Patents
Literature
400 results about "Chemical shift" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
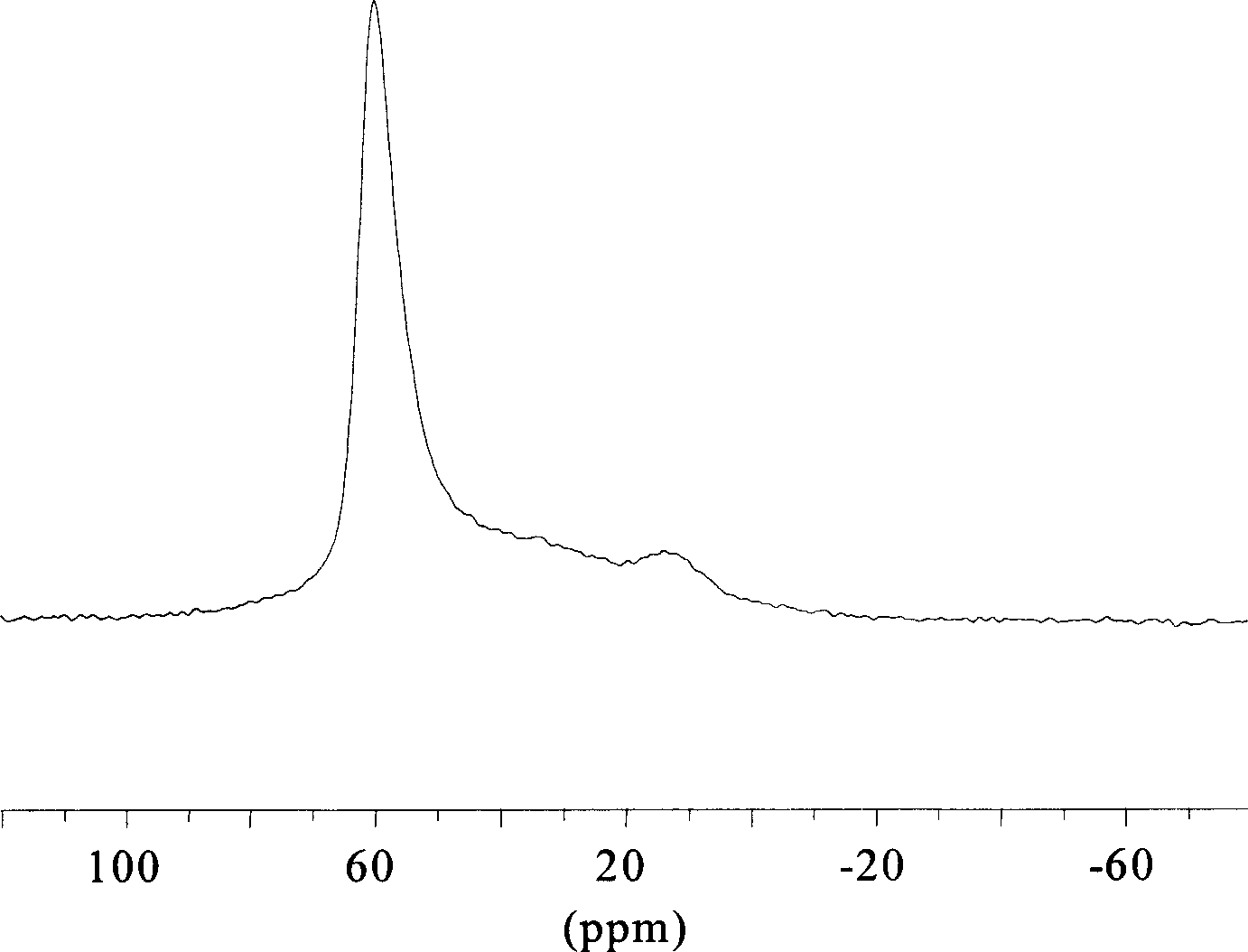
In nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of a nucleus relative to a standard in a magnetic field. Often the position and number of chemical shifts are diagnostic of the structure of a molecule. Chemical shifts are also used to describe signals in other forms of spectroscopy such as photoemission spectroscopy.
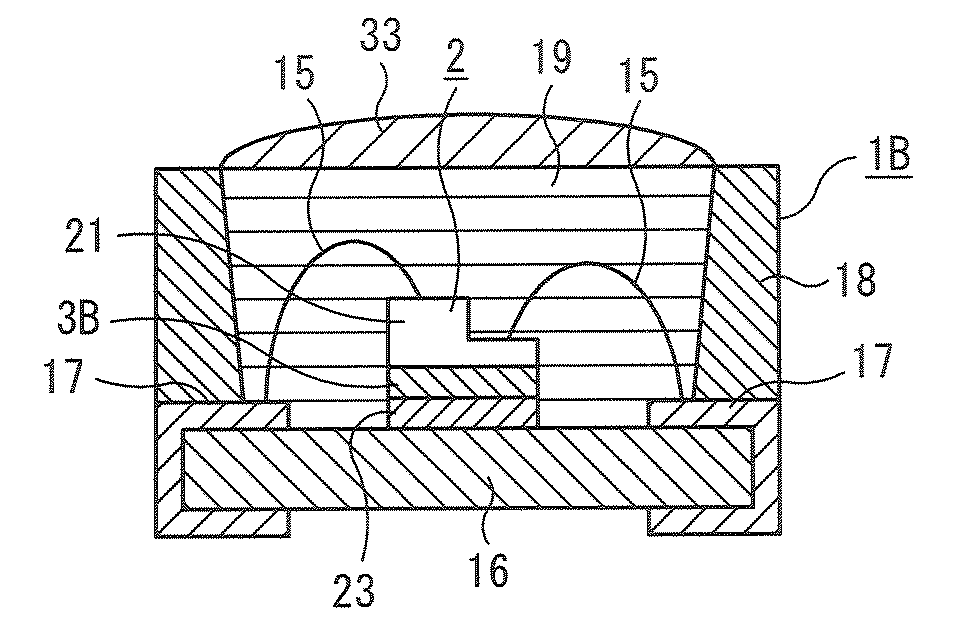
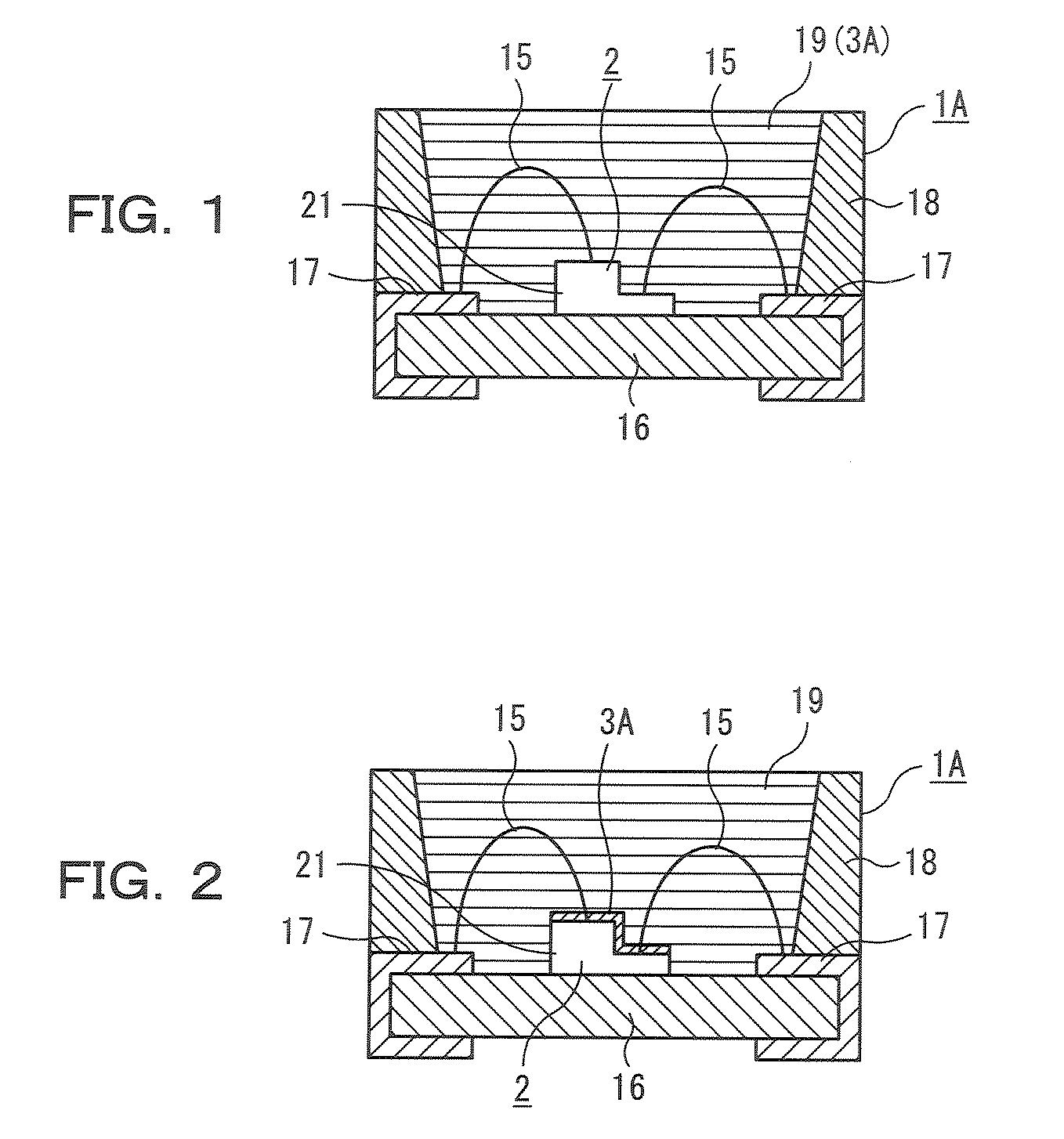
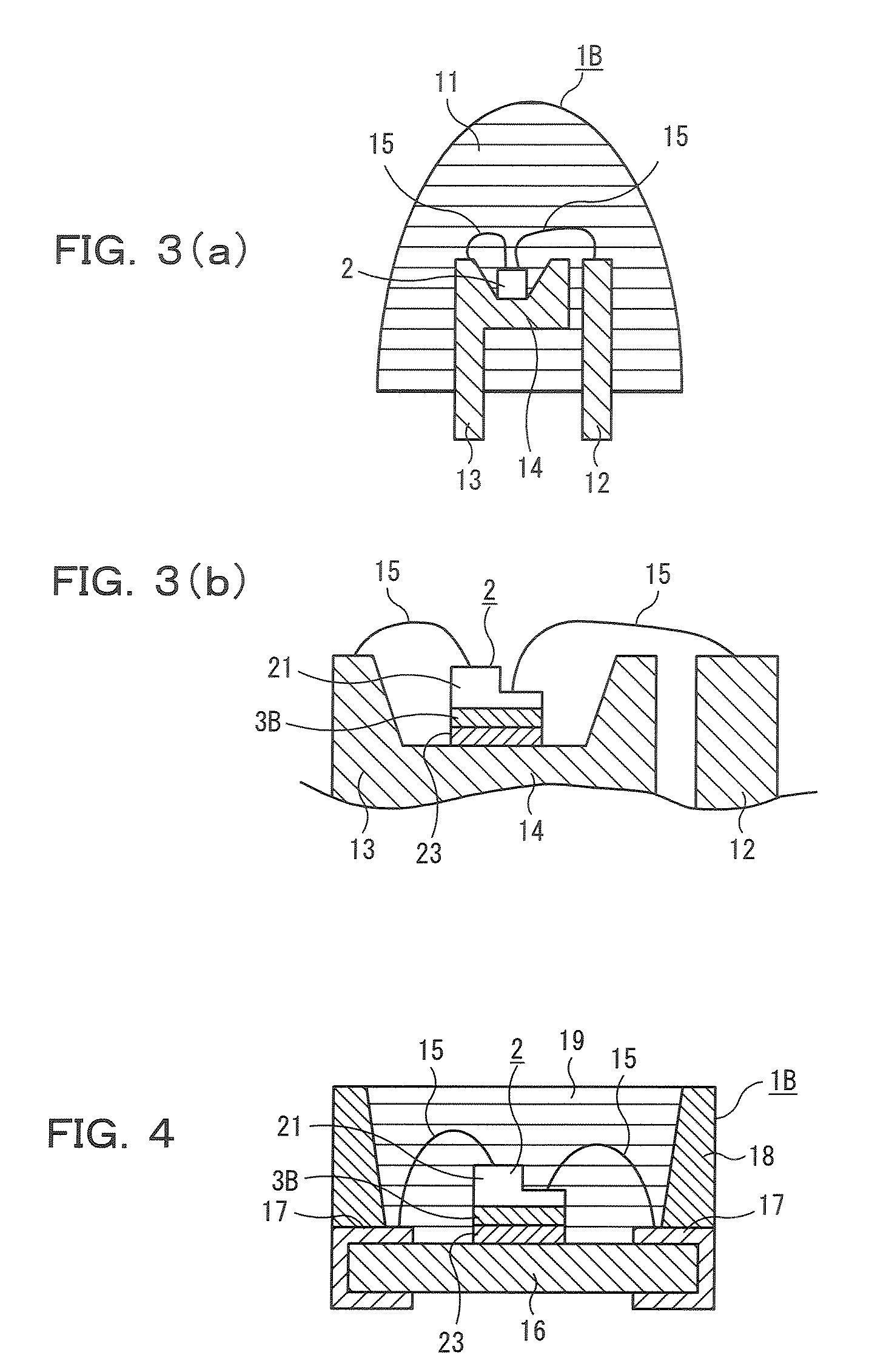
Semiconductor Light Emitting Device Member, Method for Manufacturing Such Semiconductor Light Emitting Device Member and Semiconductor Light Emitting Device Using Such Semiconductor Light Emitting Device Member
ActiveUS20090008673A1Improve sealingImprove heat resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceHeat resistance
A semiconductor light-emitting device member excellent in transparency, light resistance, and heat resistance and capable of sealing a semiconductor light-emitting device without causing cracks and peeling even after a long-time use is provided. Therefore, a semiconductor light-emitting device member that comprises (1) in a solid Si-nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum, at least one peak selected from a group consisting of (i) peaks whose peak top position is in an area of a chemical shift of −40 ppm to 0 ppm inclusive, and whose full width at half maximum is 0.3 ppm to 3.0 ppm inclusive, and (ii) peaks whose peak top position is in an area of the chemical shift of −80 ppm or more and less than −40 ppm, and whose full width at half maximum is 0.3 ppm to 5.0 ppm inclusive, wherein (2) silicon content is 20 weight % or more and (3) silanol content is 0.1 weight % to 10 weight % inclusive is used.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Polypropylene type aqueous dispersion, polypropylene type composite aqueous emulsion composition and its use
A polypropylene type aqueous dispersion comprising the following components (a) to (c): (a) a polypropylene type polymer100parts by weightand / or a modified polypropylene typepolymer(b) a surfactant1 to 100parts by weight, and(c) water100 to 1,000parts by weight,wherein the component (a) has a main chain having the following features (1) and (2) and dispersion particles in the dispersion have an average particle size of at most 0.5 μm, Feature (1) when observing a peak derived from a carbon atom of a methyl group in a propylene unit chain part comprising a head-to-tail bond by 13C-NMR and fixing a chemical shift of a peak top at a peak attributable to pentad expressed by mmmm to 21.8 ppm, a ratio (S1 / S) of an area S1 of a peak of a peak top at 21.8 ppm to a total area S of peaks at from 19.8 ppm to 22.1 ppm is at least 10% and at most 60%, and when an area of a peak (mmmr) of a peak top at 21.5 to 21.6 ppm is expressed as S2, 4+2S1 / S2>5, and Feature (2) a content ratio (mol ratio) of propylene unit (A): other olefin unit (B) is from 100:0 to 90:10.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
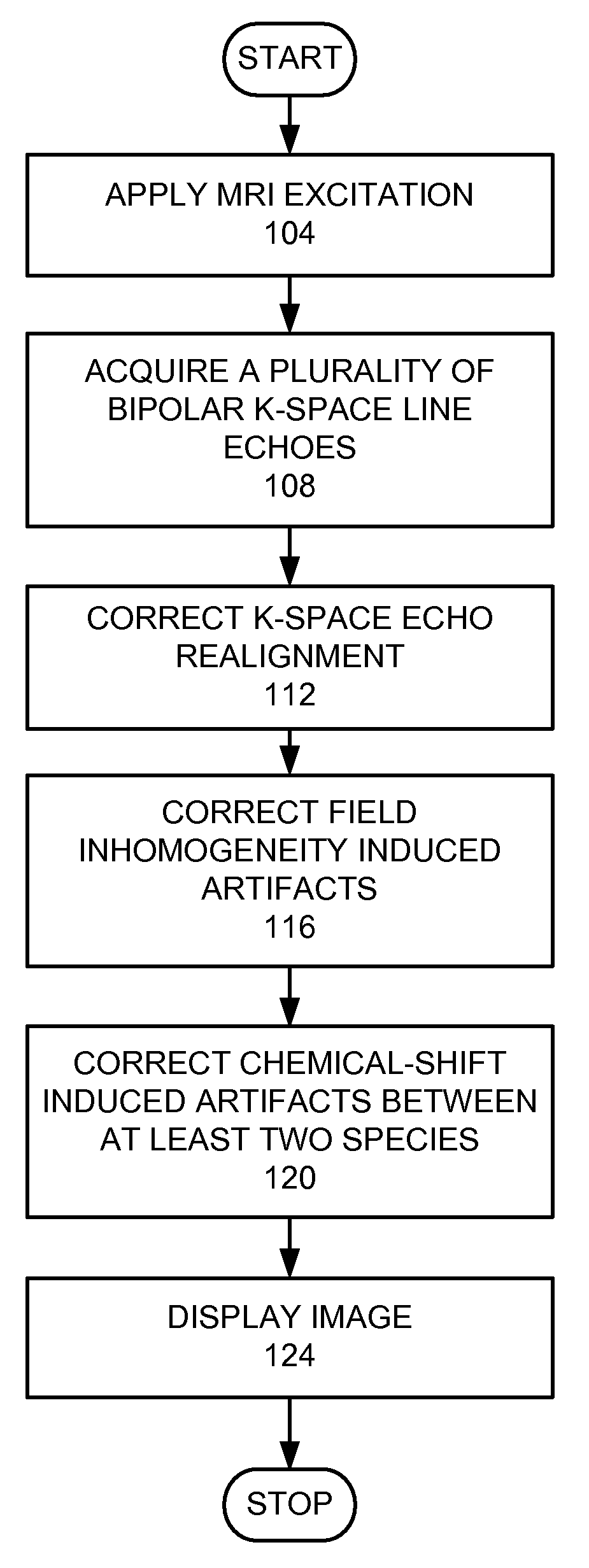
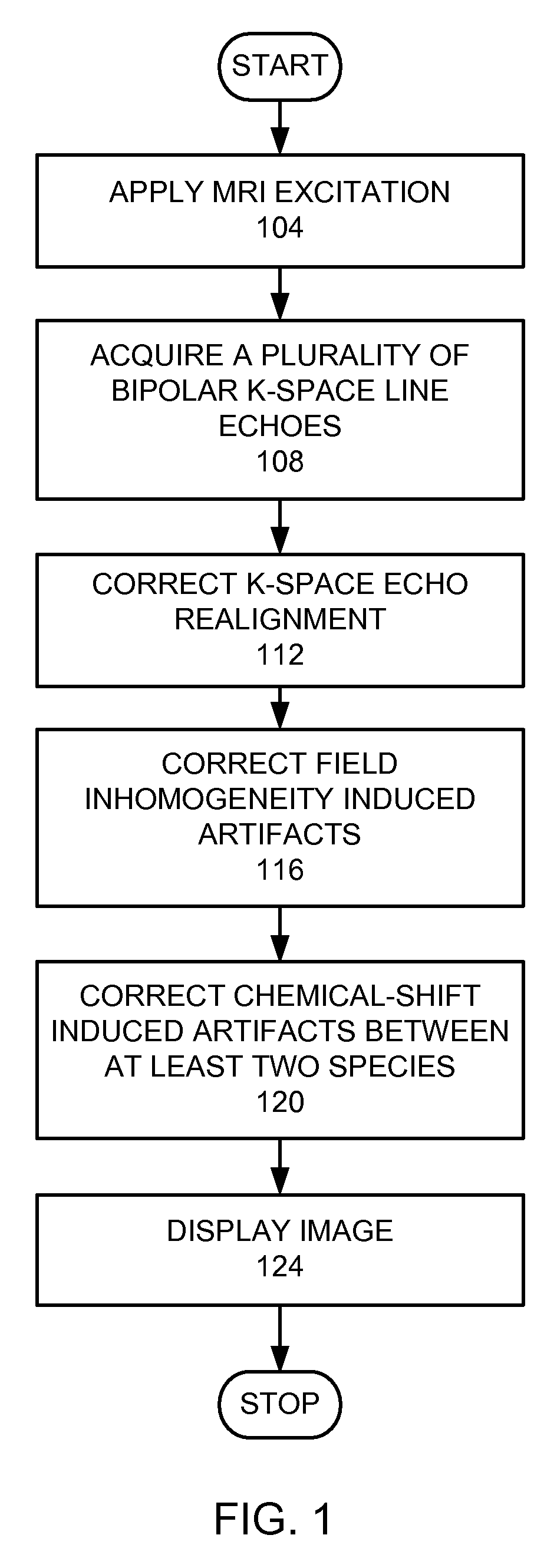
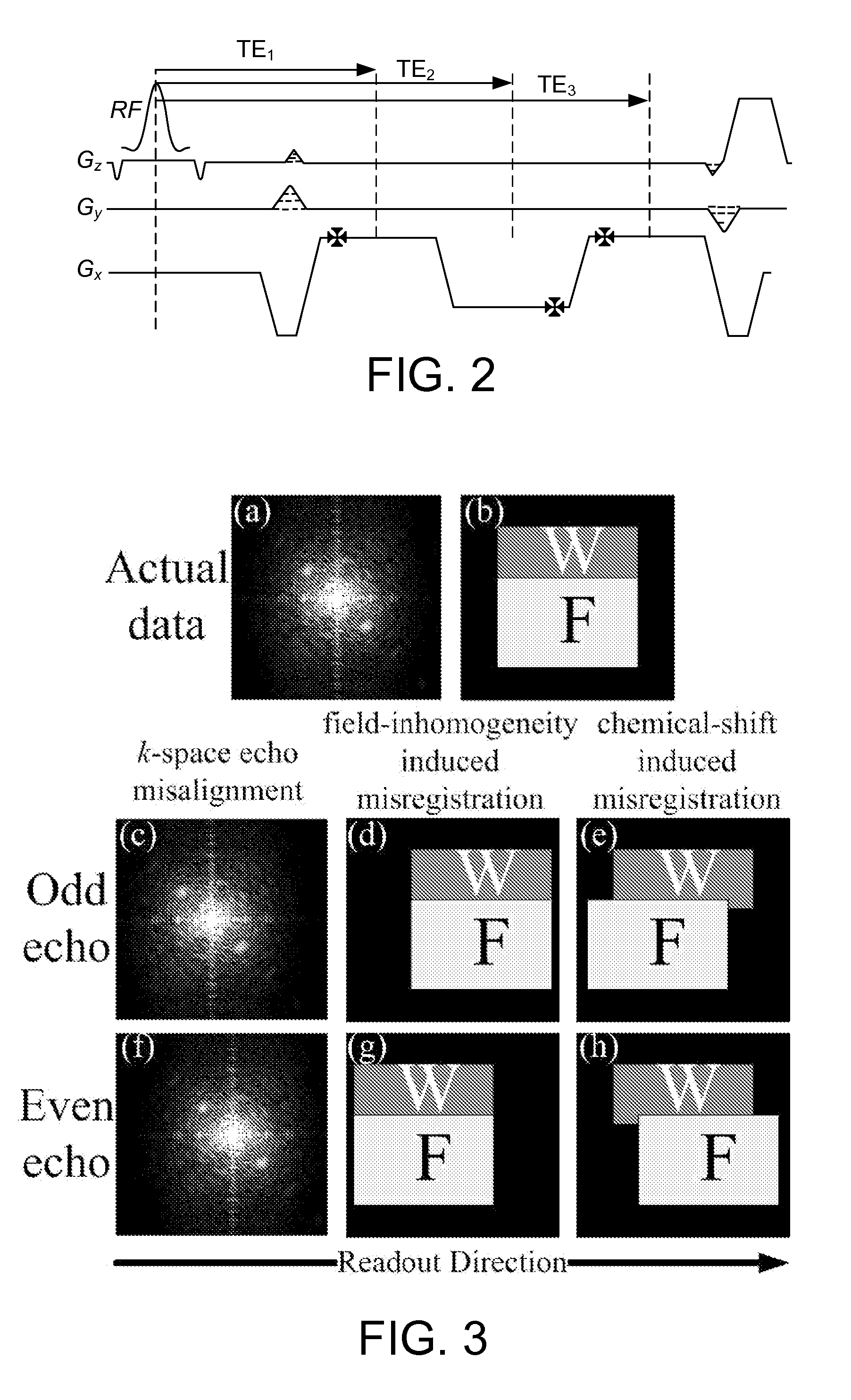
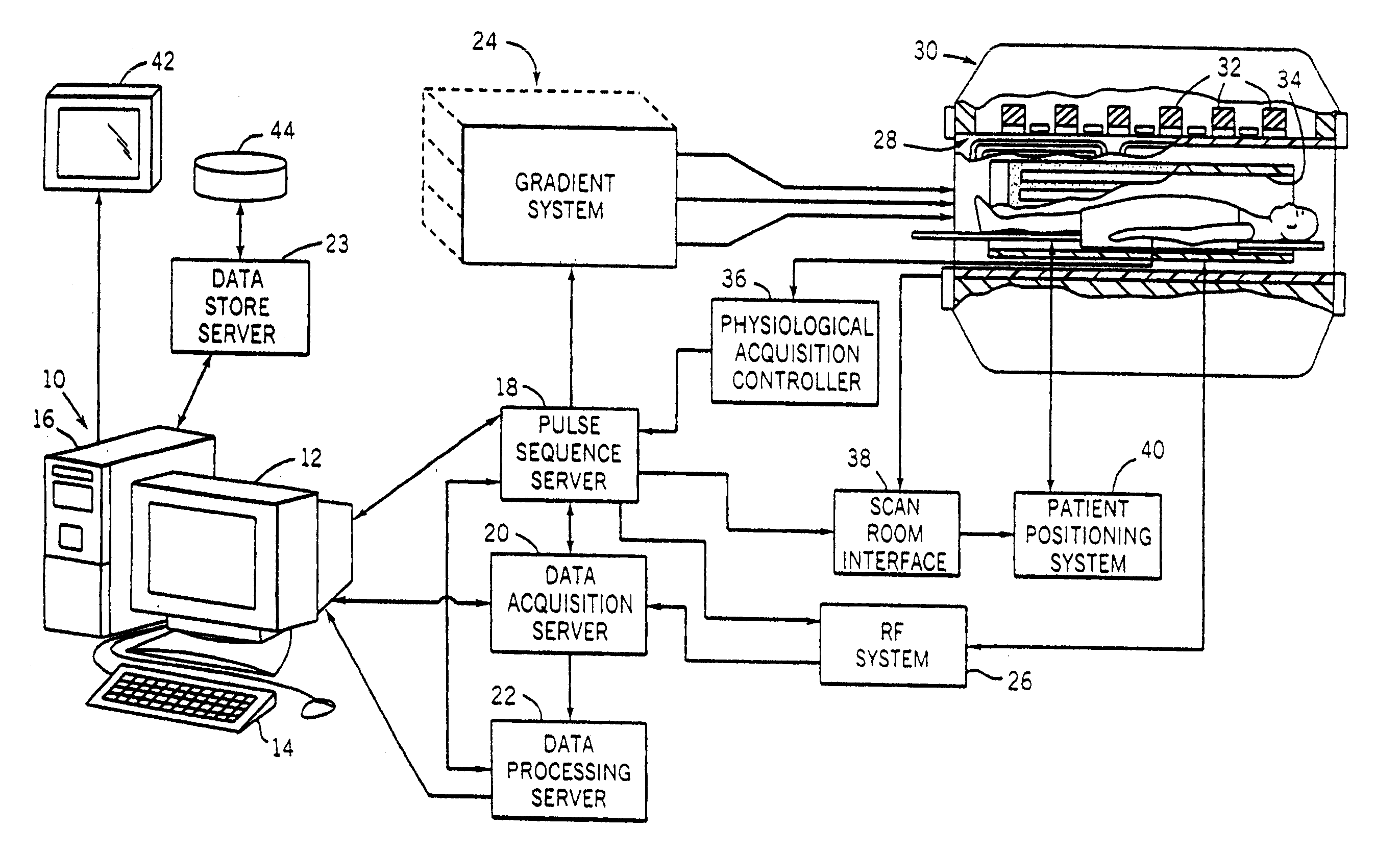
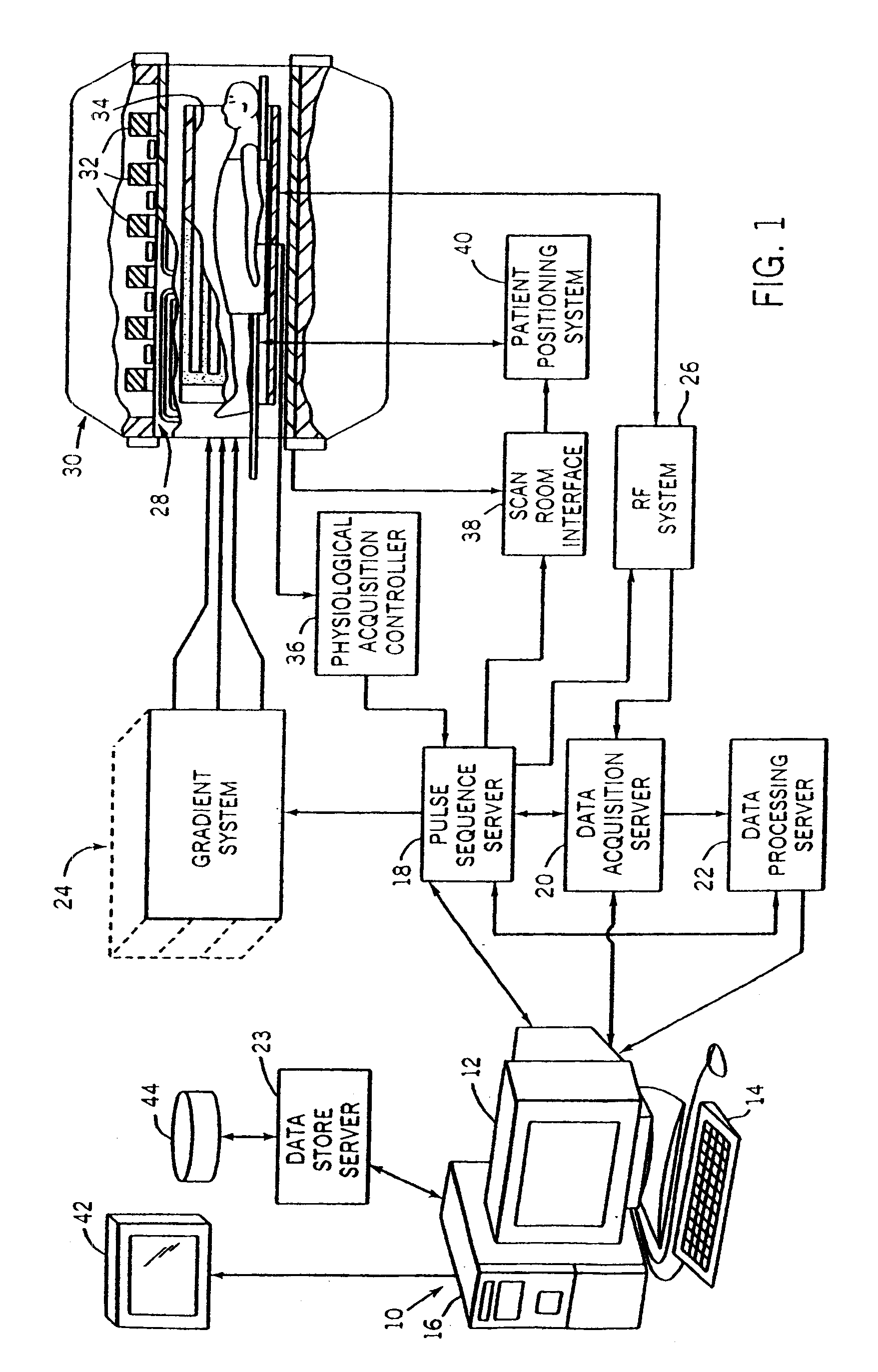
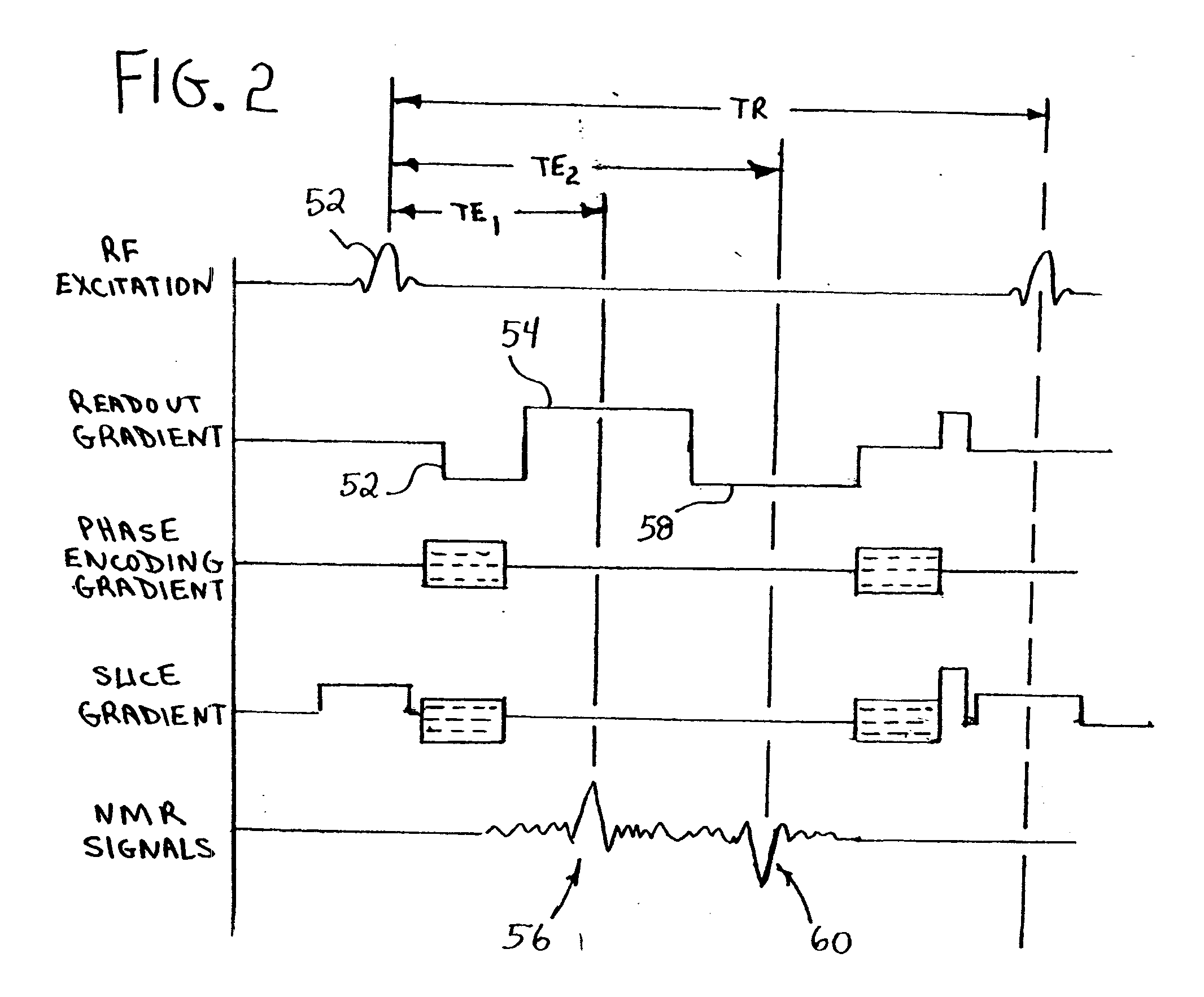
Magnetic resonance imaging with bipolar multi-echo sequences
ActiveUS7777486B2Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionProton magnetic resonanceResonance excitation
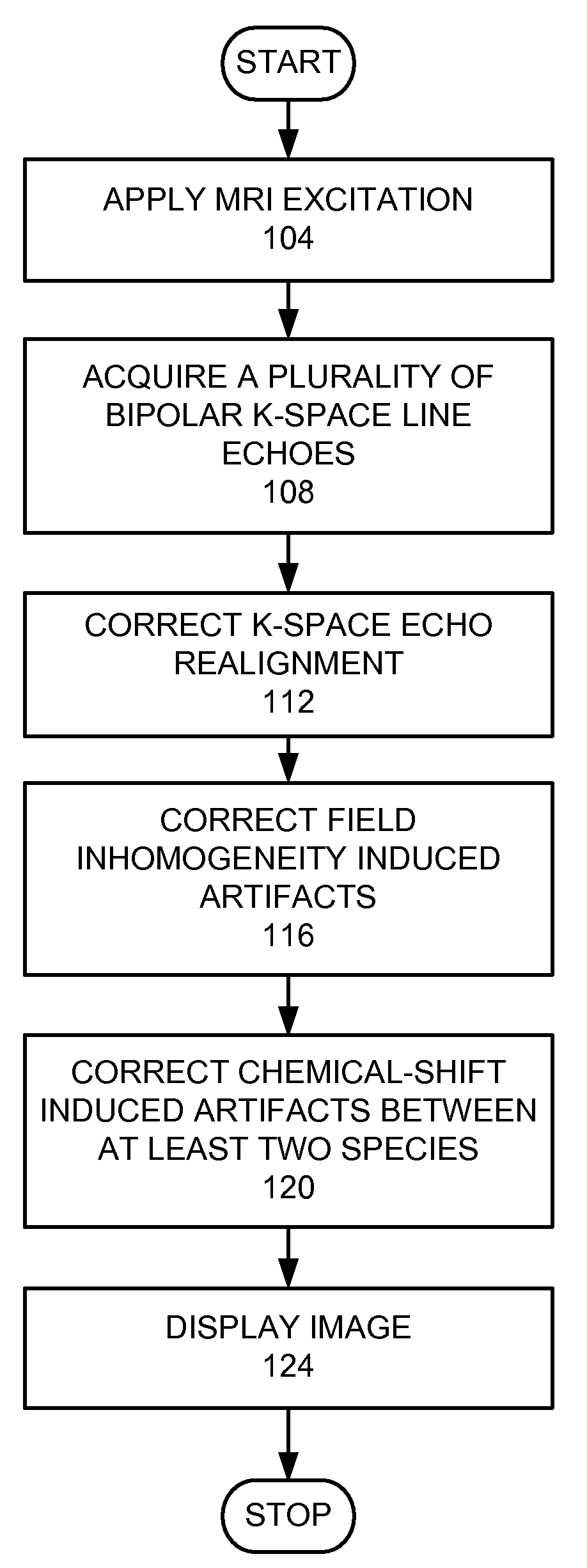
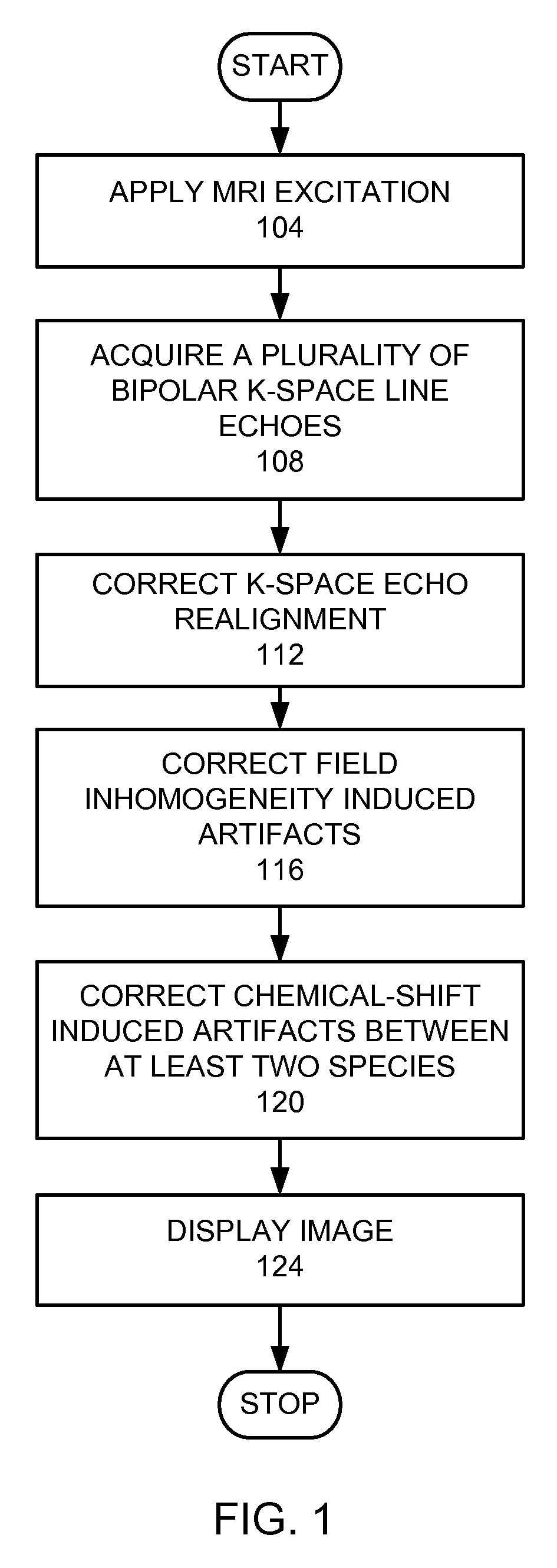
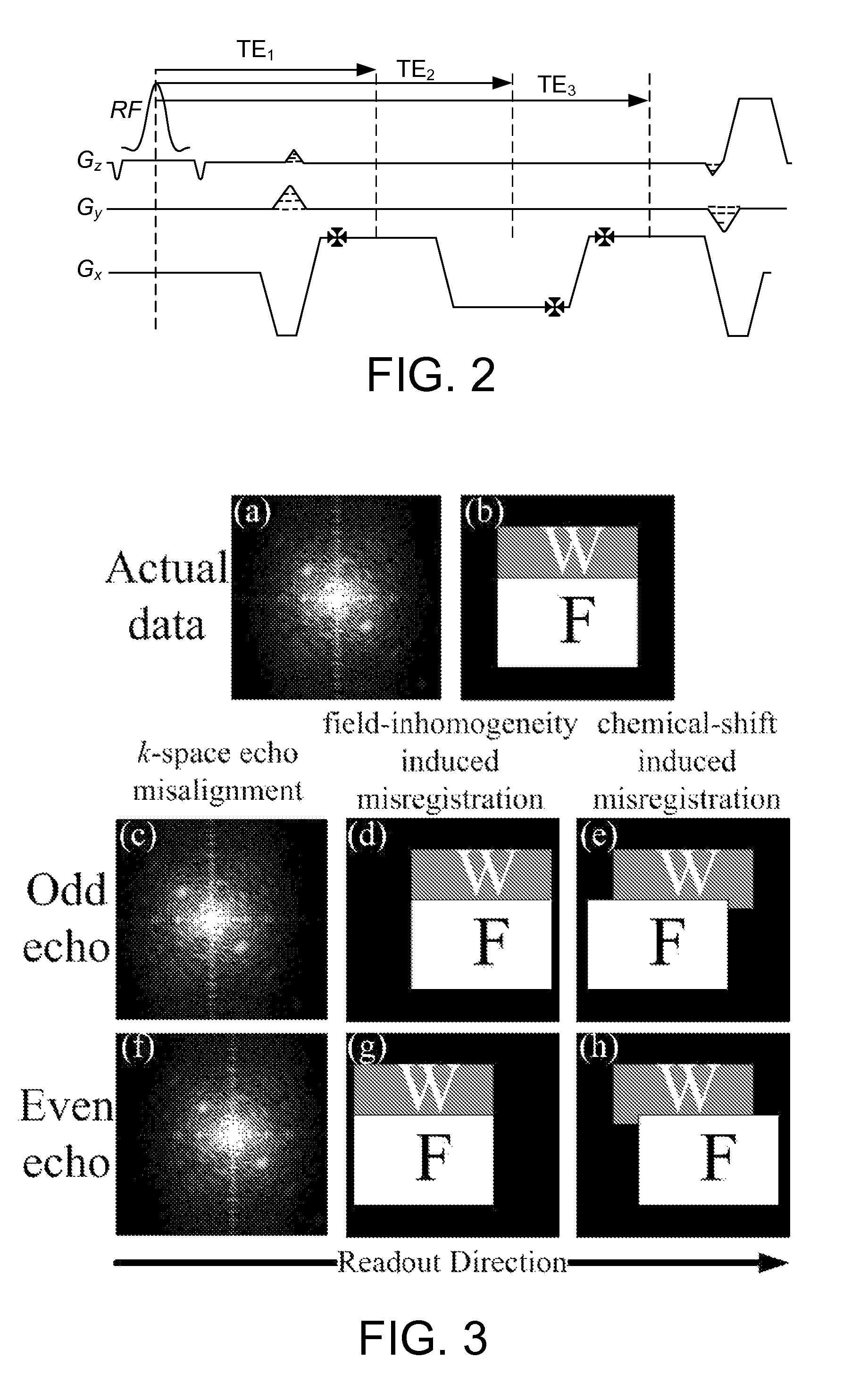
A method for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is provided. A magnetic resonance excitation is provided. A plurality of k-space echoes is acquired bi-directionally wherein at least one echo is an even echo acquired in a first direction and at least one echo is an odd echo acquired in a second direction opposite from the first direction. K-space echo realignment is corrected between the even and odd echoes. Field inhomogeneity induced artifacts are corrected. Chemical shift induced artifacts between at least two species are corrected.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Rare earth Y molecular screen and process for preparing the same
This invention discloses a rare earth Y molecular sieve and preparation; wherein, the rare earth content is 12~22 w.t% considering the quantity of rare earth oxide in molecular sieve, all rare earth ion is in molecular sieve small cage; there is no peak at 0ppm in 27Al M AS NMR spectrogram. The step to obtain molecular sieve comprises: exchanging NaY molecular sieve liquid with ammonium salt or not, taking ion exchange with rare earth chloride by weight ratio of NaY dry basis:RECl3=1:0.17~0.35 at temperature 5~100Deg; pH=2.5~7.5, water: NaY=3~50; adjusting pH value to 8~11 with alkaline solution; mixing, filtering, cleaning, drying; baking for more than 0.1h with 0~100% vapor at temperature 200~950Deg; then, dealing with the molecular sieve according to weight ratio molecular sieve dry basis: ammonium salt :water=1:0~1:2~50 at temperature 60~100Deg; finally, cleaning, filtering, drying and obtaining the product.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Localized two-dimensional shift correlated MR spectroscopy of human brain
InactiveUS7200430B2Measurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringWhole bodySpectroscopy
A two-dimensional (2D) chemical shift correlated MR spectroscopic (COSY) sequence integrated into a new volume localization technique (90°-180°-90°) for whole body MR Spectroscopy. Using the product operator formalism, a theoretical calculation of the volume localization as well as the coherence transfer efficiencies in 2D MRS is presented. A combination of different MRI transmit / receive rf coils is used. The cross peak intensities excited by the proposed 2D sequence are asymmetric with respect to the diagonal peaks. Localized COSY spectra of cerebral frontal and occipital gray / white matter regions in fifteen healthy controls are presented.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cest MRI methods for imaging of metabolites and the use of same as biomarkers
ActiveUS20120019245A1Improve spatial resolutionEasy to detectMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionEndogenous metabolismMetabolite
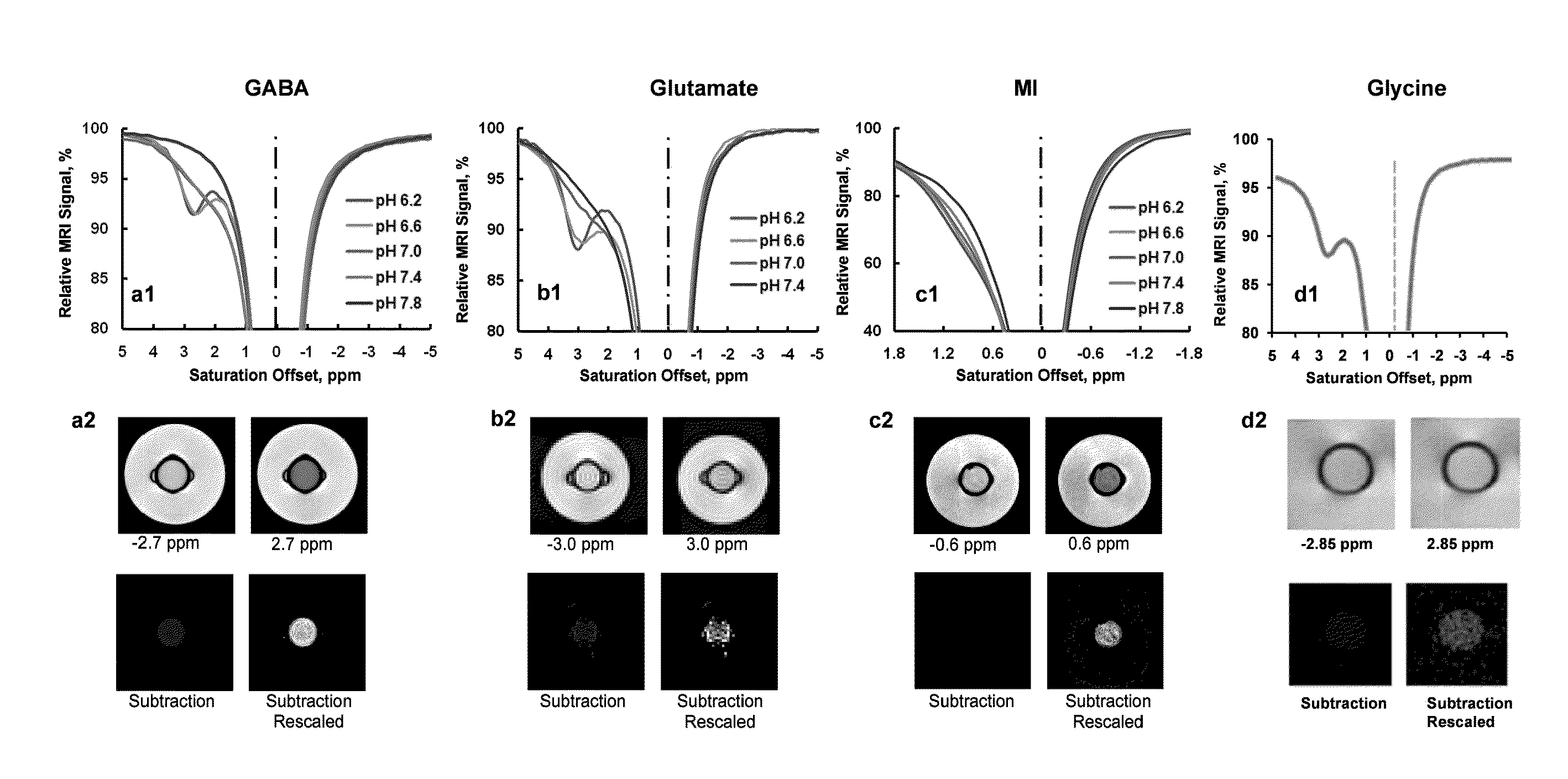
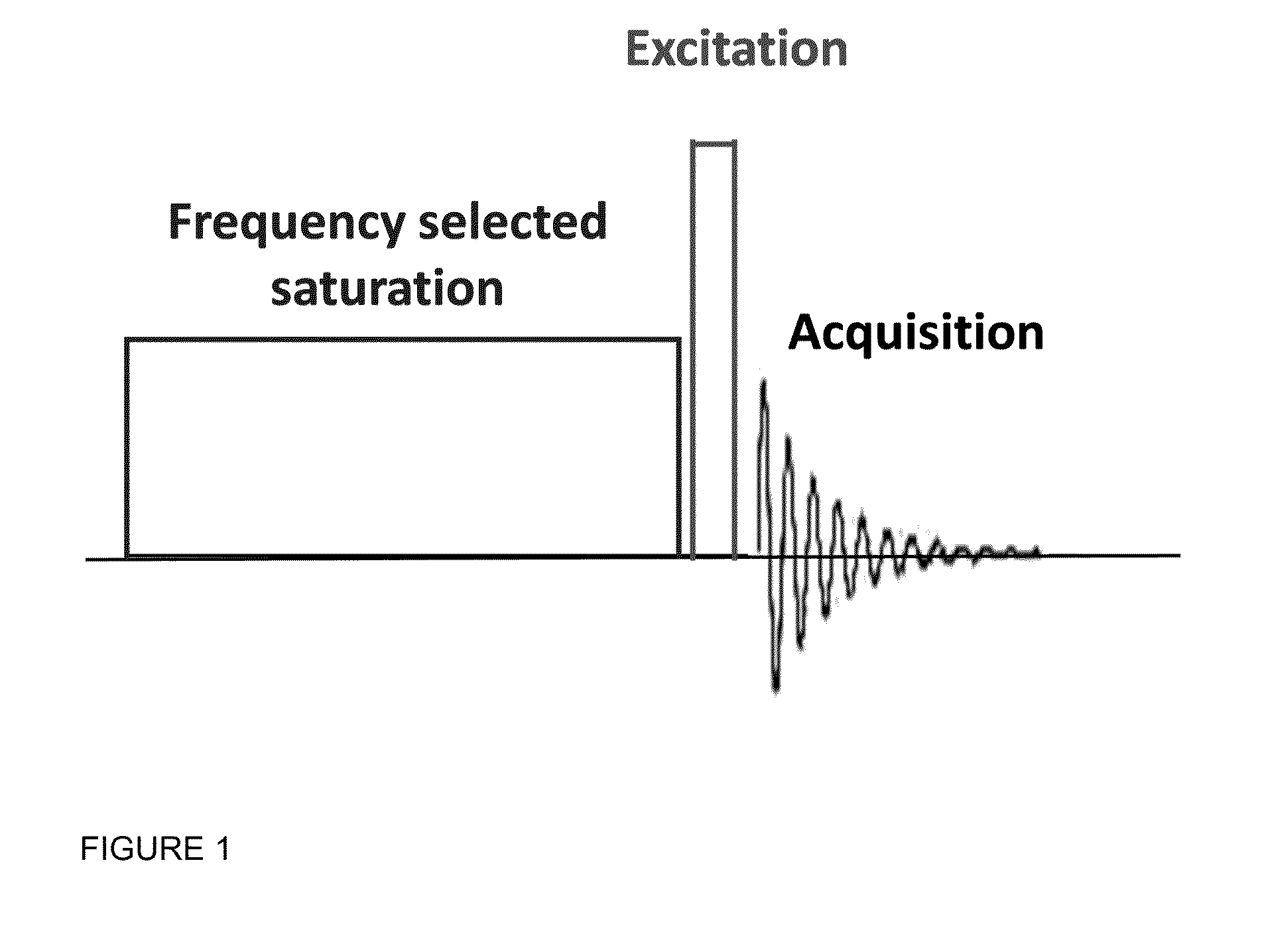
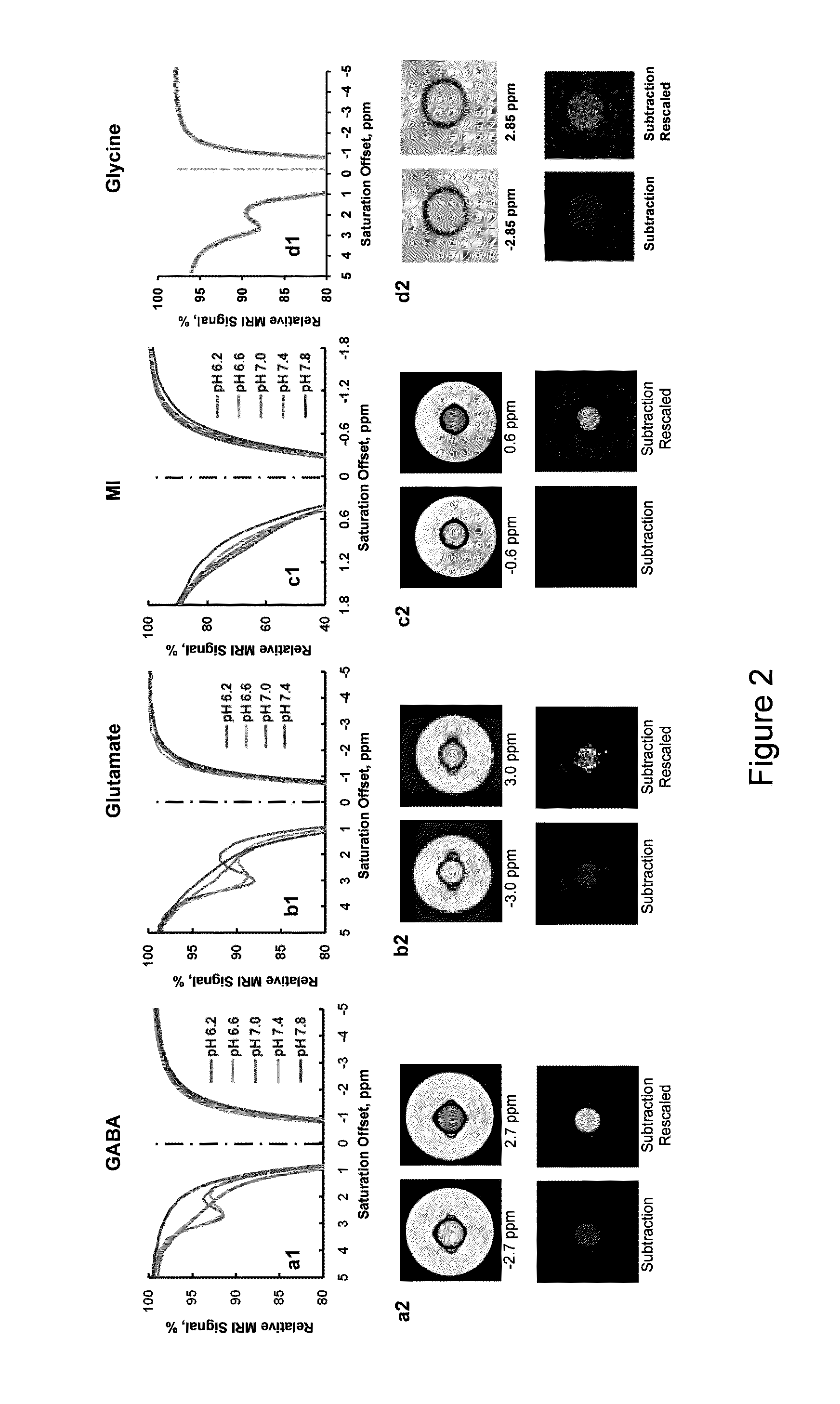
The CEST effect for various neurotransmitters and energy metabolites in the brain and muscles and various endogenous metabolites in the liver, brain, and myocardium are imaged using MR imaging to illustrate a unique CEST effect that may be used to monitor the concentration of the metabolite and hence to characterize and monitor various disease states in the body correlated to the concentration of that metabolite. By adjusting the timing, amplitude, and length of the RF pulse as well as other parameters of the CEST pulse sequence to address the unique chemical shifts and exchange rates of the target, new targets with unique characteristics may be acquired using CEST MR imaging.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
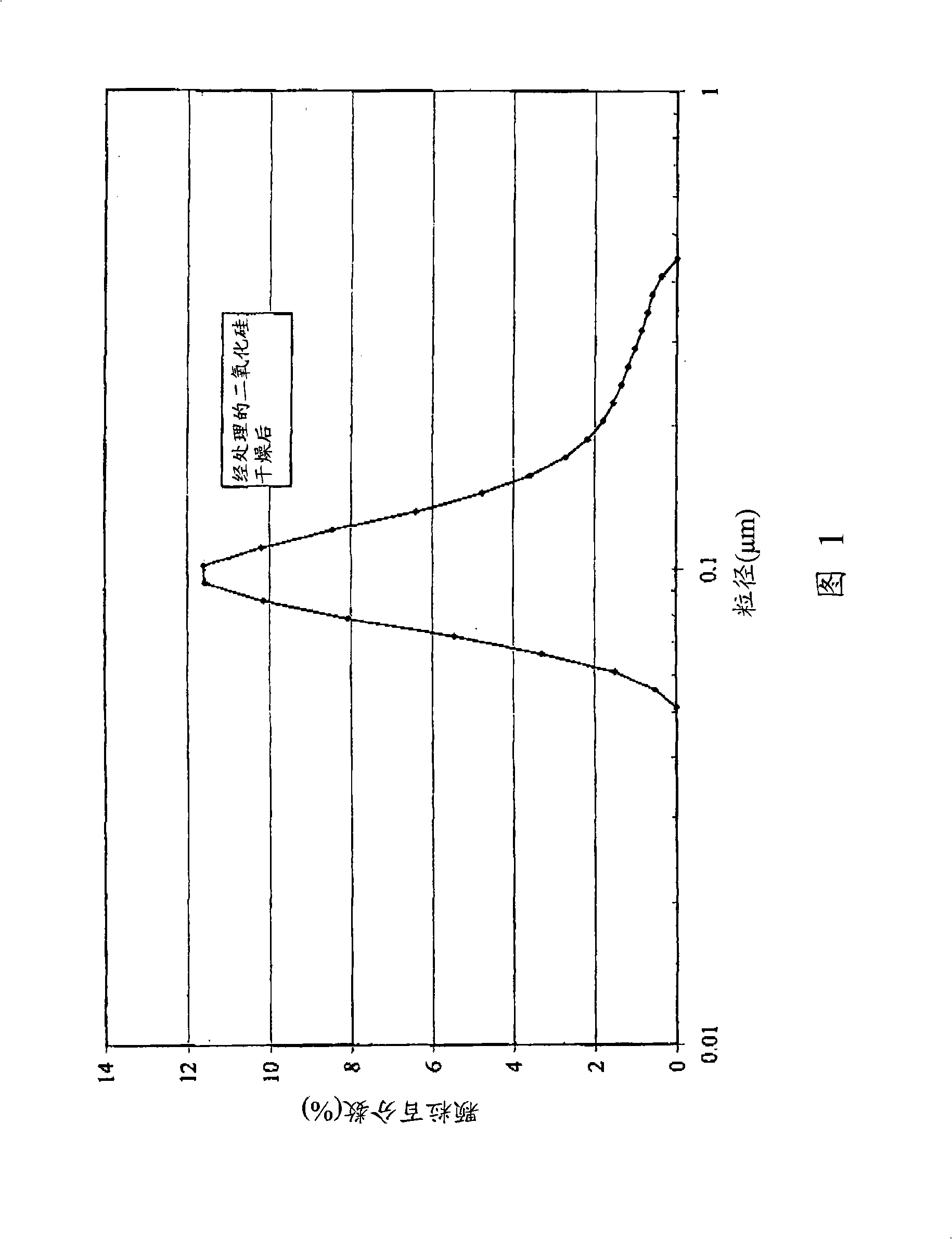
Method of preparing hydrophobic silica
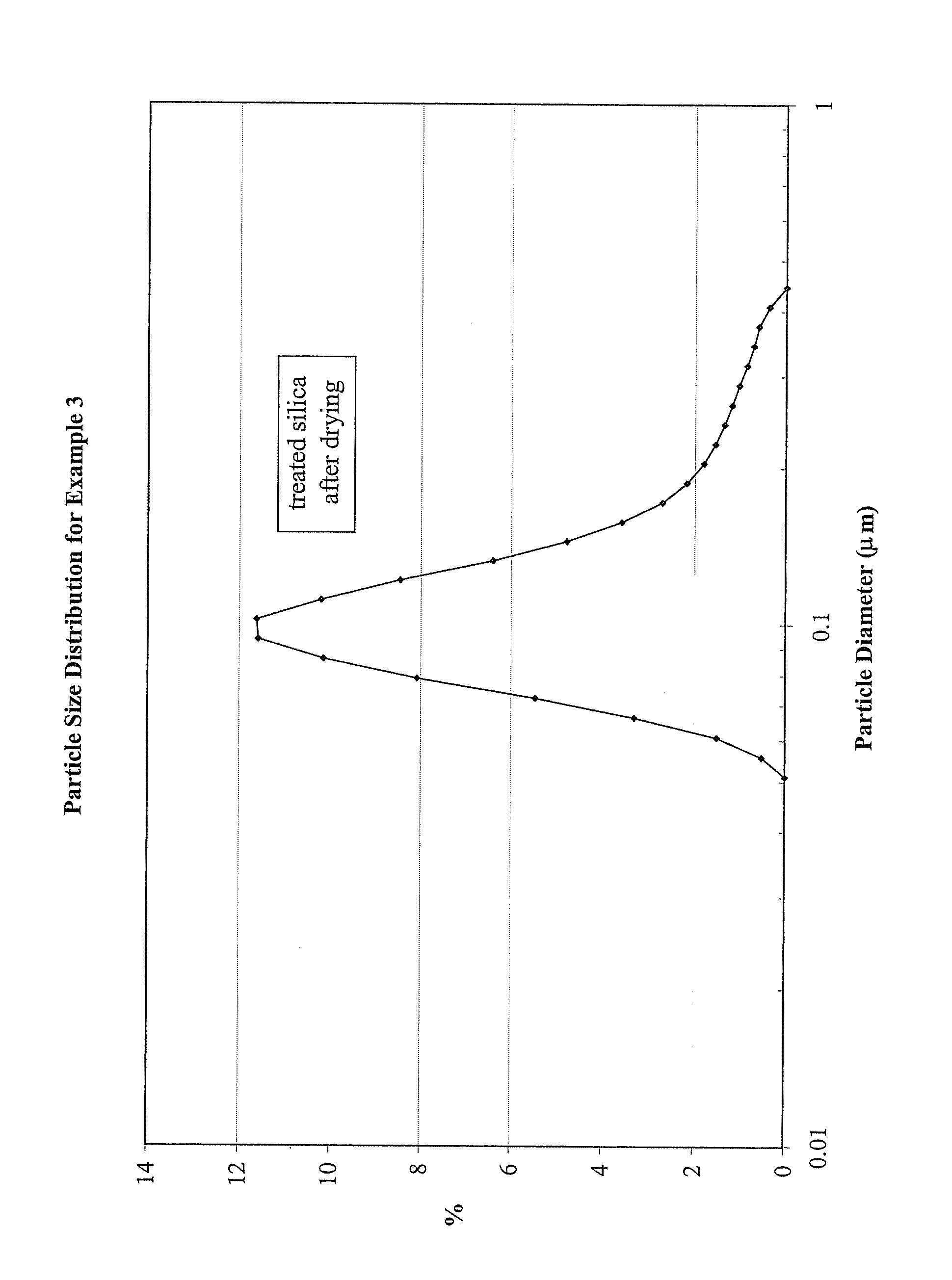
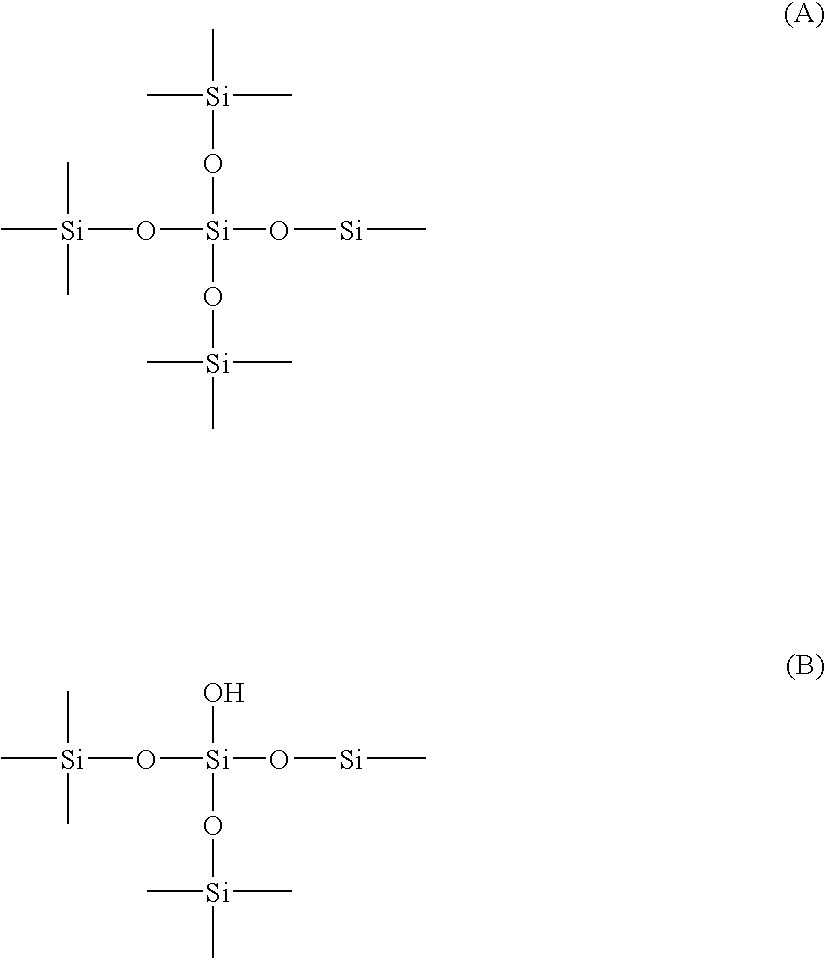
The invention provides hydrophobic surface-treated silica particles having (1) a ratio T2:T3 of about 0.4 or more, wherein T2 is the intensity of a peak having a chemical shift in the CP / MAS 29Si NMR spectrum centered within the range of −56 ppm to −59 ppm, and wherein T3 is the intensity of a peak having a chemical shift in the CP / MAS 29Si NMR spectrum centered within the range of −65 ppm to −69 ppm, and (2) a ratio (T2+T3) / (T2+T3+M) of greater than about 0.05, wherein M is the intensity of a peak having a chemical shift in the CP / MAS 29Si NMR spectrum centered within the range of +7 ppm to +18 ppm. The invention also provides a method of preparing hydrophobic surface-treated silica particles.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Catalytic cracking catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103785460AGood choiceHigh yieldCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMagic angle spinningAdhesive
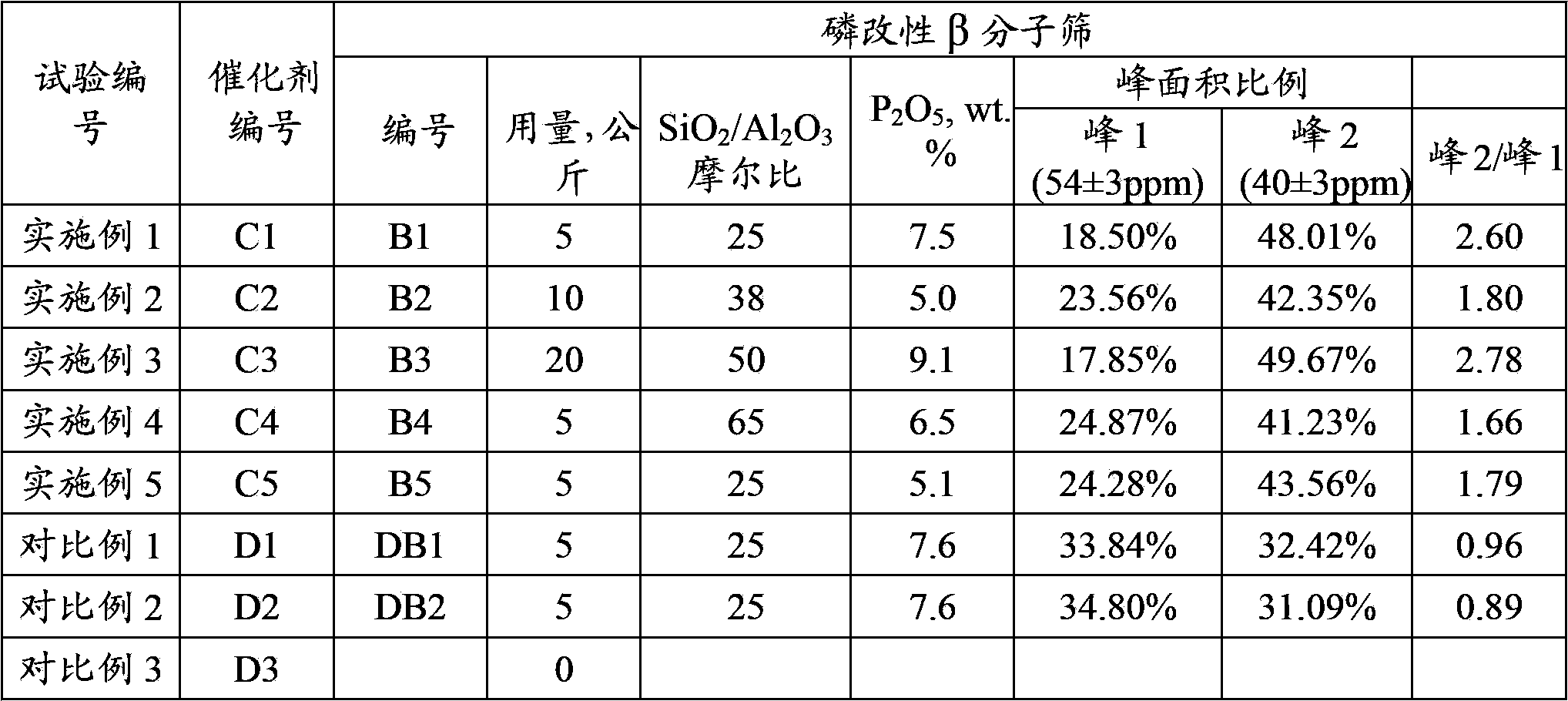
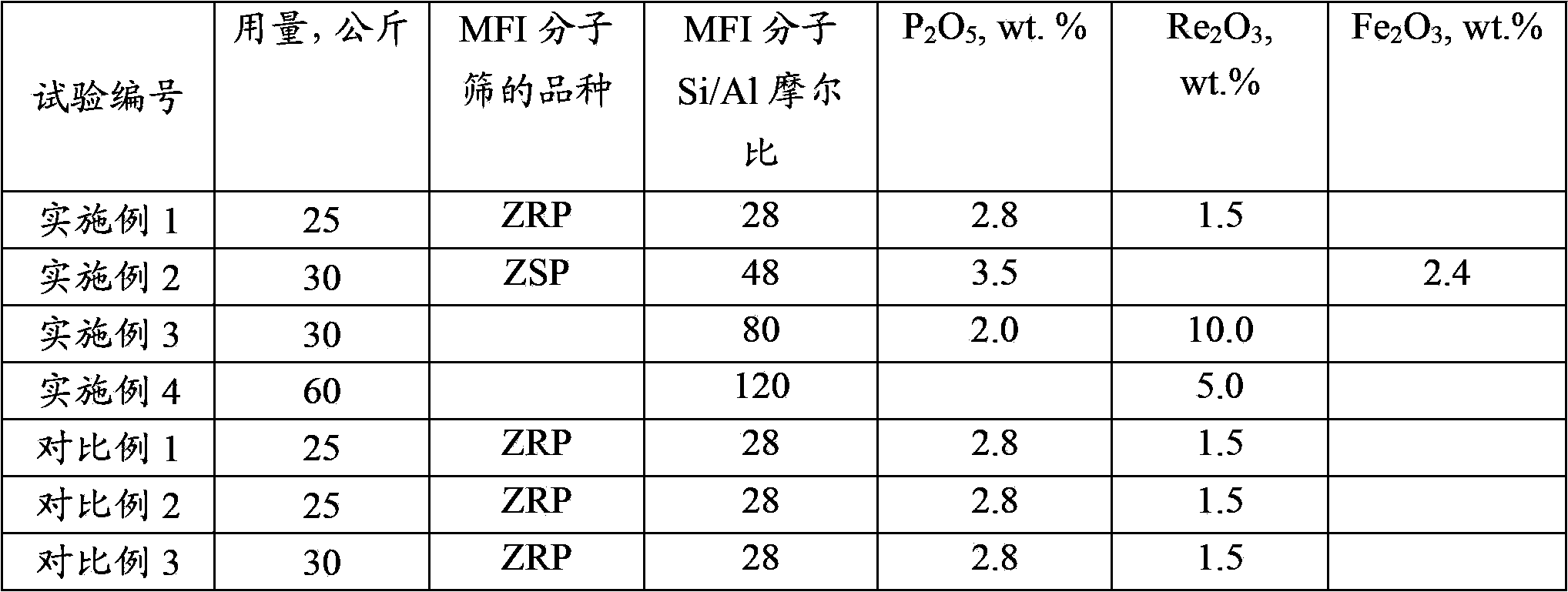
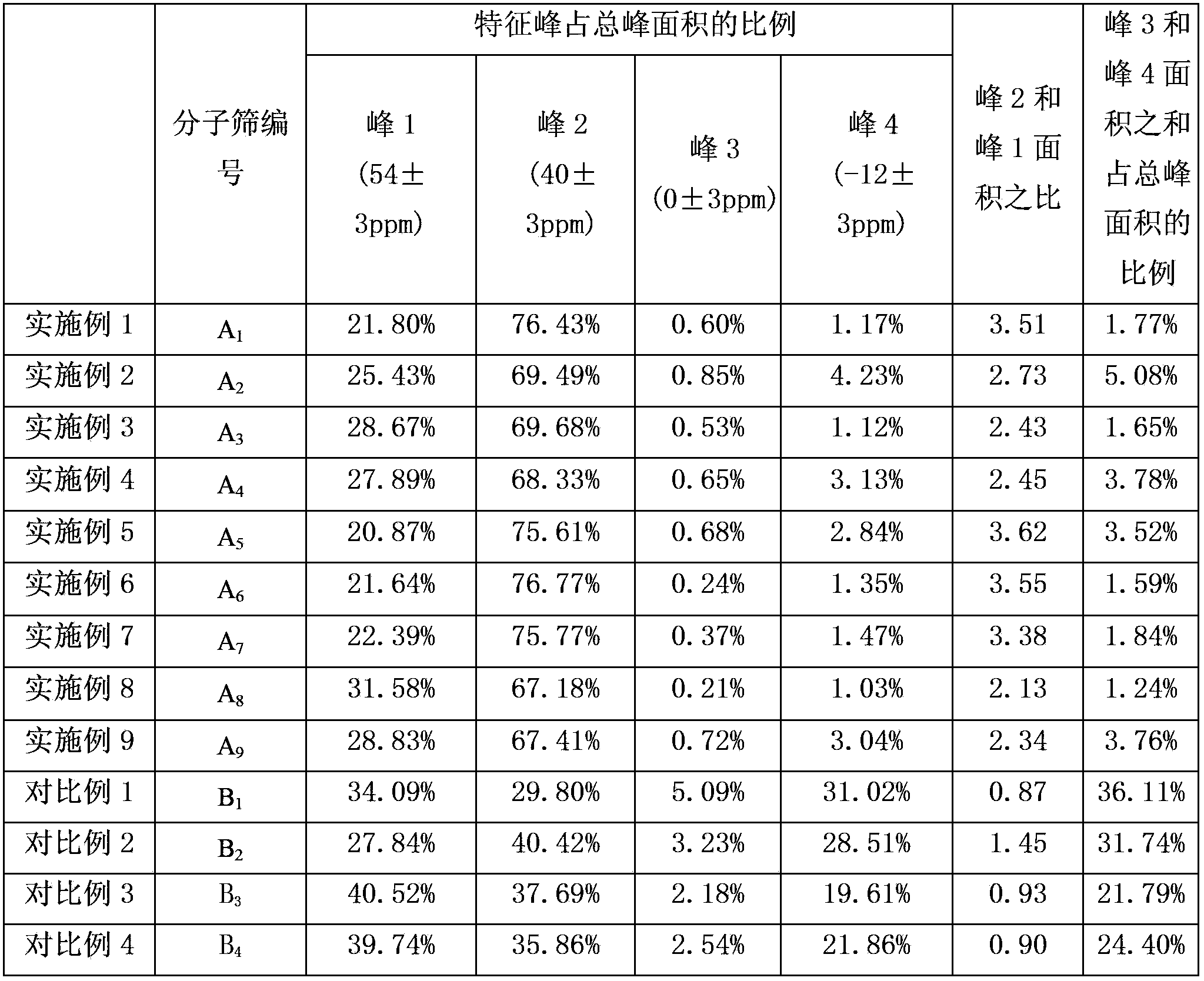
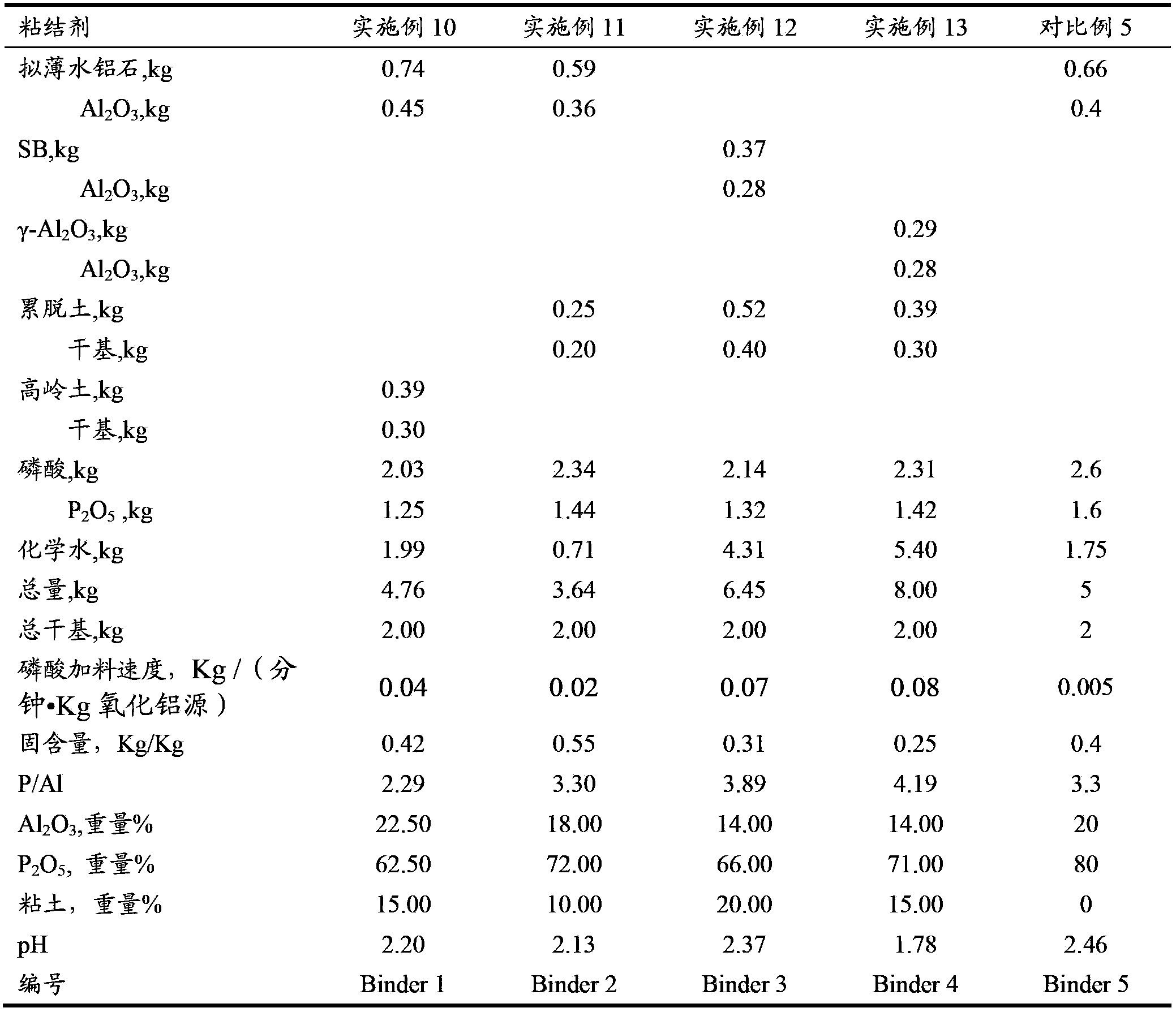
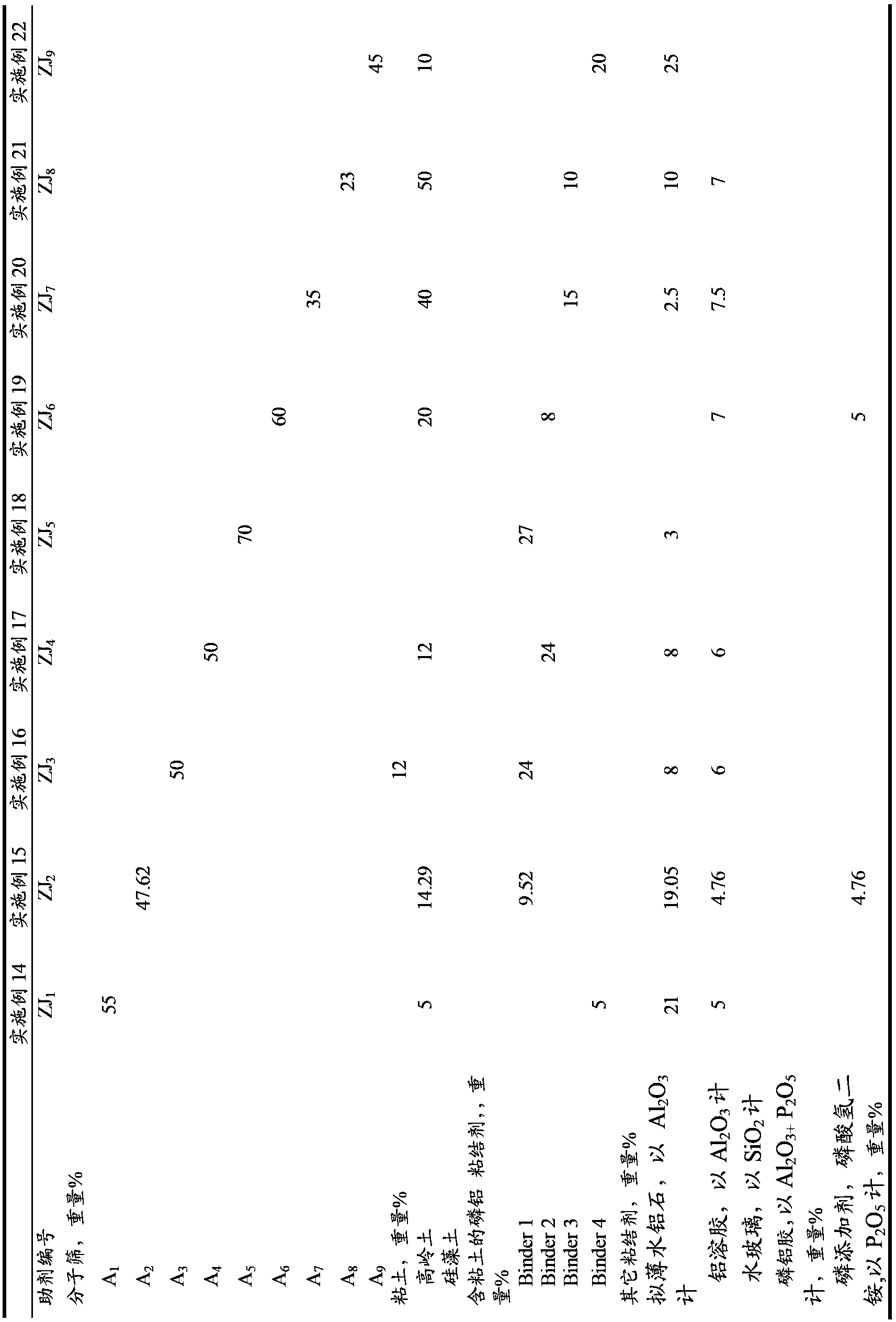
The invention discloses a catalytic cracking catalyst and a preparation method thereof, the catalytic cracking catalyst includes (a)15%-65% of a natural mineral, (b) 10%-30% of an oxide and (c) 25%-75% of a mixture of a MFI structure molecular sieve and a phosphorus-modified beta molecular sieve; the phosphorus-modified beta molecular sieve comprises 3-10 wt% by P2O5 of phosphorus, and in the 27Al MAS NMR (Magic Angle Spinning Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) of the molecular sieve, the ratio of resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of 40+-3ppm to resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of 54+-3ppm is greater than or equal to 1. The preparation method of the catalyst comprises the steps of mixing and pulping of the phosphorus-modified beta molecular sieve, the natural mineral and a non-polar oxide adhesive, and spray drying, and the preparation method of the phosphorus-modified beta molecular sieve is as follows: programmed heating of beta molecular sieve raw powder to bake to remove a template agent, and then phosphorus modification. The catalytic cracking catalyst is applied to preparation of propylene by catalytic cracking of naphtha, and the low-carbon olefin production rate is higher.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Silica
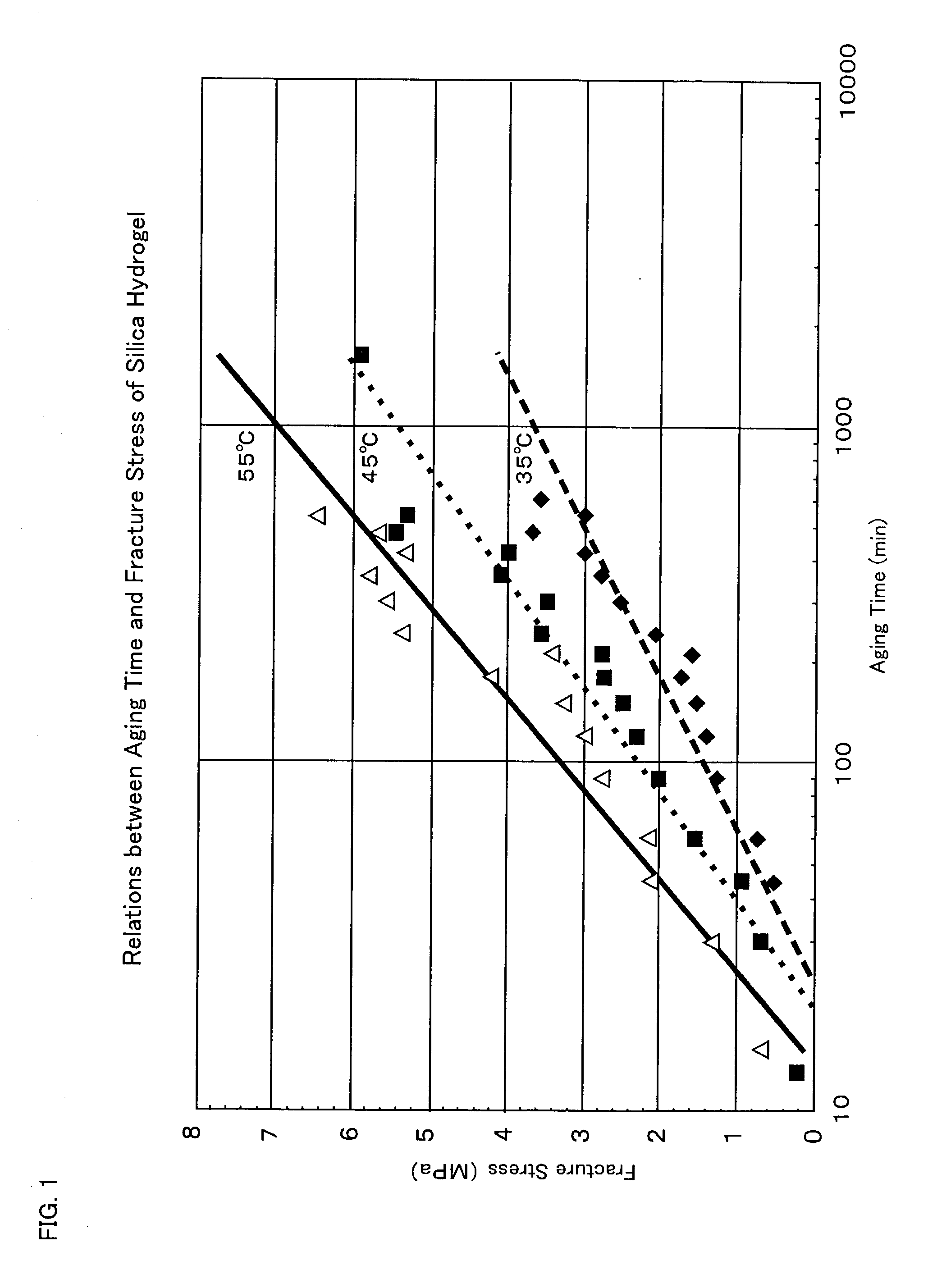
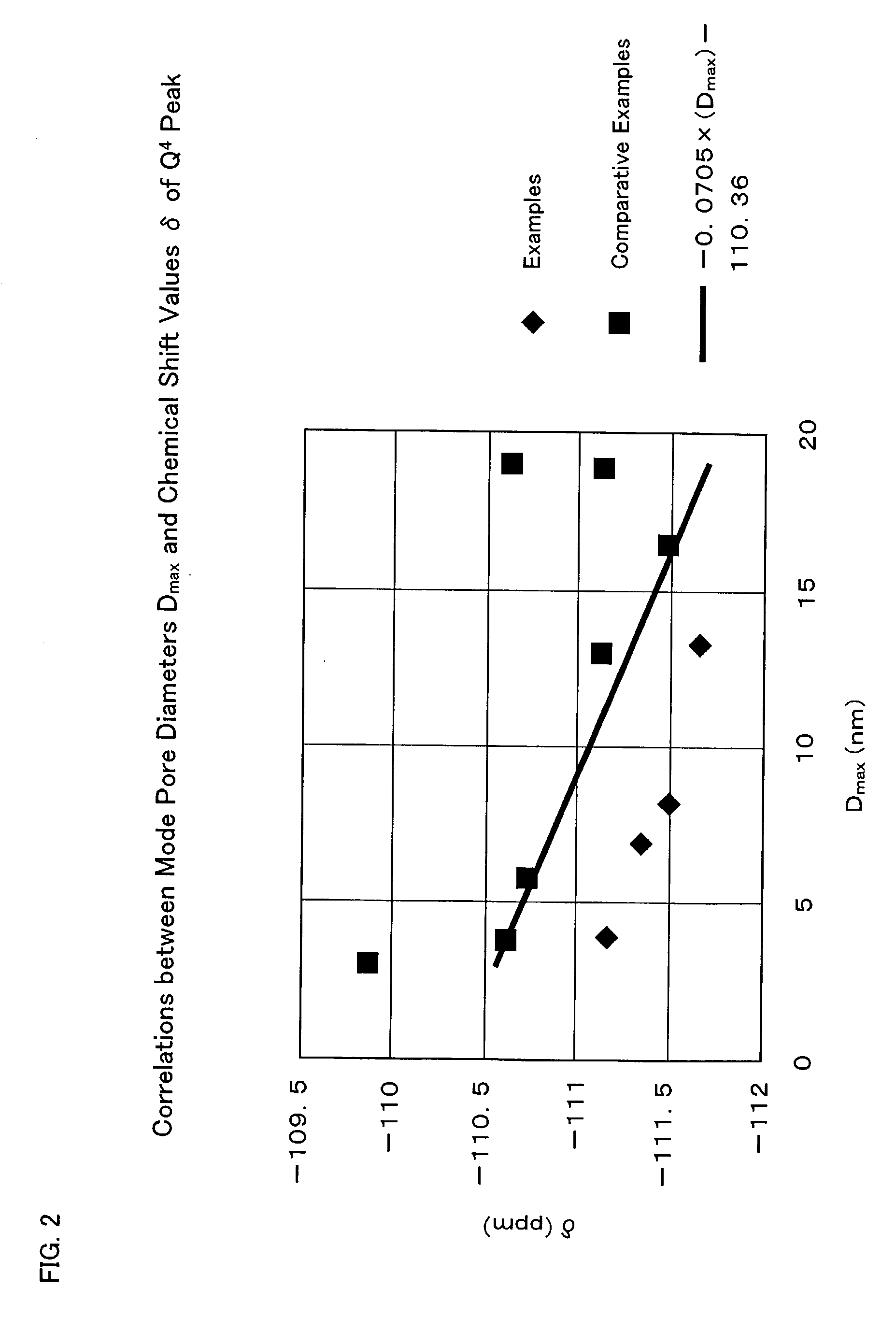
Silica with a large pore volume, a large specific surface area, a narrow pore distribution, low contents of unwanted metal impurities, and excellent physical properties such as high heat-resistance and water-resistance is provided. The silica has a mode pore diameter (Dmax) of 20 nm or less, and a solid-state Si nuclear magnetic resonance (hereinafter called solid-state Si NMR) spectrum of the silica includes a chemical shift (δ ppm) of Q4 peak meeting the following inequality (I). −0.0705×(Dmax)−110.36>δ (I) The silica with such properties can be suitably used in fields of which particularly excellent heat resistance and water resistance are required, and moreover controlled pore properties, and the fact that physical properties scarcely change over a long period of time are required among the above-mentioned applications.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Cracking catalyst for reducing alkene content in catalytically cracked gasoline
ActiveCN1733363AReduce olefin contentStrong ability to convert heavy oilCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveRare earth ions
This invention discloses crack catalyst to decrease olefin content in catalytic cracking gasoline, which is characterized in that there is 10~50 w.t% CDY molecular sieve in the catalyst that is prepared by exchanging method of solid-liquid combination; the rare earth content is 12~22 w.t% considering the quantity of rare earth oxide; all rare earth ion is in molecular sieve small cage; there is no peak at 0ppm in 27Al M AS NMR spectrogram. The catalyst can decrease olefin content in catalytic cracking gasoline greatly with well heavy oil conversion ability.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Magnetic resonance imaging with bipolar multi-echo sequences
ActiveUS20090072826A1Analysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonance excitationMulti echo
A method for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is provided. A magnetic resonance excitation is provided. A plurality of k-space echoes is acquired bi-directionally wherein at least one echo is an even echo acquired in a first direction and at least one echo is an odd echo acquired in a second direction opposite from the first direction. K-space echo realignment is corrected between the even and odd echoes. Field inhomogeneity induced artifacts are corrected. Chemical shift induced artifacts between at least two species are corrected.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Metabolite detection using magnetic resonance
InactiveUS20080081375A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationMagnetic measurementsMetaboliteDisease cause
Methods using magnetic resonance, such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), are provided for detecting metabolites in a sample. The methods are useful for the diagnosis or prognosis of a disease such as cancer and can also be used to determine or monitor a treatment protocol. The methods are useful in characterizing speciation in biological samples where mixtures are often encountered and chemical shifts of the same structural group of similar molecules can produce complicated overlapping resonances.
Owner:OKLAHOMA MEDICAL RES FOUND
Method of preparing hydrophobic silica
The invention provides hydrophobic surface-treated silica particles having (1) a ratio T2:T3 of about 0.4 or more, wherein T2 is the intensity of a peak having a chemical shift in the CP / MAS<29>Si NMR spectrum centered within the range of -56 ppm to -59 ppm, and wherein T3 is the intensity of a peak having a chemical shift in the CP / MAS <29>Si NMR spectrum centered within the range of -65 ppm to -69 ppm, and (2) a ratio (T2 +T3) / (T2 +T3 +M) of greater than about 0.05, wherein M is the intensity of a peak having a chemical shift in the CP / MAS <29>Si NMR spectrum centered within the range of +7 ppm to +18 ppm. The invention also provides a method of preparing hydrophobic surface-treated silica particles.
Owner:CABOT CORP
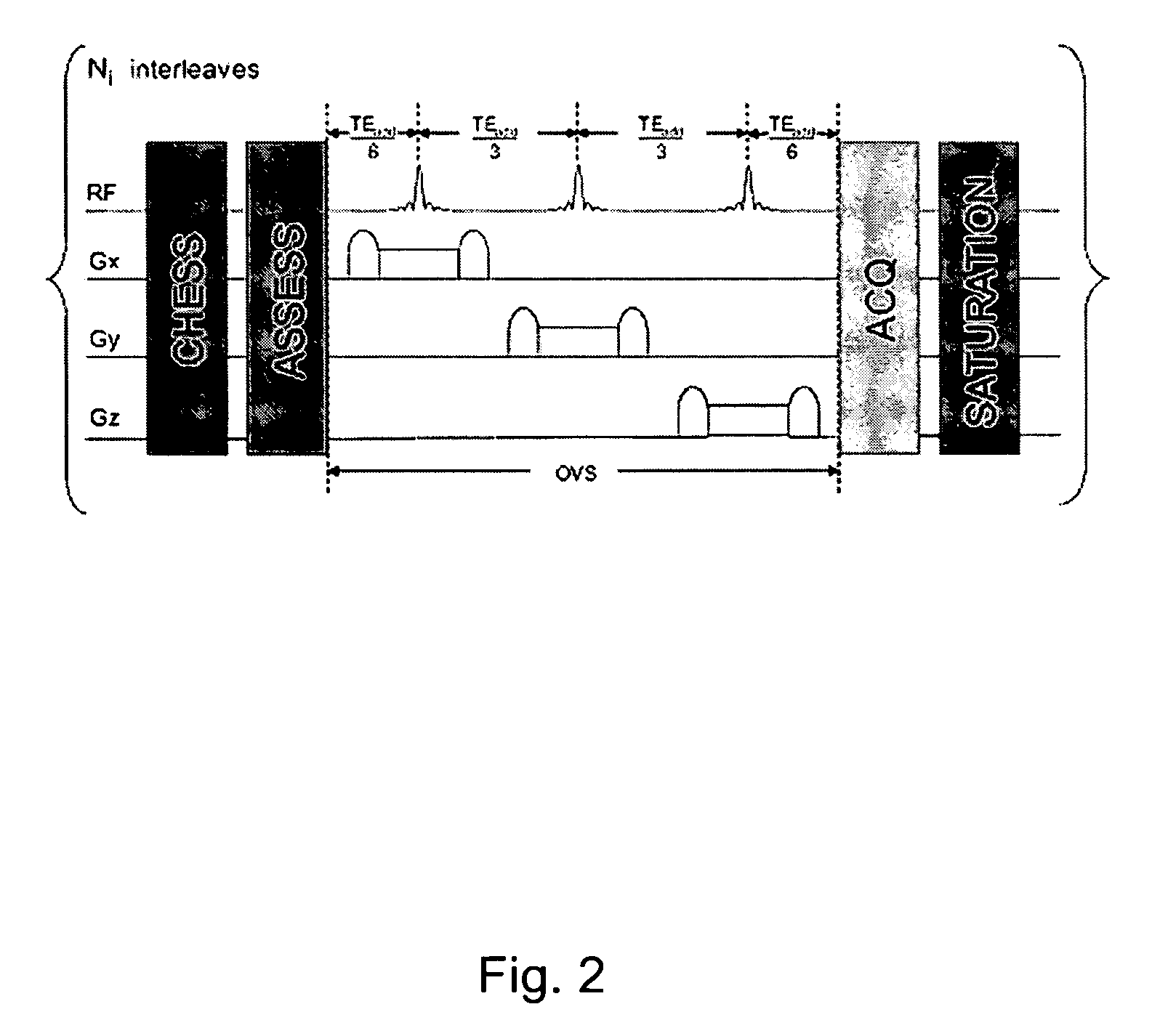
Dynamic contrast enhanced mr imaging with compressed sensing reconstruction
ActiveUS20130089271A1Improve diagnostic qualityQuality improvementImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionData setDynamic contrast
The present invention relates to a method of performing dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of an object (10) with signal separation for water and fat, the method comprising acquiring magnetic resonance datasets in the k-space using Dixon acquisition in a chemical shift encoding space and dynamic time resolution in a dynamic time space, wherein the dataset acquisition is performed employing undersampling, wherein the method further comprises: applying a compressed sensing reconstruction technique in the k-space, the chemical shift encoding space and the dynamic time space, said compressed sensing reconstruction resulting in reconstructed datasets, —performing Dixon reconstruction on the reconstructed datasets and dynamic contrast analysis on the Dixon reconstructed datasets.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
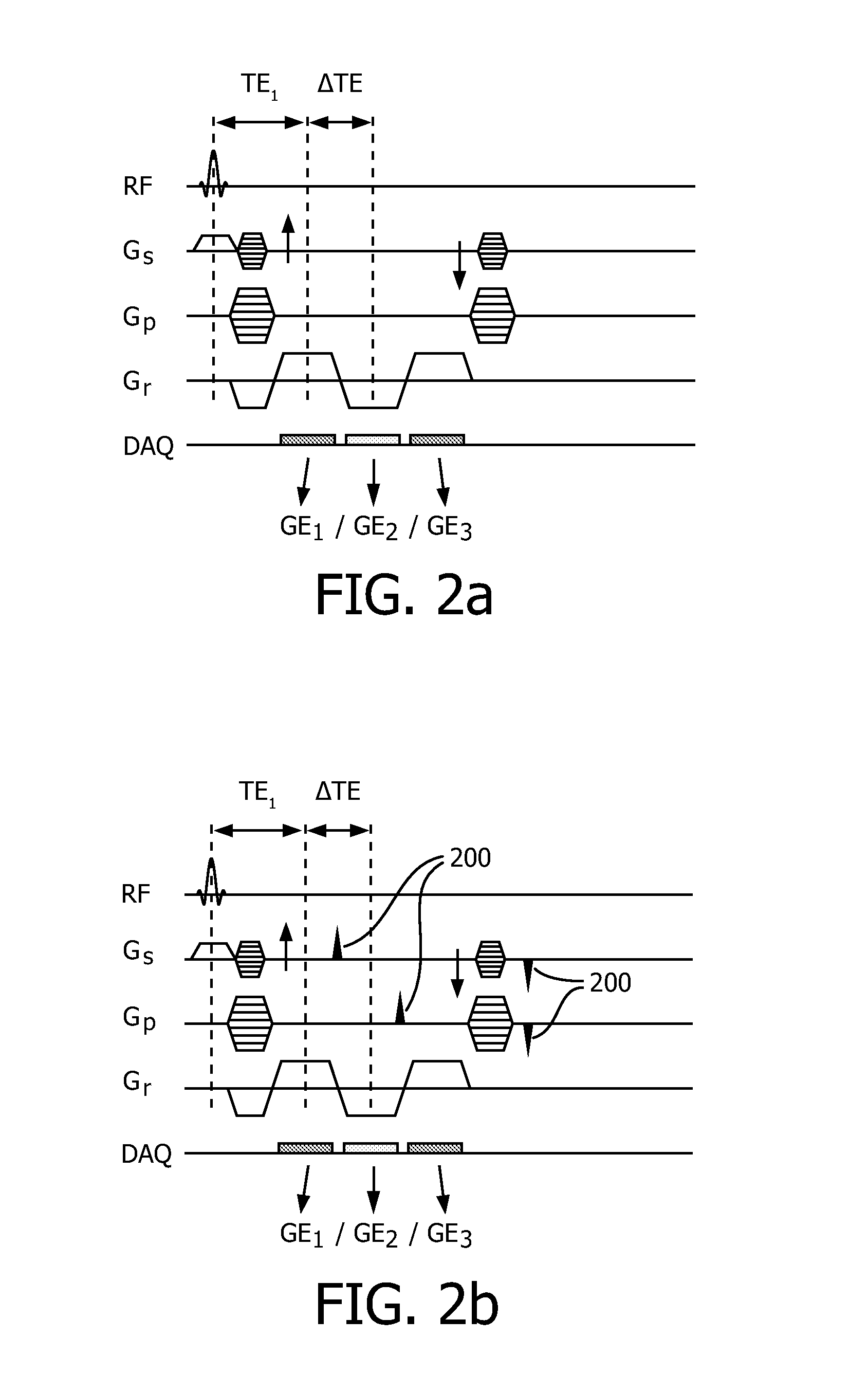
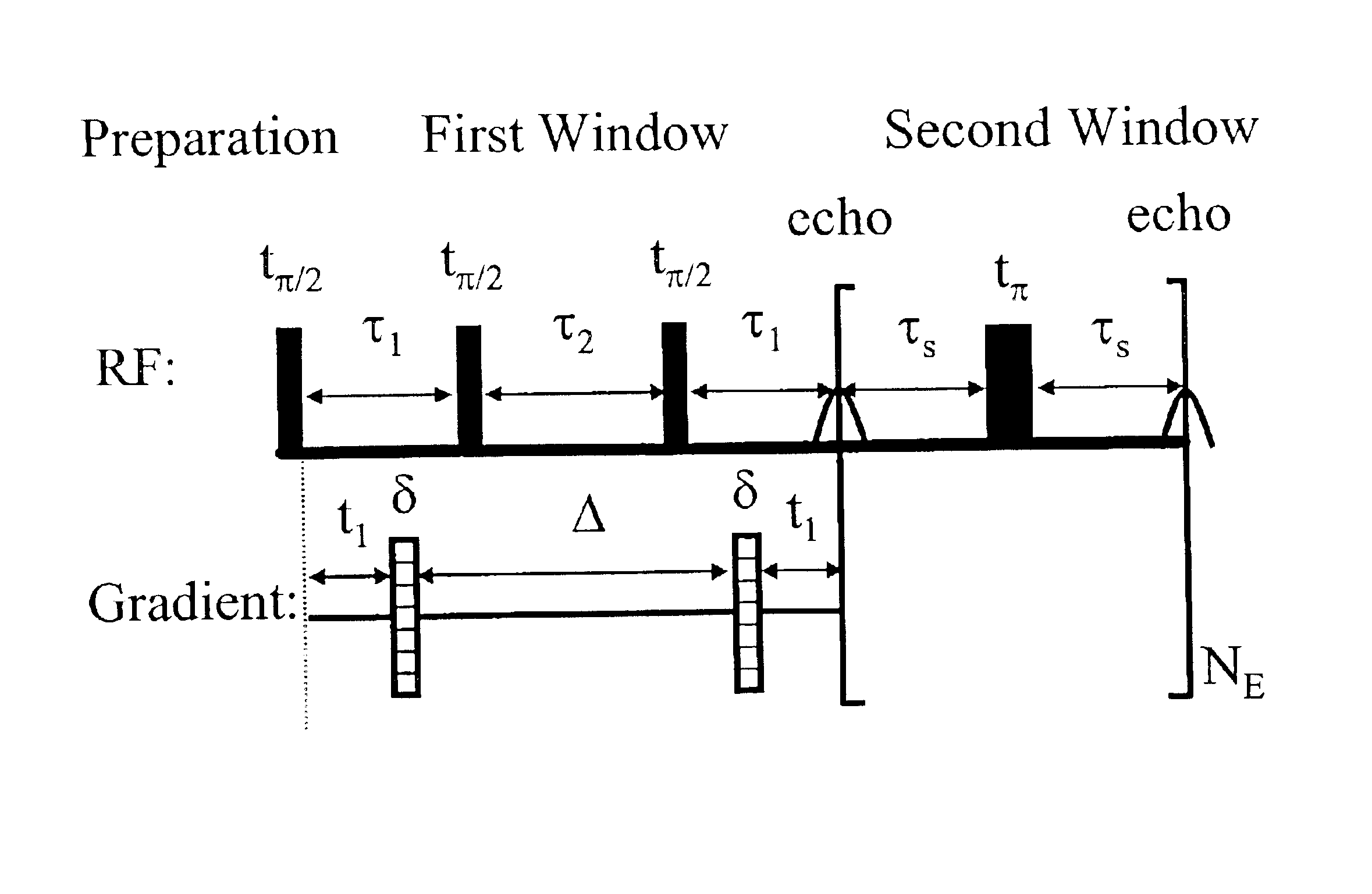
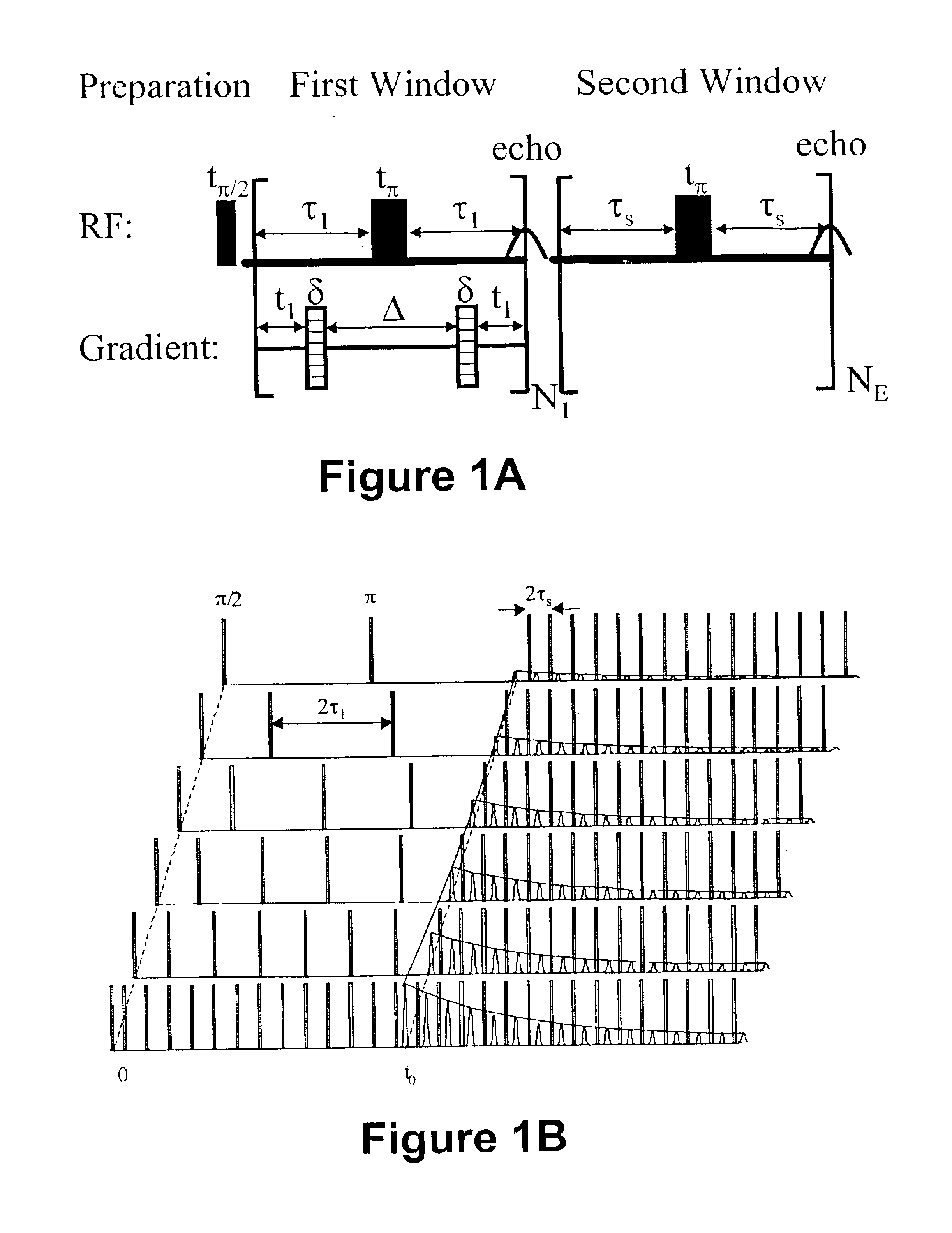
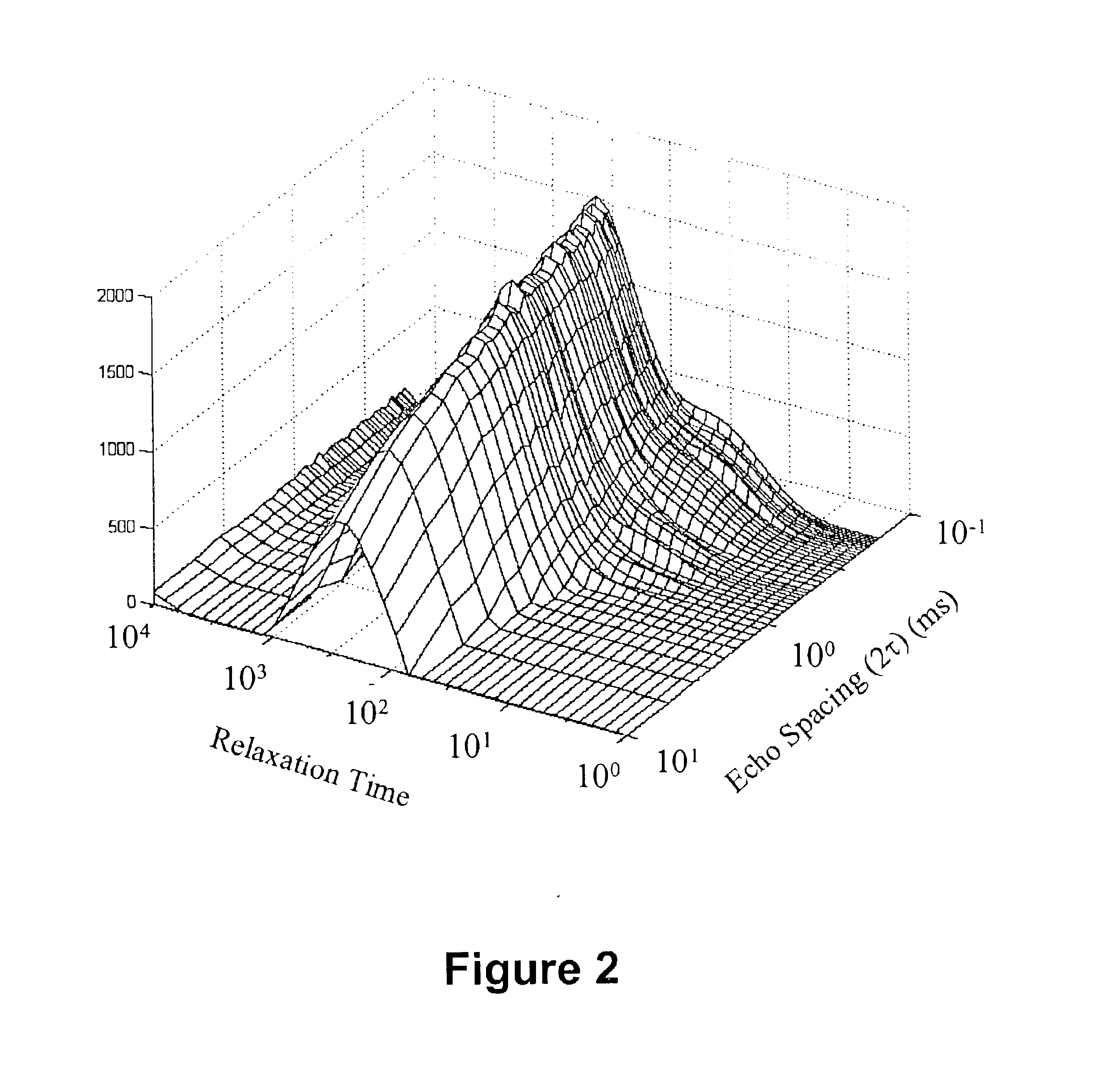
Methods of decoupling diffusion effects from relaxation times to determine properties of porous media containing fluids
InactiveUS6833698B2Remove and minimizes effectElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonancePore fluidPorous medium
Novel pulse sequences are used to probe the properties of porous media, such as are found in subterranean formations and core samples. This use allows diffusion effects to be uncoupled from the overall T2 relaxation time of the sample. Properties such as internal field gradient and distribution of diffusion coefficients may be determined. A series of pulse sequences are applied to the media to be evaluated. The series of pulse sequences include first and second windows. The first windows include pulse sequences have varying characteristics, such as increasing echo spacing, while the second windows preferably utilize similar pulse sequences which have very small echo spacing. Apparent internal field gradient distribution and apparent diffusion coefficient may be determined as a function of T2 relaxation time. These properties are readily visualized in a two-dimensional map with a first axis being the apparent internal field gradient or alternatively the diffusion coefficient of pore fluids, a second axis being the T2 relaxation times, and the vertical amplitudes being proportional to the proton population. Other properties which may be determined from use of this method include porosity, pore size distribution, oil and water saturation, oil viscosity, oil wettability, and permeability. Also, a method for determining and plotting a T1-MAS 2D spectrum is provided where T1 relaxation time and chemical shift are plotted on x,y axes while intensity of proton population is displayed along a third axis.
Owner:CHEVRONTEXACO US
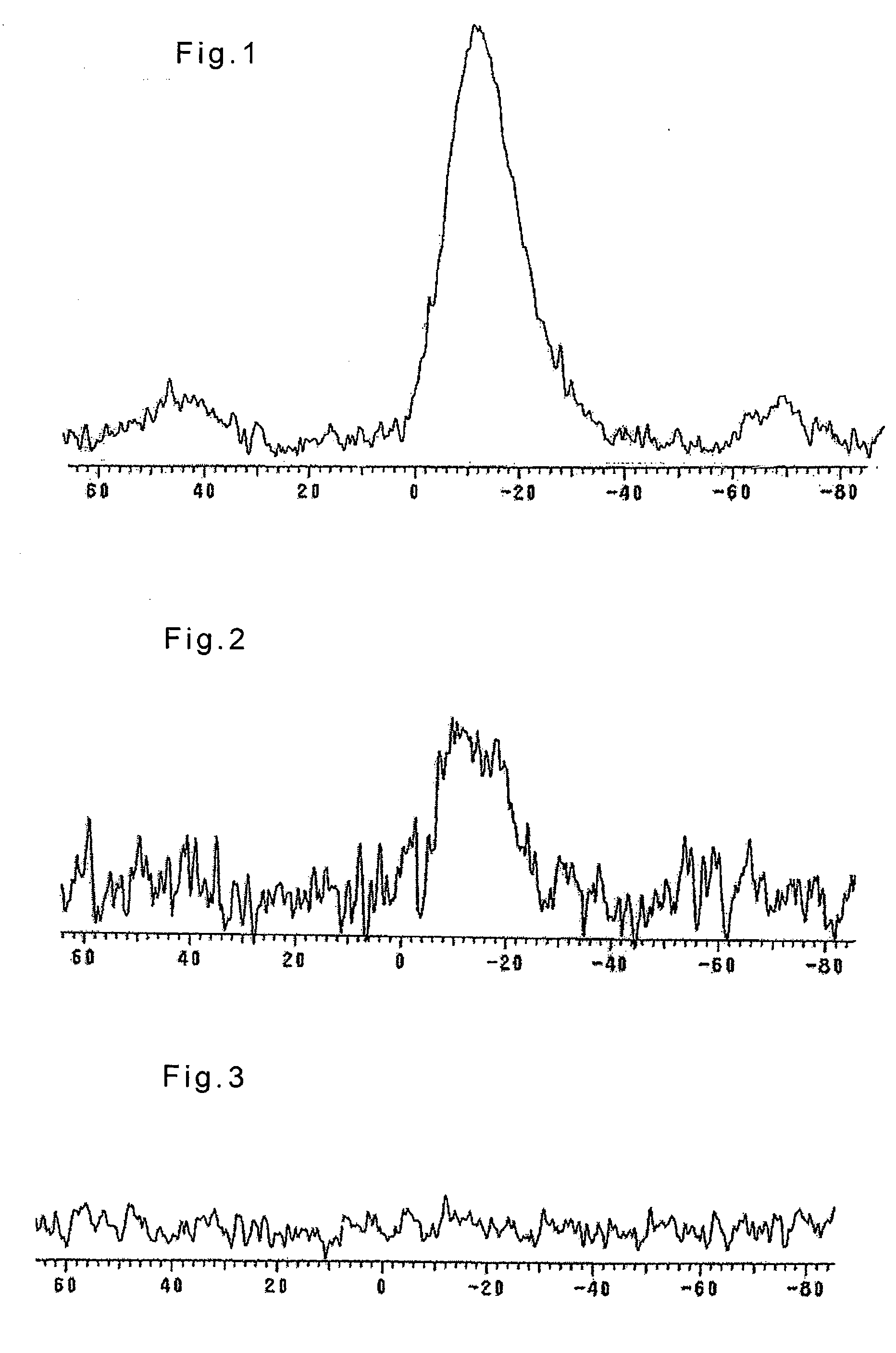
Silica-rich carrier, catalyzer for heterogeneous reactions and method for the production thereof
InactiveUS7060651B2Improve the situationEasy to fixCatalyst carriersSilicaCompound (substance)Silicon dioxide
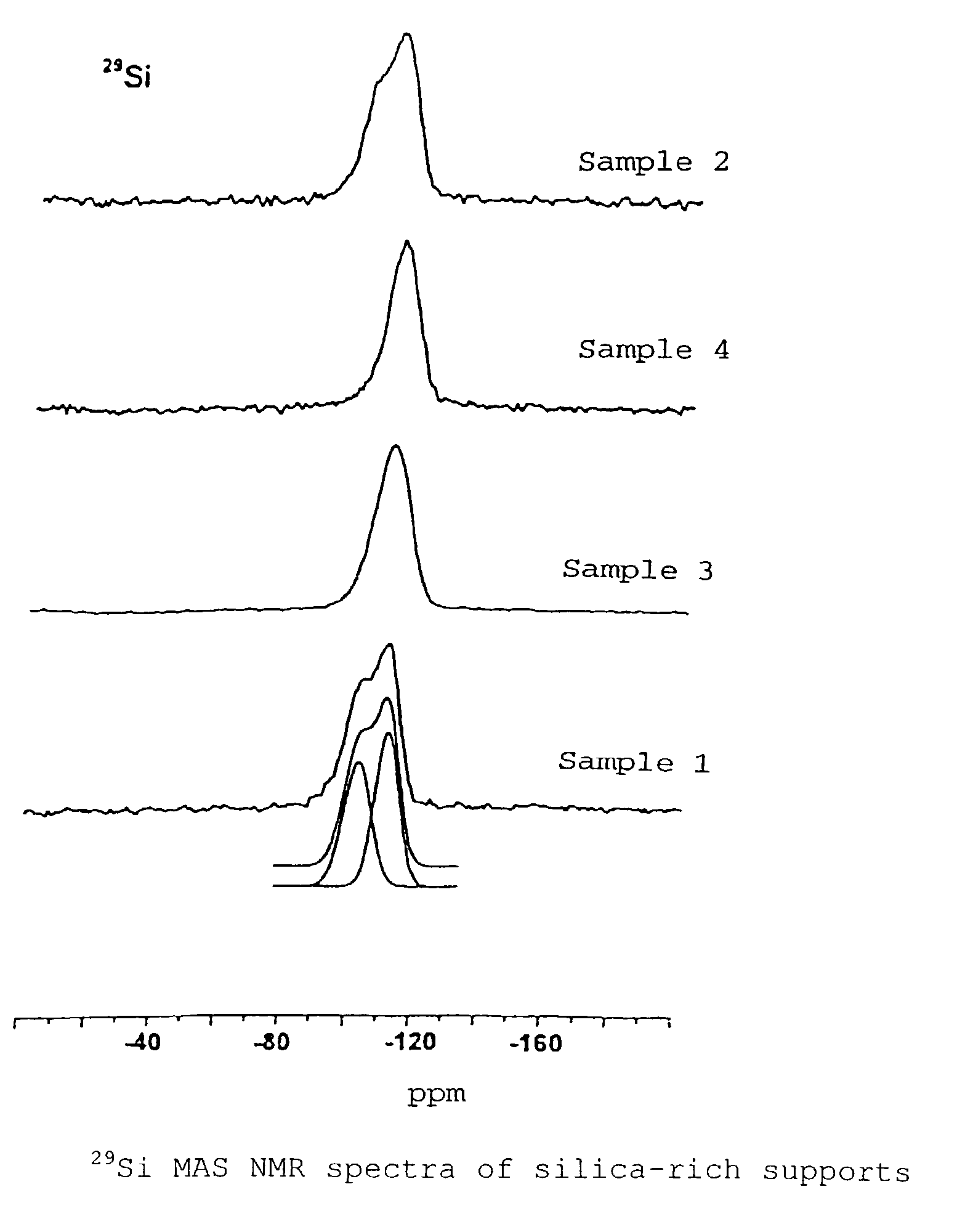
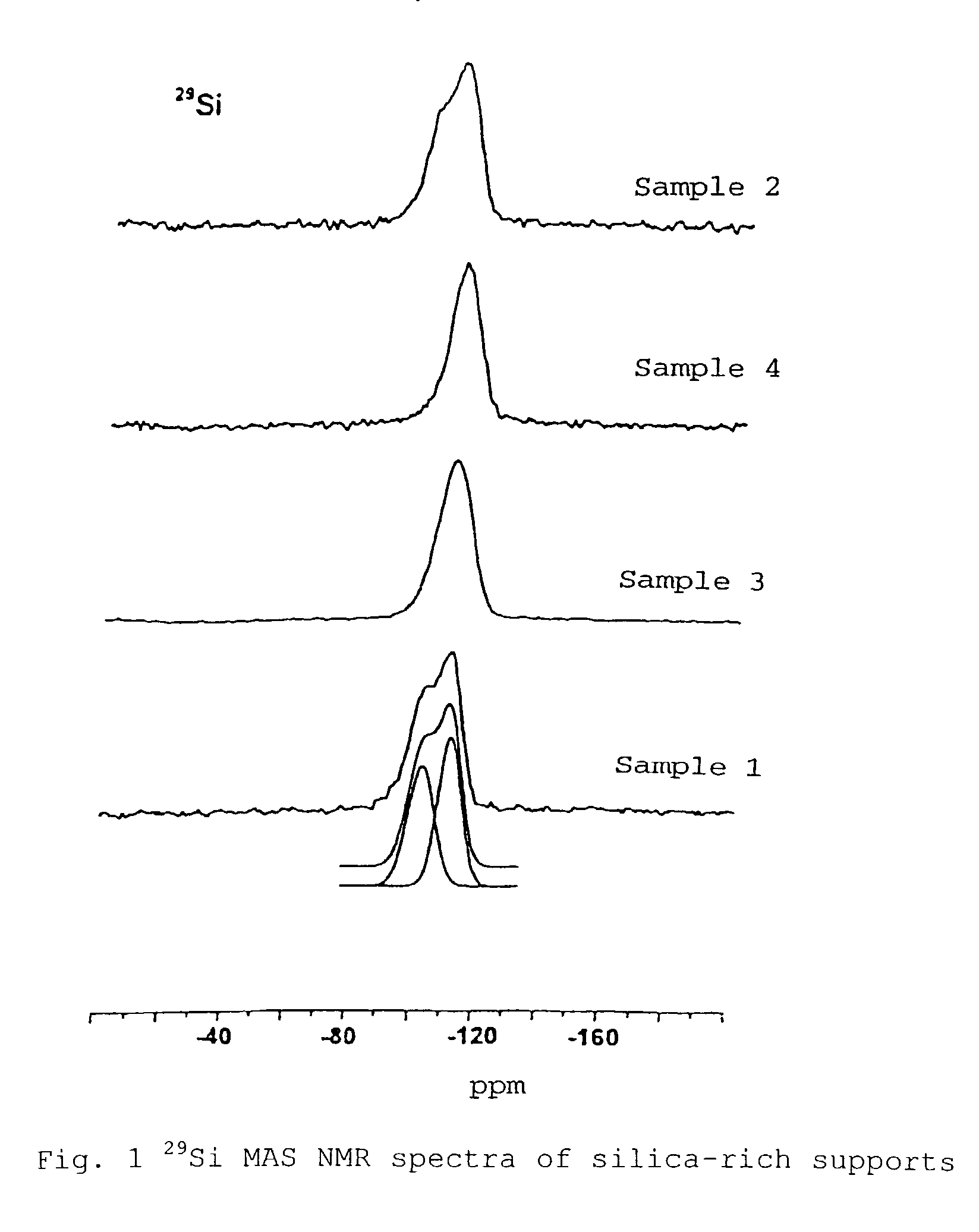
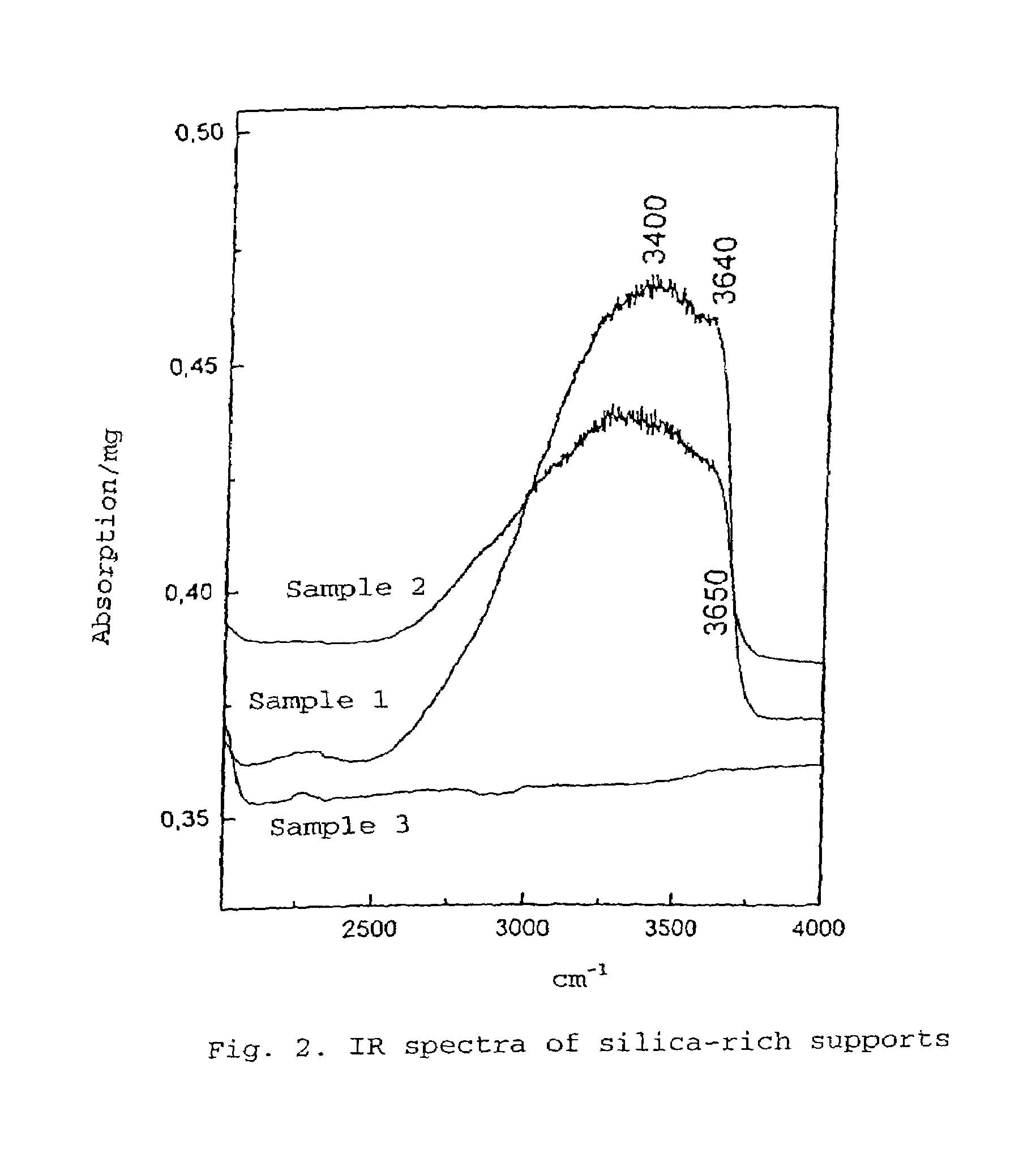
A silica-rich support and a catalyst containing the silica-rich support and a catalytic component. The support has a specific structure characterized by a set of claimed physicochemical properties: in the 29Si MAS NMR spectrum the state of silicon is characterized by the presence of lines with chemical shifts −100±3 ppm (line Q3) and −110±3 ppm (line Q4), with the ratio of the integral intensities of the lines Q3 / Q4 of from 0.7 to 1.2 (FIG. 1); in the IR spectrum there is an absorption band of hydroxyl groups with the wave number 3620–3650 cm−1 and half-width 65–75 cm−1 (FIG. 2); the carrier has a specific surface area, as measured by the BET techniques from the thermal desorption of argon, SAR=0.5–30 m2 / g and the surface, as measured by alkali titration techniques, SNa=10–250 m2 / g, with SNa / SAr=5–30.
Owner:INST KATALIZA IMENI GK BORESKOVA SIBIRSKOGO OTDELENIA ROSSIISKOI ACAD NAUK
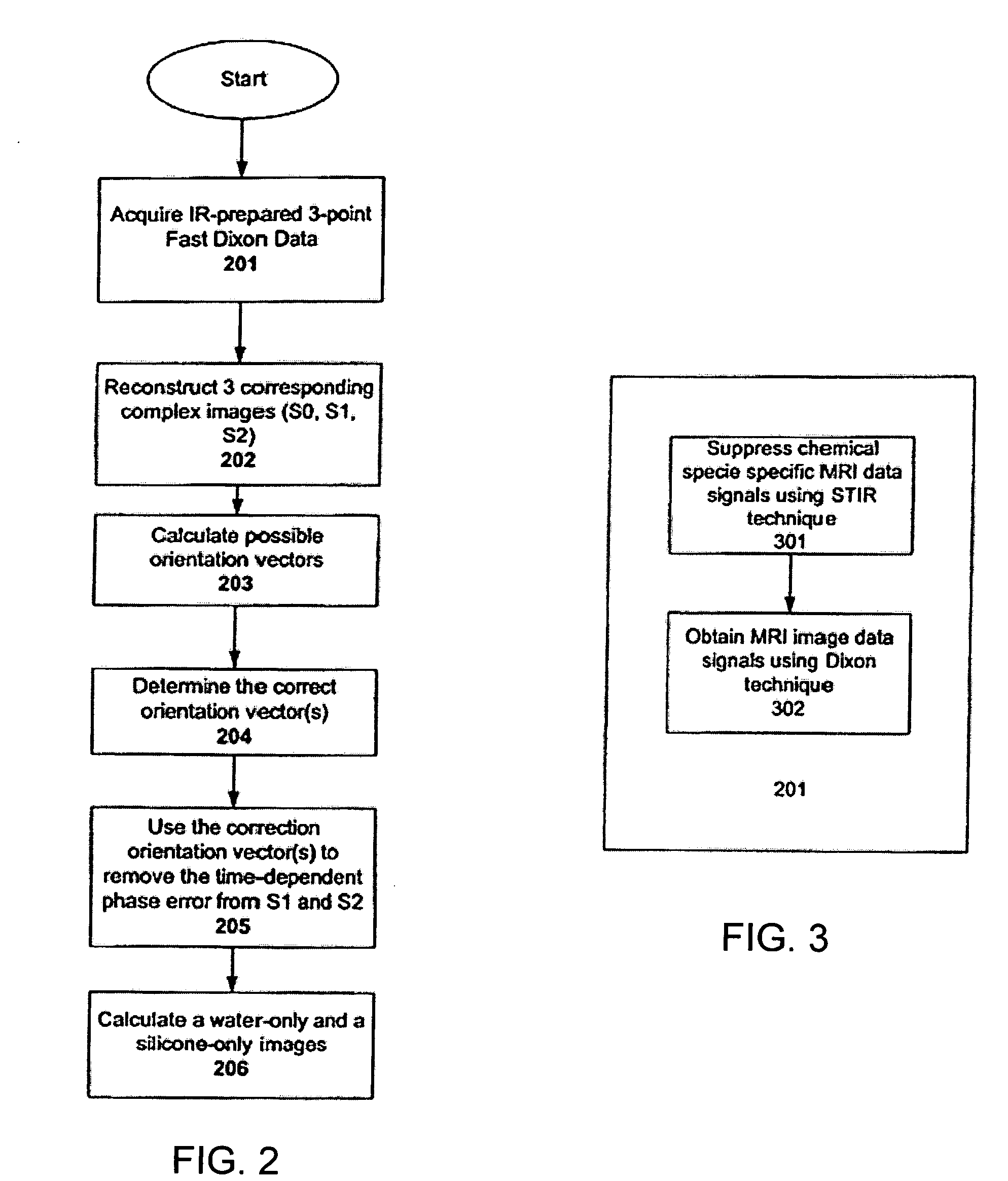
Methods and apparatuses for fast chemical shift magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20060094952A1Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsInversion recoveryChemical species
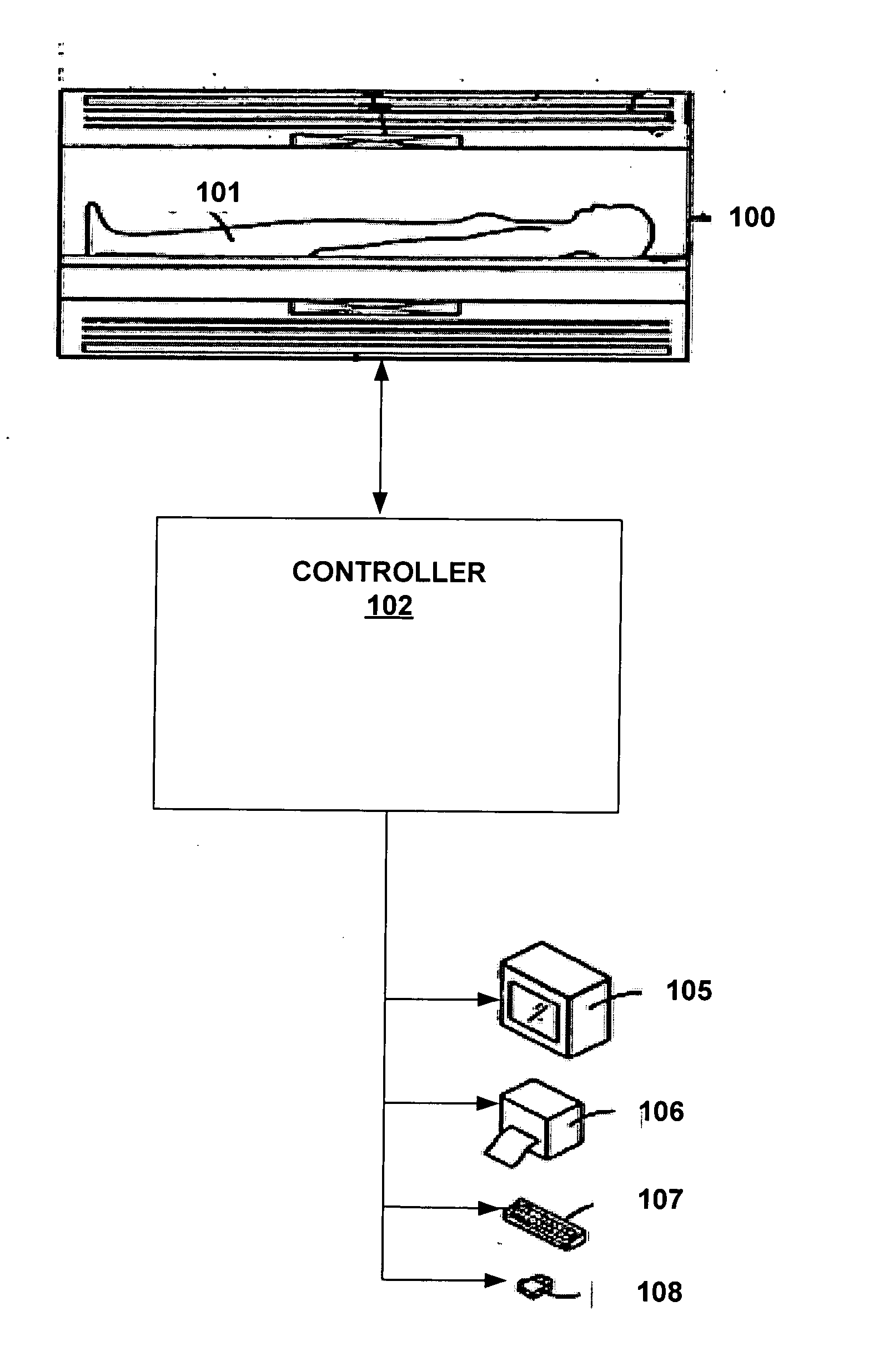
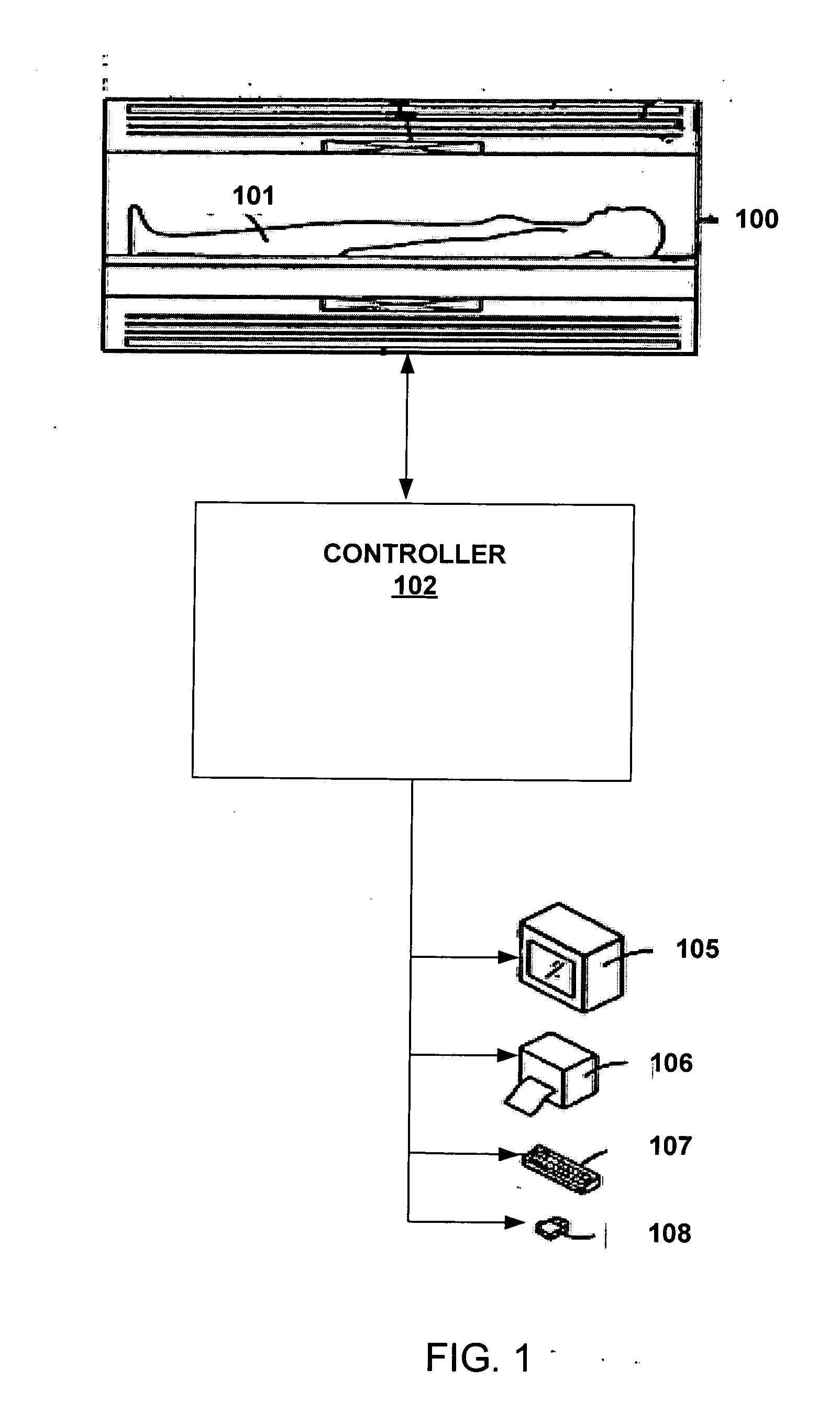
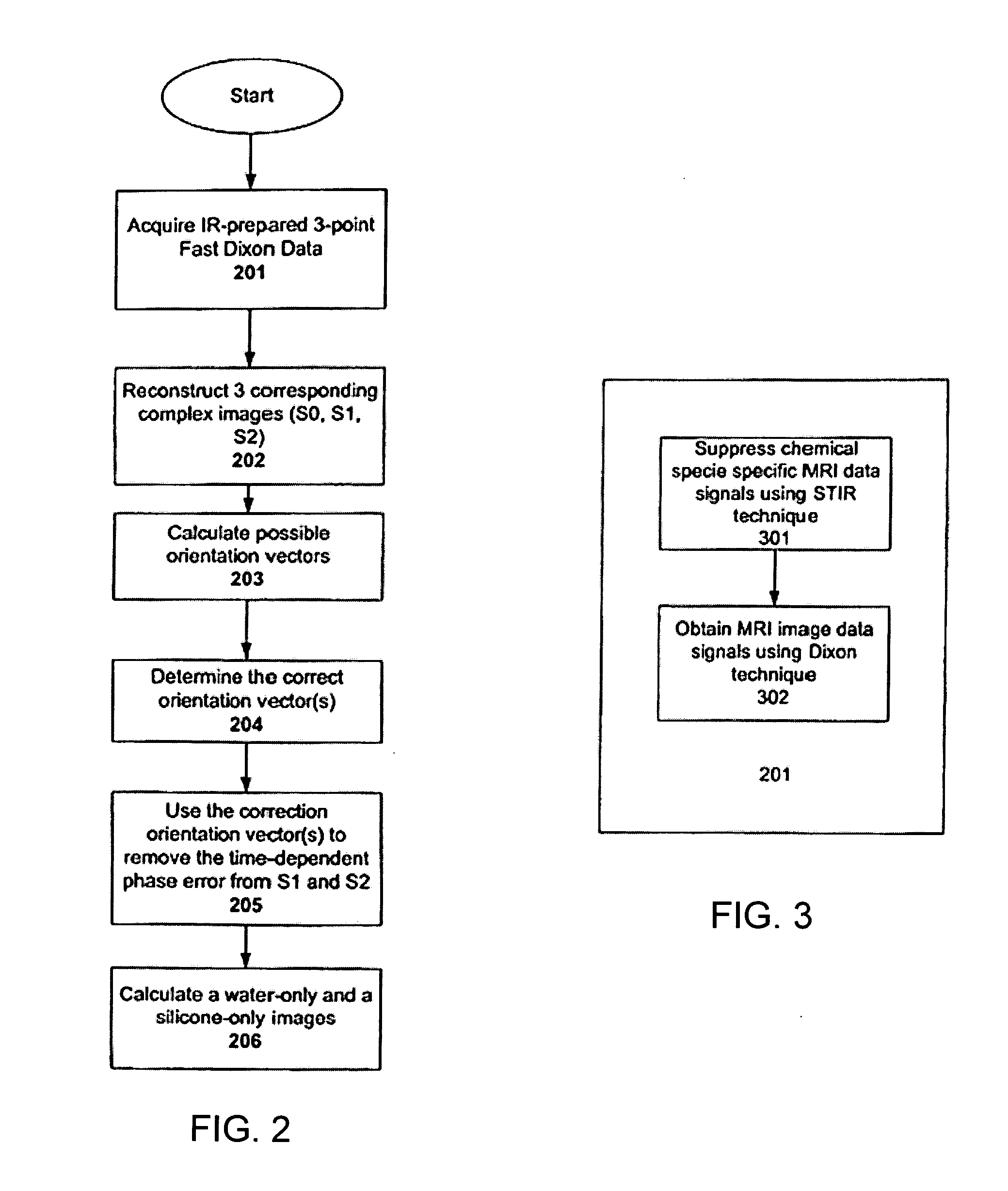
Systems and methods are described for chemical shift magnetic resonance imaging in the presence of multiple chemical species. A method includes obtaining a plurality of MRI data signals using a Dixon technique in combination with partially parallel imaging techniques and / or inversion recovery techniques, and processing the plurality of MRI data signals using a Dixon reconstruction technique to create a chemical specific shift image. An apparatus includes a MRI scanner for obtaining images, a controller configured to provide input to the scanner to acquire images using a Dixon technique in combination with partially parallel imaging techniques and / or inversion recovery techniques to produce a plurality of MRI data signals, and processing the plurality of MRI data signals using a Dixon reconstruction technique to create a chemical specific shift image, and an output device to display the resulting image.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Magnetic resonance method and apparatus for generating respective images from spin ensembles exhibiting different chemical shift
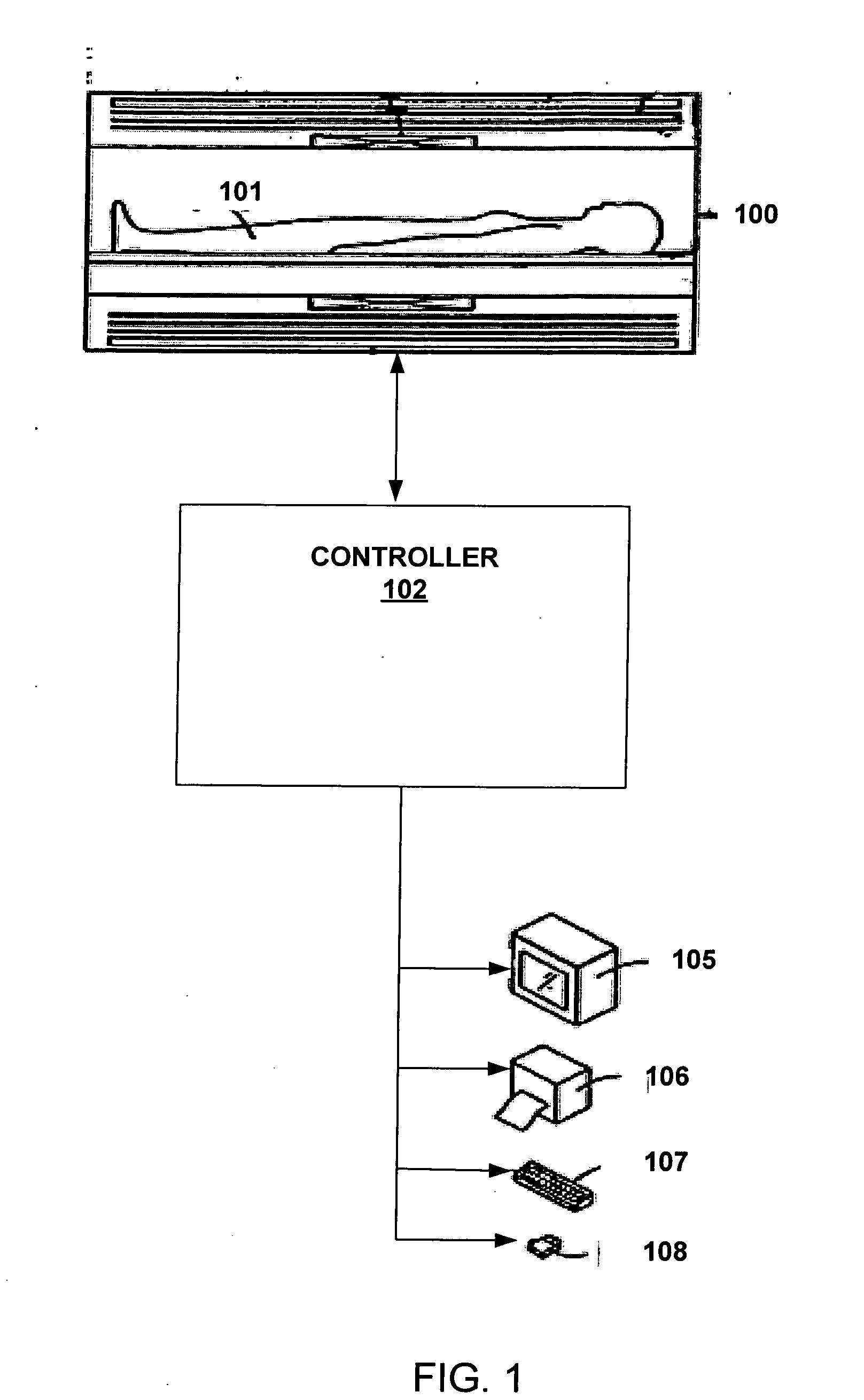
InactiveUS6841997B2Ensure consistencySimple classificationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceResonance
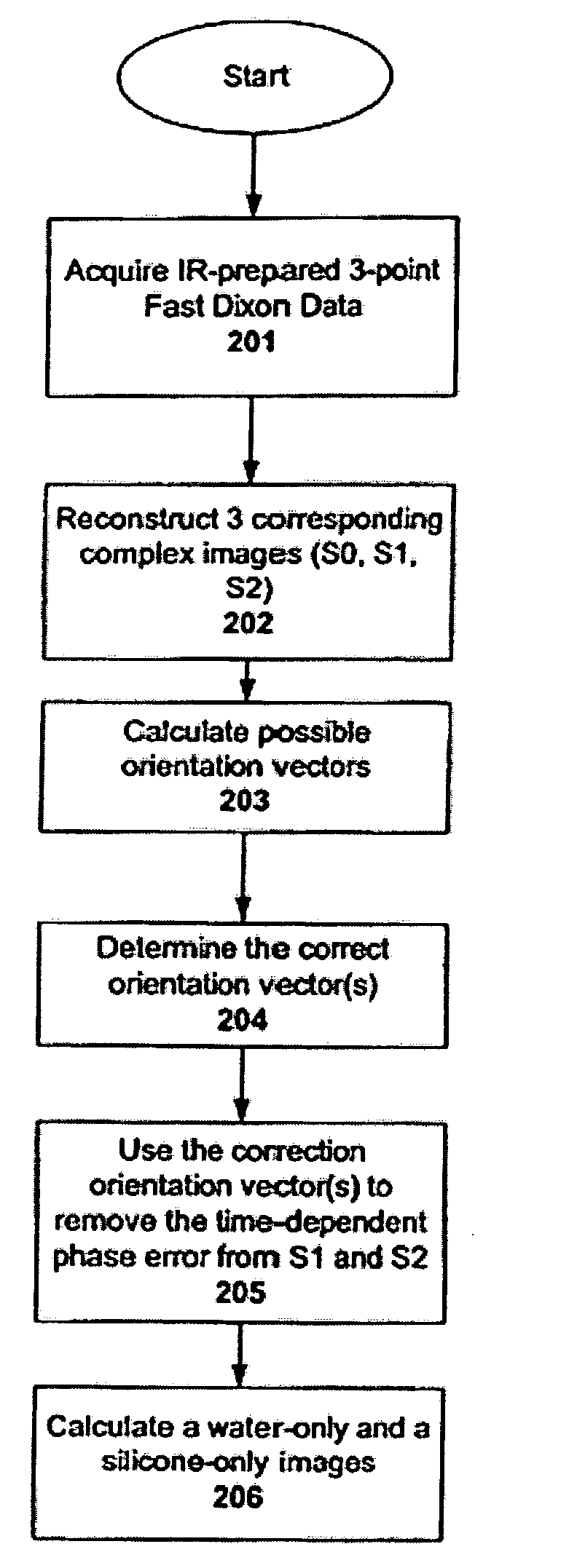
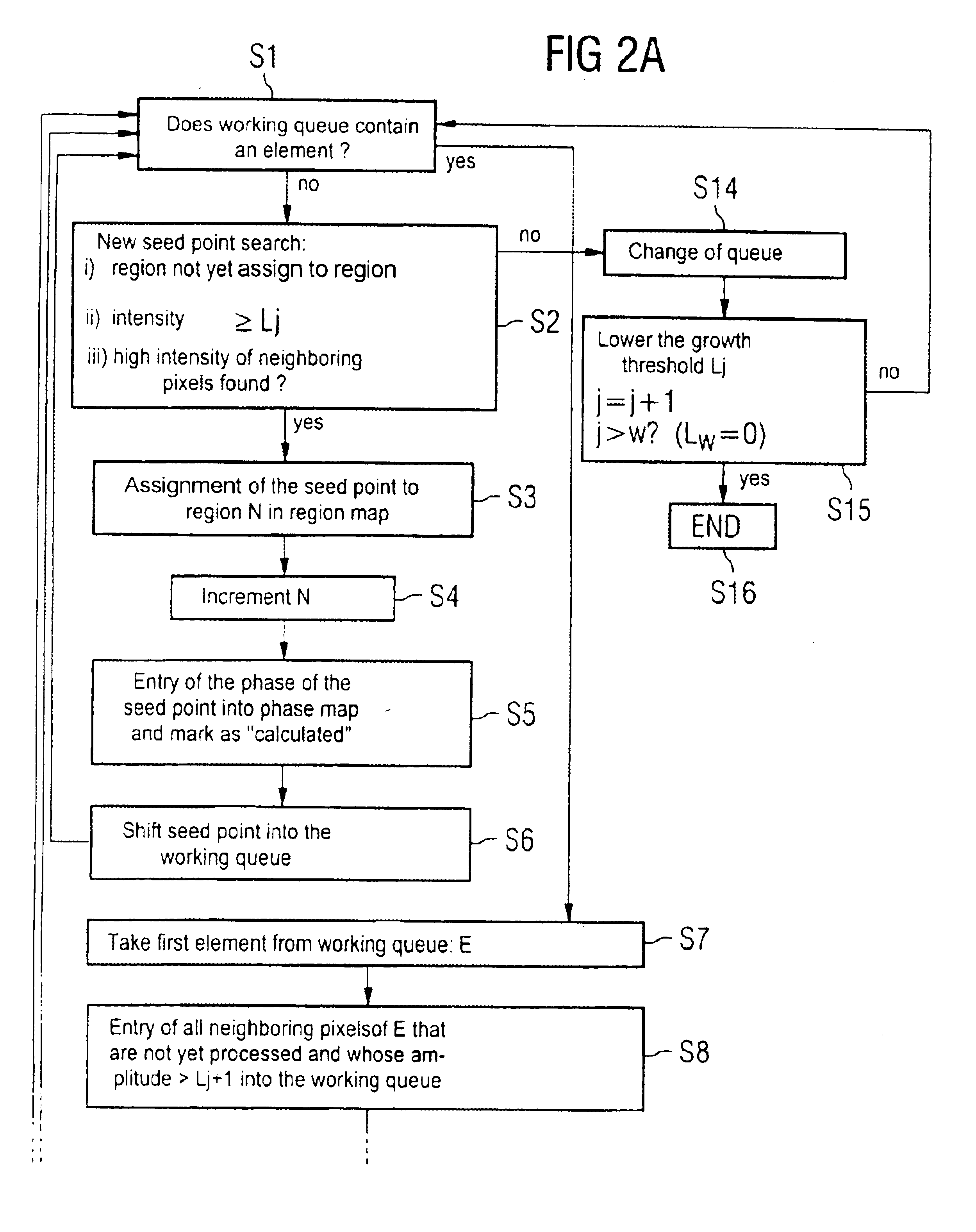
In a nuclear magnetic resonance tomography apparatus and a method for the operation thereof, on the basis of the 3-point Dixon method, spin collectives having different chemical shifts are separated by means of information maximization despite great field inhomogeneities. The unwrapping of the phases is implemented over interconnected pixel regions (phase unwrapping) proceeds initially only in regions with high signal amplitude and the regions of lower amplitudes are only successively acquired by increments. These are then assigned to the respectively correct spin type, such as fat or water.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Methods and apparatuses for fast chemical shift magnetic resonance imaging
Systems and methods are described for chemical shift magnetic resonance imaging in the presence of multiple chemical species. A method includes obtaining a plurality of MRI data signals using a Dixon technique in combination with partially parallel imaging techniques and / or inversion recovery techniques, and processing the plurality of MRI data signals using a Dixon reconstruction technique to create a chemical specific shift image. An apparatus includes a MRI scanner for obtaining images, a controller configured to provide input to the scanner to acquire images using a Dixon technique in combination with partially parallel imaging techniques and / or inversion recovery techniques to produce a plurality of MRI data signals, and processing the plurality of MRI data signals using a Dixon reconstruction technique to create a chemical specific shift image, and an output device to display the resulting image.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
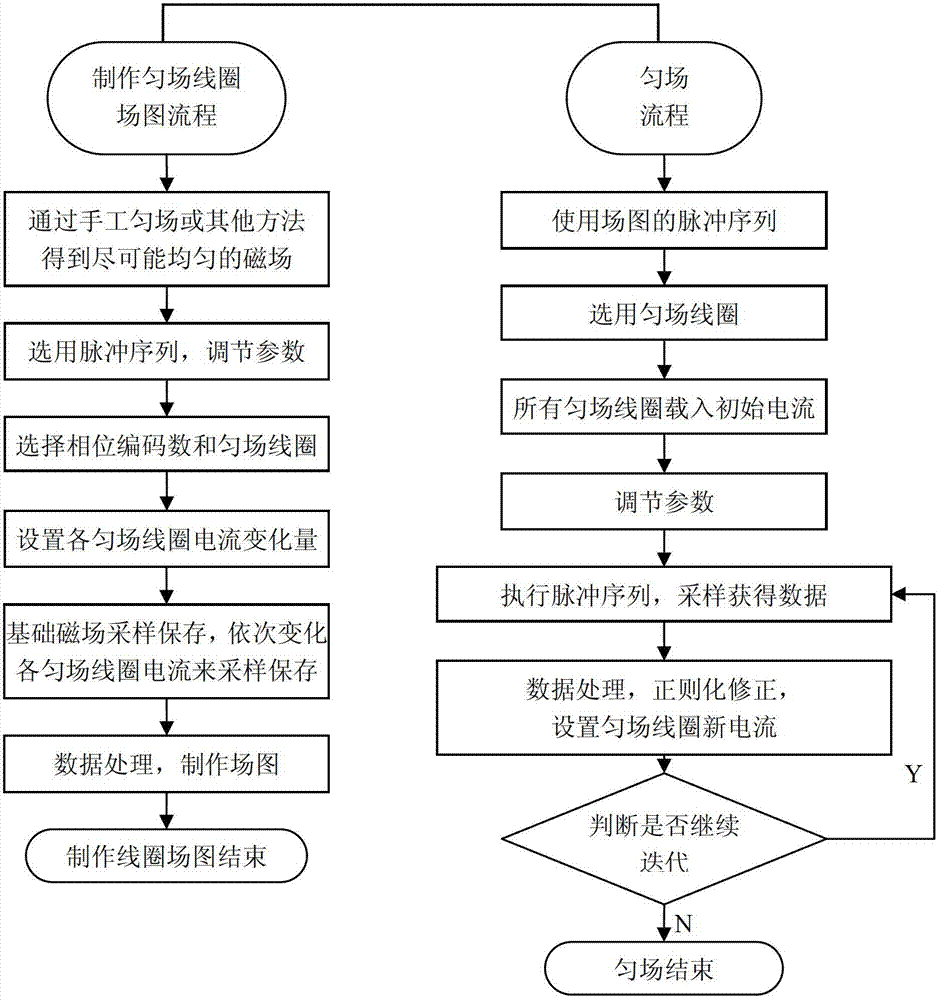
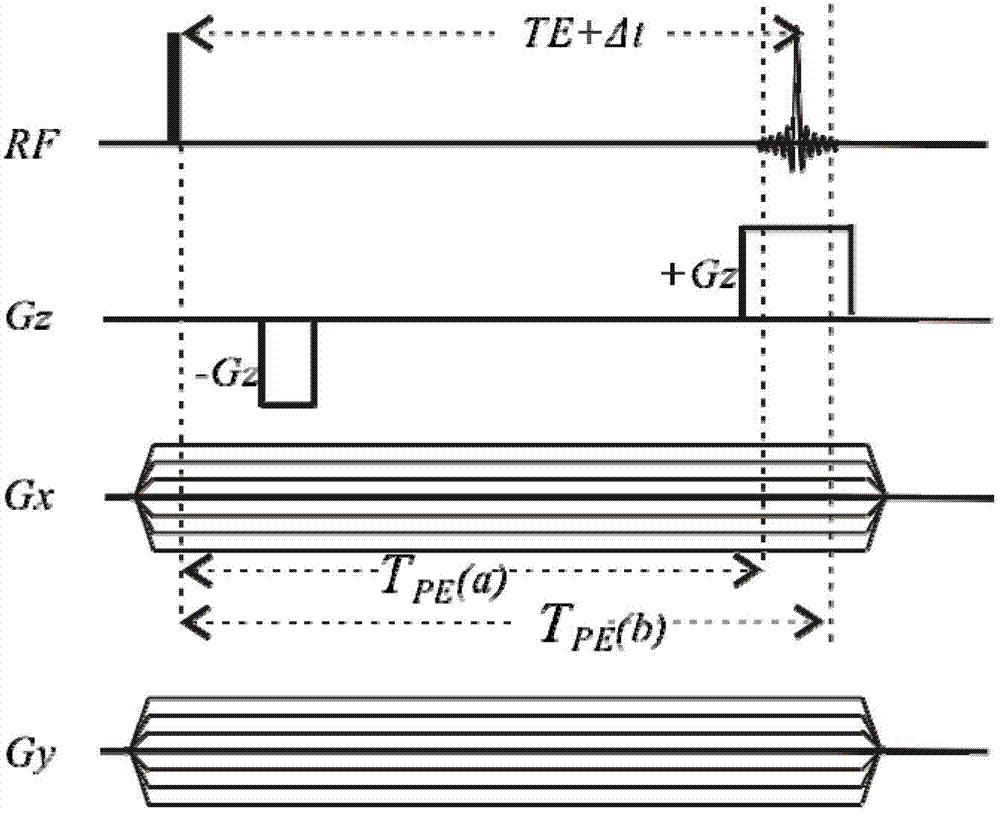
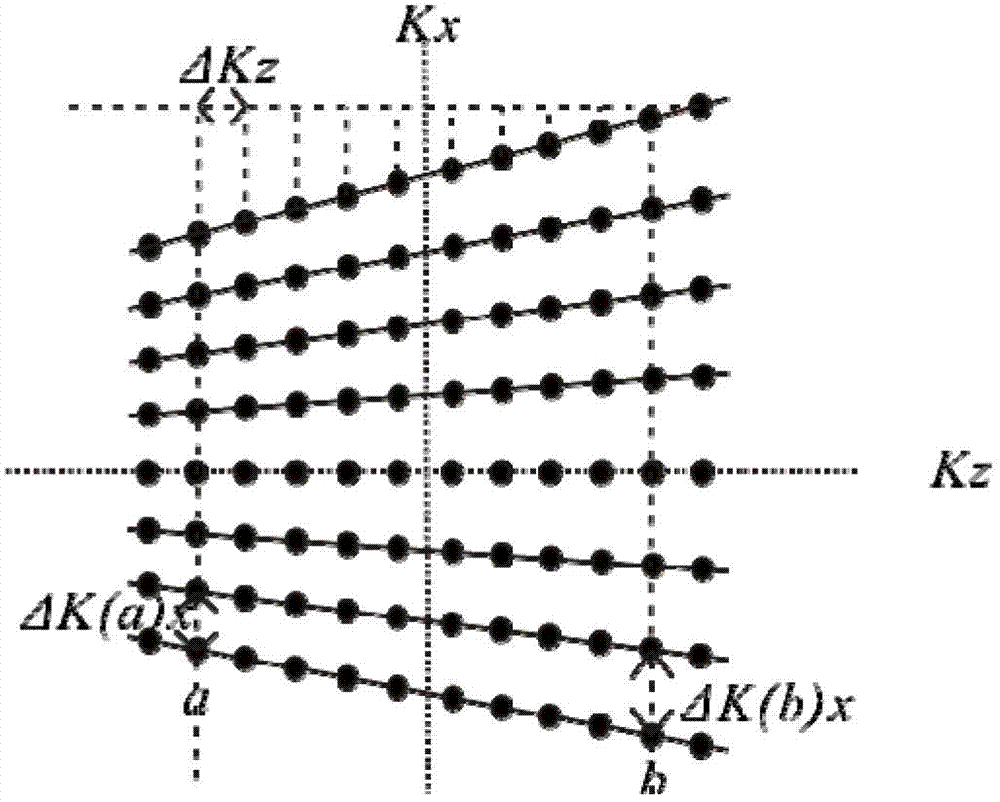
Rapid three-dimensional gradient shimming method for reducing phase encoding number on nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer
InactiveCN102768347AAvoid mutual interferenceGet rid of dependenceMeasurements using magnetic resonanceHydrogenSelective excitation
The invention discloses a rapid three-dimensional gradient shimming method for reducing phase encoding number on a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, which relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer. A method of shimming coils is selected according to the phase encoding number, X and Y high-order shimming coils are deducted, on this basis, a proper revised regularization method can be added to the calculation, a good shimming effect can still be achieved when the phase encoding number can be reduced to be 3*3 or 2*2. These few 2*2 and 3*3 phase codes are widely applied to all three-dimensional gradient shimming pulse sequences of the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, such as a three-dimensional gradient echo pulse sequence, a tilt three-dimensional gradient echo pulse sequence, and a pulse gradient field excitation echo pulse sequence. The mutual interference of multiple spectral peaks with farer chemical shifts can be overcome in the phase measurement. The three-dimensional gradient shimming in which the hydrogen nuclear is selectively excited enable the shimming method to get rid of the dependence on deuterium reagent, brings speed increase in cooperation with few phase encoding number and small-angle excitation, and has wide application range.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
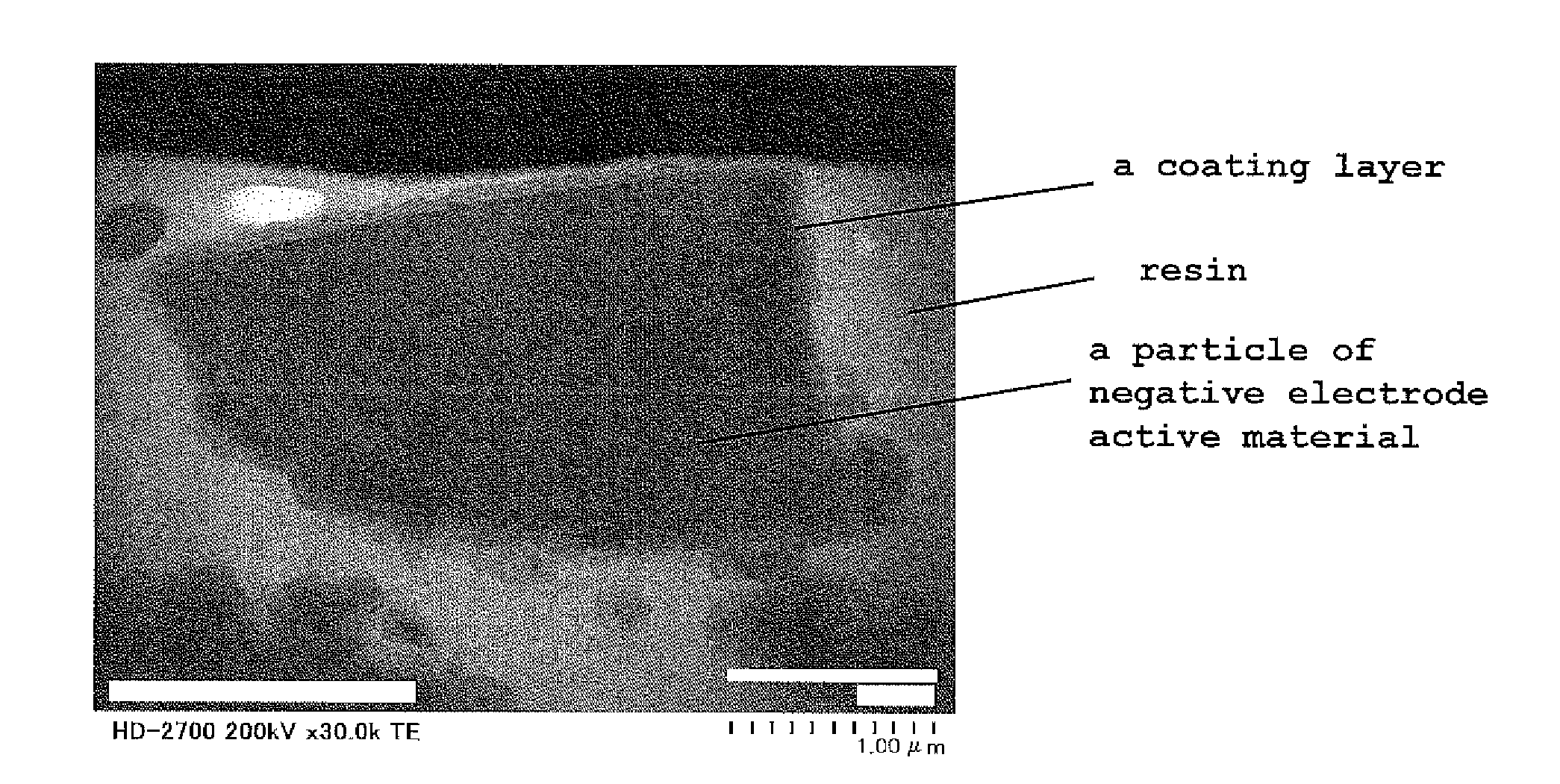
Negative electrode active material, raw material for a negative electrode active material, negative electrode, lithium ion secondary battery, method for producing a negative electrode active material, and method for producing a lithium ion secondary battery
ActiveUS20160233484A1Large capacityImprove featuresNegative electrodesSilicon oxidesLithiumUltimate tensile strength
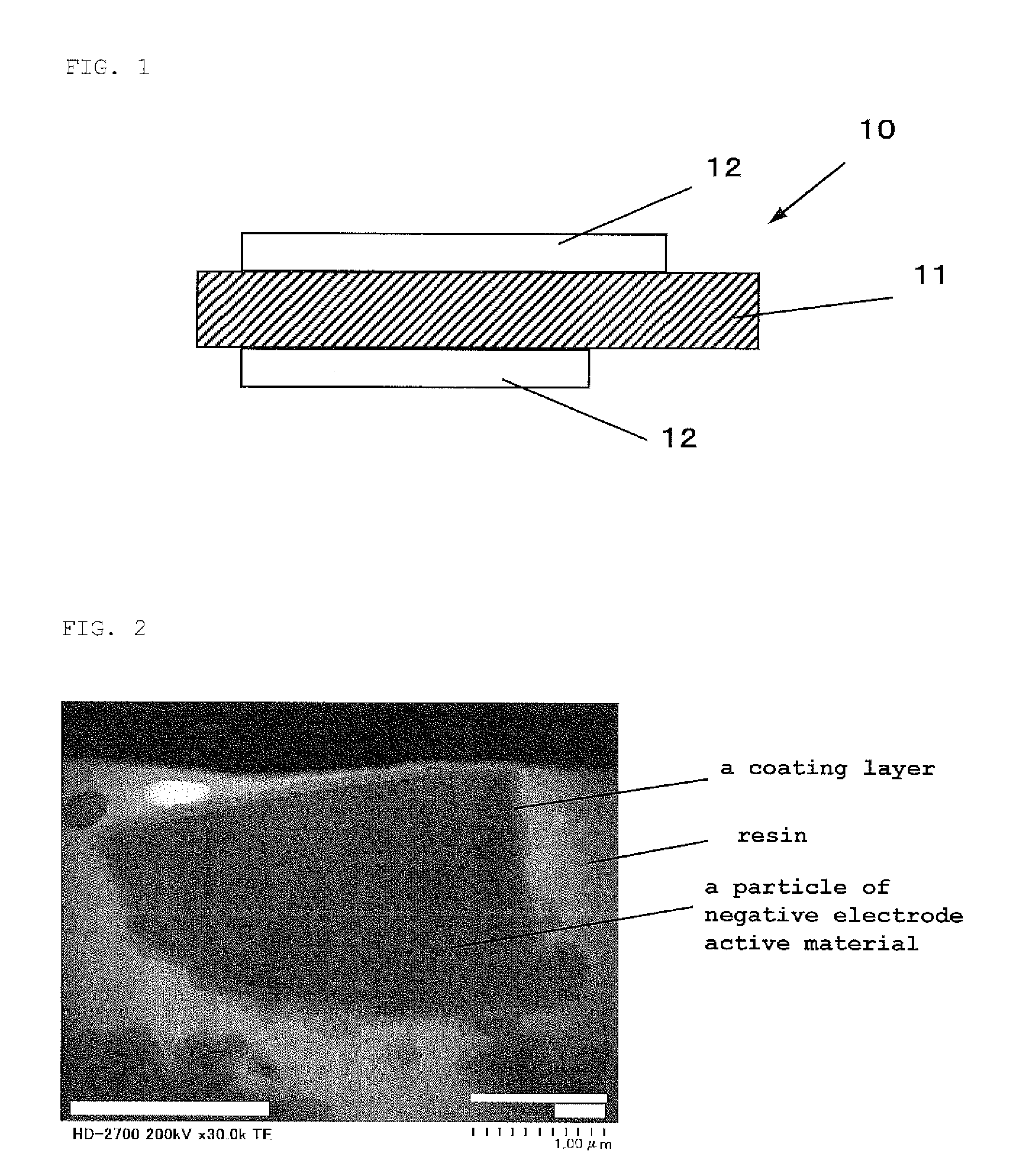
A negative electrode active material including: a particle of negative electrode active material containing silicon-based material of SiOx (0.5≦x≦1.6); wherein the intensity A of a peak in a Si-region given in the chemical shift region of from −50 to −95 ppm and the intensity B of a peak in a SiO2-region given in the chemical shift region of from −96 to −150 ppm in a 29Si-MAS-NMR spectrum of the silicon-based material satisfy a relationship that A / B≧0.8. This provides a negative electrode active material which can increase a battery capacity, and can improve cycle characteristics and initial charge / discharge characteristics when used as a negative electrode active material for a lithium ion secondary battery.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Polybenzimidazole-base complex, crosslinked material of polybenzoxazines formed thereof, and fuel cell using the same
ActiveUS20090098437A1Solid electrolytesFinal product manufactureNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceCoordination complex
A polybenzimidazole-base complex includes a polybenzimidazole-based material and a base, wherein a peak corresponding to NH of an imidazole ring of the polybenzimidazole-based material does not appear at a chemical shift of 12 to 15 ppm in a 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR) spectrum of the polybenzimidazole-base complex. A crosslinked material may be formed as a polymerization product of a polybenzimidazole-base complex and a benzoxazine-based monomer. The crosslinked material may be used an electrolyte membrane for a fuel cell comprising the crosslinked material, and a fuel cell may include the electrolyte membrane.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
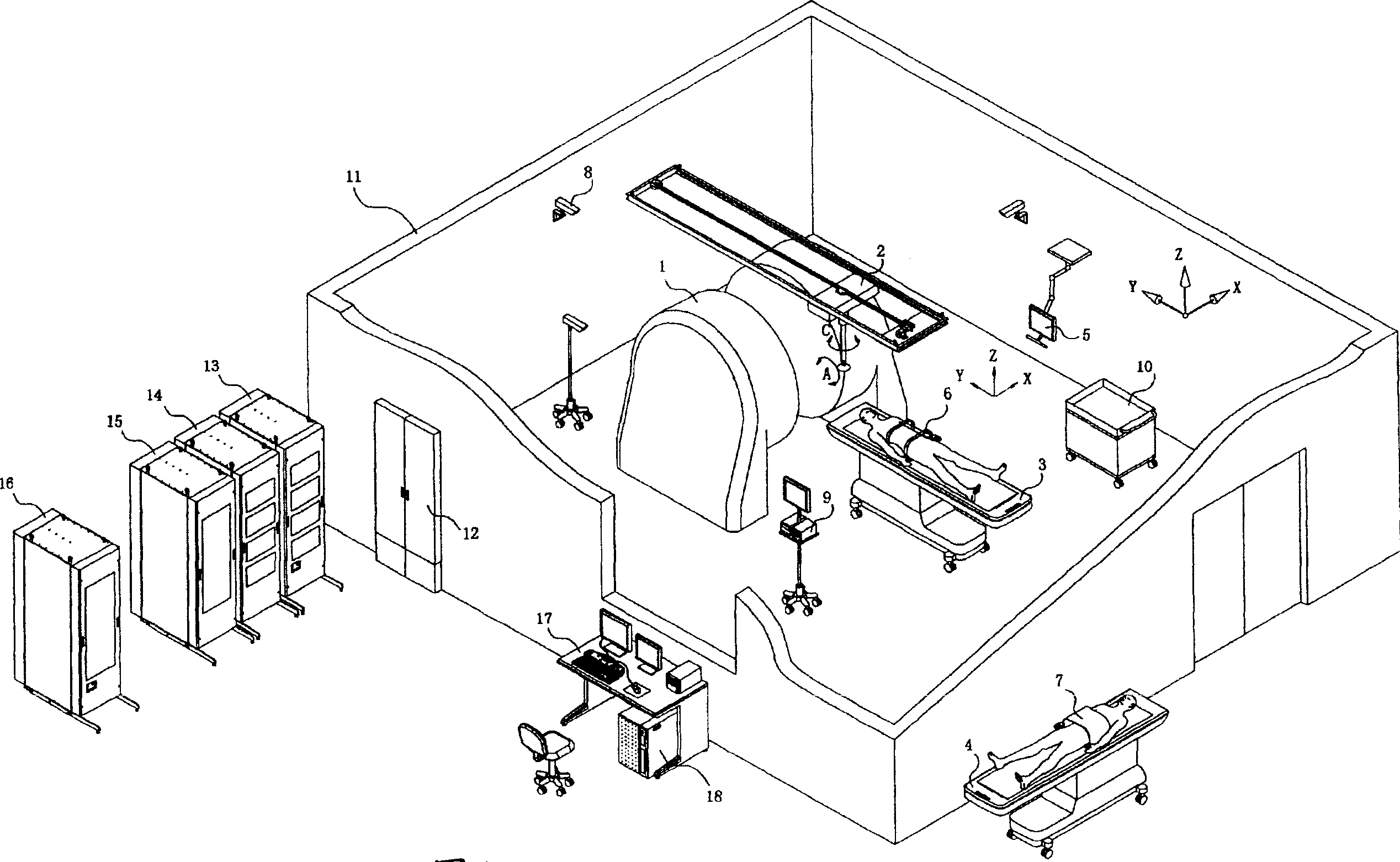
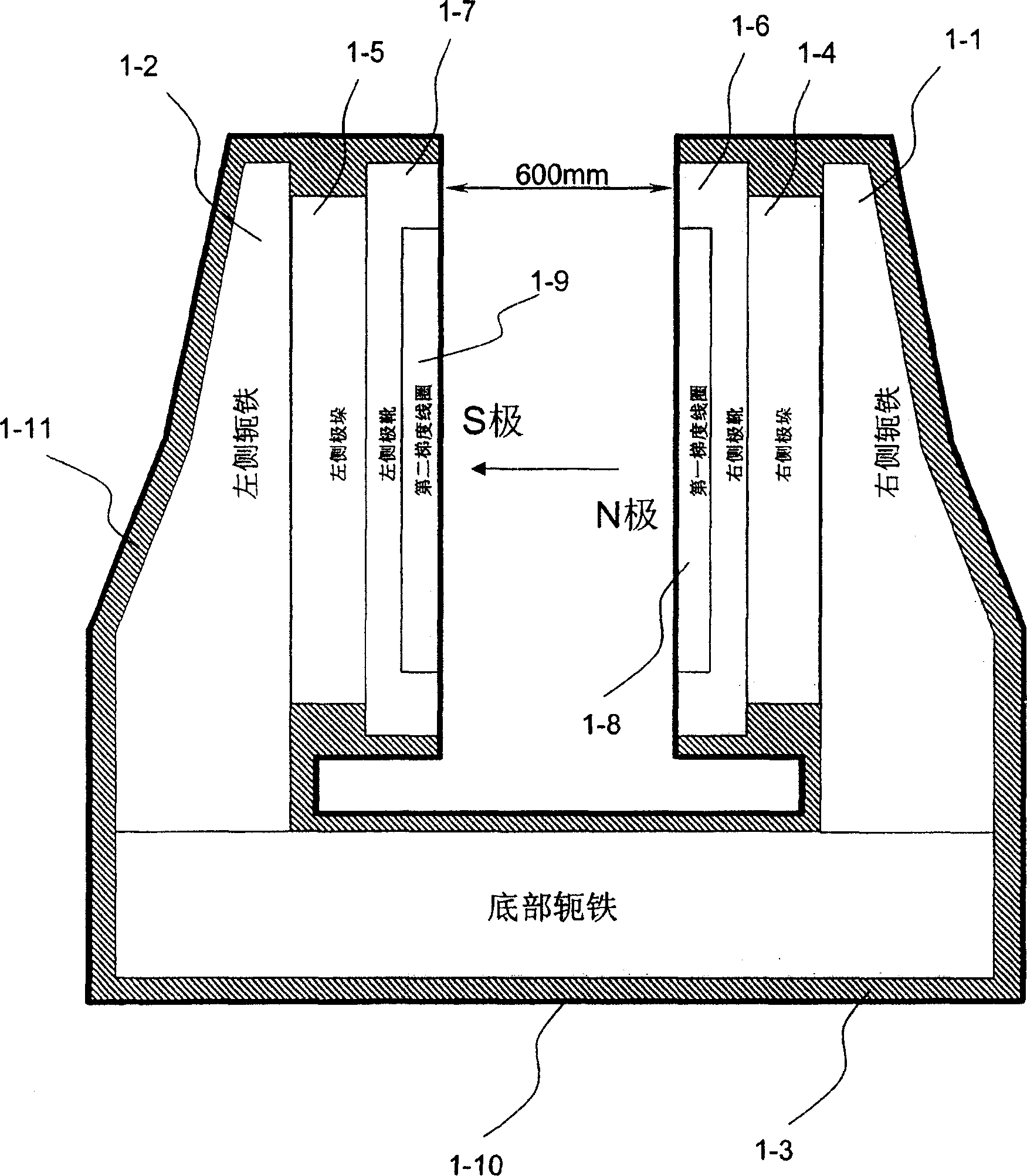
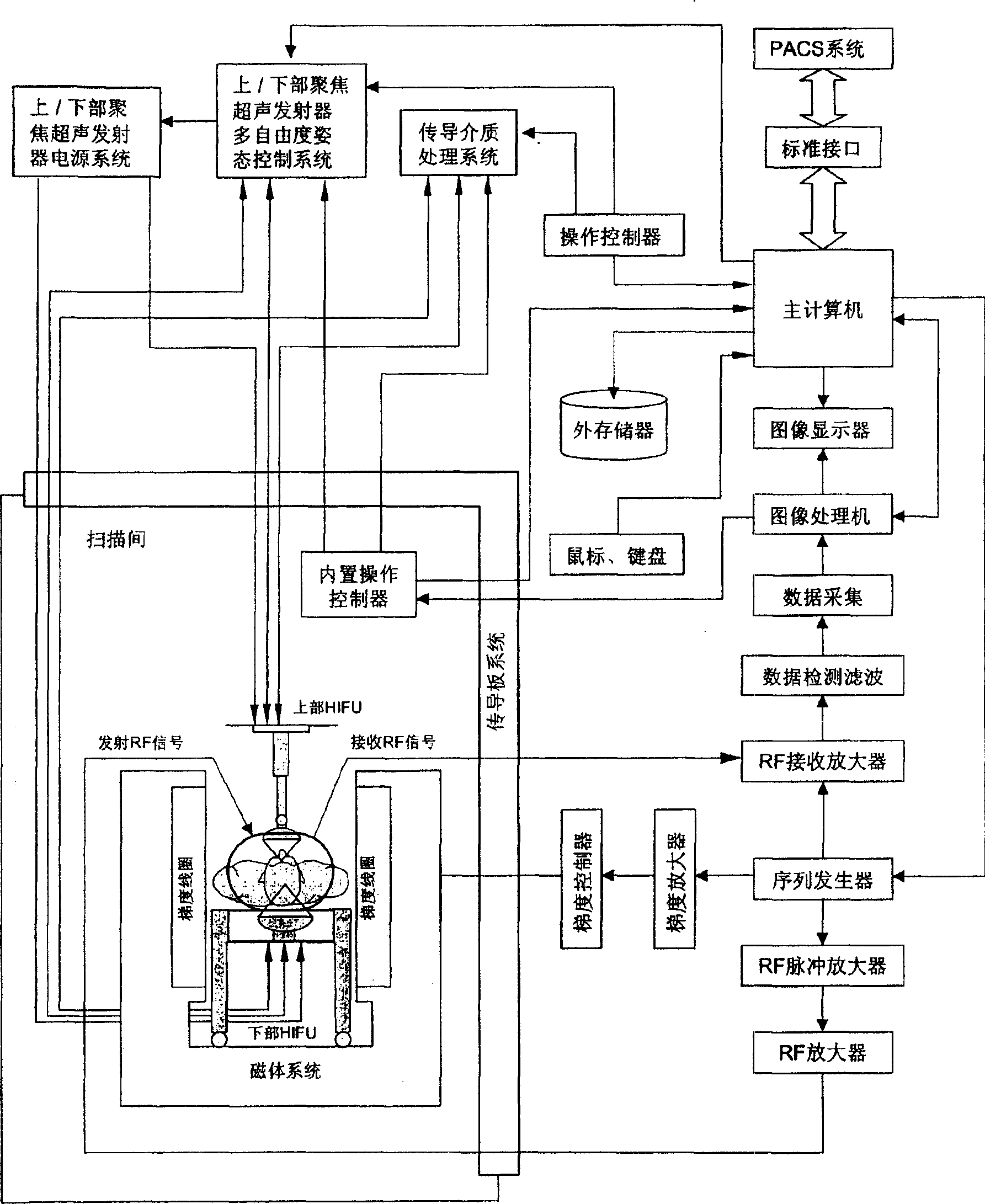
Extracorporeal high energy focusing ultrasonic system guided by permanent magnet type magnetic resonance image and method thereof
InactiveCN1903121ARealize integrationReduce the numberUltrasound therapySurgeryHigh energyTumor Examination
A high energy focusing ultrasonic system based on permanent-magnet magnetic resonance imaging system is composed of a U-shaped 0.35T / 0.45T permanent-magnet magnetic resonance imaging system consisting of permanent magnet, gradient coil, RF receiving emitting coil, and high-energy focusing ultrasonic emitter, and an examining bed (or chair) for patient. It can perform real-time tumor examination, therapy and temp control.
Owner:海扶宁高强超声技术(北京)有限公司
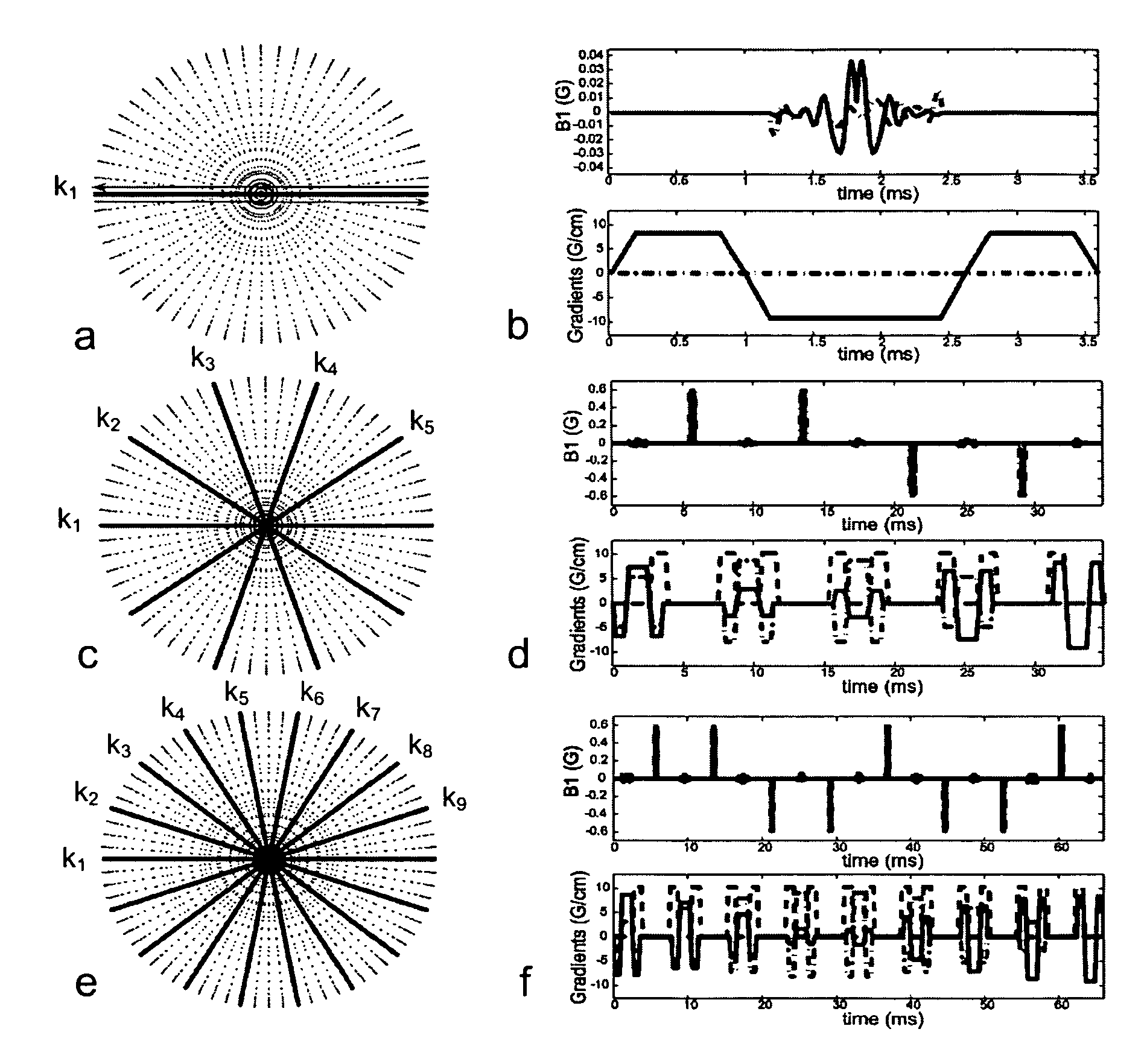
Generalized Method for MRI Chemical Species Separation Using Arbitrary k-space Trajectories
ActiveUS20080048659A1Eliminate the effects ofMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionData setChemical species
A method for producing images of a subject containing M spin species using a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system includes obtaining N k-space data matrices from N k-space data sets acquired with the MRI system using a pulse sequence with an individual associated echo time. The k-space data matrices each include corresponding data at the same plurality of k-space locations and time stamps are tracked for each k-space location. For each k-space location, a set of linear equations in k-space is solved. The set of linear equations relates corresponding data from the N k-space data matrices, echo times and time stamps to desired calculated k-space data. Calculated data in k-space which is corrected for chemical shift is produced corresponding to each k-space location and aggregated to obtain a k-space calculated data set. The k-space calculated data set is transformed to image space to obtain a corresponding image.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
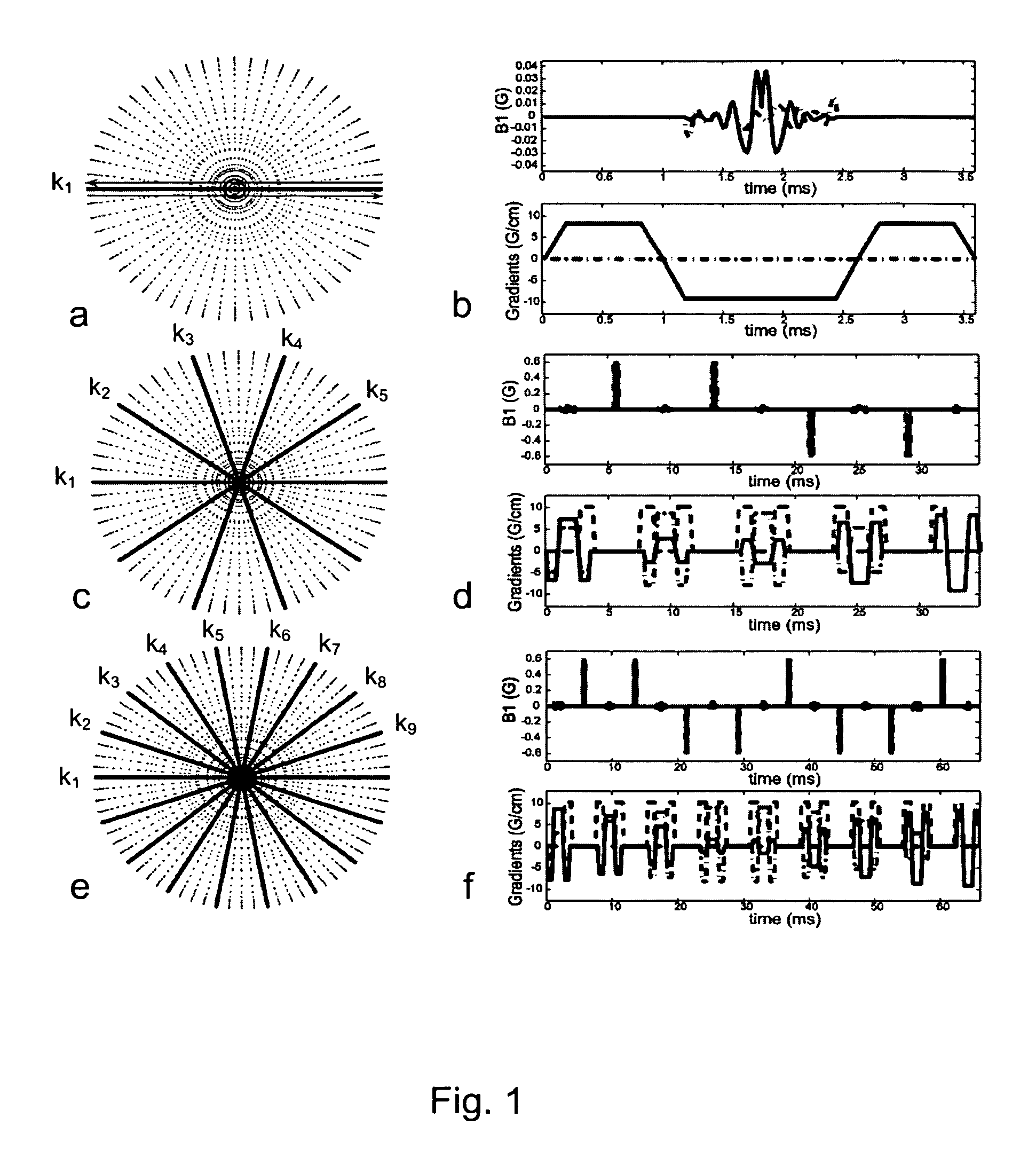
Methods for arbitrary shape selective excitation summed spectroscopy and applications of same
InactiveUS7777488B2Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionBiological bodySelective excitation
In another aspect, the present invention relates to a method for NMR measurements of an arbitrarily shaped region of interest of a living subject. In one embodiment, the method comprises the steps of applying a broad bandwidth of RF pulses to the arbitrarily shaped region of interest to obtain a corresponding spectrum, wherein substantially entire range of chemical shifts in the spectrum is excited from the arbitrarily shaped region of interest, interleaving a plurality of radial k-lines in radial k-space per excitation with non-selective refocusing pulses and obtaining spatial localization for the spectrum of the arbitrarily shaped region of interest.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Polypropylene type aqueous dispersion, polypropylene type composite aqueous emulsion composition and its use
A polypropylene type aqueous dispersion comprising the following components (a) to (c): (a) a polypropylene type polymer and / or a modified polypropylene type polymer 100 parts by weight (b) a surfactant 1 to 100 parts by weight, and (c) water 100 to 1,000 parts by weight, wherein the component (a) has a main chain having the following features (1) and (2) and dispersion particles in the dispersion have an average particle size of at most 0.5 mu m, Feature (1) when observing a peak derived from a carbon atom of a methyl group in a propylene unit chain part comprising a head-to-tail bond by <13>C-NMR and fixing a chemical shift of a peak top at a peak attributable to pentad expressed by mmmm to 21.8 ppm, a ratio (S1 / S) of an area S1 of a peak of a peak top at 21.8 ppm to a total area S of peaks at from 19.8 ppm to 22.1 ppm is at least 10% and at most 60%, and when an area of a peak (mmmr) of a peak top at 21.5 to 21.6 ppm is expressed as S2, 4+2S1 / S2>5, and Feature (2) a content ratio (mol ratio) of propylene unit (A): other olefin unit (B) is from 100:0 to 90:10.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Hydrogenation catalyst for hydrocarbon oil and process for hydrogenation using the catalyst
InactiveUS20070084753A1Good effectMolecular sieve catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationNitrogenSilicon
A hydrogenation catalyst for a hydrocarbon oil, includes an inorganic porous support composed of at least the oxides of aluminum, phosphorus, and silicon, and supporting at least one active metal selected from the metals of Group 8 of the periodic table, at least one active metal selected from the metals of Group 6 of the periodic table, and phosphorus, the phosphorus chemical shift value of the inorganic support determined by 31P-CPMAS-NMR having the peak within the range of 0 to −20 ppm. The catalyst can achieve an extremely high level of hydrogenation wherein the hydrocarbon is decreased in sulfur content to 10 ppm by mass or less and in nitrogen content to 3 ppm by mass or less.
Owner:NIPPON OIL CORP
Cracking assistant for improving low-carbon olefin concentration
ActiveCN103785458AImprove wear resistanceGood catalytic cracking performanceCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMagic angle spinningPeak area
The invention discloses a cracking assistant for improving the low-carbon olefin concentration. The cracking assistant comprises a phosphorus and transition metal-containing beta molecular sieve, a first-clay-containing phosphorus aluminum inorganic binder, other inorganic binder and second clay; the first-clay-containing phosphorus aluminum inorganic binder comprises 15-40 wt% by Al2O3 of an aluminum component, 45-80 wt % by P2O5 of a phosphorus component and 1-40 wt % by dry basis of first clay, the weight ratio of P to Al is 1-6; the phosphorus and transition metal-containing beta molecular sieve comprises 1-10wt% by P2O5 of phosphorus and 0.5-10 wt % by metallic oxide of a metal; and in the 27Al MAS NMR (Magic Angle Spinning Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) of the phosphorus and transition metal-containing beta molecular sieve, the ratio of resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of 40+-3ppm to resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of 54+-3ppm is greater than 1, and the percentage of the sun of the resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of 0+-3ppm and the resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of-12+-3ppm to the total peak area is less than 10%. The cracking assistant is used for catalytic cracking, and can improve ethylene concentrations in a catalytic cracking dry gas, and improve propylene and isobutylene concentration in a liquefied gas.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
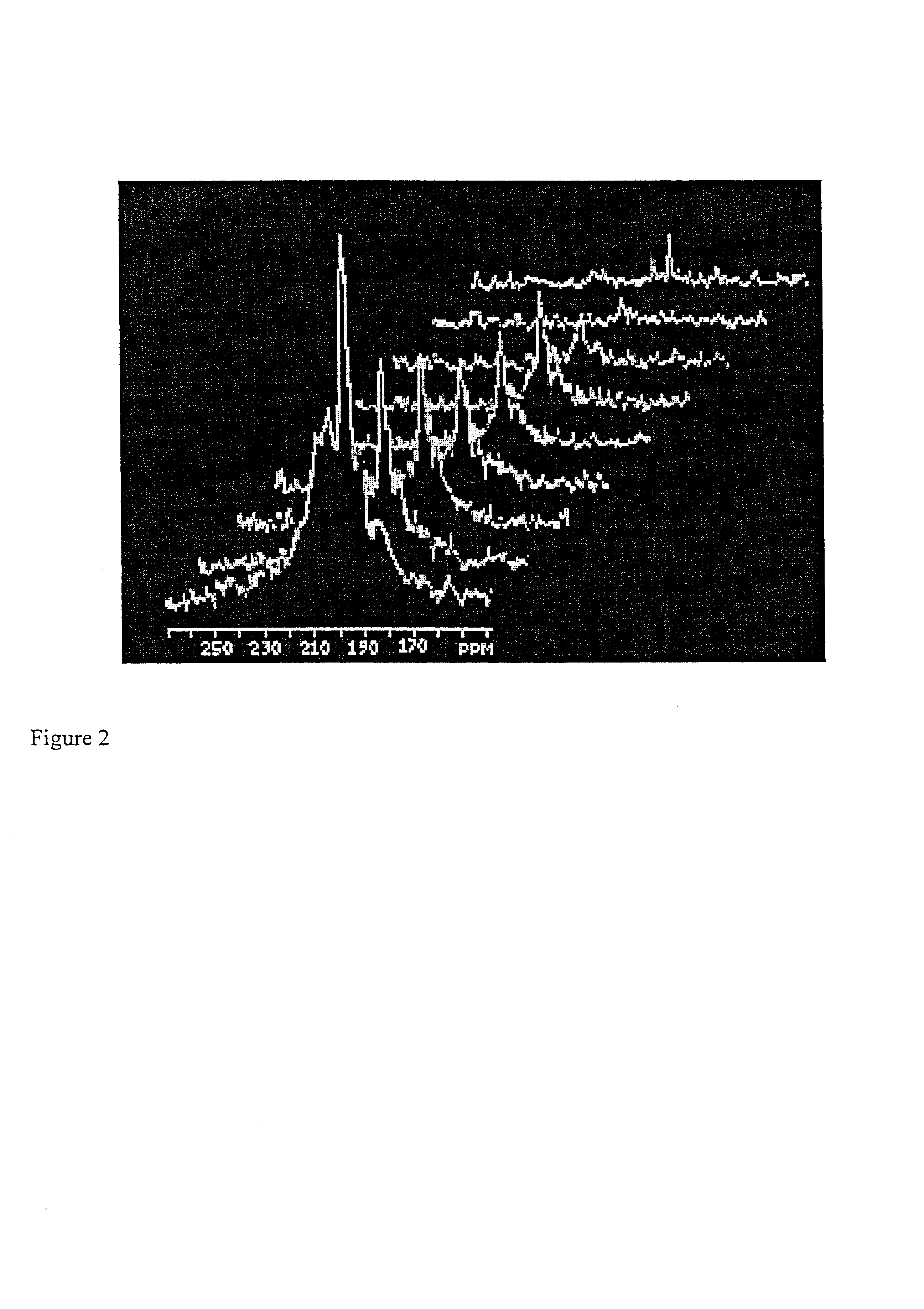
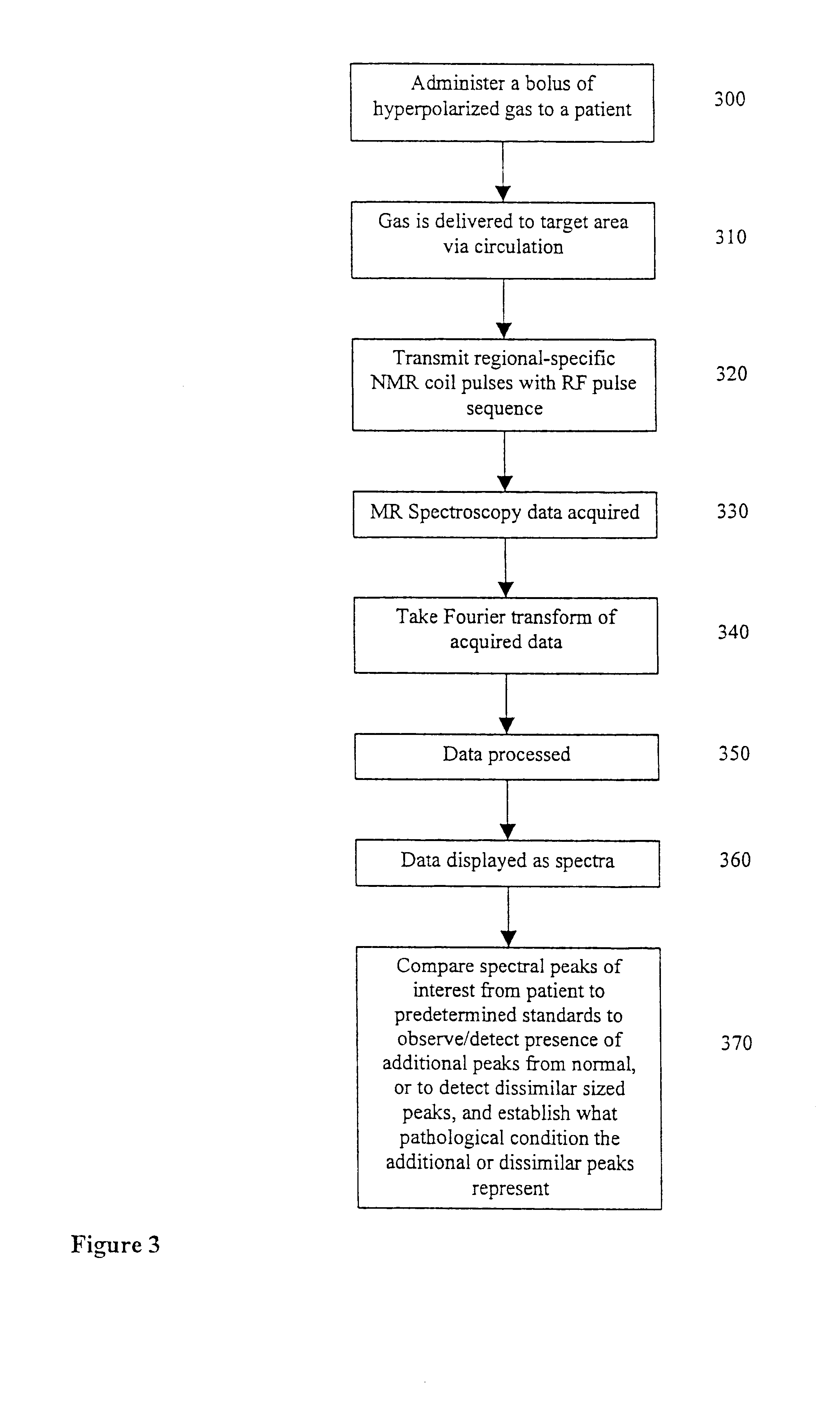
Diagnostic procedures using 129Xe spectroscopy characteristic chemical shift to detect pathology in vivo
InactiveUS6696040B2Reduce impactLarger flip anglesMeasurements using NMR spectroscopySensorsMedicineSpectroscopy
An in vivo non-invasive method for detecting and / or diagnosing a pathological condition using hyperpolarized <129>Xe spectroscopy is disclosed. Generally stated, the method includes determining the magnitude of spectral peaks which represent particular chemical shifts and comparing the observed magnitudes to those of healthy individuals. Preferably, the method includes subtracting substantial backgrounds and accounting for secondary conditions such as the polarization of hyperpolarized gas administered. Additionally, a quantitative analysis of hyperpolarized <129>Xe spectra advantageously allows a physician to establish the extent of disease progression. Advantageously, this method can be used regardless of the method of hyperpolarized <129>Xe administration.
Owner:POLAREAN
All-silicon molecular sieve and synthetic method thereof
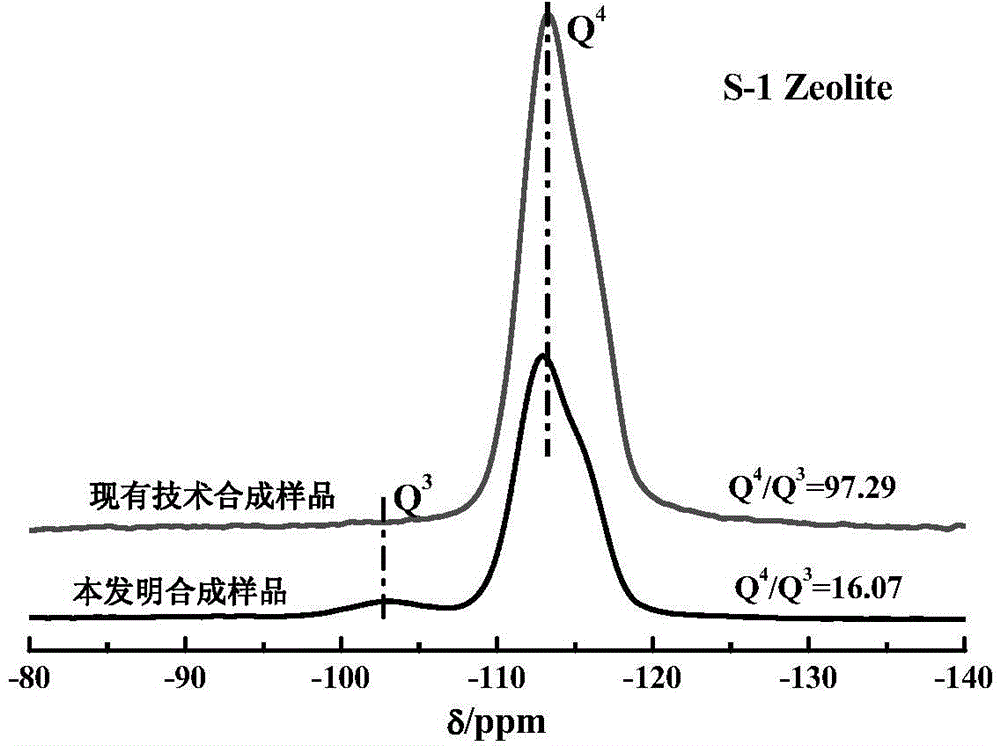
ActiveCN104556087AHigh catalytic activityFlexible adjustment of particle sizeLactams preparationSilicaMolecular sieveBeckmann rearrangement
The invention provides an all-silicon molecular sieve and a synthetic method thereof. Q4 / Q3 of the all-silicon molecular sieve is (10-90):1, wherein Q4 is the peak intensity expressed by the peak height at the chemical shift of -112+ / -2ppm in a 29SiNMR spectrogram of the all-silicon molecular sieve, and Q3 is the peak intensity expressed by the peak height at chemical shift of -103+ / -2ppm in the 29SiNMR spectrogram of the all-silicon molecular sieve. The synthetic method of the all-silicon molecular sieve comprises the following steps: mixing a template agent, an organic silicon source, an inorganic ammonium source and water to be subjected to hydrolytic alcohol removal, aging the obtained product, mixing the aging product with a solid silicon source, crystallizing the mixture in a closed reaction kettle, and recovering the all-silicon molecular sieve. The all-silicon molecular sieve provided by the invention has higher activity in cyclohexanone-oxime beckmann rearrangement.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com