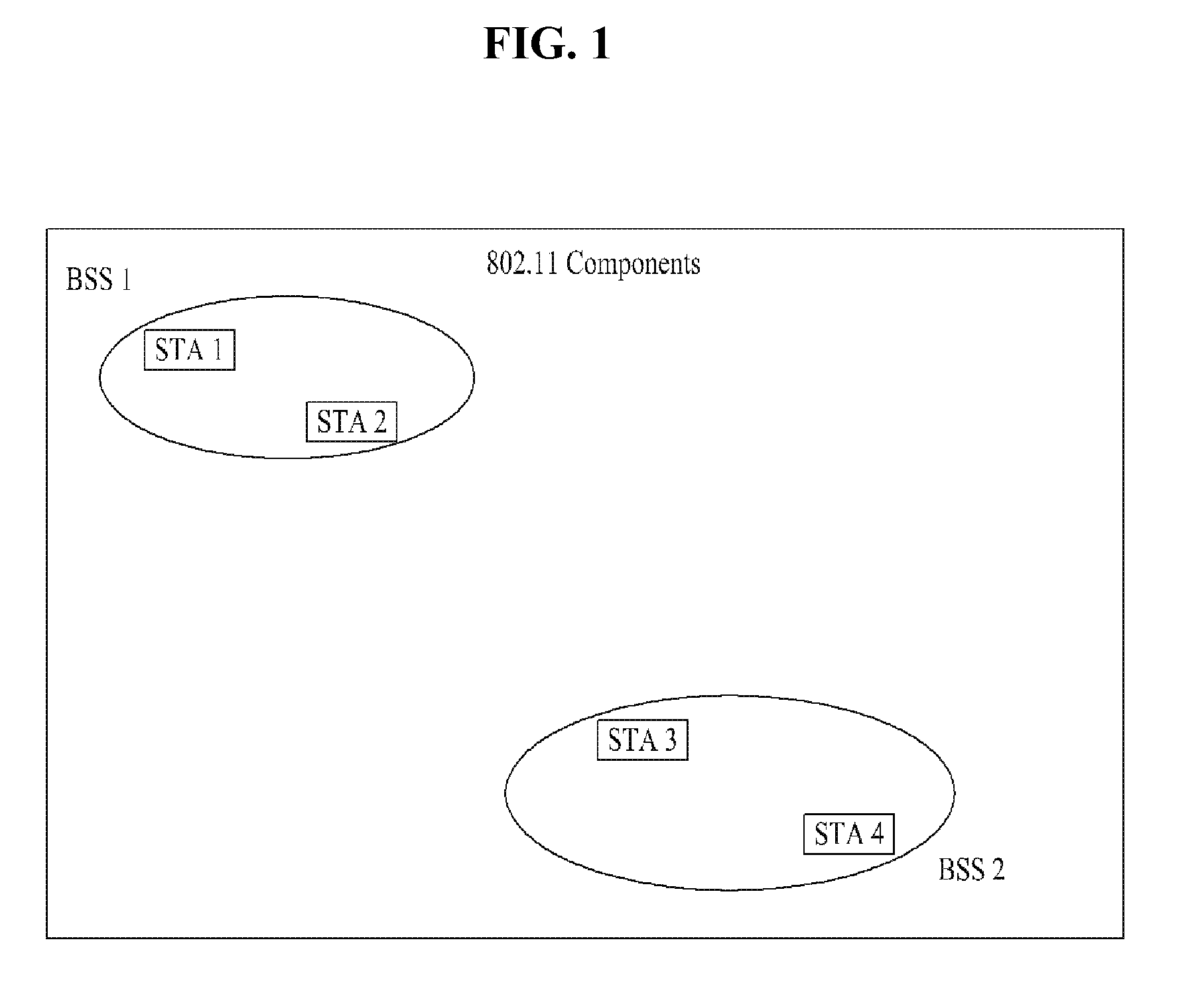
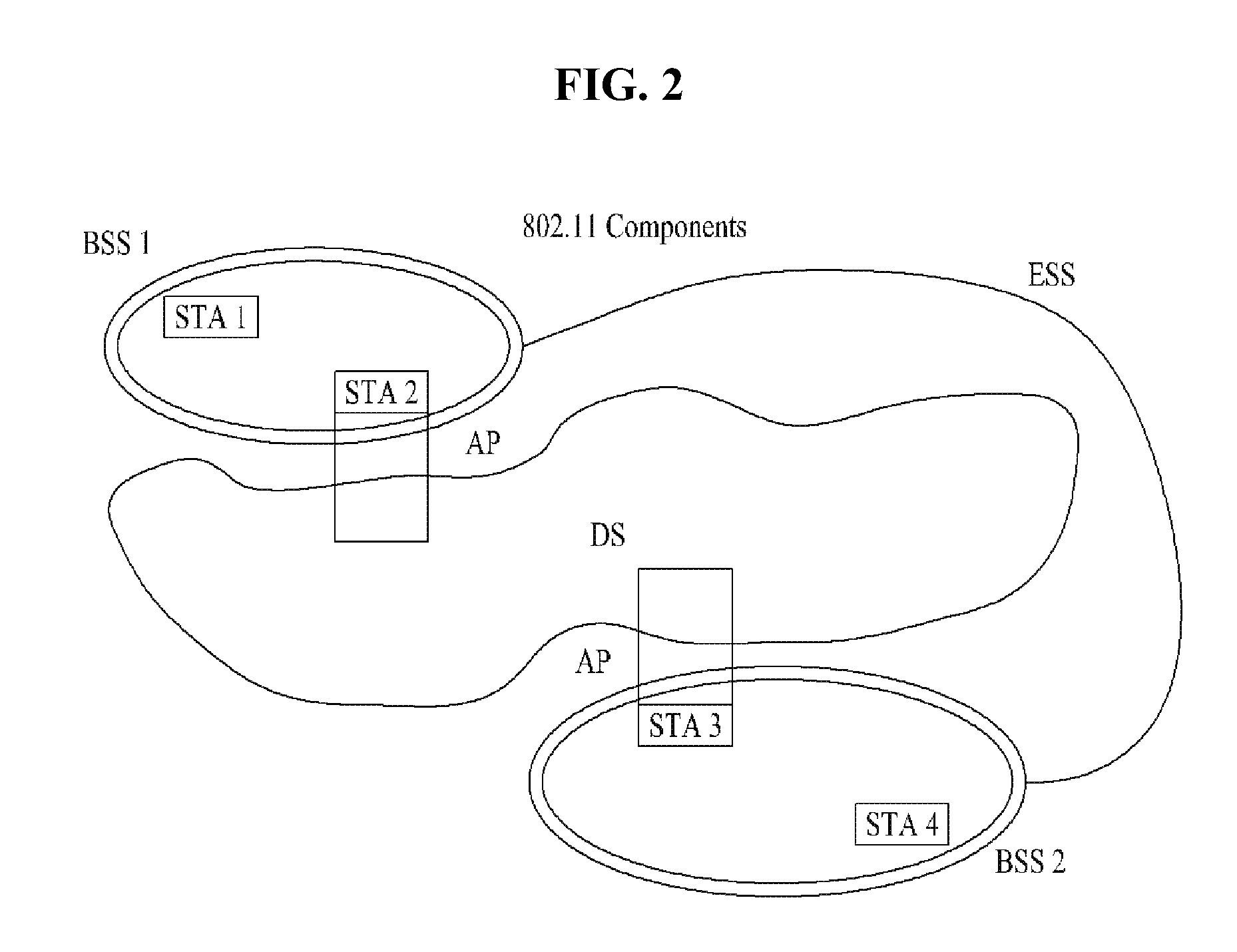
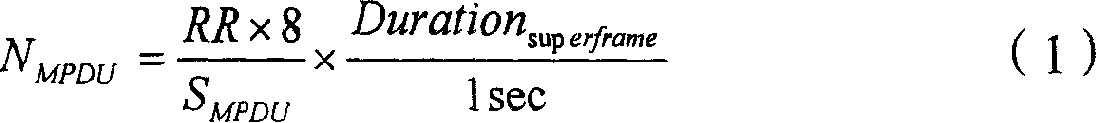Patents
Literature
64 results about "Distributed coordination function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
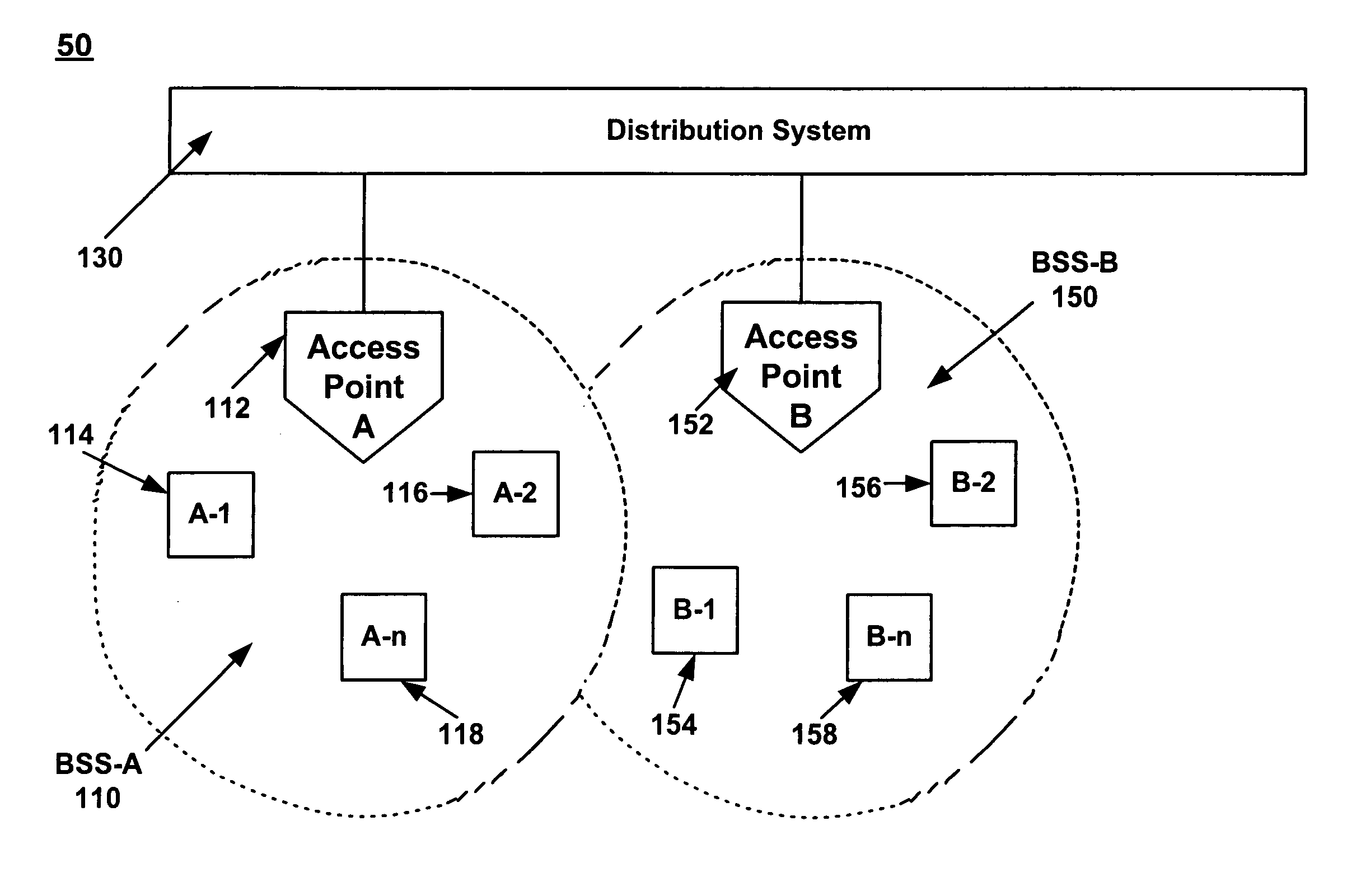
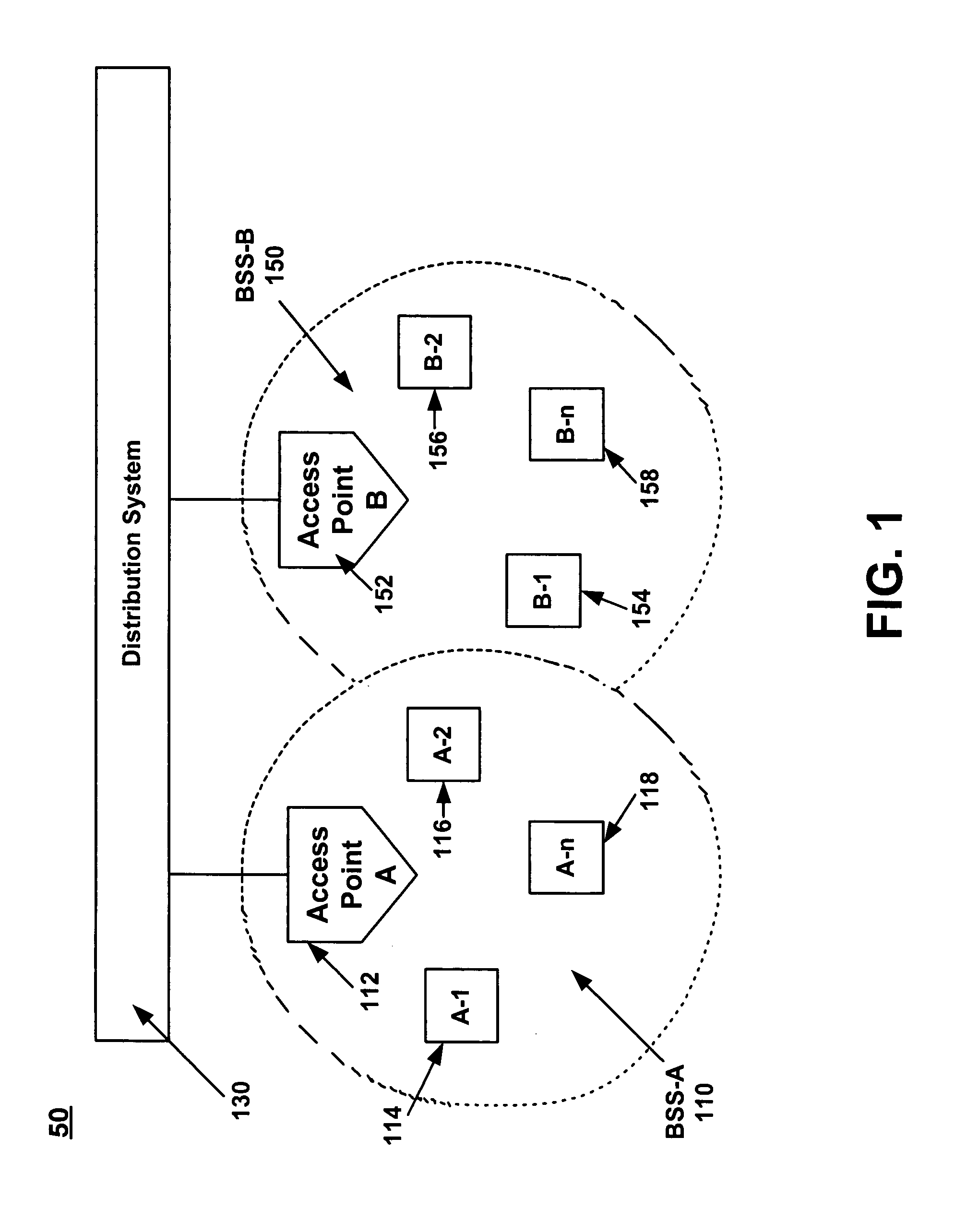
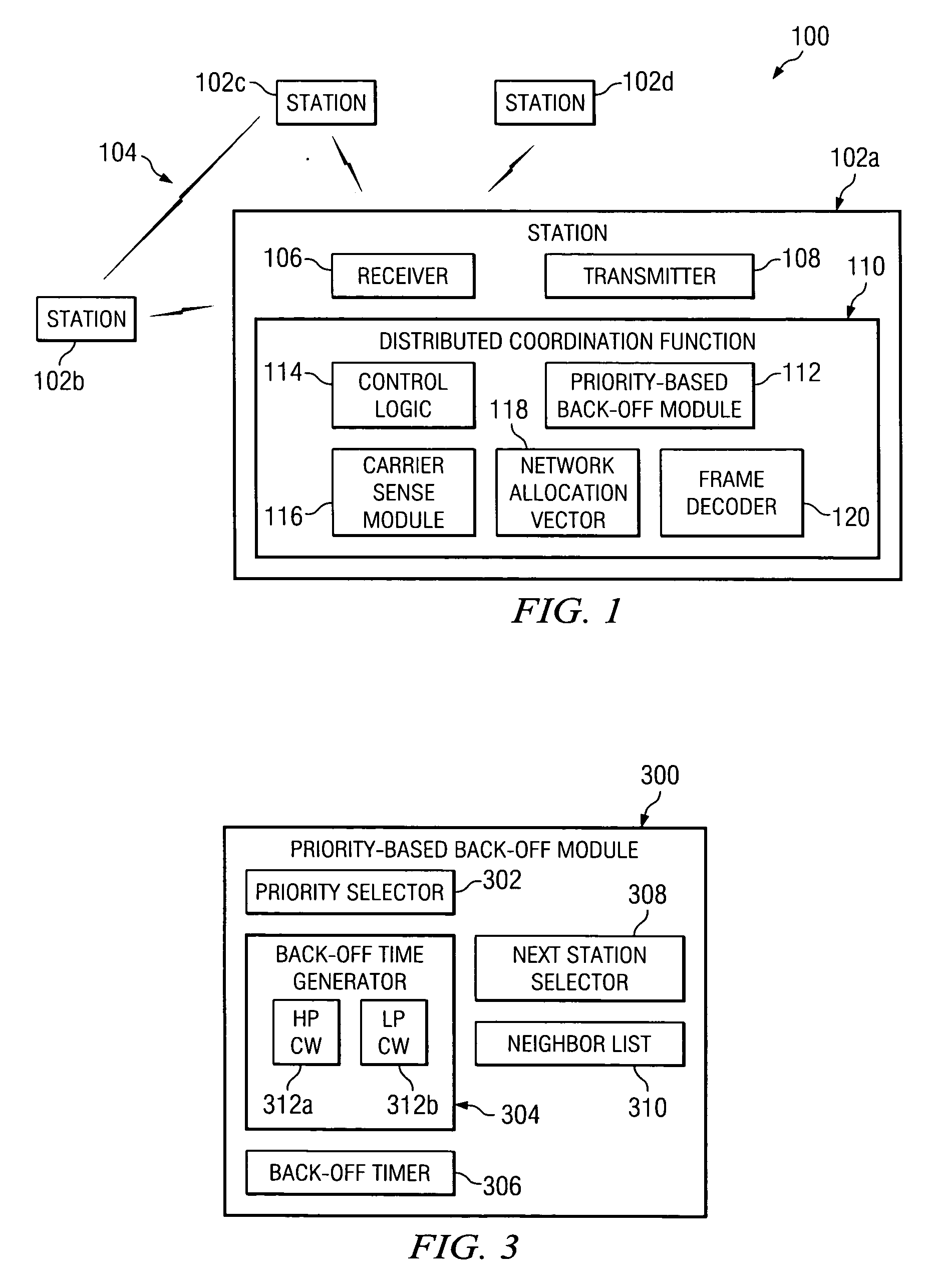
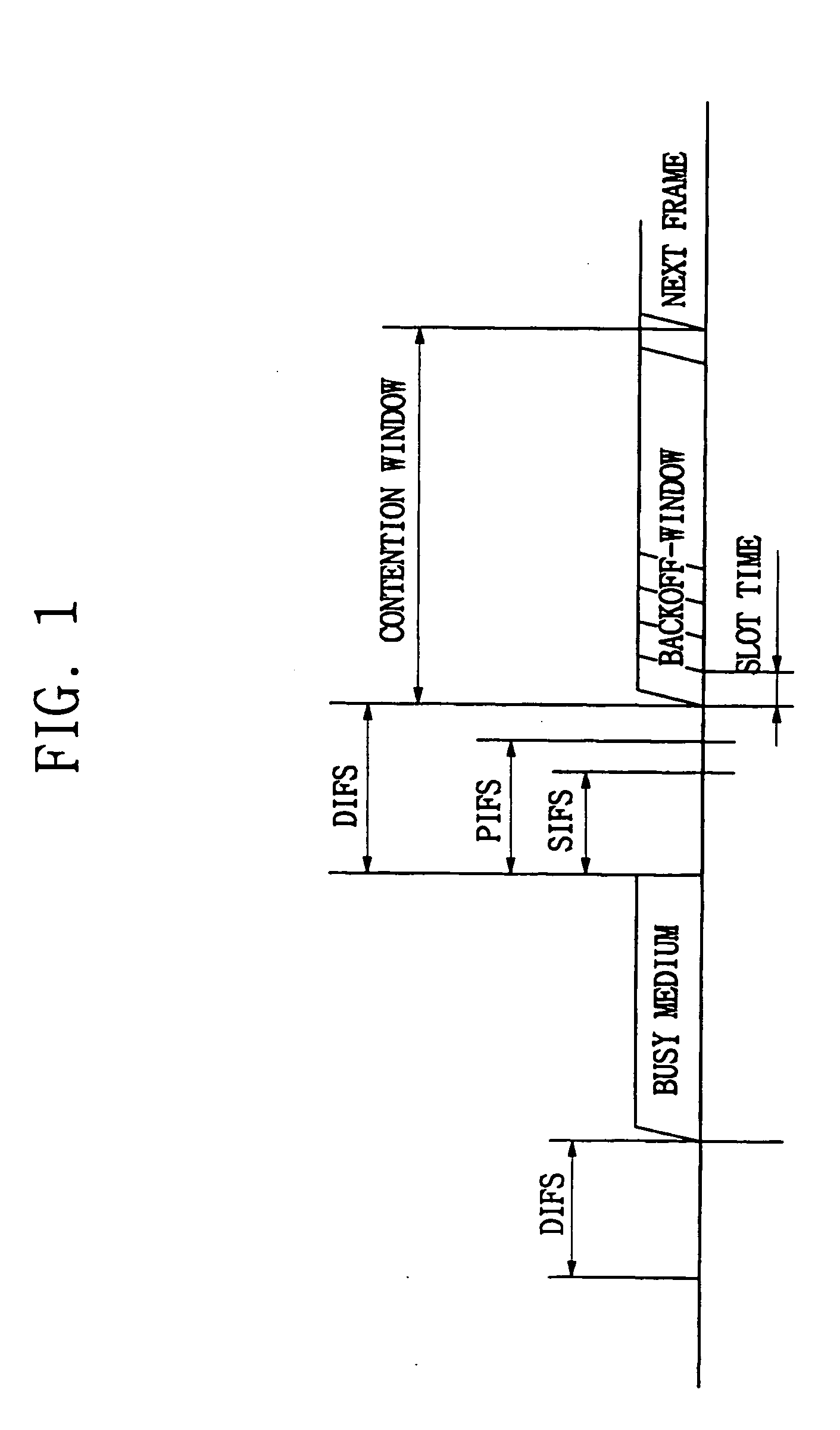
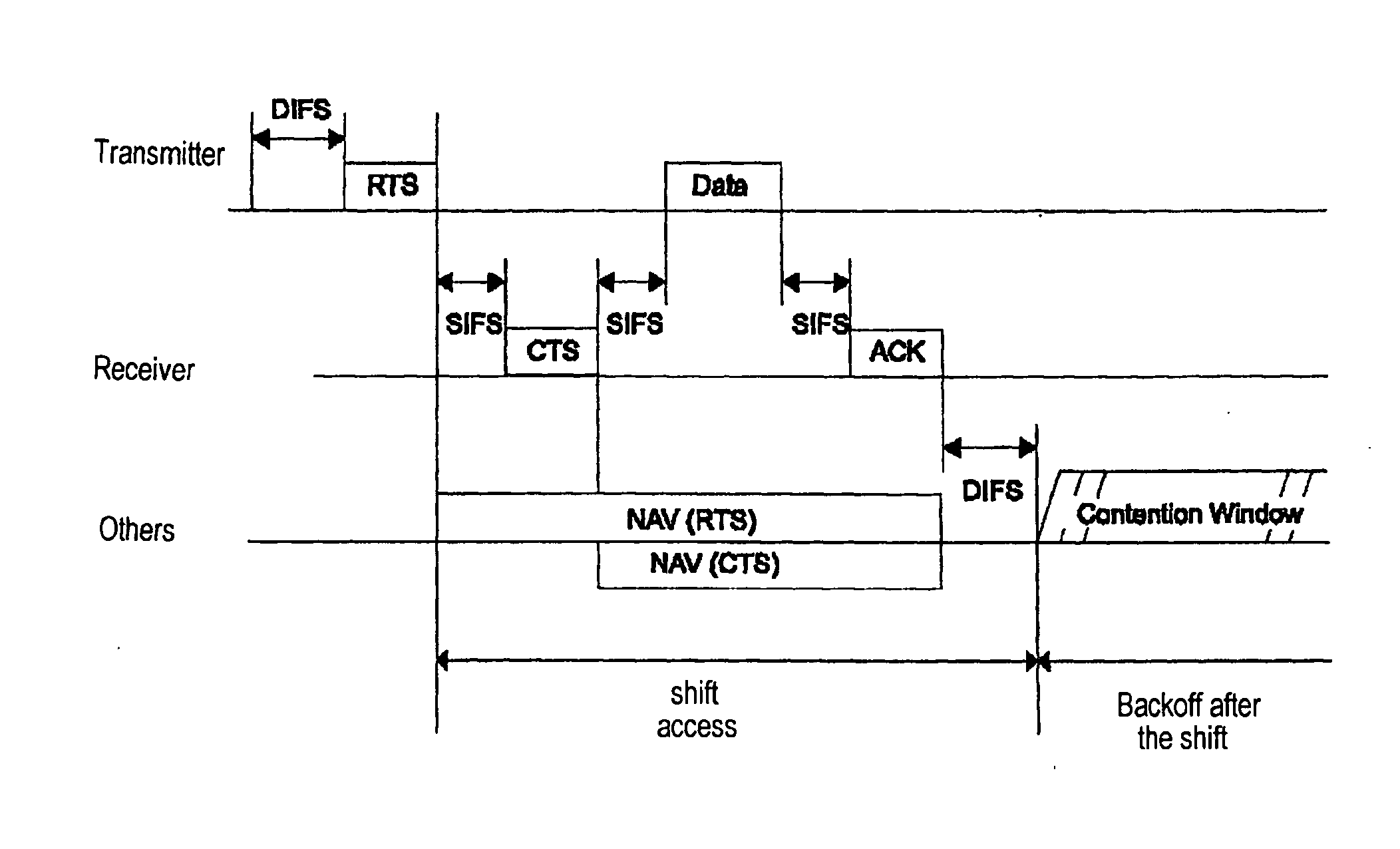
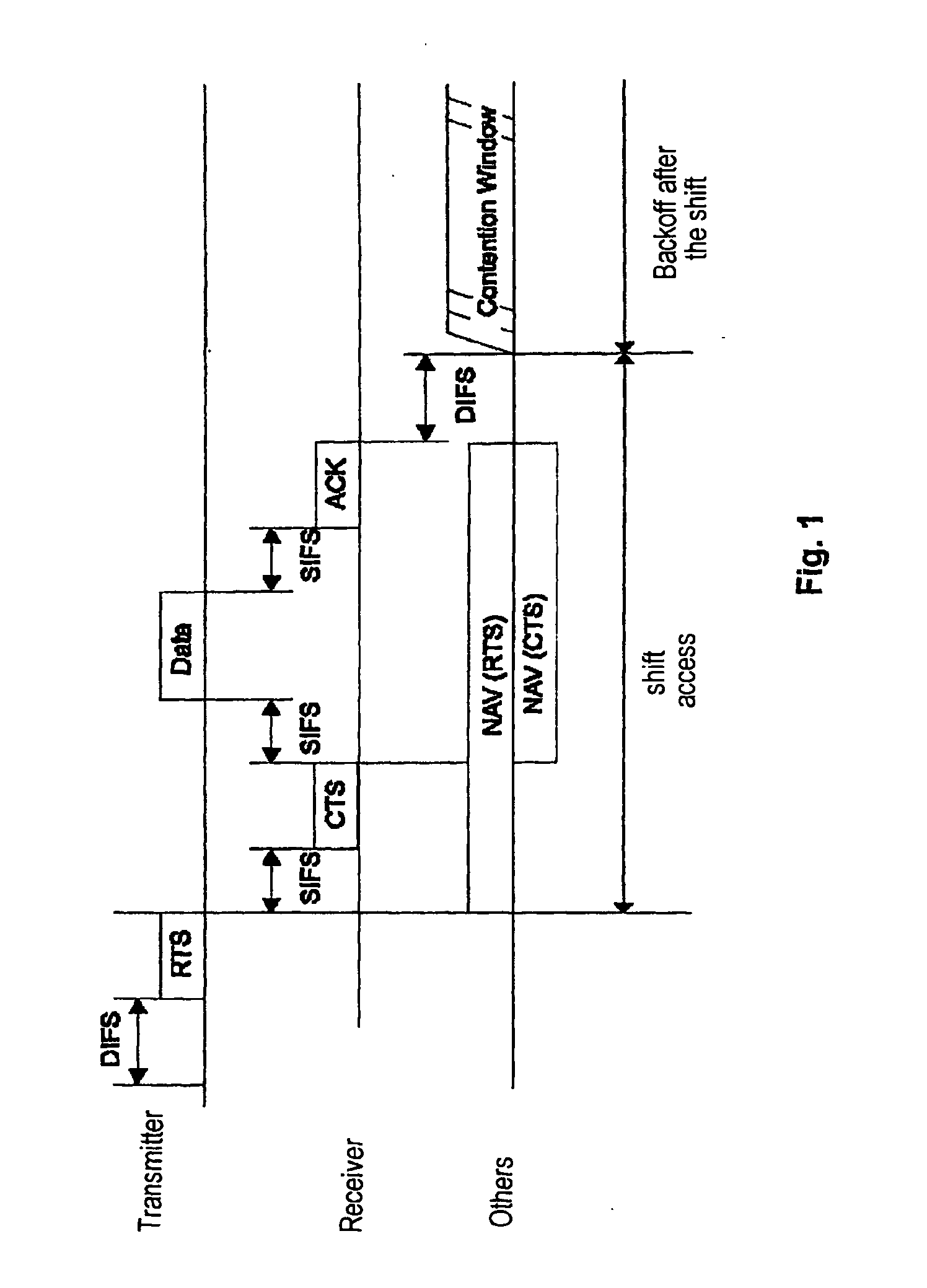
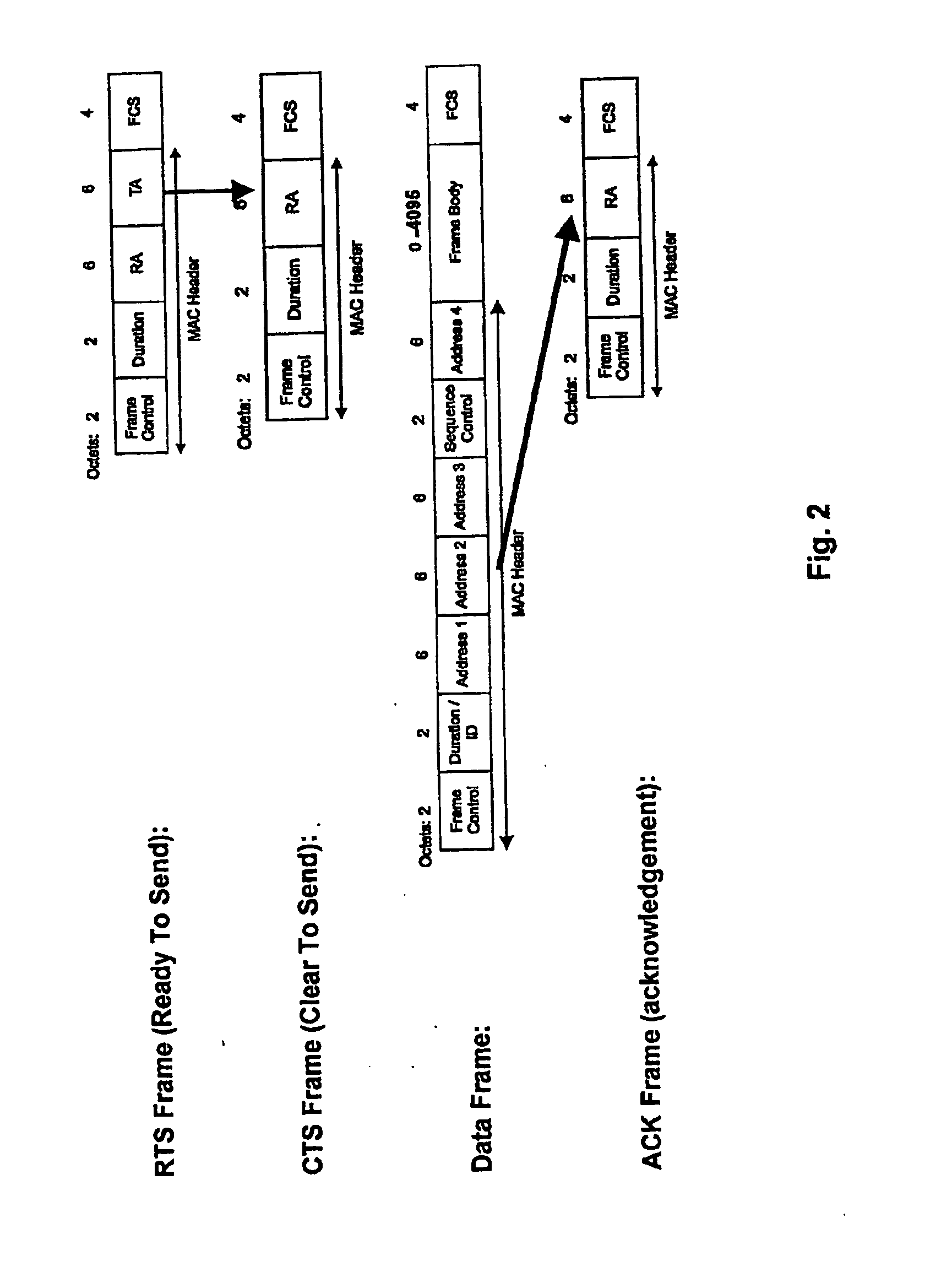
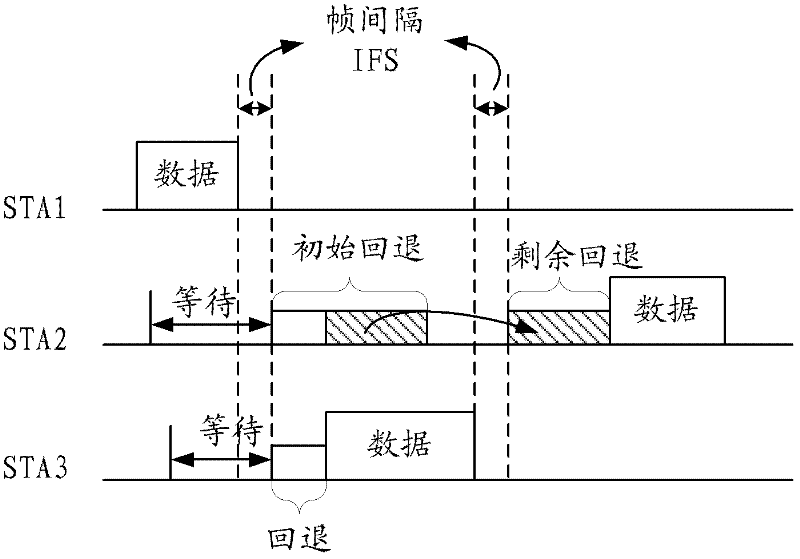
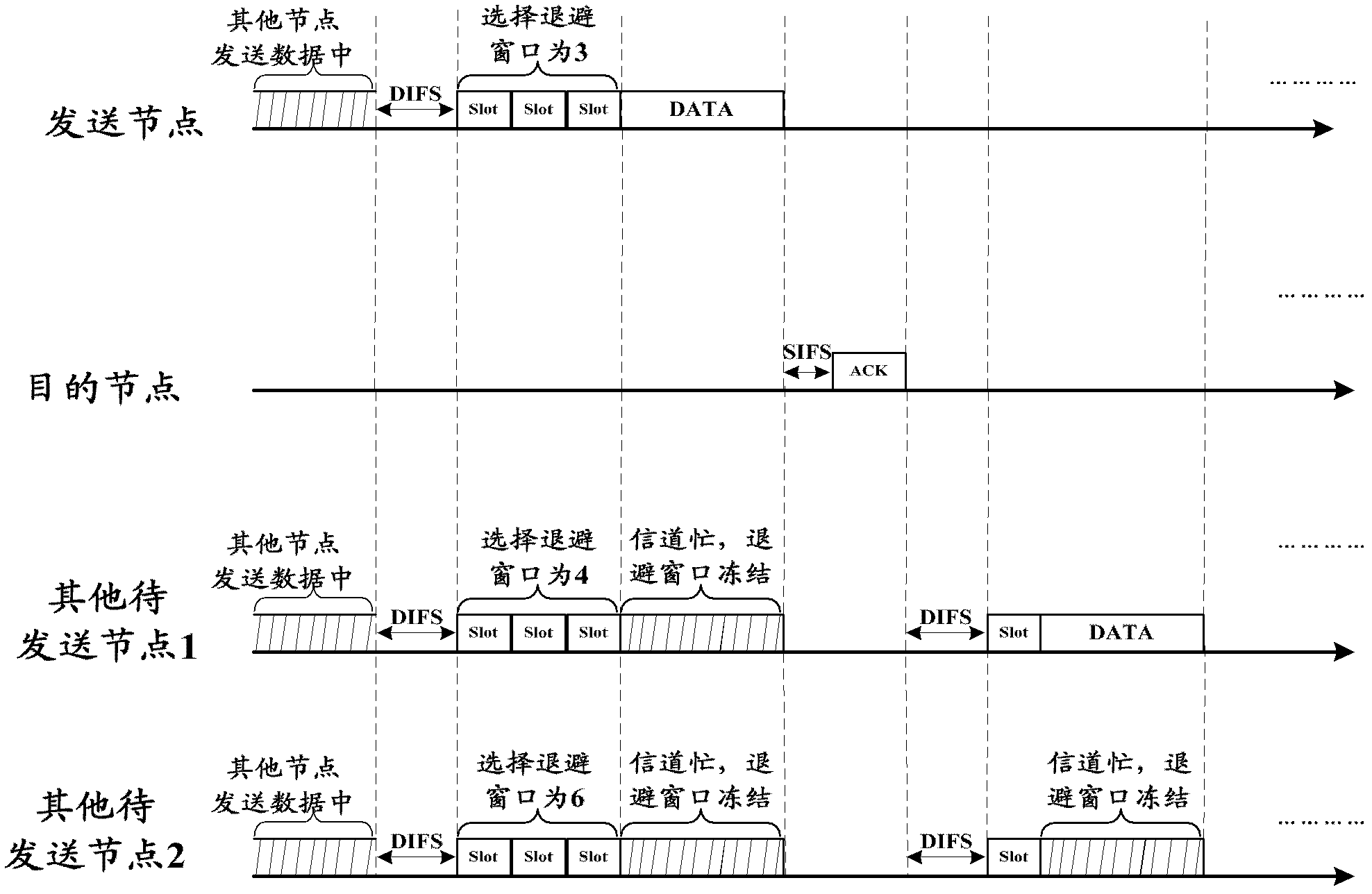
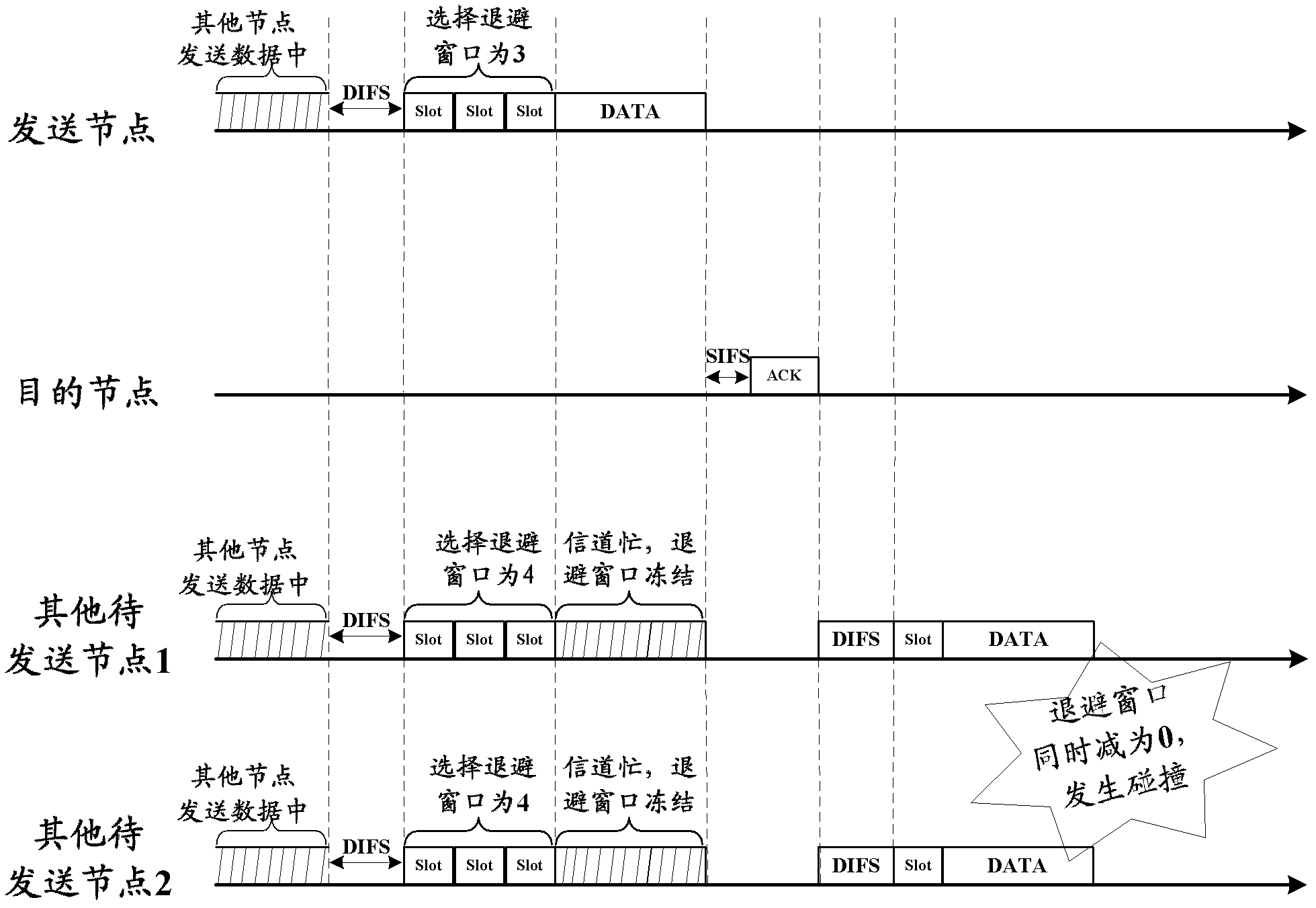
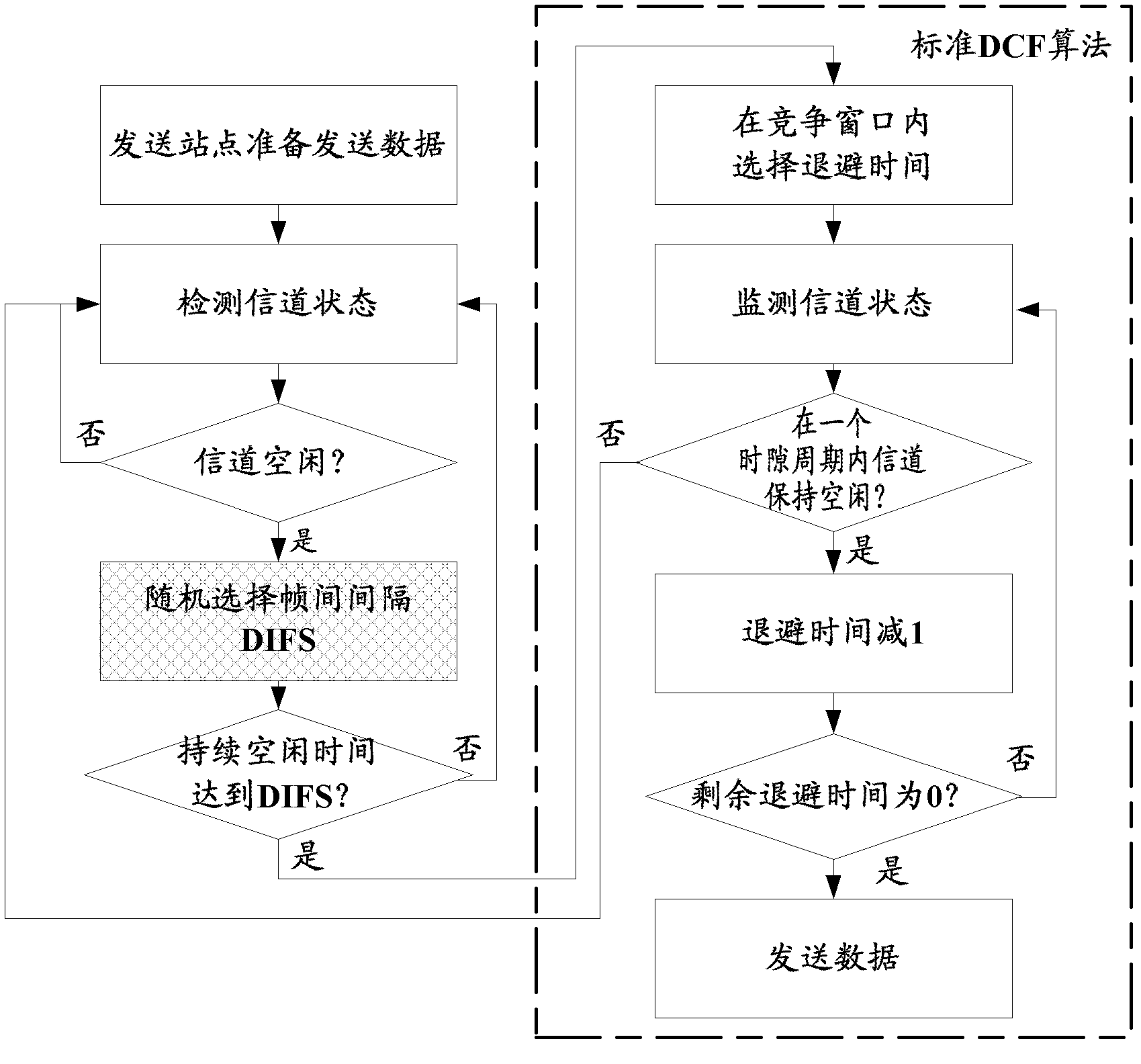
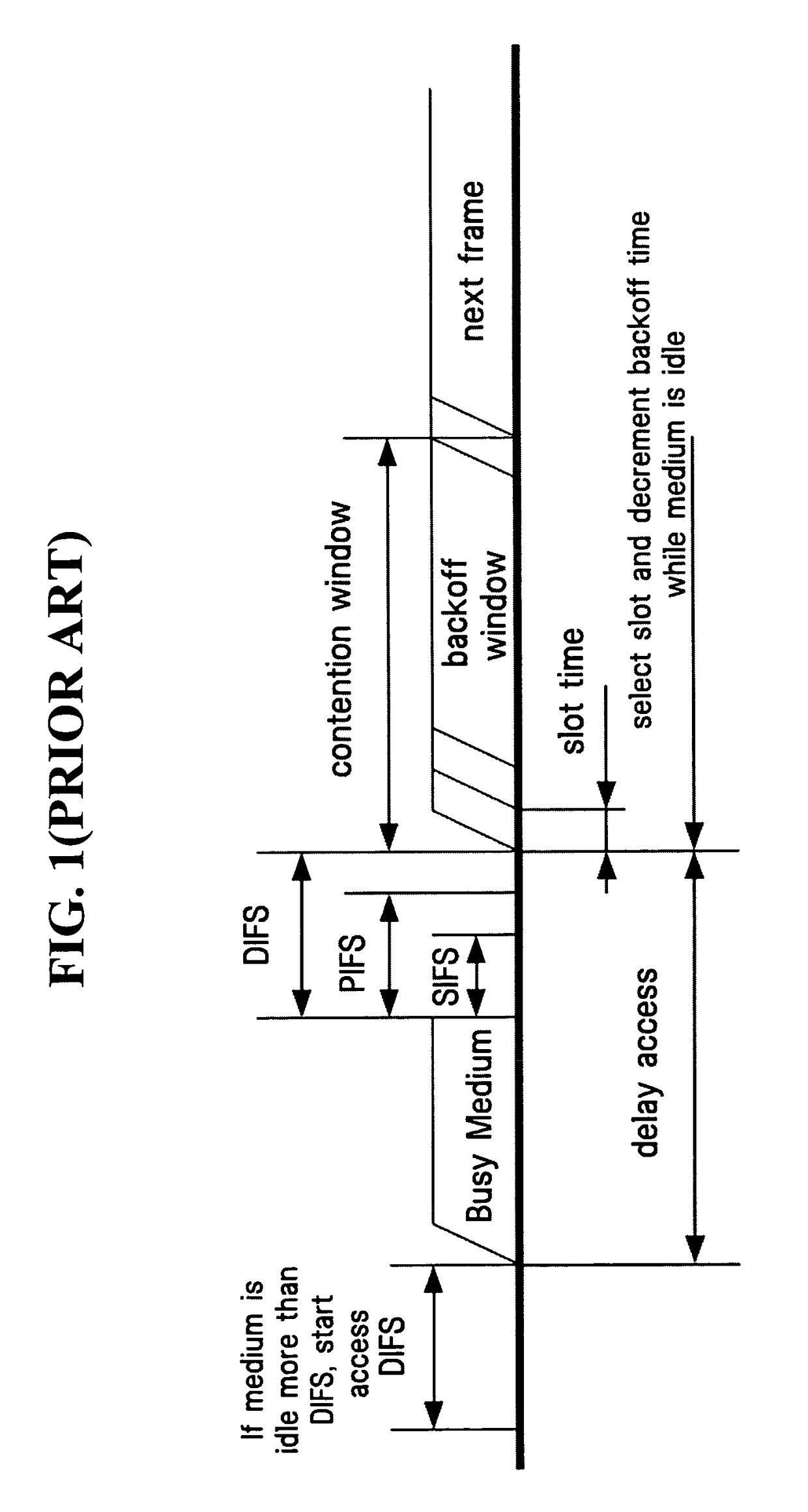
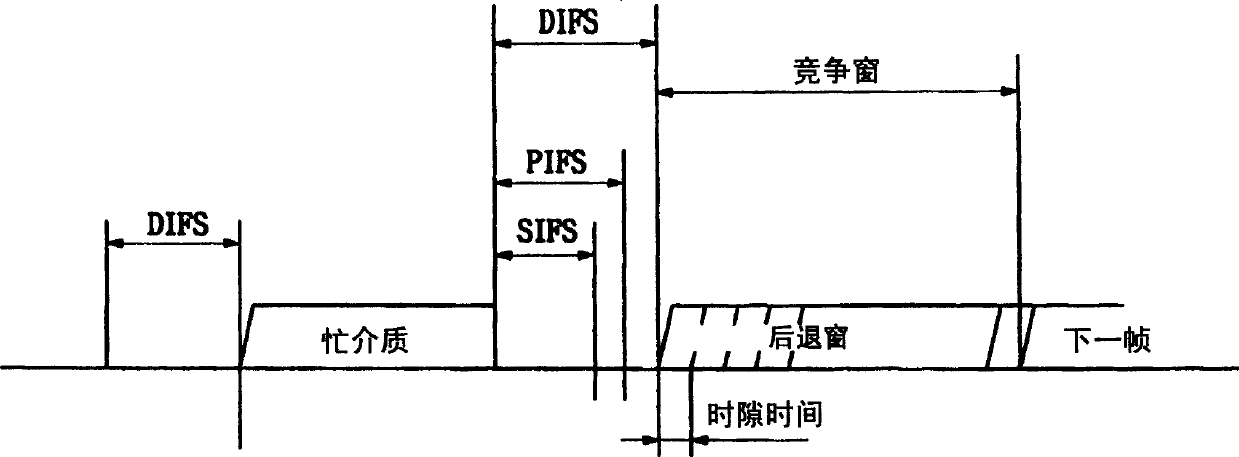
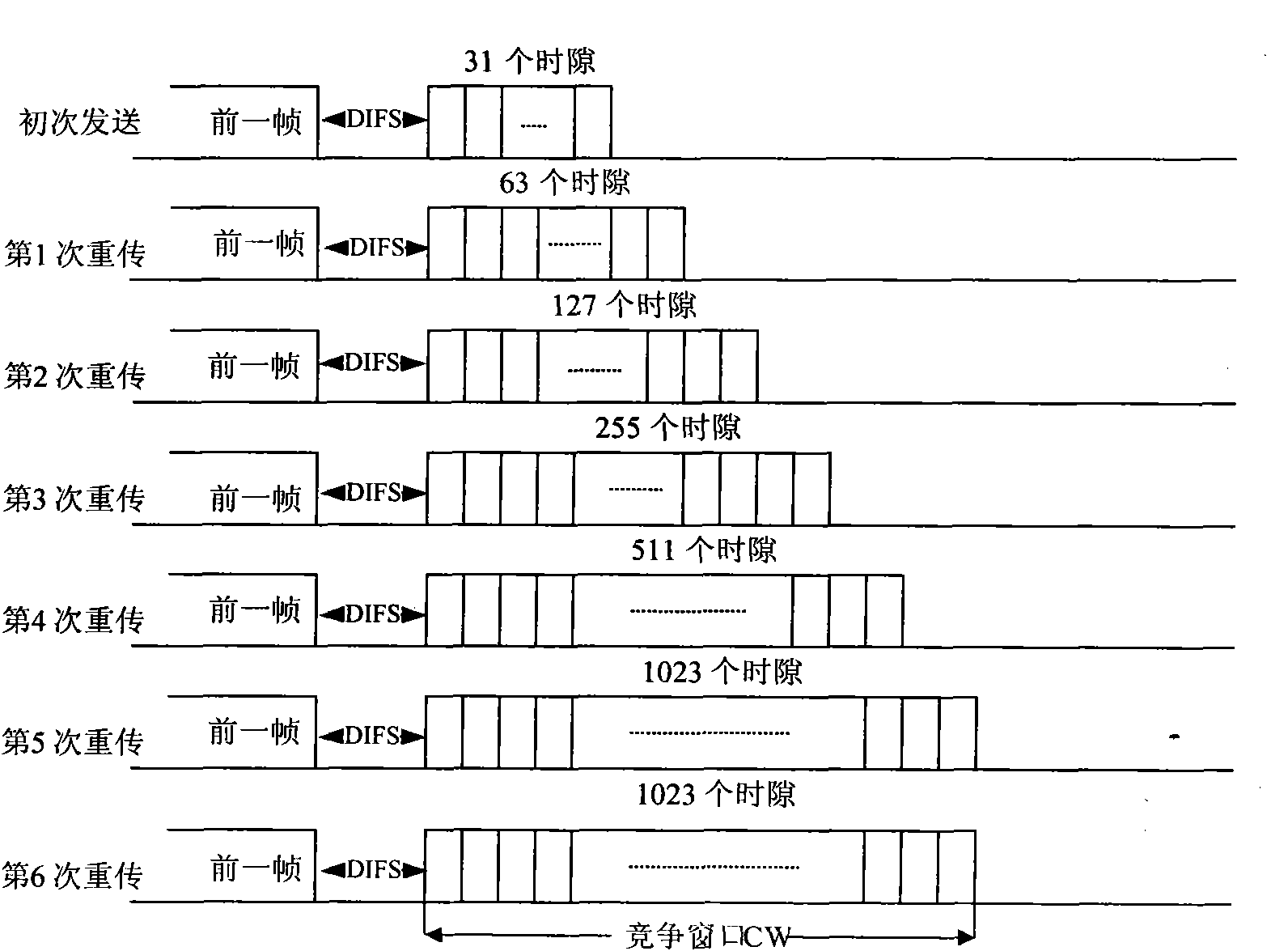
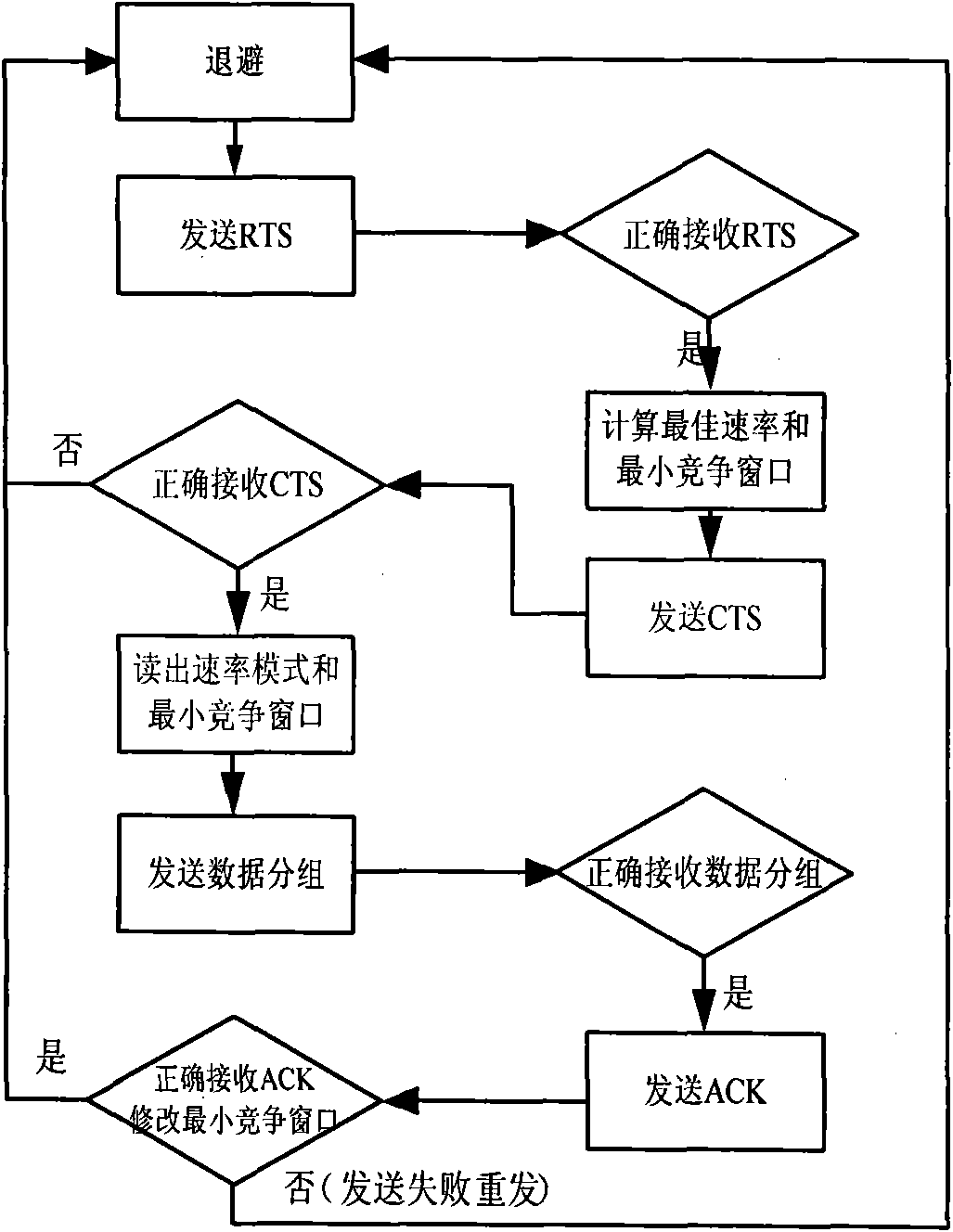
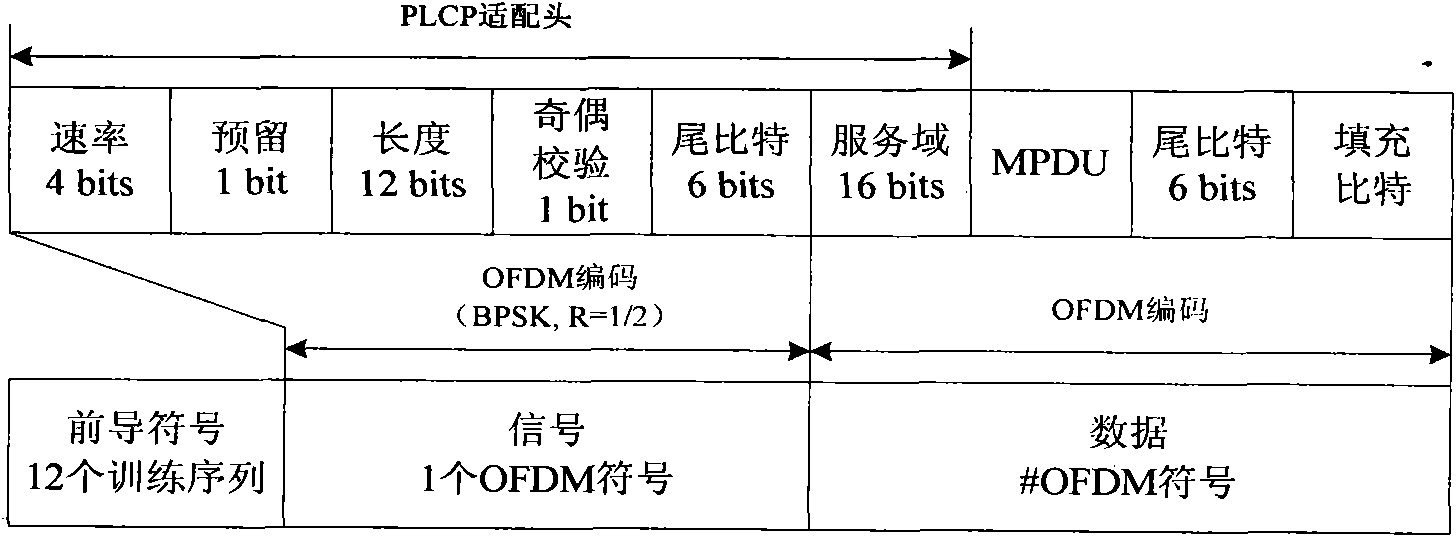
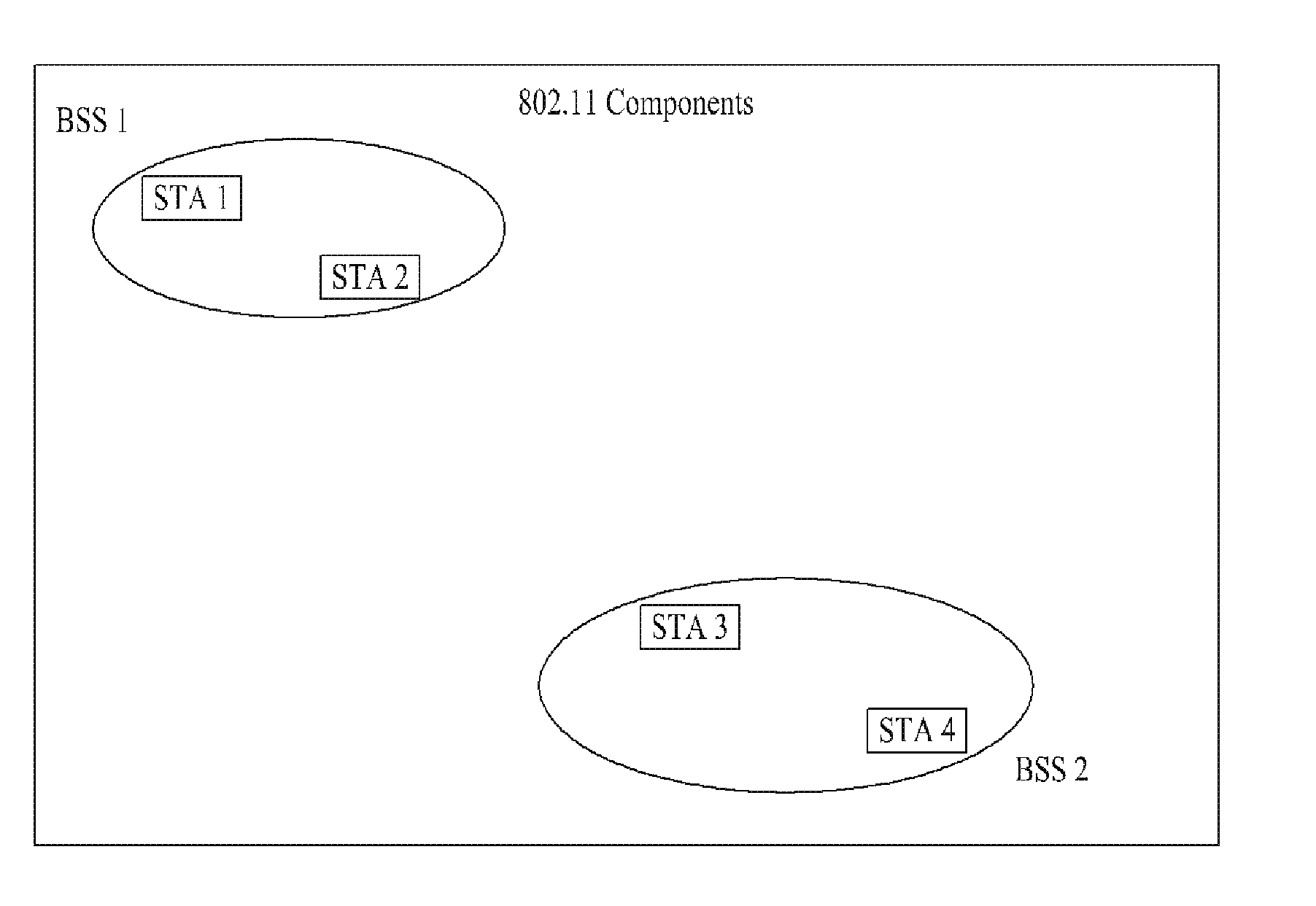
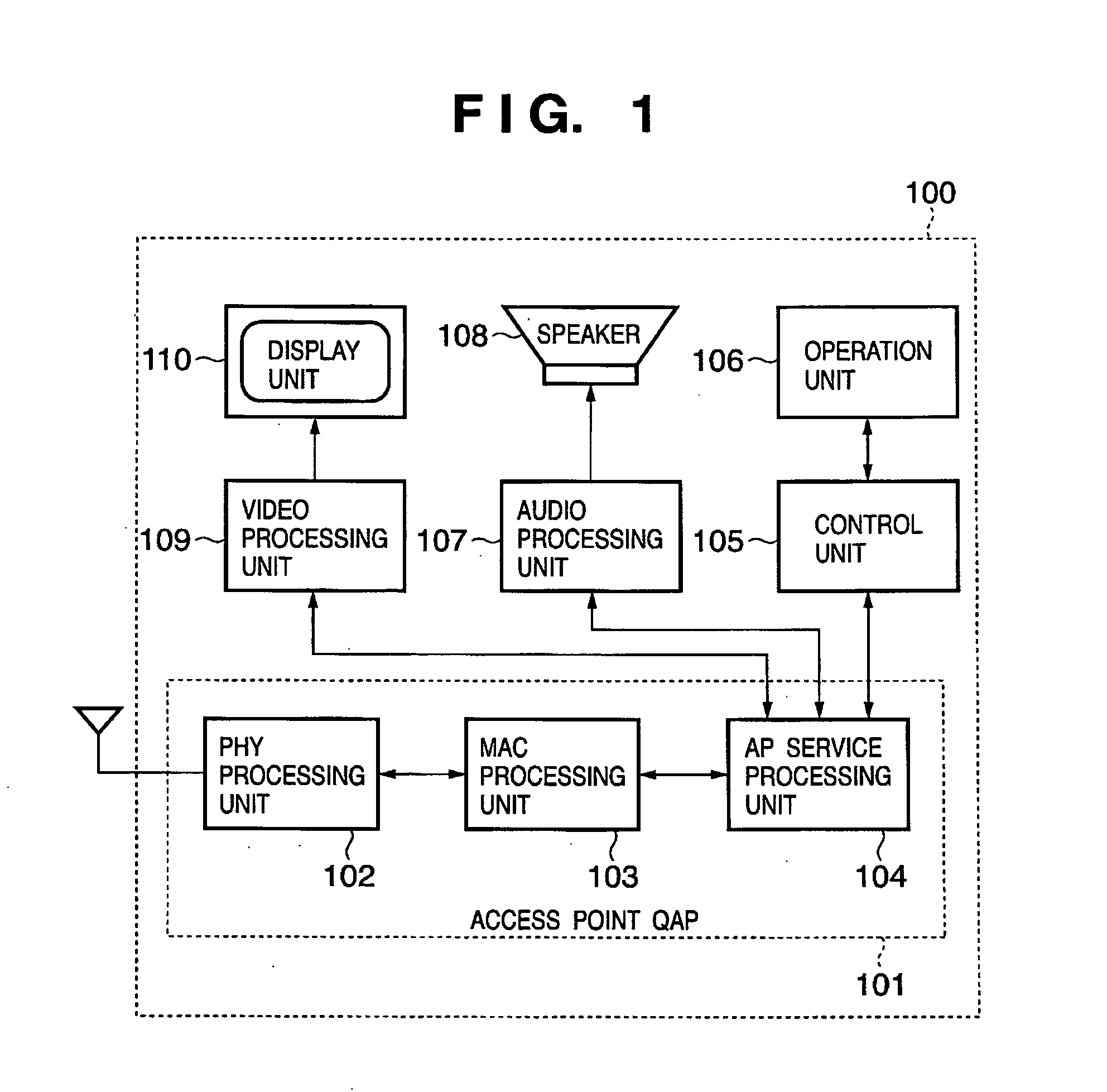
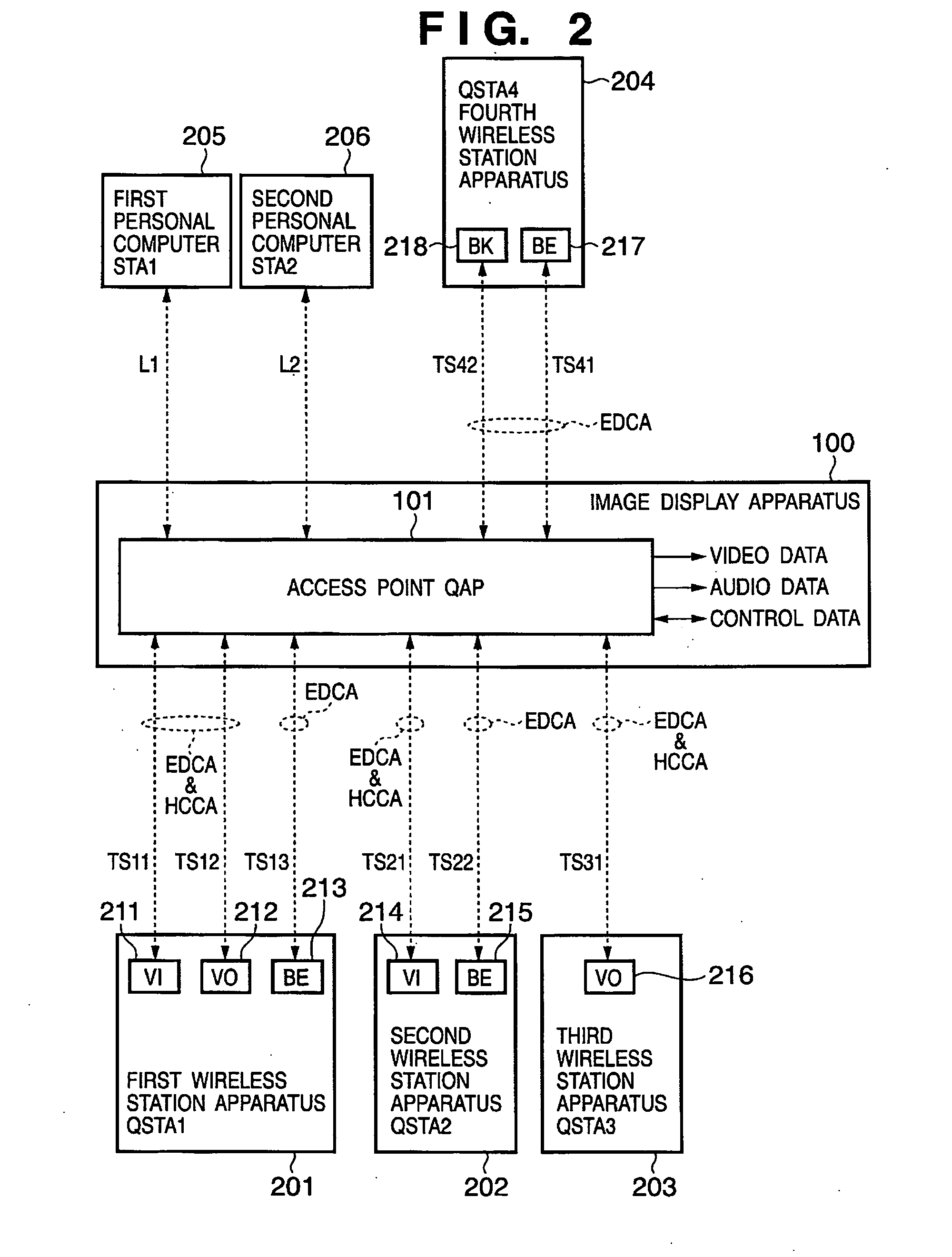
Distributed coordination function (DCF) is the fundamental medium access control (MAC) technique of the IEEE 802.11-based WLAN standard (including Wi-Fi). DCF employs a carrier-sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) with binary exponential backoff algorithm. DCF requires a station wishing to transmit to listen for the channel status for a DIFS interval. If the channel is found busy during the DIFS interval, the station defers its transmission.
Method and system for improving throughput over wireless local area networks with mode switching
InactiveUS6990116B1Improve throughputNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexDistributed coordination functionStation
A method and system for increasing the overall network throughput over a wireless local area network (WLAN). Specifically, in one embodiment of the present invention, the dynamic switching between the Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) and Point Coordination Function IEEE 802.11 access modes is determined according to the load conditions over the WLAN in a method and system. Stations and access points within a WLAN monitor conditions within the network to determine which access mechanism is most optimum for the current load conditions. Some factors to consider in determining the load conditions include but are not limited to the number of transmissions, number of receptions, and number of collisions.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
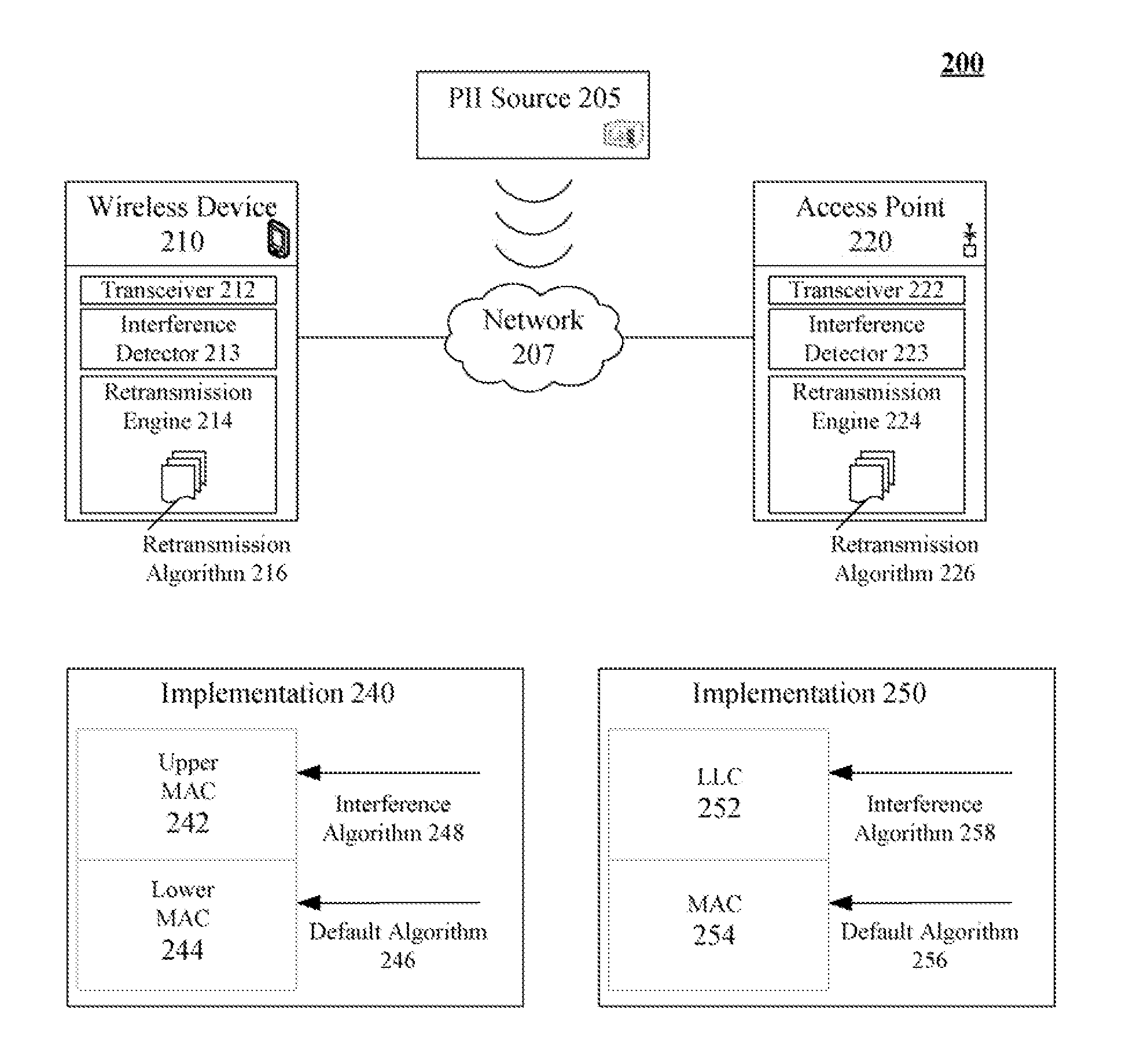
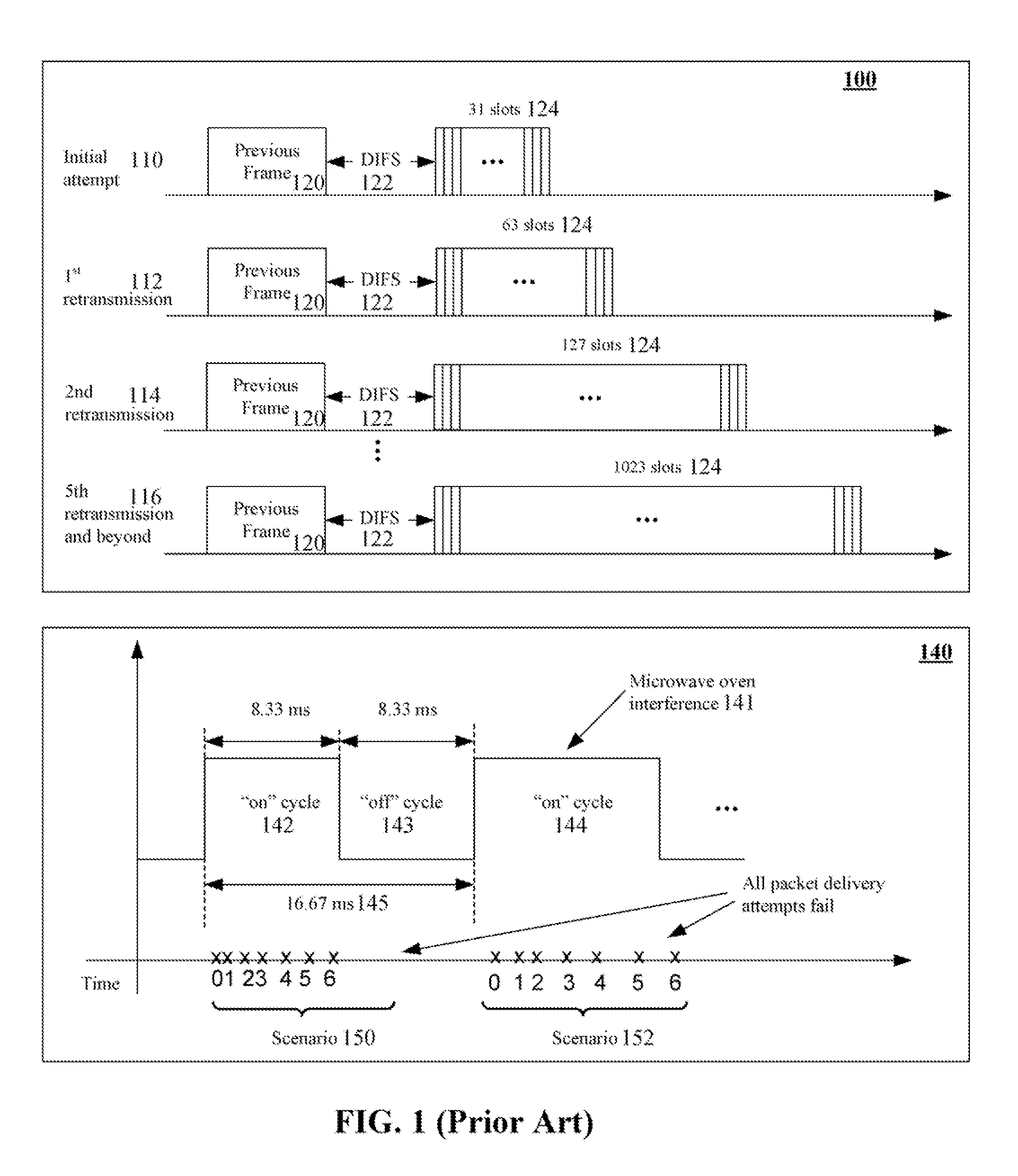
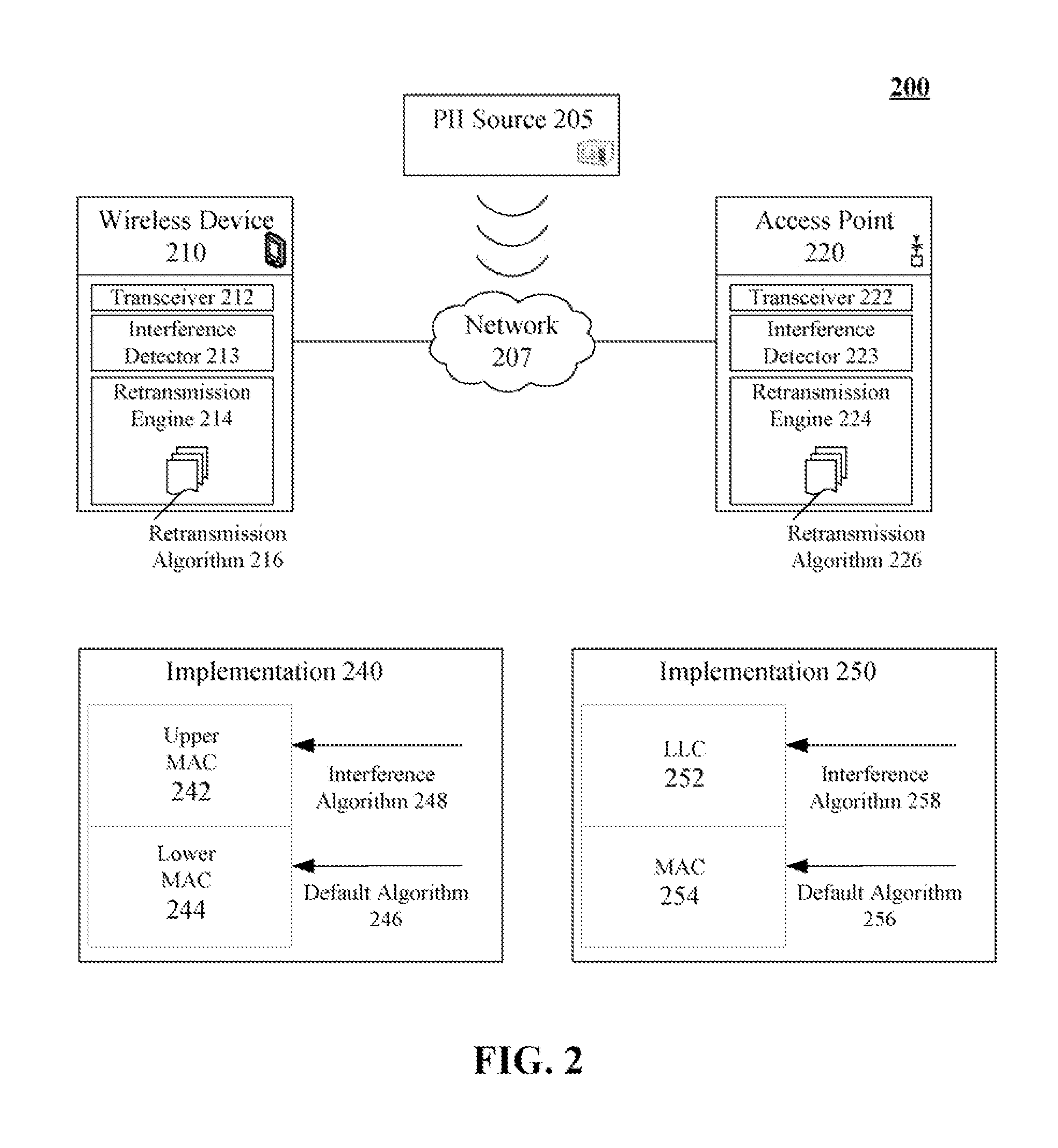
Retransmission scheme for maintaining performance for wireless communications in the presence of periodic intermittent interference
InactiveUS20080144550A1Enhanced PII performanceExtended durationError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementDistributed coordination functionMicrowave oven
The invention can establish a default retransmission algorithm and an interference retransmission algorithm. The default retransmission algorithm can be a Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) based algorithm implemented in a MAC layer in conformance with an IEEE 802.11 based standard. The minimum cumulative back-off time for the default transmission algorithm can be less a minimum cumulative back-off time for the interference retransmission algorithm. The minimum cumulative back-off time for the interference retransmission algorithm can be greater than an on-cycle of the PII and less than a sum of the one and off-cycles of the PII (e.g., between ˜8.3 ms and ˜16.7 ms for microwave oven generated PII). A determination can be made whether periodic intermittent interference is present. If so, the default retransmission algorithm can be automatically utilized for wireless data conveyances. When PII is present, the interference retransmission algorithm can be automatically utilized.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
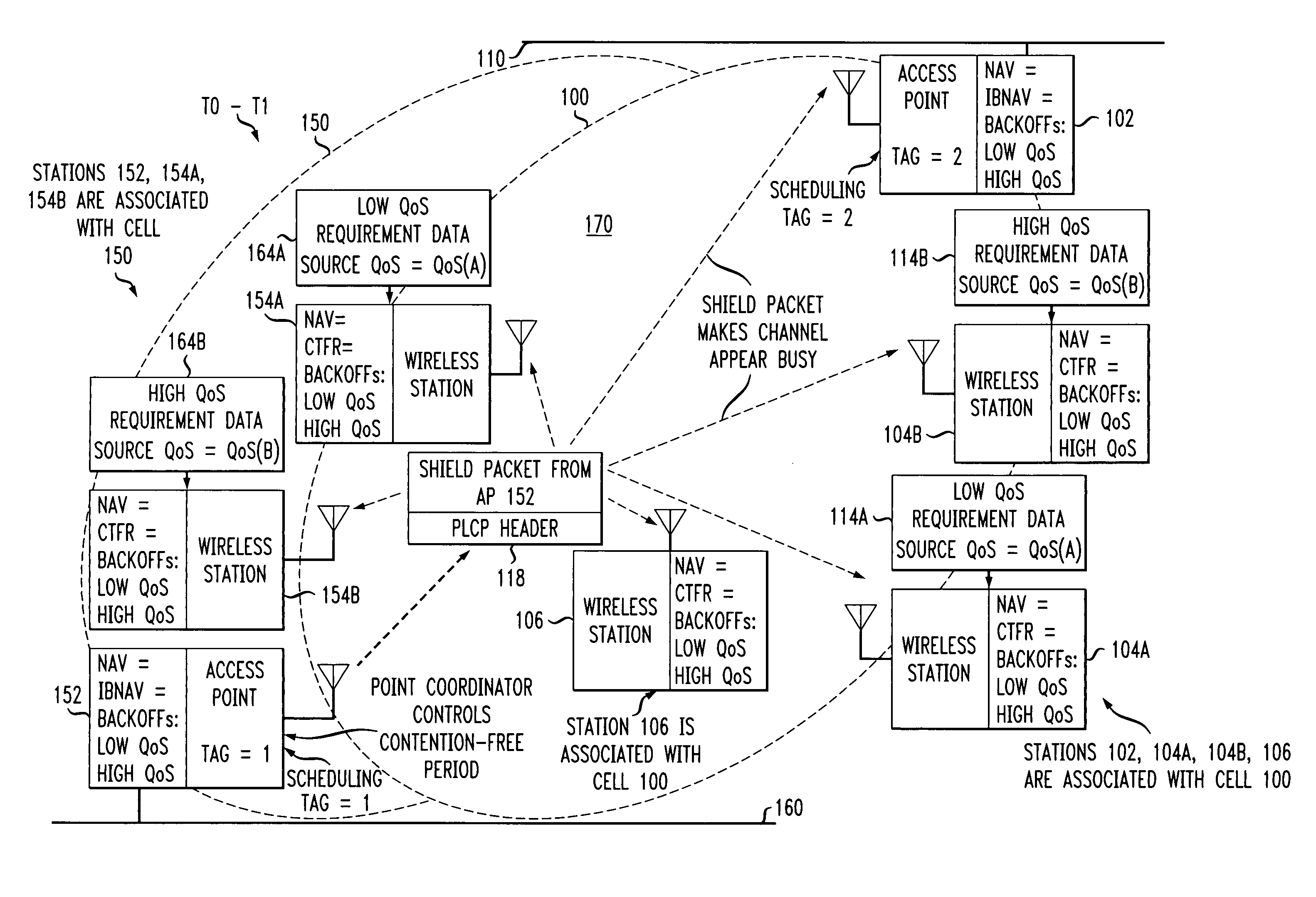
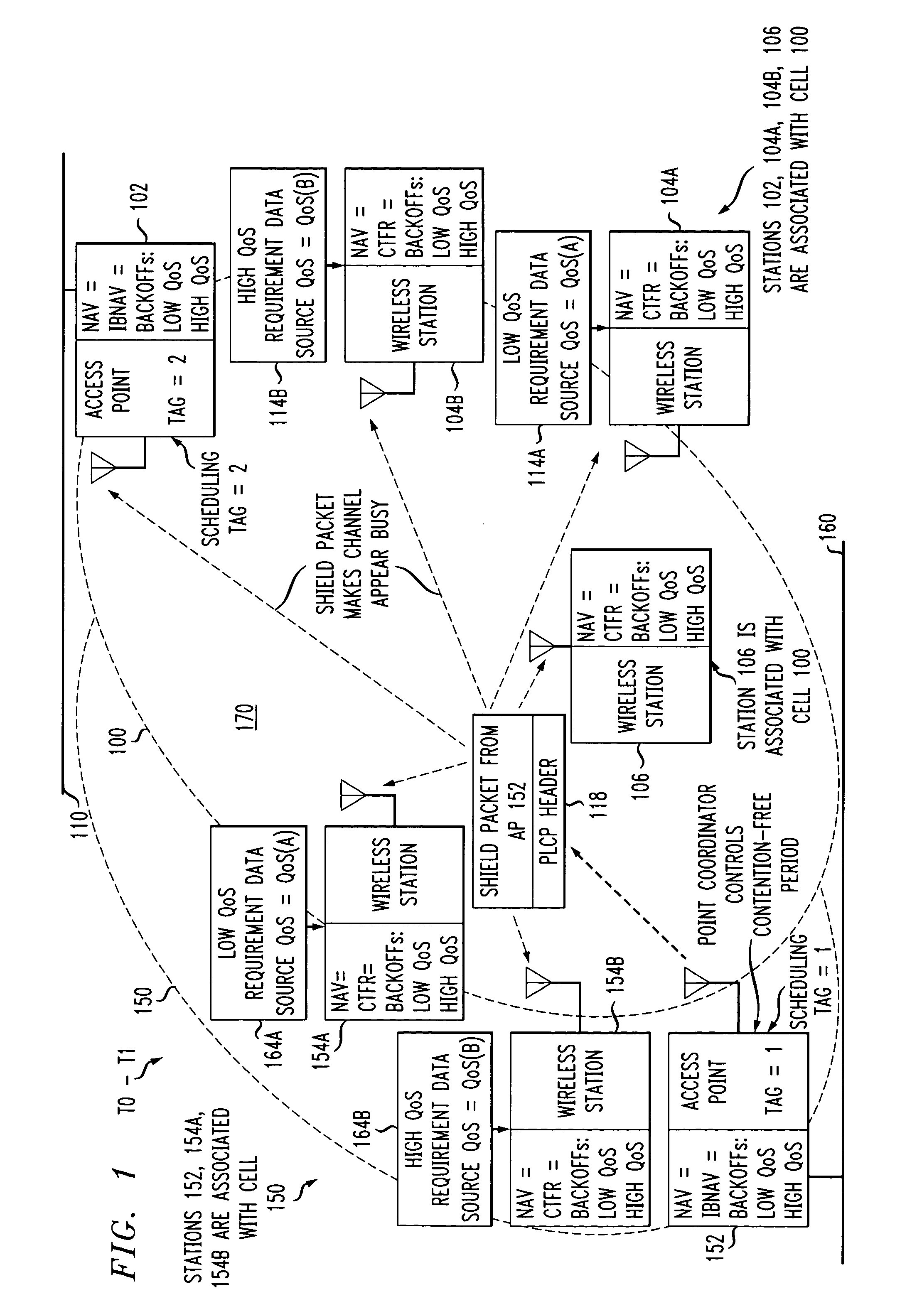
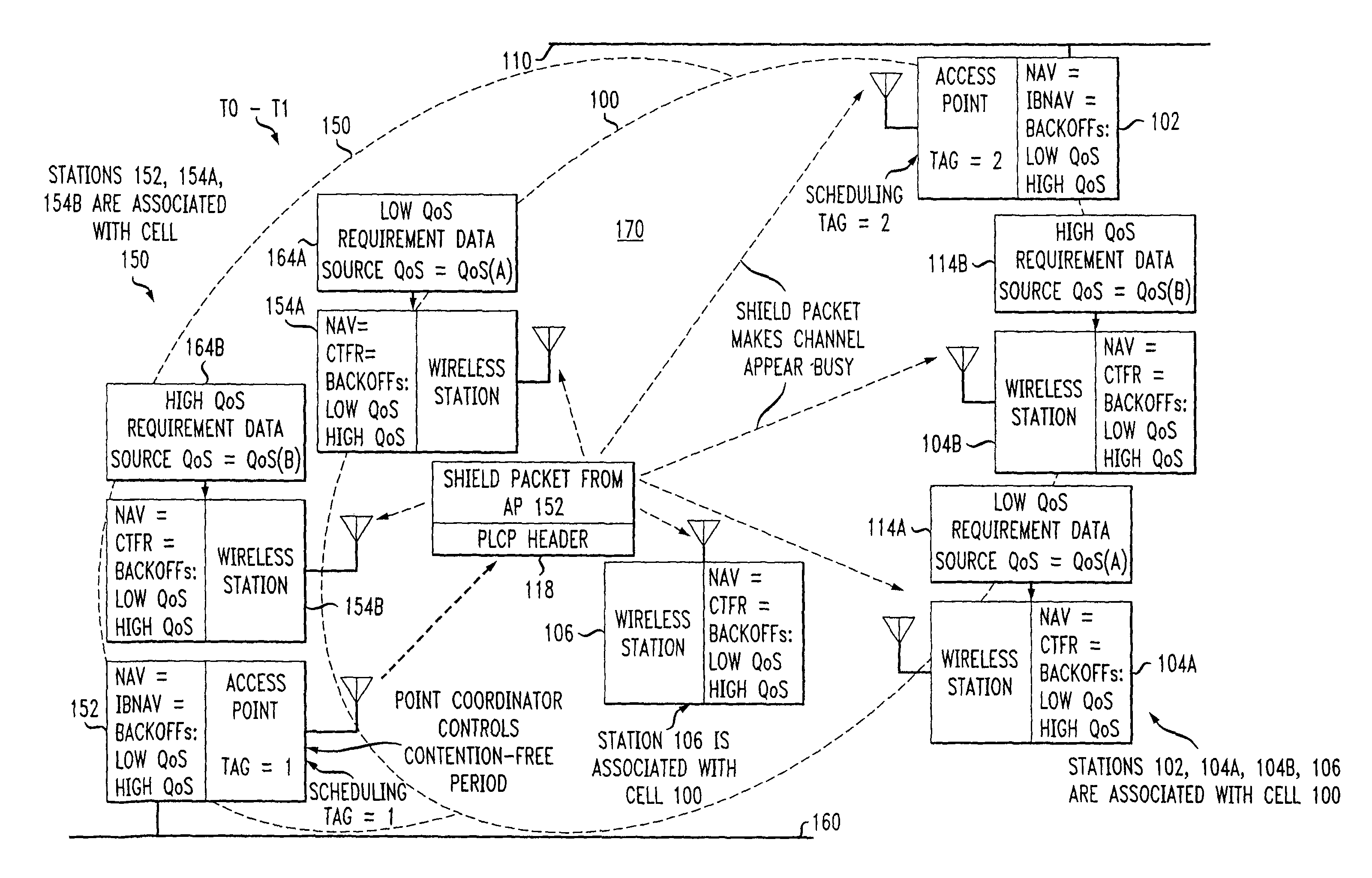
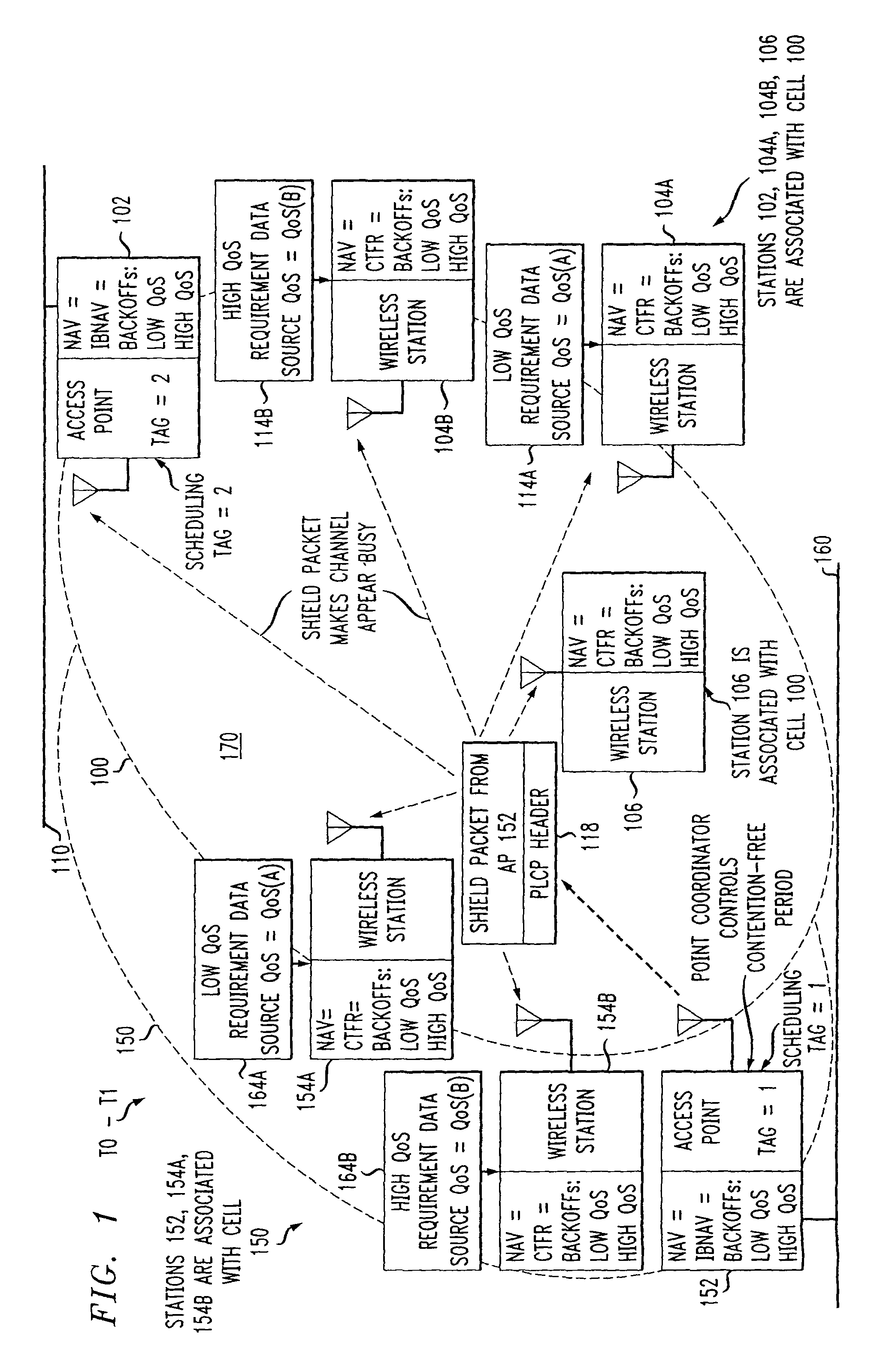
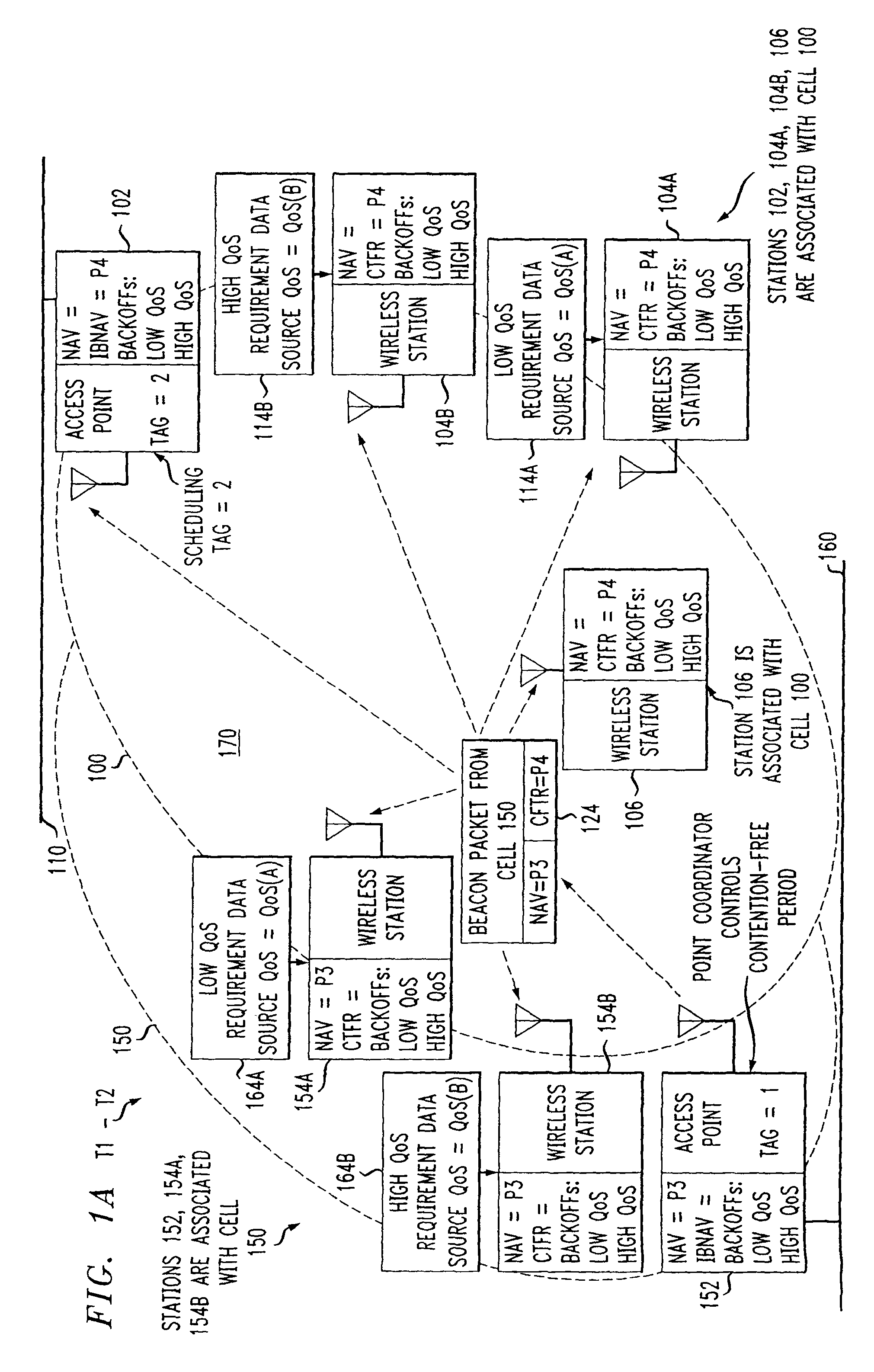
Preemptive packet for maintaining contiguity in cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) contention-free sessions
InactiveUS7245605B2Reduce usageSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesTraffic capacityDistributed coordination function
An access point transmits a preemptive peg packet when it has no data to transmit in order to maintain the contiguity of its transmission timing position with respect to the timing position of other contention-free sessions (CFS) transmitted by other access points in an existing, periodic sequence. The cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) method establishes the transmission timing position of contention-free sessions (CFS) between overlapping first and second wireless LAN cells contending for the same medium. Each cell includes a respective plurality of member stations. If an access point has no traffic, it will transmit a short, preemptive pegging packet and reset its backoff timer. In this manner, no gaps longer than the distributed coordination function (DCF) Interframe Space (DIFS) are left idle. This prevents other stations from using DCF contention to seize the channel, until all access points have completed one contention-free session (CFS) per periodic cycle.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
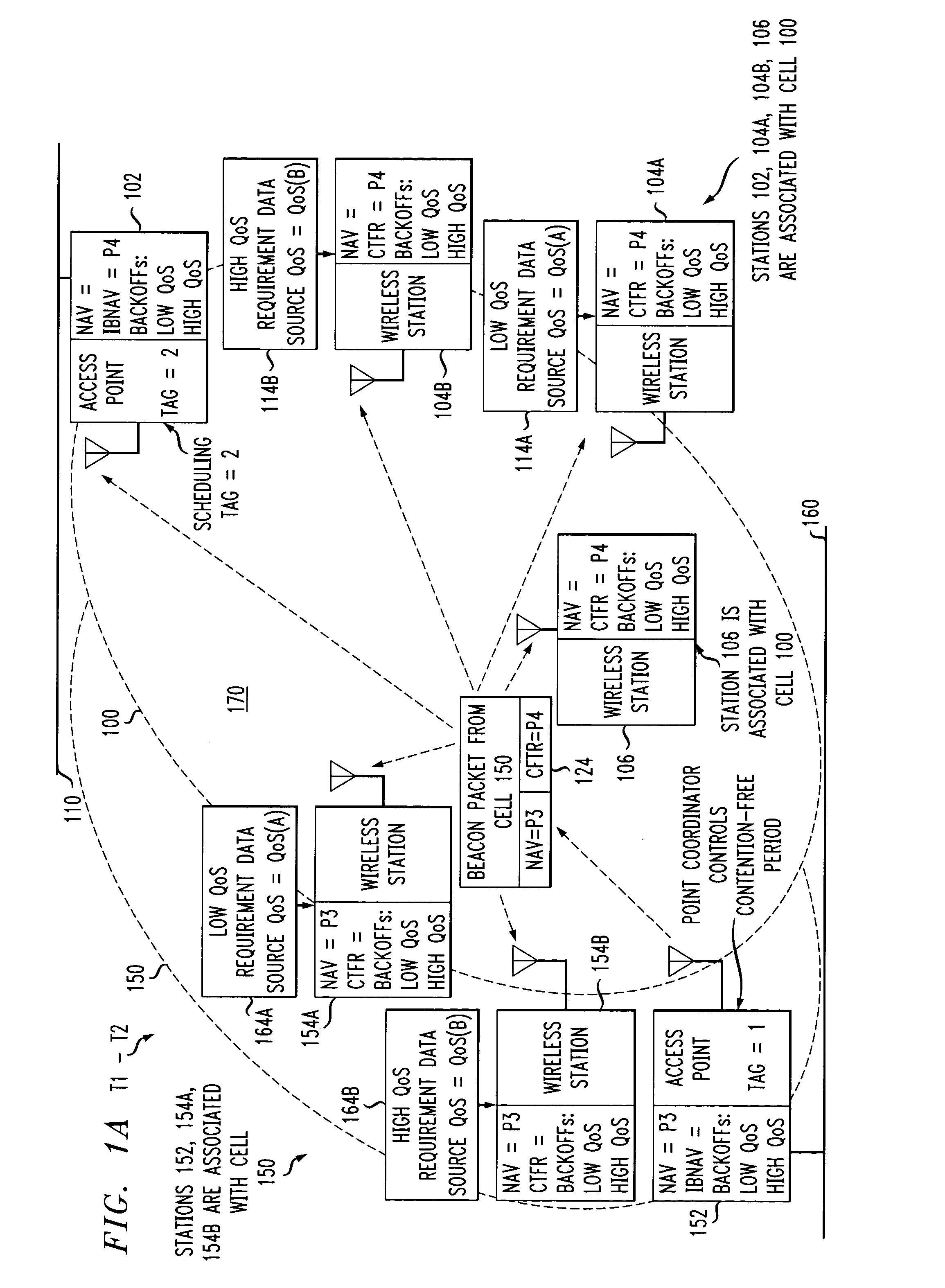
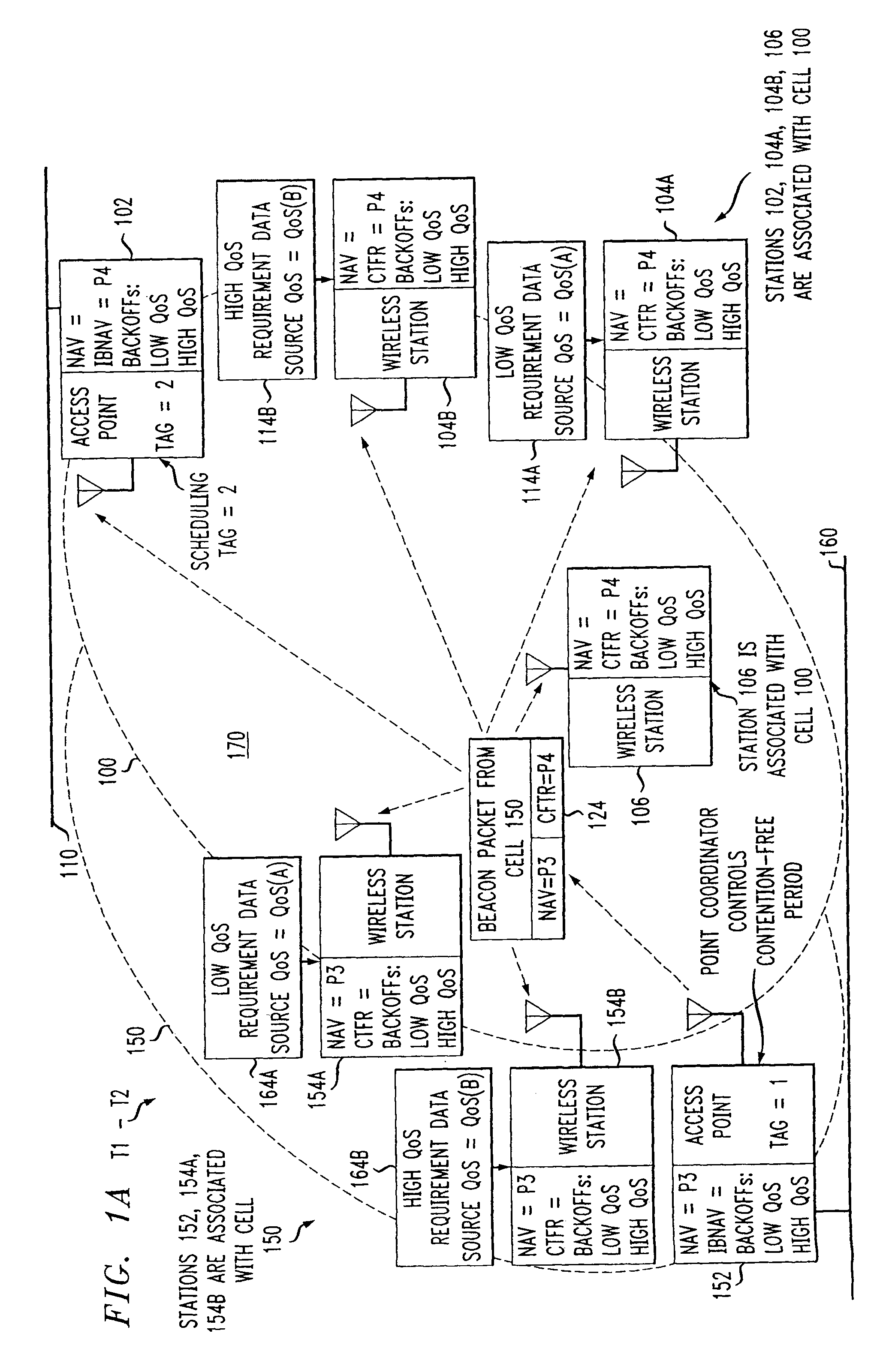
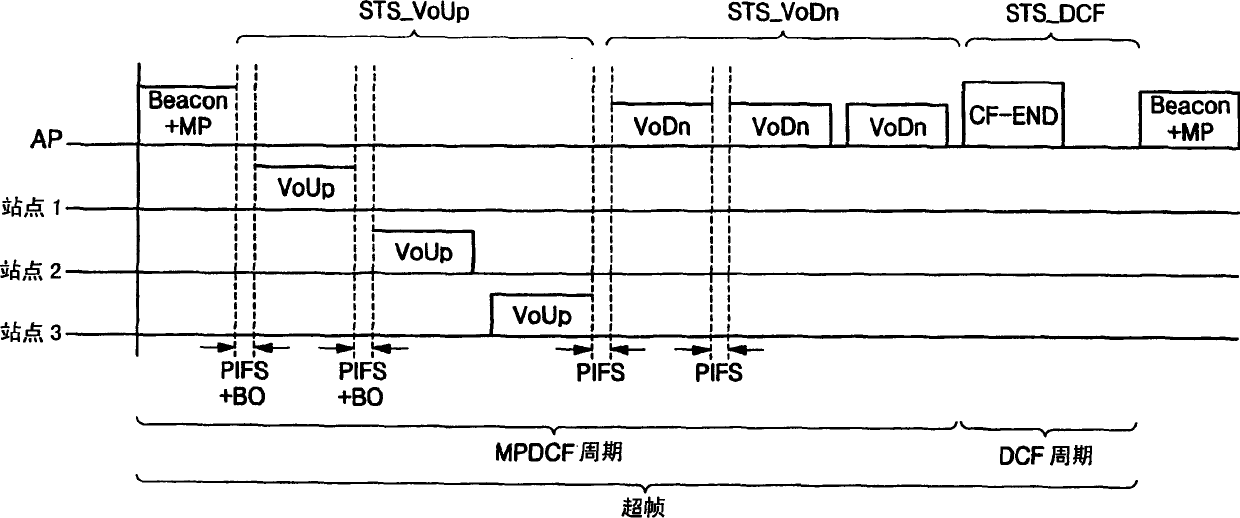
Method and system for providing a priority-based, low-collision distributed coordination function using a super-frame structure
ActiveUS20060034199A1Great probability of successful transmissionSimple methodTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationDistributed coordination functionDistribute coordination function
A method for providing a priority-based, low-collision distributed coordination function (DCF) in a wireless network is provided. The network includes an access point and a plurality of stations. The method includes receiving at a first station a super-frame from the access point. The super-frame is operable to define a service period for each of the stations. A priority for the first station is determined based on the super-frame. A back-off time is selected for the first station based on the priority.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Wireless communication method following DCF rule
ActiveUS20050157747A1Improve reliabilityNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexDistributed coordination functionTelecommunications
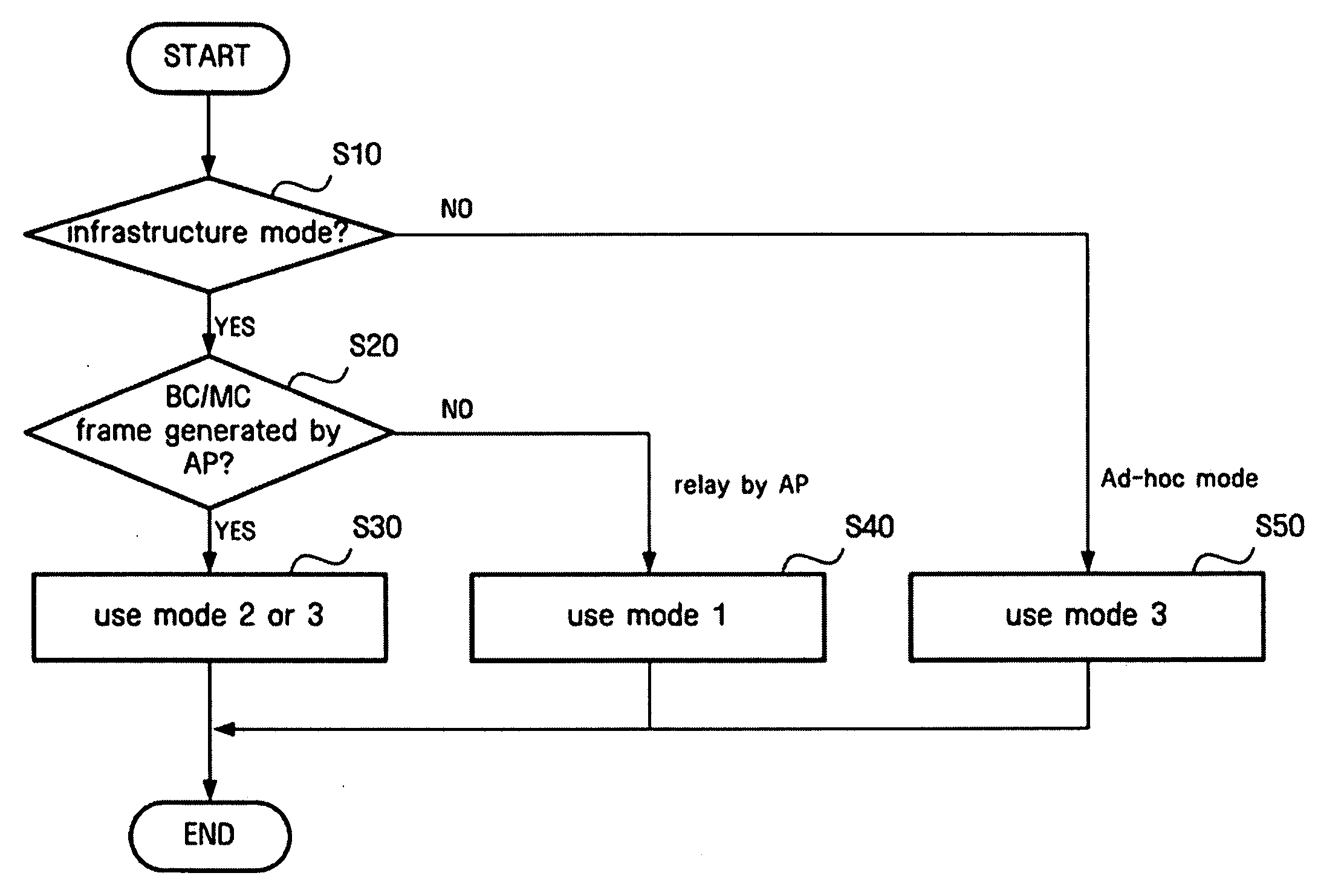
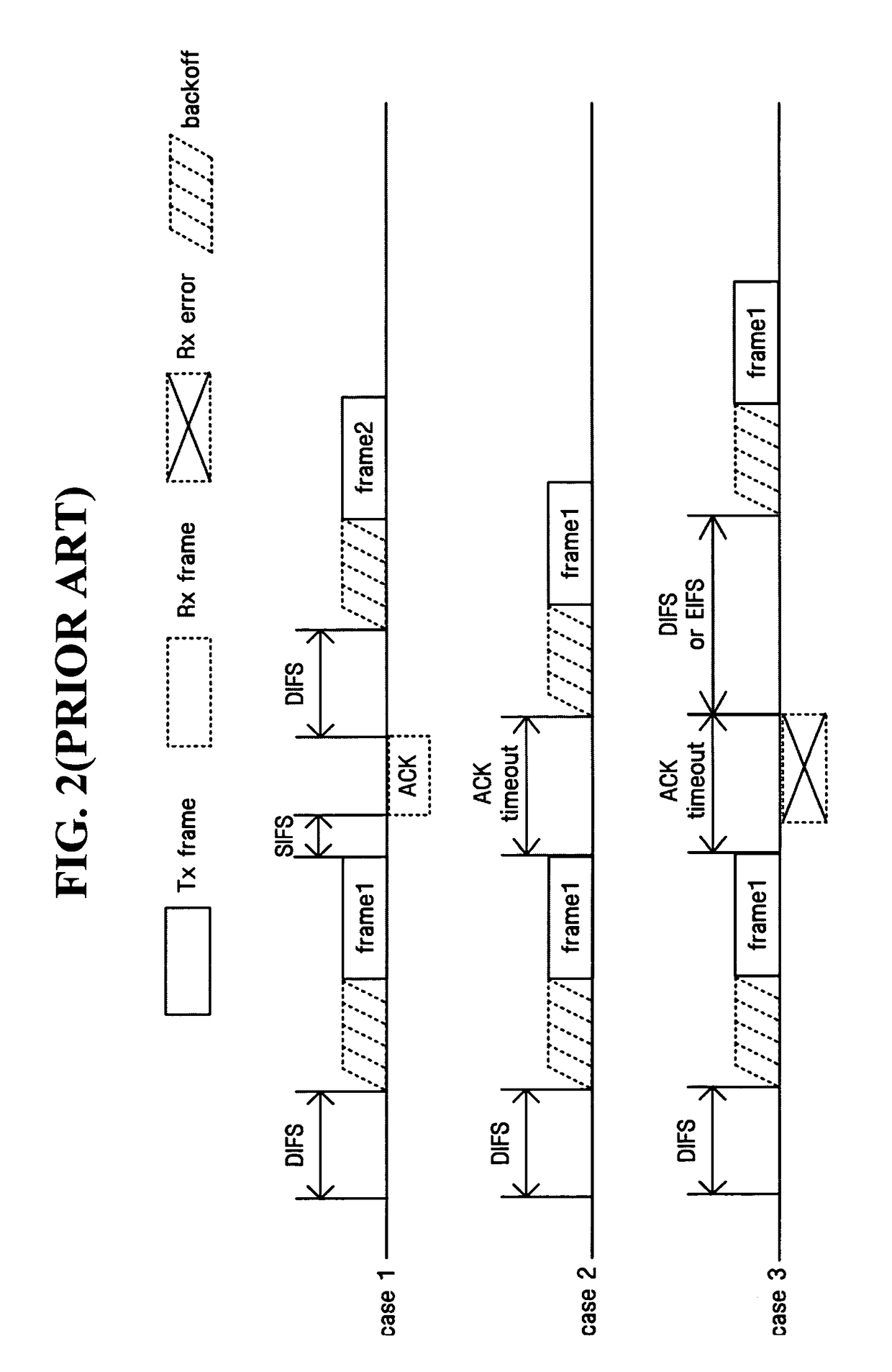
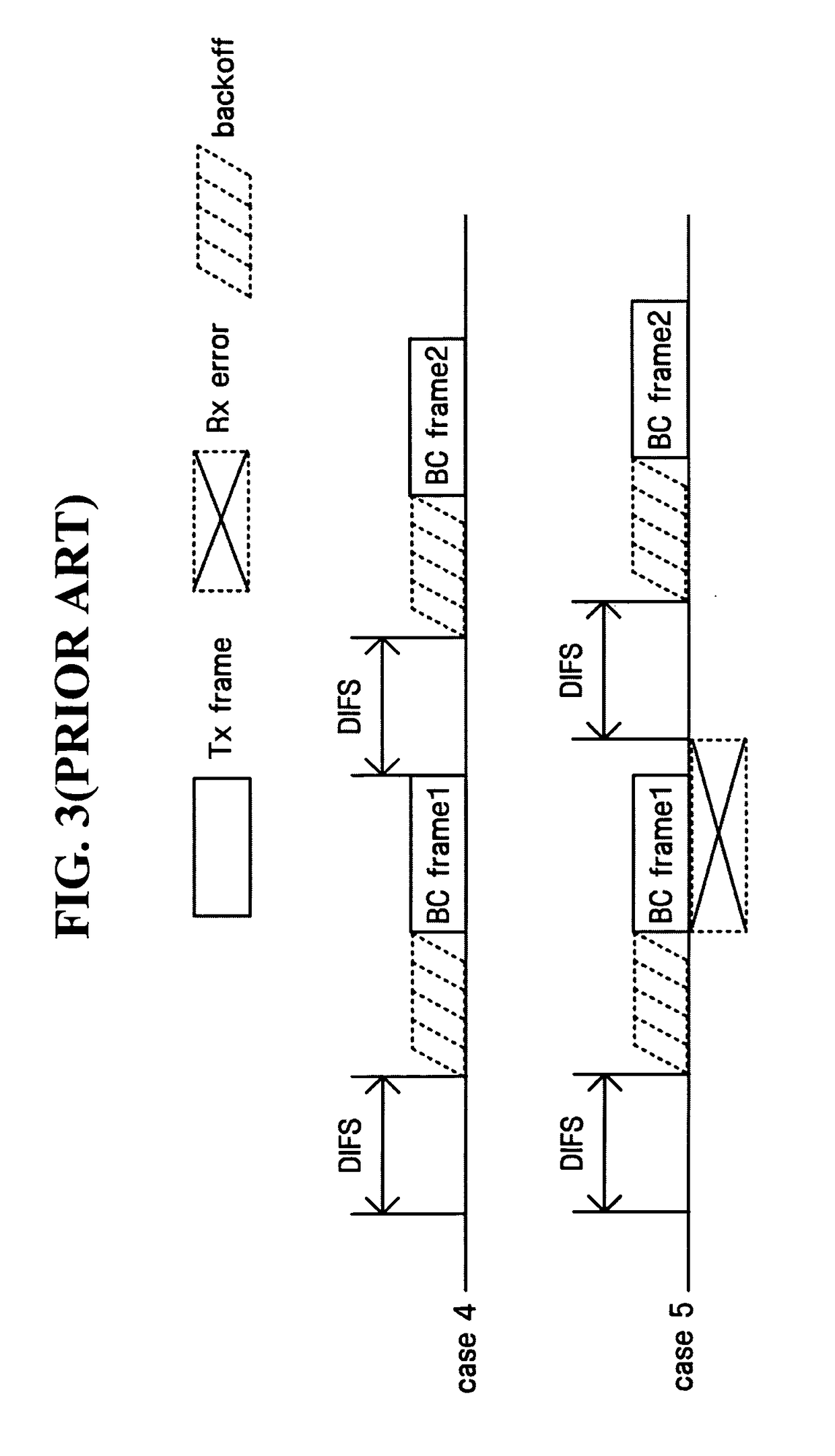
Provided are a method and apparatus which can reduce the possibility of collision with other frames when transmitting a broadcast / multicast frame in a wireless local area network (LAN) following a Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) rule, thereby ensuring reliable transmission. The wireless communication method for sending or receiving a predetermined frame through contention between an access point and one or more stations according to DCF is characterized in that the access point uses the shortest of interframe space (IFS) intervals for access to a wireless medium. Therefore, when wireless LAN STAs operate in a DCF mode, the possibility of collision during broadcast or multicast frame transmission can be reduced while adopting conventional CSMA / CA mechanism, thereby improving reliability in successful frame transmission.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
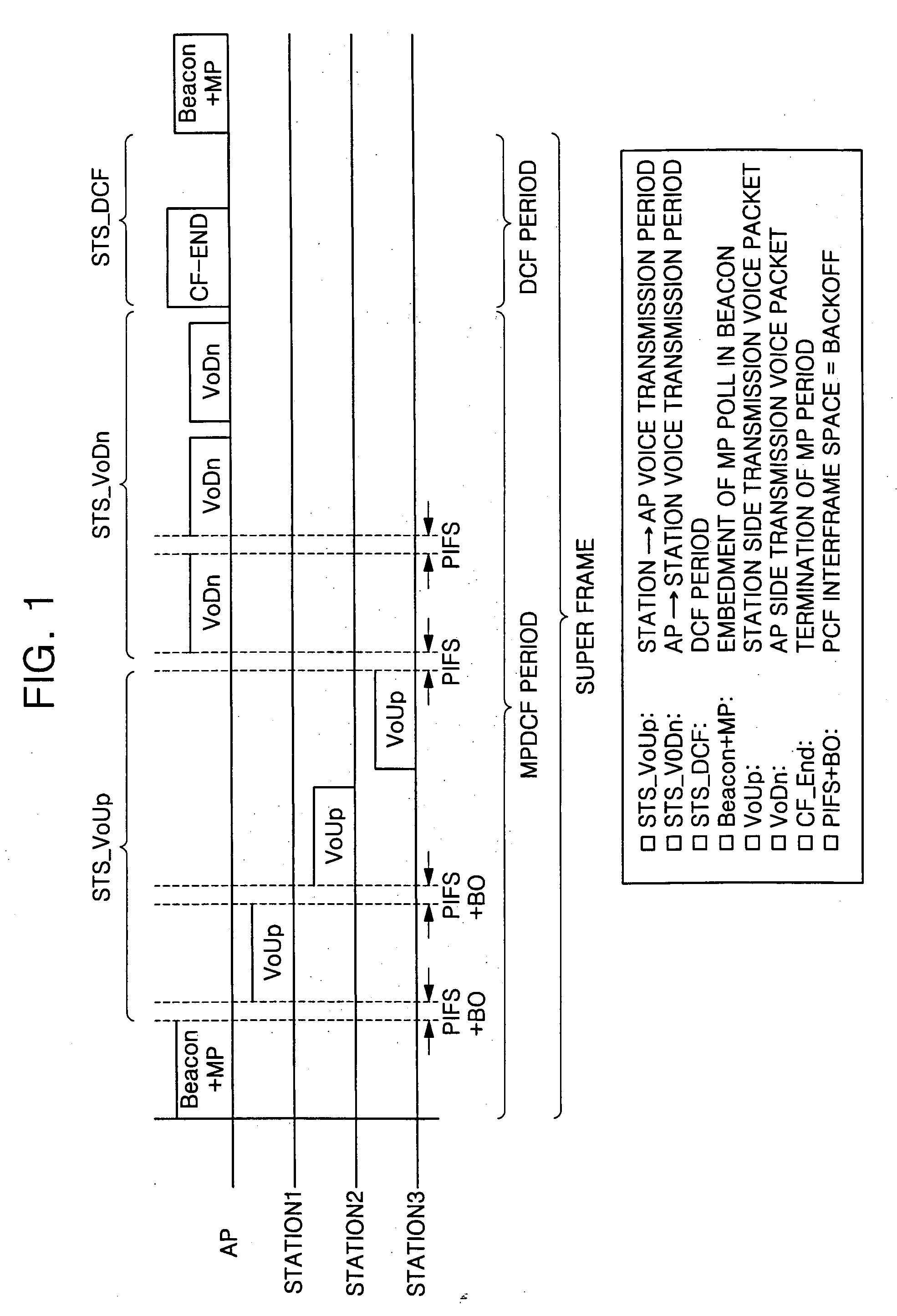
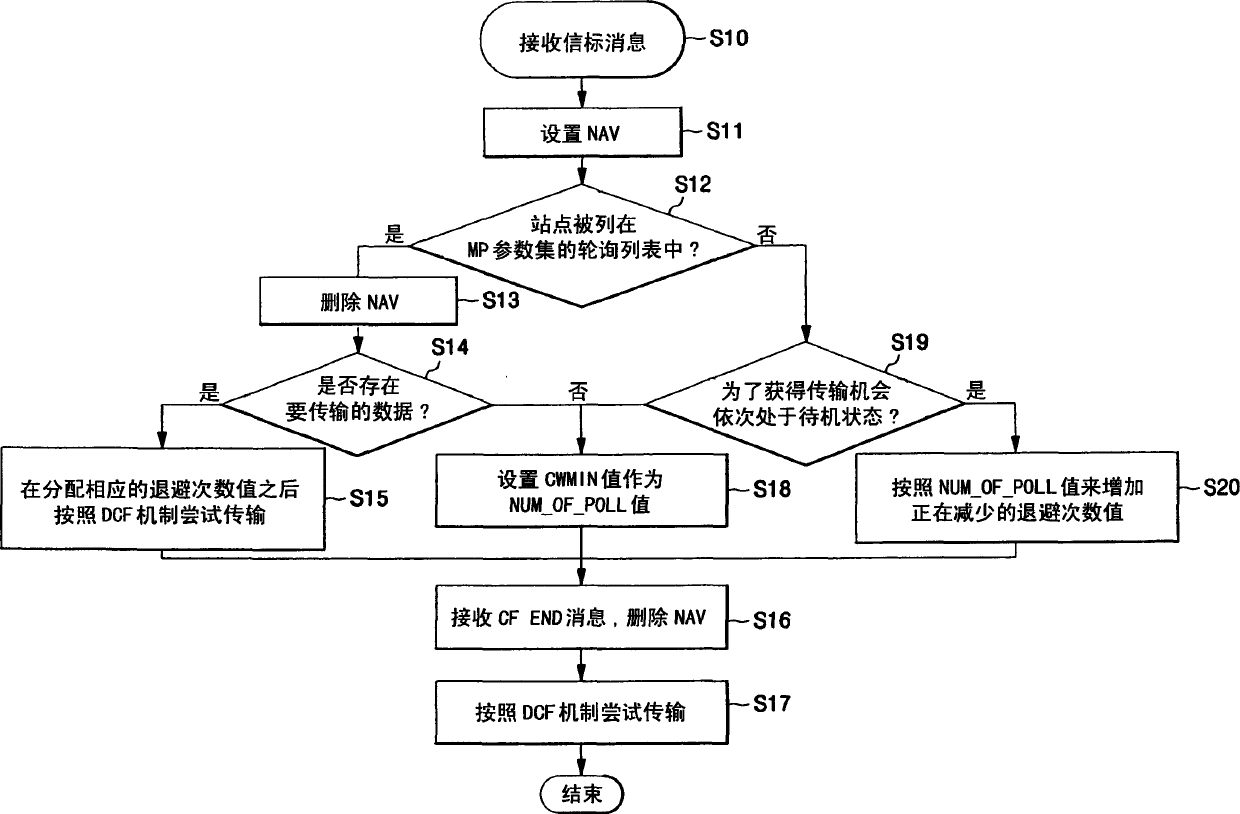
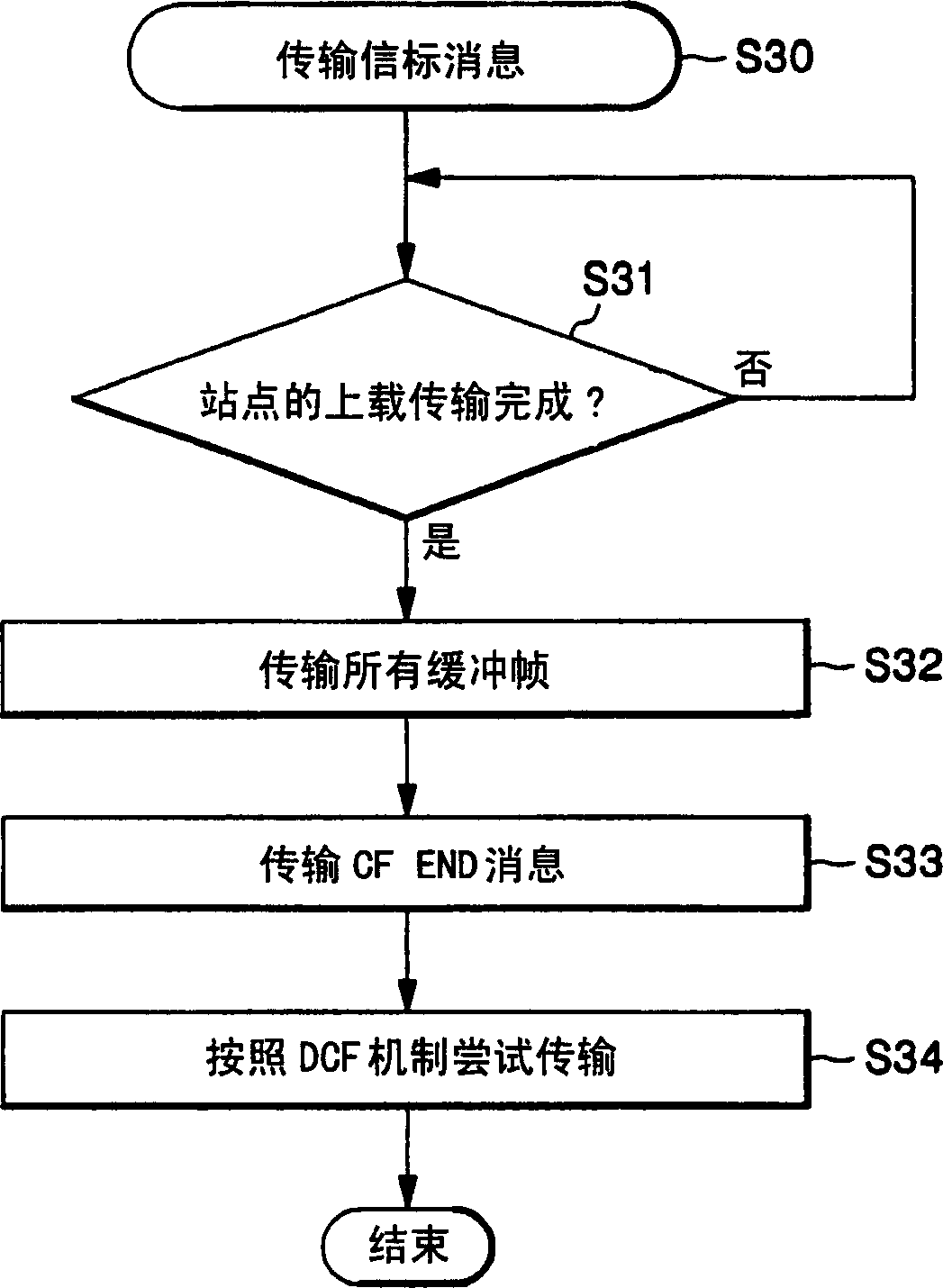
Medium access method for contention and non-contention
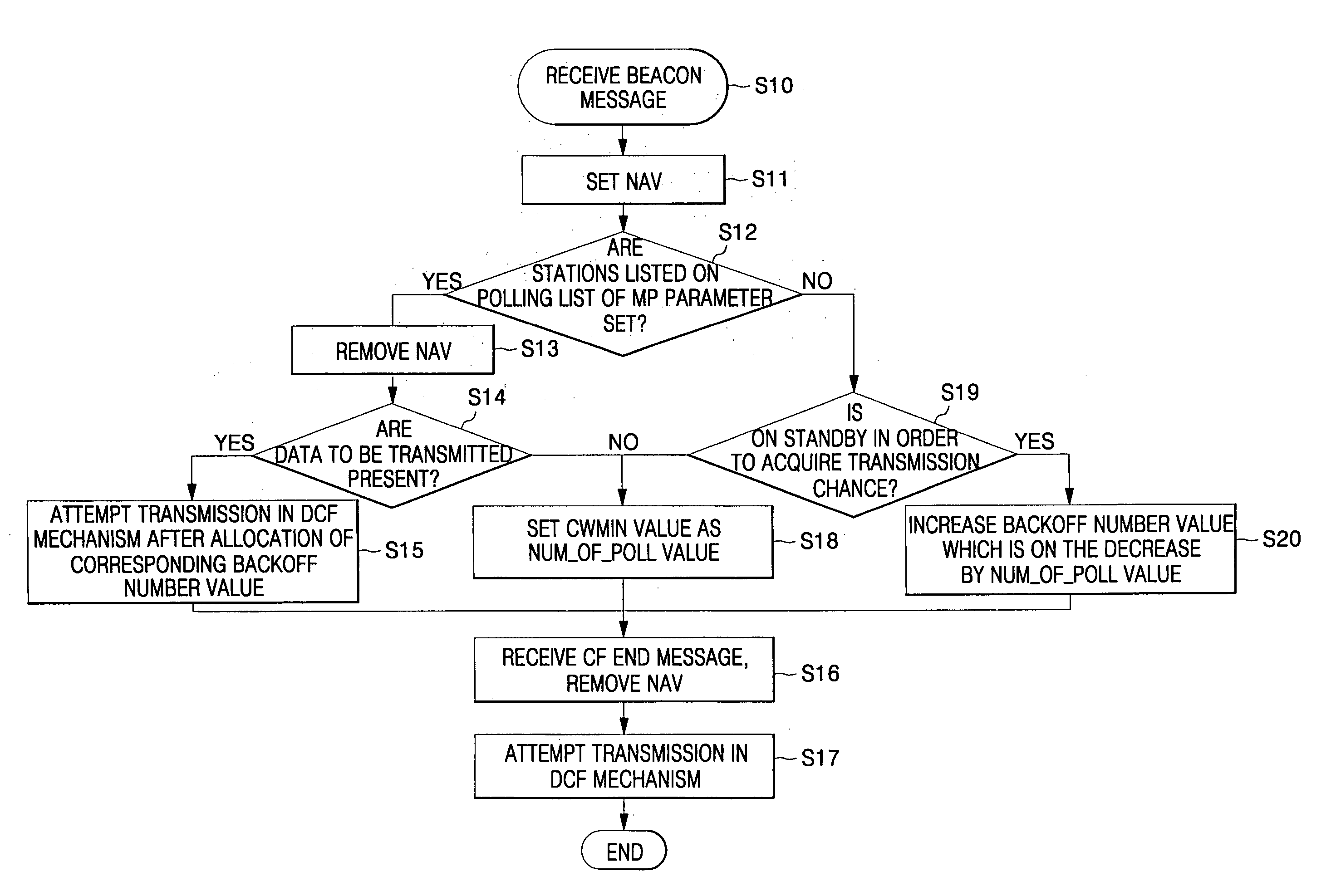
In a medium access method for contention and non-contention, a poll number for stations, or wireless terminals for communication, is managed by a base station so as to guarantee smooth traffic and improved Quality of Service (QoS). A first group of stations is provided for the non-contention, and a second group of stations is provided for the contention. The method includes (a) preparing a contention-free access message attempting access of the first group, (b) detecting a transmission time of a contention access message attempting access of the second group, (c) embedding the contention-free access message in the contention access message so as to transmit the embedded message to at least one of the first and second groups, and (d) receiving the contention access message, in which the contention-free access message is embedded, at the at least one of the first and second groups, and endowing any one of the first and second groups with a priority to attempt access to a medium in turn. Thereby, a poll number control-based multi-polling distributed coordination function (MP-DCF) mechanism is shared with the commercial stations to which no MP-DCF module is provided, so that it is possible to solve a drawback in that all stations should have the MP-DCF module provided therein, as well as to constantly maintain throughput even though the number of stations is gradually increased.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Medium access control in wireless local area network
InactiveUS20050025131A1Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsDistributed coordination functionTelecommunications
A medium access control method of a CSMA / CA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance) based wireless LAN (Local Area Network) provides contention-free medium access authority to a station or access point receiving a request signal by: transmitting a request signal frame from an arbitrary station to another arbitrary station or to an access point via a medium occupied in transmission contention with a CSMA / CA algorithm using a DCF (Distributed Coordination Function) interframe space; and transmitting an acknowledgment signal frame from the station or the access point receiving the request signal frame to the station transmitting the request signal frame via an occupied medium using a short interframe space.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Adaptive modulation and other extensions of the physical layer in multiple access systems
ActiveUS20050141448A1Less susceptible to packet errorEasy to useTransmission control/equlisationFrequency-division multiplex detailsDistributed coordination functionCommunications system
The present invention seeks to improve data exchange in a communications system that is especially standardized according to IEEE 802.11a. For this purpose, when the transmission medium, preferably an IEEE 802.11 system with a distributed coordination function (DCF) is accessed in a decentralized manner, pilot signals are transmitted from the transmitter to the recipients using a number of transmission modes and then an allocation table regarding the transmission modes is calculated by the recipient on the basis of the pilot symbols received. The recipient transmits the allocation table to the transmitter so that the subsequent data exchange can proceed on the basis of the allocation table. In the case of centralized access, preferably an IEEE 802.11 system with a point coordination function (PCF), data exchange is improved in that the subsequent data are adaptively modulated already when the allocation table is transmitted.
Owner:GIGASET COMMUNICATIONS
Method for avoiding network congestion in 802.11 competition type data transmission process
ActiveCN102413579AAvoid occupyingAvoid congestionWireless communicationDistributed coordination functionBasic service
The invention discloses a method for avoiding network congestion in a 802.11 competition type data transmission process. The method comprises the following steps that: making each sta-tion (STA) in an infrastructure basic service set (BSS) network respectively belong to at least one priority group; respectively setting a transmission factor to the each priority group; after the STA is associated in the infrastructure BSS network, before using a distributed coordination function (DCF) or an enhanced distributed channel access (EDCA) mode to compete a channel, determining whether the STA competes the channel according to the transmission factor of the priority group that the STA belongs to . In the method, before using the DCF or the EDCA mode compete the channel, the priority group mode is used to carry out priority classification to the each STA in the infrastructure BSS network. When a plurality of the STAs simultaneously carry out data transmission, on one hand, all the STAs can be guaranteed to carry out the data transmission according to a priority sequence of the STAs themselves so as to avoid the network congestion; on the other hand, the partial important STAs which are in the high priority can firstly complete the data transmission.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF INFORMATION & COMM
Distributed media access method used in wireless local area network
ActiveCN102625466AImprove effective utilizationReduce the probability of data collisionNetwork topologiesDistributed coordination functionAccess method
The invention discloses a distributed media access method used in a wireless local area network. According to the method, on the basis of a distributed coordination function (DCF)-based media access method specified in the conventional standard, the time length of DCF inter-frame space (DIFS) is set by randomizing: namely, a random time length deltaDIFS is added on the basis of the set time length of the DIFS specified in a protocol; moreover, in order not to add excessive channel overhead, the time length deltaDIFS is recommended to be set within a set time slot length, namely, delta DIFS=random (0, Slot_time); the time length of the DIFS is used for avoiding a phenomenon that different users synchronously enter a random backoff window wait state because of selecting contention windows (CWs) with the same time length, so that data collision probability and retransmission numbers among different users are reduced; channel utilization rate is improved; and system throughput is increased. Because only the time length of the DIFS is modified (namely the time length of the DIFS is subjected to randomization processing), the method is simple in operation and easy to develop, cannot increase system complexity, and does not need to update conventional sites; and new sites are compatible with old sites mutually, so that the application range of the method is enlarged, and the method has very good popularization and application prospect.
Owner:上海润欣科技股份有限公司
Preemptive packet for maintaining contiguity in cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) contention-free sessions
ActiveUS20080013509A1Synchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesTraffic capacityDistributed coordination function
An access point transmits a preemptive peg packet when it has no data to transmit in order to maintain the contiguity of its transmission timing position with respect to the timing position of other contention-free sessions (CFS) transmitted by other access points in an existing, periodic sequence. The cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) method establishes the transmission timing position of contention-free sessions (CFS) between overlapping first and second wireless LAN cells contending for the same medium. Each cell includes a respective plurality of member stations. If an access point has no traffic, it will transmit a short, preemptive pegging packet and reset its backoff timer. In this manner, no gaps longer than the distributed coordination function (DCF) Interframe Space (DIFS) are left idle. This prevents other stations from using DCF contention to seize the channel, until all access points have completed one contention-free session (CFS) per periodic cycle.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
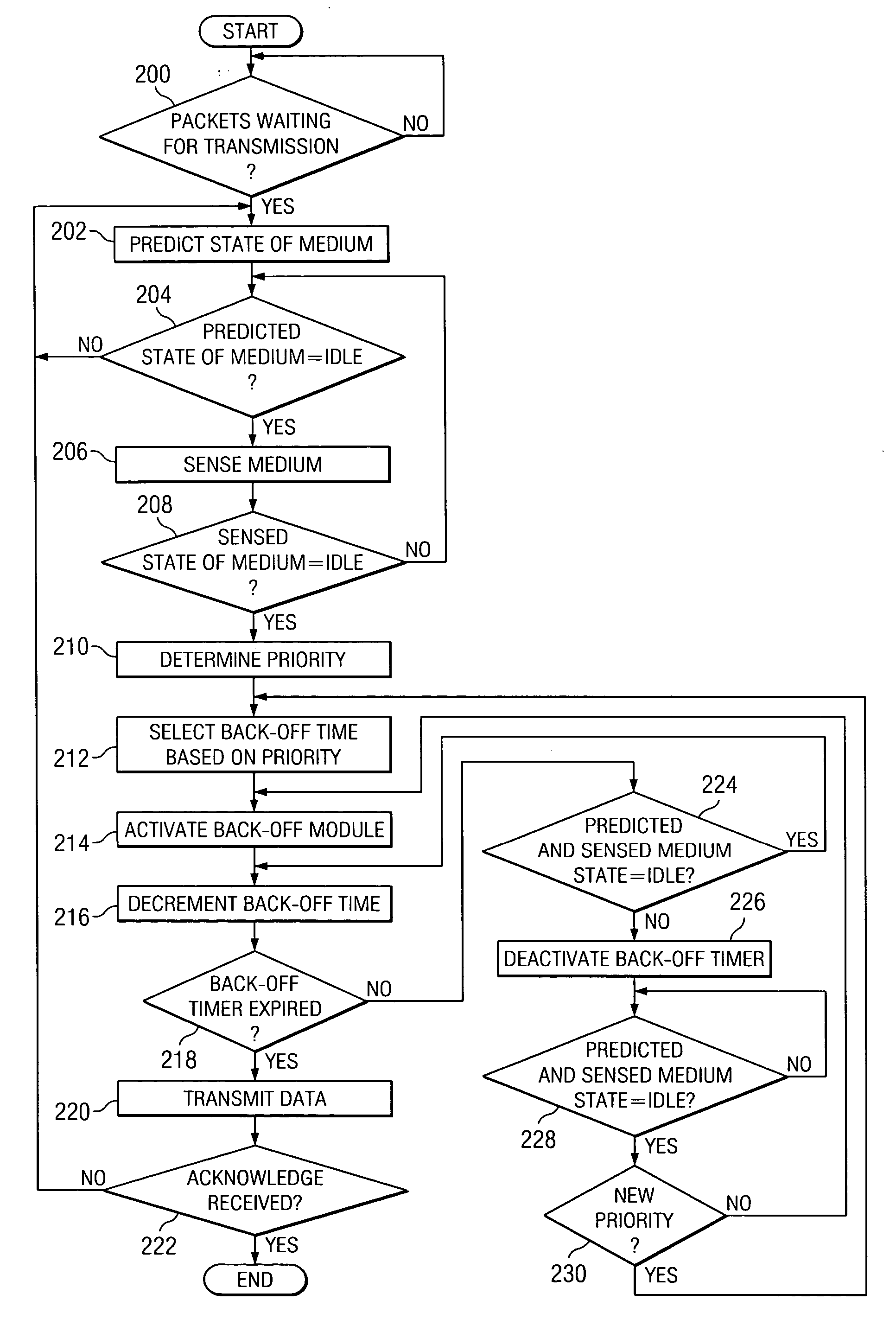
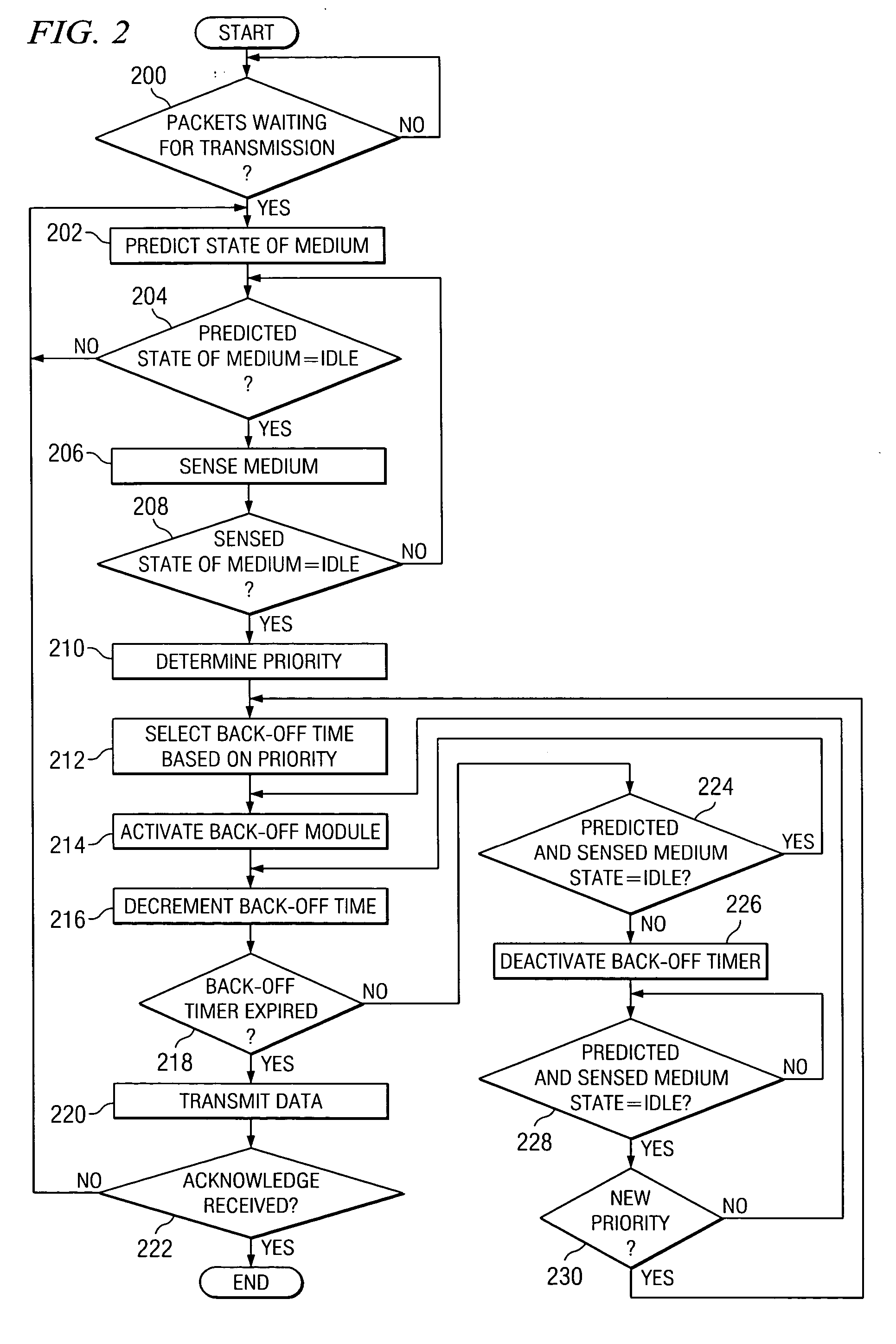
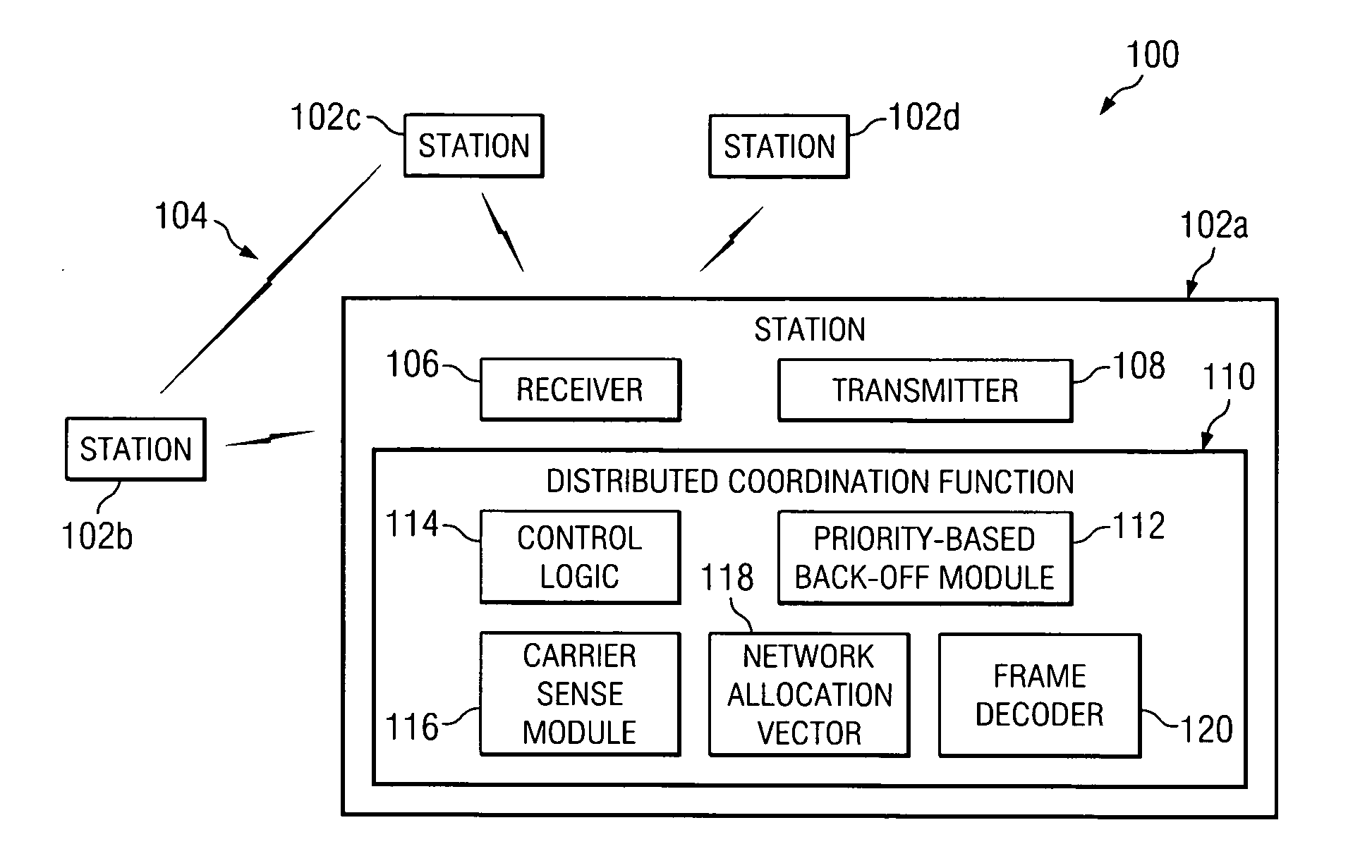
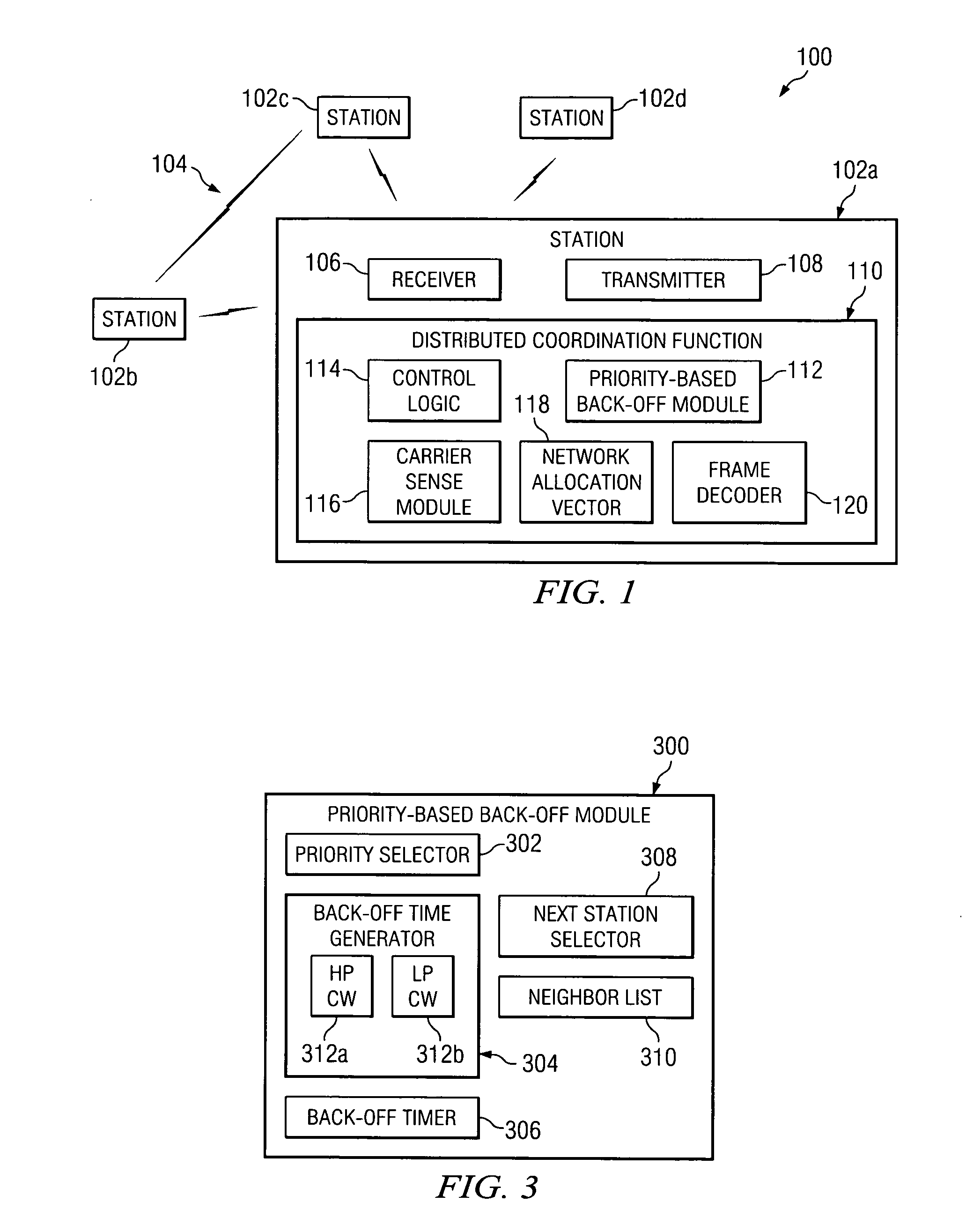
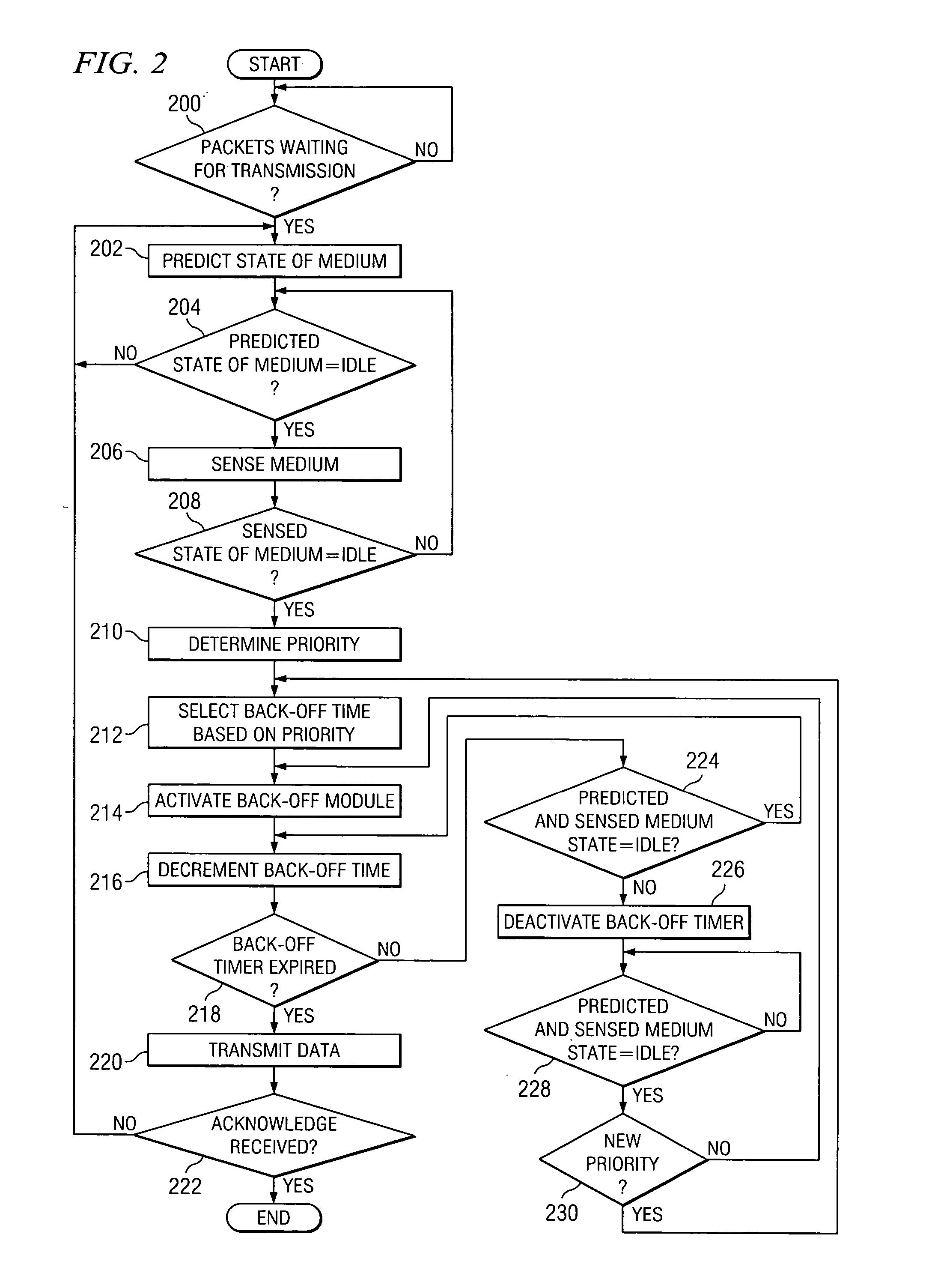
Method and system for providing a priority-based, low-collision distributed coordination function
ActiveUS20060034210A1Great probability of successful transmissionSimple methodRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesDistributed coordination functionDistribute coordination function
A method for providing a priority-based, low-collision distributed coordination function in a wireless network that includes a plurality of stations is provided. The method includes determining a priority for a first station and selecting a back-off time for the first station based on the priority.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
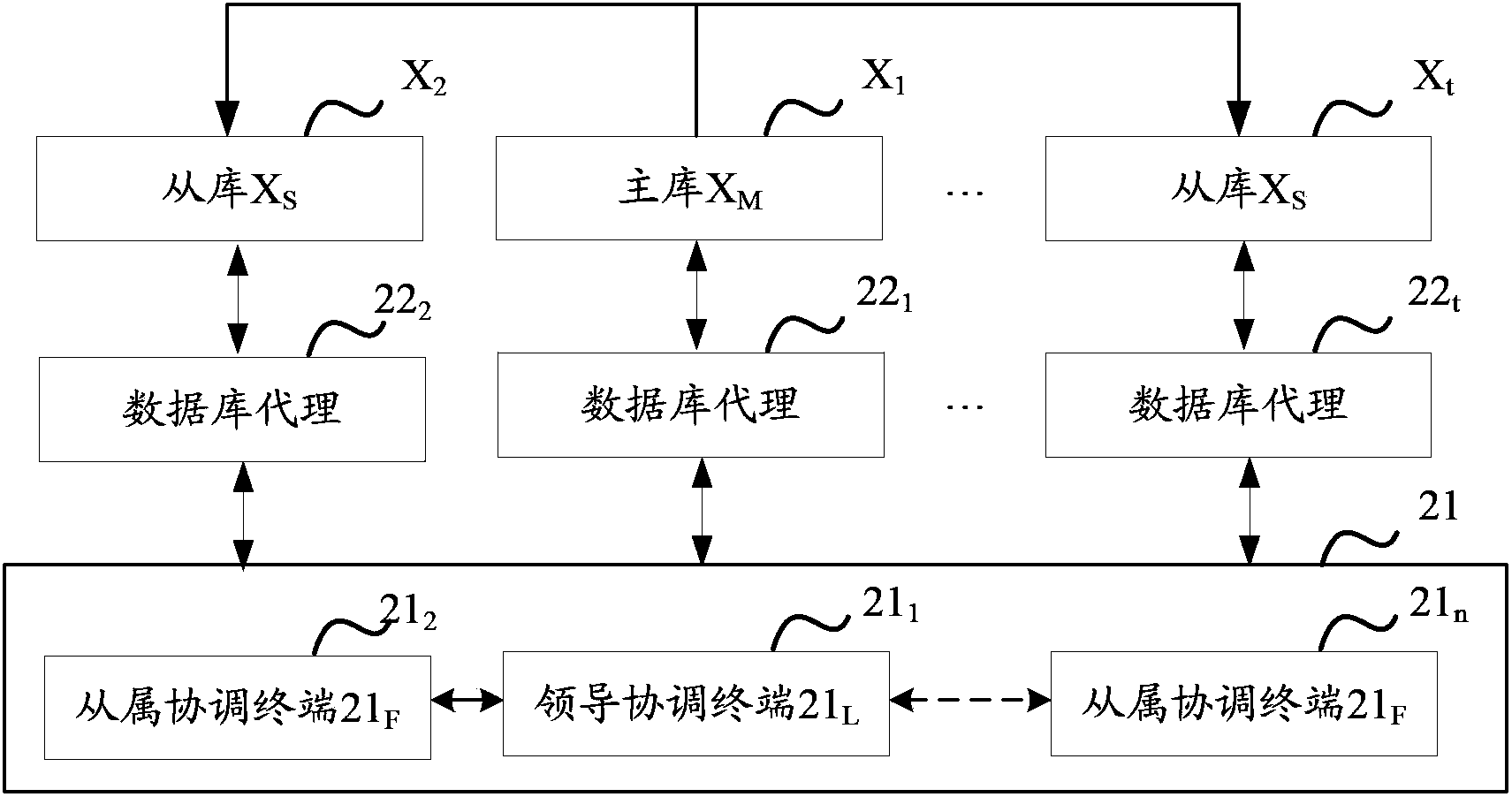
Monitoring system and monitoring method for single point of failure of database cluster
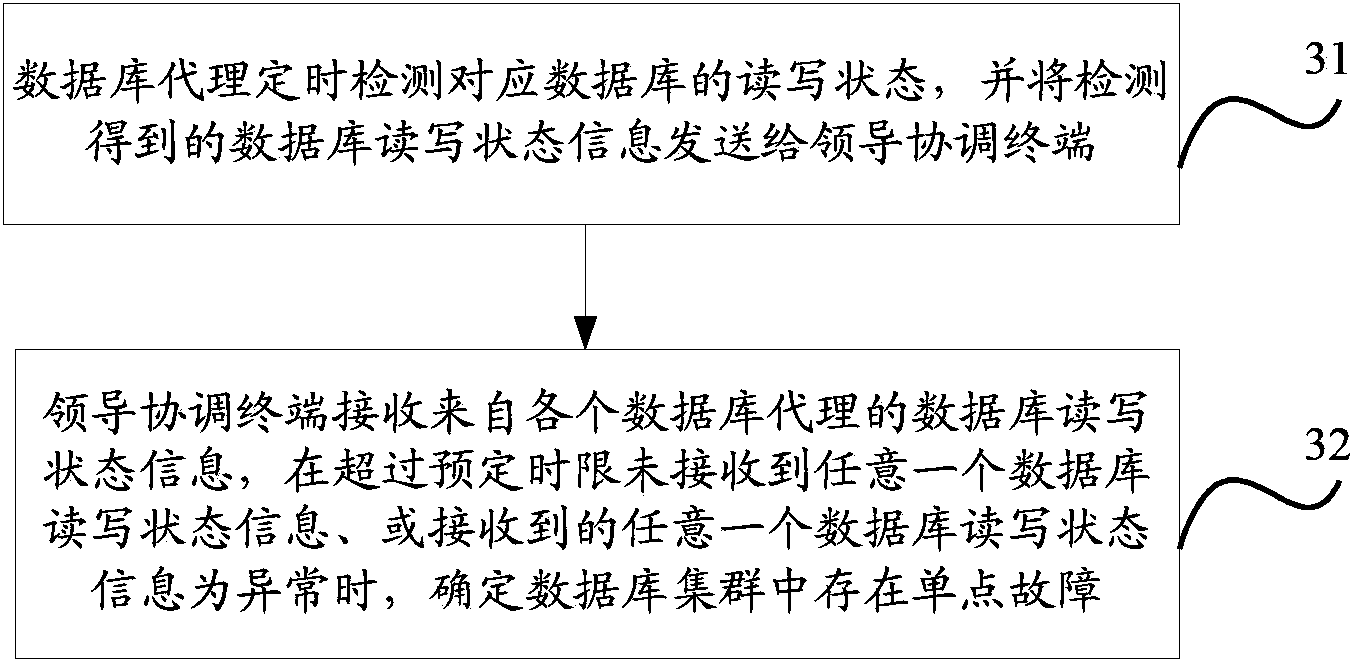
ActiveCN103425645AEfficient identificationReliable identificationSpecial data processing applicationsSingle point of failureDistributed coordination function
The invention discloses a monitoring system and a monitoring method for a single point of failure of a database cluster. The monitoring system and the monitoring method are applied to the database cluster of a plurality of databases. The databases include primary databases or secondary databases. The monitoring system comprises a plurality of database agents and at least three mutually-communicated coordinating terminals on the basis of a distributed coordination function. The coordinating terminals include a lead coordinating terminal. A database agent and a database in the database cluster are arranged on a server correspondingly, and addresses of the coordinating terminals are stored in each database agent. The database agents detect read-write states of corresponding databases regularly, and the lead coordinating terminal recognizes the single point of failure in the database cluster according to database write-read state information from the databases agents, so that the single point of failure in the database cluster can be recognized efficiently and reliably, and the problem of low efficiency of a solution to a distributed MySQL (my structured query language) database single point of failure in the prior art can be solved.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
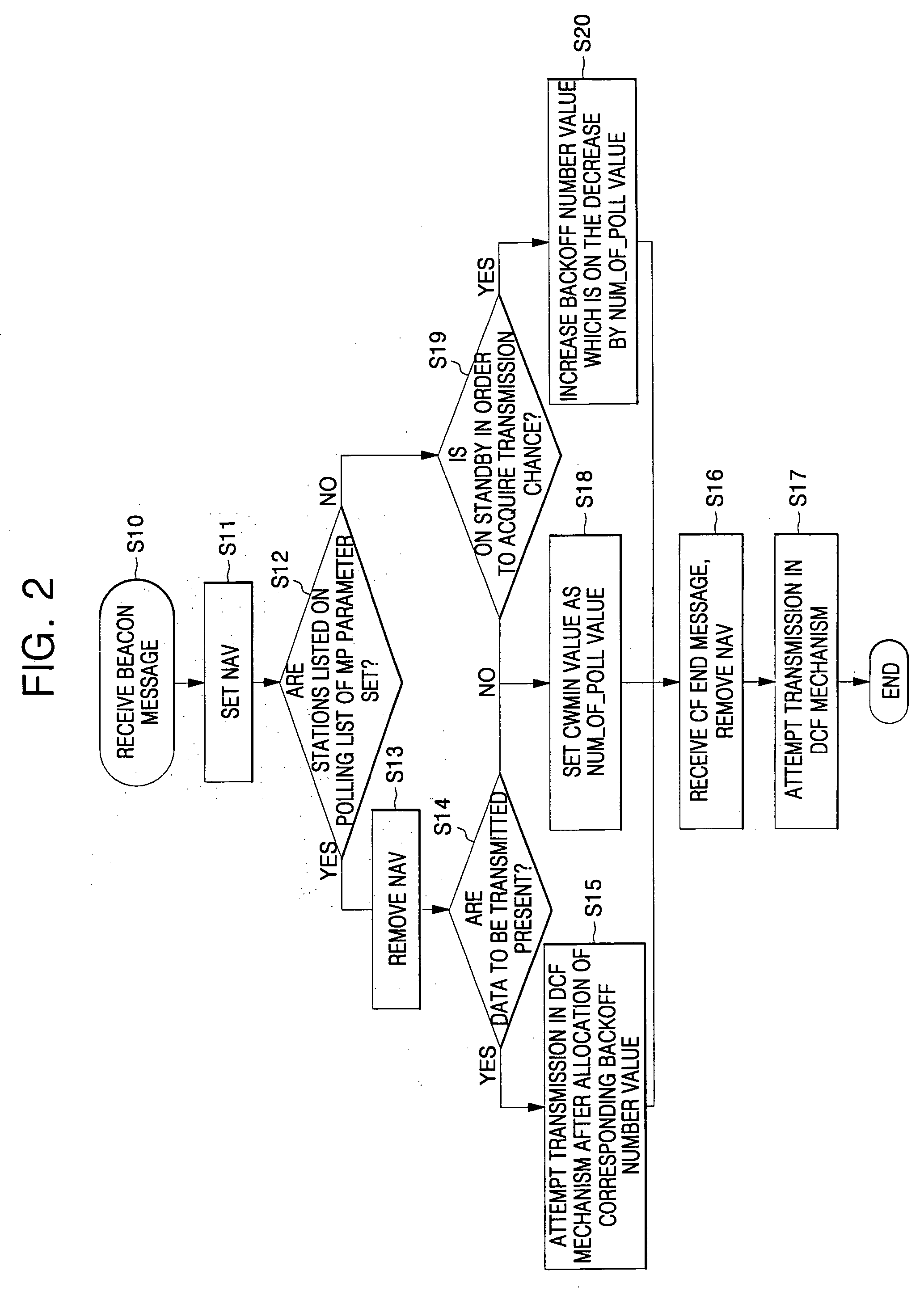
Medium access method for contention and non-contention
InactiveCN1780246AGuaranteed QoSData switching by path configurationWireless communicationFree accessDistributed coordination function
In contention and contention-free medium access methods, a first set of stations is used for no-contention and a second set of stations is used for contention. The method comprises (a) preparing a contention-free access message attempting to access a first group; (b) detecting a transmission time of a contention-free access message attempting to access a second group; (c) embedding the contention-free access message into contention access message to transmit the embedded message to at least one of the first and second groups; and (d) receiving at least one of the first and second groups a contention-free access message embedded Access messages are contended for and priority is given to either of the first and second groups to access the medium in turn. Therefore, the multi-poll distribution coordination function (MP-DCF) mechanism based on the control of polling times is shared with the commercial sites without MP-DCF modules, in order to solve the shortcomings that all sites need to have MP-DCF modules, and despite the site's The number is gradually increased to be able to maintain the throughput stably.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
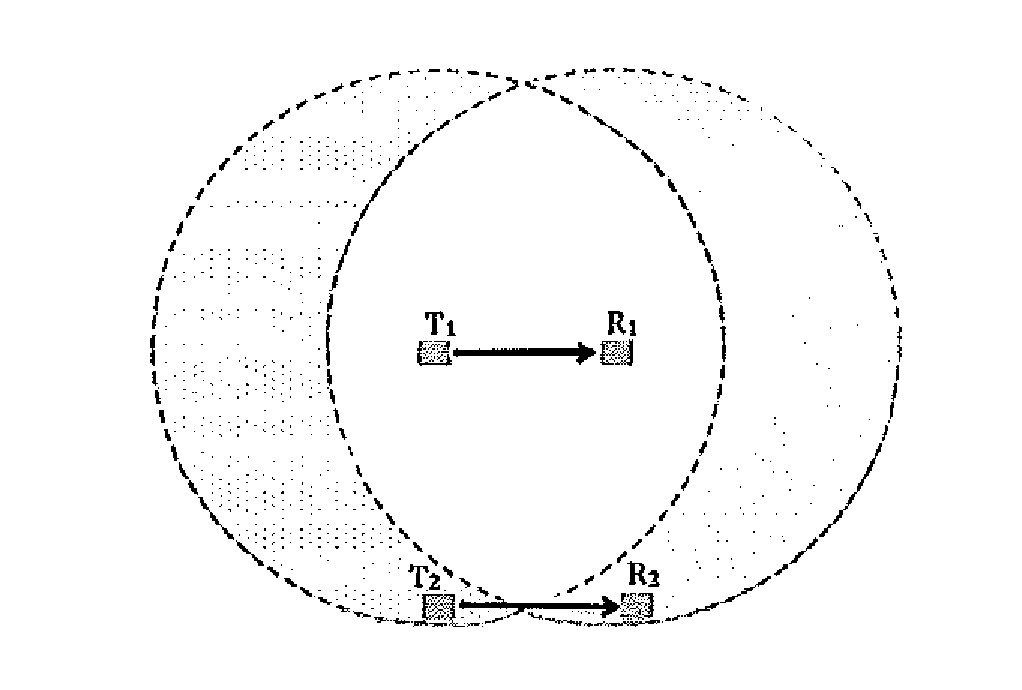
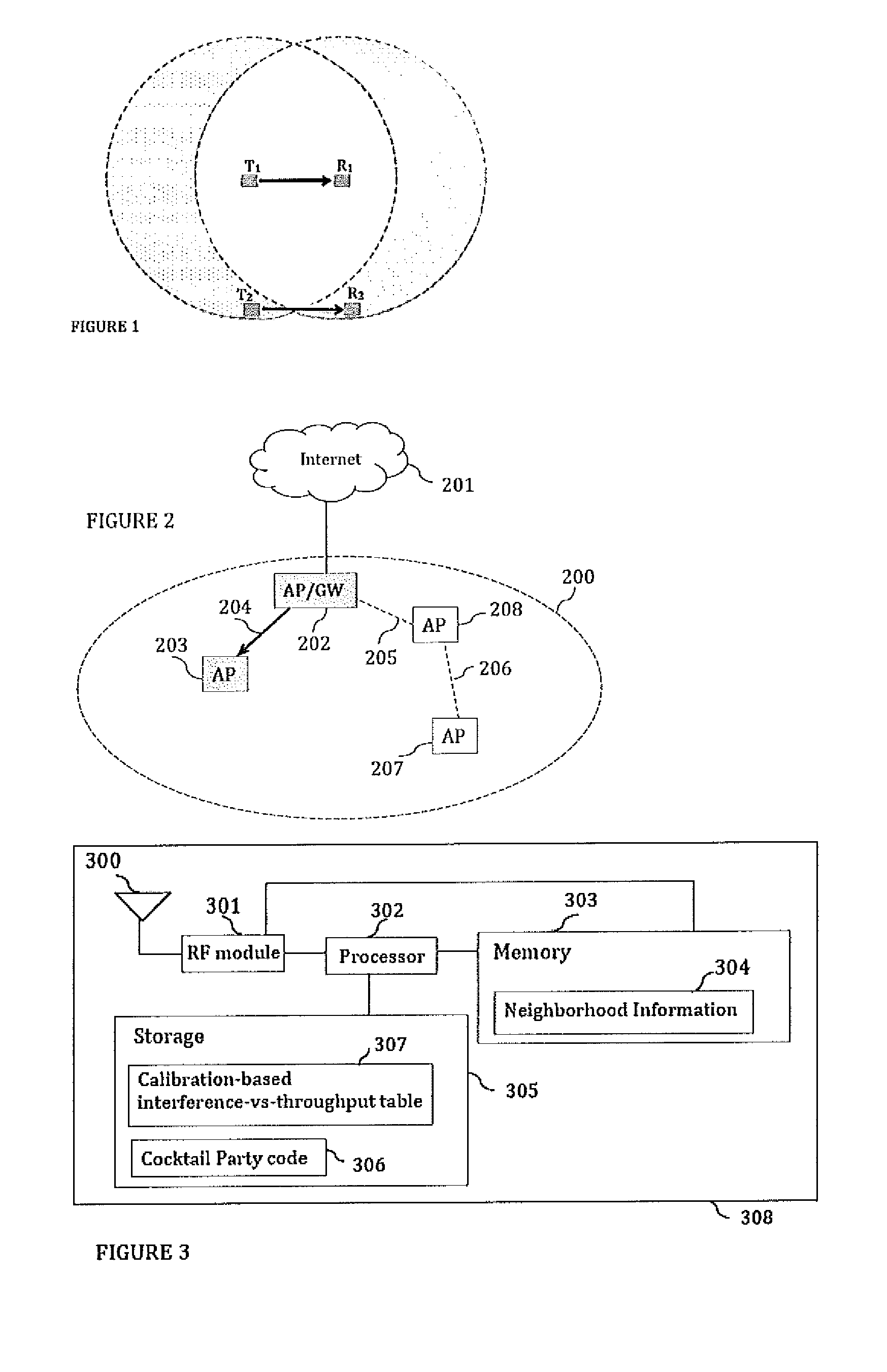
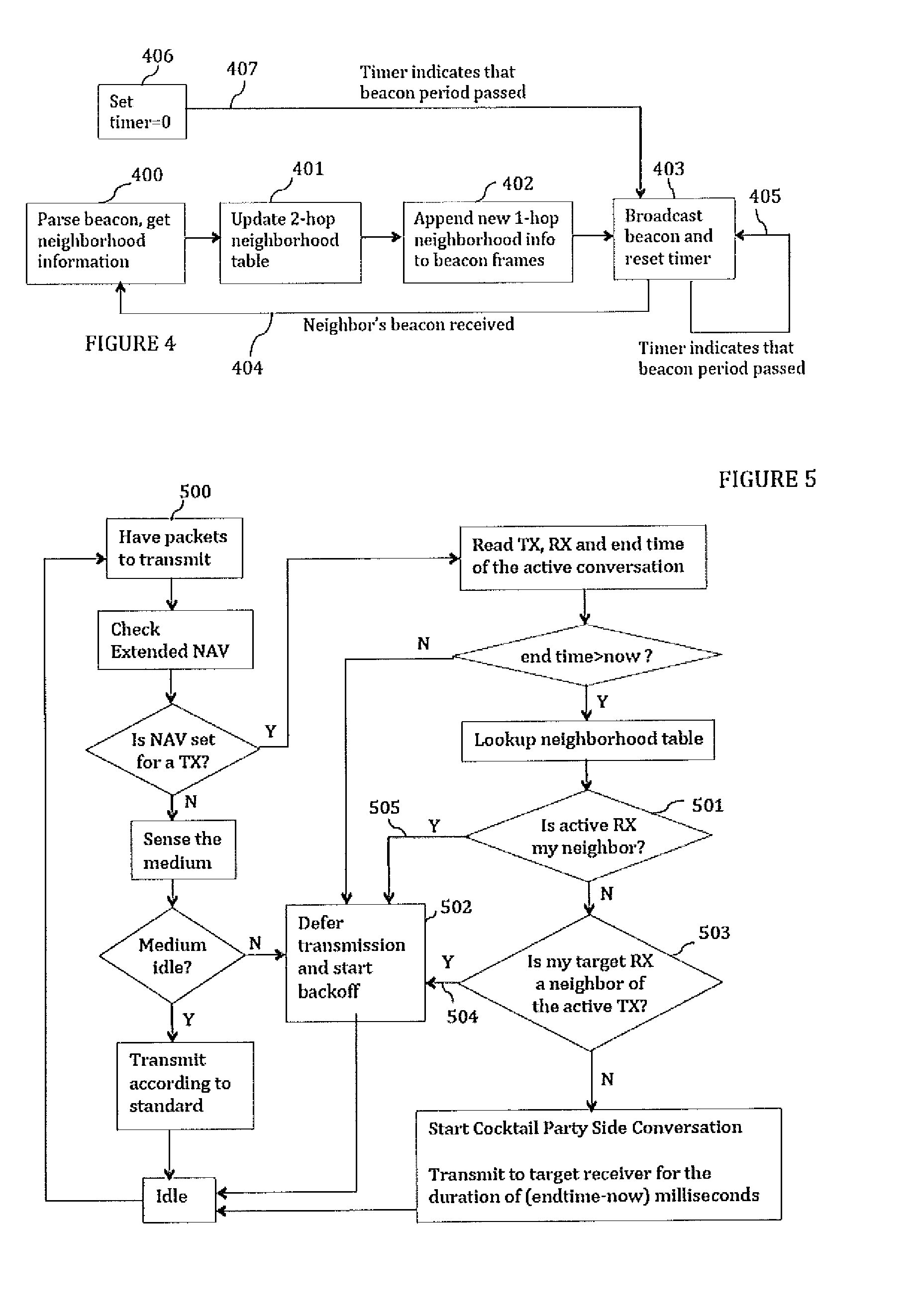
Cocktail party: side conversations and talking over in wireless mesh networks
ActiveUS20140254459A1Minimize jitterSpecial service provision for substationNetwork topologiesDistributed coordination functionProtocol design
The present disclosure proposes a method for minor modifications to the Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) channel access mechanism in order to enable a greater number of concurrent communications in a unit area in compliance with the current protocol design. The method comprises equipping nodes with wider neighborhood information than what is obtained with IEEE 802.11, and with a device calibration that equips the device with the knowledge of its performance in the presence of interference. The present disclosure medium access mechanism increases the aggregate throughput with every additional concurrent communication that is enabled in the shared medium. Cocktail Party-capable devices can fairly coexist with 802.11 legacy DCF devices, and co-operate with these devices in the same network without changes to those devices or to the standard. The same or similar mechanisms can be applied to other systems and standards in order to enable concurrent communications in the same contention area.
Owner:AIRTIES SAS
Preemptive packet for maintaining contiguity in cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) contention-free sessions
InactiveUS8068470B2Synchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesTraffic capacityDistributed coordination function
An access point transmits a preemptive peg packet when it has no data to transmit in order to maintain the contiguity of its transmission timing position with respect to the timing position of other contention-free sessions (CFS) transmitted by other access points in an existing, periodic sequence. The cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) method establishes the transmission timing position of contention-free sessions (CFS) between overlapping first and second wireless LAN cells contending for the same medium. Each cell includes a respective plurality of member stations. If an access point has no traffic, it will transmit a short, preemptive pegging packet and reset its backoff timer. In this manner, no gaps longer than the distributed coordination function (DCF) Interframe Space (DIFS) are left idle. This prevents other stations from using DCF contention to seize the channel, until all access points have completed one contention-free session (CFS) per periodic cycle.
Owner:AT & T INTPROP II LP
Resource competition method and station
ActiveCN102387592AGuaranteed reliabilityImprove resource competitive advantageWireless communicationDistributed coordination functionDistribute coordination function
The invention discloses a resource competition method and a station. The resource competition method comprises the following steps that: during multi-user multiple input multiple output (MU-MIMO) data downlink transmission, a source station selects a target station from a group of target stations according to a predetermined rule, wherein a parameter which corresponds to the selected target station is taken as a parameter of distributed coordination function (DCF) or enhanced distributed channel access (EDCA) resource competition; and the source station competes against other source stations for resources by using the DCF resource competition parameter or the EDCA resource competition parameter.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Wireless communication method following DCF rule
ActiveUS7907627B2Improve reliabilityNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexDistributed coordination functionReliable transmission
Provided are a method and apparatus which can reduce the possibility of collision with other frames when transmitting a broadcast / multicast frame in a wireless local area network (LAN) following a Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) rule, thereby ensuring reliable transmission. The wireless communication method for sending or receiving a predetermined frame through contention between an access point and one or more stations according to DCF is characterized in that the access point uses the shortest of interframe space (IFS) intervals for access to a wireless medium. Therefore, when wireless LAN STAs operate in a DCF mode, the possibility of collision during broadcast or multicast frame transmission can be reduced while adopting conventional CSMA / CA mechanism, thereby improving reliability in successful frame transmission.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multi-channel multiple access method based on reliable multi-step channel reservation mechanism
InactiveCN104902577AReduce congestionSolve the hidden terminal problemWireless communicationDistributed coordination functionTransceiver
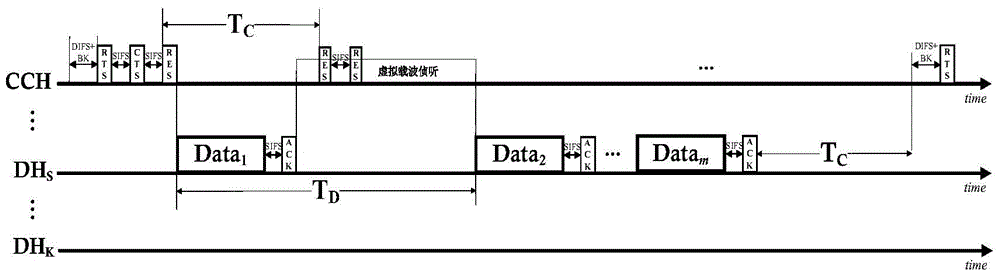
The present invention provides a multi-channel multiple access method based on a reliable multi-step channel reservation mechanism. The method mainly comprises control channel reservation and data channel reservation. When a node competes successfully in a common control channel according to a distributed coordination function mechanism, a sending node and a receiving node exchange requests on a control channel to send information, and the selection of a data channel, the reservation on the control channel and the reservation on the data channel are completed. According to the method, the multichannel hidden terminal problem is solved by using the control channel reservation, through using multi-step data channel reservation, the data packet transmission without a conflict can be realized with only one control handshake, the control channel congestion is effectively alleviated and the MAC efficiency is improved, and the system performance is greatly improved, which means that the network throughput is improved and the average packet delay is reduced. According to the method, only one set of transceiver is needed, the realization is simple, a central control nodes and entire network synchronization are not needed, and the realization cost and complexity are reduced.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Medium access control in wireless local area network
InactiveCN1578239AData switching by path configurationWireless communicationDistributed coordination functionTelecommunications
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for designing WLAN (wireless local area network) MAC (medium access control) layer protocol based on cooperative communication
InactiveCN104780619AImprove performanceImprove execution efficiencyError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork topologiesDistributed coordination functionNetwork code
The invention provides a method for designing a WLAN (wireless local area network) MAC (medium access control) layer protocol based on cooperative communication. According to the method, the design work of a network coding based cooperative communication MAC protocol is mainly completed. Mechanisms involved in the whole protocol comprise a network coding mechanism, frame format design and a competition-based DCF (distributed coordination function) channel access mechanism. The invention provides a novel network coding based cooperative communication MAC protocol, the complexity of the access mechanism is reduced, introduction of a large quantity of control frames is avoided, the protocol is well compatible with an existing protocol, meanwhile, the network performance is effectively improved, and the error code rate is reduced.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method for optimizing passing rate performance in wireless ad hoc network
InactiveCN102104447AShorten the timeIncrease the probability of conflictError prevention/detection by using return channelWireless communicationDistributed coordination functionEngineering
The invention discloses a method for optimizing passing rate performance in a wireless ad hoc network. By adopting the method, the following defects are overcome: the traditional IEEE802.11DCF (distributed coordination function) mechanism adopts the minimum contention window of the BEB (binary exponential backoff) algorithm, so the processing nodes are not timely enough to contend and are too passive. The method has the following beneficial effects: dynamically detecting the number of the transmitting nodes of the contention channels, then computing the next minimum contention window after the transmitting nodes successfully complete the current transmission according to the frame error rate of the RTS (request to send) packet, optimizing the backoff timeslot and reducing the average time of access of the nodes to the channels. The backoff mechanism is superior to the traditional BEB algorithm.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Data transmission method and device in wireless LAN system supporting downlink oriented channel
ActiveUS20170019927A1Improve system performanceReduce data transferAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesDistributed coordination functionCommunications system
The present disclosure relates to a wireless communication system, and in particular to a data transmission operation of an AP in a wireless LAN system. To this end, the AP may obtain information on a STA located at an overlapping basic service set (OBSS) from among STAs connected to the AP, and determines, based thereon, (1) whether to transmit data from the AP through a downlink oriented channel or a general channel different from the downlink oriented channel, or (2) whether to use one or more of a distributed coordination function (DCF) procedure and an enhanced distributed channel access (EDCA) procedure.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Powerline communications (PLC) network routing method and system
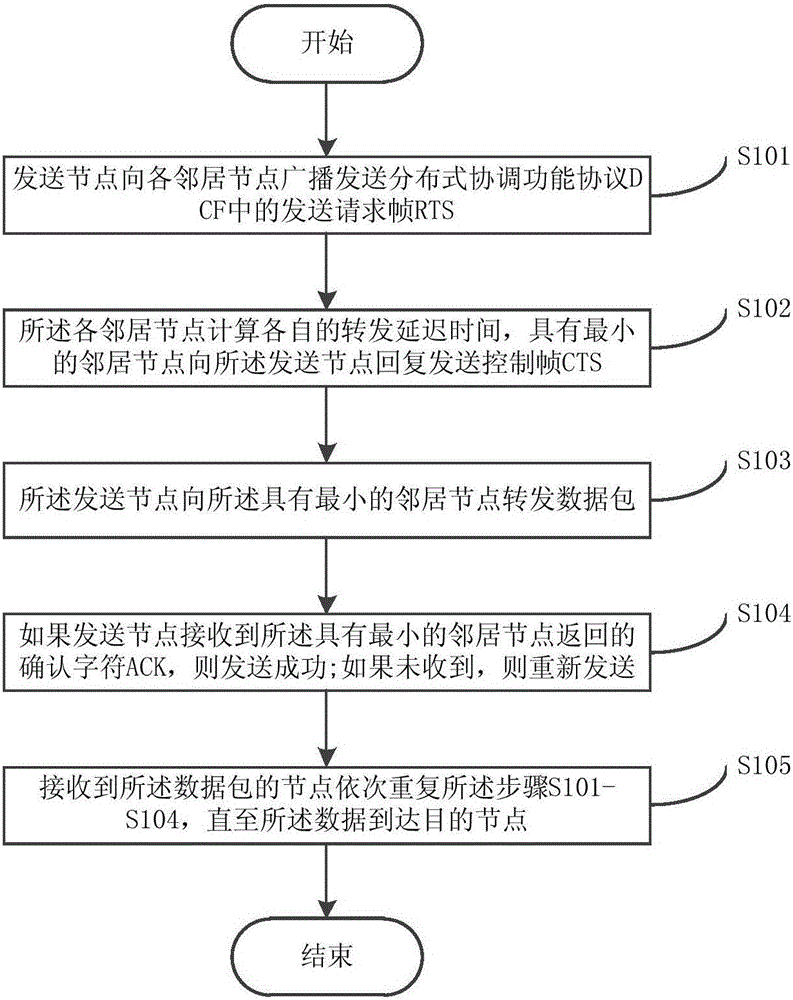
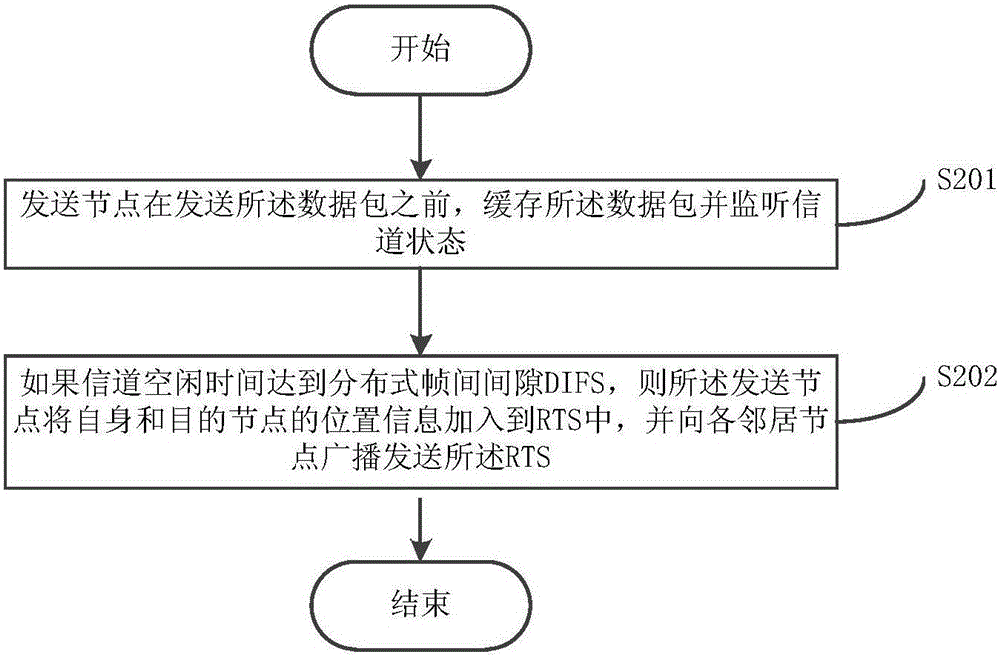
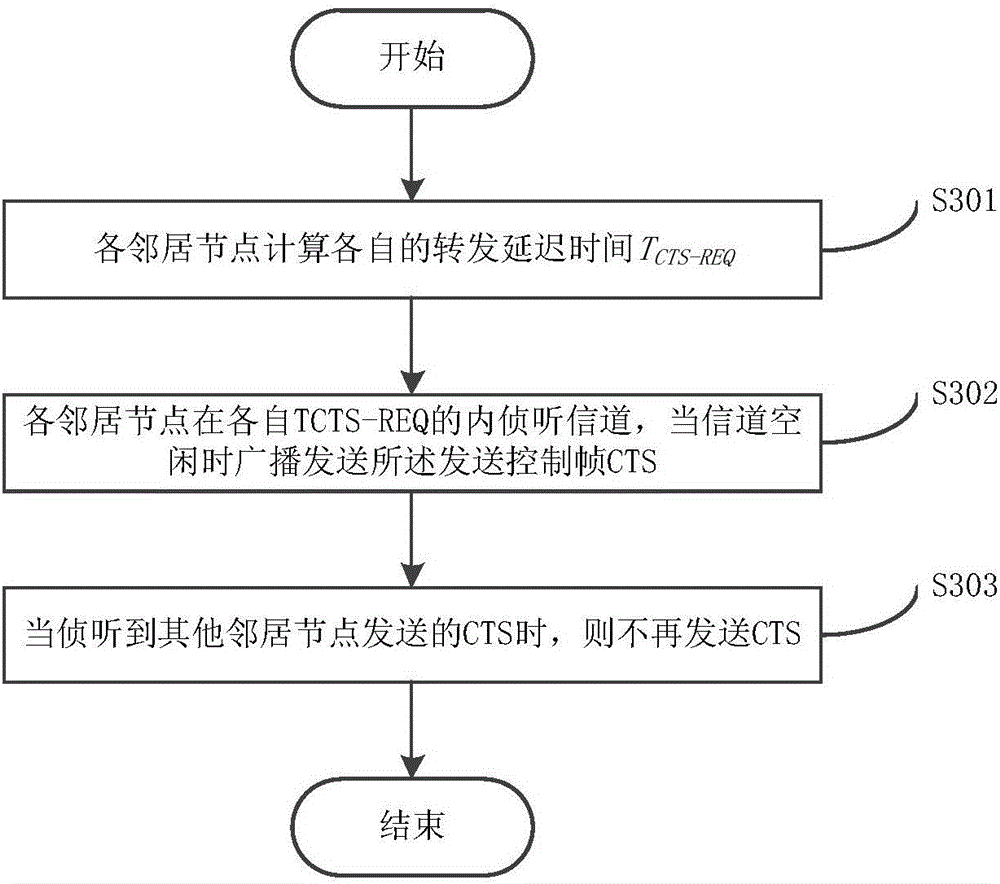
InactiveCN105072034AReduce routing conflictsReduce signaling message volumePower distribution line transmissionData switching networksDistributed coordination functionNetwork packet
The invention discloses a powerline communications (PLC) network routing method and system. The method comprises the following steps: step A, a transmitting node transmits a frame of Request To Send (RTS) in a Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) protocol to each neighboring node in a broadcasting manner; step B, each neighboring node calculates own forwarding delay time TCTS_REQ, and the neighboring node having the minimal TCTS_REQ replies to the transmitting node with a frame of Control To Send (CTS); step C, the transmitting node forwards a data packet to the neighboring node having the minimal TCTS_REQ; step D, if the transmitting node receives an acknowledgement character (ACK) returned by the neighboring node having the minimal TCTS_REQ, the transmission is successful; and step E, each node receiving the data packet orderly repeats the steps A to D until the data reaches a target node.
Owner:BEIJING SMARTCHIP MICROELECTRONICS TECH COMPANY +3
Determining inactivity timeout using distributed coordination function
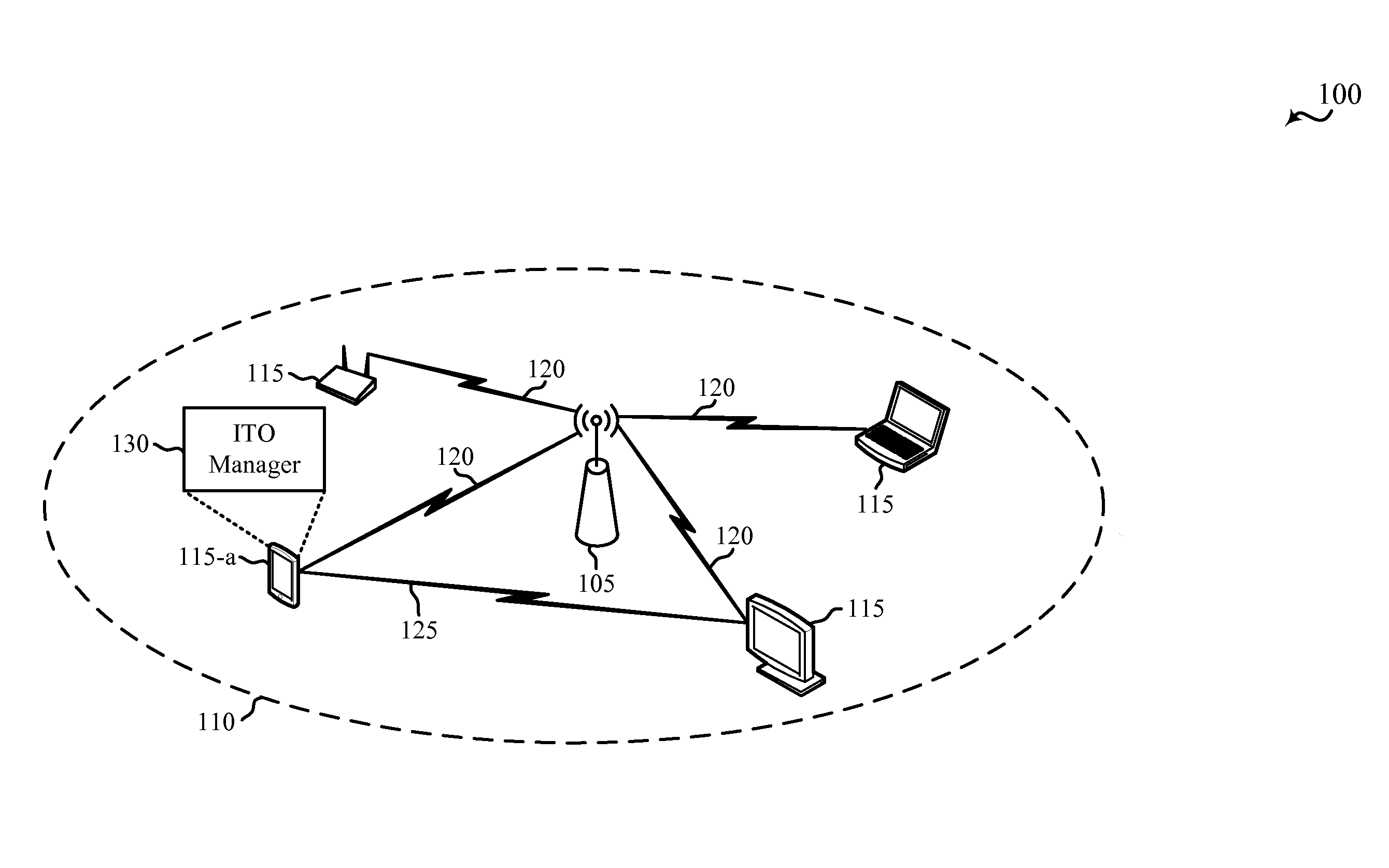
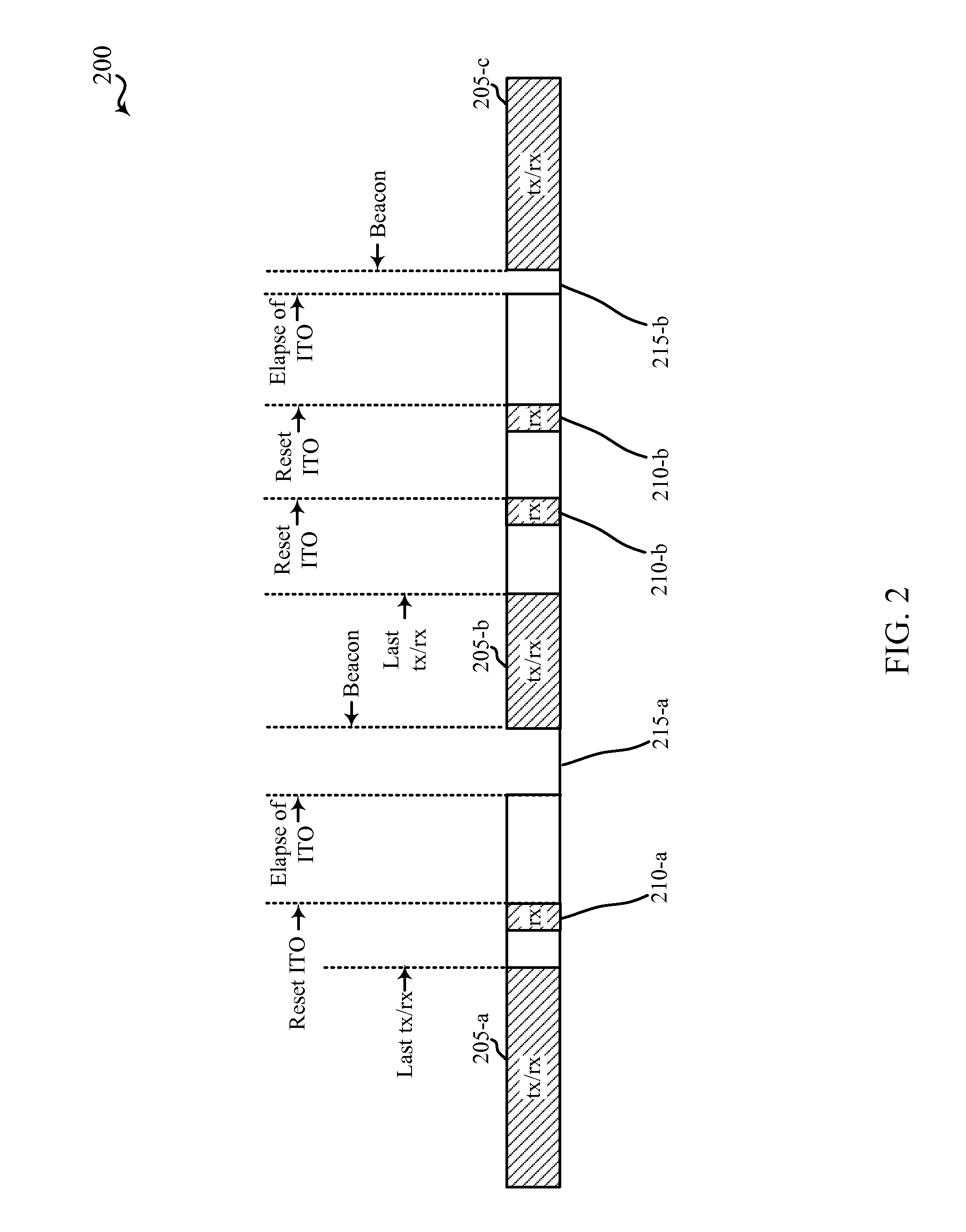
InactiveUS20160295509A1Good power savingSave powerPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementTraffic capacityDistributed coordination function
Methods, systems, and devices are described for power management in wireless devices. Power saving for a device of a wireless network may be improved by appropriately setting an inactivity timeout (ITO), and thus the amount of time, after a last transmission or reception of data traffic, that the device remains in an awake mode listening for more data traffic before the device enters a sleep mode. Distributed coordinated function (DCF) information may be used for determining the ITO. For example, the DCF information may be used to determine a channel congestion metric, which may be used to set the ITO for the device.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Resource competition method and station
ActiveCN102387538AGuaranteed reliabilityImprove resource competitive advantageError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementDistributed coordination functionDistribute coordination function
The invention discloses a resource competition method and a station. The method comprises the following steps that: during multi-user multiple input multiple output (MU-MIMO) data are in downlink transmission, a source station judges minimum back-off time in back-off time which corresponds to an MU-MIMO physical frame, and takes the minimum back-off time as a parameter of distributed coordination function (DCF) or enhanced distributed channel access (EDCA) resource competition; and the source station competes against other source stations for resources by using the DCF resource competition parameter or the EDCA resource competition parameter.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Media access control method based on WLAN system in 802.11ac protocol
ActiveCN105682247AImprove throughputImprove spectrum utilizationWireless communicationDistributed coordination functionFrequency spectrum
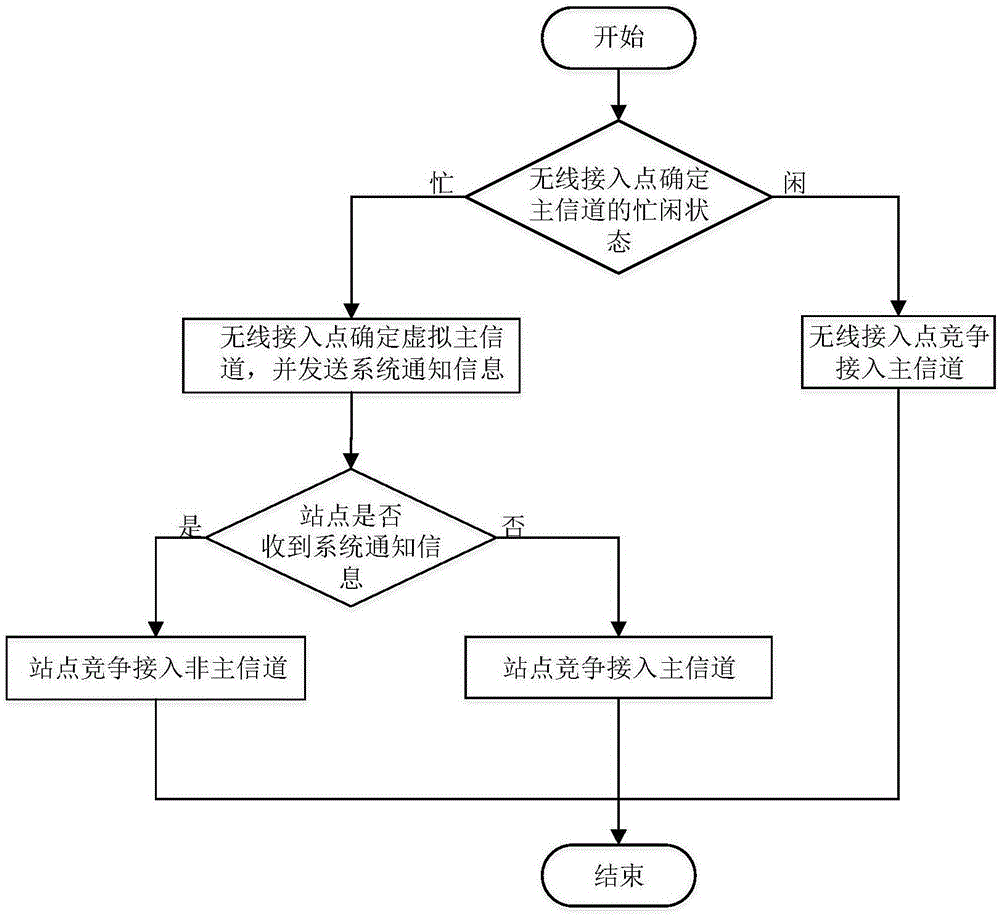
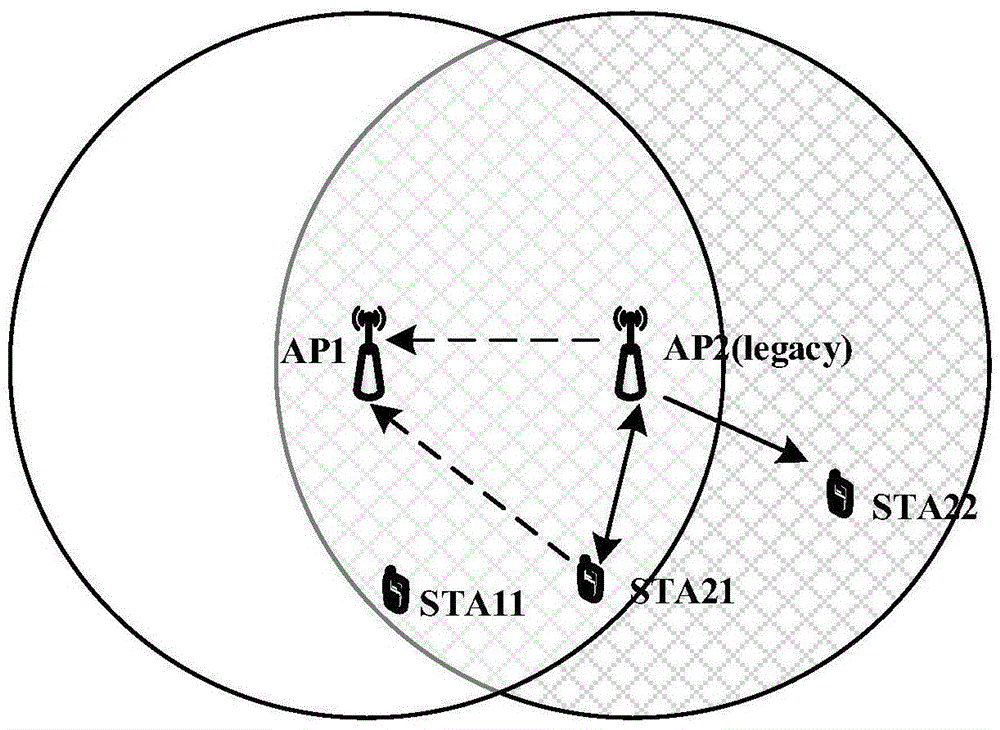
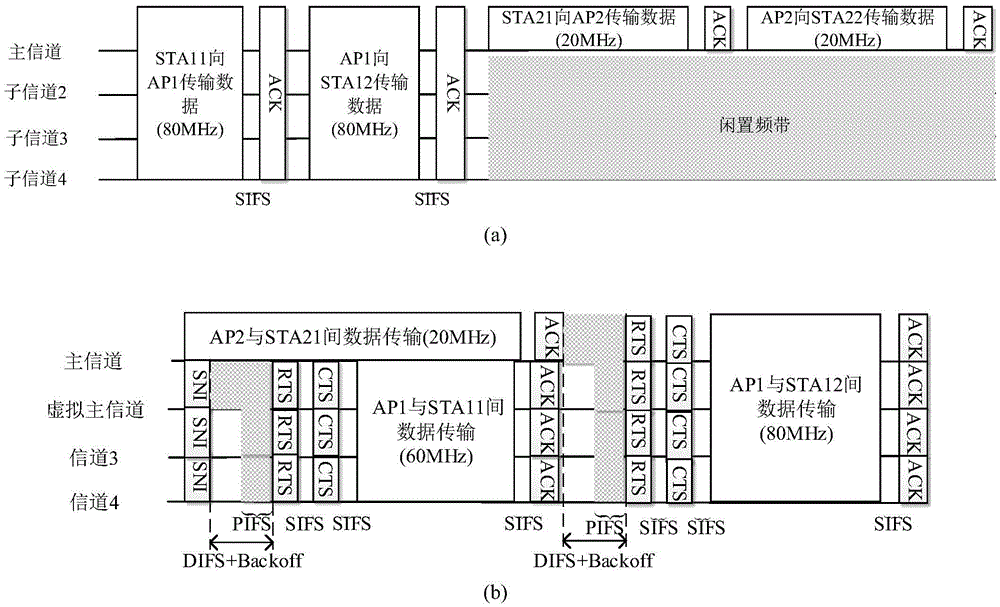
The invention discloses a media access control method based on a WLAN system in an 802.11ac protocol. The method mainly is used for solving the problem of low spectrum utilization rate resulted from overlapped basic service sets. The method comprises that a wireless access point AP invokes a carrier monitoring mechanism on a master channel so as to determine the busy and idle states of the master channel; when the master channel is in an idle condition, the wireless access point and stations STA access the master channel by a distributed coordination functional channel access method; when the master channel is in a busy condition, the wireless access point selects a first channel in non-master channels as a virtual master channel and sends system notice information SNI to the stations in a basic service set in which the wireless access point is located; SNI copies are sent to the other non-master channels; and the stations access the non-master channels on the virtual master channel according to a point coordination functional interframe interval channel access algorithm. According to the method provided by the invention, the non-master channel is utilized fully; the spectrum utilization rate and system throughput are improved; and the method can be used for optimizing the MAC layer protocol in the 802.11ac protocol.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Wireless access control station and wireless access control method
InactiveUS20060109816A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsDistributed coordination function
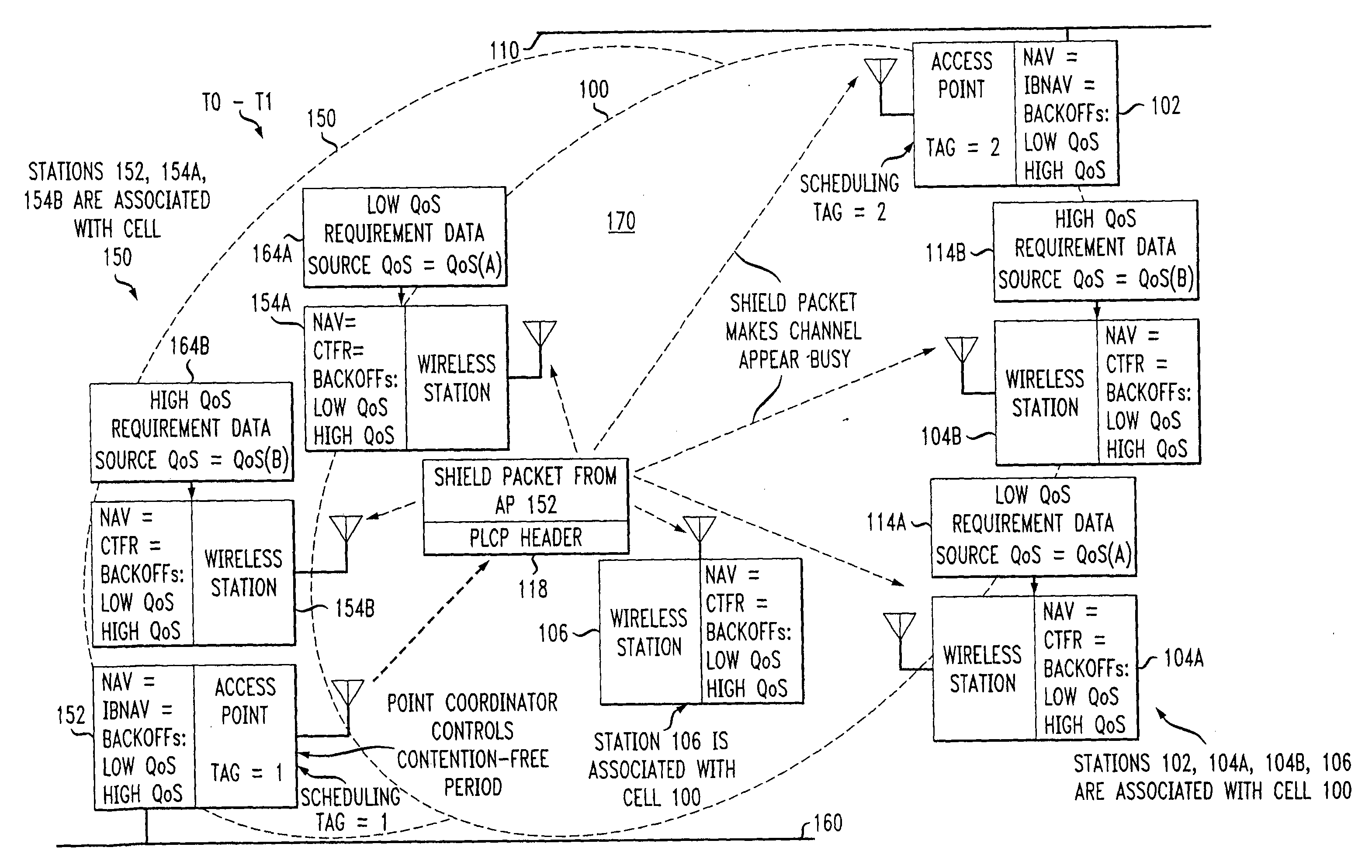
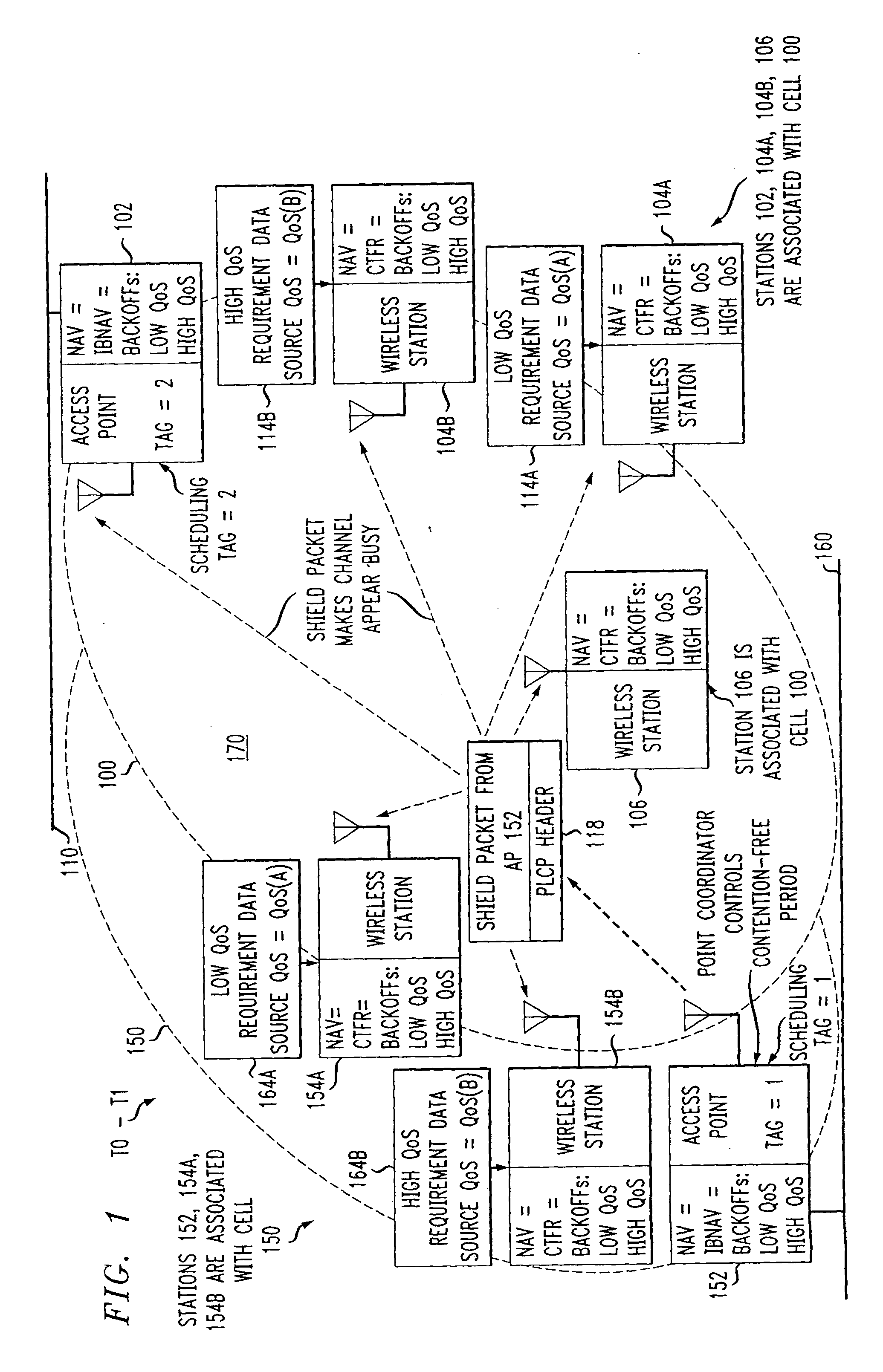
Even in a wireless station only having a distributed coordination function, a fair connection chance can be provided. A wireless access control station comprising a determination unit which determines a wireless connection count of a predetermined access category, and a change unit which changes, in accordance with determination obtained by said determination unit, wireless connection of a wireless communication apparatus satisfying a predetermined condition from a wireless connection of distributed coordination function to a wireless connection of point coordination function, or from the wireless connection of point coordination function to the wireless connection of distributed coordination function.
Owner:CANON KK
Method of transmitting multimedia data over wlan and point coordinator in wlan
InactiveCN1523846ASuccessfully transmittedReduce overheadSpecial service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelDistributed coordination functionDistribute coordination function
Transmitting multimedia data over a wireless local area network (WLAN), guaranteeing the full length of a multimedia point coordination function (mPCF) period in a WLAN, and dynamically allotting a length of the mPCF period, by receiving a request for multimedia resource from a predetermined device connected to the WLAN, during a distributed coordination function (DCF) period when a right to use a channel is distributed through contention and unilaterally transmitting the requested multimedia resource to the predetermined device during the mPCF period when the right to use a channel is distributed in a centralized manner.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Strict priority distributed coordination function in wireless networks
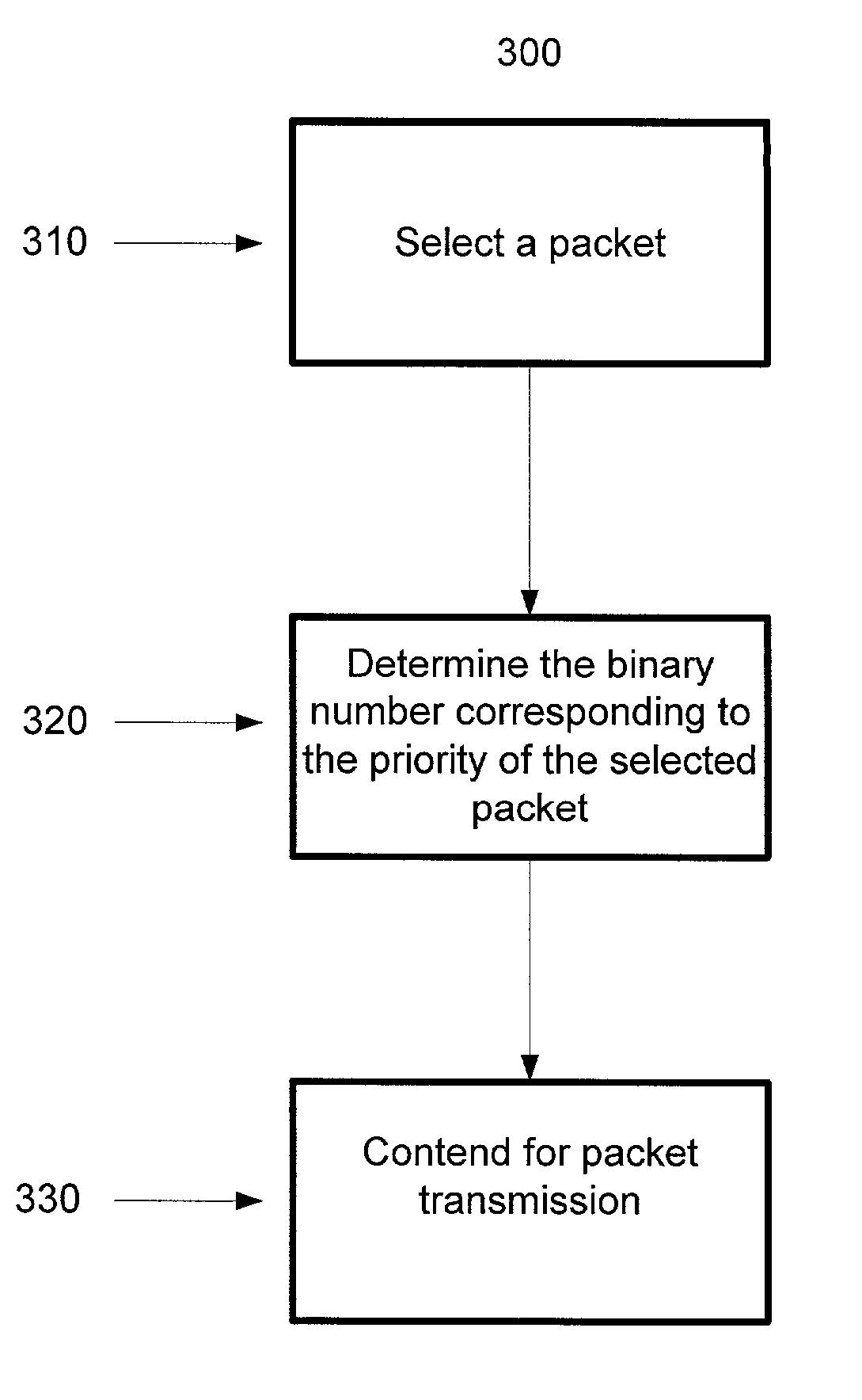
ActiveUS20060083166A9Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionDistributed coordination functionWireless lan
A system and method for prioritizing the transmission of packets in a wireless local area network. A station selects a packet from local priority queuing and identifies the priority bits of the packet. The station declares the priority of the selected packet based on the binary value of the priority bits. If the station detects that another station has selected a packet with a higher priority, then the station ceases to contend for transmission during the current transmission cycle.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com