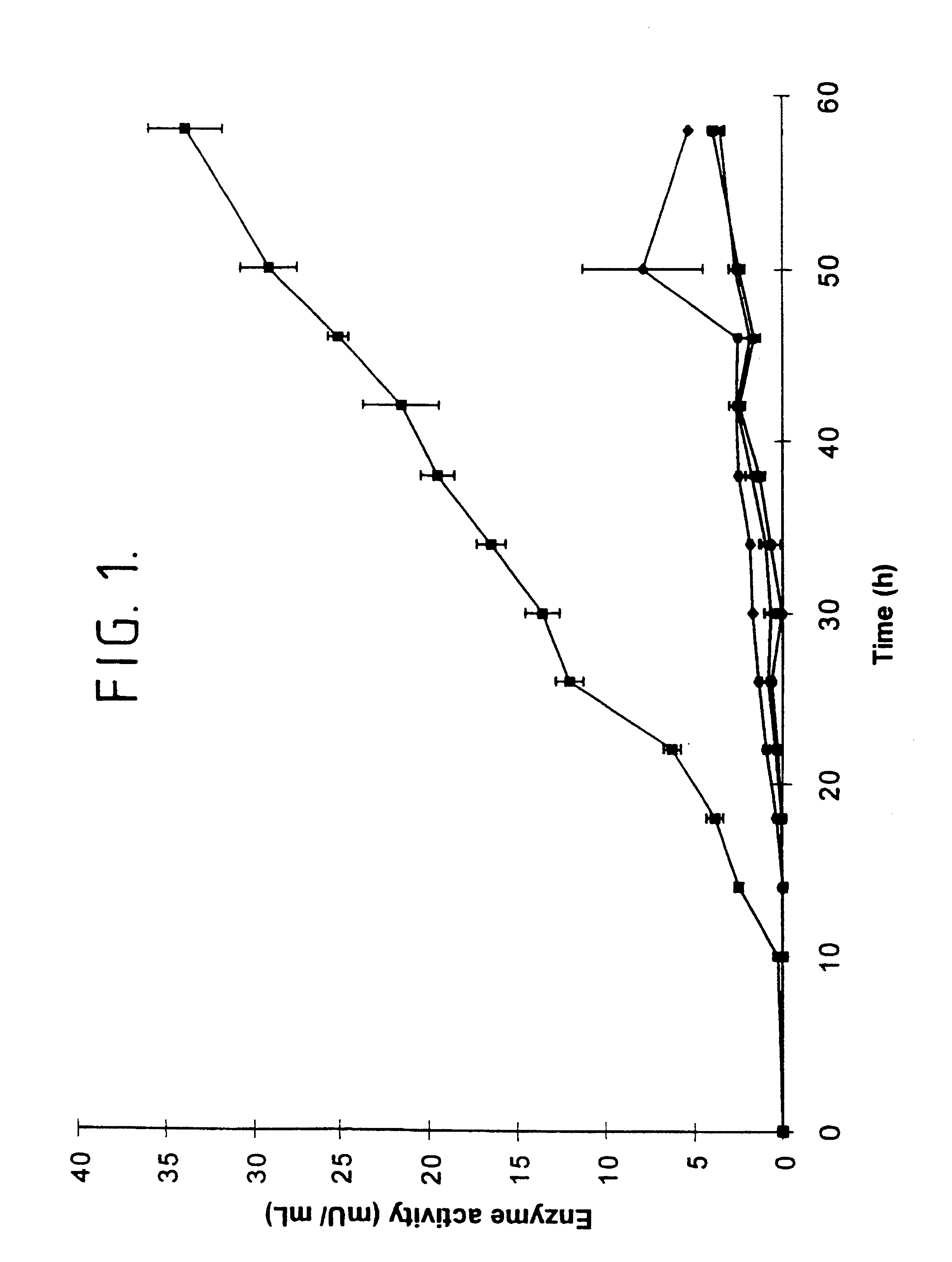
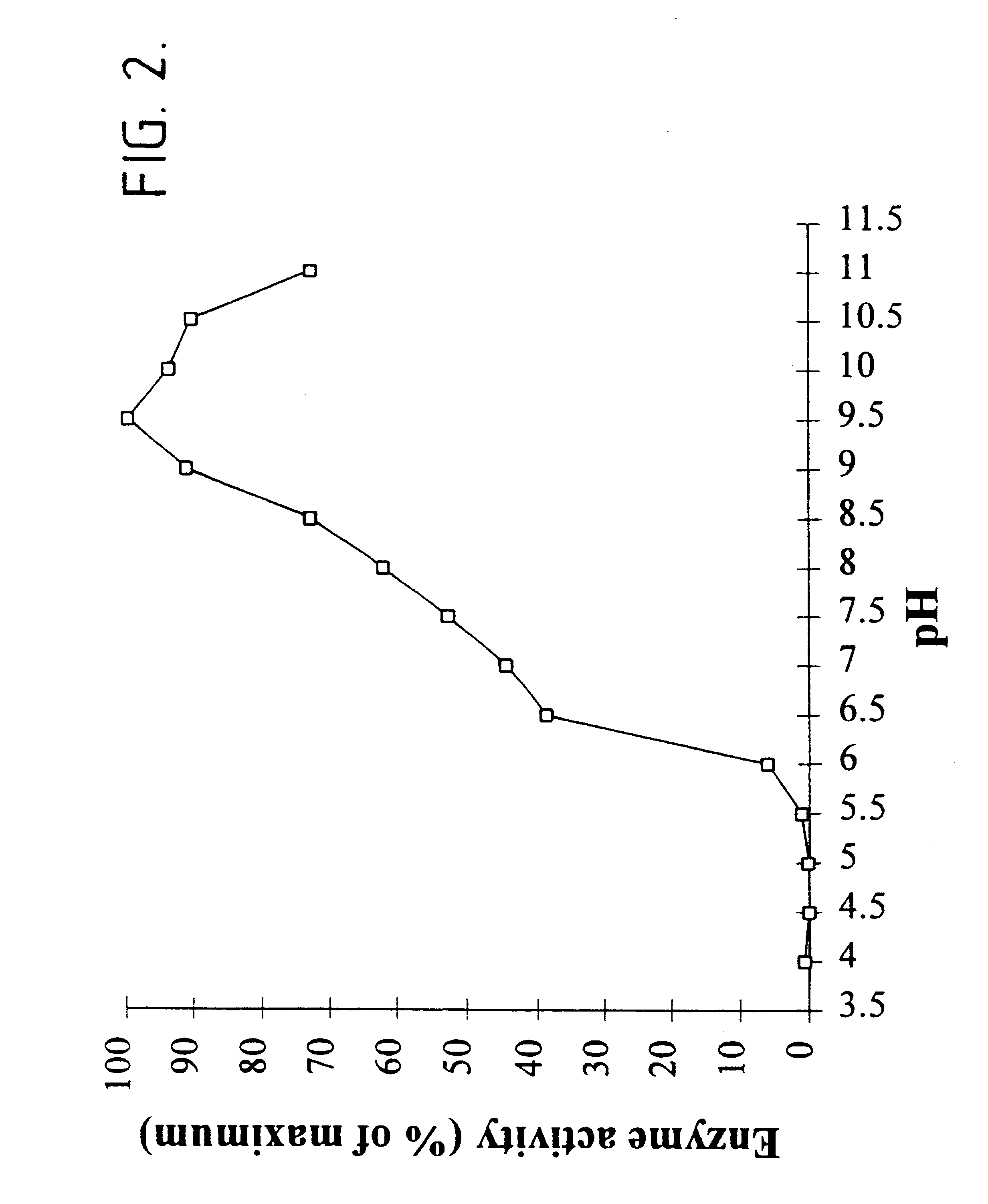
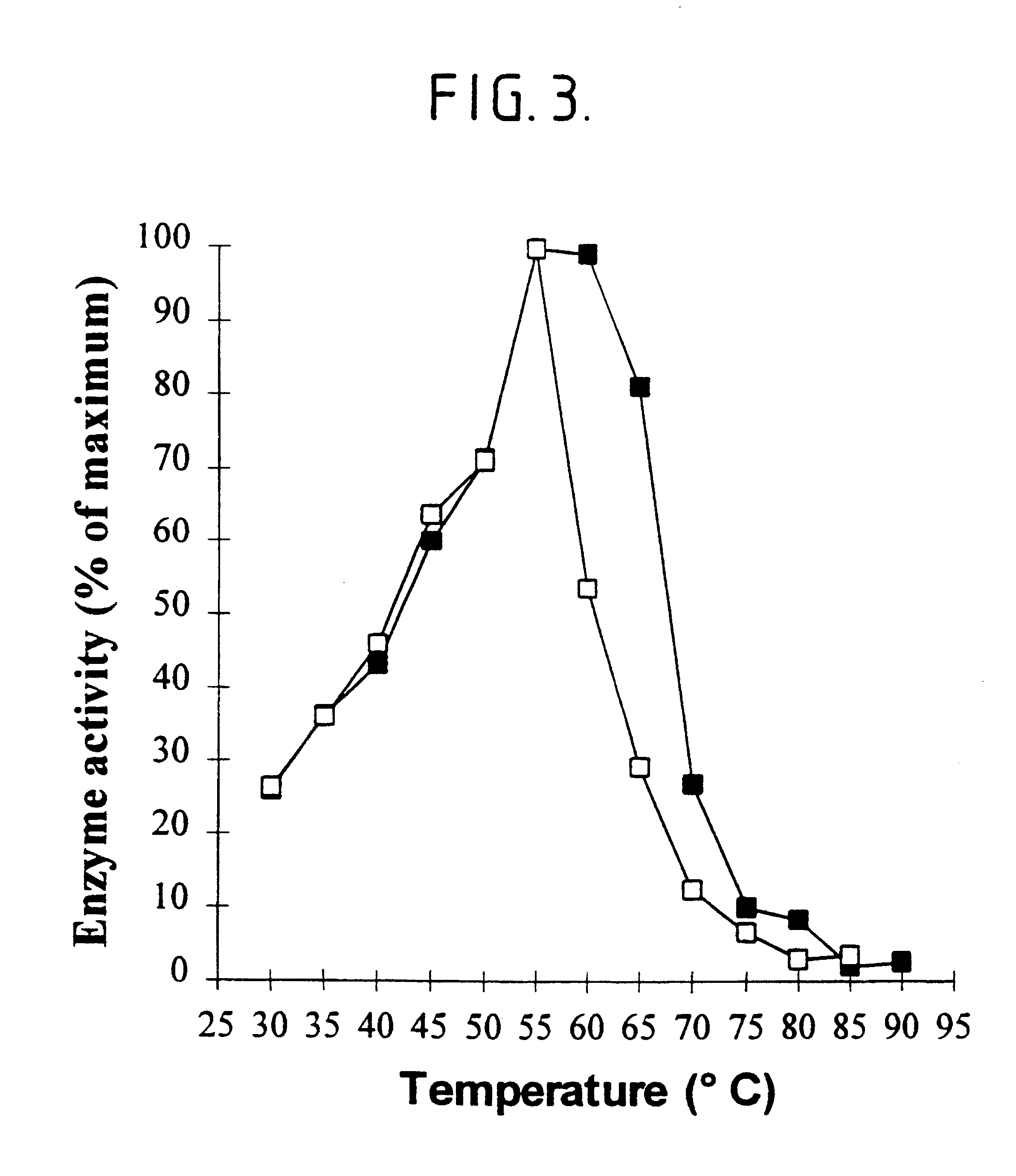
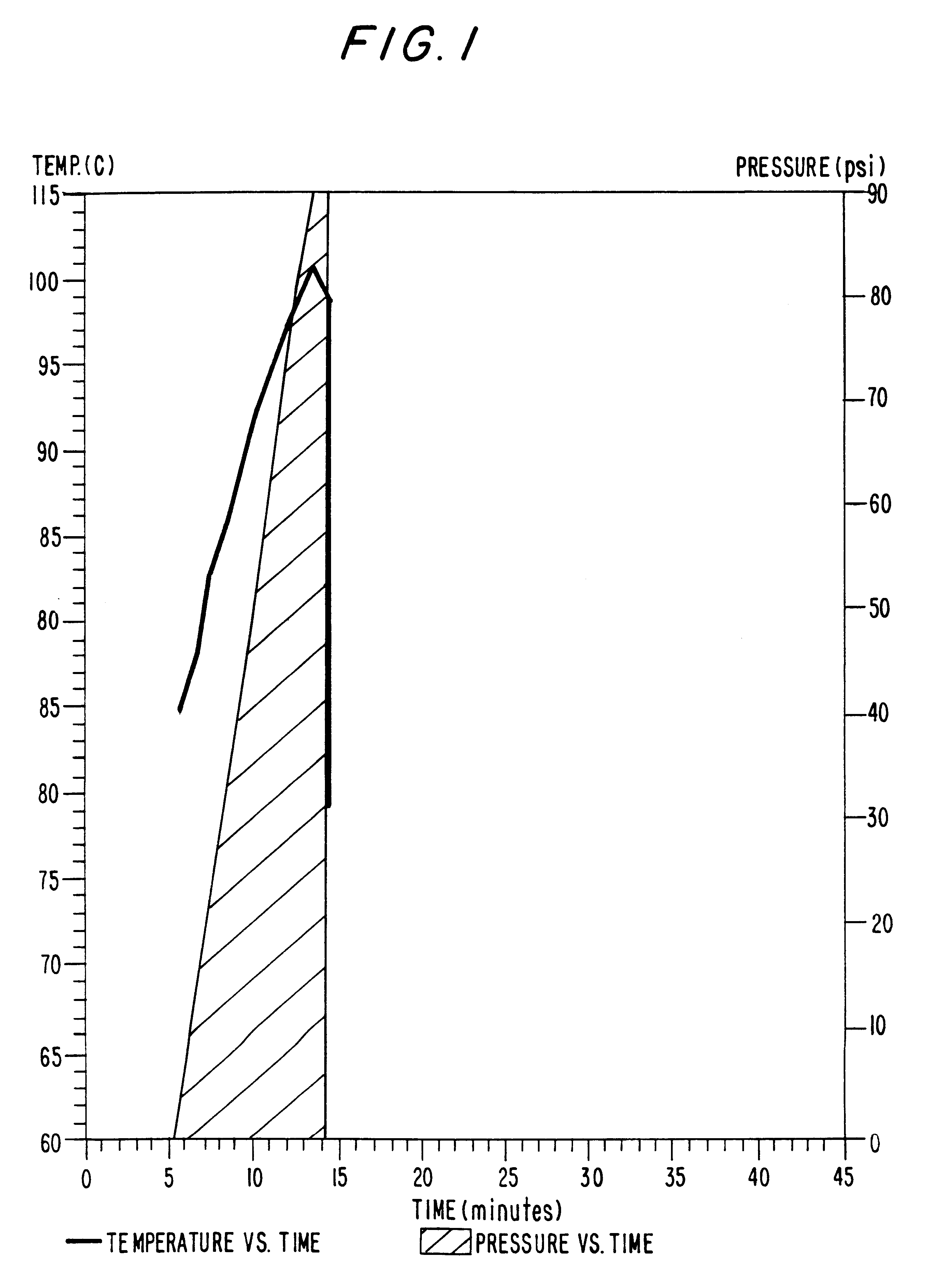
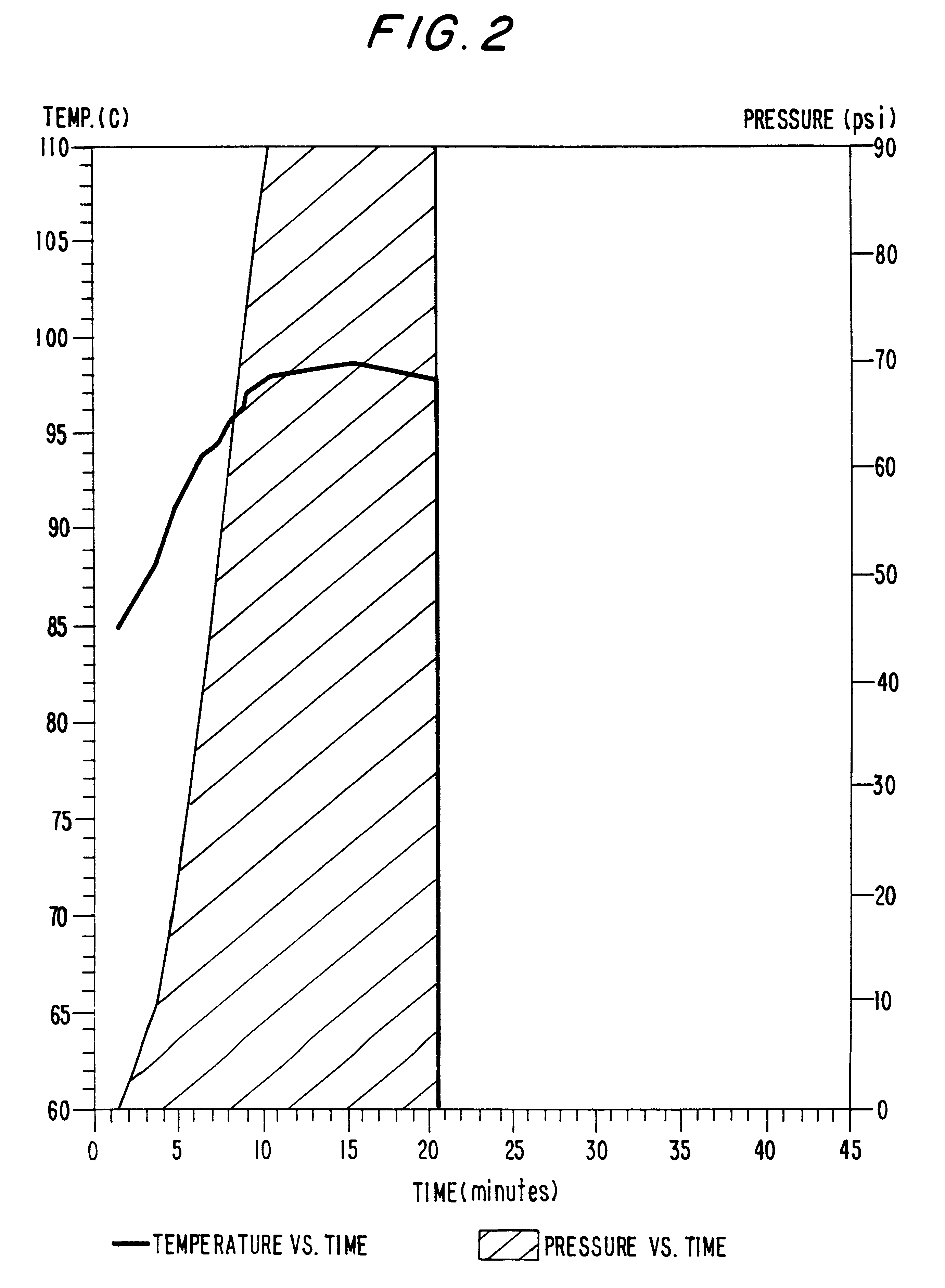
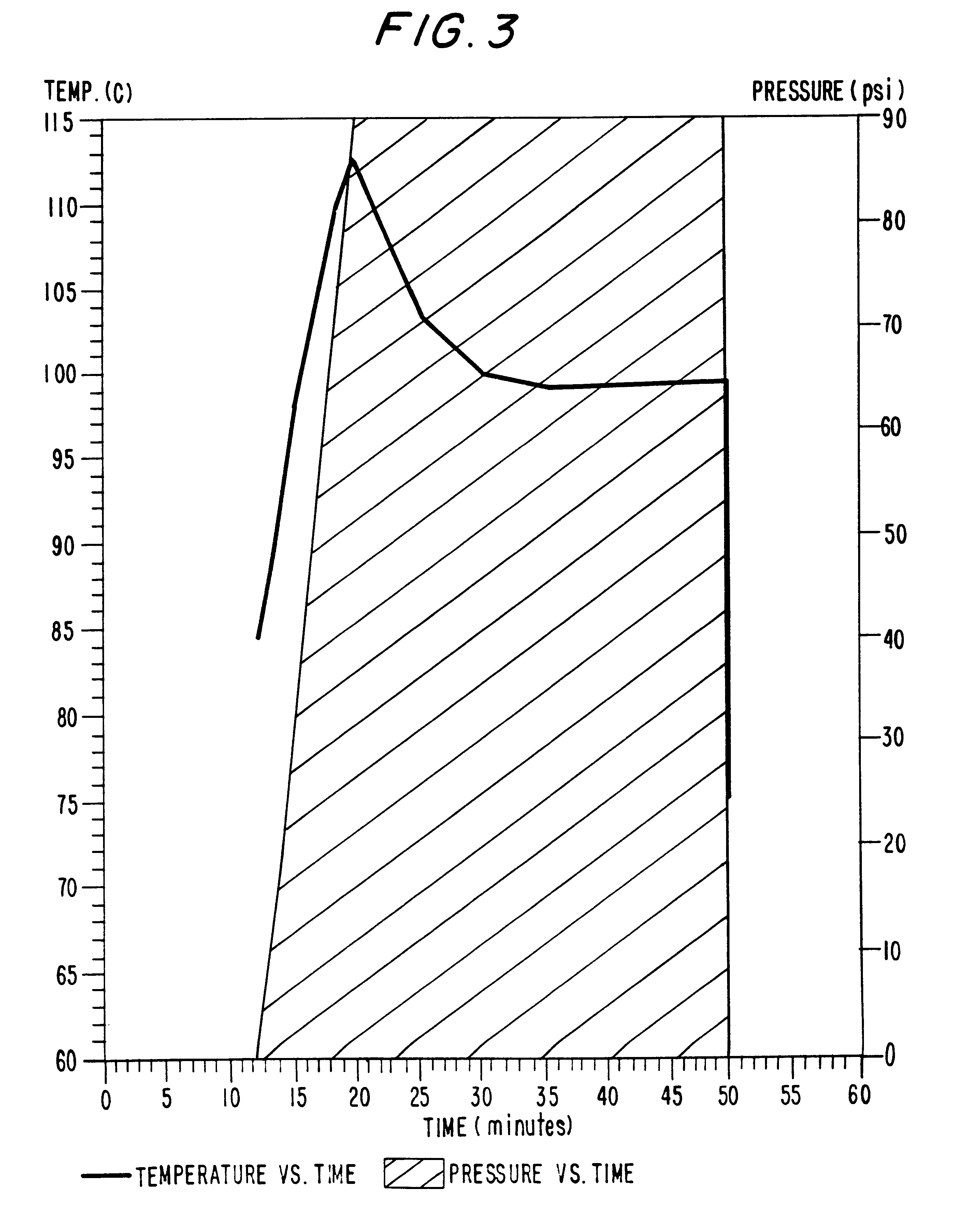
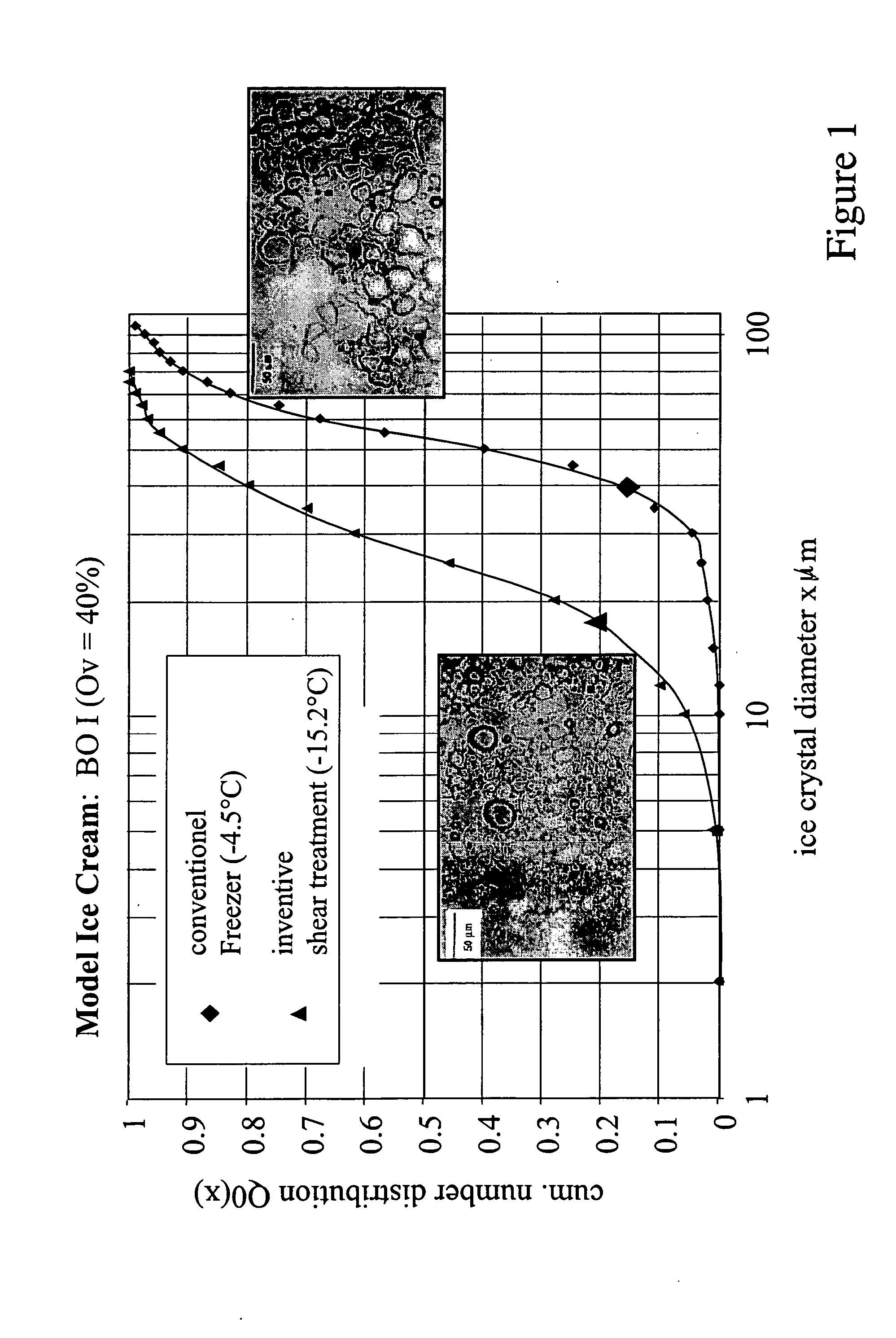
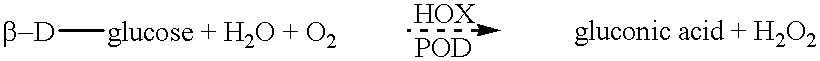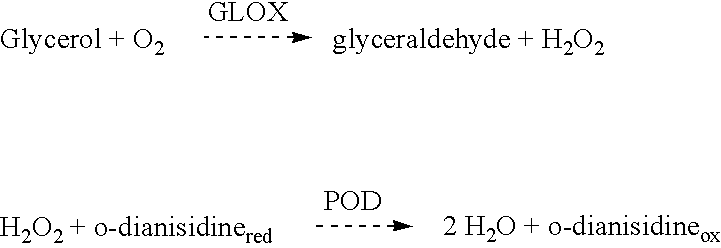Patents
Literature
1669results about "Wort preparation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
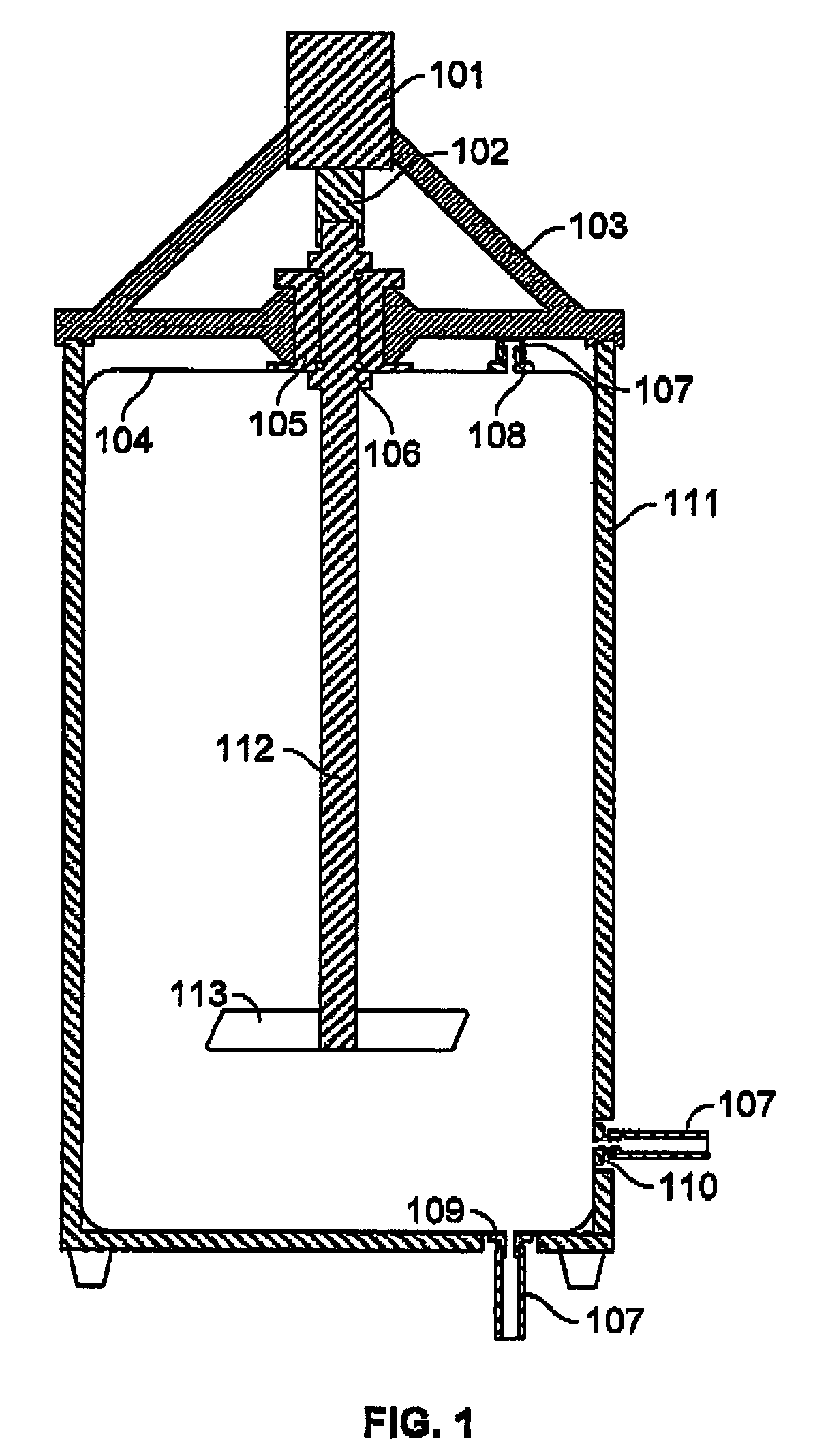
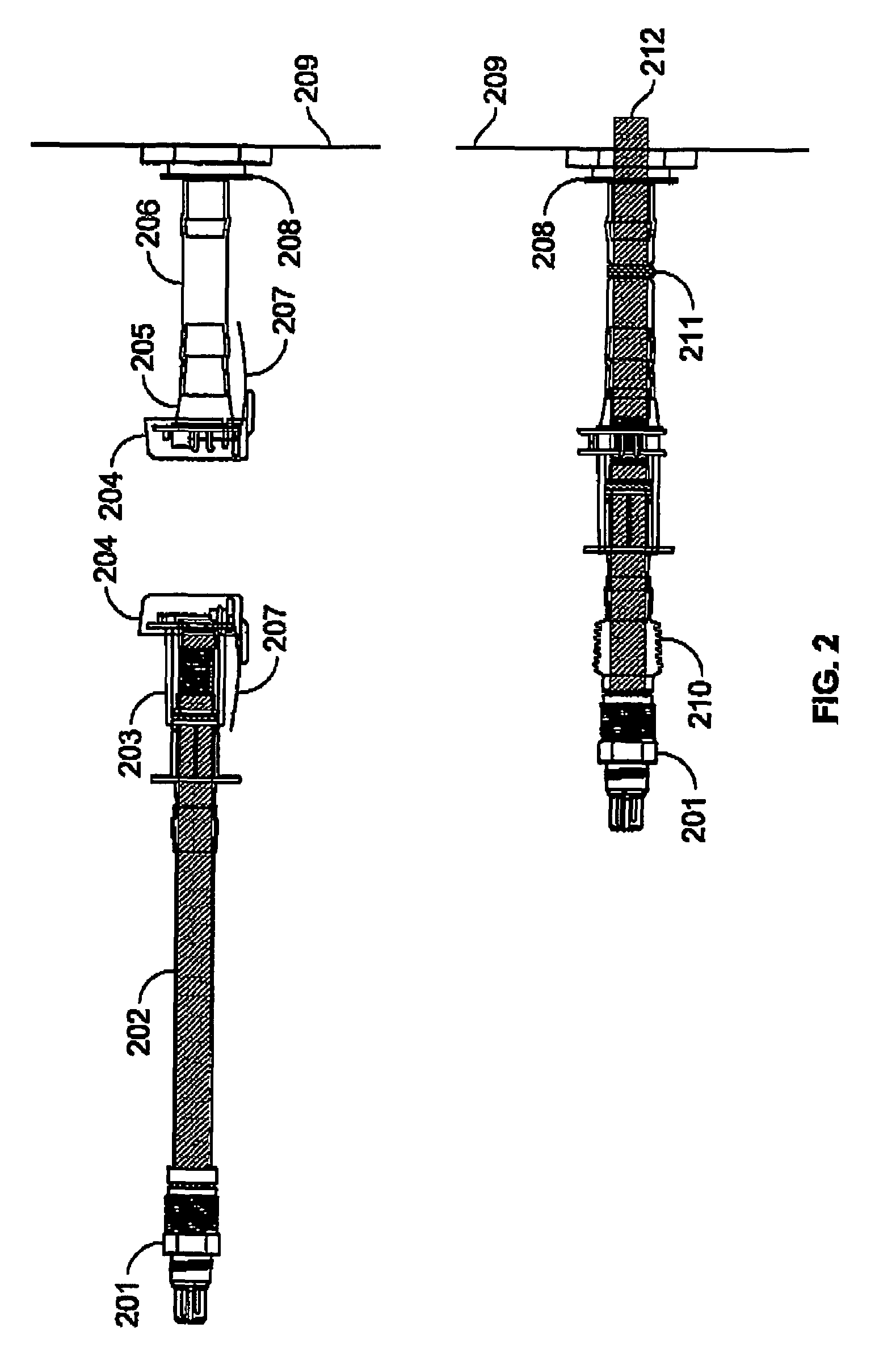
Stirred-tank reactor system
ActiveUS7384783B2Less regulatory controlMinimal or no preparation priorBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReactor systemNuclear engineering
The present invention relates to a stirred-tank reactor system and methods of preparing such systems. The present invention further encompasses the use of the stirred-tank reactor system as a disposable bioreactor and in kits with disposable elements.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD +1
Stirred-tank reactor system
ActiveUS20050239199A1Less regulatory controlConsiderable cost advantageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReactor systemNuclear engineering
The present invention relates to a stirred-tank reactor system and methods of preparing such systems. The present invention further encompasses the use of the stirred-tank reactor system as a disposable bioreactor and in kits with disposable elements.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD +1
Silicone hydrogel lenses with water-rich surfaces
ActiveUS8480227B2Meet actual needsPretreated surfacesAlcoholic beverage preparationHigh water contentHigh oxygen
The invention is related to a hydrated silicone hydrogel contact lens having a layered structural configuration: a lower water content silicone hydrogel core (or bulk material) completely covered with a layer of a higher water content hydrogel totally or substantially free of silicone. A hydrated silicone hydrogel contact lens of the invention possesses high oxygen permeability for maintaining the corneal health and a soft, water-rich, lubricious surface for wearing comfort.
Owner:ALCON INC
Morinda citrifolia (Noni) enhanced animal food product
The present invention advances prior art animal food products by providing an animal food product formulated with Morinda Citrifolia, or Noni, from the Indian Mulberry plant. The addition of Noni to the animal food product of the present invention serves to provide significant health advantages not found in prior art animal food products.
Owner:TAHITIAN NONI INT INC
Non-maltogenic exoamylases and their use in retarding retrogradation of starch
InactiveUS6667065B1Highly effective in retarding or reducing detrimental retrogradationImprove propertiesDough treatmentHydrolasesAmylosucrase activitySide chain
The present invention relates to a process for making a bread product. The process includes the addition of a non-maltogenic exoamylase that hydrolyses starch to a starch medium, and the application of heat to the starch medium. The non-maltogenic exomylase cleaves one or more linear malto-oligosaccharides, predominantly consisting of from four to eight D-glucopyranosyl units, from non-reducing ends of amylopectin side chains. The non-maltogenic exoamylase has an endoamylase activity of less than 0.5 endoamylase units (EAU) per unit of exoamylase activity.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Method of improving the properties of a flour dough, a flour dough improving composition and improved food products
InactiveUS6358543B1Reduce disadvantagesReduce stickinessDough treatmentHydrolasesIridophycus flaccidumEuthora cristata
A method of improving the rheological properties of a flour dough and the quality of the finished product made from such a dough, including adding an effective amount of an oxido-reductase capable of oxidizing maltose, in particular a hexose oxidase, e.g. isolated from an algal species such as Iridophycus flaccidum, Chondrus crispus or Euthora cristata and a dough improving composition containing the oxidore-ductase.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Reduced Pigmentation Microalgae Strains and Products Therefrom
InactiveUS20100297292A1Reduced colorationIncrease rangeMilk preparationDough treatmentHypopigmentationCarotenoid
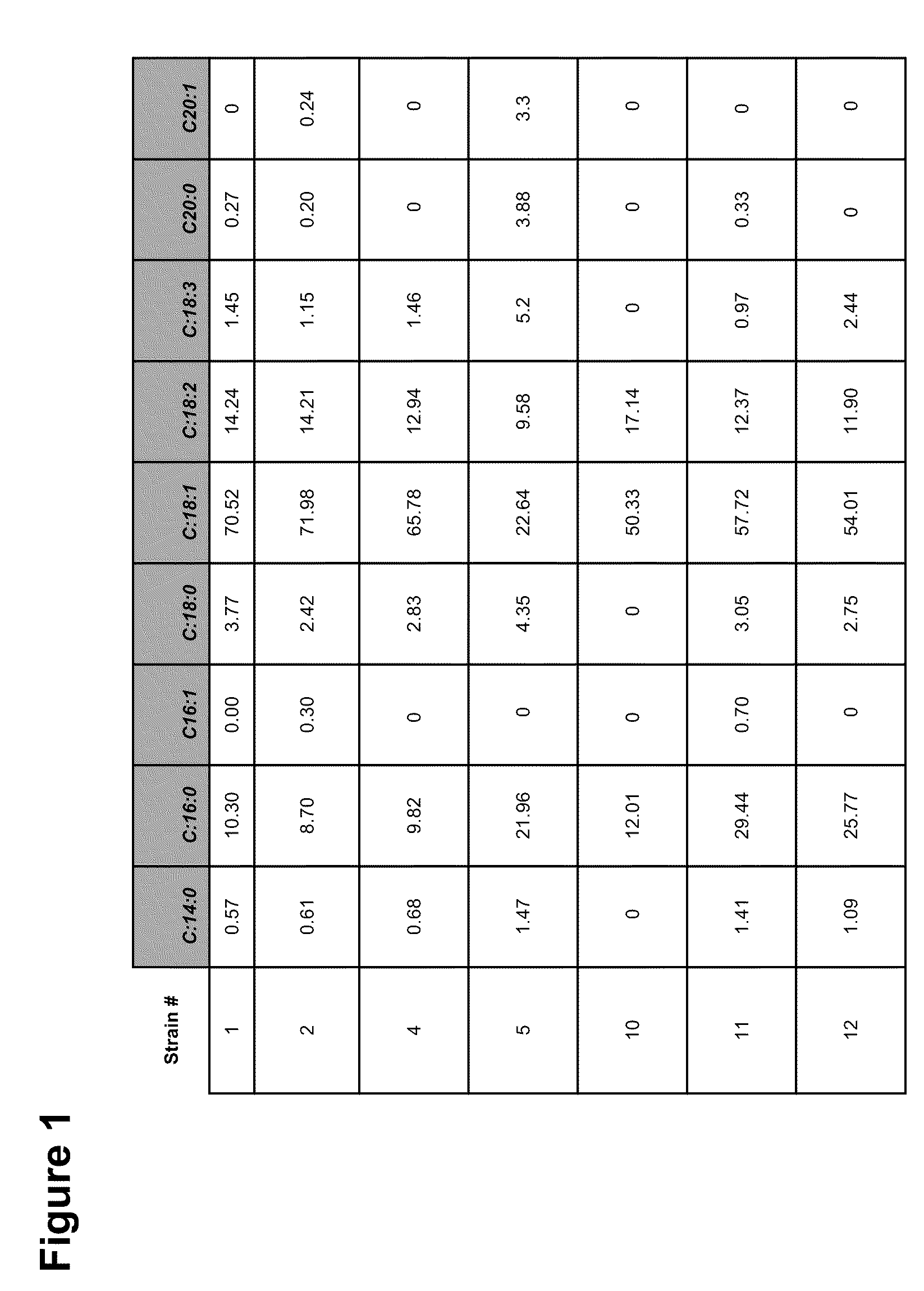
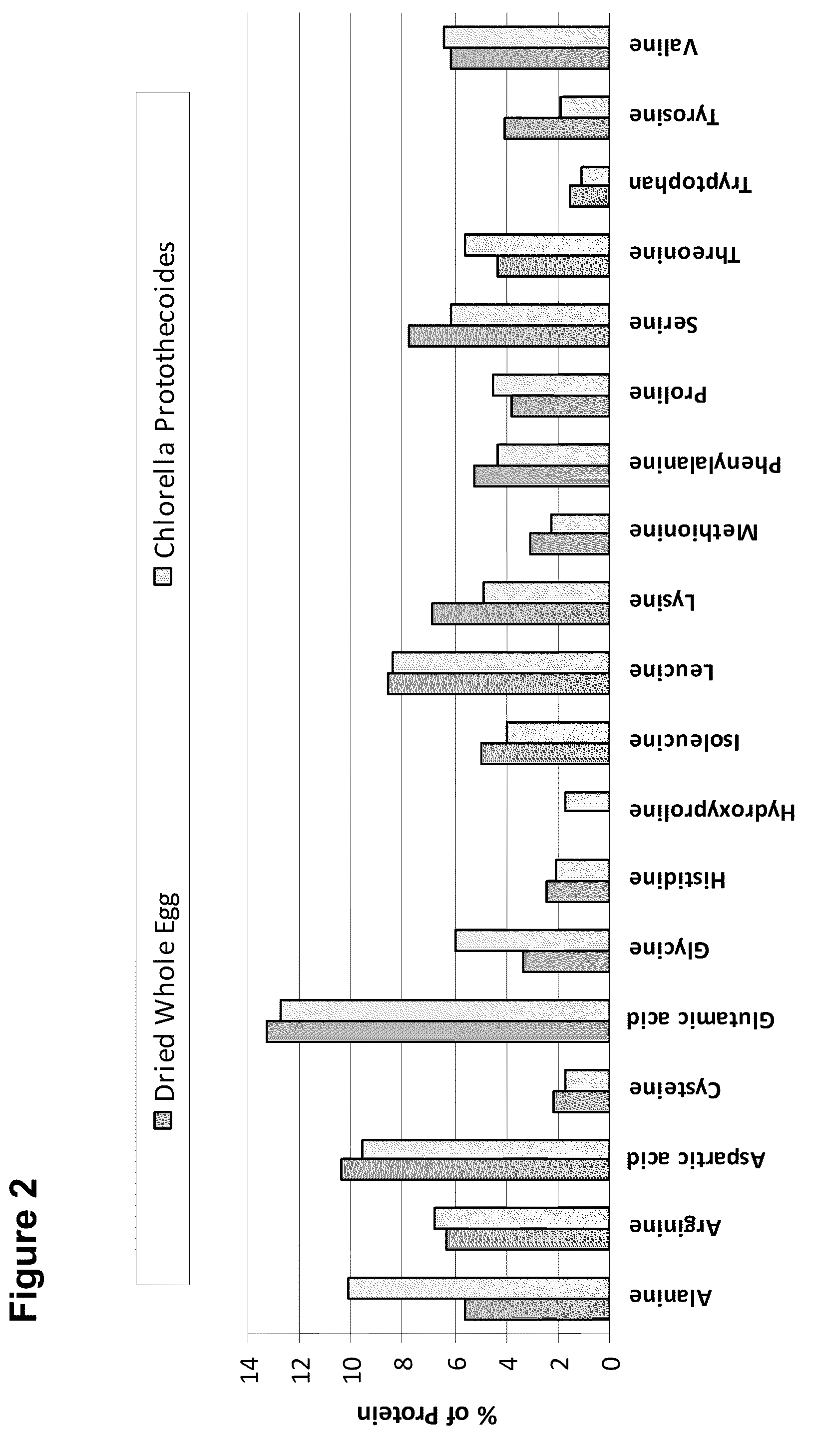
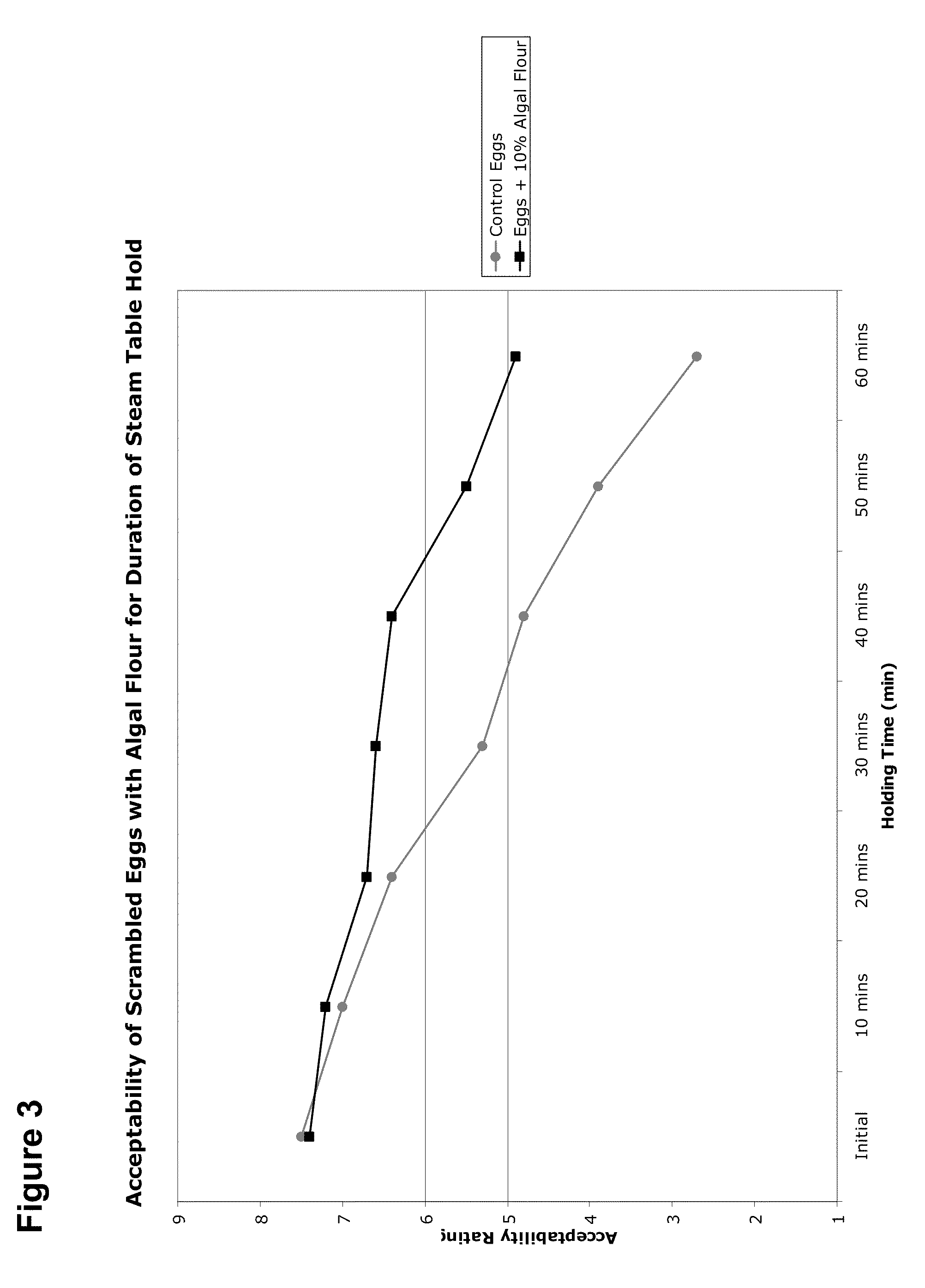
The invention provides unique and novel strains of microalgae that have been subjected to non-transgenic methods of mutation sufficient to reduce the coloration of biomass produced by the strains. Biomass produced from such strains can be used in the manufacture of baked goods, gluten free foods, beverages, high lipid algal flours, and other foods. Pigments such as carotenoids and chlorophyll can be undesirable for consumer acceptance when incorporated into foods such as mayonnaise, yogurt, and white sauces that are not traditionally associated with colors such as yellow, red, orange and green. Some pigments, such as chlorophyll, can also create undesirable taste profiles. Use of reduced pigment microalgal biomass expands the range of food products that can be manufactured with healthy lipid profiles. High protein containing biomass of the invention, also reduced in pigmentation, is also incorporated into products such as meat analogues, nutritional bars and meal replacement beverages. The reduced pigmentation microalgae also allow for incorporation of higher amounts of biomass into certain food products that could otherwise be achieved using highly pigmented microalgal biomass. Methods of generating novel reduced pigment microalgae are disclosed herein. The strains provided by the invention are also useful in the manufacture of healthy, neutral colored extracted triglyceride oils.
Owner:TERRAVIA HLDG INC
Processes of improving the quality of oil and products produced therefrom
ActiveUS20070141222A1Decreasing anisidine valueExtended service lifeWort preparationFatty substance preservation using additivesProduction qualityFood products
Oil of improved quality is produced by treating the oil with an active substance capable of reducing the anisidine value of the oil. Food products comprising the oil of improved quality are also disclosed.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
High temperature/ultra-high pressure sterilization of foods
InactiveUS6086936AImprove efficiencyFaster and more energy efficientMilk preservationMeat/fish preservation by heatingUltra high pressureProcess engineering
Method for sterilizing foods using both ultra-high pressures and high temperatures. The instantaneous temperature change that occurs when pressure is applied combines a high-temperature short-time process with ultra-high pressure to deliver a fast and therefore gentle thermal process to a pre-packaged product. The process involves heating a food to a pre-pressurized temperature, subjecting the food to ultra-high pressure, which instantaneously raises the temperature of the food, and then releasing the pressure so that the temperature returns to the original pre-pressurized temperature. The method leverages the adiabatic temperature rise which occurs when the food is hydrostatically pressurized, coupled with the lethality of the pressure, to achieve appropriate sterilization conditions.
Owner:KAL KAN FOODS
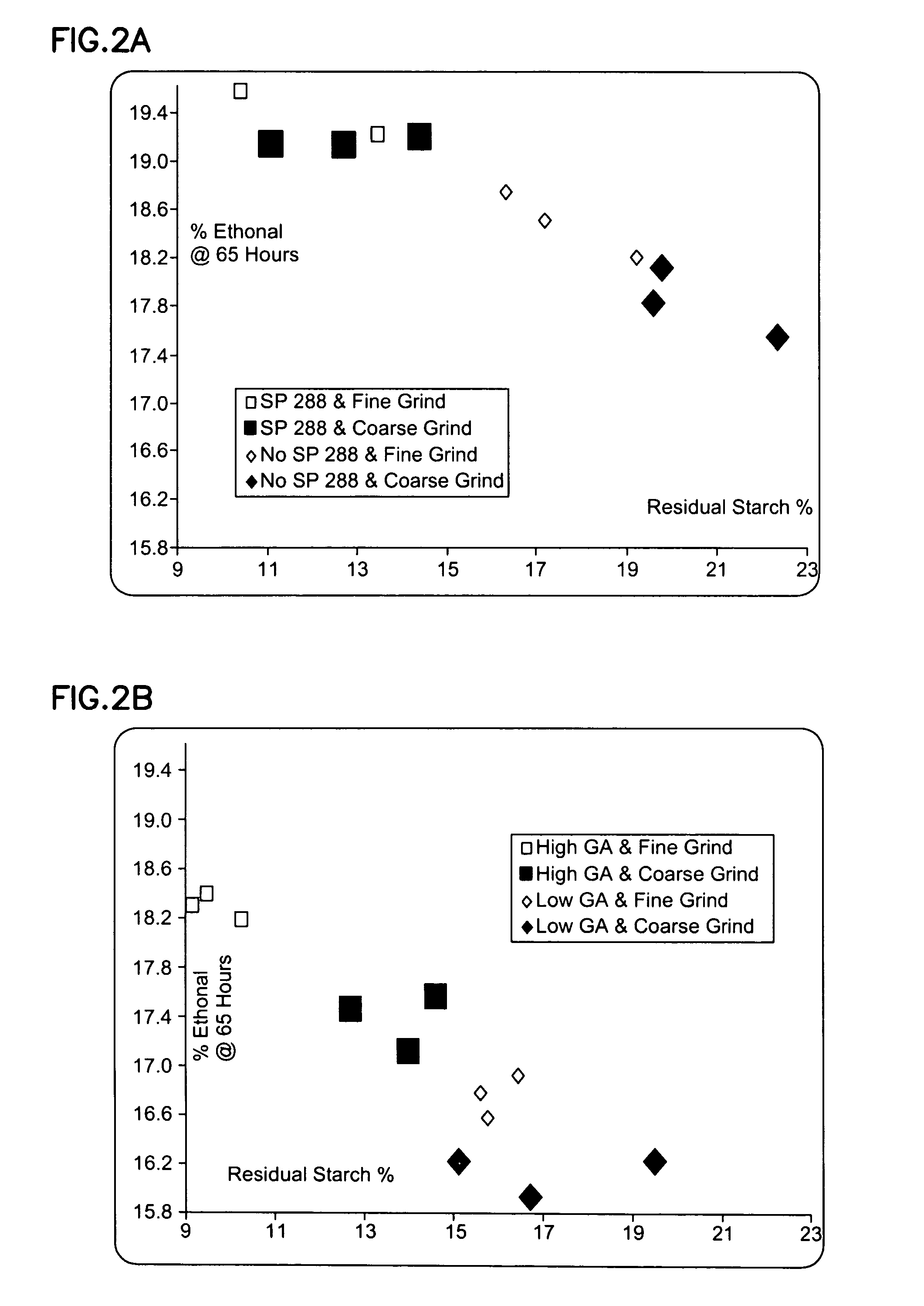
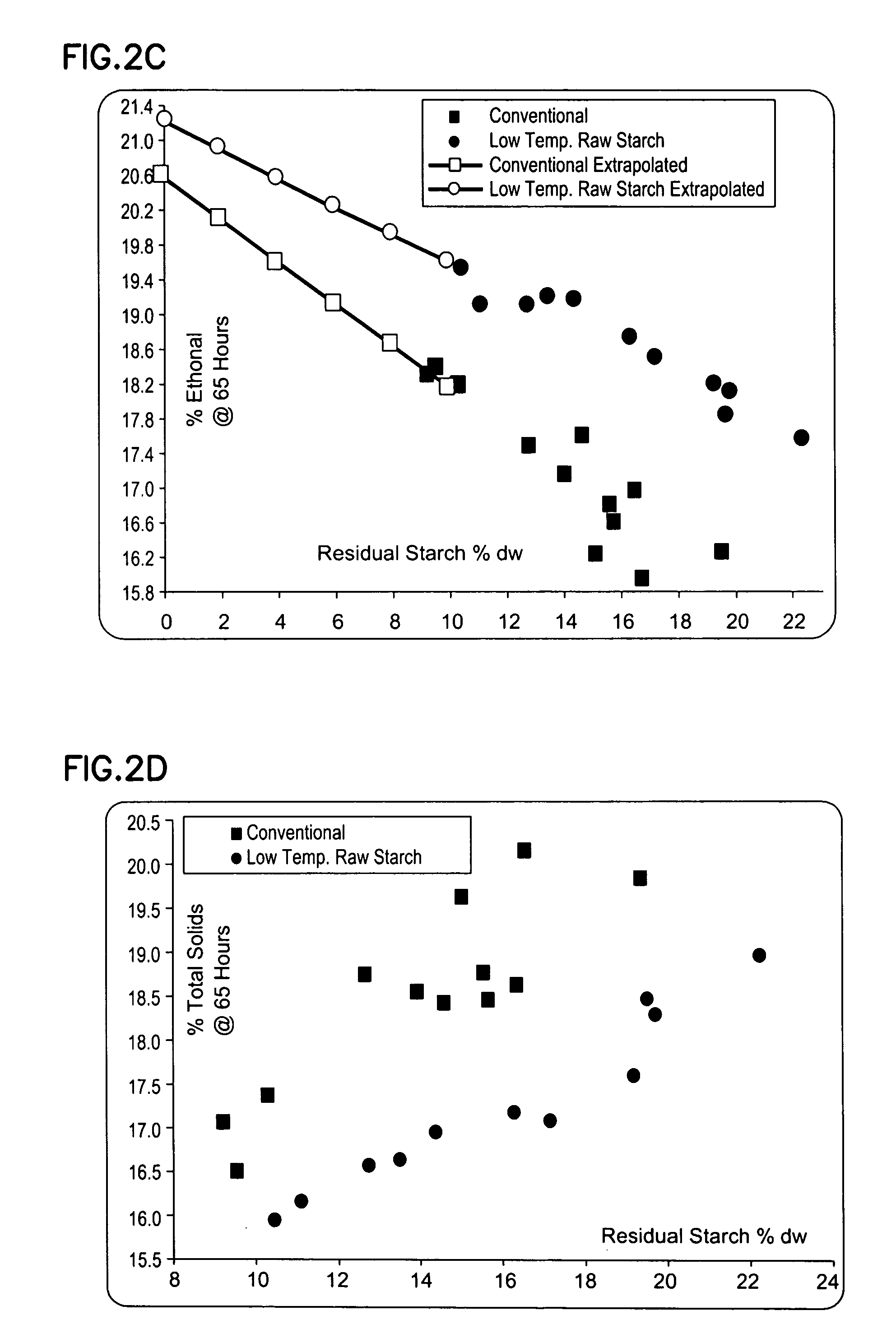
Methods and systems for producing ethanol using raw starch and selecting plant material
ActiveUS20070178567A1Improve the level ofDough treatmentWort preparationHigh alcohol beerStarch production
The present invention relates to methods for producing high levels of alcohol during fermentation of plant material, and to the high alcohol beer produced. The method can include selecting plant material. Selecting can include excluding plant material that has been exposed to high temperatures or that has had high moisture content.
Owner:POET RES INC
Biopolymer structures and components
InactiveUS20050019545A1Keep shapeIncrease valueVehicle arrangementsAlcoholic beverage preparationBiopolymerEngineering
Structures can be formed from a composition, which can be referred to as a biopolymer, that includes fermentation solids and thermoactive material. Methods of making biopolymer products include for example extruding, injection molding, or compounding fermentation solid and thermoactive material. Structures formed from biopolymer can include lumber replacements, window components, door components, siding assemblies, and other structures.
Owner:POET RES INC
Oil recovery from dry corn milling ethanol production processes
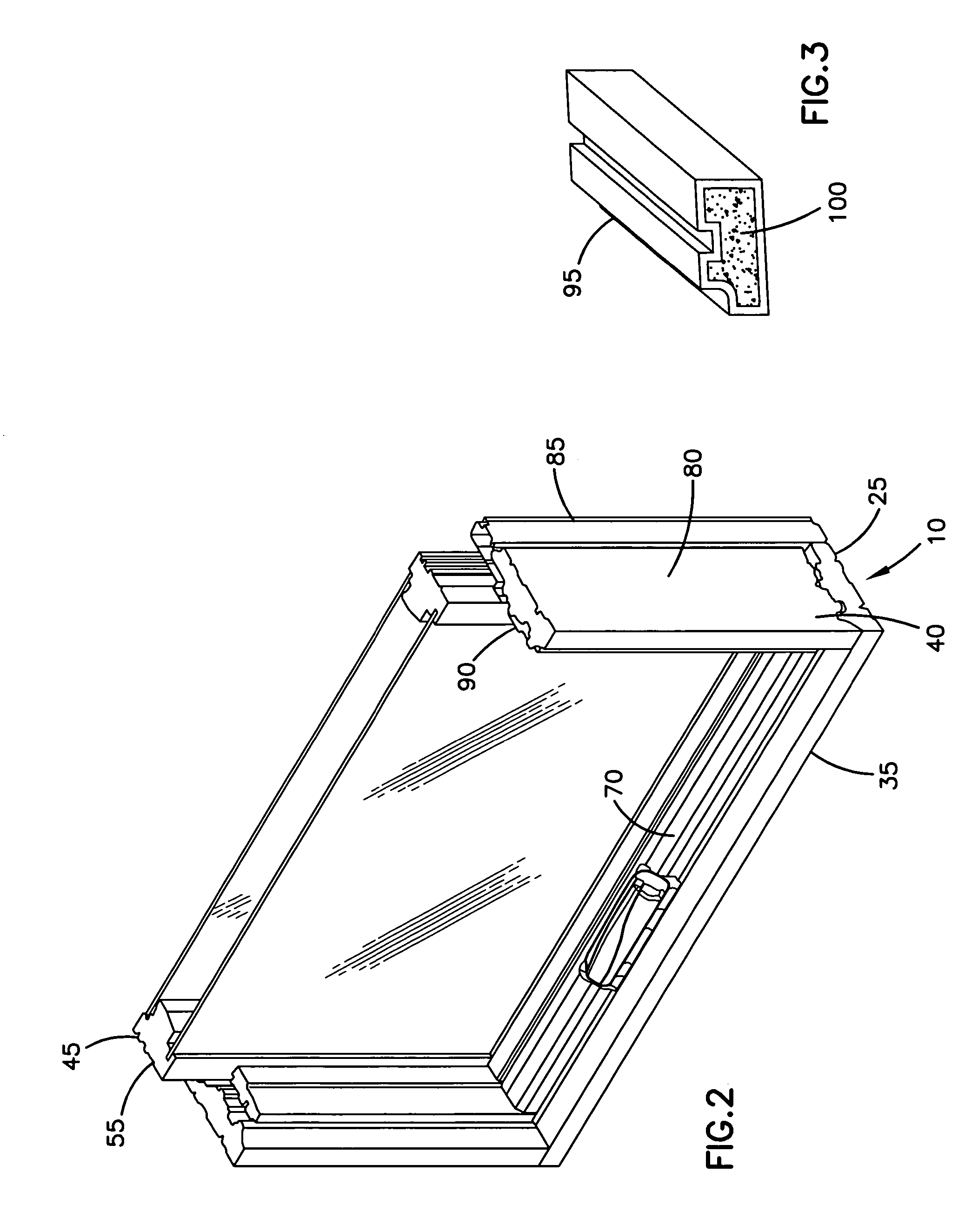
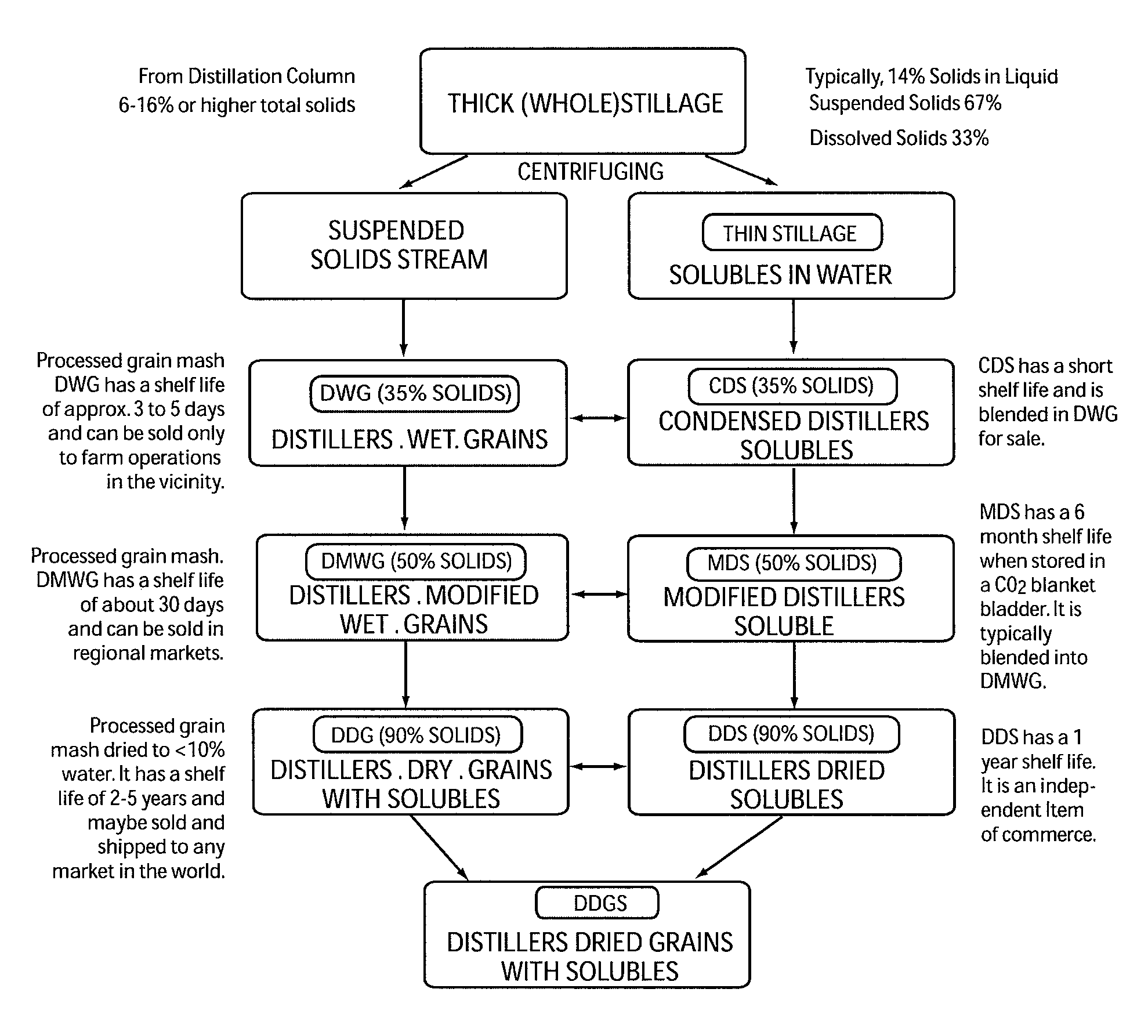
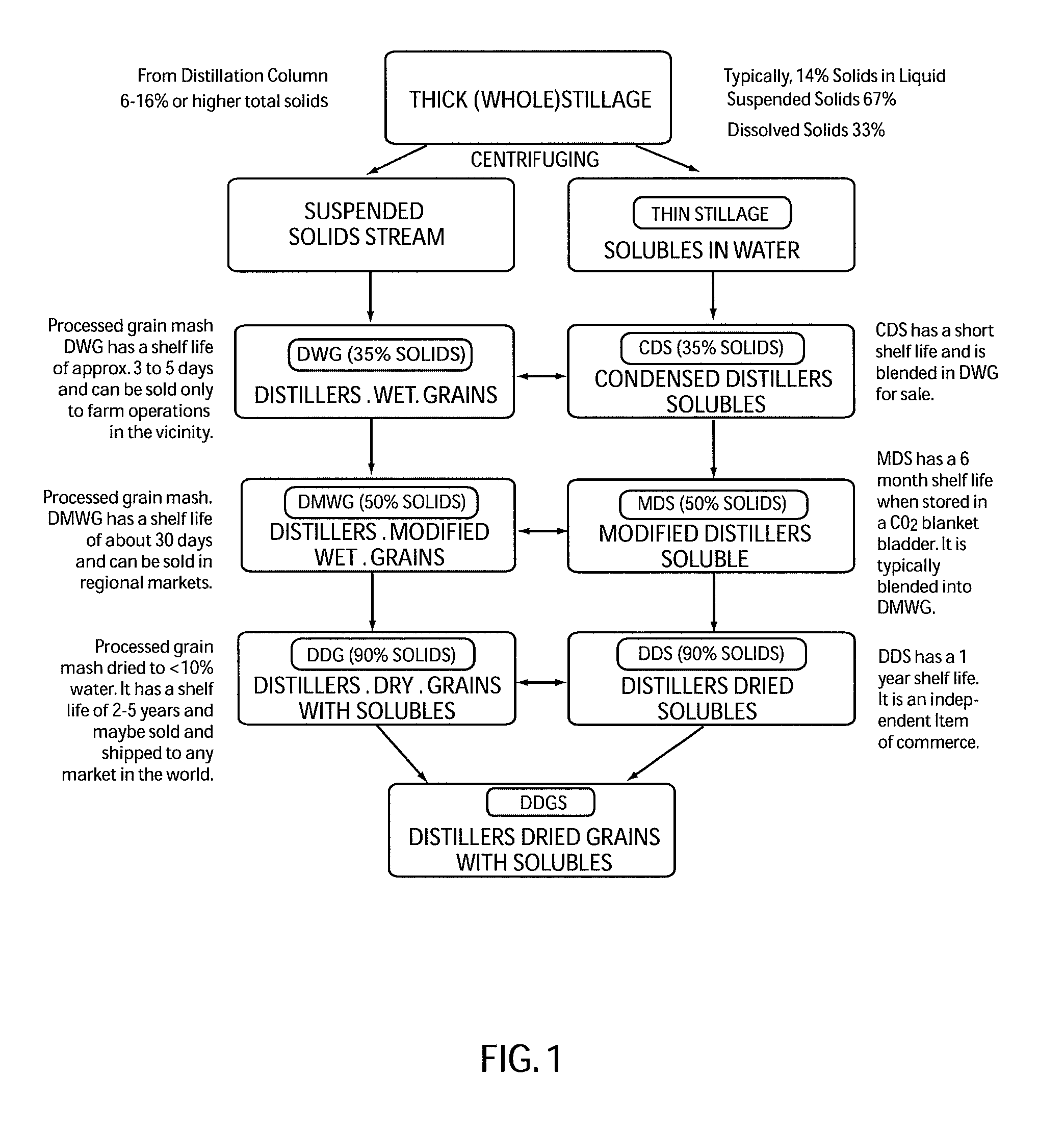
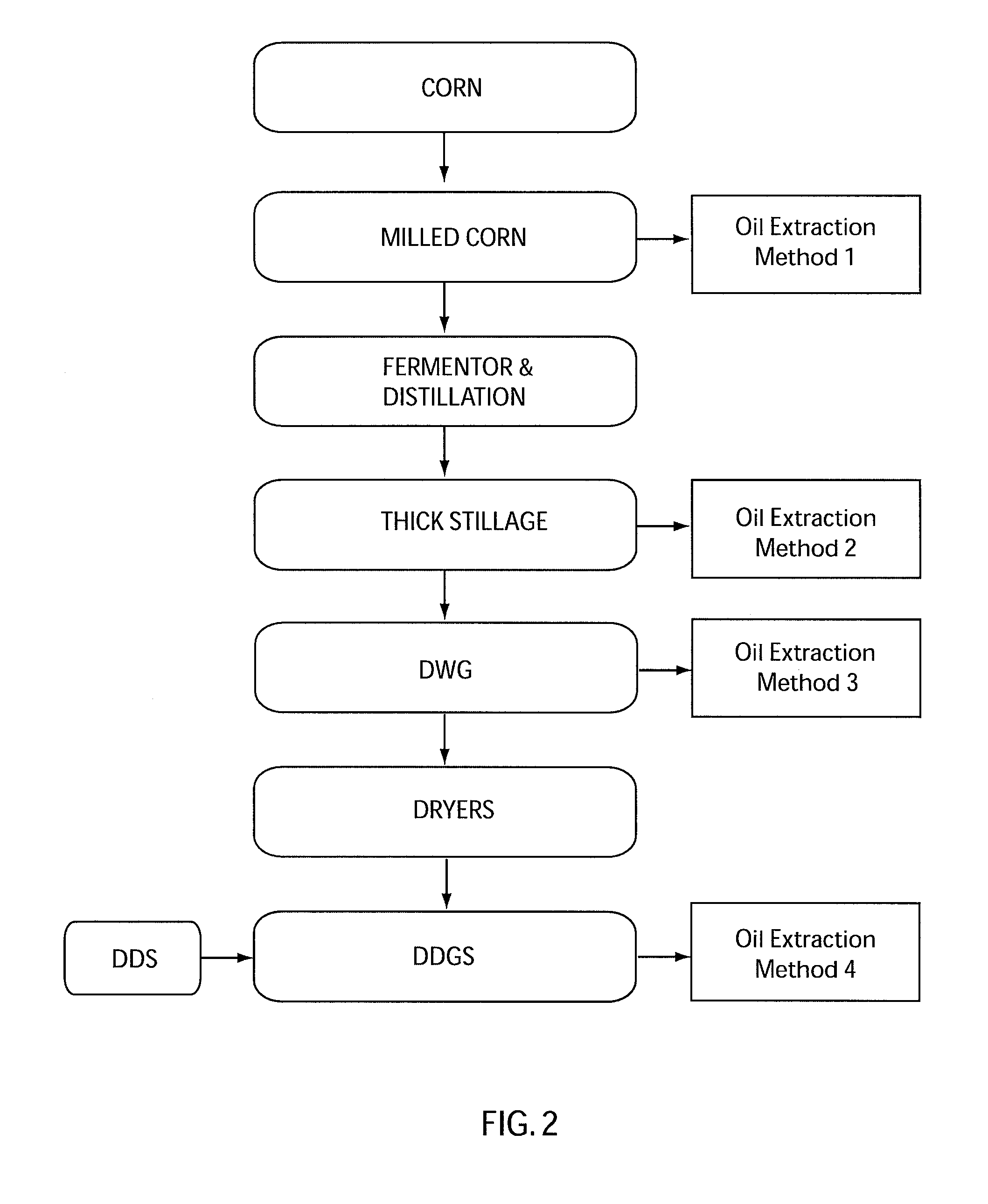
A corn oil extraction process is disclosed. The process includes the recovery of corn oil and other co-products, including but not limited to steam, electric power and chemicals, from an ethanol production process and in particular, a process that involves dry corn milling methods. The process involves extraction of oil from milled corn and residues from the fermentation step, including thick stillage, distillers wet grain, distillers dry grain and distillers dry grains with solubles, by the application of an alkyl acetate, phase separation and recovery of the separated matter. A process of drying wet co-product using ethanol and carbon dioxide from the production facility is also disclosed.
Owner:GROWMARK
Method for preparing flour doughs and products made from such doughs using lipase
InactiveUS6852346B2Improve the immunityLess-prone to mechanical deformationFungiDough treatmentPore diameterSpecific volume
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Process for the production of animal feed and ethanol and novel animal feed
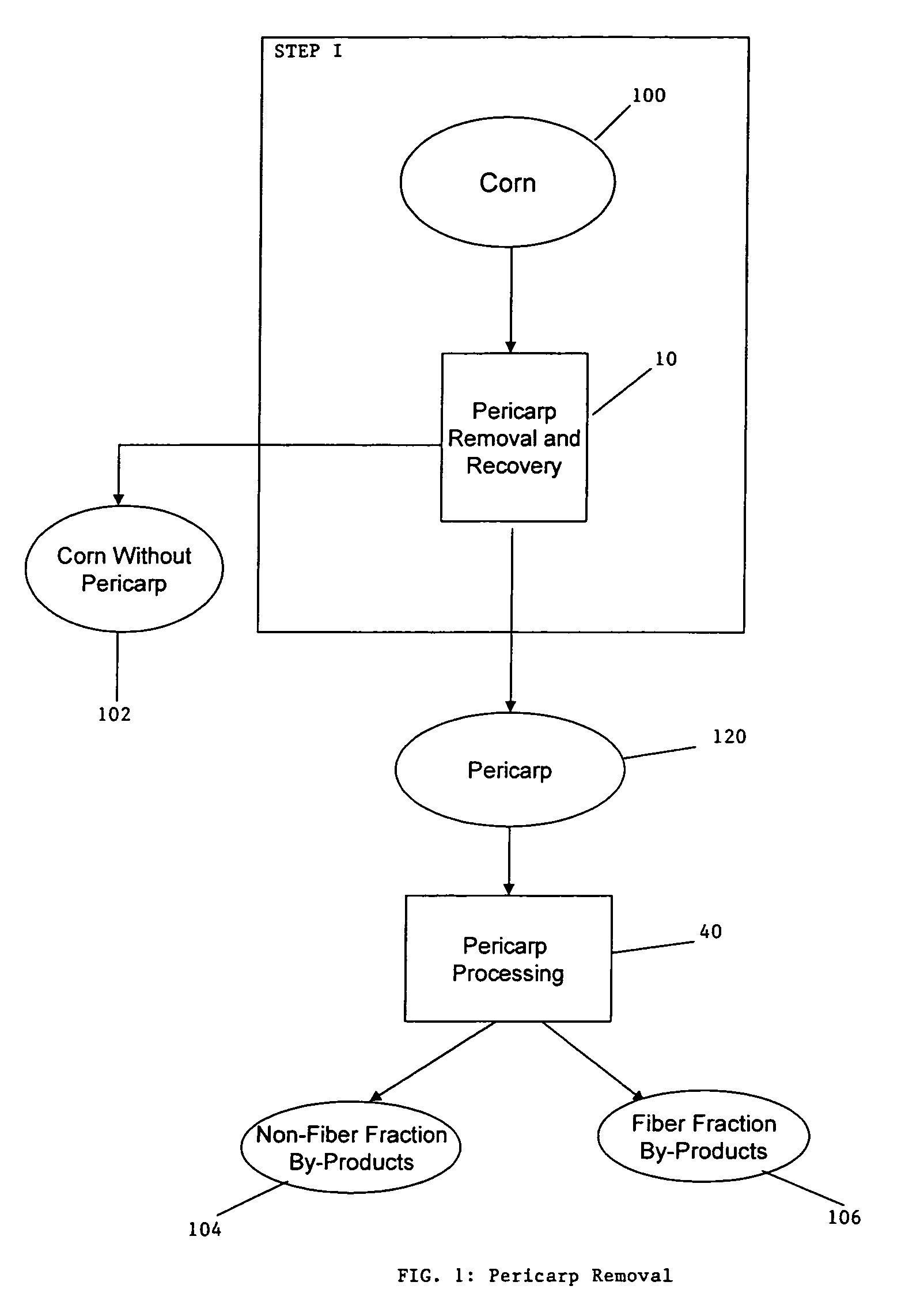
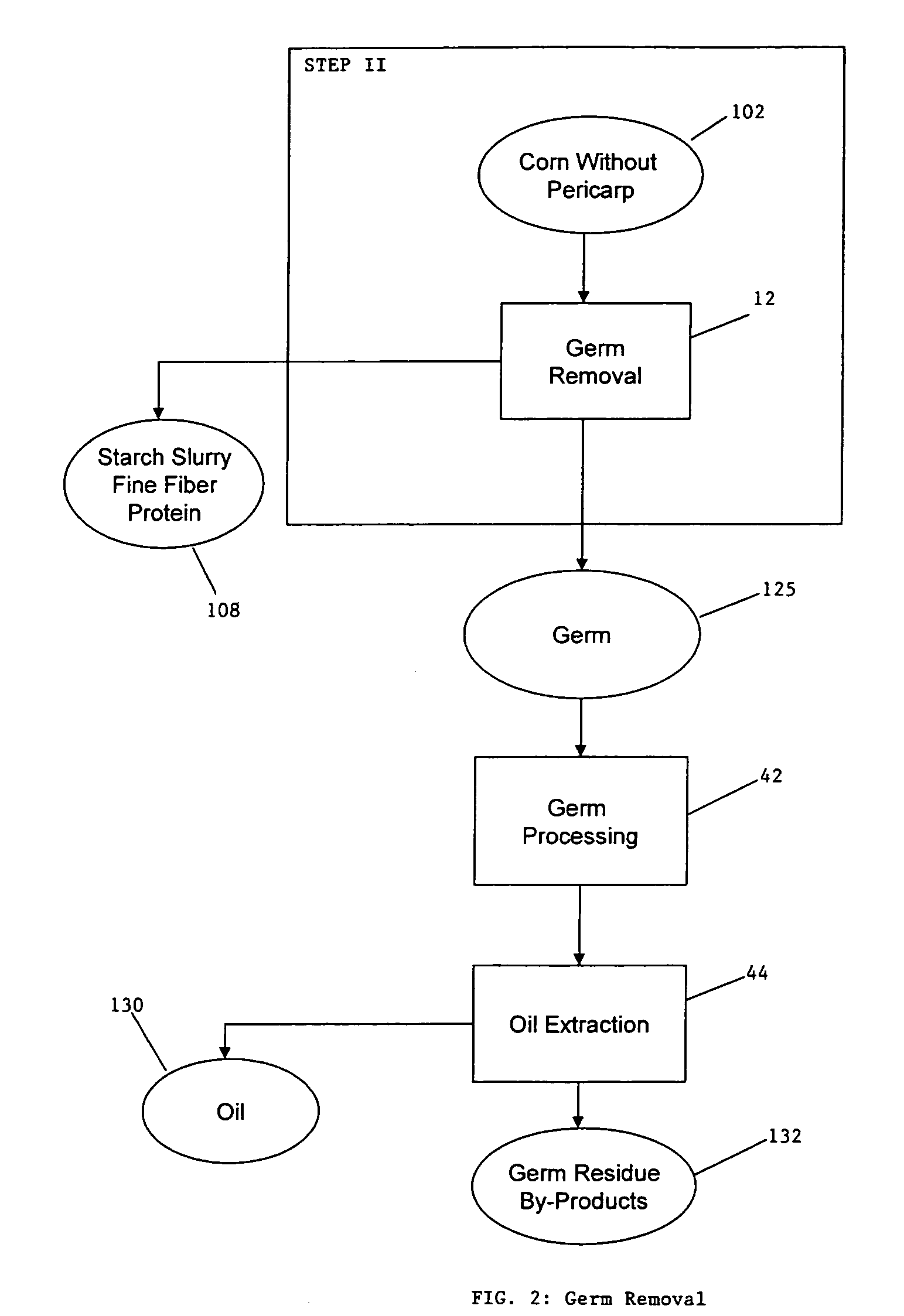
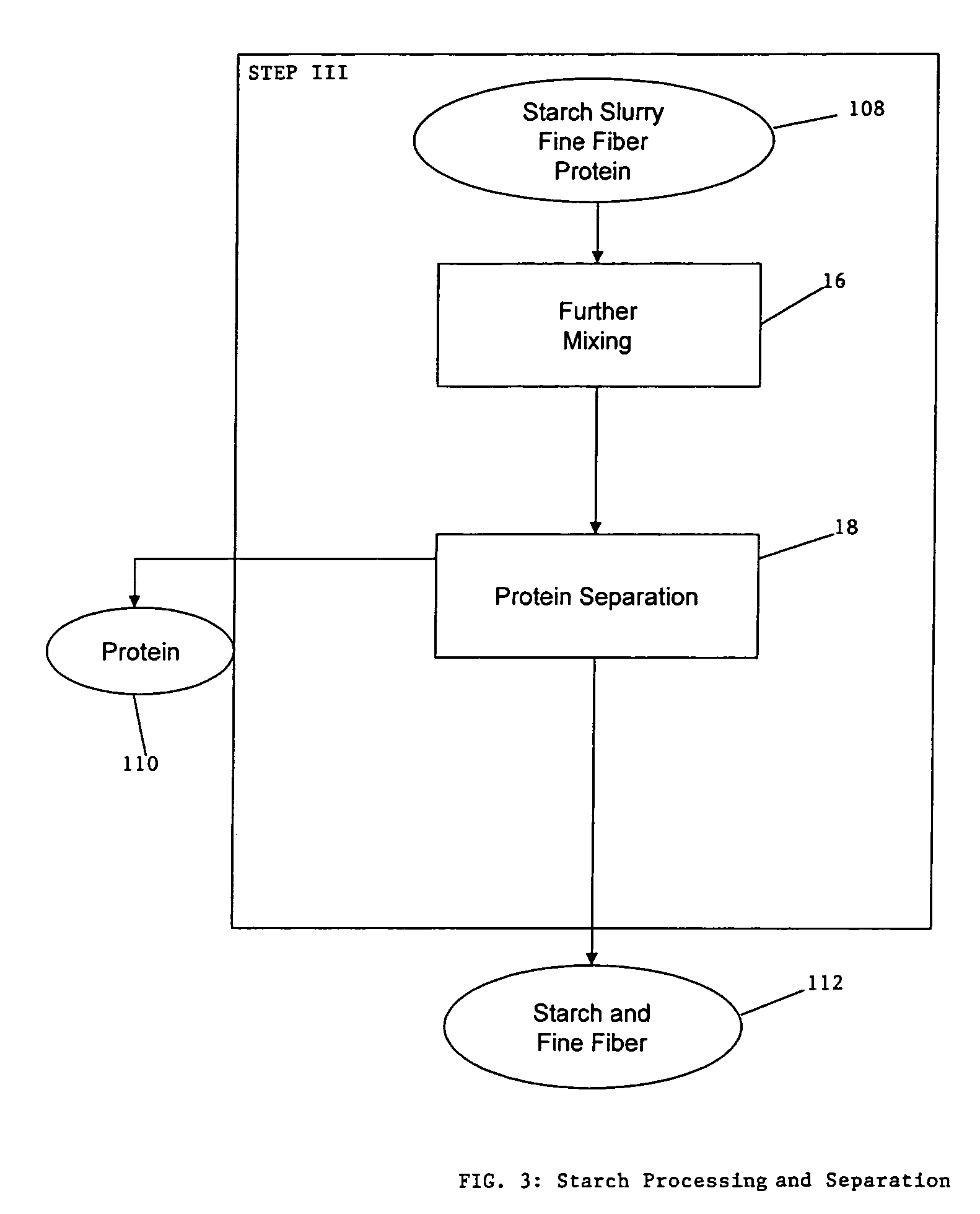
A method for the production of ethanol and a modified animal feed is provided. The method replaces the starch in known corn-based animal feed with biomass fiber treated to make it more digestible by animals. The process includes wherein the pericarp and germ are removed from the corn kernel and processed for by-products. The starch and protein are also removed and separated. The starch is then fermented and distilled to ethanol and stillage. The bioavailable modified animal feed comprises the pericarp and germ removed from corn kernels and optionally by-products of the pericarp and germ processing, and lignocellulosic materials. The modified animal feed may optionally include energy materials such as animal and vegetable fats, vegetable soapstocks, or glycerin, and combinations thereof.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
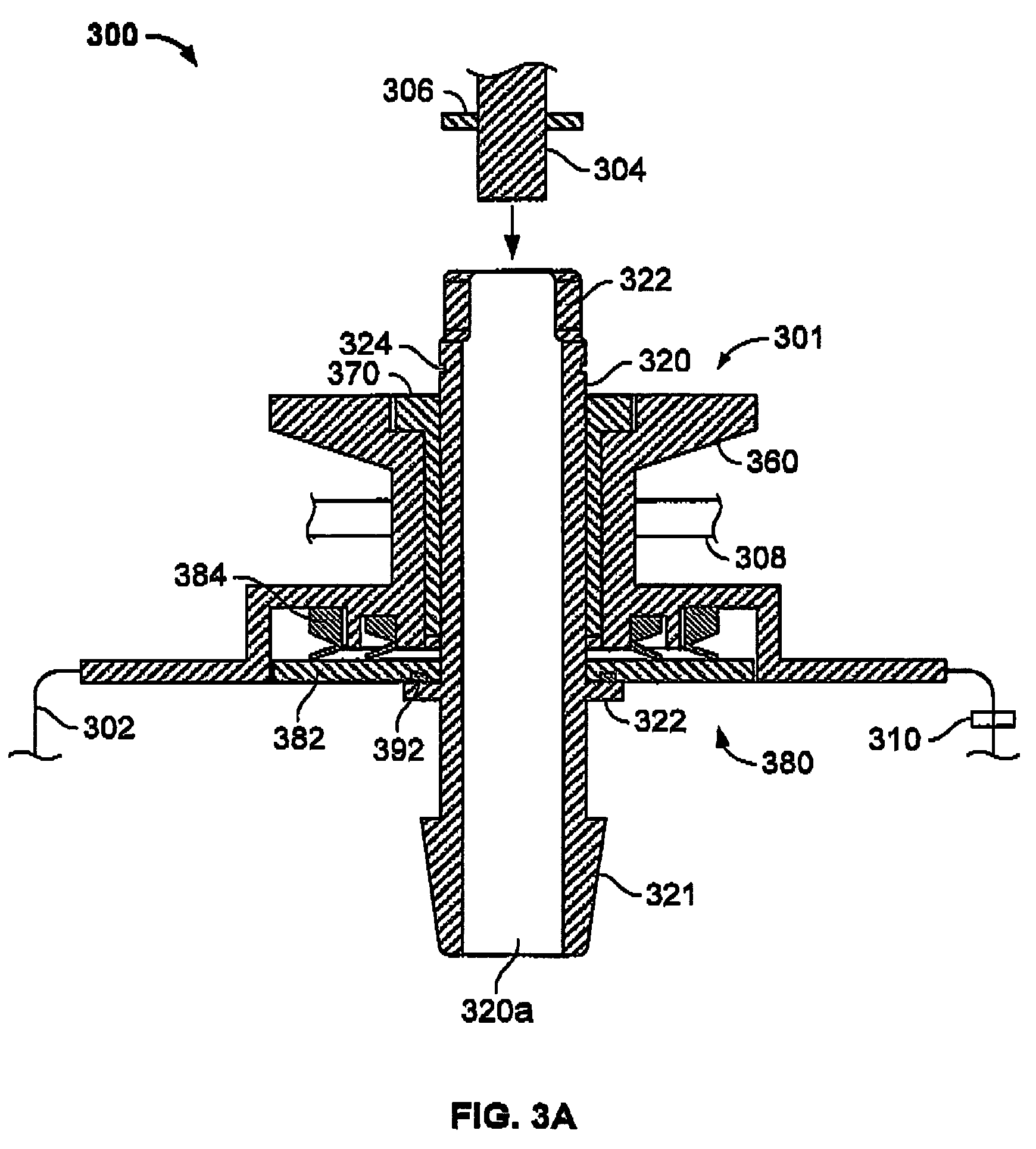
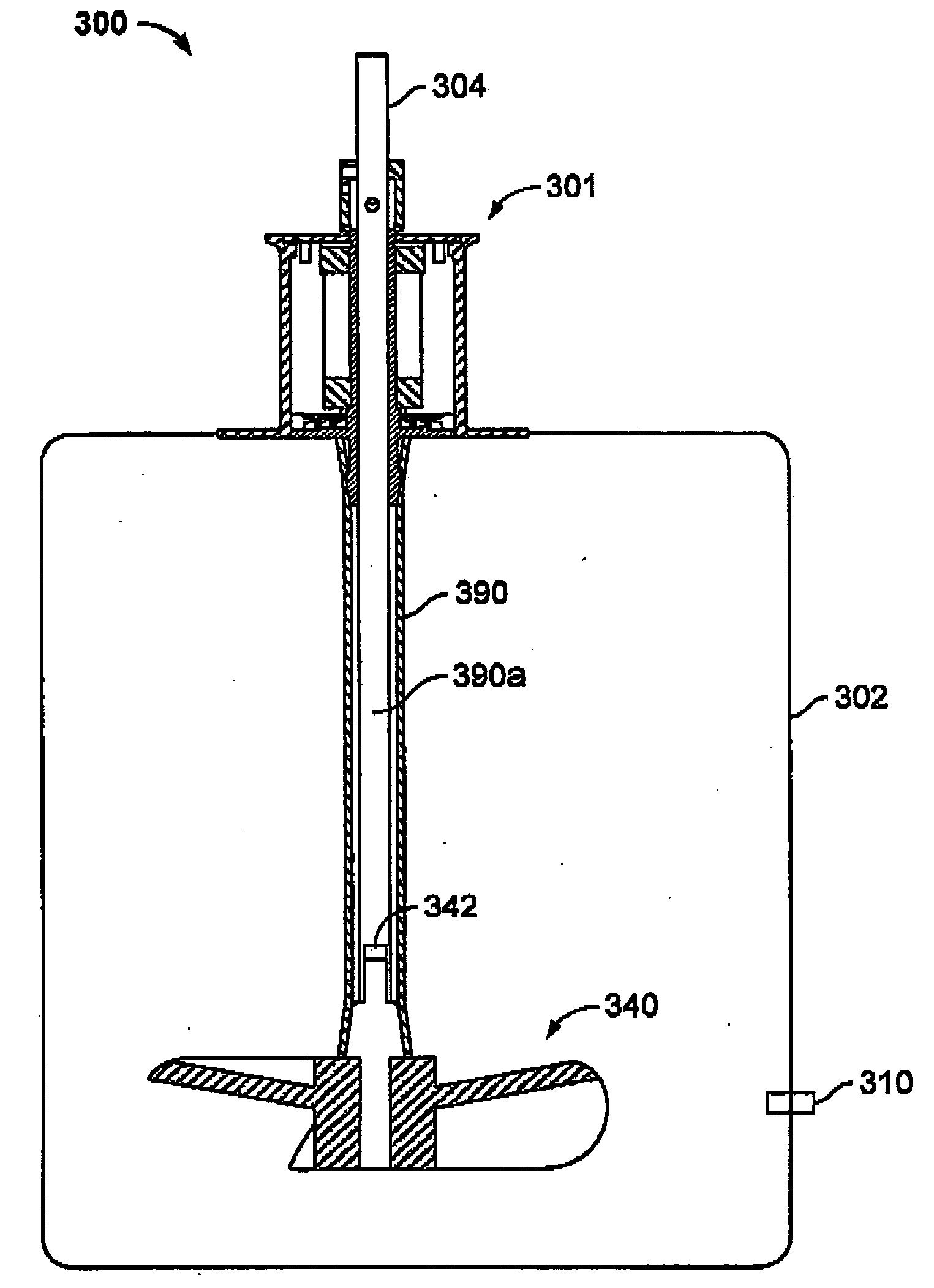
Bioreactor for growing cell or tissue cultures
ActiveUS20060019388A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMetaboliteCultured cell
The invention relates to a bioreactor comprising a chamber for containing cells or tissue cultures within a culture medium. The bioreactor also comprises a detector capable of detecting a change in one or more metabolites associated with growth of the cell or tissue cultures within the chamber and a chamber drive capable of rotating the chamber at a first speed about a first axis and a second speed about a second axis, the second axis being disposed at an angle relative to the first axis. In use, the magnitude of the first speed and the second speed are independently variable of each other.
Owner:SINGAPORE POLYTECHNIC +1
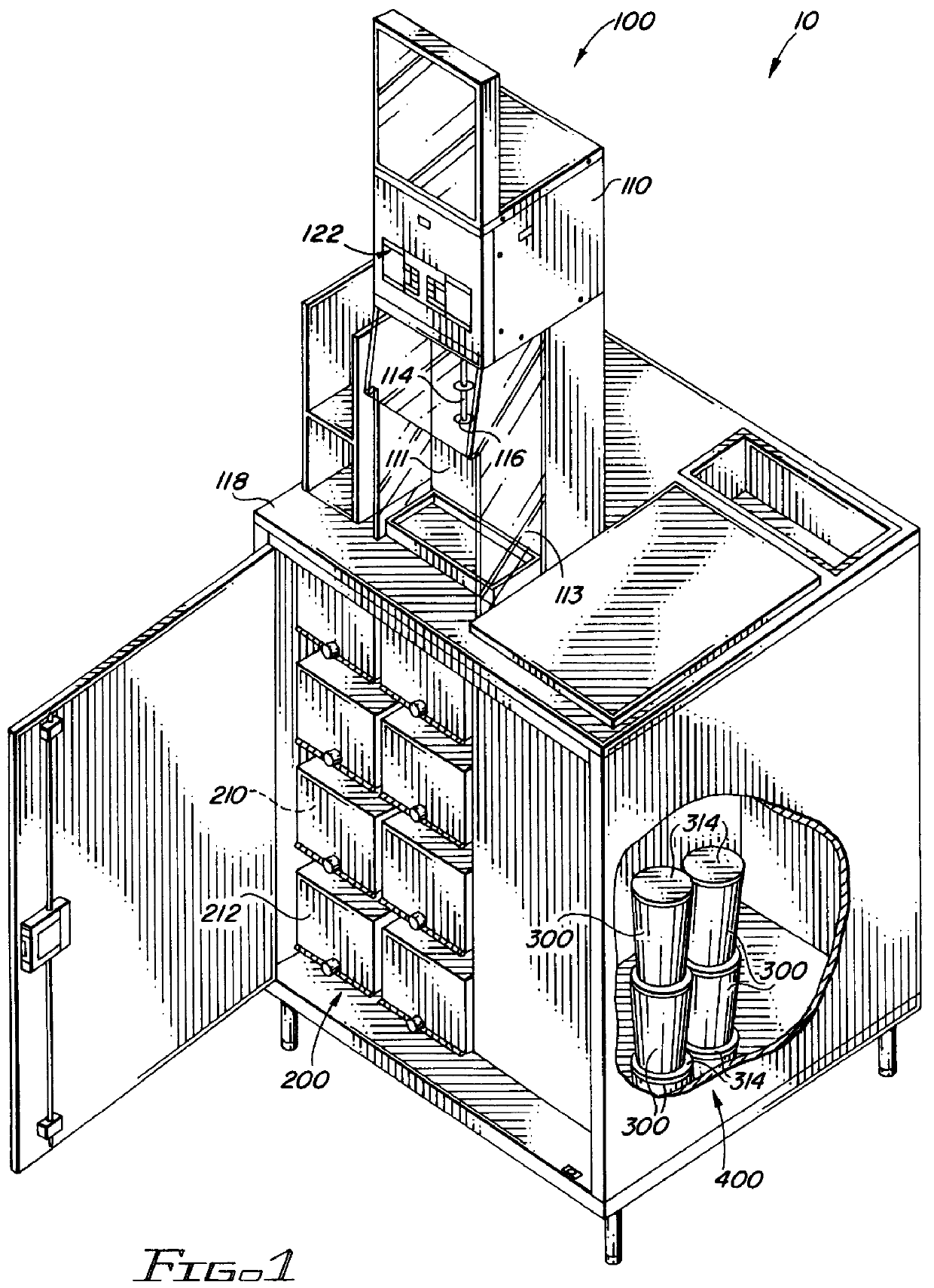
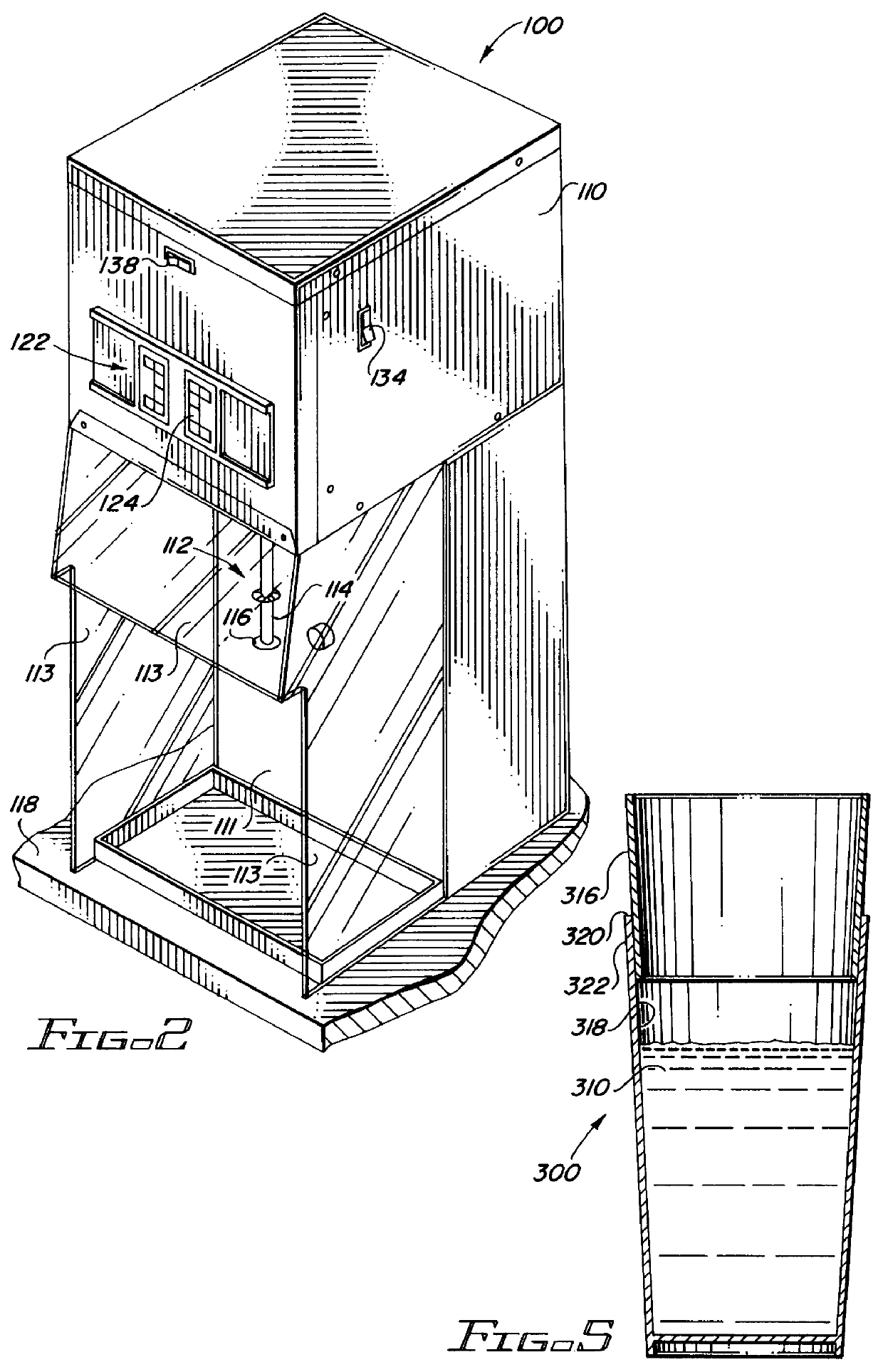
Apparatus for and method of making a frozen confectionery product
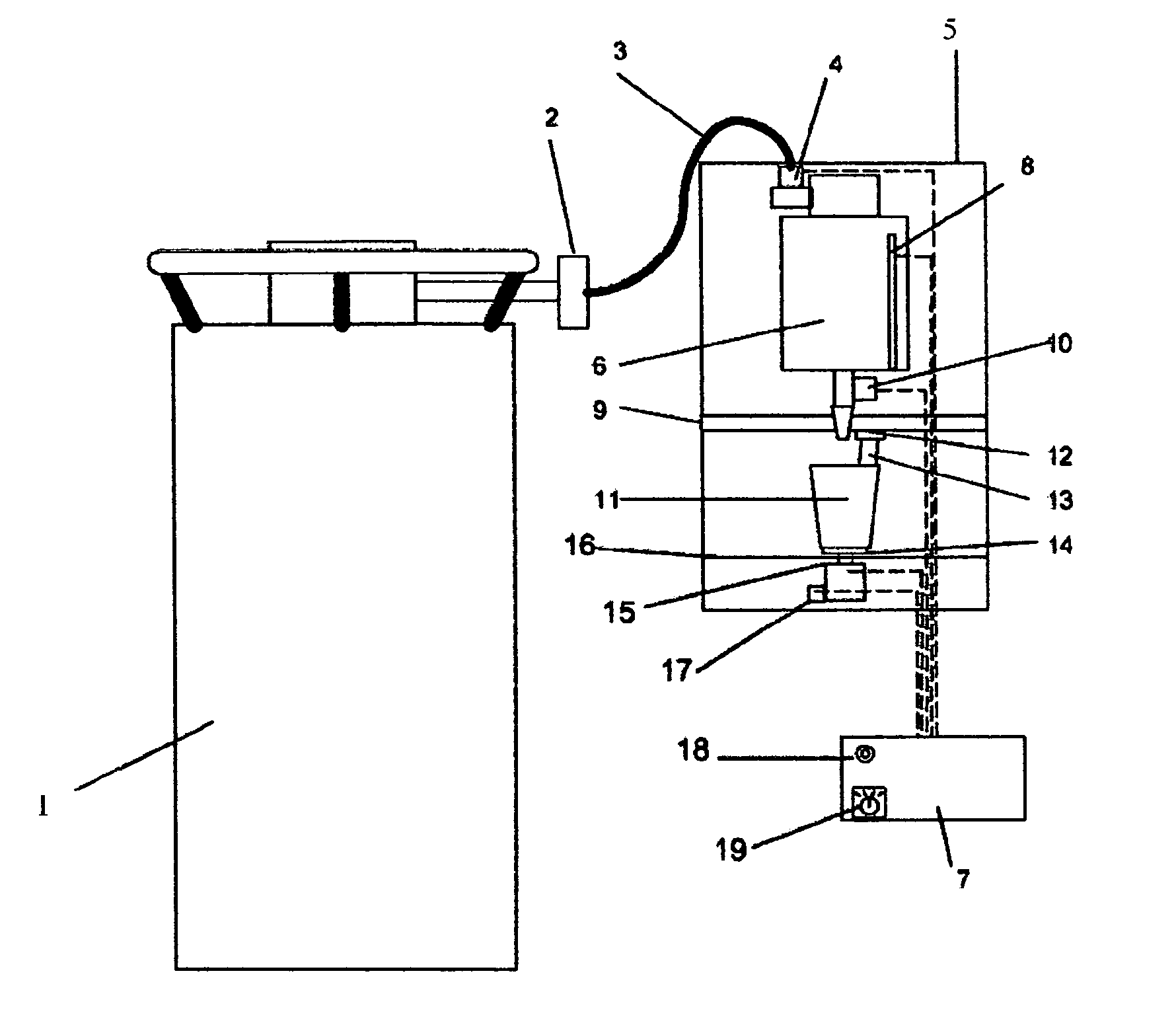
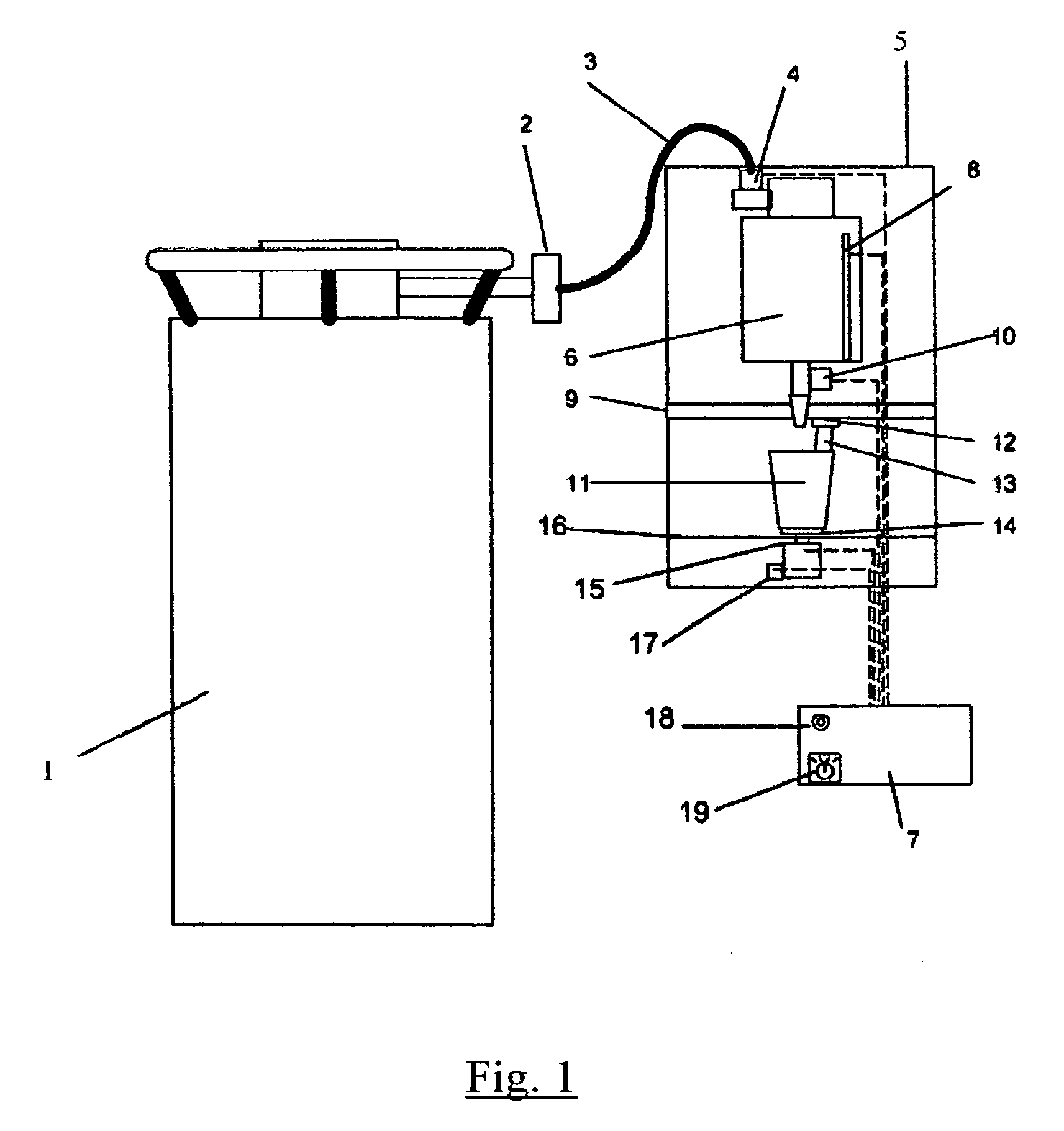
ActiveUS20060110515A1Short timeAvoid cross contaminationMilk preservationWort preparationEvaporationRelative motion
Apparatus for producing a serving of frozen confectionery product is characterized by a supply of liquid gas, a support for removably carrying a disposable container that holds a volume of unfrozen confectionery mix, and a holder for releasably holding a disposable agitator, such that the agitator extends into confectionery mix in the container. A valve controllably dispenses liquid gas into the confectionery mix in the container while relative motion is imparted to the container and agitator to agitate and admix the confectionery mix and liquid gas while the liquid gas mix evaporates to cool and freeze the confectionery mix, through a transfer of heat from the confectionery mix to the liquid gas and through the latent heat of evaporation of the liquid gas, to produce the frozen confectionery product.
Owner:SMITTEN VENTURES
Whole grain non-dairy milk production, products and use
ActiveUS20070014892A1Increase coverageReserved functionDough treatmentWort preparationSlurryWhole milk
A method comprising selection of unbroken whole grain rice that are first washed, or whole grain corn that is first reduced in size, and then making an aqueous slurry that is subsequently wet milled to release all the protein, fat, fiber, and starch components normally held in the structure of the grain. The resulting slurry can be reacted with heat to gelatinize the starch and the subsequent product dried. Also, the heated slurry containing the liberated components can be treated to enzymatic hydrolysis via the process of liquefaction and optionally saccharification, producing whole grain rice milk products having diverse carbohydrate compositions. The whole grain milk products are characterized by a nutritional composition containing substantially all the nutritional components of the whole grain, being an opaque whole milk colloid, having smooth texture versus pulpiness, lacking in all bitterness normally associated with whole grain products, and having a variety of sweetness levels from non-sweet to very sweet.
Owner:STEUBEN FOODS
Method of treating a food object in an electrostatic field
Owner:MARS COMPANY
Process for manufacturing chewable dosage forms for drug delivery and products thereof
ActiveUS7955632B2Without risk of cross-contaminatingParticularly palatable to pet animalsOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryFood gradeAdditive ingredient
A palatable, edible soft chewable medication vehicle for delivery of a pharmaceutically acceptable active ingredient, such as a drug, to an animal or human subject. The edible soft chews contain only food grade or better inactive ingredients, and preferably do not contain ingredients of animal origin. Processes for manufacturing the edible soft chews do not require the use of heat or the addition of water during mixing of active and inactive ingredients, provide stable concentrations of the active ingredient, and produce chews of consistent weight and texture.
Owner:ELANCO US INC
Biopolymer and methods of making it
The present invention relates to a composition, which can be referred to as a biopolymer, including fermentation solid and thermoactive material. The present invention also includes methods of making the biopolymer, which can include compounding fermentation solid and thermoactive material. The present biopolymer can be formed into an article of manufacture.
Owner:POET RES INC
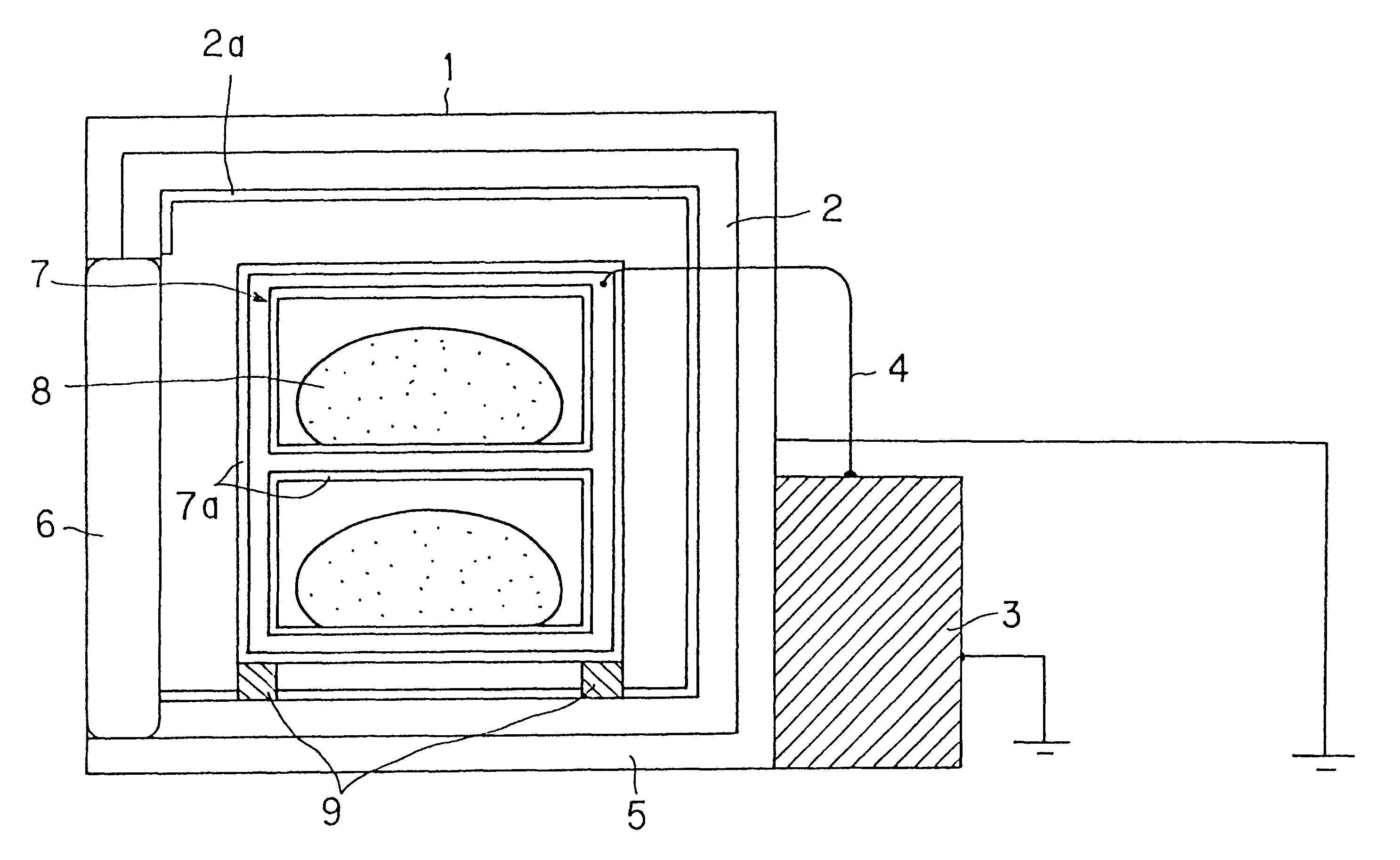
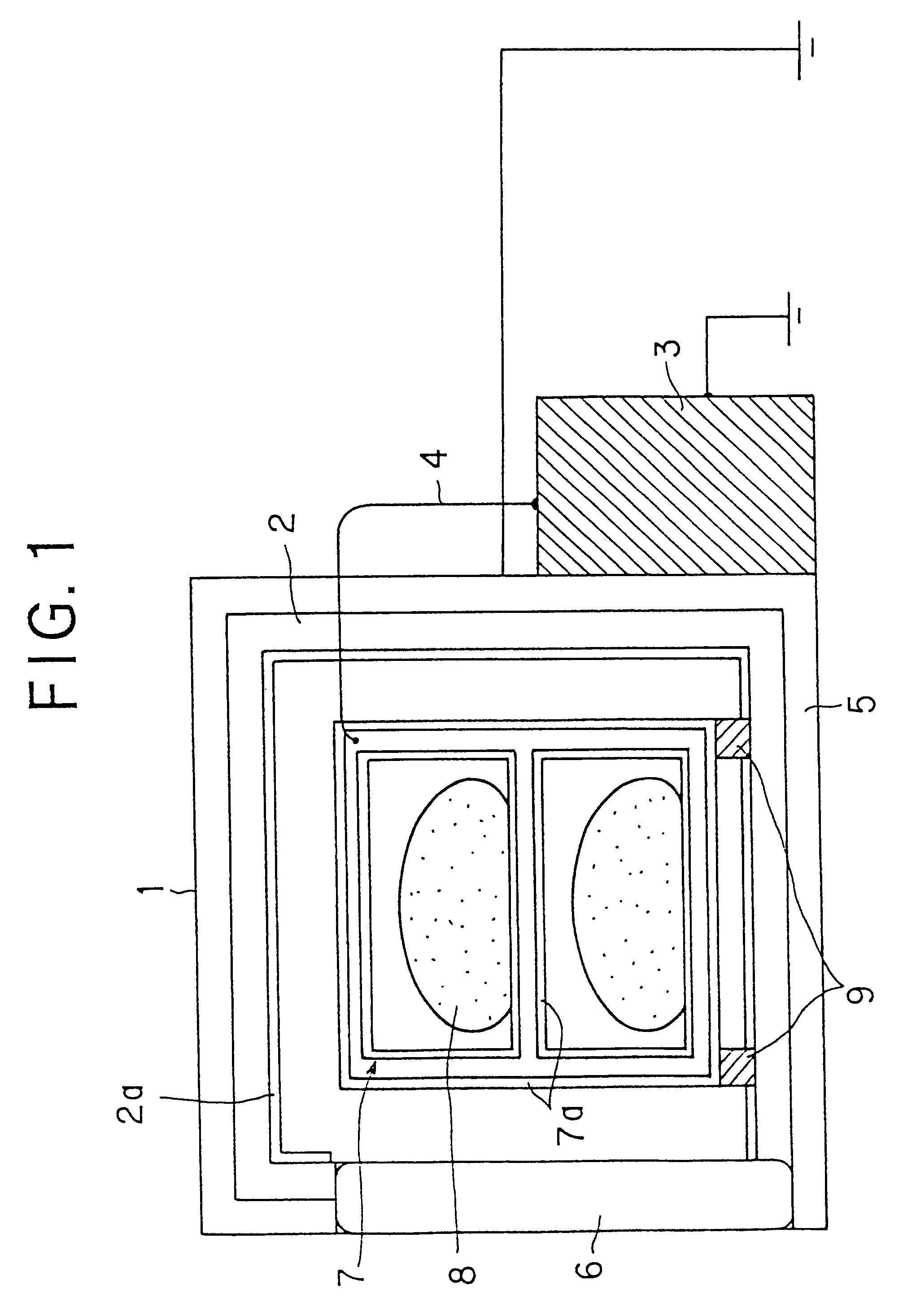
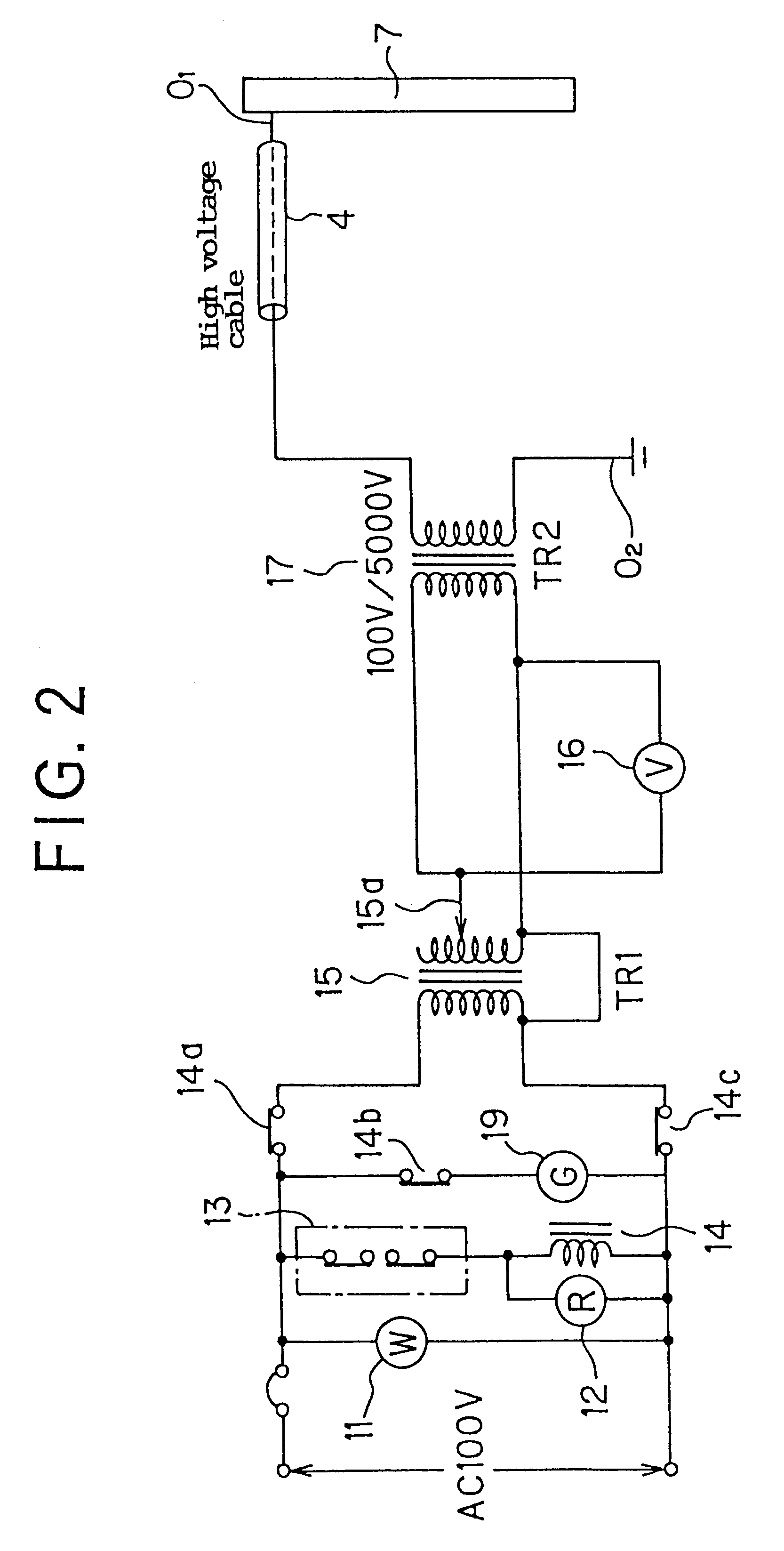
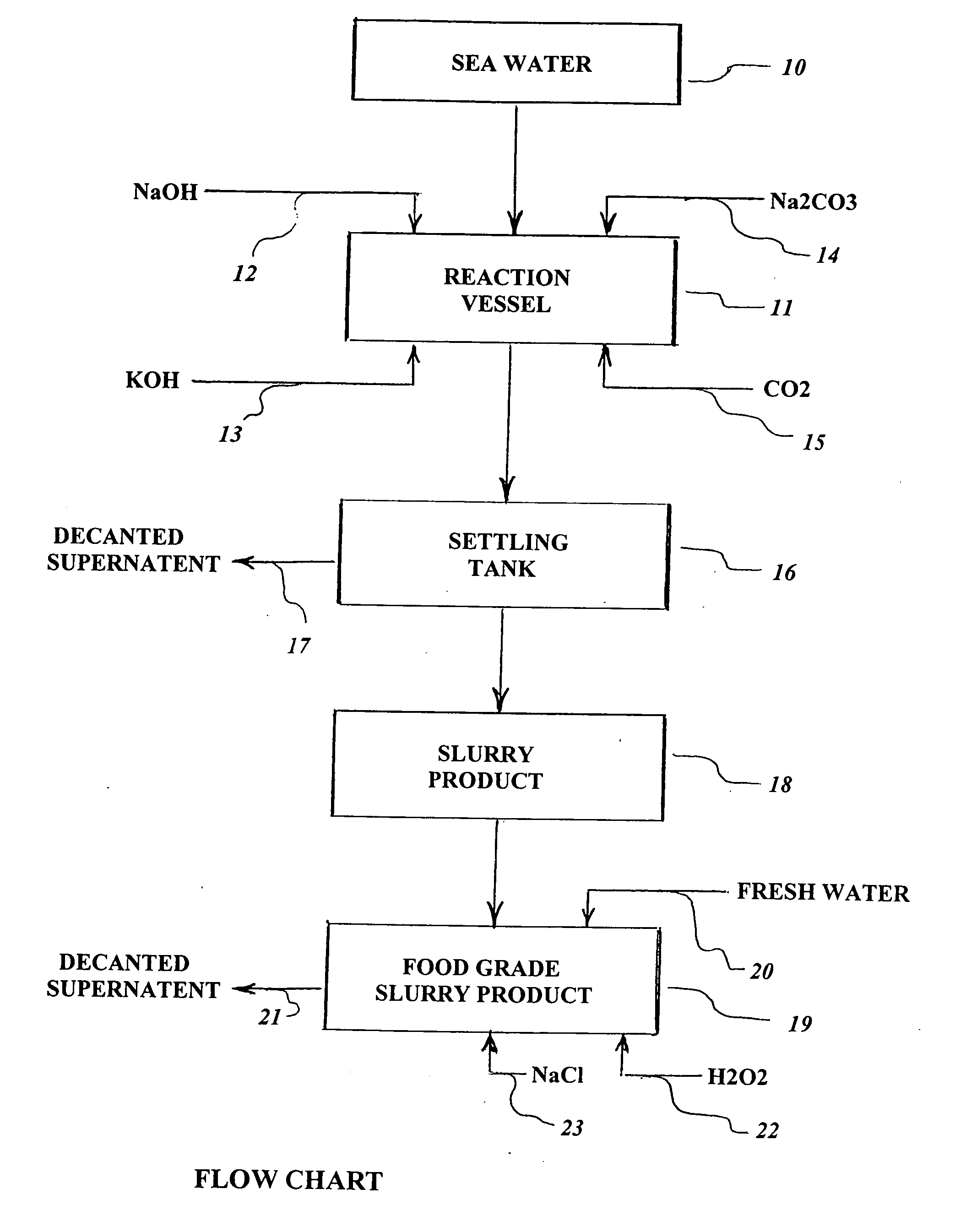
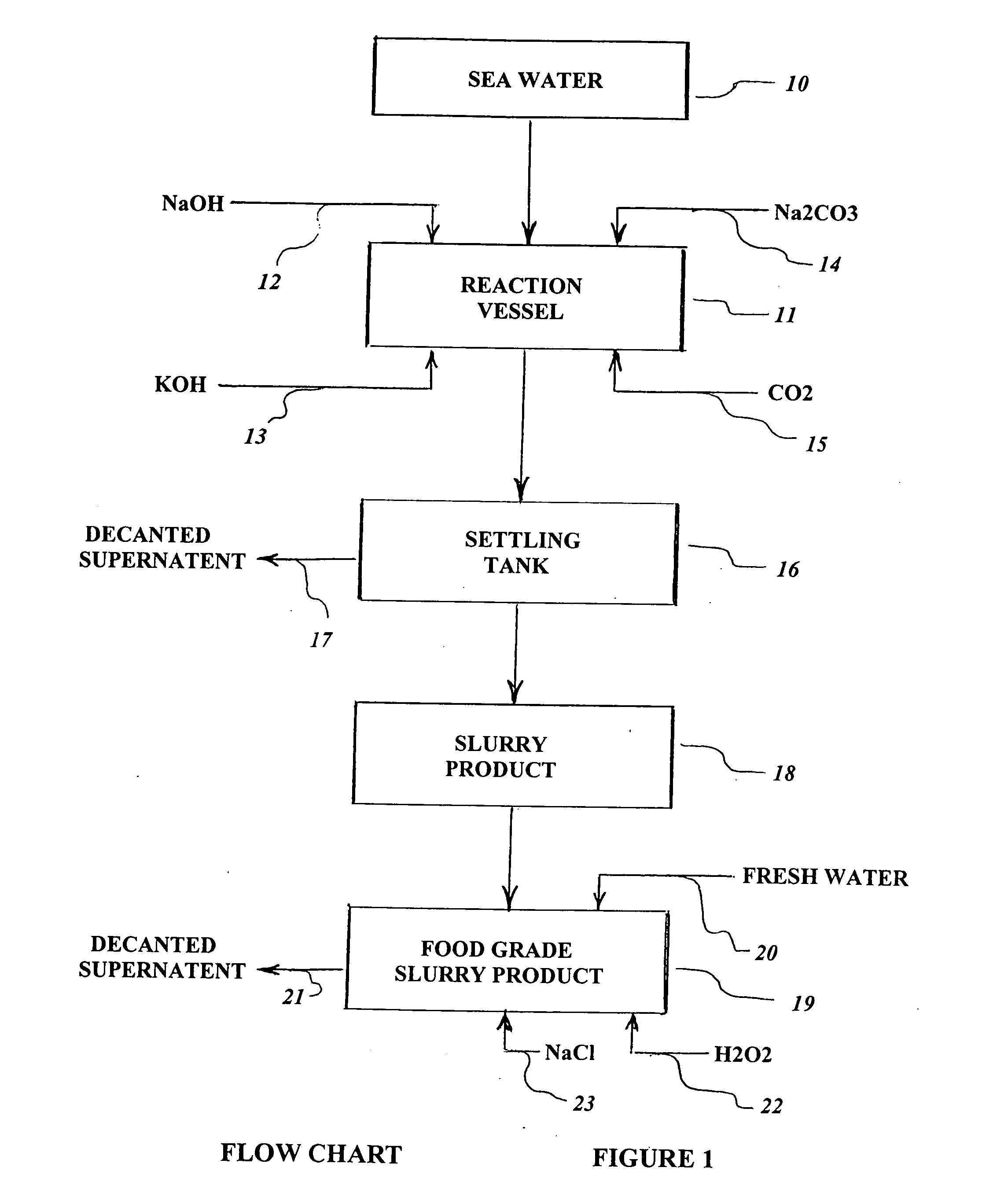
Method of producing useful products from seawater and similar brines
ActiveUS20060105082A1Increase in sizeHigh in sugarMagnesium fertilisersWort preparationParticulatesSlurry
A process is provided for the recovery of useful products, including fertilizers and nutritional supplements, from the organic matter and minerals contained in seawater and other brines. The dissolved organic carbon-based chemicals and suspended particulate carbon-based organic matter are co-precipitated together with the contained magnesium and / or calcium, along with incidental trace minerals, entrained water and water of hydration. Caustic soda (NaOH) and other alkali base or alkaline earth bases and / or carbon dioxide (CO2) are added to the brine until a pH of 10.75 to 11.0 is achieved. The settled or non-dry filtered or centrifuged precipitate is utilized as a slurry and the supernatant brine is discarded.
Owner:ZEIGLER ARTHUR WILLIAM
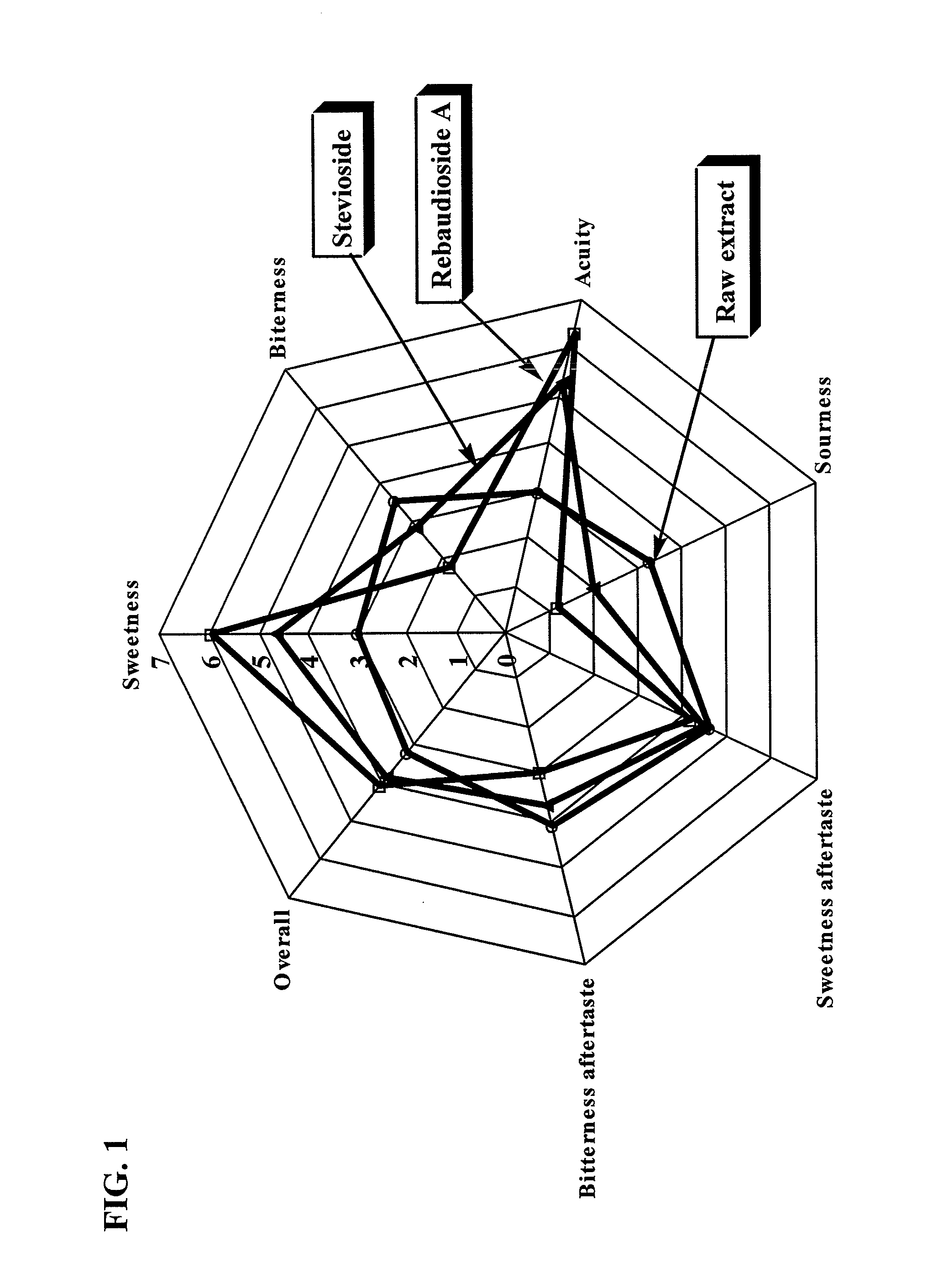
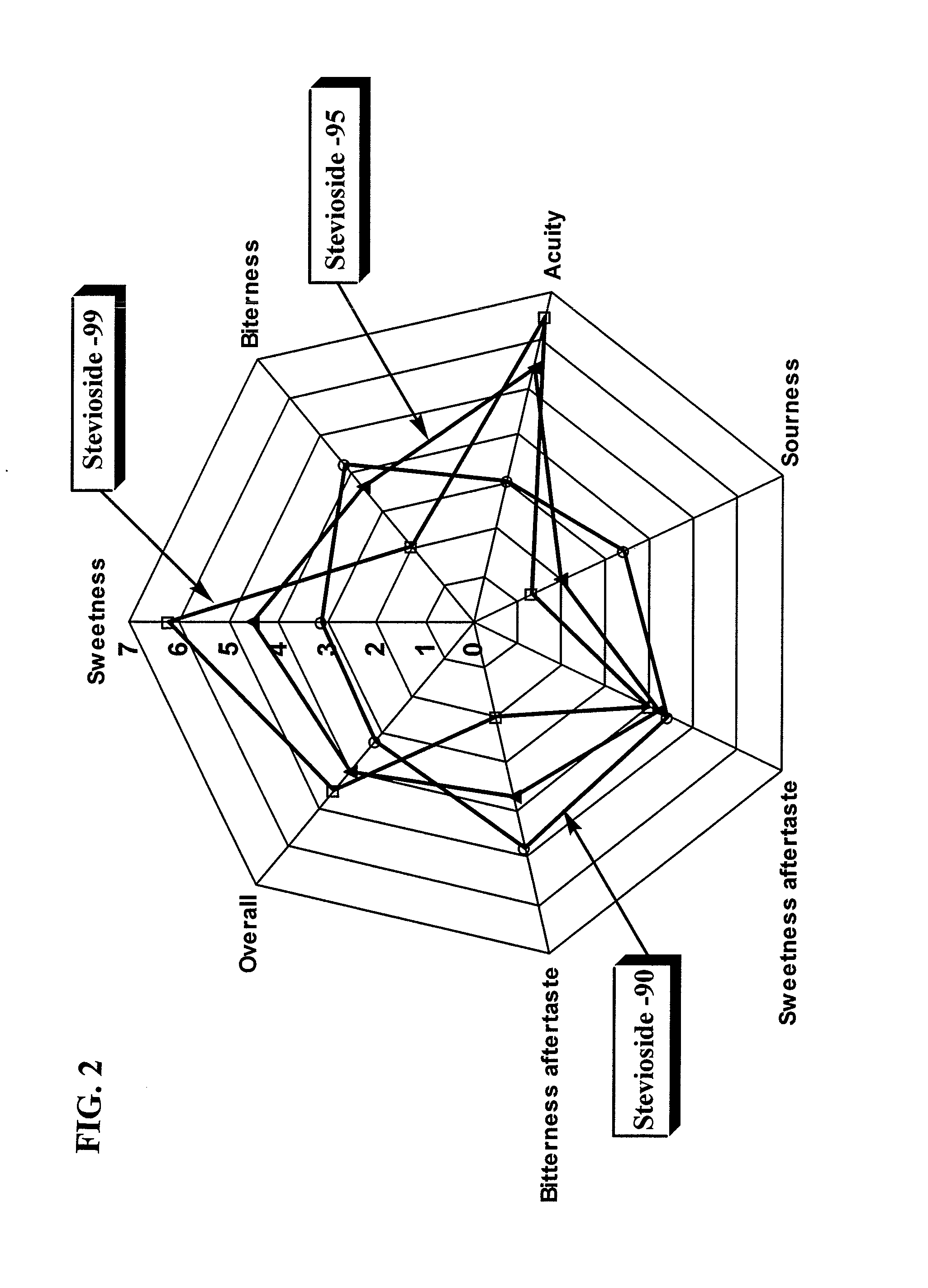
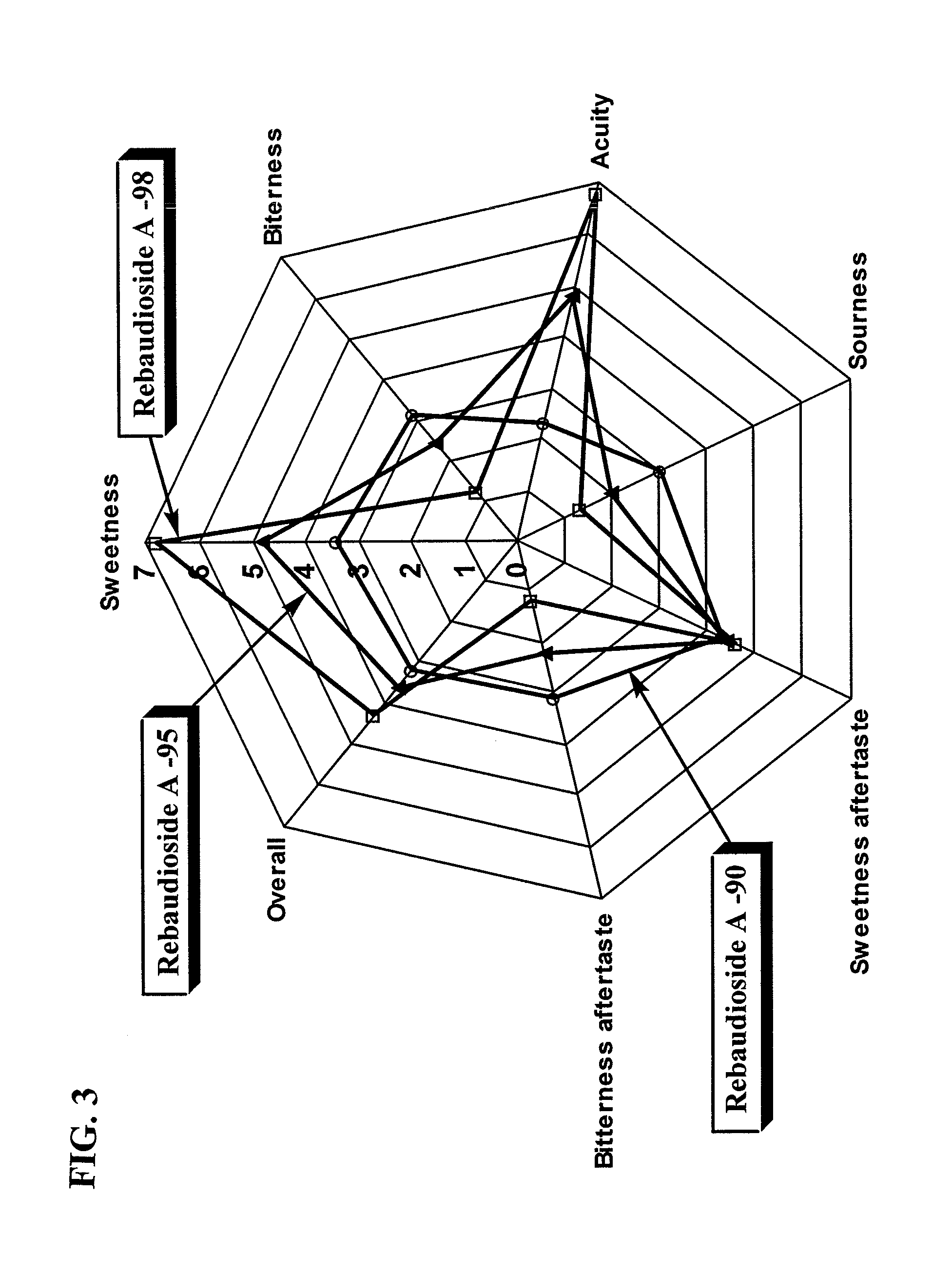
Process for Manufacturing a Sweetener and Use Thereof
Highly purified Stevioside, Rebaudioside A and a purified sweet steviol glycoside mixture were prepared from sweet glycoside extracts obtained from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni leaves. The resulting sweeteners are suitable as non-calorie, non-cariogenic, non-bitter, non-lingering sweeteners, which may be advantageously applied in foods, beverages, and milk products.
Owner:PURECIRCLE SDN BHD
High temperature/ultra high pressure sterilization of foods
InactiveUS6207215B1Fresh lookAchieves commercial sterility of low acid food productsMilk preservationMeat/fish preservation by heatingUltra high pressureEngineering
Method for sterilizing foods using both ultra-high pressures and high temperatures. The instantaneous temperature change that occurs when pressure is applied combines a high-temperature short-time process with ultra-high pressure to deliver a fast and therefore gentle thermal process to a pre-packaged product. The process involves heating a food to a pre-pressurized temperature, subjecting the food to ultra-high pressure, which instantaneously raises the temperature of the food, and then releasing the pressure so that the temperature returns to the original pre-pressurized temperature. The method leverages the adiabatic temperature rise which occurs when the food is hydrostatically pressurized, coupled with the lethality of the pressure, to achieve appropriate sterilization conditions. The disclosure also includes foods which have been sterilized using both ultra-high pressures and high temperatures.
Owner:KAL KAN FOODS
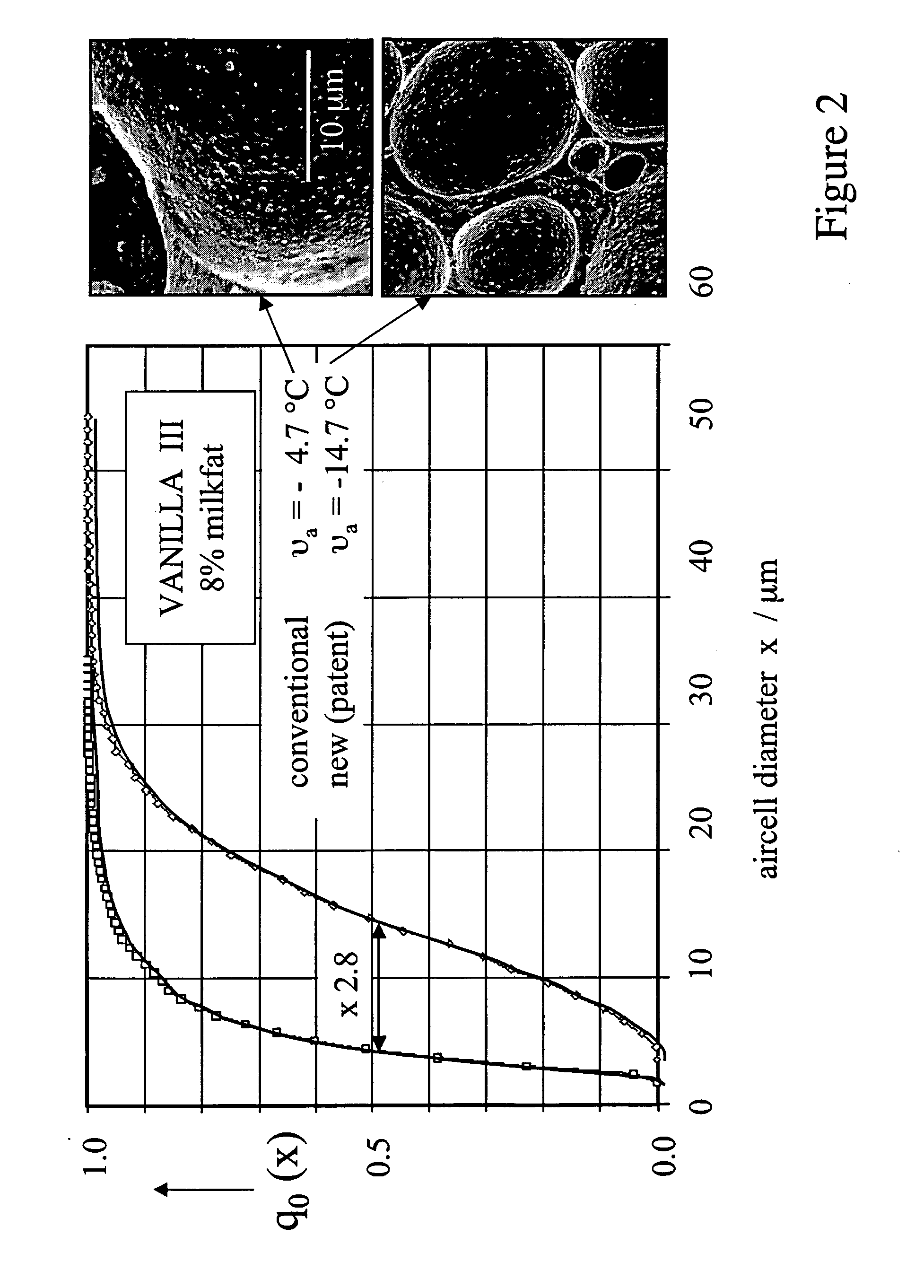
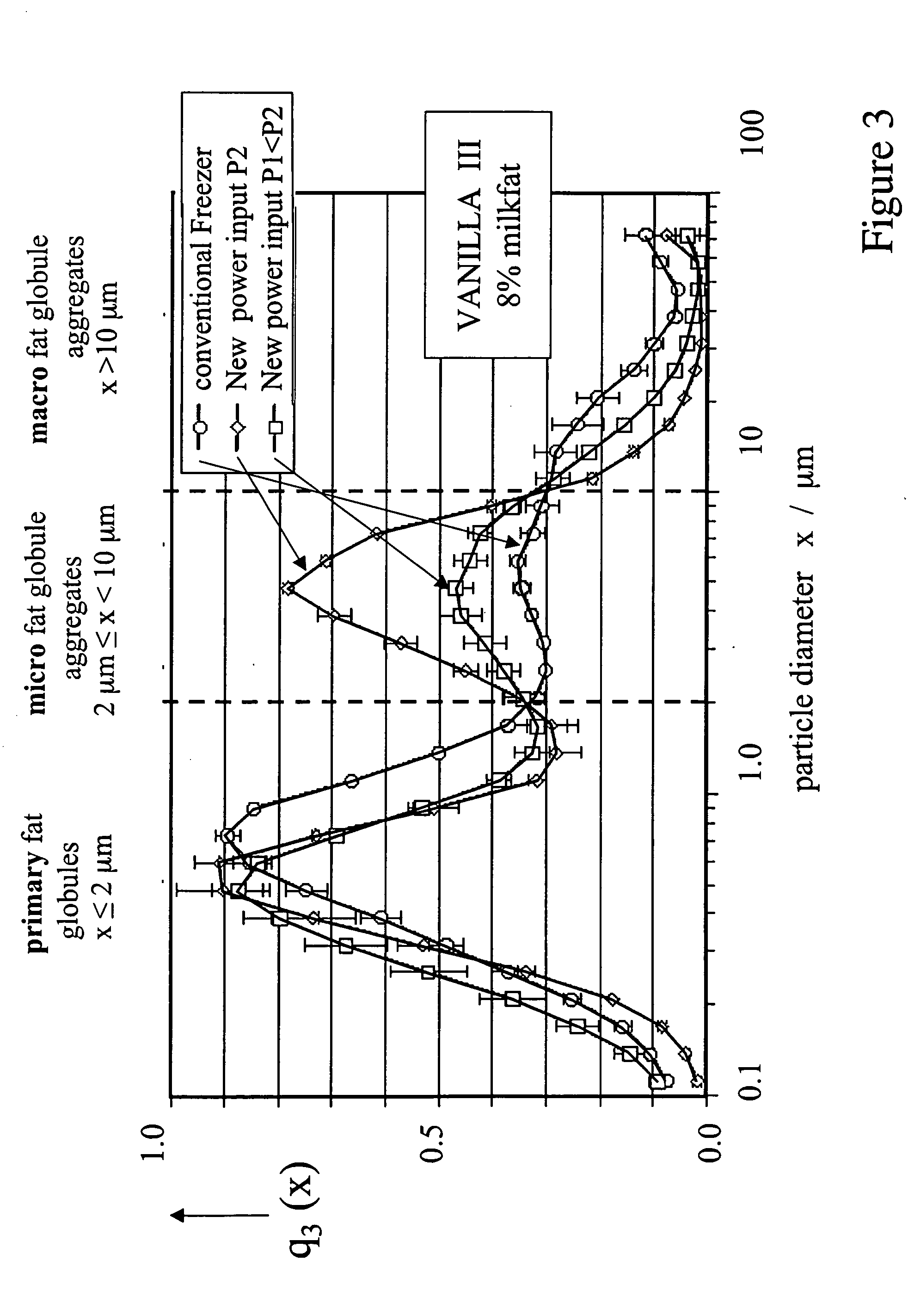
Aerated frozen suspensions with adjusted creaminess and scoop ability based on stress-controlled generation of superfine microstructures
Products that are aerated multiphase systems containing an aqueous continuous fluid phase which may include solutes thus forming an aqueous syrup and disperse phases like gas / air cells, water ice crystals and solid / semi-solid fat globules or aggregates thereof, whereas the disperse phases are that finely structured that their mean diameters are below phase specific critical maximum values and thereby generate a most preferred by consumers, full rich silky-creamy mouth feel at much lower fat content than usual in conventional related products like premium and super premium ice creams.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Method of preparing a multi-flavored shake
InactiveUS6126983AEfficiently and effectively preparingMinimize storageRotary stirring mixersFrozen sweetsEngineeringFood flavor
A flavored shake drink is prepared from a prepackaged neutral flavored mix stored within a serving cup. A flavored syrup is selected and dispensed through a dedicated nozzle carried by a housing. Each of a plurality of nozzles is in fluid communication with a corresponding solenoid control valve which controls the flow of the selected syrup pumped from a bag-in-the-box styled reservoir. One reservoir is provided for each of the selected flavors. A manually activated programmable timer controls the length of time that the solenoid activated valve remains opened thus providing a preselected amount of syrup into the cup. Switches are provided for doubling and halving the amount of the preselected quantity of syrup when creating varying single flavored and combination flavored shakes. In addition to shielding provided around the blender spindle carried by the housing for maintaining the surrounding area in a clean condition, a protective sleeve is placed within the cup for limiting the amount of mix splashed from the cup during blending of the selected syrup and neutral flavored mix. Prior to adding a selected syrup, the cup of unflavored mix is stored in a tempering freezer where it is maintained at a pre-selected temperature suitable for providing desirable blending of the syrups with the mix.
Owner:ARCHIBALD BROS FINE BEVERAINC
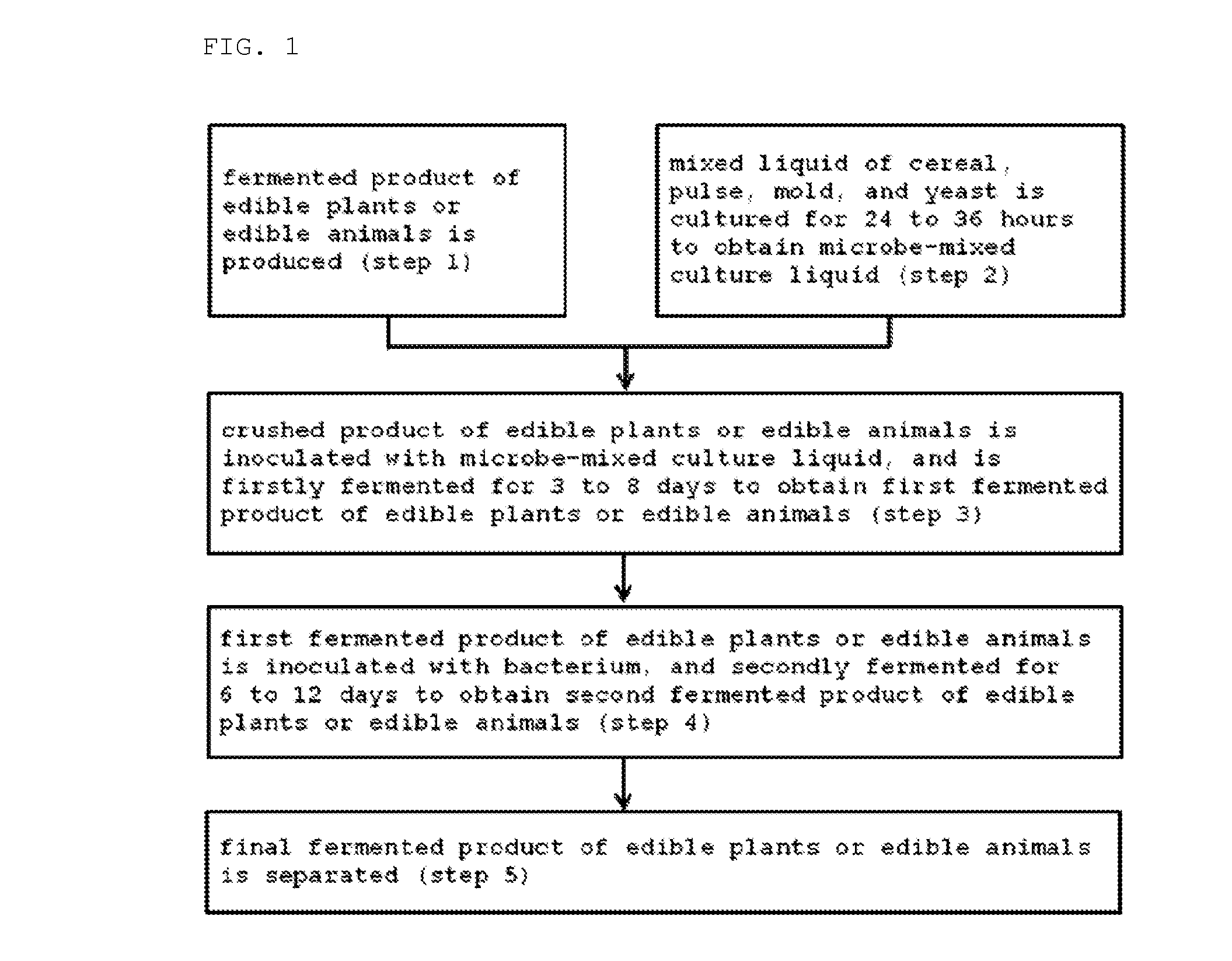
Method for producing fermented edible plants or edible animal/plants, fermented edible plants or edible animal/plants produced by same, and foods containing same
ActiveUS20100316763A1Increase heightPrevent invasionDough treatmentEdible seed preservationFood flavorOrganism
The present invention relates to a method for producing fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants, to fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants produced by same, and to foods containing same. The method for producing fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants includes the steps of: producing crushed edible plants or edible animal / plants; culturing a liquid mixture of grains, saccharides, filamentous fungi, and yeast for 24 to 36 hours to produce a mixed microbial broth; inoculating the edible plants or edible animal / plants with the mixed microbial broth, and firstly fermenting the edible plants or edible animal / plants for 3 to 8 days to produce first fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants; and inoculating the first fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants with bacteria, and secondly fermenting the first fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants for 6 to 12 days to produce second fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants. Whereby, a fermentation period can be shortened, and food deterioration and the growth of pathogenic microorganisms can be suppressed. Further, adding the fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants produced by the above-described method into foods can provide storage stability, increase bioavailability, and improve flavor.
Owner:PHARVIS R&D KOREA
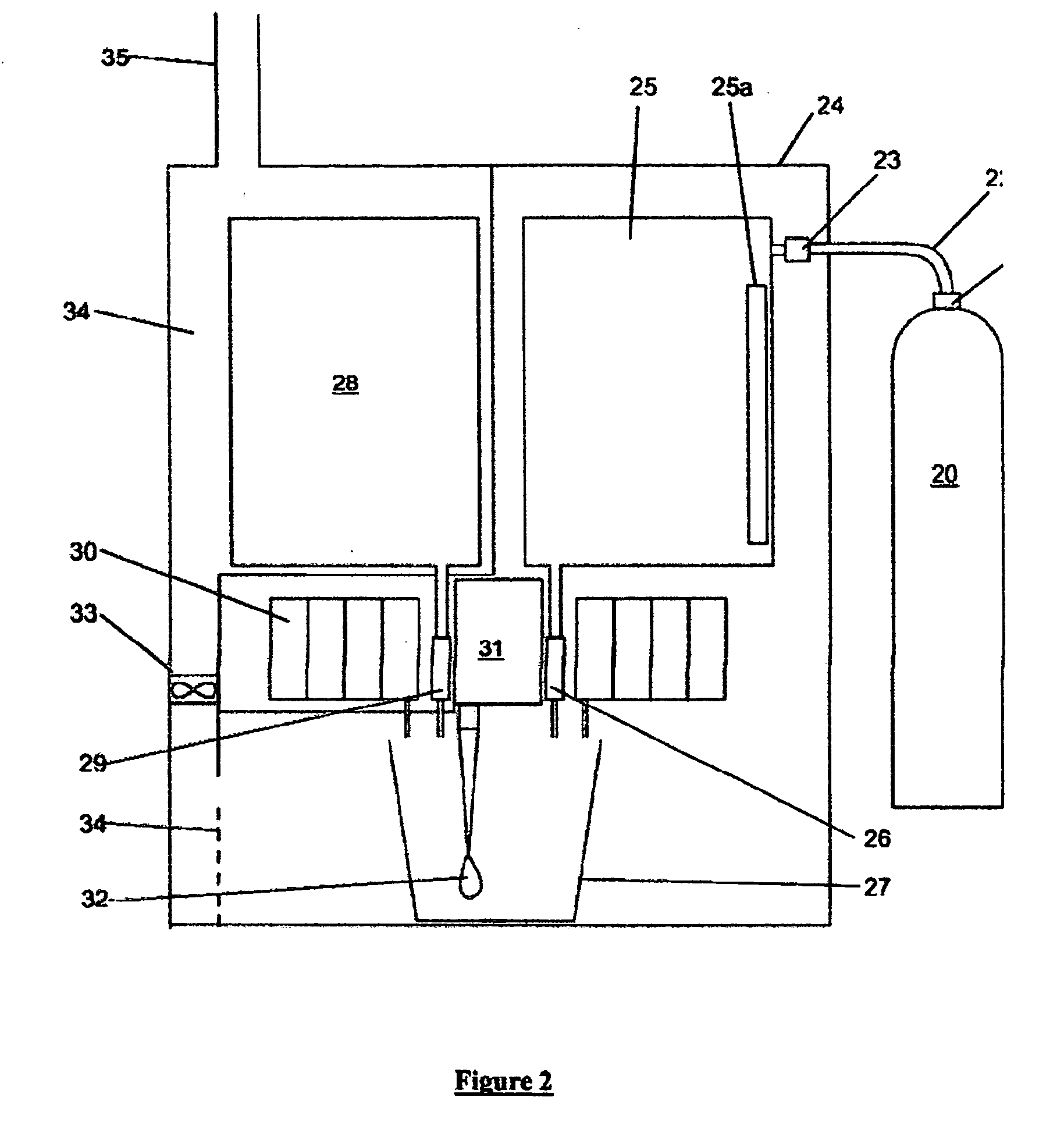
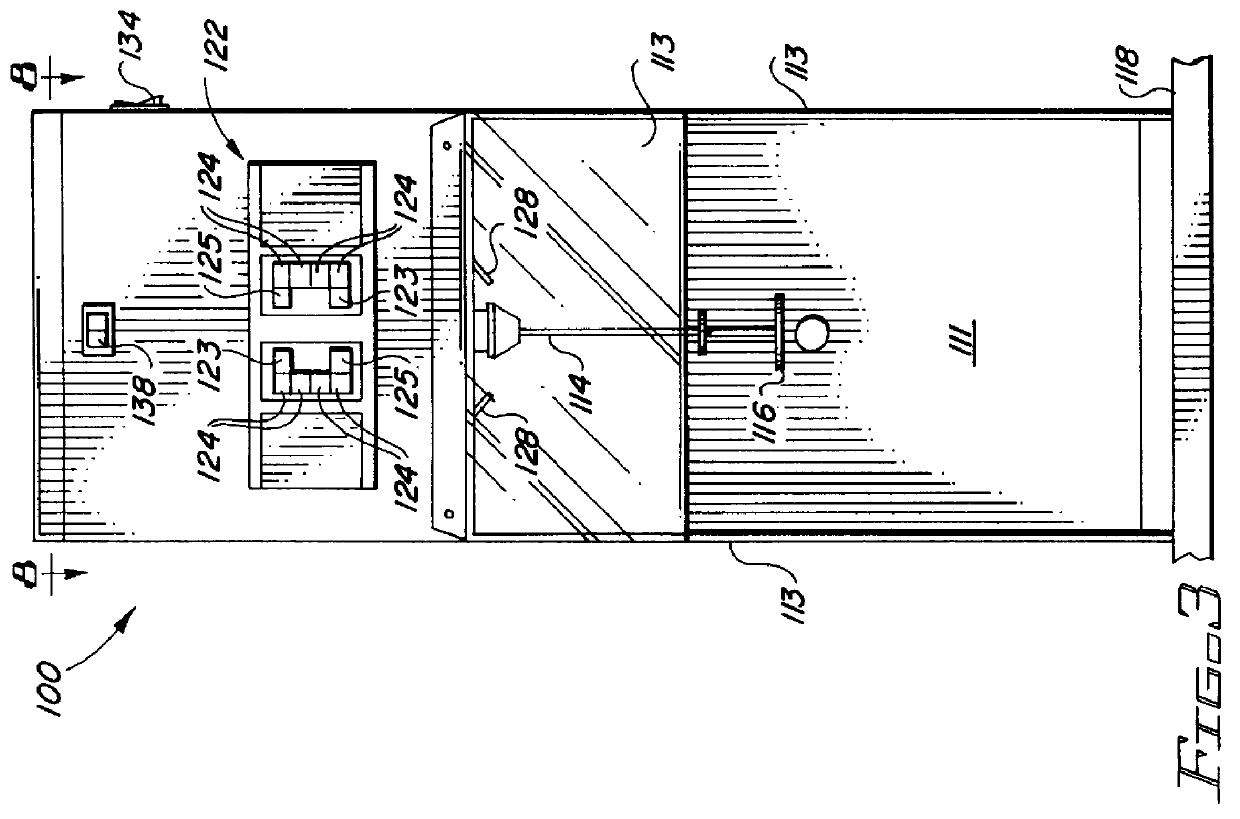
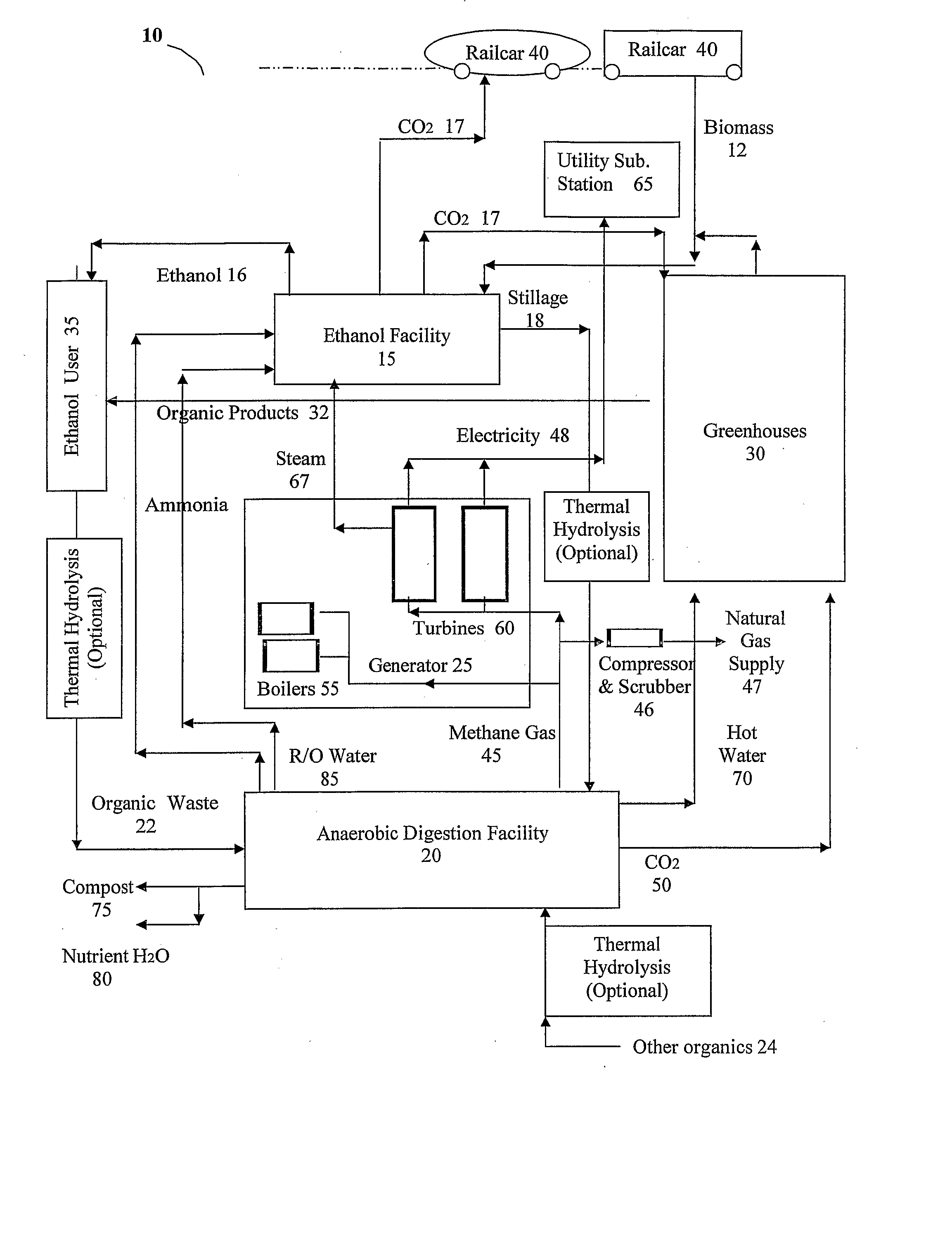
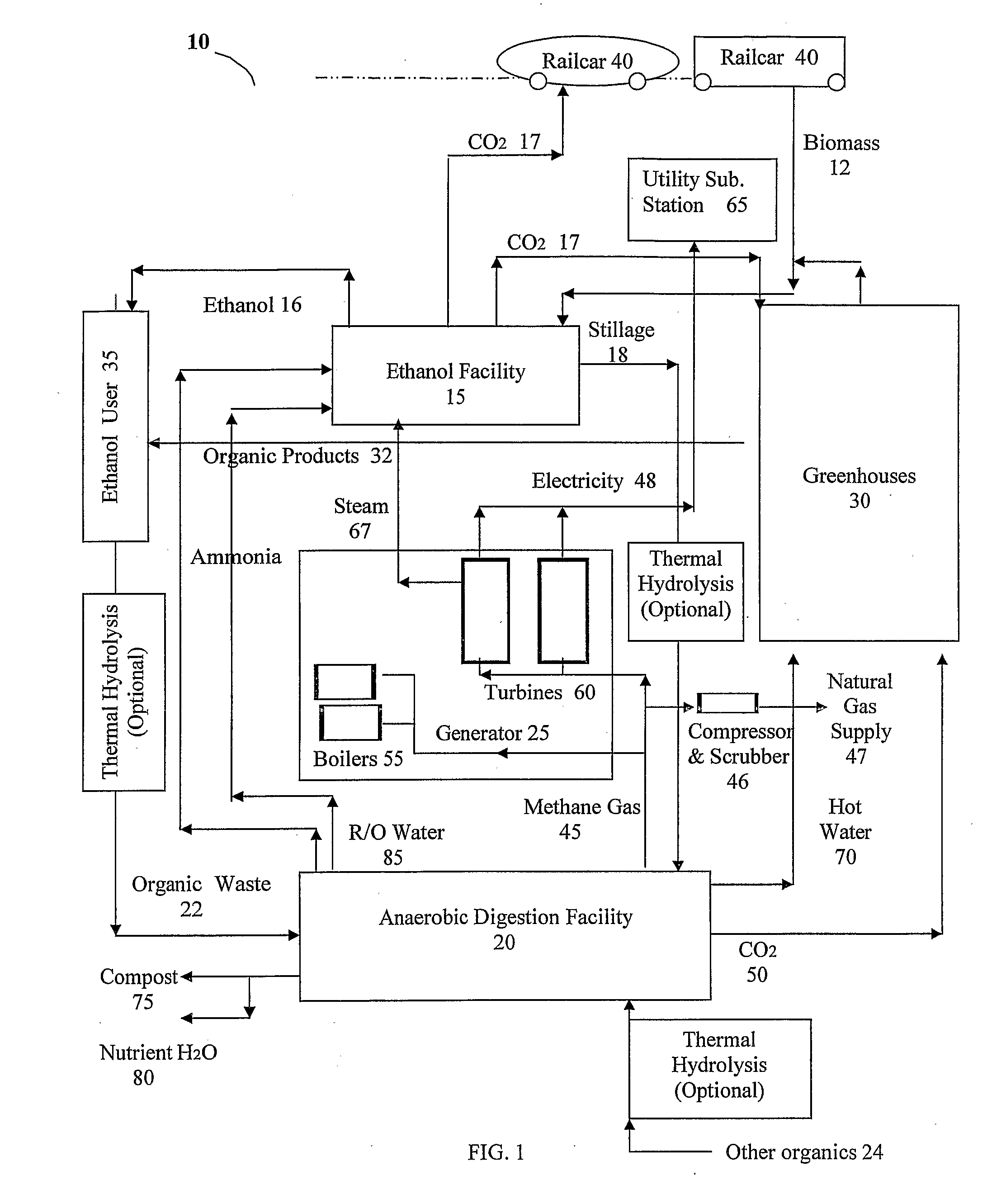
Self-Sustaining and Continuous System and Method of Anaerobically Digesting Ethanol Stillage
A system and method of anaerobically digesting ethanol stillage and reintegrating substantially all by-products thereof back into the system is disclosed. The system includes an ethanol producing facility for producing ethanol and an anaerobic digestion facility for anaerobically digesting stillage from the ethanol producing facility to produce a plurality of by-products. A plurality of sub-systems utilize the plurality of by-products from anaerobic digestion to produce a plurality of end-products. At least one of the plurality of end-products from the various sub-systems is integrated back into the ethanol producing facility and into at least one of the sub-systems such that the system of anaerobically digesting stillage is a continuous and self-sustaining operation.
Owner:ENVIROPLUS
Method of improving the properties of a flour dough, a flour dough improving composition and improved food products
InactiveUS6936289B2Reduce certain disadvantageous effectsReduce stickinessDough treatmentHydrolasesFood productsRheology
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Roasting system
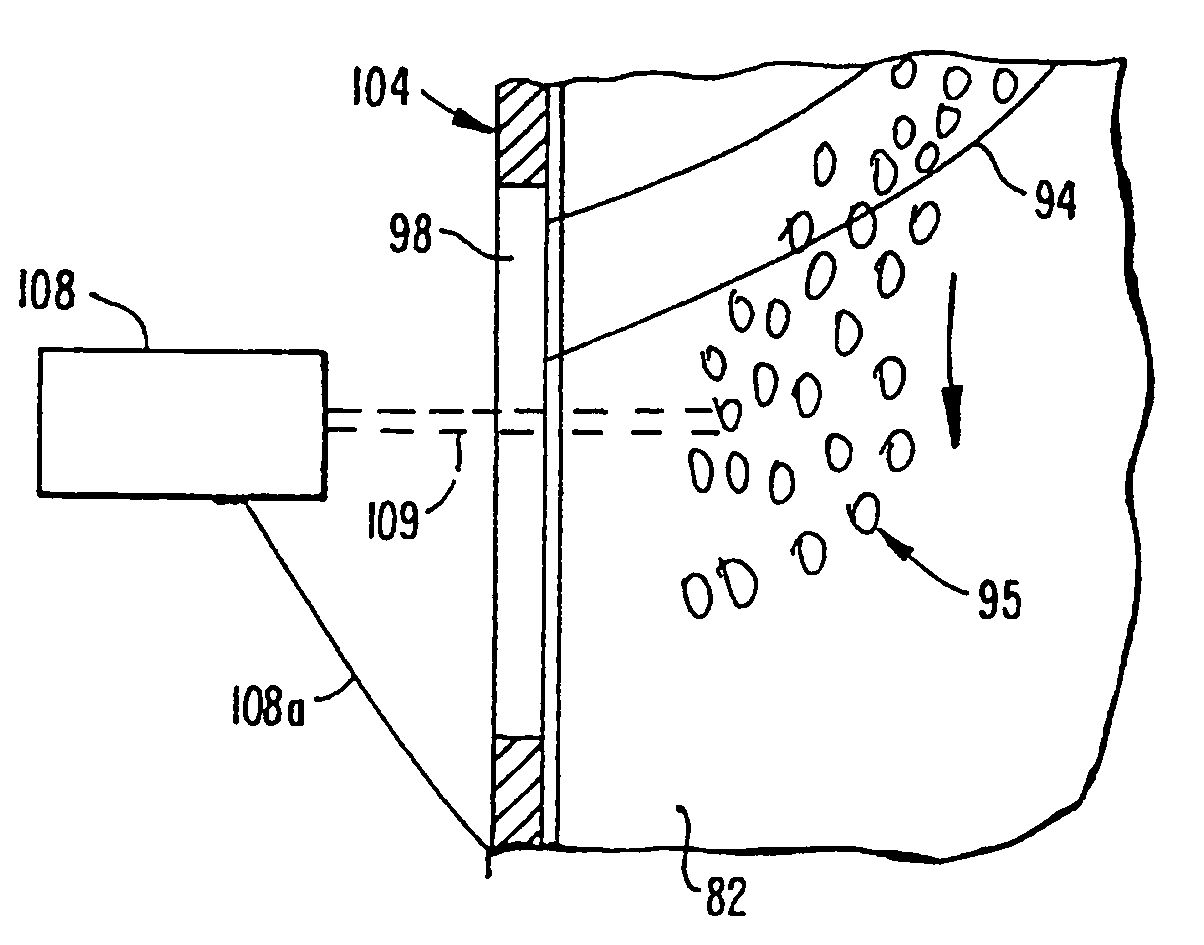
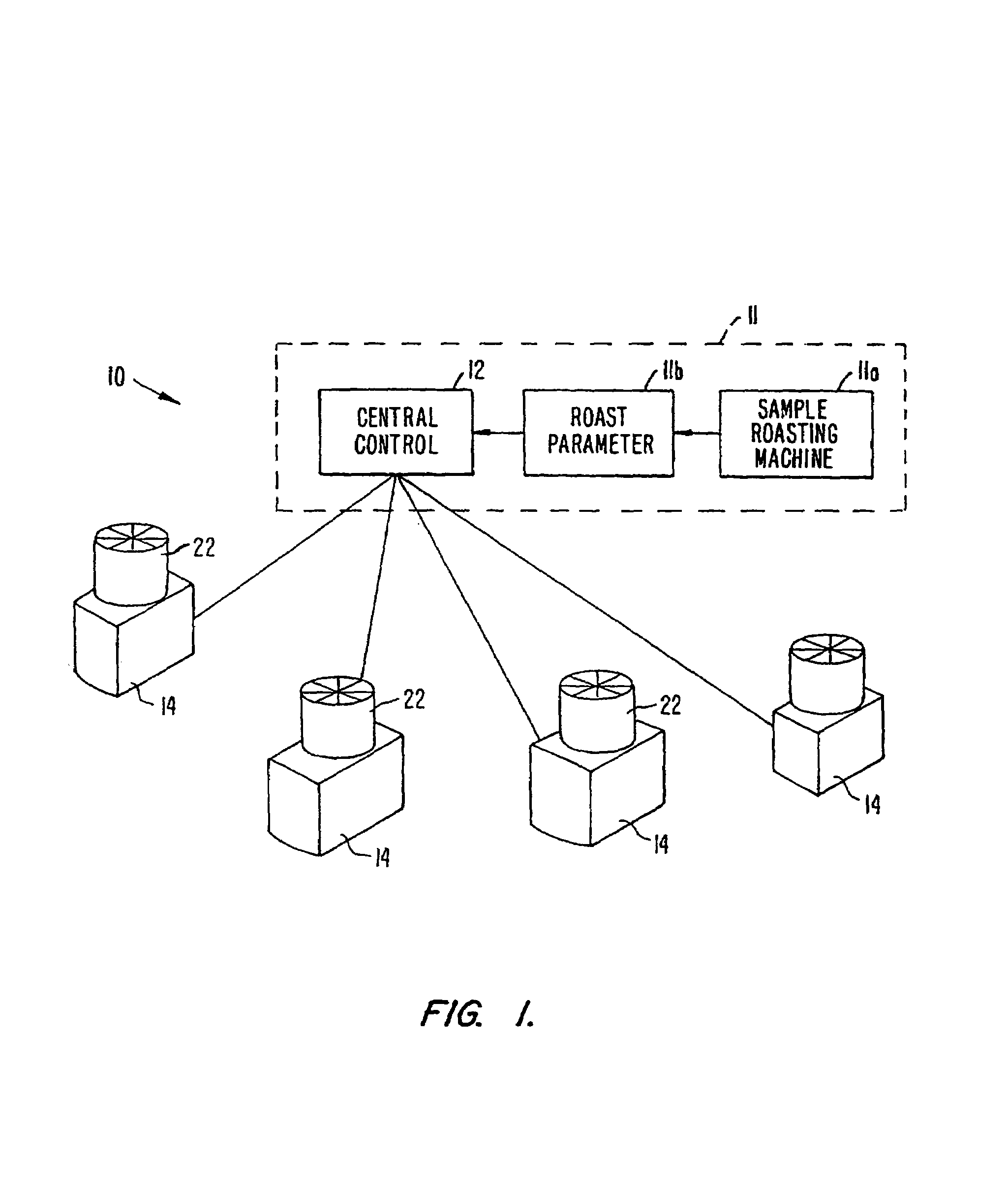
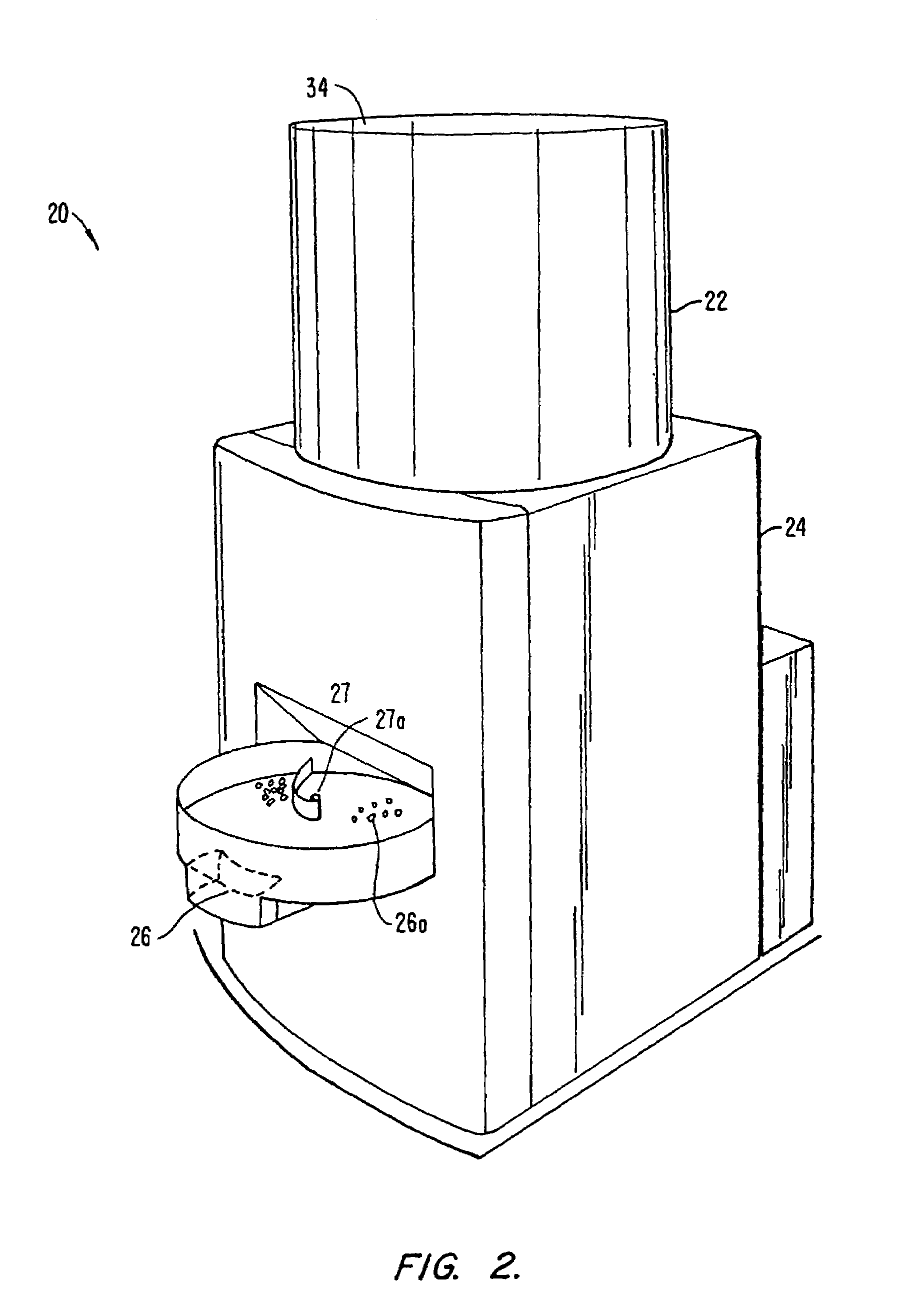
InactiveUS7285300B1Maintain consistencyEasy to downloadMilk preservationWort preparationParticulatesAir cycle
An apparatus and method of roasting foodstuff such as coffee beans employ a roasting chamber for roasting the beans. An air circulation system operatively coupled with the chamber flows heated air over the beans and thereby roasts the beans, and an air cleaning arrangement is operatively coupled with the air circulation system and located downstream of the chamber for removing substantially all particulates, smoke and volatiles entrained in the used air as it flows through the container and into the air cleaning arrangement to provide substantially pollutant-free used air. The circulation system uses atmospheric air and heats, cleans and cools it within as little as ¼ second. Sensors and a electronic controller are provided to monitor various parameters in the roasting apparatus and control the roasting characteristics. The darkness and / or color of the beans during roasting is monitored to ensure proper roasting. The roasting in roasting machines at a plurality of geographically separate locations is controlled by equipping each roasting machine with a computer with memory and providing a central control station for downloading control signals to the computer to control roasting.
Owner:GROUP 32 DEVMENT & ENG
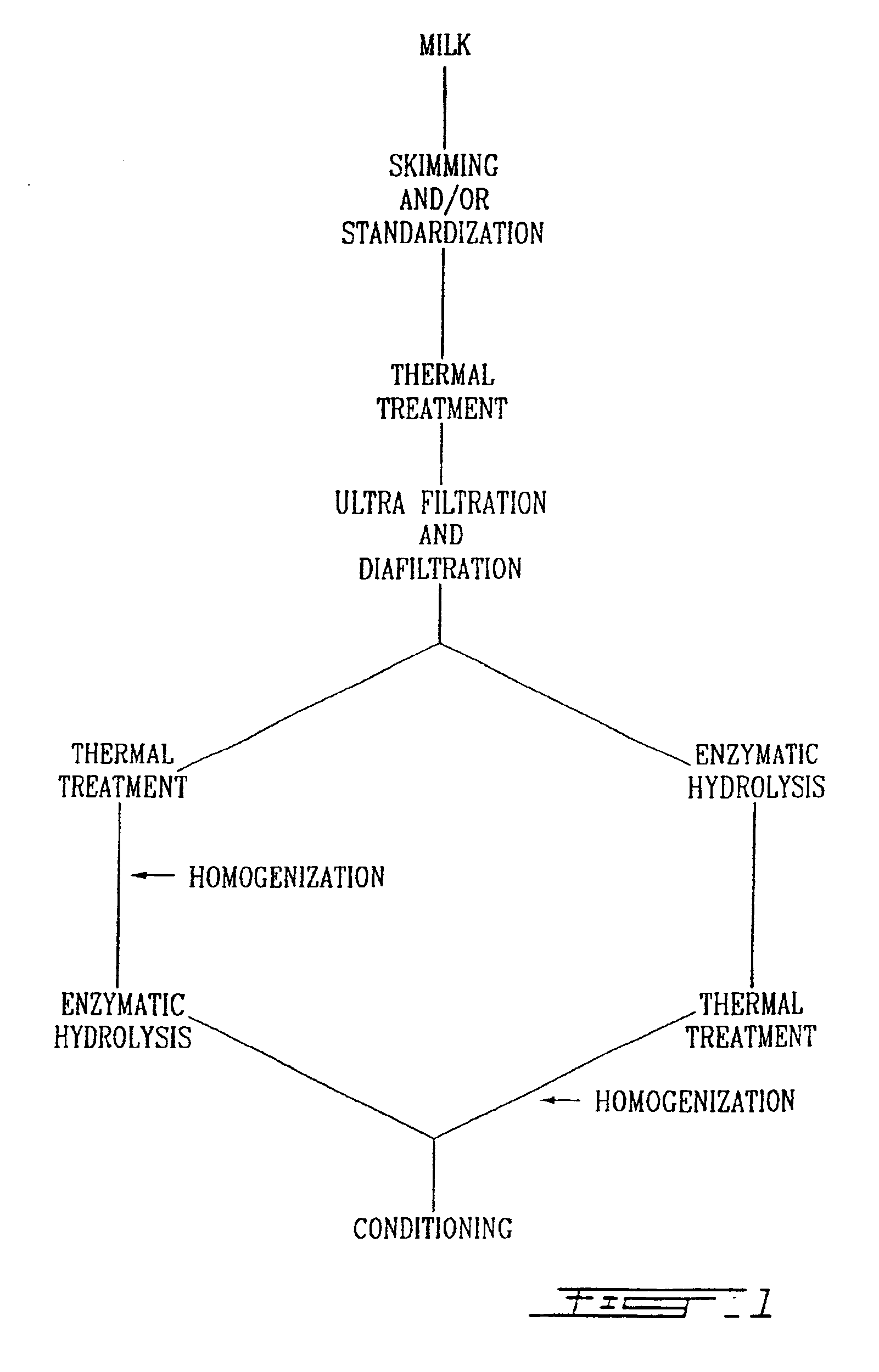
Process for making a lactose-free milk and milk so processed
InactiveUS6881428B2Affecting tasteLactose is reduced or substantially eliminated from milkMilk preparationWort preparationBiotechnologyLactose free milk
This invention relates to a process for producing a lactose-free milk which does not confer a sweet taste to the milk normally resulting from the hydrolysis of lactose into monosaccharides. The process comprises the step of reducing the lactose content of the milk to about 3% prior to hydrolysis with lactase. When the milk is skimmed milk, the protein content may be increased to about 3.8-4.0% or greater, which further improves the organoleptic properties of the milk. Milk so processed and dairy products derived therefrom are also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:AGROPUR COOP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com