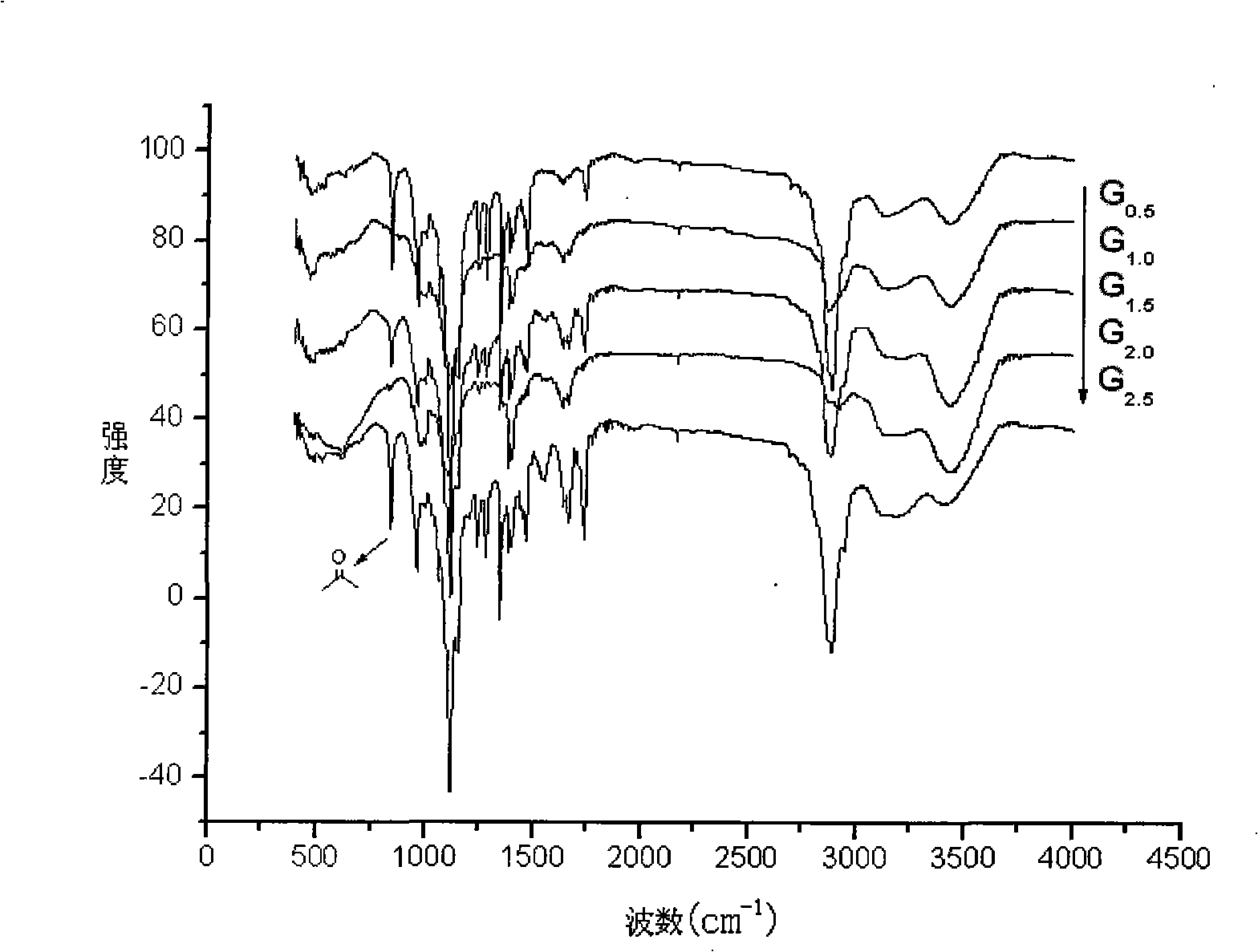
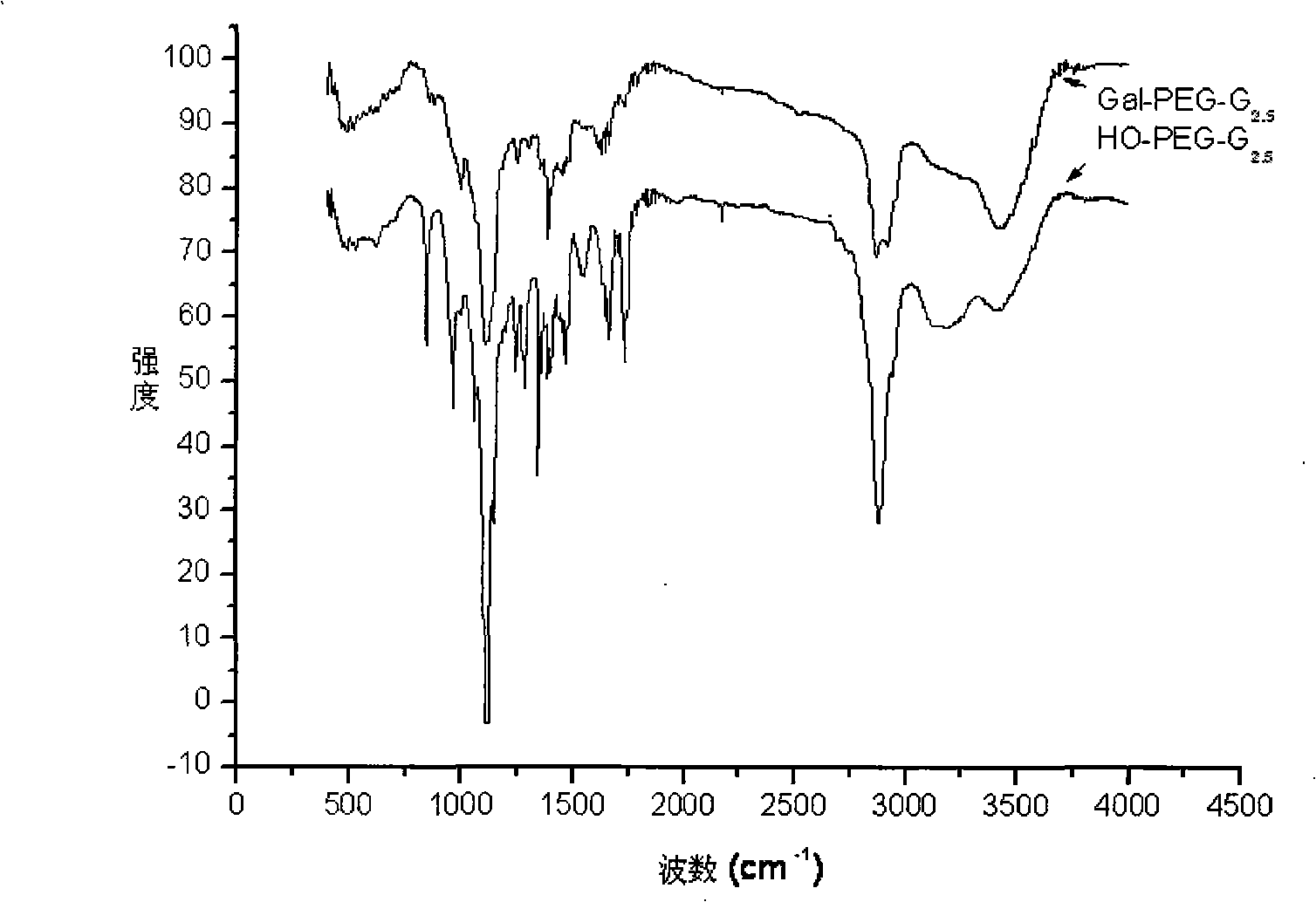
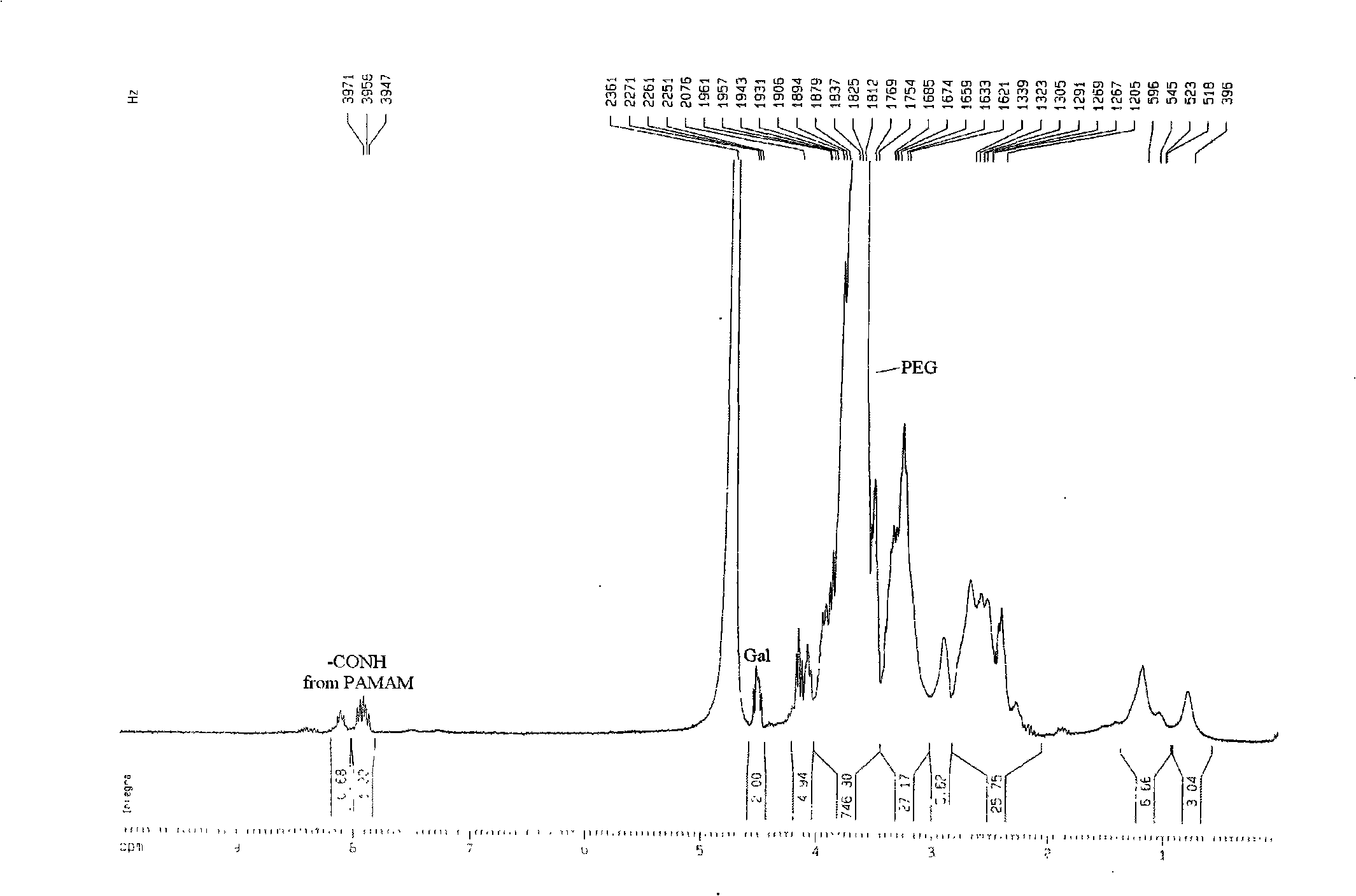
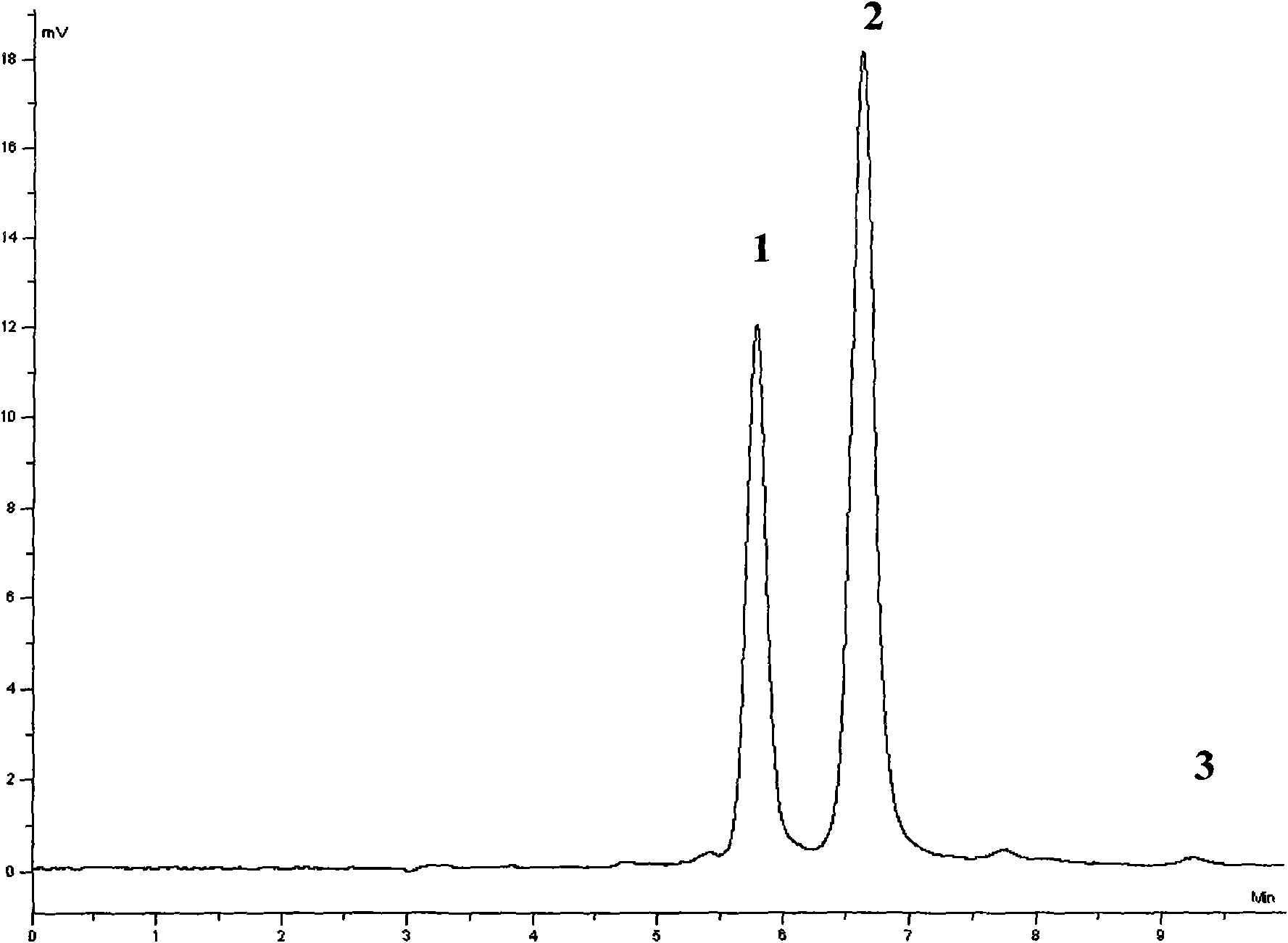
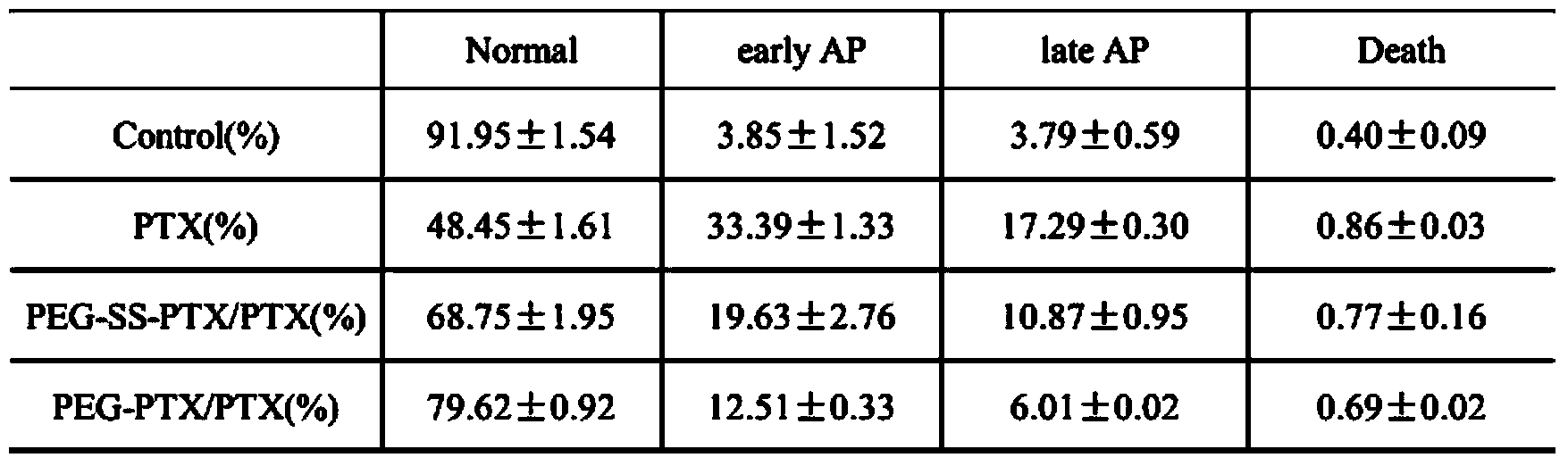
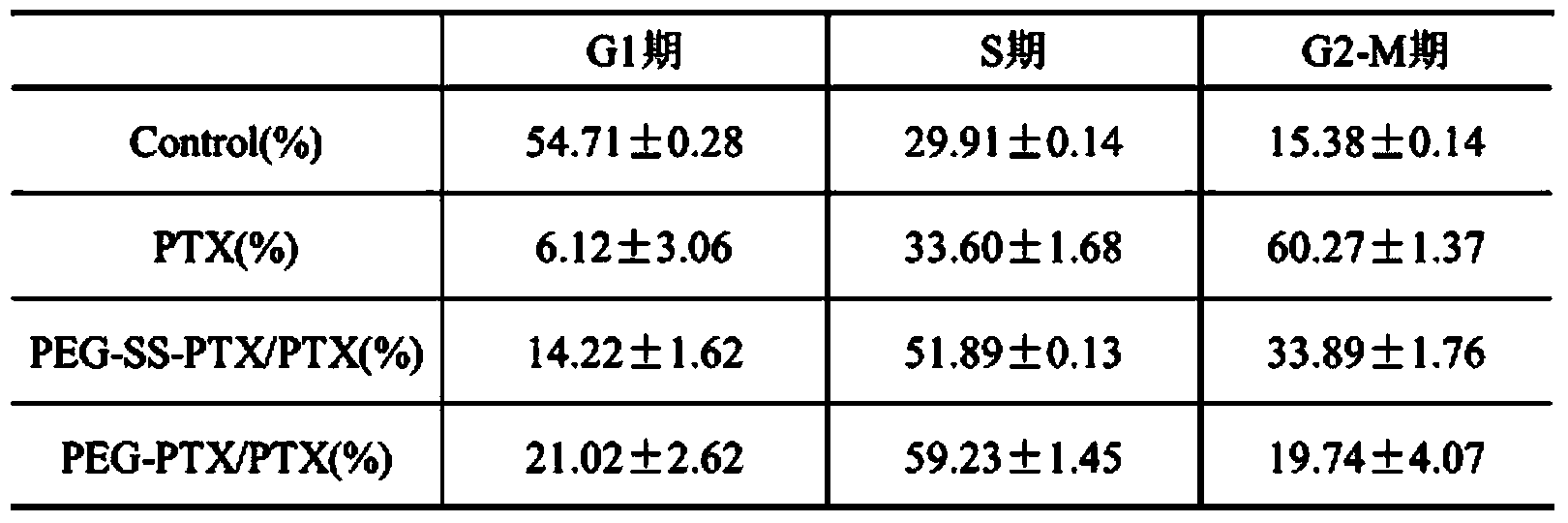
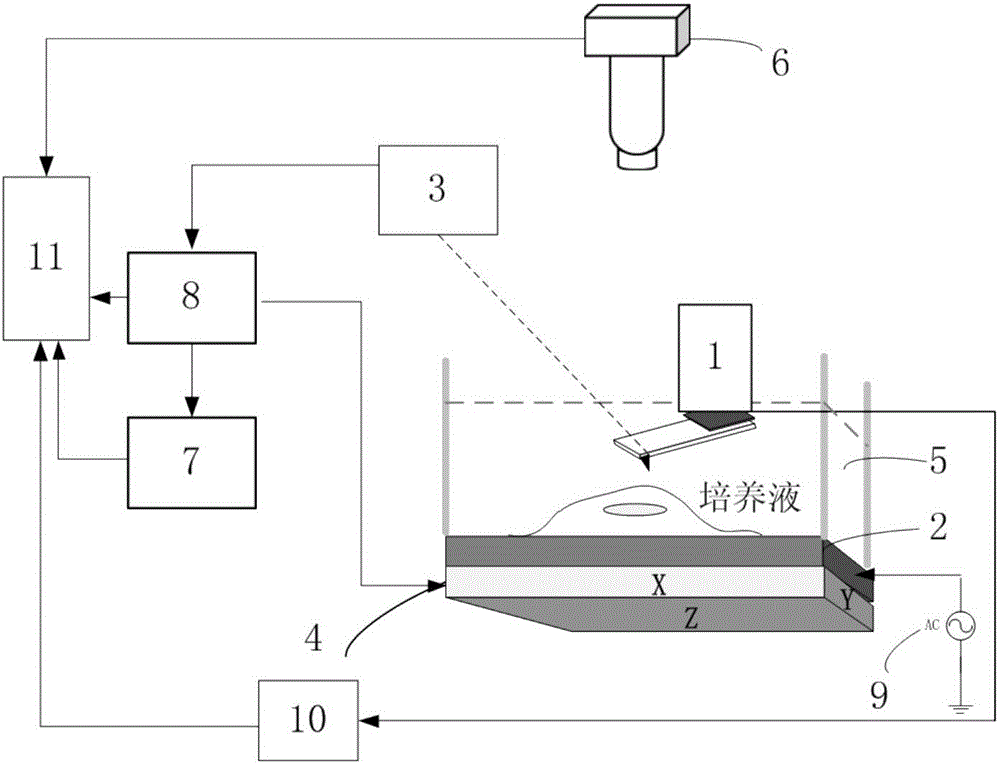
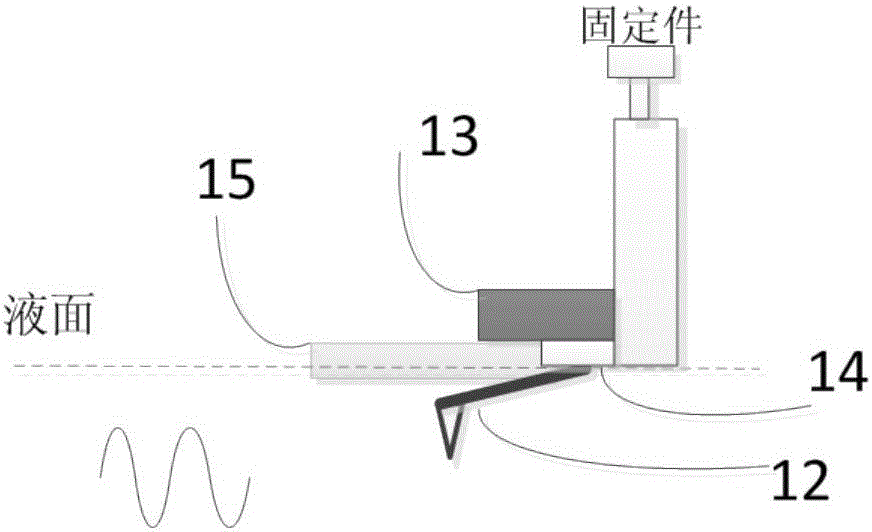
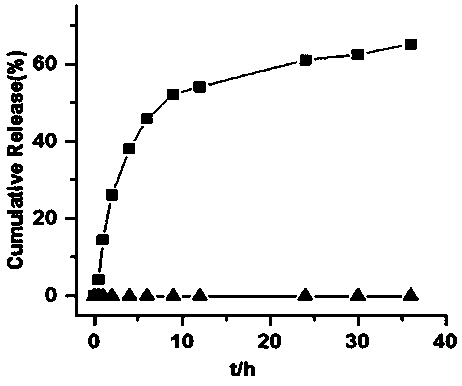
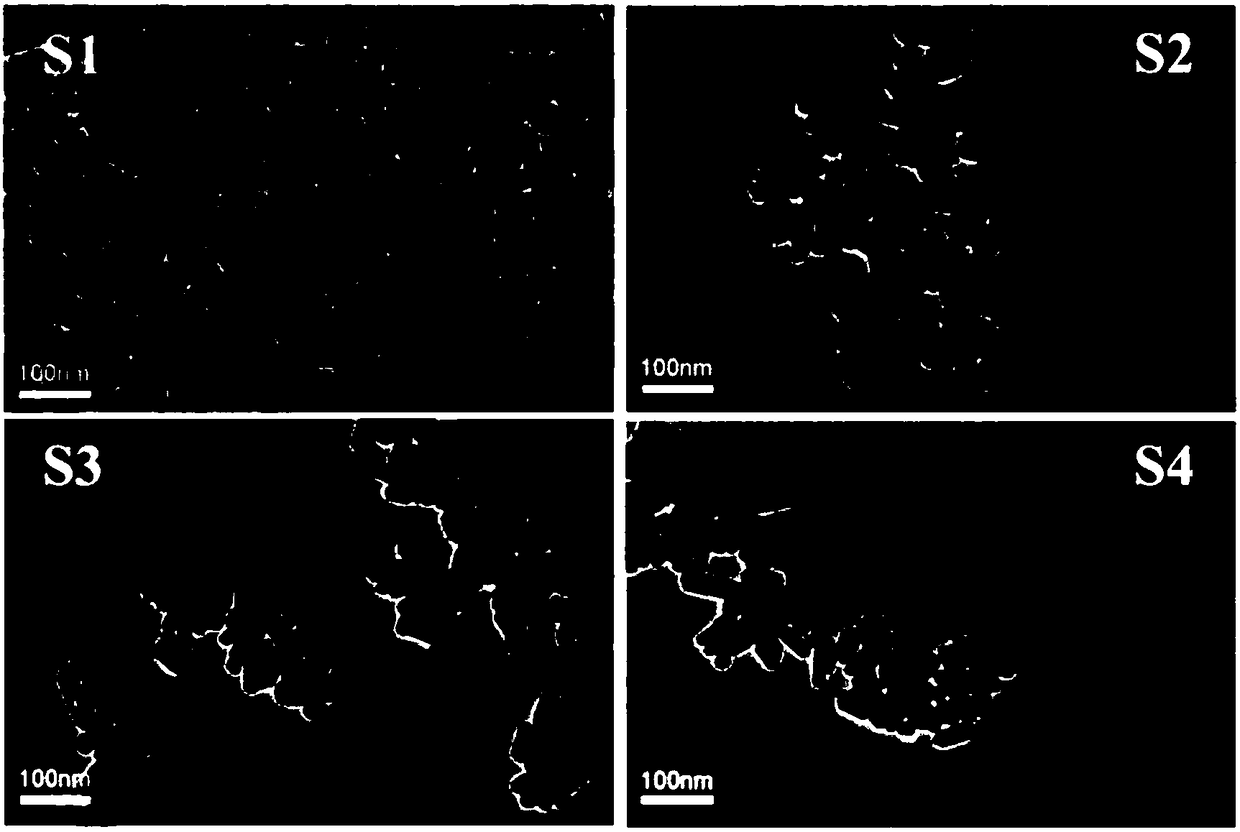
Patents
Literature
227 results about "Nanomedicine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nanomedicine is the medical application of nanotechnology. Nanomedicine ranges from the medical applications of nanomaterials and biological devices, to nanoelectronic biosensors, and even possible future applications of molecular nanotechnology such as biological machines. Current problems for nanomedicine involve understanding the issues related to toxicity and environmental impact of nanoscale materials (materials whose structure is on the scale of nanometers, i.e. billionths of a meter).
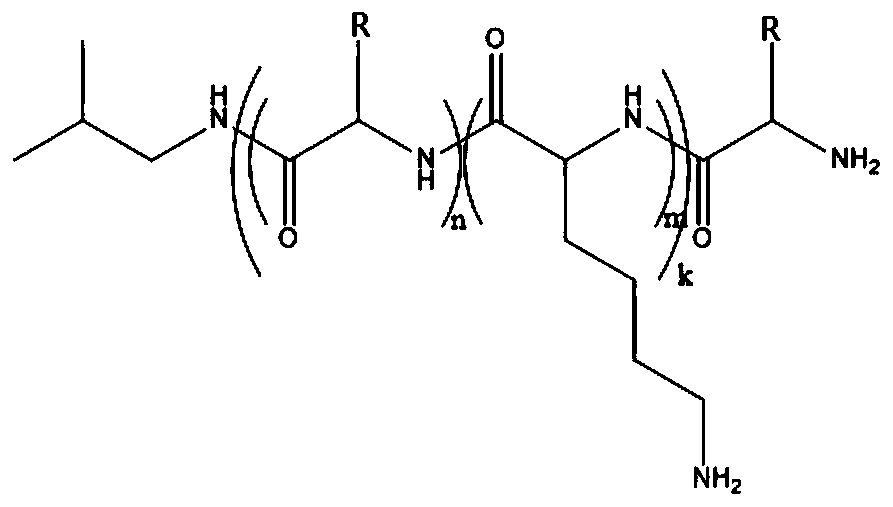
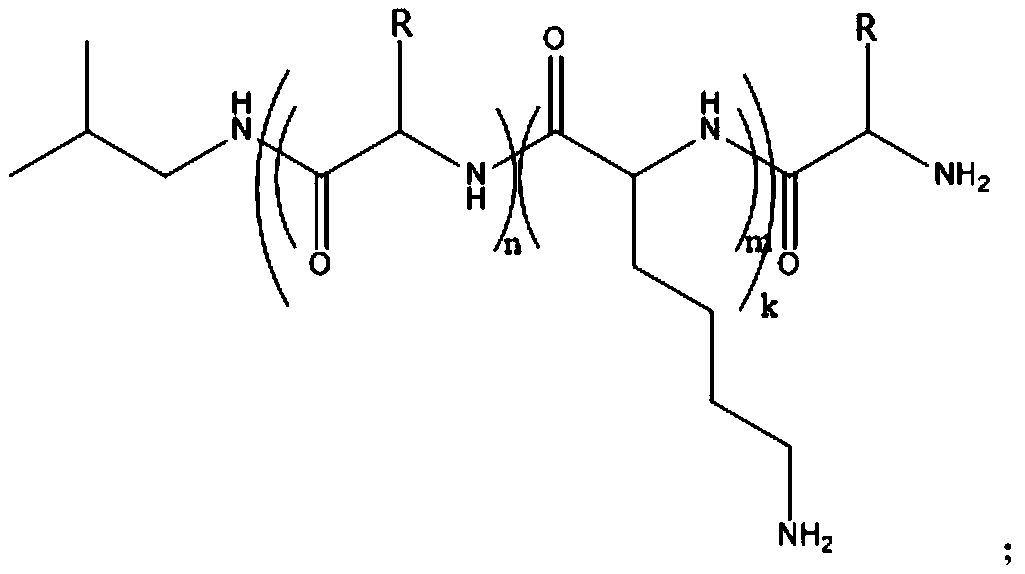
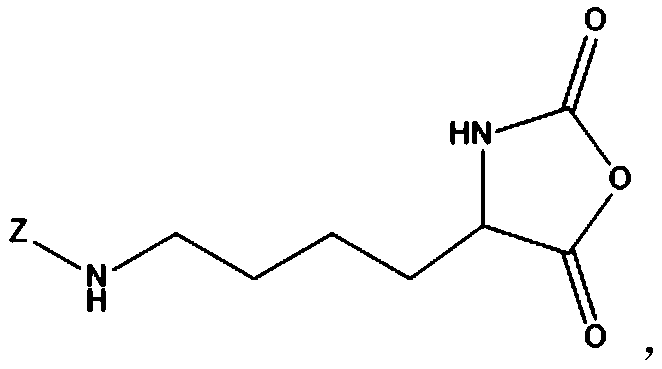
Liver target anticancer nano prodrug system based on tree shaped polymer, preparation and use
InactiveCN101259284ALong-term cycleEnhance phagocytosisOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemSide effectClinical efficacy
The invention relates to a liver targeting anticancer nanometer prodrug system basing on dendritic polymer, provides a method for preparing the prodrug system and the uses thereof and belongs to the technical field of biological medicine as well as the technical field of nano medicine. With the polyethylene glycol modified PAMAM treelike polymer of distal liver targeting group (T) as a carrier (T-PEG-PAMAM) and Doxorubicin (DOX) as treatment drug, the invention obtains the prodrug (T-PEG-PAMAM-DOX) through the covalent bond connection with degradable lysosome between the carrier and the Doxorubicin. The invention further provides the application of the liver targeting anticancer nanometer prodrug system basing on the dendritic polymer in the preparation of drugs for treating solid tumors. With the long-acting cycle in blood, the liver targeting anticancer nanometer prodrug system basing on the dendritic polymer can enhance the phagocytosis of hepatoma cells on polymers nano-micelles, realize the active and passive targeting on liver tumor tissues, improve the clinical efficacy and the bioavailability of present liver cancer therapeutic drugs and lower toxic and side effects.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Anti-tumor nano prodrug system based on dendrimer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101879313AHigh molecular weightImprove hydrophilicityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDendrimerCyclic peptide
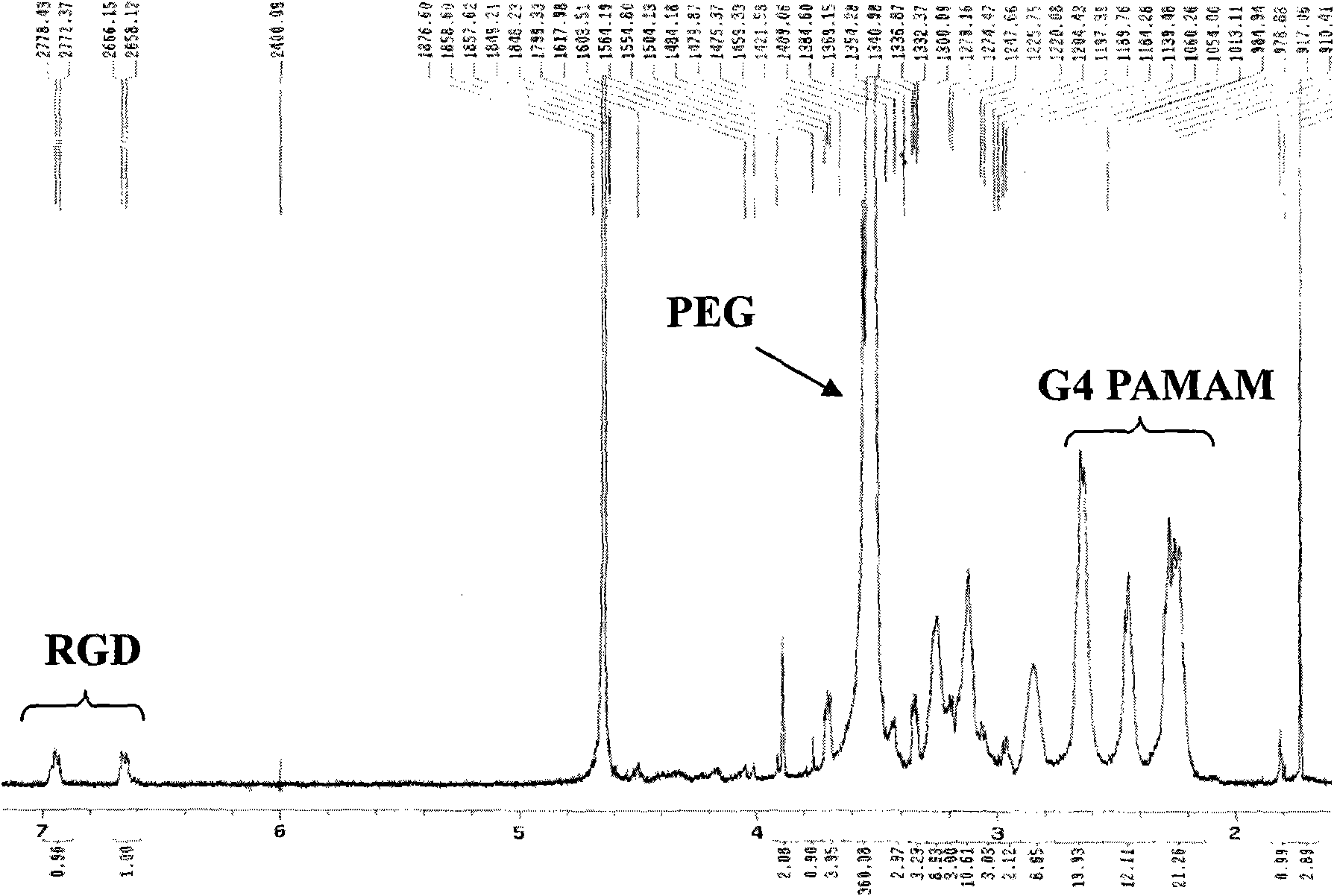
The invention relates to a multi-function nano prodrug system based on a dendrimer, which belongs to the technical field of biomedicines and nano medical science. The nano system comprises four function parts: an outermost layer RGD (arginyl-glycocoll-aspartate) cyclic peptide as an active targeting head group (1), a polyethylene glycol (PEG) hydrophilic chain segment (2) connected with the targeting head group and the dendrimer, an anti-tumour drug (3) connected with the dendrimer by an acid sensitive chemical bond and a dendrimer kernel (4). The general formula of the nano system is RGD-PEG-Dendrimer-DOX (doxorubicine), wherein the macromolecule attribute of a dendrimer vector makes a vector system passively target to tumor tissues through an EPR (Enhanced Permeability and retention) effect; the RGD cyclic peptide makes the vector system actively target to the tumor tissues through the interaction of a ligand and a receptor and promotes the endocytosis of the tumor tissues; the acid sensitive chemical bond ensures that a drug-carrying system is stable in systemic circulation and releases active drugs after arriving tumor positions and entering an acid organelle to perform the function of cytotoxicity.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Device for capture, enumeration, and profiling of circulating tumor cells
InactiveUS20120100560A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSpatial mappingBiology
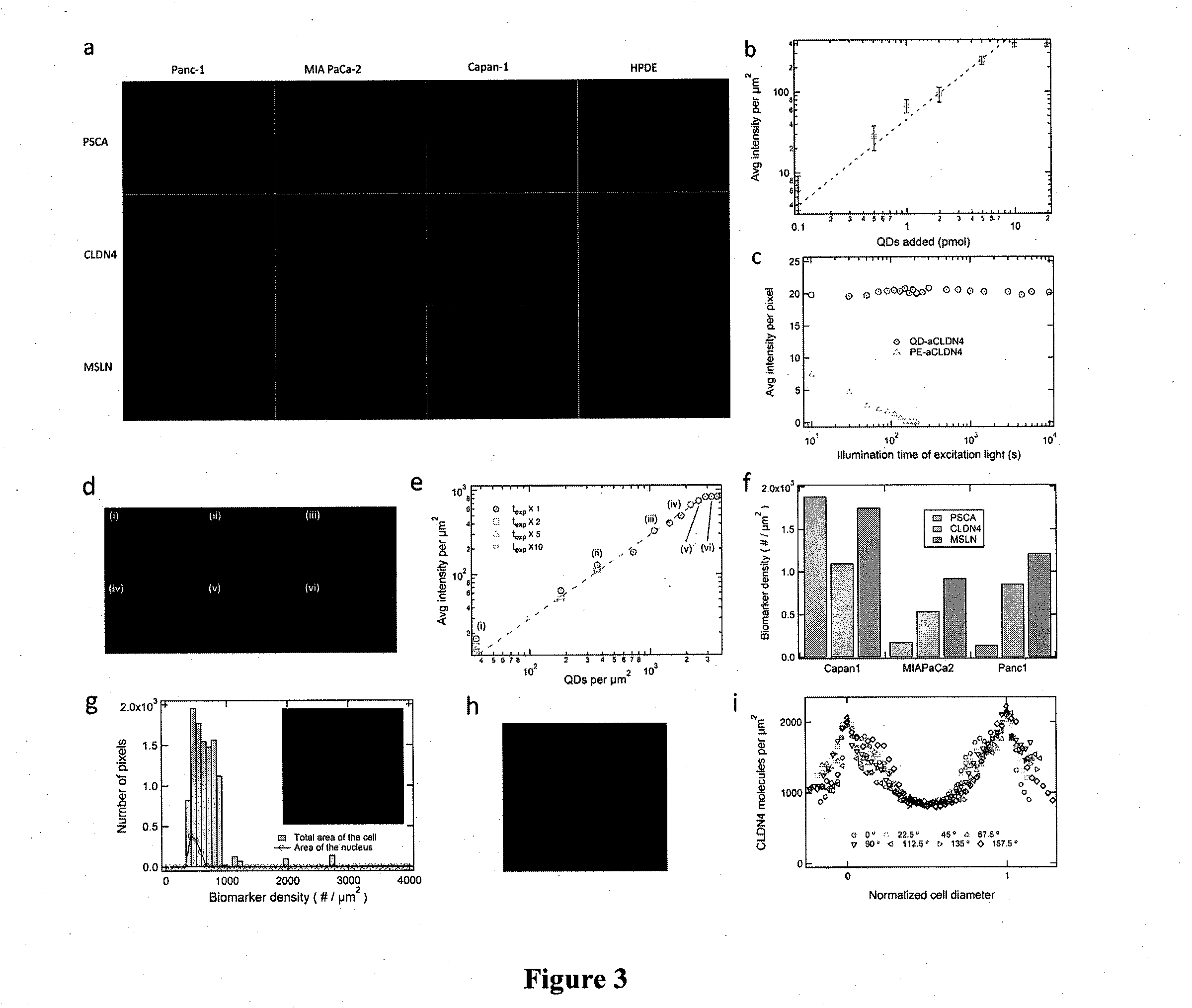
Applications in nanomedicine, such as diagnostics and targeted therapeutics, rely on the detection and targeting of membrane biomarkers. The present invention, in one embodiment, utilizes quantitative profiling, spatial mapping, and multiplexing of cancer biomarkers using functionalized quantum dots. This approach provides highly selective targeting molecular markers for pancreatic cancer with extremely low levels of non-specific binding and provides quantitative spatial information of biomarker distribution on a single cell, which is important since tumors cell populations are inherently heterogeneous. The quantitative measurements (number of molecules per square micron) is validated using flow cytometry and demonstrated using multiplexed quantitative profiling using color-coded quantum dots.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Reducible and degradable nano medicine-carrying micelle and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102085177AEfficient methodSimple methodPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolyethylene glycolCaprolactone
The invention relates to a reducible and degradable nano medicine-carrying micelle and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the fields of biomedical technology and nano medical technology. The reducible and degradable nano medicine-carrying micelle is characterized by having the following structural general formula: MPEG-CA-PCL, wherein the CA is poly-cystamine containing disulfide bonds, the MPEG is methoxy polyethylene glycol the molecular weight of which is 475-5000DA, and the PCL is polycaprolactone. The preparation method of the reducible and degradable nano medicine-carrying micelle comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out Michael addition to N,N'-bis (acrylic) cystamine and ethanolamine to obtain hydroxy poly-cystamine containing disulfide bonds, and then, carrying out ring opening reaction on caprolactone by utilizing a hydroxy group to obtain a CA-PCL polymer; and (2) mixing the CA-PCL polymer obtained in the step (1) and carboxyl-terminated MPEG, and adding paclitaxel (PTX) to prepare the nano medicine-carrying micelle through a dialysis method. The method is efficient and simple.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method and application of reduction-response-type pegylation (PEG) nanomedicine composition
ActiveCN103705943AImprove securityEliminate hidden dangers such as allergiesPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDisulfide bondingDrug conjugation
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a reduction-response-type pegylation (PEG) nanomedicine composition. The nanomedicine composition is characterized by being prepared by coupling the PEG with a medicine via disulfide bonds which are sensitive in reduction. Thus, the water solubility of the medicine is improved; the in-vivo behavior of the medicine is also improved. Meanwhile, the full release and the activity of the medicine are ensured by utilizing the characteristic that the disulfide bonds in the PEG medicine, which are sensitive in reduction, can be specifically degraded in a tumor site. Thus, a good tumor treatment scheme is provided.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Biological cell ultrasonic atomic force microscopic detection system and method
ActiveCN105910560ASuitable for non-destructive inspectionAvoid destructionUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansCancer cellSonification
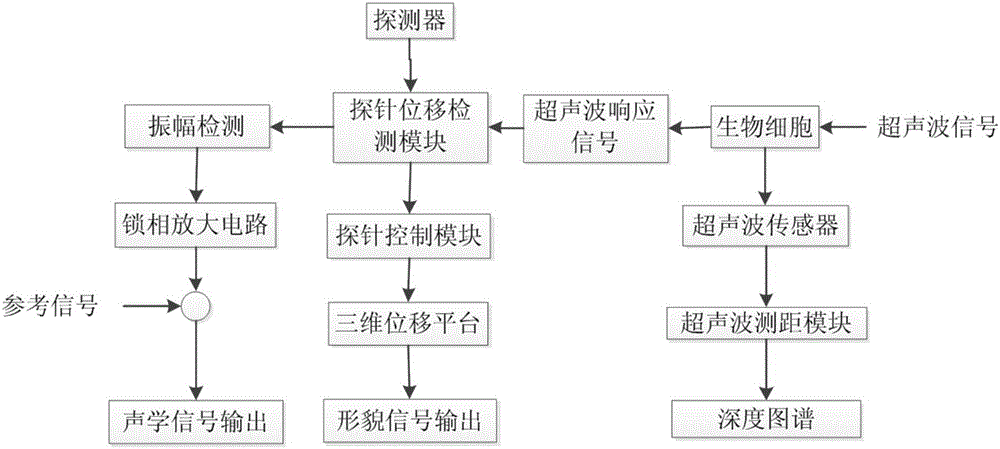
The invention relates to a biological cell ultrasonic atomic force microscopic detection system and method under the physiological environment. The system is composed of a detector, a piezoelectric transducer, a probe control module, a phase-locked amplifier and an ultrasonic ranging module. The detector is arranged in the physiological environment to scan biological cells, and the piezoelectric transducer vibrates at ultrasonic frequency. Ultrasonic signals penetrate through the biological cells to generate different signal responses. The system acquires the response signals so as to obtain the biological cell morphology and internal maps. The ultrasonic ranging module records and processes echo delay signals and quantitatively expresses an acoustic path of a vertical direction so as to reconstruct the depth map of the biological cells. Nanoscale ultra-micro internal structural analysis of the biological cells can be realized, a probe can be accurately located and guided to inject drug loading nanoparticles into cancer cells and the stress changes of the morphology and the internal structure can be observed so that the system and the method can be used for nanoscale lossless measurement of the living cells under the physiological environment and have a directive significance for nano-biotechnology and nano-medicine.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Nanobioprocessor for protein and cell therapy
InactiveUS20050214380A1Increase relative motionSuperior and stable diagnostic and treatment agentHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideSelective excitationQuantum dot
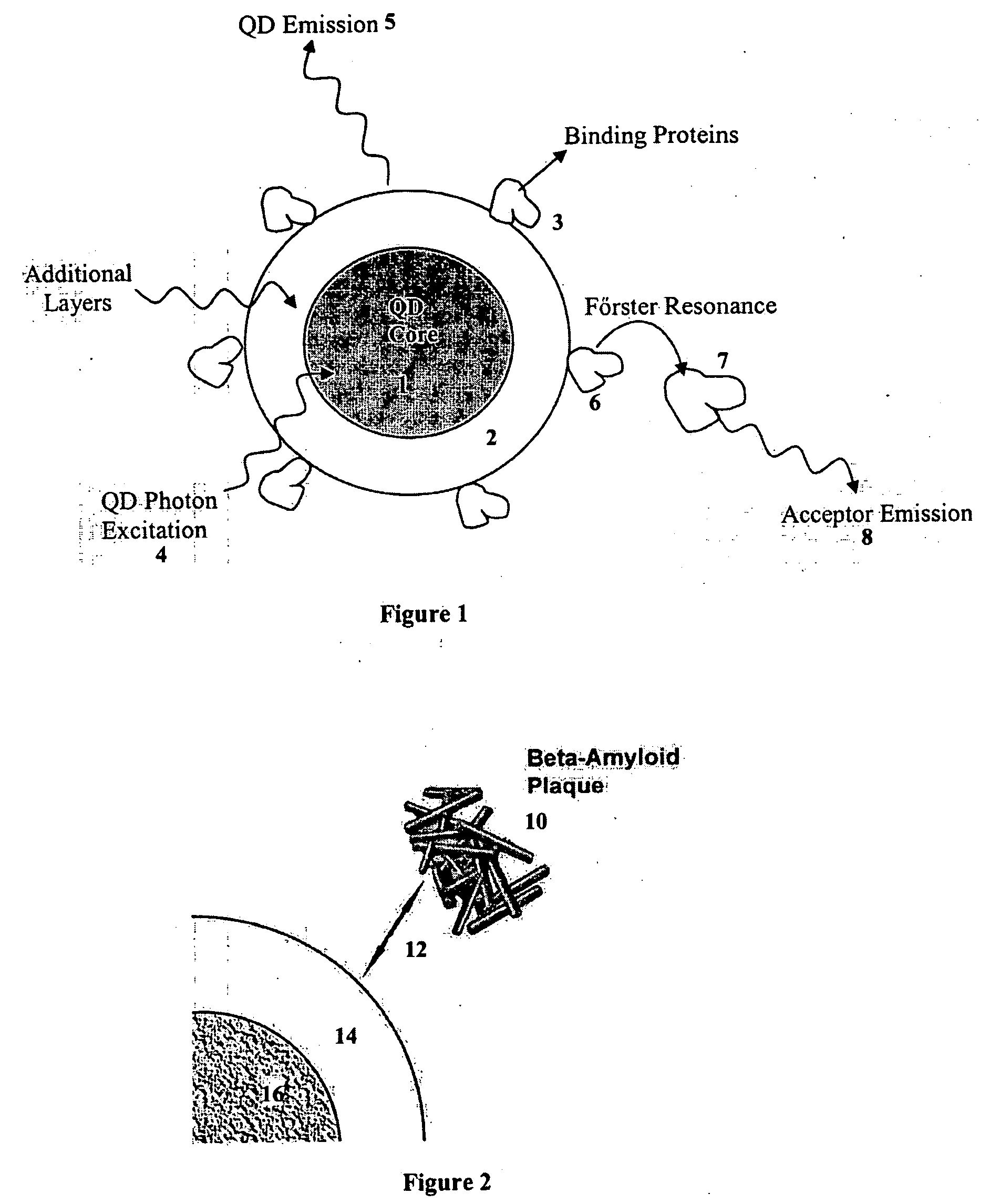
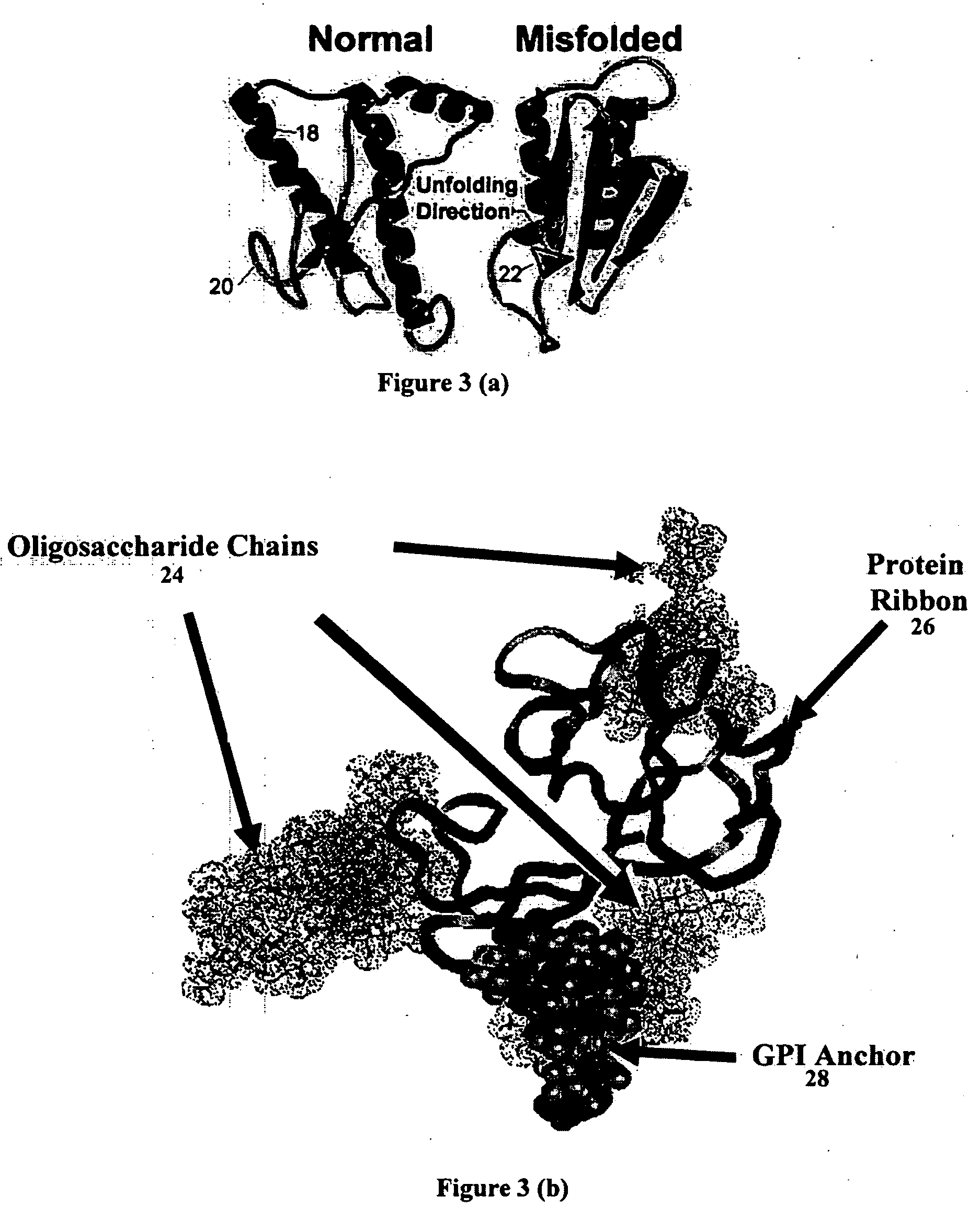
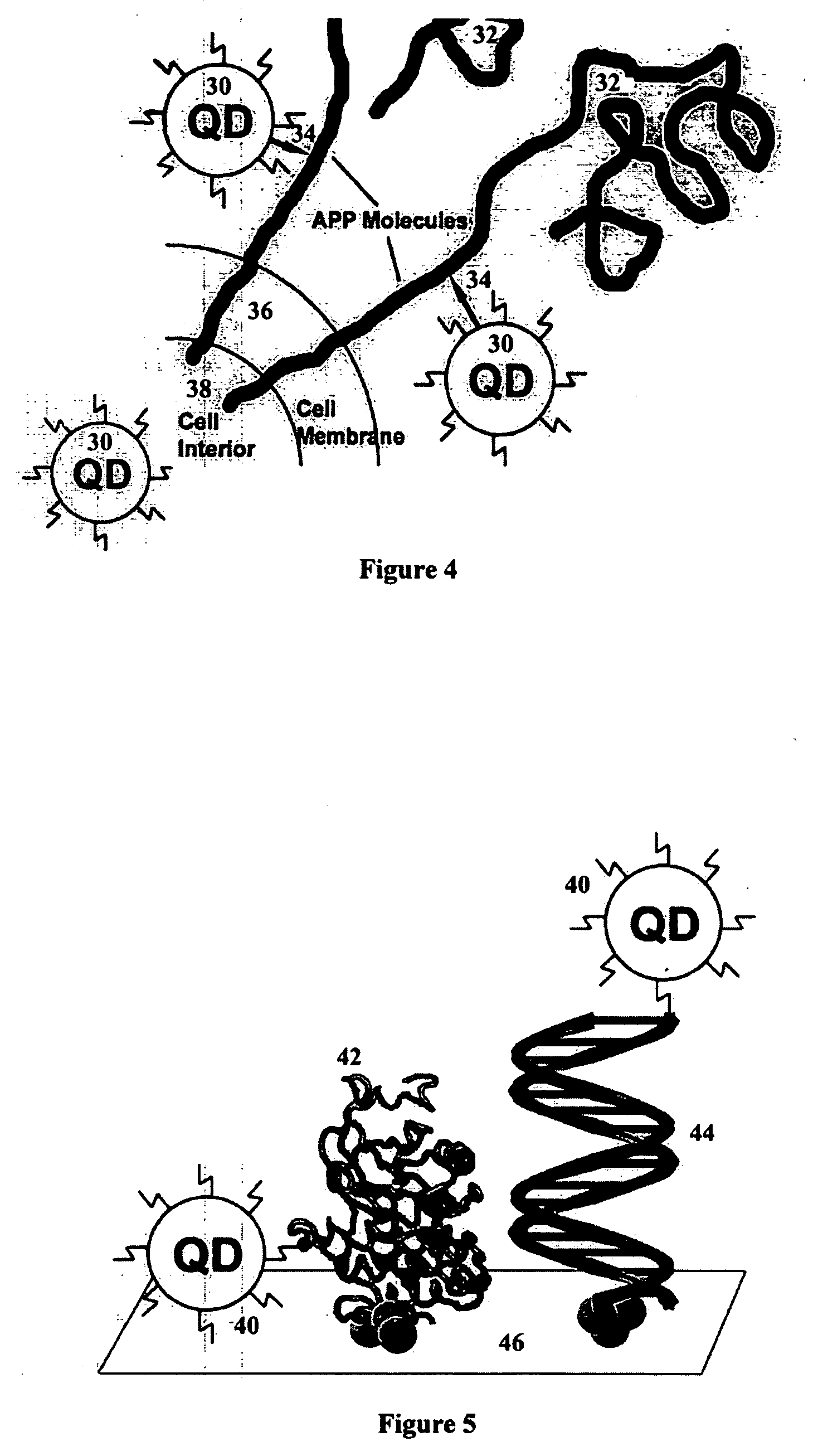
A nanobioprocessor for protein and cell therapy comprises a selectively coated quantum dot having selected band gap energies, characteristic absorption, emission spectra and outer coatings for therapy and diagnostic purposes in biophotonics and nanomedicine, and an electromagnetic radiation and detector source configured to remotely heat and / or selectively excite the quantum dot to associate with target specific misfolded or anomalous proteins, diseased cells and tissue.
Owner:APPLIED PHOTONICS WORLDWIDE
Nanoparticle drug loading system and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110859817AGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsTumor therapyTreatment field
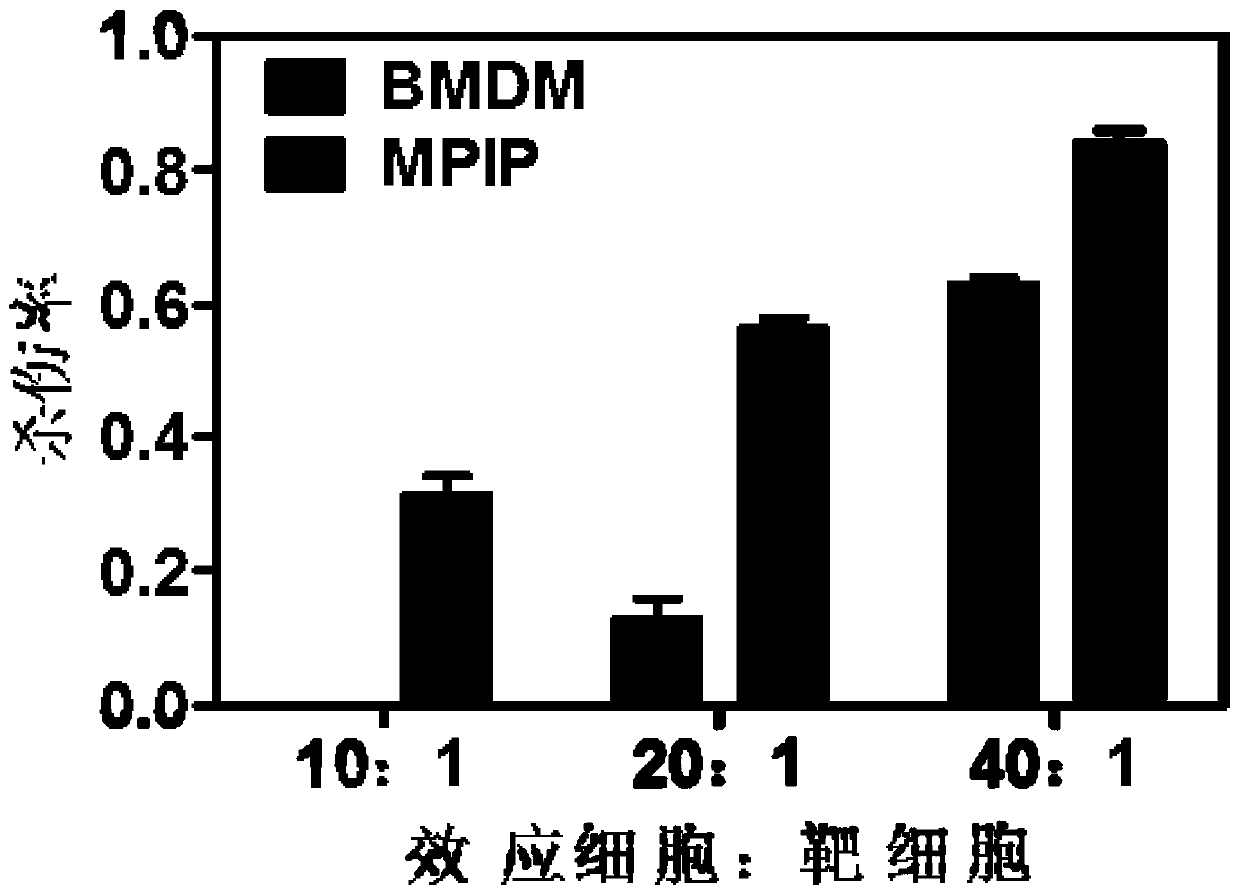
The preparation provides a nano drug loading system, which is simple is a preparation method, mature in process, stable in property and good in biocompatibility. According to the nano drug loading system, nano particles are coupled to the surfaces of macrophages through maleic amide bonds; the tumor is jointly treated through the immune regulation function of macrophages and the functions of the nanoparticles, so that the anti-tumor curative effect is improved; the problem that in the prior art, drug micromolecules cannot be effectively enriched and targeted at tumor sites is solved, and the nano drug loading system has important application prospects in the nano medical field and the tumor treatment field.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Nanometer material of mesoporous silica coated trimanganese tetroxide for modifying CuS nano particles, as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104027806ARealize the combinationTherapeuticEnergy modified materialsNMR/MRI constrast preparationsCancer cellBiocompatibility Testing
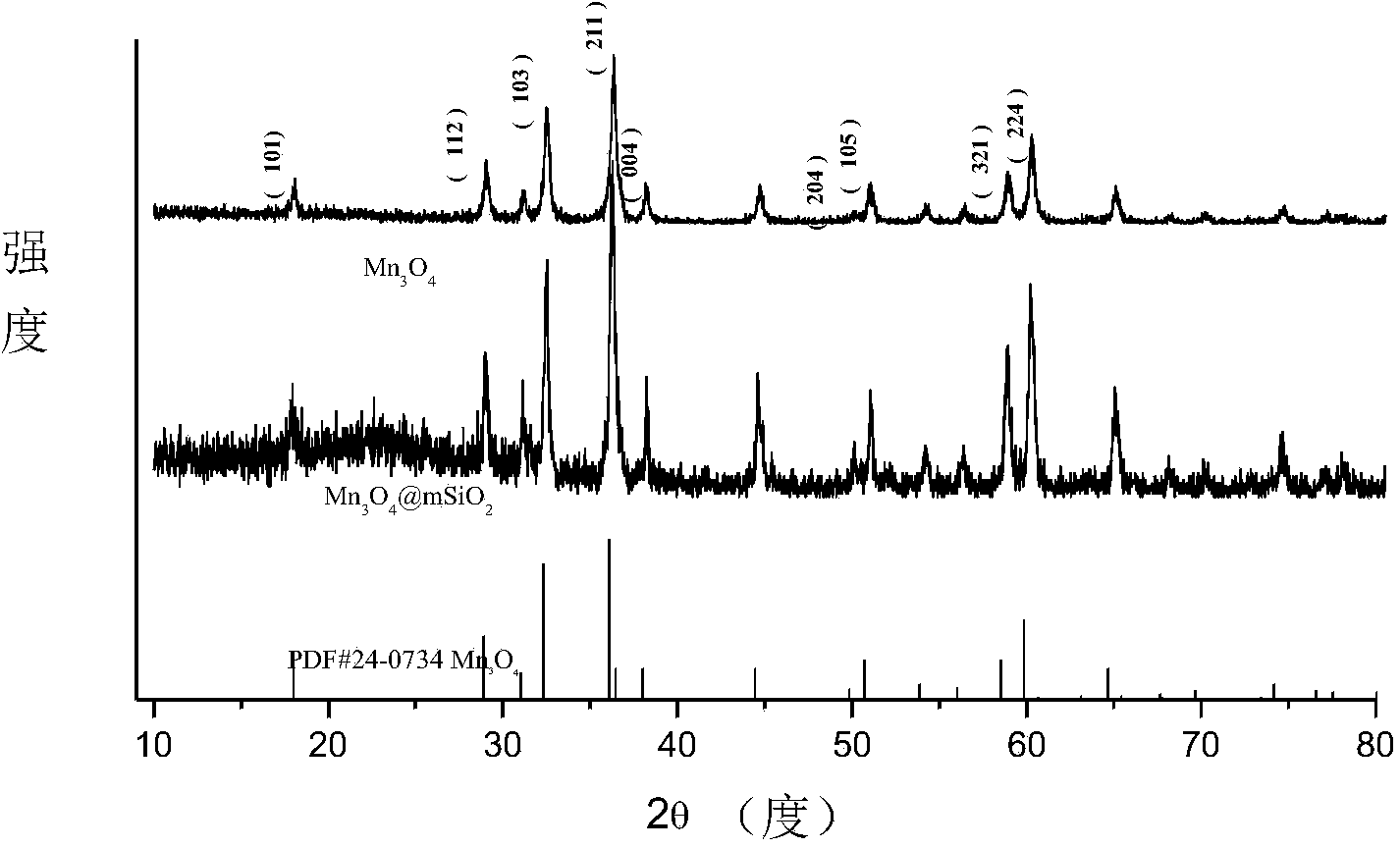
The invention discloses a nanometer material (Mn3O4@mSiO2@CuS) of mesoporous silica coated trimanganese tetroxide for modifying CuS nano particles, as well as a preparation method and an application thereof; the particle size of the nanometer material is about 70 nm; modified photosensitizer molecule methylene blue (MB) can generate singlet oxygen under excitation of 632.8 nm laser so as to kill cancer cells; and CuS can generate heat under irradiation of 980 nm laser to kill cancer cells more effectively. In cellular level experiments, the nanometer material disclosed by the invention has good biocompatibility; cancer cells can be effectively killed under the synergistic effect of optical thermal therapy and photodynamic therapy in the therapeutic process; and the nanometer material disclosed by the invention is expected to be further researched and applied as a multifunctional material in combination with diagnosis and therapy in the field of nanometer medicines.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Nested nanostructured electrostatic spinning fiber membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102071541ASolve the sudden release problemGuaranteed stabilityFilament/thread formingNon-woven fabricsFiberElectrospinning
The invention discloses a nested nanostructured electrostatic spinning fiber membrane and a preparation method thereof. The nested nanostructured electrostatic spinning fiber membrane comprises nanofibers and nanoparticles, wherein the nanoparticles are encapsulated in the nanofibers, and the nanofibers and the nanoparticles are all biodegradable materials. The method for preparing the nested nanostructured electrostatic spinning fiber membrane comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing a polymer solution prepared from the nanoparticles and the nanofiber materials; and then carrying out electrostatic spinning on the obtained mixture so as to obtain the nested nanostructured electrostatic spinning fiber membrane the nanoparticles of which are encapsulated in the nanofibers. The structure of the nested nanostructured electrostatic spinning fiber membrane disclosed by the invention is novel and practical; because the electrostatic spinning fiber membrane is in a bilayer nanostructure, the problem of initial burst release existing in the process of loading medicaments in the nanoparticles is effectively solved; and the nested nanostructured electrostatic spinning fiber membrane is simple in preparation method, and has a broad application prospect in nano-medicines, nano-pharmacology and other release fields such as agriculture.
Owner:WUXI ZHONGKE GUANGYUAN BIOMATERIALS
Nanotechnology Based Medicine for Biodefense
A composition and methods to bind and remove toxic agents from a subject exposed to the toxic agents are described herein. The composition comprises a stealth agent and scavenging agent bound to a nanoparticle platform. The stealth agent prevents the nanomedicine from detection and elimination by the immune system allowing the scavenging agent to bind the target toxic agent. The stealth agent comprises an exposing group that once removed from the stealth agent allows the nanomedicine and bound toxic agent to be detected and eliminated from the subject's body.
Owner:CYTIMMUNE SCI
Synthesis for biodegradable amphiphilic block copolymerization antibacterial peptoids, preparation method of antibacterial peptoid vesicles and applications of antibacterial peptoid vesicles
InactiveCN107513145ANon-cytotoxicGood biocompatibilityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrophobic polymerBiocompatibility Testing
The invention provides synthesis for biodegradable amphiphilic block copolymerization antibacterial peptoids, a preparation method of antibacterial peptoid vesicles and applications of the antibacterial peptoid vesicles. The synthesis for the antibacterial peptoids comprises the following steps: a hydrophilic polypeptide chain segment containing an amino protective group, a hydrophobic polymer chain segment of which one end is amino-terminated and isocyanate radicals of a diisocyanate unit are connected through covalent bonds, and therefore the antibacterial peptoids are obtained; and the antibacterial peptoid vesicles are formed by self assembly of the antibacterial peptoids, and the antibacterial peptoid vesicles can be used as antibacterial agents or drug carriers to be applied to aspects such as clinical inflammation resistance, anti-cancer drug targeting release, or nanomedicine. The antibacterial peptoid vesicles select and use the biodegradable hydrophobic polymer chain segment to replace a hydrophobic amino acid chain segment in an antibacterial peptide, thus the antibacterial peptoid vesicles do not have cytotoxicity, and have excellent biocompatibility and biodegradability; and besides, the antibacterial peptoid vesicles have a broad-spectrum antibacterial property, and a membrane damage antibacterial mechanism which is similar to that of a natural antibacterial peptide, and therefore drug tolerance of germs is not easily induced.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Tumor-targeted nanomedicine and application and preparation method
InactiveCN110433145AThe synthesis process is simpleHigh synthesis efficiencyHeavy metal active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsTumor targetMesoporous silica
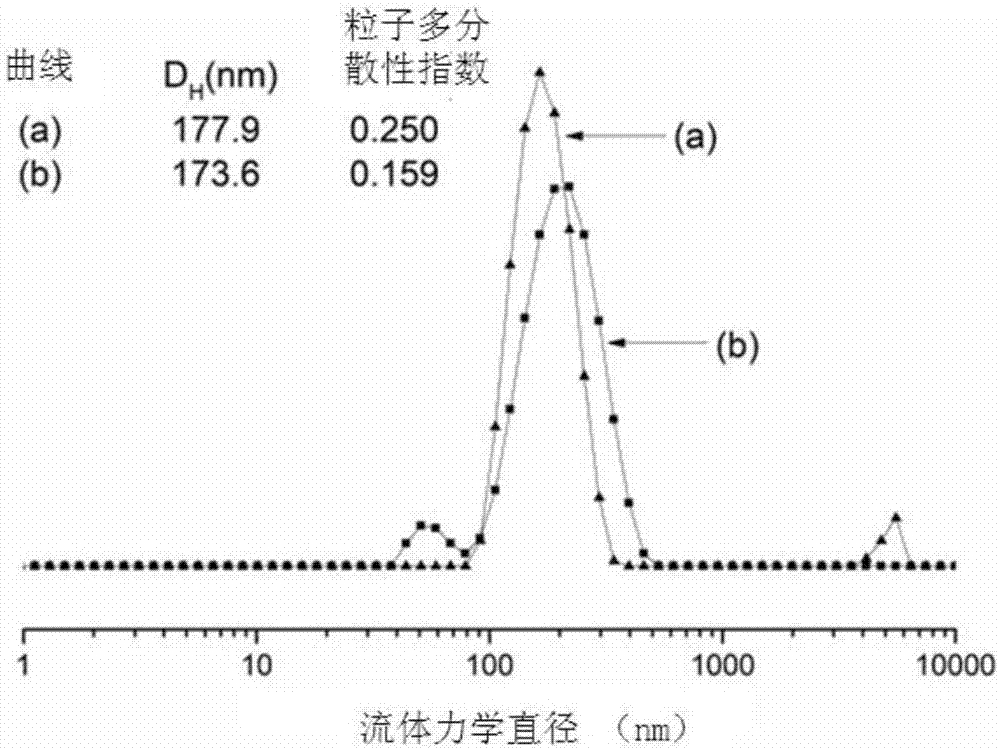
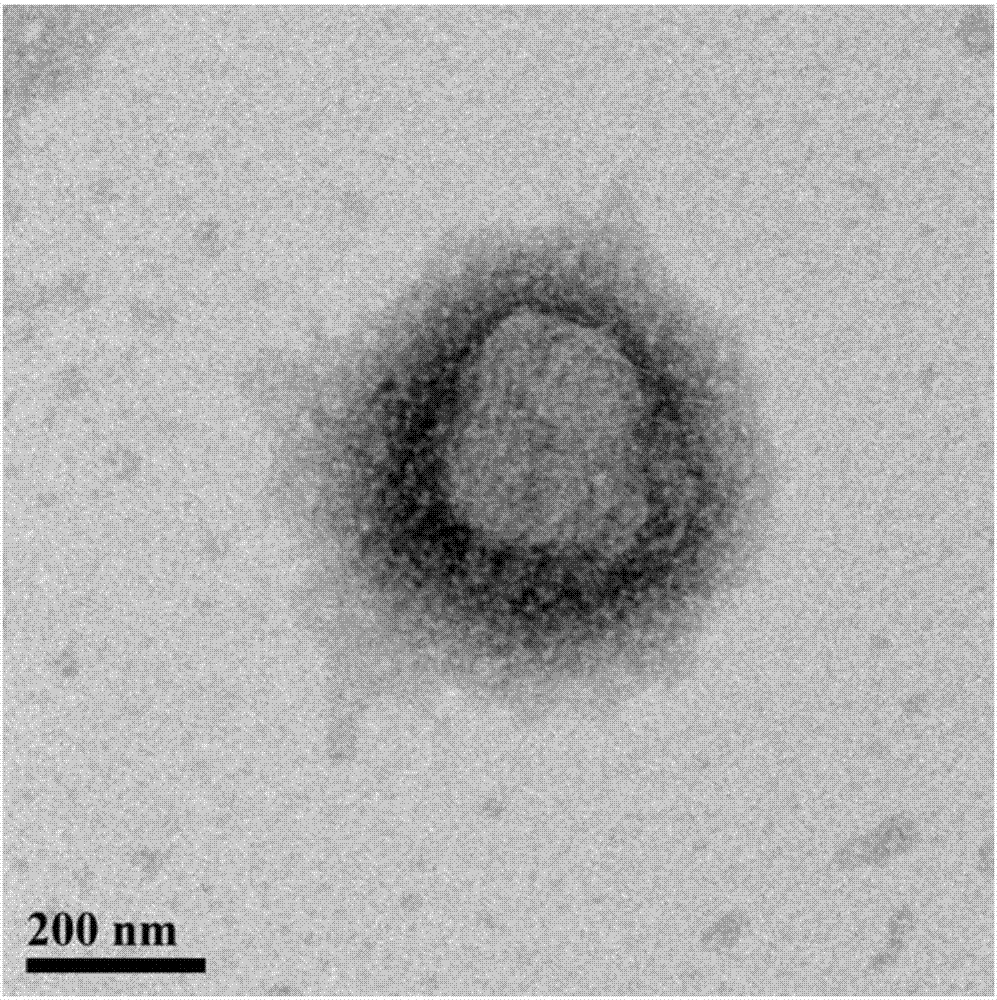
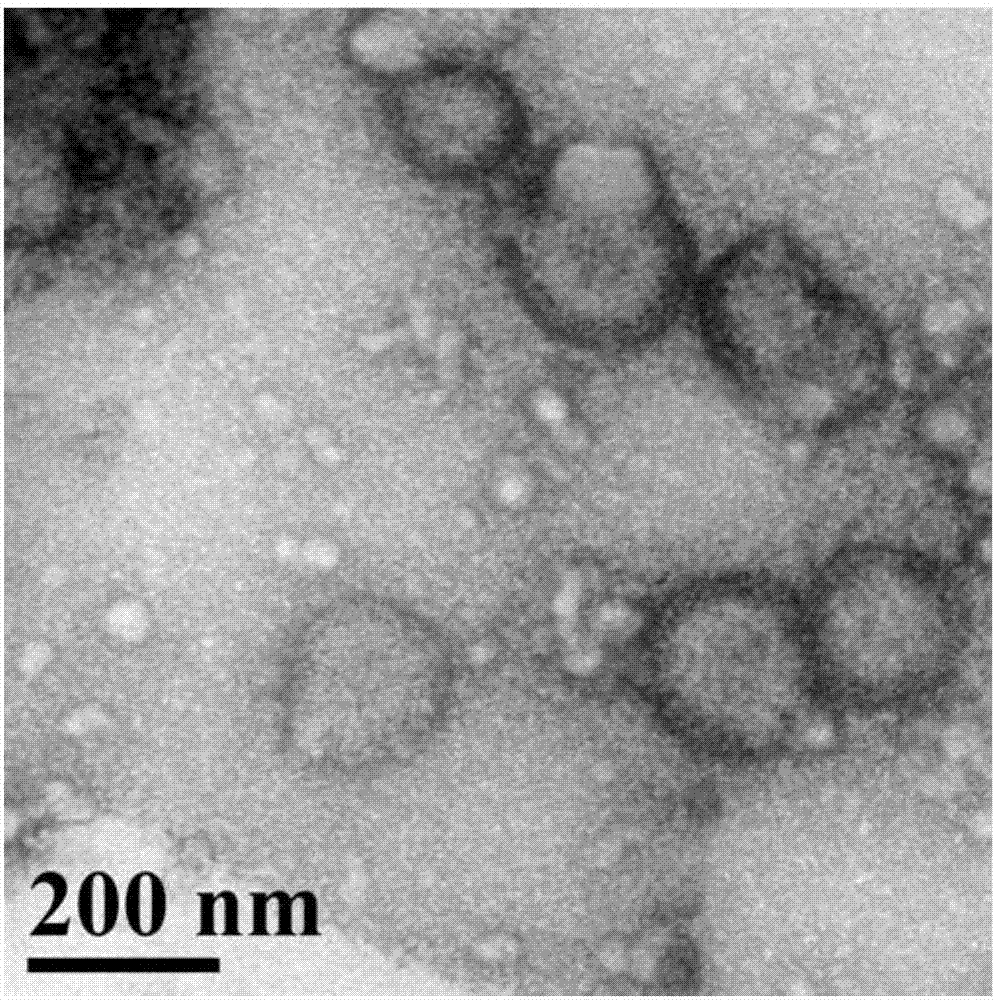
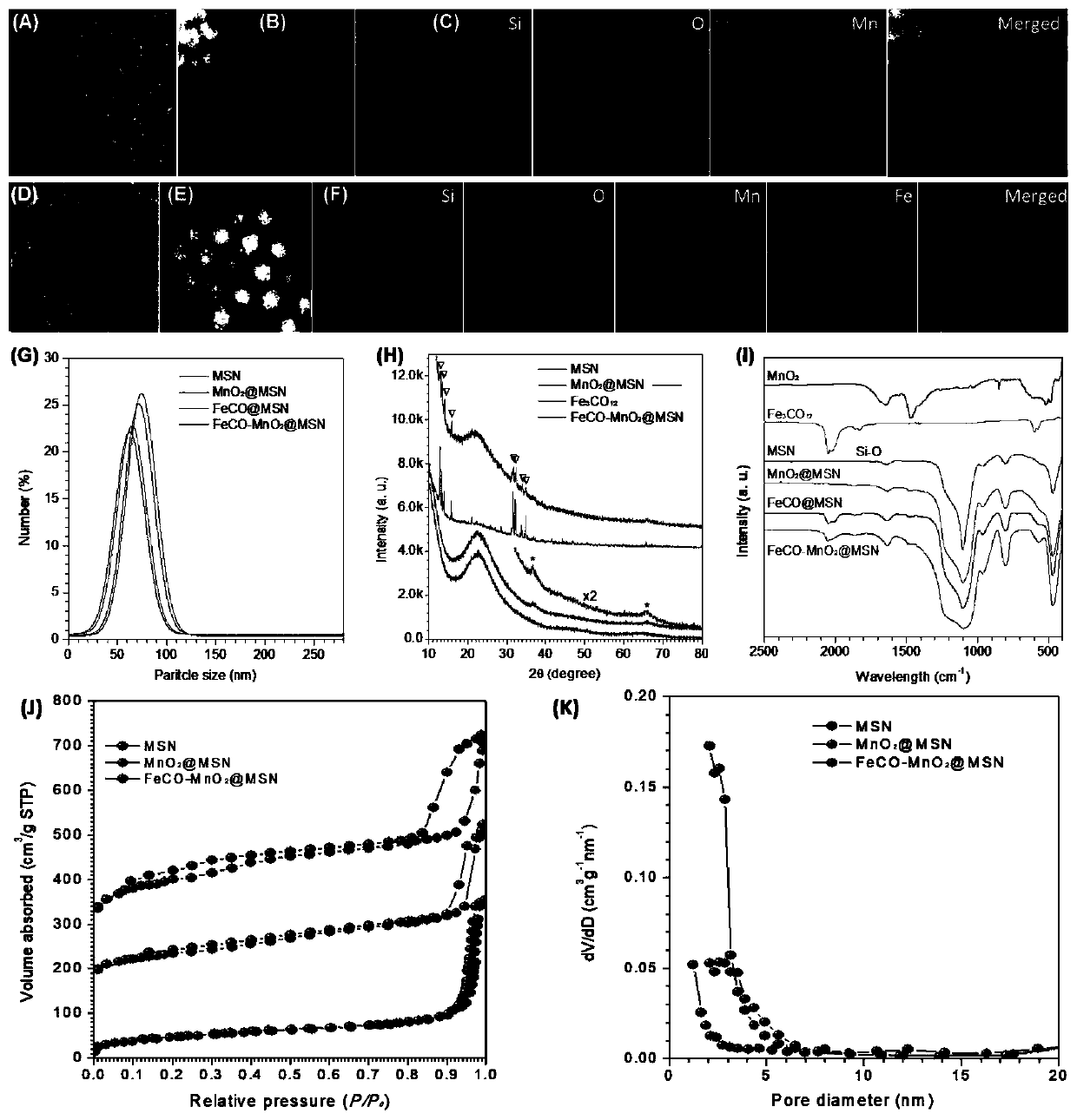
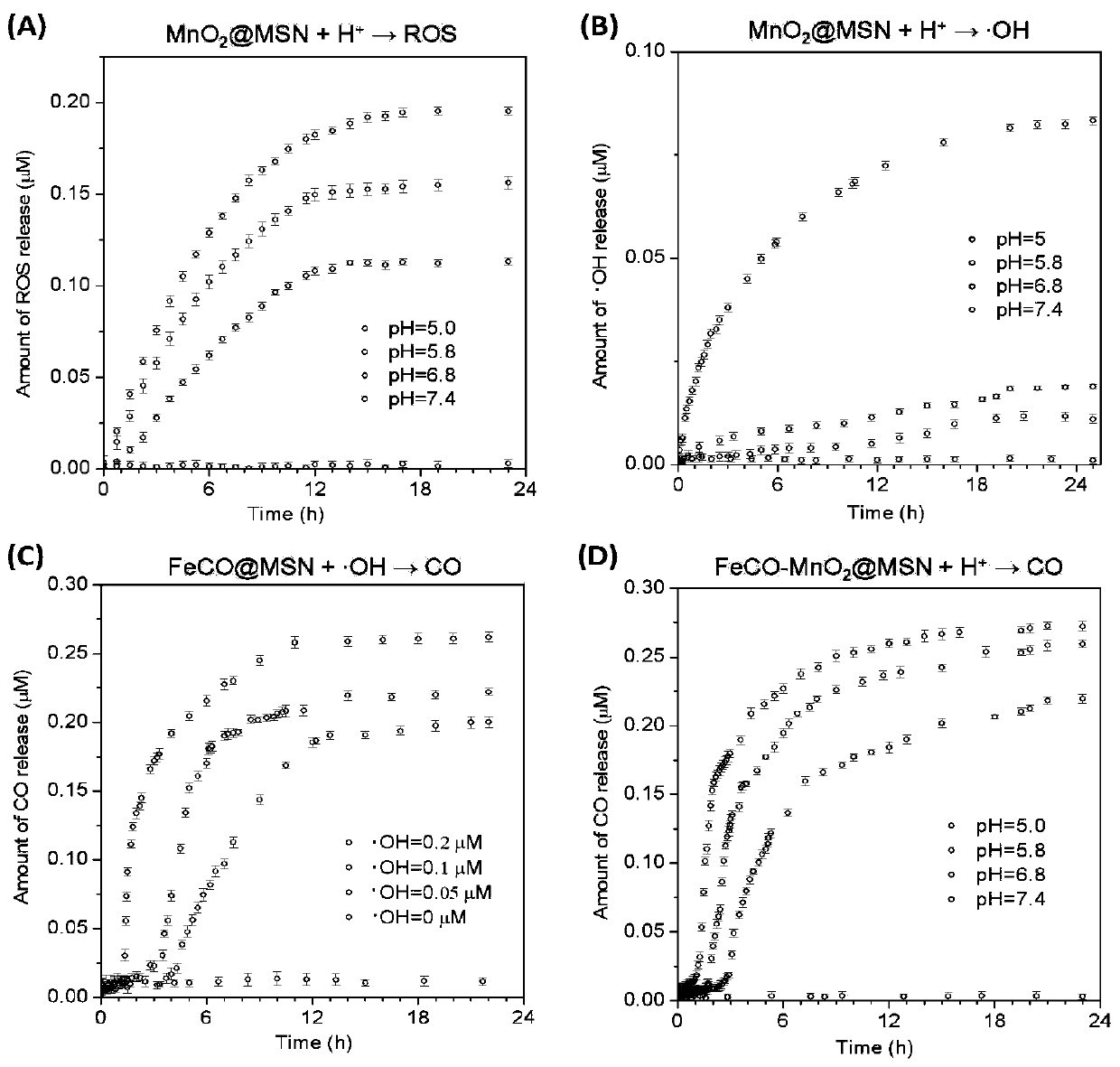
The present invention relates to a tumor-targeted nanomedicine and an application and preparation method. The tumor-targeted nanomedicine comprises MSN nanoparticles with mesoporous channels and transition metal oxides and transition metal carbonyl compounds loaded in the mesoporous channels of the MSN nanoparticles. Acid-responsive nano drug (MnO2) is loaded on mesoporous silica channels by the in-situ reduction method, and then drug dodecacarbonyltriiron (Fe3CO12) before gas (CO) release is co-loaded on the mesoporous silica channels through the nano-perfusion method. The preparation processis simple, the cost is low the gas loading efficiency is high, and the nano drug has passive targeting tumor transport and response to release of ROS and CO gas in the tumor microenvironment, low-toxicity and high-efficiency of tumor chemical kinetic therapy and gas therapy are achieved, the therapy efficiency is greatly improved, and clinical application is facilitated.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Nanometer vesicle capable of simultaneously achieving RNA interference and MR imaging and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105999310APromote differentiationGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsDispersion deliveryMagnetite NanoparticlesTherapeutic effect
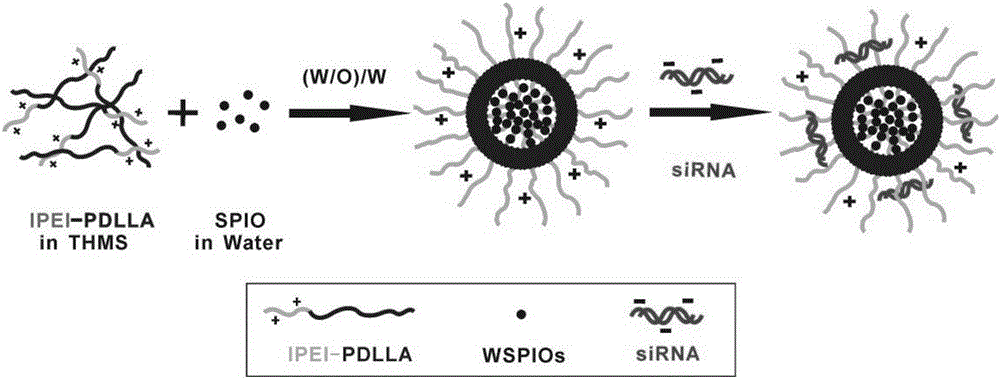
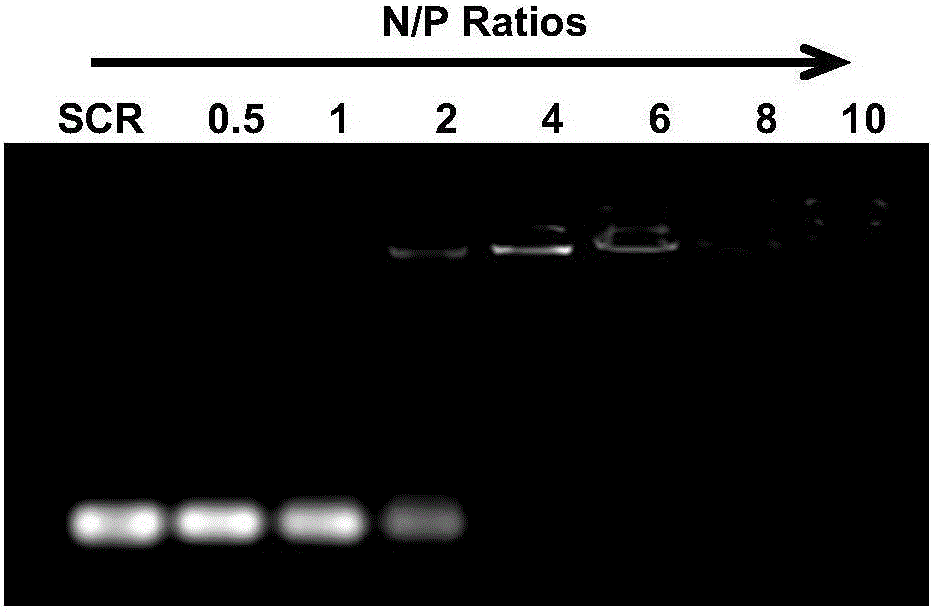
The invention belongs to the field of nanometer medicine and biomedical engineering, and particularly discloses a nanometer vesicle capable of simultaneously achieving RNA interference and MR imaging and a preparation method and application thereof. The nanometer vesicle is based on amphipathy block polymer carrier linear polymine-polyactic acid. A hydrophobic cavity of the nanometer vesicle is used for performing loads on hydrophilic magnetic nanoparticles SPIO, siRNA is composited on the surface PEI, neural stem cells are effectively marked in vitro, nerve cell differentiation genes are restrained silently, stem cells are positioned in real time after in-vivo transplanting, the stem cells are promoted to be differentiated to nerve cells, the cerebral infarction treatment effect is improved, and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Degradable nano-micelle capable of performing MR-fluorescence bimodal imaging as well as preparation method and application of degradable nano-micelle
ActiveCN106822924AImprove loading efficiencyEnables efficient bimodal labelingDispersion deliveryEmulsion deliveryResonanceFluorescence
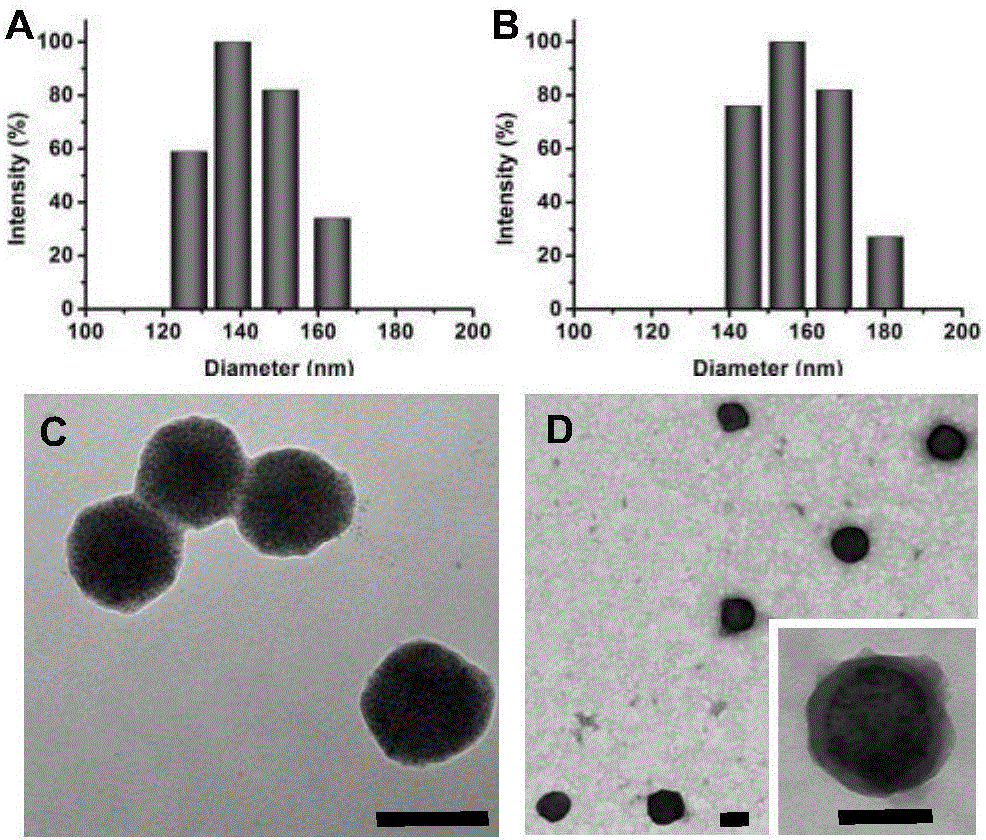
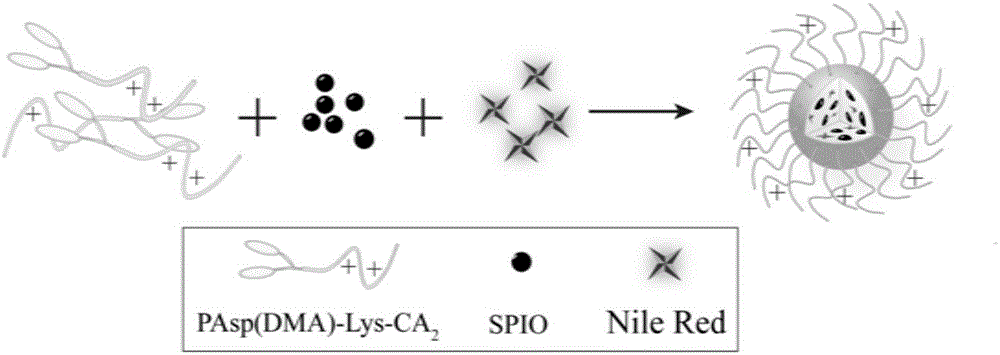
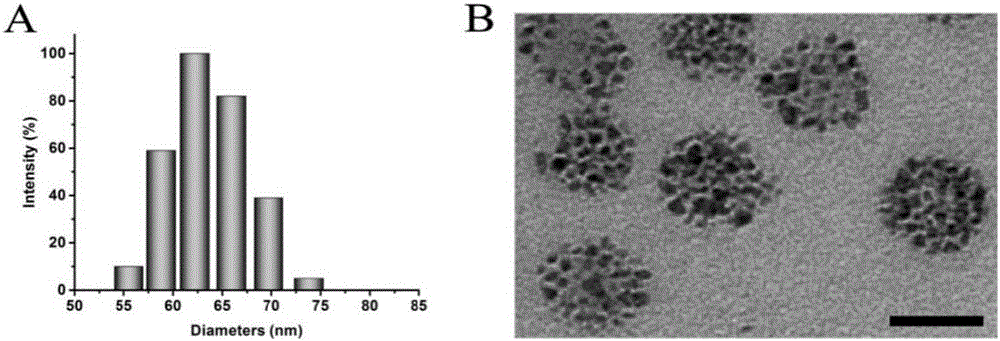
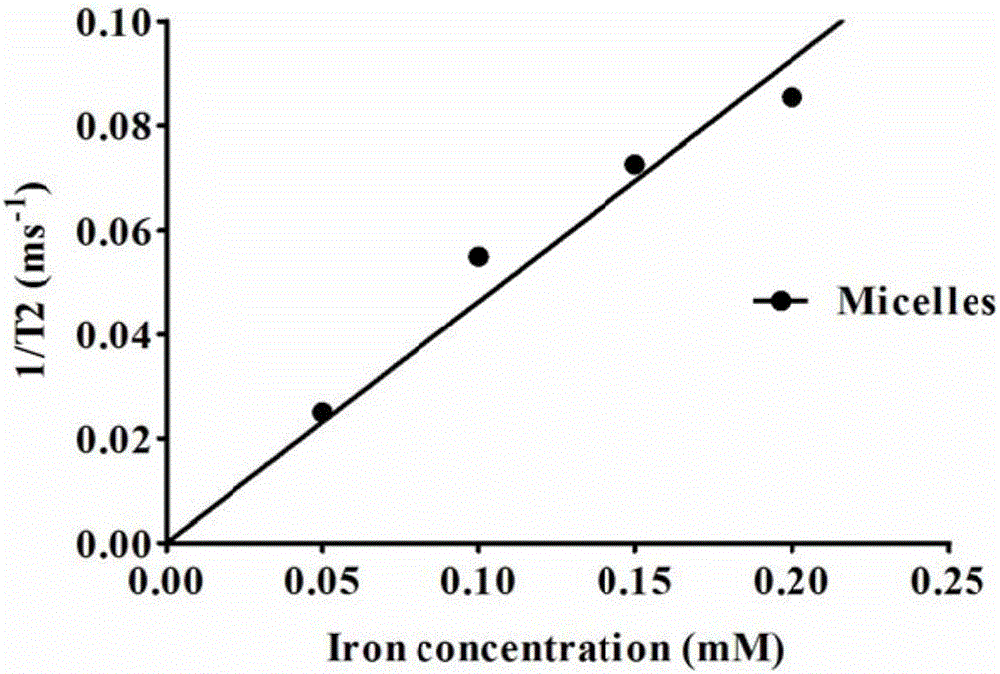
The invention belongs to the field of nano medicine and biomedical engineering and particularly discloses degradable nano-micelle capable of performing MR (magnetic resonance)-fluorescence bimodal imaging as well as a preparation method and an application of the degradable nano-micelle. The nano-micelle is based on amphipathic block polymer support PAsp(DMA)-CA2. A hydrophobic core of the micelle is used for supporting hydrophobic SPIO (superparamagnetic iron oxide) and fluorescent dye Nile red, neutral stem cells can be labeled in vitro safely and efficiently, after in-vivo transplantation of the neutral stem cells, distribution and migration conditions of the neutral stem cells in vivo can be traced in real time, safe and efficient MR-fluorescence bimodal imaging tracing of the stem cells can be realized, and the nano-micelle has broad application prospects.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Amphiphilic multi-block antibacterial peptide copolymer, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110527080AGood broad-spectrum antibacterial propertiesLow cytotoxicityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCell membraneCytotoxicity
The invention provides anamphiphilic multi-block antibacterial peptide copolymer, and a preparation method and application thereof. According to the amphiphilic multi-block antibacterial peptide copolymer,a hydrophobic amino acid block and a hydrophilic amino acid block are selected and usedfor simulating and replacingan amino acid composition in natural antibacterial peptide, therefore, excellentbroad-spectrum antibacterial performance, low cytotoxicity, excellent biocompatibility and biodegradability are achieved, an antibacterial mechanism of the amphiphilic multi-block antibacterial peptide copolymer is the same as that of the natural antimicrobial peptide, bacteria die by destroying bacterial cell membranes, andthe bacteria is not prone to being inducedto produce drug resistance.According to synthesis steps of the preparedamphiphilic multi-block antimicrobial peptide copolymer is simpler, efficient and lower in production cost compared with step-by-step synthesis reaction, and the amphiphilic multi-block antibacterial peptide copolymer can be used as an antimicrobial agent or drug carriers to be used in aspects of clinical anti-infection, targeted release of anticancer drugsor nanomedicine.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
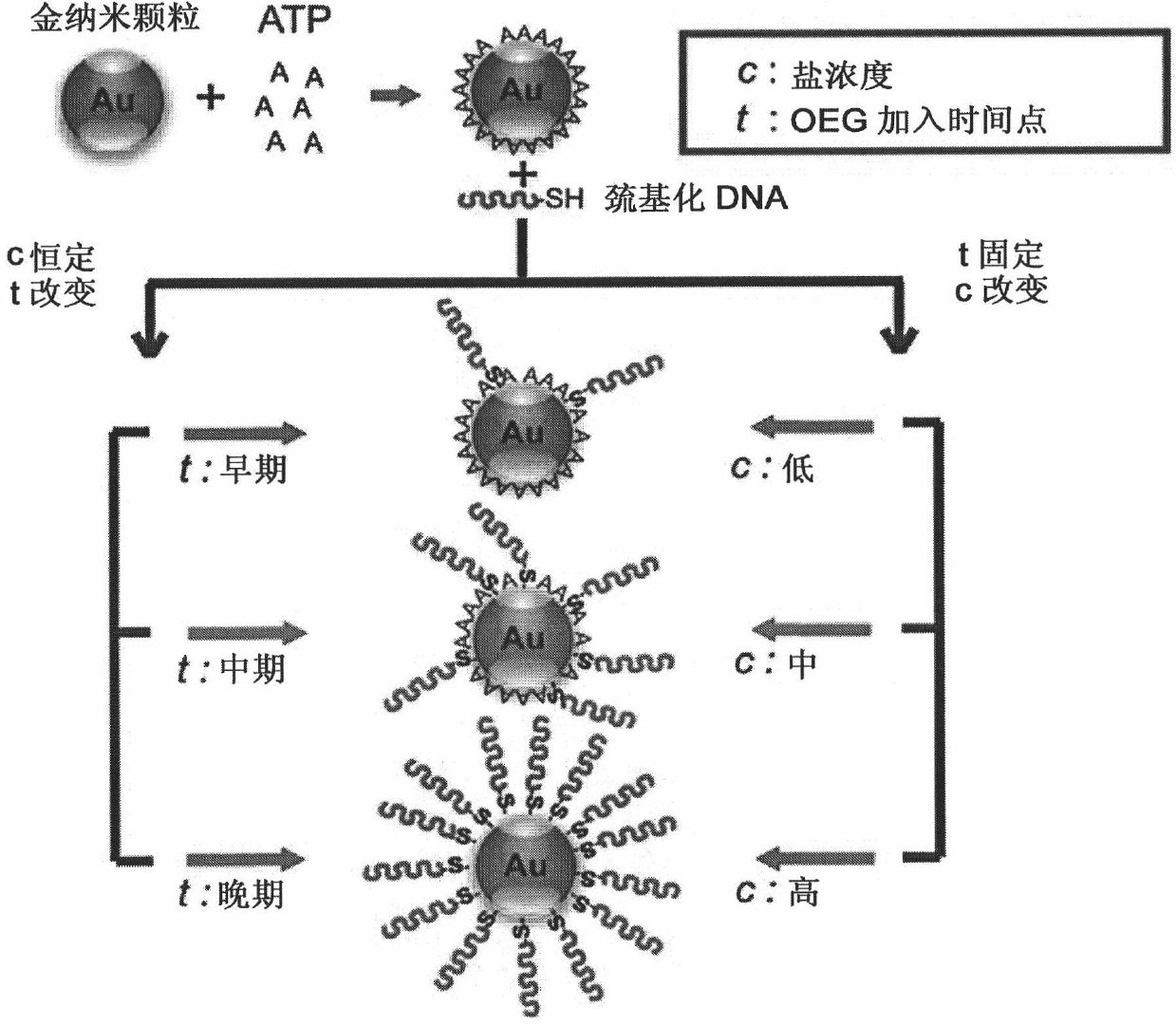
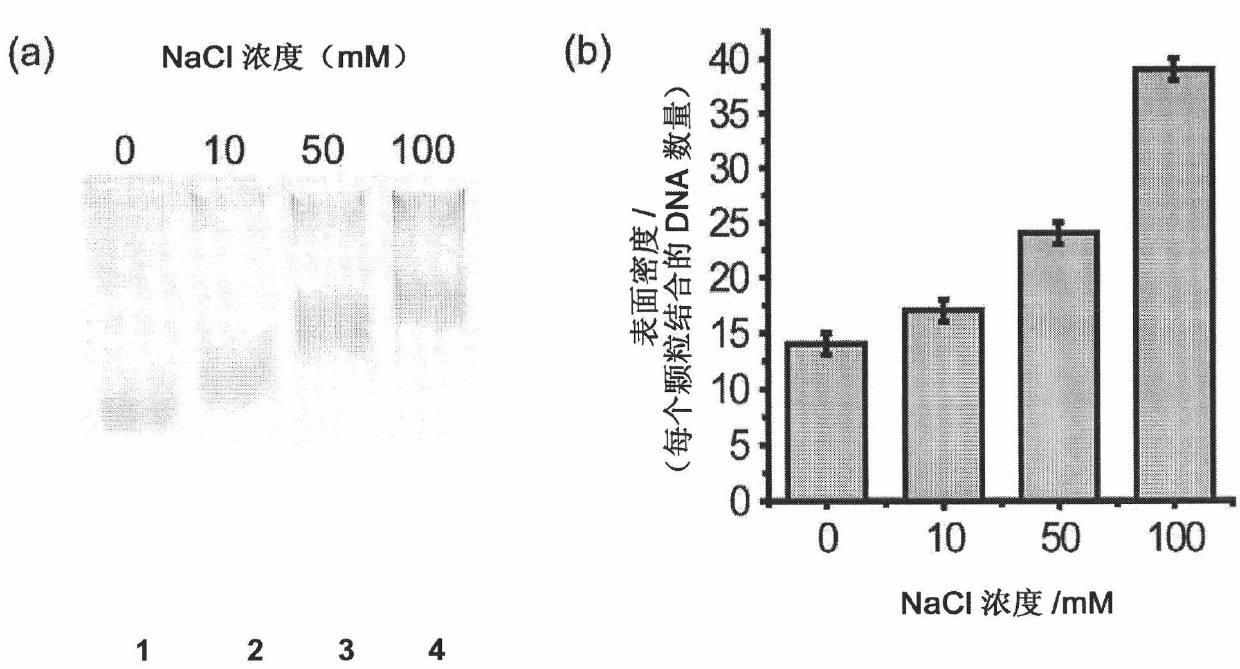
Method of manipulating the surface density of functional molecules on nanoparticles
ActiveCN101993467ALarge range of binding density controlSimple methodMaterial nanotechnologySugar derivativesNucleotidePolythylene glycol
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Nano co-delivery system for co-delivering NO donor and nanomedicine
InactiveCN109395087AImprove permeabilityPromote accumulationPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsNanocarriersCurative effect
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Therapeutic protein-loaded nanoparticle and method for preparing the same
ActiveCN108778257ASustainable preparationLarge-scale preparationPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseaseTherapeutic protein
The present invention belongs to the technical field of nanomedicine, and relates to a method for preparing a therapeutic protein-loaded nanoparticle, as well as a therapeutic protein-loaded nanoparticle, a suspension and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the nanoparticle, and a pharmaceutical preparation comprising the nanoparticle, the suspension or the pharmaceutical composition. The present invention further relates to a use of the nanoparticle in manufacture of a pharmaceutical composition, wherein the pharmaceutical composition is useful in prevention or treatment of a disease thatcan be prevented or treated by the therapeutic protein comprised in the nanoparticle.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
Stem cell tumor targeting system with internal nano-prodrug and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105457037AProlong lifeNormal neurobehavioral featuresOrganic active ingredientsUnknown materialsTumor targetingEndocytosis
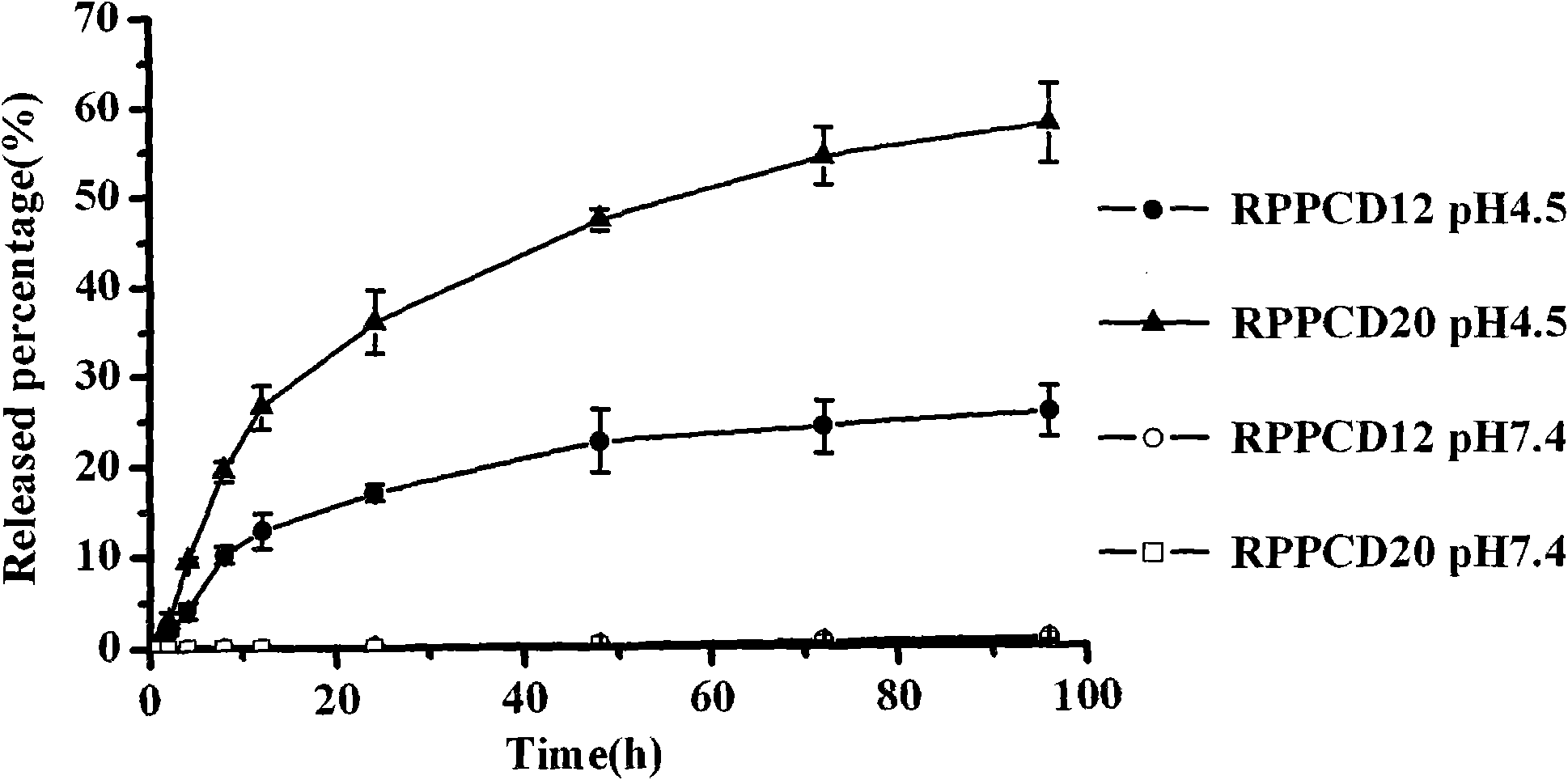
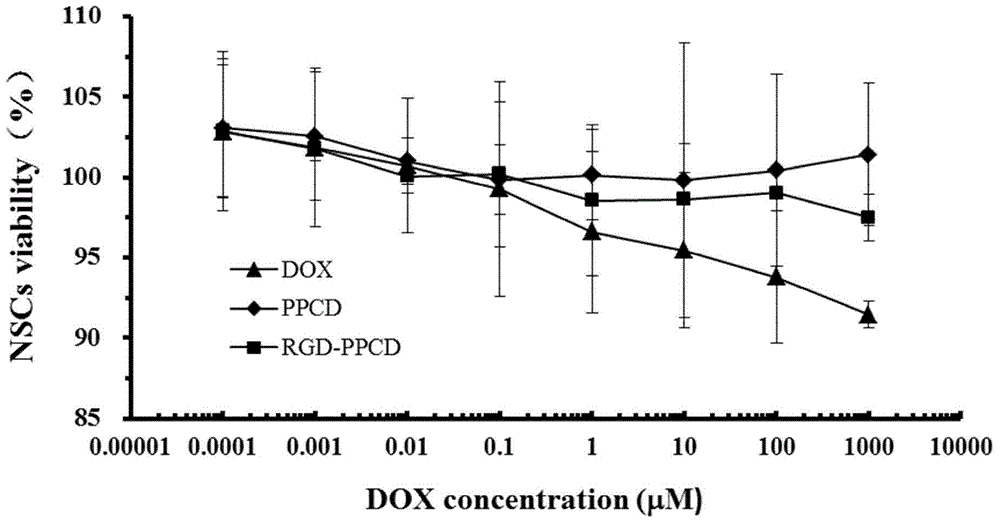
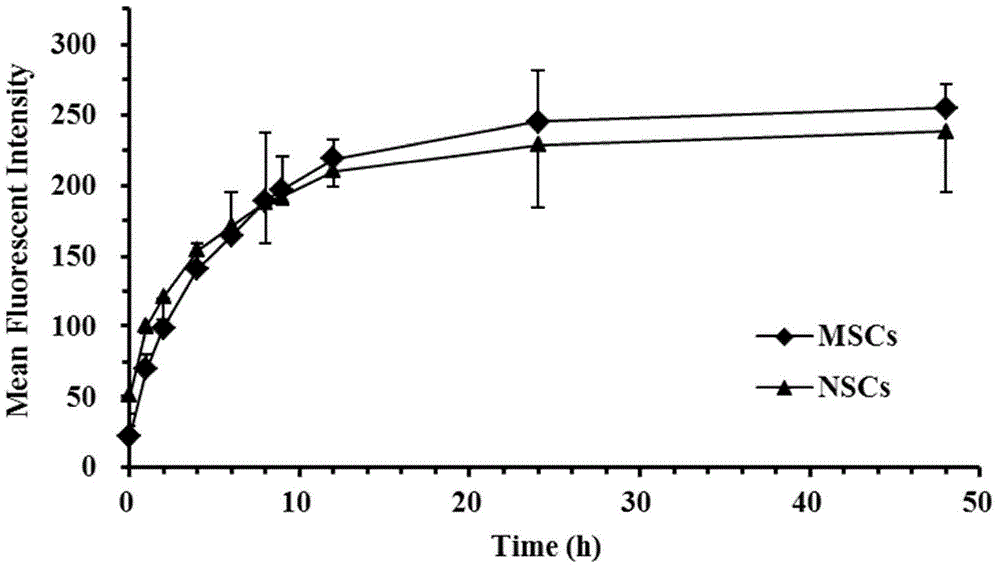
The present invention belongs to the technical fields of biomedical medicine and nano-medicine, and relates to a stem cell tumor targeting system with internal nano prodrug and a preparation method thereof. The method uses stem cells as cell carriers to prepare an anti-tumor targeting system with general formula of Stem cells-(RGD-PPCD)n through endocytosis and inner load of nano prodrug. The nano prodrug has the characteristics of targeting, sustained release and acid sensitivity release; and the stem cell carrier can remotely target primary lesion and metastasis of tumor. In vitro experimental results show that the stem cells after drug load can retain the proliferation capacity and tumor migration characteristics; and the constructed system is stable to ensure that the drug stays in the form of nano-prodrug for several days in the cells, and can slowly release the drug. In vivo experimental results show that the constructed stem cell targeting system can significantly prolong the survival time of tumor-bearing animals and can maintain normal neurobehavioral characteristics of tumor-bearing animals in comparison with the original drug and nano prodrugs, so as to play the efficient, secure and long-lasting anti-tumor effect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Macromolecule based preparation method of pH-responsive metal-organic coordination polymer
InactiveCN101947324AControl releasePowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMetal nitrateNitrate
The invention relates to a macromolecule based preparation method of pH-responsive metal-organic coordination polymer in the technical field of nanomedicine, comprising the steps of: dissolving the biocompatible macromolecule in the deionized water, orderly adding the medicinal solution and the metal nitrate solution while stirring and adjusting the pH to be neutral with the alkali, then orderly adding the poor solvent and the metal sulfate solution, and centrifugally washing and drying to obtain the pH-responsive metal-organic coordination polymer. In the invention, the medicine is prepared into the nanoscale metal-organic coordination polymer by means of the biocompatible macromolecule and the metal ion, and the invention can perform controllable release to the medicine according to the small change of the pH.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
DNA tetrahedral nucleic acid framework type gastric cancer diagnosis-treatment integrated reagent and preparation method and application thereof
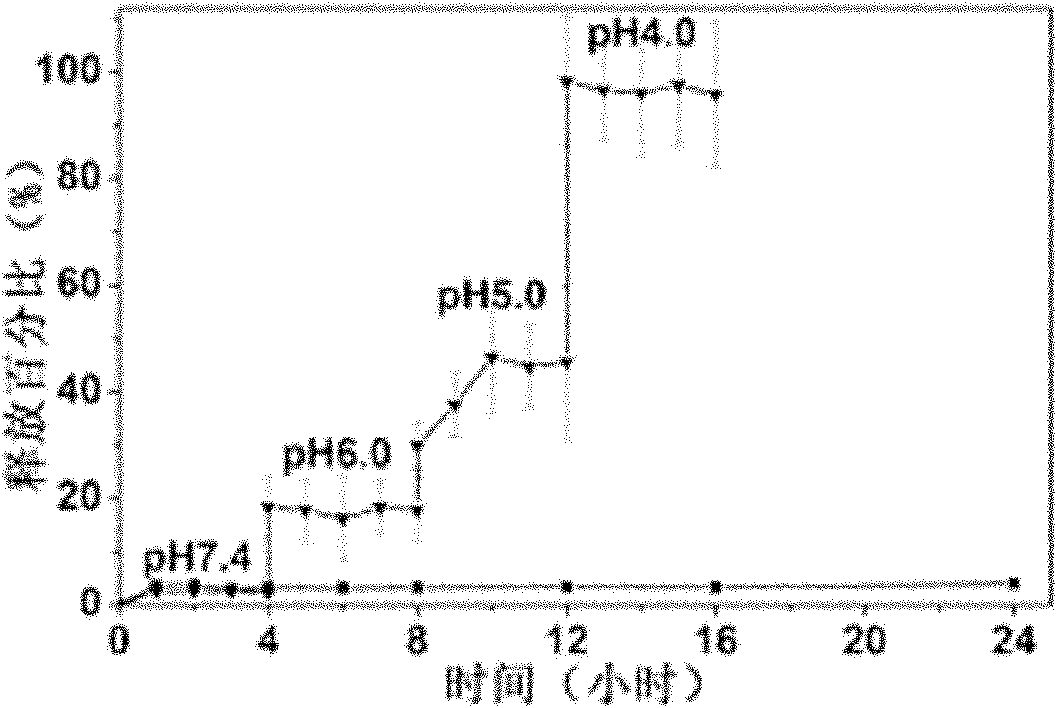
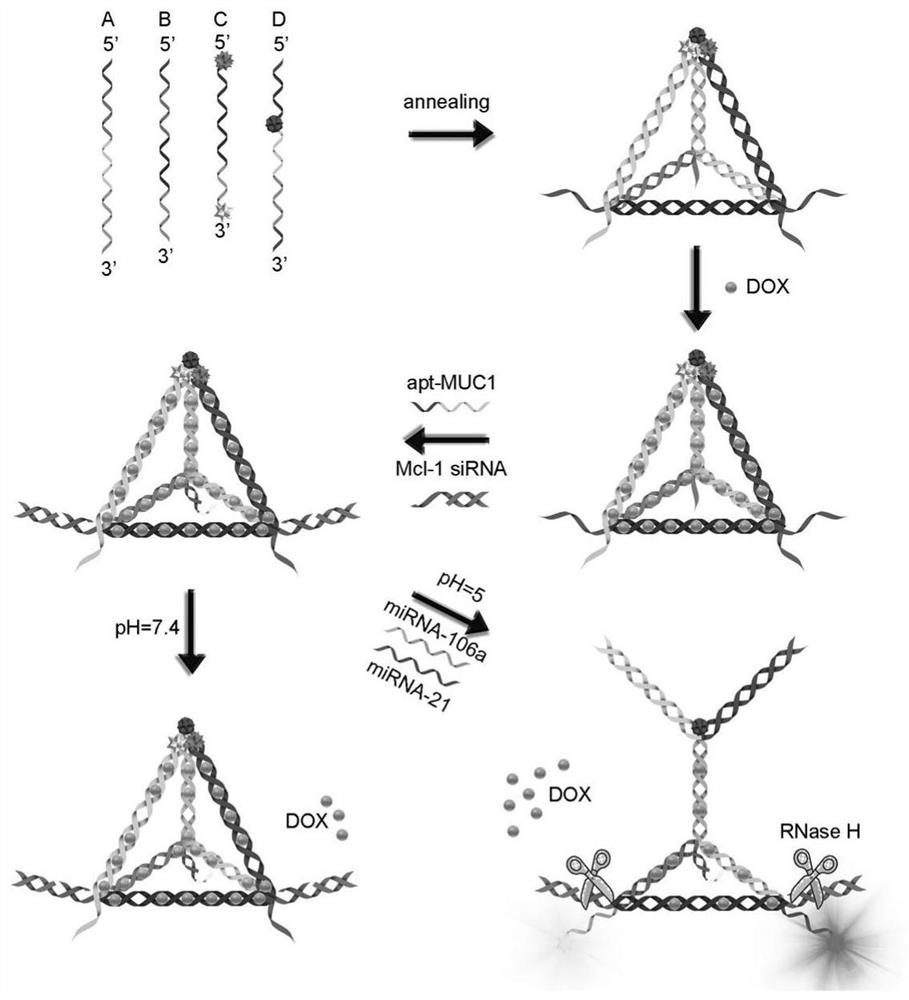
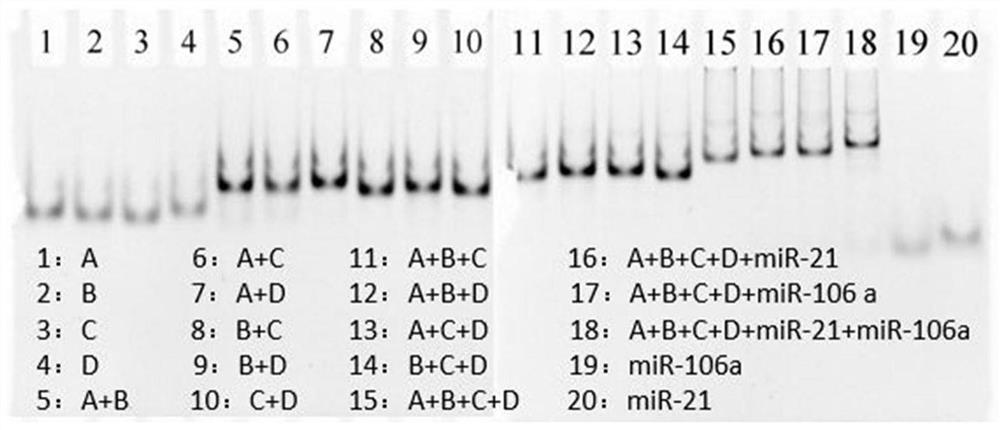
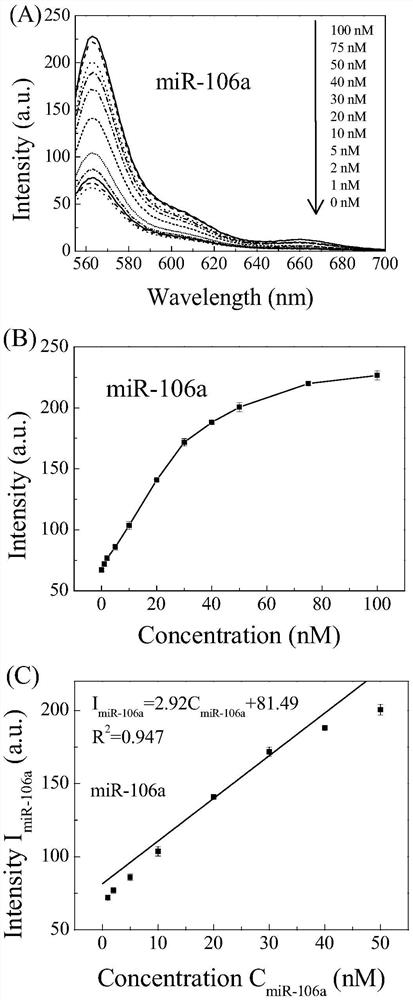
ActiveCN111803511AQuick releaseGood treatment effectOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCancers diagnosisTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a DNA tetrahedral nucleic acid framework type gastric cancer diagnosis-treatment integrated reagent which includes a DNA tetrahedral nucleic acid framework which is loaded withchemotherapeutic drugs, and is obtained by connecting a MUC1 targeting aptamer with Mcl-1 siRNA. The invention further discloses a preparation method and application of the integrated reagent. The integrated reagent can perform targeting recognition of drug-resistant gastric cancer cells SGC-7901 / ADR, miRNA detection imaging and chemical drugs and gene silencing combined synergistic treatment, the internalization efficiency of the reagent in the drug-resistant gastric cancer cells and the detection efficiency of miRNA are improved, and by using the structural changes of the nucleic acid framework in a miRNA detection process, the rapid release of DOX loaded in a DNA double strand is realized. The reagent is further combined with Mcl-1 siRNA, the gene silencing of the Mcl-1 siRNA significantly improves the therapeutic effect of DOX, and the drug resistance problem in the application of nanomedicine in biological systems is solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
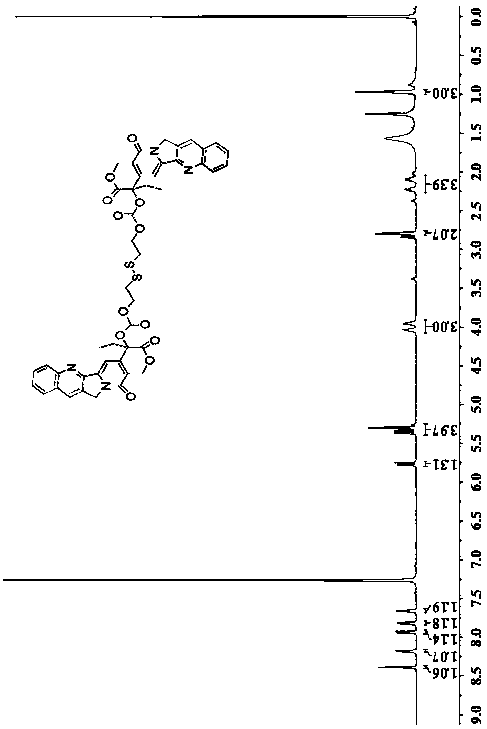
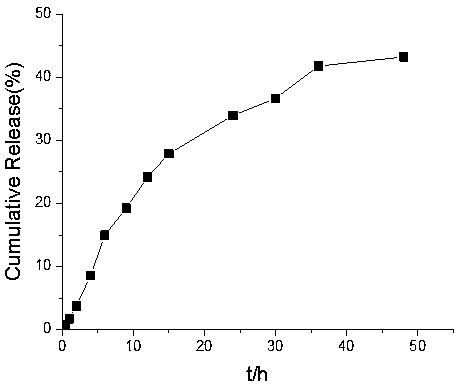
Reduction-responsive type camptothecin dimer and reduction-sensitive drug delivery system based on the camptothecin dimer
InactiveCN109293683AReduction sensitiveHigh drug loadingOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryBiocompatibility TestingStructural formula
The present invention discloses a reduction-responsive type camptothecin dimer and a reduction-sensitive drug delivery system based on the camptothecin dimer, and belongs to the technical field of biomedicines and nano-medicines. Technical scheme main points are as follows: dibromomaleimide sequentially reacts with triethylene glycol monomethyl ether, 2,2-dihydroxyethyl disulfide and camptothecinto obtain the reduction-responsive type camptothecin dimer. The camptothecin dimer has a shown structural formula. The present invention also discloses a preparation method of the camptothecin dimer and a reduction-sensitive drug delivery system based on the camptothecin dimer. Compared with a camptothecin delivery system, the drug delivery system has a drug loading amount increased from 1 wt% to9.6 wt%. Besides, the drug delivery system has reduction sensitivity, good biocompatibility, and tumor cell proliferation inhibition ability. The reduction-responsive type camptothecin dimer can be used to prepare an anticancer drug delivery system with controlled release and targeting.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Method for preparing small-sized nano-hydroxyapatite by using carbon dots (CDs) as template
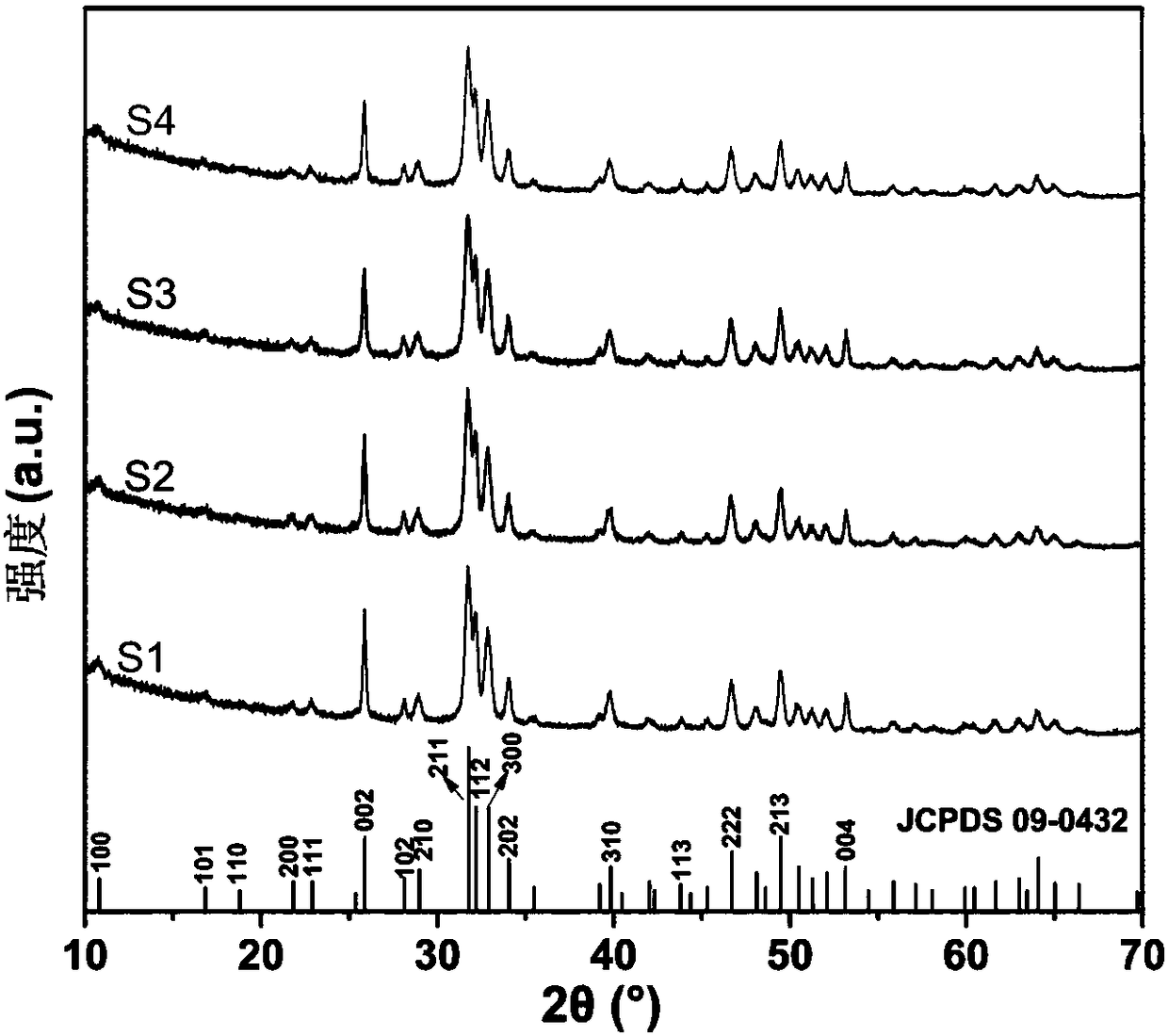
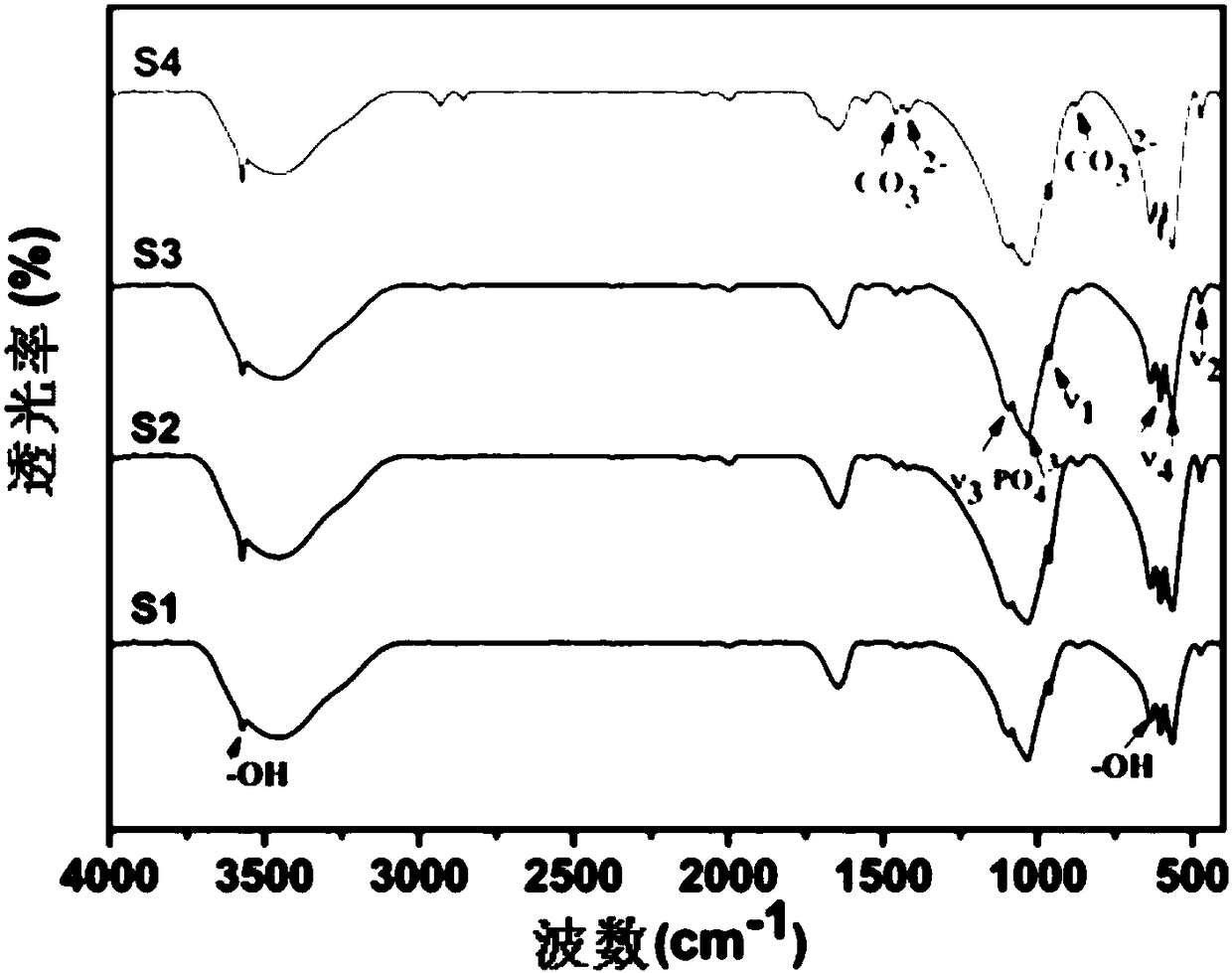
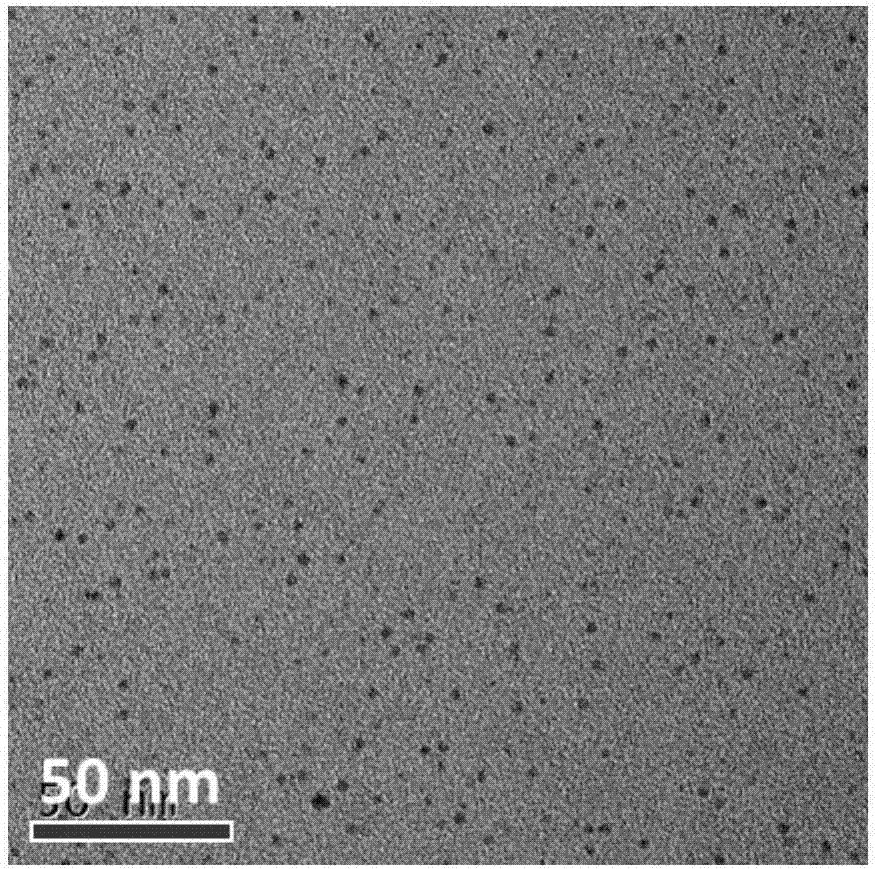
The invention belongs to the field of nano-biological materials, and discloses a method for preparing small-sized nano-hydroxyapatite by using carbon dots (CDs) as a template. The method comprises thefollowing steps: weighing solids H2N(CH2)10COOH and NaOH and dissolving in deionized water, then adding a citric acid solution and stirring for reacting, collecting white precipitate, drying, grinding, and then carrying out a thermal oxidization reaction at 300 DEG C to obtain the CDs; adjusting the pH of a Ca(NO3)2 solution to 10.5 with an alkaline solution, then dropwise adding the CDs to carryout a complexation precipitation reaction, dropwise adding an Na3PO4 solution, carrying out a hydrothermal reaction at 140 to 180 DEG C, and washing and drying a product to obtain the small-sized nano-hydroxyapatite. Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles prepared by the method are shaped like short rods, are smaller in size than particles without the CDs, can be reduced in particle size through the increase of the CD content, and have a potential application prospect in the field of nanomedicine.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method and application of reduction-sensitive drug delivery system with high drug loading rate
InactiveCN107669626AHigh drug loadingIncrease profitOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPolyethylene glycolBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a reduction-sensitive drug delivery system with a high drug loading rate, belonging to the technical field of biomedicine and nanomedicine. According to a technical scheme in the invention, 2,2-dihydroxyethyl disulfide is bonded with camptothecin via a carbonate bond to construct a camptothecin dimer with reduction sensitivity; and then the camptothecin dimer is encapsulated into an amphiphilic block copolymer polyethylene glycol-polycaprolactone by using a dialysis method so as to prepare the reduction-sensitive drug delivery system with a high drug loading rate, wherein the camptothecin dimer has a structure formula as described in the specification. The invention also specifically discloses application of the reduction-sensitive drug delivery system with a high drug loading rate to preparation of sustained-release and controlled-release drugs with targeted anti-cancer effect. Compared with a camptothecin delivery system, the drug loading rate of the drug delivery system provided by the invention is increased from 1% to 12.6%, and the drug delivery system has reduction sensitivity, good biocompatibility and capacityof inhibiting proliferation of tumor cells.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Bacterium-photothermal nanoparticle composite and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN111358811AImprove securityImprove targetingPowder deliveryBacteria material medical ingredientsTumor therapyEngineering
The present invention provides a bacterium-photothermal nanoparticle composite and a preparation method and an application thereof, and relates to the technical field of nanomedicine. The bacterium-photothermal nanoparticle composite comprises photothermal nanoparticles and bacteria. The bacteria and the photothermal nanoparticles are connected by chemical bonds A technical problem of a poor therapeutic effect of using the bacteria to treat tumors currently is solved. In the provided bacterium-photothermal nanoparticle composite, safety and targeting of the bacteria in body are improved and combination of bacterial therapy and photothermal therapy are combined by chemically bonding the photothermal nanoparticles to the bacteria, and at the same time, the bacterium-photothermal nanoparticlecomposite can also trace and image the bacteria and tumors, and can effectively improve effectiveness of tumor treatment.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Multi-modality imaging microbubble structure, preparation method and applications
InactiveCN102772808AStable in natureEasy to storeEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsEmulsion deliverySolubilityFreeze-drying
The invention relates to the cross field of chemical engineering, materials and nanomedicines, and specifically discloses a multi-modality imaging probe structure and a preparation method thereof. A multi-modality imaging probe is a microbubble with a putamen structure, a shell membrane material is composed of a high polymer material and a phospholipid material which are biodegradable and good in biocompatibility, water-solubility quantum dot solutions with different fluorescent characteristics are embedded at the center, a perfluor carbon alkyl gas is fed, and the multi-modality probe which is controllable in grain diameter, good and stable in dispersion and easy to store are prepared by a double-emulsion-freeze-drying gas feeding method. According to the multi-modality imaging probe structure the preparation method thereof, the microbubble is a reticuloendothelial system specificity contrast agent, the fluorescent imaging is achieved, the enhancement for ultrasonoscopy and magnatic resonance imaging (MRI) display and the microbubble multi-mode imaging can be achieved, and the multi-modality imaging probe structure the preparation method thereof have a wide application prospect.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Flexible mesoporous organosilicone nanorods and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109771666ALower requirementLow costPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsIn-vivo testing preparationsGold nanorodYoung's modulus
The invention discloses flexible mesoporous organosilicone nanorods and a preparation method and application thereof. The flexible mesoporous organosilicone nanorods have a stick-like morphology, crimping surfaces, large internal cavities and mesoporous channels; during preparation, gold nanorods are used as an inner core, a flexible mesoporous organic silicon oxide shell layer is obtained throughetching of an alkaline solution, and a skeleton contains organic silicon oxide and inorganic silicon oxide at the same time. The preparaiton technology process of the flexible mesoporous organosilicone nanorods is simple, the finished product is lower in Young modulus and higher in cytophagy efficiency, and the flexible mesoporous organosilicone nanorods have a great application potential in thefields of drug delivery, nanometer medical imaging and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Targeted Nanocarriers For Targeted Drud Delivery Of Gene Therapeutics
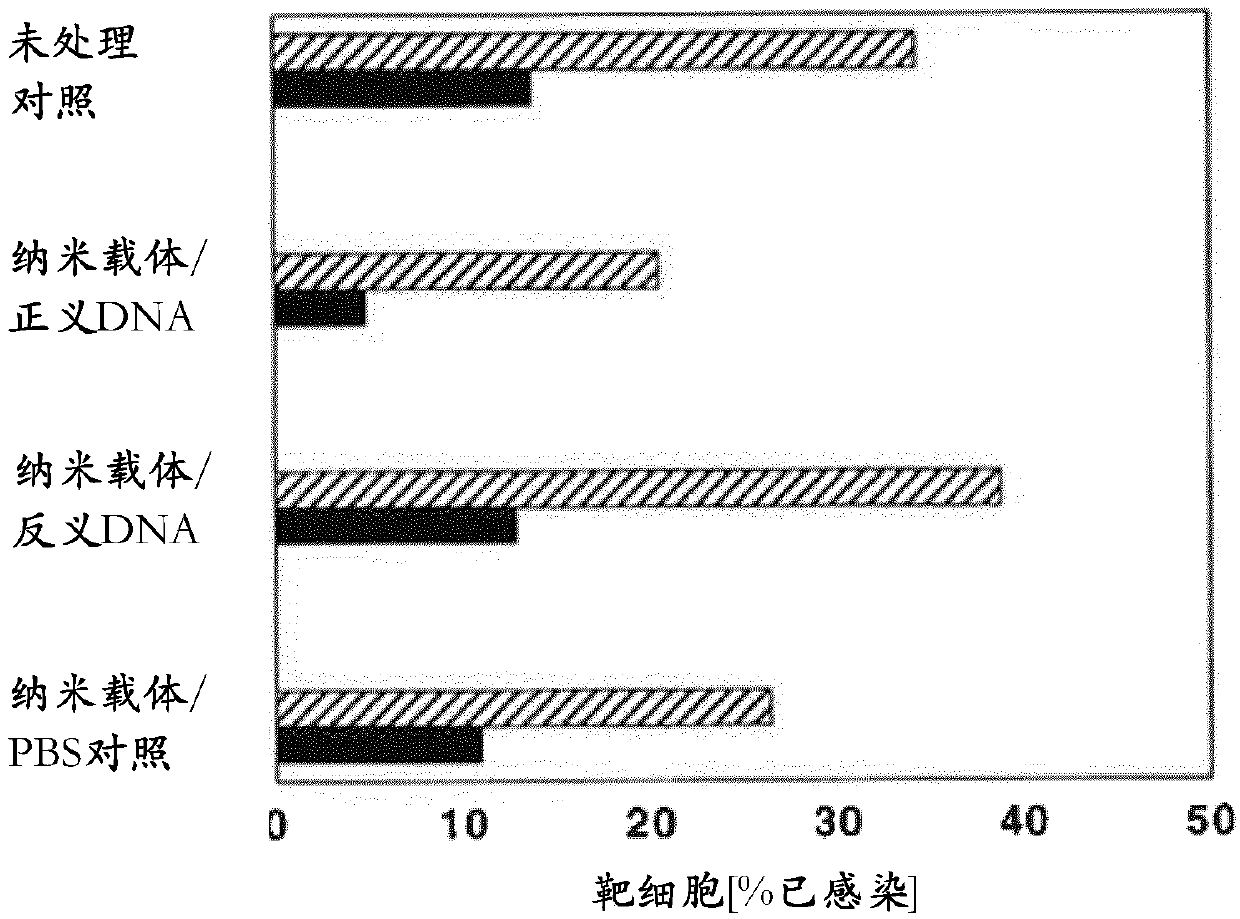
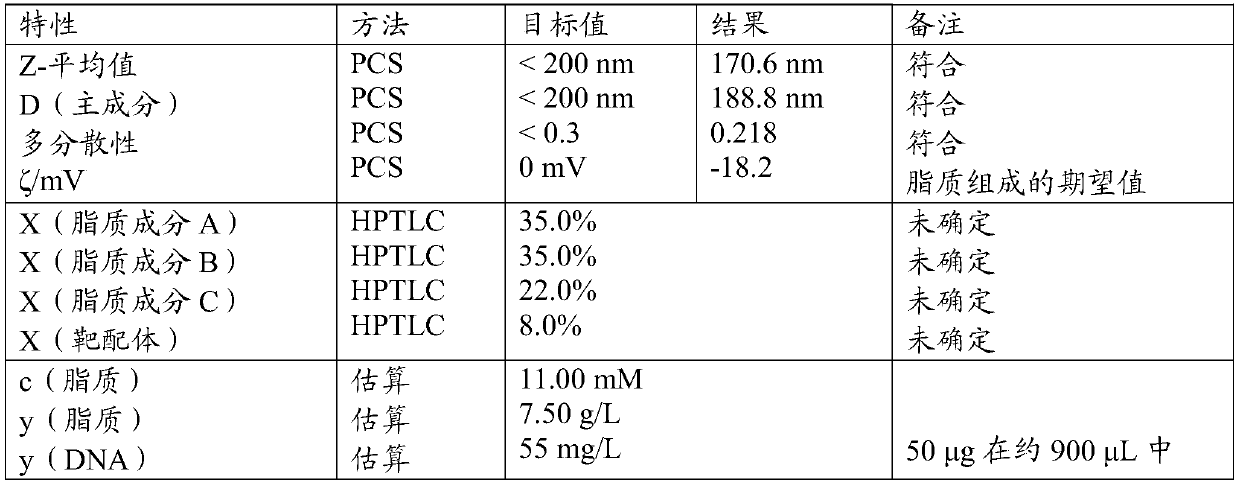
The present invention relates to targeted nanocarriers - also termed nanomedicines - and methods of preferentially, or actively, targeting and delivering a tool for gene transfer or genome editing (i.e., a plasmid or a restriction enzyme - such as a zinc finger nuclease, a CRISPR / Cas system, or a TALEN) or a tool for gene silencing or post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression (i.e., a microRNA, a siRNA, a mRNA, an antisense oligonucleotide, or a sense oligonucleotide) to a range of mammalian cell species. Cell- specific targeting is achieved by using nanocarriers featuring suitable targeting anchors having a targeting moiety that can be a carbohydrate, an antibody or an antibody fragment, a non-antibody protein derivative, an aptamer, a lipoprotein or a fragment thereof, a peptidoglycan, a lipopolysaccharide or a fragment thereof, or a CpG DNA. Such targeting anchors may or may not include a polymeric spacer like polyethylene glycol. The nanomedicines shall allow to therapeutically address a range of mammalian disease entities via various application routes. These indications include malignant diseases, autoimmune diseases, inherited disorders, metabolic disorders, or infectious diseases.
Owner:RODOS BIOTARGET
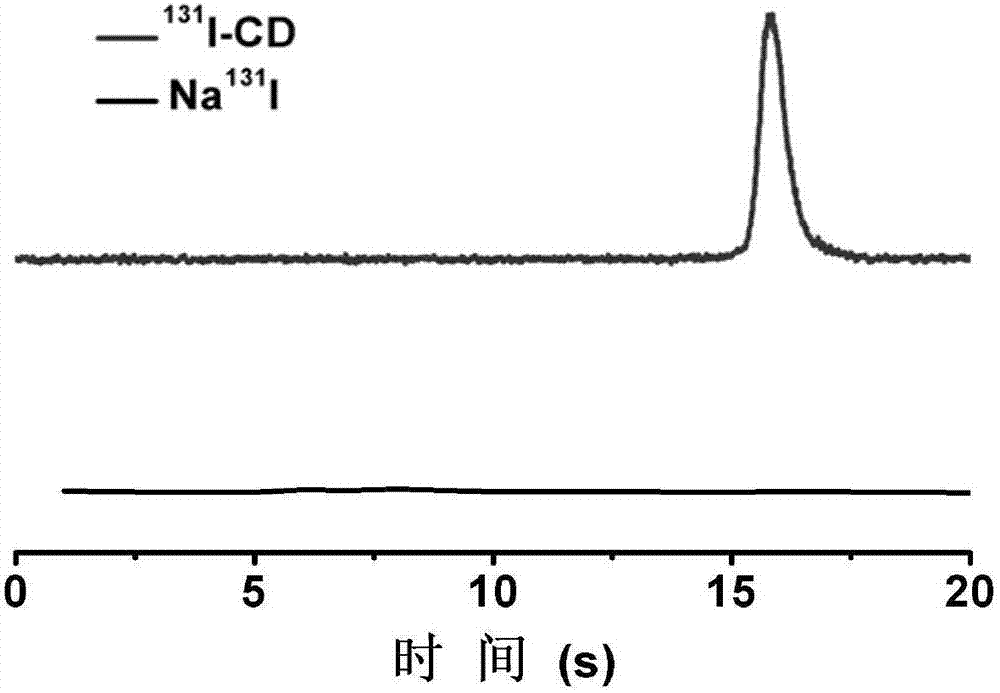
Fluorescent carbon dot for labeling of radionuclide iodine, synthetic method and application
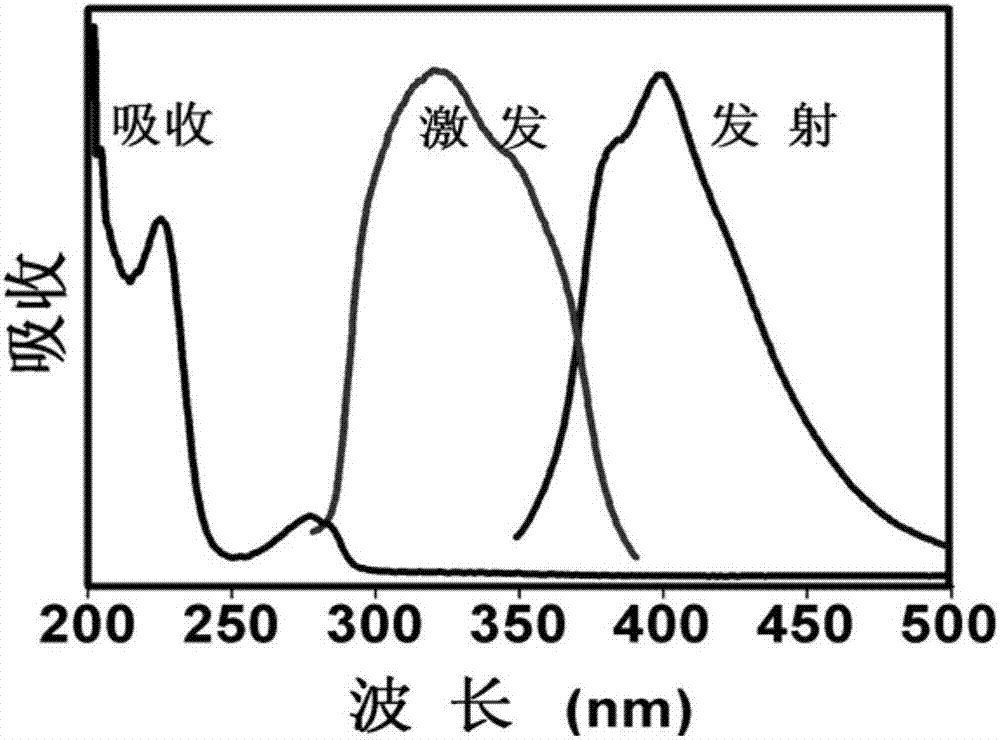
ActiveCN107118767AHigh fluorescence yieldGood water solubilityRadioactive preparation carriersLuminescent compositionsPhoton emissionBiocompatibility
The invention belongs to the field of nano-medicine and molecular imaging, and particularly relates to a fluorescent carbon dot for labeling of radionuclide iodine, a synthetic method of the fluorescent carbon dot and application in tumor imaging. The carbon dot is synthesized in one step and can be directly labeled with radionuclide iodine. A labeled product has excellent radiochemical stability and physicochemical stability and can be directly used for 124I-based PET (positron emission tomography), SPECT(125I-based single-photon emission computed tomography) imaging and 131I radiotherapy of a tumor region. The synthetic method of the fluorescent carbon dot is simple, price of raw materials is low, fluorescence efficiency is high, and biocompatibility is good; the fluorescent carbon dot has the advantage of rapid metabolism in vivo like small molecules, and can also be well enriched in the tumor region by effects of high permeability and long retention of nanoparticles to diagnose and treat a tumor.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com