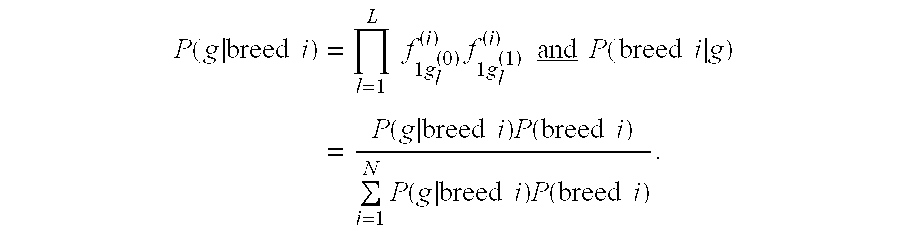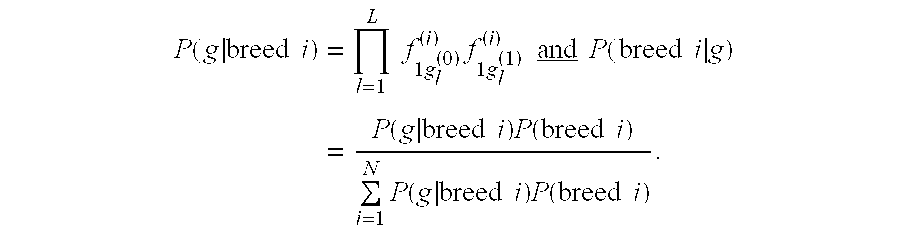Patents
Literature
117 results about "Animal genome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Massively parallel contiguity mapping
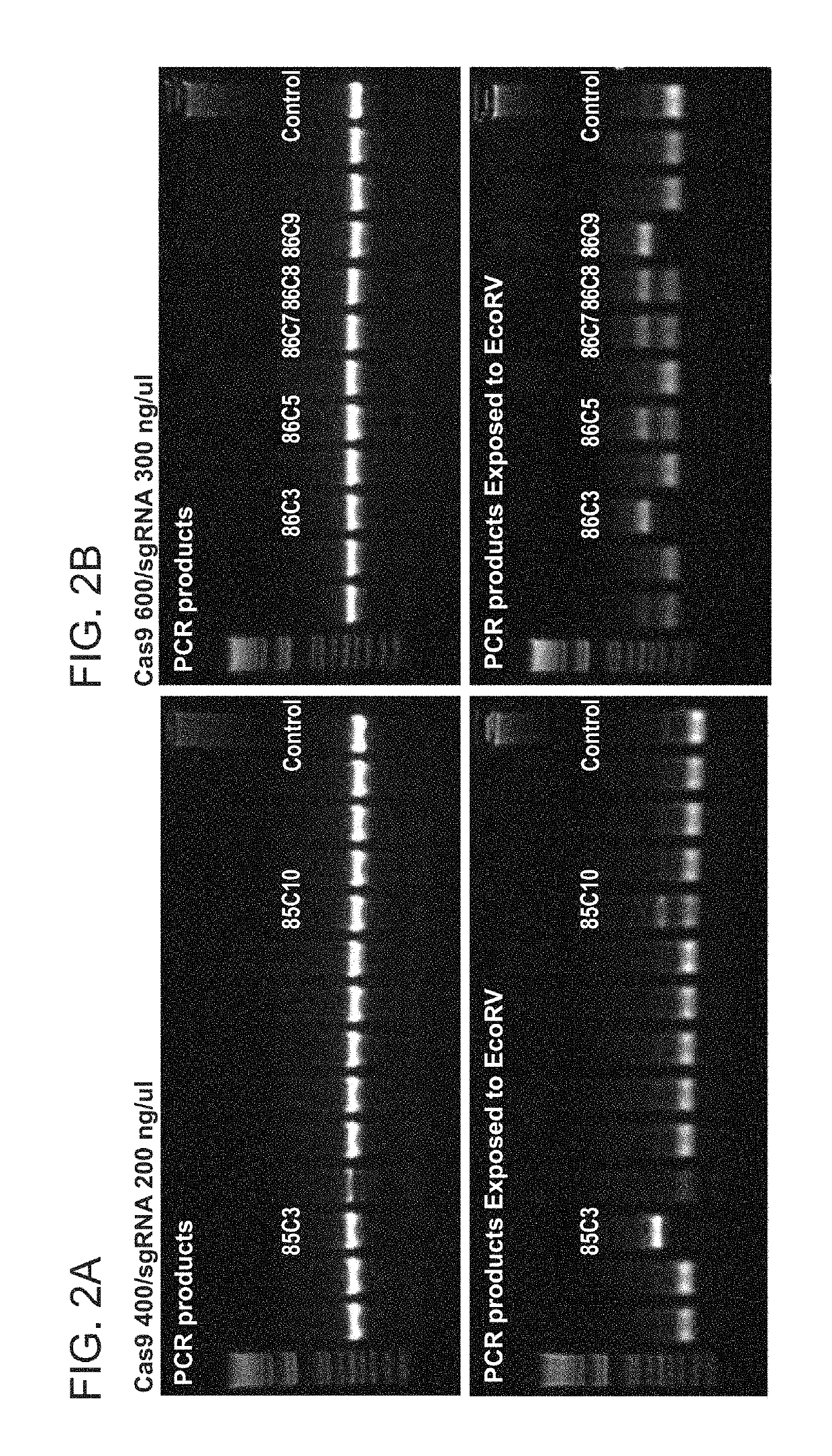
ActiveUS20130203605A1Reducing sequenceLimited to sequenceLibrary member identificationChemical recyclingHuman DNA sequencingMammalian genome
Contiguity information is important to achieving high-quality de novo assembly of mammalian genomes and the haplotype-resolved resequencing of human genomes. The methods described herein pursue cost-effective, massively parallel capture of contiguity information at different scales.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Tool for efficient site-specific transposition of genes and application of tool
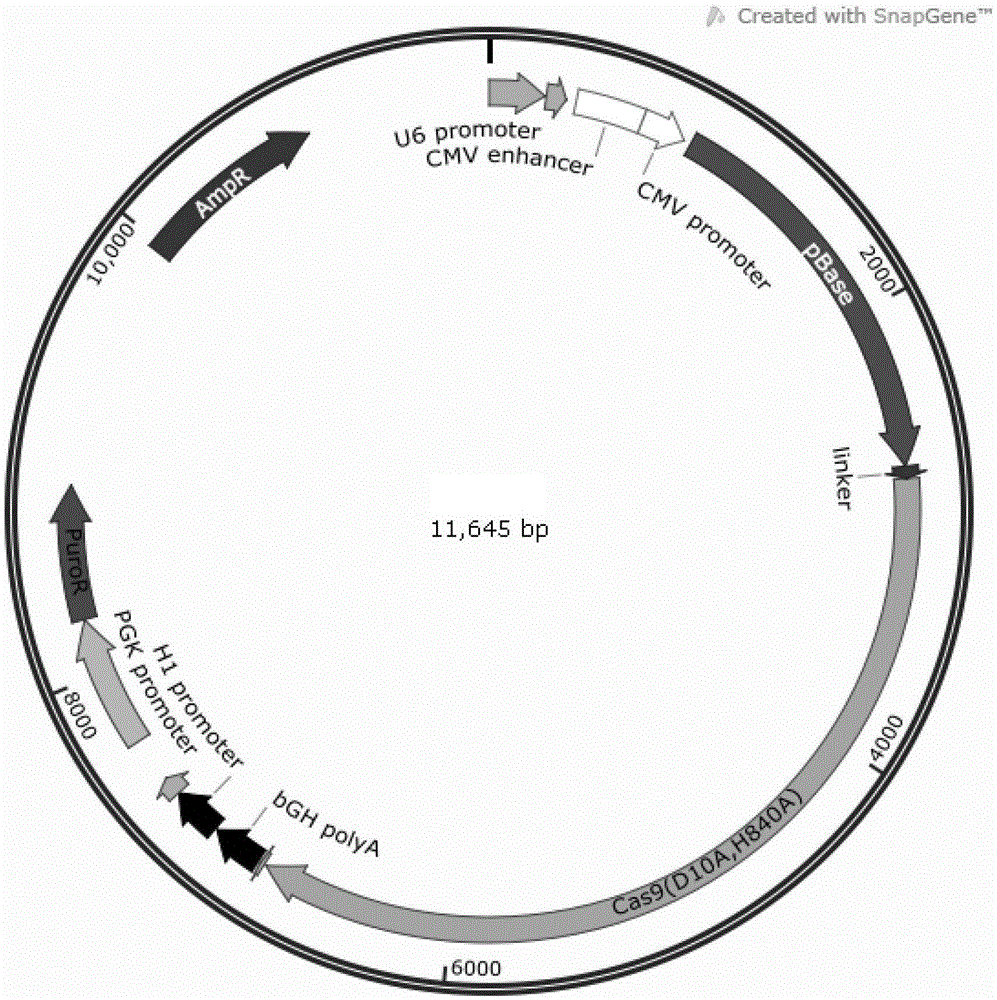
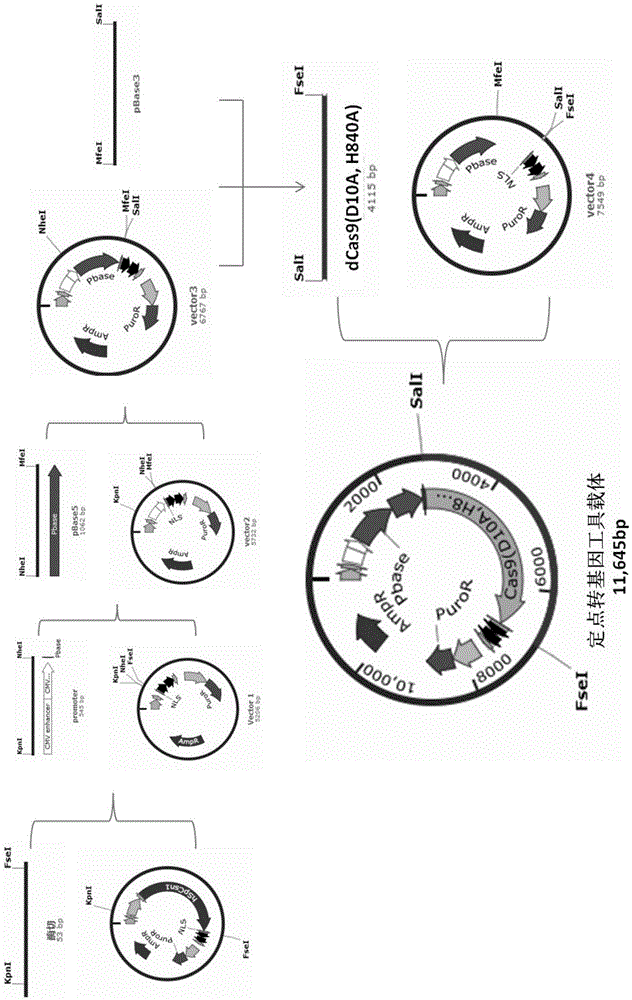
ActiveCN105646719ARealize transposition functionRealize site-specific transgeneHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGene engineeringAnimal genome
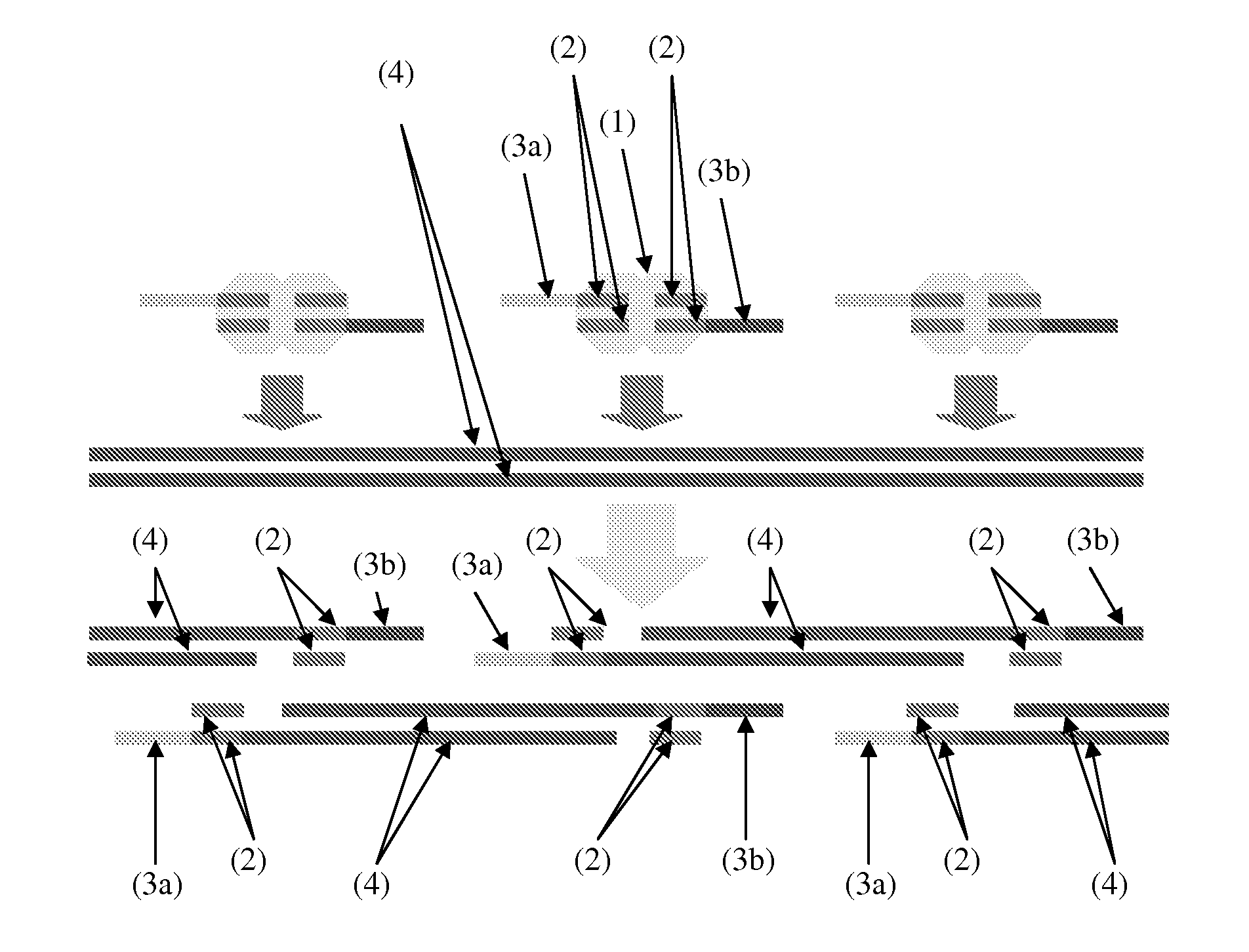
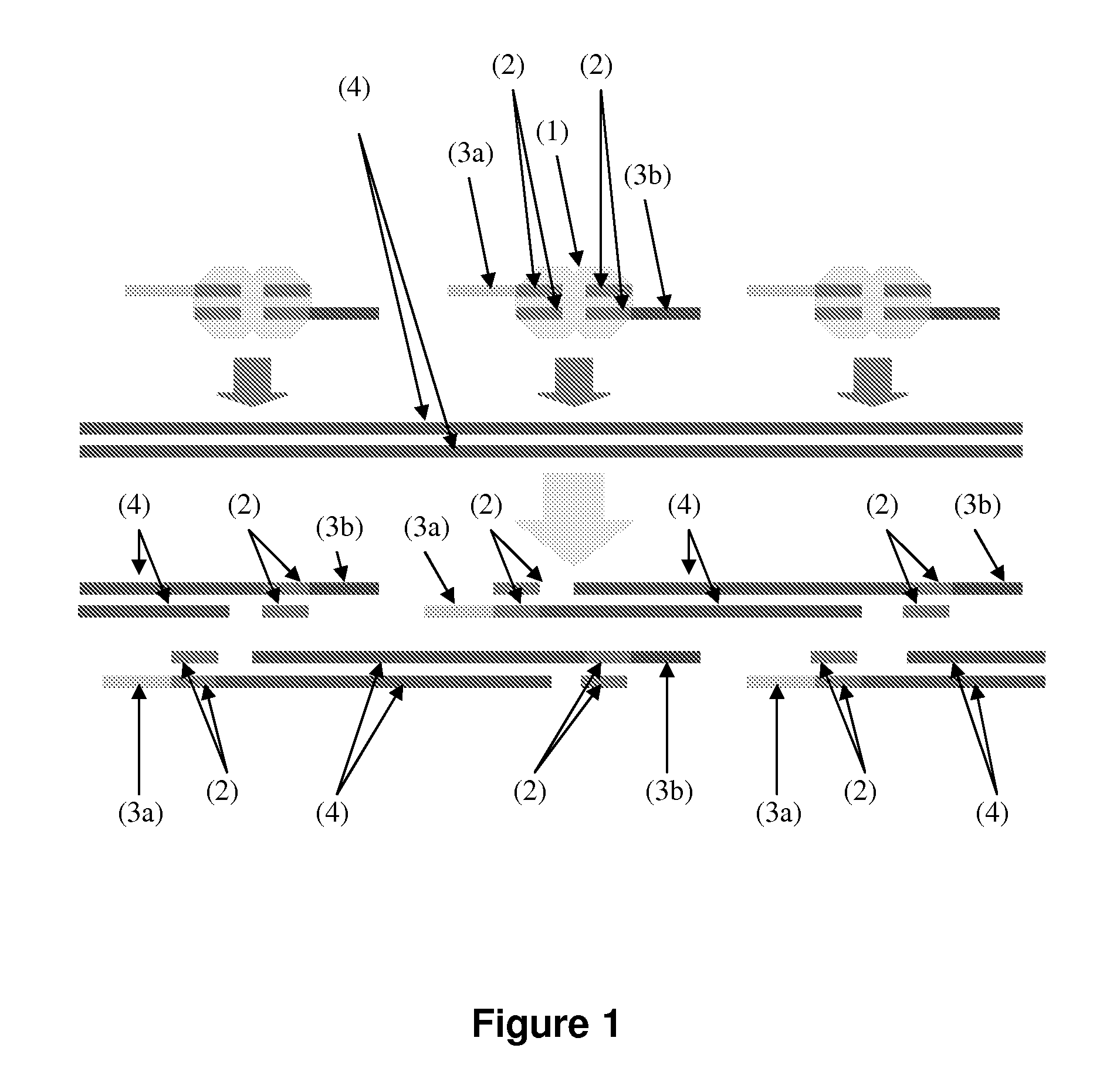
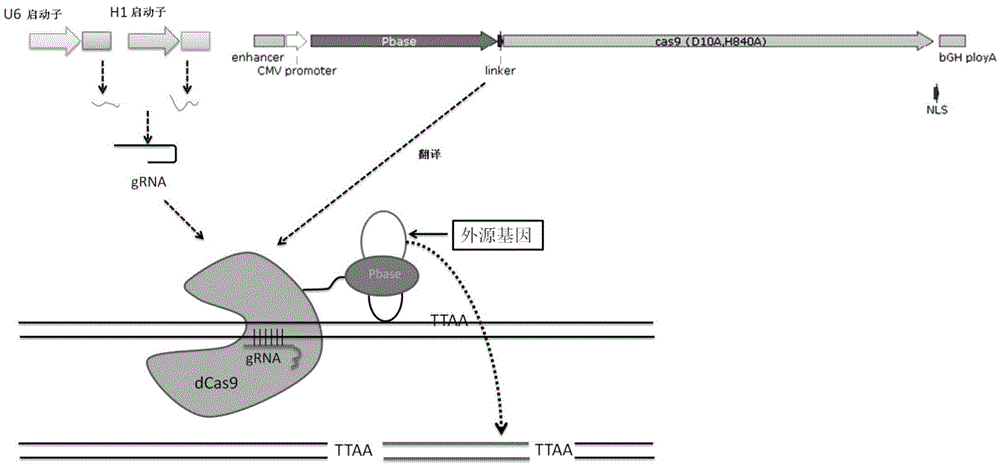
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering and particularly discloses a tool for efficient site-specific transposition of genes. The tool comprises or can produce a gRNA-Cas9 protein (without incision enzyme activity)-PB transposase compound, and gRNA targets the specific site of a genome; the Cas9 protein without incision enzyme activity is double-mutant Cas9 protein with 10th-site amino acid residue D mutating into A and 840th-site amino acid residue H mutating into A. Through design of gRNA (guide RNA) targeting the animal genome, under the coexpression condition of gRNA and site-specific transposase, PB transposase is targeted to a specific position of the genome along with a CRISPR / cas9 and gRNA compound, the PB transposase realizes a transposition function at the specific site, accordingly, donor plasmids (carriers containing exogenous target genes) are simultaneously co-transfected, the exogenous target carriers can be transposed to the specific site in the genome through transposition, and site-specific transposition of the genes is realized.
Owner:WUXI MATERNAL & CHILD HEALTH HOSPITAL
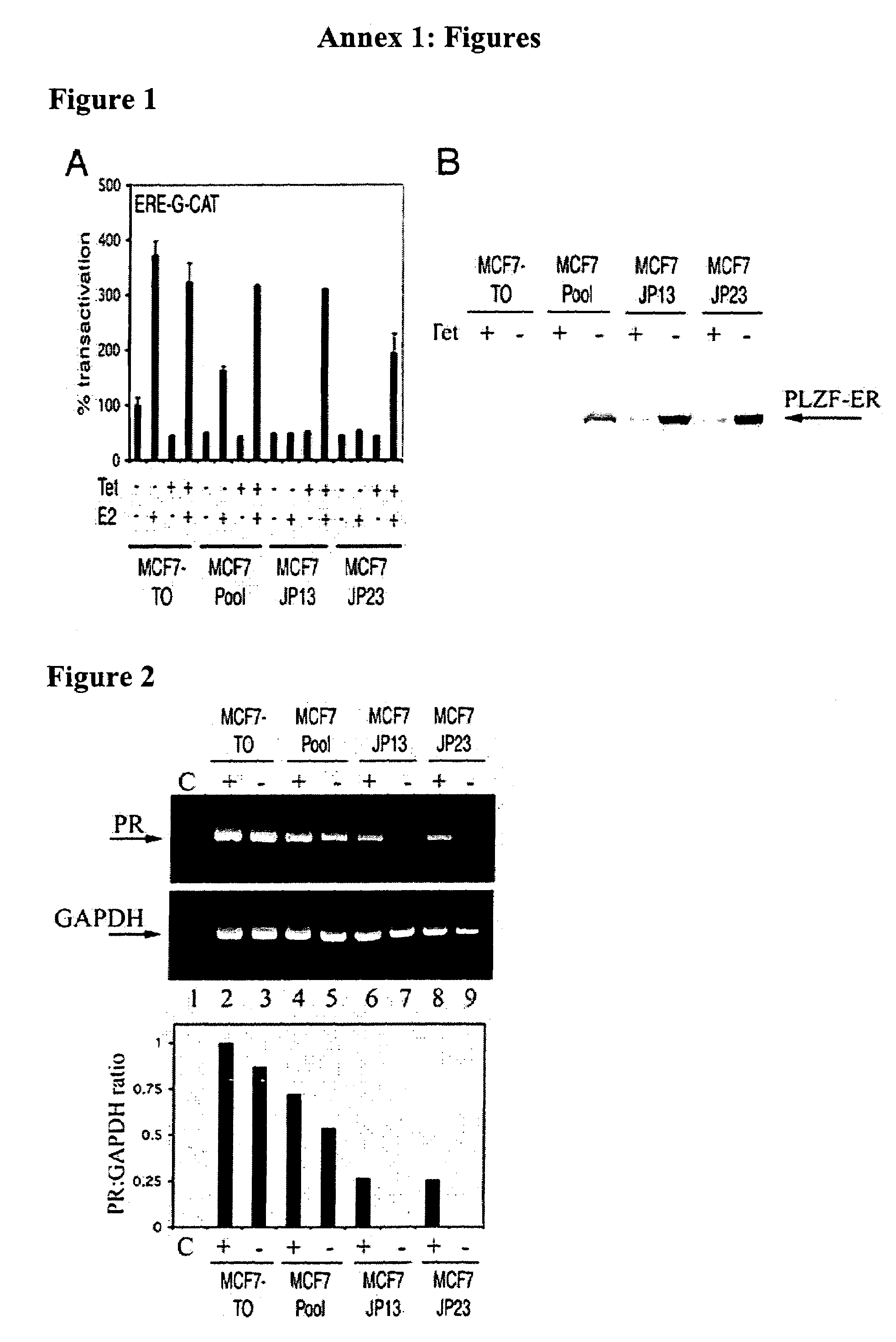
Genetically modified non-human animals expressing human epo
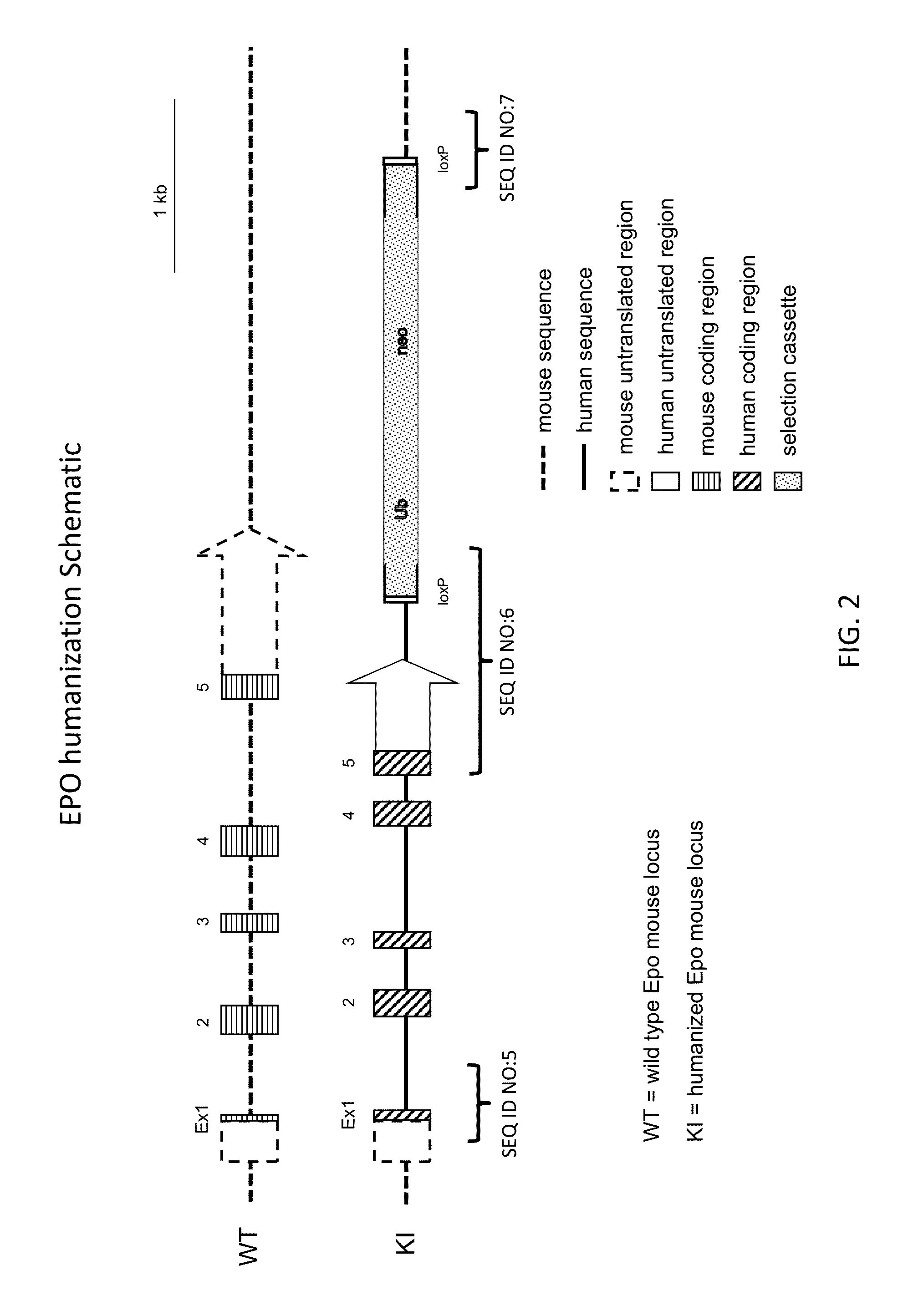
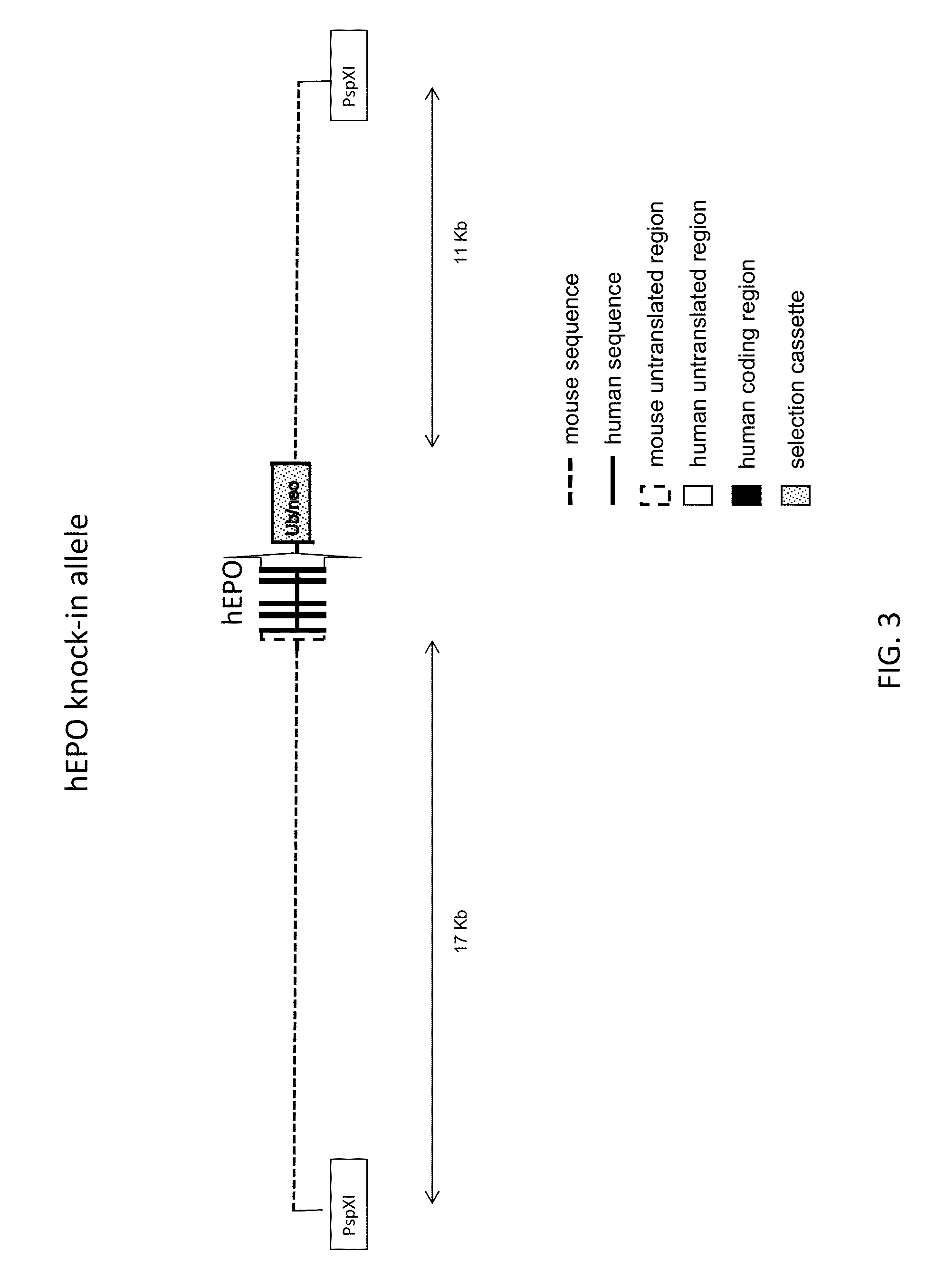
ActiveUS20150327524A1Reduce the amount requiredConducive to survivalCompounds screening/testingHydrolasesDiseaseProgenitor
Genetically modified non-human animals expressing human EPO from the animal genome are provided. Also provided are methods for making non-human animals expressing human EPO from the non-human animal genome, and methods for using non-human animals expressing human EPO from the non-human animal genome. These animals and methods find many uses in the art, including, for example, in modeling human erythropoiesis and erythrocyte function; in modeling human pathogen infection of erythrocytes; in in vivo screens for agents that modulate erythropoiesis and / or erythrocyte function, e.g. in a healthy or a diseased state; in in vivo screens for agents that are toxic to erythrocytes or erythrocyte progenitors; in in vivo screens for agents that prevent against, mitigate, or reverse the toxic effects of toxic agents on erythrocytes or erythrocyte progenitors; in in vivo screens of erythrocytes or erythrocyte progenitors from an individual to predict the responsiveness of an individual to a disease therapy.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC +2
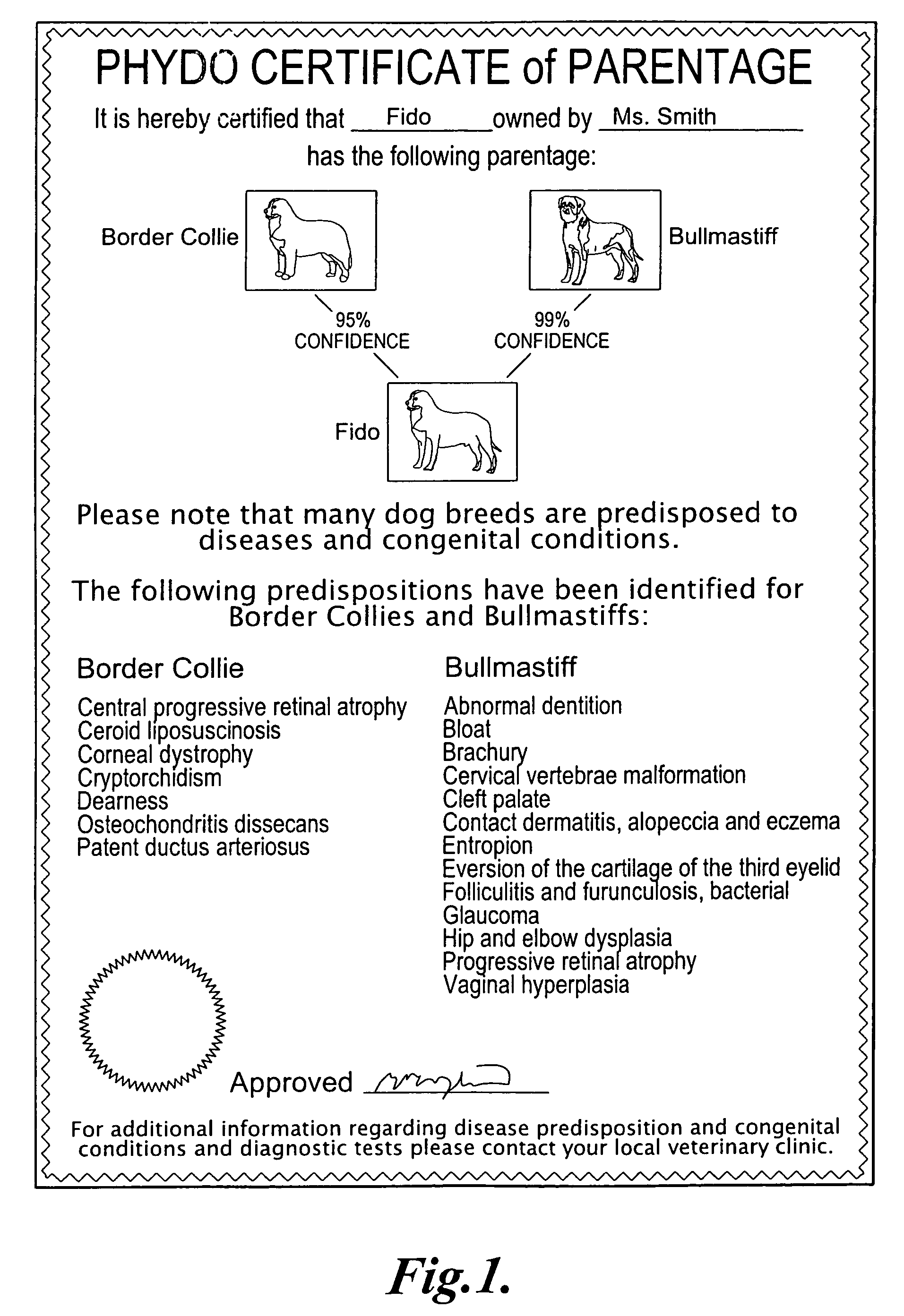
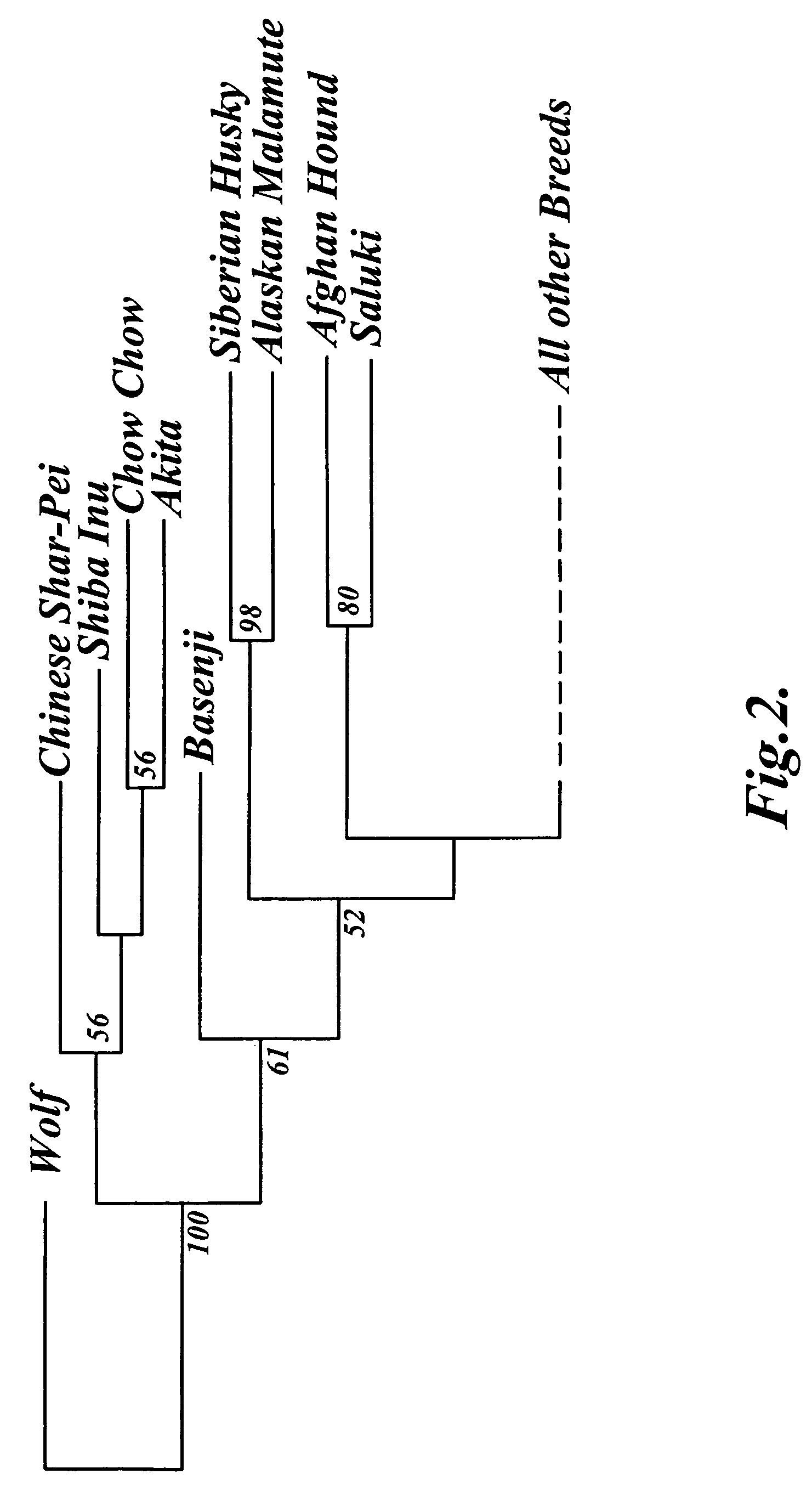
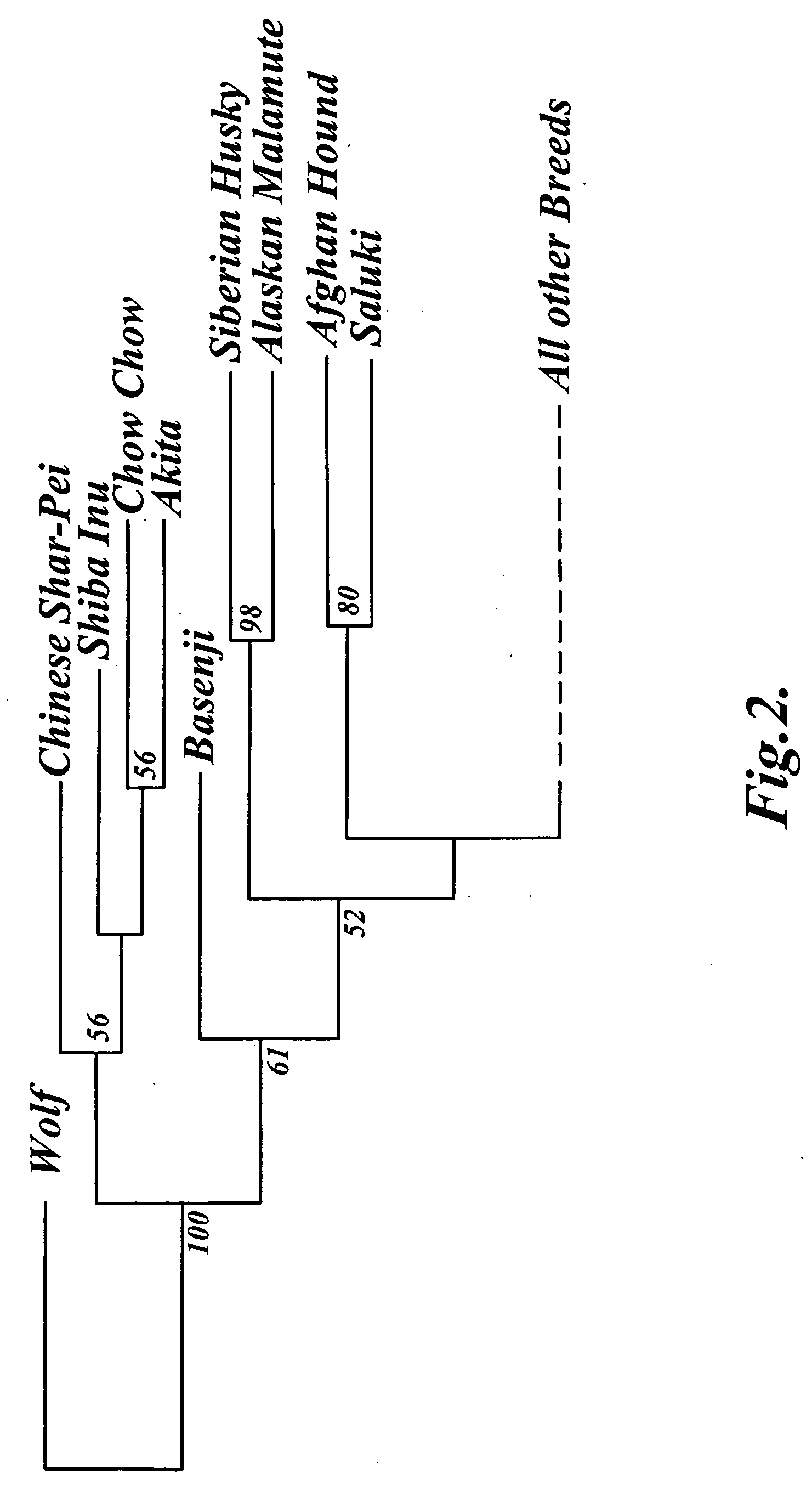
Methods and materials for canine breed identification
In one aspect, the invention provides methods for determining the contributions of canid populations to a canid genome. The methods comprise the steps of: (a) obtaining the identity of one or both alleles in a test canid genome for each of a set of markers; and (b) determining the contributions of canid populations to the test canid genome by comparing the alleles in the test canid genome to a database comprising canid population profiles, wherein each canid population profile comprises genotype information for the set of markers in the canid populations.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER CENT
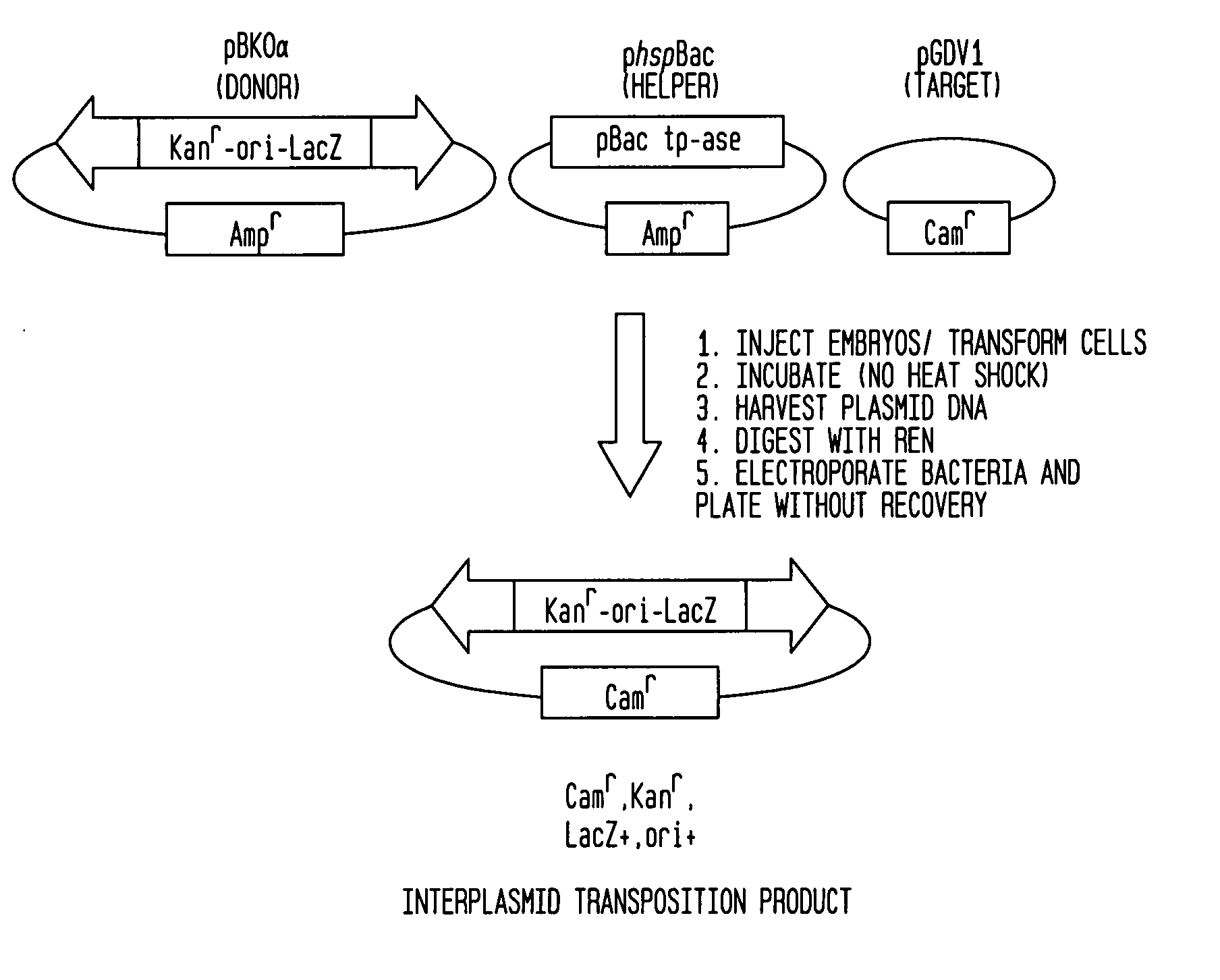
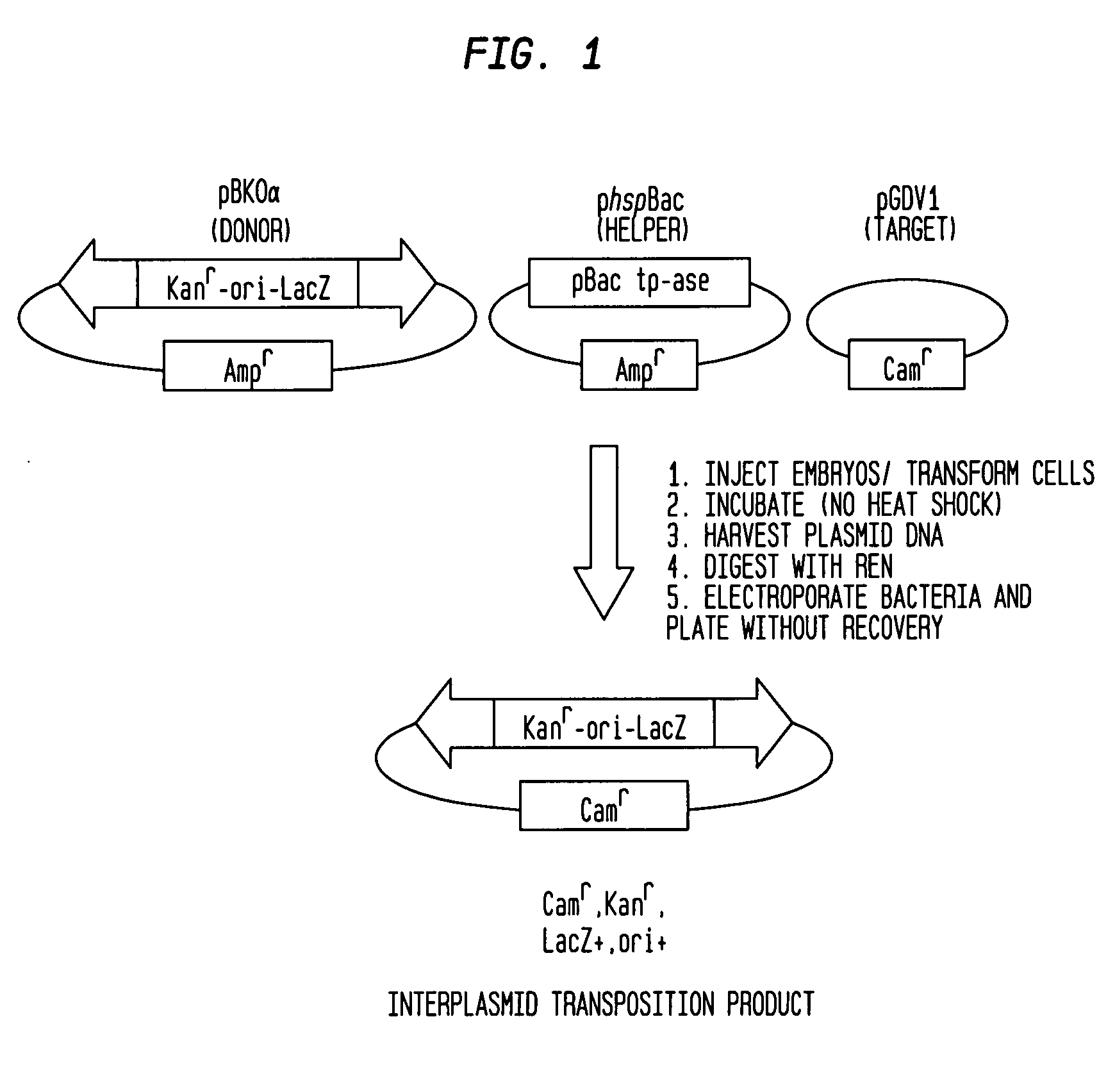
PiggyBac constructs in vertebrates
The piggyBac transposon is disclosed herein as an extremely versatile helper-dependent vector for gene transfer and germ line transformation in a wide range of vertebrate species. Presented are methods wherein genome sequencing databases may be examined using piggyBac, as homologues of piggyBac have been found among several sequenced animal genomes, including the human genome. This transposon is demonstrated to provide transposition in primate cells and embryos of the zebra fish, Danio rerio. PiggyBac mobility is demonstrated using an interplasmid transposition assay that consistently predicts the germ line transformation capabilities of this mobile element in several species. Both transfected COS-7 primate cells and injected zebrafish embryos supported the helper-dependent movement of tagged piggyBac element between plasmids in a cut-and-paste, TTAA target-site specific manner. The present invention discloses the use of piggyBac as a tool for genetic analysis of vertebrates.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
Massively parallel continguity mapping
Contiguity information is important to achieving high-quality de novo assembly of mammalian genomes and the haplotype-resolved resequencing of human genomes. The methods described herein pursue cost-effective, massively parallel capture of contiguity information at different scales.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Universal markers of transgenesis
InactiveUS20030154502A1Genetic engineeringFermentationHeterologousTranscriptional Regulatory Elements
The invention relates to methods, cells and nucleic acids for making transgenic animals. The methods generally comprise introducing into a genome of an animal a genetic construct comprising a transcriptional regulatory element operably linked to a heterologous marker gene encoding a marker, wherein the element drives expression of the marker across genera transgenic in the construct sufficient to visually detect the marker in photoreceptive cells or organs, and selecting for transgenesis by visually detecting the marker in a photoreceptive cell or organ of the animal.
Owner:WIMMER ERNST A +2
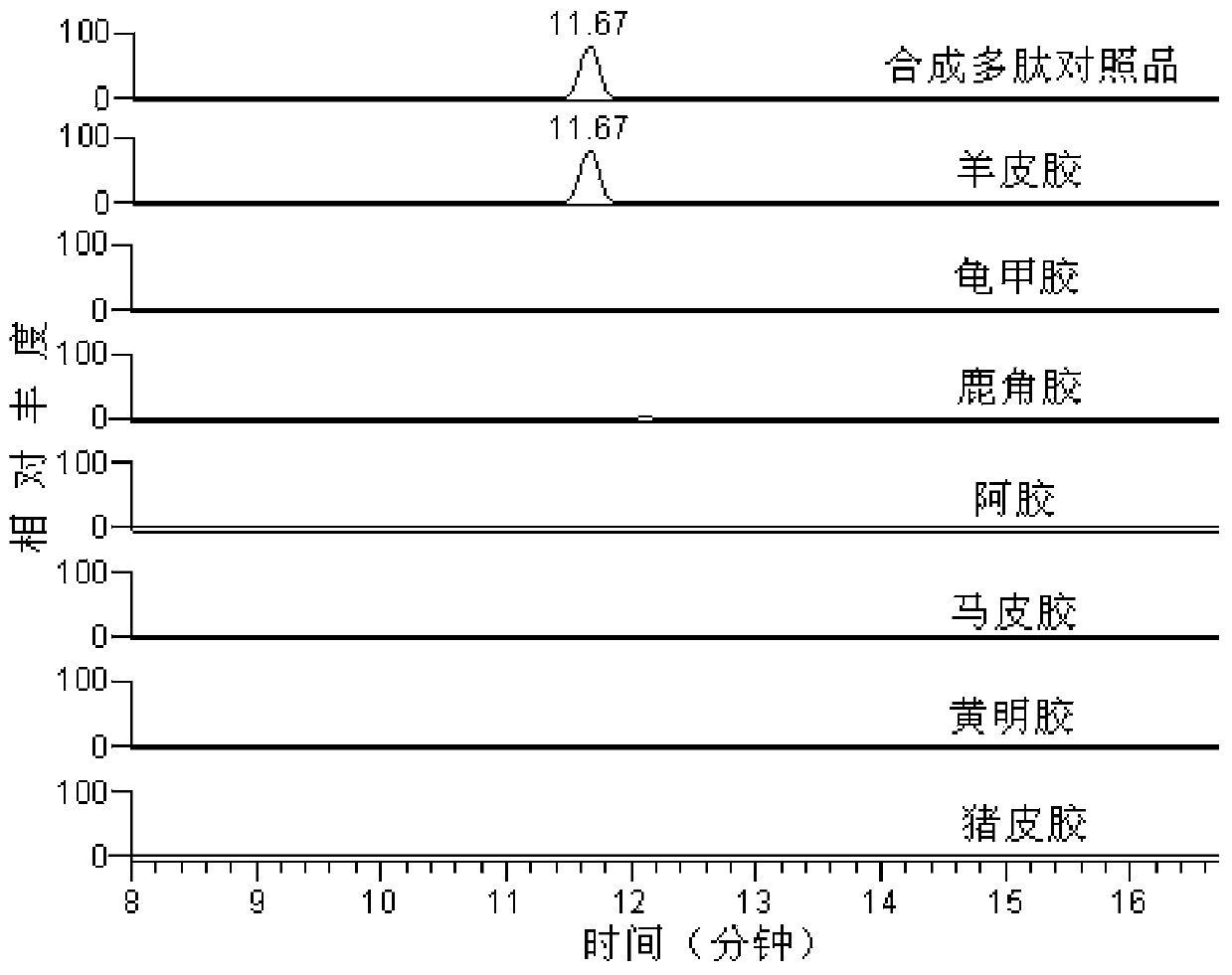
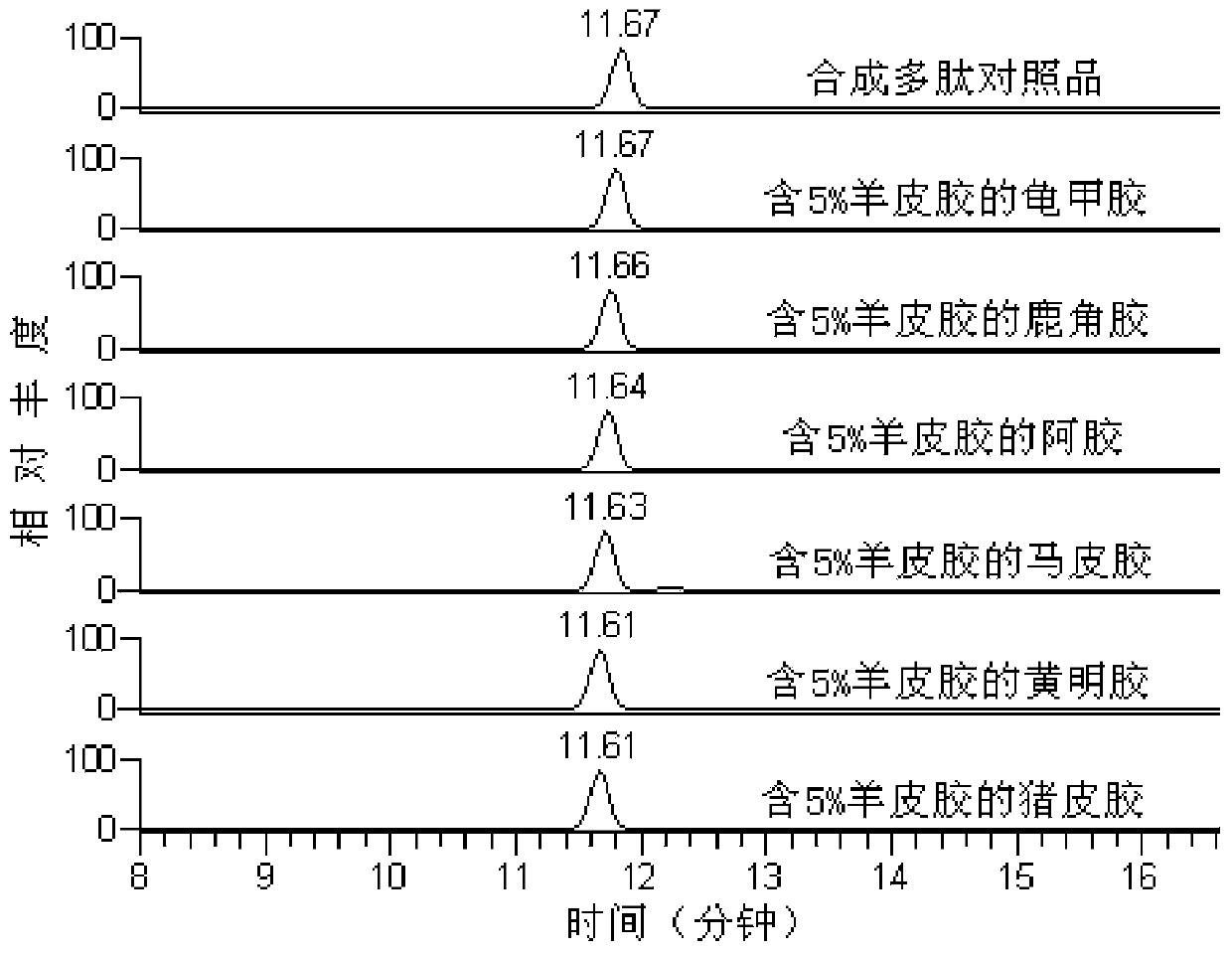
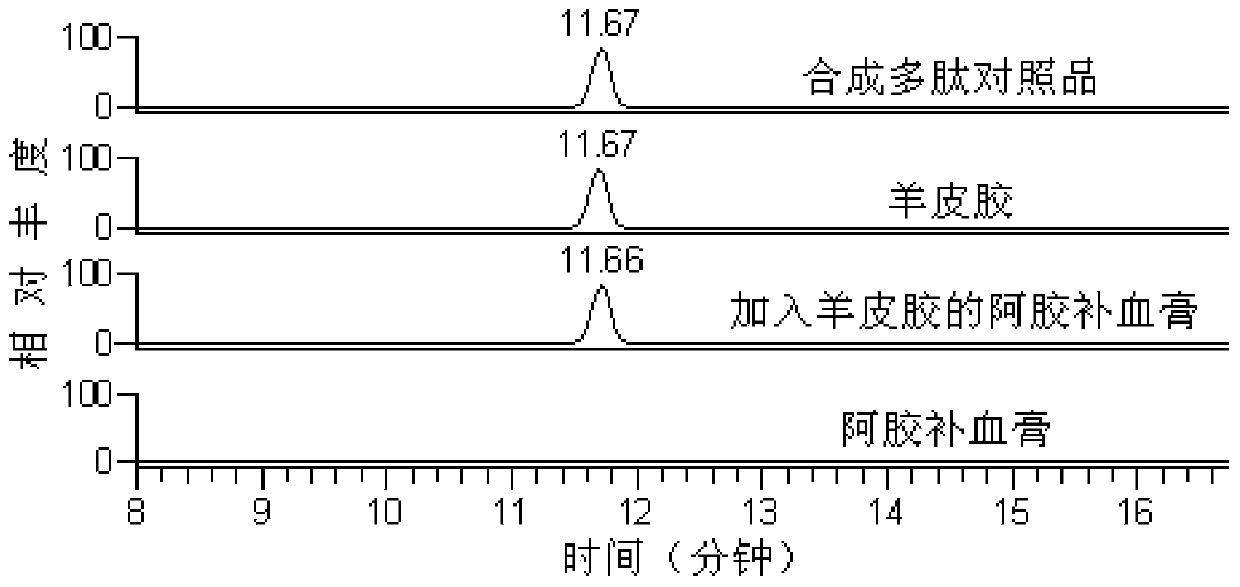
Method for detecting sheep-derived ingredients in glue type traditional Chinese medicines and products thereof
ActiveCN103630621AIncrease contentAvoid damageComponent separationPeptidesAdditive ingredientSubfamily
The invention provides a method for detecting sheep-derived ingredients in glue type traditional Chinese medicines and products thereof. The method provided by the invention comprises the step of detecting by using the difference of a specific nucleotide sequence or amino acid sequence in a genome of a sheep subfamily animal, wherein the specific amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ. ID No1. By adopting the method provided by the invention, whether the glue type traditional Chinese medicines contain the sheep-derived ingredients or not can be detected rapidly, so as to distinguish the authenticity; although polypeptides of collagen in the glue type traditional Chinese medicines are subjected to certain hydrolysis and destruction, the sheep-derived ingredients in the glue type traditional Chinese medicines and products thereof can be identified on the basis that differential polypeptides in a main ingredient, namely collagen, of the glue type traditional Chinese medicine are high in content and little in damaged extent.
Owner:SHAN DONG DONG E E JIAO
Methods and materials for canine breed identification
In one aspect, the invention provides methods for determining the contributions of canid populations to a canid genome. The methods comprise the steps of: (a) obtaining the identity of one or both alleles in a test canid genome for each of a set of markers; and (b) determining the contributions of canid populations to the test canid genome by comparing the alleles in the test canid genome to a database comprising canid population profiles, wherein each canid population profile comprises genotype information for the set of markers in the canid populations.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER CENT
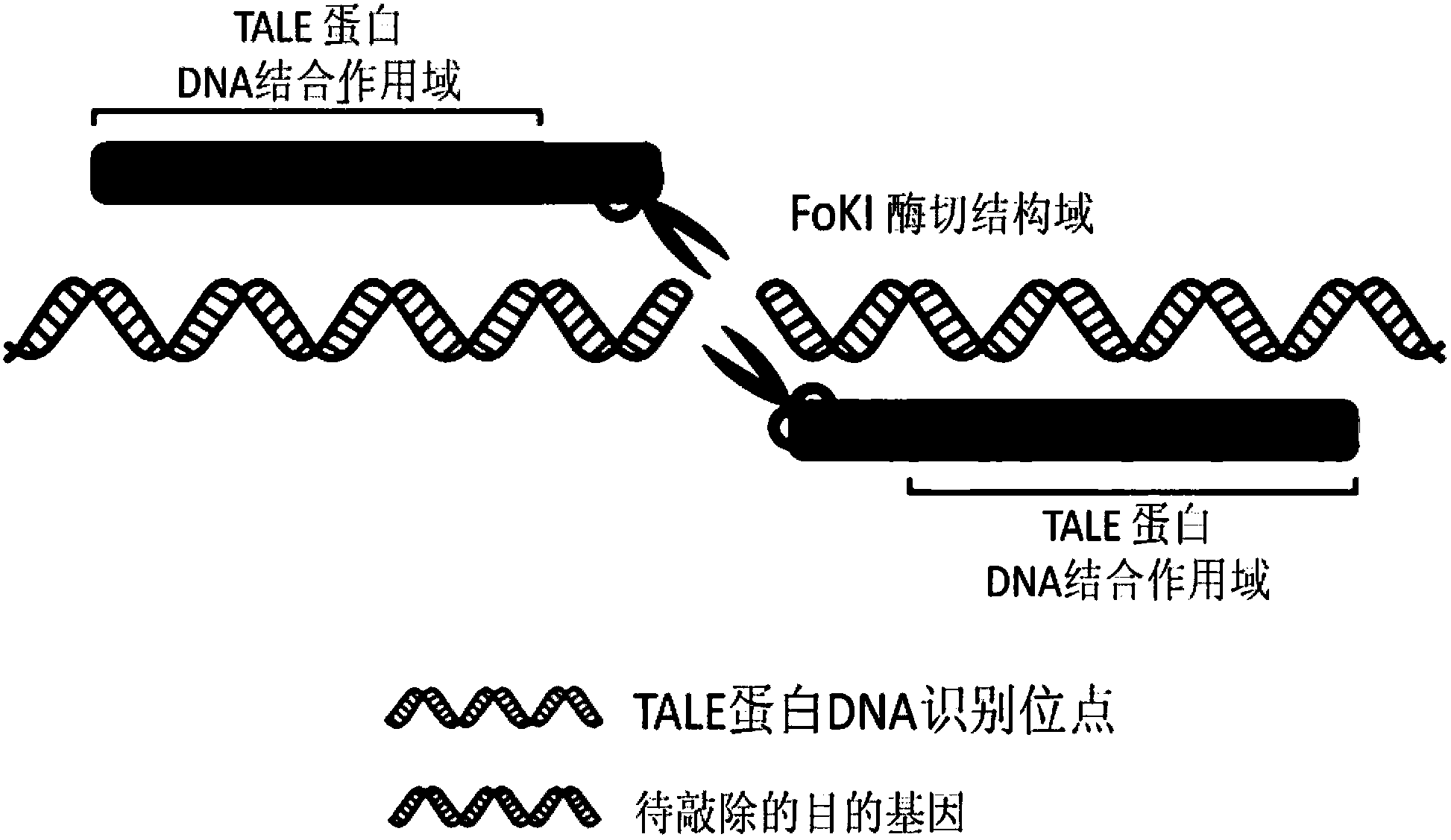
Directional modification method of specific gene of animal genome and application thereof
ActiveCN102653756AInefficient cutting mutagenesisHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementZinc finger nucleaseEmbryo
The invention relates to a method for modifying an animal genome by directed mutagenesis, in particular relates to a novel directional transformation method of a specific gene of an animal genome by utilizing zinc finger nuclease. The method comprises the following steps: designing the zinc finger nuclease which specifically identifies and cuts a targeting gene according to a sequence in a target animal target gene region; validating the directional cutting capability and efficiency of the zinc finger nuclease to the target gene by using an independent expression system; and carrying out directional genetic modification on the target gene of the embryo of a target animal to obtain a stable genetic character by utilizing the selected zinc finger nuclease. Furthermore, the invention also relates to a main gene mutation mode which is obtained by using the independent expression system, selecting and utilizing the zinc finger nuclease, and a filial generation obtained through efficient screening and oriented genetic modification by utilizing the selected gene mutation mode. On the other hand, the invention relates to the zinc finger nuclease which is obtained by utilizing the method and is capable of specifically identifying the myostatin gene of pelteobagrus fulvidraco and directionally knocking out the myostatin gene of the pelteobagrus fulvidraco.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
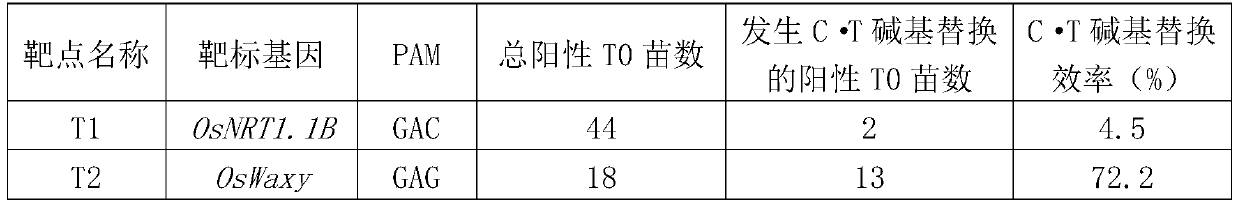
XCas9n-epBE base editing system and application thereof in genome base substitution
The invention discloses an xCas9n-epBE base editing system and an application thereof in genome base substitution. The xCas9n-epBE base editing system comprises xCas9n, PmCDA1, UGI and tRNA-esgRNA; tRNA-esgRNA targets a target sequence; and tRNA-esgRNA is represented as formula I shown as a tRNA-target sequence transcripted RNA-esgRNA skeleton. Experiments prove that the xCas9n-epBE base editing system can realize target sequence editing in plant genomes, and particularly realize the base substitution from base C to base T in the target sequence when the PAM sequence is GAC or GAG. The xCas9n-epBE base editing system has broad application prospects in the base substitution in plant or animal genomes.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Construction method and application of humanized cell factor IL15 gene modified non-human animal
The invention provides a construction method of a humanized IL15 gene modified non-human animal. A nucleotide sequence encoding a human protein IL15 is introduced into a genome of an animal by using ahomologous recombination mode, so as to construct a gene modified humanized animal. A body of the animal can normally express the human or humanized protein IL15, promote development of human T cellsand NK cells and can serve as an animal model for human IL15 signal mechanism researching and screening of drugs for diseases such as tumors, and thus, the animal has an important application value in research and development of new drugs for immunization target points.
Owner:BIOCYTOGEN JIANGSU CO LTD +1
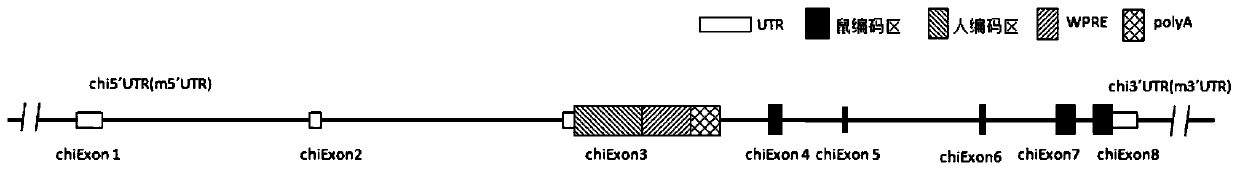
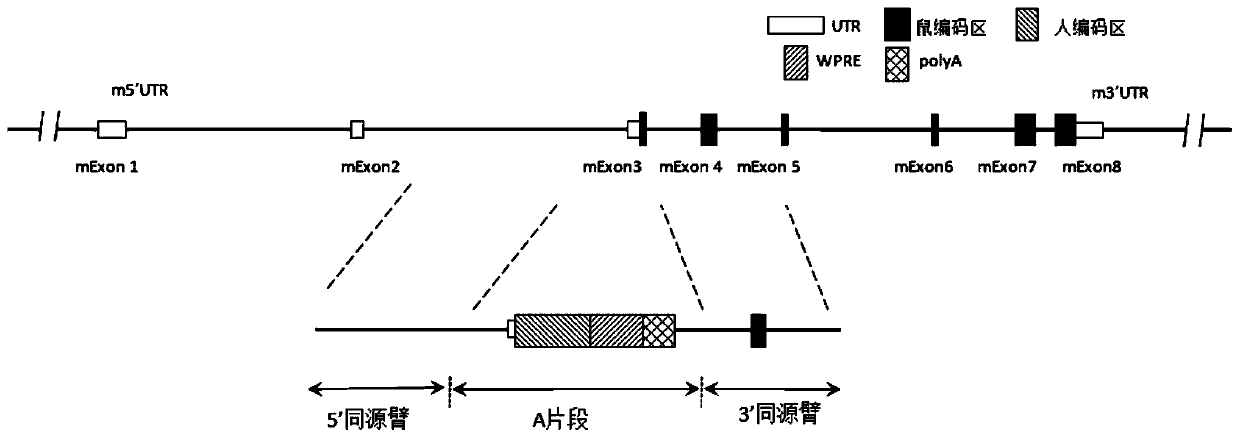
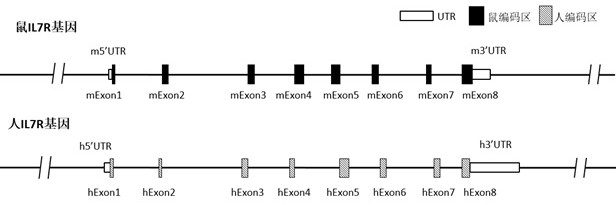
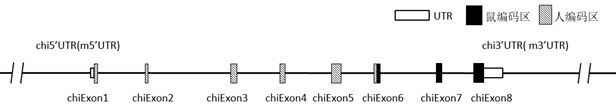
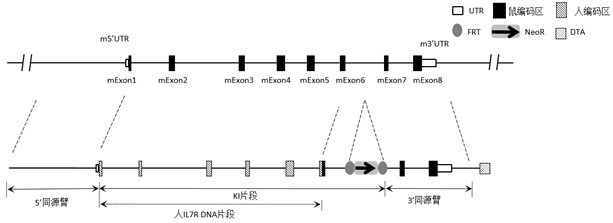
Construction method of IL7R gene humanized modified animal model and corresponding application
The invention provides a construction method of an IL7R gene humanized modified animal model, a humanized IL7R protein, a humanized IL7R gene, a targeting vector of the IL7R gene and an application ofthe targeting vector in the field of biological medicines. A part of nucleotide sequences for coding the human IL7R protein are introduced into a non-human animal genome in a homologous recombinationmanner, and the animal model can normally express the humanized IL7R protein in vivo, and can be used for human IL7R signal mechanism research, tumor and immune related disease drug screening, and important application value is realized on the research and development of new drugs of immune targets.
Owner:BIOCYTOGEN PHARMACEUTICALS (BEIJING) CO LTD
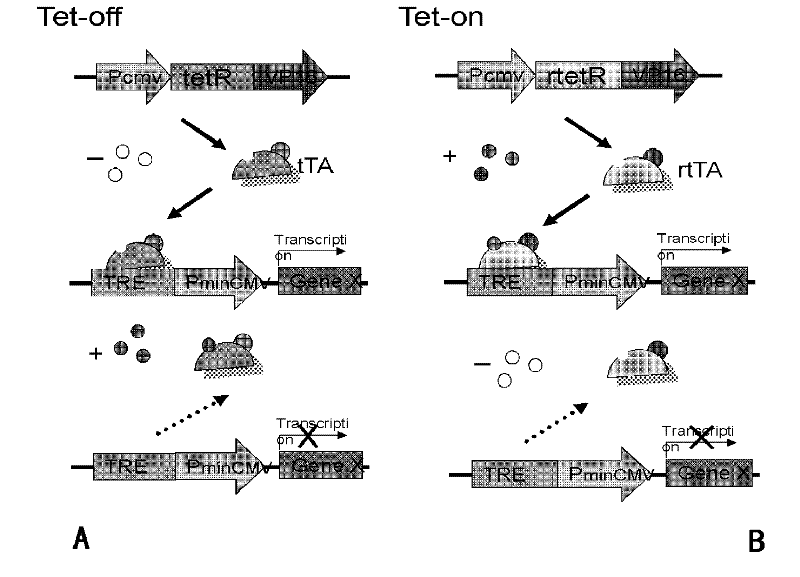
Genetic modification method for regulating and controlling animal endogenous gene expression
ActiveCN102669057AInducibleReversibleMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionDiseaseResponse element
The invention relates to a genetic modification method for regulating and controlling animal endogenous gene expression. Tetracycline response elements are inserted into proper positions of endogenous genes of animals to be regulated and controlled according to fixed points through the gene recombination technology; and regulation and control genes are transferred into animal genomes by a transgene method, transgene animals are obtained, and the reversible expression regulation and control on the endogenous genes is realized under the effect of inductors of tetracycline or other analogues. A mouse endogenous gene induction expression regulation and control model built according to the method can be widely applied to the fields of gene function study, disease animal model building and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI BIOMODEL ORGANISM SCI & TECH DEV +1
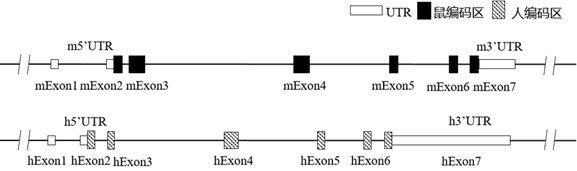
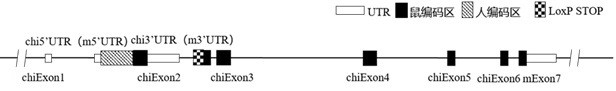
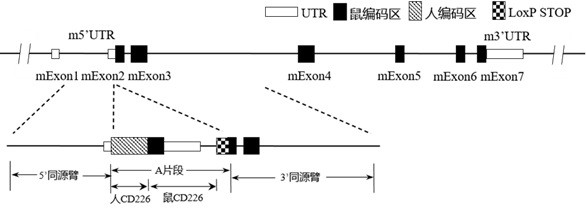
Construction method and application of CD226 gene-humanized non-human animal
ActiveCN111793647ASpeed up the R&D processShorten the timeCompounds screening/testingImmunoglobulin superfamilyBiotechnologyImmunologic disorders
The invention provides a construction method of a CD226 gene humanized modified non-human animal. By utilizing a homologous recombination manner, a nucleotide sequence for encoding a human CD226 protein is introduced into a non-human animal genome. The humanized CD226 protein can be normally expressed in an animal body, and the non-human animal can be used as an animal model for researching humanCD226 signal mechanism and screening drugs for tumor and immune diseases, and has important application value for research and development of new drugs for immune targets. The invention also providesa CD226 chimeric protein, a CD226 chimeric gene, a targeting vector of the CD226 gene, the non-human animal constructed by the construction method, and an application of the non-human animal in the field of biological medicines.
Owner:BIOCYTOGEN PHARMACEUTICALS (BEIJING) CO LTD
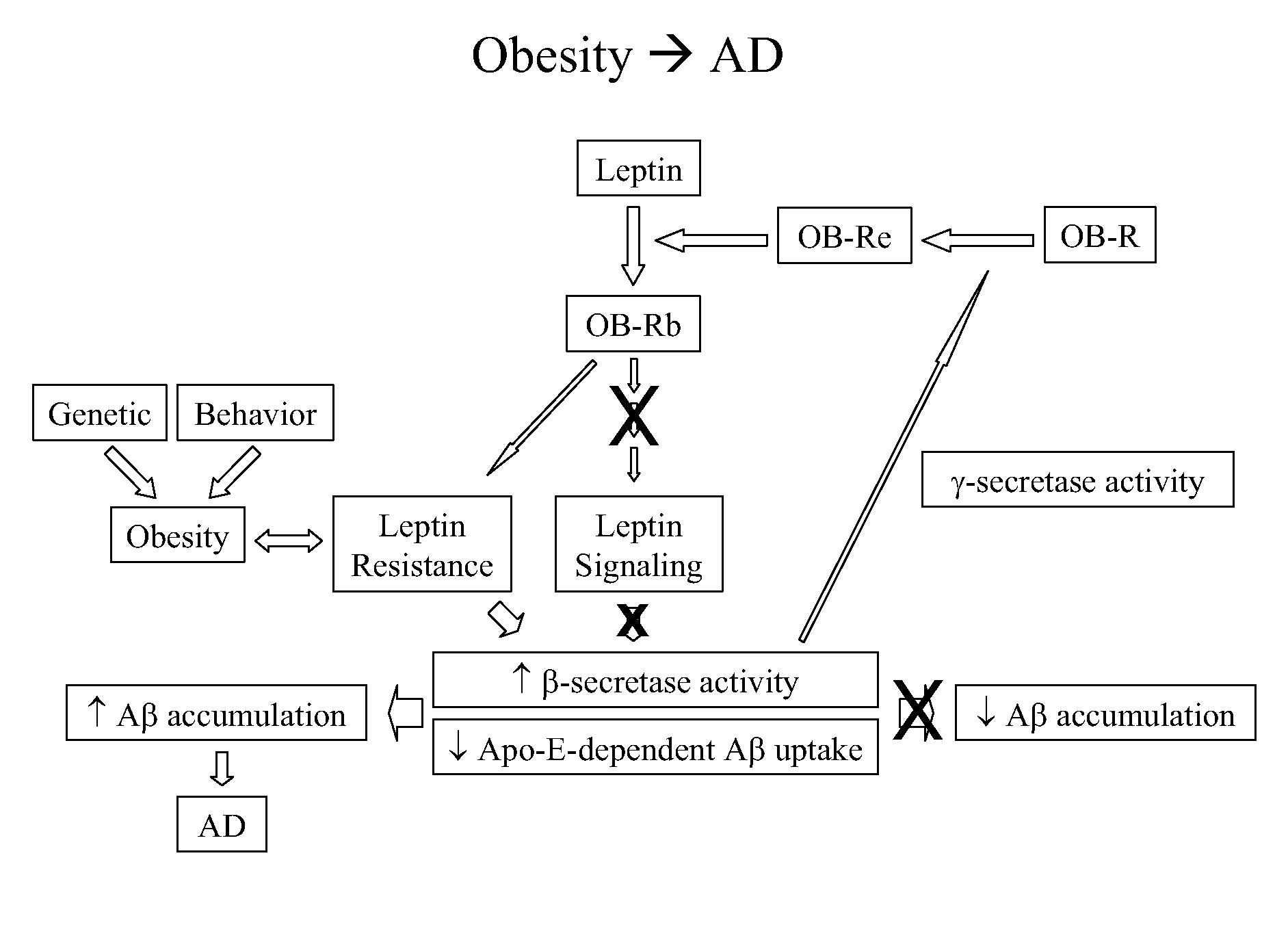
Animal models for obesity and neurodegenerative diseases
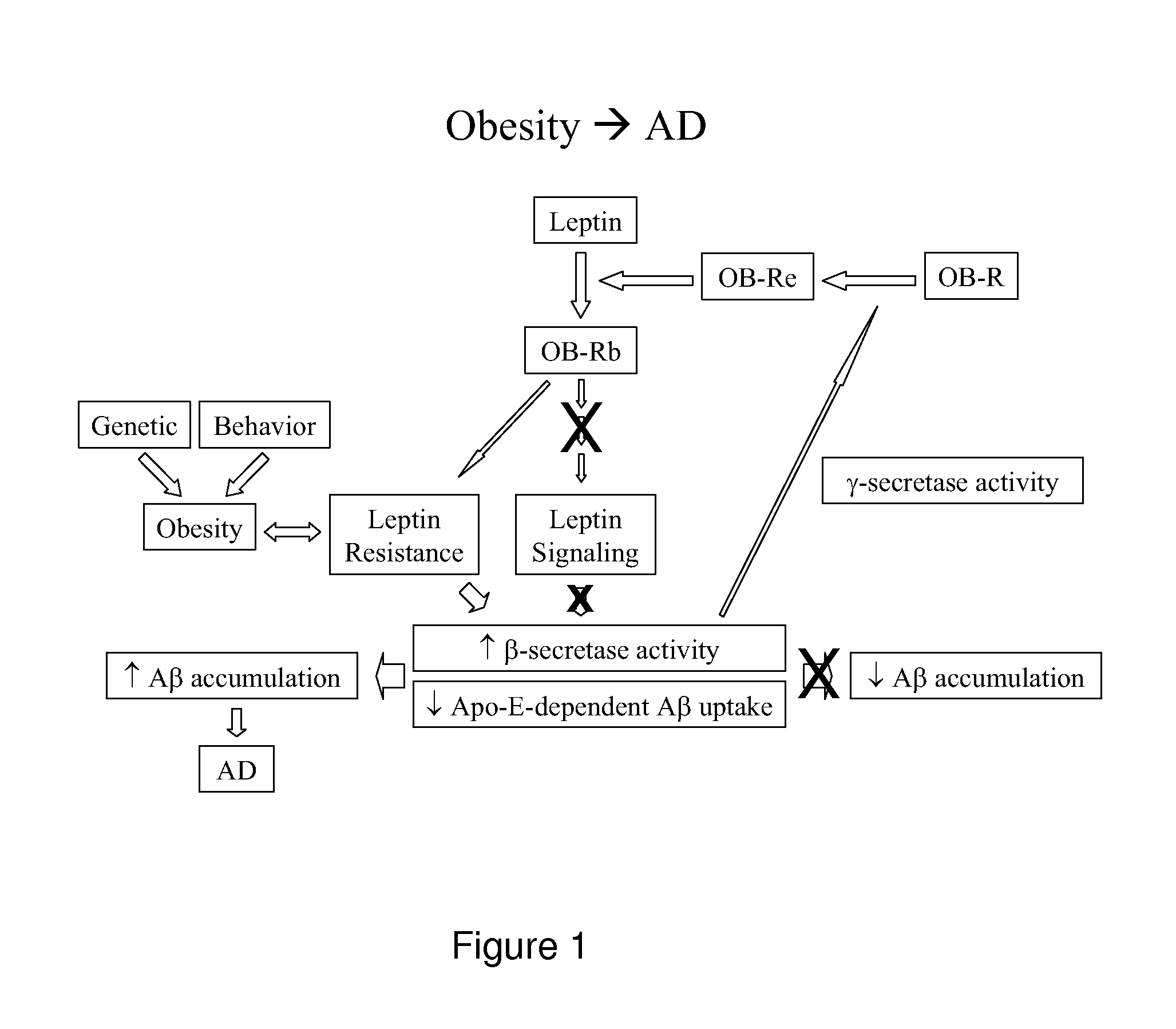
InactiveUS20090031434A1Reduce weight gainLow weight gainCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesNucleotideTransgene
A transgenic non-human animal is disclosed, the animal having a nucleic acid inserted in its genome, wherein the presence of the inserted nucleic acid in the genome of the animal results in expression of an agent, which agent is encoded by a nucleotide sequence in the genome of the animal, and wherein the agent inhibits the ability of a leptin to activate an Ob-Rb receptor. Uses of the animal and methods of identifying compounds using the animal are also disclosed.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Construction of interleukin 1beta specific mouse optical imaging system and use thereof
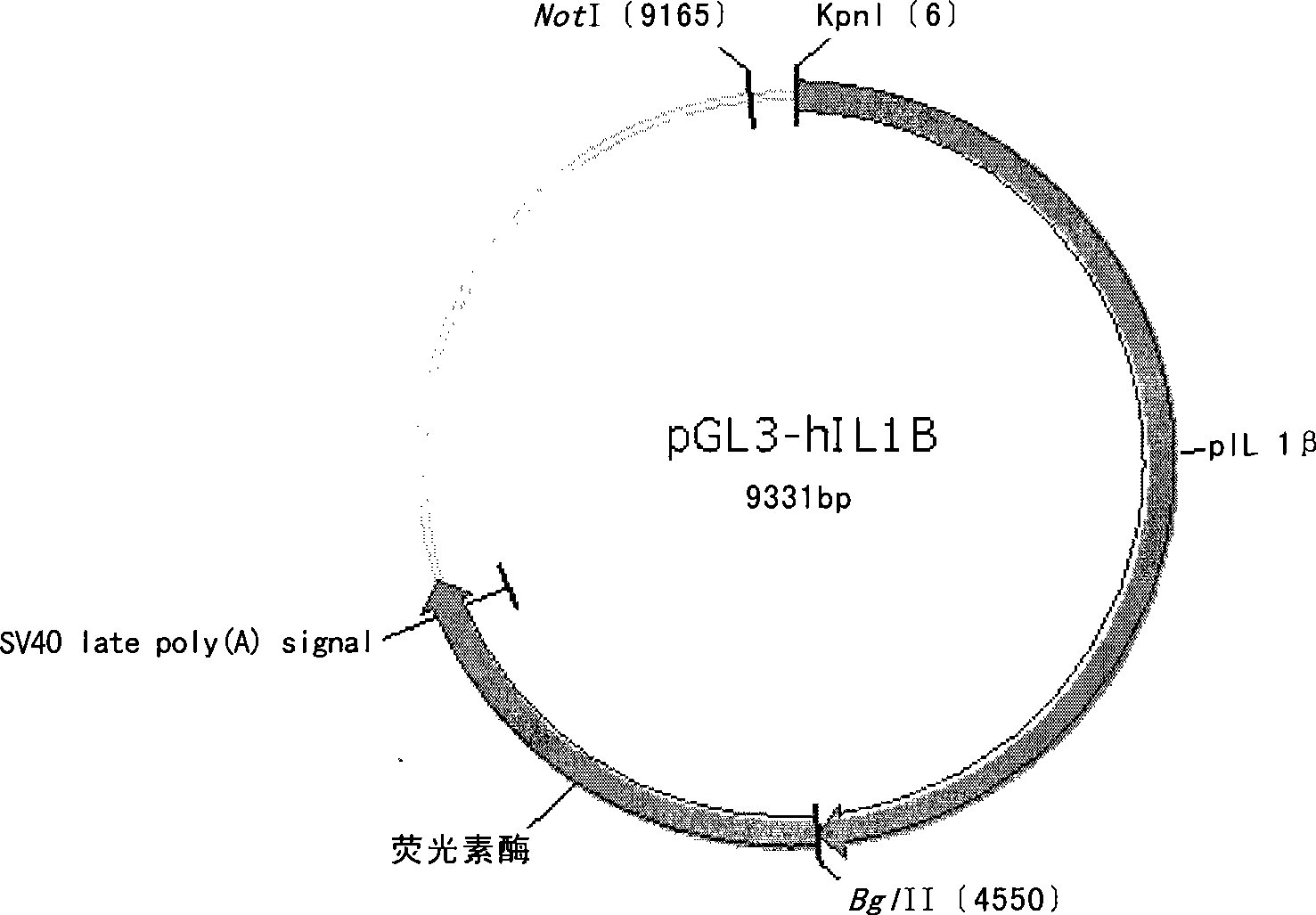
ActiveCN101469346AMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionScreening methodInterleukin-1beta
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and discloses the establishment of an optical imaging system for an interleukin 1beta specific molecular mouse and application of the optical imaging system. The invention also discloses application of a transgenic animal, which is used for screening a substance with anti-inflammation effect. A 5' upstream regulatory region containing an interleukin 1beta gene is taken as a promoter to drive a reporter gene to serve as a vector to transfer into an animal genome through transgenic technology to obtain the transgenic animal; and the animal can quickly and sensitively be detected the change of the reporter gene in the body in an in vivo imaging system, the expression condition of interleukin 1beta is reflected in the body in a real-time and effective mode. The animal transferred with the gene can be taken as a model and used for screening the substance with the anti-inflammation effect; and a screening method has the advantages of simple operation, intuitivity and high sensitivity, has small damage to the animal, and can observe the dynamic reaction process of the reporter gene driven by an interleukin 1beta promoter in the body ofthe animal under the action of related substances in a real-time and continuous mode.
Owner:SHANGHAI BIOMODEL ORGANISM SCI & TECH DEV +1
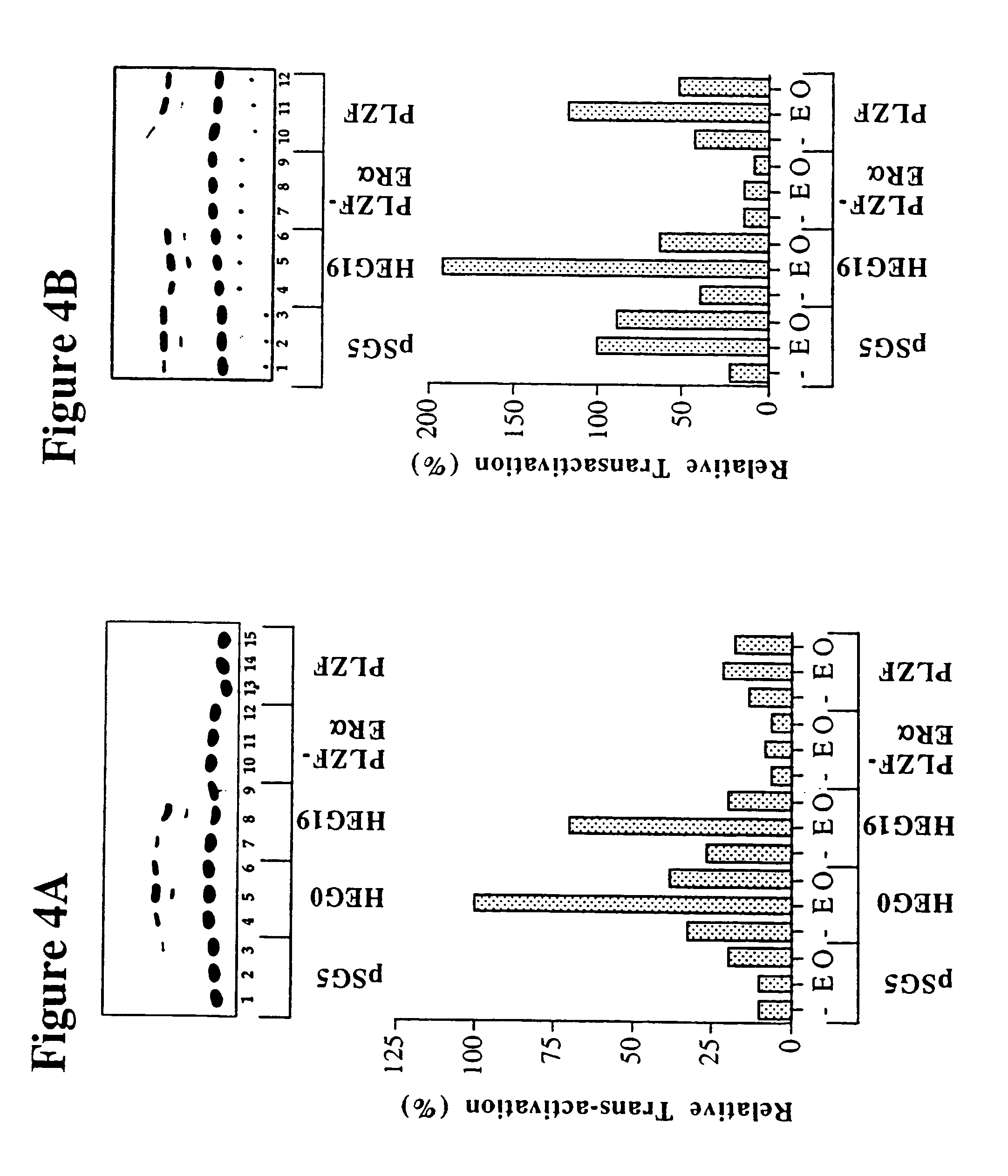
Gene knock-in non-human animal
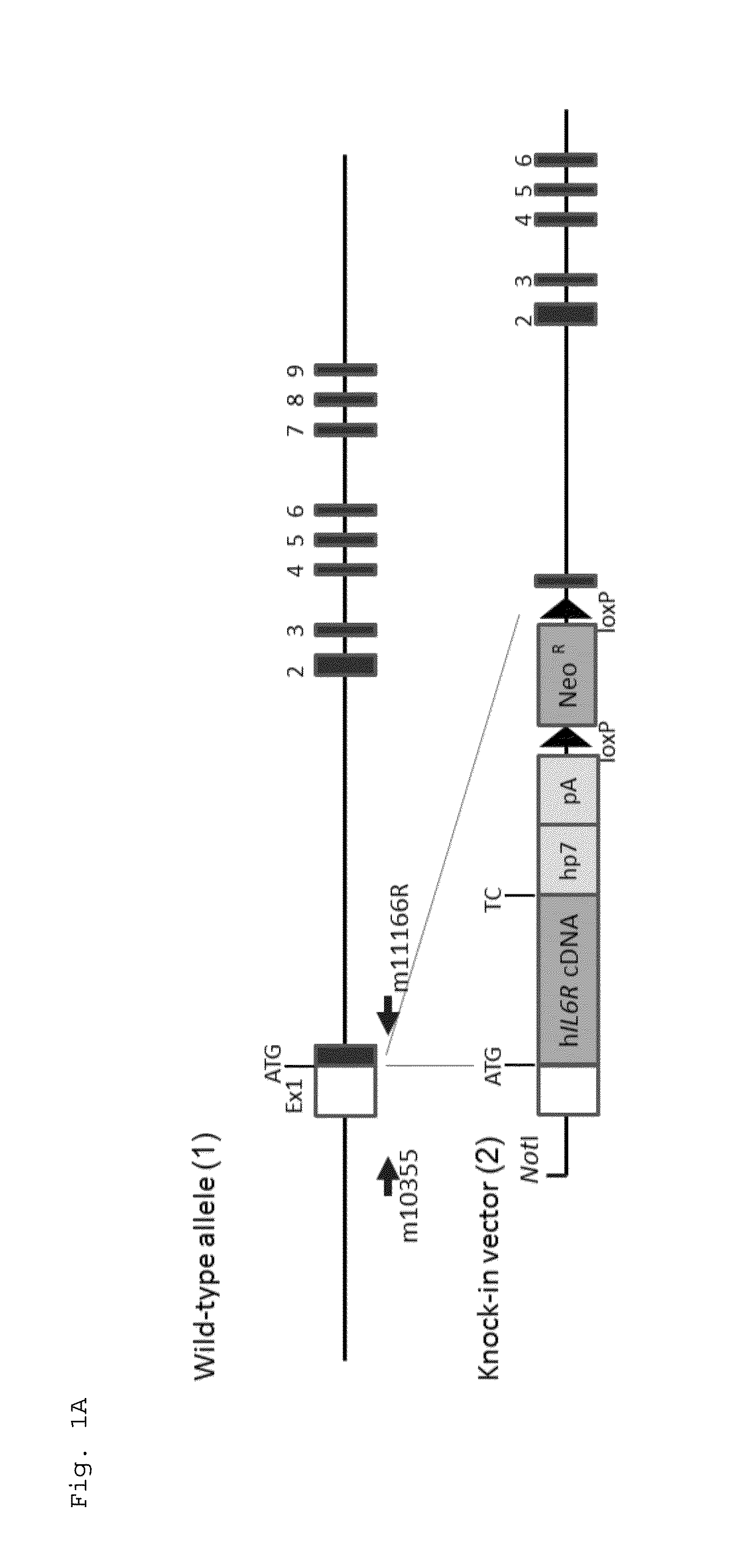
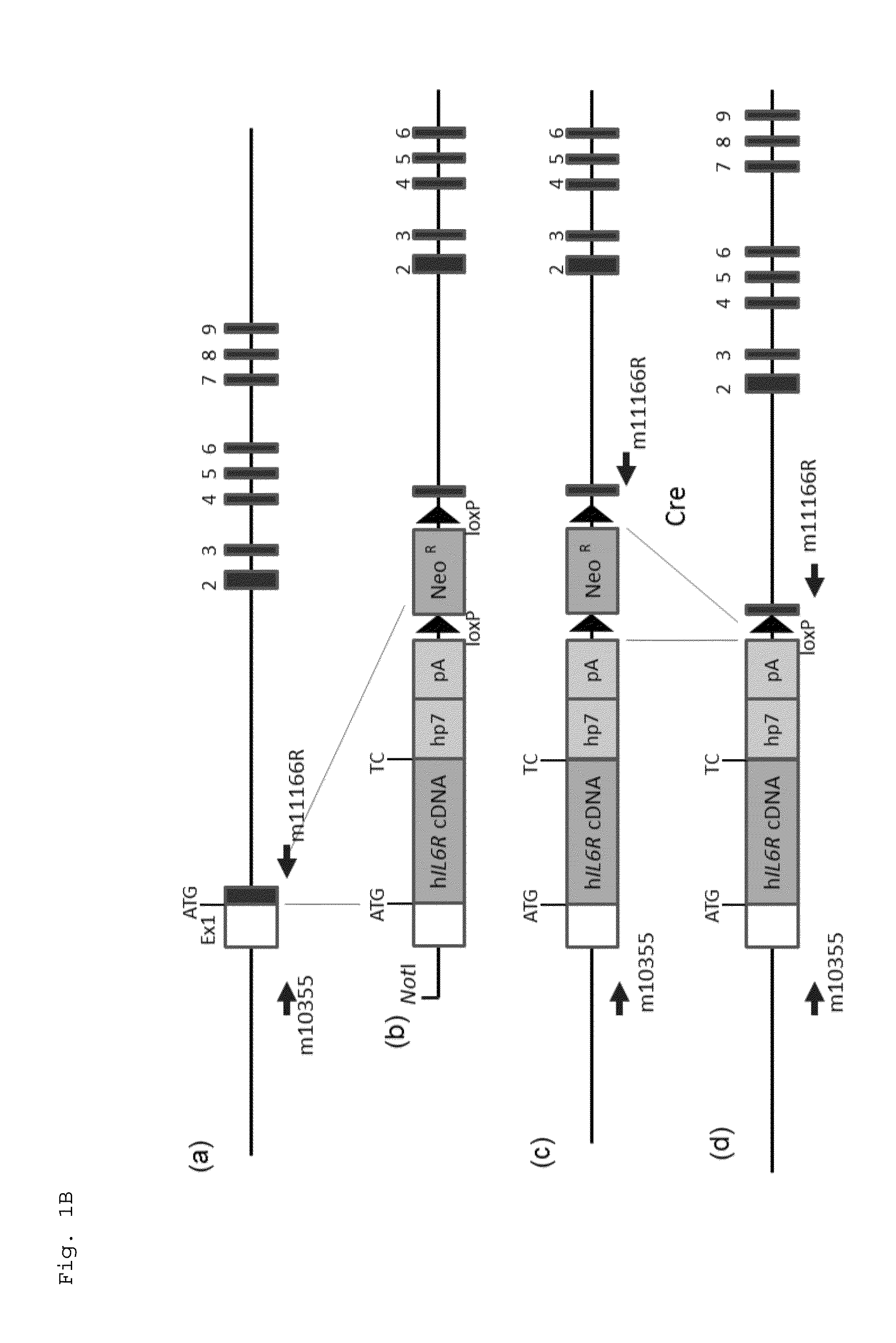
ActiveUS20150225481A1Suppressing expression of its endogenous geneAccurate assessmentCompounds screening/testingAntipyreticHuman animalA-DNA
The present invention provides a non-human animal in which a DNA comprising an hp7 sequence-encoding DNA and a poly A addition signal-encoding DNA added on the 3′ side of a DNA encoding an arbitrary foreign gene is inserted in the same reading frame as that of an arbitrary target gene present on the genome of the non-human animal.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Construction method and application of thrombopoietin (THPO) gene humanized non-human animal
The invention provides a construction method and application of a thrombopoietin (THPO) gene humanized non-human animal. The method comprises the following steps: introducing a sequence for encoding human THPO protein into an animal genome by using a homologous recombination manner; the animal can normally express the human or humanized THPO protein in vivo, to promote the development of human T cells and NK cells; the non-human animal can be used as an animal model for human THPO signal mechanism research and drug screening for diseases including tumors and the like, and has important application value for new drug research and development of immune targets. The invention further provides a targeting vector of a THPO gene, sgRNA of the target THPO gene and application of the targeting vector and the sgRNA to preparation of a humanized THPO gene.
Owner:BIOCYTOGEN PHARMACEUTICALS (BEIJING) CO LTD
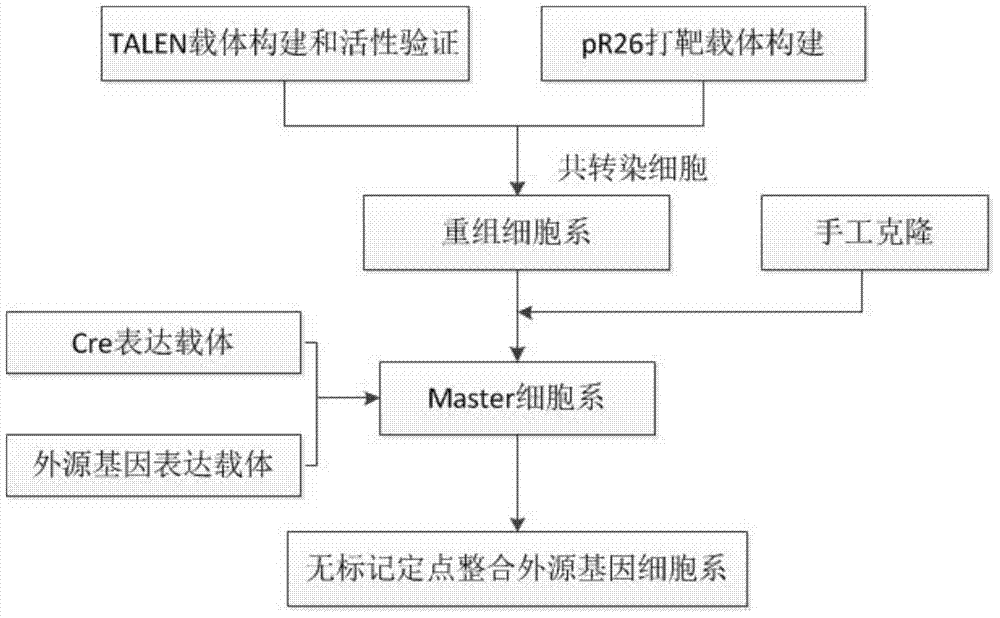
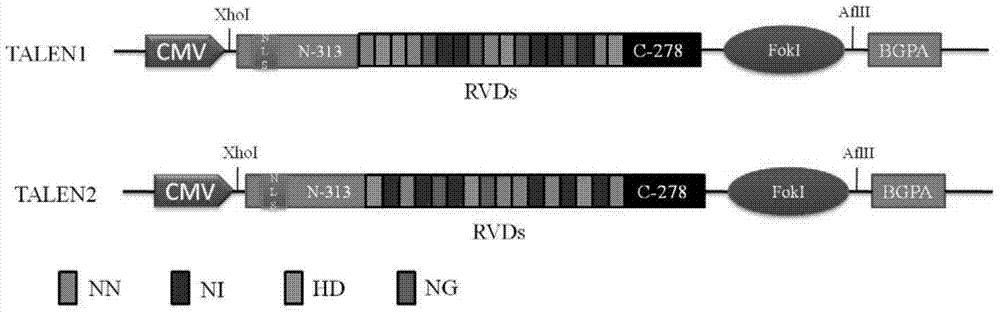
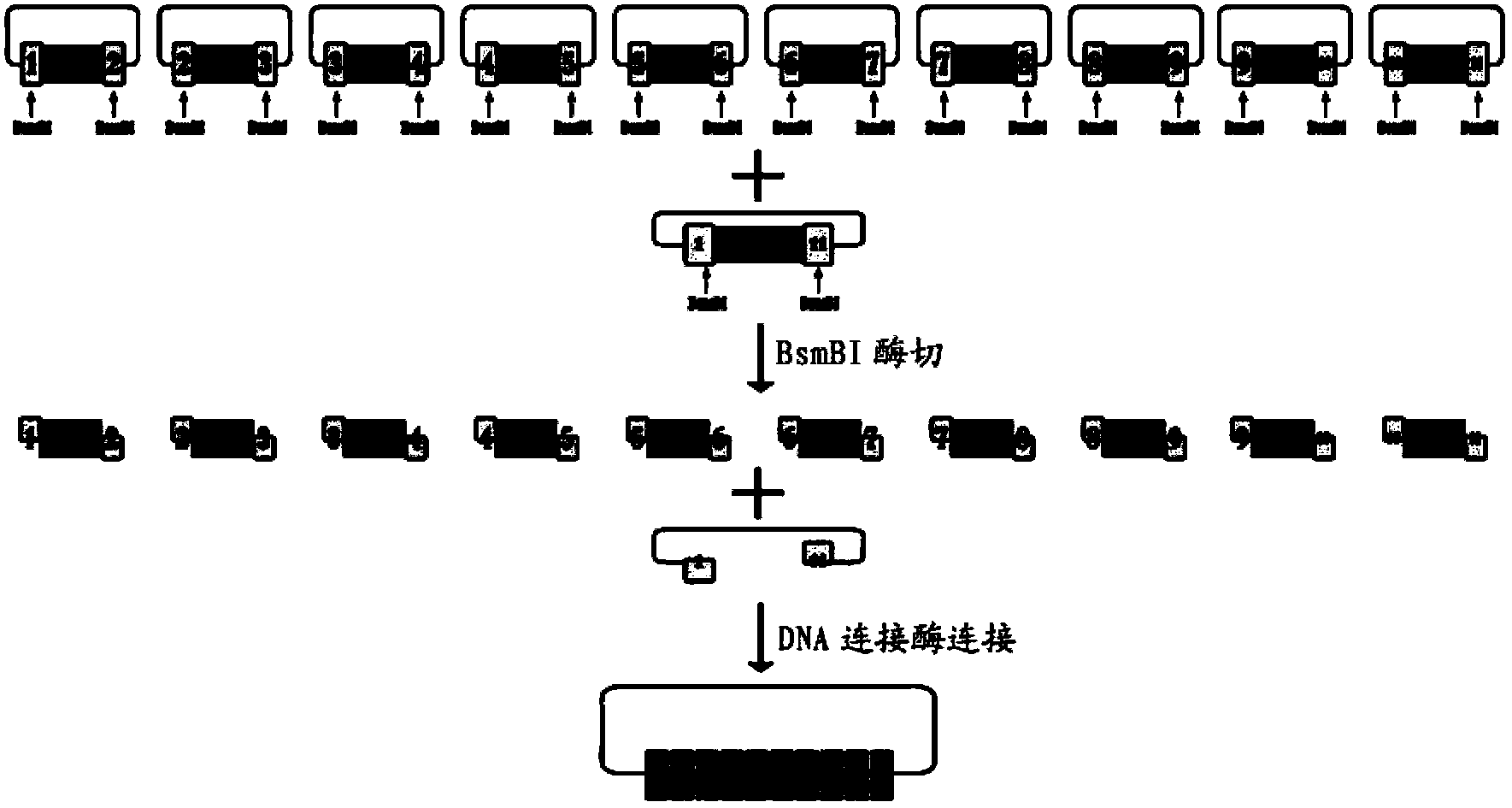
Multiple-exchange unmarked site-specific integration transgenic system and application thereof
ActiveCN104774870AVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsBiotechnologyIntegrases
Provided are multiple-exchange unmarked site-specific integration transgenic system and an application thereof, wherein the transgenic system includes: a first construction body which is a TALEN carrier, wherein the TALEN carrier identifies and cuts friendly site sequences; a second construction body including a left homologous arm, a right homologous arm, a selective marker expression cassette, a first integrase recognition sequence loxp and a first integrase recognition sequence lox2272; a third construction body including a targeted exogenous gene, a second integrase recognition sequence loxp' and a second integrase recognition sequence lox2272'; and a fourth construction body including an integrase gene Cre expression cassette. The transgenic system can simply, fast and efficiently achieve site-specific insertion of a targeted exogenous gene in an animal genome, and prepared transgenic animal cells do not contain any resistant marker gene, the preparation cycle is short, preparation is safe and reliable, and the targeted exogenous gene can stably inherited to a next generation.
Owner:深圳华大基因农业控股有限公司
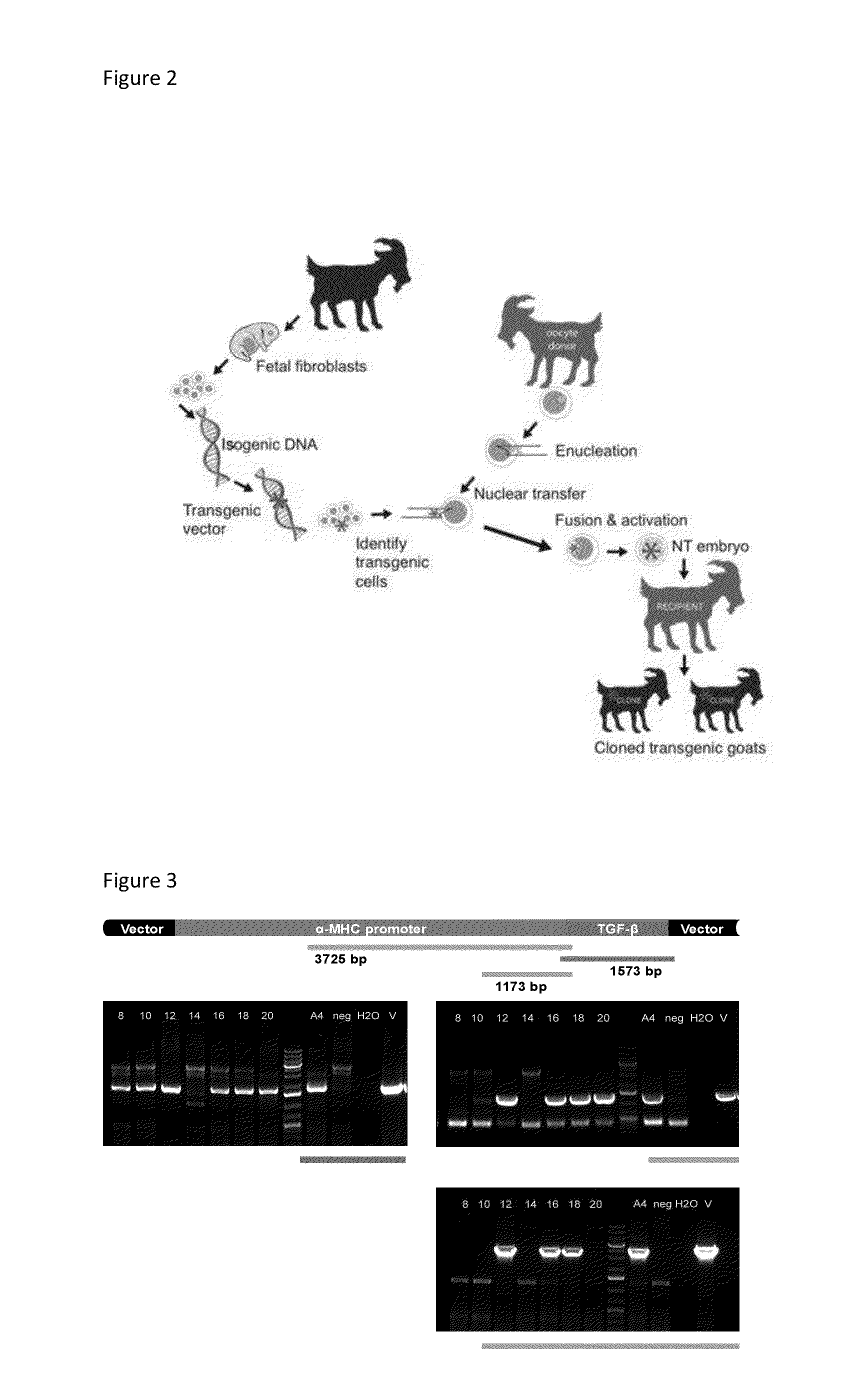
Model and method for a transgenic bovidae expressing cardiac fibrosis and associated pathology
ActiveUS20150033370A1Improve expression levelImprove the level ofAnimal reproductionObstetrical instrumentsCardiac fibrosisCardiac muscle
Herein provided are a model and method for a transgenic a bovidae having an TGF-β1 gene inserted into the bovidae genome and capable of expressing higher than normal levels of TGF-β1 in cardiac muscle.
Owner:THE UNIV OF UTAH +1
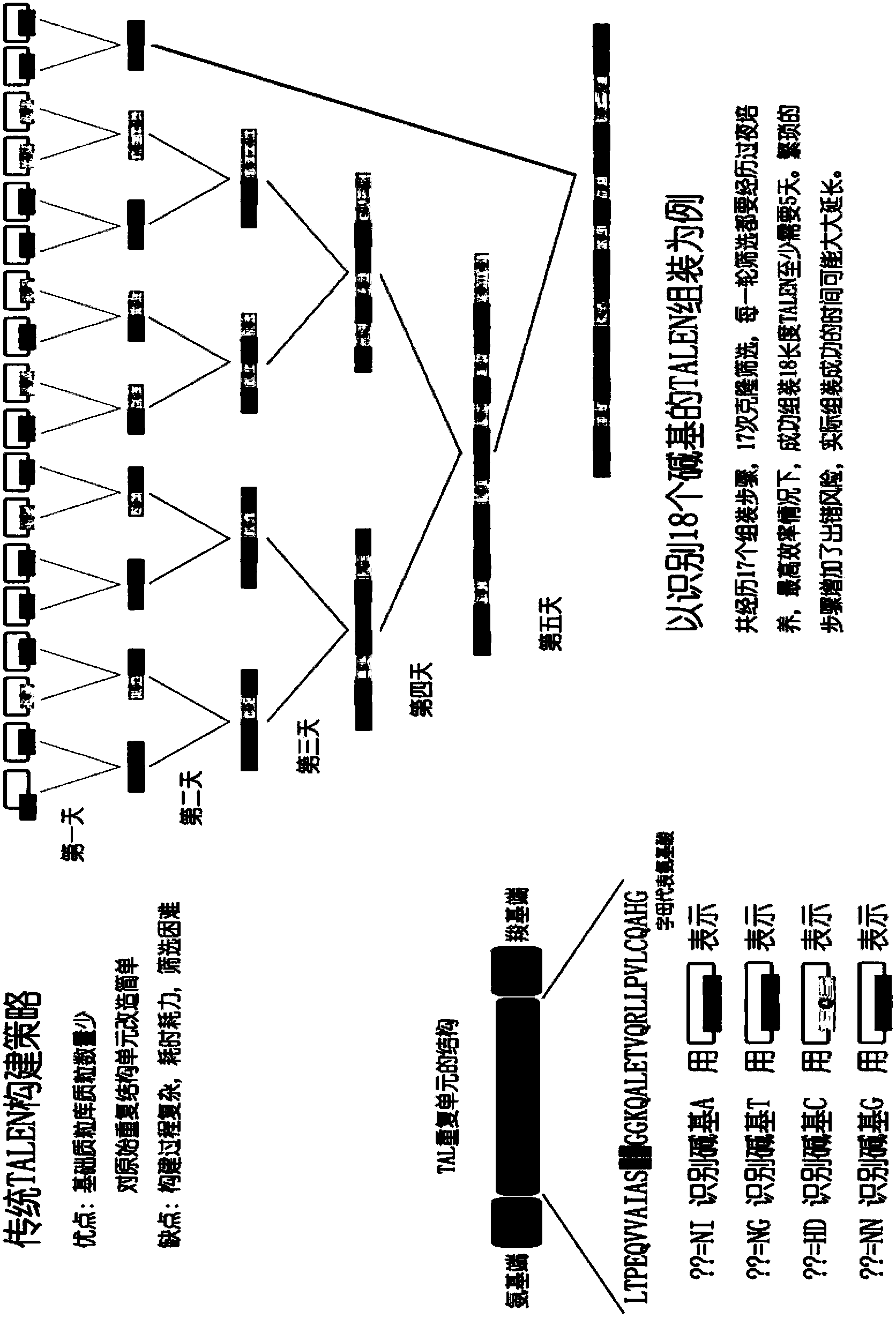
Method of achieving protein expression vector capable of genome site-specific modification
ActiveCN103898099AVector-based foreign material introductionDNA preparationAnimal geneIndividual animal
The invention relates to a biological gene clone expression technology, and particularly relates to a method of rapidly and efficiently constructing an expression vector of a transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALEN). The method is particularly suitable for constructing an expression vector aiming at higher animal genome genetic modification in large scale so as to study functions of animal genes.
Owner:BEIJING PERCANS ONCOLOGY CO LTD
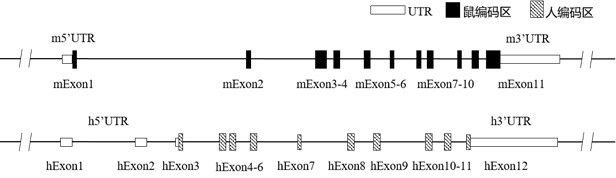
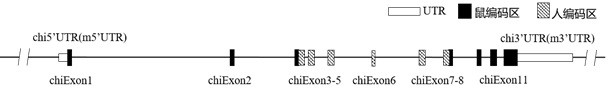
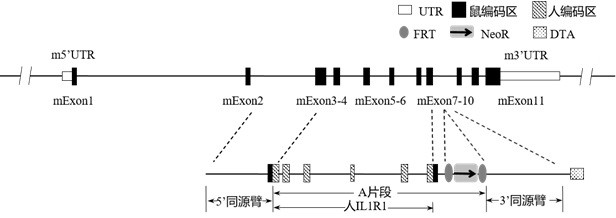
Construction method and application of IL1R1 gene-humanized modified non-human animal
ActiveCN111793646ACompounds screening/testingBiological material analysisImmunologic disordersHumanin
The invention provides a construction method of an IL1R1 gene-humanized modified non-human animal, a humanized IL1R1 protein, a humanized IL1R1 gene, a targeting vector of the IL1R1 gene and application of the targeting vector in the field of biological medicine. By utilizing a homologous recombination manner, a part of nucleotide sequences for encoding human IL1R1 protein are introduced into a non-human animal genome. The humanized IL1R1 protein can be normally expressed in a non-human animal body, and the non-human animal can be used for researching a human IL1R1 signal mechanism and screening drugs for cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases, degenerative diseases, sleep diseases, tumors or inflammation-related diseases, and has important application value forresearch and development of new drugs of immune targets.
Owner:BIOCYTOGEN PHARMACEUTICALS (BEIJING) CO LTD
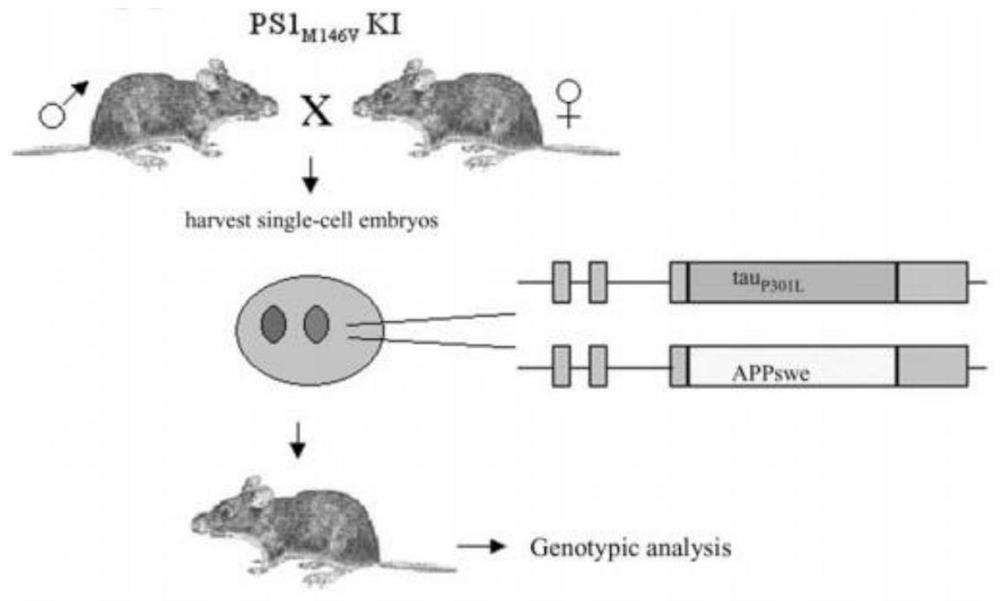
Construction method for constructing Alzheimer's disease animal model and nucleic acid composition and application thereof
PendingCN113957095AConvenient and effective wayVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryPhysiologyGenetic engineering
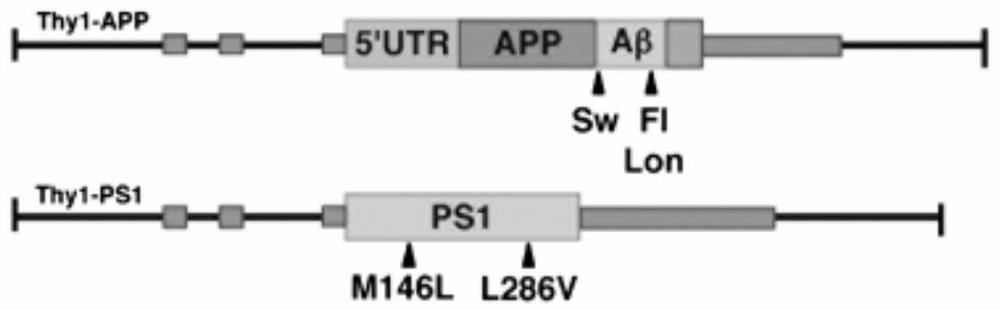
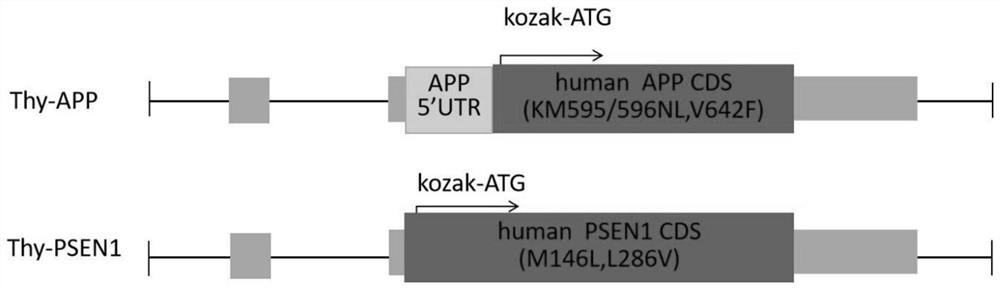
The invention discloses a construction method for constructing an Alzheimer's disease animal model and a nucleic acid composition and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the invention, Thy1-hAPP Sweep, Indiana and Thy1-hPSEN1 M146V and L286V are inserted into a target animal genome and are specifically expressed in a brain region, so that an animal model which can be stably inherited and has a spontaneous classic phenotype of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is obtained. Amyloid protein deposition occurs when the animal model is 1.5 months old, and the amyloid protein deposition increases along with age and is age-dependent. Pathologically along with glial cell hyperplasia, the appearance time is earlier than that of a common AD model. Besides, on the basis that the animal model generates a large amount of A beta deposition, the cognitive and memory ability declines when the animal model is 5 months old, and a convenient and effective way is provided for function analysis of AD related genes, research of disease pathogenesis and drug research and development.
Owner:GEMPHARMATECH CO LTD
High efficiency, high throughput generation of genetically modified non-human mammals by multi-cycle electroporation of cas9 protein
The invention described herein provides high throughput methods and reagents for generating transgenic animals (e.g., non-human mammals) through introducing a CRISPR / Cas9 system comprising a Cas9 protein into gametes or preimplantation stage embryos (e.g., one-cell embryos or zygotes) via multiple cycles (e.g., 4-10 cycles) of electroporation, leading to genetically inheritable modification to the genome of the animal.
Owner:JACKSON LAB THE
Control of gene expression
A method of suppressing the expression of a selected gene in a eukaryotic cell the method comprising introducing into the cell (a) a polypeptide comprising a DNA binding portion which binds to a site at or associated with the selected gene which site is present in a plant r animal genome and a chromatin inactivation portion, or (b) a polynucleotide encoding said polypeptide.
Owner:GENE EXPRESSION TECH
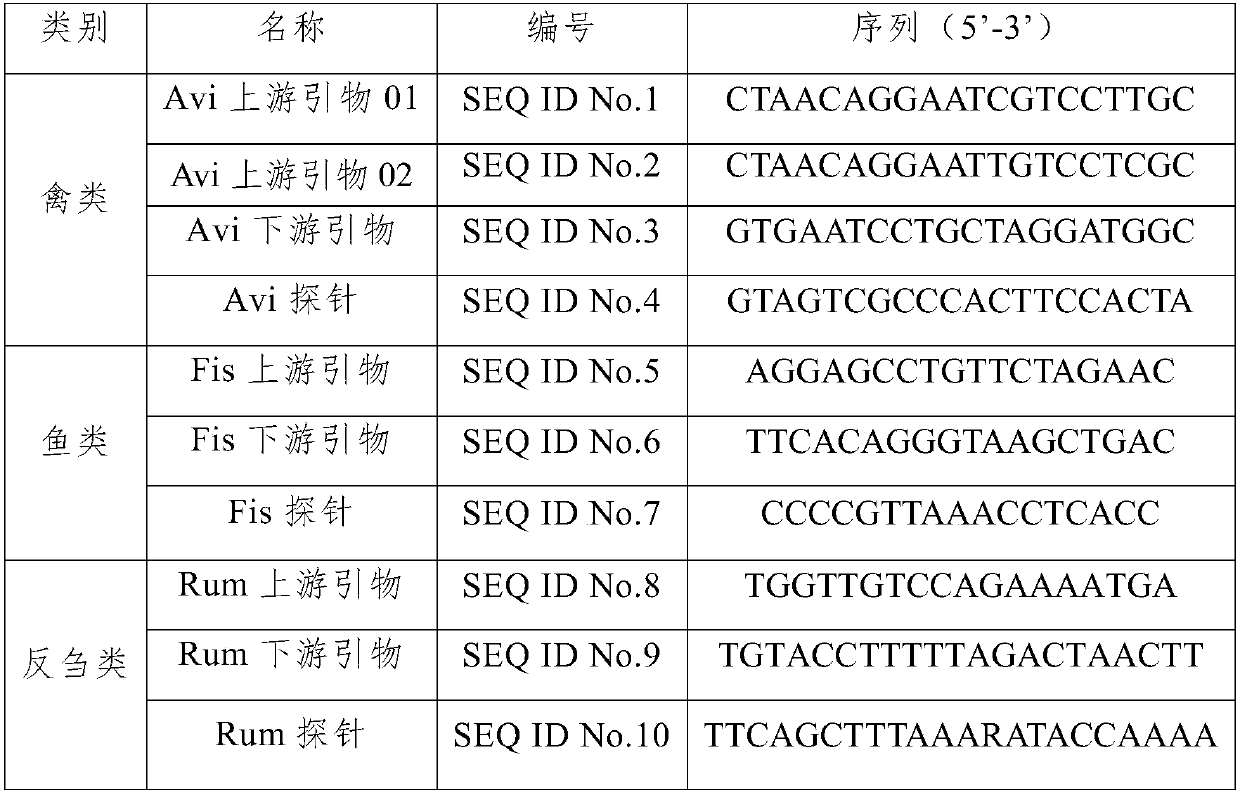
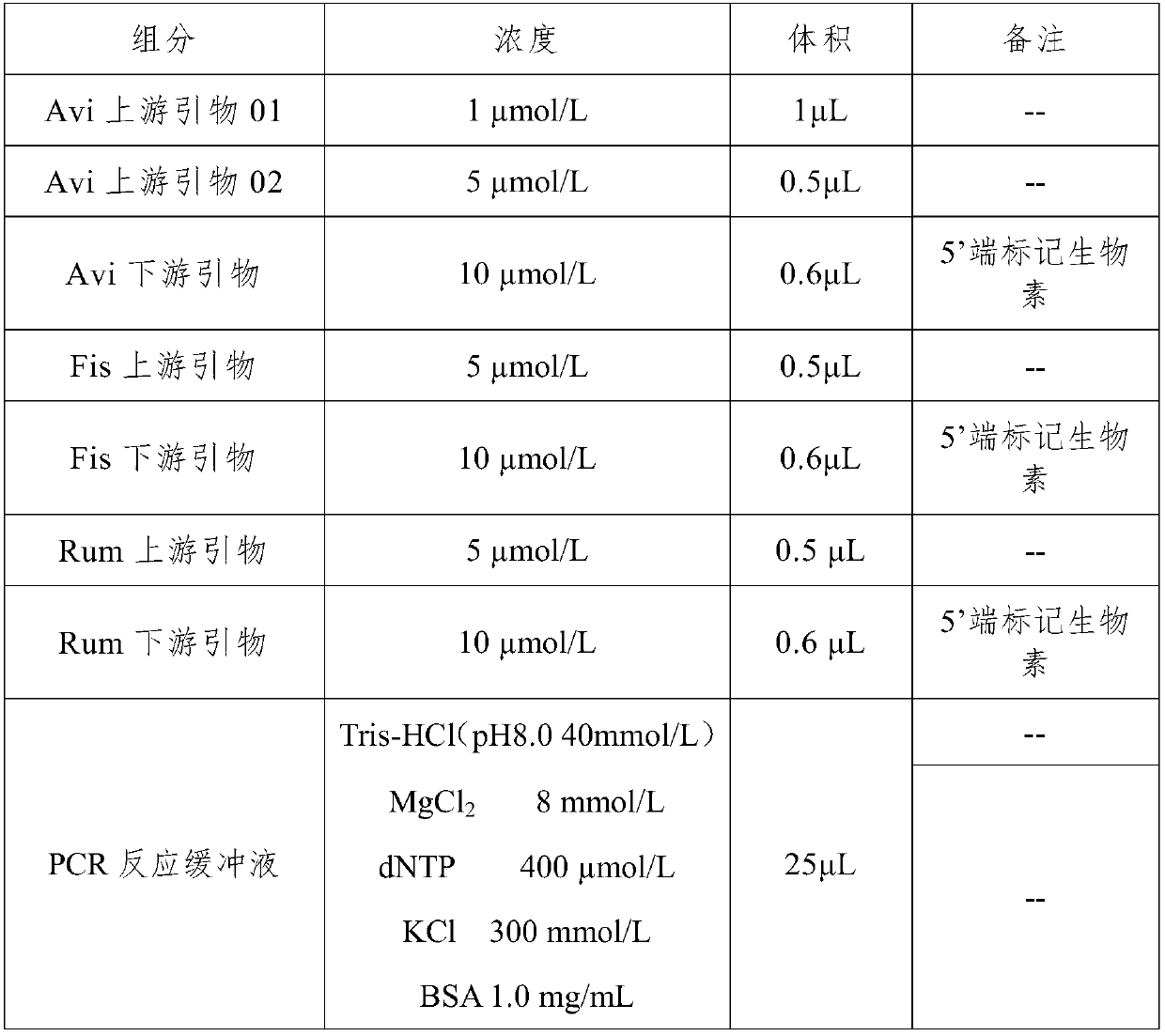
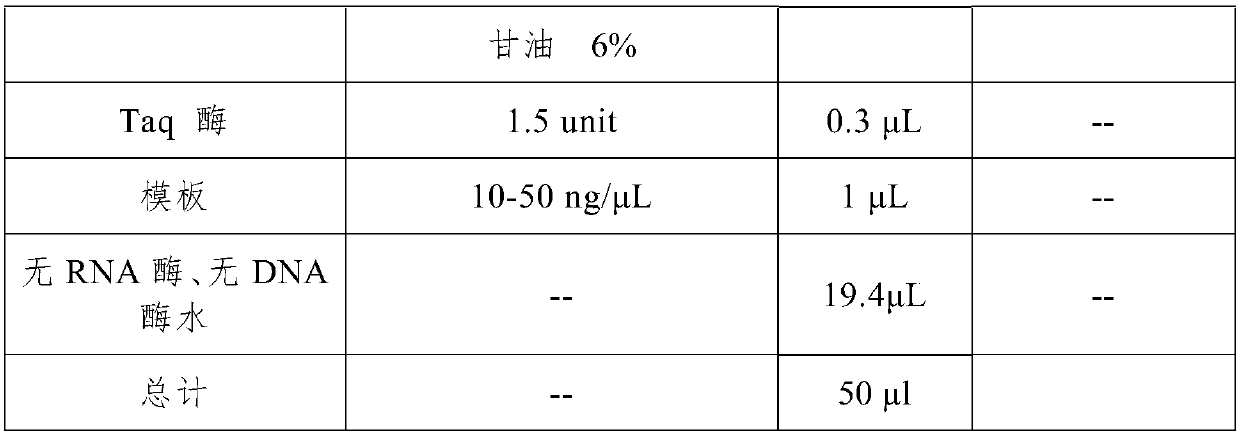
Nucleic acid, method and kit for multi-liquid phase gene chip for simultaneously detecting and identifying components of three major categories of poultry, fish and ruminants
ActiveCN109609662AImprove stabilityHigh speedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFowlMicrosphere
Owner:TECH CENT OF GUANGZHOU CUSTOMS
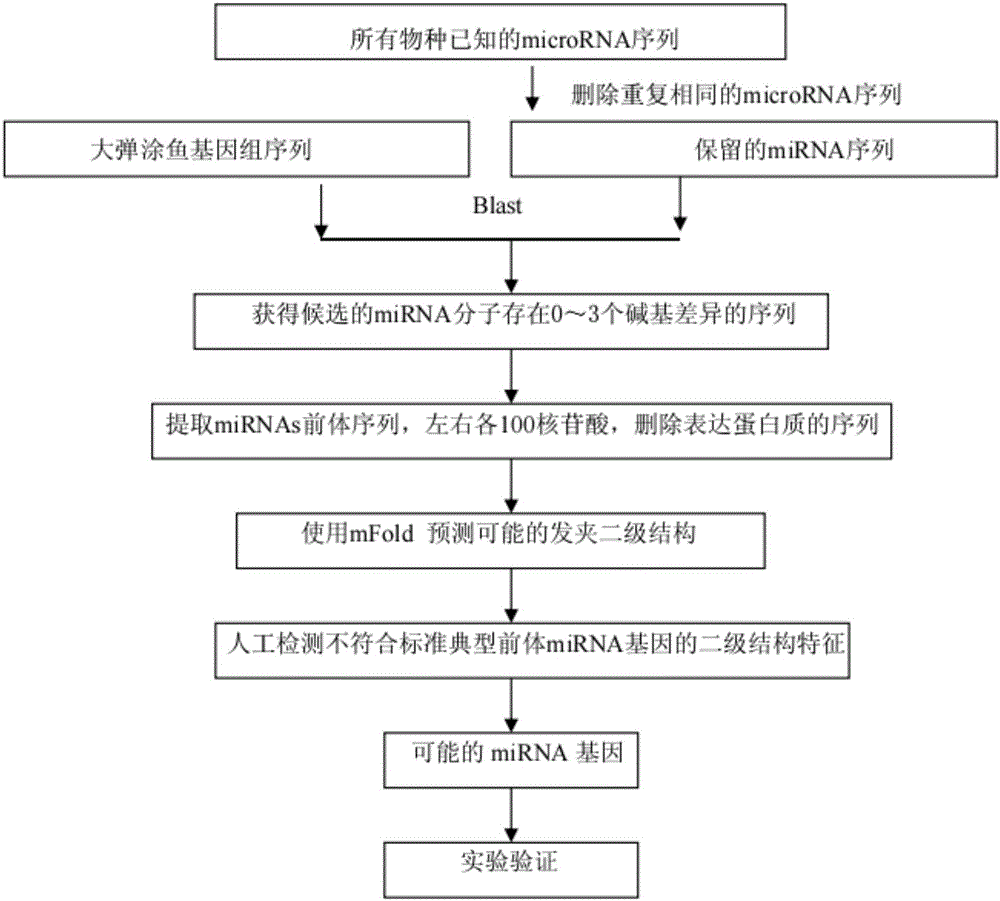
Biological genome sequence-based microRNA predicting method
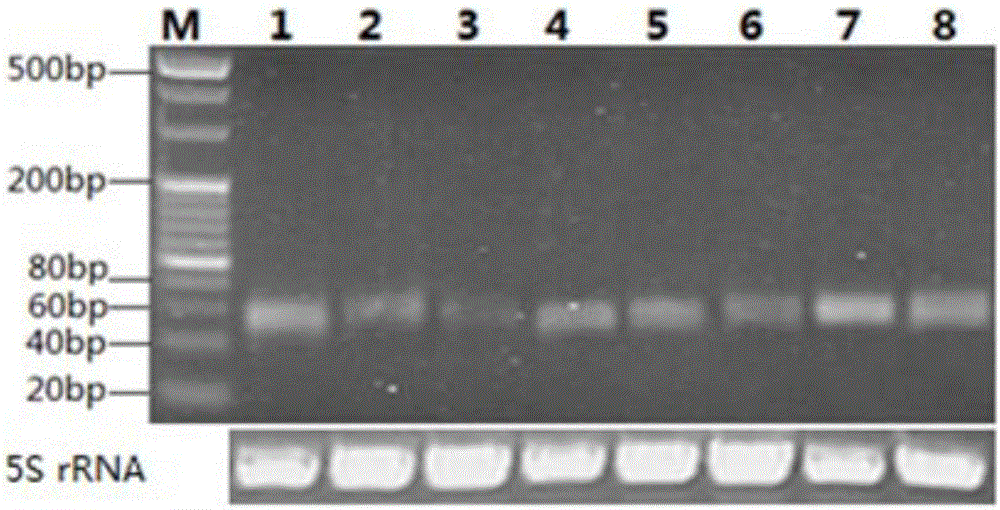
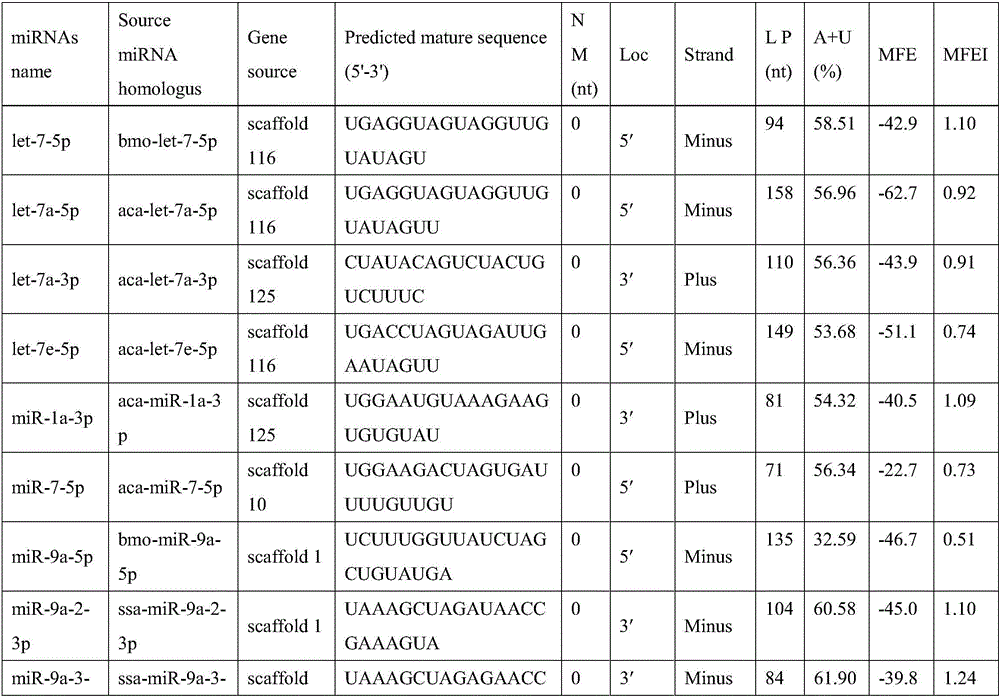
InactiveCN107523631AFast wayEfficient methodMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisMiRNA GeneAnimal genome
The invention discloses a biological genome sequence-based microRNA predicting method. According to the invention, a method for predicting microRNA in an animal genome sequence is designed and experimental verification is performed. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, downloading genome sequences and mature miRNAs sequences of biological species from a website; secondly, removing the sequences with inconsistent number of matched bases by performing genome balst comparison by utilizing downloaded miRNAs of other species, and extracting a precursor sequence of the microRNA for performing stem-and-loop structure predicting; thirdly, deleting predicted stem-and-loop sequences which contain encoding protein from the genome; fourthly, screening and deleting the sequences which have inappropriate AU content and are not accordance with typical structural characteristics of the precursor miRNA; fifthly, acquiring possible miRNAs genes; sixthly, verifying the predicted microRNA by utilizing a stem-loop RT-PCR experiment.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
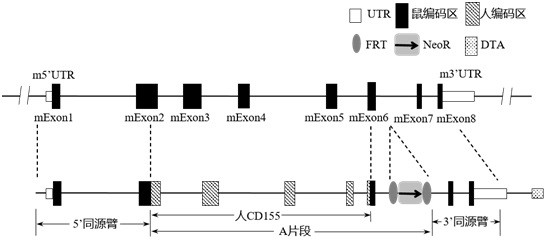
Construction method of CD155 gene humanized non-human animal and application
ActiveCN112458117ACompounds screening/testingImmunoglobulin superfamilyBiotechnologyImmunologic disorders
The invention provides a construction method of a CD155 gene humanized non-human animal. A nucleotide sequence for encoding human CD155 protein is introduced into a non-human animal genome in a homologous recombination manner; the humanized CD155 protein can be normally expressed in the animal; and the animal can be used as an animal model for human CD155 signal mechanism research and tumour and immune disease drug screening. The important application value is realized on the research and development of new drugs of immune targets. The invention also provides humanized CD155 protein, a humanized CD155 gene, a targeting vector of the CD155 gene, a non-human animal obtained by the construction method, and application of the non-human animal in the field of biological medicines.
Owner:BIOCYTOGEN PHARMACEUTICALS (BEIJING) CO LTD
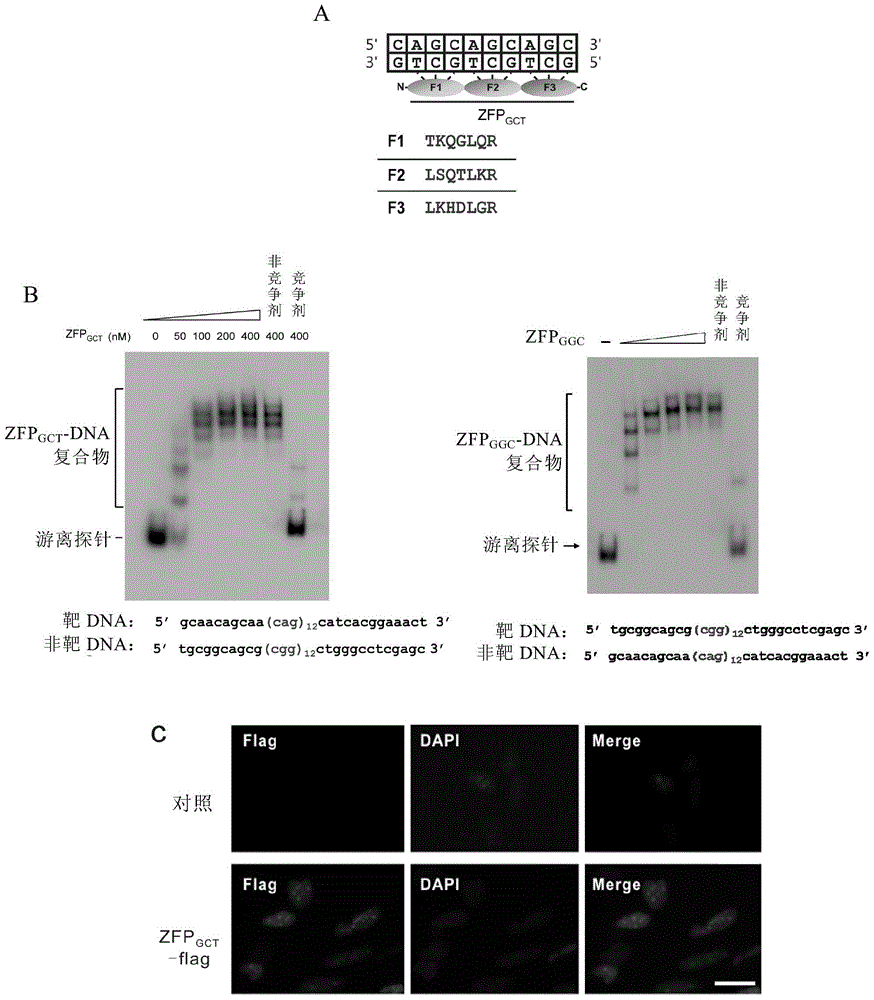
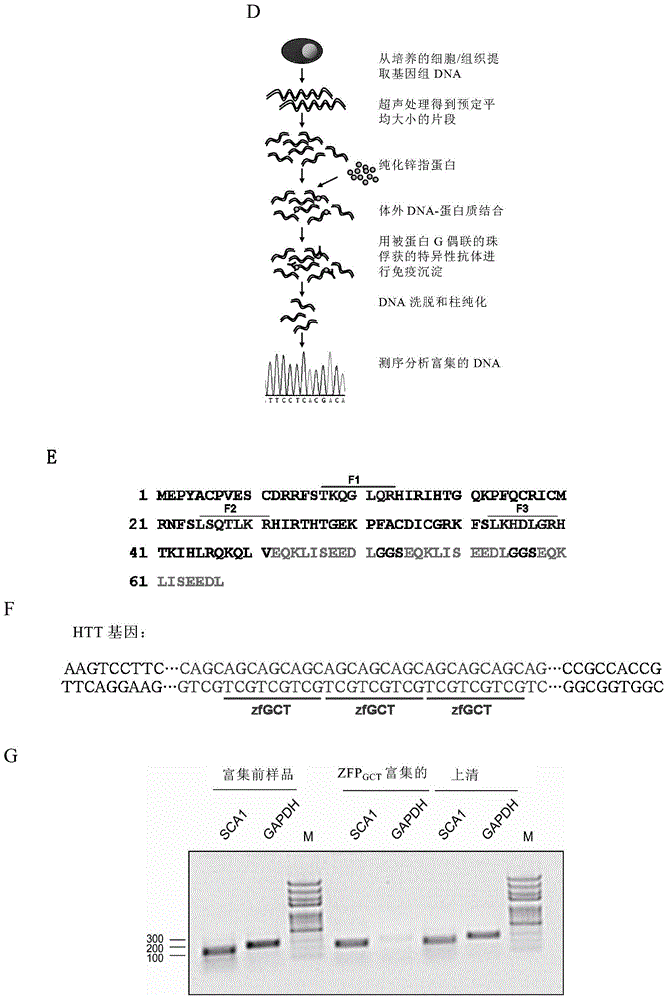
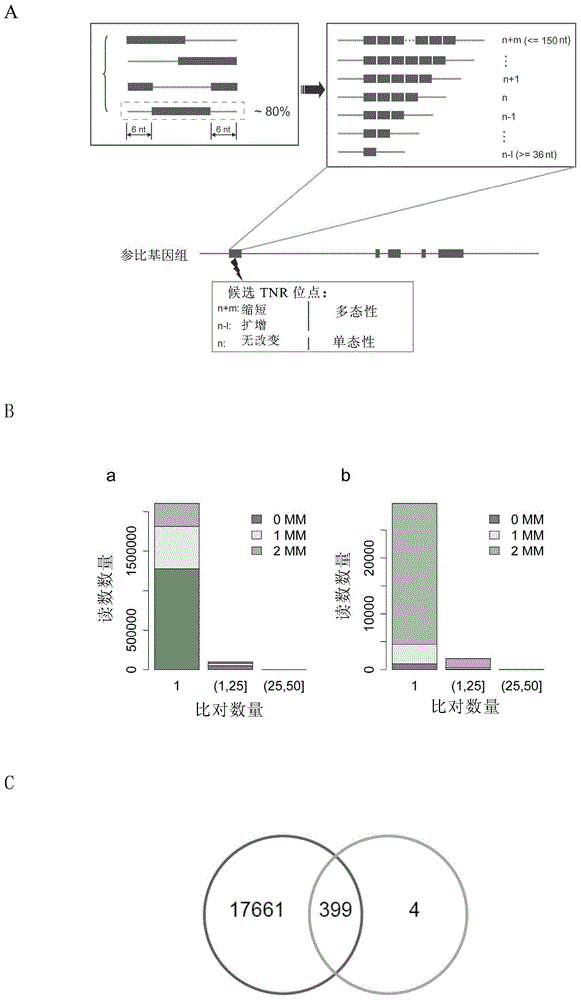
Method for detecting trinucleotide repeated sequence of mammal genome and application thereof
The invention relates to a method for detecting a trinucleotide repeated sequence of a mammal genome and an application thereof, and specifically, the invention relates to a method for detecting the trinucleotide repeated sequence of the mammal genome by using C2H2 zinc finger protein. The invention also relates to the specific C2H2 zinc finger protein, a coding sequence of the specific C2H2 zinc finger protein, polynucleotide constructs containing the coding sequence of the specific C2H2 zinc finger protein, cells, and an application of the C2H2 zinc finger protein, the coding sequence, the polynucleotide constructs and the cells.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR CELL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com