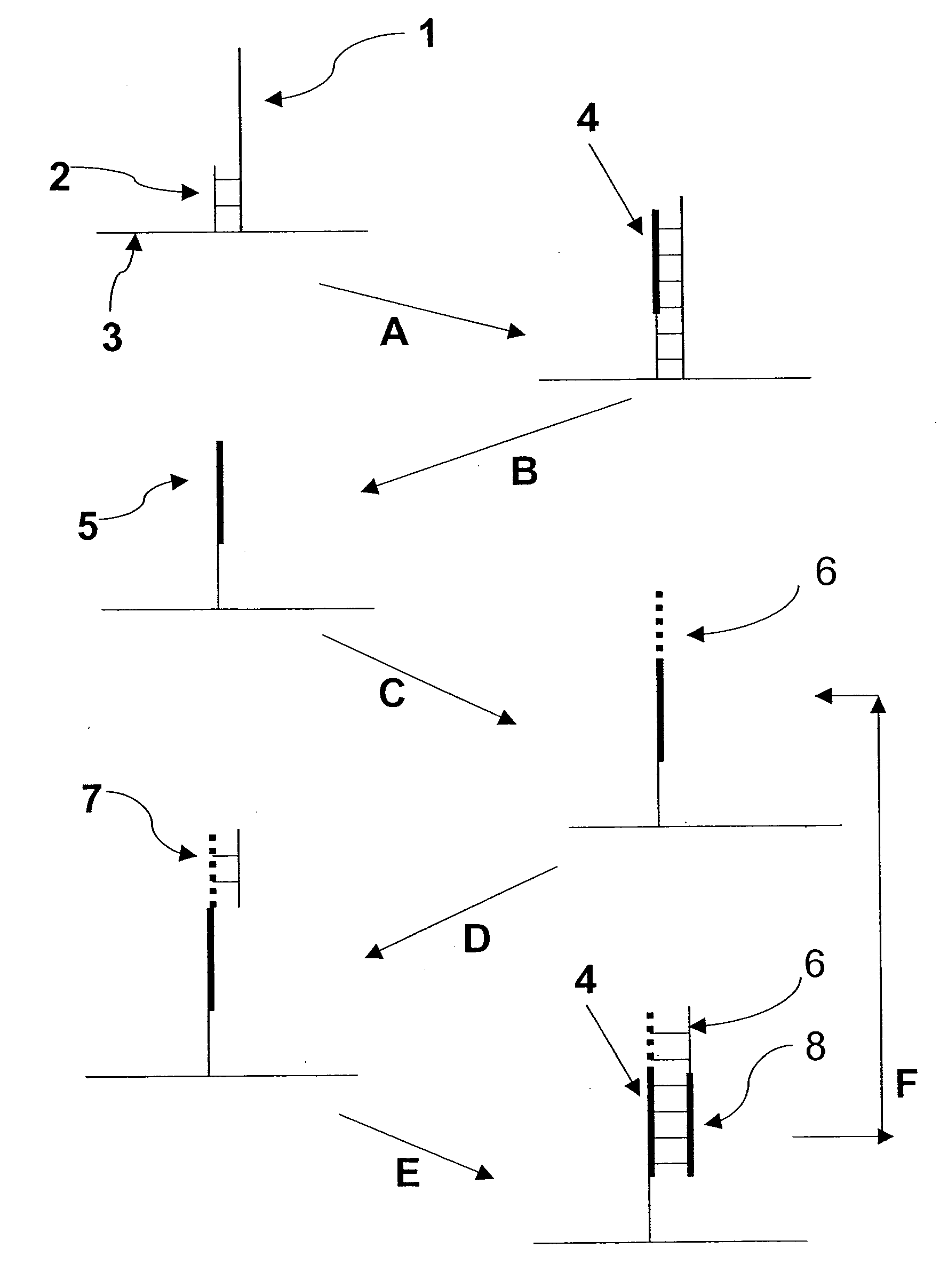
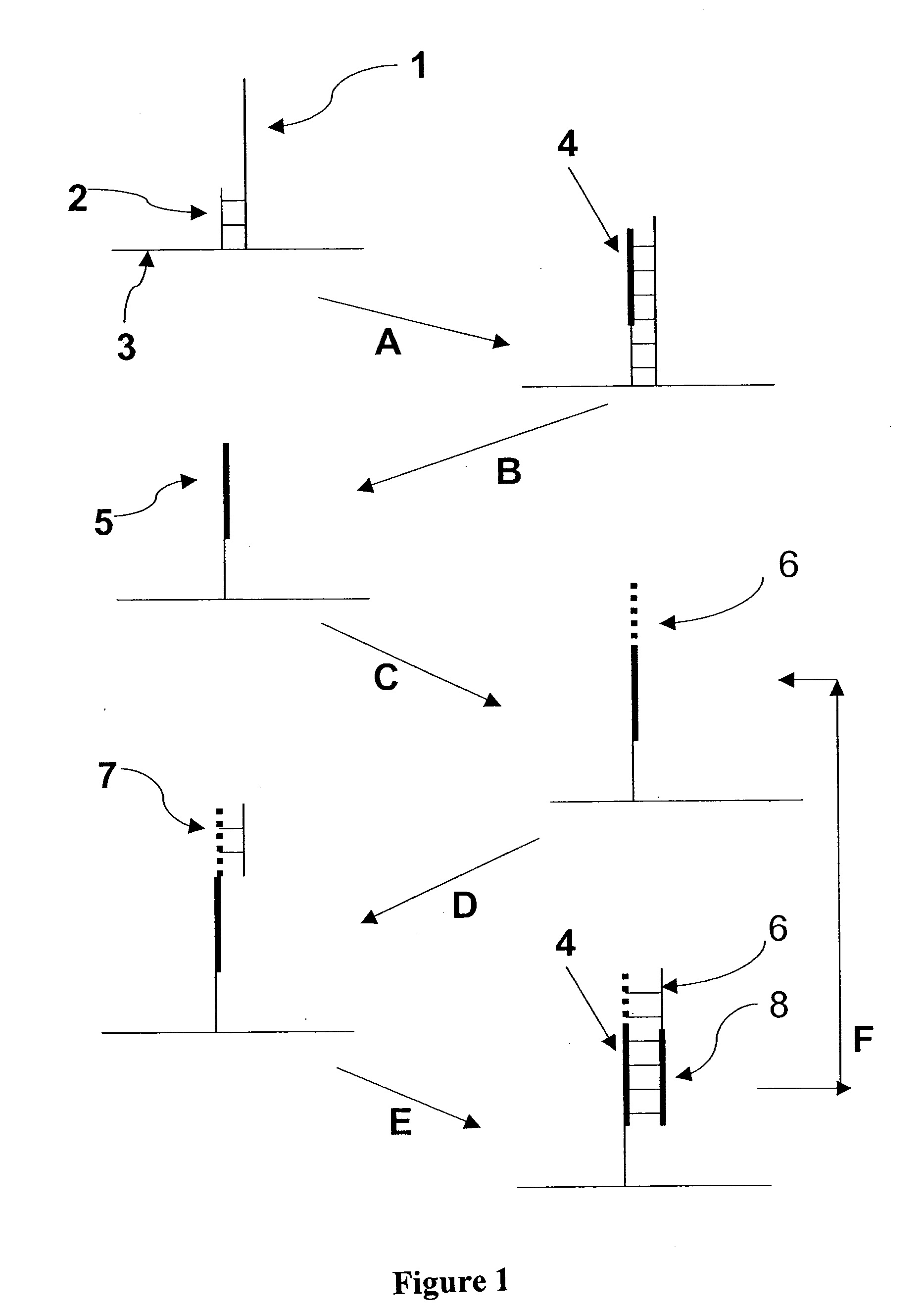
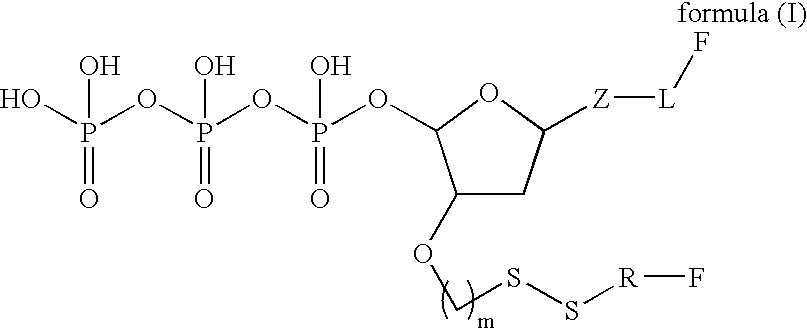
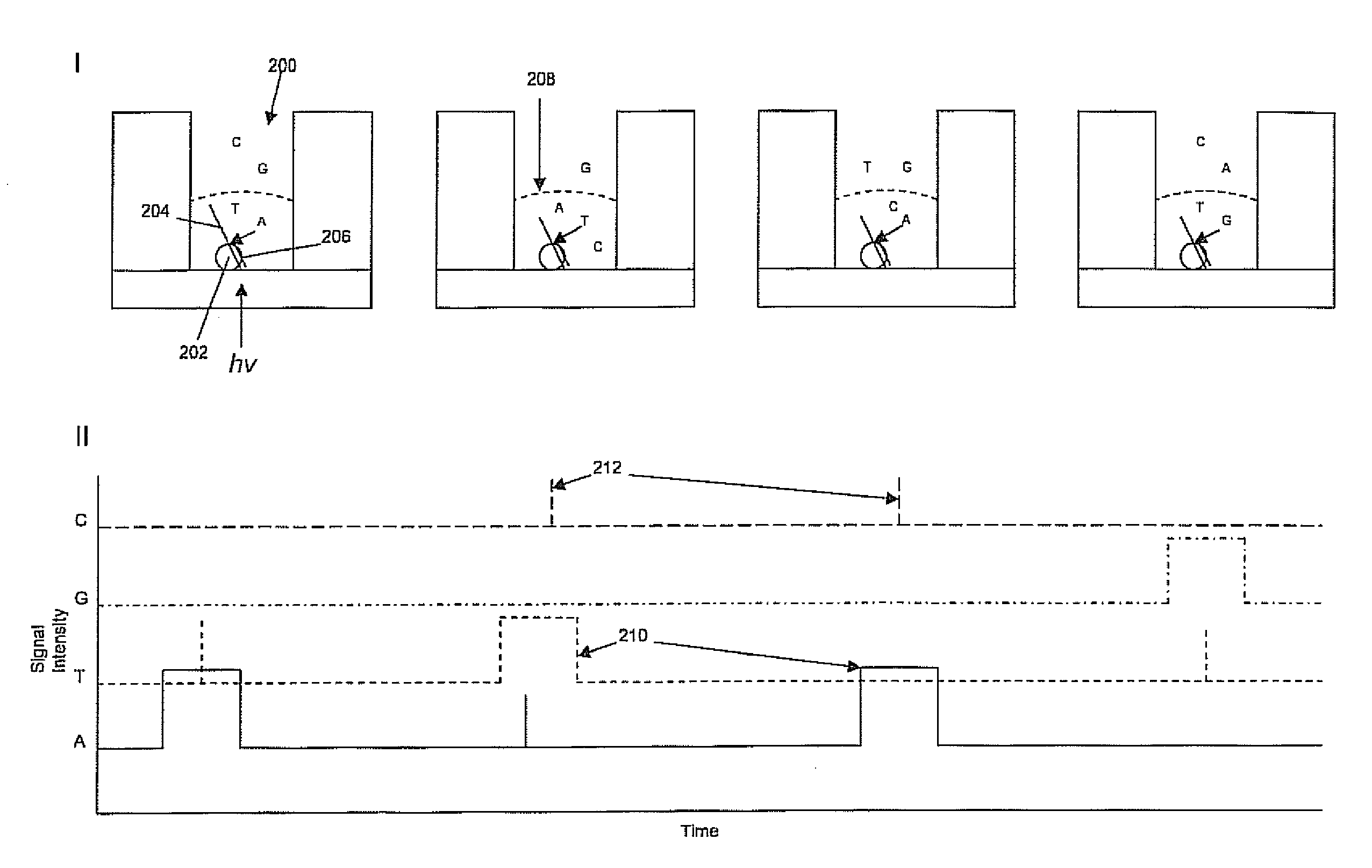
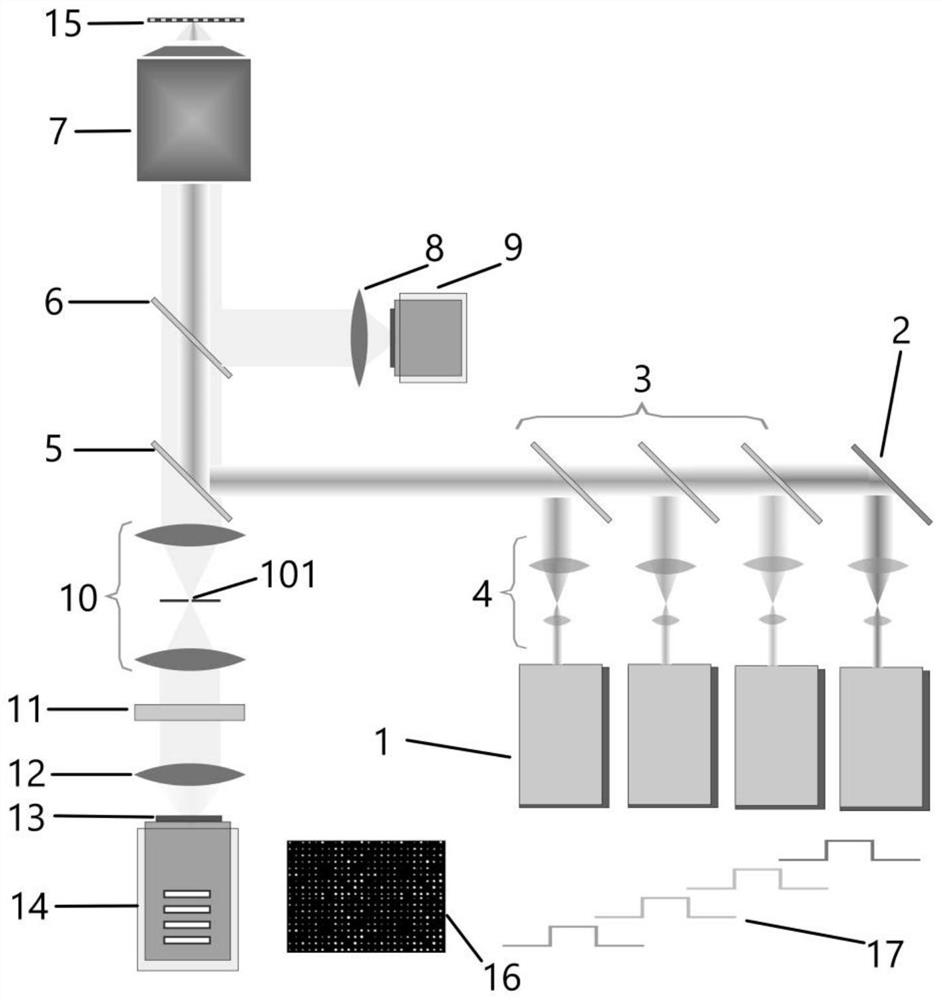
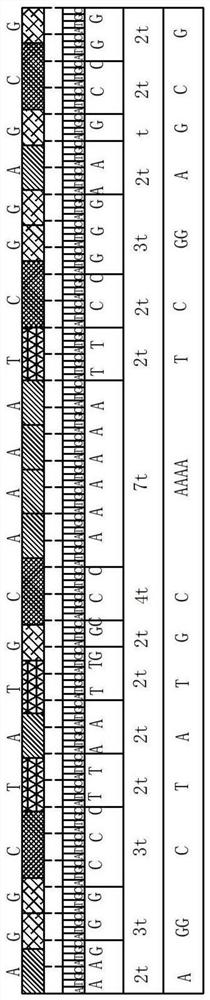
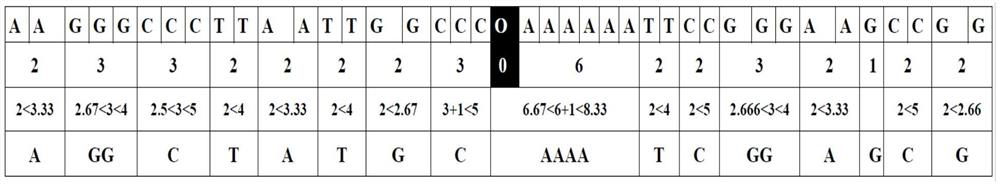
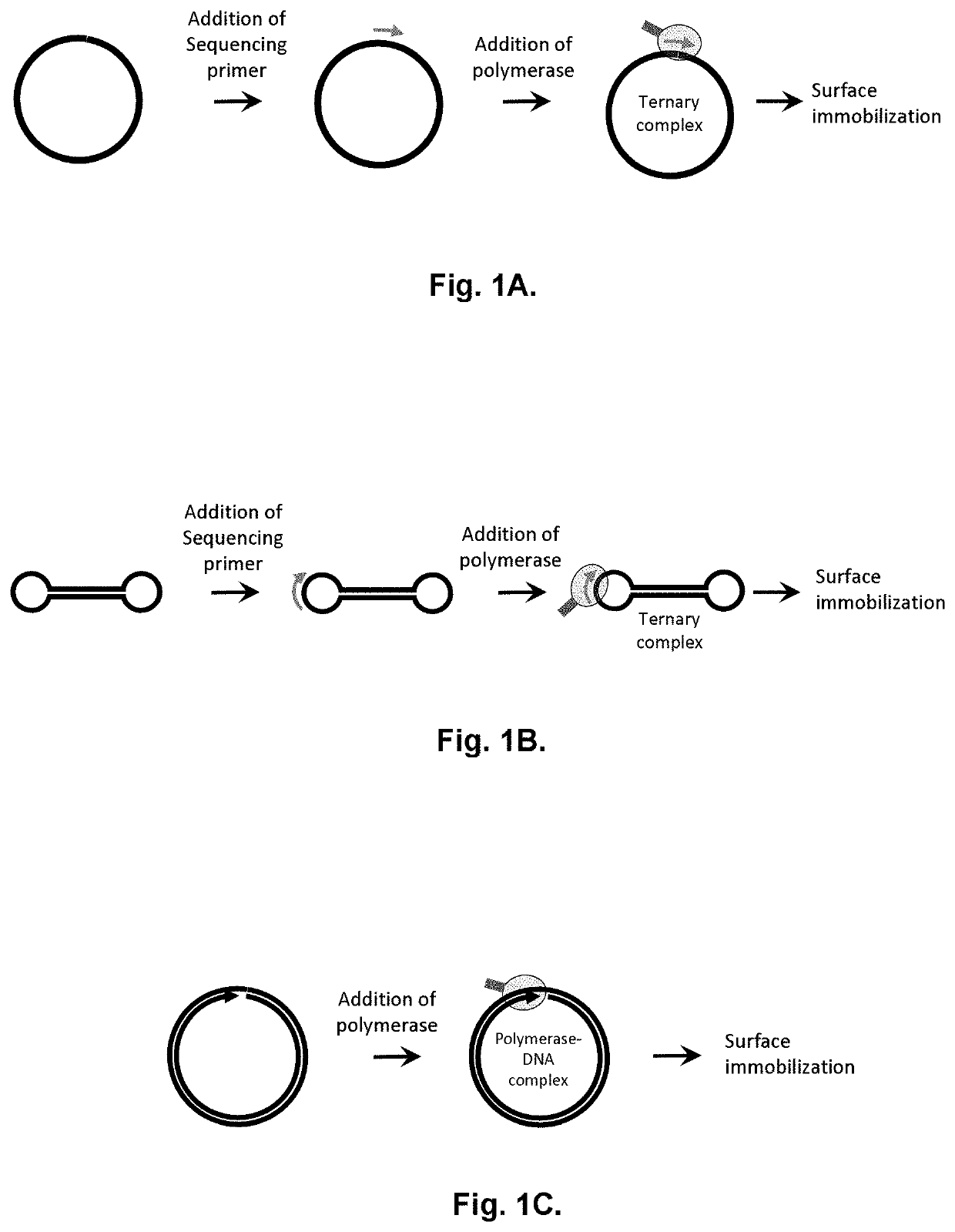
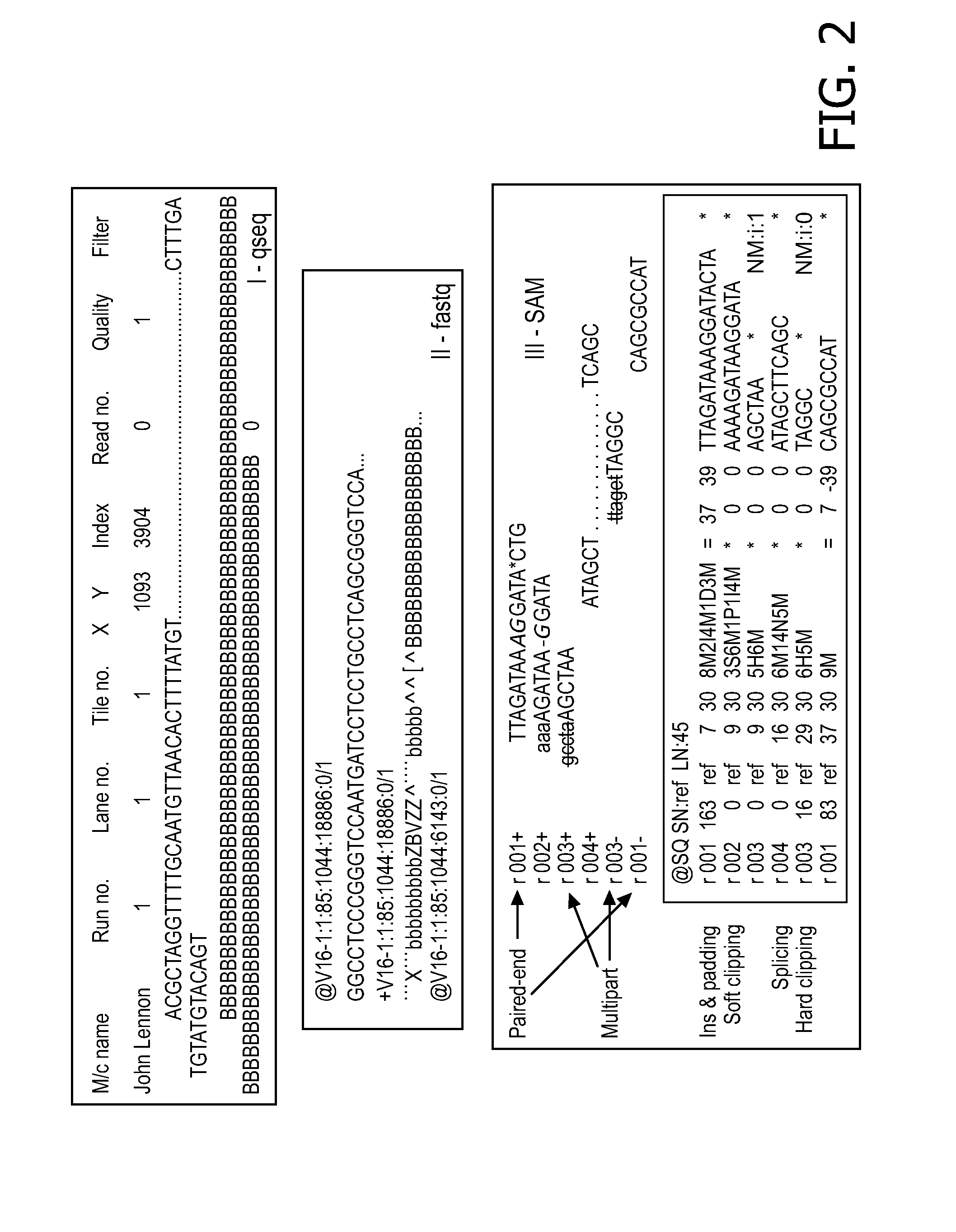
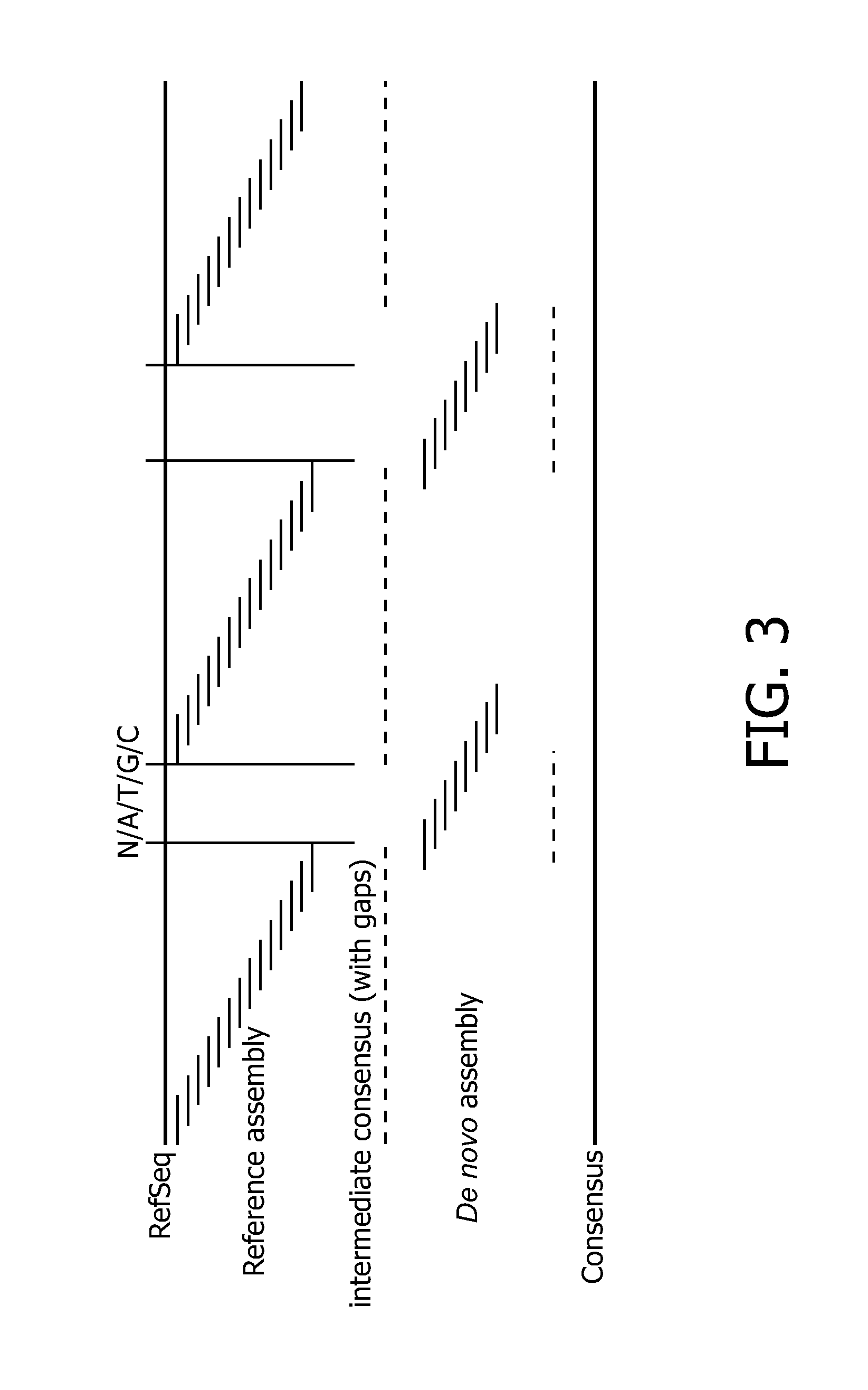
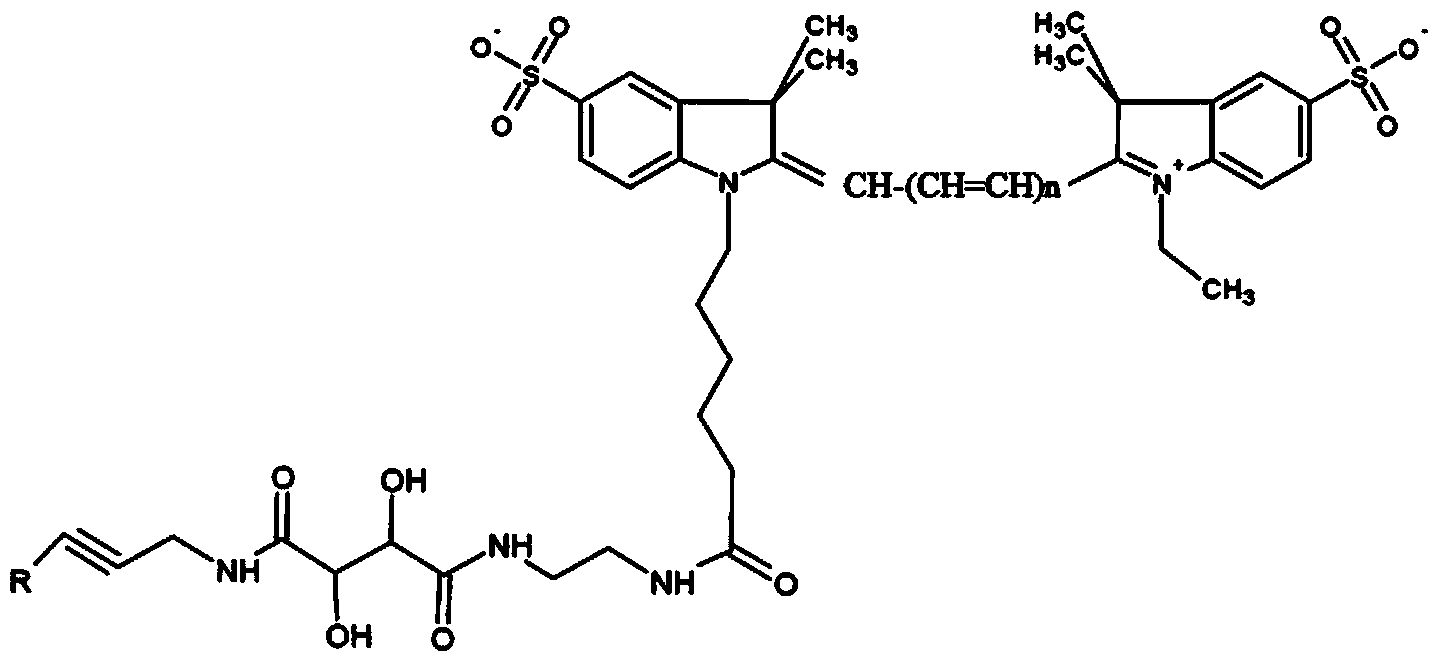
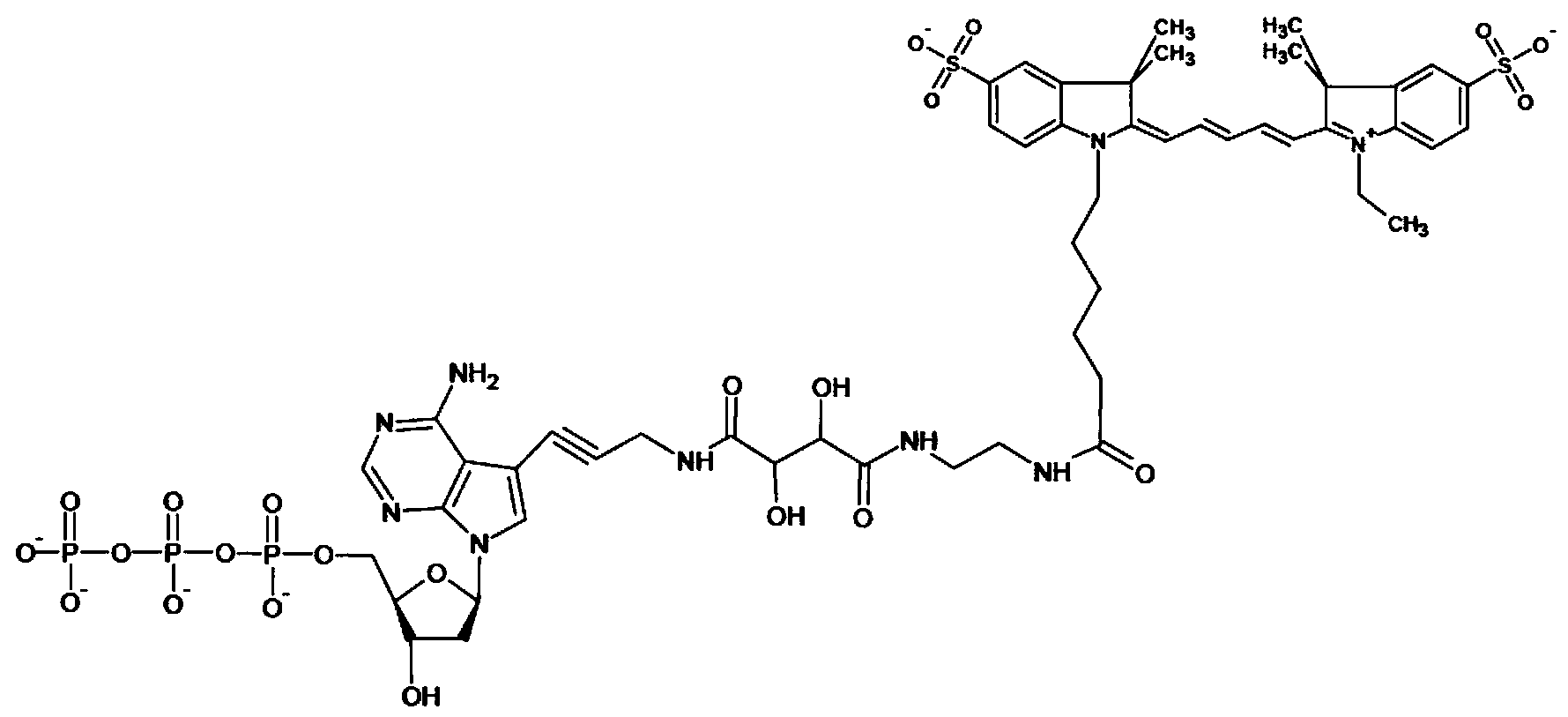
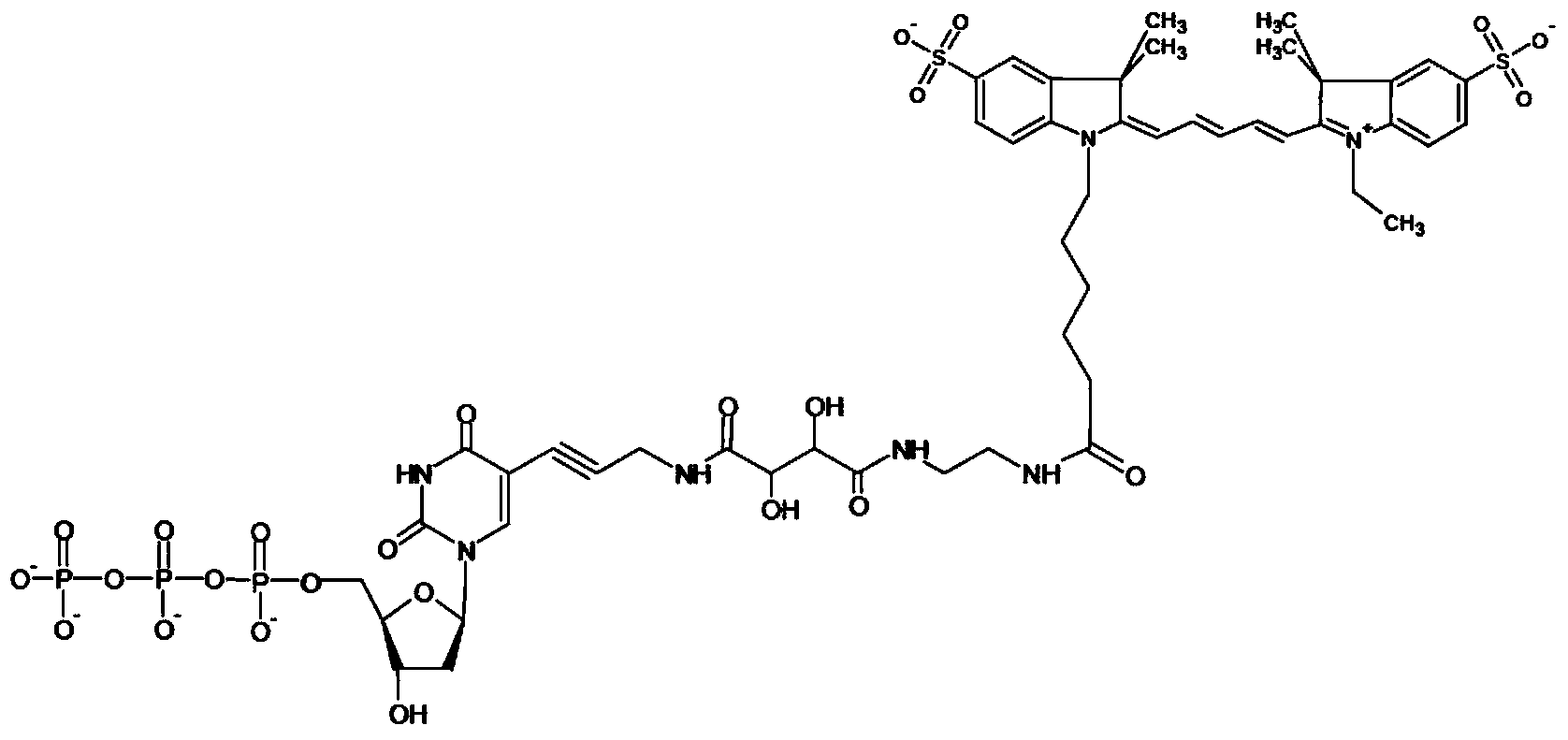
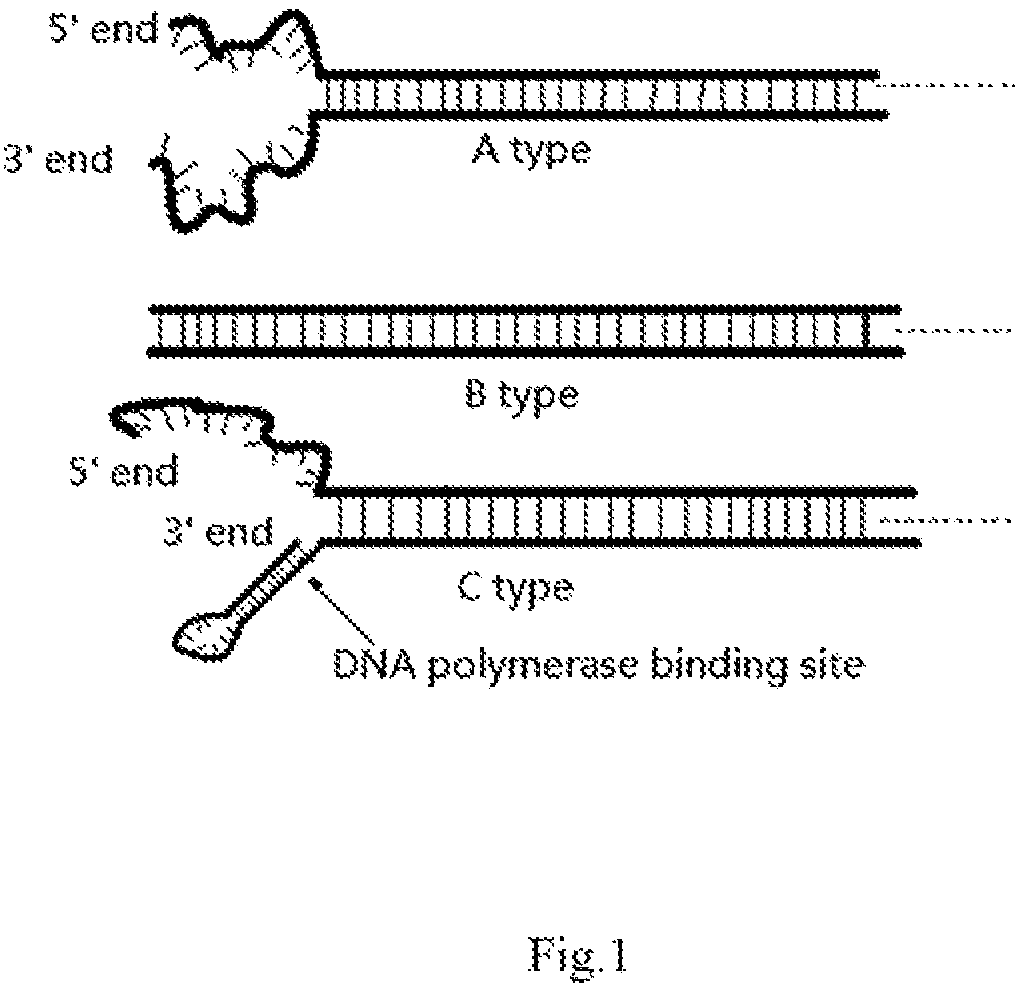
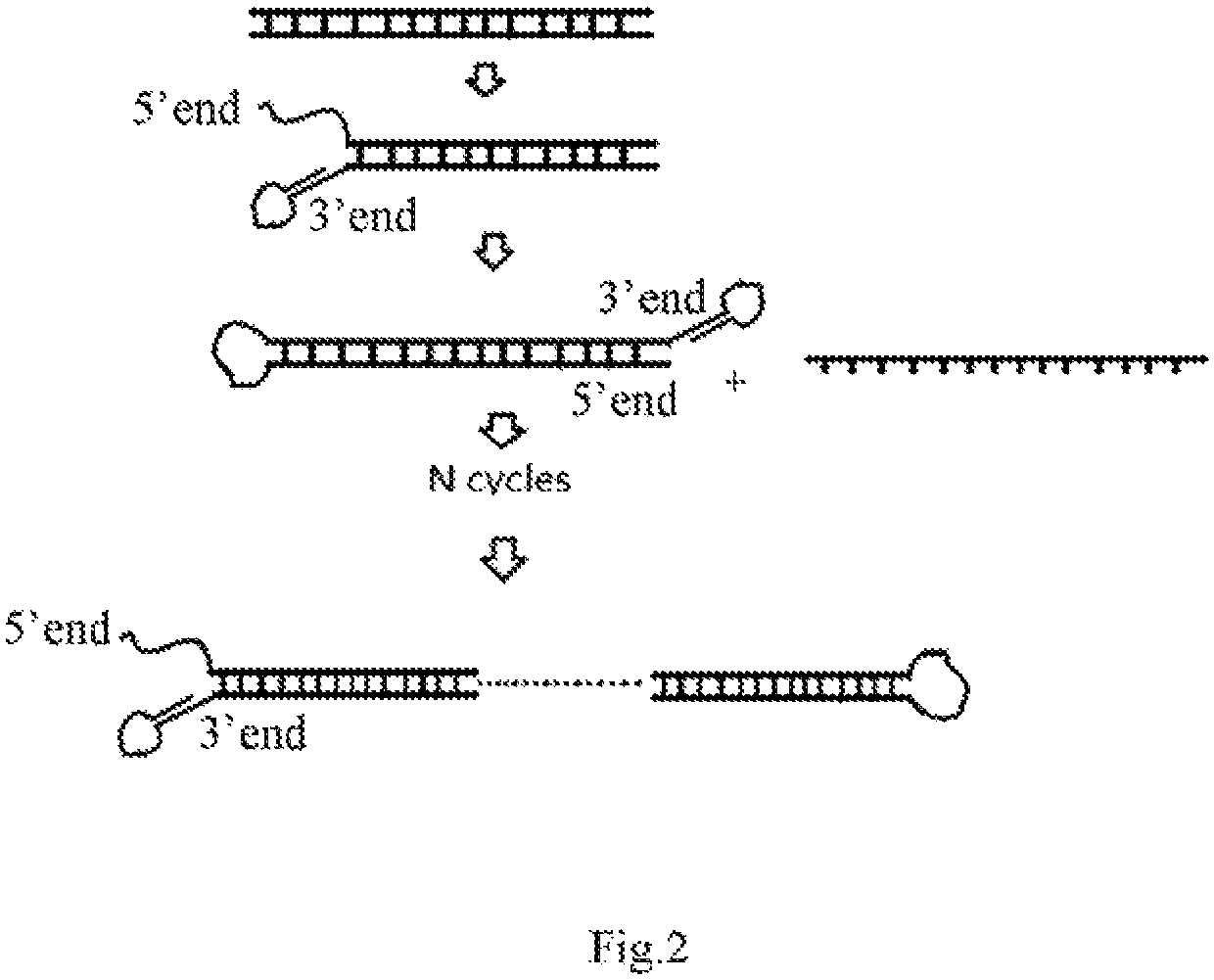
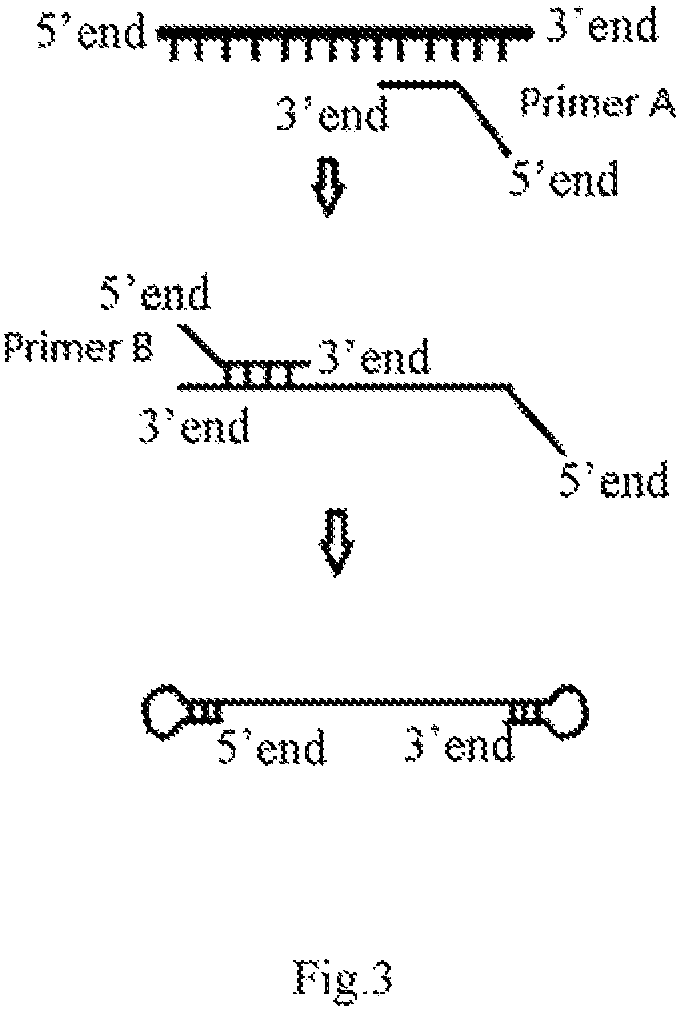
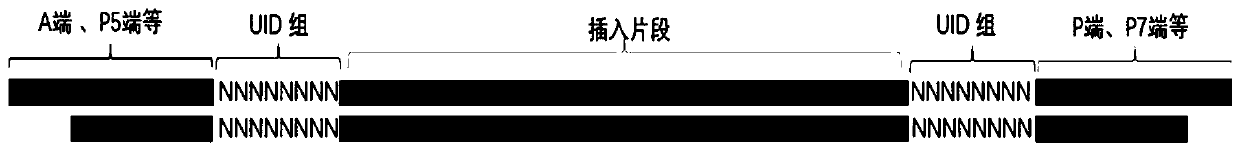
Patents
Literature
49results about How to "Improve Sequencing Accuracy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods for increasing accuracy of nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS7282337B1Improve accuracyImprove Sequencing AccuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Two slow-step polymerase enzyme systems and methods
ActiveUS20090286245A1Accurate determinationReduce numberSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyEnzyme system
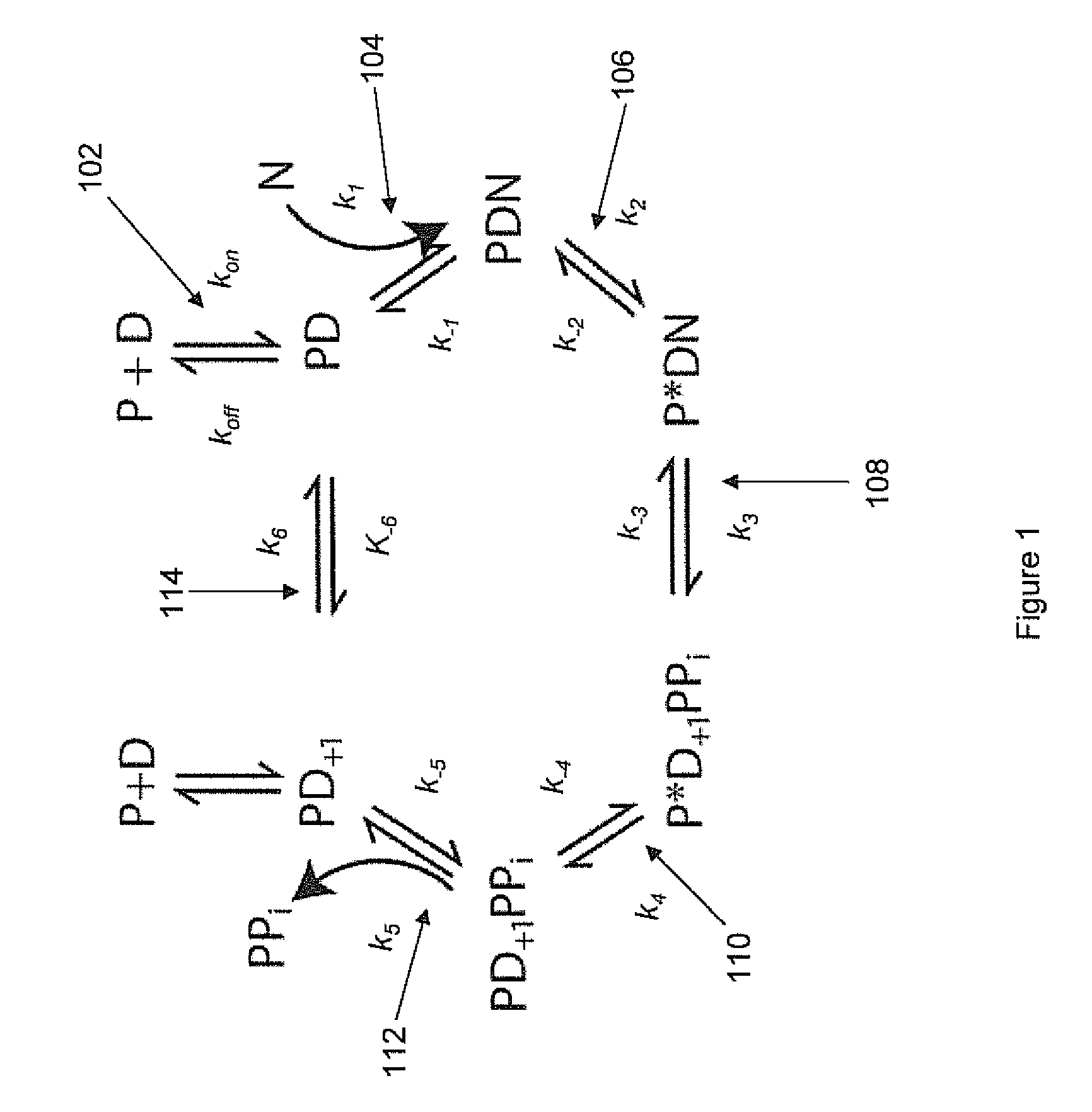
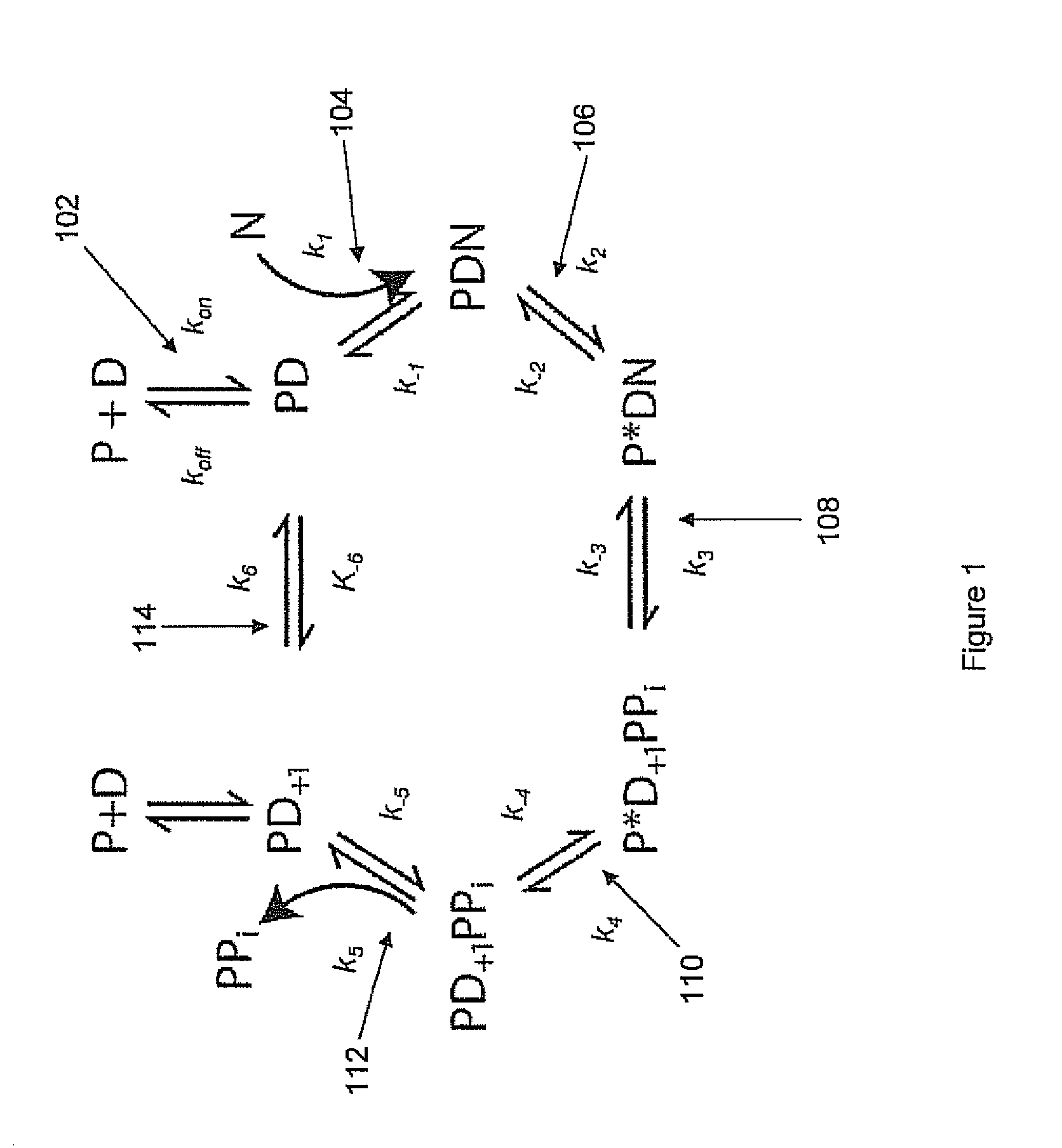
Compositions, kits, methods and systems for nucleotide sequencing comprising producing polymerase reactions that exhibit two kinetically observable steps within an observable phase of the polymerase reaction. Two slow step systems can be produced, for example, by selecting the appropriate polymerase enzyme, polymerase reaction conditions including cofactors, and polymerase reaction substrates including the primed template and nucleotides.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Molecules and methods for nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS20080103058A1Improve efficiencyImprove Sequencing AccuracySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingBiology
The invention provides molecules and methods for nucleic acid synthesis reactions useful in sequencing-by-synthesis processes.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Nucleic acid synthesis compositions and methods and systems for using same
ActiveUS20100047802A1Accurate sortingReduce in quantityMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesPolymerase LDivalent metal ions
The Application relates to compositions, kits, methods, and systems for nucleotide sequencing comprising producing polymerase reactions that comprise both catalytic and non-catalytic divalent metal ions. Effective ratios and amounts of catalytic and non-catalytic divalent metal ions are described.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
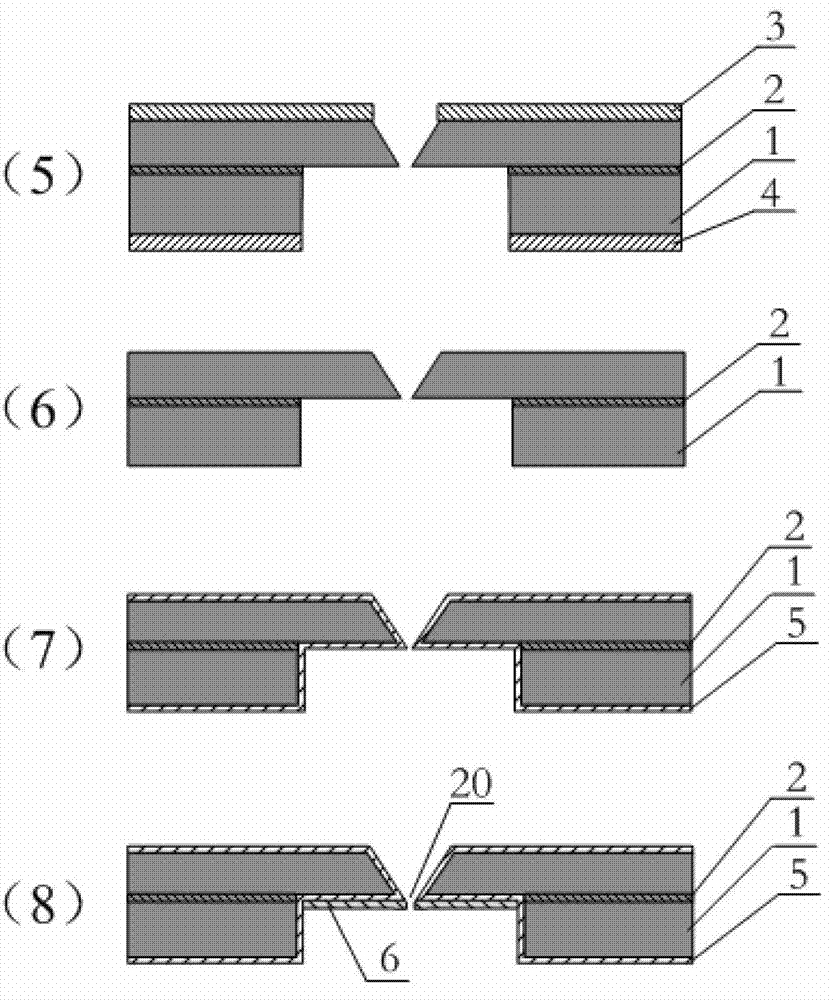
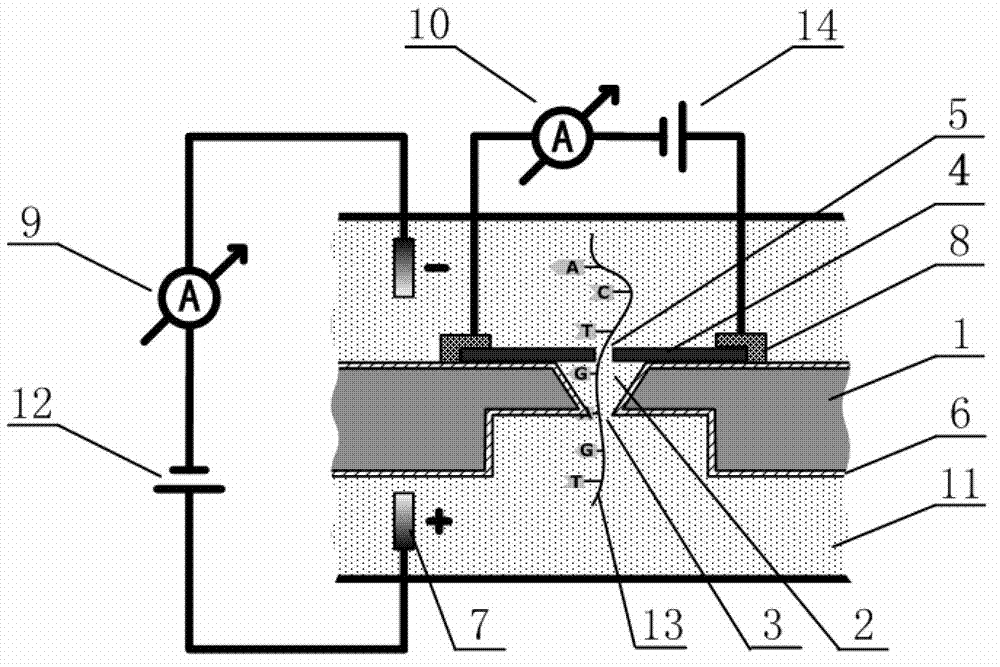
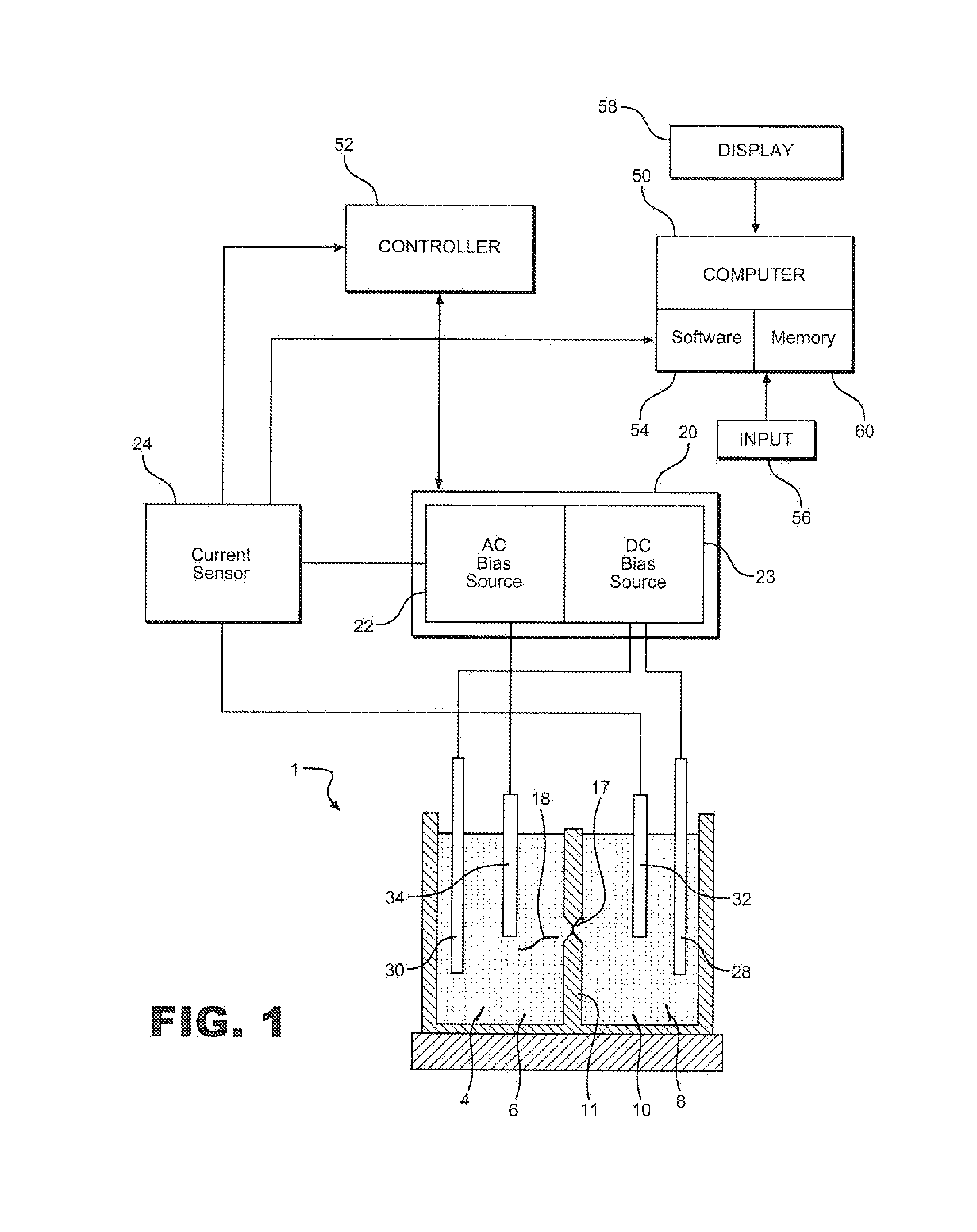
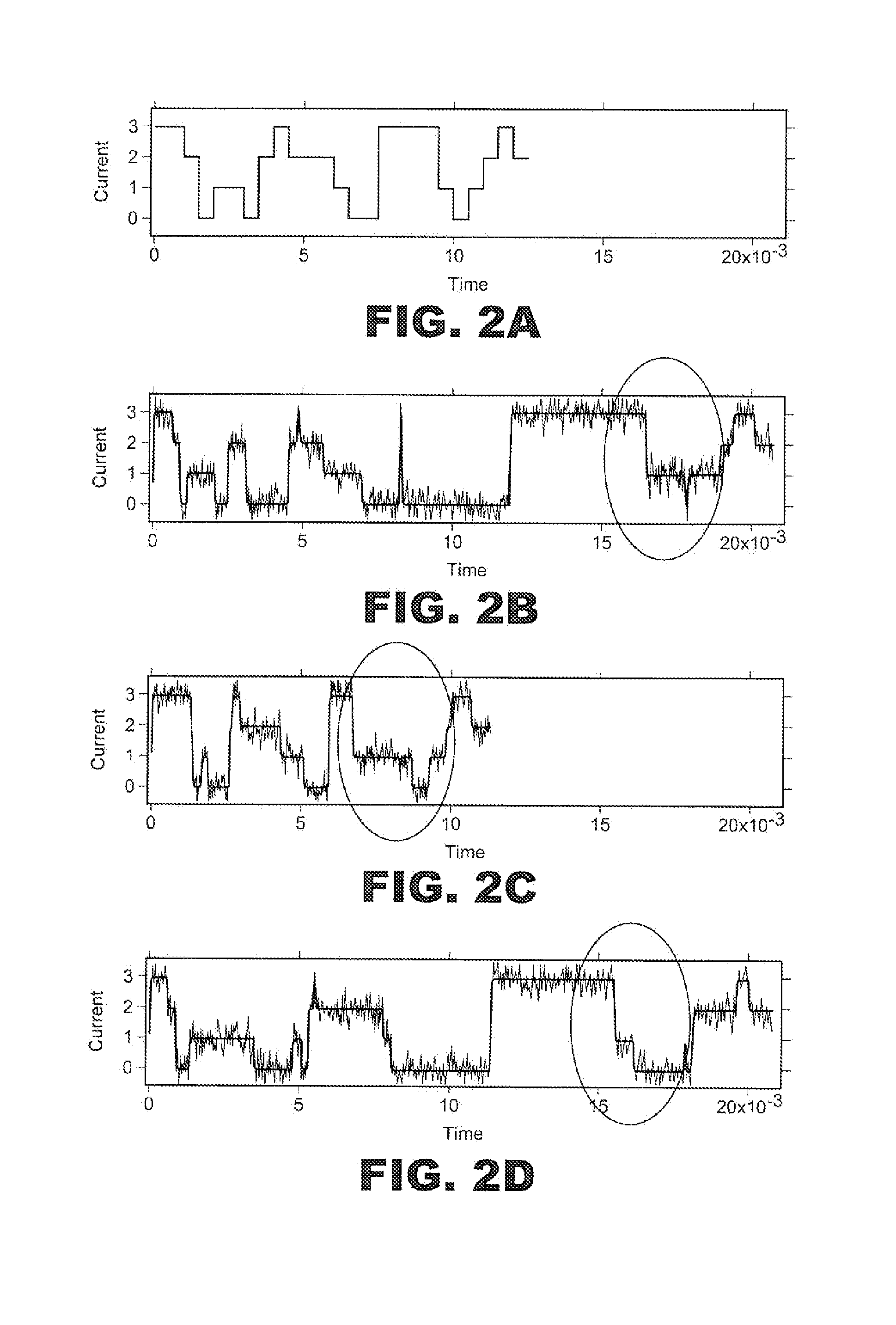
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequencing device based on graphene nanopore-microcavity-solid-state nanopore and manufacturing method
ActiveCN102901763AAvoid instabilityOvercome instabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNanotechnologyGraphiteGraphene
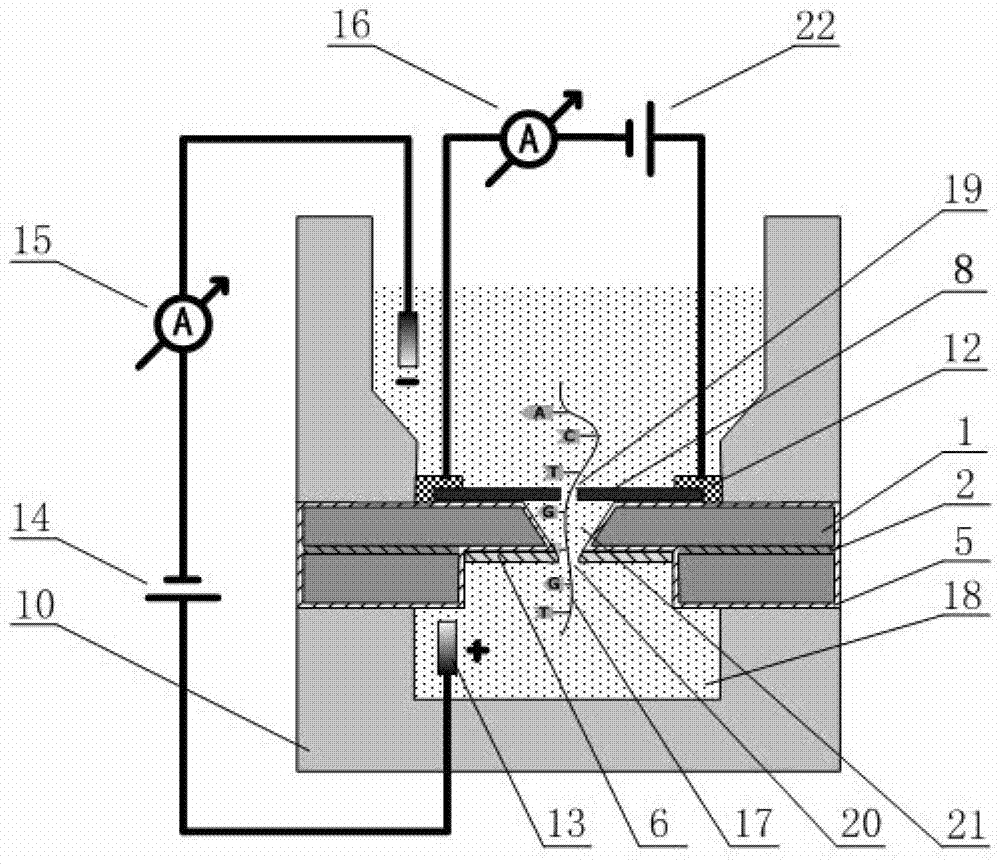
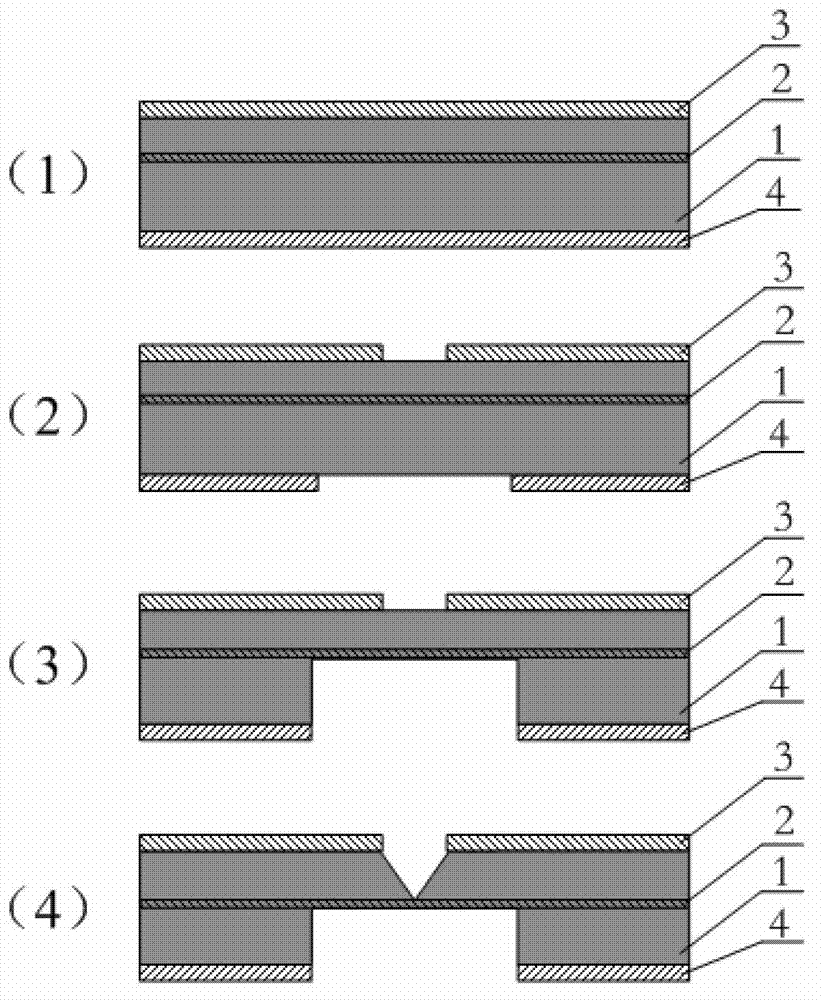
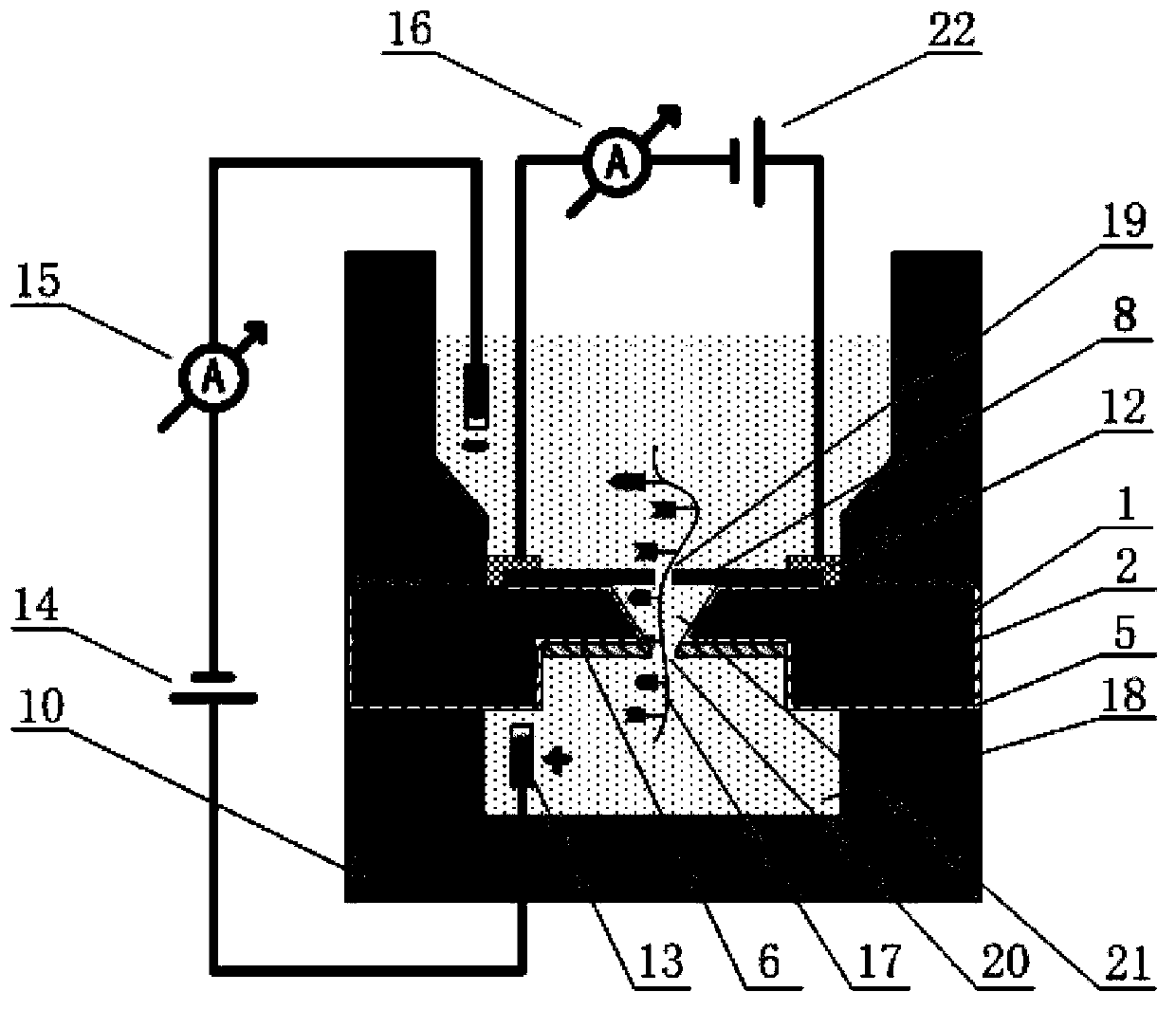
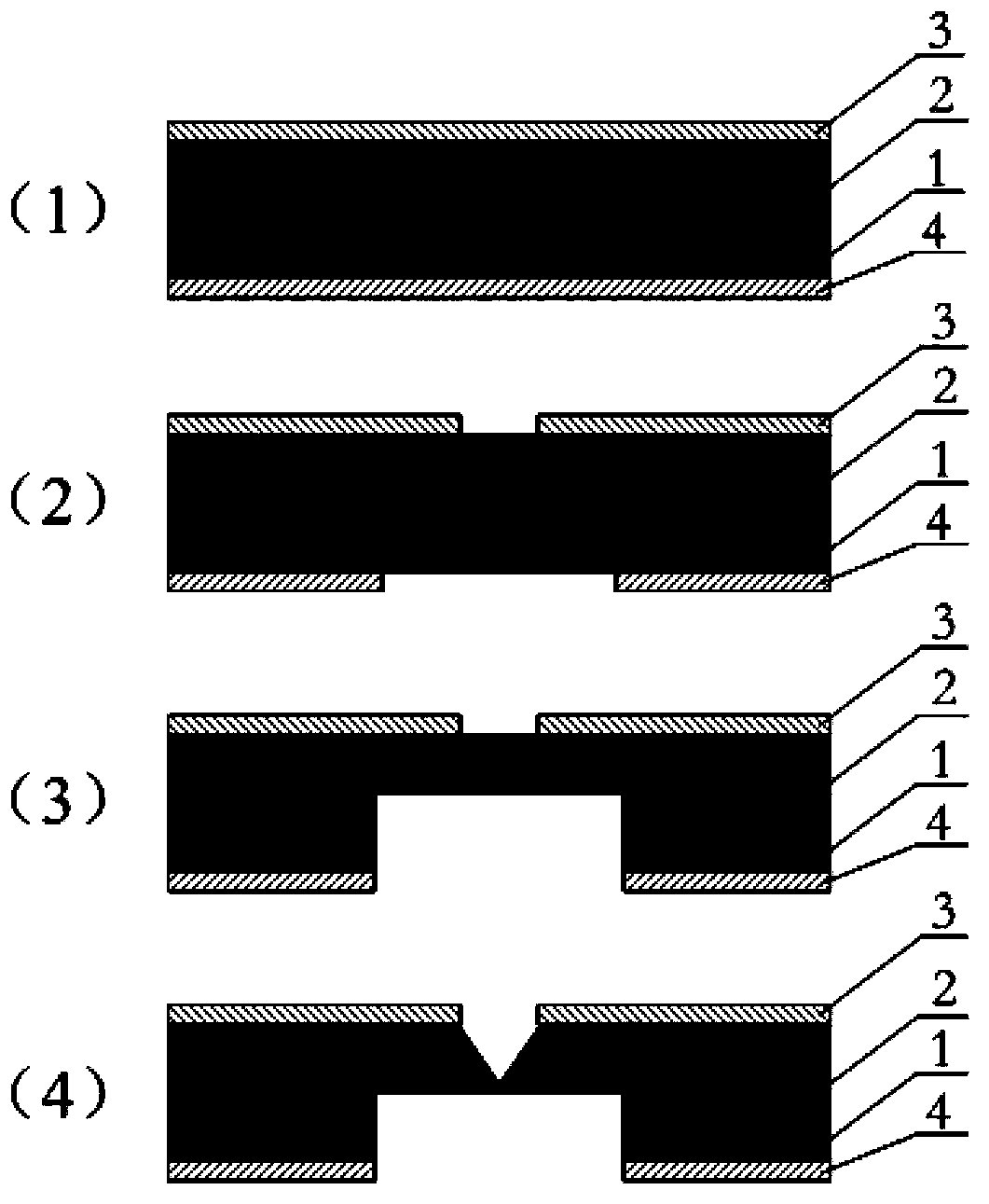
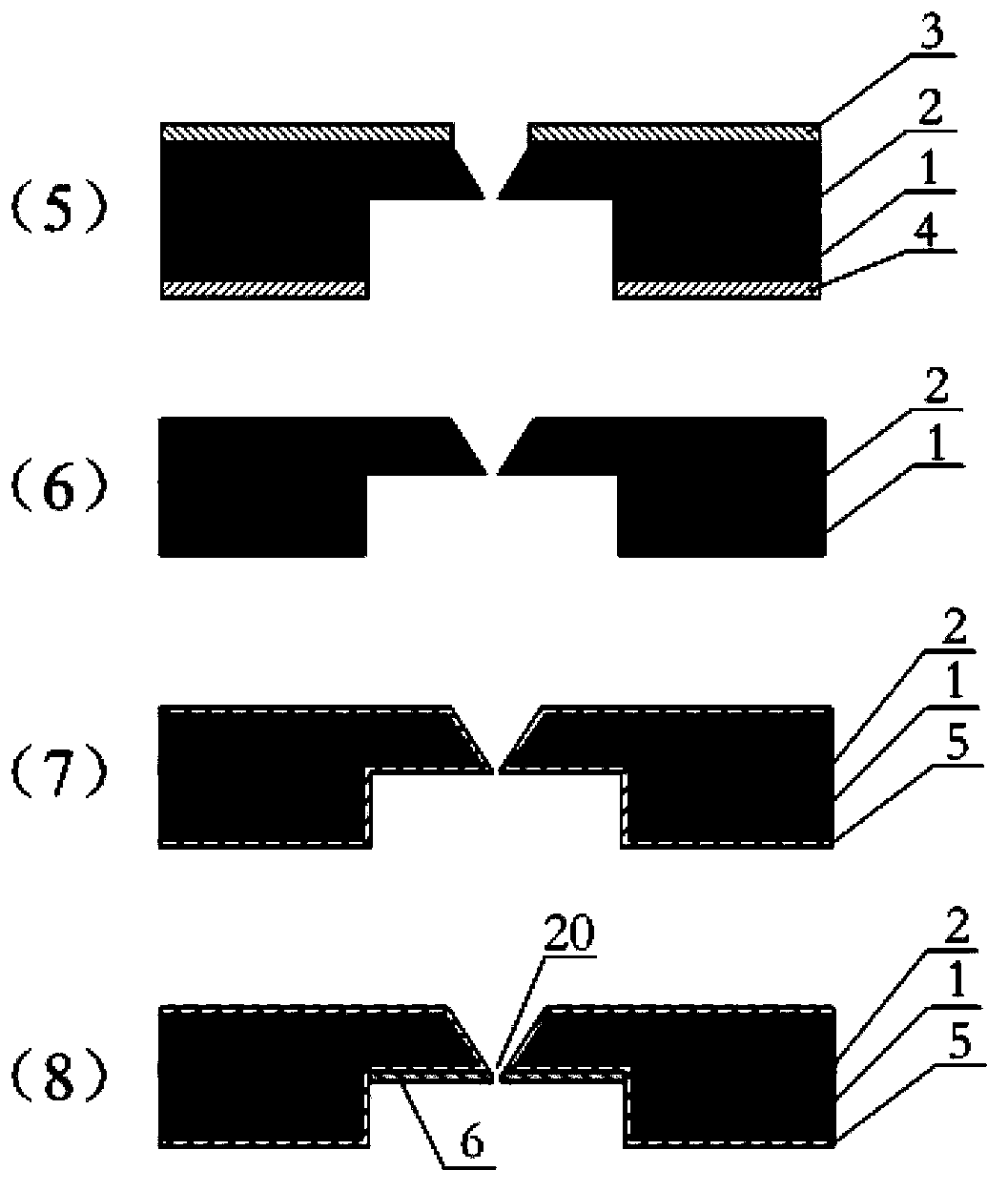
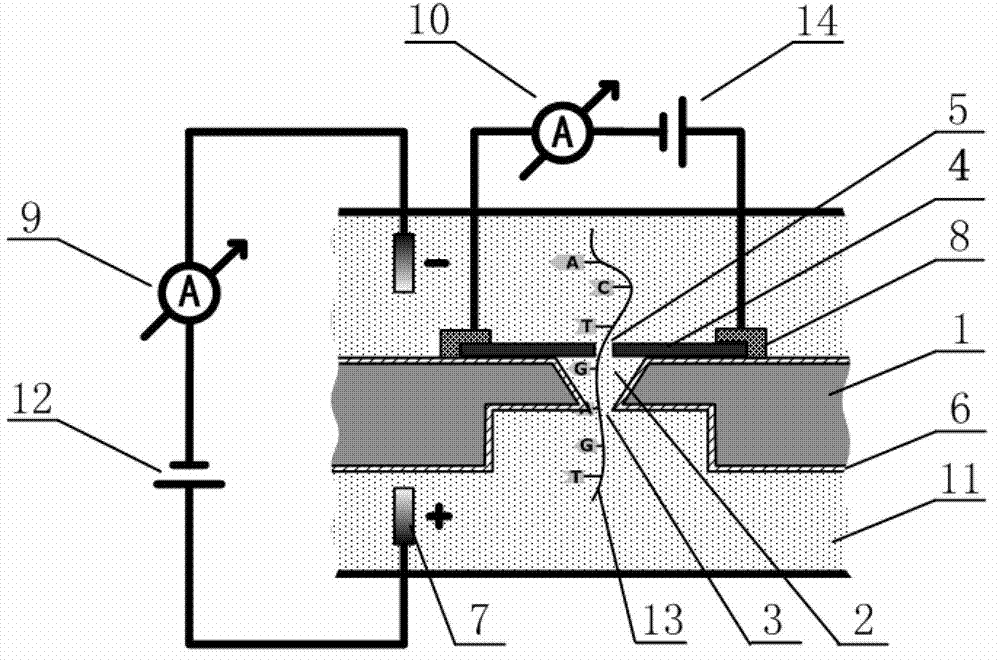
The invention discloses a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequencing device based on a graphene nanopore-microcavity-solid-state nanopore and a manufacturing method. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of etching an inverted-pyramid-shaped microcavity in the upper part of a silicon on insulator (SOI) silicon wafer; etching a columnar hole on the lower part of the SOI silicon wafer, wherein the tower top of the inverted-pyramid-shaped microcavity is the solid-state nanopore; etching the graphene on the upper part of the inverted-pyramid-shaped microcavity; etching the graphene nanopore in the center of the graphene, wherein a platinum electrode and a longitudinal weak current measurement device as well as a power supply form a longitudinal weak current measurement loop, and a gold electrode and a transverse weak current measurement device as well as the power supply form a transverse weak current measurement loop; etching an inverted cone cavity in the front side of the SOI silicon wafer; etching a vertical columnar hole at the back of the SOI silicon wafer; corroding an oxidized buried layer on the SOI silicon wafer to form the solid-state nanopore; transferring the prepared graphene to the surface of the SOI silicon wafer; etching the graphene nanopore coaxial to the fixed nanopore in the center of the graphene; and enabling a chip, the power supply and an ampere meter to form a circuit so as to realize the sequencing of the DNA by testing the change of current intensity in the circuit when the DNA penetrates through the nanopore.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Graphene nanopore-microcavity-solid-state nanopore structure based DNA sequencing device and method
ActiveCN102899243AOvercome instabilityOvercome uncontrollabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsComing outSequence analysis
The invention discloses a graphene nanopore-microcavity-solid-state nanopore structure based DNA sequencing device and a method. The sequencing device is mainly composed of a graphene nanopore-equipped graphene microstrip, an inverted pyramid-shaped microcavity in a silicon-based substrate, and a solid-state nanopore at the top of the microcavity. During sequencing, a sequencing reaction chamber is divided into two parts by the graphene nanopore-microcavity-solid-state nanopore structure. A single-stranded DNA molecule passes through the graphene nanopore linearly under the effect of an electrostatic field, then enters the inverted pyramid-shaped microcavity, and finally comes out from the solid-state nanopore. Weak current measuring equipment is utilized to measure longitudinal ionic current blocking caused by the DNA molecule passing activity in the nanopore and the transverse conductance change around the nanopore in the graphene microstrip. Further, a synchronous data recording and processing system is employed for analytical calculation of bi-directional data, thus realizing sequence analysis of the single-stranded DNA molecule.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Sequencing reactions with alkali metal cations for pulse width control
ActiveUS8986930B2Improve Sequencing AccuracyModulate the kinetics of the polymerase enzymeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPotassiumPolymerase
Compositions, kits, methods and systems for single molecule nucleotide sequencing comprising producing polymerase reactions having monovalent cations that control the median pulse width for incorporated nucleotides are disclosed. The levels of alkali metals such as lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, and cesium in the polymerization are used to control pulse width while allowing other sequencing parameters to remain within a desirable range.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Method for deducing a polymer sequence from a nominal base-by-base measurement
ActiveUS8452546B1Improve Sequencing AccuracyLimited to sequenceMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsHigh probabilityStochastic variation
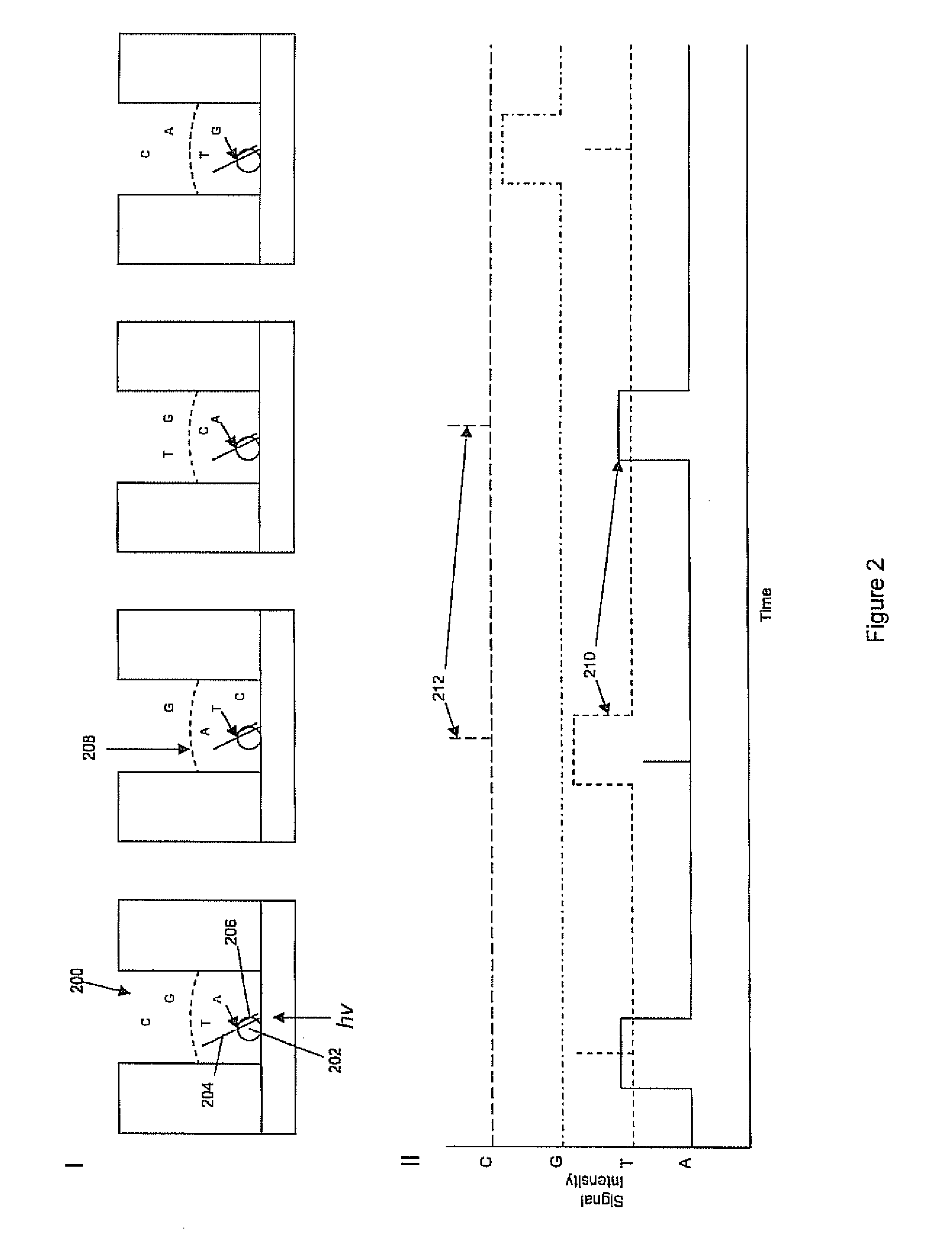
A method of processing sequencing data obtained with a polymer sequencing system identifies the most likely monomer sequence of a polymer, regardless of stochastic variations in recorded signals. Polymer sequencing data is recorded and two or more distinct series of pore blocking signals for a section of the polymer are recorded. A value is assigned to each series of pore blocking signals to obtain multiple trial sequences. The probability that each of the trial sequences could have resulting in all of trial sequences is calculated to determine a monomer sequence with the highest probability of resulting in all of the trial sequences, termed the first iteration sequence. The first iteration sequence is systematically altered to maximize the combined probability of the first iteration sequence leading to all the trial sequences in order to obtain a most likely sequence of monomers of the polymer.
Owner:ELECTRONICS BIOSCI
Molecules and methods for nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS20080269476A1Improve efficiencyImprove Sequencing AccuracySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingMolecular biology
The invention provides molecules and methods for nucleic acid synthesis reactions useful in sequencing-by-synthesis processes.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
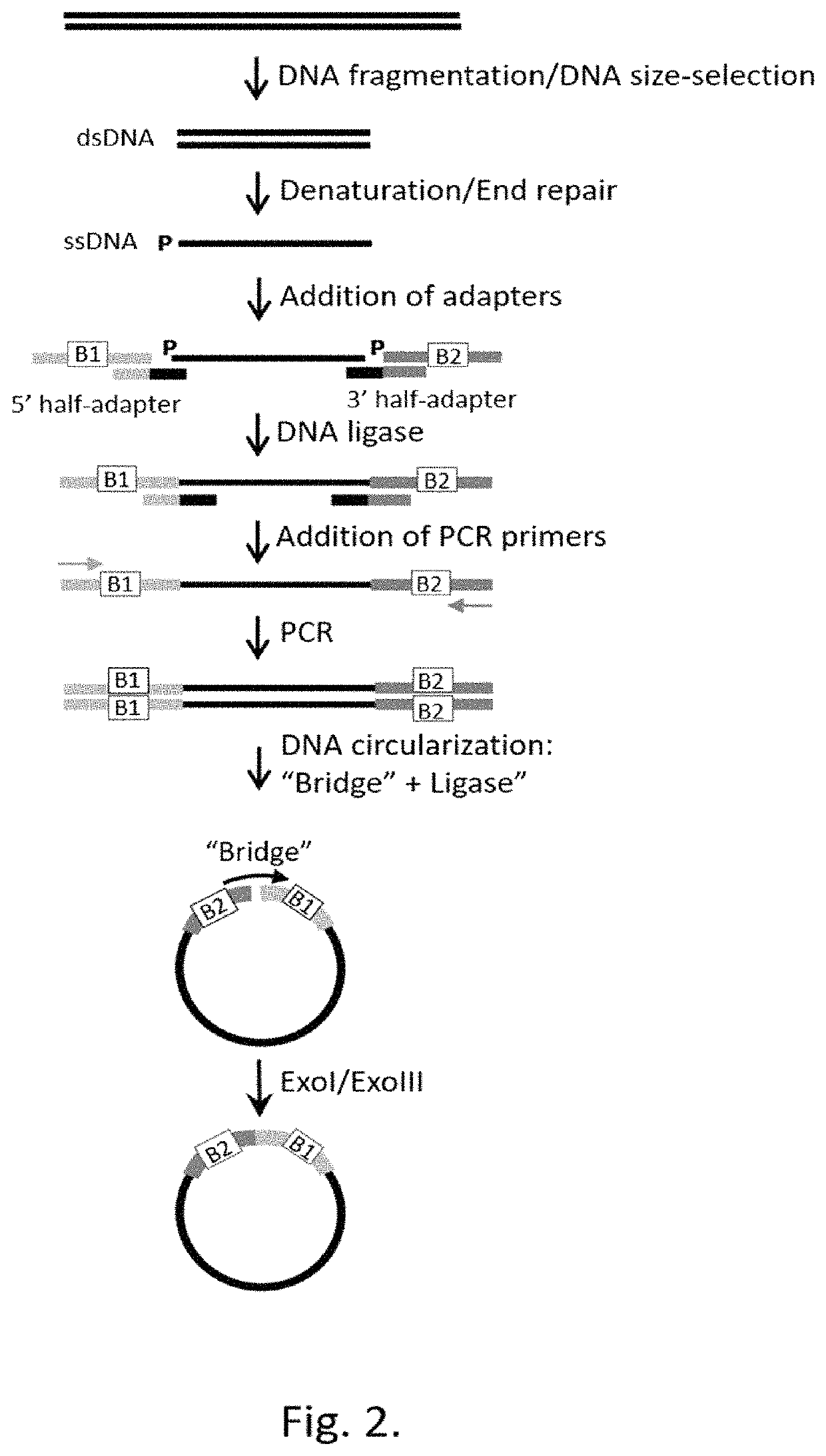
Adapter for next-generation sequencing
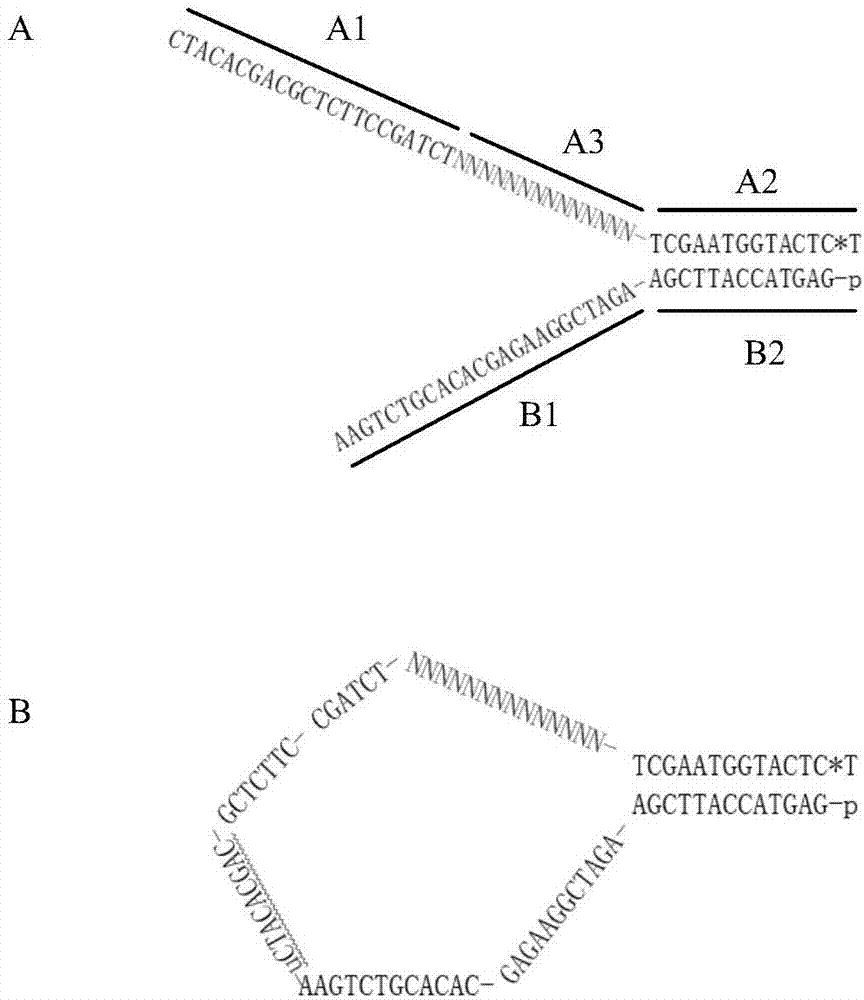
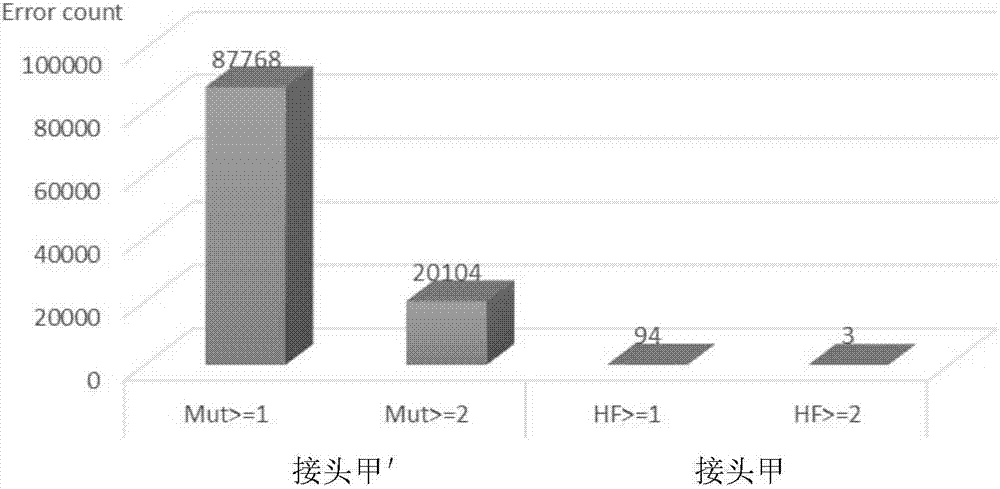
ActiveCN106939344AReduce false positive mutationsImprove Sequencing AccuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideSingle strand dna
The invention discloses an adapter for next-generation sequencing. The adapter disclosed in the invention is composed of a single-stranded DNA A and a single-stranded DNA B or composed of a single-stranded DNA C and a single-stranded DNA D. The single-stranded DNA A, from terminal 5' to terminal 3', is as shown in a formula (I), i.e., A1-A3-A2, wherein each nucleotide of A3 is A, T, C or G; the single-stranded DNA B, from terminal 3' to terminal 5', is as shown in a formula (II), i.e., B1-B2, wherein A2 and B2 are complementary, A1 and B1 are not complementary, A3, B1 and A1 are not complementary, the sequences of A1 and A2 are different, and the sequences of B1 and B2 are different; the single-stranded DNA C is composed of A1 and A2; and the single-stranded DNA D is composed of B1, B2 and A3. Experimental results show that the adapter provided by the invention can easily and efficiently reduce false positive mutation in next-generation sequencing so as to realize more sensitive detection of low-frequency mutation in heterogeneous mixed samples like heterogeneous samples and chimera samples of tumors.
Owner:北京迈基诺基因科技股份有限公司
Hairpin-like adapter, construct and method for characterizing double-stranded target polynucleotide
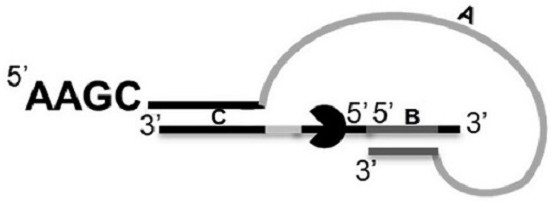
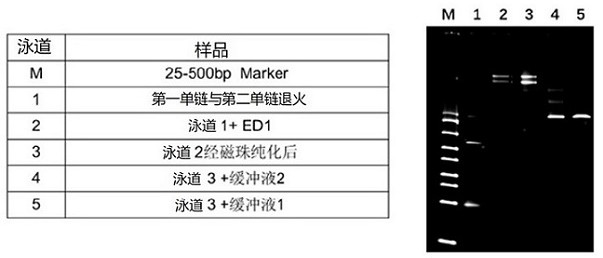
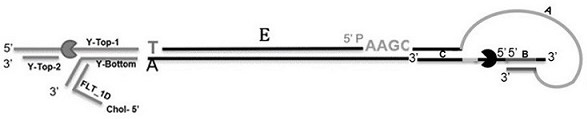
ActiveCN113462764AEffective combinationHigh reliability quadrature correction read capabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSingle strandPolynucleotide
The present invention provides a hairpin-like adaptor, a construct and a method for characterizing a double-stranded target polynucleotide. The hairpin-like adaptor comprises a first single strand and a second single strand which are respectively connected with a template strand and a complementary strand of the double-strand target polynucleotide, and the first single strand and the second single strand form at least one double-strand nucleic acid region which is used for enabling the complementary strand to be close to a transmembrane pore after the template strand passes through the transmembrane pore. Also provided are a construct comprising the hairpin-like adapter, as well as a method, a kit, and the like for characterizing double-stranded target polynucleotides. The characterization method disclosed by the invention has many advantages, such as balancing the translocation speed of the template strand and the complementary strand of the target polynucleotide, improving the sequencing accuracy and the like.
Owner:QITAN TECH LTD
Single-molecule fluorescent gene sequencing optical system
ActiveCN112646703ALight damage is smallImprove Sequencing AccuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotideLaser scanning
The invention provides a single-molecule fluorescent gene sequencing optical system which is a novel single-molecule real-time sequencing technology based on frequency scanning. The single-molecule fluorescent gene sequencing optical system comprises a sequencing chip and a plurality of single-wavelength pulse laser groups for exciting fluorescent signals, wherein exciting light of the pulse laser groups sequentially irradiates the sequencing chip through a laser light path, and a gene sequence to be detected is sequentially subjected to frequency scanning; then, optical imaging is performed through a fluorescent light path; and sequencing is performed on four basic group phosphoric acid segments of nucleotide molecules modified with different fluorescent molecules. A pulse laser scanning illumination mode is used, so that the light damage of the laser light intensity on DNA polymerase by continuous illumination in the conventional three-generation single-molecule real-time sequencing can be effectively reduced; the pulse scanning time is selected to be shorter than the polymerization extension time, so that in the ATGC cyclic sequencing process, before the next basic group starts to be detected, the sequencing accuracy can be improved through repeated measurement on the previous basic group.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
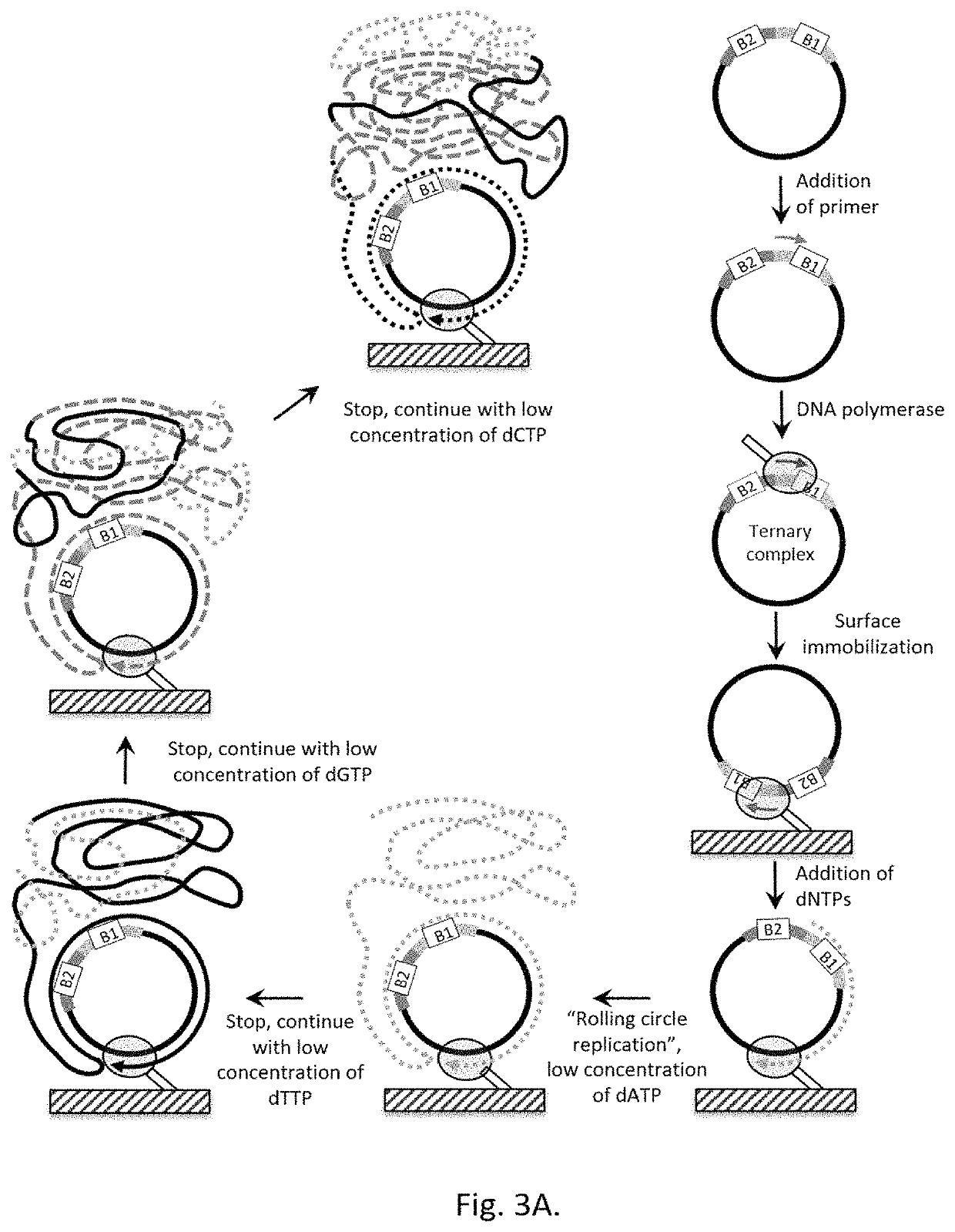
Method for label-free single-molecule DNA sequencing and device for implementing same
ActiveUS20190360039A1Lower device costReduce reagent consumptionHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolymerase L
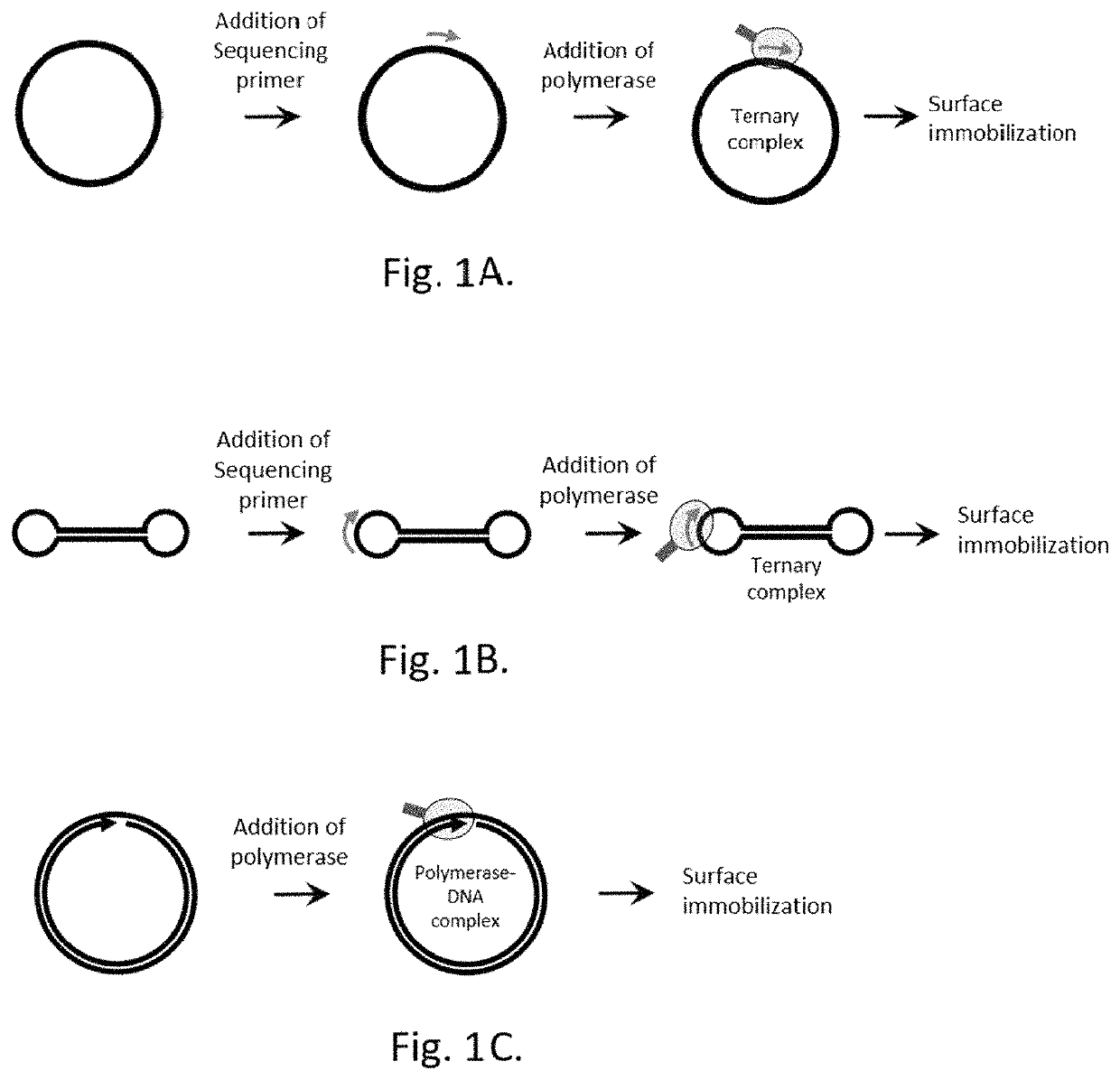
A method and a device for determining a nucleotide sequence are proposed. The method comprises immobilising looped fragments of a nucleic acid and a polymerase on a sensor surface and adding a mixture of unlabelled nucleotides onto the sensor surface. Moreover, in the mixture added, one nucleotide type is present at a much lower concentration compared to the other nucleotides. Time intervals between each of the charge separation events are determined and the mixture addition and the registration steps are repeated. Moreover, at each repetition, the nucleotide type present at a much lower concentration compared to the other nucleotides in the mixture added is changed. The nucleotide sequence of a nucleic acid molecule is determined by the analysis of the time intervals between each of the charge separation events registered, which result from the insertion, facilitated by the polymerase, of said unlabelled nucleotides into the growing nucleic acid chain. The device comprises a matrix having a plurality of sensor cells, and a digital-analog circuit, a microfluidic apparatus for feeding working solutions to the sensors, and data processing and display means.
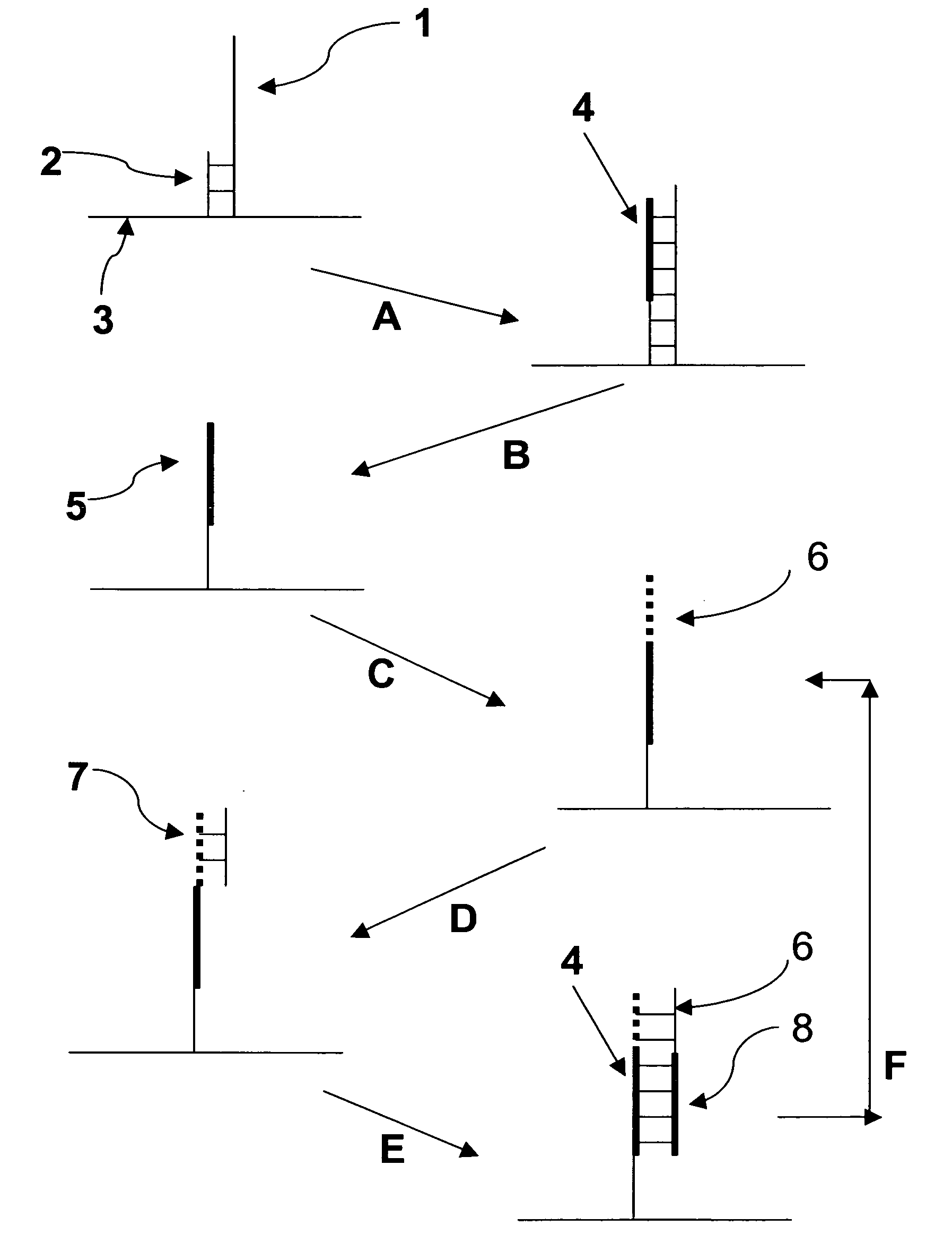
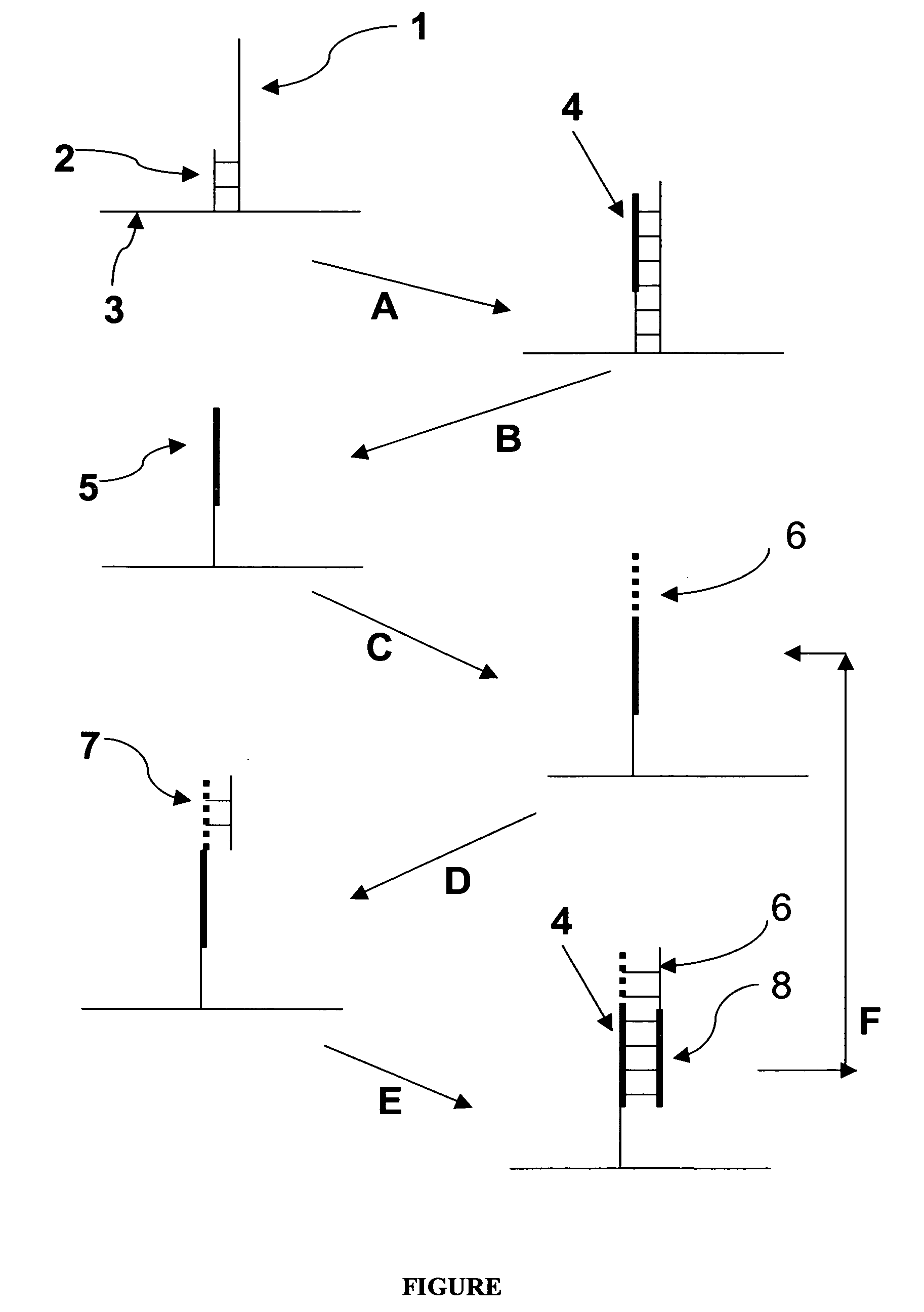
Methods for increasing accuracy of nucleic acid sequencing
InactiveUS20070243535A1Improve accuracyImprove Sequencing AccuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic acid sequencingComputational biology
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Method for Assembly of Nucleic Acid Sequence Data
InactiveUS20140249764A1Improve Sequencing AccuracyAvoids reference sequence associated bias problemBiological testingSequence analysisNucleic acid sequencingSequence assembly
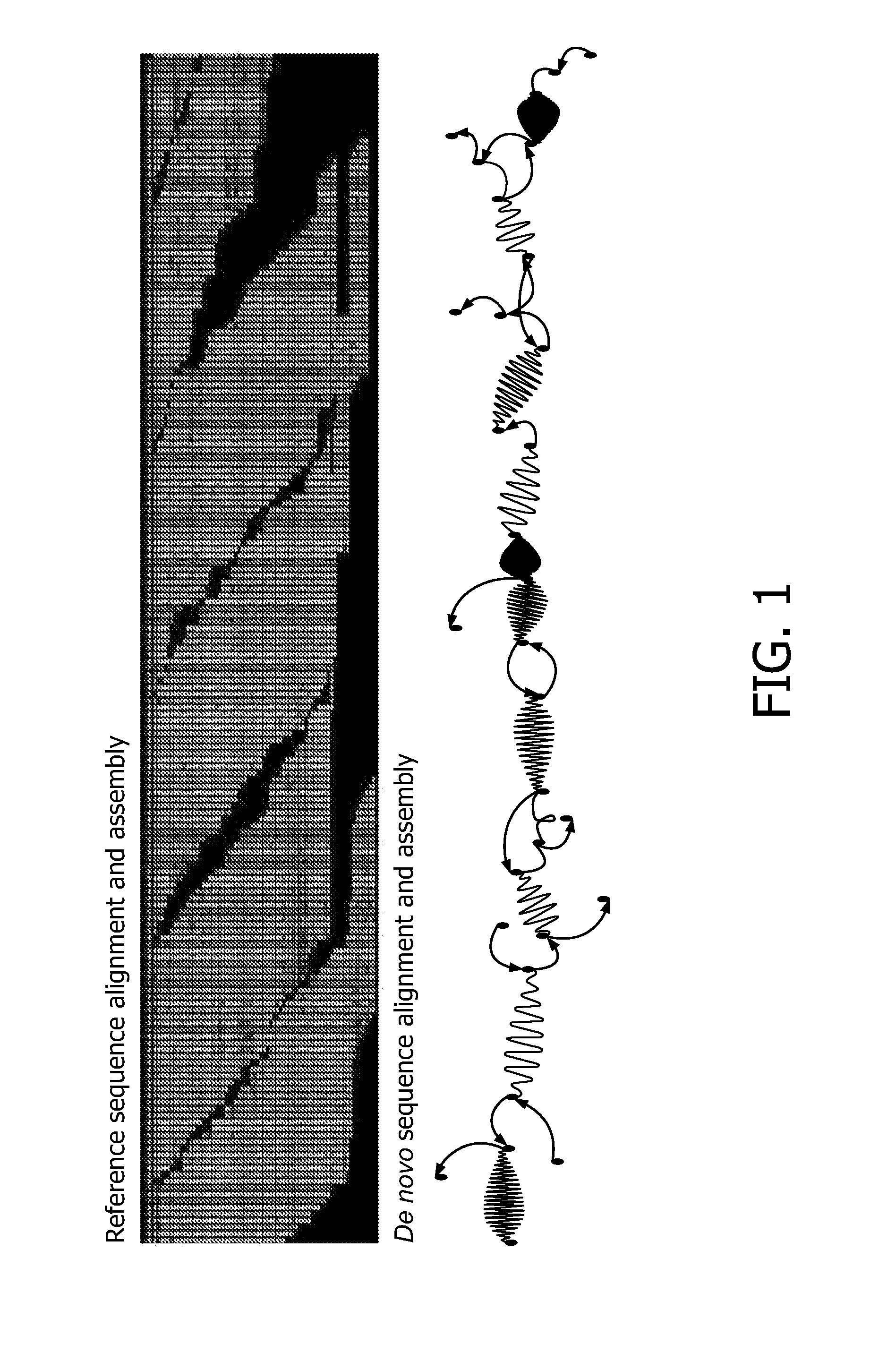
The present invention relates to a method for assembly of nucleic acid sequence data comprising nucleic acid fragment reads into (a) contiguous nucleotide sequence segment(s), comprising the steps of: (a) obtaining a plurality of nucleic acid sequence data from a plurality of nucleic acid fragment reads; (b) aligning said plurality of nucleic acid sequence data to a reference sequence; (c) detecting one or more gaps or regions of non-assembly, or non-matching with the reference sequence in the alignment output of step (b); (d) performing de novo sequence assembly of nucleic acid sequence data mapping to said gaps or regions of non-assembly; and (e) combining the alignment output of step (b) and the assembly output of step (d) in order to obtain (a) contiguous nucleotide sequence segment(s). In addition, a corresponding program element or computer program for assembly of nucleic acid sequence data and a sequence assembly system for transforming nucleic acid sequence data comprising nucleic acid fragment reads into (a) contiguous nucleotide sequence segment(s) is provided.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
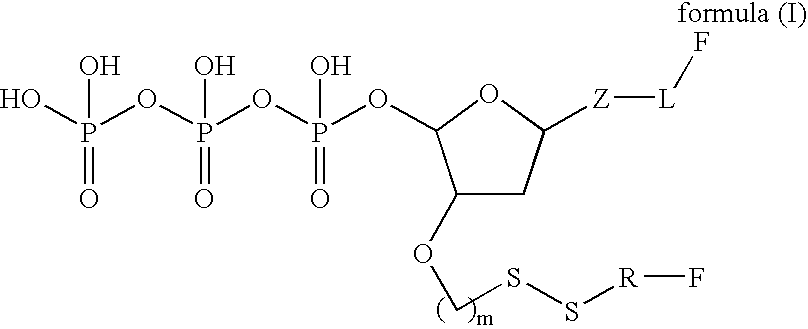
Specially modified nucleotide as well as application thereof in high-throughput sequencing
InactiveCN103951724AAchieve chemical cuttingMature and reliable technologySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideDiol
The invention discloses a specially modified nucleotide as well as an application thereof in high-throughput sequencing. A fluorescence marked group of the nucleotide and a nucleotide matrix are linked through a linker arm containing a vicinal diol bond; vicinal diol hydroxyl is oxidized by a strong oxidant, so that a single bond adjacent to carbon is broken off and a fluorescent group is chemically cut simply and effectively; the same template to be sequenced is subjected to sequencing reactions in two groups, each sequencing is finished by two nucleotide dNTPs cycles marked by two pairs of different fluorescences; in a mode that each nucleotide can only be used once in one cycle, a code composed of a nucleotide fragment is obtained by each sequencing reaction, and nucleotide sequence information composed of a group of codes is obtained after the first group of sequencing reaction is finished; then the second group of sequencing reaction is performed to obtain a plurality of code information ranked by the second group of sequencing reaction; the two groups of code information are encoded according to the sequencing order, and the two groups of encoded information are combined to form the specific base sequence of a nucleotide fragment to be sequenced.
Owner:南京普东兴生物科技有限公司
Position anchoring bar code system for nanopore sequencing library building
ActiveCN111440846AAccurate resolutionReduce classification errorsLibrary tagsMicrobiological testing/measurementEngineeringComputer science
The invention relates to a position anchoring bar code system for nanopore sequencing library building, and a preparation method and application of the position anchoring bar code system. The positionanchoring bar code system provided by the invention has higher resolution and higher classification accuracy, can significantly reduce the false positive rate of identification, improves the nanoporesequencing precision on the whole, and reduces the sequencing cost.
Owner:SIMCERE DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD +1
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequencing device based on graphene nanopore-microcavity-solid-state nanopore and manufacturing method
ActiveCN102901763BAvoid instabilityOvercome instabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNanotechnologyMeasurement deviceWeak current
The invention discloses a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequencing device based on a graphene nanopore-microcavity-solid-state nanopore and a manufacturing method. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of etching an inverted-pyramid-shaped microcavity in the upper part of a silicon on insulator (SOI) silicon wafer; etching a columnar hole on the lower part of the SOI silicon wafer, wherein the tower top of the inverted-pyramid-shaped microcavity is the solid-state nanopore; etching the graphene on the upper part of the inverted-pyramid-shaped microcavity; etching the graphene nanopore in the center of the graphene, wherein a platinum electrode and a longitudinal weak current measurement device as well as a power supply form a longitudinal weak current measurement loop, and a gold electrode and a transverse weak current measurement device as well as the power supply form a transverse weak current measurement loop; etching an inverted cone cavity in the front side of the SOI silicon wafer; etching a vertical columnar hole at the back of the SOI silicon wafer; corroding an oxidized buried layer on the SOI silicon wafer to form the solid-state nanopore; transferring the prepared graphene to the surface of the SOI silicon wafer; etching the graphene nanopore coaxial to the fixed nanopore in the center of the graphene; and enabling a chip, the power supply and an ampere meter to form a circuit so as to realize the sequencing of the DNA by testing the change of current intensity in the circuit when the DNA penetrates through the nanopore.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for label-free single-molecule DNA sequencing and device for implementing same
ActiveUS11034998B2Rapid, highly accurate, and inexpensive method for determiningEliminate needHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideCharge separation
A method and a device for determining a nucleotide sequence are proposed. The method comprises immobilising looped fragments of a nucleic acid and a polymerase on a sensor surface and adding a mixture of unlabelled nucleotides onto the sensor surface. Moreover, in the mixture added, one nucleotide type is present at a much lower concentration compared to the other nucleotides. Time intervals between each of the charge separation events are determined and the mixture addition and the registration steps are repeated. Moreover, at each repetition, the nucleotide type present at a much lower concentration compared to the other nucleotides in the mixture added is changed. The nucleotide sequence of a nucleic acid molecule is determined by the analysis of the time intervals between each of the charge separation events registered, which result from the insertion, facilitated by the polymerase, of said unlabelled nucleotides into the growing nucleic acid chain. The device comprises a matrix having a plurality of sensor cells, and a digital-analog circuit, a microfluidic apparatus for feeding working solutions to the sensors, and data processing and display means.
Method for deducing a polymer sequence from a nominal base-by-base measurement
ActiveUS9558319B1Improve Sequencing AccuracyLimited to sequenceDigital computer detailsSpecial data processing applicationsHigh probabilityStochastic variation
A method of processing sequencing data obtained with a polymer sequencing system identifies the most likely monomer sequence of a polymer, regardless of stochastic variations in recorded signals. Polymer sequencing data is recorded and two or more distinct series of pore blocking signals for a section of the polymer are recorded. A value is assigned to each series of pore blocking signals to obtain multiple trial sequences. The probability that each of the trial sequences could have resulting in all of trial sequences is calculated to determine a monomer sequence with the highest probability of resulting in all of the trial sequences, termed the first iteration sequence. The first iteration sequence is systematically altered to maximize the combined probability of the first iteration sequence leading to all the trial sequences in order to obtain a most likely sequence of monomers of the polymer.
Owner:ELECTRONICS BIOSCI
Nucleic acid indexing techniques
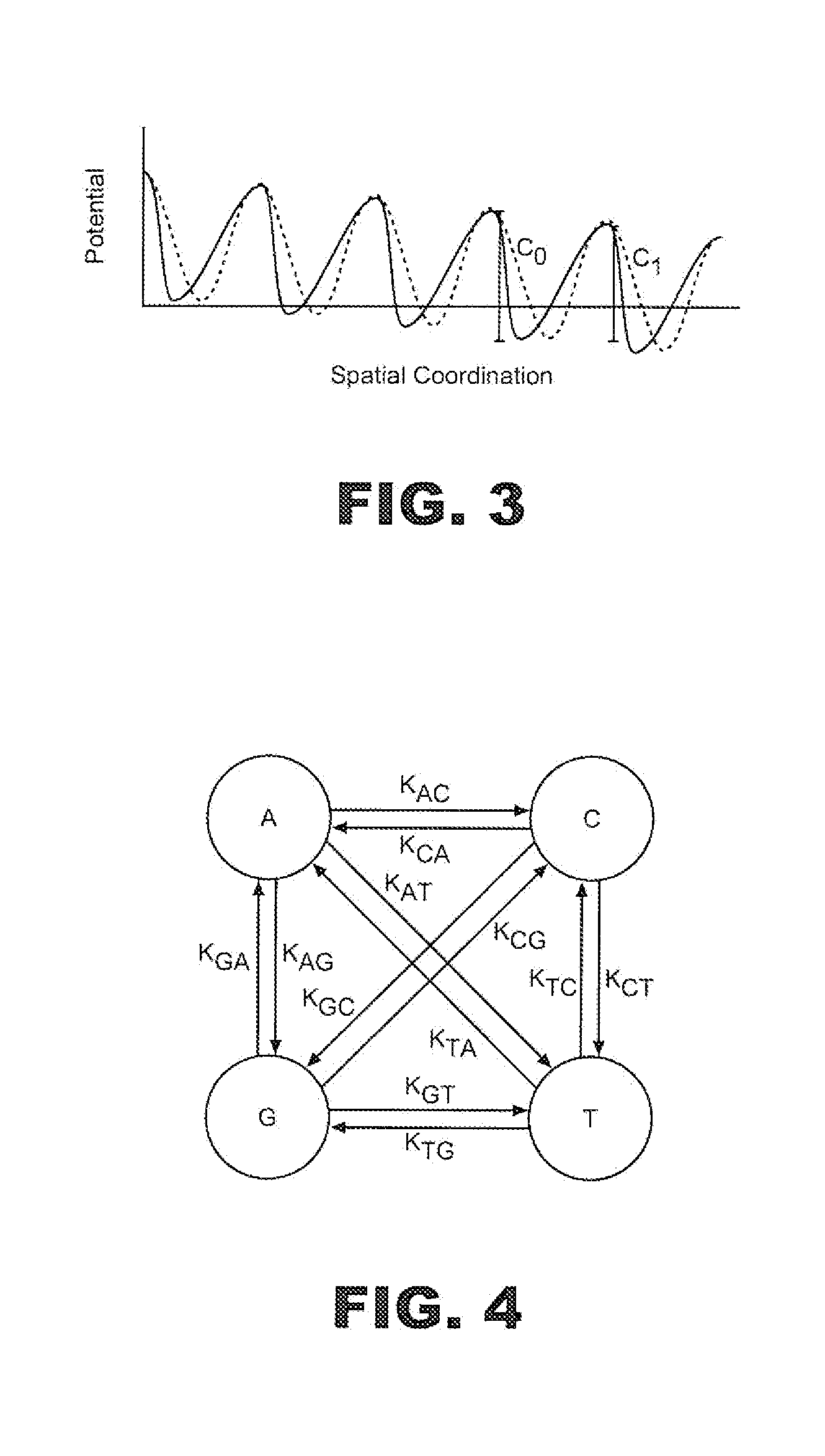
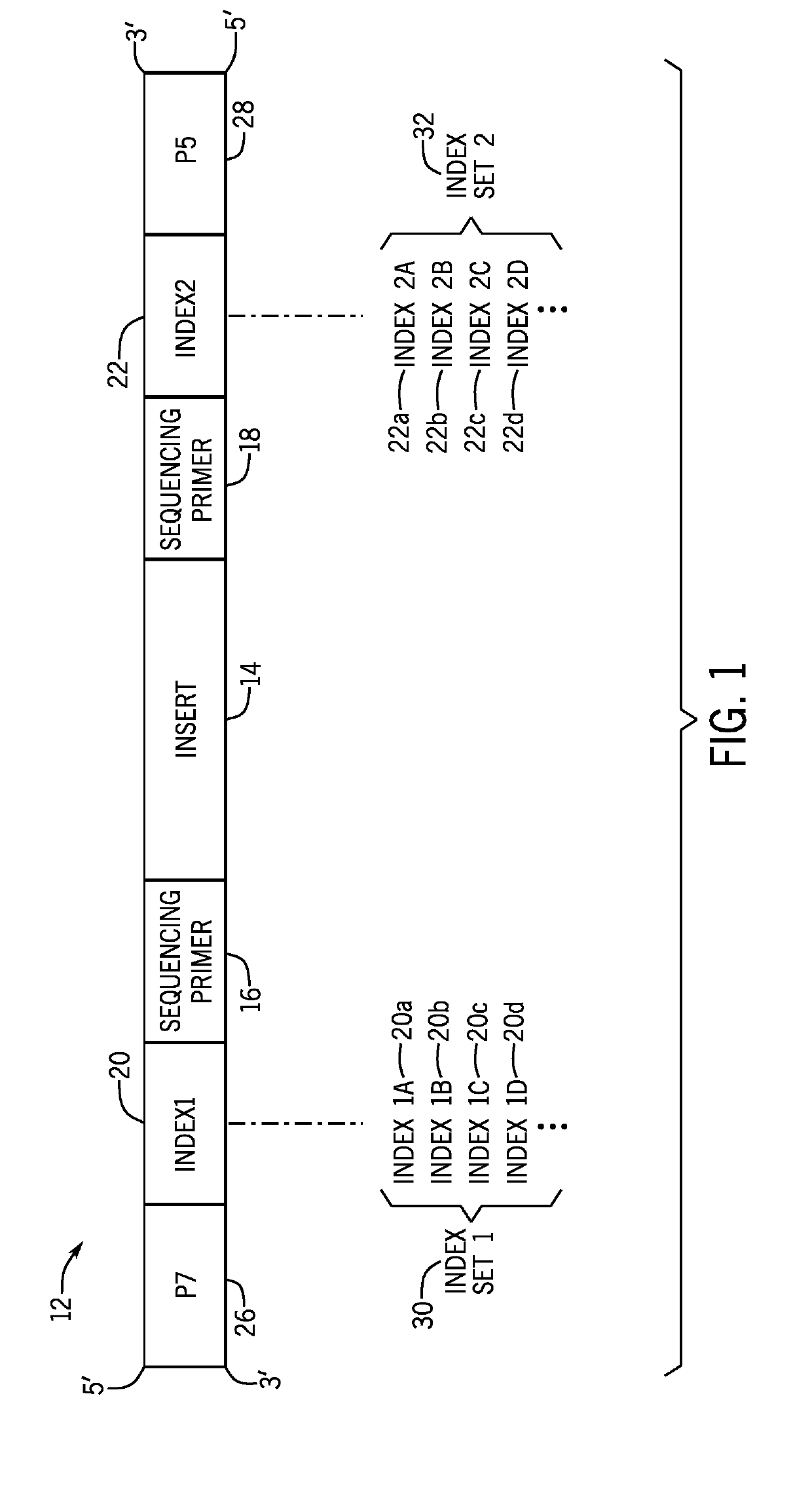
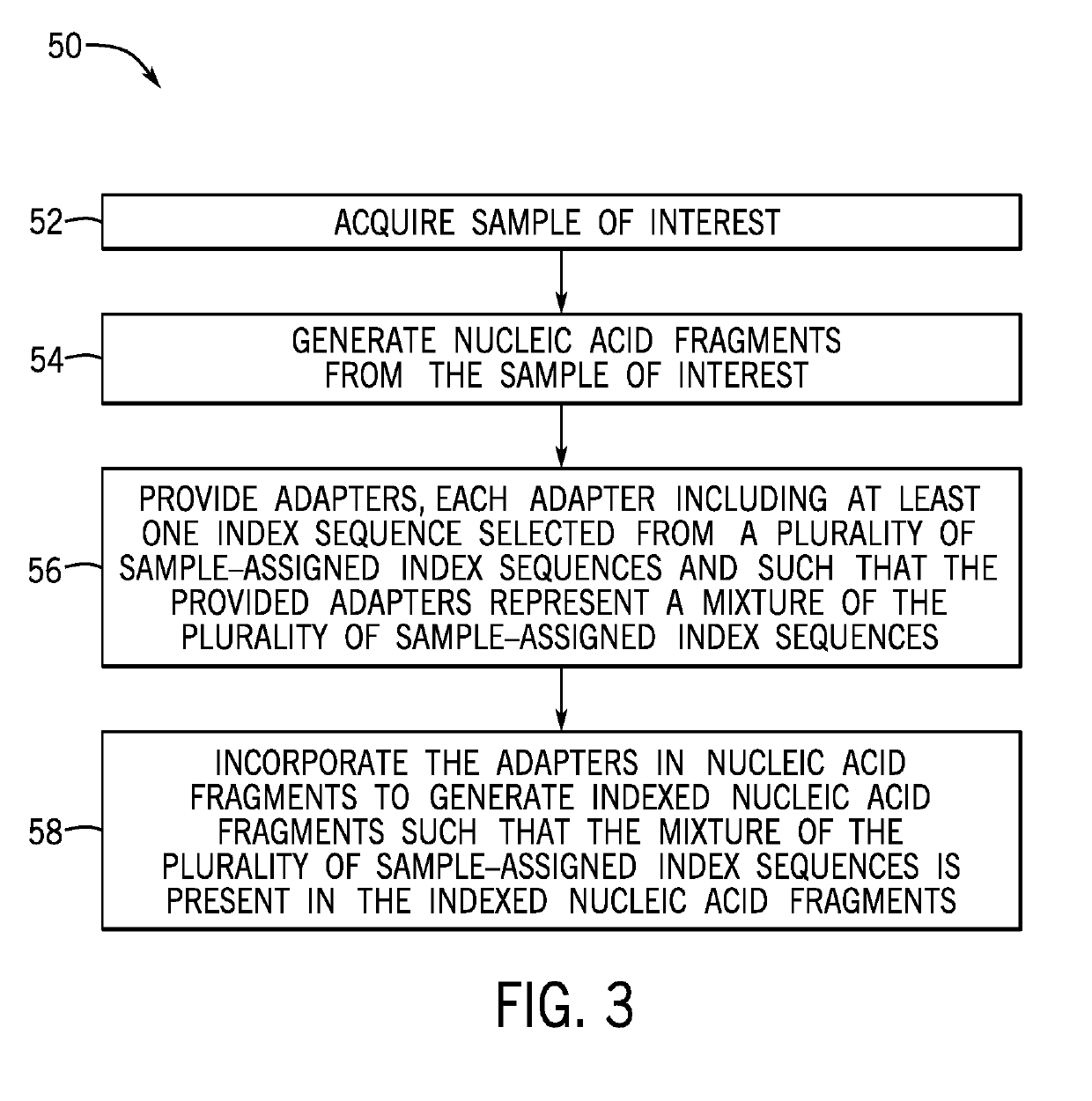
PendingUS20190218545A1Introduce contaminationImprove Sequencing AccuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisSingle sampleNucleic acid
Presented herein are techniques for indexing of nucleic acid, e.g., for use in conjunction with sequencing. The techniques include generating indexed nucleic acid fragments from an individual sample, whereby the index sequence incorporated into each index site of the nucleic acid fragment is selected from a plurality of distinguishable of index sequences and such that the population of generated nucleic acid fragments represents each index sequence from the plurality. In this manner, the generated indexed nucleic acid fragments from a single sample are indexed with a diverse mix of index sequences that reduce misassignment due to index read errors associated with low sequence diversity.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Nucleic acid isothermal self-amplification method
ActiveUS11268139B2Increase frequencyImprove Sequencing AccuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesSingle strandA-DNA
Provided is a nucleic acid isothermal self-amplification method comprising, adding suitable palindrome complementary sequences at both ends of a target template to form a stem-loop structure spontaneously, and providing reagents and conditions as needed to perform self-amplification. The method does not require addition of additional amplification primers. The reagent comprises a DNA polymerase having a strand displacement activity. The method does not rely on exogenous amplification primers for amplification, has a constant amplification temperature without a complex temperature control equipment, and achieves rapid amplification. The amplification product is a long single-stranded DNA of a continuous complementary sequence and can be applied to special occasions. In addition, the amplification has no GC bias.
Owner:LU XINHUA
Linker sequence and application thereof
ActiveCN111575349ARealize the marking functionImprove Sequencing AccuracyLibrary tagsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNABioinformatics
The invention provides a linker sequence and an application thereof. The linker sequence comprises a molecular tag composed of a plurality of bases and sequencing linkers based on sequencing platforms; the molecular tag is located at the 3' end of the sequencing linker; and the linker sequence is linked to fragmented DNA by the molecular tag. The molecular tag composed of the plurality of bases iscombined with the sequencing linkers based on different sequencing platforms, and the constructed linker sequence is connected to one end and / or two ends of the fragmented DNA in the early stage of library construction, so that the marking effect on an original DNA fragment is realized; after the sequencing linkers are connected, the DNA is directly subjected to computer sequencing, so that an original sequence is reserved, and the technical effect of tracing the original source of the DNA fragment is achieved; and repeated fragments in the read length are removed according to the molecular tag in a sequencing result analysis process, and the sequencing accuracy is improved.
Owner:CAPITALBIO GENOMICS
Targeted capture sequencing detection method for pathogenic microorganisms of respiratory system
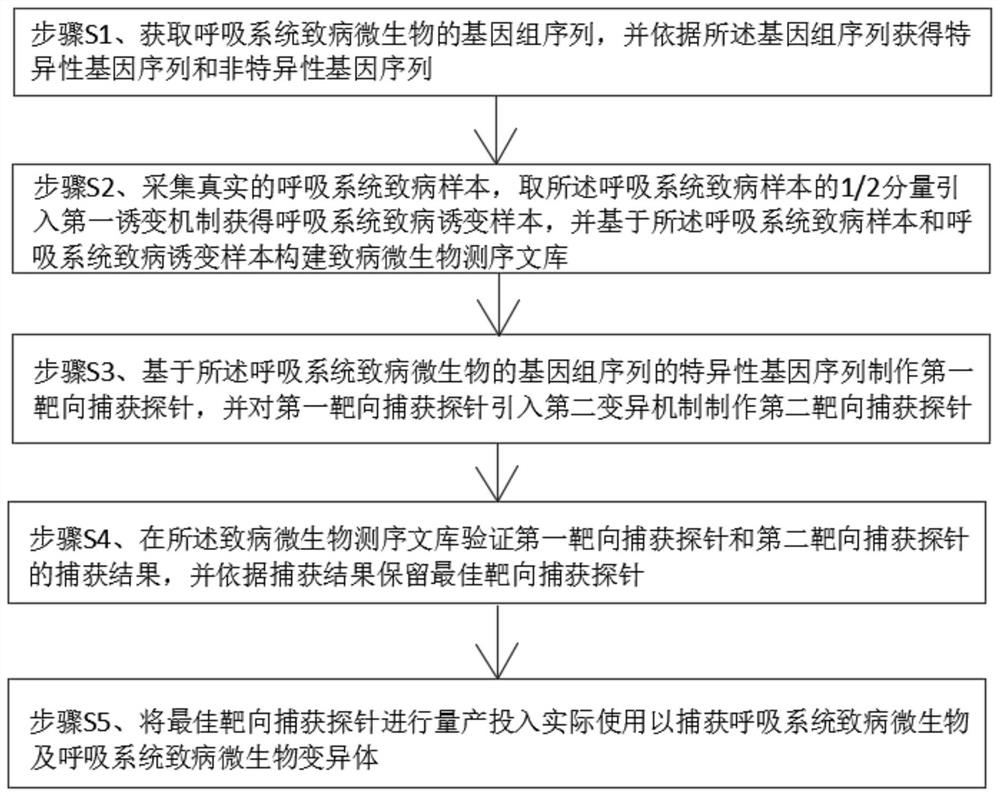
InactiveCN113046478AIncrease gene sequence abundanceAvoid Sequencing ResultsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationPathogenic microorganismTarget capture
The invention discloses a targeted capture sequencing detection method for pathogenic microorganisms of a respiratory system. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, acquiring a genome sequence of the pathogenic microorganisms of the respiratory system, and acquiring a specific gene sequence and a non-specific gene sequence according to the genome sequence; and S2, collecting a real pathogenic sample of the respiratory system, introducing a first mutagenesis mechanism into a half component of the pathogenic sample of the respiratory system to obtain a pathogenic mutagenesis sample of the respiratory system, and constructing a pathogenic microorganism sequencing library based on the pathogenic sample of the respiratory system and the pathogenic mutagenesis sample of the respiratory system. According to the method, a mutation mechanism is introduced into the preparation of the pathogenic microorganism sequencing library to simulate a microorganism mutation process, so that the gene sequence abundance of the microorganisms is increased, a sequencing result of the mutated virus microorganisms is prevented from being false negative, and the sequencing accuracy is improved.
Owner:深圳人体密码基因科技有限公司
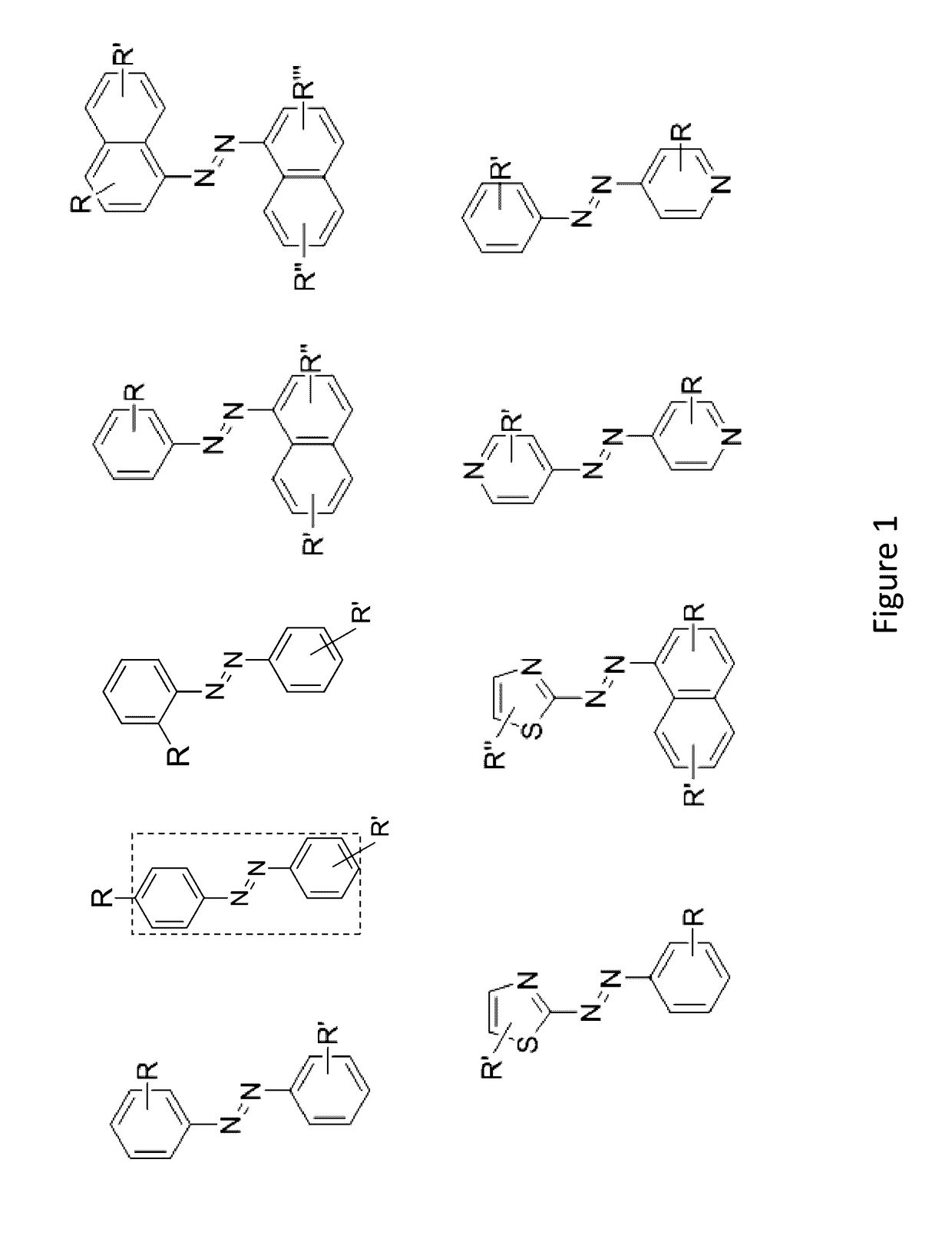
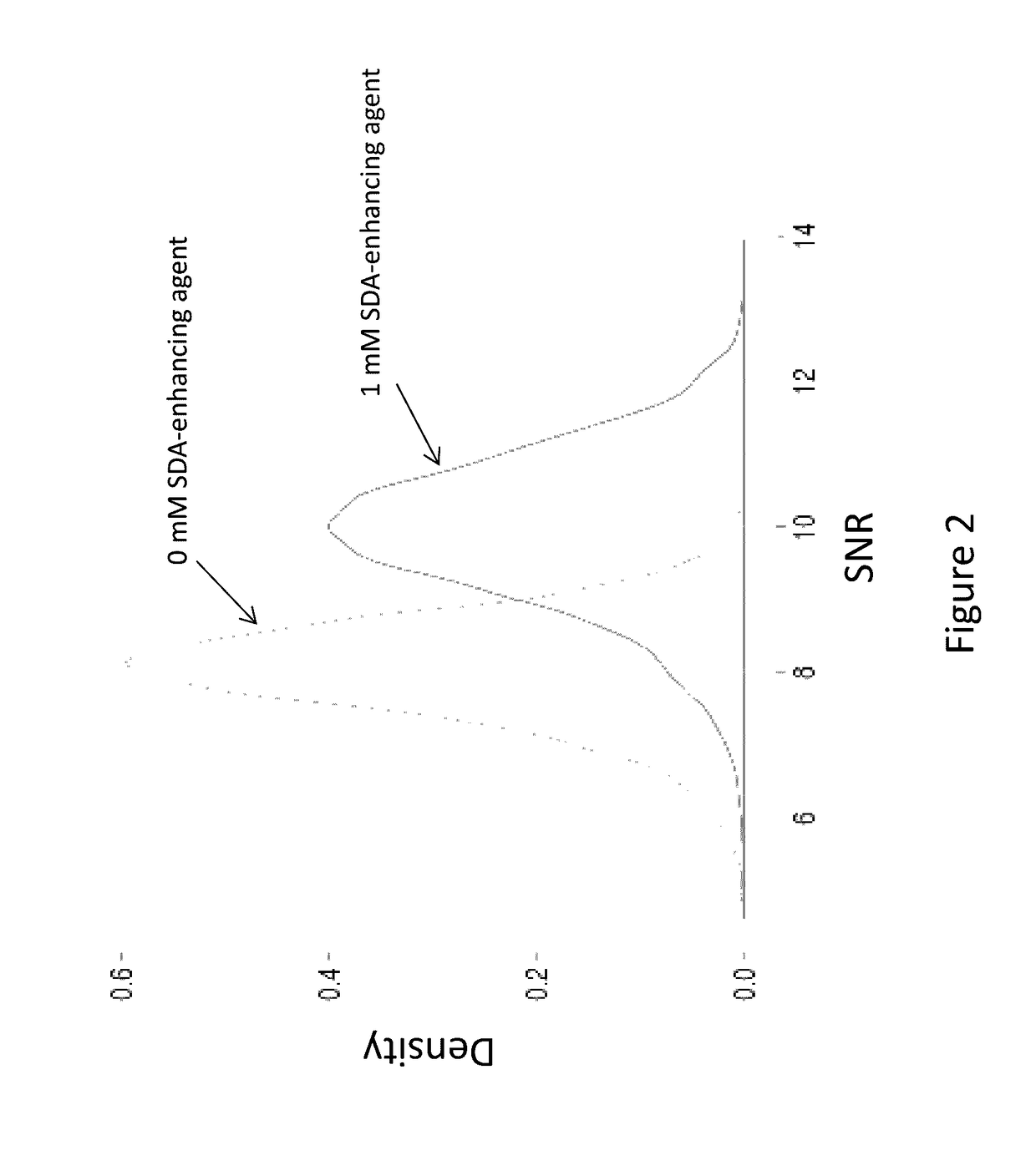
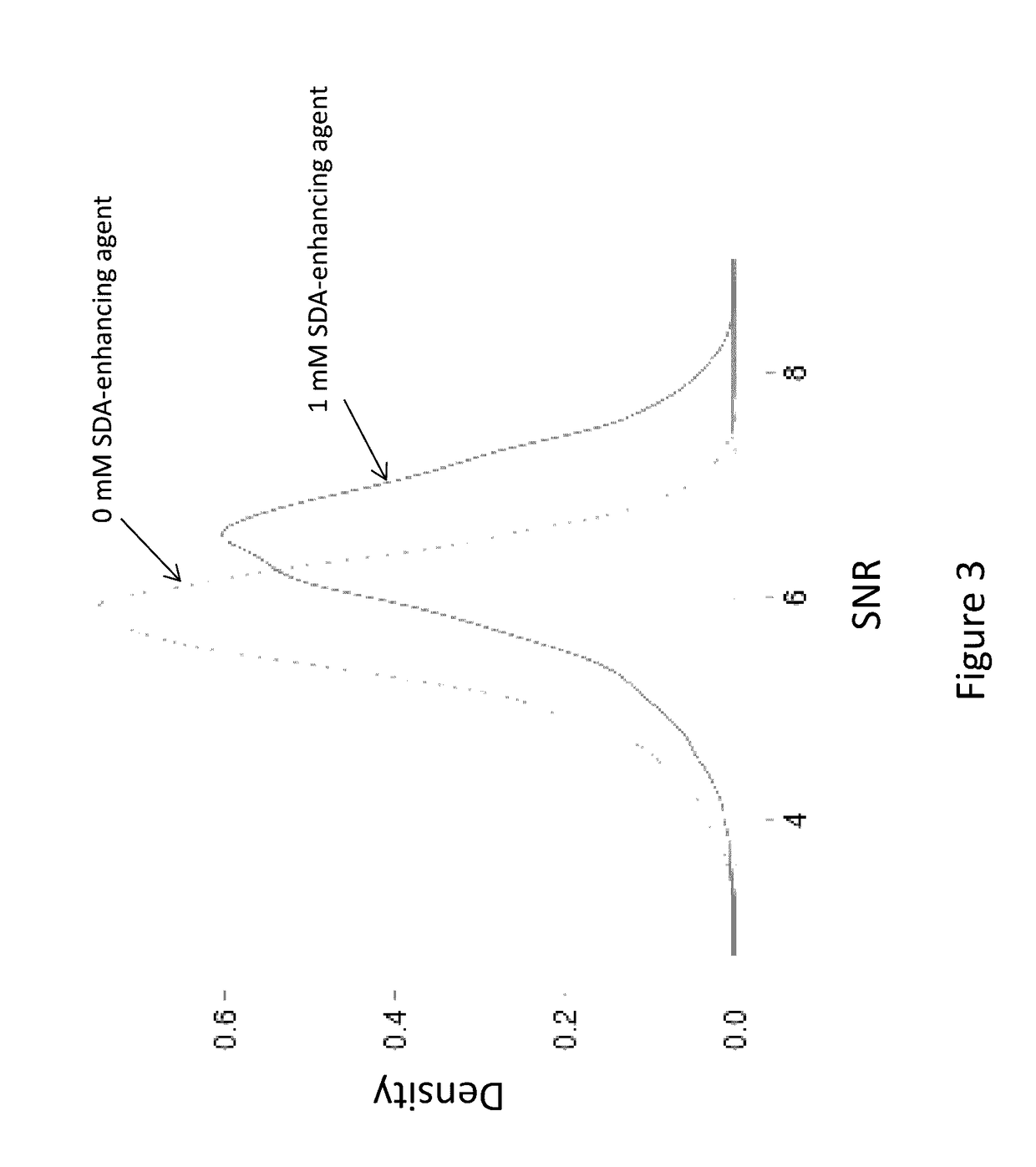
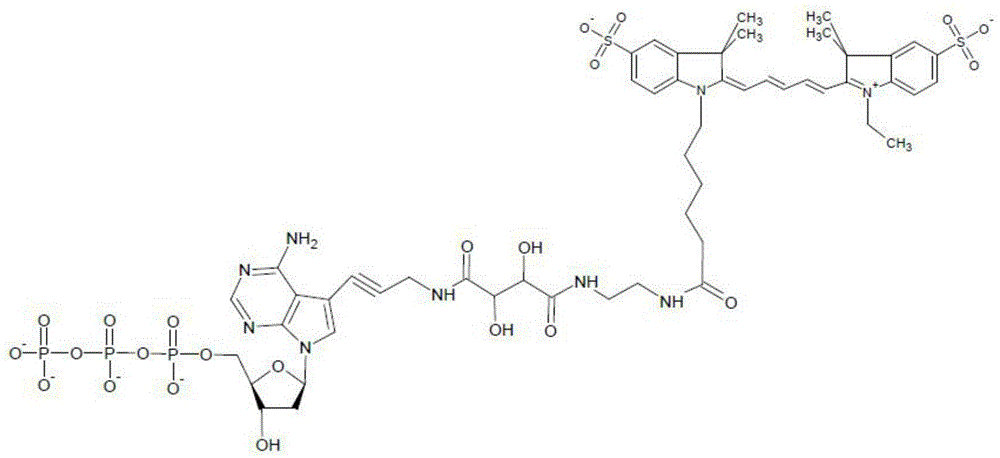
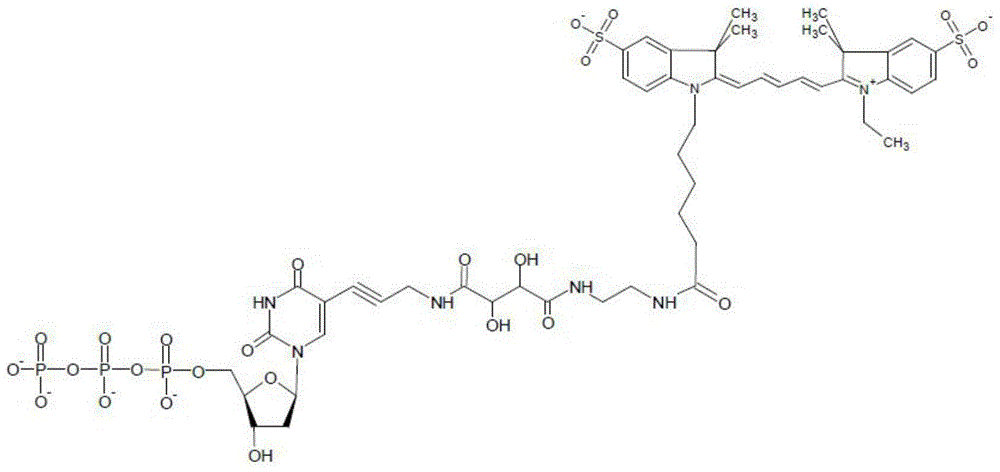
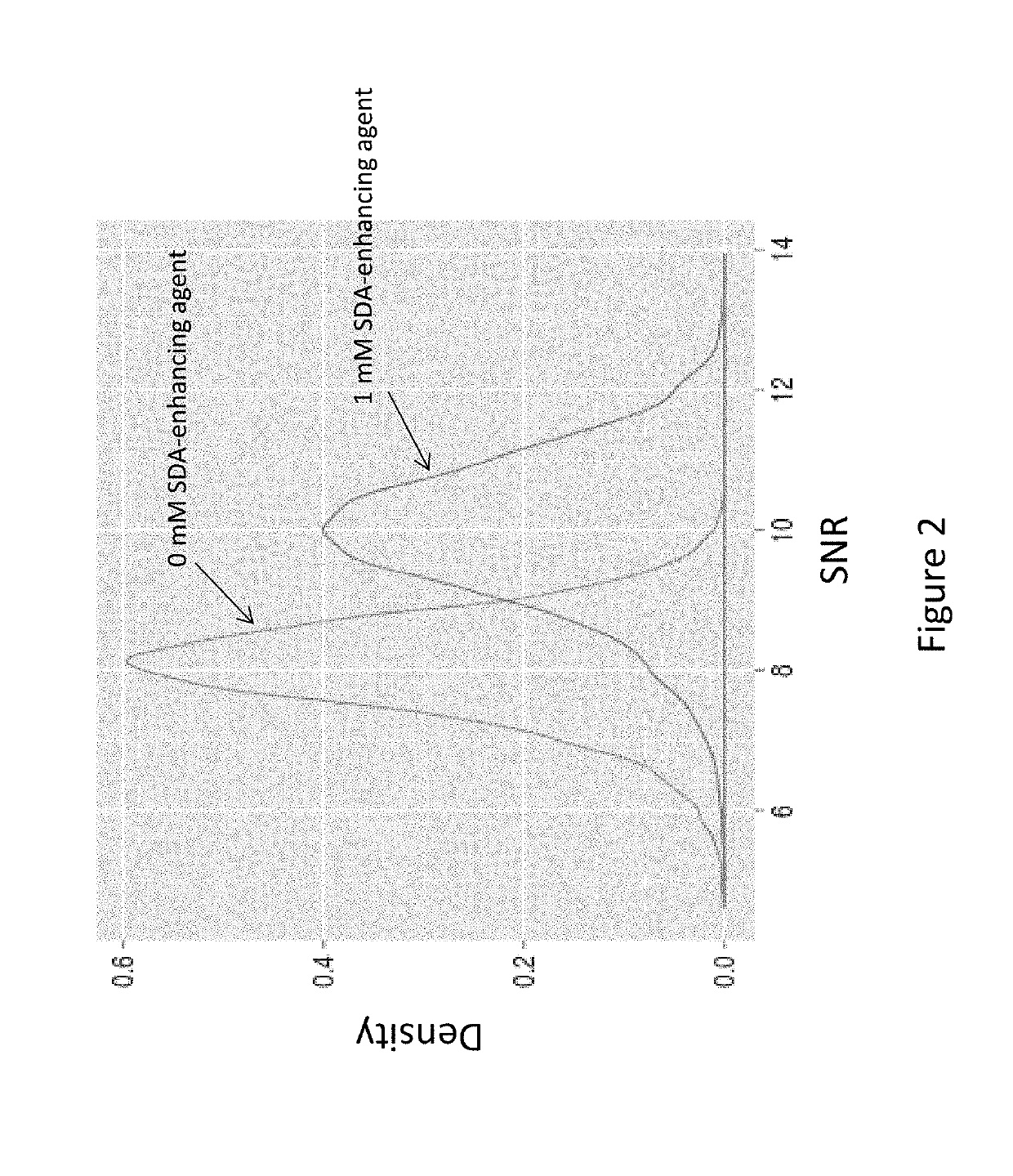
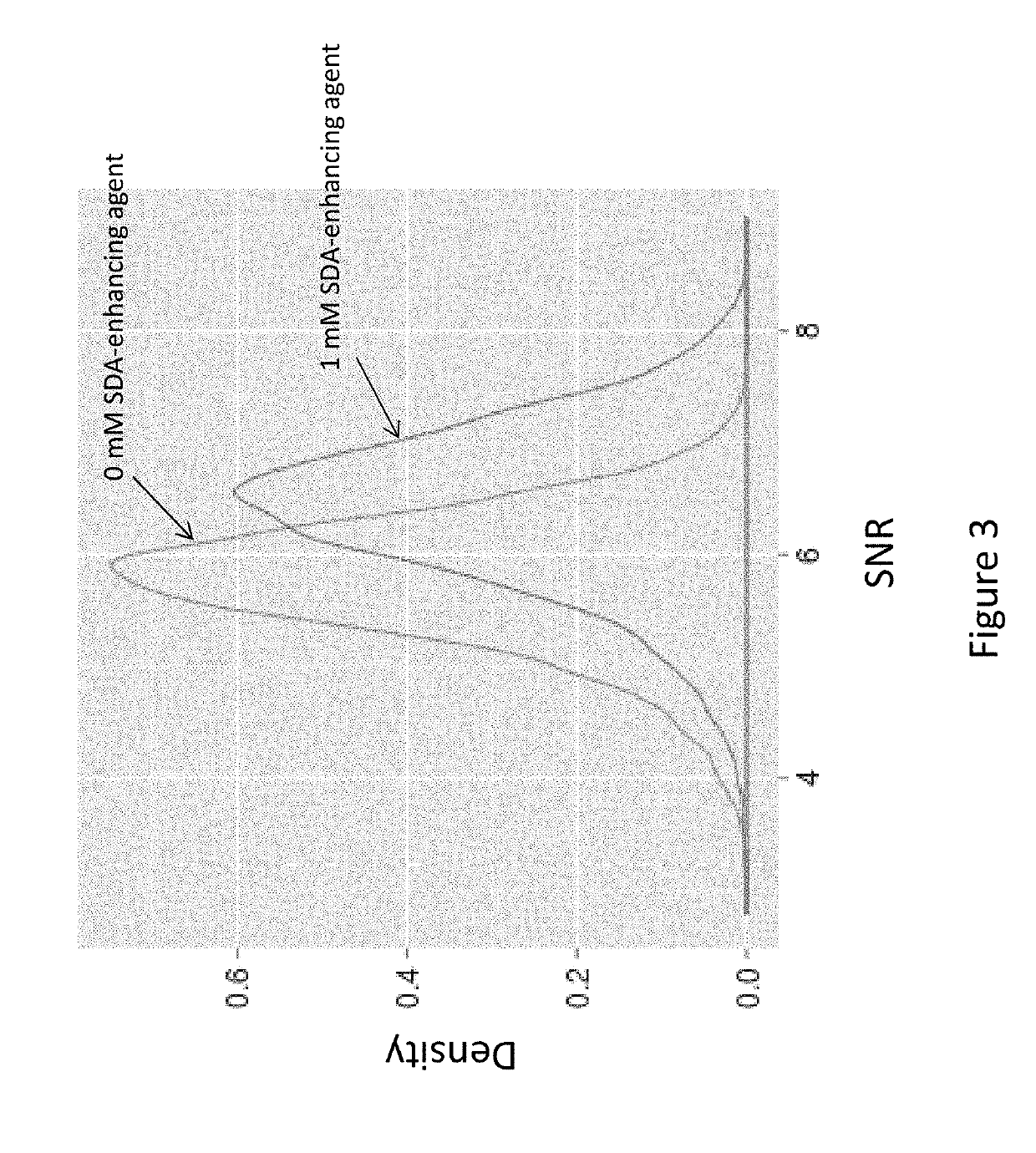
Compounds and systems for improving signal detection
ActiveUS20170145494A1Reduce restrictionsEasy to detectMonoazo dyesMicrobiological testing/measurementSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Photoprotection
Compositions, devices, systems and methods for increasing the signal to noise ratio (SNR) and / or enhancing photoprotection in an illuminated analytical reaction by addition of one or more signal detection assay (SDA)-enhancing agents to the reaction mixture.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
DNA sequencing device, solid-state nanopore array and preparation method of solid-state nanopore array
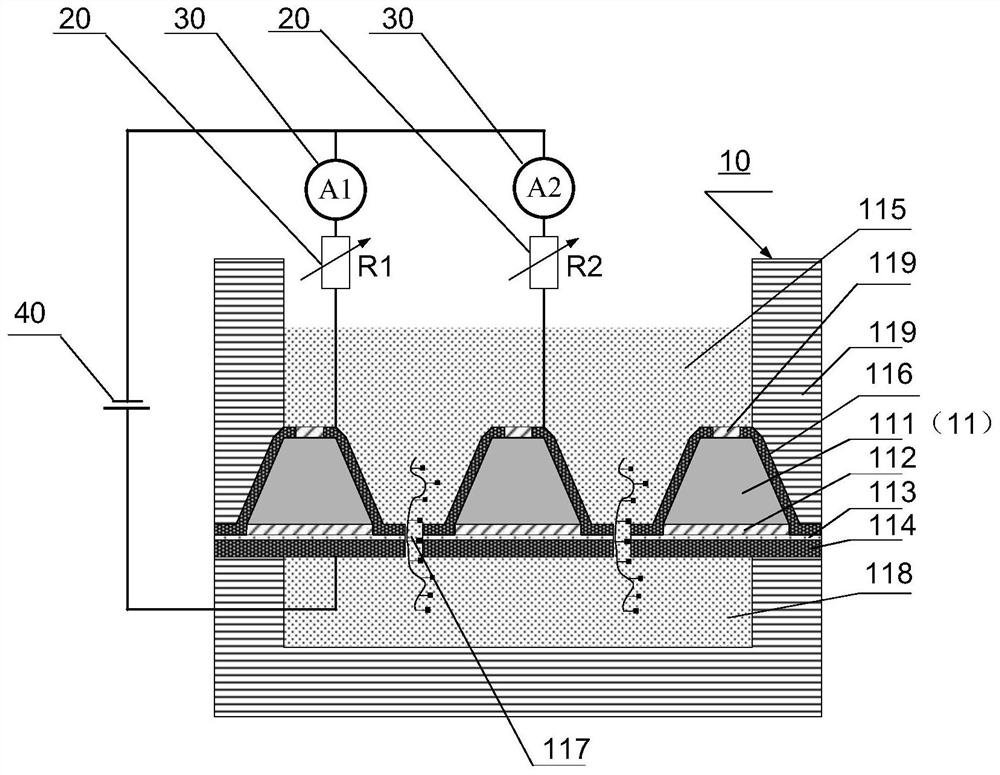
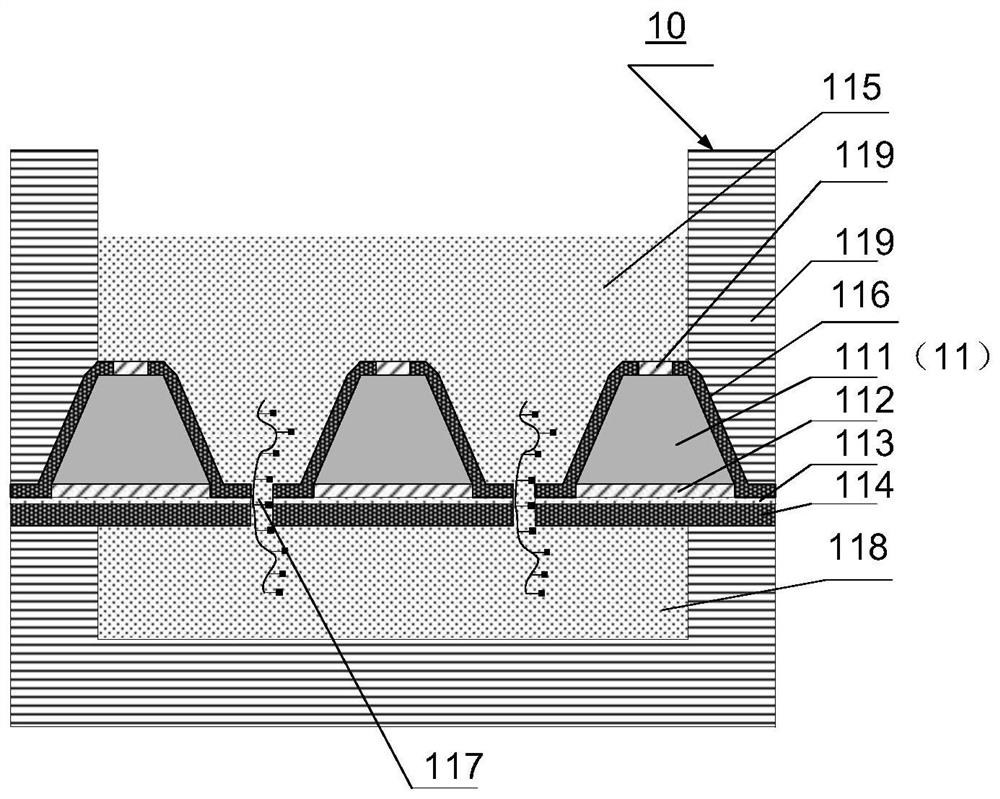
PendingCN112300913ASolve the problem that only the same gene sequence can be testedImprove stabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSilicon oxideA-DNA
The invention discloses a DNA sequencing device, a solid-state nanopore array and a preparation method of the solid-state nanopore array. The solid-state nanopore array comprises a plurality of pyramids etched on a silicon wafer, silicon oxide grows below each pyramid, silicon nitride is deposited below the silicon oxide, and a first metal electrode is- evaporated below the silicon nitride; secondmetal electrodes are evaporated on the two sides of each pyramid, an inverted pyramid-shaped micro-cavity is formed between the second metal electrodes on the two sides of the adjacent pyramids, a solid-state nanopore is formed in the tower top of each inverted pyramid-shaped micro-cavity, and each solid-state nanopore forms a solid-state nanopore array; the first metal electrode, a variable resistor, a current measuring device, a power supply and the second metal electrodes form a plurality of longitudinal weak current measuring loops; and by adjusting the variable resistor, the current measuring device measures the longitudinal weak current of the longitudinal weak current measuring loops to sequence a DNA sequence passing through the solid-state nanopore array. According to the embodiment of the invention, the DNA sequencing precision and sequencing efficiency can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN RUHAN GENE SCI & TECH LTD
Graphene nanopore-microcavity-solid-state nanopore structure based DNA sequencing device and method
ActiveCN102899243BOvercome instabilityChange componentsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSequence analysisComing out
The invention discloses a graphene nanopore-microcavity-solid-state nanopore structure based DNA sequencing device and a method. The sequencing device is mainly composed of a graphene nanopore-equipped graphene microstrip, an inverted pyramid-shaped microcavity in a silicon-based substrate, and a solid-state nanopore at the top of the microcavity. During sequencing, a sequencing reaction chamber is divided into two parts by the graphene nanopore-microcavity-solid-state nanopore structure. A single-stranded DNA molecule passes through the graphene nanopore linearly under the effect of an electrostatic field, then enters the inverted pyramid-shaped microcavity, and finally comes out from the solid-state nanopore. Weak current measuring equipment is utilized to measure longitudinal ionic current blocking caused by the DNA molecule passing activity in the nanopore and the transverse conductance change around the nanopore in the graphene microstrip. Further, a synchronous data recording and processing system is employed for analytical calculation of bi-directional data, thus realizing sequence analysis of the single-stranded DNA molecule.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A position-anchored barcoding system for nanopore sequencing library construction
ActiveCN111440846BAccurate resolutionReduce classification errorsLibrary tagsMicrobiological testing/measurementBarcodeBioinformatics
The present application relates to a position-anchored barcode system for nanopore sequencing library construction, a preparation method and an application thereof. The position-anchored barcode system described in this application has higher resolution and higher classification accuracy, can significantly reduce the false positive rate of identification, improve the accuracy of nanopore sequencing as a whole, and reduce the cost of sequencing.
Owner:SIMCERE DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD +1
A special modified nucleotide and its application in high-throughput sequencing
InactiveCN103951724BAchieve chemical cuttingMature and reliable technologySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideFluorescence
The invention discloses a specially modified nucleotide as well as an application thereof in high-throughput sequencing. A fluorescence marked group of the nucleotide and a nucleotide matrix are linked through a linker arm containing a vicinal diol bond; vicinal diol hydroxyl is oxidized by a strong oxidant, so that a single bond adjacent to carbon is broken off and a fluorescent group is chemically cut simply and effectively; the same template to be sequenced is subjected to sequencing reactions in two groups, each sequencing is finished by two nucleotide dNTPs cycles marked by two pairs of different fluorescences; in a mode that each nucleotide can only be used once in one cycle, a code composed of a nucleotide fragment is obtained by each sequencing reaction, and nucleotide sequence information composed of a group of codes is obtained after the first group of sequencing reaction is finished; then the second group of sequencing reaction is performed to obtain a plurality of code information ranked by the second group of sequencing reaction; the two groups of code information are encoded according to the sequencing order, and the two groups of encoded information are combined to form the specific base sequence of a nucleotide fragment to be sequenced.
Owner:南京普东兴生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com