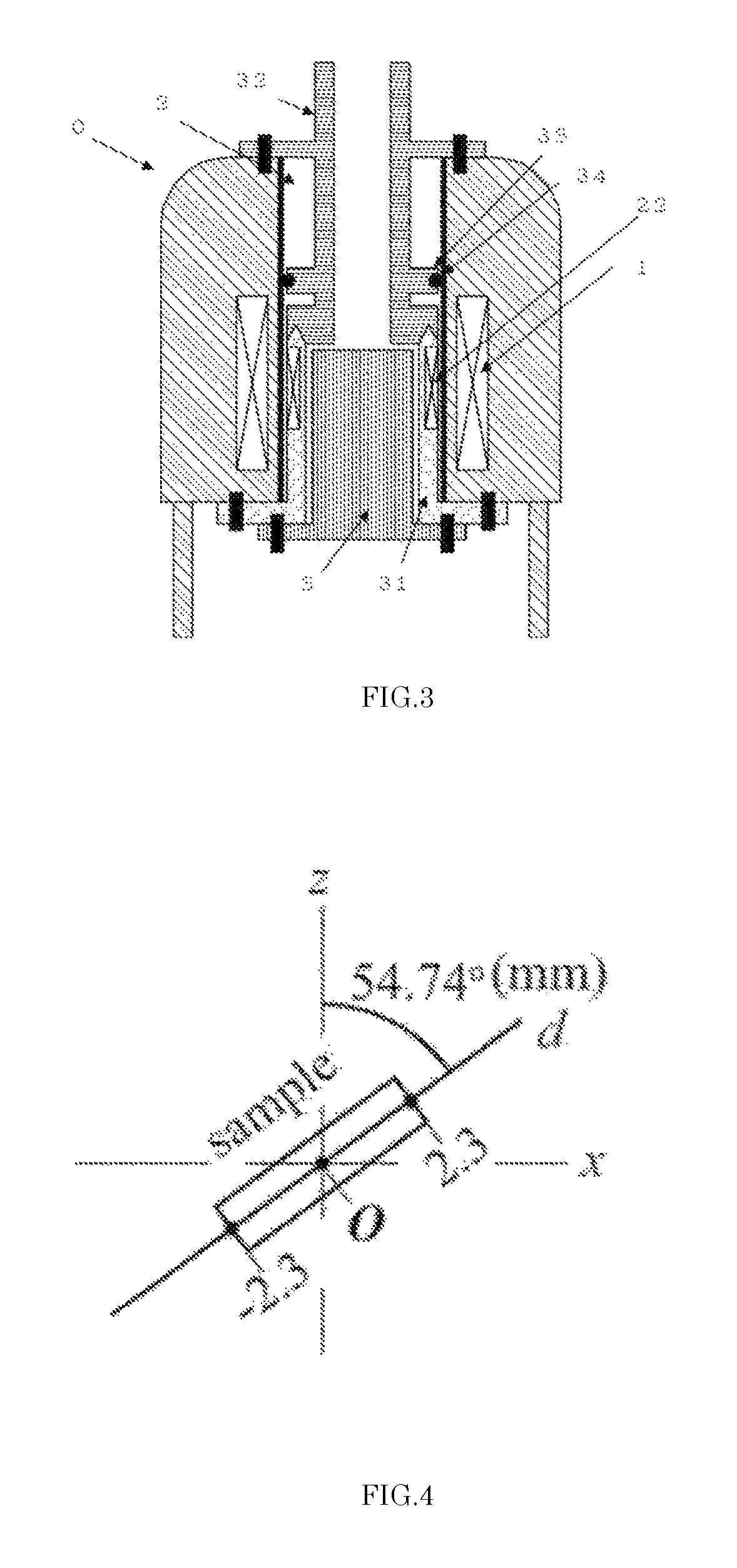
Coil assembly for accurate adjustment of magic angle in solid-state NMR apparatus and method of adjusting magic angle using such coil assembly
ActiveUS10048335B2Minimize impactAvoids increases in linewidthsMeasurements using NMR spectroscopySample rotationImage resolution
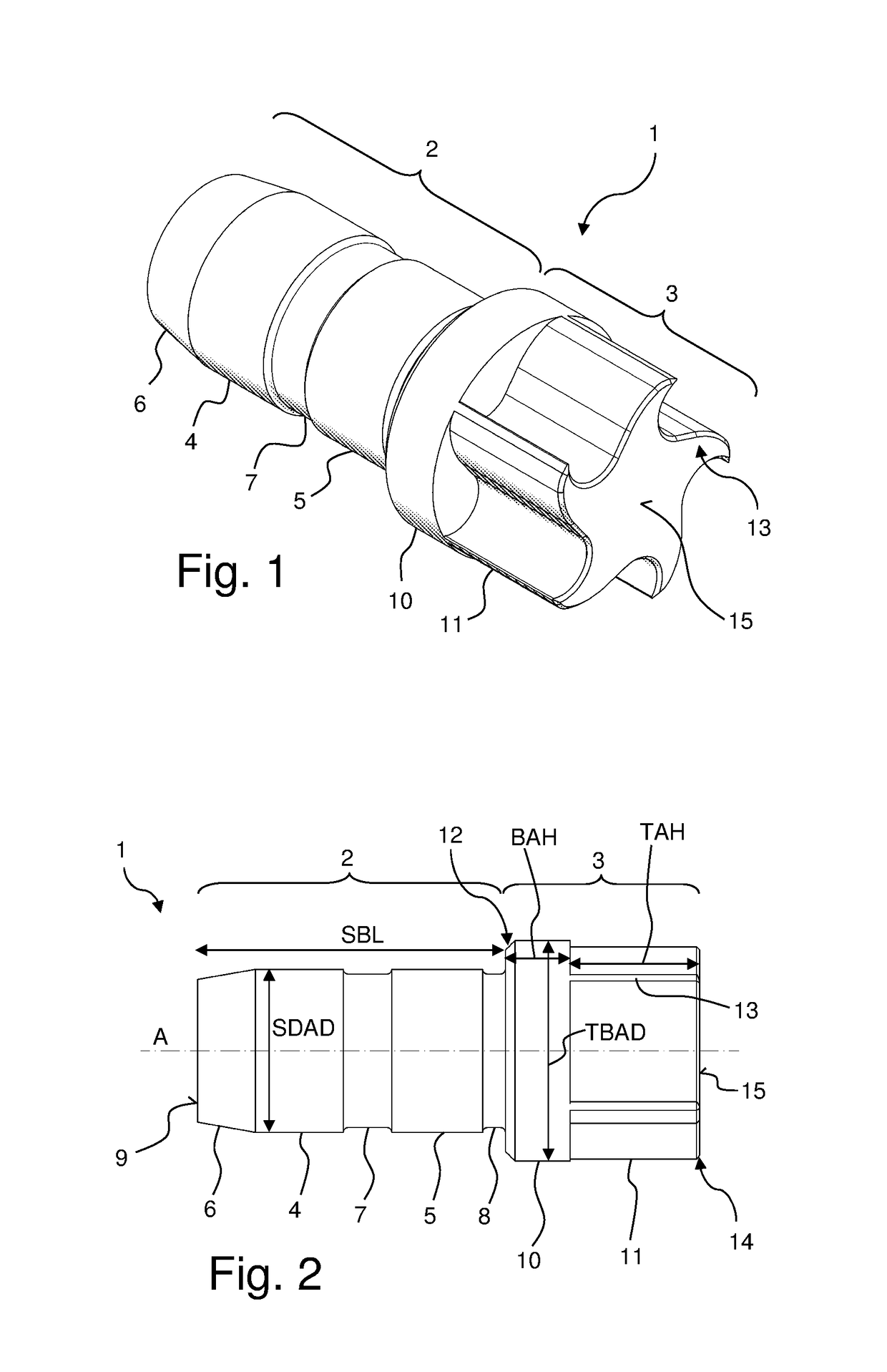
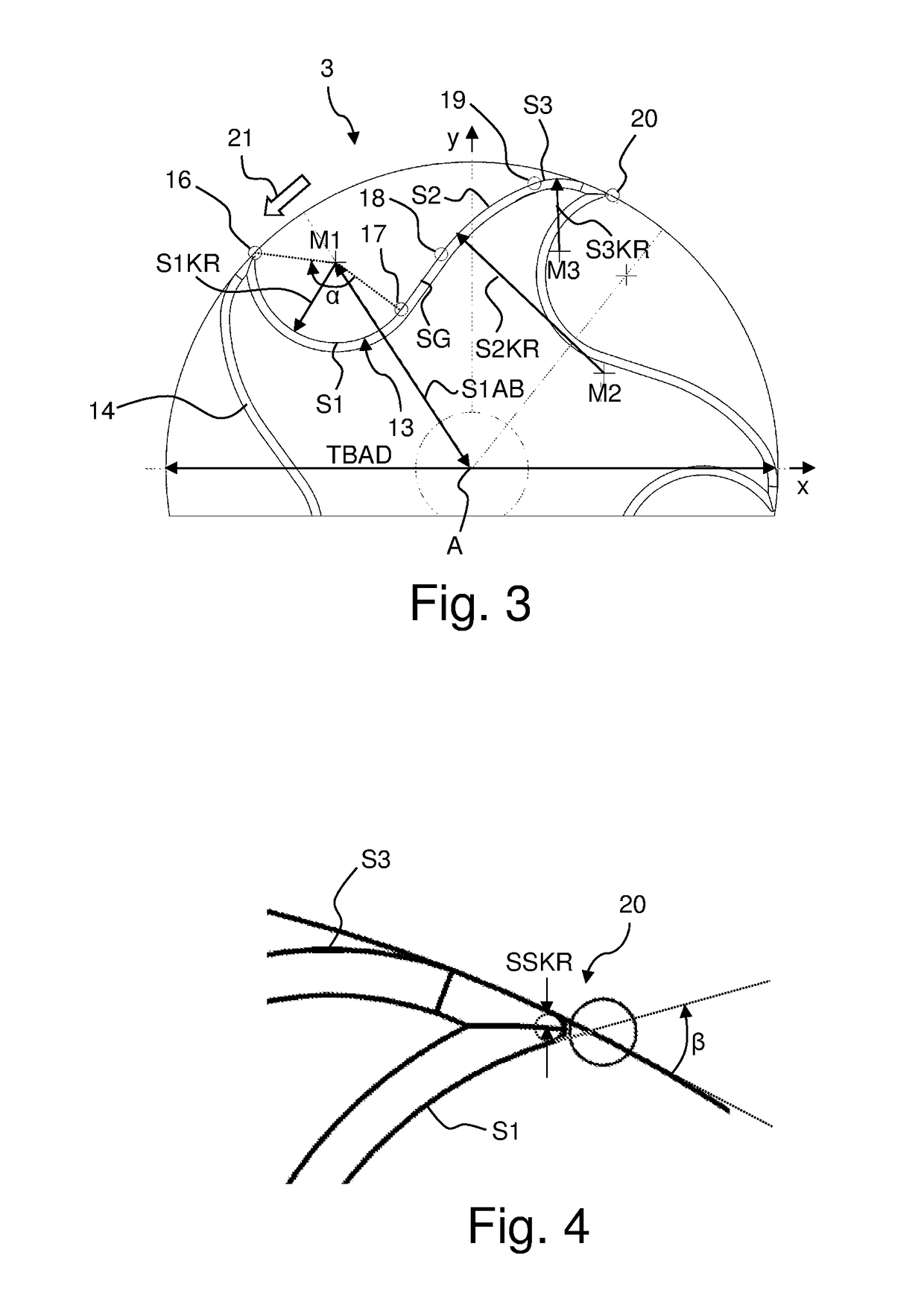
A specially shaped coil assembly for accurate adjustment of the magic angle is provided to permit accurate adjustment of an angle made between the direction of a static magnetic field and the axis of sample spinning without impairing the resolution of NMR signals. The sample is placed within the external static magnetic field B0. The coil assembly is for use in a solid-state NMR apparatus that performs NMR detection while spinning the sample about an axis tilted at the magic angle relative to the external static magnetic field B0. The coil assembly comprises a pair of arcuate conductor lines and a pair of straight conductor lines. Each of the arcuate lines has a diameter of 2a. Each of the straight lines has a length of 2L. The diameter 2a and the length 2L are so selected as to satisfy the relationship: 1.91≤2L / 2a≤2.15.
Owner:JEOL LTD
Sample tube for solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus magic angle high-speed rotation method and method for measuring nuclear magnetic resonance absorption spectrum employing it
InactiveUS7482810B2High sensitivityMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The present invention discloses a sample tube for the magic angle high-speed rotation method used in a solid nuclear magnetic resonance device probe wherein a radio wave irradiation / detection coil is disposed close to a sample and a method of measuring a high resolution nuclear magnetic resonance absorption spectrum using the same. This tube is suitable for solid nuclear magnetic resonance (solid NMR) measurements of minute amounts of sample. The sample tube has a capillary part filled with a sample and non-capillary parts situated at its two ends, and a spinner which can be detachably inserted into at least one of the outer ends of the non-capillary parts. The capillary part and non-capillary parts are made of a ceramic and / or polymer material.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP TOKYO UNIV OF AGRI & TECH
Method for NMR spectroscopy
ActiveUS20120229137A1Reduce signal lossIncrease in signal intensityMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse magnetizationSpectroscopy
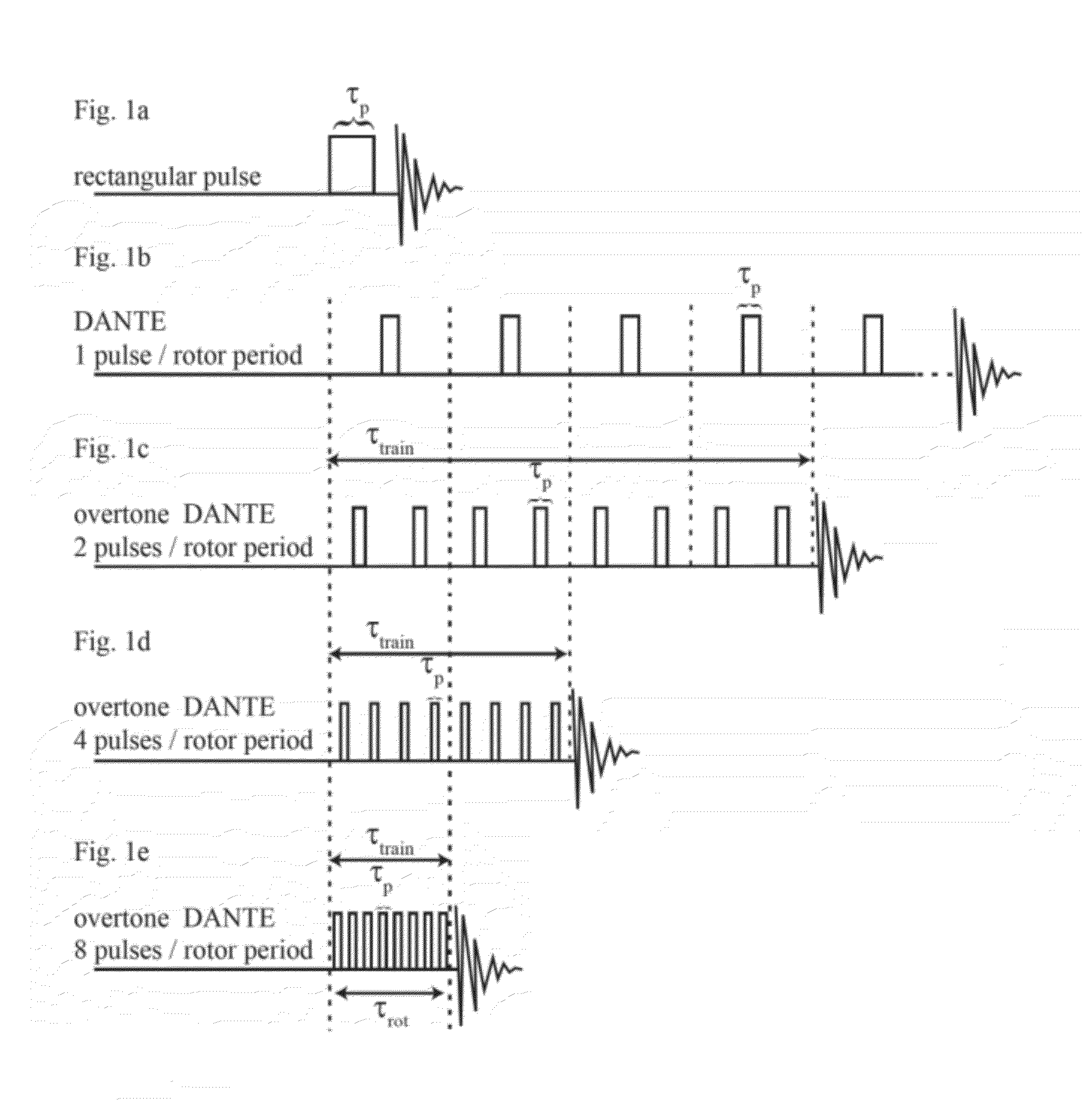
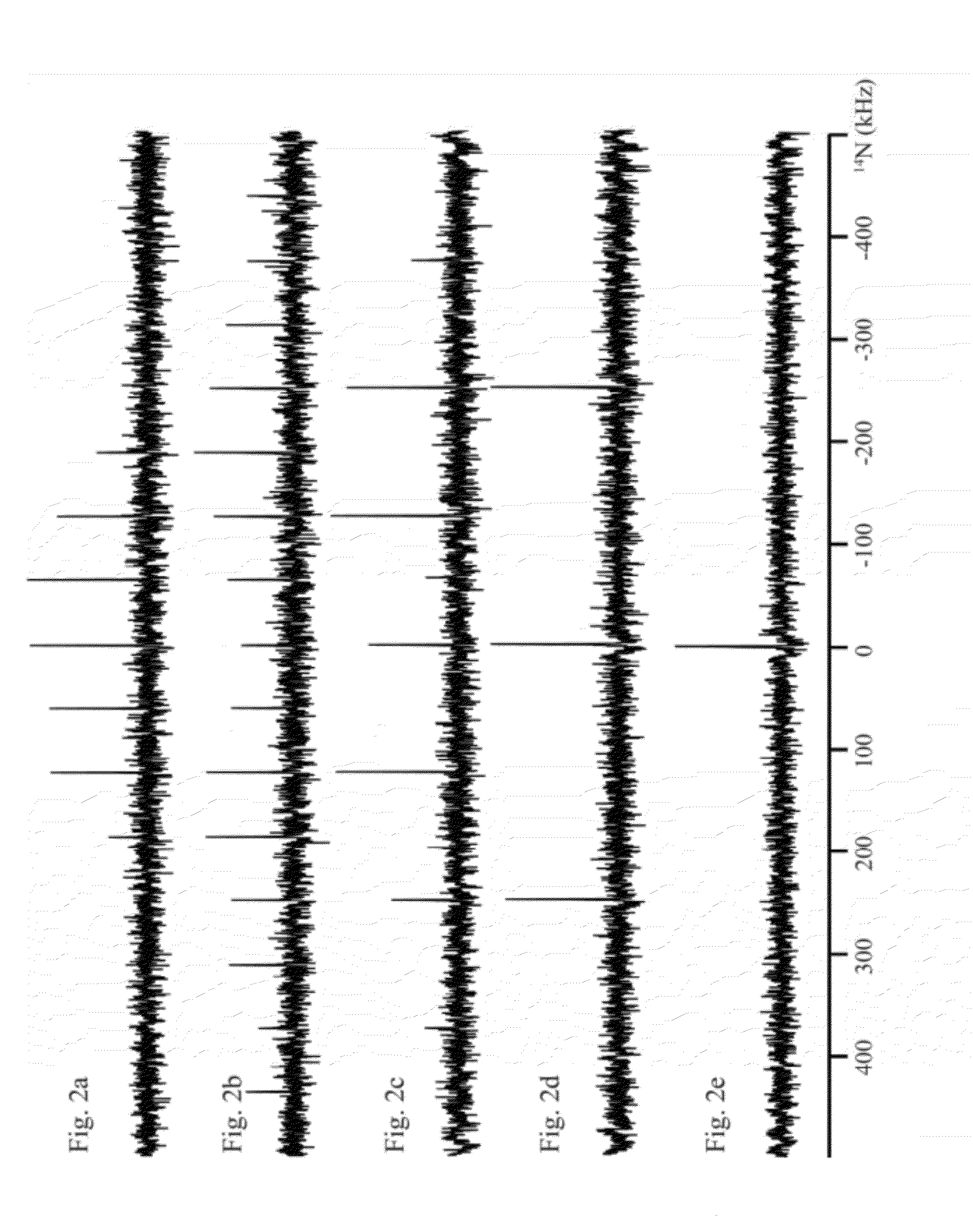
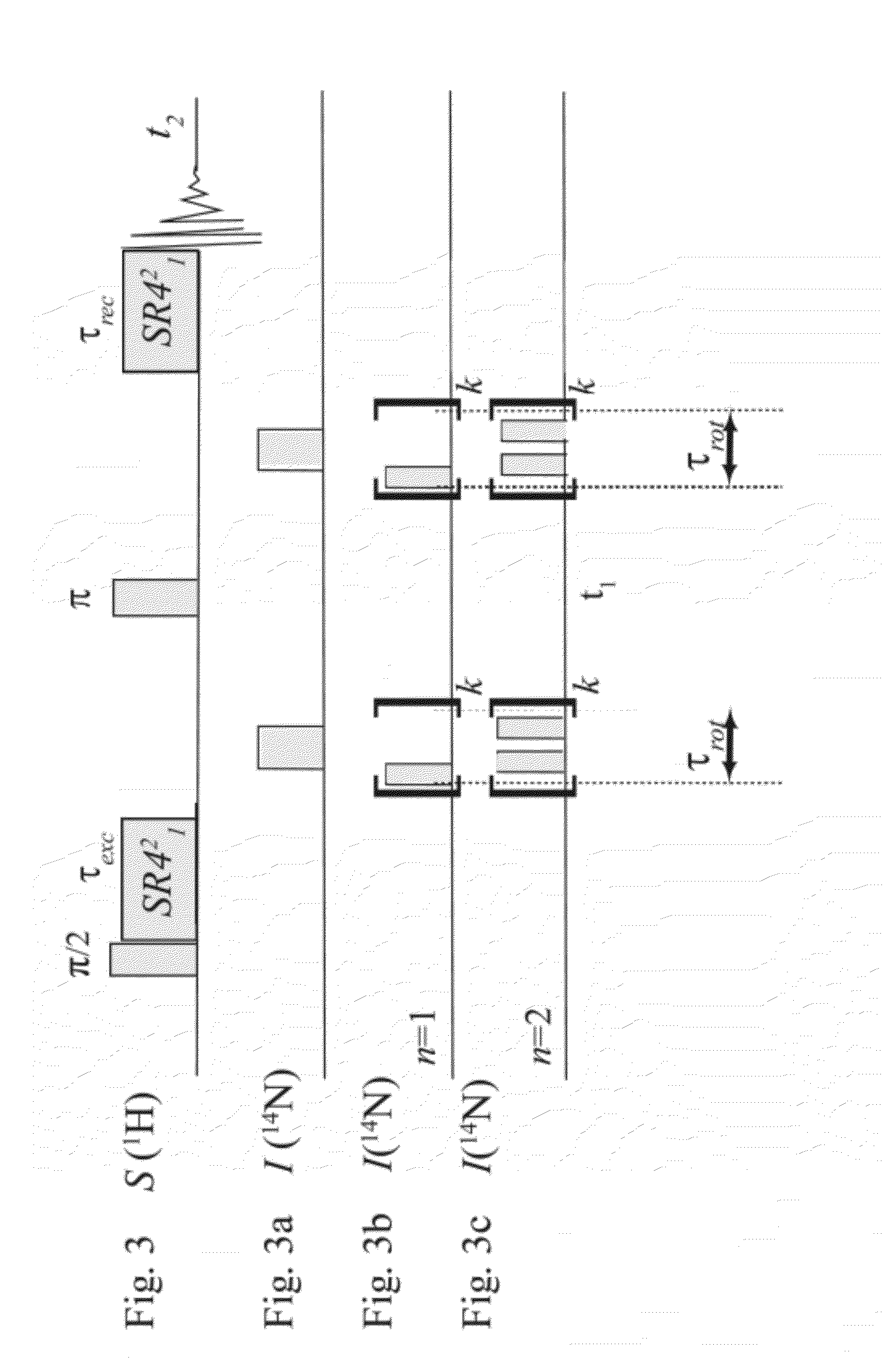
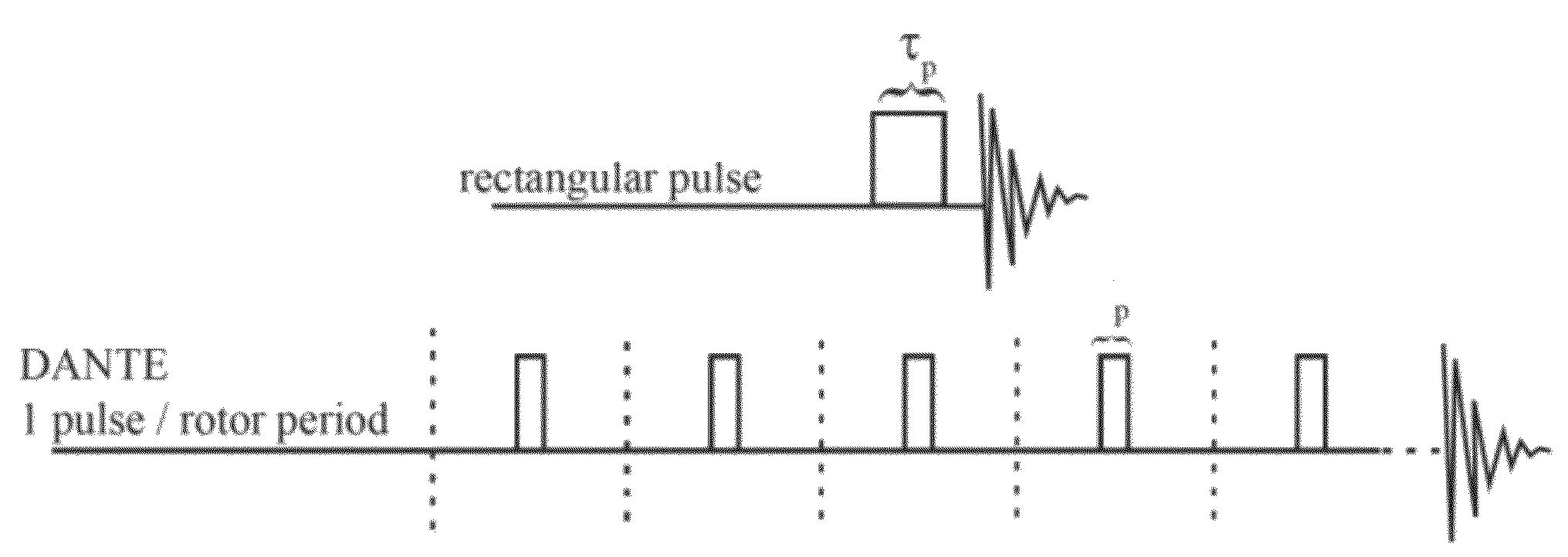
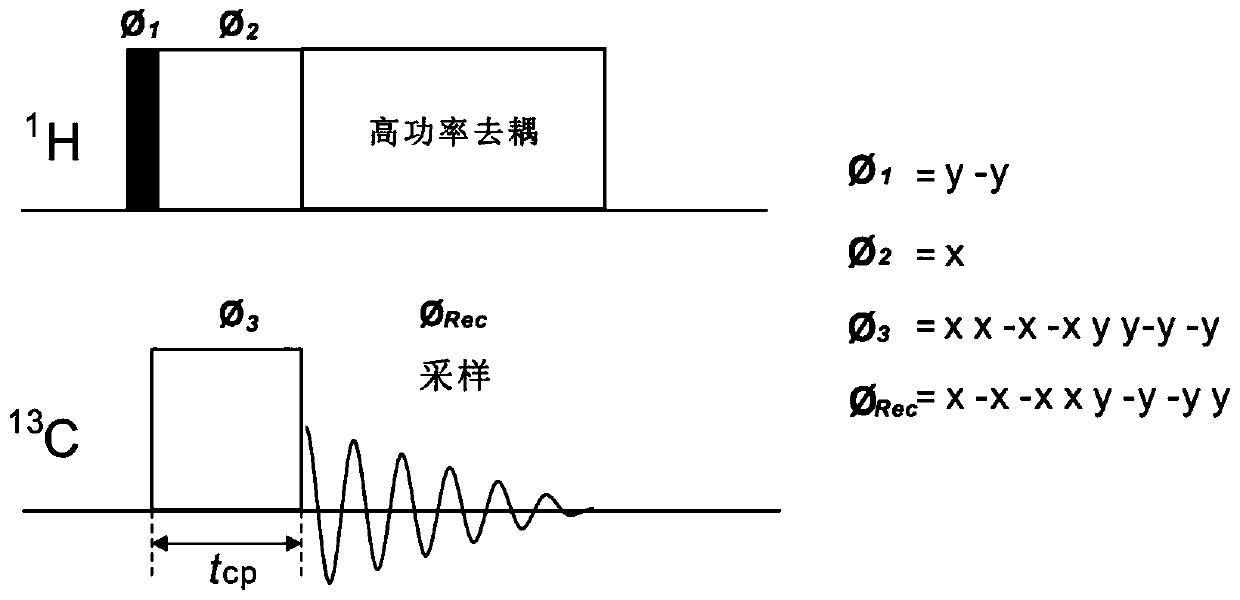
A method for performing magnetic resonance spectroscopy on solid samples containing nuclei of interest with spin quantum number I subjects the sample to a static magnetic field. The sample is spun at the magic angle and broad-band excitation of transverse magnetization of the nuclei of interest is effected by applying a first train of rotor-synchronized rf-pulses, having a carrier frequency, to the nuclei of interest with a pulse duration 0.1 μs<τp<2 μs, the first train of rf-pulses comprising k·n pulses extending over k rotor periods τrot with n pulses per rotor period τrot, wherein n is an integer n>1. Uniform excitation of a great number of spinning sidebands or families of sidebands that arise from large first-order quadrupole or hyperfine interactions is enabled and signal intensity is thereby improved.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG +1
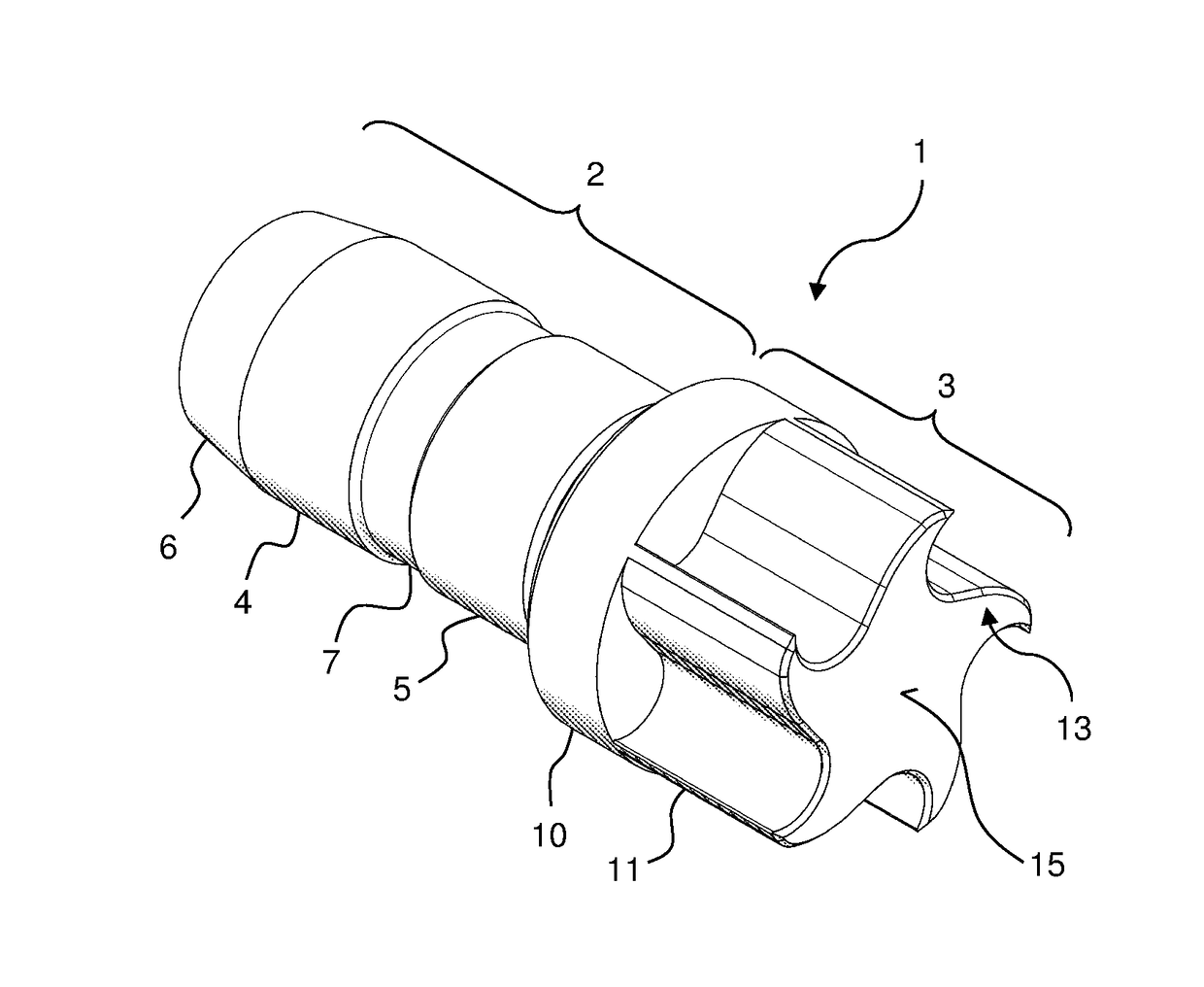
Nmr-mas turbine assembly
ActiveUS20170108561A1Easy to produceImprove running stabilityEngine manufactureBlade accessoriesMagic angle spinningNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A nuclear magnetic resonance-magic angle spinning (NMR-MAS) turbine assembly has a MAS rotor with turbine cap having a stopper region and a turbine region. The stopper region allows feeding into a rotor tube and has at least one sealing section for resting against an inner wall of the rotor tube. The turbine region has a collar section for resting against a face side of the rotor tube and a turbine section that forms the turbine blades, which protrude axially from the collar section without extending radially further than the collar section. The arrangement of the rotor allows for very high rotation frequencies that, correspondingly, reduce line broadening in NMR measurements.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
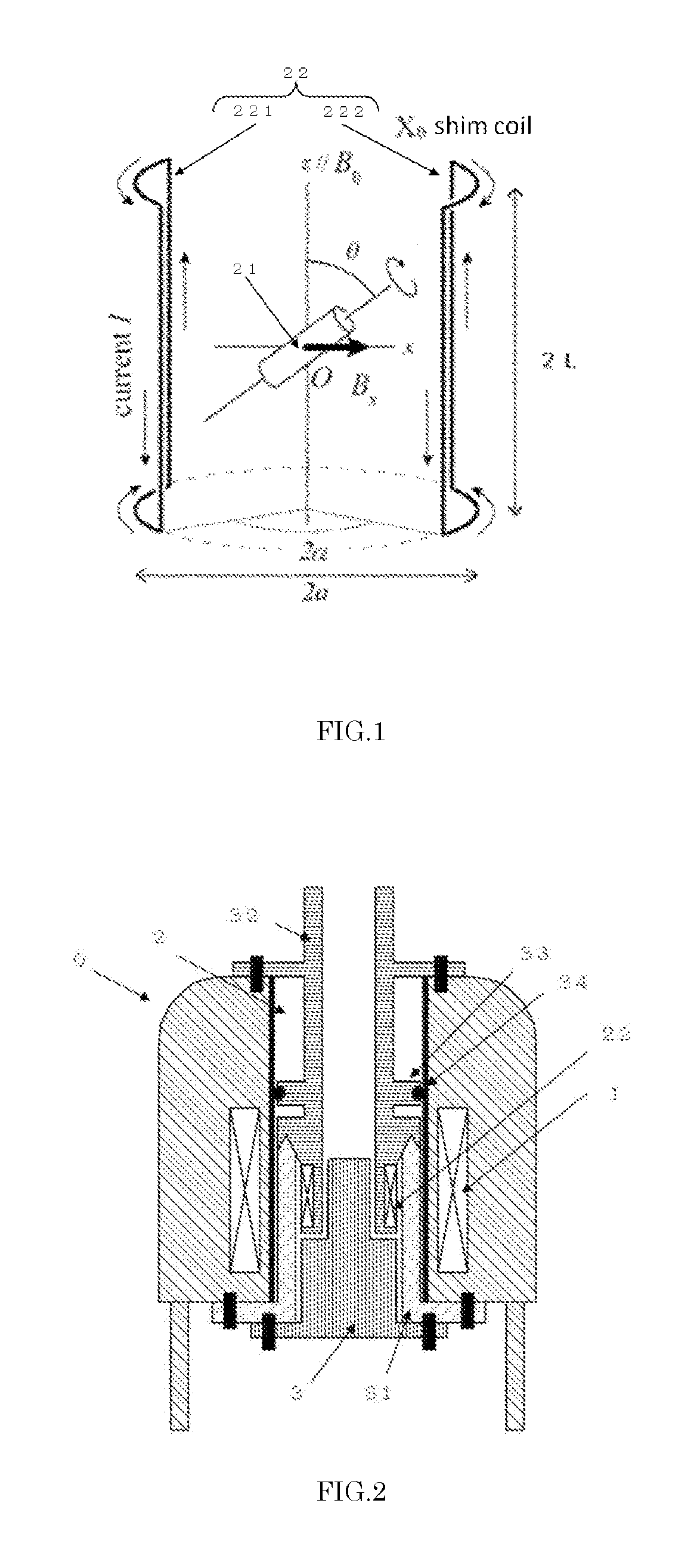
Coil Assembly for Accurate Adjustment of Magic Angle in Solid-State NMR Apparatus and Method of Adjusting Magic Angle Using Such Coil Assembly
ActiveUS20160291102A1Minimize impactAvoids increases in linewidthsMeasurements using NMR spectroscopySample rotationMagic angle
A specially shaped coil assembly for accurate adjustment of the magic angle is provided to permit accurate adjustment of an angle made between the direction of a static magnetic field and the axis of sample spinning without impairing the resolution of NMR signals. The sample is placed within the external static magnetic field B0. The coil assembly is for use in a solid-state NMR apparatus that performs NMR detection while spinning the sample about an axis tilted at the magic angle relative to the external static magnetic field B0. The coil assembly comprises a pair of arcuate conductor lines and a pair of straight conductor lines. Each of the arcuate lines has a diameter of 2a. Each of the straight lines has a length of 2L. The diameter 2a and the length 2L are so selected as to satisfy the relationship: 1.91≦2L / 2a≦2.15.
Owner:JEOL LTD
Method for NMR spectroscopy
ActiveUS8963546B2Increase signal strengthReduce signal lossMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse magnetizationSpectroscopy
A method for performing magnetic resonance spectroscopy on solid samples containing nuclei of interest with spin quantum number I subjects the sample to a static magnetic field. The sample is spun at the magic angle and broad-band excitation of transverse magnetization of the nuclei of interest is effected by applying a first train of rotor-synchronized rf-pulses, having a carrier frequency, to the nuclei of interest with a pulse duration 0.1 μs<τp<2 μs, the first train of rf-pulses comprising k·n pulses extending over k rotor periods τrot with n pulses per rotor period τrot, wherein n is an integer n>1. Uniform excitation of a great number of spinning sidebands or families of sidebands that arise from large first-order quadrupole or hyperfine interactions is enabled and signal intensity is thereby improved.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG +1
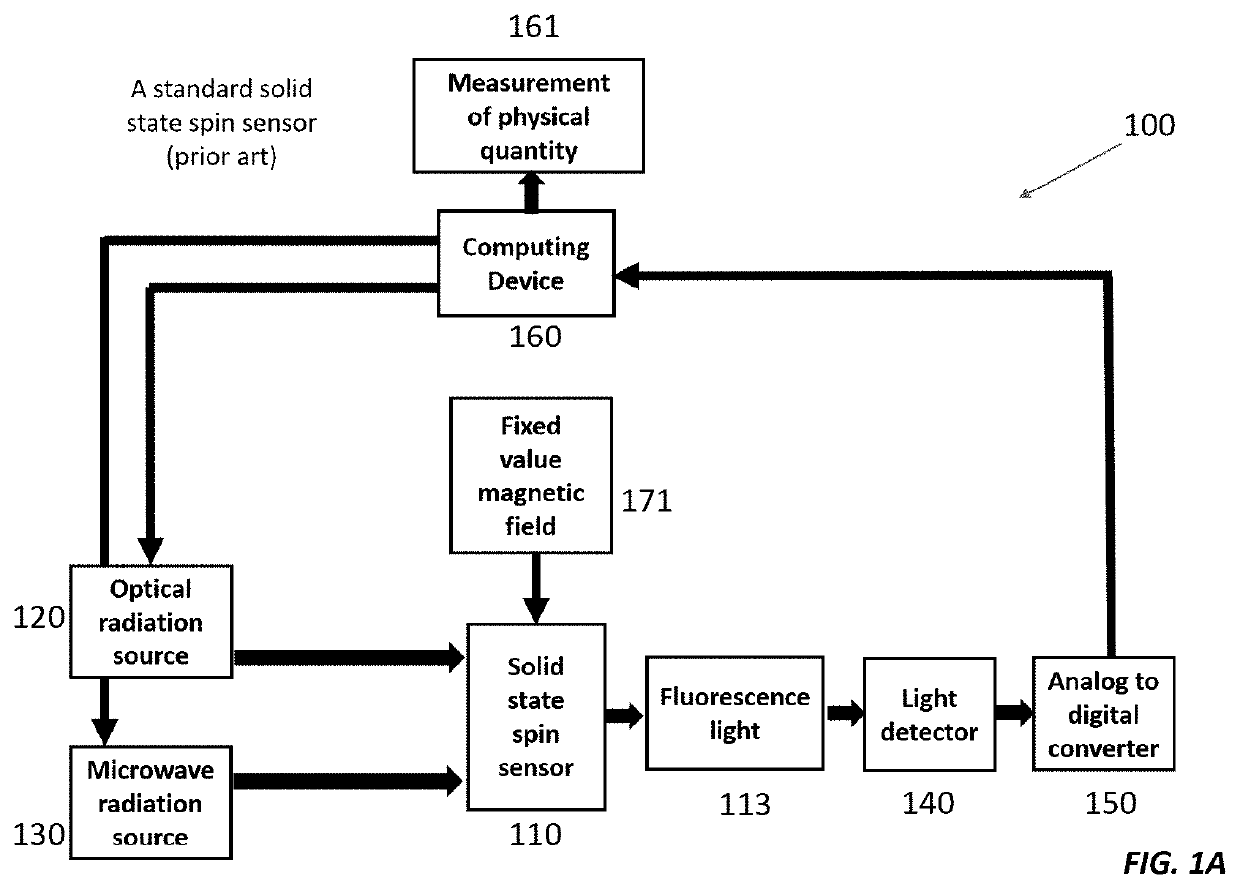
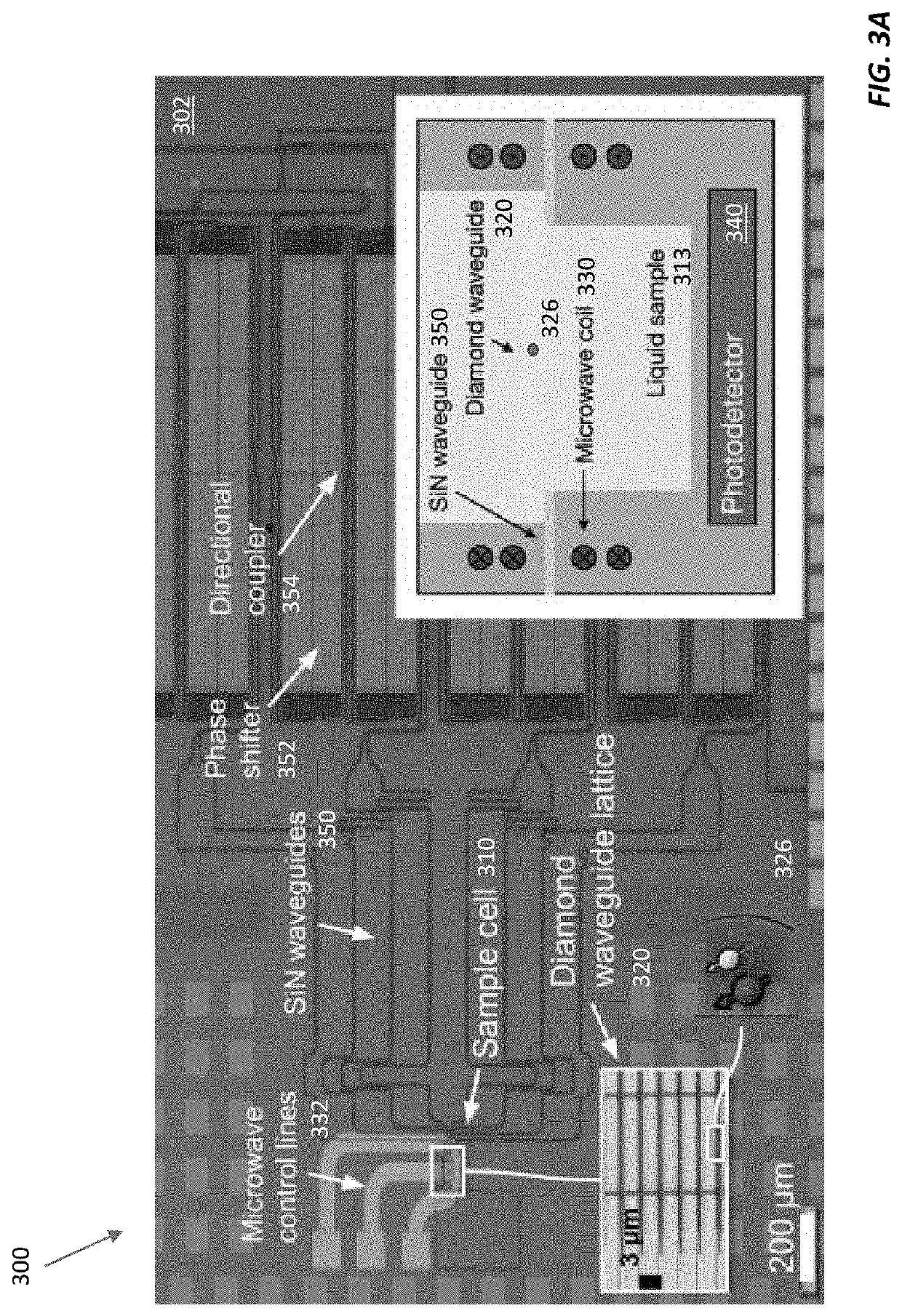
Stationary magic angle spinning enhanced solid state spin sensor
ActiveUS10705163B2Increases dephasing timeAnalysis using double resonanceMeasurements using NMRMagic angle spinningHelmholtz coil
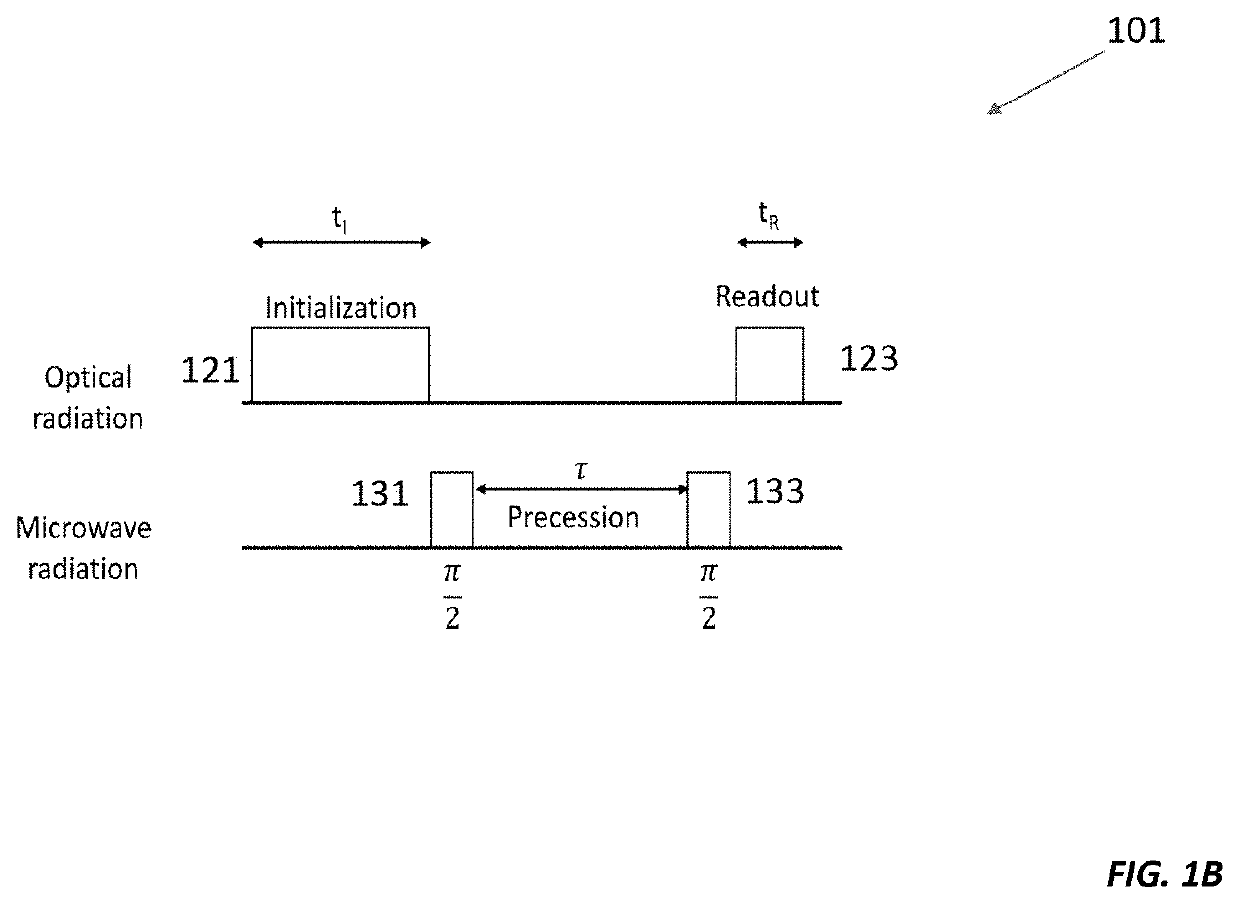
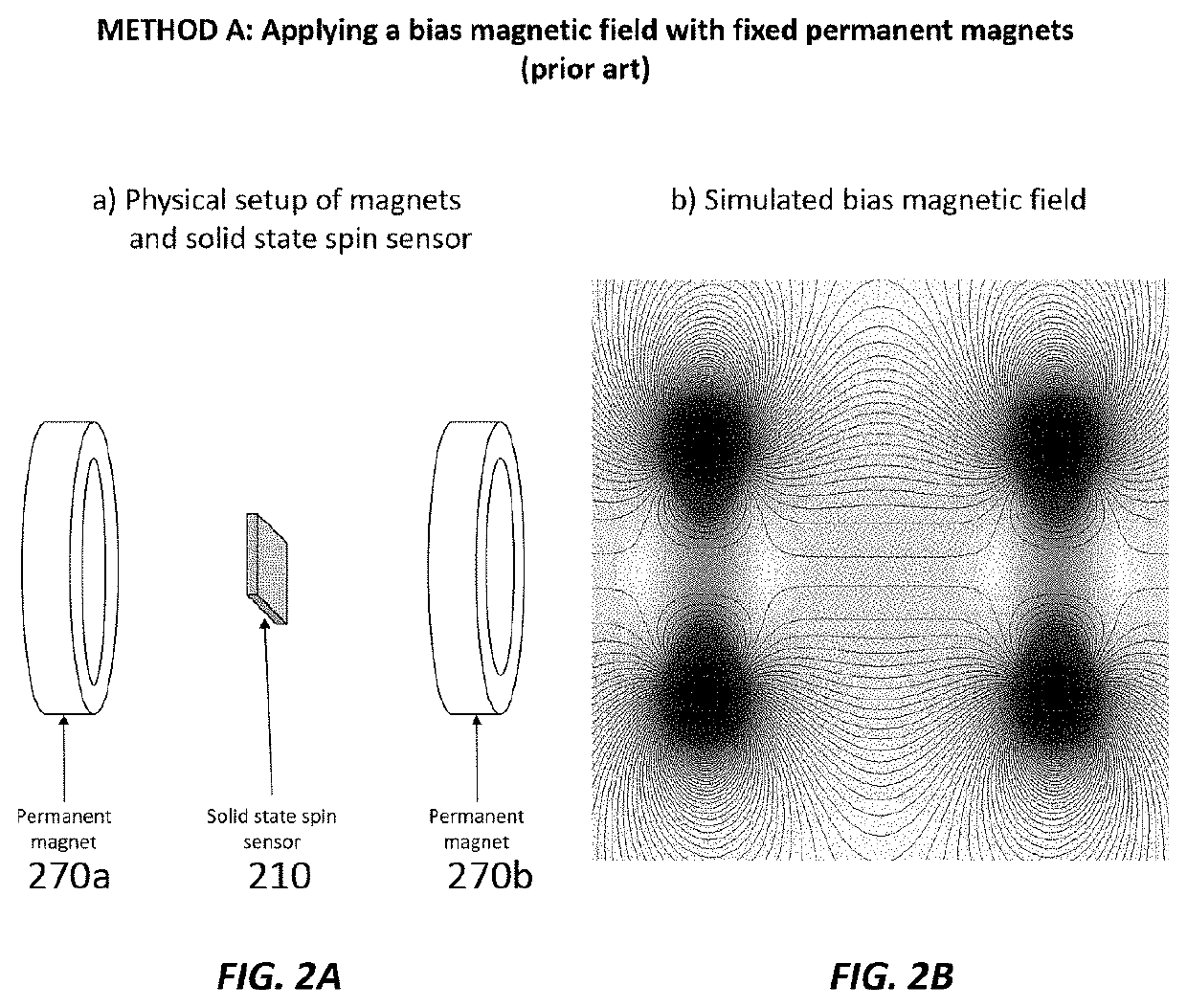
Here we present a solid-state spin sensor with enhanced sensitivity. The enhanced sensitivity is achieved by increasing the T2* dephasing time of the color center defects within the solid-state spin sensor. The T2* dephasing time extension is achieved by mitigating dipolar coupling between paramagnetic defects within the solid-state spin sensor. The mitigation of the dipolar coupling is achieved by applying a magic-angle-spinning magnetic field to the color center defects. This field is generated by driving a magnetic field generator (e.g., Helmholtz coils) with phase-shifted sinusoidal waveforms from current source impedance-matched to the magnetic field generator. The waveforms may oscillate (and the field may rotate) at a frequency based on the precession period of the color center defects to reduce color center defect dephasing and further enhance measurement sensitivity.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Cryogenic Integrated Circuits Architecture for Multiplexed Chemical-Shift NMR
PendingUS20220137169A1Small sample volumeMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyMagnetic variable regulationMagic angle spinningResonance measurement
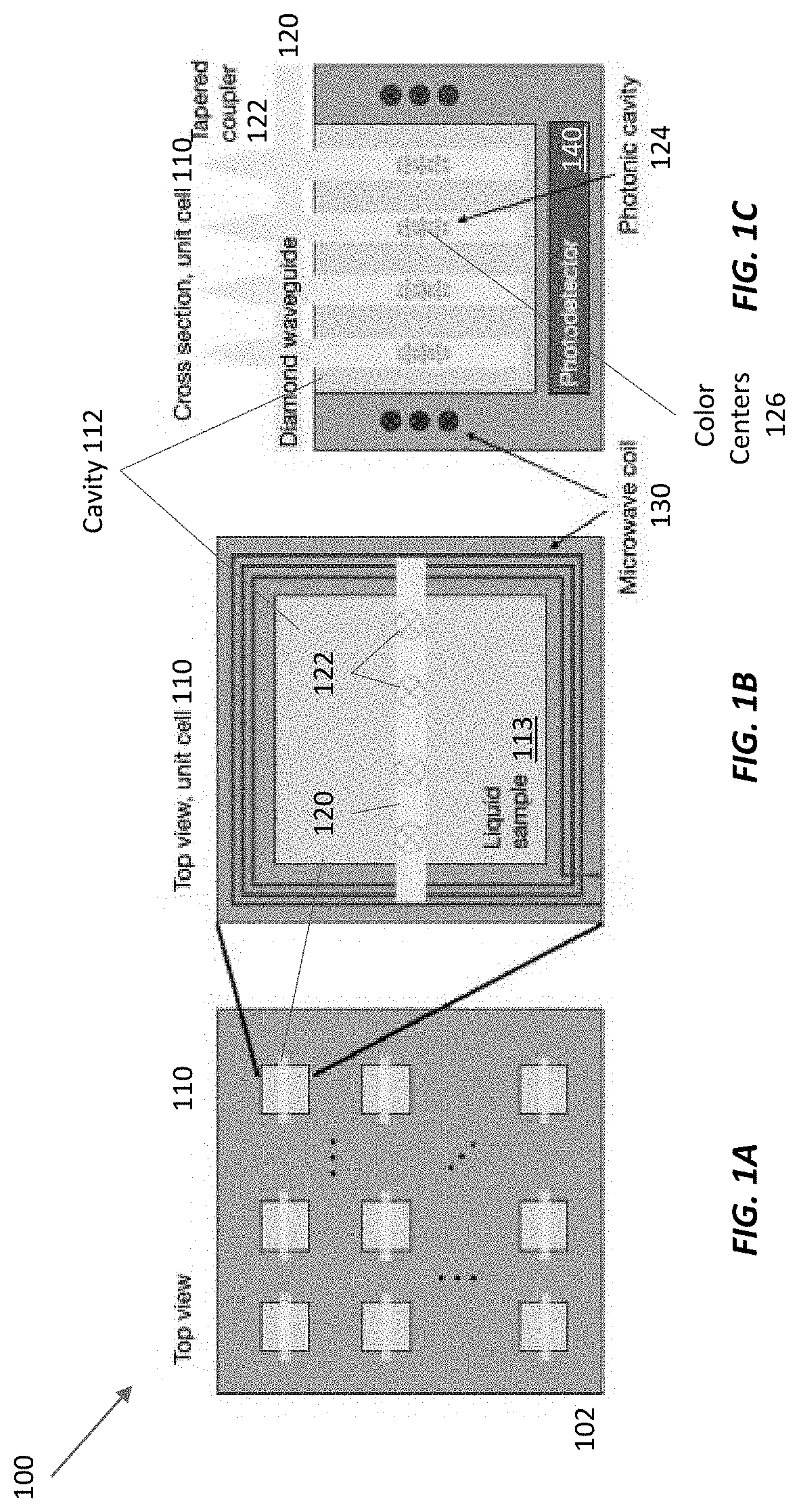
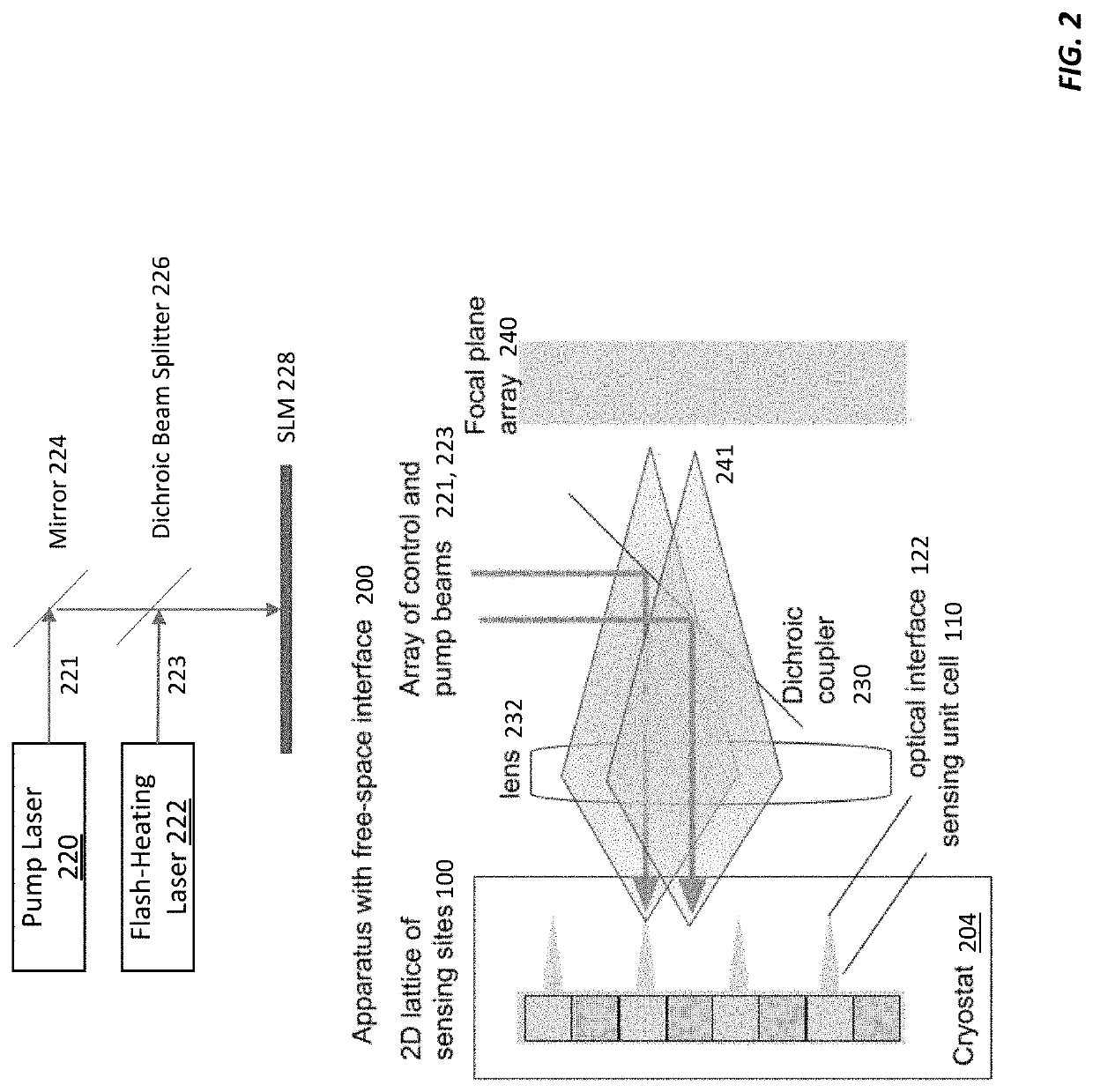
Chemical-shift nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy involves measuring the effects of chemical bonds in a sample on the resonance frequencies of nuclear spins in the sample. Applying a magnetic field to the sample causes the sample nuclei to emit alternating current magnetic fields that can be detected with color centers, which can act as very sensitive magnetometers. Cryogenically cooling the sample increases the sample's polarization, which in turn enhances the NMR signal strength, making it possible to detect net nuclear spins for very small samples. Flash-heating the sample or subjecting it to a magic-angle-spinning magnetic field (instead of a static magnetic field) eliminates built-in magnetic field inhomogeneities, improving measurement sensitivity without degrading the sample polarization. Tens to hundreds of small, cryogenically cooled sample chambers can be integrated in a semiconductor substrate interlaced with waveguides that contain color centers for optically detected magnetic resonance measurements of the samples' chemical-shift NMR frequencies.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method for the In Vitro Determination of Cellular Uptake of Exogenous and Endogenous Substances Using Nmr Shift Agents and the Magic Angle Nmr Technique
InactiveUS20080003632A1Promote differentiationEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceSubstance useQuantitative determination
The present invention relates to a method for the in vitro quantitative determination of cellular uptake of exogenous or endogenous substances which method comprises applying MAS-NMR spectroscopy technique to an in vitro cellular sample, in combination with a shift agent. The said method is particularly advantageous as it find general applicability for a variety of substances and cell samples.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus and process for high-resolution in situ investigations
ActiveUS9194920B2Raise the ratioHigh sensitivityMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyMaterial analysis by using resonanceMagic angle spinningContinuous flow
A continuous-flow (CF) magic angle sample spinning (CF-MAS) NMR rotor and probe are described for investigating reaction dynamics, stable intermediates / transition states, and mechanisms of catalytic reactions in situ. The rotor includes a sample chamber of a flow-through design with a large sample volume that delivers a flow of reactants through a catalyst bed contained within the sample cell allowing in-situ investigations of reactants and products. Flow through the sample chamber improves diffusion of reactants and products through the catalyst. The large volume of the sample chamber enhances sensitivity permitting in situ 13C CF-MAS studies at natural abundance.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Solid nuclear magnetic resonance quantitative detection method and device based on successive cross polarization
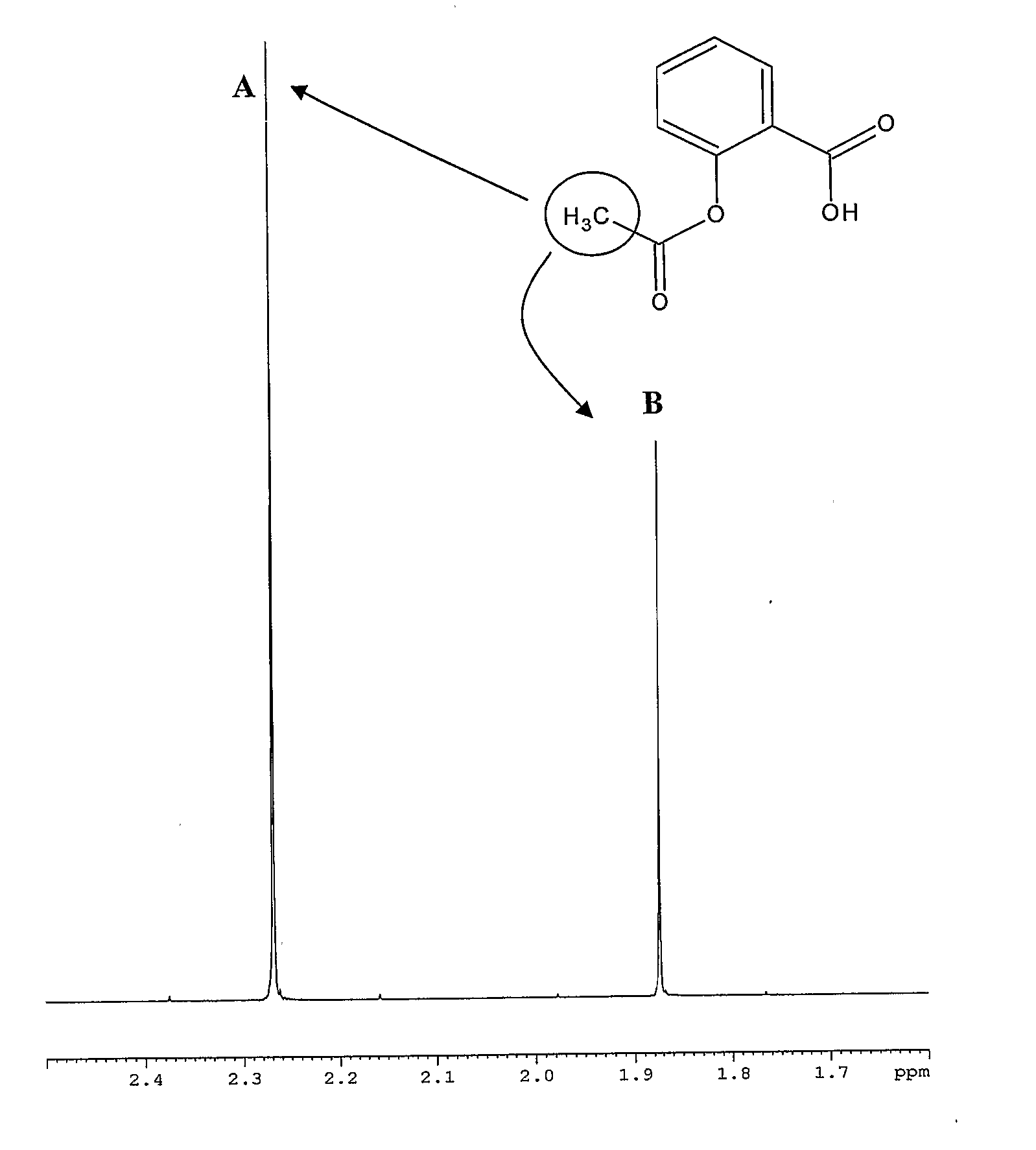
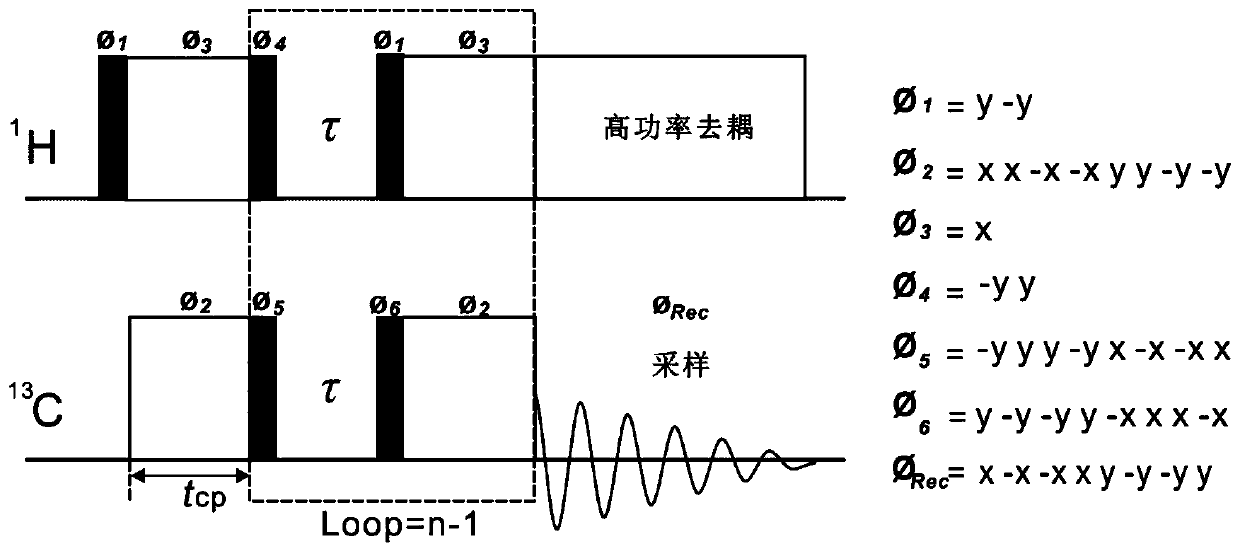
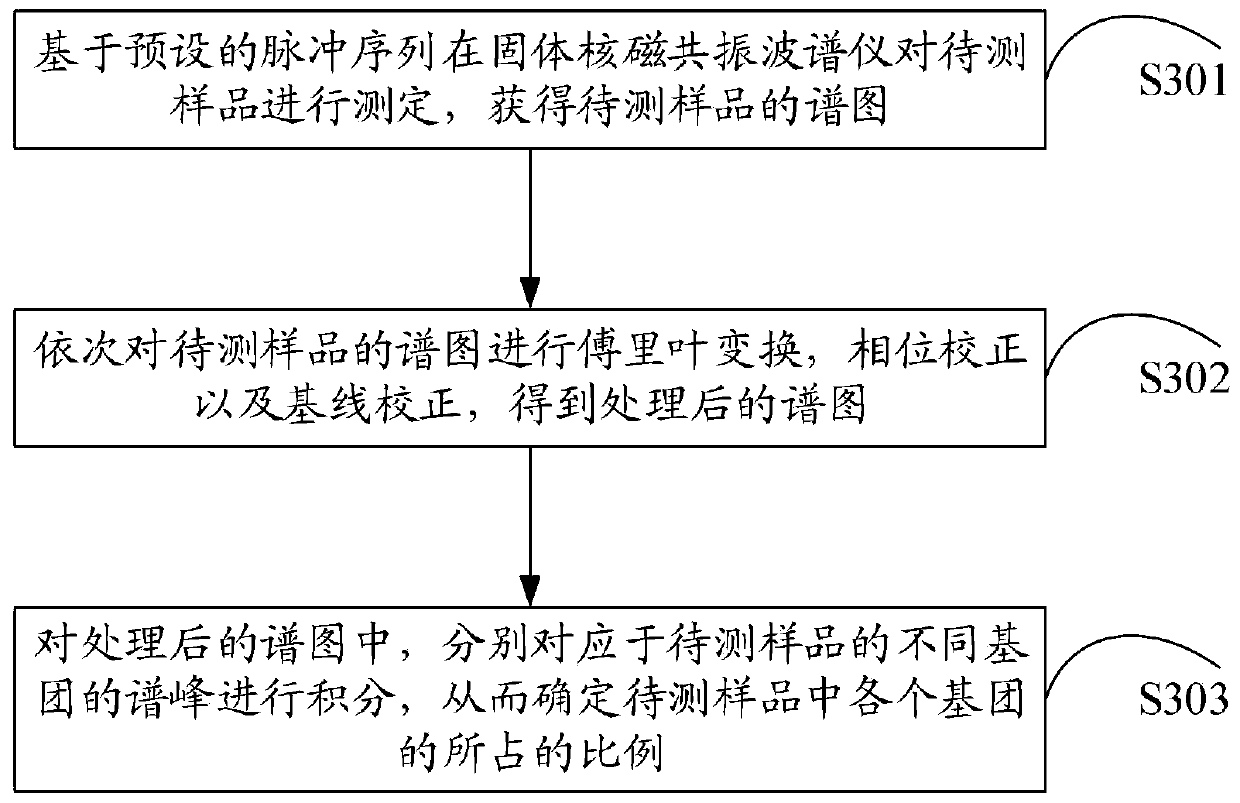
ActiveCN111044960AIncrease the enhancement factorImprove accuracyMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMagic angle
The invention provides a solid nuclear magnetic resonance quantitative detection method and device based on successive cross polarization. The method comprises the steps of determining a to-be-detected sample in a solid nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer based on a preset pulse sequence to obtain a spectrogram of the to-be-detected sample, wherein the pulse sequence comprises a plurality of first pulse units and a second pulse unit, and the first pulse units are used for increasing enhancement coefficients of signals of 13C nucleuses located in different groups in the to-be-detected sample; and the second pulse unit is used for fixing a magnetization vector of a 1H nucleus of the to-be-detected sample in the magic angle direction, carrying out cross polarization on the 1H nucleus andthe 13C nucleus of the to-be-detected sample, and calculating the proportion of each group in the to-be-detected sample according to the spectrogram of the to-be-detected sample. According to the scheme, the second pulse unit fixes the magnetization vector of the 1H nucleus in the to-be-detected sample in the magic angle direction, so that the T1[rho]H of the 1H nucleus in the to-be-detected sample is prolonged, and the effect of improving the accuracy of quantitative detection is achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
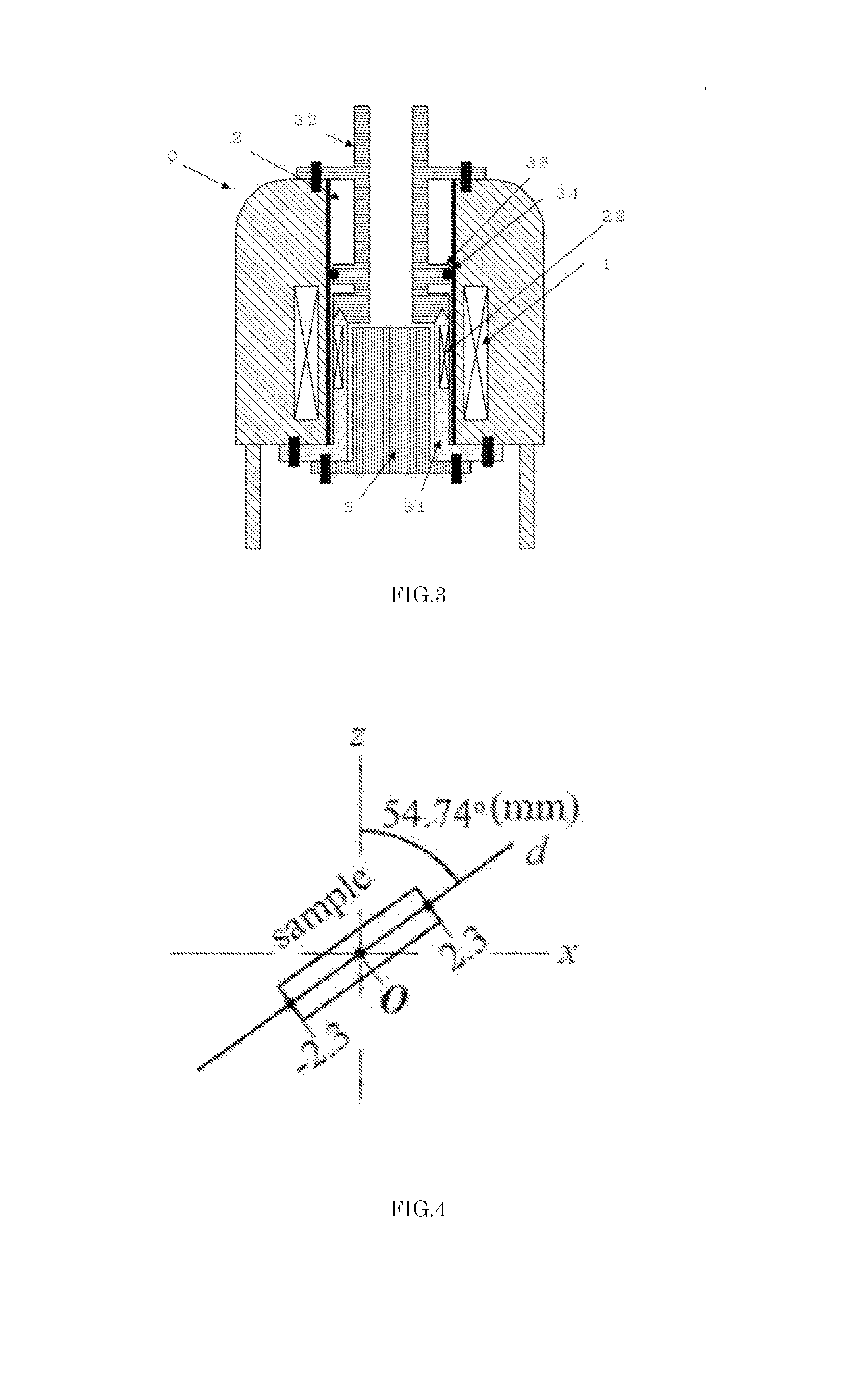
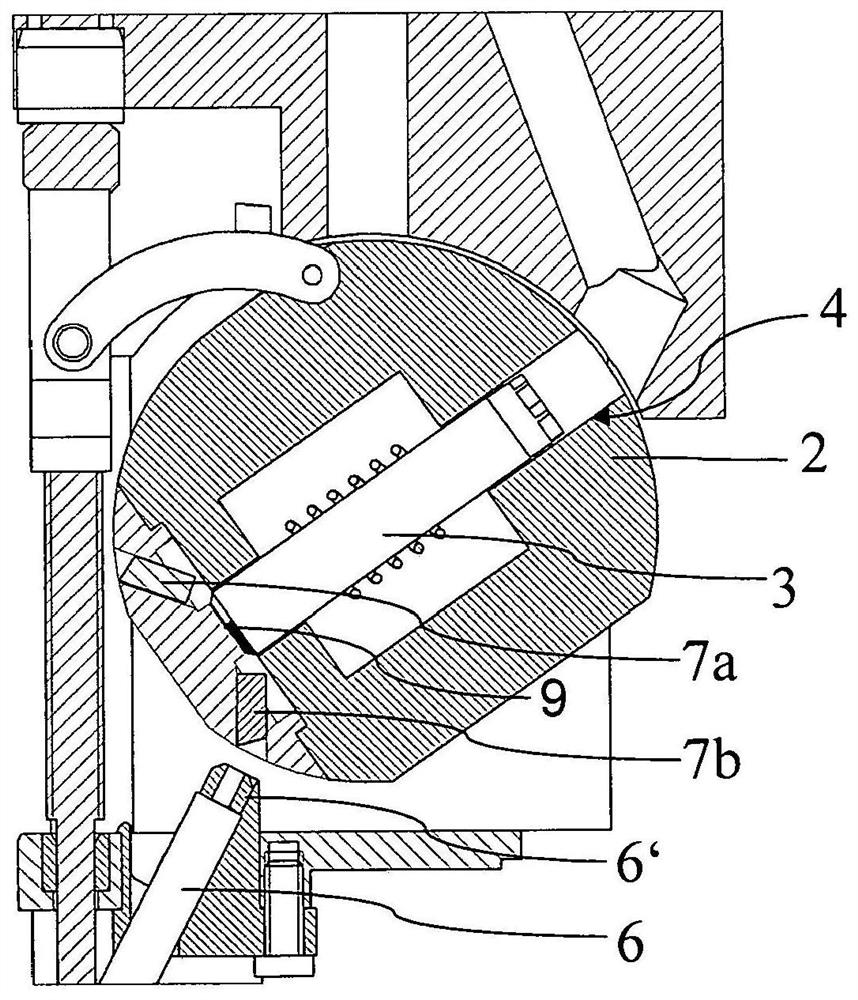
NMR-Magic Angle Rotary Probe with Oscillable Stator
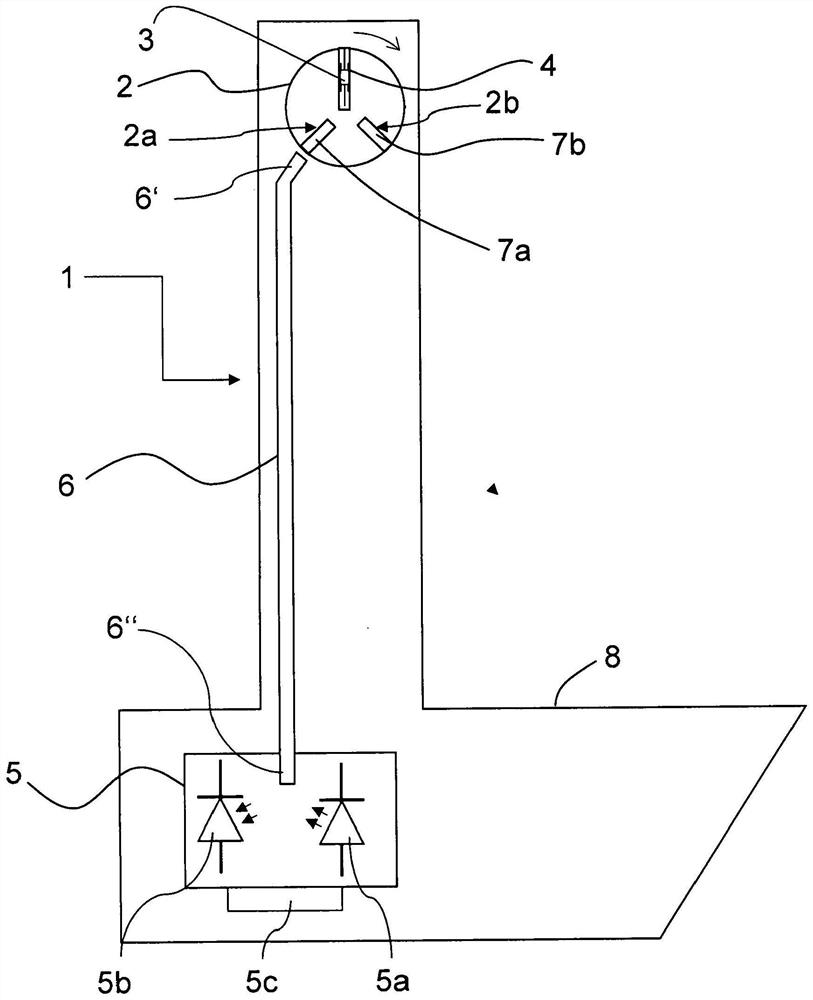
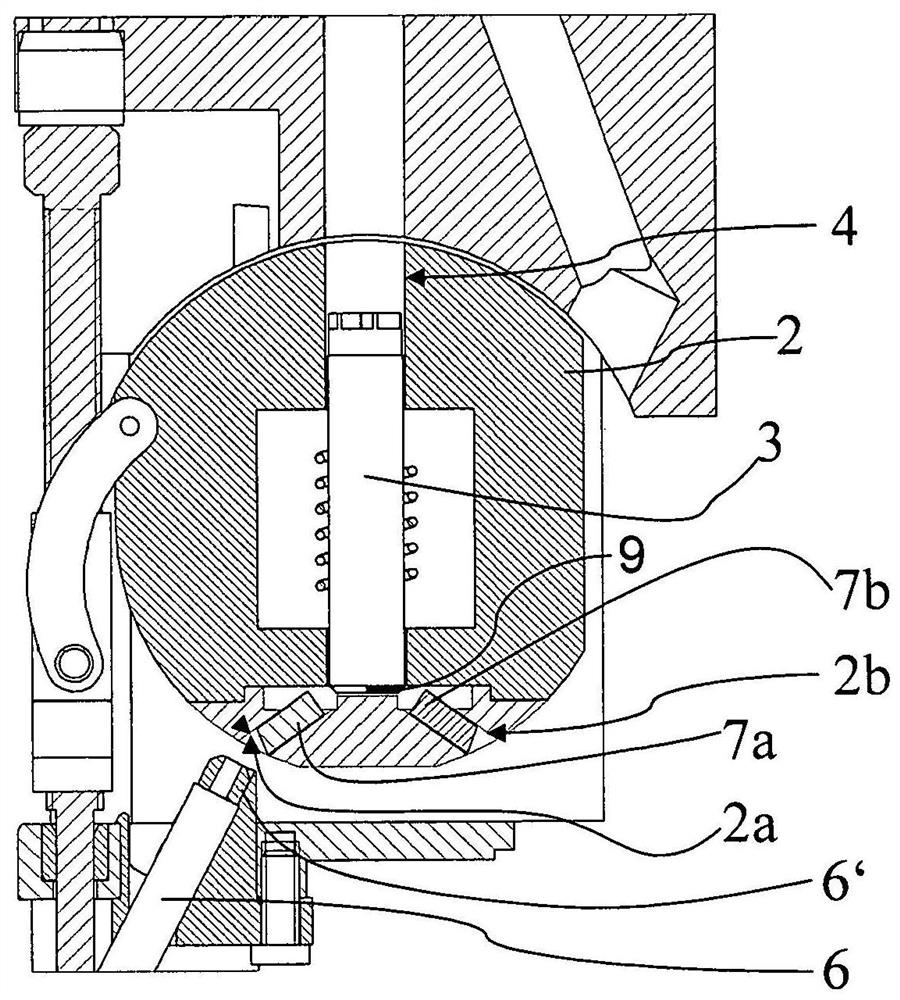
A probe head (1) of an NMR-MAS assembly has a stator (2) with an opening (4) receiving a rotor (3) which, in a measuring position, rotates at the magic angle to the B0 field. The stator is pivotable between the measuring position and a loading position of the rotor. A detection device (5) permits external, contactless identification of whether the opening of the stator is fitted with a rotor. The detection device has a light source (5a), from which light is introduced into a lower end (6″) of a light guide (6). The stator has a first bore (2a), in which a first light guide stump (7a) is positioned such that, in the loading position of the stator, it produces an optical connection between a rotor inserted in the stator and an upper end (6′) of the light guide opposite the lower end.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Nano polysaccharide compound and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN112807487AImprove water retentionSignificant effectPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationXerophthalmiaNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention provides a nano polysaccharide compound and a preparation method and application thereof, and the nano polysaccharide compound comprises beta-1, 3-glucan and chitin, wherein the nano polysaccharide compound has a spectrum of solid carbon-13 cross polarization magic angle rotation nuclear magnetic resonance, and the spectrum comprises the following peak values: 176 + / -0.2 ppm, 103 + / -0.2 ppm, 87 + / -0.2 ppm and 74 + / -0.2 ppm. The nano polysaccharide compound has the effects of promoting wound healing, treating xerophthalmia and promoting bone regeneration.
Owner:PANION & BF BIOTECH INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com