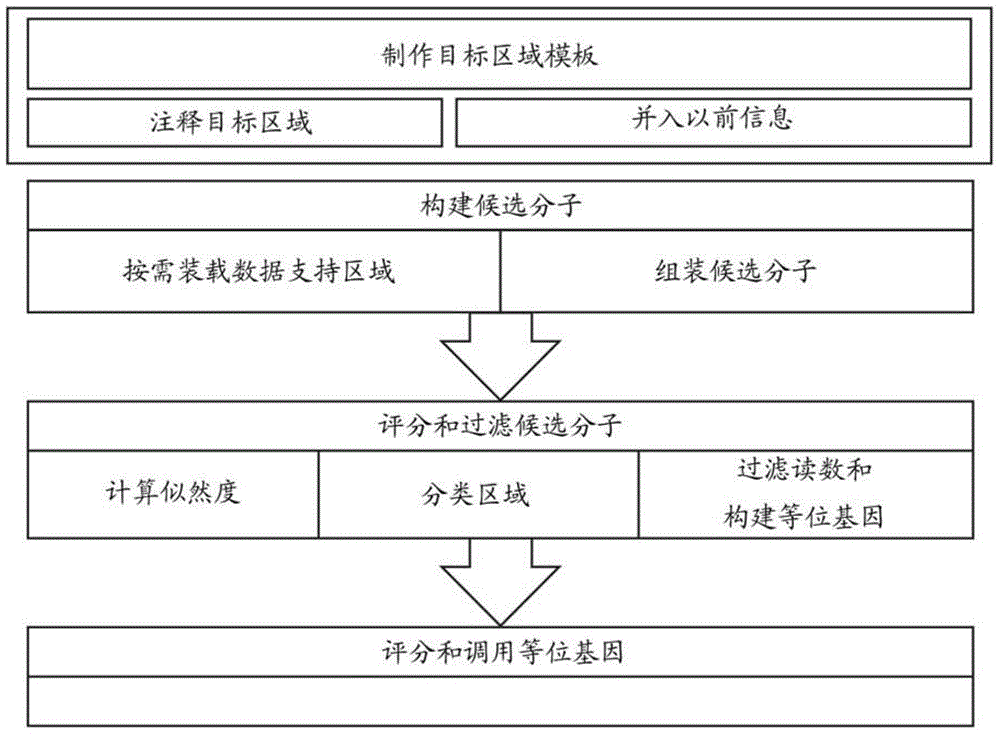
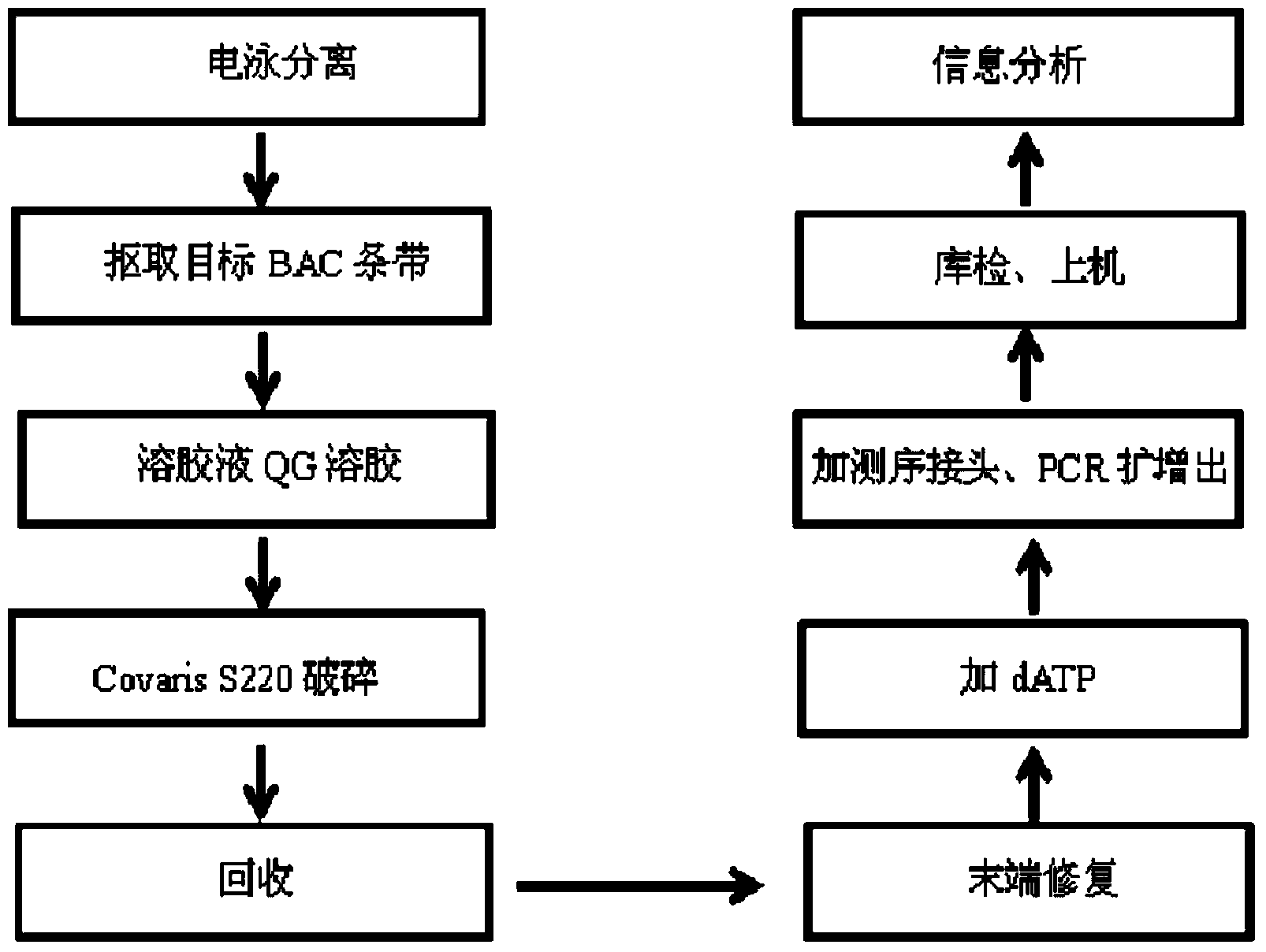
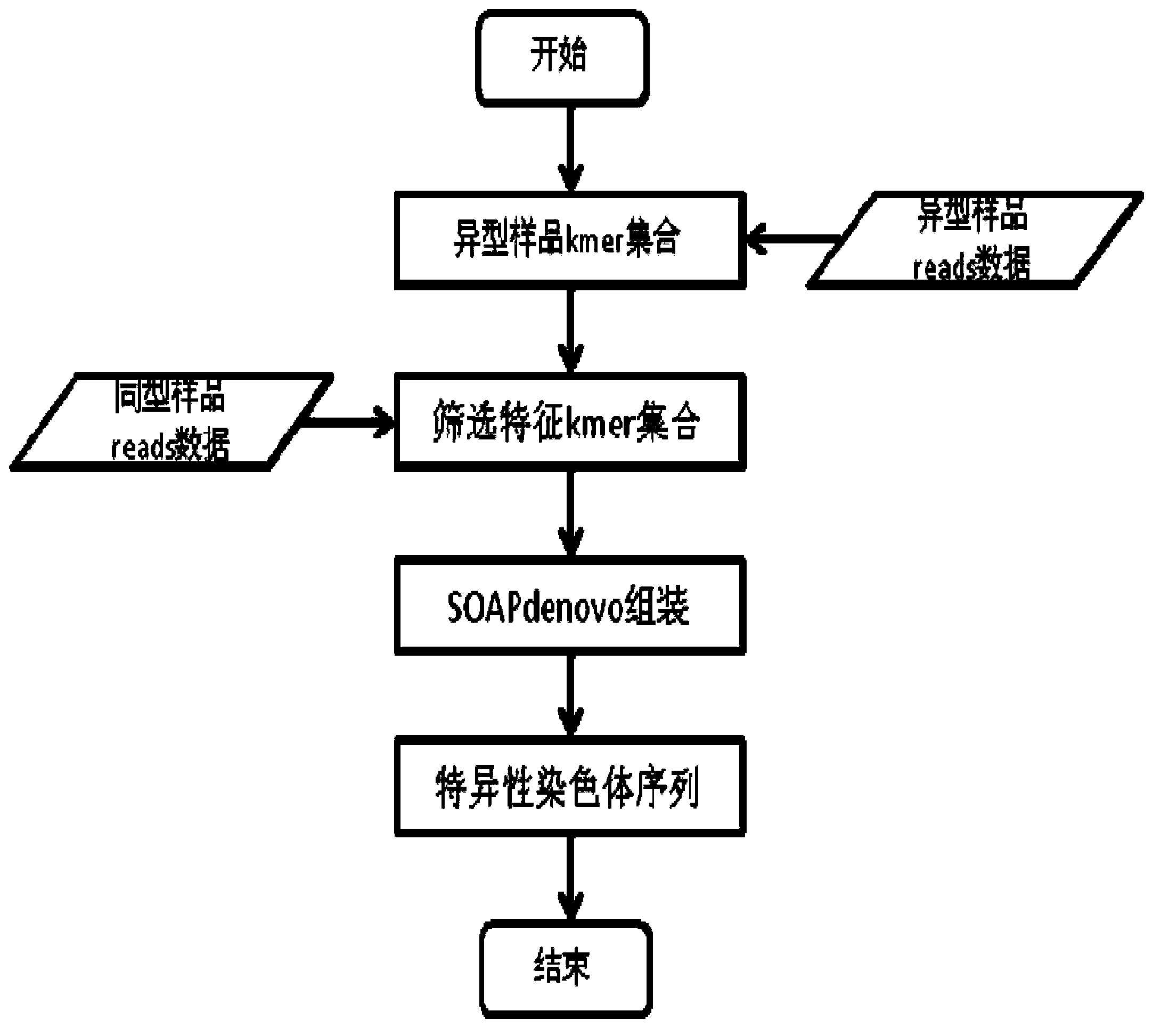
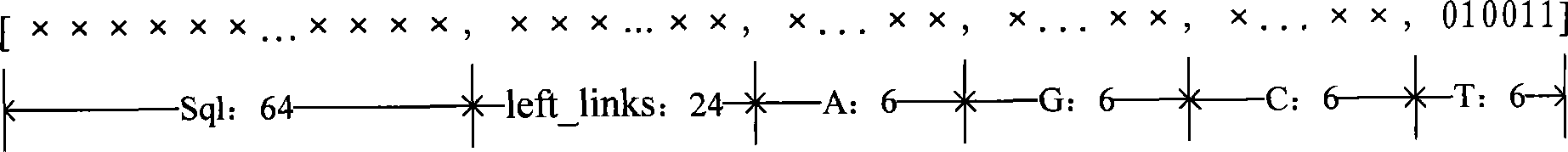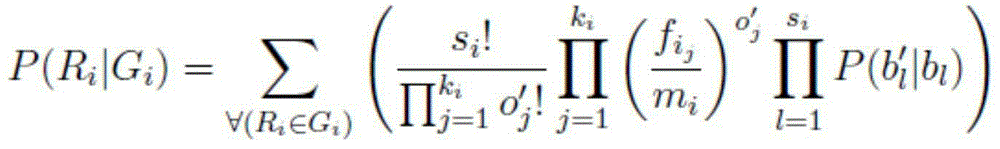Patents
Literature
104 results about "Sequence assembly" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
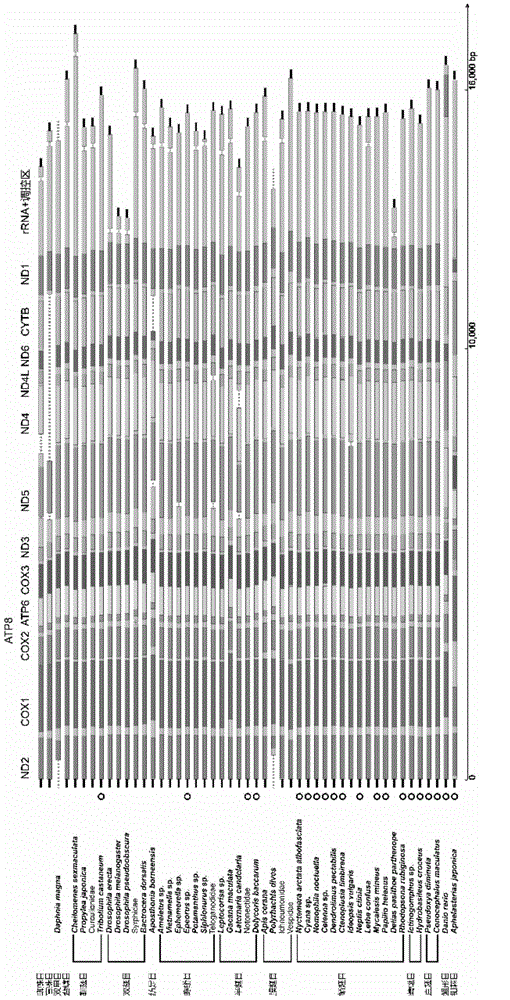
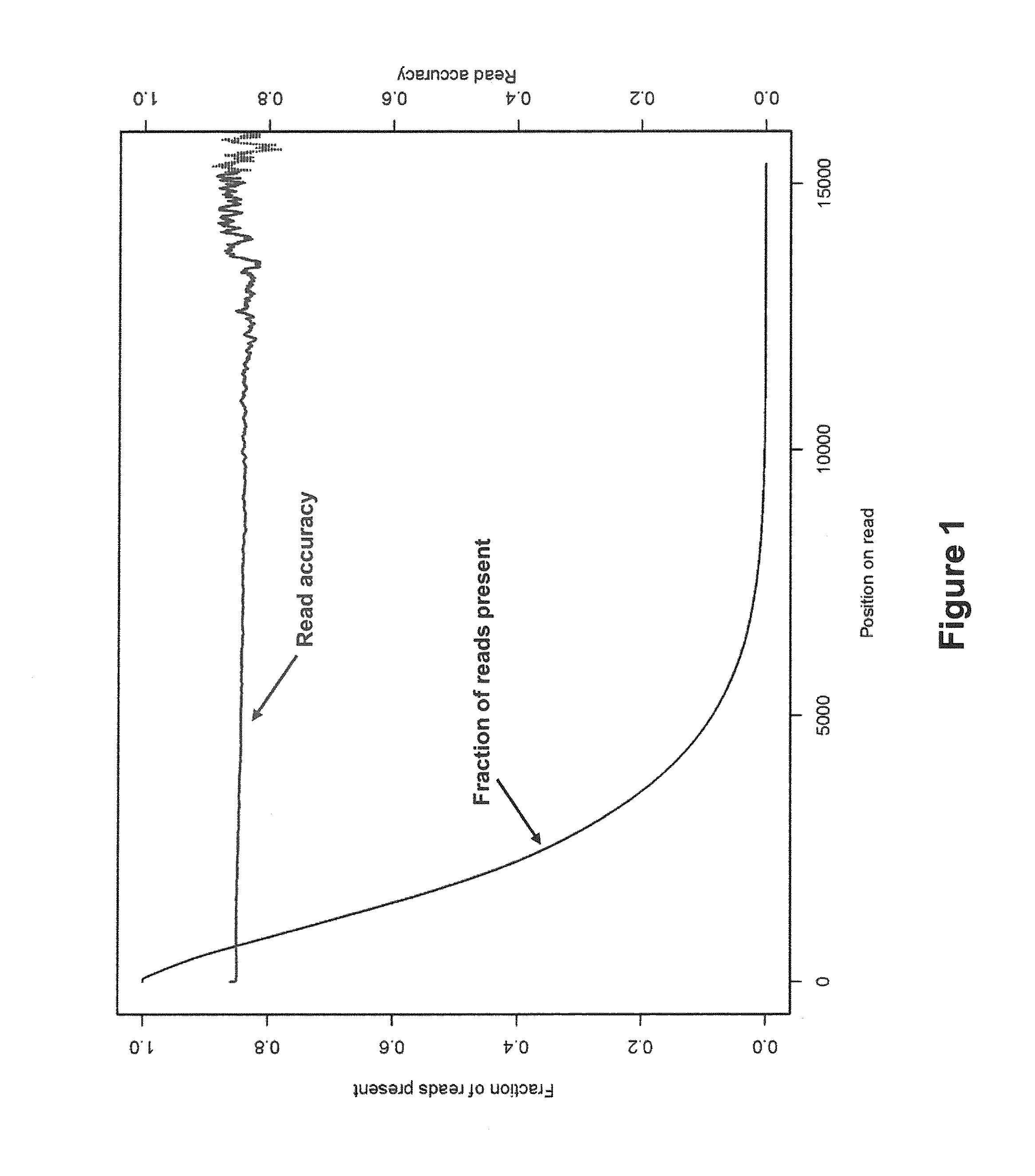
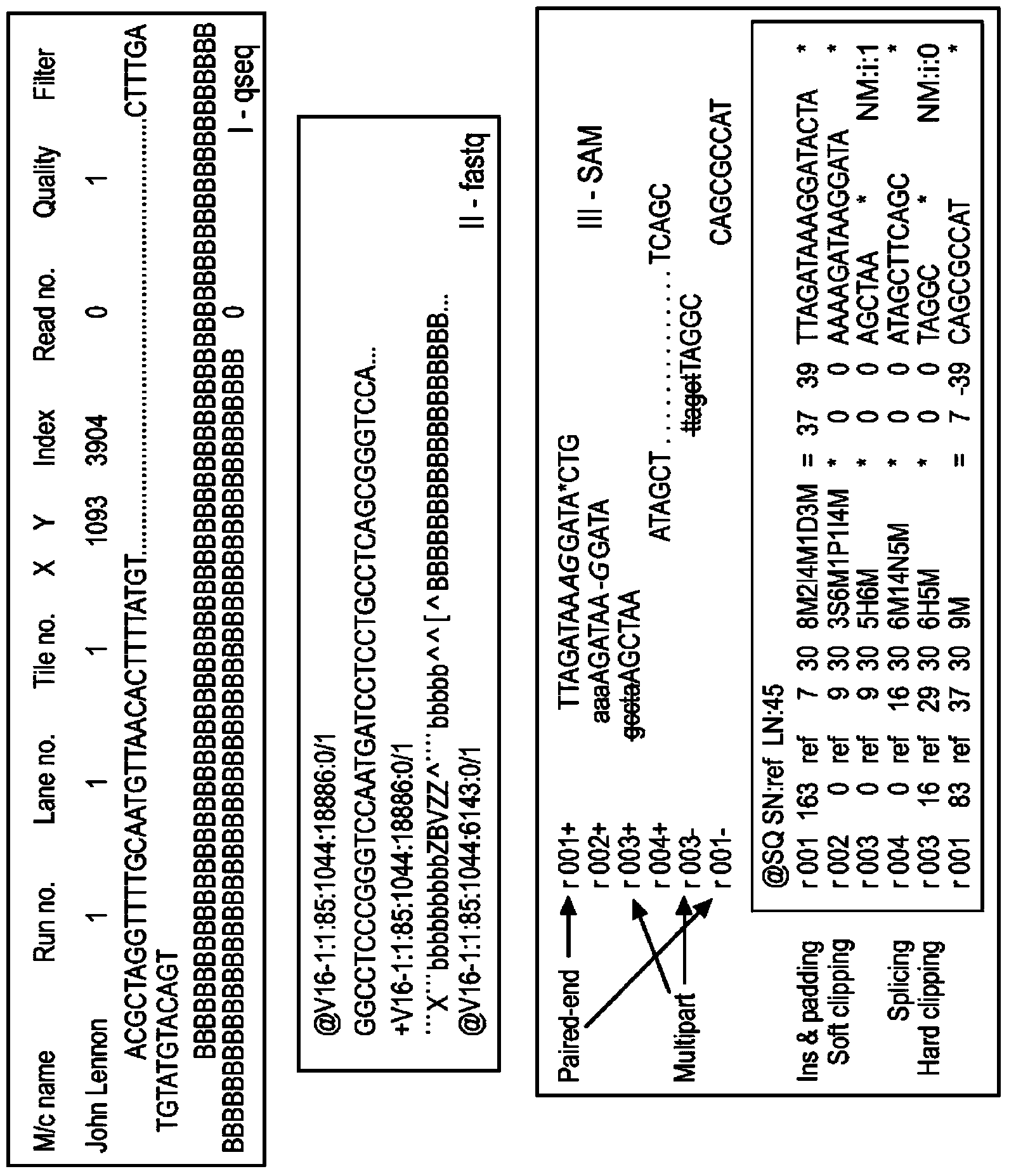
In bioinformatics, sequence assembly refers to aligning and merging fragments from a longer DNA sequence in order to reconstruct the original sequence. This is needed as DNA sequencing technology cannot read whole genomes in one go, but rather reads small pieces of between 20 and 30000 bases, depending on the technology used. Typically the short fragments, called reads, result from shotgun sequencing genomic DNA, or gene transcript (ESTs).
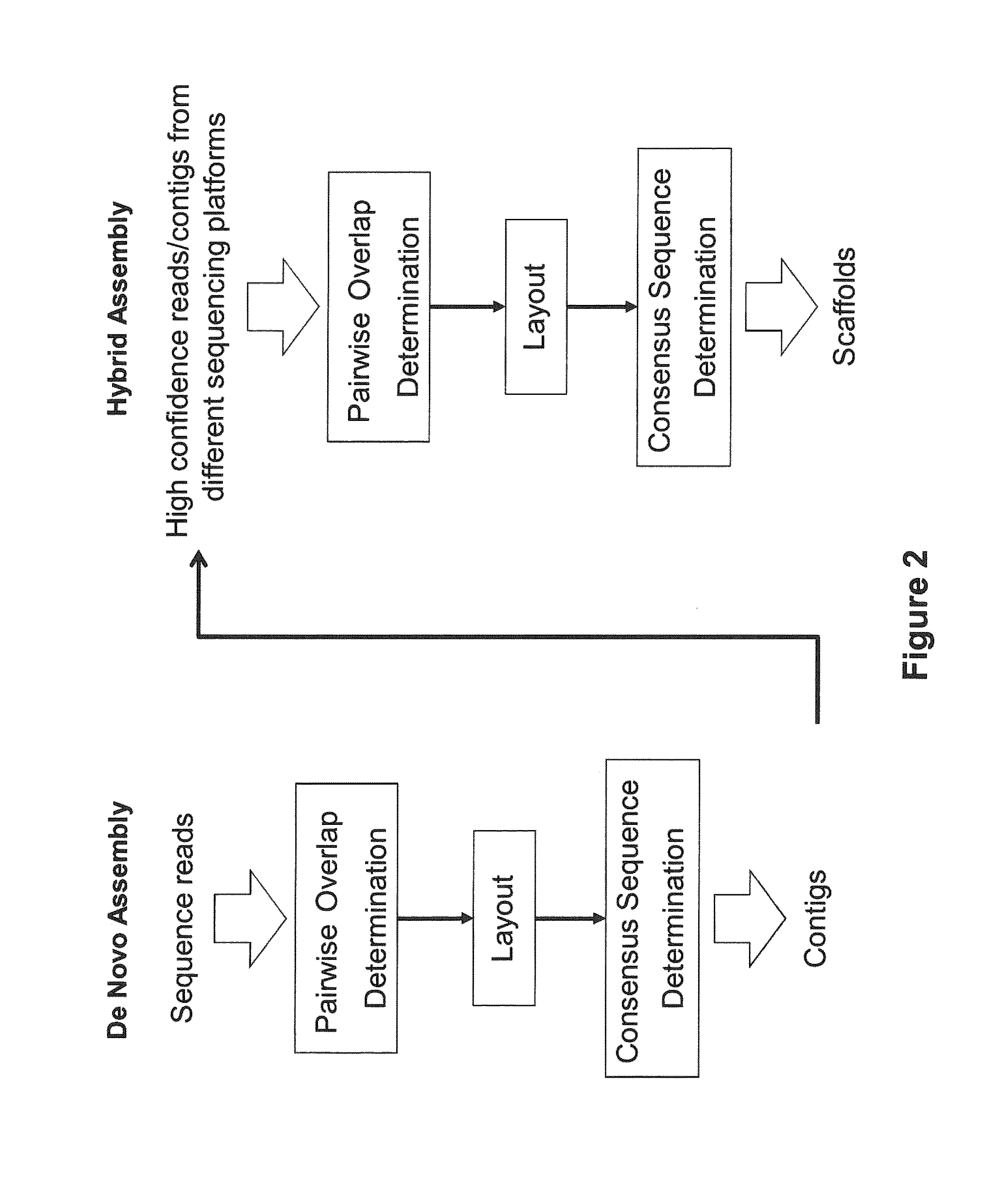
Sequence assembly and consensus sequence determination
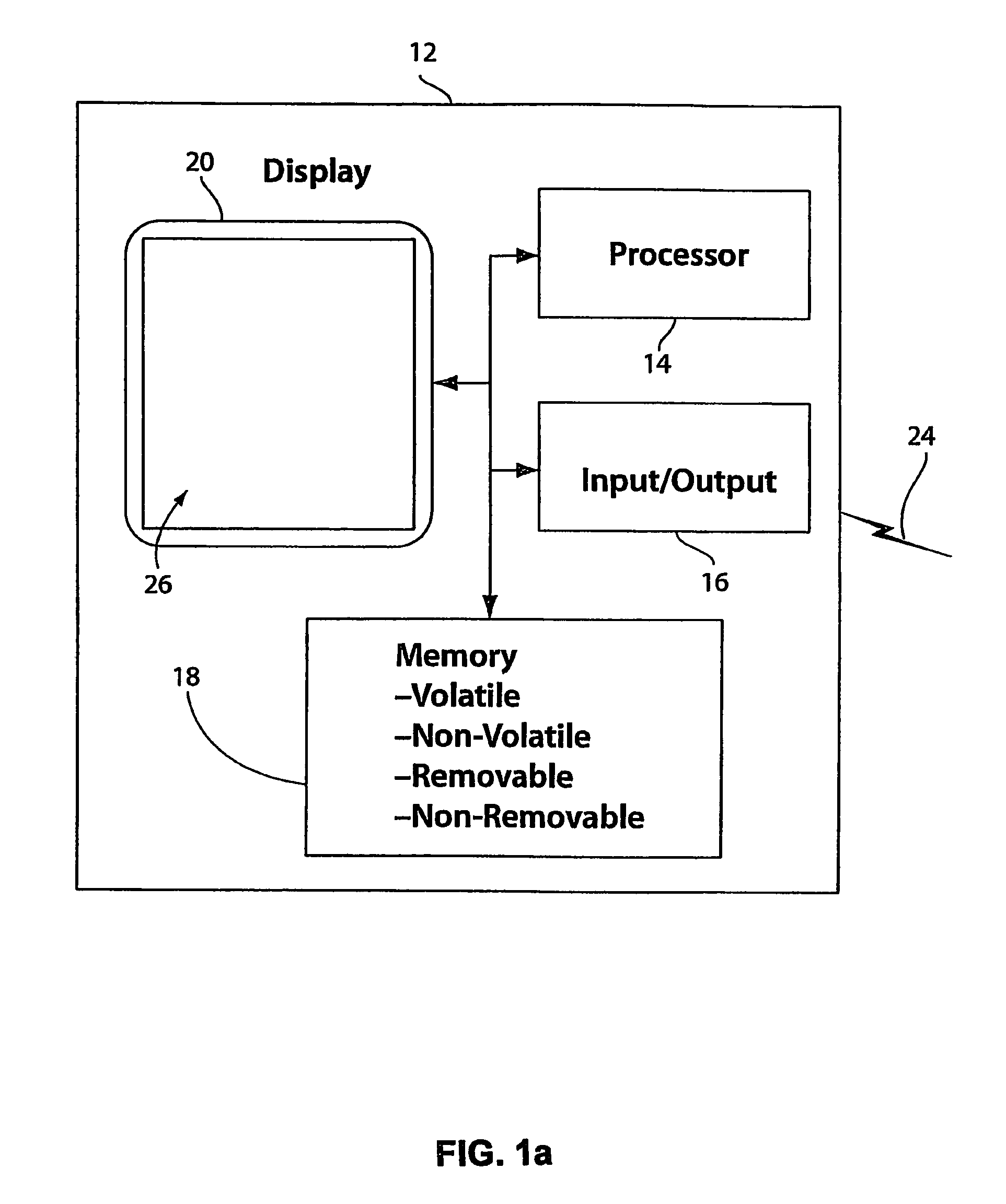
ActiveUS20120330566A1Maximum flexibilitySubstantial sensitivityBiostatisticsBiological testingNucleotideNucleic acid sequencing
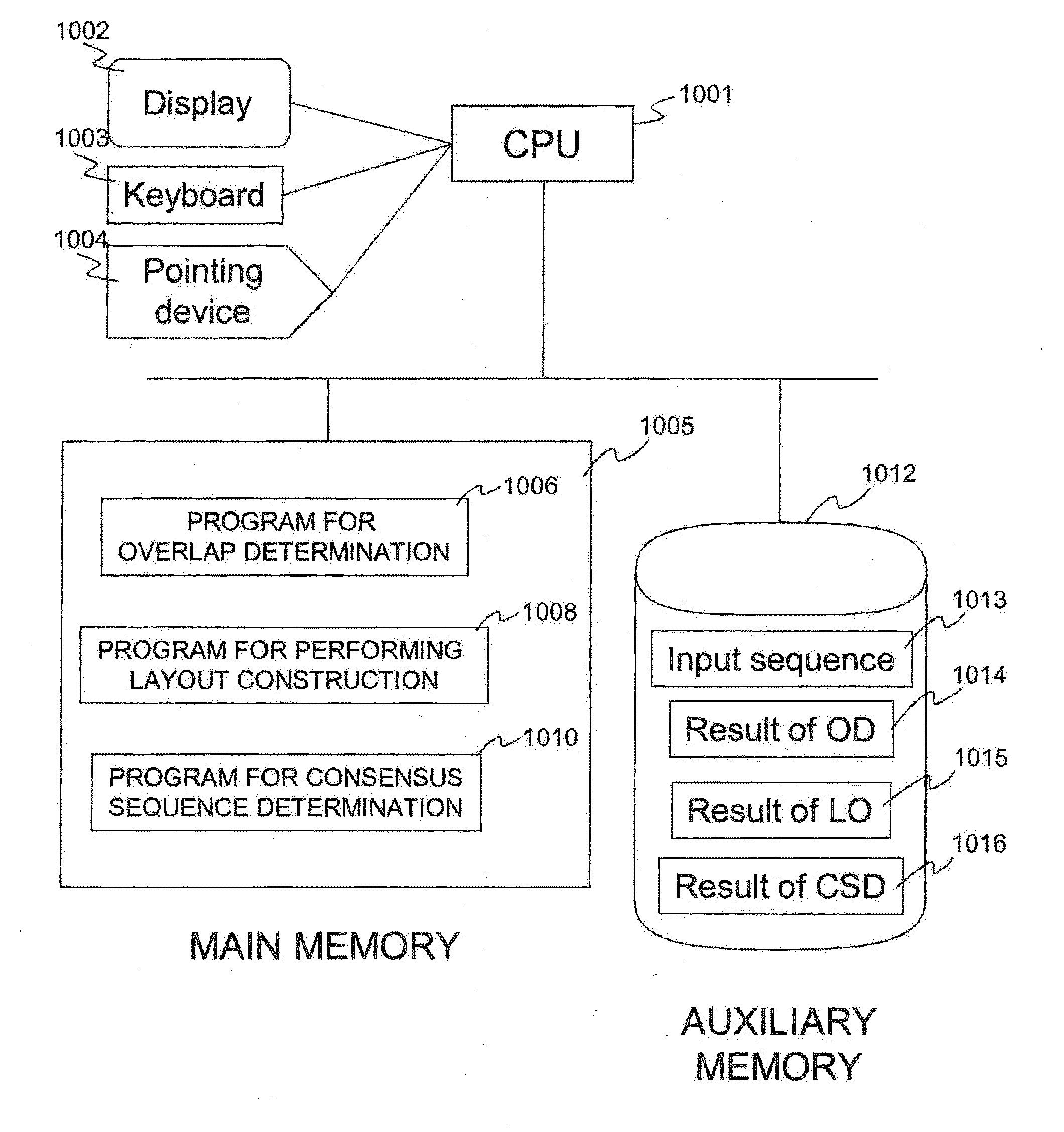
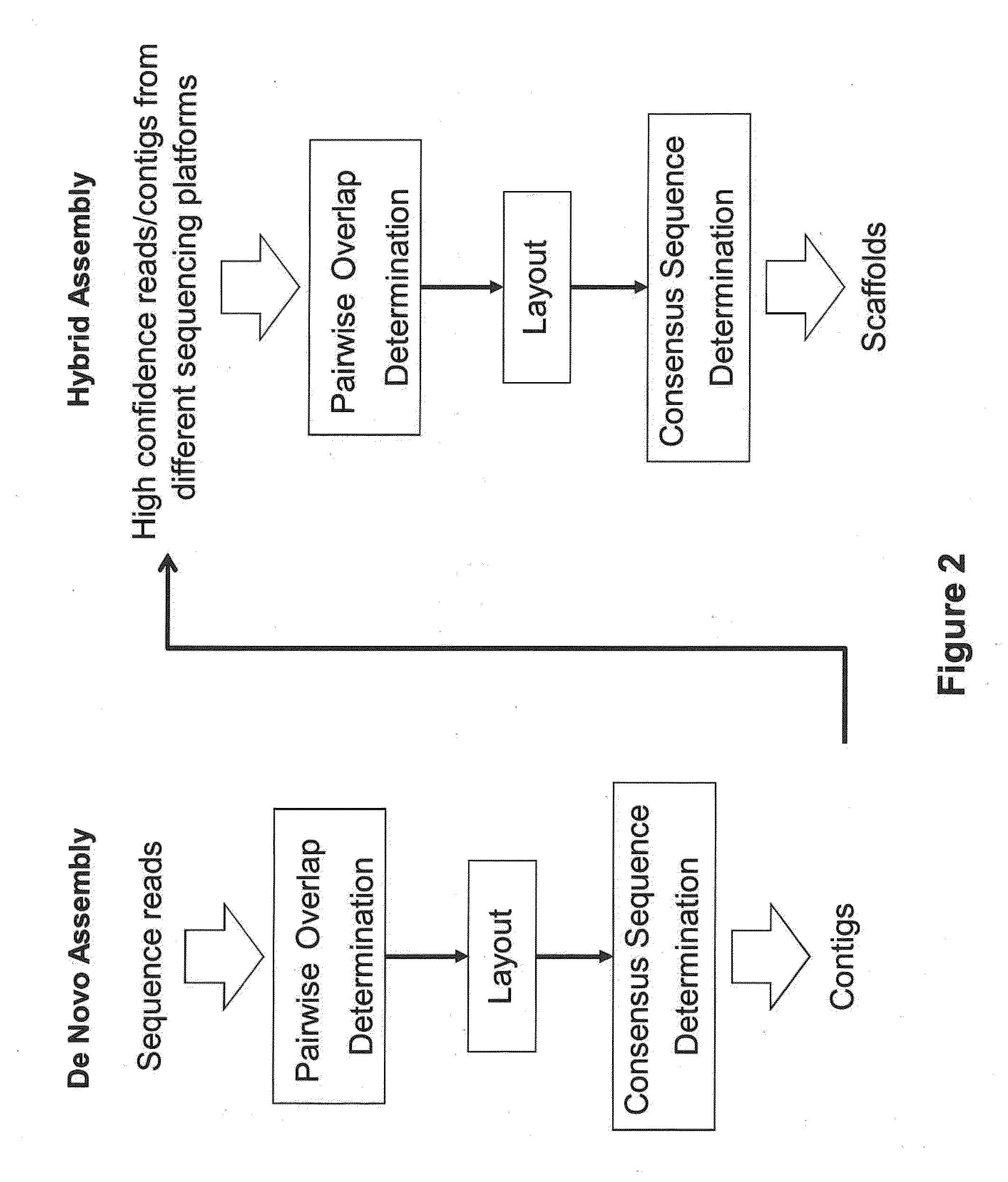
Computer implemented methods, and systems performing such methods for processing signal data from analytical operations and systems, and particularly in processing signal data from sequence-by-incorporation processes to identify nucleotide sequences of template nucleic acids and larger nucleic acid molecules, e.g., genomes or fragments thereof. In particularly preferred embodiments, nucleic acid sequences generated by such methods are subjected to de novo assembly and / or consensus sequence determination.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
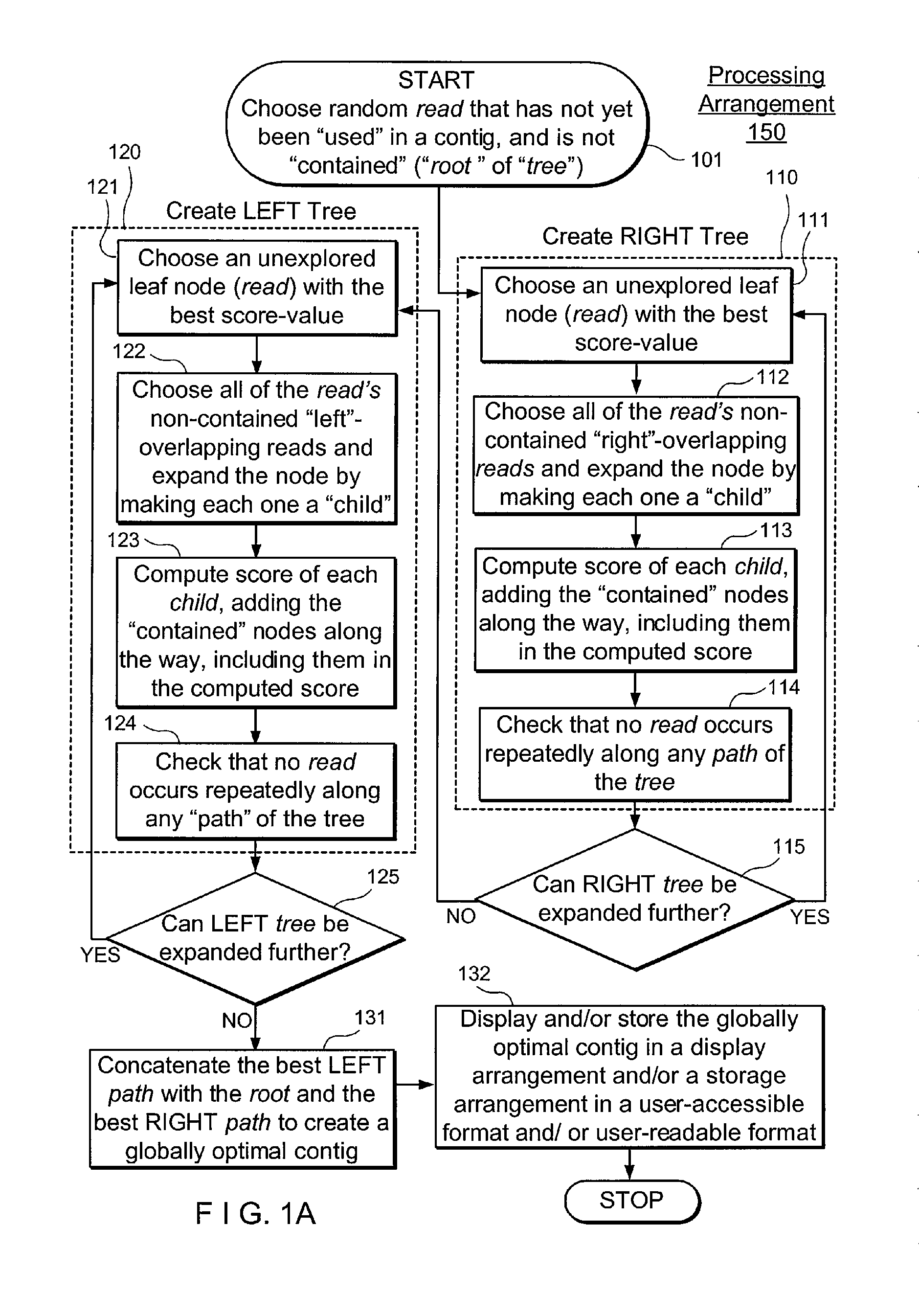
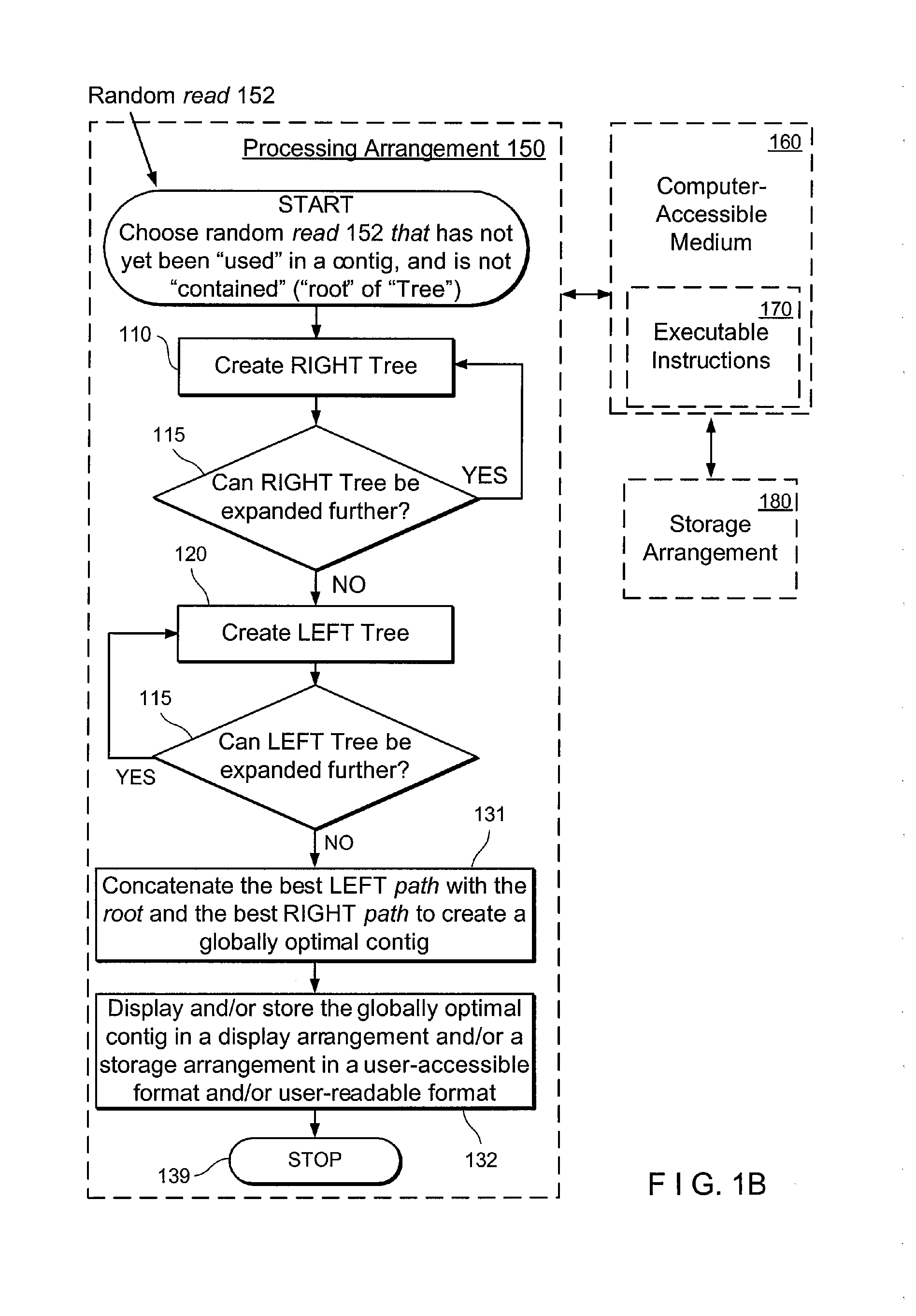
Method, computer-accessible medium and systems for score-driven whole-genome shotgun sequence assemble
ActiveUS20120041727A1Computation using non-denominational number representationSequence analysisHaplotypeData mining
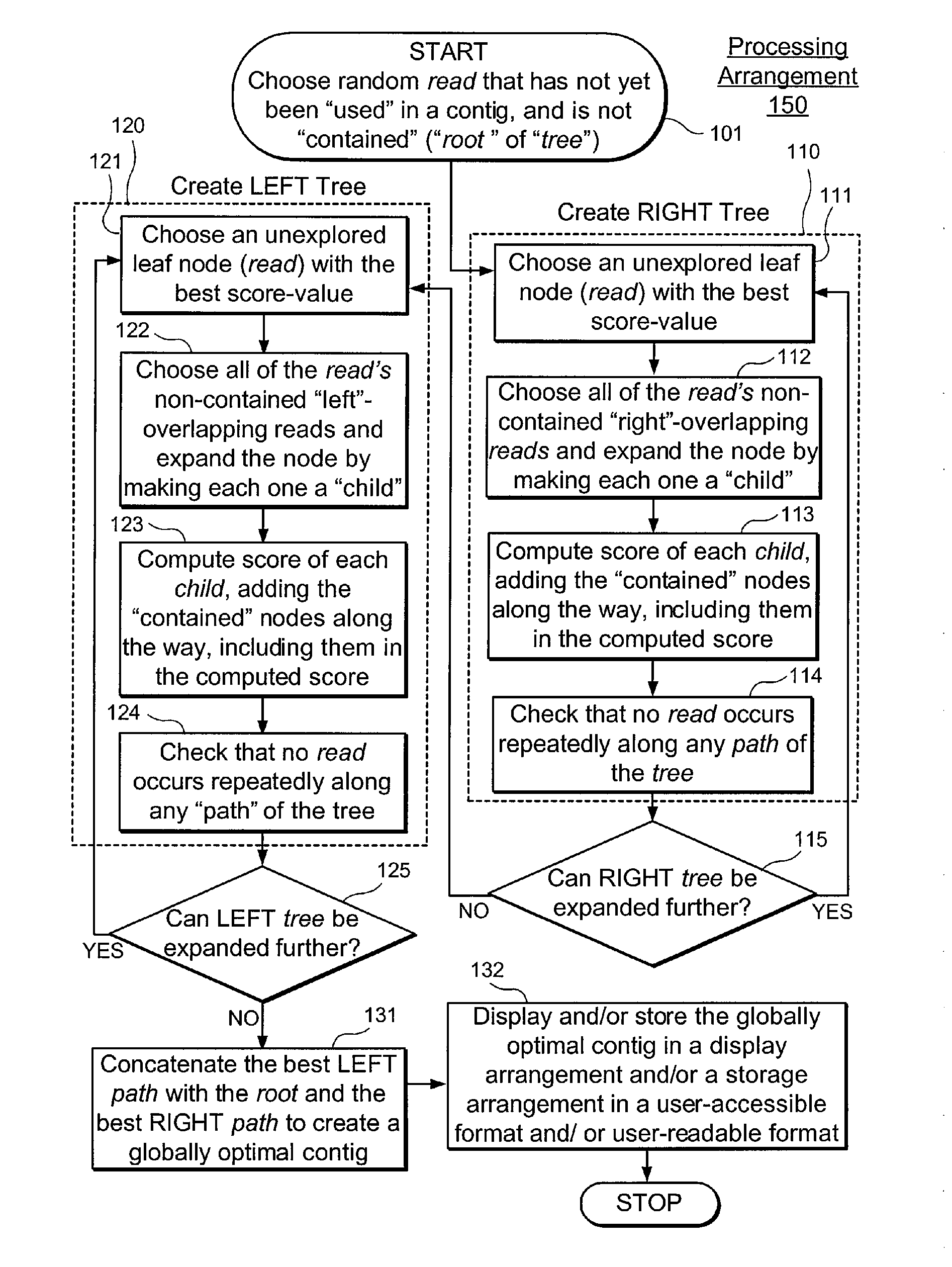
Exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure relate generally to methods, computer-accessible medium and systems for assembling haplotype and / or genotype sequences of at least one genome, which can be based upon, e.g., consistent layouts of short sequence reads and long-range genome related data. For example, a processing arrangement can be configured to perform a procedure including, e.g., obtaining randomly located short sequence reads, using at least one score function in combination with constraints based on, e.g., the long range data, generating a layout of randomly located short sequence reads such that the layout is globally optimal with respect to the score function, obtained through searching coupled with score and constraint dependent pruning to determine the globally optimal layout substantially satisfying the constraints, generating a whole and / or a part of a genome wide haplotype sequence and / or genotype sequence, and converting a globally optimal layout into one or more consensus sequences.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
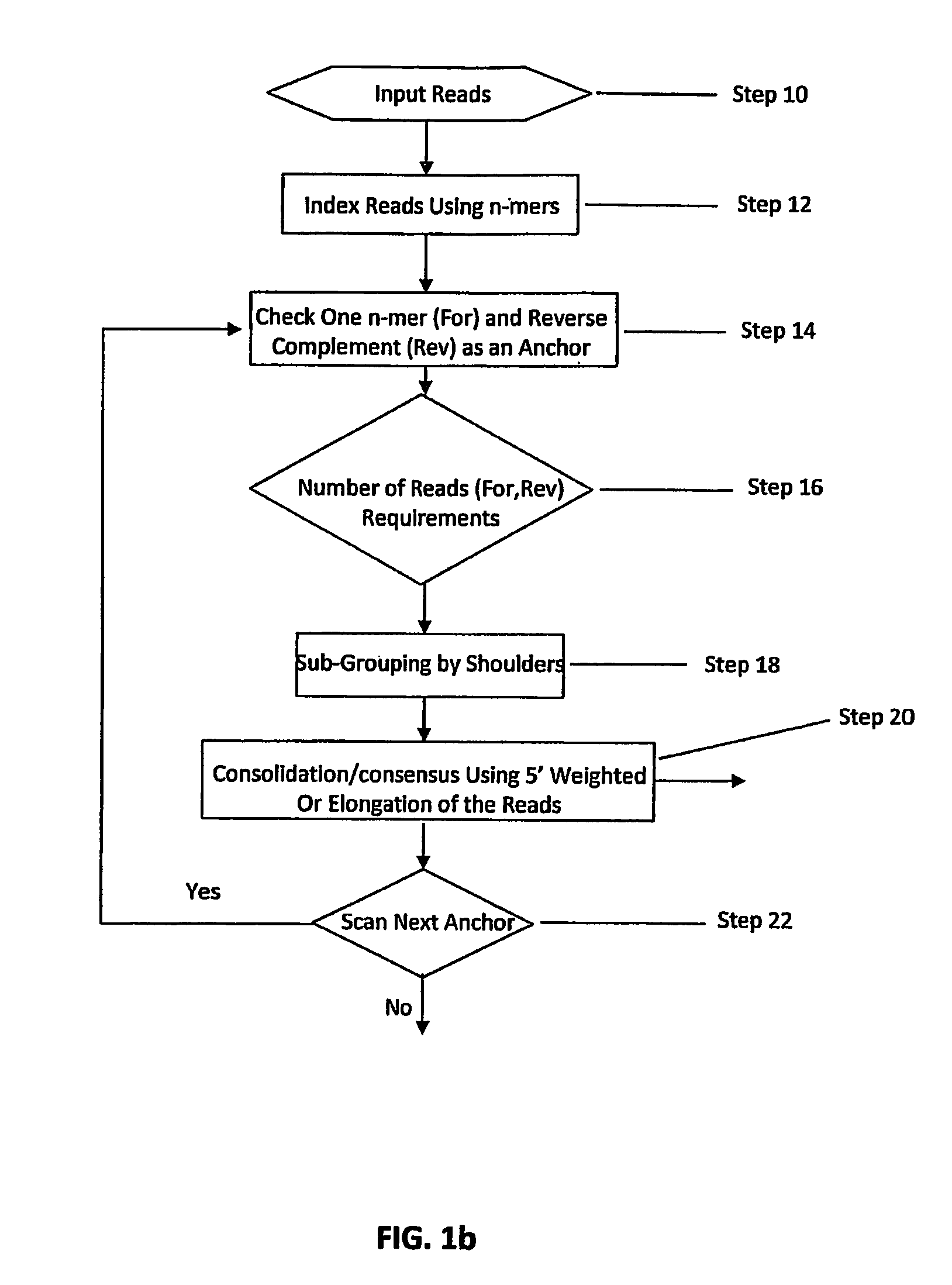
DNA Sequence Assembly Methods of Short Reads
ActiveUS20090318310A1Shorten the counting processReducing sequenceSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsDNA fragmentationComputerized system
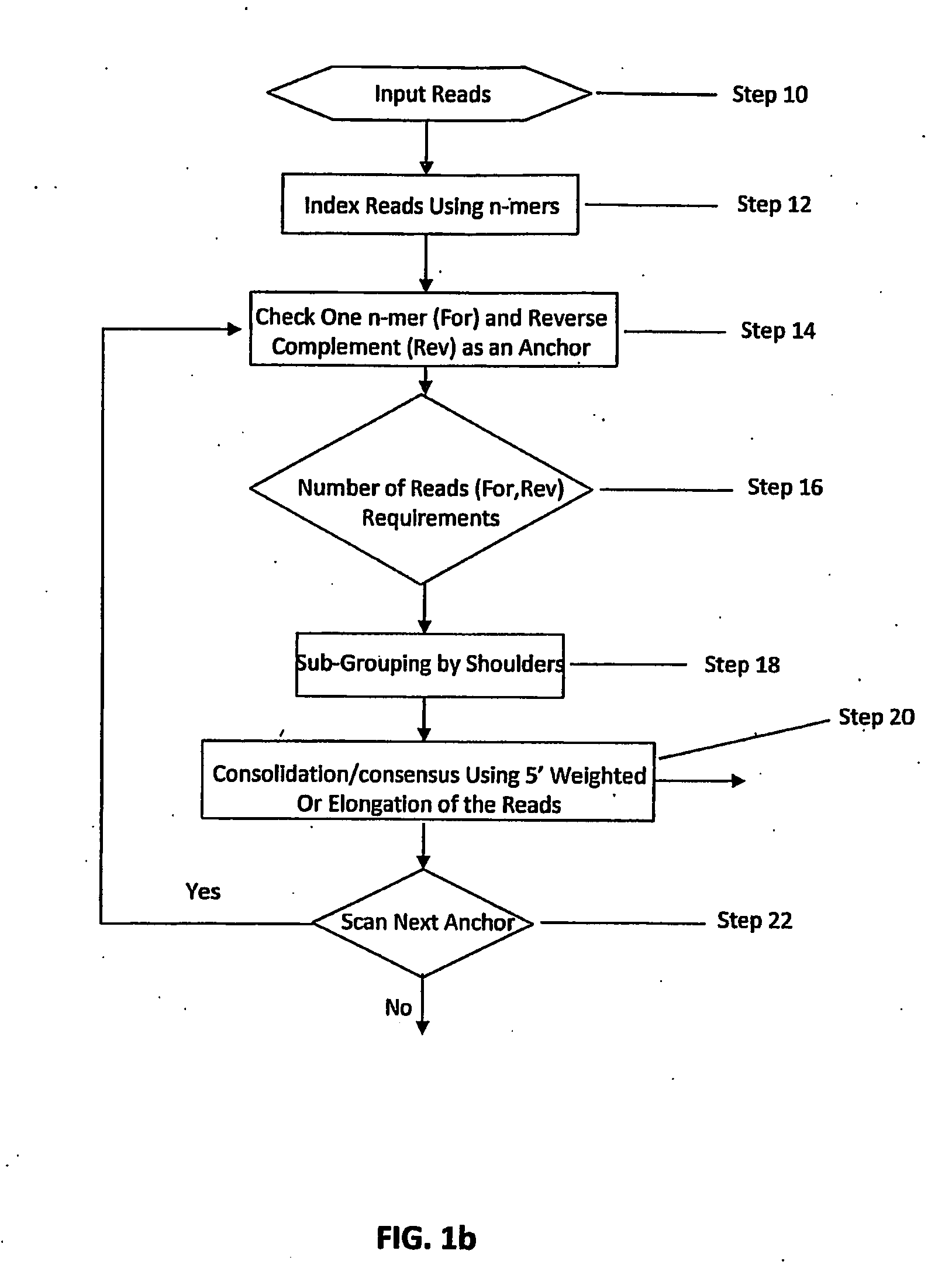
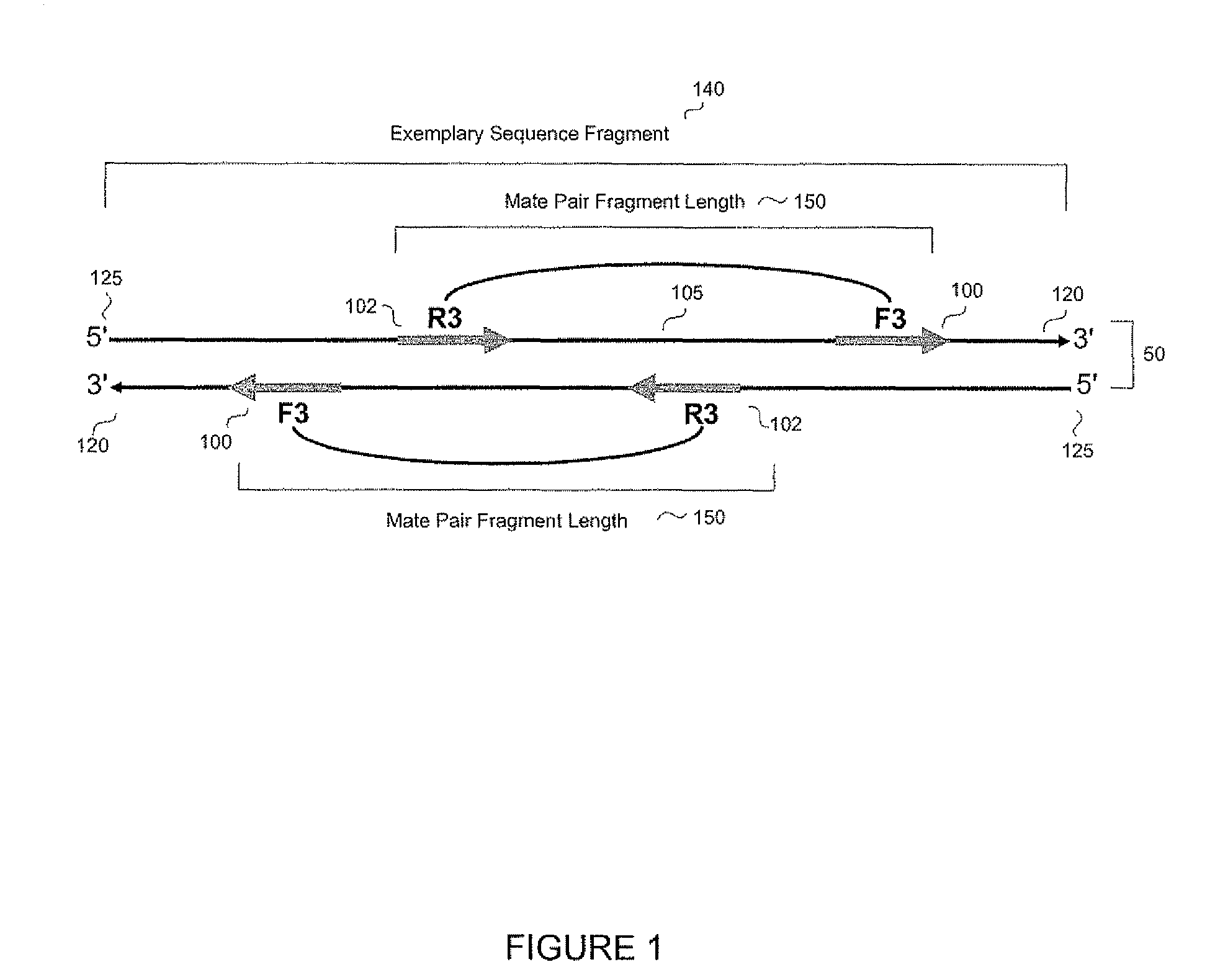
Certain embodiments of the invention provide systems and methods for the automated assembly of DNA sequence data into contiguous DNA segments using a computer a system. DNA sequence data is entered into the system. The system indexes and groups a plurality of DNA fragment reads utilizing an anchor sequence and consolidates the fragments into larger sequences by merging the fragment reads within a group.
Owner:SOFTGENETICS
System and methods for indel identification using short read sequencing
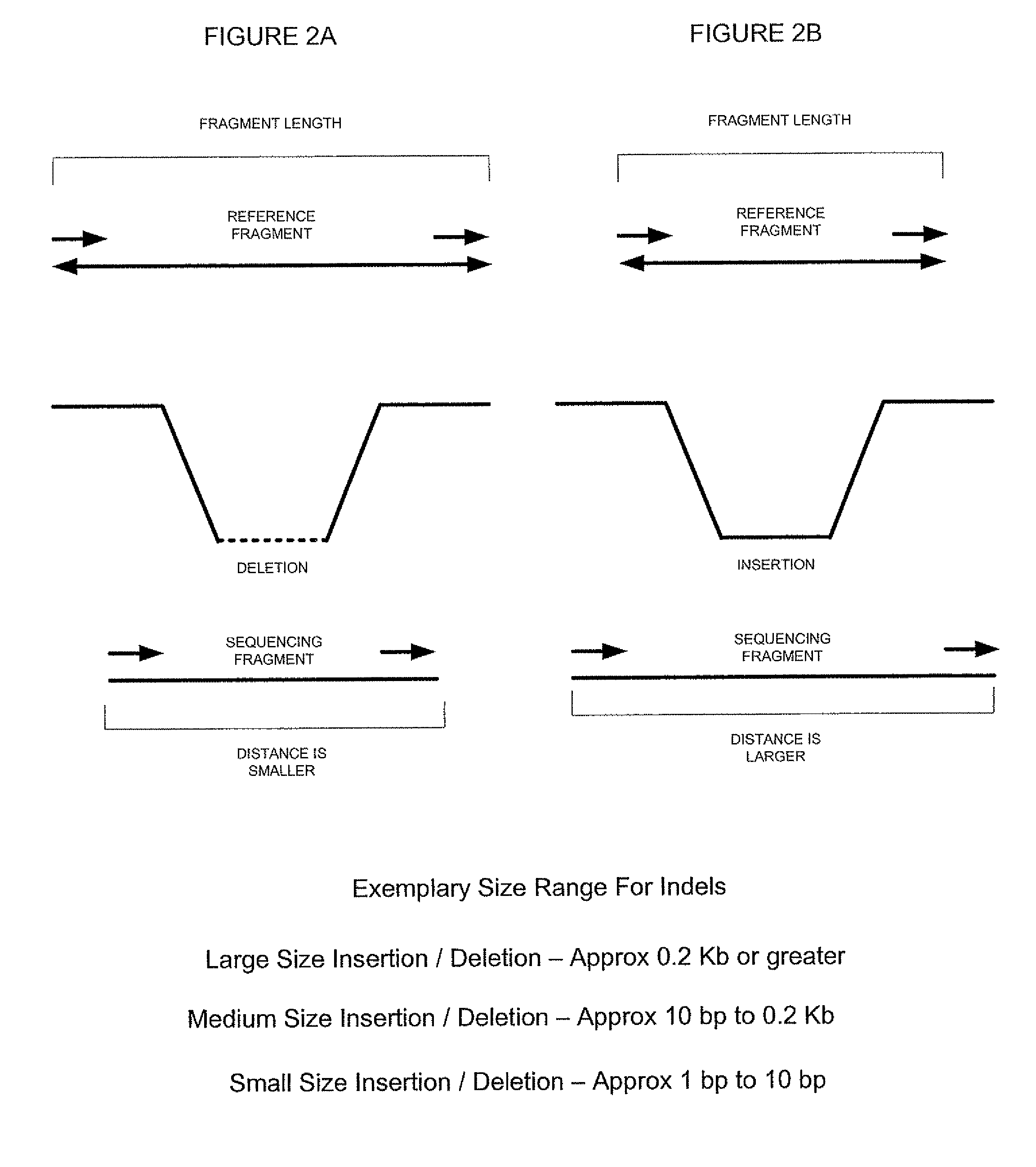
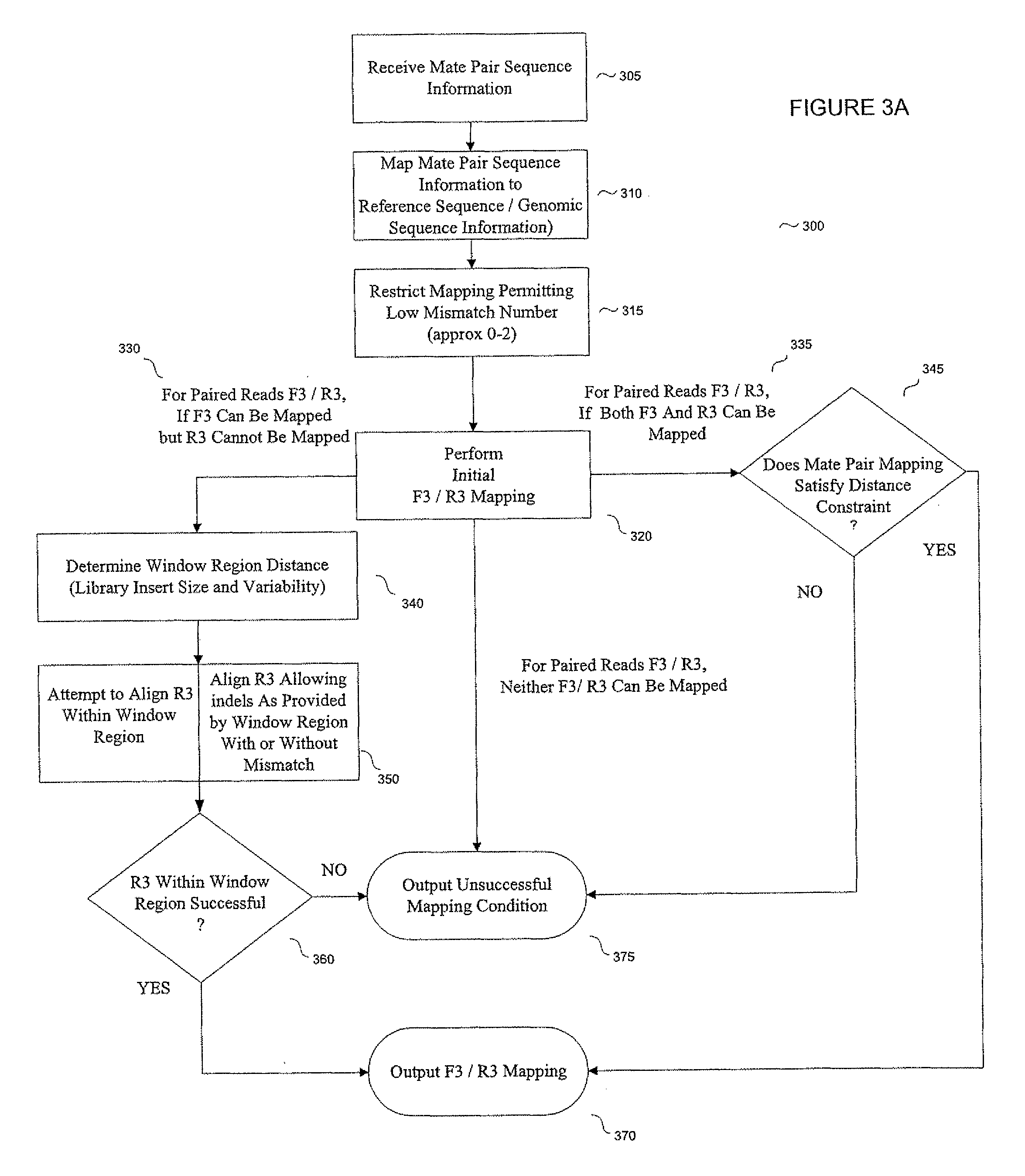
ActiveUS8165821B2Reduce in quantityReduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesParallel computingShort read
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Method for detecting mutation information in multiplex amplification sequencing product of genome
ActiveCN106202991AEfficient identificationQuick identificationHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsReference genesNatural abundance
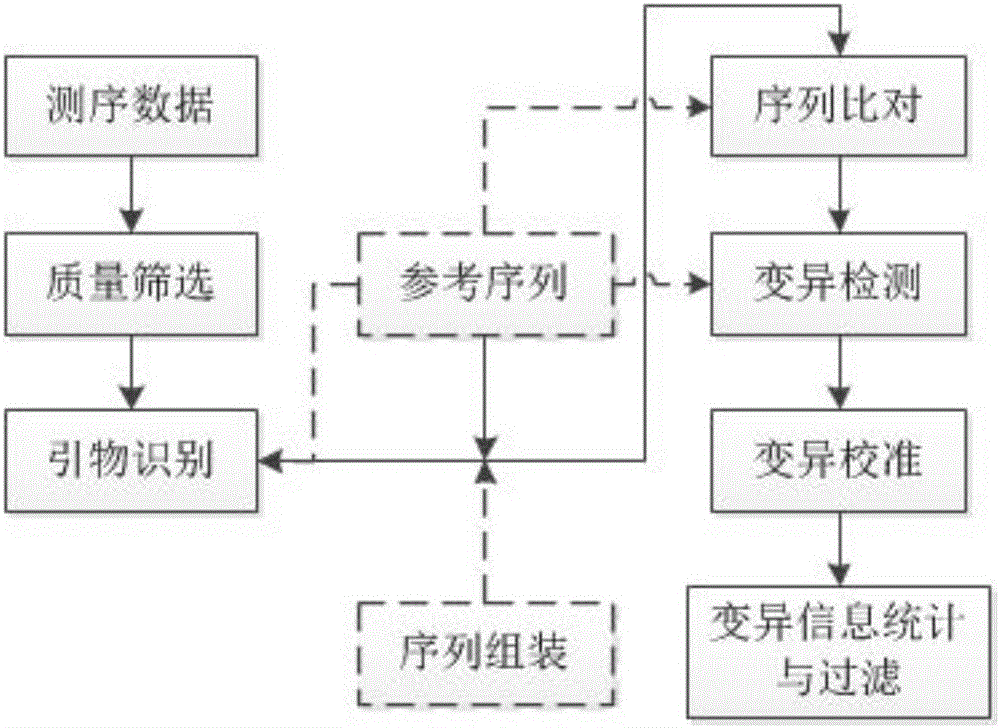
The invention discloses a method for detecting mutation information in a multiplex amplification sequencing product of a genome. The method comprises steps as follows: sequencing data are subjected to quality assessment and preprocessing; a recognizable sequencing sequence is selected for sequence assembling; the recognizable sequencing sequence or a sequence obtained through assembling is compared with a reference gene sequence, and preliminary variation information is obtained; fine calibration of sequence variation is performed according to different types of conditions; a calibrated sequencing fragment is obtained; the homozygosis or heterozygosis state of a target fragment is obtained according to the type of the sequencing fragment with the highest abundance; finally, the mutation information in the multiplex amplification sequencing product of the genome is obtained. By means of the method, the amplification product can be rapidly, efficiently and accurately recognized, and the calculation resources are saved; the sequence assembling process is compatible, and the problem of reduction of the quality value of basic groups produced in the sequencing process can be effectively solved; the homozygosis / heterozygosis state of variation information can be more effectively and stably judged, and random errors introduced in the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) process and the sequencing process are eliminated.
Owner:AMOY DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD +1
Recursive categorical sequence assembly
InactiveUS20050227278A1Microbiological testing/measurementData visualisationHardware architectureDatabase
The present invention provides a method for efficiently creating assemblies. The present invention also provides a web-based system for scientists to interact with a computer to implement the method. Further the scientist is able to upload and download information to and from the method to and from a database. The present invention also provides an efficient hardware architecture to implement the method.
Owner:LARGE SCALE BIOLOGY
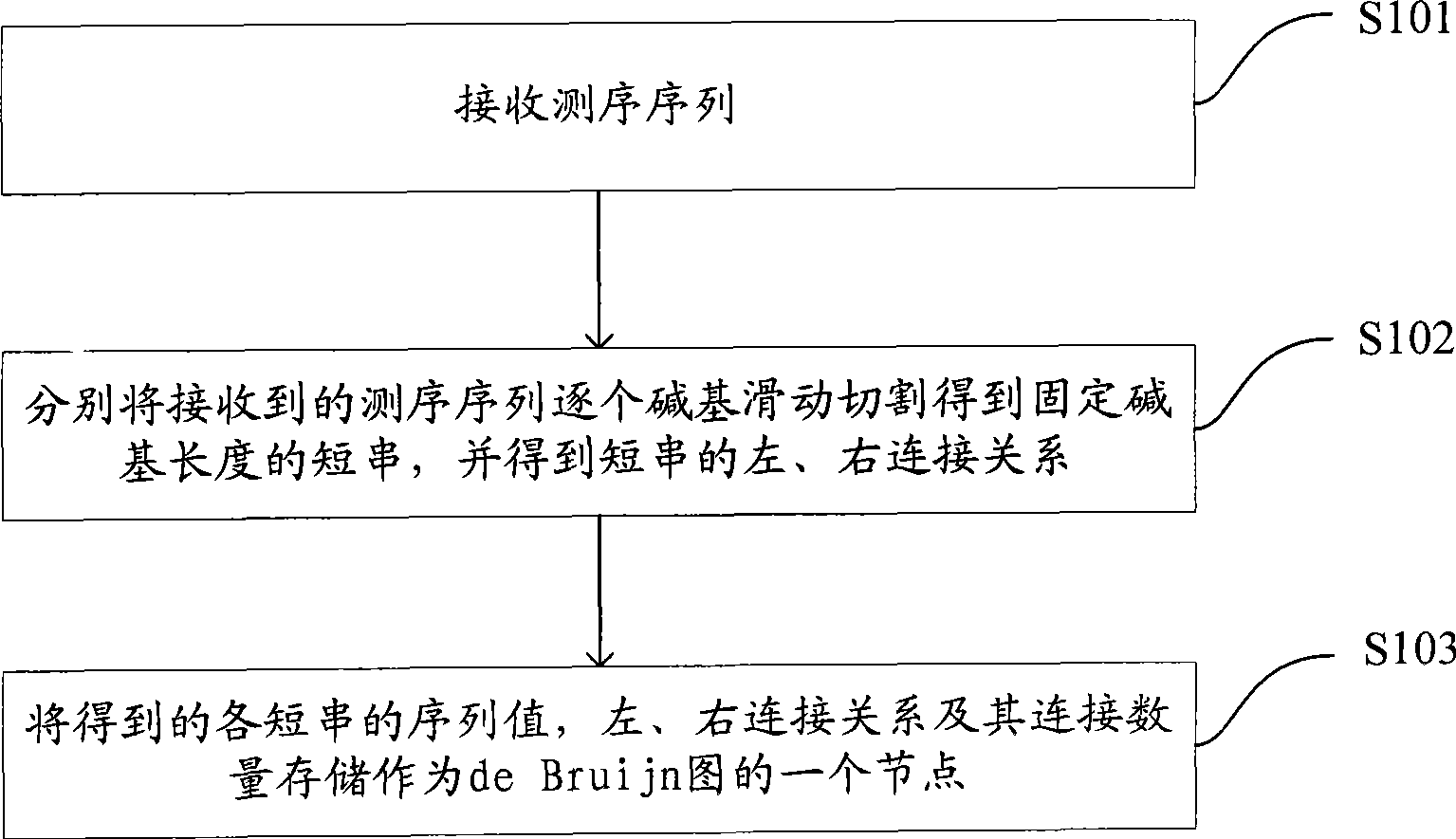
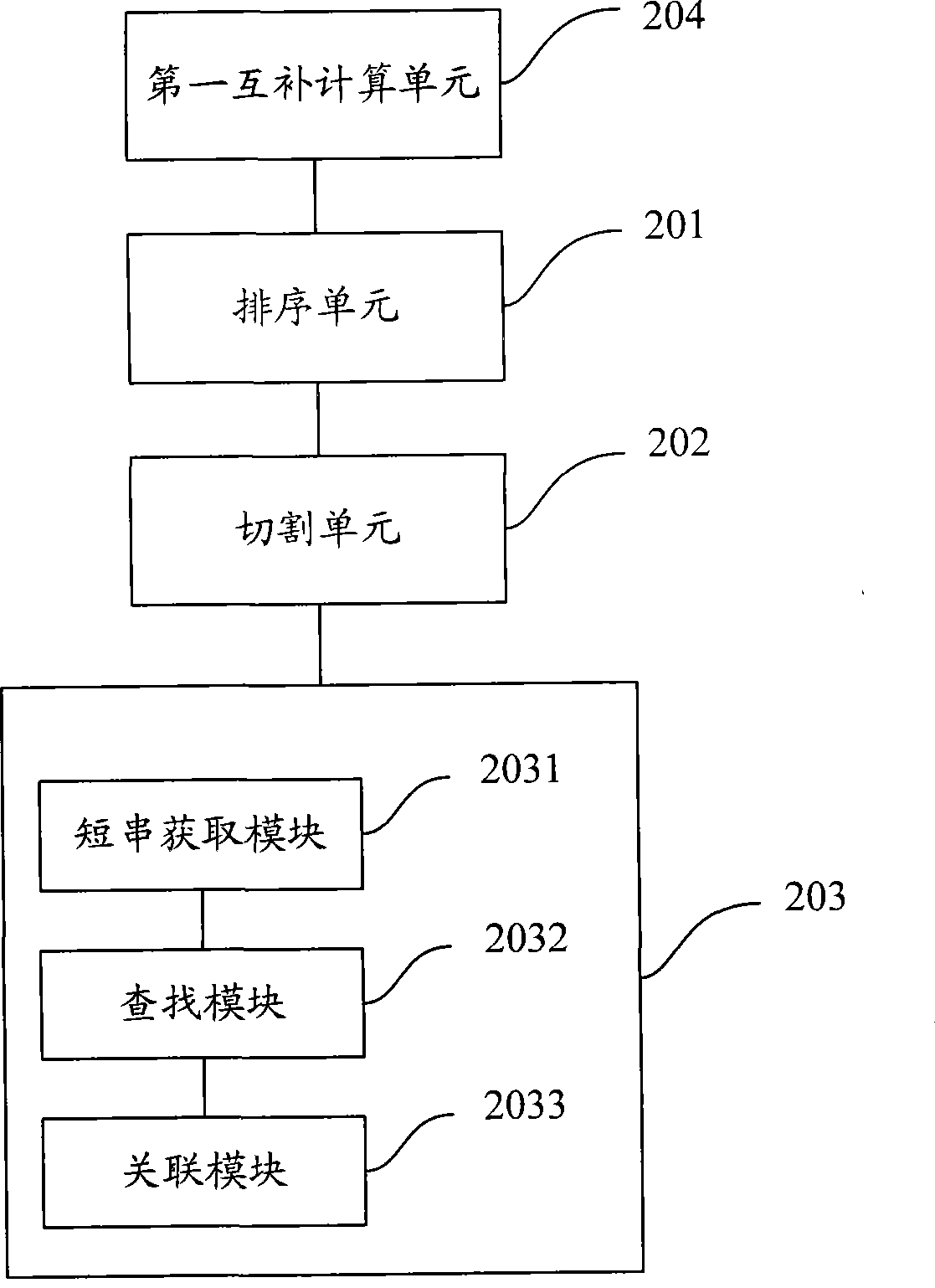
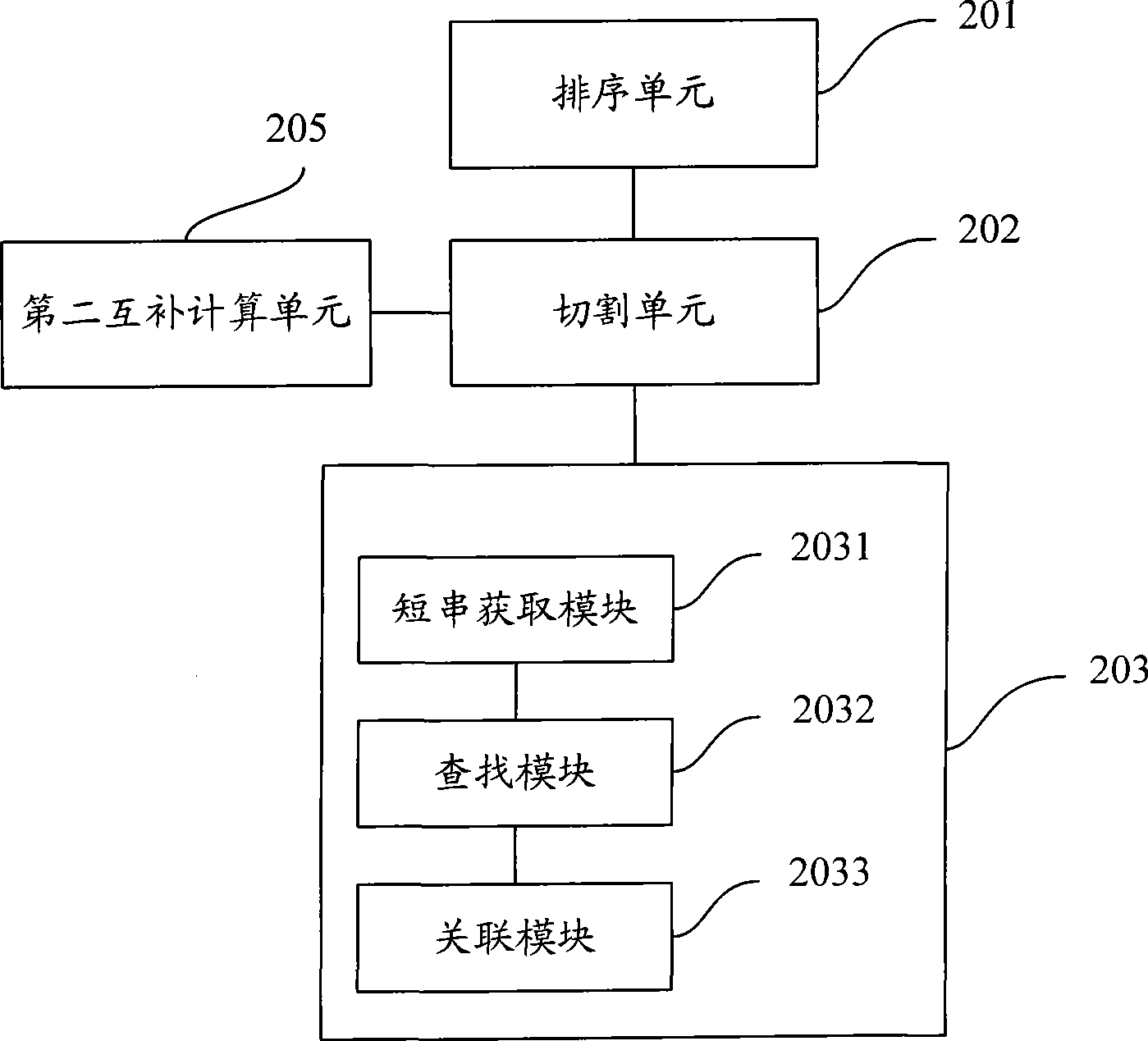
Method and system for drawing construction in short sequence assembly
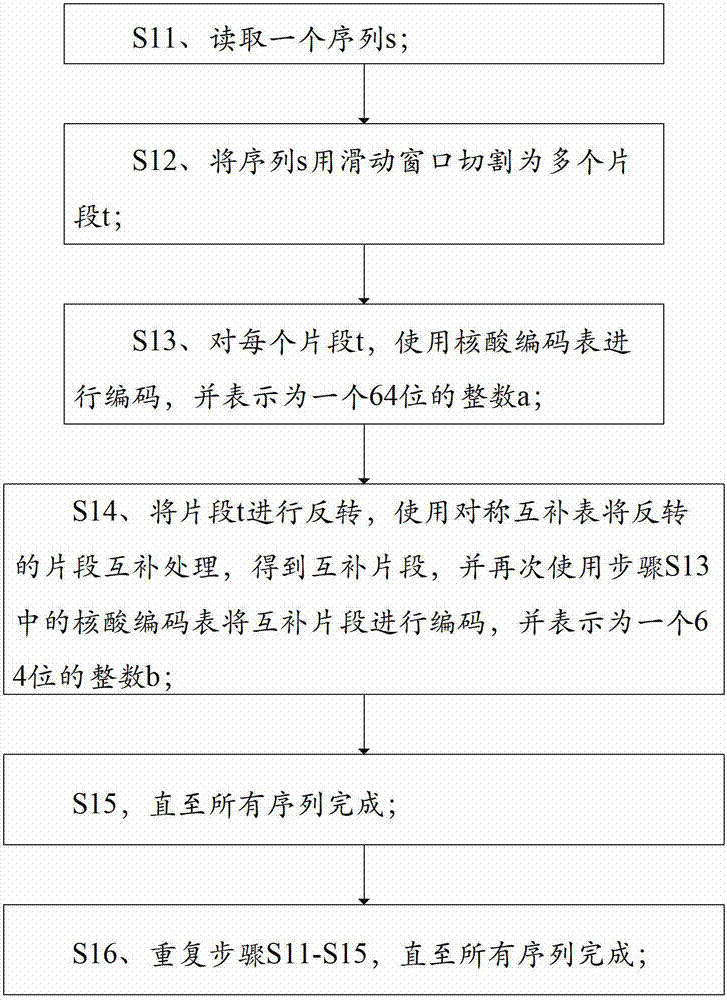
ActiveCN101430742ASmall footprintHigh speedMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisShort stringConnection number
The invention is applicable to the technical field of gene engineering, and provides a method for constructing a graph in a short sequence assembly and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: receiving an order-checking sequence; carrying out sliding cutting on each base of the received order-checking sequence to obtain a short string with a fixed base length and a left and right connecting relation of the short string; storing a sequence value of the obtained short string, the left and right connecting relation and a connection number as a node of a de Bruijn graph. In the invention, the method for constructing the graph in the short sequence assembly can be realized by slidingly cutting the base of the received order-checking sequence one by one to obtain the short string with the fixed base length and the left and right connecting relation of the short string, and storing the sequence value of the obtained short string, the left and right connecting relation and the connection number as the node of the de Bruijn graph. The method can assemble a large genome with small occupied memory and fast speed.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
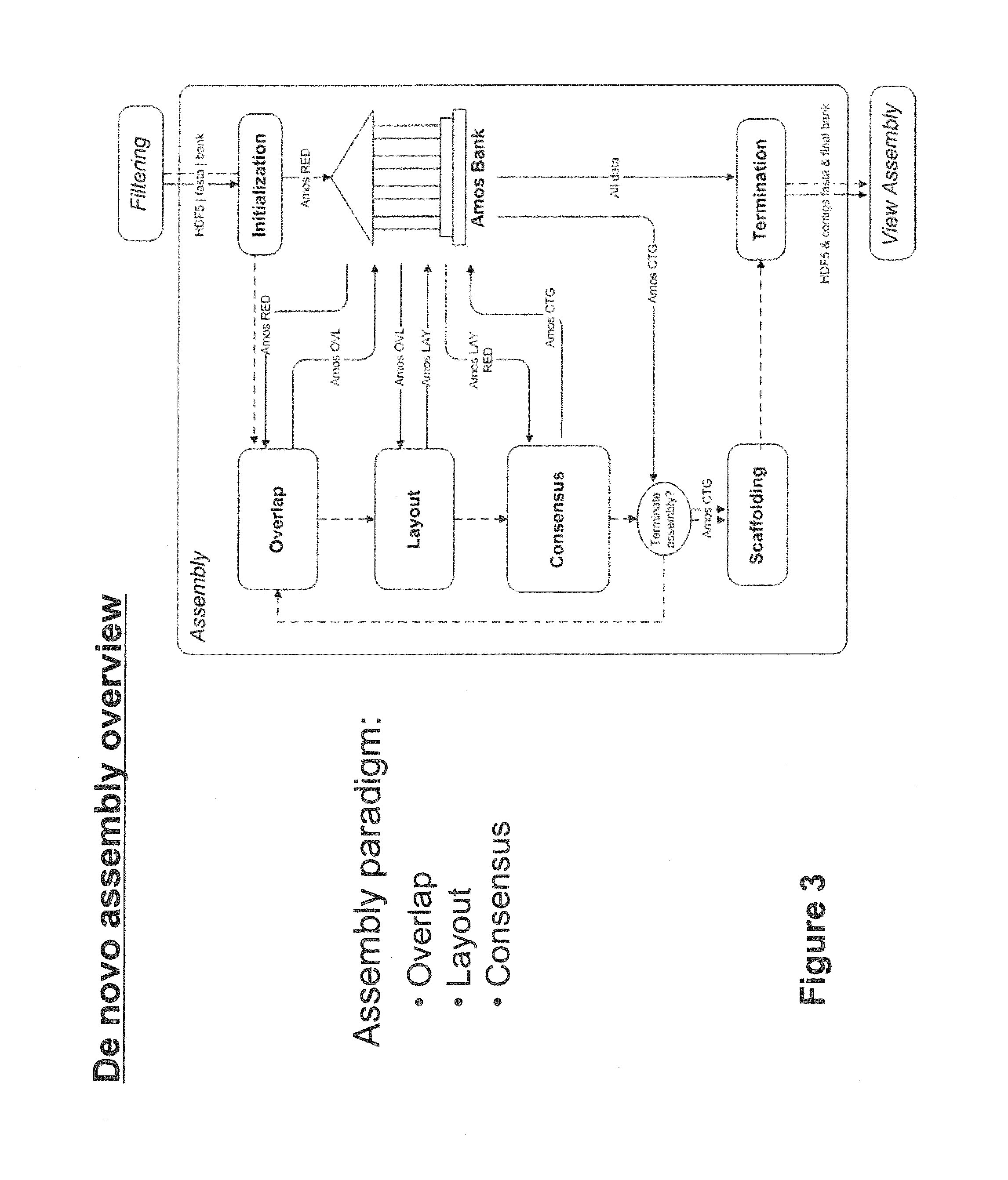
Sequence assembly and consensus sequence determination
Computer implemented methods, and systems performing such methods for processing signal data from analytical operations and systems, and particularly in processing signal data from sequence-by-incorporation processes to identify nucleotide sequences of template nucleic acids and larger nucleic acid molecules, e.g., genomes or fragments thereof. In particularly preferred embodiments, nucleic acid sequences generated by such methods are subjected to de novo assembly and / or consensus sequence determination.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Compressed storage and construction method of two-way multi-step deBruijn graph
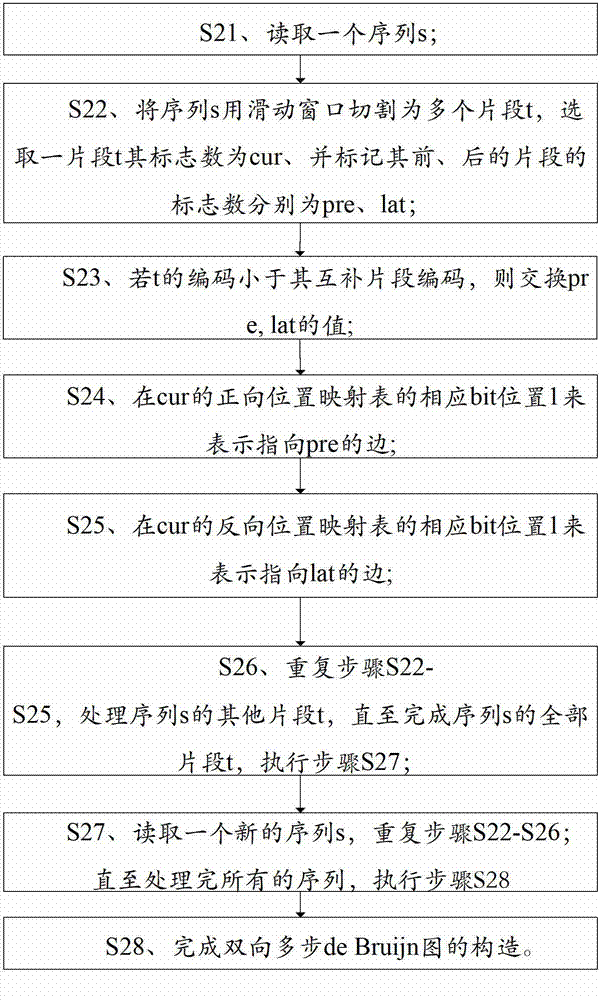
ActiveCN103093121AIncrease stitching run speedReduce consumptionSpecial data processing applicationsTheoretical computer scienceHelix structure
The invention relates to a compressed storage and construction method of a two-way multi-step de Bruijn graph, and the compressed storage and construction method of the two-way multi-step de Bruijn graph includes compressed storage steps and de Bruijn graph construction steps. The compressed storage and construction method of the two-way multi-step de Bruijn graph includes the steps of (1) carrying out a structure optimization for the de Bruijn graph by combining with the characteristics of the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) order complementary double-helix structure, and halving nodes of the graph to be stored by using two-way multi-step de Bruijn graph, (2) using a compressed storage technology of the two-way multi-step de Bruijn graph to enable memory consumption of storing the two-way multi-step de Bruijn graph to be controlled within 100 times size of a reference sequence so that the problem that the sequence-assembled original de Bruijn graph scale is enormous unusually so as to bring a storage pressure to the memory consumption can be solved, and (3) constructing two-way multi-step de Bruijn graph, the DNA sequence assembling problem being capable of being decomposed into the edge fusant problem, and suitable for parallel computing.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
System and Method for Detecting Population Variation from Nucleic Acid Sequencing Data
InactiveUS20160034638A1Microbiological testing/measurementProteomicsPopulation variationNucleic acid sequencing
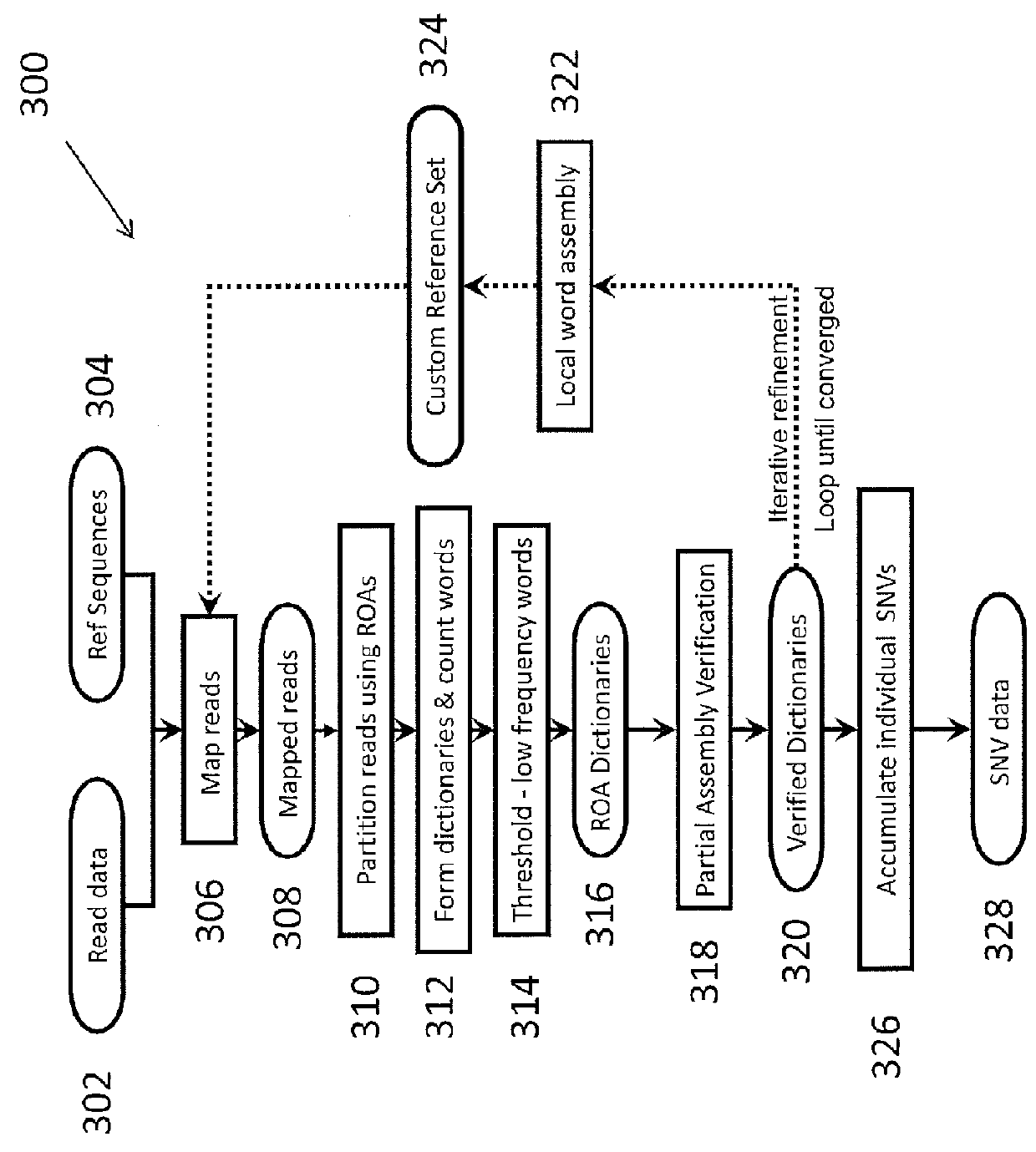
The present invention relates to a method of identifying genetic variants within a population of sequences. The method includes the steps of aligning a set of sequence data reads to reference sequences, dividing reference sequences into multiple tracks of overlapping regions of analysis (ROAs), partitioning each read into a ROA, identifying a plurality of sequence patterns in the reads, setting a sequence pattern frequency threshold value, eliminating any sequence pattern that has a value below the frequency threshold value forming a plurality of dictionaries from the sequence patterns having a value above the frequency threshold value, and cross-validating sequence patterns via partial sequence assembly. The method may optionally include amending the reference sequences used in iterative re-alignment of sequence data.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
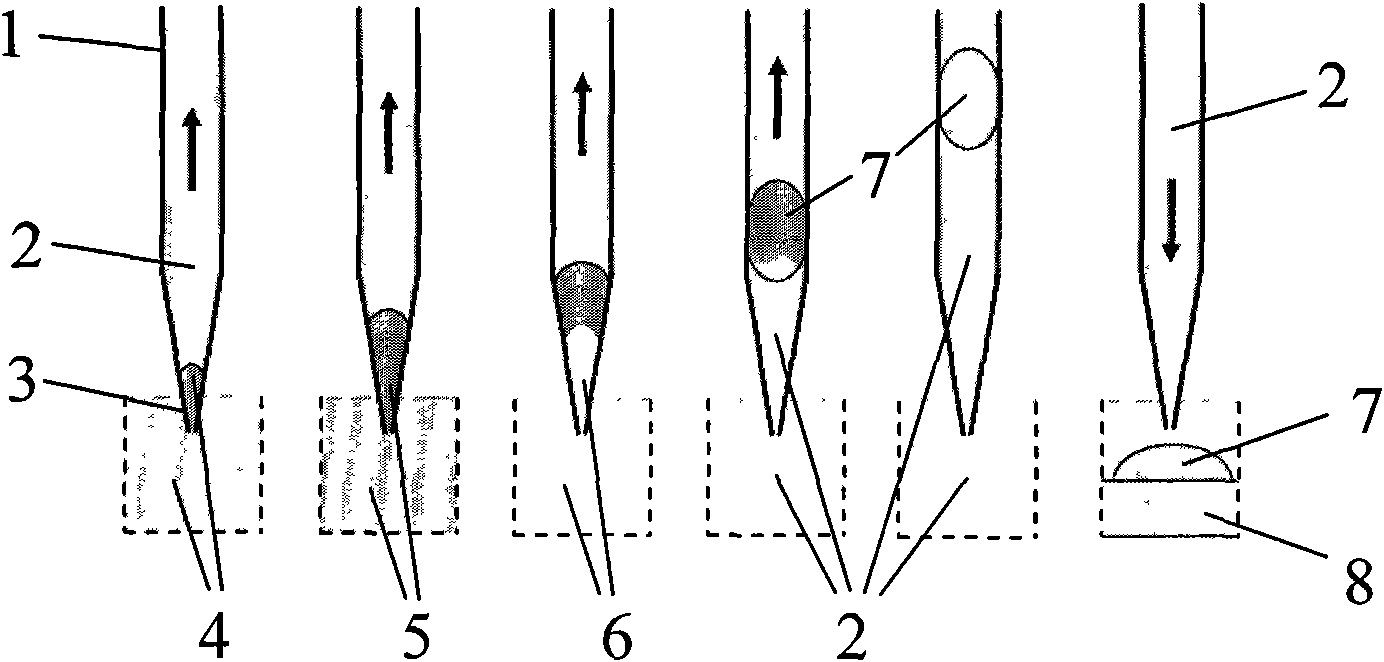
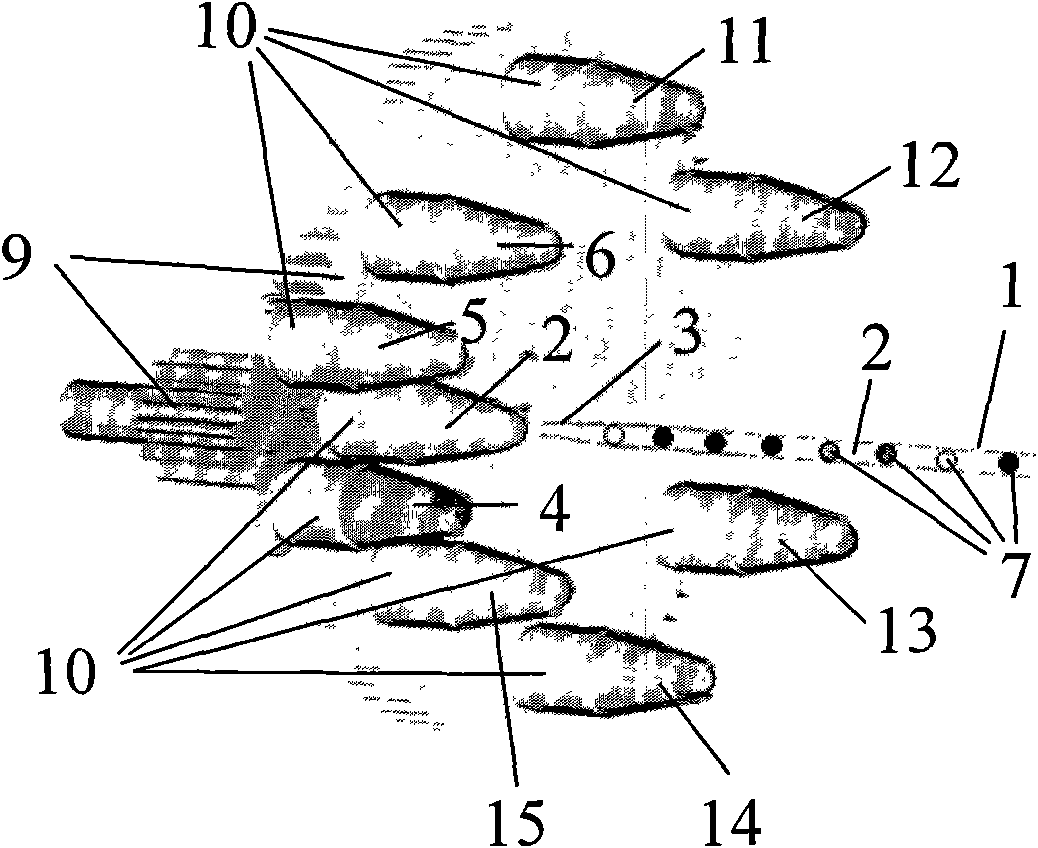
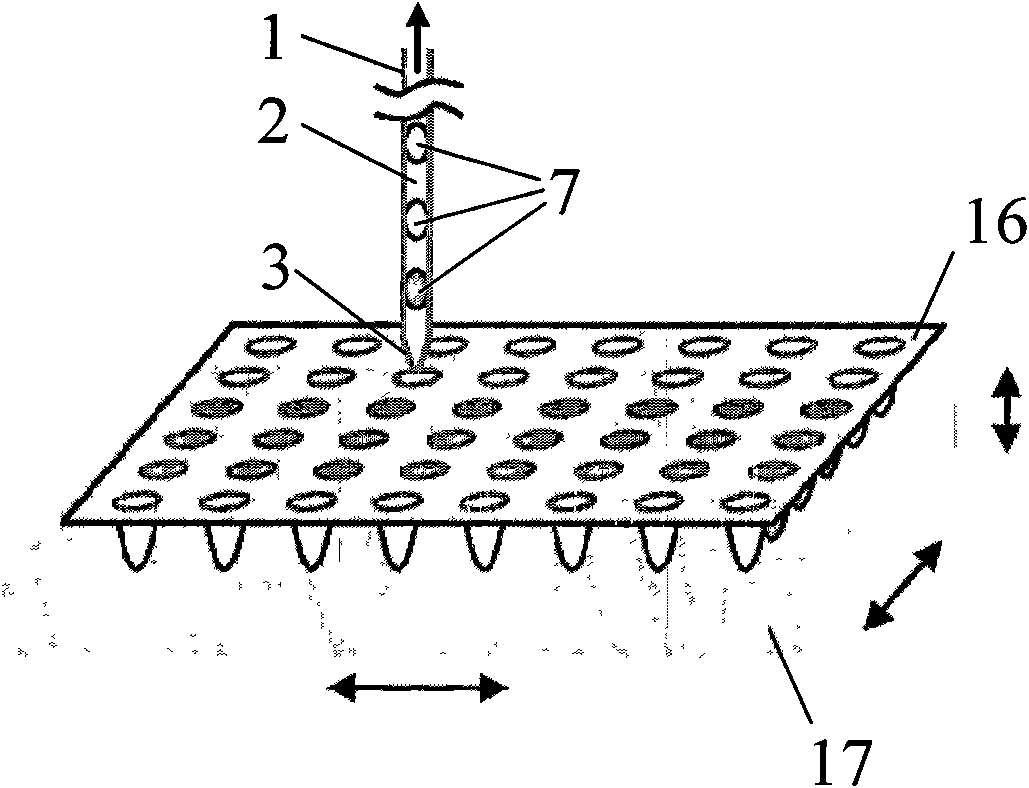
Micro-fluid control liquid drop generation system based on liquid drop sequence assembly technology and use method
The invention relates to the field of liquid drop analysis, in particular to a micro-fluid control liquid drop generation system based on a liquid drop sequence assembly technology. In the invention, the micro-fluid control liquid drop generation system based on the liquid drop sequence assembly technology comprises an automatic liquid presenting device, a liquid drive device, a capillary and a liquid drop array plate, wherein the automatic liquid presenting device is connected with the liquid drop array plate, and the liquid drive device is connected with the capillary. The invention has the advantages that: (1) the construction of the system is simple and convenient without the complicated micro-processing technology and expensive processing equipment, so that the micro-fluid control liquid drop generation system is beneficial to wide application in a conventional laboratory; (2) the category and the mixture proportion of the liquid in the liquid drop can be optionally changed to generate liquid drops with different compositions; and (3) the generation of high flux automation of the liquid drops with the different compositions can be realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
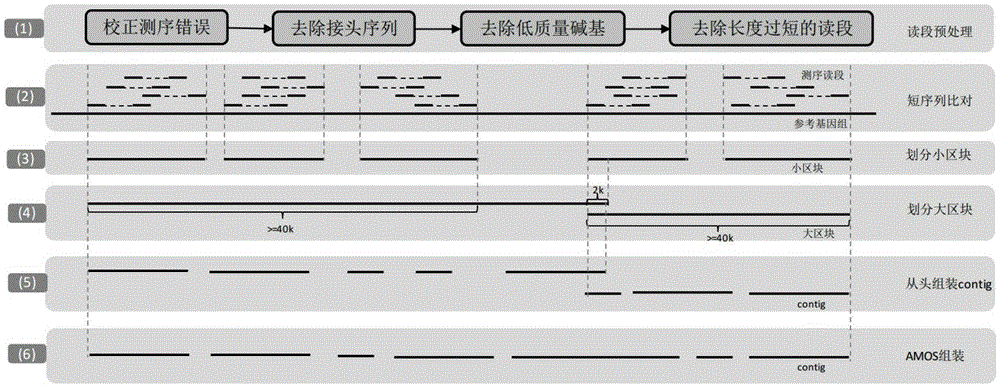
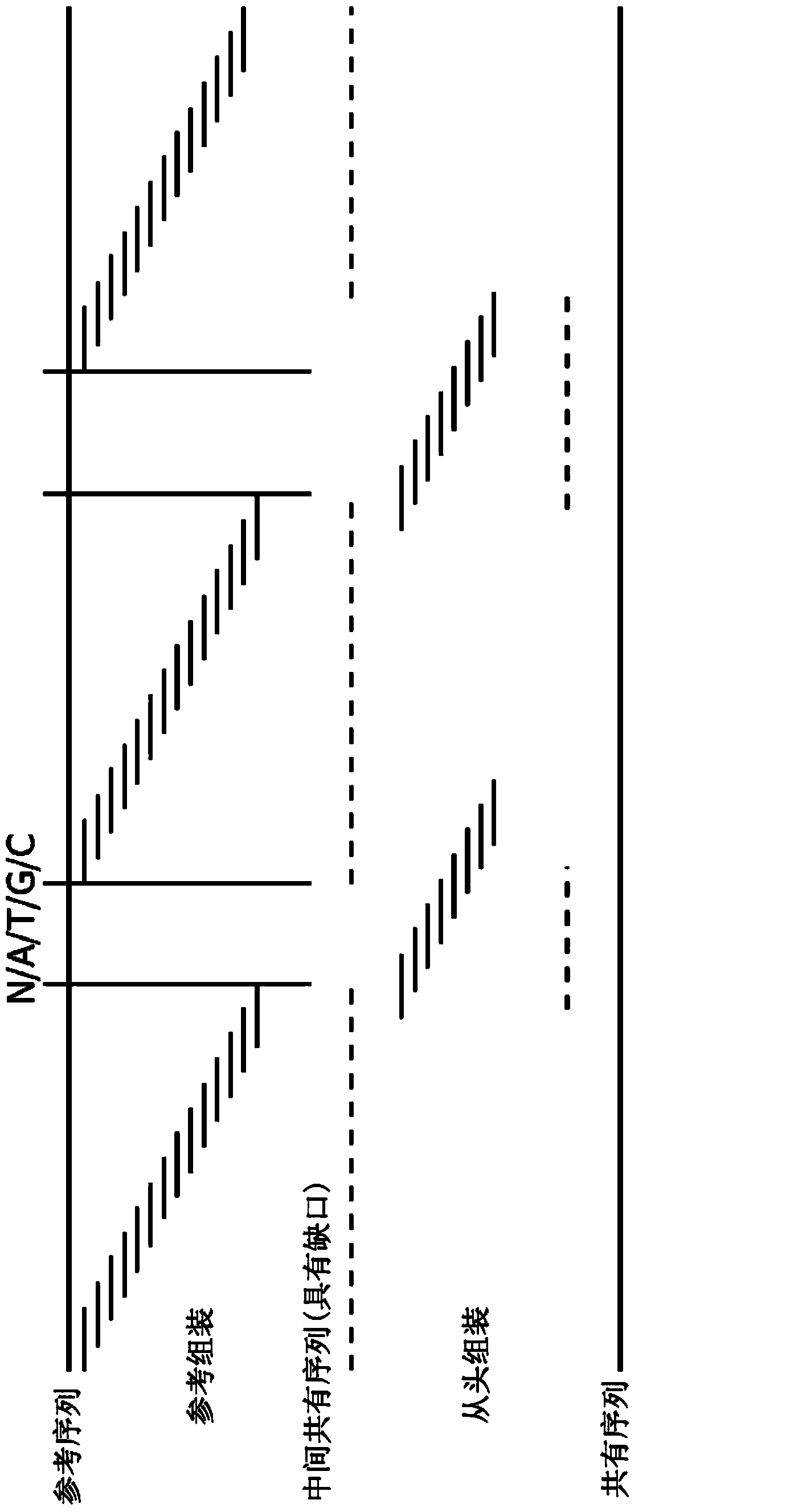
Reference genome and de novo assembly combination based next-generation sequencing data assembly method
InactiveCN105303068AQuality improvementImprove continuitySpecial data processing applicationsReference genomeSequencing data
The invention relates to a reference genome and de novo assembly combination based next-generation sequencing data assembly method. Two policies based on reference genome assembly and genome de novo assembly are combined for overcoming the disadvantages of the two policies, and the advantages of the two policies are fully utilized. The method comprises: firstly, obtaining a genome sequence relatively high in continuity and accuracy by utilizing the reference genome based policy; secondly, obtaining a genome subjected to de novo assembly by utilizing the de novo assembly policy, wherein the genome is relatively good in performance of specific sequence assembly of species; and finally, integrating the two genomes to generate a genome relatively high in accuracy, continuity and integrity.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
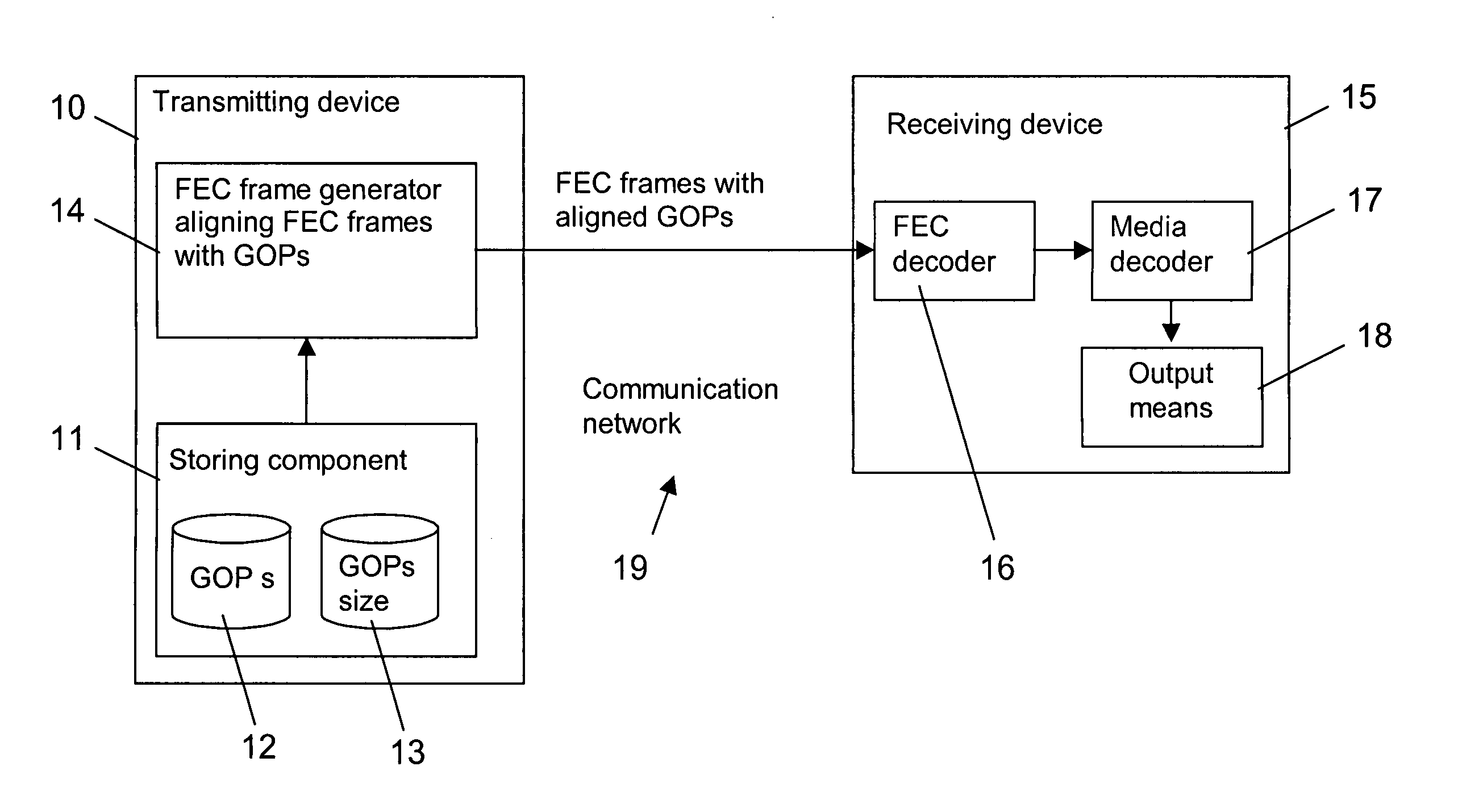
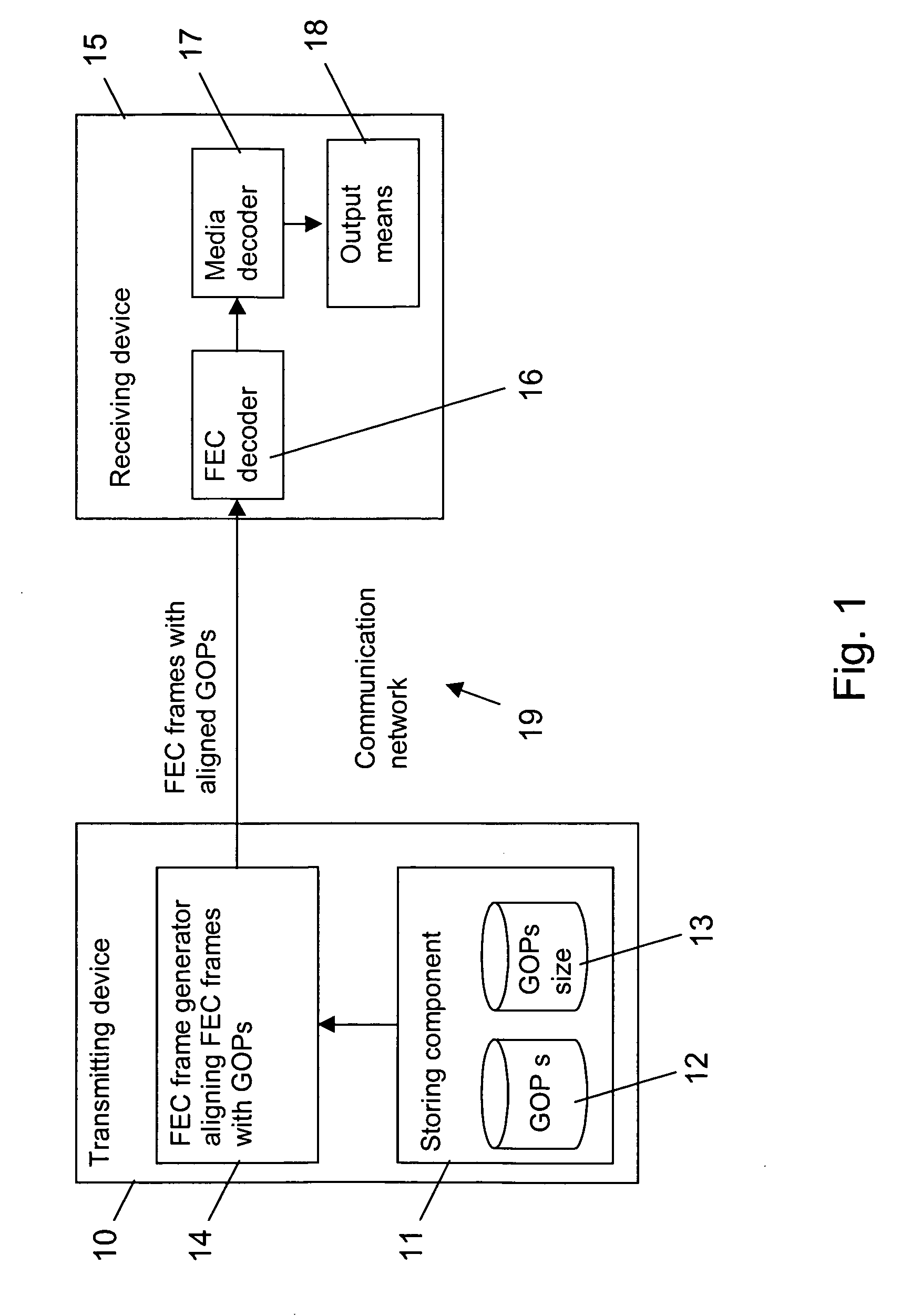
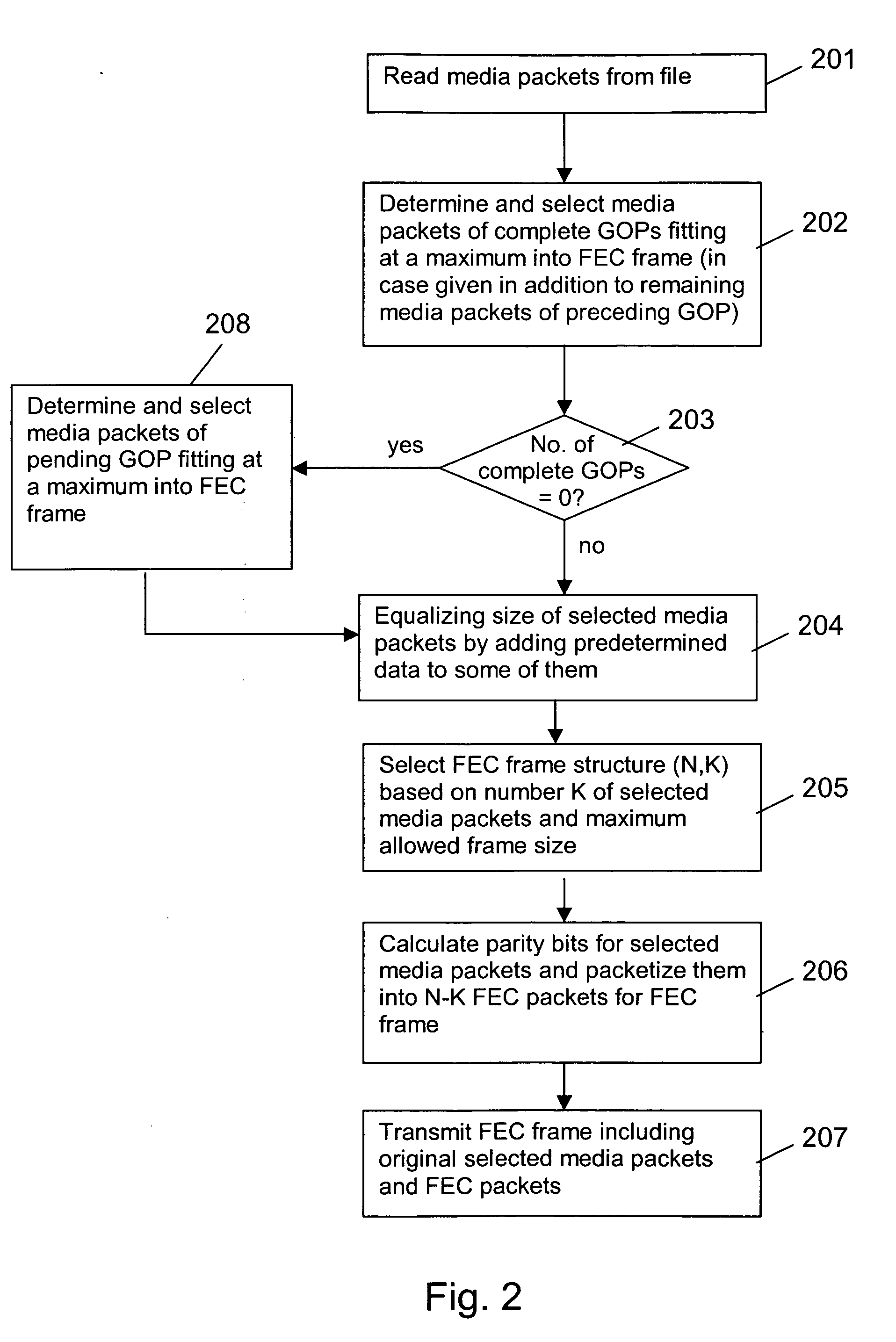
Assembling forward error correction frames
InactiveUS20060107189A1Reduce buffering delayReduce size requirementsError preventionTransmission control/equalisingReal-time computingSequence assembly
The invention relates to a method for assembling FEC frames for a sequence of groups of coded media packets. In order to reduce a buffer delay at a decoding end (15), it is proposed that the FEC frame is aligned with the groups of media packets. To this end, a number of next subsequent groups are determined, which fit completely into a FEC frame. All coded media packets associated to this determined group or groups, if any, are selected for the FEC frame (step 202,402). Then, the selected coded media packets are encoded to obtain at least one FEC packet for the FEC frame (step 206,406). For fixed FEC frame structures, moreover the introduction of padding packets as additional media packets, if required, is proposed.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Method for assembly of nucleic acid sequence data
InactiveCN103797486ASolve deviationIncrease sequence precisionSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsNucleotideNucleic acid sequence
The present invention relates to a method for assembly of nucleic acid sequence data comprising nucleic acid fragment reads into (a) contiguous nucleotide sequence segment(s). The method comprises steps of: (a) obtaining a plurality of nucleic acid sequence data from a plurality of nucleic acid fragment reads; (b) aligning the plurality of nucleic acid sequence data to a reference sequence; (c) detecting one or more gaps or regions of non-assembly, or non-matching with the reference sequence in the alignment output of the step (b); (d) performing de novo sequence assembly of nucleic acid sequence data mapping to the gaps or regions of non-assembly; and (e) combining the alignment output of the step (b) and the assembly output of the step (d) in order to obtain (a) contiguous nucleotide sequence segment(s).The present invention further relates to a method, wherein the detection of gaps or regions of non-assembly is performed by implementing a base quality, coverage, complexity of the surrounding region, or length of mismatch filter or threshold. Also envisaged is the masking out of nucleic acid sequence data relating to known polymorphisms, disease related mutations or modifications, repeats, low map ability regions, CPG islands, or regions with certain biophysical features. In addition, a corresponding program element or computer program for assembly of nucleic the sequence data and a sequence assembly system for transforming the nucleic acid sequence data comprising nucleic acid fragment reads into (a) contiguous nucleotide sequence segment(s) are provided.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
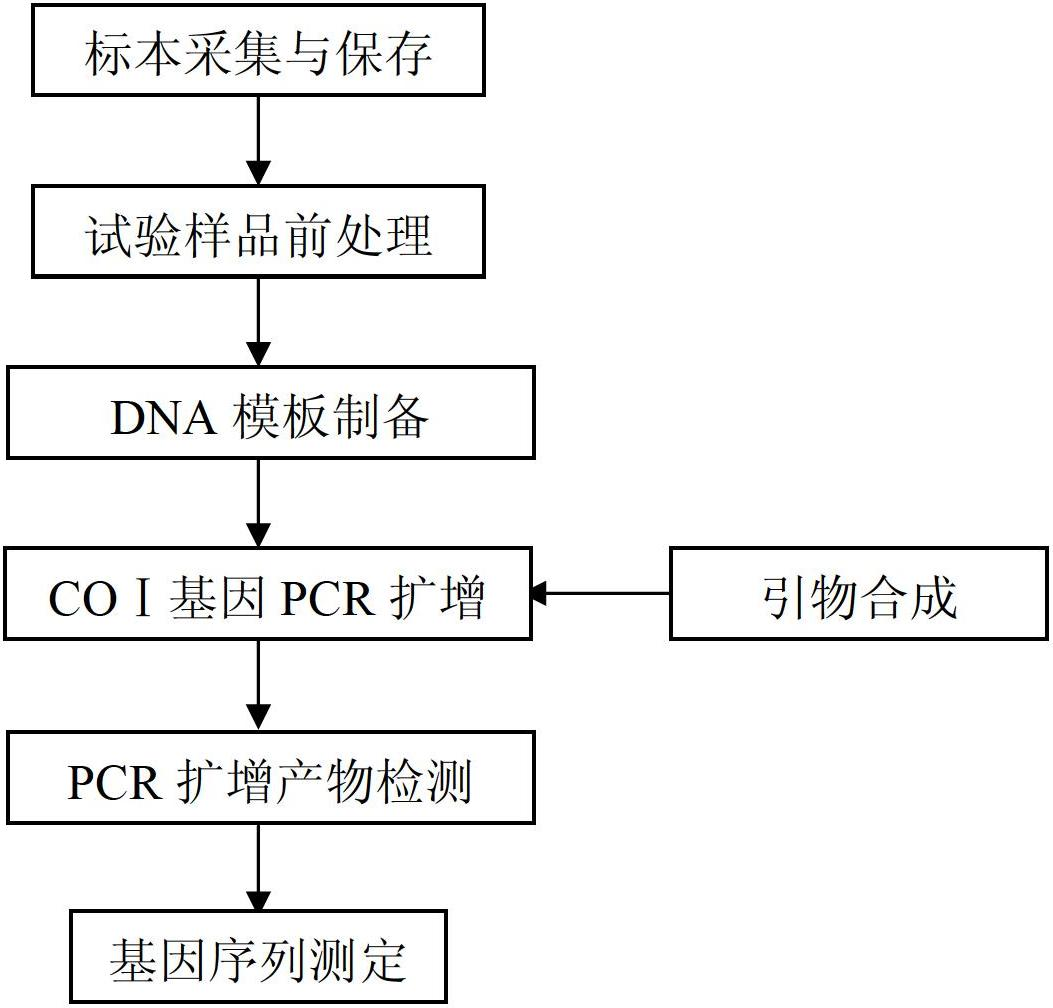
A DNA bar code standard gene sequence for Taiwan Lasiohelea
ActiveCN102690829AFacilitate the realization of molecular identificationShorten identification timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationRapid identificationLasiohelea
The invention discloses a DNA bar code standard gene sequence for Taiwan Lasiohelea, which is characterized in that a bar code standard detection gene is COI gene, possessing gene sequence SEQ ID NO.1. Manual proofreading and sequence assembly are carried out to the sequencing result and Blast similarity search is carried out in NCBI to ensure that the obtained sequence is the target sequence. Species identification of Taiwan Lasiohelea is realized through morphological identification, thereby result reliability is guaranteed. The DNA bar code standard gene sequence for Taiwan Lasiohelea provided in the invention is in favor of realizing rapid identification of Taiwan Lasiohelea, and reduces identification time.
Owner:FUJIAN INT TRAVEL HEALTH CARE CENT
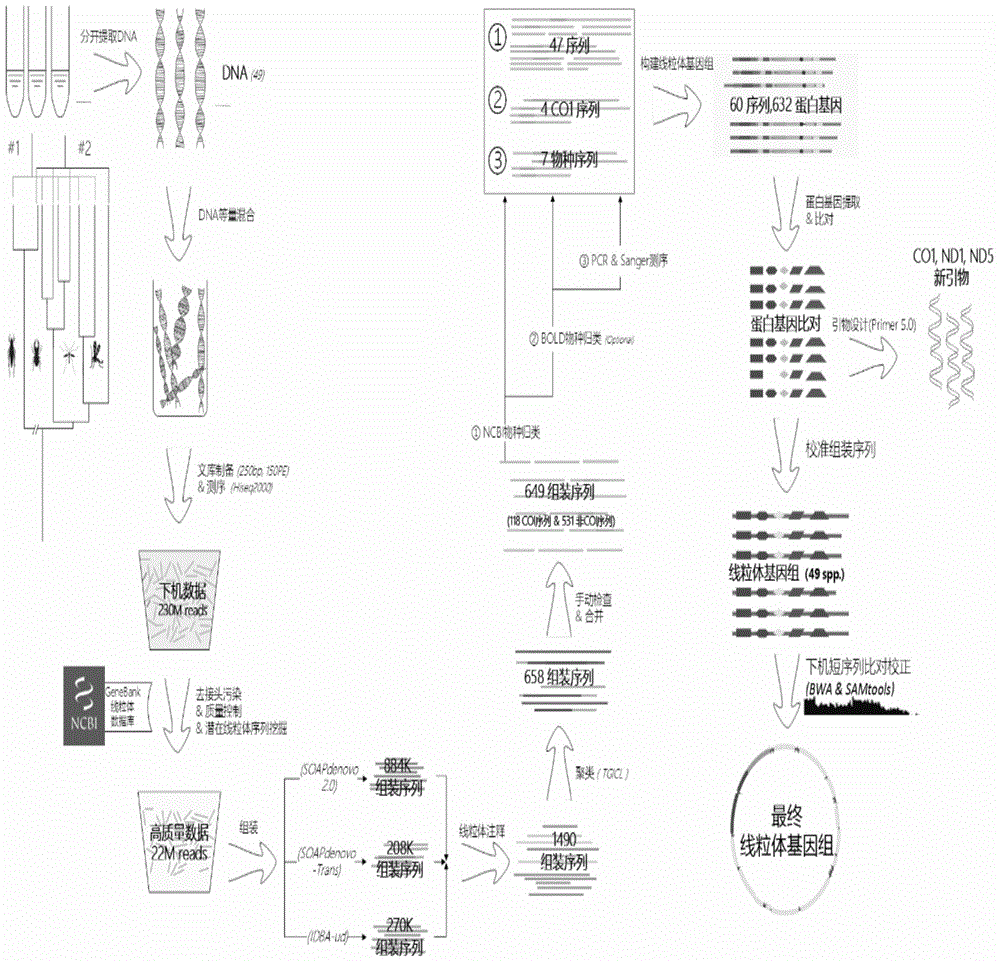
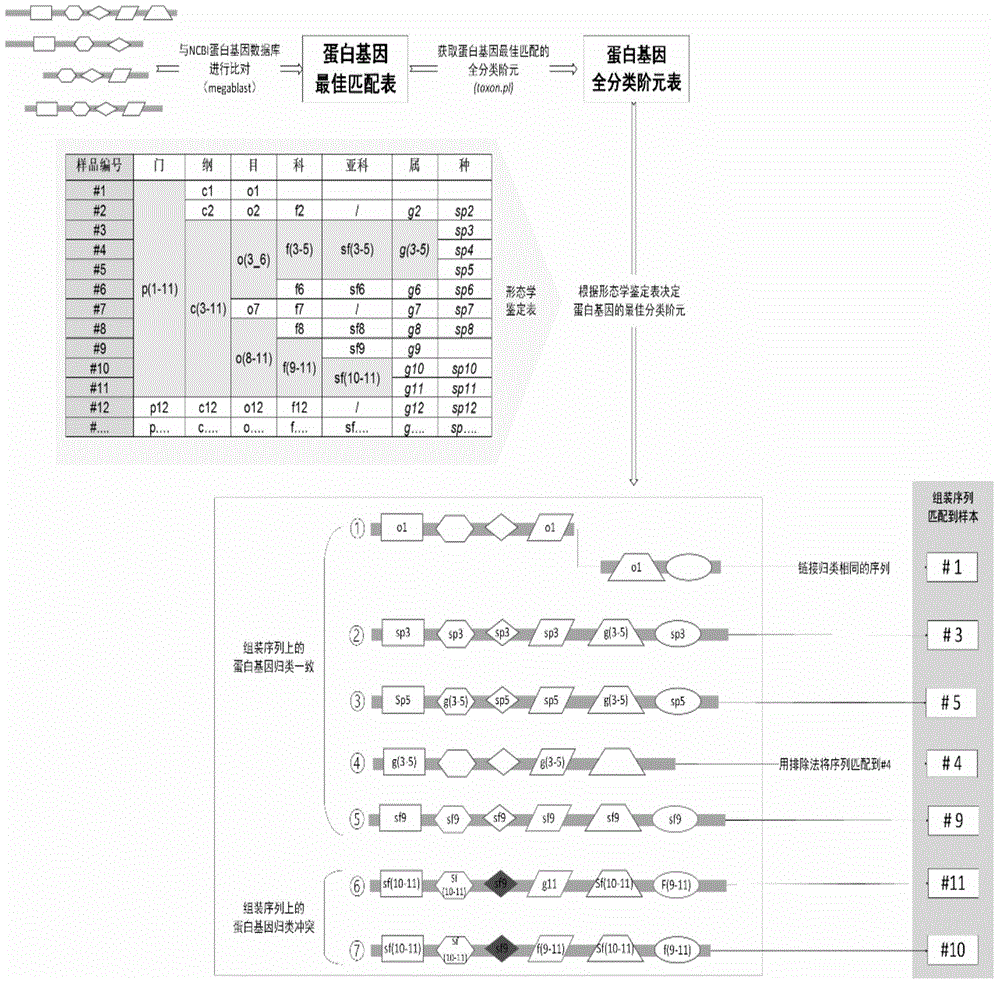
Method and system for determining mitochondria genome sequence information of various samples at the same time
ActiveCN105653899ALower requirementReduce labor costsSpecial data processing applicationsMitophagyMitochondrial protein
The invention discloses a method and system for determining mitochondria genome sequence information of various samples at the same time, wherein the various samples belong to different species. The method includes the following steps of: providing genome DNA of each of the various samples and mixing the genome DNA; performing library construction on the DNA mixture; performing sequencing on the DNA sequencing library; performing screening on the plurality of sequencing sequences to obtain a target sequence; performing sequence assembly on the target sequence to obtain the plurality of assembled sequences; performing morphological species taxonomy on each of the various samples to obtain morphological species taxonomy information of the various samples; performing species distribution on the assembled sequences based on the morphological species taxonomy information of the various samples and reference to a mitochondria protein gene database to determine the assembled sequence of each of the various samples; and respectively constructing a mitochondria genome of each of the samples based on the assembled sequence of each of the various samples, and determining the mitochondria genome sequence information.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
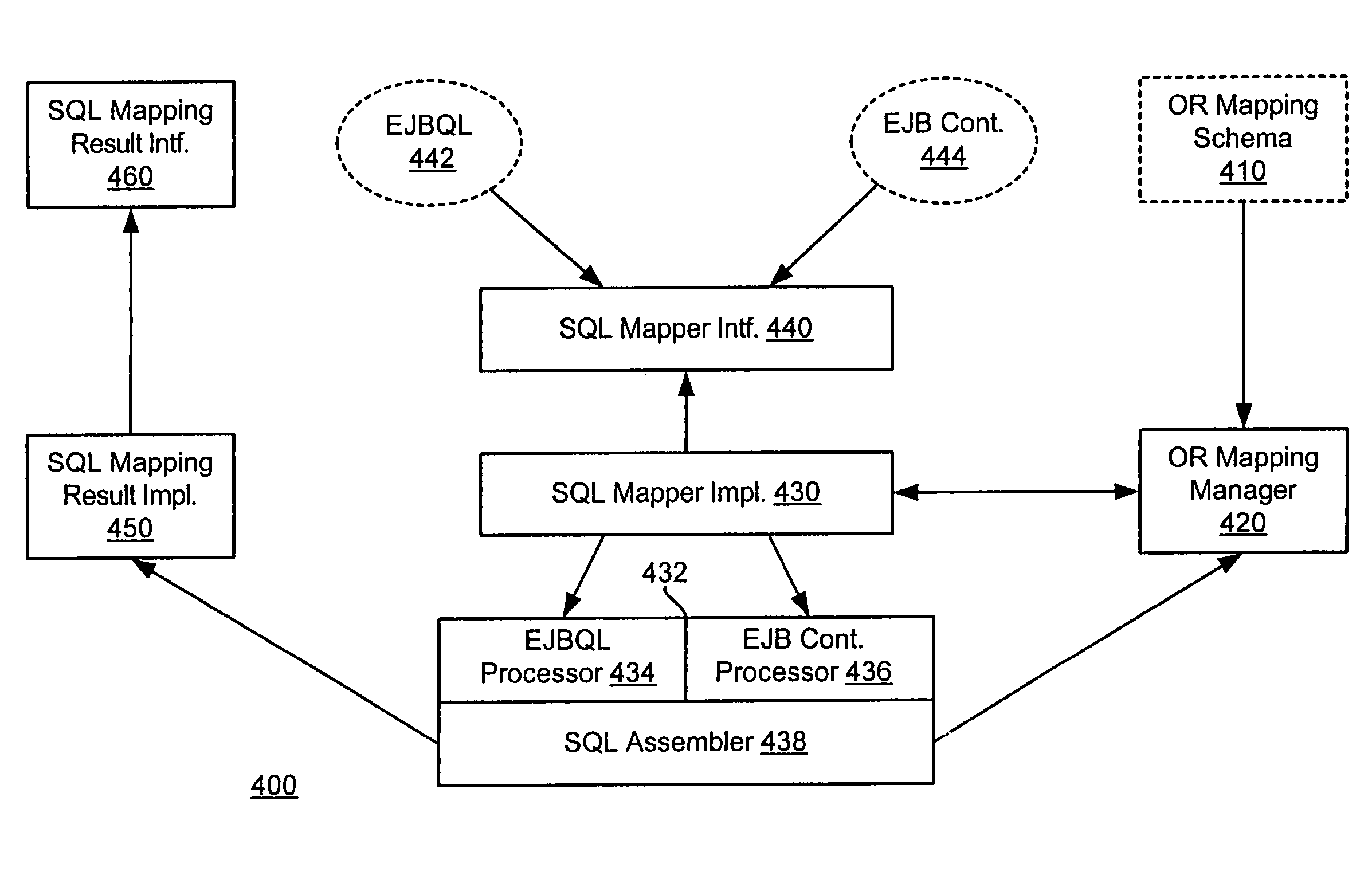
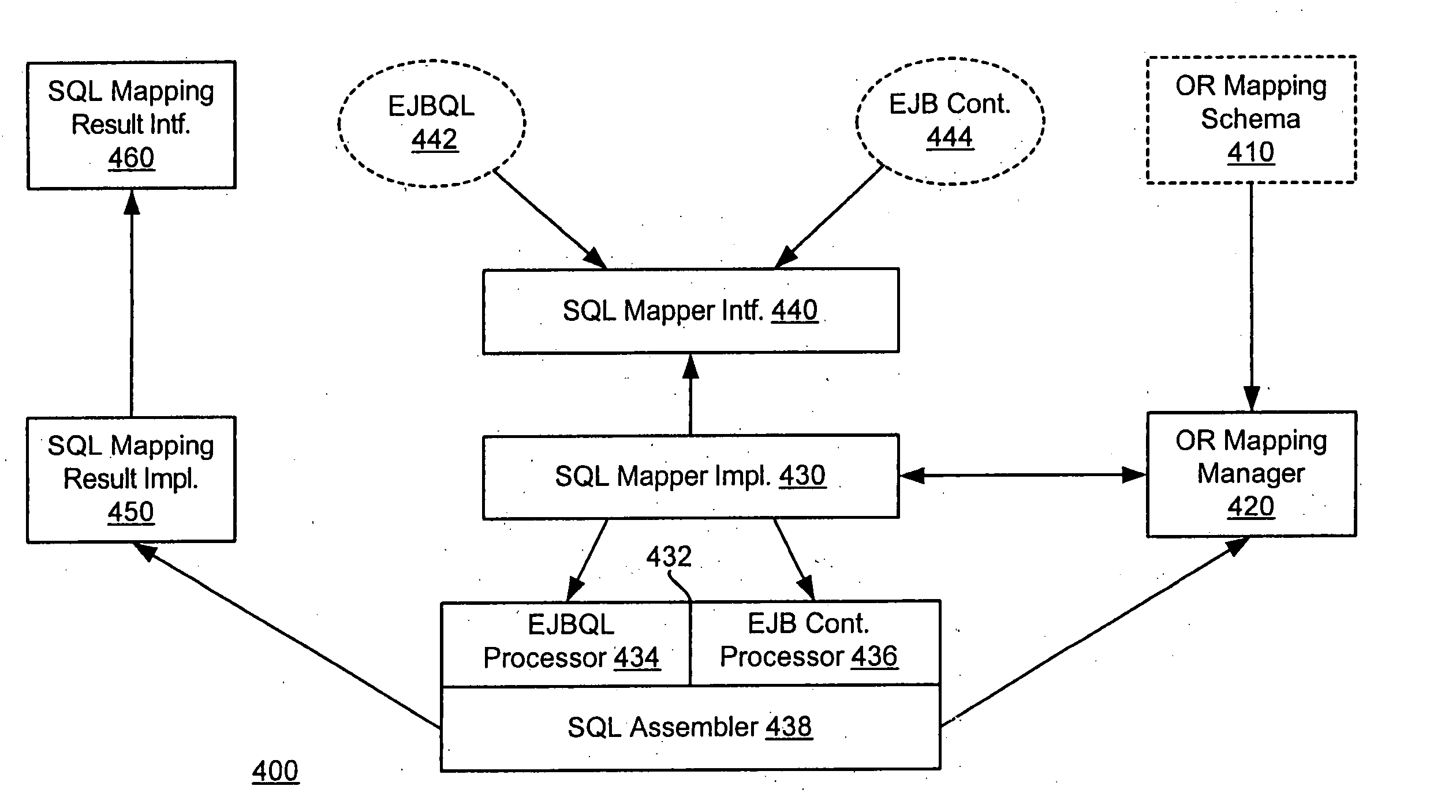
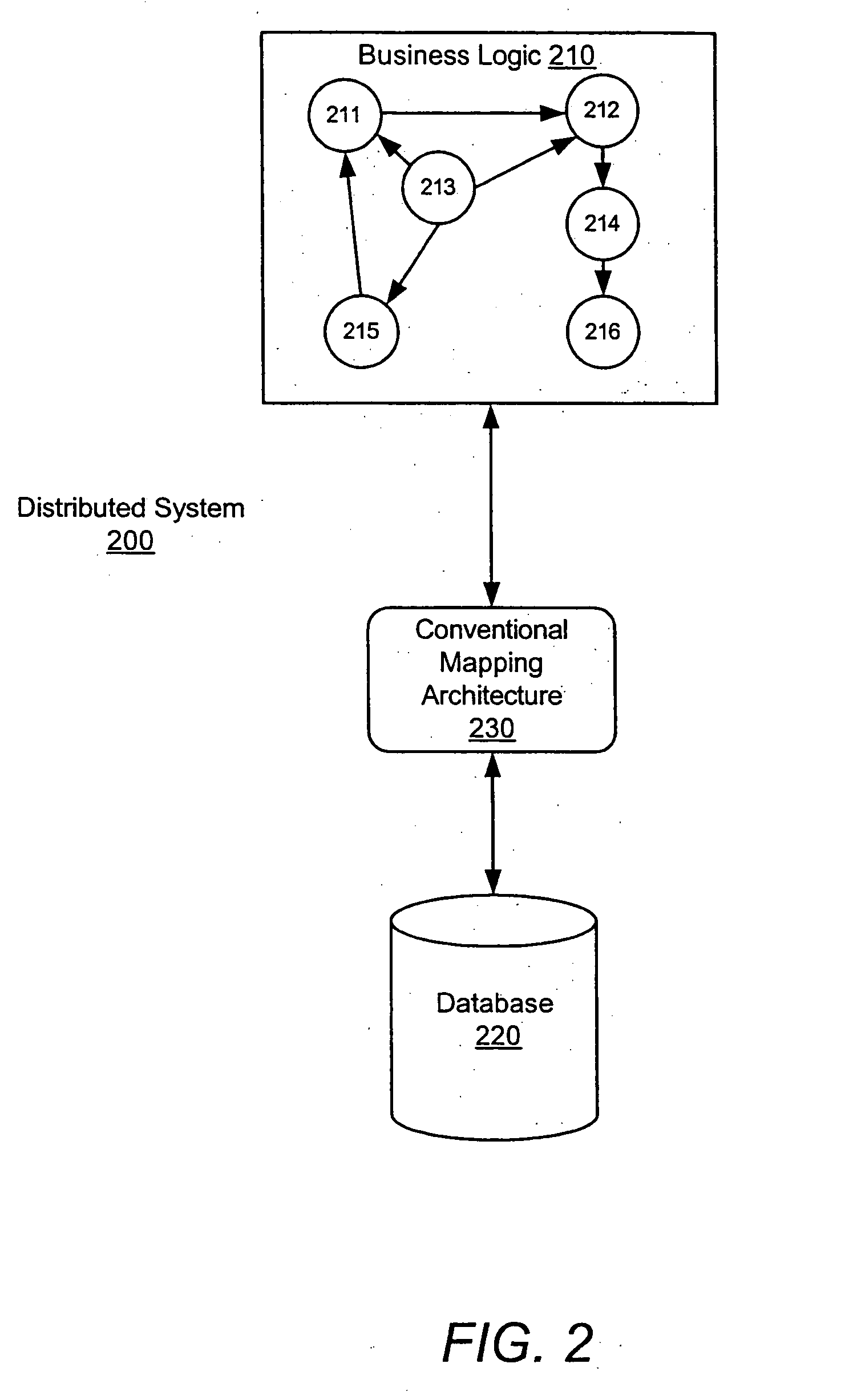
System and method for a query language mapping architecture
A system and method are provided for a query language mapping architecture. In an embodiment, the query language mapping architecture includes an Enterprise Java Bean (EJB) interpreting layer to receive one or more EJB persistence requests and to translate the one or more EJB persistence requests to command sequences. In an embodiment, the query language mapping architecture may also include a Structured Query Language (SQL) assembly layer to receive the command sequences from the EJB interpreting layer and to assemble one or more SQL statements based, at least in part, on the command sequences.
Owner:SAP AG
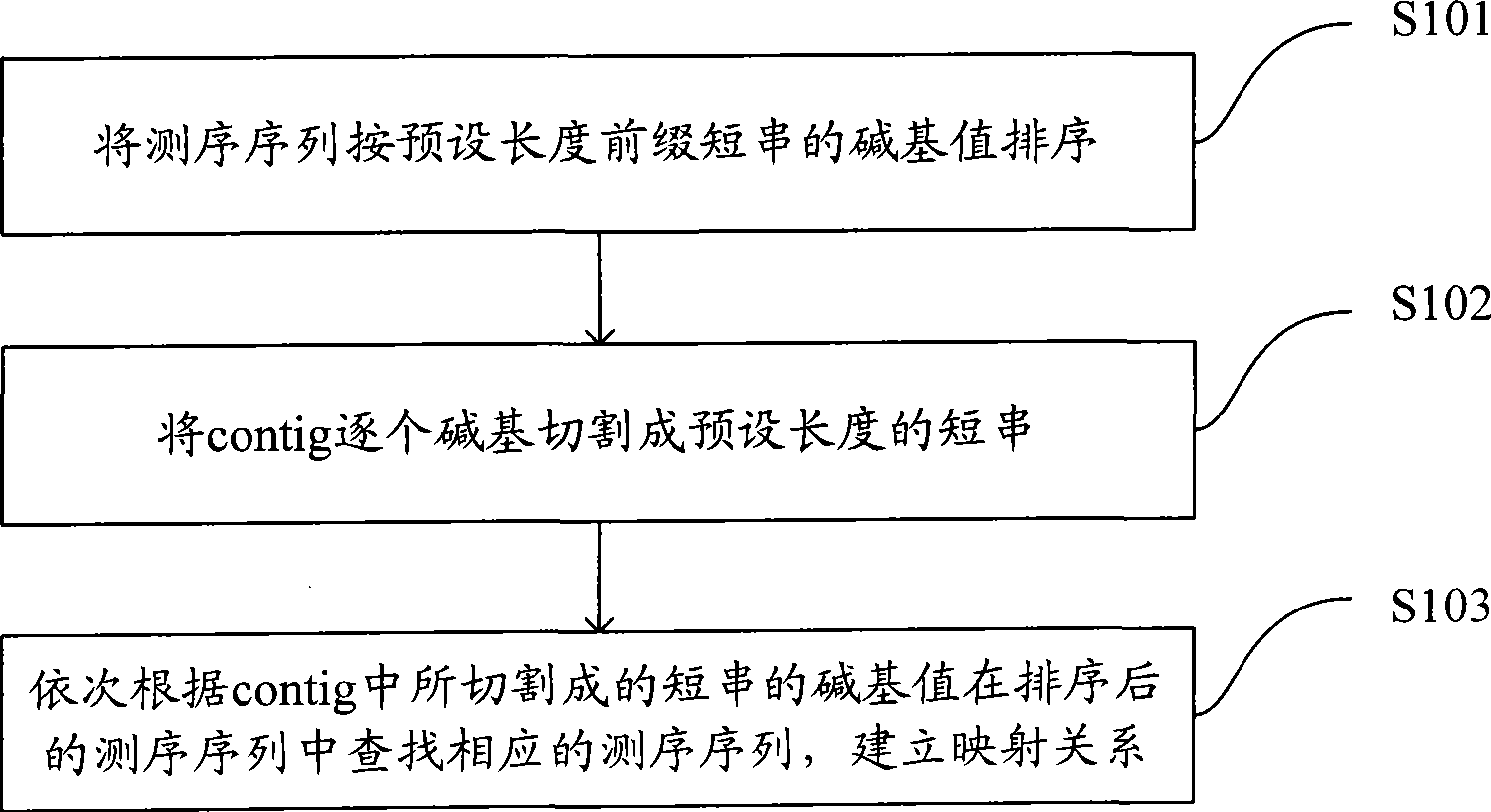
Short sequence mapping method and system
InactiveCN101430741AExtended processing timeLength prefix short processing timeMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsContigShort string
The invention is applicable to the technical field of gene engineering, and provides a method for mapping a short sequence and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: ordering an order-checking sequence according to base values of prefixed short strings with predetermined length; cutting each base of a contig to a short string with the predetermined length; searching a corresponding order-checking sequence in an ordered order-checking sequence in sequence according to the base value of the cut short string in the contig so as to establish a mapping relation. In the invention, the method for mapping the short sequence used in a short sequence assembly is realized by ordering the order-checking sequence according to the base values of the prefixed short strings with the predetermined length, cutting each base of the contig to the short string with the predetermined length and searching the corresponding order-checking sequence in the ordered order-checking sequence in sequence according to the base value of the cut short string in the contig so as to establish the mapping relation. Therefore, the method has short treatment time and high efficiency.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
System and method for a query language mapping architecture
ActiveUS20060004831A1Data processing applicationsDatabase queryingEnterprise Java BeanQuery language
A system and method are provided for a query language mapping architecture. In an embodiment, the query language mapping architecture includes an Enterprise Java Bean (EJB) interpreting layer to receive one or more EJB persistence requests and to translate the one or more EJB persistence requests to command sequences. In an embodiment, the query language mapping architecture may also include a Structured Query Language (SQL) assembly layer to receive the command sequences from the EJB interpreting layer and to assemble one or more SQL statements based, at least in part, on the command sequences.
Owner:SAP AG
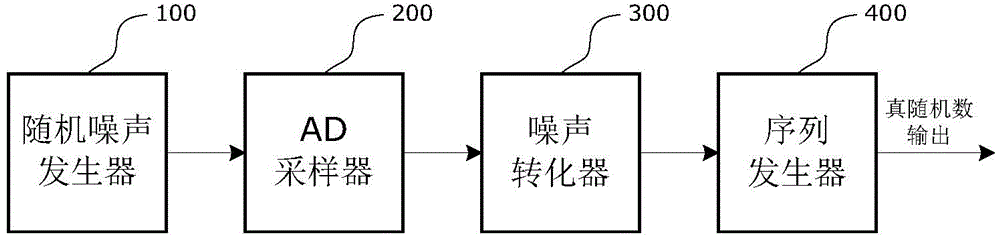
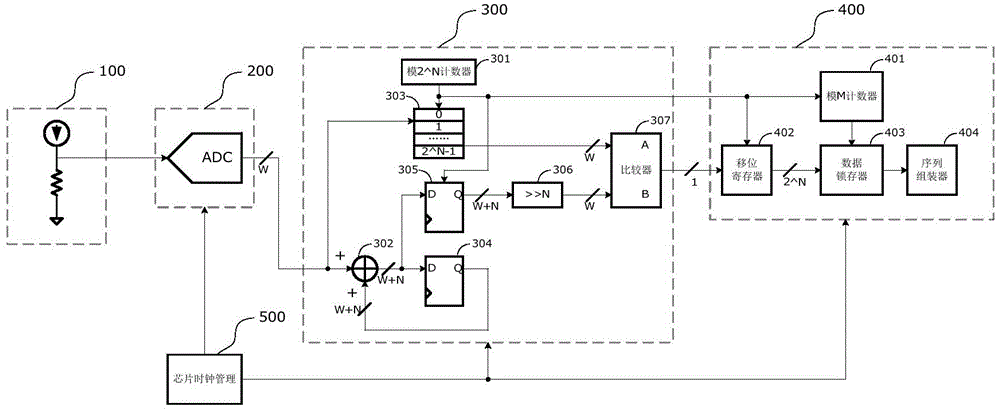
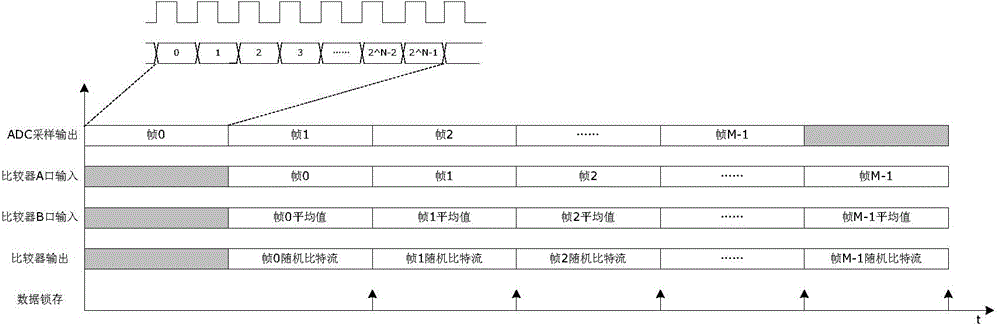
On-chip true random number generator
InactiveCN104133658AEvenly distributedQuality improvementRandom number generatorsProduction lineRandom noise
The invention relates to an on-chip true random number generator, which comprises a random noise generator, an AD (Analog to Digital) sampler, a noise converter and a sequence generator. The on-chip true random number generator is characterized in that an on-chip temperature sensor is used as a noise source of the true random number generator; a temperature value is converted into a digital signal through AD sampling; the digital signal obtained through sampling is subjected to noise extraction conversion, and a group of true random sequences is obtained; and finally, a plurality of groups of random sequences are assembled through the sequence generator, and true random numbers in any bit are generated. An on-chip noise signal is used as a signal source of the true random number, so the characteristics of randomness, unpredictability and the like are realized, and the generated random numbers are in uniform distribution, comfort to the characteristics of irrelevance and the like and belongs to high-quality true random numbers. The on-chip true random number generator belongs to an on-chip true random number generator realized by using an integrated circuit; the technologies of chip design production line, synchronous processing, resource reuse and the like are utilized; and the on-chip true random number generator has the advantages that the cost is low, the stability is good, the velocity is high, the realization is easy, and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU HONGYUN TECH
Method and system for filtering sequence segments in short-sequence assembly
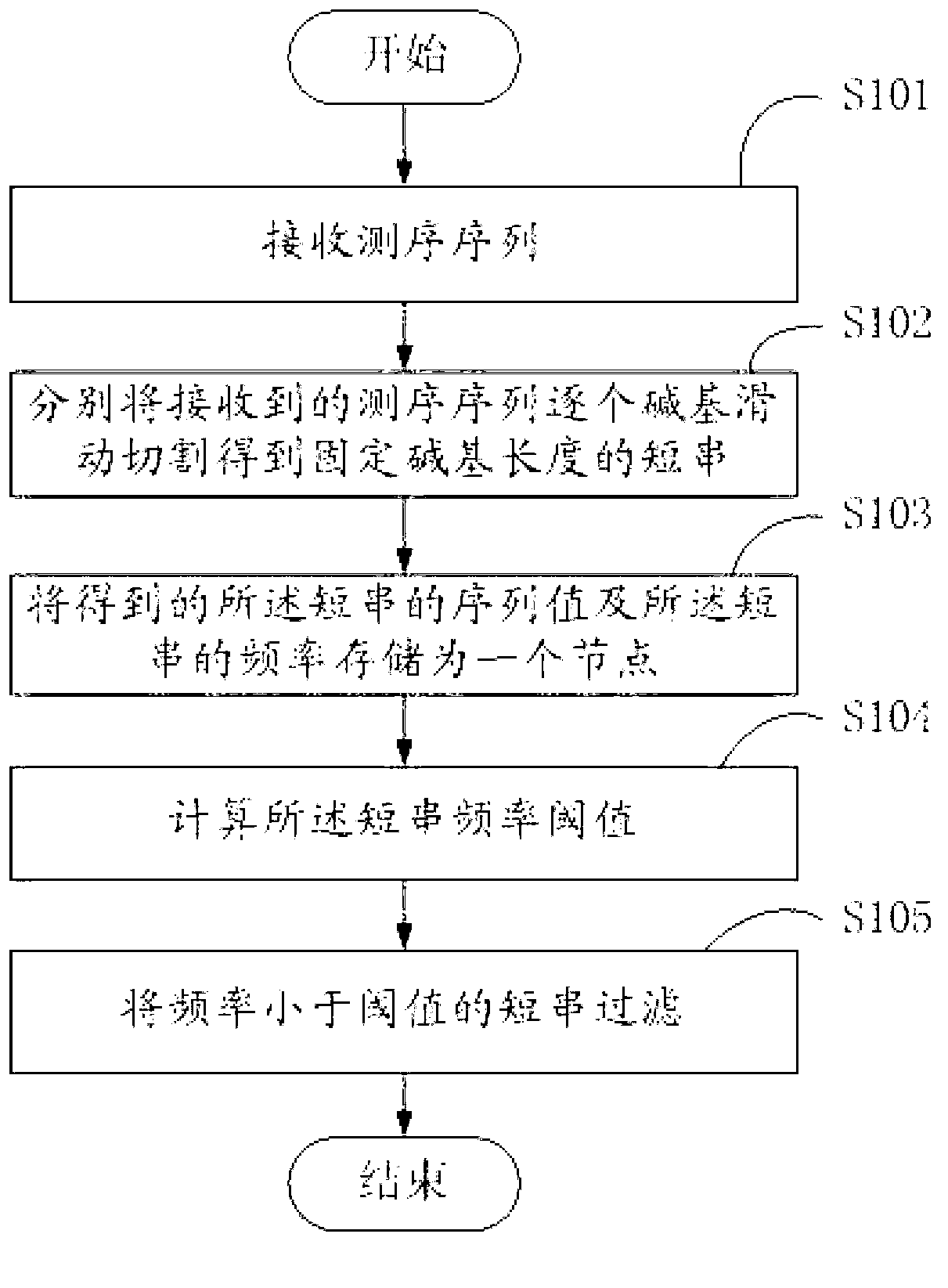
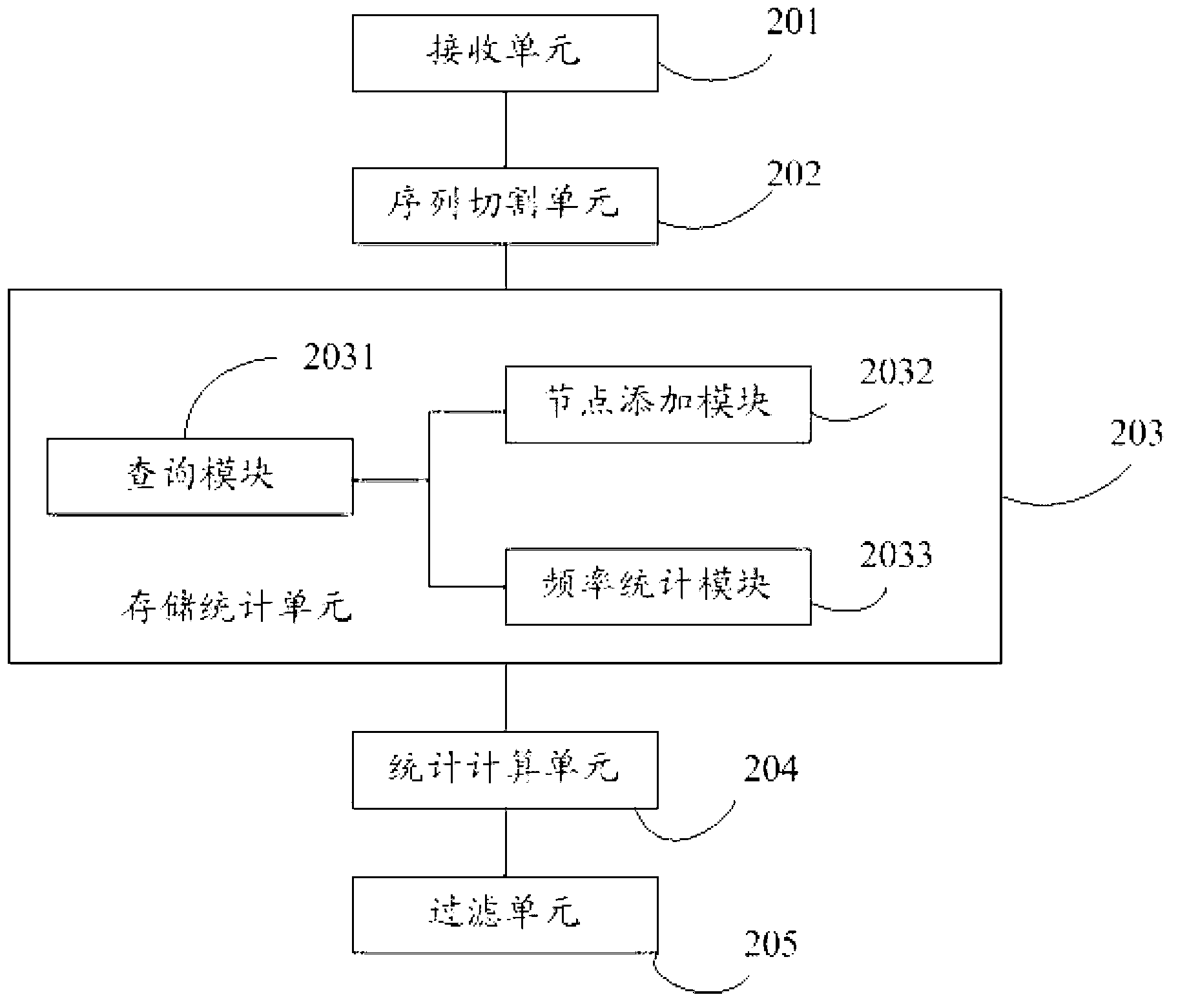
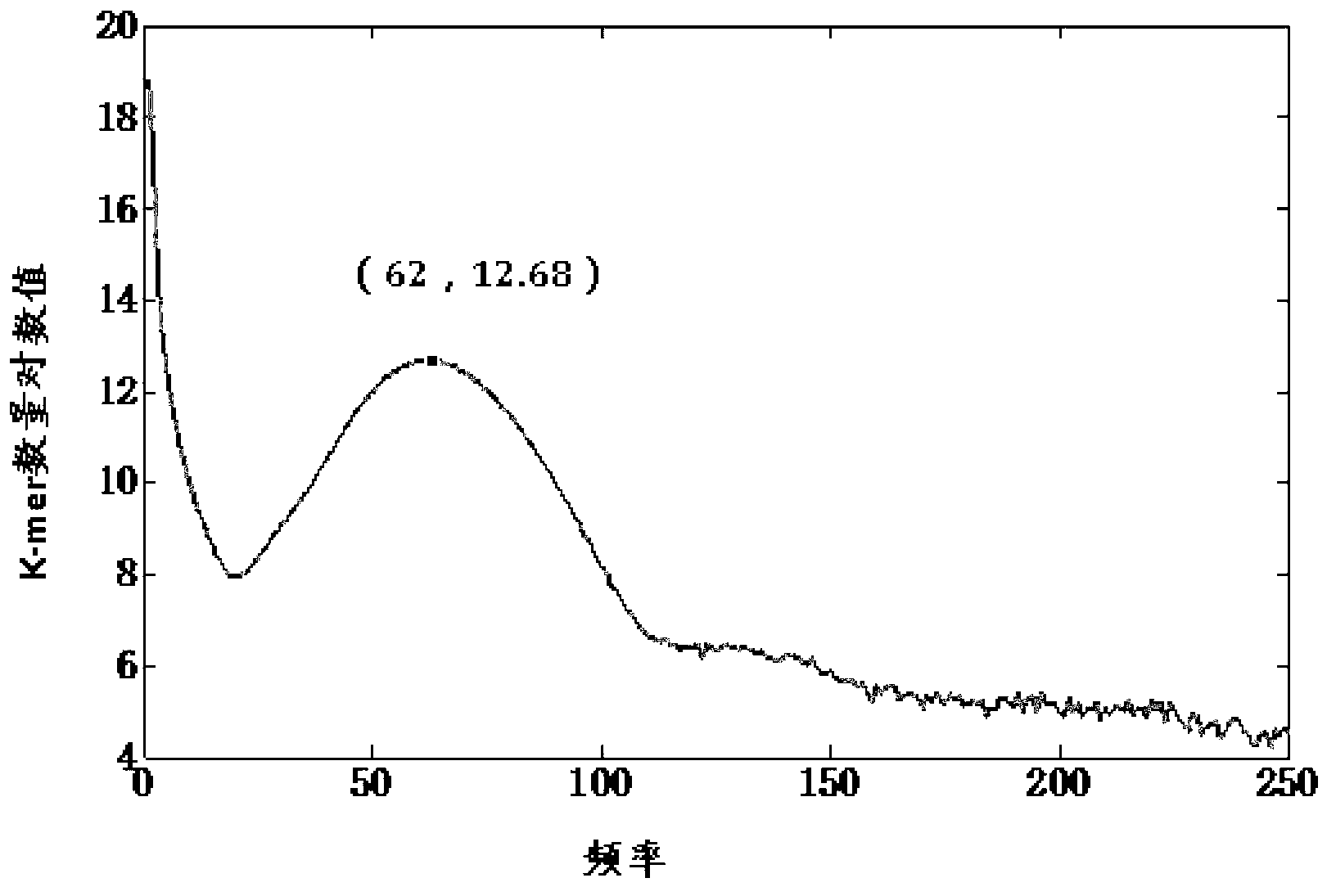
ActiveCN103065067ASave memoryImprove performanceSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringSequence assembly
The invention discloses a method for filtering sequence segments in a short-sequence assembly. The method comprises the following steps: receiving measured sequences, respectively performing base slide cutting to received measured sequences one by one to obtain short strings with fixed base length; storing sequence values and occurrence frequency of the short strings as a node; calculating a short string frequency threshold value; and filtering the short strings with frequency smaller than the threshold value. The invention further provides a system for filtering sequence segments in the short-sequence assembly. The method and system for filtering sequence segments in the short-sequence assembly has the advantages of filtering wrong short strings, decreasing assembled and spliced short string sets, reducing internal memory required by assembling and splicing programs, improving the performance of the assembling and splicing programs, performing statistics to the frequency of the short strings while storing short string modes, and being simple in operation and small in error.
Owner:深圳市弘志拓新创业投资企业(有限合伙)
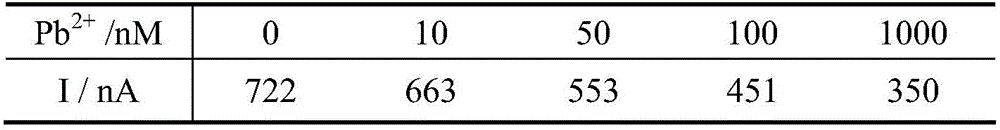
Photo-electrochemical DNA biosensor based lead ion determination method
The invention provides a photo-electrochemical DNA biosensor based lead ion determination method. According to the method, a DNA sequence containing partial Pb<2+> which can be specifically identified is assembled on the surface of an ITO electrode; and with Ru(bpy)2(dppz)<2+> as a photo-electrochemical signal probe, after the Pb<2+> acts with DNA on the surface of the electrode, the probe is separated from a DNA chain, so that a photo-electrochemical signal is weakened, and photo-electrochemical detection of Pb<2+> is achieved. The DNA biosensor with the ITO electrode provided by the invention is simple in preparation, low in cost, high in response speed, convenient in detection, short in period, high in stability and good in repeatability, and has mild reaction conditions. Furthermore, the photo-electrochemical sensor has the advantages of high selectivity, high sensitivity and the like on Pb<2+>.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Computer display tool for visualizing relationships between and among data
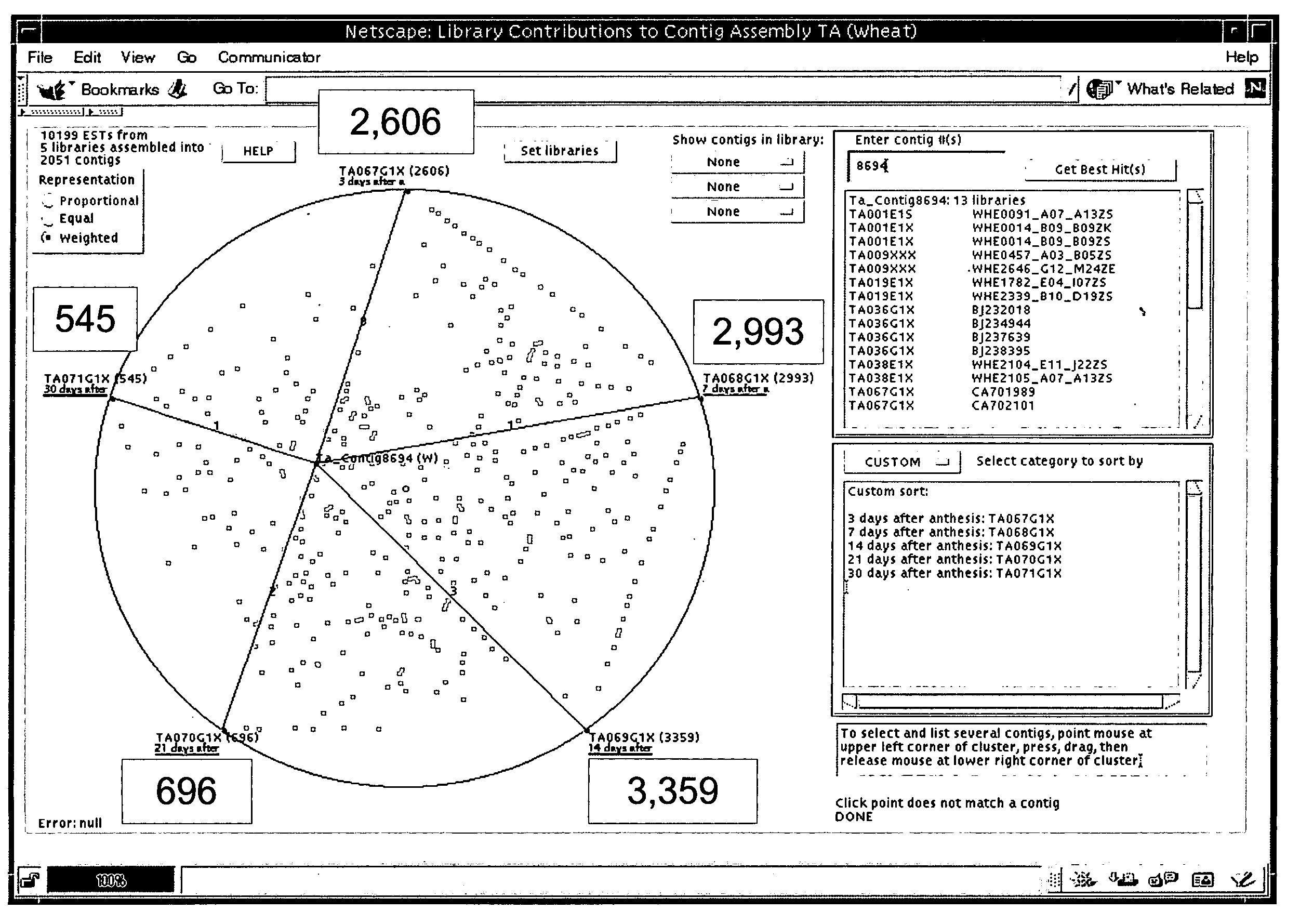
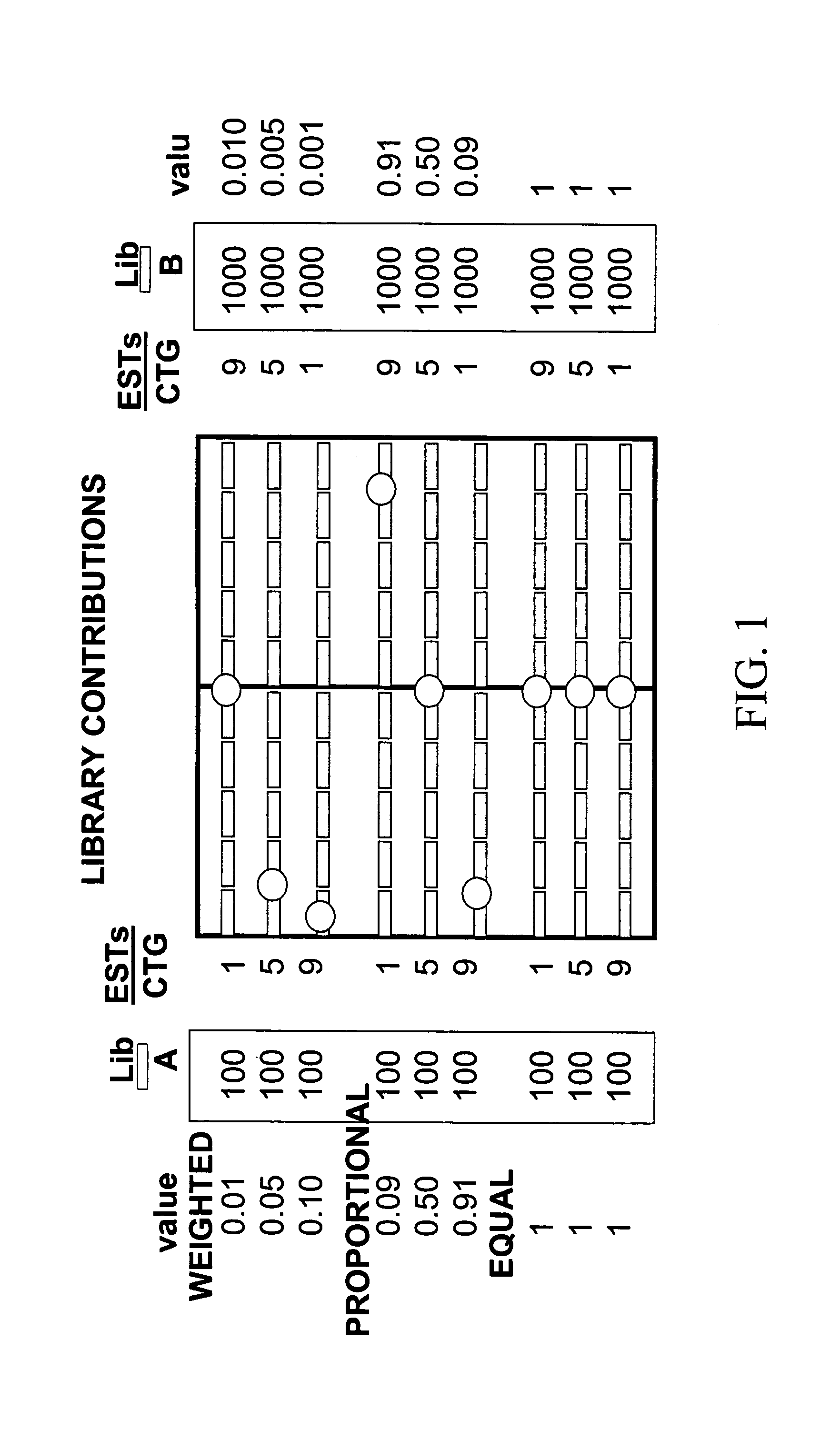
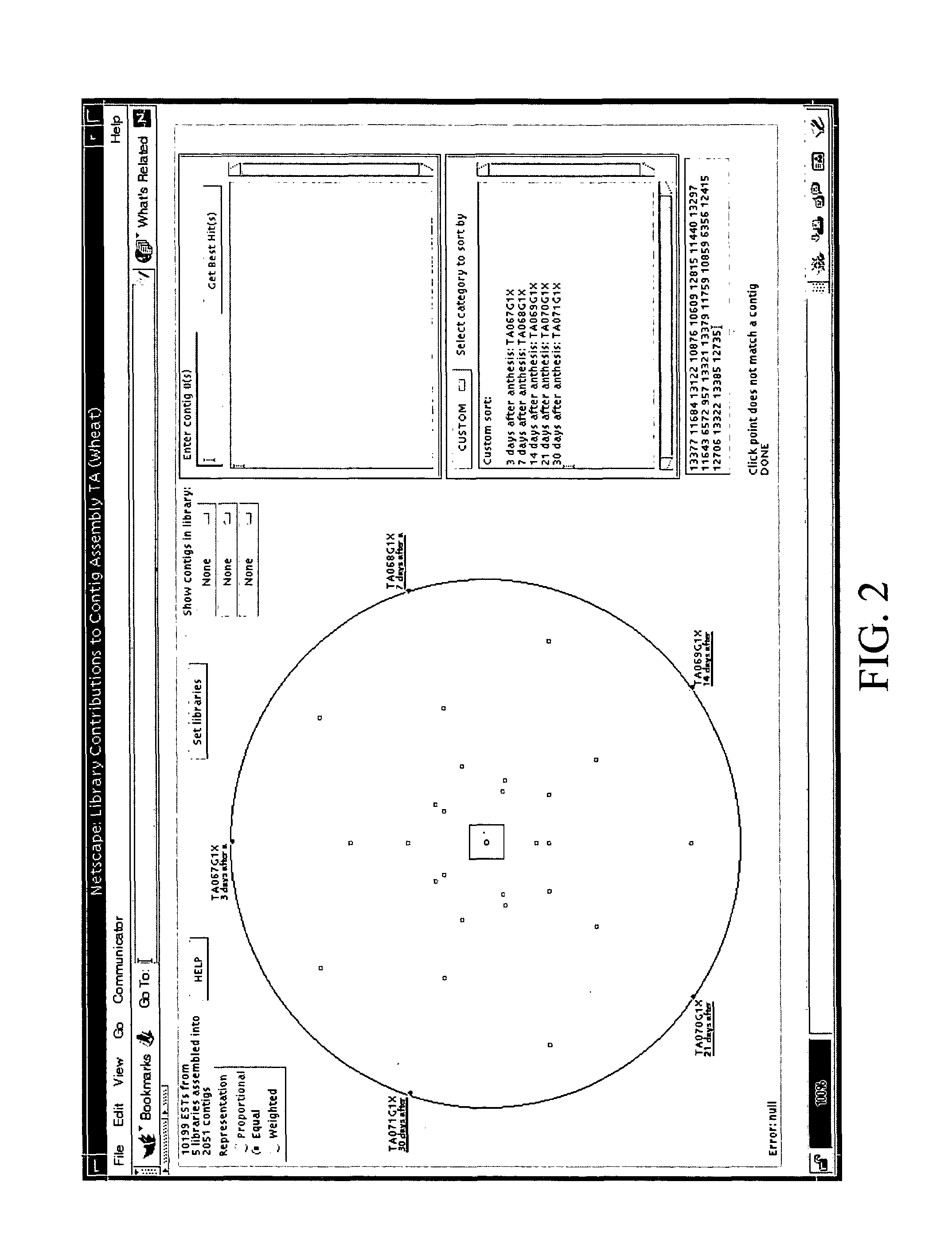
InactiveUS7475087B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsGenomicsRelational database
The invention is directed to a tool for visualizing relationships between and among data. It uses existing relational databases, and provides the means to view these databases in order to reveal degrees of relatedness between and among various data clusters. An illustrative use of said database tool is for analyzing genomics data. A test platform for this tool used EST data for the wheat tribe Triticeae, but can easily be extended for applications where other sequence assembly procedures are implemented, particularly those which use alphanumeric characters to represent data. The implementation of algorithms to manipulate the data points for investigative functions may be adapted to serve other applications.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Gene engineering method for preparing a recombinant glutathion peroxidase
ActiveCN103224915AHigh activity of recombinant GPXAvoid yieldEnzymesFermentationInclusion bodiesPeroxidase
The invention provides a gene engineering method for preparing a recombinant glutathion peroxidase, which belongs to the field of biological technology. The method comprises the following steps: assembling a target gene to a secretion type prokaryotic expression vector, introducing a catalytic group SeCys of GPX into a substrate combination position of GPX by a gene mutant method in an auxotroph prokaryotic expression system or an auxotroph and SPP combined expression system, thereby the activity of the GPS is very high; or assembling the target gene with the SeCys insertion sequence into a secretion type mammalia cell expression vector, assembling a SeCys insertion sequence binding protein 2 into an intracellular type mammalia cell expression vector, and cotransfecting the two vectors into the same lactation cell strain, and synthesizing the GPX under the existence of sodium selenite. The invention the advantages of simple method, recombined GPX vitality, high output and good stability, thereby avoiding decreased yield and inactivation caused by renaturation of an inclusion body, and solving the problem that the natural GPX source is limited and the property is not stable.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Full-automatic production line and process of inductor
InactiveCN108735490ARealize automatic film windingRealize automatic outputInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureProduction lineEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of inductor production, and provides a full-automatic production line and process of an inductor. The full-automatic production line comprises an assemblymechanism, a transfer mechanism, a film winding mechanism and a tin dipping output mechanism, wherein the assembly mechanism comprises a rack, a sequence assembly A, a sequence assembly B, a sequenceassembly C and a jacked-up assembly, an assembly region is formed on the jacked-up assembly, the transfer mechanism comprises a positioning assembly, a telescopic assembly and a translation assembly,the film winding mechanism comprises a bearing rack, a placement assembly, a transmission assembly, a pre-tightening assembly and a cutter, the pre-tightening assembly and the positioning assembly arearranged in an interrupt contact way, and the tin dipping output mechanism comprises a tin liquid bin, a guide assembly and a receiving bin. An assembly body is driven to be interrupt transmission with the film winding mechanism by the transfer mechanism during the transferring process, a thin film is wound around the assembly body in an automatic rotation mode, automatic film winding of the assembly body during the transferring process is achieved, and the technical problem of low production efficiency caused by independence of each process in the prior art is solved.
Owner:CHANGXING SOFITEL ELECTRONICS
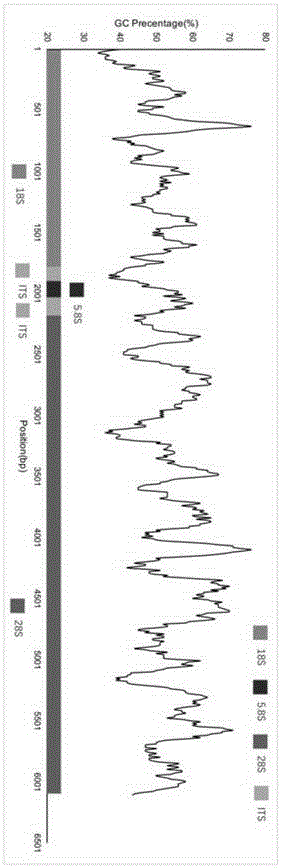
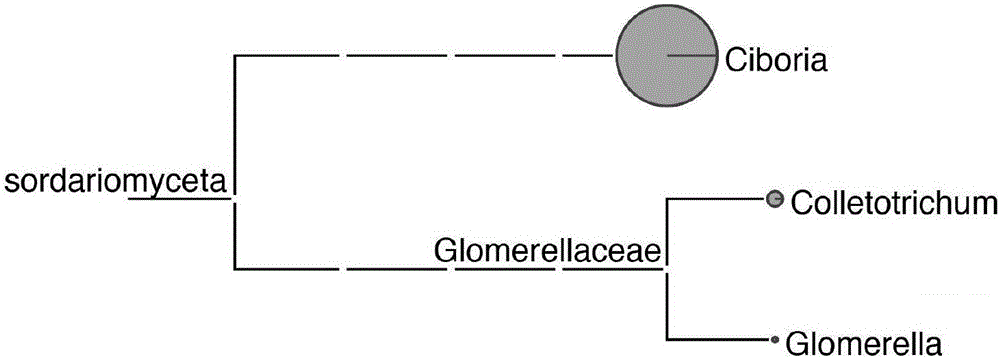
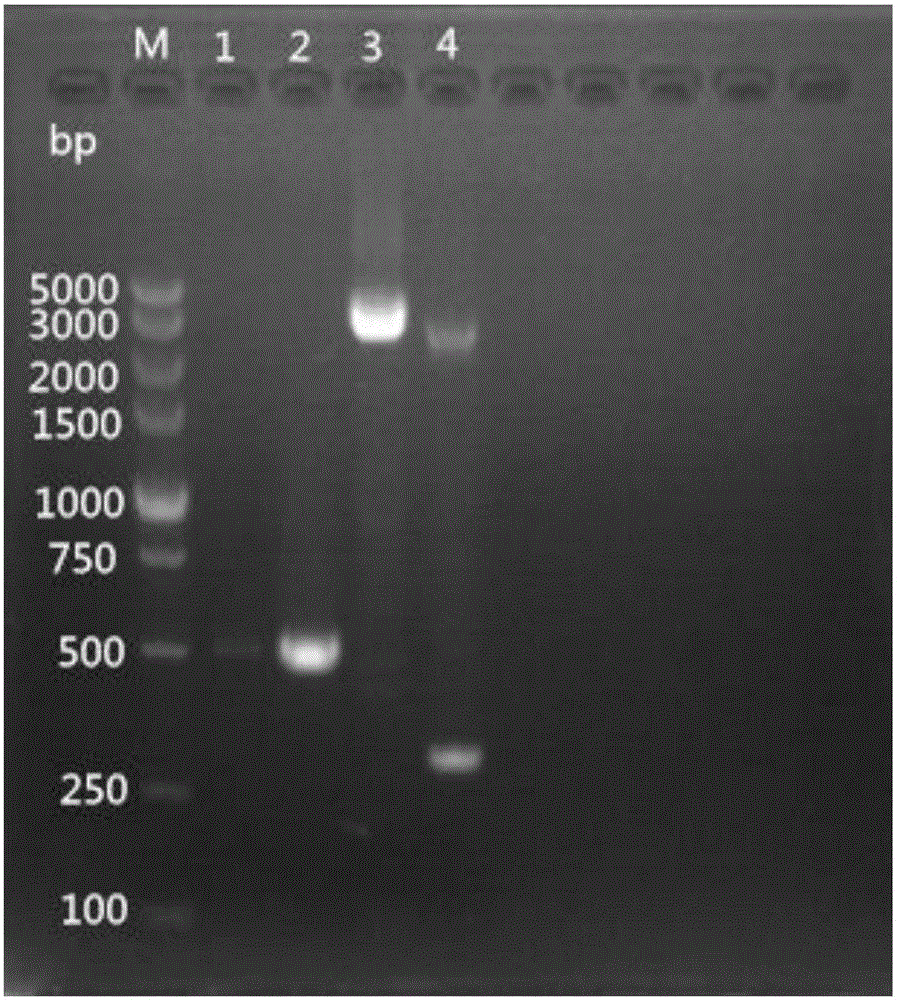
High-throughput mulberry pathogenic bacteria identification and species classification method and application thereof
ActiveCN106636433AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseRibosomal DNA
The invention discloses a high-throughput mulberry pathogenic bacteria identification and species classification method. The method comprises the following steps that diseased mulberries are collected; the total DNA of the diseased mulberries is extracted; an Illumina DNA library is created; Illumina high-throughput sequencing is carried out; a mulberry genome sequence in sequencing data is removed; microbial genome sequences are assembled; complete ribosomal DNA sequences are assembled; microbial ribosomal DNA sequences are screened and labeled; the ribosomal DNA sequences are comparatively analyzed to classify species, and thereby the mulberry pathogenic bacteria identification and species classification are fulfilled. A result shows that three species of fungi are identified in total when the method disclosed by the invention is applied to carry out the identification of pathogenic bacteria of popcorn disease and species classification, wherein the Ciboria pathogenic bacteria has the highest relative abundance, hereby the pathogenic Ciboria shiraiana is determined as Ciboria, and according to a comparison result, the pathogenic Ciboria shiraiana is determined as Ciboria carunculoides. Most of the species are phytopathogenic bacteria, and can lead to symptoms, such as mummification and swelling, appearing on fruits and seeds of plants, which are identical with the symptoms of the popcorn disease.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
A method for finding variants from targeted sequencing panels
Provided herein is a method for identifying a sequence variant in an enriched sample. In certain embodiments, the method may comprise: (a) obtaining: (i) a plurality of sequence reads from a sample that has been enriched for a genomic region and (ii) a reference sequence for the genomic region; (b) assembling the sequence reads to obtain a plurality of discrete sequence assemblies that correspond to potential variants; (c) determining which of the potential variants are true and which are artifacts by examining the sequence reads that make up each of the discrete sequence assemblies; (d) optionally determining whether each of the true potential variants contains a mutation that is known to be associated with the reference sequence; and (e) outputting a report indicating whether the sample comprises a sequence variant.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method for building high throughput sequencing library of low-quality sample deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
ActiveCN104005090AReduce lossesHigh yieldMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationElectrophoresisDNA
The invention discloses a method for building a high throughput sequencing library of a low-quality sample deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). The building method comprises the following steps: carrying out electrophoretic separation on the low-quality sample DNA, and directly obtaining the sample DNA free of a purification step; and directly building a fragmentation library from the sample DNA which is directly obtained without the purification step, so as to obtain the high throughput sequencing library. According to the building method disclosed by the invention, the fragmentation library is directly built by the sample DNA after electrophoretic separation, so that not only is the target of purifying the sample DNA achieved, but also the loss of the sample DNA is reduced, the yield of the sample DNA is improved, the quantity of the low-quality sample DNAs can meet the requirements of building the high throughput sequencing library, and pollution to protein, bacterial genome DNA or other impurities DNAs can be effectively avoided by the built high throughput sequencing library, so as to avoid the effect on following sequence assembly.
Owner:BEIJING NOVOGENE TECH CO LTD
Characteristic kmer based metatypic chromosomal sequence assembly method and application thereof
ActiveCN103805689ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWhole genome sequencingComplete sequence
The invention relates to a characteristic kmer based metatypic chromosomal sequence assembly method and application thereof. The characteristic kmer based metatypic chromosomal sequence assembly method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: performing whole-genome sequencing for a homoplastic (like XX or ZZ) sample and a metatypic (like XY or ZW) sample; analyzing kmer difference between the two samples based on the data to obtain the characteristic kmer of the metatypic chromosome; and then performing metatypic chromosomal sequence assembly based on the characteristic kmer so as to obtain the complete sequence information of metatypic chromosome. The invention also provides an assembly unit on the basis of the method above.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
DNA sequence assembly methods of short reads
Certain embodiments of the invention provide systems and methods for the automated assembly of DNA sequence data into contiguous DNA segments using a computer a system. DNA sequence data is entered into the system. The system indexes and groups a plurality of DNA fragment reads utilizing an anchor sequence and consolidates the fragments into larger sequences by merging the fragment reads within a group.
Owner:SOFTGENETICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com