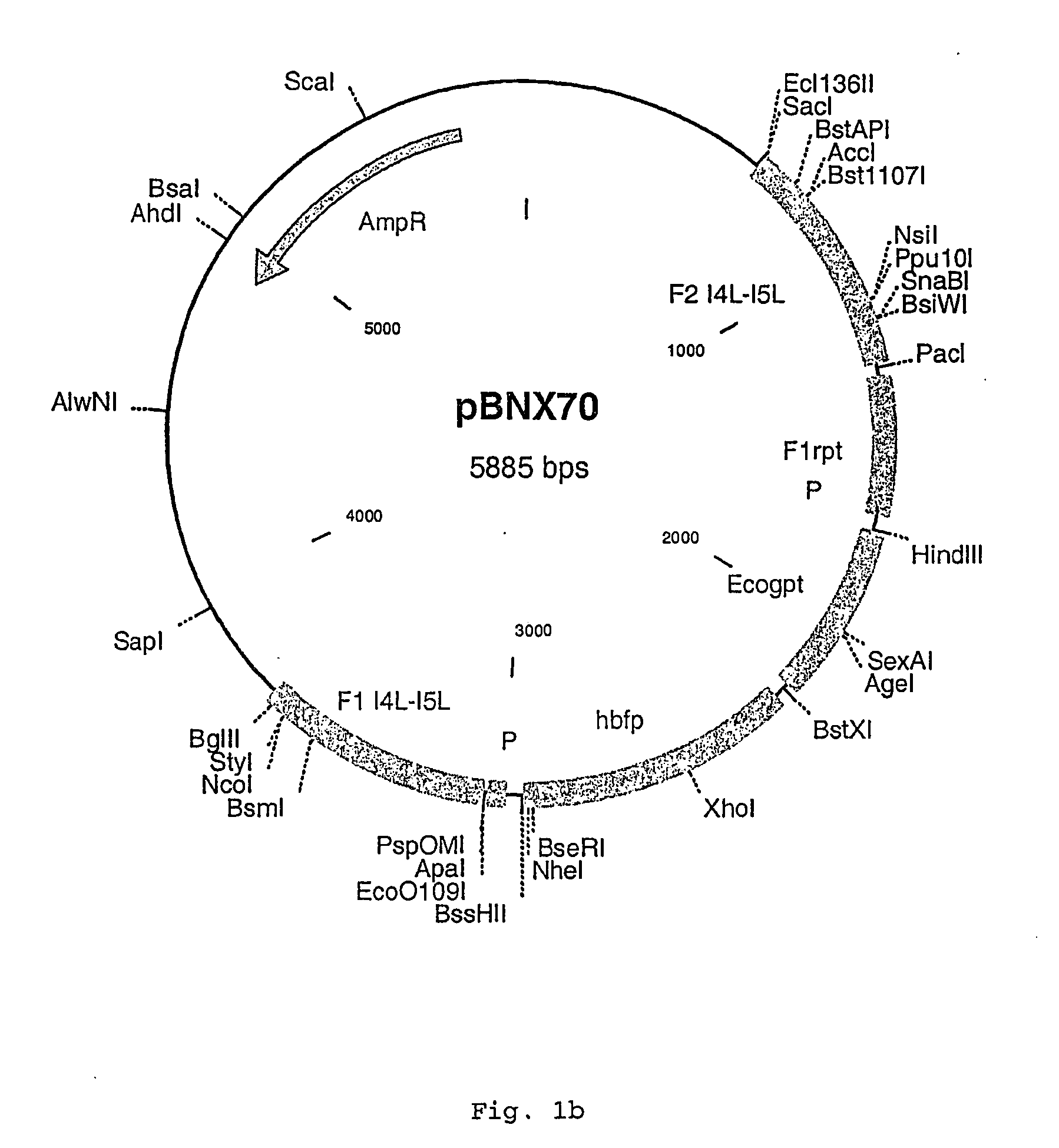
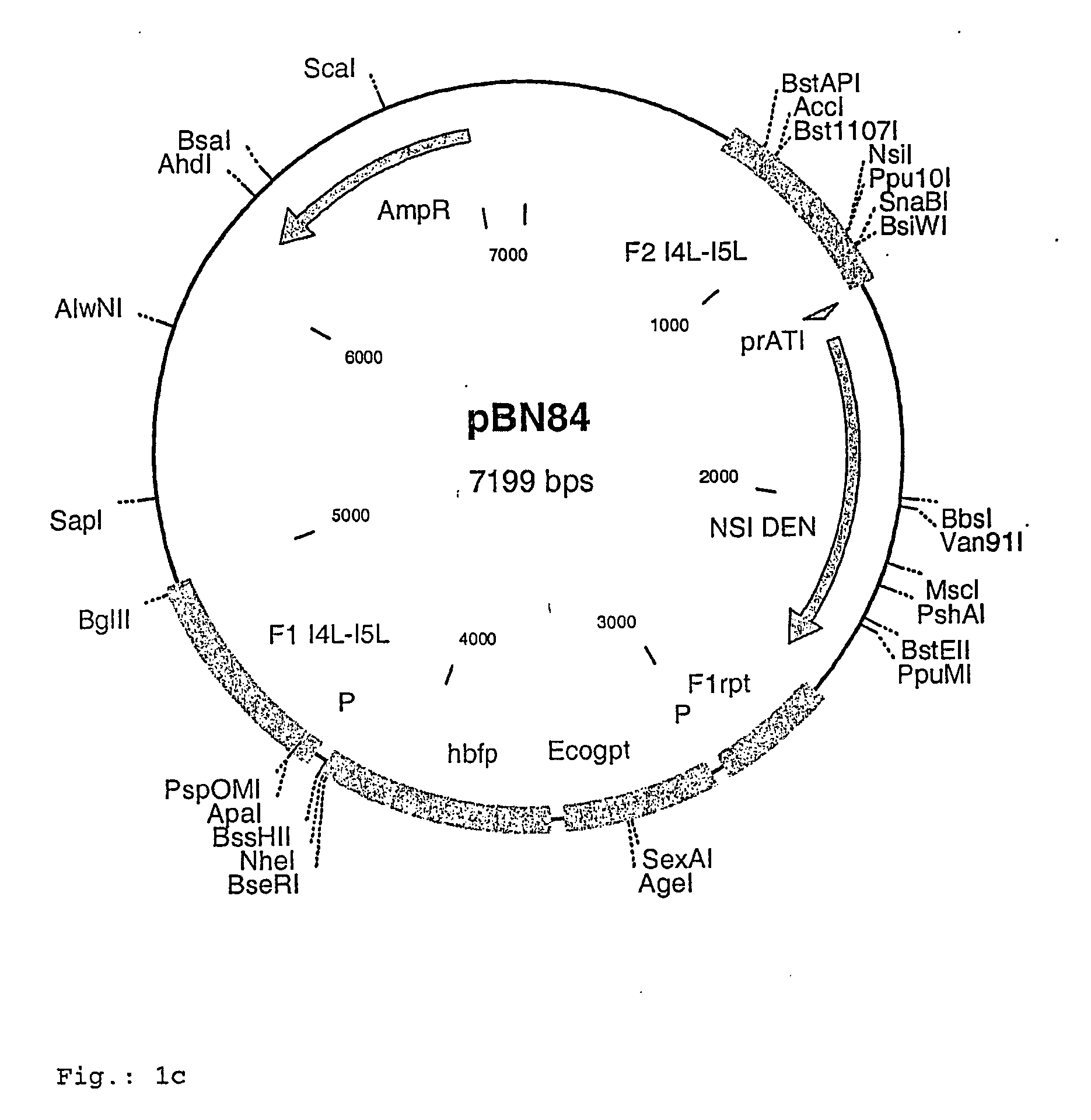
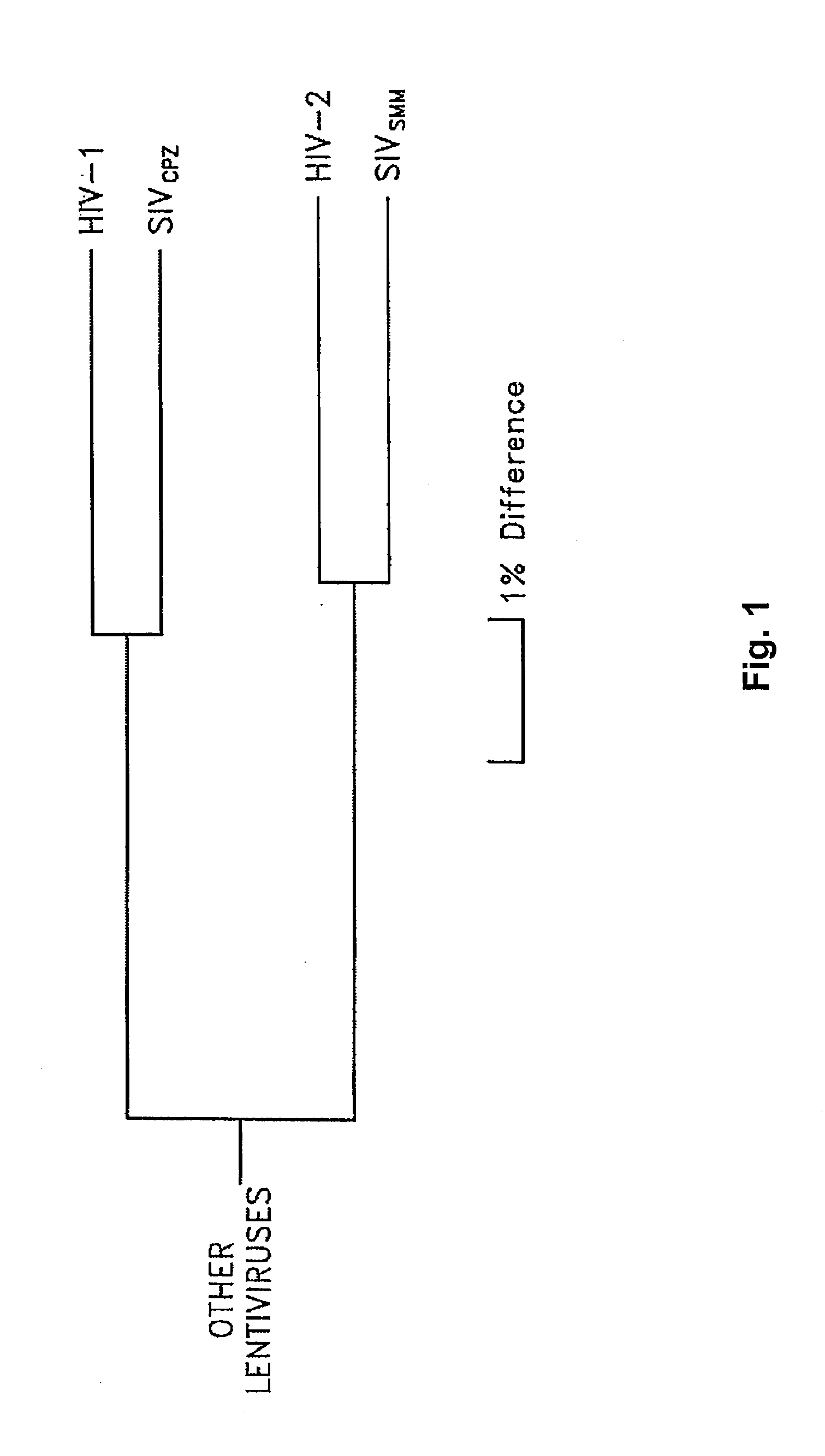
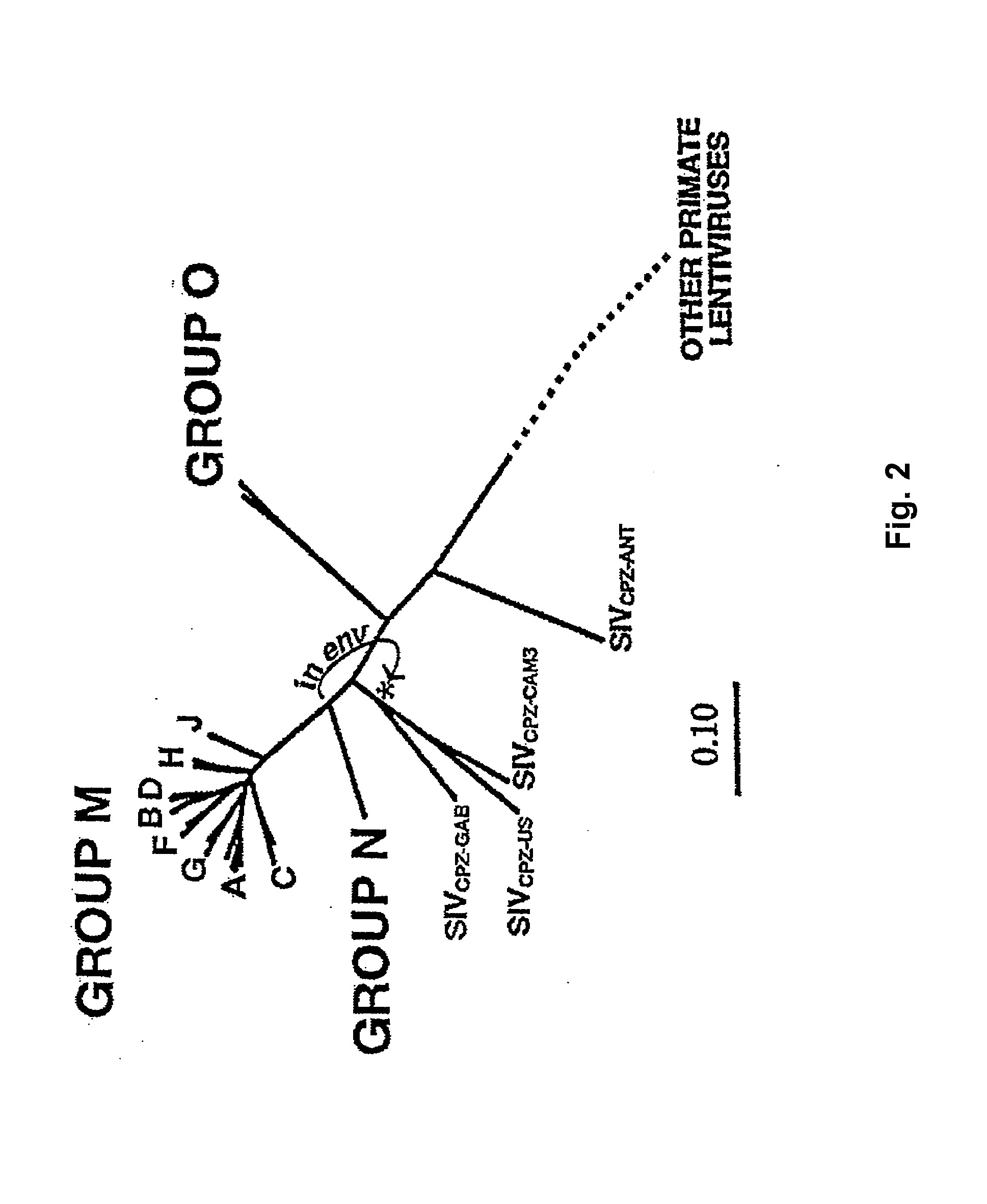
Patents
Literature
45 results about "Intergenic region" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
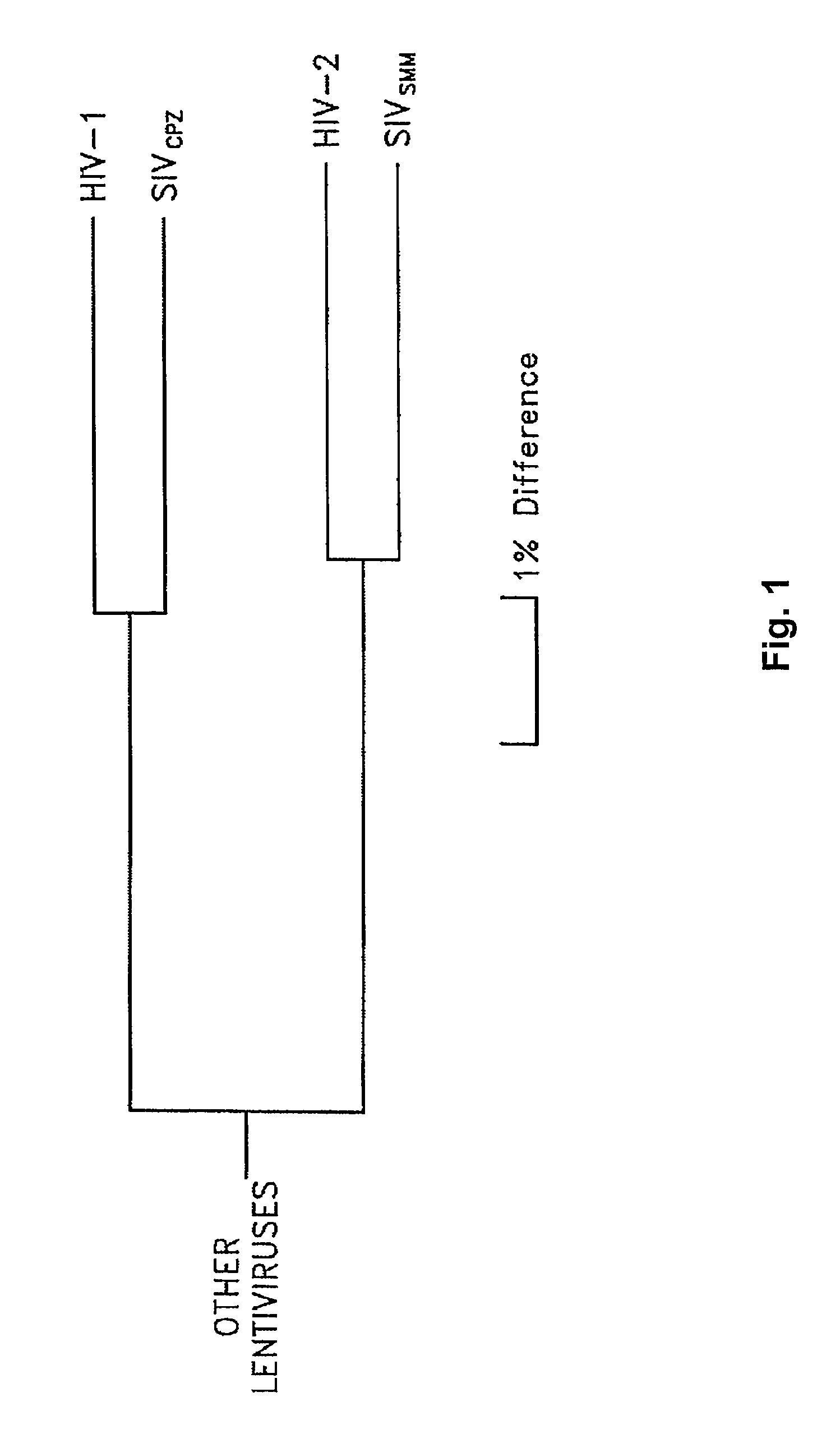
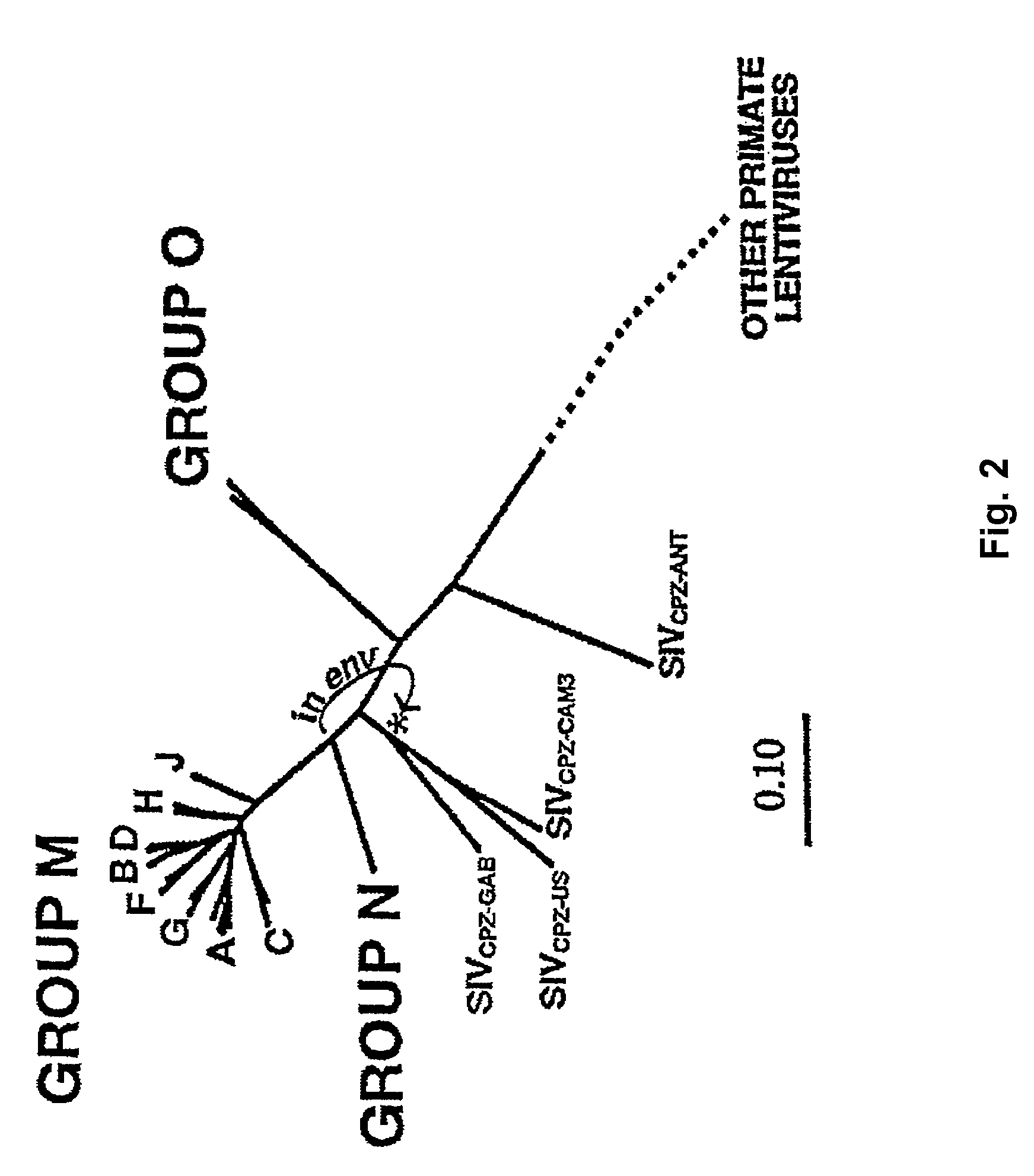
An Intergenic region (IGR) is a stretch of DNA sequences located between genes. Intergenic regions are a subset of noncoding DNA. Occasionally some intergenic DNA acts to control genes nearby, but most of it has no currently known function. It is one of the DNA sequences sometimes referred to as junk DNA, though it is only one phenomenon labeled such and in scientific studies today, the term is less used. Recently transcribed RNA from the DNA fragments in intergenic regions were known as "dark matter" or "dark matter transcripts".
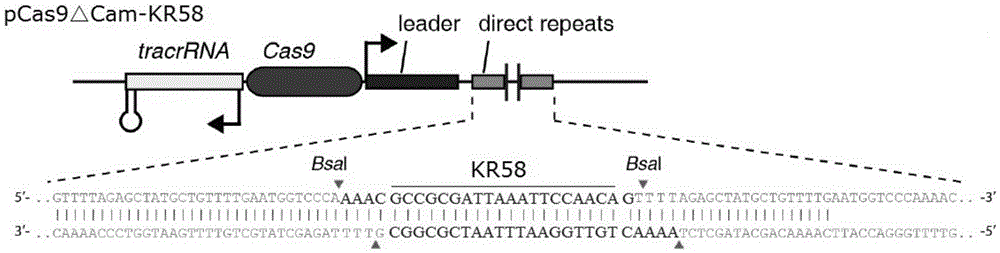
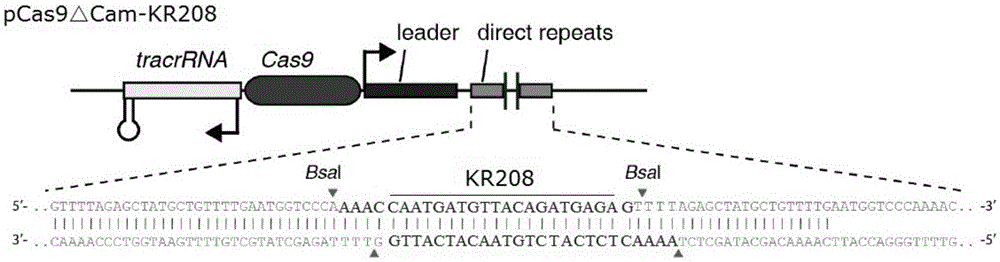
Recombinant vector for eliminating activity of kanamycin drug resistance gene and building method of recombinant vector
InactiveCN105463003AInhibitory activityHigh copy numberNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionNovel geneOrganism
The invention provides a recombinant vector for eliminating the activity of a kanamycin drug resistance gene, and aims at eliminating drug resistance germs in organisms and solving the problem of kanamycin drug resistance of the germs. The recombinant vector for eliminating the activity of the kanamycin drug resistance gene is characterized by comprising a pCas9 vector subjected to chloramphenicol resistance elimination and a gRNA nucleotide sequence KR58 or KR208 aiming at a kanamycin resistance gene kan; the concrete nucleotide sequence of the KR58 is GCCGCGAT TAAATTCCAACA, and the concrete nucleotide sequence of the KR208 is CAATGATG TTACAGATGAGA. A building method of the recombinant vector mainly comprises the steps of carrying intergenic region nucleic acids by a novel gene editing tool CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) / Cas9 system; removing a chloramphenicol resistance gene on the recombinant vector; transforming the gene into vaccine vector bacteria such as attenuated salmonella typhimurium; performing co-culture on the recombinant bacteria and the kanamycin drug resistance gene so that the recombinant vector in the recombinant bacterium cell enters the kanamycin drug resistance bacteria in an engaging mode. The activity of the kanamycin resistance gene kan is effectively inhibited, so that the original drug resistance bacterium cannot grow on a kanamycin culture medium.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
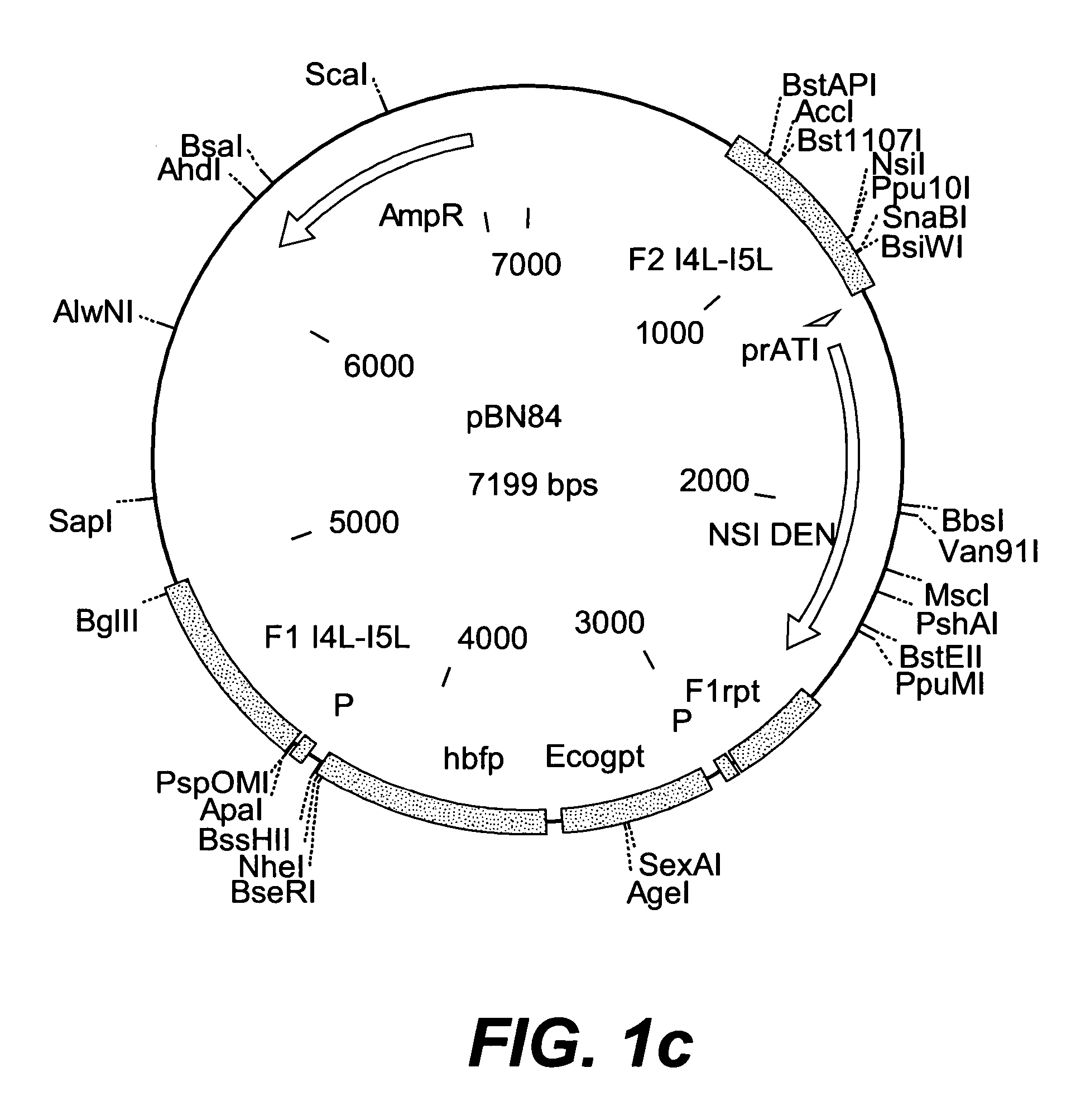
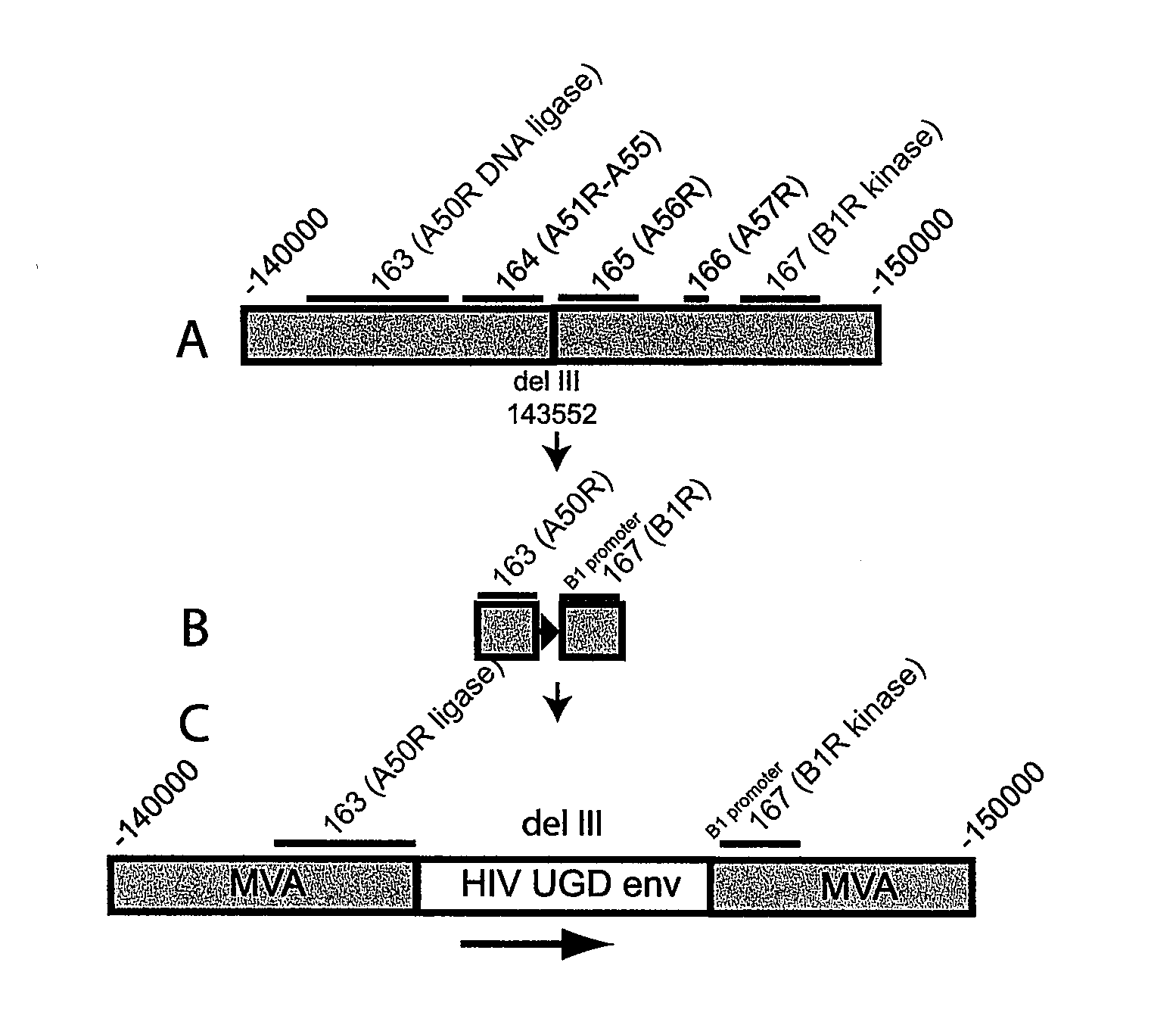
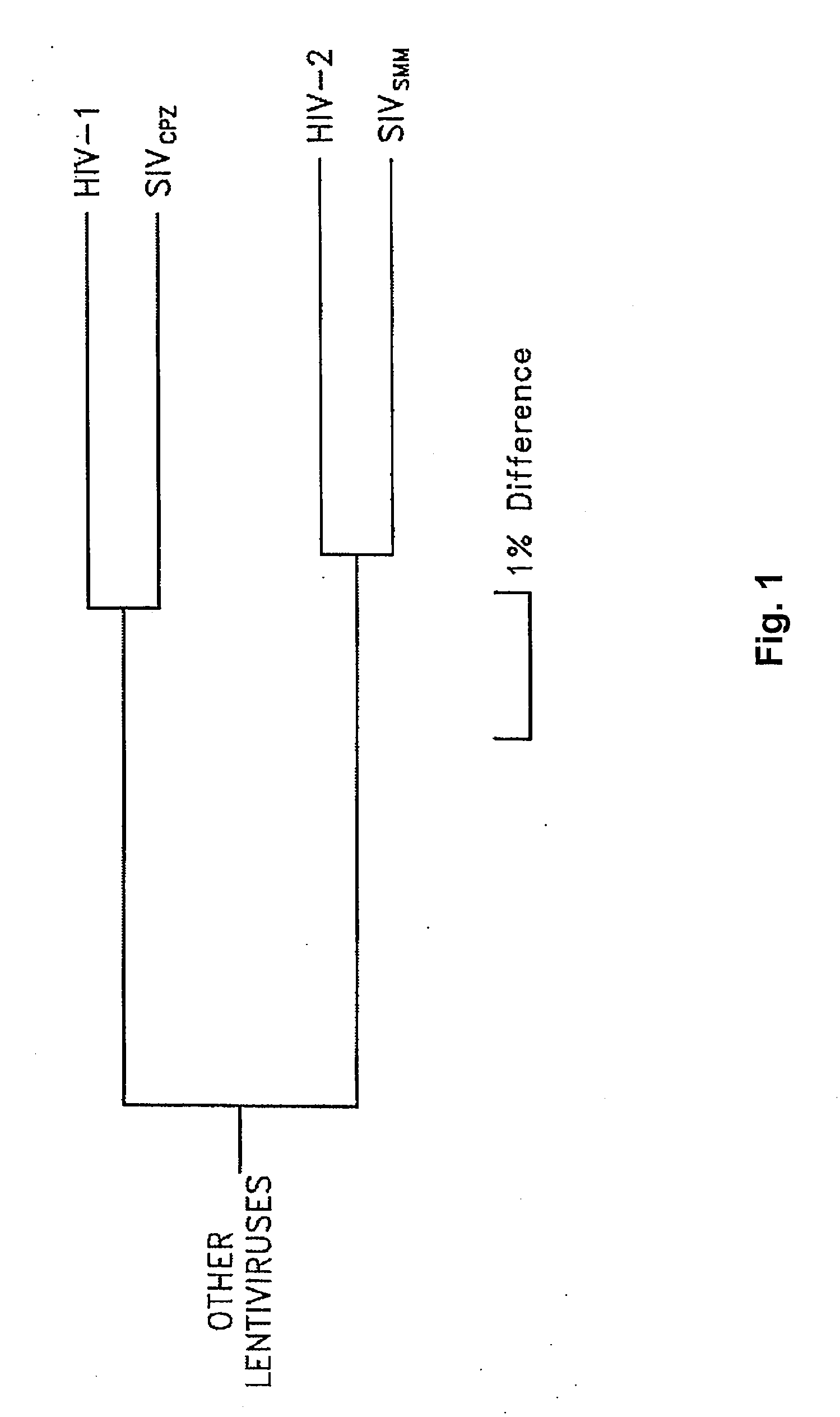
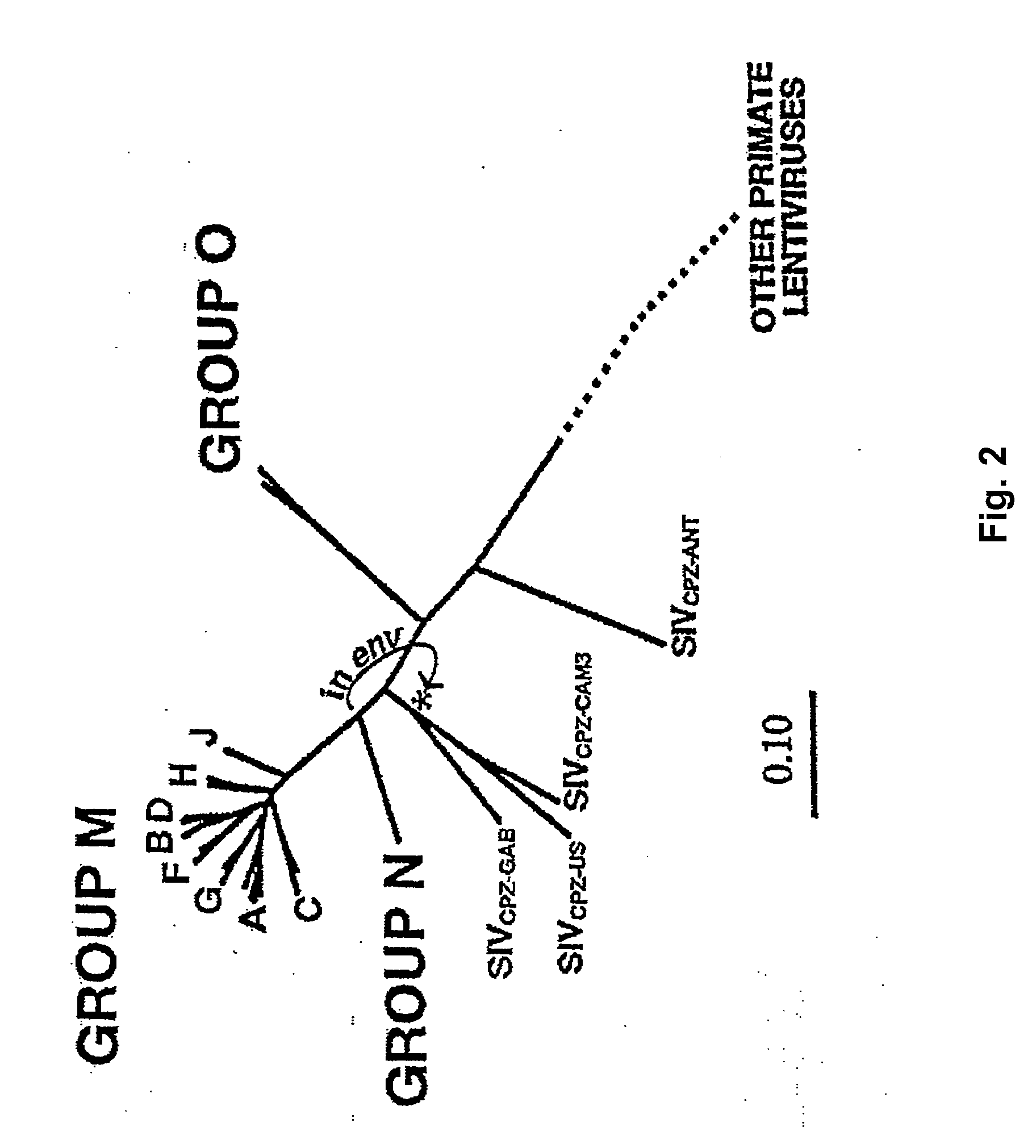
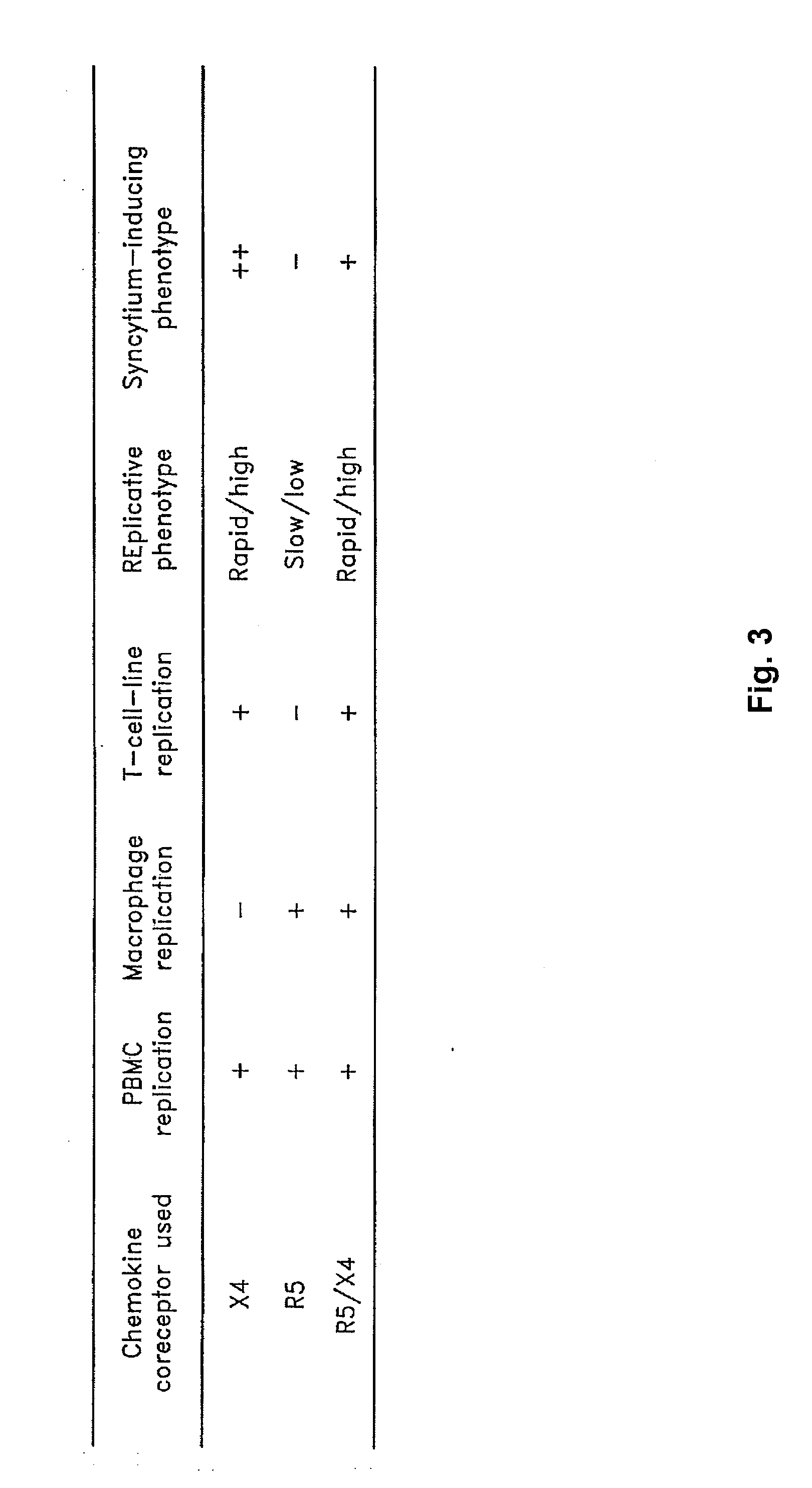
Intergenic regions as novel sites for insertion of HIV DNA sequences in the genome of Modified Vaccinia virus Ankara
ActiveUS7501127B2Stably express multiple HIV proteinsRaise the possibilitySsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesVacciniaInsertion site
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
Recombinant modified vaccinia ankara (MVA) vaccinia virus containing restructured insertion sites
The present invention relates to recombinant modified vaccinia Ankara (MVA) virus containing restructured sites useful for the integration of heterologous nucleic acid sequences into an intergenic region (IGR) of the virus genome, where the IGR is located between two adjacent, essential open reading frames (ORFs) of the vaccinia virus genome, wherein the adjacent essential ORFs are non-adjacent in a parental MVA virus used to construct the recombinant MVA virus, and to related nucleic acid constructs useful for inserting heterologous DNA into the genome of a vaccinia virus, and further to the use of the disclosed viruses as a medicine or vaccine.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
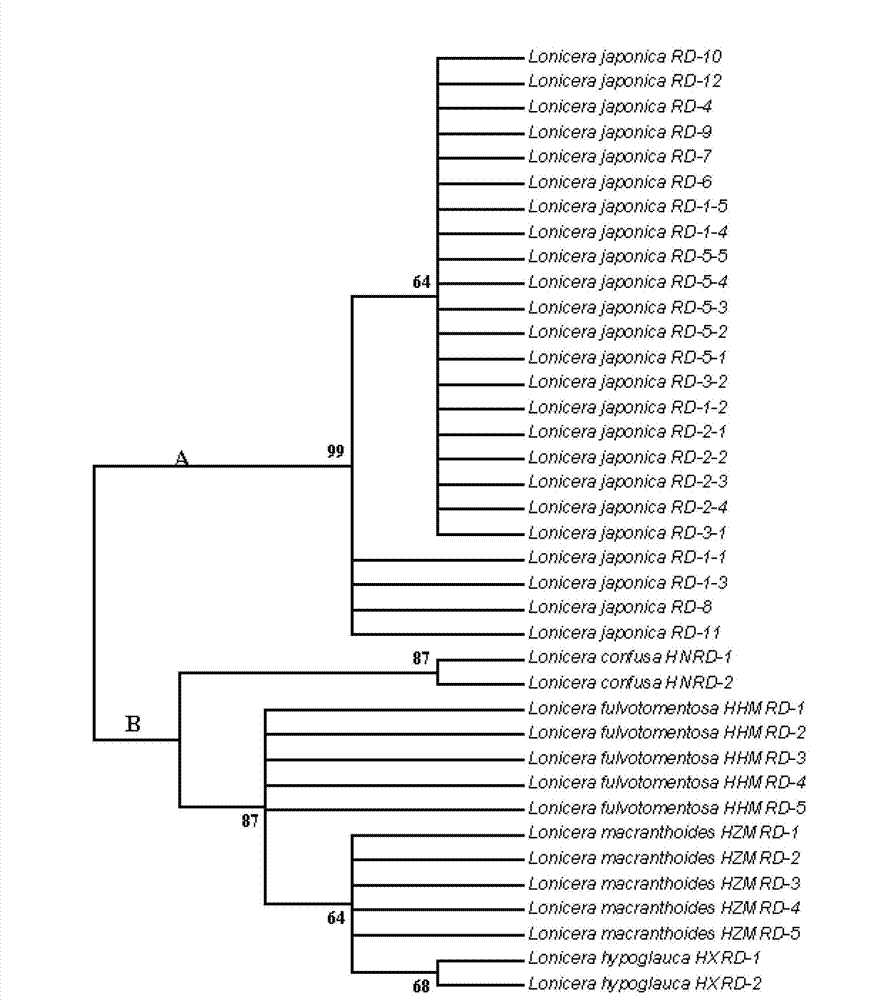
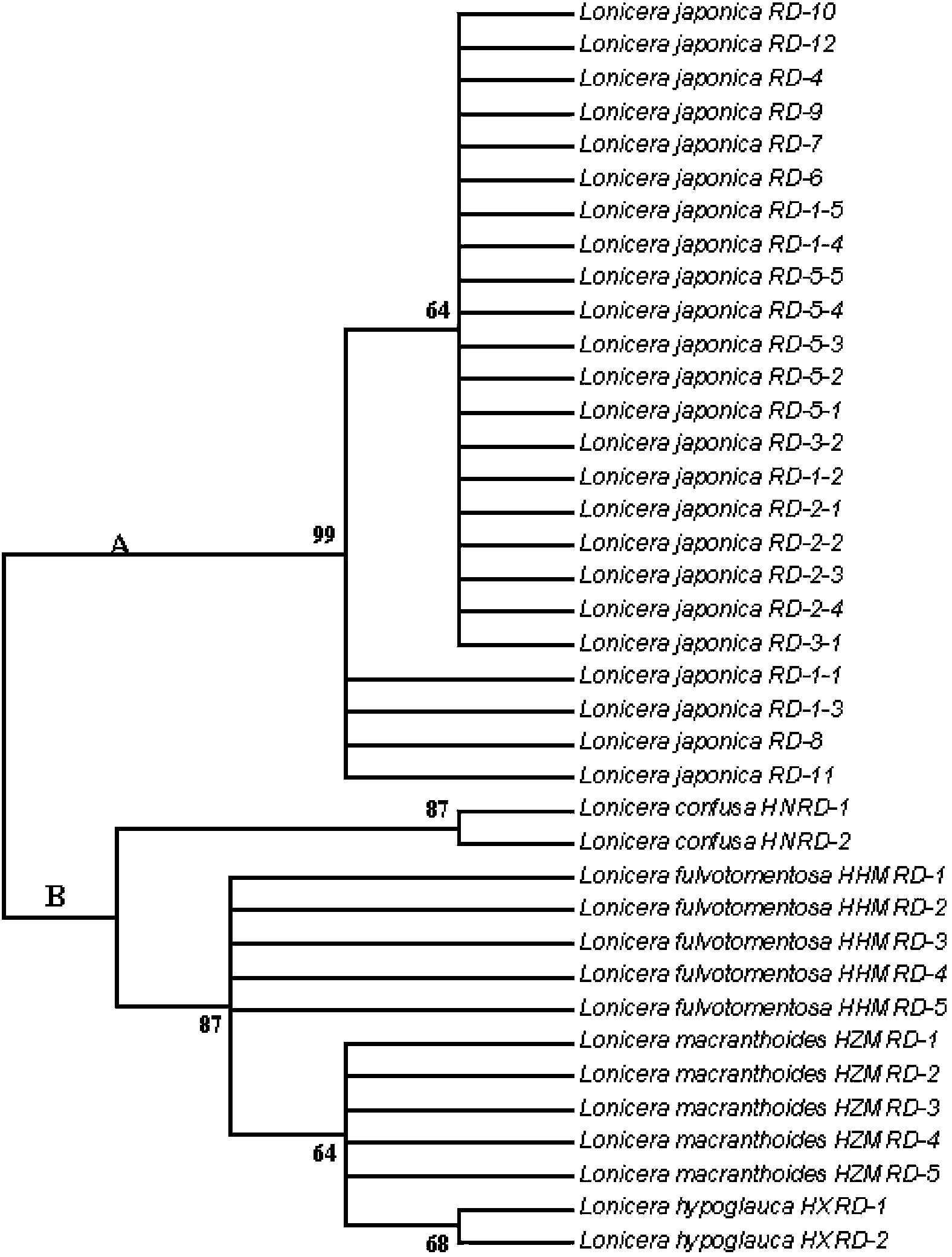
Method for identifying honeysuckle and lonicera confuse and application of same
ActiveCN103173532AEfficient extractionQuick extractionMicrobiological testing/measurementGermplasmRibosomal DNA
The invention relates to a method for identifying honeysuckle and lonicera confuse and an application of the method. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the step of performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on ITS2 nucleotide sequence, and particularly comprises the steps of 1) extracting the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a sample; 2) performing PCR amplification on the segments of the ITS2 sequence containing ribosome DNA; 3) splicing the amplification products to obtain a complete ITS2 intergenic region; and 4) establishing the NJ (neighbour-joining) tree of the ITS2 sequence of the sample. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively solving the problems of variety identification, variety improvement and breeding of honeysuckle medicinal materials, development and utilization of germplasm resources, and the like; and the method disclosed by the invention is wide in applicability, simple to operate, easy to grasp, high in accuracy, and capable of successfully realizing rapid and accurate identification on honeysuckle medicinal materials or powder and lonicera confuse medicinal materials or powder.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI +1
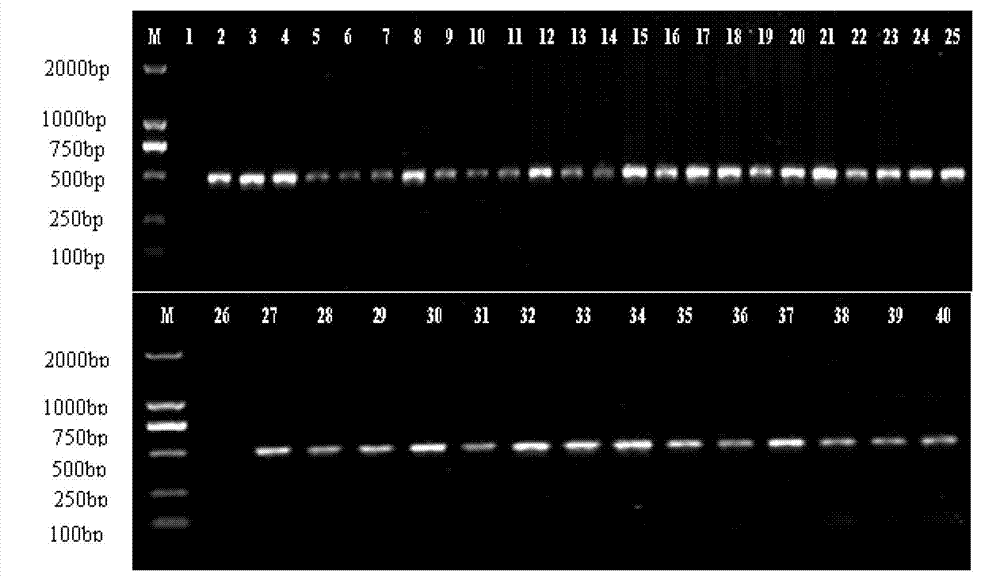
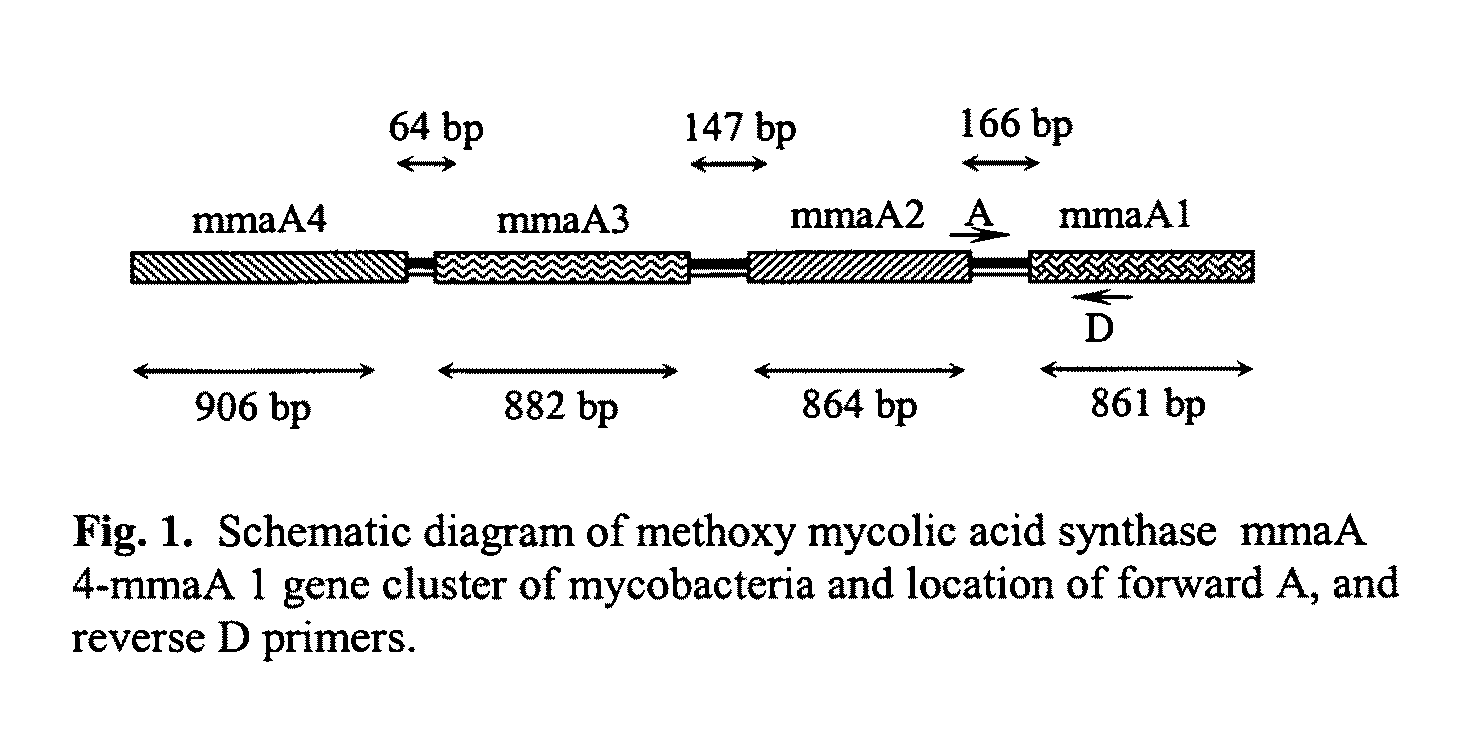
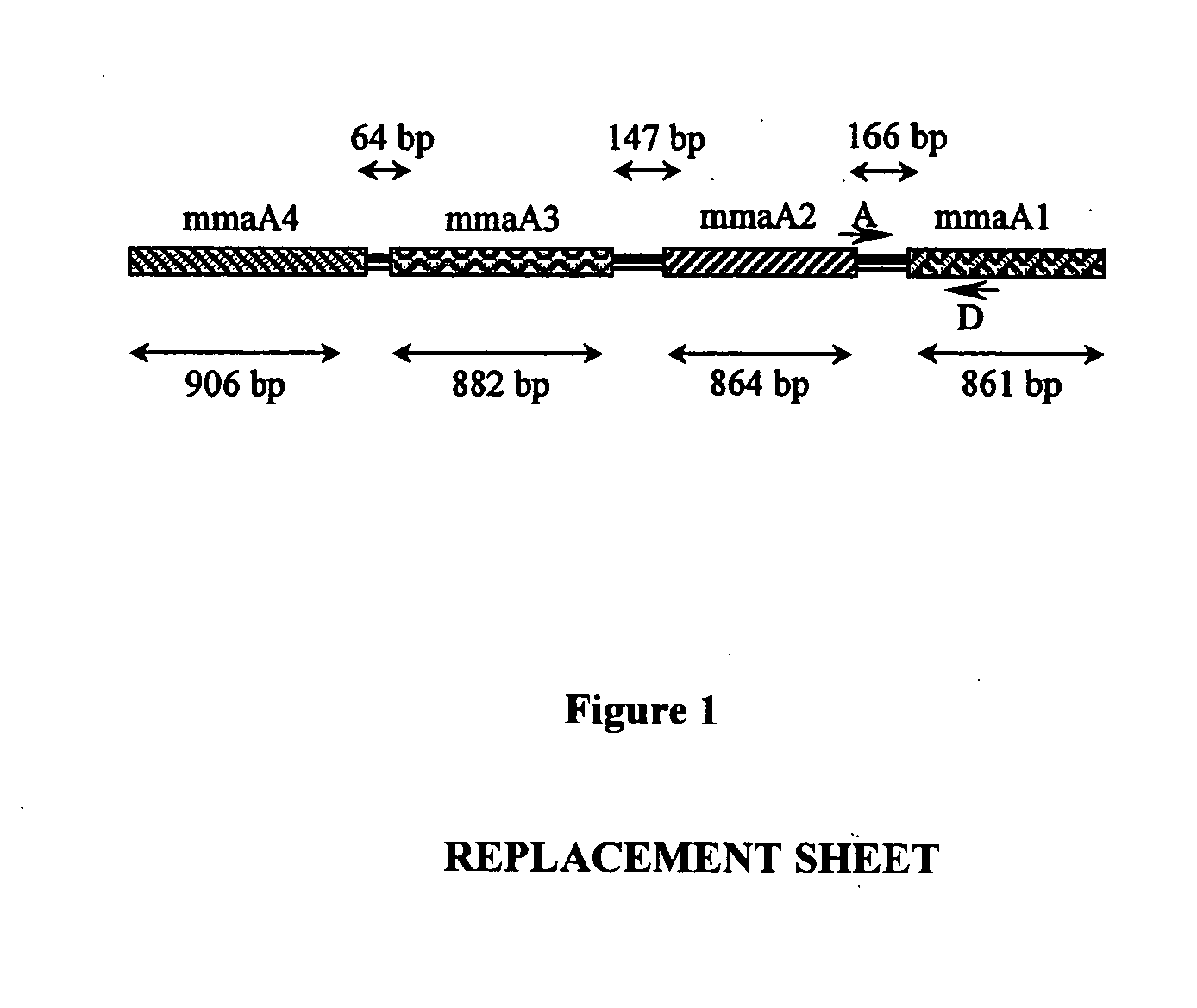
Method for detecting pathogenic mycobacteria in clinical specimens
The present invention relates to detection of pathogenic mycobacteria in clinical specimens such as sputum, cerebrospinal fluid, gastric lavage and tissue biopsies etc., wherein the novel stretch of DNA that lies in the intergenic region between methyl mycolic acid synthase genes mmaA1 and mmaA2 and the flanking region in mmaA1 and mmaA2 genes and is the invention uses a pair of designed oligonucleotide primers that specifically amplifies the target DNA from the clinical specimens.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Intergenic regions as insertion sites in the genome of modified vaccinia virus ankara (mva)
ActiveUS20050244428A1Insert firmlyFungiSsRNA viruses positive-senseModified vaccinia AnkaraPlasmid Vector
The present invention relates to novel insertion sites useful for the integration of exogenous sequences into the Modified Vaccinia Ankara (MVA) virus genome. The present invention further provides plasmid vectors to insert exogenous DNA into the genome of MVA. Furthermore, the present invention provides recombinant MVA comprising an exogenous DNA sequence inserted into said new insertion site as medicine or vaccine.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
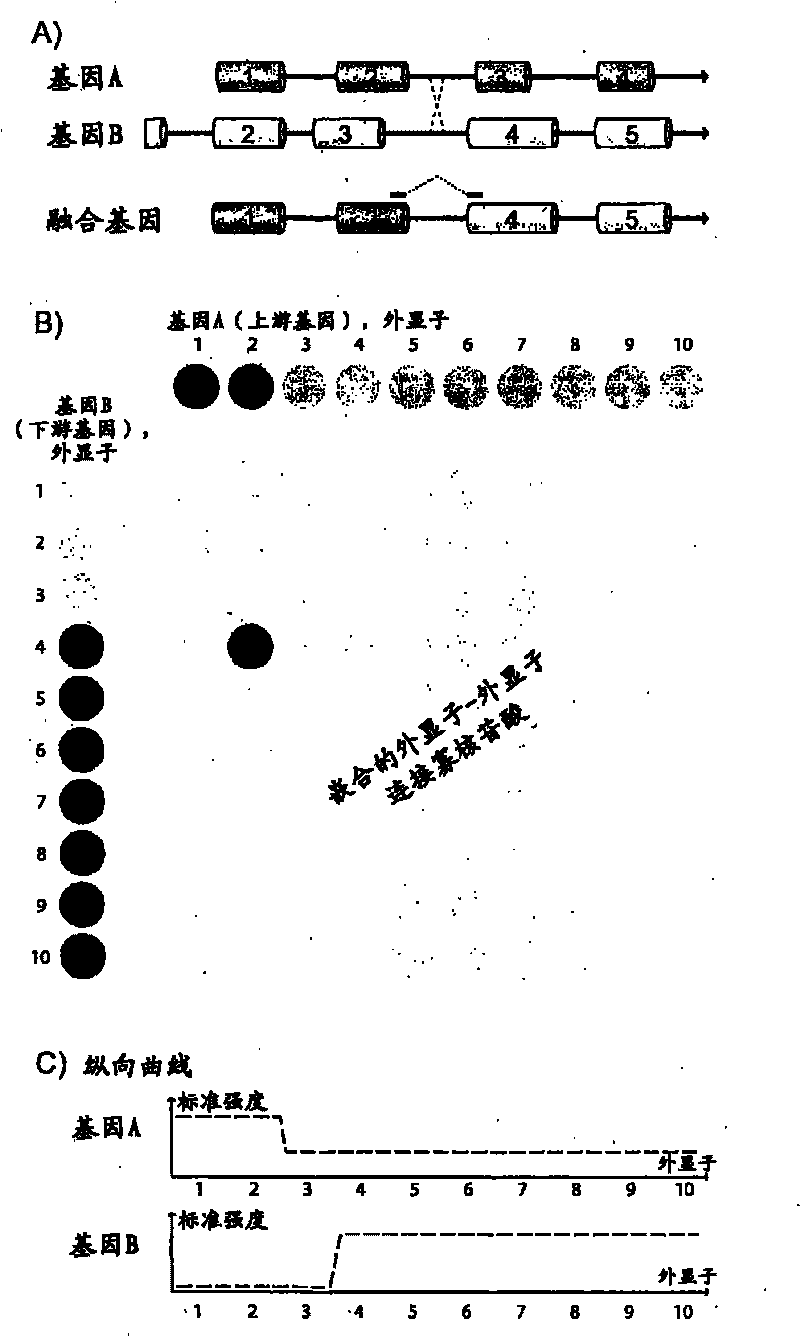
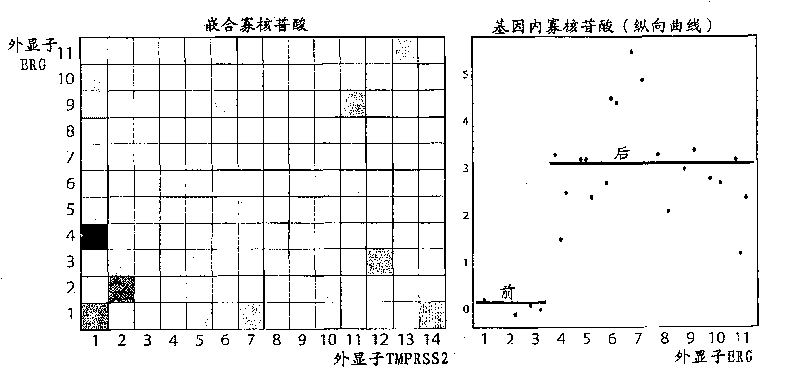
Fusion gene microarray
The present invention relates to a microarray comprising a chimeric probe for an intergenic exon-to-exon junction of a fusion gene and at least two intragenic probes for a fusion gene partner of the fusion gene. The invention further relates to a method of detecting a fusion gene and a kit suitable for detecting fusion genes.
Owner:UNIV OSLO HF
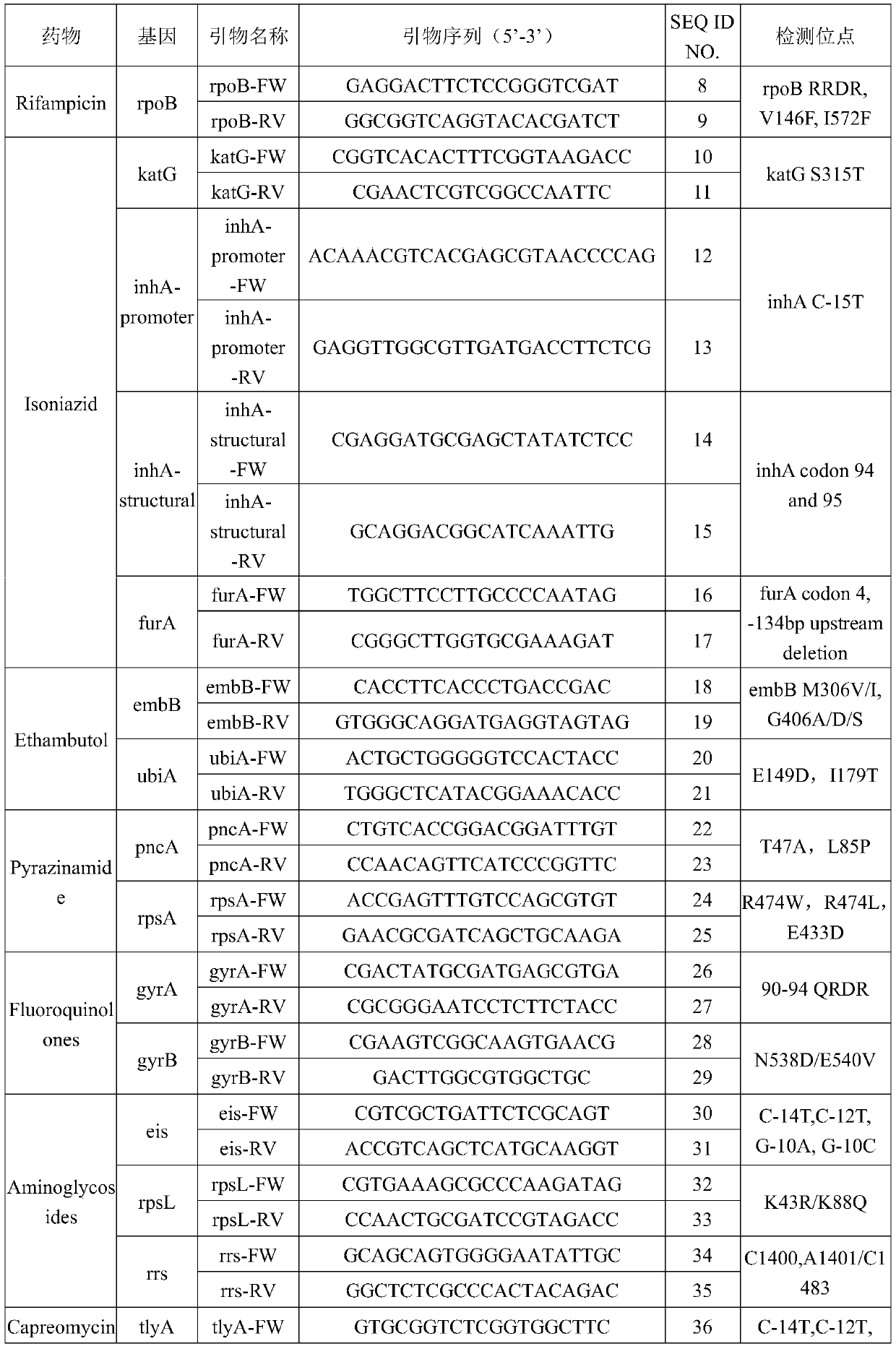
Tubercle bacillus drug tolerance detection reagent kit and tubercle bacillus drug tolerance detection method
PendingCN111172303AWide range of drug resistance detectionEasy constructionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationAntituberculosis drugTuberculosis bacillus
The invention provides a tubercle bacillus drug tolerance detection reagent kit and method. The tubercle bacillus drug tolerance detection reagent kit comprises a tubercle bacillus drug tolerance detection reagent, wherein the tubercle bacillus drug tolerance detection reagent comprises a sequencing primer in accordance with a tubercle bacillus drug tolerance gene; the tubercle bacillus drug tolerance gene comprises one or more genes of rpoB, katG, inhA-promoter, inhA-structural, furA, embB, ubiA, pncA, rpsA, gyrA, gyrB, eis, rpsL, rrs, tlyA, rplC and rrl; and further, the reagent kit also contains a tubercle bacillus nucleic acid detection reagent, and the tubercle bacillus nucleic acid detection reagent comprises a primer pair 1 in accordance with IS6110, a primer pair 2 in accordance with the IS6110 and a probe primer in accordance with the IS6110. Through the adoption of the tubercle bacillus drug tolerance detection reagent kit disclosed by the invention, tubercle bacillus nucleicacid in samples can be quickly detected, and positive samples can be further subjected to drug tolerance detection; and the tubercle bacillus drug tolerance detection reagent kit has good sensitivity, good specificity and good accuracy, and can perform mutation detection on 48 sites of 17 drug tolerance genes of common antituberculosis drugs and fragment deficiency detection of an intergenic region, so that the tuberculosis medication can be more accurately and comprehensively guided.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KINGMED DIAGNOSTICS GRP CO LTD +1
Recombinant modified vaccinia ankara (MVA) vaccinia virus containing restructured insertion sites
ActiveUS20120263750A1Viral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesModified vaccinia AnkaraOpen reading frame
The present invention relates to recombinant modified vaccinia Ankara (MVA) virus containing restructured sites useful for the integration of heterologous nucleic acid sequences into an intergenic region (IGR) of the virus genome, where the IGR is located between two adjacent, essential open reading frames (ORFs) of the vaccinia virus genome, wherein the adjacent essential ORFs are non-adjacent in a parental MVA virus used to construct the recombinant MVA virus, and to related nucleic acid constructs useful for inserting heterologous DNA into the genome of a vaccinia virus, and further to the use of the disclosed viruses as a medicine or vaccine.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Improved PCR detection method of dwarfing bacteria of sugarcane persistent roots
InactiveCN101633956ASimple extraction methodHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesImproved methodNucleotide sequencing
The invention provides an improved PCR detection method of the dwarfing bacteria of sugarcane persistent roots. A pair of specific primers Lxx1 / Lxx2 are designed according to an RSD pathogenic bacterium Lxx 16S-23SrDNA intergenic region nucleotide sequence, and a PCR multiplication method is adopted to detect the dwarfing bacteria of sugarcane persistent roots after the improved method is used for extracting the total DNA of sugarcane juice; the method overcomes the defects of the prior detection technique; and the invention provides the PCR detection method of the dwarfing bacteria of the sugarcane persistent roots, which has the advantages of high speed, stability, accuracy, high sensitivity and strong specificity.
Owner:SUGARCANE RES INST OF YUNNAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
New mutation site related to isoniazide resistance of mycobacterium tuberculosis and application thereof
InactiveCN103820440AImproving Molecular DetectionShorten diagnostic timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNew mutationDrug resistance
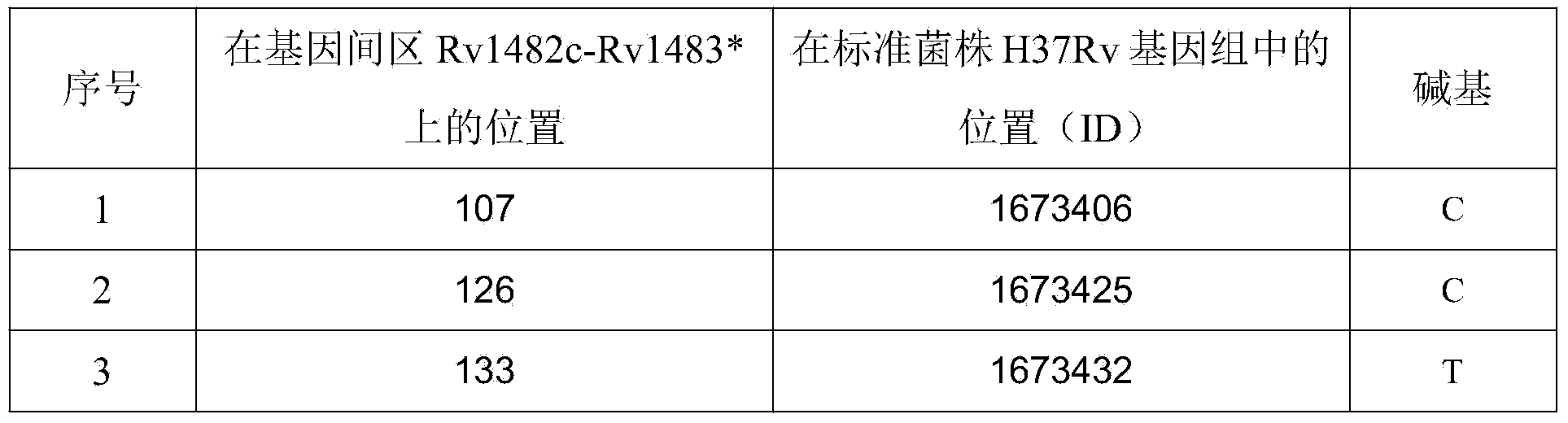
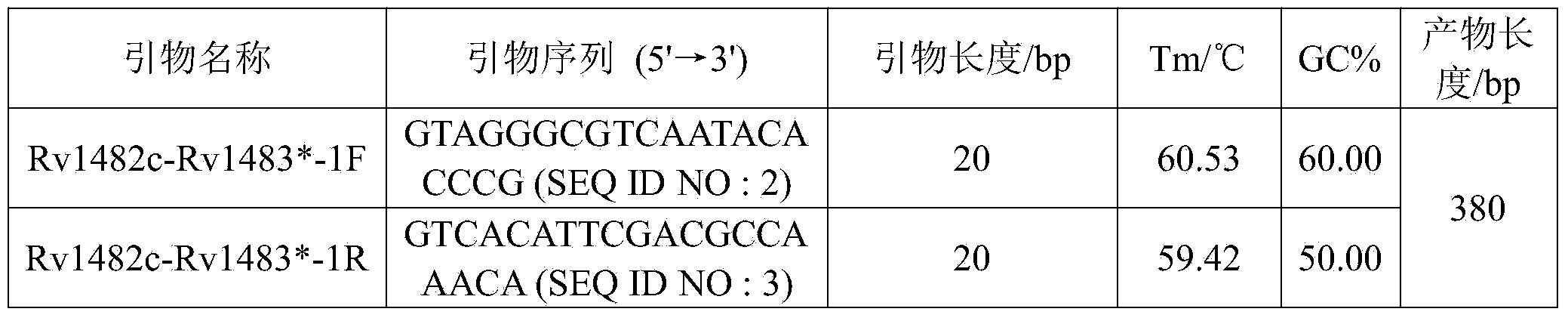
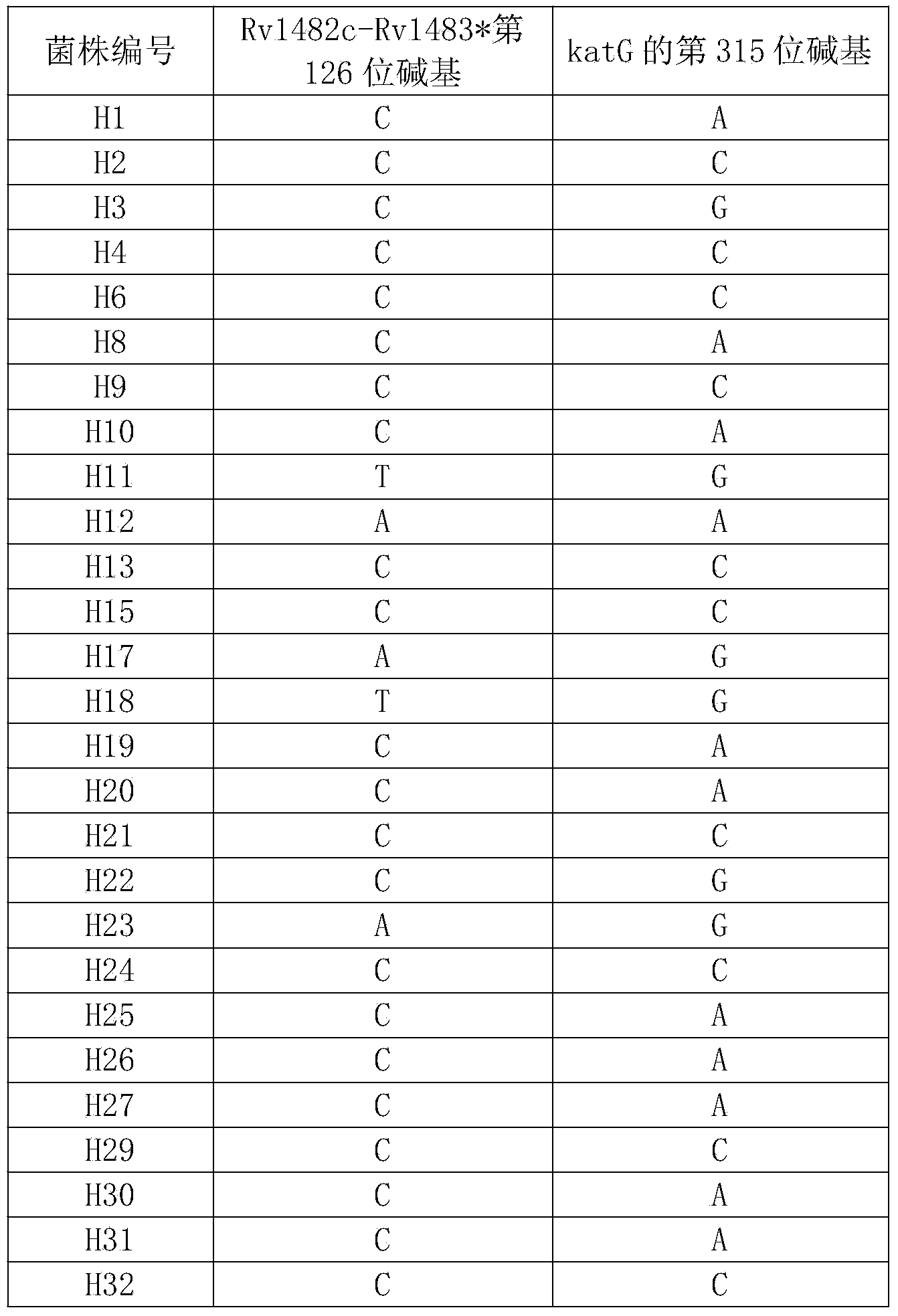
The invention discloses a new mutation site related to isoniazide resistance of mycobacterium tuberculosis and an application thereof. The new mutation site is positioned at a 1673425th site of a standard strain H37Rv genome, that is a 126th base in an intergenic region of Rv1482c to Rv1483*, and the generated point mutation comprises that a base C is mutated into a base T or a base A. The found new mutation site can be used as a detection target applied in detection of the isoniazide resistance of mycobacterium tuberculosis, improves the molecular detection level of the isoniazide resistance of mycobacterium tuberculosis, shortens the diagnosis time of patients, and saves the treating time and cost for the patients. The mycobacterium tuberculosis drug-resistant mutation site is explained to possibly occur in a non-coding region, the base mutation of the intergenic region is prompted to be possibly related to the drug resistance, and a drug-resistant biomarker also exists. The invention provides a new idea for finding out a new and more effective mycobacterium tuberculosis drug-resistant molecular marker.
Owner:广东省结核病控制中心
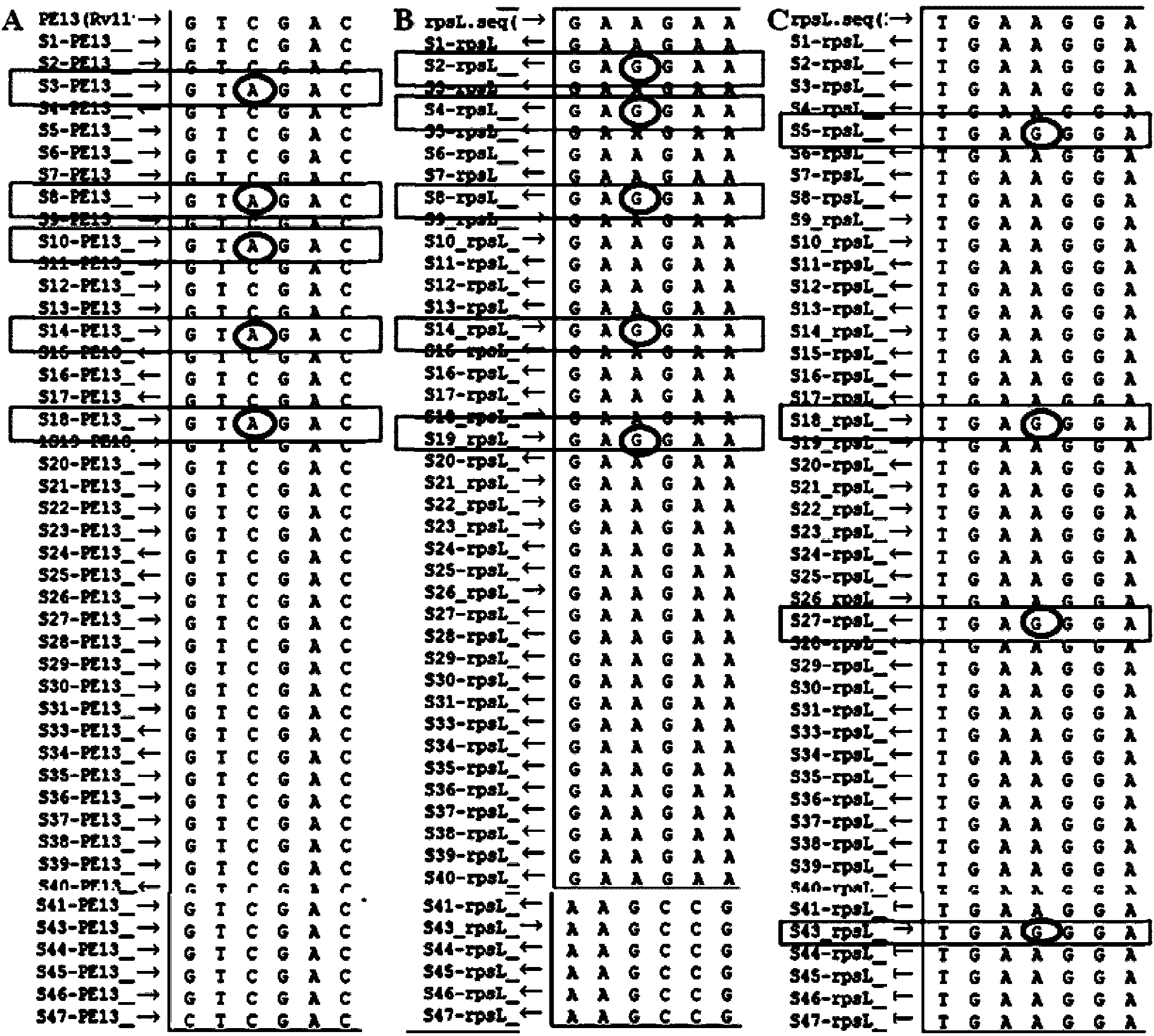
New mutation site related to streptomycin resistance of mycobacterium tuberculosis and application thereof
InactiveCN103820439AImproving Molecular DetectionShorten diagnostic timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNew mutationStreptomycin
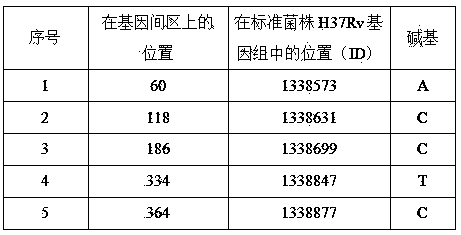
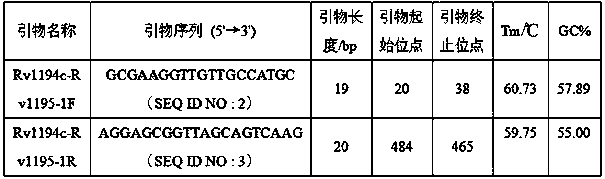
The invention discloses a new mutation site related to streptomycin resistance of mycobacterium tuberculosis and an application thereof. The new mutation site is positioned at a 1338631st site of a standard strain H37Rv genome, that is a 47th base in an intergenic region of Rv1194c to Rv1195, and the generated point mutation comprises that a base C is mutated into a base A. The found new mutation site can be used as a detection target applied in detection of the streptomycin resistance of mycobacterium tuberculosis, improves the molecular detection level of the streptomycin resistance of mycobacterium tuberculosis, shortens the diagnosis time of patients, and saves the treating time and cost for the patients. The mycobacterium tuberculosis drug-resistant mutation site is explained to possibly occur in a non-coding region, the base mutation of the intergenic region is prompted to be possibly related to the drug resistance, and a drug-resistant biomarker also exists. The invention provides a new idea for finding out a new and more effective mycobacterium tuberculosis drug-resistant molecular marker.
Owner:广东省结核病控制中心
Recombinant Modified Vaccinia Ankara (MVA) Vaccinia Virus Containing Restructured Insertion Sites
The present invention relates to recombinant modified vaccinia Ankara (MVA) virus containing restructured sites useful for the integration of heterologous nucleic acid sequences into an intergenic region (IGR) of the virus genome, where the IGR is located between two adjacent, essential open reading frames (ORFs) of the vaccinia virus genome, wherein the adjacent essential ORFs are non-adjacent in a parental MVA virus used to construct the recombinant MVA virus, and to related nucleic acid constructs useful for inserting heterologous DNA into the genome of a vaccinia virus, and further to the use of the disclosed viruses as a medicine or vaccine.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Method for detecting pathogenic mycobacteria in clinical specimens
InactiveUS20050123928A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue biopsyGastric lavage
The present invention relates to detection of pathogenic mycobacteria in clinical specimens such as sputum, cerebrospinal fluid, gastric lavage and tissue biopsies etc., wherein the novel stretch of DNA that lies in the intergenic region between methyl mycolic acid synthase genes mmaA1 and mmaA2 and the flanking region in mmaA1 and mmaA2 genes and is the invention uses a pair of designed oligonucleotide primers that specifically amplifies the target DNA from the clinical specimens
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
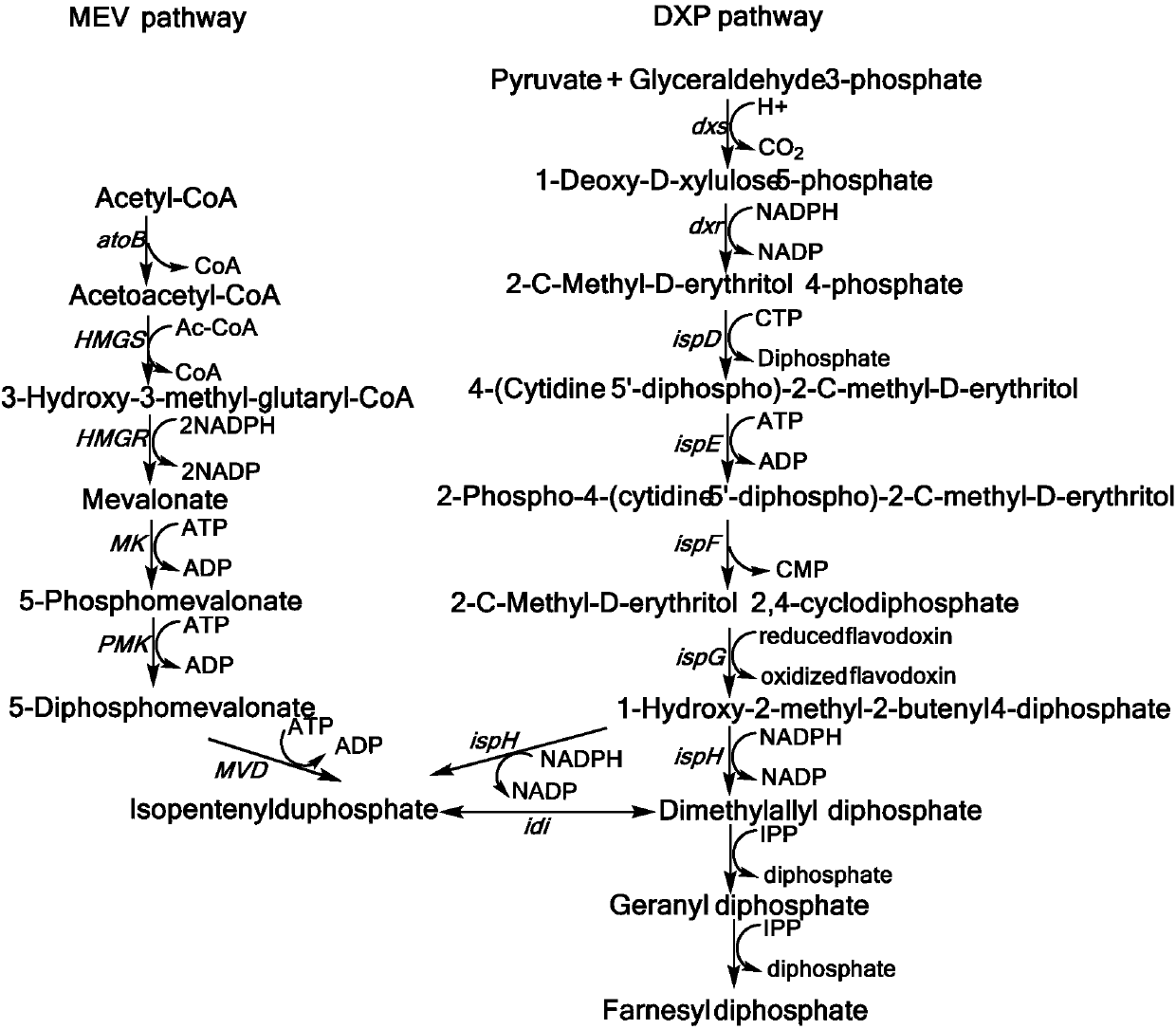
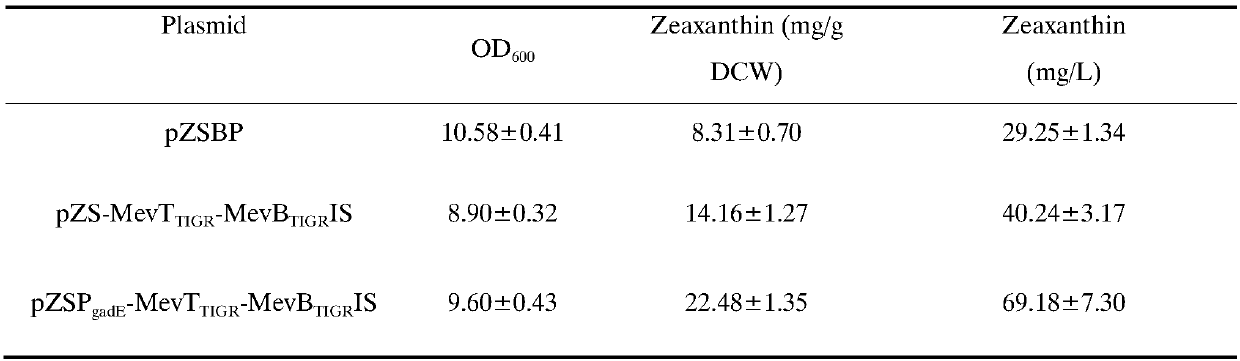
Mevalonic acid pathway tuned by TIGR
InactiveCN107190004AIncrease productionAvoid toxicityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliZeaxanthin
The invention belongs to the field of biochemistry, and relates to an MEV (mevalonic acid) pathway tuned by TIGR (tunable intergenic regions) to produce isopentene compounds, especially zeaxanthin. In particular, the exogenous MEV pathway is introduced into the engineered escherichia coli (ZEAX) for producing zeaxanthin, especially an upstream pathway and a downstream pathway of MEV tuned by the TIGR are introduced to coordinate the production of intermediate products and reduce the toxicity to cells due to the accumulation of intermediate products, and finally the yield of zeaxanthin is increased.
Owner:辛珉
Heat-resistant serum 4 type fowl adenovirus genetic engineering vaccine candidate strain and construction method thereof
InactiveCN110607285ASsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsHeat stabilityGenetic engineering
The invention relates to a heat-resistant serum 4 type fowl adenovirus genetic engineering vaccine candidate strain and a construction method thereof. The candidate strain is a thermal-stability newcastle disease virus (Newcastle Disease Virus) rAHR09-4F2 expressing serum 4 type fowl adenovirus spike protein 2, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: V201932. The candidate strain is obtained through using a heat-resistant newcastle disease attenuated virus strain rAHR09 as a carrier, inserting a serum 4 type fowl adenovirus (FAdV4) spike protein (fiber2) gene between a P intergenic region andan M intergenic region, and adopting a backward heredity technique. The result of evaluating the biological characteristics and the immunoprotection efficacy of the candidate strain displays that therecombinant virus has favorable heat stability and immunogenicity and provides favorable immunoprotection on FAdV4 infection.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method
InactiveUS20100216664A1Improve the level ofGood effectNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyIntergenic region
The present invention relates, in one aspect, to a method for determining the severity of a disease attributed to at least one genetic mutation in one or more of the genes encoding haemoglobin polypeptide chains, comprising the steps of: (a) providing a sample from said subject; and (b) determining the presence of one or more diagnostic markers:(i) within a 127 kb segment on chromosome 2p15;(ii) within MYB and / or HBSIL and / or the intergenic region between MYB and HBSIL located on the 6q23 QTL interval; and / or(iii) within one of the chromosomal loci given in Table 14; wherein the presence of said marker(s) in said sample is indicative that the severity of said disease in said subject will be or is less severe in said subject in comparison to a subject that does not possess said marker(s).
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Intergenic rnas and methods for modulating gene expression and pathogenesis in candida
Intergenic non-coding RNA molecules that regulate the expression of HWP1 and ALS3 of Candida are provided as are methods of using the non-coding RNA molecules and complementary molecules thereof in modulating HWP1 or ALS3 expression; adherence, yeast-to-hyphal transition, or biofilm development of Candida; and preventing or treating candidiasis.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Method for identifying honeysuckle and lonicera confuse and application of same
ActiveCN103173532BSolving Variety IdentificationSolution BreedingMicrobiological testing/measurementGermplasmRibosomal DNA
The invention relates to a method for identifying honeysuckle and lonicera confuse and an application of the method. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the step of performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on ITS2 nucleotide sequence, and particularly comprises the steps of 1) extracting the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a sample; 2) performing PCR amplification on the segments of the ITS2 sequence containing ribosome DNA; 3) splicing the amplification products to obtain a complete ITS2 intergenic region; and 4) establishing the NJ (neighbour-joining) tree of the ITS2 sequence of the sample. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively solving the problems of variety identification, variety improvement and breeding of honeysuckle medicinal materials, development and utilization of germplasm resources, and the like; and the method disclosed by the invention is wide in applicability, simple to operate, easy to grasp, high in accuracy, and capable of successfully realizing rapid and accurate identification on honeysuckle medicinal materials or powder and lonicera confuse medicinal materials or powder.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Gene chip and kit for detecting common pathogenic bacteria in food
InactiveCN101967510BImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyShigella sp
The invention provides a gene chip and a kit for detecting common pathogenic bacteria in food. The gene chip comprises a solid phase carrier and an oligonucleotide probe fixed on the solid phase carrier, wherein the oligonucleotide probe comprises DNA sequences which are selected from an nuc gene of staphylococcus aureus, an speB gene of streptococcus pyogenes, an invA gene of salmonella, an ipaHgene of Shigela, a zpx gene of Enterobacter sakazakii, a 16S-23S intergenic region of Klebsiella pneumoniae, a toxR gene of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and 16SDNA of the seven bacteria. The kit comprisesthe gene chip. By utilizing the gene chip and the kit to detect the seven common pathogenic bacteria in food, the invention has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, high accuracy and good repeatability.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD
Novel isothermal loop-mediated vibrio parahaemolyticus nucleic acid marker detection reagent
InactiveCN105803057AAvoid pollutionHave immunityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesAntigenVibrio parahemolyticus
The invention relates to a novel isothermal loop-mediated vibrio parahaemolyticus nucleic acid marker detection reagent. According to the reagent, an antigen is marked for a front inner primer in a primer group used in isothermal loop-mediated amplification, meanwhile another antigen is marked for a rear inner primer, the operation can be performed when a vibrio parahaemolyticus specific 16S-23S rRNA intergenic region sequence is amplified, subsequently a piece of colloidal gold test paper in match is adopted to detect an amplification product, and then vibrio parahaemolyticus can be detected. As the primer for the 16S-23S rRNA intergenic region sequence is designed for RNA secondary structure prediction, the situation that the detection sensitivity and the specificity can be influenced by mutation caused if other protein genes are used or the rRNA gene is blindly used can be avoided as much as possible, and the detection reagent provided by the invention is good in specificity and sensitivity.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
SNP marker of medicinal plant murraya paniculata as well as identifying method and application thereof
InactiveCN105821128ARapid identificationAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideMurraya paniculata
The invention provides an SNP marker of a medicinal plant murraya paniculata. In the SNP marker, the nucleotide on the 75th site from the 5' terminal in the sequence shown by SEQ ID No.1 is T, the nucleotide on the 109th site is T and / or the nucleotide on the 173rd site is A; the sequence shown by SEQ ID No.1 is the ITS2 intergenic region sequence of murraya paniculata. By adopting the SNP marker, the medicinal murraya paniculata can be quickly and accurately identified; the SNP marker has wide applicability and can guarantee the stability and reliability of the identification result from the source; and compared with traditional morphological identification method, the SNP marker of the medicinal plant murraya paniculata can realize quick and accurate identification of the medicinal murraya paniculata.
Owner:CHINA RESOURCES SANJIU MEDICAL & PHARMA +1
Quick identification method for paniculate swallowwort root medicinal material and counterfeit species thereof
InactiveCN107619877ARapid identificationEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementMedicinal herbsRibosomal DNA
The invention discloses a quick identification method for a paniculate swallowwort root medicinal material and counterfeit species thereof, namely rhizoma cynanchi stauntonii and blackend swallowwortroots. The quick identification method comprises the following steps: 1) extracting DNA of a to-be-detected sample; 2) taking the DNA of the to-be-detected sample as a template, and performing PCR amplification on a fragment of an ITS2 sequence containing ribosomal DNA; 3) splicing amplification products to obtain a complete ITS2 intergenic region; 4) analyzing interspecific variation sites of paniculate swallowwort root and counterfeit species thereof, namely rhizoma cynanchi stauntonii and blackend swallowwort roots, identifying as paniculate swallowwort roots if the 50-th site is a basic group C, and identifying as counterfeit species of paniculate swallowwort roots if the 50-th site is basic group deletion. The quick identification method is strong in applicability, is simple to operate, can realize quick and accurate identification for the paniculate swallowwort root medicinal material and counterfeit species thereof, and can identify a great number of samples within a short time.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
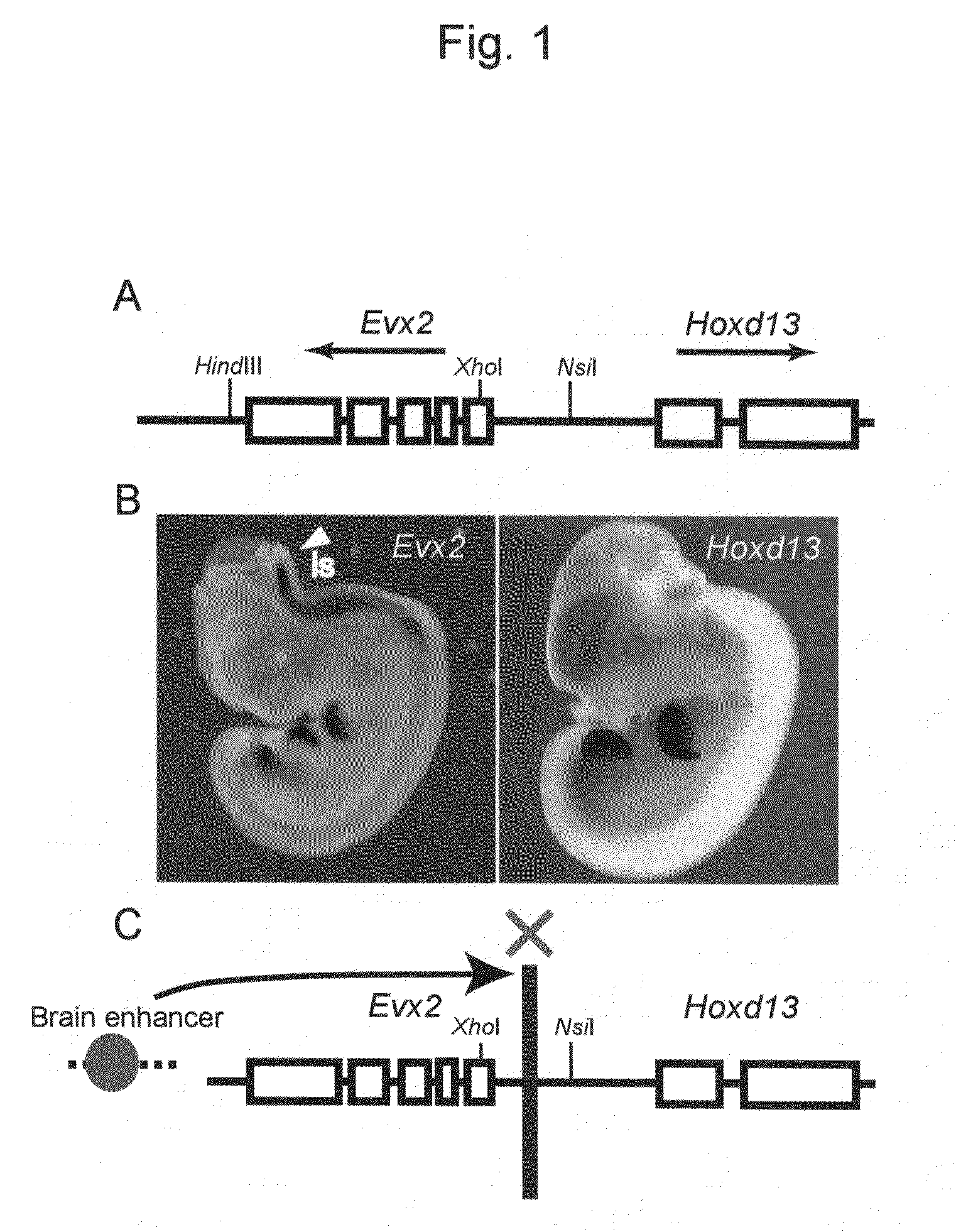
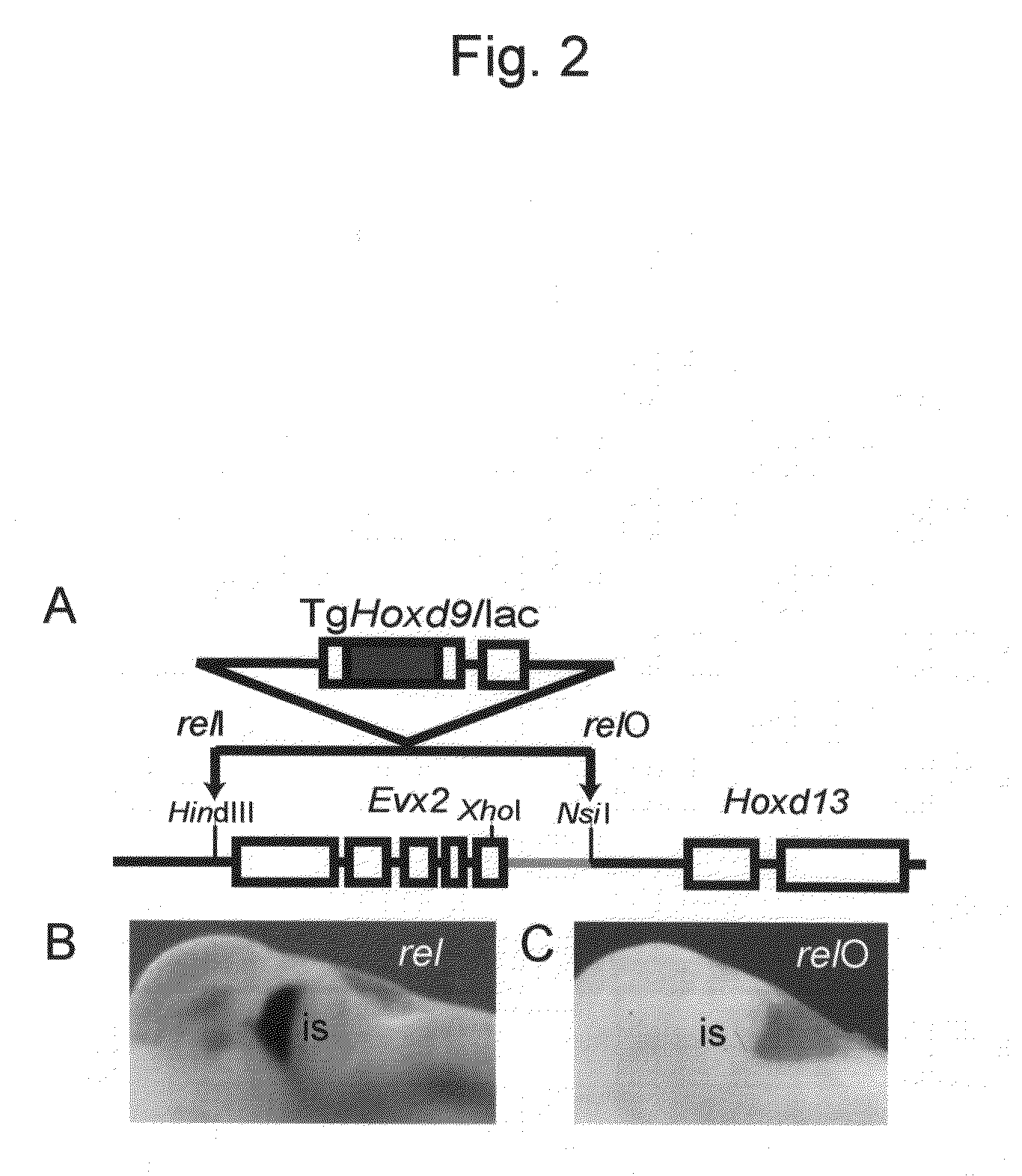
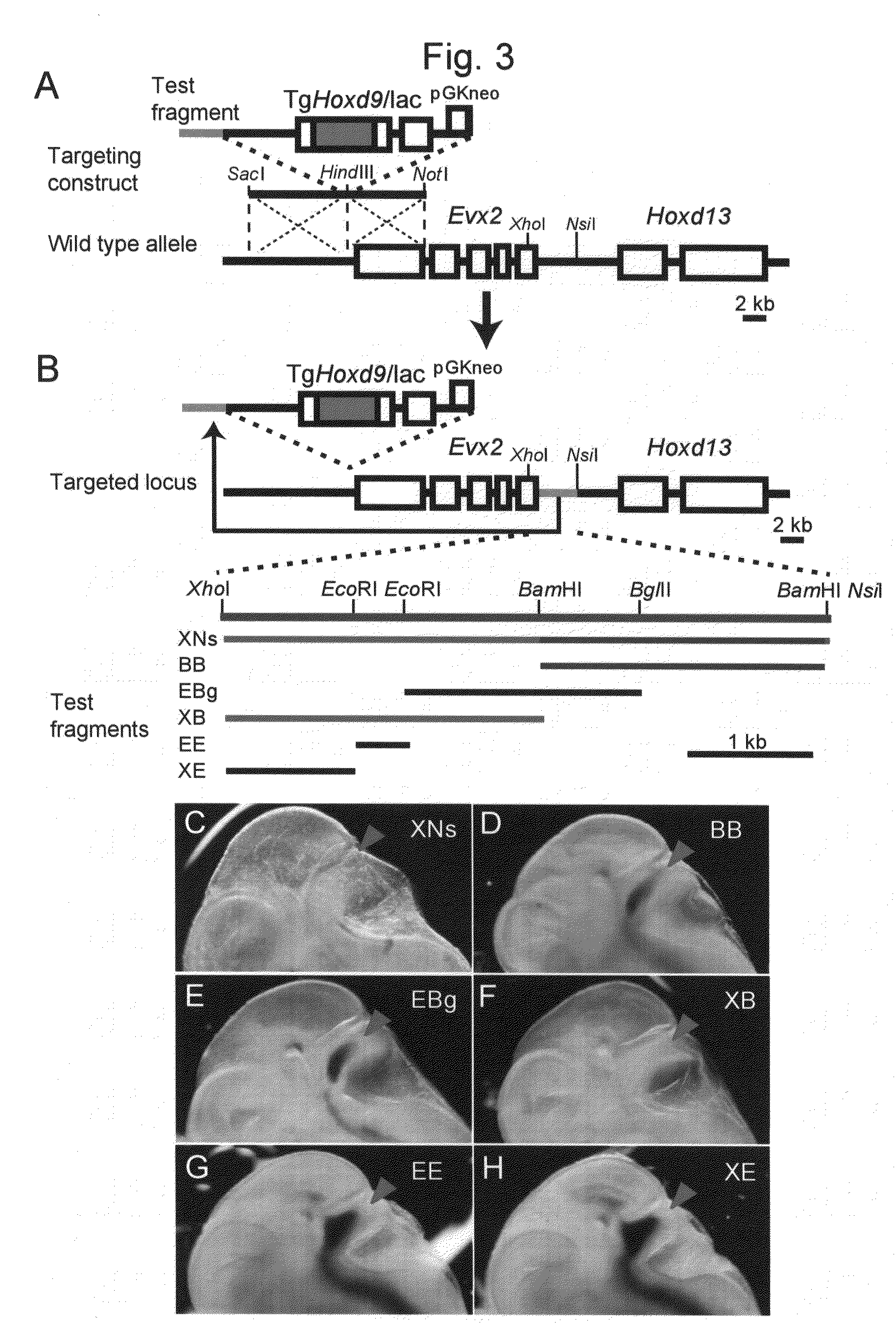
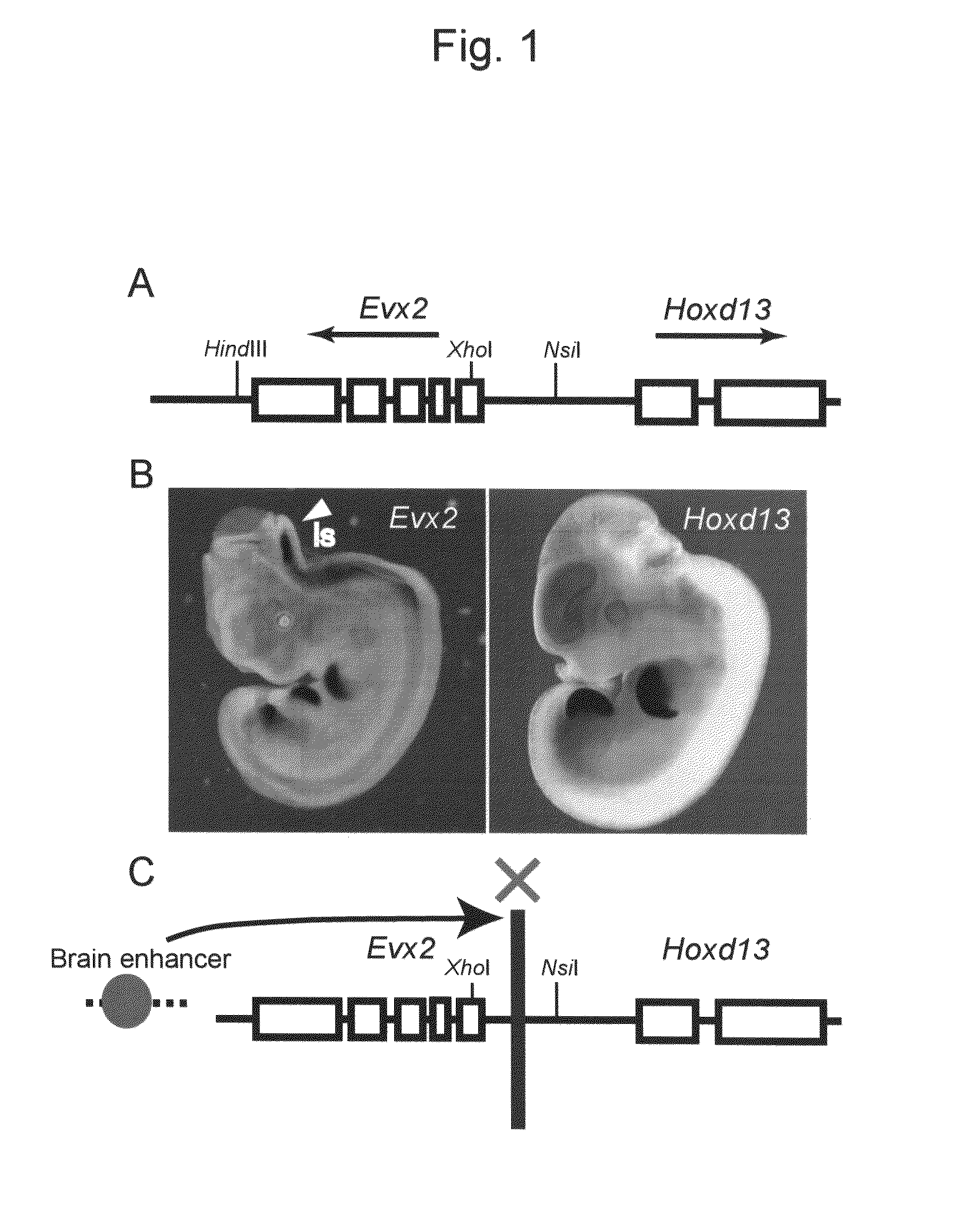
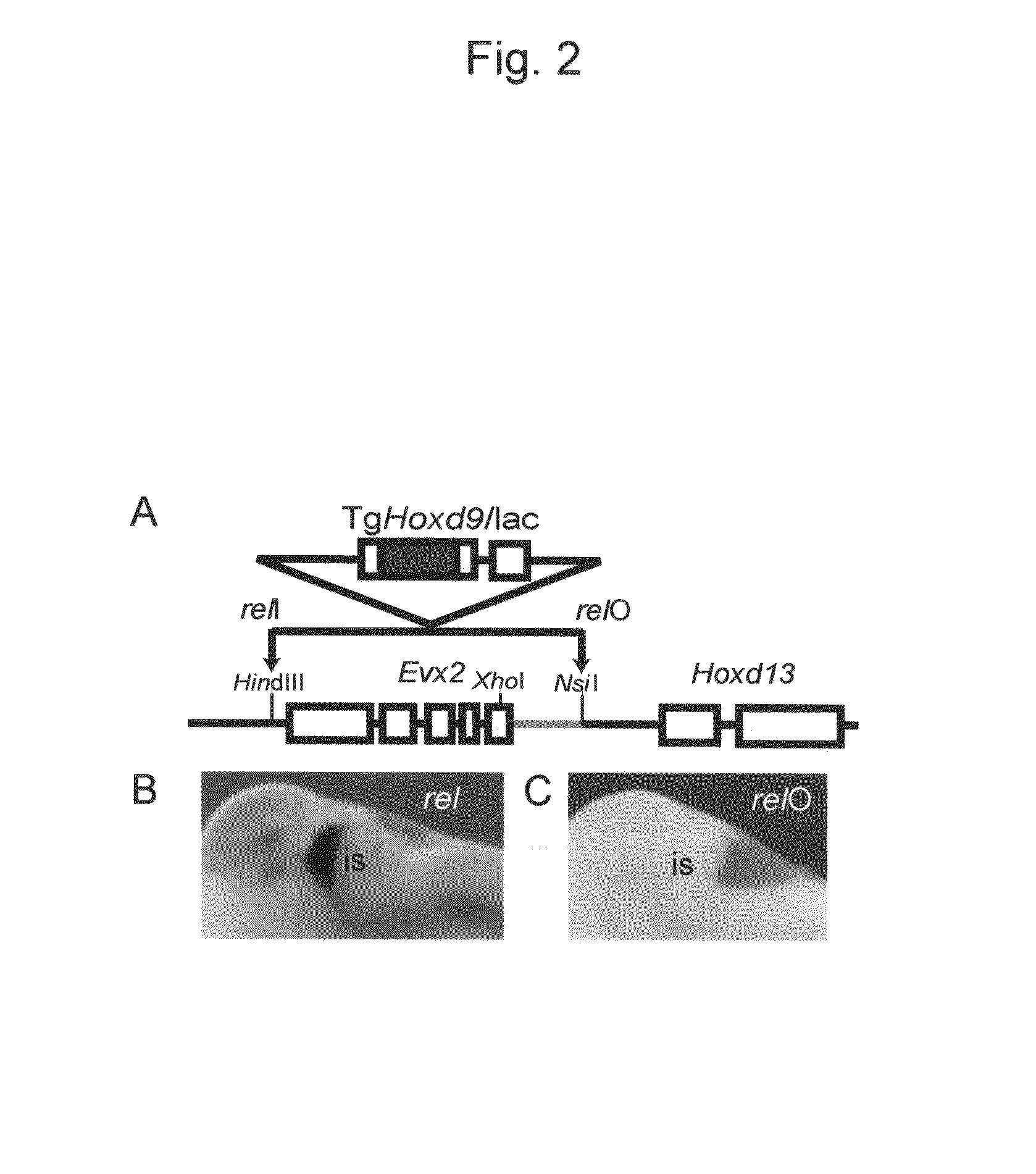
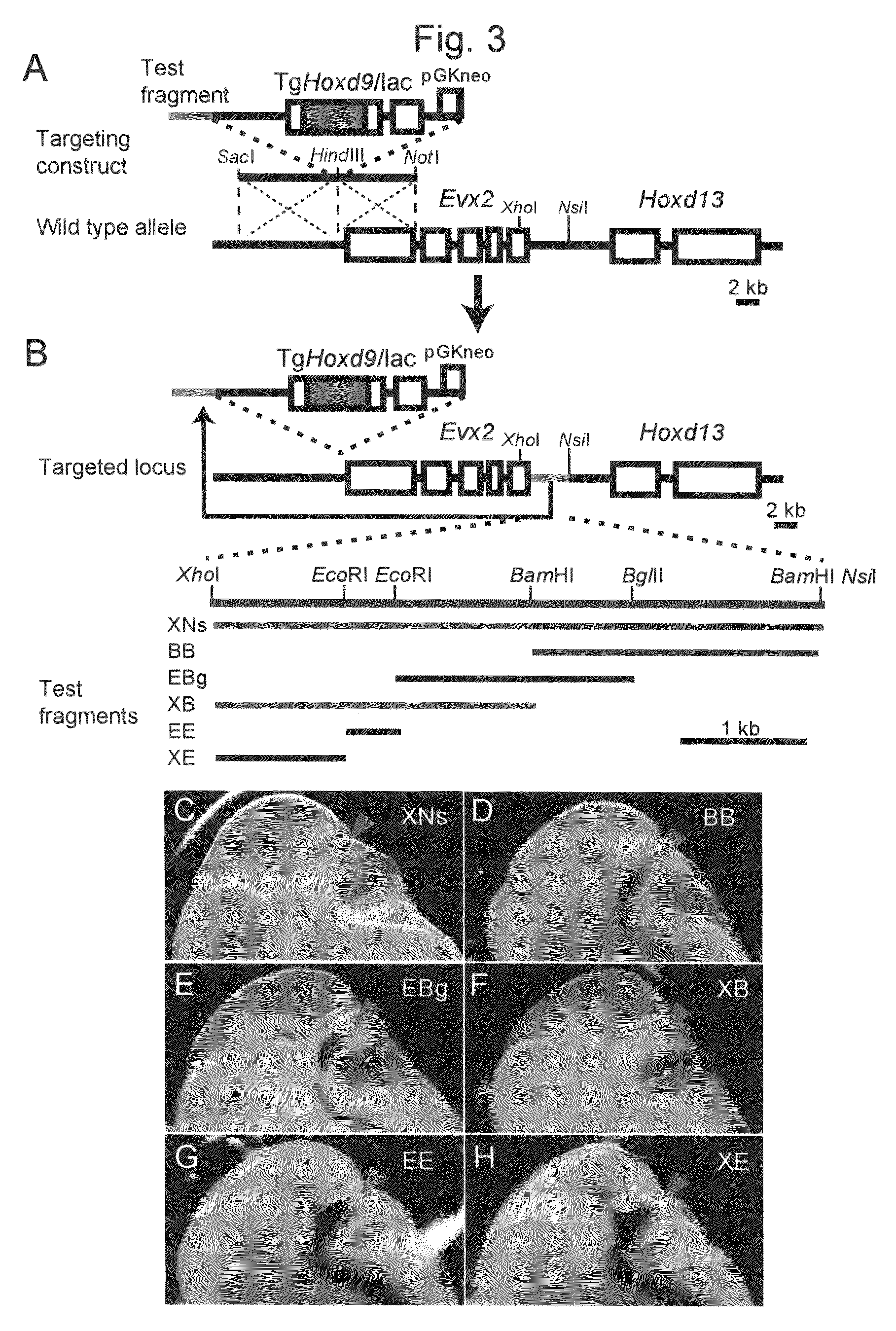
Method for enabling stable expression of transgene
This invention relates to a method for stably expressing a transgene integrated into the genome of an animal cell or of an animal over a long period. Specifically, this invention provides: an approximately 2.5 kb XhoI-BamHI fragment (or XB fragment) derived from the Evx2-Hoxd13 intergenic region of the animal genome, or a homologue thereof; a DNA containing a foreign DNA wherein the DNA has been inserted between the two essentially identical XB fragments or homologues thereof; a vector, animal cell, or nonhuman mammalian animal containing said DNA; and use of the vector, animal cell, or nonhuman mammalian animal for production of a substance or therapy.
Owner:RIKEN
Molecular marker primer and method used for identification of prunus pedunculata, prunus mongolica, and prunus triloba
ActiveCN108998567AQuick identificationSusceptible to the environmentMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerAgricultural science
The invention discloses a molecular marker primer and a method which are used for identification of prunus pedunculata, prunus mongolica, and prunus triloba. The molecular marker primer comprises a forward primer and a reverse primer; the sequence of the forward primer tKF is ACTCGAACCCGGAACTAG, and the sequence of the reverse primer tKR is CGACCGATTTCTGCGTAT. The identification method comprises following steps: 1, leaf sample collecting; 2, leaf sample total genome DNA extraction; 3, amplification of target genes in leaf sample total genome DNA obtained in step 2 using the molecular marker primer used for identification of prunus pedunculata, prunus mongolica, and prunus triloba, and obtaining of amplification products; 4, purifying and sequencing of the amplification products obtained instep 3; and 5, comparison analysis on sequencing results obtained in step 4. According to the method, trnK-UUU intergenic region based base difference can be taken as the molecular marker primer usedfor identification of prunus pedunculata, prunus mongolica, and prunus triloba germplasm distinguishing, the identification method is simple, and operation is convenient.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Mitochondria molecular marker primer of enteromorpha population and application thereof
ActiveCN108315468ARapid identificationEasy identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPropaguleAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the technical field of algae molecular markers, and particularly relates to a mitochondria molecular marker primer of enteromorpha population and application thereof. The mitochondria molecular marker primer is applied to identify a high-resolution mitochondria molecular marker (the sequence of a rps2-trnL intergenic region) of the enteromorpha population. The method can detect an algae sample and a microcosmic propagule sample, and is more reliable and practical compared with a conventional method, and accordingly the application of the mitochondria molecular marker primer of the enteromorpha population has significant meaning on the aspects of green tide disaster research, enteromorpha germplasm identification, phylogeny, systematic geography research and protection and utilization of enteromorpha resources.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Molecular marker closely linked with tomato neck and root rot resistant gene Frl, and application of molecular marker
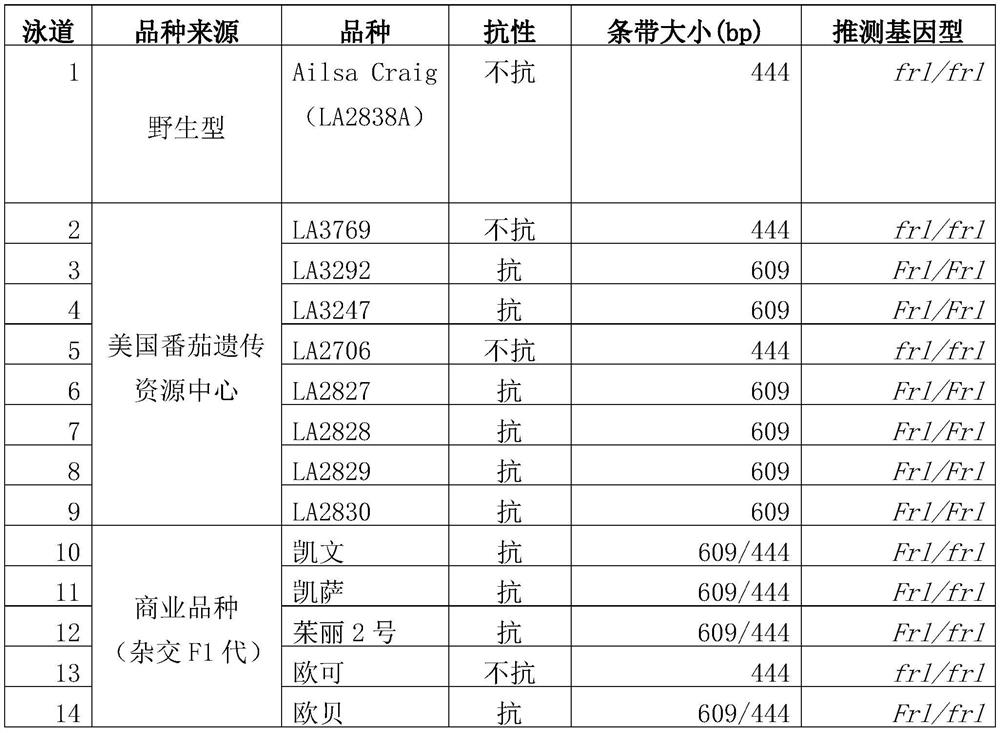
ActiveCN113943826AImprove accuracyShorten the breeding cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementResistant genesRoot rot
The invention discloses a molecular marker closely linked with a tomato neck and root rot resistant gene Frl, and application of the molecular marker. The invention provides application of a substance for detecting whether a 165bp fragment is contained in a positioning interval of an Frl gene in the genome of a tomato variety or not in identification or auxiliary identification of tomato neck and root rot resistance of tomatoes. The invention discovers that 165bp large fragment insertion related to the tomato neck and root rot resistance is in the presence in an intergenic region in the positioning interval (an interval of 4.2-5.1 Mb of a tomato No.9 chromosome) of the Frl gene in the genome of the tomato variety, a PCR-based molecular marker is designed according to the fragment, whether a tomato material to be detected contains the Frl gene or not and whether the tomato material is homozygous or not can be detected, a breeding period can be shortened, and the accuracy of breeding selection is improved.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
A high-efficiency and controllable expression system of exogenous genes carried by endogenous
ActiveCN111088254BImprove controllabilityImprove stabilityFungiVectorsHeterologousTranscriptional expression
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, and discloses an efficient and controllable expression system of an exogenous gene carried by an endogenous source, which includes a sequentially connected sequence: a host target gene stop codon upstream segment containing a stop codon, and a fungal operon gene interval region, the target gene, and the DNA fragment downstream of the stop codon of the host target gene, the target gene is connected using the fungal operon intergenic region sequence, and inserted into the downstream of the stop codon of the host cell expression gene by site-directed gene insertion. The promoter of the target gene completes the transcriptional expression of the target gene. The expression system simplifies the experimental operation steps, improves work efficiency, increases the controllability and stability of target gene expression, and reduces the requirement for known promoter diversity for multi-gene heterologous expression. The excavation of natural products, the improvement of production and the creation of unnatural compounds have high practical application value.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Protozoan expression system
InactiveUS20010010928A1Improve purification effectHigh densityPeptide/protein ingredientsProtozoaBiotechnologyDisease
A method for the high level production of active, properly processed recombinant protein in trans-splicing organisms is disclosed. The method involves the integration of the gene encoding the recombinant protein of interest into a chromosomal locus where it is transcribed under the direction of the rRNA promoter. The gene is also operably linked to intergenic regions allowing the protein to be translated in these organisms. The recombinant organisms expressing a therapeutic protein can also be used to treat a disease or undesirable condition which is characterized by a deficiency in that protein.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Method for enabling stable expression of transgene
This invention relates to a method for stably expressing a transgene integrated into the genome of an animal cell or of an animal over a long period. Specifically, this invention provides: an approximately 2.5 kb XhoI-BamHI fragment (or XB fragment) derived from the Evx2-Hoxd13 intergenic region of the animal genome, or a homologue thereof; a DNA containing a foreign DNA wherein the DNA has been inserted between the two essentially identical XB fragments or homologues thereof; a vector, animal cell, or nonhuman mammalian animal containing said DNA; and use of the vector, animal cell, or nonhuman mammalian animal for production of a substance or therapy.
Owner:RIKEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com