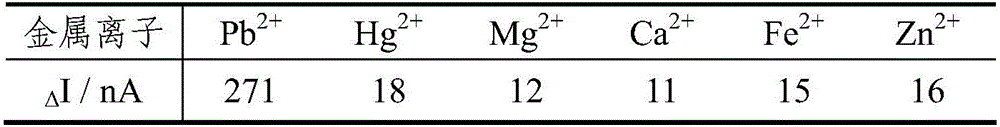Photo-electrochemical DNA biosensor based lead ion determination method
A biosensor, photoelectrochemical technology, applied in the fields of analytical chemistry and photoelectrochemical sensing, can solve the problems of low sensitivity, high background signal, interference, etc., and achieve the effects of high sensitivity, broad application prospects and high selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1 Preparation of DNA-modified ITO electrode and biosensor thereof
[0029] The preparation method of the DNA-modified ITO electrode prepared in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0030] (1) Clean the ITO glass electrode with detergent, acetone, isopropanol, etc. for 5 minutes, and finally clean it with ultrapure water and dry it in an oven. The concentration of 10% SnO 2 The nano-sol was spin-coated on the surface of ITO conductive glass. After natural air-drying, it was calcined in a muffle furnace at 350°C for 3 hours. After natural cooling, it was cut into 0.5cm×3cm glass pieces with a glass knife to obtain SnO-modified glass pieces. 2 The ITO electrode spare;
[0031] (2) Dilute the solid DNA sample with Tris-HClO 4 The buffer solution was dissolved, placed in a water bath at 85° C. for 10 minutes, then naturally cooled to room temperature, and set aside; wherein, the nucleotide sequence of the DNA is shown in SEQ ID NO:1;
[0032] (3) Apply ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2 Based on the lead ion determination method of photoelectrochemical DNA biosensor
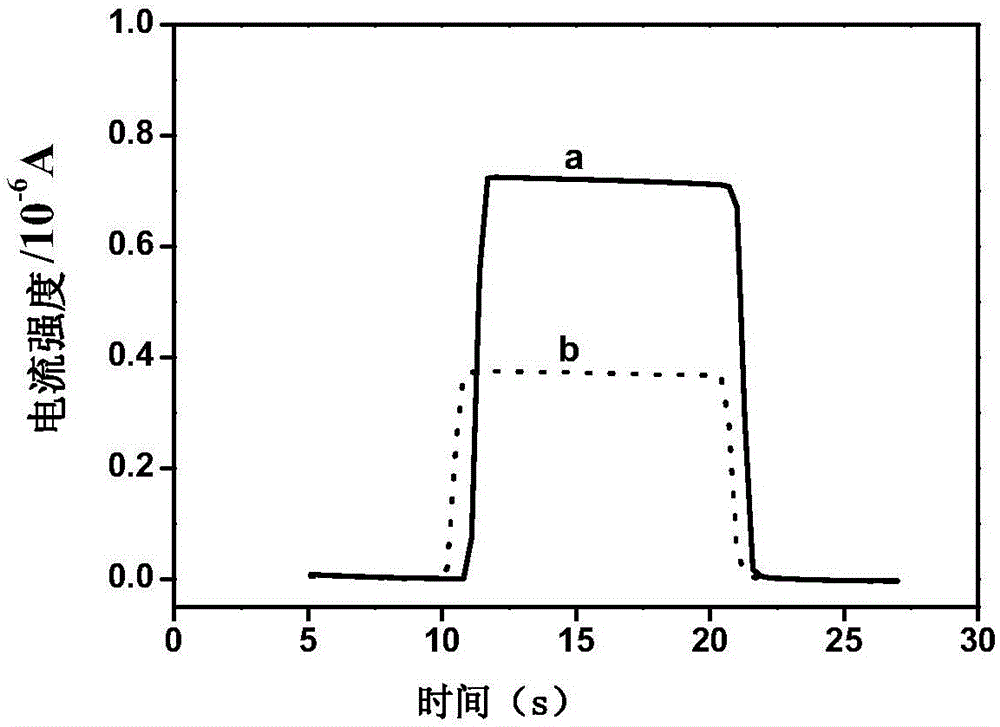
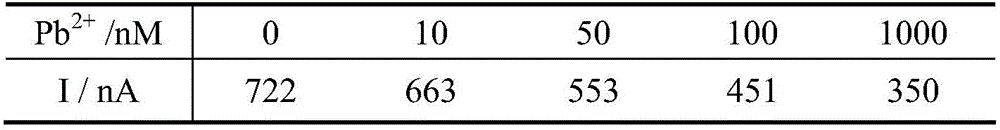
[0037] Different concentrations of Pb 2+ The solution was dropped on the surface of the DNA-modified ITO electrode prepared in Example 1 and incubated for 2 hours. After the electrode was taken out, it was washed three times with ultrapure water and dried with nitrogen gas. Then add 10μM Ru(bpy) 2 (dppz) 2+ The probe solution was dropped on the surface of the above-mentioned DNA electrode and incubated for 1 h. After washing with ultrapure water for three times, dry it with nitrogen gas, connect it to an electrochemical workstation, and perform cyclic voltammetry scanning under the irradiation of 473nm blue light to realize the detection of Pb 2+ determination. Different concentrations of Pb 2+ The photoelectrochemical signals generated after interacting with the ITO electrode DNA-modified membrane are shown in Table 1.
[0038] Table 1 Different concentrations of Pb 2...
Embodiment 3Pb2
[0041] Example 3Pb 2+ selective research
[0042] With 100nM metal ion Pb 2+ , Hg 2+ , Mg 2+ , Ca 2+ , Fe 2+ , Zn 2+ Instead of Pb in Example 2 2+ , other experimental conditions are identical with embodiment 2. Changes of photoelectrochemical signals produced by different metal ions interacting with DNA-modified membranes of ITO electrodes Δ I see Table 2.
[0043] Table 2 Changes in photoelectrochemical signal ΔI produced by different heavy metal ions
[0044]
[0045] It can be seen from Table 2 that when Pb 2+ After interacting with the surface of the DNA-modified ITO electrode, the change in the photoelectrochemical signal is the largest, while the change in the photoelectrochemical signal produced by several other metal ions is small. The results show that the photoelectrochemical DNA biosensor can realize the detection of Pb 2+ selective detection.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com