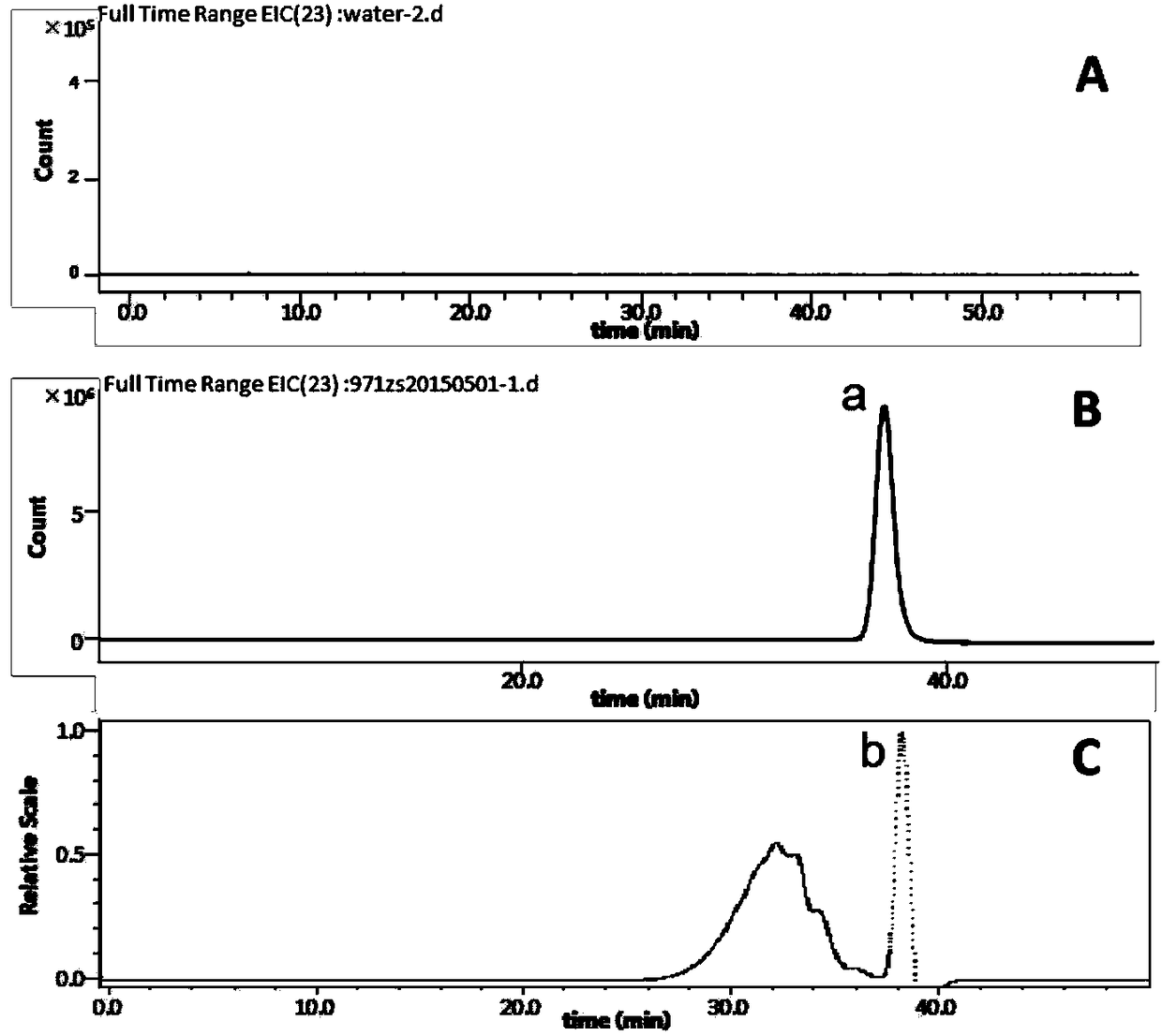
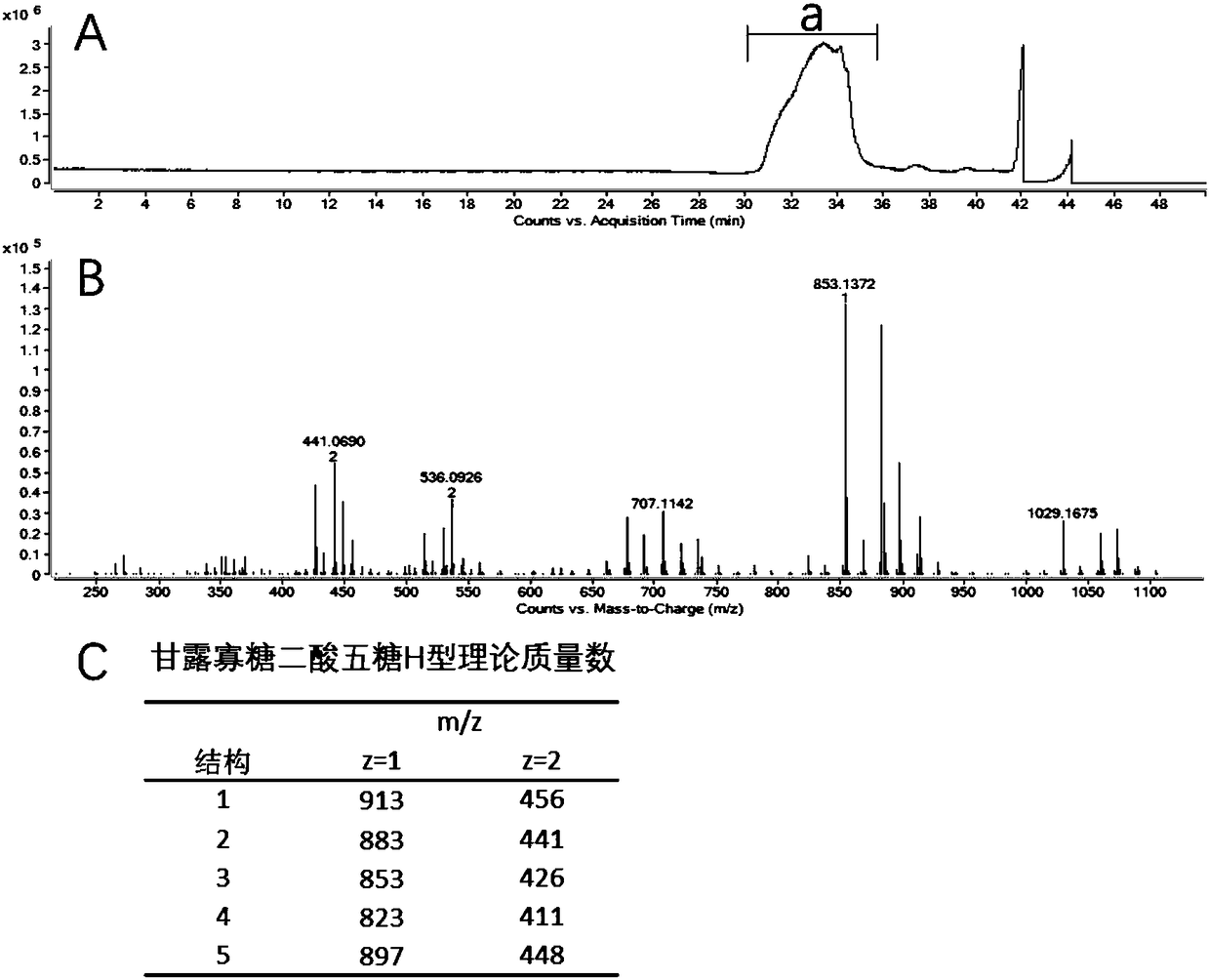
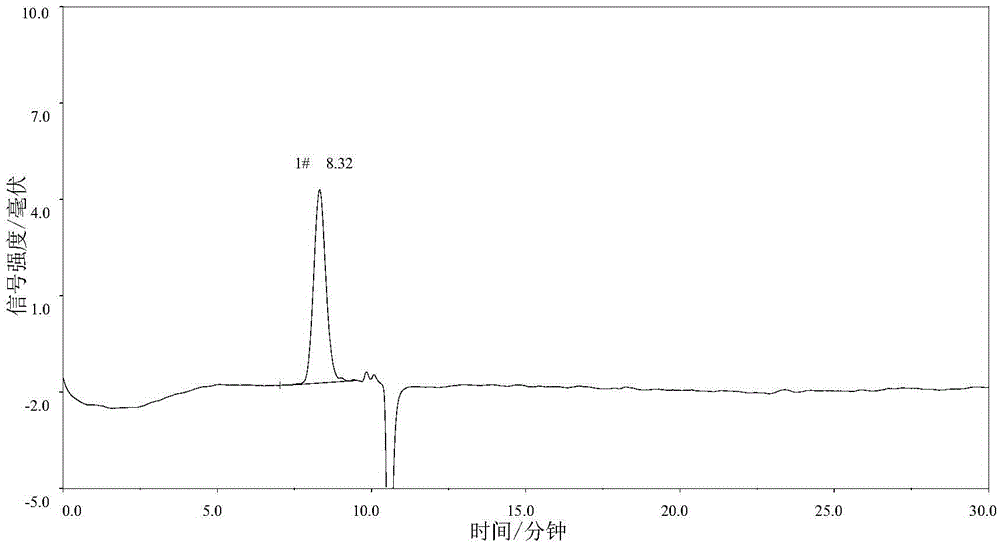
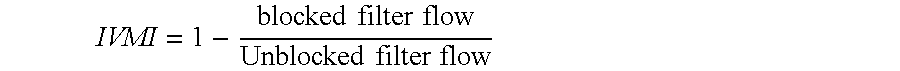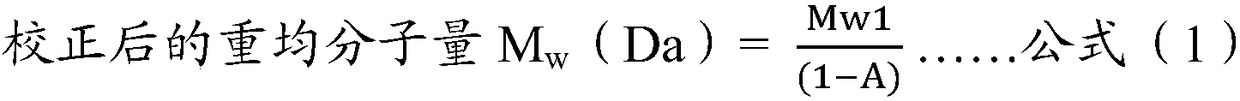Patents
Literature
181 results about "Size-exclusion chromatography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
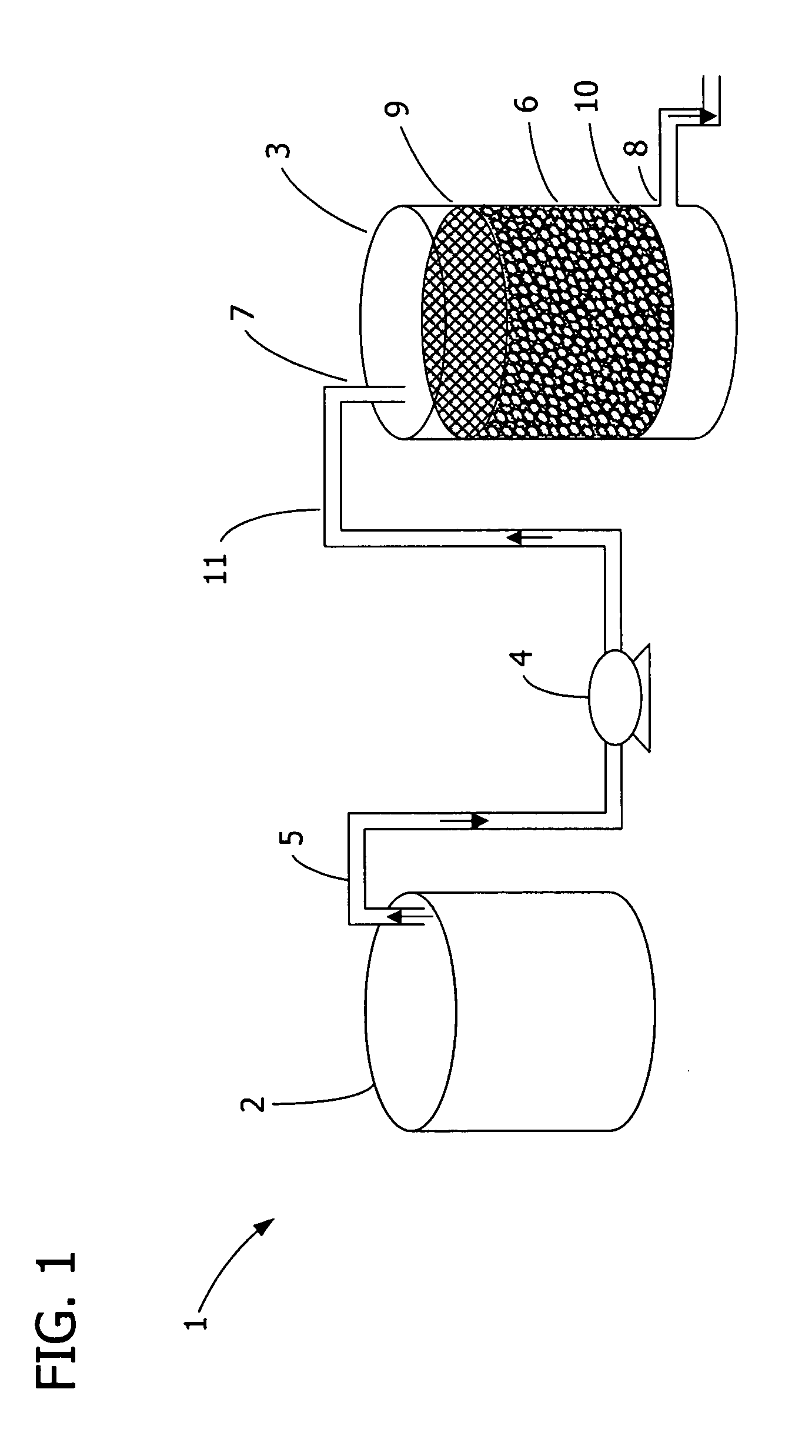
Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC), also known as molecular sieve chromatography, is a chromatographic method in which molecules in solution are separated by their size, and in some cases molecular weight. It is usually applied to large molecules or macromolecular complexes such as proteins and industrial polymers. Typically, when an aqueous solution is used to transport the sample through the column, the technique is known as gel-filtration chromatography, versus the name gel permeation chromatography, which is used when an organic solvent is used as a mobile phase. The chromatography column is packed with fine, porous beads which are composed of dextran polymers (Sephadex), agarose (Sepharose), or polyacrylamide (Sephacryl or BioGel P). The pore sizes of these beads are used to estimate the dimensions of macromolecules. SEC is a widely used polymer characterization method because of its ability to provide good molar mass distribution (Mw) results for polymers.
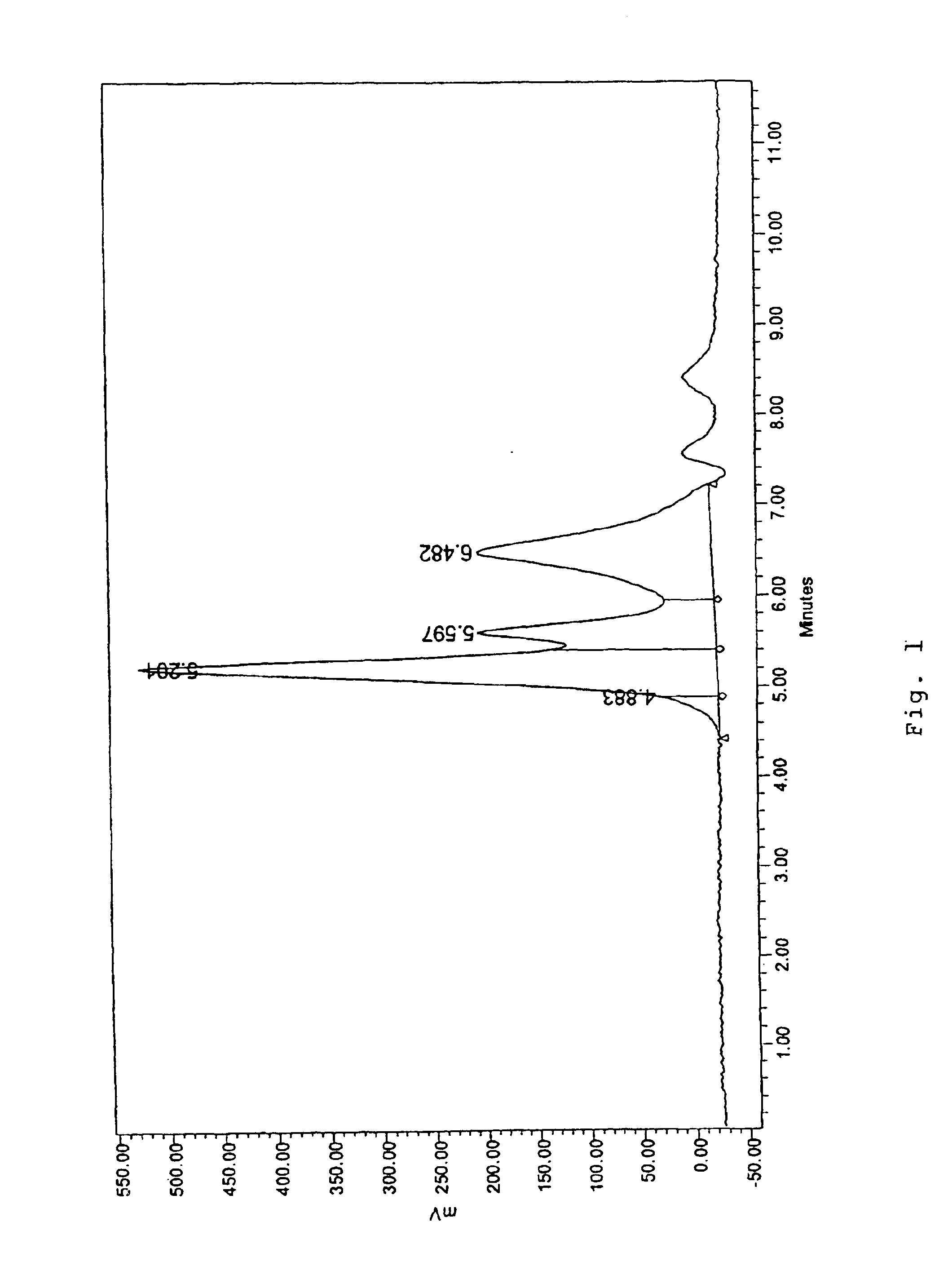
Chromatographic method for mutation detection using mutation site specifically acting enzymes and chemicals
InactiveUS6027898AHighly reproducibleEasy to implementSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChromatographic separationRetention time
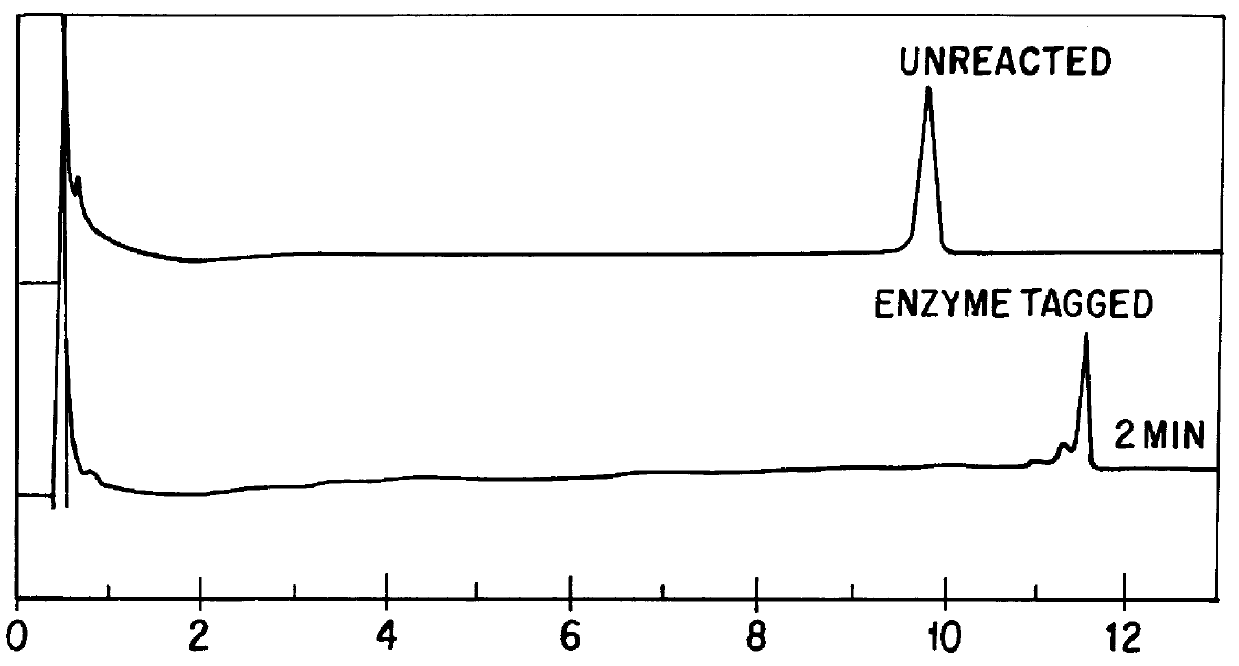
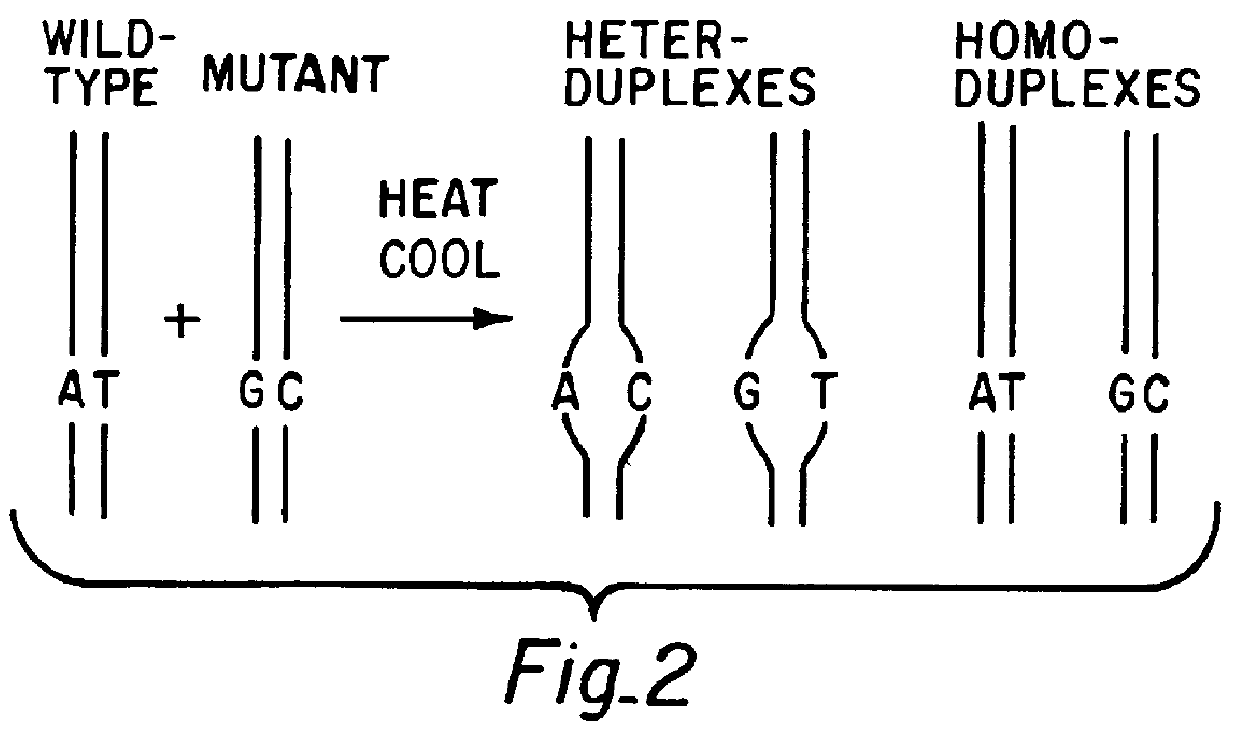
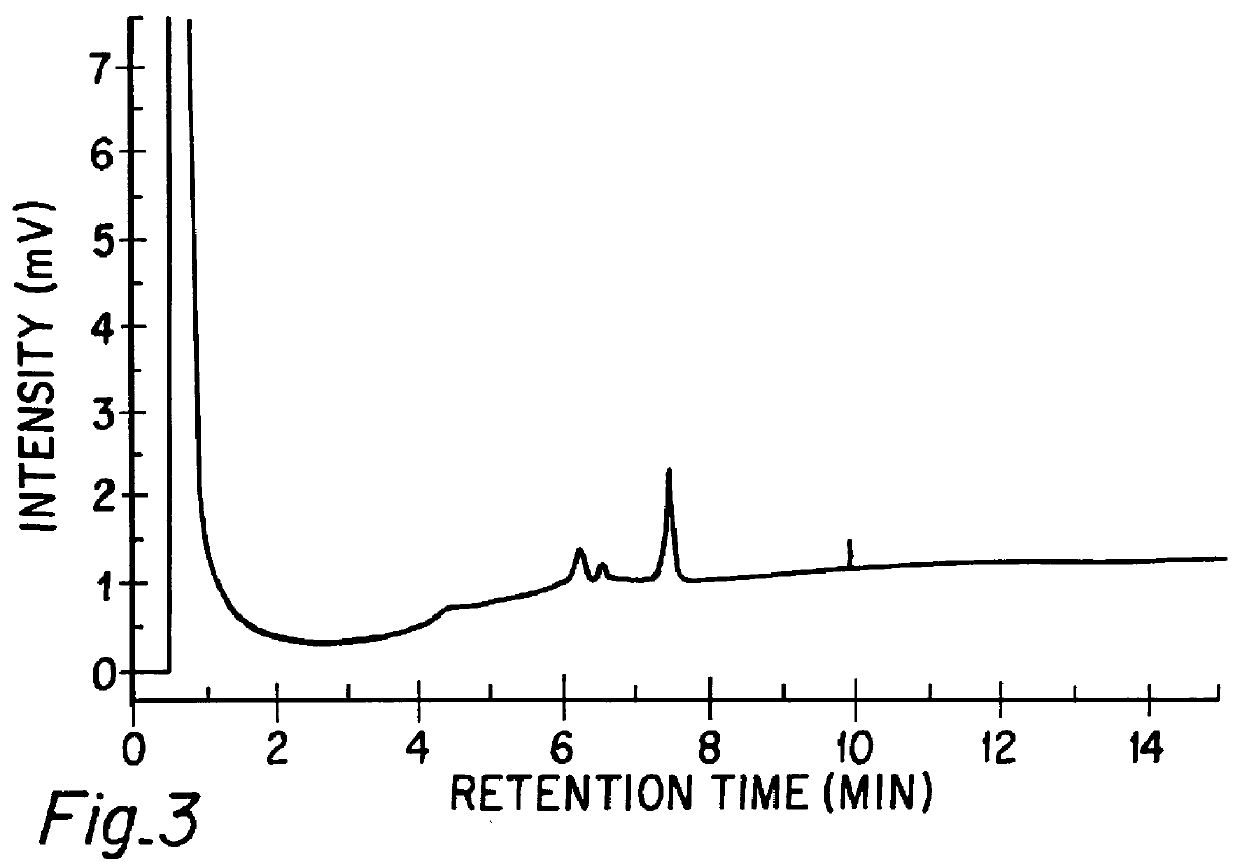
A method for analyzing a sample of double stranded DNA to determine the presence of a mutation therein comprises contacting the sample with a mutation site binding reagent, and chromatographically separating and detecting the product. The chromatographic separation can be performed using Matched Ion Polynucleotide Chromatography, size exclusion chromatography, ion exchange chromatography, or reverse phase chromatography. The mutation site binding reagent can be an enzyme or a non-proteinaceous chemical reagent. In one embodiment, a mutation site binding reagent binds to the site of mutation and alters the chromatographic retention time. In another embodiment, a mutation site binding reagent cleaves at the site of mutation, resulting in an increase in the number of fragments.
Owner:ADS BIOTEC INC
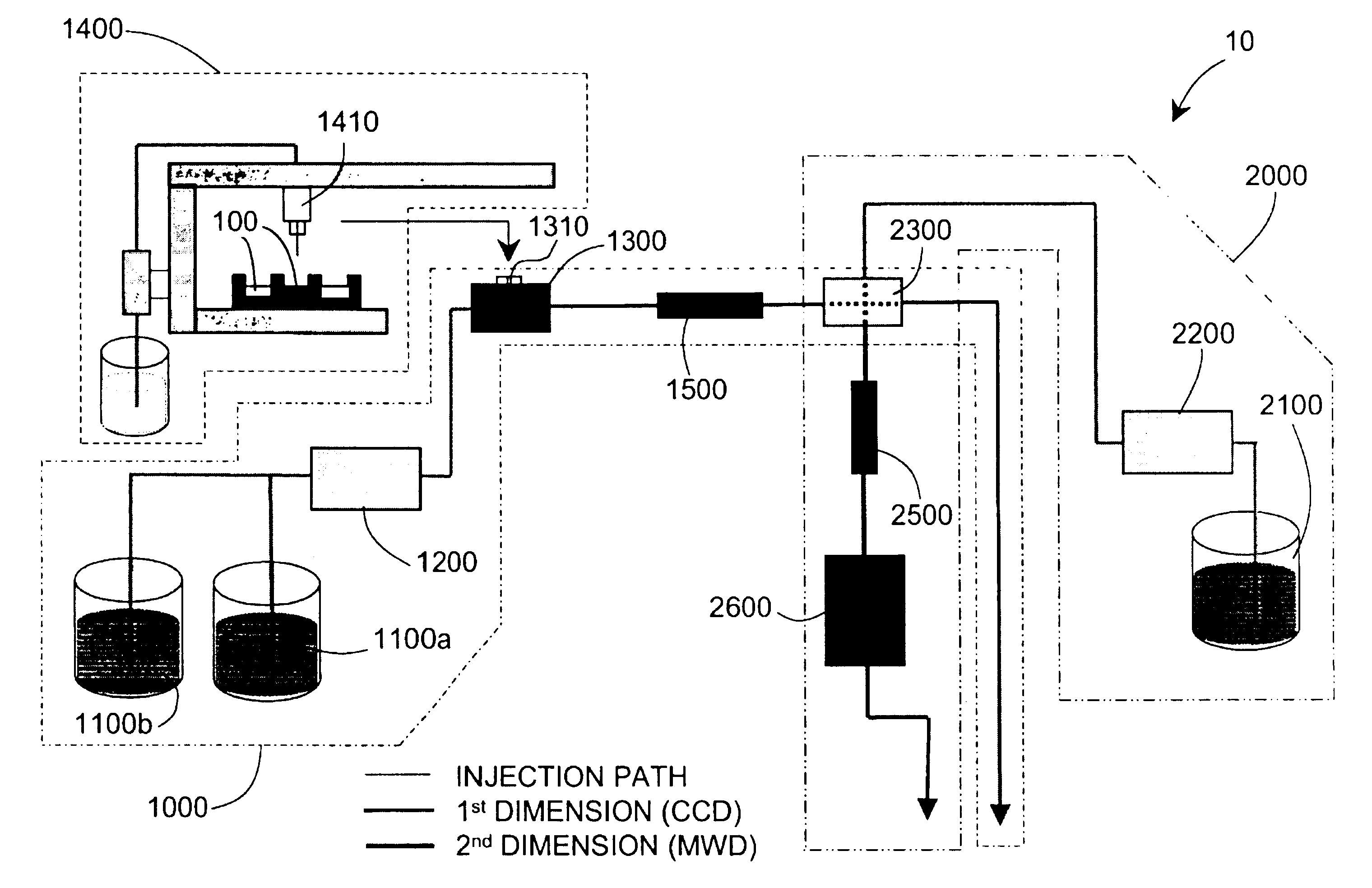
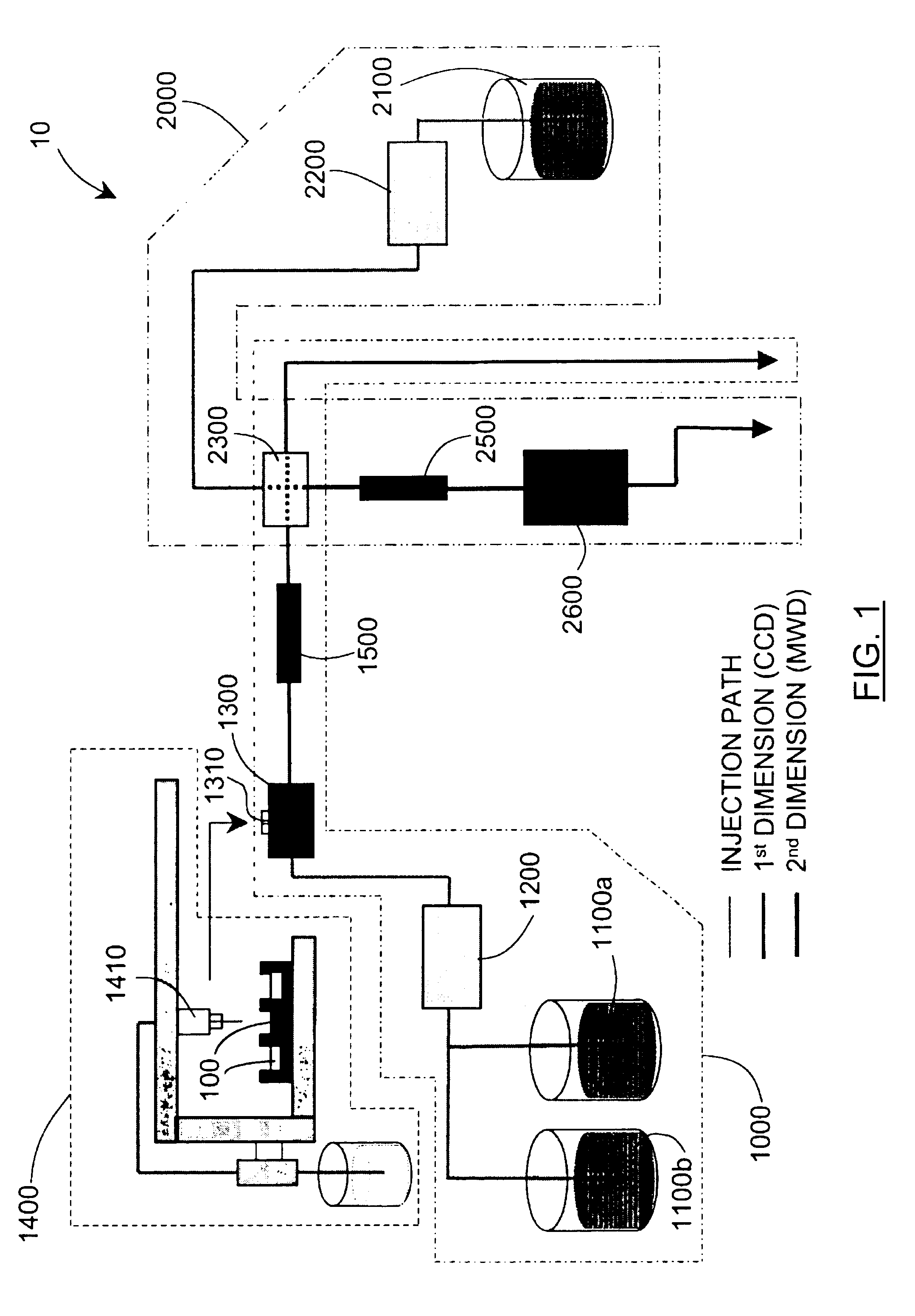
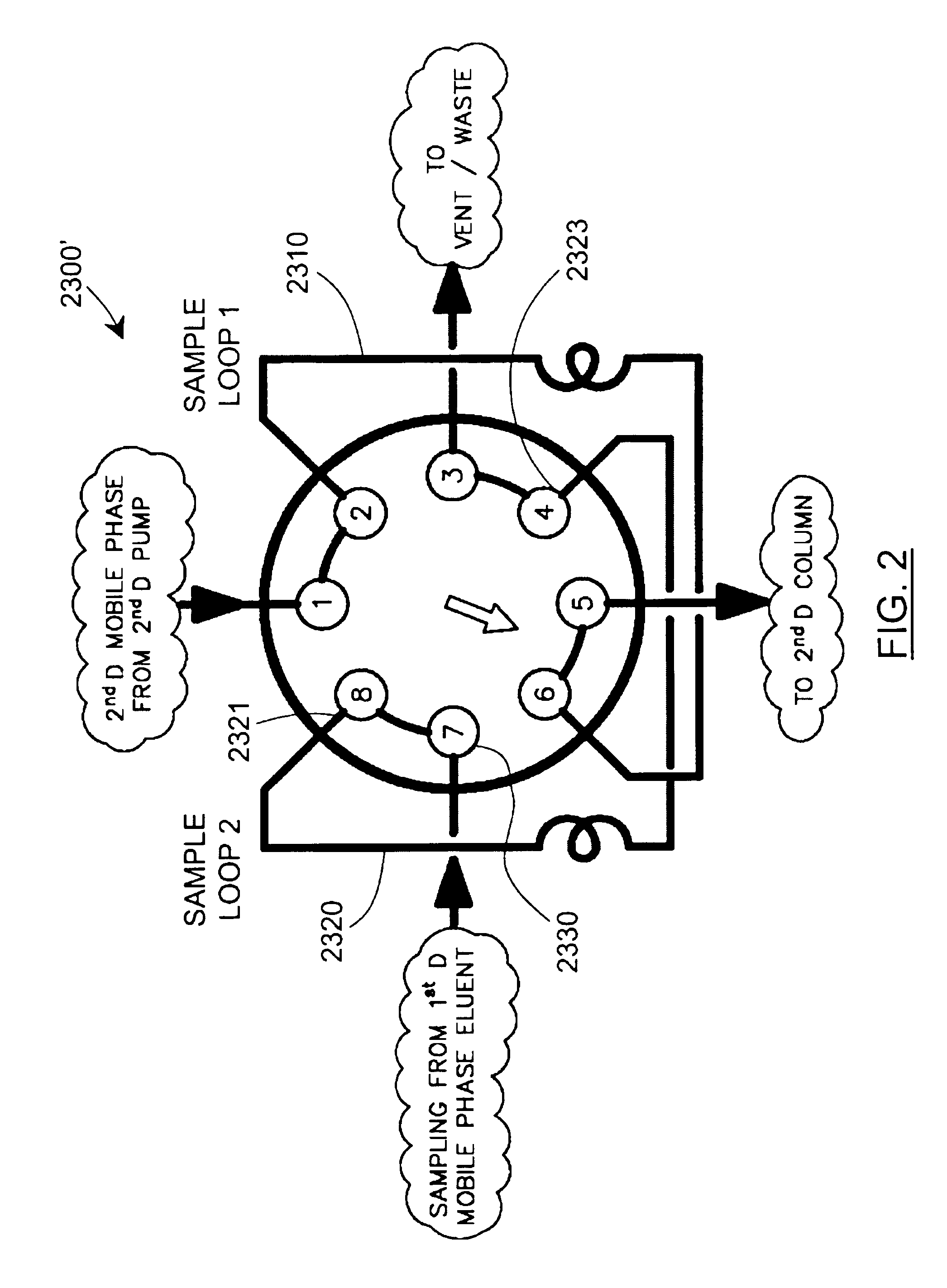
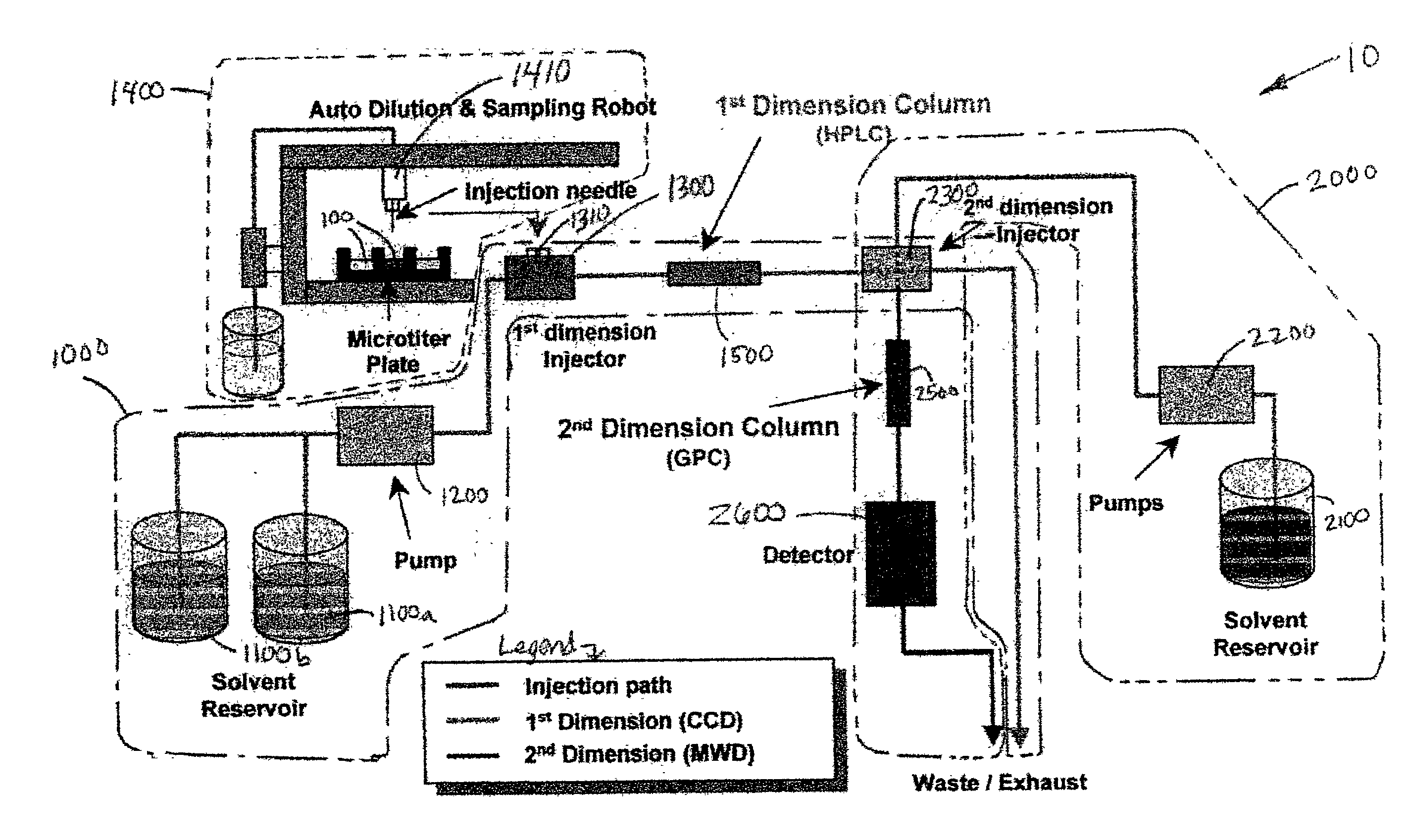
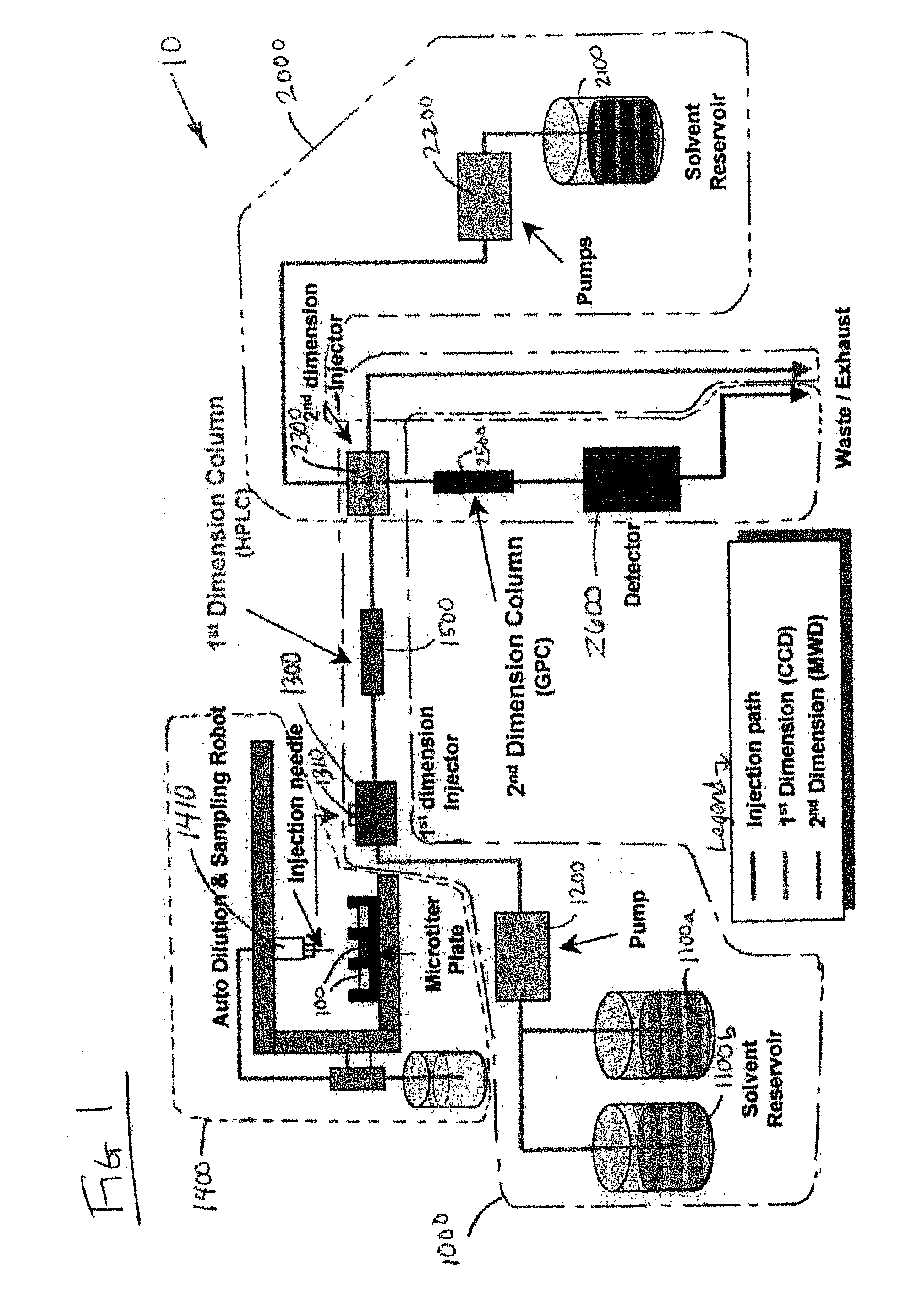
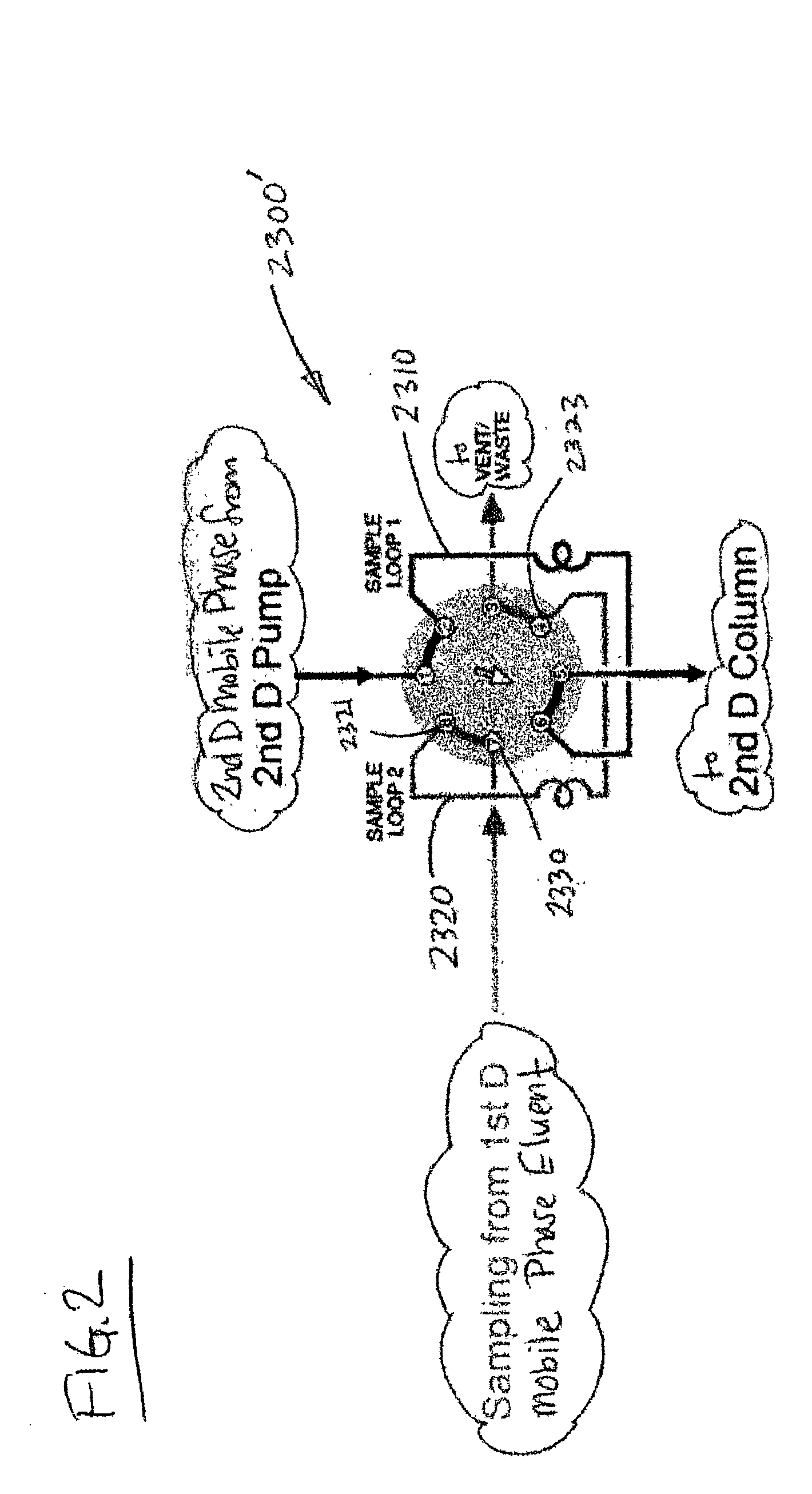
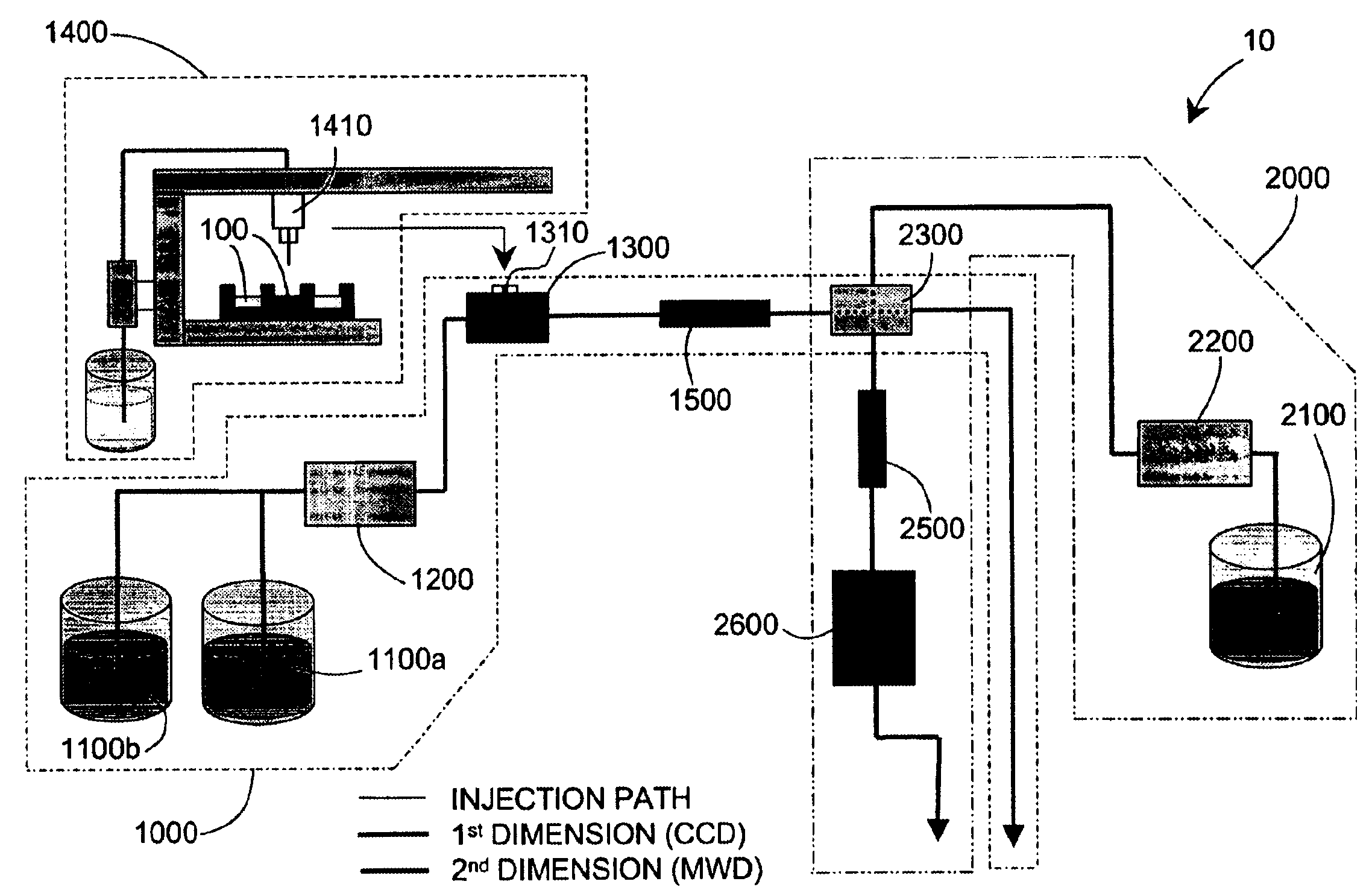
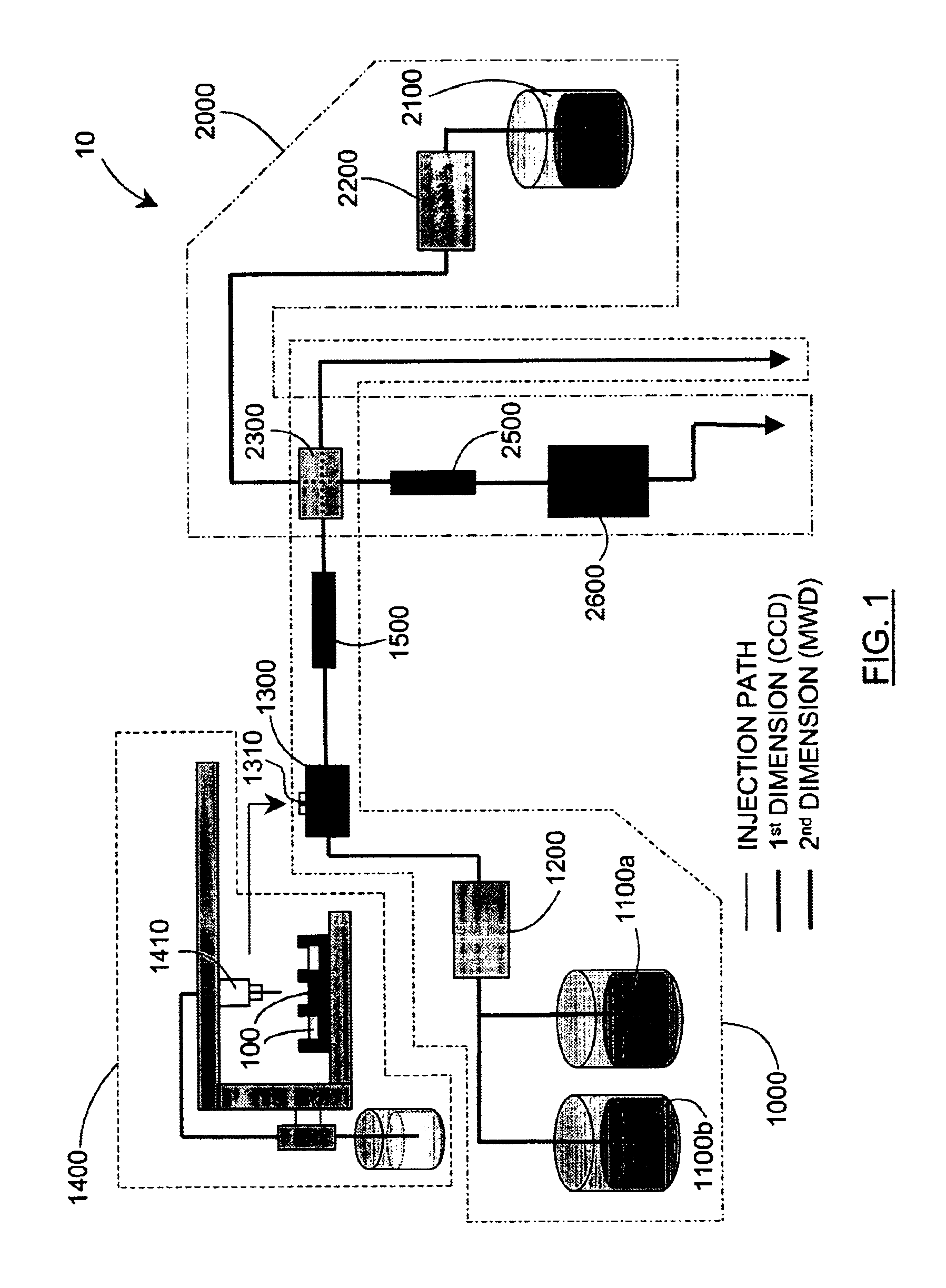
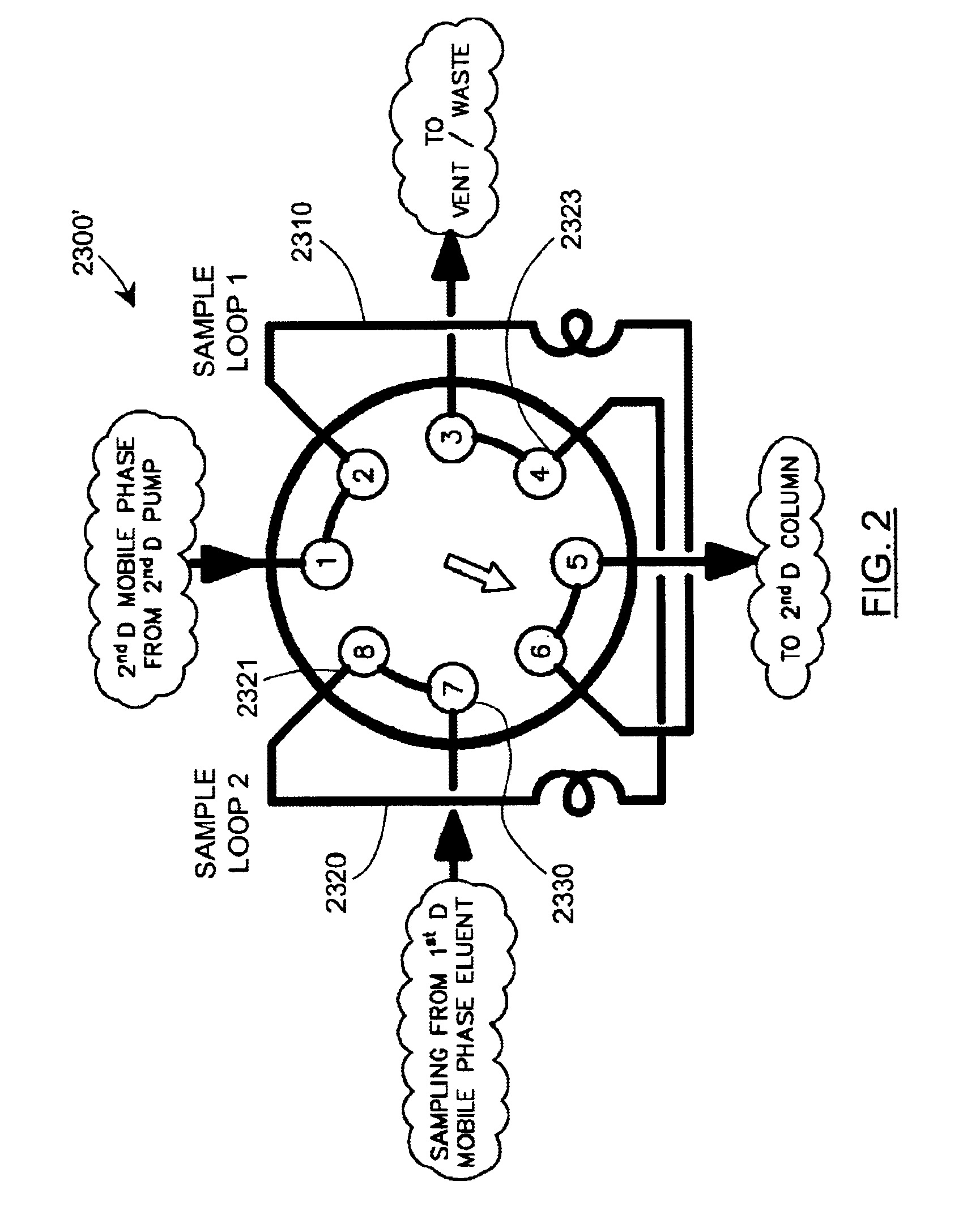
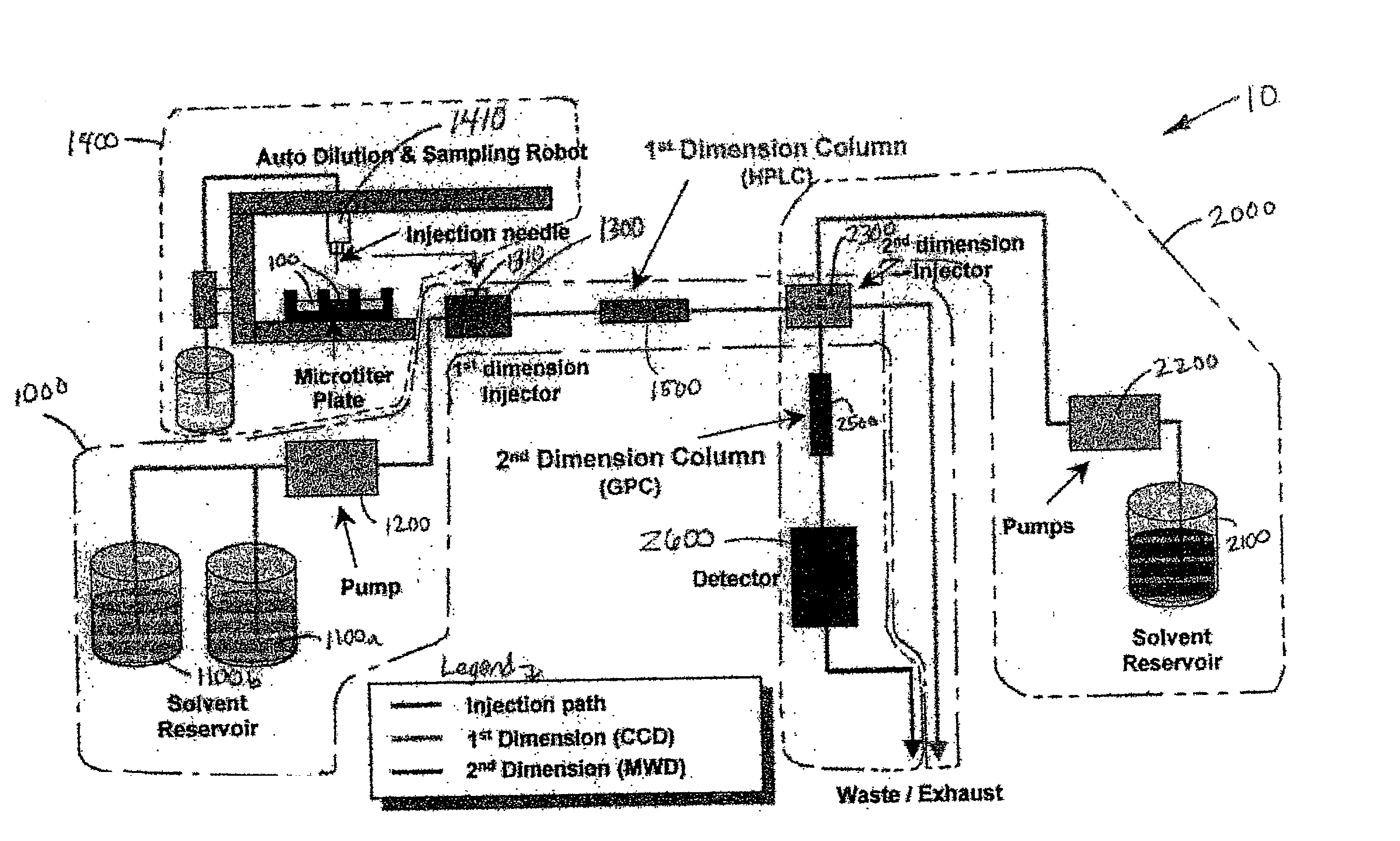
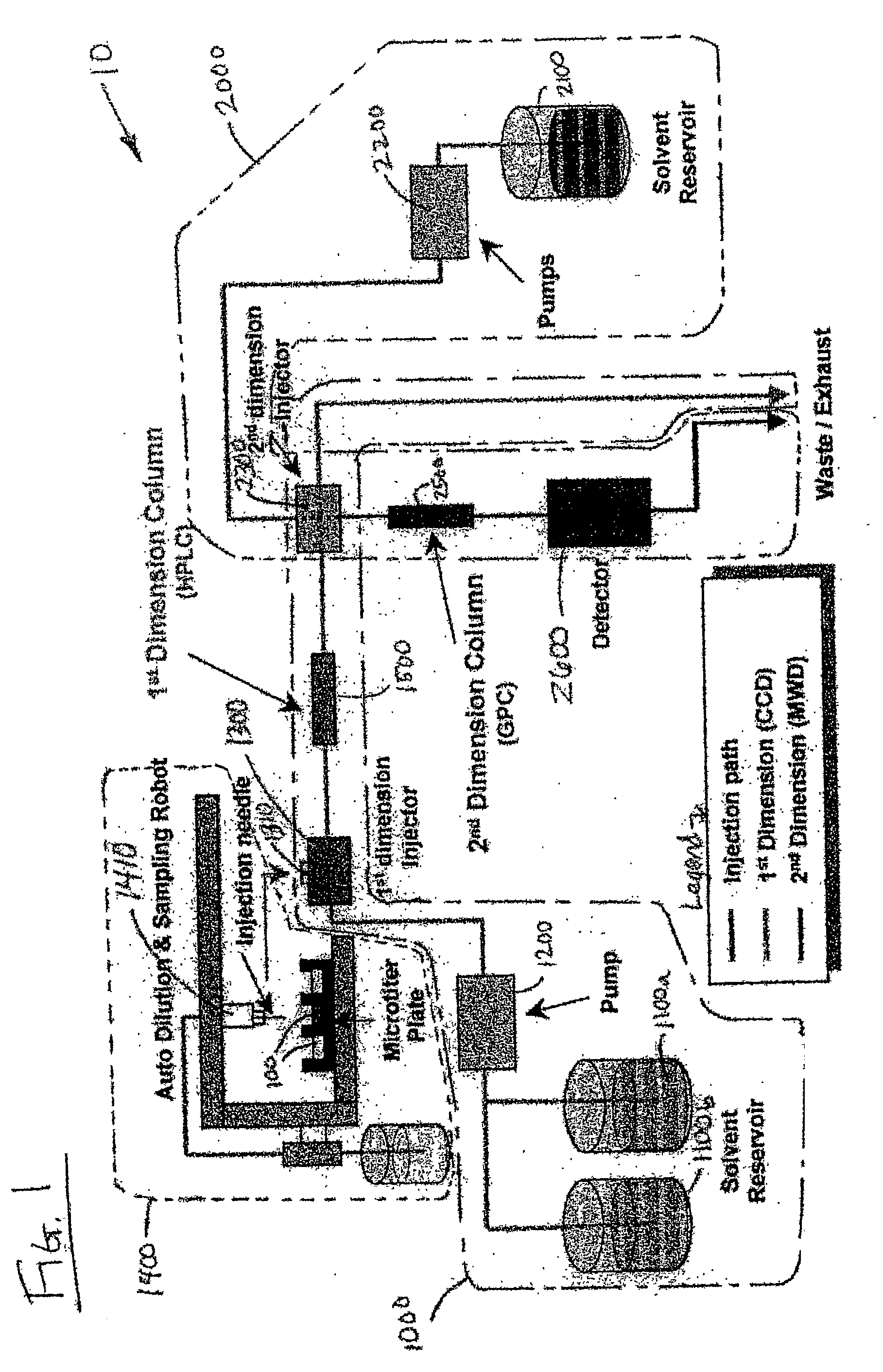
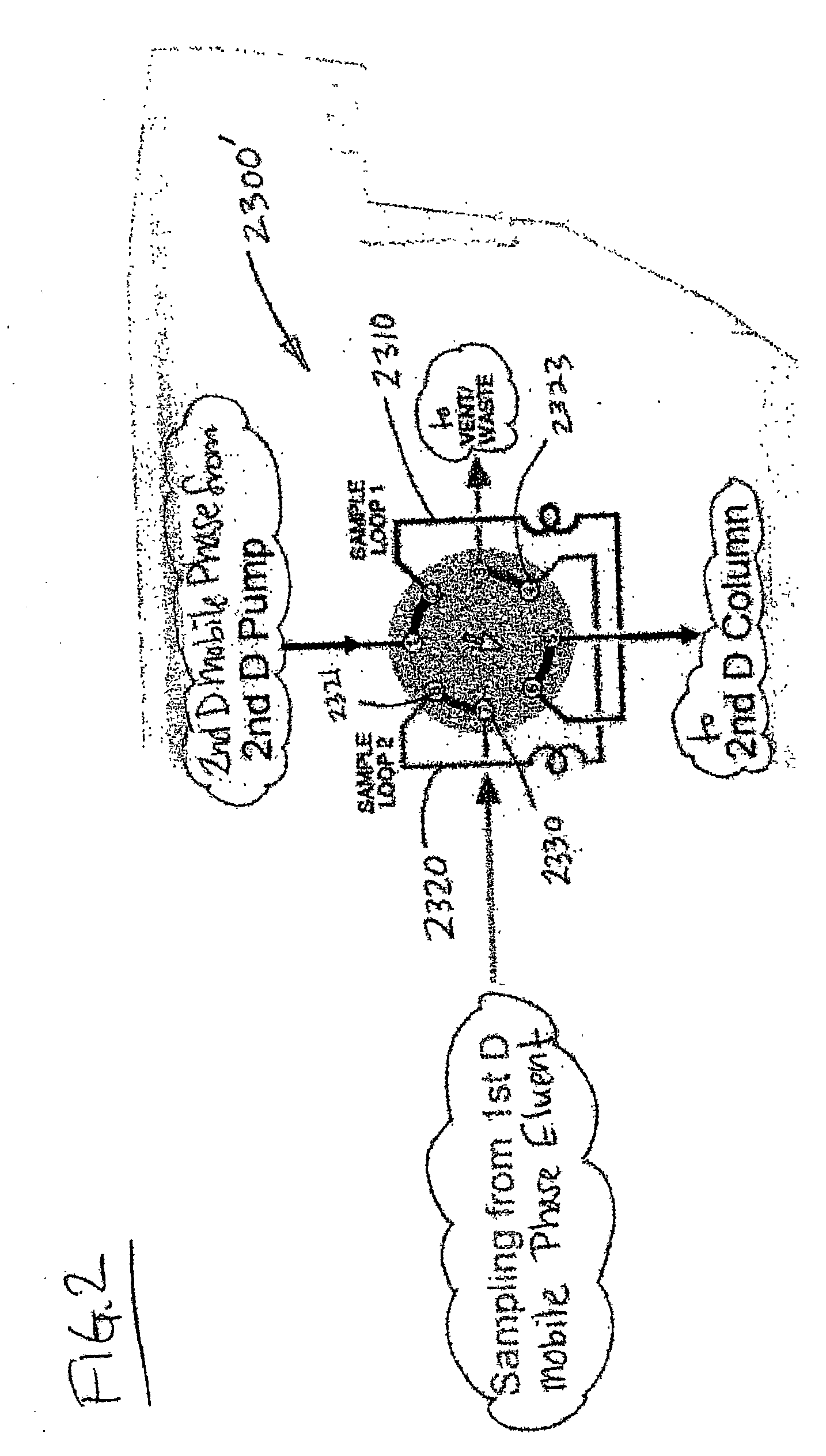
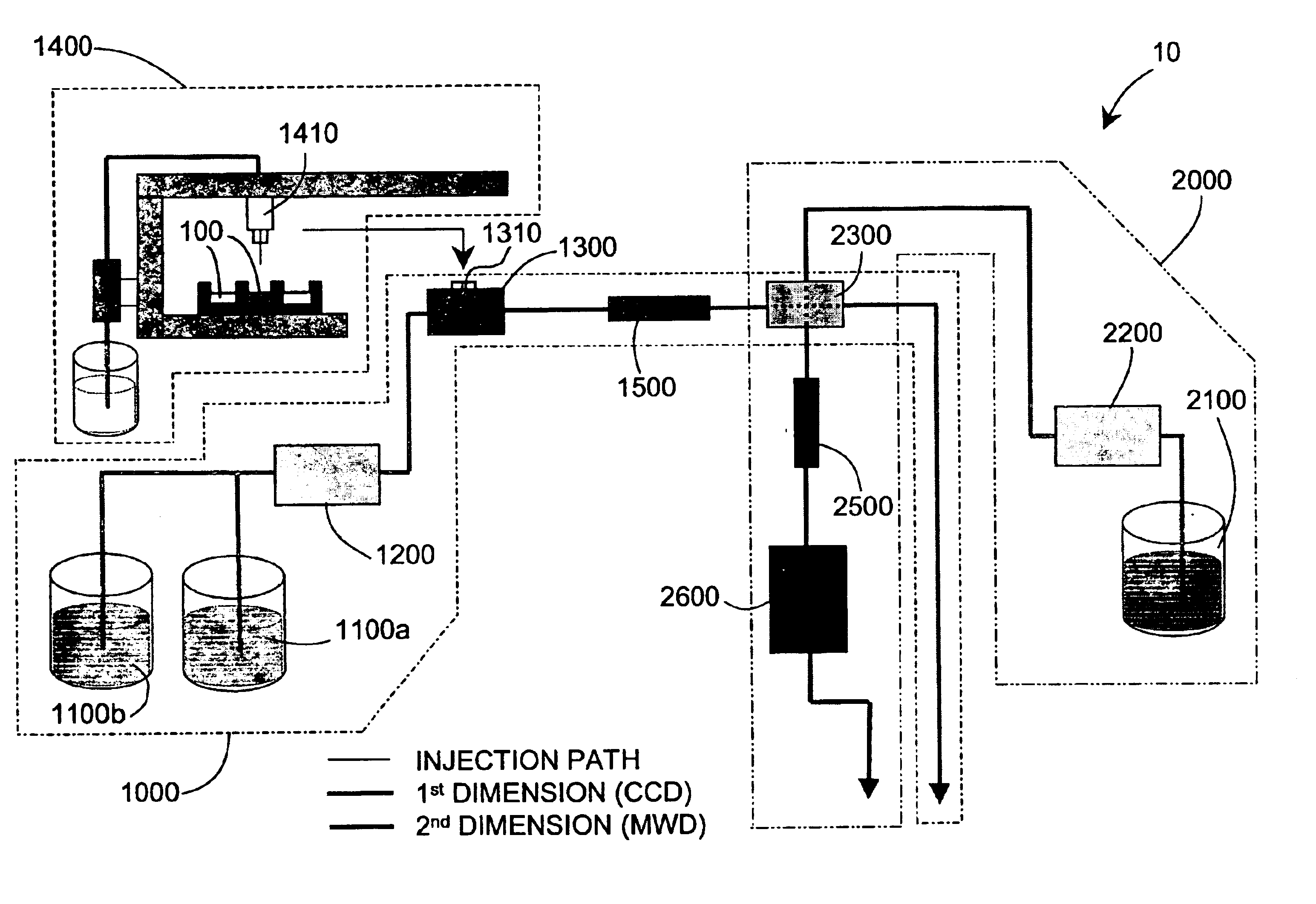
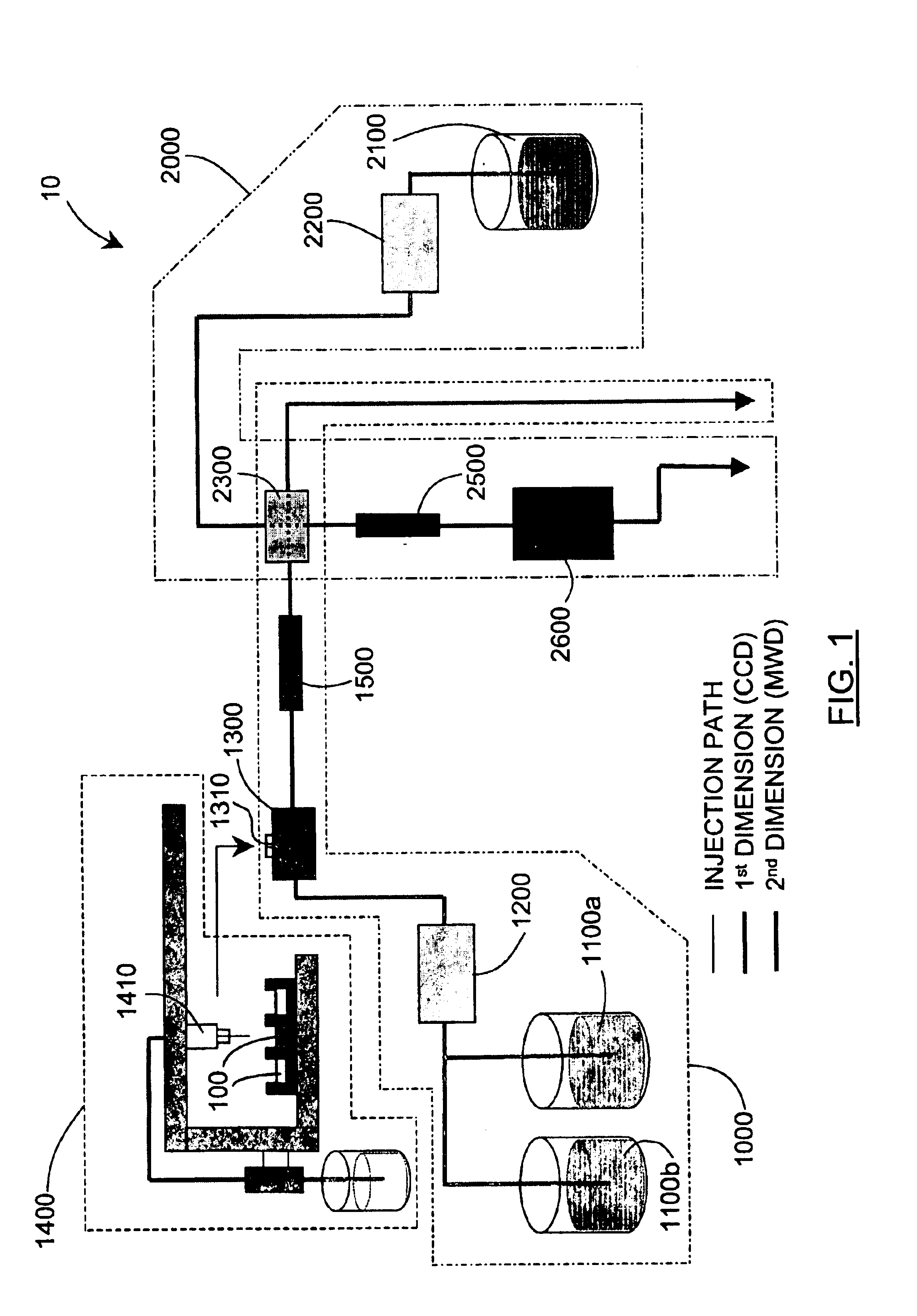
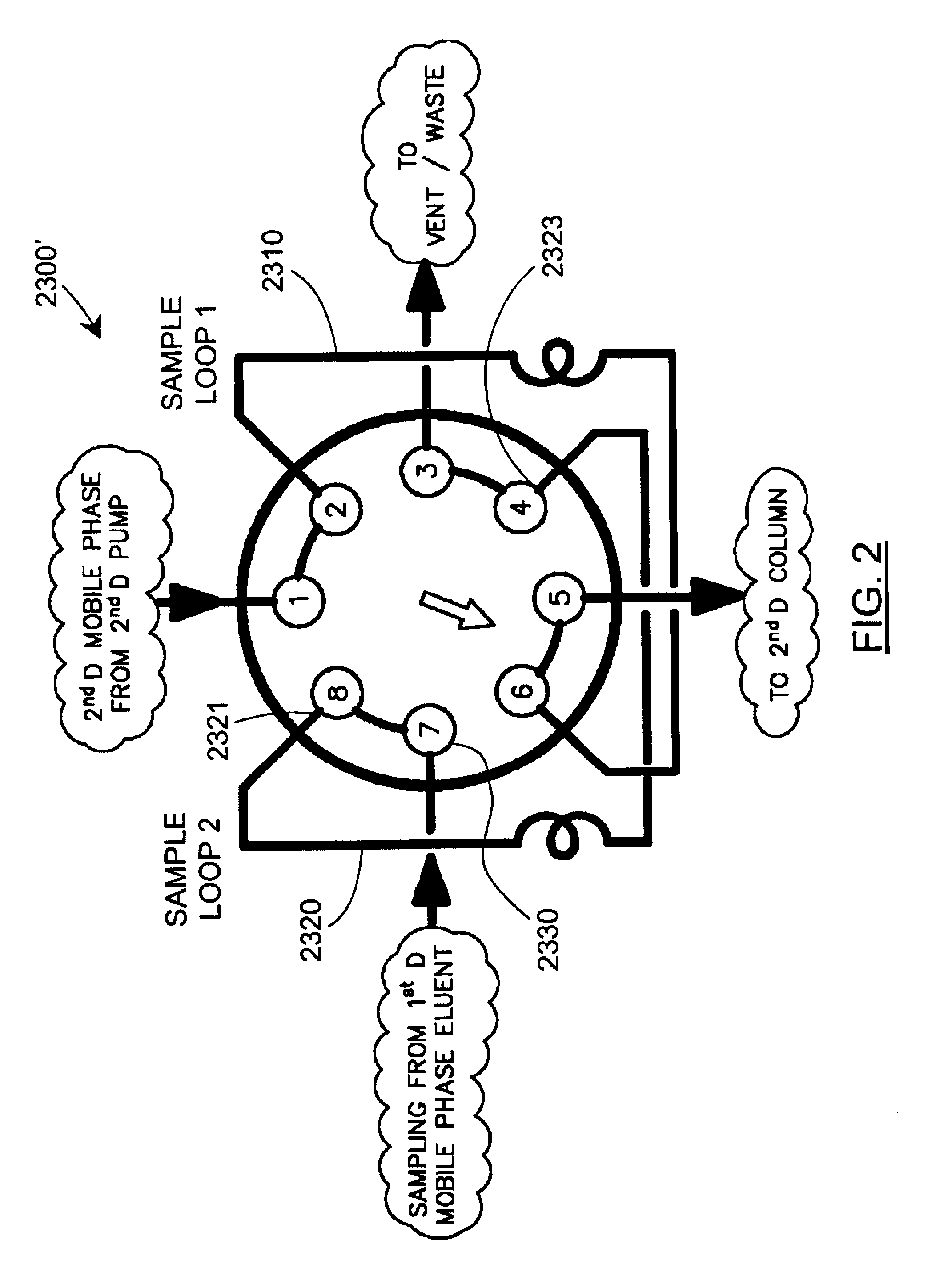
Methods and apparatus for characterization of polymers using multi-dimensional liquid chromatography with regular second-dimension sampling
InactiveUS6730228B2Less complicatedUniversal applicabilityIon-exchange process apparatusSequential/parallel process reactionsGradient elutionPhase gradient
Methods and apparatus for characterizing a polymer sample and in preferred embodiments, libraries of polymer samples, in a comprehensive, directly-coupled multi-dimensional liquid chromatography system are disclosed. The first and second dimensions are preferably high-performance liquid chromatography dimensions, such as for example, a first dimension adapted for determining composition (e.g. adapted for mobile-phase gradient elution chromatography, including reverse phase chromatography, adsorption chromatography and the like), and a second dimension adapted for determining molecular weight or particle size (e.g., adapted for size exclusion chromatography, including gel permeation chromatography).
Owner:FREESLATE
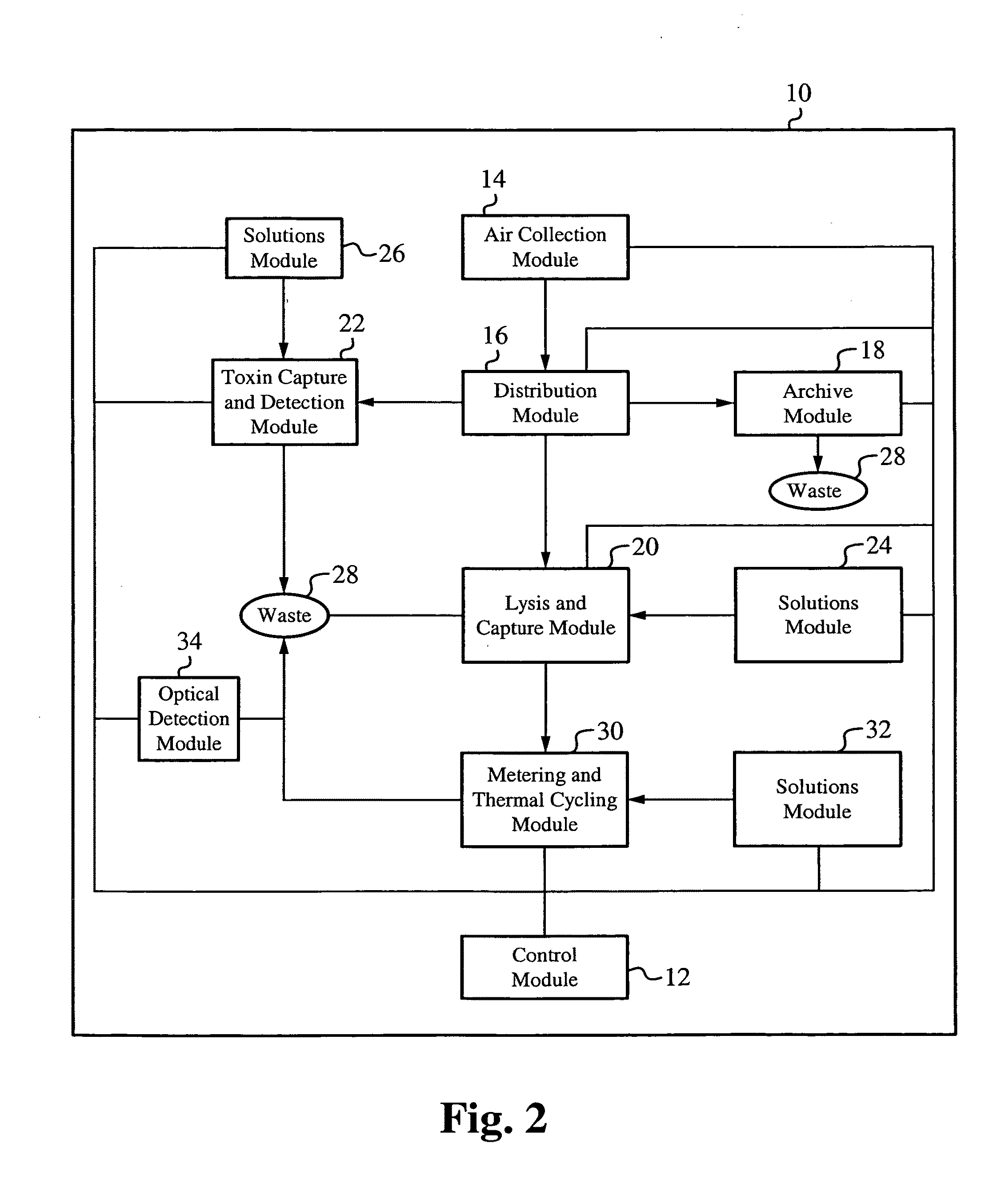
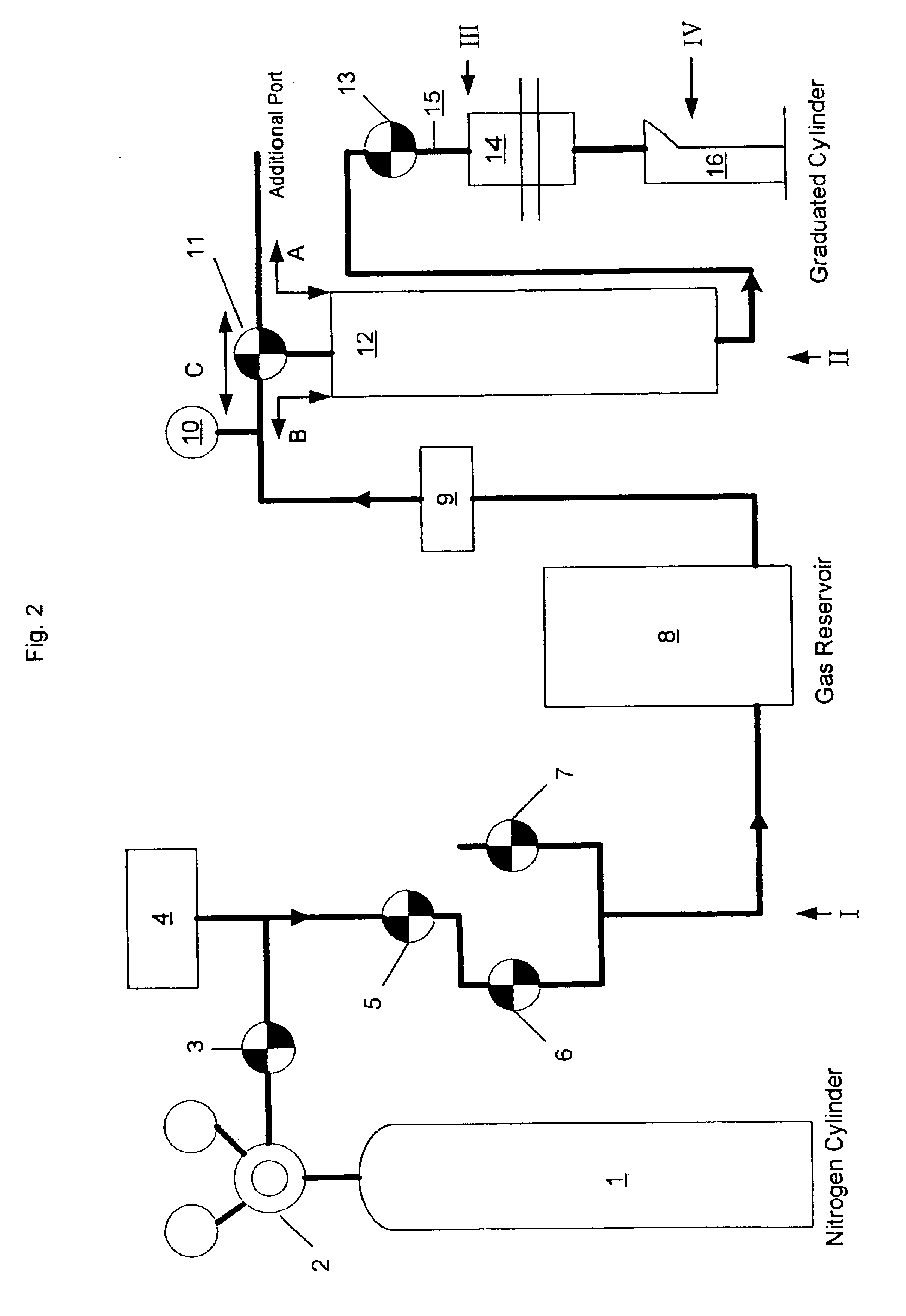
Sample preparation apparatus
InactiveUS20100050749A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLysisAnalyte
A capture and purification apparatus is configured as a stand-alone apparatus or as part of a larger system. The capture and purification apparatus can be configured as a microfluidic cartridge that includes microfluidic circuitry and individually controlled valves. The microfluidic cartridge can be configured to function independently, or can be configured to be coupled to a separate instrument that provides the actuation to perform the capture and purification process. The capture and purification apparatus is configured as a volume-driven system that applies single-direction valves, a single fluid driving device, and fluid lines to control and discretely direct fluid flow within a full-loaded fluidic system. Such control enables various fluid sample processing techniques to be performed including, but not limited to, lysis, thermal cycling, and / or target analyte capture and purification, for example using a combination of ion-exchange chromatography and size-exclusion chromatography (SEC).
Owner:MICROFLUIDIC SYST
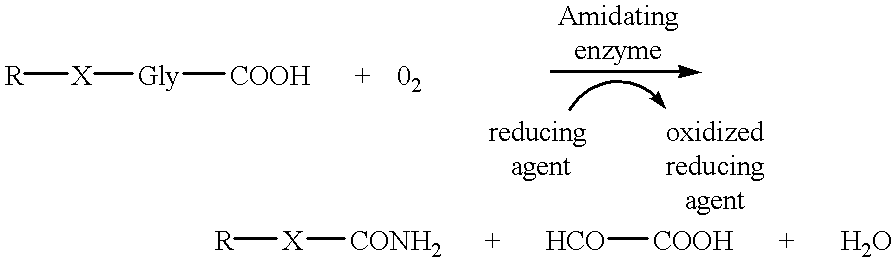
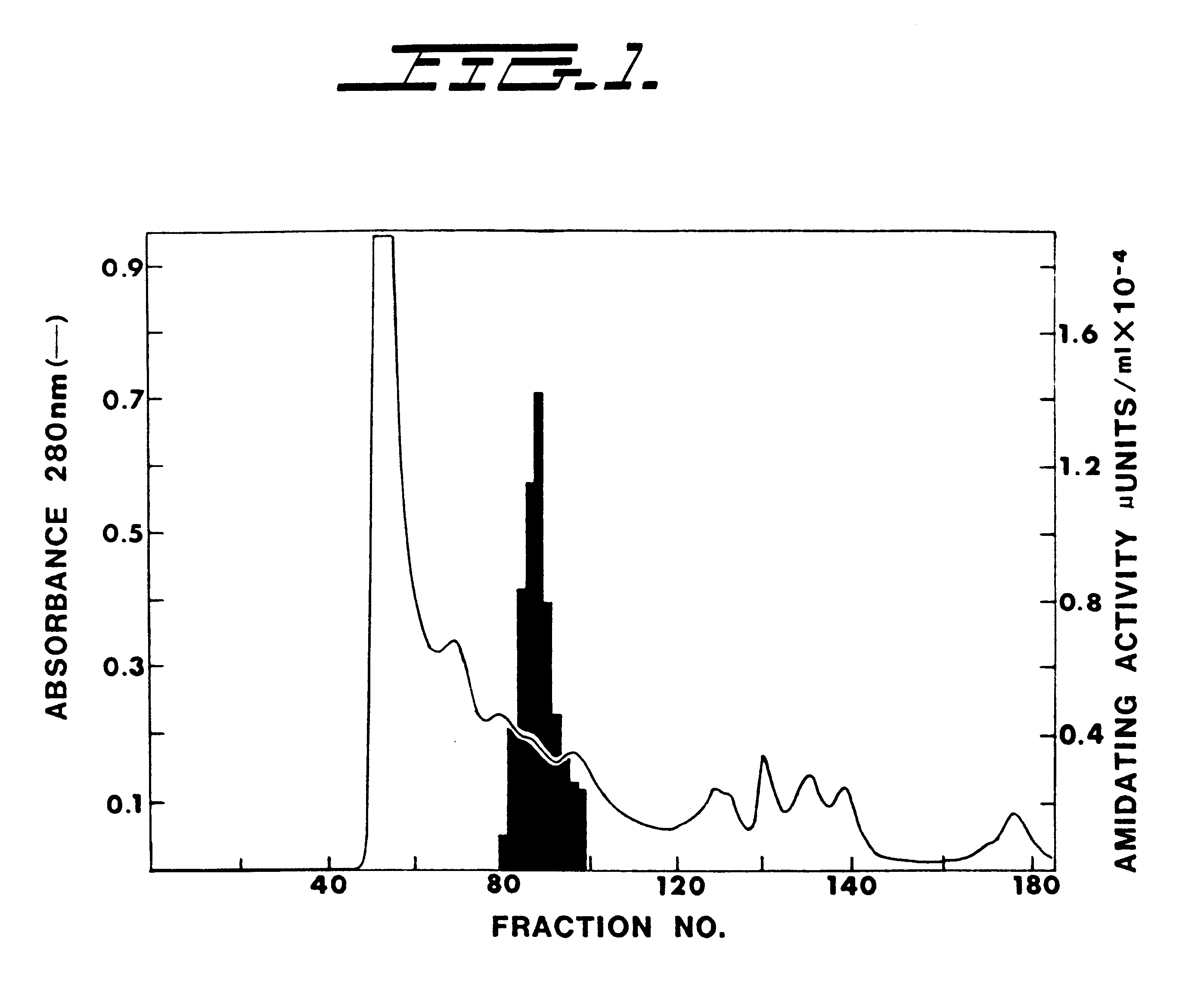
Alpha-amidating enzyme compositions and processes for their production and use
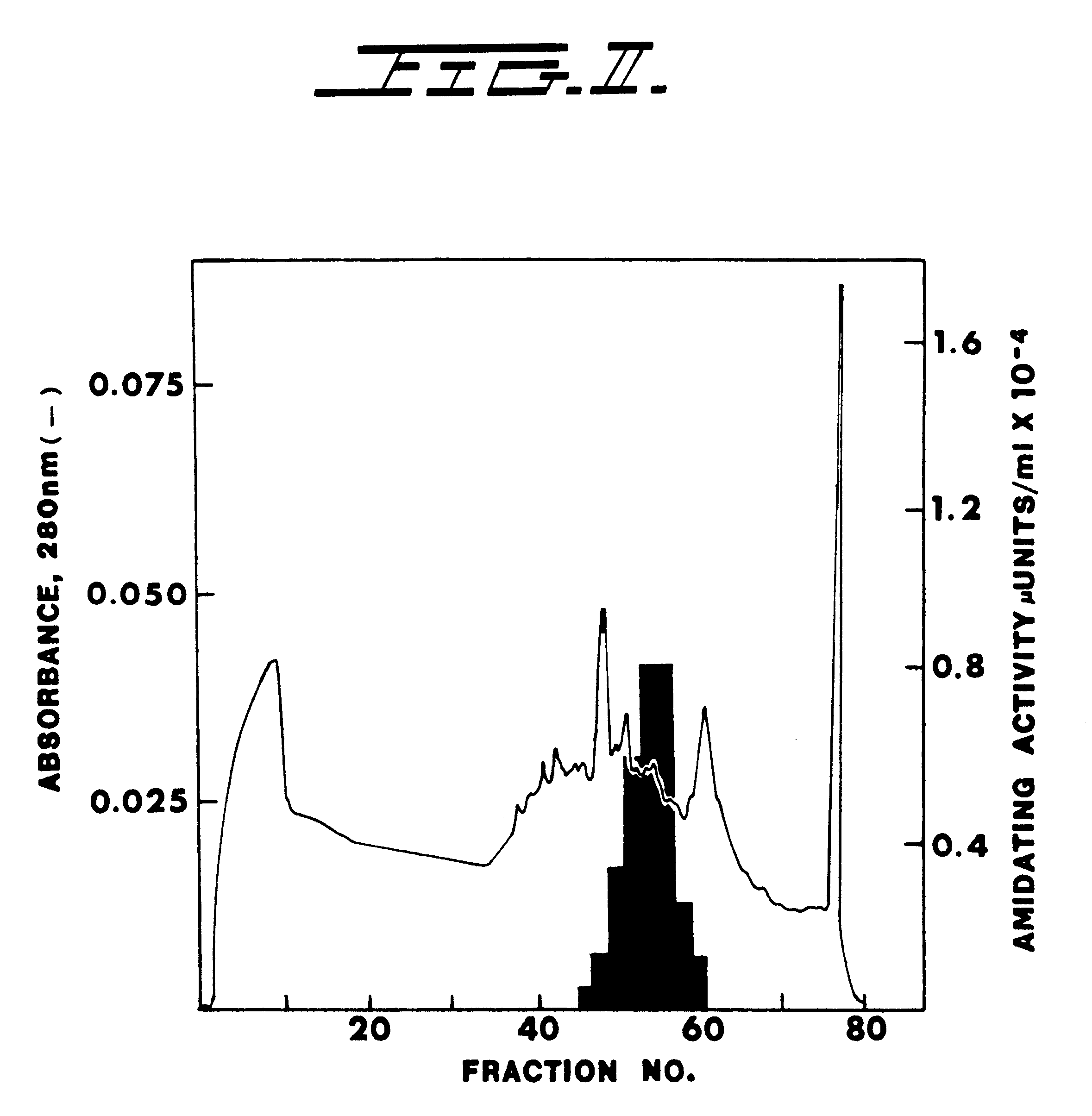
InactiveUS6319685B1Efficient productionImprove efficiency and reusabilityImmobilised enzymesBacteriaADAMTS ProteinsSize-exclusion chromatography
Purified enzymatic compositions are provided having alpha-amidating enzymes capable of catalyzing the conversion of a peptidyl compound having a C-terminal glycine residue to a corresponding peptidyl amide having an amino group in place of the C-terminal glycine. The purified compositions have specific activities above 25 mU per mg protein and are sufficiently free of proteases to allow effective catalysis of even peptidyl compounds having L-amino acids. Biologically important alpha-amidated products such as calcitonin and other regulatory hormones are efficiently produced using the alpha-amidation reaction catalyzed by the enzymes. Purification by size exclusion chromatography in combination with strong anion exchange chromatography results in homogeneous enzyme species which are used to prepare antibodies specific for the alpha-amidating enzyme. A gene capable of expressing the alpha-amidating enzyme is ligated into an expression vector and transformed into a host cell capable of expressing the gene.
Owner:MICROCAP FUND INC THE A CORP OF MD
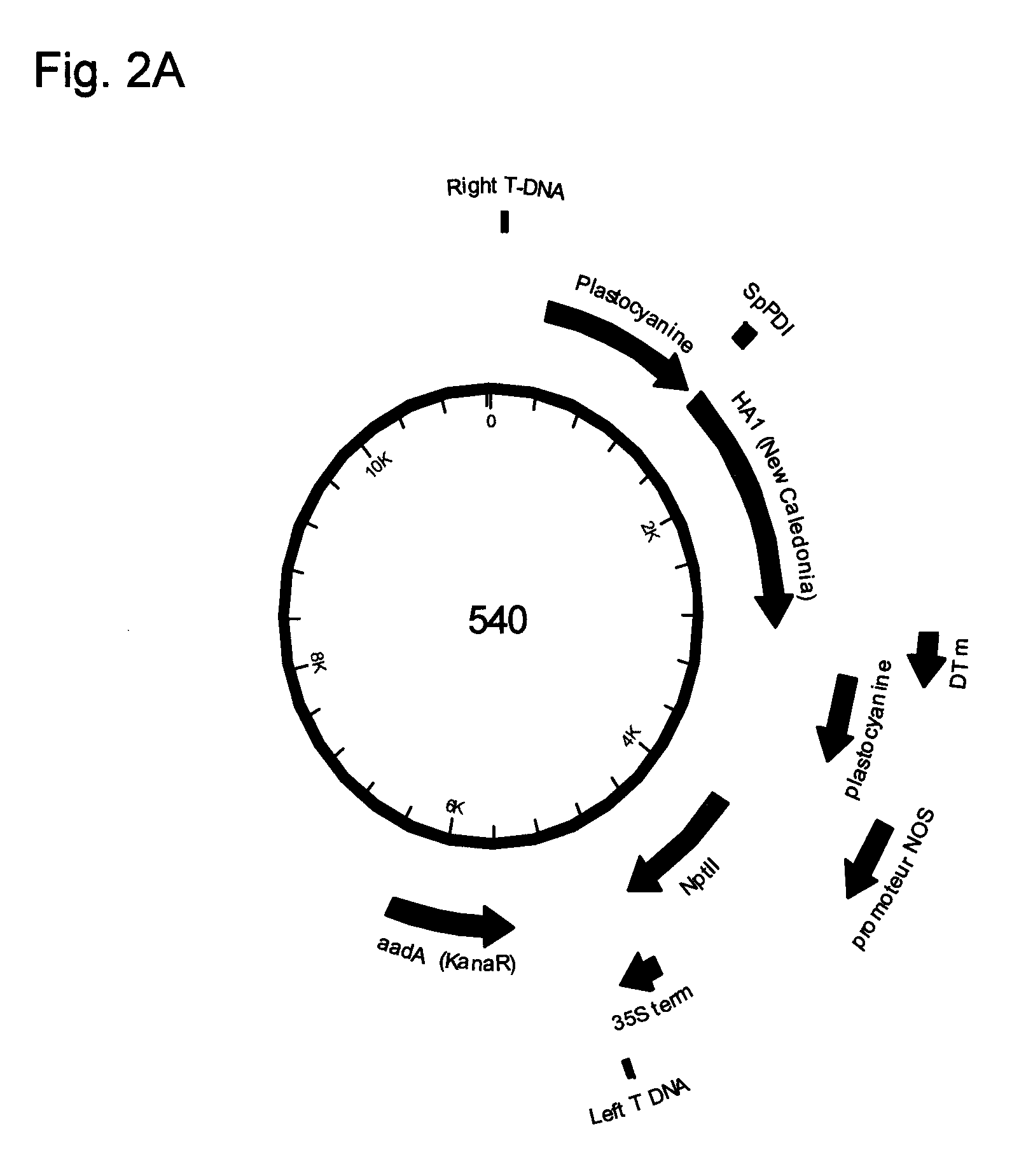
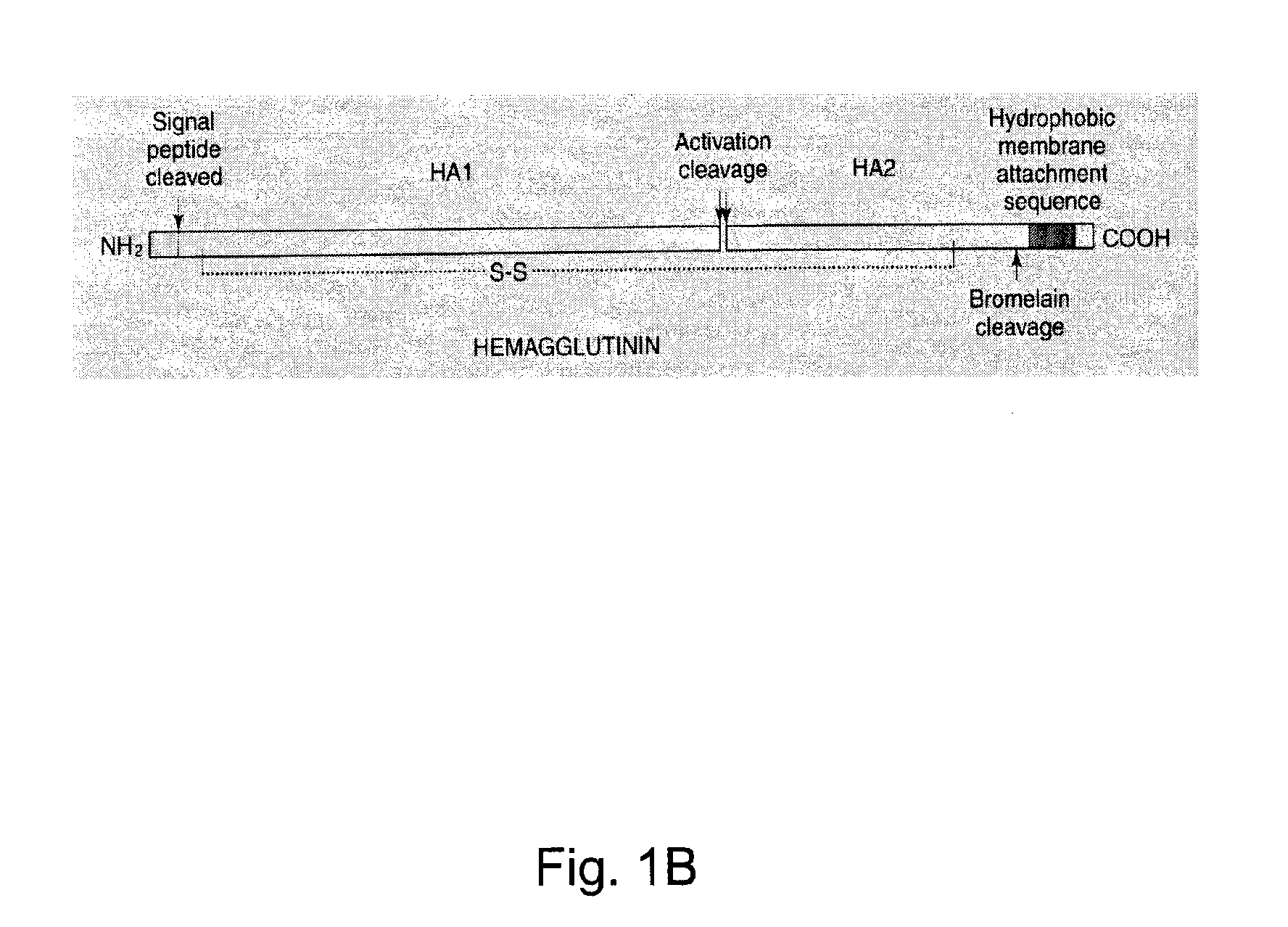
Influenza virus-like particles (VLPS) comprising hemagglutinin produced within a plant
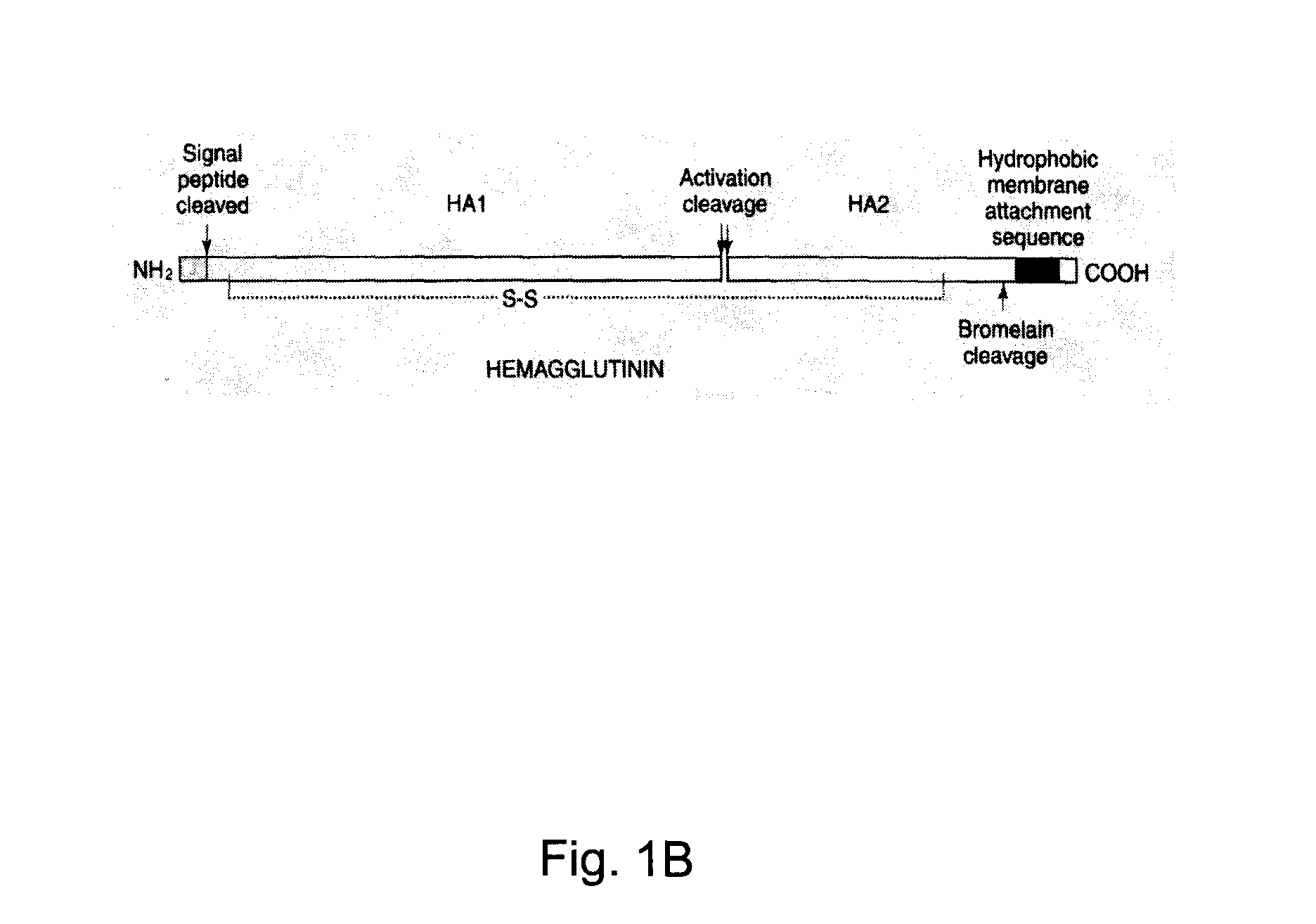
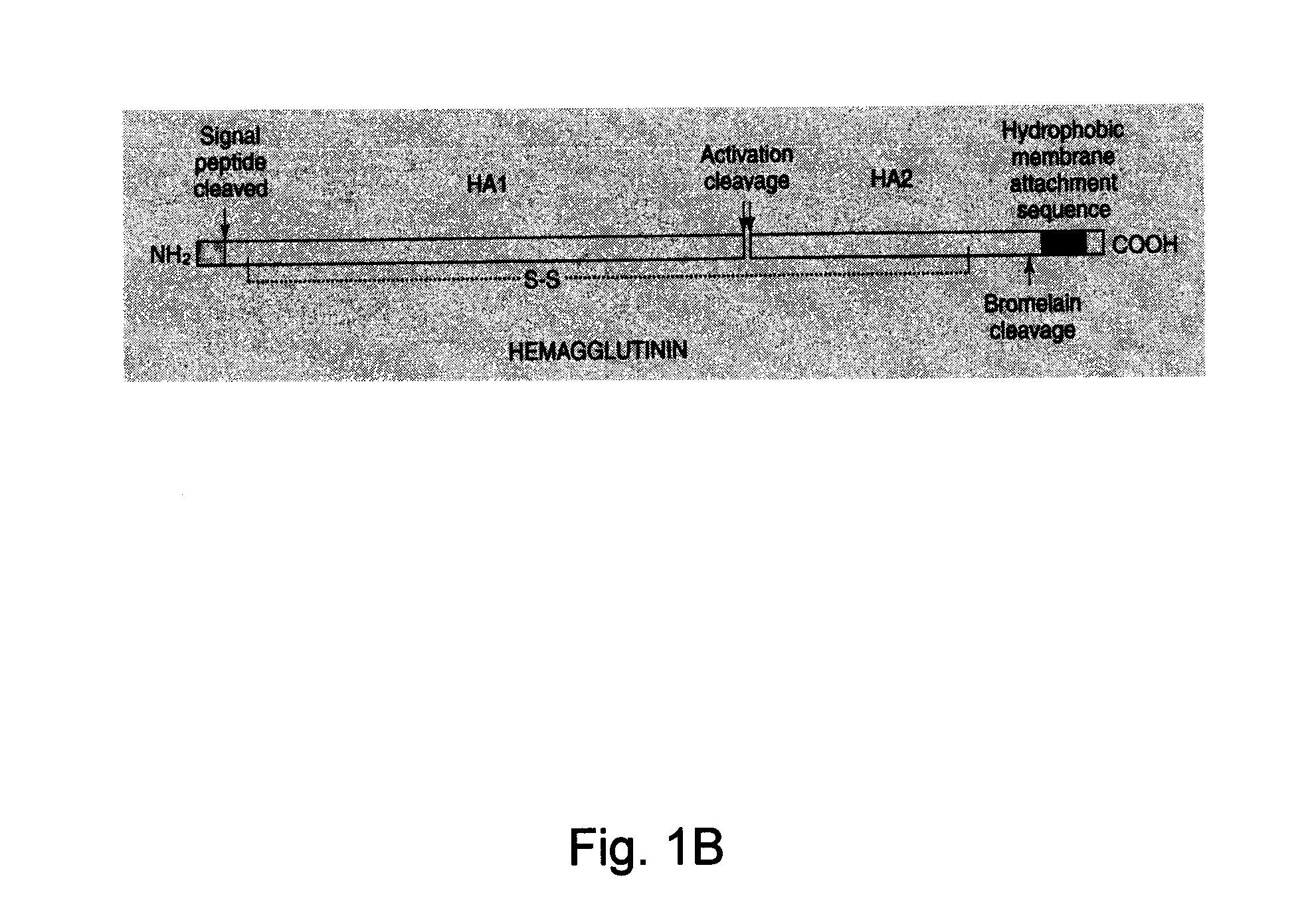
InactiveUS20100239610A1Enhance immune responseEasy to captureSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesHemagglutininLipid formation
A method for synthesizing influenza virus-like particles (VLPs) within a plant or a portion of a plant is provided. The method involves expression of influenza HA in plants and the purification by size exclusion chromatography. The invention is also directed towards a VLP comprising influenza HA protein and plants lipids. The invention is also directed to a nucleic acid encoding influenza HA as well as vectors. The VLPs may be used to formulate influenza vaccines, or may be used to enrich existing vaccines.
Owner:MEDICAGO INC
Methods and apparatus for characterization of polymers using multi-dimensional liquid chromatography with parallel second-dimension sampling
InactiveUS20030089663A1Less complicatedUniversal applicabilityIon-exchange process apparatusSamplingGradient elutionPhase gradient
Methods and apparatus for characterizing a polymer sample and in preferred embodiments, libraries of polymer samples, in a comprehensive, directly-coupled multi-dimensional liquid chromatography system are disclosed. The first and second dimensions are preferably high-performance liquid chromatography dimensions, such as for example, a first dimension adapted for determining composition (e.g. adapted for mobile-phase gradient elution chromatography, including reverse phase chromatography, adsorption chromatography and the like), and a second dimension adapted for determining molecular weight or particle size (e.g., adapted for size exclusion chromatography, including gel permeation chromatography).
Owner:FREESLATE
Enhanced efficacy basic aluminum halides, antiperspirant active compositions and methods for making
InactiveUS6902724B1Good curative effectImprove skinCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAluminium chloridePharmacology
Disclosed are basic aluminum halides having enhanced antiperspirant efficacy; methods of making such materials and antiperspirant compositions containing such basic aluminum halides, and optionally an amino acid, salts of amino acids, antimicrobial agents, or an organic solvent having at least two carbon atoms and at least one hydroxy group and mixture thereof and methods of making such mixtures. Basic aluminum halides having enhanced antiperspirant efficacy are produced by reacting (a) aluminum powder; (b) an aluminum halide; and (c) water at a temperature greater than about 85° C. This reaction is maintained until reaction products having an Al:halide ratio of about 1.2:1 to 1.5:1 and preferably 1.3 to 1.4:1; and a solution solids concentration of about 30-40 weight percent on an anhydrous basis are obtained. The products are characterized as having a Size Exclusion Chromatography (HPLC) Test Band I of less than 5%, preferably less than 1%, Band II percent aluminum value of 20-60% preferably about 35 to 55%, Band III percent aluminum value of 10 to 35% preferably 15-30% and Band IV value of 15 to 50% and preferably 25 to 35% and sum of peak 3 and 4 areas of at least 45% and no more than 70% and preferably 65%. The enhanced efficacy basic aluminum chloride salts of this invention are more economical to produce, show enhanced efficacy and are more stable compared to the conventional enhanced efficacy aluminum salts which show rapid degradation of Band III to Band II peak areas ratio are less irritant and more skin friendly.
Owner:SUMMIT RES LAB
Methods for characterization of polymers using multi-dimensional liquid chromatography with parallel second-dimension sampling
InactiveUS6855258B2Less complicatedUniversal applicabilityIon-exchange process apparatusSamplingGradient elutionPhase gradient
Methods and apparatus for characterizing a polymer sample and in preferred embodiments, libraries of polymer samples, in a comprehensive, directly-coupled multi-dimensional liquid chromatography system are disclosed. The first and second dimensions are preferably high-performance liquid chromatography dimensions, such as for example, a first dimension adapted for determining composition (e.g. adapted for mobile-phase gradient elution chromatography, including reverse phase chromatography, adsorption chromatography and the like), and a second dimension adapted for determining molecular weight or particle size (e.g., adapted for size exclusion chromatography, including gel permeation chromatography).
Owner:FREESLATE
Methods and apparatus for characterization of polymers using multi-dimensional liquid chromatography with regular second-dimension sampling
InactiveUS20030080062A1Less complicatedUniversal applicabilityIon-exchange process apparatusSequential/parallel process reactionsGradient elutionPhase gradient
Methods and apparatus for characterizing a polymer sample and in preferred embodiments, libraries of polymer samples, in a comprehensive, directly-coupled multi-dimensional liquid chromatography system are disclosed. The first and second dimensions are preferably high-performance liquid chromatography dimensions, such as for example, a first dimension adapted for determining composition (e.g. adapted for mobile-phase gradient elution chromatography, including reverse phase chromatography, adsorption chromatography and the like), and a second dimension adapted for determining molecular weight or particle size (e.g., adapted for size exclusion chromatography, including gel permeation chromatography).
Owner:FREESLATE
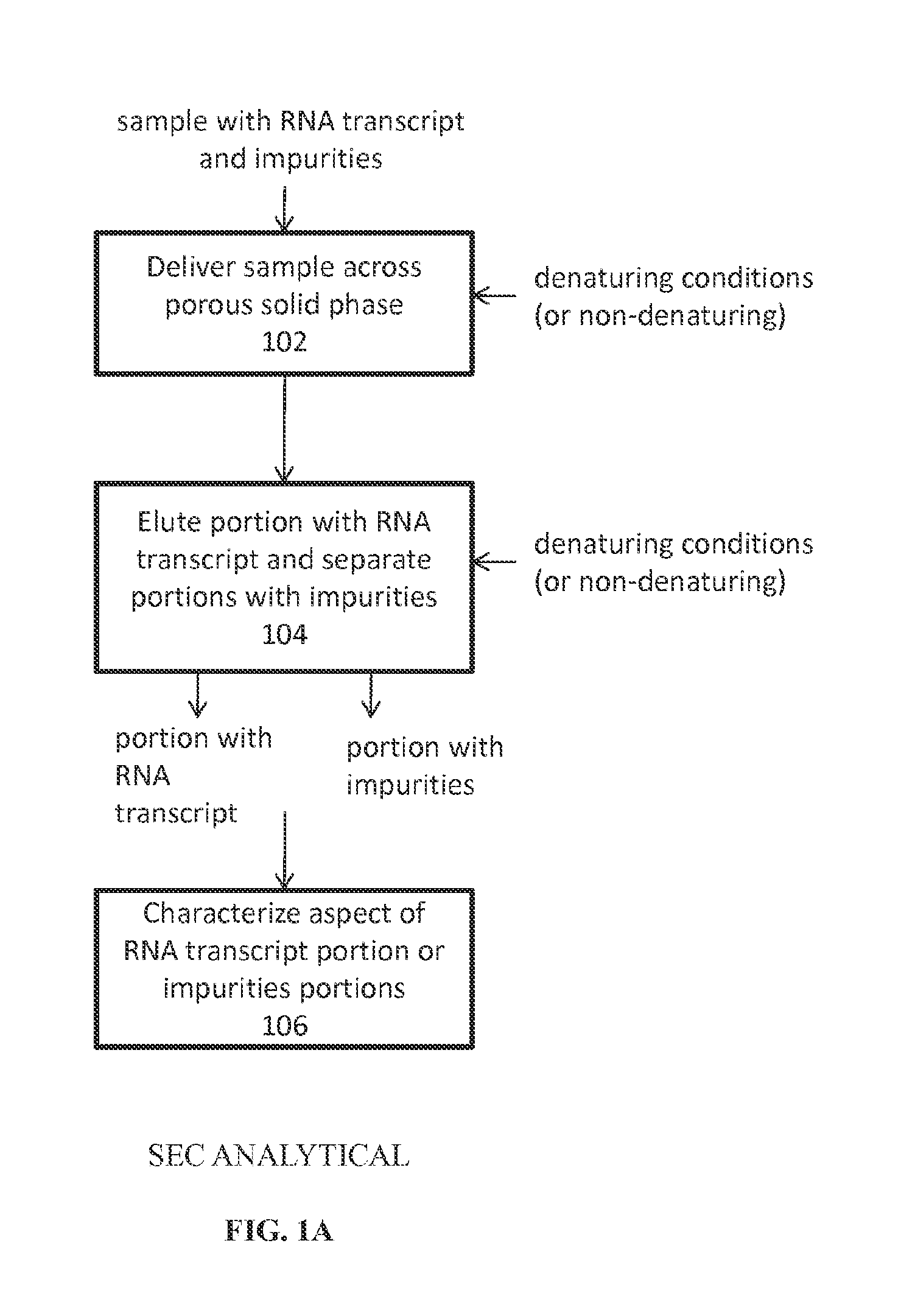
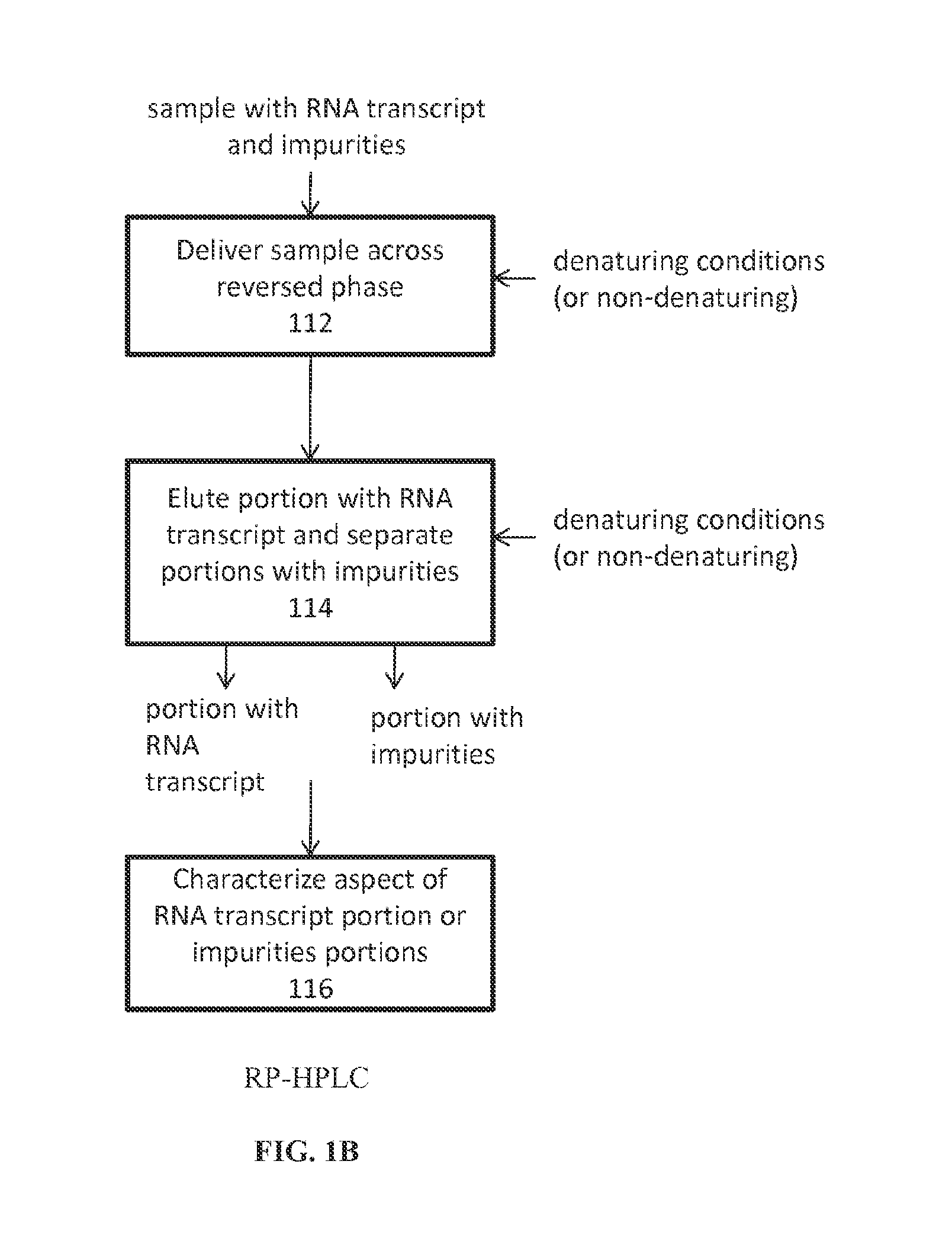
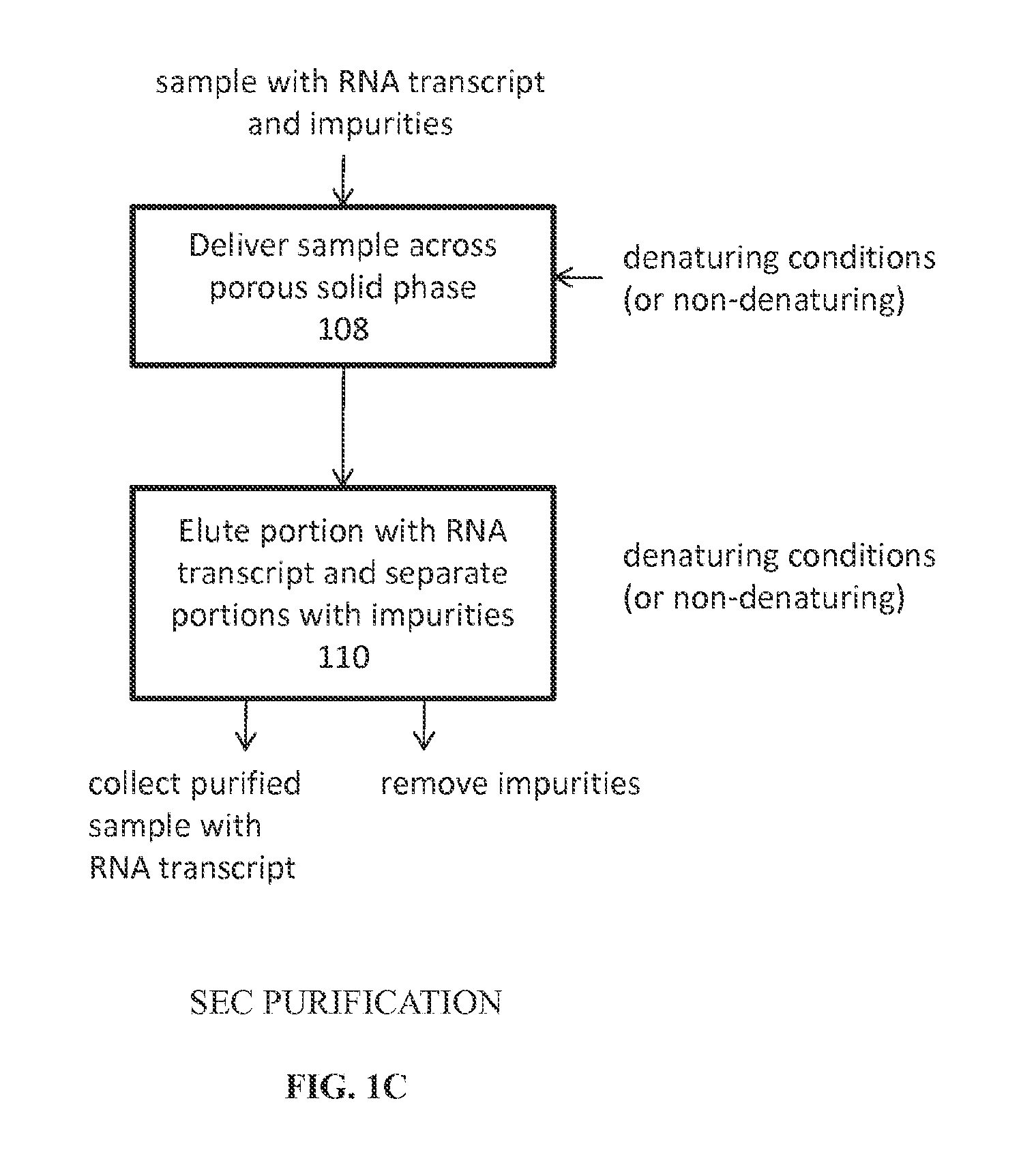
Analysis of mRNA heterogeneity and stability
InactiveUS20160017313A1Simple preparation processDemonstrate success of the manufacturing processElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementNucleotideQualitative analysis
Reversed phase-High Performance (High Pressure) Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC) and Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) methods have been developed for monitoring structural and size heterogeneity as well as stability of large RNA transcripts, including lengths of up to at least 10,000 nucleotides. The methods are designed for significantly larger mRNAs that could be monitored in the past, including lengths of up to at least 10,000 nucleotides, and including chemically modified RNA transcripts. SEC techniques are also used in the preparative purification of large RNA transcripts to remove impurities, including hybridized nucleic acid impurities and multimeric RNA species. All of these techniques are also beneficial in that they can be used for large scale manufacturing of therapeutics.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
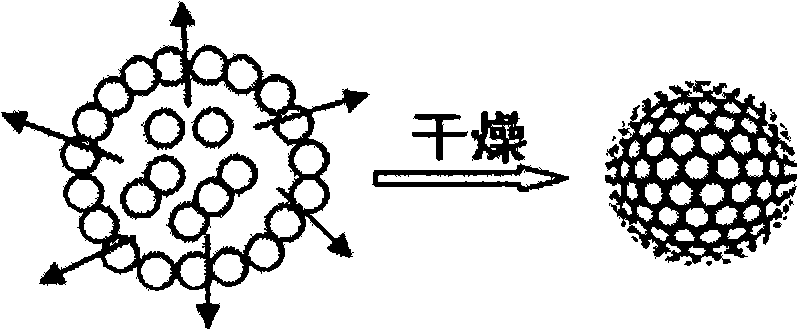
Method for self-assembling preparing colloidal photonic crystals and improving mechanical stability
InactiveCN101280455ALarge specific surface areaMeet the requirements of special useFrom gel stateMicroballoon preparationEvaporationSolvent
Disclosed is a self-assembly and preparation device of colloidal photonic crystals and the method thereof to improve the mechanical stability; the colloidal particle solution is distributed to a continuous phase and in the formation of colloidal solution droplets. Through the evaporation of the solution in the droplet, the colloidal particle in the solution is self-assembled to become the colloidal photonic crystal while the droplet is taken as a template. For the mechanical stability of the photonic crystal, the mutual cementation of the colloidal particles inside a crystal is greatly enhanced through the heat treatment. The three-dimensional colloidal photonic crystals with high mechanical stability and prepared through such a method has a potential value in the aspects of size exclusion chromatography, enzyme or zymophore, adsorption medium, bio-molecule detection carrier, filter, light switches, photonic paper and so on.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Rapid characterization of polymers
InactiveUS6866786B2Less complicatedUniversal applicabilitySequential/parallel process reactionsComponent separationGradient elutionPhase gradient
Methods and apparatus for characterizing a polymer sample and in preferred embodiments, libraries of polymer samples, in a comprehensive, directly-coupled multi-dimensional liquid chromatography system are disclosed. The first and second dimensions are preferably high-performance liquid chromatography dimensions, such as for example, a first dimension adapted for determining composition (e.g. adapted for mobile-phase gradient elution chromatography, including reverse phase chromatography, adsorption chromatography and the like), and a second dimension adapted for determining molecular weight or particle size (e.g., adapted for size exclusion chromatography, including gel permeation chromatography).
Owner:FREESLATE
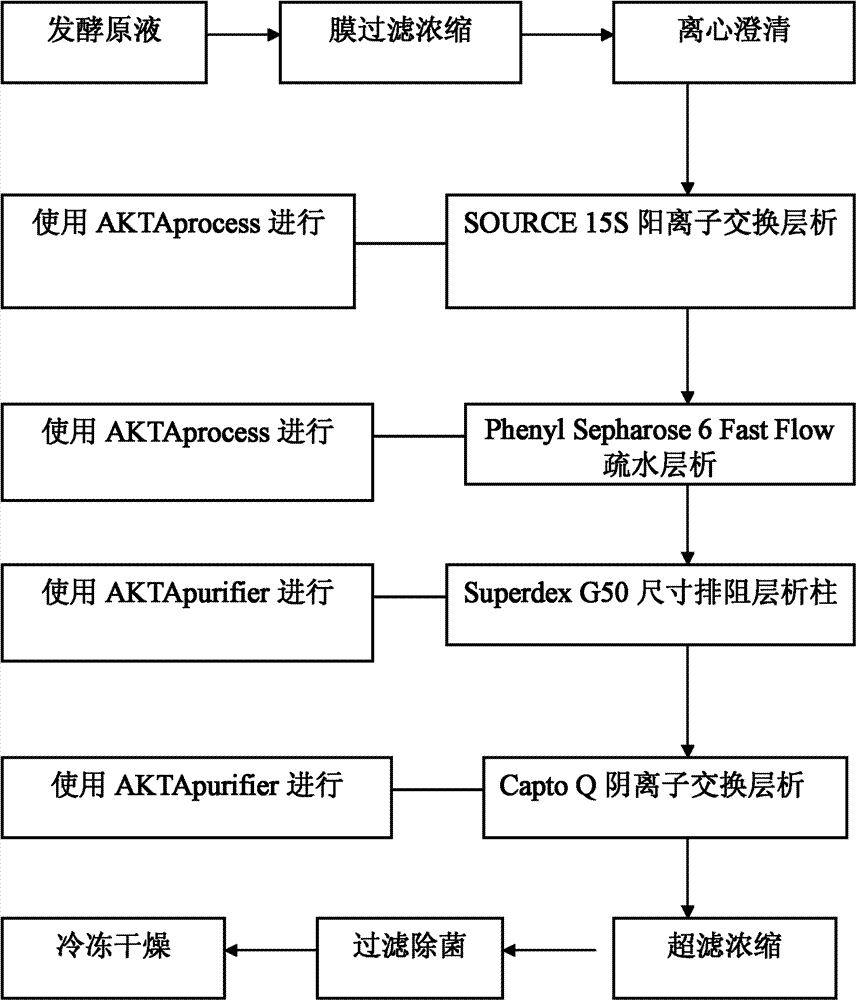
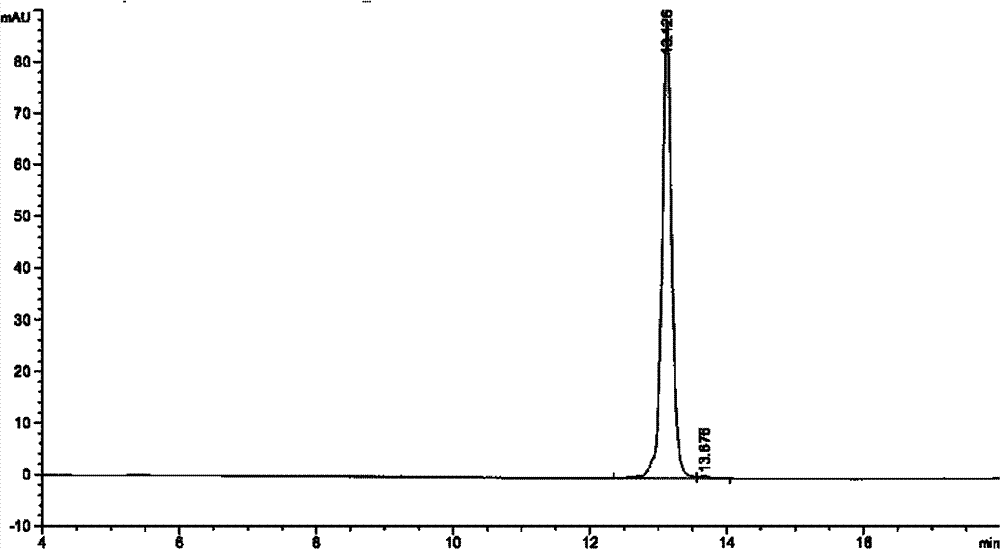
Production method of Sublancin antibacterial peptide
InactiveCN102851339AIncrease productionHigh purityMicroorganism based processesDepsipeptidesCentrifugationUltrafiltration
The invention provides a preparation method of Sublancin antibacterial peptide, which comprises the following steps: (1) inoculating bacillus subtilis into a medium for fermentation, filtering the fermentation liquor; (2) orderly performing centrifugation, cation exchange chromatography, hydrophobic chromatography, size exclusion chromatography, and anion exchange chromatography of the fermentation liquor in step (1), finally performing ultrafiltration concentration and drying to obtain the Sublancin antibacterial peptide. The method of the invention is low in cost, increased in production efficiency, and high in product purity; the prepared Sublancin antibacterial peptide has purity of up to more than 99%; the process is simple, and easy to popularize and apply, and can realize large-scale production.
Owner:中农颖泰林州生物科园有限公司
Extraction separation method of algae polysaccharide
InactiveCN1412203AIncrease profitAchieve co-extractionDrug biological activitySize-exclusion chromatography
The extraction and separation method of algae polysaccharide is characterized by that the present invention utilzies the characteristics of polysaccharide and glucoprotein which are dissolved in water, adopts water extraction method to make extraction, uses ethyl alcohol to make fractional precipitation to make separation, finally adopts the anion-exchange column and gel exclusion chromatography to purity polysaccharide, in which the biological activity of protein and protein polysaccharide can be retained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
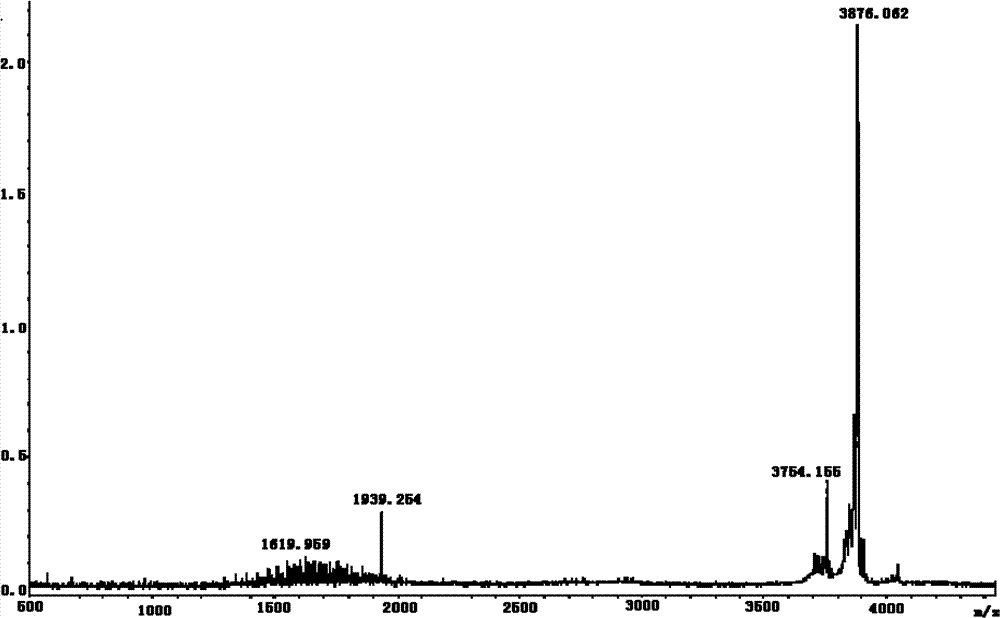
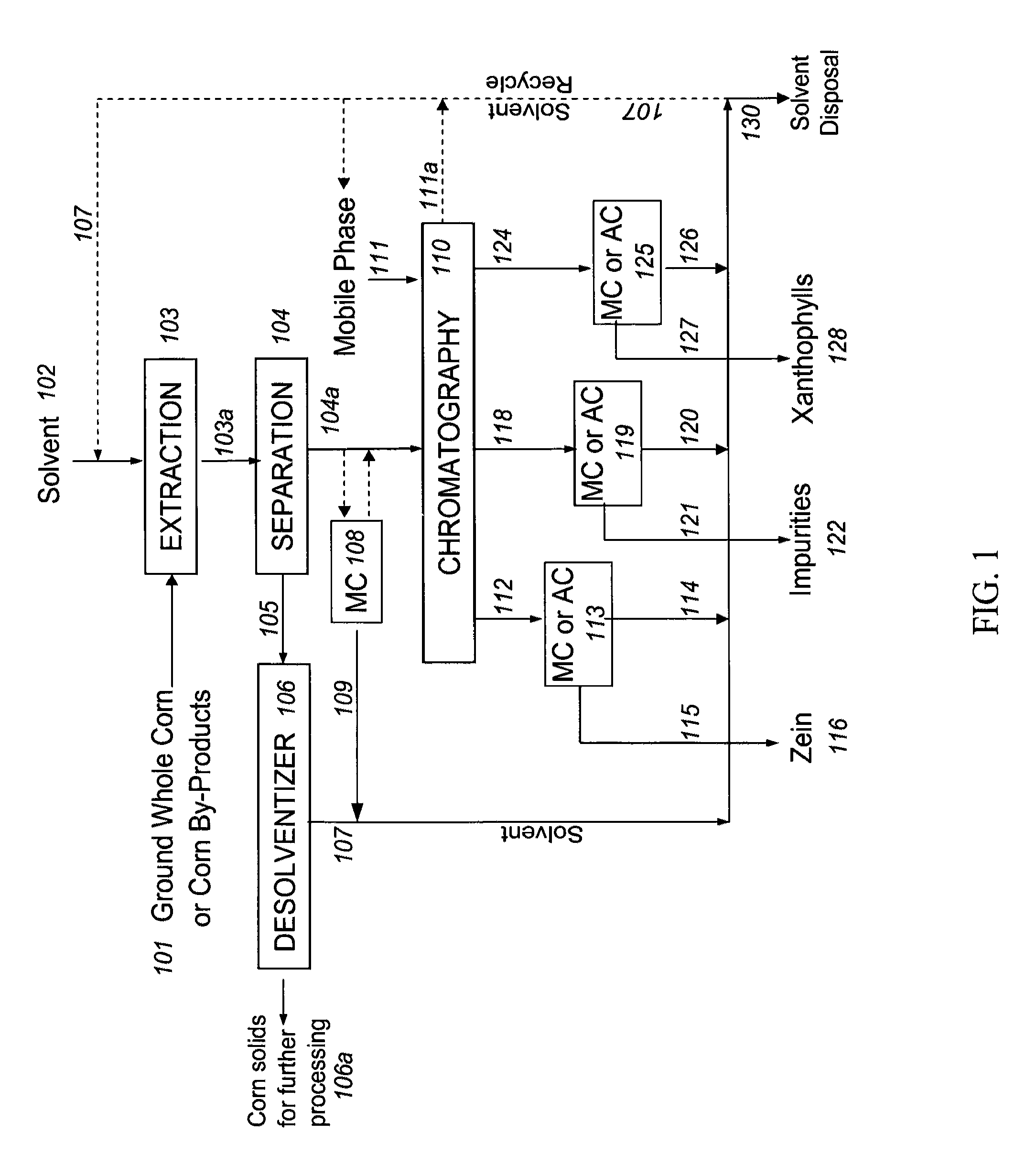
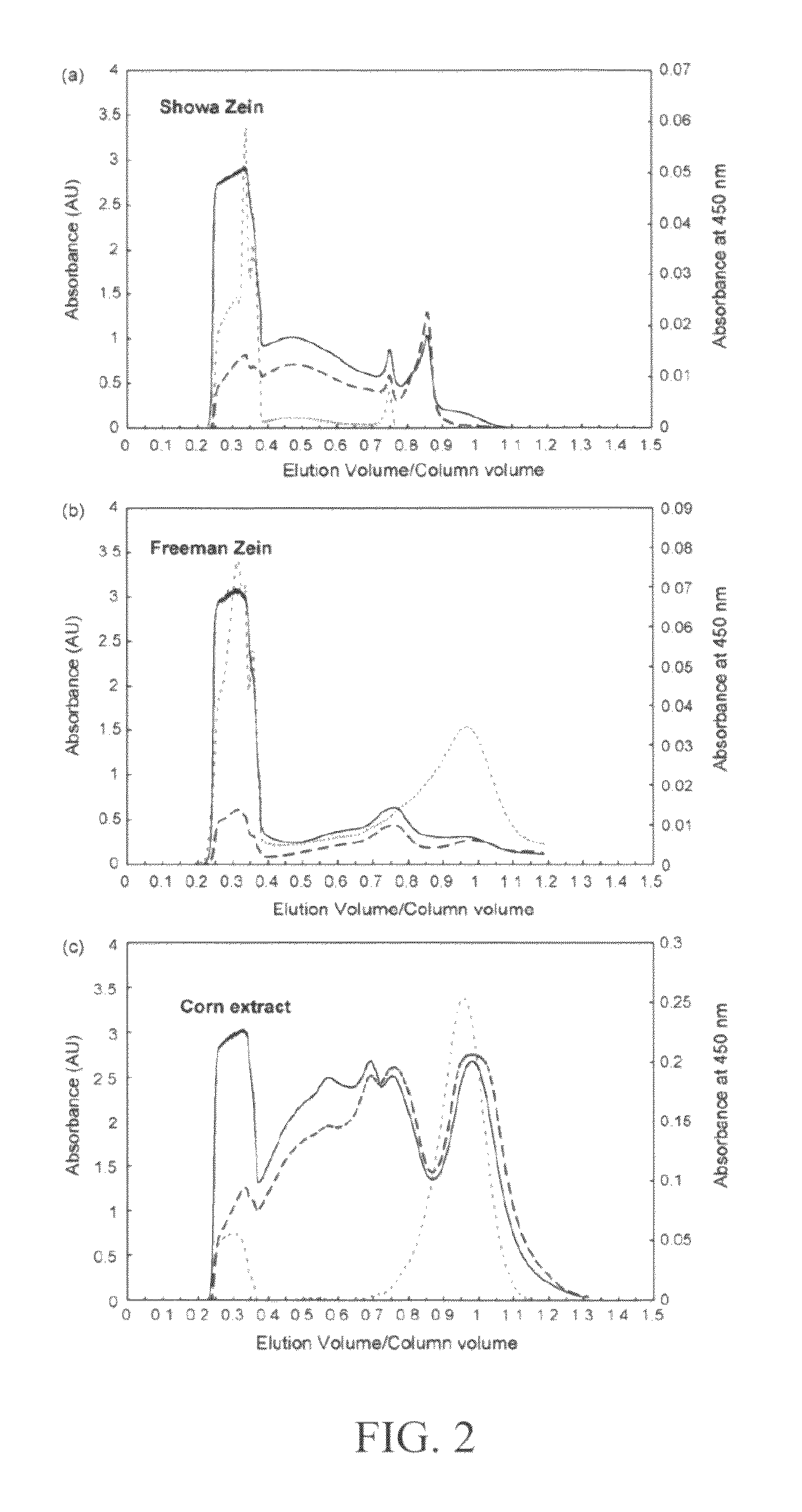
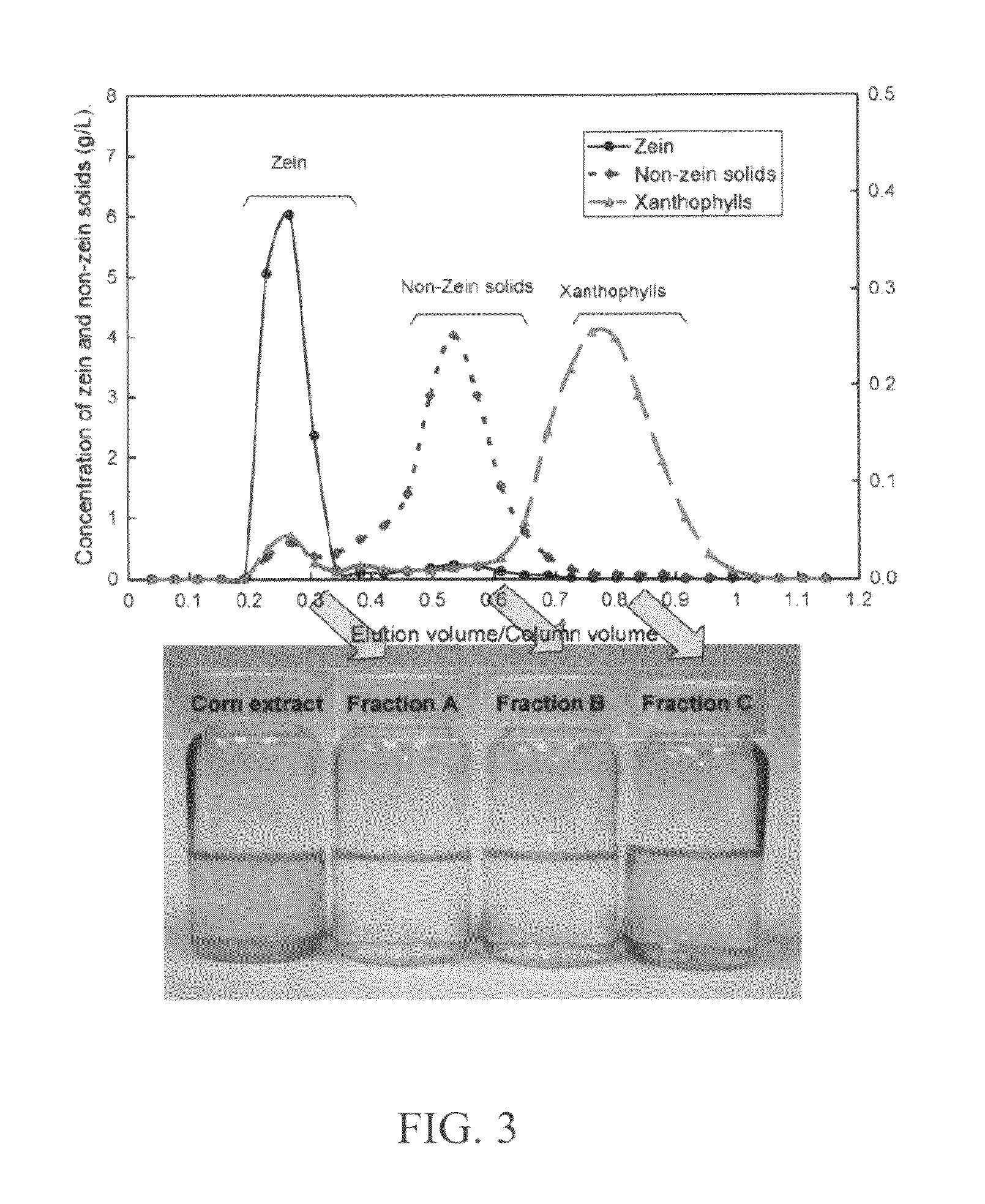
Method and system for production of zein and/or xanthophylls using chromatography
Methods and systems for obtaining zein and / or xanthophylls in highly pure form. Zein is first extracted from corn using aqueous ethanol. Suspended corn solids are separated, and the resulting extract is purified in a single size-exclusion chromatography step to separate impurities and produce substantially purified zein. The chromatography step may simultaneously produce substantially purified xanthophylls.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Recombinant influenza virus-like particles (VLPS) produced in transgenic plants expressing hemagglutinin
InactiveUS20100310604A1Easy to captureEnhance immune responseVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsLipid formationHemagglutinin
A method for synthesizing influenza virus-like particles (VLPs) within a plant or a portion of a plant is provided. The method involves expression of influenza HA in plants and the purification by size exclusion chromatography. The invention is also directed towards a VLP comprising influenza HA protein and plants lipids. The invention is also directed to a nucleic acid encoding influenza HA as well as vectors. The VLPs may be used to formulate influenza vaccines, or may be used to enrich existing vaccines.
Owner:MEDICAGO INC
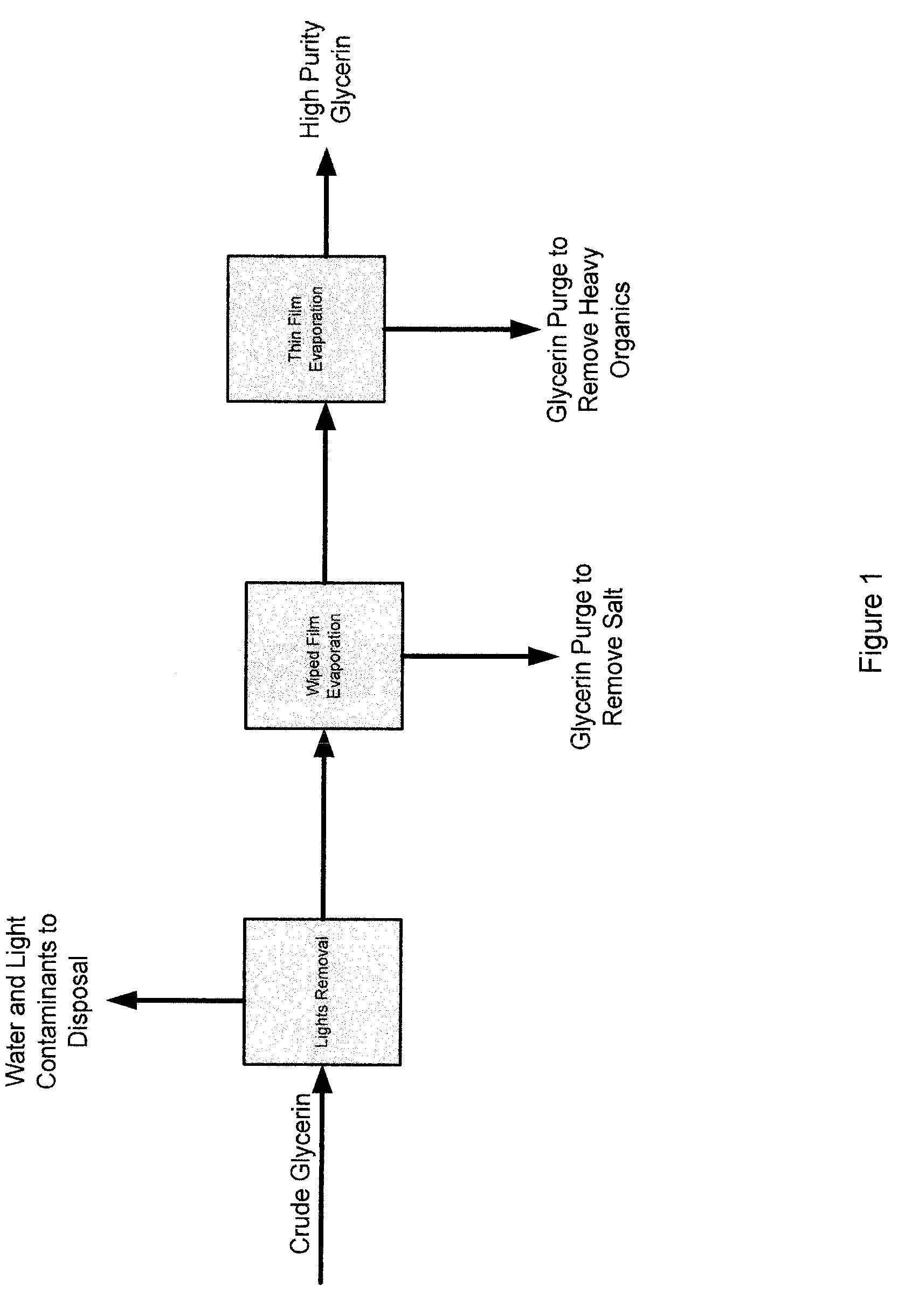
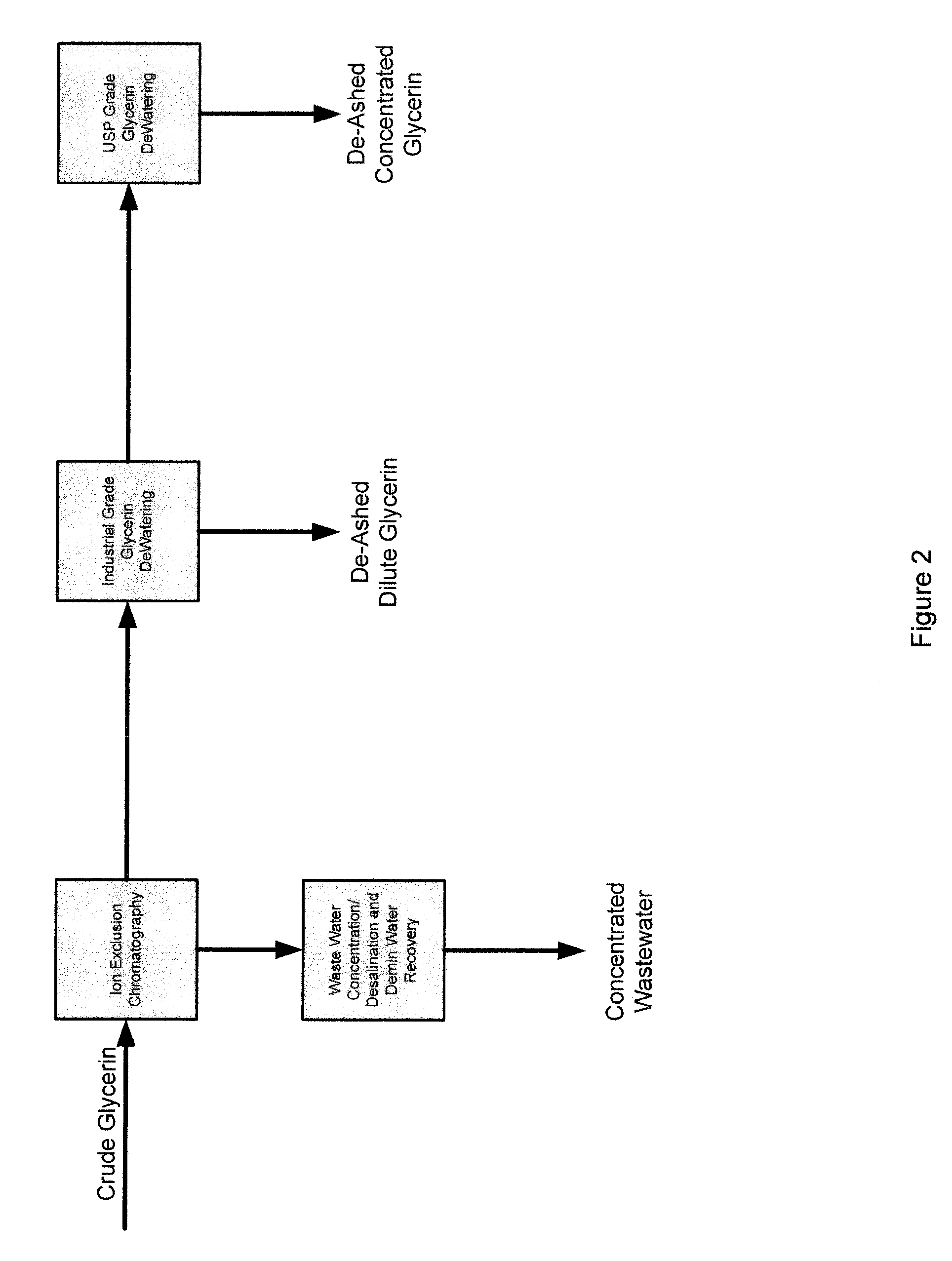
Process for the purification of crude glycerin utilizing ion exclusion chromatorgraphy and glycerin concentration
InactiveUS20090198088A1Organic compound preparationSolid sorbent liquid separationChromatographic separationFractionation
A process for the purification of crude glycerin utilizing ion exclusion chromatography fractionation, and one or more dewatering steps under moderate temperatures and pressures.
Owner:LANXESS CORP
High amylose dog chew formulation
InactiveUS7722911B2Resist formationReducing of choking and intestinal blockageBaking mixturesFrozen sweetsThermoplasticPlasticizer
Owner:B&S PLASTICS
Chromatographic methods for assessing adenovirus purity
InactiveUS20080299545A1Improve performanceSolving precise measurementsMicrobiological testing/measurementDsDNA virusesBiologyVirus
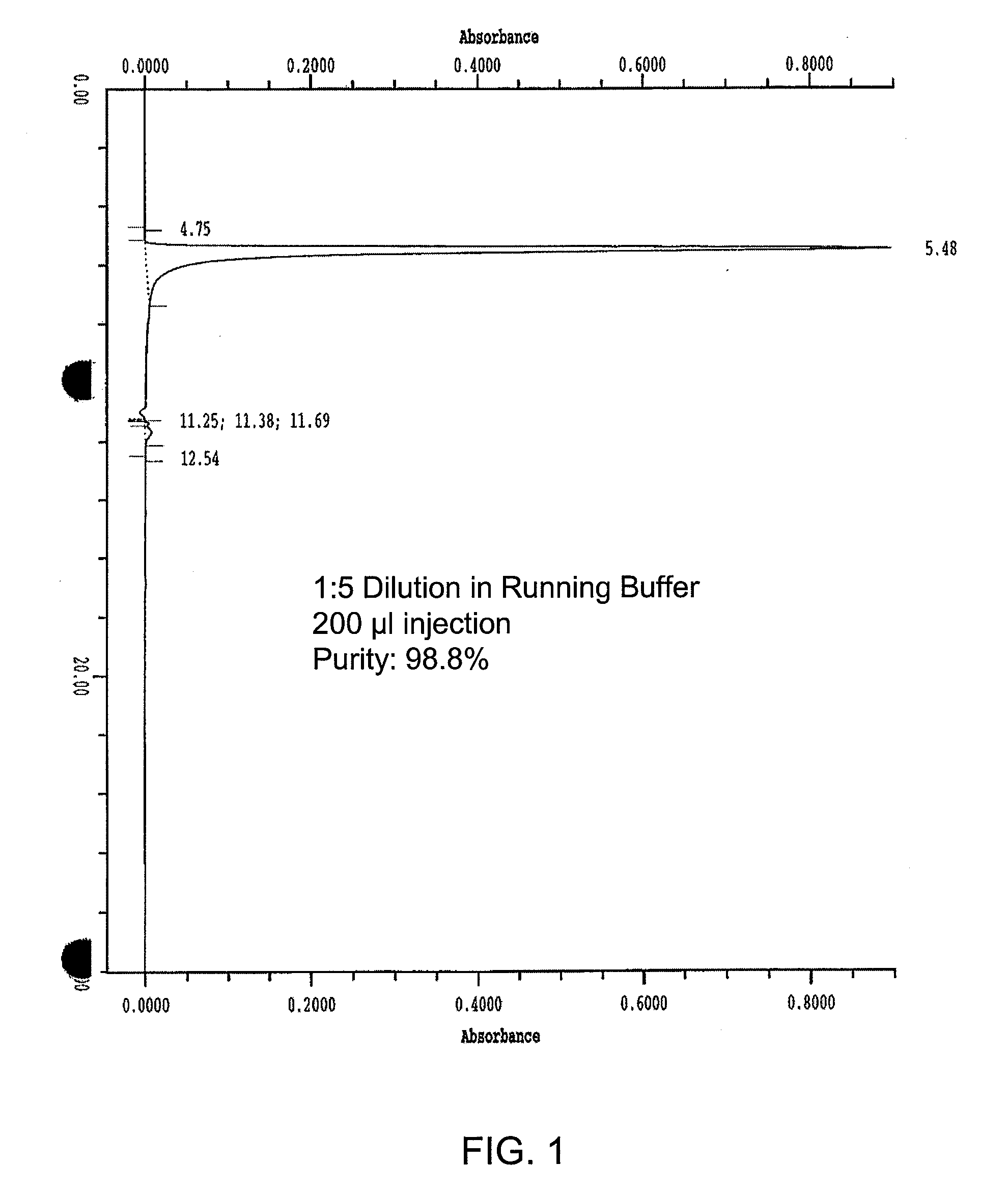
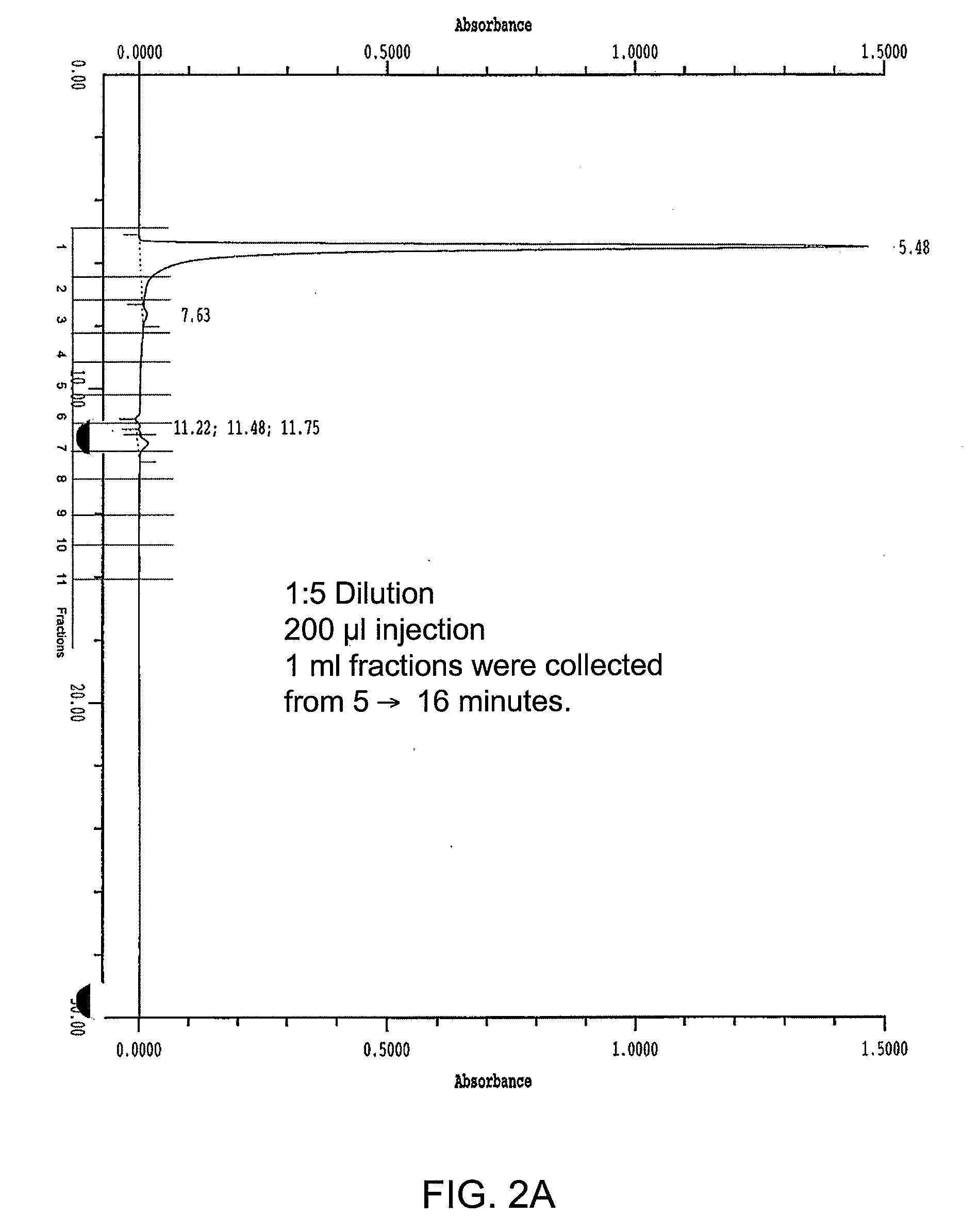
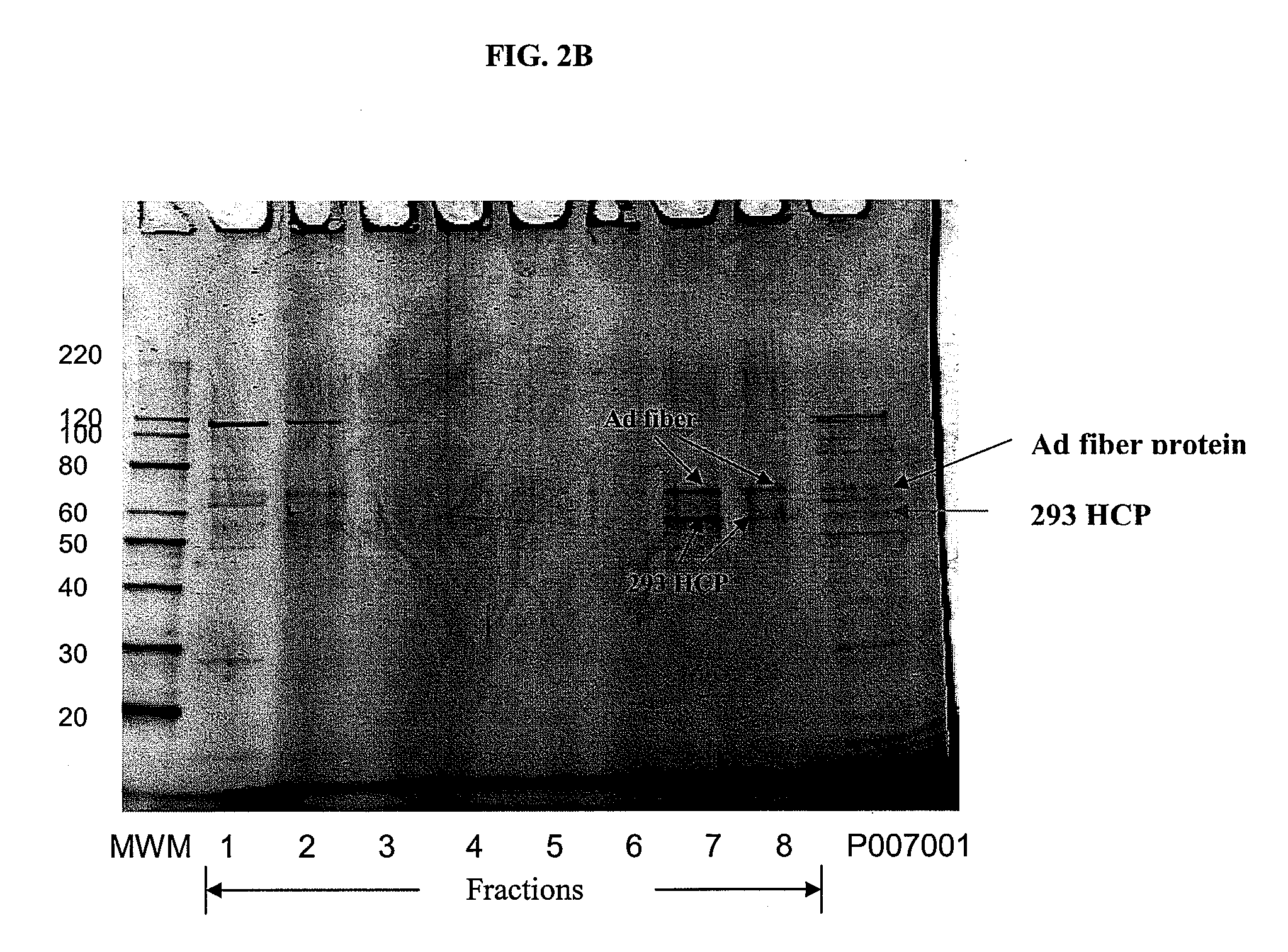
Methods for determining the quantity, quality and purity of a previously purified virus sample are disclosed. Such methods, which include the use of high performance size exclusion chromatography to determine these attributes are also disclosed.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
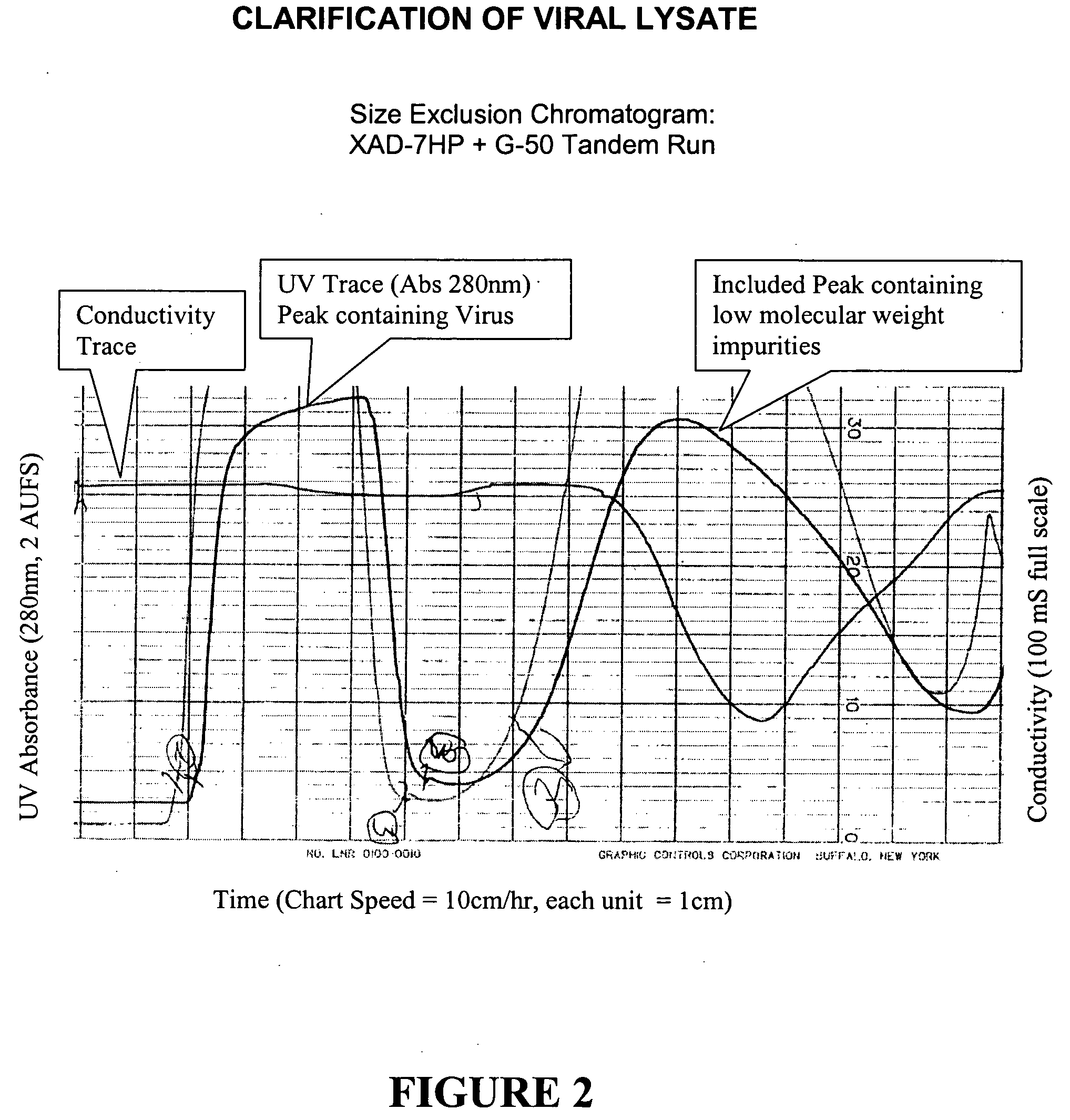
Method for purifying virus
InactiveUS20050003507A1Avoiding chromatography buffer conductivity adjustmentClarifying a cell lysate preparationRecovery/purificationMedical preparationsAnion-exchange chromatographyCell lysates
A process for the purification of viruses from a cell lysate preparation is described, consisting of preferably two successive chromatographic steps; the first a clarification step utilizing size exclusion chromatography, and the second, a virus capture and release step using anion exchange chromatography, which successive chromatographic steps have the advantage of purifying virus, and avoiding chromatography buffer conductivity adjustments.
Owner:ONYX PHARMA INC
Influenza virus-like particles (VLPS) comprising hemagglutinin
ActiveUS20110293650A1Easy to captureEnhance immune responseVirusesAntiviralsHemagglutininVirus-like particle
A method for synthesizing influenza virus-like particles (VLPs) within a plant or a portion of a plant is provided. The method involves expression of influenza HA of type A / California / 04 / 09 in plants and the purification by size exclusion chromatography. The invention is also directed towards a VLP comprising influenza HA protein of type A / California / 04 / 09 and plants lipids. The invention is also directed to a nucleic acid encoding influenza HA of type A / California / 04 / 09 as well as vectors. The VLPs may be used to formulate influenza vaccines, or may be used to enrich existing vaccines.
Owner:MEDICAGO INC
Size exclusion chromatography process for the preparation of an improved soy protein-containing composition
InactiveUS20060062878A1Add flavorImprove odorWort preparationProtein composition from vegetable seedsFood flavorSize-exclusion chromatography
Relatively low molecular weight components which contribute undesirable flavor, odor, appearance, functionality, and / or other characteristics to soy protein materials may be removed, in accordance with the present invention, by treating the materials with a size exclusion resin selective for removal of the low molecular weight components.
Owner:SOLAE LLC
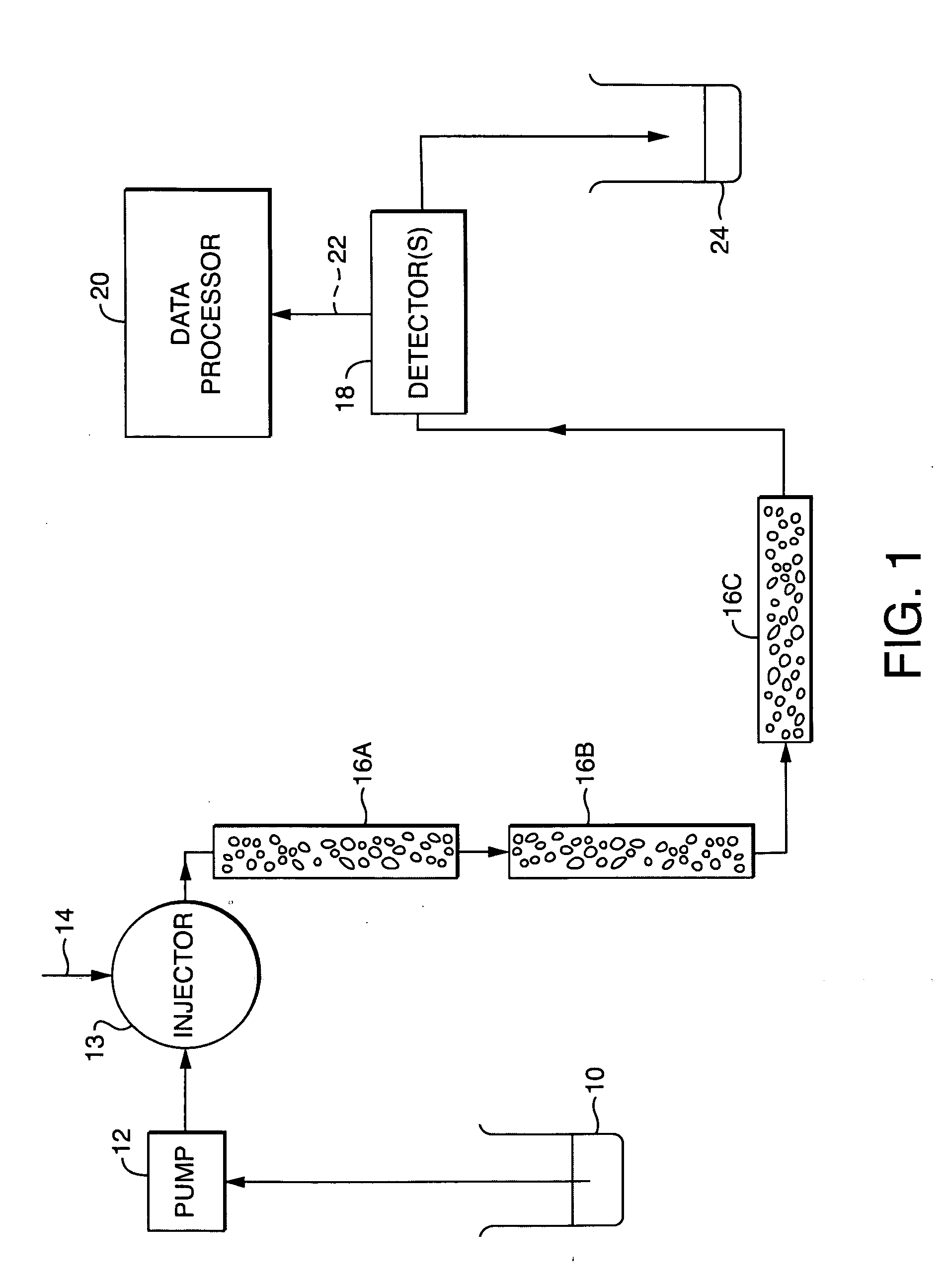
System and method for determining radius of gyration, molecular weight, and intrinsic viscosity of a polymeric distribution using gel permeation chromatography and light scattering detection
InactiveUS20050240385A1Component separationPhase-affecting property measurementsLight scatter measurementRefractive index
A system and method for analyzing data from a gel permeation chromatography (GPC) or size exclusion chromatography (SEC) system fro determining a polymeric sample's radius of gyration. Data from two or more detectors is used with a least-squares minimization fit. A novel method includes the simultaneous determination of a sample's radius of gyration using data from a light scattering detector that collects data from at least two incident angles. Detectors within the inventive method include a multi-angle light scattering (LS) detector, viscometer (V) and a refractive index (RI) detector.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for characterizing impurity profile of organic materials
InactiveUS20150177199A1Simple methodComponent separationSurface/boundary effectAntigenSolid phase extraction
Method and apparatus for characterizing drug-modified polymers, macromolecules, proteins, antigens, antibodies or nanoparticles and quantitative determination of their impurity profile by two-dimensional liquid chromatography analysis. The first dimension is preferably size exclusion chromatography (SEC)—which is also known as gel permeation chromatography in case of non-aqueous samples (GPC)—for complete molecular weight analysis of nanoscale particles. It is not just included the application of separating small molecules from big molecules, but it is also the separation of different sorts of oligomers (e.g. monomers, dimers, trimers, tetramers). The second dimension is adapted for separating and characterizing small molecules which can be impurities or non-reacted modifiers with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Between the dimensions it is feasible to use solid phase extraction column(s) to collect small molecules, wash off or change solvent, or minimize broadening of their peaks.
Owner:BBS NANOTECH
Purification of her-2 variants
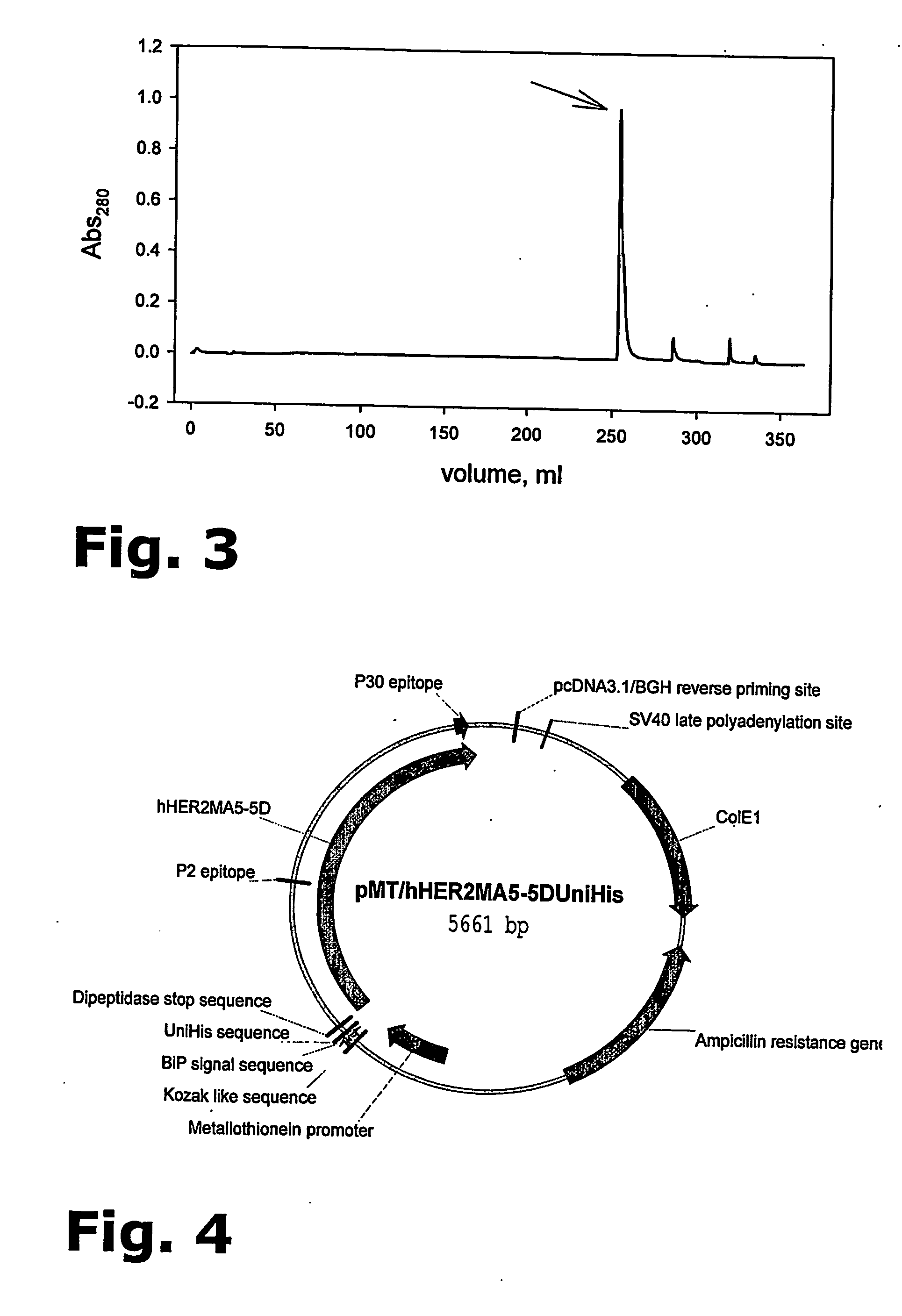
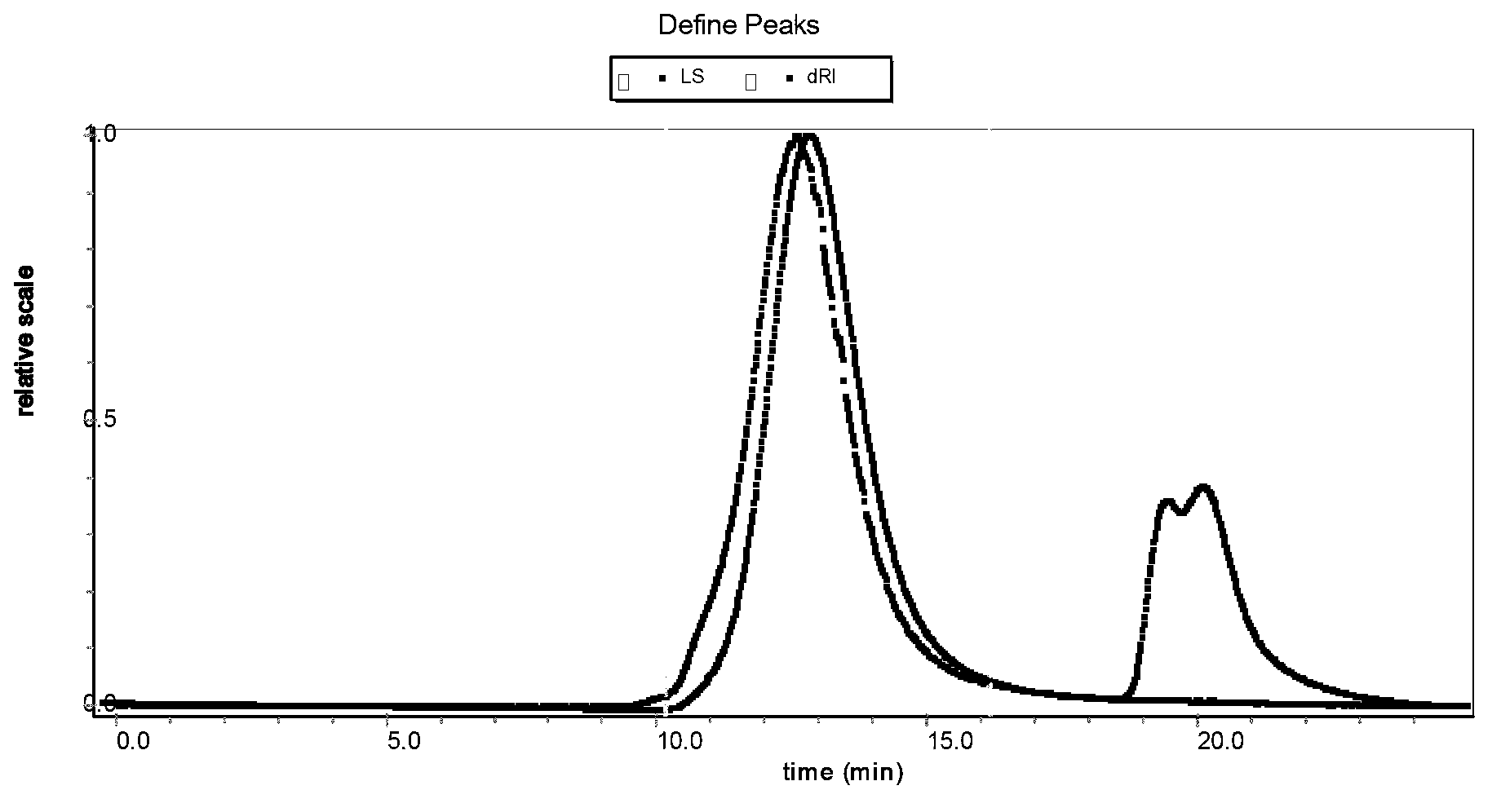
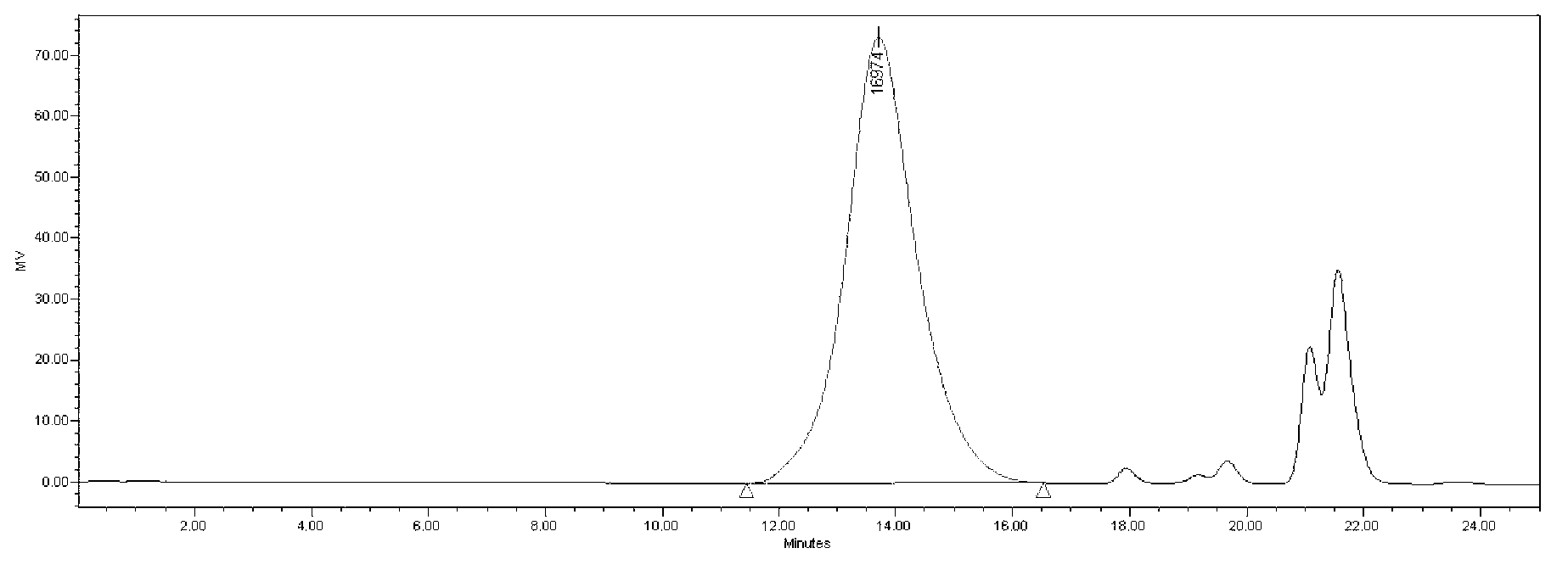
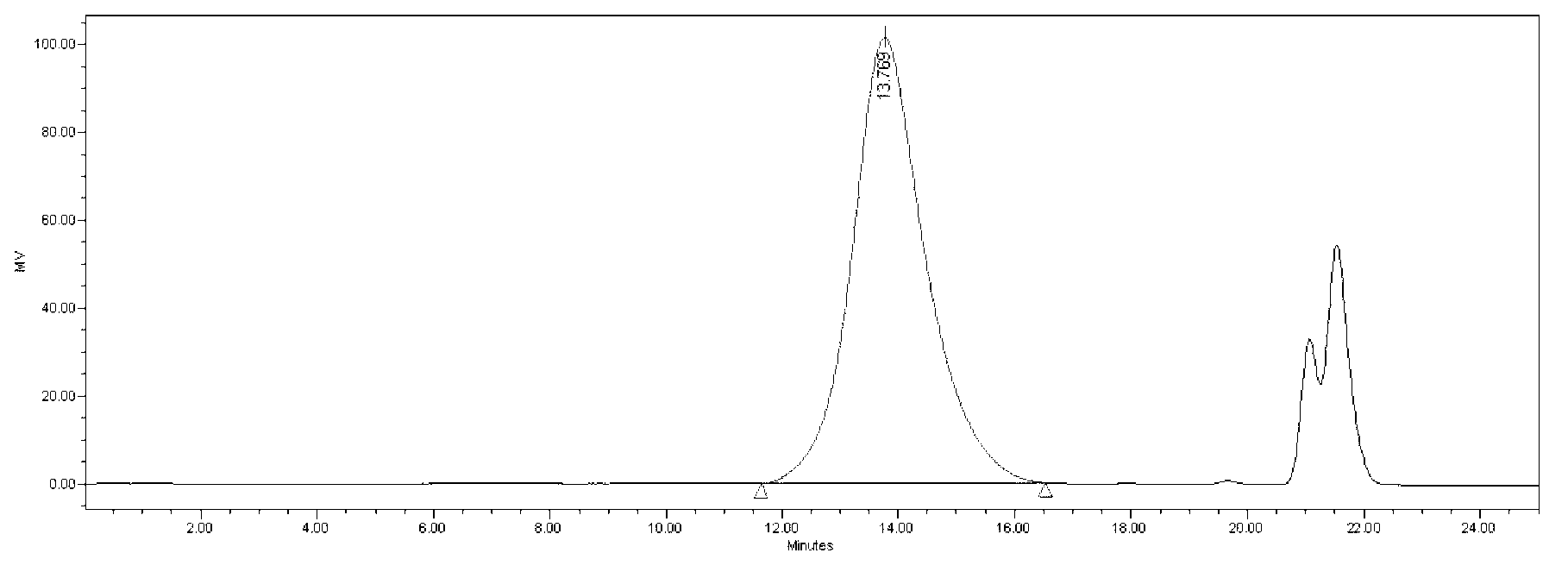
The present invention provides for a novel method for purification of EGFR family proteins obtained from cultures of insect cells. The process comprises subsequent steps of a) diafiltration and exchange of culture medium with buffer, b) immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC), c) size exclusion chromatography (SEC), and d) anion exchange chromatography (AIE). The method also provides for an immunogenic variant of HER-2 protein which for which the purification process has been especially adapted, as well as means for the preparation of the variant.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
Reference substance for measuring relative molecular weight and molecular weight distribution of heparin and salt thereof
The invention discloses a reference substance for measuring the relative molecular weight and the molecular weight distribution of heparin and salt thereof. The reference substance comprises heparin sodium and a molecular weight range distribution standard sample list thereof, wherein heparin sodium is solid; and the molecular weight of heparin sodium, measured according to HPSEC (high performance size exclusion chromatography)-MALLS (Multi-angle Laser Light Scattering), is 3000 to 40000. The invention further discloses a method for measuring the relative molecular weight and the molecular weight distribution of heparin samples. The method comprises the following steps: (1), taking heparin samples of which the molecular weights range from 3000 to 40000 as reference substances; (2), drawing a molecular weight range distribution standard sample list; and (3), measuring the heparin samples according to HPSEC, and calculating the relative molecular weight and the molecular weight distribution, so as to carry out quality control. The reference substance and the method for measuring the relative molecular weight and the molecular weight distribution of the heparin samples according to the reference substance are the first in the world, and have higher utility values; the method is strict, scientific and simple; the measured results are accurate; and the popularization and application prospect is excellent.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Functionalised Triblock Copolymers and Compositions Containing Such Polymers
ActiveUS20130017189A1Expand the scope ofTuning timeOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderEnd-groupKetone
Amphiphilic triblock copolymers B-A-B, wherein A is a linear poly(ethylene glycol) block, having a number average molecular weight (Mn) of between 900 and 3000 Daltons, determined with size exclusion chromatography; wherein B are hydrophobic blocks with at least two cyclic monomers selected from the group consisting of glycolide, lactide, 1,3-dioxan-2-one, 5,5-dimethyl-1,3--dioxan-2-one, 1,4-dioxan-2-one, 1,4-dioxepan-2-one, 1,5-dioxepan-2-one, each B-block having a number average molecular weight (Mn) of between 400 and 2000 Daltons, determined with size exclusion chromatography; and wherein 25% to 100% of the polymer hydroxyl end-groups are covalently modified with at least one derivative of a C2-C20 fatty acid. The invention also relates to compositions with such polymers and the use thereof.
Owner:INGELL TECH HLDG
Method for measuring weight-average molecular weight and content of mannuronic acid substances
ActiveCN109459505ASolve the large deviation of weight average molecular weight determinationSolve the problem of inaccurate content quantificationComponent separationIon contentQuality control
The invention belongs to the field of natural medicine chemistry and quality control, and relates to a method for measuring the weight-average molecular weight and the content of soluble salt of mannuronic acid substances. Weight-average molecular weight and content results of acid sugar measured by an SEC-MALS (size exclusion chromatography with multi-angle laser scattering detector) are corrected by the aid of the metal ion content of soluble salt samples of the mannuronic acid substances. The weight-average molecular weight and the content of the soluble salt w of the mannuronic acid substances can be rapidly and accurately measured by the method.
Owner:GREEN VALLEY (SHANGHAI) PHARM CO LTD
Detection method for polyethylene glycol content
ActiveCN105548422AExtended elution timeEasy to separateComponent separationMedical equipmentPolyethylene glycol
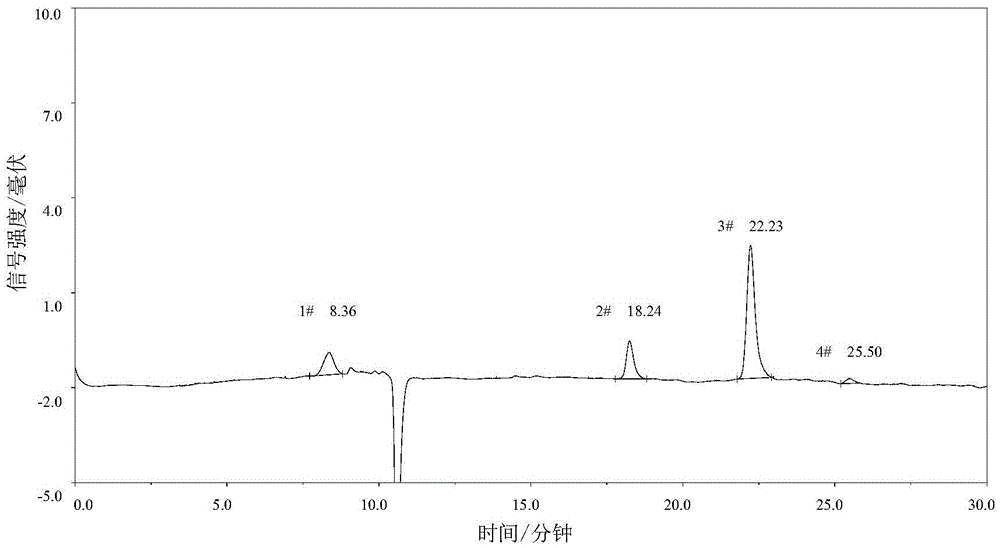
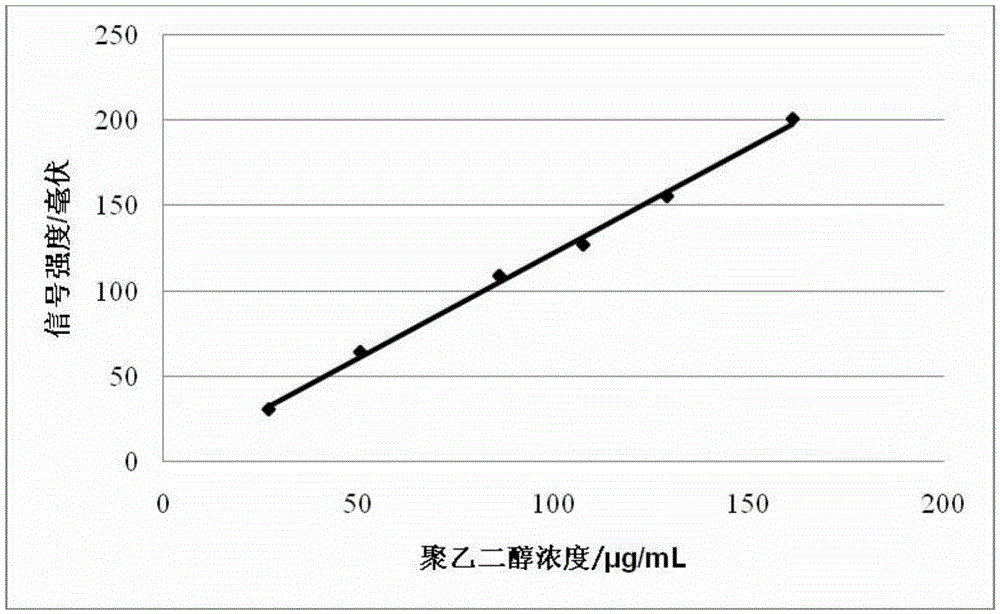
The invention discloses a detection method for polyethylene glycol content. The detection method utilizes the differences among the hydromechanical volumes of all components in a sample and, by optimizing chromatographic conditions, chooses a size exclusion chromatography column with appropriate grain size and aperture of chromatographic column packing to carry out high-quality separation, the chromatographic peak of polyethylene glycol is identified by a conventional common detector for laboratories, regression is carried out by an external standard method, and the absolute content of the polyethylene glycol in the sample is then quantified. The detection method disclosed by the invention solves the limitation in conventional methods, such as poor separation degree, low trace content test accuracy and test results only being capable of being expressed by percentage content, and the detection method is particularly suitable for detecting polyethylene glycol content or polyethylene glycol residue quantity in drugs or drug-carrying medical equipment, food, health-care products and other biological products.
Owner:LIFETECH SCIENTIFIC (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Exosome separation and purification method
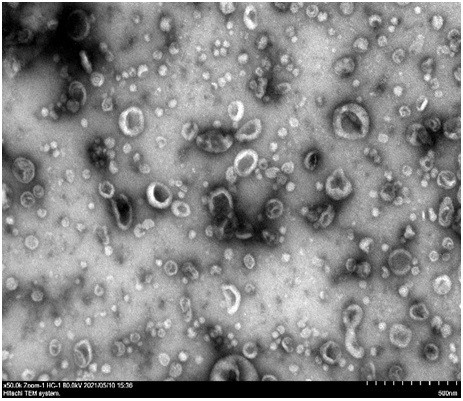
InactiveCN113444682AImprove efficiencyHigh purityCell dissociation methodsArtificial cell constructsMolecular sieveUltrafiltration
The invention relates to an exosome separation and purification method, which comprises the following steps of: taking a body fluid or a culture solution containing exosome, and carrying out anion exchange chromatography and / or molecular sieve chromatography to obtain a purified exosome solution. By means of the purification method, the high-purity exosome can be obtained by low cost and high efficiency even in a large-scale exosome requirement. Compared with the existing exosome purification methods, including a centrifugation method, a PEG polymer precipitation method, an affinity chromatography method, an ultrafiltration method and a molecular sieve size exclusion chromatography method, the exosome separation and purification method disclosed by the invention can be used for purifying exosomes with different volumes (100ml to 500L), and especially for milk-derived products with more impurity proteins, the milk-derived exosome of which the purity is 99% or above can be obtained. Meanwhile, the exosome separation and purification method has the advantages of la ow cost and a high recovery rate, and can meet the requirements of industrial production.
Owner:天九再生医学(天津)科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com