Patents
Literature
93 results about "Contiguity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A contiguity is a continuous mass, or a series of things in contact or in proximity. In a different meaning, contiguity is the state of being contiguous. The concept was first set out in the Law of Contiguity which states that things that occur near each other in time or space are readily associated.
Face feature analysis for automatic lipreading and character animation
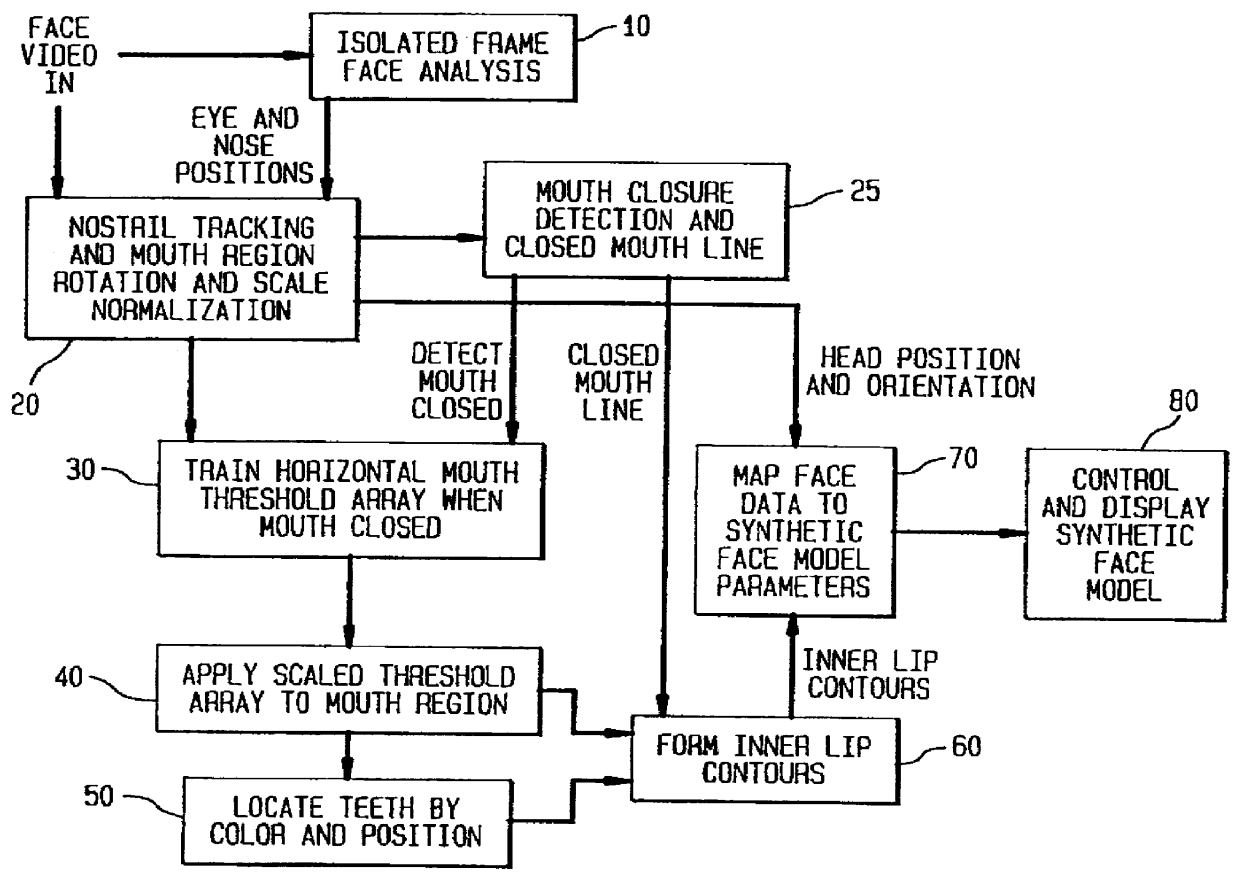
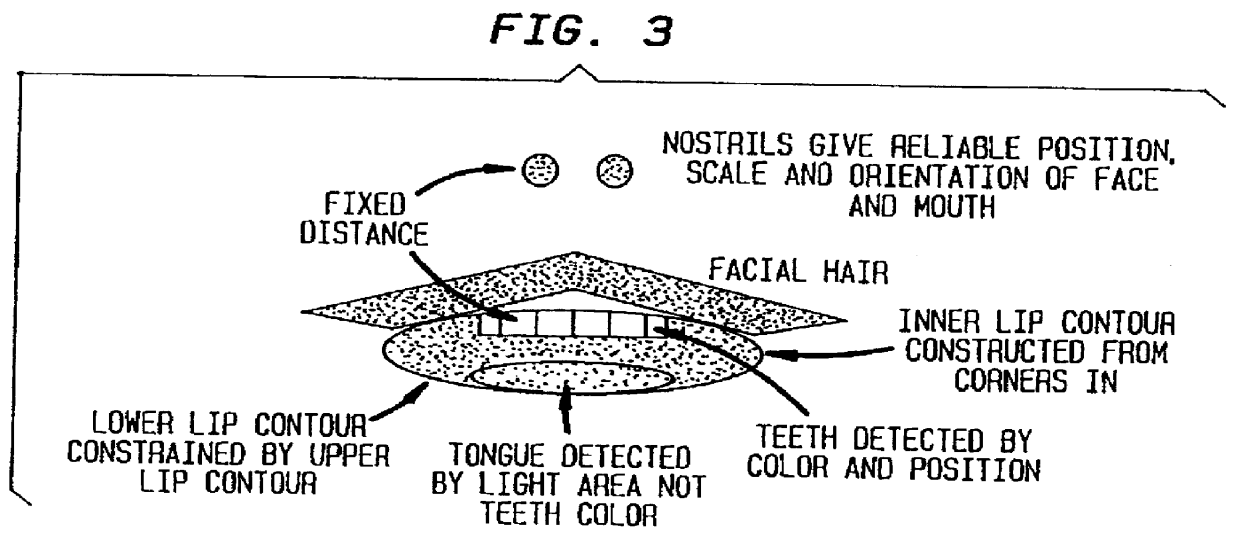
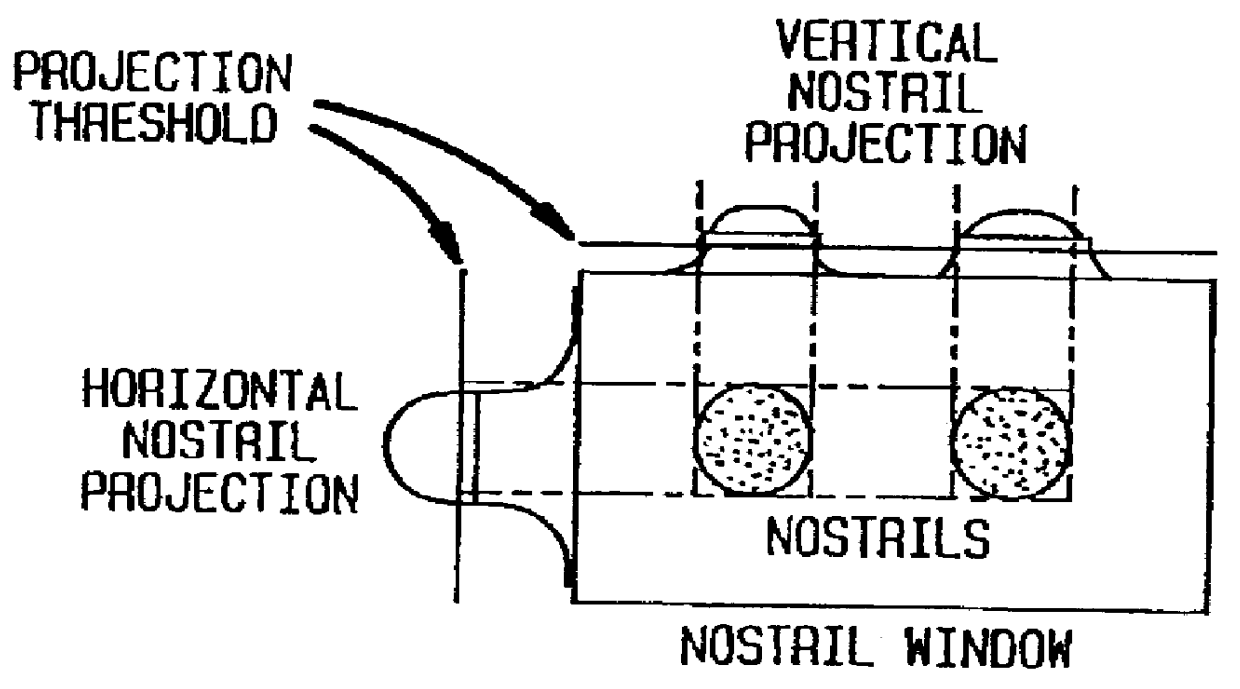
A face feature analysis which begins by generating multiple face feature candidates, e.g., eyes and nose positions, using an isolated frame face analysis. Then, a nostril tracking window is defined around a nose candidate and tests are applied to the pixels therein based on percentages of skin color area pixels and nostril area pixels to determine whether the nose candidate represents an actual nose. Once actual nostrils are identified, size, separation and contiguity of the actual nostrils is determined by projecting the nostril pixels within the nostril tracking window. A mouth window is defined around the mouth region and mouth detail analysis is then applied to the pixels within the mouth window to identify inner mouth and teeth pixels and therefrom generate an inner mouth contour. The nostril position and inner mouth contour are used to generate a synthetic model head. A direct comparison is made between the inner mouth contour generated and that of a synthetic model head and the synthetic model head is adjusted accordingly. Vector quantization algorithms may be used to develop a codebook of face model parameters to improve processing efficiency. The face feature analysis is suitable regardless of noise, illumination variations, head tilt, scale variations and nostril shape.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Massively parallel contiguity mapping
ActiveUS20130203605A1Reducing sequenceLimited to sequenceLibrary member identificationChemical recyclingHuman DNA sequencingMammalian genome
Contiguity information is important to achieving high-quality de novo assembly of mammalian genomes and the haplotype-resolved resequencing of human genomes. The methods described herein pursue cost-effective, massively parallel capture of contiguity information at different scales.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
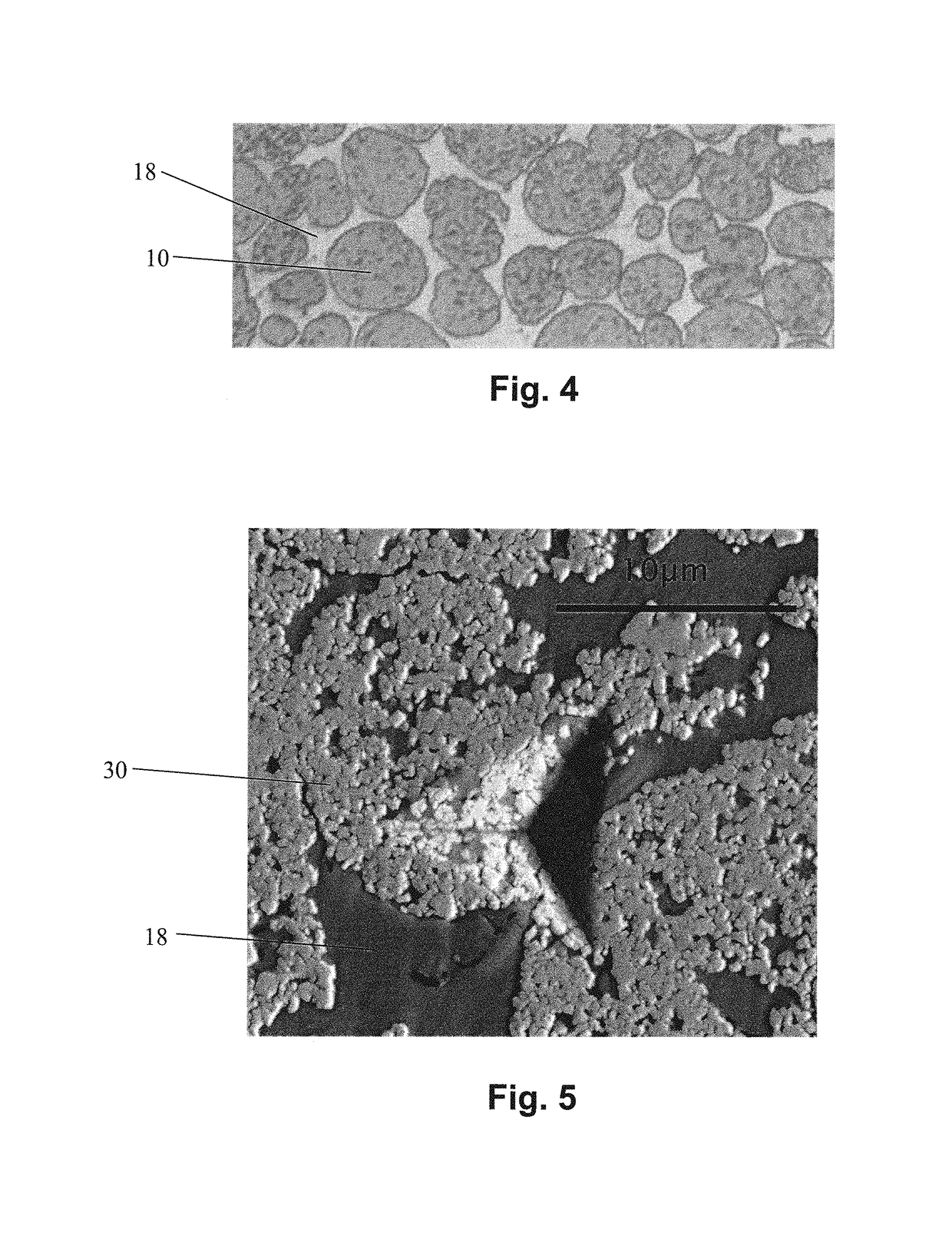
Heterogeneous composite bodies with isolated cermet regions formed by high temperature, rapid consolidation
ActiveUS9943918B2Increase spacingUniform compositionRolling contact bearingsTransportation and packagingNanoparticleNanometre
A heterogeneous composite consisting of near-nano ceramic clusters dispersed within a ductile matrix. The composite is formed through the high temperature compaction of a starting powder consisting of a core of ceramic nanoparticles held together with metallic binder. This core is clad with a ductile metal such that when the final powder is consolidated, the ductile metal forms a tough, near-zero contiguity matrix. The material is consolidated using any means that will maintain its heterogeneous structure.
Owner:POWDERMET
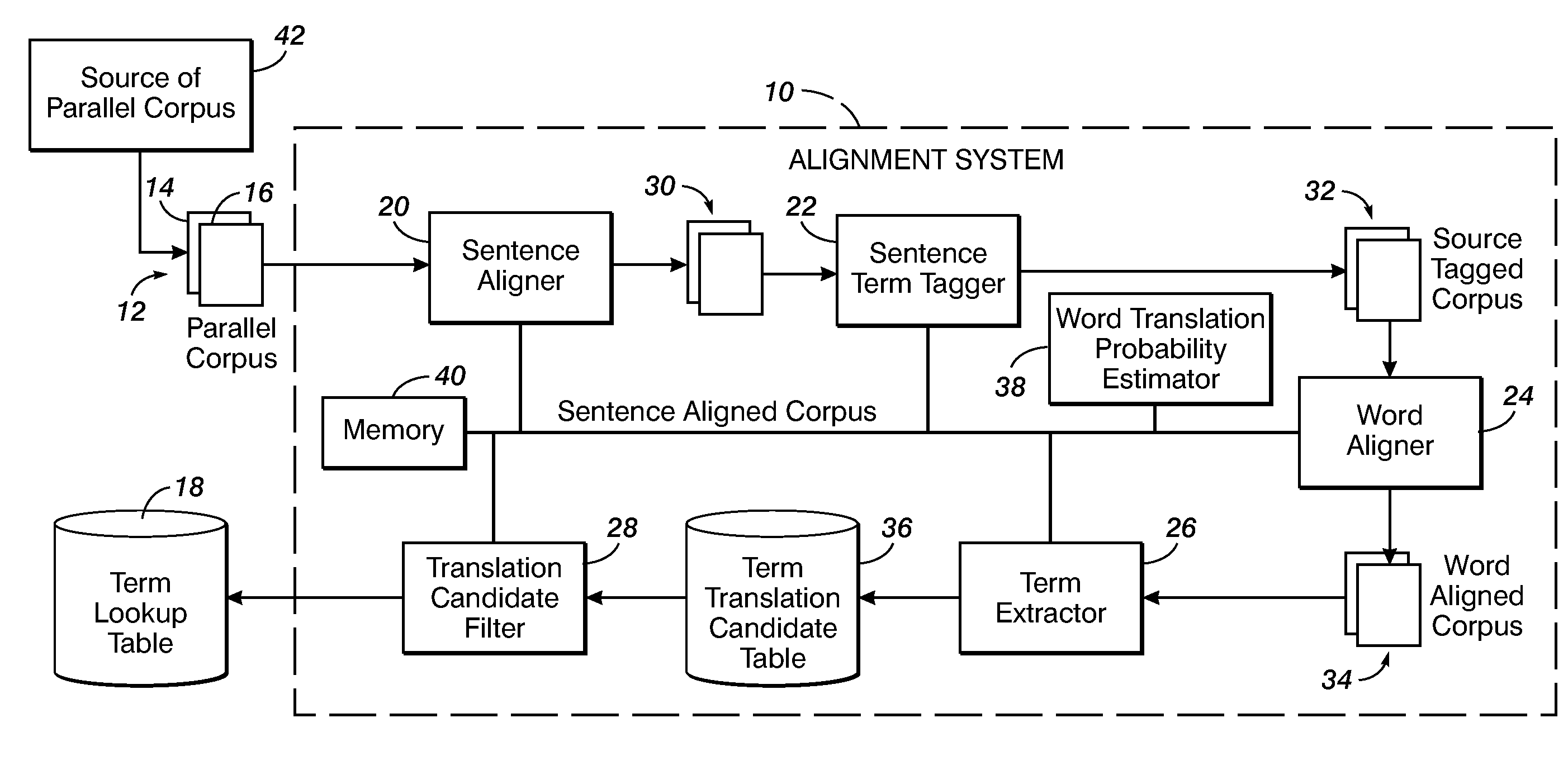
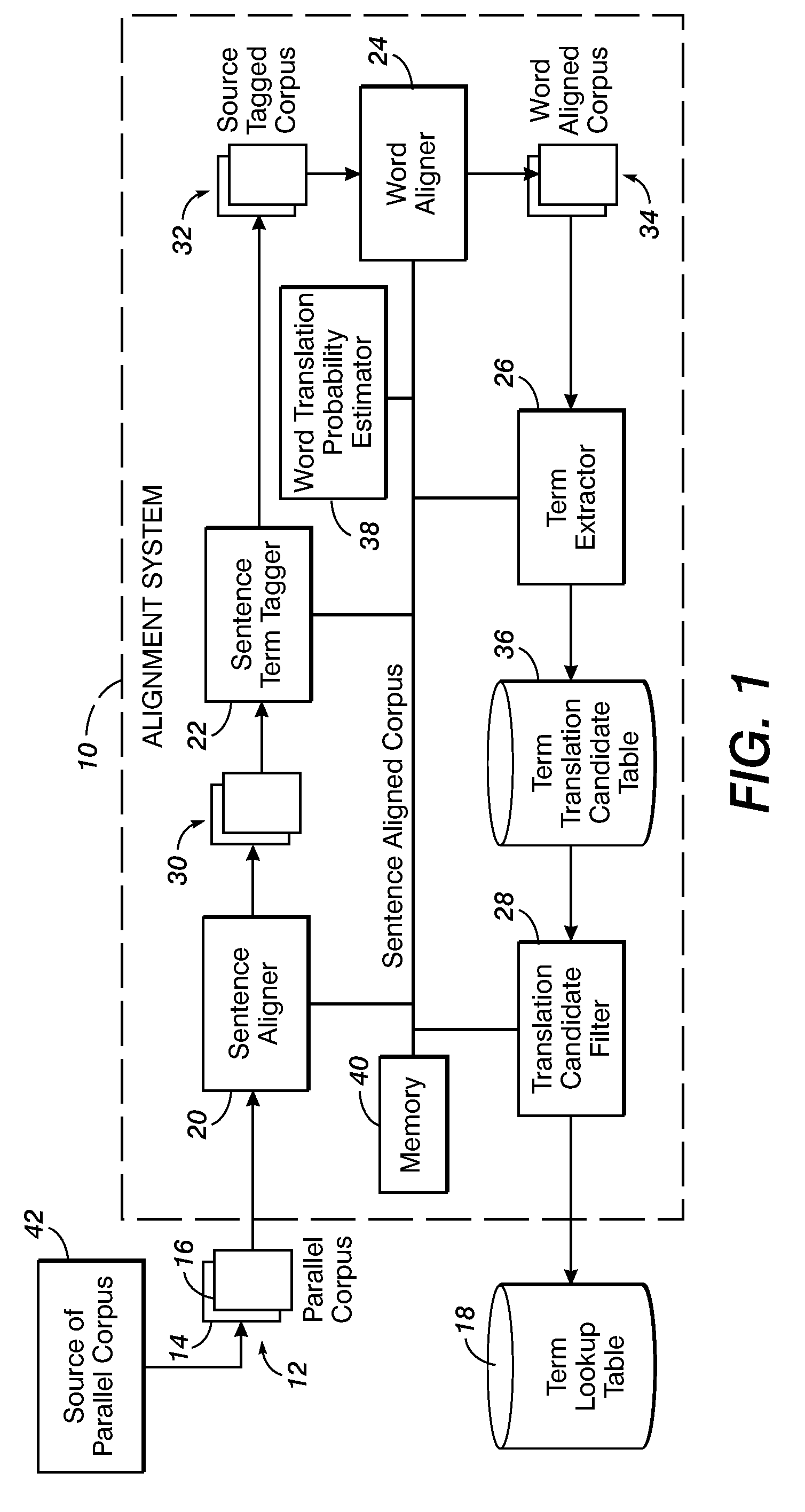
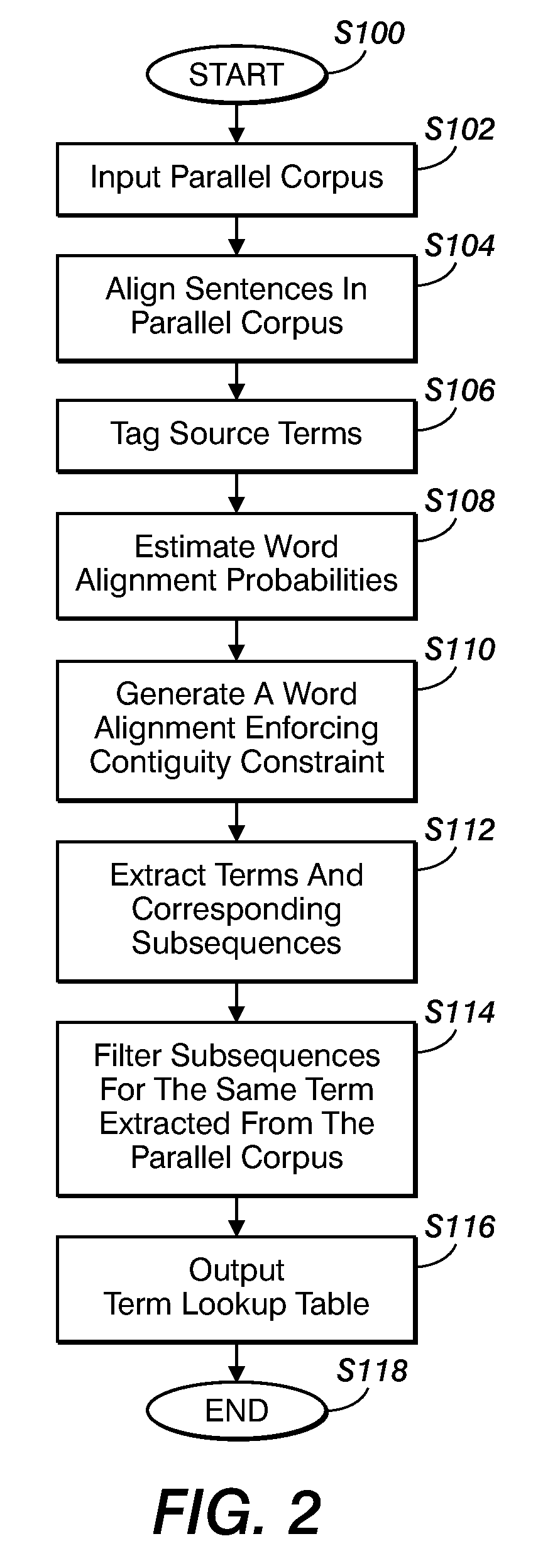
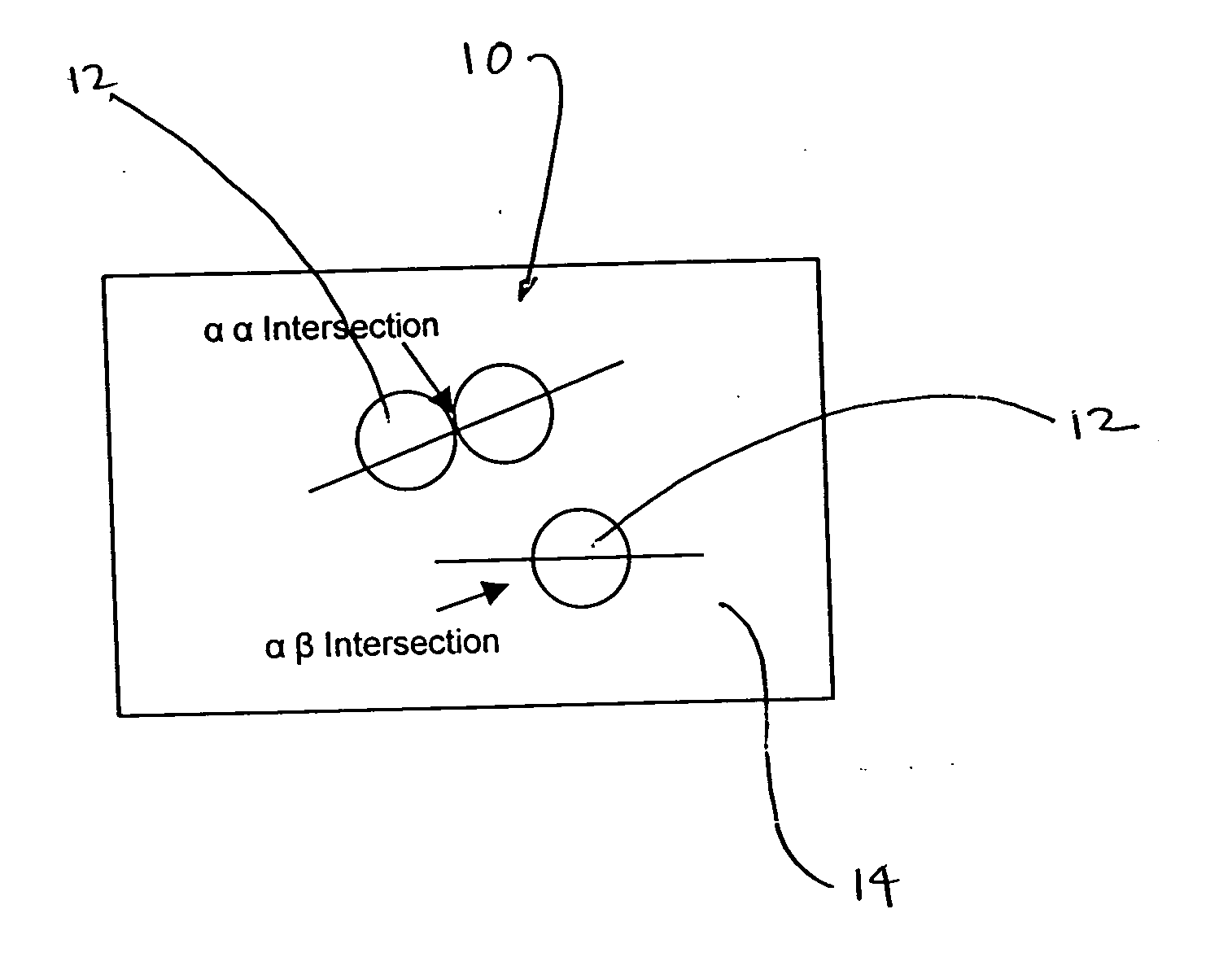
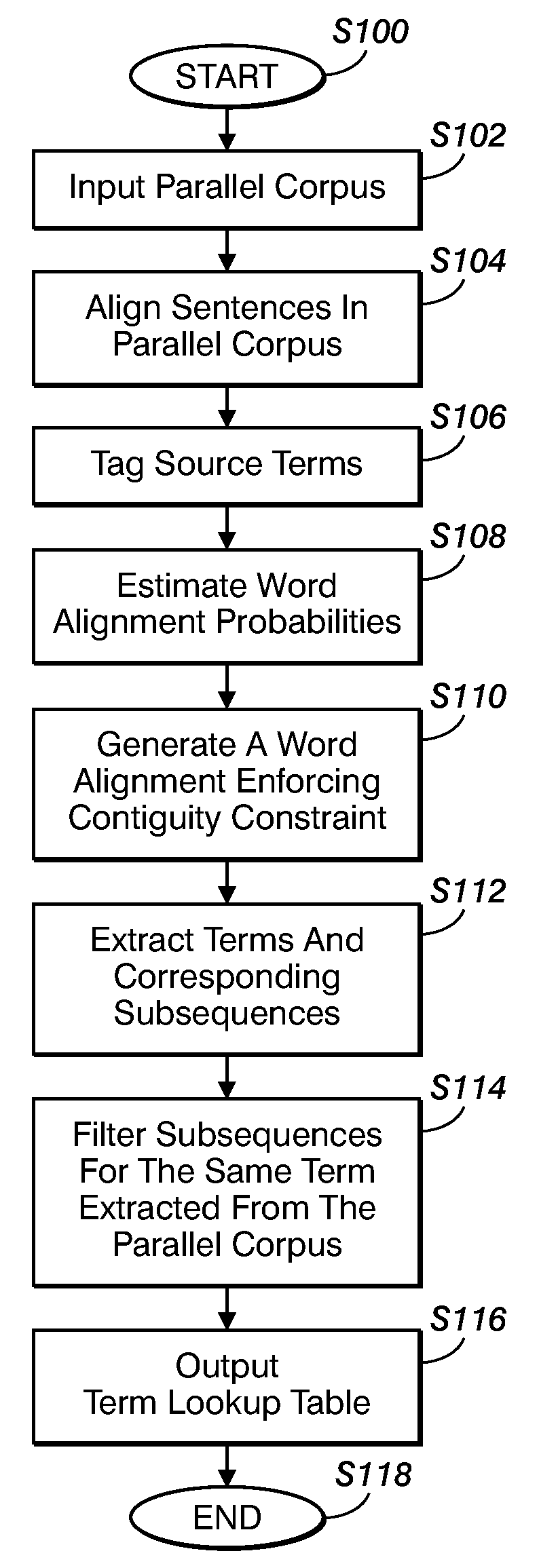
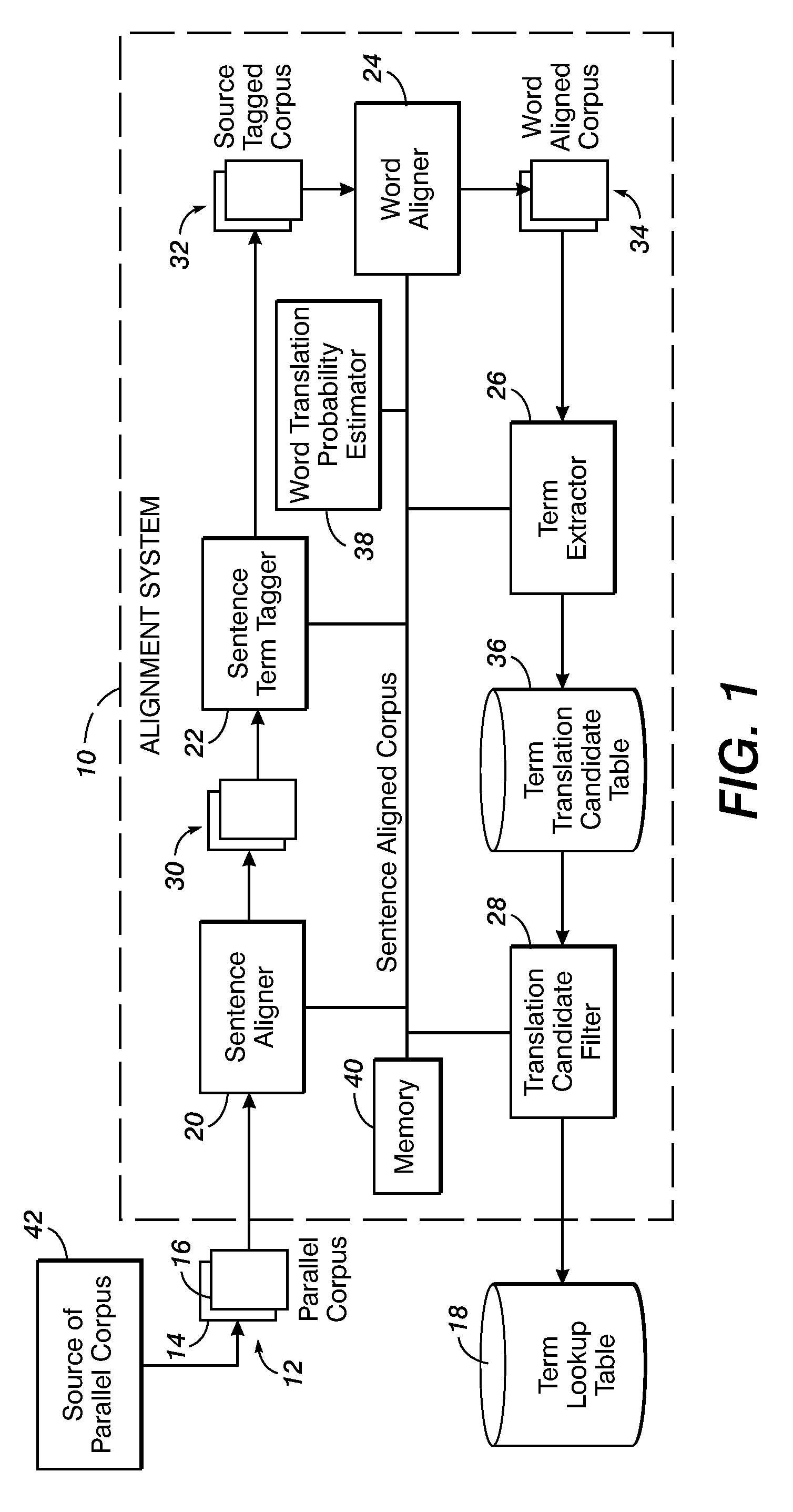
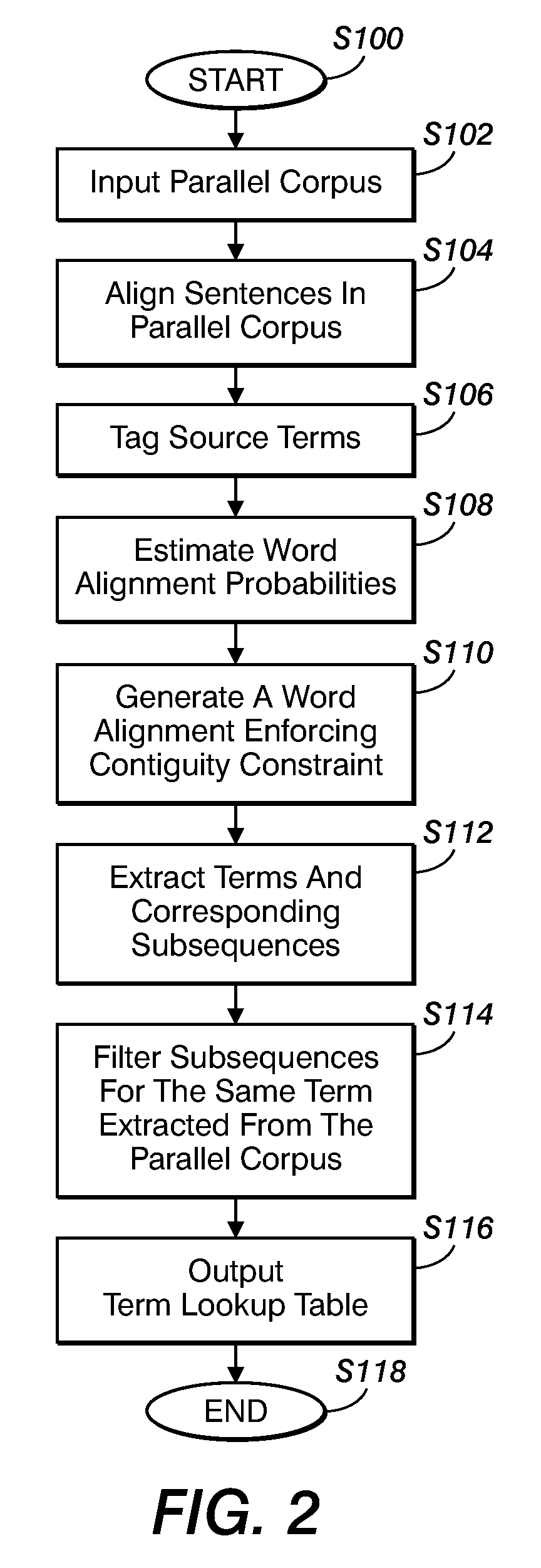
Method for aligning sentences at the word level enforcing selective contiguity constraints
InactiveUS9020804B2Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsProbit modelConditional probability
An alignment method includes, for a source sentence in a source language, identifying whether the sentence includes at least one candidate term comprising a contiguous subsequence of words of the source sentence. A target sentence in a target language is aligned with the source sentence. This includes developing a probabilistic model which models conditional probability distributions for alignments between words of the source sentence and words of the target sentence and generating an optimal alignment based on the probabilistic model, including, where the source sentence includes the at least one candidate term, enforcing a contiguity constraint which requires that all the words of the target sentence which are aligned with an identified candidate term form a contiguous subsequence of the target sentence.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Hybrid cemented carbide composites
Embodiments of the present invention include hybrid composite materials comprising a cemented carbide dispersed phase and a cemented carbide continuous phase. The contiguity ratio of the dispersed phase of embodiments may be less than or equal to 0.48. The hybrid composite material may have a hardness of the dispersed phase that is greater than the hardness of the continuous phase. For example, in certain embodiments of the hybrid composite material, the hardness of the dispersed phase is greater than or equal to 88 HRA and less than or equal to 95 HRA and the hardness of the continuous phase is greater than or equal to 78 and less than or equal to 91 HRA. Additional embodiments may include hybrid composite materials comprising a first cemented carbide dispersed phase wherein the volume fraction of the dispersed phase is less than 50 volume percent and a second cemented carbide continuous phase, wherein the contiguity ratio of the dispersed phase is less than or equal to 1.5 times the volume fraction of the dispersed phase in the composite material. The present invention also includes a method of making a hybrid cemented carbide composite by blending partially and / or fully sintered granules of the dispersed cemented carbide grade with “green” and / or unsintered granules of the continuous cemented carbide grade to provide a blend. The blend may then be consolidated to form a compact. Finally, the compact may be sintered to form a hybrid cemented carbide.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Method for aligning sentences at the word level enforcing selective contiguity constraints
InactiveUS20080300857A1Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsProbit modelConditional probability
An alignment method includes, for a source sentence in a source language, identifying whether the sentence includes at least one candidate term comprising a contiguous subsequence of words of the source sentence. A target sentence in a target language is aligned with the source sentence. This includes developing a probabilistic model which models conditional probability distributions for alignments between words of the source sentence and words of the target sentence and generating an optimal alignment based on the probabilistic model, including, where the source sentence includes the at least one candidate term, enforcing a contiguity constraint which requires that all the words of the target sentence which are aligned with an identified candidate term form a contiguous subsequence of the target sentence.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Hybrid cemented carbide composites
Embodiments of the present invention include hybrid composite materials comprising a cemented carbide dispersed phase and a cemented carbide continuous phase. The contiguity ratio of the dispersed phase of embodiments may be less than or equal to 0.48. The hybrid composite material may have a hardness of the dispersed phase that is greater than the hardness of the continuous phase. For example, in certain embodiments of the hybrid composite material, the hardness of the dispersed phase is greater than or equal to 88 HRA and less than or equal to 95 HRA and the hardness of the continuous phase is greater than or equal to 78 and less than or equal to 91 HRA.Additional embodiments may include hybrid composite materials comprising a first cemented carbide dispersed phase wherein the volume fraction of the dispersed phase is less than 50 volume percent and a second cemented carbide continuous phase, wherein the contiguity ratio of the dispersed phase is less than or equal to 1.5 times the volume fraction of the dispersed phase in the composite material.The present invention also includes a method of making a hybrid cemented carbide composite by blending partially and / or fully sintered granules of the dispersed cemented carbide grade with “green” and / or unsintered granules of the continuous cemented carbide grade to provide a blend. The blend may then be consolidated to form a compact. Finally, the compact may be sintered to form a hybrid cemented carbide.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
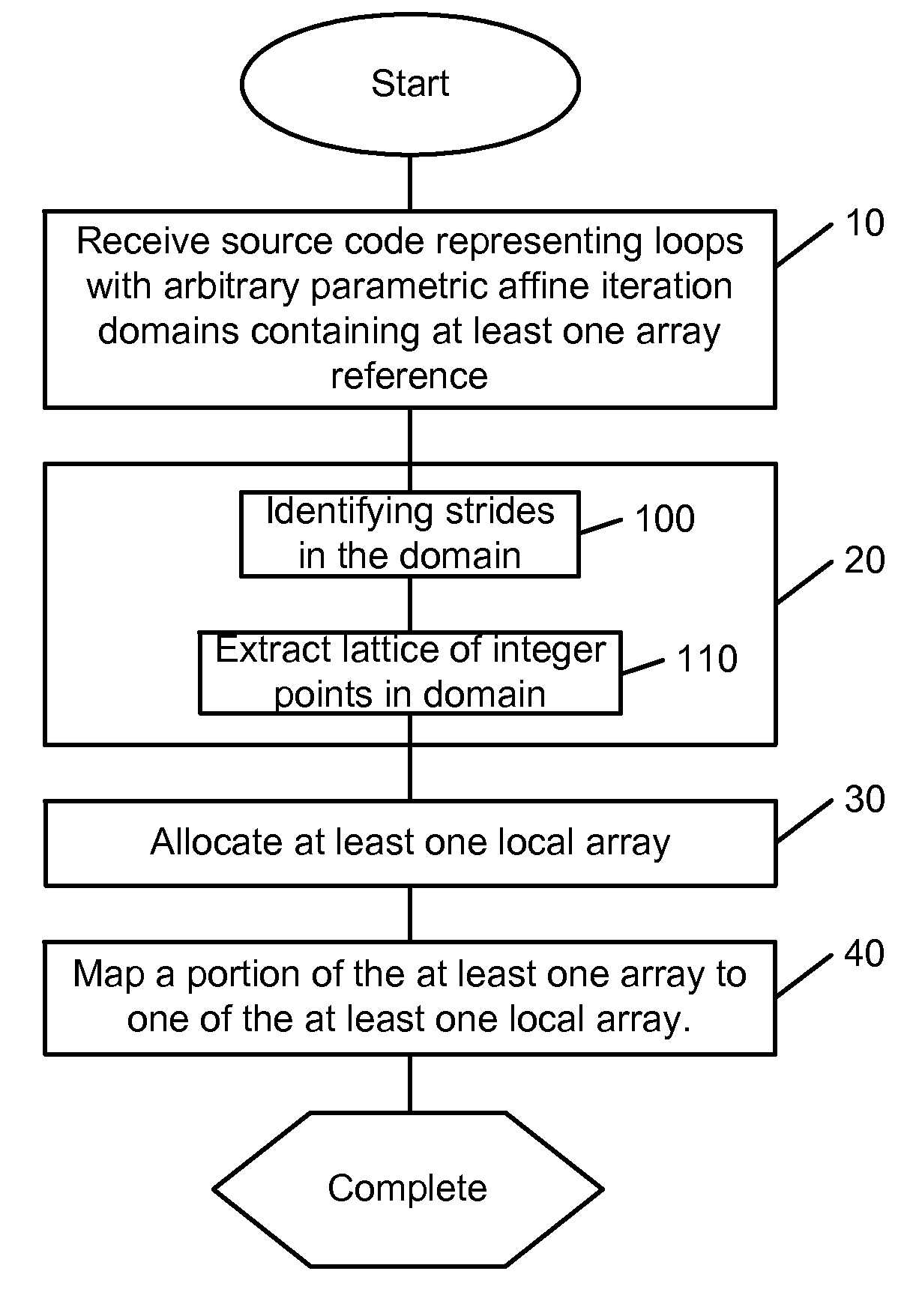
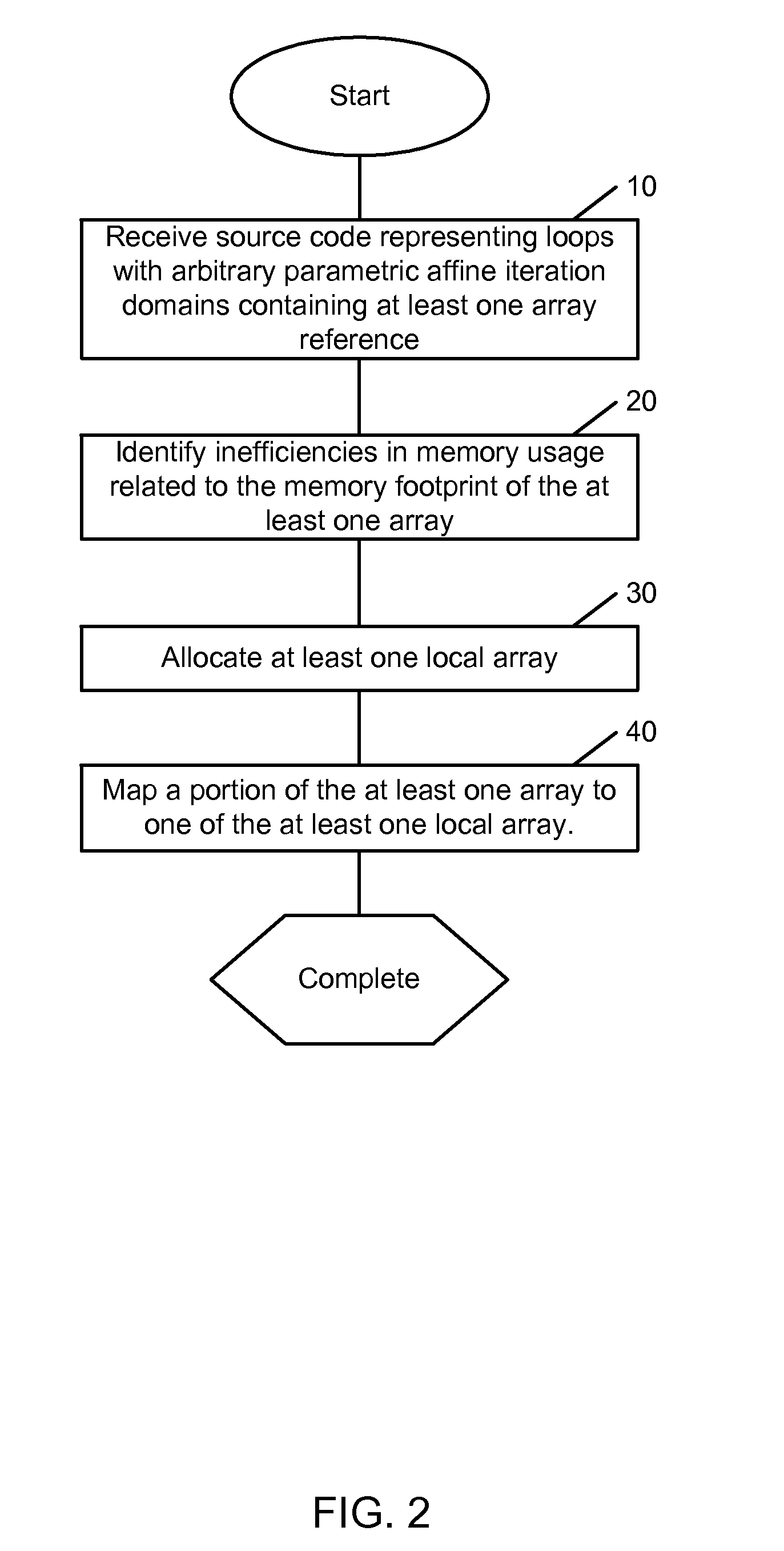
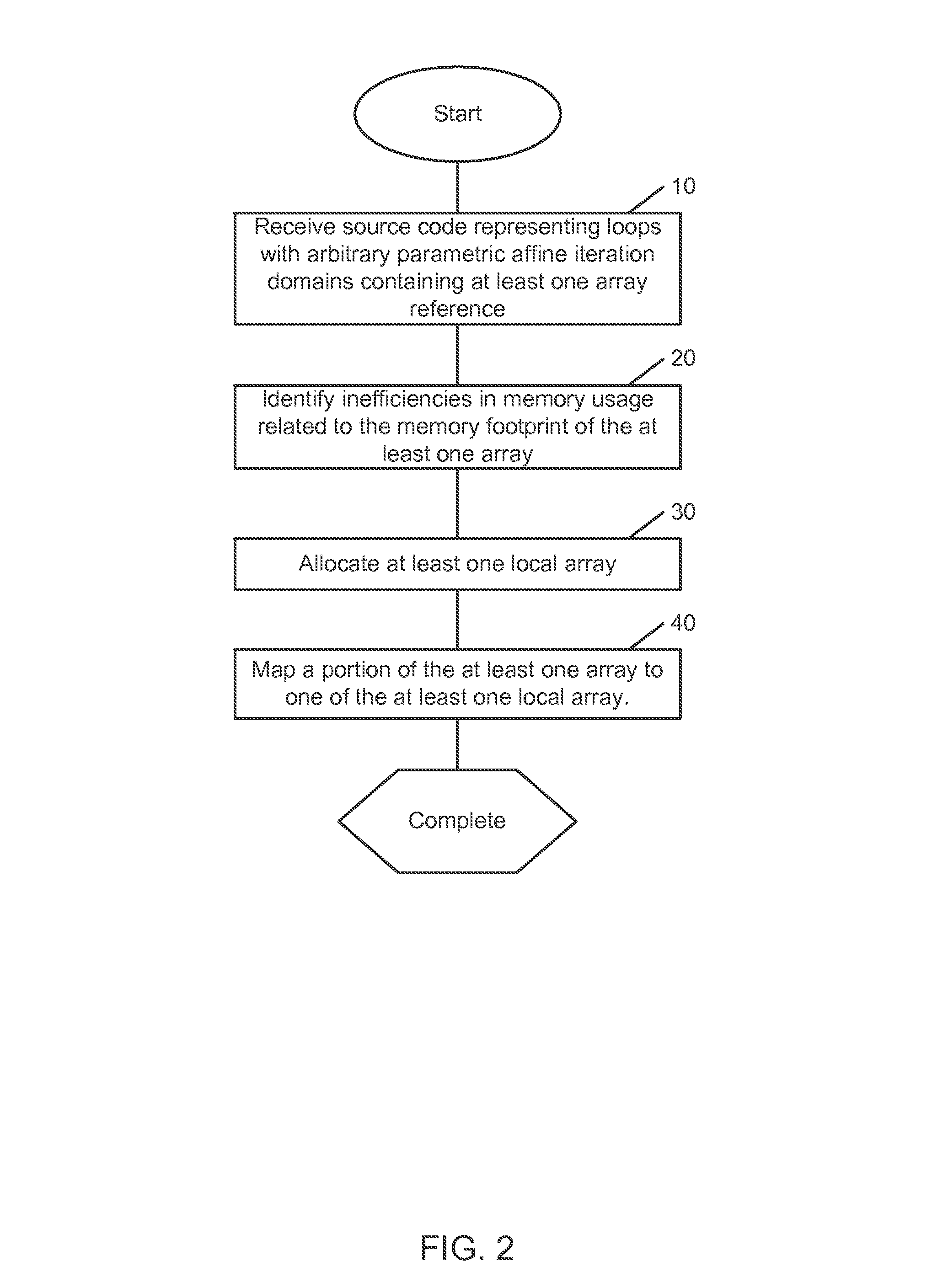
System, methods and apparatus for program optimization for multi-threaded processor architectures
ActiveUS20100218196A1Low costEasy to implementSoftware engineeringMultiprogramming arrangementsParallel computingExecution unit
Owner:QUALCOMM TECHNOLOGIES INC
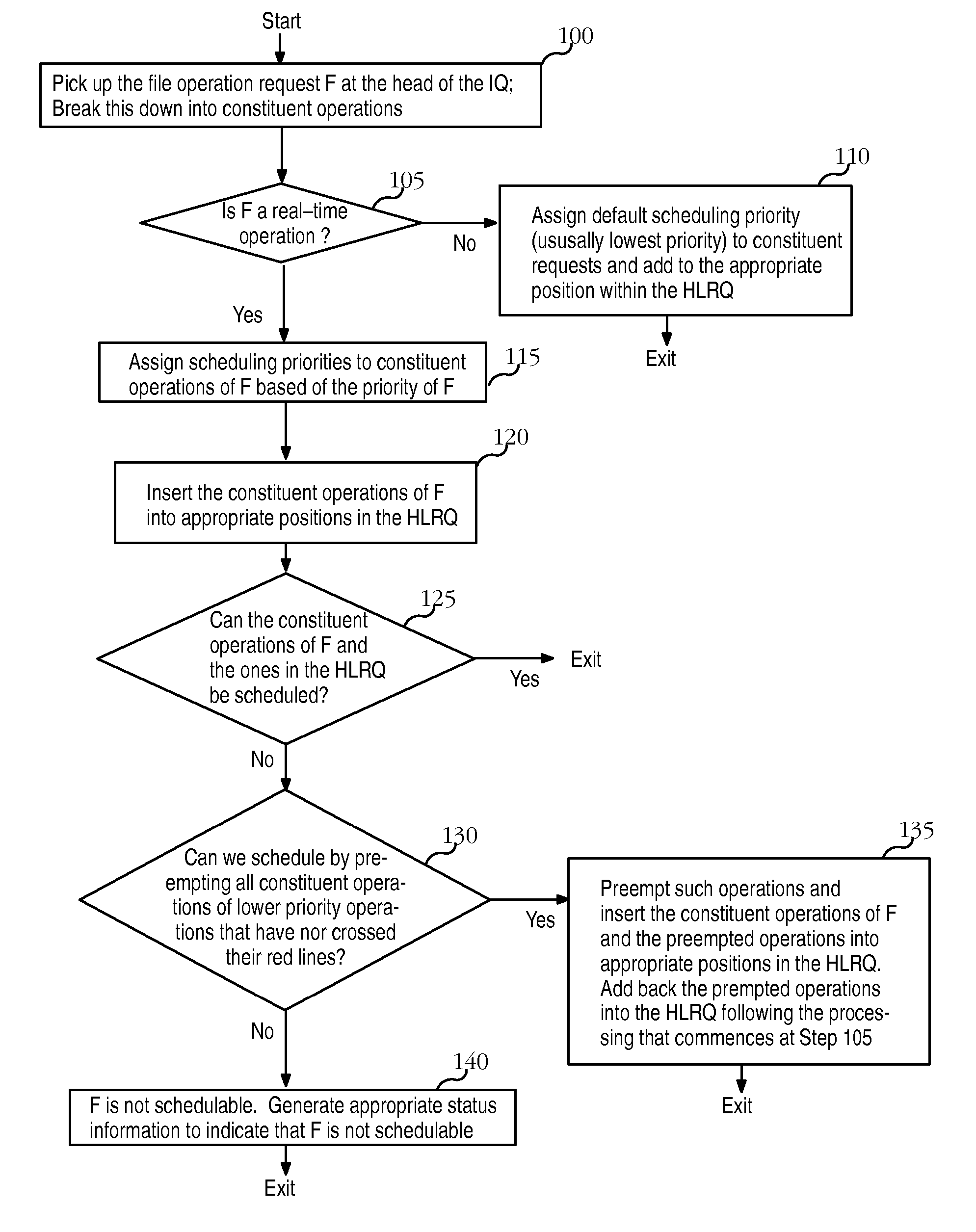
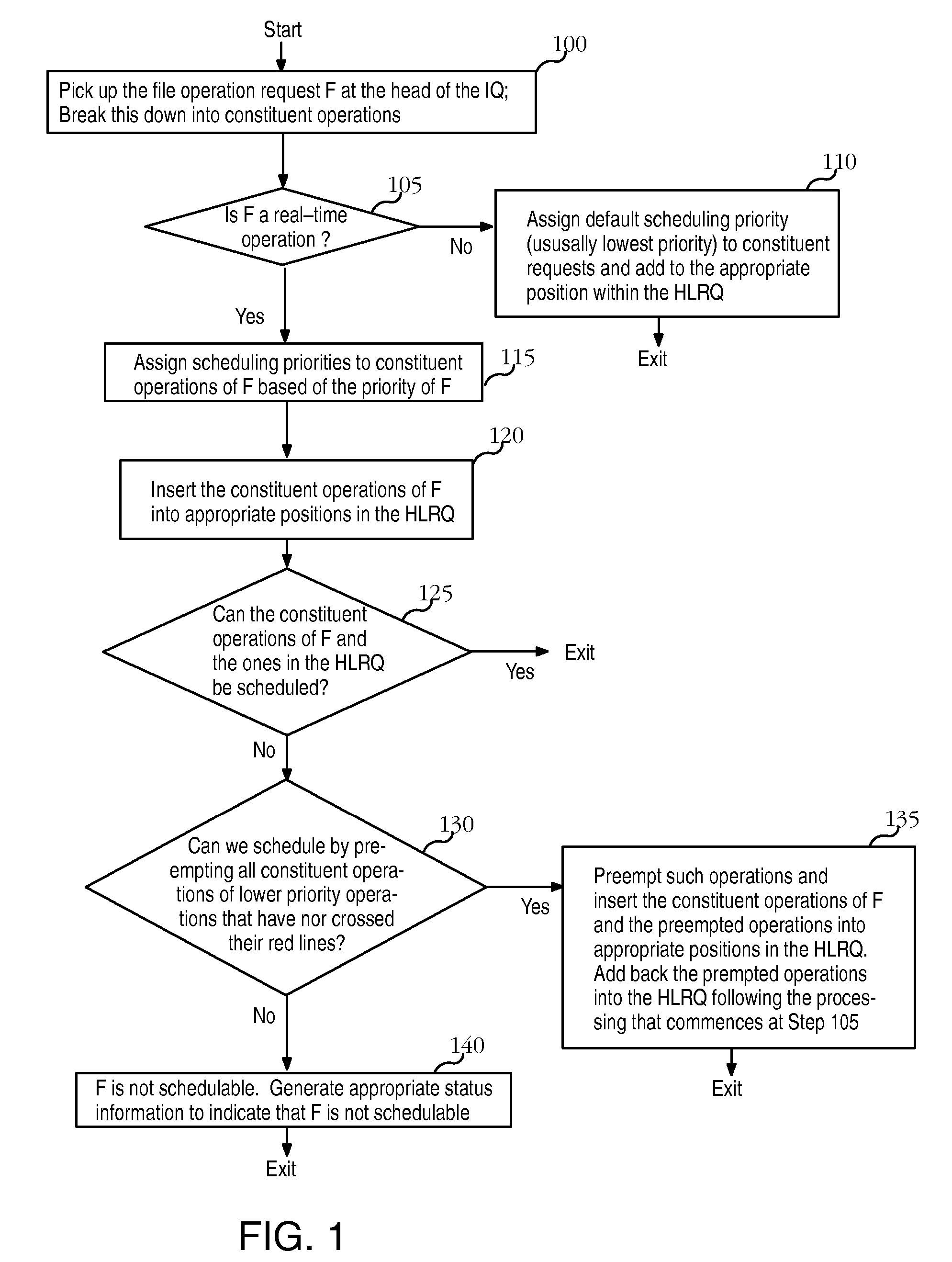
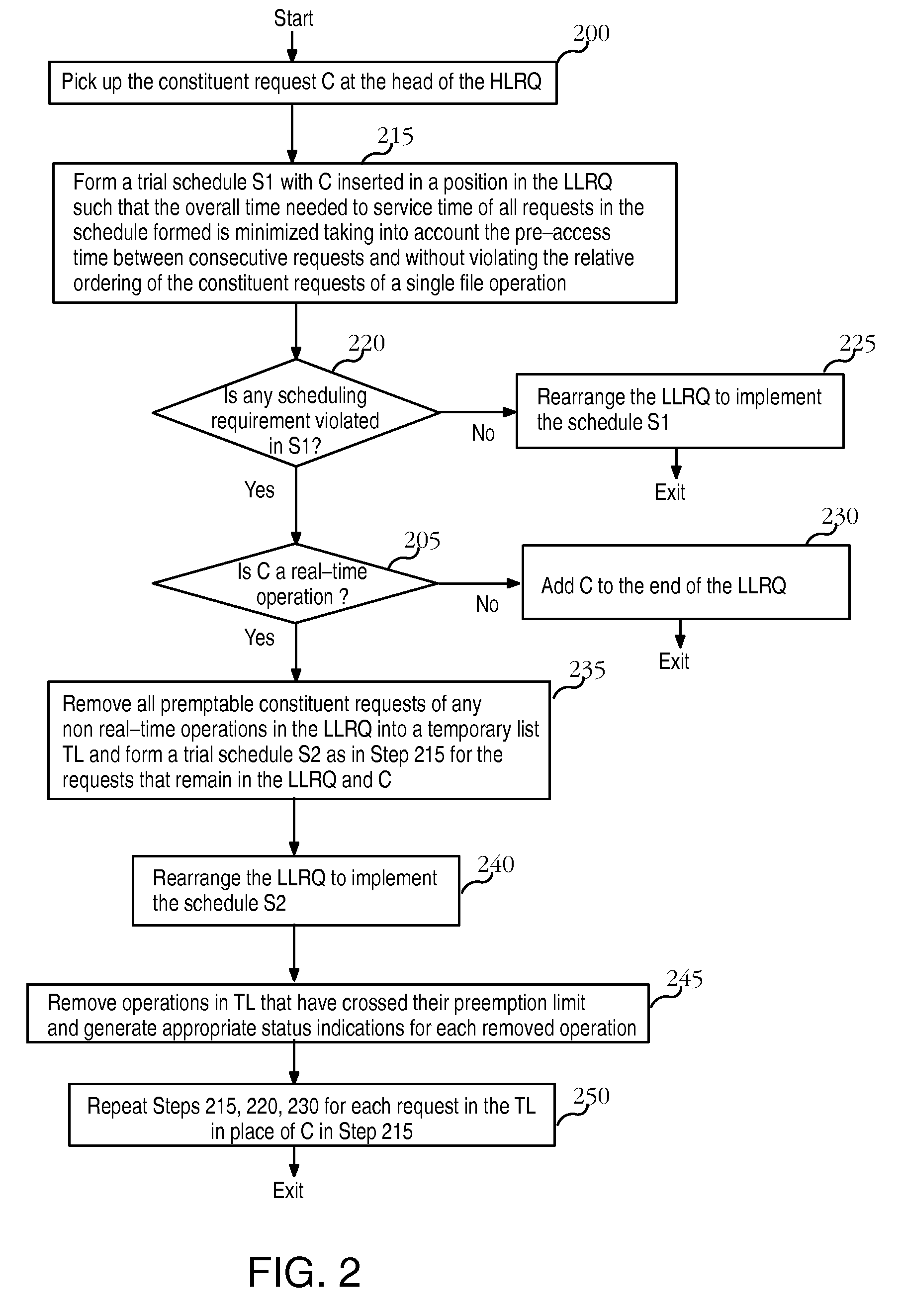
File system having predictable real-time performance
InactiveUS20070067595A1Improve abilitiesTime requiredDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsNon real timeQuality of service
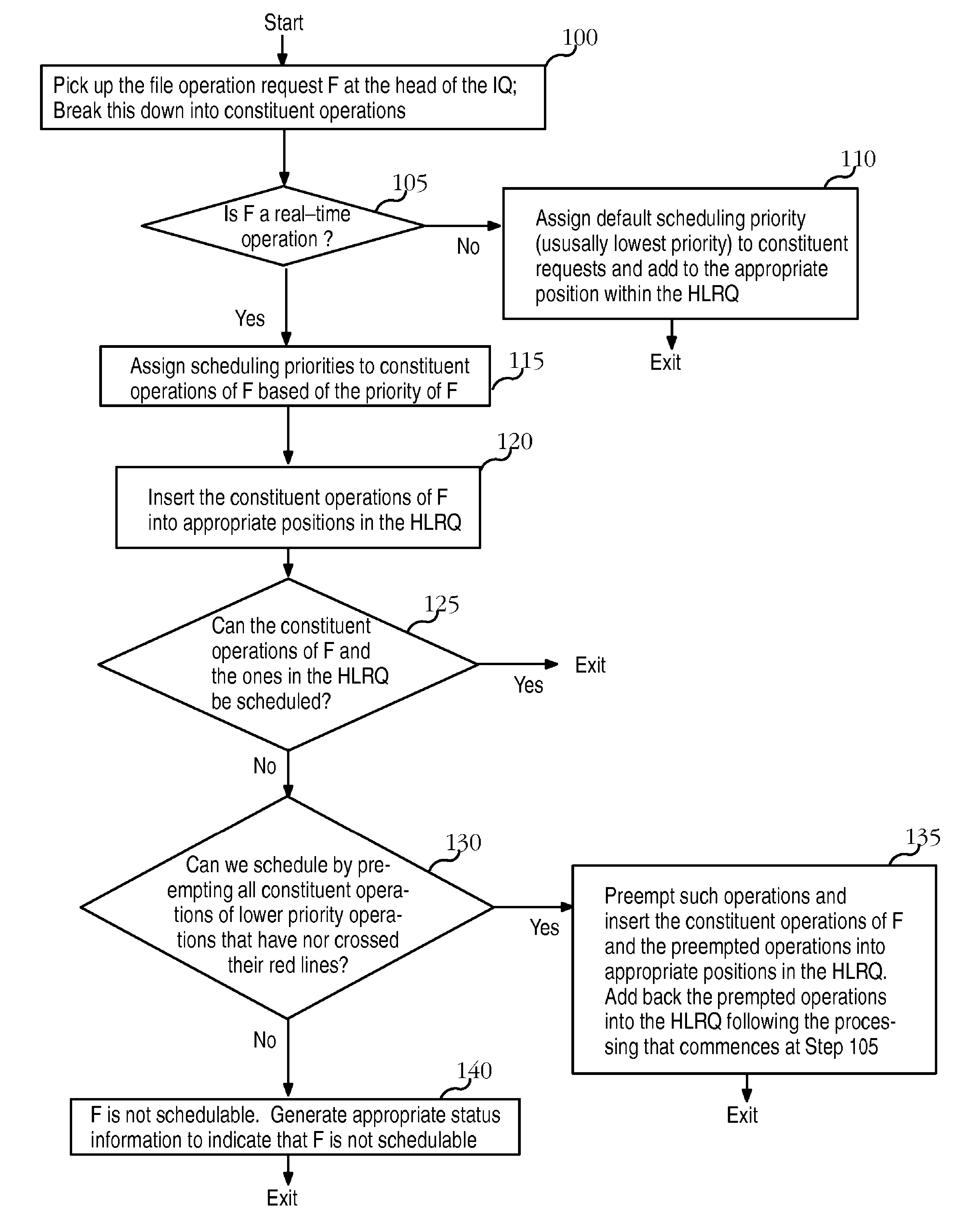
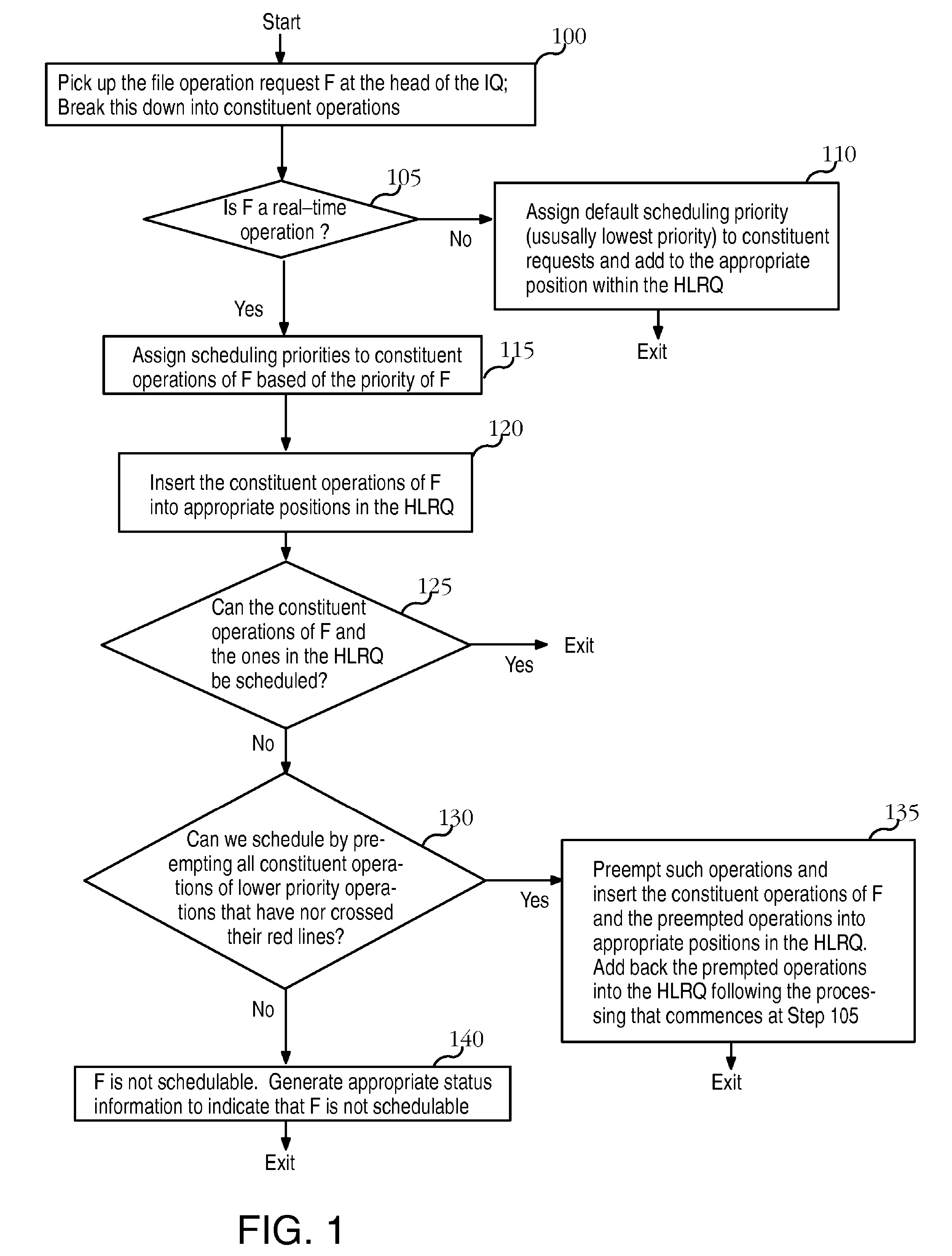
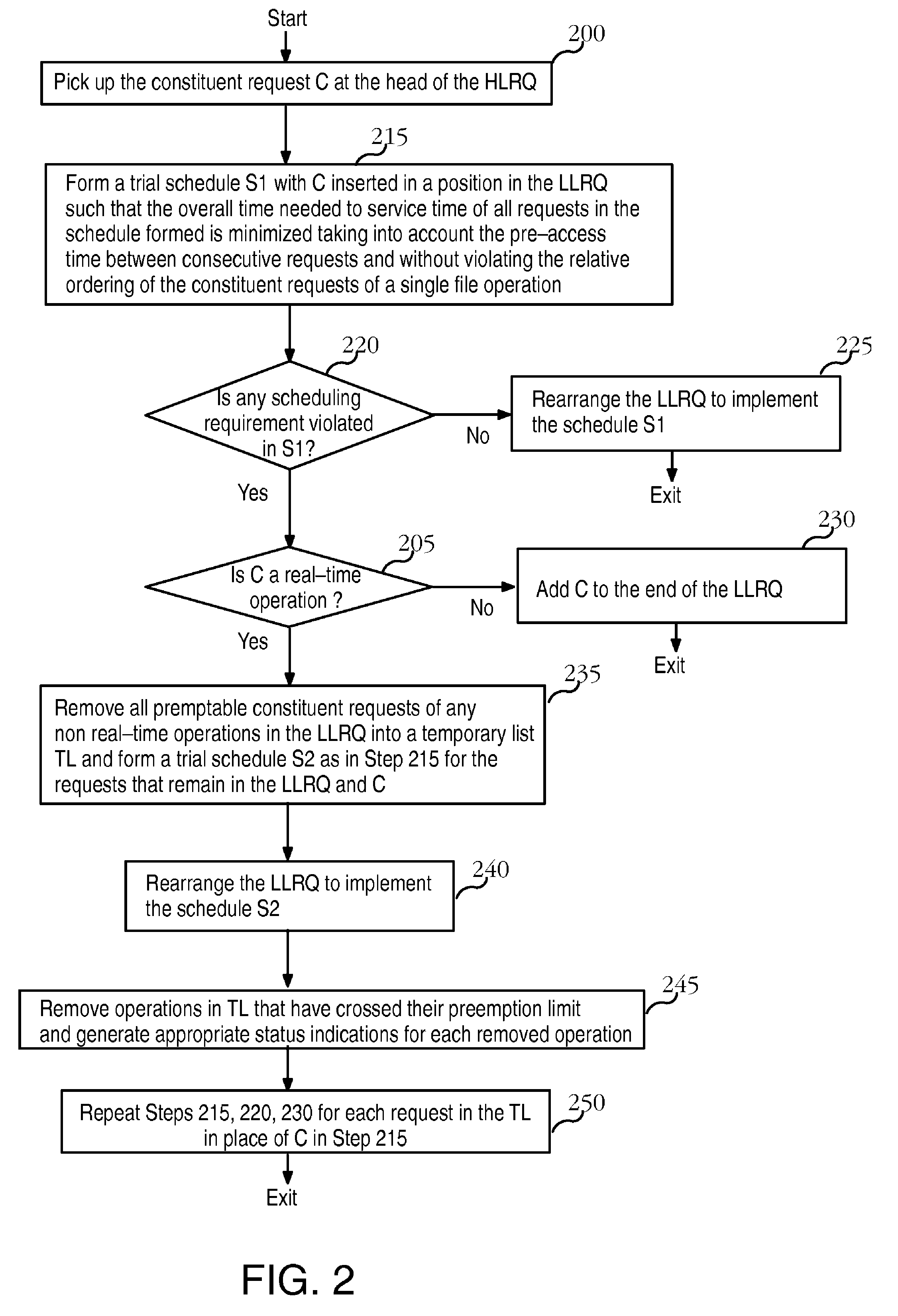
A file system that permits predictable accesses to file data stored on devices that may have a variable access latency dependent on the physical location of the file on the physical storage device. A variety of features that guarantee timely, real-time response to I / O file system requests that specify deadlines or other alternative required quality-of-service parameters. The file system addresses needs to accommodate the file systems of storage devices such as disks that have an access time dependant on the physical location of the data within the storage device. A two-phase, deadline-driven scheduler considers the impact of disk seek time on overall response times. Non real-time file operations may be preempted. Files may be preallocated to help avoid access delay caused by non-contiguity. Disk buffers may also be preallocated to improve real-time file system performance.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
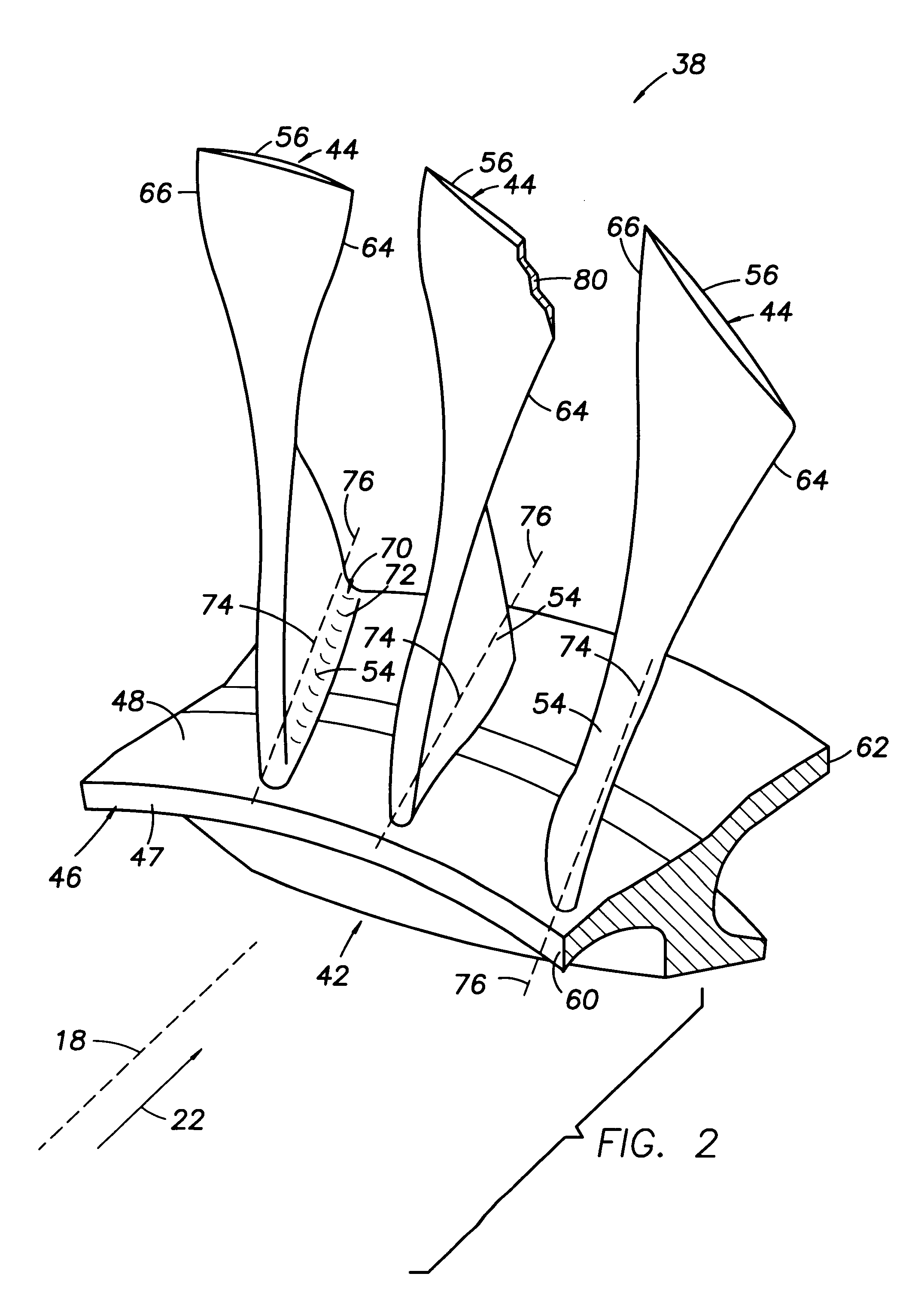
Method for linear friction welding and product made by such method
A process for joining a base for an airfoil to a disk for an integrally bladed rotor stage in a gas turbine engine includes providing a disk having a radially outer rim with a slot defined therein by a recessed surface, and further includes providing a base having a longitudinally extending root portion facing opposite a longitudinally extending support portion for supporting the airfoil. The root portion has a root surface and the support portion has an outer surface. The process further includes bringing the root surface of the root portion into contact with the recessed surface bounding the slot, applying pressure and relative movement between the base and the rim to achieve during welding, substantial contiguity between the root surface and the recessed surface over the area of the recessed surface, resulting in a substantially continuous linear friction weld between the base and the rim.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
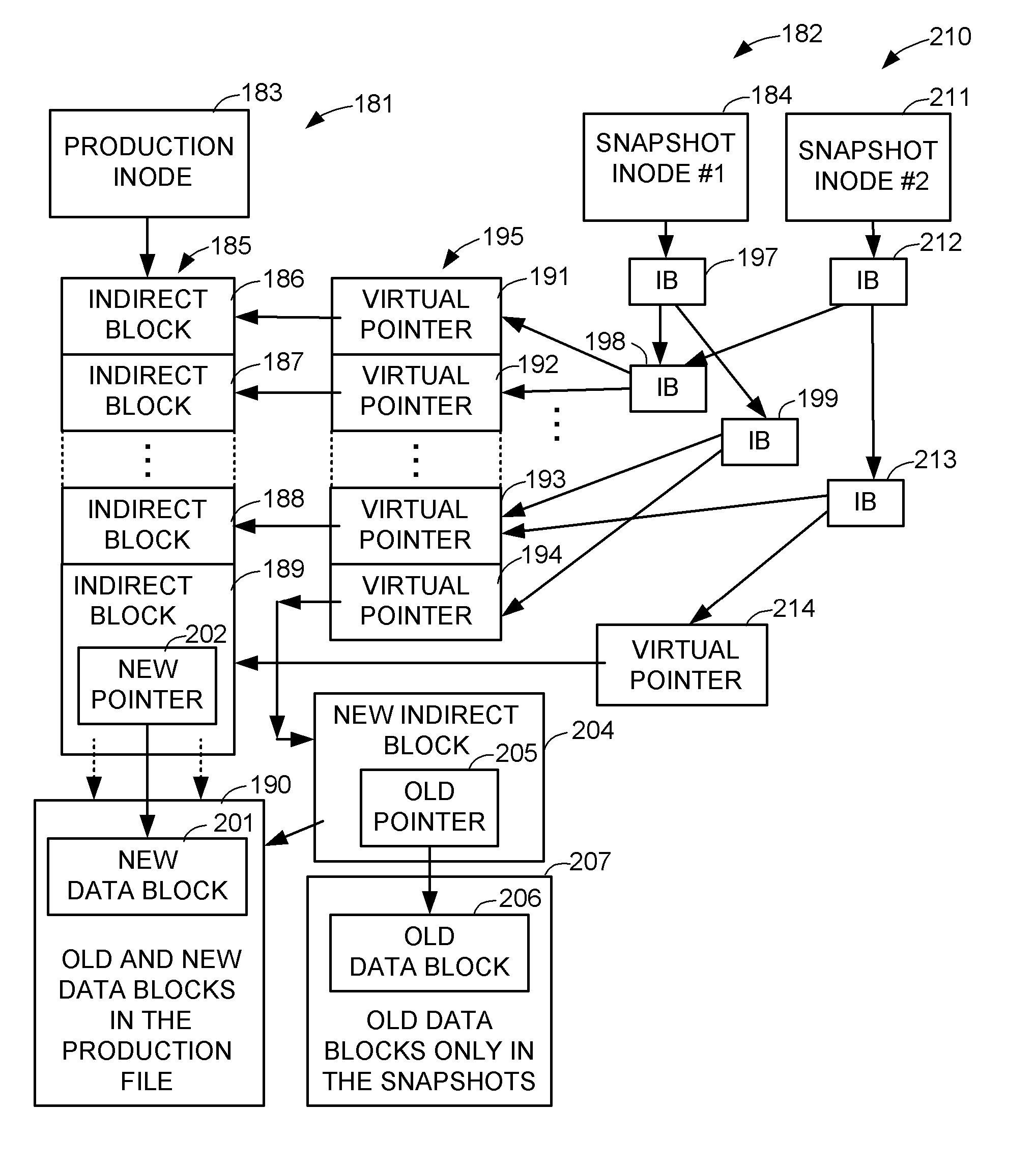
Creating point-in-time copies of file maps for multiple versions of a production file to preserve file map allocations for the production file
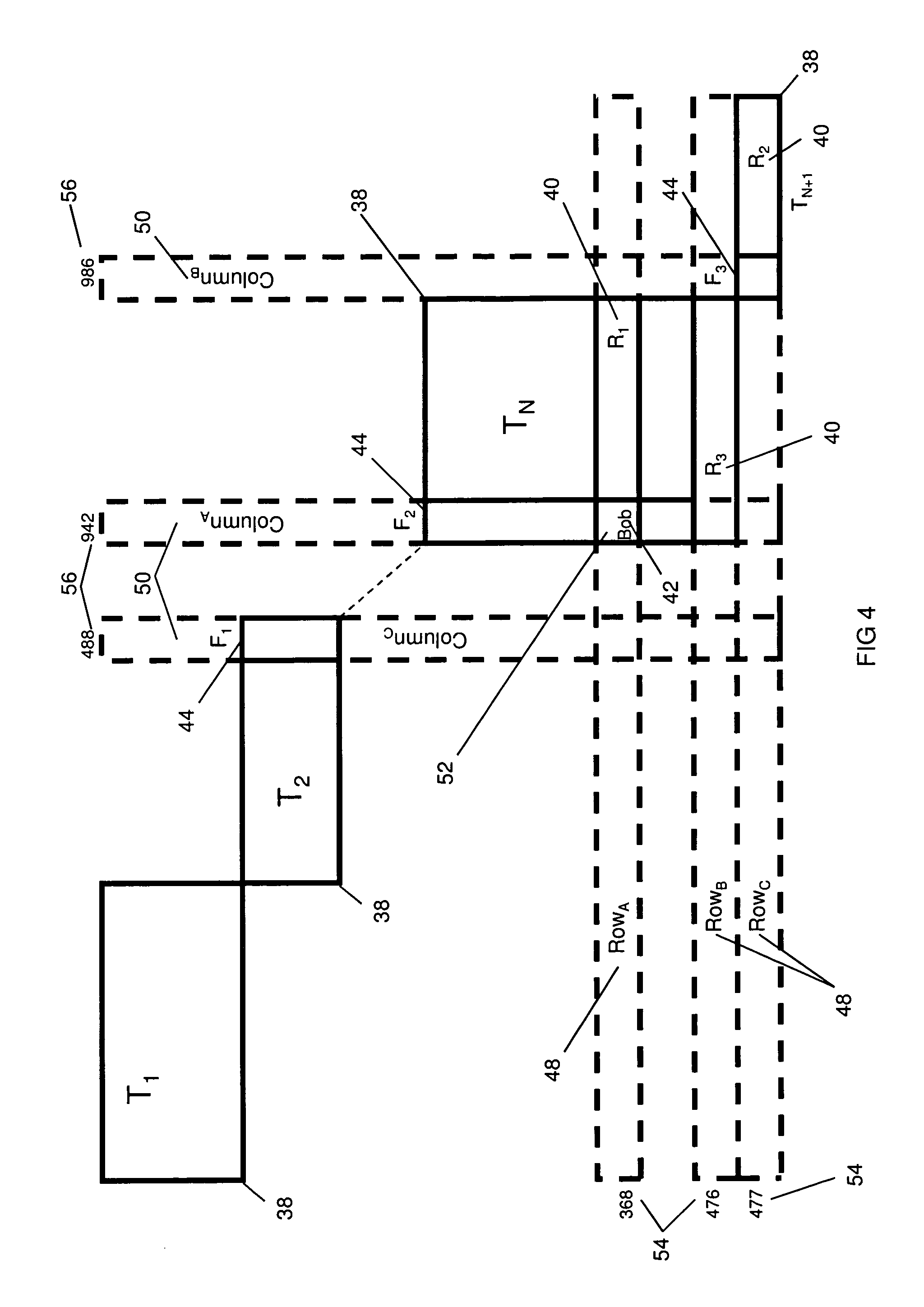
ActiveUS8620973B1Easy to solveDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsMetadataContiguity
To preserve the contiguity of file map extents of a production file when making a series of snapshot copies, the snapshots share indirect blocks of the production file through virtual pointers. When a write to a data block of the production file is first done since the time of the most recent snapshot so that the most recent snapshot can no longer share one of the contiguous indirect blocks, a new indirect block is allocated to store the file mapping metadata for the most recent snapshot, and a virtual pointer for the snapshots is changed to point to this new indirect block. Therefore the change in the virtual pointer changes the file mapping metadata for any number of snapshots sharing the new indirect block so that the method is scalable.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
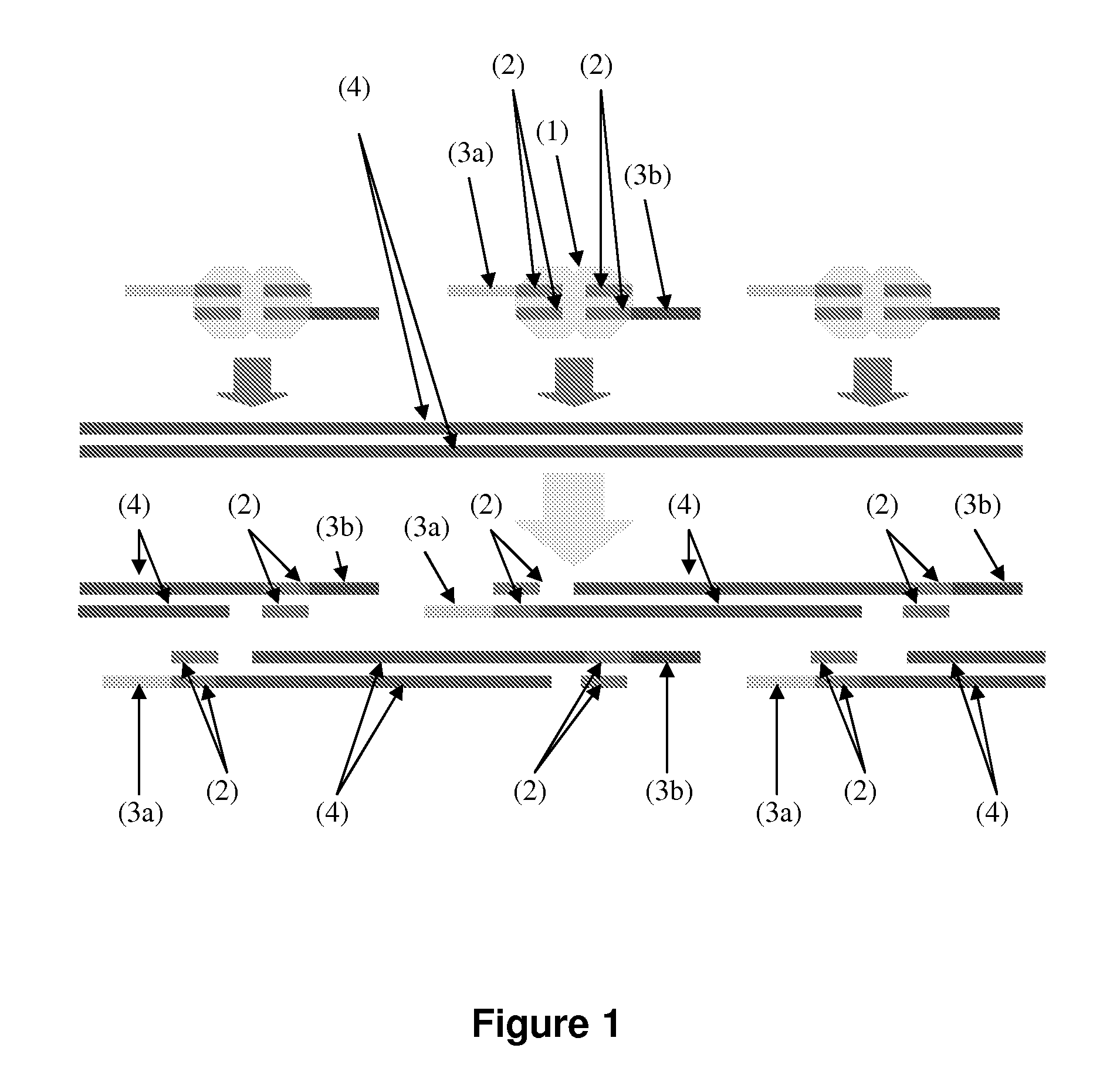
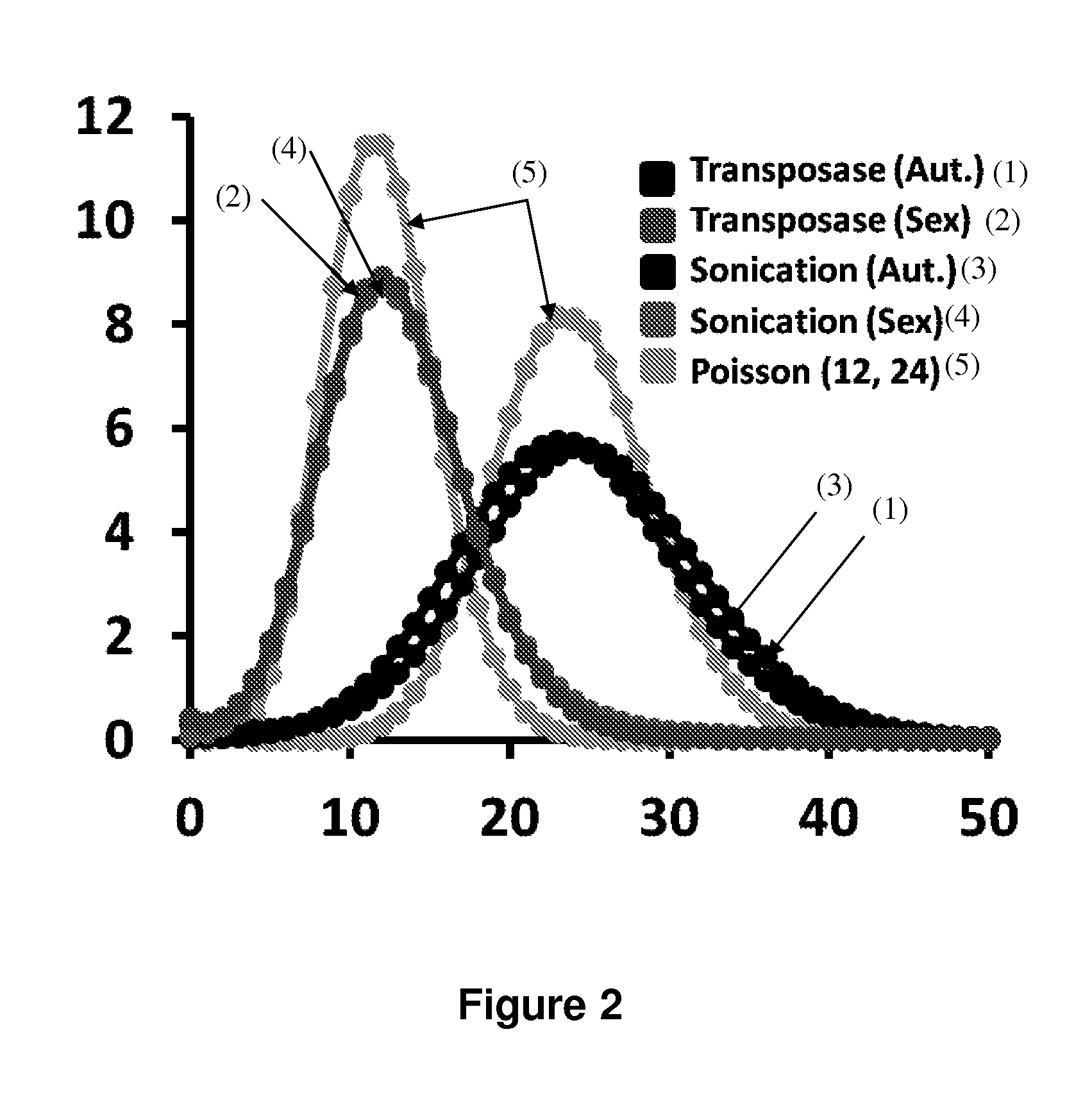
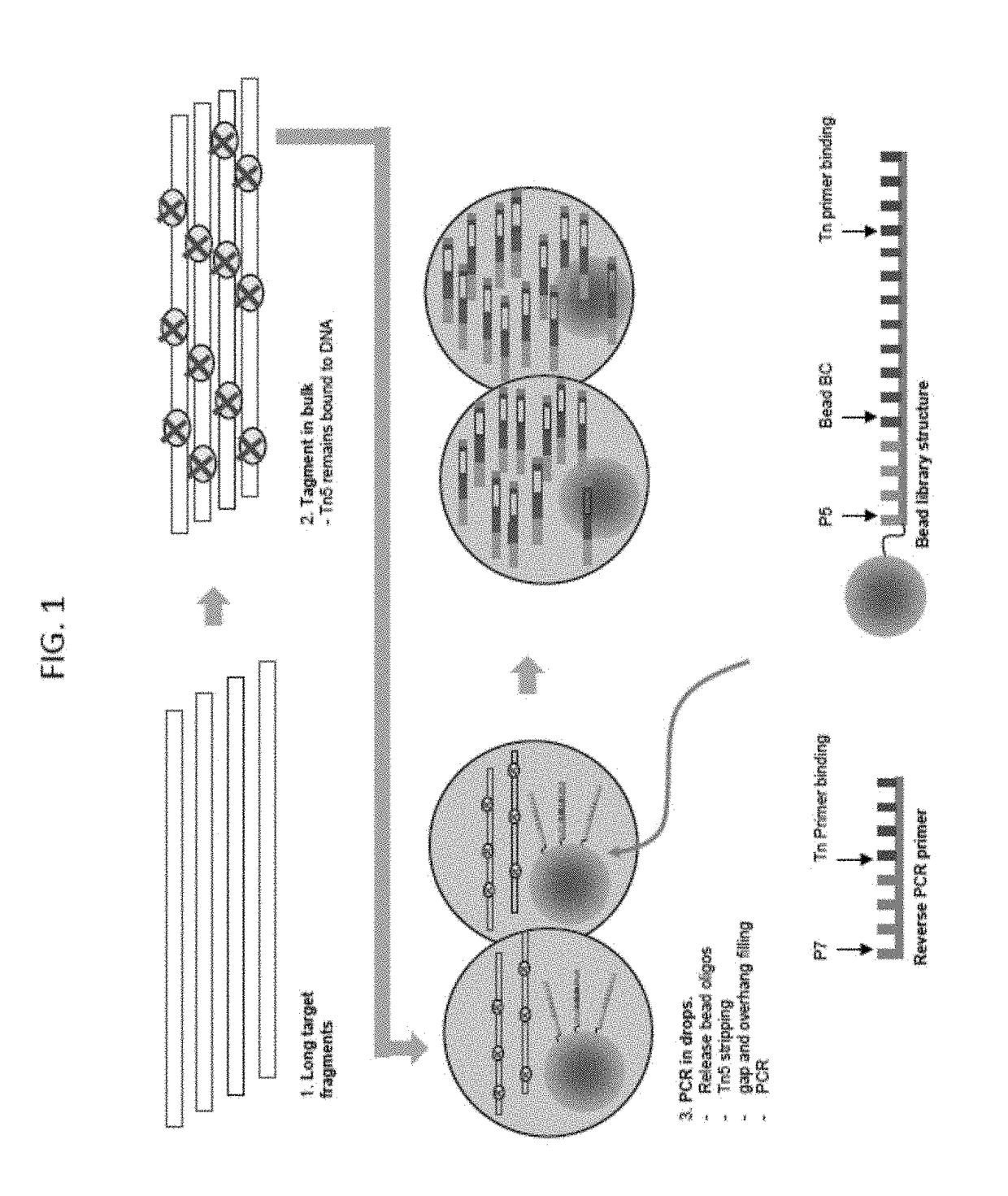
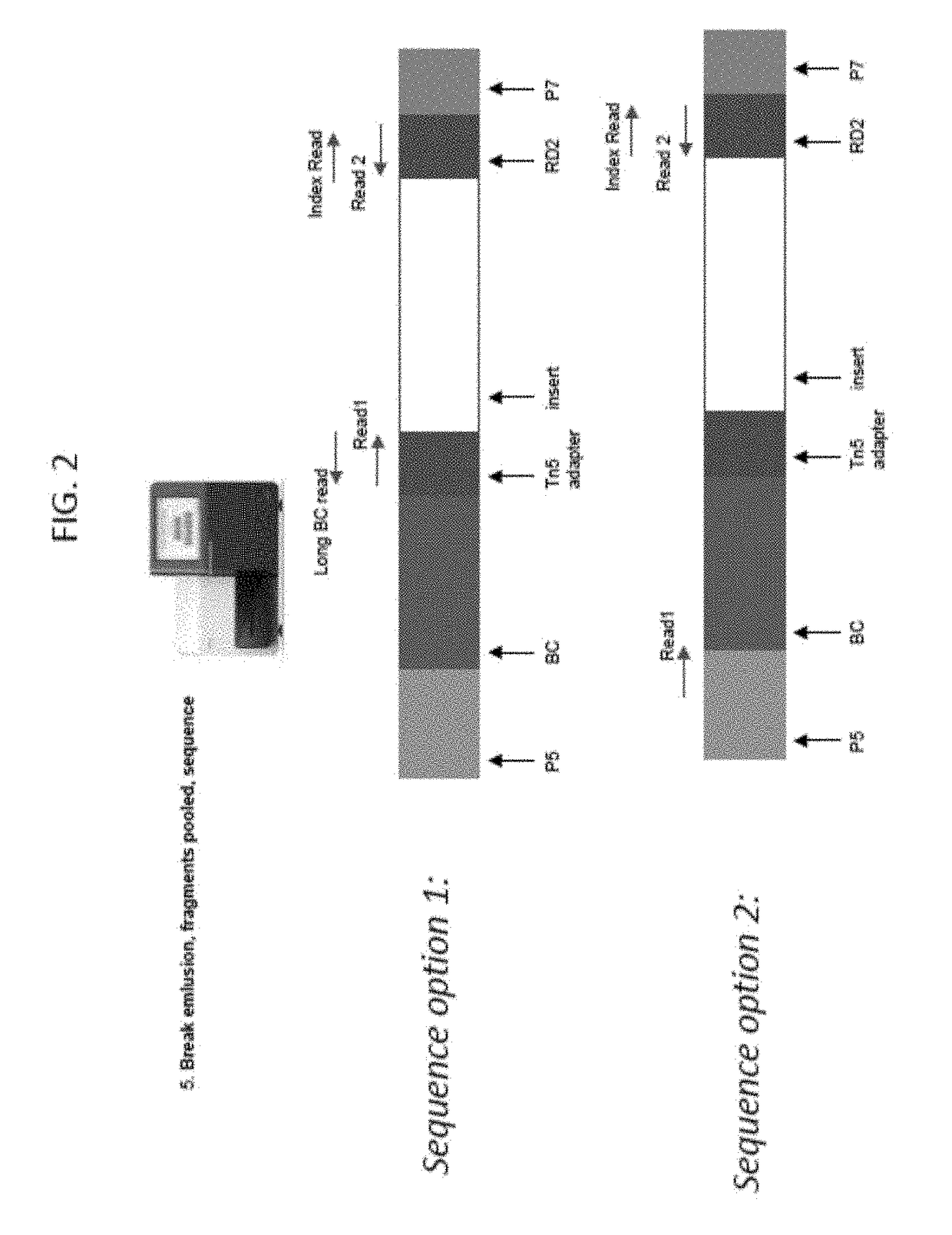
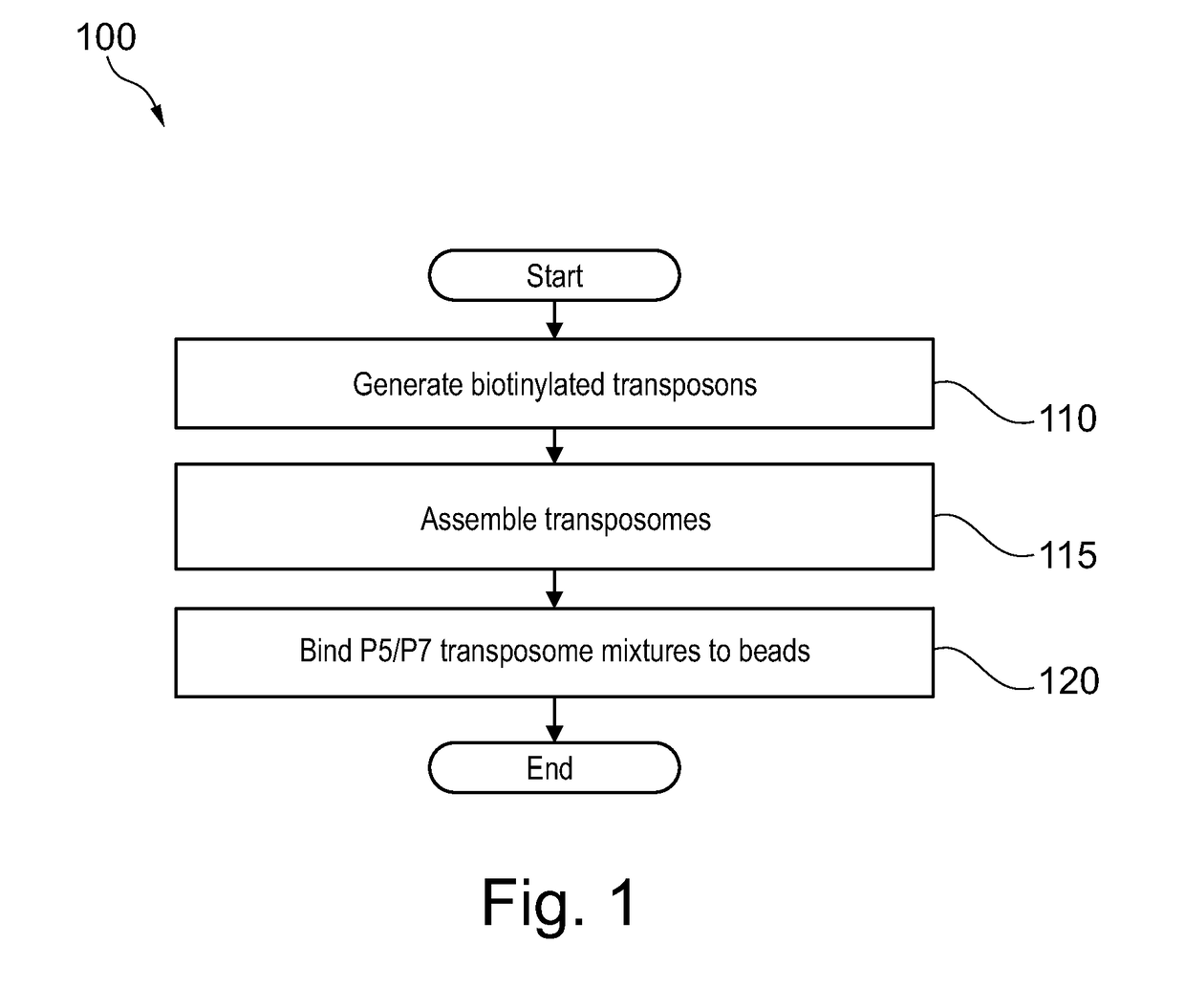
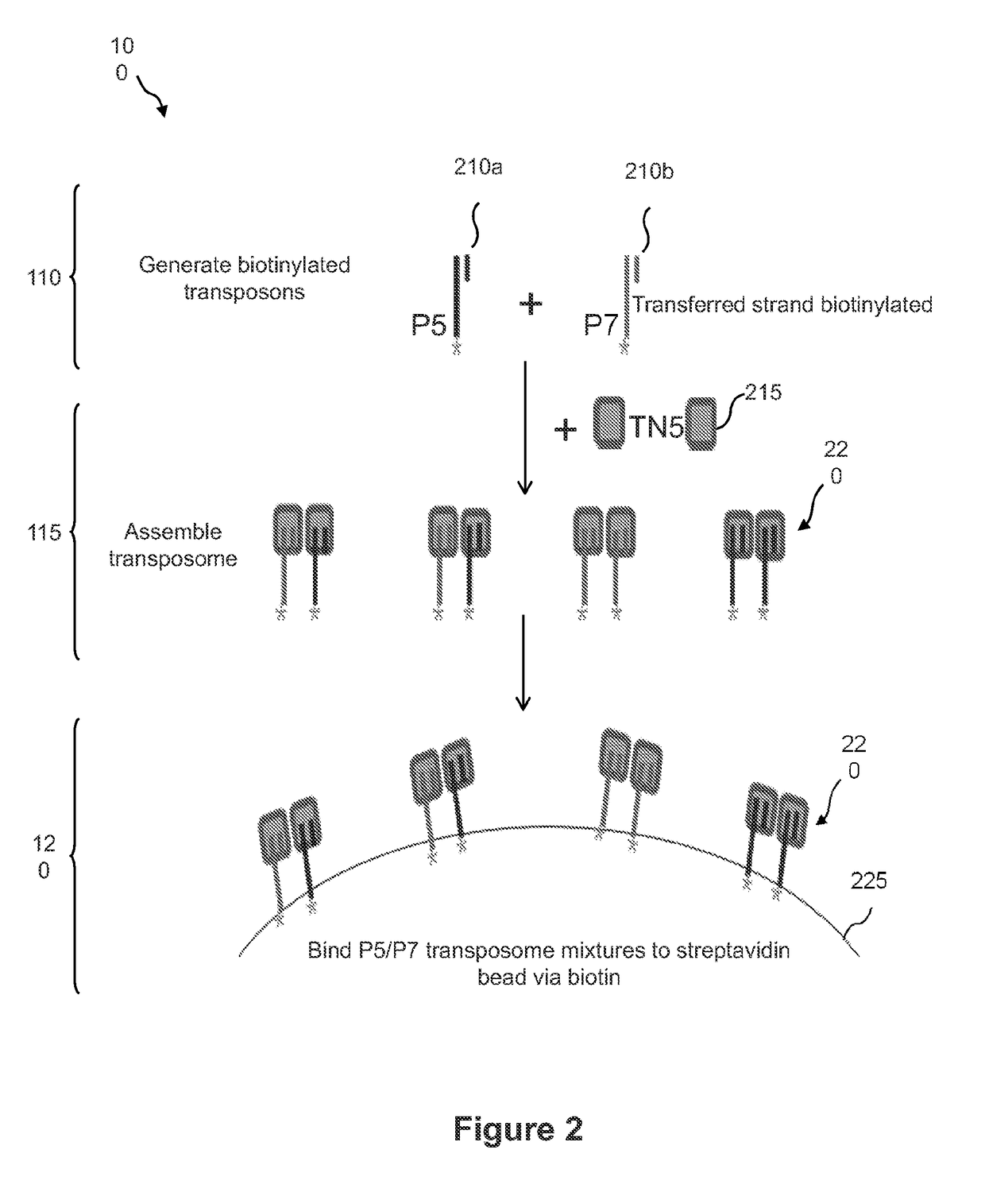
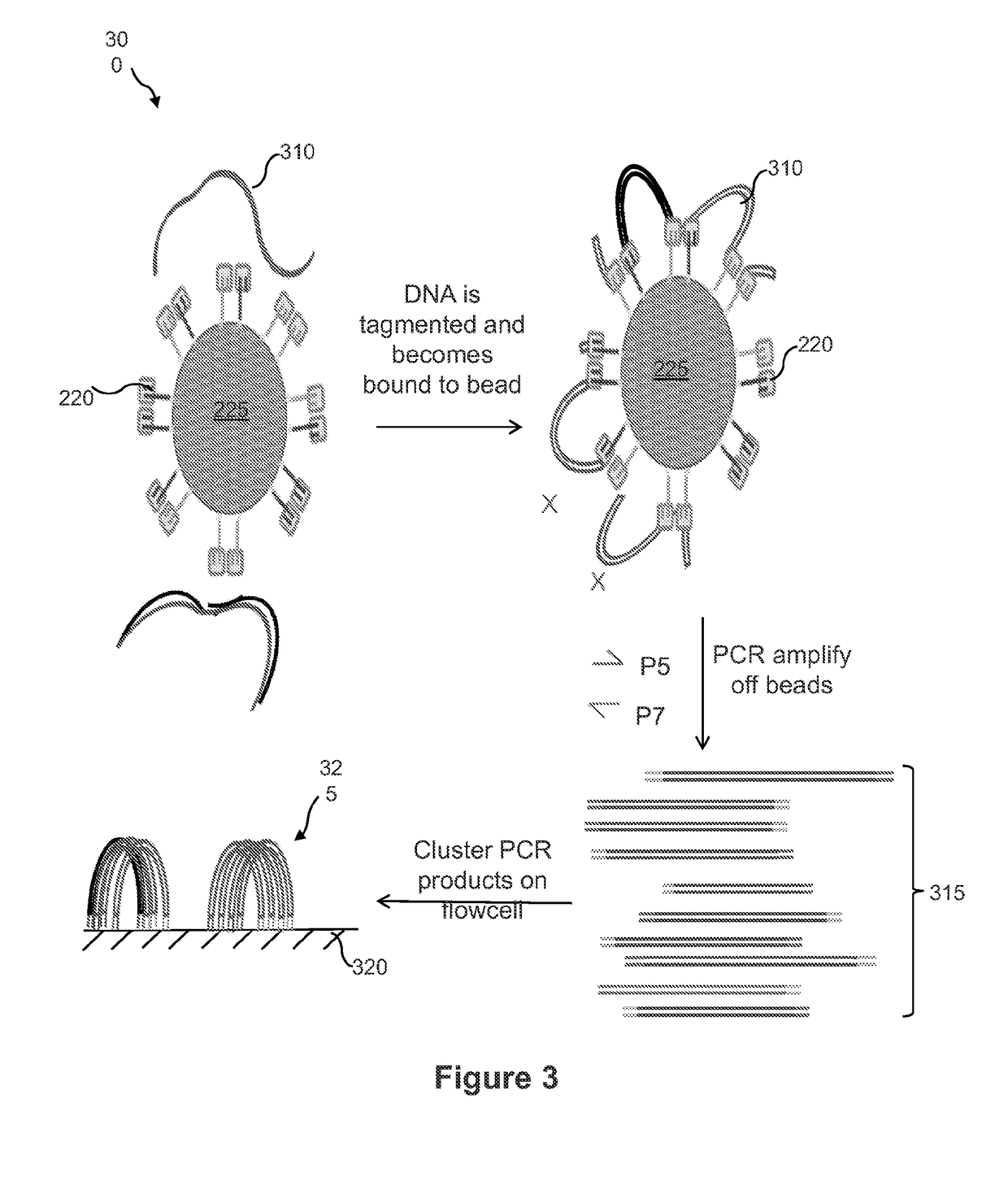
Droplet tagging contiguity preserved tagmented DNA
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Contiguity preserving transposition
Embodiments provided herein relate to methods and compositions for preparing an immobilized library of barcoded DNA fragments of a target nucleic acid, identifying genomic variants, determining the contiguity information, phasing information, and methylation status of the target nucleic acid.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
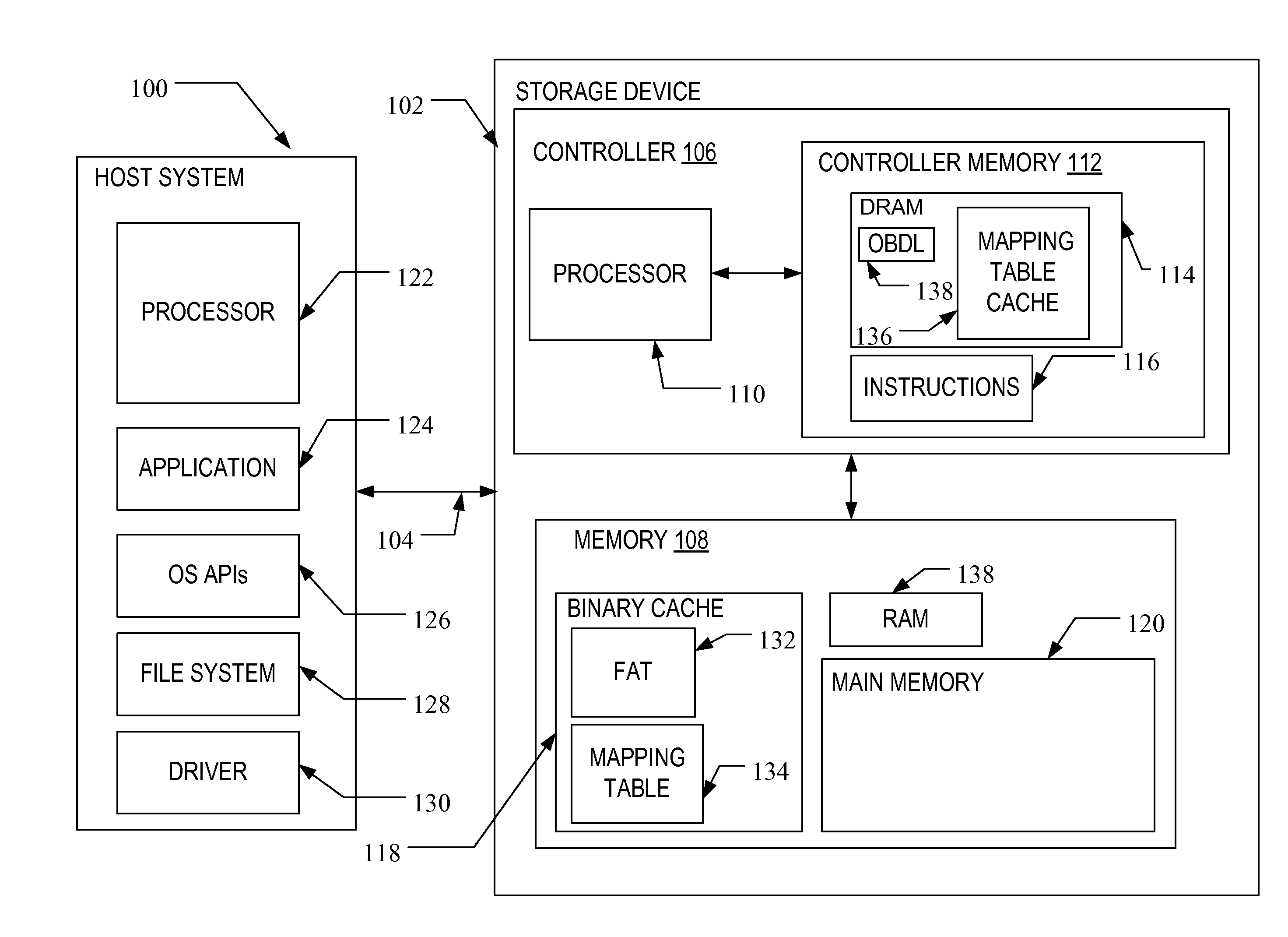
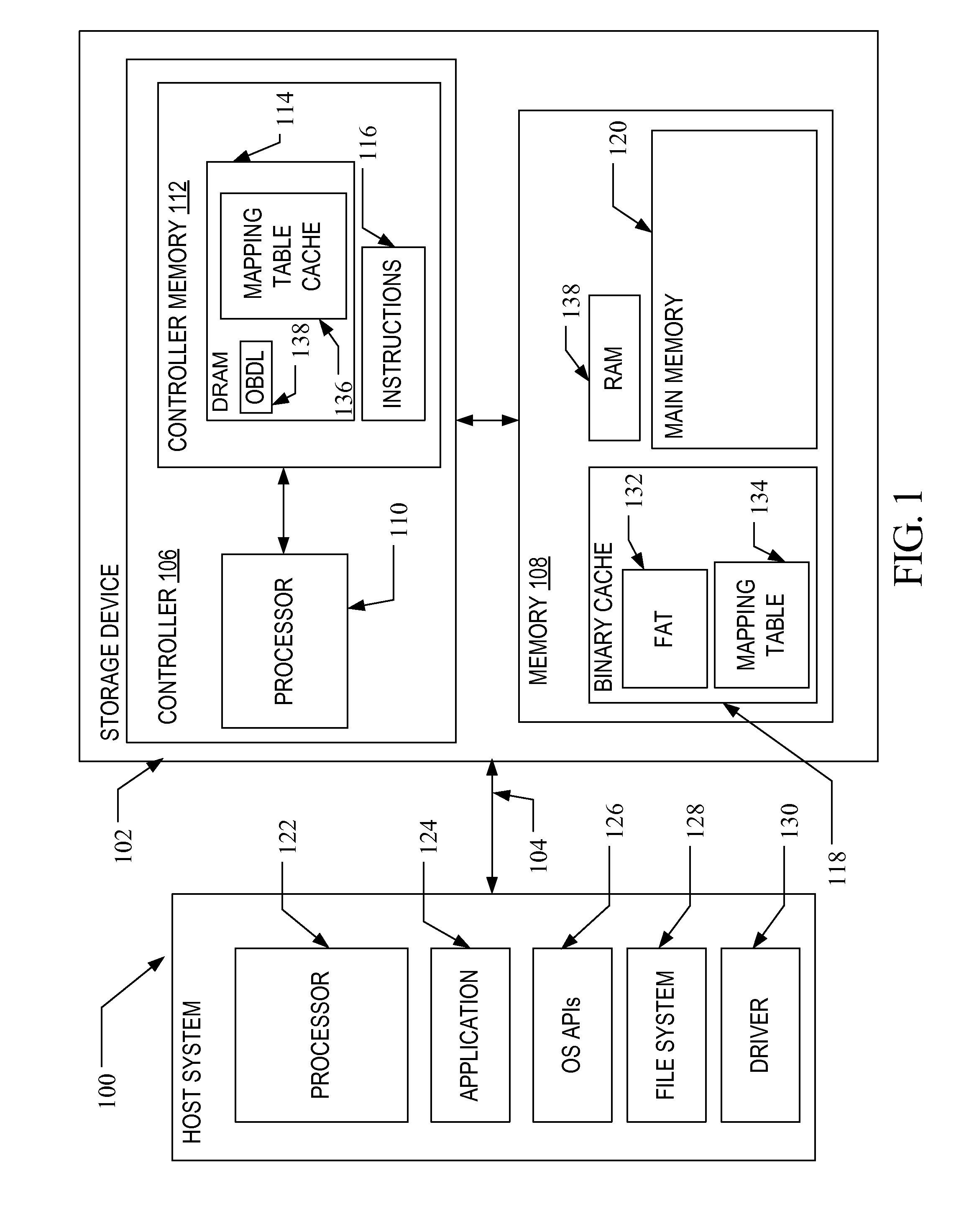
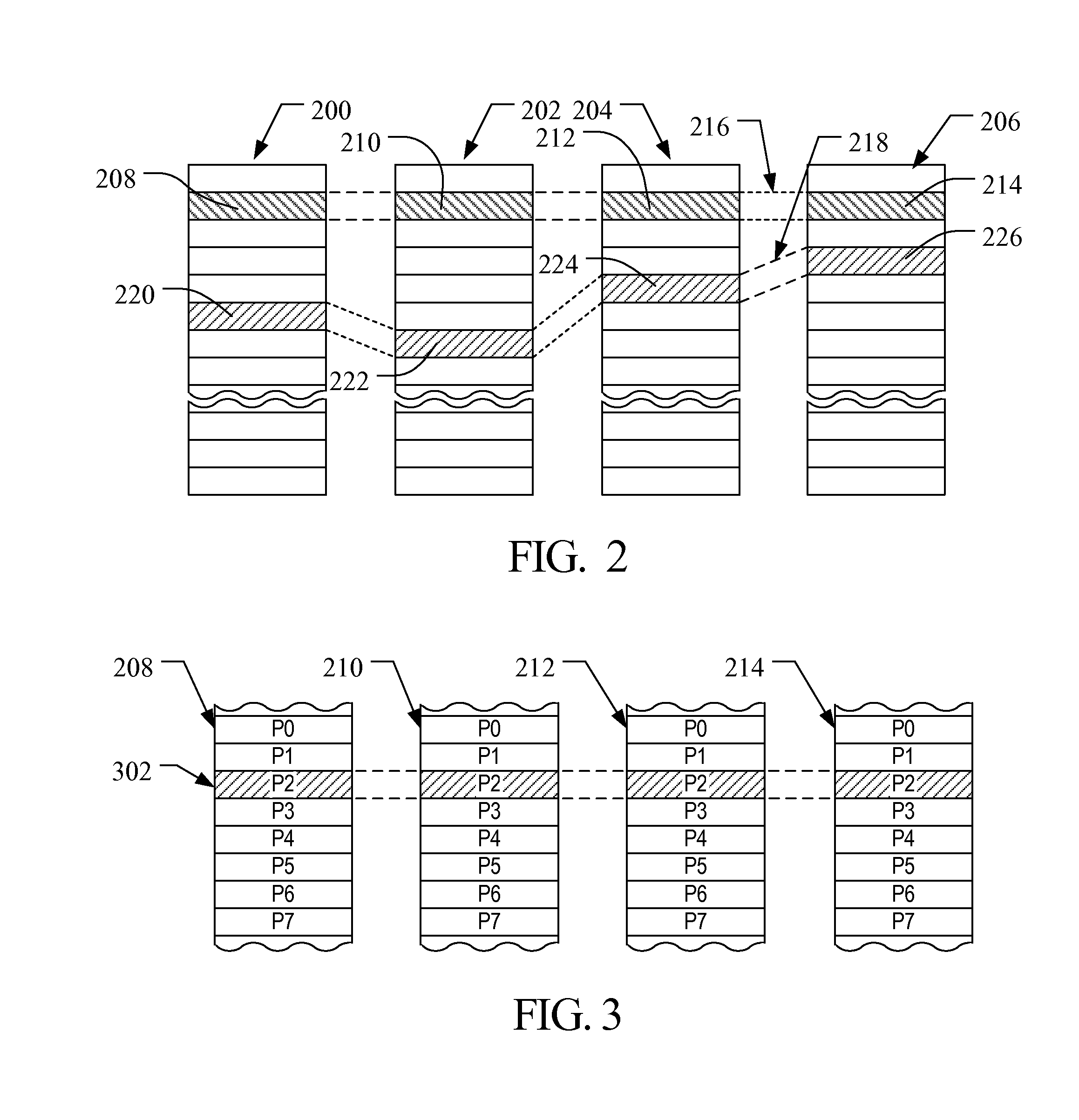
Method and system for interleaving pieces of a mapping table for a storage device
ActiveUS20150347026A1Improve efficiencyImprove read performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersContiguityVolatile memory
A method and system are disclosed for handling logical-to-physical mapping in a storage device. The method includes the storage device storing in fast access memory, such as DRAM, only a fixed-size subset of the primary mapping table in non-volatile memory, along with contiguity information of physical addresses for logical address not in the subset that are adjacent to the logical addresses in the subset. The system includes a storage device having volatile memory, non-volatile memory and a controller in communication with the volatile and non-volatile memory that is configured to carry out the method noted above.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
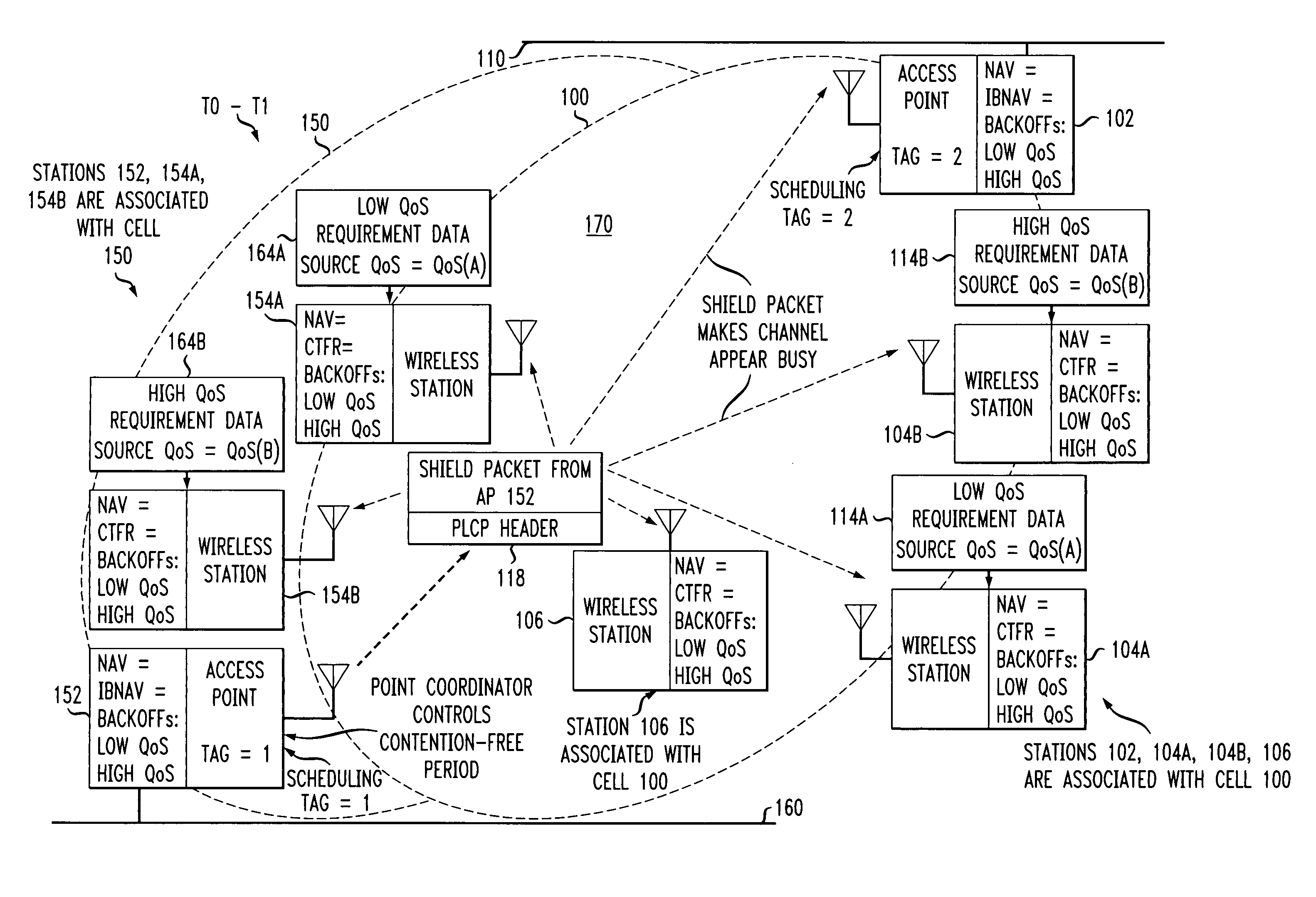
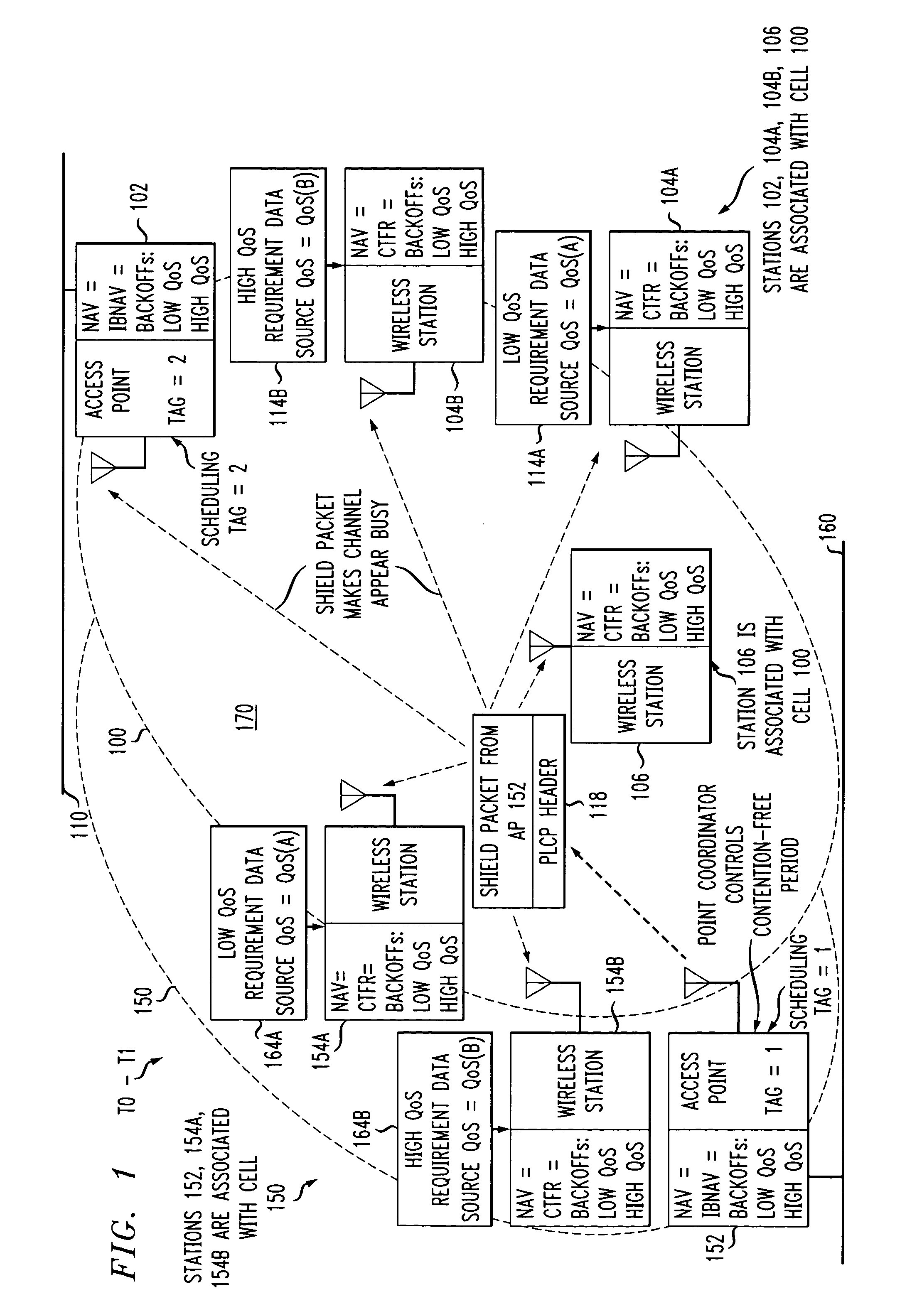
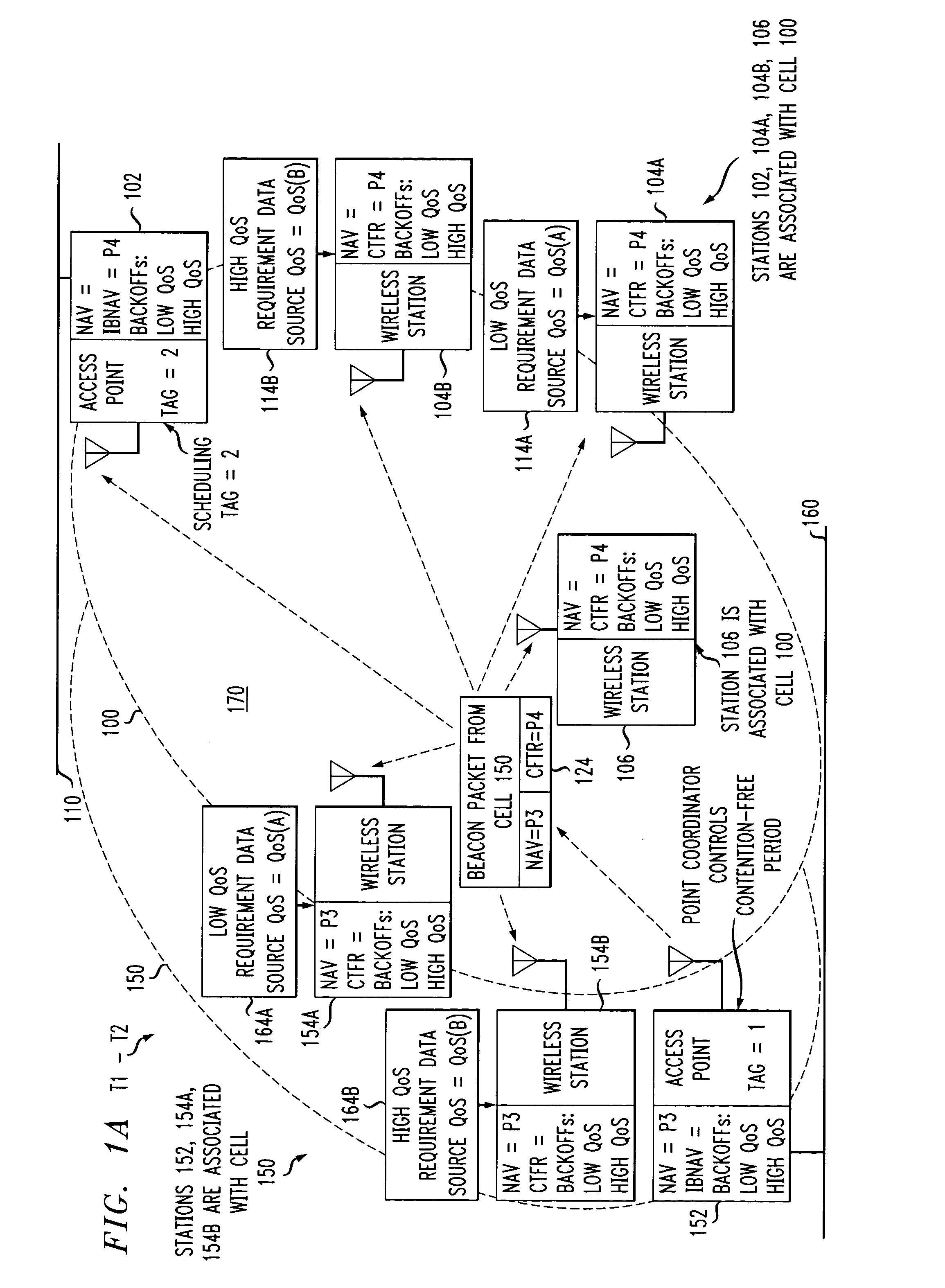
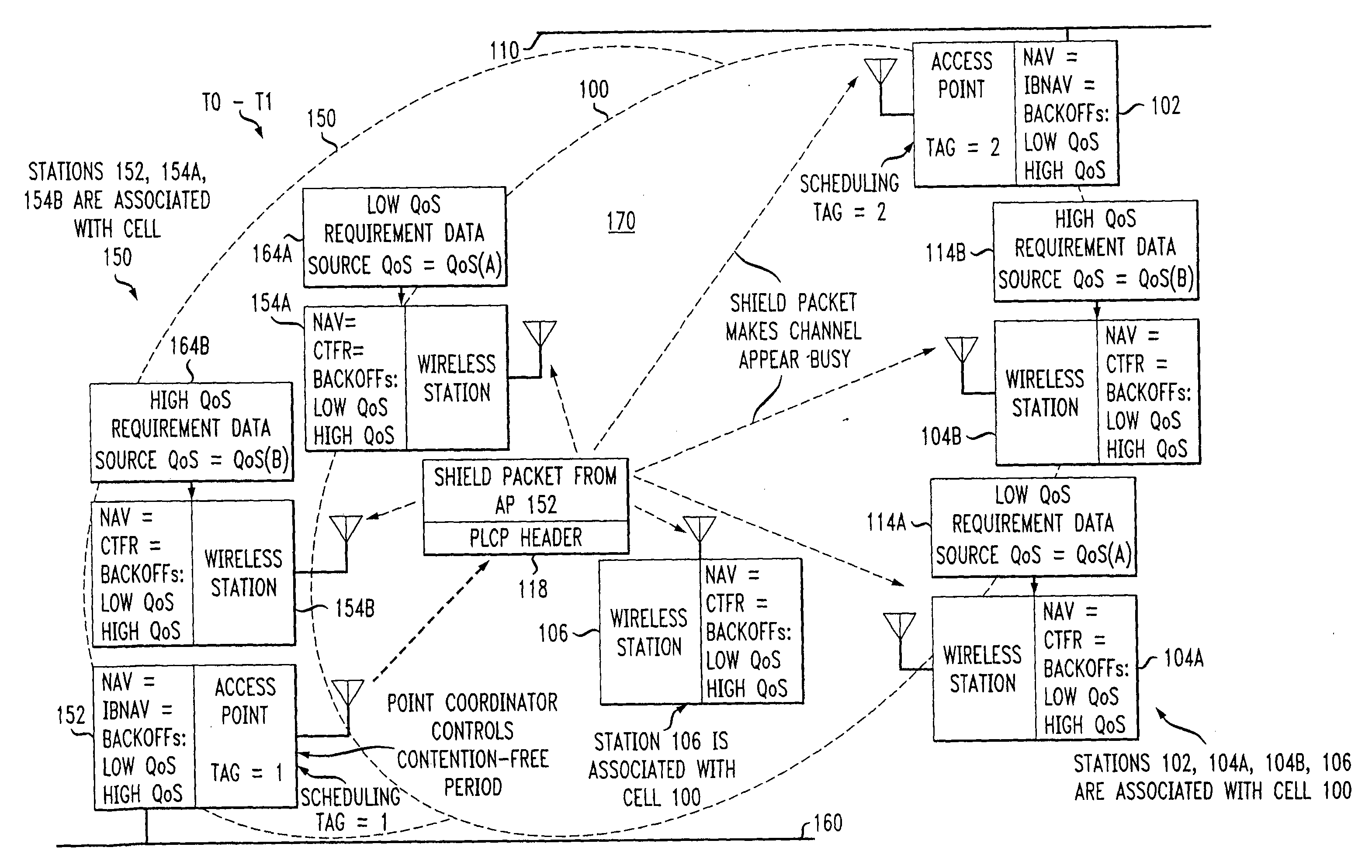
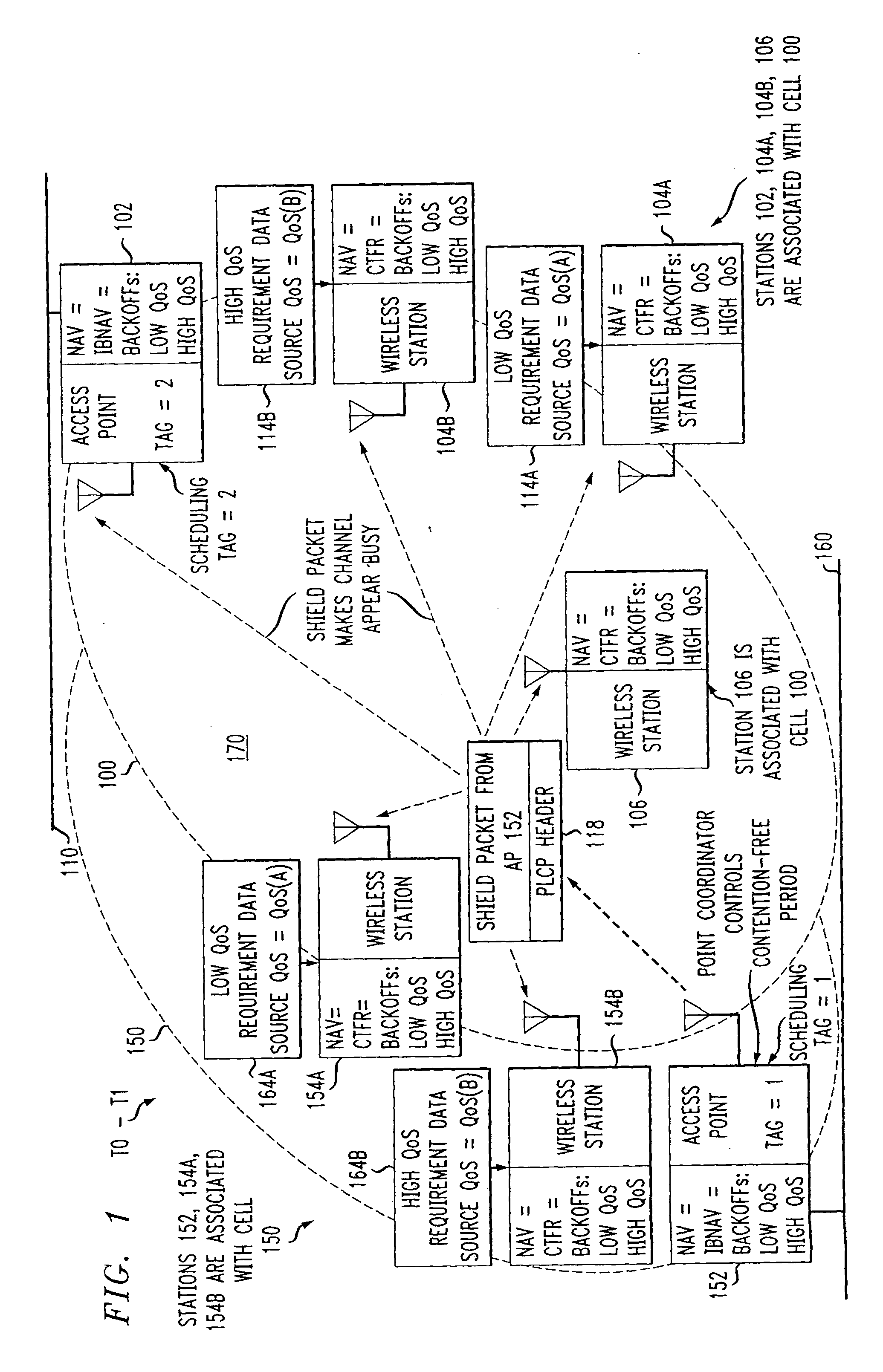
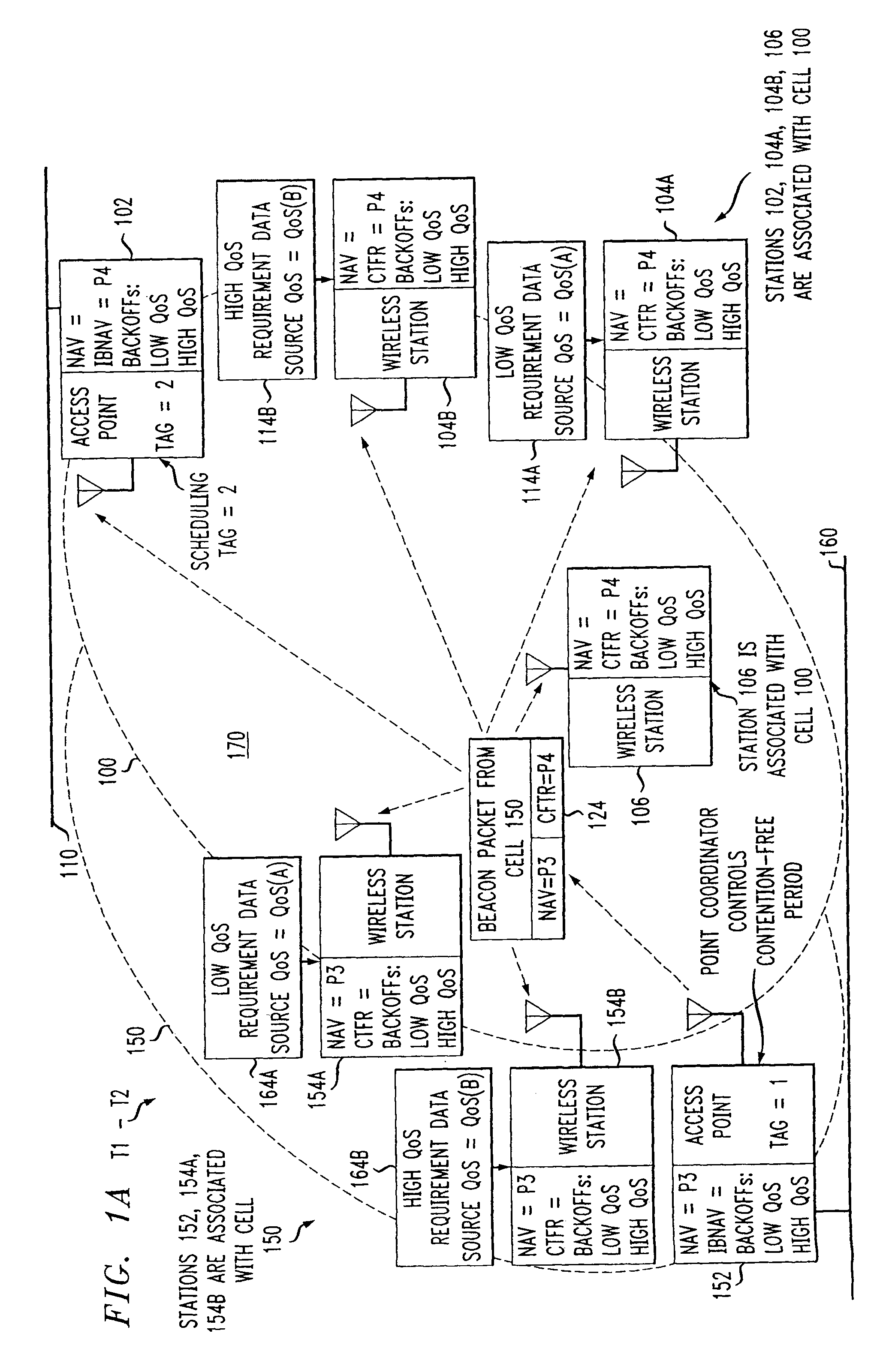
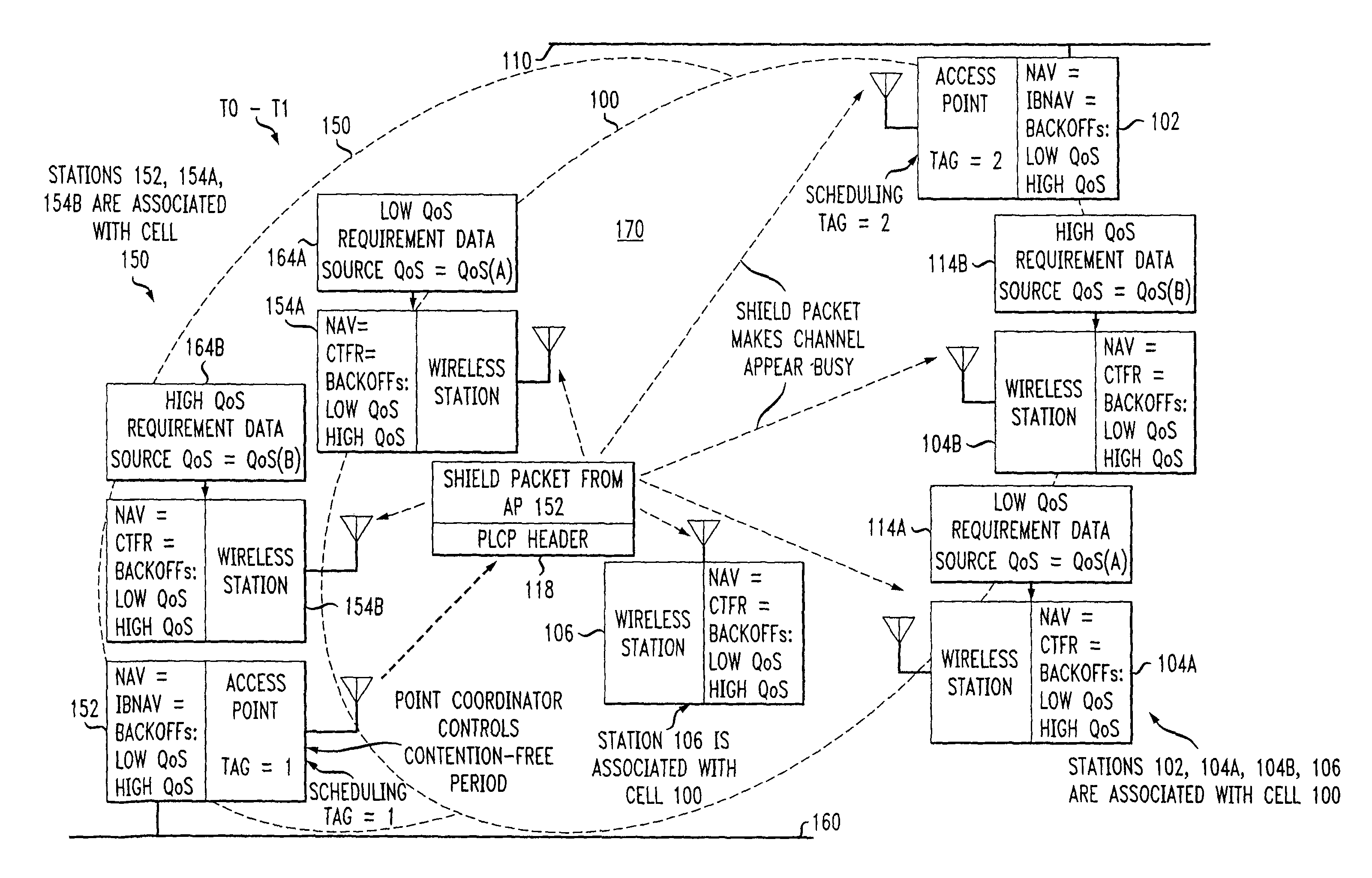
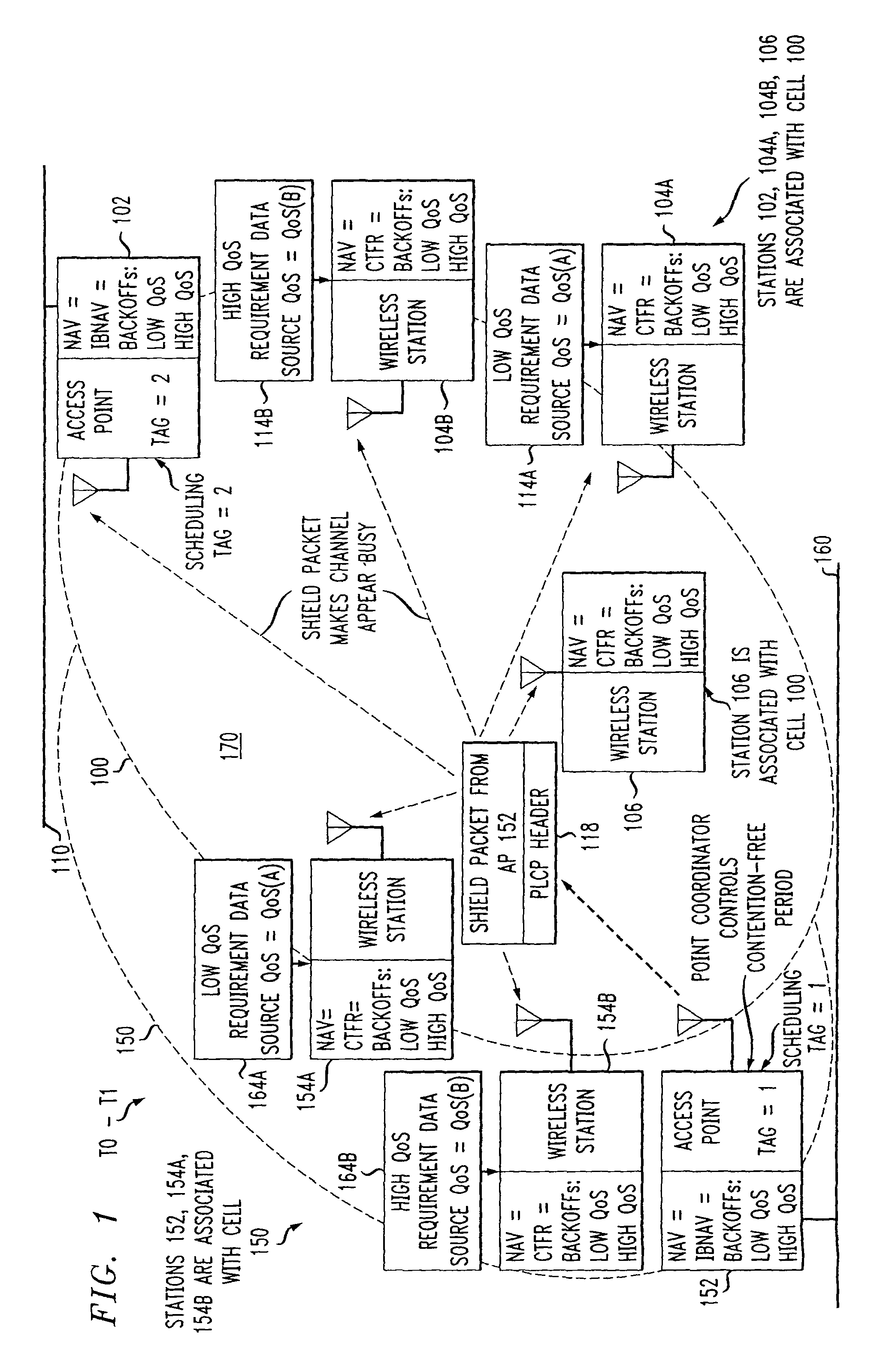
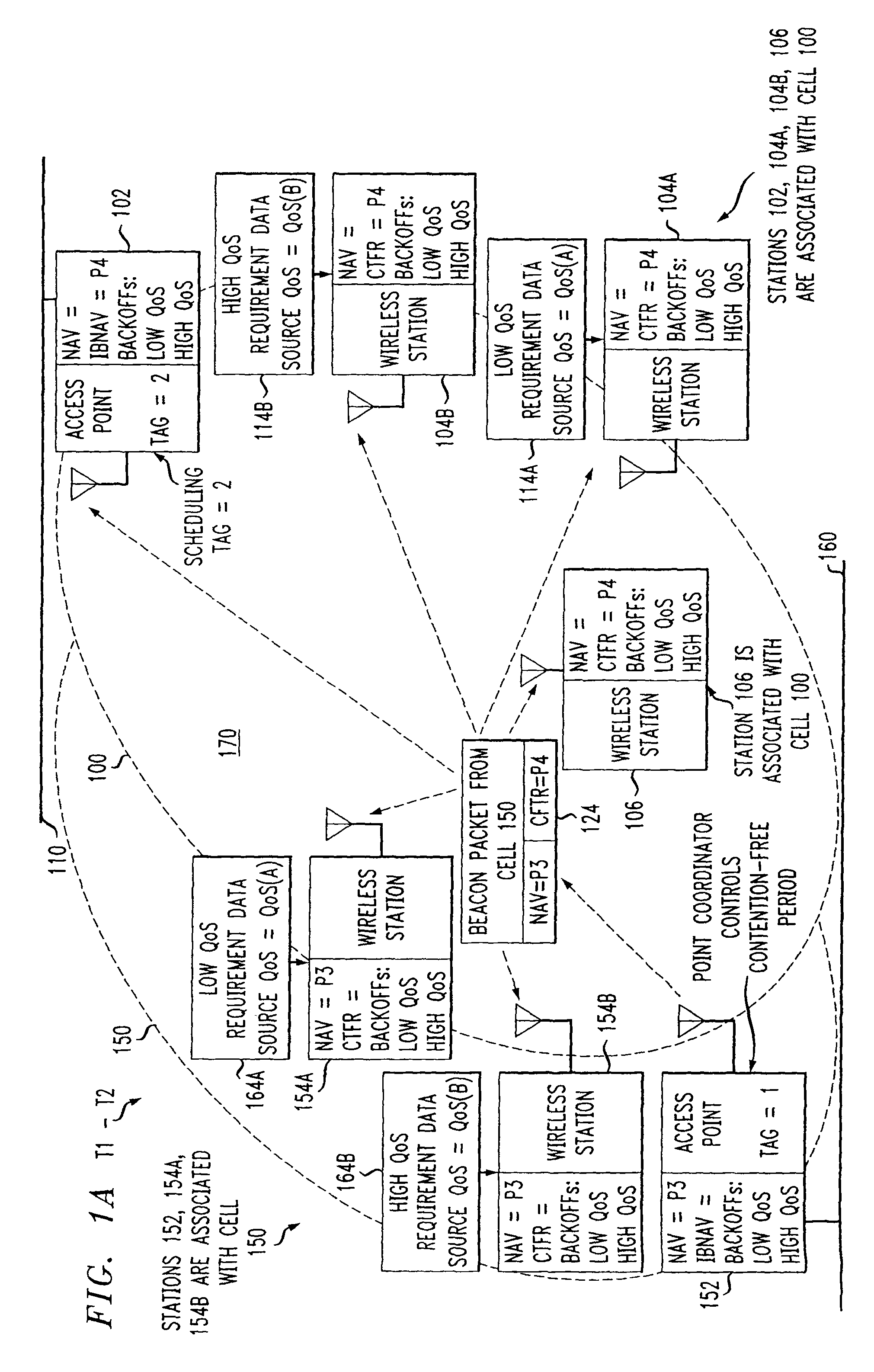
Preemptive packet for maintaining contiguity in cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) contention-free sessions
InactiveUS7245605B2Reduce usageSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesTraffic capacityDistributed coordination function
An access point transmits a preemptive peg packet when it has no data to transmit in order to maintain the contiguity of its transmission timing position with respect to the timing position of other contention-free sessions (CFS) transmitted by other access points in an existing, periodic sequence. The cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) method establishes the transmission timing position of contention-free sessions (CFS) between overlapping first and second wireless LAN cells contending for the same medium. Each cell includes a respective plurality of member stations. If an access point has no traffic, it will transmit a short, preemptive pegging packet and reset its backoff timer. In this manner, no gaps longer than the distributed coordination function (DCF) Interframe Space (DIFS) are left idle. This prevents other stations from using DCF contention to seize the channel, until all access points have completed one contention-free session (CFS) per periodic cycle.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Expandable belt and tread drum
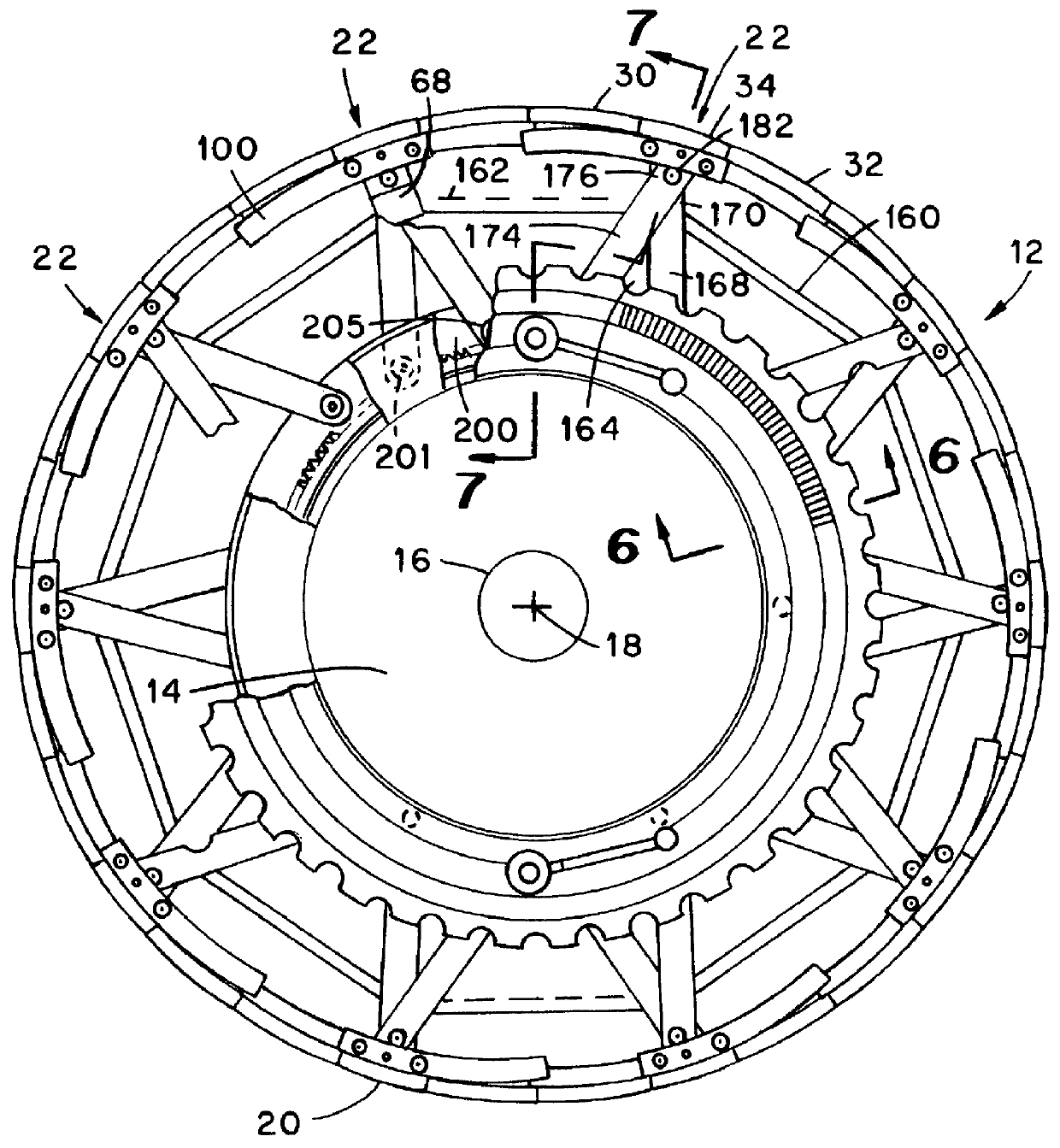
A belt and tread drum having an annular shell comprising a plurality of circumferentially spaced segments, each of which is mounted on a carrier which disposed in circumscribing relationship to a generally cylindrical actuator rotatably connected with a reciprocating piston disposed within a cavity defined between the actuator and a hub fixed to a central core of the drum. Translational movement of the piston between extended and retracted positions in a direction parallel to the rotational axis of the drum is converted into selected rotational movement of the actuator relative to the hub. A plurality of sets of links interposed between the segments and the actuator and hub have their first ends commonly pivotally pinned to a segment. The second end of one link of each set of links is pivotally pinned to the actuator and the second end of the other link of each set of links is pivotally pinned to the hub. Rotation of the actuator relative to the hub controls the arcuate separation of these second ends such that bringing these second ends toward contiguity moves the segments radially outwardly, and conversely, moving these second ends arcuately apart serves to move the segments radially inwardly of the drum. A hand wheel establishes maximum and minimum rotational movement of the actuator and provides a visual indication of the radial positions of the several segments, i.e. the diameter of the drum.
Owner:DAVIAN ENTERPRISES LLC
System, methods and apparatus for program optimization for multi-threaded processor architectures
ActiveUS8930926B2Low costEasy to implementSoftware engineeringMultiprogramming arrangementsParallel computingExecution unit
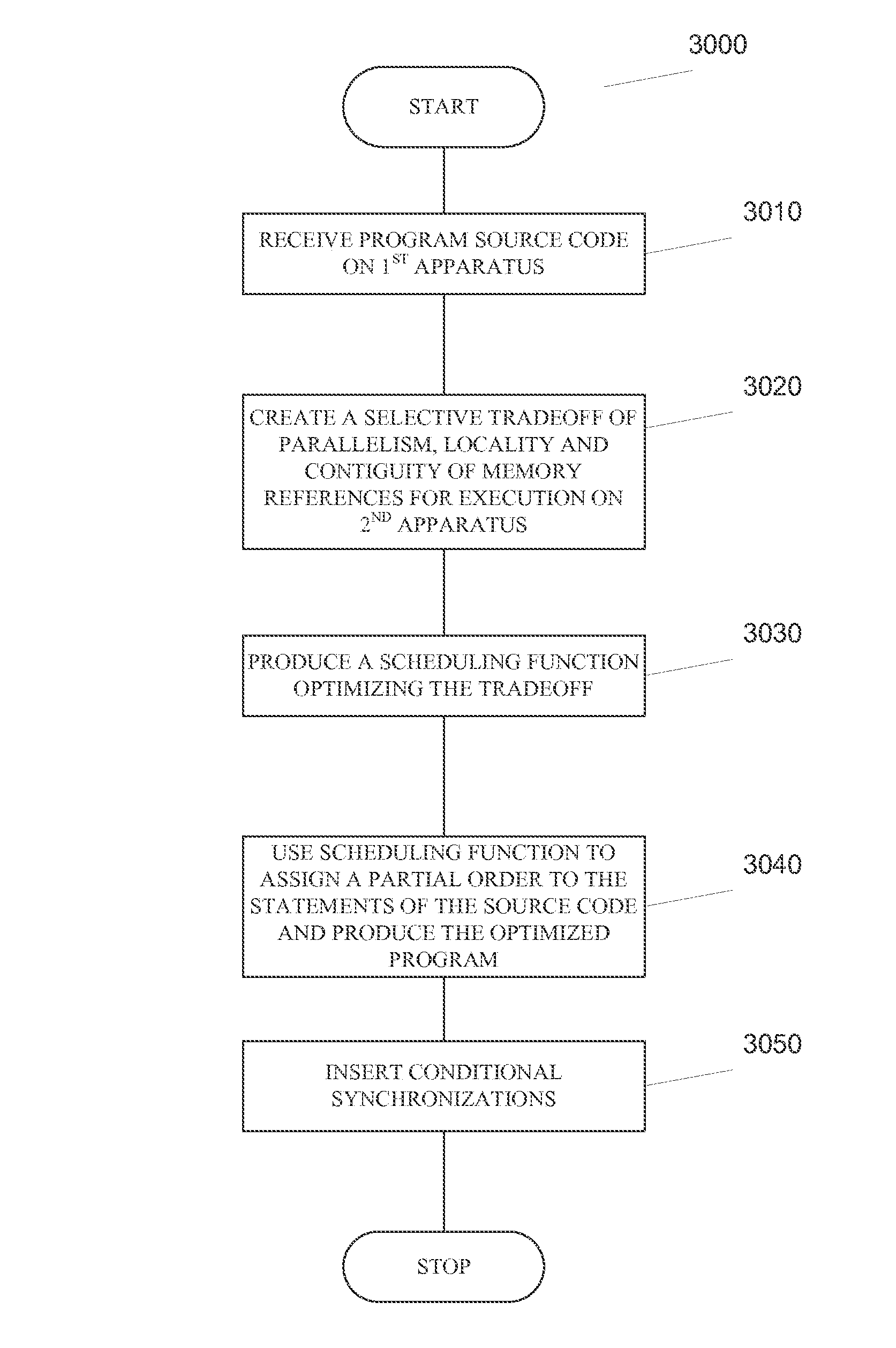
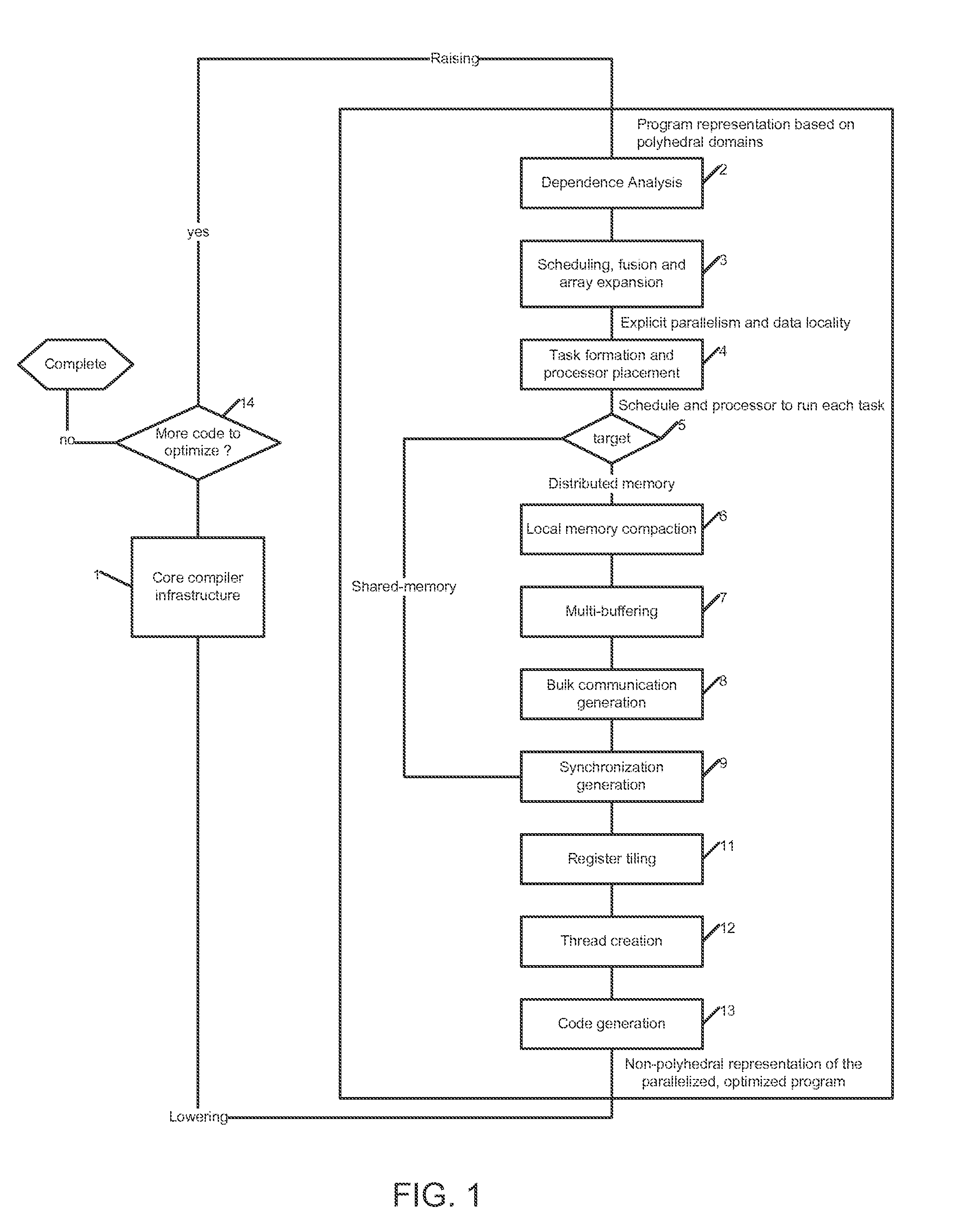
Methods, apparatus and computer software product for source code optimization are provided. In an exemplary embodiment, a first custom computing apparatus is used to optimize the execution of source code on a second computing apparatus. In this embodiment, the first custom computing apparatus contains a memory, a storage medium and at least one processor with at least one multi-stage execution unit. The second computing apparatus contains at least two multi-stage execution units that allow for parallel execution of tasks. The first custom computing apparatus optimizes the code for parallelism, locality of operations and contiguity of memory accesses on the second computing apparatus. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
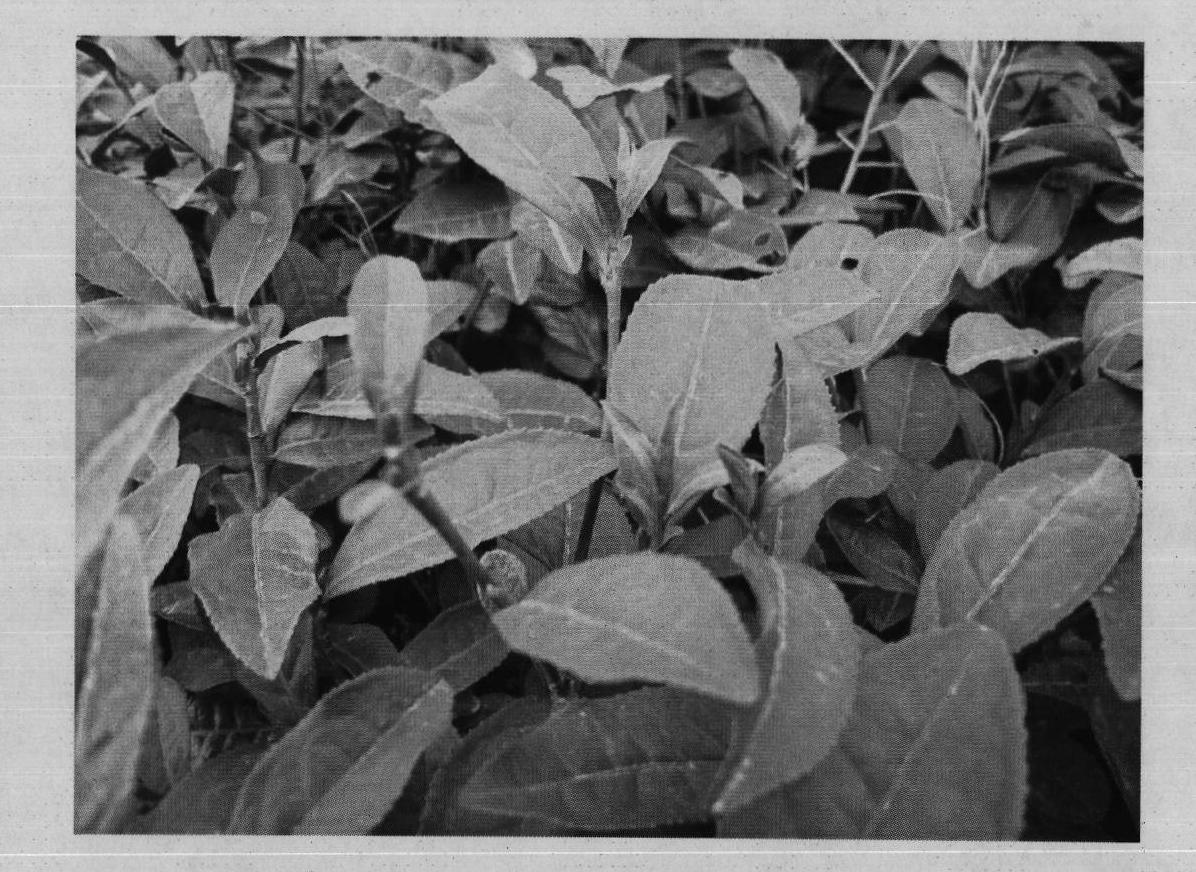
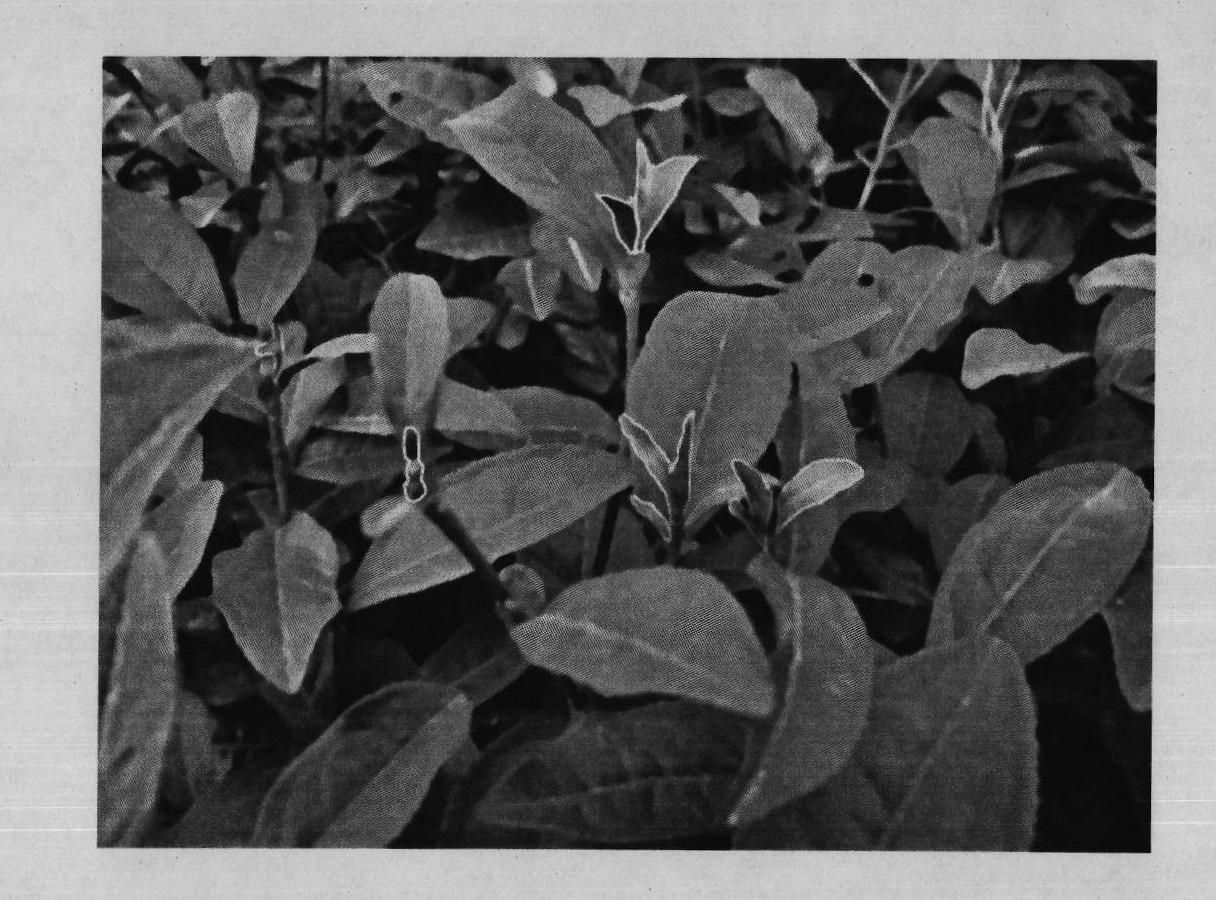
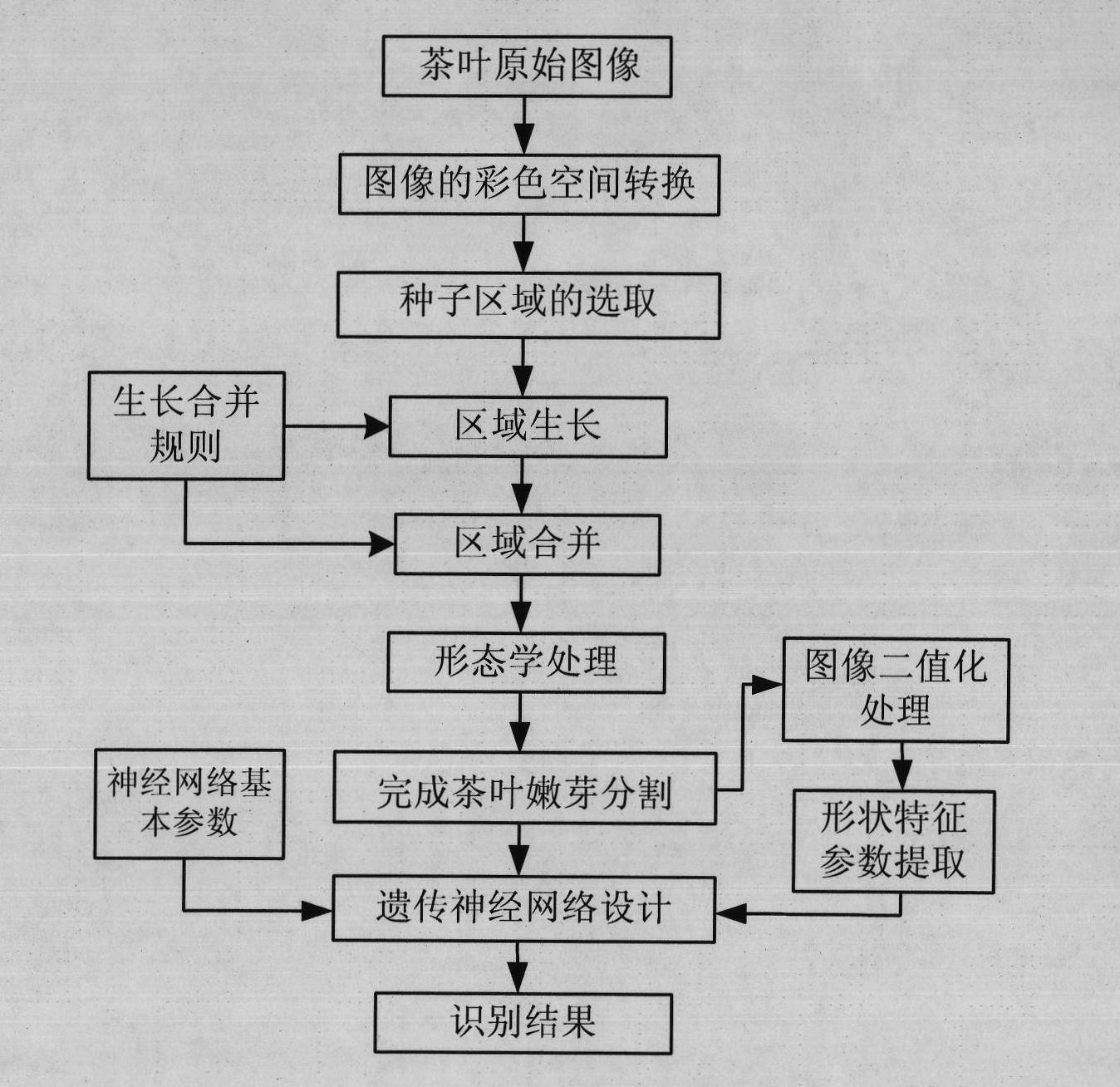
Tea tender shoot segmentation and identification method based on color and region growth
InactiveCN102013021AEasy to divideOvercome the shortcoming of easy to fall into local minimumImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageImaging processing
The invention provides a novel tea tender shoot segmentation and identification method based on color and region growth, relating to the technical field of image processing. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, converting the original tea RGB (Red, Green, Blue) color image into an HIS color space, and carrying out initial seed selection according to the parameters of hue H and saturation S therein; then carrying out region growth on a seed region according to the color similarity and region contiguity; carrying out region growth and combination by combining with color distance and edge distance to segment tea tender shoots; then extracting the shape feature parameters of binarized color and tender shoot images; and finally finishing identification through an improved hereditary neural network. Through a segmentation and identification experiment on the tea tender shoots in the tea image, the result shows that the algorithm can well separate the tea tender shoots from the tea image, well store the outline information of the tea tender shoots and obtain very good identification results.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Packaging substrate having pattern-matched metal layers
InactiveUS20090114429A1Maximum flexibilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsElectricityMetal interconnect
A pattern matched pair of a front metal interconnect layer and a back metal interconnect layer having matched thermal expansion coefficients are provided for a reduced warp packaging substrate. Metal interconnect layers containing a high density of wiring and complex patterns are first developed so that interconnect structures for signal transmission are optimized for electrical performance. Metal interconnect layers containing a low density wiring and relatively simple patterns are then modified to match the pattern of a mirror image metal interconnect layer located on the opposite side of the core and the same number of metal interconnect layer away from the core. During this pattern-matching process, the contiguity of electrical connection in the metal layers with a low density wiring may become disrupted. The disruption is healed by an additional design step in which the contiguity of the electrical connection in the low density is reestablished.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Preemptive packet for maintaining contiguity in cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) contention-free sessions
ActiveUS20080013509A1Synchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesTraffic capacityDistributed coordination function
An access point transmits a preemptive peg packet when it has no data to transmit in order to maintain the contiguity of its transmission timing position with respect to the timing position of other contention-free sessions (CFS) transmitted by other access points in an existing, periodic sequence. The cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) method establishes the transmission timing position of contention-free sessions (CFS) between overlapping first and second wireless LAN cells contending for the same medium. Each cell includes a respective plurality of member stations. If an access point has no traffic, it will transmit a short, preemptive pegging packet and reset its backoff timer. In this manner, no gaps longer than the distributed coordination function (DCF) Interframe Space (DIFS) are left idle. This prevents other stations from using DCF contention to seize the channel, until all access points have completed one contention-free session (CFS) per periodic cycle.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
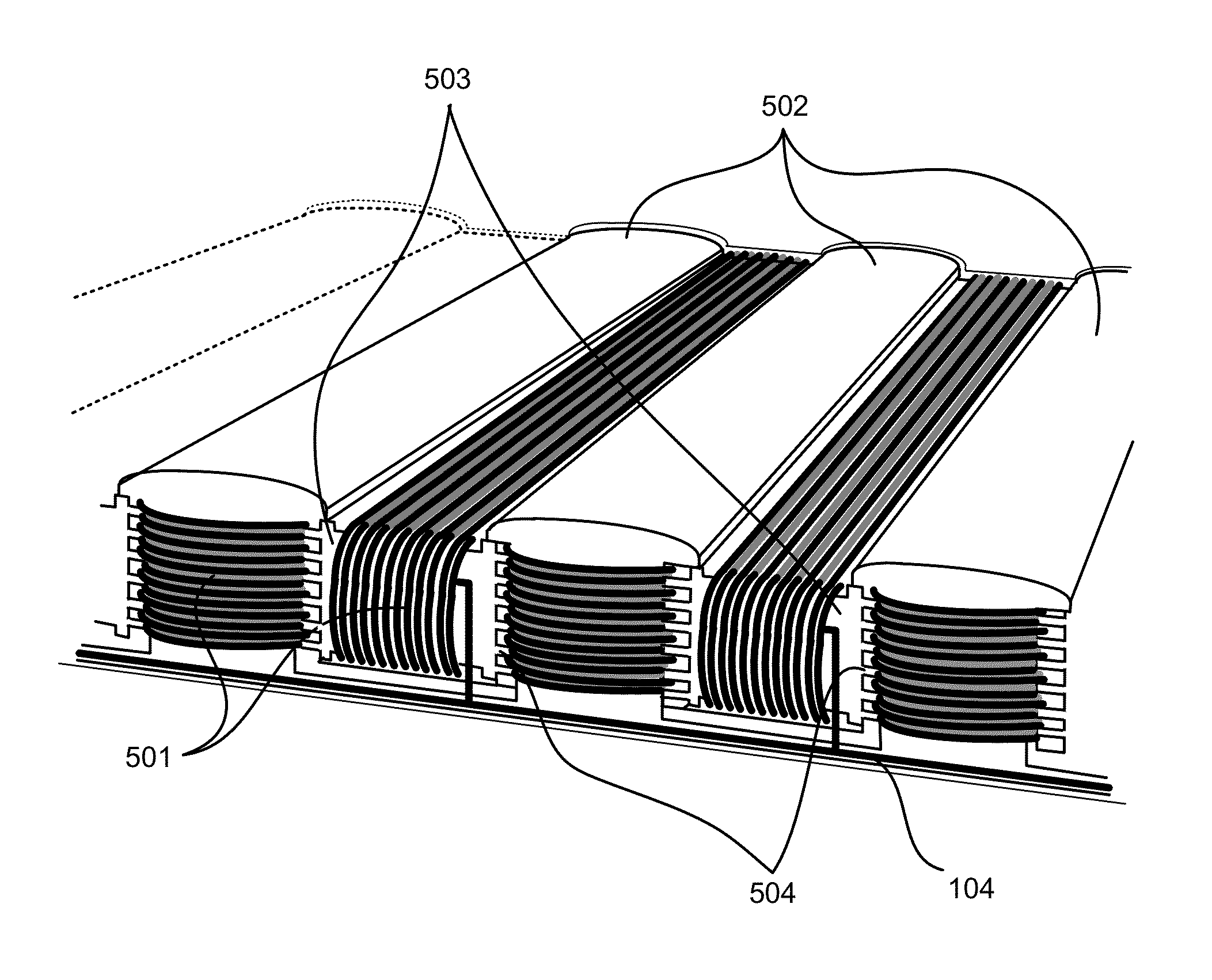
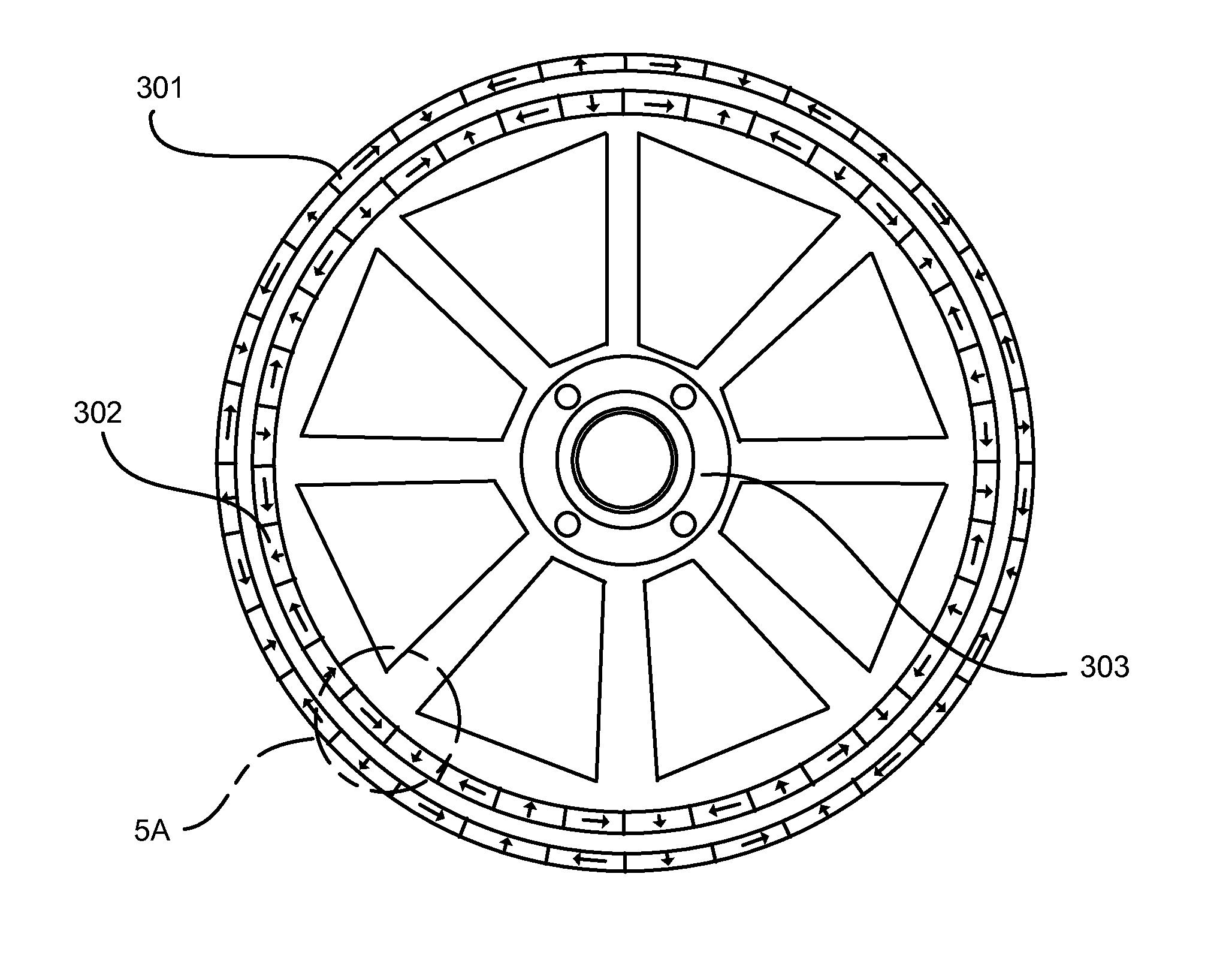
Halbach array electric motor with substantially contiguous electromagnetic cores
Dual Halbach array element electric motor / generator with paired enhanced sides and substantially contiguous vertical and horizontal electromagnetic cores, comprised of a plurality of electromagnets arranged in Halbach array sequence, with horizontal cores equipped with fork-like prongs to provide substantial contiguity with vertical cores, assembled to serve as a circular or linear stator, rotor, or both, and a plurality of permanent magnets likewise arranged in a Halbach array sequence, assembled to serve as a circular or linear stator or rotor where required, with the enhanced sides of each Halbach array element, as rotor and stator, are paired together.
Owner:CATALAN ROBERTO SANCHEZ
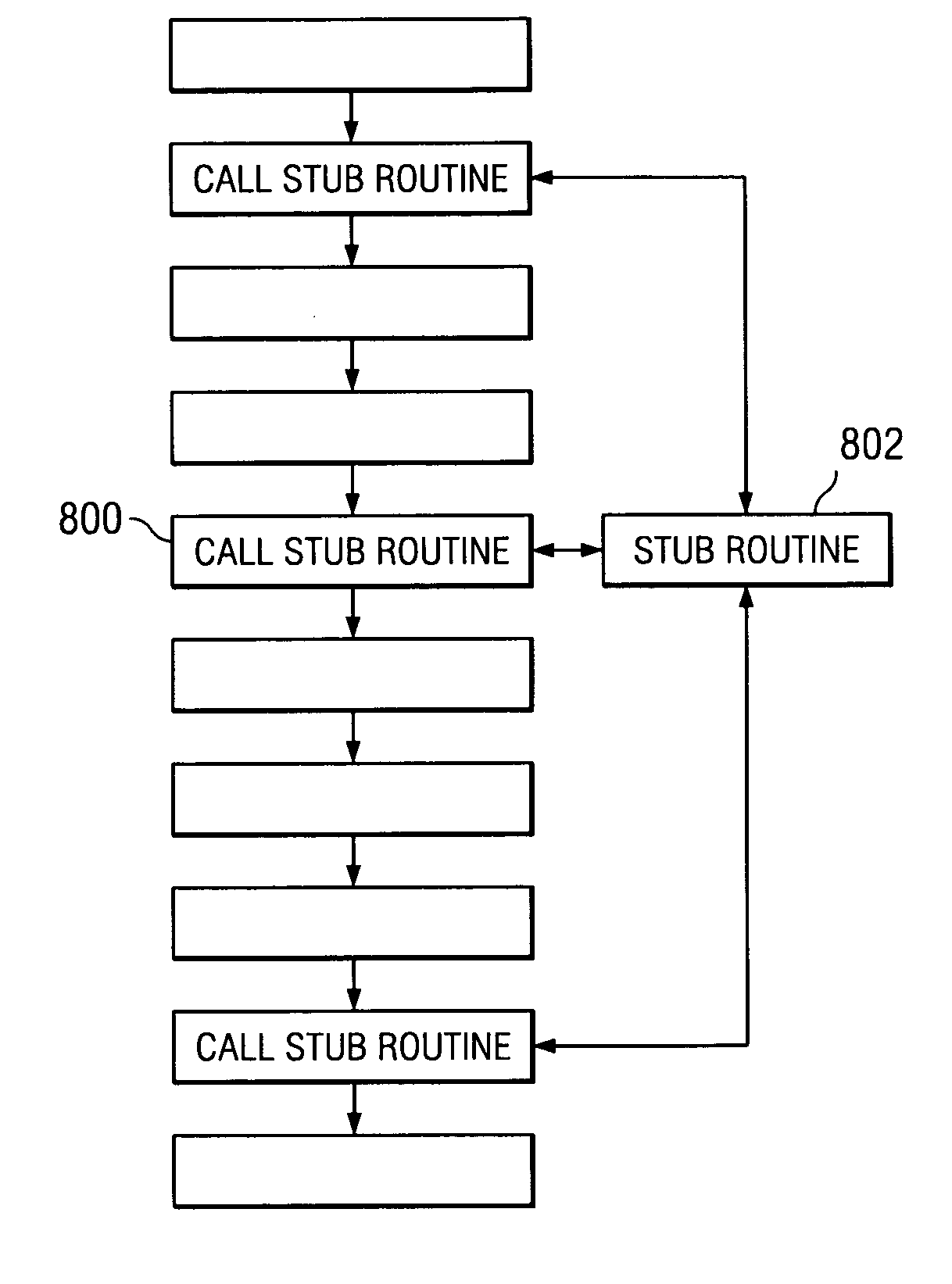
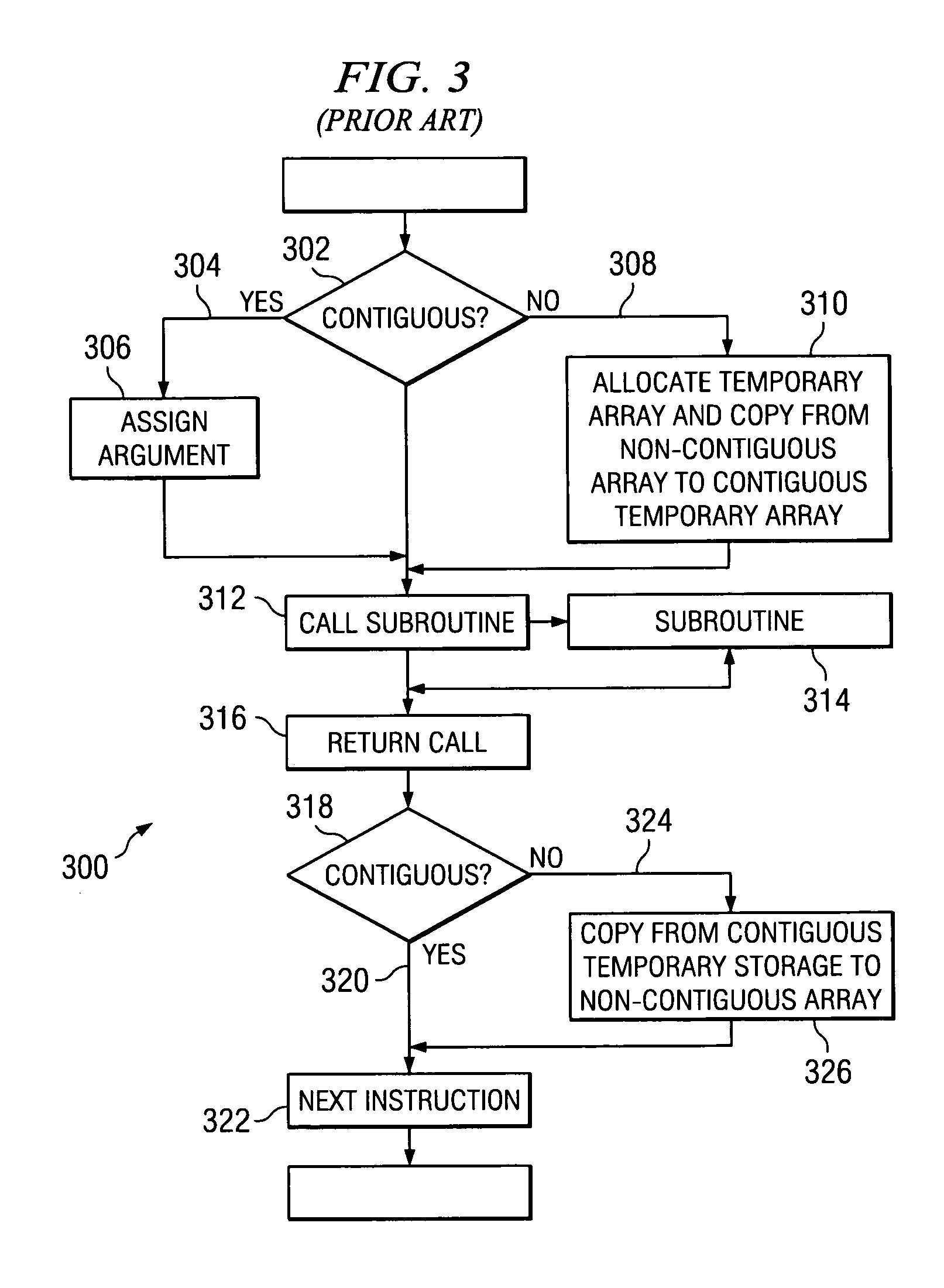
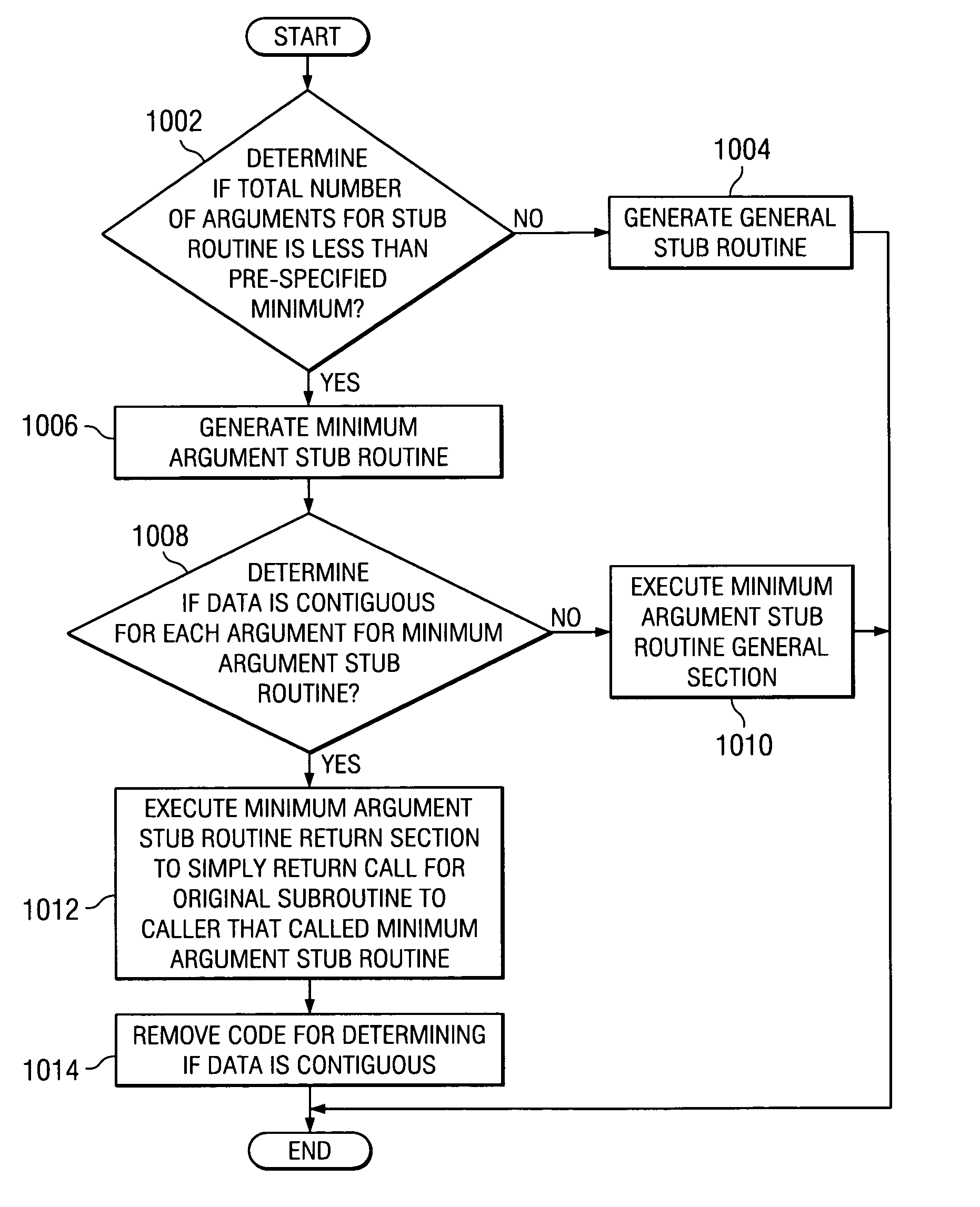
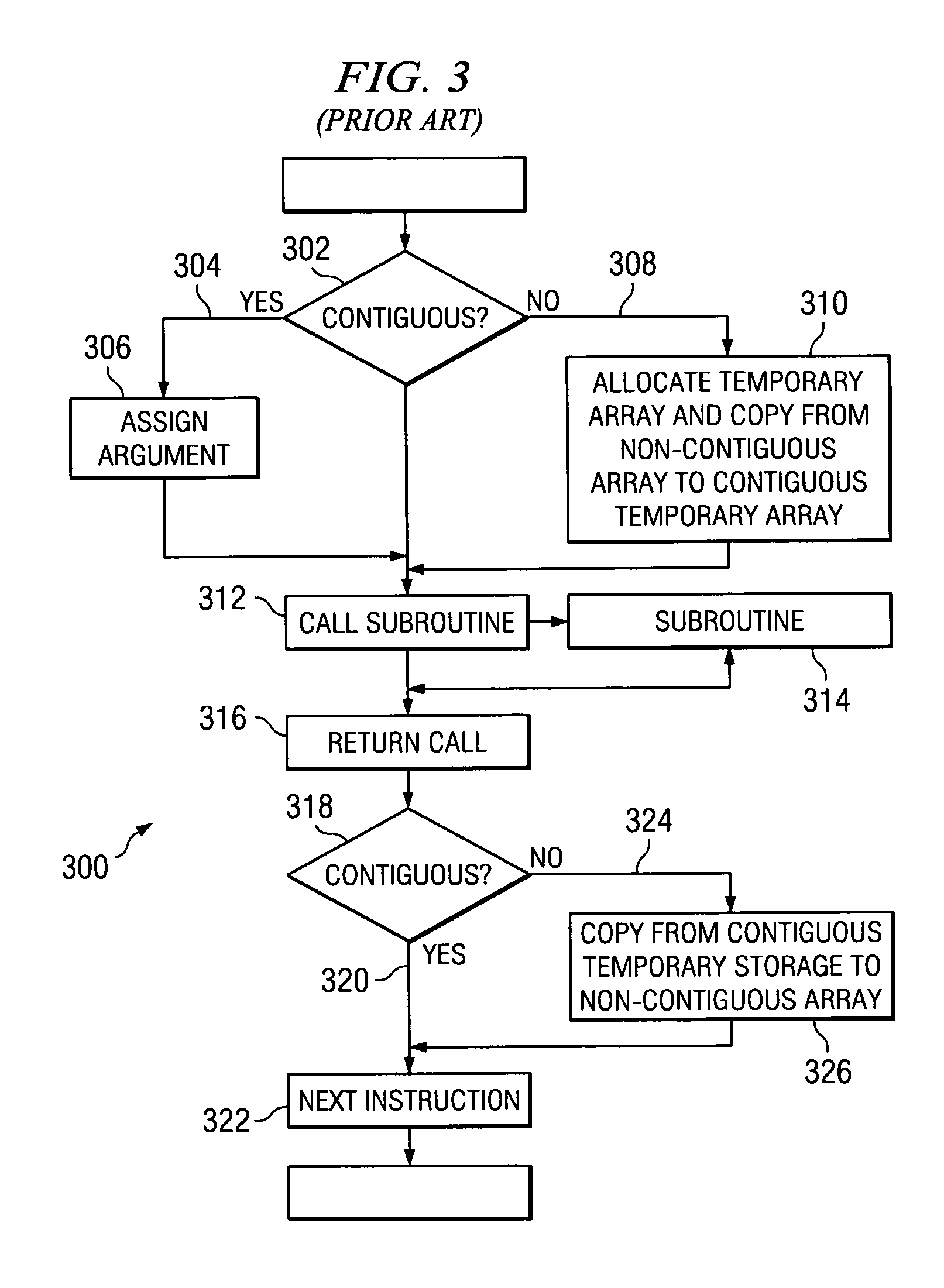
Method for simplifying compiler-generated software code
A computer implemented method, system, and computer usable program code for simplifying compiler-generated software code by creating a stub routine for checking storage contiguity. A stub routine is generated for a subroutine. The stub routine is used to determine whether data is contiguous for the subroutine. A subroutine call in the code is replaced with a stub routine call for the stub routine. The subroutine call has at least one argument. The stub routine call includes each argument for the subroutine call. The code is executed. The stub routine is called by the stub routine call to determine whether data is contiguous for the subroutine.
Owner:IBM CORP
Halbach Array Electric Motor with Substantially Contiguous Electromagnetic Cores
ActiveUS20150061440A1Reduce unsprung weightEasy to handleMagnetic circuit rotating partsVehicle sub-unit featuresContiguityElectromagnet
Halbach Array electric motor with substantially contiguous electromagnetic cores, comprised of a plurality of electromagnets arranged in Halbach Array sequence, whose horizontal cores are equipped with fork-like prongs to provide substantial contiguity with vertical cores, assembled to serve as a circular or linear stator, rotor or both, and a plurality of permanent magnets likewise arranged in a Halbach Array sequence, assembled to serve as a circular or linear stator or rotor where required.
Owner:CATALAN ROBERTO SANCHEZ
Wireless communication base station device, wireless communication mobile station device, and propagation path estimation method
ActiveUS20100272201A1Improve accuracySecret communicationRadio transmissionEstimation methodsControl data
A wireless communication base station device, whereby precision of propagation path estimation is improved by making possible determination of the contiguity of precoding strings contiguous in frequency regions. In this device, a pre-coding string contiguity determining portion (120) determines whether or not a plurality of pre-coding strings (?) which are input from a pre-coding string calculating portion (119) are contiguous in a frequency region. The pre-coding string contiguity determining portion (120) outputs smoothing possibility data, which indicate determination results, to a control data generating portion (104). The control data generating portion (104) generates control data indicating smoothing possibility data which is input from the pre-coding string contiguity determining portion (120).
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
Massively parallel continguity mapping
Contiguity information is important to achieving high-quality de novo assembly of mammalian genomes and the haplotype-resolved resequencing of human genomes. The methods described herein pursue cost-effective, massively parallel capture of contiguity information at different scales.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
File system having predictable real-time performance
InactiveUS8046558B2Improve abilitiesTime requiredDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsQuality of serviceNon real time
A file system that permits predictable accesses to file data stored on devices that may have a variable access latency dependent on the physical location of the file on the physical storage device. A variety of features that guarantee timely, real-time response to I / O file system requests that specify deadlines or other alternative required quality-of-service parameters. The file system addresses needs to accommodate the file systems of storage devices such as disks that have an access time dependant on the physical location of the data within the storage device. A two-phase, deadline-driven scheduler considers the impact of disk seek time on overall response times. Non real-time file operations may be preempted. Files may be preallocated to help avoid access delay caused by non-contiguity. Disk buffers may also be preallocated to improve real-time file system performance.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Packing Container
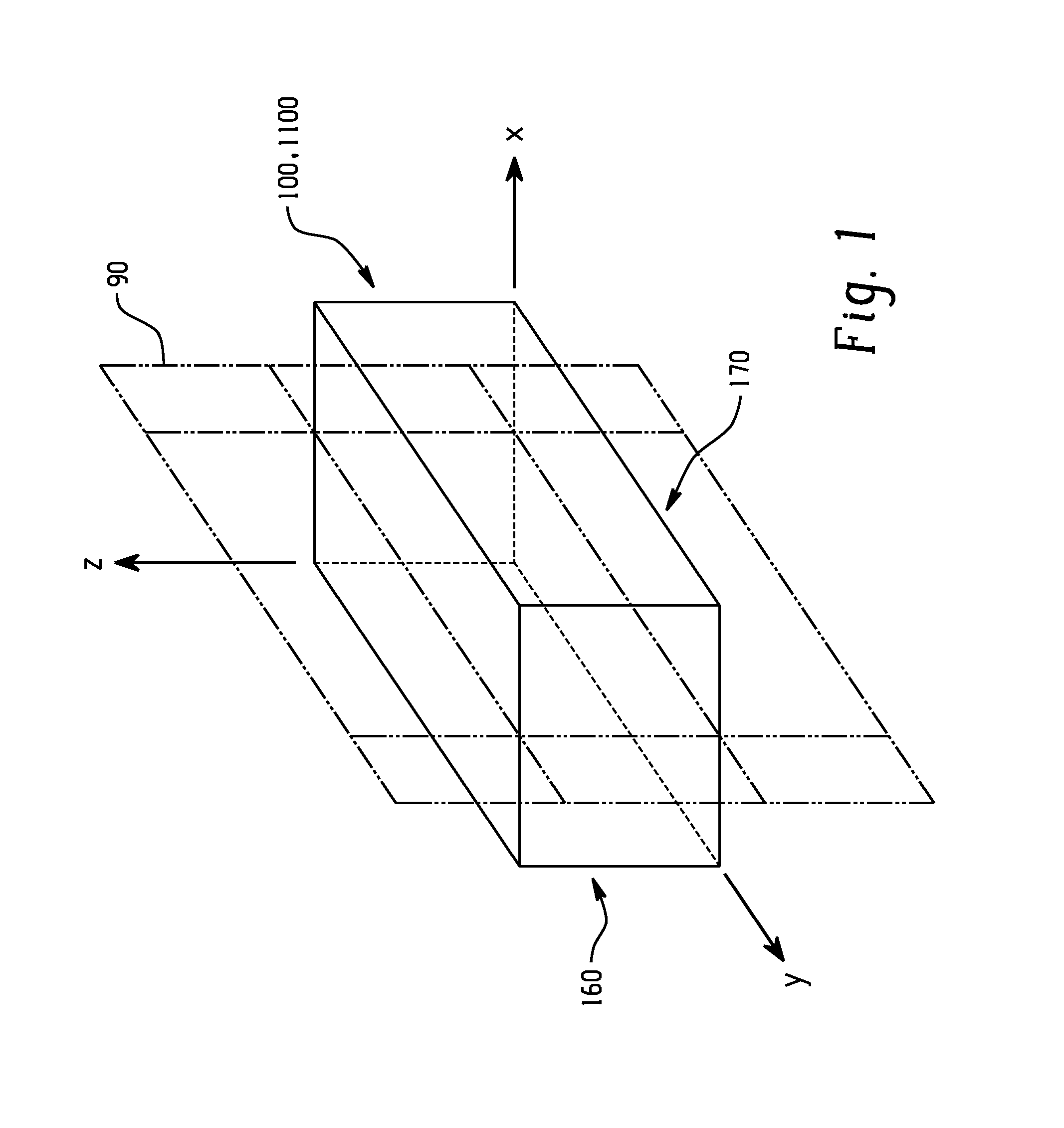
A container includes a plurality of panels integrally arranged with respect to each other and with respect to a set of orthogonal x, y and z axes, the z-axis defining a direction line in which the container is configured to support a stacking load. The plurality of panels include a first panel having a first planar surface, and a second panel having a second planar surface, wherein the first panel and the second panel form a contiguity with a fold line disposed therebetween, and wherein the first planar surface is disposed parallel to the x-z plane or the y-z plane. The container further includes a compression reinforcement feature having a planar edge oriented orthogonal to the first planar surface and perpendicular to the z-axis, the planar edge being disposed a distance away from the fold line but at a distance no greater than half a thickness of the first panel, the first panel having a void between the fold line and the planar edge.
Owner:GEORGIA PACIFIC CORRUGATED
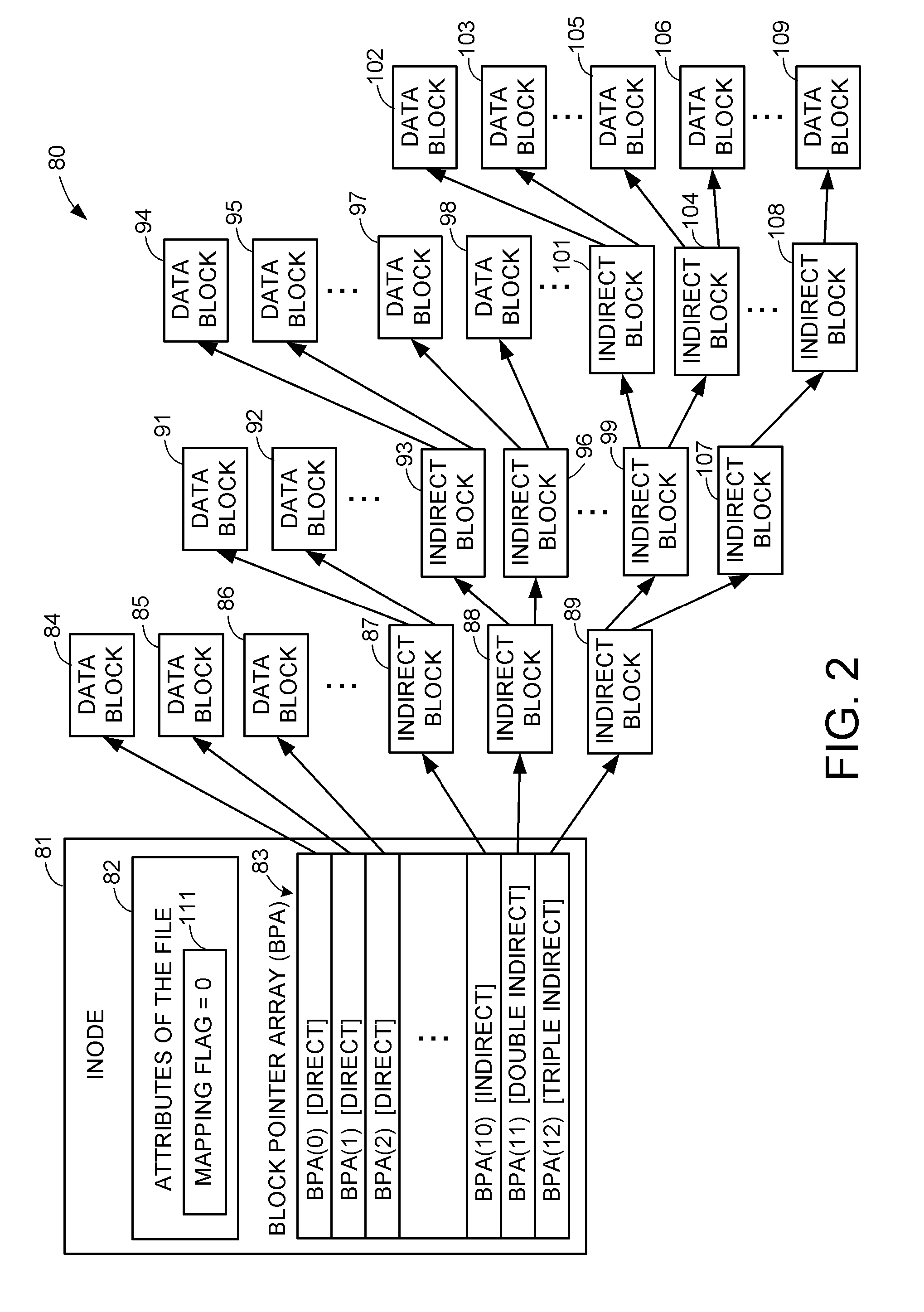
Two-dimensional data storage system
InactiveUS8108431B1Facilitates field-level lockingSimplify access operationsDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsArray data structureData access
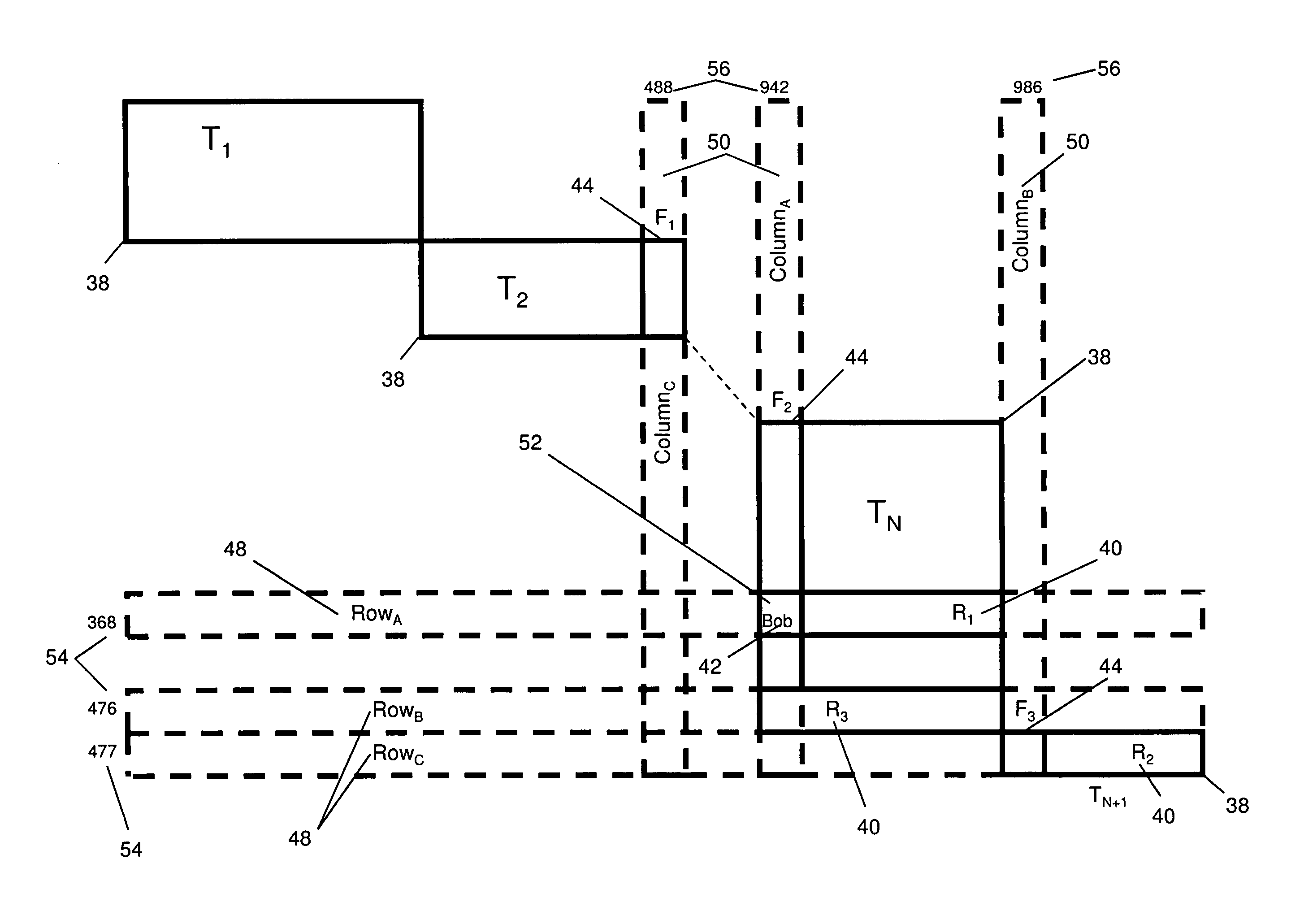
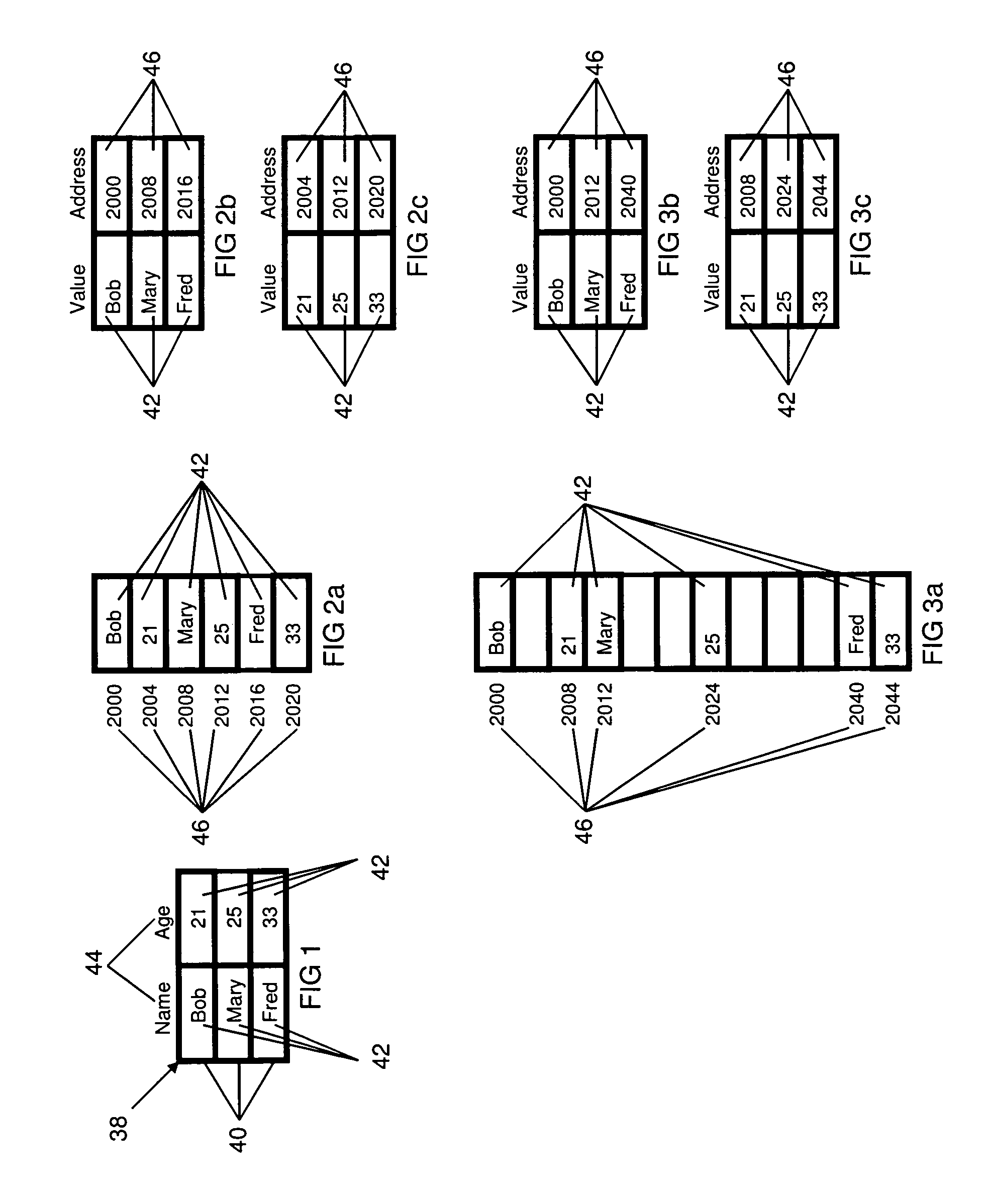
A method providing a level of indirection that abstracts the details of physical data storage, requiring neither indexing nor contiguity of data elements in physical storage for efficient data access. Tables are organized in a diagonal pattern (with a natural implementation in electronic spreadsheets), where the region occupied by each table is expandable and shrinkable. A novel query processing mechanism applies successive expressions in a query to progressively smaller arrays of references to a table's records. A novel method for implementing join operations avoids data replication, where the table derived from the join contains a matrix of references to values in the original tables. The derived table can subsequently be used to update the original tables via references, where this capability can be utilized in a user interface supporting atomic data entry transactions, where users may edit the derived table, and the corresponding original tables are atomically updated.
Owner:AUTOTELIKA
Method for simplifying compiler-generated software code
A computer implemented method, system, and computer usable program code for simplifying compiler-generated software code by creating a stub routine for checking storage contiguity. A stub routine is generated for a subroutine. The stub routine is used to determine whether data is contiguous for the subroutine. A subroutine call in the code is replaced with a stub routine call for the stub routine. The subroutine call has at least one argument. The stub routine call includes each argument for the subroutine call. The code is executed. The stub routine is called by the stub routine call to determine whether data is contiguous for the subroutine.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Preemptive packet for maintaining contiguity in cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) contention-free sessions
InactiveUS8068470B2Synchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesTraffic capacityDistributed coordination function
An access point transmits a preemptive peg packet when it has no data to transmit in order to maintain the contiguity of its transmission timing position with respect to the timing position of other contention-free sessions (CFS) transmitted by other access points in an existing, periodic sequence. The cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) method establishes the transmission timing position of contention-free sessions (CFS) between overlapping first and second wireless LAN cells contending for the same medium. Each cell includes a respective plurality of member stations. If an access point has no traffic, it will transmit a short, preemptive pegging packet and reset its backoff timer. In this manner, no gaps longer than the distributed coordination function (DCF) Interframe Space (DIFS) are left idle. This prevents other stations from using DCF contention to seize the channel, until all access points have completed one contention-free session (CFS) per periodic cycle.
Owner:AT & T INTPROP II LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com