Patents
Literature
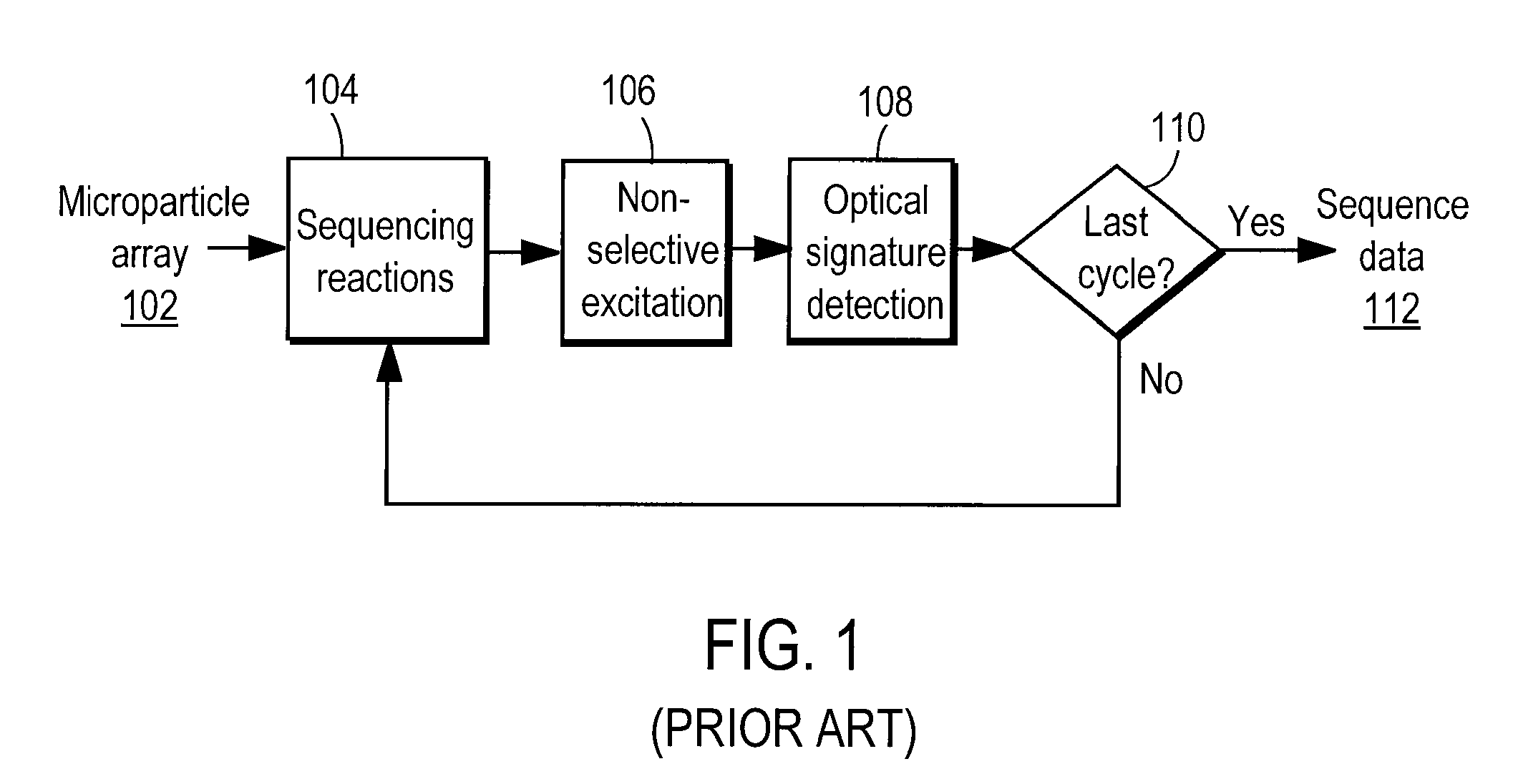
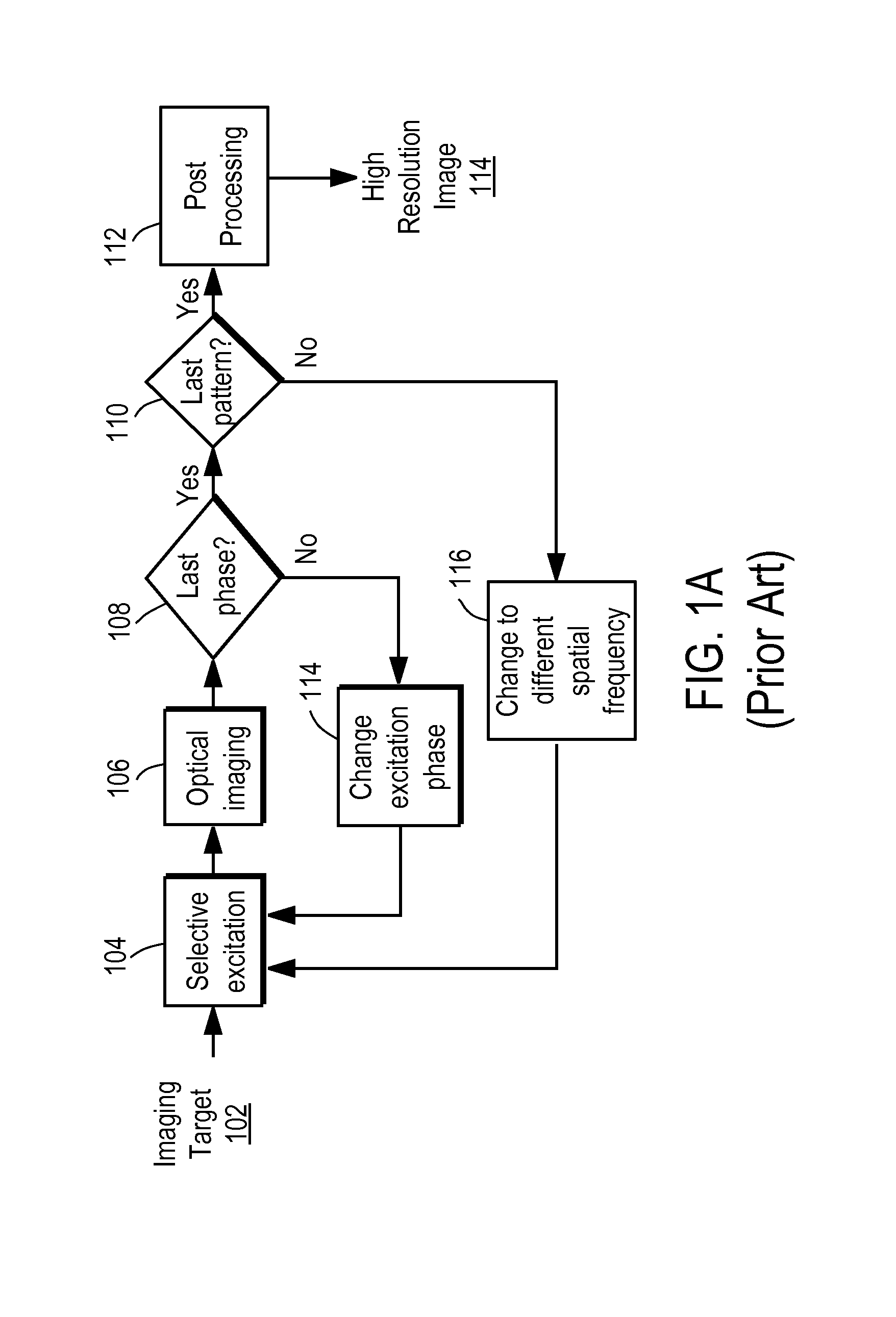
153 results about "Selective excitation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electronic lighting unit and photographic equipment with the electronic lighting unit
InactiveUS20050168965A1Efficient productionEnsure normal power onTelevision system detailsBuilding locksSelective excitationExtinction
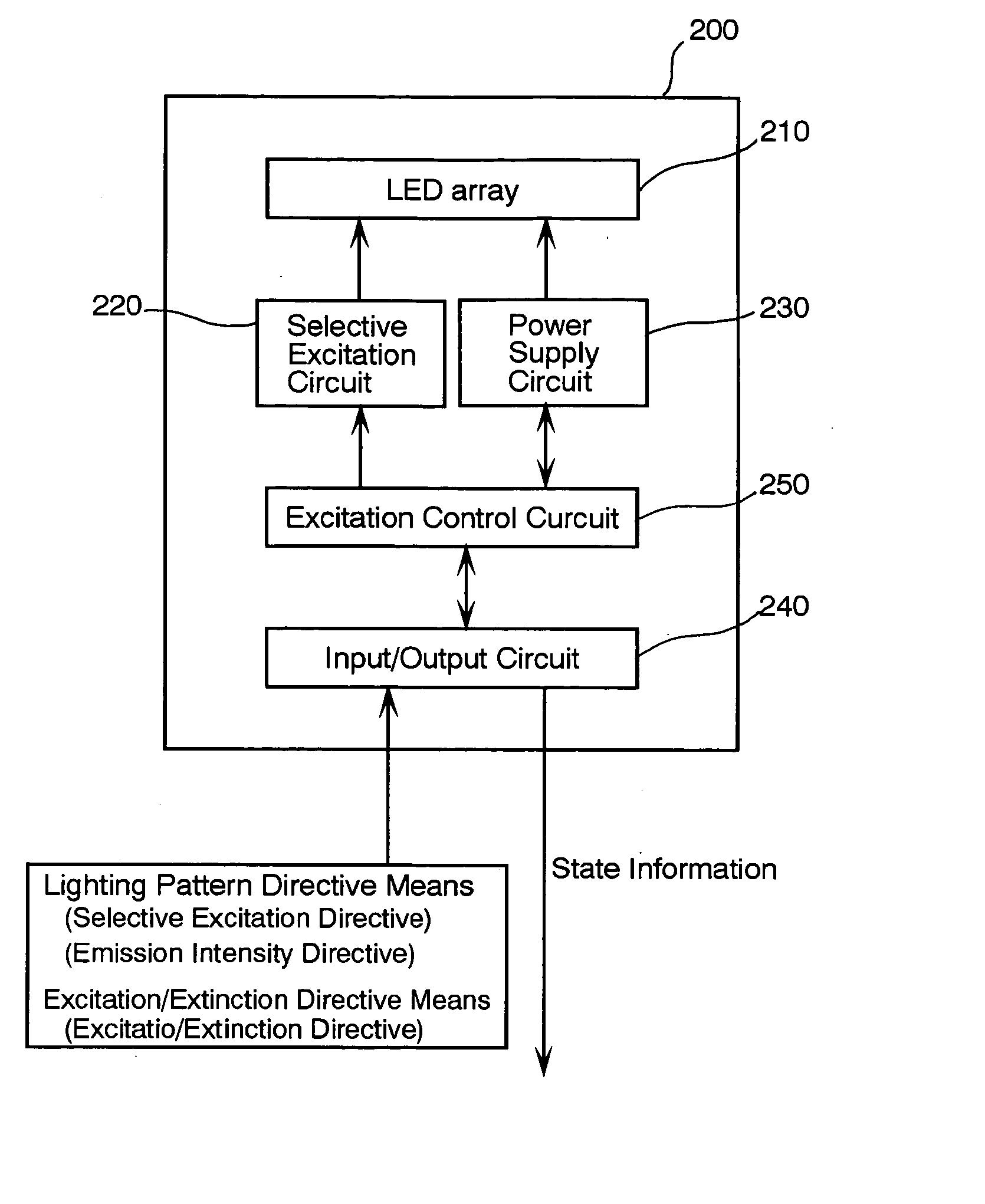
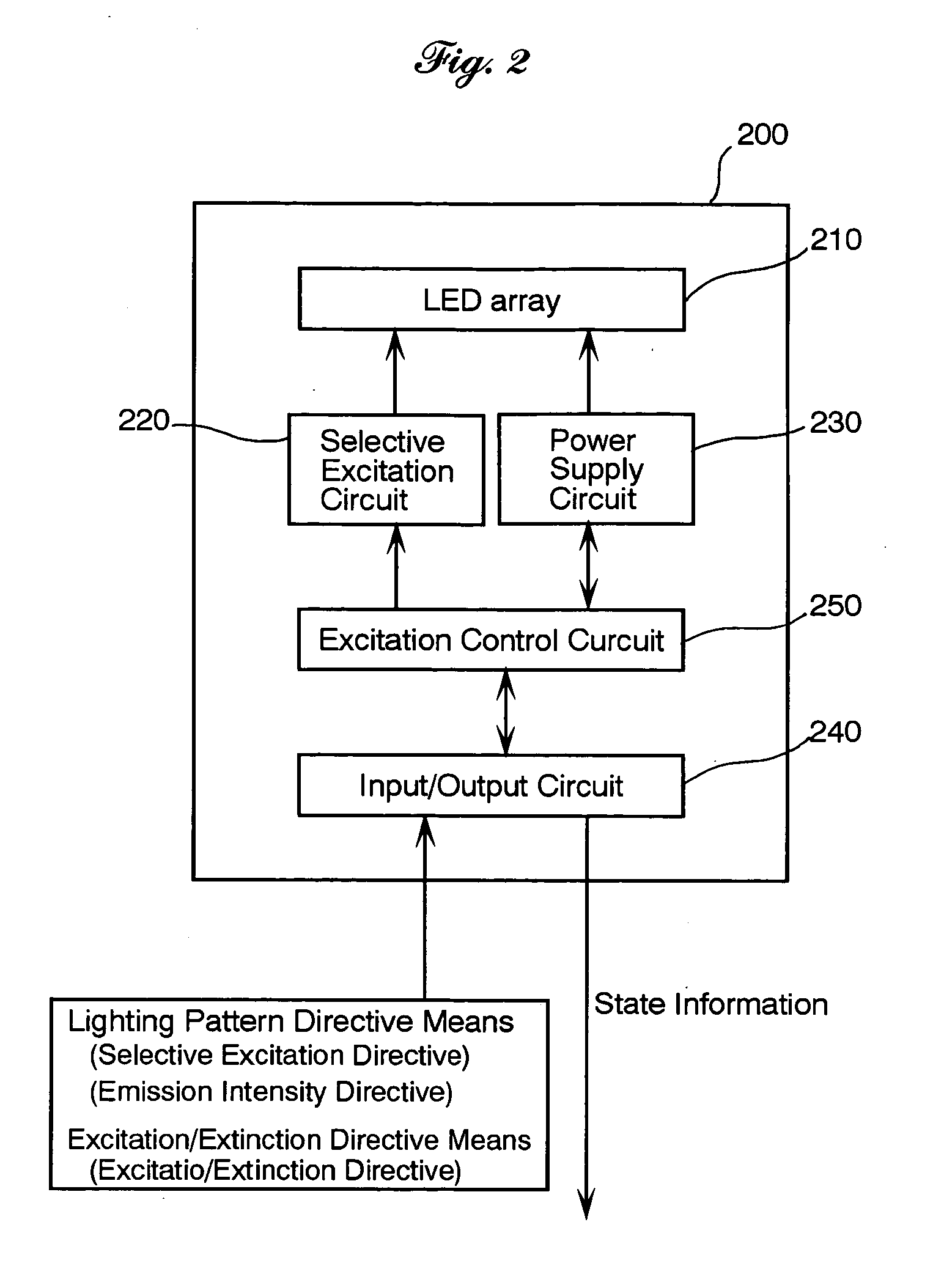
A lighting unit for producing flash light toward subjects in a photographic scene comprises an matrix array of light emitting elements arranged so as to have individual lighting fields different from one another, a selective excitation circuit for exciting selectively the light emitting elements so as to produce flash light, different in intensity as appropriate, in predetermined lighting patterns and an excitation / extinction circuit 250 for exciting or extinguishing the light emitting elements. A photographic equipment equipped with the lighting unit has directive switches or buttons for directing the lighting unit to select lighting pattern according to focal lengths, zoom rations, operation modes including a communication mode, and / or demands of pre-lighting,
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
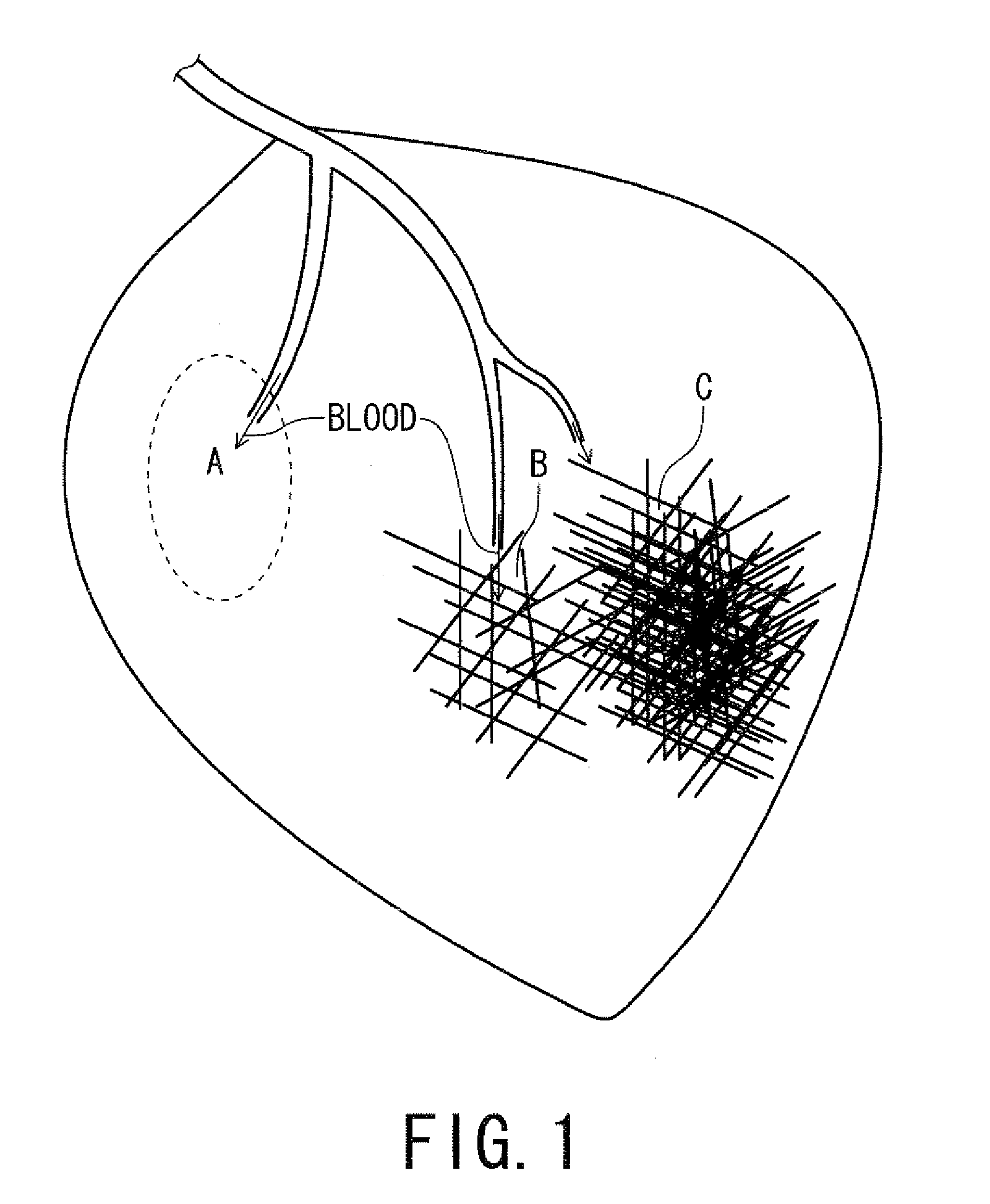
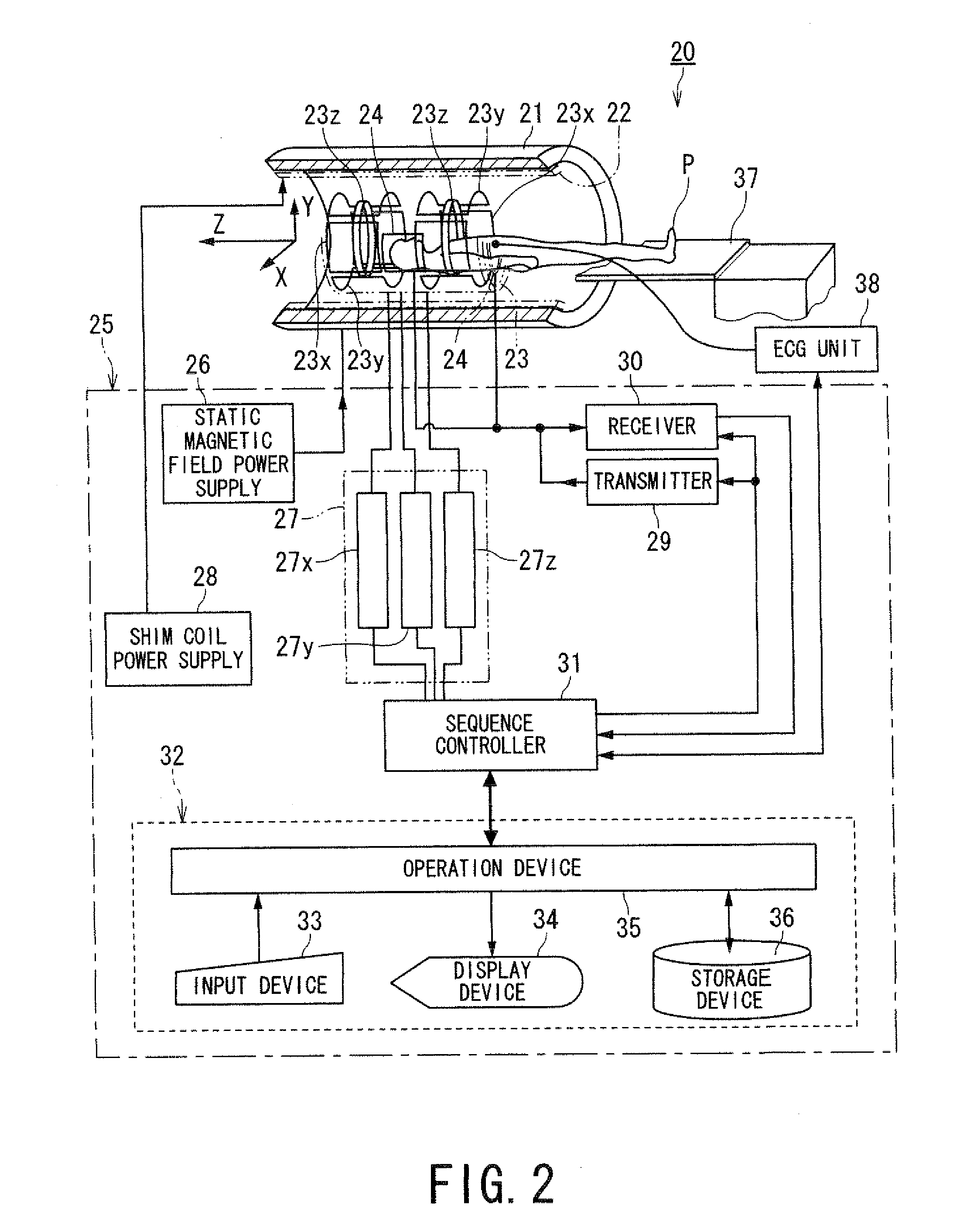
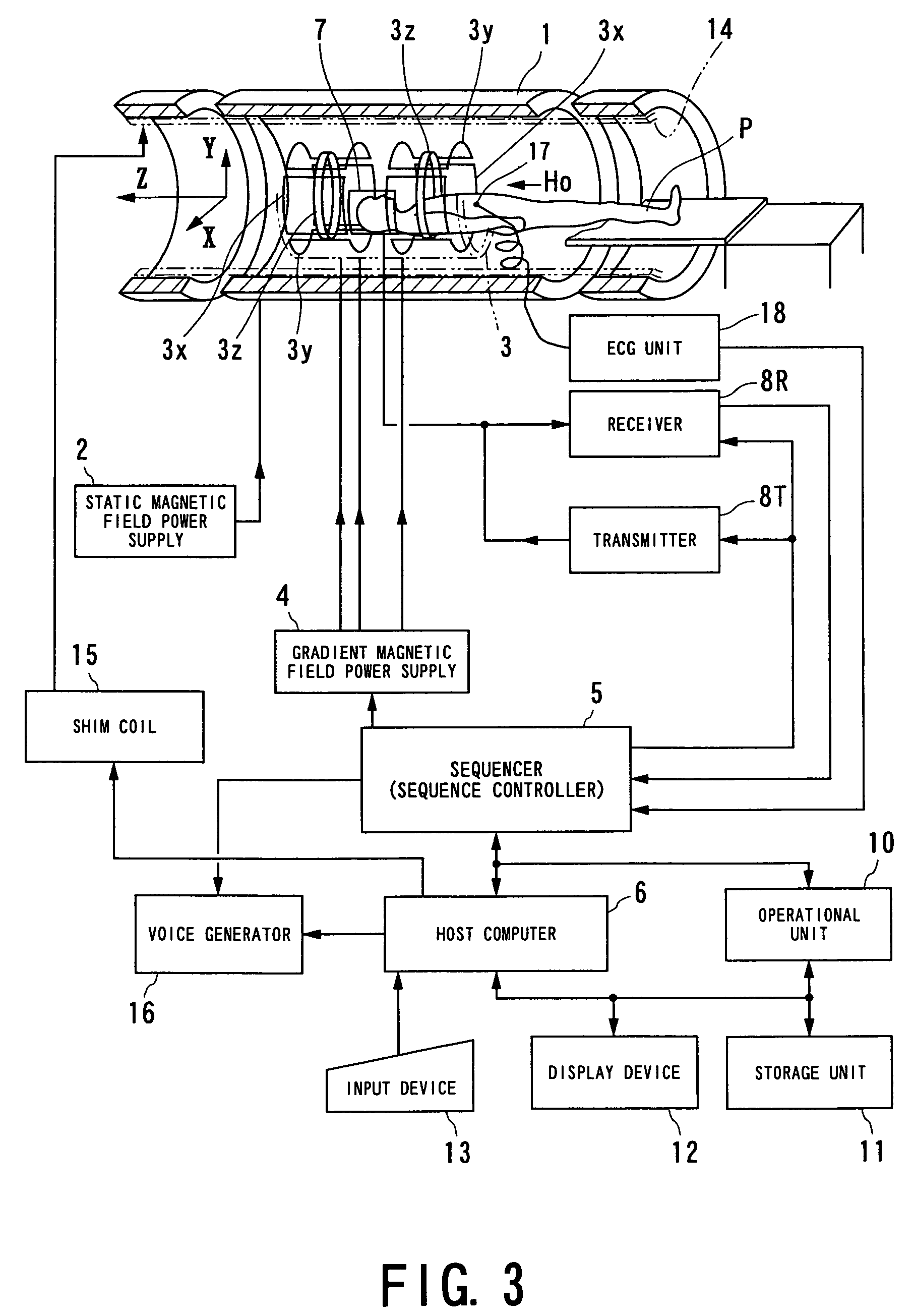
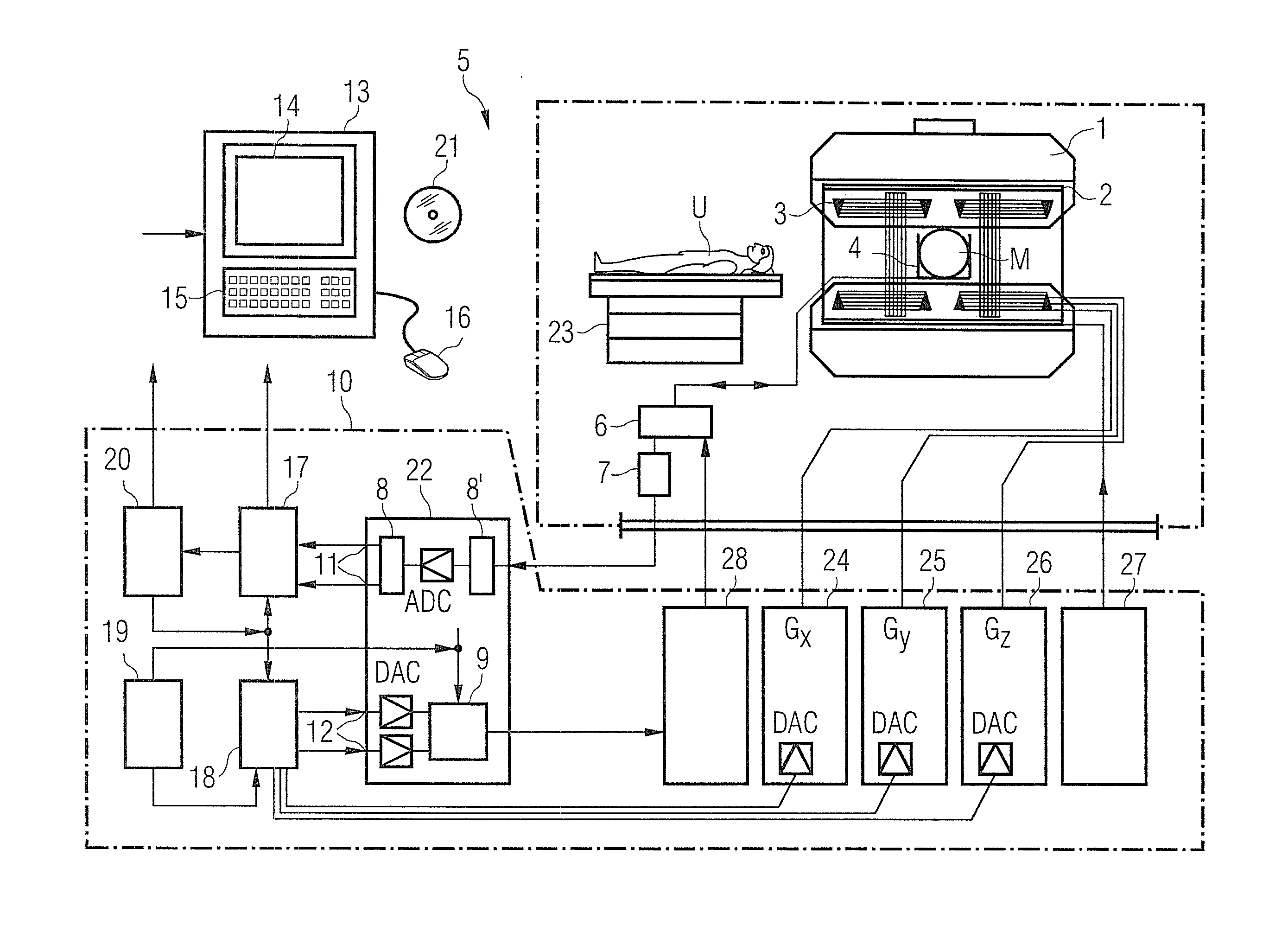
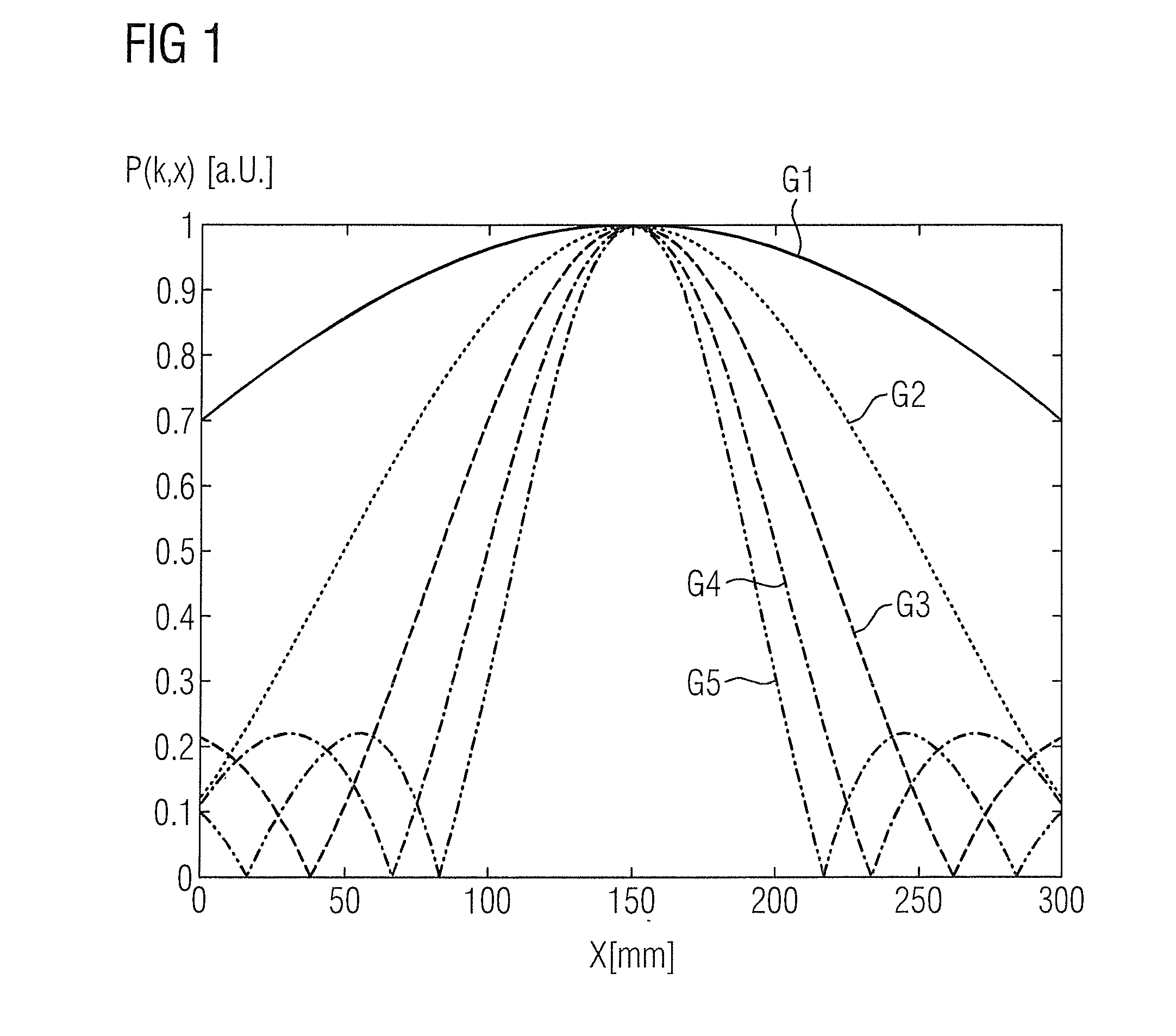
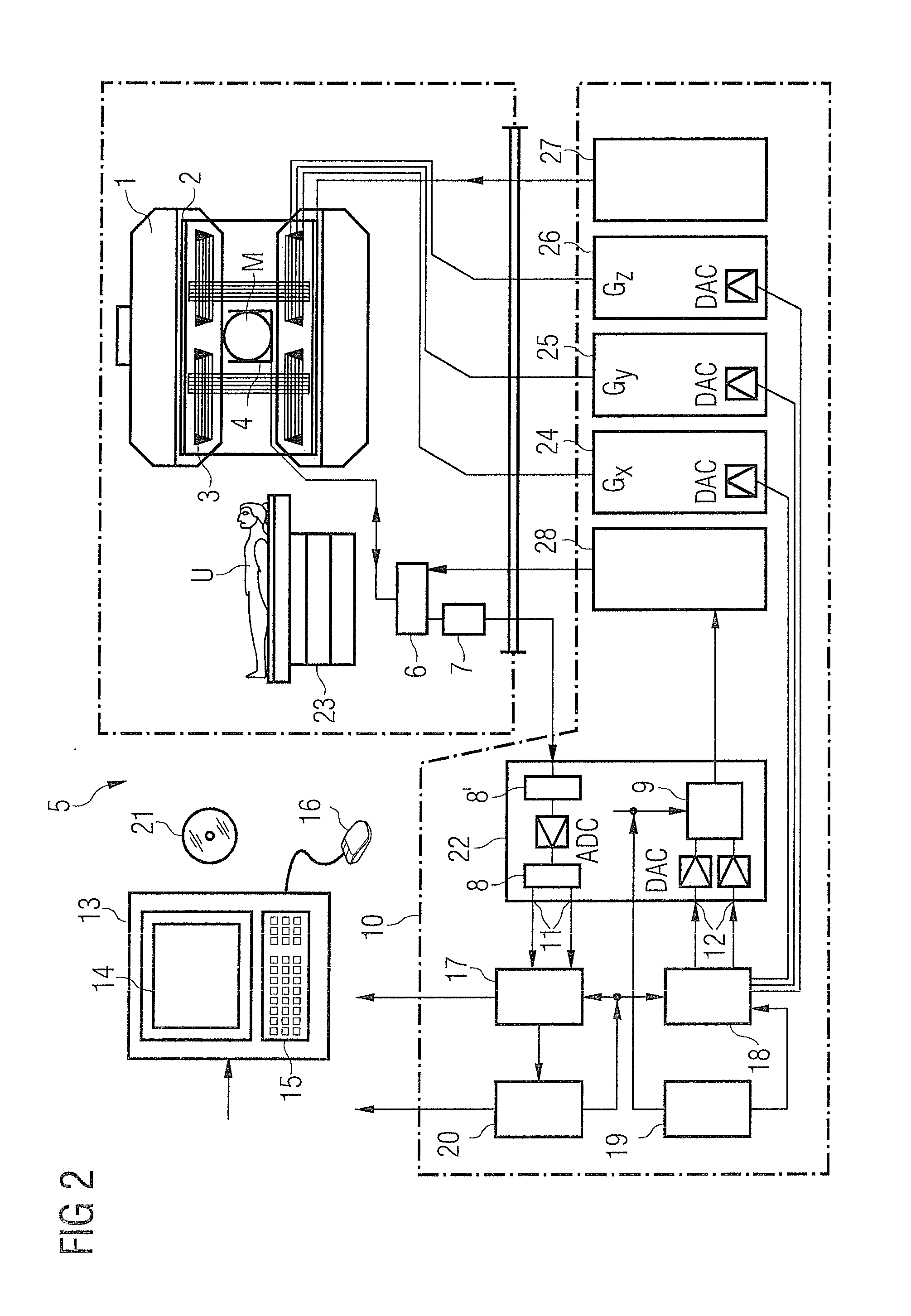
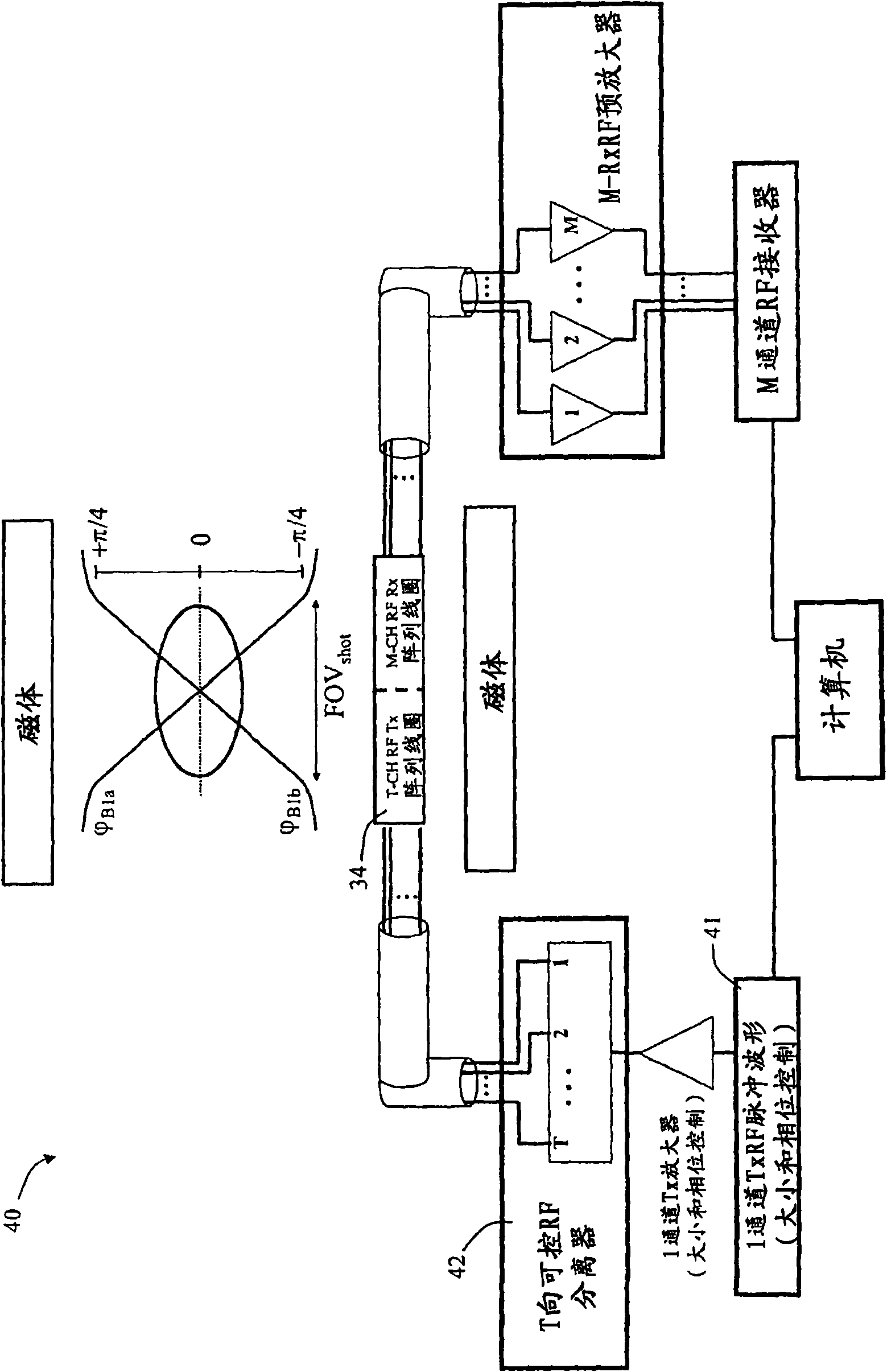
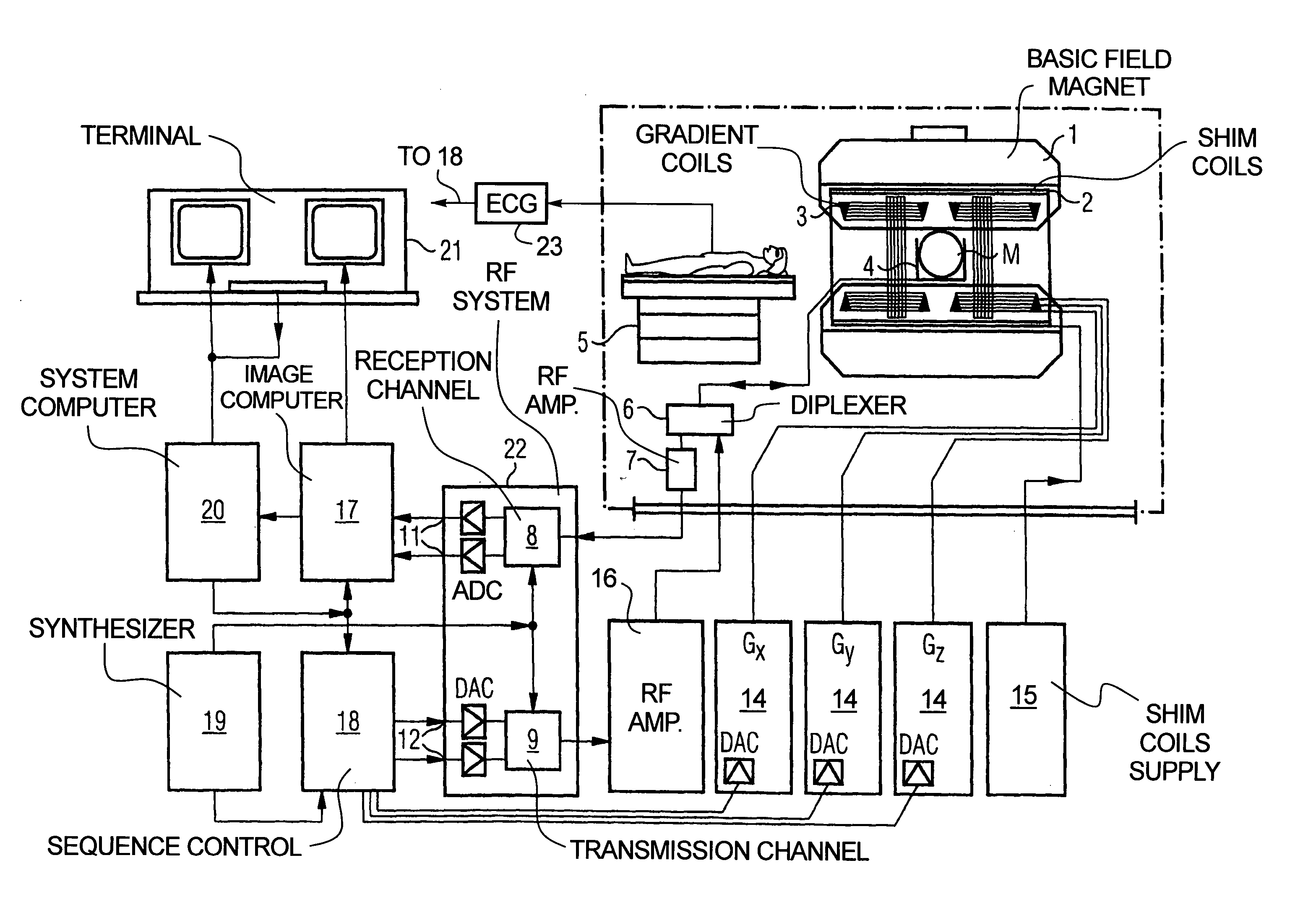
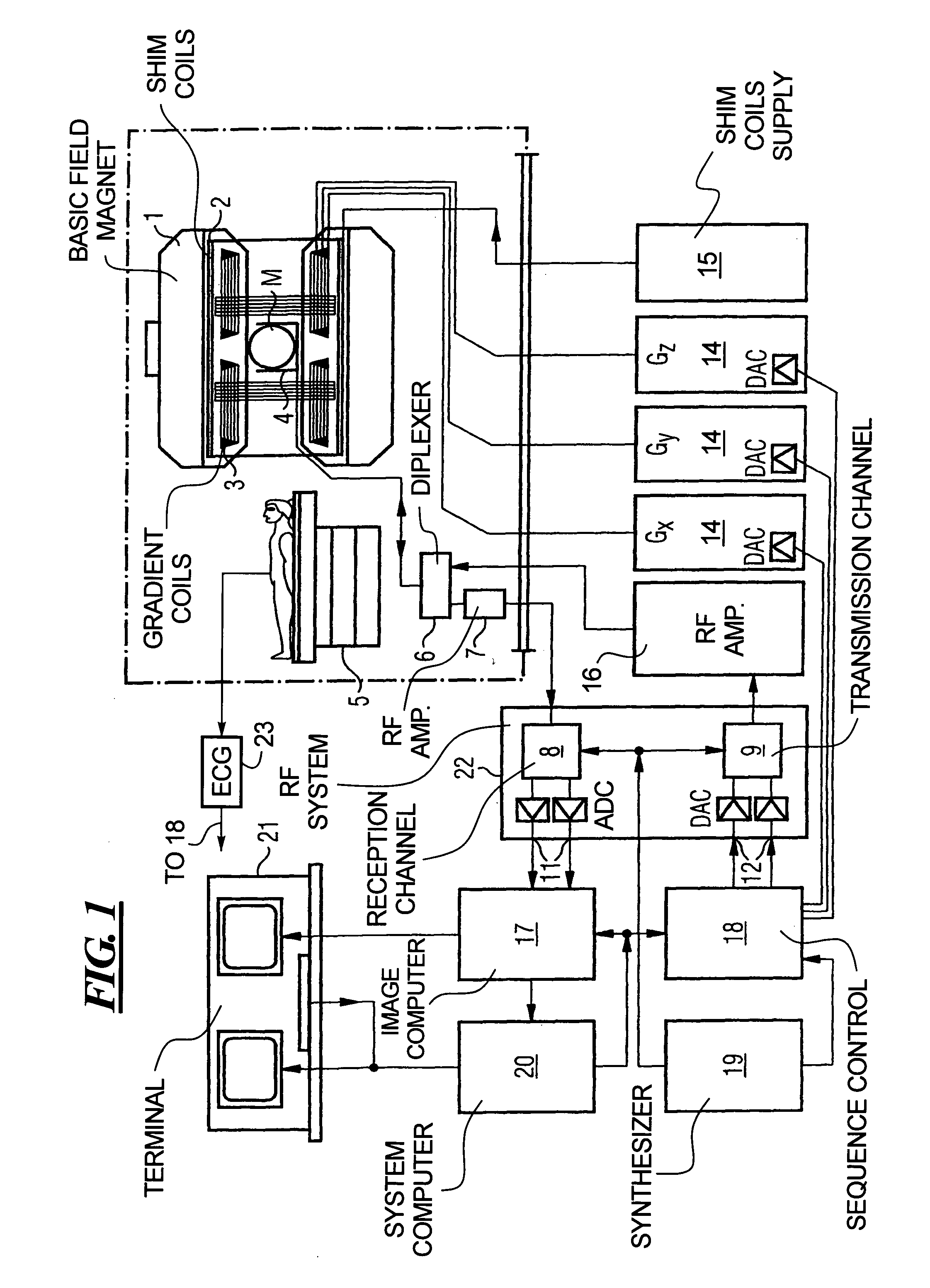
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
ActiveUS20110071382A1Easy accessSatisfactory resolutionMagnetic measurementsSensorsAscending aortaProton magnetic resonance
According to one of the aspects of an MRI apparatus of the present invention, the MRI apparatus includes an imaging data acquiring unit and a blood flow information generating unit. The imaging data acquiring unit acquires imaging data from an imaging region including myocardium, without using a contrast medium, by applying a spatial selective excitation pulse to a region including at least a part of an ascending aorta for distinguishably displaying inflowing blood flowing into the imaging region. The blood flow information generating unit generates blood flow image data based on the imaging data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
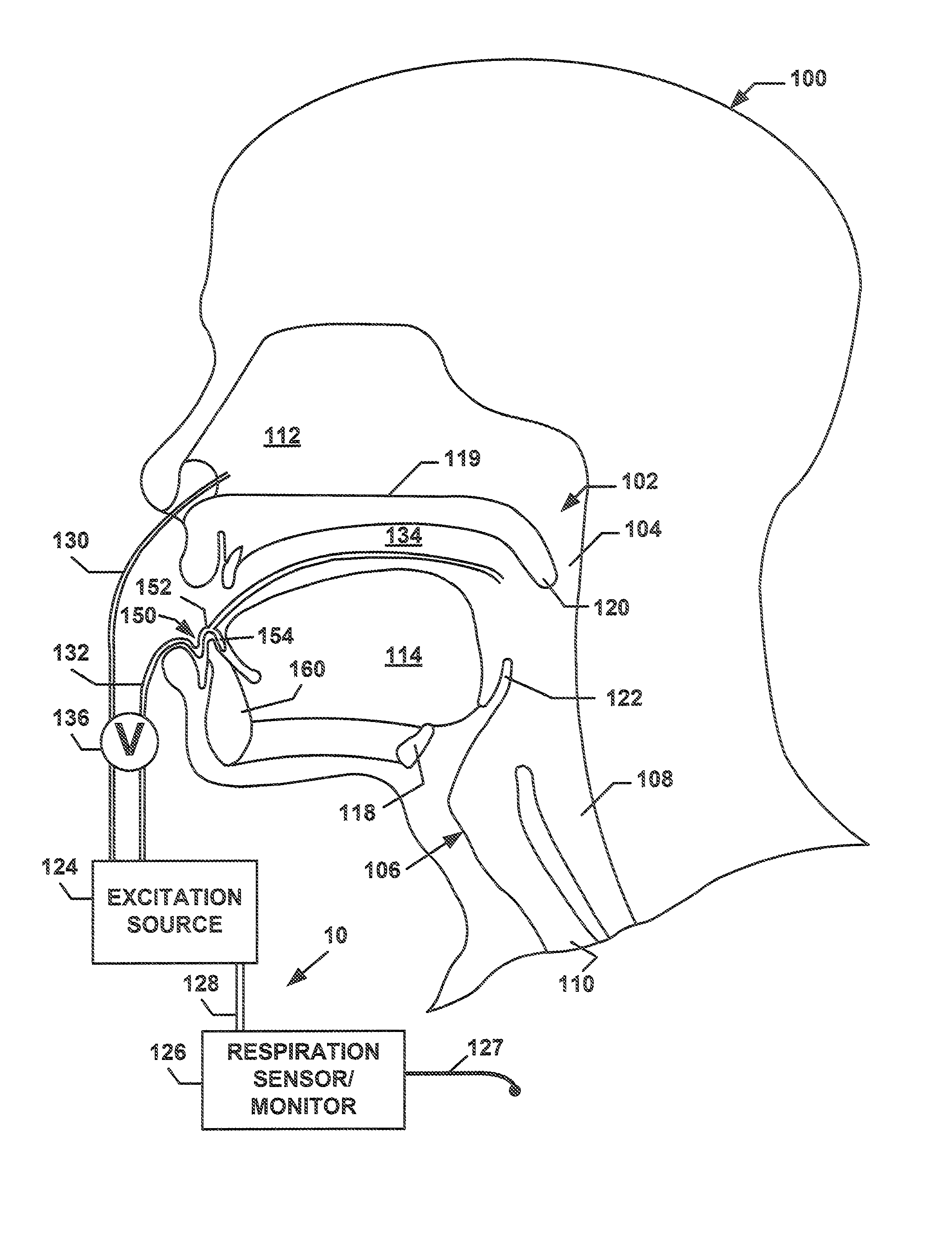
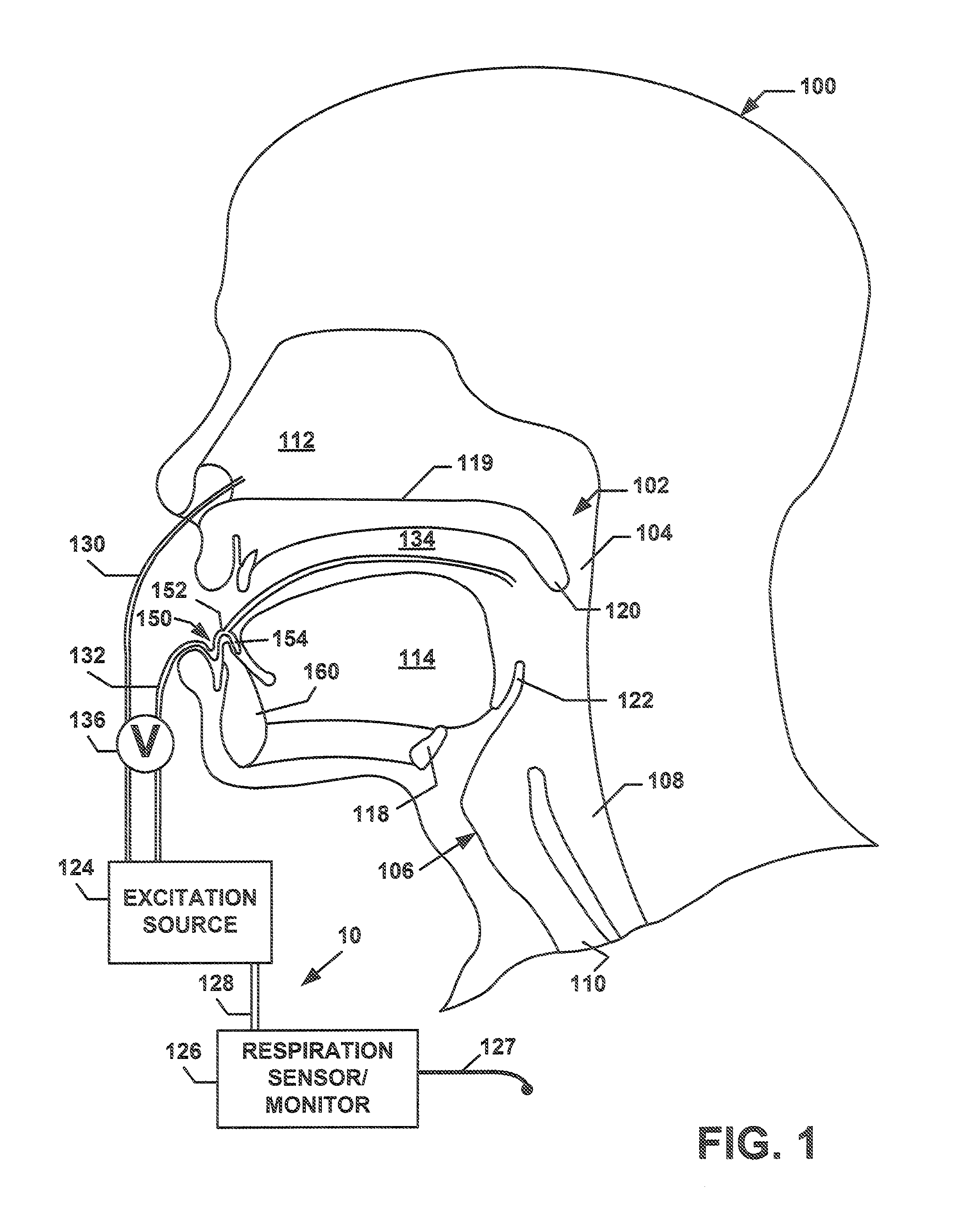
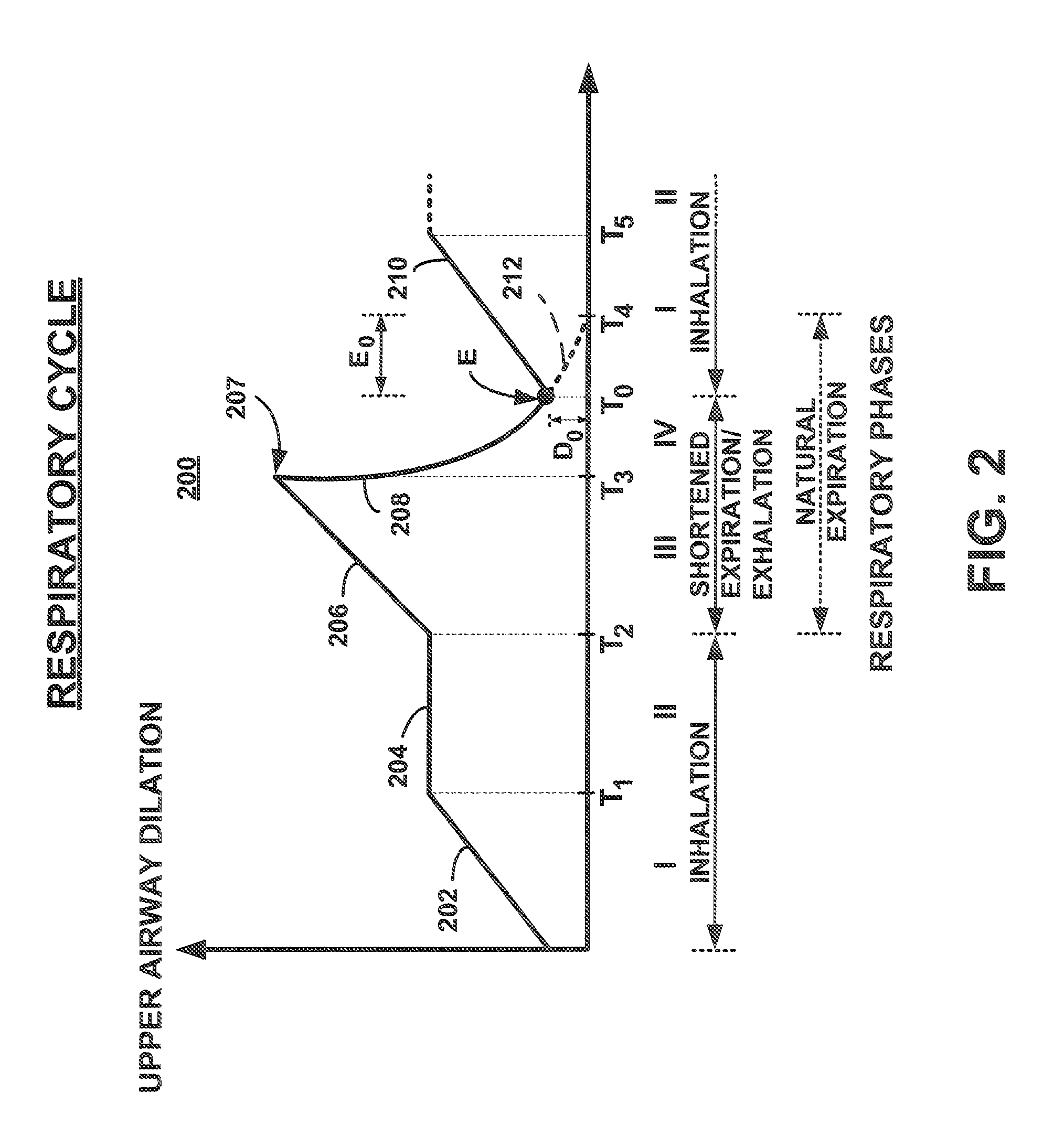
Discontinuous Positive Airway Pressure Device And Method Of Reducing Sleep Disordered Breathing Events
ActiveUS20110071444A1Reducing sleep disordered breathing eventRespiratorsHead electrodesPharyngeal conduitSelective excitation
A Discontinuous Positive Airway Pressure (DPAP) device and method of using the same for reducing sleep disordered breathing events, such as sleep apnea and snoring. The DPAP device provides selective excitation to the pharyngeal conduit or another muscle or cartilage along the respiratory path, a predetermined period of time before the end of the expiration stage, in order to prematurely reverse the respiratory cycle before the total collapse of the pharyngeal conduit, thus enabling the inhalation stage to reopen and refill the pharyngeal conduit.
Owner:KASSATLY L SAMUEL A +3
Sensor apparatus and cantilever for it
InactiveUS20020092359A1Highly sensitive chemicalEasy to adaptNanotechForce measurementSelective excitationCondensed matter physics
A magnetically excited, resonant cantilever sensor apparatus has a cantilever as the transducer element. A static magnetic field is directed in the plane of the cantilever(s) cooperating with a current loop in / on the latter. Orienting the magnetic field along or perpendicular to the cantilever axis and controlling the current apprpriately allows for selective excitation of resonance or non-resonance modes and / or in a self-oscillation mode. The deflection of the cantilever is detected using piezoresistive or magnetic readout. The apparatus may be used as gas sensor, scanning force microscope, mechanical filter, temperature sensor or the like.
Owner:SWISS FEDERAL INST OF TECH ZURICH
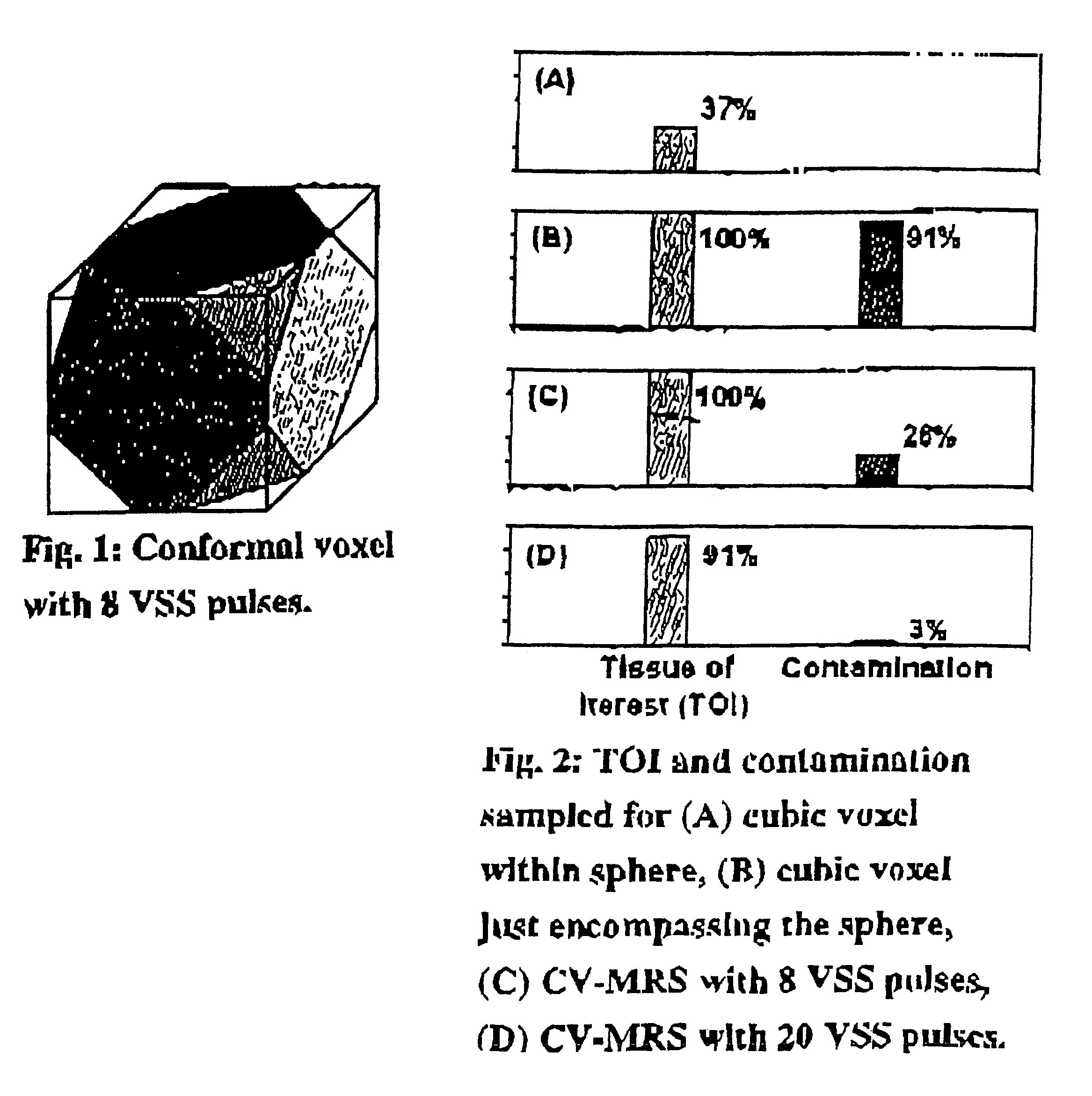
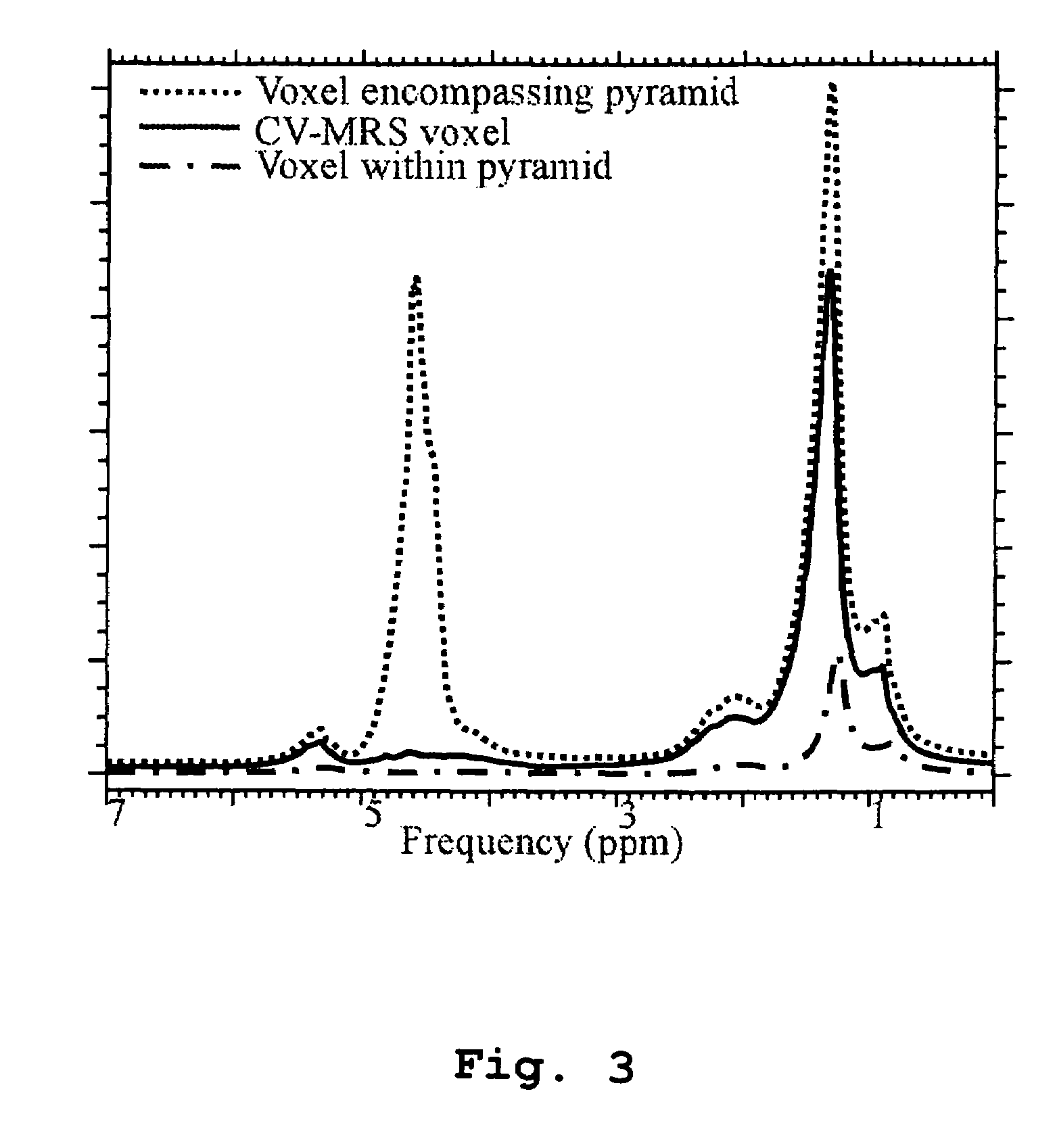
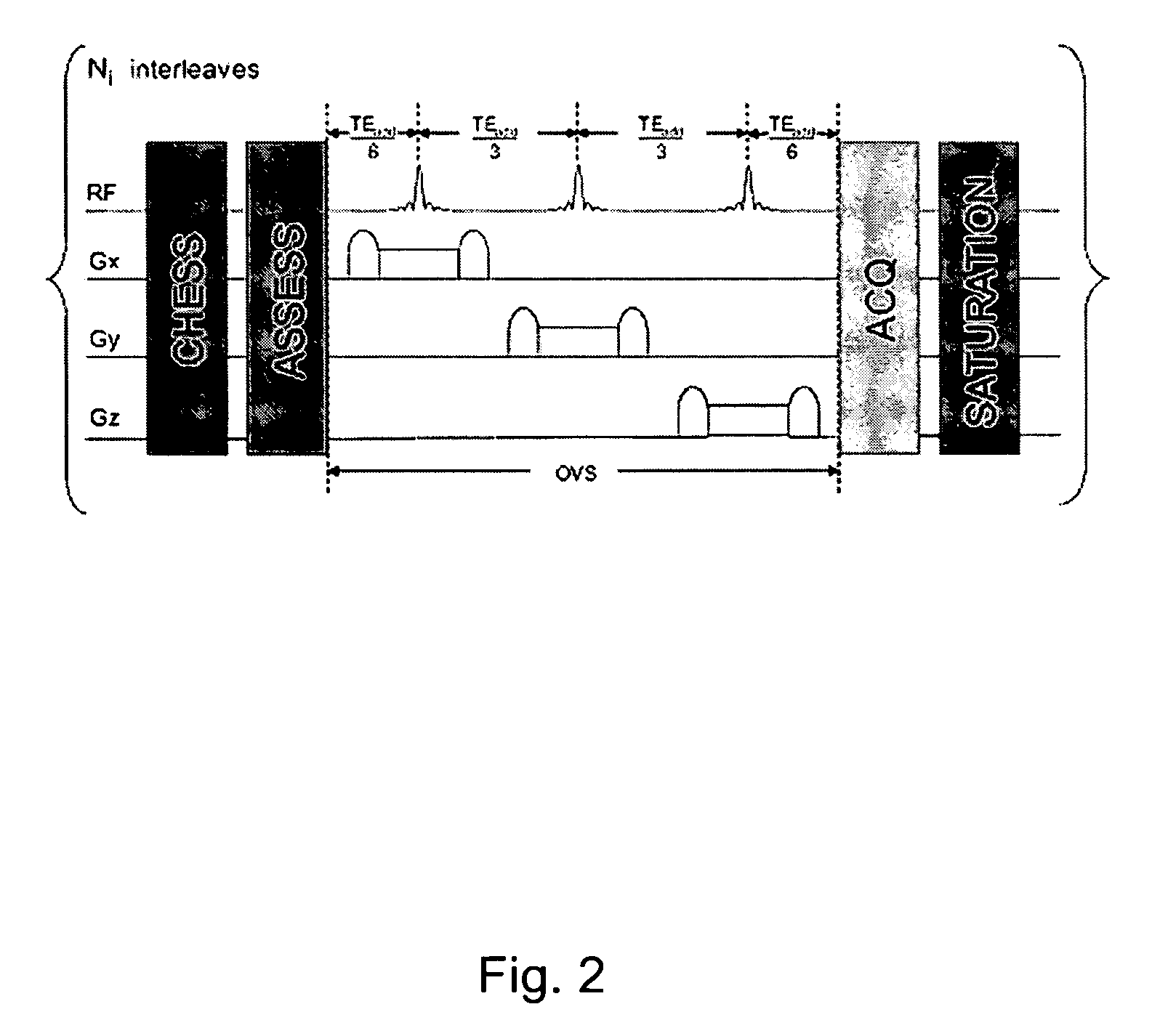
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy using a conformal voxel
InactiveUS7319784B2Improving prescriptionAdd featureMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionVoxelSelective excitation
The goal was to automate and optimize the shaping and positioning of a shape-specific / conformal voxel that conforms to any volume of interest, such as a cranial lesion, to allow conformal voxel magnetic resonance spectroscopy (CV-MRS). We achieved this by using a computer program that optimizes the shape, size, and location of a convex polyhedron within the volume of interest. The sides of the convex polyhedron are used to automatically prescribe the size and location of selective excitation voxels and / or spatial saturation slices. For a spherically-shaped, phantom-simulated lesion, CV-MRS increased the signal from the lesion by a factor of 2.5 compared to a voxel completely inside the lesion. CV-MRS reduces the voxel prescription time, operator subjectivity, and acquisition time.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
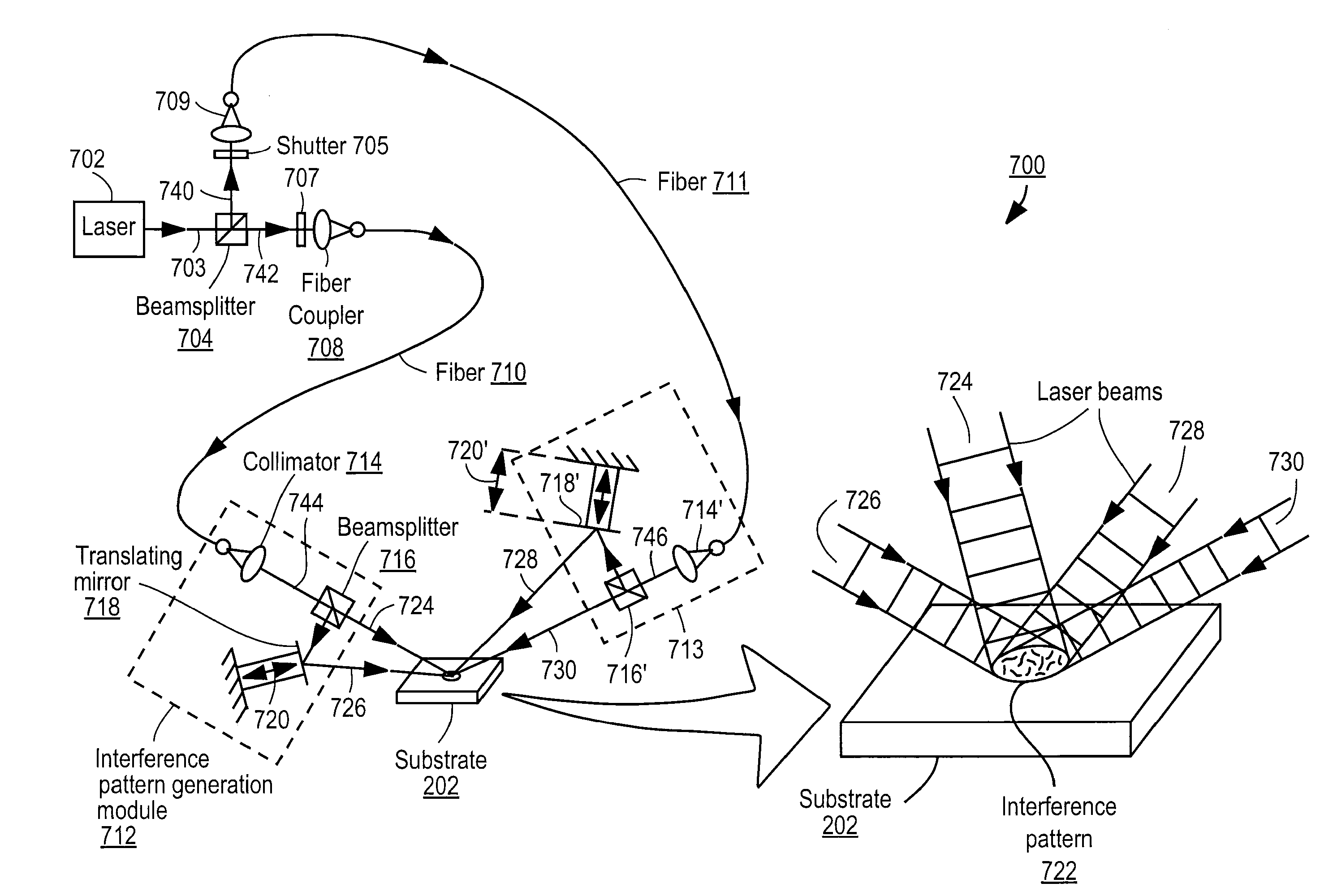
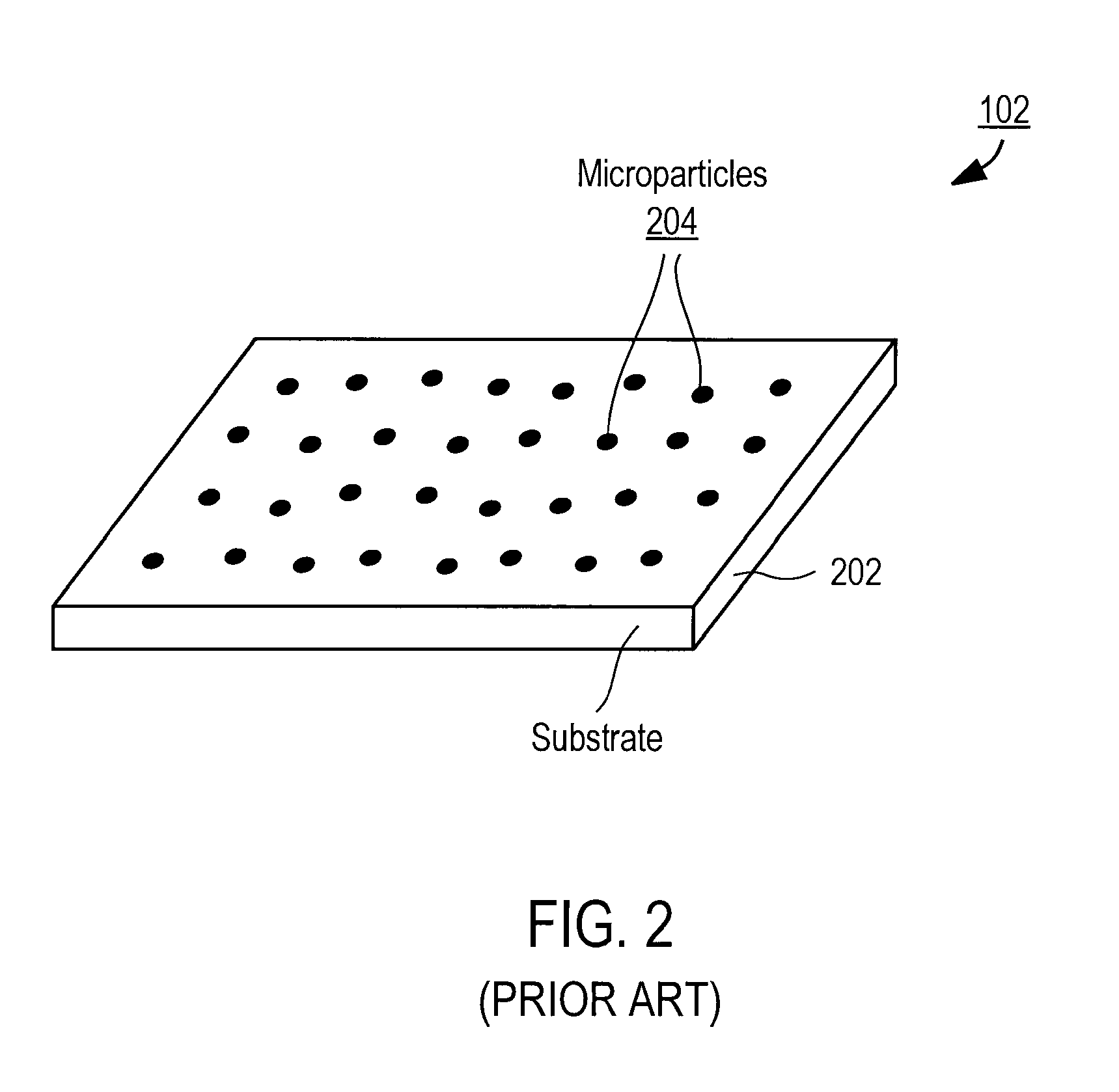
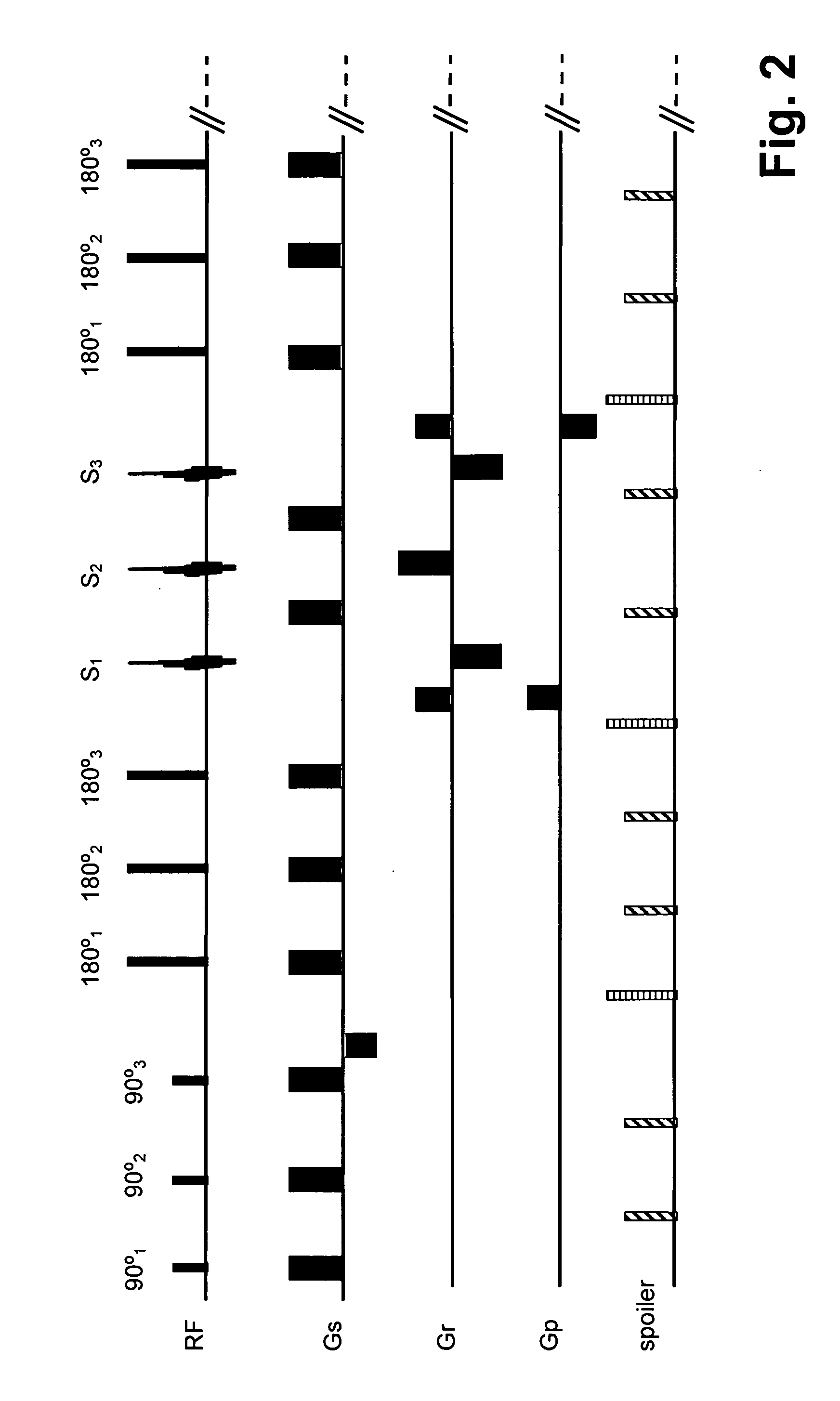
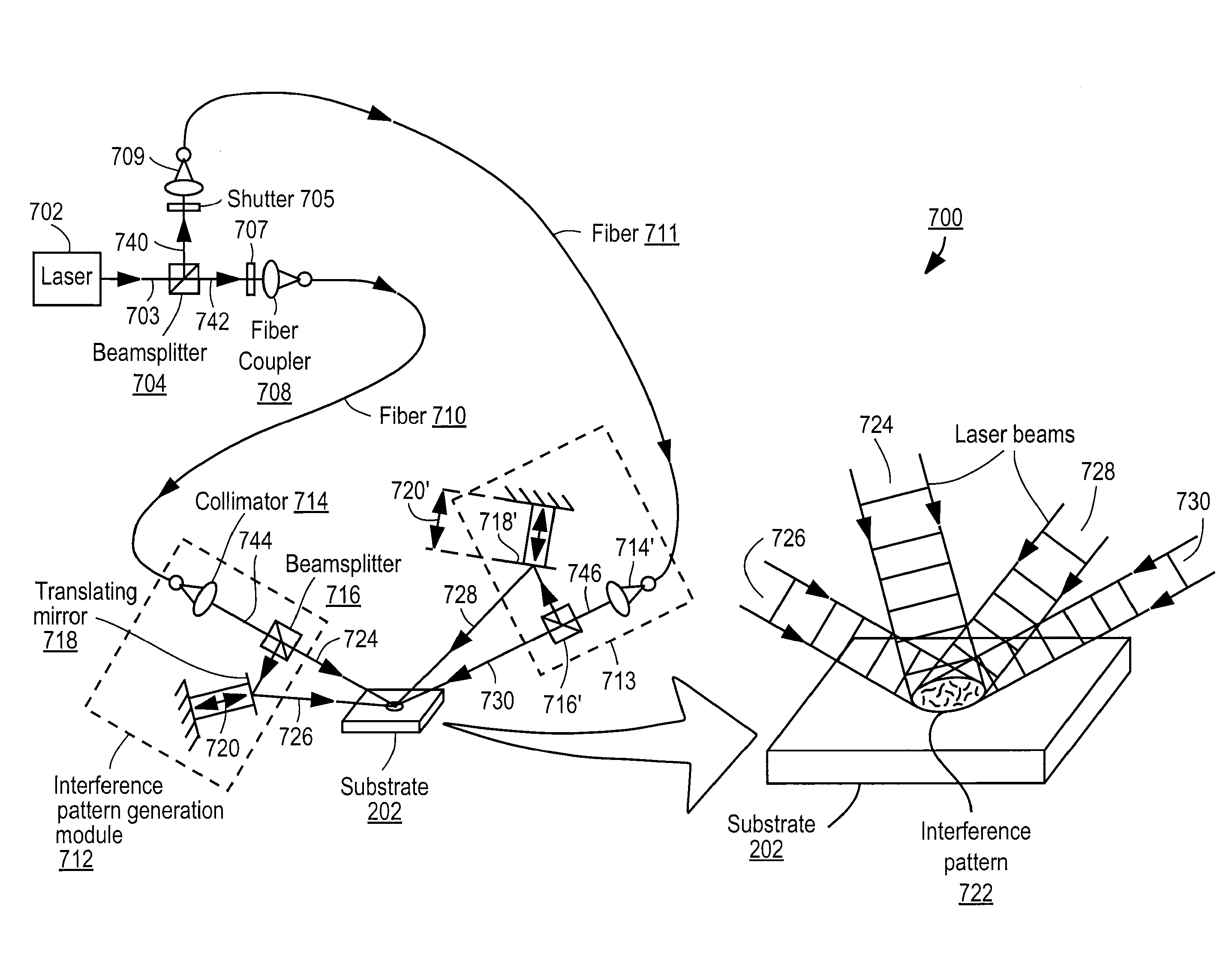
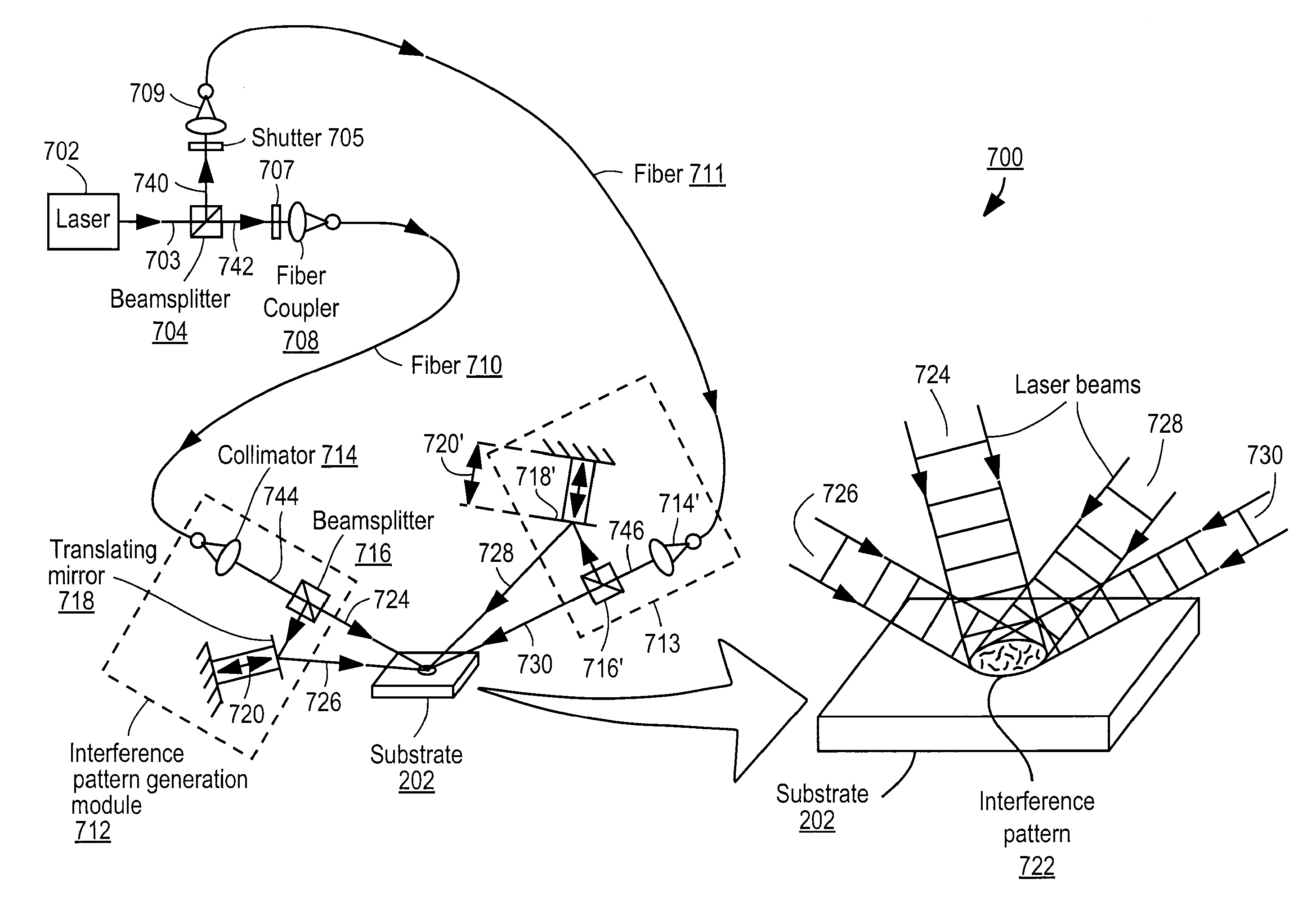
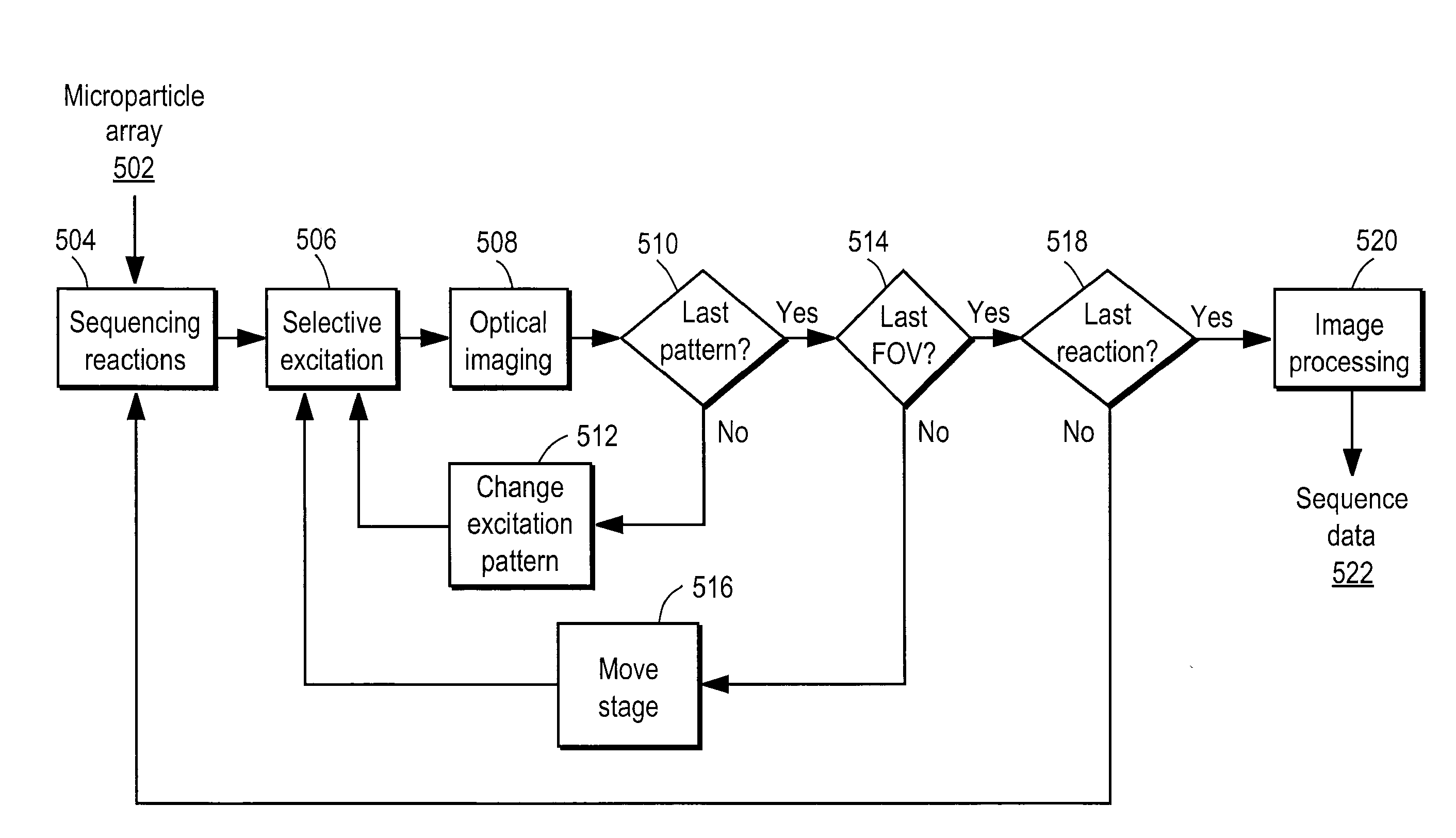
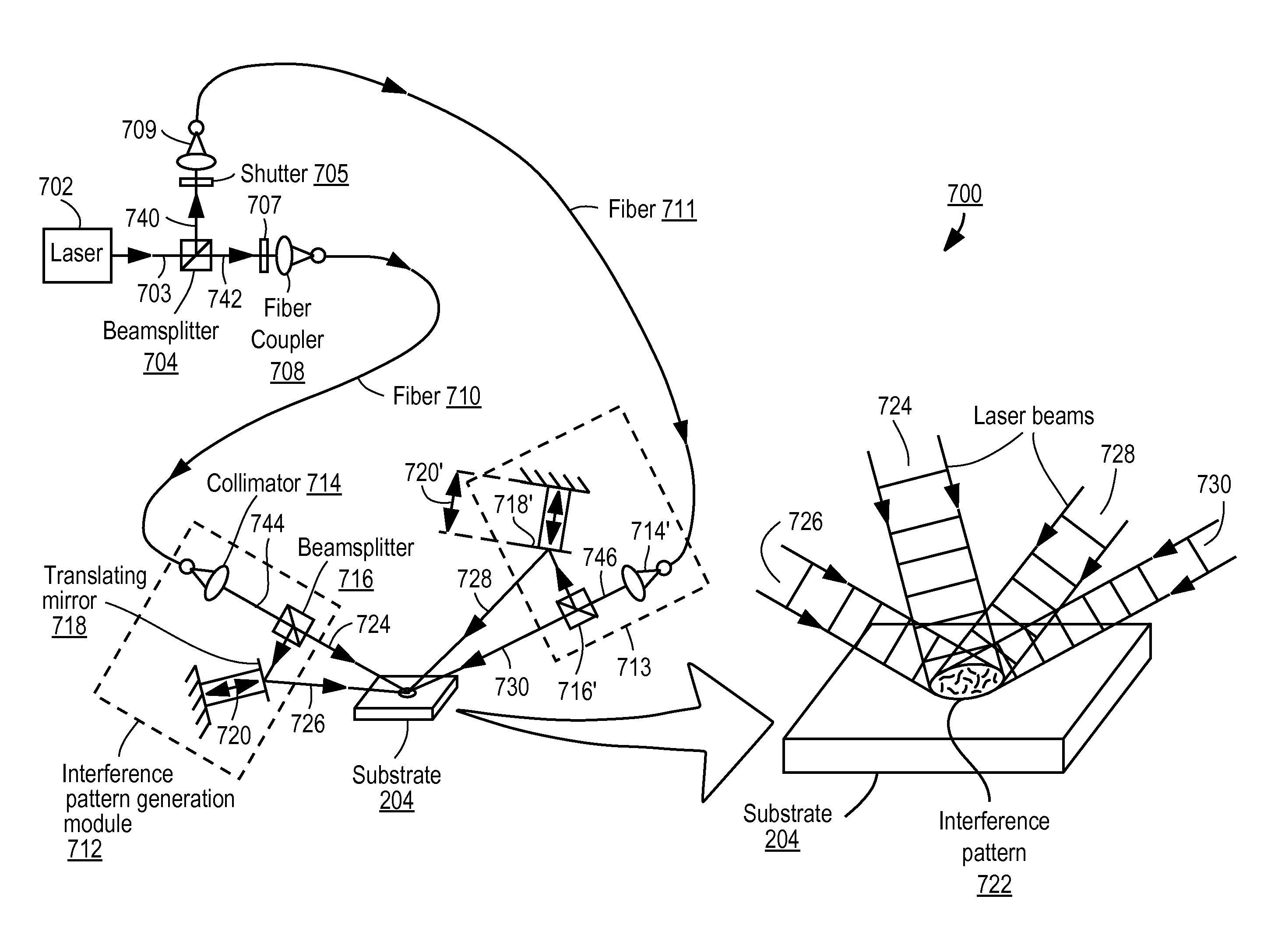
Apparatus for selective excitation of microparticles
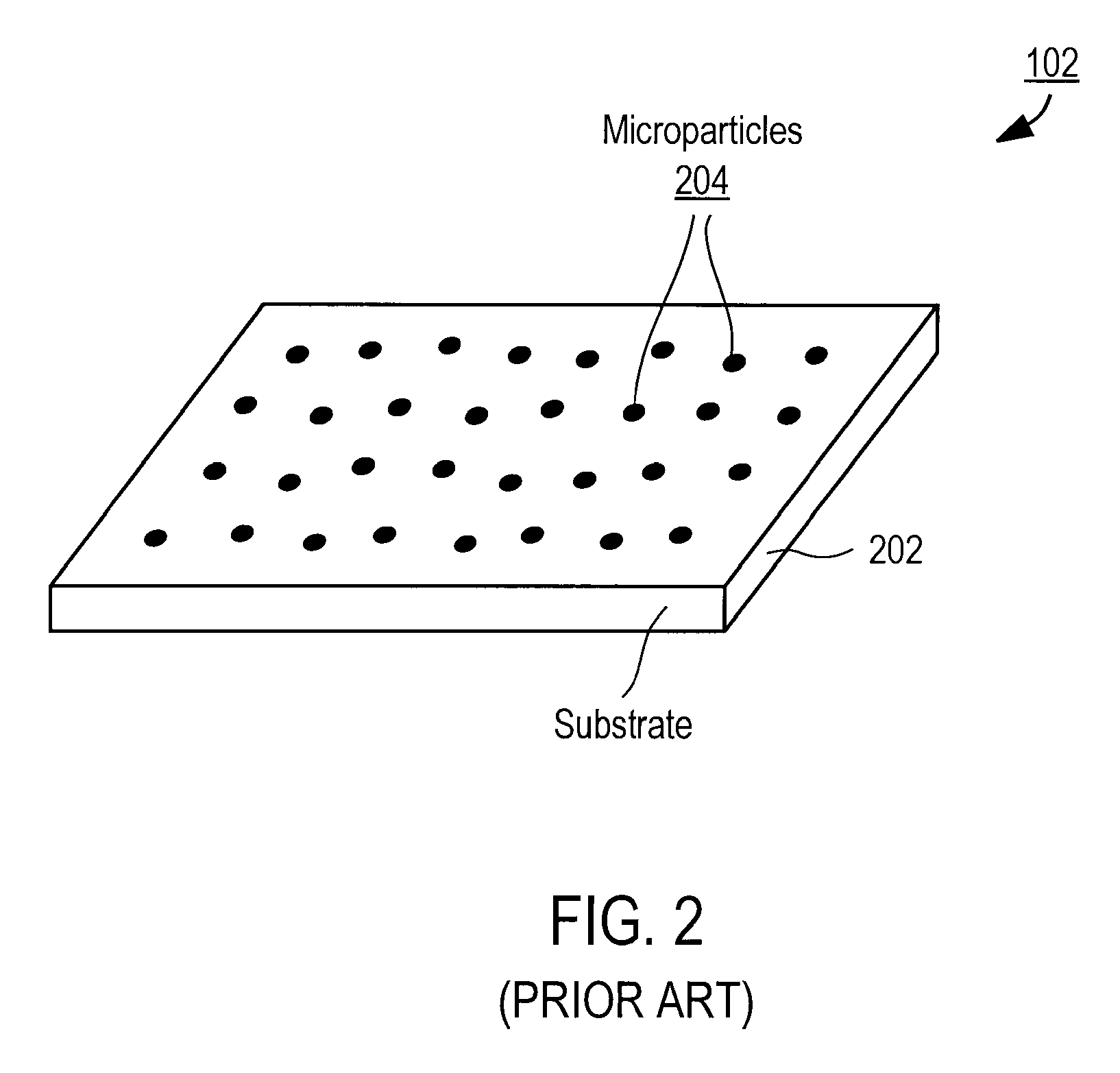
ActiveUS20090061505A1High speedEfficient data representationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsImage resolutionSelective excitation
Nucleic acid microparticles are sequenced by performing a sequencing reaction on the microparticles using one or more selectively exciting the microparticles in an excitation pattern, optically imaging the microparticles at a resolution insufficient to resolve individual microparticles, and processing the optical images of the microparticles using information on the excitation pattern to determine the presence or absence of the optical signature, which indicates the sequence information of the nucleic acid. An apparatus for optical excitation of the microparticles comprises an optical fiber delivering a first laser beam, and an interference pattern generation module coupled to the optical fiber. The interference pattern generation module splits the first laser beam into second and third laser beams and generates the excitation pattern for selectively exciting the microparticles by interference between the second and third laser beams.
Owner:REBUS BIOSYSTEMS INC
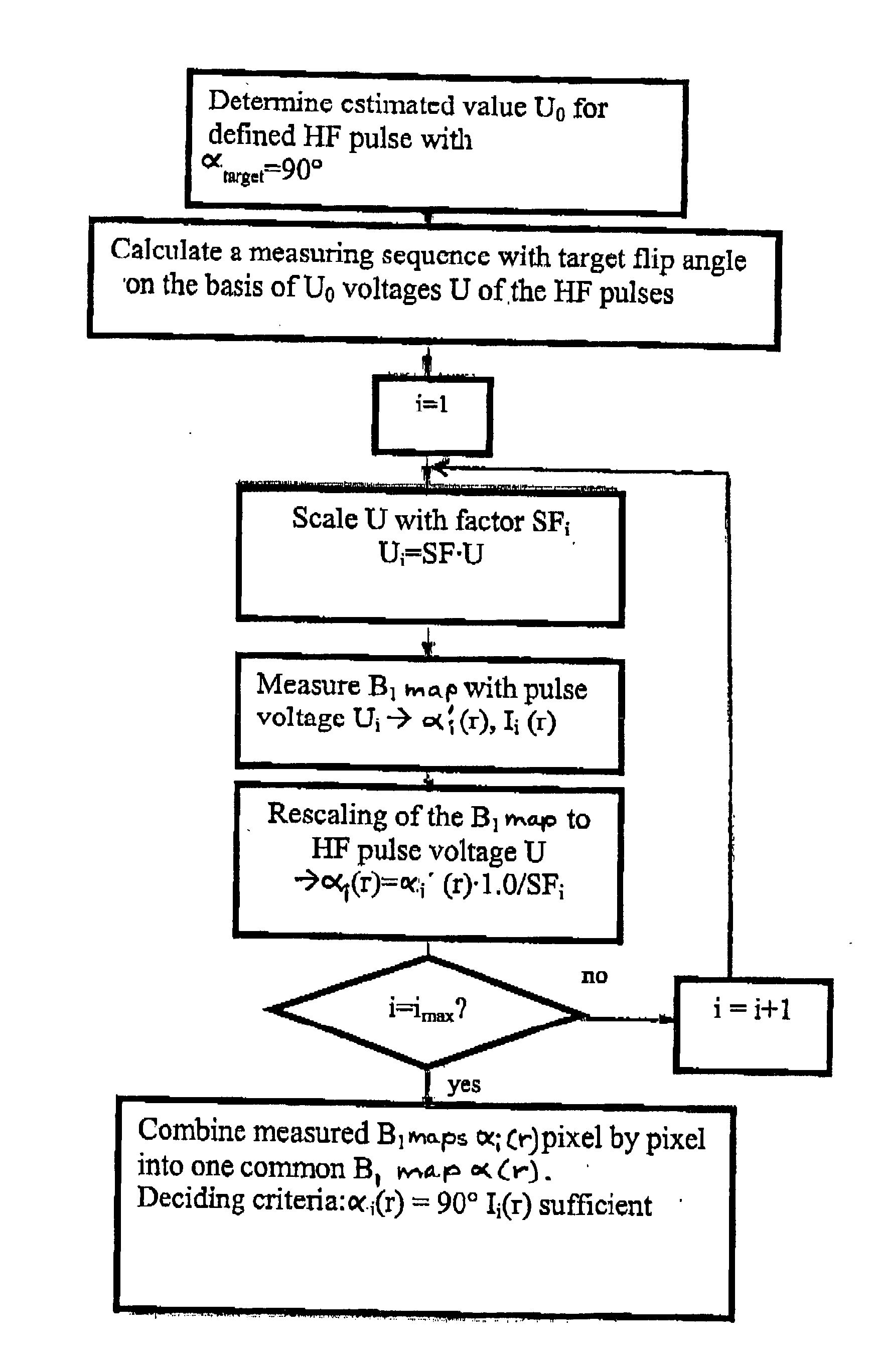
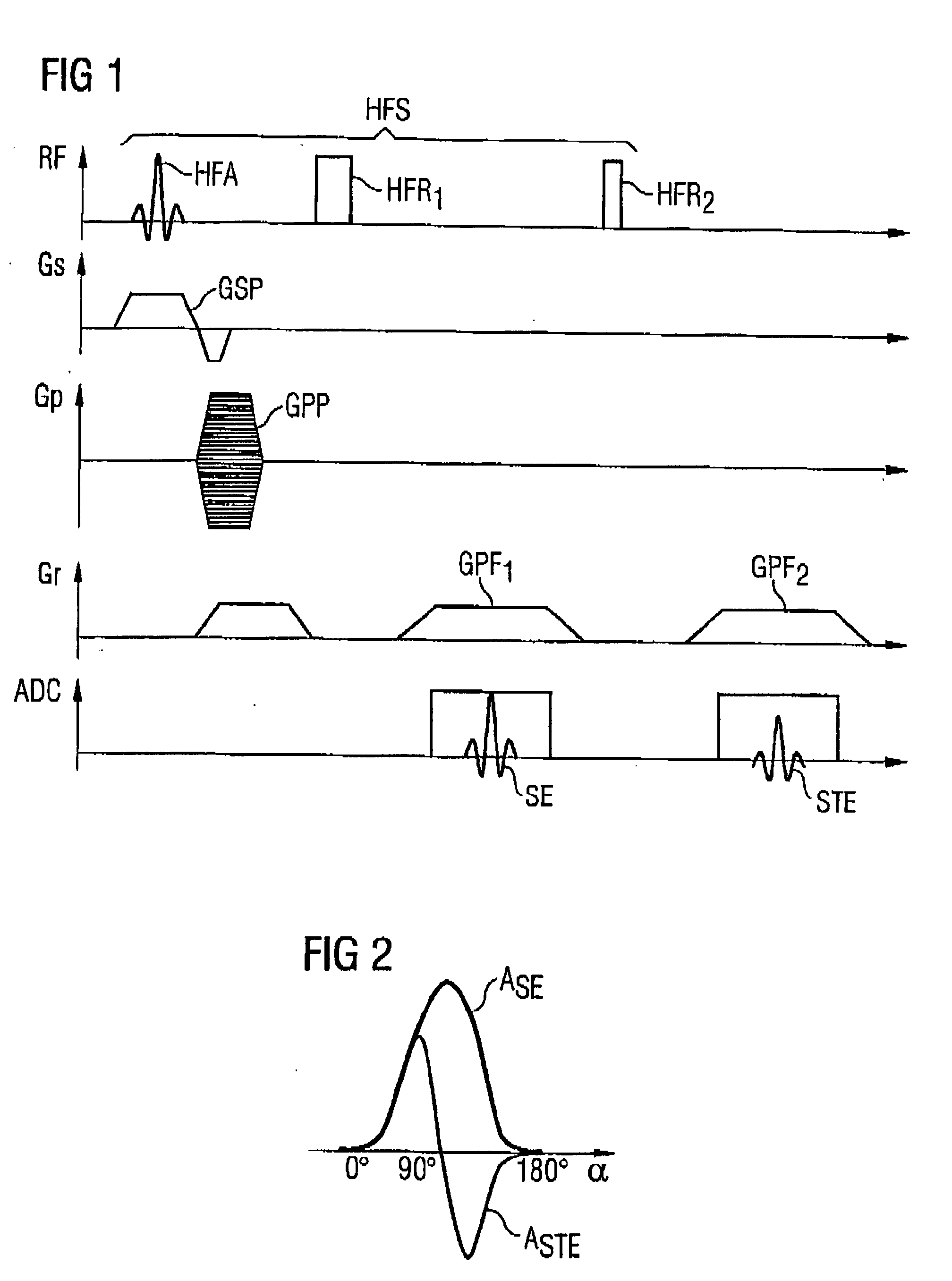
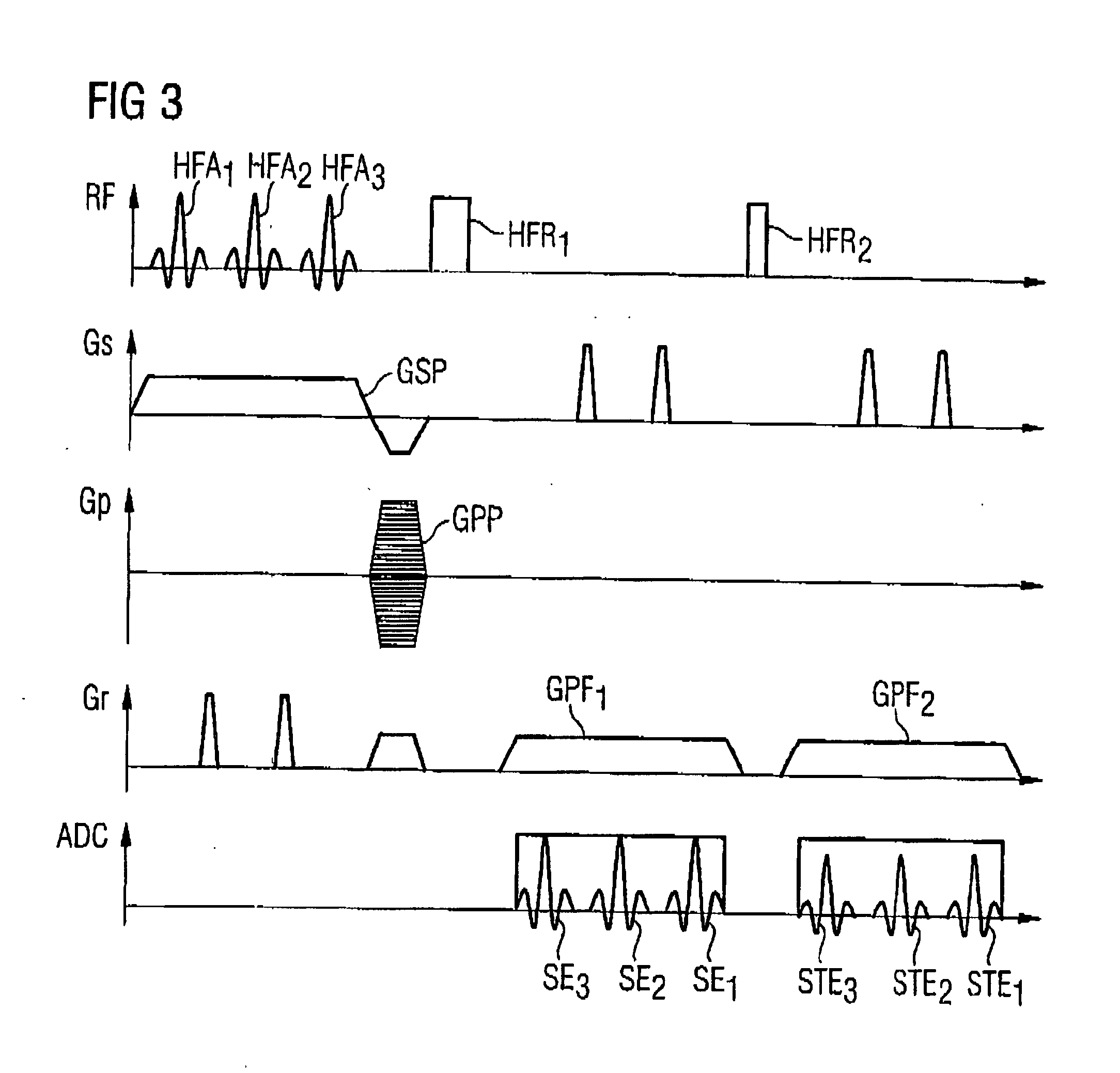
Method and magnetic resonance tomography apparatus for spatially resolved measurement of the B1 field distribution
ActiveUS20050073304A1High overall measuring timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurement deviceSelective excitation
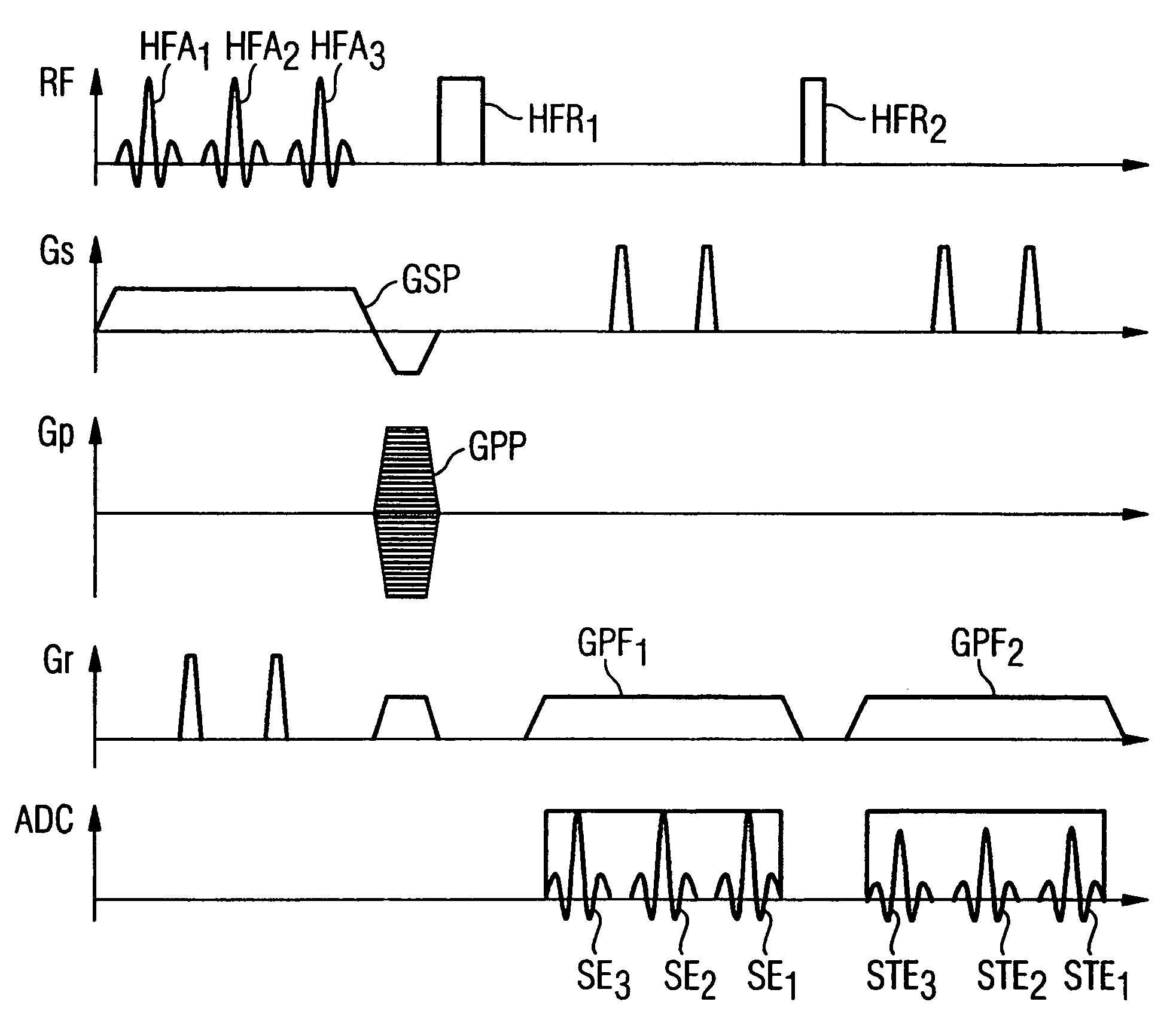
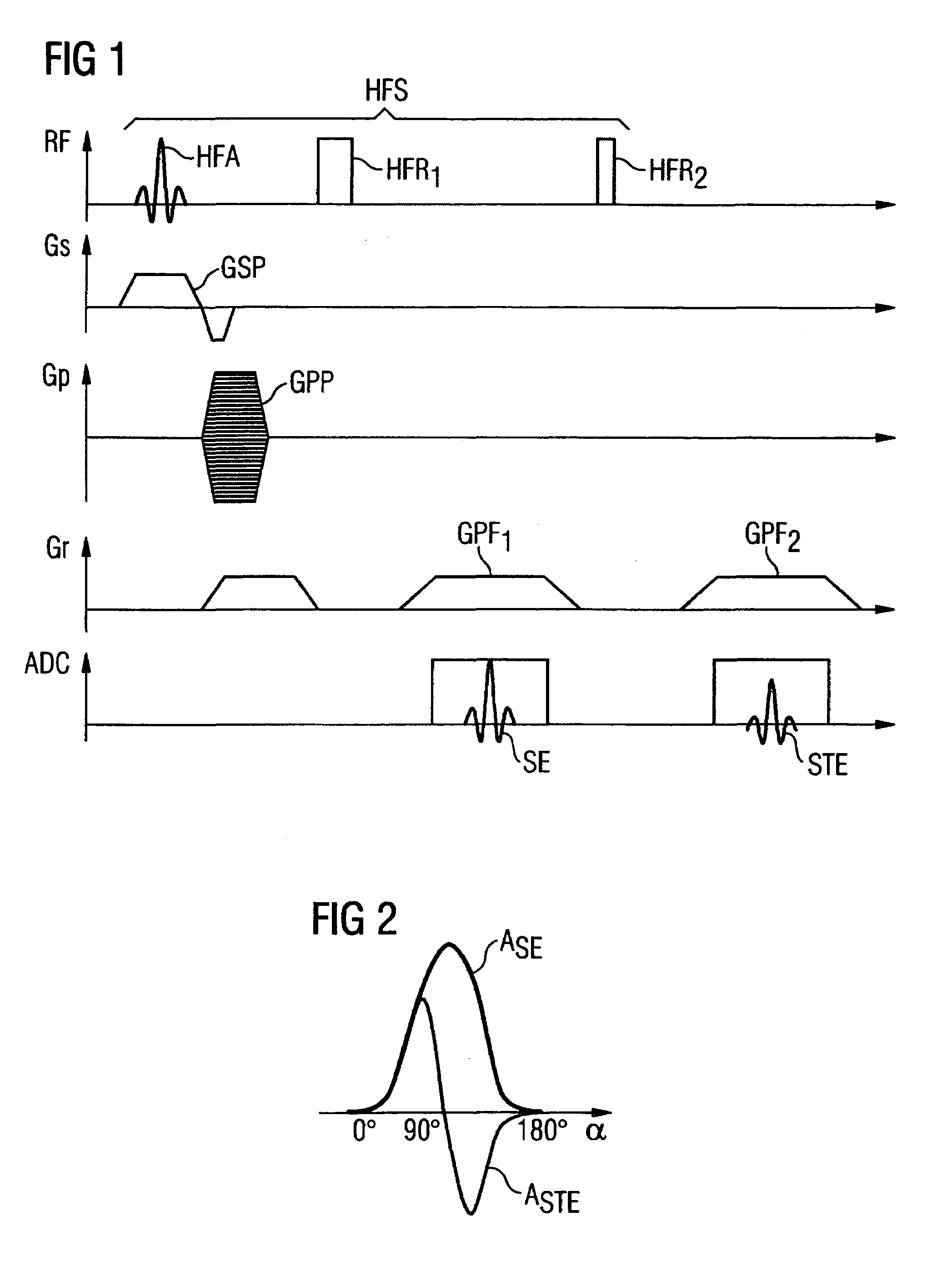
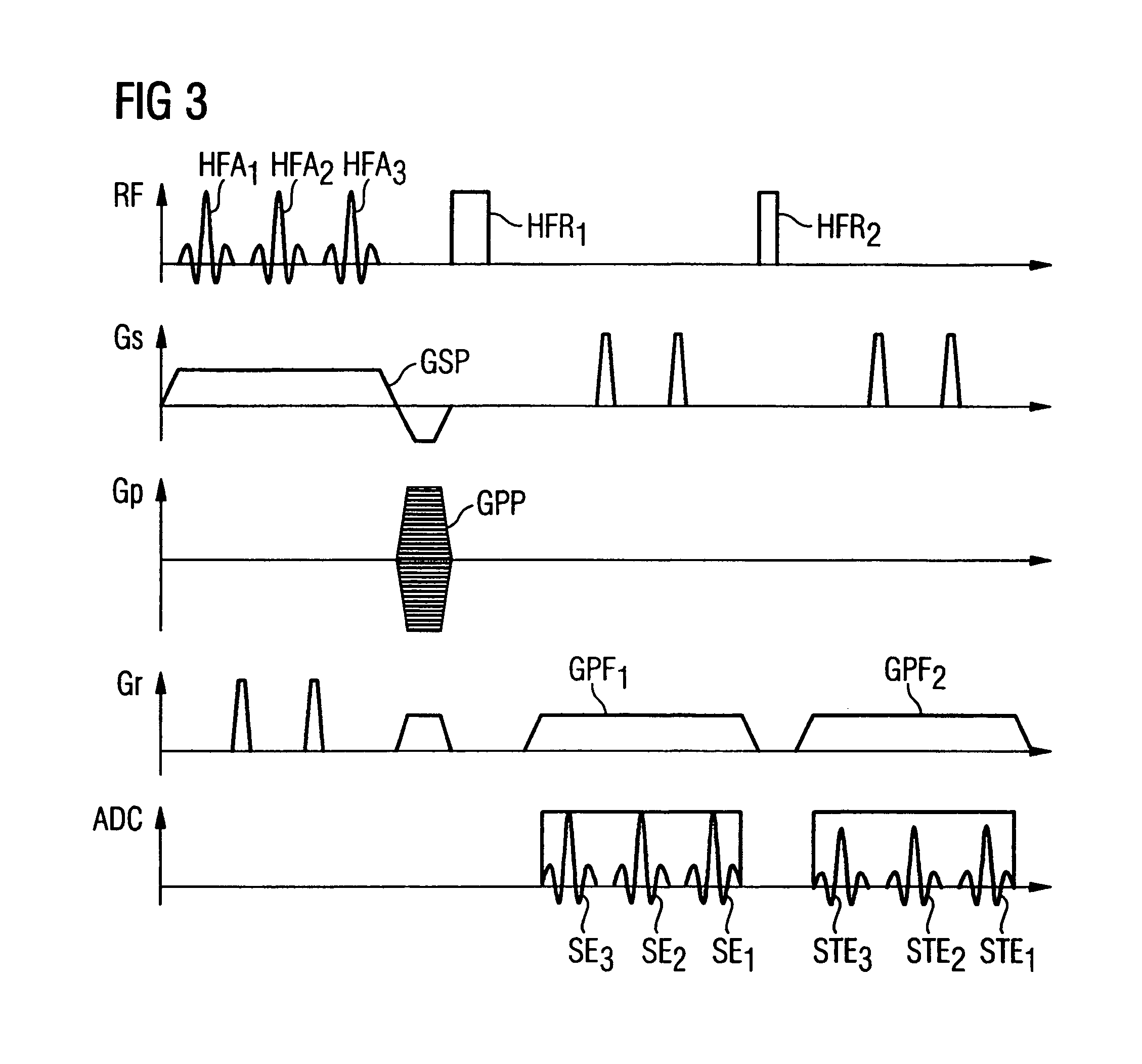
In a method and magnetic resonance tomography apparatus for spatially resolved measurement of the magnetic high frequency field distribution in the apparatus, a double echo high frequency pulse sequence with a first excitation pulse following by at least two refocusing pulses are emitted for generation of a first echo and a following second echo. At least the excitation pulse is slice selective. In an excitation layer defined by the slice selective excitation pulse a first echo image and second echo image are spatially resolved by using suitable gradient pulses for phase or frequency encoding Using the relationships of the amplitudes of the first and second echo image in the various locations the flip angles representing the field strength at the relevant locations in the relevant slice are determined.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Magnetic resonance imaging for a plurality of selective regions set to object continuously moved
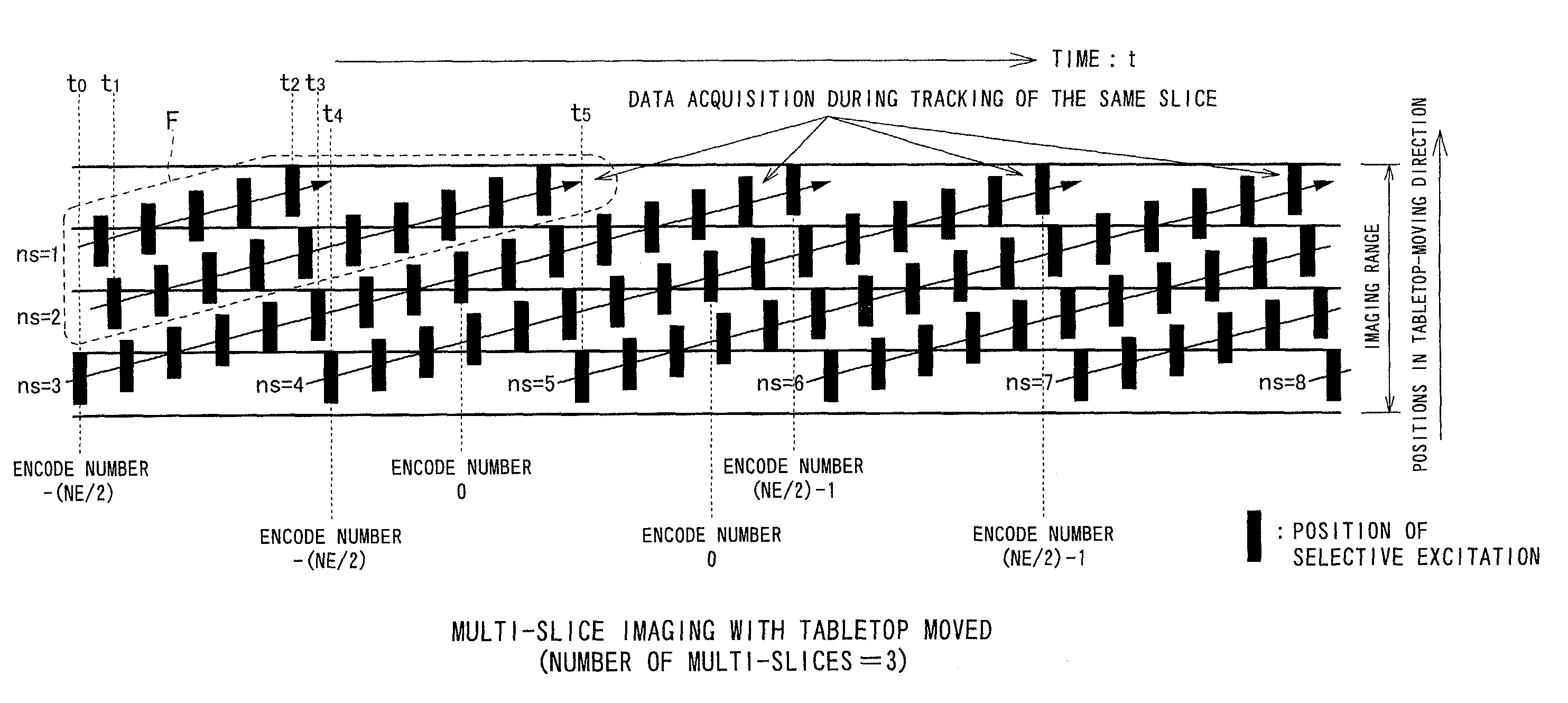
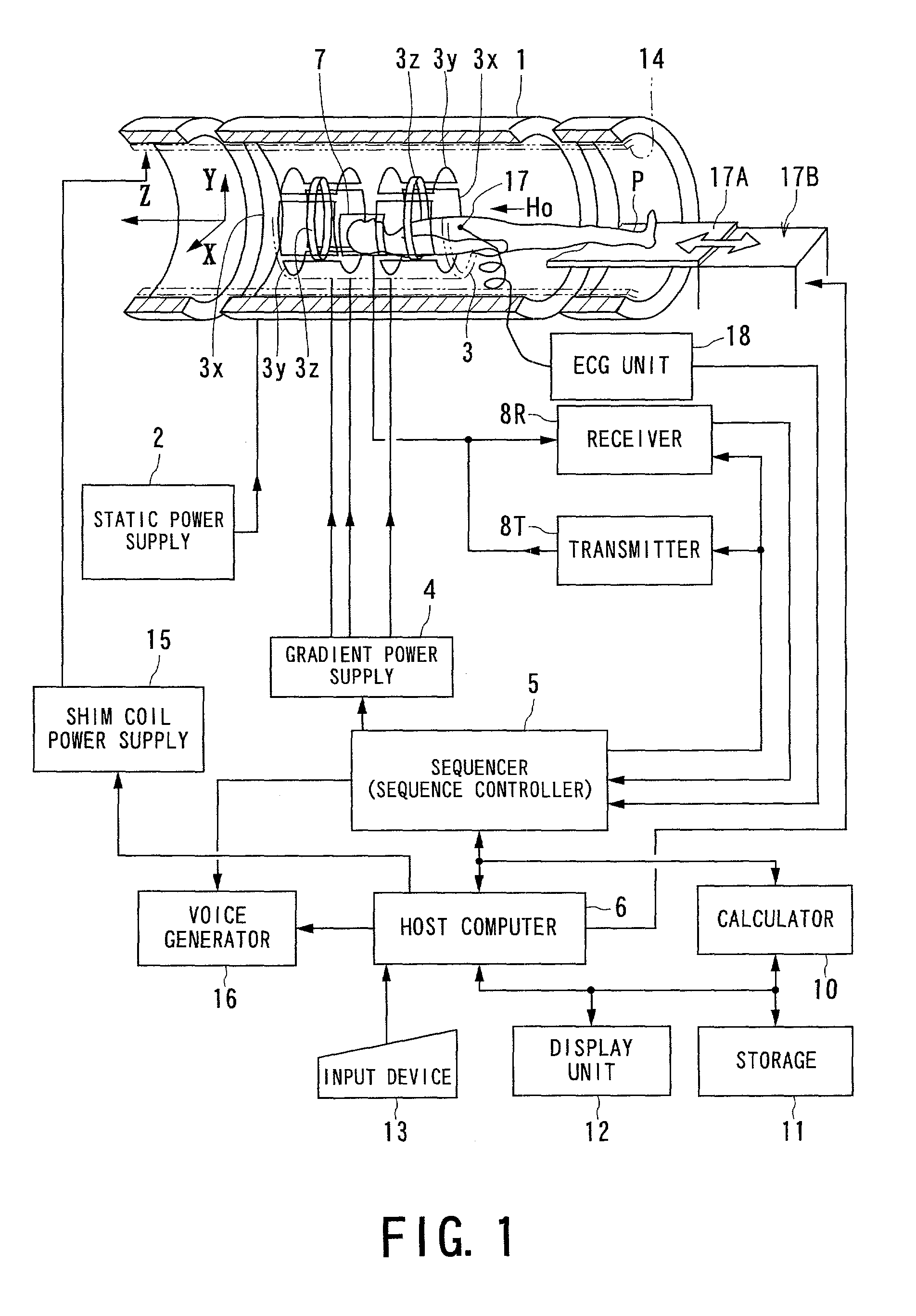
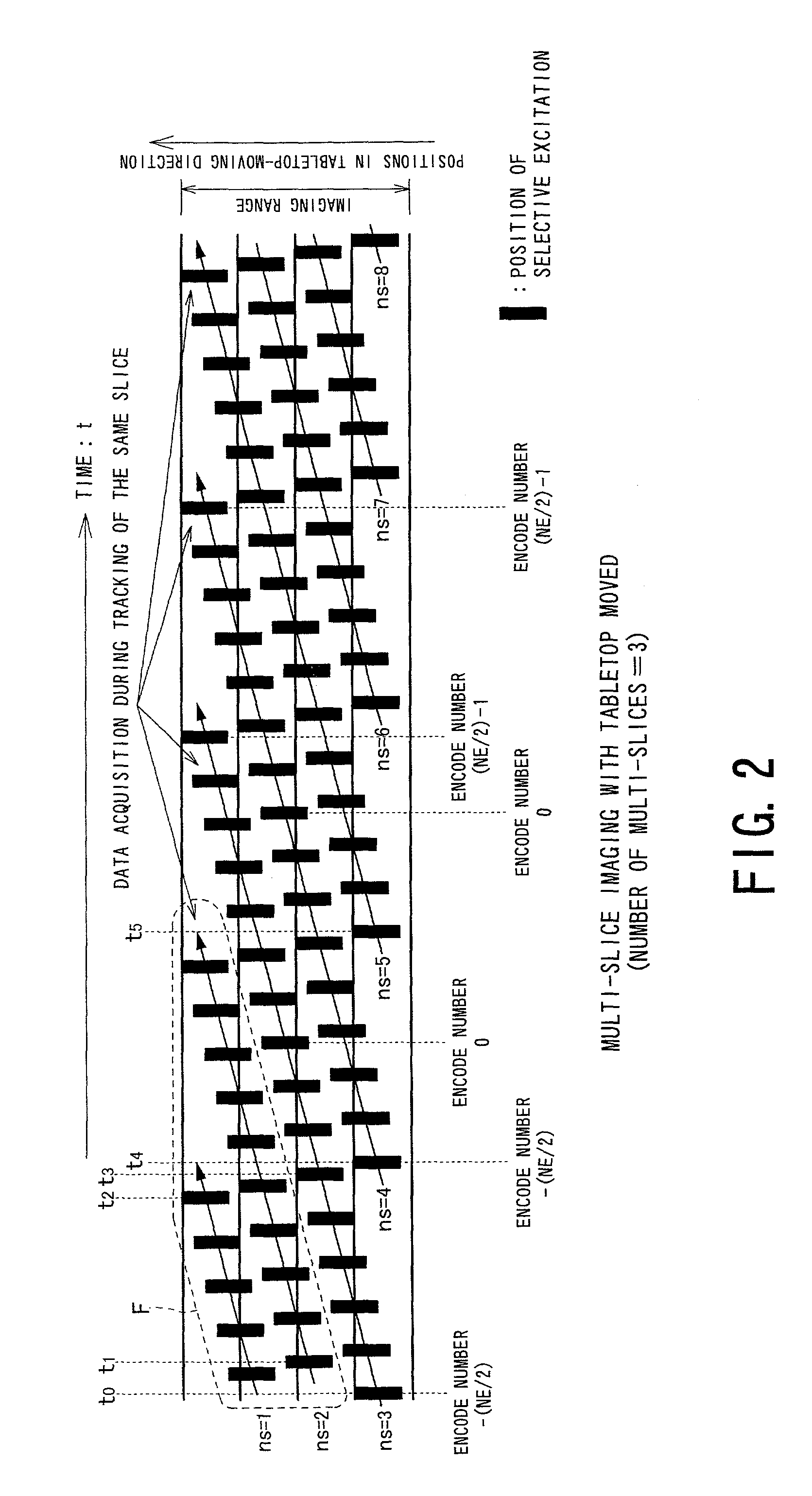
InactiveUS7110805B2Suppress artifactsEffective treatmentDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMulti sliceSelective excitation
MRI echo data is acquired by performing selective-excitation on regions composed of multi-slices of an object, while the object is moved continuously. The positions of the multi-slices are moved within a predetermined imaging range fixedly determined by an MRI system, according to object movement. This allows positions of the multi-slices to be changed in compliance with the moved object, so that the multi-slices positionally track with the object within the imaging range. Accordingly, a multi-slice imaging technique can be provided, which is executable during even continuous movement of the object.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
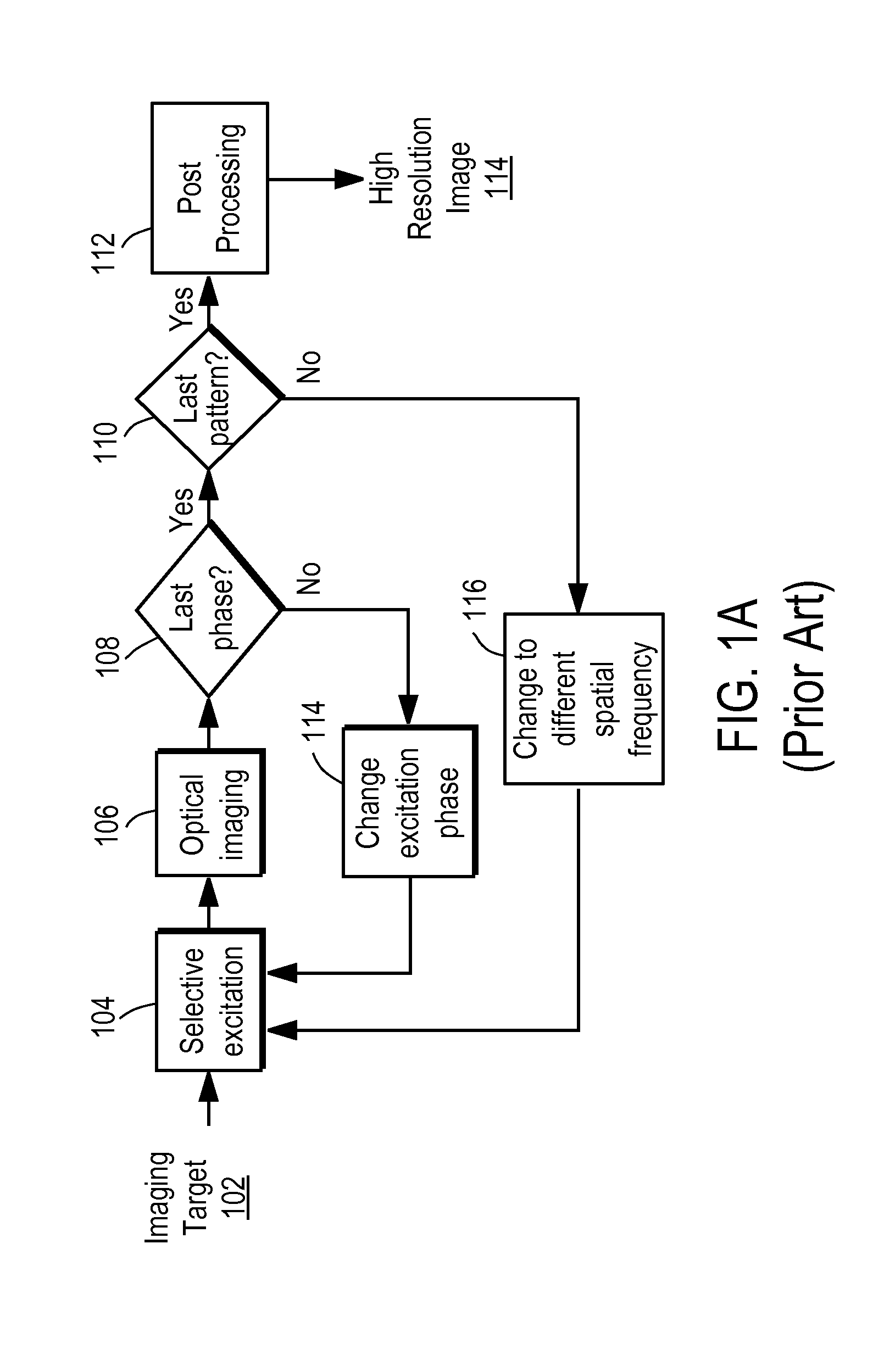
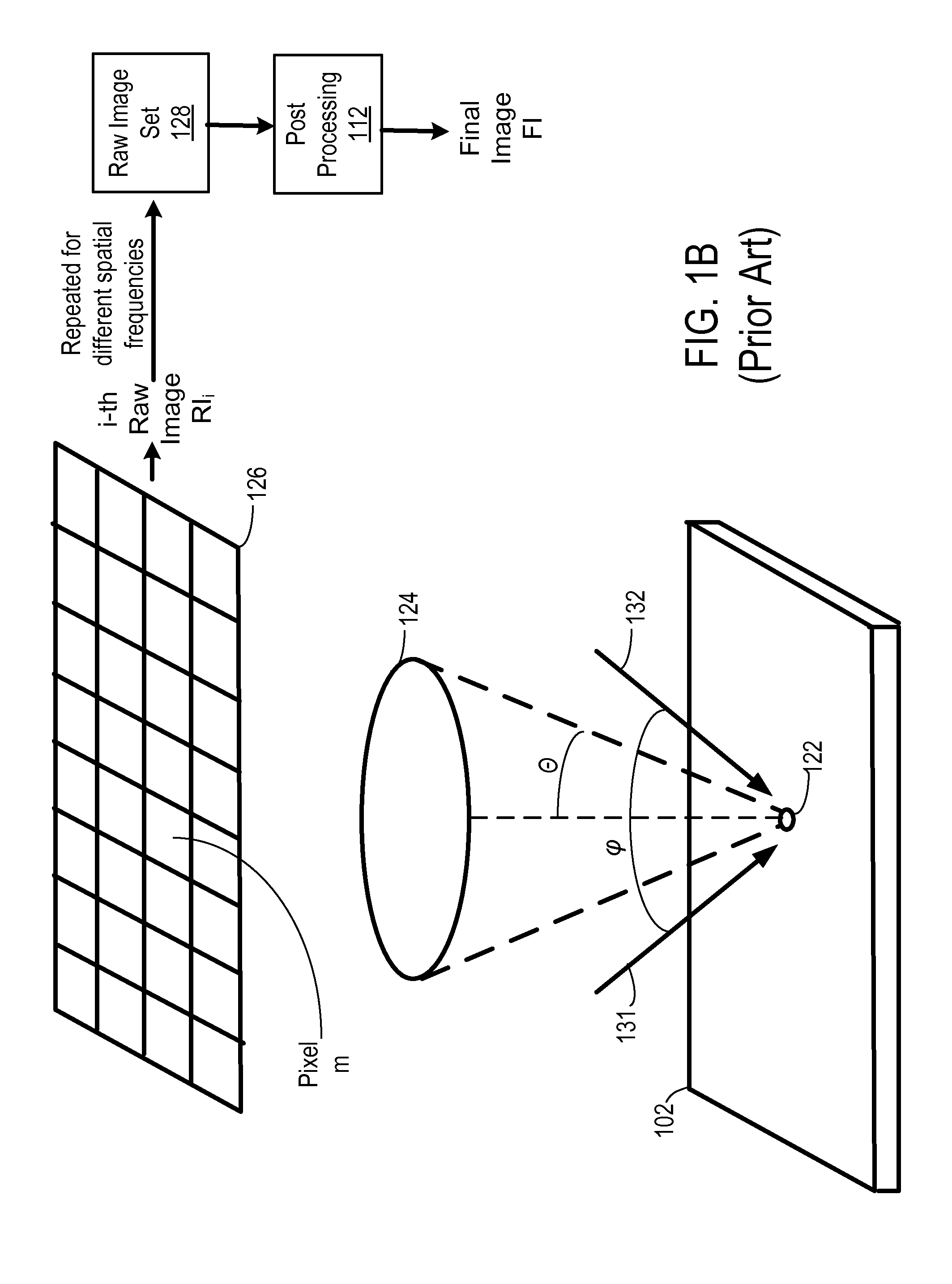
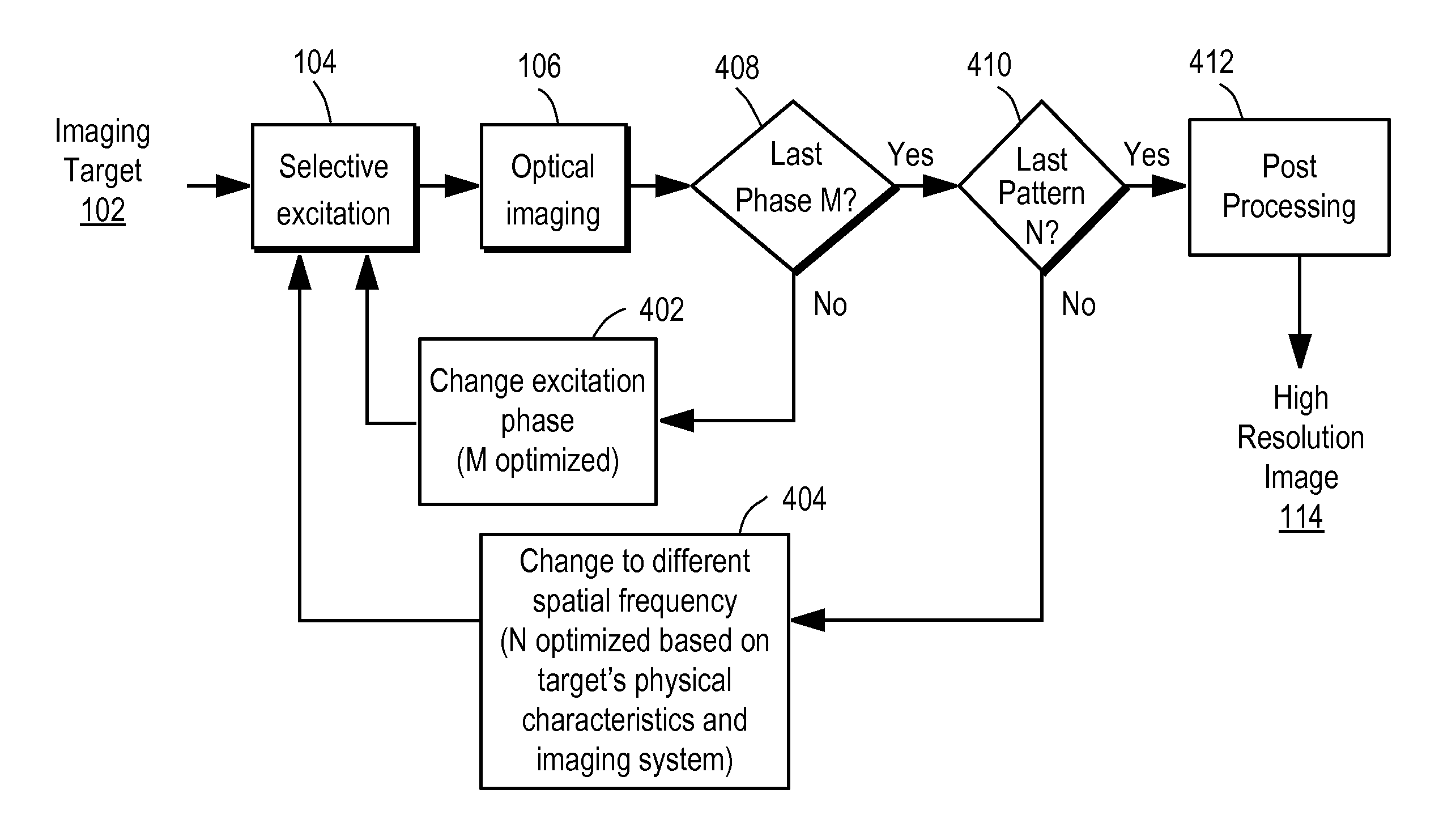
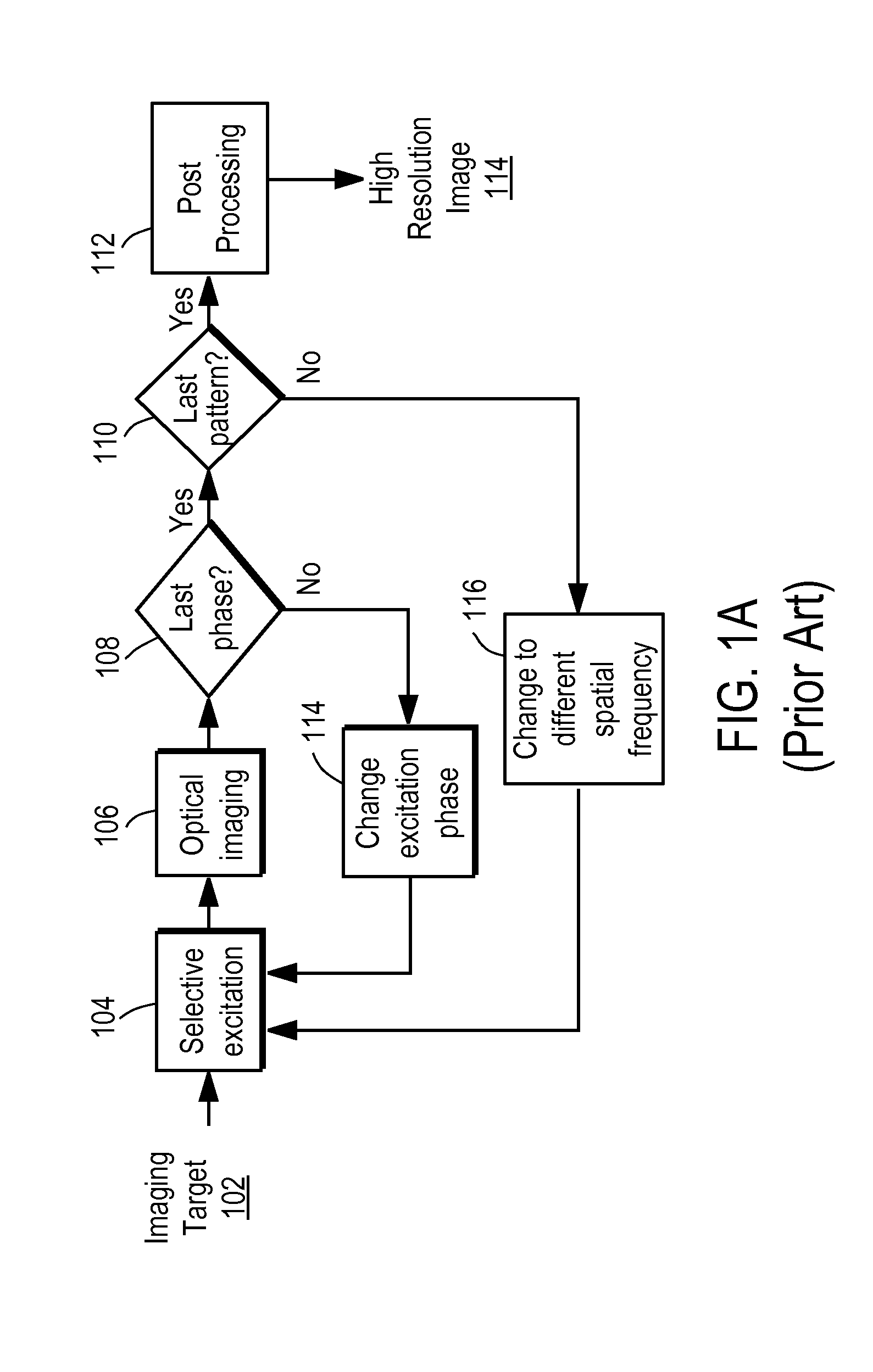
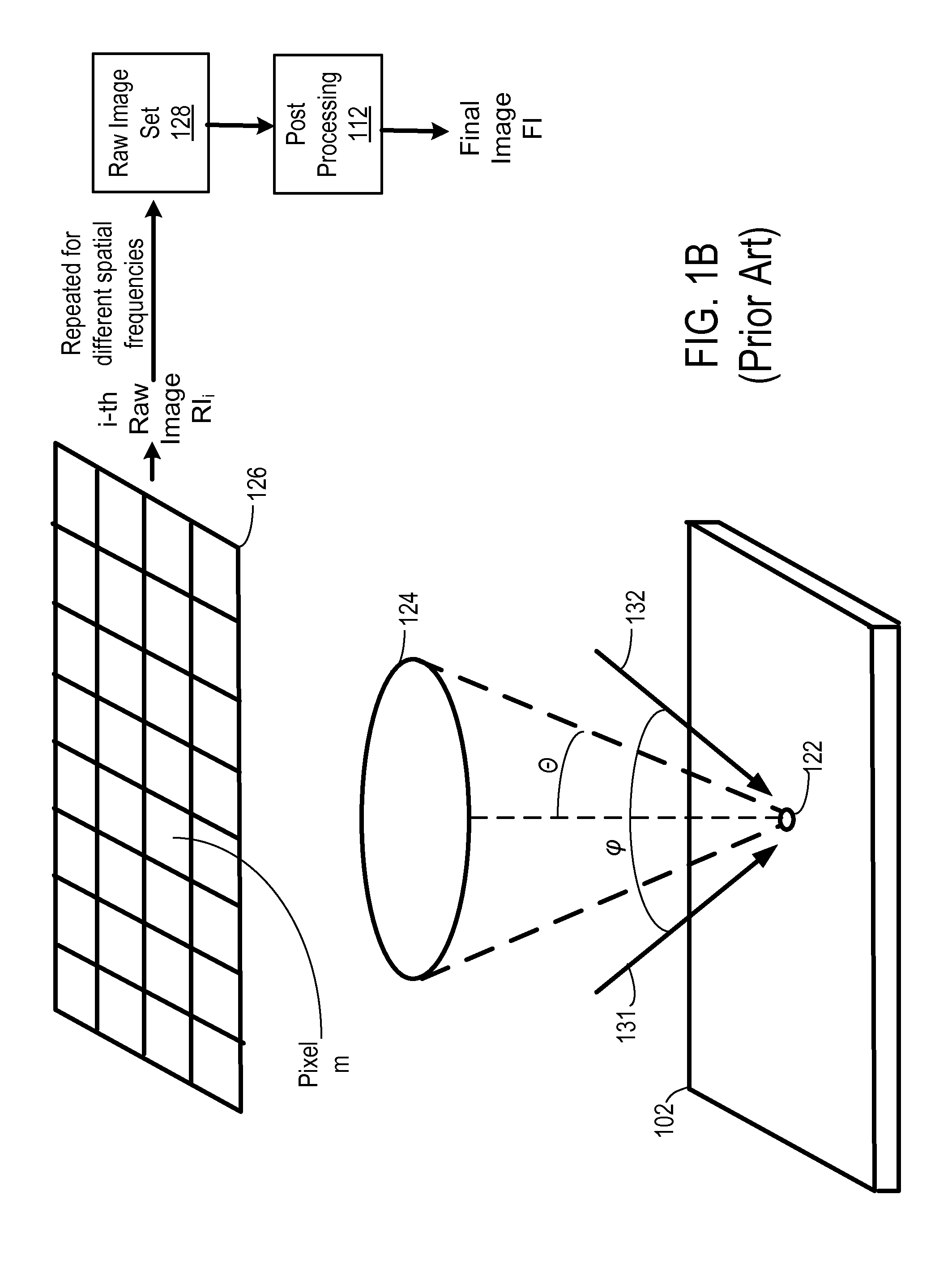
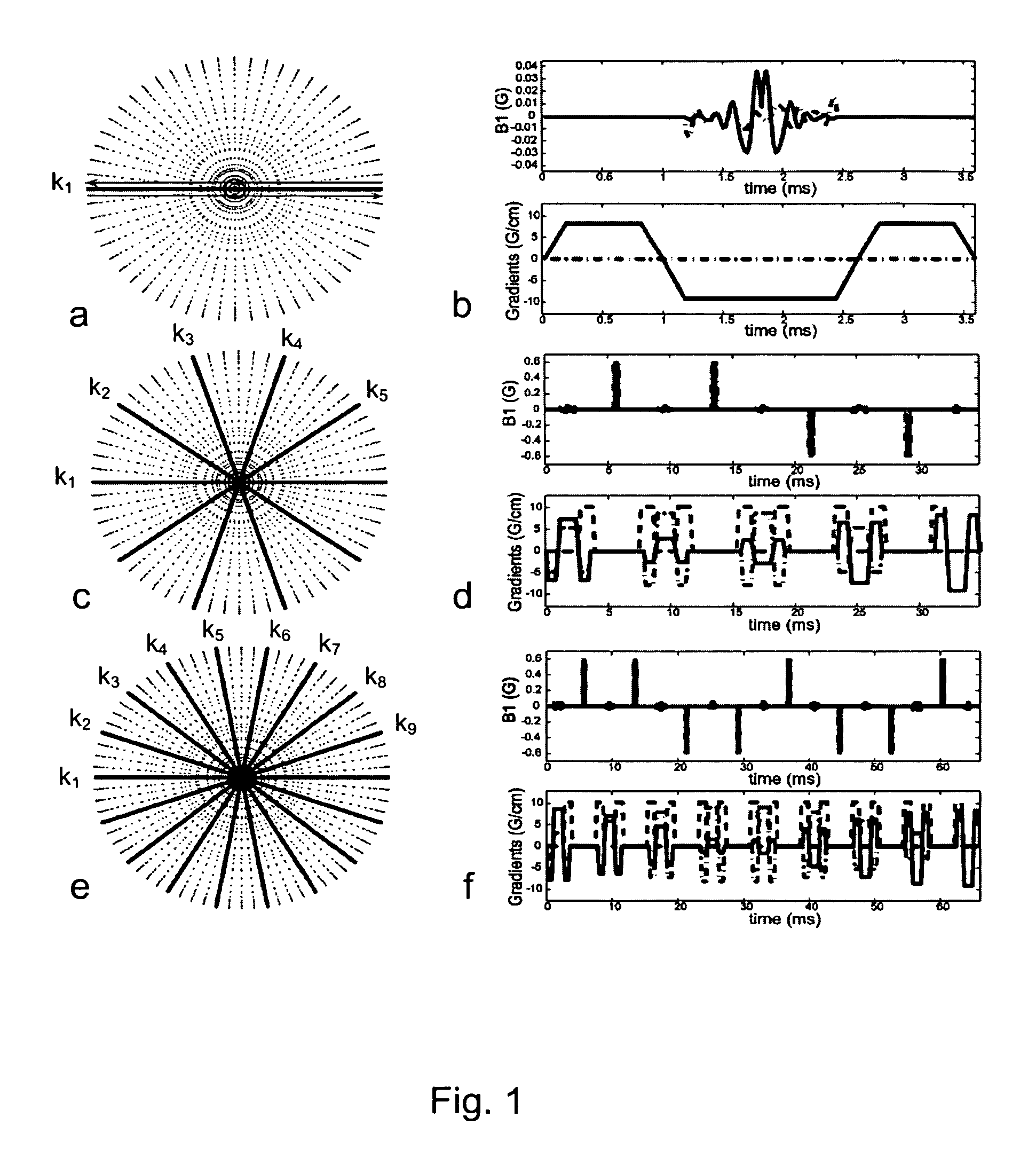
Synthetic aperture optics imaging method using minimum selective excitation patterns
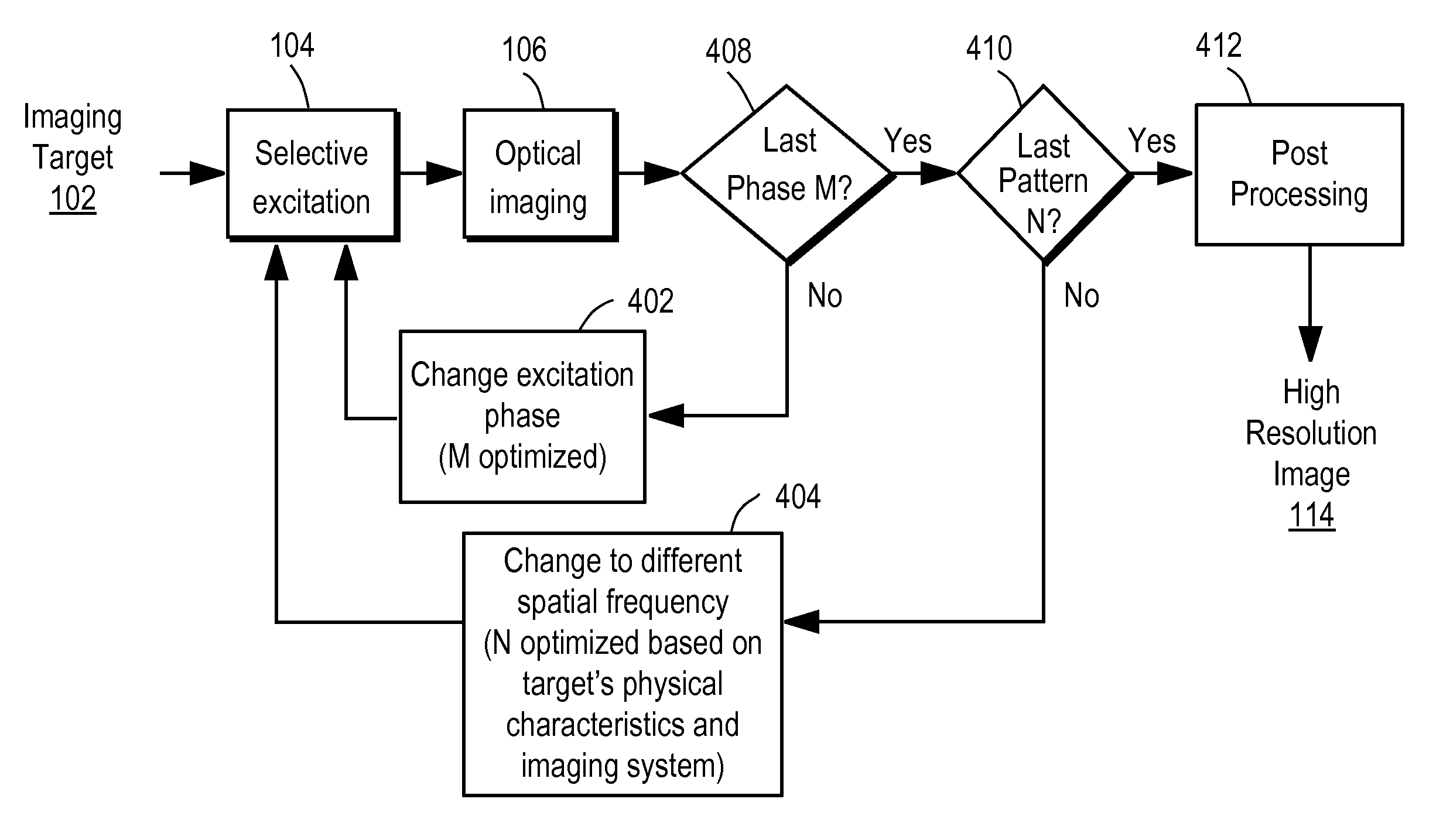
ActiveUS8502867B2Minimize the numberLow costMaterial analysis by optical meansColor television detailsSelective excitationComputer module
A synthetic aperture optics (SAO) imaging method minimizes the number of selective excitation patterns used to illuminate the imaging target, based on the objects' physical characteristics corresponding to spatial frequency content from the illuminated target and / or one or more parameters of the optical imaging system used for SAO. With the minimized number of selective excitation patterns, the time required to perform SAO is reduced dramatically, thereby allowing SAO to be used with DNA sequencing applications that require massive parallelization for cost reduction and high throughput. In addition, an SAO apparatus optimized to perform the SAO method is provided. The SAO apparatus includes a plurality of interference pattern generation modules that can be arranged in a half-ring shape.
Owner:REBUS BIOSYSTEMS INC
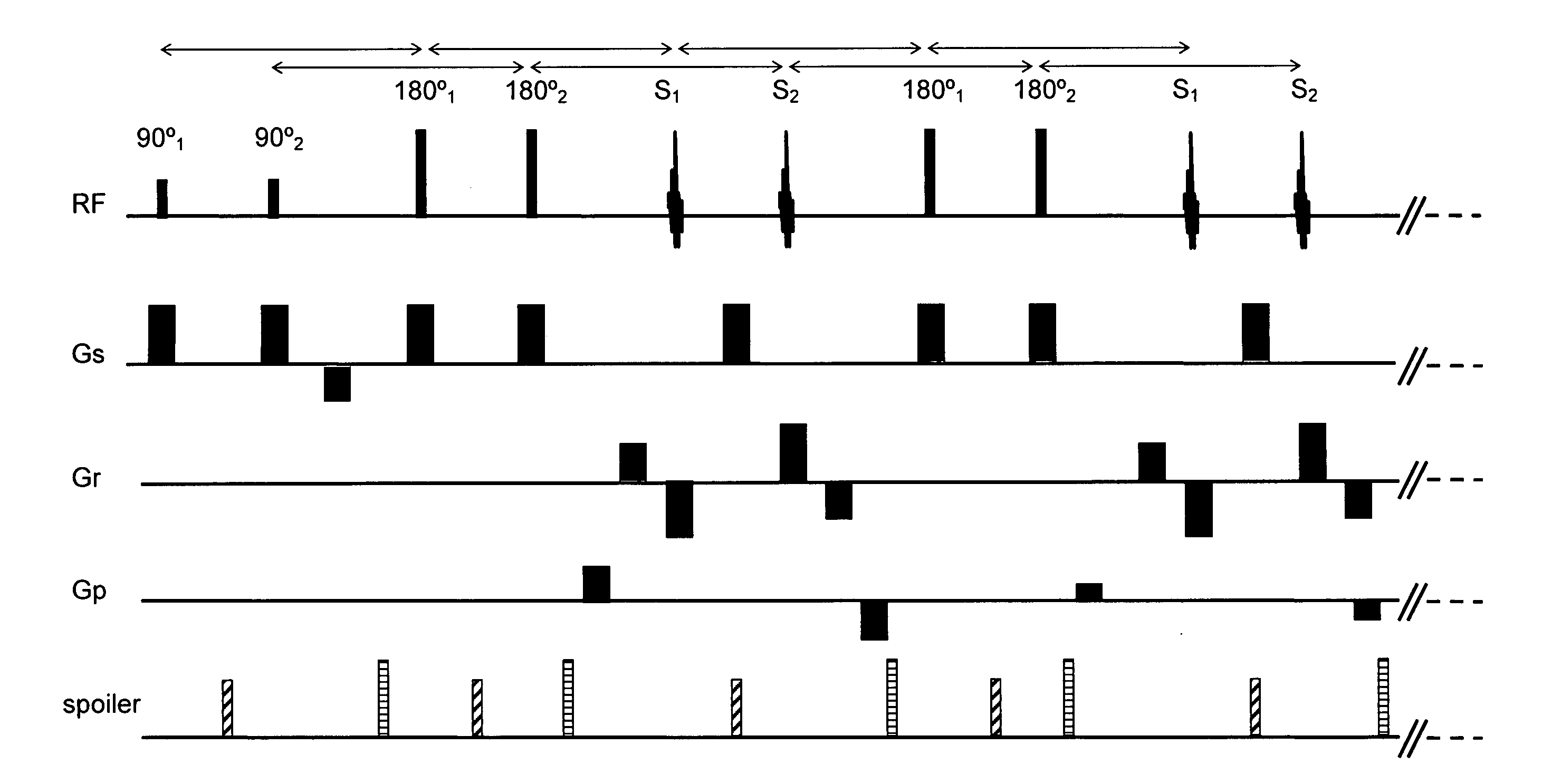
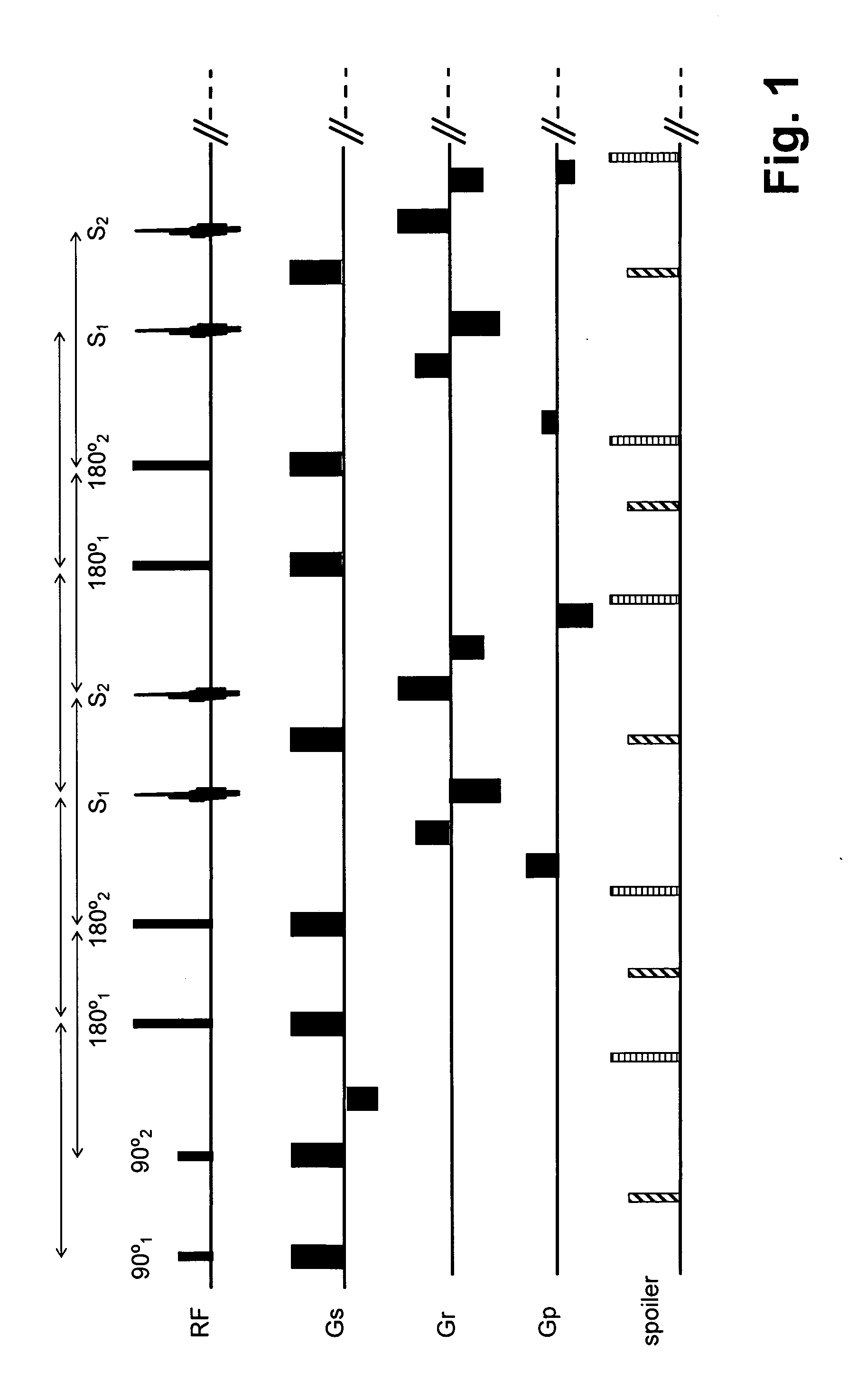
Simultaneous excitation and acquisition of signal from multiple slices in the RARE sequence (multiplex RARE)
InactiveUS20100259260A1Improve efficiencyEasy to useMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionStimulated echoSelective excitation
A method for RARE magnetic resonance imaging comprising slice selective excitation of two or more slices and of one or more nuclei, followed by refocusing of these slices and application of gradient pulses which cause a diversion of the signal into spin echoes and stimulated echoes, is characterized by application of refocusing slice selective RF pulses, which are placed to fulfill the echo-spacing CPMG condition for each slice and by arrangement of gradient pulses which cause the phase accumulated by spins in each slice between two consecutive refocusing RF pulses corresponding to that slice to be equal, thus fulfilling the CPMG phase accumulation condition. Thereby, the obtainable signal can be increased and stabilized.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
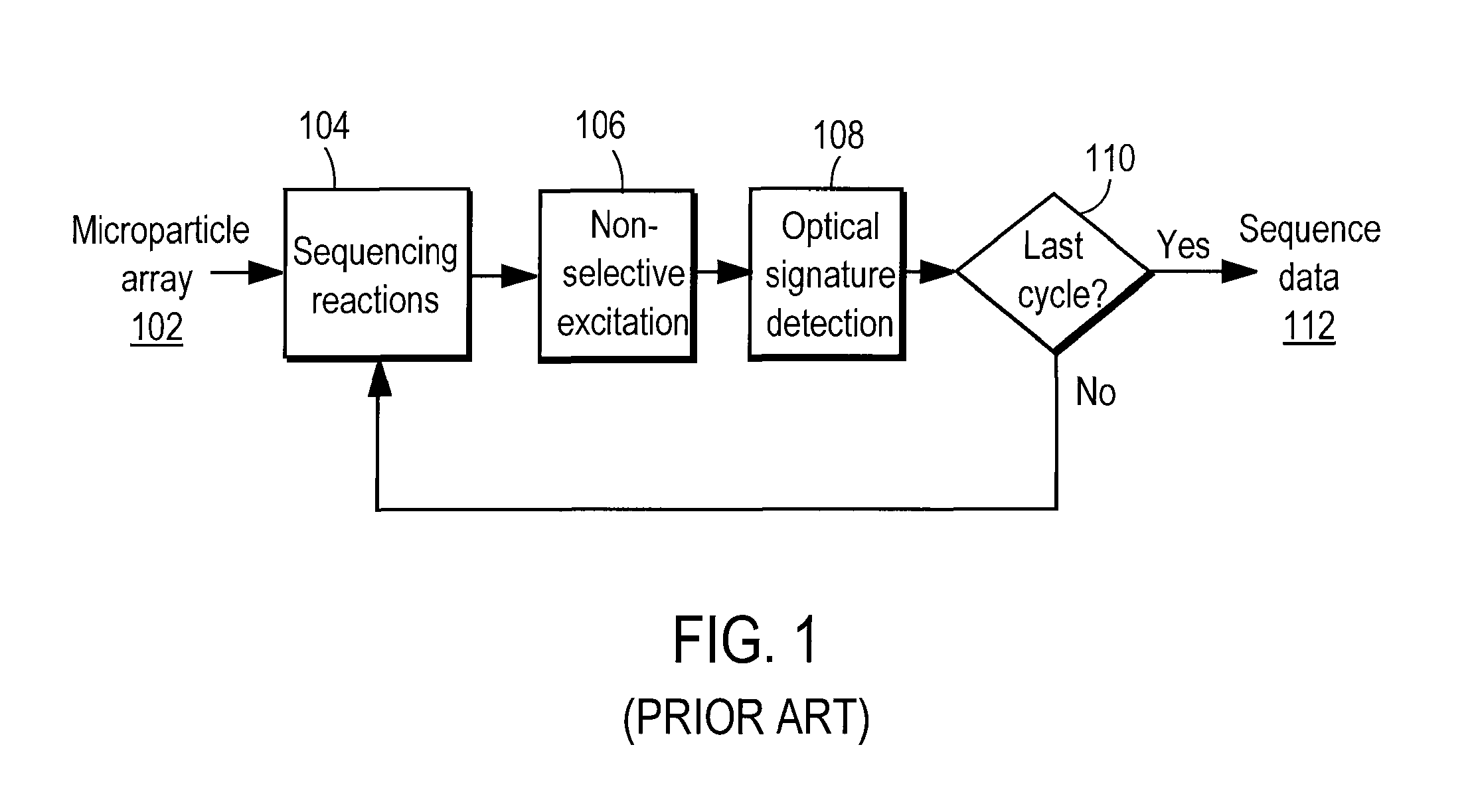
Nucleic acid sequencing by selective excitation of microparticles
ActiveUS20090061526A1High speedData efficientBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSelective excitationImage resolution
Nucleic acid microparticles are sequenced by performing a sequencing reaction on the microparticles using one or more reagents, selectively exciting the microparticles in an excitation pattern, optically imaging the microparticles at a resolution insufficient to resolve individual microparticles, and processing the optical images of the microparticles using information on the excitation pattern to determine the presence or absence of the optical signature, which indicates the sequence information of the nucleic acid. An apparatus for optical excitation of the microparticles comprises an optical fiber delivering a first laser beam, and an interference pattern generation module coupled to the optical fiber. The interference pattern generation module splits the first laser beam into second and third laser beams and generates the excitation pattern for selectively exciting the microparticles by interference between the second and third laser beams.
Owner:REBUS BIOSYSTEMS INC
Apparatus for selective excitation of microparticles
ActiveUS8759077B2High speedData efficientBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsExcitation patternSelective excitation
Owner:REBUS BIOSYSTEMS INC
Synthetic aperture optics imaging method using minimum selective excitation patterns
ActiveUS20110228068A1Minimize the numberLow costMaterial analysis by optical meansColor television detailsSelective excitationExcitation pattern
A synthetic aperture optics (SAO) imaging method minimizes the number of selective excitation patterns used to illuminate the imaging target, based on the objects' physical characteristics corresponding to spatial frequency content from the illuminated target and / or one or more parameters of the optical imaging system used for SAO. With the minimized number of selective excitation patterns, the time required to perform SAO is reduced dramatically, thereby allowing SAO to be used with DNA sequencing applications that require massive parallelization for cost reduction and high throughput. In addition, an SAO apparatus optimized to perform the SAO method is provided. The SAO apparatus includes a plurality of interference pattern generation modules that can be arranged in a half-ring shape.
Owner:REBUS BIOSYSTEMS INC
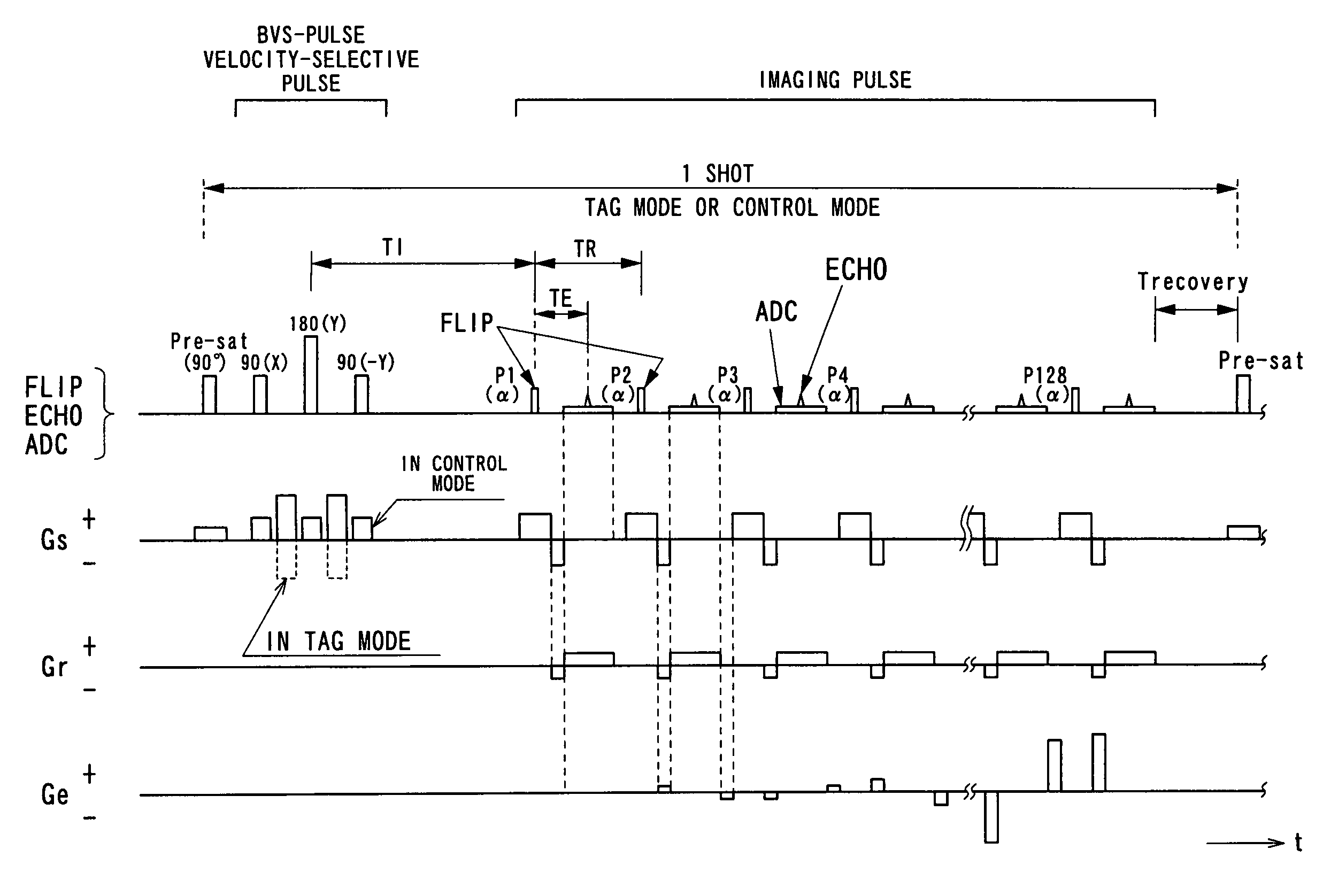
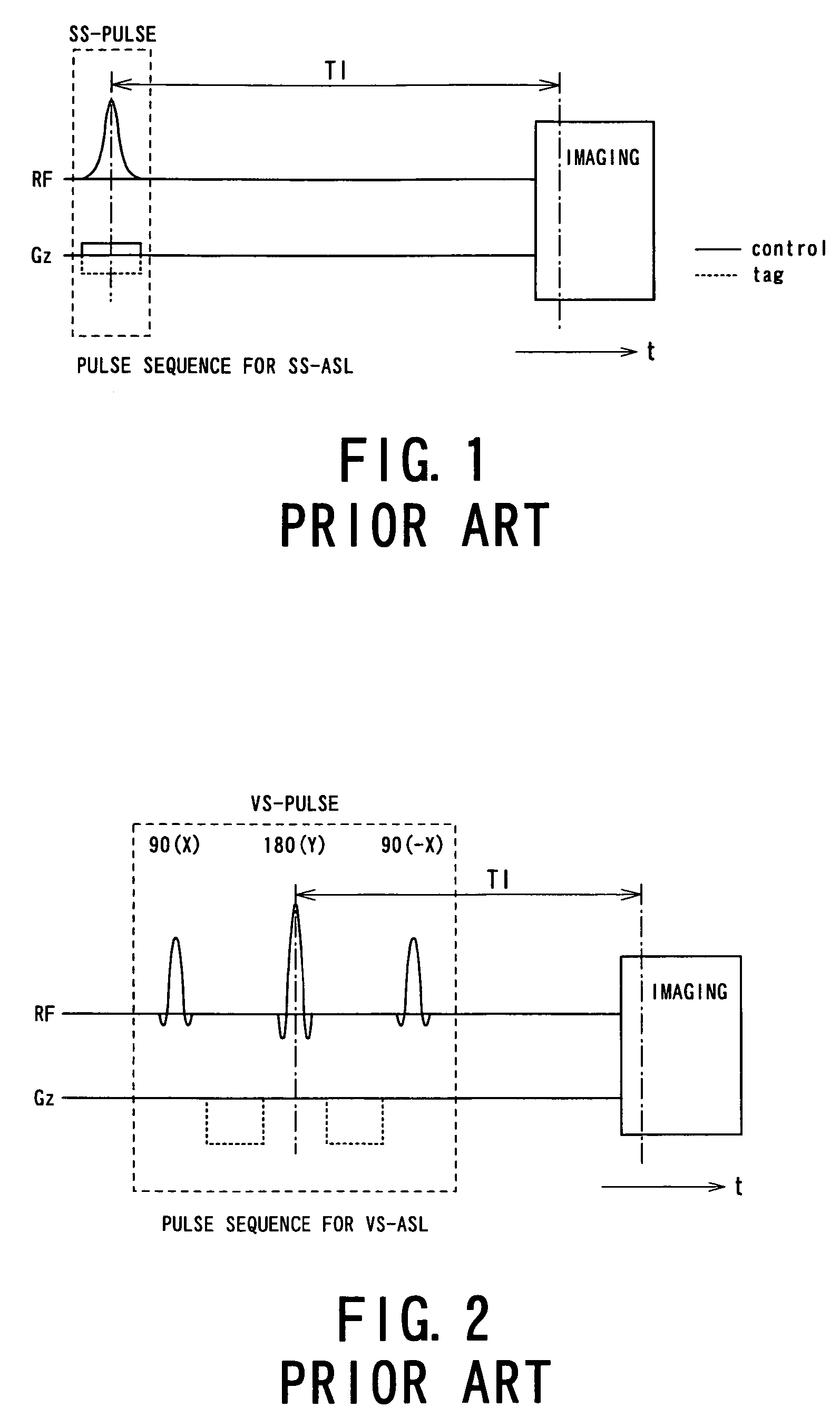
MRI apparatus and ASL imaging technique
ActiveUS7545141B2Reducing Td time-induced errorHigh sensitivityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhase shiftedSelective excitation
An MRI apparatus obtains an ASL (Arterial Spin Labeling) image of a region to be imaged in a subject by performing a scan to the region to be imaged independently in a control mode and in a tag mode according to a pulse sequence based on an ASL technique. The pulse sequence includes a velocity-selective pulse, BVS (Band-limited Velocity-Selective)-pulse, that selectively excites magnetization spins in a blood flow passing through the region to be imaged and having a constant velocity range for the spins to undergo transition to transverse magnetization, and then performs excitation to cause the transverse magnetization to flip back to longitudinal magnetization. The velocity-selective pulse is formed in such a manner that the transverse magnetization excited in each of the control mode and the tag mode gives rise to a phase shift in an opposite polarity upon velocity-selective excitation.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Nucleic acid sequencing by selective excitation of microparticles
ActiveUS8222040B2High speedData efficientBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSelective excitationMicroparticle
Owner:REBUS BIOSYSTEMS INC
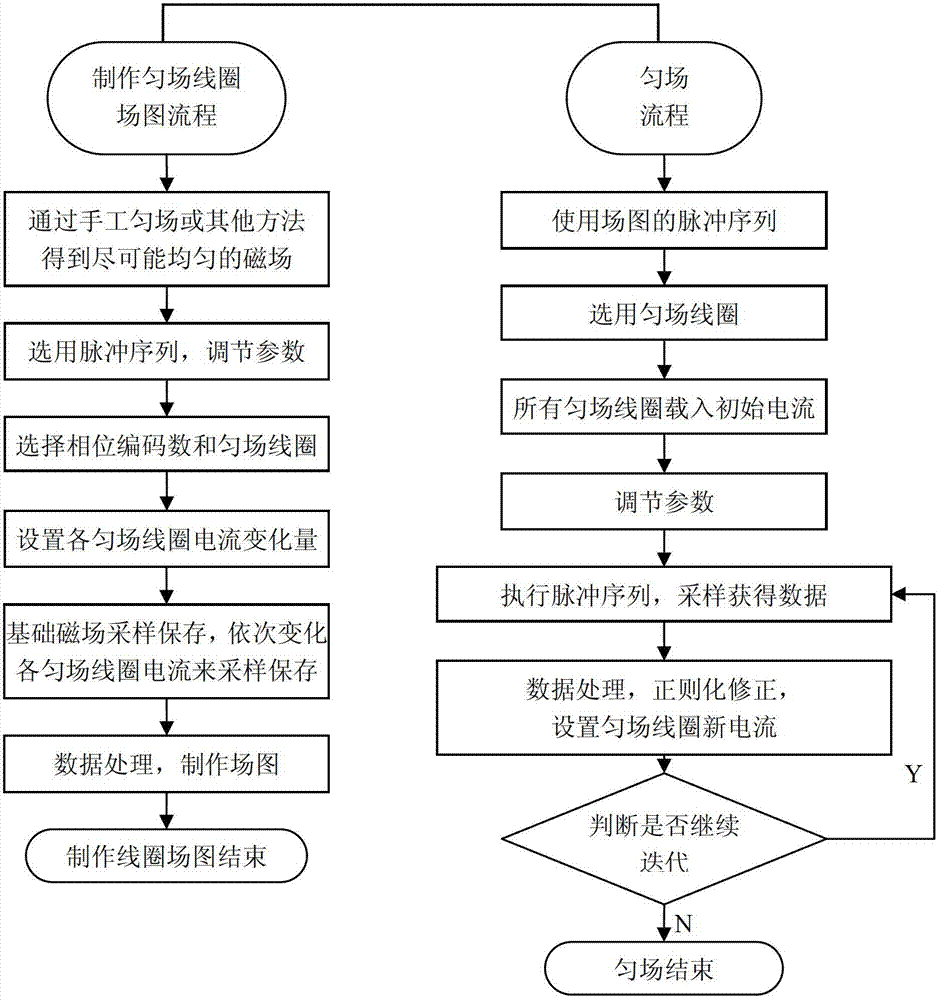
Rapid three-dimensional gradient shimming method for reducing phase encoding number on nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer
InactiveCN102768347AAvoid mutual interferenceGet rid of dependenceMeasurements using magnetic resonanceHydrogenSelective excitation
The invention discloses a rapid three-dimensional gradient shimming method for reducing phase encoding number on a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, which relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer. A method of shimming coils is selected according to the phase encoding number, X and Y high-order shimming coils are deducted, on this basis, a proper revised regularization method can be added to the calculation, a good shimming effect can still be achieved when the phase encoding number can be reduced to be 3*3 or 2*2. These few 2*2 and 3*3 phase codes are widely applied to all three-dimensional gradient shimming pulse sequences of the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, such as a three-dimensional gradient echo pulse sequence, a tilt three-dimensional gradient echo pulse sequence, and a pulse gradient field excitation echo pulse sequence. The mutual interference of multiple spectral peaks with farer chemical shifts can be overcome in the phase measurement. The three-dimensional gradient shimming in which the hydrogen nuclear is selectively excited enable the shimming method to get rid of the dependence on deuterium reagent, brings speed increase in cooperation with few phase encoding number and small-angle excitation, and has wide application range.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Methods for arbitrary shape selective excitation summed spectroscopy and applications of same
InactiveUS7777488B2Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionBiological bodySelective excitation
In another aspect, the present invention relates to a method for NMR measurements of an arbitrarily shaped region of interest of a living subject. In one embodiment, the method comprises the steps of applying a broad bandwidth of RF pulses to the arbitrarily shaped region of interest to obtain a corresponding spectrum, wherein substantially entire range of chemical shifts in the spectrum is excited from the arbitrarily shaped region of interest, interleaving a plurality of radial k-lines in radial k-space per excitation with non-selective refocusing pulses and obtaining spatial localization for the spectrum of the arbitrarily shaped region of interest.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Illumination apparatus optimized for synthetic aperture optics imaging using minimum selective excitation patterns
ActiveUS20110228073A1Minimize the numberLow costImage enhancementImage analysisLight equipmentSelective excitation
A synthetic aperture optics (SAO) imaging method minimizes the number of selective excitation patterns used to illuminate the imaging target, based on the objects' physical characteristics corresponding to spatial frequency content from the illuminated target and / or one or more parameters of the optical imaging system used for SAO. With the minimized number of selective excitation patterns, the time required to perform SAO is reduced dramatically, thereby allowing SAO to be used with DNA sequencing applications that require massive parallelization for cost reduction and high throughput. In addition, an SAO apparatus optimized to perform the SAO method is provided. The SAO apparatus includes a plurality of interference pattern generation modules that can be arranged in a half-ring shape.
Owner:REBUS BIOSYSTEMS INC
Blood flow gated MRI
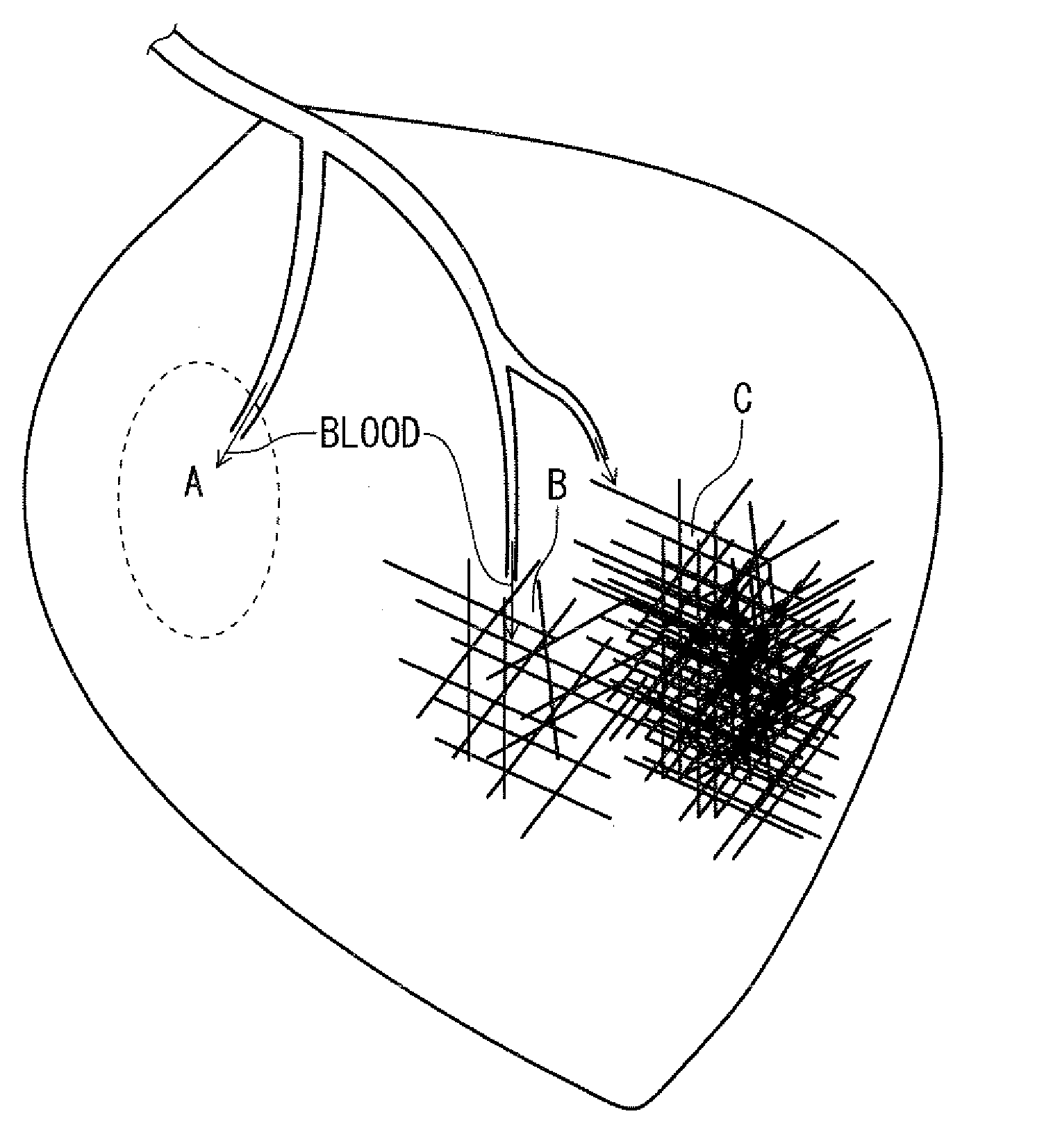
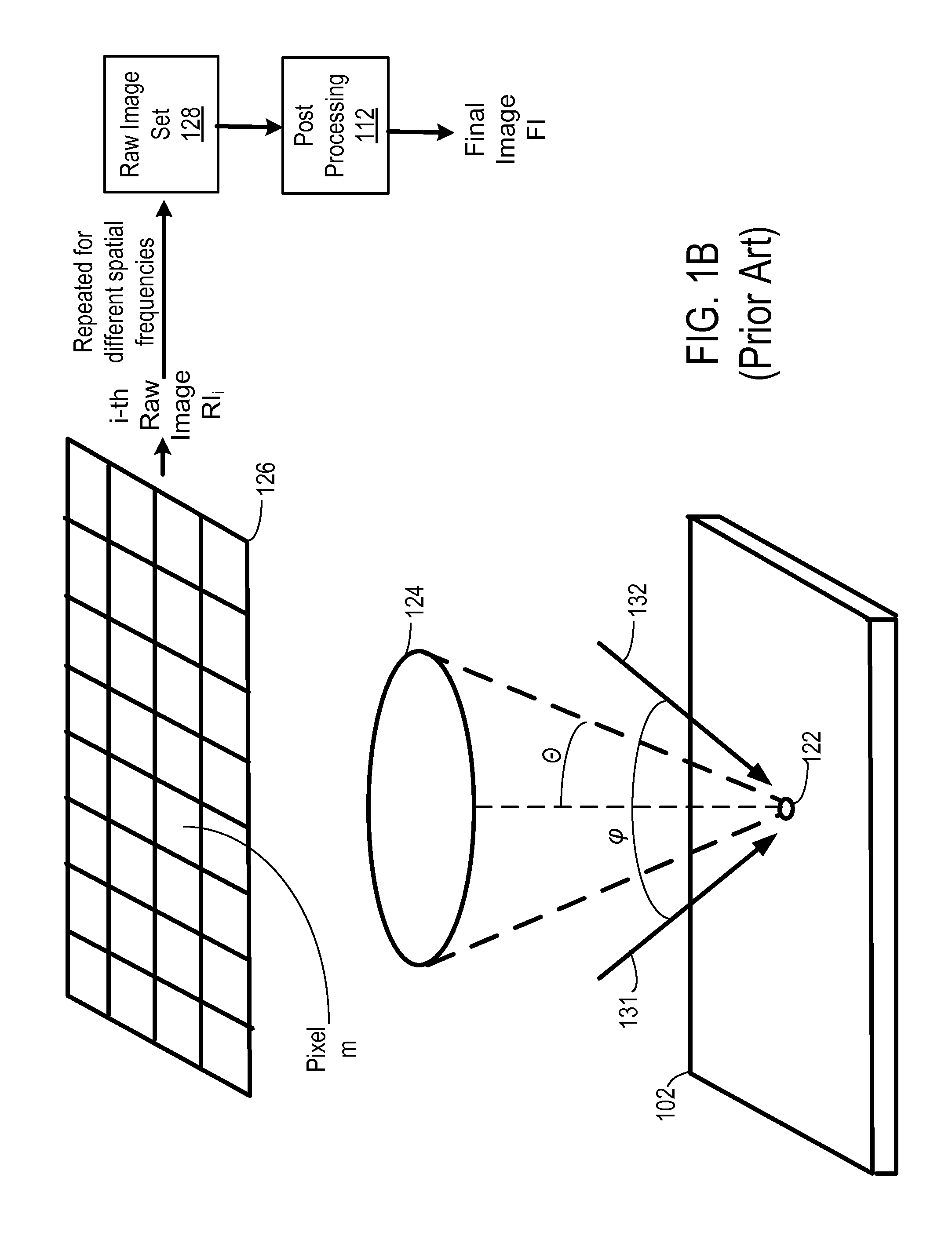
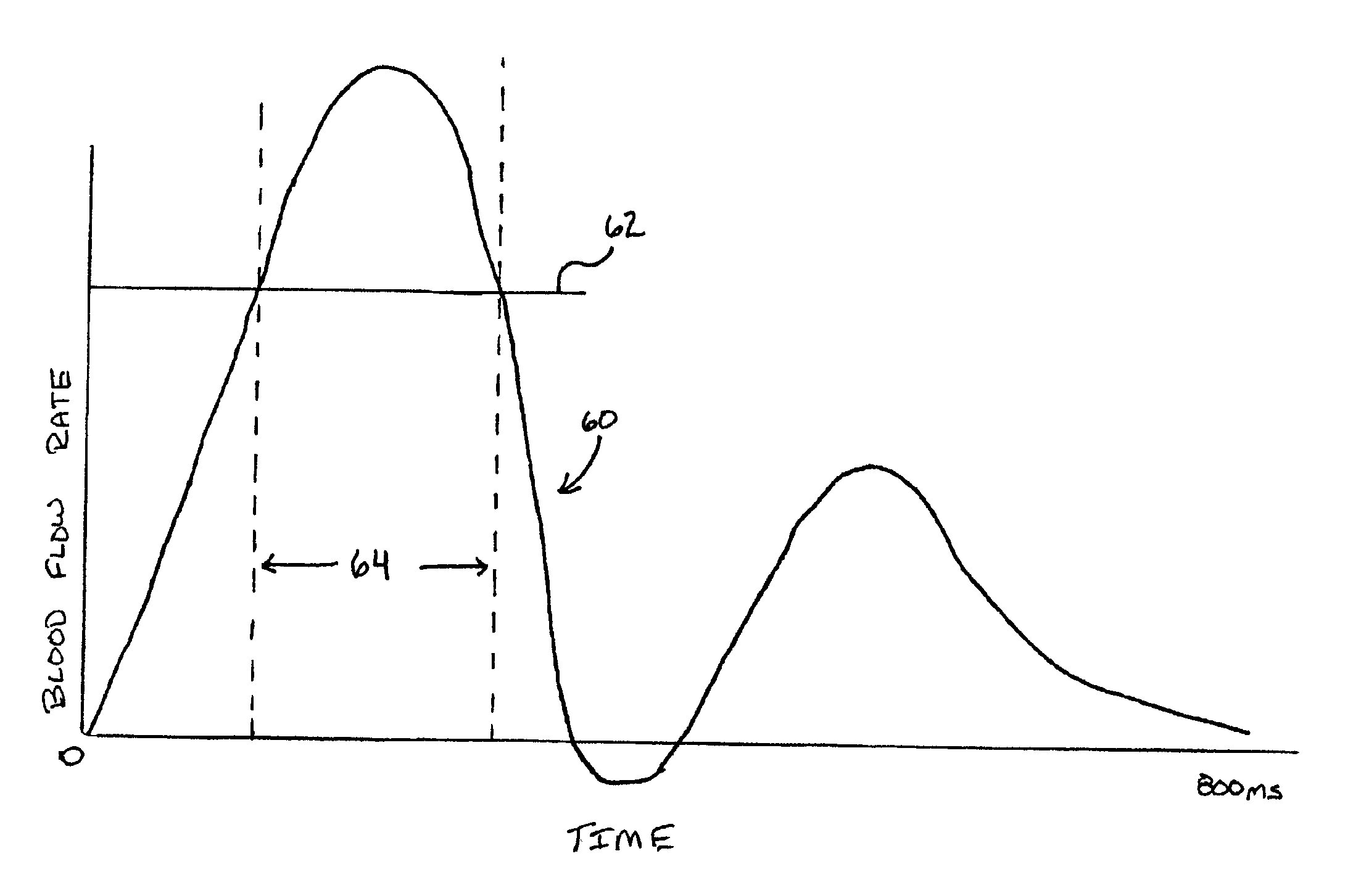
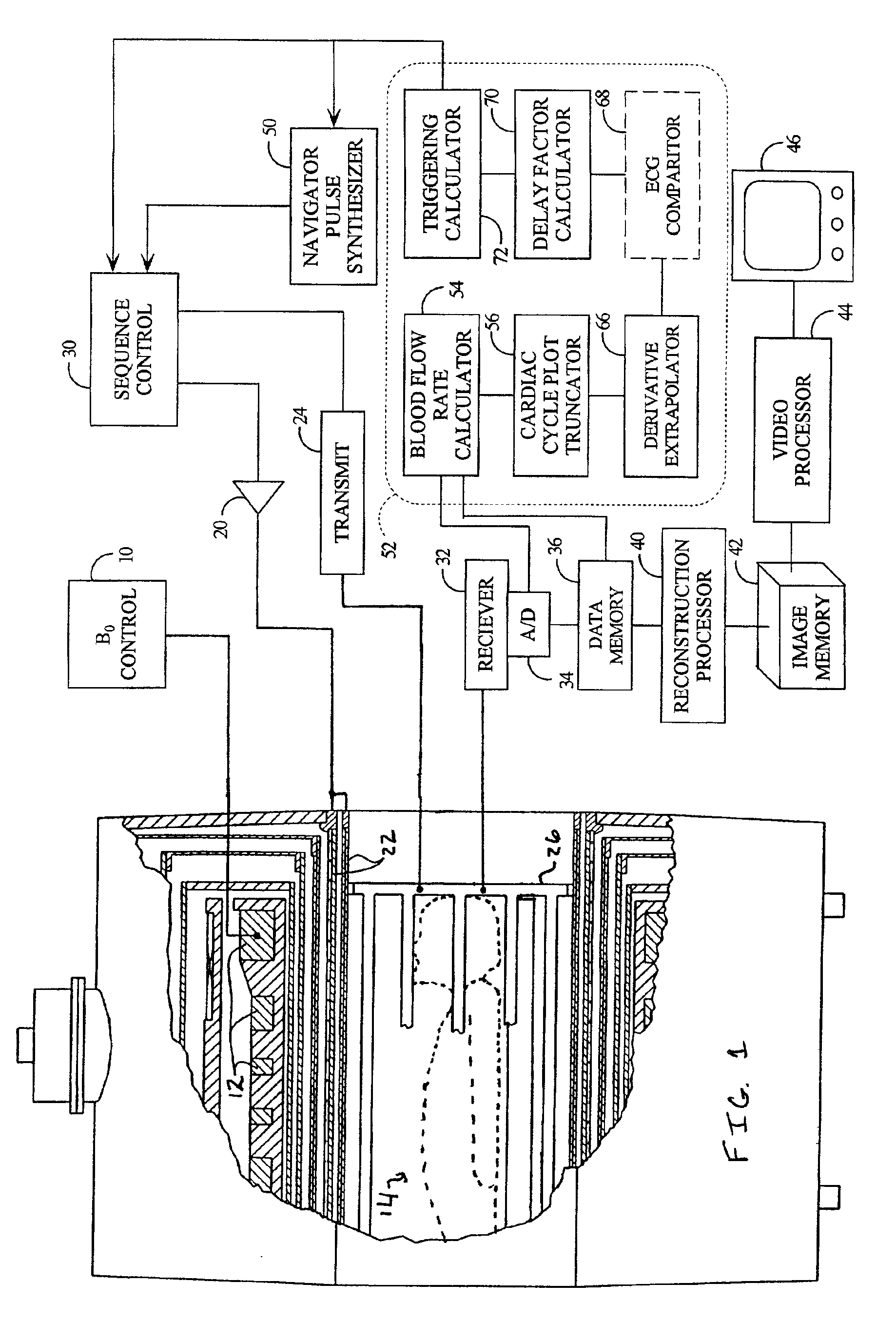
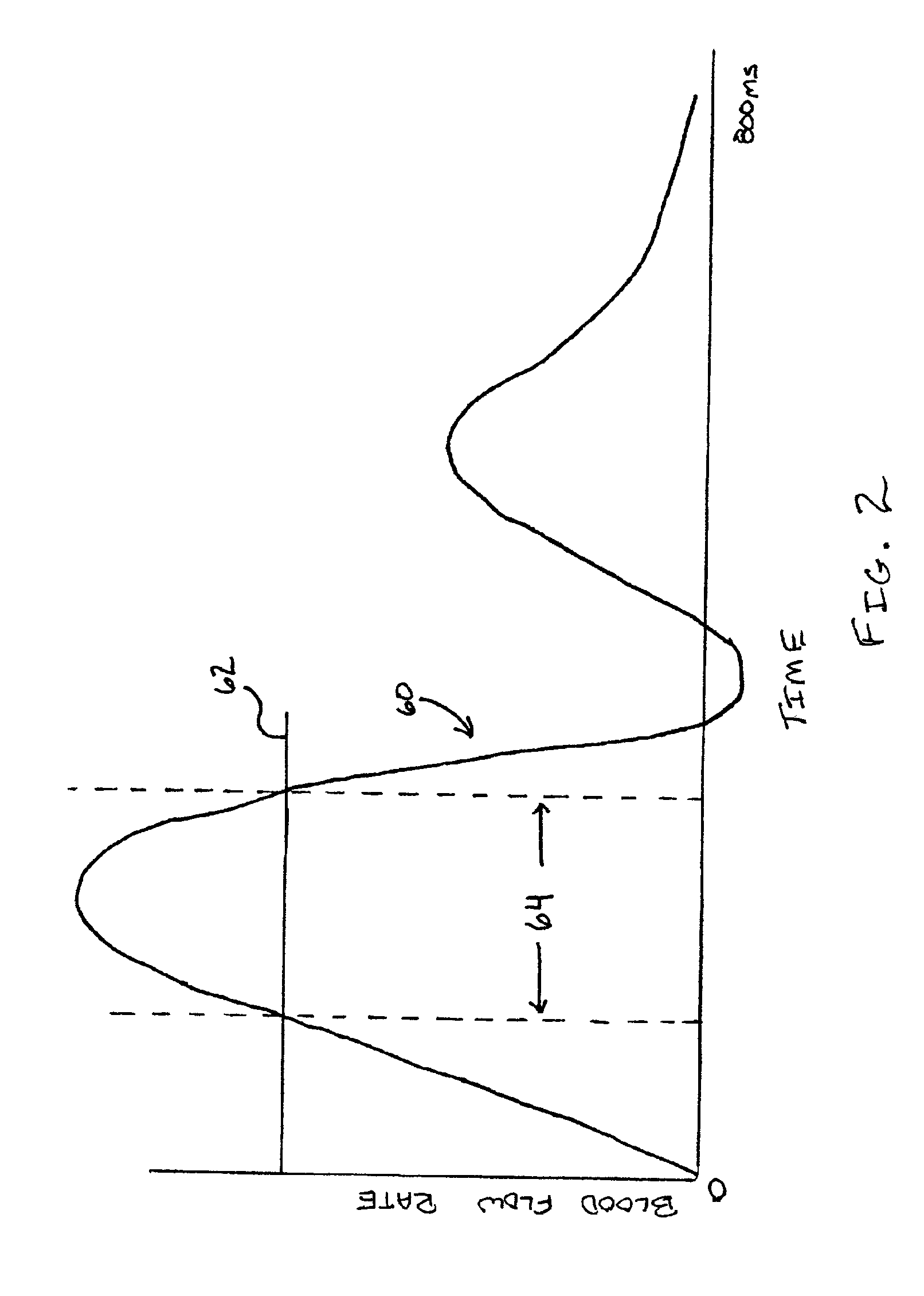
A magnetic resonance imaging method and apparatus includes a navigator region defined within the subject by selective excitation. Blood flow is measured within the selected region using the principles of phase contrast MR angiography. A cardiac cycle plot is constructed from Fourier transformed data that represents measured velocity of blood flow through the navigator region as a function of time. On the basis of the cardiac cycle plot and the navigator measurements, data acquisition is synchronized or gated to portions of the cardiac cycle.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
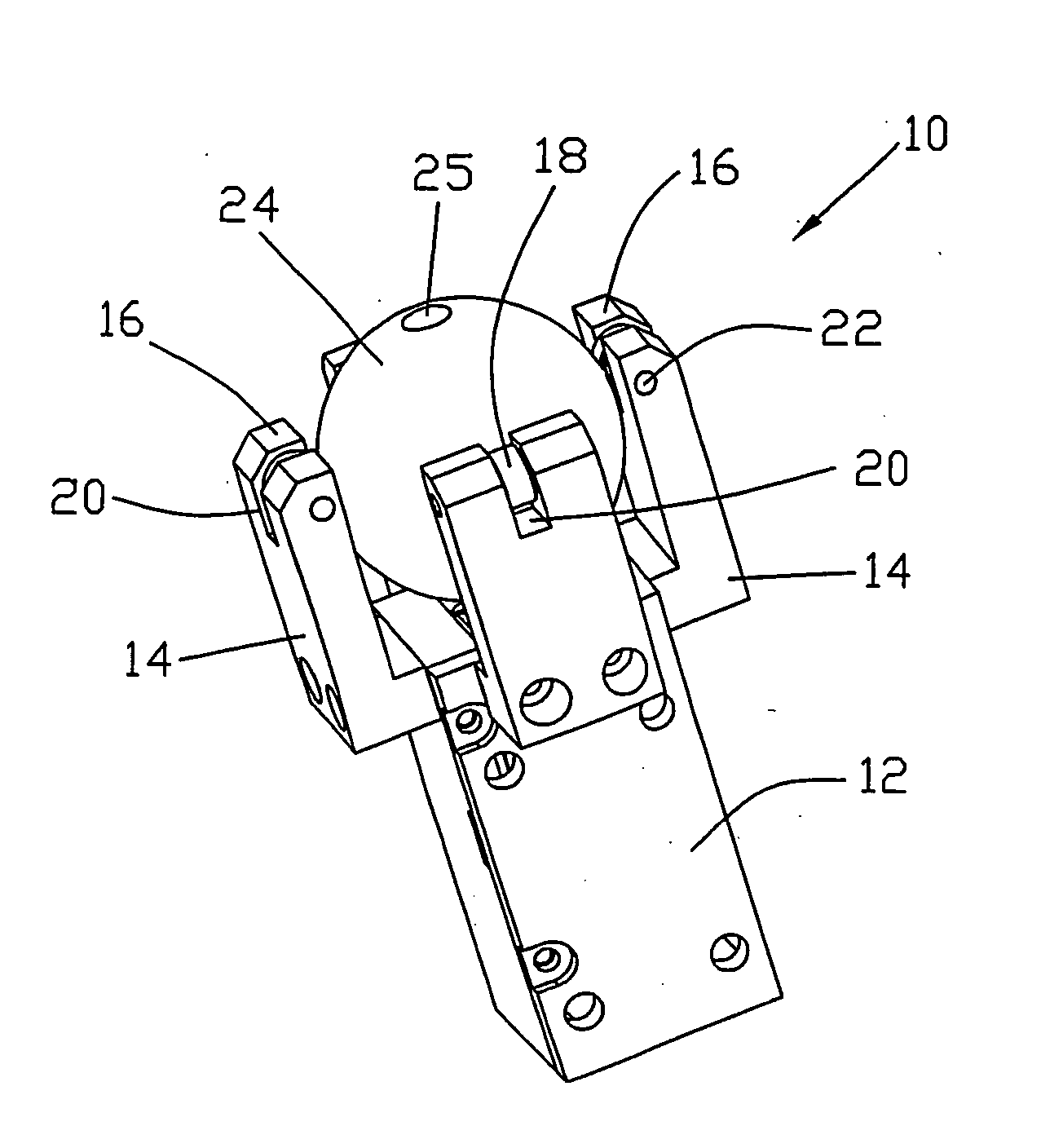
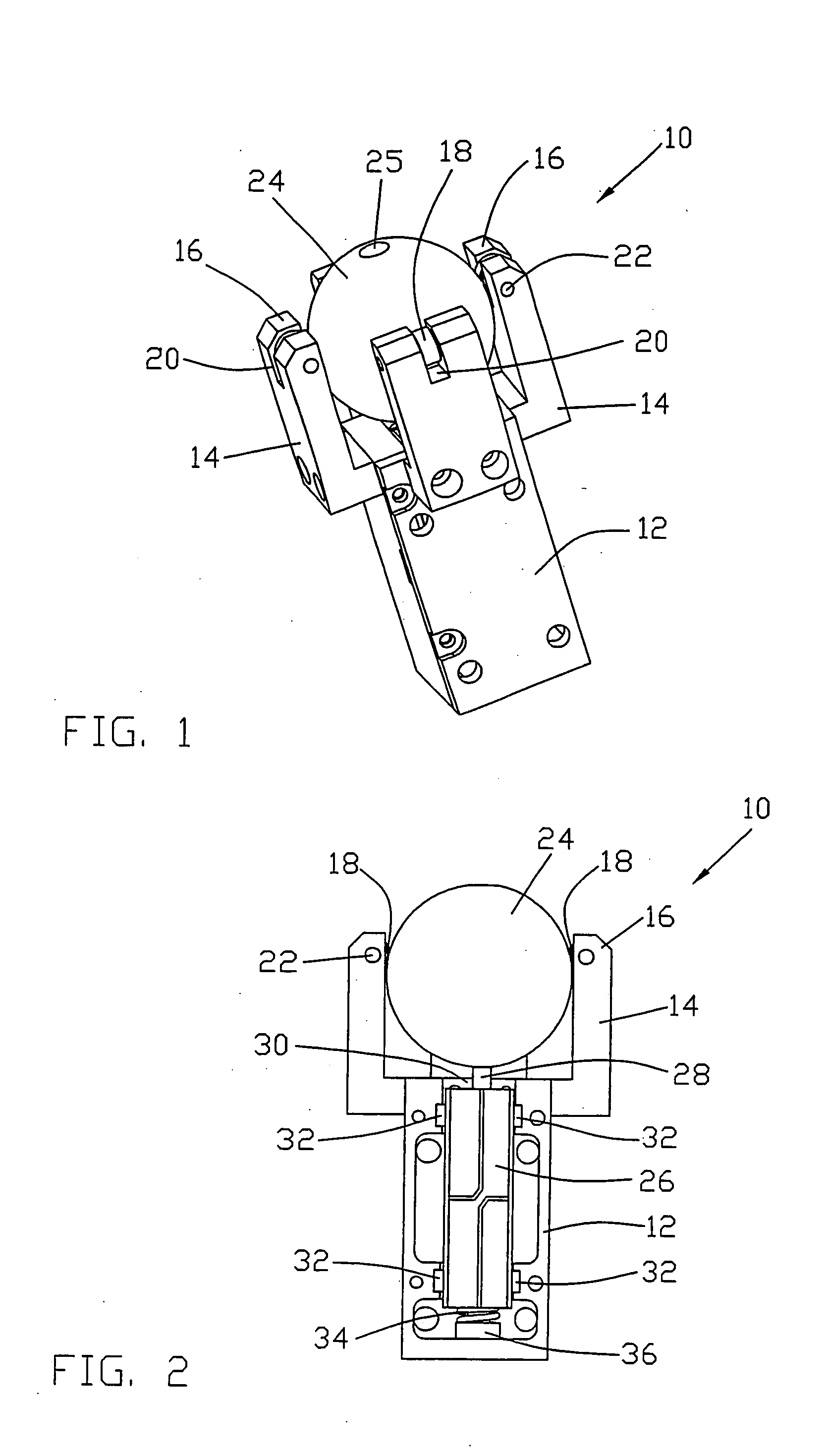
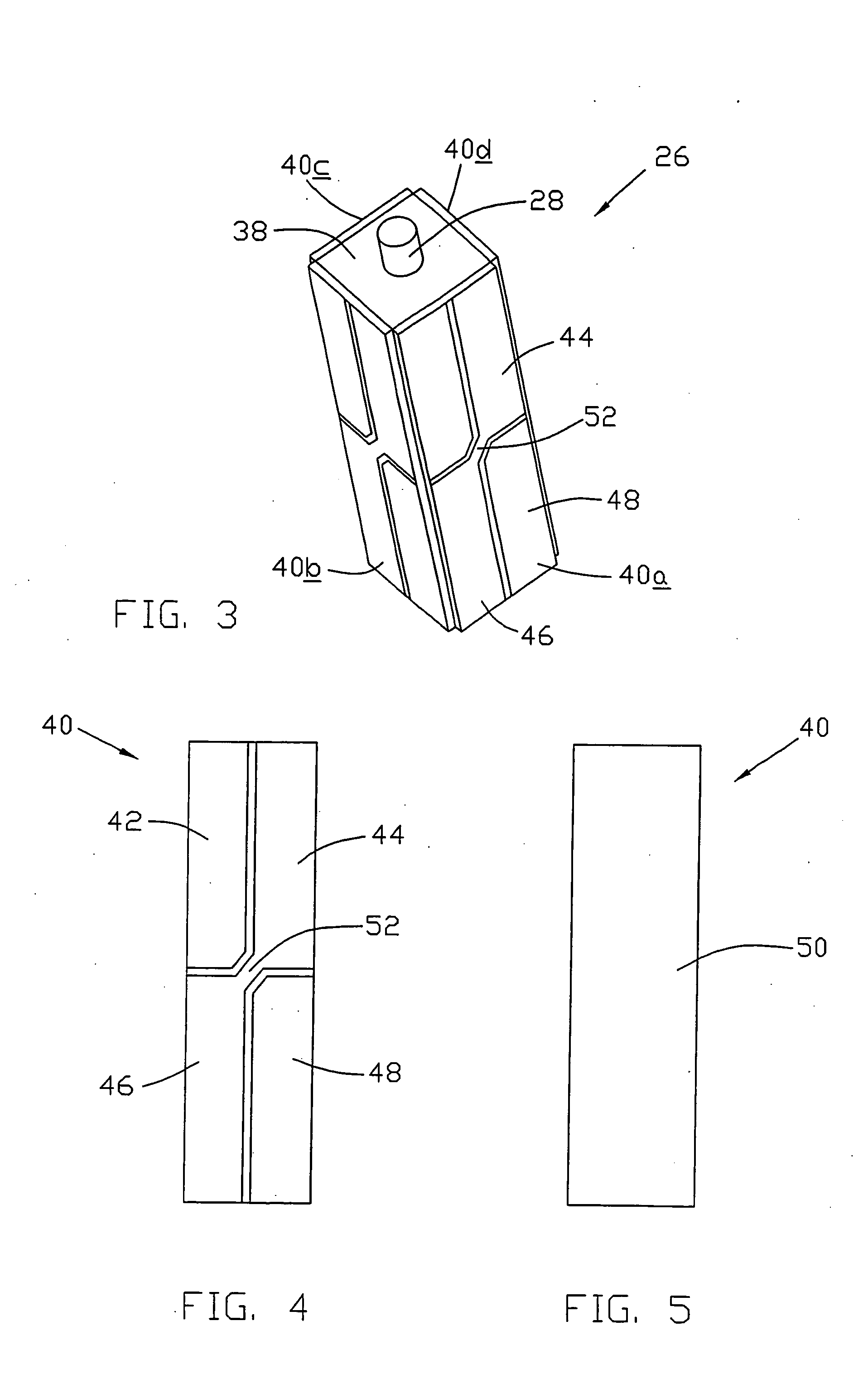
Electric motor
InactiveUS20050082947A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device detailsFour quadrantsSquare cross section
A piezoelectric motor has an actuator 26 which drives a slider 24. The actuator has a rectangular steel core of square cross-section with an axially projection driving tip 28. A ceramic piezoelectric element 40 is bonded to each of the four faces of the core. Each piezoelectric element has four quadrants covered by quadrant electrodes 40a-40d on one side and a common or earth electrode on the other side contacting the core which electrically joins the common electrodes. By selective excitation of corresponding diagonally opposite quadrants of opposite piezoelectric elements, the actuator is made to drive the tip in either the X direction or the Y direction. The preferred slider is a spherical ball held captive within arms extending from a housing of the actuator. The driving tip is pressed against the ball by a preload spring 34 acting on the actuator. Operation of the actuator causes the ball 24 to rotate about an X axis or about a Y axis producing a two dimensional movement from a single motor and single actuator.
Owner:JOHNSON ELECTRIC SA
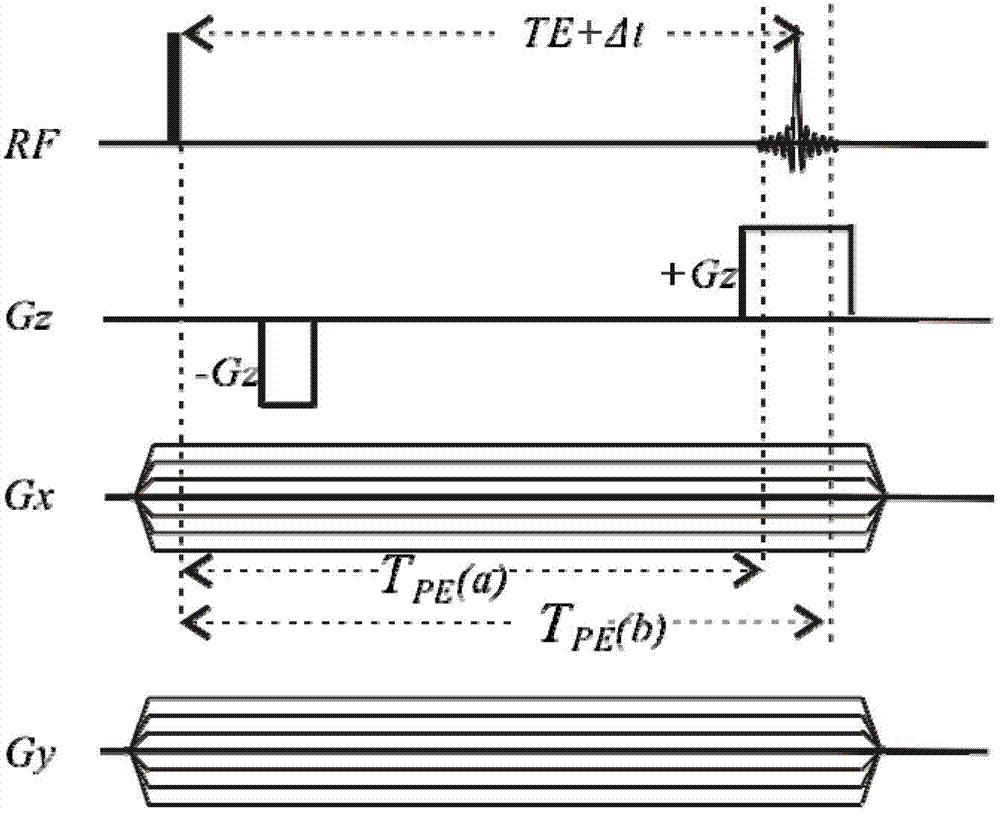
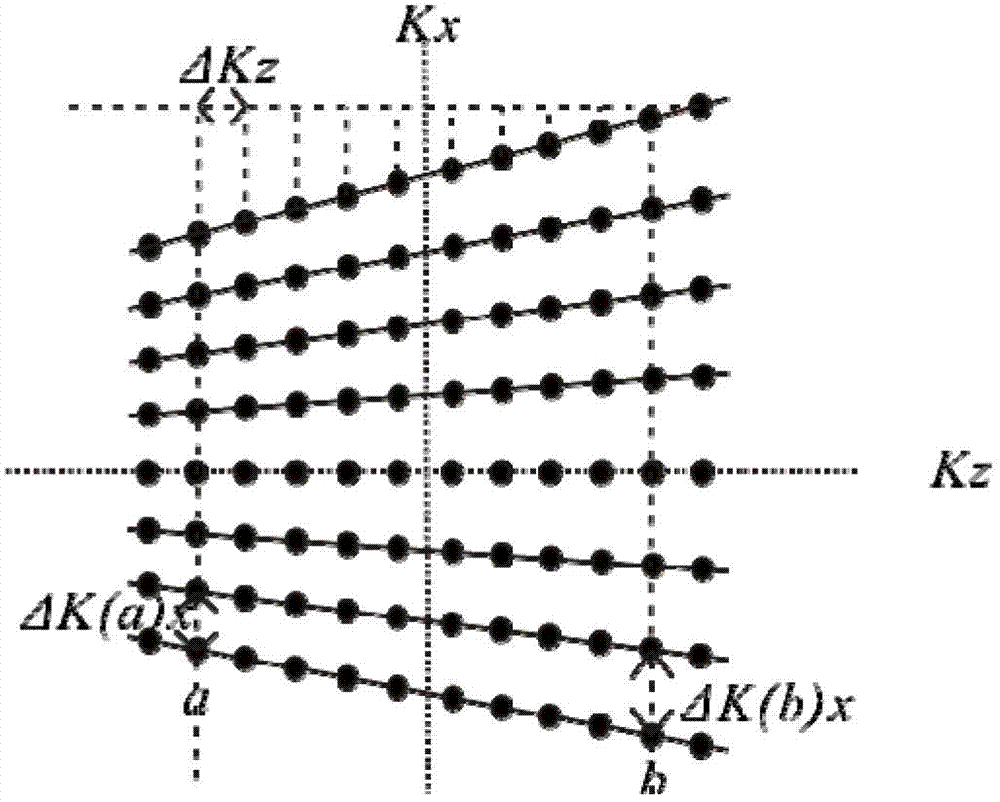
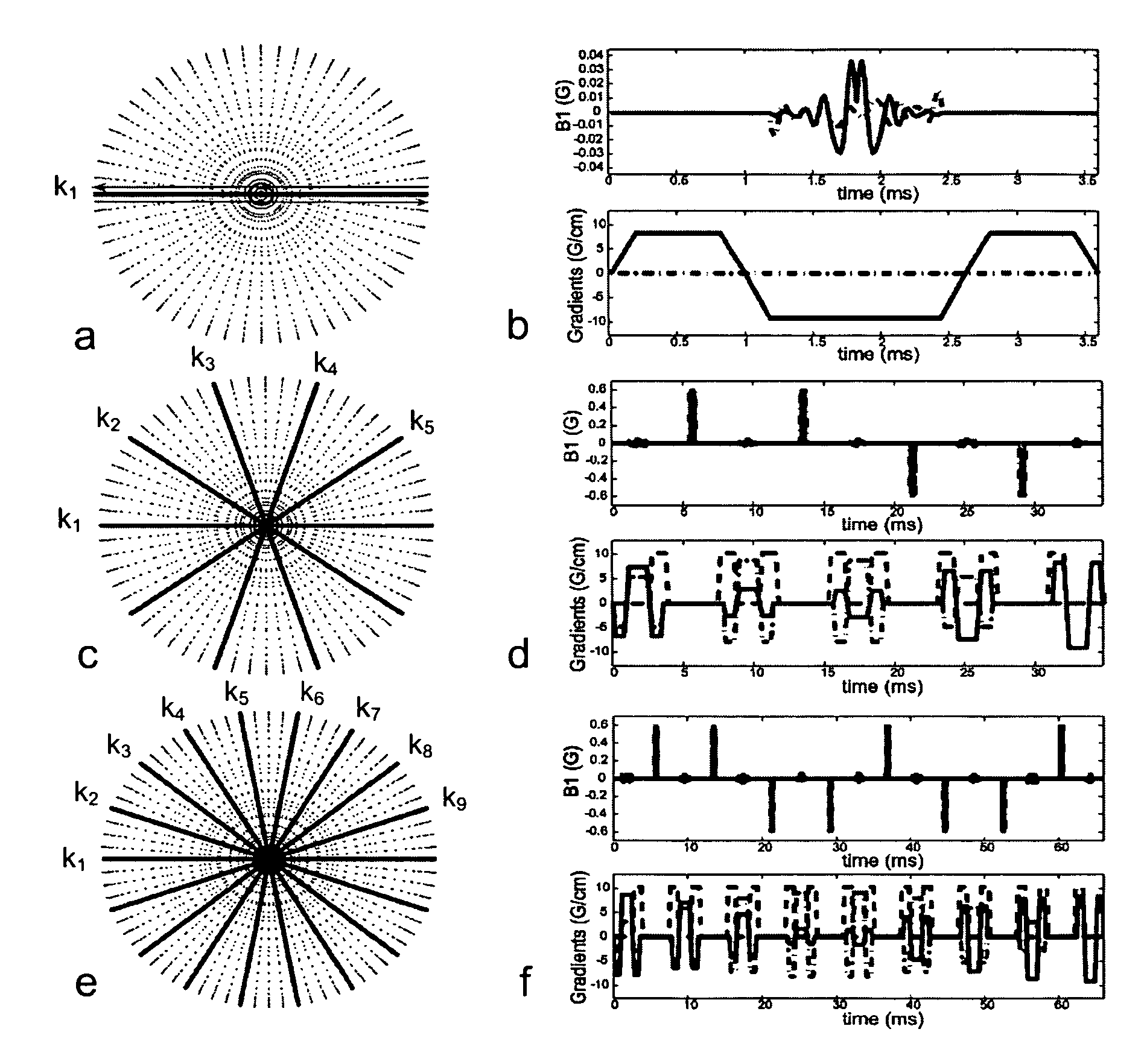
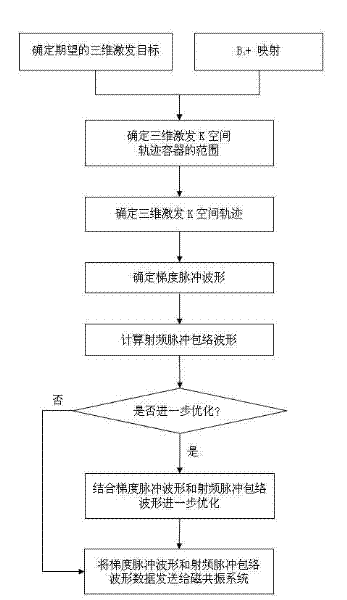
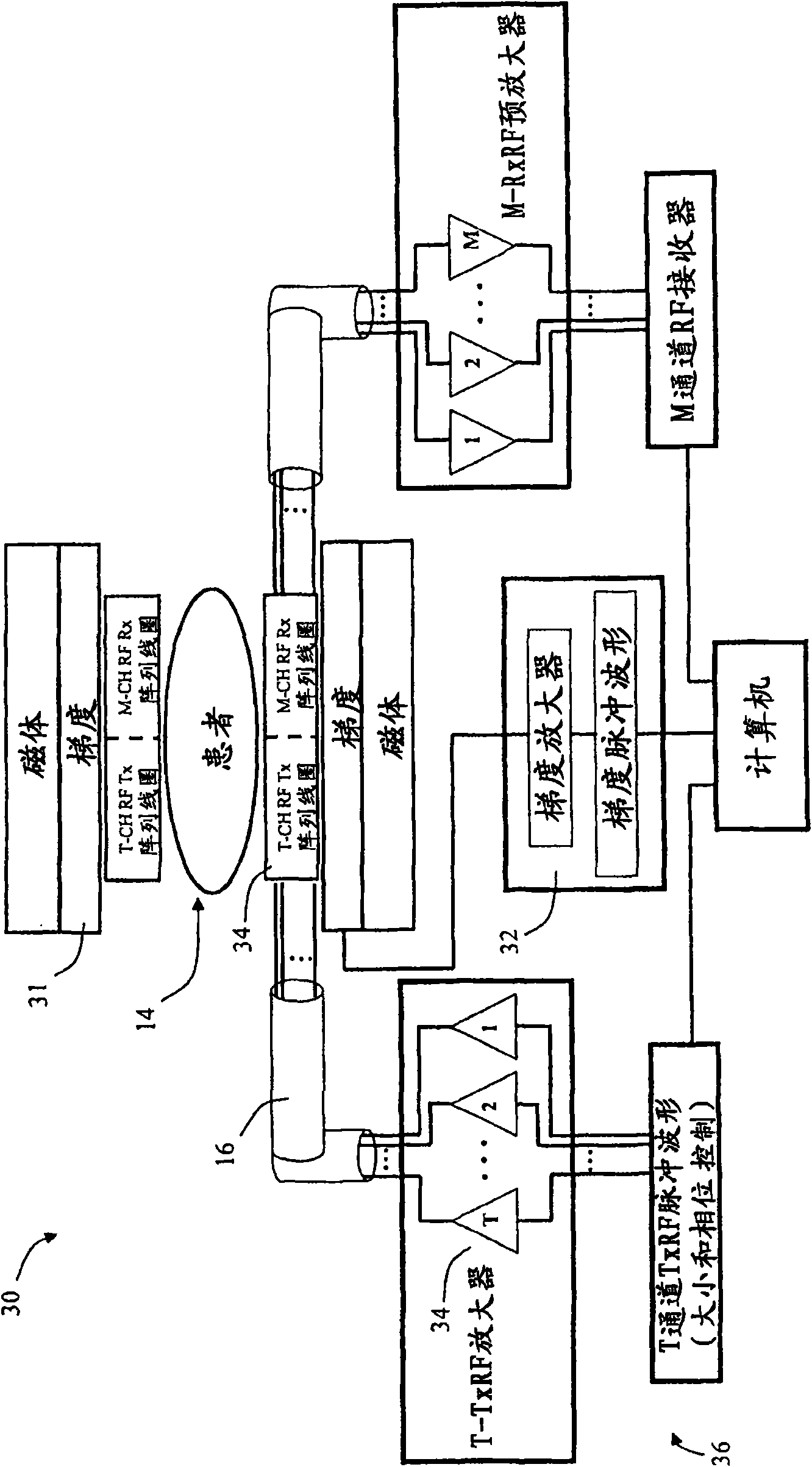
A Sequence Design Method for Three-Dimensional Spatially Selective Excitation for Magnetic Resonance Imaging
InactiveCN102283649AImprove sampling efficiencyImprove securityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSequence designPulse envelope
The invention discloses a selective excitation sequential design method for magnetic resonance imaging in a three-dimensional space. According to the sequential design method disclosed by the invention, a proper excitation K space track is optimally determined according to space sensitive conditions of an excitation target and a plurality of transmitting channels of a radio-frequency coil, thereby a gradient pulse waveform and a radio frequency pulse envelope waveform corresponding to each transmitting channel are determined. A gradient driving unit and a radio-frequency driving unit in a magnetic resonance system can be used for generating gradient pulse and radio frequency pulse according to the radio frequency pulse envelope waveform and the gradient pulse waveform and driving a gradient coil and the radio frequency coil to apply the gradient pulse and radio frequency pulse in a scanning space, thereby the expected selective excitation target in the three-dimensional space is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
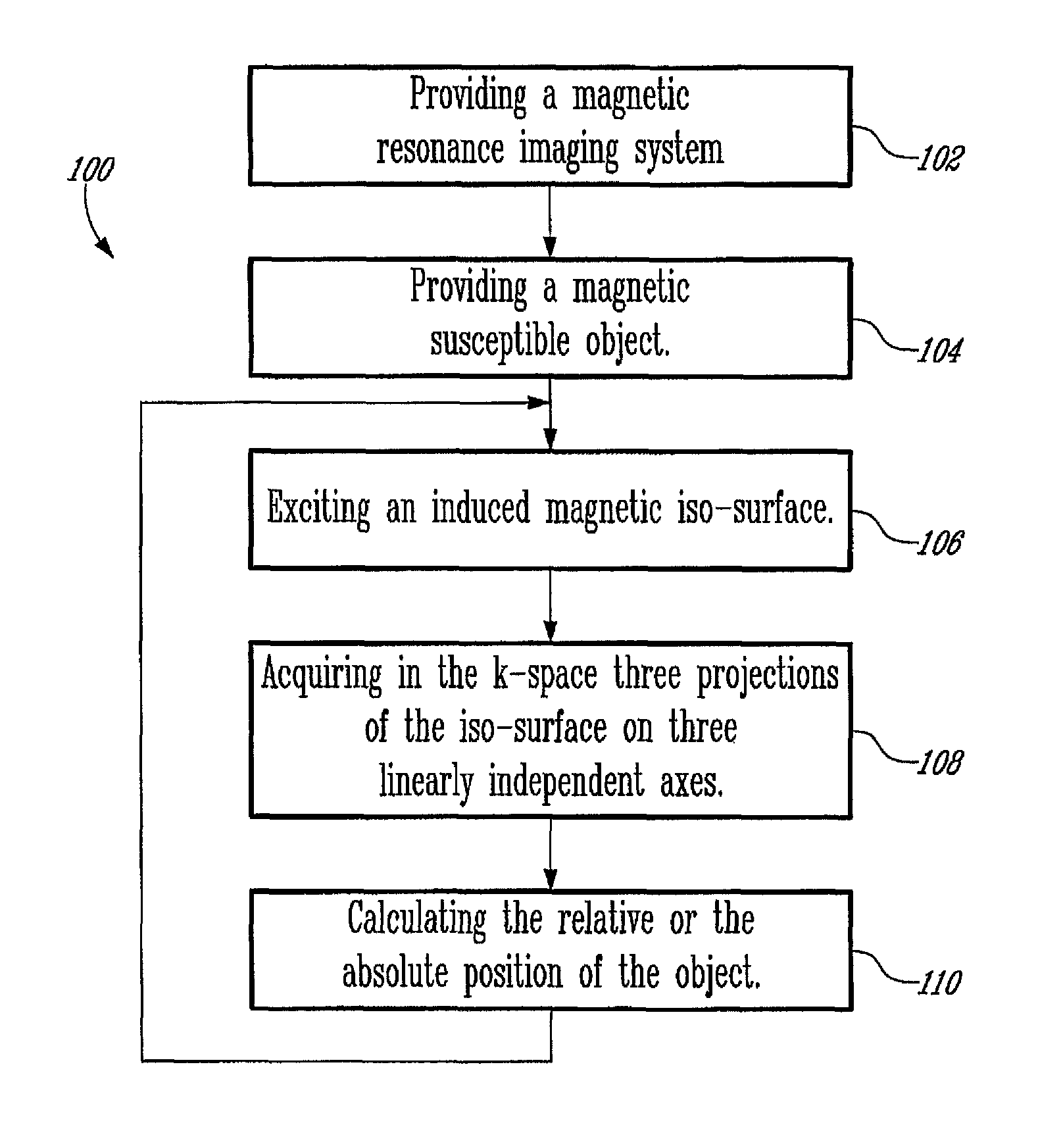
MR-tracking based on magnetic signature selective excitation
ActiveUS8948841B2Overcome disadvantagesEasy to useSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceSelective excitation
The present invention relates to a MR tracking method and device. More specifically, the present invention relates to a magnetic resonance tracking method and device, using a magnetic-susceptible object. A magnetic iso-surface induced by the object is selectively excited with a corresponding frequency offset; the magnetic iso-surface is then projected on three axes of a k-space, from which projections the spatial position of the object is calculated.
Owner:VAL CHUM PARTNERSHIP +1
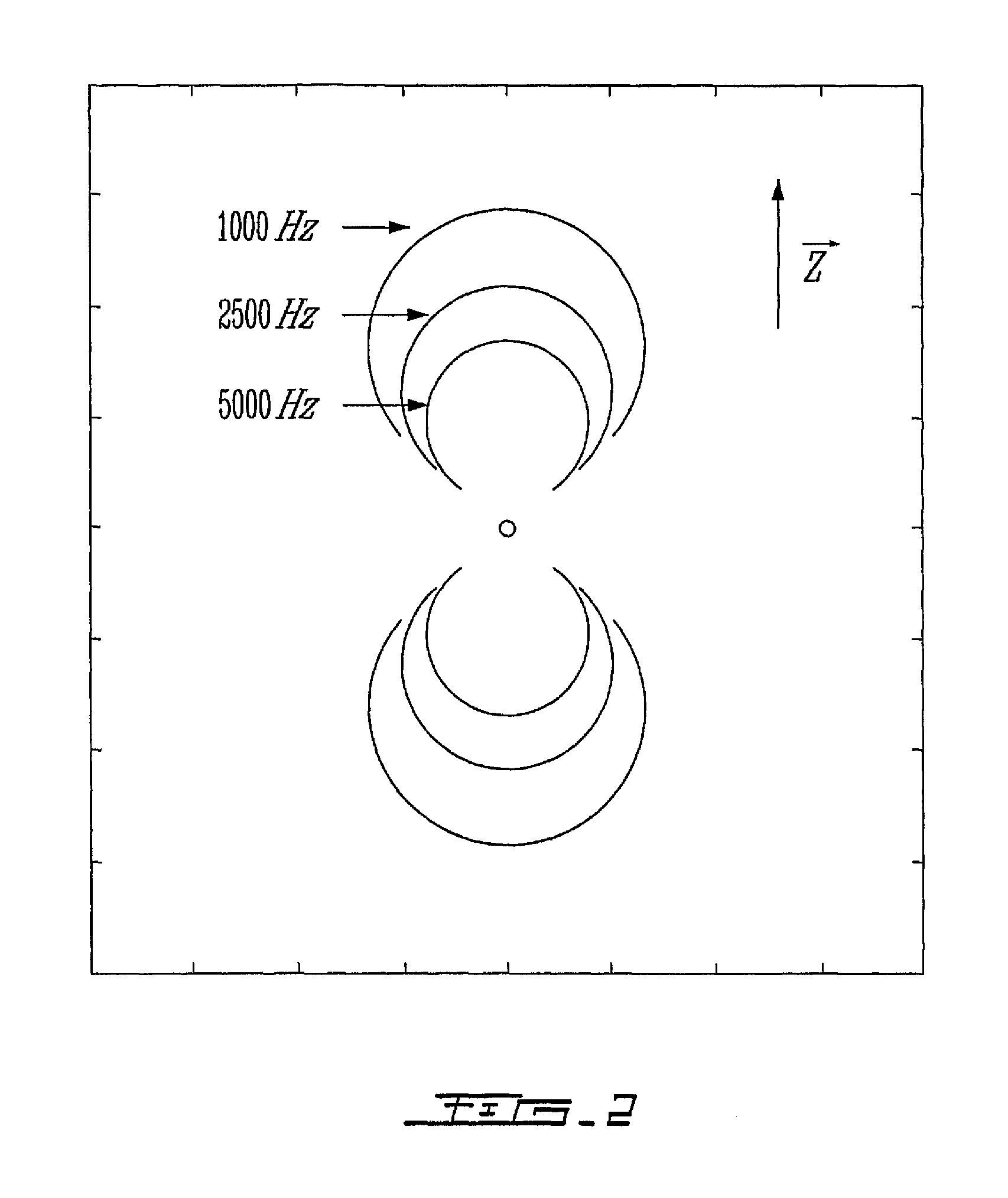
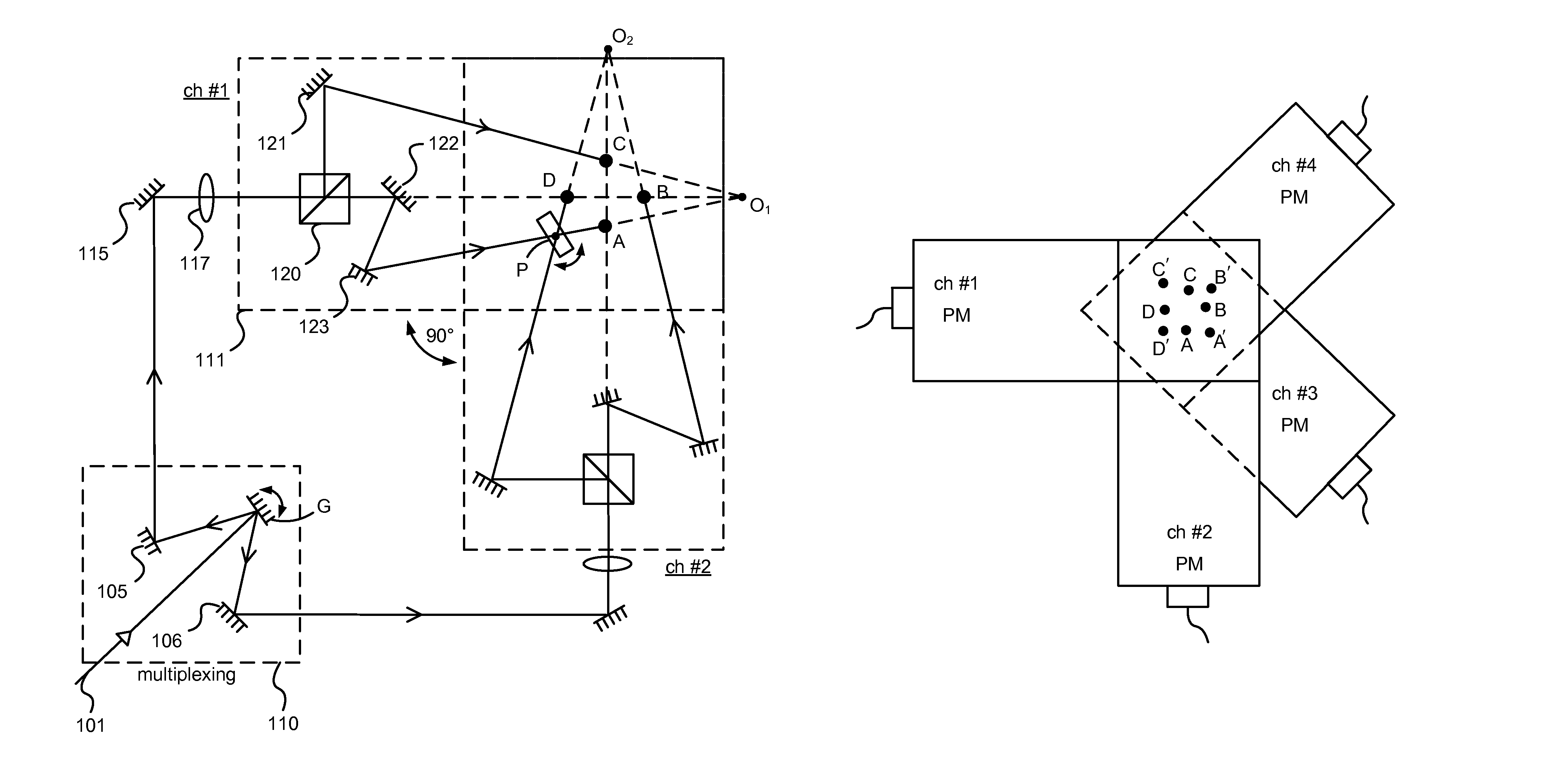
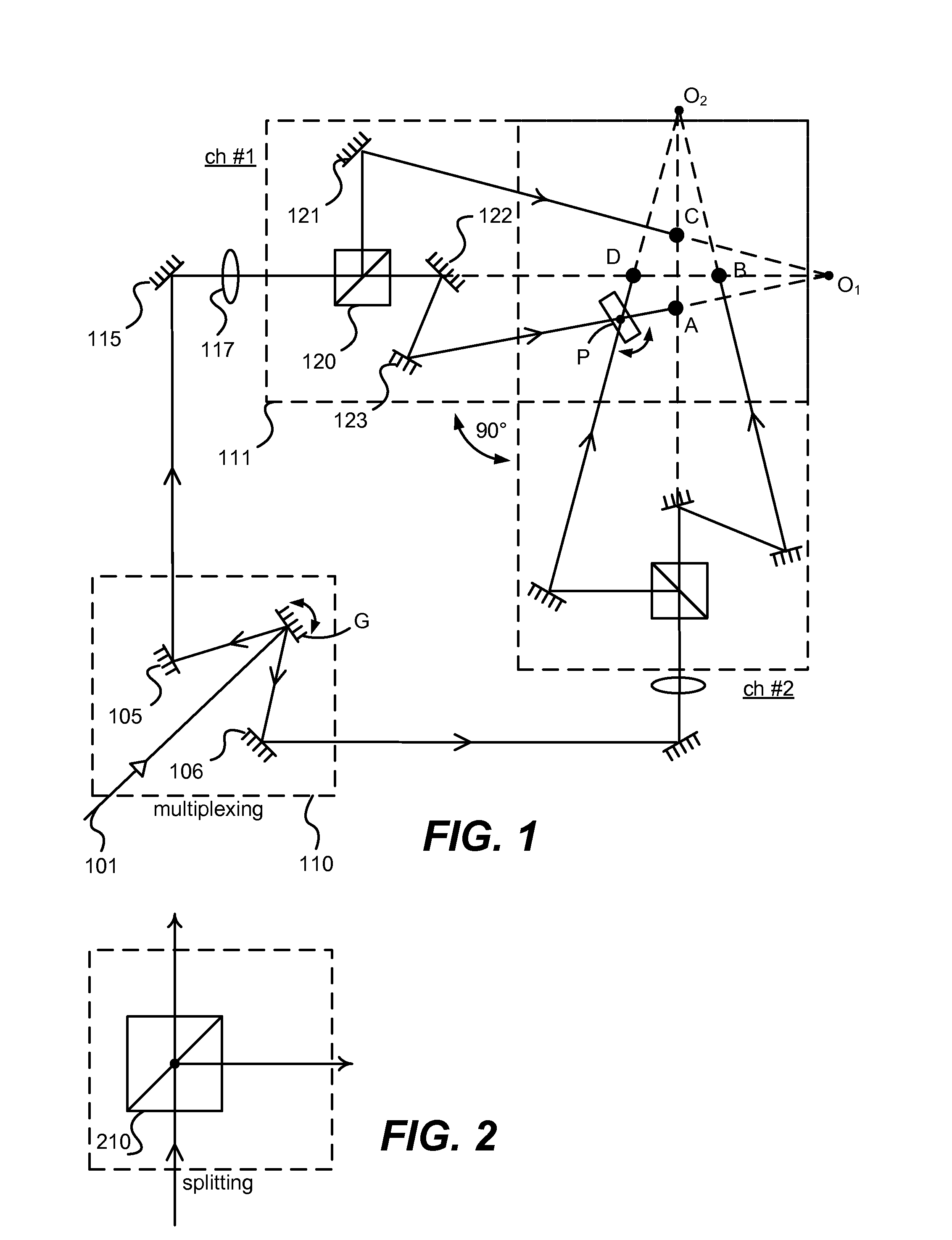
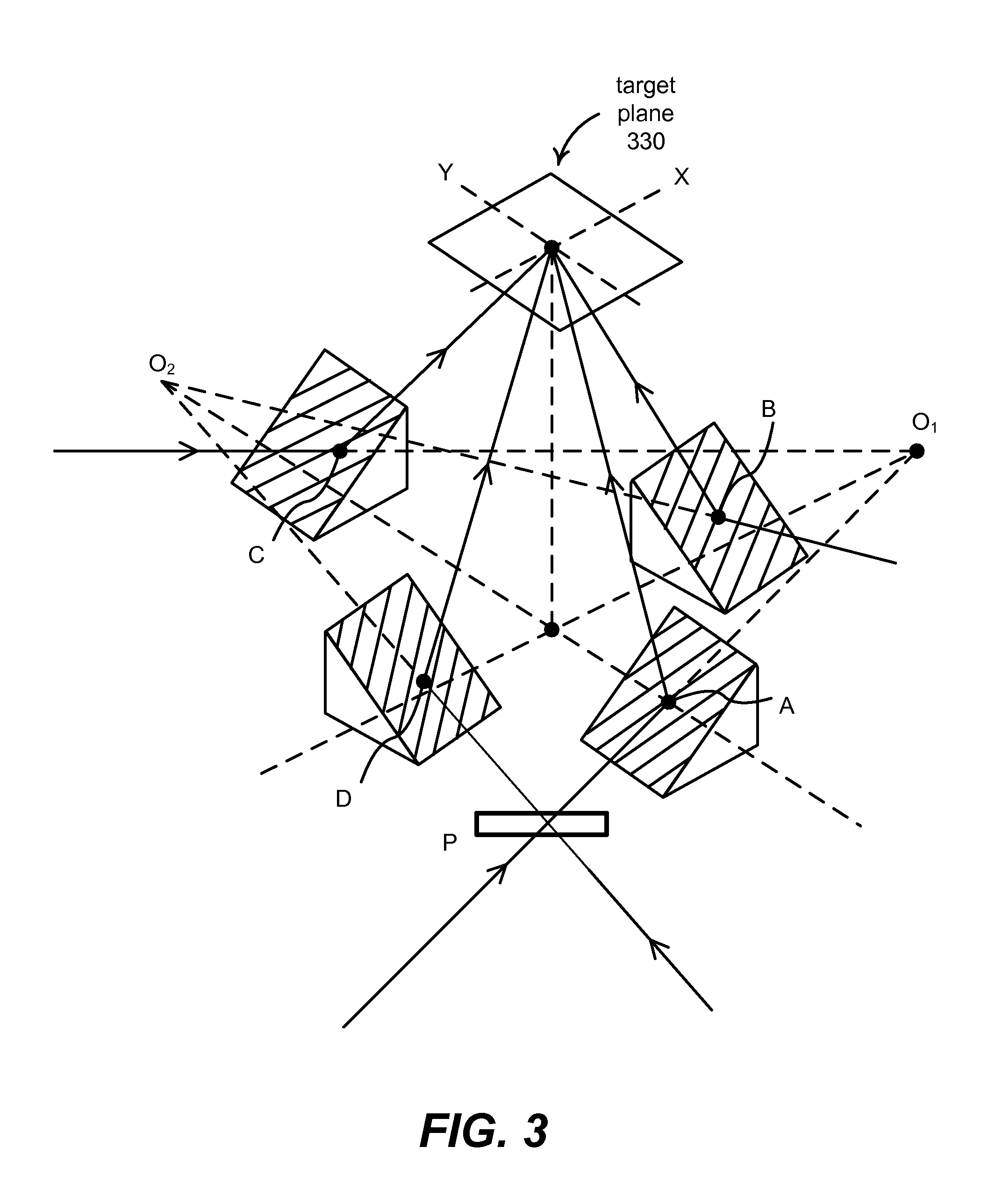
Modular pattern illumination and light beam multiplexing for selective excitation of microparticles
ActiveUS8817362B2Cosmonautic condition simulationsLaser using scattering effectsMultiplexingPhase shift module
A modular approach to a pattern illumination system for selective excitation of microparticles is used. A dual-channel pattern module having two single-channel pattern modules are oriented at a non-zero offset angle to each other. In this arrangement, a galvo-scanner based phase-shifting module is shared between the two channels. A set of tilt mirrors are used to direct the beams from the pattern modules onto the target plane. Additional layers of pattern modules can be added to accommodate any desirable number of additional channels. The additional layer(s) may be rotationally off-set from the other layer(s) by an angular amount to simplify the layout of optical components. A remote light source module may be connected to the pattern modules through optical fiber.
Owner:REBUS BIOSYSTEMS INC
Method and apparatus for correction of artifacts in magnetic resonance images
ActiveUS20130101198A1Reduce artifactsWithout limiting MR measurementGenetic material ingredientsCharacter and pattern recognitionResonanceSelective excitation
In a method and apparatus for the correction of artifacts in magnetic resonance images (MR) acquired with an MR pulse sequence in which gradients are switched simultaneously during the radiation of at least one non-selective excitation pulse, measurement data acquired with the pulse sequence in k-space are loaded into a processor, in which a perturbation matrix is determined on the basis of spatial and k-space point data of the acquired measurement data and the gradients used during the excitation. A corrected image is calculated from the acquired measurement data in k-space and the perturbation matrix, with the calculation of the corrected image including a matrix inversion of the perturbation matrix. The corrected image is then stored or displayed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
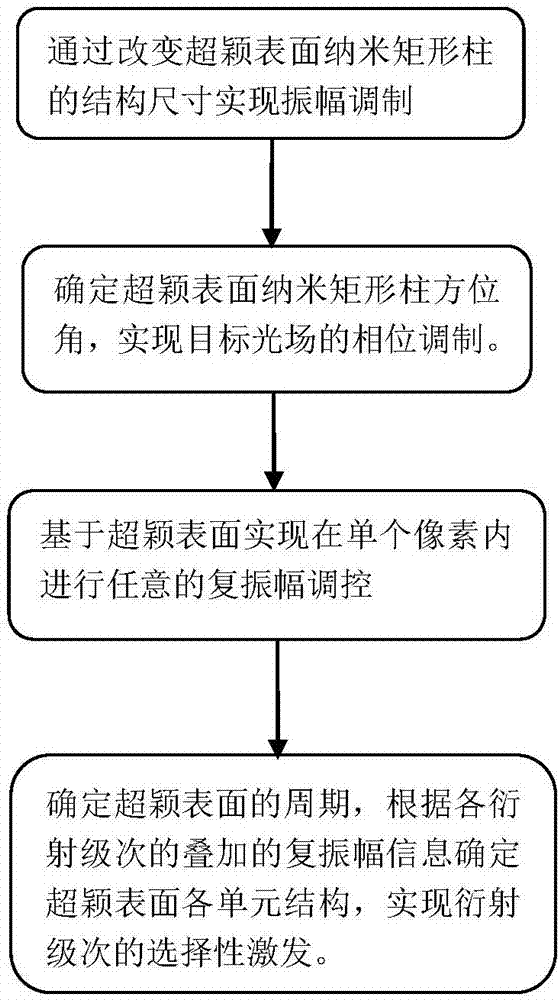
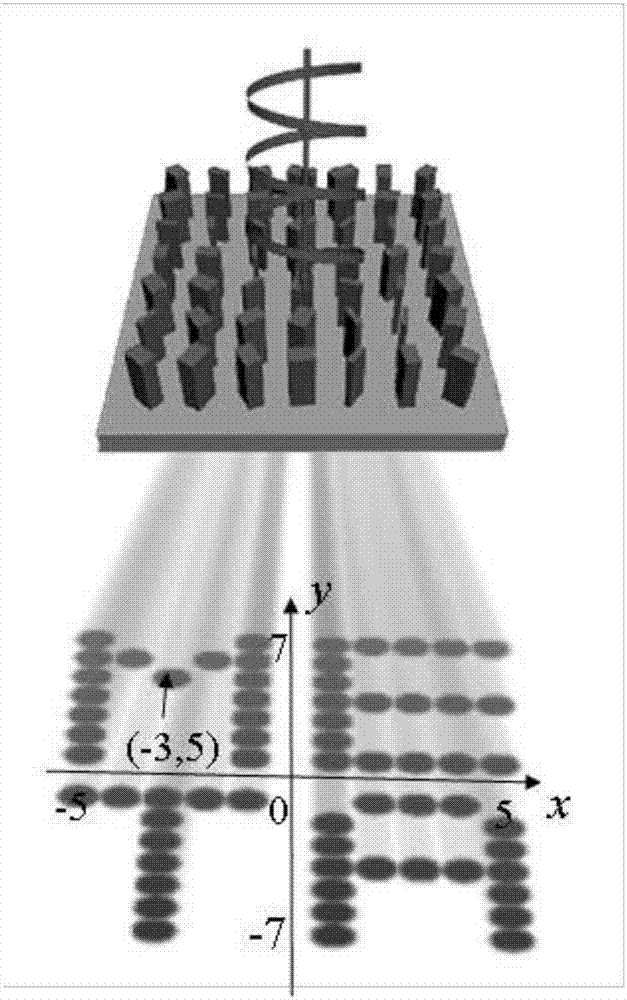
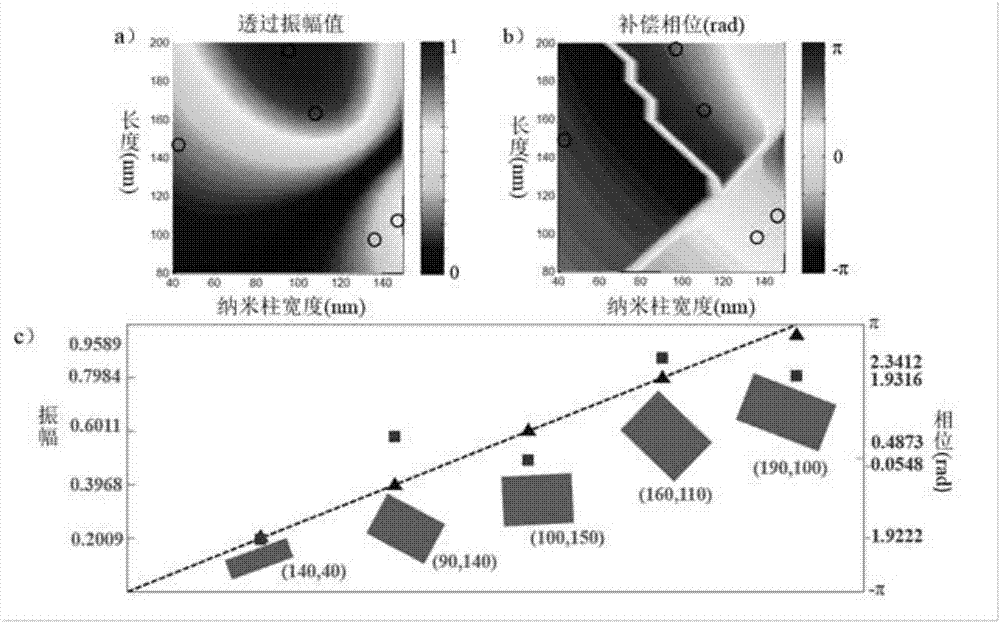
Method for selectively exciting diffraction levels on basis of metasurface complex amplitude modulation
ActiveCN107991771AAchieve distributionRealize disseminationOptical elementsMicro nanoComplex amplitude
The invention discloses a method for selectively exciting diffraction levels on the basis of metasurface complex amplitude modulation, and belongs to the field of micro-nano optics. The structure sizes of nano rectangular columns of metasurfaces are changed to obtain amplitudes and dynamic phase information of target light fields, and azimuth angles theta of the nano rectangular columns of the metasurfaces are determined, and accordingly phases of the target light fields can be modulated; the amplitudes and the phase information are combined with one another, and accordingly complex amplitudescan be arbitrarily regulated and controlled in a single pixel; the periods of the metasurfaces are determined, Fourier levels corresponding to all the selected diffraction levels are superimposed, accordingly, complex amplitude information of various unit structures of the metasurfaces can be set, and the spatial propagation diffraction levels can be selectively excited. The method has the advantages that amplitude values of the target light fields can be processed by stages, and the phases of the target light fields can be continuously changed; the metasurface design and processing complexity can be lowered by the aid of the method, and the method can be widely applied to the fields of light field shaping, laser parallel processing, micro-nano optical detection and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
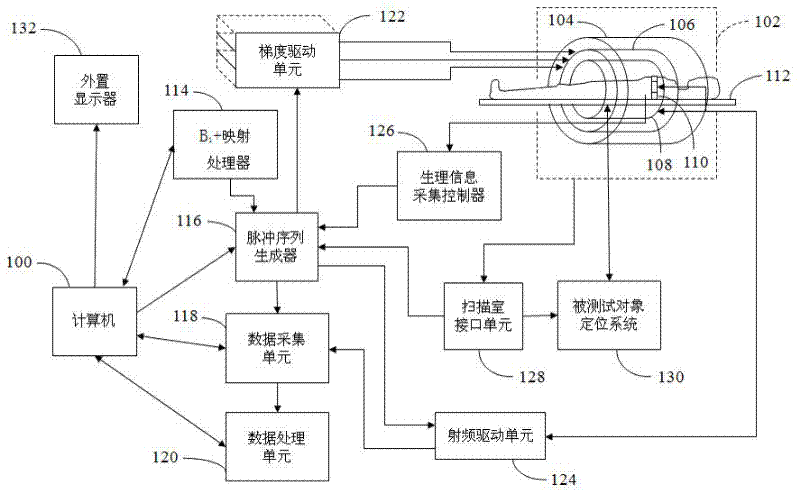
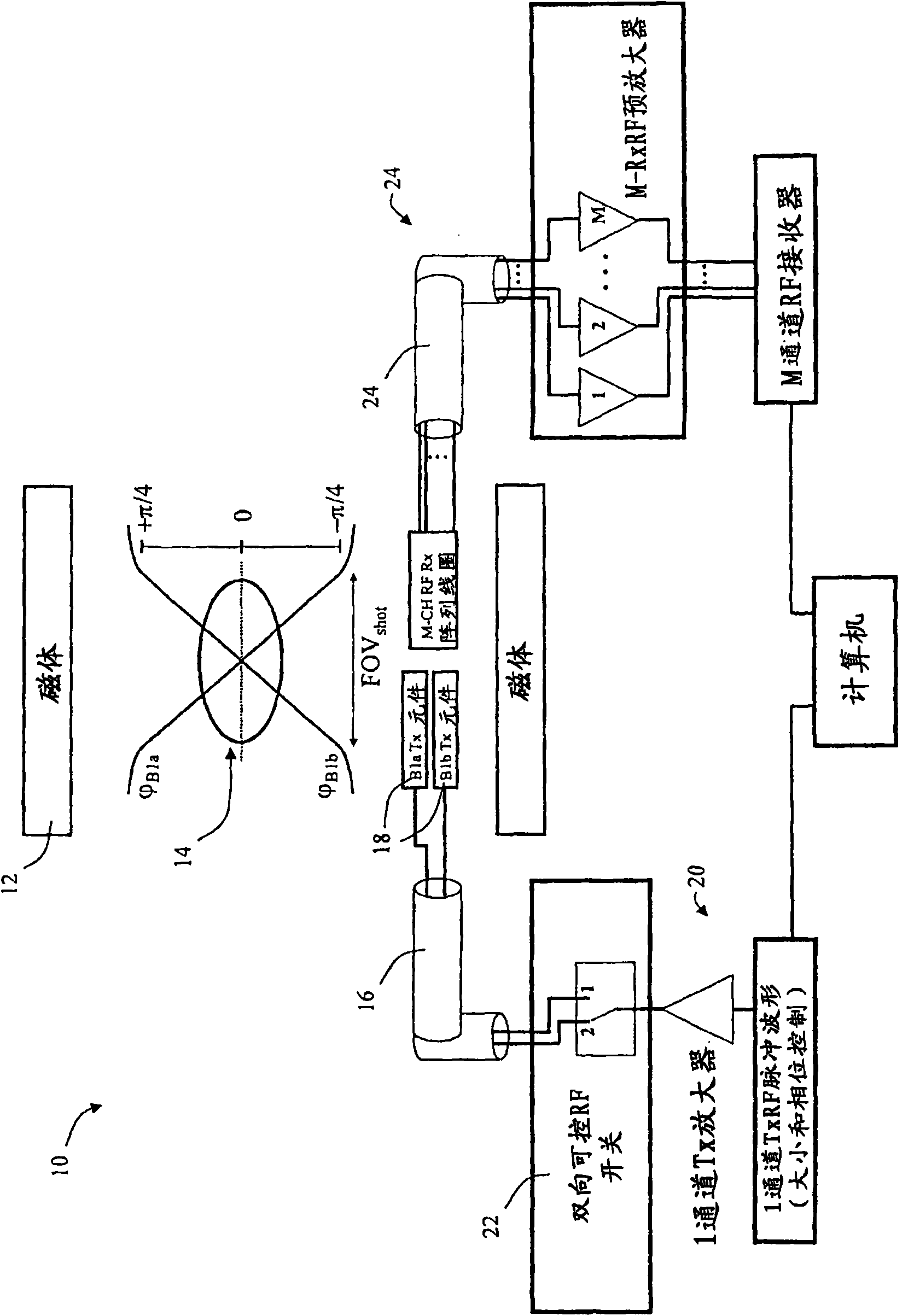
RF based spatially selective excitation in mri
InactiveCN101688909AMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSelective excitationFourier transform on finite groups
The invention relates to an RF based spatially selective excitation in MRI. Herein a method for slice selection is provided in an MRI process, the method involves controlling a transmit array by adding low flip angle RF pulses interspersed between refocusing pulses that are used to move a k-space weighting function with respect to one or more B l fields used to deposit energy according to a desired k-space weighting function. The low flip angle pulses deposit energy so that an envelope traced by the low flip angle pulses in the k-space weighting function is related to a desired spatially excited region of the sample volume, for example by a Fourier transform, if the phase encoding directions are linear axes that coordinatize the sample volume, and the Bl fields have linear phase gradients.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
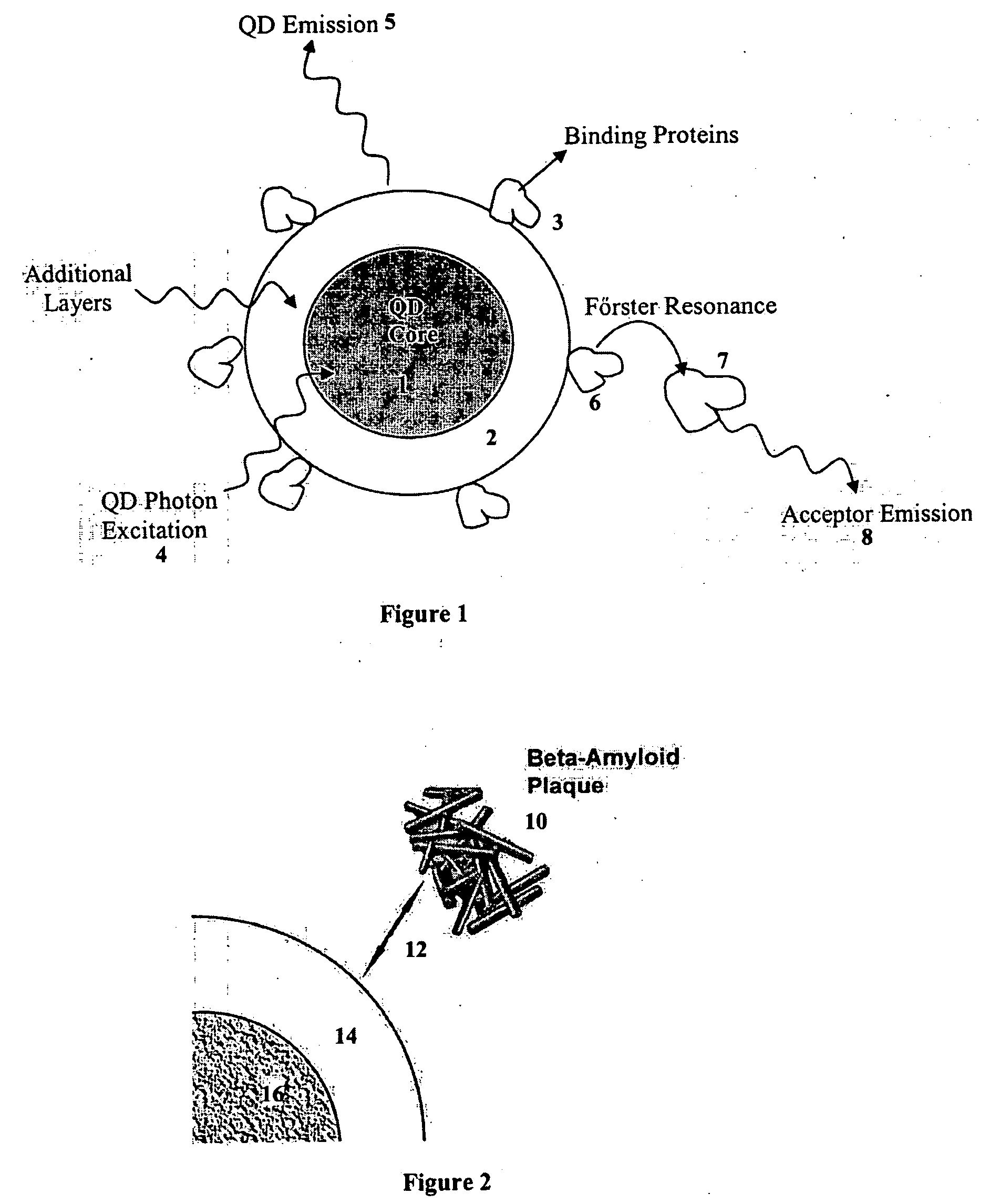
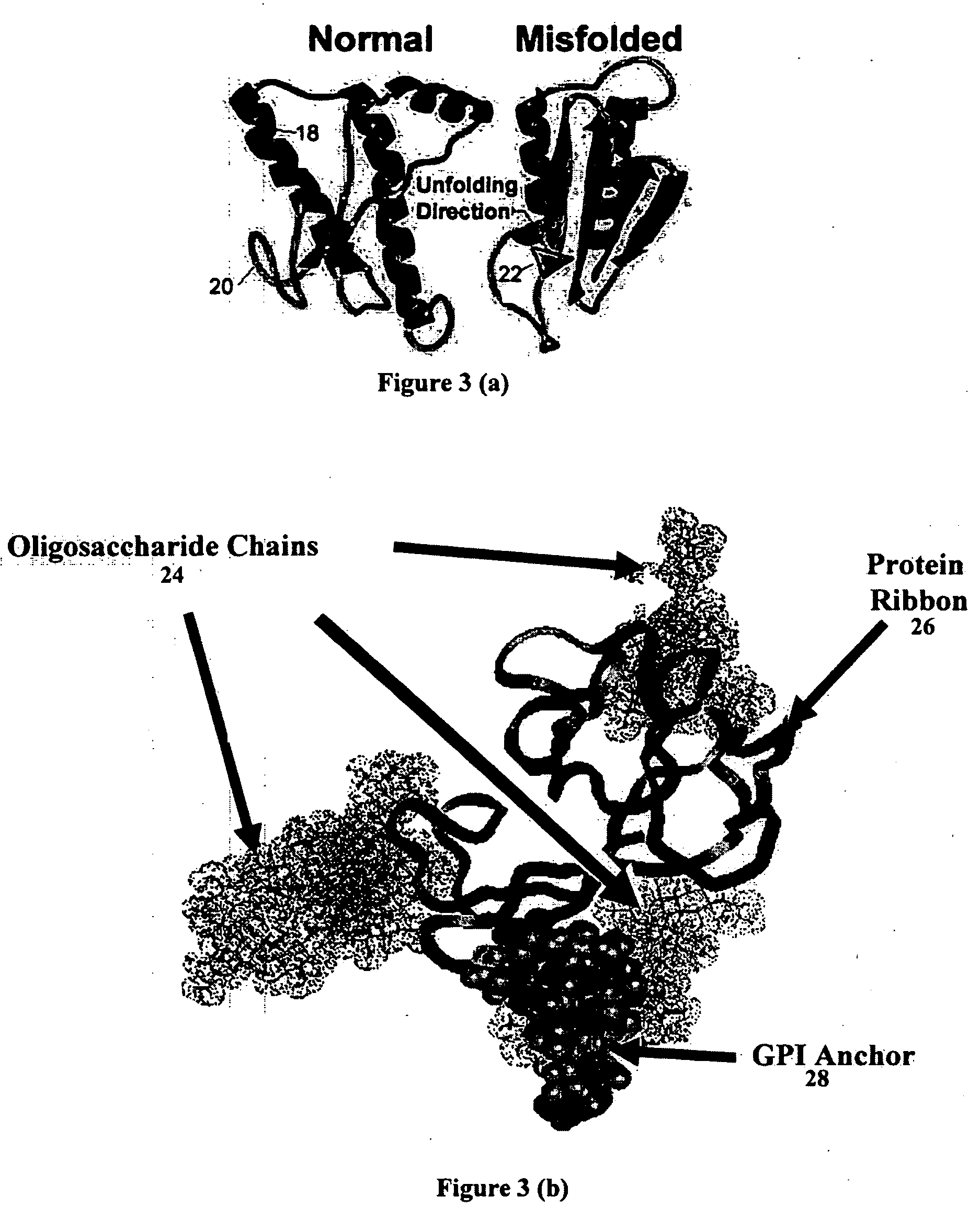
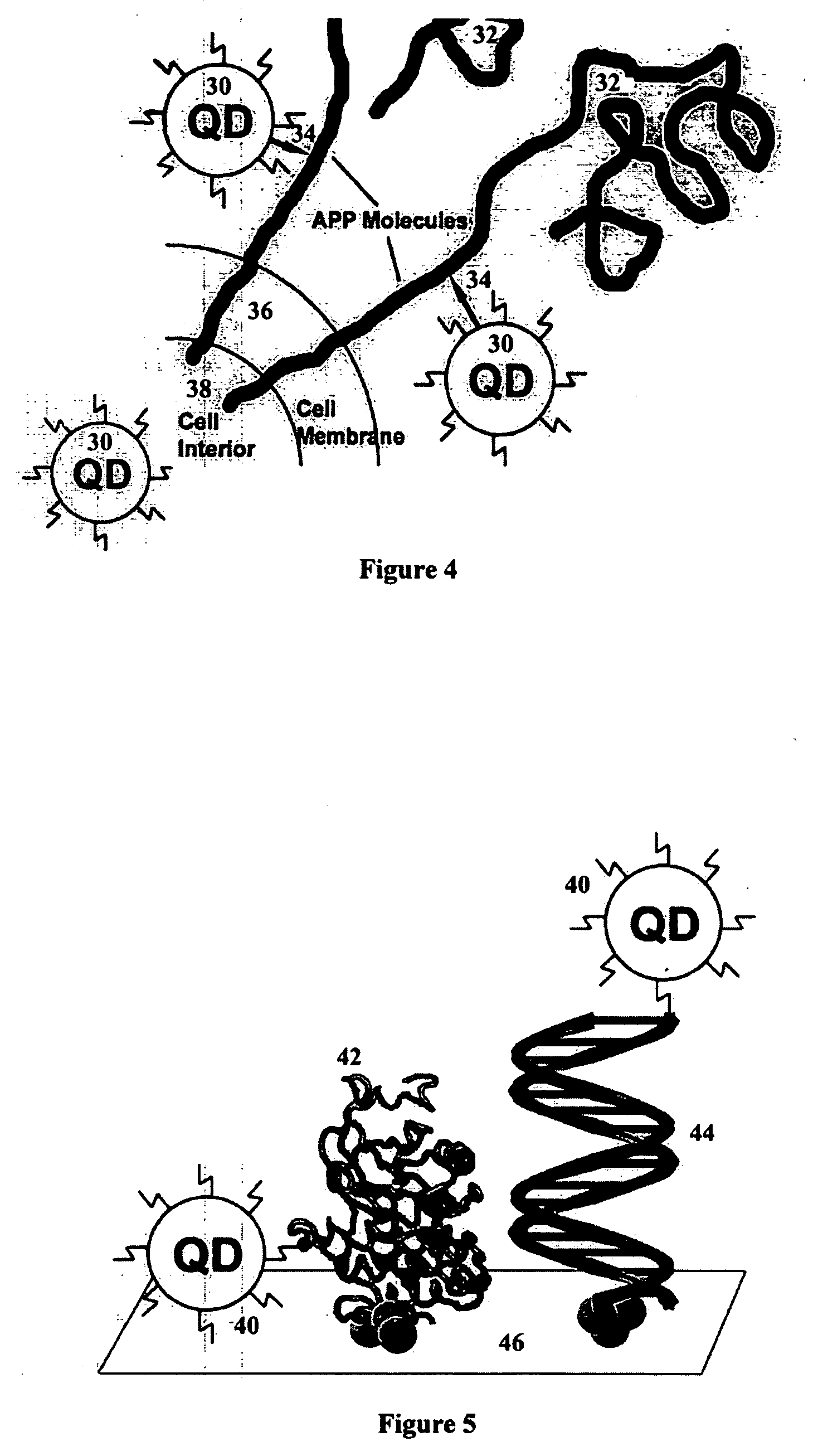
Nanobioprocessor for protein and cell therapy
InactiveUS20050214380A1Increase relative motionSuperior and stable diagnostic and treatment agentHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideSelective excitationQuantum dot
A nanobioprocessor for protein and cell therapy comprises a selectively coated quantum dot having selected band gap energies, characteristic absorption, emission spectra and outer coatings for therapy and diagnostic purposes in biophotonics and nanomedicine, and an electromagnetic radiation and detector source configured to remotely heat and / or selectively excite the quantum dot to associate with target specific misfolded or anomalous proteins, diseased cells and tissue.
Owner:APPLIED PHOTONICS WORLDWIDE
Method and magnetic resonance tomography apparatus for spatially resolved measurement of the B1 field distribution
ActiveUS7038453B2High overall measuring timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionSelective excitationPulse sequence
In a method and magnetic resonance tomography apparatus for spatially resolved measurement of the magnetic high frequency field distribution in the apparatus, a double echo high frequency pulse sequence with a first excitation pulse following by at least two refocusing pulses are emitted for generation of a first echo and a following second echo. At least the excitation pulse is slice selective. In an excitation layer defined by the slice selective excitation pulse a first echo image and second echo image are spatially resolved by using suitable gradient pulses for phase or frequency encoding Using the relationships of the amplitudes of the first and second echo image in the various locations the flip angles representing the field strength at the relevant locations in the relevant slice are determined.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
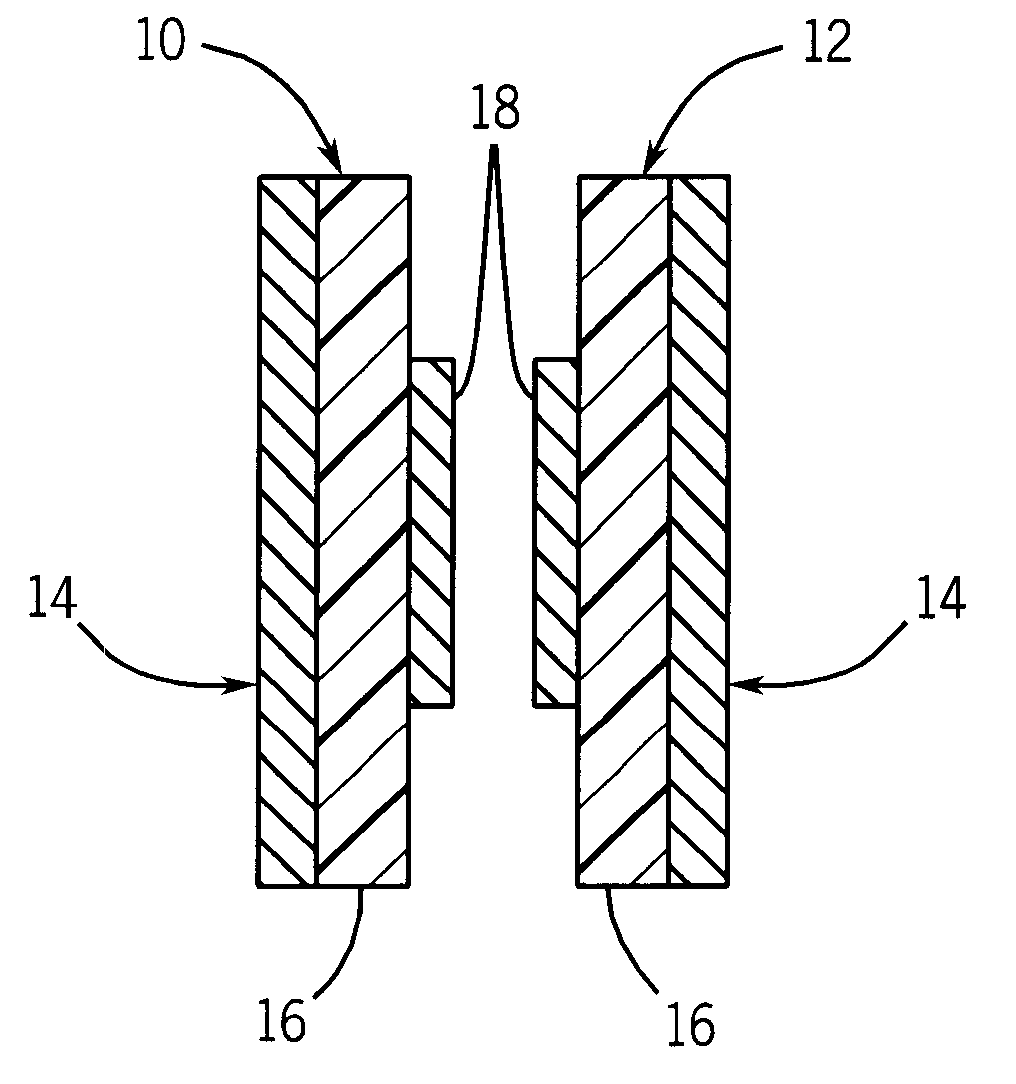
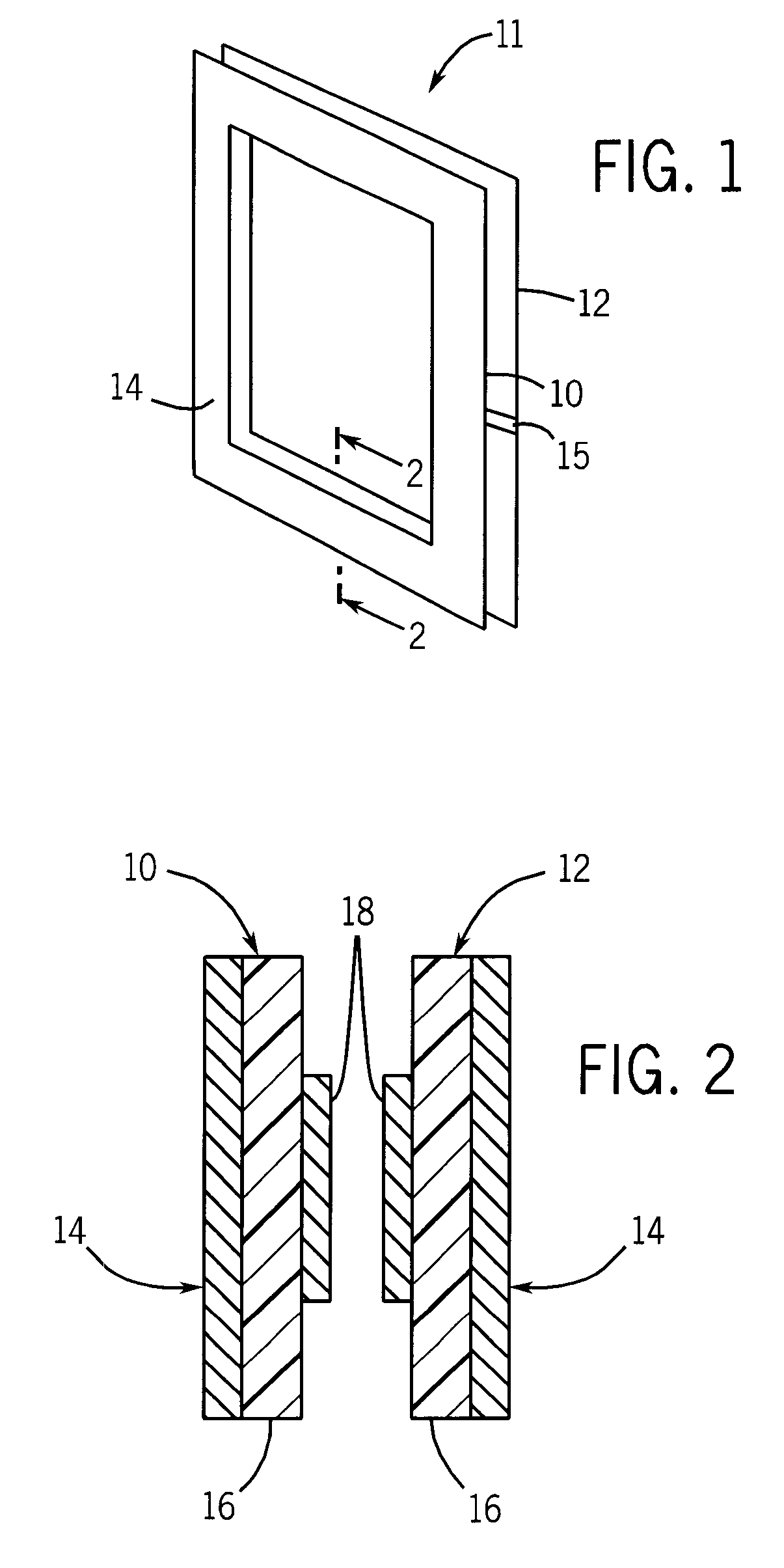
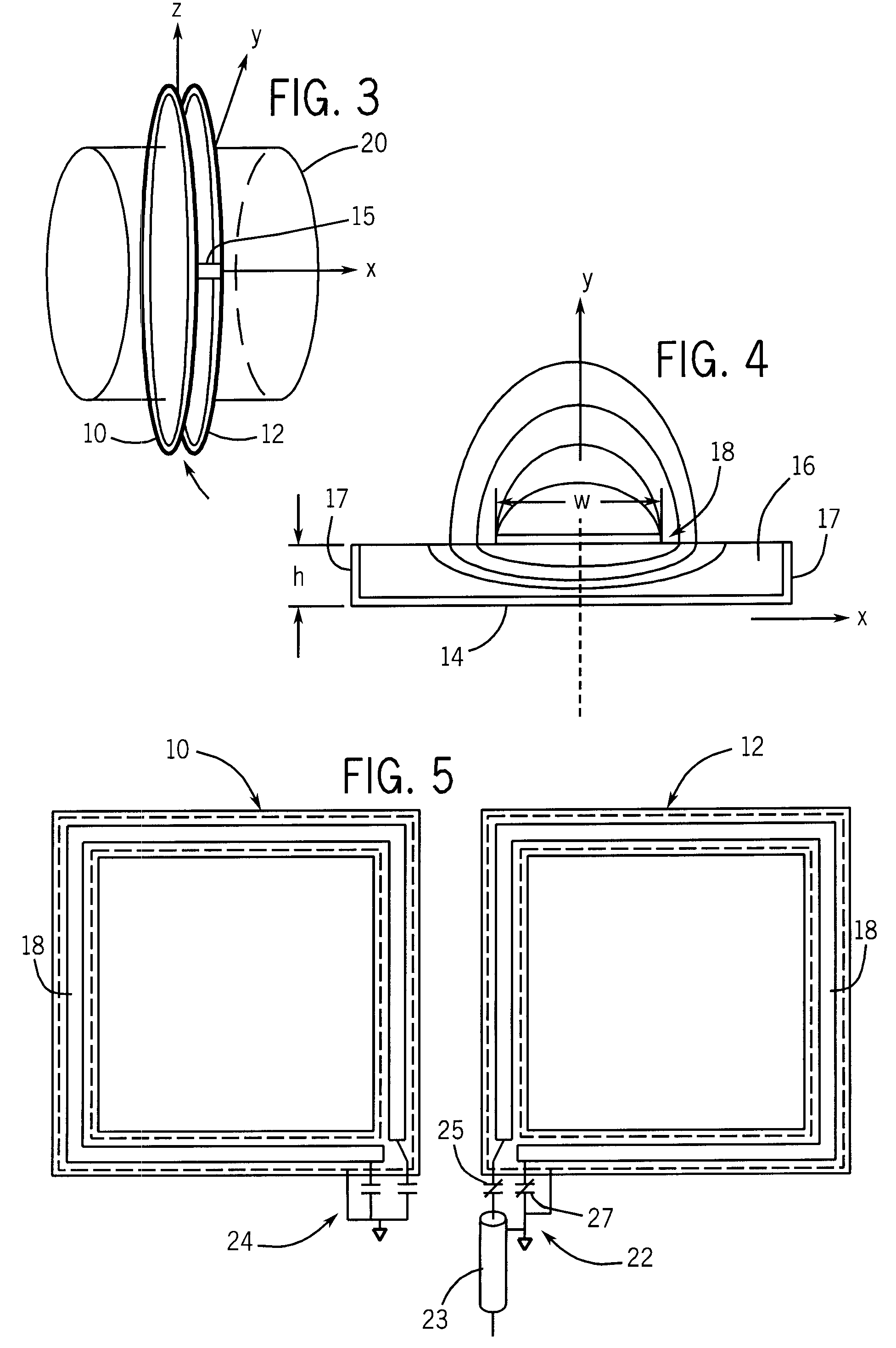
Slab-selective RF coil for MR system
ActiveUS7420371B2High sensitivityImprove field uniformityMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionRf fieldSelective excitation
An RF coil includes two coil portions that are spaced apart to define a slab therebetween. Each coil portion is a microstrip transmission line formed as a loop wherein the microstrip includes a conductive strip disposed on one side of a dielectric material and a ground plane disposed on the other side of the dielectric material. When energized, a uniform RF field is produced in the slab. An array of such RF coils arranged back to back can be formed to allow for the selective excitation of a desired slab.
Owner:NORTHSHORE UNIV HEALTHSYST RES INST
Magnetic resonance imaging method and apparatus with non-selective excitation of the examination subject
InactiveUS20070191705A1Short timeShorter spacingMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSelective excitationRadio frequency
In a magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and a method for operating the apparatus, a trueFISP sequence is used, but is modified to employ non-selective, rectangular radio frequency pulses. The use of non-selective excitation pulses reduces the sensitivity to off-resonance and allows excitation to be achieved in a shorter time compared to selective excitation, thereby shortening the time between echoes and minimizing slice profile issues.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com