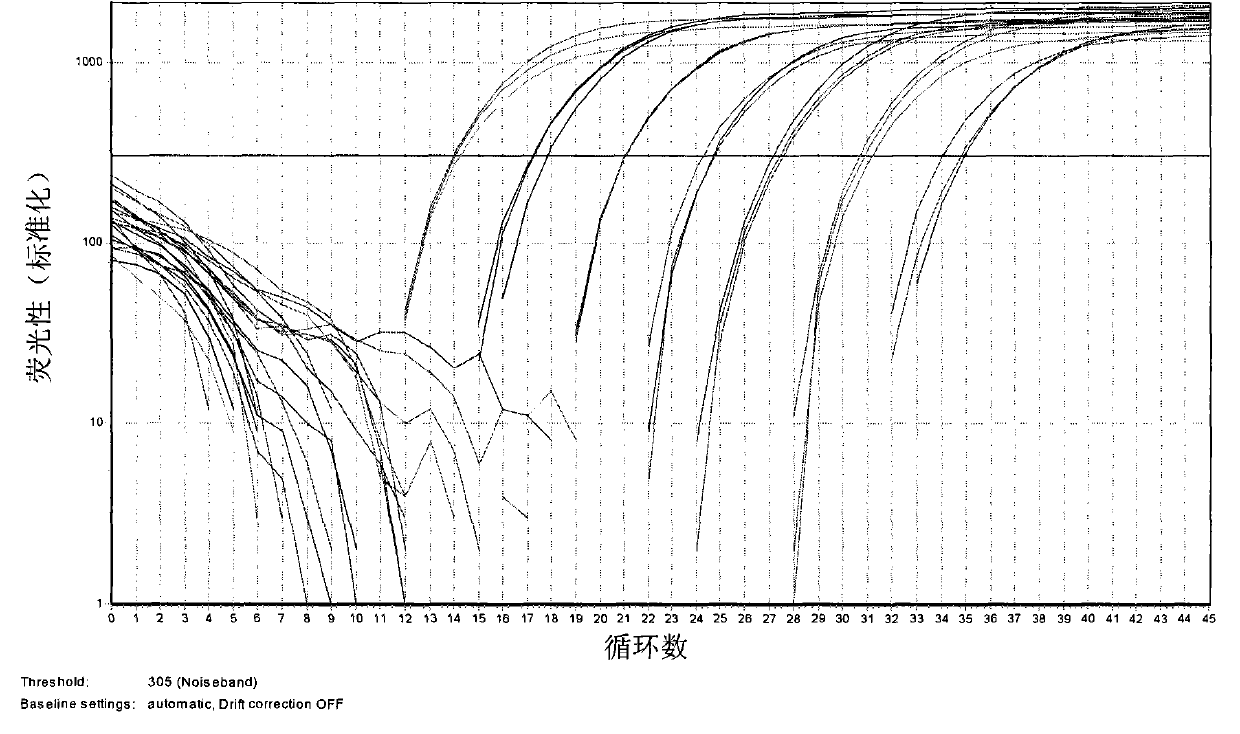
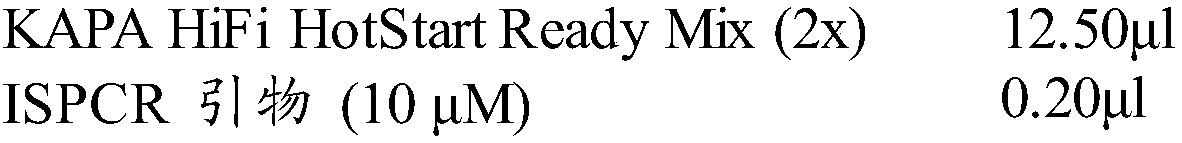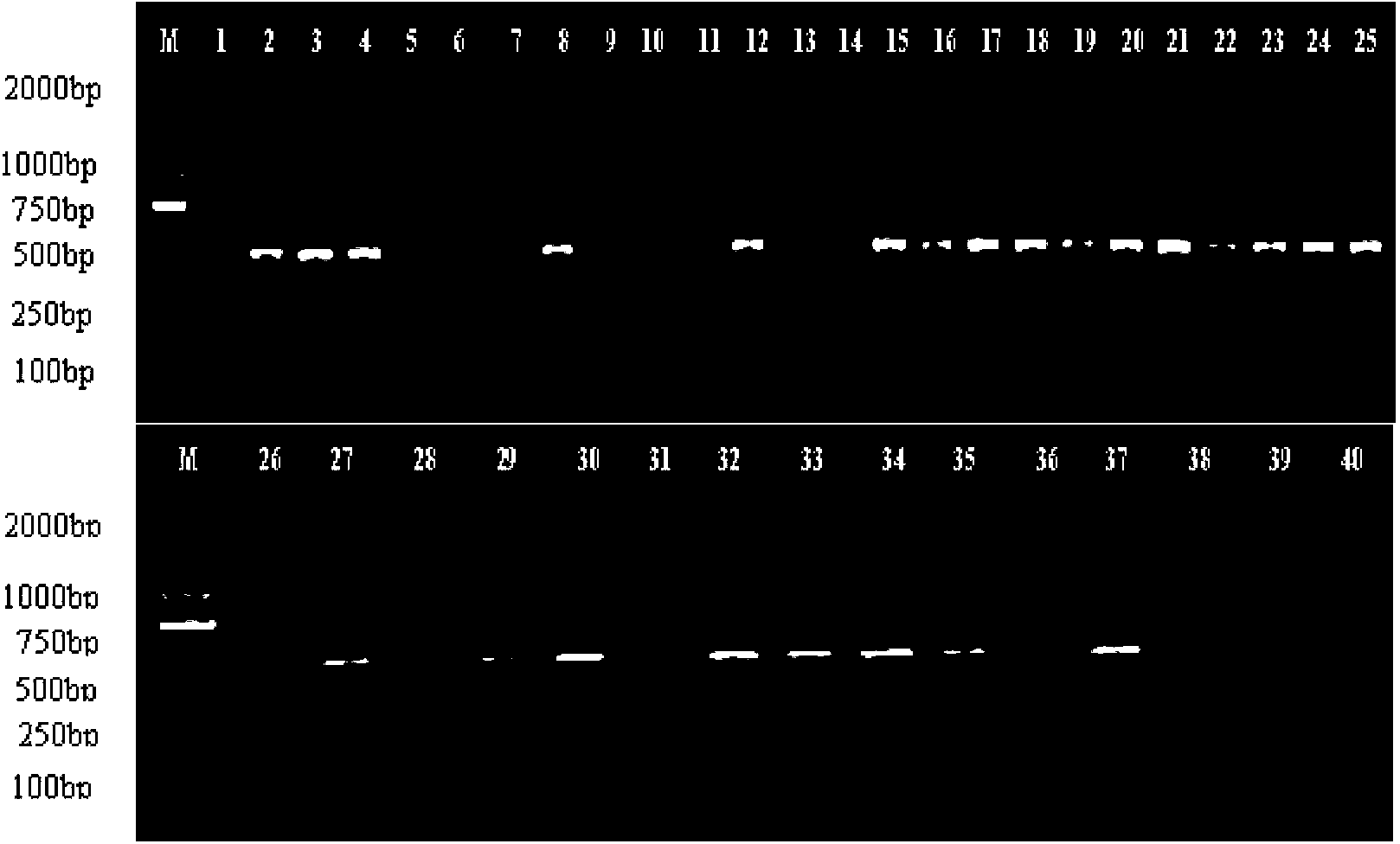Patents
Literature
58 results about "Ribosomal DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
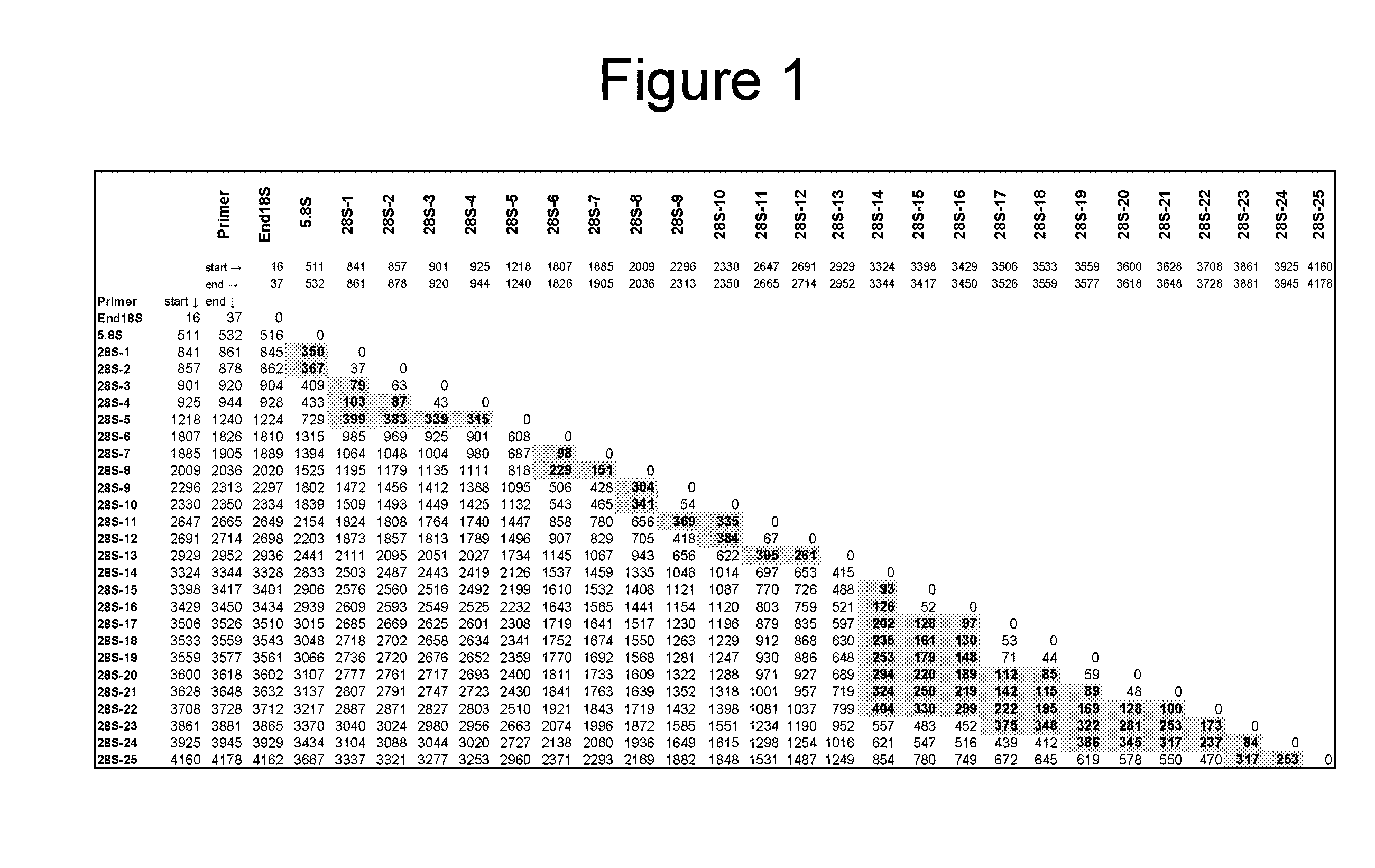
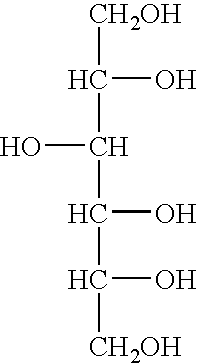
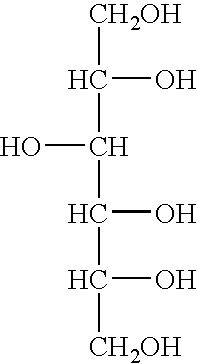
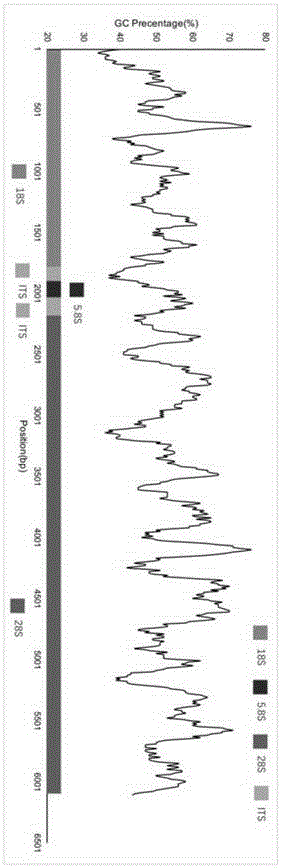
Ribosomal DNA (rDNA) is a DNA sequence that codes for ribosomal RNA. Ribosomes are assemblies of proteins and rRNA molecules that translate mRNA molecules to produce proteins. As shown in the figure, rDNA of eukaryotes consists of a tandem repeat of a unit segment, an operon, composed of NTS, ETS, 18S, ITS1, 5.8S, ITS2, and 28S tracts. rDNA has another gene, coding for 5S rRNA, located in the genome in most eukaryotes. 5S rDNA is also present in tandem repeats as in Drosophila. In the nucleus, the rDNA region of the chromosome is visualized as a nucleolus which forms expanded chromosomal loops with rDNA. These rDNA regions are also called nucleolus organizer regions, as they give rise to the nucleolus. In the human genome there are 5 chromosomes with nucleolus organizer regions: the acrocentric chromosomes 13 (RNR1), 14 (RNR2), 15 (RNR3), 21 (RNR4) and 22 (RNR5). In Bacteria, Archaea, and chloroplasts the rRNA is composed of different (smaller) units, the large (23S) ribosomal RNA, 16S ribosomal RNA and 5S rRNA. The 16S rRNA is widely used for phylogenetic studies.
Broad range pcr-based compositions and methods for the detection and identification of fungal pathogens
InactiveUS20100129821A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurement28S ribosomal RNARibosomal DNA
Disclosed herein are methods for detecting a fungal pathogen in a patient sample, involving isolating the sample, carrying out a PCR reaction on the sample to generate an amplicon that includes a region of the fungal 28S ribosomal RNA gene, and detecting the PCR amplicon. Also disclosed are sequences of primers for specifically detecting a broad range of fungal pathogens in the presence of human ribosomal DNA. In certain embodiments, the amplicon is detected by sequencing or by two-dimensional melt-curve analysis. In yet other embodiments, more than one fungal pathogen is detected in a sample using the methods disclosed herein.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
Method of reducing non-specific amplification in PCR
InactiveUS20030104395A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAmplification dnaRibosomal DNA
The invention provides methods for reducing non-specific amplification DNA in a polymerase chain reaction comprising providing a sample comprising a target DNA sequence of interest; contacting the sample with at least one enzyme having nucleic acid polymerase activity; and incubating the sample with said enzyme for a time and under conditions sufficient to amplify the target DNA sequence, forming amplified target sequence; wherein the incubation is performed in the presence of an amount of sorbitol, or sorbitol and DMSO effective to reduce the non-specific amplification relative to the amount of non-specific amplification observed in the absence of sorbitol, or sorbitol and DMSO. The methods are suitable for amplification of ribosomal DNA, particularly from clinical samples. Compositions and kits containing sorbitol, or sorbitol and DMSO for reducing non-specific amplification are also provided.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Method of reducing non-specific amplification in PCR
InactiveUS6783940B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAmplification dnaPolymerase L
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
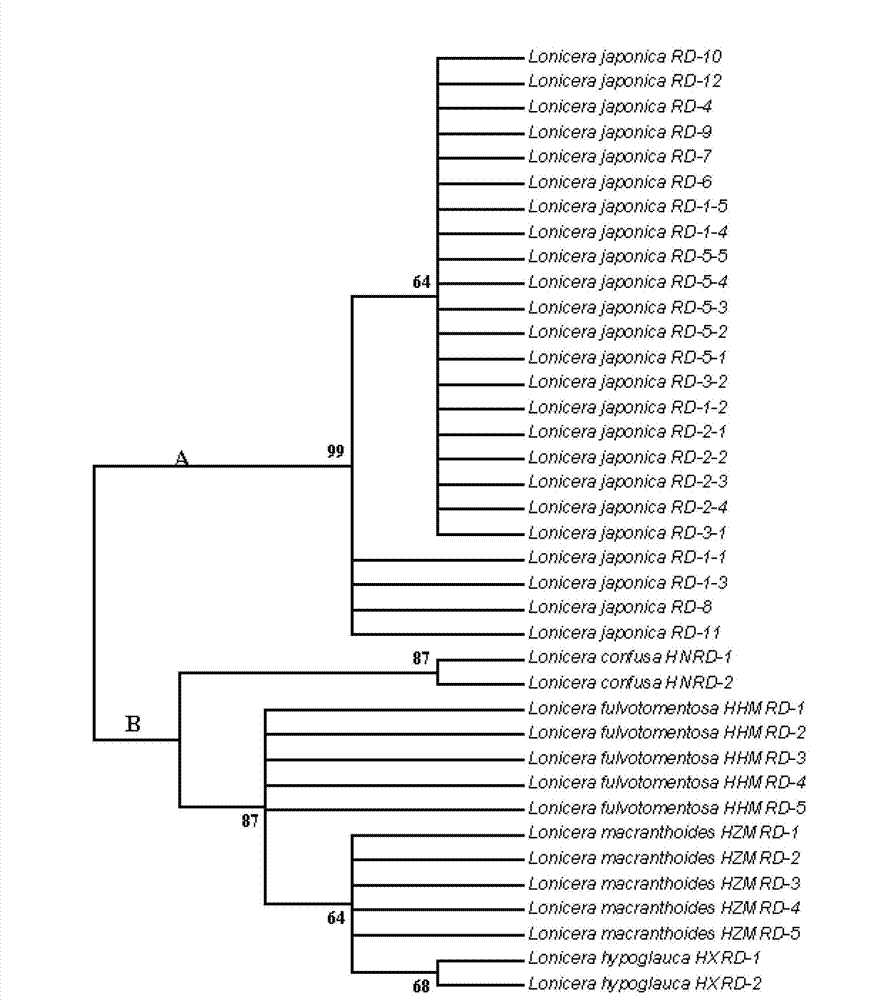
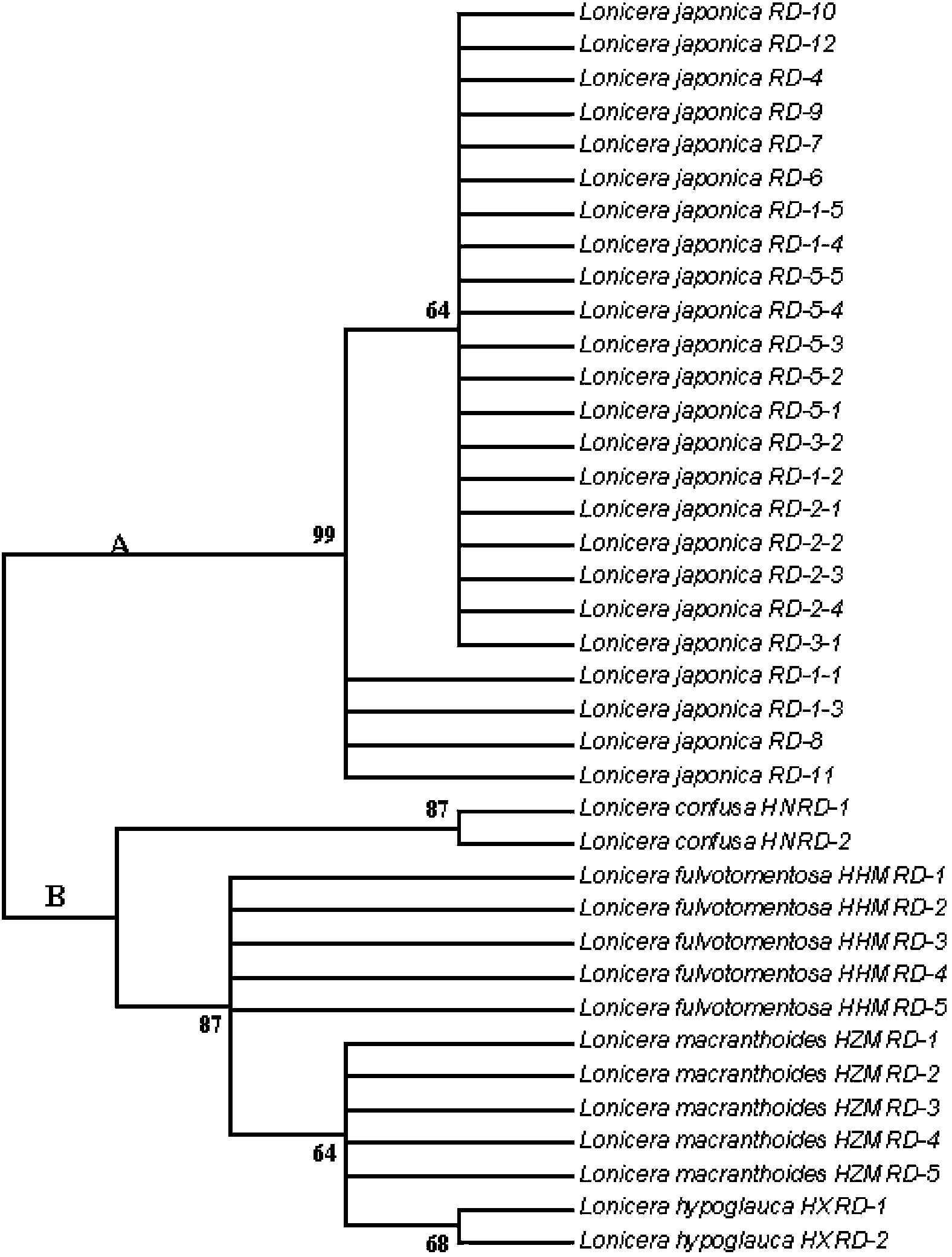
Method for identifying honeysuckle and lonicera confuse and application of same
ActiveCN103173532AEfficient extractionQuick extractionMicrobiological testing/measurementGermplasmRibosomal DNA
The invention relates to a method for identifying honeysuckle and lonicera confuse and an application of the method. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the step of performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on ITS2 nucleotide sequence, and particularly comprises the steps of 1) extracting the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a sample; 2) performing PCR amplification on the segments of the ITS2 sequence containing ribosome DNA; 3) splicing the amplification products to obtain a complete ITS2 intergenic region; and 4) establishing the NJ (neighbour-joining) tree of the ITS2 sequence of the sample. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively solving the problems of variety identification, variety improvement and breeding of honeysuckle medicinal materials, development and utilization of germplasm resources, and the like; and the method disclosed by the invention is wide in applicability, simple to operate, easy to grasp, high in accuracy, and capable of successfully realizing rapid and accurate identification on honeysuckle medicinal materials or powder and lonicera confuse medicinal materials or powder.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Microchip for identifying phellinus species and the method thereof
InactiveUS20110111970A1Improve accuracyLess time-consumingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRapid identificationRibosomal DNA
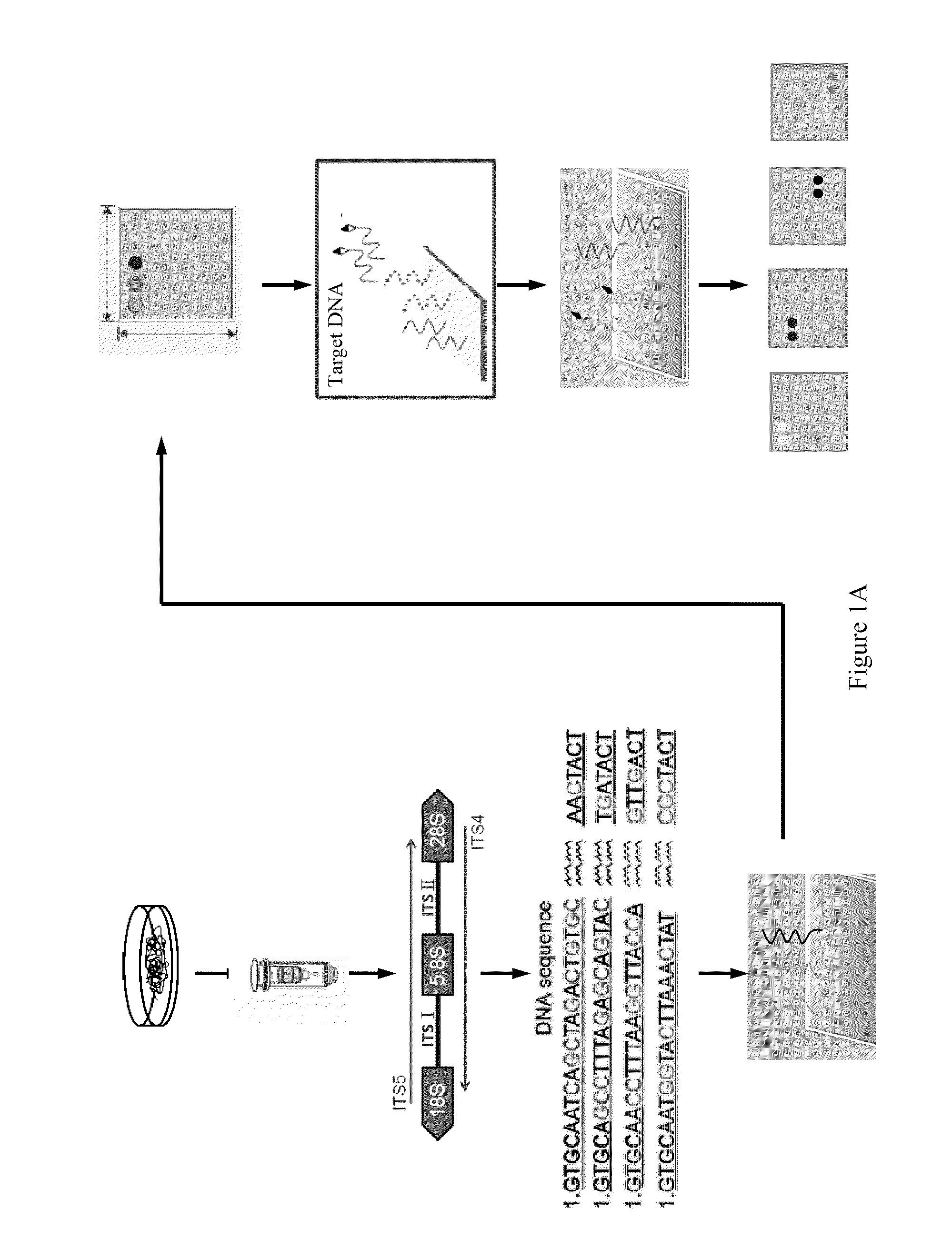
The developed oligonucleotide microchip for simultaneous, rapid identification of multiple crucial forest Phellinus pathogens was based on the DIG or biotin-labeled specific probes derived form ribosomal DNA genes (ITS1-5.8S-ITS2), by using reverse-dot hybridization. The chip can precisely and accurately identify and diagnose seventeen Phellinus species, including notorious hardwood and conifer tree killer, P. noxius and P. weirii, with a sensitivity of 1 pg DNA / μl on Nylon membrane, and 100 fg DNA / μl on plastic chip, respectively. Verification and identification of forest Phellinus pathogens infested authentic samples or voucher specimens can be accomplished within 7 hr.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Method for detecting enteritis pathogenic bacteria
ActiveCN102154450AAvoid damageCause drug resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesRibosomal DNA
The invention relates to a method for detecting bacteria, in particular to a method for detecting enteritis pathogenic bacteria. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) extracting DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of one or more bacteria samples; (2) amplifying full length of 16S rDNA (ribosomal DNA) of a sample by using a primer of 16S rDNA of bacteria; (3) breaking an amplified PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) product; (4) repairing ends of the broken product from each bacteria sample and connecting deoxyadenosine at the end 3' of the product, and then connecting different PCR-free joints; (5) sequencing a connection product by using a second-generation sequencing technology to obtain a sequence of the connection product; and (6) comparing the sequence with 16S rDNA reference sequences of all existing bacteria to determine types of bacteria existing in each sample.
Owner:深圳华大因源医药科技有限公司
Process for preparing a protein by a fungus transformed by multicopy integration of an expression vector
InactiveUS6090574AImproved stability against attack by proteaseImprove stabilityFungiHydrolasesYeastAspergillus
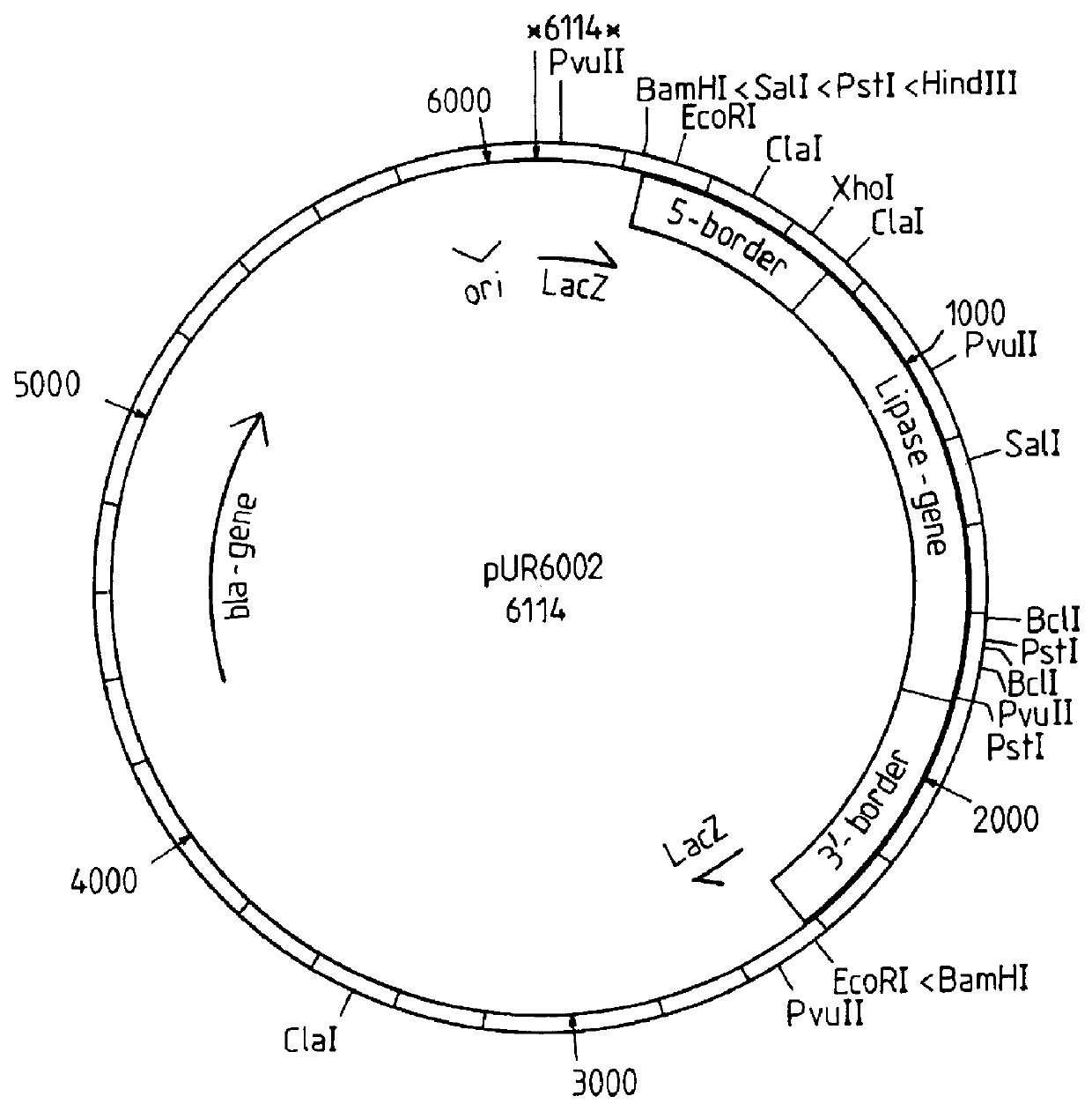
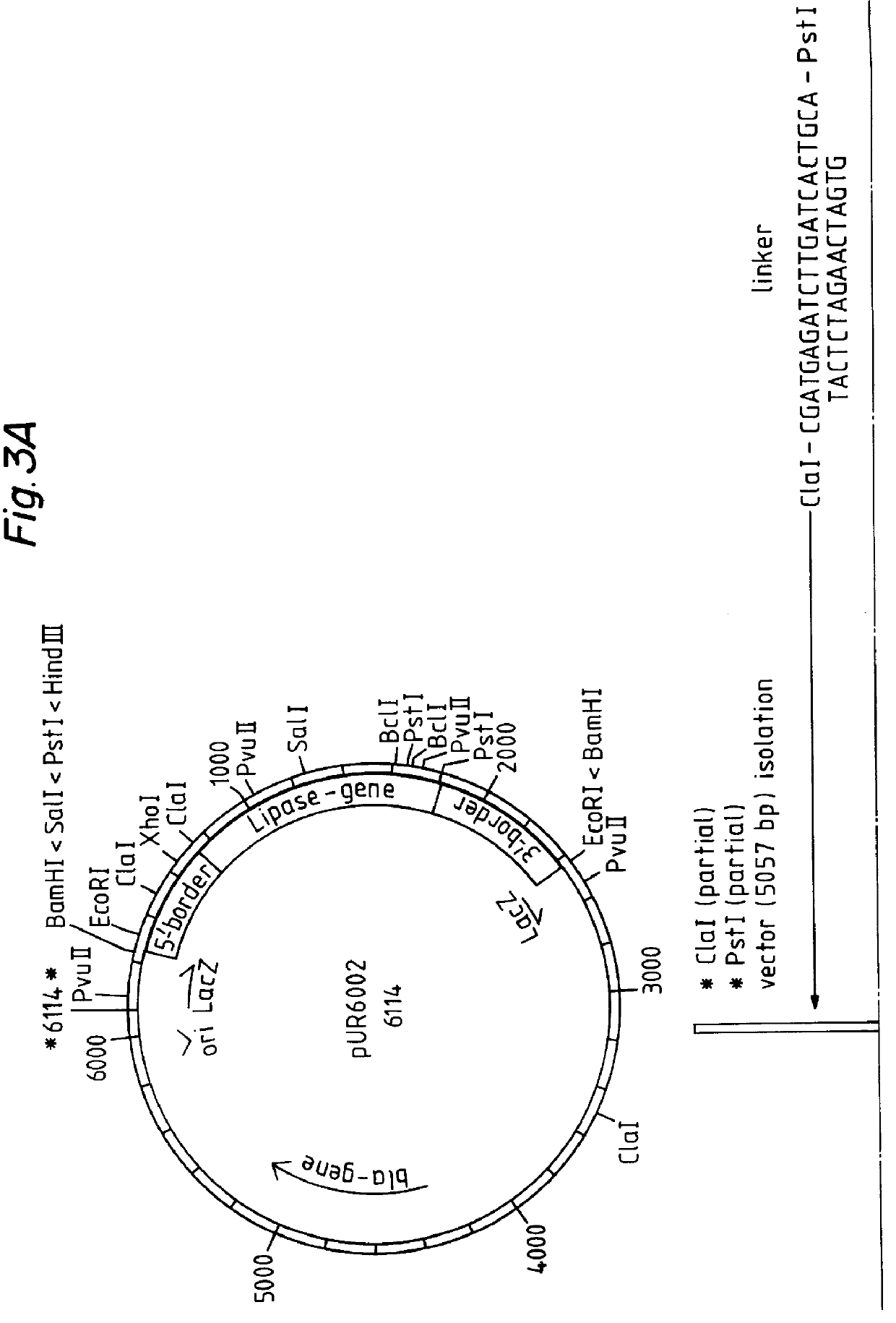
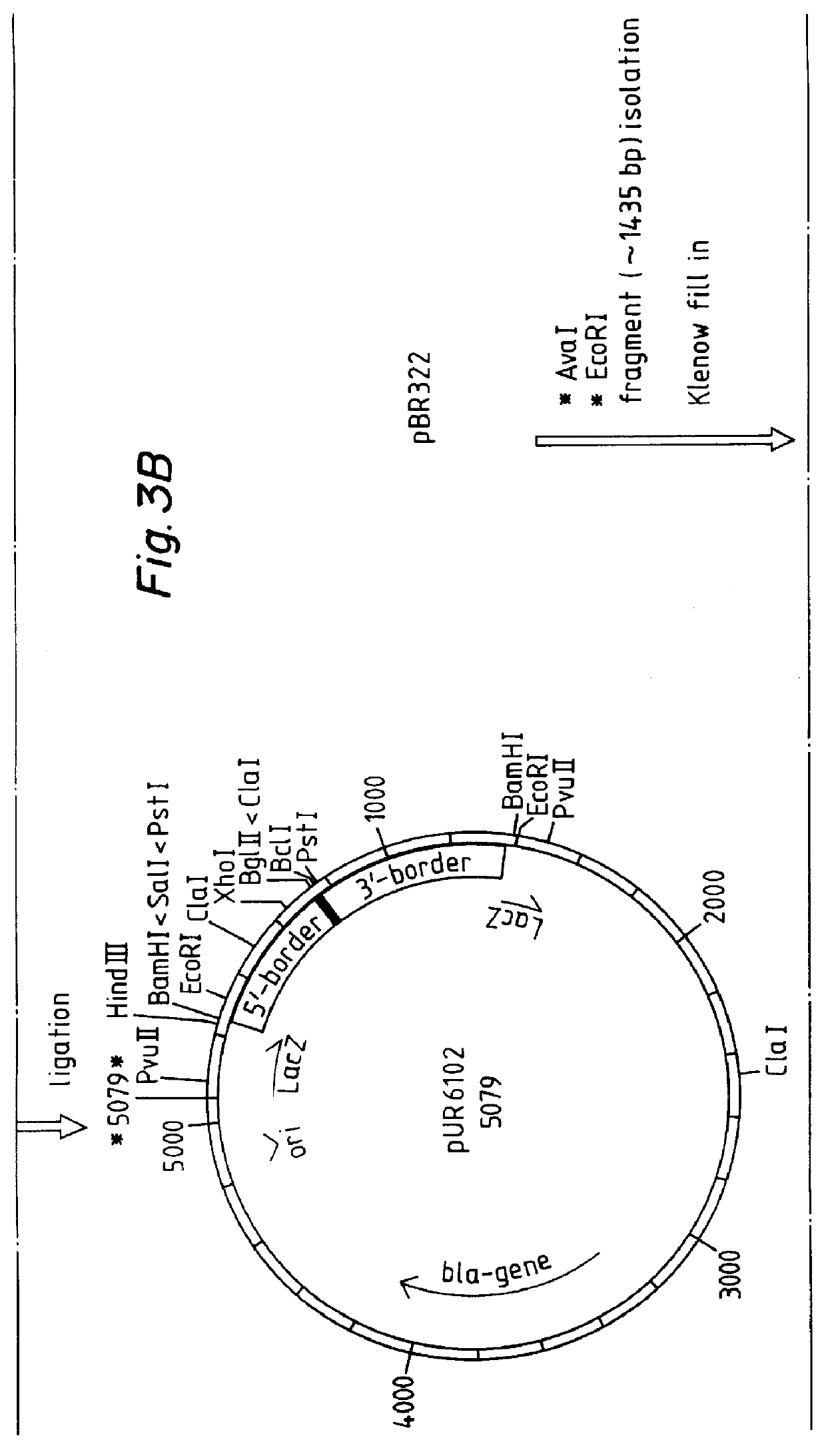
A process is disclosed for preparing a protein by a eukaryote transformed by multicopy integration of an expression vector into the genome of a yeast, such as Saccharomyces, Hansenula, and Kluyveromyces, or of a mould such as Aspergillus, Rbizopus and Trichoderma, the expression vector containing both an "expressible gene" encoding the protein and a so-called "deficient selection marker meeded for the growth of the yeast or mould in a specific medium", such as the LEU2d, TRP1d or URA3d gene, in combination witha ribosomal DNA sequence, resulting in stable high copy integration of 100-300 copies per cell. This multicopy integration results in an increased production of the desired protein, which can be guar alpha -galactosidase, an oxidase or a hydrolytic enzyme such as a lipase.
Owner:BAC IP
High through-put detection of pathogenic yeasts in the genus trichosporon
InactiveUS20060216723A1Rapid and simple to performSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisPresent method
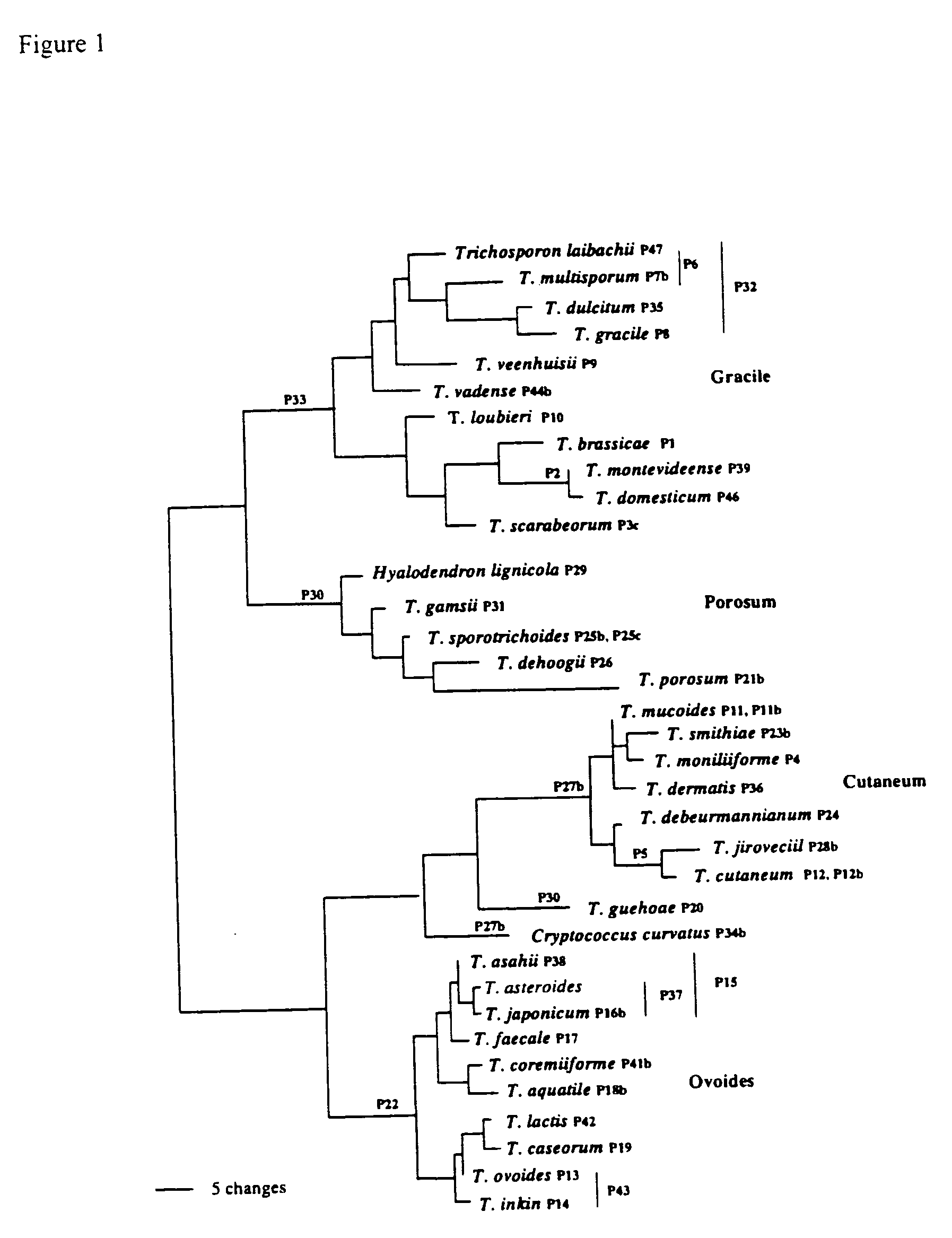
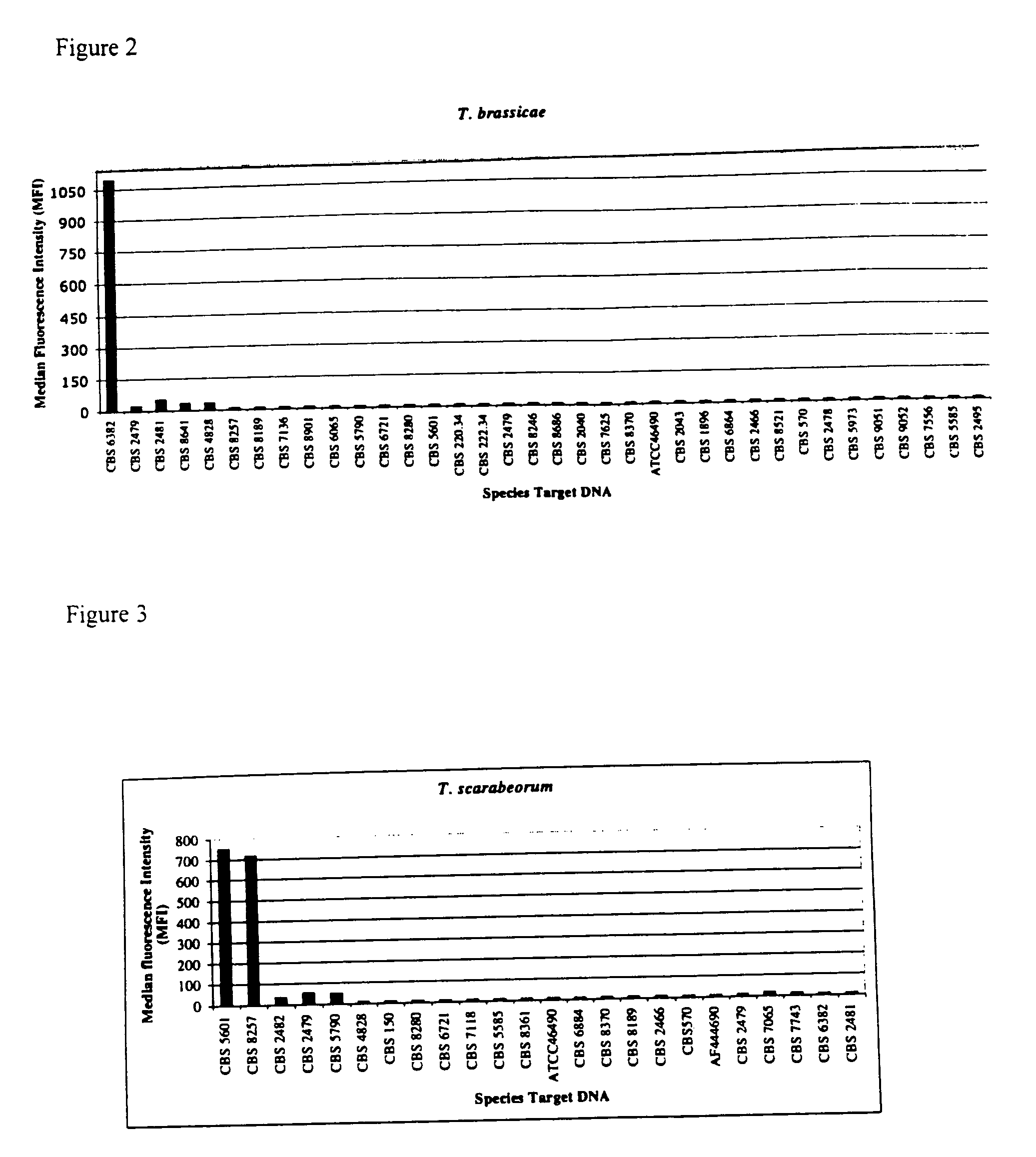
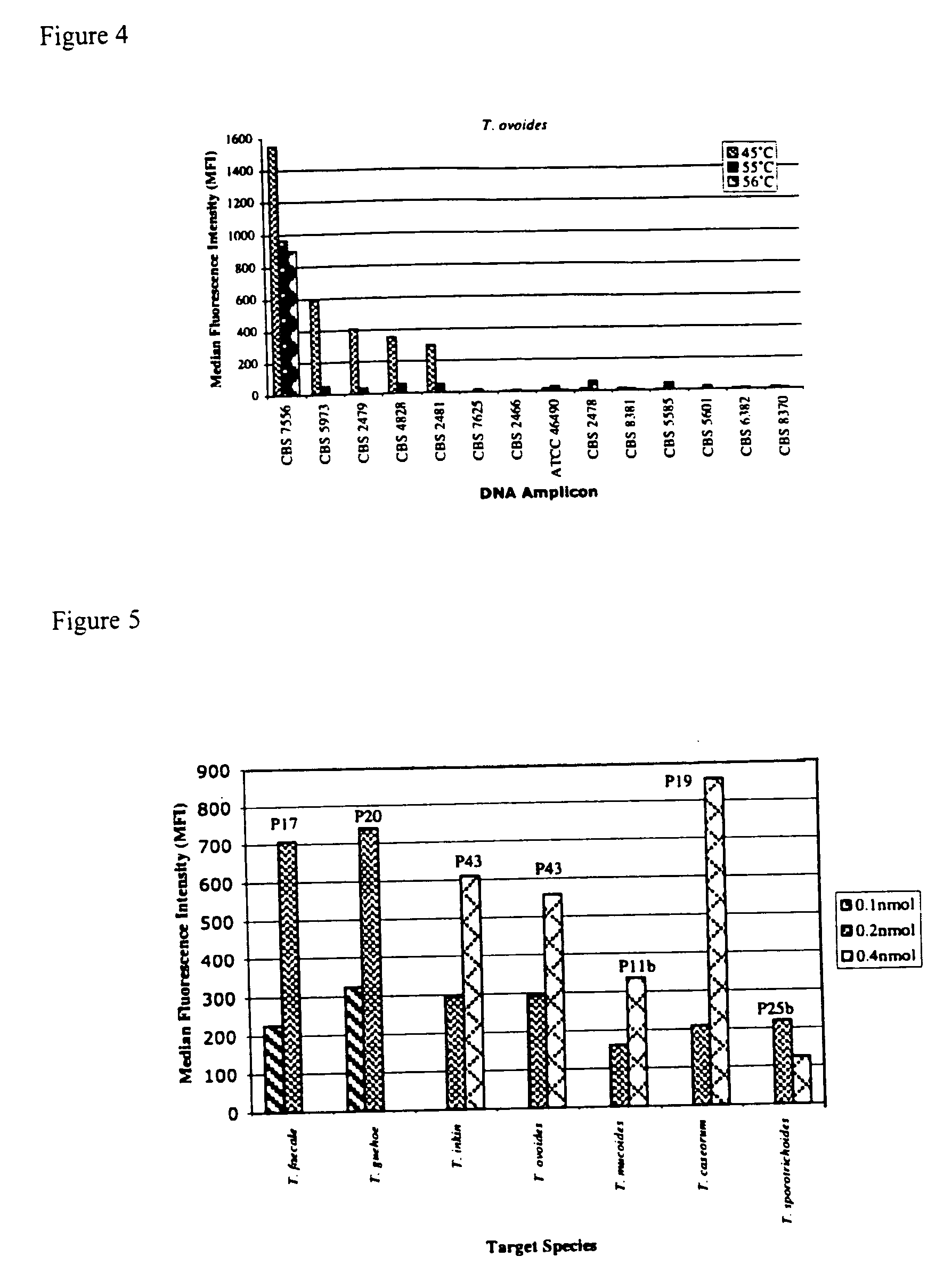
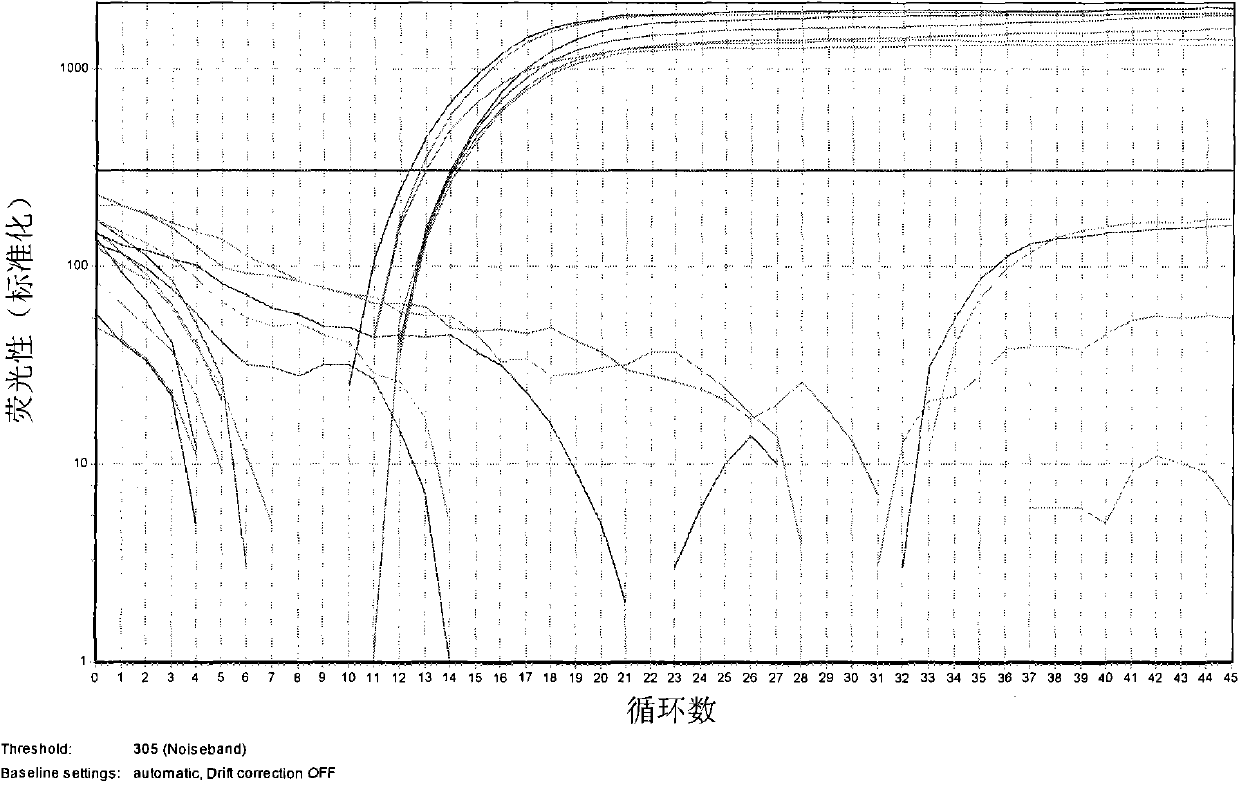
The emergence of opportunistic and antifungal resistant strains has given rise to an urgent need for a rapid and accurate method for the detection of fungal pathogens. In this application, we demonstrate the detection of medically important fungal pathogens at the species level. The present method, which is based on a nucleotide hybridization assay, consists of a combination of different sets of fluorescent beads covalently bound to species specific capture probes. Upon hybridization, the beads bearing the target amplicons are classified by their spectral addresses with a 635 nm laser. Quantitation of the hybridized biotinylated amplicon is based on the fluorescent detection with a 532 nm laser. Using this technology we designed and tested various multiplex formats, the performance of forty eight species specific and group specific capture probes designed from sequence analysis in the D1 / D2 region of ribosomal DNA, internal transcribed spacer regions (ITS), and intergenic spacer region (IGS). Species-specific biotinylated amplicons (>600 bp) were generated with three sets of primers to yield fragments from the three regions. The developed assay was specific and relatively fast, as it discriminated species differing by one nucleotide and required less than 50 min following amplification to process a 96 well plate with the capability to detect up to 100 species per well. The sensitivity of the assay allowed the detection as low as 102 genome molecules in PCR reactions and 107 to 108 molecules of biotinylated amplification product. This technology provided a rapid means of detection of Trichosporon species and had the flexibility to identify species in a multiplex format by combining different sets of beads. The assay can be expanded to include all known pathogenic fungal species.
Owner:MIAMI UNIVERISTY OF
Kit and method for identifying and detecting Cordyceps sinensis
InactiveCN102086471AStrong specificityQuantitative detection of contentMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceRibosomal DNA
The invention provides a method for identifying and detecting Cordyceps sinensis, wherein the method comprises steps of: (a) extracting ribosome DNA from a sample to be detected; (b) applying DNA extracted in step (a) as a template to perform real time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using a primer pair shown by SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2 and a probe shown by SEQ ID NO.3 to obtain amplification products; and (c) determining the authenticity and contents of the Cordyceps sinensis in dependence on the existence and intensity of the fluorescences of the amplification products. The invention also provides a kit which comprises the primer pair and the probe. The invention can qualitatively identify the authenticity of the Cordyceps sinensis and detect the Cordyceps sinensis contents of a sample with a lowest detection limitation of 0.0001 ng / ul, thus the invention is more sensitive than prior arts; and the invention can also effectively detect the Cordyceps sinensis samples in which nucleic acid is severely degraded after processing, and detecting results are more accurate and more effective than those obtained using prior arts.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT OF GUANGDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU +1
PCR-RFLP method for rapidly identifying radix tetrastigme and various counterfeits and adulterants of radix tetrastigme
ActiveCN104611424ARapid identificationImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMedicinal herbsEnzyme digestion
The invention belongs to the field of molecular markers and discloses a PCR-RFLP method for rapidly identifying radix tetrastigme and various counterfeits and adulterants of the radix tetrastigme. The method comprises the following steps: 1, extracting the NDA of the medicinal material (namely the radix tetrastigme); 2, carrying out PCR amplification by forward and reverse primers of internal transcribed spacer ITS2 sequences of a pair of amplified ribosomal DNAs; 3, digesting the PCR product by restriction enzyme NCO I; 4, carrying out agarose gel electrophoresis analysis. After the enzyme digestion of amplified products of the DNA of the radix tetrastigme, two DNA fragments with sizes about 335 bp and 200 bp are generated, and the various counterfeits and adulterants are not identified by the NCO I enzyme. By utilizing the differences between the DNA sequences of radix tetrastigme and the counterfeits and adulterants of the radix tetrastigme, a quick, convenient and reliable PCR-RFLP identification method is established and used for identifying whether counterfeits and adulterants are mixed in the radix tetrastigme or not, so that the technical problem that the truth and false cannot be identified by sensory or physical and chemical analysis methods is solved, and the medication safety of the radix tetrastigme is ensured.
Owner:ZHEJIANG PHARMA COLLEGE
Production of artificial hybrid lingzhi and uses thereof
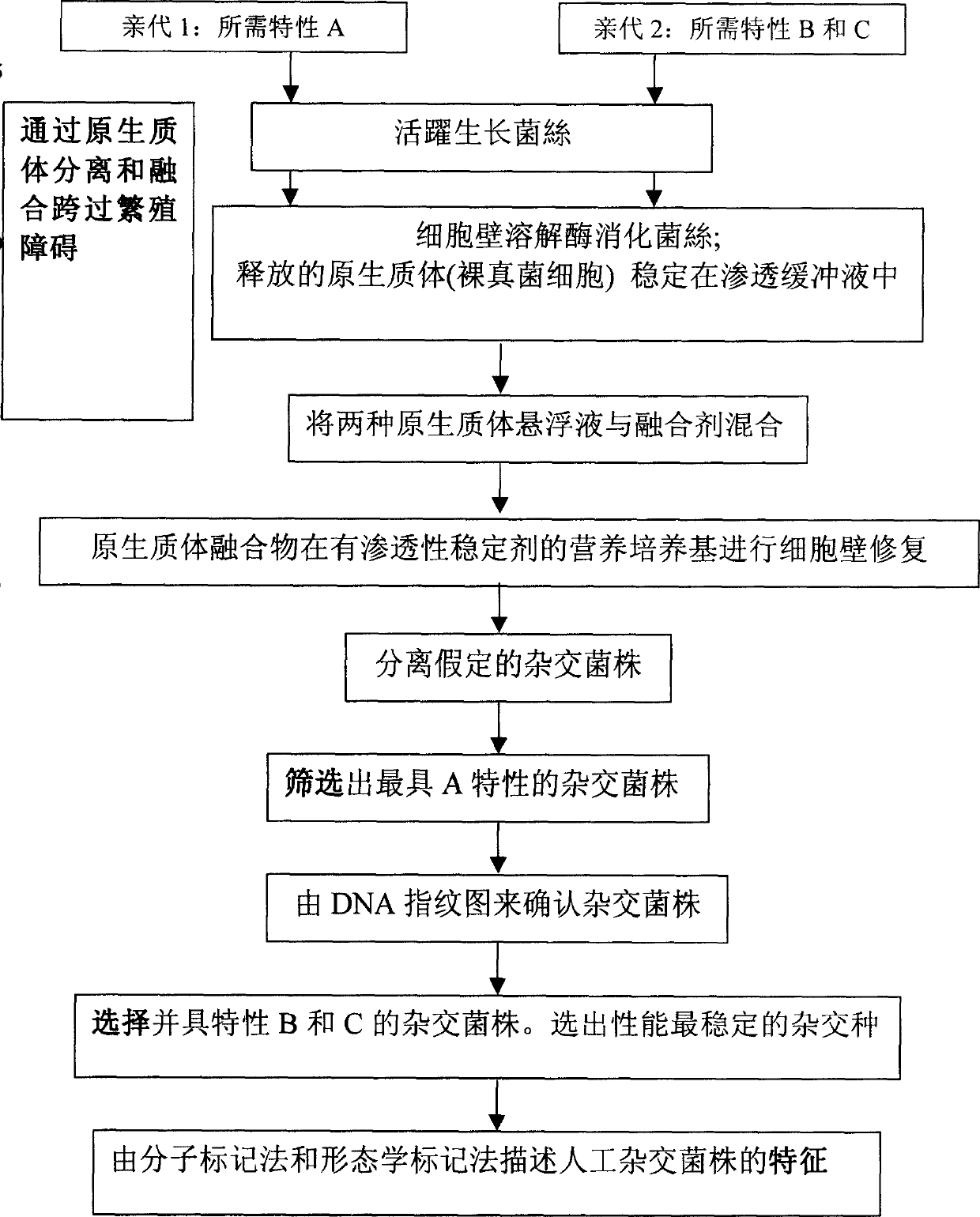
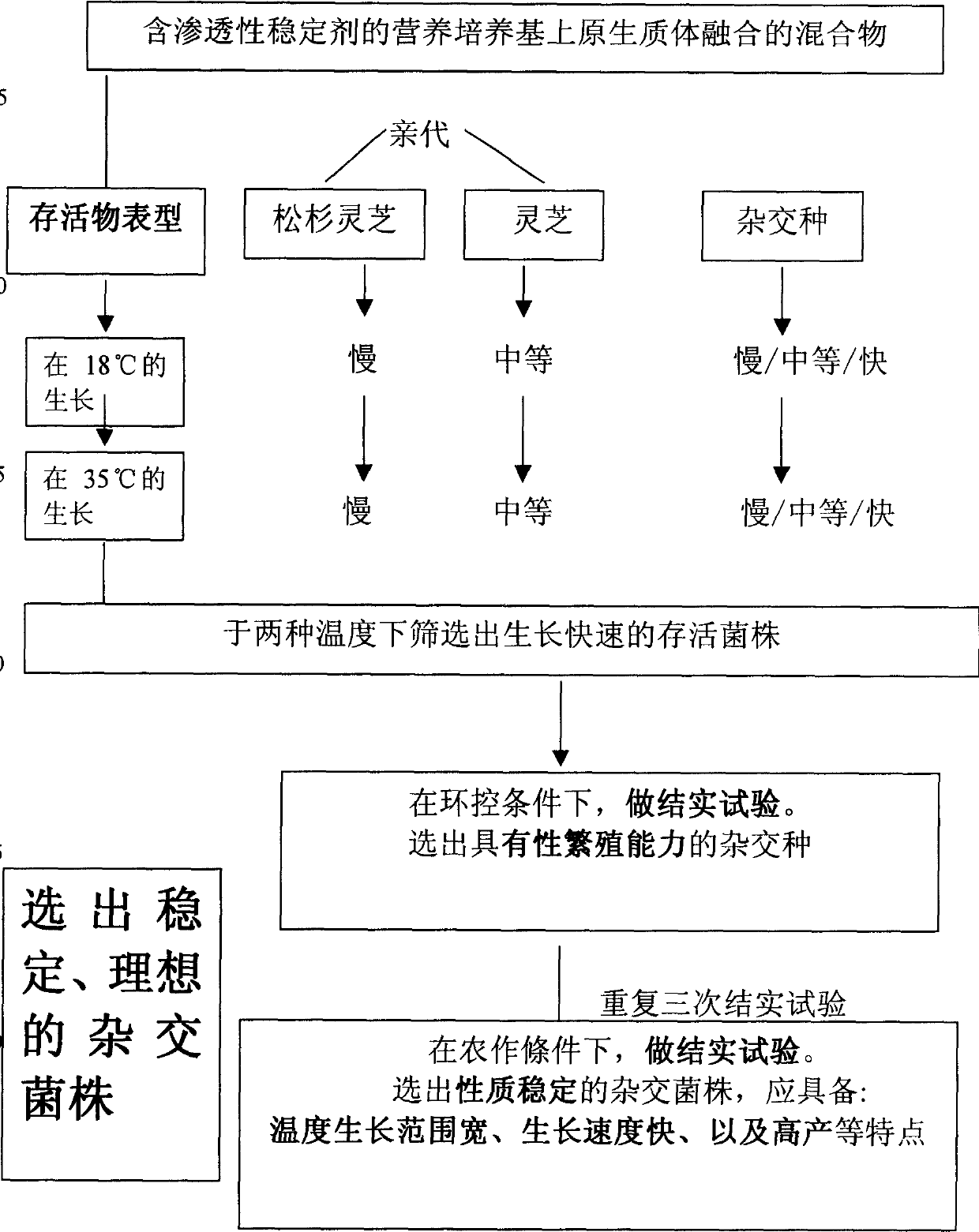
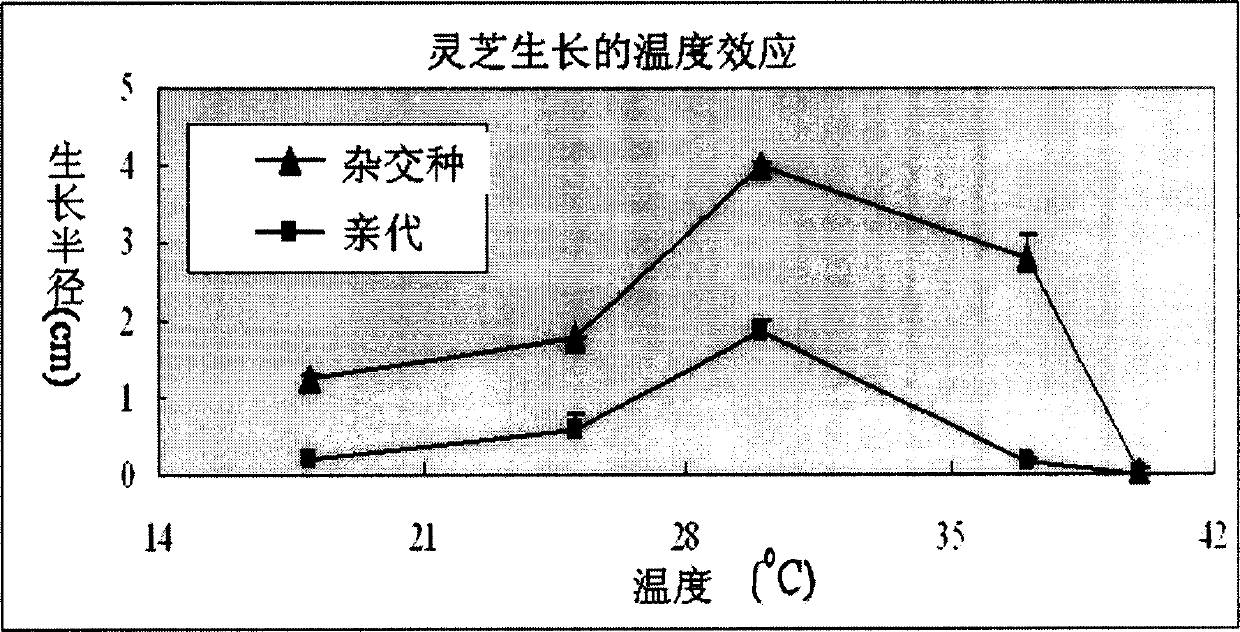
InactiveCN1742555AStable Product Development CapabilitiesWide temperature growth rangePlant genotype modificationHorticultureRibosomal DNAProtoplast
An artificial hybrid lingzhi was created by protoplast fusion between a cultivar DEG C, and was characterized by unique DNA fingerprints by random amplified polymorphic DNA markers using arbitrary primers: PP4L, PS3L, PS1L, POM and UK, and sequences of nuclear ribosomal DNA gene and mitochondrial ribosomal DNA gene different from those of the parental cultivar.
Owner:赵绍惠
High-throughput mulberry pathogenic bacteria identification and species classification method and application thereof
ActiveCN106636433AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseRibosomal DNA
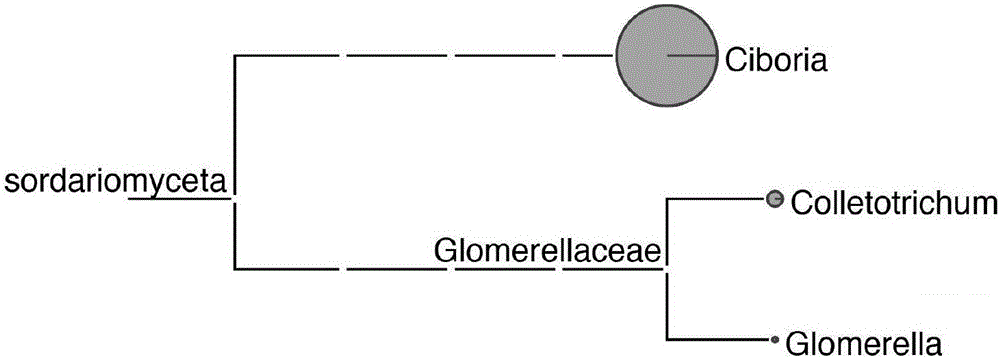
The invention discloses a high-throughput mulberry pathogenic bacteria identification and species classification method. The method comprises the following steps that diseased mulberries are collected; the total DNA of the diseased mulberries is extracted; an Illumina DNA library is created; Illumina high-throughput sequencing is carried out; a mulberry genome sequence in sequencing data is removed; microbial genome sequences are assembled; complete ribosomal DNA sequences are assembled; microbial ribosomal DNA sequences are screened and labeled; the ribosomal DNA sequences are comparatively analyzed to classify species, and thereby the mulberry pathogenic bacteria identification and species classification are fulfilled. A result shows that three species of fungi are identified in total when the method disclosed by the invention is applied to carry out the identification of pathogenic bacteria of popcorn disease and species classification, wherein the Ciboria pathogenic bacteria has the highest relative abundance, hereby the pathogenic Ciboria shiraiana is determined as Ciboria, and according to a comparison result, the pathogenic Ciboria shiraiana is determined as Ciboria carunculoides. Most of the species are phytopathogenic bacteria, and can lead to symptoms, such as mummification and swelling, appearing on fruits and seeds of plants, which are identical with the symptoms of the popcorn disease.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Ribosome DNA methylation marker for detection of cancer in peripheral blood and application thereof
ActiveCN110195107AHigh copy numberTimely diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCancers diagnosisRibosomal DNA
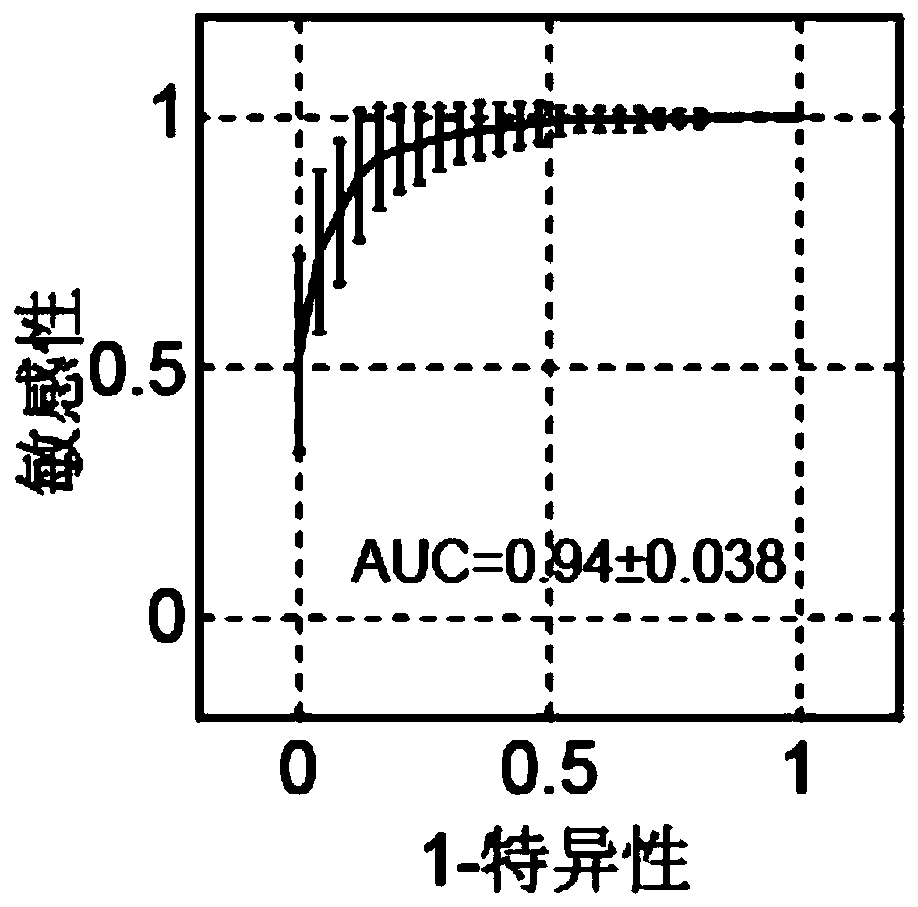
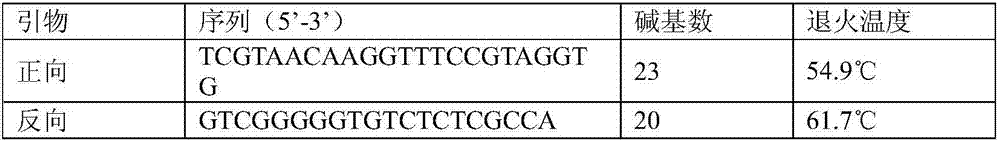
The invention provides a ribosome DNA methylation marker for detection of cancer in peripheral blood and an application thereof. The markers comprise at least one selected from the group consisting of, by taking a human ribosomal DNA repeat fragment unit reference sequence U13369.1 as a reference, CpG sites at positions of 38974, 37148, 37013, 37082, 37076, 32936, 21740, 23407, 34657, and 28277 orthe modified CpG site. The invention also provides a system, a kit, and the like for any combination of the markers for cancer diagnosis. The methylation status of the markers is significantly different between tumor tissues and non-tumor tissues, and the markers are hypomethylated in tumor tissues, and the ROC of combination of the markers in a test set to distinguish patients with liver cancer,lung cancer, and colorectal cancer can respectively reach 96%, 94%, and 92%.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method of identifying molecules of culter alburnus, triangular bream and hybrid generation of culter alburnus and triangular bream
ActiveCN106868112AStrong specificityIncrease credibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementRibosomal DNACulter alburnus
The invention discloses a method of identifying molecules of culter alburnus, triangular bream and a hybrid generation of culter alburnus (female) and triangular bream (male), and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. According to the method, by selecting genes of first internal transcribed spacers (ITS1) of ribosome DNA of the culter alburnus, the triangular bream and the hybrid generation of the culter alburnus and the triangular bream, the genes have remarkable difference in the size of amplified fragments of three types of fish; and a pair of universal primers are designed, and the culter alburnus, the triangular bream and the hybrid generation of the culter alburnus and the triangular bream are distinguished by amplifying the ITS1 region by PCR. The method established by the invention has strong specificity and high reliability and can be applied to variety identification of the culter alburnus, the triangular bream and the hybrid generation of the culter alburnus and the triangular bream.
Owner:ZHEJIANG INST OF FRESH WATER FISHERIES
Quick quantitative detection of genetic marker of skeletonema costatum japonicum and its method
The present invention provides a genetic marker and method for quickly quantitatively detecting skeletonema costatum. It provides skeletonema costatum ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and transcription unit internal spacer (ITS) nucleotide sequence, and oligonucleotide probe designed by using said sequence as basis. The invention utilizes the sequence comparison and experiment to show that these probes are genetic marker peculiary to the skeletonema costatum. The invention also provides the method for quickly quantitatively detecting skeletonema costatum.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA +1
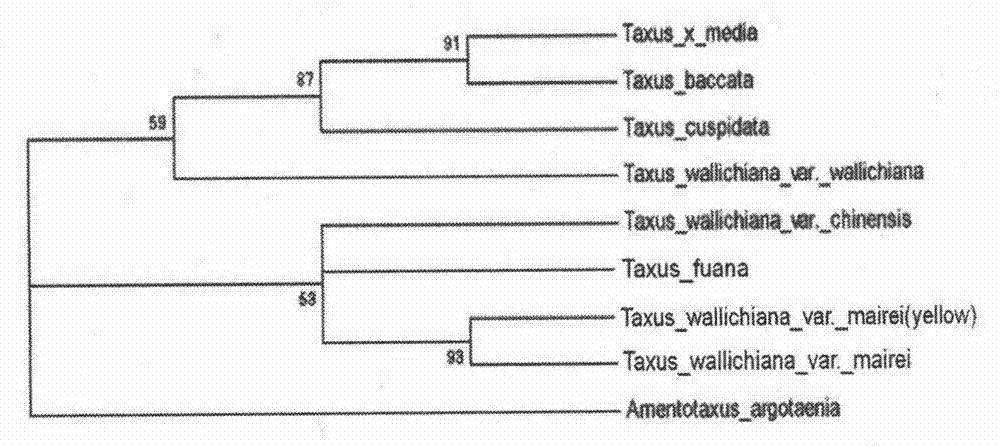
Nucleotide sequence and method used for identifying and differentiating species and varieties of Taxus chinensis
The invention discloses a nucleotide sequence used for identifying and differentiating species and varieties of Taxus chinensis. The sequence is originated from an internal transcribed spacer (ITS1) sequence of ribosome DNA (rDNA) of a proto-variety of Taxus wallichiana, and can be used for contrast and identification of the species and varieties of Chinese yew; and through analysis of the genetic characteristics of the germplasm resource of Taxus chinensis at a DNA level, effective molecular marks are provided for differentiation of the species and varieties of Taxus chinensis, and a good base is laid for identification, differentiation and screening of excellent germplasm of the species and varieties of Taxus chinensis. Meanwhile, the invention provides a method for identifying the species of Taxus chinensis by using the nucleotide sequence. The method is simple and practical to operate and can realize convenient, rapid, objective and accurate differentiation of different species and varieties of Taxus chinensis.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
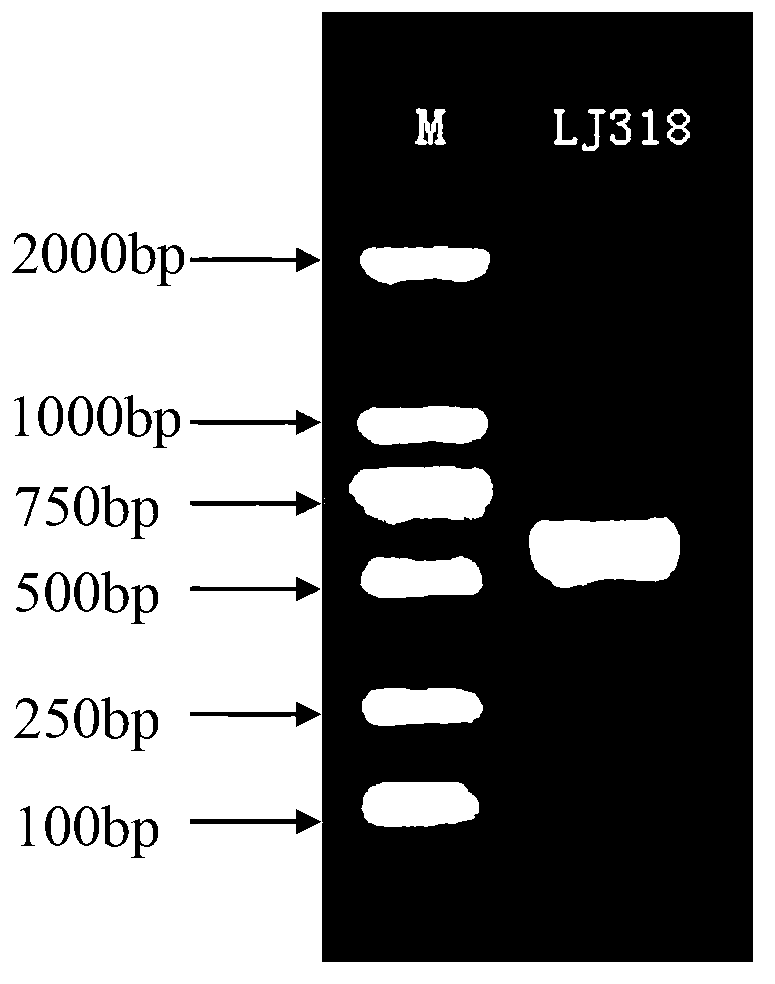
Penicillium citrinum LJ318 for degrading chlortetracycline
InactiveCN103289904APromote degradationGrow fastFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismRibosomal DNA
The invention relates to a strain of Penicillium citrinum LJ318 capable of degrading chlortetracycline and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) in March 3rd, 2012, and the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No.5850. An rDNA-ITS (Ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer) gene sequence of the chlortetracycline degrading strain LJ318 consists of 544 basic groups. The strain is wide in chlortetracycline-tolerating range and has relatively good degradation effects on the residual chlortetracycline in both liquid and solid wastes.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
Fungus strain and its application
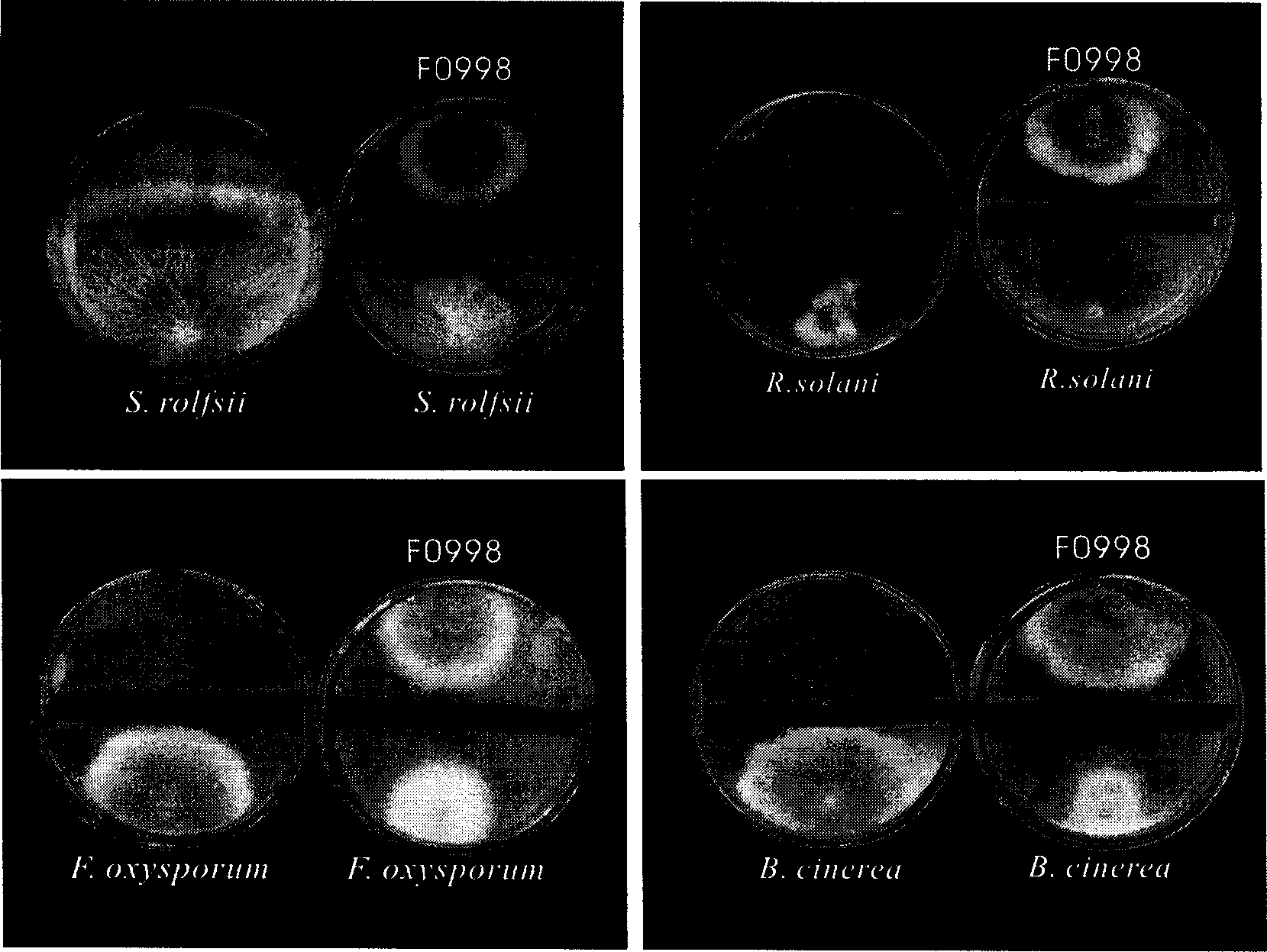
InactiveCN1693446AGrowth inhibitionEnhance natural healing powerBiocideFungiBiotechnologyMicroorganism
A fungus strain Fusarium tricinctum-ZJUF0998 (CGMCC No.1331), belnoging to Fusarium, Nectriaceae, Hypocreales, Sordariomycetidae, Ascomycetes, Ascomycota, fungi, and the complete sequence of its internal transcription spacer rebosomal DNA are disclosed. It can generate the volatile aromatic gas to suppress the growth of plant pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Eriocheir sinensis Microsporidia in-situ hybridization detection probe and kit
InactiveCN105177165AIntuitive combinationEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesInfection rateSpiroplasma
The invention discloses an Eriocheir sinensis Microsporidia in-situ hybridization detection probe and kit. The sequence of the probe is disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1. After the probe is labeled by digoxin and combined with Microsporidia 18S subunit ribosome DNA (18S SSU rDNA) by hybridization, the Microsporidia infection can be judged under a microscope after alkaline phosphatase detection system color development. The invention also discloses a kit containing the probe, which has favorable specific, is simple to operate and can intuitively combine the pathogen detection and pathological changes. On the premise of efficiently and accurately detecting the Spiroplasma, the kit can analyze the infection rate and infection intensity of the sample section. The hybridization between the probe and 18S SSU rDNA is specific, the signal is progressively amplified, and thus, the kit disclosed by the invention is more sensitive and accurate than the conventional dyeing observation detection. The detection result proves that the section subjected to hybridization color development can be stored for a long time.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES INSITUTE OF JIANGSUPROVINCE
DNA barcode identification method of traditional She medicinal Shiliang herb tea based original species and related confusable species
InactiveCN106834471AResolve Species IdentificationSolve resource problemsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA barcodingGermplasm
The invention relates to the field of Chinese herbal medicine based original plant species identification technology, specifically to a method for identifying traditional She medicinal Shiliang herb tea based original species and related confusable species by the utilization of ITS2 fragments of ribosomal DNA and application thereof. A DNA barcode identification method of traditional She medicinal Shiliang herb tea based original species and related confusable species comprises the following steps: 1) DNA sample extraction; 2) PCR amplification of fragments containing ITS2 sequences; 3) splicing of PCR amplification products; 4) comparison of ITS2 sequences of multiple species; and 5) construction of phylogenetic tree based on the ITS2 sequences. The DNA extraction method of traditional She medicinal Shiliang herb tea based original species and related confusable species and the ITS2 preparation method can effectively solve the problems such as species identification of Shiliang herb tea and related species, development and utilization of germplasm resources, etc. The method of the invention has extensive applicability, is simple to operate, is easy to grasp and has high accuracy. By the method, rapid and accurate identification of the Shiliang herb tea based original species and related confusable species can be successfully realized.
Owner:LISHUI AGRI SCI +1
Bupleurum DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) identifying kit and identifying method
The invention relates to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicine detection, in particular to a bupleurum DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) identifying kit and identifying method. The identifying kit comprises a DNA extraction reagent, a bupleurum identifying system and a bupleurum scorzonerifolium willd identifying system. The bupleurum DNA identifying method comprises the steps of: designing two pairs of specific oligonucleotide primers of the bupleurum ribosomal DNA, artificially synthesizing two pairs of primers, establishing a bupleurum DNA identifying kit, determining a reaction process, judging the result, and the like. The bupleurum DNA identifying kit and identifying method can be used for identifying and detecting traditional Chinese medicines, the bupleurum DNA identifying kit can accurately identify the specificity of bupleurum and can simultaneously identify the bupleurum, the bupleurum scorzonerifolium willd and confusing species thereof, and the identifying method has the advantages of simplicity, quickness and the like.
Owner:BEIHUA UNIV
Method for identifying traditional she medicine Rubi Radix et Rhizoma original plant and congeneric similar confusable species thereof on the basis of ITS2 sequence gene fragments
InactiveCN107541547AAccurate identificationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRibosomal DNARubus
The invention relates to the field of traditional Chinese medicinal material original plant species identification technology, specifically to a method for identifying leaf, root and fruit of traditional she medicine Rubi Radix et Rhizoma original plant and congeneric similar confusable species thereof by the utilization of ITS2 fragments of ribosome DNA and application thereof. The method for identifying traditional she medicine Rubi Radix et Rhizoma original plant and congeneric similar confusable species thereof on the basis of ITS2 sequence gene fragment comprises the following steps: 1) extraction of multiple rubus plant leaf, root and fruit DNA samples; 2) PCR amplification of fragments containing ITS2 sequence; 3) assembling of PCR amplification fragments; 4) comparison of ITS2 sequences of multiple rubus species; and 5) construction of a phylogenetic tree on the basis of ITS2 sequence. The method of the invention has extensive applicability, is simple and convenient to operate,is easy to master, has high accuracy, and can successfully realize efficient and accurate identification of Rubi Radix et Rhizoma original plant and congeneric similar confusable species thereof.
Owner:LISHUI AGRI SCI
Sequencing method for single cell transcriptome
ActiveCN109971843AGet rid of application limitationsImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementEucaryotic cellMagnetic bead
The present invention belongs to the field of biotechnology and discloses a sequencing method for a single cell transcriptome. PAP / PGP is used to add poly A / G to a tail part of a RNA strand to increase RNA stability and at the same time produces an extended strand used for reverse transcription and cDNA synthesis. When effective RNA enrichment is carried out downstream, a small-fragment PCR non-specific product is purified by magnetic beads labeled with ribosomal DNA probes, a half-annealed splint hybridization is used to remove rRNA in a cDNA form having a size of 5s, 5.8s, 18s and 28s, and besides, a large amount of invalid Reads during sequencing are reduced. The sequencing method can conduct one-stop non-coding RNA, microRNA and mRNA total transcriptome sequencing of a single eukaryocyte, produces an expression matrix of the transcriptome and frees an application limitation that one cell can only perform one sequencing.
Owner:复旦大学泰州健康科学研究院
Method for building nucleotide formula to identify plant variety by using ribosome deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
InactiveCN103757114ASpeed up breedingIncrease productivityMicrobiological testing/measurementRibosomal DNASingle strand dna
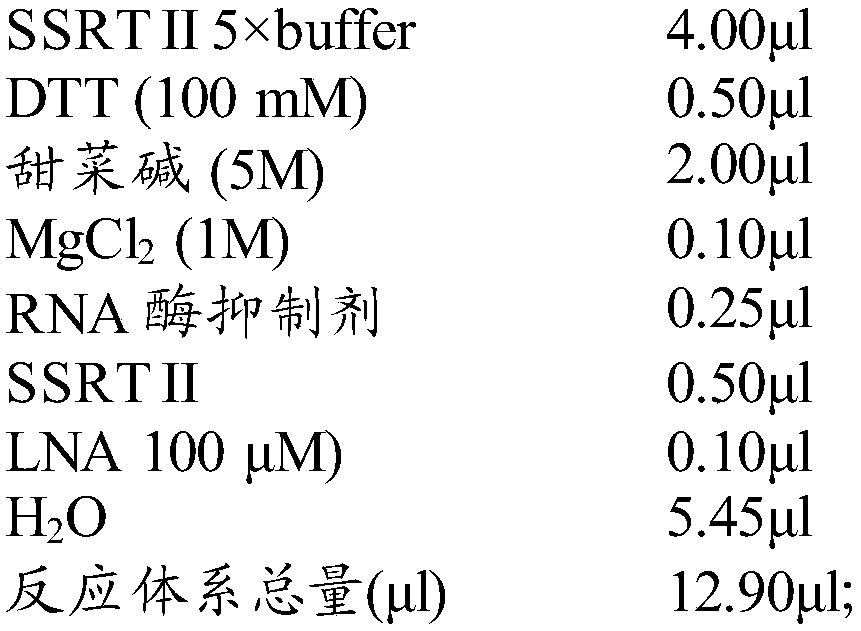
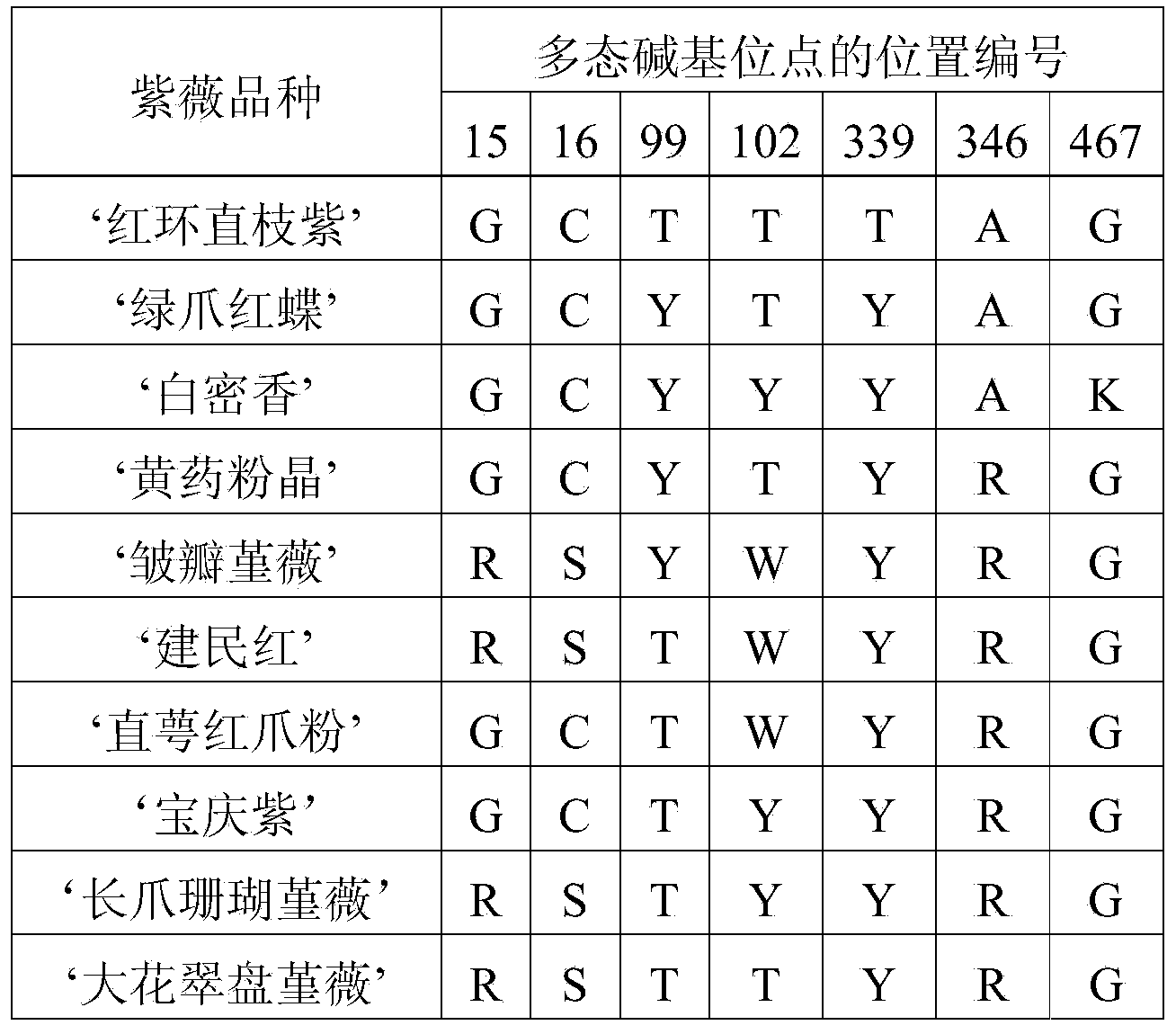
The invention discloses a method for identifying plant variety, and provides a method for identifying crape myrtle variety. The method comprises the following steps: 1) carrying out polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification by taking a genome deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of to-be-detected crape myrtle as a template and using a primer composed of two single-chain DNA molecules shown in a sequence 1 and a sequence 2, so as to obtain a PCR product; 2) sequencing the PCR product, and listing the nucleotide formulas of the to-be-detected crape myrtle according to the sequencing result; 3) comparing the nucleotide formulas obtained in the step 2) with corresponding nucleotide formulas of a plurality of crape myrtle varieties, so as to determine the variety of the to-be-detected crape myrtle. An experiment proves that the method is accurate, and simple and fast to operate, the production efficiency and the quality monitoring level of related enterprises can be improved, and the defects of the traditional method are effectively compensated. In addition, identification of a non-flowering phase (for example, a seedling stage) is simultaneously achieved. The method has important significance on facilitation of development of new variety breeding of the crape myrtle, crape myrtle flower and wood industries and urban garden greening, and environmental protection.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Ribosomal DNA ITS1 gene-based polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification kit for detecting clonorchis sinensis metacercaria and amplification primer
InactiveCN105132539AHigh detection sensitivityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationClonorchis sinensisTrue positive rate
The invention discloses a ribosomal DNA ITS1 gene-based polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification kit for detecting clonorchis sinensis metacercaria and an amplification primer. The kit comprises a PCR amplification reaction solution, wherein the PCR amplification reaction solution comprises 10 mmol / L of Tris-HCl, 50 mmol / L of KCl, 1.5 mmol / L of MgCl2, 0.8 mmol / L of dNTPs, 0.4 [mu]mol / L of positive primer, 0.4 [mu]mol / L of negative primer, 20 ng / [mu]L of DNA template, and 0.075 U / [mu]L of Taq enzyme. The kit disclosed by the invention is high in sensitivity and specificity, the detection is fast in speed and accurate, and an effective technical means is provided for making a diagnosis, giving treatment and preventing clonorchis sinensis infection.
Owner:舟山出入境检验检疫局综合技术服务中心
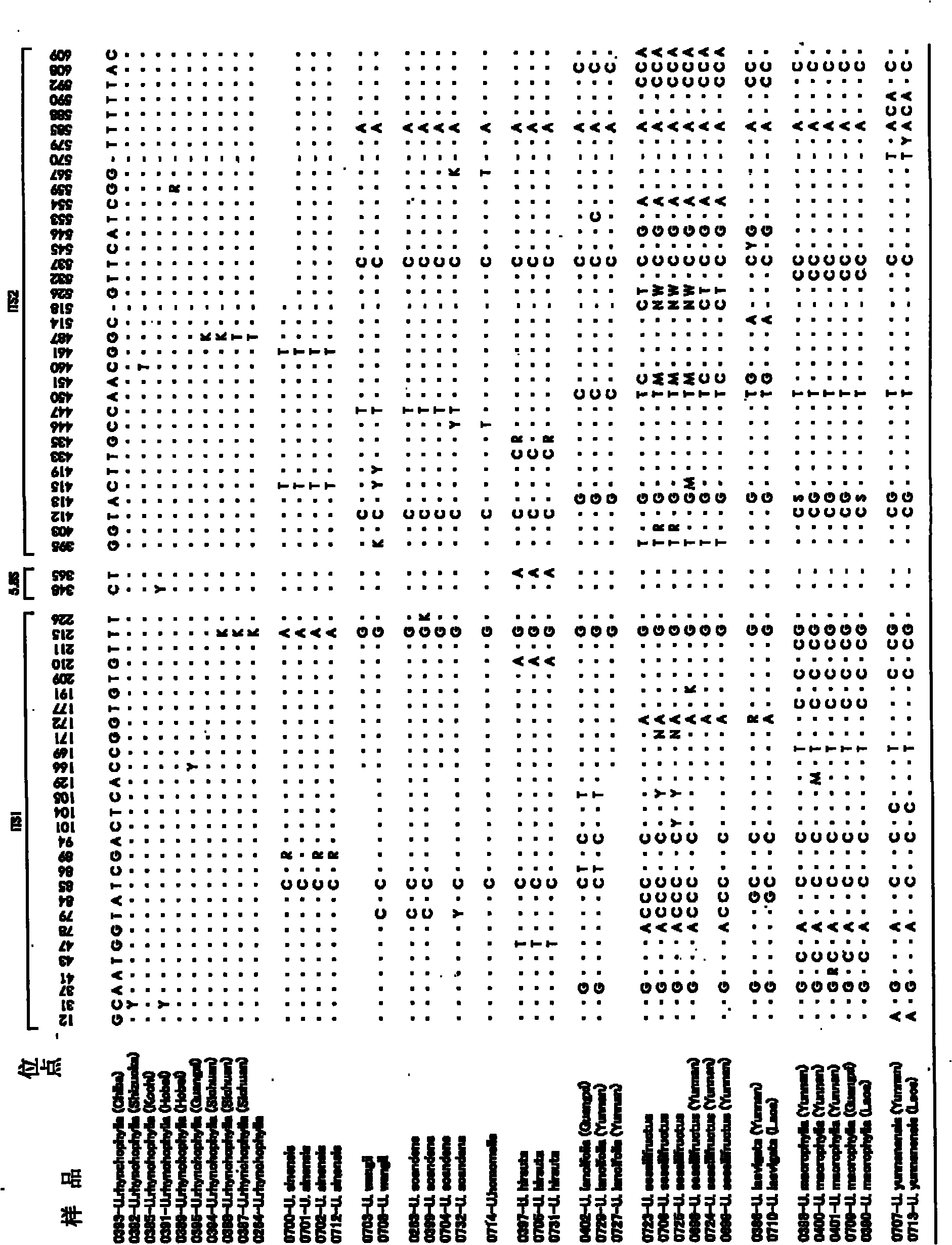
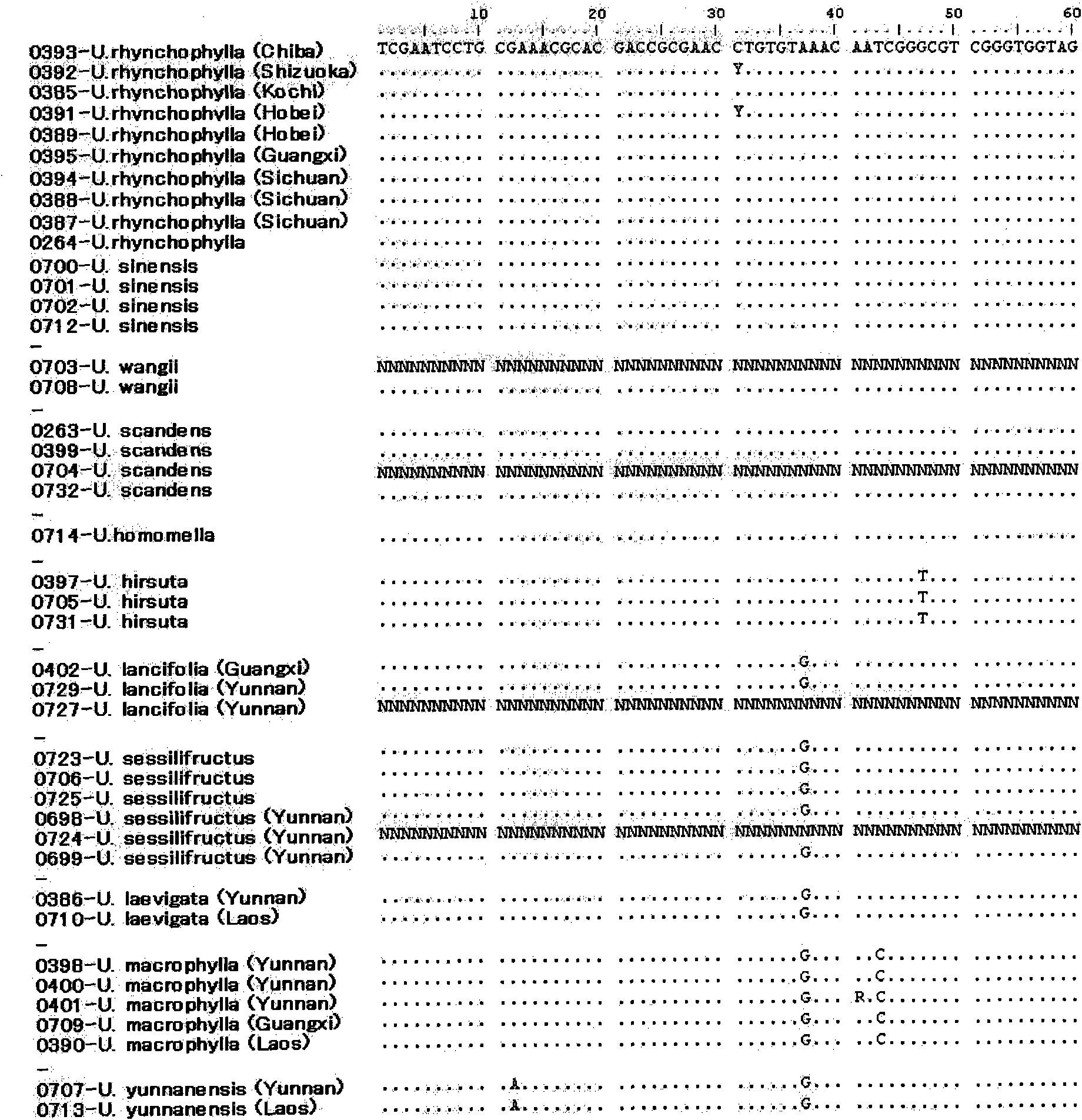
Method of identifying the species of plant belonging to the genus uncaria
ActiveCN101772579AMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyIts regionTest sample
It is intended to provide a method whereby the species of a plant belonging to the genus Uncaria can be identified at a high accuracy. Namely, a method of identifying the species of a plant belonging to the genus Uncaria contained in a test sample which comprises comparing the base sequence in the ITS region of the ribosomal DNA of the plant contained in the test sample with at least one base sequence in the ITS region selected from among the base sequences represented by SEQ ID NOS:1 to 11.
Owner:TSUMURA
ITS fragment of skunk bush ribosome DNA and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101285067AIncrease varietySolution BreedingFermentationPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologySkunk
The invention relates to an ITS fragment of a dogwood ribosomal DNA and a method for producing the same, effectively solving the problems of variety identification, variety improvement, breeding and exploitation and use of germplasm resources. The ITS fragment consists of three parts which are ITS1, 5.8 S, and ITS2. The method comprises the following steps of: grinding leaves of a dogwood tree; adding PVP powder into the ground leaves and grinding the mixture into fine powder; placing the fine powder into an extraction buffer solution for configuration; removing supernatant; adding beta-Mercaptoethanol and extract made of Vc+2xCTAB into the residuum and mixing the mixture uniformly; adding a solution made of saturated phenol chloroform isoamyl alcohol twice at the same volume; removing impurities and configuring; getting supernatant and adding isopropyl alcohol into the supernatant; collecting sedimentations; and draining off alcohol, and thus obtaining the DNA; carrying out PCR amplification and purification to the DNA by a primer; and sequencing the purified PCR resultant to obtain the ITS fragment. The method is simple, scientific, economic and excellent in social effect.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Method for identifying honeysuckle and lonicera confuse and application of same
ActiveCN103173532BSolving Variety IdentificationSolution BreedingMicrobiological testing/measurementGermplasmRibosomal DNA
The invention relates to a method for identifying honeysuckle and lonicera confuse and an application of the method. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the step of performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on ITS2 nucleotide sequence, and particularly comprises the steps of 1) extracting the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a sample; 2) performing PCR amplification on the segments of the ITS2 sequence containing ribosome DNA; 3) splicing the amplification products to obtain a complete ITS2 intergenic region; and 4) establishing the NJ (neighbour-joining) tree of the ITS2 sequence of the sample. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively solving the problems of variety identification, variety improvement and breeding of honeysuckle medicinal materials, development and utilization of germplasm resources, and the like; and the method disclosed by the invention is wide in applicability, simple to operate, easy to grasp, high in accuracy, and capable of successfully realizing rapid and accurate identification on honeysuckle medicinal materials or powder and lonicera confuse medicinal materials or powder.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Probe and method for detecting heterosigma akashiwo
InactiveCN1699599AObjective detectionAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesRibosomal DNA
The present invention belongs to the field of environment microbe inspection technology with molecular biological method. The invention discloses red tide heterosigma akashiwo alga ribosome DNA(rDNA)and the nucleic acid sequence of interval area of transcription unit (ITS) as well as the oligonucleotide probe based on the design of this sequence. This nucleic acid probe is used as a pair of guide object to carry out PCR reaction. Accurate and fast inspection of red tide heterosigma akashiwo alga can be realized through predicting whether there is the PCR product of corresponding size. The present invention also discloses a fast and accurate inspection quantitative counting method of red tide heterosigma akashiwo alga by fluorescent quantitative PCR technology with the probe.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification kit for detecting metacercaria of Cs (clonorchis sinensis) on basis of ribosomal DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) ITS2 (internal transcribed spacer 2) and amplification primer
InactiveCN105154535AEasy to judgeHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerClonorchis sinensis
The invention discloses a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification kit for detecting metacercaria of Cs (clonorchis sinensis) on the basis of ribosomal DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) ITS2 (internal transcribed spacer 2) and an amplification primer. The PCR amplification kit comprises a PCR amplification reaction liquid, wherein the PCR amplification reaction liquid comprises 10 mmol / L of Tris-HCl , 50 mmol / L of KCl, 1.5 mmol / L of MgCl2, 0.8 mmol / L of dNTPs (deoxyribonucleoside-5'-triphosphate), 0.4 mu mol / L of a forward primer, 0.4 mu mol / L of a reverse primer, 20 ng / mu L of a DNA template and 0.075 U / mu L of a Taq enzyme. The PCR amplification kit is high in sensitivity and high in specificity, can detect metacercaria of Cs quickly and accurately and provides an effective technical means for diagnosis and prevention of Cs infection.
Owner:舟山出入境检验检疫局综合技术服务中心
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com