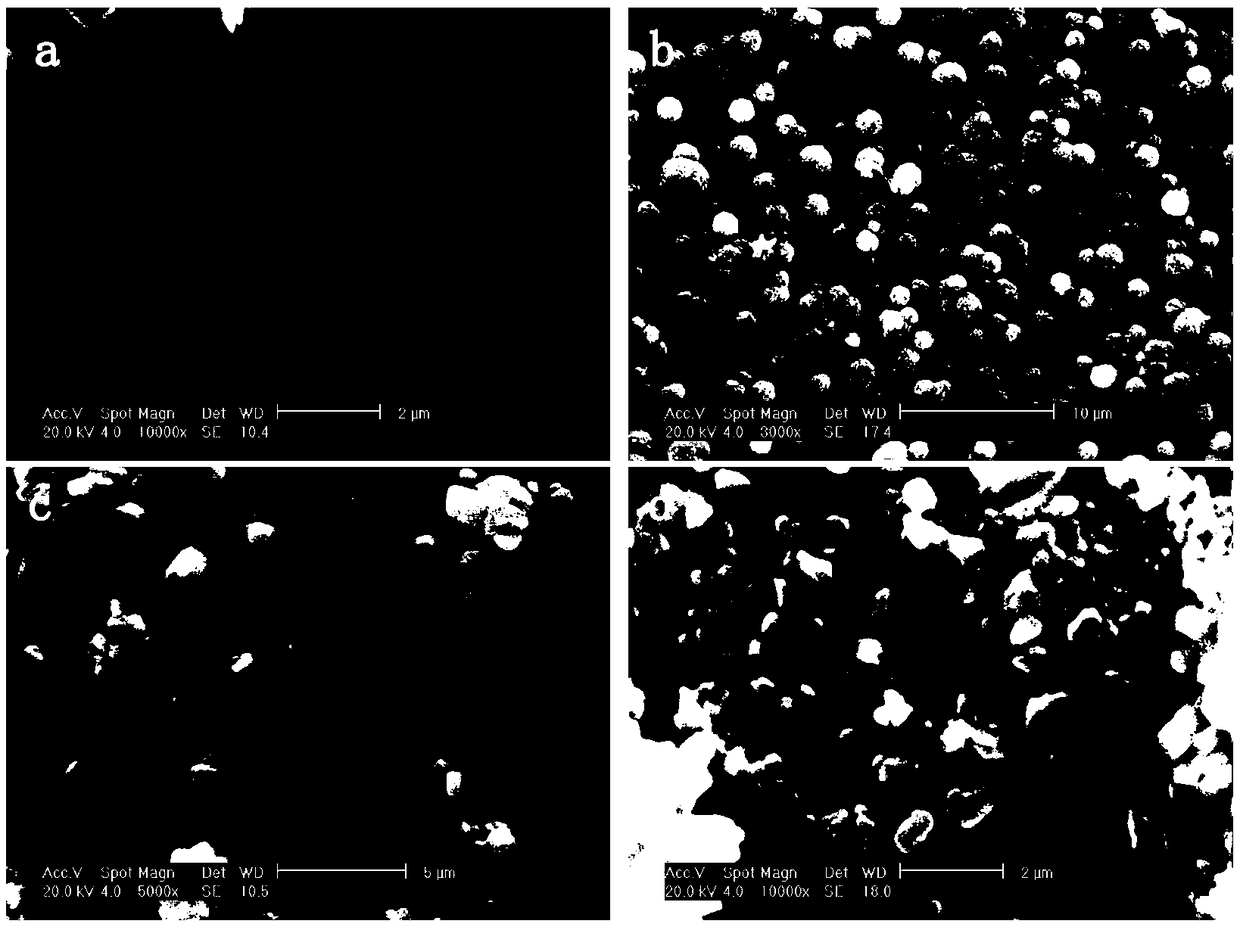
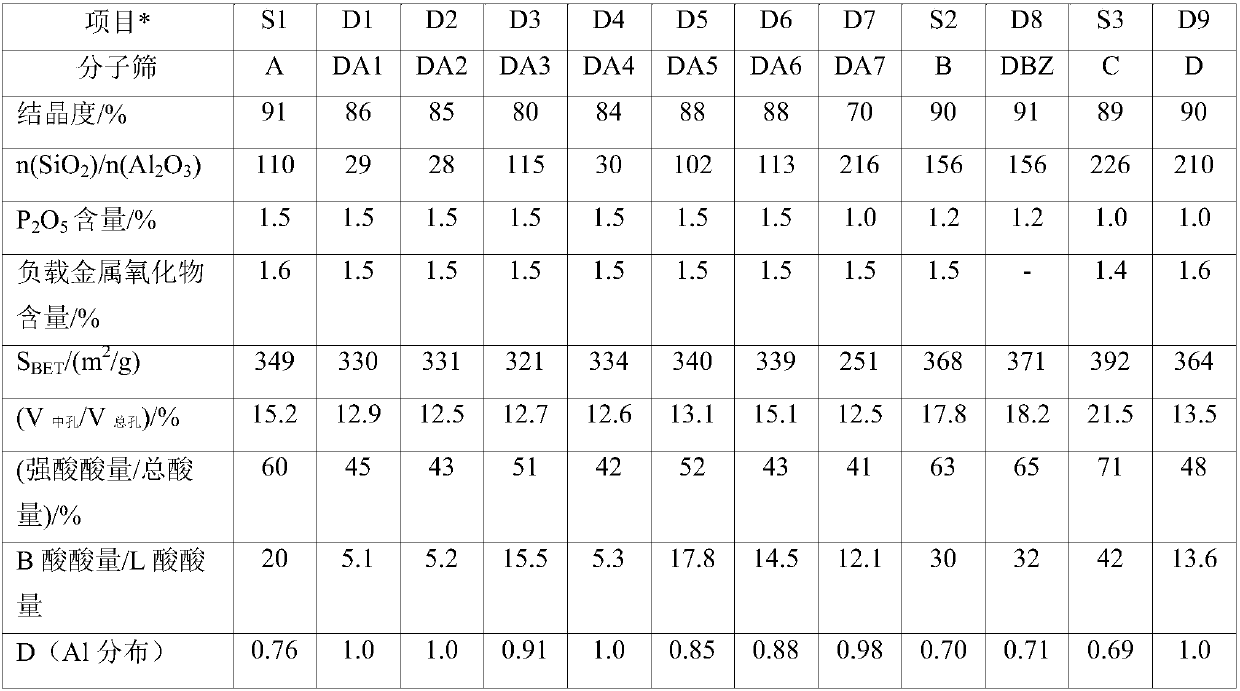
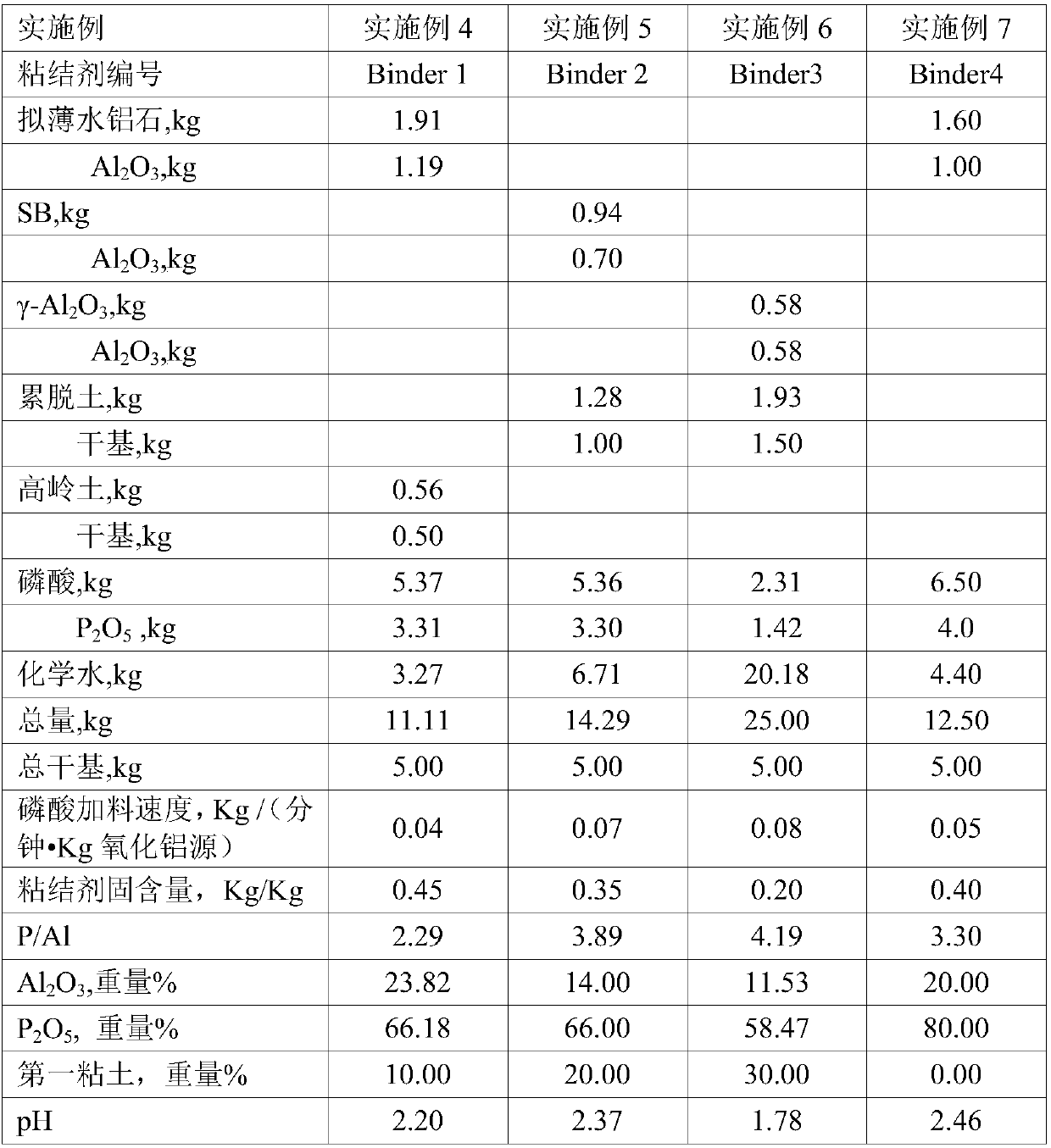
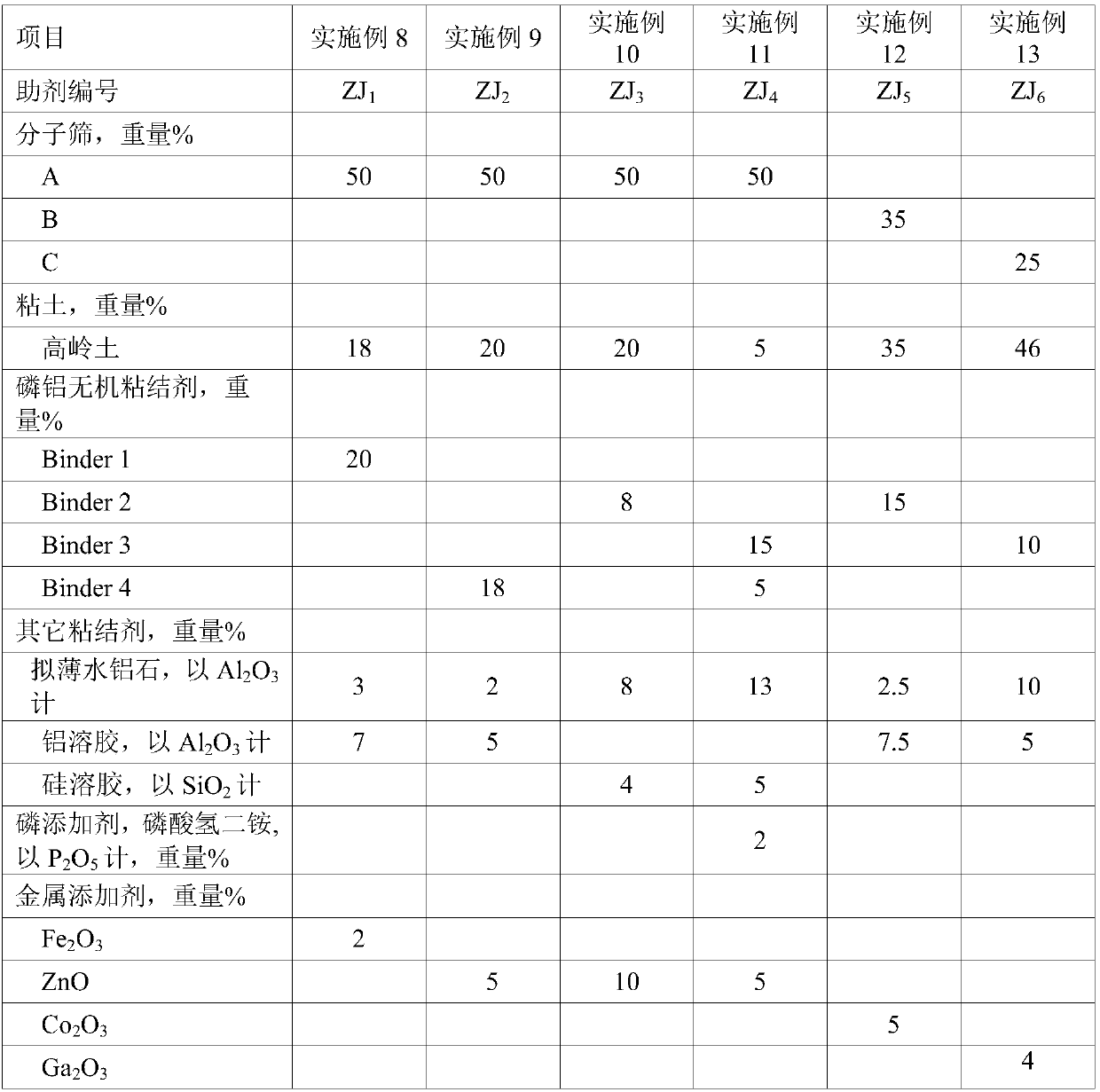
Patents
Literature
88results about How to "Good catalytic cracking performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
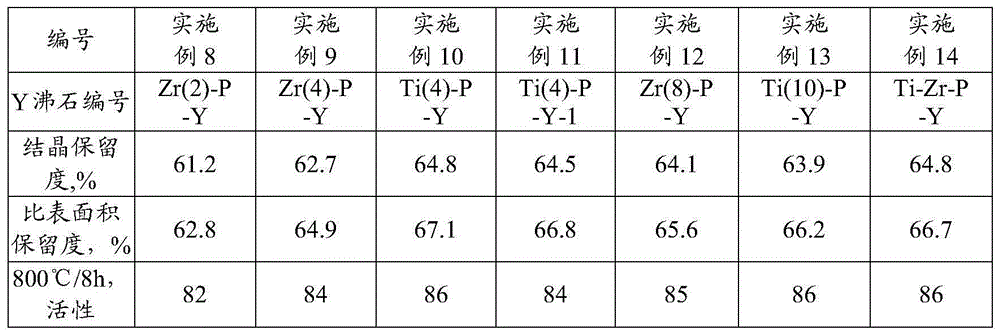
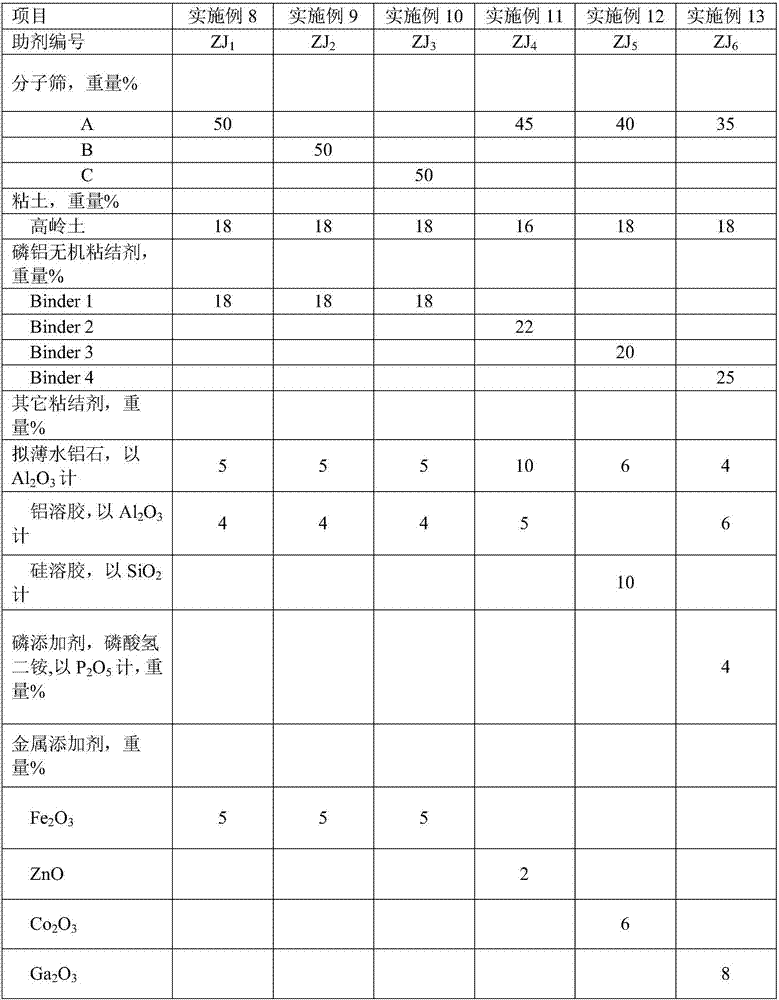
Catalyst of catalyzing, cracking for reducing sulfur content in gasoline and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN1597850AGood dispersionGood hydrothermal stabilityCatalytic crackingMolecular sieveIn situ crystallization
The invention is a catalytic cracking catalyst to reduce sulfur content of gasoline and its preparing method, synthesis gama-type molecular sieve by kaoline in-situ crystallization and making exchange sodium reduction or / and rare-earth ion exchange processing to prepare it, and its characteristic: the weight percent of sodium oxide contained in it is less than 0.75%, the ratio of zeolite to silica-alumina is above 4.5, and it adds one or several of the sourish metal elements: Cu, Zn, Fe, Al, Ni, Zr, Sn, Ga, Ti and V in weight percent of 0.1-10%. It has good zeolite dispersivity and excellent hydrothermal stability, good catalytic cracking property, and excellent function of reducing sulfur content of gasoline. It can be used by mixing with routine FCC catalyst and also be singly applied in the catalytic cracking process course.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Light oil type hydrocracking catalyst with composite molecular sieve as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103394368BGood catalytic cracking performanceGood catalyticMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon oil crackingMolecular sieveNaphtha
The invention discloses a light oil type hydrocracking catalyst with a composite molecular sieve. The hydrocracking catalyst comprises the composite molecular sieve consisting of a modified Y-molecular sieve and a modified ZSM-23 molecular sieve, a carrier composed of micropore aluminum oxides, and a hydrogenation activity component composed of a VIB group metal and a VIII group metal. The hydrocracking catalyst is characterized in that the composite molecular sieve comprises the modified Y-molecular sieve and the modified ZSM-23 molecular sieve, and the Y-molecular sieve is modified and dealuminized, so that heat stability and hydrothermal stability are stably enhanced, the hydrophobicity is enhanced, the absorption and desorption properties of the molecular sieve are improved, and the catalyst achieves a high catalytic cracking property. The pore passages of the modified SM-23 molecular sieve are unobstructed, the number of the acid sites is small, the isomerism property is outstanding, and the octane value of the molecular sieve is increased because of light naphtha components. The modified Y-molecular sieve and the modified ZSM-23 molecular sieve are mixed and used according to a formula ratio of the hydrocracking catalyst, so that both the cracking activity and the isomerism property are considered, and the final catalyst achieves an ideal catalytic effect.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +3
Cracking assistant for improving low-carbon olefin concentration
ActiveCN103785458AImprove wear resistanceGood catalytic cracking performanceCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMagic angle spinningPeak area
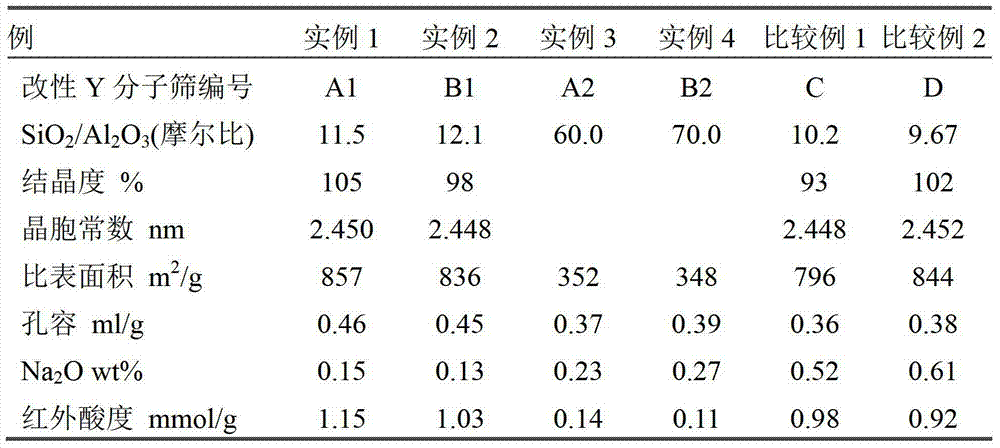
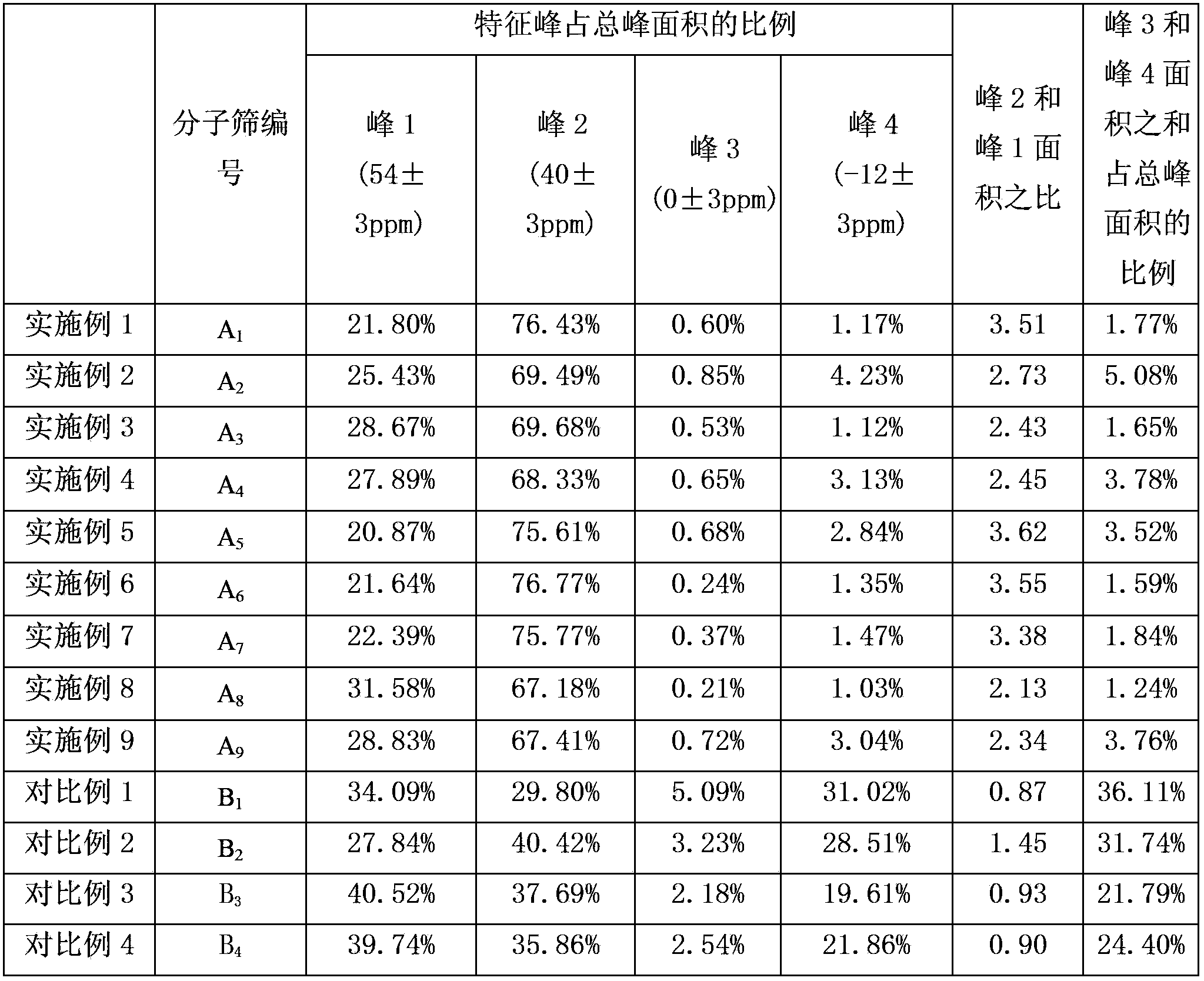
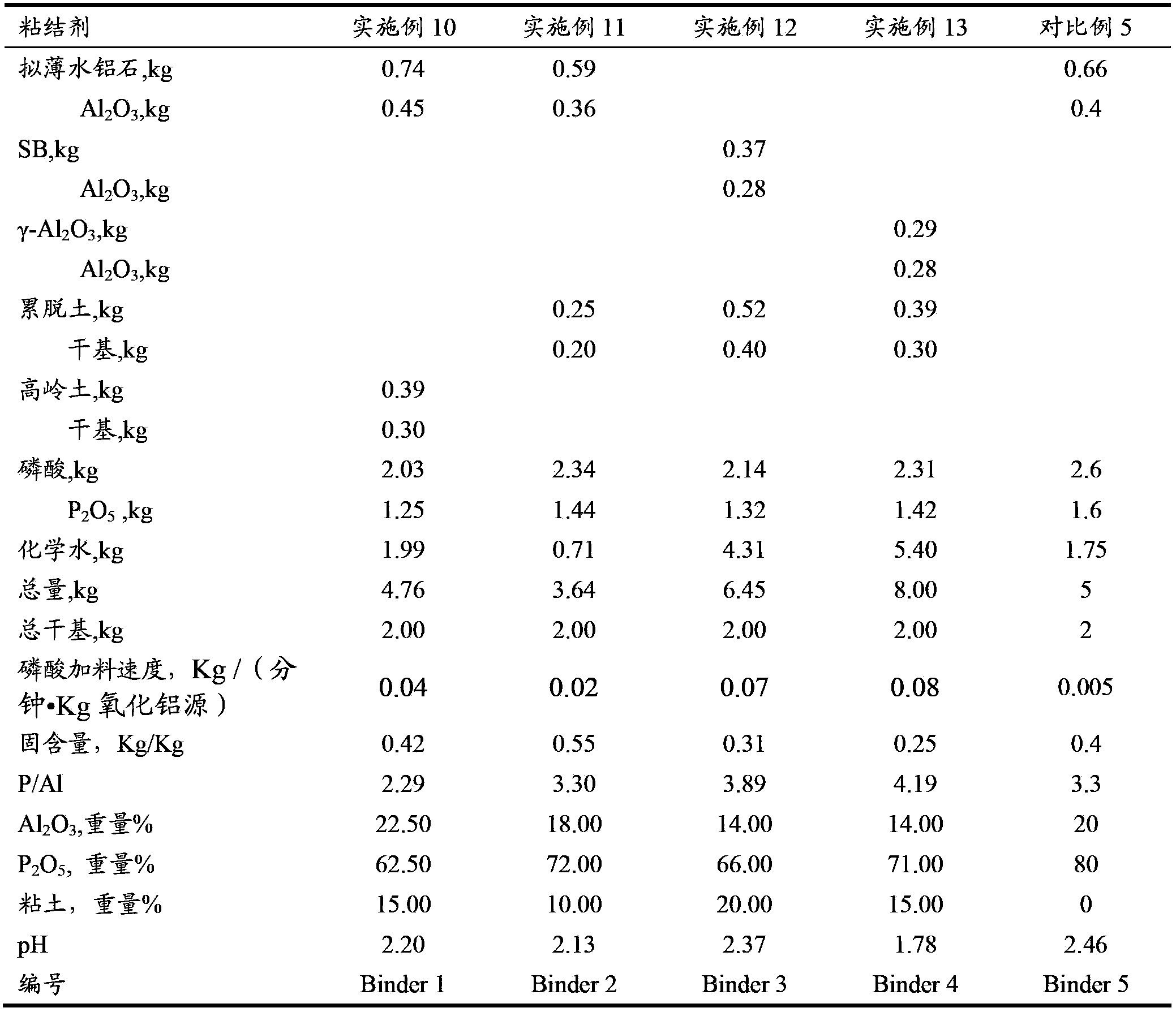
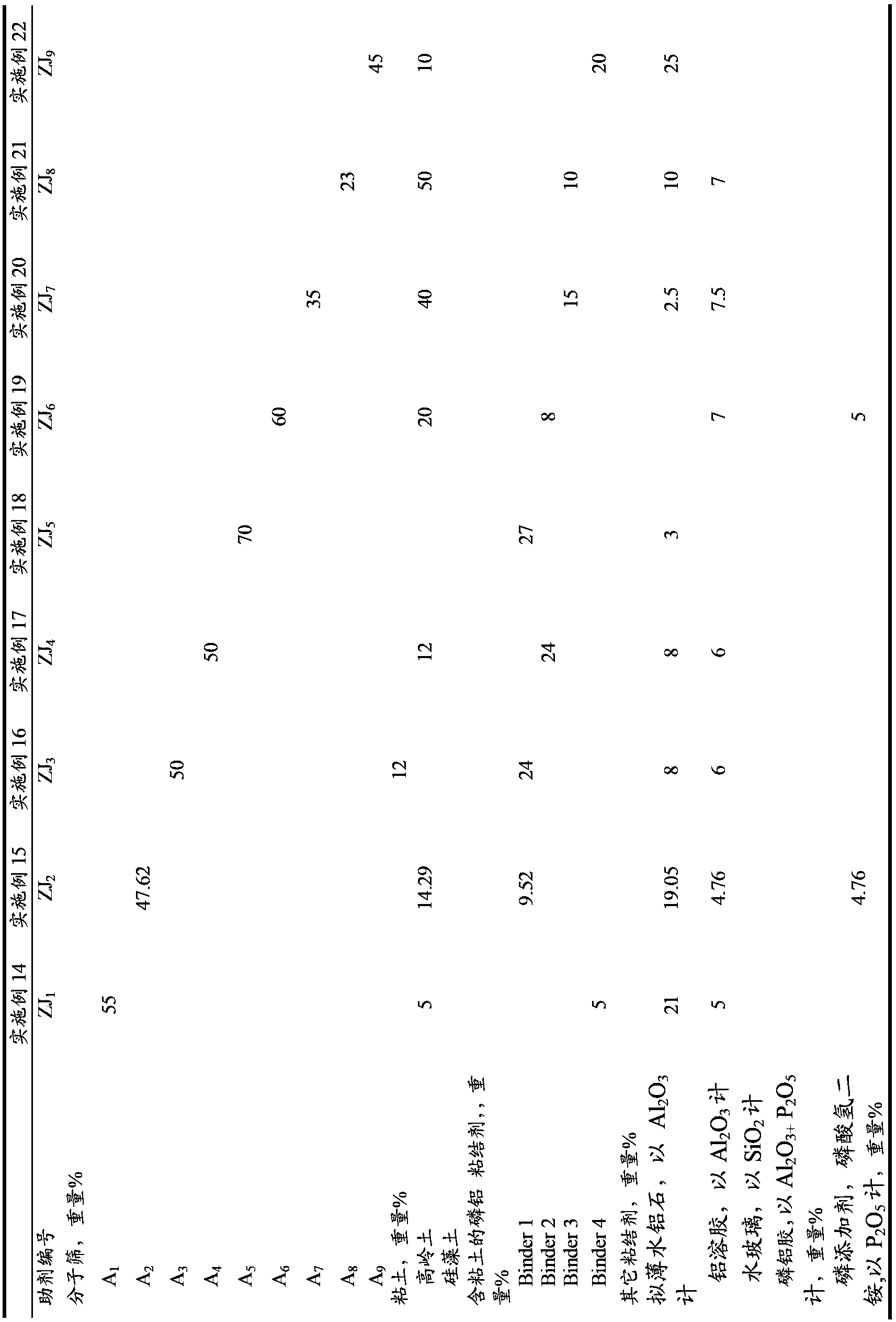
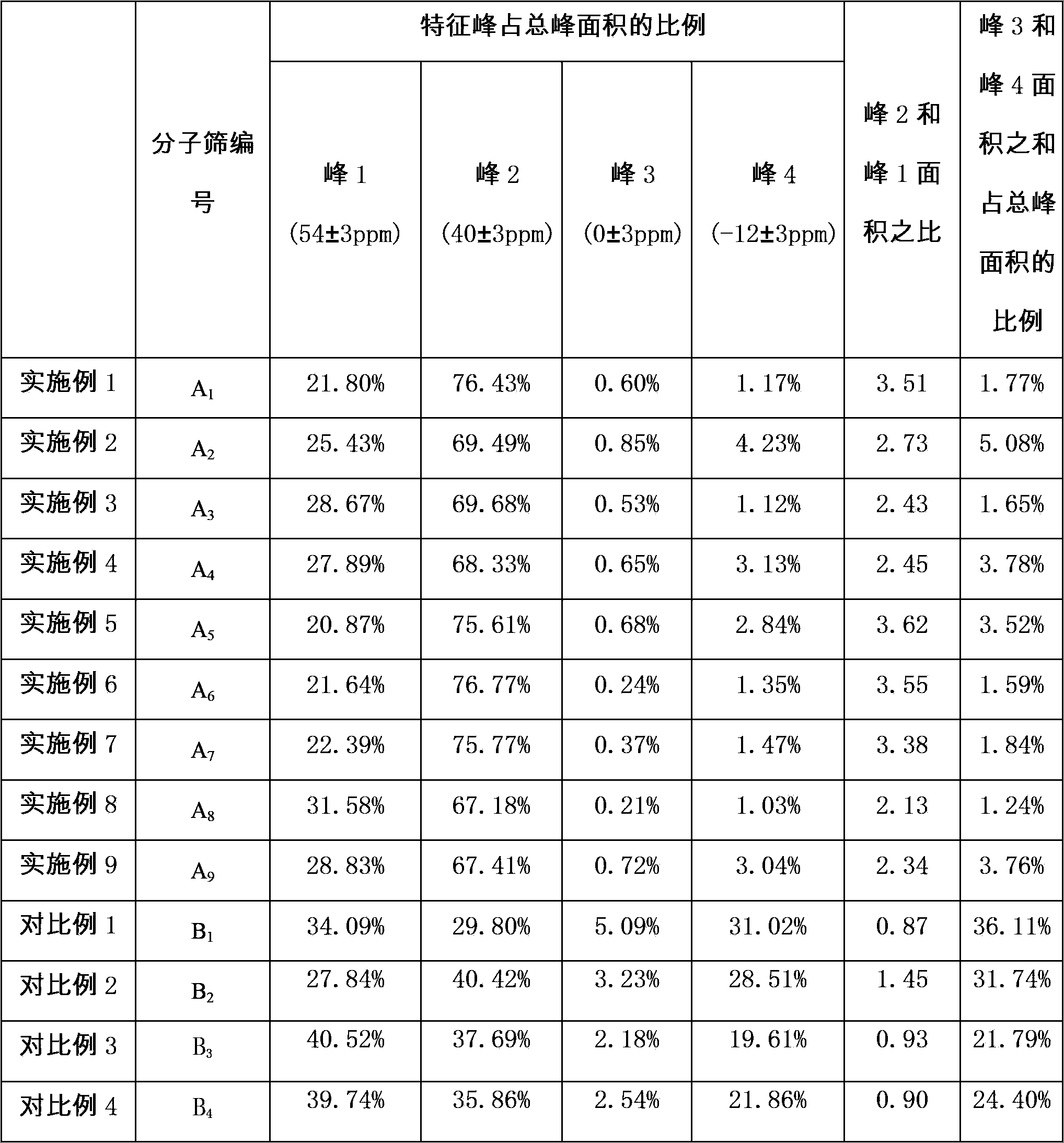
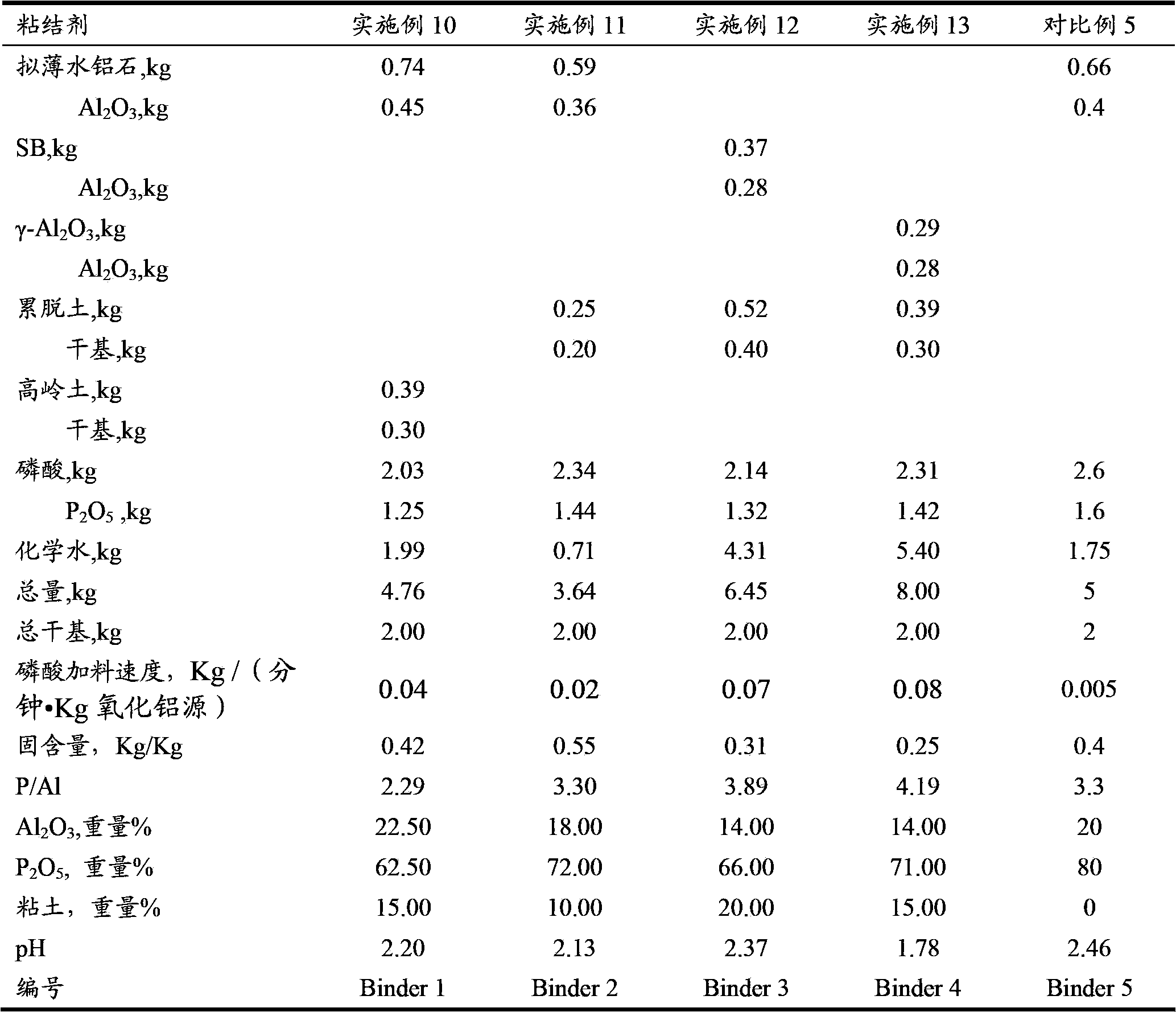
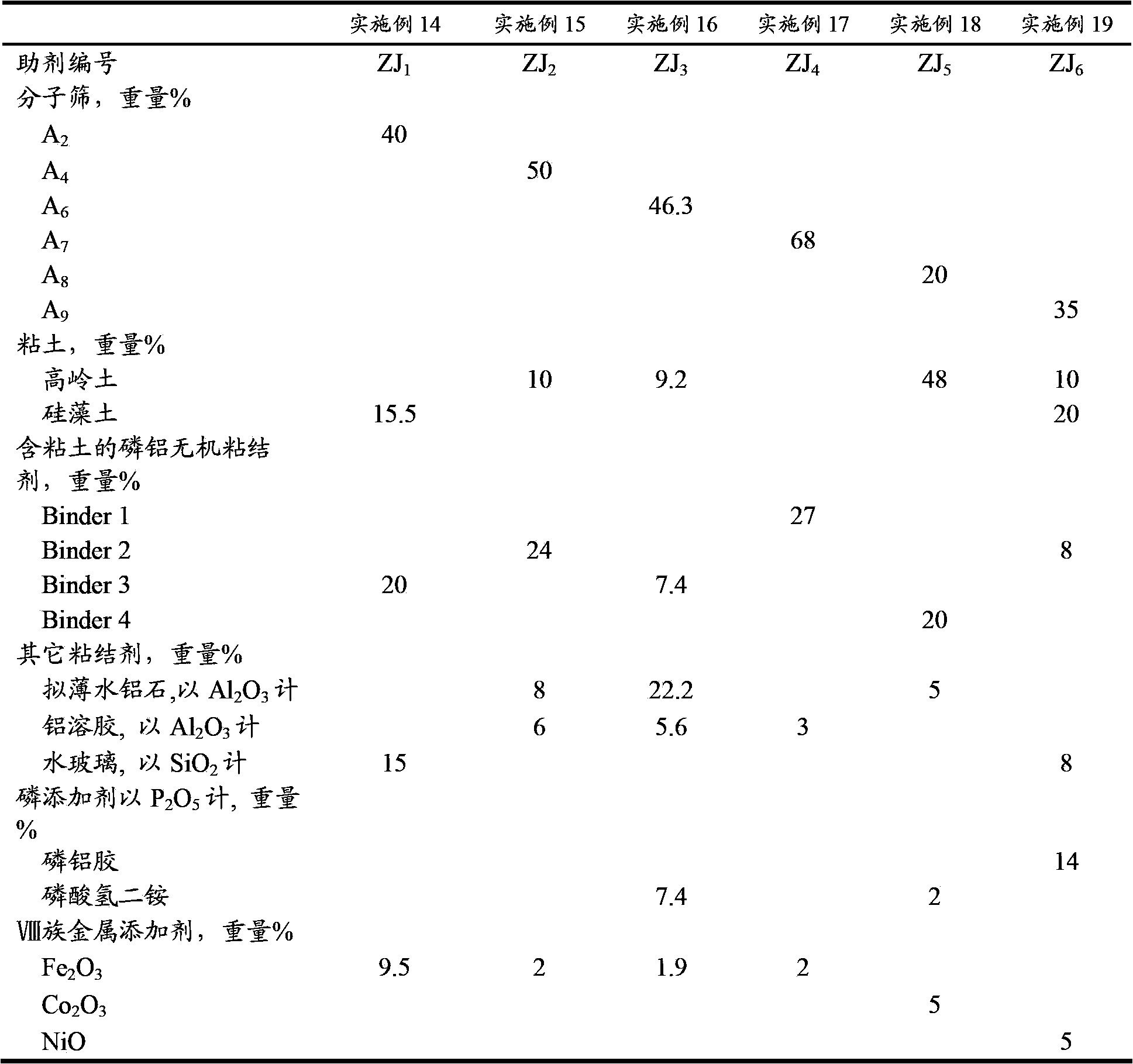
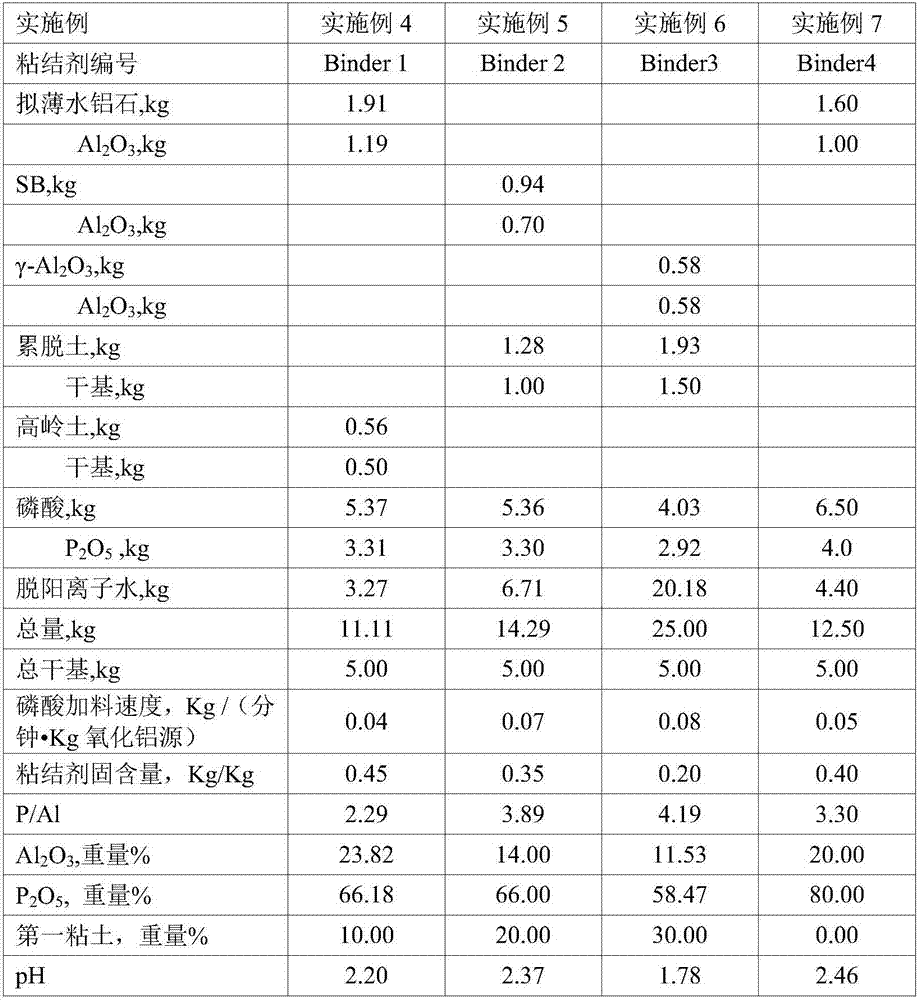
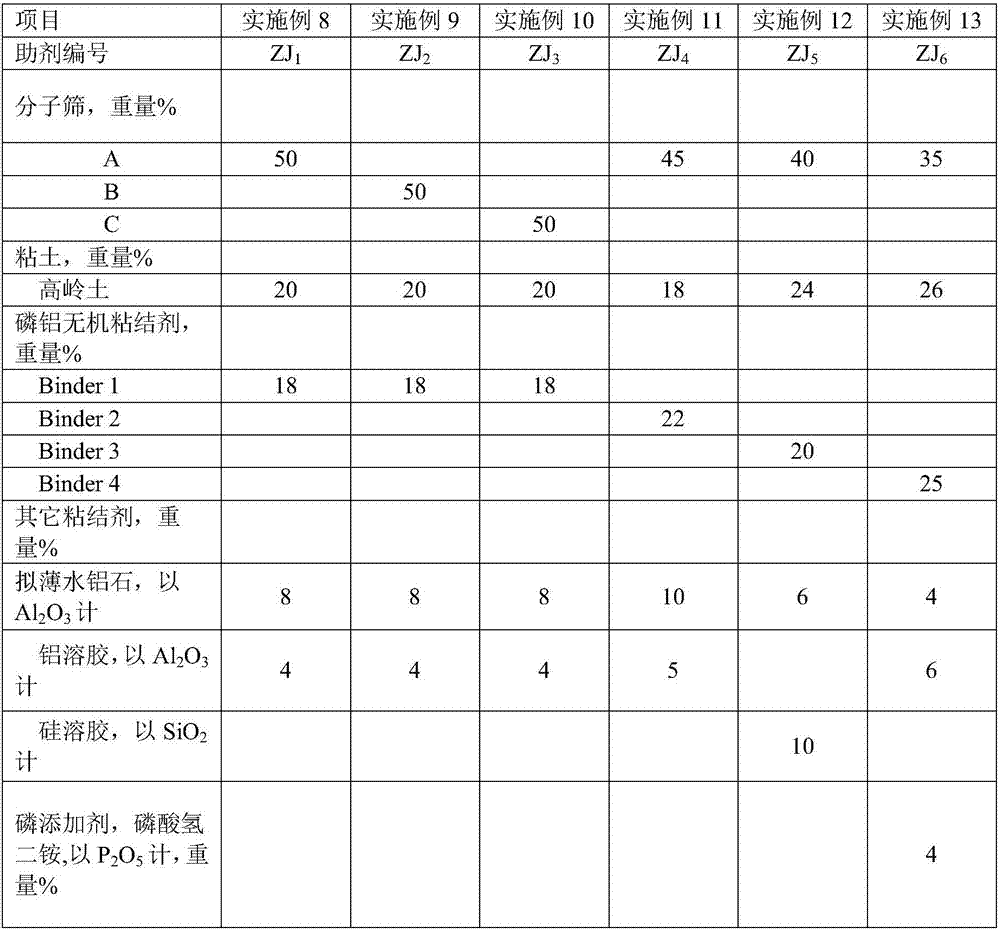
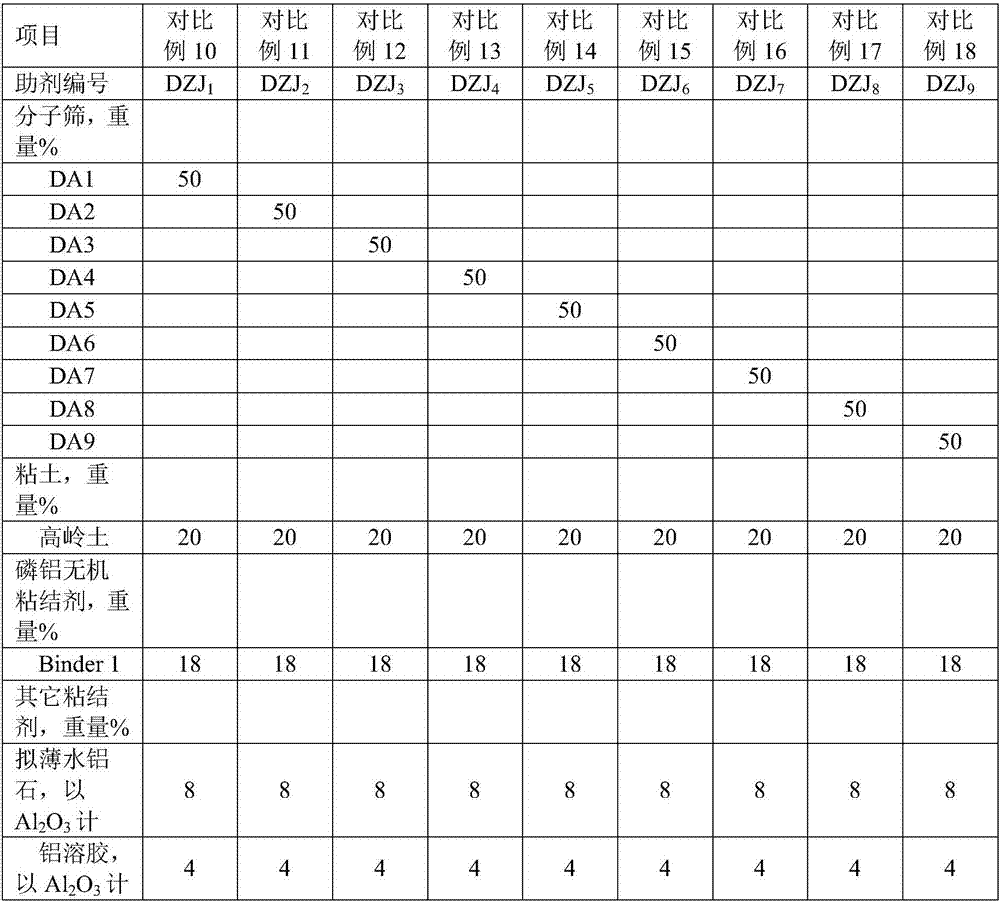
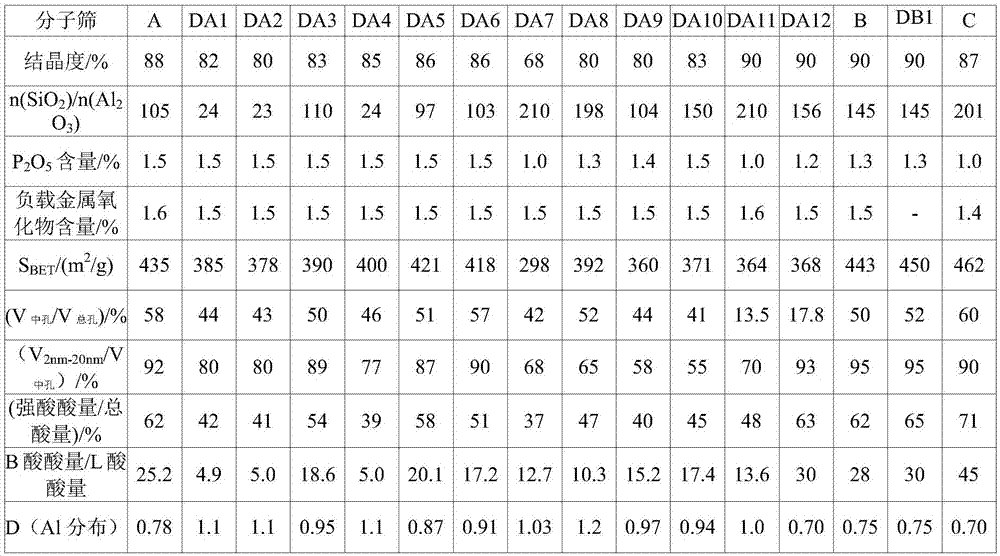
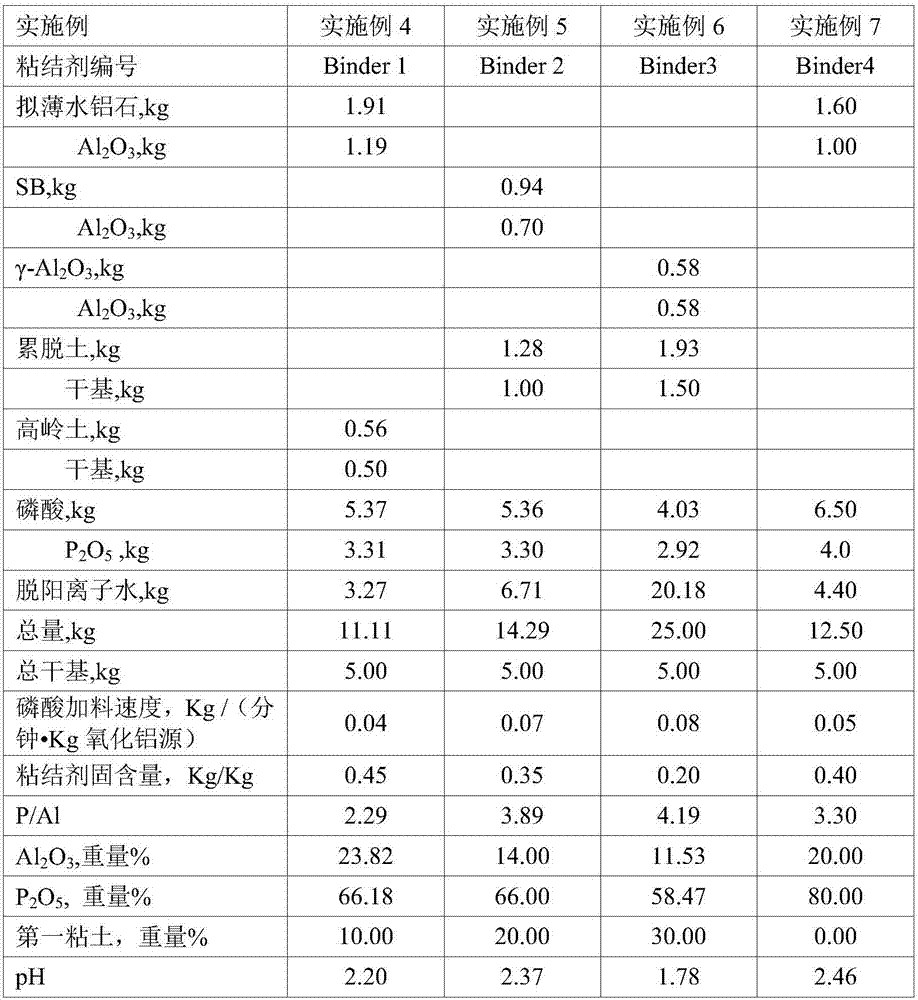
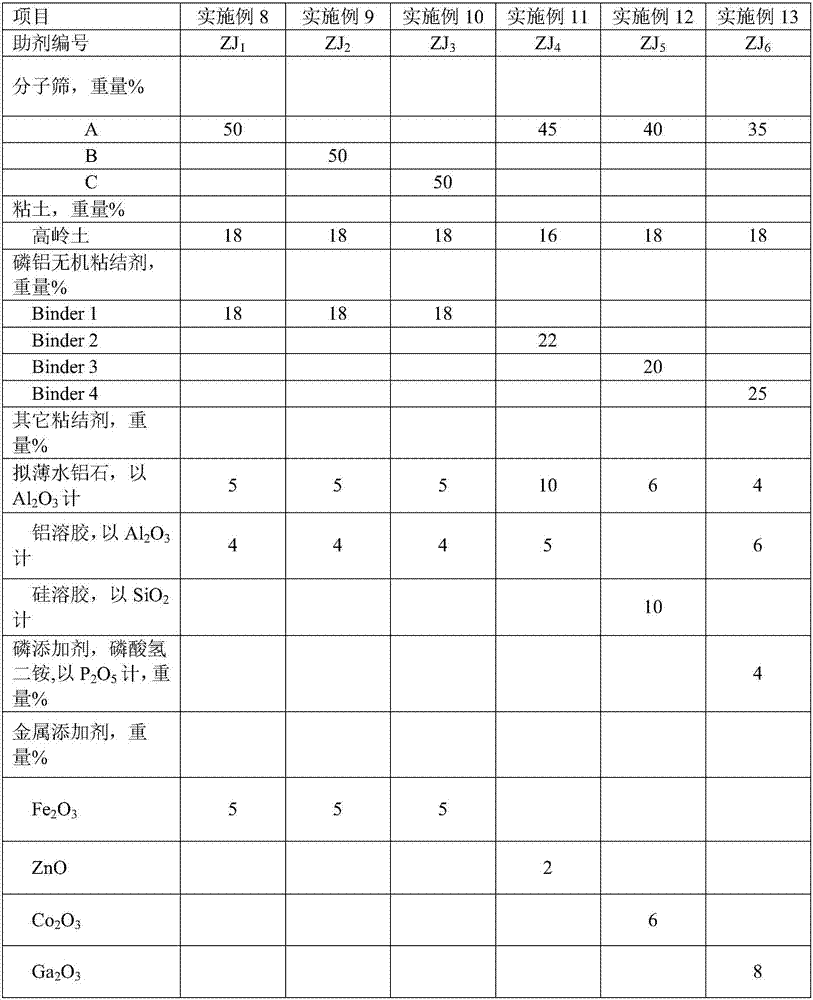
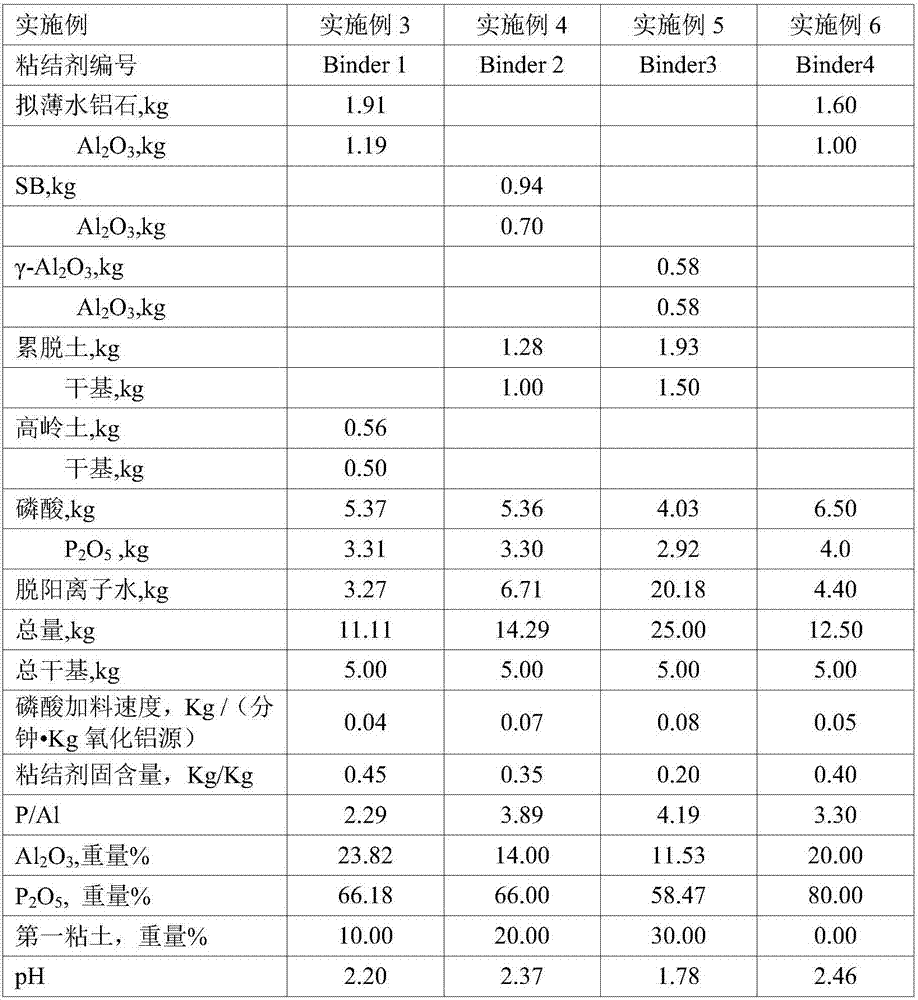
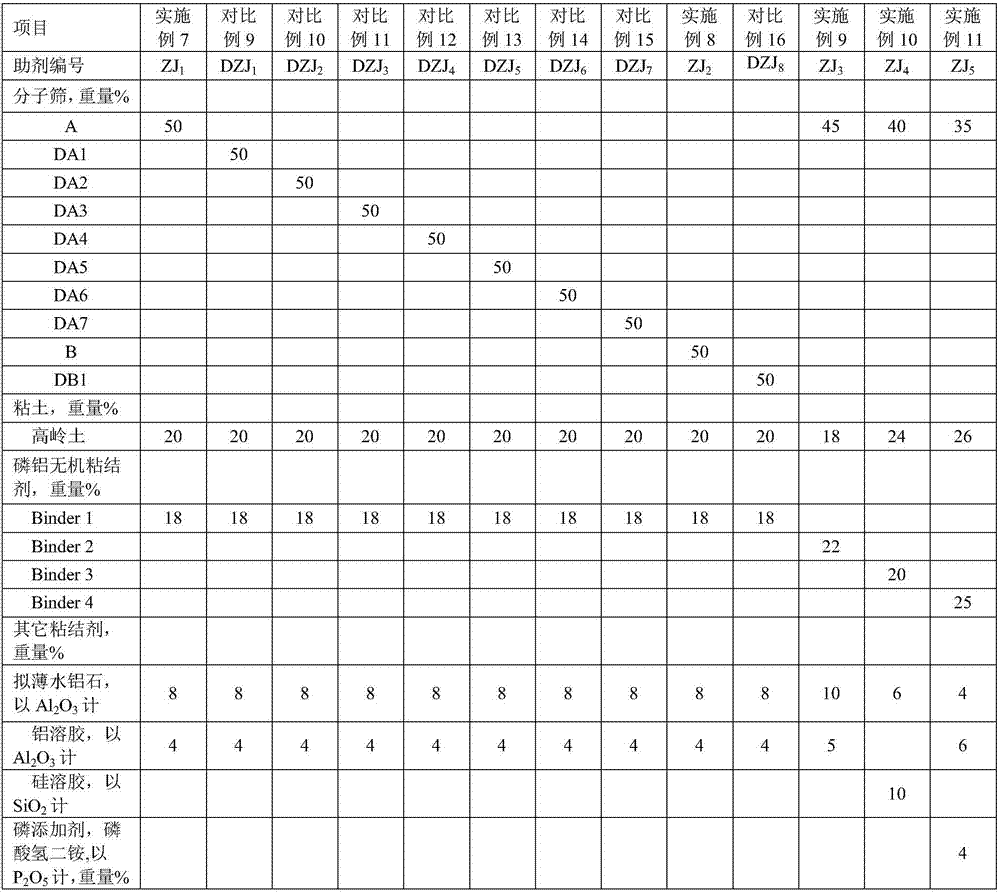
The invention discloses a cracking assistant for improving the low-carbon olefin concentration. The cracking assistant comprises a phosphorus and transition metal-containing beta molecular sieve, a first-clay-containing phosphorus aluminum inorganic binder, other inorganic binder and second clay; the first-clay-containing phosphorus aluminum inorganic binder comprises 15-40 wt% by Al2O3 of an aluminum component, 45-80 wt % by P2O5 of a phosphorus component and 1-40 wt % by dry basis of first clay, the weight ratio of P to Al is 1-6; the phosphorus and transition metal-containing beta molecular sieve comprises 1-10wt% by P2O5 of phosphorus and 0.5-10 wt % by metallic oxide of a metal; and in the 27Al MAS NMR (Magic Angle Spinning Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) of the phosphorus and transition metal-containing beta molecular sieve, the ratio of resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of 40+-3ppm to resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of 54+-3ppm is greater than 1, and the percentage of the sun of the resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of 0+-3ppm and the resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of-12+-3ppm to the total peak area is less than 10%. The cracking assistant is used for catalytic cracking, and can improve ethylene concentrations in a catalytic cracking dry gas, and improve propylene and isobutylene concentration in a liquefied gas.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Cracking auxiliary agent for increasing low-carbon olefin concentration
ActiveCN103785456AImprove wear resistanceGood catalytic cracking performanceCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsFuel oilPeak area
The invention relates to a cracking auxiliary agent for increasing low-carbon olefin concentration. The cracking auxiliary agent contains a modified beta molecular sieve, a first clay-containing phosphorus-aluminum inorganic binder, and other inorganic binders and VIII group metal additives, and contains or does not contain second clay, wherein the first clay-containing phosphorus-aluminum inorganic binder comprises an aluminum component, a phosphorus component and first clay, the modified beta molecular sieve containing the phosphorus and the transition metal comprises 1-10 wt% (calculated as P2O5) of the phosphorus and 0.5-10 wt% (calculated as metal oxide) of the metal, and in the 27Al MAS NMR of the molecular sieve, a ratio of the resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of 40+ / -3 ppm to the resonance signal peak area at the chemical shift of 54+ / -3 ppm is more than or equal to 1, and the sum of the resonance signal peak areas at the chemical shifts of 0+ / -3 ppm and -12+ / -3 ppm accounts for less than or equal to 10% of the total peak area. According to the present invention, the cracking catalyst composition is used for catalytic cracking of petroleum hydrocarbons, and can be provided for increasing the catalytic cracking liquefied gas yield, increasing the concentration of the low-carbon olefin in the liquefied gas, especially the concentration of isobutene, increasing the ratio of ethylene to dry gas, and increasing the gasoline octane number, and the heavy oil conversion capacity of the main catalyst is not affected when the auxiliary agent is blended in the large proportion manner.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
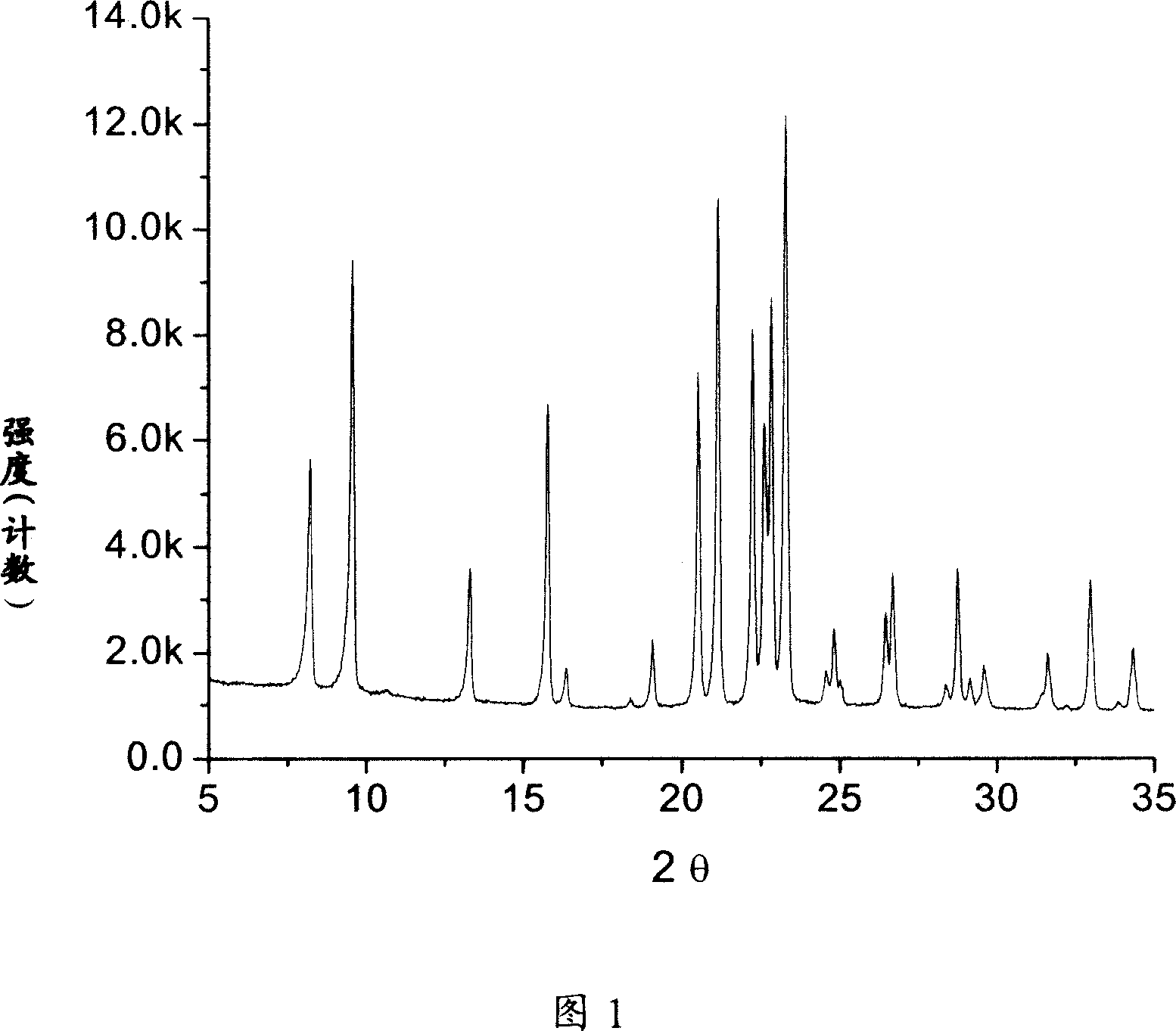
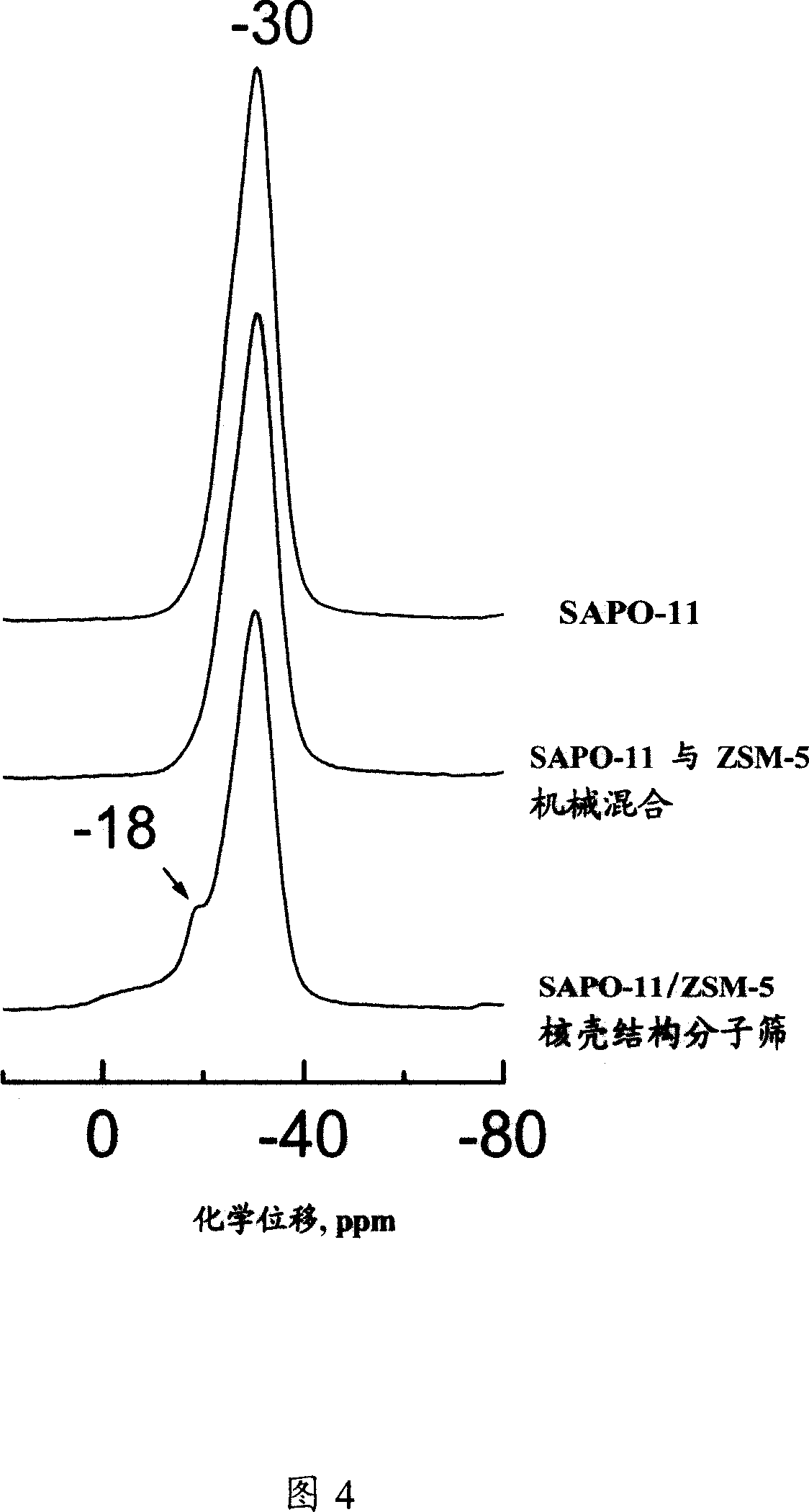
Core-shell structured molecular sieve, its production and use
ActiveCN1982215AHigh yieldGood catalytic cracking performanceMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular-sieve and base-exchange phosphatesMolecular sieveCracking reaction
A molecular sieve with aluminum phosphor-silicate molecular sieve kernel and Pentasil molecular sieve shell structure in proportion of 1:1-20:1 proportion and its production are disclosed. The process is carried out by mixing silicate-containing compound with aluminum-containing compound solution, agitating, adding into organic template agent to obtain mixture, mixing it with dispersed aluminum phosphor-silicate molecular sieve in proportion of SiO2:Al203:Na2O:P2O5:R:H2O=(10-500): 1(5-100): (0.1-20): (3-100): (1000-10000), crystallizing at 120-200degree, filtering, washing, drying and sintering. It can be used for light-hydrocarbon cracking reaction and has more output.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Light-oil-type hydrocracking catalyst carrier, preparation method thereof and applications thereof
ActiveCN103406143AIncreased acid center strengthIncrease reaction rateMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon oil crackingMolecular sieveAluminium
The invention discloses a light-oil-type hydrocracking catalyst carrier comprising a modified Y molecular sieve, a modified ZSM-23 molecular sieve and foraminate aluminium oxide. The light-oil-type hydrocracking catalyst carrier comprises the modified Y molecular sieve with high cracking activity, and the modified ZSM-23 molecular sieve with excellent isomerization performance, and therefore the carrier has more comprehensive catalytic performances. A Y molecular sieve is modified to remove aluminium and improve the Si / Al skeleton, thus generating unit cell contraction, reducing the concentration of surface acid sites, and enhancing intensity of the acid sites and producing rich secondary mesopores, thereby facilitating improvement of adsorption and desorption performances of the molecular sieve, reducing diffusion resistance of reactant and resultant and improving the reaction speed, and therefore a catalyst can obtain a high catalytic cracking performance and more light distillates can be produced. The modified ZSM-23 molecular sieve has unobstructed pore channels, a little amount of the acid sites and an outstanding isomerization performance, thereby facilitating isomerization of the light distillates to improve the octane value.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +3
Binder-free zsm-5 molecular sieve catalyst and its preparation and use method
ActiveCN103785449BGood catalytic cracking performanceHigh yieldMolecular sieve catalystsBulk chemical productionLanthanideSilicon dioxide
The invention relates to a binder-free ZSM-5 molecular sieve catalyst, a preparation method thereof and a using method thereof, mainly solving a technical problem, namely the utilization rate reduction of molecular sieve pore channels due to addition of binders in forming processes. A ZSM-5 molecular sieve, solid powder silica and modifying components are mixed, extruded into bars and formed, and subjected to solid crystallization in organic amine vapour, wherein the crystallization time is 16-150 h and the crystallization temperature is 40-200 DEG C. In the binder-free ZSM-5 molecular sieve catalyst with fine crystal grains, the weight ratio of silicon to aluminum based on oxides is Al2O3:SiO2(by weight)=0-6:100 and the grain size of the molecular sieve is smaller than 1 [mu]m. The modifying component phosphorous accounts for 0.1-10% of the whole catalyst and the modifying component lanthanide series metal accounts for 0.01-5% of the whole catalyst. The binder-free ZSM-5 molecular sieve catalyst can be used in the fields of catalysts used for low-carbon olefin preparation through petroleum hydrocarbon cracking, and the fields of preparation and applications of the catalysts.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for high-yield low carbon olefin and system for high-yield low carbon olefin
ActiveCN107779226AGenerate moreImprove conversion rateTreatment with hydrotreatment processesHydrocarbon oils treatment productsWaxNaphtha
The invention relates to the field of residual oil utilization and discloses a method for high-yield low carbon olefin and a system for high-yield low carbon olefin. The method comprises the followingsteps: introducing a residual oil raw material into a fluidized bed hydrocracking reaction zone, performing a hydrocracking reaction, separating a hydrocracking reaction effluent, introducing a wax oil fraction into a first reactor and a second reactor in sequence, carrying out a catalytic cracking reaction, and introducing first light naphtha into a third reactor in a catalytic cracking reactionzone, and performing another catalytic cracking reaction; separating catalytic cracking products obtained from the second reactor and the third reactor in the catalytic cracking reaction zone, respectively circulating circulation oil and second light naphtha into the first reactor and the third reactor in the catalytic cracking reaction zone, and circulating catalytic cracking oil pulp into the fluidized bed hydrocracking reaction zone. With the organic combination of a fluidized bed residual oil hydrogenation process with a catalytic cracking process, the yield of high-value products such aspropylene and ethylene in the combined processes can be remarkably increased.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Cracking assistant for improving low-carbon olefin concentration
ActiveCN103007993AImprove wear resistanceGood catalytic cracking performanceCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sievePhosphor
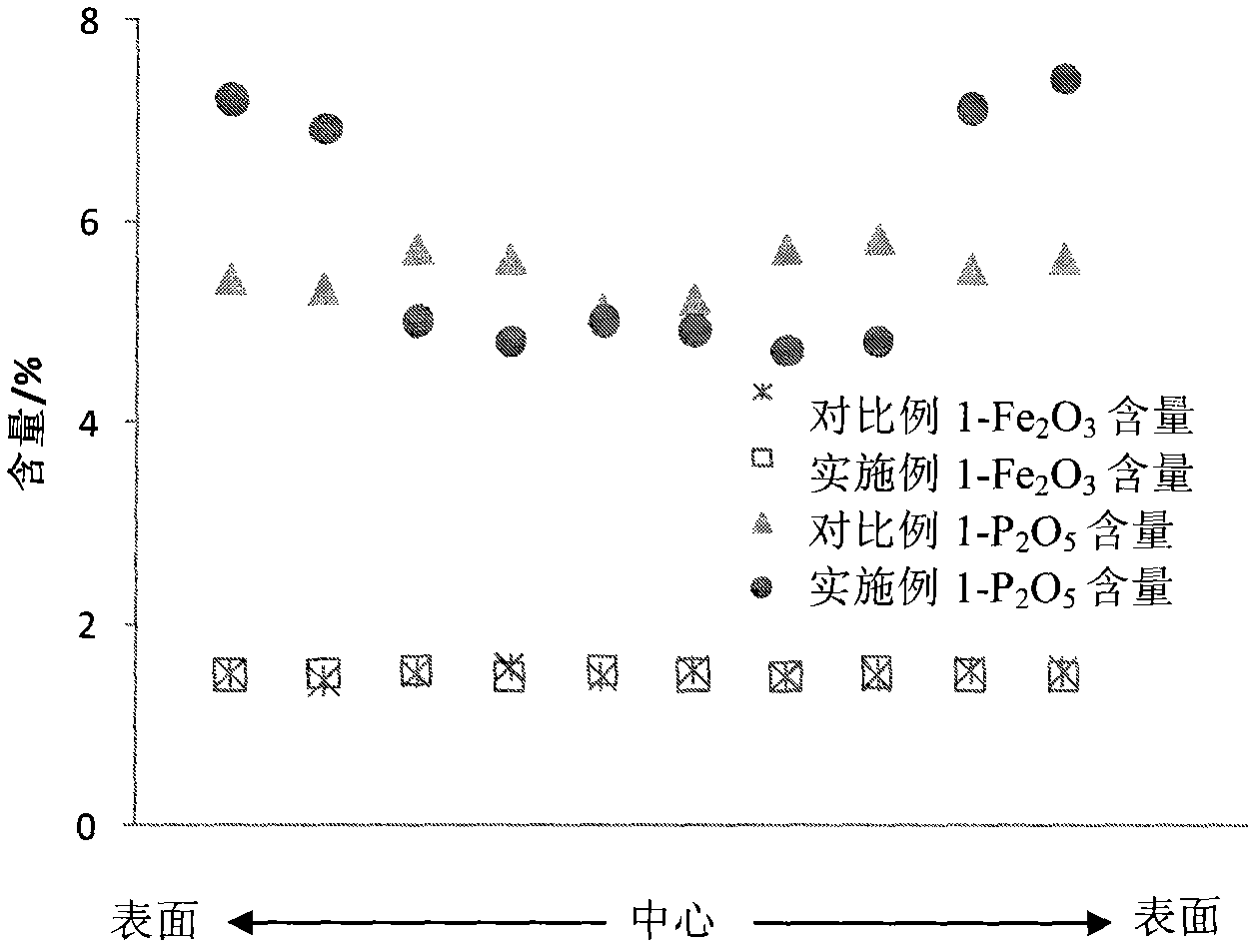
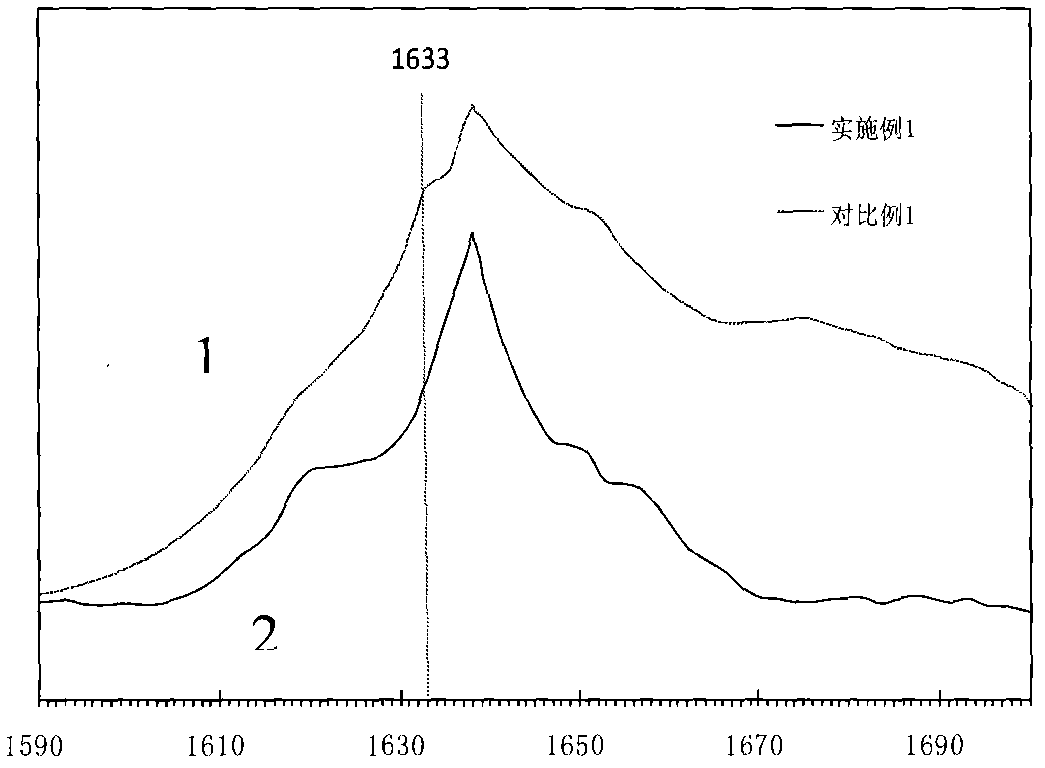
The invention discloses a cracking assistant for improving a low-carbon olefin concentration. The cracking assistant comprises a modified MFI molecular sieve, a first clay-containing phosphor-aluminum inorganic binder, other inorganic binders and a VIII metal additive, and / or second clay. The first clay-containing phosphor-aluminum inorganic binder comprises an aluminum component, a phosphor component and first clay. The modified MFI molecular sieve contains phosphor and one or more of transition metals of Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Mn, Zn, Sn and Bi. There is not an absorption peak at the wavelength of 1633cm<-1> in a modified MFI molecular sieve infrared spectra obtained by trimethylpyridine as a probe molecule. The cracking assistant is used for catalytic cracking, can improve a catalytic cracking liquefied gas yield, can obviously improve a concentration of a low-carbon olefin in catalytic cracking liquefied gas, can especially improve a concentration of propylene in catalytic cracking liquefied gas, and can improve the selectivity of dry gas and coke.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Carrier containing dual-molecular sieves, catalyst containing dual-molecular sieves and preparation methods and application of carrier and catalyst
ActiveCN108067290AImprove stabilityReduced Diffusion ResistanceMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon oils refiningMolecular sievePtru catalyst
The invention provides a carrier containing dual-molecular sieves, a catalyst containing dual-molecular sieves and preparation methods and application of the carrier and the catalyst. The carrier is prepared from 48.5wt%-89.9wt% of a modified Y molecular sieve, 0.1wt%-1.5wt% of an SBA-15 molecular sieve and 10wt%-50wt% of aluminum oxide by weight of the carrier; the catalyst is prepared from 28.5wt%-74.9wt% of the modified Y molecular sieve and 0.1wt%-1.5wt% of an SBA-15 mesoporous molecular sieve by weight of the catalyst; and group VIB metal accounts for 10.0-25.0wt% in terms of its oxides,group VIII metal accounts for 3.0-8.0wt% in terms of its oxides, and the aluminum oxide accounts for 10-30wt%. The carrier is especially suitable for preparing a light oil type hydrocracking catalystand has high catalytic cracking activity and high target product selectivity.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Preparation method of iron sulfide for catalyzing heavy oil hydrocracking, and technology using iron sulfide
ActiveCN104030364AMagnetic Fe
<sub>1-x</sub>
S has hydrogenation catalytic activityHas hydrogenation catalytic activityPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrocarbon oil crackingActive componentIron sulfide
The invention discloses a preparation method of iron sulfide for catalyzing heavy oil hydrocracking. The method comprises the following steps: placing coal in a fluid bed, and burning the coal at 500-900DEG C under normal pressure to obtain dust; and separating out iron sulfide from the dust under the action of magnetic force, wherein the molecular formula of the iron sulfide is Fe1-xSx, x is less than or equal to 0.2, and the particle size of the iron sulfide is less than or equal to 30mum. The iron sulfide is added to heavy oil in order to catalyze the hydrocracking reaction of the heavy oil, and the yield of the obtained light fractions below 350DEG C can reach above 80%. The iron sulfide prepared through the method can be used in the hydrocracking reaction of the heavy oil as an active component of a catalyst or a catalyst individually.
Owner:BEIJING SJ ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION & NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Hydrocracking catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108579777AHigh activityImprove performanceHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsCatalyst activation/preparationActive componentFixed bed
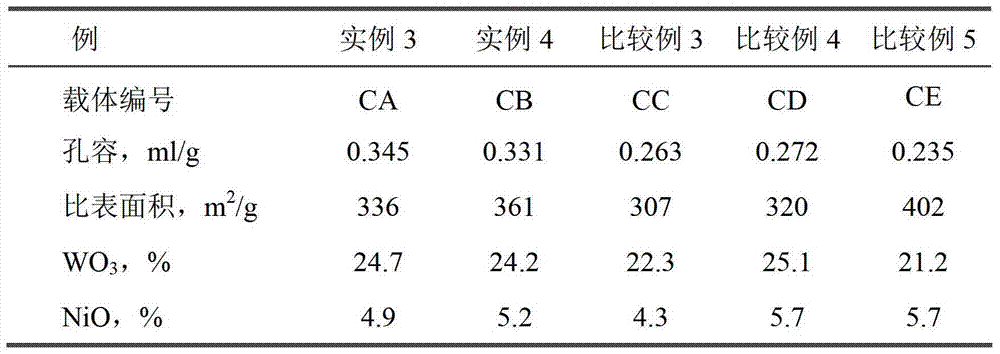
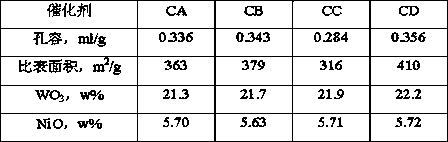
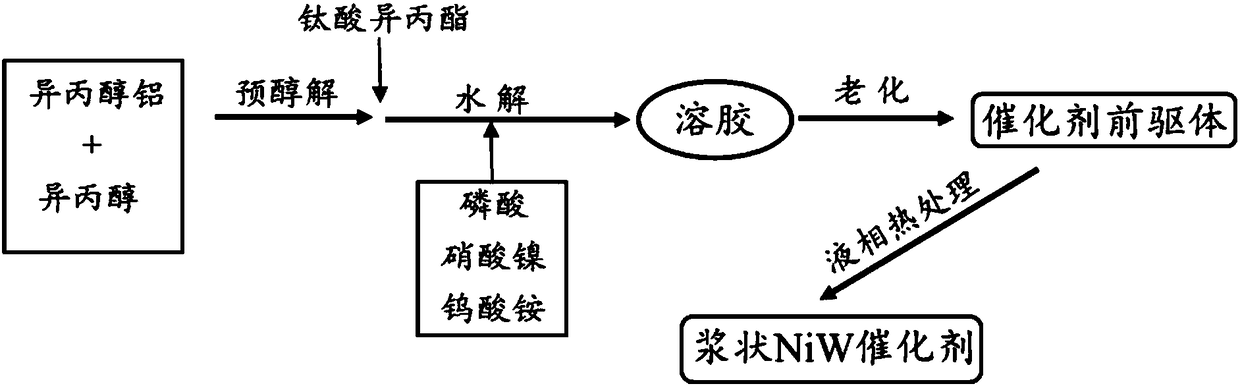
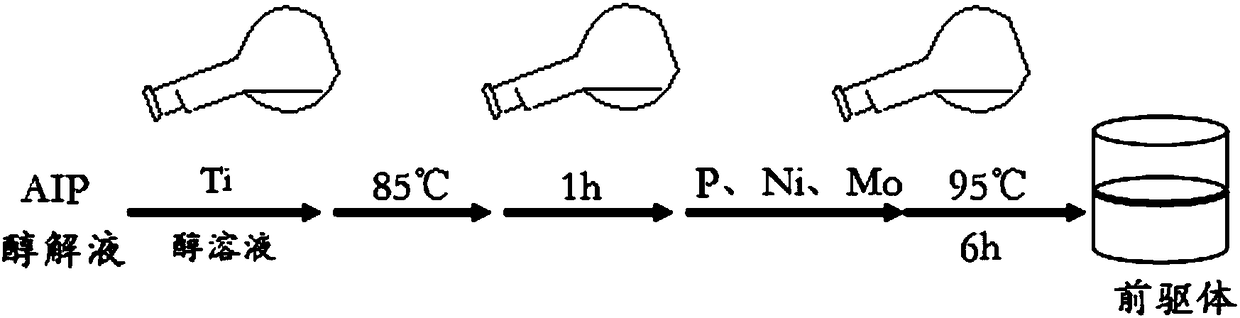
The invention discloses a hydrocracking catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The hydrocracking catalyst includes an active component and a carrier, wherein the active component is NiO and WO3 and the carrier is a composite carrier of AlOOH and TiO2; an additive contains phosphorus; the catalyst is prepared through a complete liquid-phase process. In the invention, when the hydrocracking catalyst is used for hydrocracking of medium / low-temperature coal tar, conversion to light fraction is greatly improved on the basis of guaranteeing high liquid yield, wherein H / C molar ratio of the coaltar is increased from 1.153 to more than 1.556 (fuel oil), even to 1.603 when the catalyst is optimized. The hydrocracking catalyst solves difficult problems that a fixed bed catalyst in the prior artis difficult to industrialize due to surface coking and inactivation caused by non-uniform heat distribution in a bed layer; the preparation method has simple process and simple operations.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Catalytic cracking aid for increasing propylene yield, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107970982AGood catalytic cracking performanceHigh yieldCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveDry basis
The present discloses a catalytic cracking aid for increasing propylene yield, and a preparation method thereof, wherein the catalytic cracking aid comprises 10-75 wt% of a phosphorus-containing MFI structure molecular sieve (calculated as the dry base weight), 3-40 wt% of a phosphorus-aluminum inorganic binder (calculated as the dry base weight), 1-30 wt% of other inorganic binder (calculated asthe oxide), and 0-60 wt% of second clay (calculated as the dry base weight) by using the dry base weight of the catalytic cracking aid as the reference. According to the present invention, the catalytic cracking aid can effectively improve propylene yield and propylene selectivity in the catalytic cracking.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalytic cracking aid capable of improving octane barrels of gasoline and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107971031AGood catalytic cracking performanceBoost octaneCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsManganeseChemistry
The invention discloses a catalytic cracking aid capable of improving the octane barrels of gasoline and a preparation method thereof. The catalytic cracking aid comprises, on the basis of dry base weight, 10 to 75 wt% of a MFI-structure molecular sieve containing phosphorus and loading metal in terms of the dry base weight, 3 to 40 wt% of a phosphorus-aluminum inorganic binder in terms of the drybase weight, 1 to 30 wt% of other inorganic binder in terms of oxide, 0 to 60 wt% of second clay in terms of the dry base weight and 0.5 to 15 wt% of a metallic additive in terms of oxide, wherein the metallic additive is at least one selected from a group consisting of group-VIII metal, manganese, zinc and gallium. When the catalytic cracking aid is applied to catalytic cracking process, the octane number of the gasoline is improved by increasing the content of isohydrocarbons in gasoline, and the yield of the gasoline is almost maintained unchanged, so the octane barrels of the gasoline areimproved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Modified Y zeolite and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106145154AHigh crystallinityLarge specific surface areaCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic solventRare earth
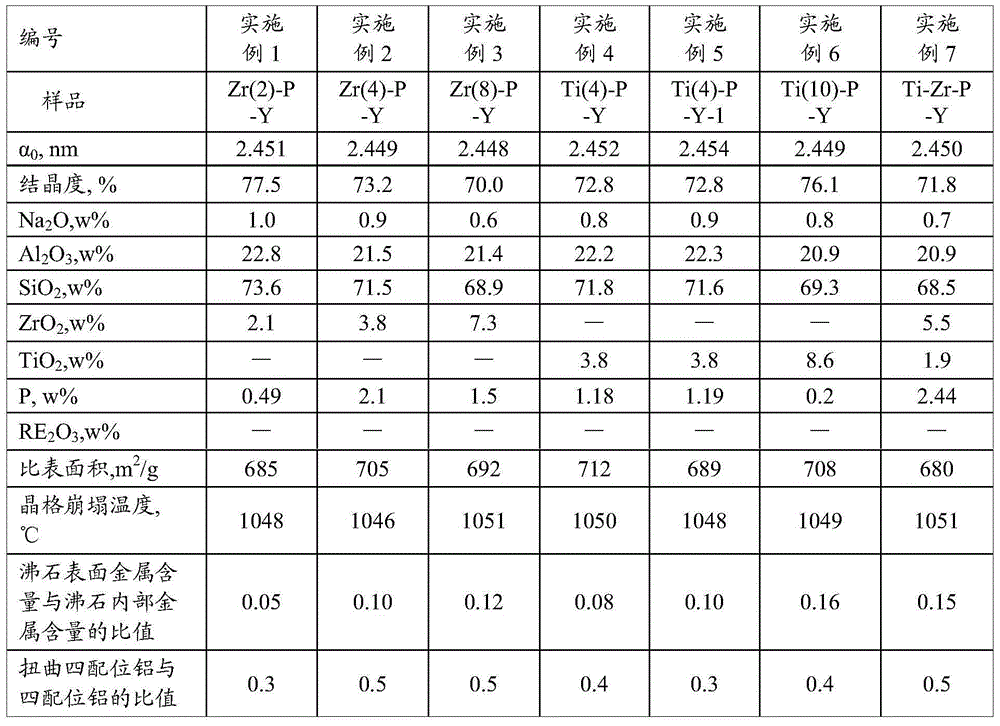
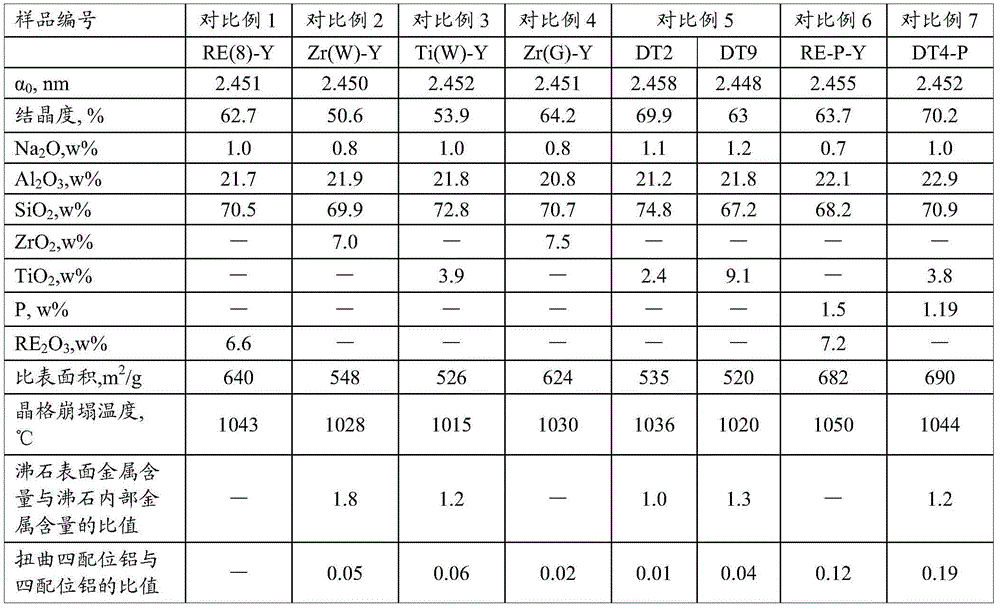
The invention provides modified Y zeolite and a preparation method thereof. The modified Y zeolite contains 1-15 wt% of IVB family metal according to oxide and 0.1-10.0 wt% of phosphorus according to P. The ratio of the content of metal on the surface of the zeolite to the content of metal in the zeolite is not higher than 0.2. The preparation method of the modified Y zeolite includes the steps of processing Y zeolite with water content not exceeding 5 wt% through organic solvent and modified metallic compound, conducting calcinating, and then conducting processing through a phosphorous containing compound and acid. The modified Y zeolite has heat and hydrothermal stability not lower than that of the rare earth modified Y zeolite and has higher coke selectivity.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
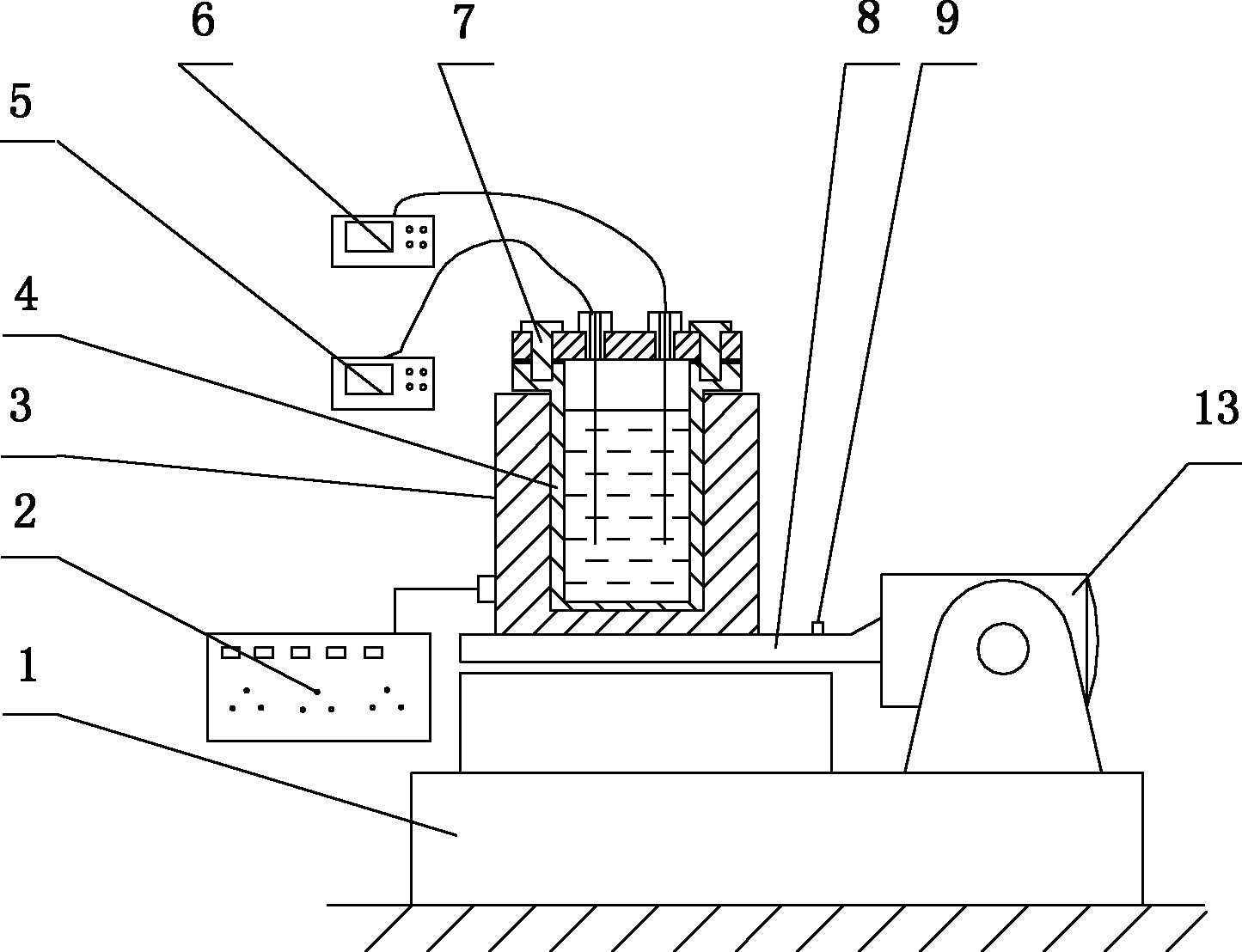
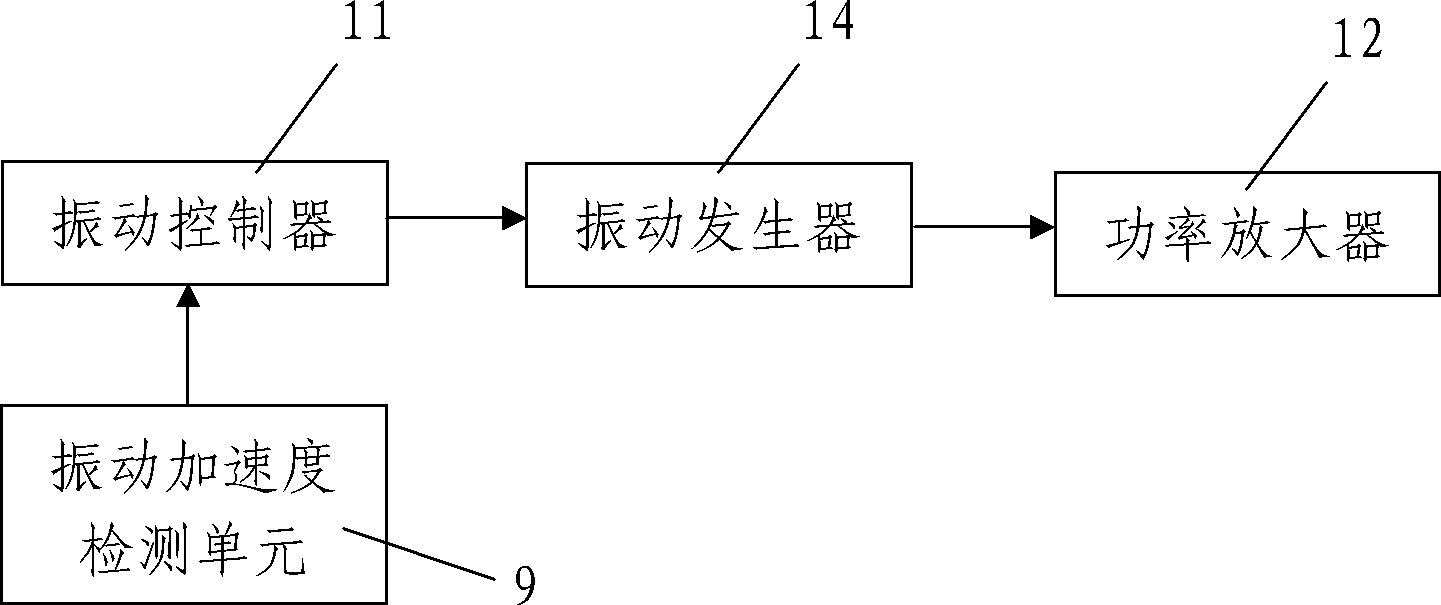
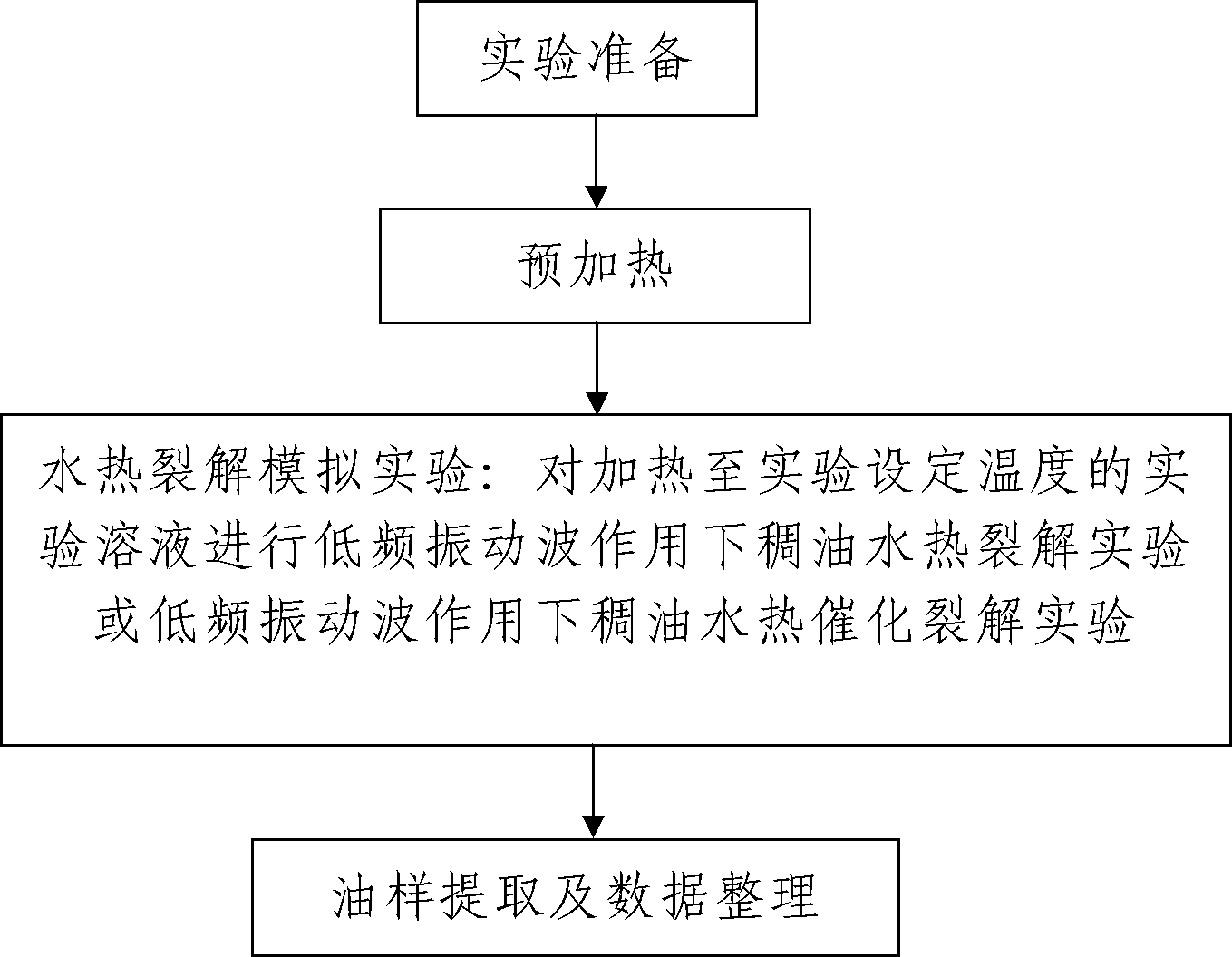
Experimental device and method for thick oil water thermal-catalytic cracking under effect of low frequency vibration waves
ActiveCN102628351ASimple structureEasy to operateSurveyFluid removalExperimental methodsVibration acceleration
The invention discloses an experimental device and a method for thick oil water thermal-catalytic cracking under the effect of low frequency vibration waves. The experimental device comprises a reaction tank, a constant temperature heating device, a temperature detecting unit, a pressure detecting unit, an electric vibration experiment stand and a vibration acceleration detecting unit, wherein the electric vibration experiment stand is used for driving the reaction tank to continuously vibrate up and down together with the constant temperature heating device; the vibration acceleration detecting unit is used for detecting the vibration acceleration of the electric vibration experiment stand in a real time manner; the reaction tank is placed in the constant temperature heating device and integrally assembled with the constant temperature heating device; the constant temperature heating device is fixed on the electric vibration experiment stand; and the vibration frequency of the electric vibration experiment stand is 5-500 Hz; and the experimental method comprises the following steps: (1) experiment preparation, (2) preheating, (3) thick oil water thermal cracking experiment under the effect of the low frequency vibration waves, and (4) oil sample extraction and data organization. The invention has the advantages of reasonable design, convenience for mounting and laying, complete functions, simplicity and convenience in use and operation, good use effect and capability of solving various actual problems in the thick oil recovery process.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Catalytic cracking aid capable of improving octane barrels of gasoline and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107970984AGood catalytic cracking performanceBoost octaneCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveCracking reaction
The invention discloses a catalytic cracking aid capable of improving the octane barrels of gasoline and a preparation method thereof. The catalytic cracking aid comprises, on the basis of dry base weight, 10 to 75 wt% of a phosphorus-containing MFI-structure molecular sieve in terms of the dry base weight, 3 to 40 wt% of a phosphorus-aluminum inorganic binder in terms of the dry base weight, 1 to30 wt% of other inorganic binder in terms of oxide and 0 to 60 wt% of second clay in terms of the dry base weight. The catalytic cracking aid provided by the invention has good catalytic cracking performance; and when the aid is blended with a main agent and applied to catalytic cracking reactions of hydrocarbon oil, the octane barrels of catalytically cracked gasoline can be improved and the content of isohydrocarbons in the gasoline is substantially increased, so the octane number of the gasoline is improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalytic cracking aid for increasing propylene yield, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107971029AGood catalytic cracking performanceHigh yieldCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveManganese
The present discloses a catalytic cracking aid for increasing propylene yield, and a preparation method thereof, wherein the catalytic cracking aid comprises 10-75 wt% of a phosphorus-containing MFI structure molecular sieve (calculated as the dry base weight), 3-40 wt% of a phosphorus-aluminum inorganic binder (calculated as the dry base weight), 1-30 wt% of other inorganic binder (calculated asthe oxide), 0-60 wt% of second clay (calculated as the dry base weight), and 0.5-15 wt% of at least a metal additive (calculated as the oxide) selected from a group VIII metal, manganese, zinc and gallium by using the dry base weight of the catalytic cracking aid as the reference. According to the present invention, the catalytic cracking aid can effectively improve propylene yield and propylene selectivity in the catalytic cracking.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
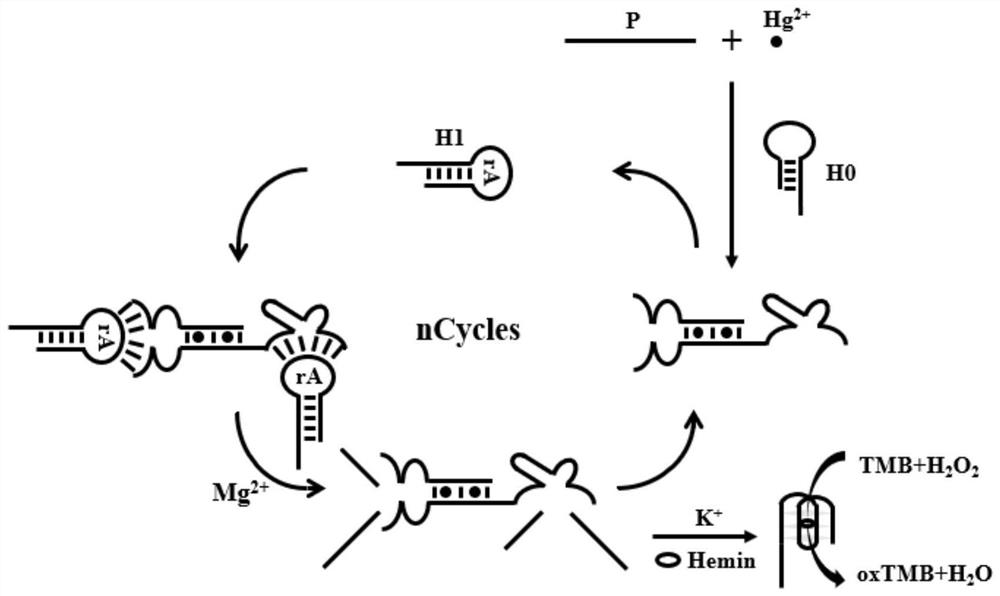
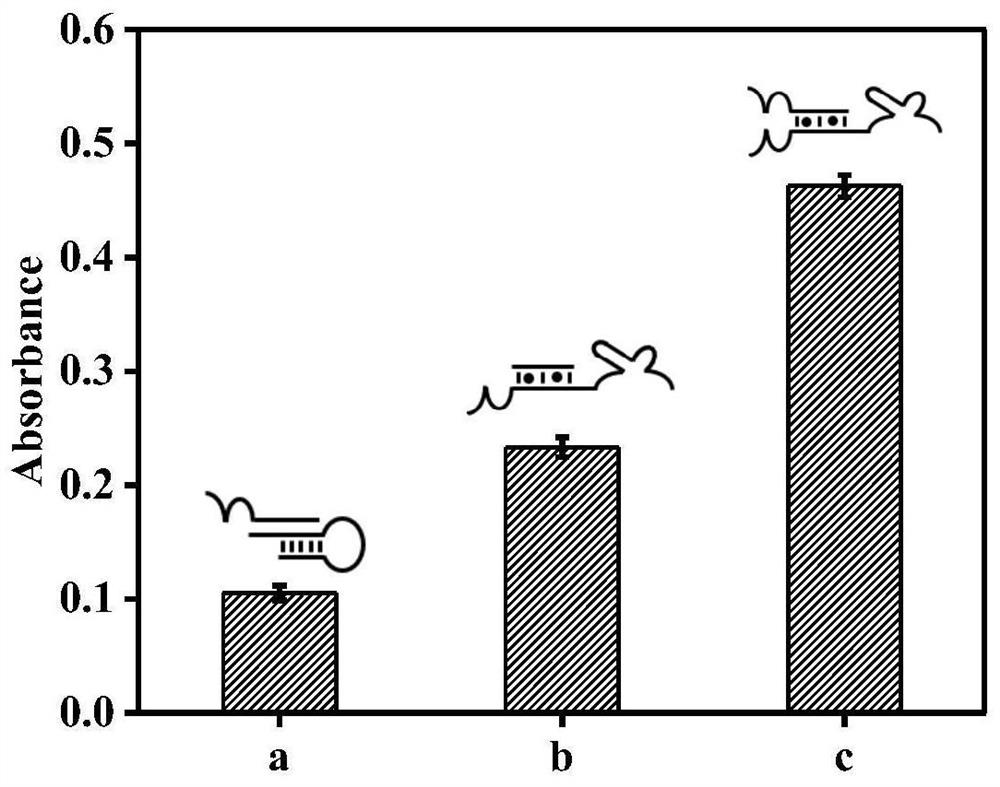
Mercury ion detection method assisted by mimic enzyme and kit
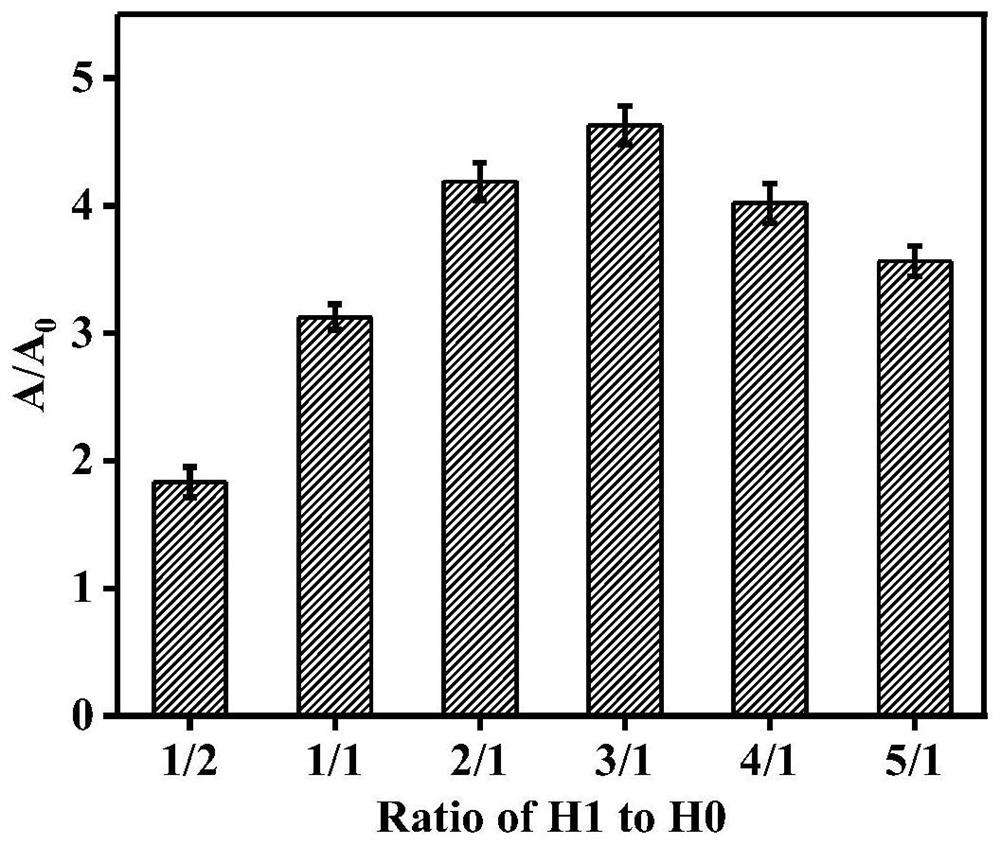
ActiveCN112924406ARealize detectionEasy to operateMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsMercuric ionHemin
The invention provides a mercury ion detection method using DNAzyme to assist amplification to generate signals and a kit. The detection method comprises an auxiliary probe P, a hairpin probe H0 and a hairpin probe H1. The auxiliary probe P and the hairpin probe H0 are combined to form two independent DNAzyme in the presence of mercury ions, the hairpin probe H1 of modified ribonuclease (rA) is subjected to catalytic cracking, and a large amount of desoxyribonucleic acid sequences rich in guanine (G) are released. In hemin (hemin) and a potassium ion solution, the released sequence forms a G-quadruplex DNA enzyme to catalyze a H2O2 mediated chromogenic substrate 3, 3', 5, 5'-tetramethyl benzidine for color development, and H2SO4 is used for termination, so that a stable yellow solution is formed. The method is used for detecting mercury ions in drinking water, has the characteristics of high sensitivity, strong specificity, low cost, simplicity in operation and the like, and has a wide application prospect in actual sample detection.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Vacuum residue processing method
InactiveCN101928597AHigh yieldGood catalytic cracking performanceTreatment with plural serial stages onlyReaction temperatureFuel oil
The invention relates to a processing method, which comprises the following steps of: coking vacuum residue serving as a raw material, denitrifying and refining coker gatch and performing catalytic cracking. The combination process improves coking processing capability, improves the yield of the coker gatch, reduces the yield of coke and improves liquid yield by reducing delayed coking recycle ratio of the vacuum residue, reaction temperature and tower top pressure, and improves the catalytic cracking property of the coker gatch by removing nitride from the coker gatch; the increased coker gatch is used as the catalytic cracking raw material instead of heavy oil; the vacuum residue does not enter a catalytic cracking device; and the total light oil yield is improved.
Owner:涿州贝尔森生化科技发展有限公司 +1
Iron modified sheet type ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst preparation method
ActiveCN108262061AAdaptableHigh catalytic cracking performanceMolecular sieve catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationSiliconFerric
An iron modified sheet type ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst preparation method includes: subjecting an aluminum source to inertia or activating treatment; adding the treated aluminum source to glue solution prepared from a silicon source and a template agent to prepare a gel mixture under the condition of stirring, wherein mole composition of the gel mixture includes: SiO2 / Al2O3=10-1000, Na2O / SiO2=0-0.5, R / SiO2=0.2-2.0, H2O / SiO2=8-100, and R refers to the template agent; well mixing the gel mixture with an iron source to obtain iron modified gel, wherein the iron source accounts for 1%-10% of the totalmass of the iron modified gel; subjecting the prepared iron modified gel to hydrothermal crystallization, and subjecting solid obtained in crystallization to filtering, washing, drying and calciningto obtain iron modified sheet type ZSM-5 zeolite. The method has advantages that introduction of the template agent and a guide agent is avoided; different iron sources are adopted for modification toobtain products through a one-step method; product synthesis is realized without subsequent modification.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Core-shell metal hybrid silicate-1/SAPO-5 composite molecular sieve ceramic membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108816269AImprove completenessHigh film forming efficiencyCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveSeed crystal
The invention relates to a core-shell metal hybrid silicate-1 / SAPO-5 composite molecular sieve ceramic membrane and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the core-shell metal hybridsilicate-1 / SAPO-5 composite molecular sieve ceramic membrane comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a silicate-1 molecular sieve synthesis solution; (2) preparing an SAPO-5 molecular sieve synthesis solution; (3) preparing core-shell metal hybrid silicate-1 / SAPO-5 molecular sieve composite seed crystals; (4) preparing the core-shell metal hybrid silicate-1 / SAPO-5 composite molecular sieve ceramic membrane. The preparation method is simple in process, shorter in consumed time, lower in cost and higher in membrane forming rate.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Catalytic cracking assistant for improving gasoline octane number barrel yield and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107583670AGood catalytic cracking performanceBoost octaneCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveManganese
The invention discloses a catalytic cracking assistant for improving gasoline octane number barrel yield and a preparation method thereof. Based on a dry base weight, the assistant comprises 10-75wt%of an MFI structural molecular sieve containing phosphorus and loaded metal in terms of the dry base weight, 3-40wt% of a phosphorus aluminum inorganic binder in terms of the dry base weight, 1-30wt%of other inorganic binder in terms of oxide, 0-60wt% of second clay in terms of the dry base weight, and 0.5-15wt% of a metal additive selected from at least one of VIII group metals and manganese, zinc, gallium. The assistant provided by the invention can be applied to a catalytic cracking process to increase the content of isohydrocarbon in gasoline so as to increase the gasoline octane number,and at the same time can maintain the gasoline yield basically unchanged, thus improving the gasoline octane number barrel yield.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalytic cracking aid for increasing propylene yield, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107971022AGood catalytic cracking performanceHigh yieldCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveDry basis
The present discloses a catalytic cracking aid for increasing propylene yield, and a preparation method thereof, wherein the catalytic cracking aid comprises 10-75 wt% of a phosphorus-containing and loaded-metal-containing IMF structure molecular sieve (calculated as the dry base weight), 3-40 wt% of a phosphorus-aluminum inorganic binder (calculated as the dry base weight), 1-30 wt% of other inorganic binder (calculated as the oxide), and 0-60 wt% of second clay (calculated as the dry base weight) by using the dry base weight of the catalytic cracking aid as the reference. According to the present invention, the catalytic cracking aid can effectively improve propylene yield and propylene selectivity in the catalytic cracking.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
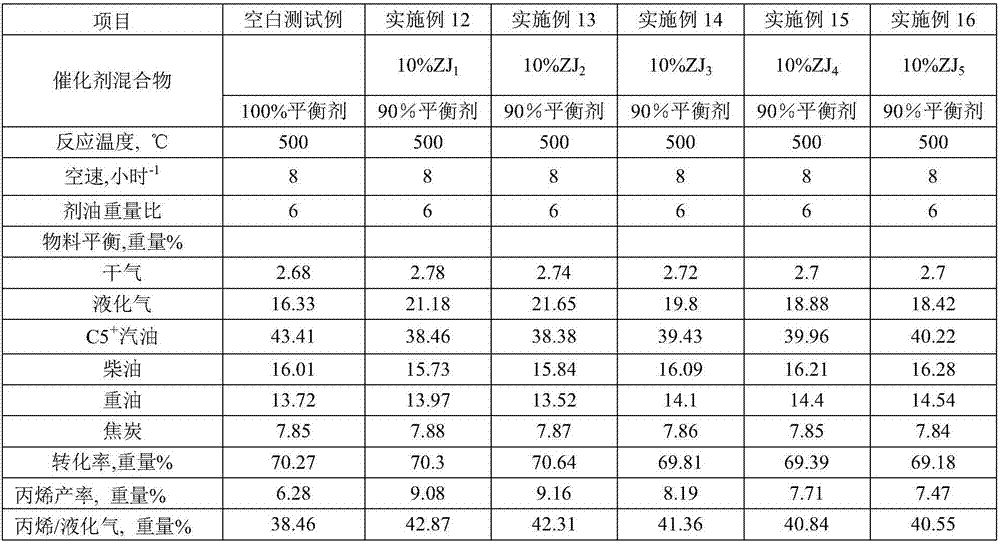
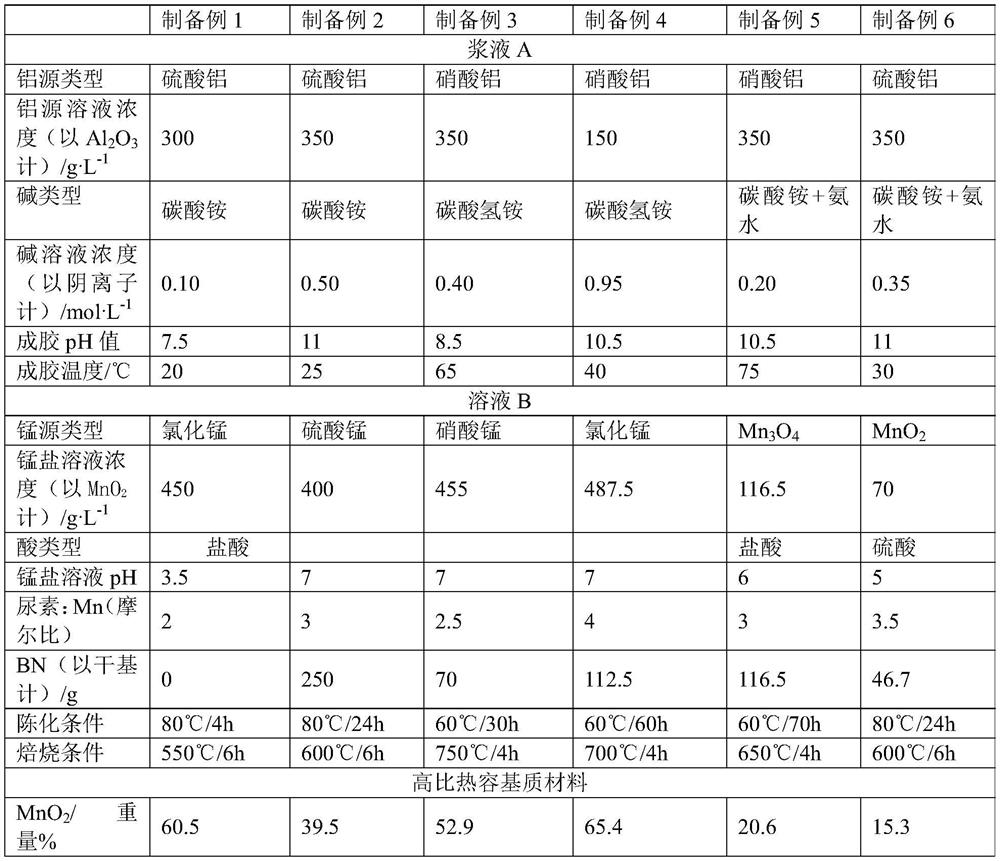
Catalytic cracking multifunctional metal trapping agent and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114425295AEasy accessImprove adsorption capacityCatalytic crackingCatalyst protectionPhysical chemistryEconomic benefits
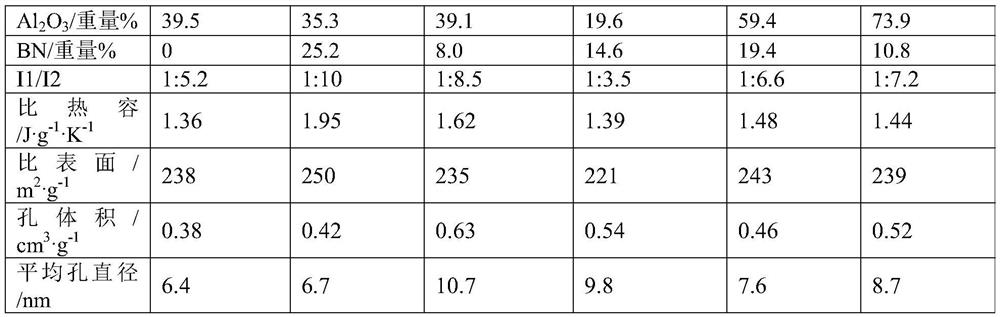
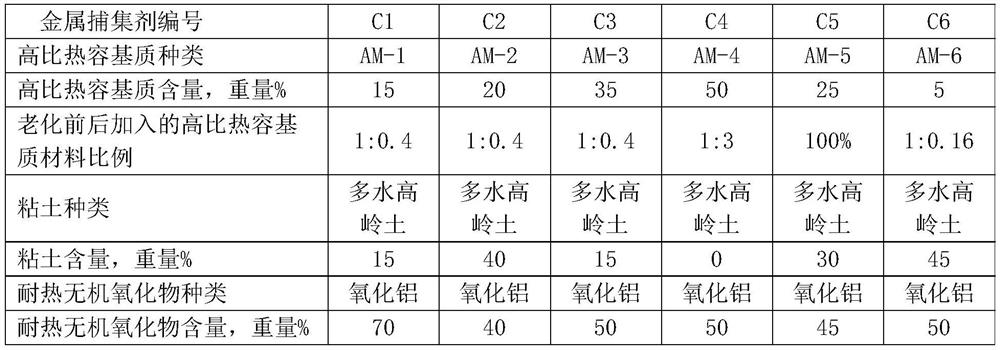
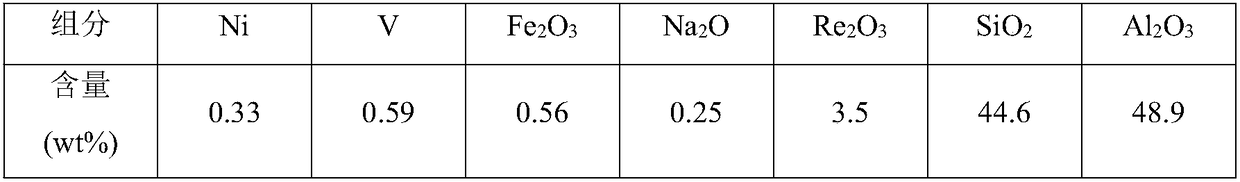
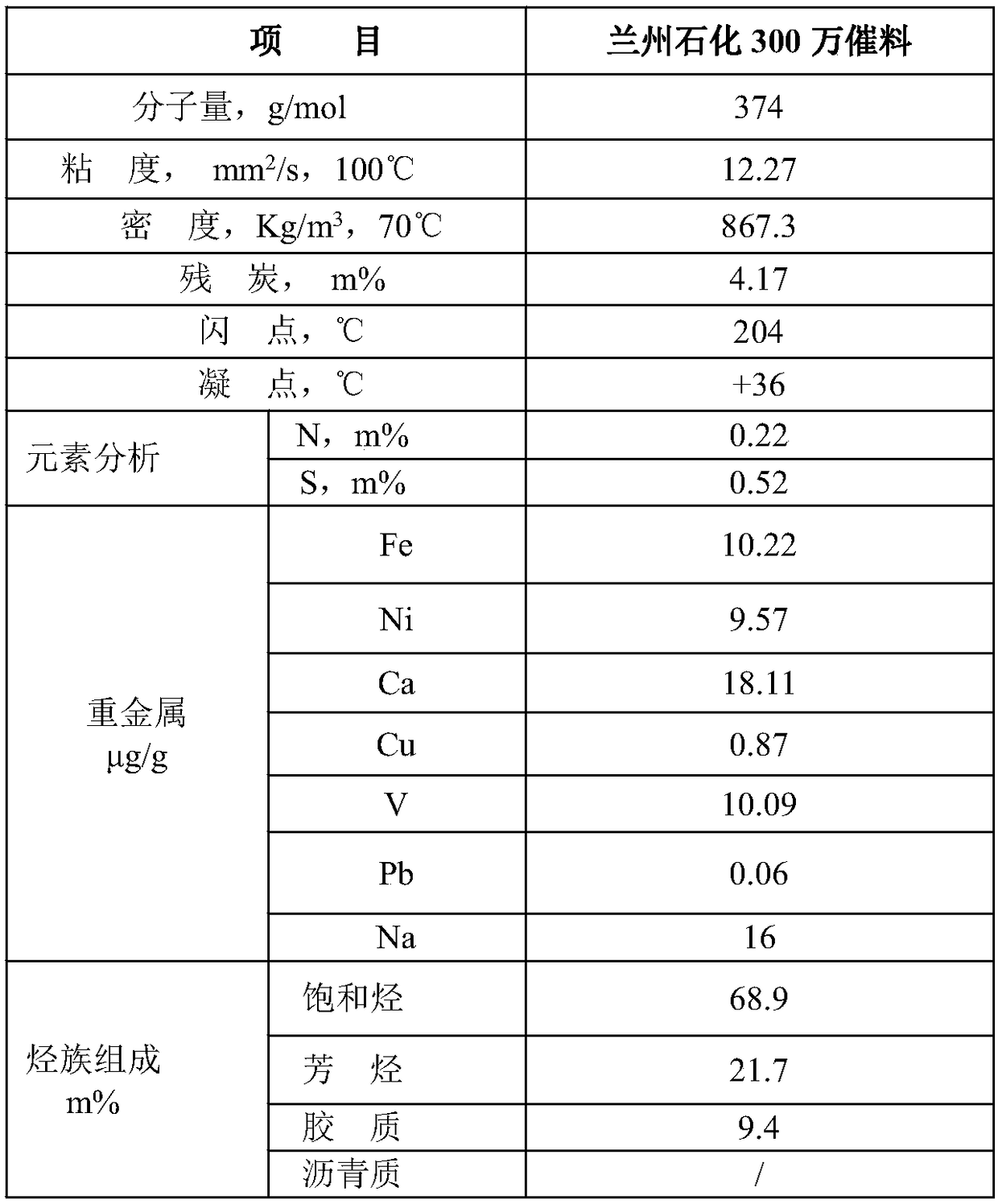
The invention provides a catalytic cracking multifunctional metal trapping agent and a preparation method thereof. The metal trapping agent contains 1-60 wt% of a high specific heat capacity matrix material, 40-99 wt% of a heat-resistant inorganic oxide and 0-50 wt% of clay, wherein the high specific heat capacity matrix material contains at least 5% by weight of manganese oxide, and the specific heat capacity of the high specific heat capacity matrix material is 1.3-2.0 J / (g.K). The preparation method of the high specific heat capacity matrix material comprises the steps of forming a mixture from preparation raw materials comprising a manganese source, and optionally washing and / or drying and / or roasting. The metal trapping agent provided by the invention can be used for processing hydrocarbon oil raw materials which are high in carbon residue value and contain various metals, can effectively trap the metals in the raw materials, is environment-friendly and pollution-free in components, and has good economic benefits.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
FCC equilibrium catalyst reactivation and modification method
ActiveCN109382146AHigh catalytic cracking activityGood choiceCatalytic crackingCatalyst regeneration/reactivationPhosphorIon exchange
The invention discloses an FCC equilibrium catalyst reactivation and modification method. The method comprises following steps: (1) ammonium ion exchange: mixing an FCC equilibrium catalyst with water, carrying out pulping to prepare FCC equilibrium catalyst slurry, heating the slurry to a temperature of 50 to 95 DEG C, mixing the slurry with ammonium salts, carrying out ammonium ion exchange for1 to 3 hours under stirring, and performing filtering, washing, and drying, wherein after ammonium ion exchange, the Na2O content of the FCC equilibrium catalyst is reduced to 0.2 wt% or less; and (2)mixing the FCC equilibrium catalyst, which has a Na2O content of 0.2 wt% or less and is obtained in the step (1), with water, carrying out pulping, mixing obtained slurry with magnesium salts and phosphor containing compounds, stirring, carrying out co-precipitation for 10 to 60 minutes, and finally performing filtering, drying, and burning to obtain reactivated FCC equilibrium catalyst. The provided method can recover the catalytic cracking activity of an FCC equilibrium catalyst and improves the selectivity of cracking products. The method is simple, is easy to perform and is environmentally friendly at the same time.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Nanocluster mesoporous ZSM-5 molecular sieve and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN114804141AGood catalytic cracking performanceImproved ring-opening cleavage performanceNanotechnologyBulk chemical productionMolecular sieveSlurry
The invention belongs to the technical field of ZSM-5 molecular sieve preparation, and relates to a nanocluster mesoporous ZSM-5 molecular sieve and a preparation method thereof.The nanocluster mesoporous ZSM-5 molecular sieve particles are formed by stacking nanocrystals and have intercrystalline pores formed by stacking the nanocrystals, the average grain size of the nanocrystals is 80-120 nm, and the average grain size of the nanocrystals is 80-120 nm. The most probable aperture of the macropores of the nanocluster mesoporous ZSM-5 molecular sieve is 250 to 350 nm, and the most probable aperture of the mesopores of the nanocluster mesoporous ZSM-5 molecular sieve is 13 to 17 nm. The preparation method comprises the following steps: forming slurry containing a template machine and a silicon source under certain conditions, forming slurry containing alkali and an aluminum source, mixing the slurry containing the template machine and the silicon source and the slurry containing alkali and the aluminum source under certain conditions to form a synthetic liquid, crystallizing and recycling. The ZSM-5 molecular sieve has relatively good performance.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalytic cracking assistant for improving gasoline octane number barrel yield and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107583666AGood catalytic cracking performanceBoost octane barrelCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveAluminium
The invention discloses a catalytic cracking assistant for improving gasoline octane number barrel yield and a preparation method thereof. Based on a dry base weight, the assistant comprises 10-75wt%of an MFI structural molecular sieve containing phosphorus and loaded metal in terms of the dry base weight, 3-40wt% of a phosphorus aluminum inorganic binder in terms of the dry base weight, 1-30wt%of other inorganic binder in terms of oxide, and 0-60wt% of second clay in terms of the dry base weight. The assistant provided by the invention can be applied to a catalytic cracking process to increase the content of isohydrocarbon in gasoline so as to increase the gasoline octane number, and at the same time can maintain the gasoline yield basically unchanged, thus improving the gasoline octanenumber barrel yield.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalytic cracking aid capable of promoting yield increase of propylene, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107971006AGood catalytic cracking performanceHigh yieldCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveManganese
The invention discloses a catalytic cracking aid capable of promoting yield increase of propylene, and a preparation method thereof. The catalytic cracking aid comprises, on the basis of dry base weight, 10 to 75 wt% of an IMF-structure molecular sieve containing phosphorus and loading metal in terms of the dry base weight, 3 to 40 wt% of a phosphorus-aluminum inorganic binder in terms of the drybase weight, 1 to 30 wt% of other inorganic binder in terms of oxide, 0 to 60 wt% of second clay in terms of the dry base weight and 0.5 to 15 wt% of a metallic additive in terms of oxide, wherein themetallic additive is at least one selected from a group consisting of group-VIII metal, manganese, zinc and gallium. The aid provided by the invention can effectively improve propylene yield and propylene selectivity when applied to catalytic cracking.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
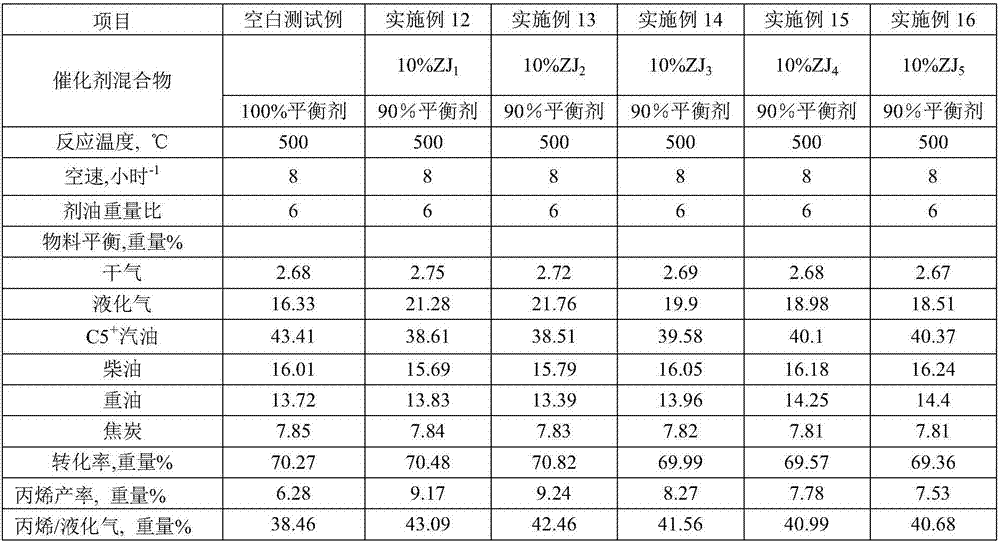
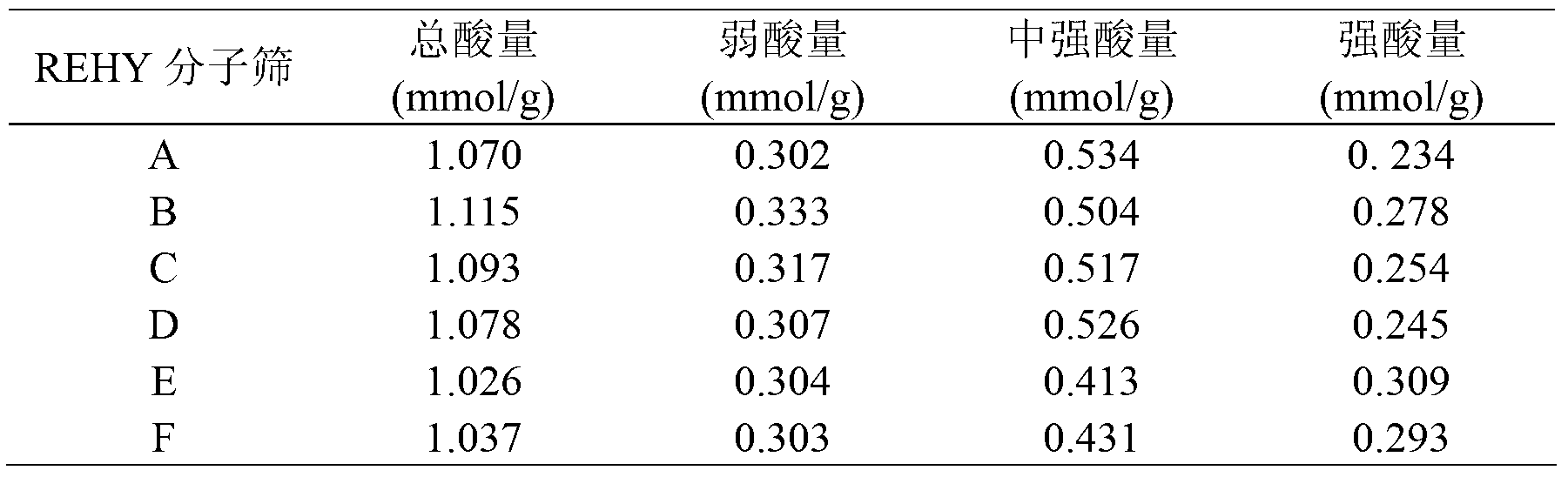
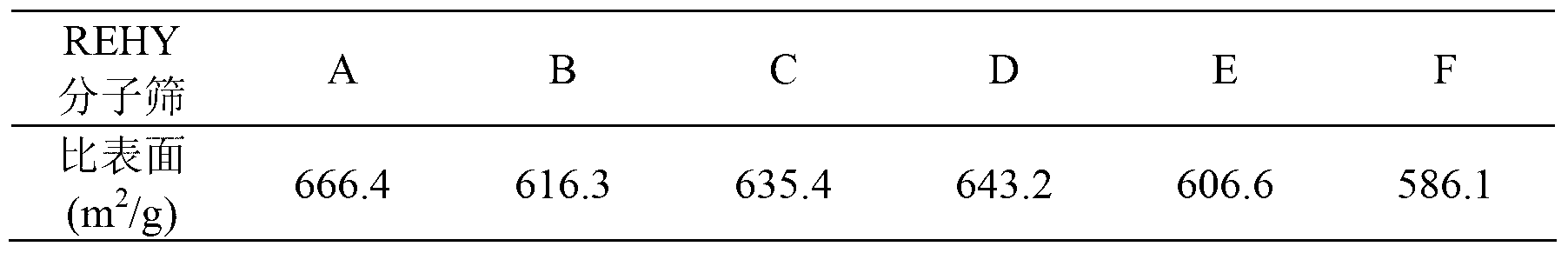
High temperature hydrothermal stability REHY molecular sieve, preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN103265052ASimple processSave energyMolecular sieve catalystsFaujasite aluminosilicate zeoliteMolecular sieveRare earth
The present invention discloses a high temperature hydrothermal stability REHY molecular sieve preparation method, which comprises: adopting NaY as a raw material, carrying out ammonium exchange, adopting step-by-step programmed temperature increase calcination, repeating the exchange and the calcination 4 times to obtain HY, and carrying out rare earth modification on the HY to obtain the molecular sieve. The method has characteristics of simple process, energy source saving and easy promotion. The obtained REHY molecular sieve has advantages of low Na content, high hydrothermal stability, high acid content, large specific surface and the like, has a high catalysis cracking performance in a catalytic cracking reaction, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com