Patents
Literature
1559results about "Treatment with plural serial stages only" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
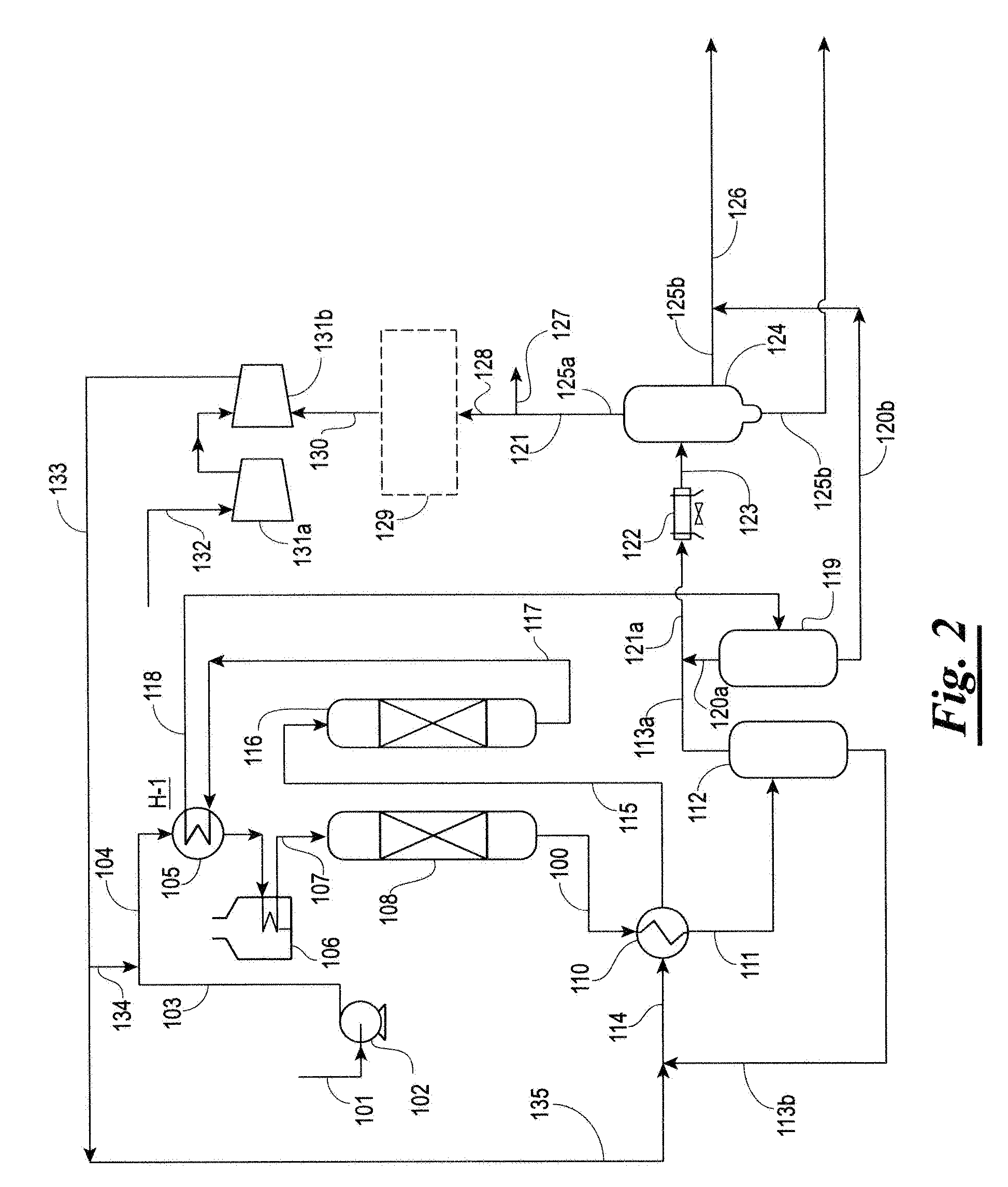
Process for Co-Producing Jet Fuel and LPG from Renewable Sources
ActiveUS20080244962A1Improve cold flowHydrocarbon by hydrogenationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionEngineeringRenewable resource
The present invention generally relates to a method for producing an isoparaffinic product useful as jet fuel from a renewable feedstock. The method may also include co-producing a jet fuel and a liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) fraction from a renewable feedstock. The method includes hydrotreating the renewable feedstock to produce a hydrotreating unit heavy fraction that includes n-paraffins and hydroisomerizing the hydrotreating unit heavy fraction to produce a hydroizomerizing unit heavy fraction that includes isoparaffins. The method also includes recycling the hydroisomerizing unit heavy fraction through the hydroisomerization unit to produce an isoparaffinic product that may be fractionated into a jet fuel and an LPG fraction. The present invention also relates to a jet fuel produced from a renewable feedstock having improved cold flow properties.
Owner:REG SYNTHETIC FUELS LLC
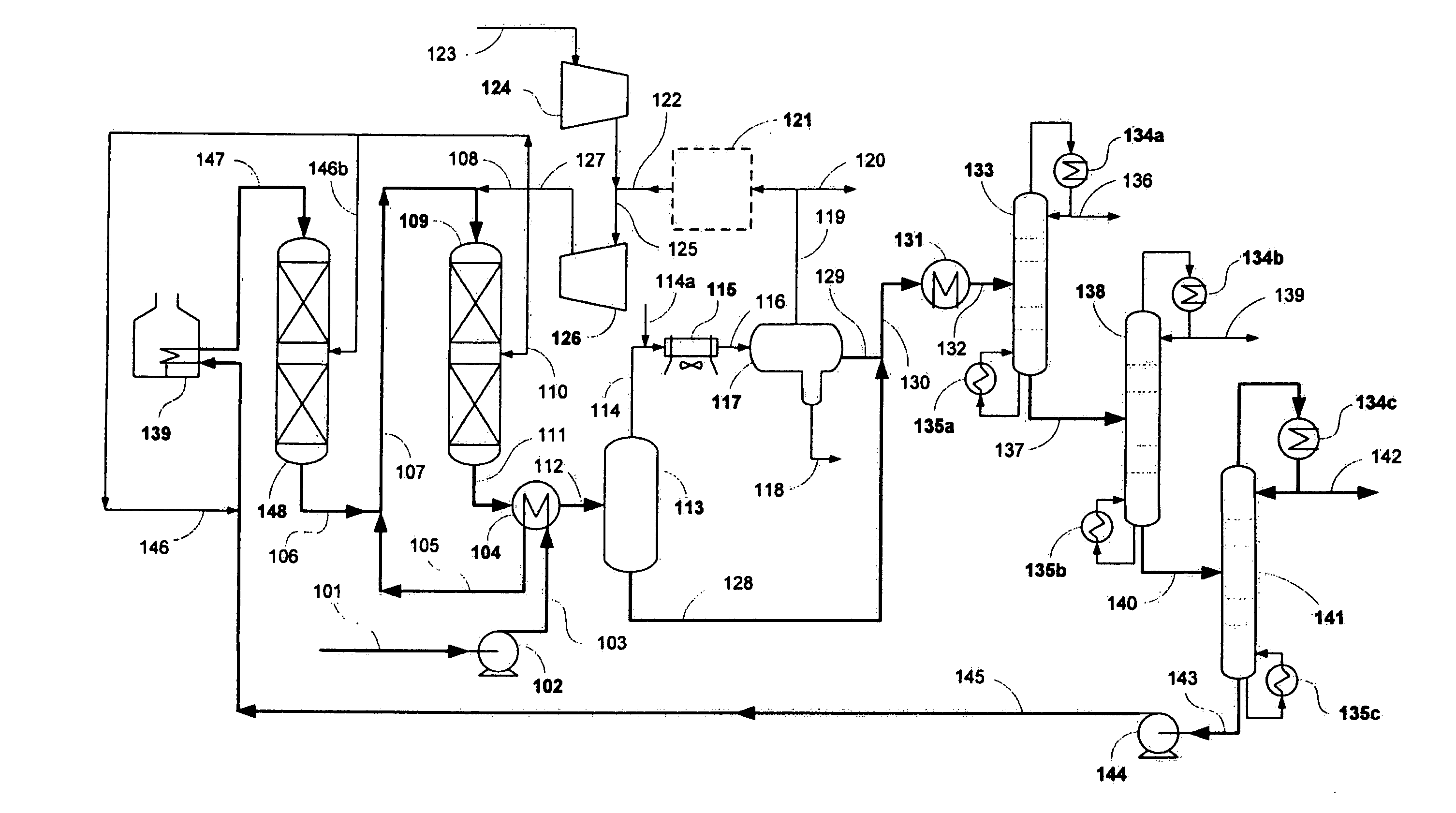
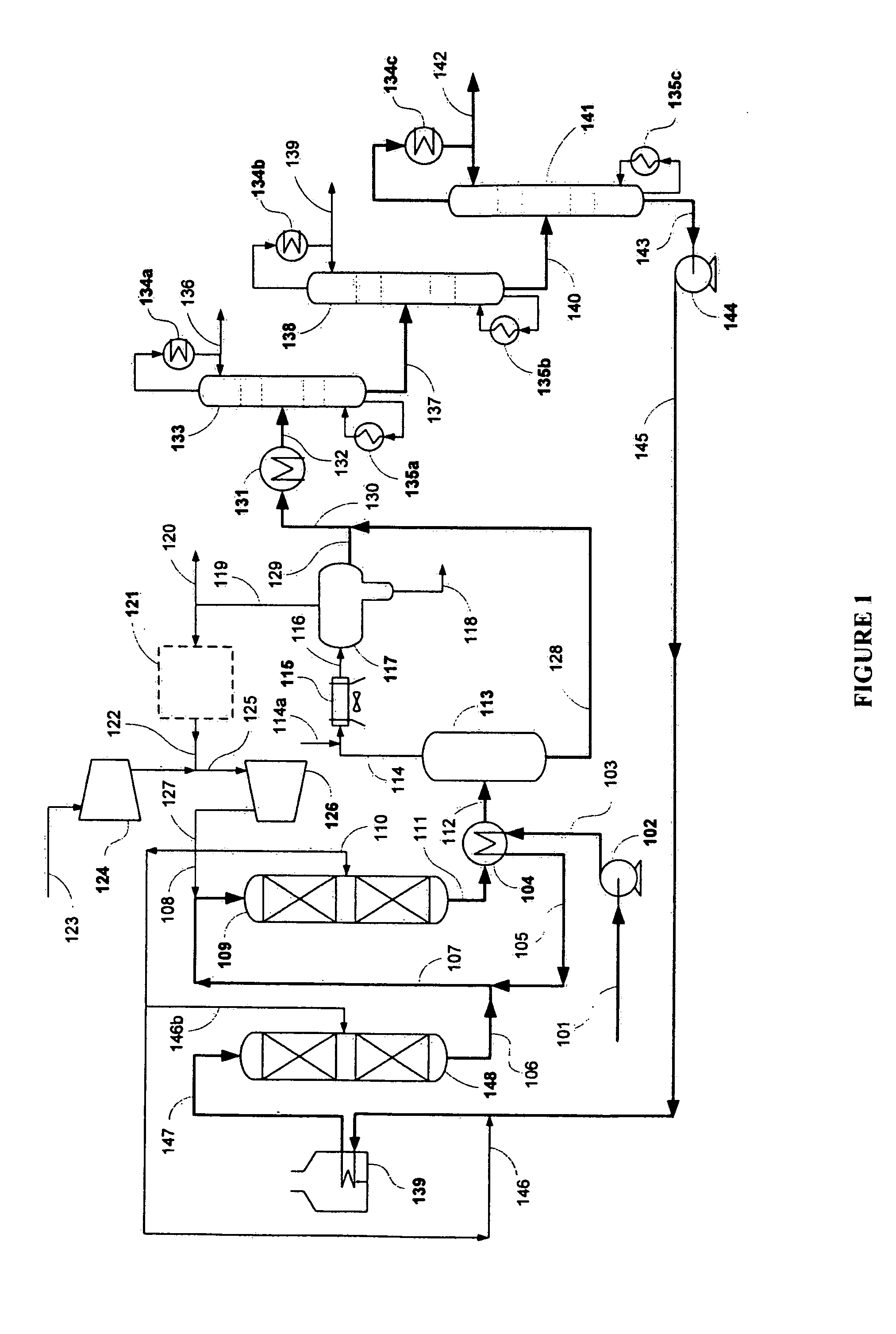
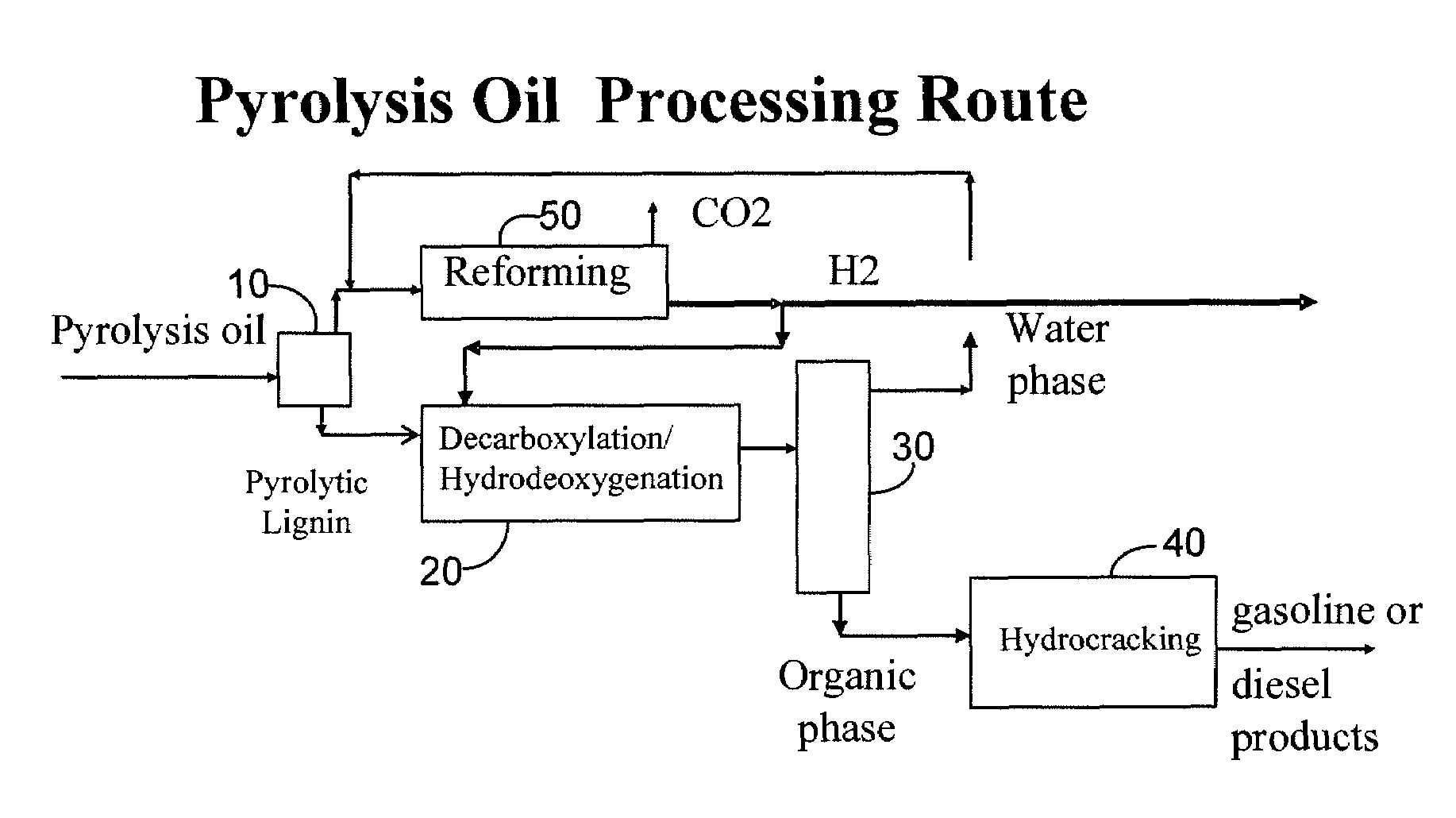
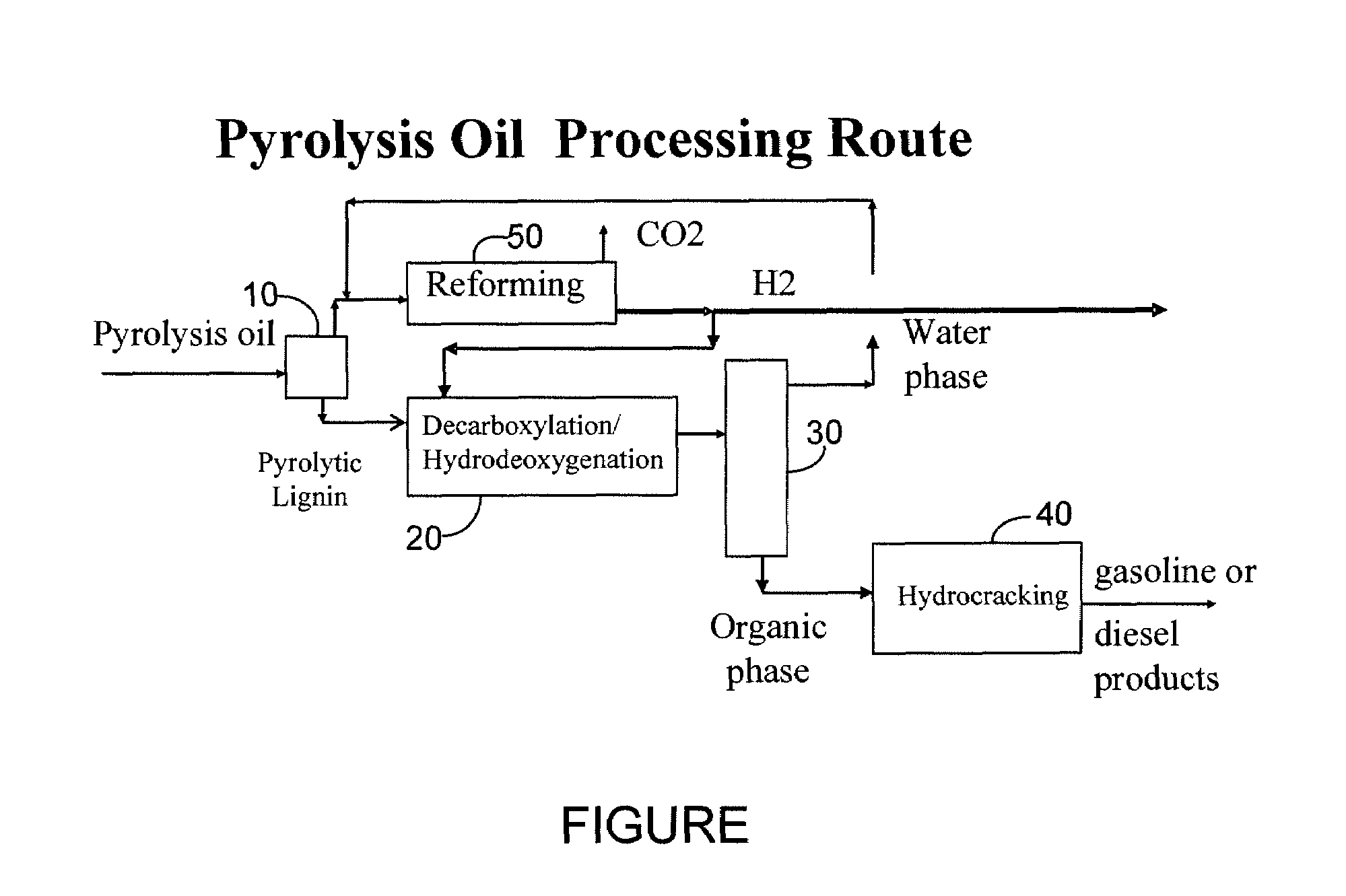
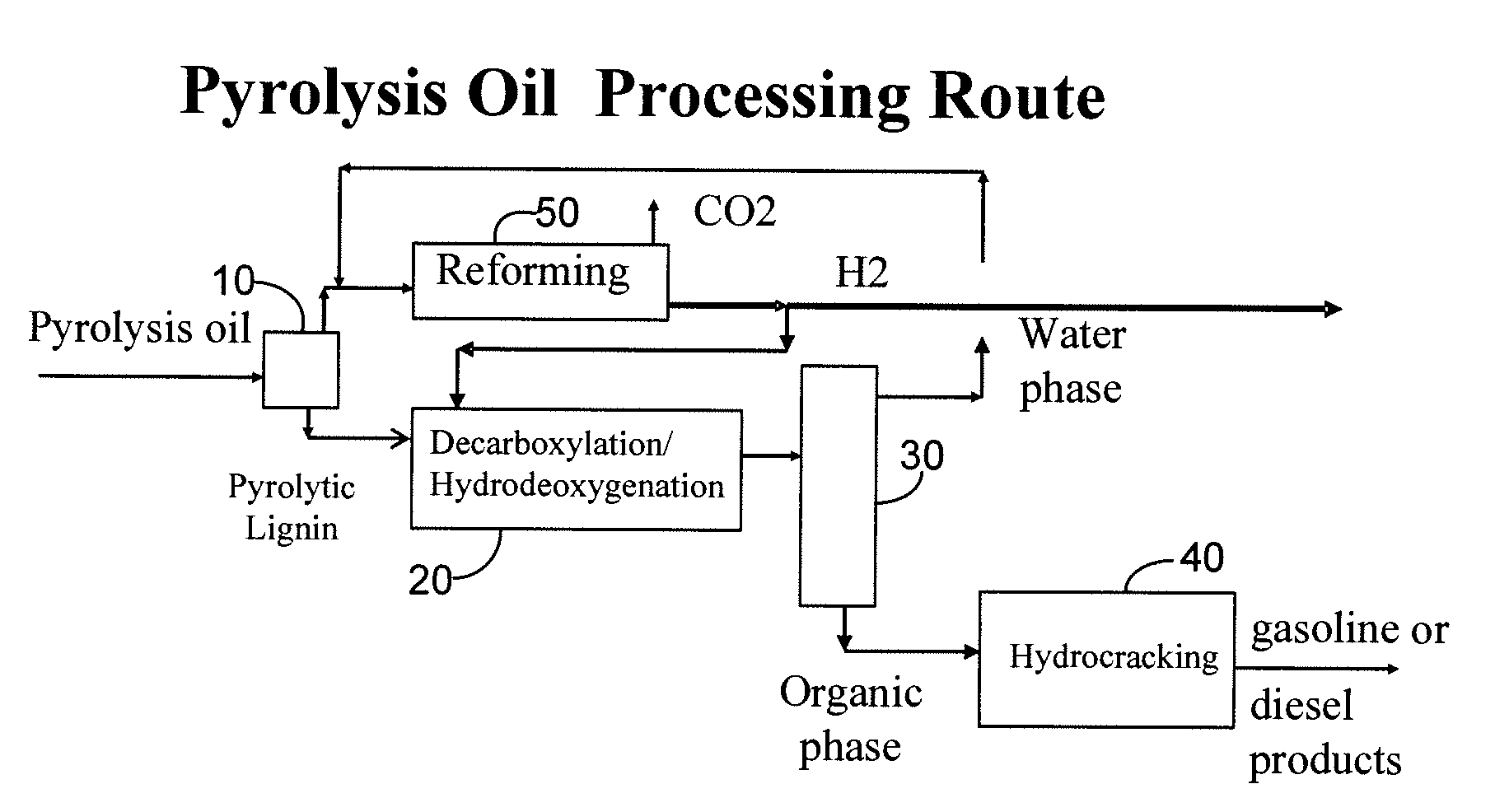
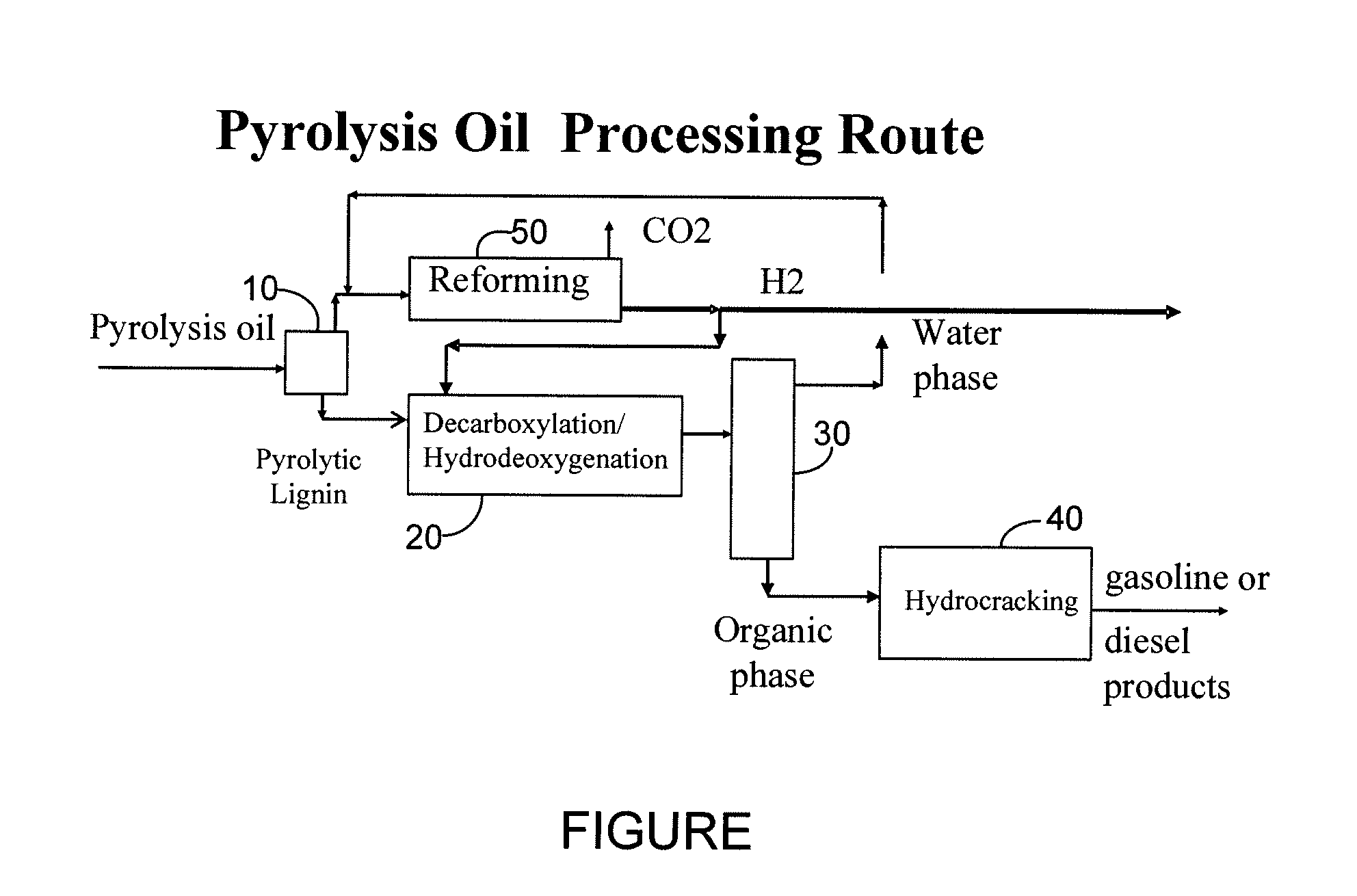
Gasoline and diesel production from pyrolytic lignin produced from pyrolysis of cellulosic waste
InactiveUS7578927B2Treatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyTreatment with plural serial stages onlyCelluloseNaphtha
A process for the conversion of biomass to a liquid fuel is presented. The process includes the production of diesel and naphtha boiling point range fuels by hydrocracking of pyrolysis lignin extracted from biomass.
Owner:UOP LLC
Complex comprising oxidative dehydrogenation unit
ActiveUS20140249339A1Consumes lotThermal non-catalytic crackingSequential/parallel process reactionsAlkaneDehydrogenation
Oxidative dehydrogenation of paraffins to olefins provides a lower energy route to produce olefins. Oxidative dehydrogenation processes may be integrated with a number of processes in a chemical plant such as polymerization processes, manufacture of glycols, and carboxylic acids and esters. Additionally, oxidative dehydrogenation processes can be integrated with the back end separation process of a conventional steam cracker to increase capacity at reduced cost.
Owner:NOVA CHEM (INT) SA
Production of Aviation Fuel from Renewable Feedstocks
ActiveUS20090283442A1Improve solubilityMinimize severityTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonIsomerizationBoiling point
A hydrocarbon product stream having hydrocarbons with boiling points in the aviation fuel range is produced from renewable feedstocks such as plant and animal oils. The process involves treating a renewable feedstock by hydrogenating, deoxygenating, isomerization, and selectively hydrocracking the feedstock to produce paraffinic hydrocarbons having from about 9 to about 16 carbon atoms and a high iso / normal ratio in a single reaction zone containing a multifunctional catalyst, or set of catalysts, having hydrogenation, deoxygenation, isomerization and selective hydrocracking functions.
Owner:UOP LLC
Premium synthetic lubricant base stock (Law734) having at least 95% noncyclic isoparaffins
A premium synthetic lubricating oil base stock having a high VI and low pour point is made by hydroisomerizing a Fischer-Tropsch synthesized waxy, paraffinic feed wax and then dewaxing the hydroisomerate to form a 650-750° F.+ dewaxate. The waxy feed has an initial boiling point in the range of about 650-750° F., from which it continuously boils up to at least 1050° F. and has a T90-T10 temperature difference of at least 350° F. The feed is preferably hydroisomerized without any pretreatment, other than optional fractionation. The 650-750° F.+ dewaxate is fractionated into two or more base stocks of different viscosity.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
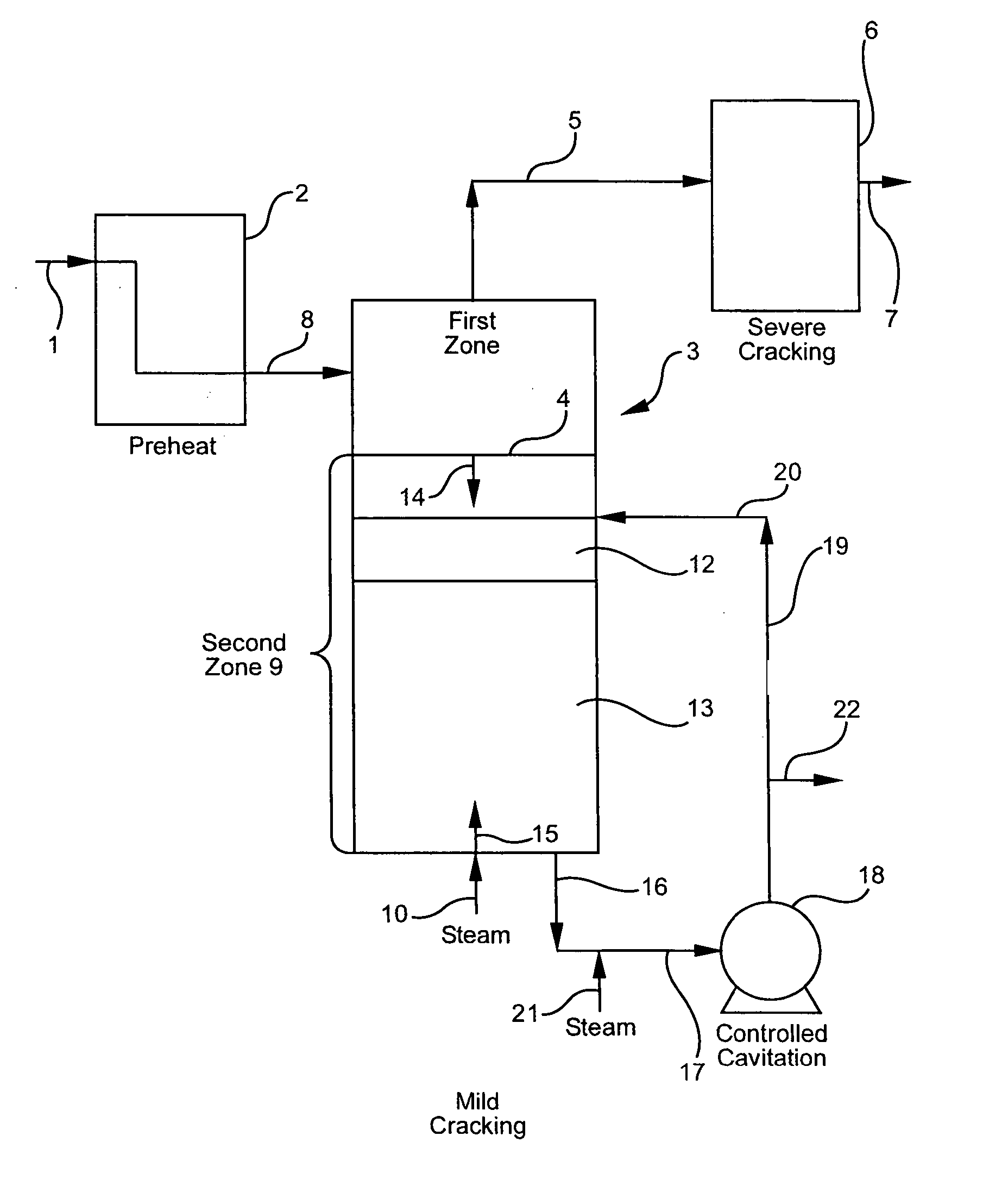
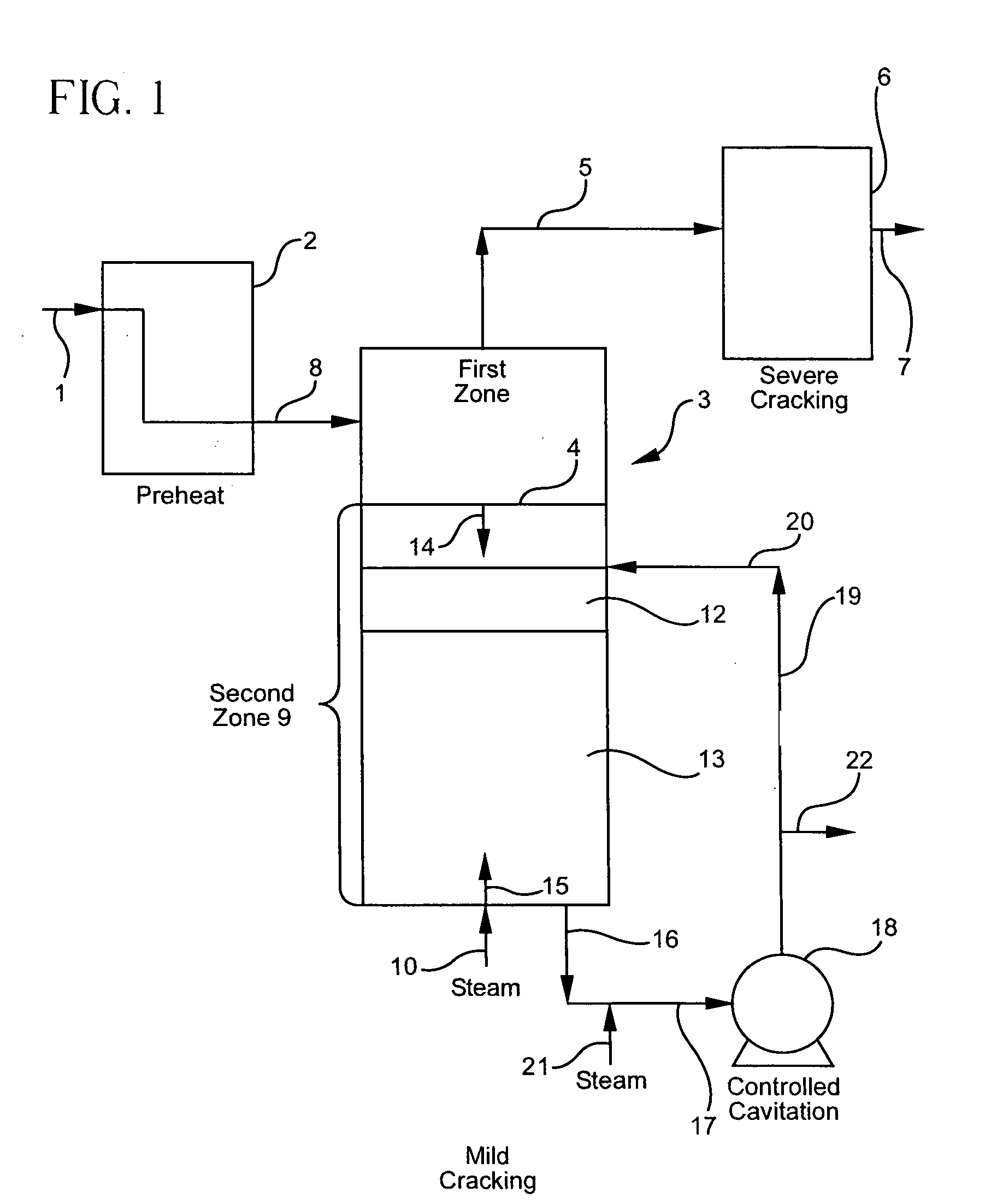
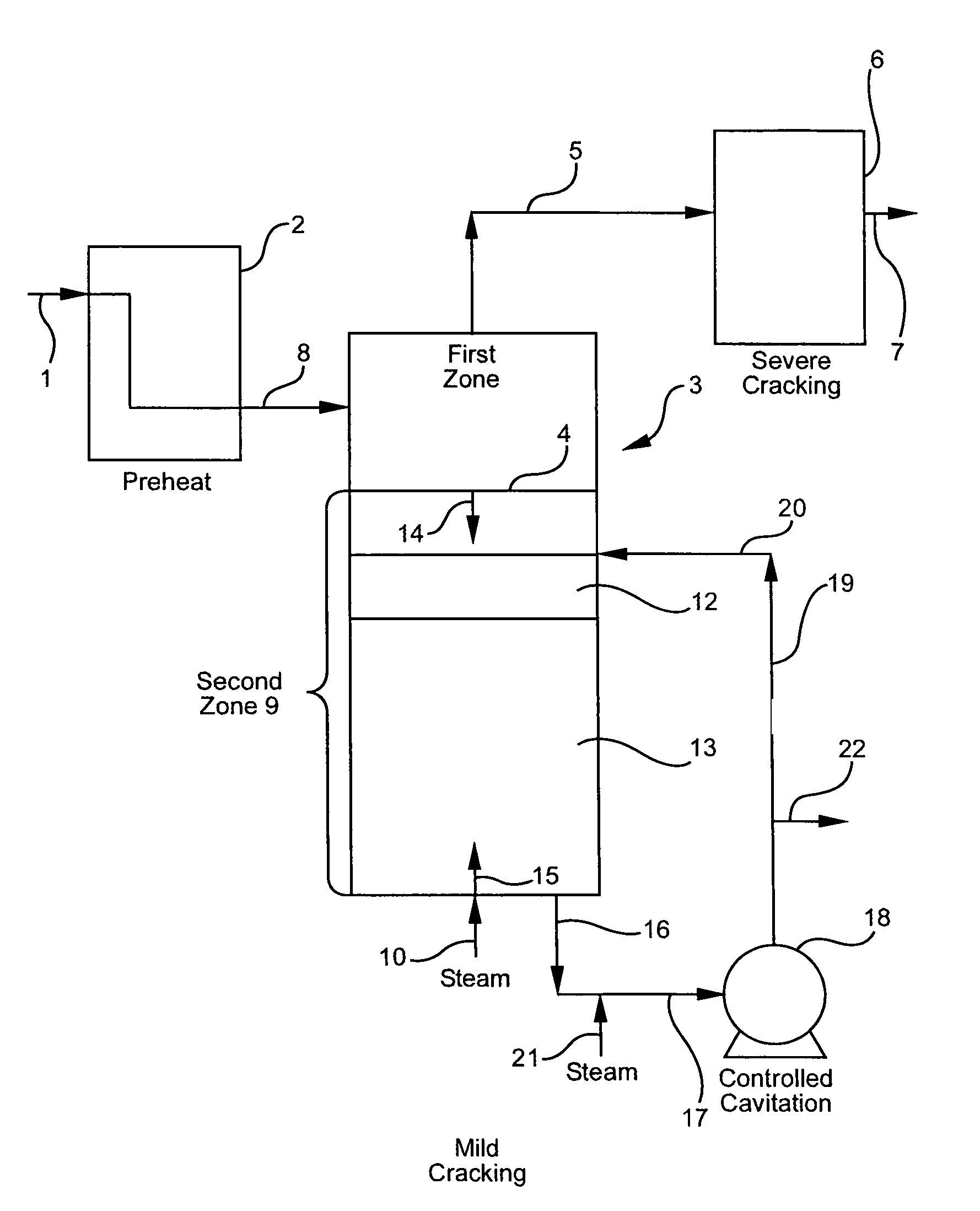
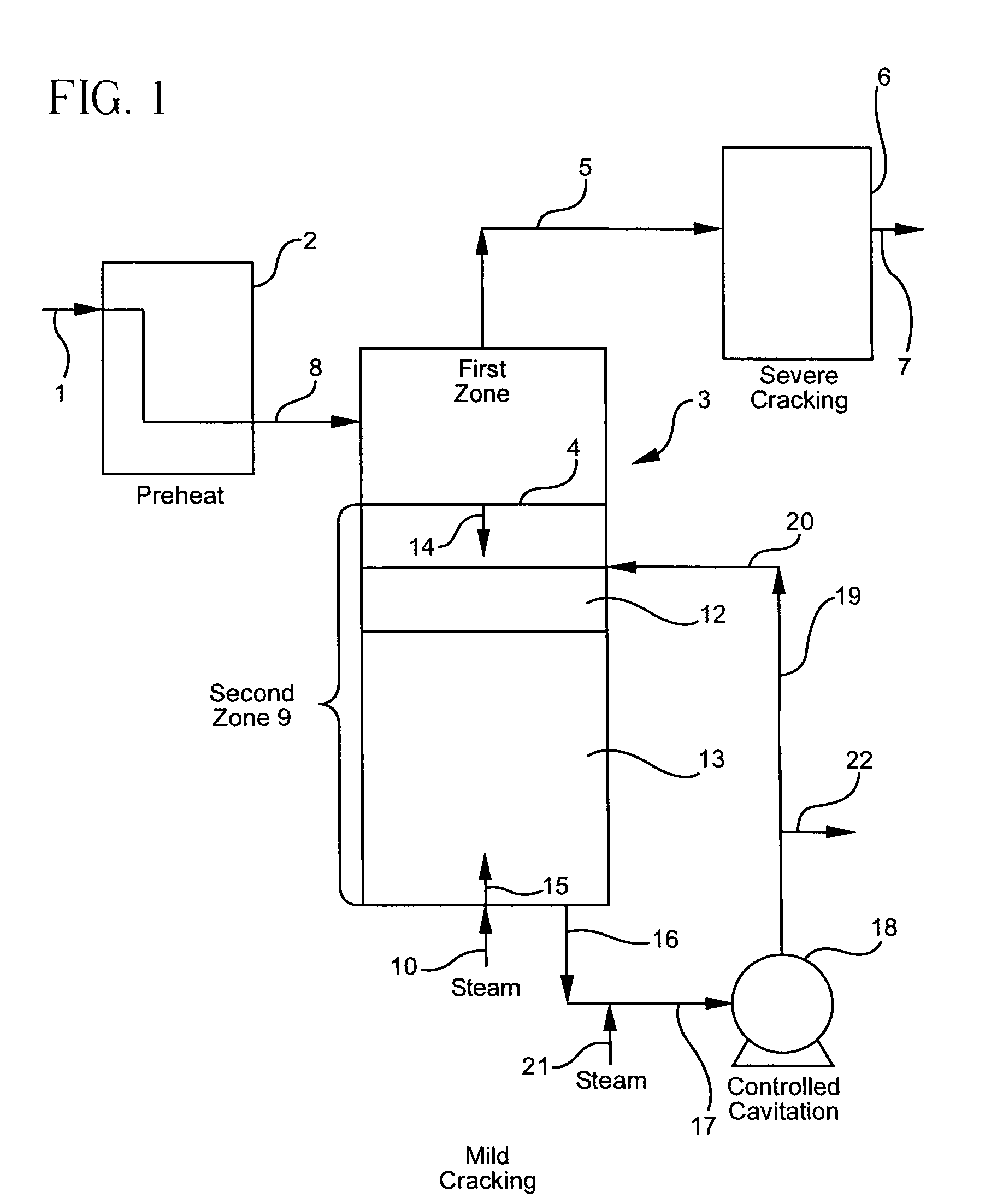
Olefin production utilizing whole crude oil and mild controlled cavitation assisted cracking
InactiveUS20050010075A1Thermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyCavitationAlkene
A method for utilizing whole crude oil as a feedstock for the pyrolysis furnace of an olefin production plant wherein the feedstock after preheating is subjected to mild thermal cracking assisted with controlled cavitation conditions until substantially vaporized, the vapors being subjected to severe cracking in the radiant section of the furnace.
Owner:EQUSR CHEM LP
Process for removal of nitrogen and poly-nuclear aromatics from hydrocracker feedstocks
A feedstream to a hydrocracking unit is treated to remove or reduce the content of polynuclear aromatics and nitrogen-containing compounds by contacting the feedstream with an adsorbent compound selected from attapulgus clay, alumina, silica gel and activated carbon in a fixed bed or slurry column and separating the treated feedstream that is lower in the undesired compounds from the adsorbent material. The adsorbent can be mixed with a solvent for the undesired compounds and stripped for re-use.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Upgrading of tar using POX/coker
ActiveUS8083931B2Reduce and eliminate needThermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyNaphthaPartial oxidation
The invention is directed to a process wherein a feedstock or stream comprising steam cracker tar is passed to a vacuum pipestill. A deasphalted cut of tar is obtained as an overhead (or sidestream) and a heavy tar asphaltenic product is obtained as bottoms. In preferred embodiments, at least a portion of the bottoms product is sent to a partial oxidation unit (POX) wherein syn gas may be obtained as a product, and / or at least a portion of the bottoms product is used to produce a light product stream in a coker unit, such as coker naphtha and / or or coker gas oil. In another preferred embodiment at least a portion of the overheads product is added to refinery fuel oil pools and in yet another preferred embodiment at least a portion of the overheads product is mixed with locally combusted materials to lower soot make. Two or more of the aforementioned preferred embodiments may be combined.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
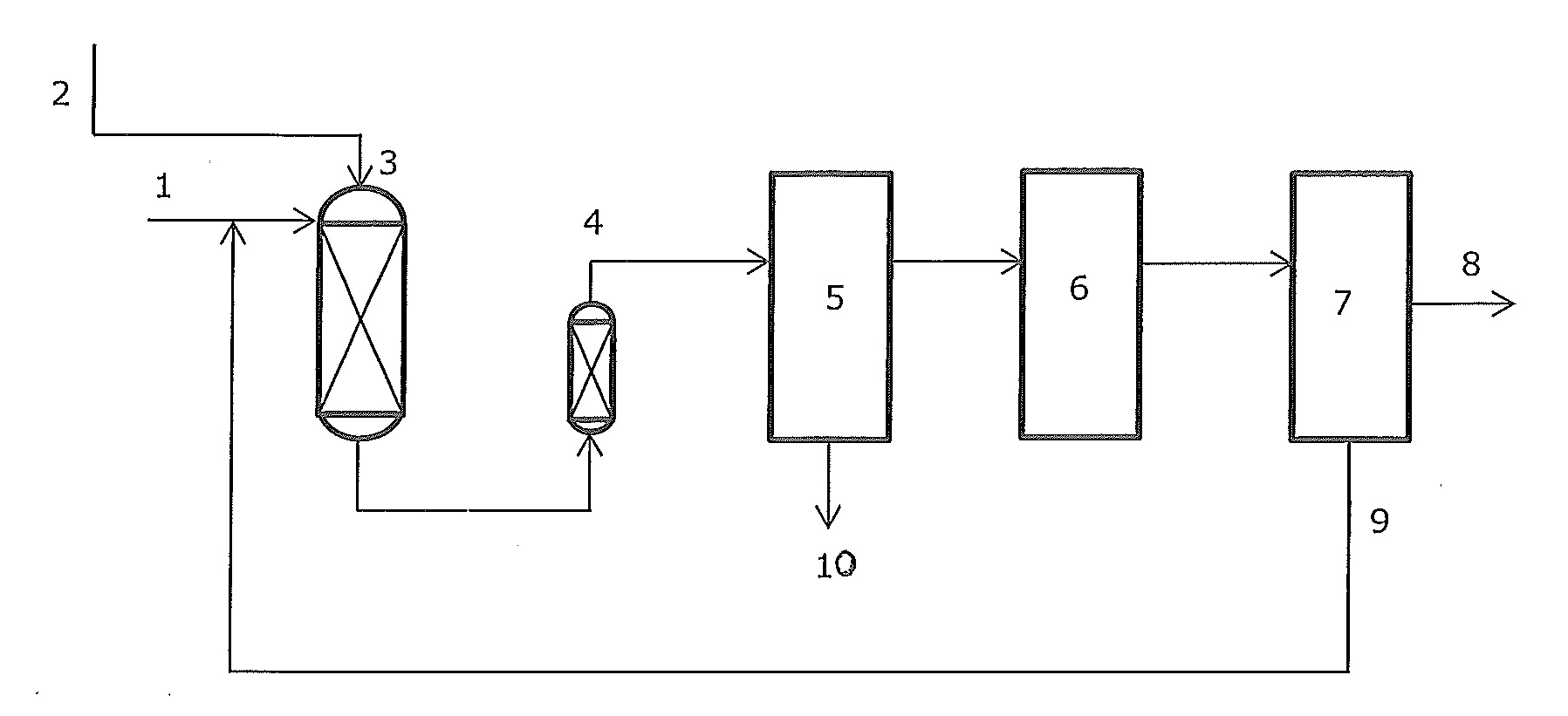
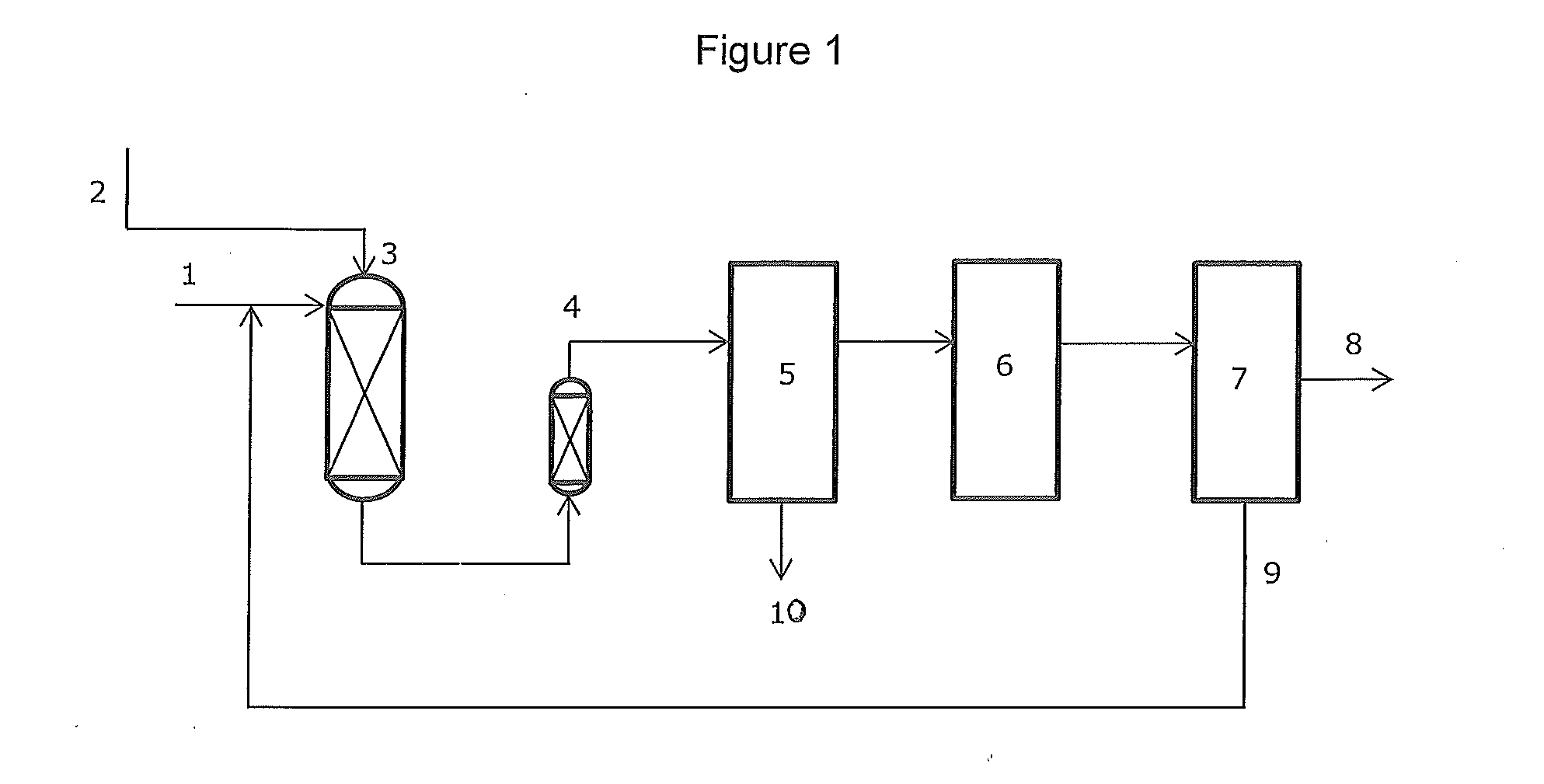
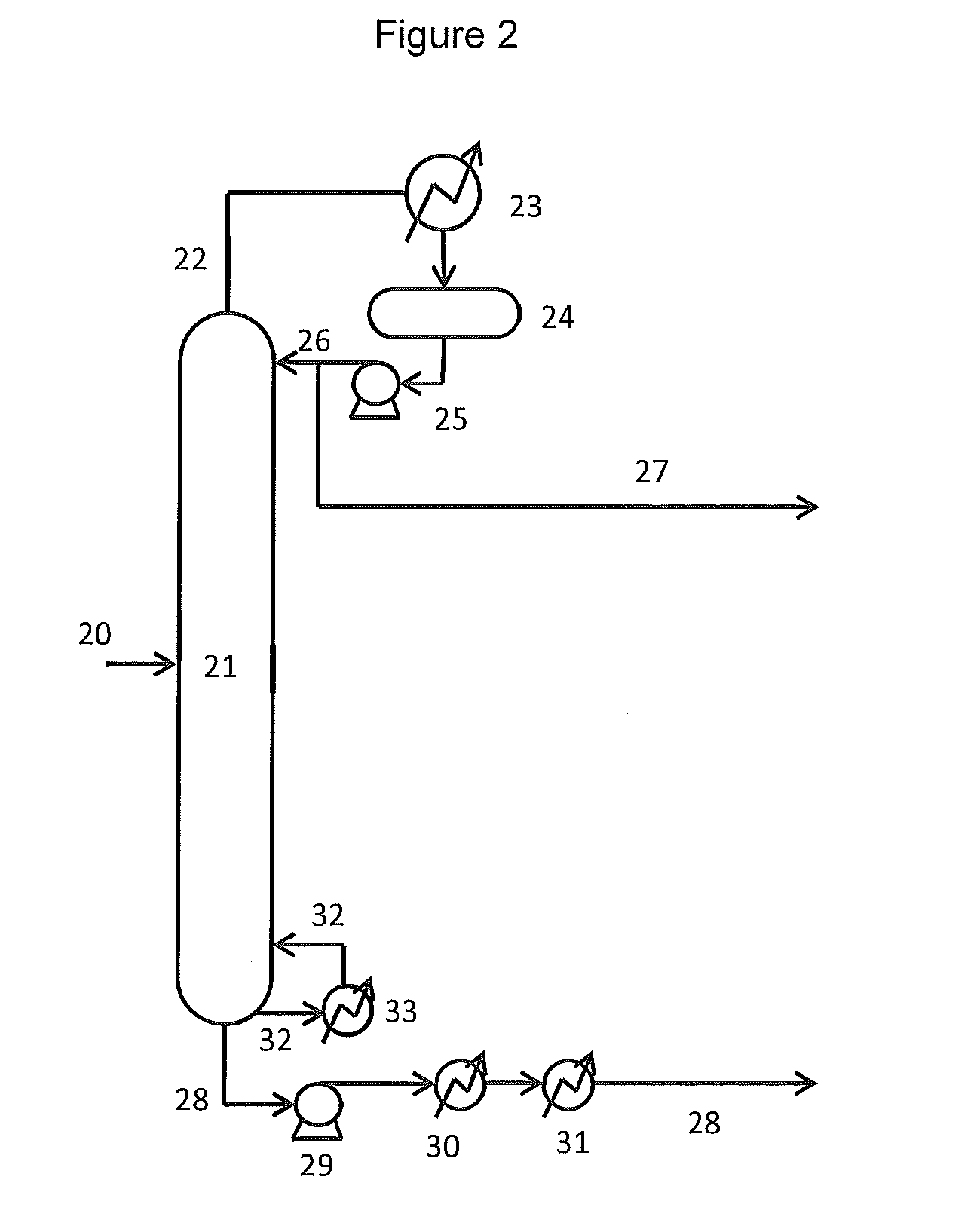
Gasoline and diesel production from pyrolytic lignin produced from pyrolysis of cellulosic waste
InactiveUS20080053870A1High yieldTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyTreatment with plural serial stages onlyCelluloseNaphtha
Owner:UOP LLC
Process to produce aromatics from crude oil
ActiveUS20150321975A1Low impurity contentHigh API gravityThermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial stages onlyVapor–liquid separatorWater flow
A process for producing aromatics from a hydrocarbon source in the presence of supercritical water comprising the steps of mixing a pressurized, pre-heated water stream with a pressurized, pre-heated petroleum feedstock, the pressurized, pre-heated water stream at a pressure above the critical pressure of water and a temperature above the critical temperature of water, feeding the combined stream to a supercritical water reactor to create a modified stream, cooling and depressurizing the modified stream, separating the depressurized stream in a vapor-liquid separator, condensing the vapor stream, separating the condensed stream into a water recovery stream and a light product recovery stream, extracting the aromatics from the light product recovery stream, depressurizing the liquid stream, separating the depressurized liquid stream in a heavy separator into an upgraded product stream, and recycling part of the upgraded product stream to the pressurized, pre-heated petroleum feedstock as a product recycle.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
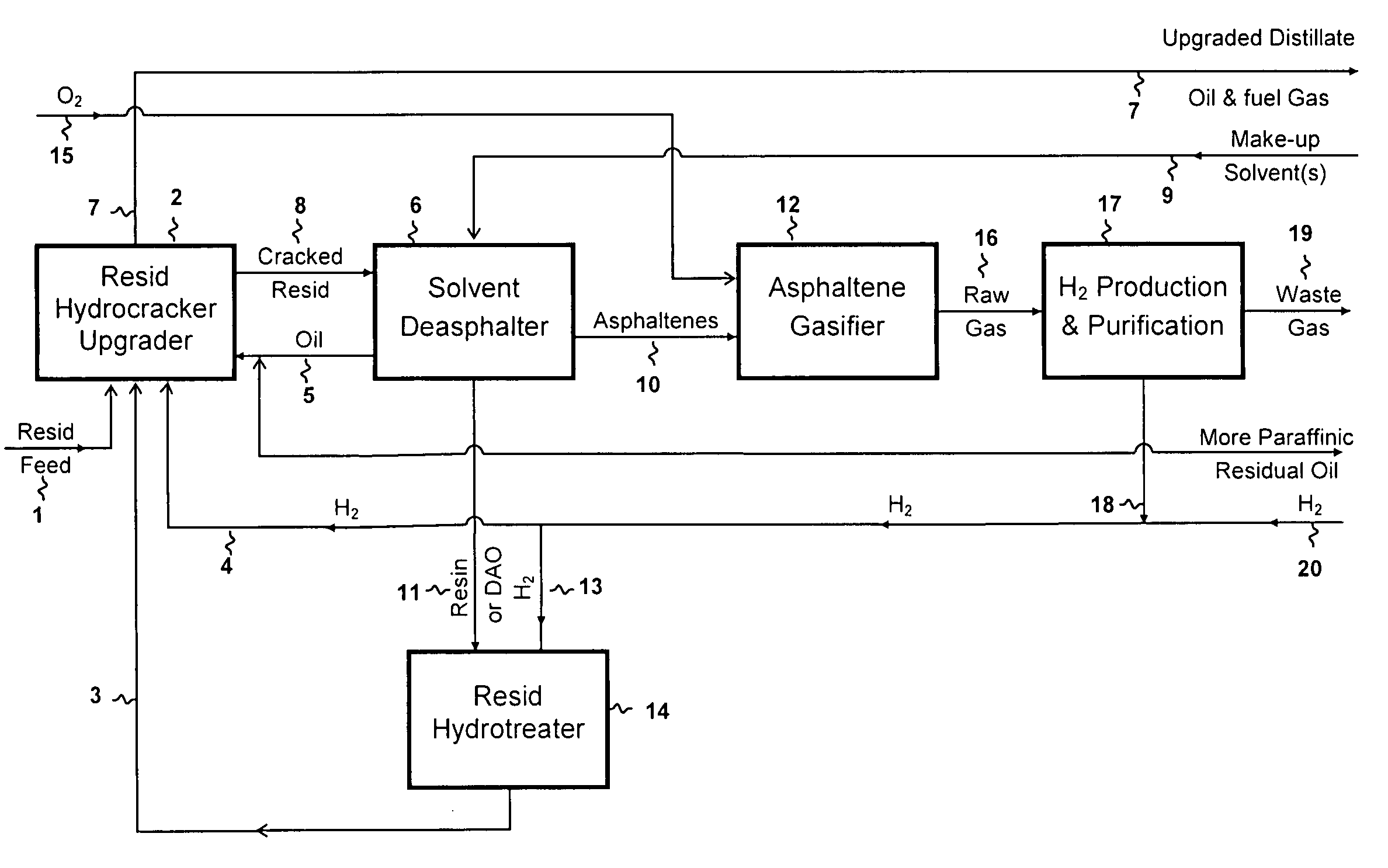
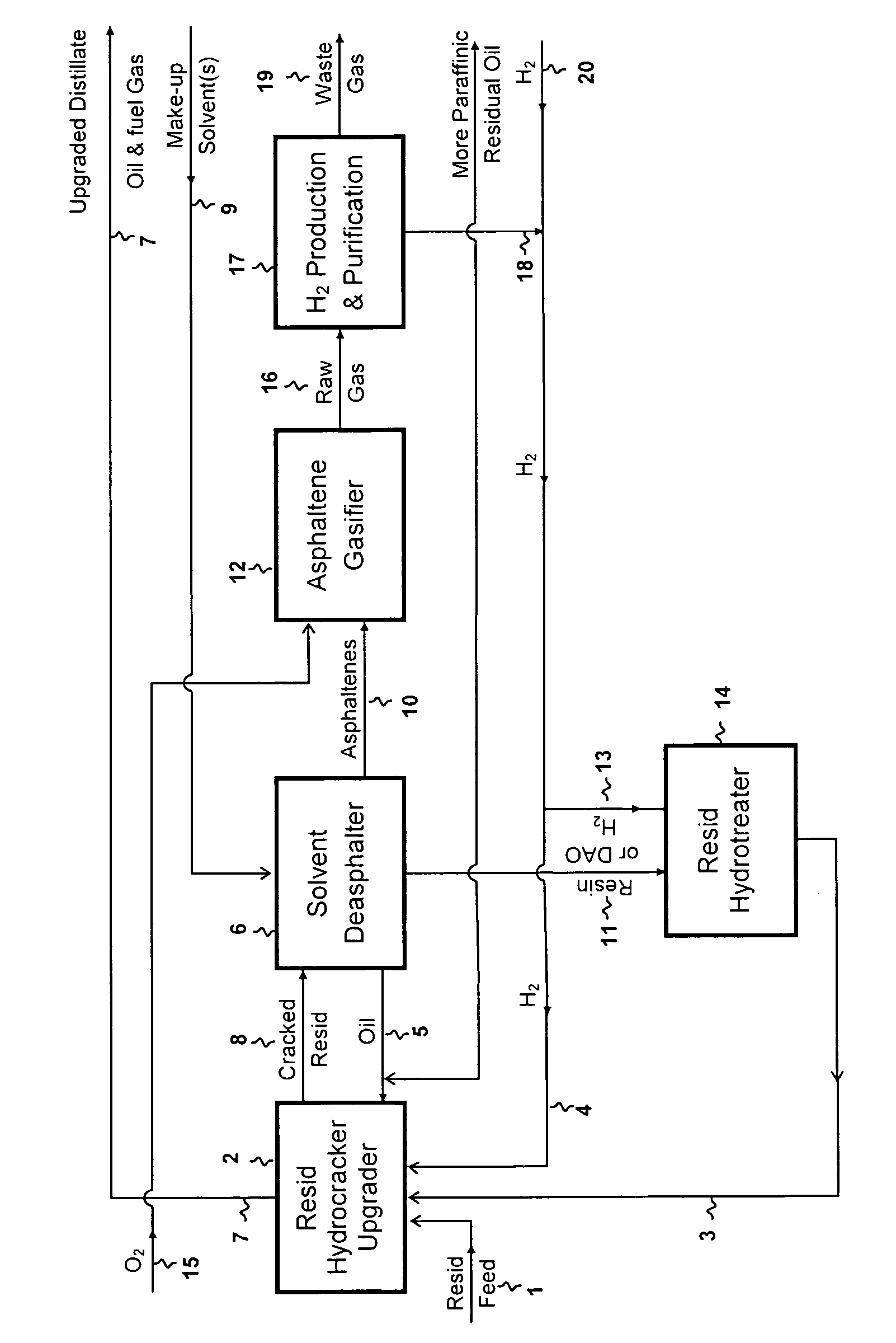
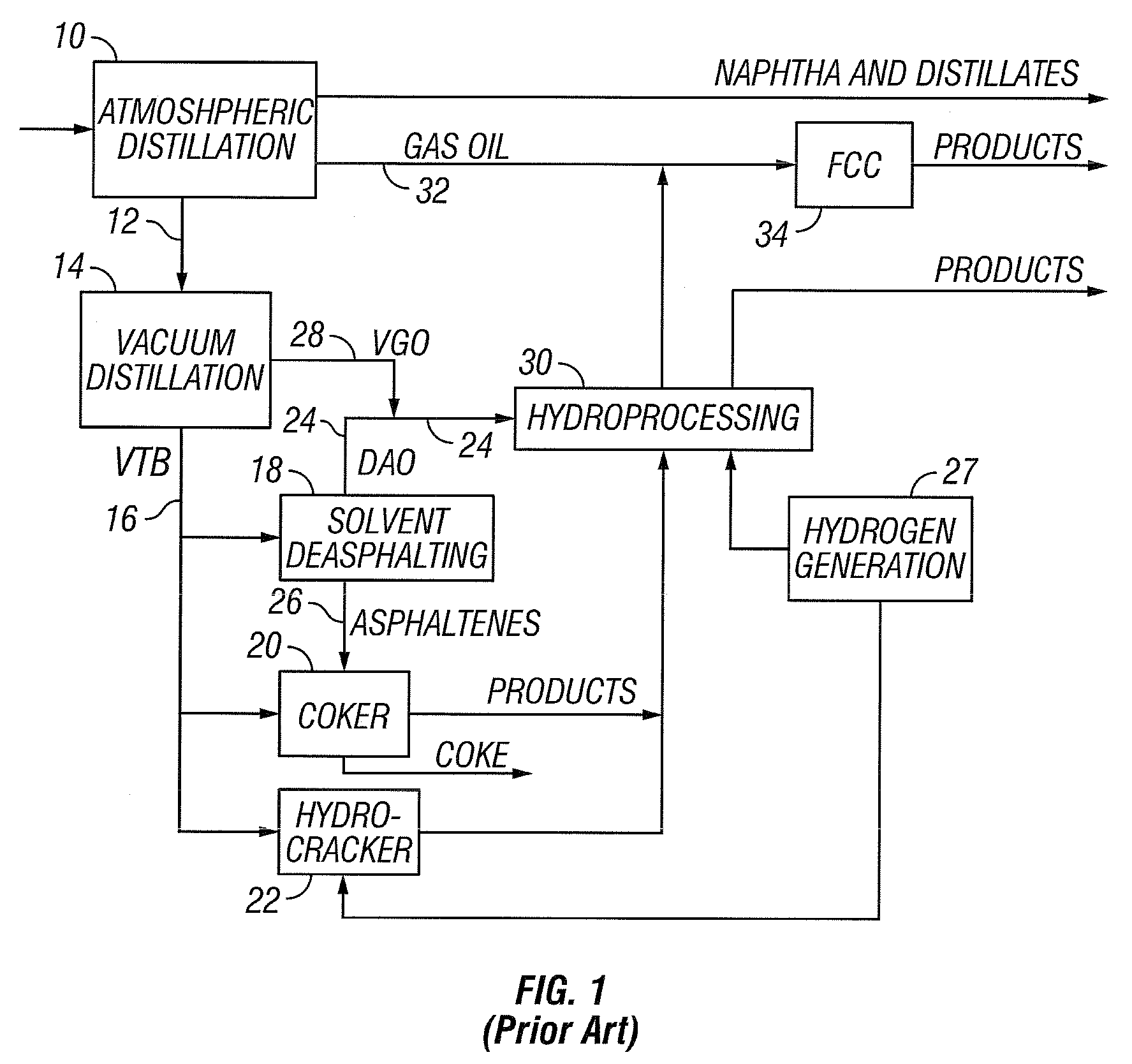
Heavy Oil and Bitumen Upgrading
ActiveUS20060042999A1Reduce metal contentEasy to liftThermal non-catalytic crackingWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by selective extractionNaphthaHydrogen
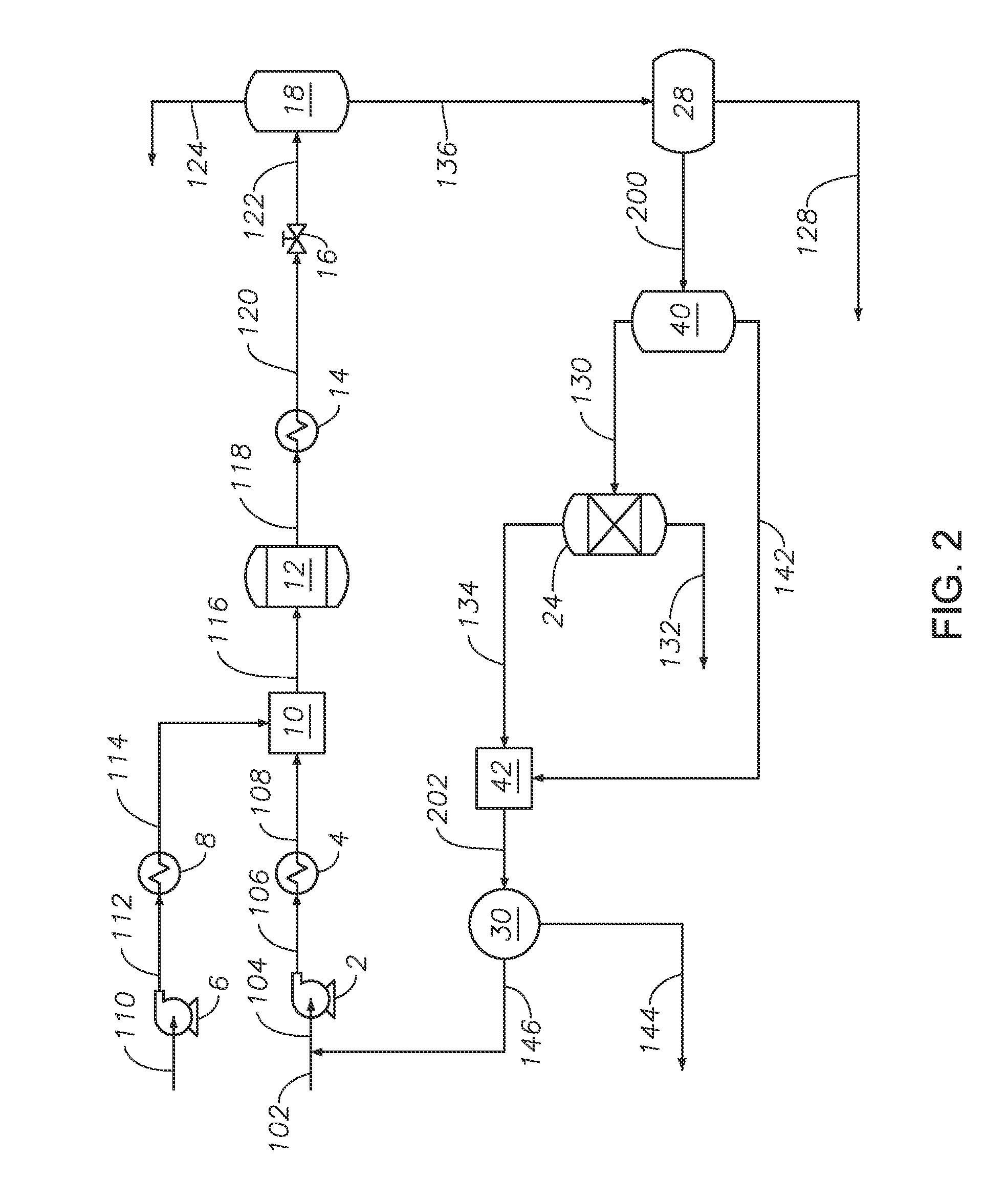
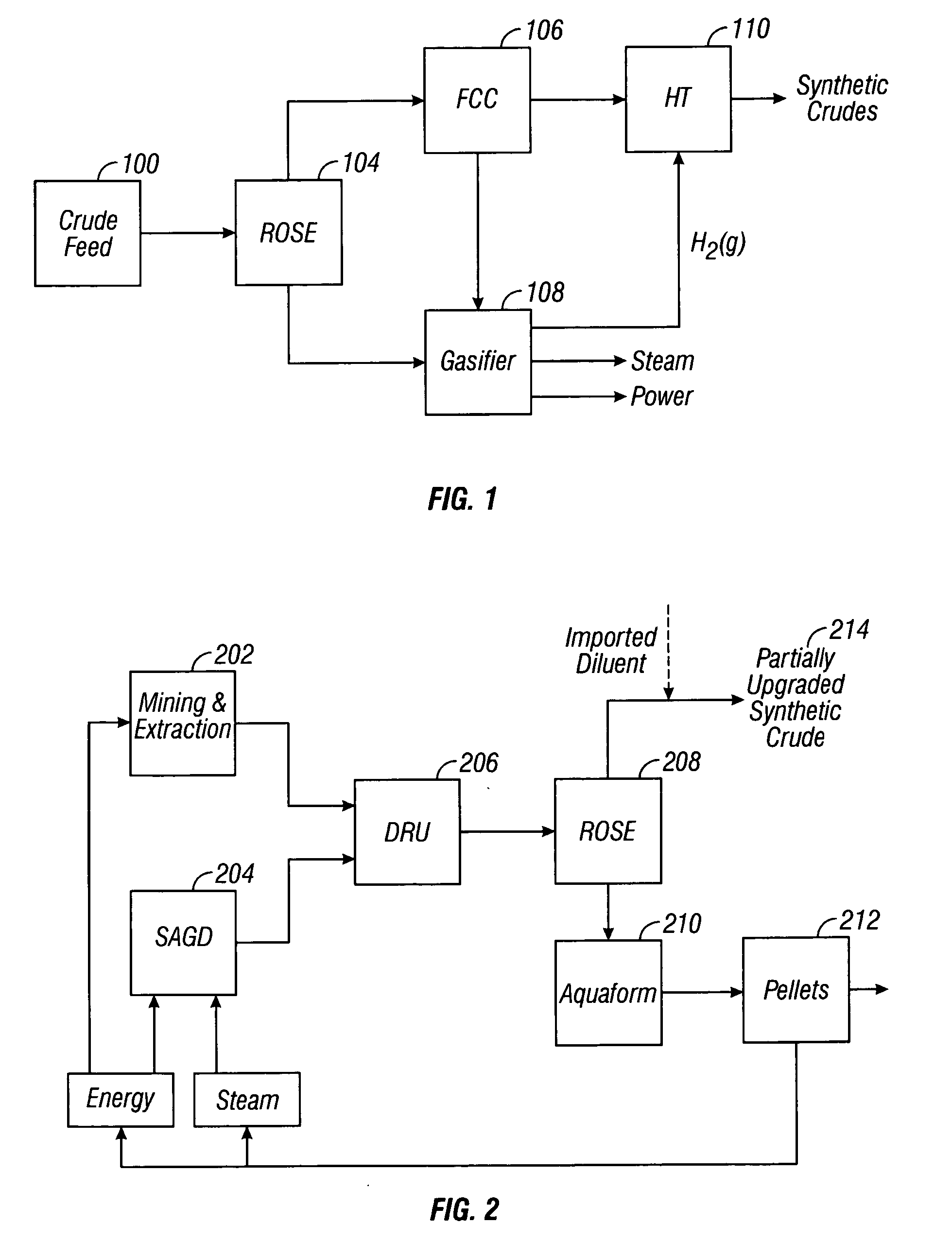
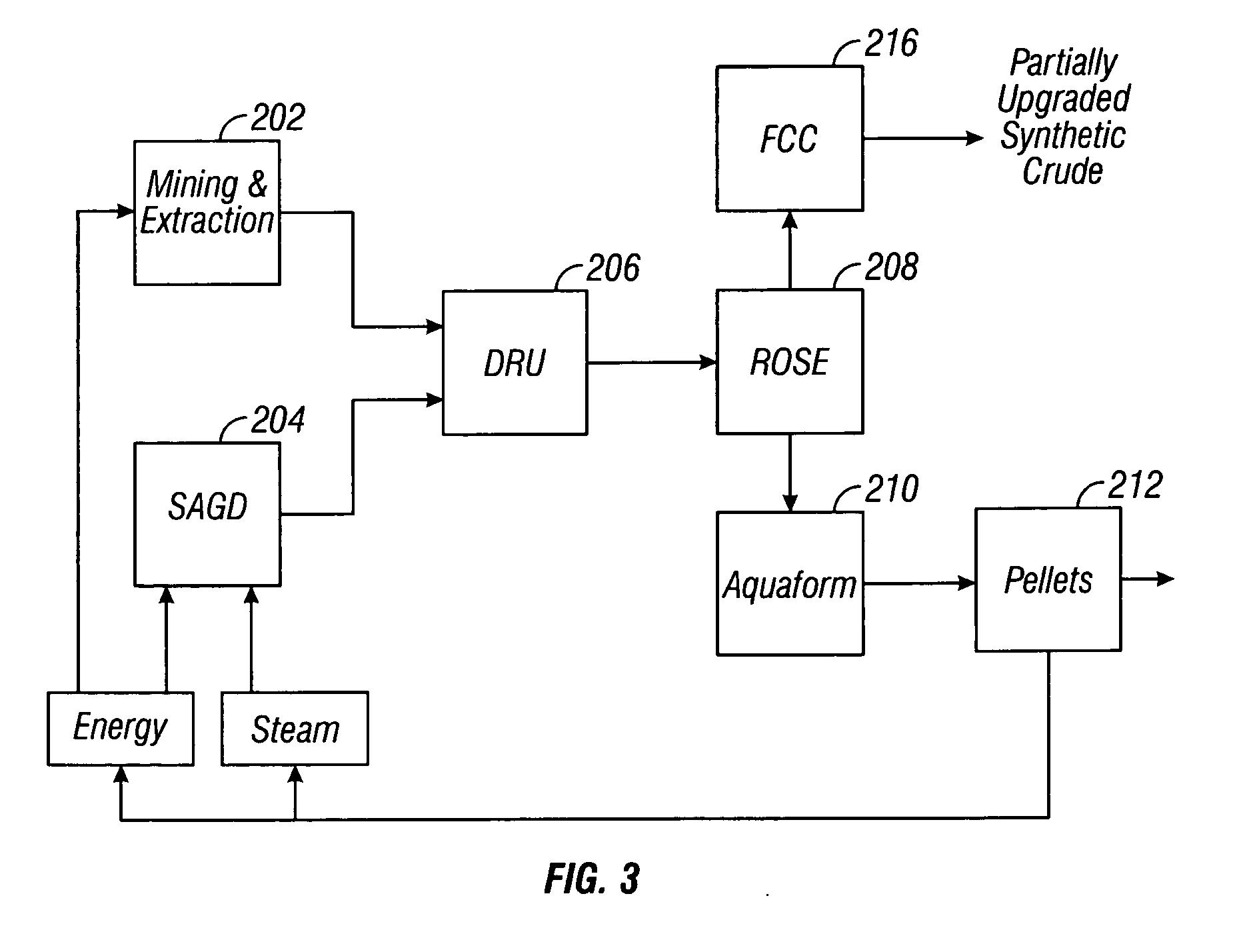
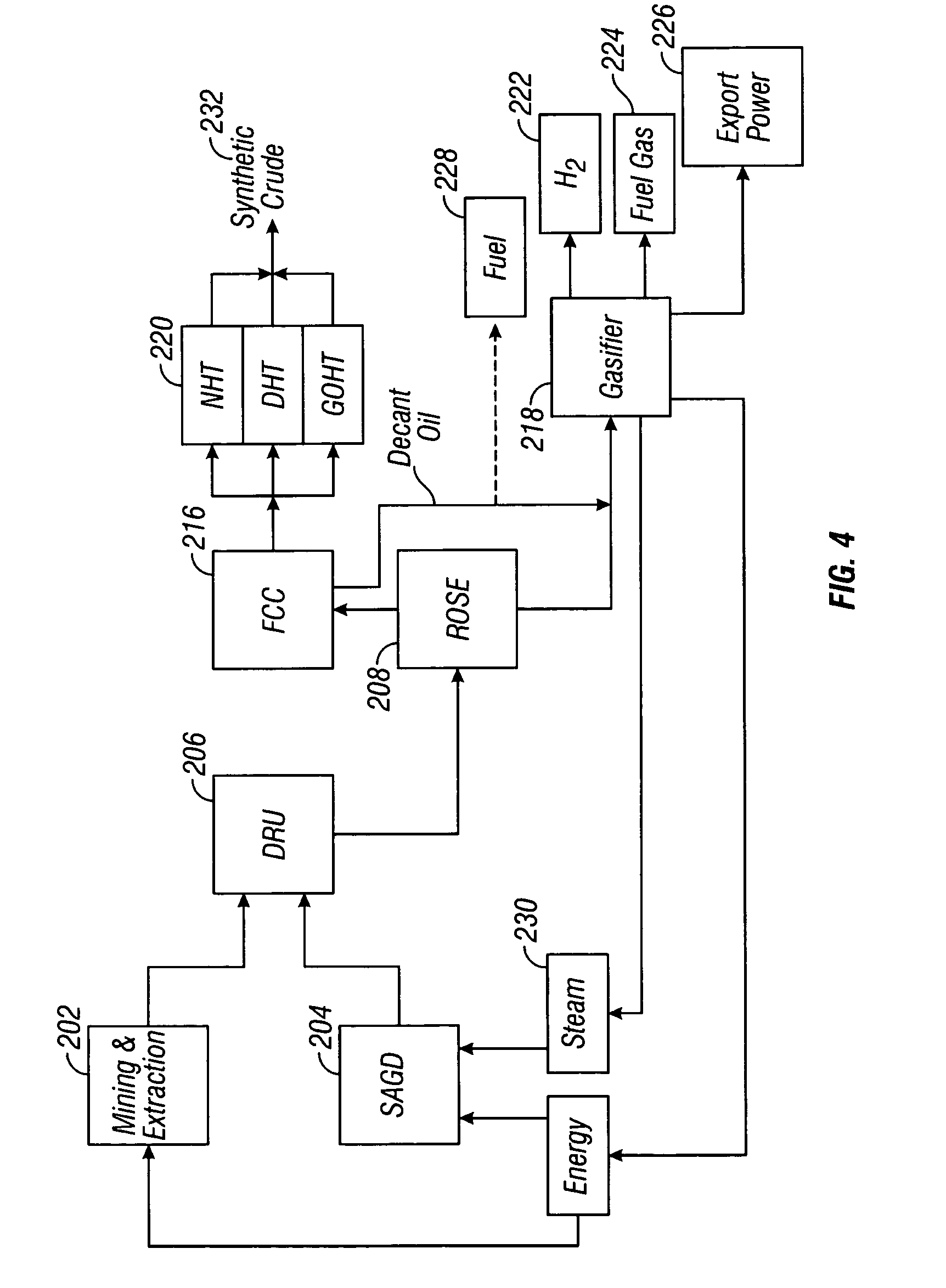
Disclosed is a process for the upgrading and demetallizing of heavy oils and bitumens. A crude heavy oil and / or bitumen feed is supplied to a solvent extraction process 104 wherein DAO and asphaltenes are separated. The DAO is supplied to an FCC unit 106 having a low conversion activity catalyst for the removal of metals contained therein. The demetallized distillate fraction is supplied to a hydrotreater 110 for upgrading and collected as a synthetic crude product stream. The asphaltene fraction can be supplied to a gasifier 108 for the recovery of power, steam and hydrogen, which can be supplied to the hydrotreater 110 or otherwise within the process or exported. An optional coker 234 can be used to convert excess asphaltenes and / or decant oil to naphtha, distillate and gas oil, which can be supplied to the hydrotreater 220.
Owner:KELLOGG BROWN & ROOT LLC
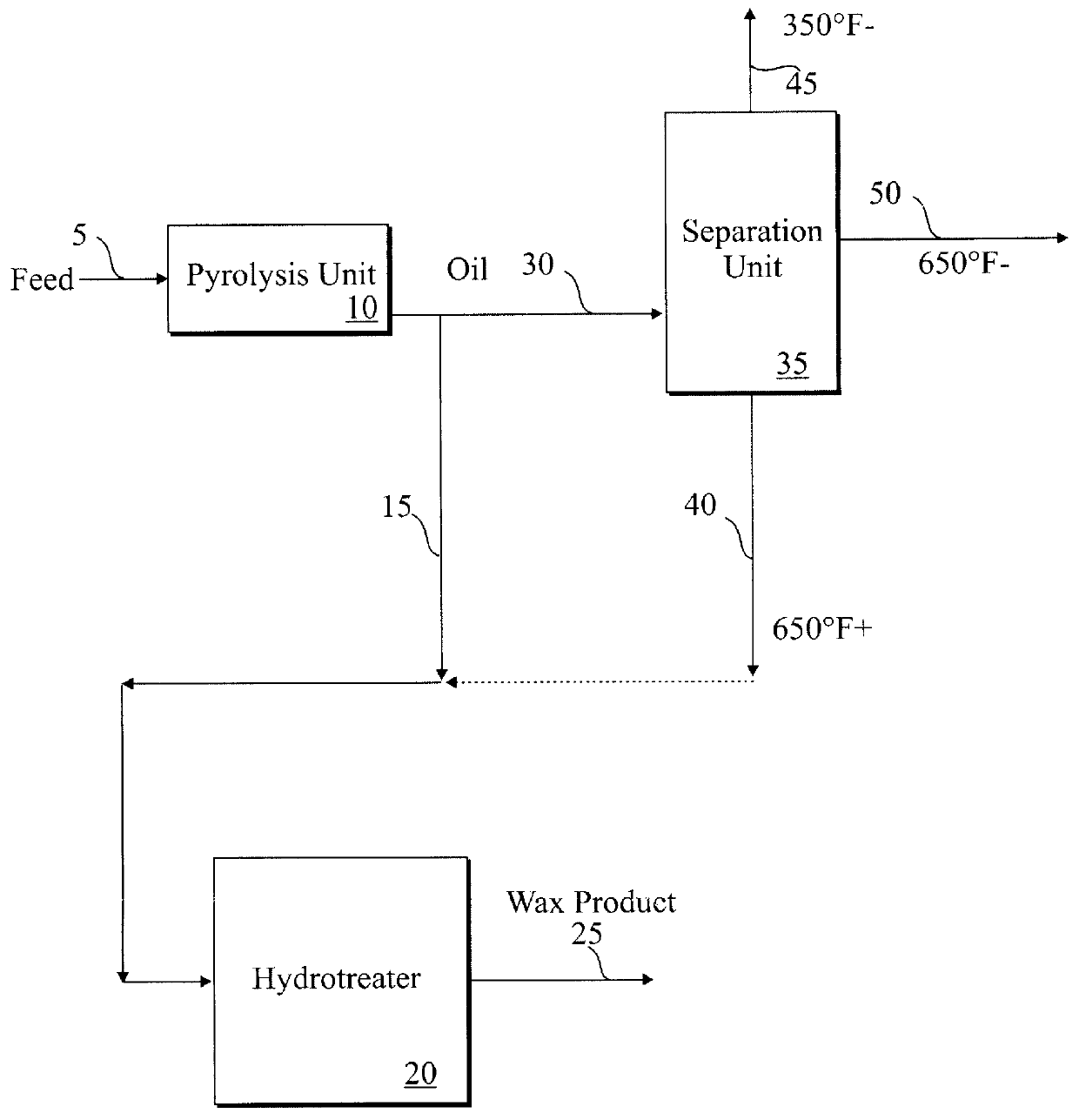
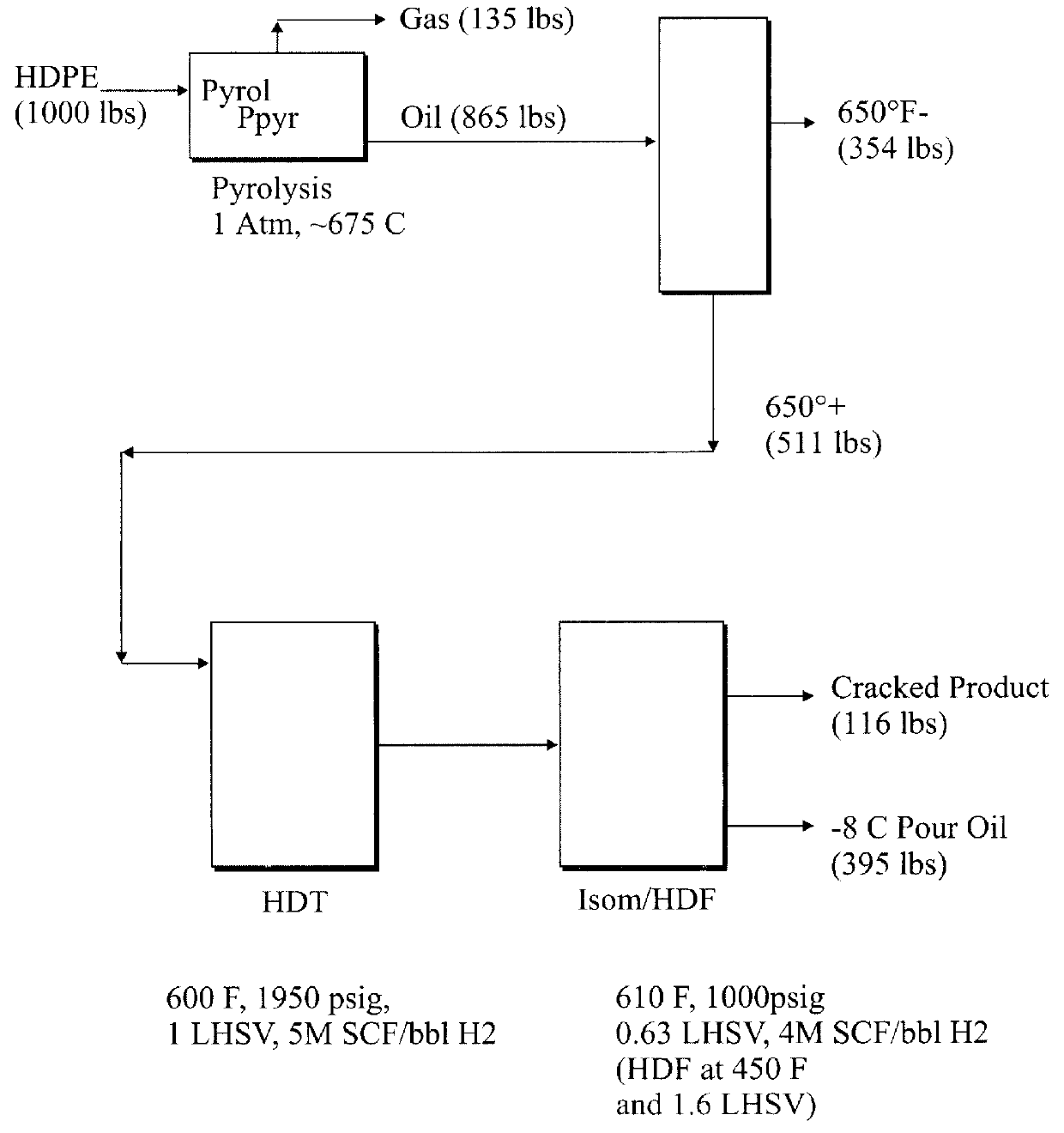
Method for making a heavy wax composition
InactiveUS6143940ATreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyTreatment with plural serial stages onlyWaxAlkane
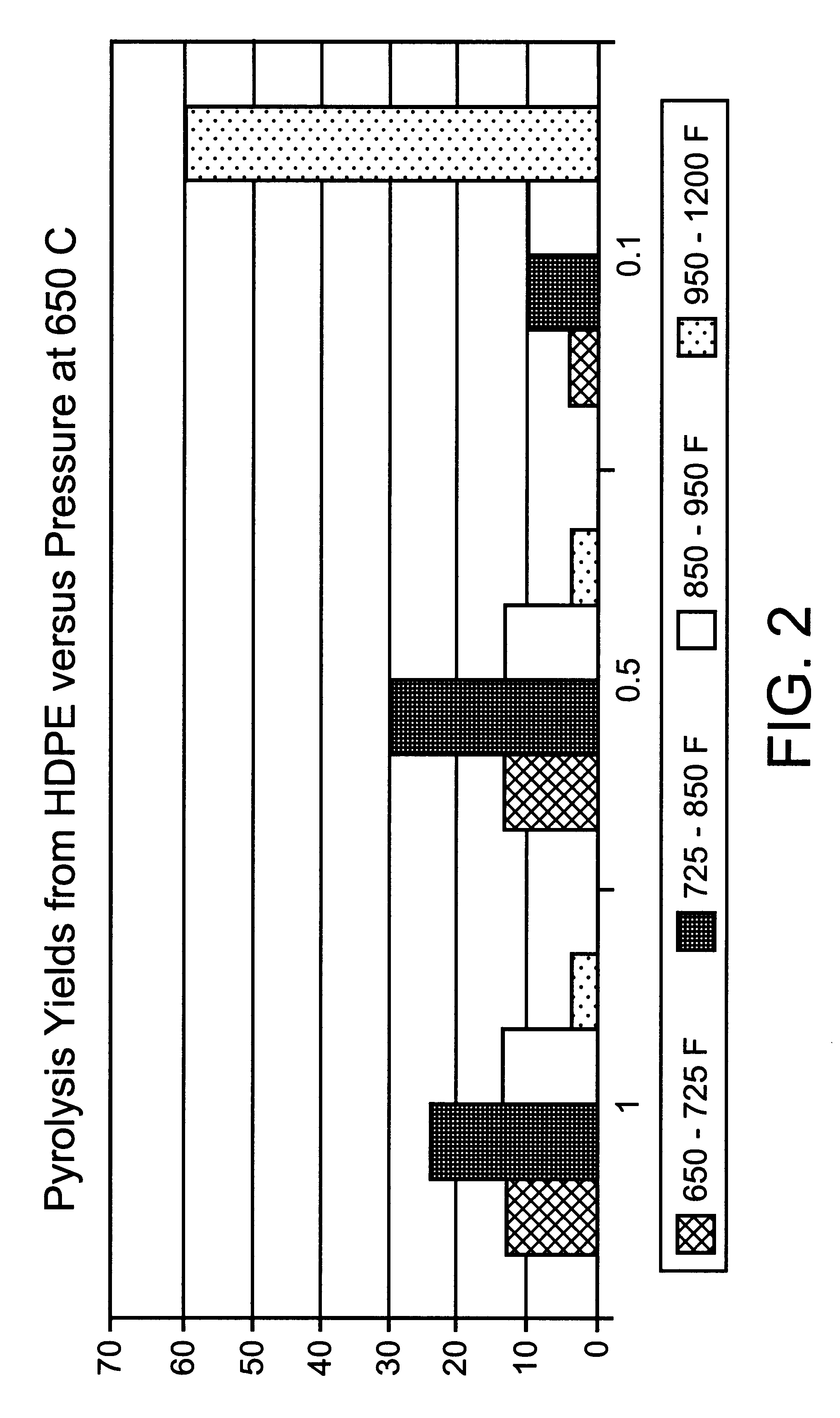
The invention includes a process of making a wax composition including: a process for making a heavy wax composition including the steps of (1) contacting a waste plastics feed containing primarily polyethylene in a pyrolysis zone at sub-atmospheric pressure, whereby at least a portion of the waste plastics feed is cracked, thereby forming a pyrolysis zone effluent including 1-olefins and n-paraffins; and (2) passing the pyrolysis zone effluent to a hydrotreating zone, for contacting with a hydrotreating catalyst at catalytic conditions.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Olefin production utilizing whole crude oil and mild controlled cavitation assisted cracking
InactiveUS6979757B2Thermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyCavitationAlkene
A method for utilizing whole crude oil as a feedstock for the pyrolysis furnace of an olefin production plant wherein the feedstock after preheating is subjected to mild thermal cracking assisted with controlled cavitation conditions until substantially vaporized, the vapors being subjected to severe cracking in the radiant section of the furnace.
Owner:EQUSR CHEM LP
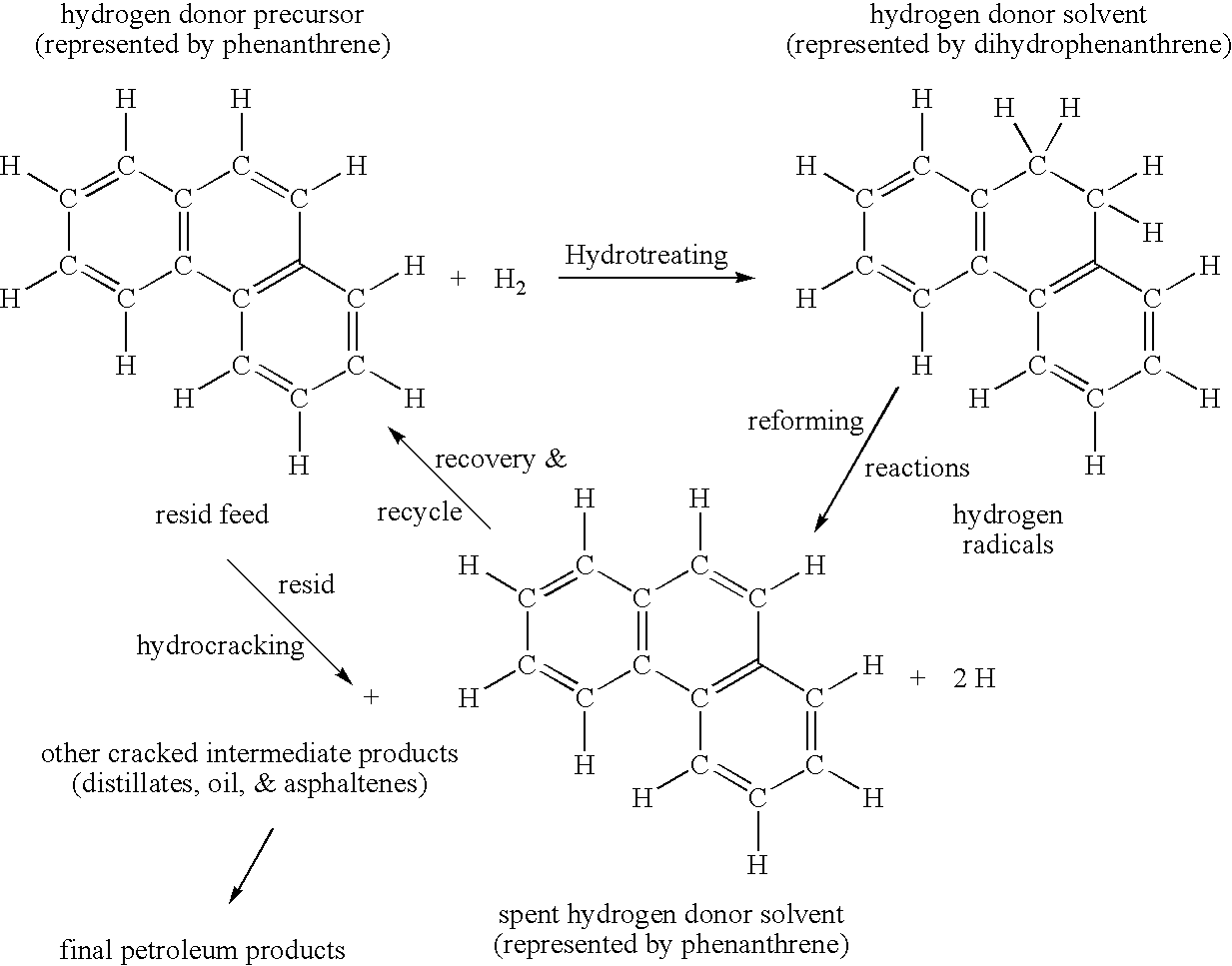
Hydrogen donor solvent production and use in resid hydrocracking processes
InactiveUS20070108100A1Treatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyCoke ovensHydrogenBoiling point
A process derived hydrogen donor solvent is used to increase the maximum resid conversion and conversion rate in an ebullated bed resid hydrocracker. The hydrogen donor solvent precursor is produced by hydroreforming reactions within the resid hydrocracker, recovered as the resin fraction from a solvent deasphalting unit, regenerated in a separate hydrotreater reactor, and recycled to the ebullated bed resid hydrocracker. The major advantage of this invention relative to earlier processes is that hydrogen is more efficiently transferred to the resin residual oil in the separate hydrotreater and the hydrogen donor solvent effectively retards the formation of coke precursors at higher ebullated bed resid hydrocracker operating temperatures and resid cracking rates.
Owner:BOC GRP INC
Hydrocarbon thermal cracking using atmospheric distillation
ActiveUS7404889B1Thermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyDistillationGasoline
A method for thermally cracking a hydrocarbonaceous feed wherein the feed is first processed in an atmospheric thermal distillation step to form a light gasoline and atmospheric residuum mixture. The light gasoline / residuum combination is gasified at least in part in a vaporization step, and the gasified product of the vaporization step is thermally cracked.
Owner:EQUSR CHEM LP
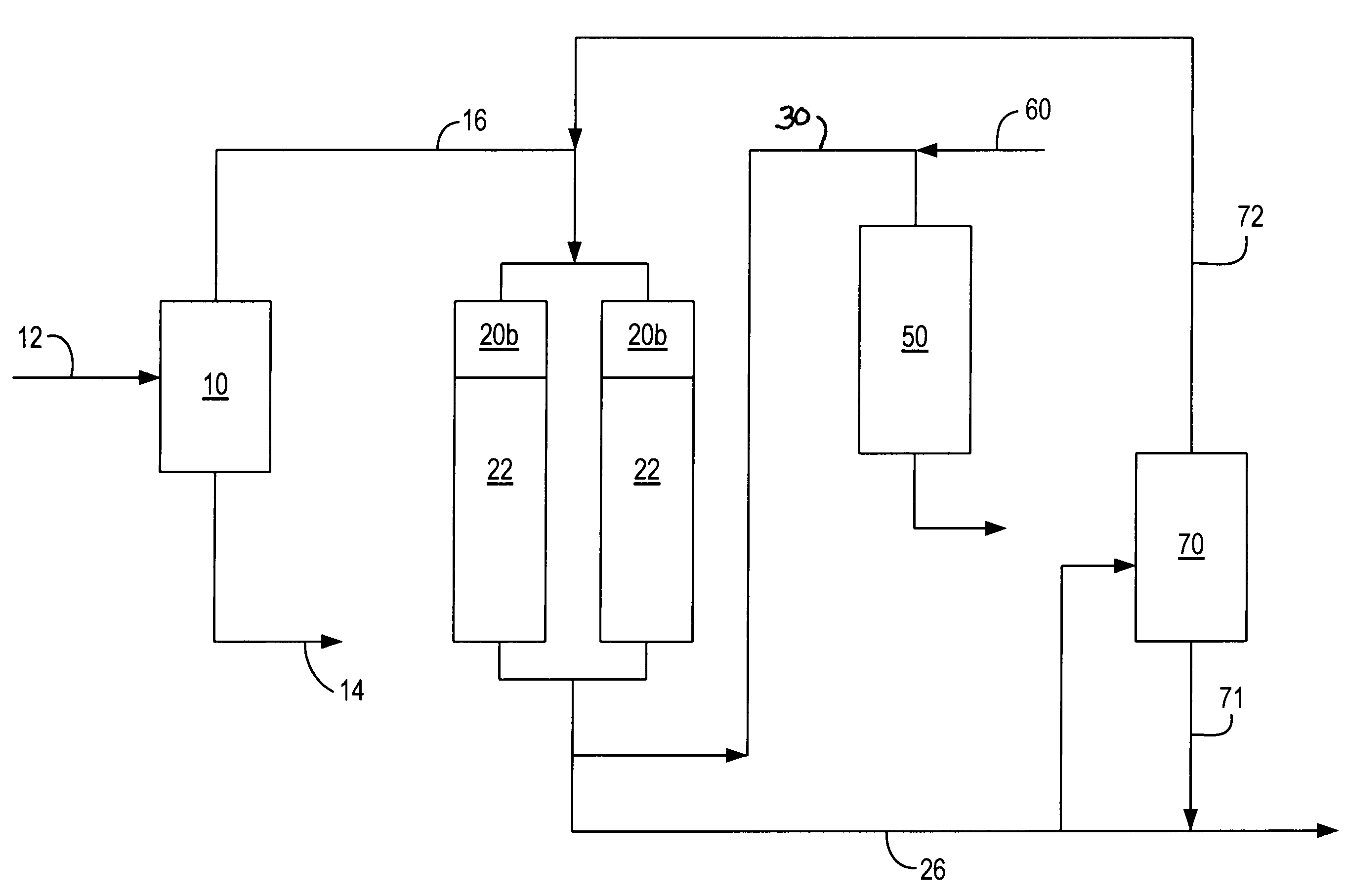
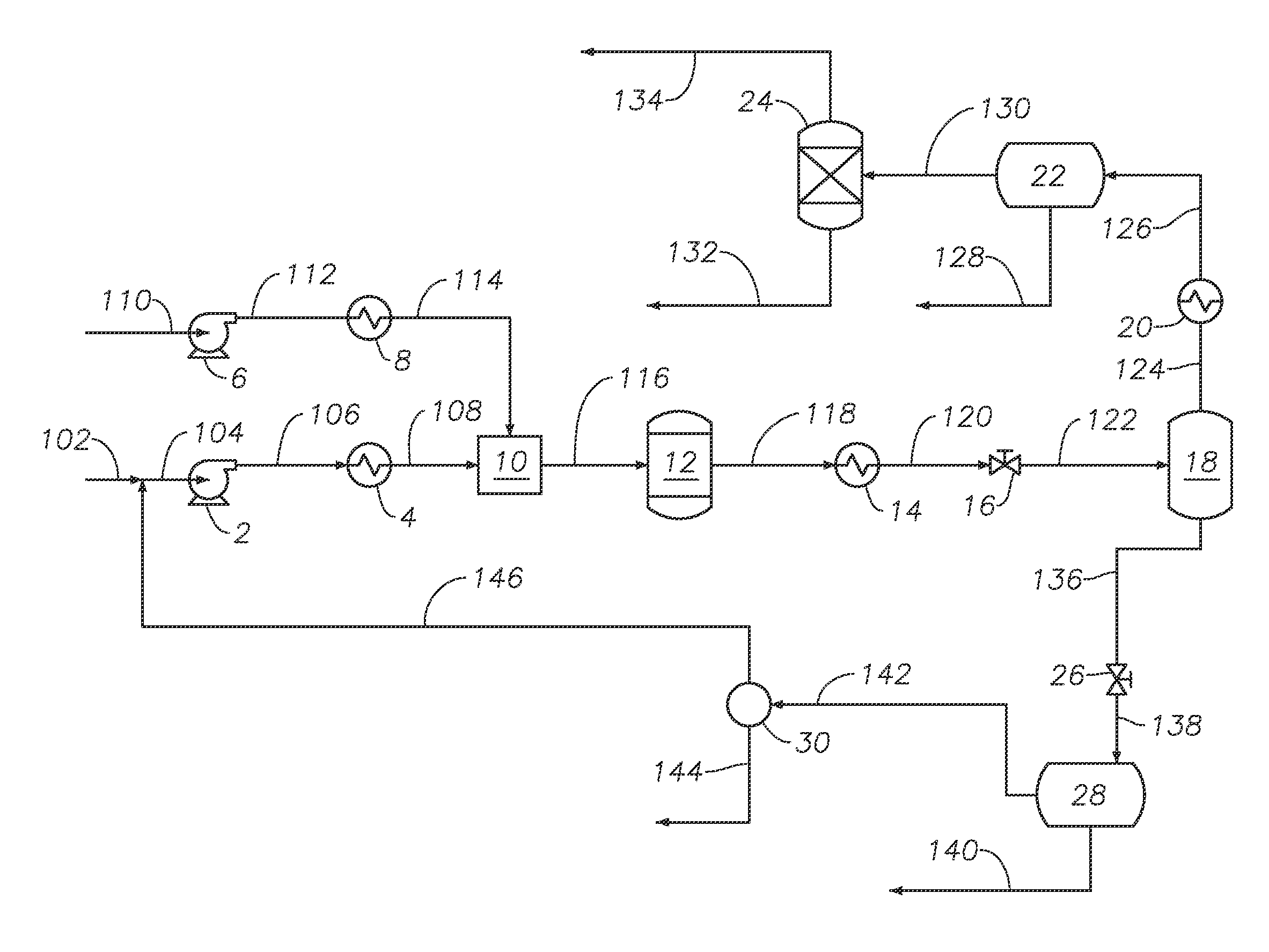
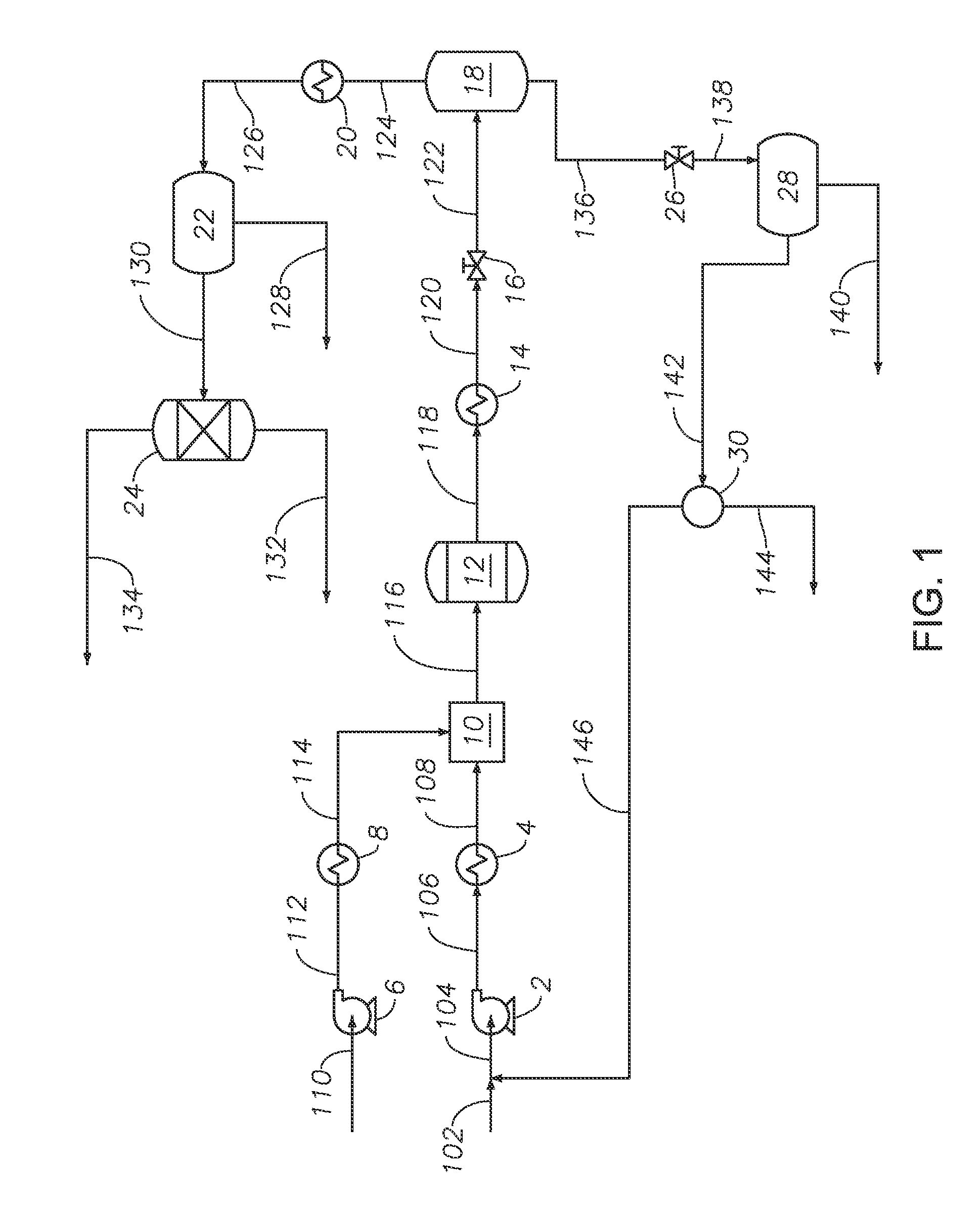
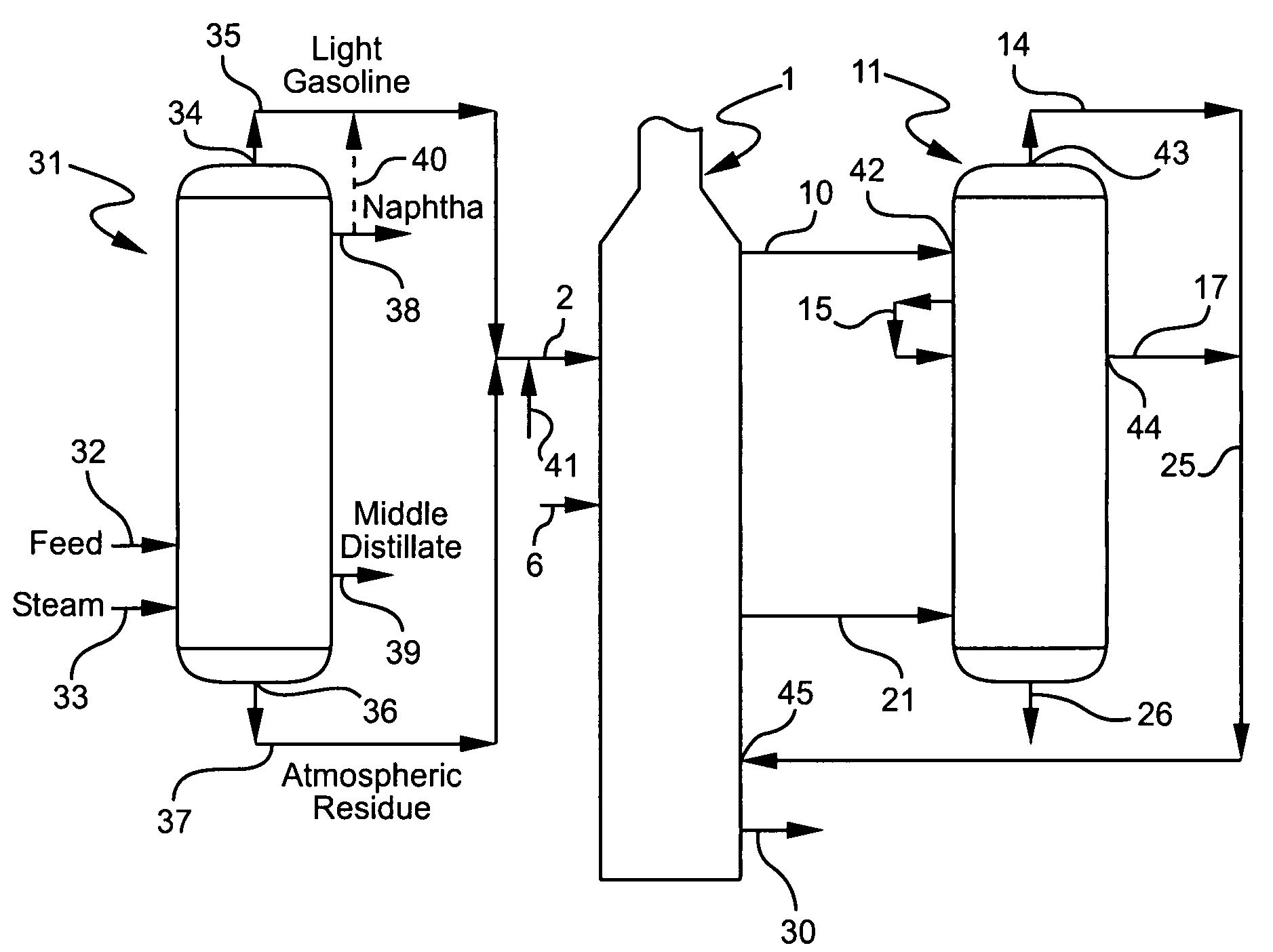
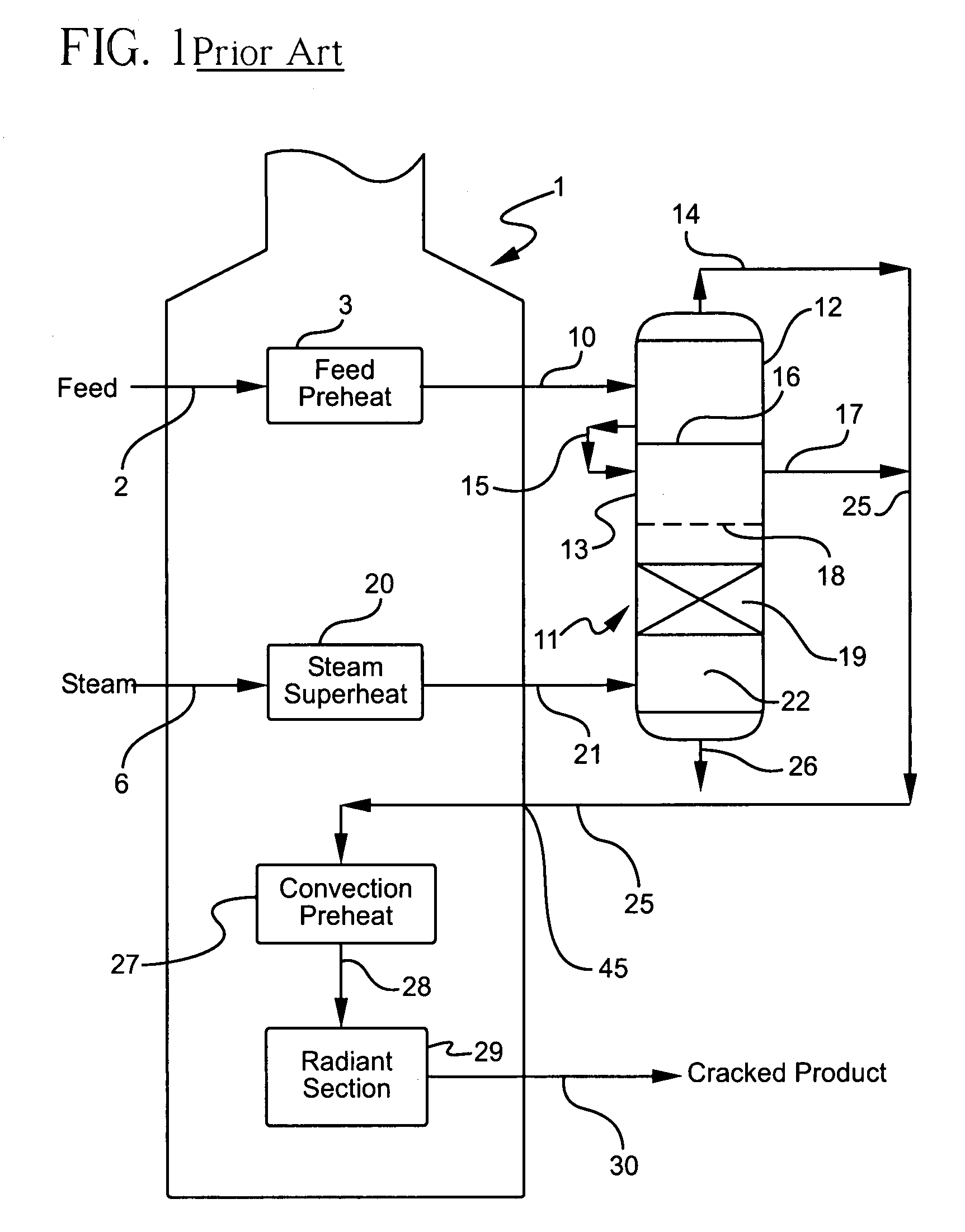
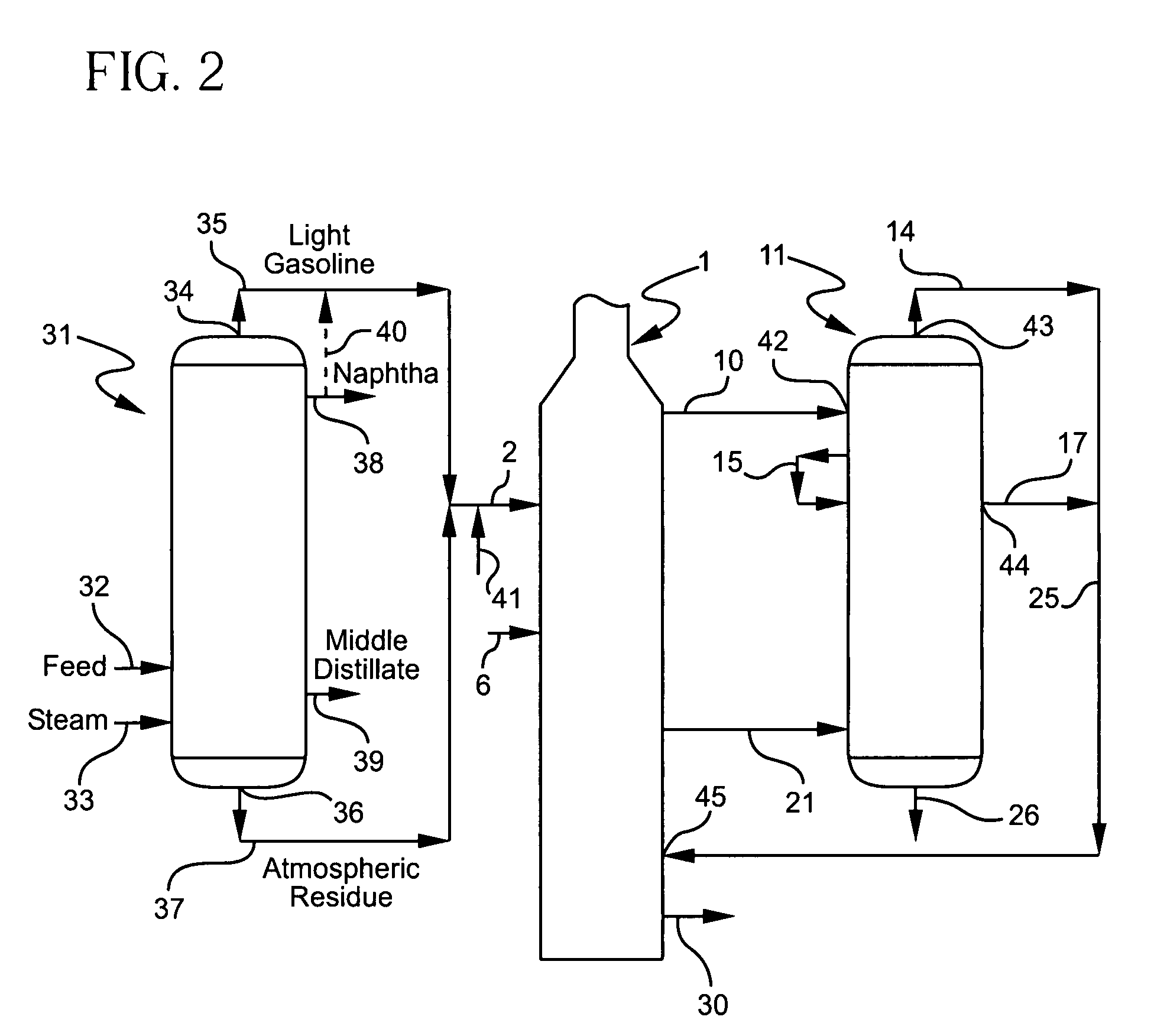
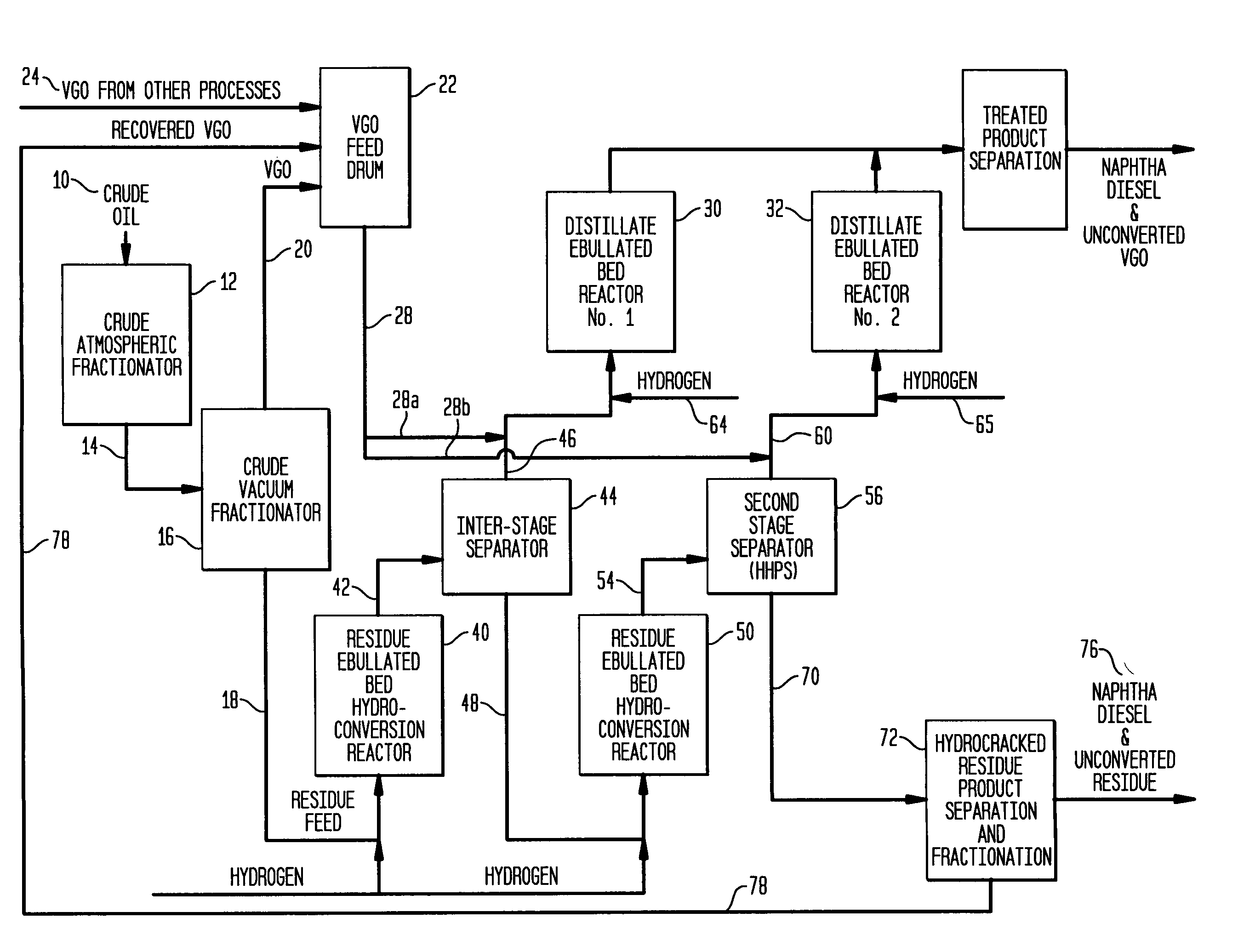
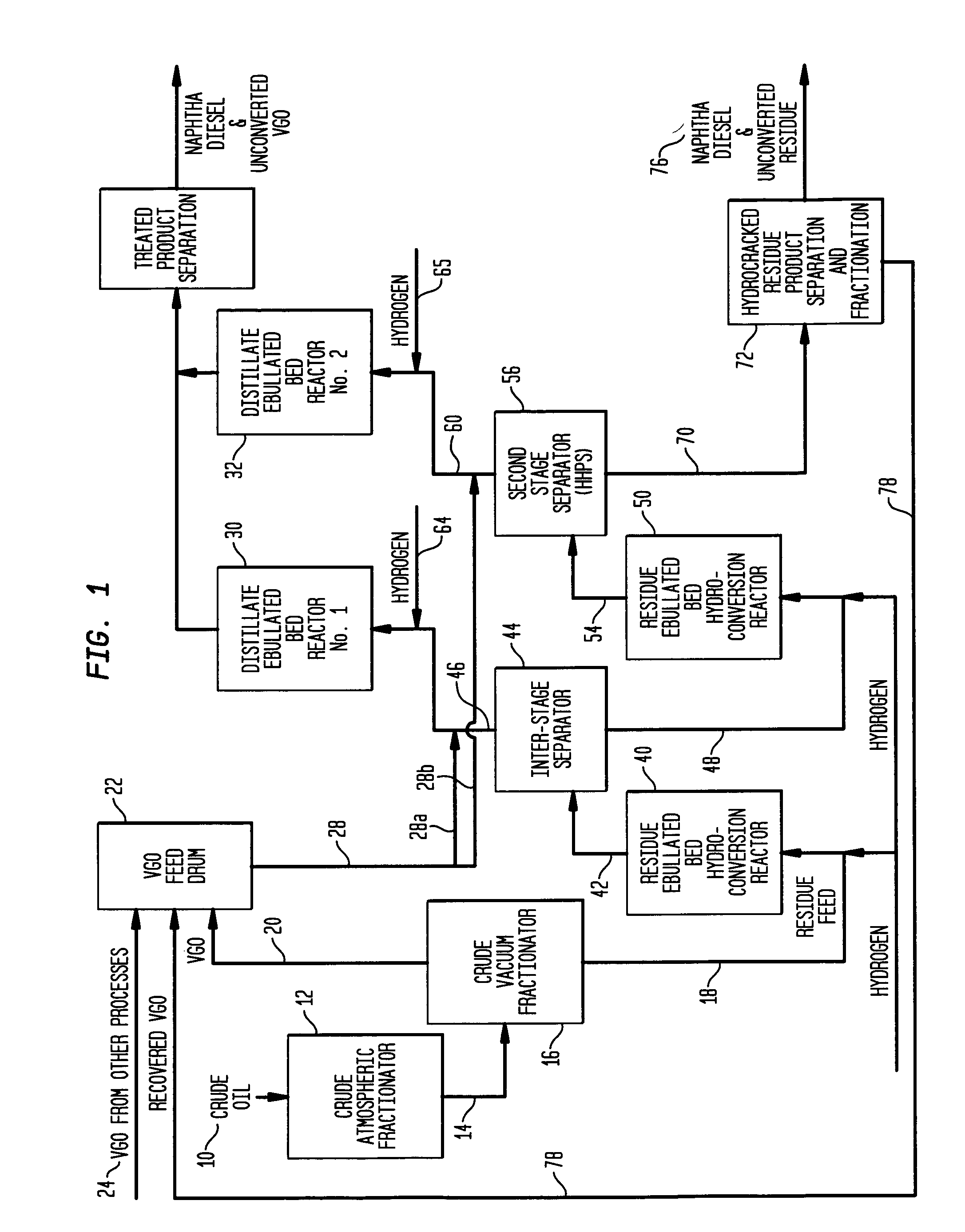
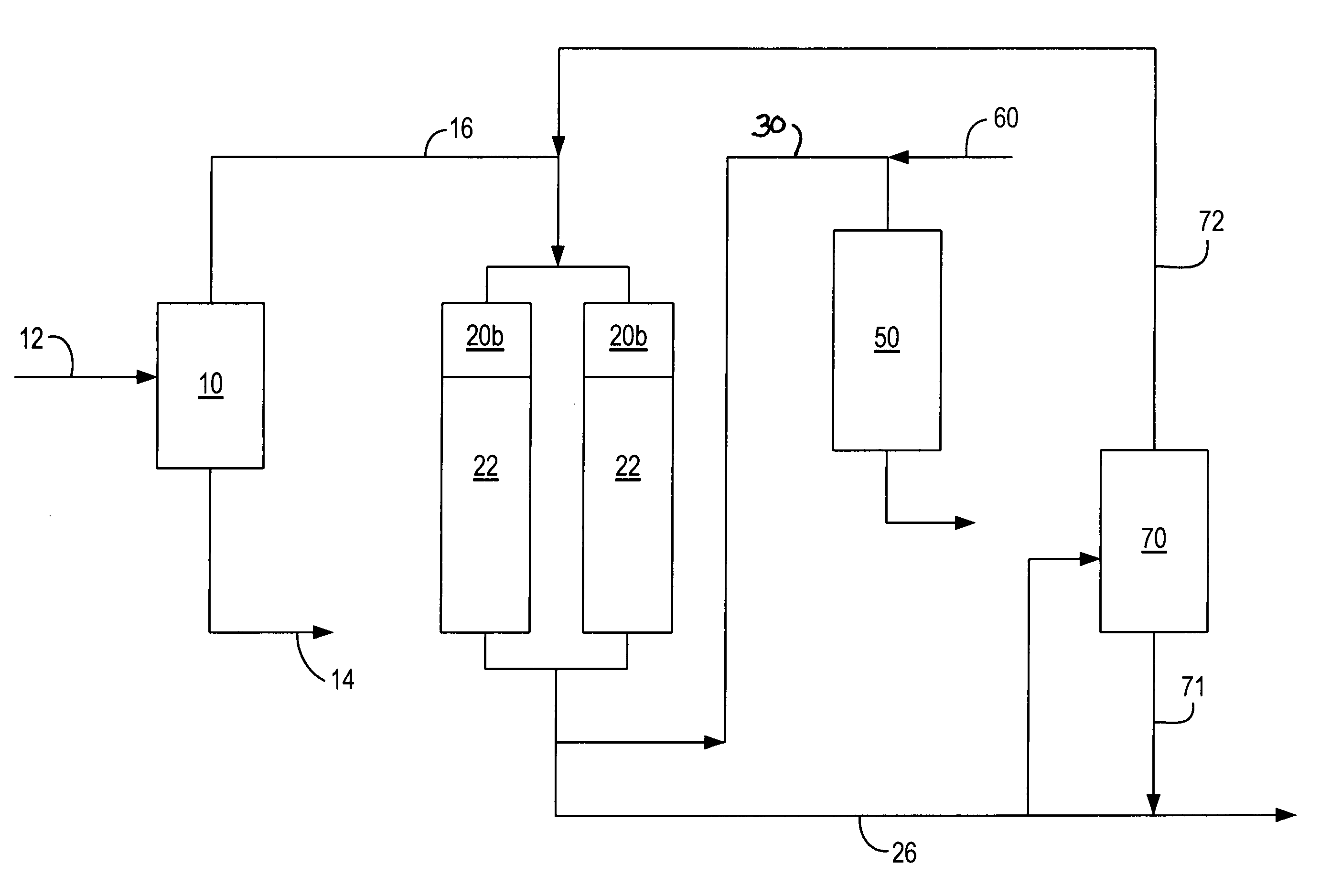
Process for multistage residue hydroconversion integrated with straight-run and conversion gasoils hydroconversion steps
InactiveUS7938952B2Improve throughputMitigate issueTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyMolecular sieve catalystsVapor liquidLiquid product
This invention relates to a novel integrated hydroconversion process for converting heavy atmospheric or vacuum residue feeds and also converting and reducing impurities in the vacuum gas oil liquid product. This is accomplished by utilizing two residue hydroconversion reaction stages, two vapor-liquid separators, and at least two additional distillate ebullated-bed hydrocracking / hydrotreating reaction stages to provide a high conversion rate of the residue feedstocks.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
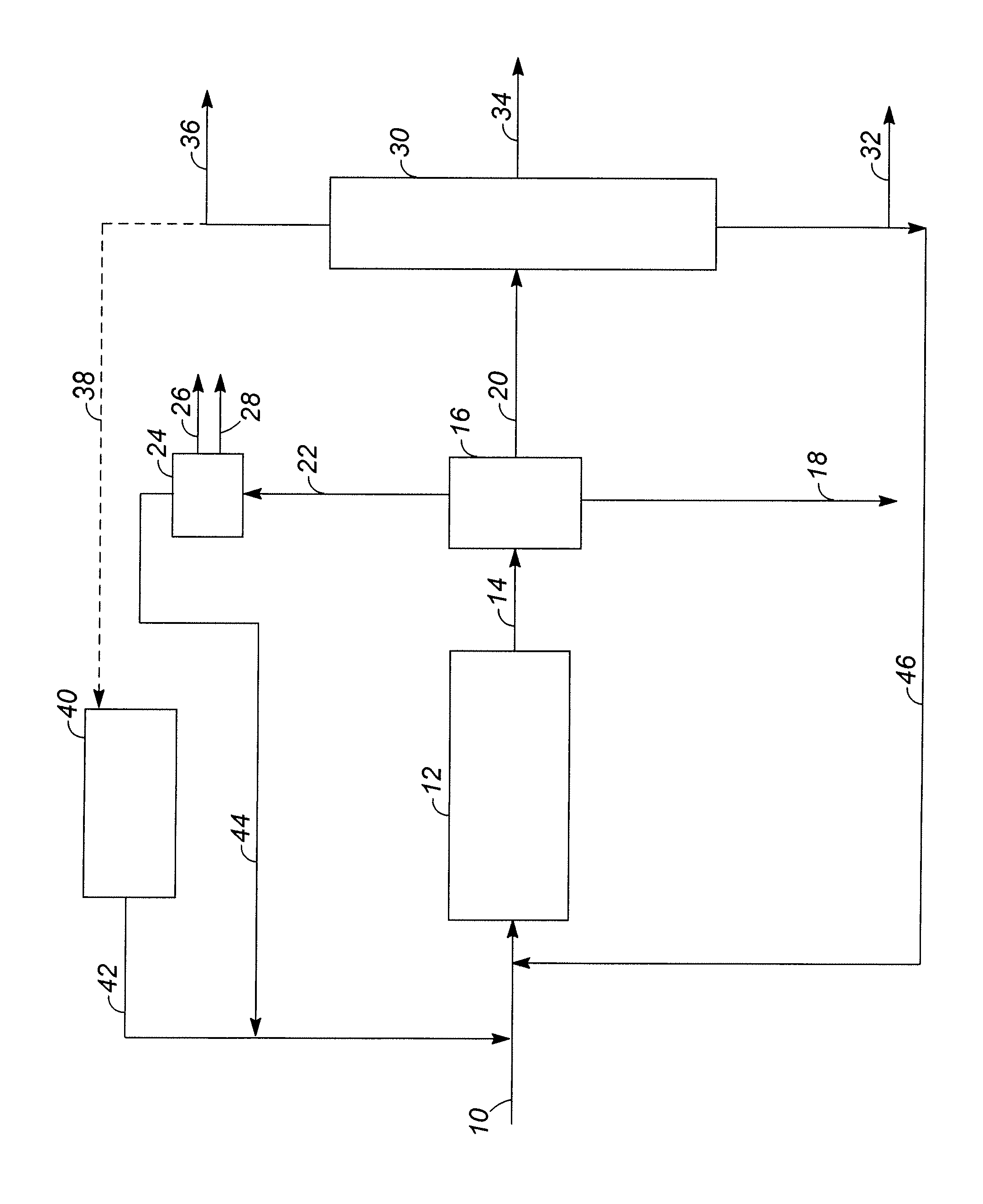
Olefin production utilizing whole crude oil/condensate feedstock with enhanced distillate production
InactiveUS7550642B2Maximize recoveryThermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial stages onlyLiquid productNatural-gas condensate
A method processing a liquid crude and / or natural gas condensate feed comprising subjecting the feed to a vaporization step to form a vaporous product and a liquid product, subjecting the vaporous product to severe thermal cracking, and subjecting the liquid product to crude oil refinery processing.
Owner:EQUSR CHEM LP
Gasoline sulfur reduction in fluid catalytic cracking
InactiveUS6852214B1Reduce sulfur contentLow sulfurCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsOxidation stateGasoline
The sulfur content of liquid cracking products, especially the cracked gasoline, of the catalytic cracking process is reduced by the use of a sulfur reduction additive comprising a porous molecular sieve which contains a metal in an oxidation state above zero within the interior of the pore structure of the sieve. The molecular sieve is normally a large pore size zeolite such as USY or zeolite beta or an intermediate pore size zeolite such as ZSM-5. The metal is normally a metal of Period 4 of the Periodic Table, preferably zinc or vanadium. The sulfur reduction catalyst may be used in the form of a separate particle additive or as a component of an integrated cracking / sulfur reduction catalyst.
Owner:MOBIL OIL CORP +1
Process for making a lubricating composition
InactiveUS6288296B1Improvement ingredientsTreatment with plural serial stages onlyHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionAlkaneIsomerization
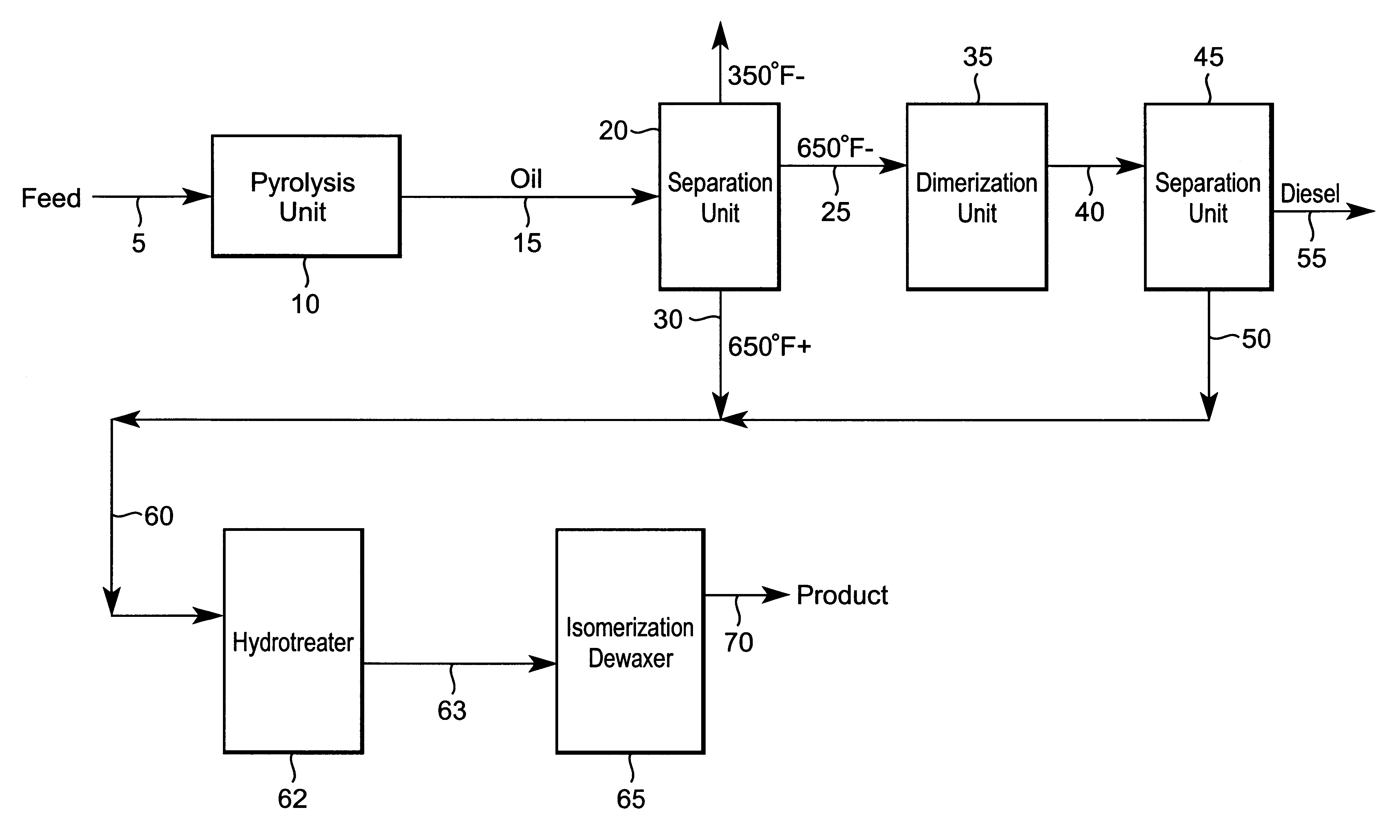
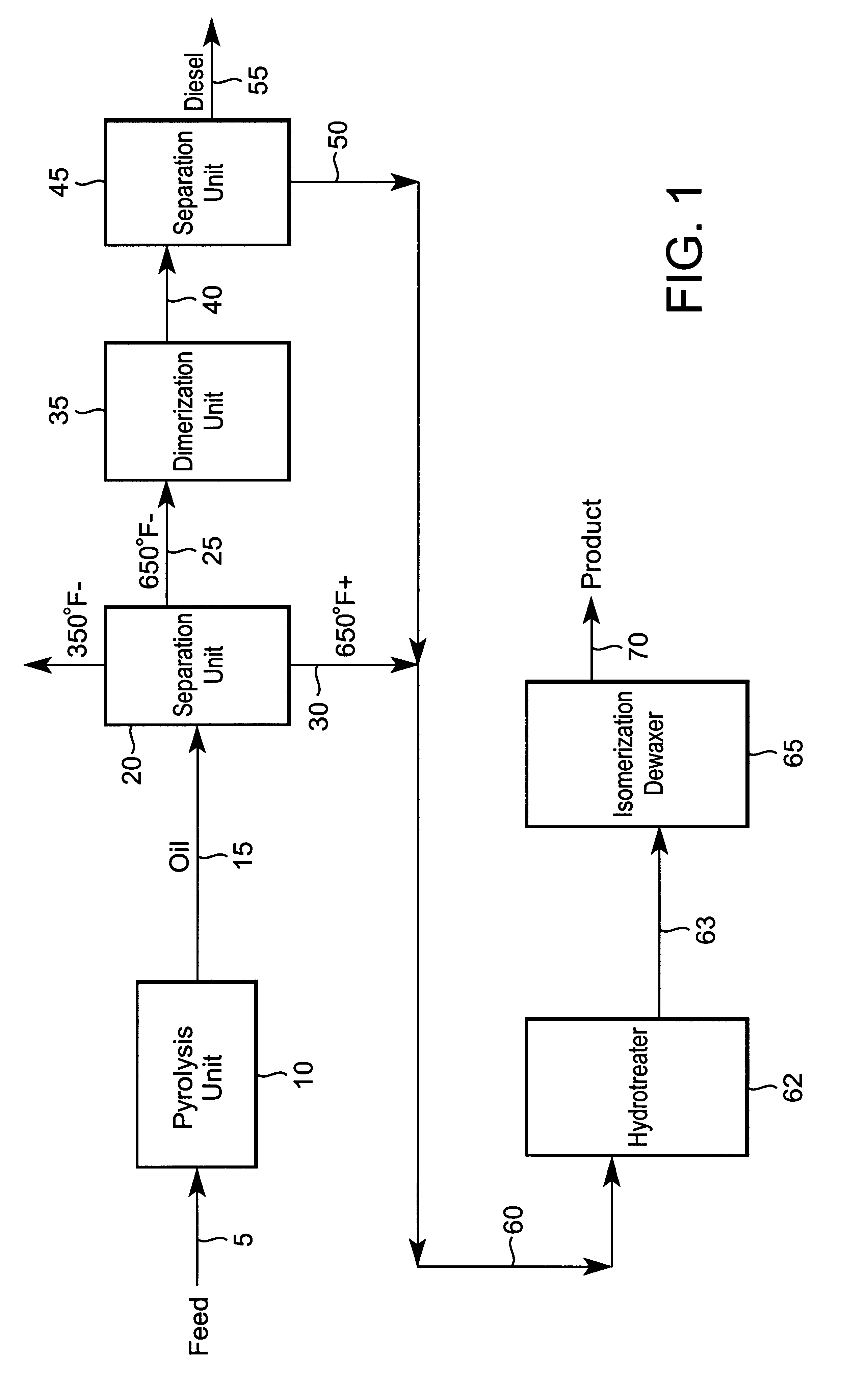
The invention includes a process of making a lubricating oil composition including: a process for making a high VI lubricating oil composition including the steps of (1) contacting a waste plastics feed including mainly polyethylene in a pyrolysis zone at pyrolysis conditions, whereby at least a portion of the waste plastics feed is cracked, thereby forming a pyrolysis zone effluent including 1-olefins and n-paraffins; (2) passing the pyrolysis zone effluent, including a heavy fraction and a middle fraction, the pyrolysis effluent middle fraction including 1-olefins, to a separations zone; where the pyrolysis effluent heavy fraction portion is separated from the pyrolysis effluent middle fraction; (3) passing the pyrolysis effluent middle fraction to a dimerization zone, where at least a portion of the pyrolysis effluent middle fraction is converted to a lube oil range material; and (4) passing at least a portion of the lube oil range material to a catalytic isomerization dewaxing zone, where at least a portion of the lube oil range material is contacted with a isomerization dewaxing catalyst at isomerization dewaxing conditions thereby forming a high VI lubricating oil composition.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Supercritical hydrocarbon conversion process
ActiveUS7144498B2Thermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyReaction temperatureUnit operation
Supercritical conversion of hydrocarbons boiling above 538° C. (1000° F.) with a solvating hydrocarbon at a weight ratio of solvating hydrocarbon to high-boiling hydrocarbons of at least 2:1 and at conditions above the critical temperature and pressure of the high-boiling hydrocarbons-solvent mixture, in the presence of hot fluidized solids. The hydrocarbons are supplied to a reaction zone at a temperature below that of the hot solids supplied thereto, whereby the resulting hydrocarbons-solids suspension has a thermal equilibrium temperature corresponding to the reaction temperature. The conversion has high rates of sulfur, nitrogen and metals removal, nearly complete conversion to lower molecular weight products, high naphtha and distillate selectivity, and low coke formation. The supercritical conversion can replace crude distillation, vacuum distillation, solvent deasphalting, coking, hydrocracking, hydrotreating, and / or fluid catalytic cracking, and / or used in parallel with such unit operations for debottle-necking or increasing capacity.
Owner:KELLOGG BROWN & ROOT LLC
Hydrodeoxygenation process
A process for producing a hydrocarbon from biomass. A feed stream having free fatty acids, fatty acid esters or combinations thereof is provided. The feed stream is heated in the presence of a first catalyst to produce a partially hydrodeoxygenated stream. The partially hydrodeoxygenated stream is heated in the presence of a second catalyst to produce an effluent stream containing the hydrocarbon.
Owner:REG SYNTHETIC FUELS LLC
Catalytic conversion method and apparatus for upgrading poor gasoline
InactiveCN1401740AReduce olefin contentReduce sulfur contentTreatment with plural serial stages onlyCatalytic transformationFuel oil
A catalytic converting process for upgrading poor-quality gasoline with high olefine content incldues a conventional catalytic cracking step for heavy oil and a catalytic converting step for upgrading said gasoline. It is characterized by in that two steps a common catalyst regenerator and a same catalyst are used. It can decrease olefine content by 15-50 vol% and S content by 5-30% and increase RON by 0.2-2 units.
Owner:SINOPEC LUOYANG PETROCHEM ENG CORP
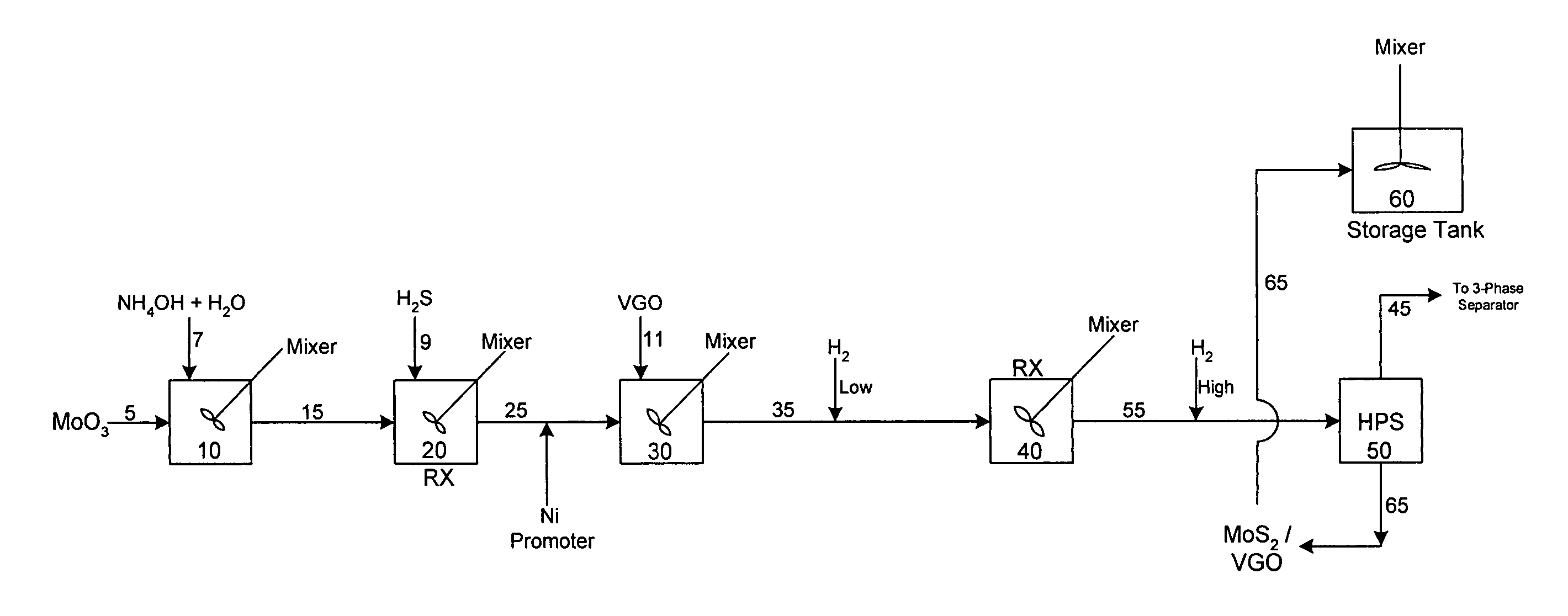
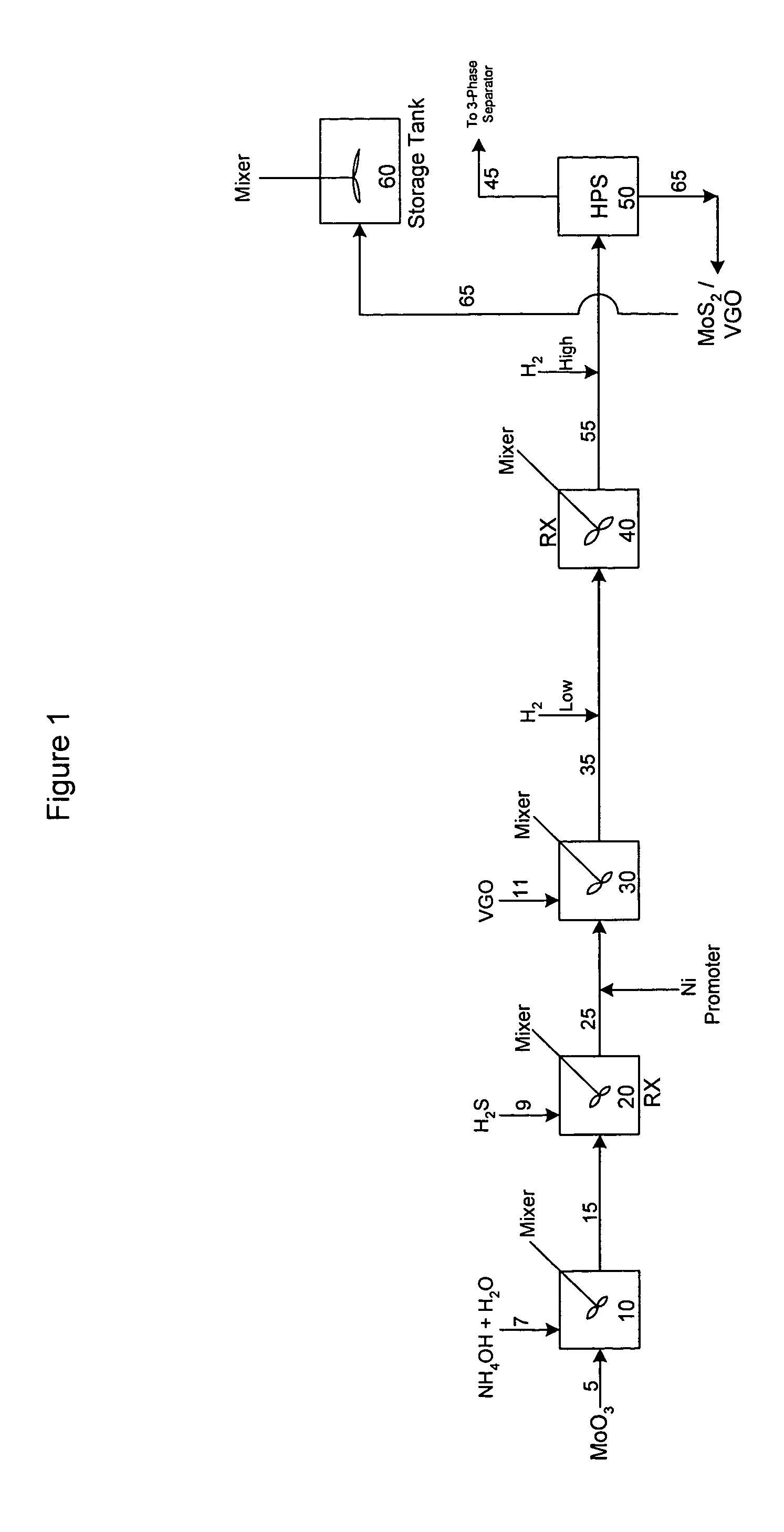
Process for upgrading heavy oil using a highly active slurry catalyst composition
ActiveUS7214309B2High viscosityTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyTreatment with plural serial stages onlyHydrogenSlurry
The instant invention is directed to a process for upgrading heavy oils using a slurry composition. The slurry composition is prepared in a series of steps, involving mixing a Group VIB metal oxide with aqueous ammonia to form an aqueous mixture and sulfiding the mixture to form a slurry. The slurry is then promoted with a Group VIII metal compound. Subsequent steps involve mixing the slurry with a hydrocarbon oil, and combining the resulting mixture with hydrogen gas (under conditions which maintain the water in a liquid phase) to produce the active slurry catalyst.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Process for removal of nitrogen and poly-nuclear aromatics from hydrocracker and FCC feedstocks
ActiveUS20080105595A1Increase heightCatalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial stages onlyActivated carbonSorbent
A feedstream to a hydrocracking unit is treated to remove or reduce the content of polynuclear aromatics and nitrogen-containing compounds by contacting the feedstream with an adsorbent compound selected from attapulgus clay, alumina, silica gel and activated carbon in a fixed bed or slurry column and separating the treated feedstream that is lower in the undesired compounds from the adsorbent material. The adsorbent can be mixed with a solvent for the undesired compounds and stripped for re-use.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Process for the manufacture of hydrocarbon components
The present invention relates to hydrocarbons and particularly to the manufacture of hydrocarbon components suitable as aviation fuels or jet fuels and as blending stocks for aviation fuels. The process comprises the stages, wherein in the first stage an oil feed of biological origin and hydrogen gas are subjected to conditions sufficient to effect hydrodeoxygenation in the presence of a hydrodeoxygenation catalyst to yield n-paraffins;in the second stage the n-paraffins and hydrogen gas are subjected to conditions sufficient to effect isomerisation in the presence of an isomerisation catalyst to yield isoparaffins and separating fractions; andrecycling the fraction boiling at a temperature above 200° C. under atmospheric pressure obtained from the second stage to reisomerisation, where isomerisation is effected in the presence of an isomerisation catalyst.
Owner:NESTE OIL OY
Two stage fluid catalytic cracking process for selectively producing C2 to C4 olefins
InactiveUS7323099B2Treatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyCatalytic naphtha reformingPtru catalystNaphtha
A process for selectively producing C2 to C4 olefins from feedstock such as a gas oil or resid. The feedstock is reacted in a first stage comprising a fluid catalytic cracking unit wherein it is converted in the presence of a mixture of conventional large pore zeolitic catalyst and a medium pore zeolitic catalyst to reaction products, including a naphtha boiling range stream. The naphtha boiling range stream is introduced into a second stage where it is contacted with a catalyst containing from about 10 to about 50 wt. % of a crystalline zeolite having an average pore diameter less than about 0.7 nanometers at reaction conditions which include temperatures ranging from about 500 to about 650° C. and a hydrocarbon partial pressure from about 10 to about 40 psia (about 70 to about 280 kPa).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
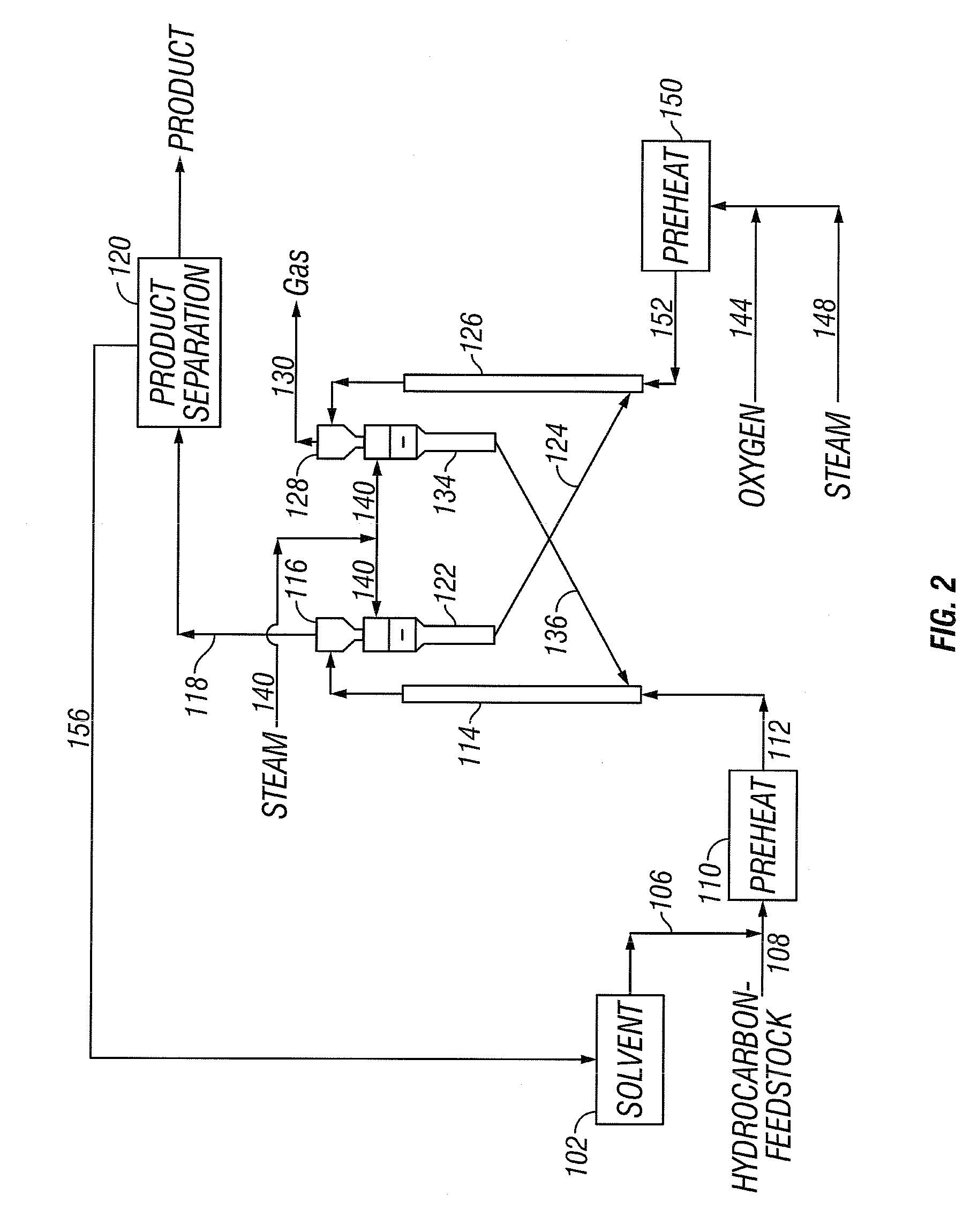
Integrated solvent deasphalting, hydrotreating and steam pyrolysis process for direct processing of a crude oil
ActiveUS9284502B2Thermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlySteam pyrolysisFuel oil
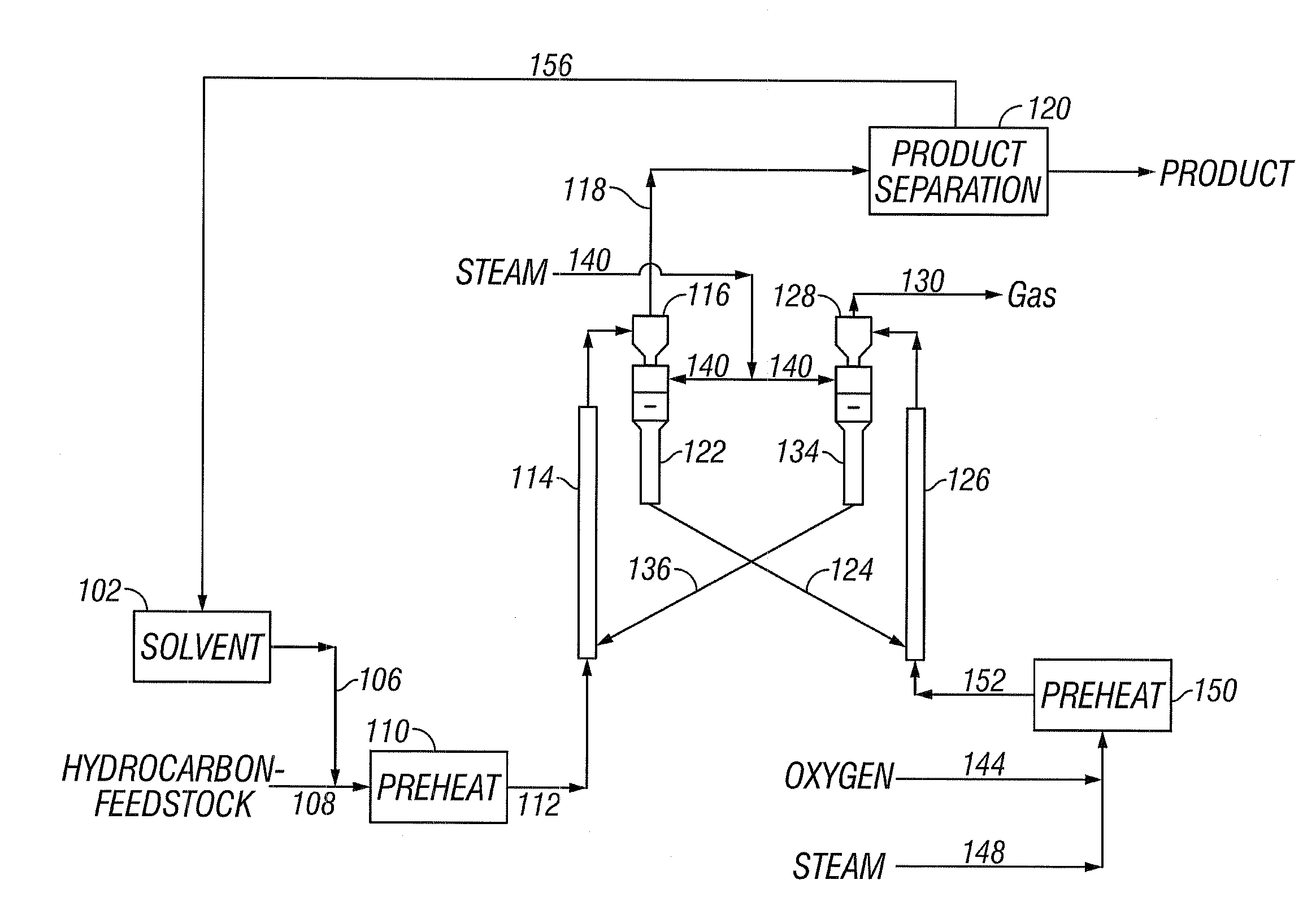
A process is provided that is directed to a steam pyrolysis zone integrated with a solvent deasphalting zone and a hydrotreating zone to permit direct processing of crude oil feedstocks to produce petrochemicals including olefins and aromatics. The integrated solvent deasphalting, hydrotreating and steam pyrolysis process for the direct processing of a crude oil to produce olefinic and aromatic petrochemicals comprises: charging the crude oil to a solvent deasphalting zone with an effective amount of solvent for producing a deasphalted and demetalized oil stream and a bottom asphalt phase; charging the deasphalted and demetalized oil stream and hydrogen to a hydroprocessing zone operating under conditions effective to produce a hydroprocessed effluent reduced having a reduced content of contaminants, an increased paraffinicity, reduced Bureau of Mines Correlation Index, and an increased American Petroleum Institute gravity; thermally cracking the hydroprocessed effluent in the presence of steam to produce a mixed product stream; separating the mixed product stream; purifying hydrogen recovered from the mixed product stream and recycling it to the hydroprocessing zone; recovering olefins and aromatics from the separated mixed product stream; and recovering pyrolysis fuel oil from the separated mixed product stream.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Methods and Systems for Producing Reduced Resid and Bottomless Products from Heavy Hydrocarbon Feedstocks
InactiveUS20080230440A1Cost controlReduce operating costsThermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyParticulatesLiquid product
The present invention is directed to the upgrading of heavy petroleum oils of high viscosity and low API gravity that are typically not suitable for pipelining without the use of diluents. The method comprises introducing a particulate heat carrier into an up-flow reactor, introducing the feedstock at a location above the entry of the particulate heat carrier, allowing the heavy hydrocarbon feedstock to interact with the heat carrier for a short time, separating the vapors of the product stream from the particulate heat carrier and liquid and byproduct solid matter, collecting a gaseous and liquid product mixture comprising a mixture of a light fraction and a heavy fraction from the product stream, and using a vacuum tower to separate the light fraction as a substantially bottomless product and the heavy fraction from the product mixture.
Owner:IVANHOE HTL GASOLINEEUM
Flow-through cavitation-assisted rapid modification of crude oil
ActiveUS20100101978A1Improve effectivenessThermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyCavitationChemical composition
A device and method are provided for manipulating petroleum, non-conventional oil and other viscous complex fluids made of hydrocarbons that comprise enforcement of fluid in a multi-stage flow-through hydrodynamic cavitational reactor, subjecting said fluids to a controlled cavitation and continuing the application of such cavitation for a period of time sufficient for obtaining desired changes in physical properties and / or chemical composition and generating the upgraded products. The method includes alteration of chemical bonds, induction of interactions of components, changes in composition, heterogeneity and rheological characteristics in order to facilitate handling, improve yields of distillate fuels and optimize other properties.
Owner:CAVITATION TECH
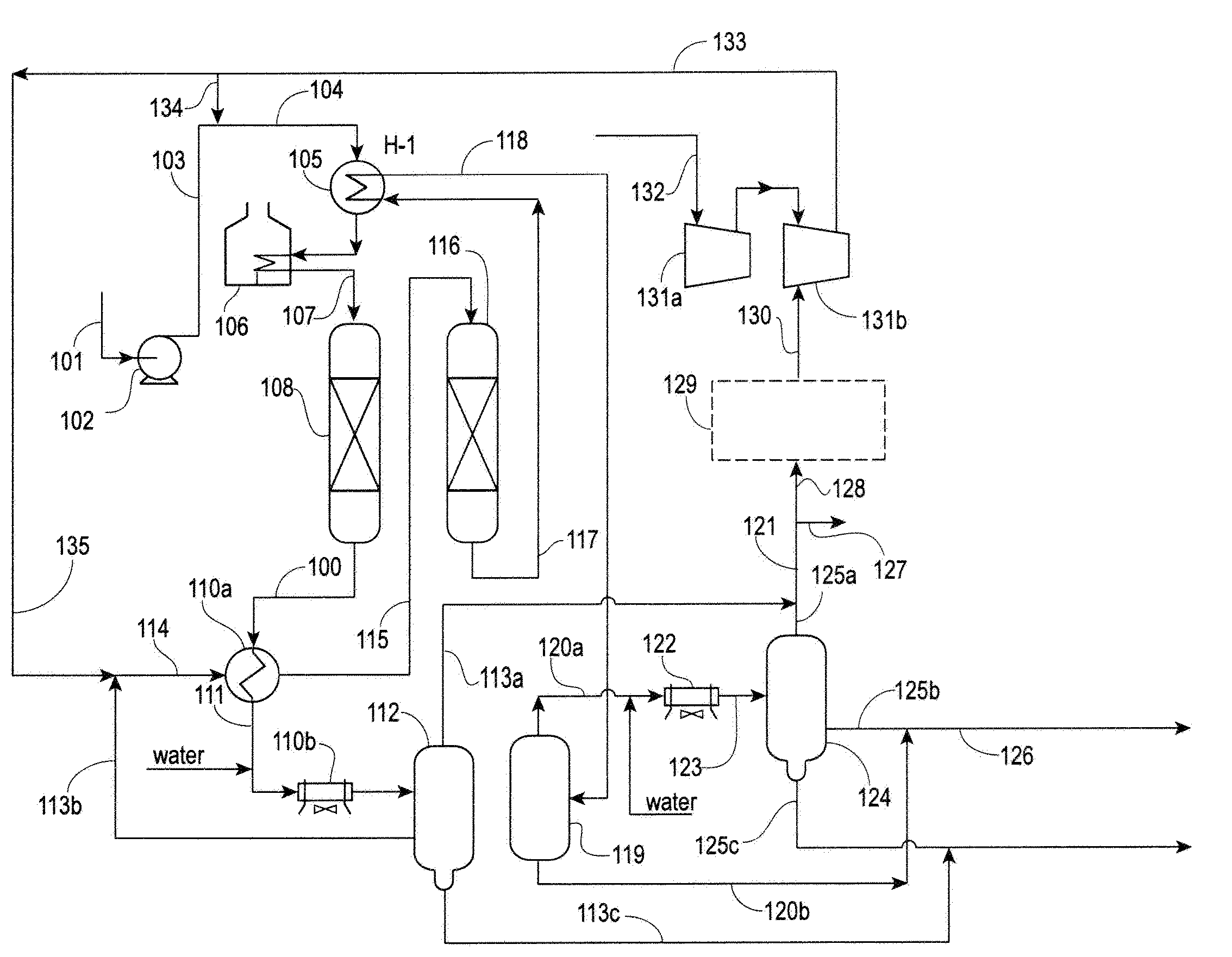
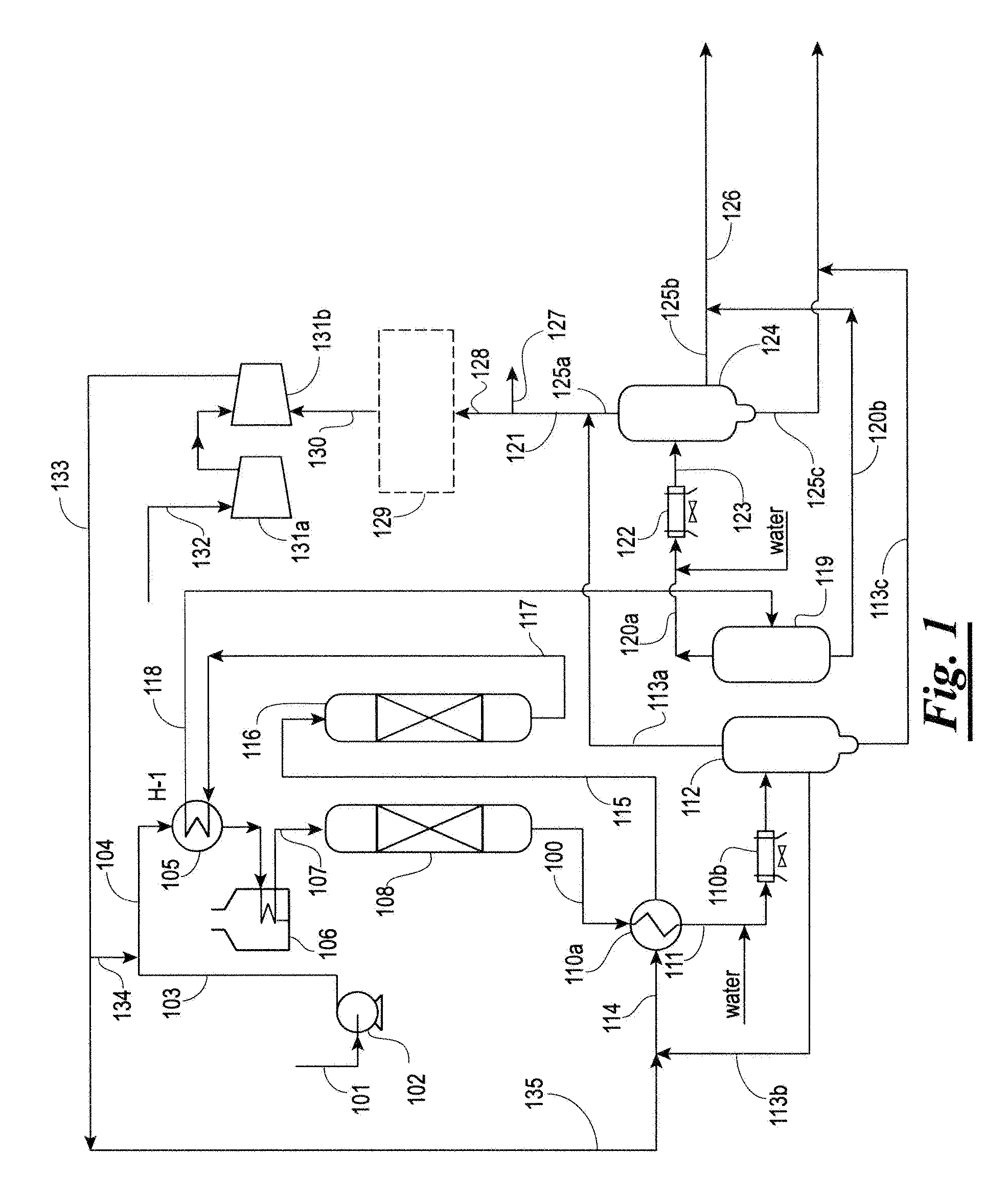
Integrated hydrotreating and steam pyrolysis process for direct processing of a crude oil
ActiveUS9255230B2Thermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlySteam pyrolysisCorrelation index
An integrated hydrotreating and steam pyrolysis process for the direct processing of a crude oil is provided to produce olefinic and aromatic petrochemicals. Crude oil and hydrogen are charged to a hydroprocessing zone operating under conditions effective to produce a hydroprocessed effluent reduced having a reduced content of contaminants, an increased paraffinicity, reduced Bureau of Mines Correlation Index, and an increased American Petroleum Institute gravity. Hydroprocessed effluent is thermally cracked in the presence of steam to produce a mixed product stream, which is separated. Hydrogen from the mixed product stream is purified and recycled to the hydroprocessing zone, and olefins and aromatics are recovered from the separated mixed product stream.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com