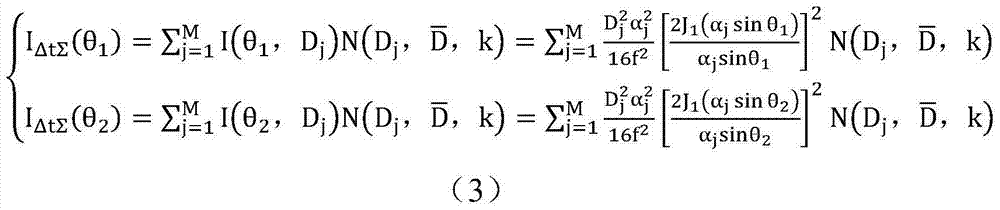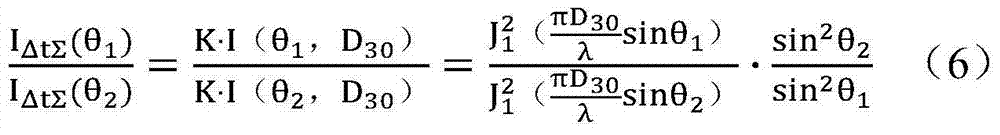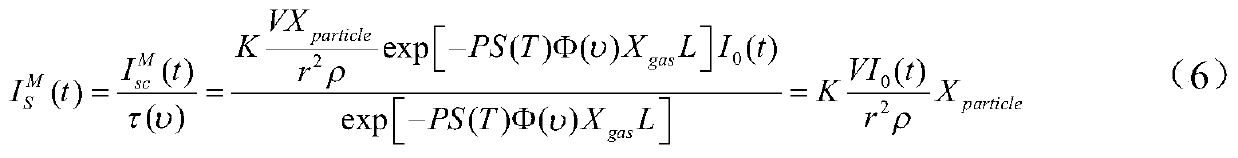Patents
Literature
74 results about "Light scatter measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
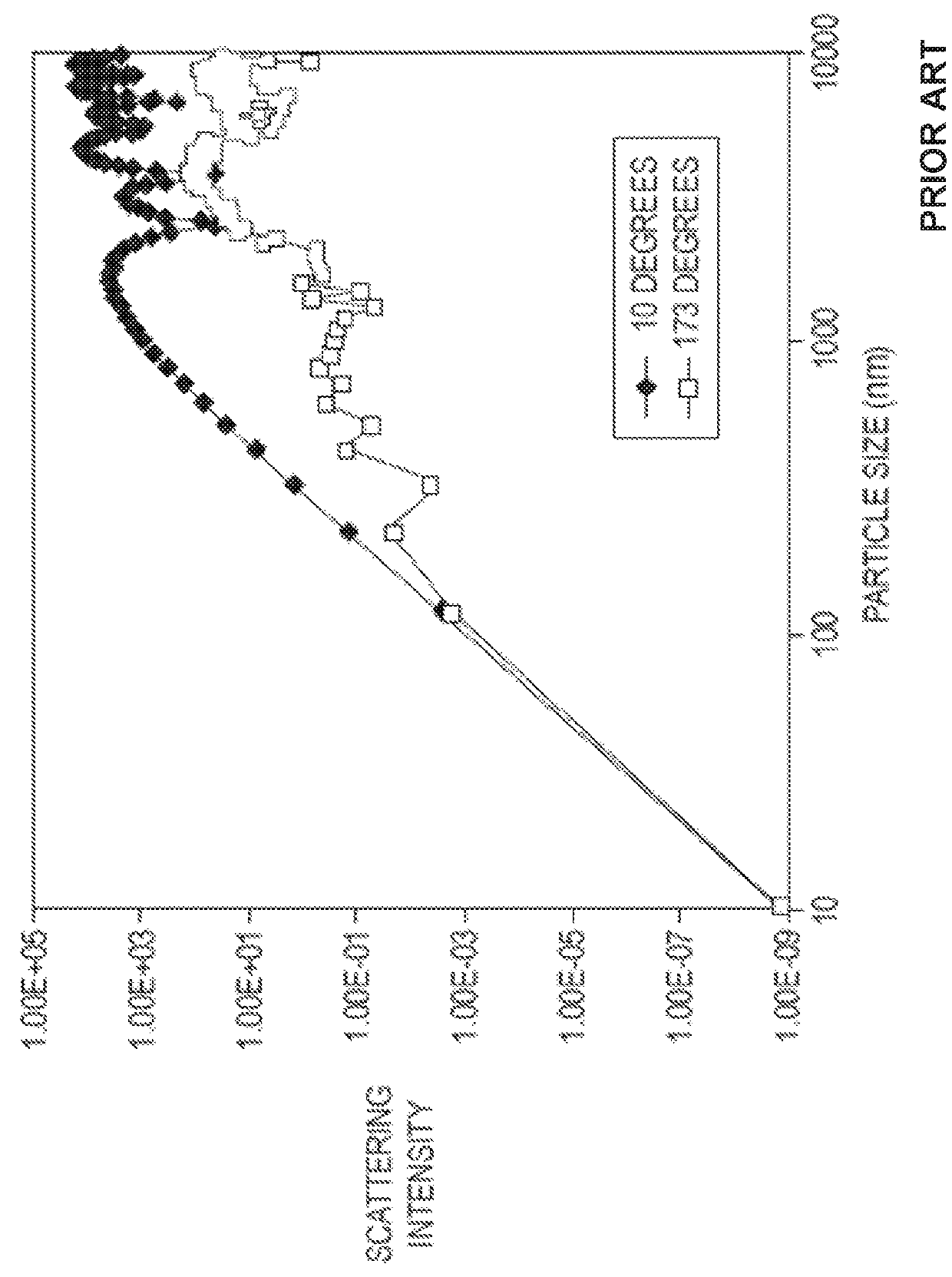
Multiangle light scattering (MALS) describes a technique for measuring the light scattered by a sample into a plurality of angles. It is used for determining both the absolute molar mass and the average size of molecules in solution, by detecting how they scatter light.
System and method for nanostructure apodization mask for transmitter signal suppression in a duplex telescope
Disclosed herein is a system for an apodization mask composed of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) for absorbing unwanted stray light. An apodization mask is a precise pattern or shape that is mathematically derived using light scattering measurement techniques to achieve optimal light absorption.Also disclosed herein is an apparatus for a duplex telescope with stray light suppressing capabilities comprising: a primary mirror for transmitting and receiving light; a secondary mirror for defocusing transmitted light onto the primary mirror and for focusing received light; a photodetector which receives light; a laser transmitter which transmits light; and an apodization mask for absorbing stray transmitted light.
Owner:NASA
Multi-purpose reagent system and method for enumeration of red blood cells, white blood cells and thrombocytes and differential determination of white blood cells
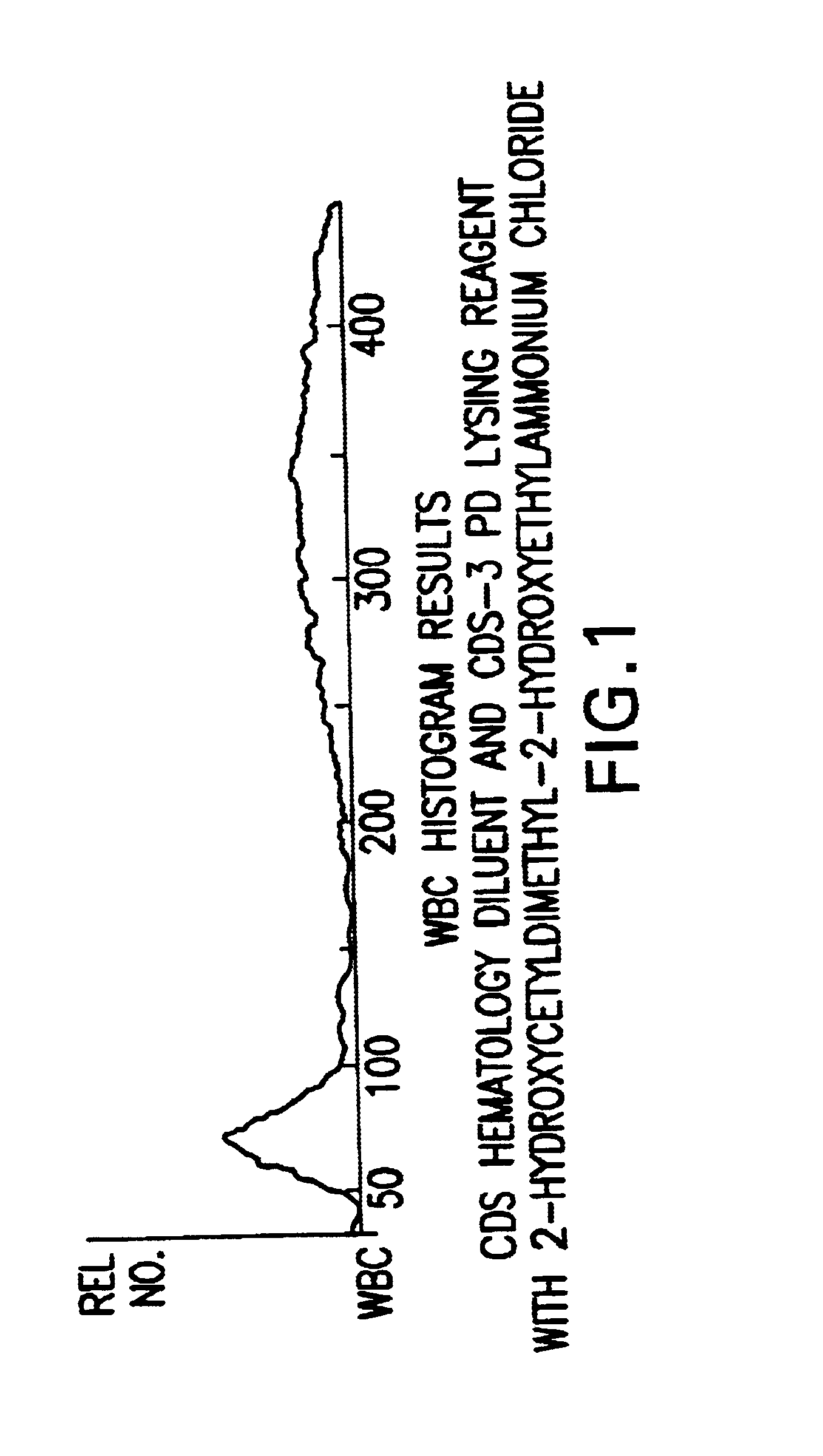
InactiveUS6632676B1Stable blood diluentWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationLight scatter measurementSystem requirements
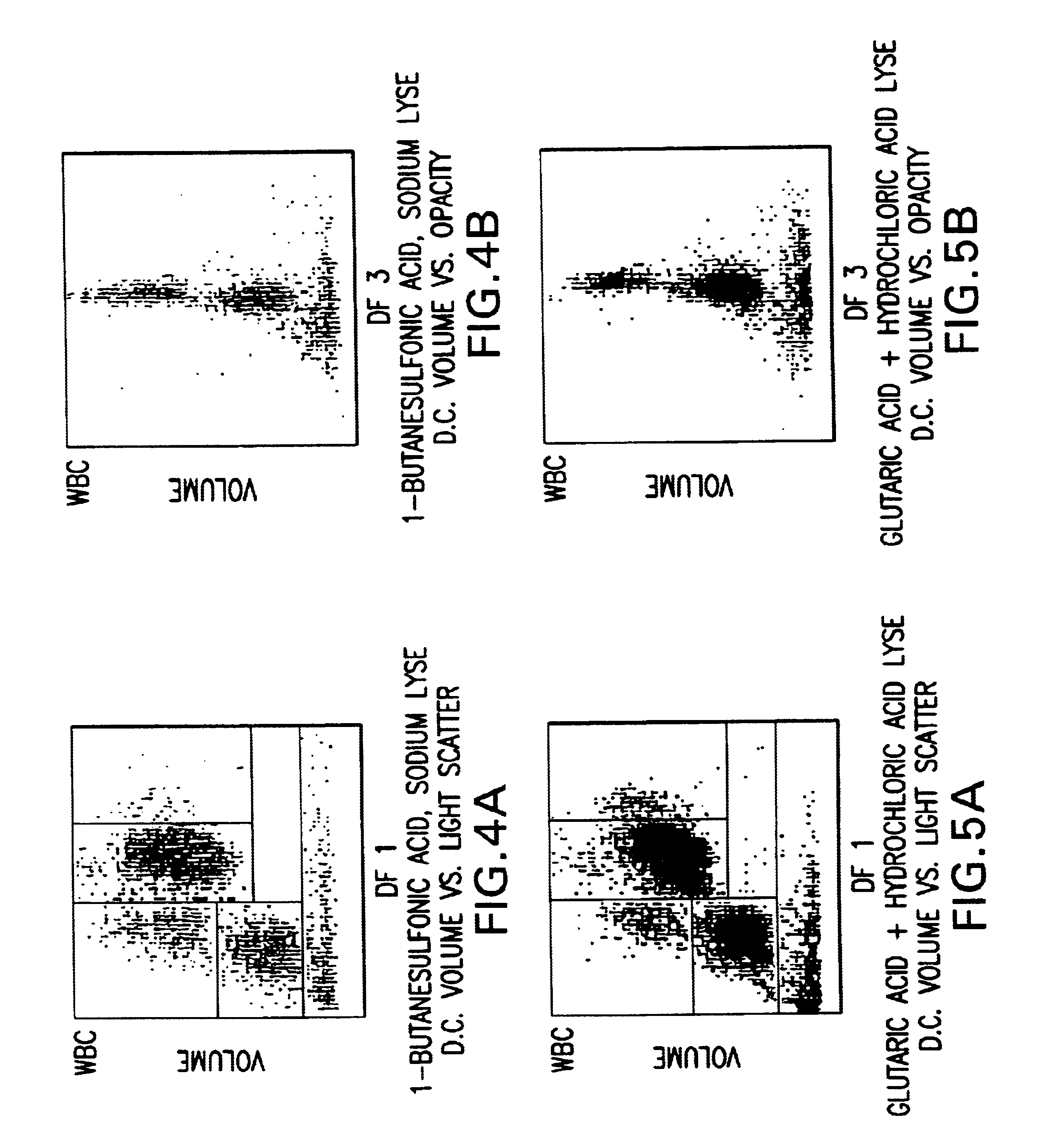
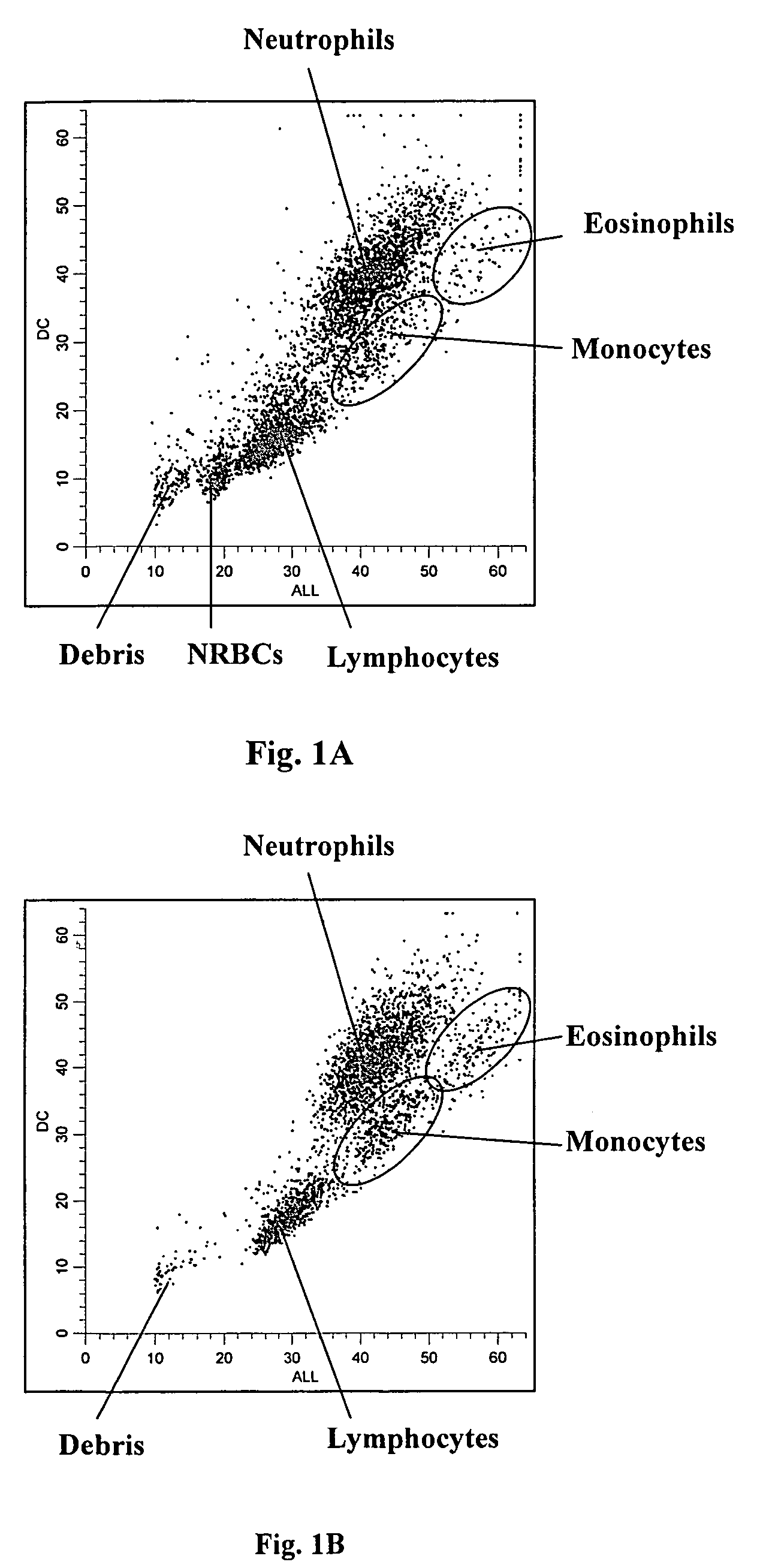
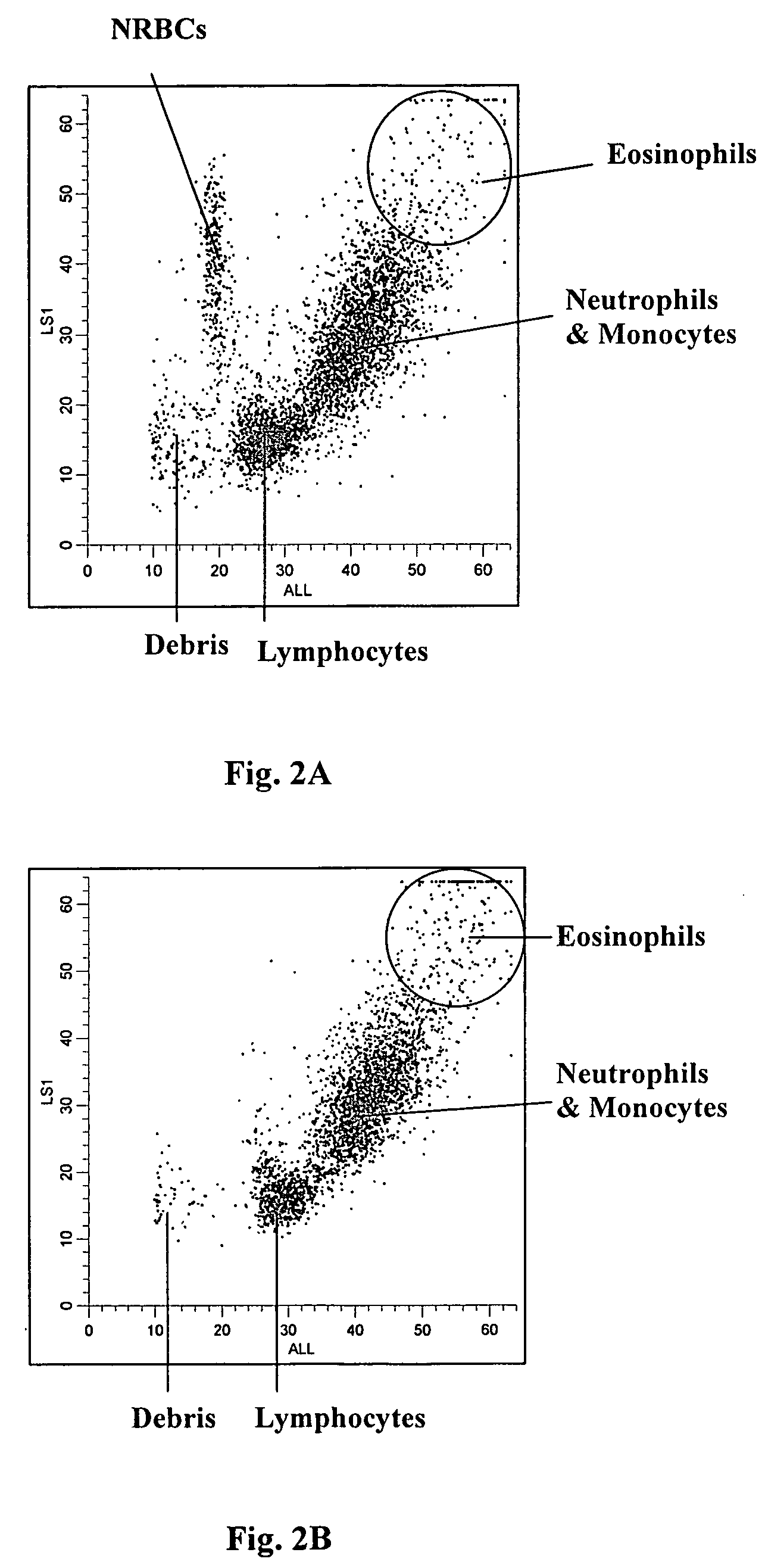
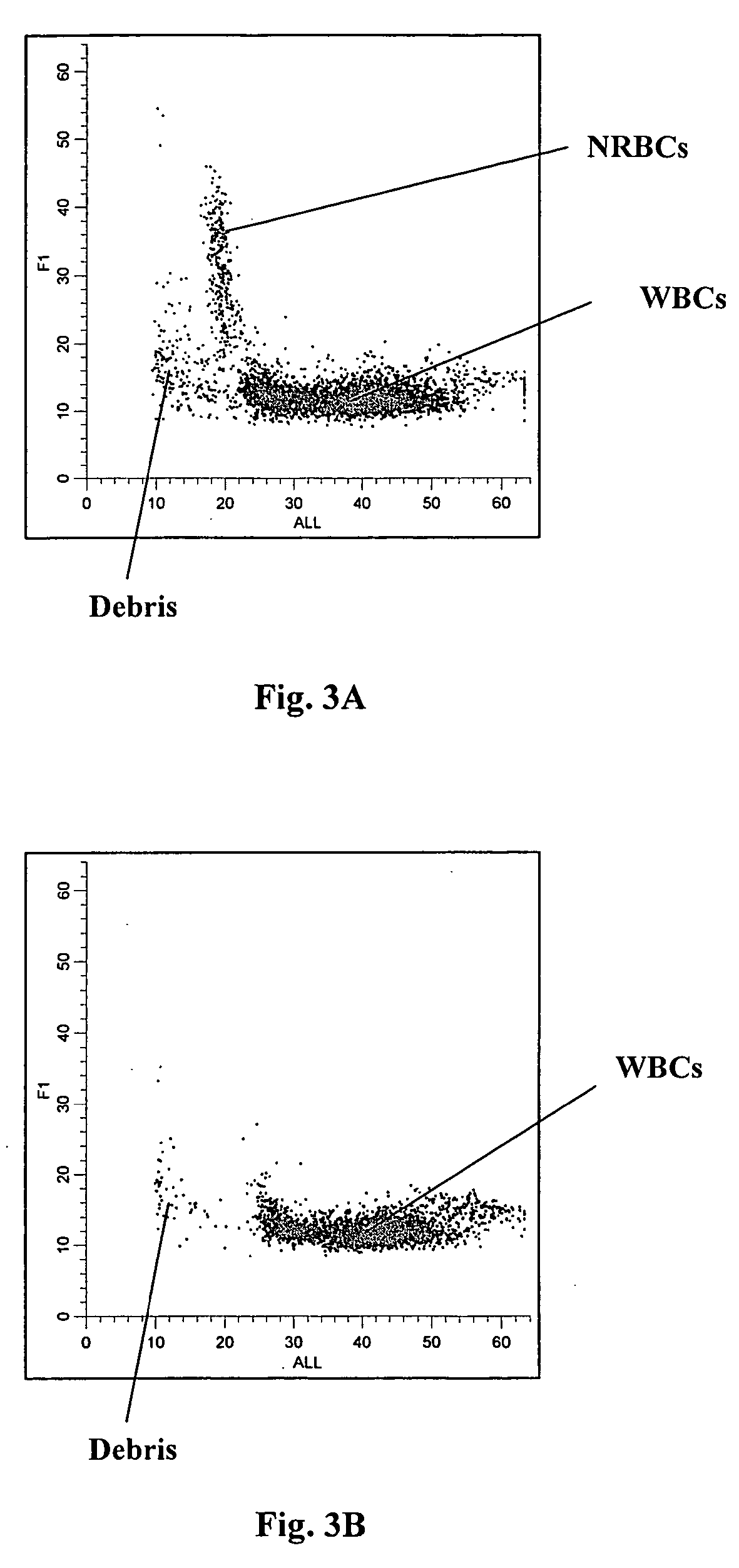
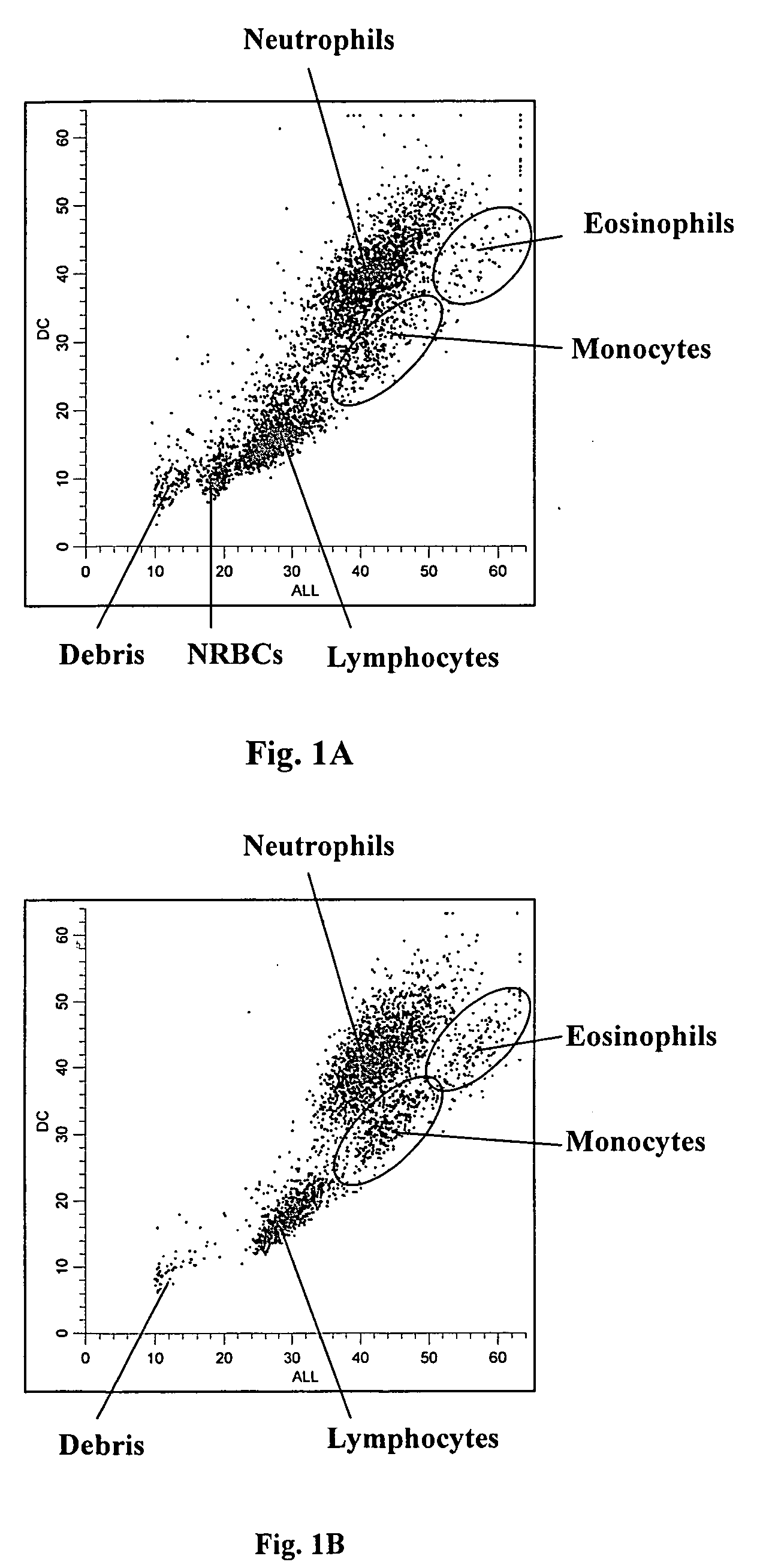
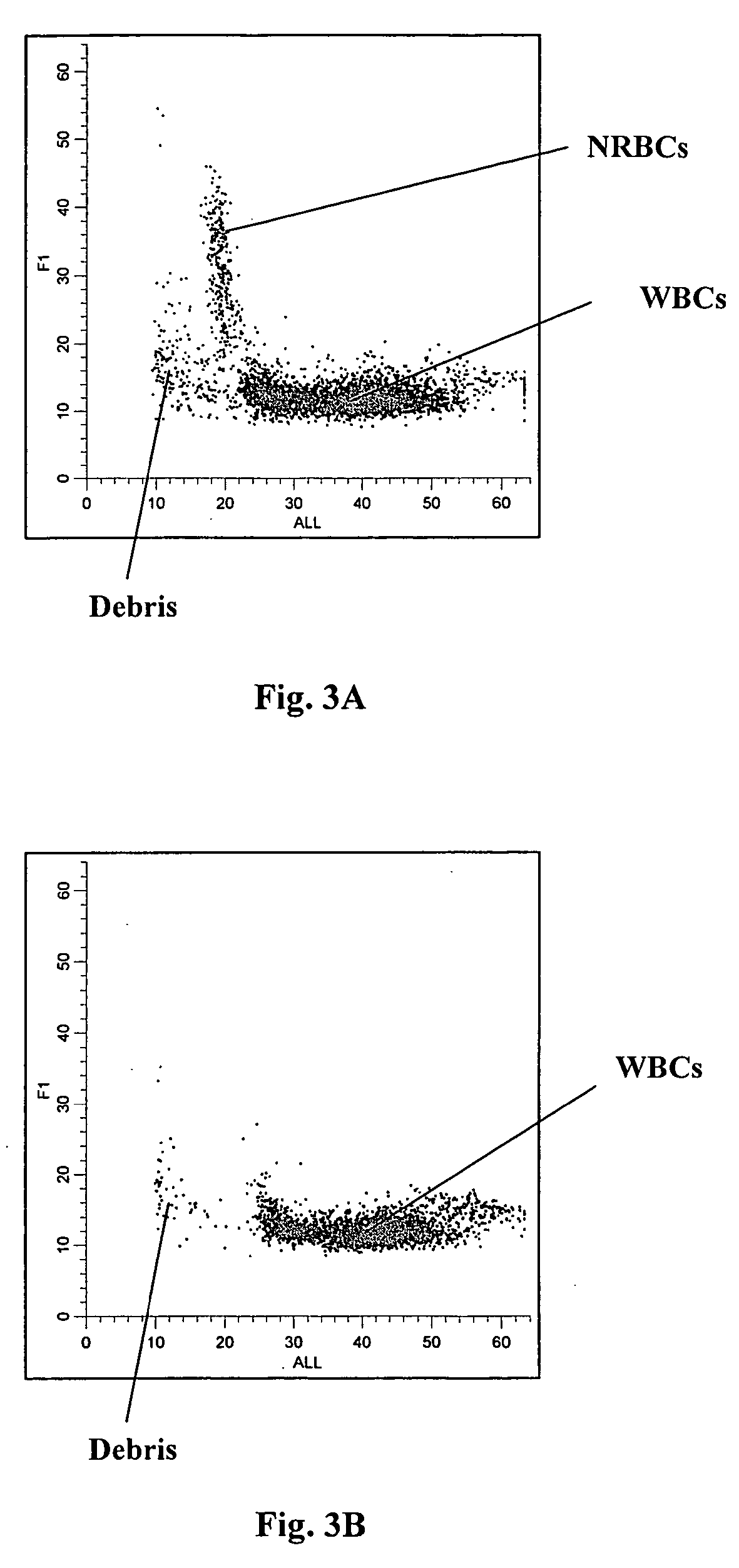
A novel reagent system for use with automated and semi-automated hematology analyzers including an essentially isotonic blood diluting reagent, a blood cell lysing and hemoglobin conversion reagent, and a second lysing reagent for differentiating white blood cells into classes by size and functional characteristics. The diluent reagent enhances properties for counting and sizing blood specimens, while stabilizing cellular volume and cellular integrity for many hours. The blood cell lysing reagent removes red blood cells and enables subsequent enumeration of white blood cells and simultaneous determination of hemoglobin without use of the toxic cyanide anion. The third lysing reagent and a companion quenching differentiates blood cells into classes by size and functional characteristics, based on d.c. impedance volume, conductivity / opacity and light scatter measurements. The companion quenching reagent adjusts pH and conductivity of the final measurement solution to match the analyzer system requirements. Novel methods for use of the reagents with automated and semi-automated hematology analyzers are also provided.< / PTEXT>
Owner:CLINICAL DIAGNOSTICS SOLUTIONS
Method of measurement of nucleated red blood cells
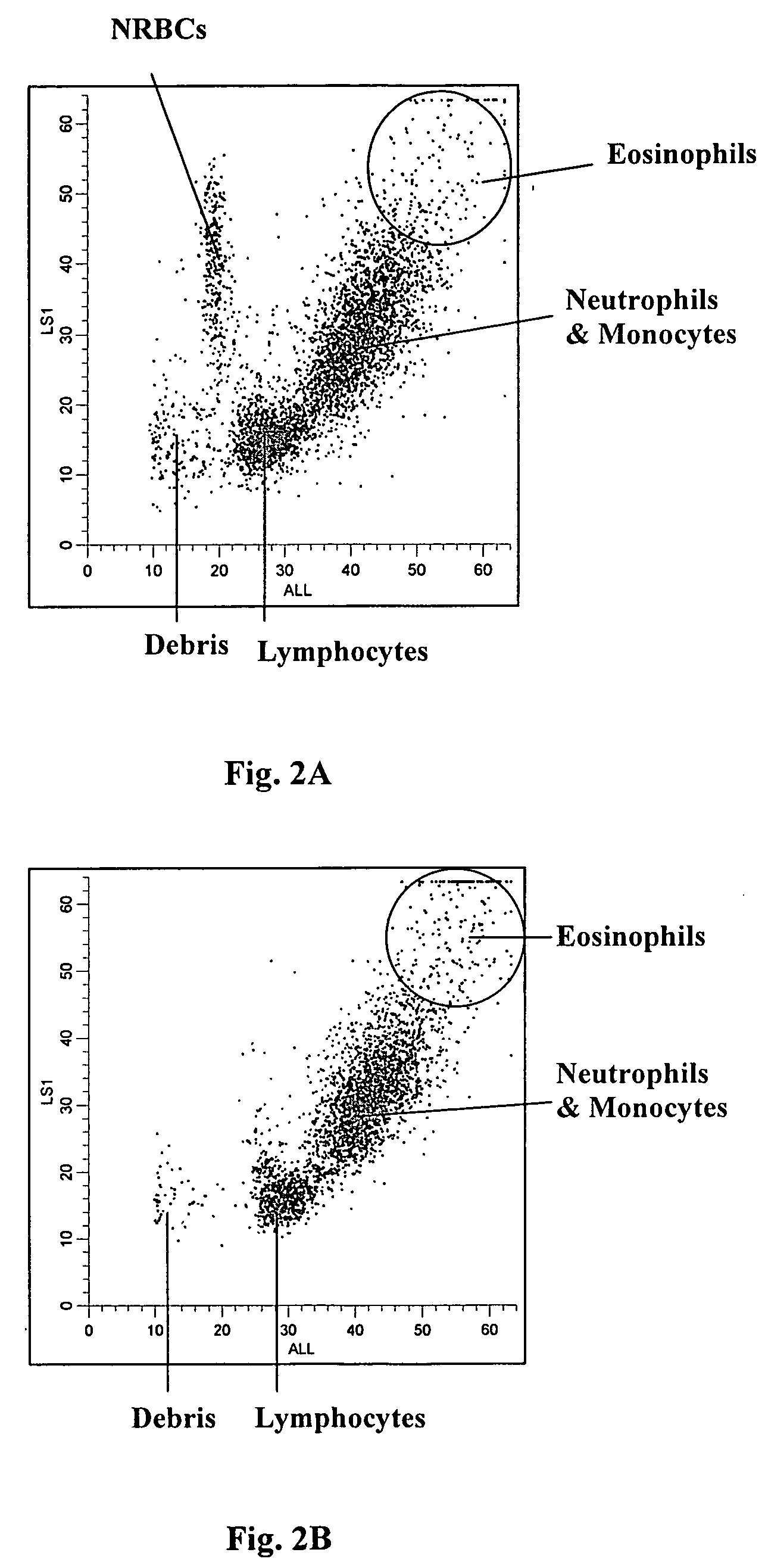
Methods are provided for measurement of nucleated red blood cells in a blood sample. The methods include exposing a blood cell sample to a reagent system to lyse mature red blood cells, subsequently analyzing nucleated red blood cells in a flow cell by axial light loss, DC impedance, and medium angle light scatter measurements; by axial light loss, low angle light scatter, and medium angle light scatter measurements; or by axial light loss, DC impedance, low angle light scatter, and medium angle light scatter measurements; and then differentiating nucleated red blood cells from other cell types by using measured signals and / or functions thereof.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Method of measurement of nucleated red blood cells
Methods are provided for measurement of nucleated red blood cells in a blood sample. The methods include exposing a blood cell sample to a reagent system to lyse mature red blood cells, subsequently analyzing nucleated red blood cells in a flow cell by axial light loss, DC impedance, and medium angle light scatter measurements; by axial light loss, low angle light scatter, and medium angle light scatter measurements; or by axial light loss, DC impedance, low angle light scatter, and medium angle light scatter measurements; and then differentiating nucleated red blood cells from other cell types by using measured signals and / or functions thereof.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Method for measuring mass concentration of particulate matter
ActiveCN104122180AEnsure consistencyVarious conditions in consistent operationParticle suspension analysisLight scatter measurementError factor
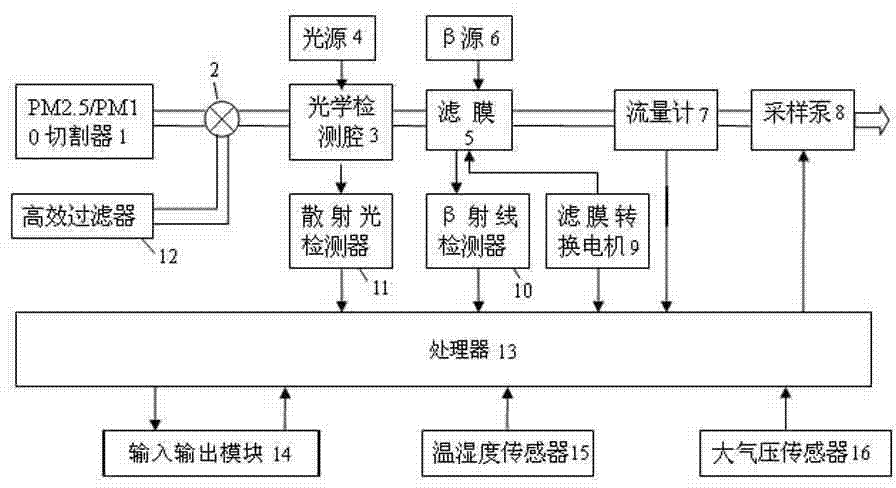
The invention relates to a method for measuring the mass concentration of a particulate matter. A processor controls a sampling pump so that airflow enters from a particulate matter collecting unit, atmospheric particulate matter information is acquired, whether an instrument needs to be calibrated is judged, a beta-ray calibration module is started to calibrate the parameter values of a light scattering measurement module if calibration is needed, and the light scattering measurement module is turned on after the parameters are calibrated; and if calibration is not needed, the light scattering measurement module directly carries out measurement. By combining a light scattering method for measuring the concentration of the particulate matter with a beta-ray method, the measurement is accurate and data are directly read on line in real time; the beta-ray calibration module and the light scattering measurement module share one gas path, so as to ensure that various conditions in the calibration process are consistent and reduce error factors; and the parameters of the light scattering measurement module are calibrated by using the beta-ray calibration module when the measurement environment is changed, and the light scattering measurement module is separately utilized to measure the concentration of the particulate matter when the measurement environment is not changed.
Owner:QINGDAO ZHONGRUI INTELLIGENT INSTR
Detecting and counting bacteria suspended in biological fluids
InactiveUS20080106737A1Light level decreaseLower Level RequirementsWithdrawing sample devicesScattering properties measurementsCuvetteForward scatter
System and method for detecting and counting bacteria suspended in a biological fluid by means of light scattering measurements is provided. In accordance with the method of the invention the level of signal to noise of the measured intensities of light scattered by a sample of the biological fluid is significantly enhanced for forwardly scattered light within a range of scattering angles which are smaller compared to a predefined maximal scattering angle. The system of the invention includes a cuvette adapted to contain a sample of the biological fluid whose sidewalls and windows are suitably constructed and arranged to significantly reduce the level of reflected light obscuring the scattering patterns measured within the range of scattering angles considered.
Owner:WEICHSELBAUM AMNON +2
Counting Bacteria and Determining Their Susceptibility to Antibiotics
ActiveUS20090325210A1Analysis material containersMicrobiological testing/measurementSuspended particlesLight scatter measurement
A method for detecting and counting particles suspended in fluids, such as bacteria suspended in urine, utilizing dynamic features of the suspended particles and employing light scattering measurements. The disclosed method is suitable for determining the susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics. A cuvette for detecting bacteria in fluids, which is especially suited for the light scattering measurements, is provided.
Owner:IP SPECIALISTS LTD
Counting bacteria and determining their susceptibility to antibiotics
ActiveUS8339601B2Analysis material containersMicrobiological testing/measurementSuspended particlesBacteriuria
A method for detecting and counting particles suspended in fluids, such as bacteria suspended in urine, utilizing dynamic features of the suspended particles and employing light scattering measurements. The disclosed method is suitable for determining the susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics. A cuvette for detecting bacteria in fluids, which is especially suited for the light scattering measurements, is provided.
Owner:IP SPECIALISTS LTD
Detecting bacteria in fluids
InactiveUS20070211251A1Microbiological testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsLight scatter measurementFiltration
A method for the detection of bacteria in aqueous fluids in the form of solutions, emulsions and or suspensions, such as drinking water, liquid food and drinks and biological fluids such as urine, spinal and / or amniotic fluids and serums by measurement of light scattering The fluid suspected of containing bacteria is filtered, first to exclude particles of sizes larger than the size of the expected bacteria. Other filtration methods are used in addition to exclude different constituents of the examined fluid. Ion exchange chromatography is such a method. The verification of bacterial contamination and the calculation of its level is performed by matching measured scattering profiles with pre-stored calibrated scattering profiles. A system for carrying out the measurements including cuvette units suited for light scattering measurements is provided.
Owner:WEISCHSELBAUM AMNON
Light scattering apparatus, light scattering measurement method, light scattering analysis apparatus and light scattering measurement analysis method
InactiveUS20060044558A1Scattering properties measurementsLight scatter measurementCorrelation function
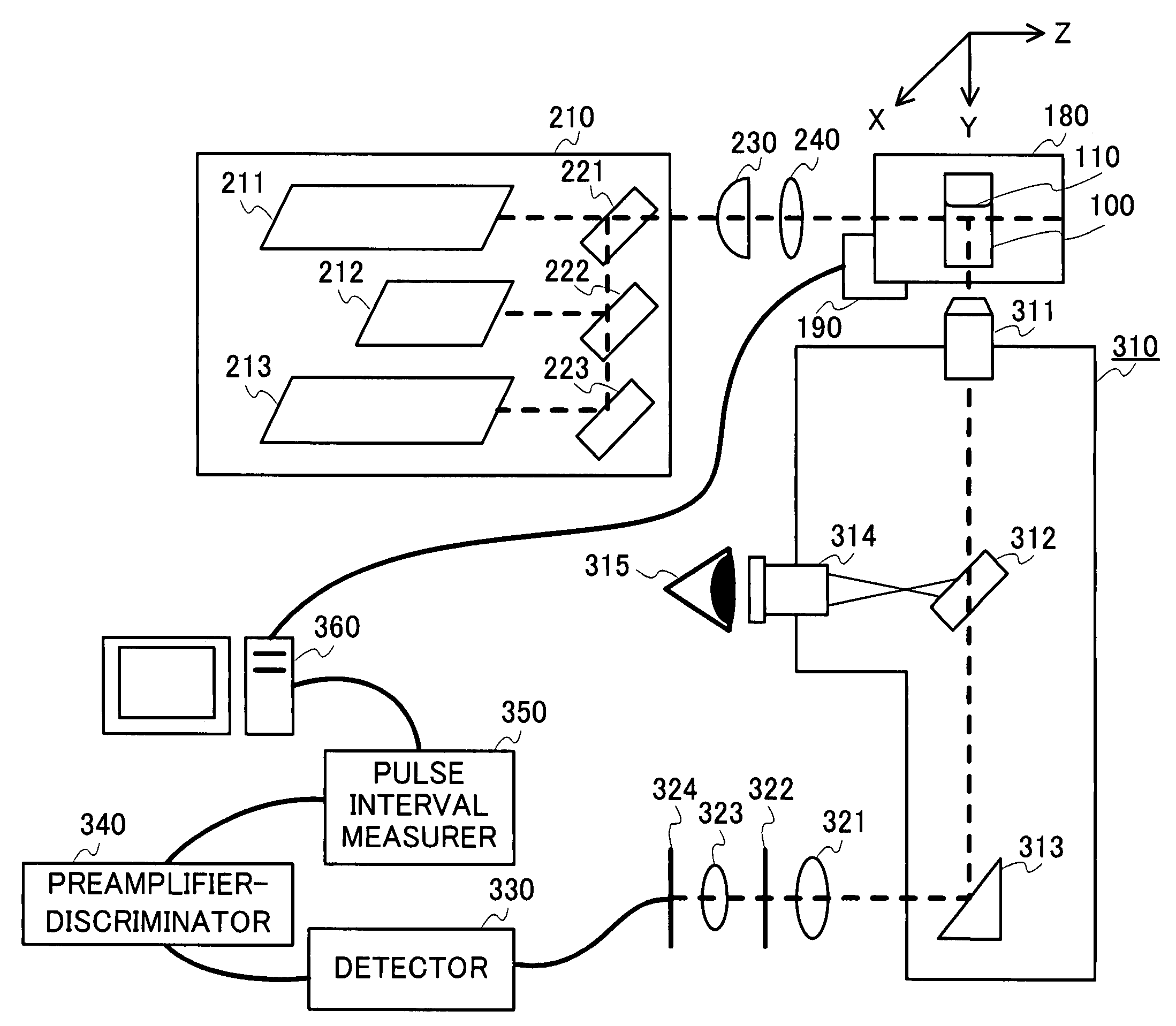
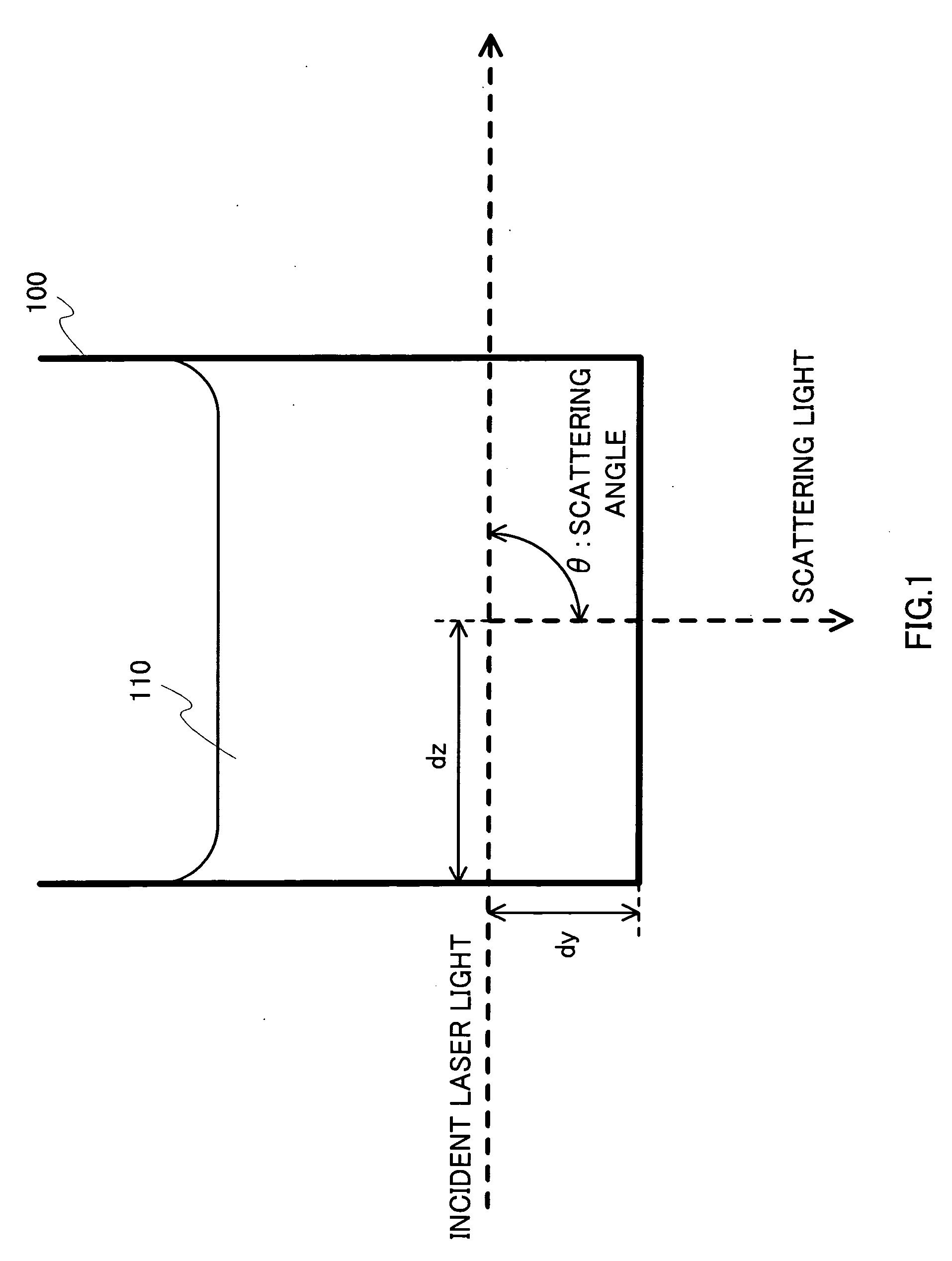
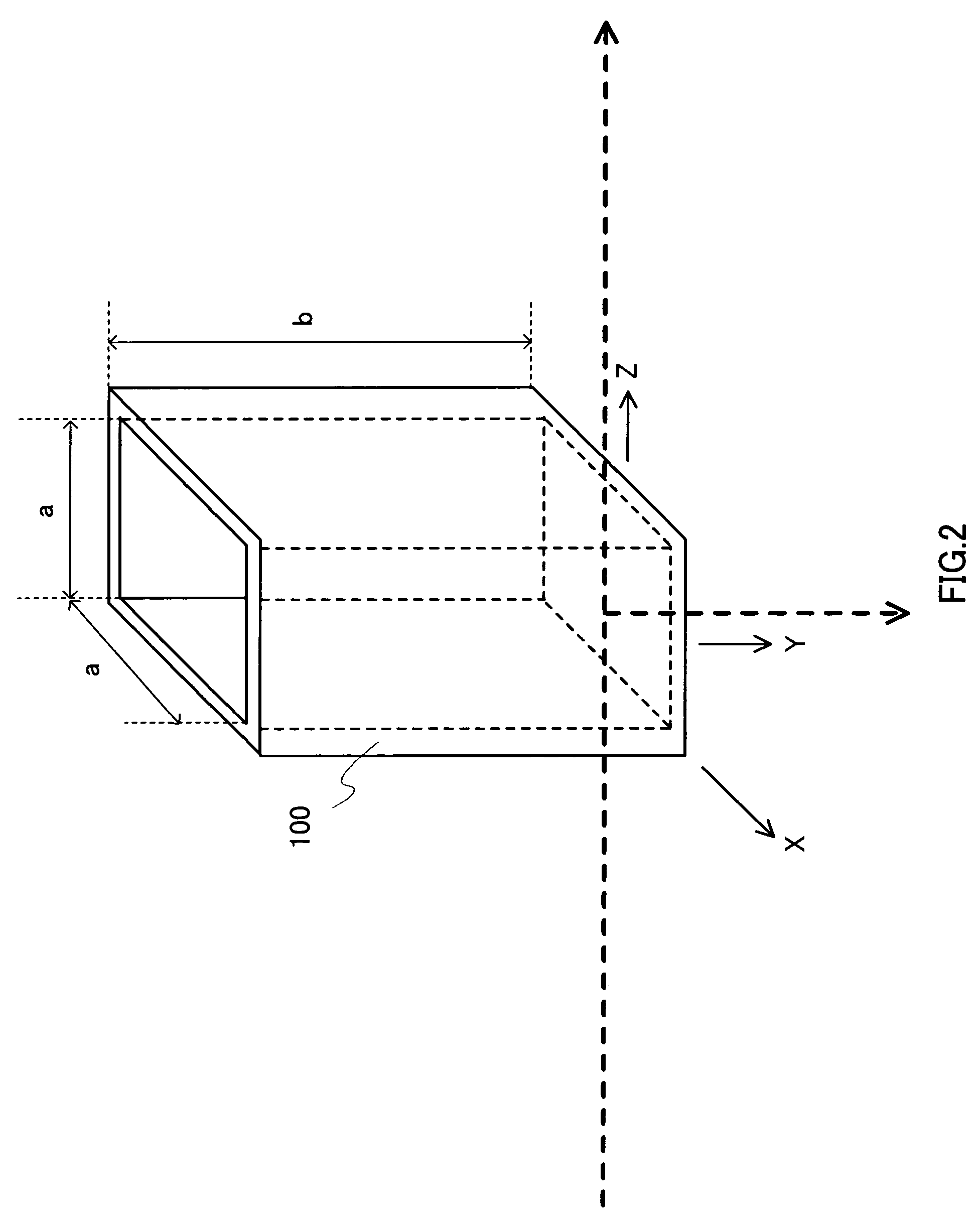
A light scattering apparatus capable of measuring light scattering of opaque samples. In the apparatus, control section 190 controls an optical path length required for laser light output from laser light source 210 to being incident on a sample and then outgoing as scattered light to approximate by zero. Detector 330 detects outgoing scattered light to output as a photon pulse. Pulse interval measurer 350 measures a time interval of the photon pulse output from detector 330. An operator in computer 360 calculates an n-order correlation function (n1) using the time interval of the photon pulse measured in pulse interval measurer 350.
Owner:GEL DESIGN
Detecting and counting bacteria suspended in biological fluids
ActiveUS20100277734A1Lower Level RequirementsImprove noiseWithdrawing sample devicesScattering properties measurementsForward scatterCuvette
System and method for detecting and counting bacteria suspended in a biological fluid by means of light scattering measurements is provided. In accordance with the method of the invention the level of signal to noise of the measured intensities of light scattered by a sample of the biological fluid is significantly enhanced for forwardly scattered light within a range of scattering angles which are smaller compared to a predefined maximal scattering angle. The system of the invention includes a cuvette adapted to contain a sample of the biological fluid whose sidewalls and windows are suitably constructed and arranged to significantly reduce the level of reflected light obscuring the scattering patterns measured within the range of scattering angles considered.
Owner:BACTERIOSCAN LTD
Method for synchronous measurement of optical constant and particle size distribution of spherical particles based on multi-angle light scattering-transmission process
ActiveCN106383072AThe inversion result is accurateHigh precisionPhase-affecting property measurementsScattering properties measurementsLight scatter measurementWeak measurement
The invention discloses a method for synchronous measurement of the optical constant and particle size distribution of spherical particles based on a multi-angle light scattering-transmission process, relates to the technical field of participating medium radiation property measurement and is aimed at solving the problems of great error of experimental measurement value and relatively weak measurement signal in participating medium radiation parameter measurement based on inverse problem solving. The method comprises the following steps: irradiating the surface of a particle system sample by using continuous steady-state laser; arranging optical detectors on different scattering-angle positions; measuring the scattering optical signal intensity and hemispherical transmission signal of the steady-state laser of different angles; and obtaining the optical constant of the spherical particles and the particle size distribution of the particle system in combination with the signals and through the inverse problem solving technology. The method disclosed by the invention is suitable for synchronous measurement of the optical constant and particle size distribution of spherical particles based on a multi-angle light scattering-transmission process.
Owner:黑龙江省工研院资产经营管理有限公司
Cuvette for light scattering measurements incorporating evaporation inhibition means
ActiveUS20140146313A1Prevent evaporationImprove usabilityWithdrawing sample devicesScattering properties measurementsCuvetteLight scatter measurement
A cuvette for use with light scattering detectors is disclosed. A trough or moat within the cuvette can be filled with solvent which is not in fluid contact with the sample to be measured. This solvent moat creates saturated vapor pressure in the chamber preventing evaporation from the sample when the cuvette is capped. The cuvette itself may be made of an inexpensive polymer which can be polished to high optical quality while still being moldable in complex forms capable of enabling further utility, such as extra griping surfaces, identification tabs allowing the detection instrument to determine the cuvette model, and various sample chamber forms. The novel cuvette may have extremely small sample volumes, while allowing significant overfill of the measurement chamber, improving ease of sample loading. The polymers used may be relatively inexpensive, and therefore the cuvette can generally be discarded after a single use.
Owner:WYATT TECH
Number concentration measurement device of atmospheric ultrafine particles
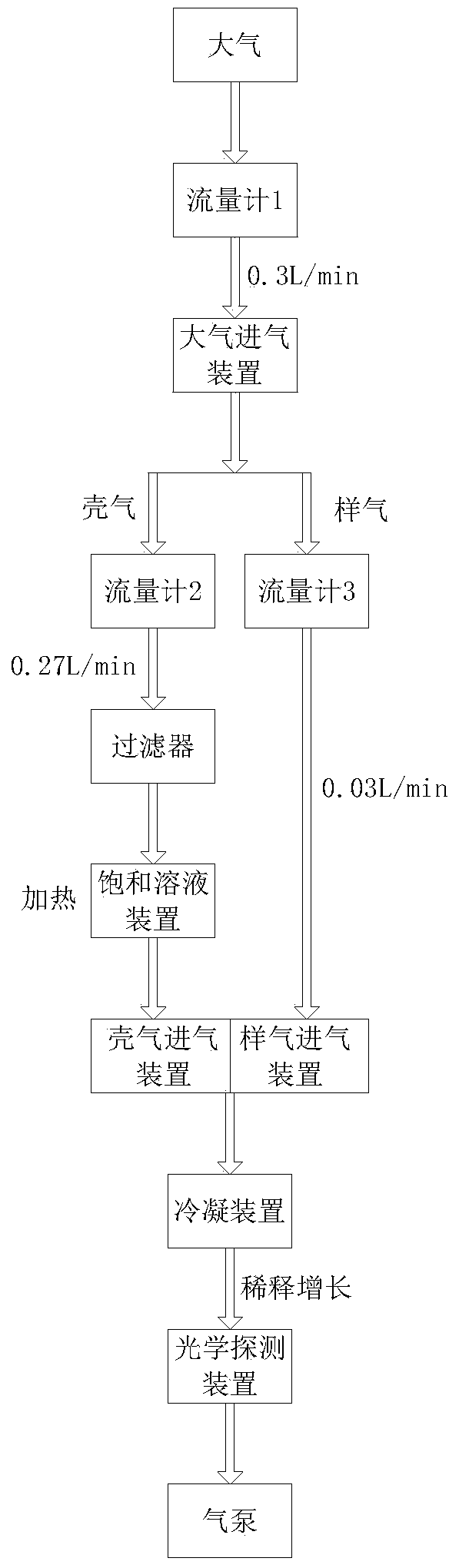
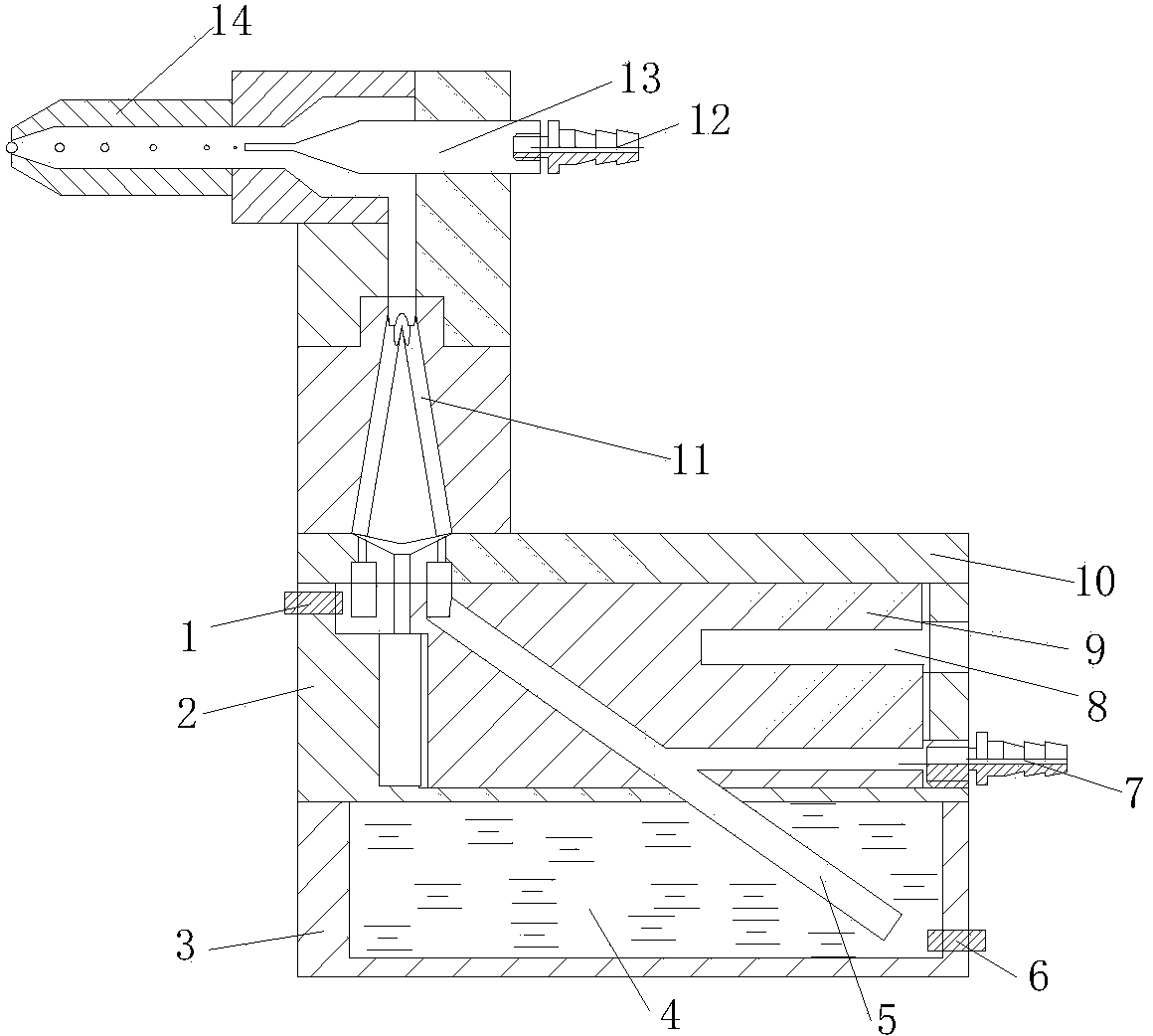
ActiveCN104297118AEnsure normal flowIncreased condensation nuclei efficiencyParticle suspension analysisParticulatesLight scatter measurement
The invention discloses a number concentration measurement device of atmospheric ultrafine particles. The number concentration measurement device comprises an atmospheric airflow channel, a sample gas flow channel, a shell gas flow channel, a gas inlet device, a saturated solution device, a condensing device and an optical detection device. According to the number concentration measurement device, on the basis of a condensation nucleus theory and a light scattering measurement theory, i.e. shell gas flow passes through steam of a heated saturated solution and then is mixed with the air flow of the atmospheric ultrafine particles, the ultrafine particles pass through the condensing device and then are condensed to grow up, and then a light scattering technique is used for measuring the particles which are condensed to grow up, so as to obtain a number concentration value of the particles. By using the shell gas flow designed in the number concentration measurement device, the loss of sample gas flow particles can be reduced, and the condensation nucleus efficiency of the ultrafine particles can be effectively improved. The number concentration measurement device has the advantages of small and compact structure and high applicability, and the number concentration of the particles with a particle diameter range between 3 nm to 5 microns can be measured.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
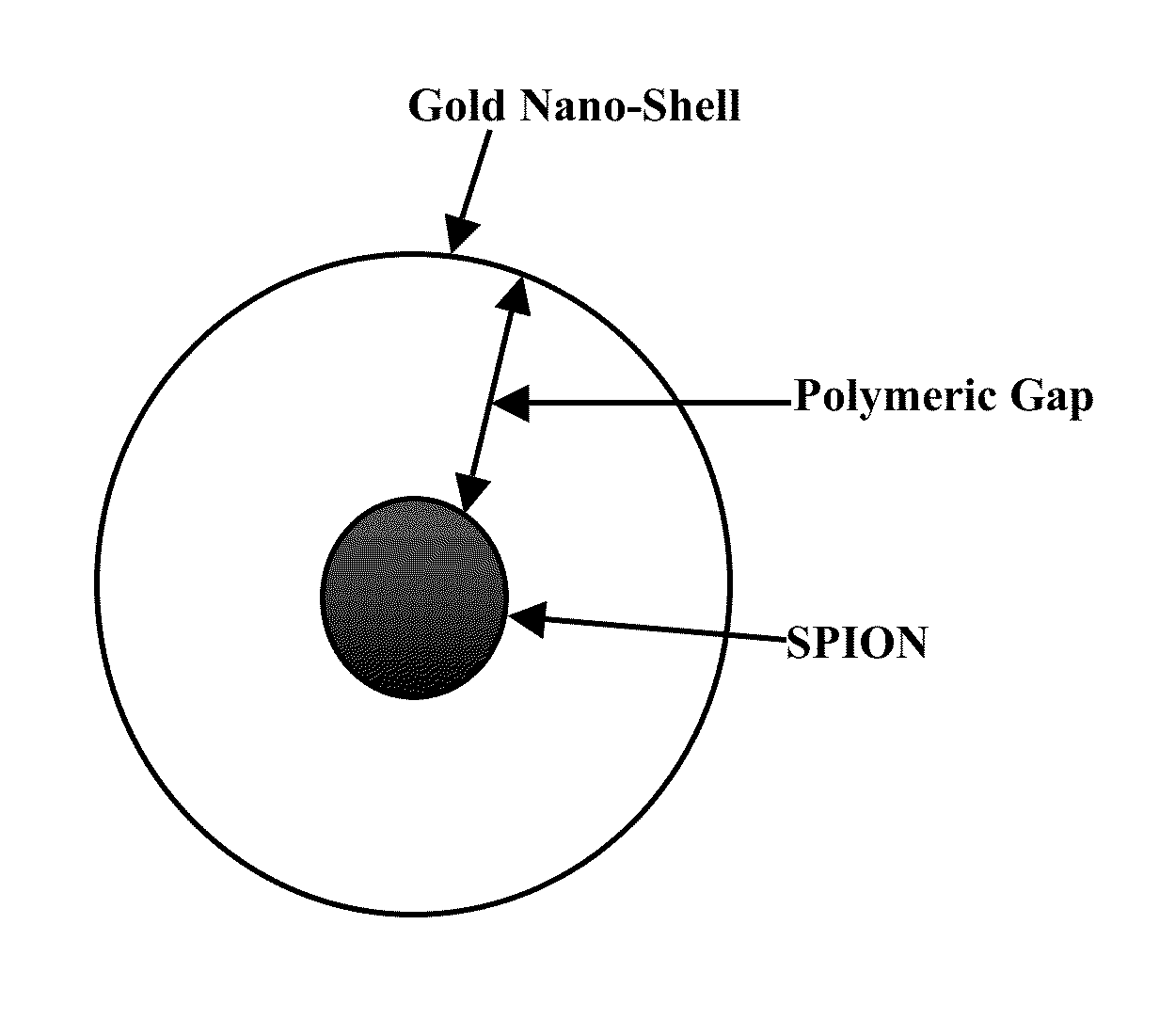
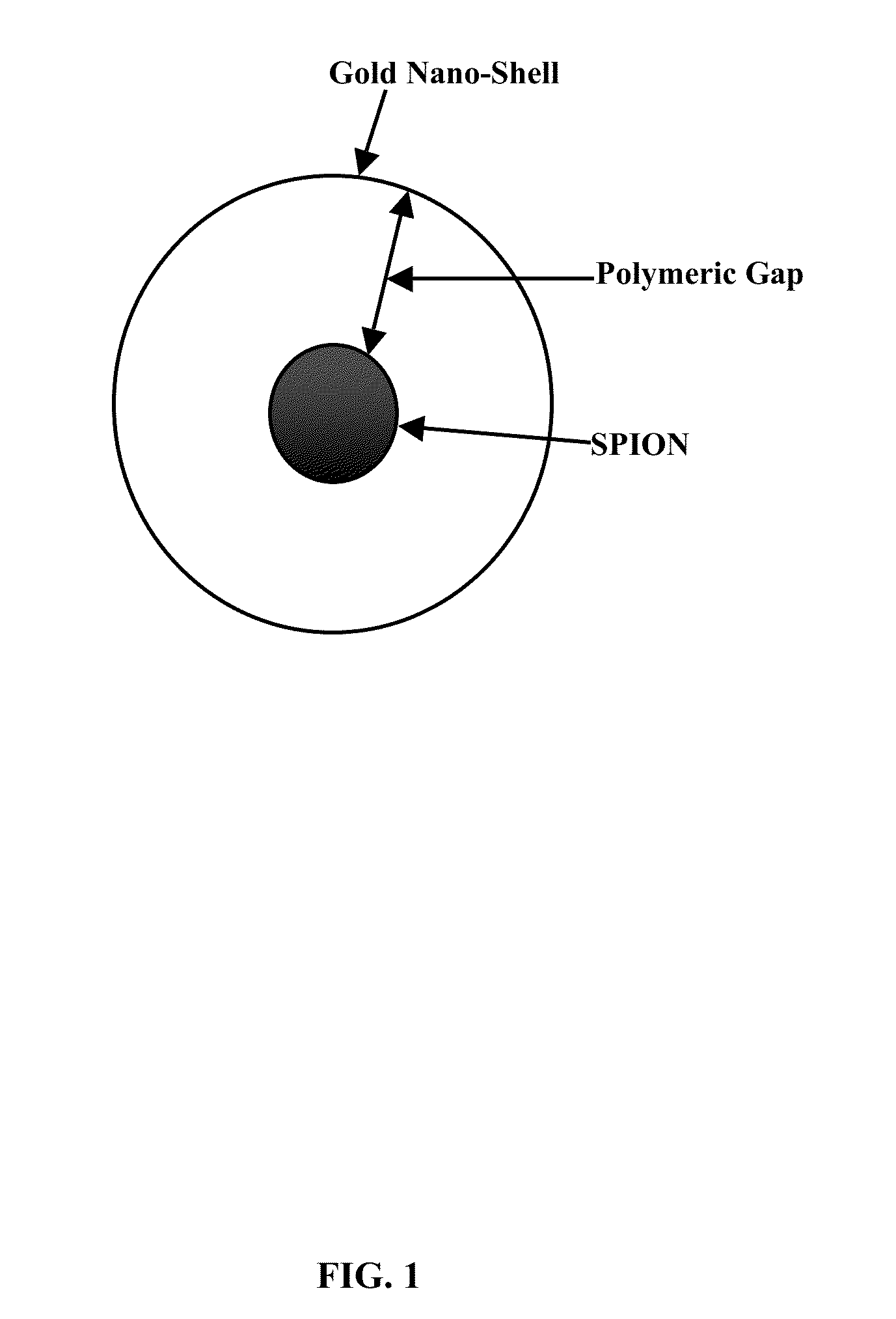
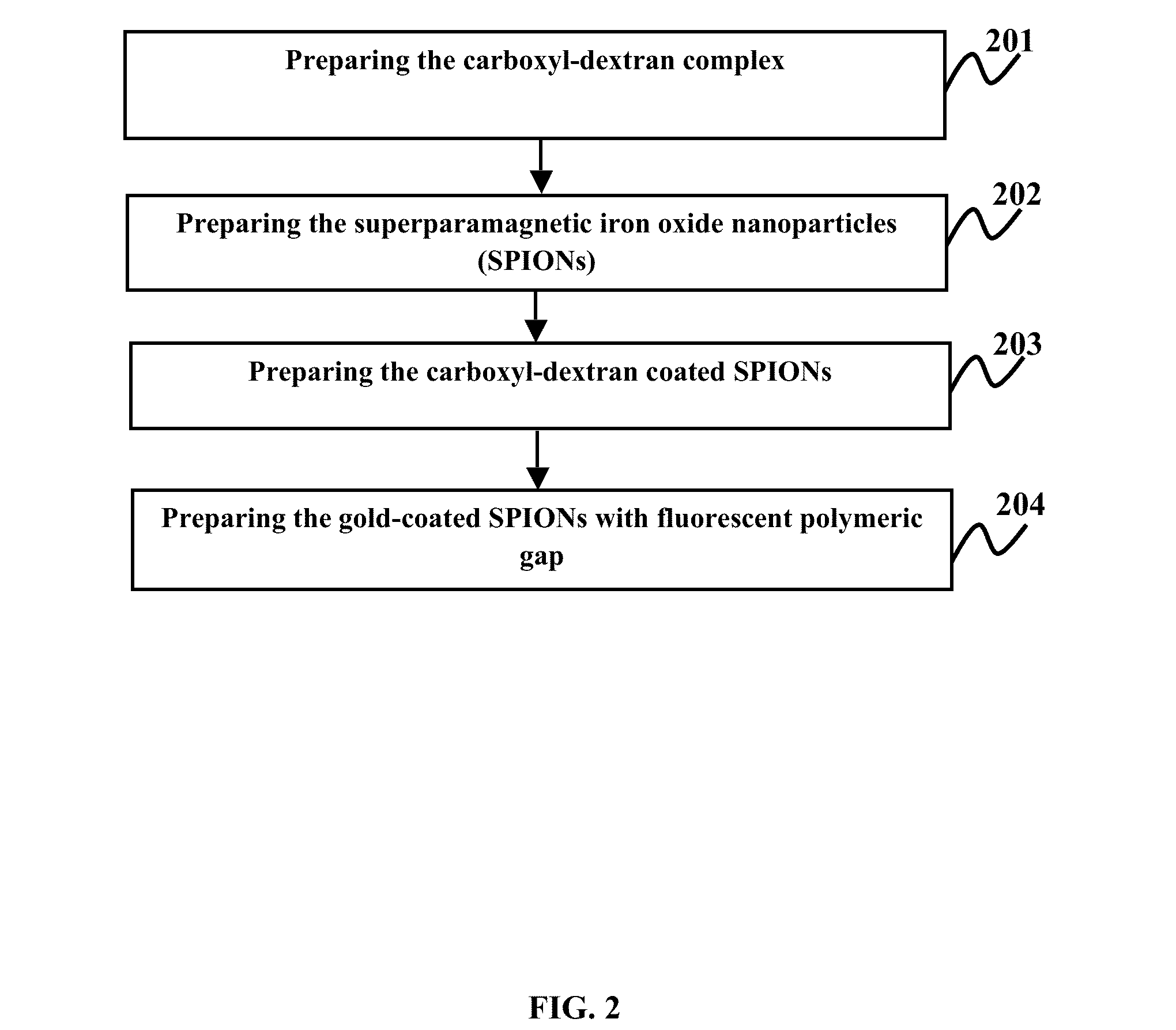
Plasmonic stable fluorescence superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and a method of synthesizing the same
The various embodiments herein provide for the engineered multimodal super paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) with a fluorescent dye. The SPIONs comprise fluorescent polymer dye arranged in a gap between a SPION core and a gold shell. The SPIONS are provided with a gold coating. The gap is made up of a polymeric molecule such as 6-arm anthracene terminated. The core of the nanoparticle is made up of a magnetic metal oxide. The method for synthesizing SPIONs involves preparing carboxyl-dextran complex and the SPIONS. The SPIONs are coated with carboxyl-dextran complex. The coated SPIONs coated are subjected to fluorescent polymer and gold nano shell coating. The prepared SPIONs are characterized by light scattering measurement and magnetization measurements.
Owner:MAHMOUDI MORTEZA +1
System and method for determining radius of gyration, molecular weight, and intrinsic viscosity of a polymeric distribution using gel permeation chromatography and light scattering detection
InactiveUS20050240385A1Component separationPhase-affecting property measurementsLight scatter measurementRefractive index
A system and method for analyzing data from a gel permeation chromatography (GPC) or size exclusion chromatography (SEC) system fro determining a polymeric sample's radius of gyration. Data from two or more detectors is used with a least-squares minimization fit. A novel method includes the simultaneous determination of a sample's radius of gyration using data from a light scattering detector that collects data from at least two incident angles. Detectors within the inventive method include a multi-angle light scattering (LS) detector, viscometer (V) and a refractive index (RI) detector.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Systems and methods to analyze multiplexed bead-based assays using backscattered light
ActiveUS20080246968A1Reduce in quantityShorten the timeColor/spectral properties measurementsLight scatter measurementMicrosphere
This invention relates to a system and method related to an epifluorescence microscope based optical system equipped with a tunable filter to localize microspheres in bead-based assays based on a back-scattered light (also known as reflected light) image. A common optical path for reflected and emitted luminescence in conjunction with a tunable filter negates the requirement of an additional sensor employed in existing technologies for localizing microspheres based on light scatter measurements.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Devices And Methods For Detection Of Microorganisms
InactiveUS20100136521A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsArduino microcontrollerLight scatter measurement
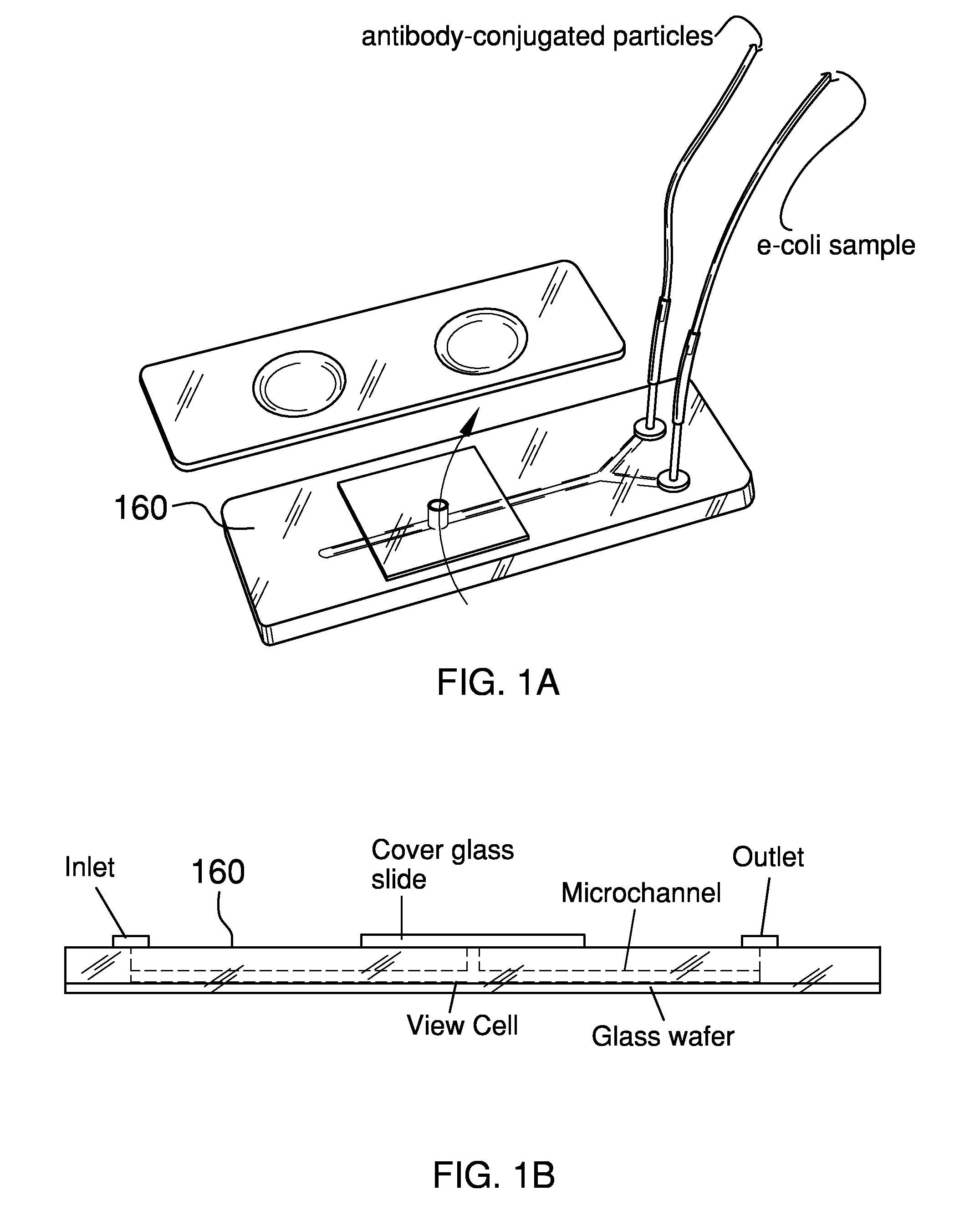
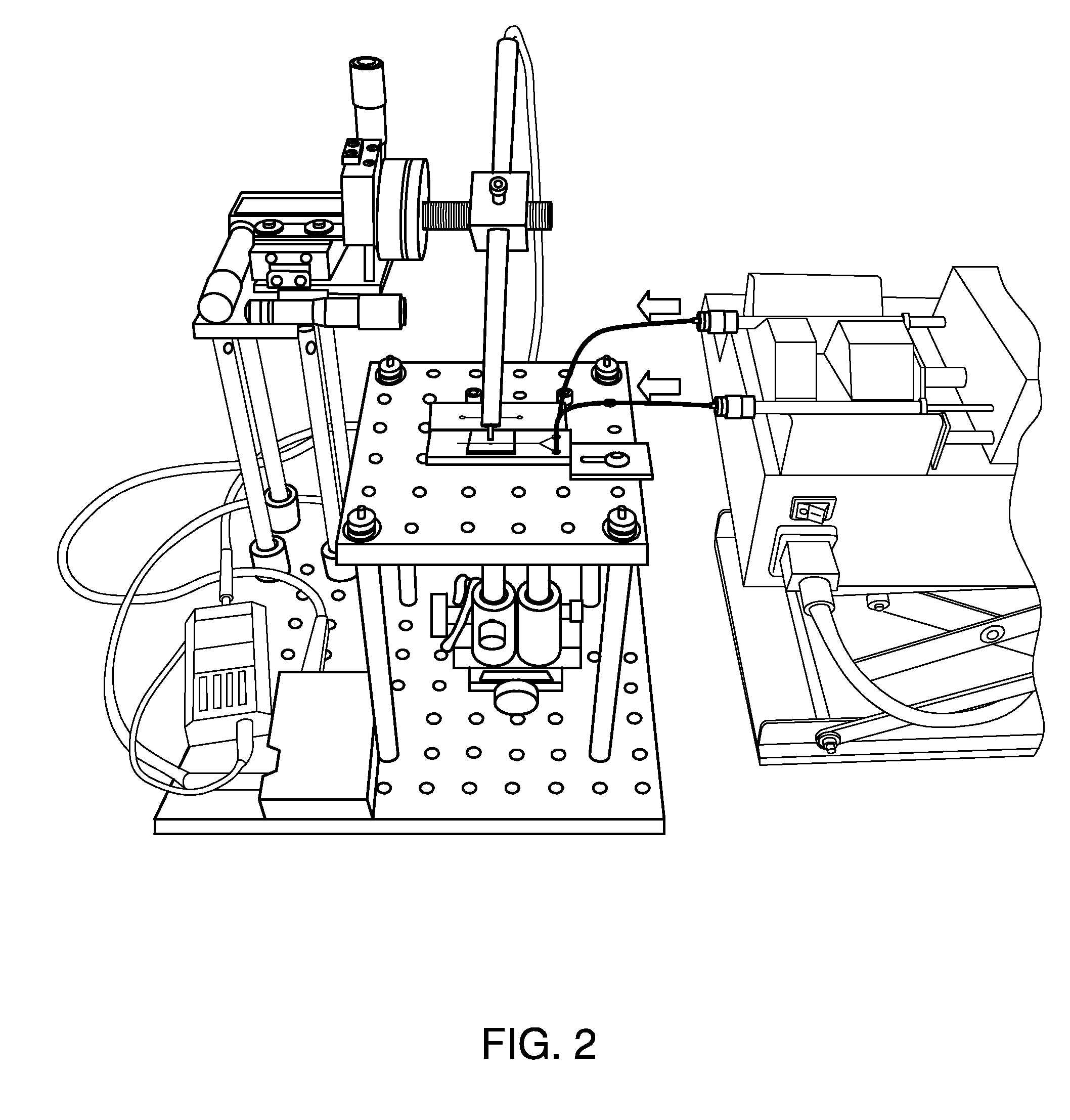
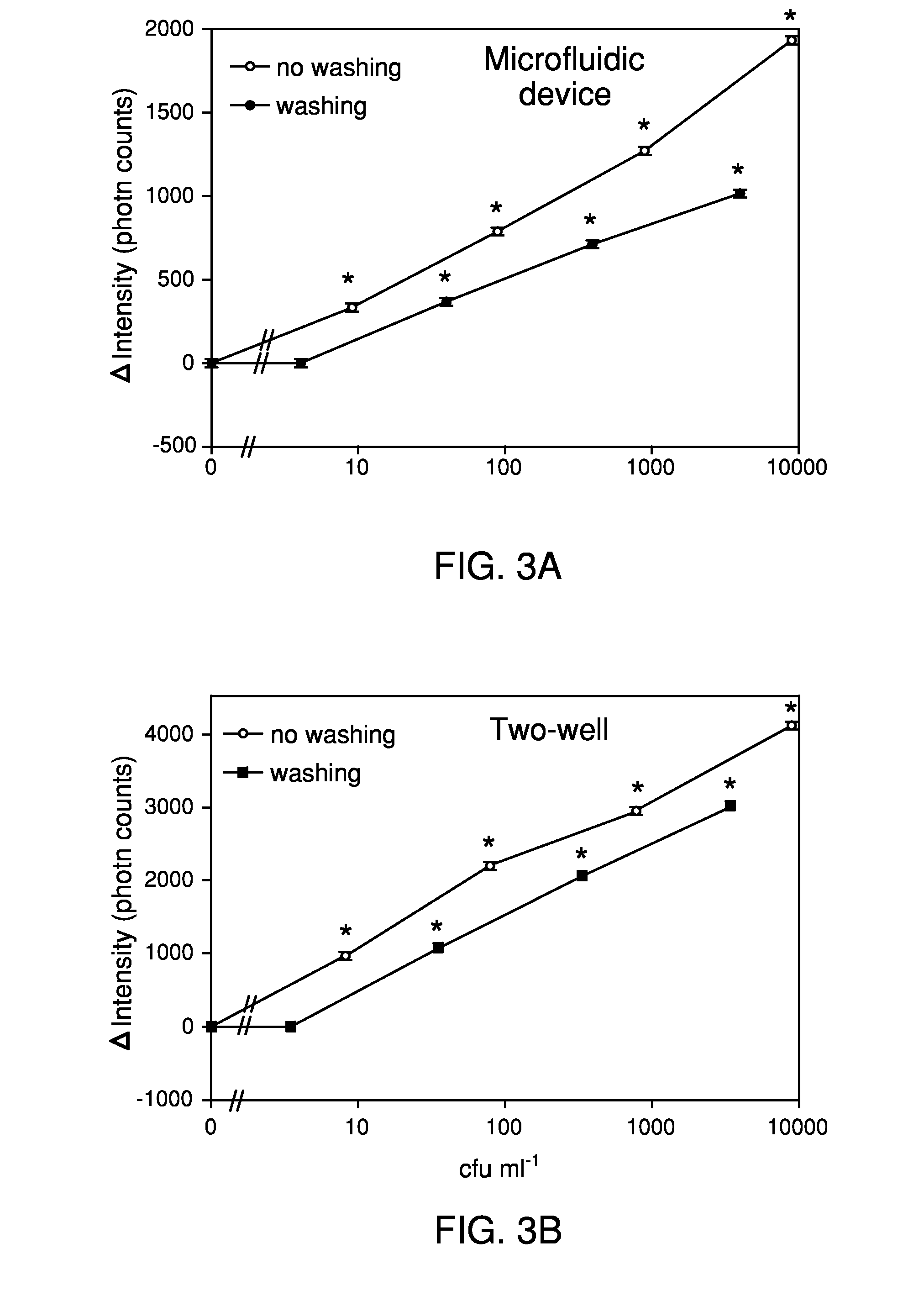
The present invention features methods and devices for microorganisms through detecting Mie light scattering from immunoagglutinated beads. The methods feature providing a first bead suspension with antibody specific for the microorganism conjugated to beads; mixing the first bead suspension with a sample to form a first mixture; irradiating the first mixture with first incident light; detecting forward light scattering at a first angle with respect to the first incident light, where the first angle being between about 30 to 60 degrees; determining l from the light scattering; providing a second bead suspension with no antibody and simultaneously measuring l0 in a similar manner; comparing l with l0. All light scattering measurements may be made in a two-well slide or a Y-channel microfluidic device. Samples, for example food samples (e.g., vegetable samples), may be prepared in a variety of ways. A vegetable sample may be chopped up and added to a buffer. In some embodiments, the sample is then filtered with a common cloth or tissue component. The present invention also features devices (or apparatuses) for detecting a microorganism in a sample. The apparatuses may be a large-scale device or a small-scale device. The large-scale device may consist of a portable spectrometer, light source, optical fibers, and adjustable positioning stages, in addition to, for example, a two-well slide or a microfluidic device. The small-scale device is made portable by using, for example, light-emitting diodes, avalanche photodiodes, an op-amp circuit, Arduino microcontroller board, an LCD display, and small batteries, in addition to, for example, a two-well slide or a microfluidic device. Therefore, the invention is adaptable for detecting microorganisms in vegetable sample preparations. Still further, the invention may be operated on a small-scale, for example, for use by workers in agriculture fields or food factories.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Light scattering measurement system and method for particulate matters
InactiveCN106018193AMeasurable particle sizeMeasurable propertiesParticle size analysisParticle suspension analysisParticulatesLight scatter measurement
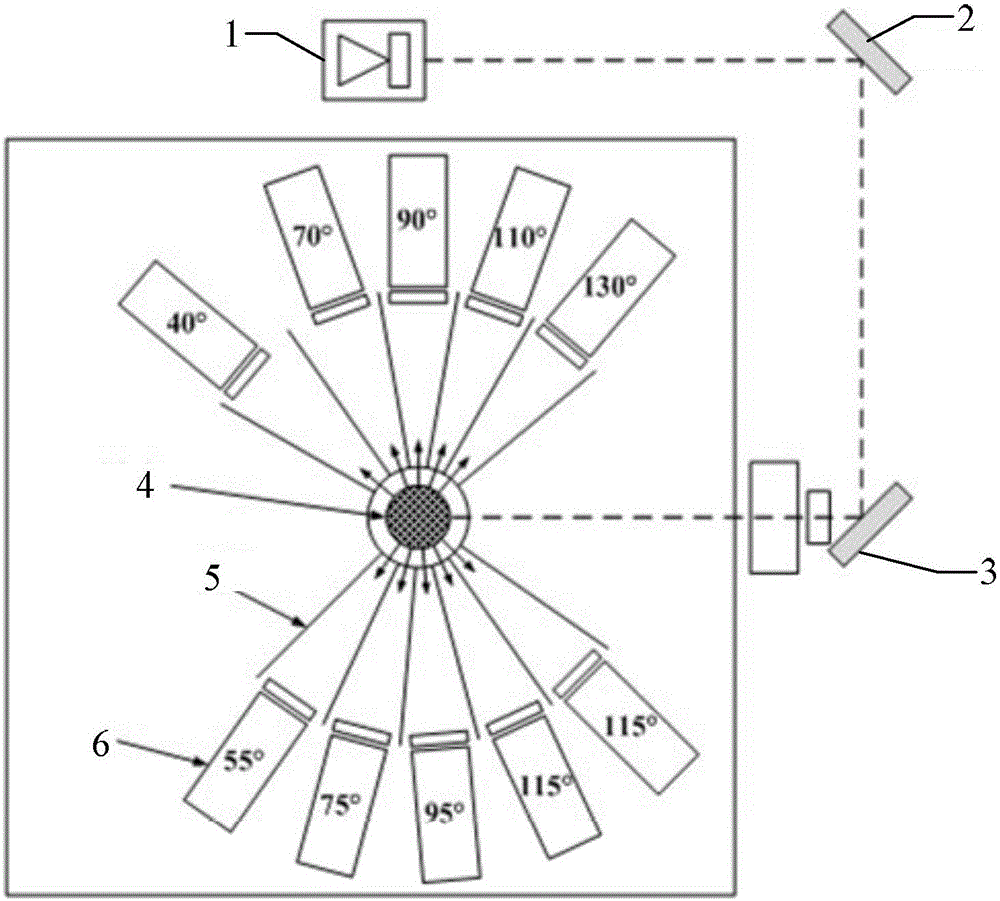
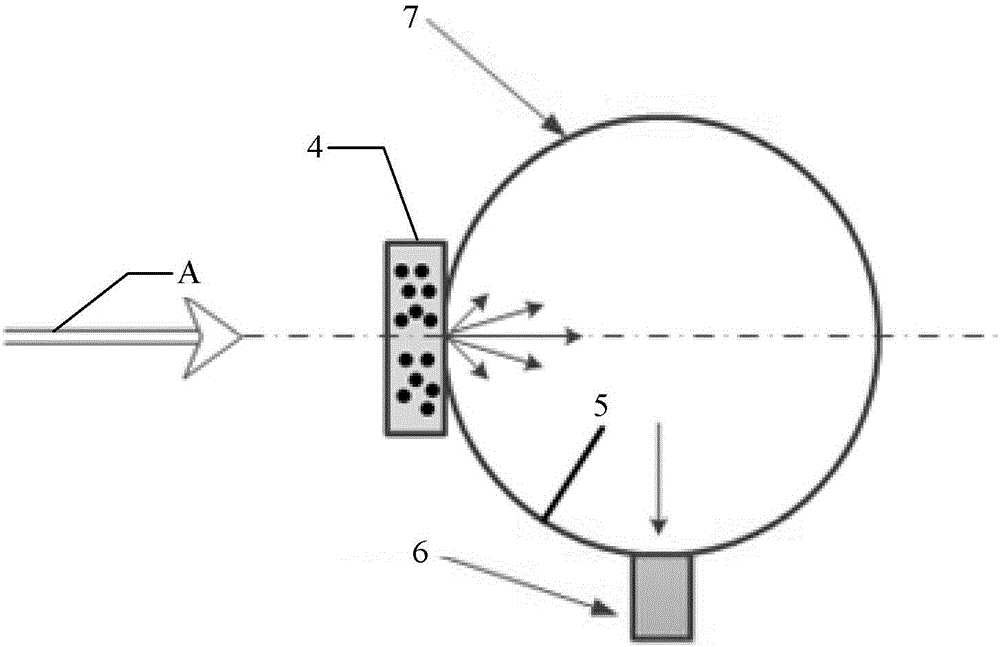
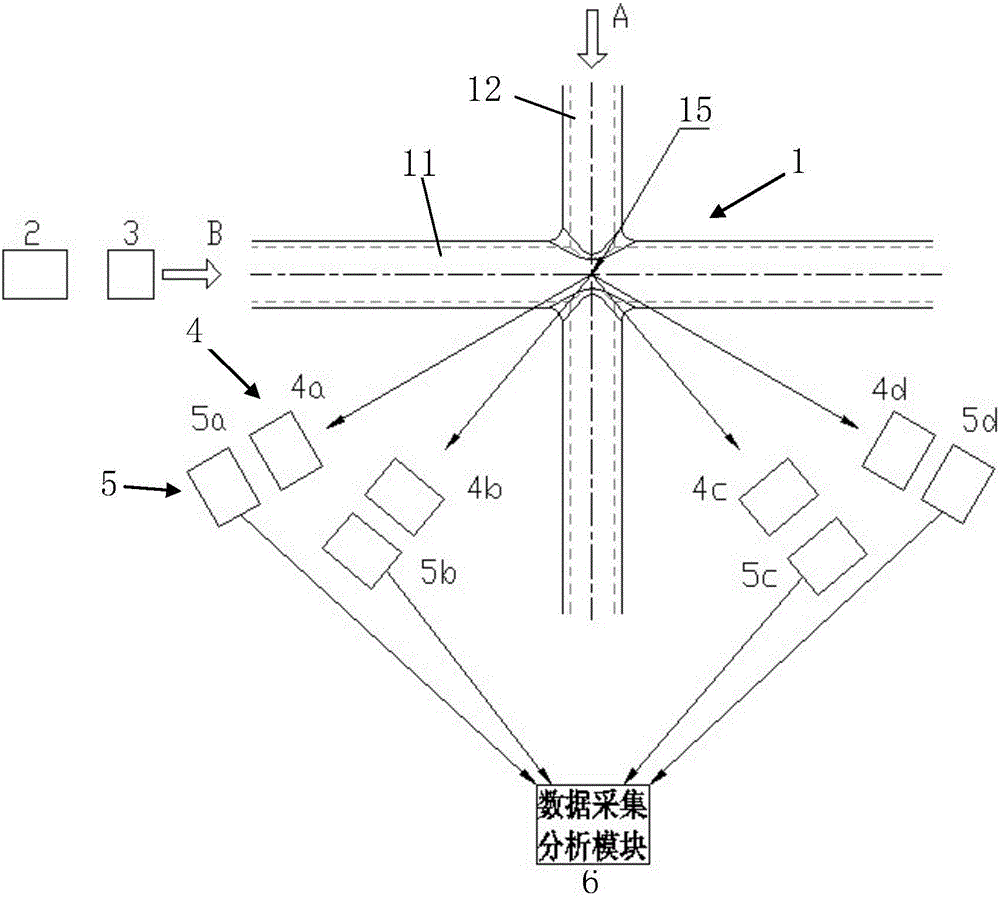
A light scattering measurement system for particulate matters comprises a scattering measurement chamber, a light source, a scattering light detector, a data acquisition and analysis module, a light source polarizing device and a plurality of scattering light polarization analyzers. The scattering measurement chamber includes a light channel and a particulate matter sample injecting channel, a center line of the light channel and a center line of the particulate matter sample injecting channel intersect at an intersection point. The light source is mounted on one side of the scattering measurement chamber. The light source polarizing device is positioned between the scattering measurement chamber and the light source. The multiple scattering light polarization analyzers are arranged at positions differently angled with the center line of the light channel from the intersection point as a start point; the scattering light detector is arranged in correspondence with the multiple scattering light polarization analyzers and used for receiving light from the multiple scattering light polarization analyzers. The invention also provides a light scattering measurement method for particulate matters. The particulate matters are measured based on a particulate matter multi-angle scattering method, and particle sizes and attributes of the particulate matters can be determined.
Owner:ZHONGXING INSTR SHENZHEN
Biological indicator system to detect effectiveness of sterilization
InactiveUS7326562B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSporeLight scatter measurement
A novel biological indicator system to detect the effectiveness of a sterilization treatment for assessing the viability of and / or changes in bacterial spores exposed to sterilization or disinfection by multi-angle light scattering thereby detecting a change in the spores as indicators of spore viability and the efficacy of the sterilization or disinfection.
Owner:ICF TECH
Particle granularity and concentration light scattering measuring method
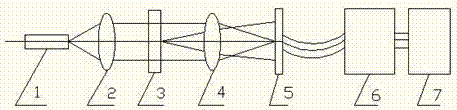
ActiveCN104515722AImprove reliabilityImprove accuracyTransmissivity measurementsParticle size analysisChemical physicsLight scatter measurement
The invention discloses a particle granularity light scattering measurement method. The method comprises the following steps: 1, measuring light intensity change values I delta t sigma (theta 1) = It + delta t sigma (theta 1)-It sigma(theta 1), I delta t sigma (theta 2) = It + delta t sigma (theta 2)-It sigma (theta 2); 2, measuring particle size distribution by substituting the light intensity change values of the two scattering angles into the following formula to obtain a particle size distribution function; and 3, measuring the average particle size by substituting the light intensity change values of the two scattering angles I delta sigma (theta 1) and I delta sigma (theta 2) into the formula below to obtain the average particle size D30. The particle granularity and concentration light scattering measuring method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple measurement process, easy calibration, and no requirement on knowing any parameter; and a twice measurement method is provided to avoid the influence of window pollution in particle size distribution solving on the measurement results.
Owner:NANJING INST OF MEASUREMENT & TESTING TECH
Device and method for detecting mass concentration of particulate matter
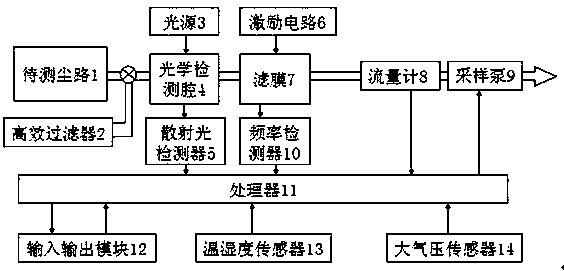
InactiveCN107607449ASame conditionsImprove quality resolutionParticle suspension analysisParticulatesResonance measurement
The invention provides a device and a method for detecting the mass concentration of a particulate matter, and relates to the technical field of concentration detection. The device for detecting the mass concentration of the particulate matter comprises a gas channel to be measured, a gas flow driver, and a light scattering measurement unit, a flow metering unit and a matched control processor which are arranged on the gas channel to be measured, and also comprises a micro-resonance measurement unit arranged on the same gas channel to be measured together with the light scattering measurementunit, the micro-resonance measurement unit includes a choked flow filter membrane arranged on the gas channel to be measured, and a frequency detector and a control circuit which are connected with the choked flow filter membrane, and the signal output end of the frequency detector is connected with the control processor. The device and the method, which adopt a micro-resonance process and a lightscattering measurement process to carry out fusion calculation, have the advantages of high mass resolution, fast response speed, suitableness for various gas channels, overcoming of the influences of the physical, chemical and flow characteristics of particles on the simple light scattering measurement process, and accuracy and reliability in the measurement result.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Atmospheric particulate single sampling channel two-parameter monitor and monitoring method
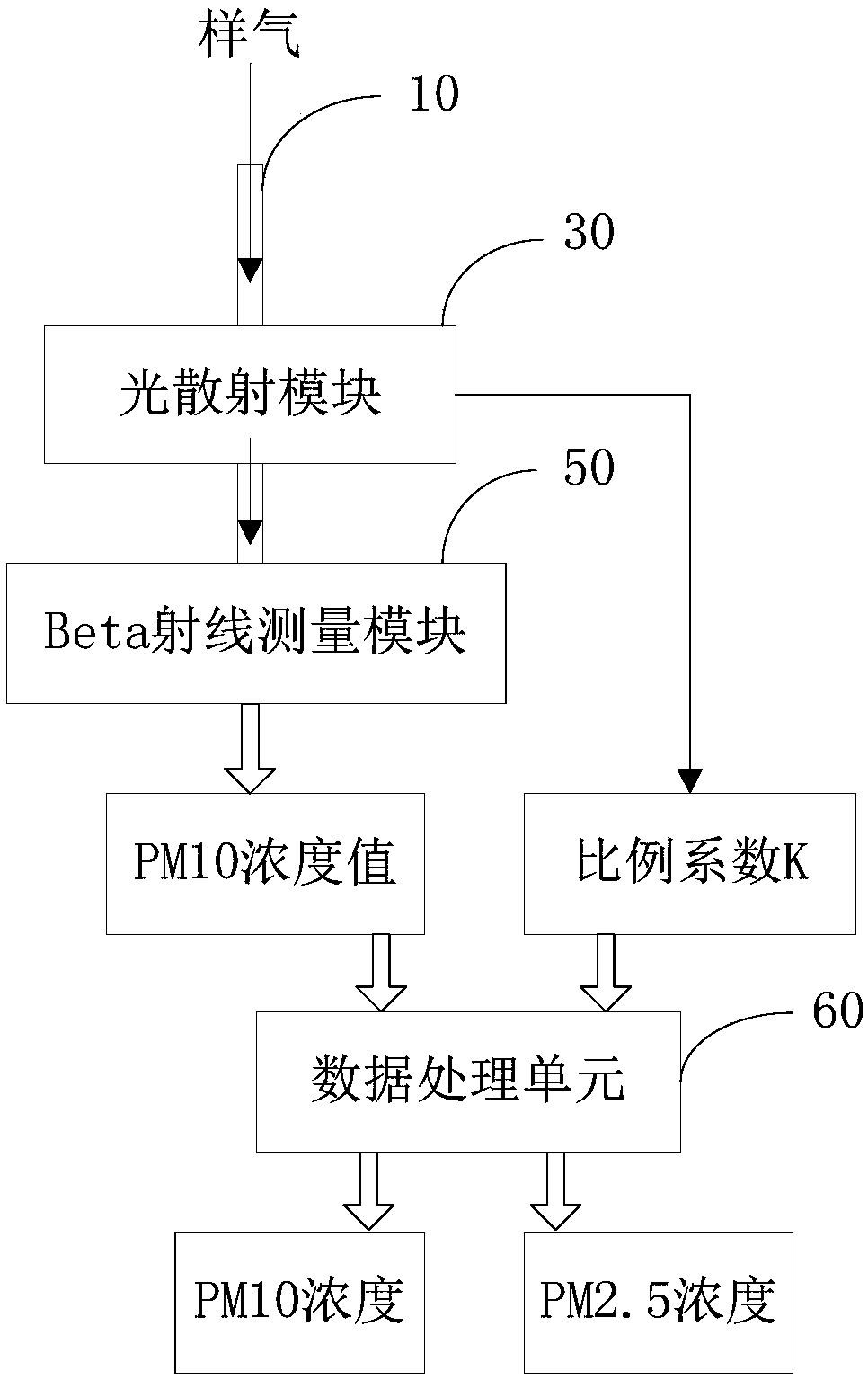
ActiveCN108303359AAvoid hanging upside downHigh measurement accuracyParticle suspension analysisParticulatesLight scatter measurement
The invention discloses an atmospheric particulate single sampling channel two-parameter monitor and a monitoring method. The monitor comprises a sample gas channel, a light scattering measurement module, a beta ray measurement module, and a data processing unit, the light scattering measurement module and the beta ray measurement module are sequentially arranged on the sample gas channel, whereinthe light scattering measurement module is used for measuring the ratio of PM10 to PM2.3 by using a light scattering method, the beta ray measurement module is used for measuring the concentration ofPM10 by using a beta ray method, and the data processing unit is used for calculating the concentration of PM2.5 according to the ratio provided by the light scattering measurement module and the concentration of the PM10 measured by the beta ray measurement module. The two particle size concentrations are measured by using one piece of equipment, and the advantages and the bridge of the beta method and the light scattering method are highly combined, so that a low-cost low-complexity product easy in equipment and maintenance is achieved.
Owner:HEFEI FUTONG PHOTOELECTRIC TECH CO LTD
Polarized light scattering measurement system and method based on magneto-optic modulation
InactiveCN103163051ANo distractionNo damagePolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsLight scatter measurementDivergence angle
The invention relates to a polarized light scattering measurement system and method based on magneto-optic modulation. Coherent light sent out by a laser is changed to linear polarized light through a polarizer, and the linear polarized light is focused into a sample matching tank through a focusing lens. Scattered light coming out from the sample matching tank passes through an expanded beam collimating lens to reduce a divergence angle of the scattered light and collimate the diameter of an outgoing beam, and then the scattered light passes through a Faraday coil, a polarization analyzer and an expanded beam lens in sequence to obtain linear polarized light with periodic changes which can be received by a photomultiplier tube after passing through an aperture diaphragm capable of limiting a photosensitive area, signals are sent into a phase-locked amplifier by the photomultiplier tube to filter and remove external noise and white noise inside equipment, and then sent into a sampling integrator and a computer for sampling integration and digital average to obtain the particle size distribution. Compared with the prior art, the polarized light scattering measurement system and method based on the magneto-optic modulation can be used for low-intensity laser measurement without interference or damage to a sample, can be used for quickly and accurately measuring the nanoparticle size, suppressing the noise to the maximum extent and improving the measurement accuracy to enable the system to be suitable to be used in various environments.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
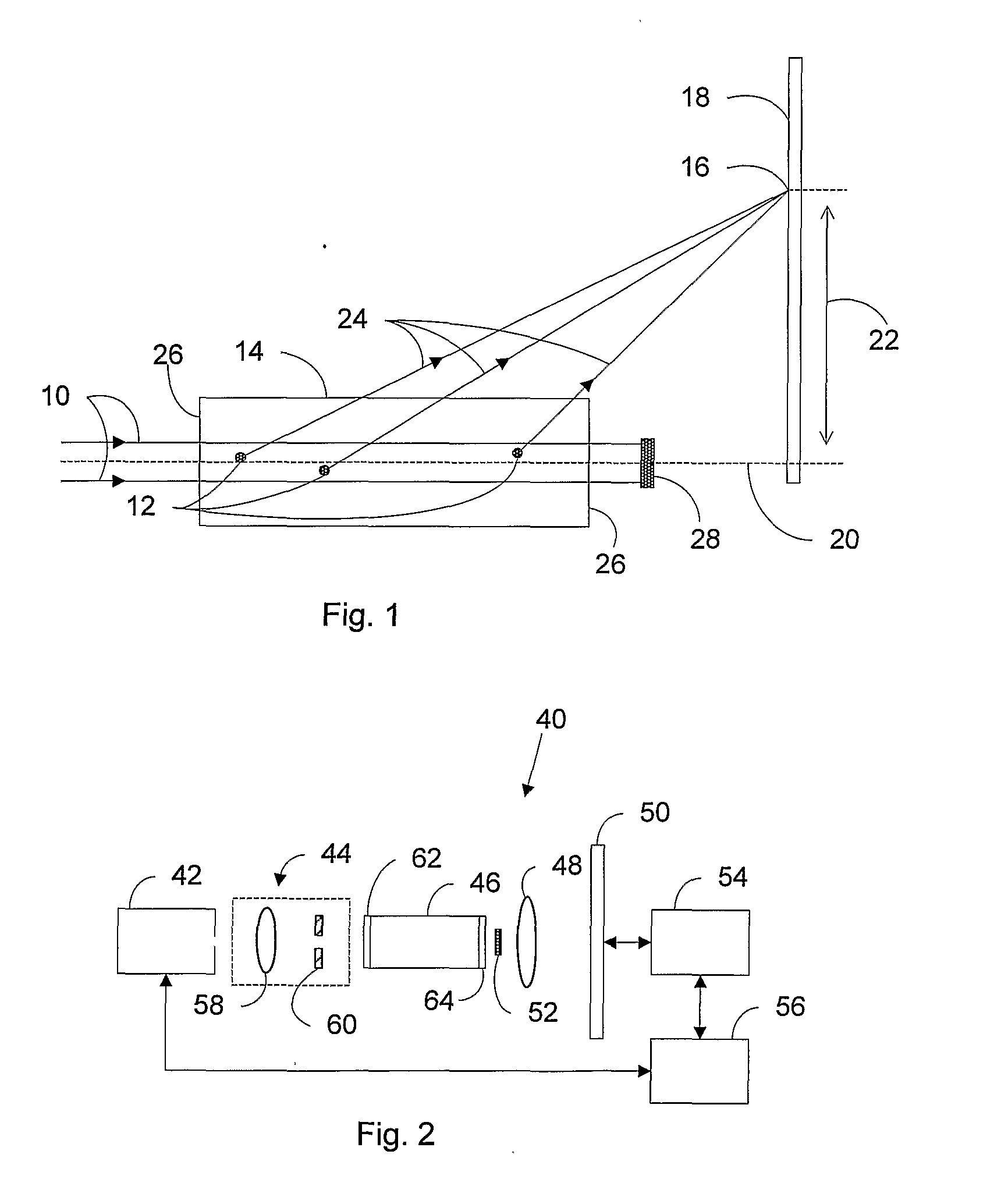
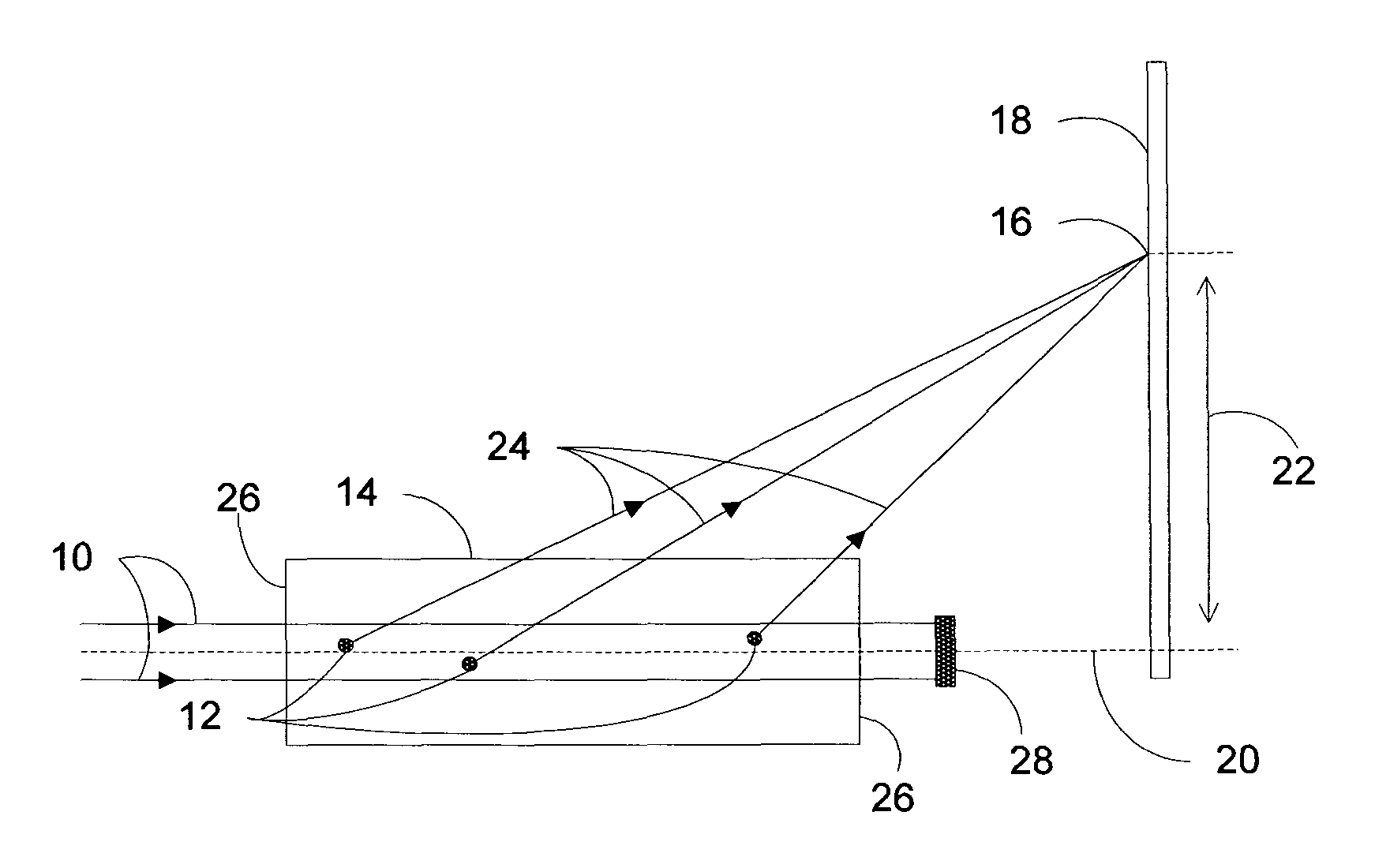
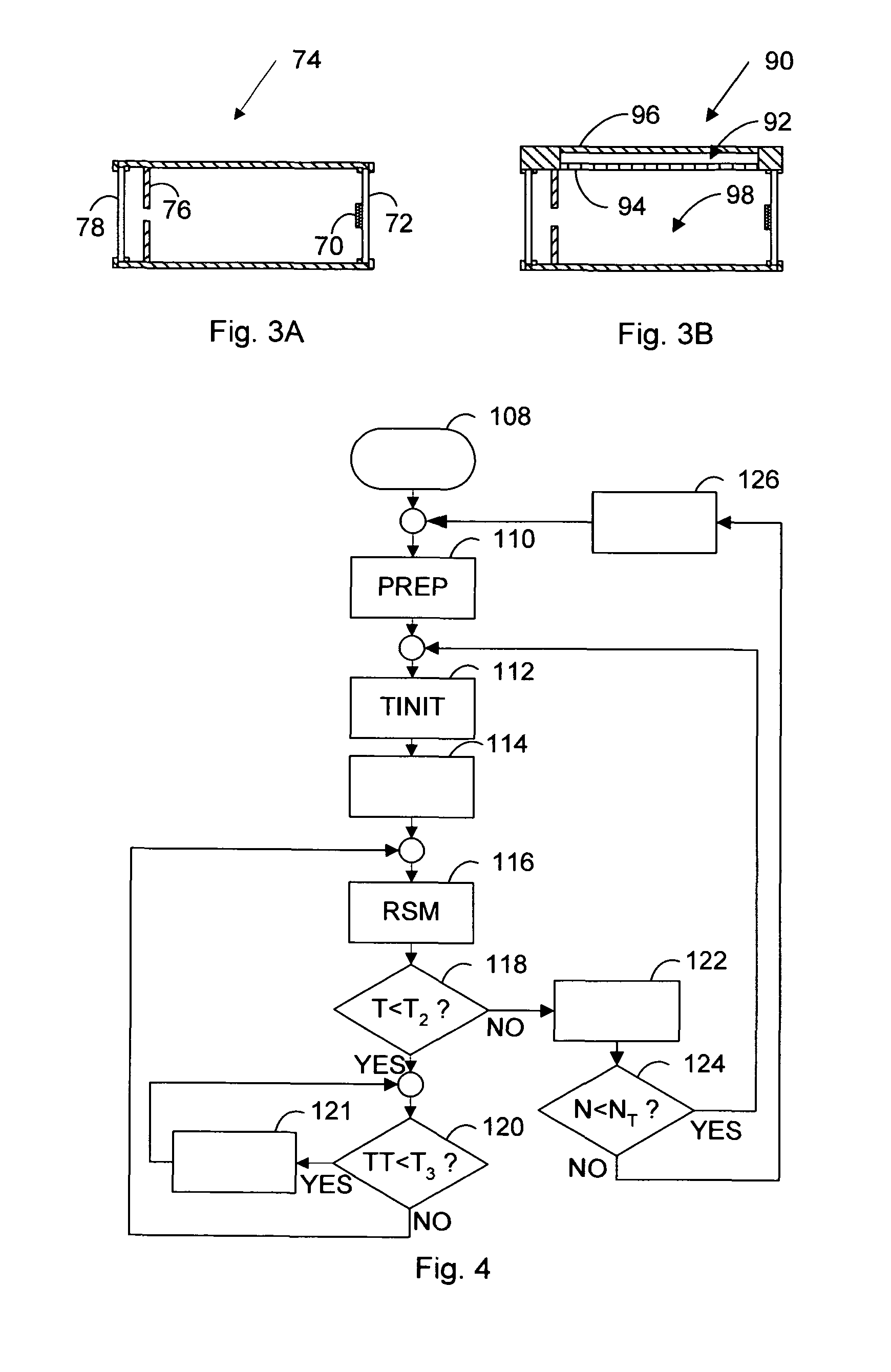
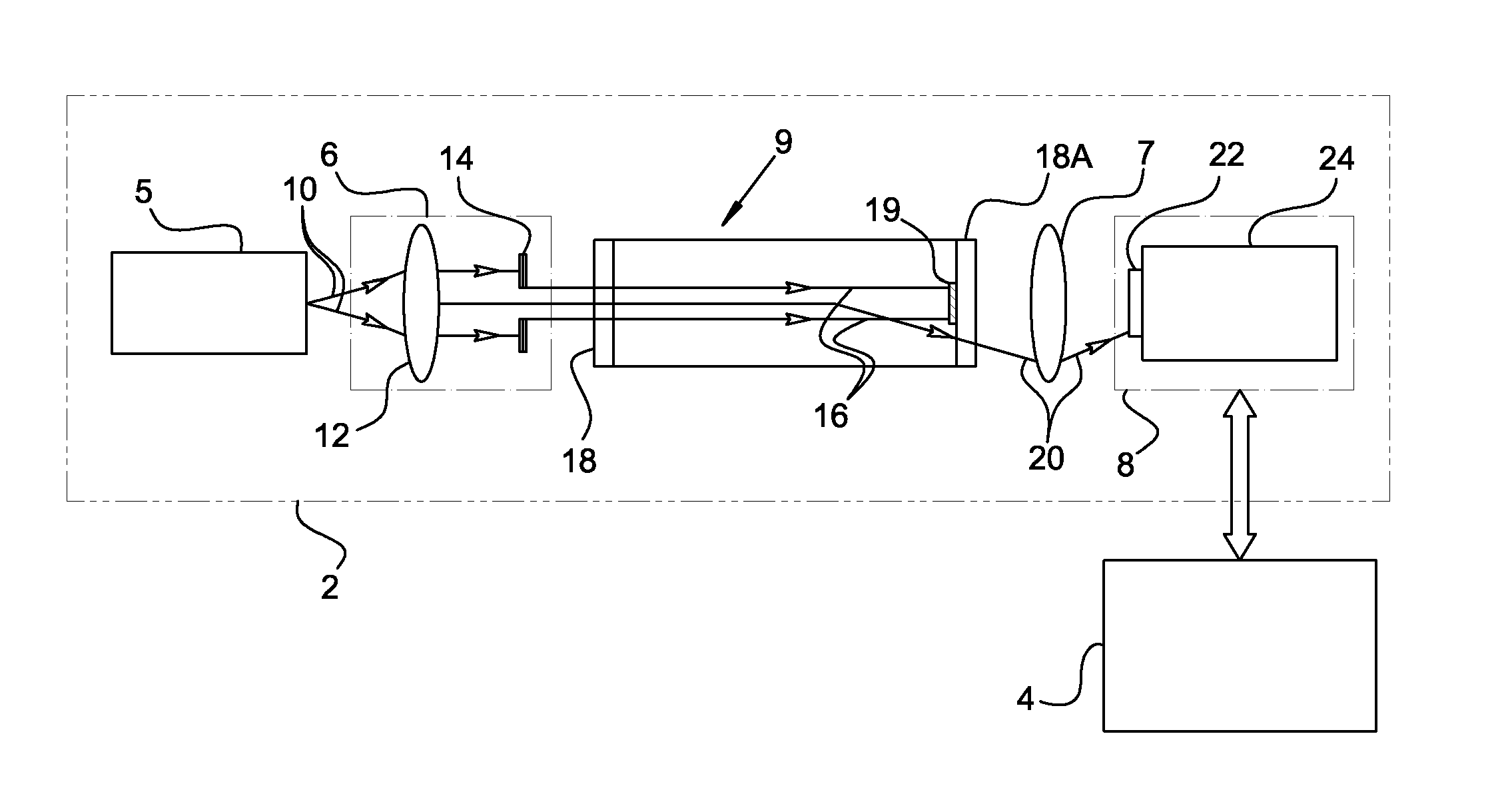
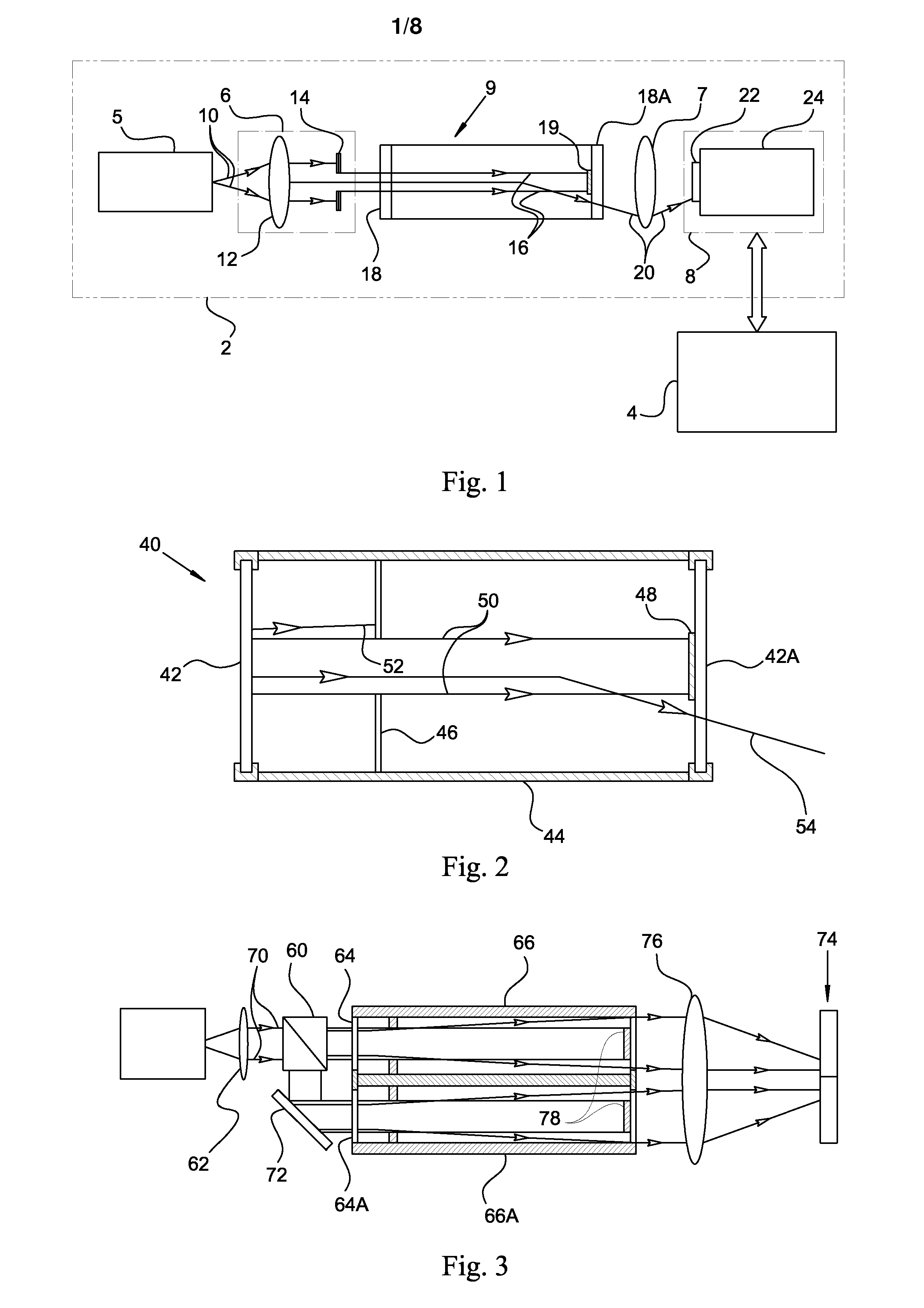
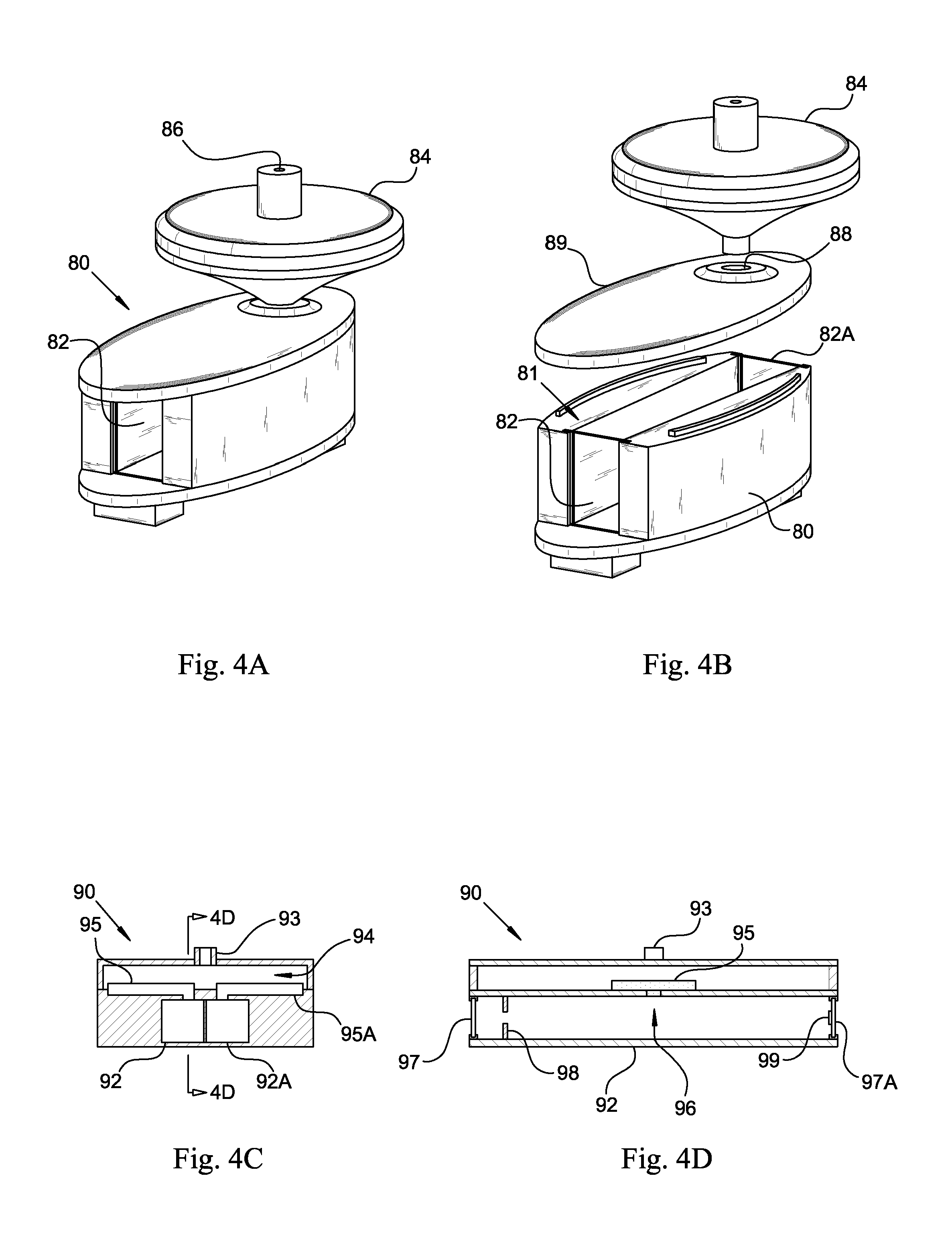
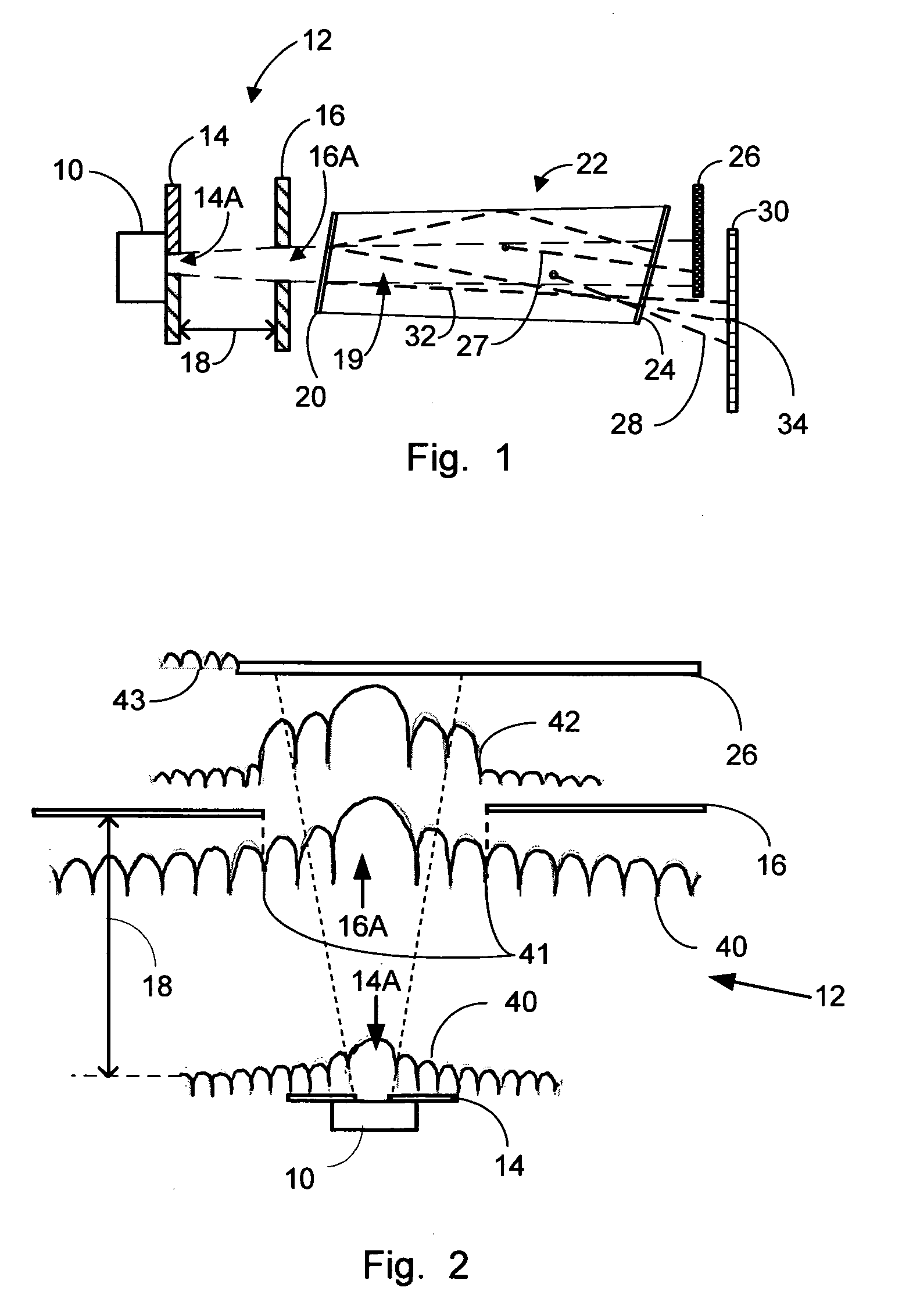
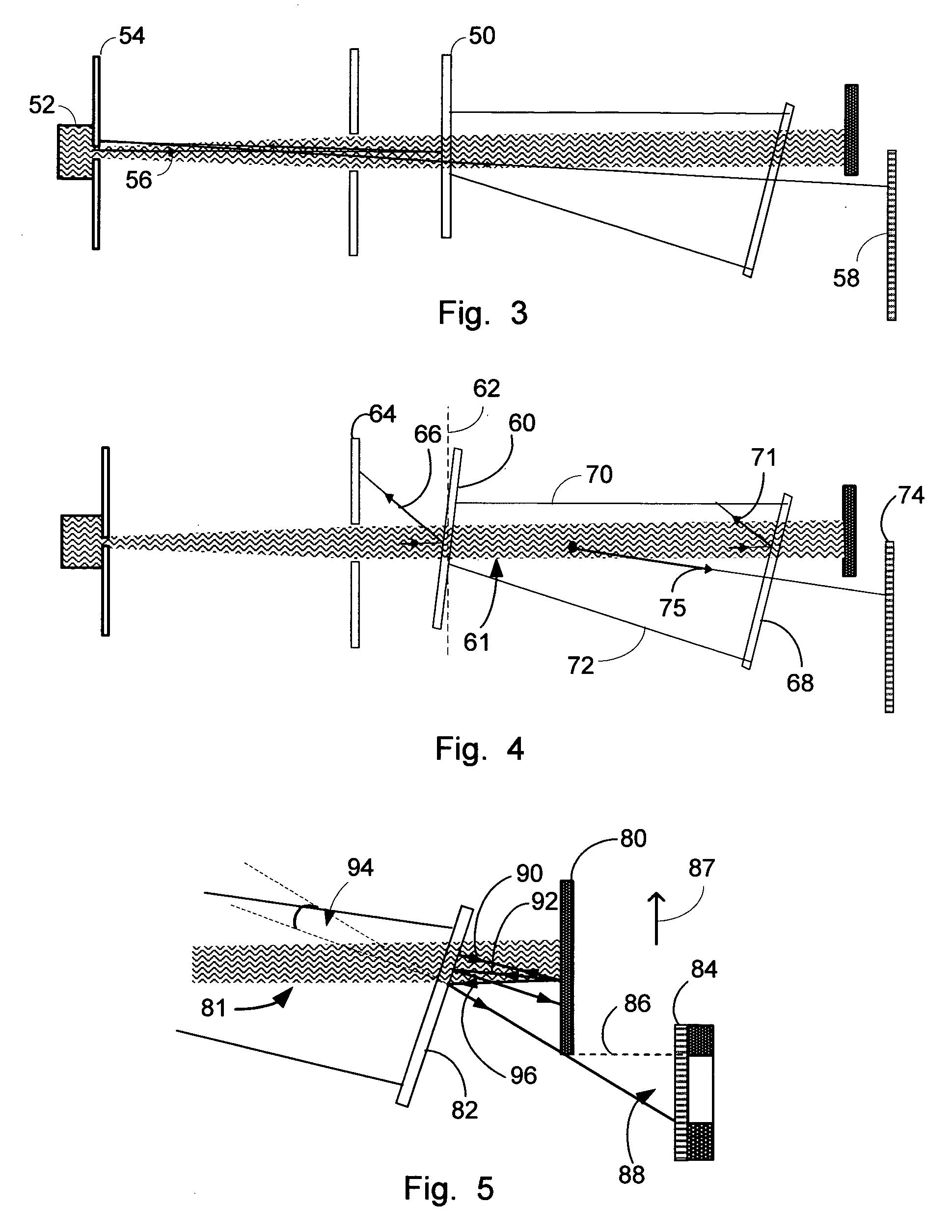
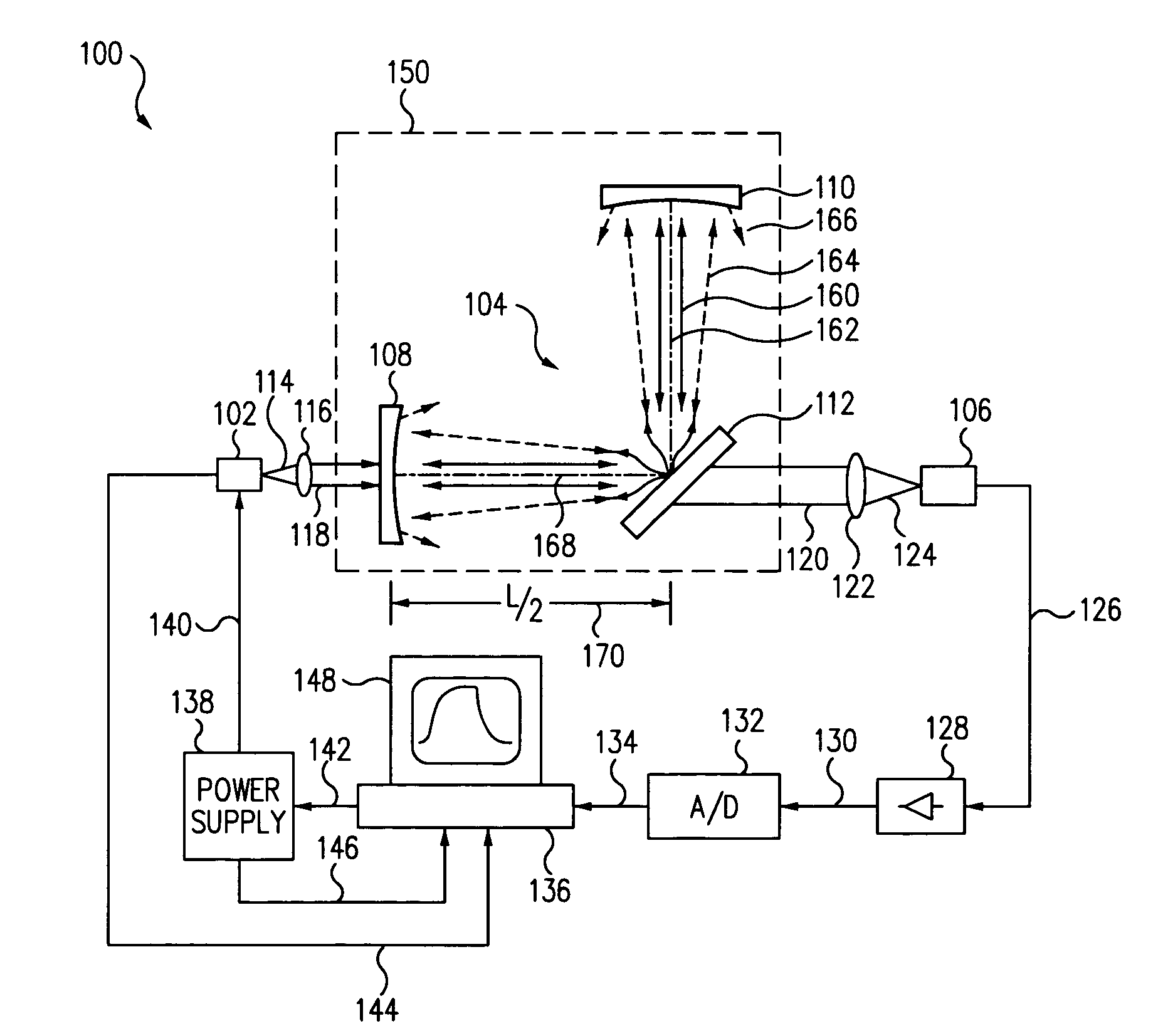
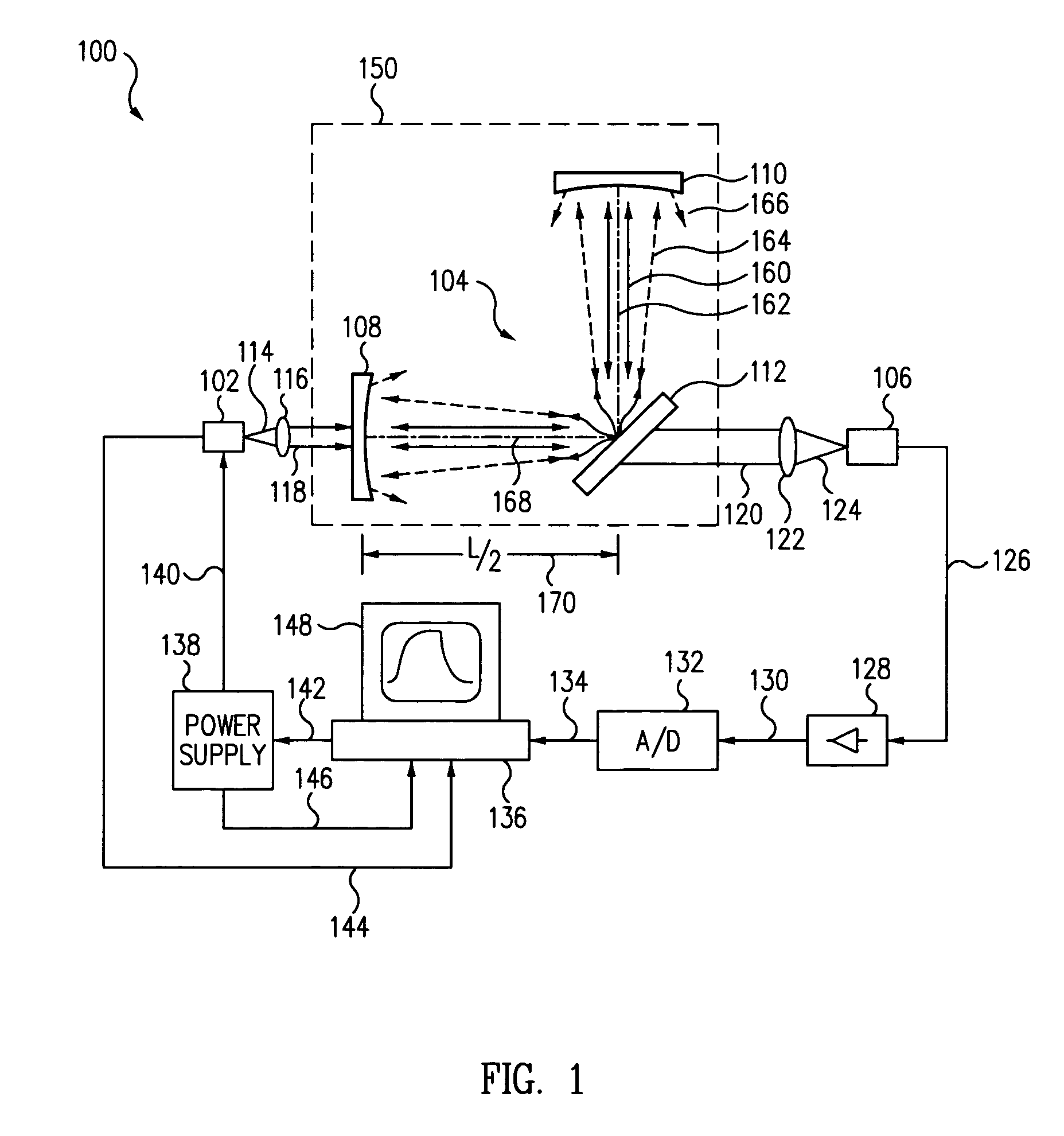
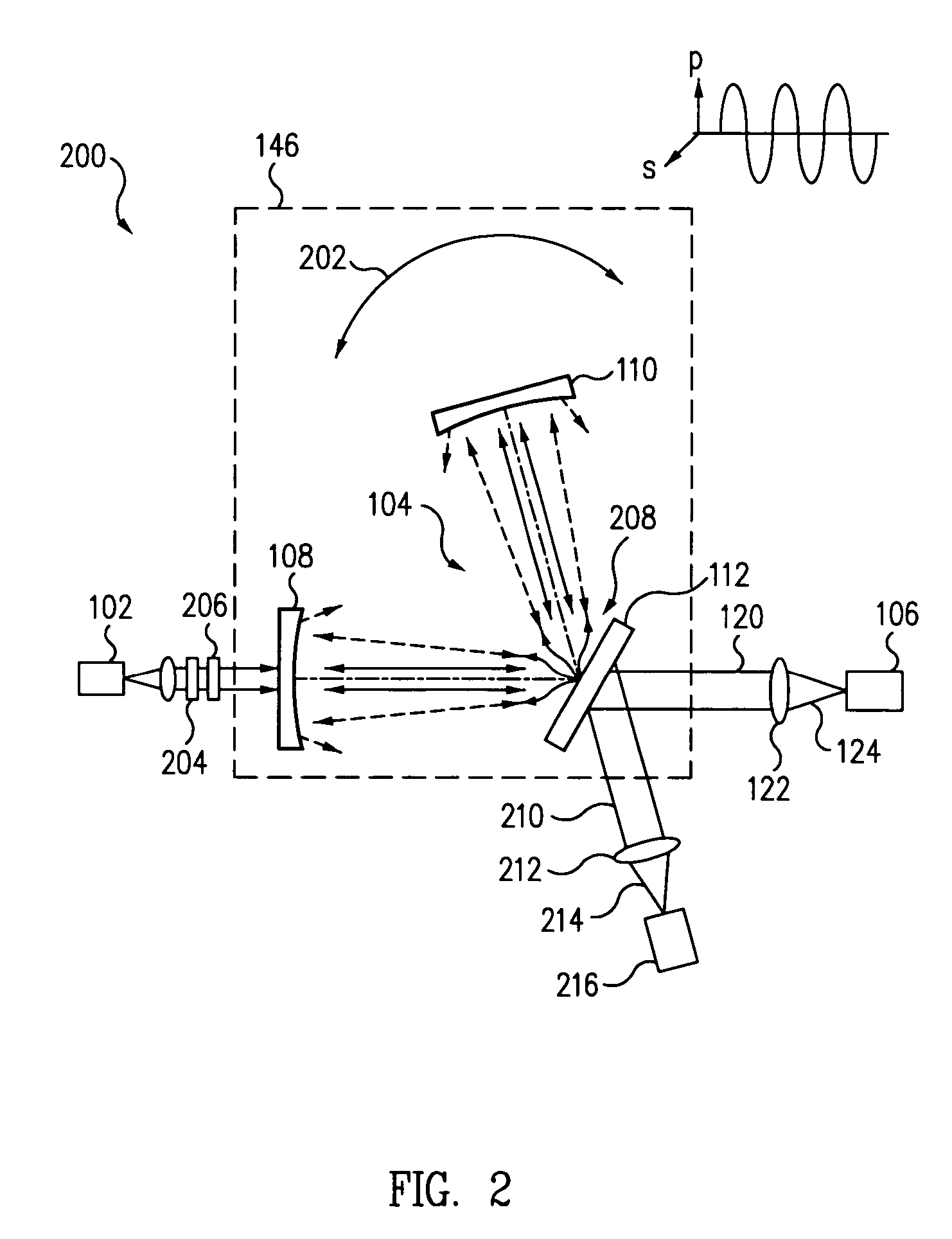
Light scatter measurement apparatus and method
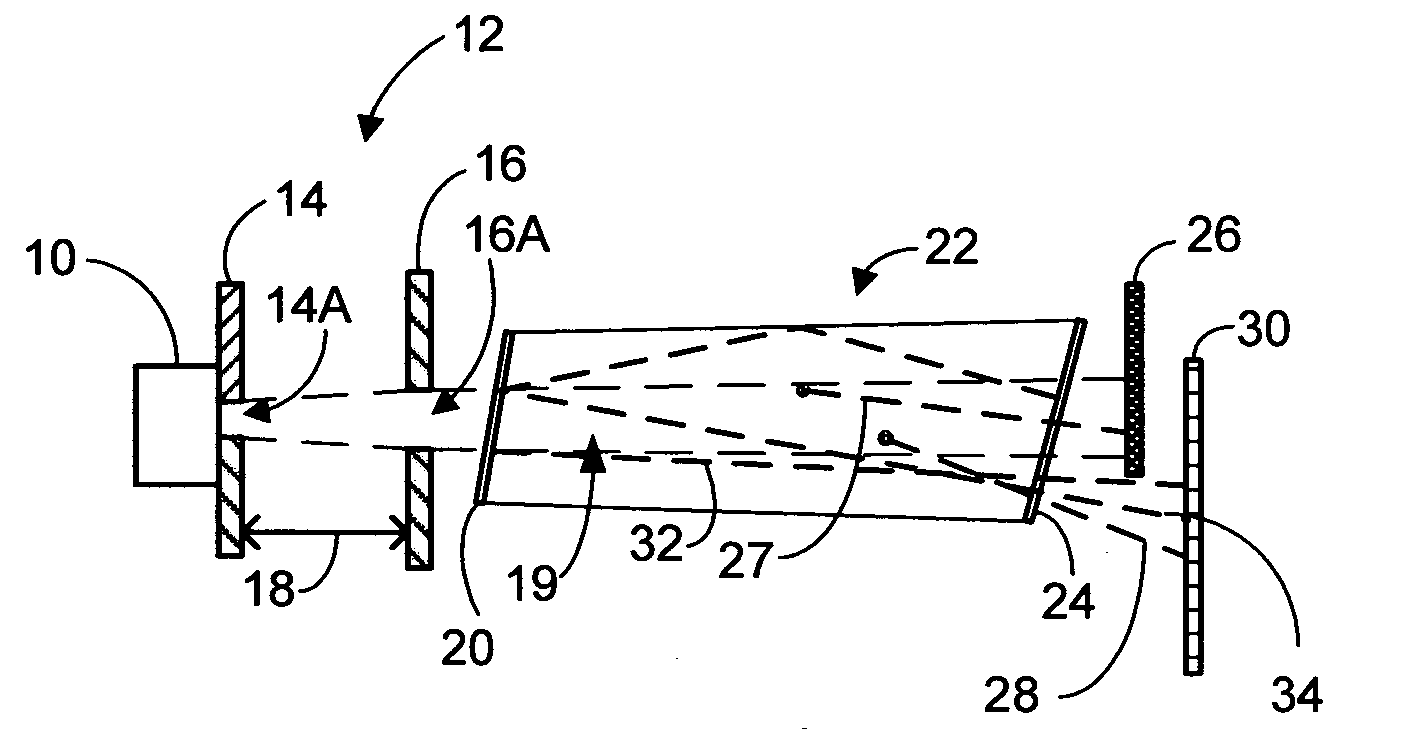
In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, an apparatus for measuring light scatter loss from a test piece includes a light source, an optical cavity including the test piece and at least one mirror located along a path, and a light detector. The cavity receives an input beam from the light source, circulates a beam within the cavity as a circulating beam, and produces an output beam. Irregularities on the surface of the test piece result in a progressive diffusion of the circulating beam about the path. The light detector provides an output signal based on the intensity of the output beam. The output signal has an initial slope that determines a first saturation value. The output signal has a second saturation value. The difference between the first saturation value and the second saturation value provides a scatter loss measurement.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Improved method and apparatus for measuring the scattered light signals from a liquid sample
ActiveCN101963579AEasy to measureEffective focusPhotometryScattering properties measurementsLight scatter measurementLight beam
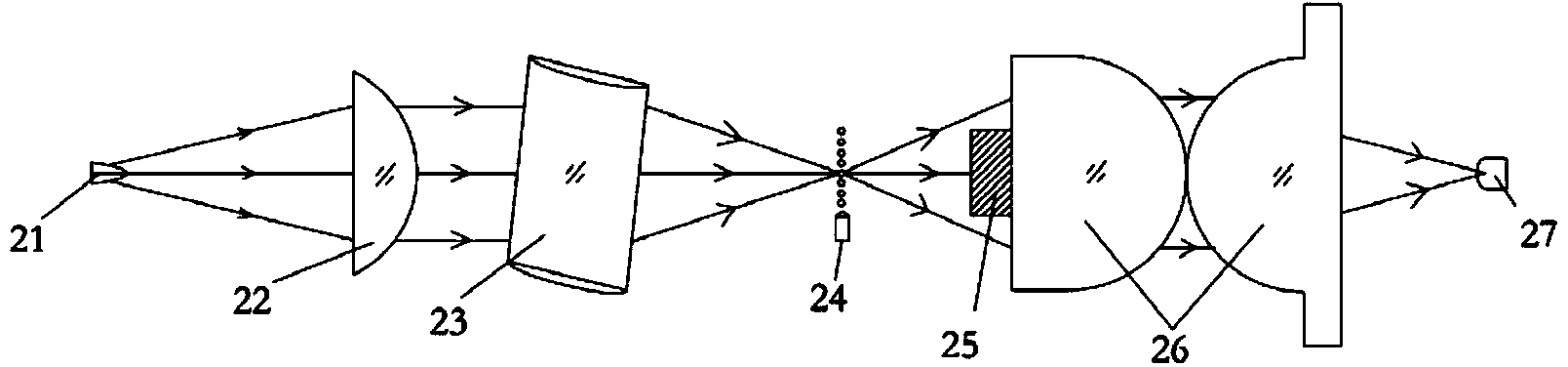
The invention relates to an improved method and apparatus for measuring the scattered light signals from a liquid sample. A sample cell for making light scattering measurements, incorporating an exterior surface acting as both a lateral and vertical lens, is described. This unique structure permits greatly improved measurement of the light scattered by molecules and particles suspended in a fluid contained therein or flowing therethrough while illuminated by a fine light beam incident thereon. The resultant lensed structure of the cell, when integrated into a scattered light photometer and combined with suitable apertures before each scattered light collecting detector, reduces significantly stray light from entering each such detector.
Owner:WYATT TECH
Aperture System for Multi-Angle Light Scattering Detectors
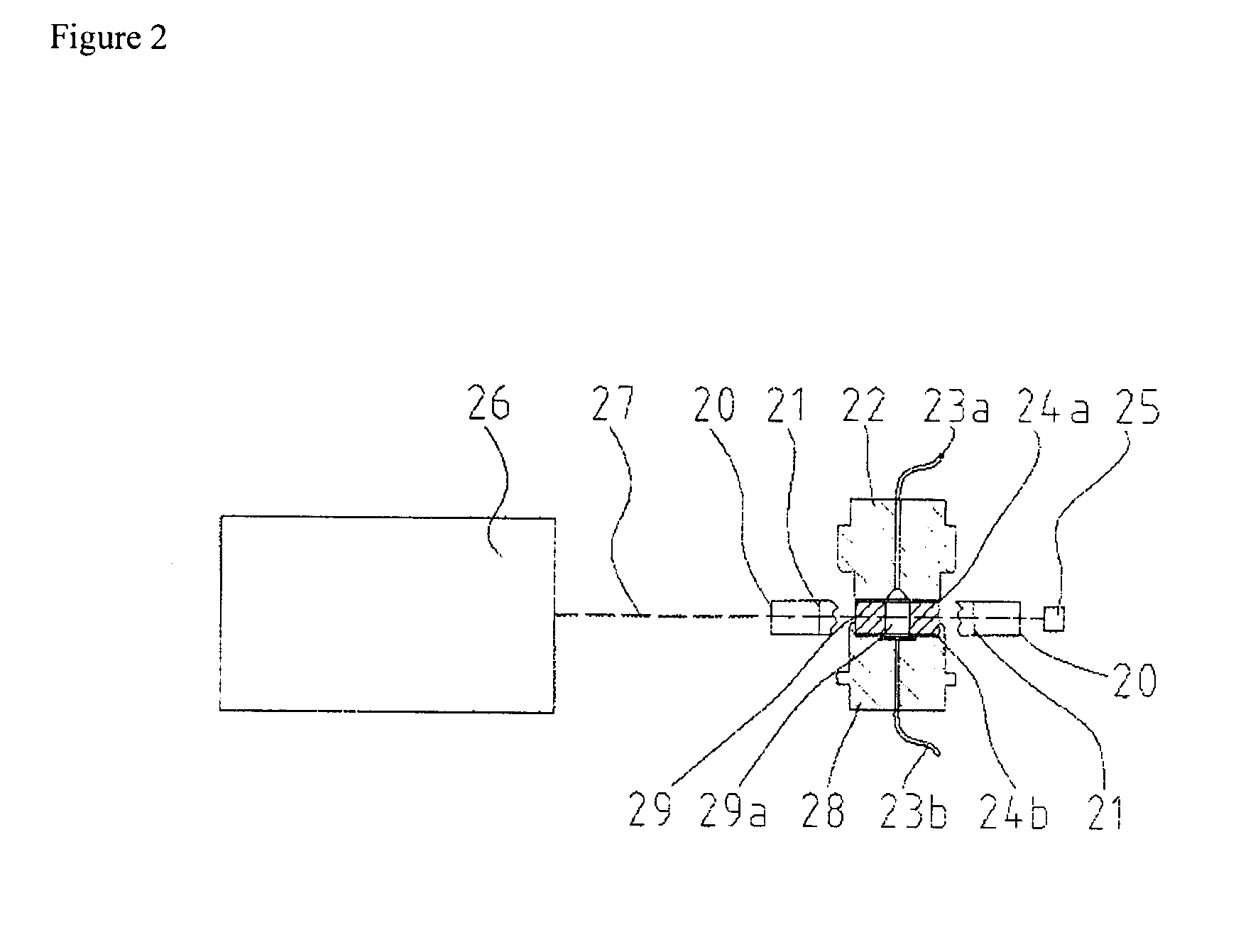
An apparatus for measuring the light scattering properties of a sample in a liquid medium, wherein the liquid medium with the sample is illuminated by a laser beam in a measuring cell transversely to the direction of filling the liquid medium in the measuring cell or transversely to the flow direction of the liquid medium within the measuring cell, comprising a laser, a cylindrical measuring cell, a first inner aperture system, a second outer aperture system and at least two detectors, wherein the detectors are arranged outside of the second outer aperture system so that they collect the light scattered on the sample within set, different angle ranges, wherein the first inner aperture system and the second outer aperture system are formed and arranged circularly and concentrically around the axis of the measuring cell. Use of the apparatus and a method that makes use of the apparatus are also disclosed.
Owner:POSTNOVA ANALYTICS
Light scattering measurements using simultaneous detection
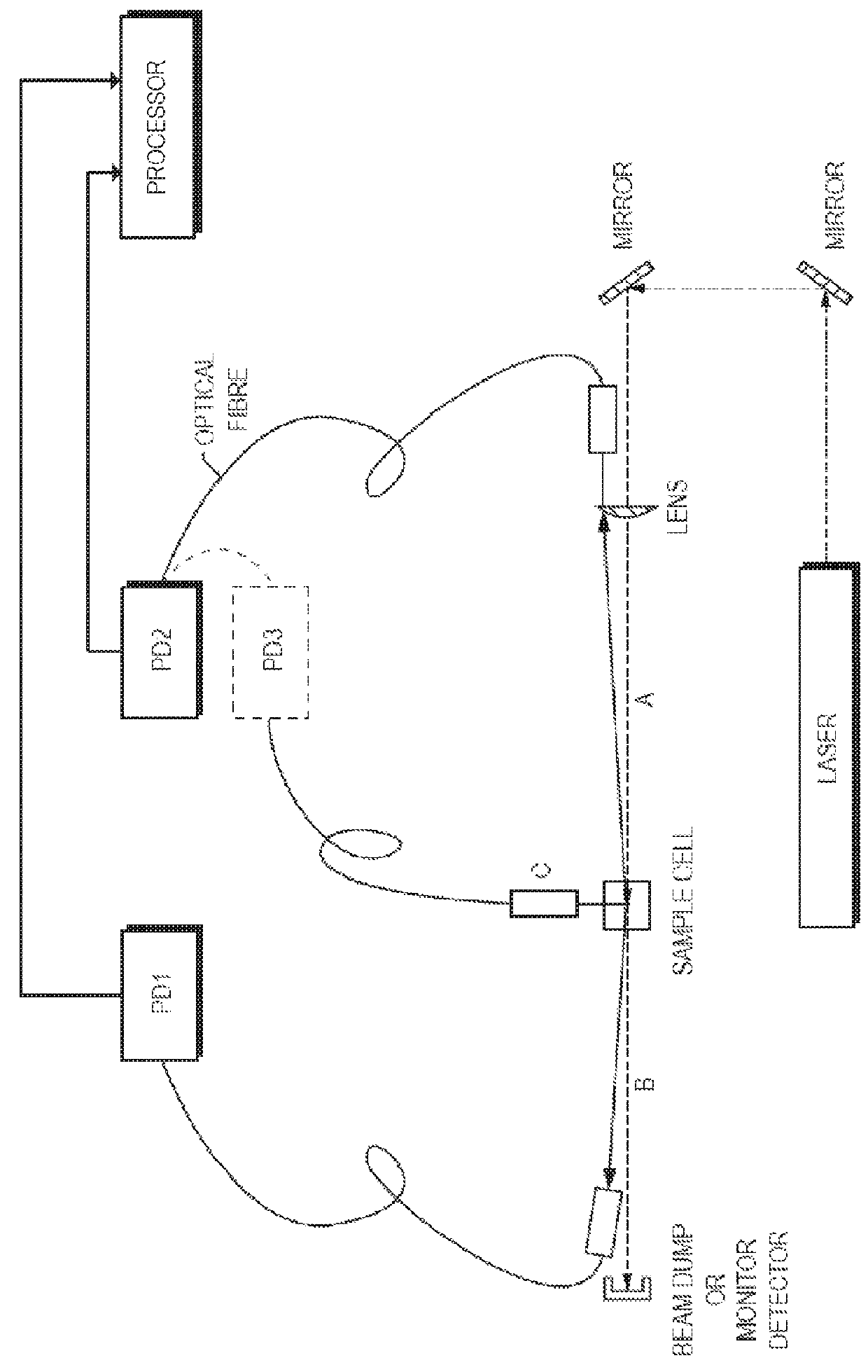
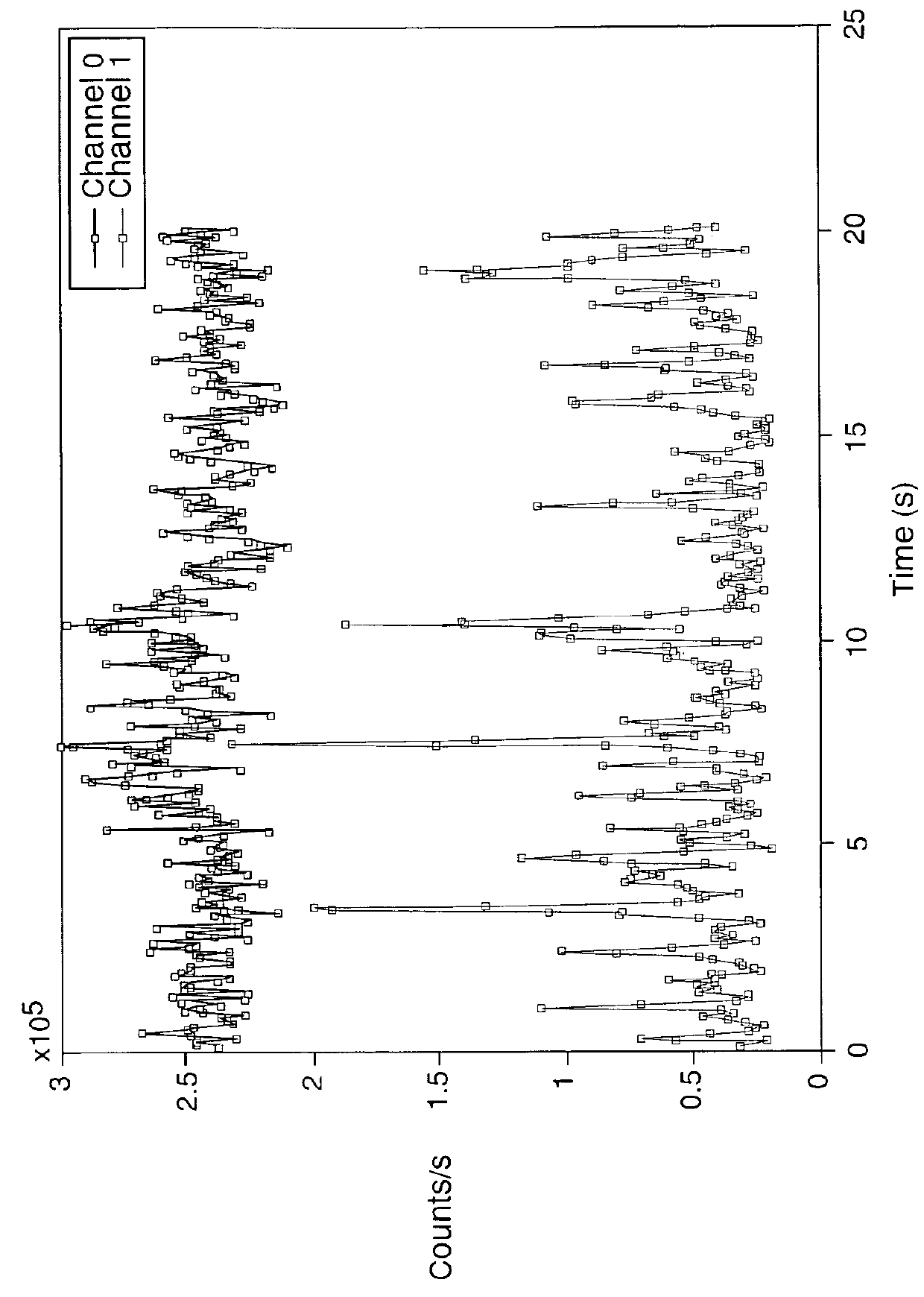
ActiveUS10006851B2Material analysis by optical meansBiological particle analysisLight scatter measurementPhoton counting
Methods and apparatus for measuring particle characteristics are disclosed. In one aspect, an amount of light arising from interaction between light and a suspended sample is detected simultaneously with the acquisition of a photon count from a different direction. At least one measure of particle characteristics can then be derived based at least in part on timing between information from the steps of acquiring and detecting.
Owner:MALVERN INSTRUMENTS
Disposable cartridge for fluid analysis
ActiveCN103217401AMicrobiological testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsLight scatter measurementAbsorbance
The present invention relates to a disposable cartridge for fluid analysis. A disposable blood analysis cartridge may include a sample collection reservoir, an absorbance measurement channel, and an optical light scattering measurement channel. One or more valves may be disposed between the sample collection reservoir and the absorbance measurement channel and / or the optical light scattering measurement channel. A negative pressure may be applied to the cartridge to pull sample from the sample collection reservoir through the one or more valves and into the absorbance measurement channel and / or the optical light scattering measurement channel. Once the sample is pulled into the absorbance measurement channel and / or the optical light scattering measurement channel, the one or more valves may be closed. With the one or more valves closed, and in some cases, a pusher fluid may be provided to push the fluid sample to other regions of the disposable fluid blood analysis cartridge.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
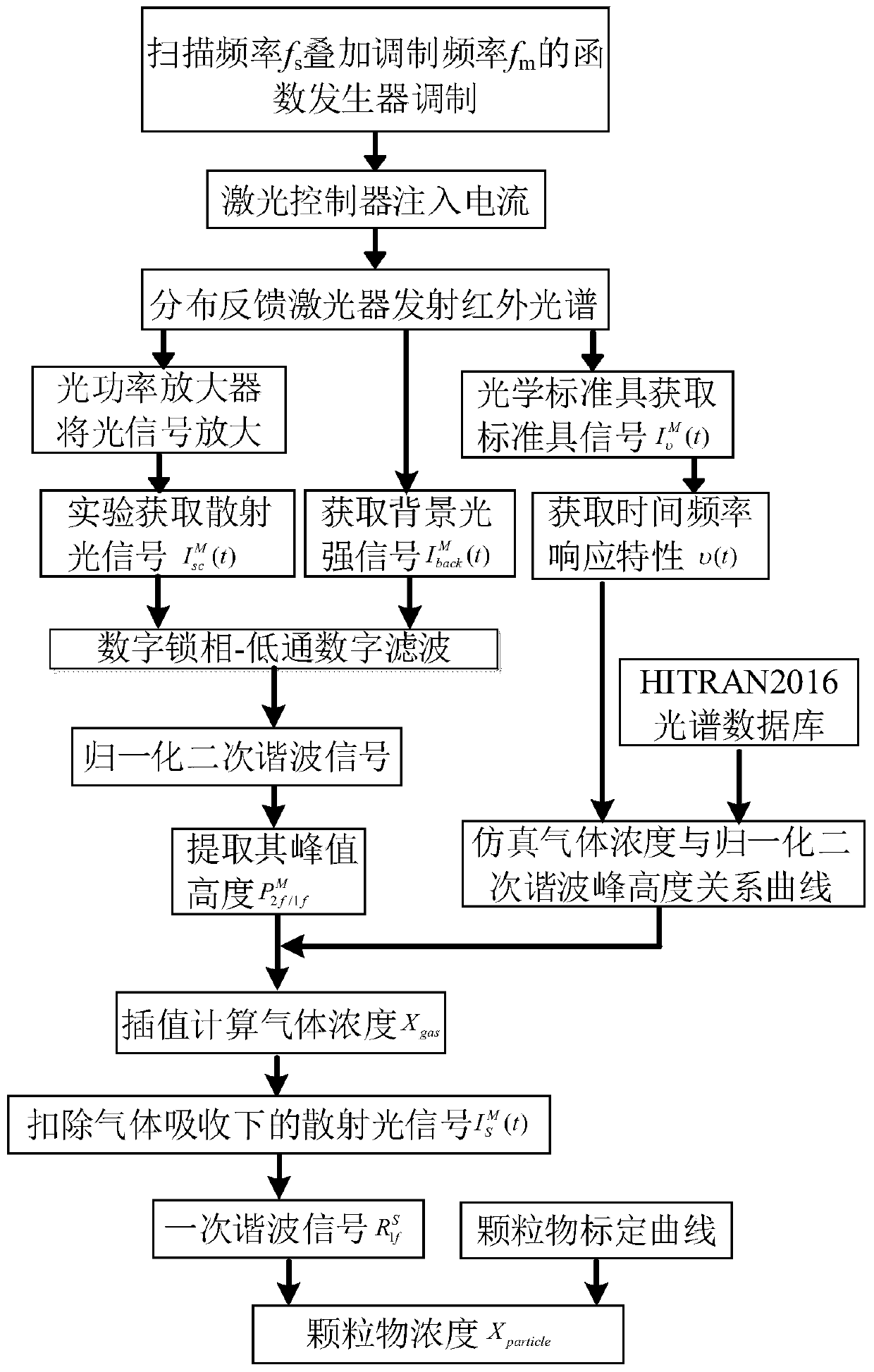
Synchronous particle and gas concentration measurement device and method based on infrared light modulation technology
ActiveCN109813639ARealize synchronized measurementsImprove signal-to-noise ratioParticle size analysisColor/spectral properties measurementsParticulatesLight scatter measurement
The invention discloses a synchronous particle and gas concentration measurement device and method based on an infrared light modulation technology. According to the method, a light scattering measurement light path is coupled with a wavelength modulation measurement light path, so that synchronous concentration measurement of low-concentration particles and gas is realized. According to the method, there is no need to additionally consider low-frequency noise such as background dark current of a detector, so that the signal-to-noise ratio of the concentration measurement of the low-concentration particles and gas is effectively increased; the sensitivity is higher; the limit to existing concentration measurement of particles and gas is lowered. Therefore, the method has an important application value in realization of synchronous online monitoring of to-be-detected particles and gas in a coal-fired power plant with ultra-low emission demands.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com