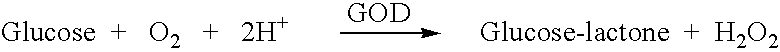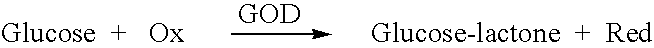Patents
Literature
19025results about "Tissue/virus culture apparatus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
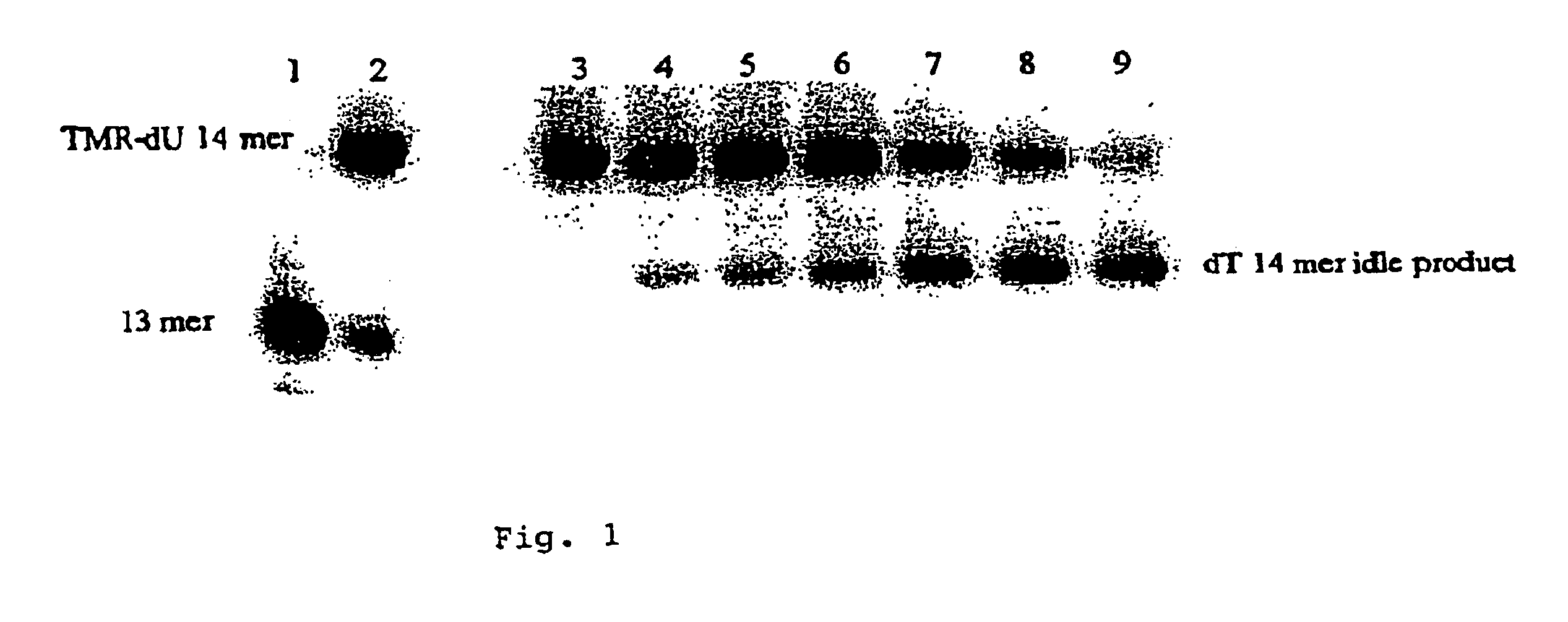
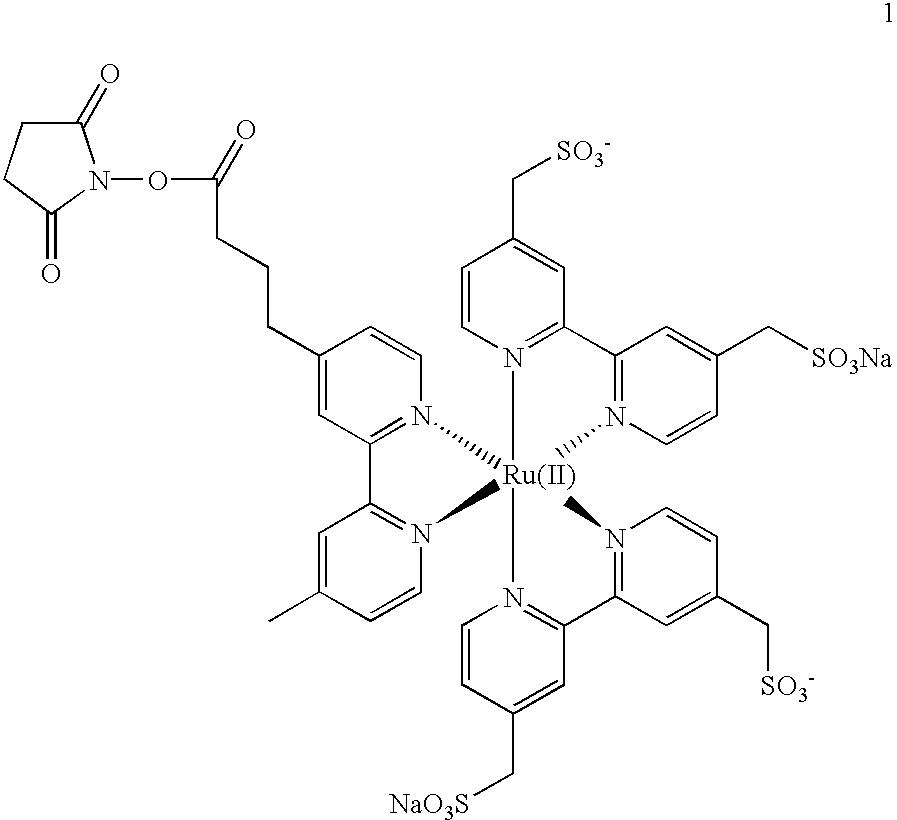
Labelled nucleotides
InactiveUS7057026B2Use of techniqueBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOrganic chemistryNucleoside
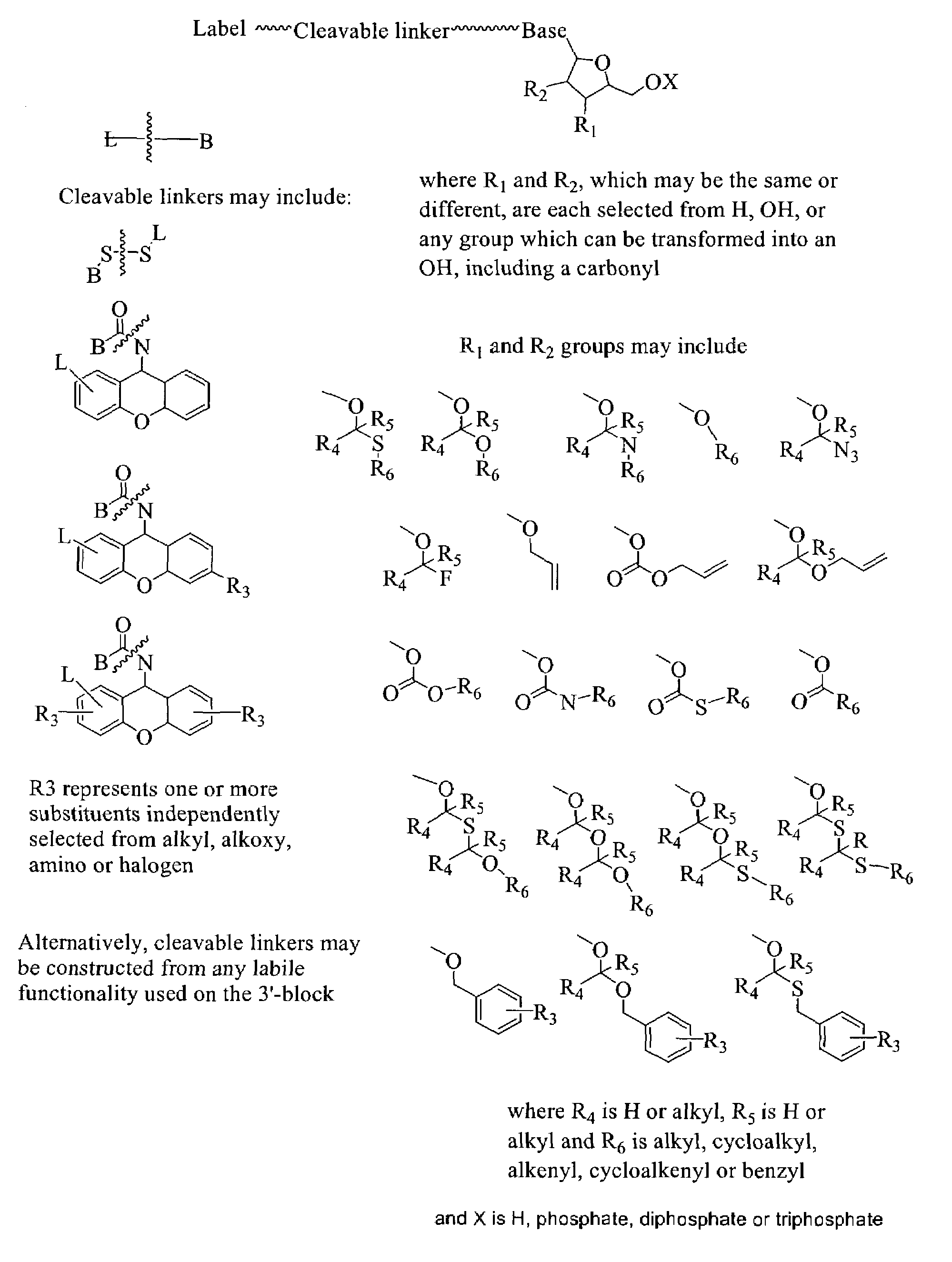
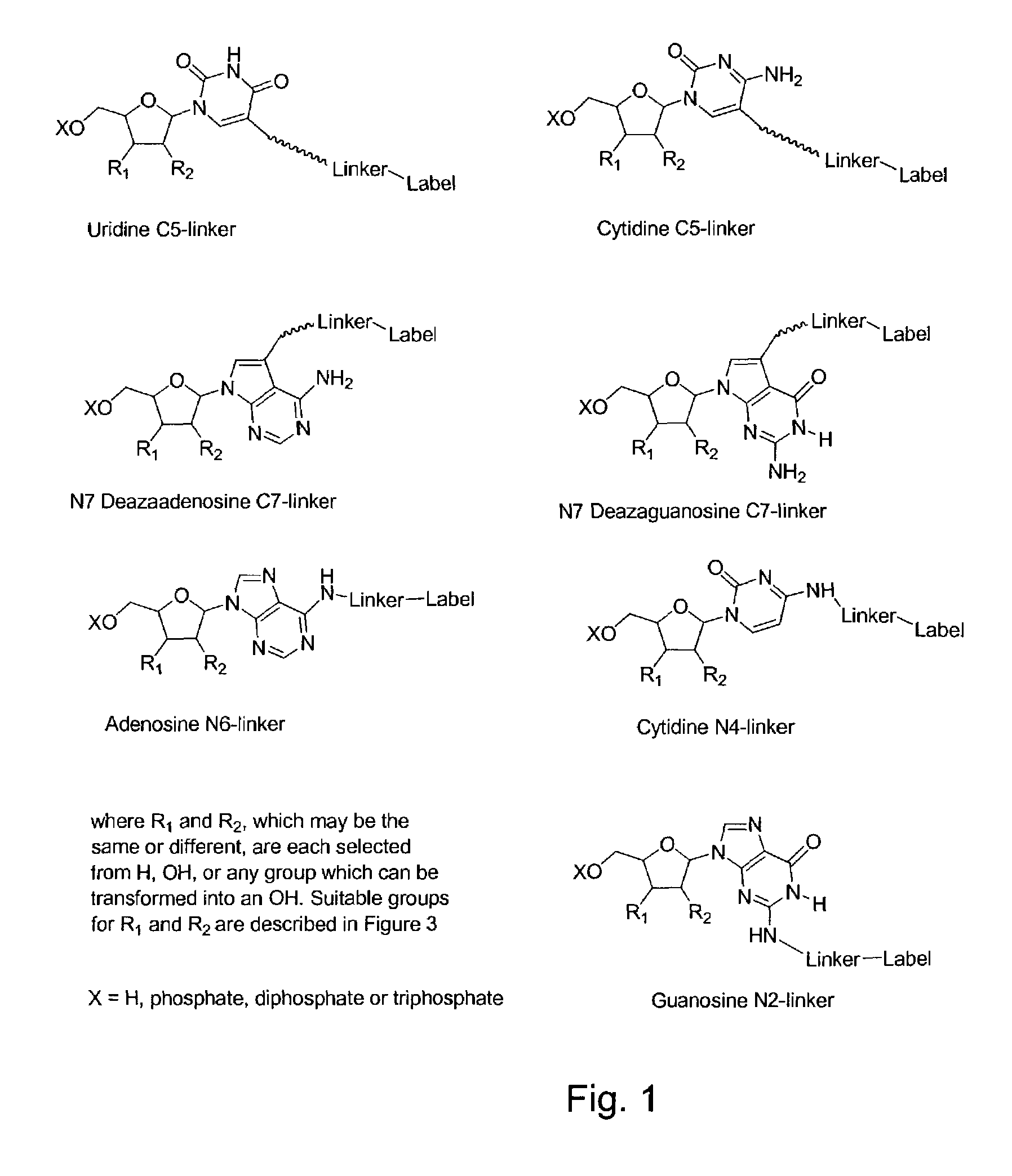
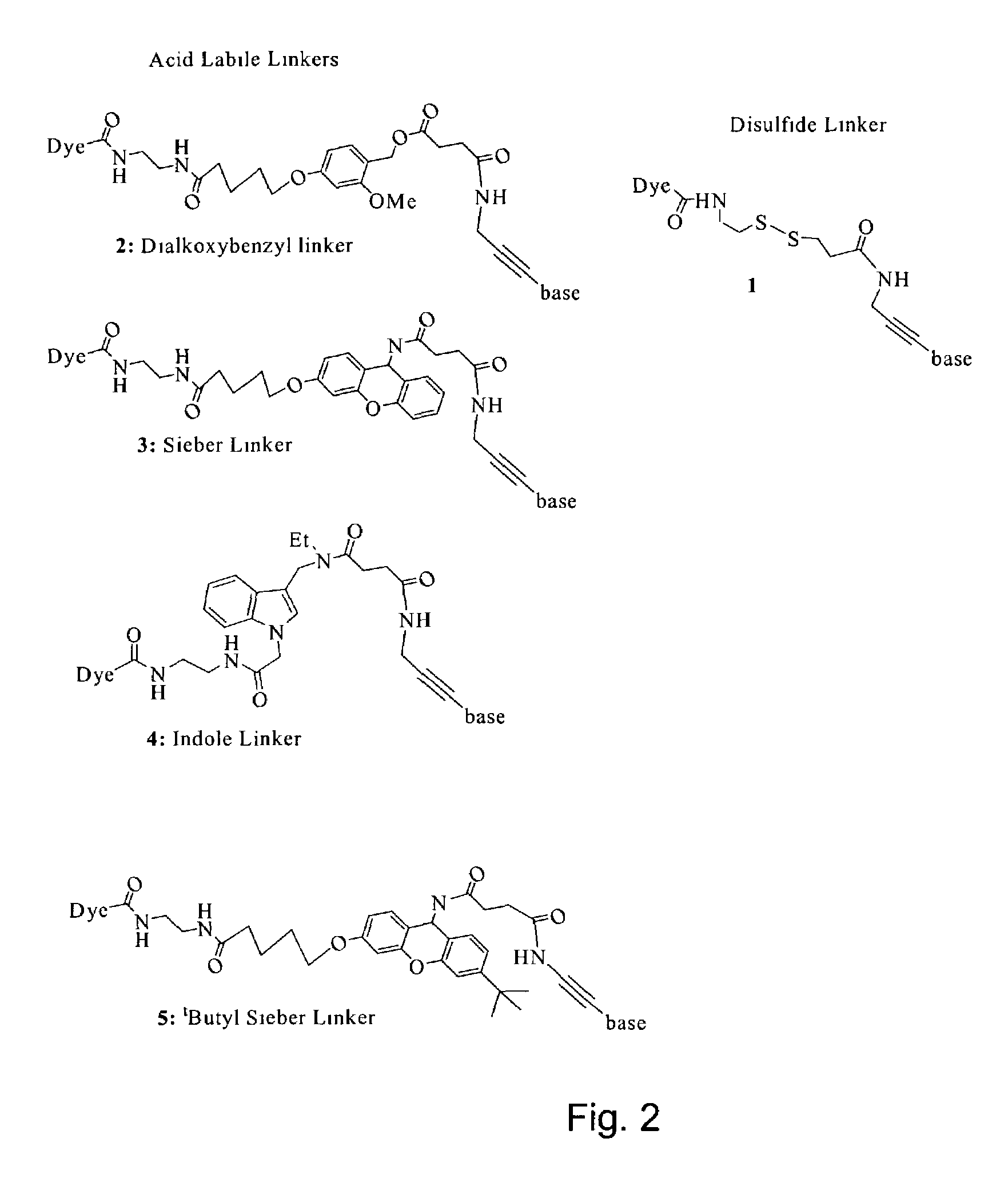
Nucleosides and nucleotides are disclosed that are linked to detectable labels via a cleavable linker group.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
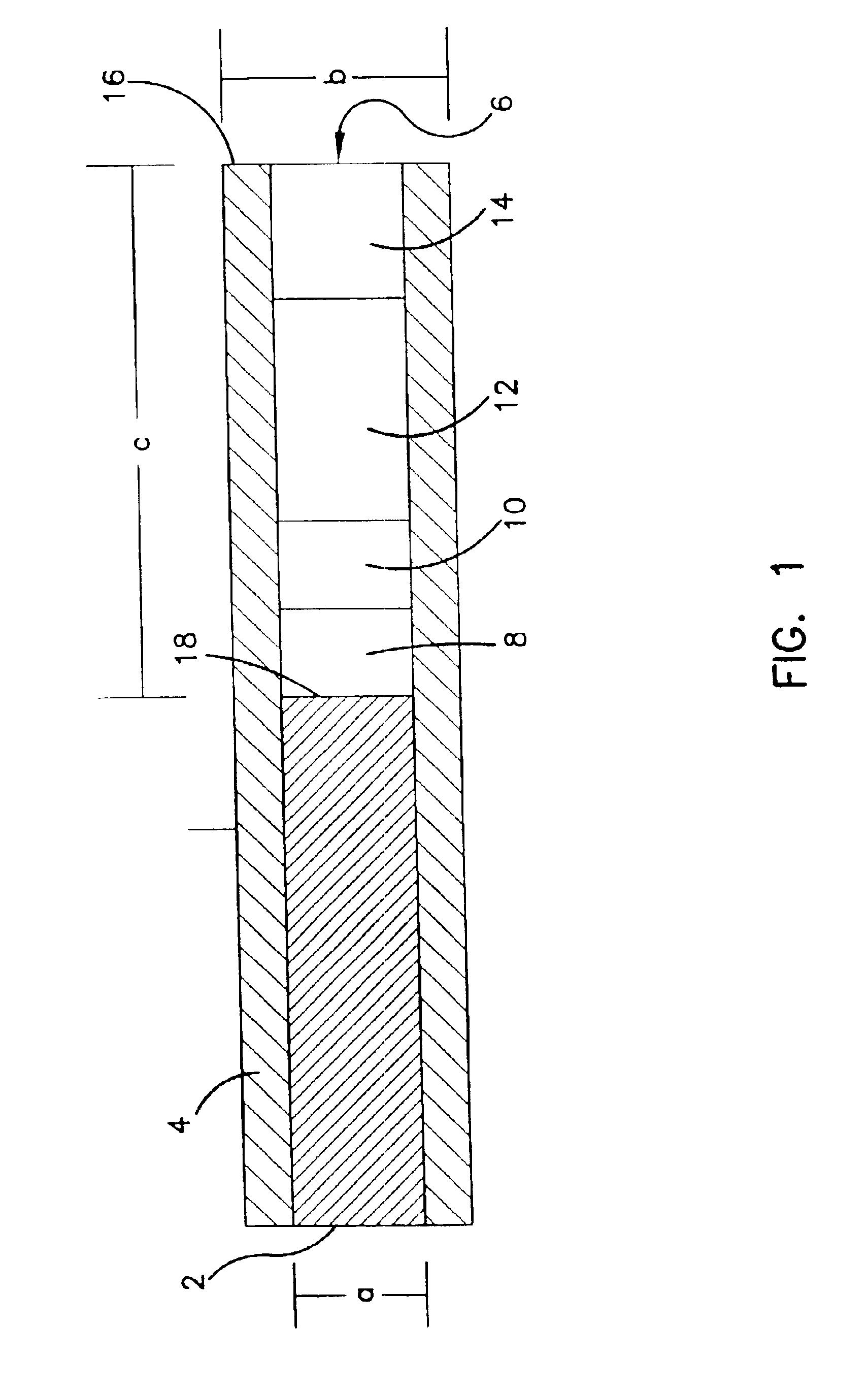
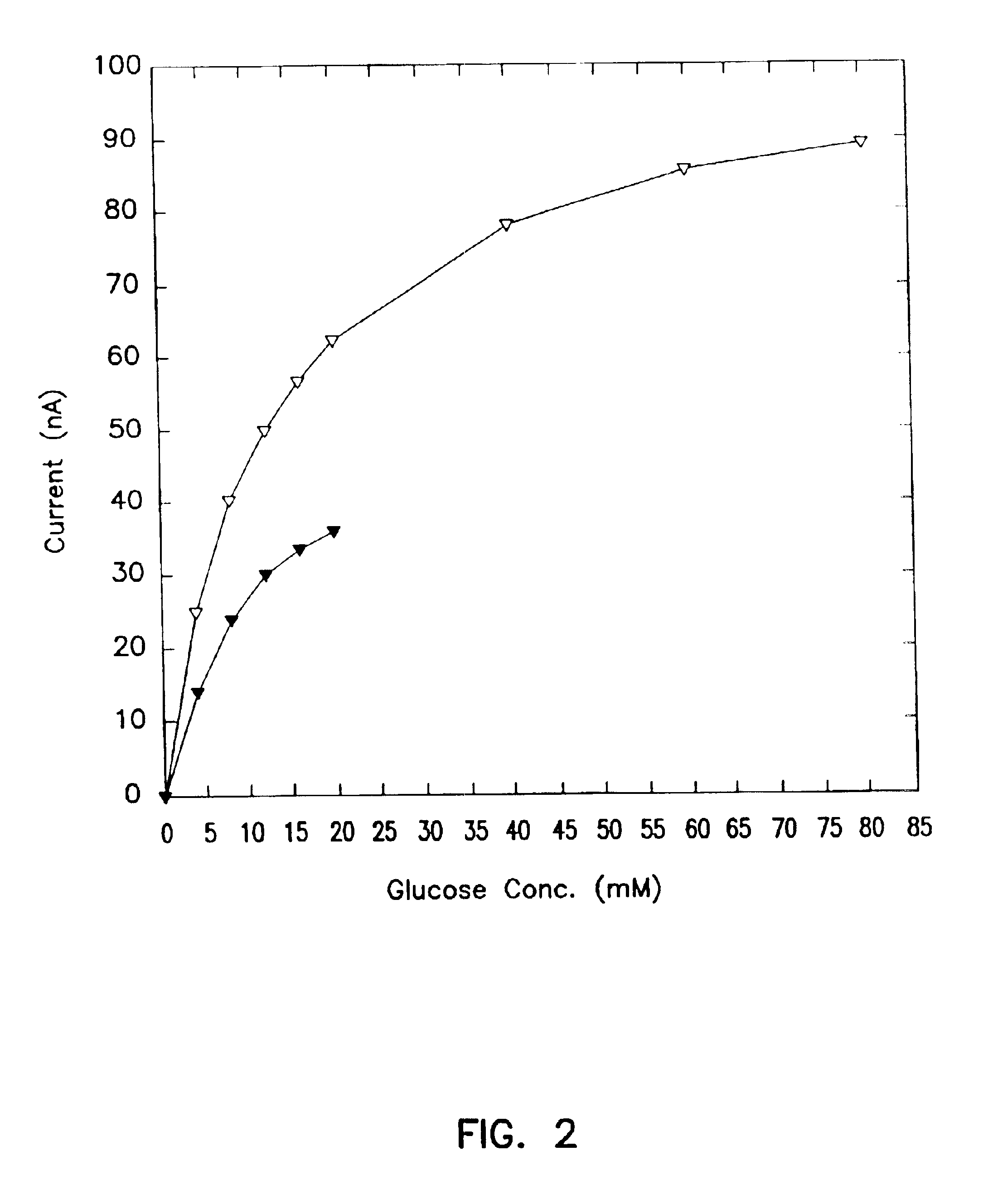
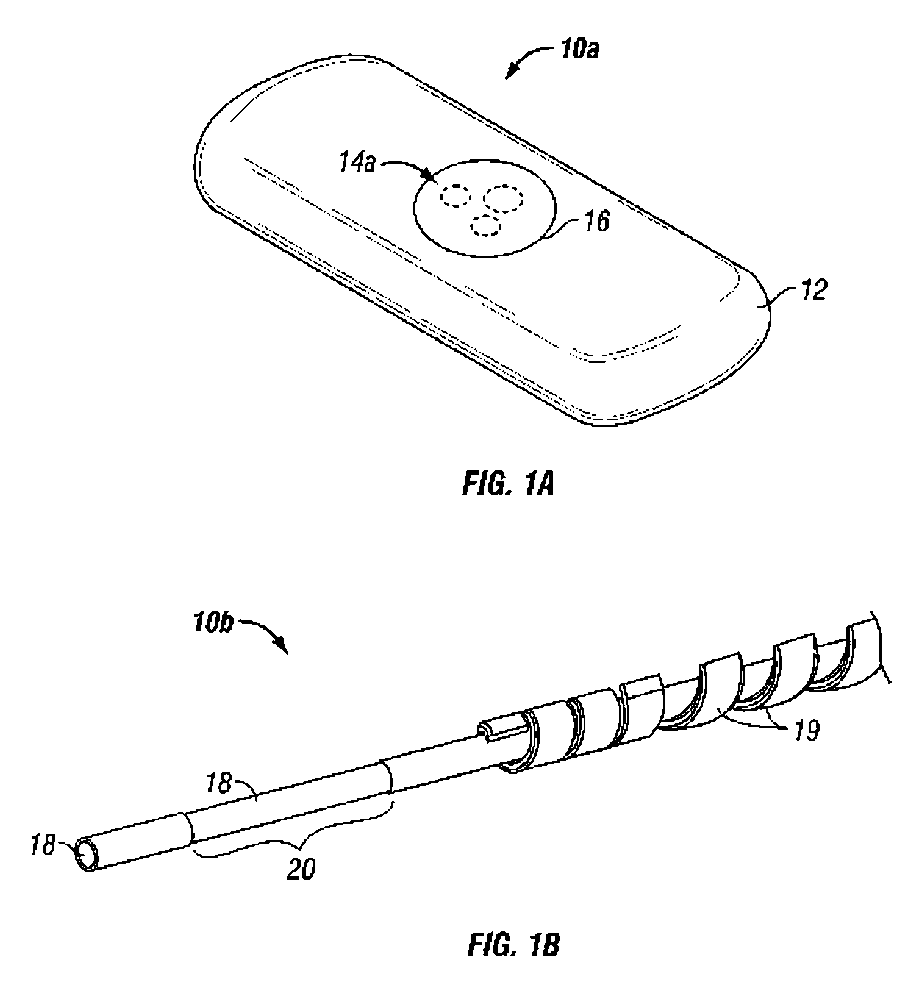
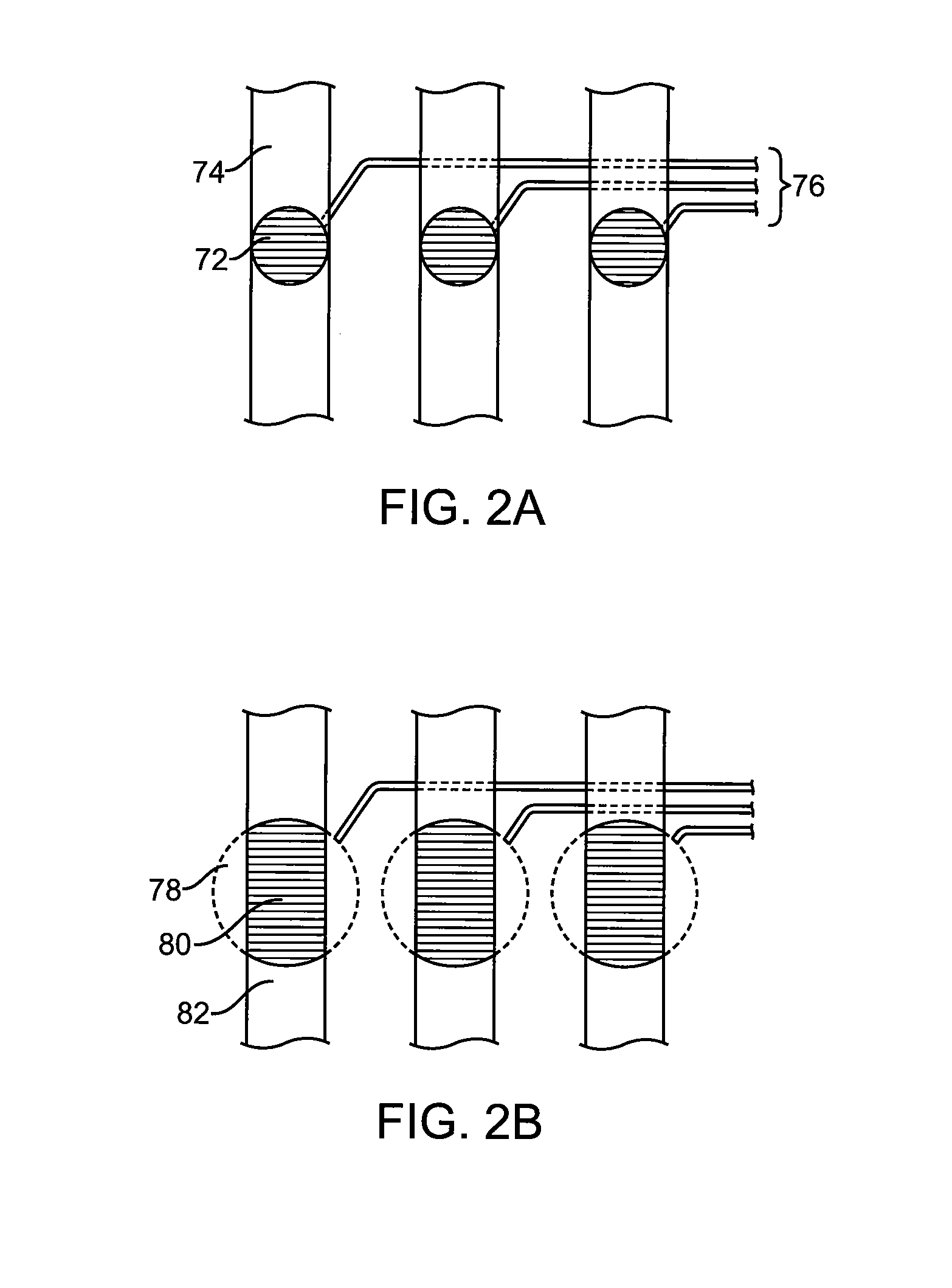
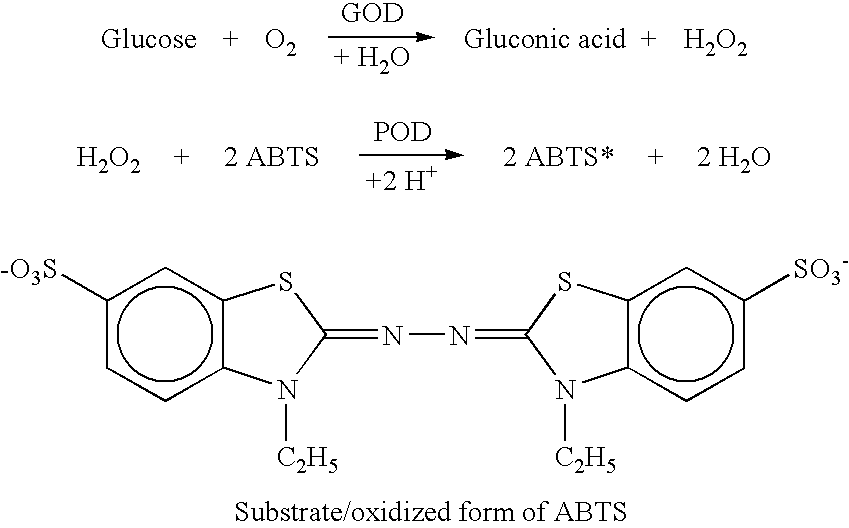
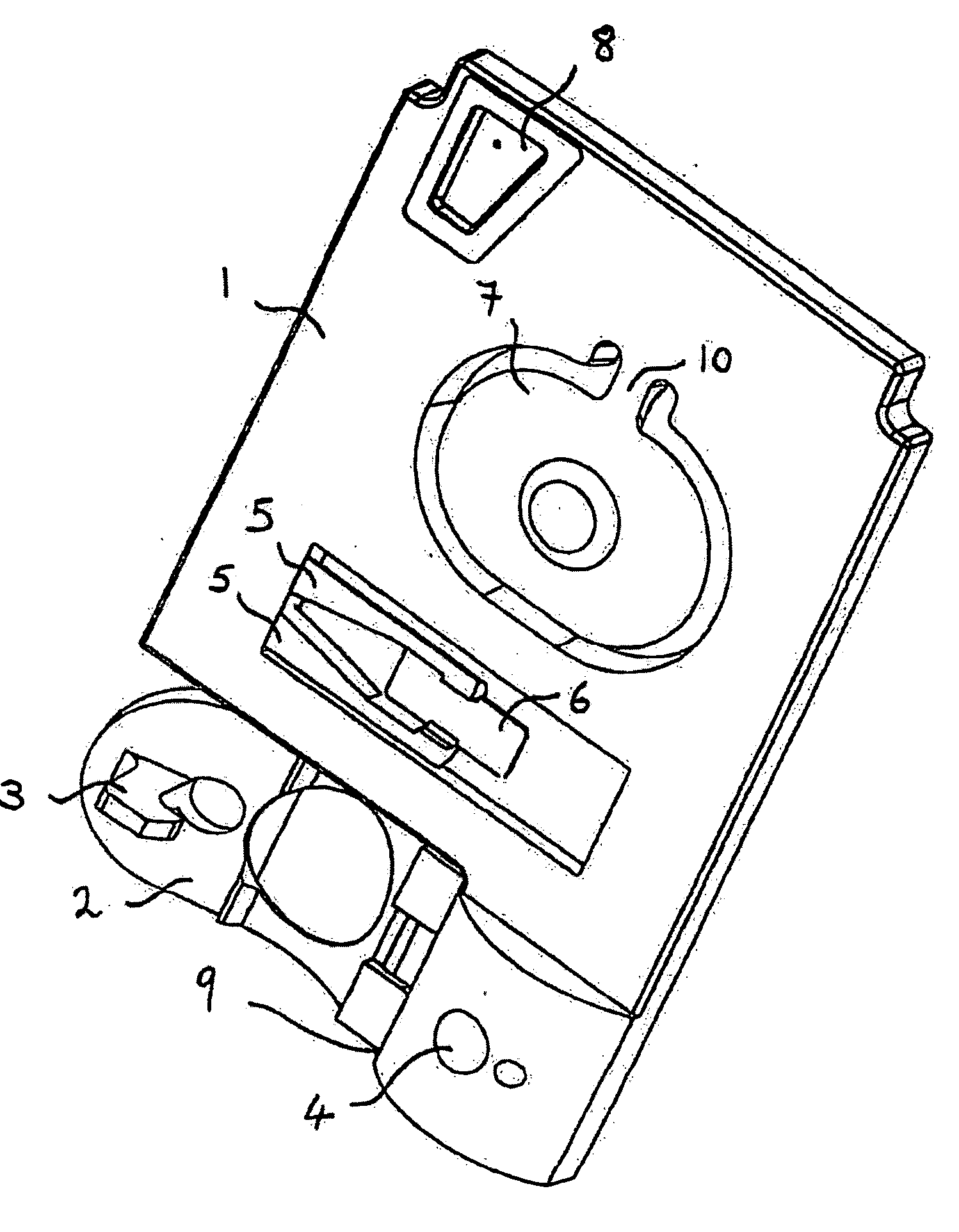
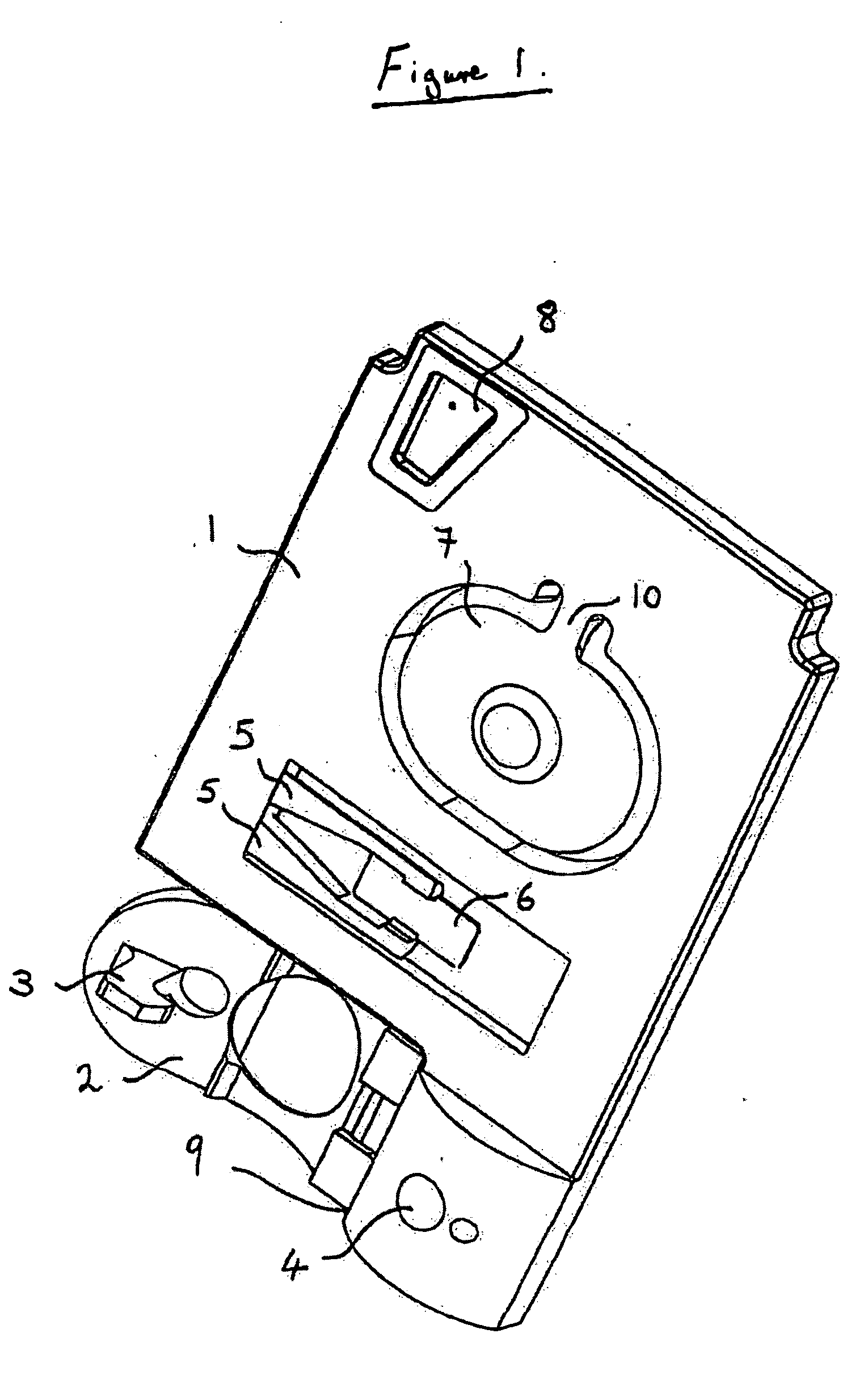
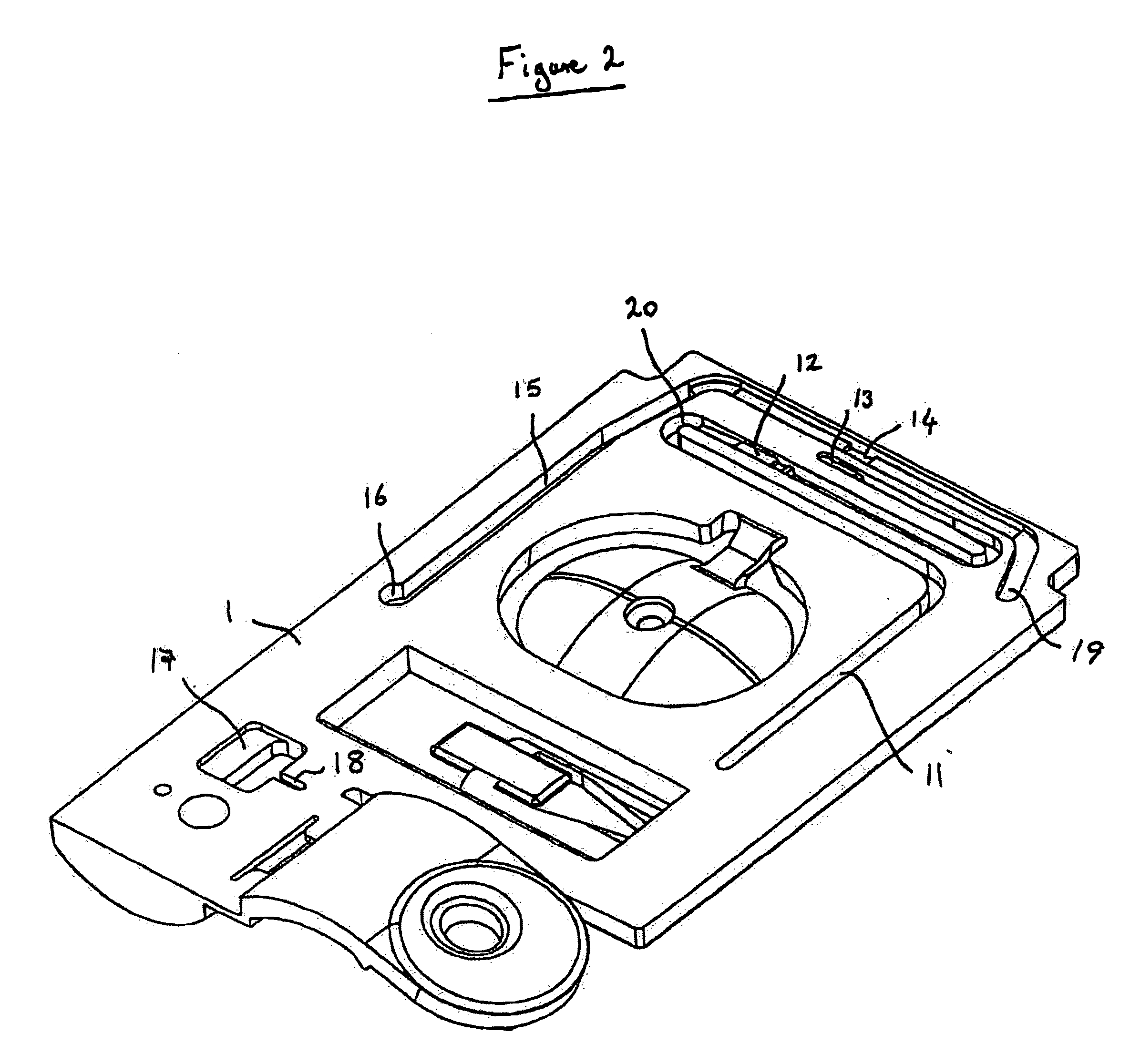
Subcutaneous glucose electrode
InactiveUS6881551B2Reduce transportationAccurate measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsConcentrations glucosePolyamide
A small diameter flexible electrode designed for subcutaneous in vivo amperometric monitoring of glucose is described. The electrode is designed to allow “one-point” in vivo calibration, i.e., to have zero output current at zero glucose concentration, even in the presence of other electroreactive species of serum or blood. The electrode is preferably three or four-layered, with the layers serially deposited within a recess upon the tip of a polyamide insulated gold wire. A first glucose concentration-to-current transducing layer is overcoated with an electrically insulating and glucose flux limiting layer (second layer) on which, optionally, an immobilized interference-eliminating horseradish peroxidase based film is deposited (third layer). An outer (fourth) layer is biocompatible.
Owner:THERASENSE
Polynucleotide sequencing
InactiveUS6833246B2Efficient and fast determinationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotidePolymerase L
The invention relates to the sequencing of a target polynucleotide sequence, immobilized on a solid support, using the polymerase reaction to extend a suitable primer and characterizing the sequential addition of labelled bases. The present invention further relates to the presence of a polymerase enzyme that retains a 3' to 5' exonuclease function, which is induced to remove an incorporated labelled base after detection of incorporation. A corresponding non-labelled base may then be incorporated into the complementary strand to allow further sequence determinations to be made. Repeating the procedure allows the sequence of the complement to be identified, and thereby the target sequence.
Owner:SOLEXA
Enzyme electrode structure
InactiveUS6071391AEasy to manufactureEasy to measureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEnzyme electrodeWorking electrode
A biosensor comprises a space part for sucking and housing a sample formed of two upper and lower plates, the two plates being stuck together by an adhesive layer, the space part for sucking and housing the sample being constituted so as to be partially opened in the peripheral part and partially closed by the adhesive layer, and has a working electrode having at least glucose oxidase immobilized thereon and a counter electrode on the same plane of the plate.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
System and apparatus for sequential processing of analytes
InactiveUS6969488B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteMicroparticle
An apparatus and system are provided for simultaneously analyzing a plurality of analytes anchored to microparticles. Microparticles each having a uniform population of a single kind of analyte attached are disposed as a substantially immobilized planar array inside of a flow chamber where steps of an analytical process are carried out by delivering a sequence of processing reagents to the microparticles by a fluidic system under microprocessor control. In response to such process steps, an optical signal is generated at the surface of each microparticle which is characteristic of the interaction between the analyte carried by the microparticle and the delivered processing reagent. The plurality of analytes are simultaneously analyzed by collecting and recording images of the optical signals generated by all the microparticles in the planar array. A key feature of the invention is the correlation of the sequence of optical signals generated by each microparticle in the planar array during the analytical process.
Owner:SOLEXA
Single molecule arrays for genetic and chemical analysis
ActiveUS20070099208A1Efficient high resolution analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanotechImage resolutionRandom array
Random arrays of single molecules are provided for carrying out large scale analyses, particularly of biomolecules, such as genomic DNA, cDNAs, proteins, and the like. In one aspect, arrays of the invention comprise concatemers of DNA fragments that are randomly disposed on a regular array of discrete spaced apart regions, such that substantially all such regions contain no more than a single concatemer. Preferably, such regions have areas substantially less than 1 μm2 and have nearest neighbor distances that permit optical resolution of on the order of 109 single molecules per cm2. Many analytical chemistries can be applied to random arrays of the invention, including sequencing by hybridization chemistries, sequencing by synthesis chemistries, SNP detection chemistries, and the like, to greatly expand the scale and potential applications of such techniques.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Afinity domain for analyte sensor
InactiveUS20050176136A1Reduce impactBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteSorbent
Abstract of the DisclosureThe preferred embodiments provide a membrane system, particularly for use on an electrochemical sensor, wherein the membrane system includes an affinity domain that dampens the effects of target interferant(s) on the sensor. The affinity domain can be layer, surface, region, and / or portion of the membrane system formed using sorbents that have an affinity for the target interferant. The sorbents can be adapted to adsorb the interferants, for example using adsorbents such as chromatography packing materials. The sorbents can also be adapted to absorb the interferants by imprinting a molecular structure on the material that forms the affinity domain such that target interferants bind to the imprinted surfaces at the molecular level.
Owner:DEXCOM
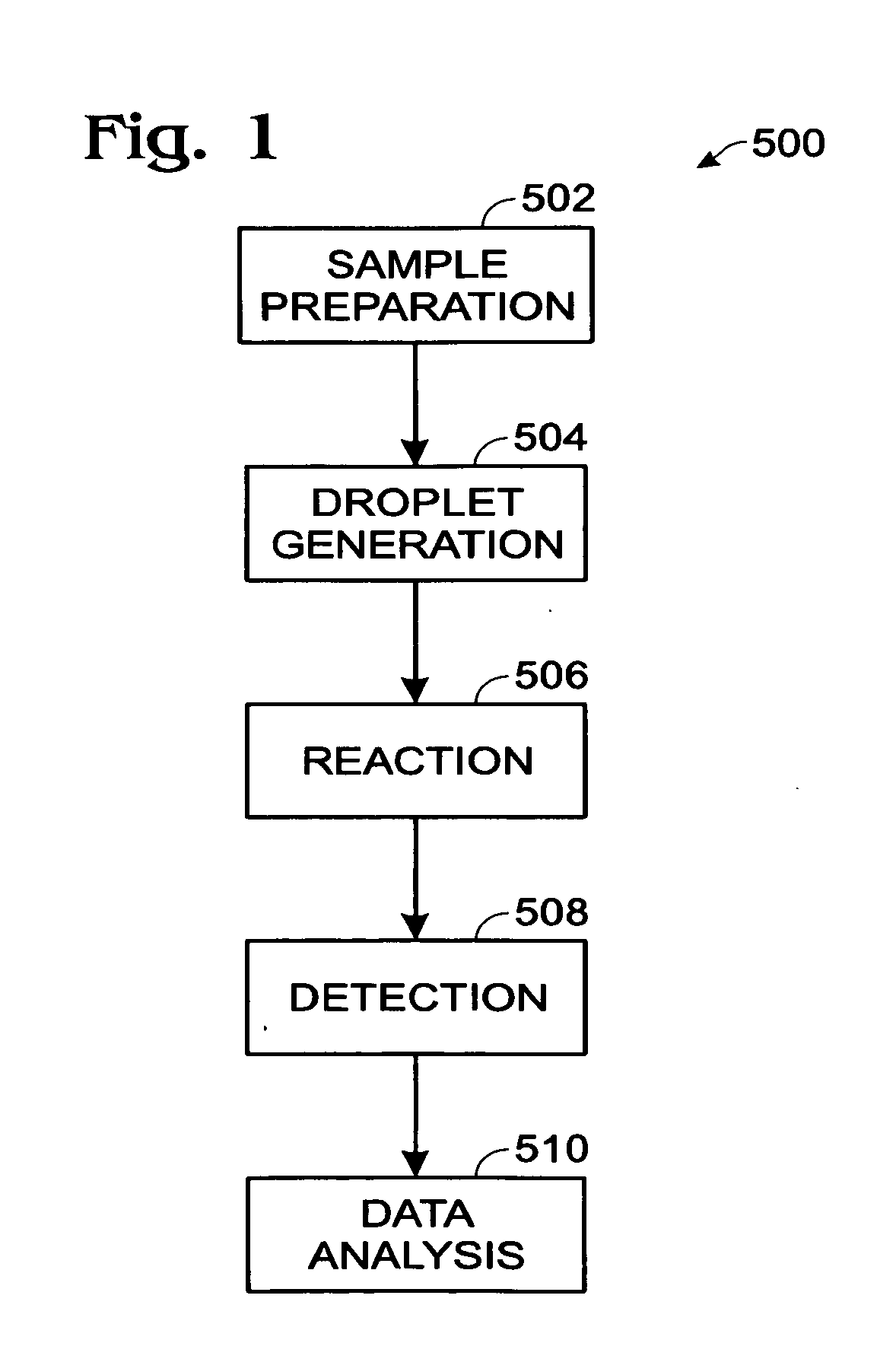
Droplet-based assay system
ActiveUS20100173394A1Easy CalibrationImprove accuracy and reliabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayBiology
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Multi-array, multi-specific electrochemiluminescence testing
InactiveUS6066448AMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProviding materialElectrochemiluminescence
Materials and methods are provided for producing patterned multi-array, multi-specific surfaces which are electronically excited for use in electrochemiluminescence based tests. Materials and methods are provided for the chemical and / or physical control of conducting domains and reagent deposition for use in flat panel displays and multiply specific testing procedures.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
Systems and devices for sequence by synthesis analysis
ActiveUS20100111768A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDNAComputational biology
The present invention comprises systems and devices for sequencing of nucleic acid, such as short DNA sequences from clonally amplified single-molecule arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Nucleic acid amplification utilizing microfluidic devices
InactiveUS6960437B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRegulation temperatureEngineering
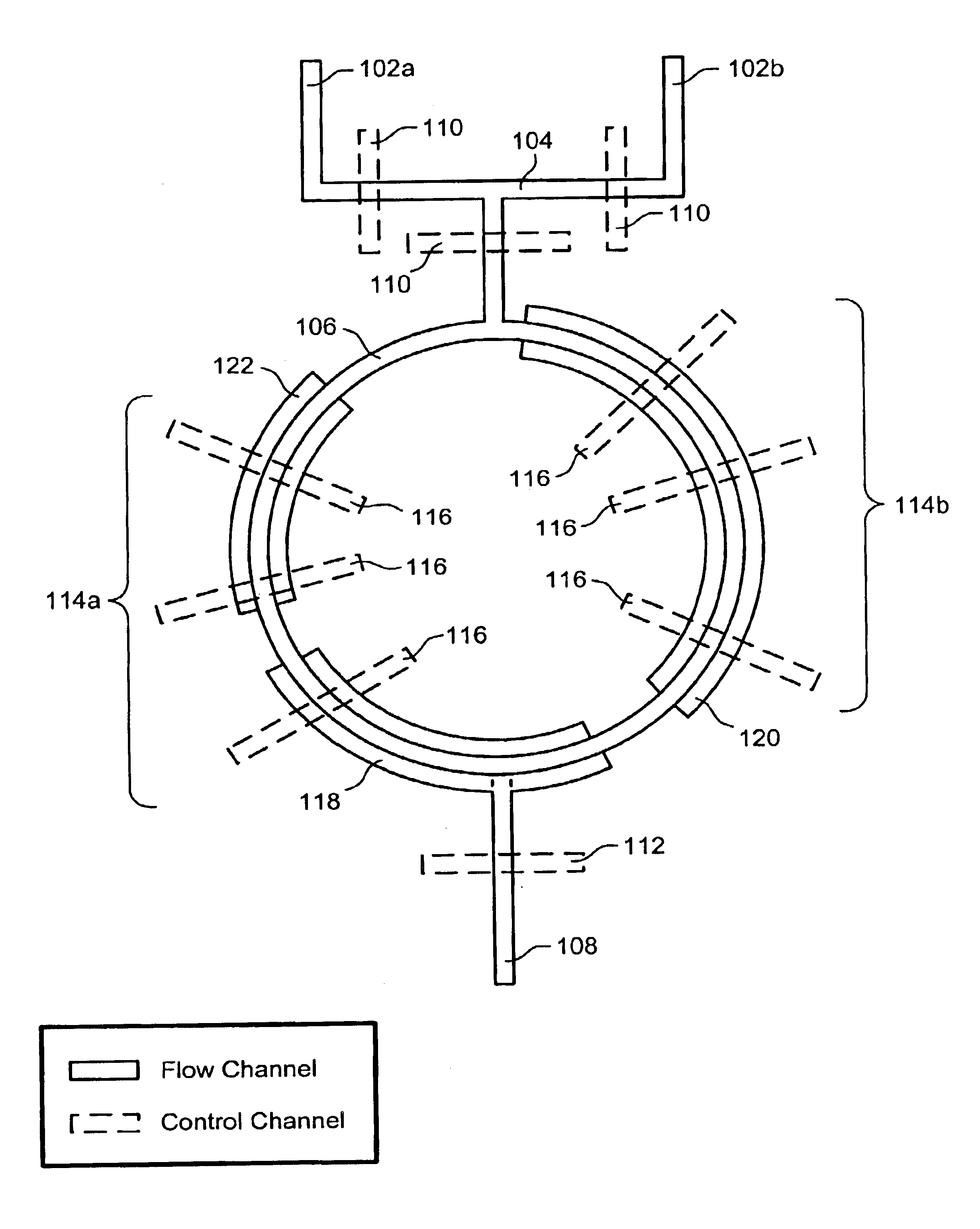
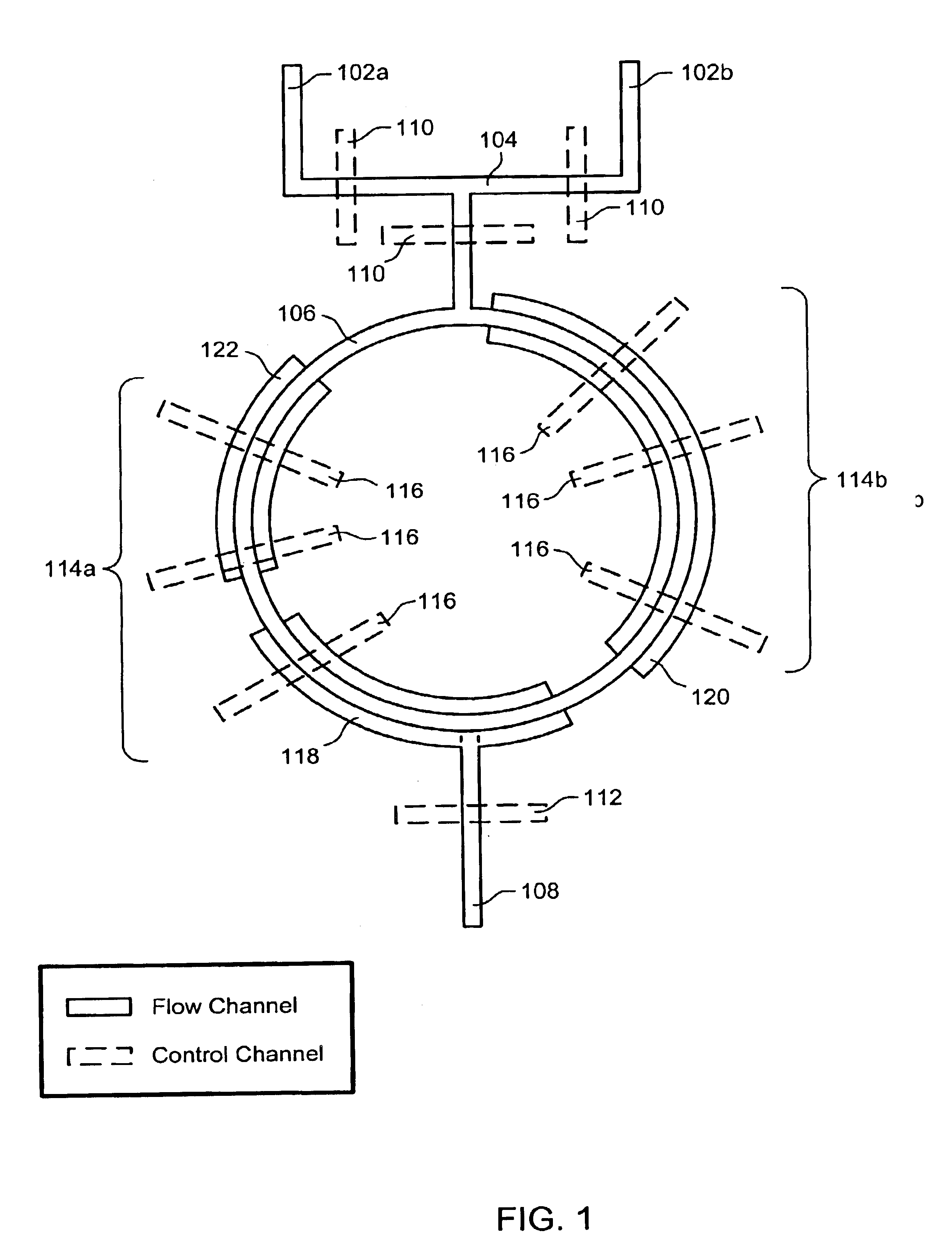
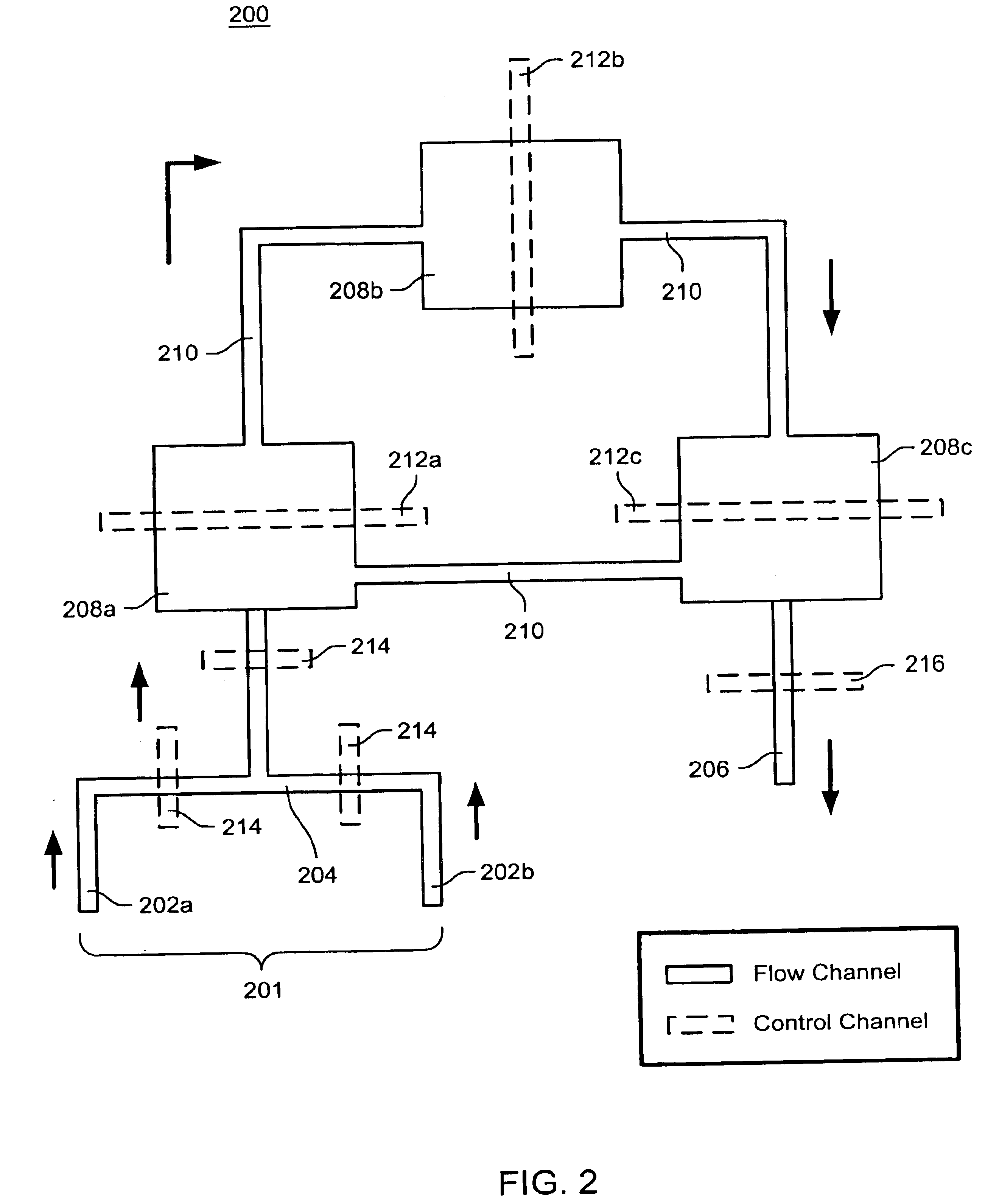
The present invention provides microfluidic devices and methods using the same in various types of thermal cycling reactions. Certaom devices include a rotary microfluidic channel and a plurality of temperature regions at different locations along the rotary microfluidic channel at which temperature is regulated. Solution can be repeatedly passed through the temperature regions such that the solution is exposed to different temperatures. Other microfluidic devices include an array of reaction chambers formed by intersecting vertical and horizontal flow channels, with the ability to regulate temperature at the reaction chambers. The microfluidic devices can be used to conduct a number of different analyses, including various primer extension reactions and nucleic acid amplification reactions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Methods for increasing accuracy of nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS7282337B1Improve accuracyImprove Sequencing AccuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
In vivo biosensor apparatus and method of use
InactiveUS6673596B1Less can be administeredCost-effective administration of drugBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIn vivoGenetically engineered
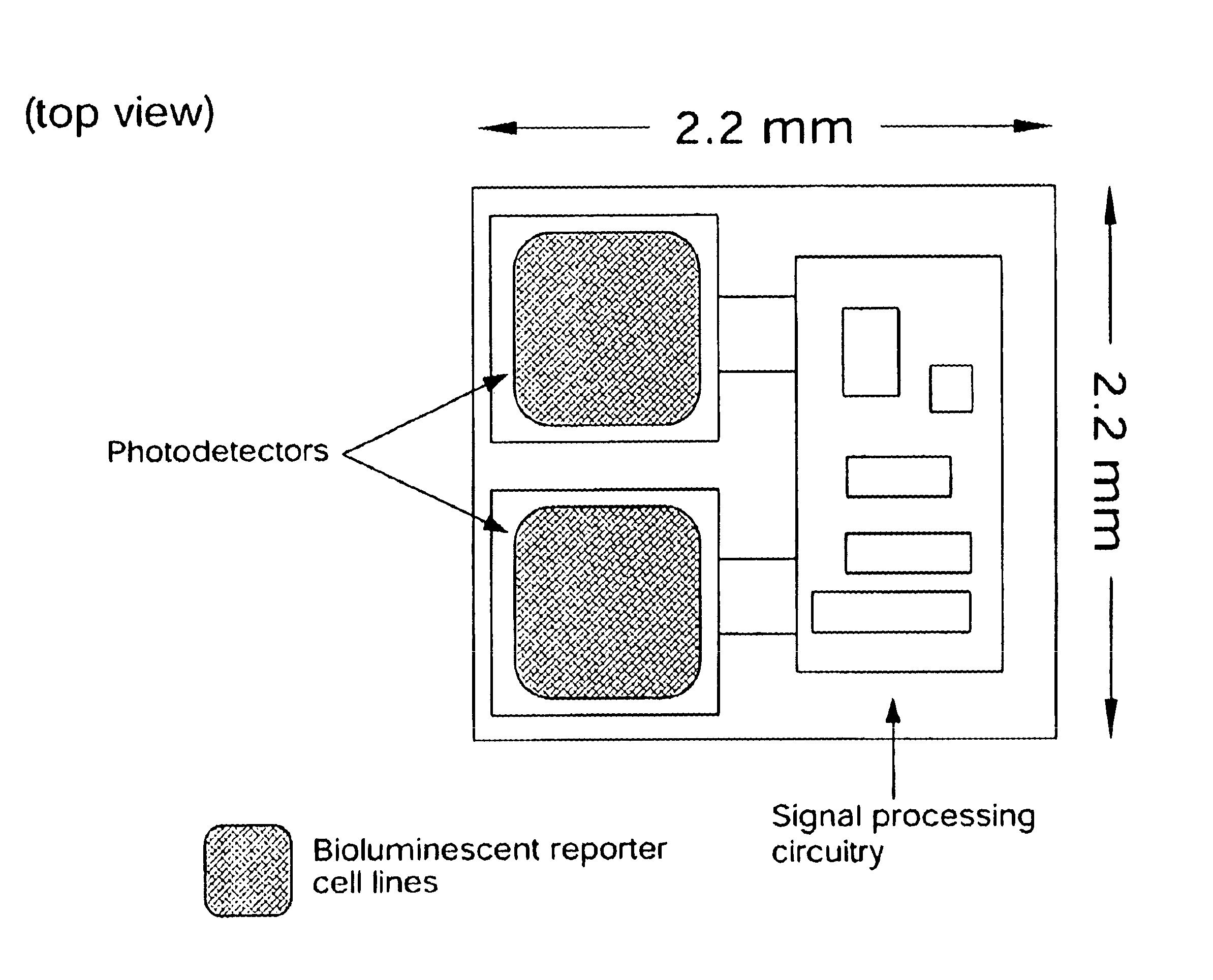
Disclosed are bioluminescent bioreporter integrated circuit devices that detect selected analytes in fluids when implanted in the body of an animal. The device comprises a bioreporter that has been genetically engineered to contain a nucleic acid segment that comprises a cis-activating response element that is responsive to the selected substance operably linked to a gene encoding a bioluminescent reporter polypeptide. In preferred embodiments, the target analyte is glucose, glucagons, or insulin. Exposure of the bioreporter to the target substance causes the response element to up-regulate the nucleic acid sequence encoding the reporter polypeptide to produce a luminescent response that is detected and quantitated. In illustrative embodiments, the bioreporter device is encapsulated on an integrated circuit that is capable of detecting the emitted light, processing the resultant signal, and then remotely reporting the results. Also disclosed are controlled drug delivery systems capable of being directly or indirectly controlled by the detection device that provide drugs such as insulin to the animal in reponse to the amount of target analyte present in the body fluids.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Scaffolded nucleic acid polymer particles and methods of making and using
ActiveUS20100304982A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsParticle compositionPolynucleotide
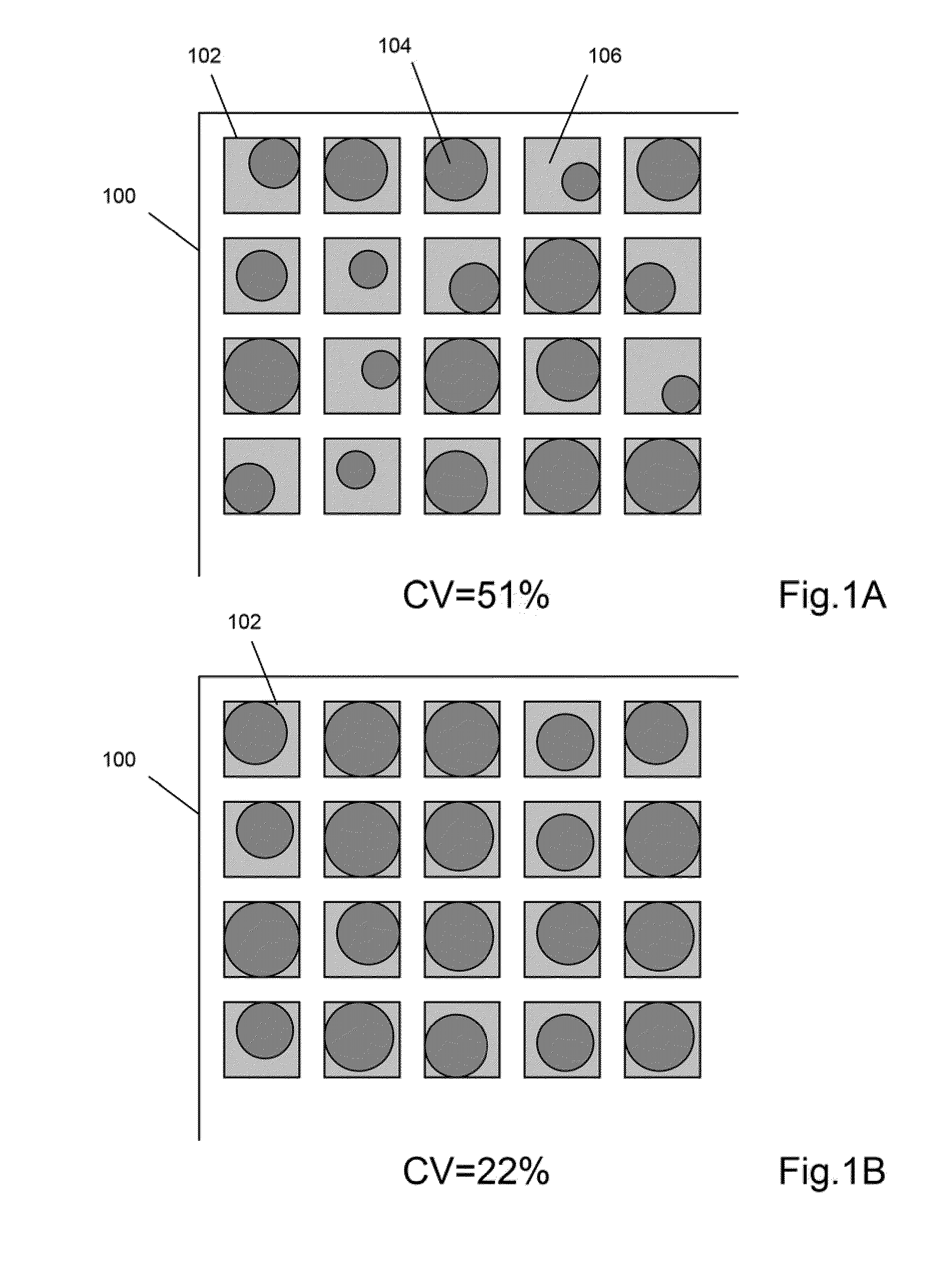
The invention provides particle compositions having applications in nucleic acid analysis. Nucleic acid polymer particles of the invention allow polynucleotides to be attached throughout their volumes for higher loading capacities than those achievable solely with surface attachment. In one aspect, nucleic acid polymer particles of the invention comprise polyacrylamide particles with uniform size distributions having low coefficients of variations, which result in reduced particle-to-particle variation in analytical assays. Such particle compositions are used in various amplification reactions to make amplicon libraries from nucleic acid fragment libraries.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
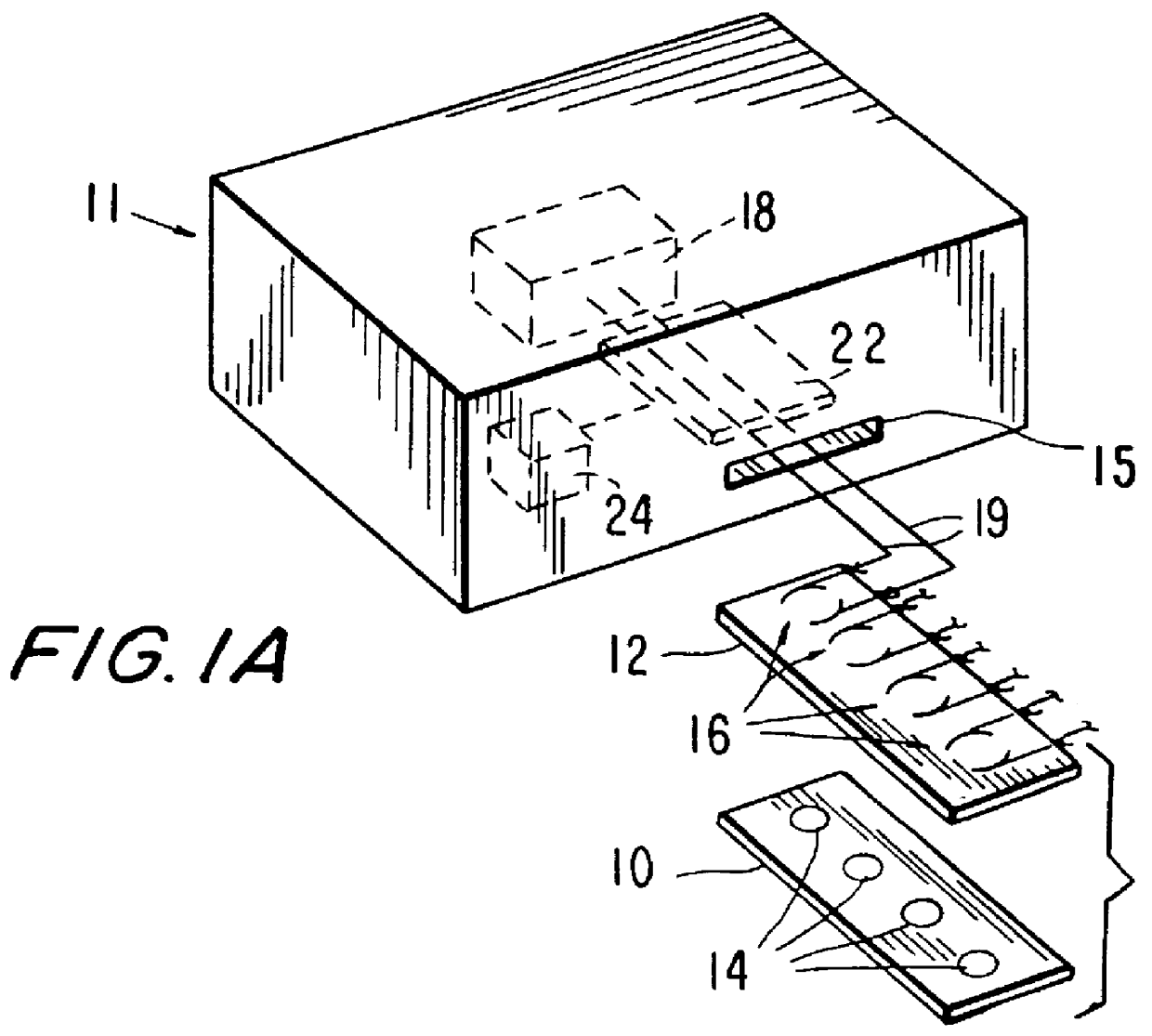
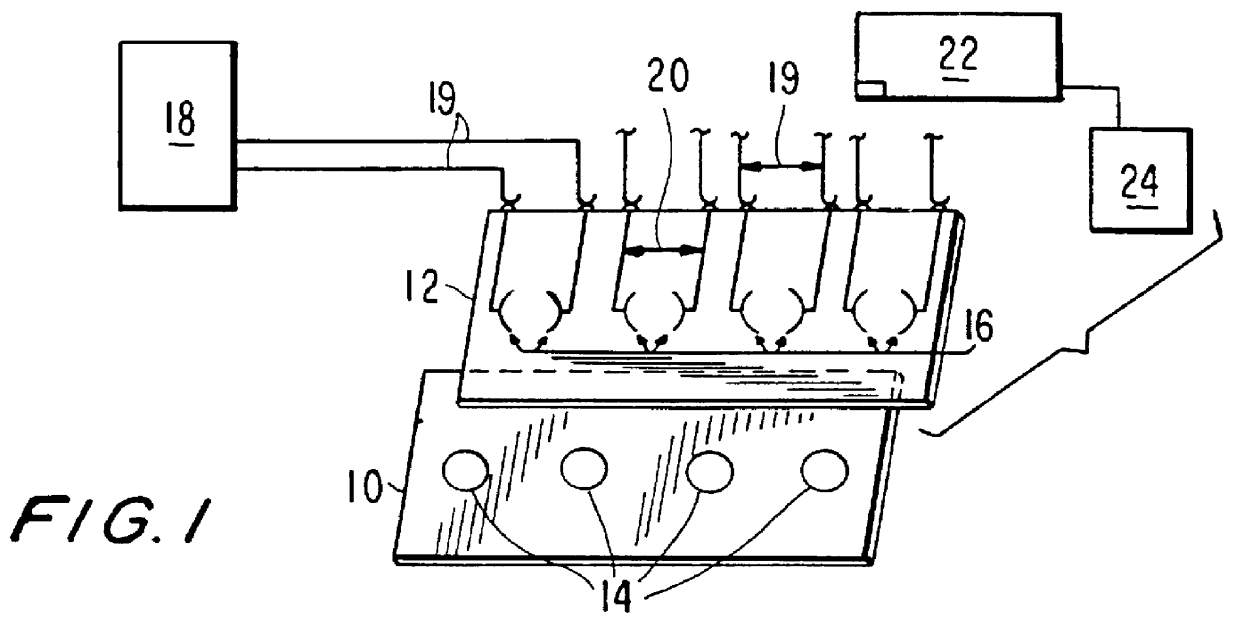
Miniaturized cell array methods and apparatus for cell-based screening
InactiveUS6103479AImprove throughputIncrease contentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyTemporal informationHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The present invention discloses devices and methods of performing high throughput screening of the physiological response of cells to biologically active compounds and methods of combining high-throughput with high-content spatial information at the cellular and subcellular level as well as temporal information about changes in physiological, biochemical and molecular activities. The present invention allows multiple types of cell interactions to be studied simultaneously by combining multicolor luminescence reading, microfluidic delivery, and environmental control of living cells in non-uniform micro-patterned arrays.
Owner:CELLOMICS
Ultra-fast nucleic acid sequencing device and a method for making and using the same
InactiveUS7001792B2Accurate identificationAccurately and effectively identifying bases of DNABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsUltra fastNucleic acid sequencing
A system and method employing at least one semiconductor device, or an arrangement of insulating and metal layers, having at least one detecting region which can include, for example, a recess or opening therein, for detecting a charge representative of a component of a polymer, such as a nucleic acid strand, proximate to the detecting region, and a method for manufacturing such a semiconductor device. The system and method can thus be used for sequencing individual nucleotides or bases of ribonucleic acid (RNA) or deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). The semiconductor device includes at least two doped regions, such as two n-typed regions implanted in a p-typed semiconductor layer or two p-typed regions implanted in an n-typed semiconductor layer. The detecting region permits a current to pass between the two doped regions in response to the presence of the component of the polymer, such as a base of a DNA or RNA strand. The current has characteristics representative of the component of the polymer, such as characteristics representative of the detected base of the DNA or RNA strand.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
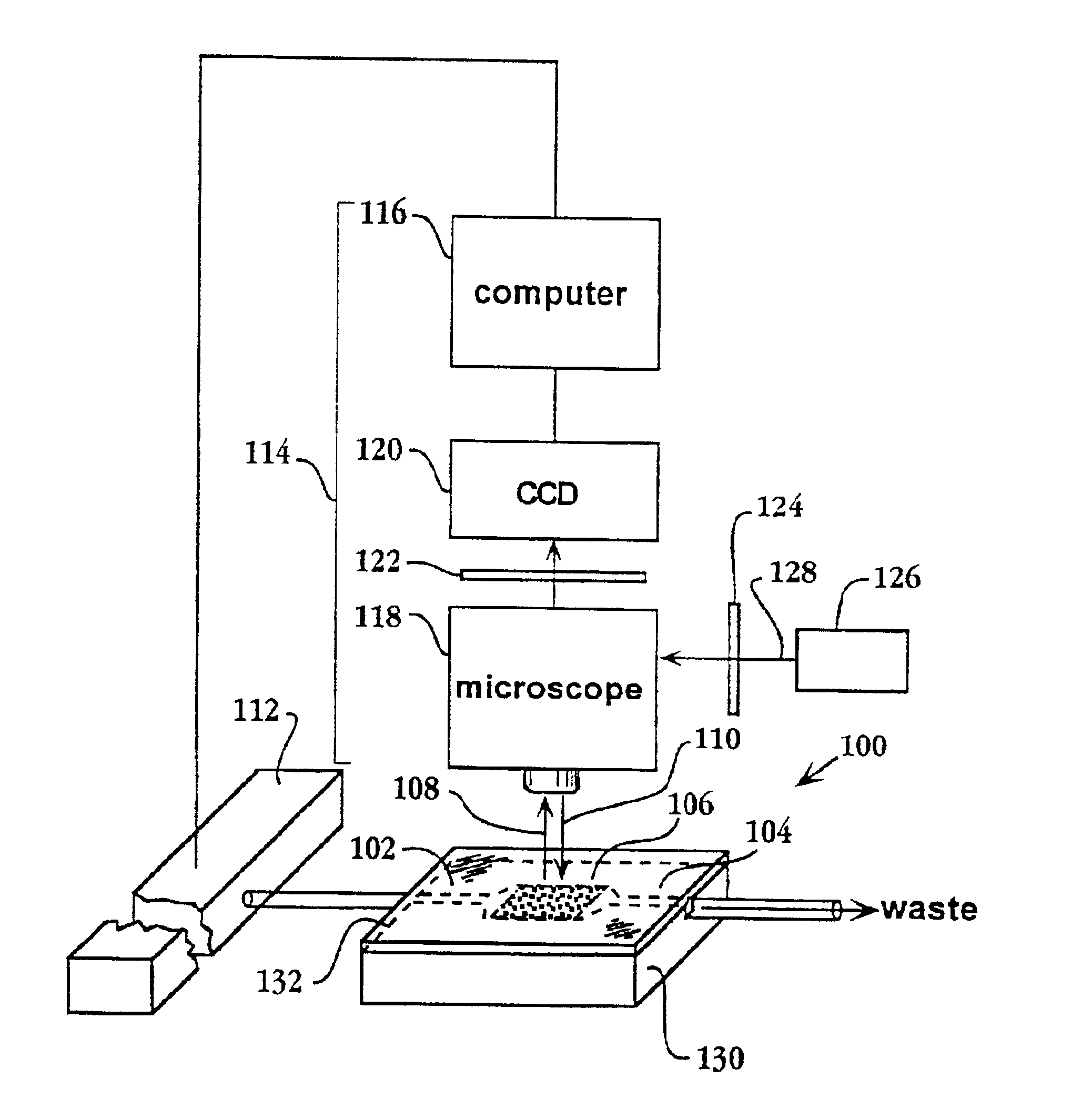
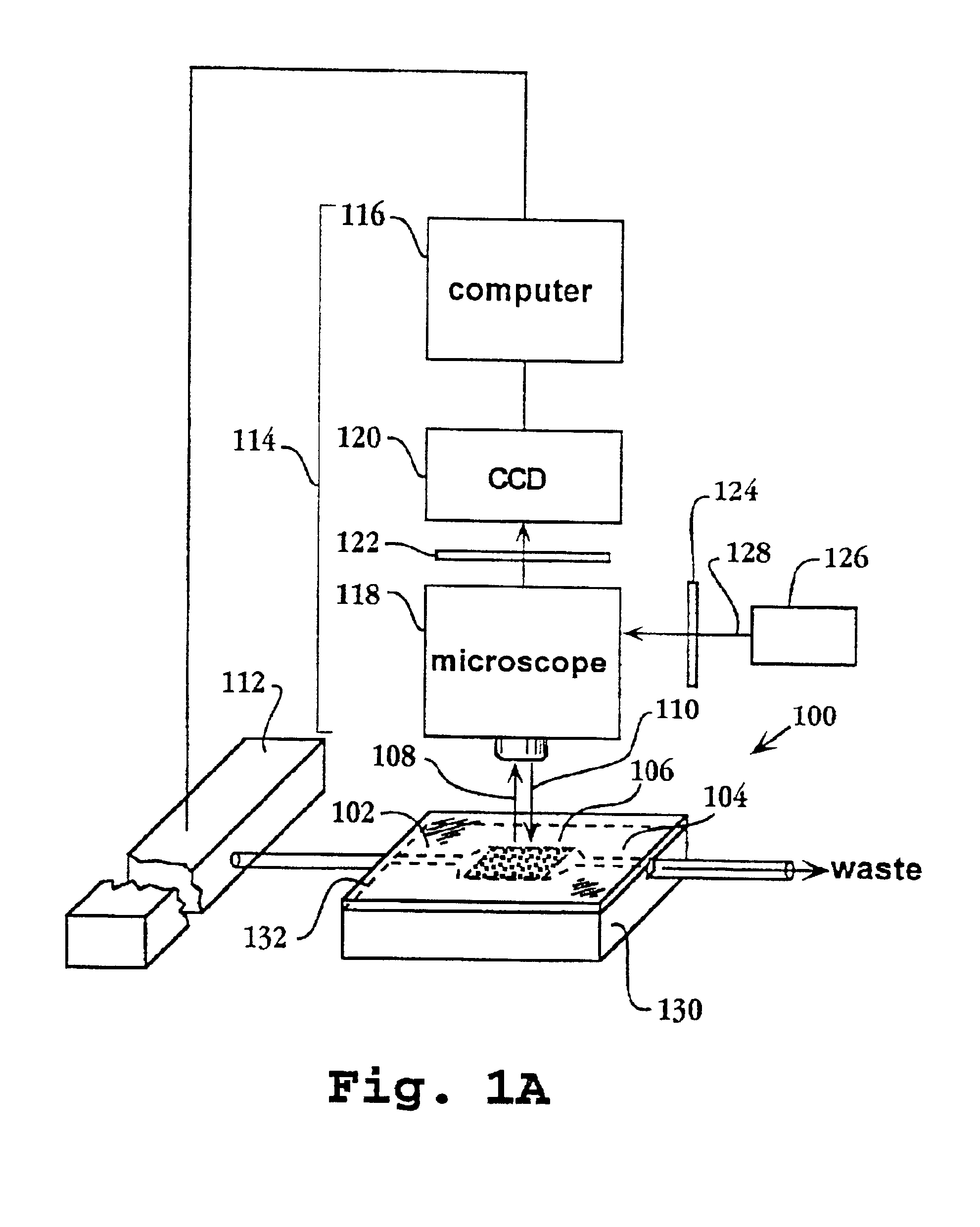
Systems, methods, and apparatuses to image a sample for biological or chemical analysis
ActiveUS20120270305A1Reduce capacityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical basisActuator
A fluidic device holder configured to orient a fluidic device. The device holder includes a support structure configured to receive a fluidic device. The support structure includes a base surface that faces in a direction along the Z-axis and is configured to have the fluidic device positioned thereon. The device holder also includes a plurality of reference surfaces facing in respective directions along an XY-plane. The device holder also includes an alignment assembly having an actuator and a movable locator arm that is operatively coupled to the actuator. The locator arm has an engagement end. The actuator moves the locator arm between retracted and biased positions to move the engagement end away from and toward the reference surfaces. The locator arm is configured to hold the fluidic device against the reference surfaces when the locator arm is in the biased position.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
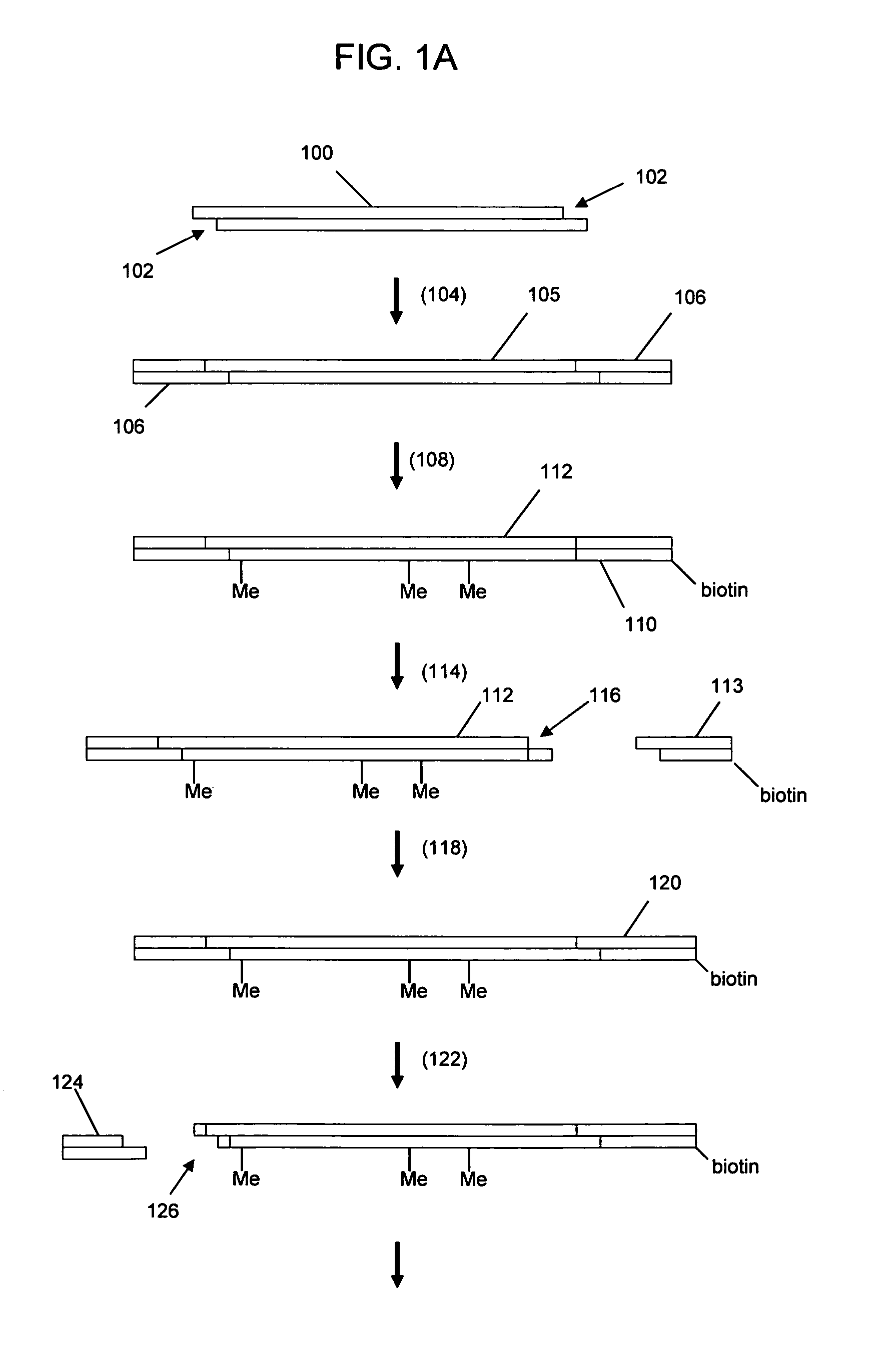
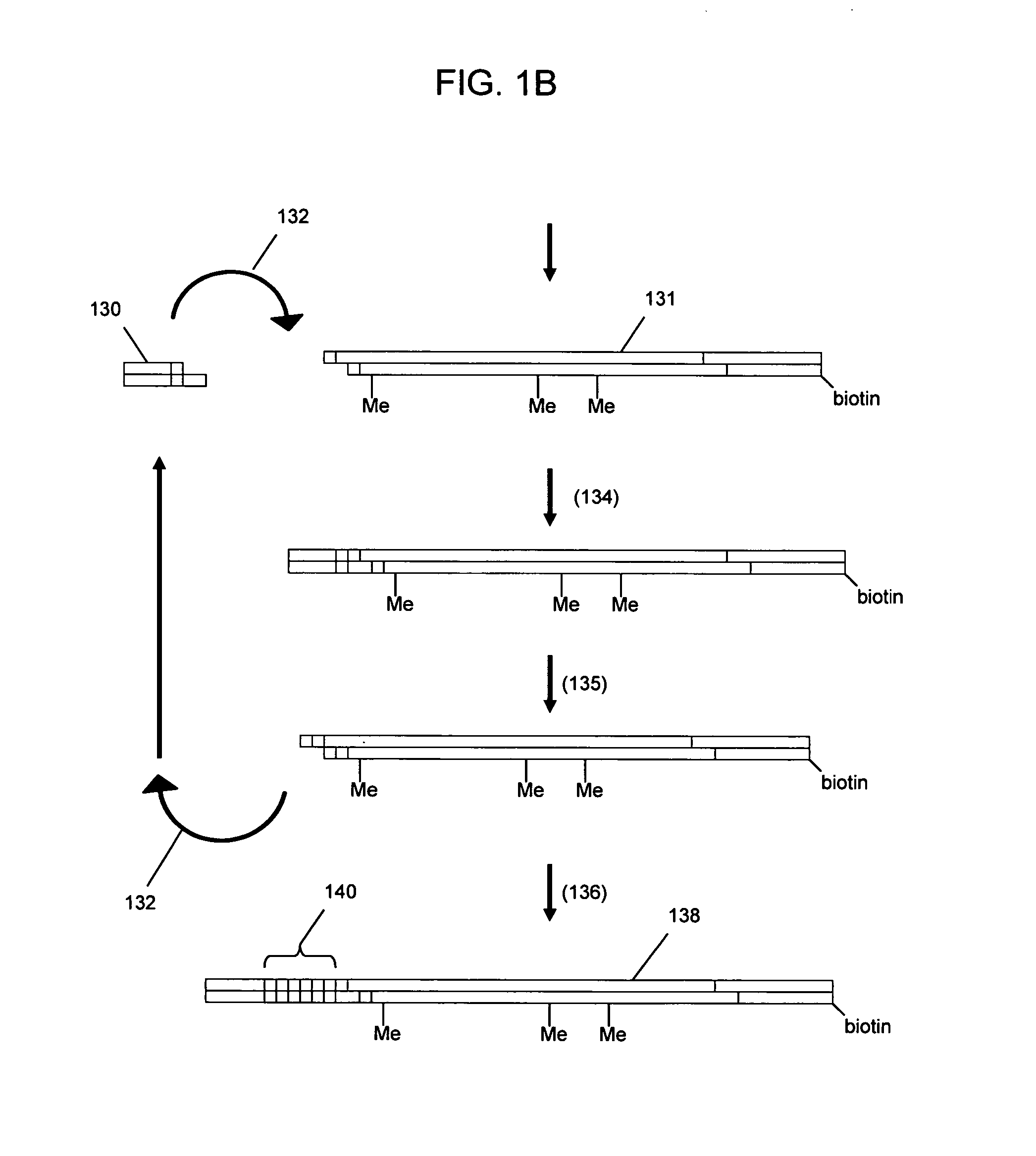
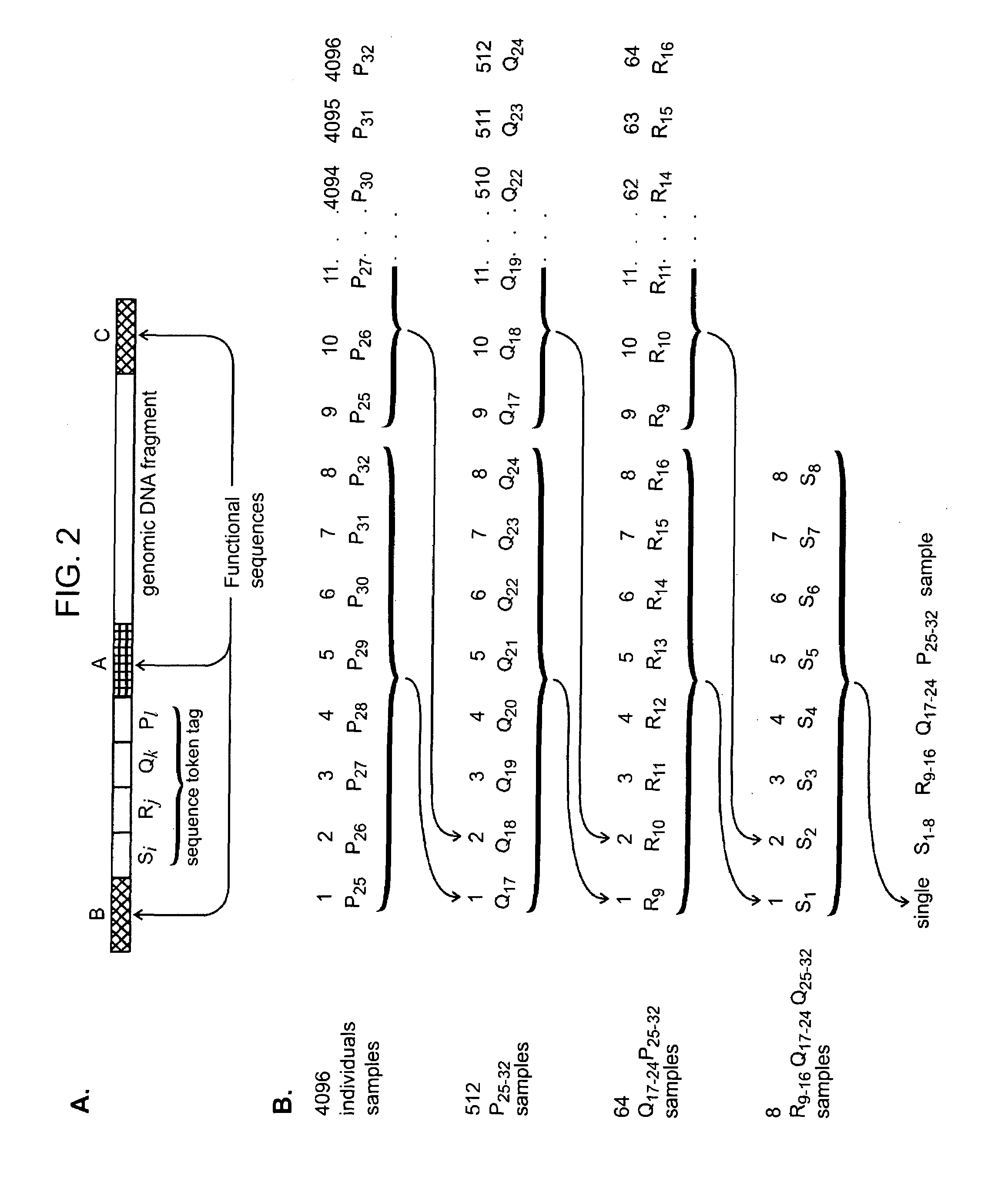
Nucleic acid analysis using sequence tokens
ActiveUS7544473B2Efficiently determine variations in nucleotide sequences in the associated nucleic acid sequence fragmentsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDon't repeat yourselfNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides methods and compositions for tagging nucleic acid sequence fragments, e.g., a set of nucleic acid sequence fragments from a single genome, with one or more unique members of a collection of oligonucleotide tags, or sequence tokens, which, in turn, can be identified using a variety of readout platforms. As a general rule, a given sequence token is used once and only once in any tag sequence. In addition, the present invention also provides methods for using the sequence tokens to efficiently determine variations in nucleotide sequences in the associated nucleic acid sequence fragments.
Owner:PERSONAL GENOME DIAGNOSTICS INC
Integrated active flux microfluidic devices and methods
InactiveUS6767706B2Rapid and complete exposureQuick and accurate and inexpensive analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFlow mixersAntigenHybridization probe
The invention relates to a microfabricated device for the rapid detection of DNA, proteins or other molecules associated with a particular disease. The devices and methods of the invention can be used for the simultaneous diagnosis of multiple diseases by detecting molecules (e.g. amounts of molecules), such as polynucleotides (e.g., DNA) or proteins (e.g., antibodies), by measuring the signal of a detectable reporter associated with hybridized polynucleotides or antigen / antibody complex. In the microfabricated device according to the invention, detection of the presence of molecules (i.e., polynucleotides, proteins, or antigen / antibody complexes) are correlated to a hybridization signal from an optically-detectable (e.g. fluorescent) reporter associated with the bound molecules. These hybridization signals can be detected by any suitable means, for example optical, and can be stored for example in a computer as a representation of the presence of a particular gene. Hybridization probes can be immobilized on a substrate that forms part of or is exposed to a channel or channels of the device that form a closed loop, for circulation of sample to actively contact complementary probes. Universal chips according to the invention can be fabricated not only with DNA but also with other molecules such as RNA, proteins, peptide nucleic acid (PNA) and polyamide molecules.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Support for high performance affinity chromatography and other uses
Multilayered particulate materials are formed by coating a particulate substrate with a metal and adsorbing an organic layer comprising a recognition moiety onto the metal film. The recognition moiety interacts with an analyte of interest allowing for its detection, purification, etc. Suitable recognition moieties can be selected from a range of species including, small molecules, polymers and biomolecules and the like. The novel particulate materials of the invention can be utilized in an array of methods including, ion-exchange, ion-selective ion-exchange, assays, affinity dialysis, size exclusion dialysis, as supports in solid phase synthesis, combinatorial synthesis and screening of compound libraries and the like.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Drug delivery system and method
InactiveUS6041252AFacilitated releaseFast wayBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyLiposomeBiomedical engineering
A method for delivering a therapeutic agent to a predetermined location in a host is disclosed, wherein a liposome-encapsulated therapeutic agent is administered to the host, and an electrical field which encompasses a predetermined region within the host is established, such that as the liposome-encapsulated agent is exposed to the electrical field the release of the agent from the liposome to the predetermined region is enhanced.
Owner:ICHOR MEDICAL SYST
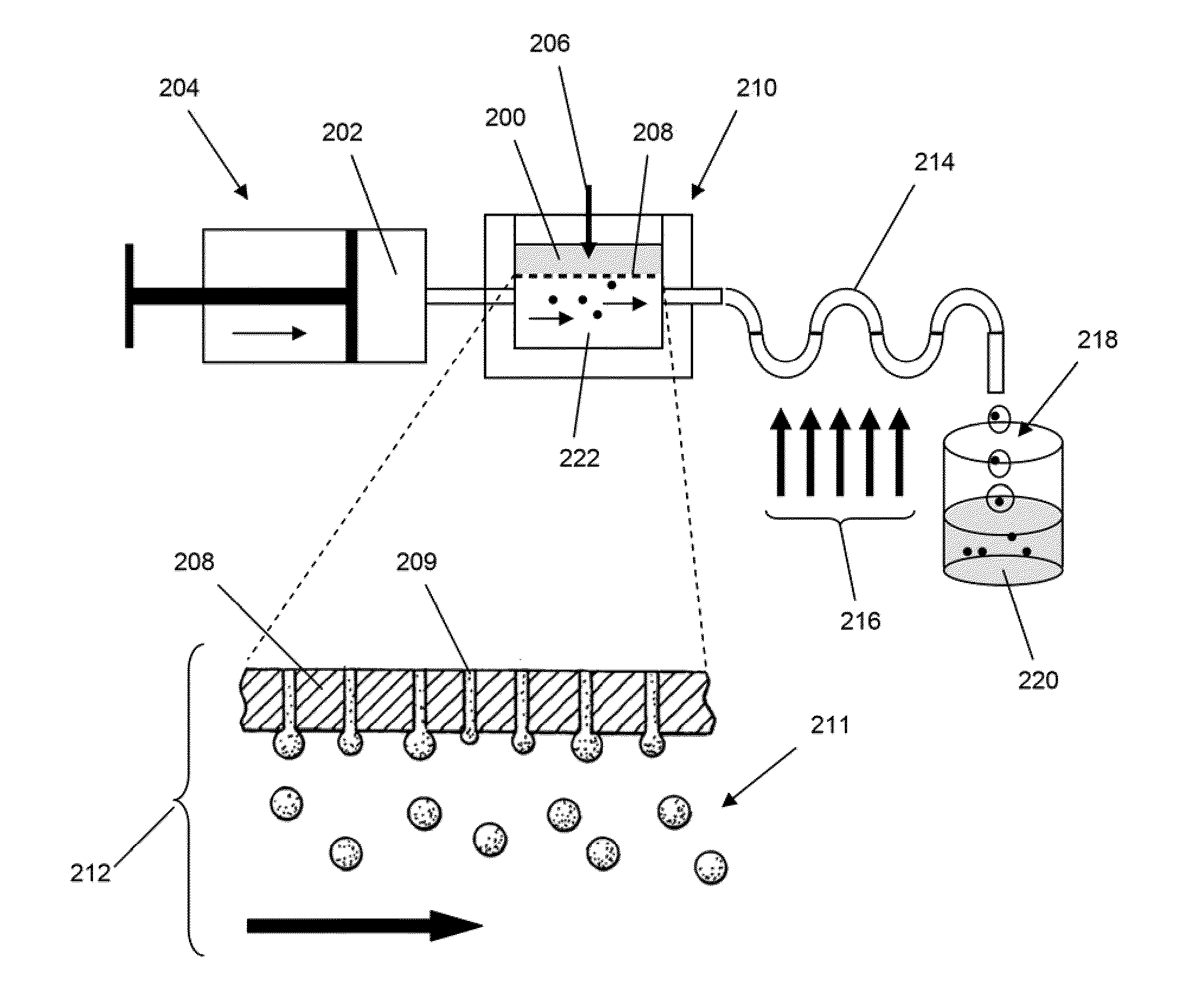
Microfabricated crossflow devices and methods
InactiveUS7294503B2Increase sensitivityHigh numberSludge treatmentFixed microstructural devicesMain channelEnzyme
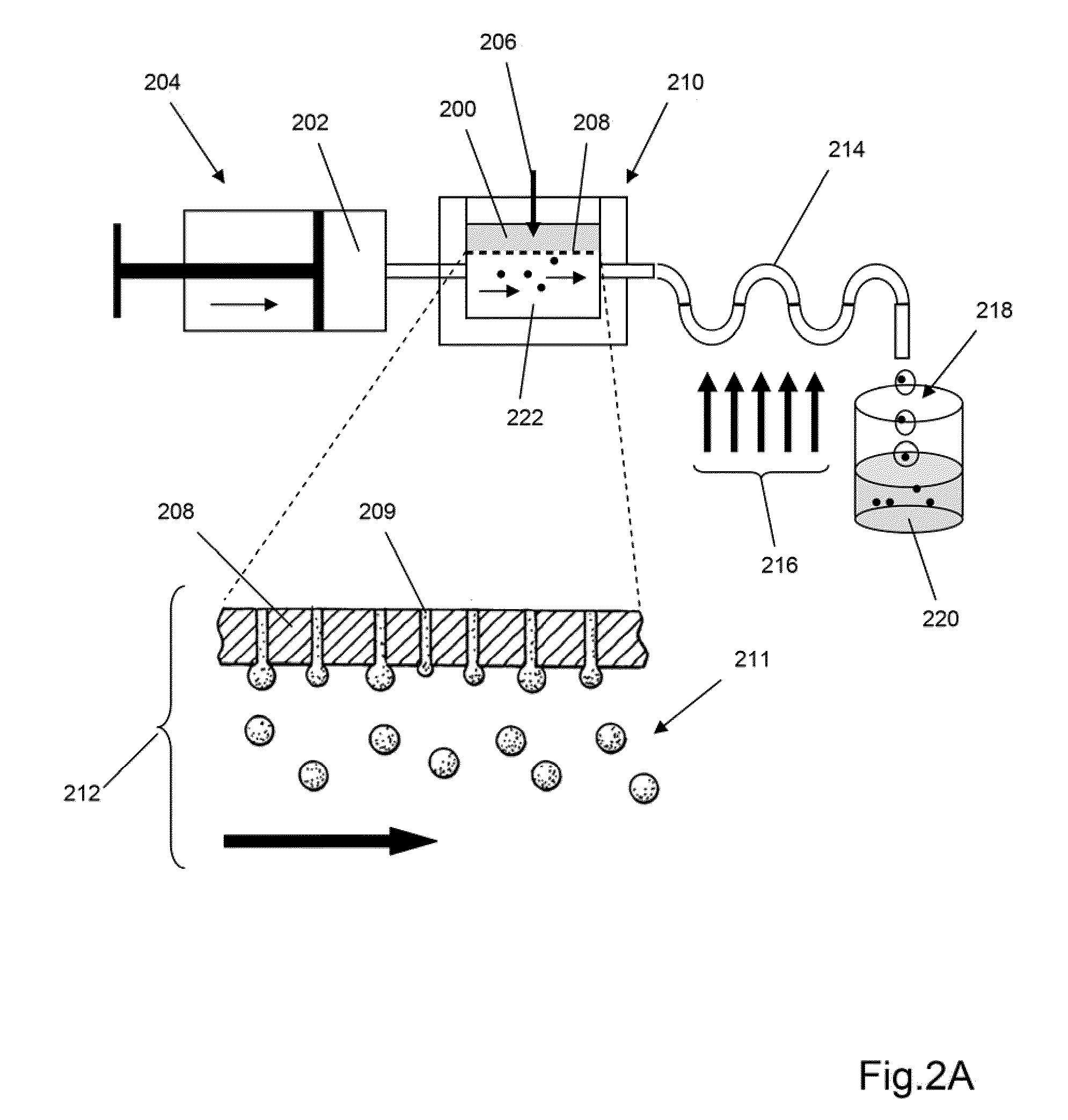
A microfluidic device for analyzing and / or sorting biological materials (e.g., molecules such as polynucleotides and polypeptides, including proteins and enzymes; viruses and cells) and methods for its use are provided. The device and methods of the invention are useful for sorting particles, e.g. virions. The invention is also useful for high throughput screening, e.g. combinatorial screening. The microfluidic device comprises a main channel and an inlet region in communication with the main channel at a droplet extrusion region. Droplets of solution containing the biological material are deposited into the main channel through the droplet extrusion region. A fluid different from and incompatible with the solution containing the biological material flows through the main channel so that the droplets containing the biological material do not diffuse or mix. Biological material within the droplets can be analyzed and / or sorted by detecting a predetermined characteristic of the biological sample in each droplet and sorting the droplet accordingly.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
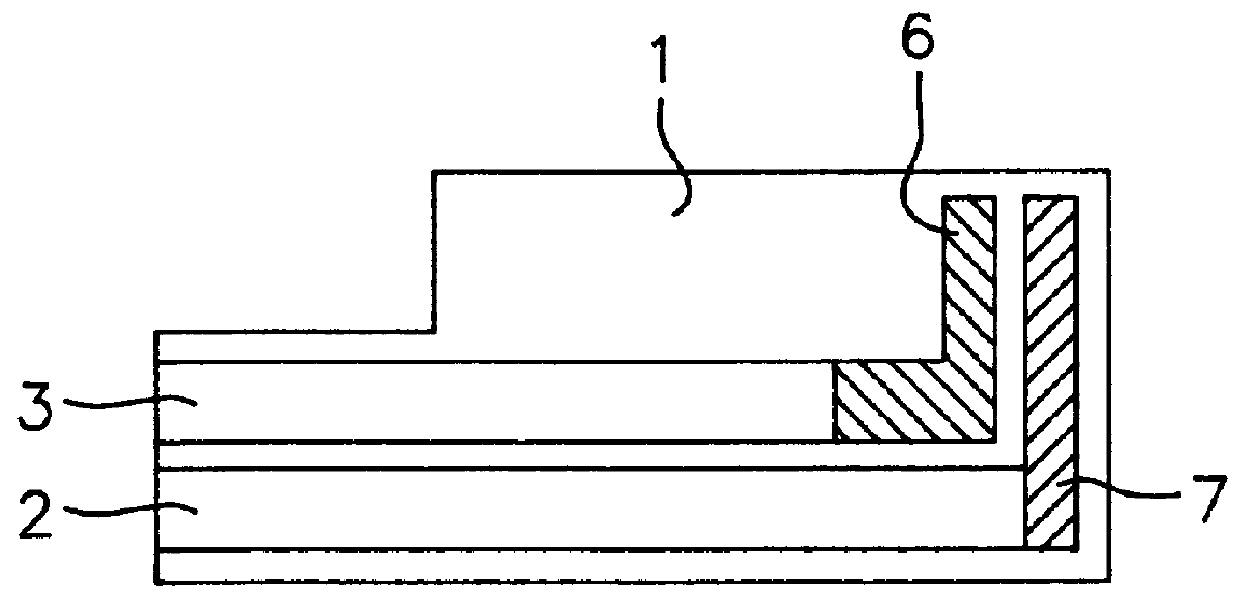
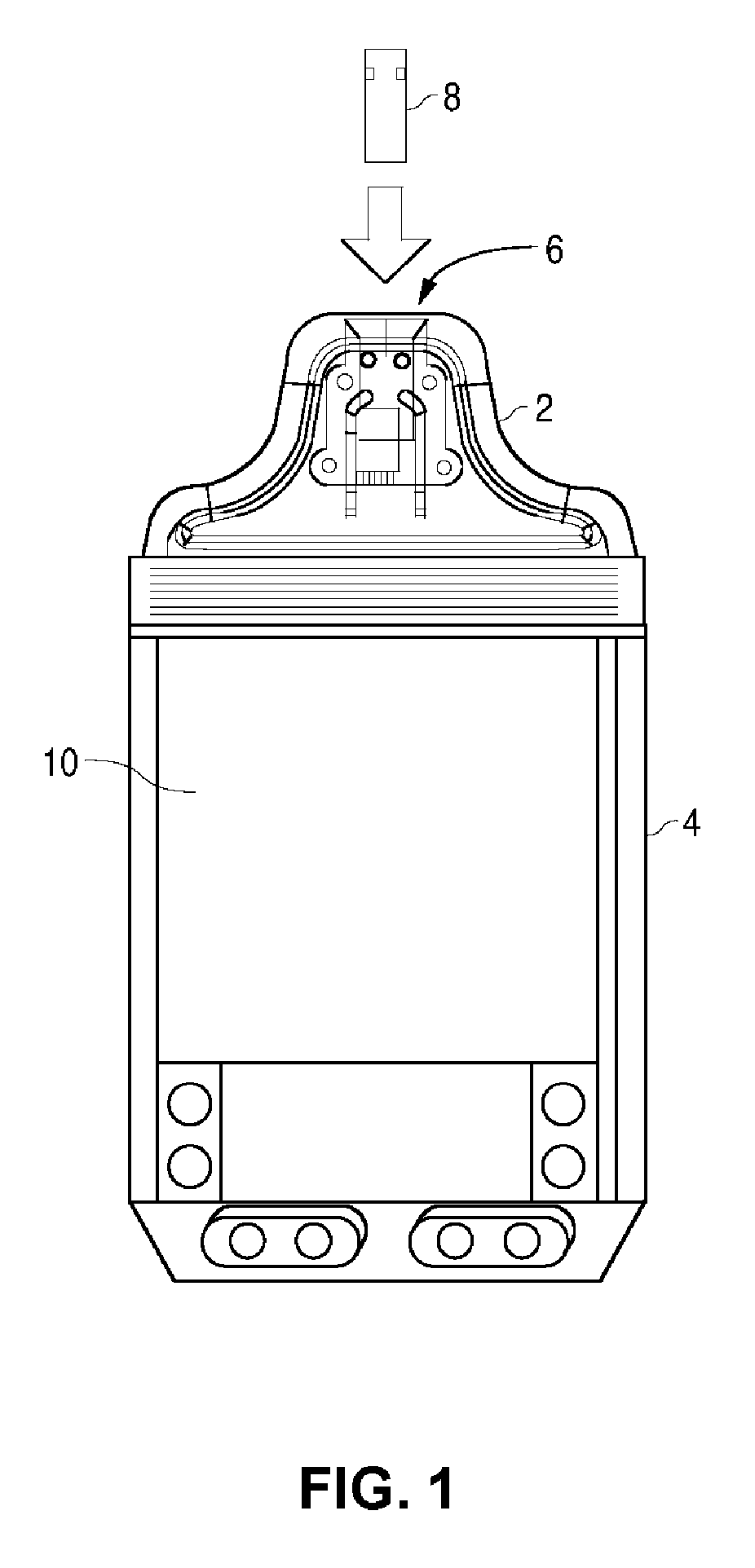
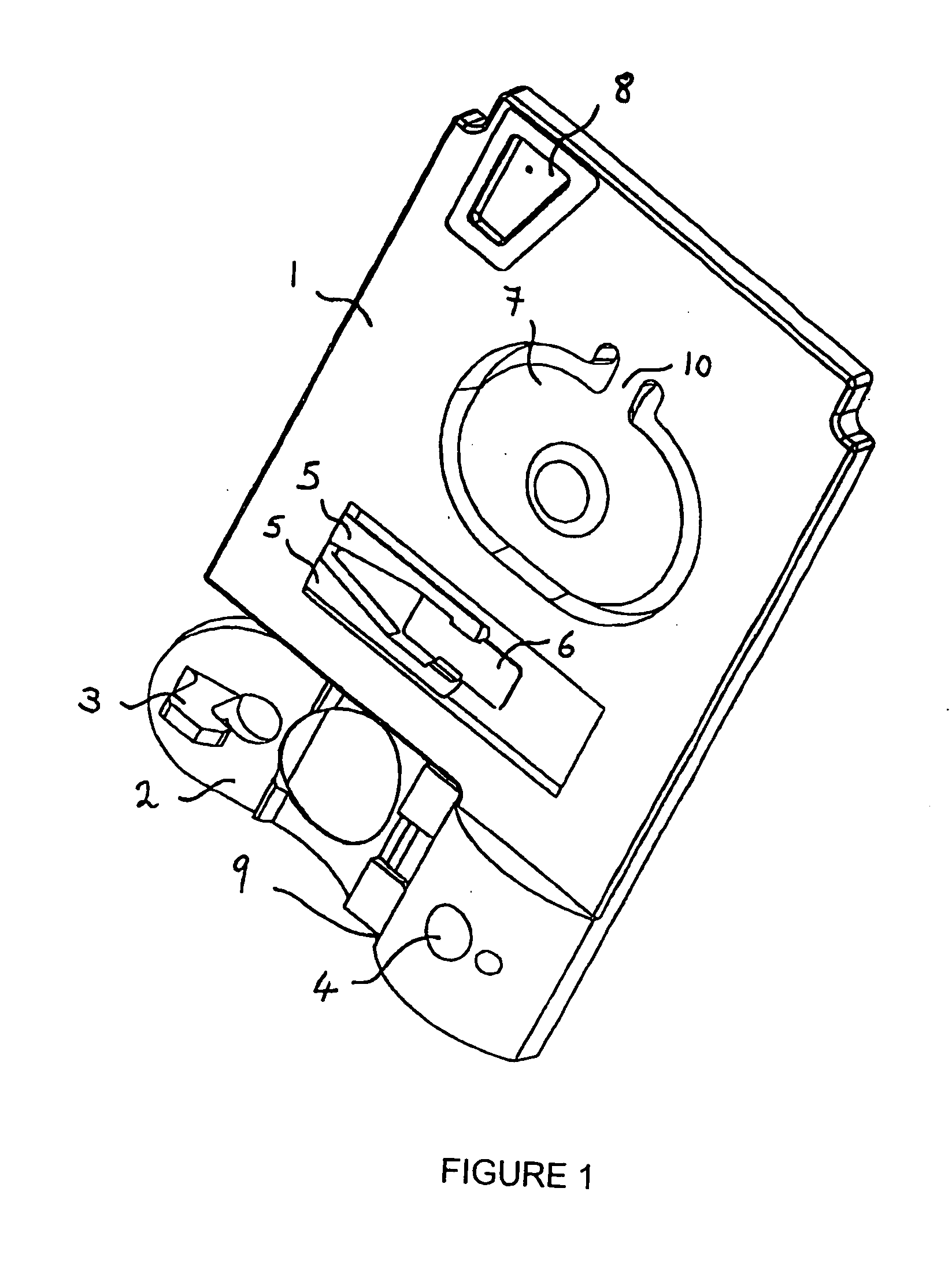
Analyte measurement
InactiveUS20040096959A1Low viscosityMore suitedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrochemical detectorAnalyte
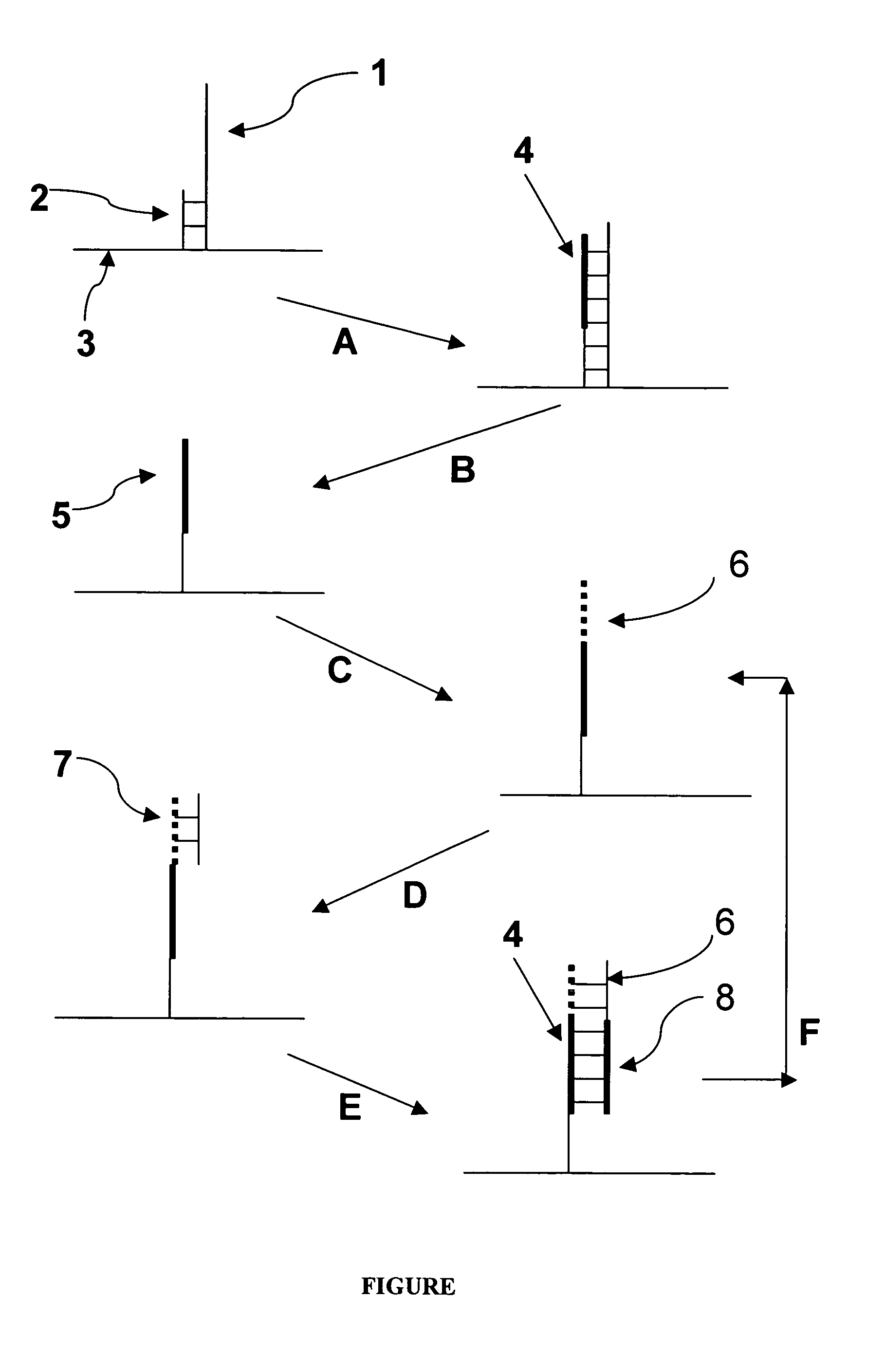
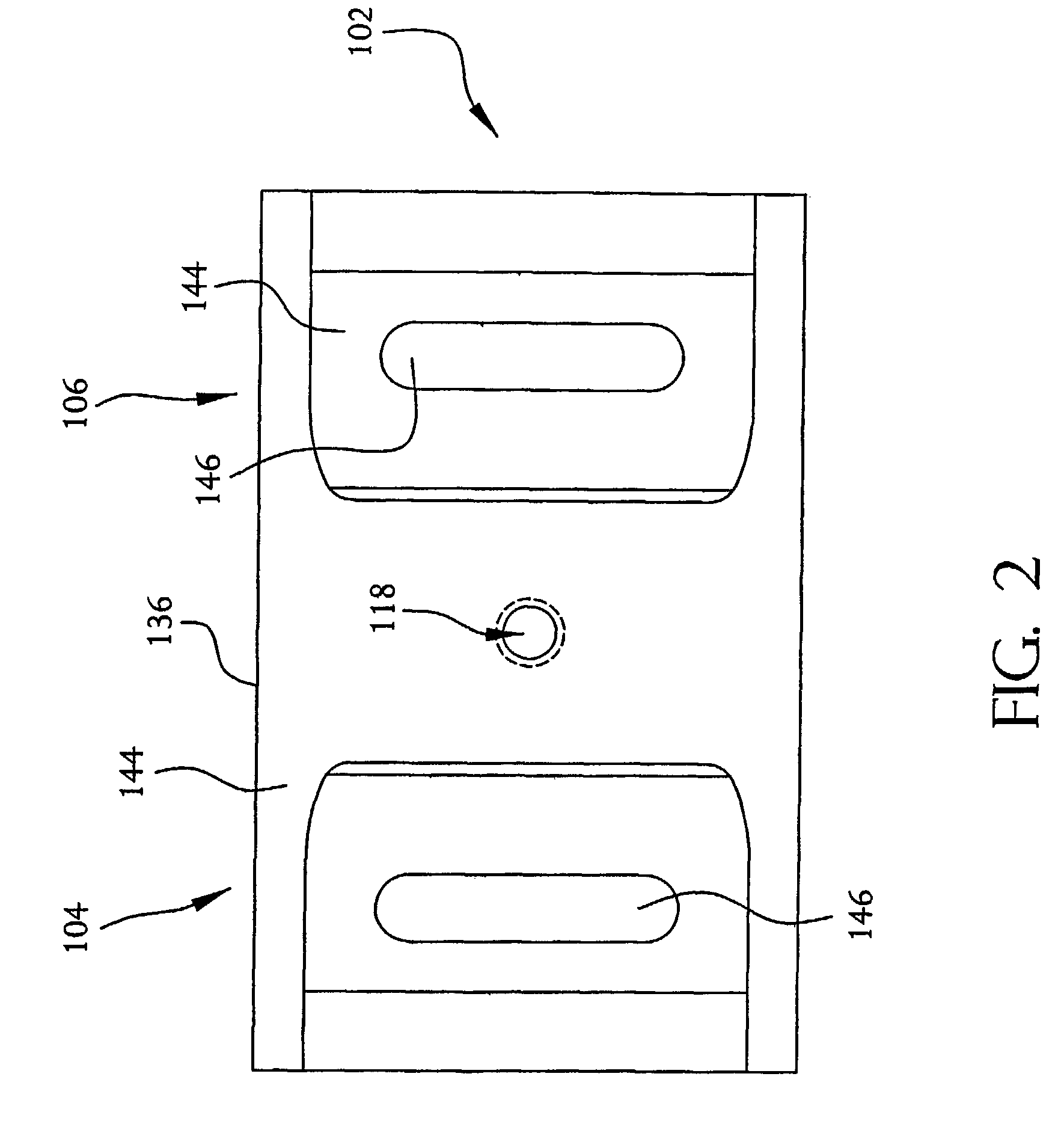
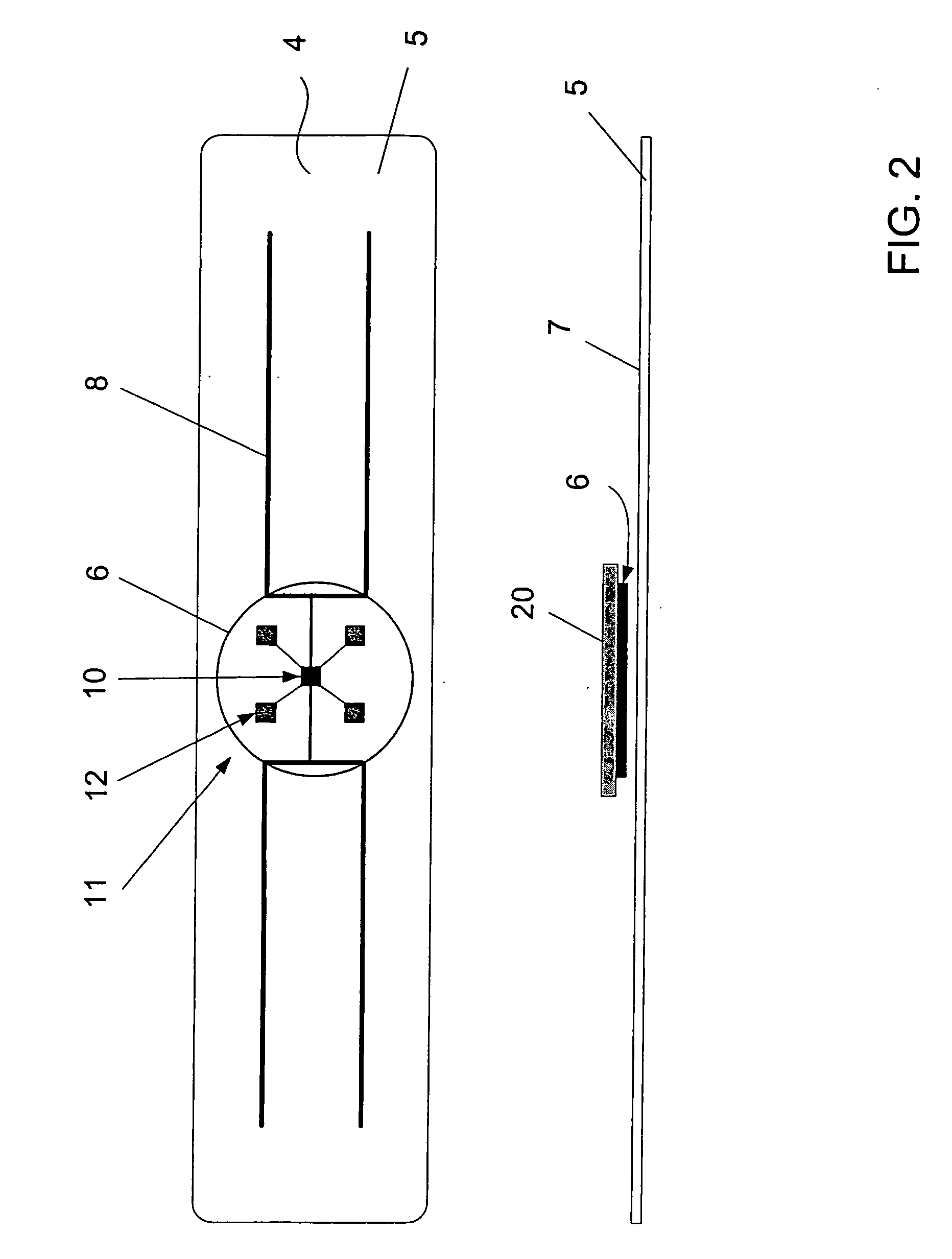
A glucose sensor in the form of a skin patch 2 has a microneedle 4 which painlessly penetrates the skin to draw out interstitial fluid. The interstitial fluid passes to a common entrance port 7. A series of microchannels 8 is provided on the skin patch. The fluid drawn onto the patch is selectively switched between a number of microchannels 8 by means of electro-osmotic pumps 10 and hydrophobic gates 12. Each microchannel 8 has an electrochemical detector 11 for sensing gluocse concentration. Also disclosed is a monlithic device with an integrated lance 83.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC +1
Immunoassay device with improved sample closure
ActiveUS20050054078A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCapillary TubingEngineering
An apparatus and method for sealing a fluid sample collection device, comprising: loading a fluid sample collection device with a fluid sample, said device comprising a housing having at least one substantially planar surface that includes an orifice in fluid communication with an internal fluid sample holding chamber which terminates at an internal capillary stop; and slidably moving a sealing element over at least a portion of said substantially planar surface in a way that displaces any excess fluid sample away from the orifice, seals the fluid sample within said holding chamber, and inhibits the fluid sample from prematurely breaking through the internal capillary stop.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
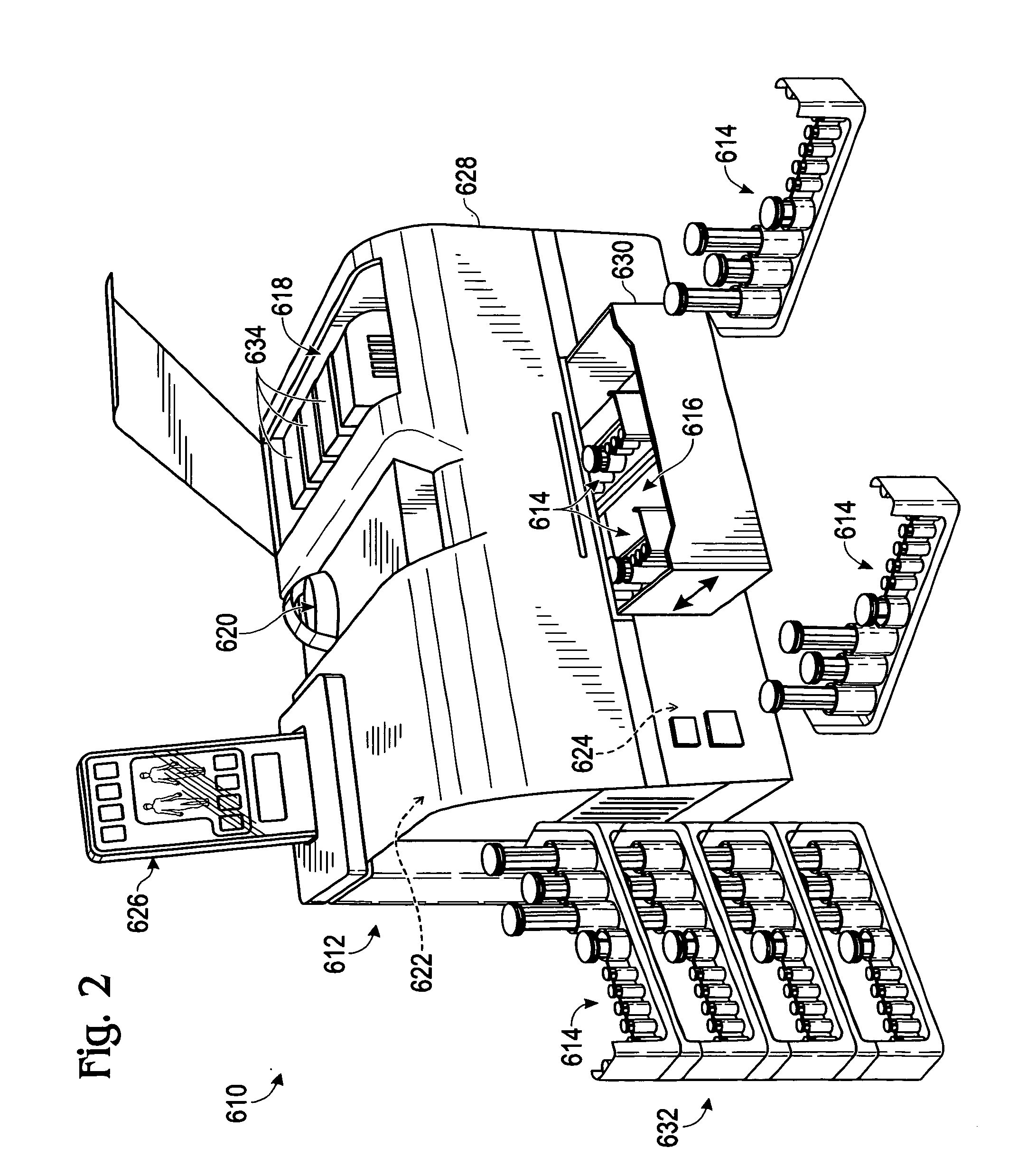
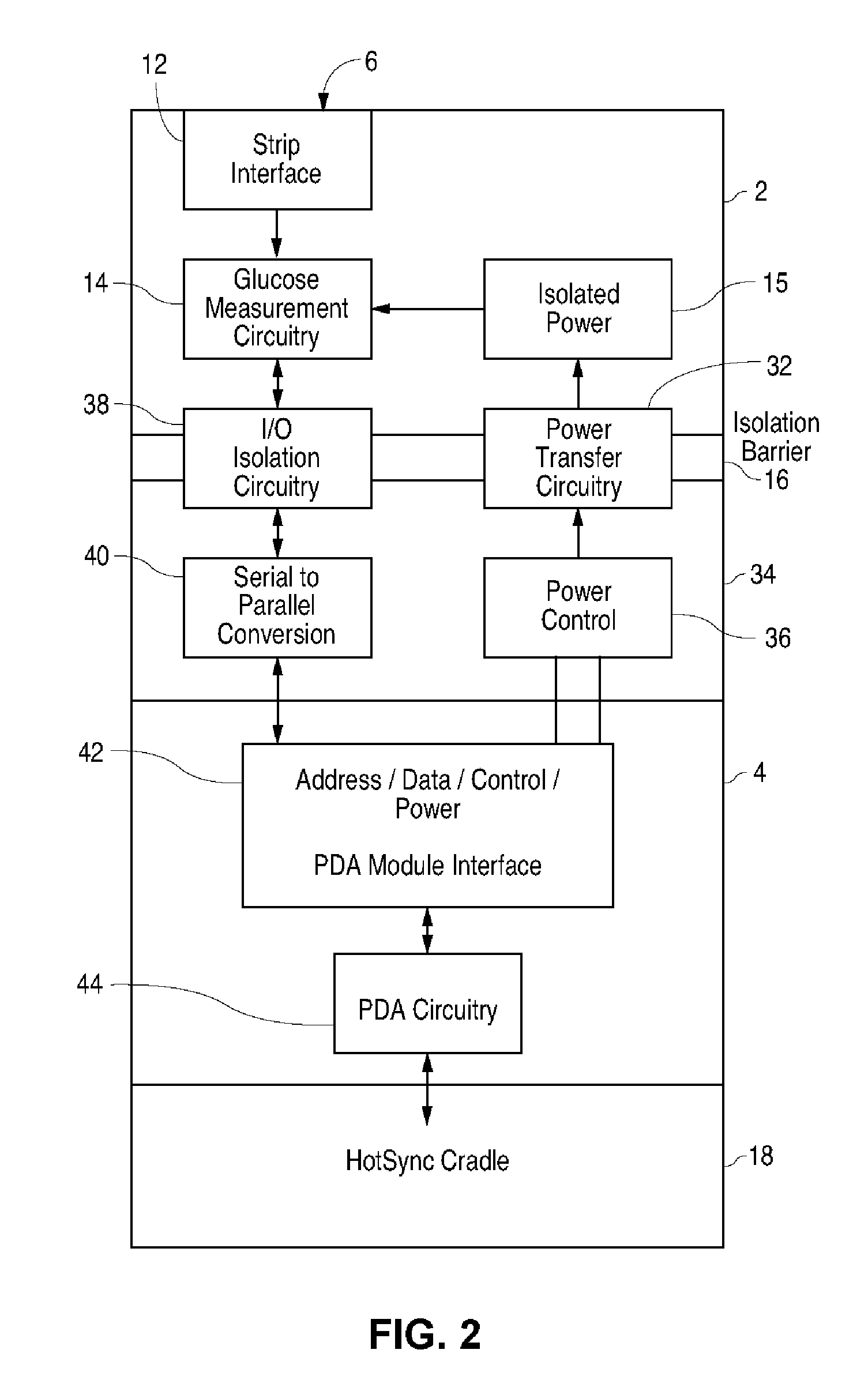
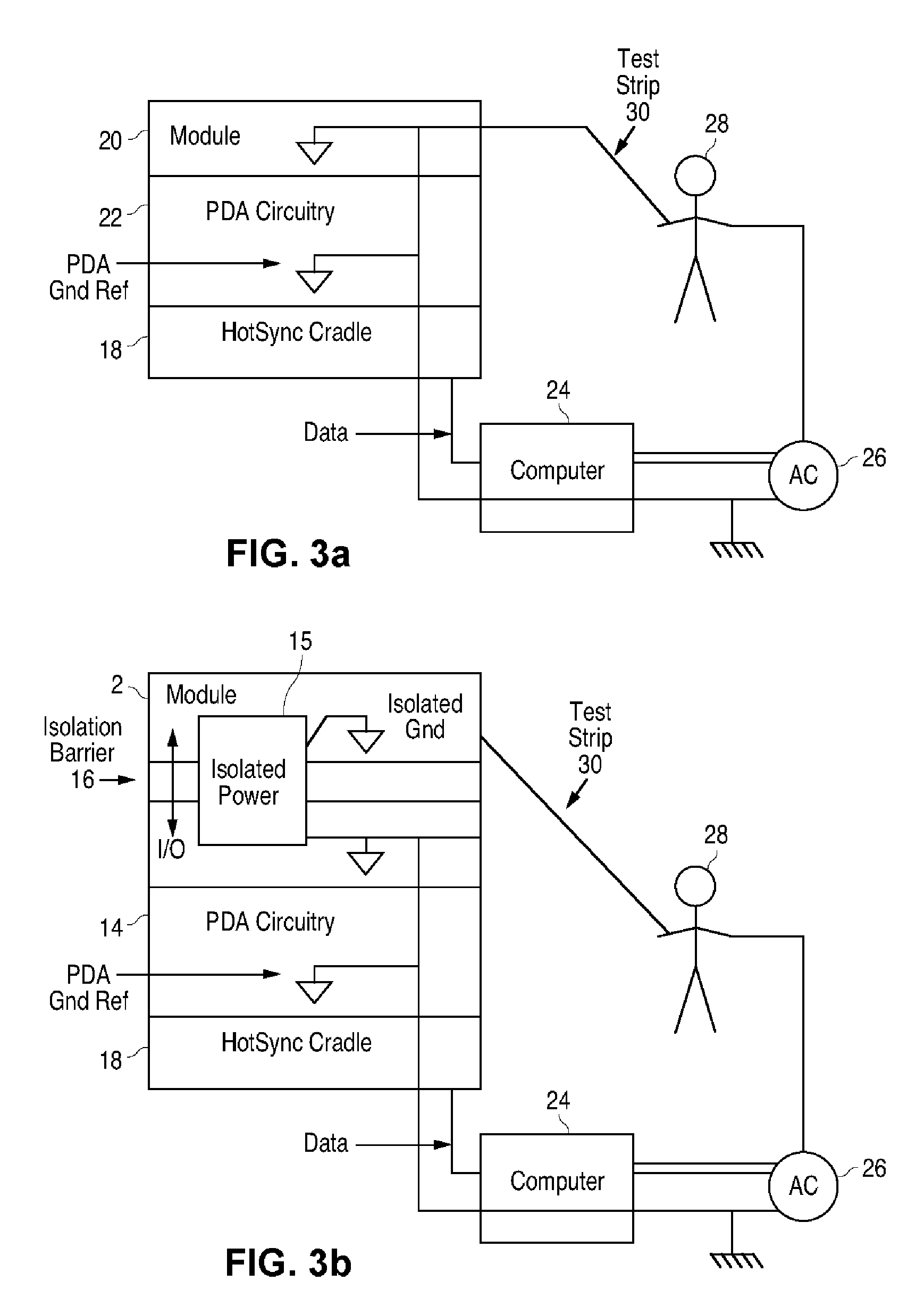
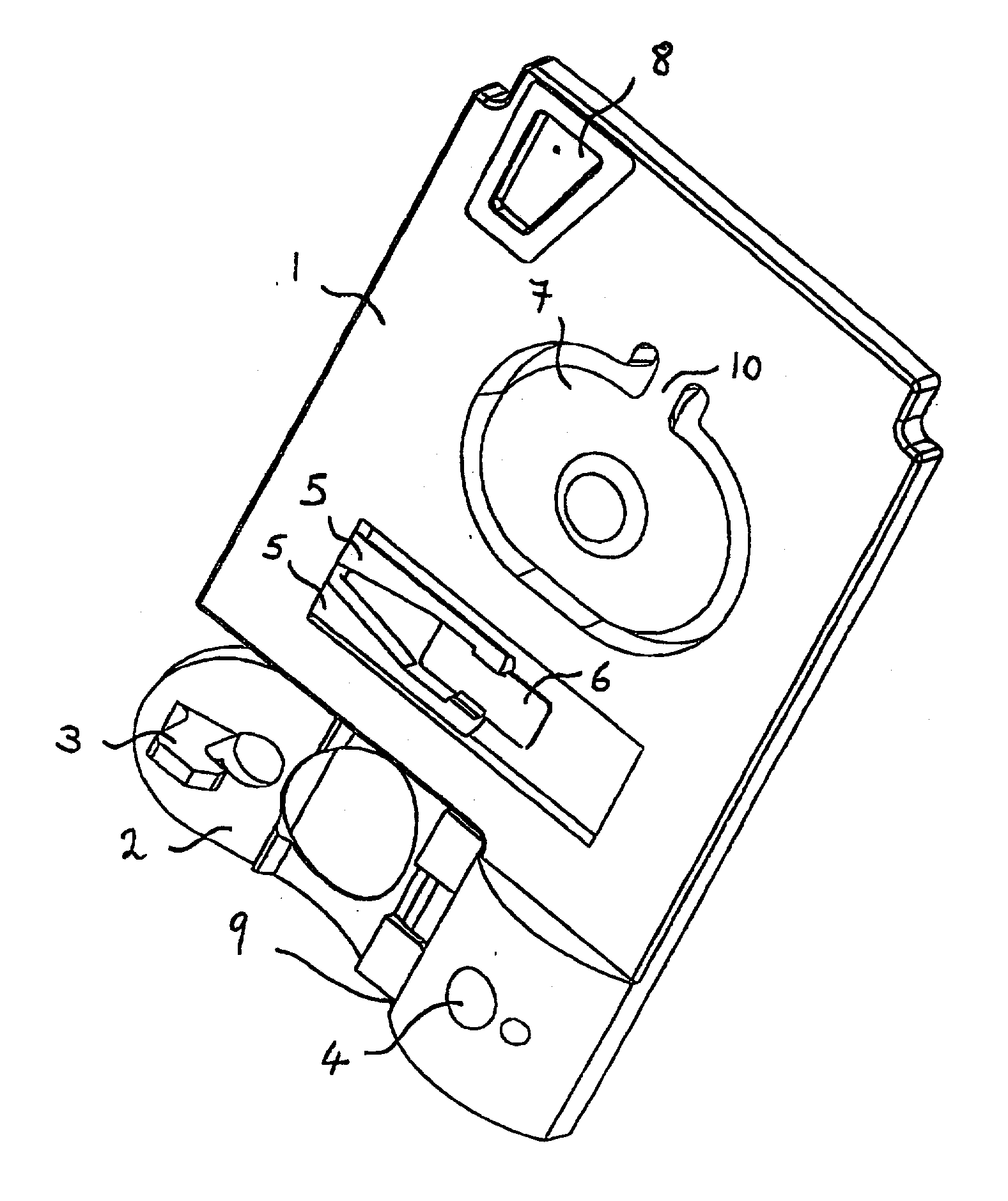
Blood glucose tracking apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20050277164A1Easy and precise applicationEfficient use ofBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHand heldComputer module
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Apparatus and methods for analyte measurement and immuno assay
ActiveUS20030170881A1Avoid disadvantagesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPoint of careOrganism
The present invention relates to an apparatus for conducting a variety of assays for the determination of analytes in liquid samples, and relates to the methods for such assays. In particular, the invention relates to a single-use cartridge designed to be adaptable to a variety of real-time assay protocols, preferably assays for the determination of analytes in biological samples using immunosensors or other ligand / ligand receptor-based biosensor embodiments. The cartridge provides novel features for processing a metered portion of a sample, for precise and flexible control of the movement of a sample or second fluid within the cartridge, for the amending of solutions with additional compounds during an assay, and for the construction of immunosensors capable of adaptation to diverse analyte measurements. The disclosed device and methods of use enjoy substantial benefits over the prior art, including simplicity of use by an operator, rapid in situ determinations of one or more analytes, and single-use methodology that minimizes the risk of contamination of both operator and patient. The disclosed invention is adaptable to the point-of-care clinical diagnostic field, including use in accident sites, emergency rooms, surgery, nursing homes, intensive care units, and non-medical environments.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Capillary immunoassay and device therefor comprising mobilizable particulate labelled reagents
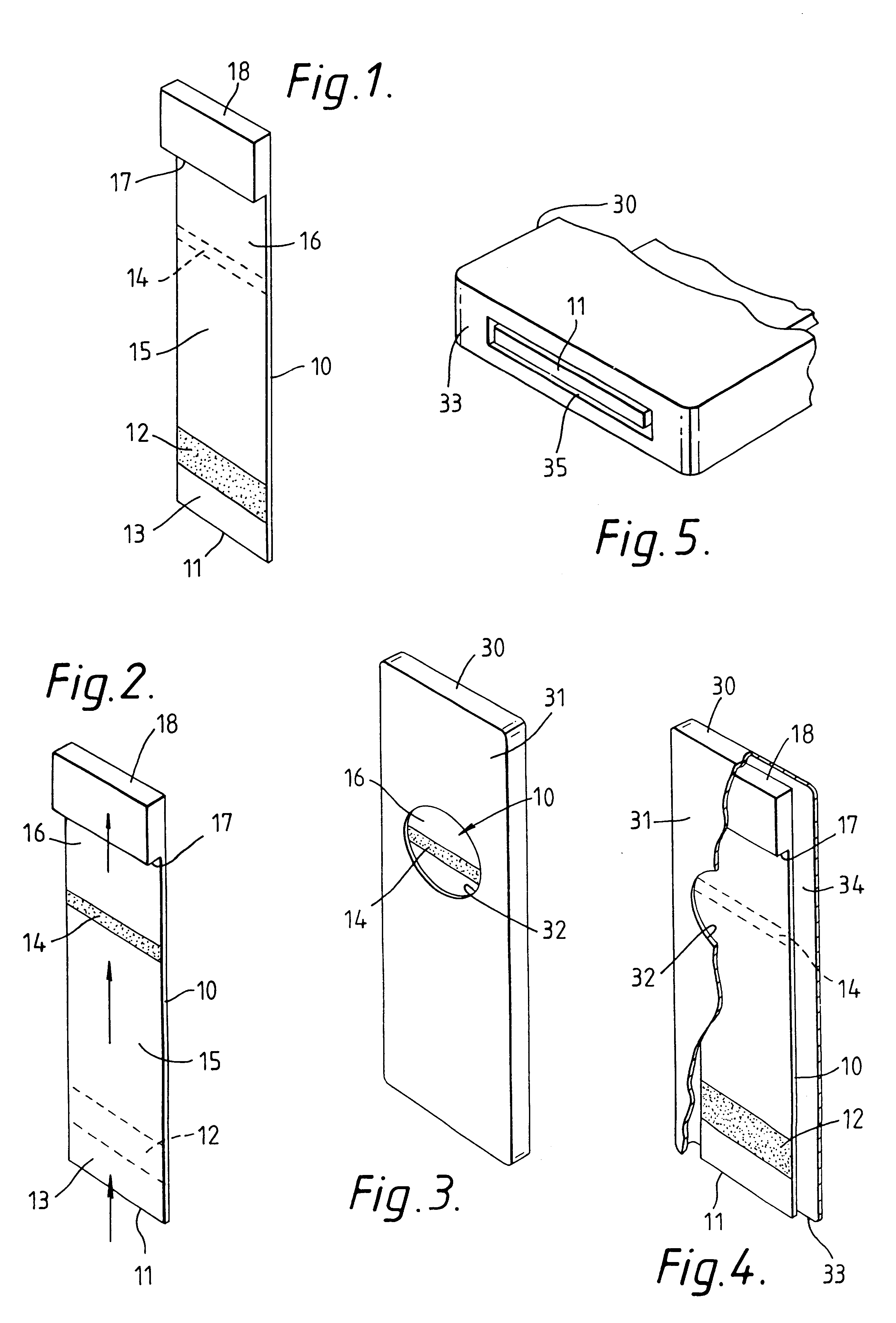
InactiveUS6187598B1Improve completenessBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPlastic materialsCapillary Tubing
An analytical test device useful for example in pregnancy testing, comprises a hollow casing (500) constructed of moisture-impervious solid material, such as plastics materials, containing a dry porous carrier (510) which communicates indirectly with the exterior of the casing via a bibulous sample receiving member (506) which protrudes from the casing such that a liquid test sample can be applied to the receiving member and permeate therefrom to the porous carrier, the carrier containing in a first zone a labelled specific binding reagent is freely mobile within the porous carrier when in the moist state, and in a second zone spatially distinct from the first zone unlabelled specific binding reagent for the same analyte which unlabelled reagent is permanently immobilised on the carrier material and is therefore not mobile in the moist state, the two zones being arranged such that liquid sample applied to the porous carrier can permeate via the first zone into the second zone, and the device incorporating means, such as an aperture (508) in the casing, enabling the extent (if any) to which the labelled reagent becomes bound in the second zone to be observed. Preferably the device includes a removable cap for the protruding bibulous member.
Owner:INVERNESS SWITZERLAND GMBH
Assay plates, reader systems and methods for luminescence test measurements
ActiveUS20040022677A1Improve collection efficiencyIncrease assayBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTest measurementBiology
Luminescence test measurements are conducted using an assay module having integrated electrodes with a reader apparatus adapted to receive assay modules, induce luminescence, preferably electrode induced luminescence, in the wells or assay regions of the assay modules and measure the induced luminescence.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
Immunoassay device with immuno-reference electrode
InactiveUS20060160164A1Reduce distractionsIncrease ionic strengthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImmune profilingImmobilized Antibodies
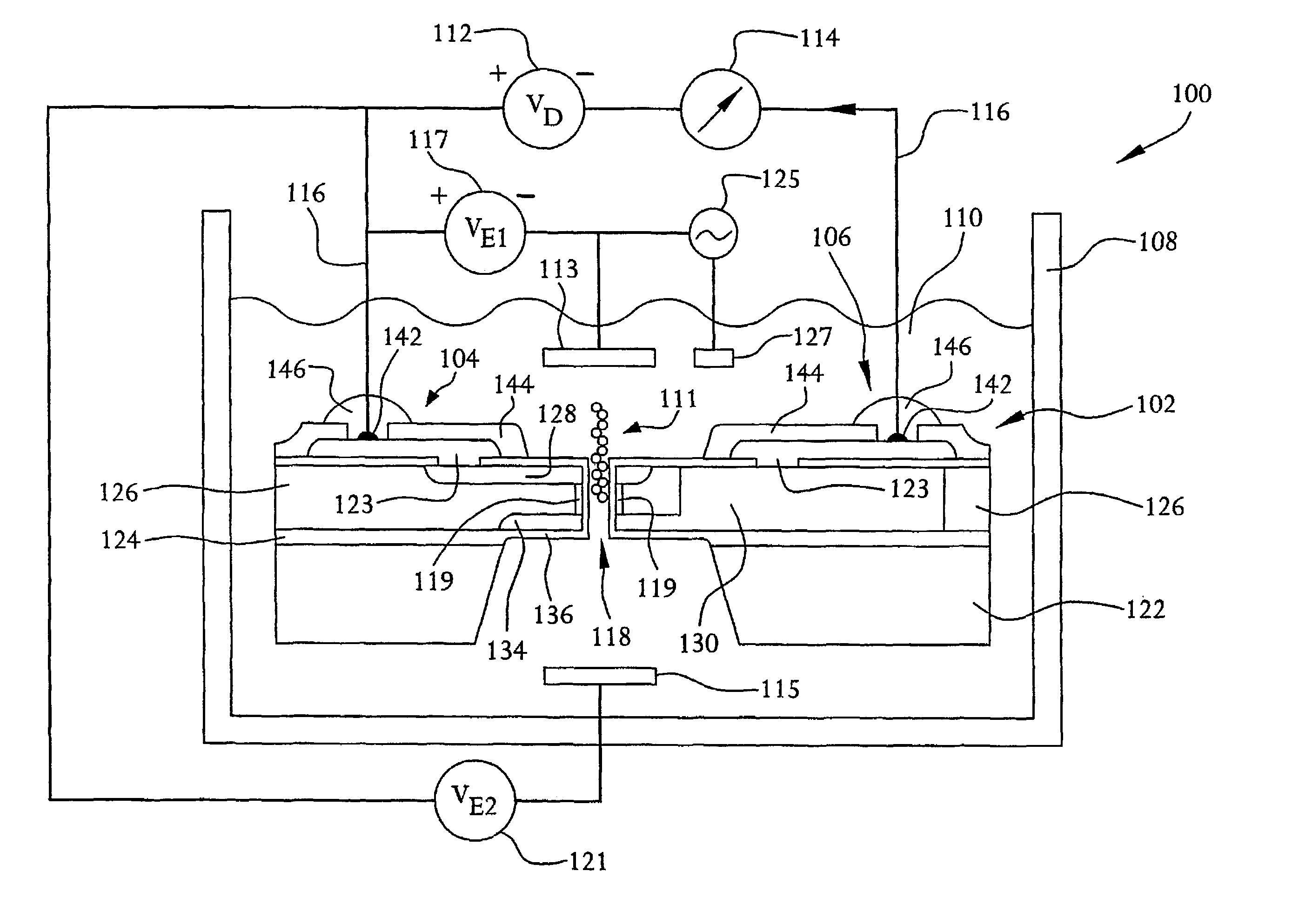
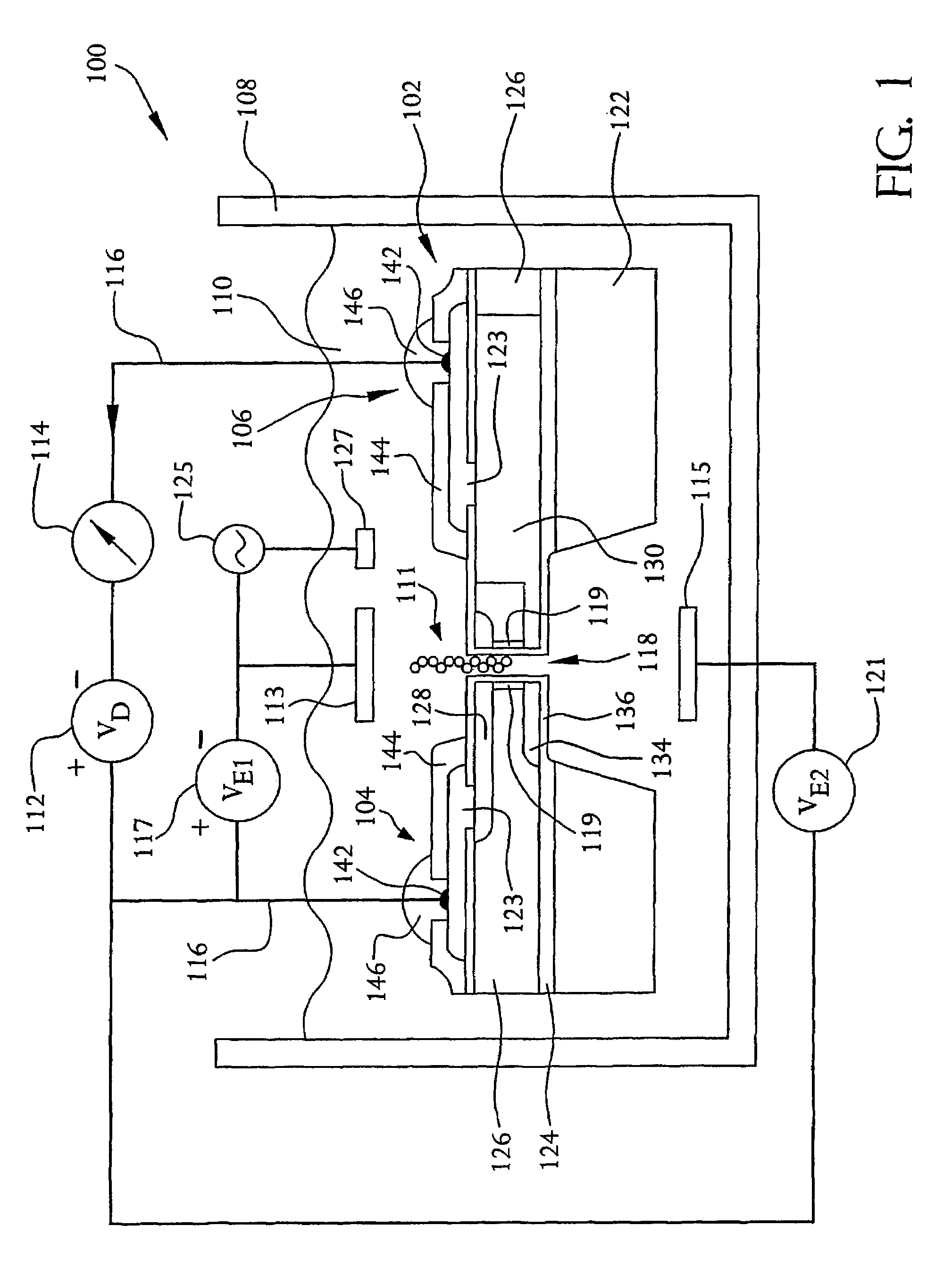
An electrochemical immunosensor system with reduced interference, comprising: a first immunosensor that generates an electrochemical signal based on the formation of a sandwich between an immobilized antibody, a target analyte and a labeled antibody, wherein a portion of the signal arises from non-specific binding of the labeled antibody in the region of the first immunosensor, and a second immunosensor that acts as an immuno-reference sensor and generates a signal that is the same as or predictably related to the degree of non-specific binding which occurs in the region of the first immunosensor, and has an immunocomplex between an immobilized antibody and an endogenous or exogenous protein that is in the sample and that is not the target analyte.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Diagnostic radio frequency identification sensors and applications thereof
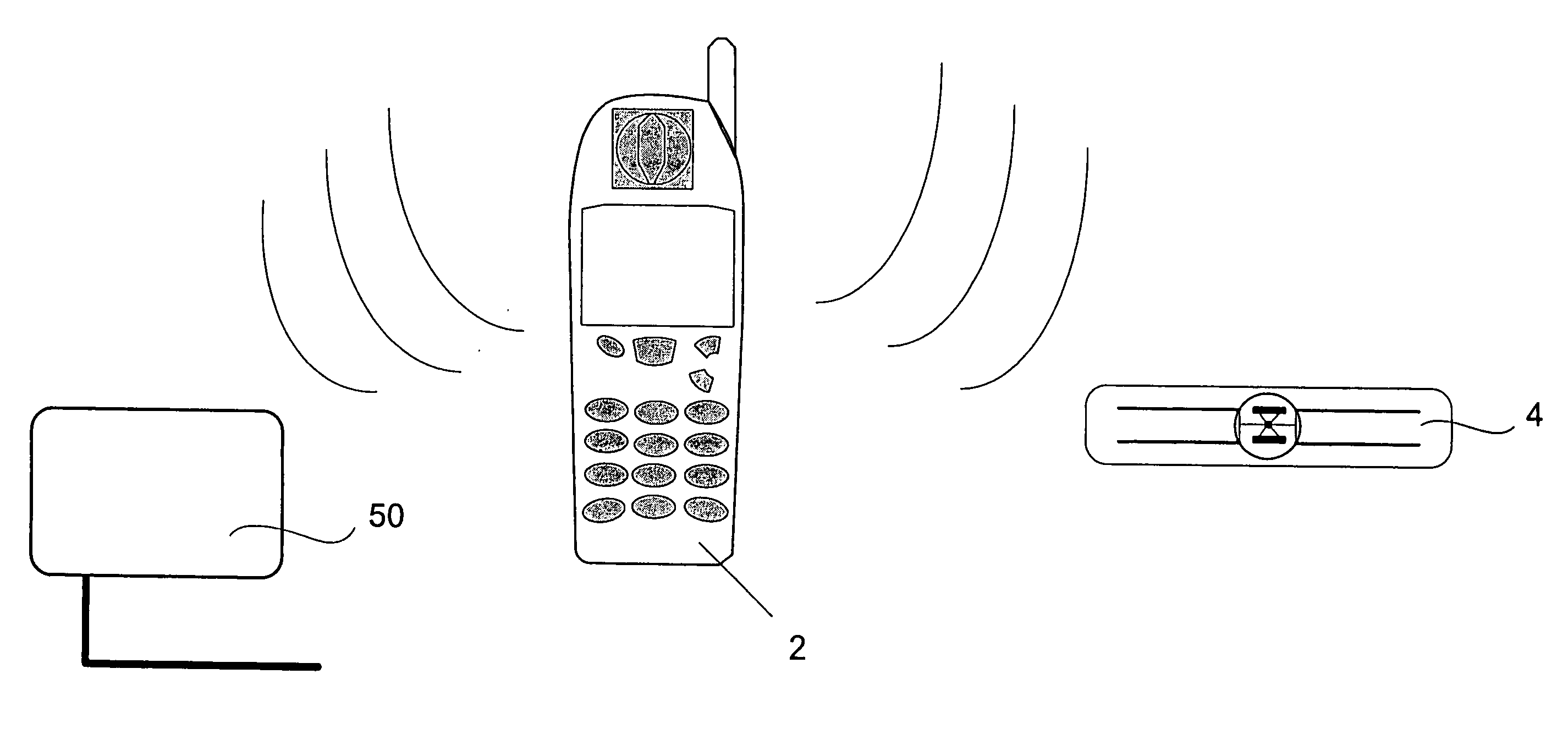
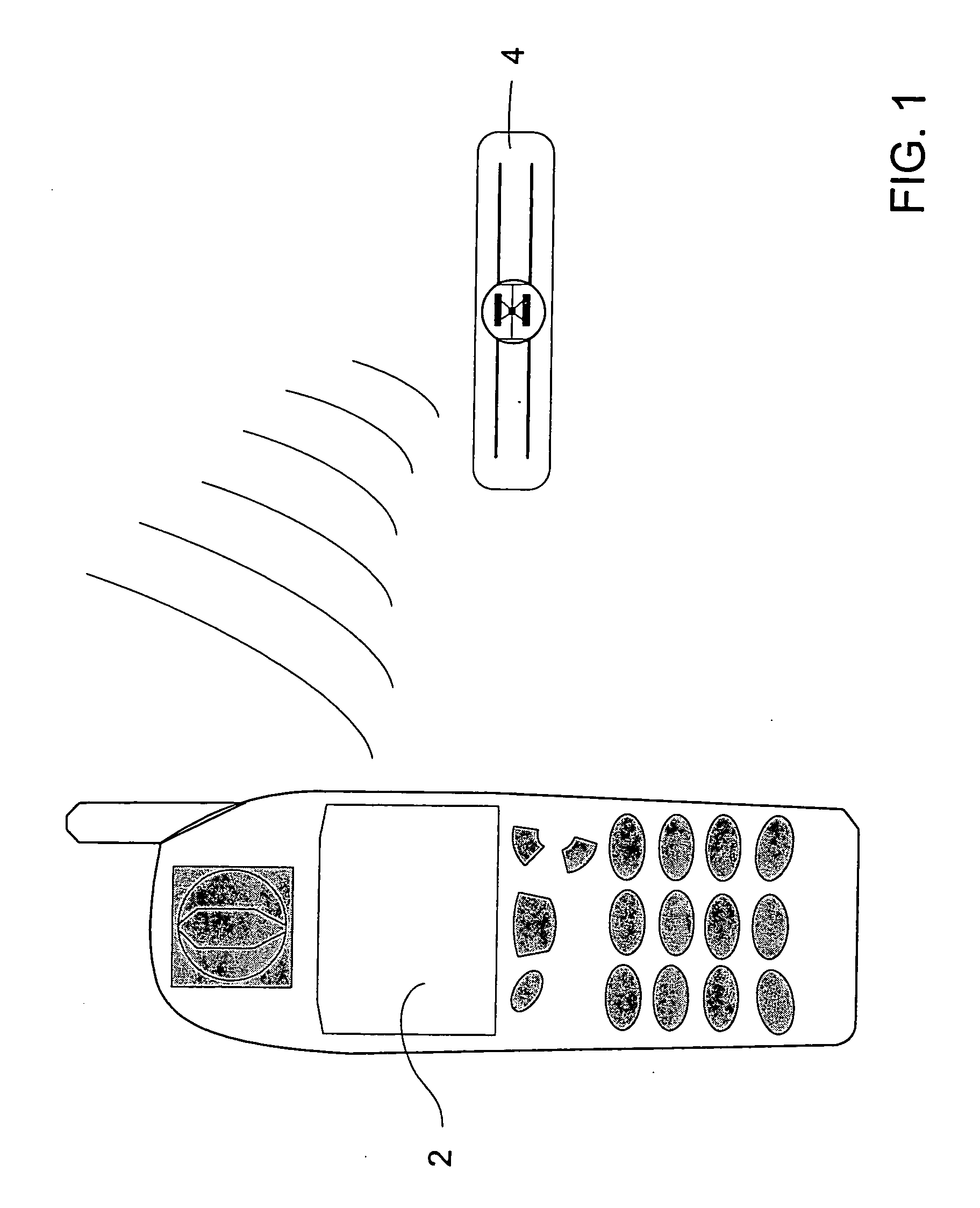
ActiveUS20060290496A1Low costDevices with bluetooth interfacesBurglar alarm mechanical actuationPower sensorPoint of care
An integrated passive wireless chip diagnostic sensor system is described that can be interrogated remotely with a wireless device such as a modified cell phone incorporating multi-protocol RFID reader capabilities (such as the emerging Gen-2 standard) or Bluetooth, providing universal easy to use, low cost and immediate quantitative analyses, geolocation and sensor networking capabilities to users of the technology. The present invention can be integrated into various diagnostic platforms and is applicable for use with low power sensors such as thin films, MEMS, electrochemical, thermal, resistive, nano or microfluidic sensor technologies. Applications of the present invention include on-the-spot medical and self-diagnostics on smart skin patches, Point of Care (POC) analyses, food diagnostics, pathogen detection, disease-specific wireless biomarker detection, remote structural stresses detection and sensor networks for industrial or Homeland Security using low cost wireless devices such as modified cell phones.
Owner:ALTIVERA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com