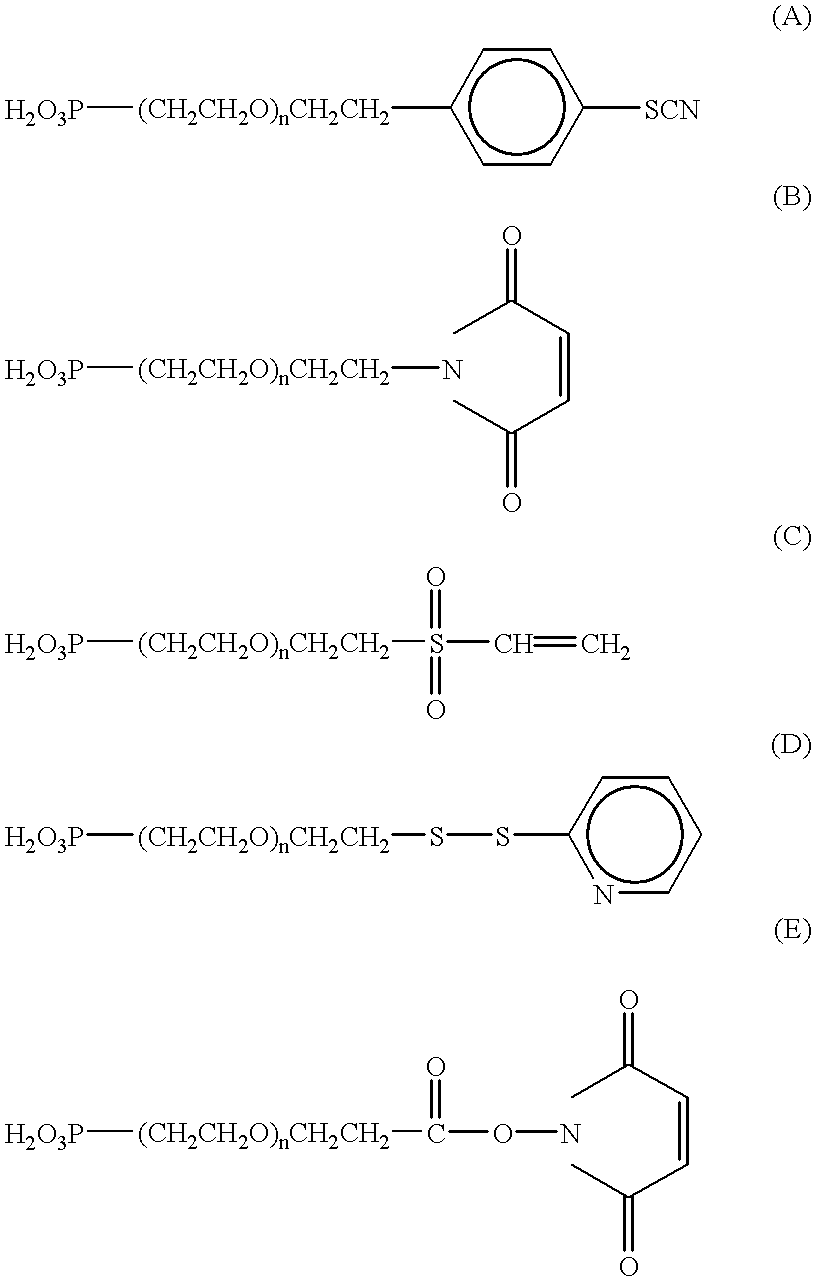
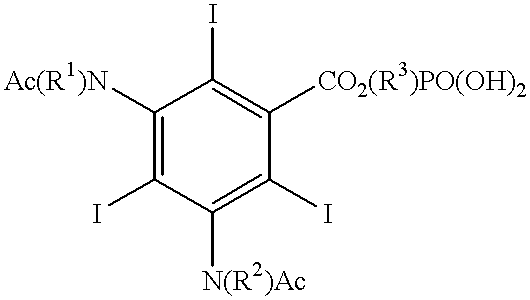
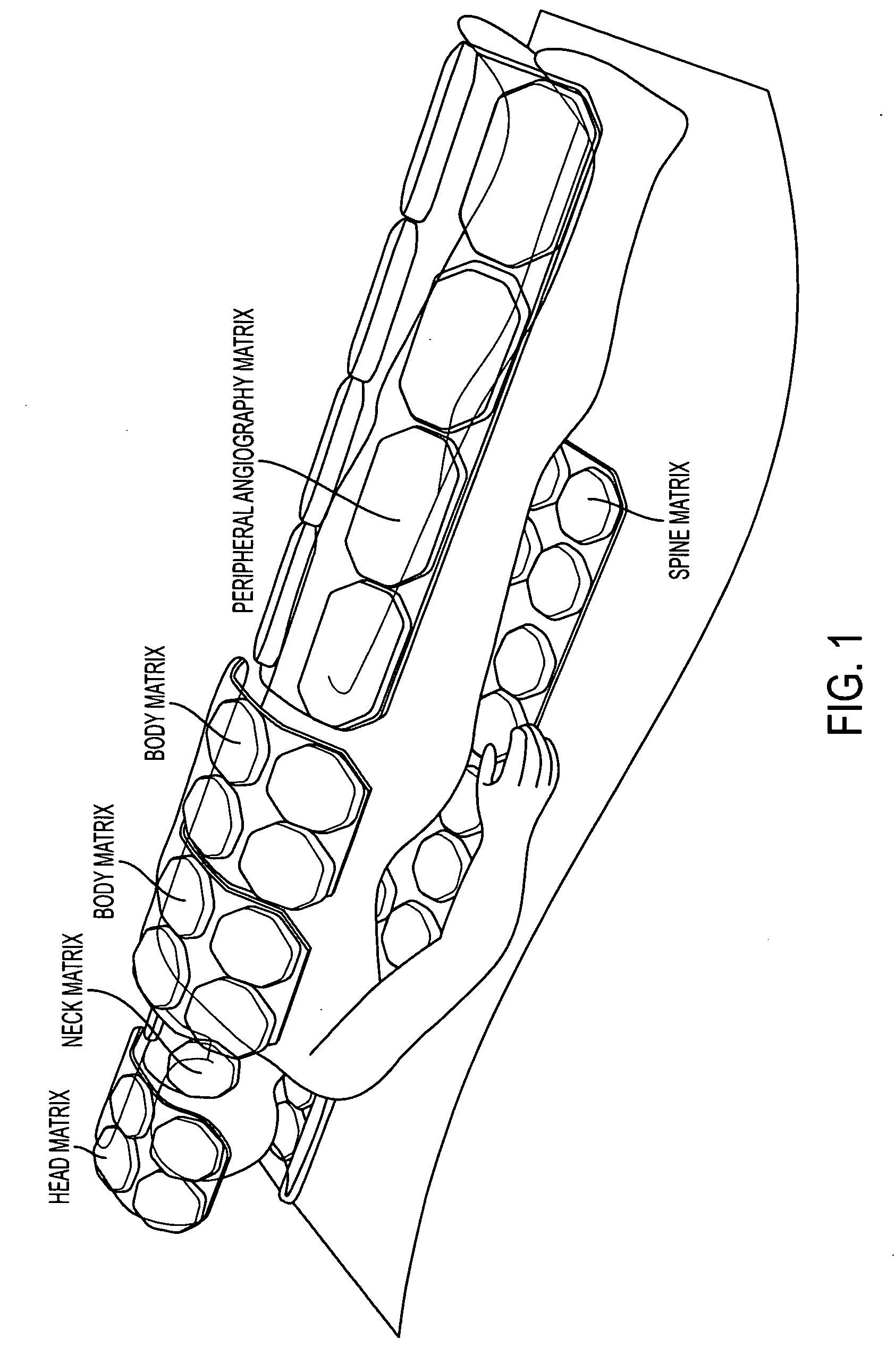
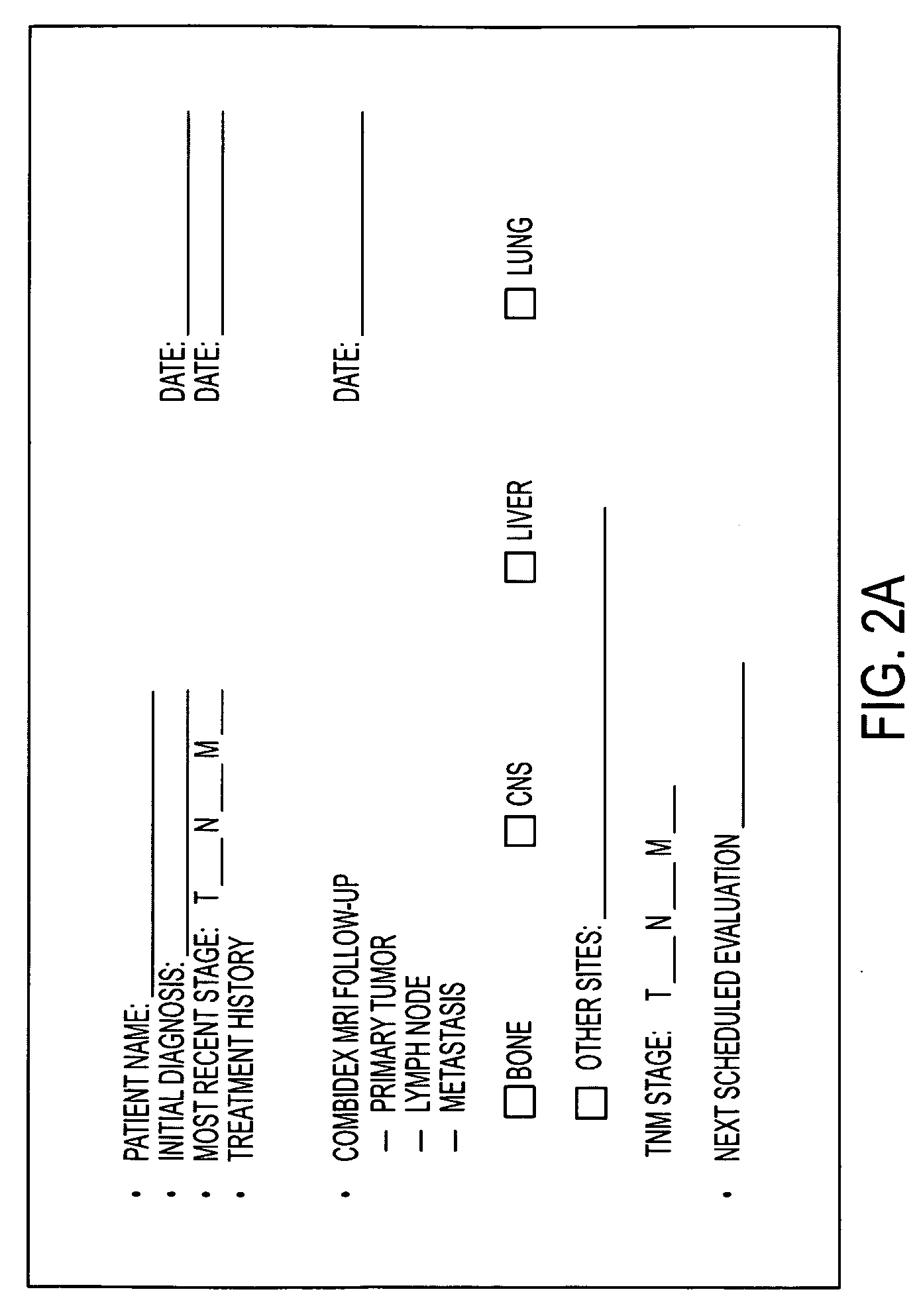
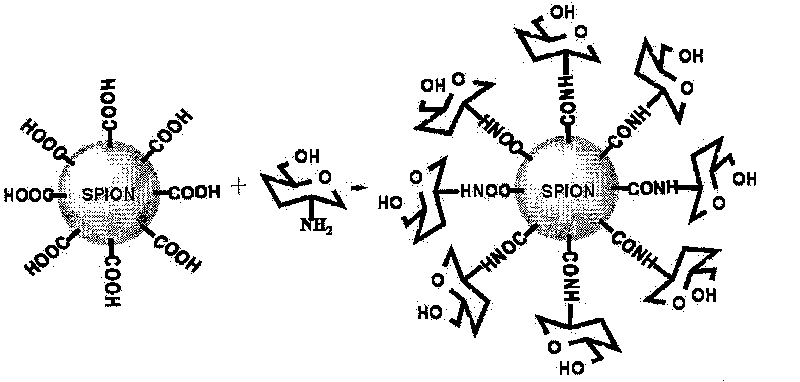
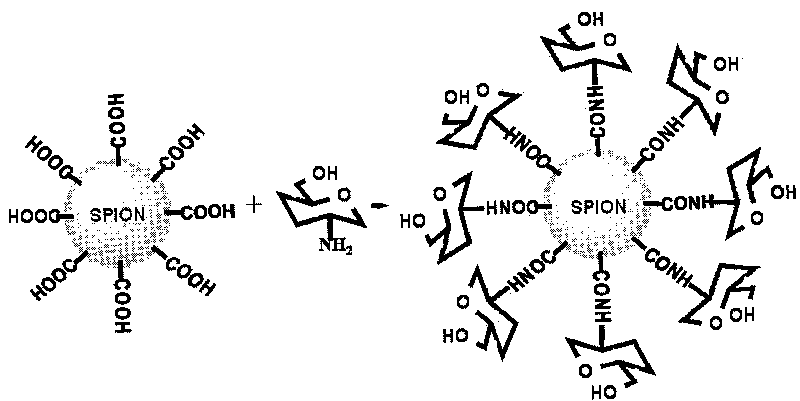
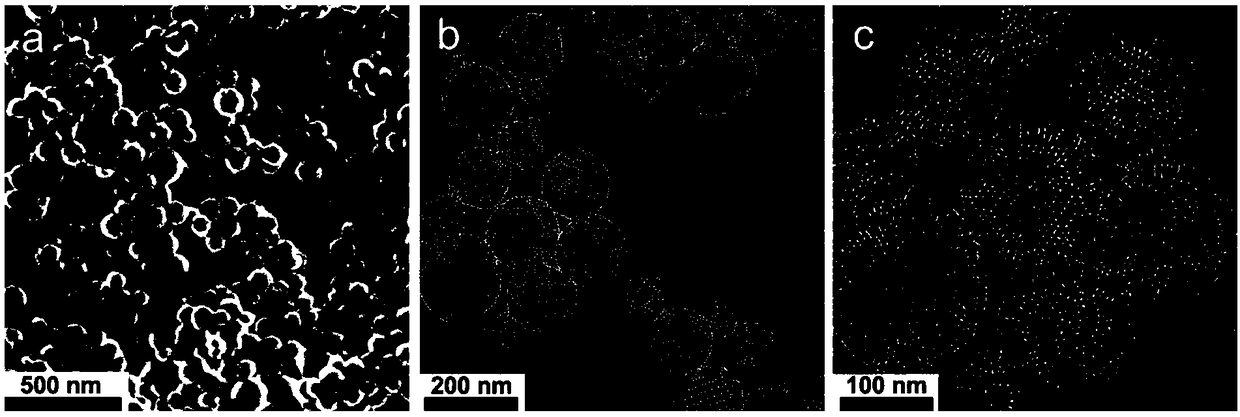
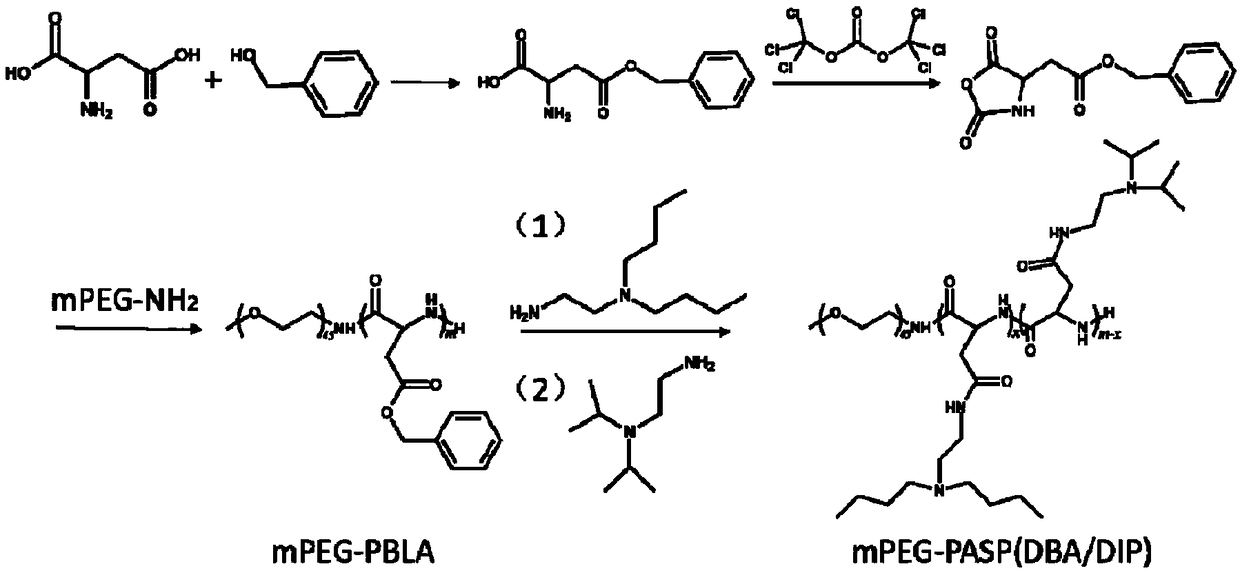
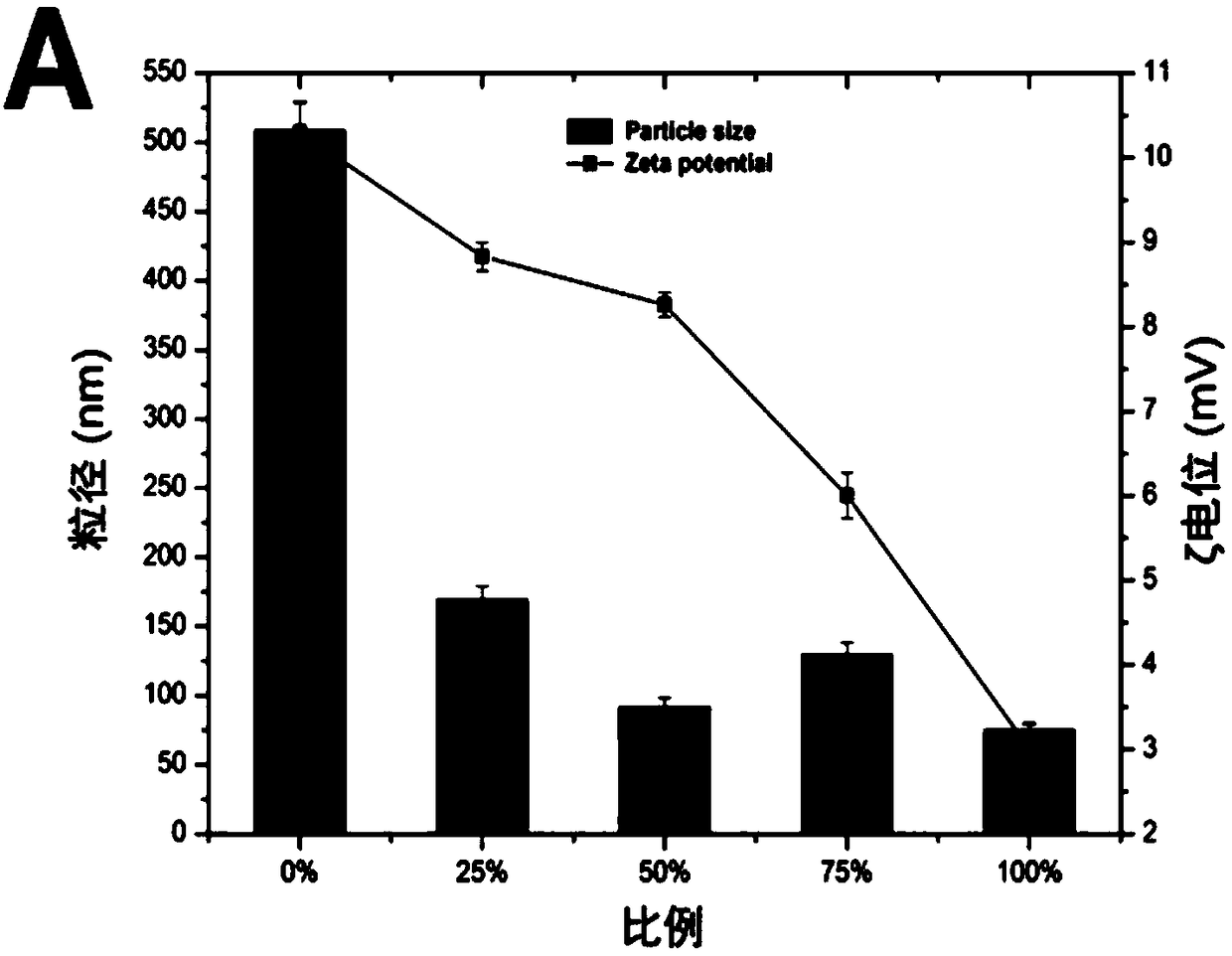
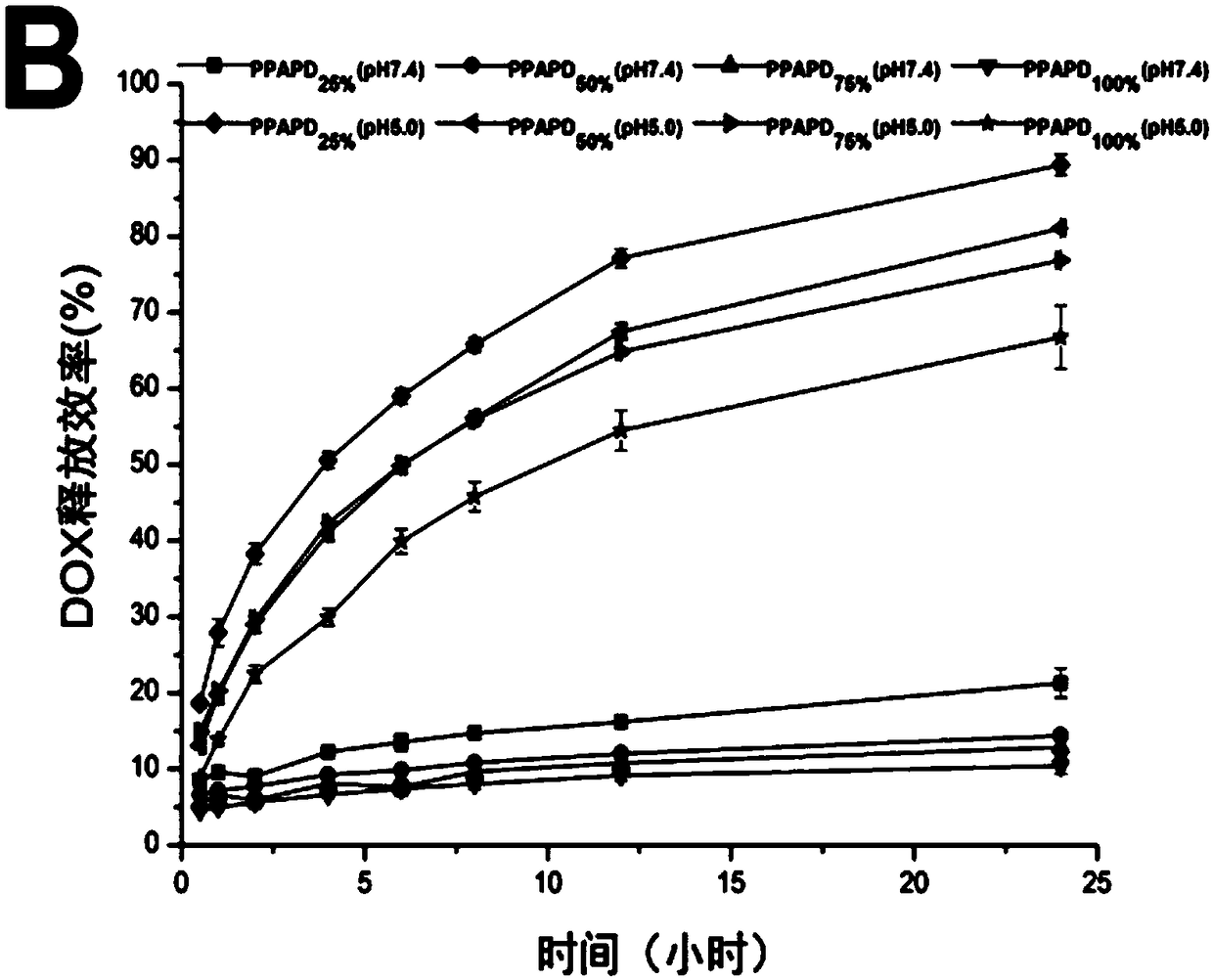
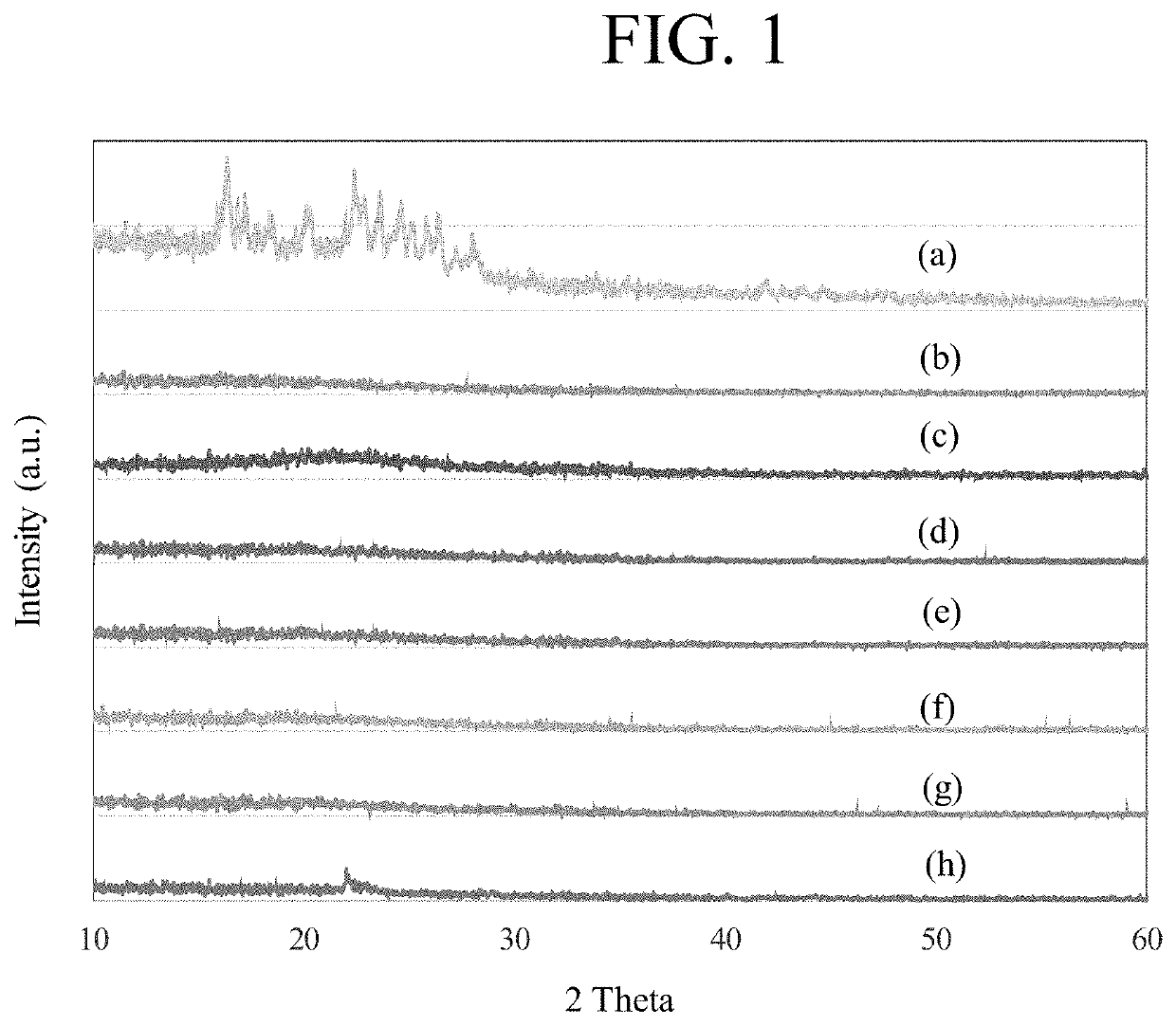
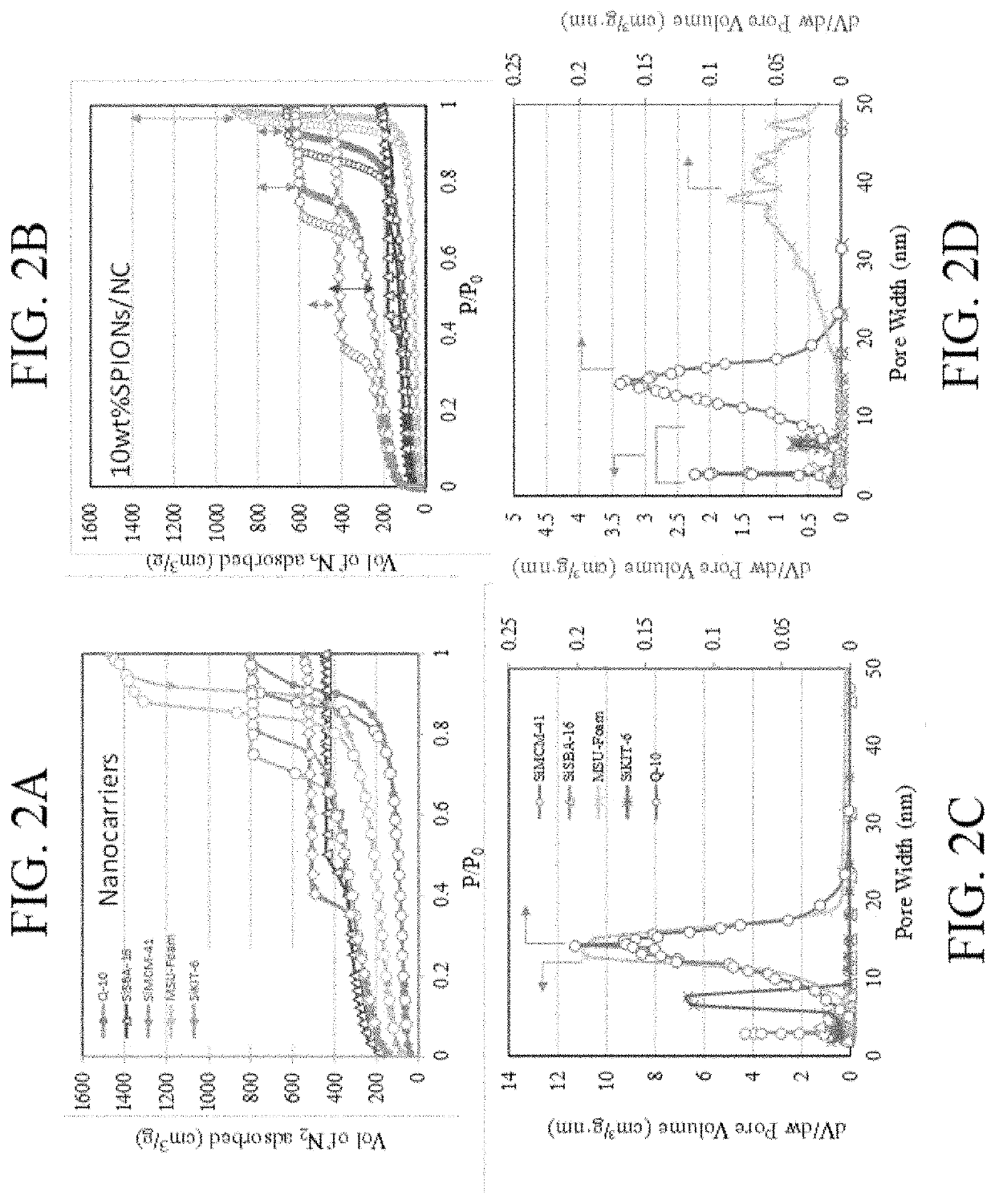
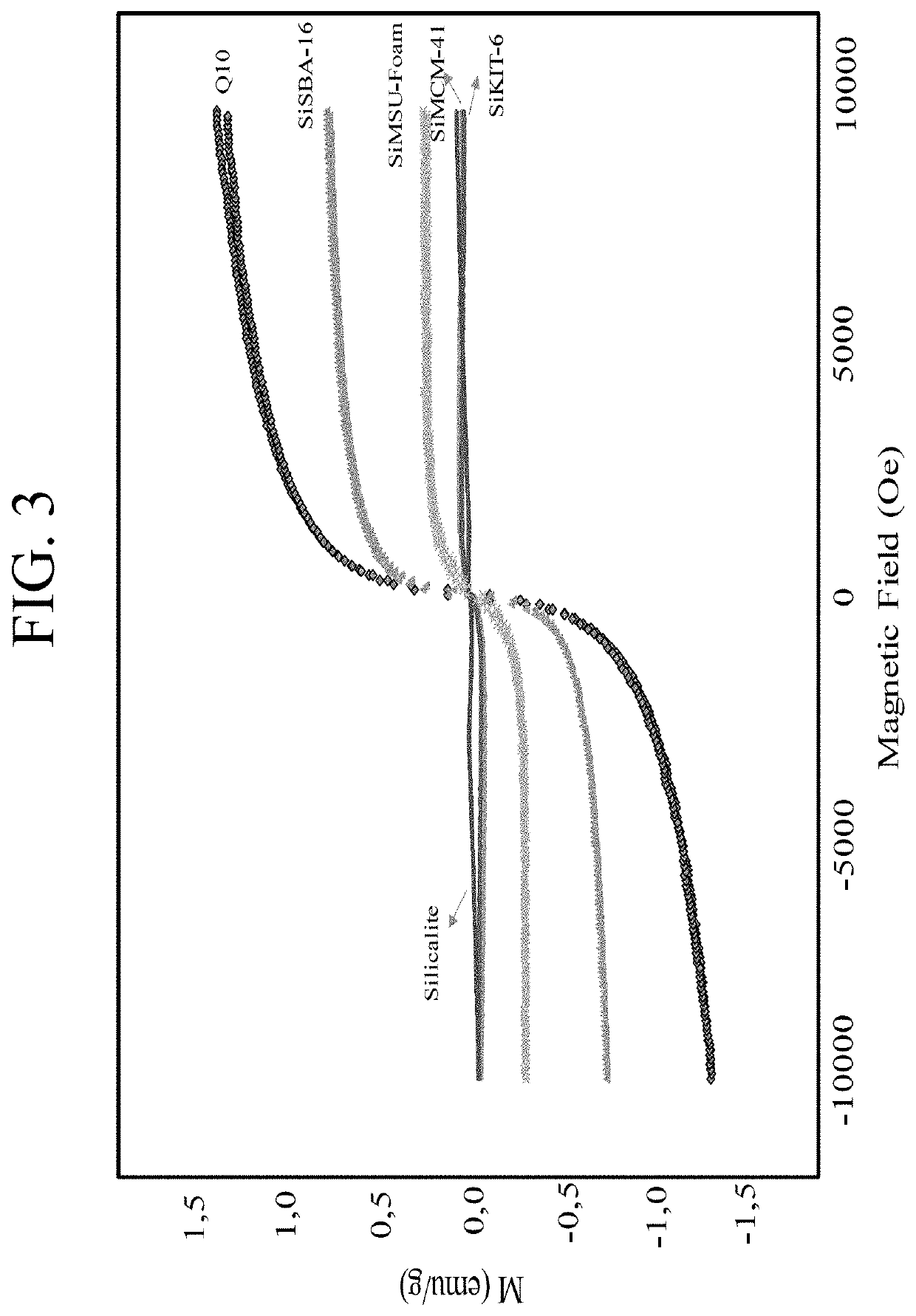
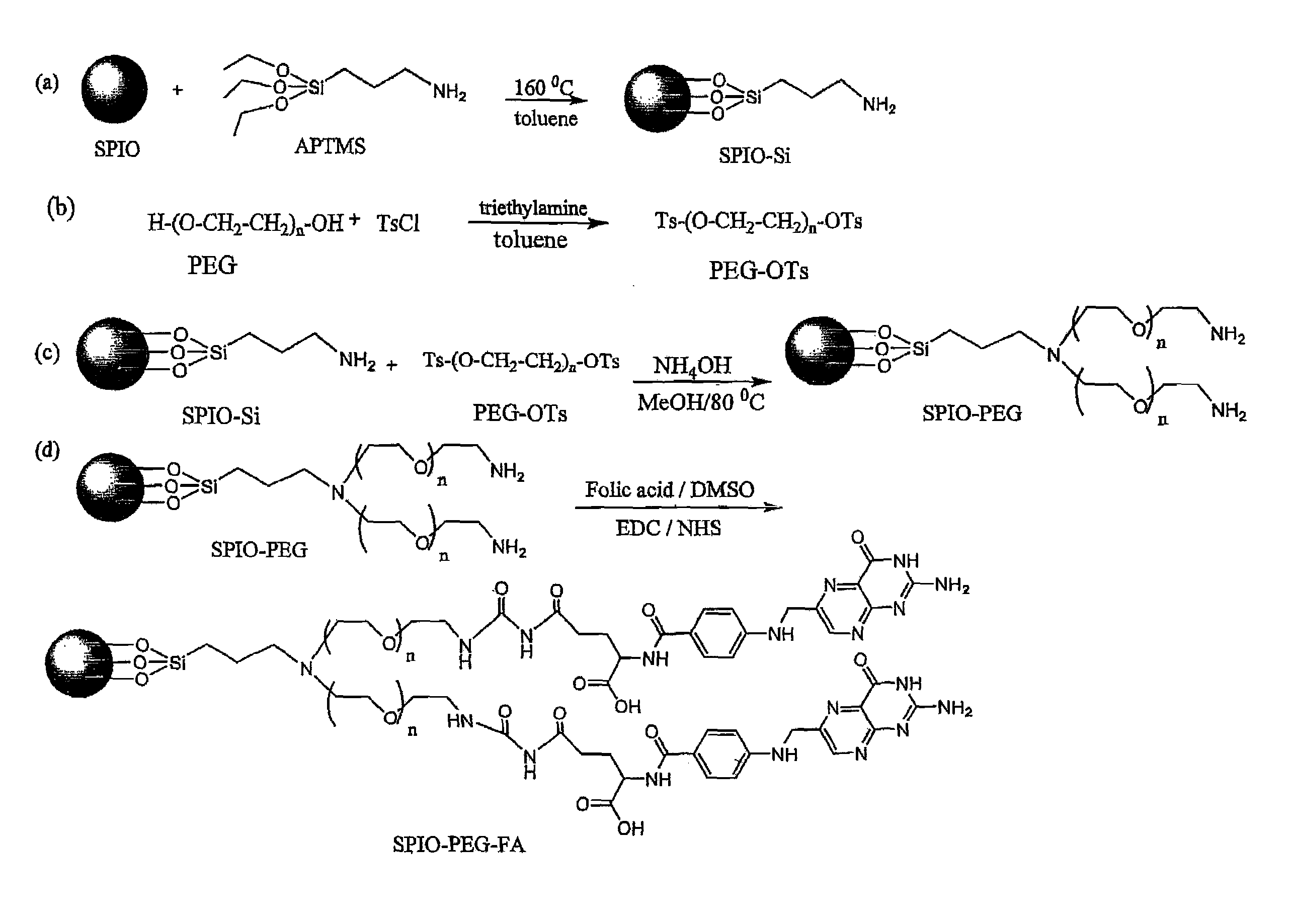
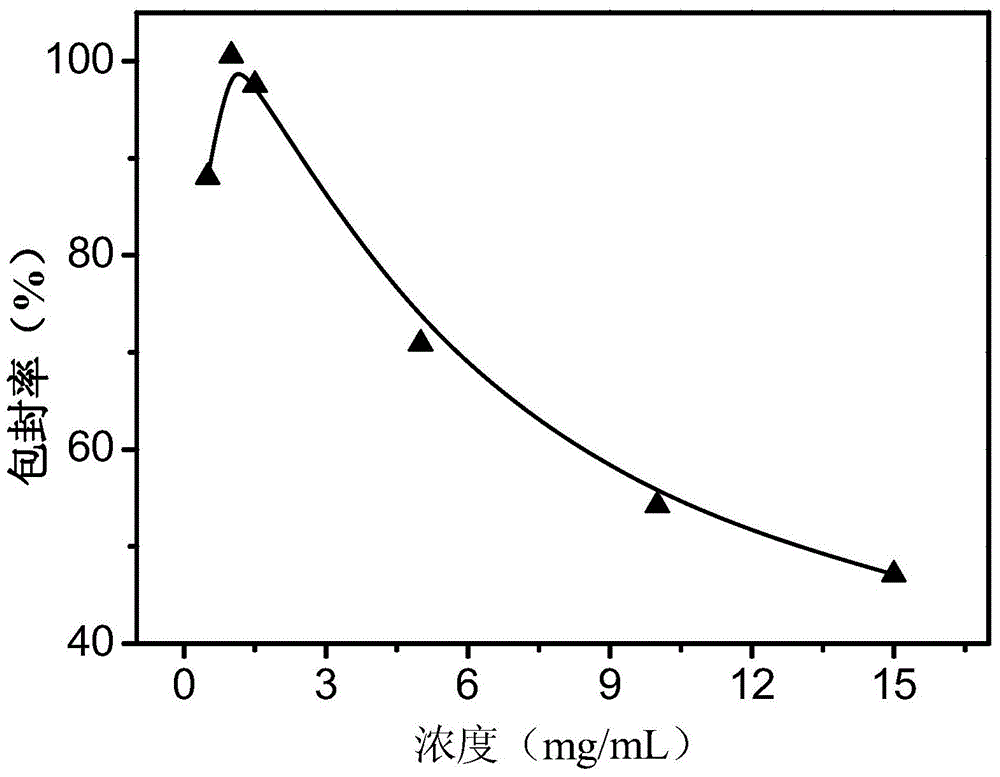
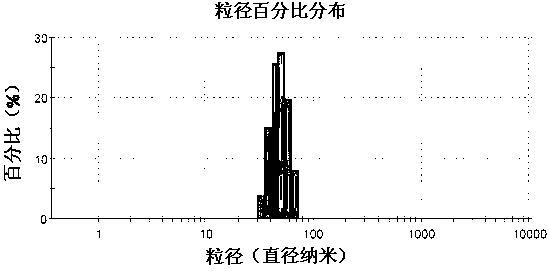
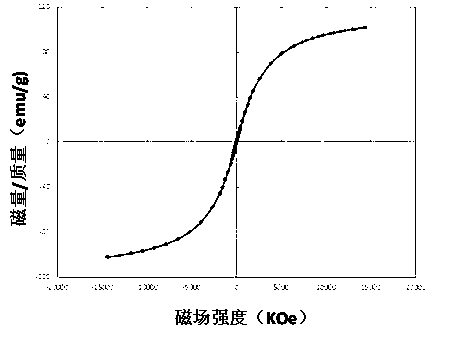
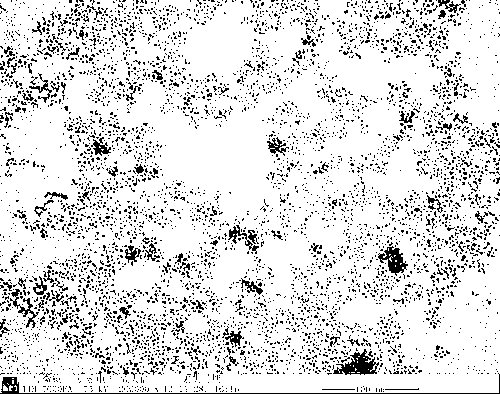
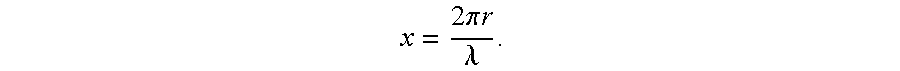Patents
Literature
158 results about "Superparamagnetic iron oxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
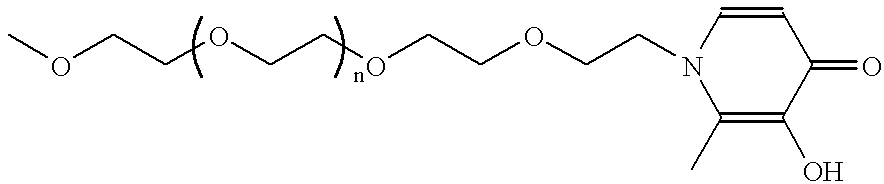
Superparamagnetic contrast media coated with starch and polyalkylene oxides
The invention relates to MR contrast media containing composite nanoparticles, preferably comprising a superparamagnetic iron oxide core provided with a coating comprising an oxidatively cleaved starch coating optionally together with a functionalized polyalkyleneoxide which serves to prolong blood residence.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE AS
Constrast media
InactiveUS6423296B1Increase productionPowder deliveryBiocideOxidative cleavageComposite nanoparticles
The invention relates to MR contrast media containing composite nanoparticles, preferably comprising a superparamagnetic iron oxide core provided with a coating comprising an oxidatively cleaved starch coating optionally together with a functionalized polyalkyleneoxide which serves to prolong blood residence.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE AS
Imaging inflammatory conditions using superparamagnetic iron oxide agents
InactiveUS20060093555A1Low toxicityImprove toleranceNanomedicineDiagnostic recording/measuringImaging conditionIron agent
The present invention is directed to the field of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) using superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) agents. In particular, the present invention is directed to cationic, nonagglomerated, nontoxic SPIO agents, methods for imaging conditions associated with inflammatory responses using the disclosed SPIO agents, and methods for managing inflammatory conditions using the disclosed SPIO agents.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Injectable superparamagnetic nanoparticles for treatment by hyperthermia and use for forming an hyperthermic implant
The injectable formulation for treatment by hyperthermia comprises a liquid carrier and heat-generating superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles having a mean diameter not greater than 20 nm. Said injectable formulation is able to form in-situ a hyperthermic solid or semi-solid implant upon contact with a body fluid or tissue. Said hyperthermic solid or semi-solid implant may be useful for treating a tumor or a degenerative disc disease by hyperthermia.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA +2
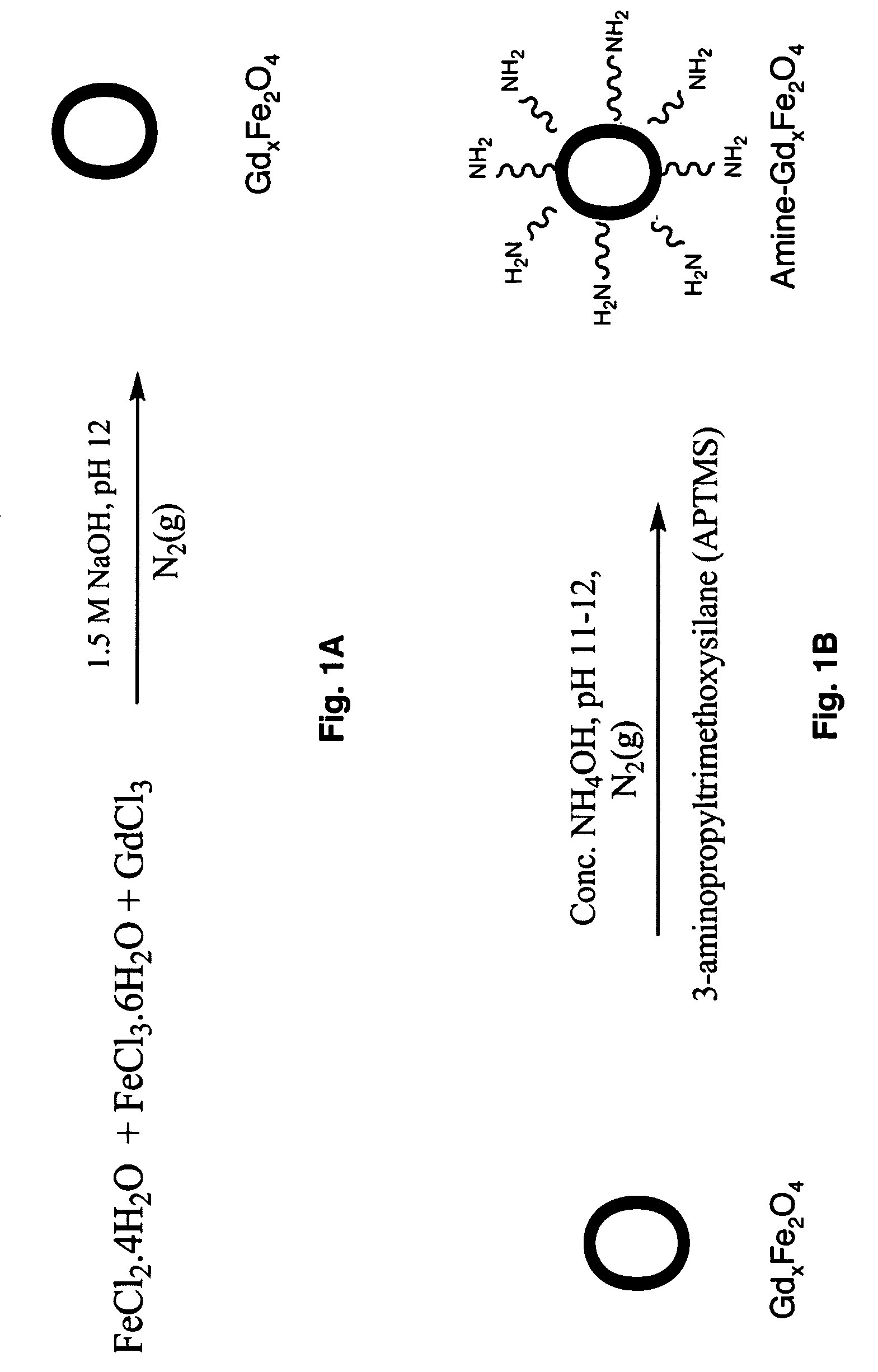
Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and uses thereof
Owner:HOUSTON SYST UNIV OF
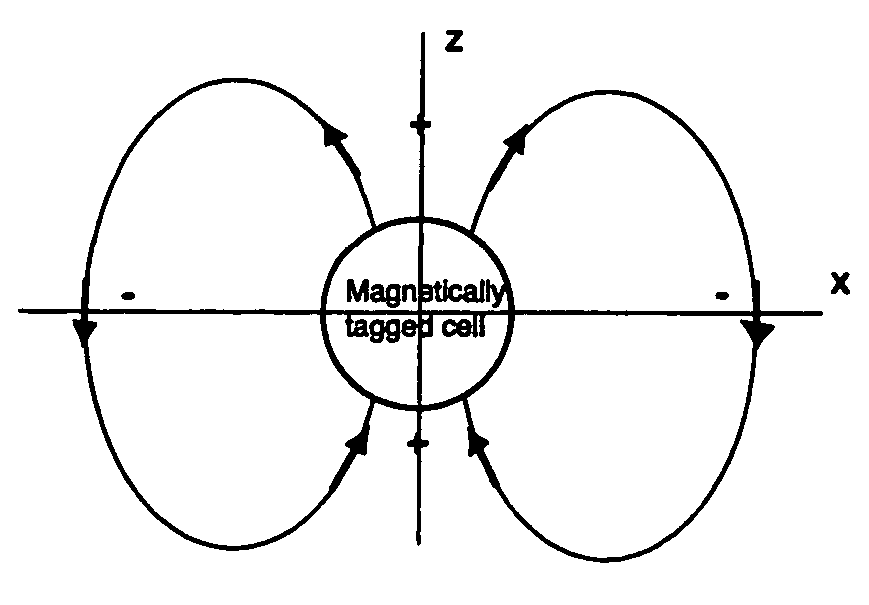
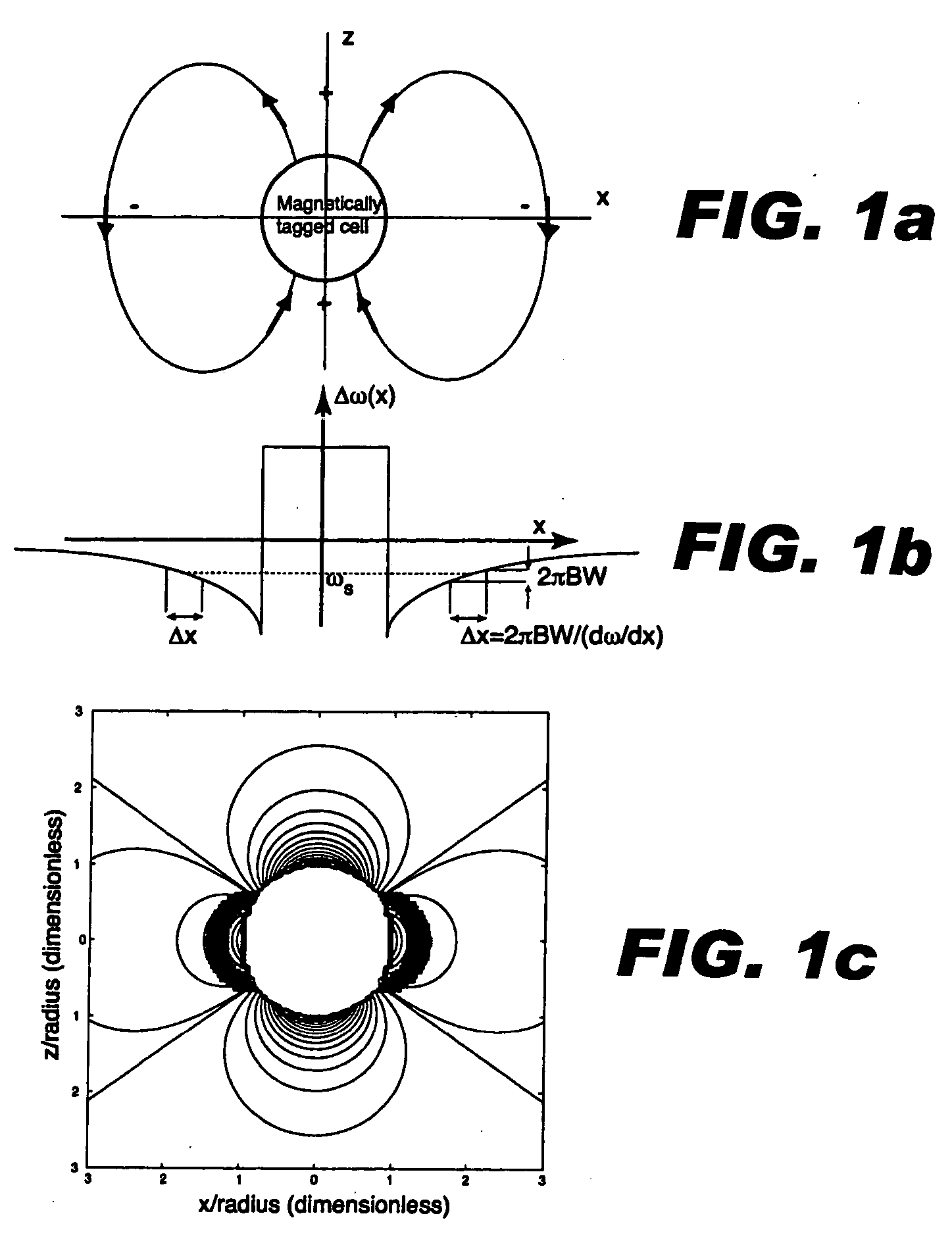
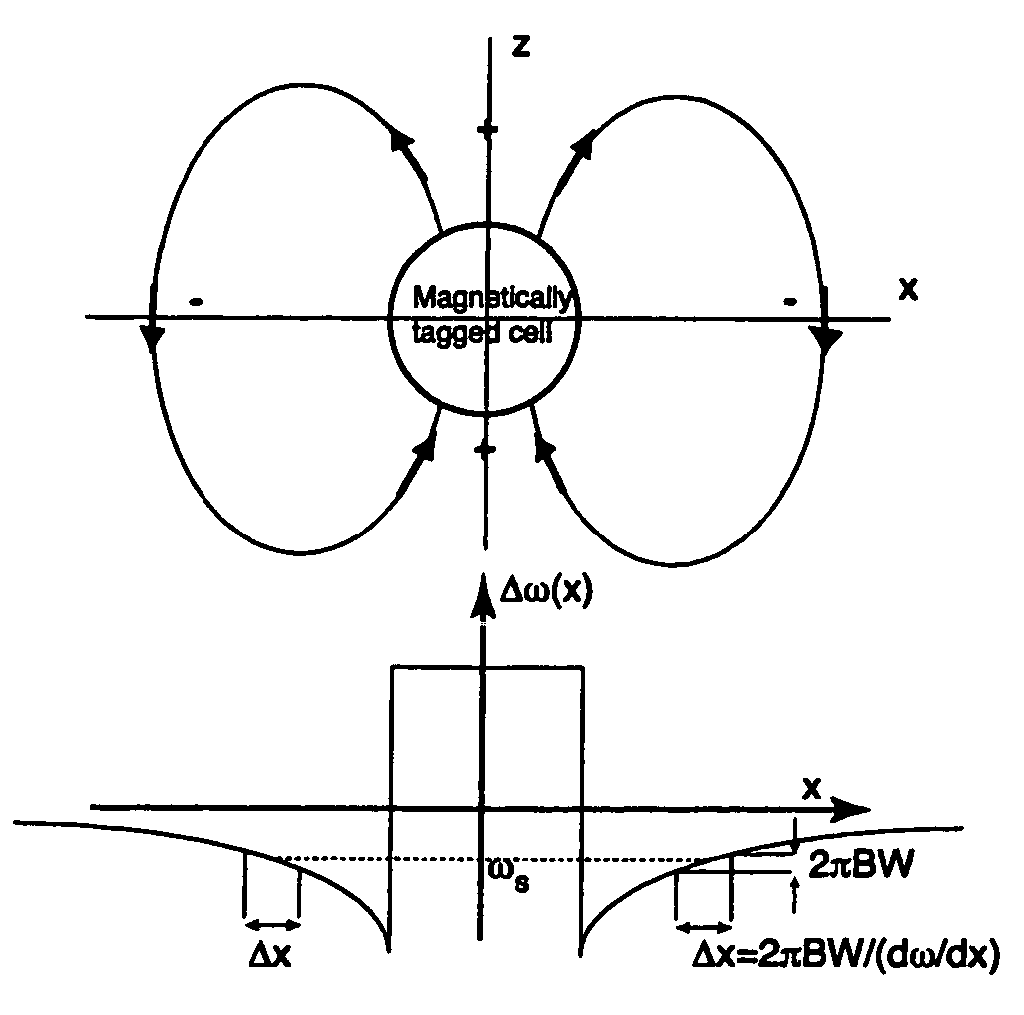
Positive contrast MRI of magnetically tagged cells, objects, tissues
ActiveUS20050261575A1Positive contrastReadily apparentDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNegative Contrast AgentMagnetic marker
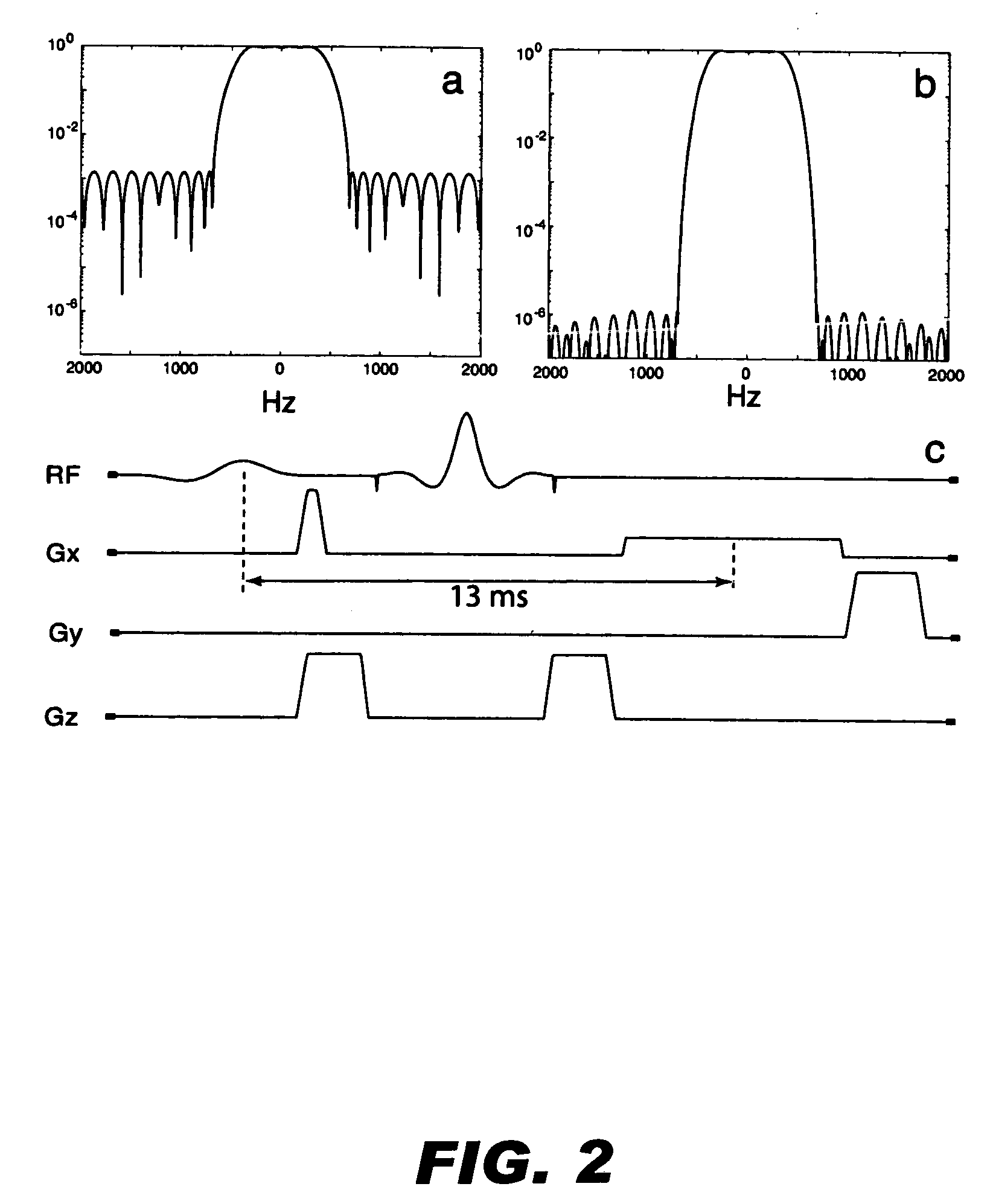
Contrast agents incorporating super-paramagnetic iron-oxide (SPIO) nanoparticles have shown promise as a means to visualize labeled cells using MRI. Labeled cells cause significant signal dephasing due to the magnetic field inhomogeneity induced in water molecules near the cell. With the resulting signal void as the means for detection, the particles are behaving as a negative contrast agent, which can suffer from partial-volume effects. Disclosed is a new method for imaging labeled cells with positive contrast. Spectrally-selective RF pulses are used to excite and refocus the off-resonance water surrounding the labeled cells so that only the fluid and tissue immediately adjacent to the labeled cells are visible in the image. Phantom, in vitro, and in vivo experiments show the feasibility of the new method. A significant linear correlation (r=0.87, p<0.005) between the estimated number of cells and the signal has been observed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and uses thereof
The present invention provides a biomimetic contrast agent comprising an amine-functionalized iron (II) oxide / iron(III) oxide nanoparticle core a targeting ligand attached to the nanoparticle core via a linker and an inert outer layer of a hydrophilic polymer conjugated to the targeting ligand and imaging methods using the biomimetic contrast agents. Also, provided is a dual functional contrast agent comprising a metal-doped iron (II) oxide / iron(III) oxide nanoparticle core, an inert layer of gold coating the nanoparticle core and a biodegradable cationic polymer linked thereto. The dual functional contrast agent is complexed to a therapeutic gene and when transfected into mesenchymal stem cells comprises a dual contrast agent and gene delivery system. In addition, methods of using the dual functional system are provided. Furthermore, kits comprising the biomimetic contrast agents and the dual contrast agent and gene delivery system are provided.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Hydrophilic polymer biomaterial having a specific magnetic resonance imaging signal and process for the preparation of said biomaterial
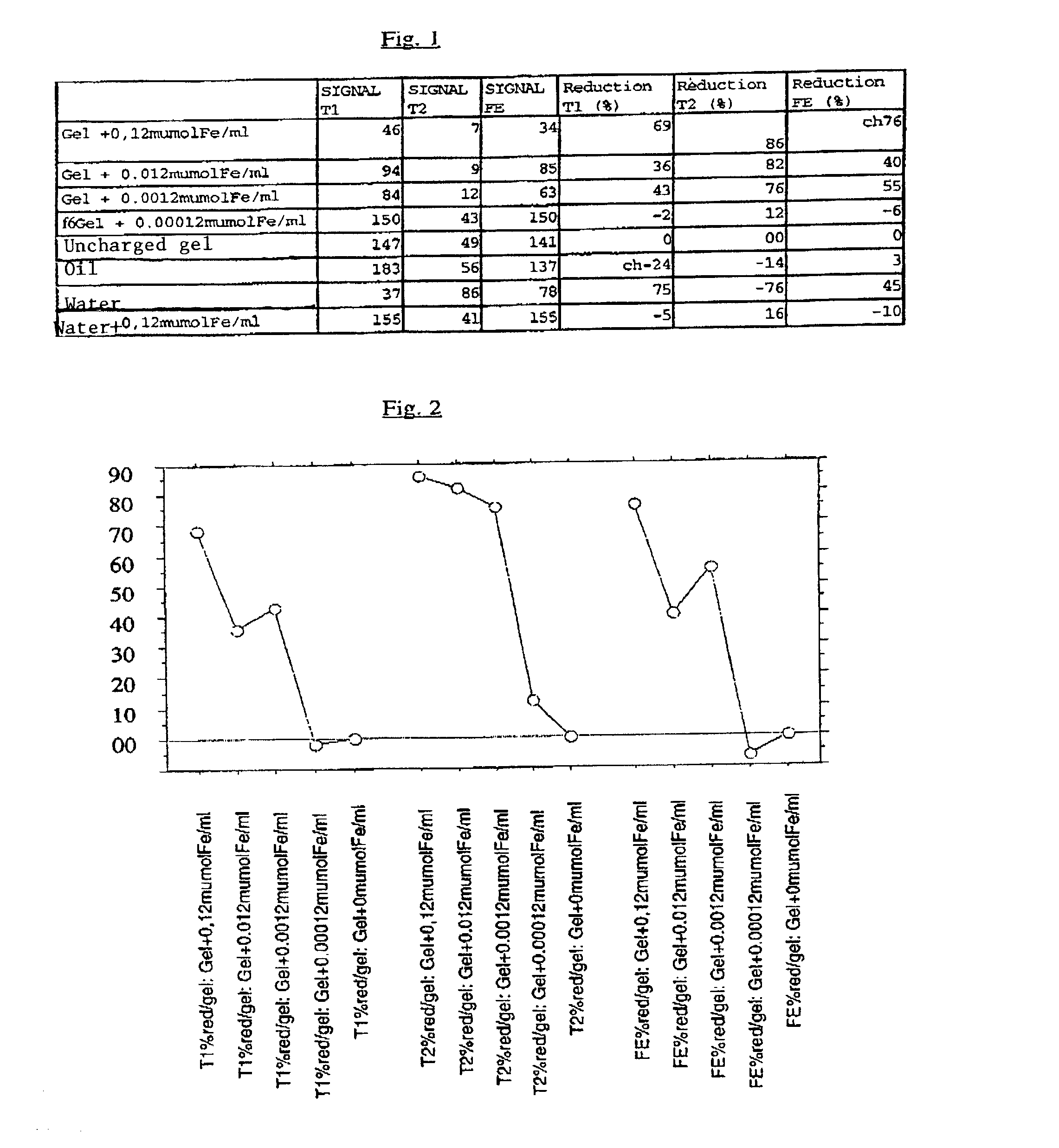
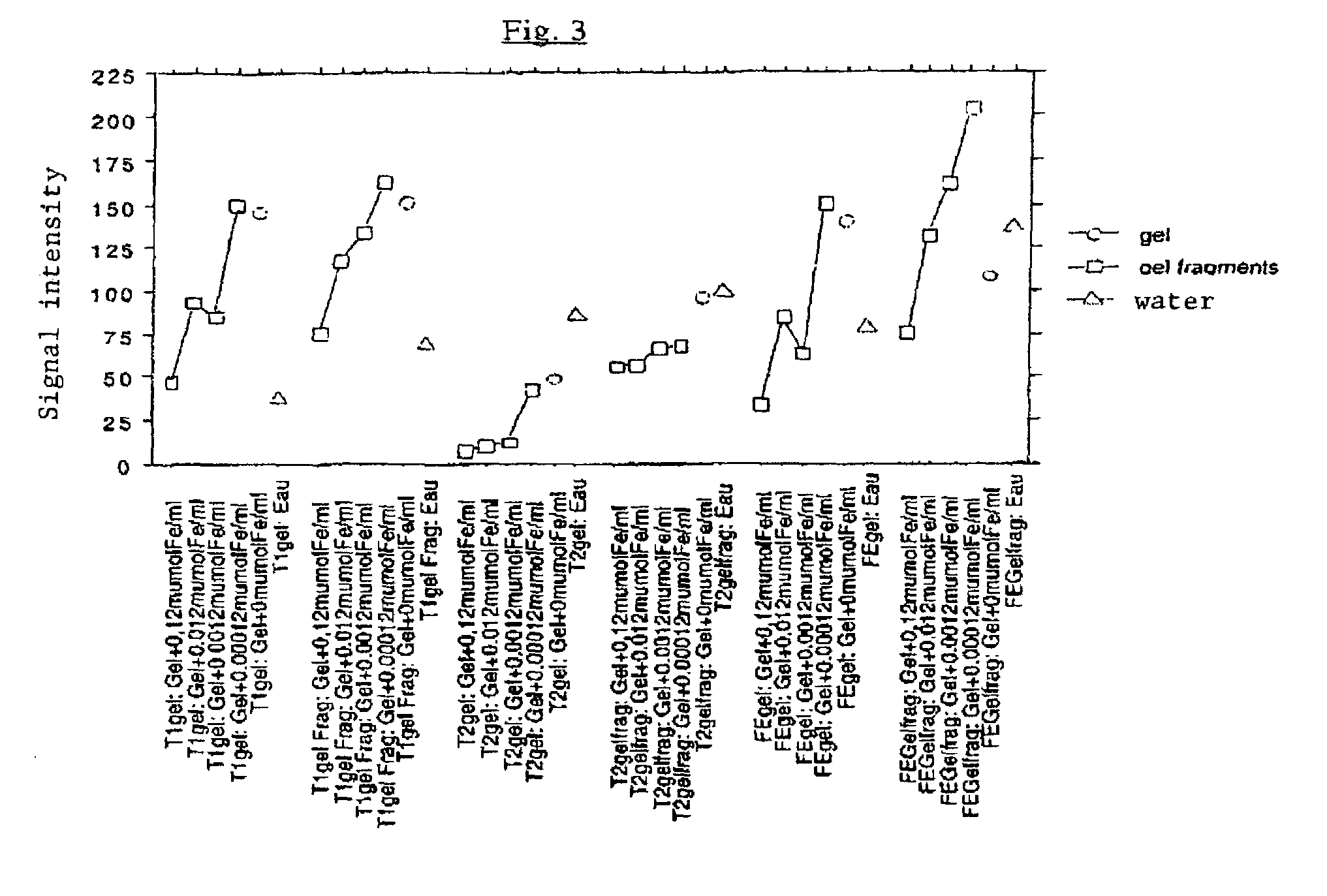
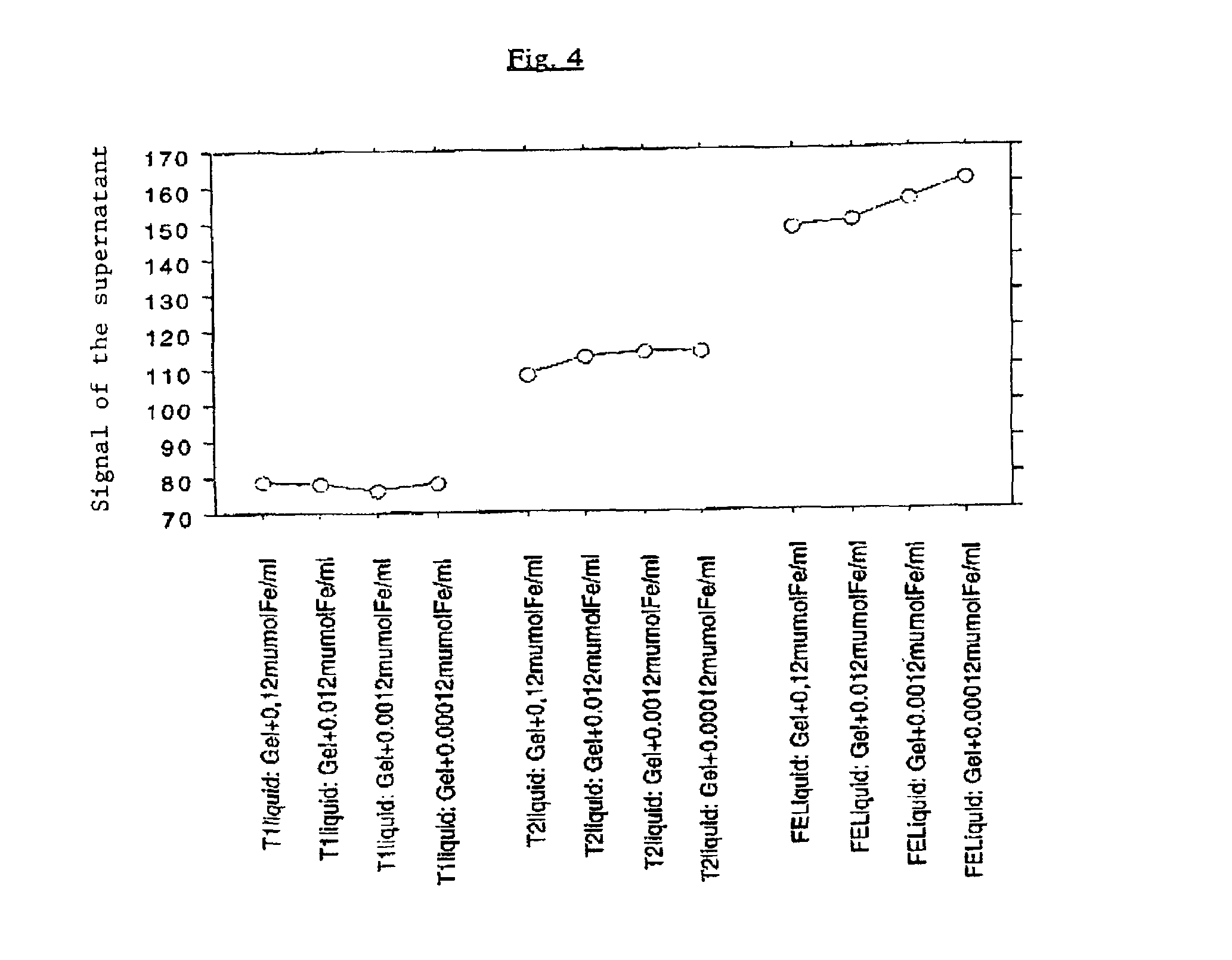
A charged biomaterial including at least one first hydrophilic polymer, and superparamagnetic iron oxide particles complexed with a second hydrophilic polymer substantially identical to or different from the first hydrophilic polymer, wherein the superparamagnetic iron oxide particles complexed with the second hydrophilic polymer are distributed substantially homogeneously and substantially without aggregates in the first hydrophilic polymer. A process for preparing a charged biomaterial including forming an aqueous solution of hydrophilic monomers and superparamagnetic iron oxide particles complexed with a hydrophilic polymer including monomers substantially identical to or different from the hydrophilic monomers, polymerizing the solution and forming a polymer hydrogel in which are distributed substantially homogeneously and substantially without aggregates the superparamagnetic iron oxide particles complexed with the hydrophilic polymer.
Owner:LASSISTANCE PUBLIQUE HOPITAUX DE PARIS ETAB PUBLIC DE SANTE
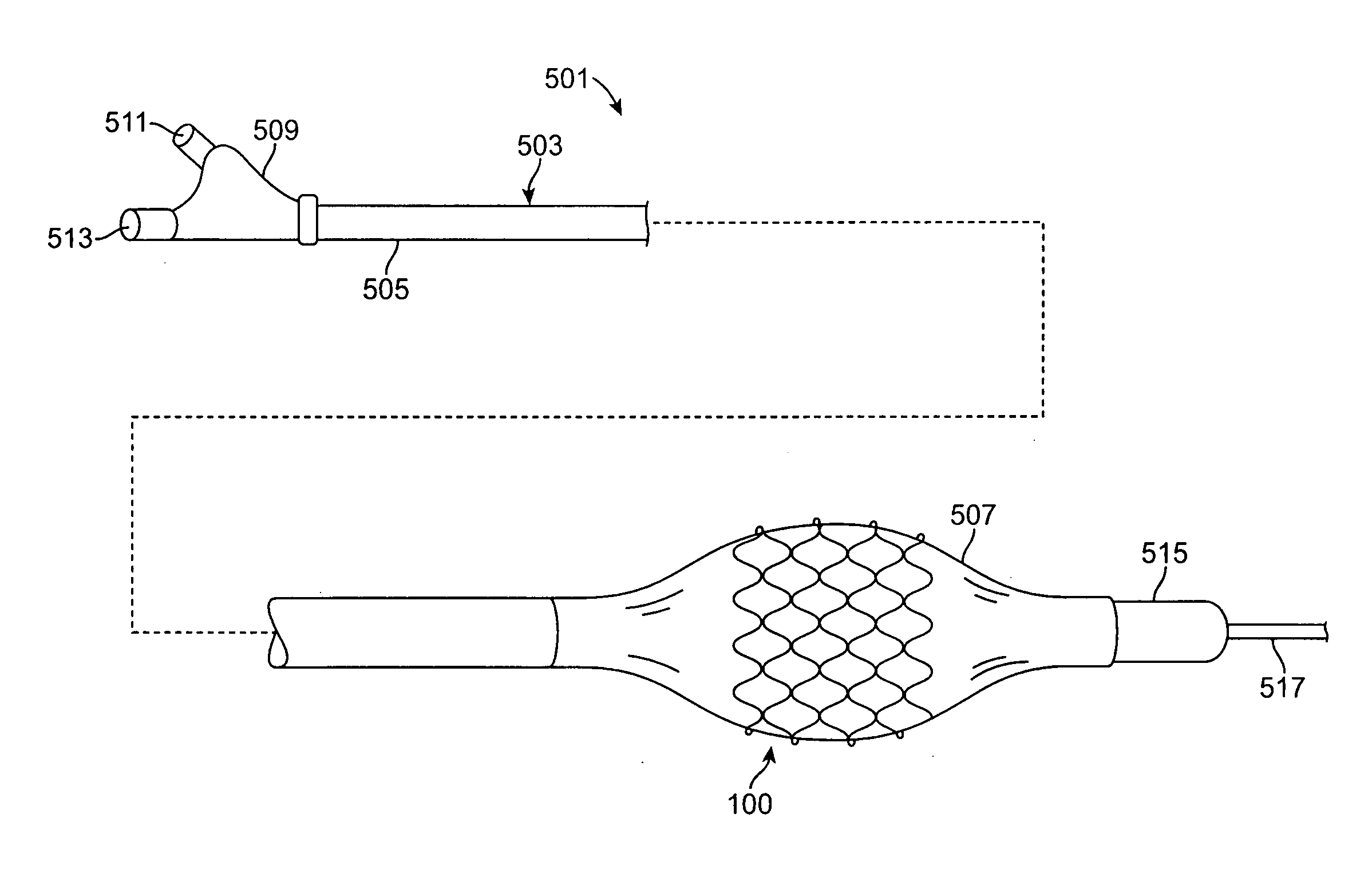
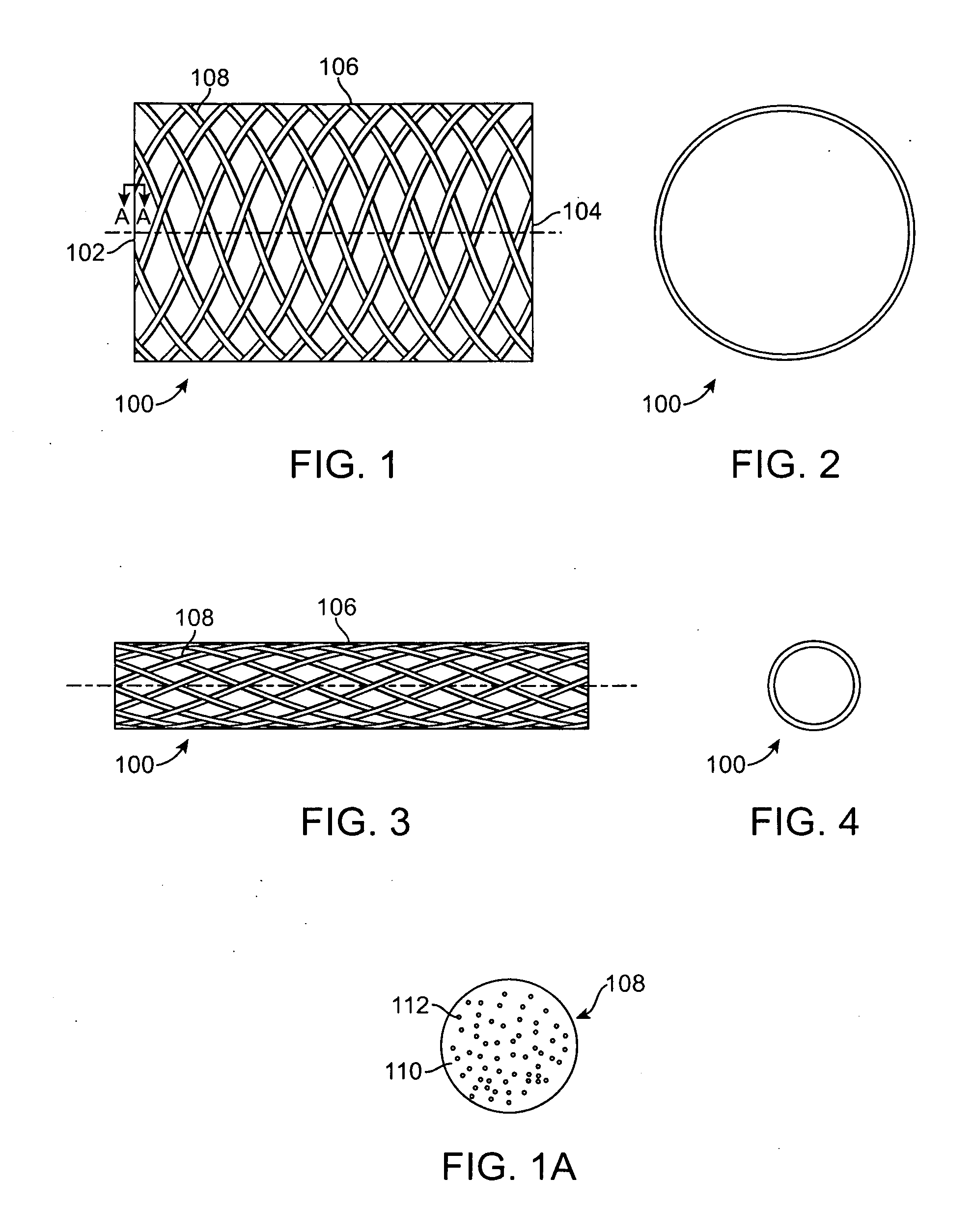
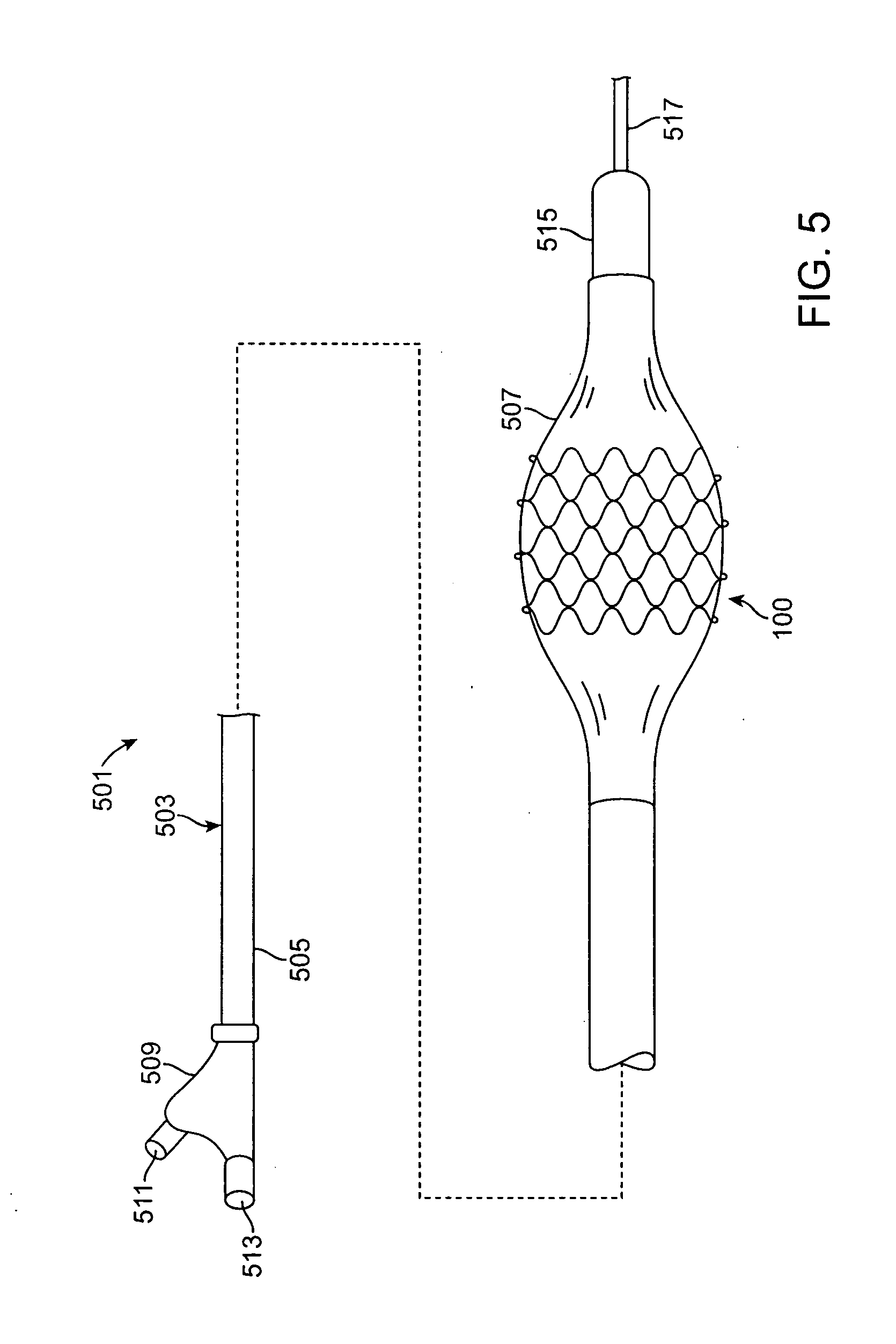
Method for Tracking Degradation of a Biodegradable Stent Having Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Particles Embedded Therein
A tubular stent formed from a plurality of filaments, the filaments constructed out of a solid bioabsorbable polymeric material having active agent particles dispersed there through that are visible by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The active agent particles are superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) particles. The SPIO particles enhance the visibility of the polymeric stent under MRI, and also allow for accurate monitoring of stent degradation. As the stent degrades, the SPIO particles are released and either flow downstream or are embedded by nearby macrophages. The amount of SPIO particles within the remaining stent body is decreased, which results in a different MRI signal. By quantifying the signal change, the amount of biodegradable stent remaining can be deduced in situ and the stent degradation rate may be accurately calculated.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
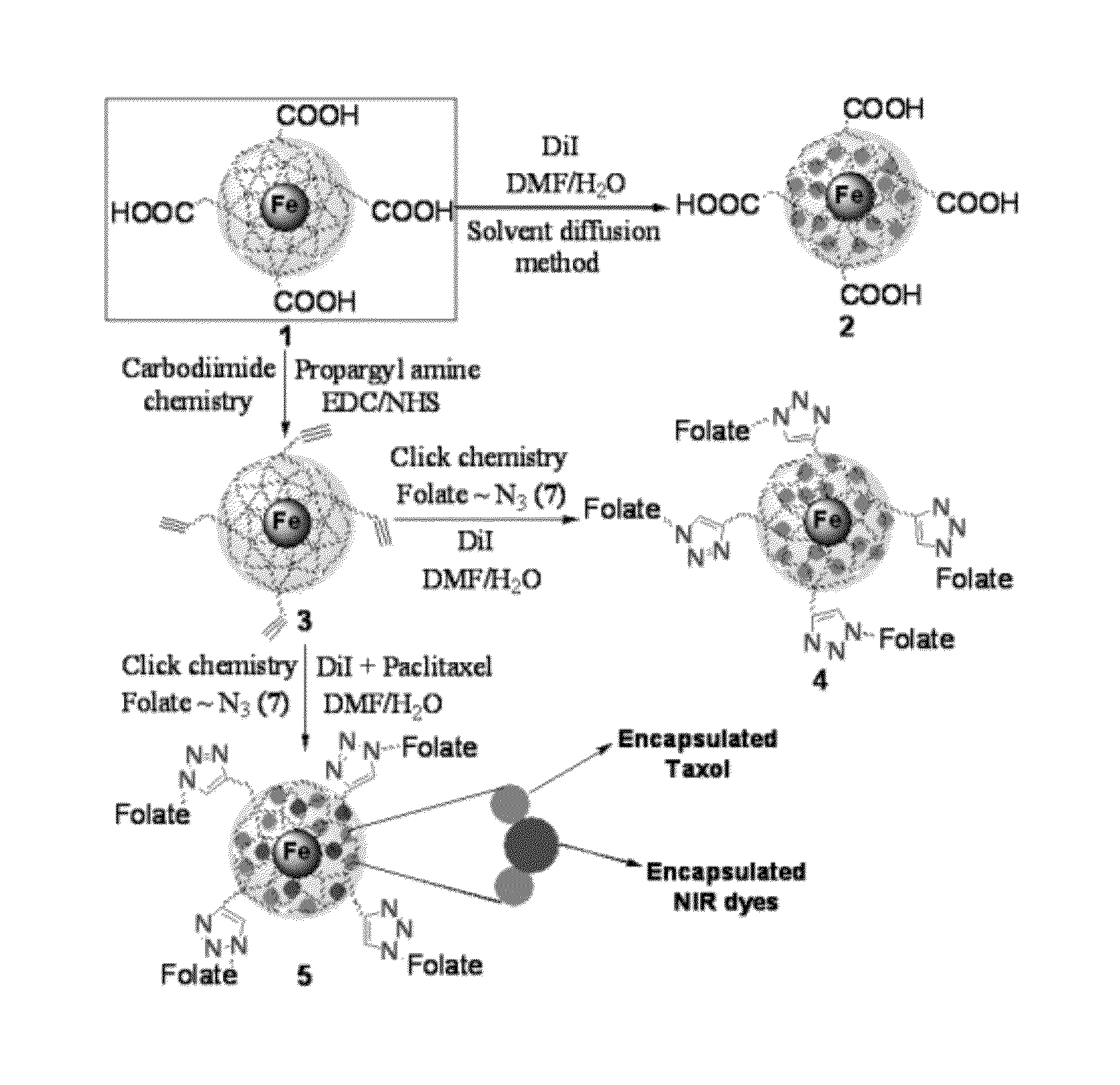
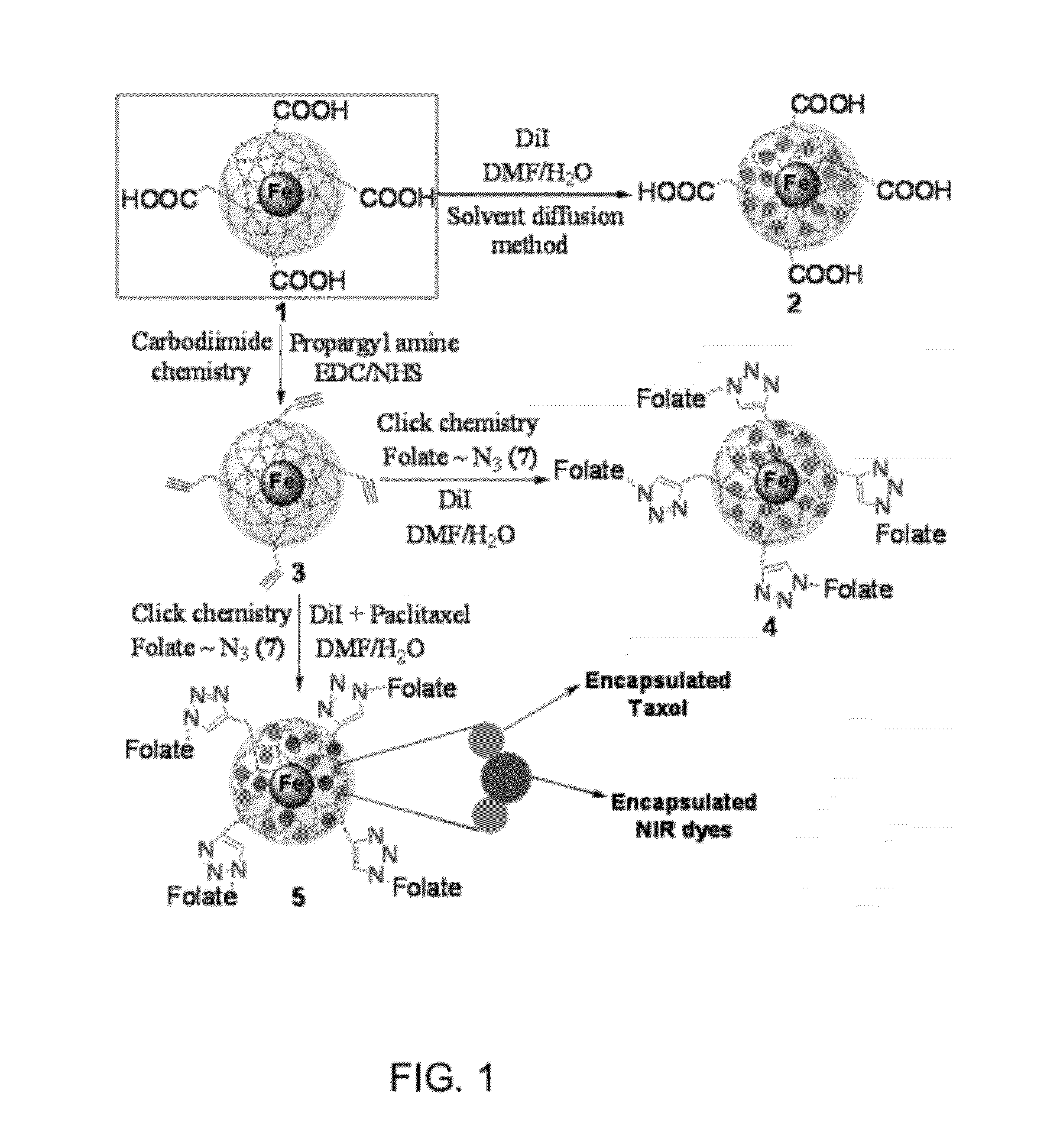
Multimodal, multifunctional polymer coated nanoparticles
InactiveUS8236284B1Maintain good propertiesImprovement factorPowder deliveryBiocideFluorescenceALLYL SUCROSE
Disclosed are nanoparticles having a metallic core consisting essentially of superparamagnetic iron oxide; a polymeric coat surrounding said core, the coat having a matrix of polyacrylic acid and forming an outer periphery of said nanoparticle; a plurality of hydrophobic pockets formed by the polymeric coat; a plurality of carboxylic groups along an outer periphery of the polymeric coat and effective to conjugate with a predetermined targeting ligand which functionalizes the nanoparticle; a lipophylic fluorescent dye encapsulated in the plurality of hydrophobic pockets; and a drug encapsulated in the plurality of hydrophobic pockets. Associated methods of making the nanoparticles and of treatments using the nanoparticles are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Control of materials and porous magnetic particles
InactiveUS20090179171A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanomagnetismAqueous dropletMagnetite Nanoparticles
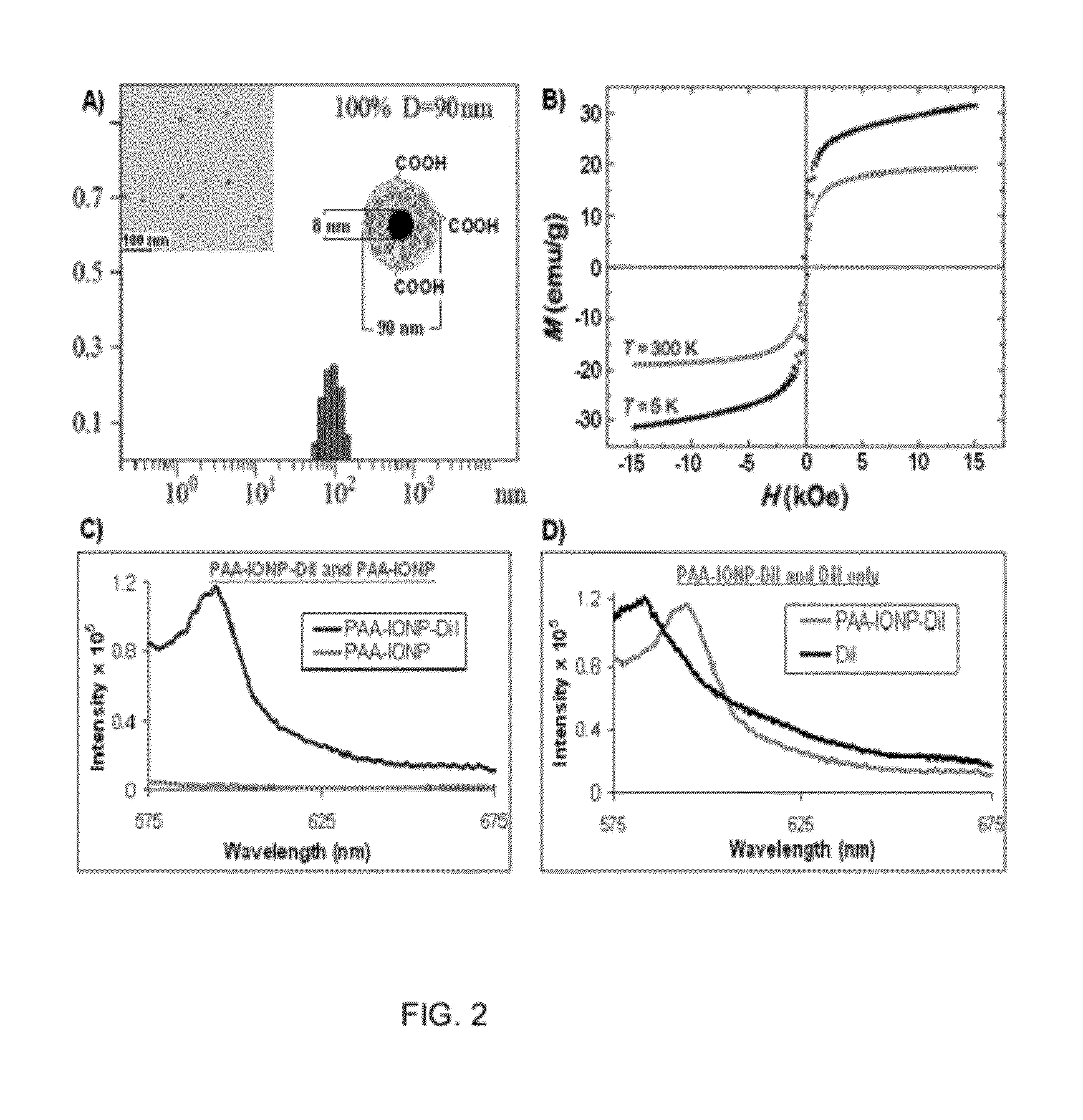
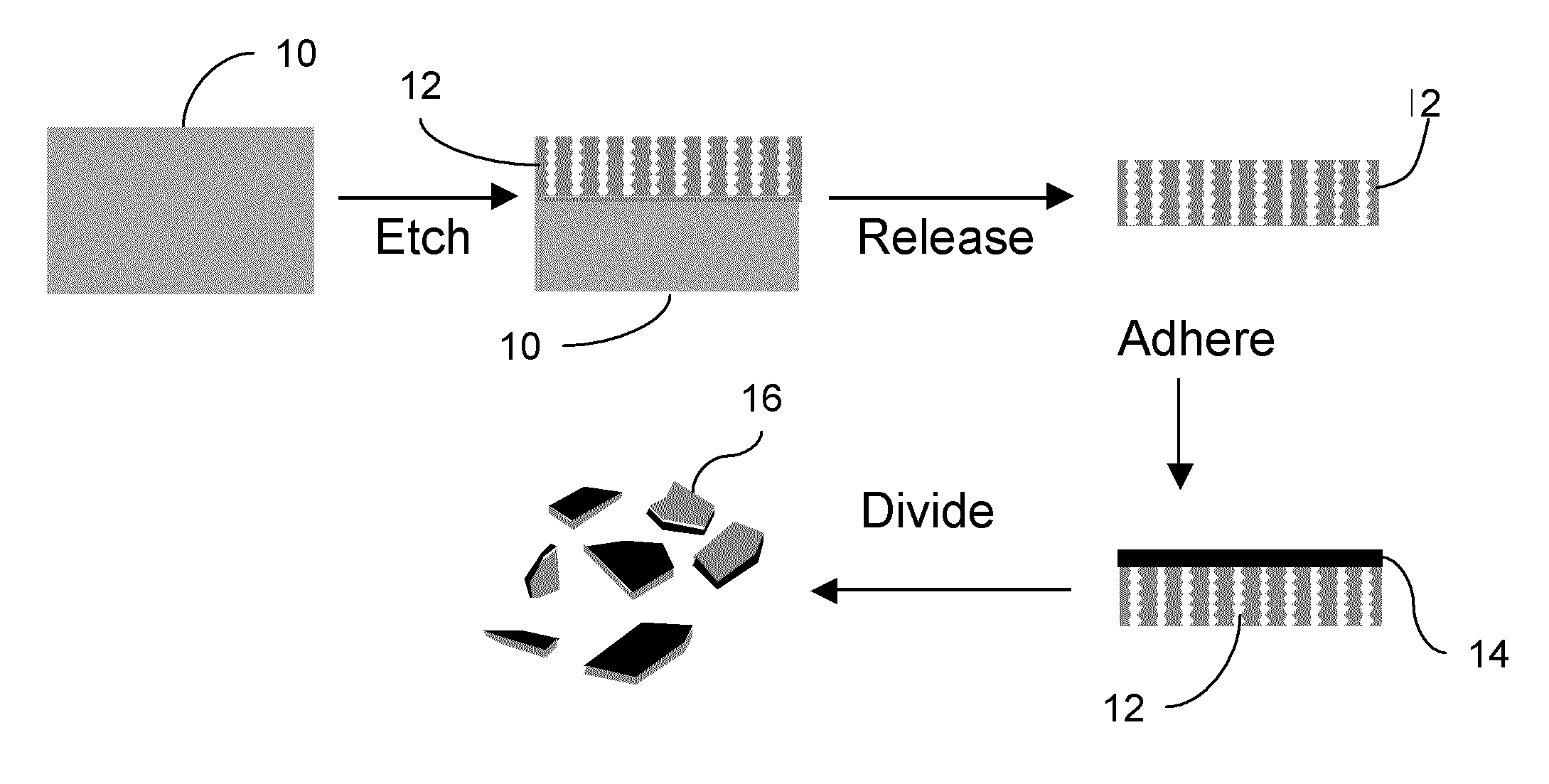
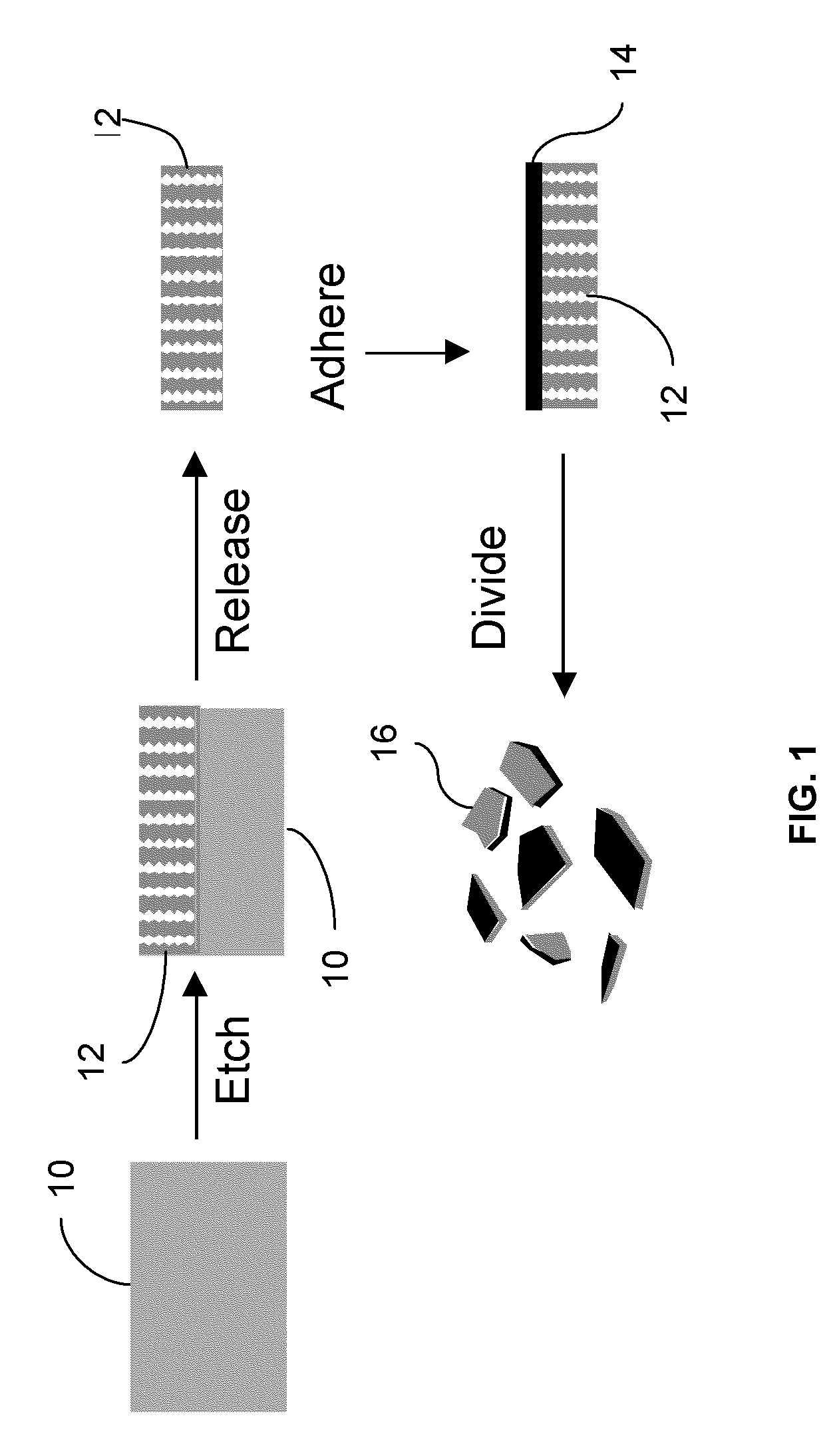
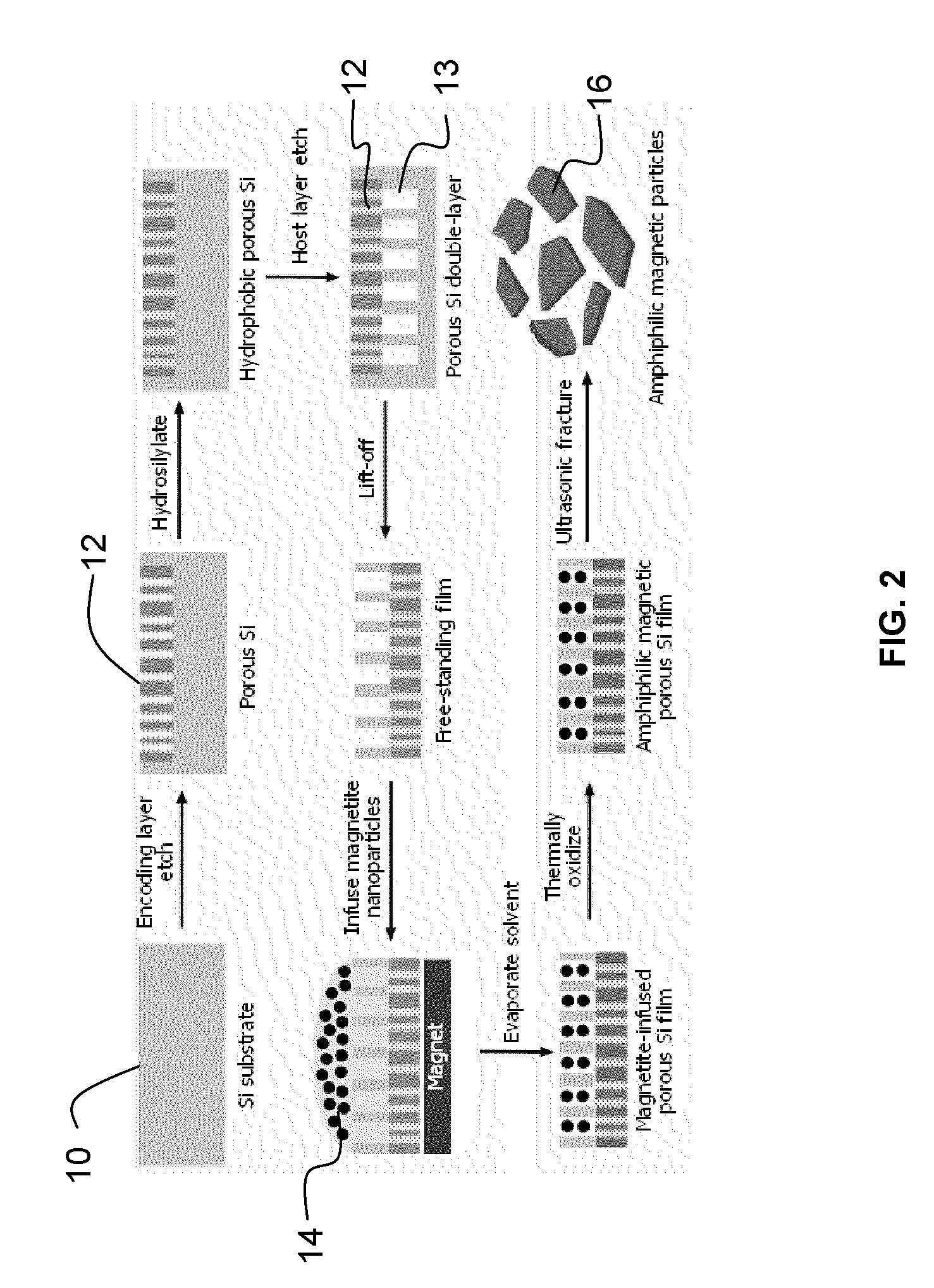
The present invention uses externally applied electromagnetic stimulus to control and heat porous magnetic particles and material associated with the particles. The particles contain magnetic material, such as superparamagnetic iron oxide and are associated with a material. Application of a DC magnetic field allows them to be moved with their associated material, and application of an AC RF electromagnetic field allows them to be heated with their associated material. The material can be associated with the particles by being contained in the pores of the particles, or in other cases the particles can adhere to the associated material, which can be an aqueous droplet. The present invention also provides a multi-layer porous magnetic particle. The particle includes a host layer having pores sized to accept magnetic nanoparticles. Magnetic nanoparticles are infused within pores of the host layer An encoding layer includes pores that define a spectral code. The pores in the encoding layer are sized to substantially exclude the magnetic nanoparticles. The encoding layer can also be a multi-layer, exhibiting, for example, a complex spectral code.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Positive contrast MRI of magnetically tagged cells, objects, tissues
Contrast agents incorporating super-paramagnetic iron-oxide (SPIO) nanoparticles have shown promise as a means to visualize labeled cells using MRI. Labeled cells cause significant signal dephasing due to the magnetic field inhomogeneity induced in water molecules near the cell. With the resulting signal void as the means for detection, the particles are behaving as a negative contrast agent, which can suffer from partial-volume effects. Disclosed is a new method for imaging labeled cells with positive contrast. Spectrally-selective RF pulses are used to excite and refocus the off-resonance water surrounding the labeled cells so that only the fluid and tissue immediately adjacent to the labeled cells are visible in the image. Phantom, in vitro, and in vivo experiments show the feasibility of the new method. A significant linear correlation (r=0.87, p<0.005) between the estimated number of cells and the signal has been observed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Macrophage-Enhanced MRI (MEMRI)
Methods for assessing stage of cancer in a subject are provided, comprising administering a macrophage imaging agent to the subject, making a magnetic resonance image of regions of the subject's body at cancer risk, and using the image to assess macrophage density and displacement associated with any primary cancer or metastatic cancer in the subject, such density and displacement being indicative of neoplasia. The macrophage imaging agent may be an ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide particle and in particular embodiments, the macrophage imaging agent has a blood half-life sufficient to permit microphage trapping throughout the regions at cancer risk. Additional embodiments provide methods for assessing efficacy of an anticancer treatment in a subject, methods for determining frequency of follow-up MEMRI evaluation in a subject, methods for determining metastatic potential of cancer foci in a subject, and methods for determining prognosis of cancer in a subject. Methods for directing site of biopsy in a subject by performing a whole body MEMRI evaluation of the subject to identify macrophage density at a tumor site of interest and assessing the macrophage density to identify the site of biopsy in the subject, macrophage density being an indicator of tumor growth are also provided, in addition to methods for providing individualized cancer treatment to a subject in need thereof using whole body MEMRI evaluation.
Owner:AMAG PHARMA
D-glucosamine-modified iron oxide nanoparticles and preparation method of lyophilized powder thereof
InactiveCN101698106AOvercome the problem of liquid instabilityFulfil requirementsNMR/MRI constrast preparationsEmulsion deliveryTumor targetSuperparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles
The invention relates to d-glucosamine-modified iron oxide nanoparticles used as a tracer for magnetic resonance, a preparation method of lyophilized powder thereof and use thereof. The d-glucosamine-modified iron oxide nanoparticles comprise superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles, wherein the surfaces of the superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles are modified by a substance having carboxyls; the carboxyls react with the aminos of the d-glucosamine to form amido bonds; and thus a structure that the surfaces of the superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles are modified by the d-glucosamine is formed. The invention provides a novel tumor-targeted MRI contrast agent which has high selectivity of tumors for the tumor targeted magnetic resonance diagnostic tests and clinic tumor diagnosis. By preserving the d-glucosamine-modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in form of the lyophilized powder, the unstable problem of the d-glucosamine-modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles is solved. The d-glucosamine-modified iron oxide nanoparticles are sterile, anhemolytic and free from vascular stimulation and can meet the requirements of tests of cells, animals and the like.
Owner:ZHENJIANG NO 1 PEOPLES HOSPITAL +1
Preparation and use of polyvinyl pyrrolidon modified superparamagnetism nano bengala
InactiveCN101475224AUniform particle sizeGood dispersionFerroso-ferric oxidesIn-vivo testing preparationsSuperparamagnetismSuperparamagnetic iron oxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing superparamagnetic iron oxide nanometer particles modified by polyvinylpyrrolidone. The method sequentially comprises the following steps that: 1) under the protection of inert gas, FeCl3.6H2O, FeCl2.4H2O and polyvinylpyrrolidone are dissolved in diglycol at the room temperature; 2) under the protection of inert gas, mixed solution of NaOH and diglycol is added to obtained tawny solution for reaction; 3) an obtained black suspension is cooled to room temperature and added with ethyl acetate for centrifugation; 4) solids obtained after centrifugation are dispersed in anhydrous ethanol, and then ethyl acetate is added for centrifugation; 5) the steps 4) is repeated twice to three times and black solids are obtained; and 6) the black solids are dispersed in deionized water, placed in a dialysis bag with the molecular weight cutoff between 10 and 15 w and dialyzed for at least 48 hours. The superparamagnetic iron oxide nanometer particles modified by polyvinylpyrrolidone are used for tracing the functions of islet graft.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Tracing method for medulla desmohemoblast stem cell
InactiveCN101002679AAccurate tracer monitoringEffective researchDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMiddle medullaSuperparamagnetic iron oxide
A tracing method for the intermedullary filling stem cells includes such steps as using transfectant to modify superparamagnetic iron oxide to make it carry positive charges, using it to mark the cultured intermedullary filling stem cells, inoculating said cells onto scaffold, transplanting it in the body of animal, and using NMR imaging instrument for tracing the cells in animal body.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Novel mesoporous silicon sphere co-loaded medicine nano-complex and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108815523AReduce releaseIncrease drug concentrationOrganic active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsSuperparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticlesMesoporous silica
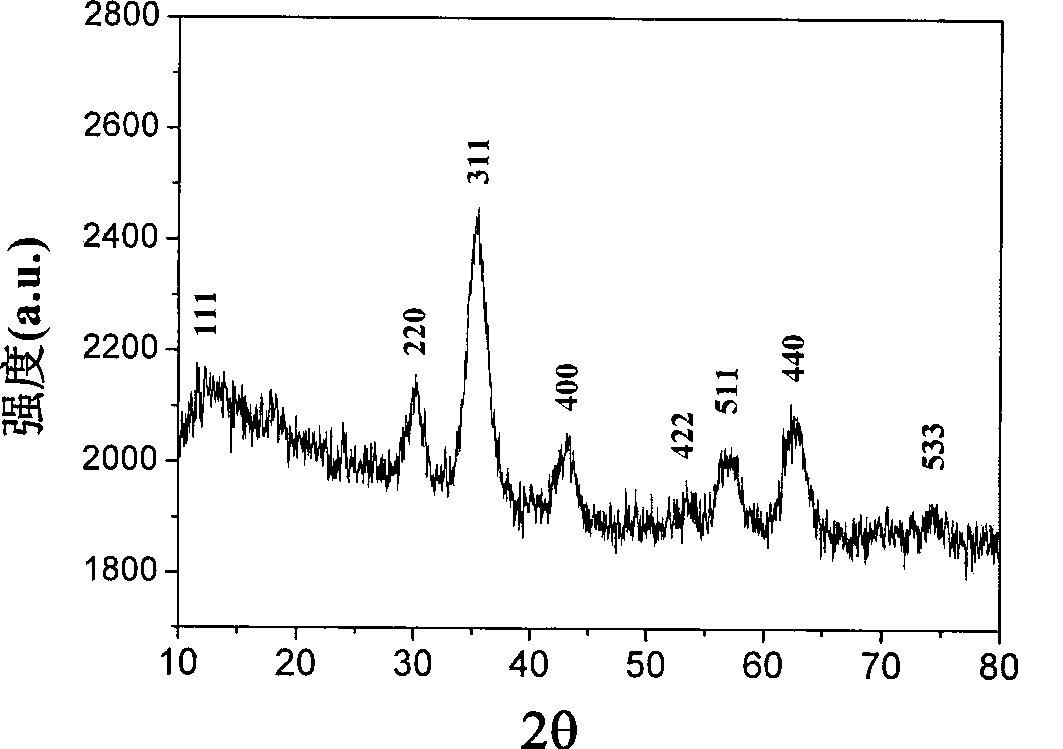
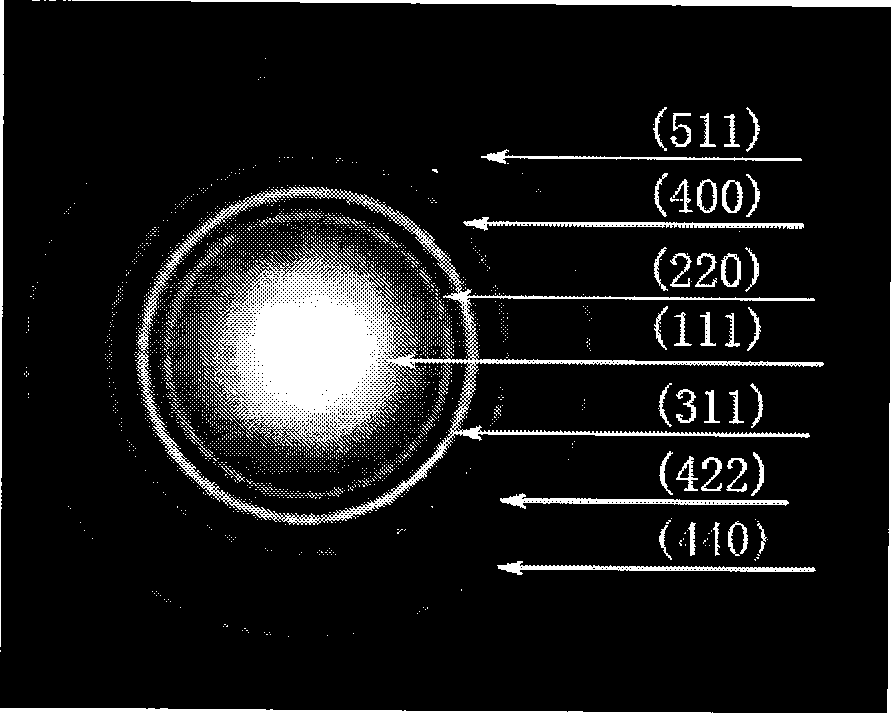
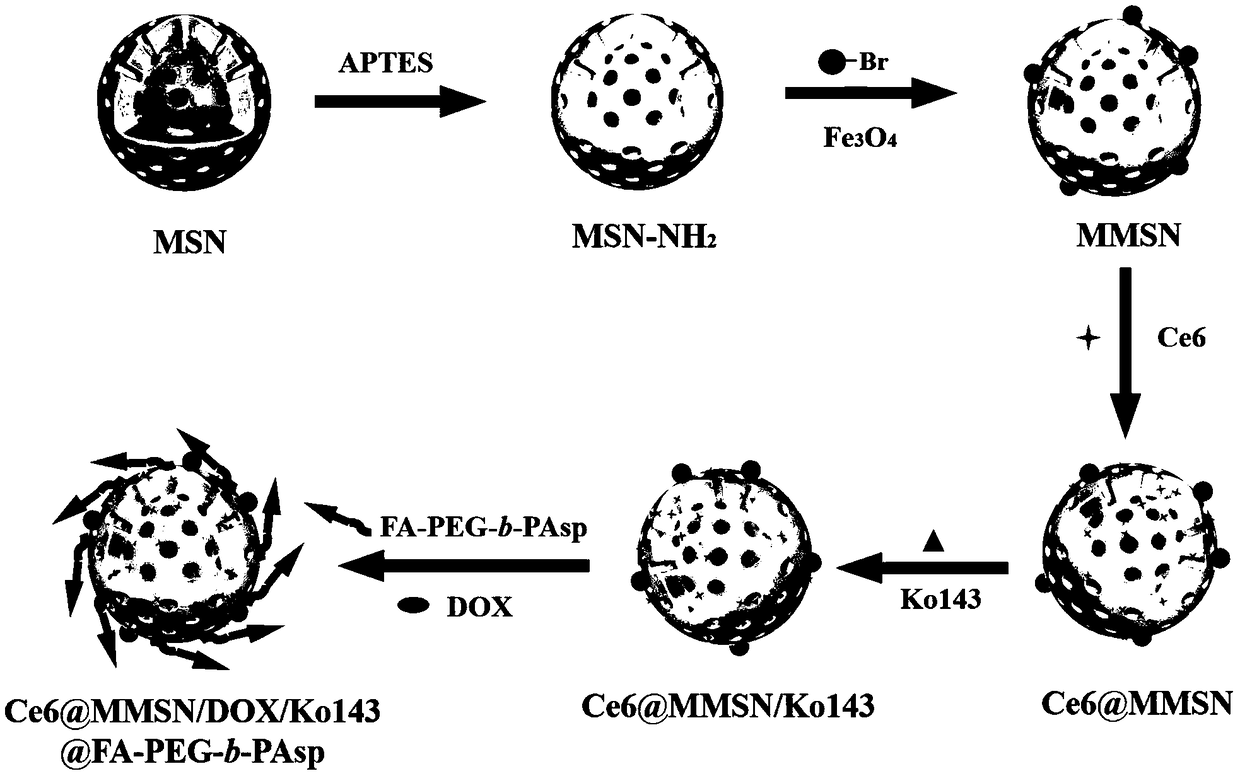
The invention discloses a novel mesoporous silicon sphere co-loaded medicine nano-complex and a preparation method thereof. The novel mesoporous silicon sphere co-loaded medicine nano-complex is Ce6@MMSN / DOX / Ko143@PAsp-b-PEG-FA; the preparation method comprises the following steps: selecting TEOS (Tetraethyl Orthosilicate) as a silicon source, CTAB (Cetyltrimethyl Ammonium Bromide) as a template agent and n-hexane as a pore expanding agent and synthesizing mesoporous silicon dioxide nanoparticles with a double-pore-channel core-shell structure; carrying out amination modification on the mesoporous silicon dioxide nanoparticles; synthesizing Fe3O4 nanoparticles by adopting an LSS (Liquid-Solid-Solution) phase transfer method and ligand exchange reaction; modifying and embedding superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles on the surface of aminated MSN through nucleophilic substitution, so as to construct magnetic mesoporous silicon dioxide nanoparticles; taking DCC (Dicyclollexyl Carbodiimide) as a condensation agent and covalently binding a photosensitizer Ce6 through amidation; meanwhile, loading a BCRP (Breast Cancer Resistance Protein) inhibitor Ko143; then crossly linking a copolymer FA-PEG-b-PAsp; finally, loading an anti-tumor medicine DOX.
Owner:SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV
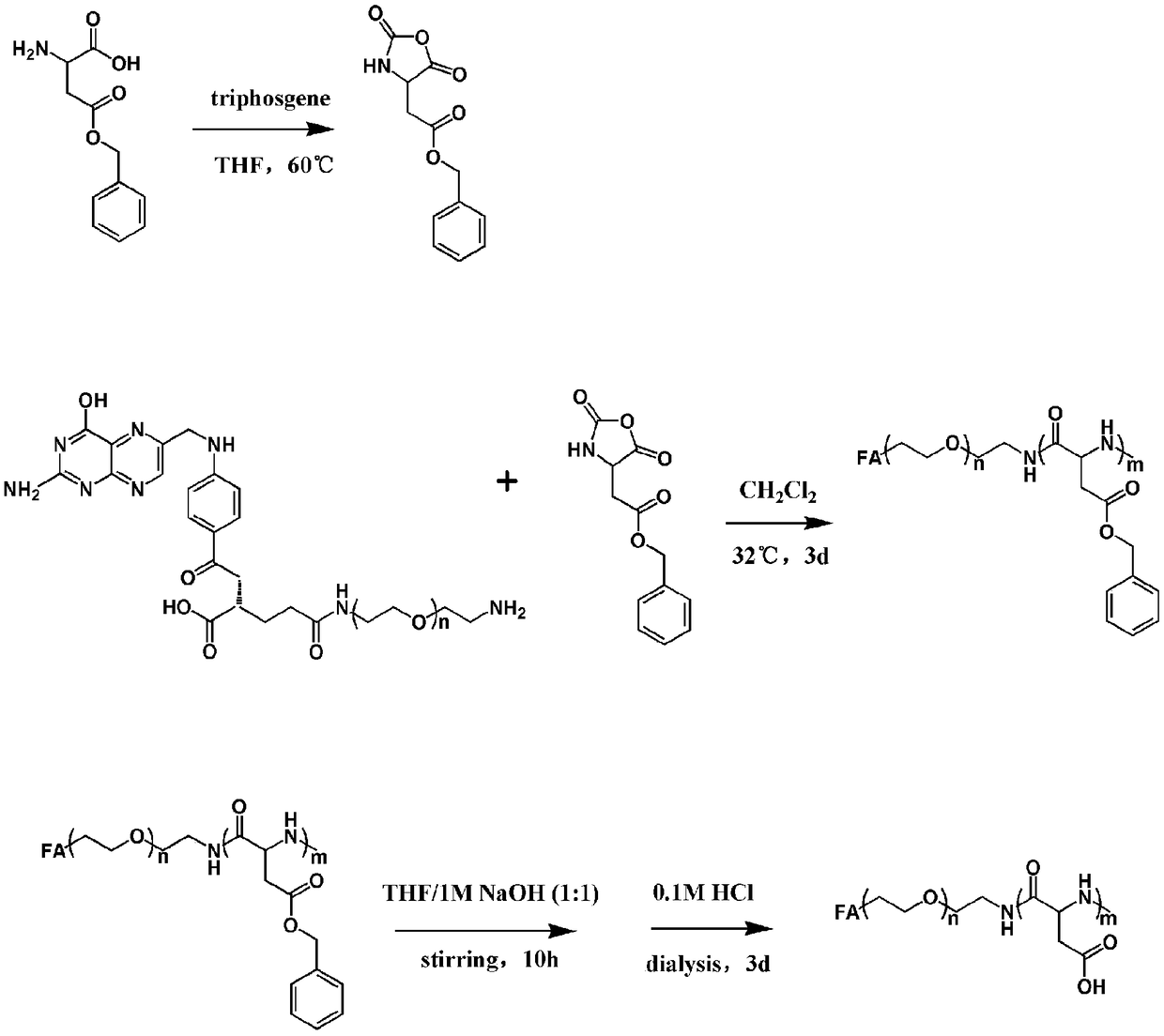
An acid-responsive nanometer micelle for drug loading, a preparation method and an application thereof
ActiveCN109172521AProlong blood circulation timeQuick releaseOrganic active ingredientsDispersion deliveryCancers diagnosisPolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses an acid-responsive nanometer micelle for drug loading, a preparation method and an application thereof. The nano-micelles were self-assembled from hydrophilic segment polyethylene glycol (PEG) and hydrophobic segment pH-sensitive polyaspartyl diisopropylethylenediamine / di-n-butylethylenediamine (PAsp (DIP / DBA)). The nano-micelles can prolong the drug circulation time, aggregate in the tumor site, increase the local drug concentration, and respond to the micro-acid environment of the tumor tissue. As a drug carrier of stimulation response, the nano-micelles can rapidly release the loaded chemotherapeutic drug adriamycin in the tumor site, and play a significant anti-tumor effect. At the same time, the nano-micelles loaded with magnetic resonance contrast agent superparamagnetic iron oxide can be used for tumor magnetic resonance imaging and monitoring drug uptake and aggregation. This method utilizes nano-drug aggregation at tumor site and acid responsiveness ofcarrier to realize rapid drug release to improve tumor therapeutic effect, and endows nano-micellar MRI visualization function, which provides a promising innovative strategy for cancer diagnosis andtreatment, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
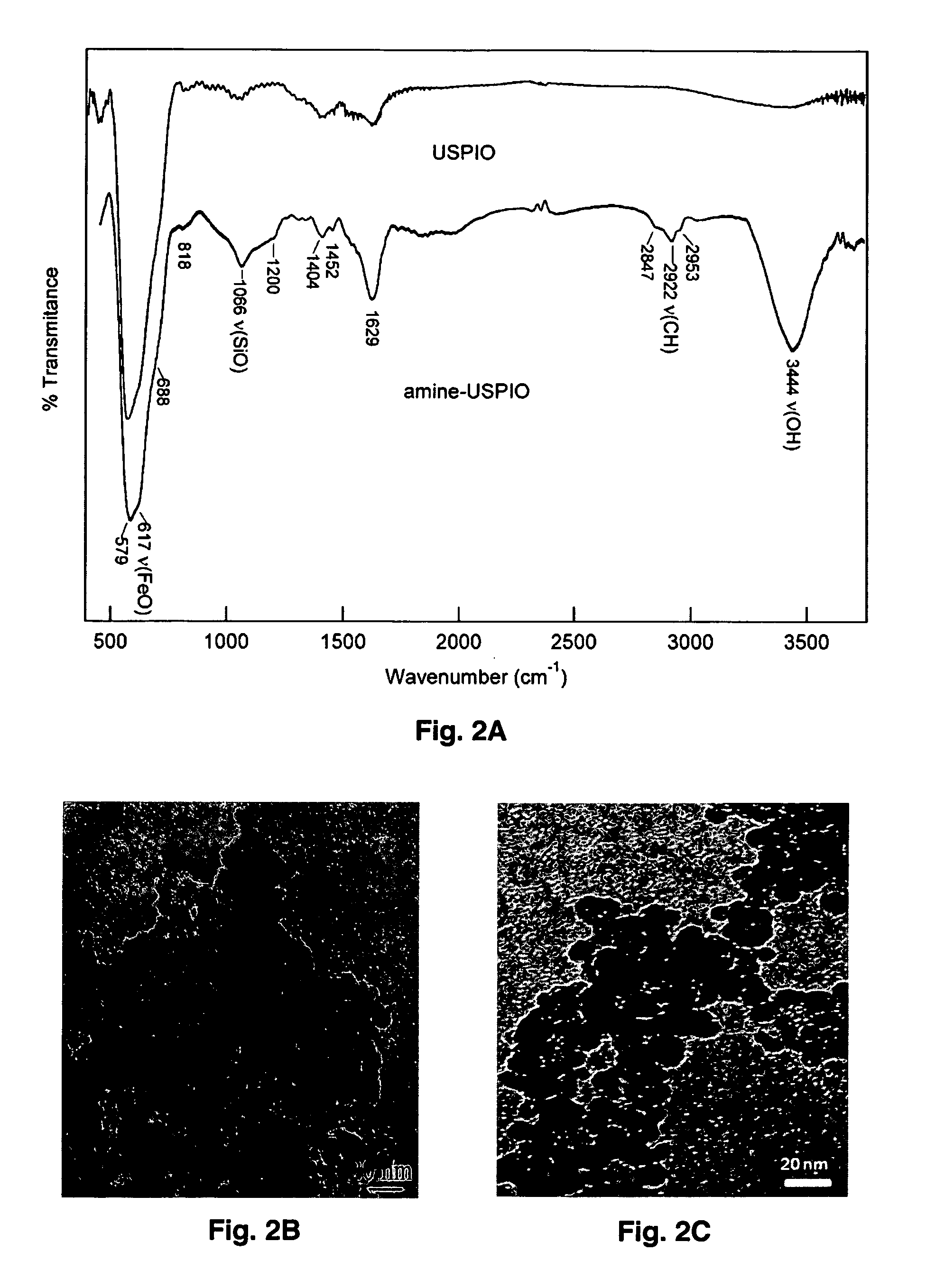
Theranosis of macrophage-associated diseases with ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (USPIO)
InactiveUS20130336897A1Promote extravasationIncrease scatteringPowder deliveryBiocideDiseaseLysosome
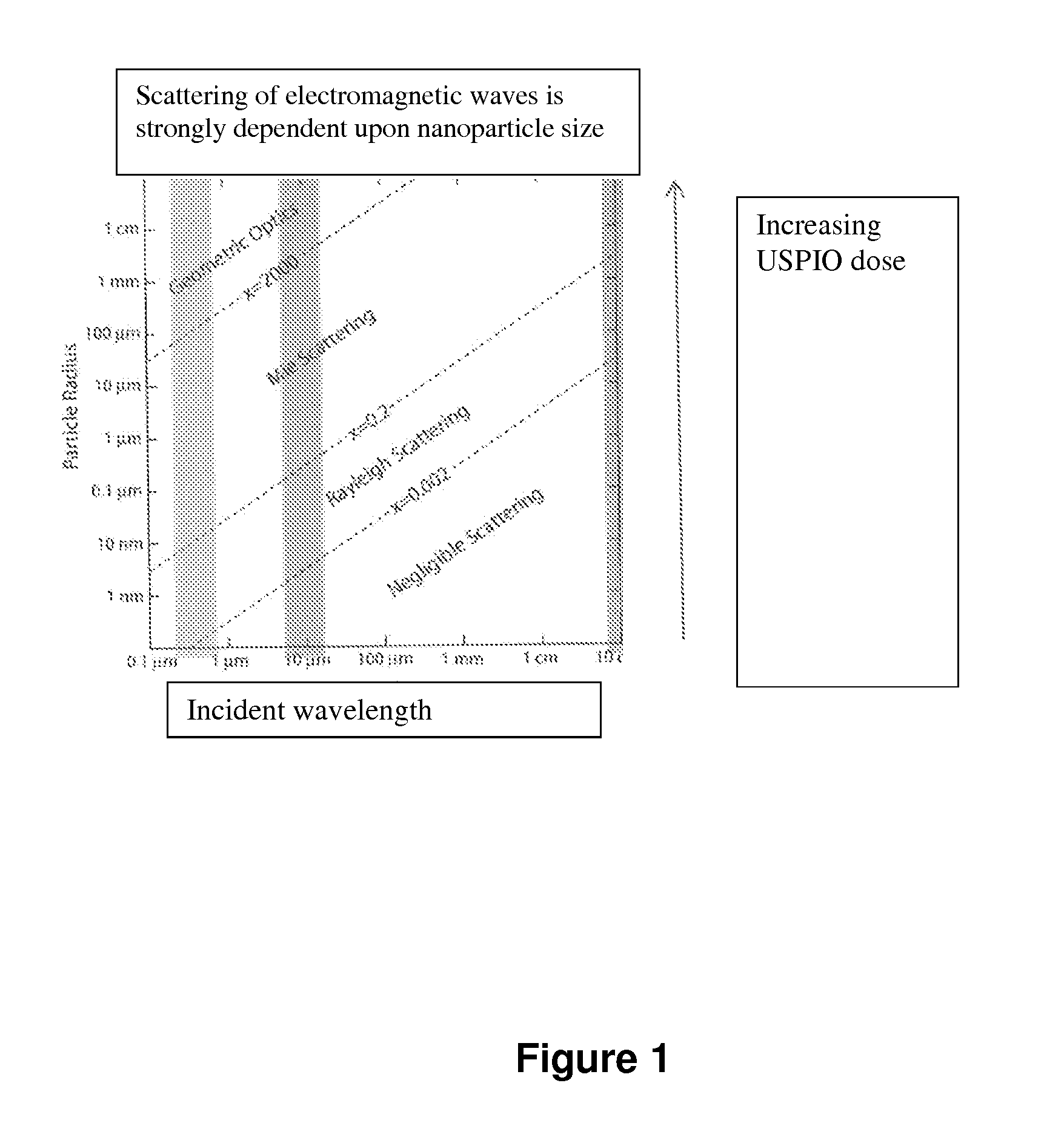
Macrophages sequester and aggregate ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (USPIO) in their lysosomes. The amount of USPIO loading of macrophages depends upon the route and dose of administration, and the pharmacokinetics of accumulation and removal. Both fixed macrophages and activated macrophages associated with inflammatory diseases and cancer phagocytize USPIOs, and the loaded macrophages can serve to identify the extent of a macrophage-dependent disease as well as to direct treatment options. Furthermore, the absorption of energy from incident electromagnetic waves by the aggregated nanoparticles can be used for conformal thermotherapy. The USPIOs can further be used to carry drugs to the same activated macrophages. The co-administered drugs can be bound to the USPIO by condition-dependent releasing links that are responsive to local pH or heating.
Owner:WOLF GERALD L +1
Preparation method of hyaluronic acid modified superparamagnetic iron oxide/gold composite nanoprobe
InactiveCN104548142ASimple operation processMild reaction conditionsX-ray constrast preparationsEmulsion deliveryTumor targetCancer cell
The invention relates to a preparation method of a hyaluronic acid modified superparamagnetic iron oxide / gold composite nanoprobe. A NaBH4 reduction method is used for preparing PEI coated Au nano-particles; Fe3O4 / Au-PEI composite nanoparticles are synthetized in one step through a modified coprecipitation method; then HA is modified on the surface of the Fe3O4 / Au-PEI composite nanoparticles, so as to prepare a Fe3O4 / Au-HA composite nanoprobe. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple in process, mild in reaction conditions, and easy to operate; the prepared Fe3O4 / Au-HA composite nanoprobe has a relatively high relaxation rate, has an excellent X-ray damping capacity, is excellent in colloidal stability and biocompatibility, and has a targeting capability of a high expression cancer cell of a specific CD44 acceptor, and has a potential application value in the field of internal tumor targeted MR / CT bimodal imaging diagnosis.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
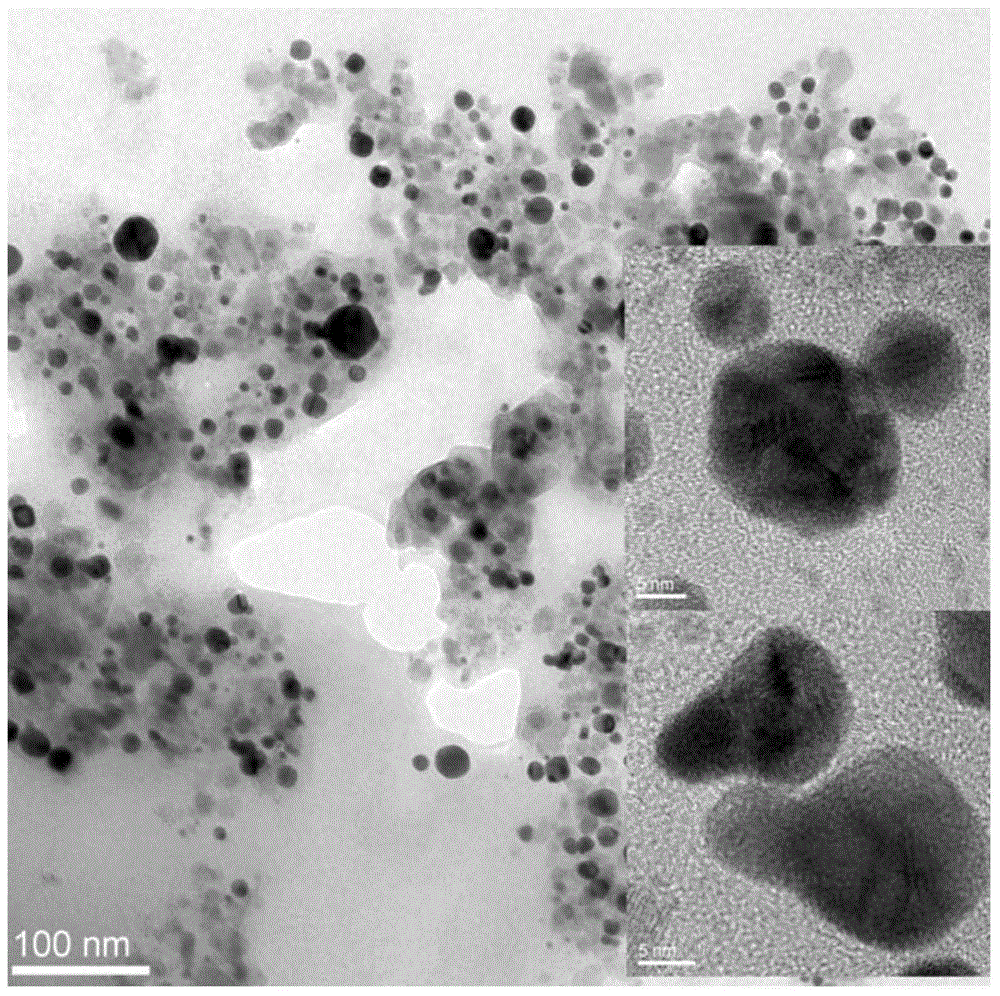
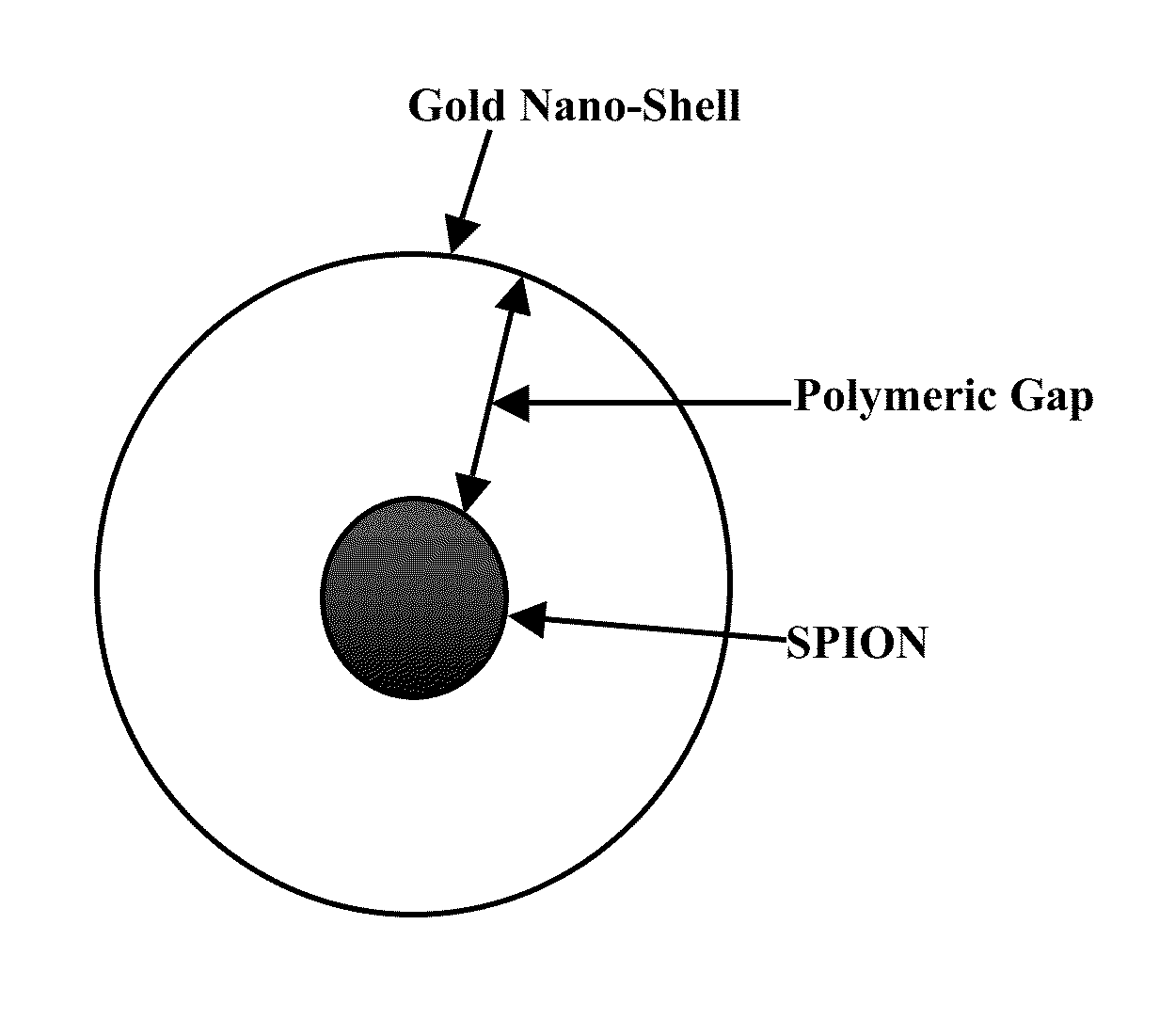
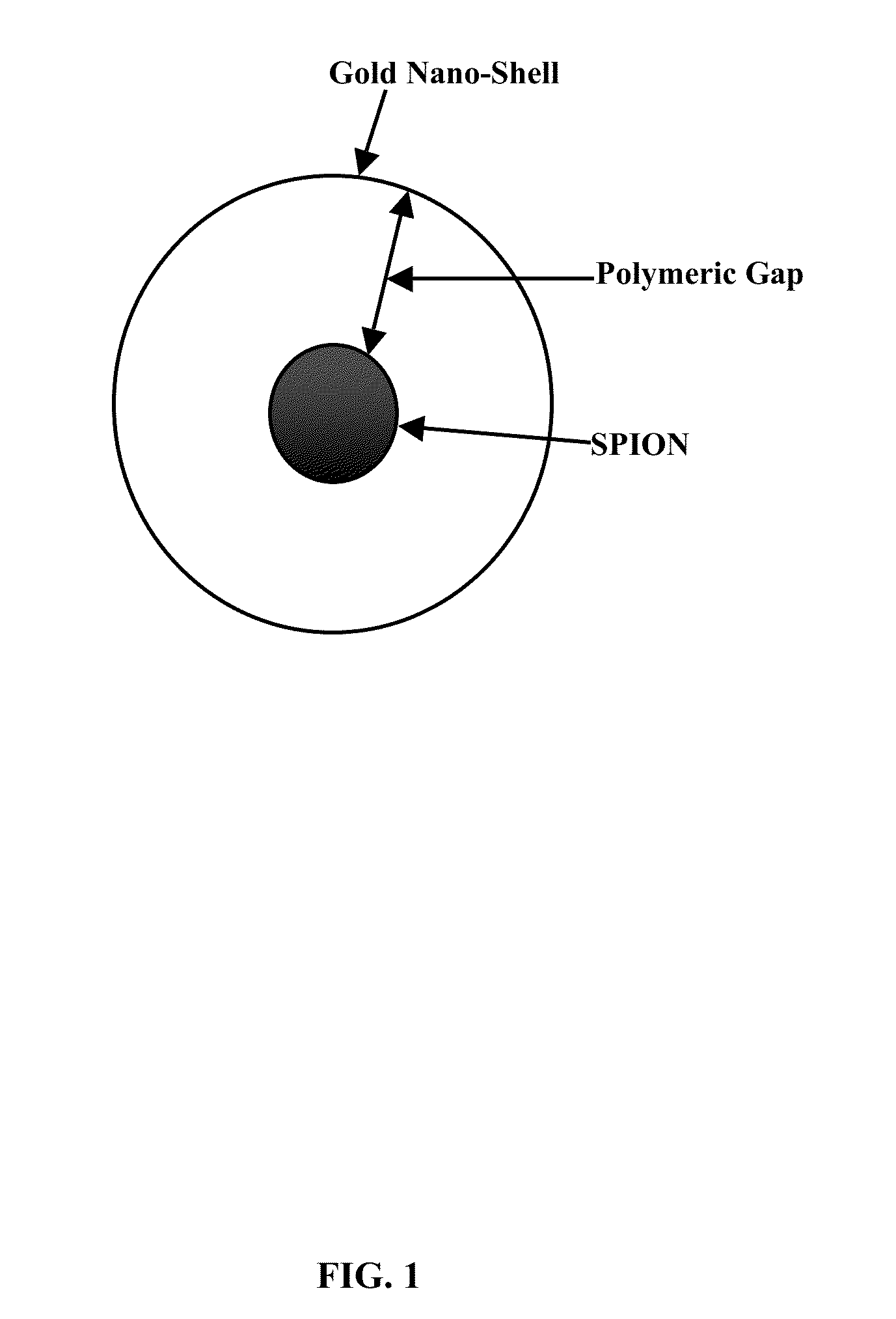
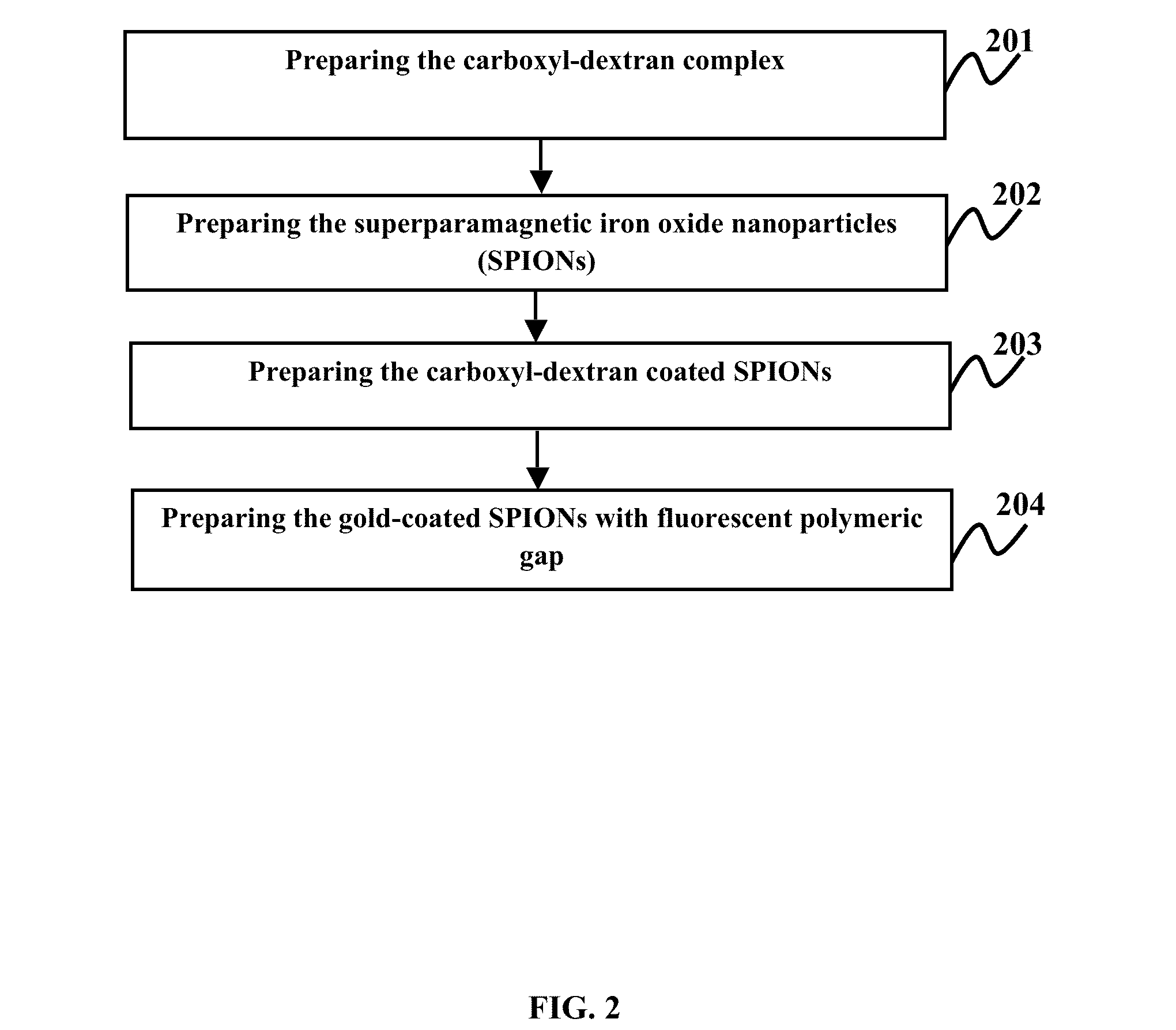
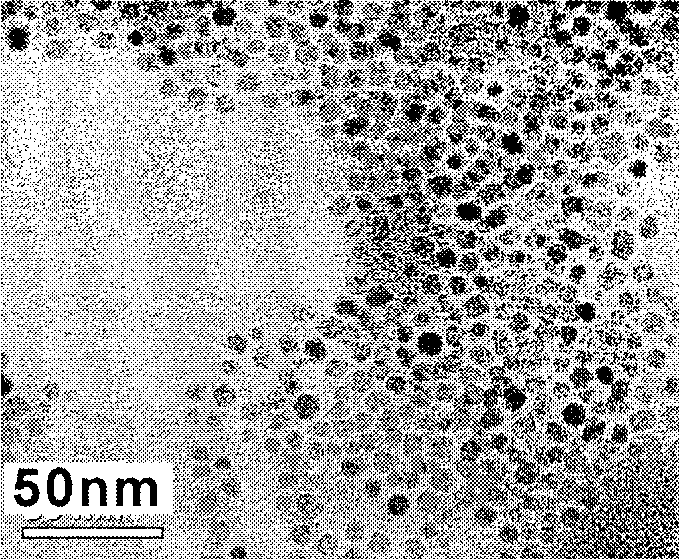
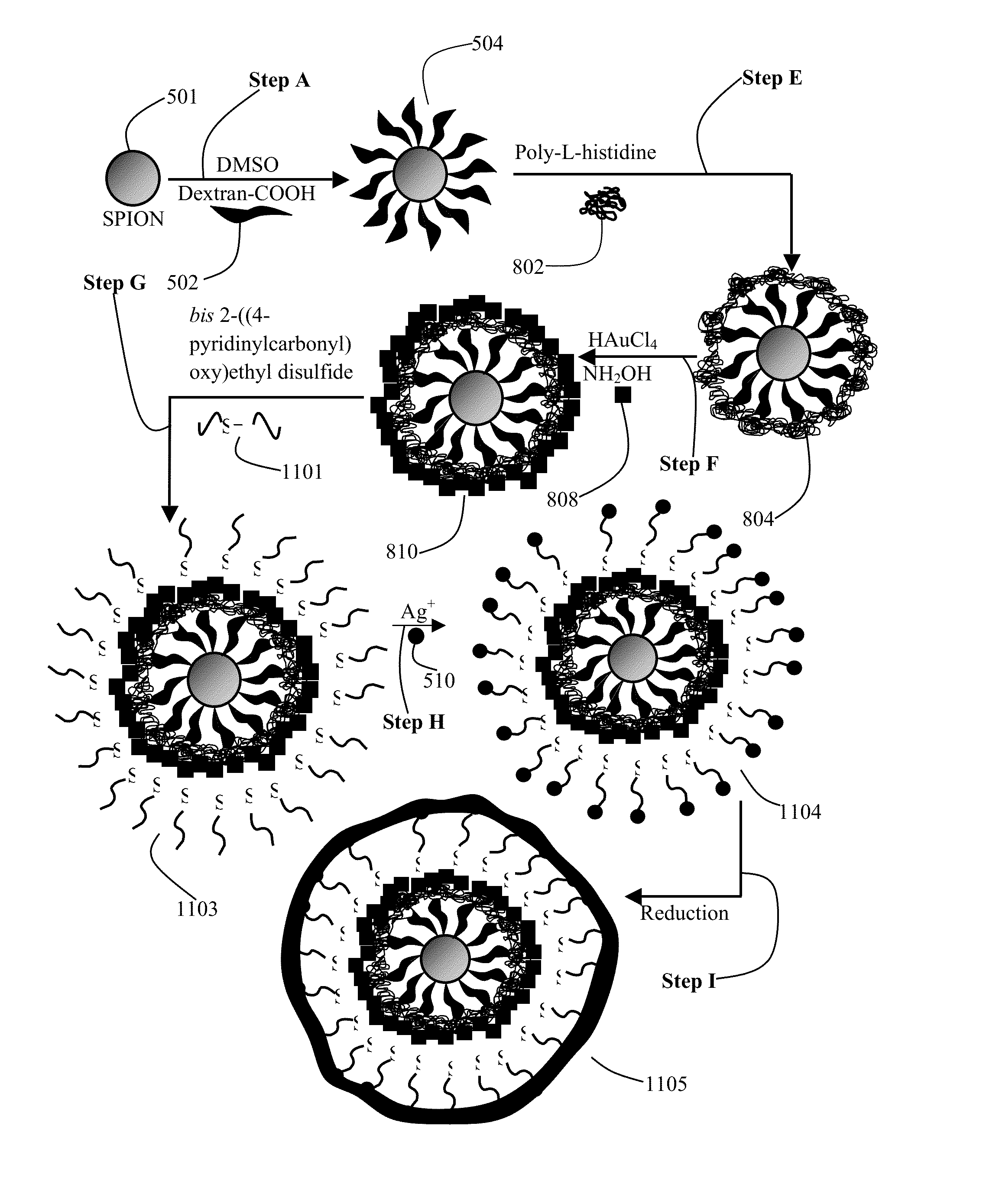
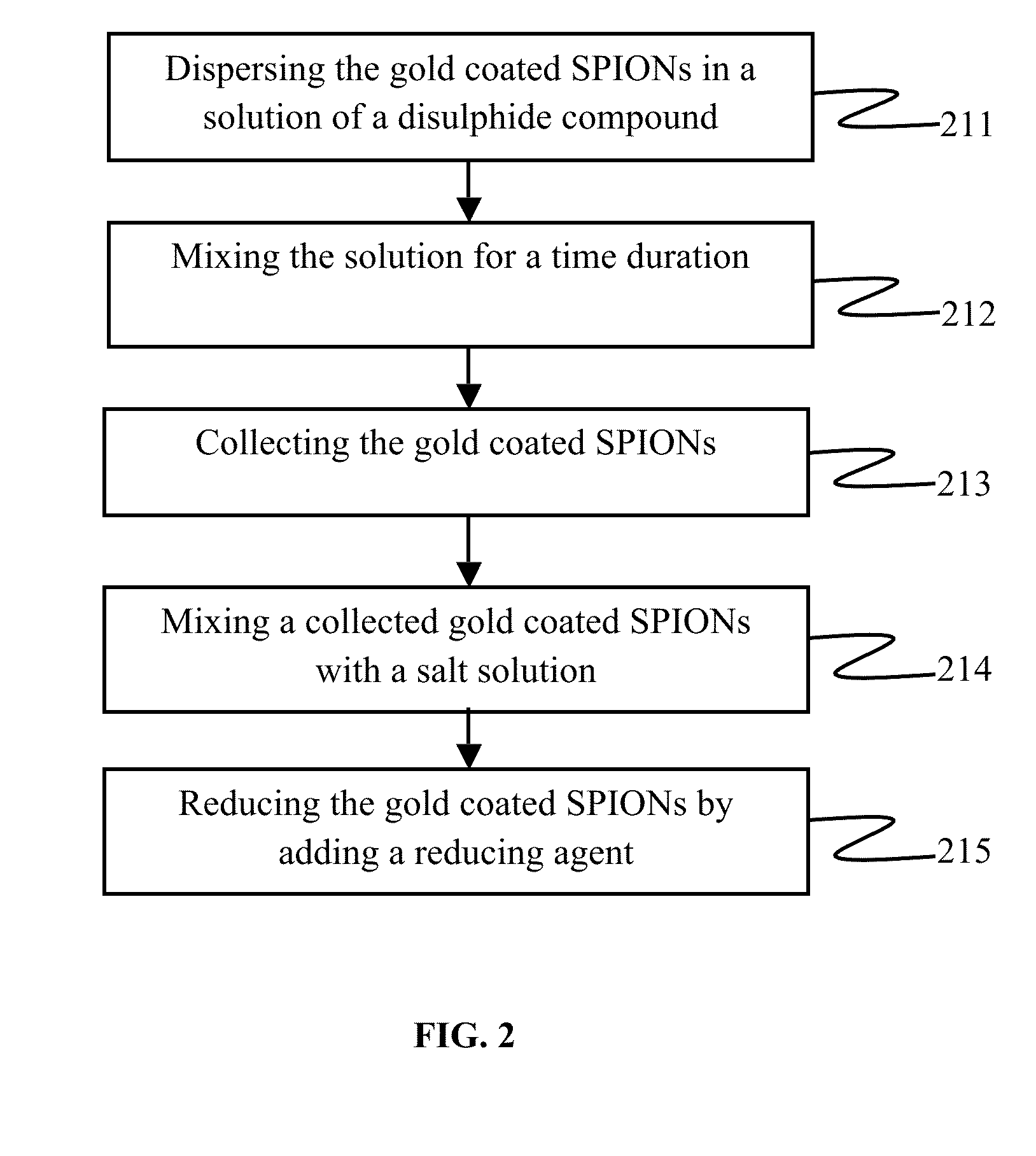
Plasmonic stable fluorescence superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and a method of synthesizing the same
The various embodiments herein provide for the engineered multimodal super paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) with a fluorescent dye. The SPIONs comprise fluorescent polymer dye arranged in a gap between a SPION core and a gold shell. The SPIONS are provided with a gold coating. The gap is made up of a polymeric molecule such as 6-arm anthracene terminated. The core of the nanoparticle is made up of a magnetic metal oxide. The method for synthesizing SPIONs involves preparing carboxyl-dextran complex and the SPIONS. The SPIONs are coated with carboxyl-dextran complex. The coated SPIONs coated are subjected to fluorescent polymer and gold nano shell coating. The prepared SPIONs are characterized by light scattering measurement and magnetization measurements.
Owner:MAHMOUDI MORTEZA +1
Curcumin-based magnetic nanostructured system for dual response of imaging and therapeutics
ActiveUS20200038525A1Reduced viabilityImprove bioavailabilityPowder deliveryNanomedicineNanocarriersDual response
Owner:IMAM ABDULRAHRNAN BIN FAISAL UNIVERSITY
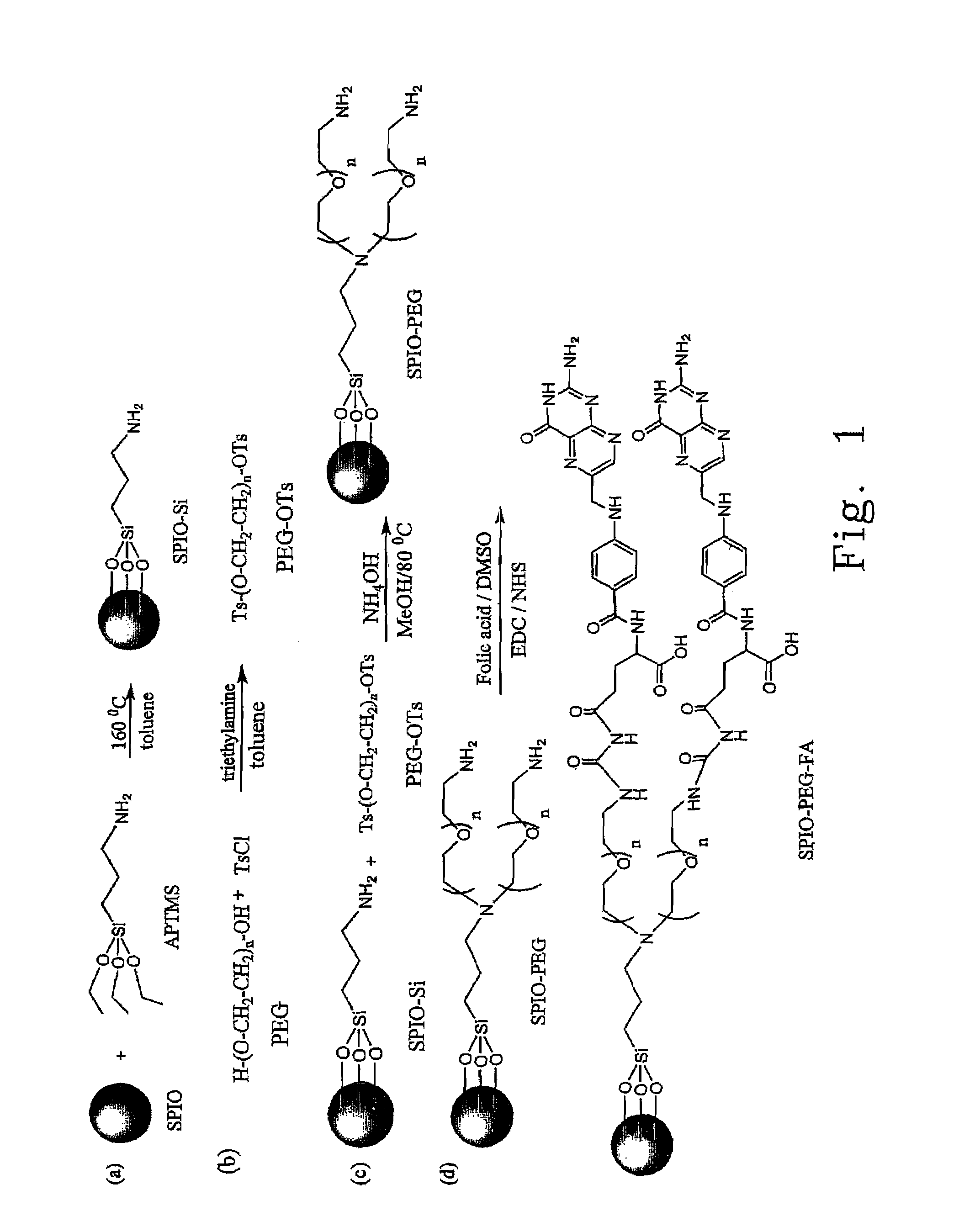
Folate-receptor-targeting iron oxide nanoparticles coated with poly(ethylene glycol)
InactiveUS7598335B2Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSynthesis methodsSuperparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle
The present invention provides the synthetic method and superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles capable of targeting to the folic acid receptors existing on the cell membranes and with high relaxivity. The iron oxide nanoparticles of the present invention can further be used as the contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Owner:KAOHSIUNG MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing high magnetic resonance sensitivity ferroferric oxide nano-particle with tumor-targeting function
InactiveCN101444630AAchieve tumor targeting functionFacilitate targeted diagnosticsIn-vivo testing preparationsTumor targetSuperparamagnetism
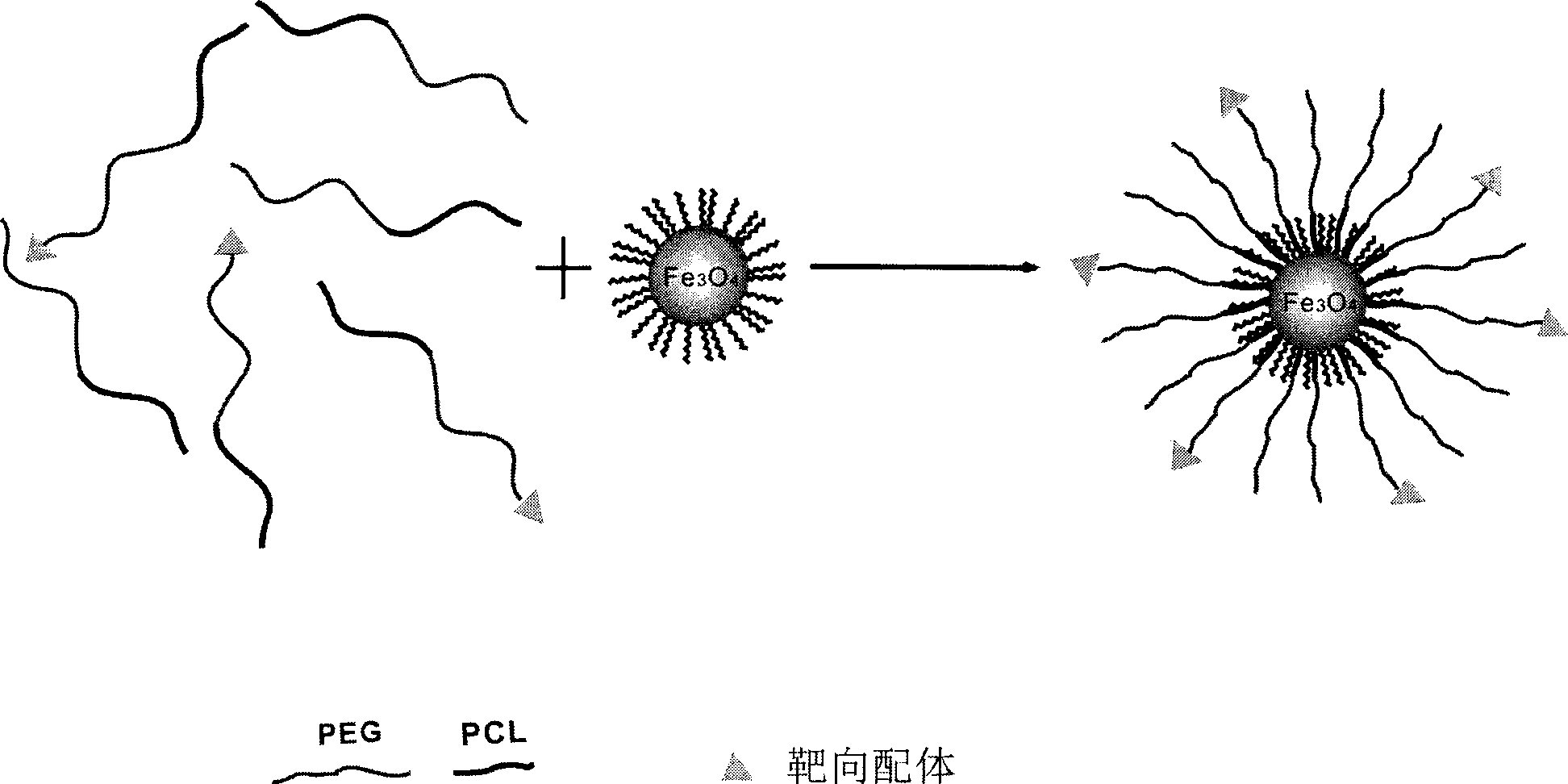
The invention discloses a method for preparing high magnetic resonance sensitivity ferroferric oxide nano-particle with tumor-targeting function. Amphiphilic block polymer of the end capping of tumor-targeted ligand and super-paramagnetic ferroferric oxide are dissolved in tetrahydrofuran, then the obtained solution is added into ionized water or distilled water, the tetrahydrofuran is volatilized, the super-paramagnetic ferroferric in the solution is separated out, washed by the distilled water, then dispersed into the ionized water or the distilled water, and finally centrifugalized, thus the nano-particle is obtained; the tumor-targeted ligand is folic acid, polypeptide or antibody. In the invention, by loading lipophilic ferroferric oxide nano-particle at self-assembled micellar inner core, the tumor-targeted and water-soluble ferroferric oxide nano-particle that is below 50 nm is developed. The tumor-targeting function is realized by coupling the folic acid or antibody at micellar surface. The invention has wide application prospect.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
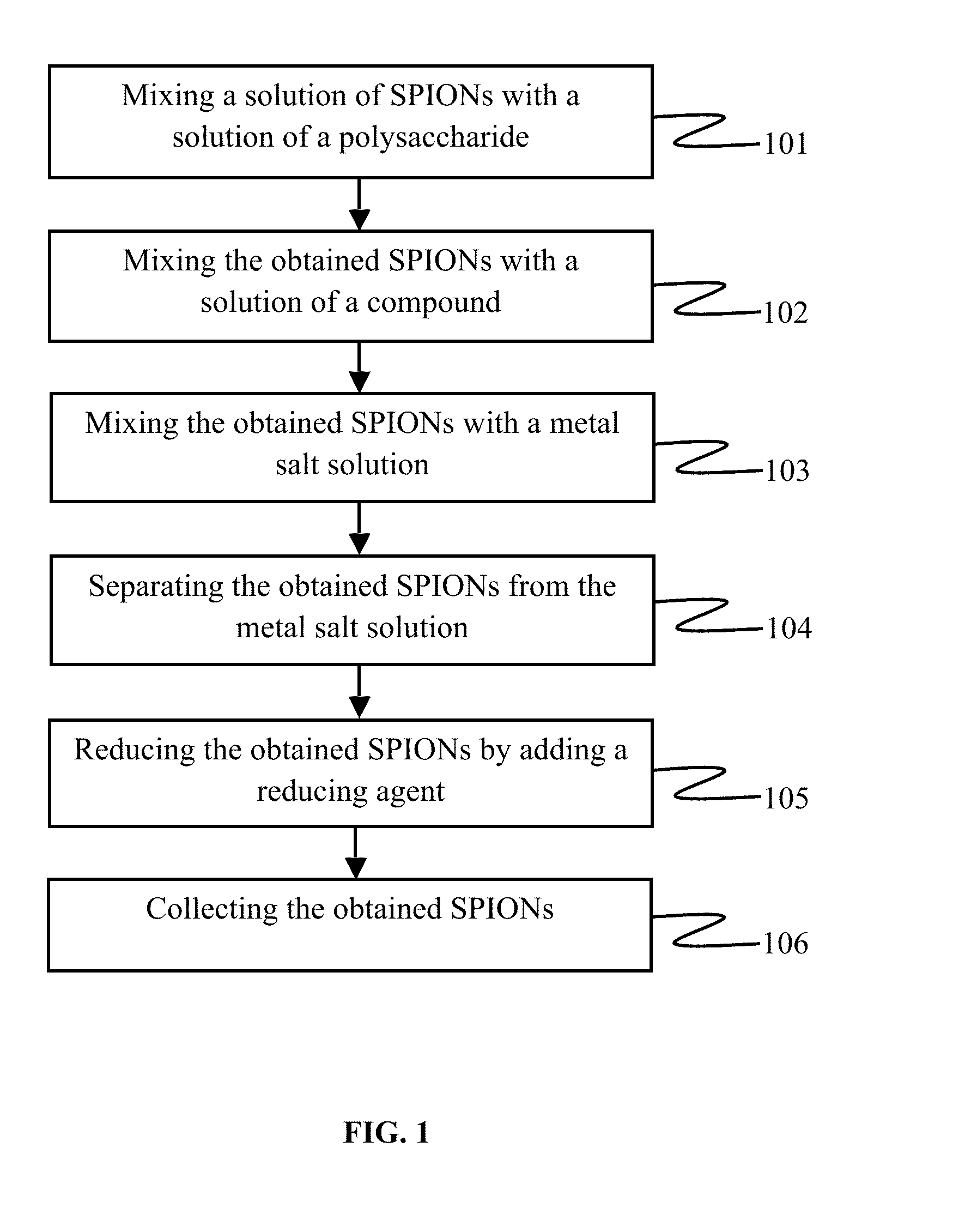
Super paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with metallic coatings and a method of syhthesizing the same
The various embodiments herein provide super paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs). The SPIONs have a plurality of metallic coatings and plurality of polymeric gaps. The embodiments herein also provide a method of synthesizing the SPIONs with metallic rings and polymeric gaps. The metallic coatings form a ring like structure on the outer surface of the SPION. The SPION has a size of 13 nm. The ring has a thickness of 2-3 nm. The rings are one or more in number. The polymeric gaps have a thickness of 3-5 nm. The polymeric gaps are one or more in number. The method involves mixing the SPIONs with a plurality of polymers and then forming a metallic ring on the outer surface of the SPIONs. The SPIONs have anti-bacterial properties and stop a growth of bacterial biofilms. The SPIONs also have SERS properties.
Owner:MAHMOUDI MORTEZA +2
Pharmaceutical raw material
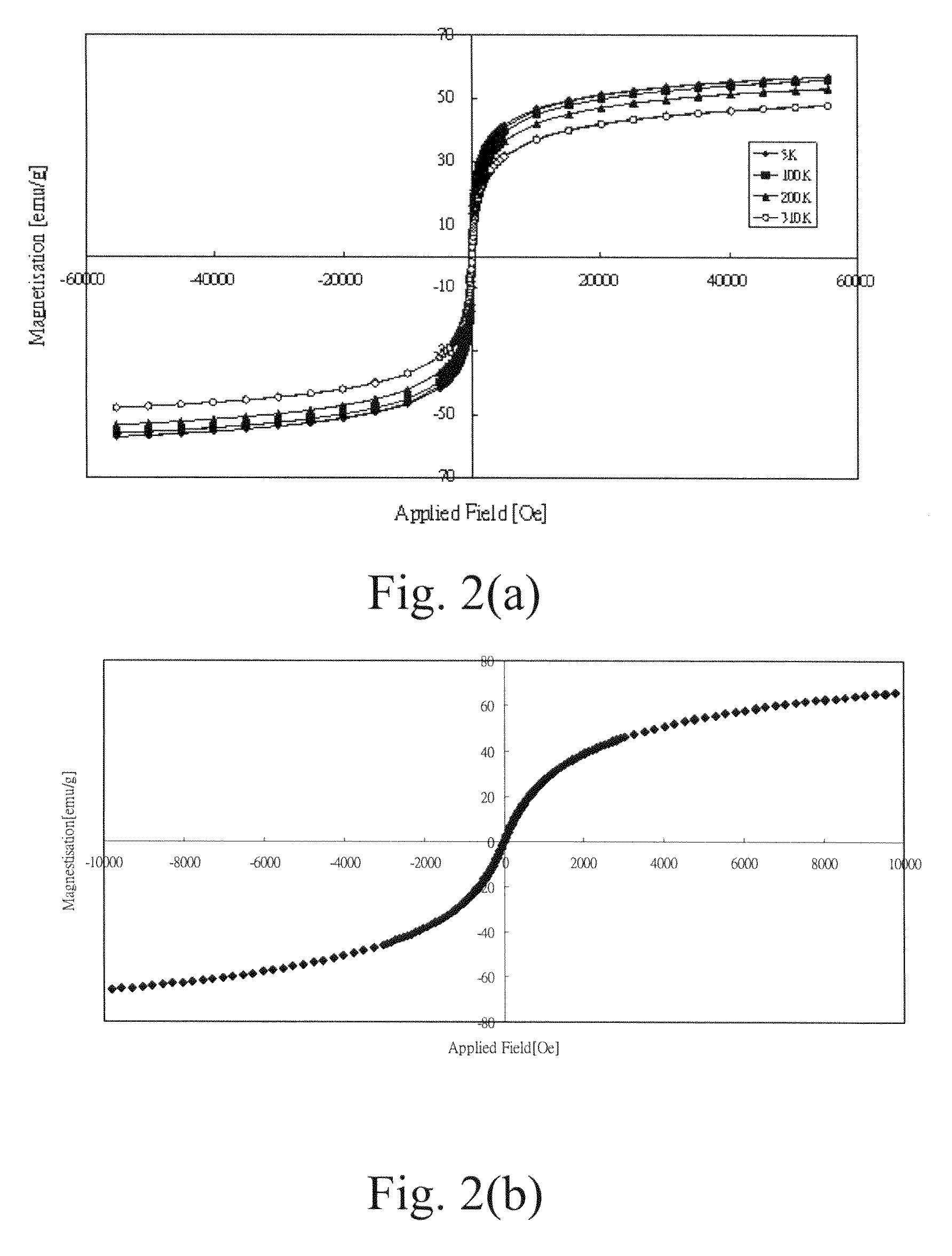
There are provided a pharmaceutical raw material capable of exhibiting a uniform functionality and producing magnetic particle-containing drugs for diagnosis and medical treatments with a high reproducibility. The pharmaceutical raw material comprises a monodisperse colloid sterile aqueous solution of magnetic iron oxide fine particles having an average particle diameter of 5 to 30 nm, a saturation magnetization of 50 to 90 Am2 / kg and a coercive force of 0.1 to 1.6 kA / m. The pharmaceutical raw material can be produced by forming magnetic iron oxide fine particles in the form of a colloid aqueous solution, purifying the resultant colloid aqueous solution of superparamagnetic iron oxide particles by water-washing and removing water-soluble salts by-produced upon the reaction from the reaction solution by an ordinary method, and replacing a dispersing medium of the purified colloid aqueous solution with ultrapure water.
Owner:TODA IND
Degradable nano-micelle capable of performing MR-fluorescence bimodal imaging as well as preparation method and application of degradable nano-micelle
ActiveCN106822924AImprove loading efficiencyEnables efficient bimodal labelingDispersion deliveryEmulsion deliveryResonanceFluorescence
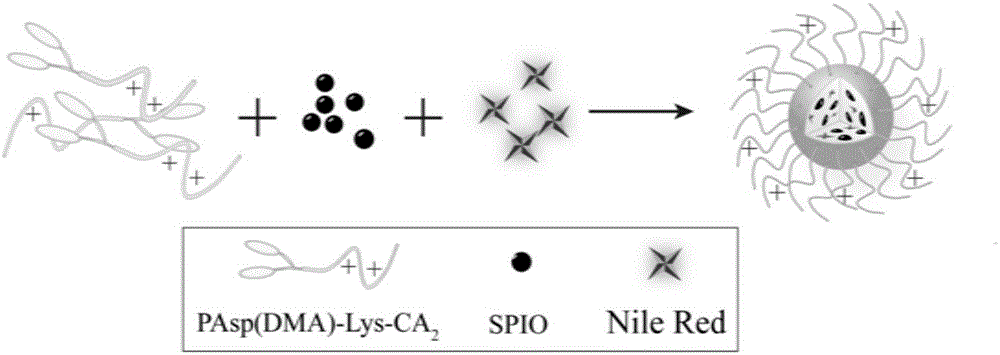
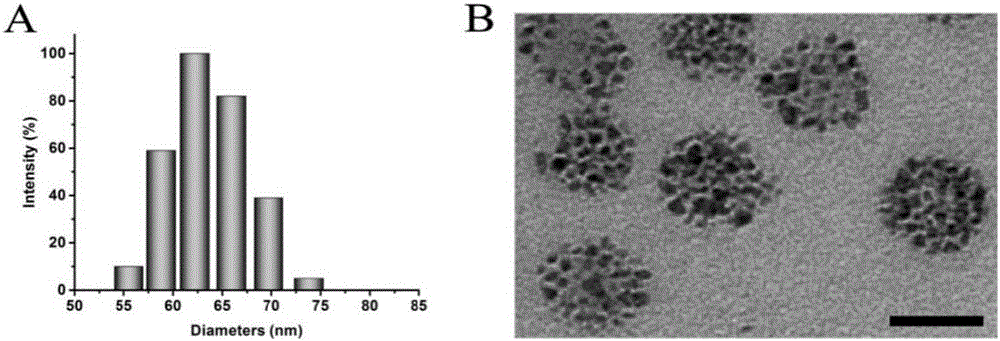
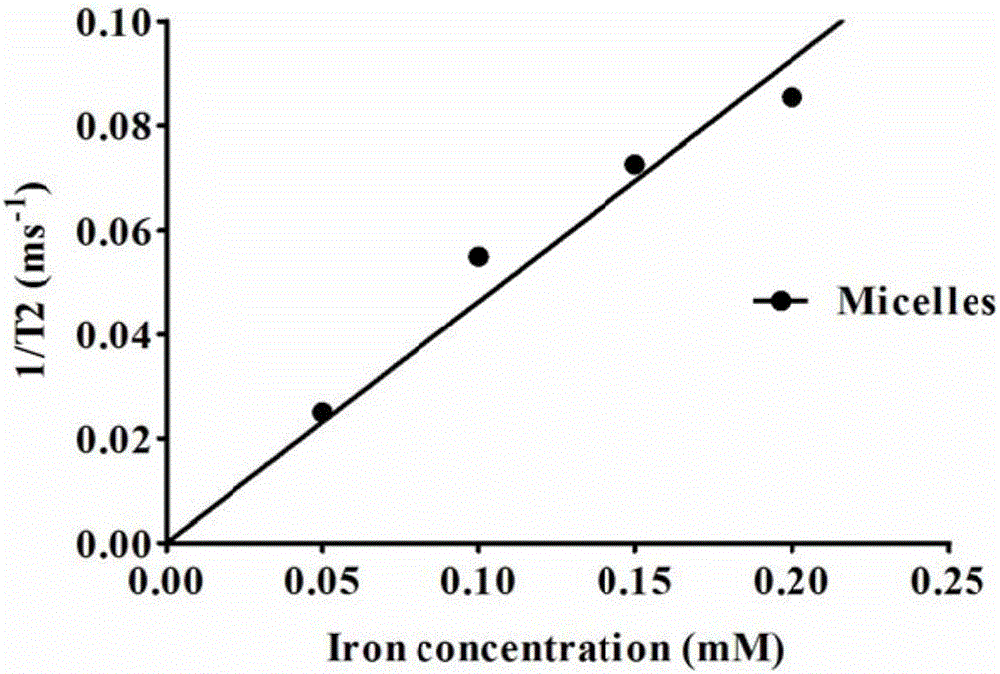
The invention belongs to the field of nano medicine and biomedical engineering and particularly discloses degradable nano-micelle capable of performing MR (magnetic resonance)-fluorescence bimodal imaging as well as a preparation method and an application of the degradable nano-micelle. The nano-micelle is based on amphipathic block polymer support PAsp(DMA)-CA2. A hydrophobic core of the micelle is used for supporting hydrophobic SPIO (superparamagnetic iron oxide) and fluorescent dye Nile red, neutral stem cells can be labeled in vitro safely and efficiently, after in-vivo transplantation of the neutral stem cells, distribution and migration conditions of the neutral stem cells in vivo can be traced in real time, safe and efficient MR-fluorescence bimodal imaging tracing of the stem cells can be realized, and the nano-micelle has broad application prospects.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
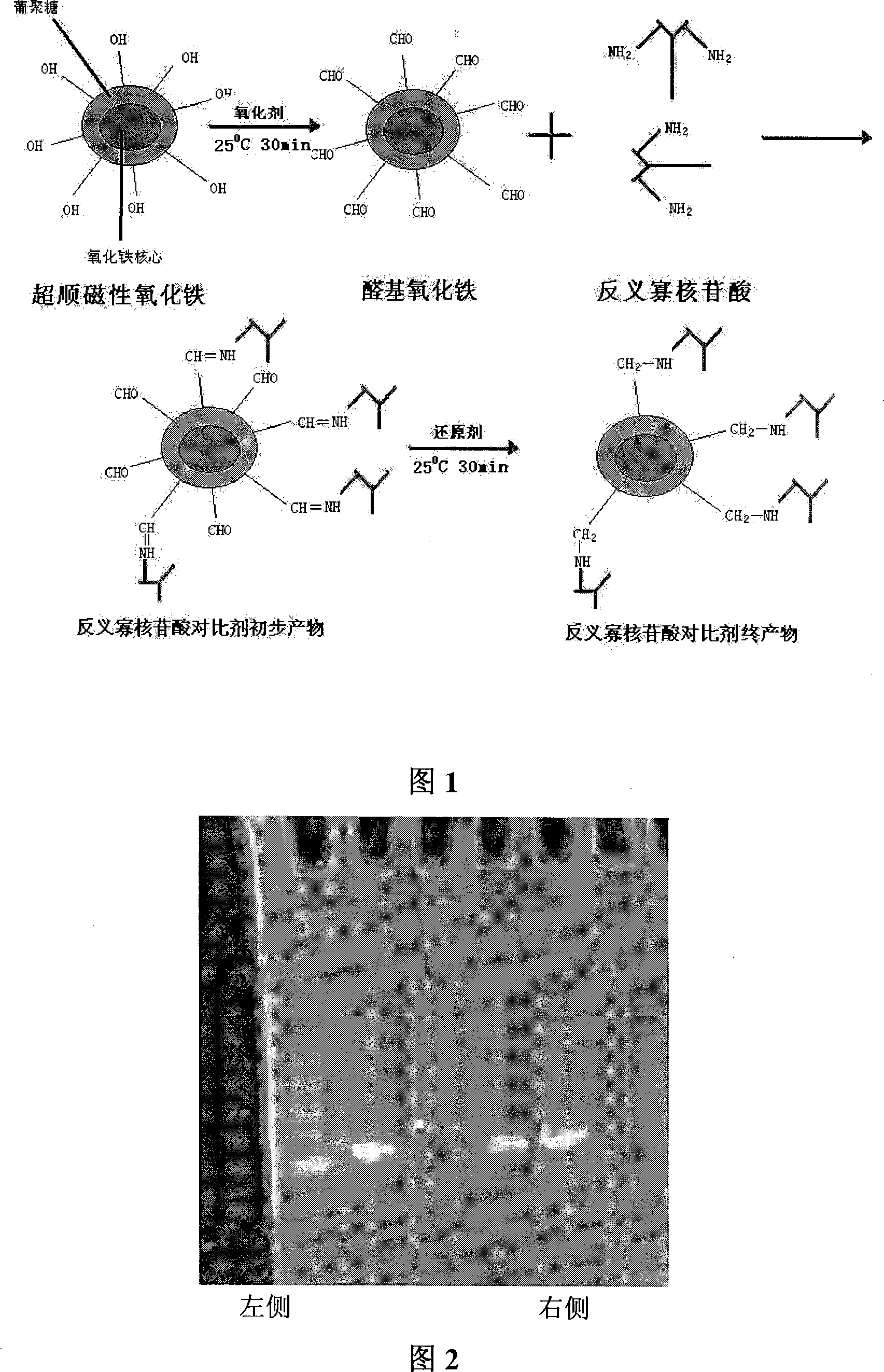
Antisense oligonucleotide probe contrast agent marked by superparamagnetism iron oxide and production of the same
InactiveCN101130093AImaging time window lengthIncrease spaceNMR/MRI constrast preparationsStage tumorSuperparamagnetism
The invention discloses a trans-oligonucleotide probe contrast-medium to mark superparamagnetism iron oxide, which consists of carrier constituted by gluglucosan enveloped by ferroferric oxide nanometer particle with superparamagnetism and trans-oligonucleotide segment of c-erbB2 cancer gene, wherein the trans-oligonucleotide connects the gluglucosan in the carrier at covalent bond. The invention also relates to a making method of the contrast-medium. The invention uses trans-gene technique of molecular biological domain into imaging diagnosis to combine the superiority and specificity of two advanced techniques, which increases the ratio of target / non-target of probe to the maximum degree to scan the size, position and anatomical relationship of adjacent structures of tumour through magnetic resonance, in order to build new imaging method of early-stage tumor diagnosis of specificity on the gene level. The invention can be applied to do early-stage imaging diagnosis for malignant tumour, epoophoron cancer, uterine neck cancer, esophagus cancer and cervical scale cancer.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
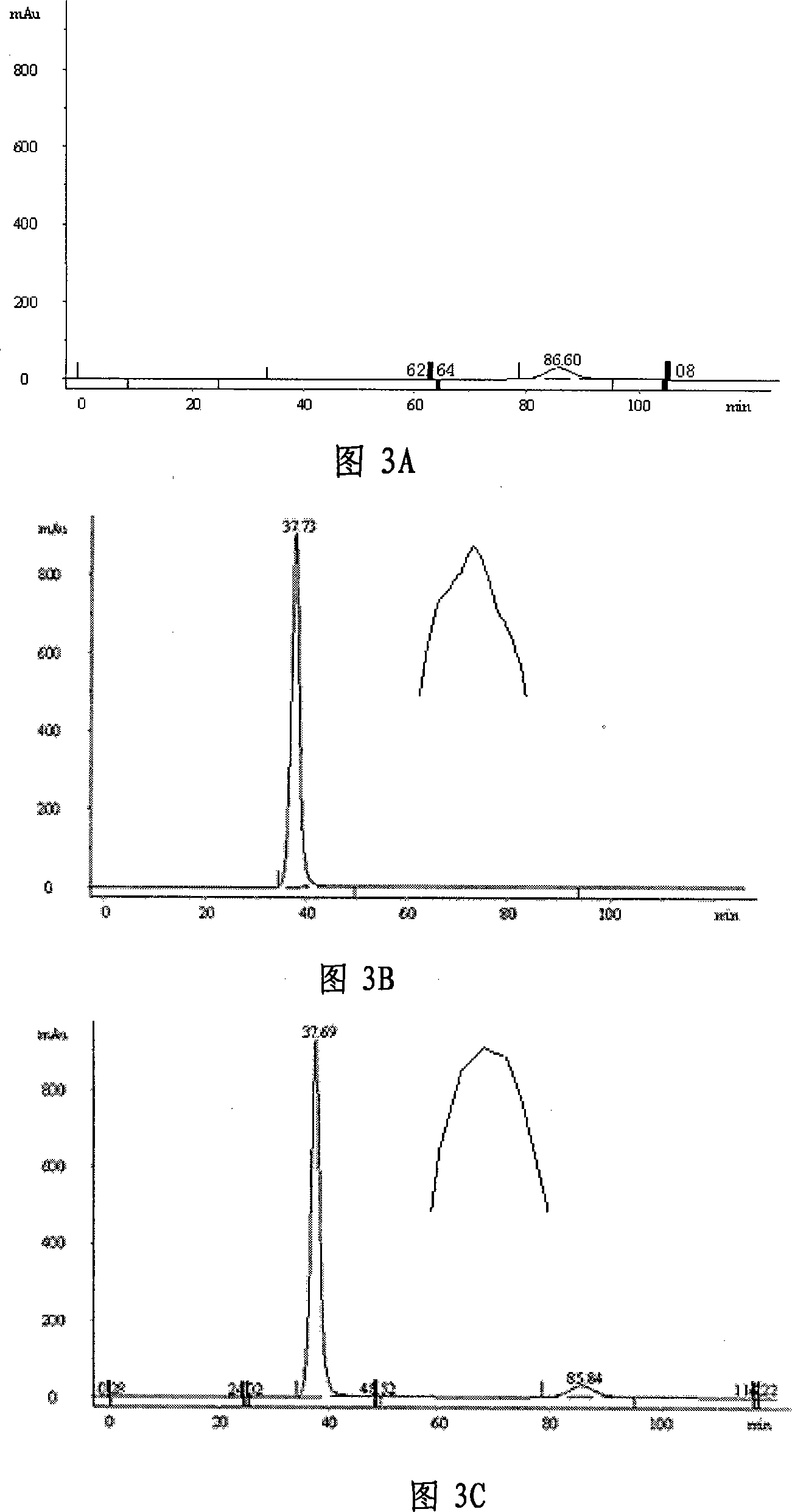
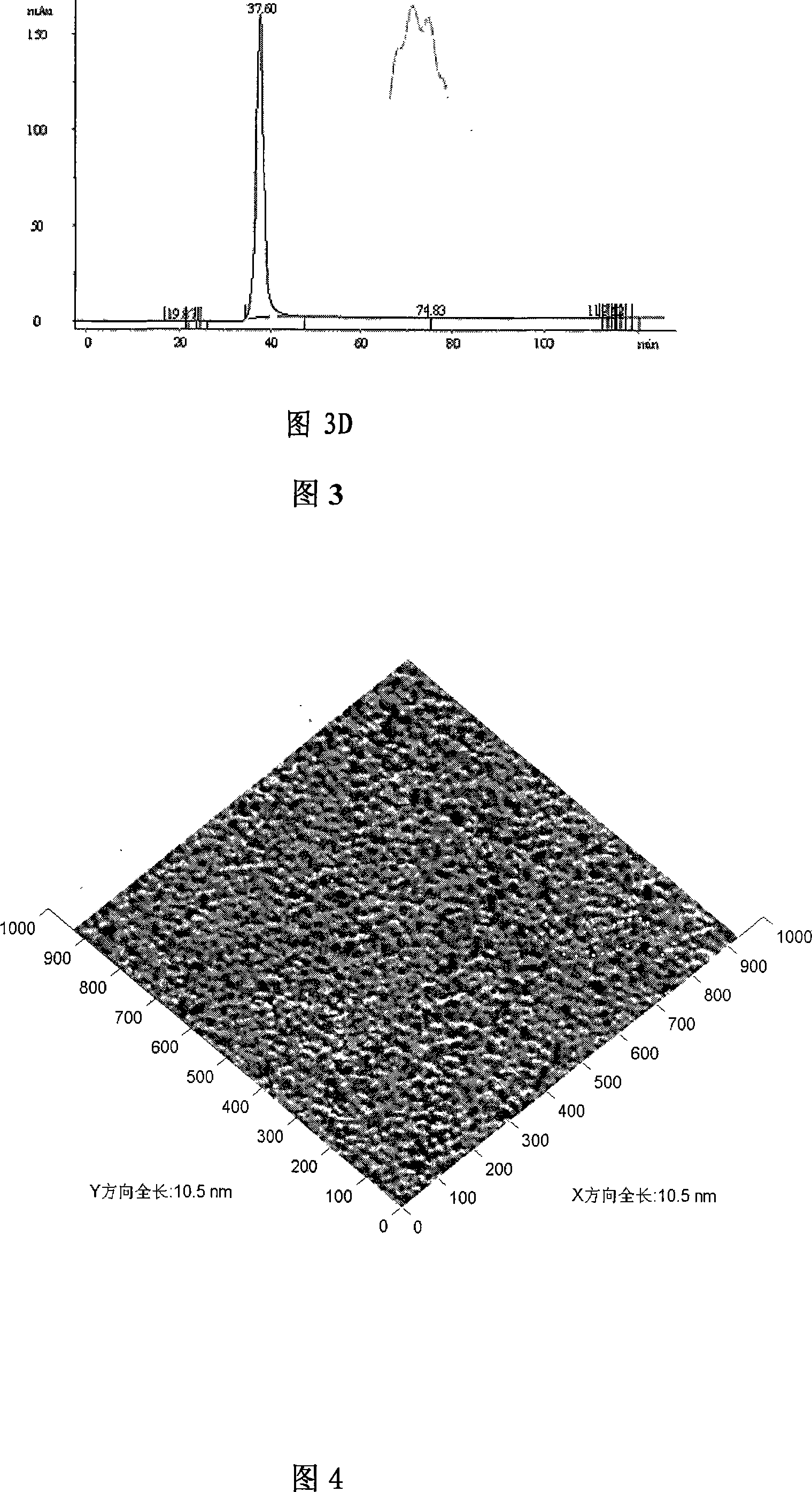
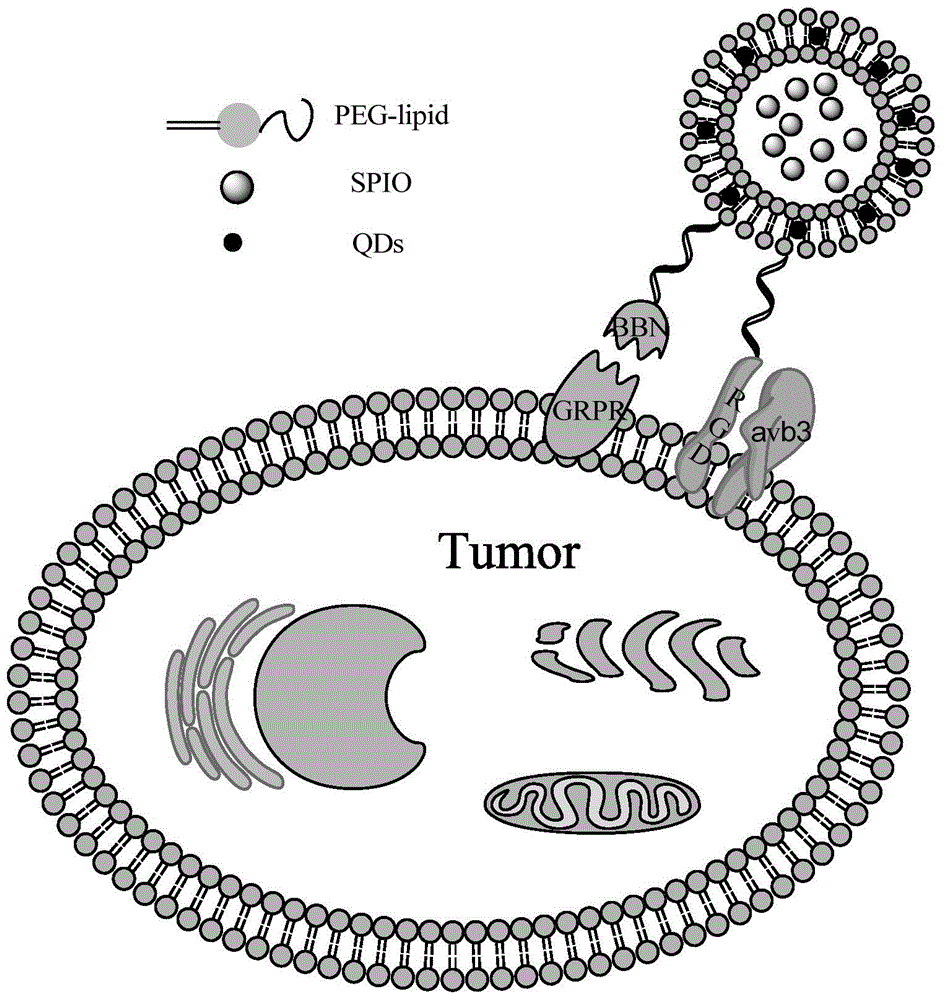
Preparation method and application of RGD@BBN double-targeted MR (magnetic resonance)/optical dual-mode molecular probe
InactiveCN105079826AGreat penetration depthGood biocompatibilityEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsImage contrastDual mode
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of an RGD@BBN double-targeted MR (magnetic resonance) / optical dual-mode molecular probe, wherein the RGD@BBN double-targeted MR / optical dual-mode molecular probe is prepared by the following steps: coating water-soluble superparamagnetic iron oxide ( SPIO) particles in hydrophilic core of lipidosome and coating oil-soluble QDs particles in hydrophobic lipid bilayer of the lipidosome by taking lipidosome as a carrier, and linking a double-targeted RGD@BBN ligand by virtue of a post-interpolation method. The RGD@BBN contained in the dual-mode molecular probe disclosed by the invention is interpolated and immobilized on the surface of the lipid bilayer by virtue of self-assembly, and the preparation method is mild in condition and is efficient and practical. According to the invention, a relatively independent space is coated by two different image contrast agents without changing the properties of the image contrast agents; and the prepared double-target dual-mode molecular probe, which simultaneously has RGD and BBN targeting functions, has targeting functions on RGD or (and) BBN receptor-positive tumors.
Owner:GUANGZHOU FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL (GUANGZHOU DIGESTIVE DISEASE CENT GUANGZHOU FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH)
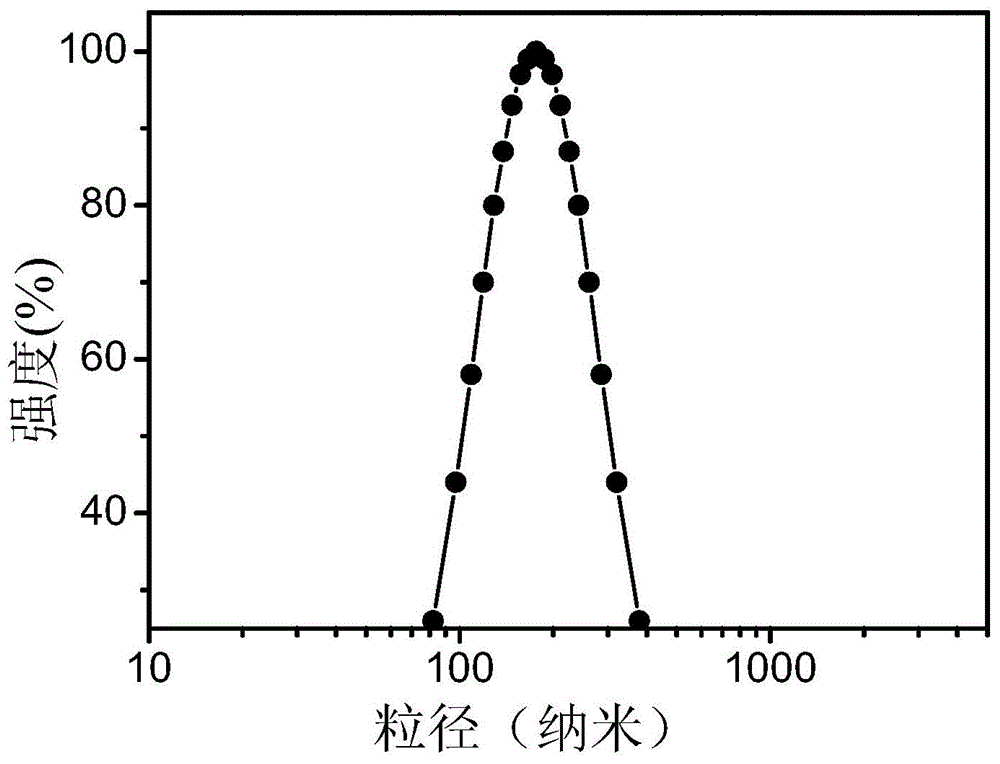
Stable nanoscale superparamagnetic iron oxide solution as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103316361AGood dispersionImprove contrast imaging capabilitiesNMR/MRI constrast preparationsStage tumorSuperparamagnetic iron oxide
The invention provides a stable nanoscale superparamagnetic iron oxide solution which is used as a contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The superparamagnetic iron oxide solution is characterized in that the particle size of nanoscale superparamagnetic iron oxide particles is stabilized to between 60 and 75 nanometers when the superparamagnetic iron oxide solution is stored for 12 months at an environmental temperature of 4 to 38 DEG C, and the nanoscale superparamagnetic iron oxide particles are in high dispersibility and free from agglomerating or precipitating. After nanoscale superparamagnetic iron oxide solution containing 25mcg of iron, provided by the invention, is subjected to intravenous injection in the MRI of an early-stage in-situ hepatic cancer tumor live model of a rat, the imaging performance of the tumor in the MRI is obviously improved, the position, boundary and size of the tumor can be clearly displayed, and the tumor image effect remains significant after 24 hours; the phenomenon that the boundary and size of the tumor are unclear occurs in the MRI of the early-stage in-situ hepatic cancer tumor live model without contrast agent. Therefore, the nanoscale superparamagnetic iron oxide solution provided by the invention has a stable nanometer solution characteristic, is obvious in tumor impacting effect under low-dosage injection, and unique in innovation and application prospect.
Owner:桑迪(武汉)生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com