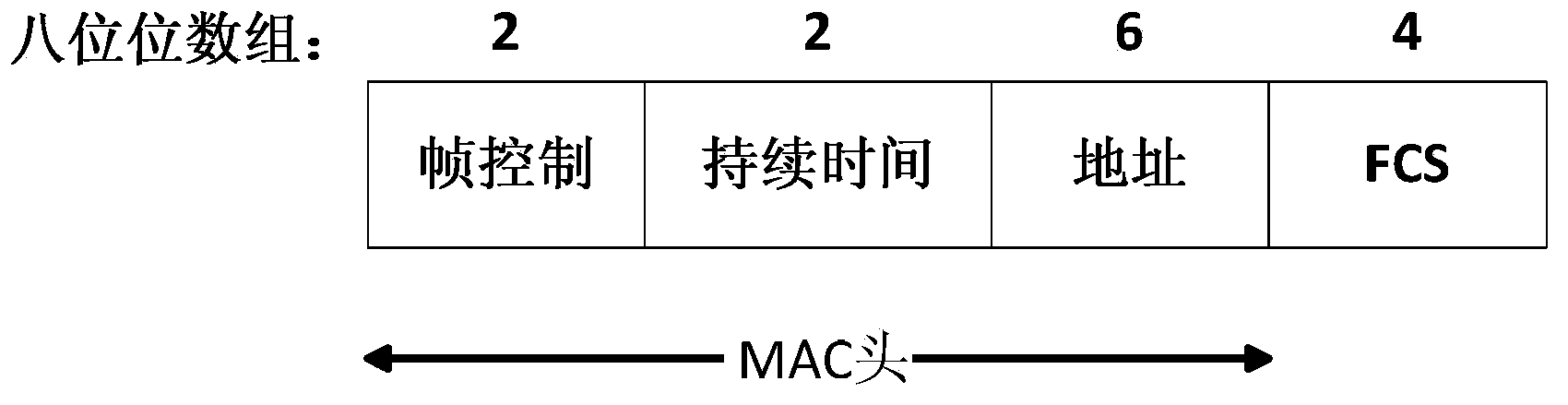
Patents
Literature
41 results about "Short Interframe Space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
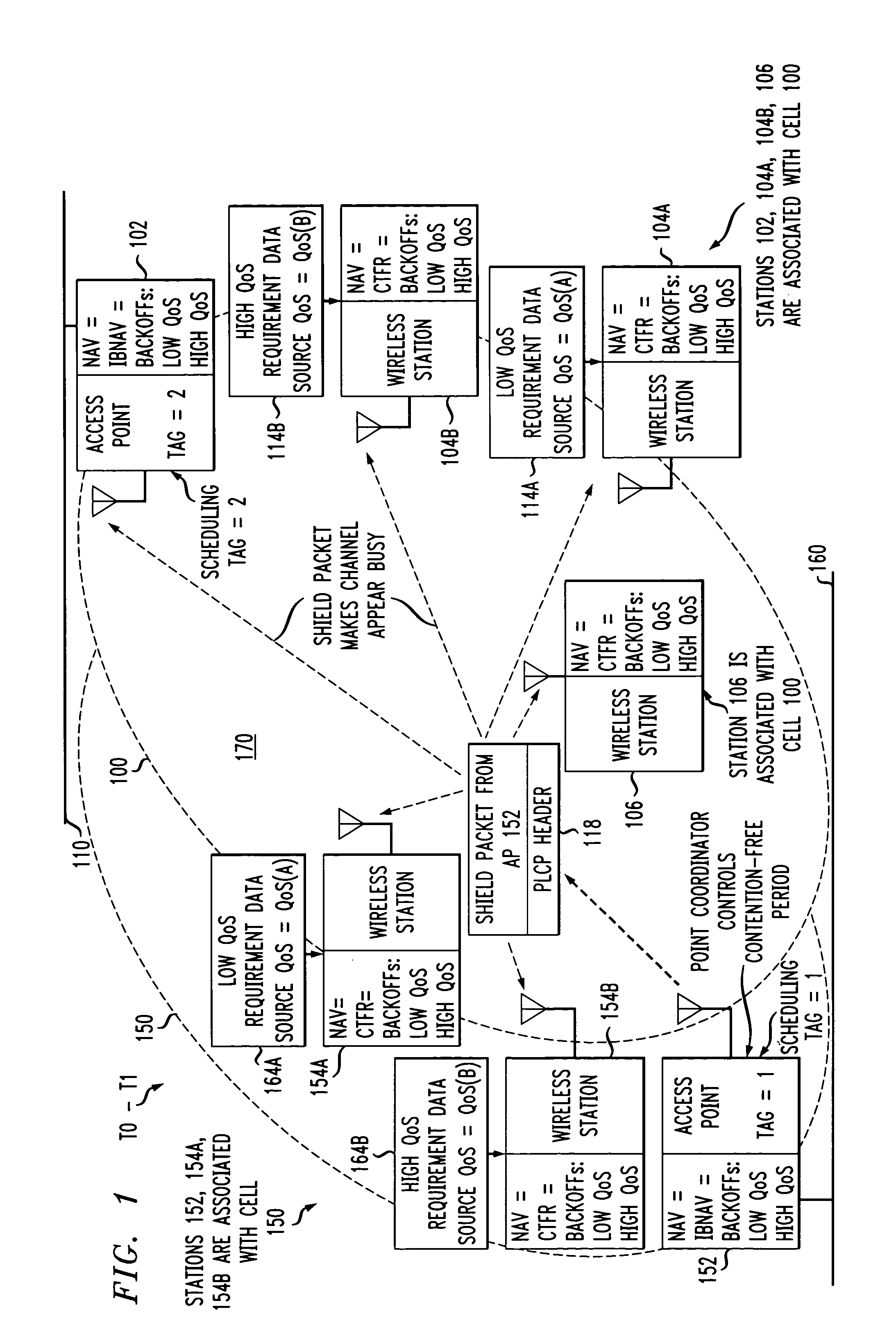
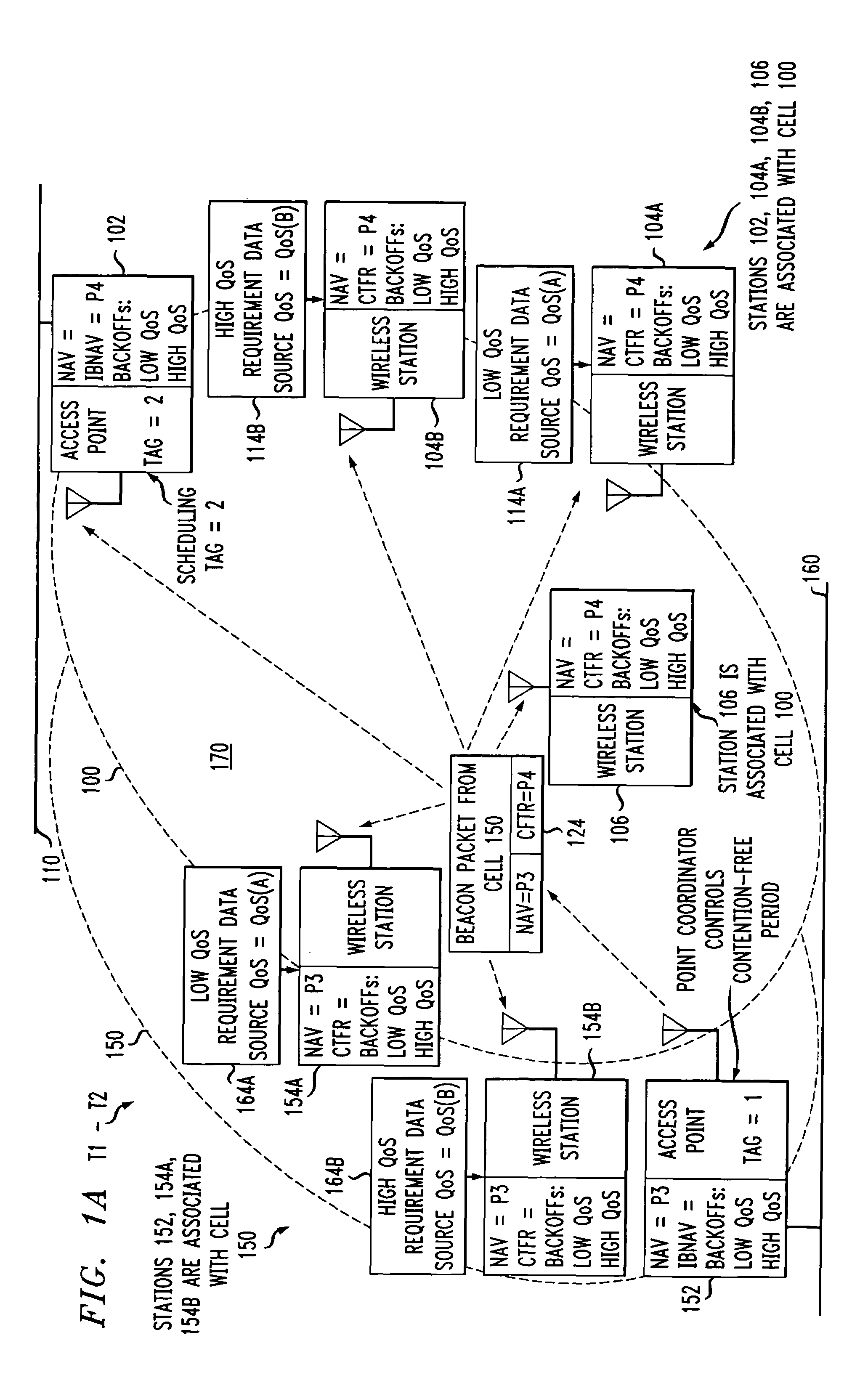
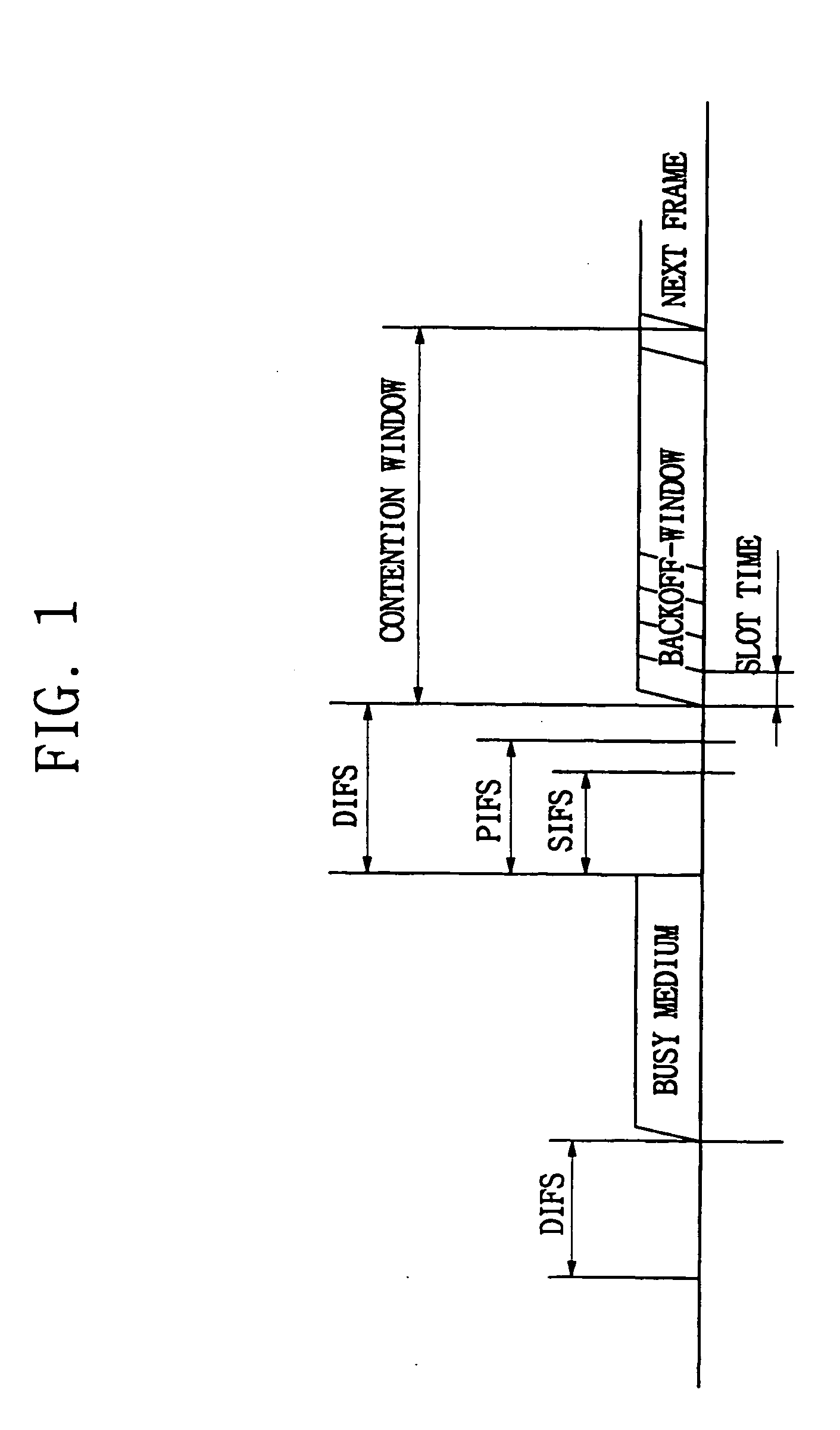
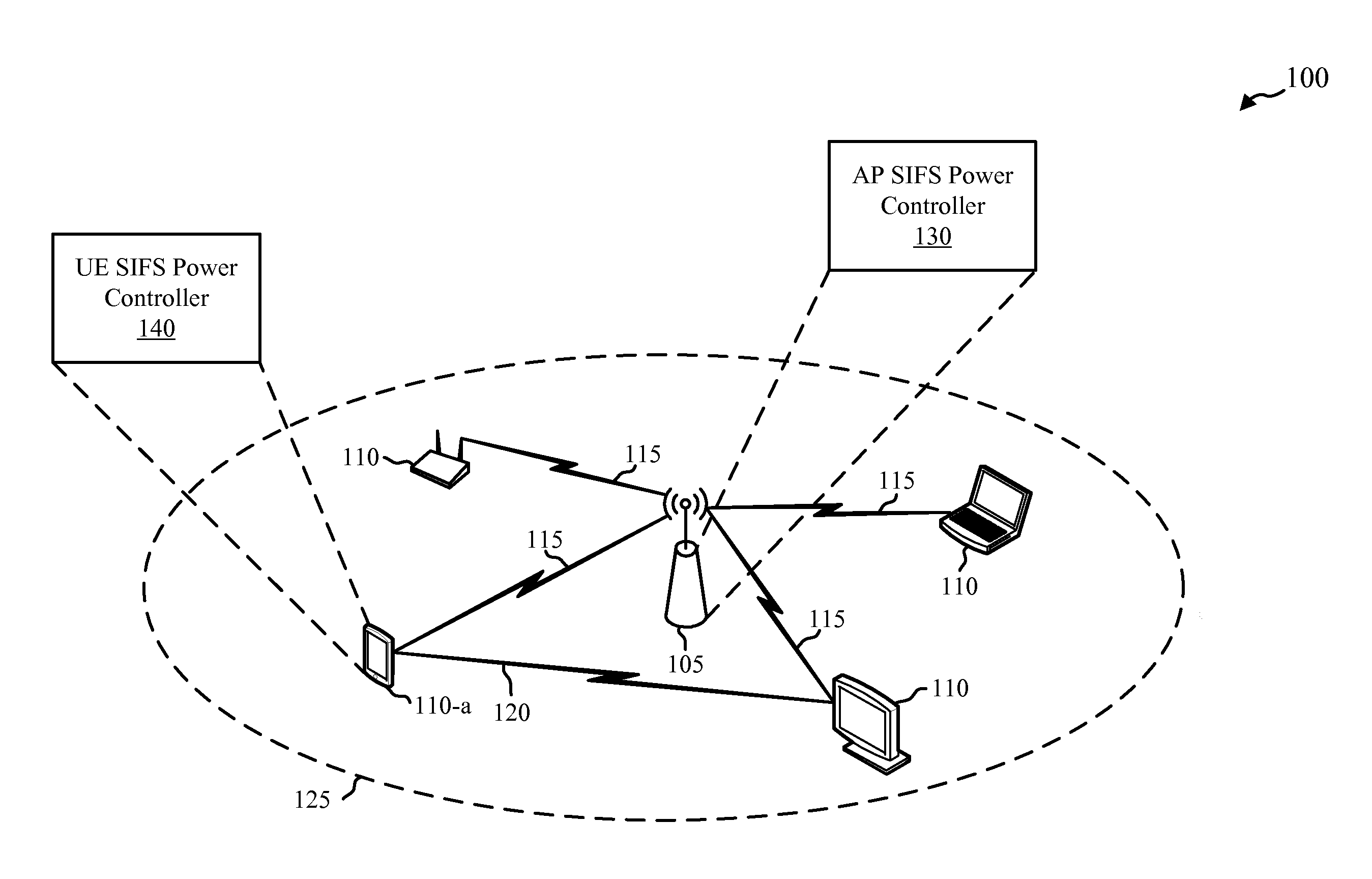
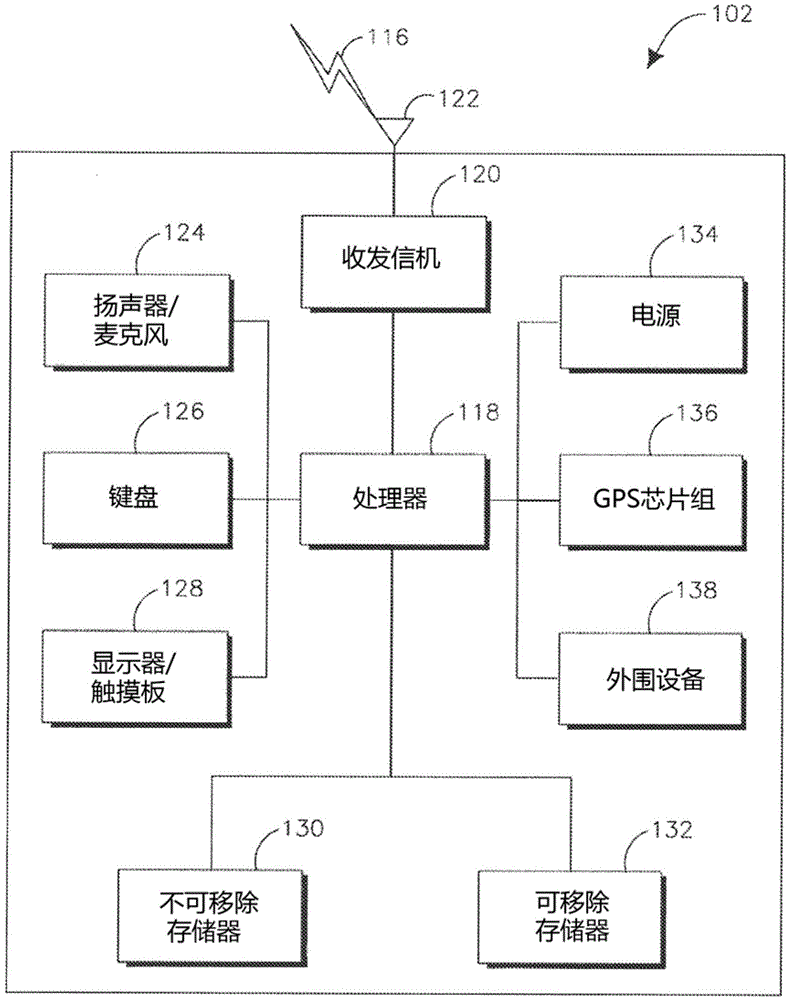
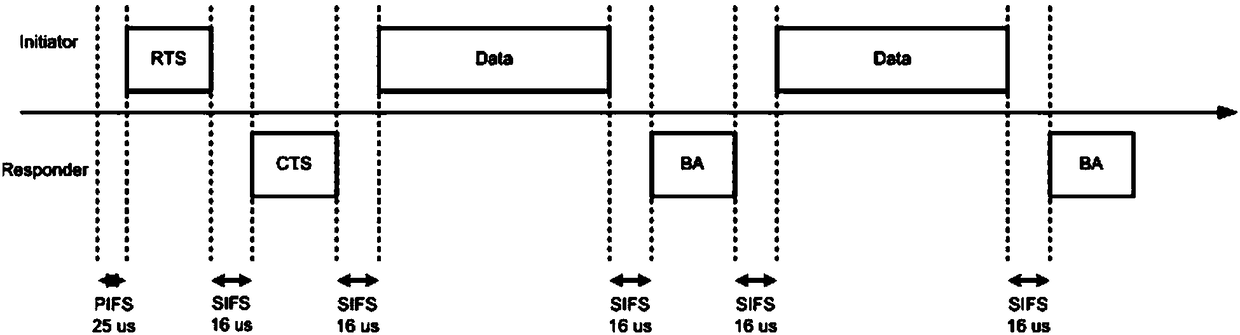
Short Interframe Space (SIFS), is the amount of time in microseconds required for a wireless interface to process a received frame and to respond with a response frame. It is the difference in time between the first symbol of the response frame in the air and the last symbol of the received frame in the air. A SIFS time consists of the delay in receiver RF, PLCP delay and the MAC processing delay, which depends on the physical layer used. In IEEE 802.11 networks, SIFS is the interframe spacing prior to transmission of an acknowledgment, a Clear To Send (CTS) frame, a block ack frame that is an immediate response to either a block ack request frame or an A-MPDU, the second or subsequent MPDU of a fragment burst, a station responding to any polling a by point coordination function and during contention free periods of point coordination function.
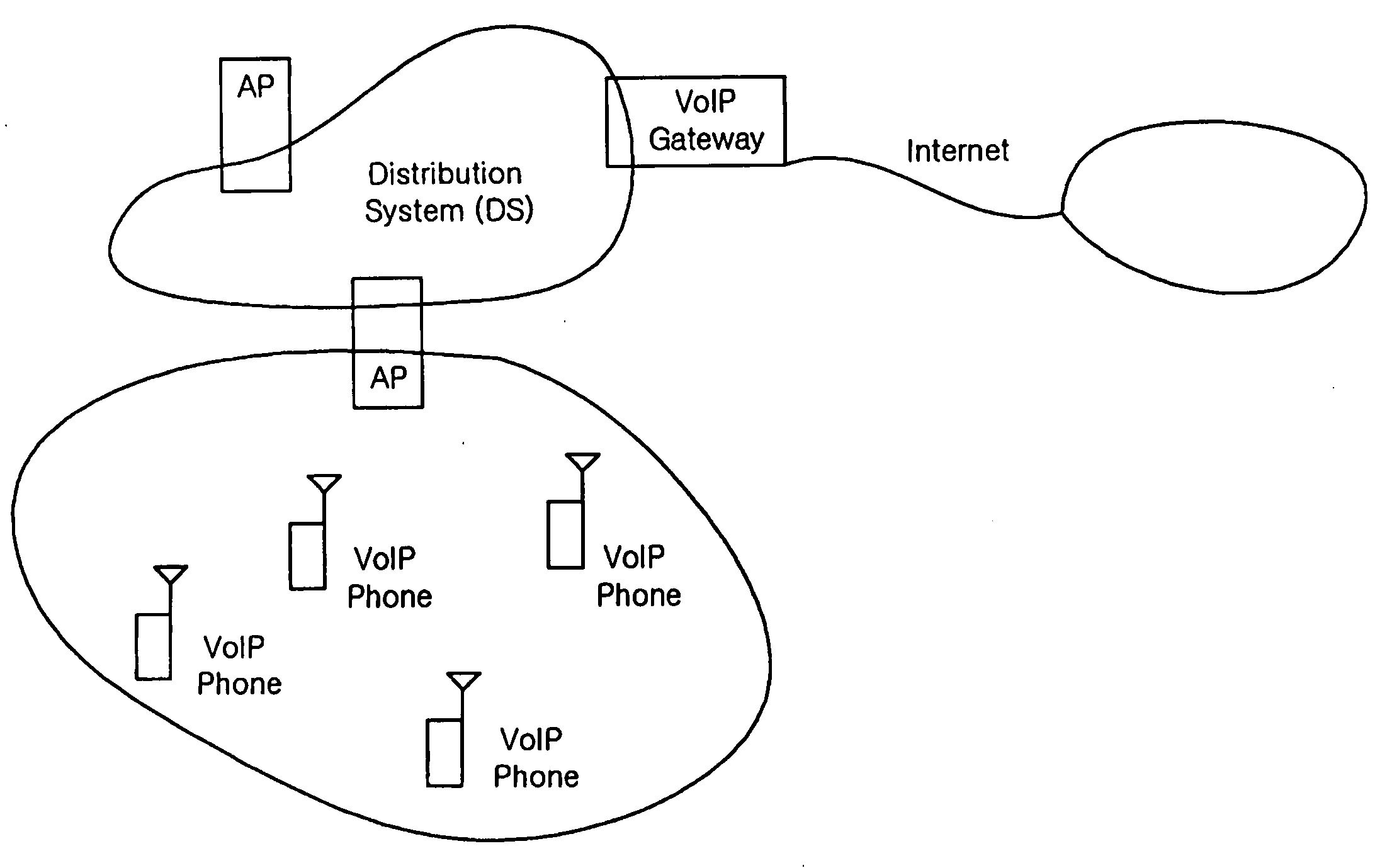
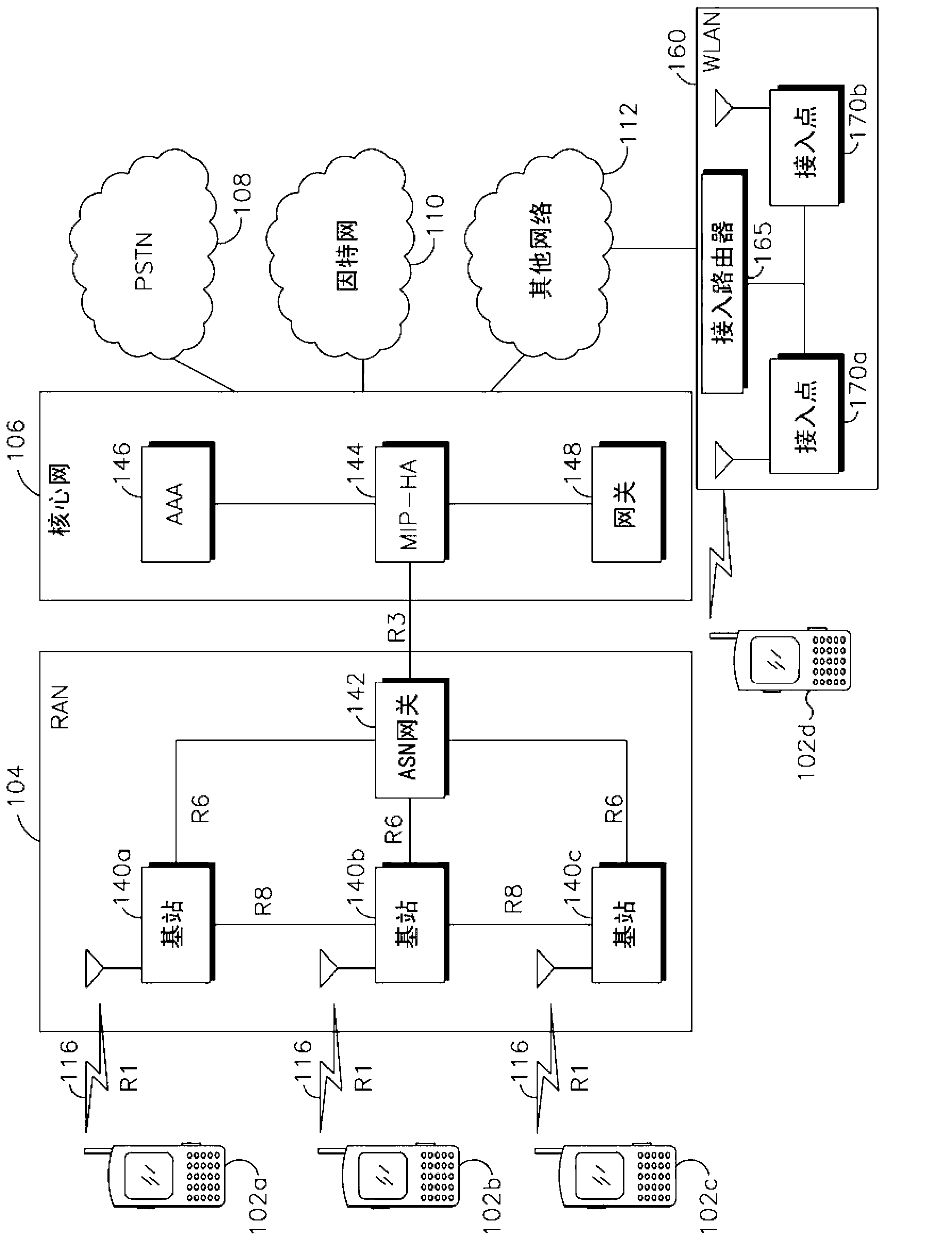
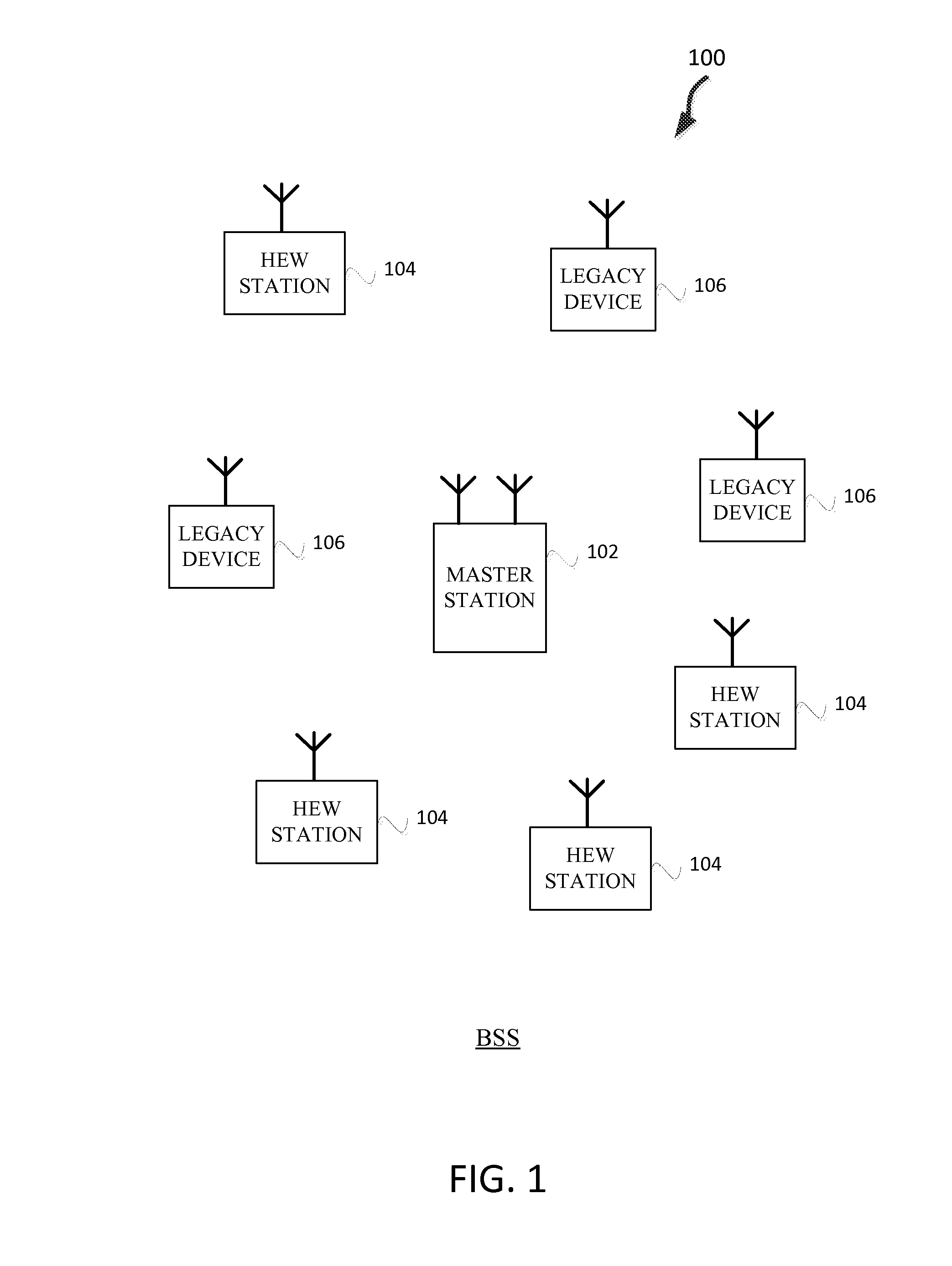
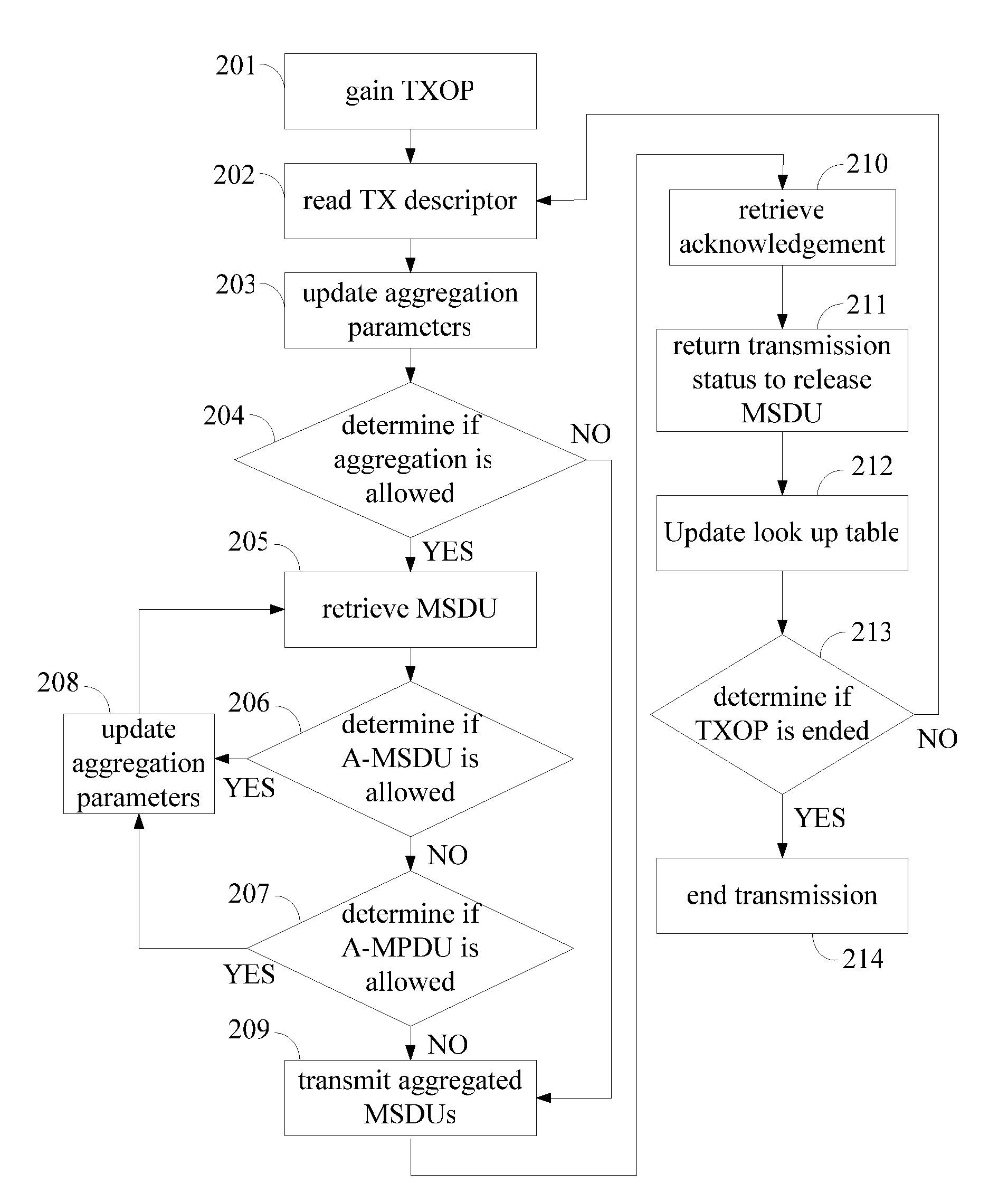
Group transmissions in wireless local area networks
A method for channel sounding by an access point includes transmitting a sounding frame to a plurality of mobile stations (STAs). The sounding frame includes training symbols to be measured by each of the plurality of STAs. A sounding response frame is received from each of the plurality of STAs. The sounding response frame received from a first STA of the plurality of STAs is received at a short interframe spacing interval delay after completion of the sounding request frame transmission.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Fixed deterministic post-backoff for cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) contention-free sessions
ActiveUS7245604B2Reduce conflictSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementIdle timeTimer
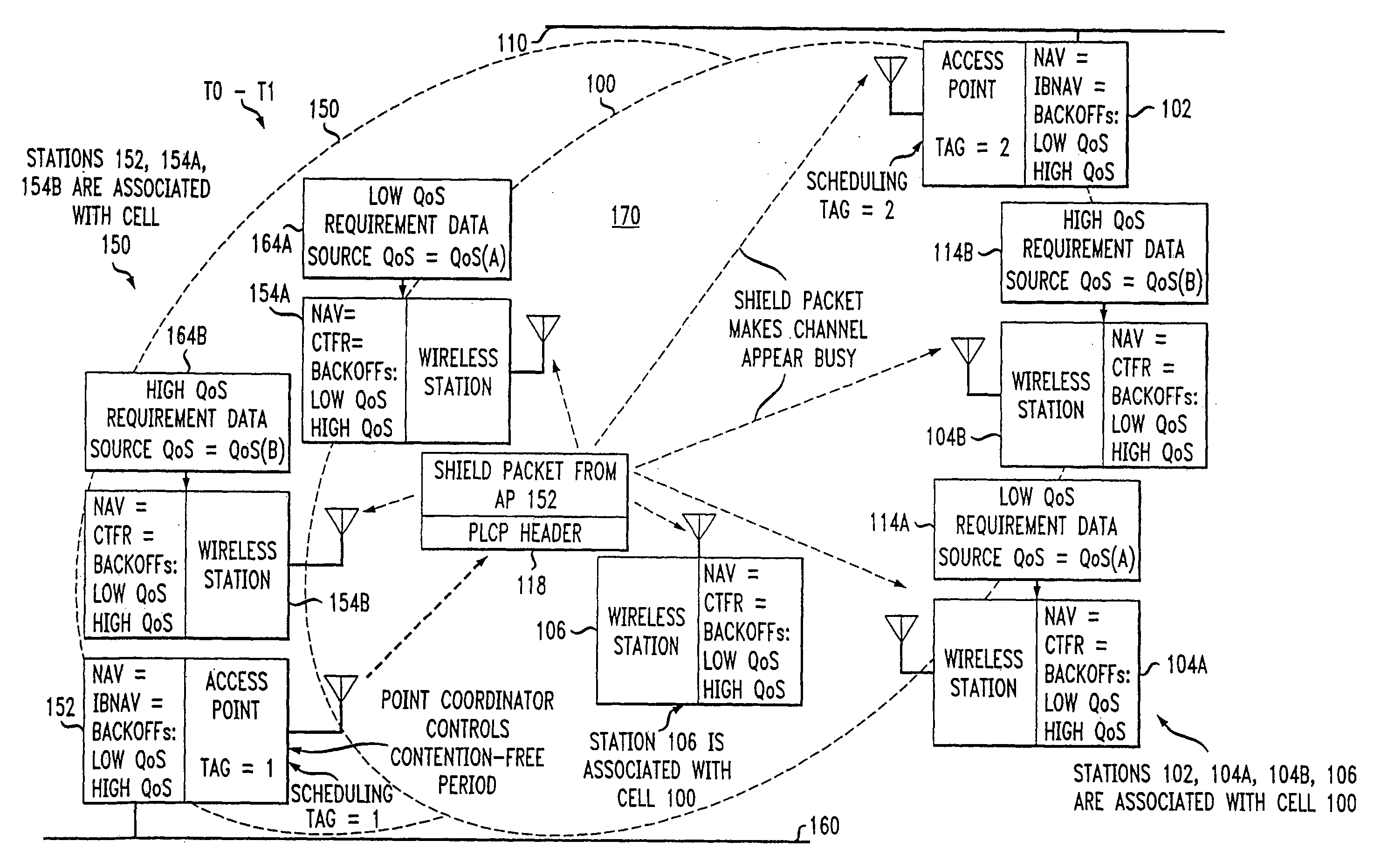
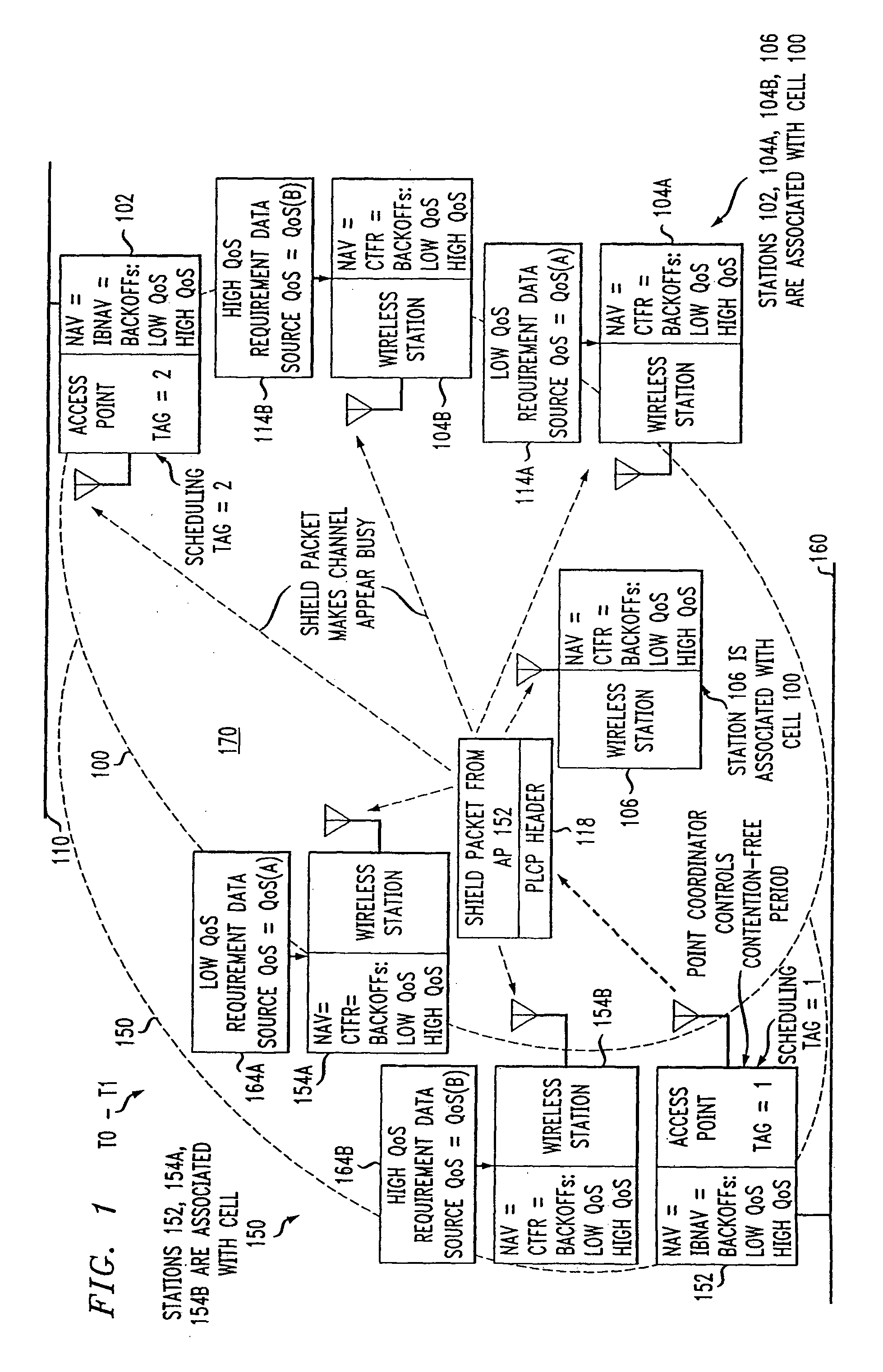
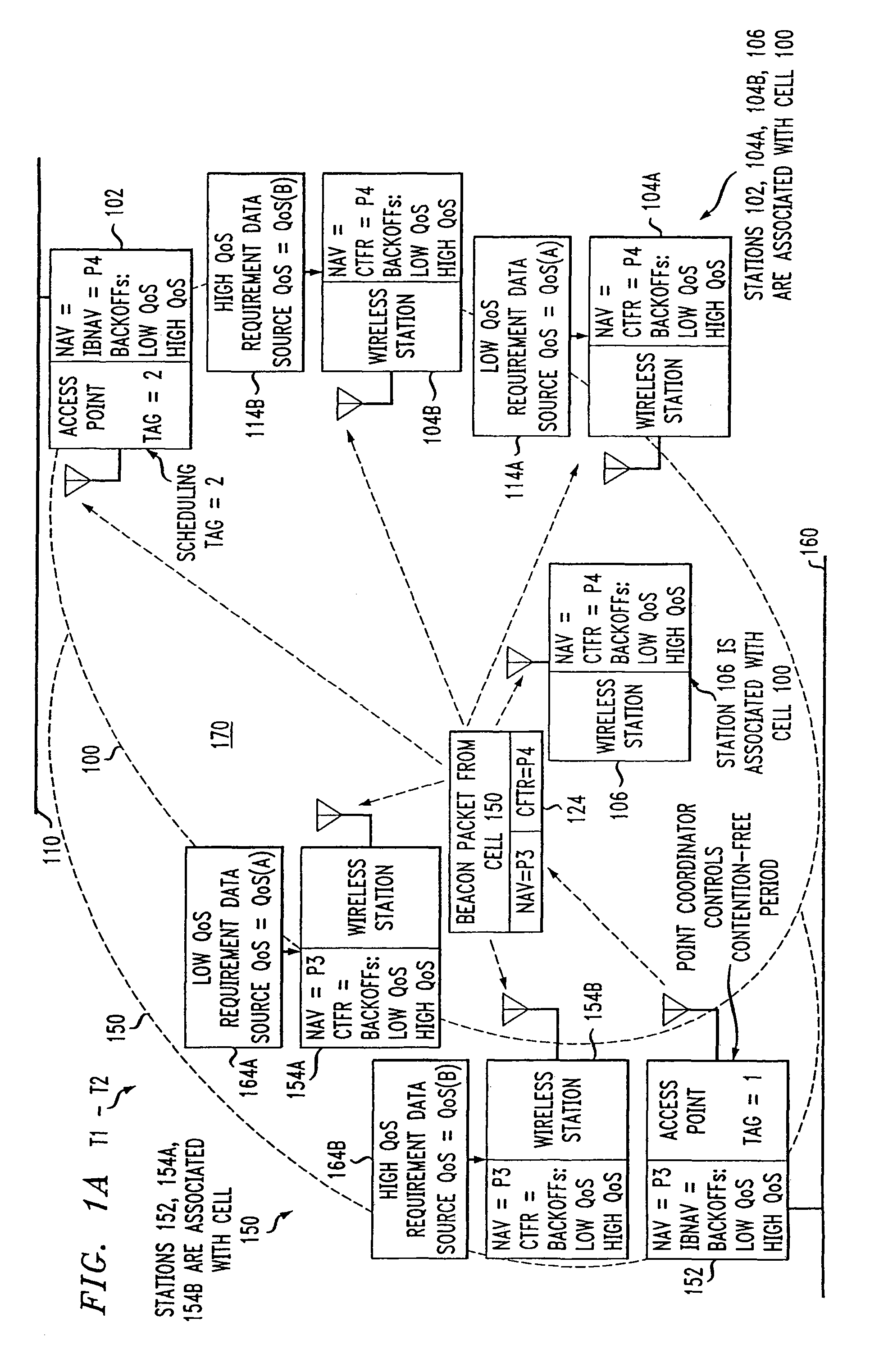
A cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) method is disclosed which includes Fixed Deterministic Post-Backoff. Fixed deterministic post-backoff reduces conflicts between access points of overlapping cells. Contention-free sessions (CFSs) can be generated, one from each overlapping cell. Each active access point engages in a fixed deterministic post-backoff. A fixed deterministic backoff delay (Bkoff times a fixed number of idle time slots) is used by all access points, with the value of Bkoff being greater than the number of overlapping cells. The Bkoff should be large enough to enable the traffic that needs to be accommodated by the channel. Each access point has a backoff timer that is counted down using the shortest interframe space possible, typically the Priority Interframe Space (PIFS). A contention-free session (CFS) is initiated when the backoff timer expires, and it is then reset to the value of Bkoff to start a new cycle. A cycle is measured in terms of idle time slots instead of a fixed time interval. Contention-based transmissions can be attempted by an access point or other stations in the cell using their assigned priority while the access point is counting down its backoff timer. A new access point can get started and resolve possible collisions by a small random backoff. Subsequent contention-free sessions (CFSs) will not conflict, given an existing sequence of non-conflicting CFSs, since the follower access point's backoff delay exceeds that of the leader's by at least one times the fixed number of idle time slots. In this manner, contention-free sessions can be conducted without interference in the first and second cells.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
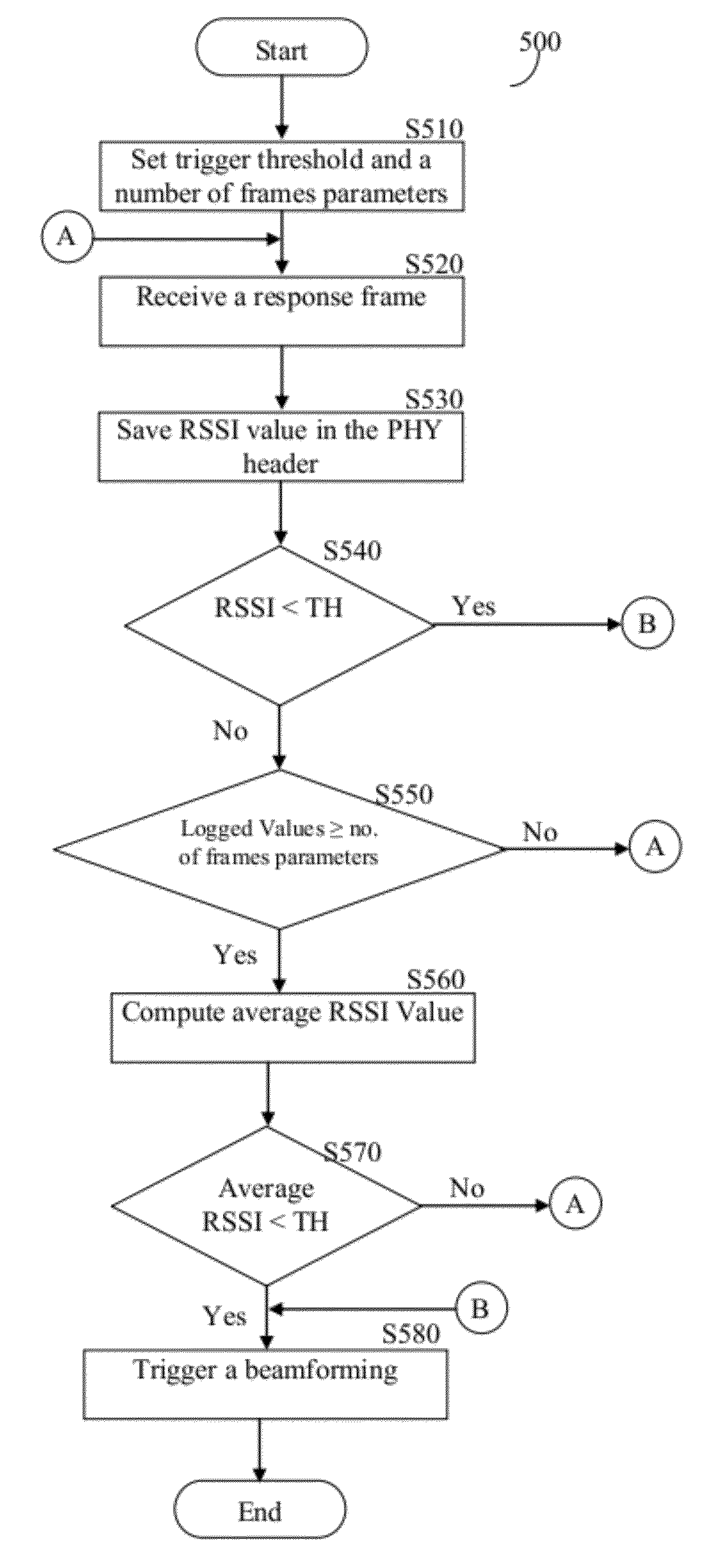
Techniques for minimizing the beam forming time in wireless local area networks
InactiveUS20120287797A1Shorten the timeError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsSignal qualityWireless lan
A method for beamforming in a wireless local area network (WLAN), the method is performed by a receiver wireless station. The method comprises receiving a frame transmitted by a transmitter wireless station over a wireless medium; analyzing a physical (PHY) header of the received frame to determine if a Short Interframe Space (SIFS) response is required; when a SIFS response is required, performing: constructing a response frame including a PHY header, wherein the PHY header includes at least a measured link quality field; inserting a measured signal quality in the measured link quality field; waiting a time equal to a SIFS period; and sending the response frame to the transmitter wireless station after the SIFS period has elapsed, wherein based on received measured values included in response frames the transmitter wireless station predicts a loss link to initiate a beamforming training, thereby reducing the beamforming time.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
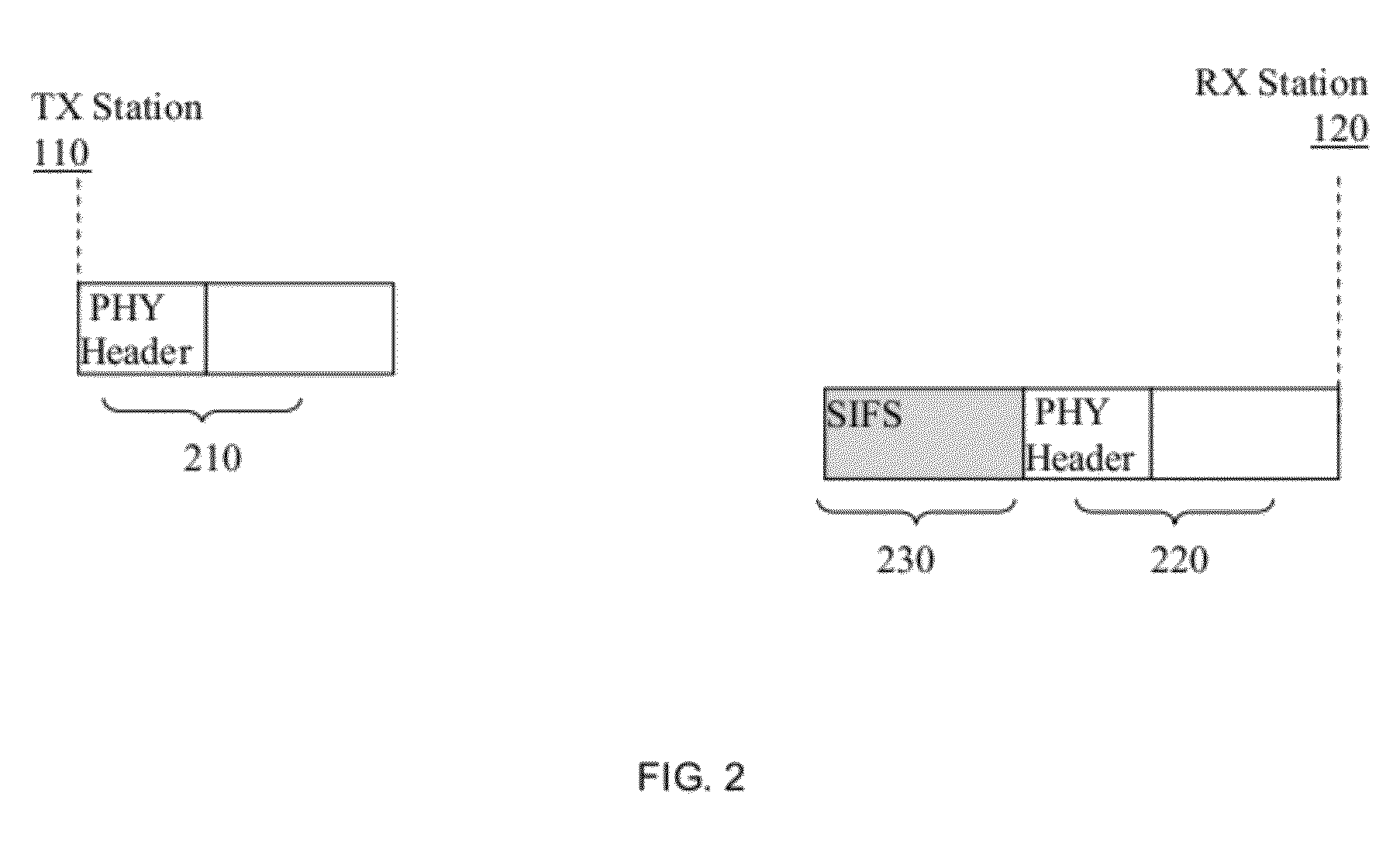
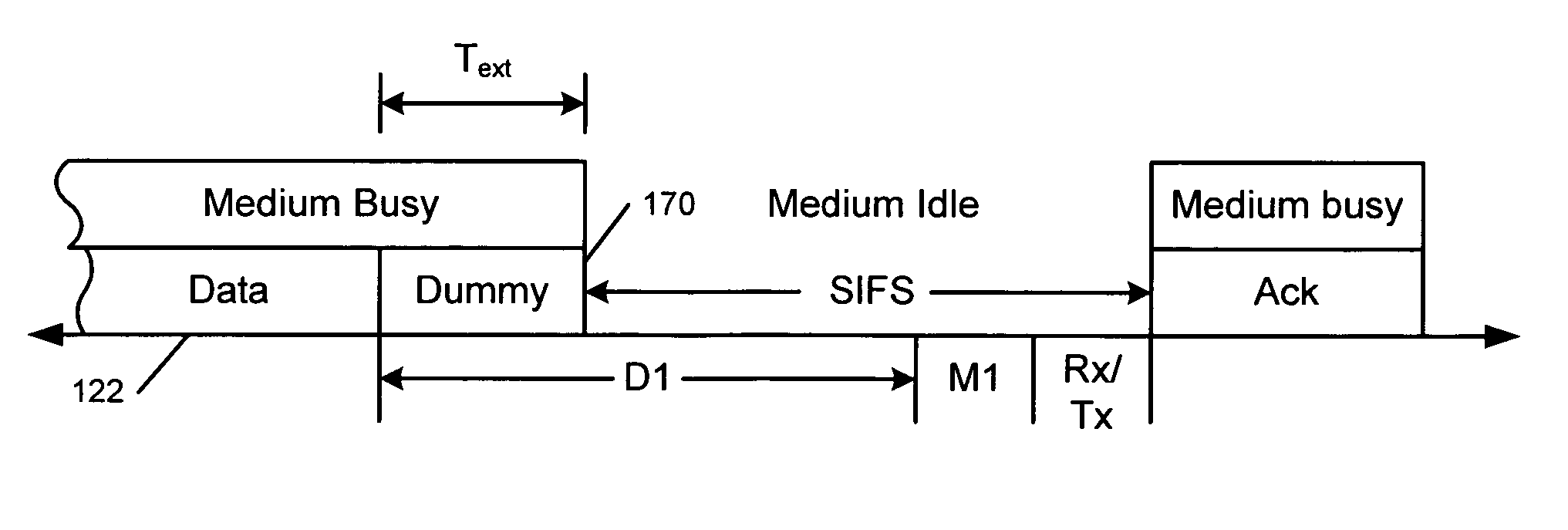
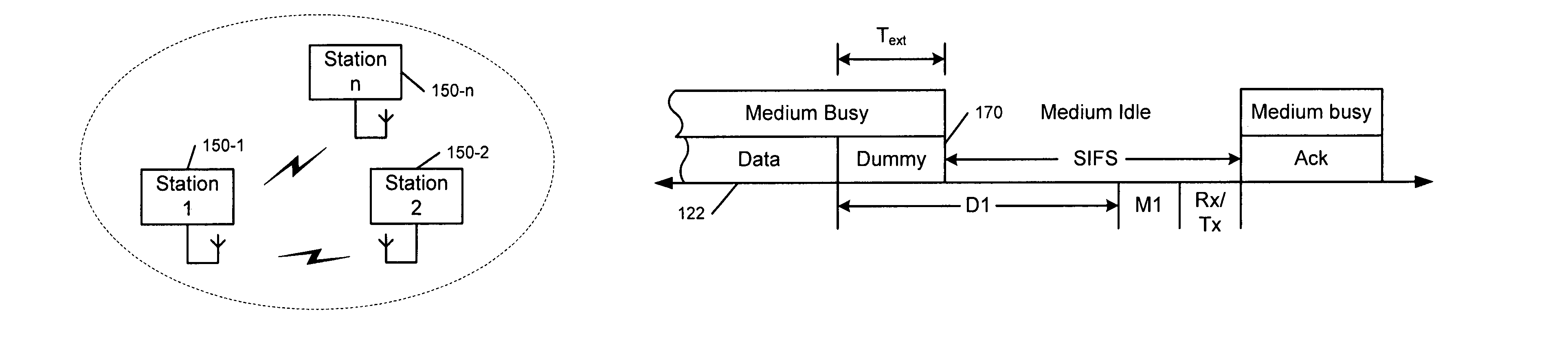
Extension mode for wireless lans complying with short interframe space requirement
A method and apparatus enables advanced signal processing in a wireless local area network (WLAN). First and second WLAN transceivers are provided with advanced signal processing capabilities. A maximum interframe period between data and an acknowledgement is required by the WLAN for compatibility. A duration of the interframe period is shorter than a duration that is required to perform the advanced signal processing. The first WLAN transceiver transmits a header and data. A first data field in the header is specified that enables the advanced signal processing. A second data field is specified that defines a data time period and an extension time period. The first WLAN transceiver transmits data during the data time period and dummy data during the extension time period. The second WLAN transceiver receives the header and initiates receiver processing during the extension time period.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Medium access control in wireless local area network
InactiveUS20050025131A1Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsDistributed coordination functionTelecommunications
A medium access control method of a CSMA / CA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance) based wireless LAN (Local Area Network) provides contention-free medium access authority to a station or access point receiving a request signal by: transmitting a request signal frame from an arbitrary station to another arbitrary station or to an access point via a medium occupied in transmission contention with a CSMA / CA algorithm using a DCF (Distributed Coordination Function) interframe space; and transmitting an acknowledgment signal frame from the station or the access point receiving the request signal frame to the station transmitting the request signal frame via an occupied medium using a short interframe space.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
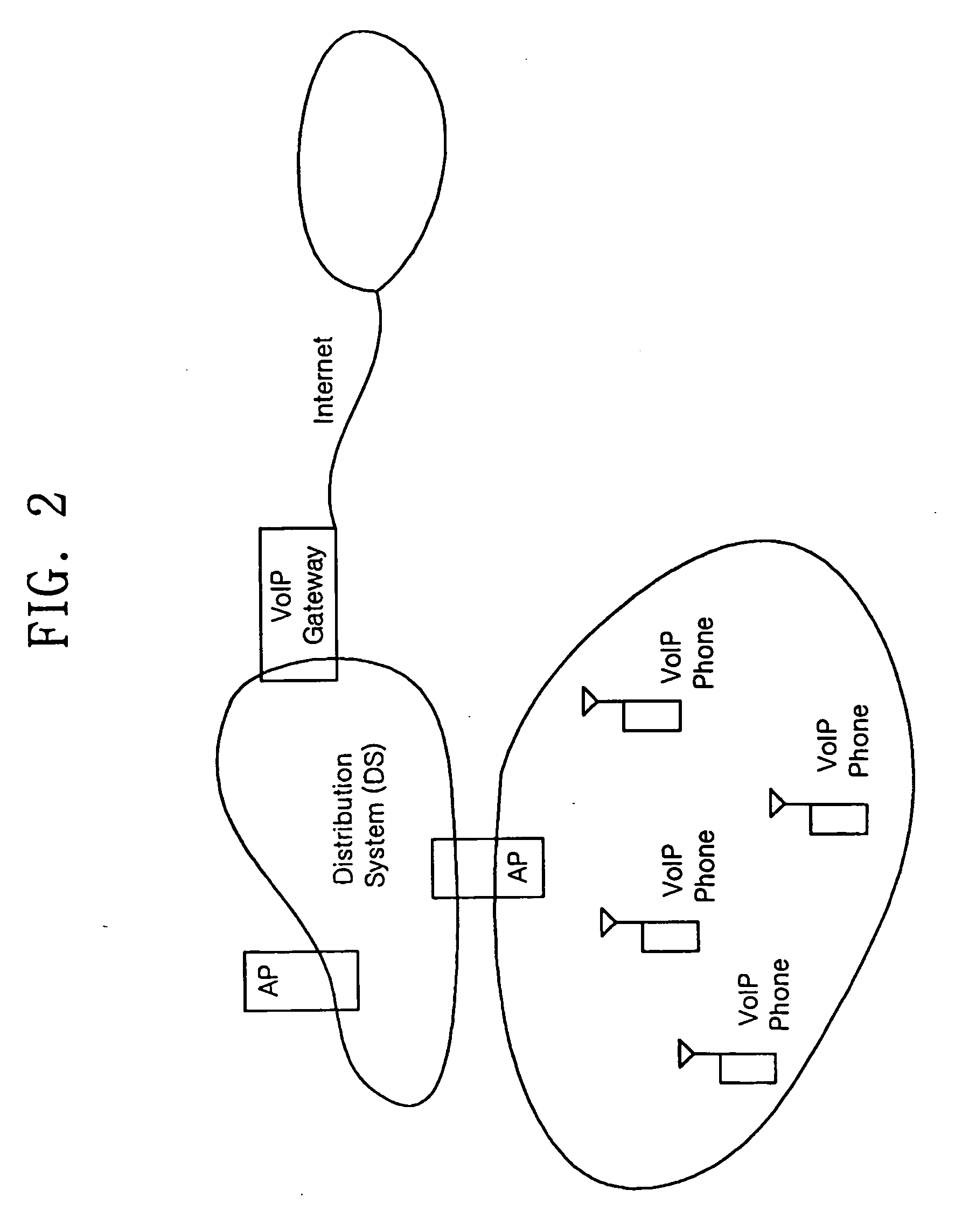
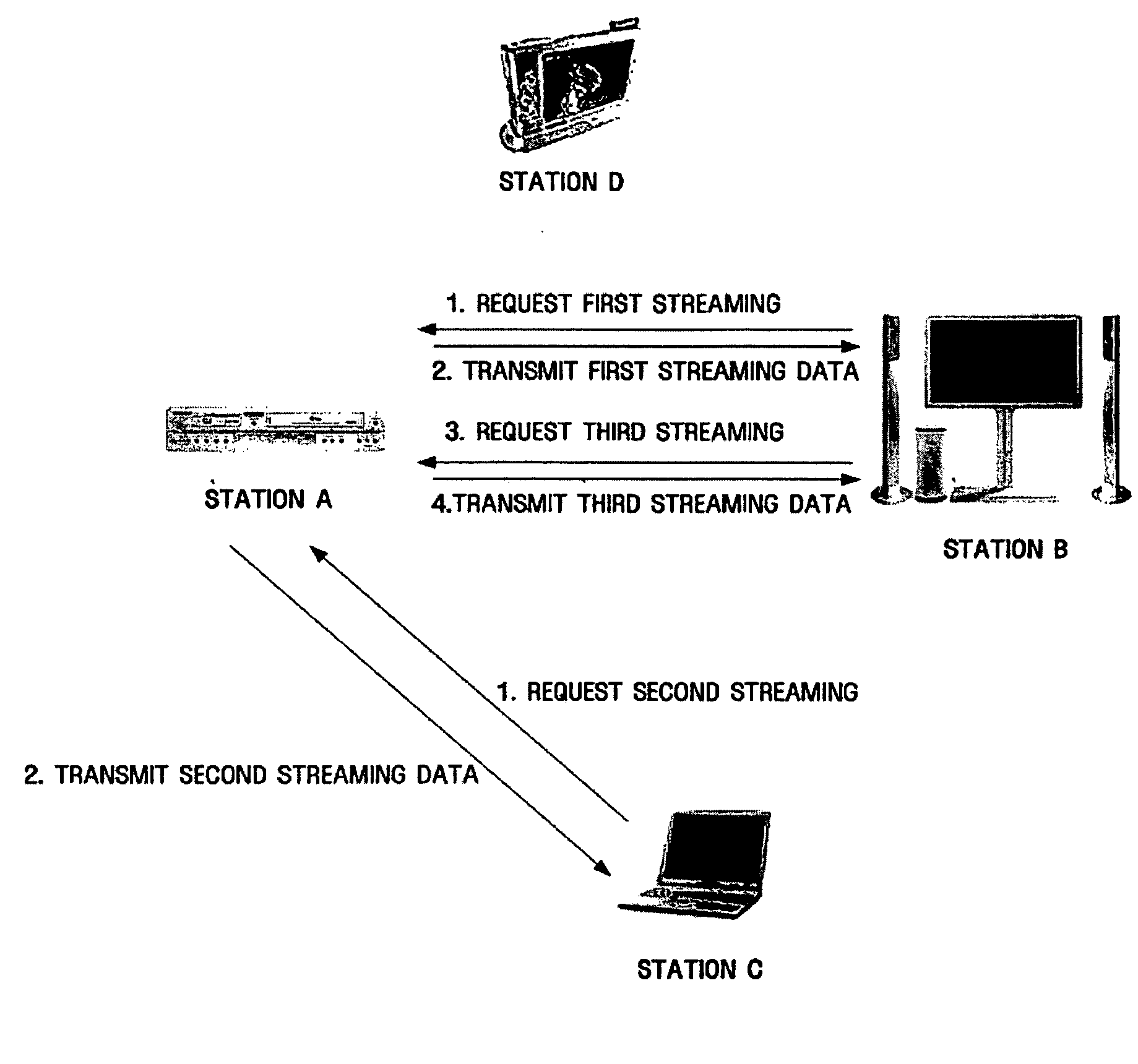
Method for data streaming in ad-hoc wireless local area network
InactiveUS20050050219A1Network topologiesData switching by path configurationStreaming dataData stream
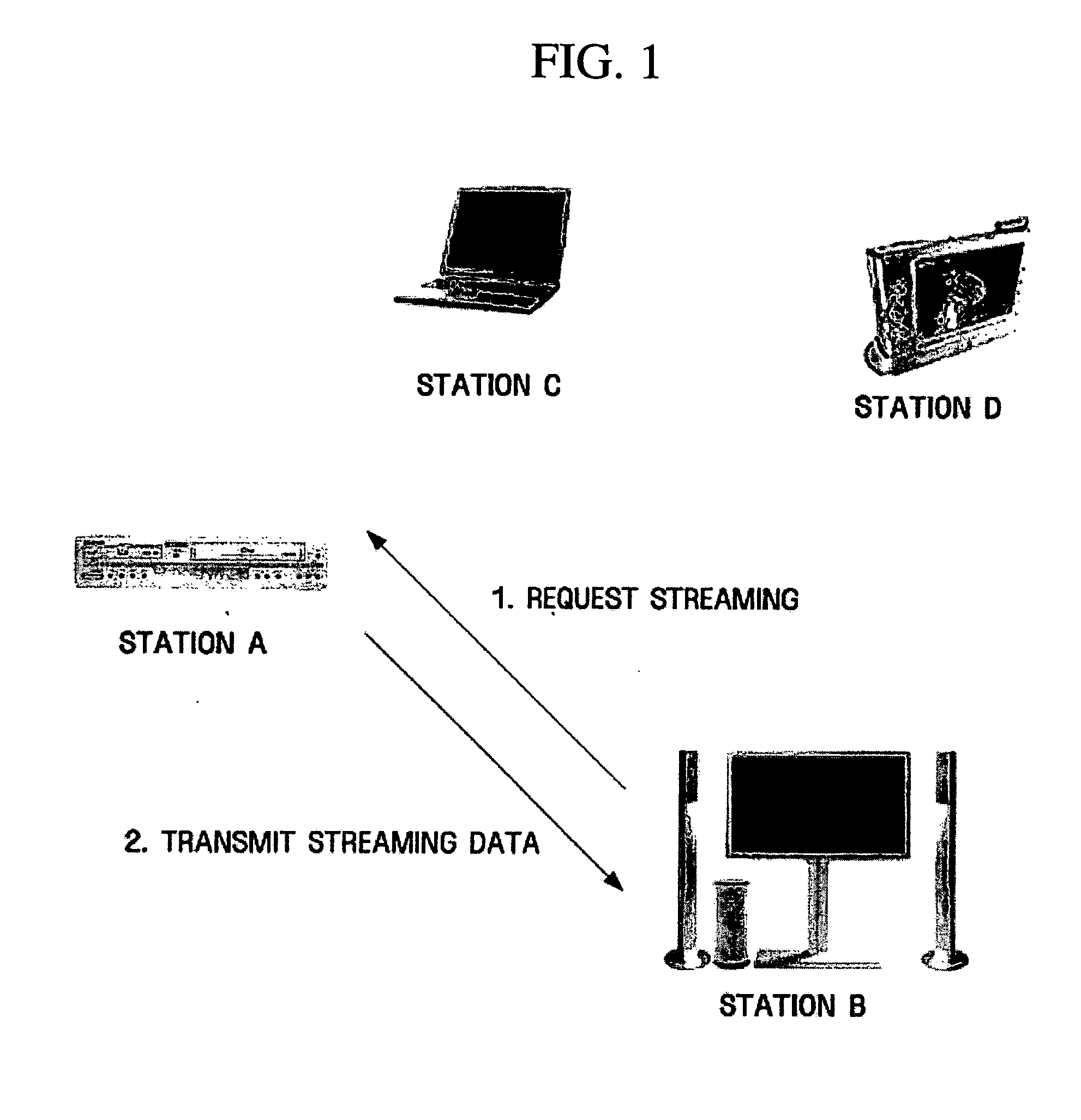
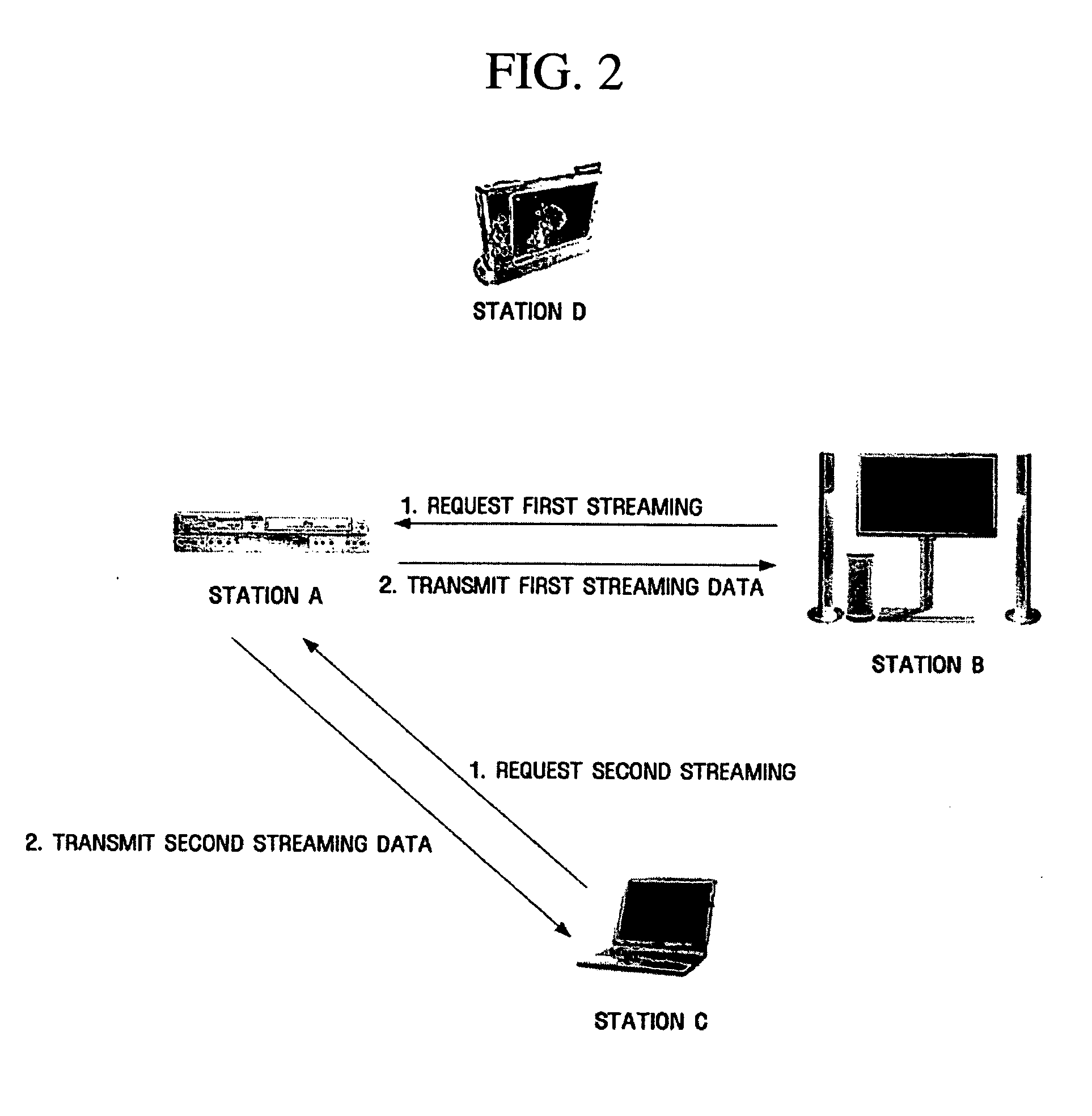
A method for data streaming in an ad-hoc wireless local area network (LAN). The method for data streaming includes receiving at least one streaming request frame that requests transmission of streaming data to at least one station, and transmitting frames containing the streaming data to at least one station with Short InterFrame Space (SIFS) interval. Streaming data is reliably transmitted in an ad-hoc wireless LAN without greatly changing existing wireless LAN standards.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Group transmissions in wireless local area networks
A method for channel sounding by an access point includes transmitting a sounding frame to a plurality of mobile stations (STAs). The sounding frame includes training symbols to be measured by each of the plurality of STAs. A sounding response frame is received from each of the plurality of STAs. The sounding response frame received from a first STA of the plurality of STAs is received at a short interframe spacing interval delay after completion of the sounding request frame transmission.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Fixed deterministic post-backoff for cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) contention-free sessions
ActiveUS20080013508A1Reduce conflictSynchronisation arrangementNetwork traffic/resource managementIdle timeTime segment
A cyclic prioritized multiple access (CPMA) method is disclosed which includes Fixed Deterministic Post-Backoff. Fixed deterministic post-backoff reduces conflicts between access points of overlapping cells. Contention-free sessions (CFSs) can be generated, one from each overlapping cell. Each active access point engages in a fixed deterministic post-backoff. A fixed deterministic backoff delay (Bkoff times a fixed number of idle time slots) is used by all access points, with the value of Bkoff being greater than the number of overlapping cells. The Bkoff should be large enough to enable the traffic that needs to be accommodated by the channel. Each access point has a backoff timer that is counted down using the shortest interframe space possible, typically the Priority Interframe Space (PIFS). A contention-free session (CFS) is initiated when the backoff timer expires, and it is then reset to the value of Bkoff to start a new cycle. A cycle is measured in terms of idle time slots instead of a fixed time interval. Contention-based transmissions can be attempted by an access point or other stations in the cell using their assigned priority while the access point is counting down its backoff timer. A new access point can get started and resolve possible collisions by a small random backoff. Subsequent contention-free sessions (CFSs) will not conflict, given an existing sequence of non-conflicting CFSs, since the follower access point's backoff delay exceeds that of the leader's by at least one times the fixed number of idle time slots. In this manner, contention-free sessions can be conducted without interference in the first and second cells.
Owner:AT & T INTPROP II LP
Solving a hidden node problem due to transmission power imbalance
InactiveUS20120243519A1Network topologiesWireless commuication servicesClear to sendHidden node problem
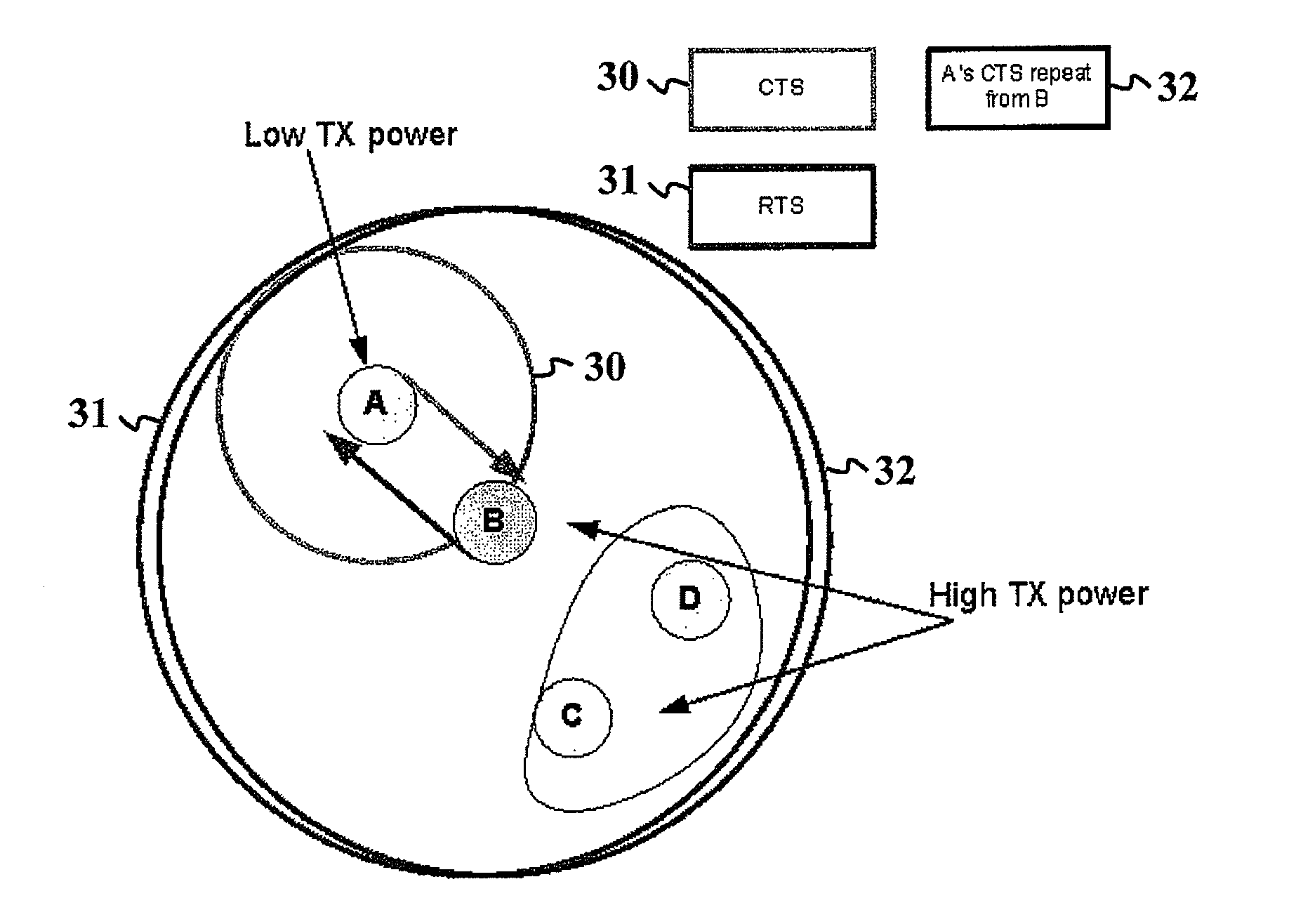
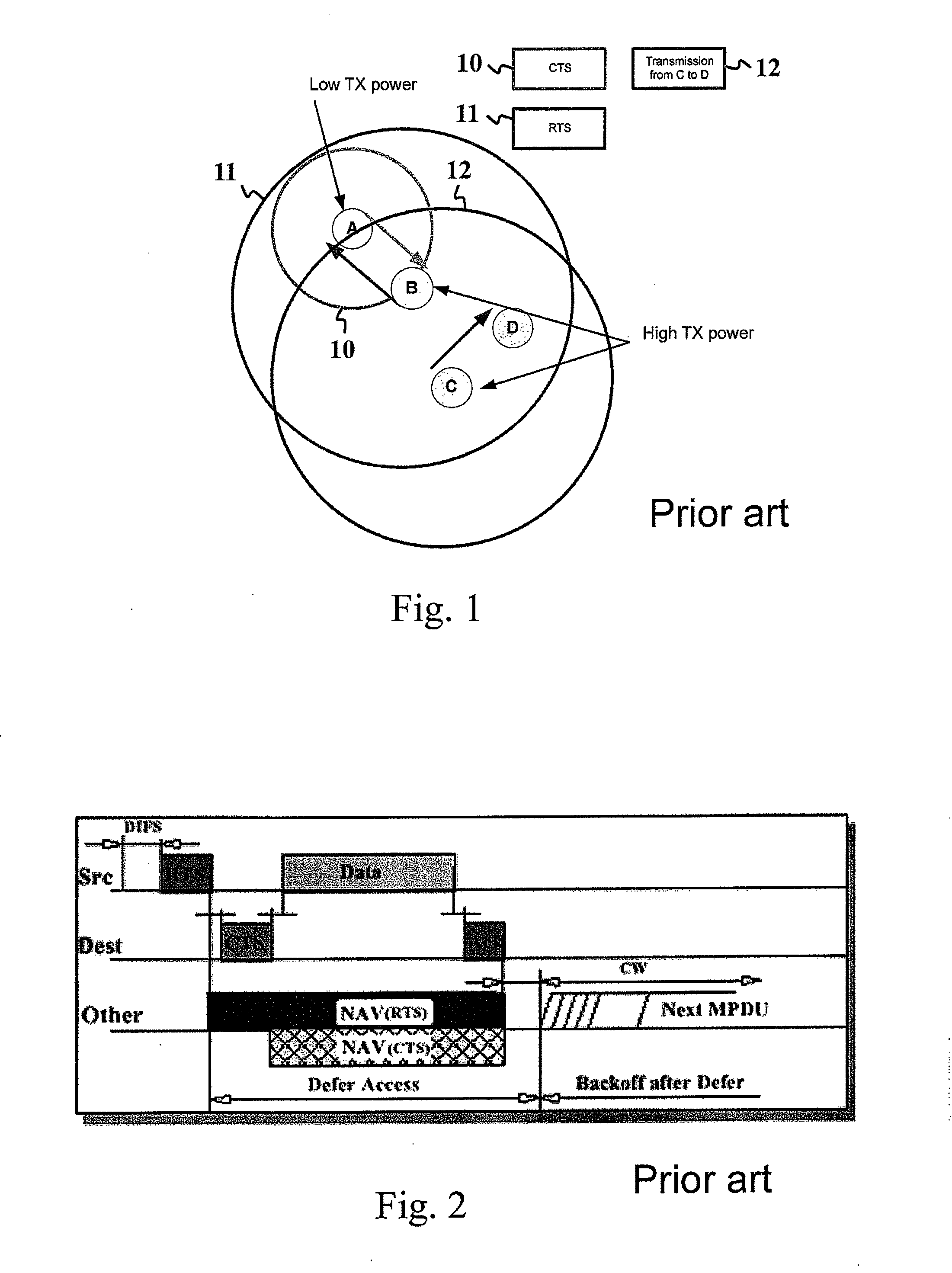
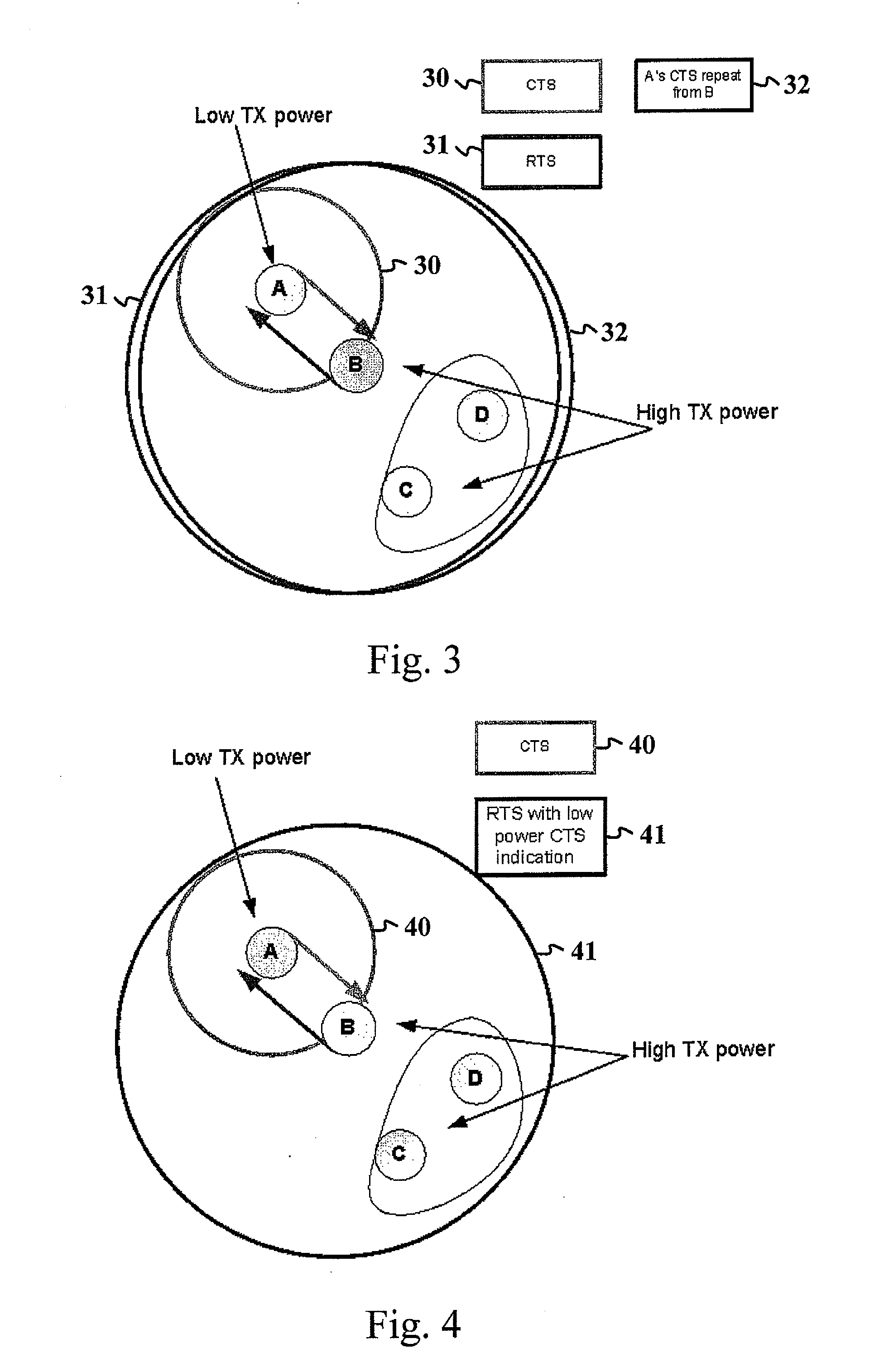
The present invention discloses an apparatus, a method and a computer program for resolving a hidden node problem in relation to handshake message transferring e.g. in WLAN networks. In one embodiment of the invention, the apparatus receiving a Clear to Send (CTS) message repeats the message after a Short Interframe Space (SIFS) time period. Stations not directly hearing the original CTS due to a low power are able to receive the repeated CTS and defer their transmissions accordingly. In another embodiment, the apparatus receiving the CTS message indicates in its Ready to Send (RTS) message that the CTS sender station has a low transmitting power. With this knowledge, the other present stations can defer their transmissions until they are sure that the data transfer between the first two stations having the RTS-CTS messaging has not been initiated or is already completed.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Medium access control in wireless local area network
InactiveCN1578239AData switching by path configurationWireless communicationDistributed coordination functionTelecommunications
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
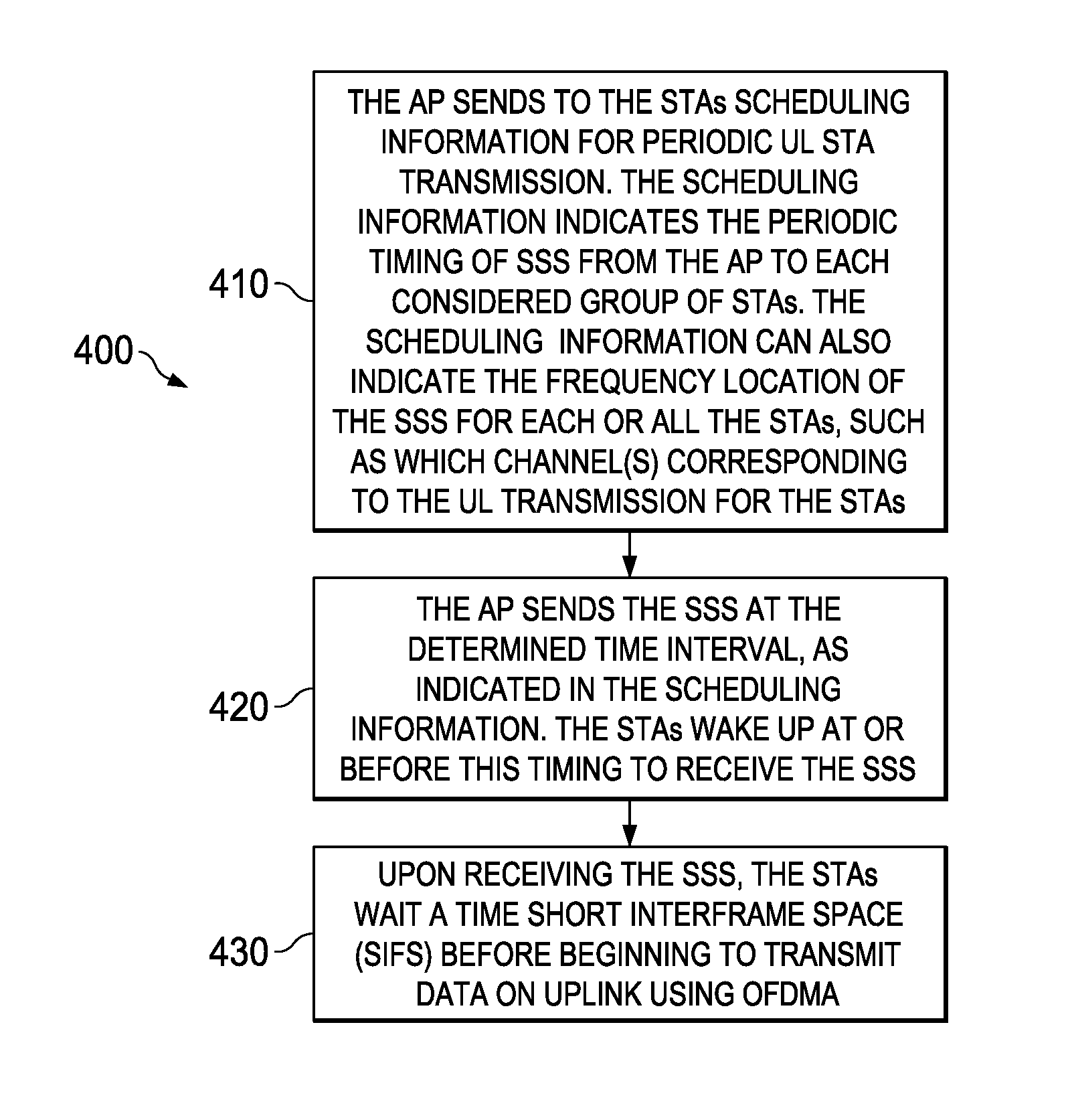
System and Method for Uplink OFDMA Transmission
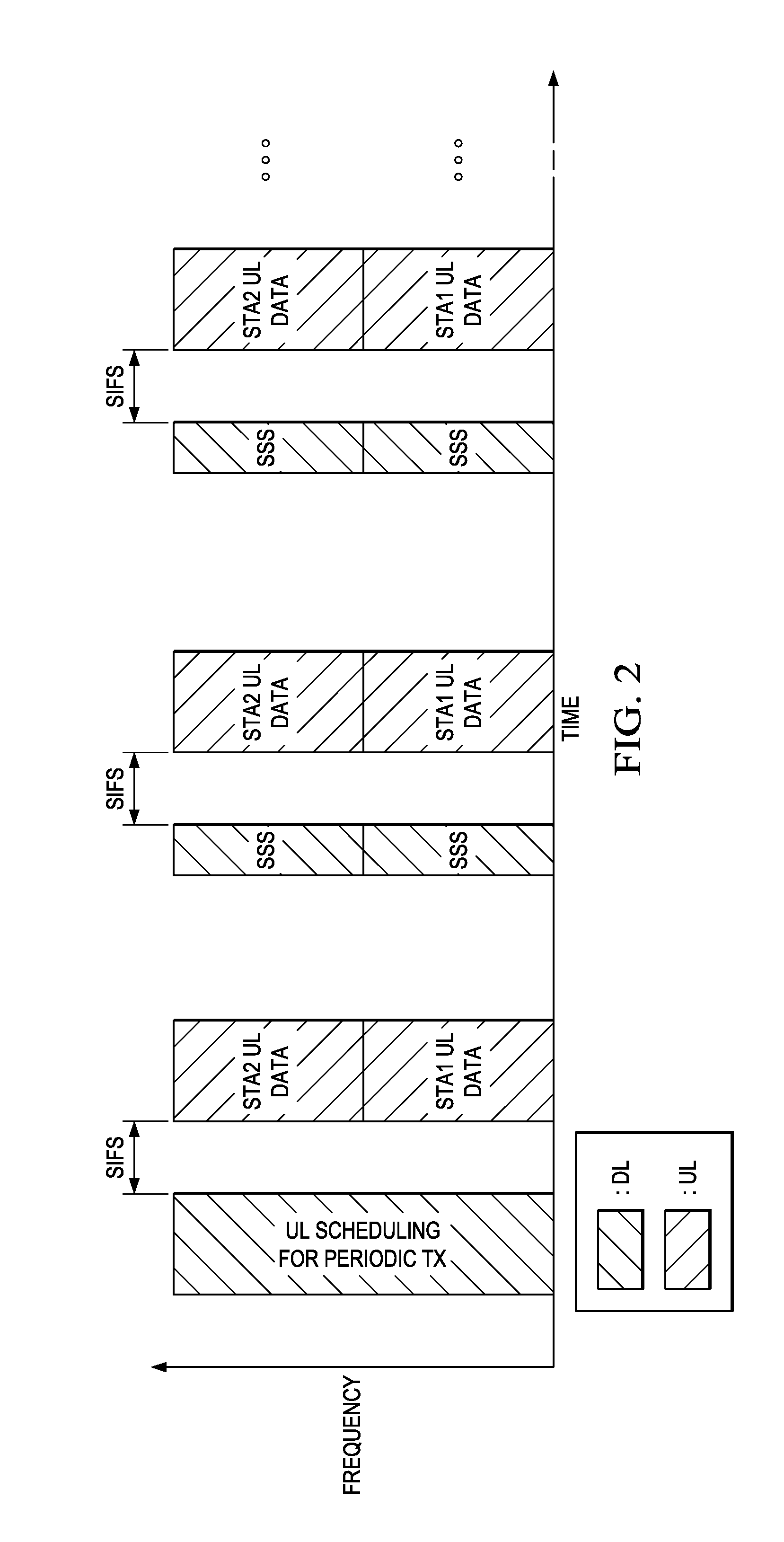
ActiveUS20150201432A1Easy to useTransmission path divisionSignal allocationTelecommunicationsWifi network
Embodiments are provided for implementing efficient uplink (UL) orthogonal frequency division-multiple access (OFDMA) transmission in wireless systems, such as in WiFi networks. An embodiment method includes sending, by an access point (AP) to a plurality of stations (STAs), scheduling information for periodic UL transmission, and sending, to the STAs, a short synchronous signal (SSS) in accordance with the scheduling information for periodic UL transmission. The method further includes receiving, from the STAs, a corresponding UL transmission in response to receiving the SSS. The UL transmission is sent by each of the plurality of the STAs at about a same time. The STAs wait for a time short interframe space (SIFS) after receiving the SSS, before sending, to the AP, the UL transmission.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Wireless MAC layer throughput improvements
ActiveUS7606213B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionRandom-access channelTransmitter
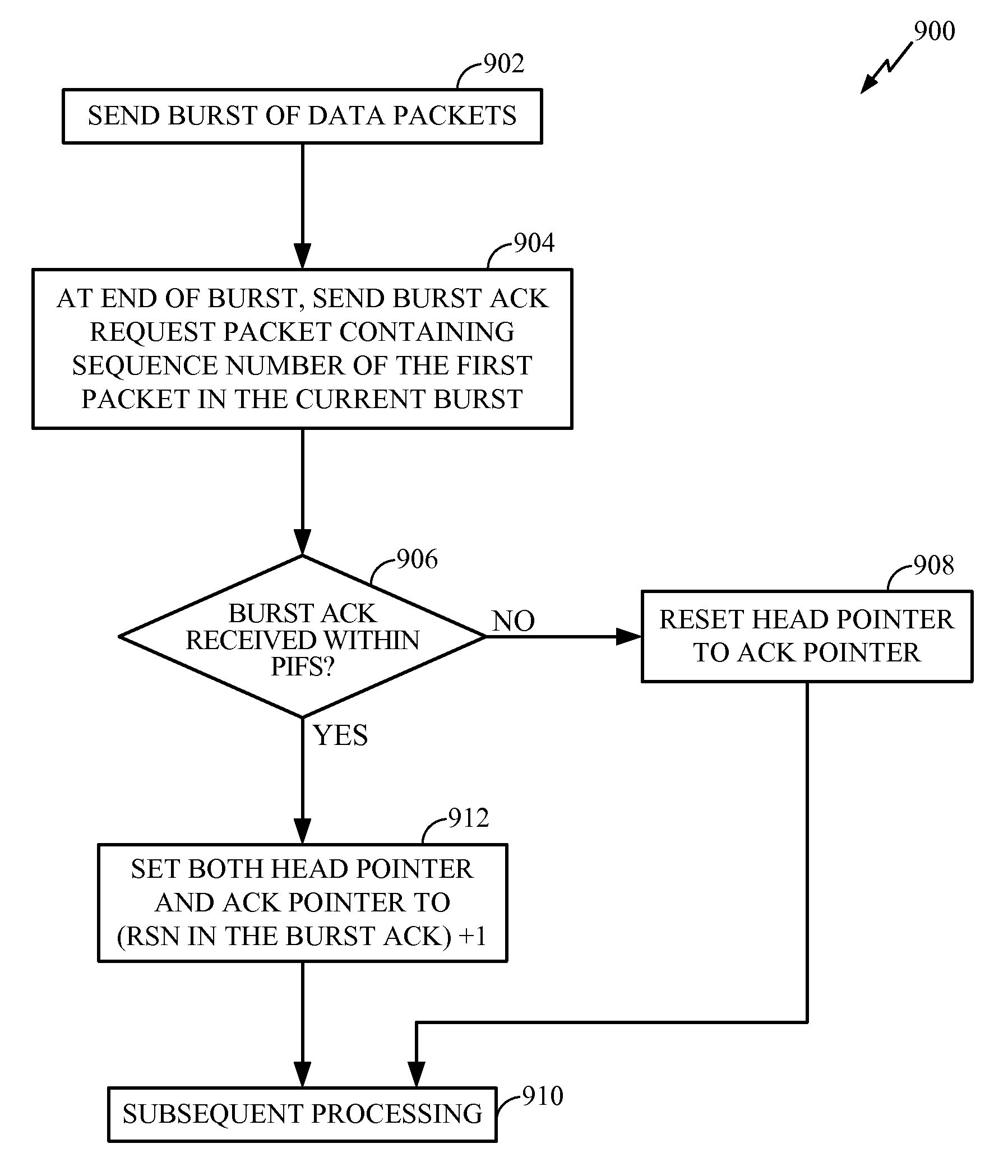
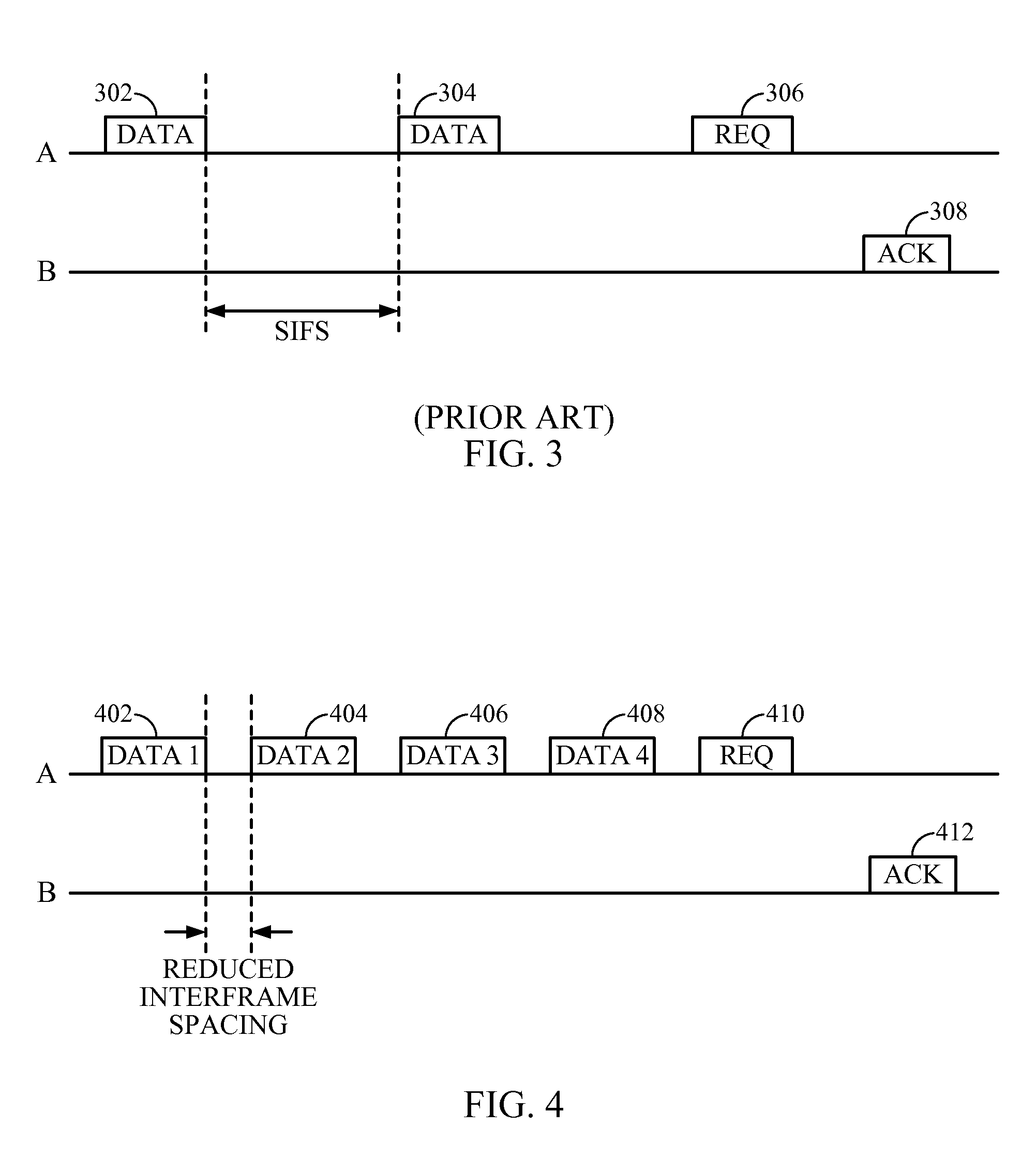
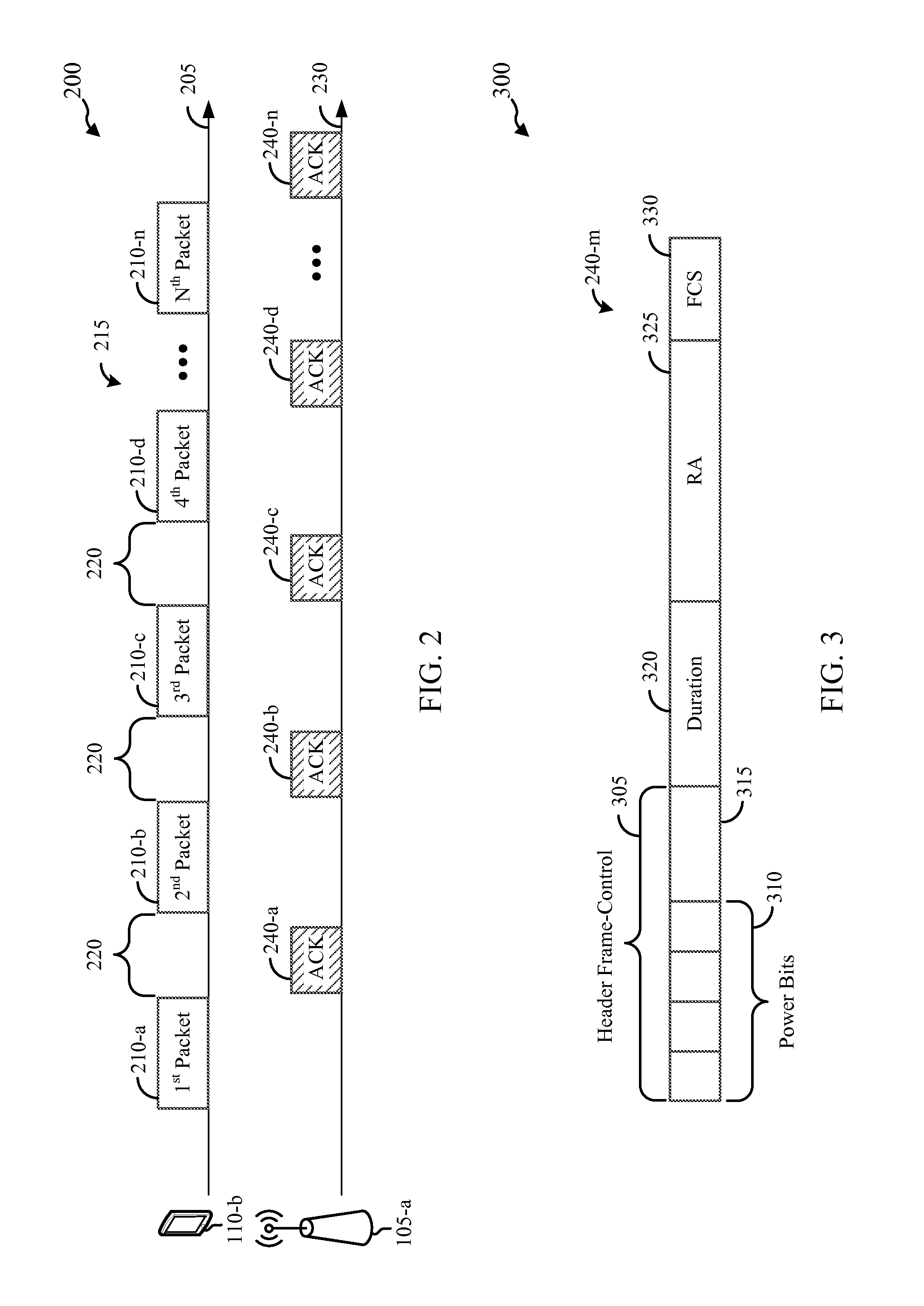
Methods, apparatuses, and systems are presented for transmitting data packets in a wireless network over a multi-access channel involving sequentially sending a plurality of medium access control (MAC) data packets from a transmitter over the multi-access channel, using a physical layer protocol based on a standard physical layer protocol having a short interframe spacing (SIFS), wherein the plurality of MAC data packets includes at least a first data packet and a second data packet separated by a reduced interframe spacing that is less than SIFS, attempting to receive the plurality of MAC data packets at a receiver using the physical layer protocol, including the first data packet and the second data packet separated by the reduced interframe spacing, and sending from the receiver a single acknowledgement packet associated with attempting to receive the plurality of MAC data packets.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Techniques for managing sifs-bursting in WLAN system
Methods and apparatuses for providing closed-loop power control during a short inter-frame space (SIFS) burst are described herein. A method includes receiving feedback associated with transmit power used to transmit a first data packet in a SIFS burst. The method also includes adjusting at least the transmit power, or a modulation and coding scheme (MCS), or a combination thereof, used to transmit a second data packet of the SIFS burst based at least in part on the received feedback.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
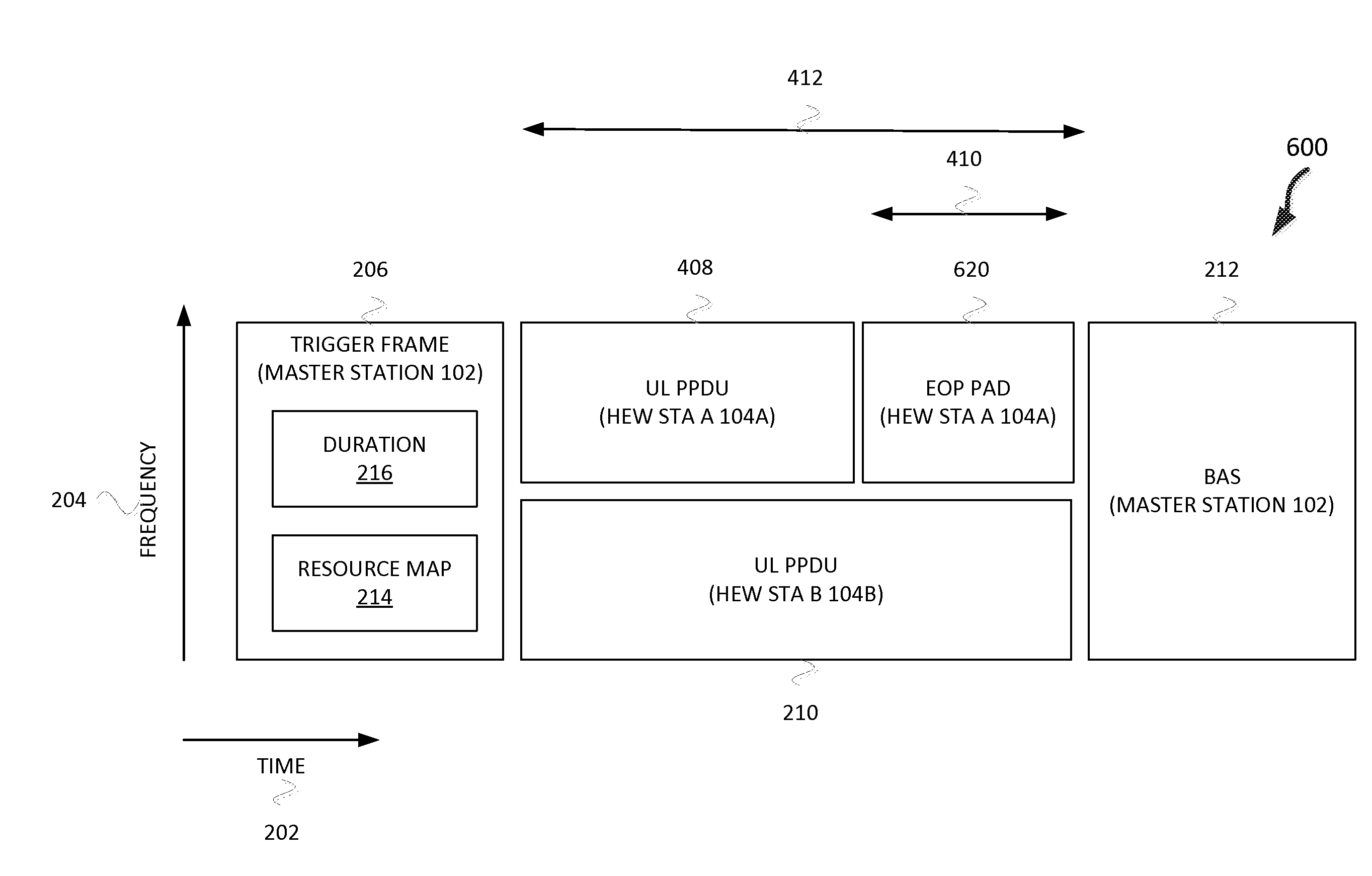
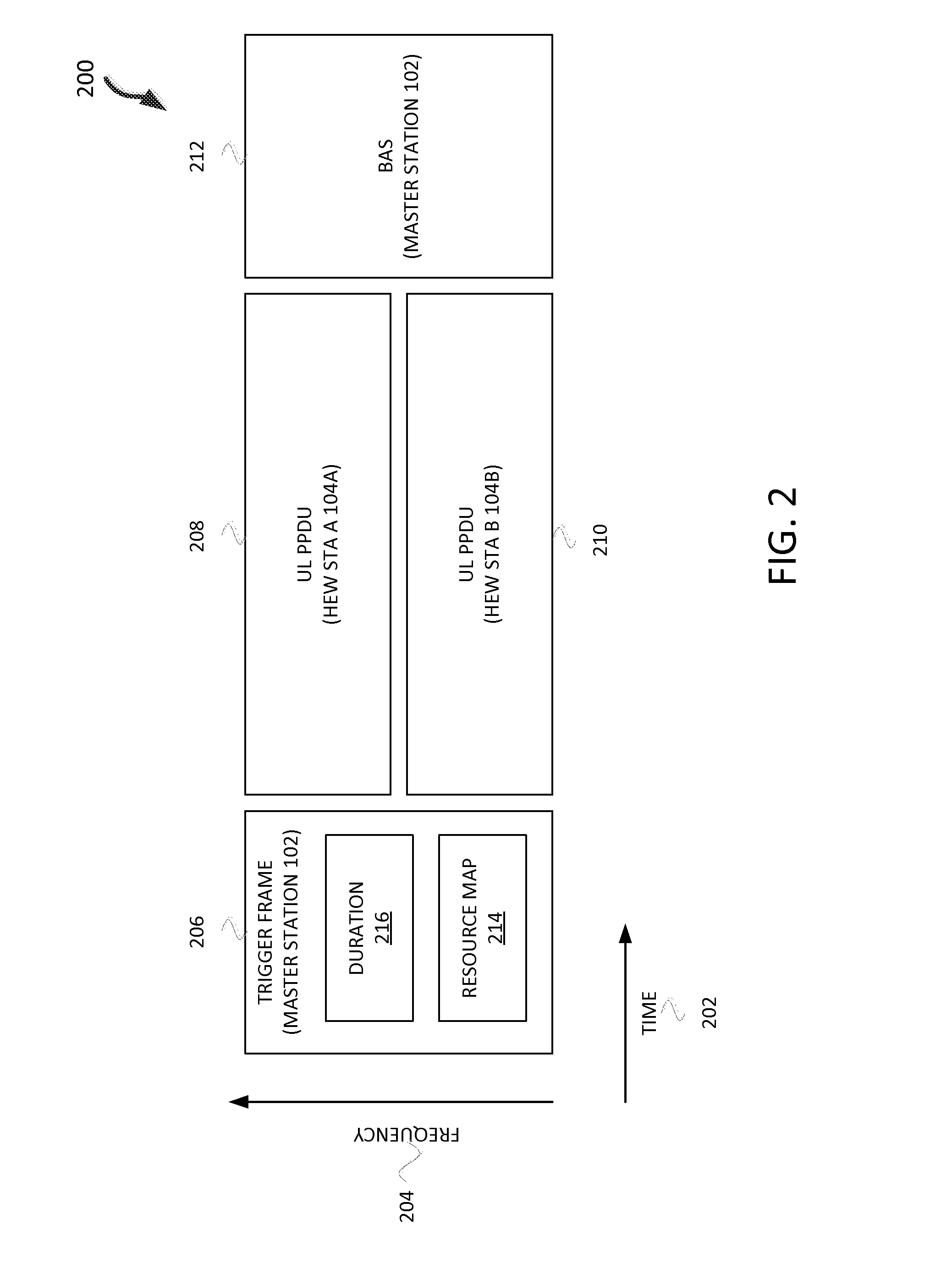
Apparatus, method, and computer readable media for uplink transmission opportunity in a high-efficiency wireless local-area network
Methods, devices and a computer-readable medium are disclosed for an uplink transmission opportunity in a high-efficiency wireless local-area network (HEW) are disclosed. A HEW station is disclosed that may include circuitry configured to receive a trigger frame with a first duration from a HEW master station, determine a second duration based on the first duration, generate a packet with the second duration, and transmit the packet with the second duration in an uplink transmission opportunity to the master station in accordance with at least one from the following group: orthogonal frequency division multiple-access and multiple-user multiple-input multiple-output. The trigger frame may include a resource map and the HEW station may transmit the packet on a channel indicated in the resource map. The second duration may be indicated in a legacy portion of the packet. The second duration may extend to one short interframe space before an acknowledgement of the packet.
Owner:INTEL CORP
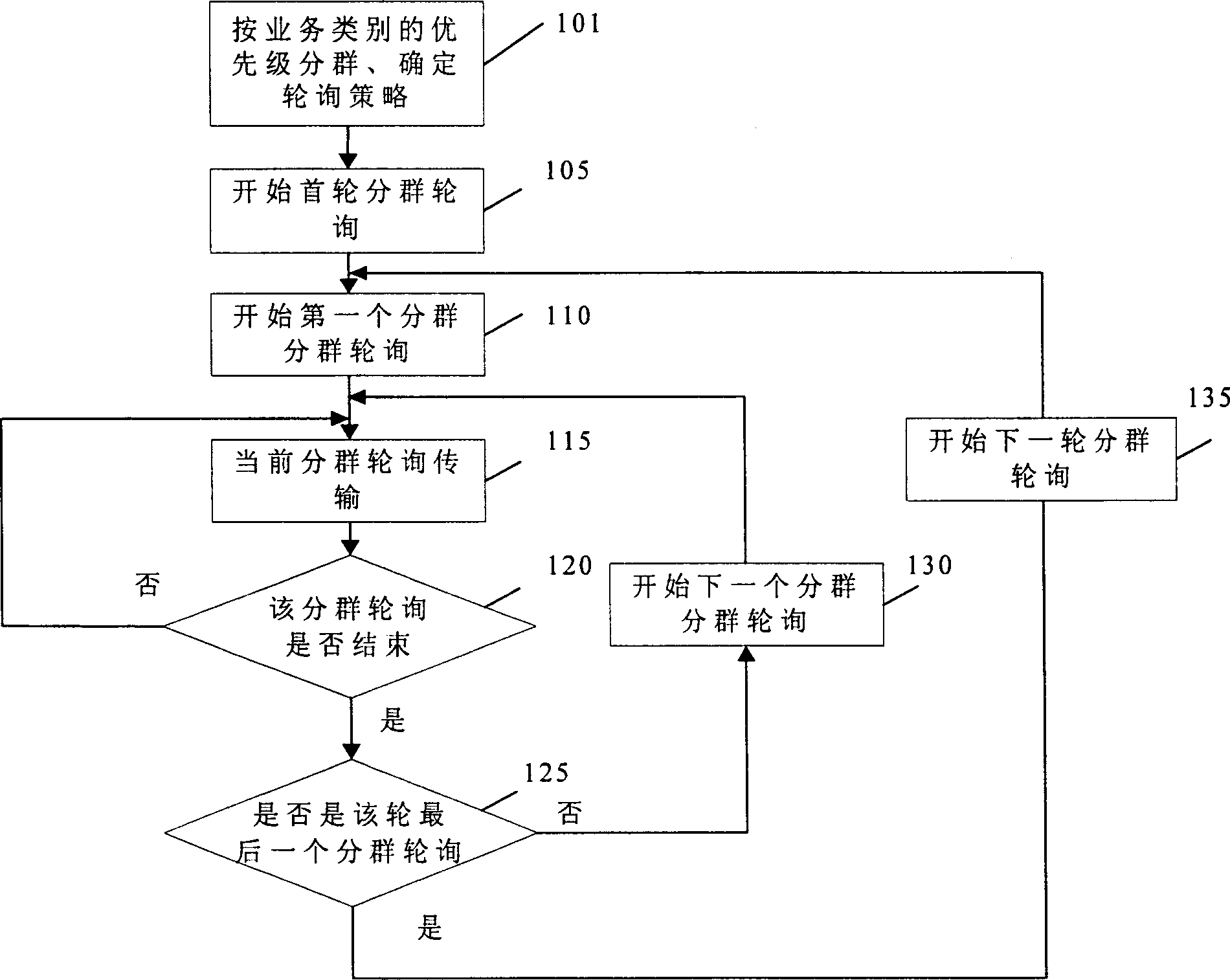
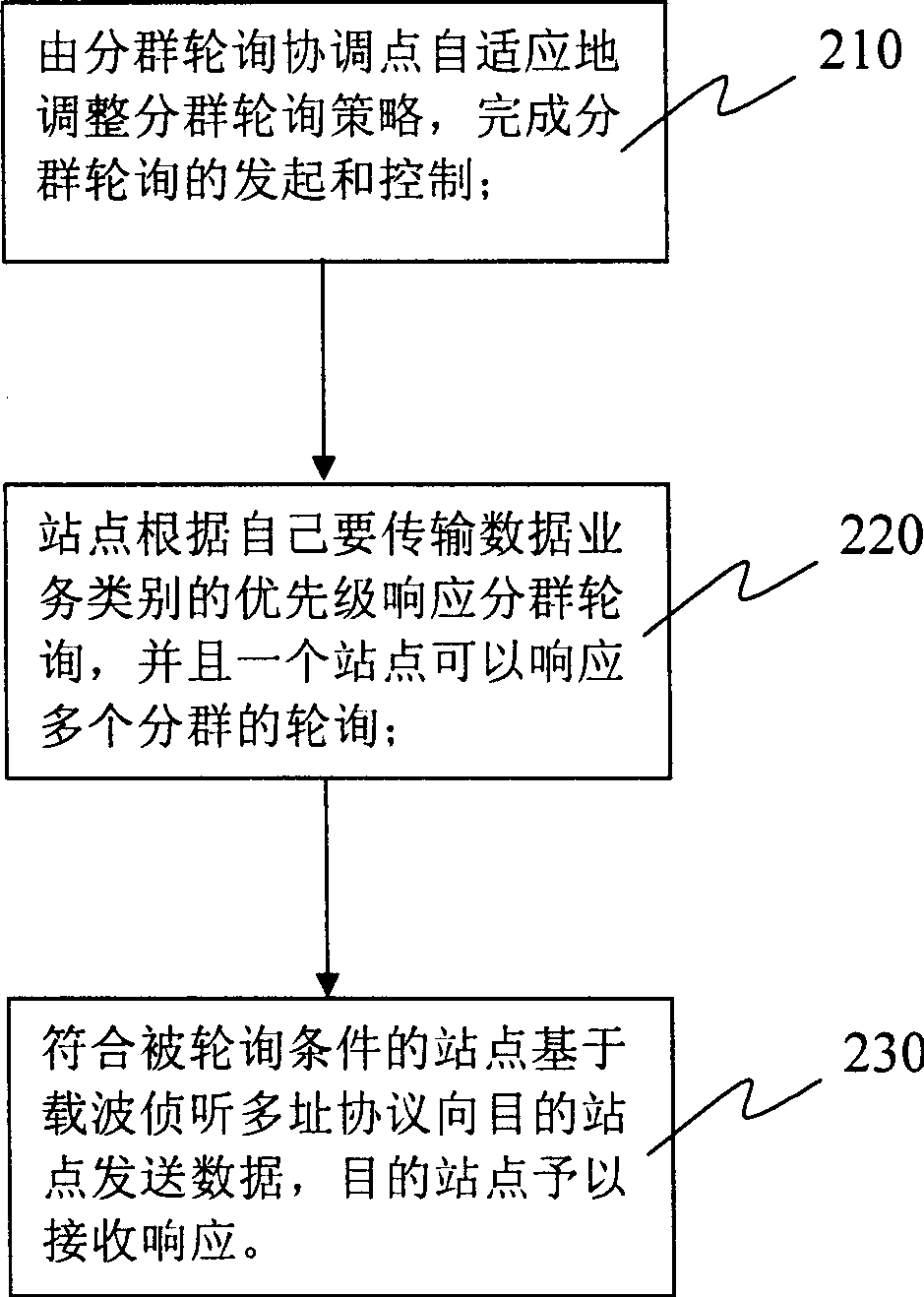
WLAN subgroup polling method based on self-adaptive service quality assurance
InactiveCN1791046AImprove throughputImprove performanceNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesAdaptive servicesWeb site
The invention discloses a wireless LAN grouping polling method based on self-adaptive service QA, which comprises: regulating grouping polling strategy according to priority of business and business type variation and current state, polling with different contents repeatedly to the grouping that may have business for transmission; the wed site responses the polling according to business type; the web site meet polling condition sends data to target site, the latter responses and receives. This invention can set the frame interval of different priority level same or different, avoids unnecessary transmission delay, and enhances network performance.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Wireless Transmission Method, Apparatus, And System
InactiveUS20100103914A1Error preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless transmissionComputer network
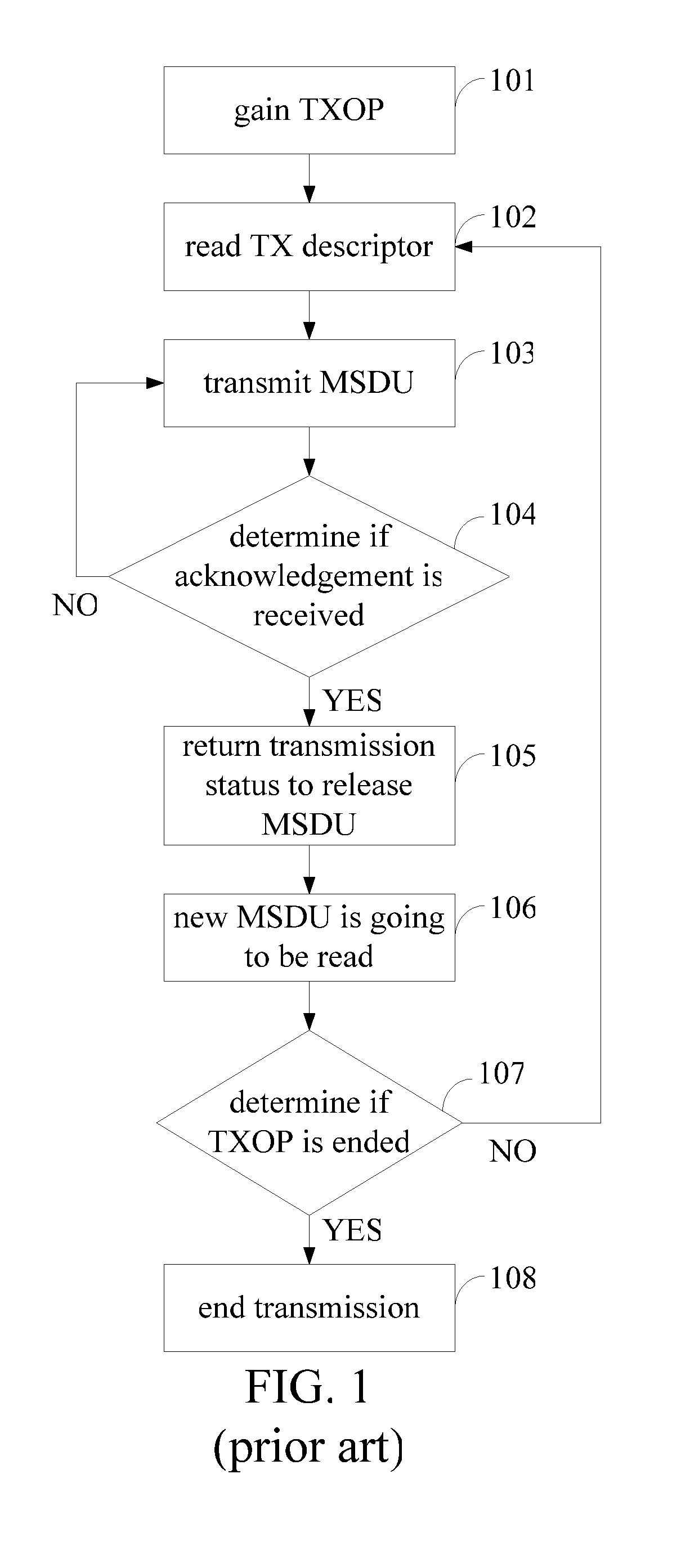
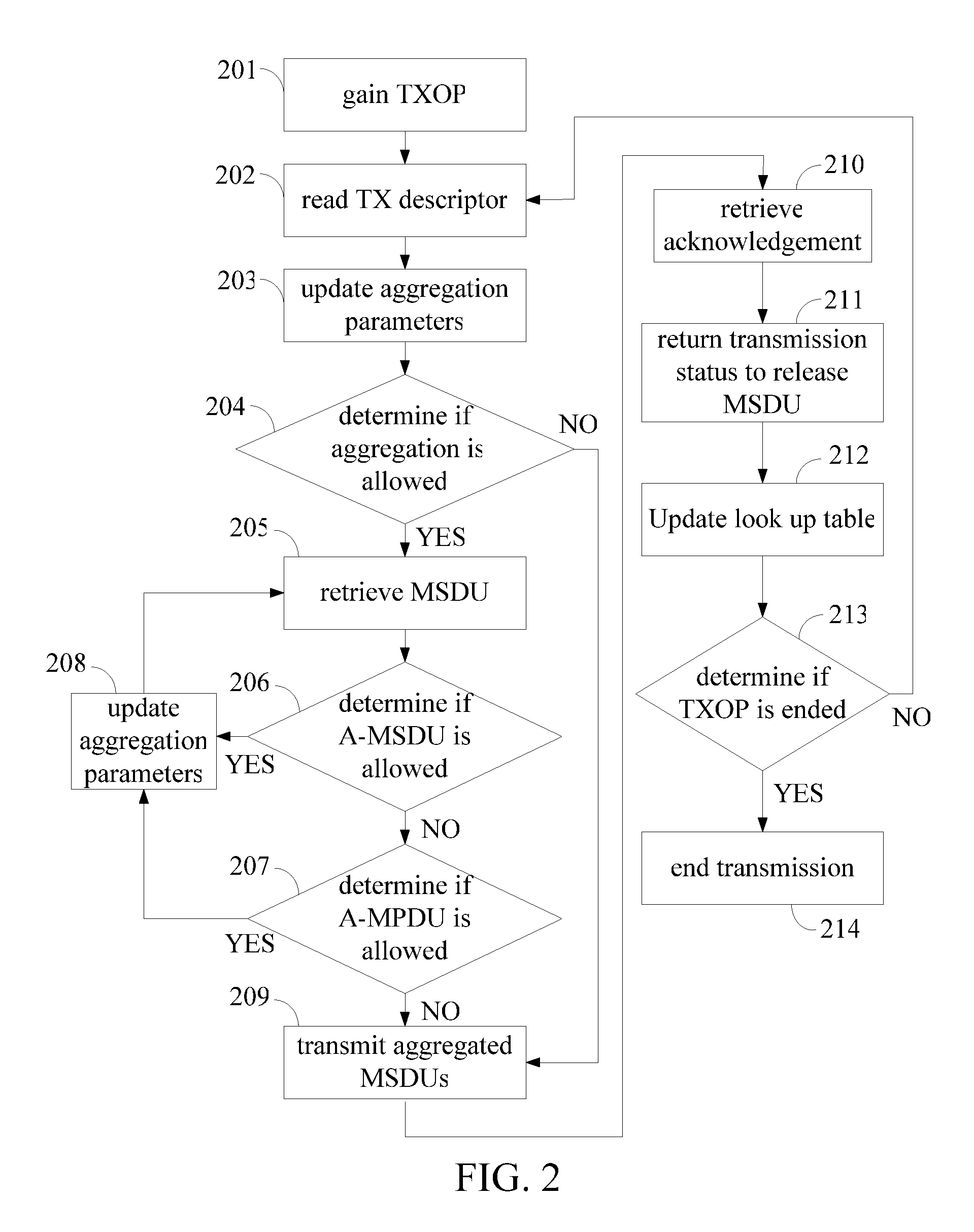
A wireless transmission method, performed in a second layer of a wireless LAN apparatus, for transmitting data from a first layer of the wireless LAN apparatus to a third layer of the wireless LAN apparatus, comprising steps of: retrieving information related to unacknowledged frames from the first layer; aggregating the unacknowledged frames into a data unit if a processing time of the retrieving and aggregating step is less than a short inter frame space corresponding to a transmission opportunity; and transmitting the data unit to the third layer in the transmission opportunity.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Adaptive short inter-frame space bursting
InactiveUS20160295580A1Improve performanceRich user experiencePower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementBurstingTelecommunications
Methods, systems, and devices are described for wireless communication at a wireless device. A wireless device (e.g., station or access point) may adapt short inter-frame space (SIFS) burst parameters to improve the performance of the overall network while providing enriched user experience. A wireless device may monitor traffic conditions on the network and dynamically adapt the SIFS burst parameters associated with one or more stations based at least in part on detected variations on the traffic channel. In other examples, the wireless device may allocate a common SIFS burst parameter to be used by a plurality of wireless devices in the basic service set (BSS).
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
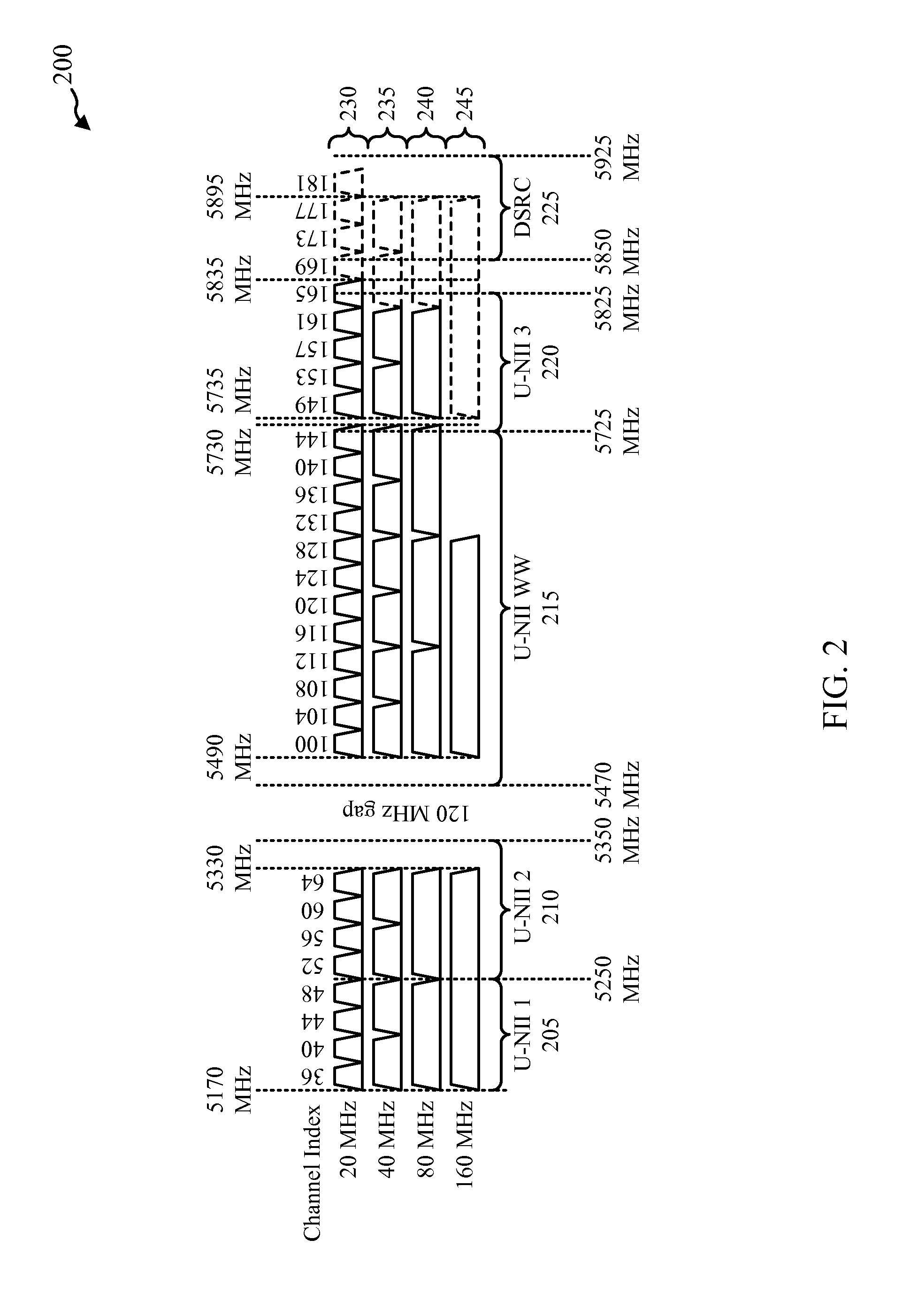
Inter-frame spacing adaptation for yielding to dsrc operation
ActiveUS20140370809A1Extended durationNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumInter frame space
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
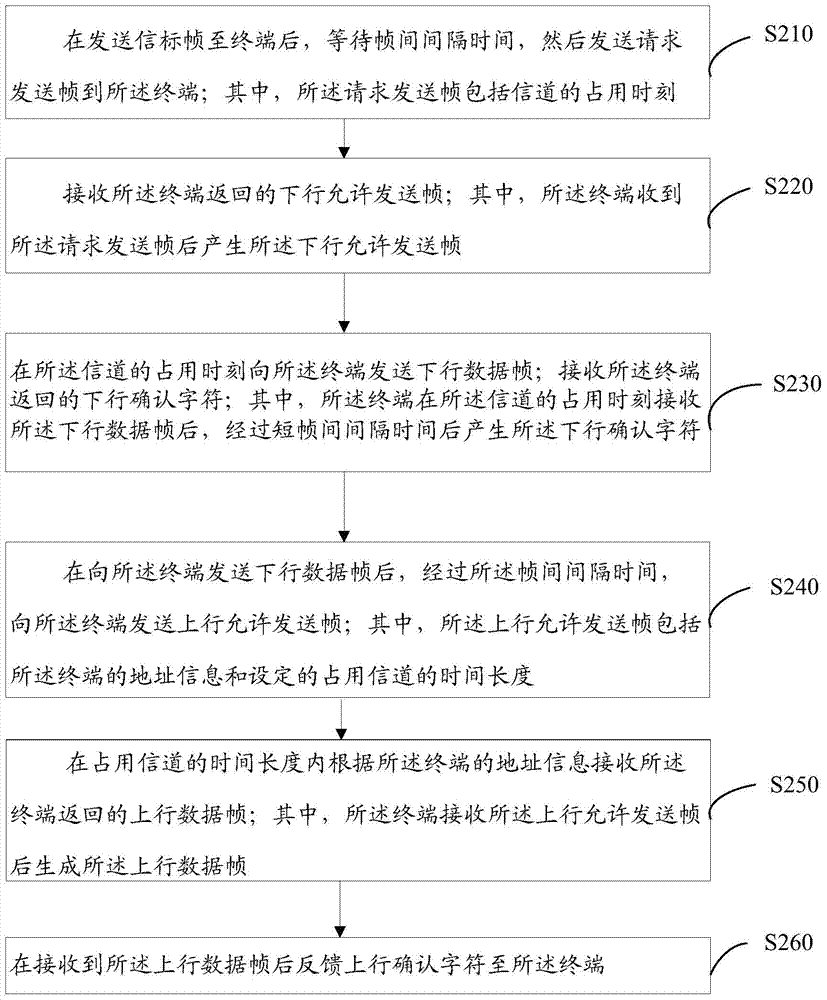
Data transmission method and system for wireless access point and terminal
ActiveCN104507174AReduce waiting timeSave resourcesError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork topologiesBeacon frameComputer terminal
The invention provides a data transmission method and a system for a wireless access point and a terminal. The method comprises the following steps: waiting for an interframe spacing interval after a beacon frame is sent to the terminal; transmitting a request transmission frame to the terminal, wherein the request transmission frame comprises occupied moment of a channel; receiving a downlink allowing transmission frame returned by the terminal, wherein the terminal generates the download allowing transmission frame after receiving the request transmission frame; transmitting a download data frame to the terminal at the occupied moment of the channel, and receiving a download acknowledge character returned by the terminal, wherein the terminal generates the download acknowledge character after a short interframe spacing interval after receiving the download data frame at the occupied moment of the channel. The request transmission frame is transmitted through the terminal during data transmission, and comprises the occupied moment of the channel, thus the problem of throughput drop of the system under the multi-user circumstance can be solved.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM SYST CHINA LTD
Uniform WLAN multi-AP physical layer methods
InactiveCN104871438ASpatial transmit diversityWireless communicationTelecommunicationsPhysical layer
A method and apparatus are disclosed for training and feedback in sectorized transmissions. An IEEE 802.11 station may receive a Sector Training Announcement frame from an AP. The station may then receive a plurality of Training frames from the AP, wherein each of the plurality of Training frames is separated by a short interframe space (SIFS) and each of the plurality of Training frames is received using a different sectorized antenna pattern. The station may generate a Sector Feedback frame indicating a sector based on the plurality of Training frames. The station may send the Sector Feedback frame to the AP. The Sector Feedback frame may indicate a desire to enroll in sectorized transmissions. Alternatively, the Sector Feedback frame may indicate a desire to change sectors.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
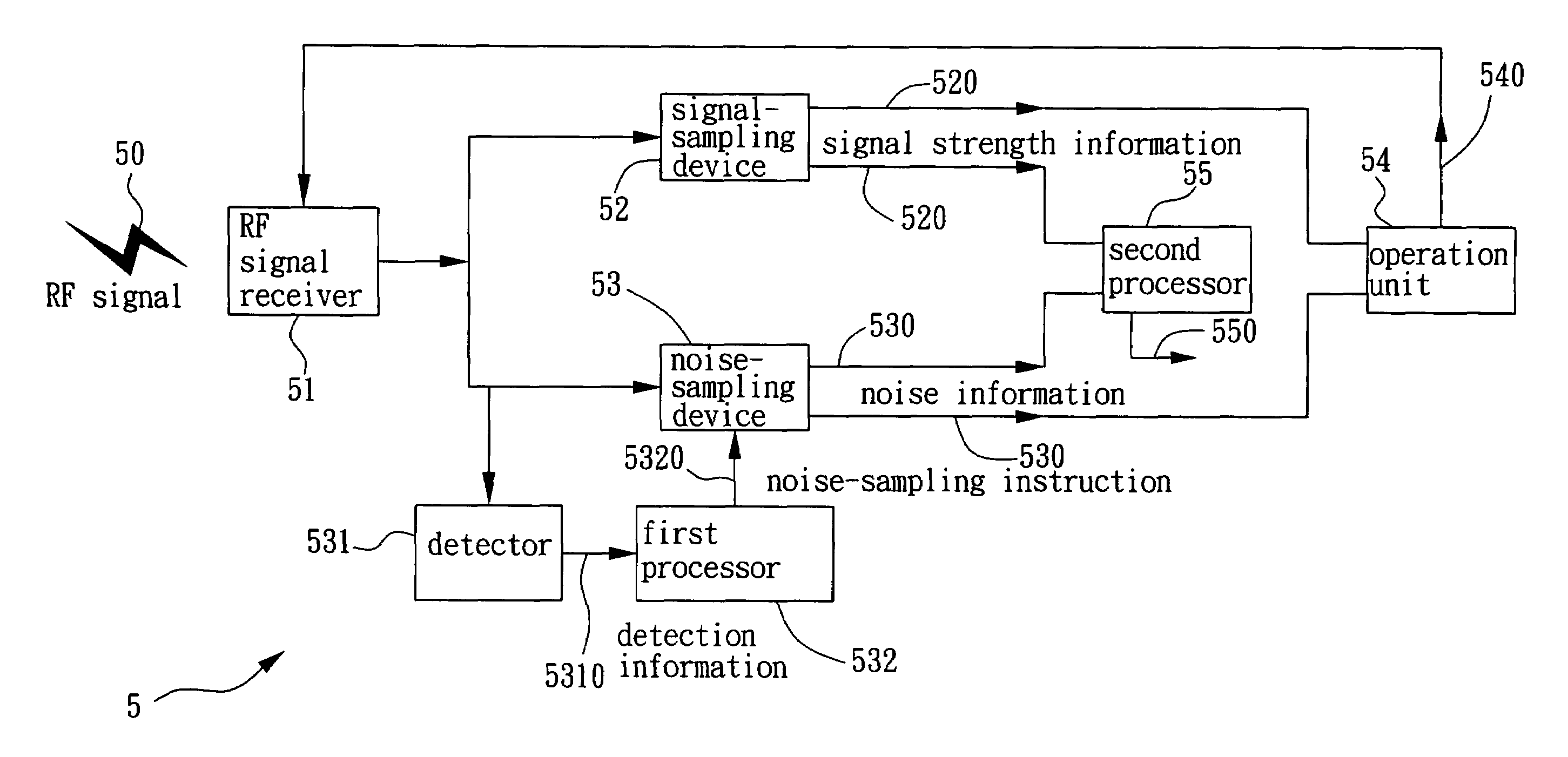
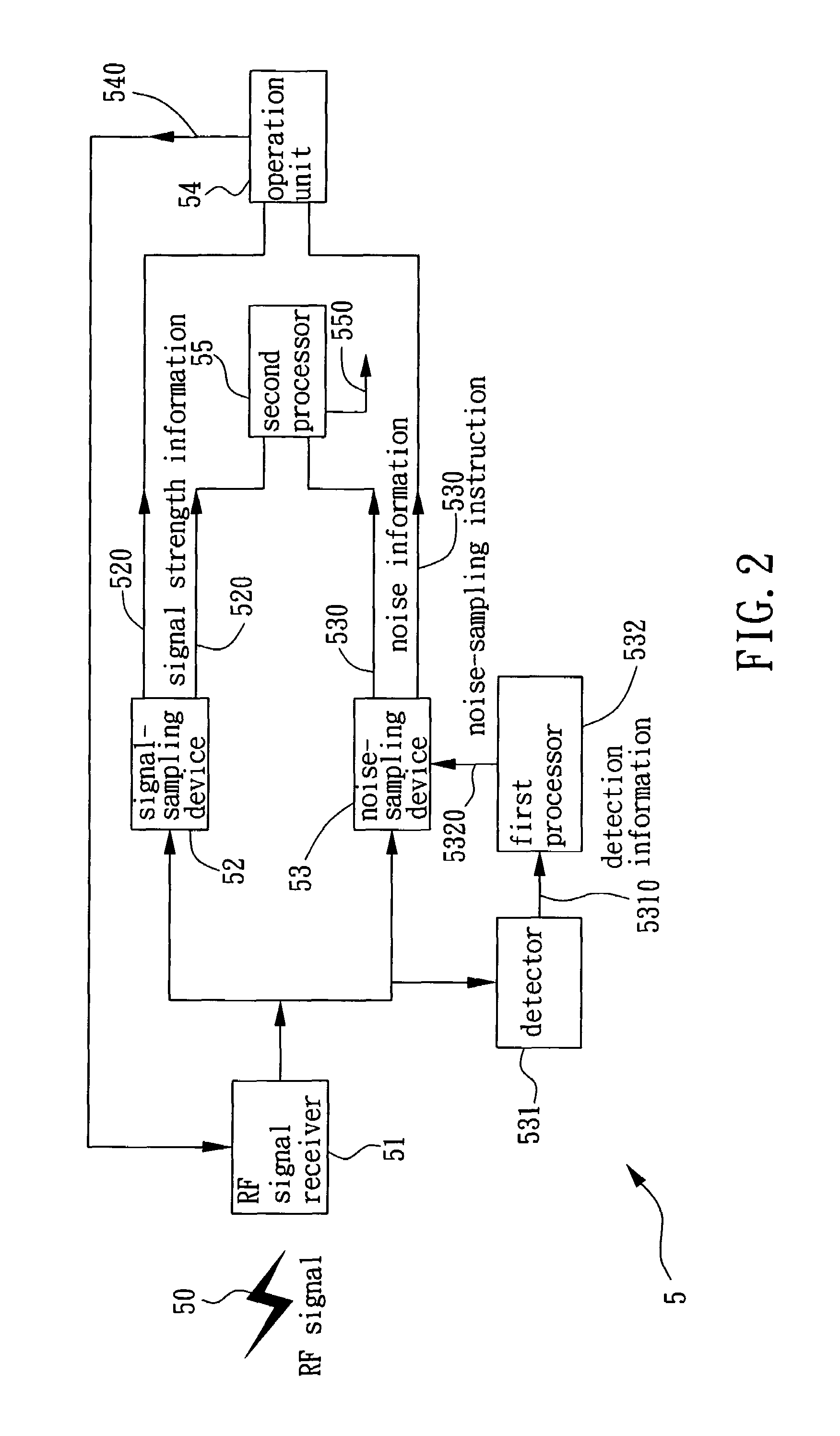
System and method for RF gain control
The present invention provides a system and method for RF gain control that extracts the background noise information of the received RF signal in the short inter-frame space (SIFS), and computes the background noise information and strength information of the received RF signal to output a feedback control signal to adjust the gain of the RF signal receiver. It optimizes the receiving system and makes the received RF signal be of sufficient strength and have a good quality as well.
Owner:ACCTON TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
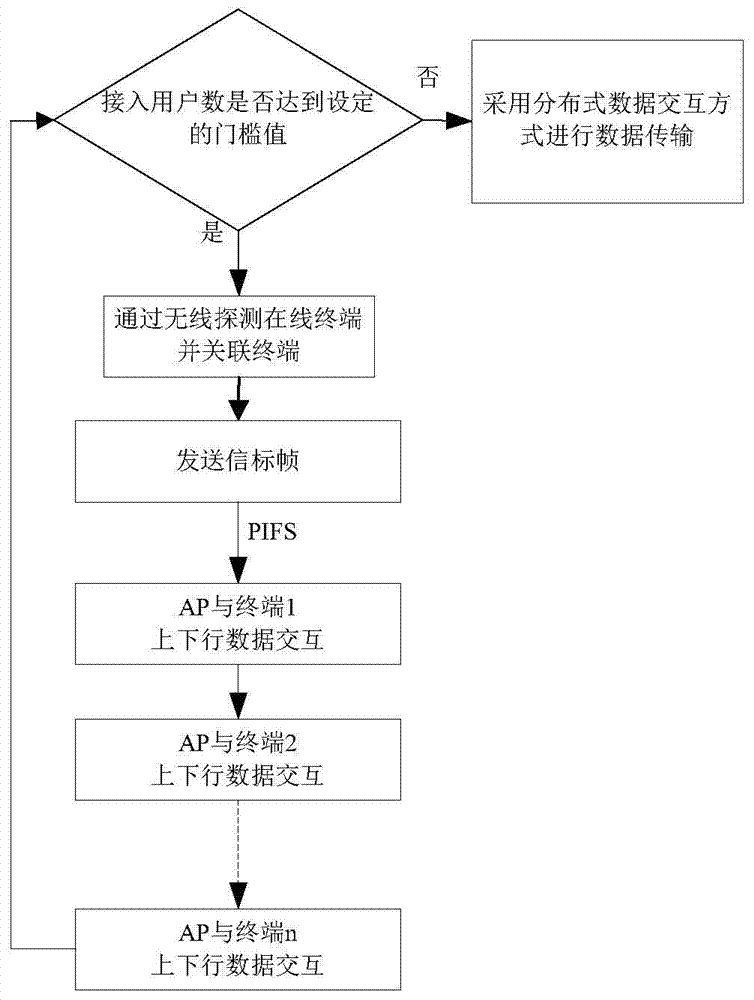
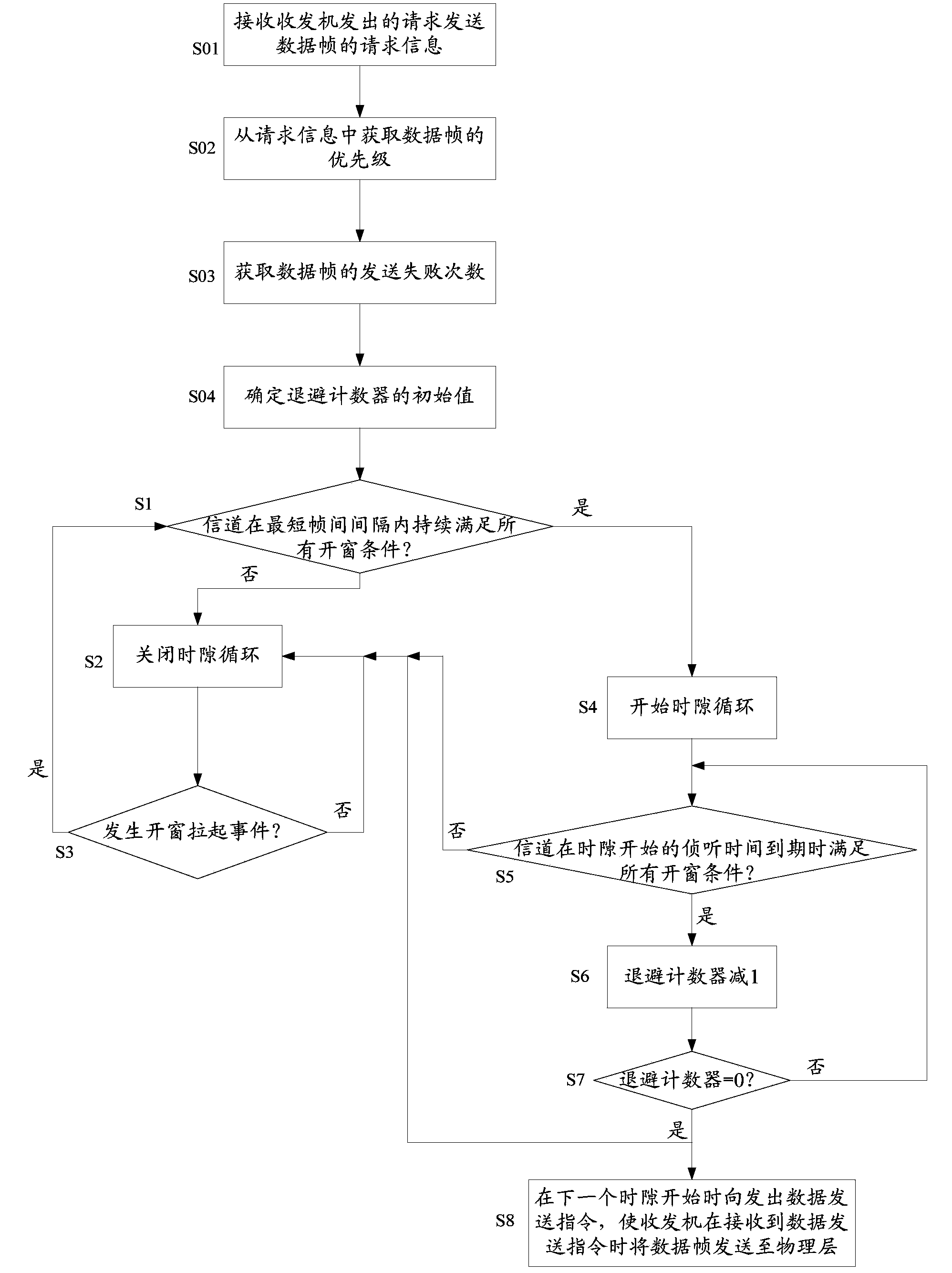
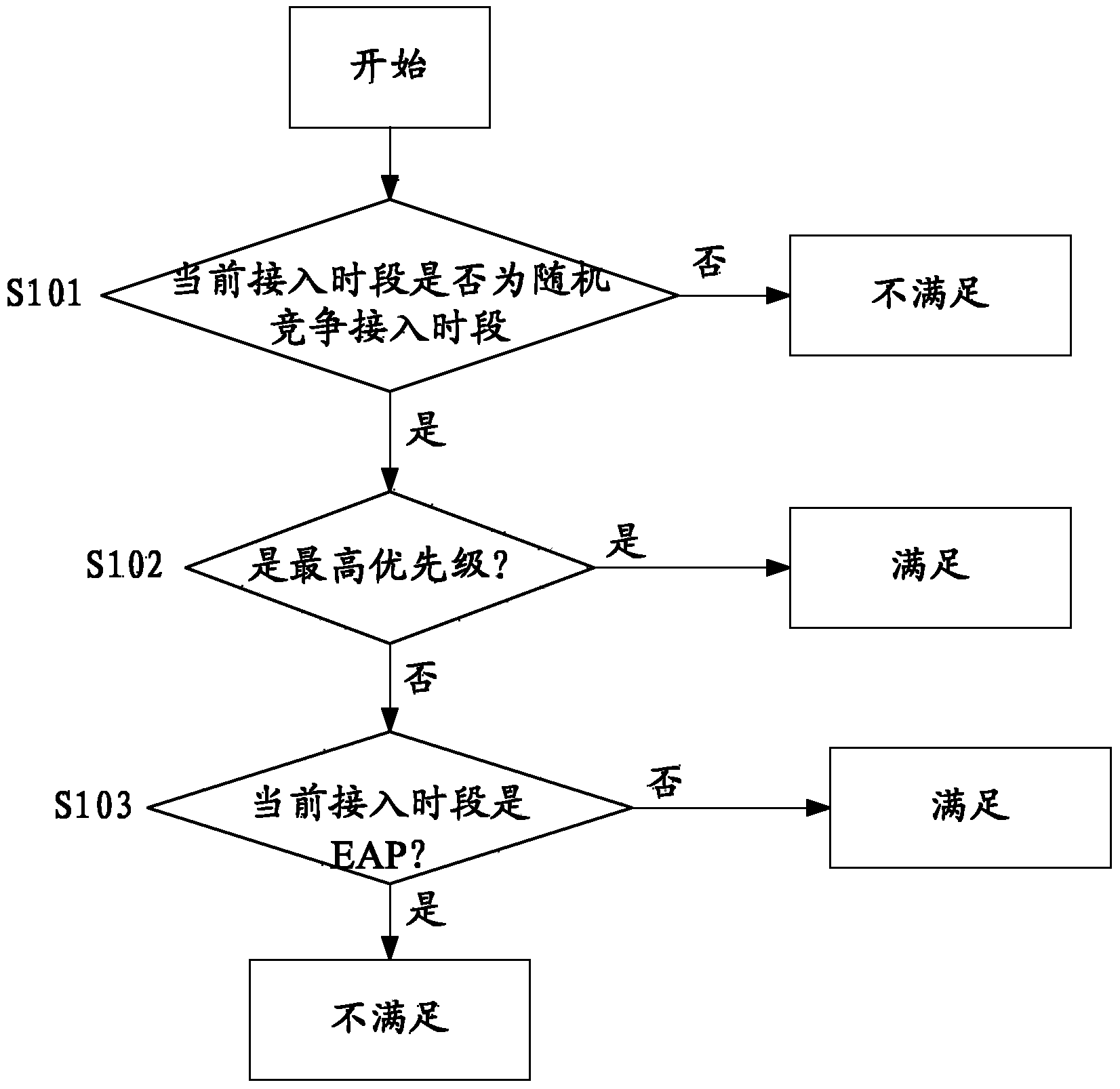
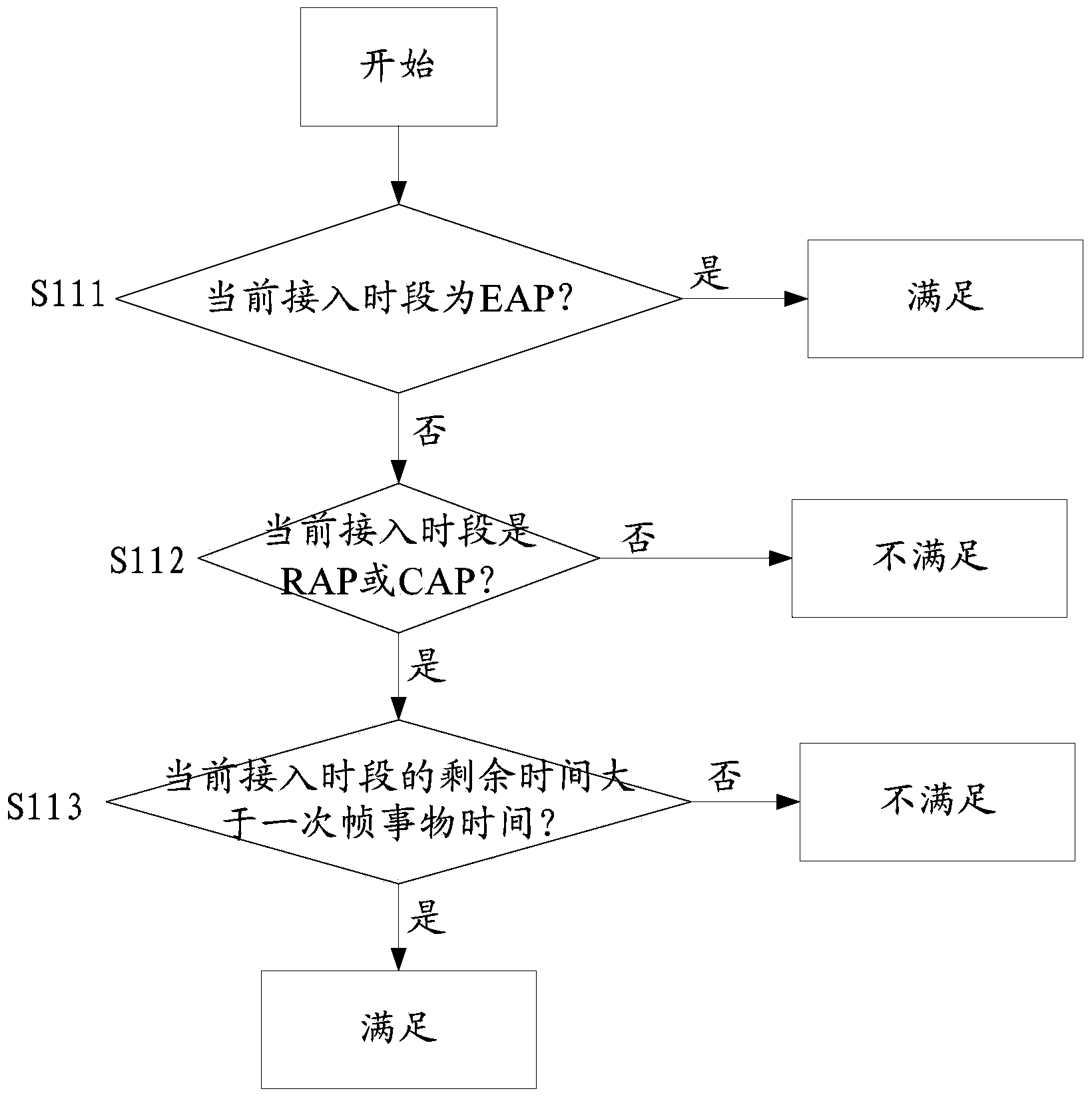
Method and system for controlling radio resource dynamic access in body area network simulation process
The invention discloses a method and system for controlling radio resource dynamic access in the body area network simulation process. The method includes the steps that request information is received; priority is acquired from the request information; an initial value of a backoff counter is determined; when any windowing pull-up event occurs in the time slot cycle stopping period and the initial value is determined, whether a channel continues to meet all windowing conditions or not in a shortest interframe interval is judged, if yes, a time slot cycle is started, and if not, the time slot cycle is stopped; whether the channel meets all the windowing conditions or not when start monitoring time of each time slot is end is judged, if yes, 1 is subtracted from the number of the backoff counter, and if not, the time slot cycle is stopped; the time slot cycle is stopped when the number of the backoff counter becomes 0 through subtraction, a data sending command is sent out when a next time slot is started, and then data frames are sent to a physical layer through a transceiver. Simulation of media access control is separated from a simulation platform structure, and by the combination of a mechanism, for receiving and sending the data frames, provided by a simulation platform, body area network simulation is achieved.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Communication managing and controlling method for wireless local area network
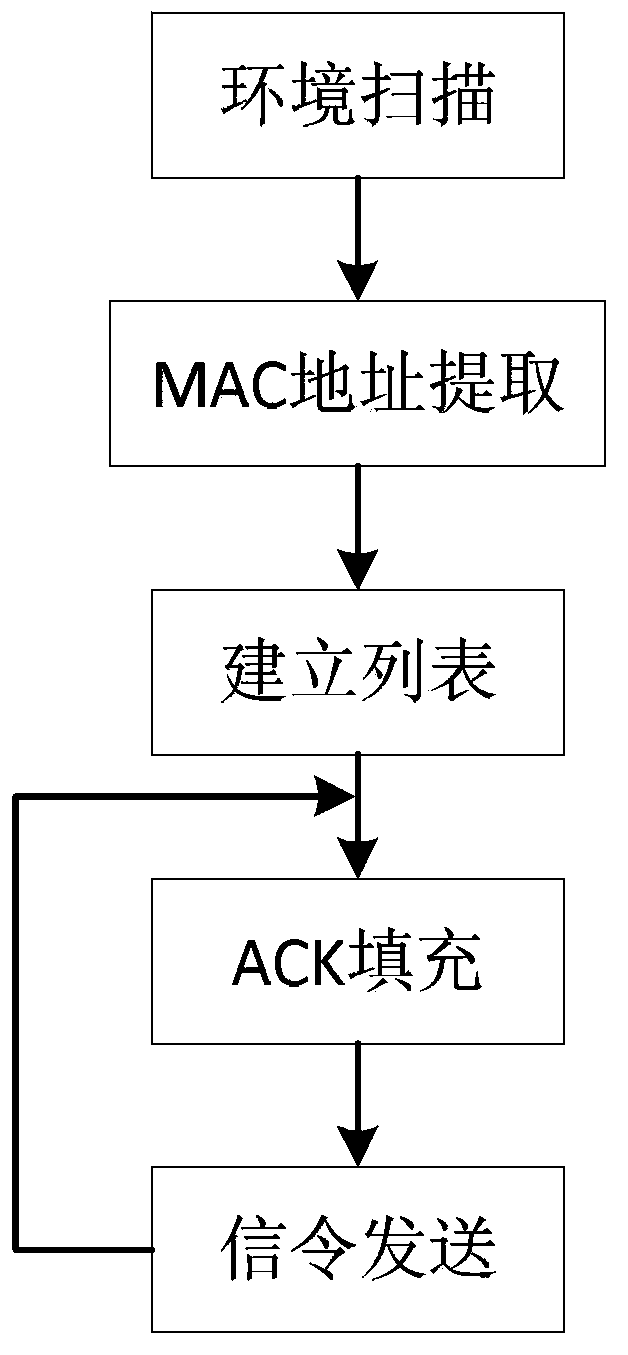
ActiveCN104333859AThe blocking effect is stableImprove applicabilityAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesPresent methodComputer terminal
The present invention discloses a communication managing and controlling method for a wireless local area network. The present method includes that 1) a network card drive of a blocking device is modified so as to enable the blocking device to send blocking frames at intervals no greater than the short interframe space (SIFS); 2) the blocking device scans the surrounding wireless local area network environment, and obtains MAC addresses of an access point (AP) and a terminal (STA) working in a to-be-blocked channel; 3) the blocking device establishes a channel MAC address list including all MAC addresses of all the access points (Aps) and terminals (STA) to be blocked of the channel regarding each channel; and 4) the blocking device fills the MAC address in the channel MAC address list of the channel into a destination address field of a blocking frame and then sends the blocking frame regarding each channel to be blocked. The communication managing and controlling method greatly increases information security of secret units or regions, and has a small effect on the surrounding electromagnetic environment.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Extension mode for wireless LANs complying with short interframe space requirement
An access point comprises a transmitter. A coding module communicates with the transmitter and generates a first packet including a first field that identifies one of a standard signal processing mode and an extension signal processing mode, a second field that selectively defines a data length based on one of a transmit time period for the first packet and the transmit time period plus an extension mode time period for performing the extension signal processing mode, and a third field that selectively comprises one of the data and the data and dummy data.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Optimizing response interframe space in communication systems
InactiveUS9231736B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCommunications systemPhysical layer
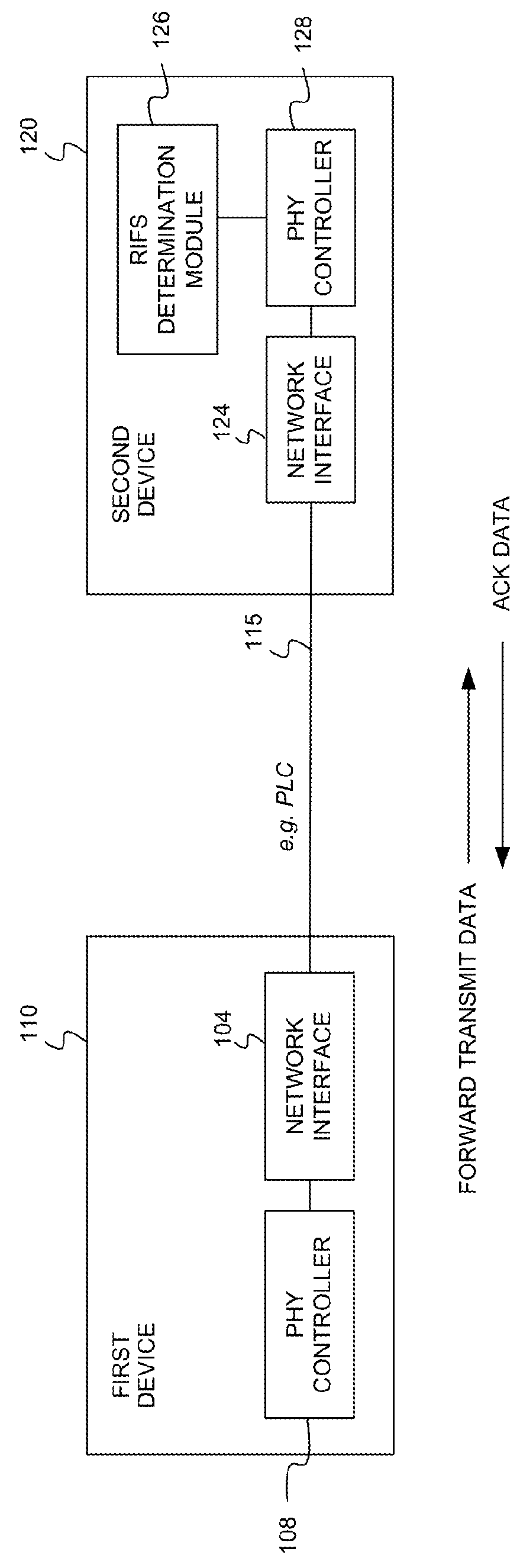
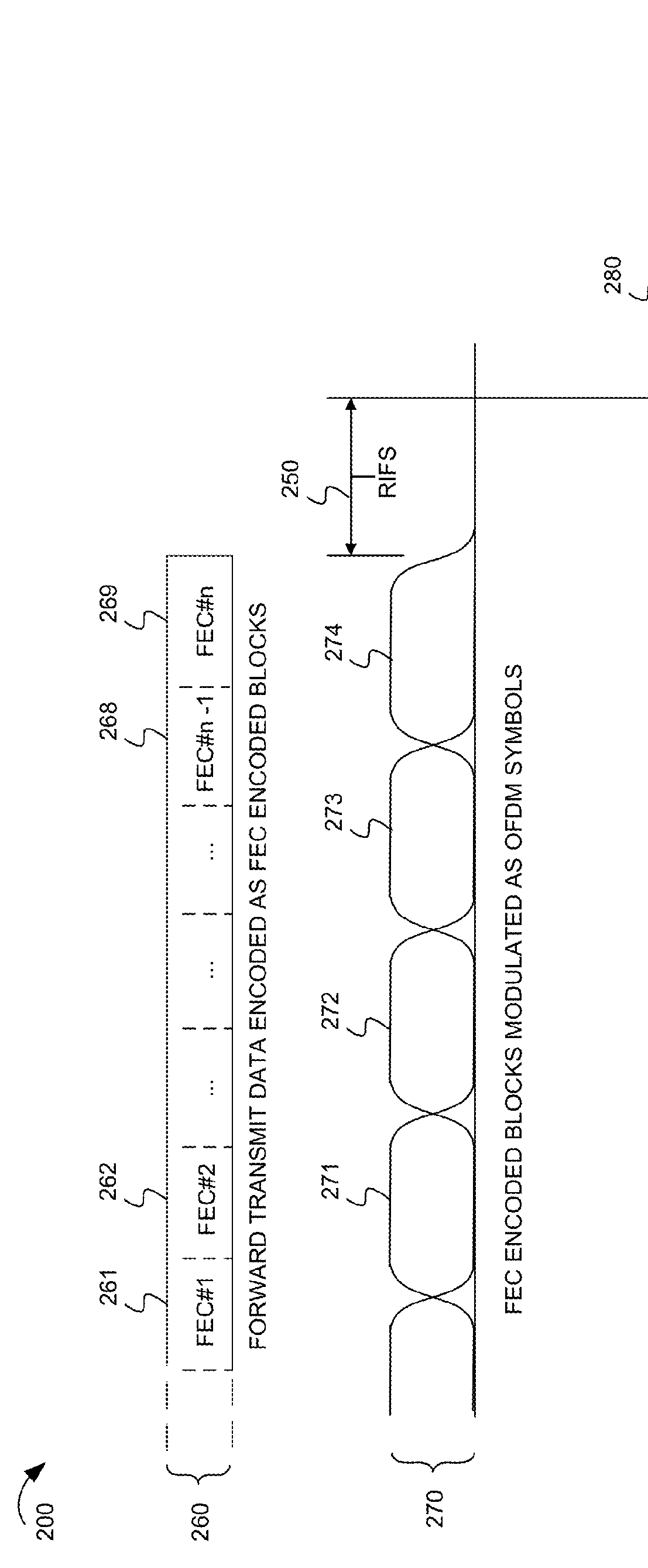
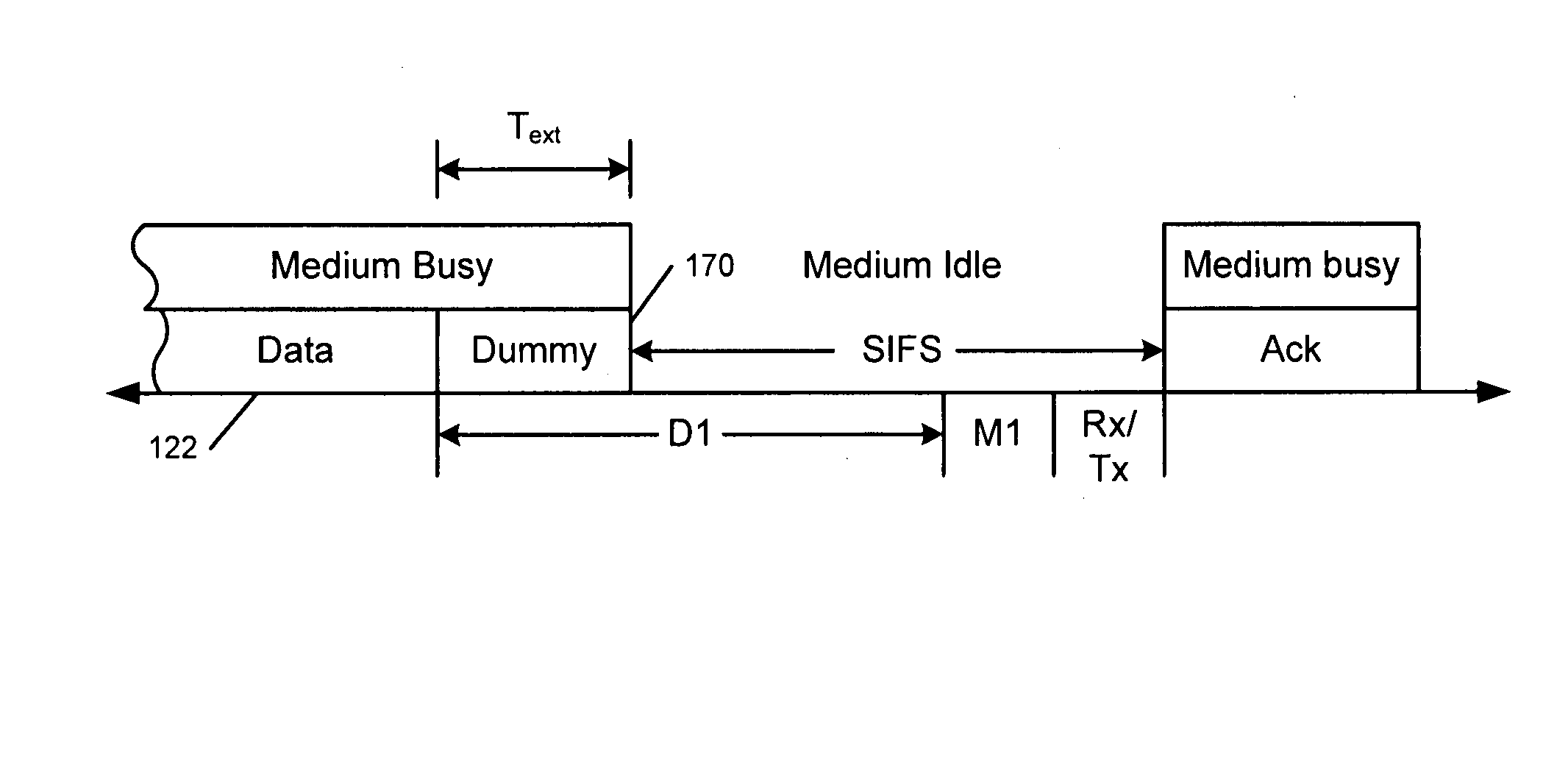
A response interframe space (RIFS) time period may be adapted in a communication system. The RIFS time period may be determined based, at least in part, on a processing time used by a receiving device to process a received physical layer transmission from a transmitting device. The RIFS may be optimized in consideration of channel conditions for a particular communications channel, capabilities of a receiving device, and / or characteristics of a particular physical layer transmission. For example, the RIFS may be dependent on characteristics of a final transmission symbol used to transmit a physical layer transmission. The RIFS may depend on a processing time associated with decoding forward error correction (FEC) encoded blocks that end in the final transmission symbol. The RIFS may depend on a quantity of decoding iterations in a communication system that uses iterative decoding of FEC encoded blocks.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Extension mode for wireless LANs compying with short interframe space requirement
A wireless station comprises a transmitter. A coding module communicates with the transmitter and generates a first packet including a first field that identifies one of a standard signal processing mode and an extension signal processing mode, a second field that selectively defines a data length based on one of a transmit time period for data of the first packet and the transmit time period plus an extension mode time period for performing the extension signal processing mode, and a third field that selectively comprises one of the data and the data and dummy data.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
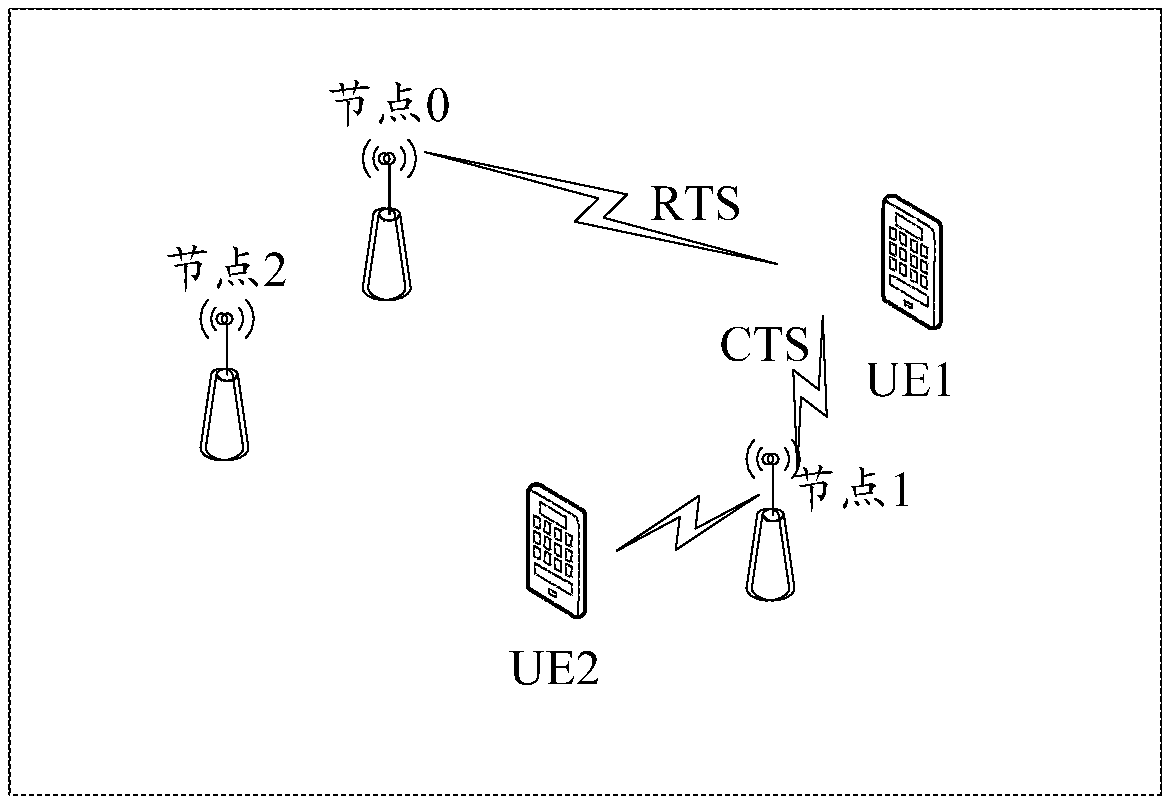
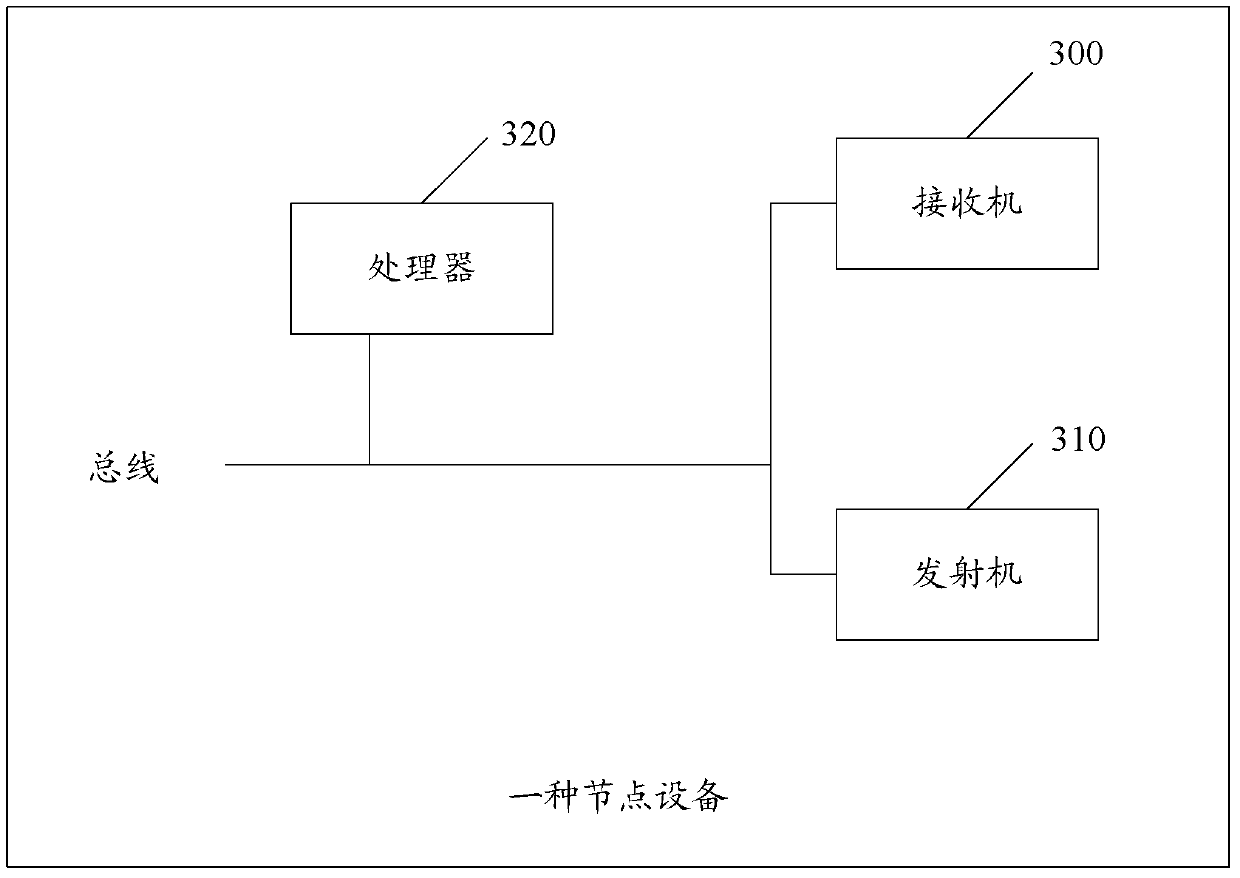
A node device, system, method for sending data, and method for receiving data
ActiveCN105850216BImprove monitoringIncrease the probability of hearing that the channel is idleNetwork planningIdle channelInter frame space
Disclosed are a node device, system, data transmission method and data receiving method. The device comprises: a transmission module, for sending a requesting to send (RTS) frame to a second node on a channel; a receiving module, for receiving from the second node a clearing to send (CTS) frame within a preset first time interval after the transmission module transmits the RTS frame, the first time interval being greater than one short inter-frame spacing (SIFS) time period; and a determination module, for determining a time interval indicated by a first silence time window included in the CTS frame received by the receiving module. The transmission module is further used to transmit data to the second node on the channel within the time interval indicated by the first silence time window included in the CTS and determined by the determination module. The present invention increases the probability of monitoring an idle channel.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
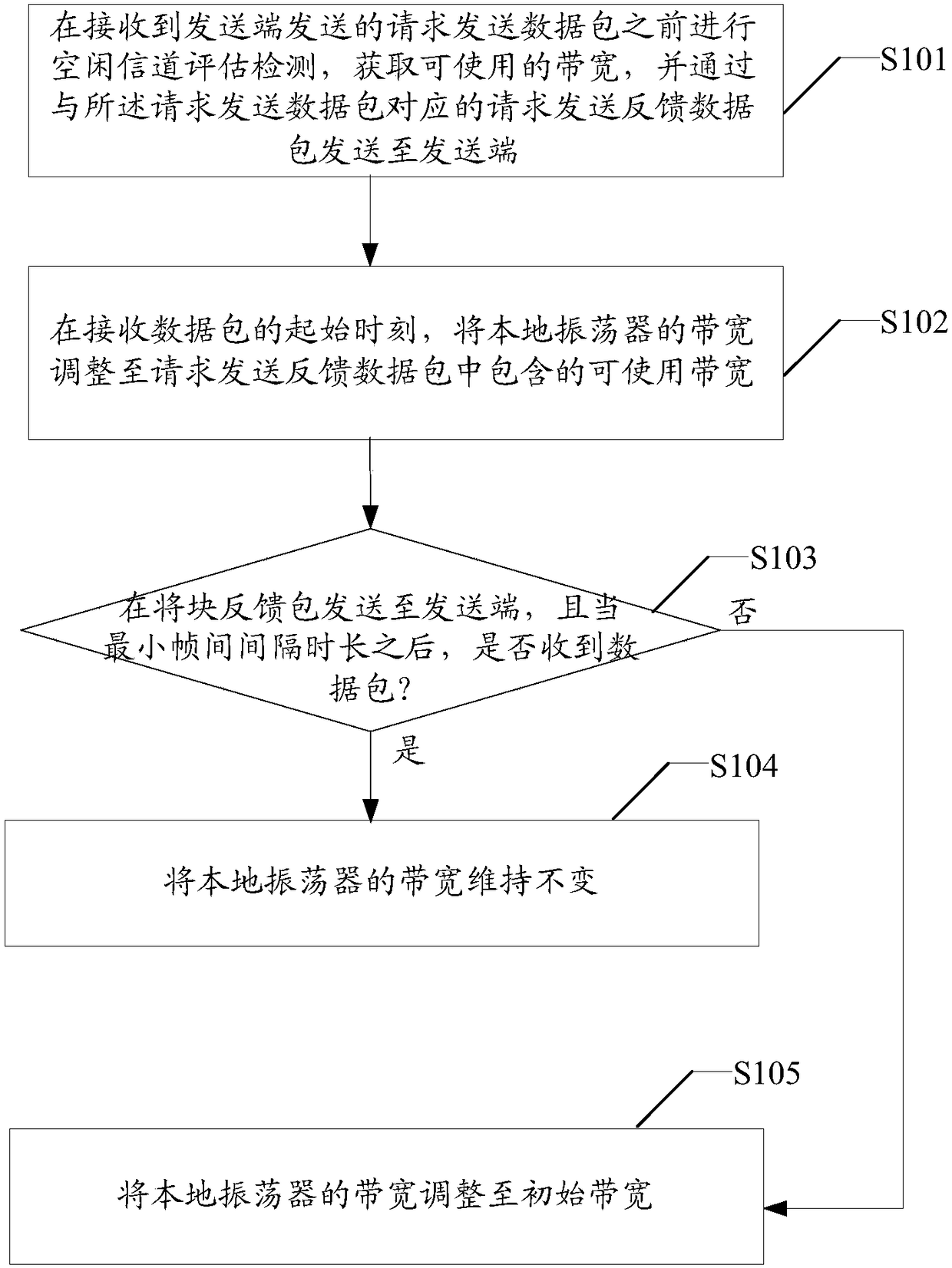
Local oscillator bandwidth adjustment method, receiver, computer medium, and system
ActiveCN109428747AAvoid interferenceNetwork topologiesData switching networksStart timeNetwork packet
The present invention provides a local oscillator bandwidth adjustment method, a receiver, a computer medium, and a system. The local oscillator bandwidth adjustment method includes: performing clearchannel assessment detection before a request-to-send data packet sent by a transmit end is received, obtaining an available bandwidth, and sending a request-to-send feedback data packet correspondingto the request-to-send data packet to the transmit end; adjusting a bandwidth of the local oscillator to the available bandwidth included in the request-to-send feedback data packet at a starting time of receiving the data packet; when a block feedback packet is transmitted to the transmit end, after a Short Interframe Space duration, determining whether the data packet is received; and if the data packet is received, maintaining the bandwidth of the local oscillator; or if the data packet is not received, the bandwidth of the local oscillator is adjusted to an initial bandwidth. When the above solution is applied, the bandwidth of the local oscillator can be dynamically adjusted according to the bandwidth used in real time, so that a received signal is prevented from being interfered byother channels.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
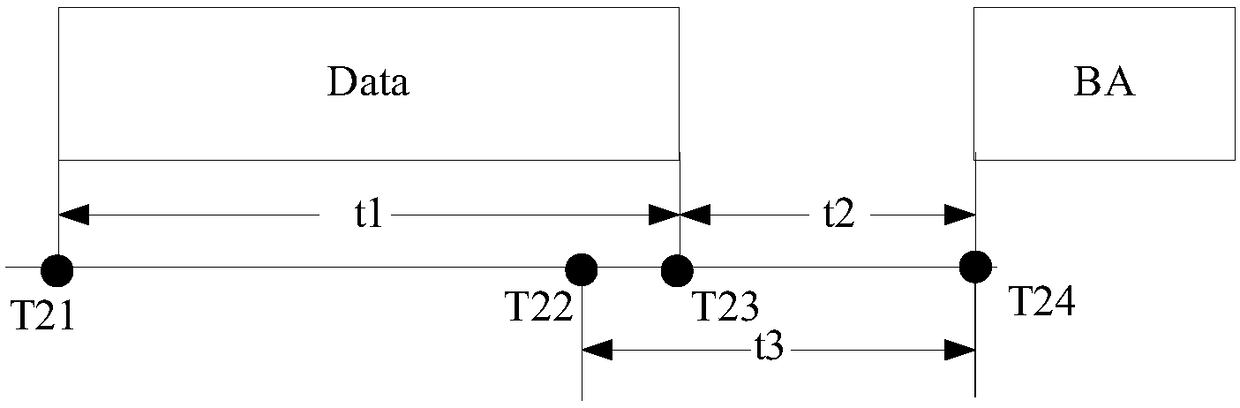
A positioning method, related equipment and system based on time measurement
ActiveCN109565779BImprove privacyPosition fixationWireless communicationEngineeringReal-time computing
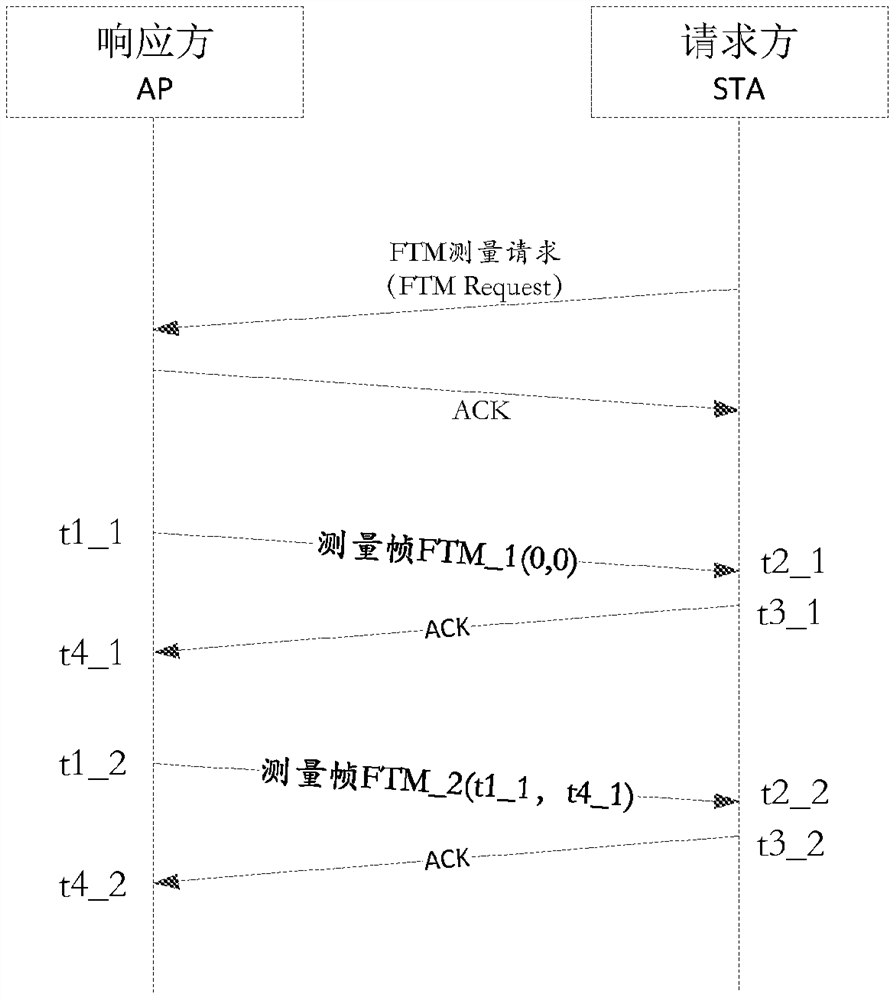
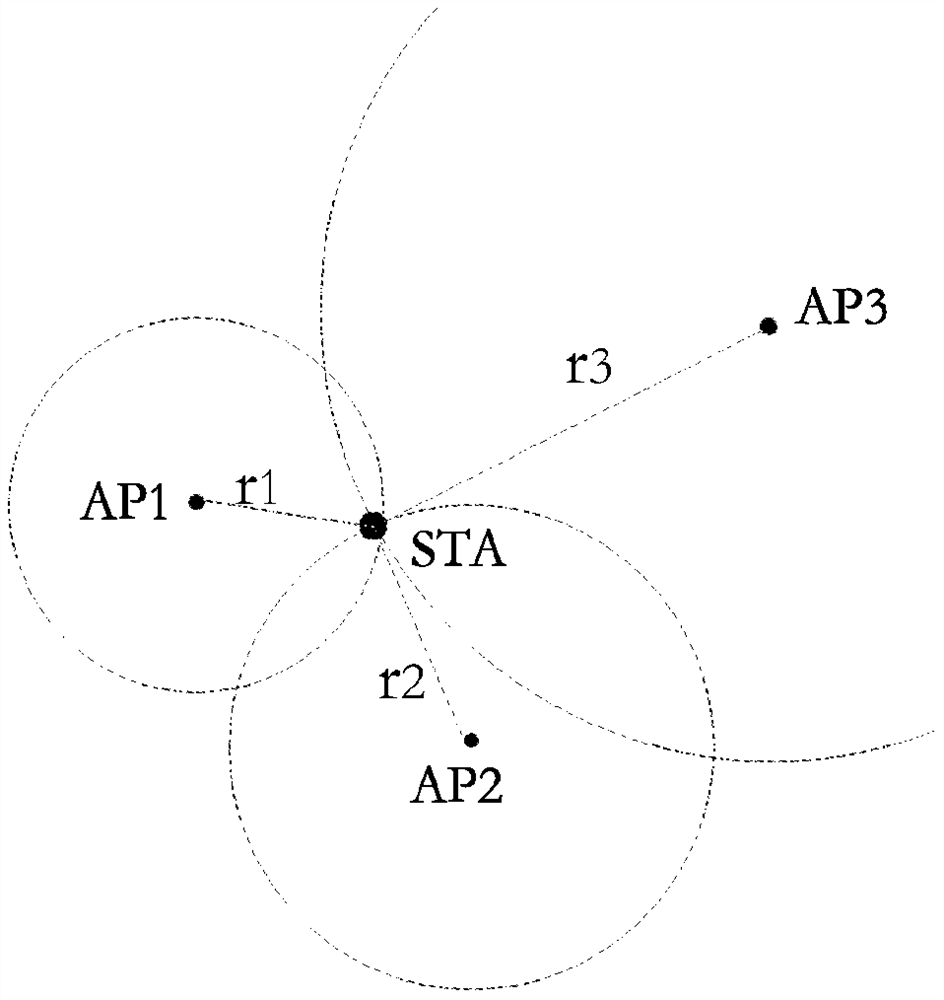
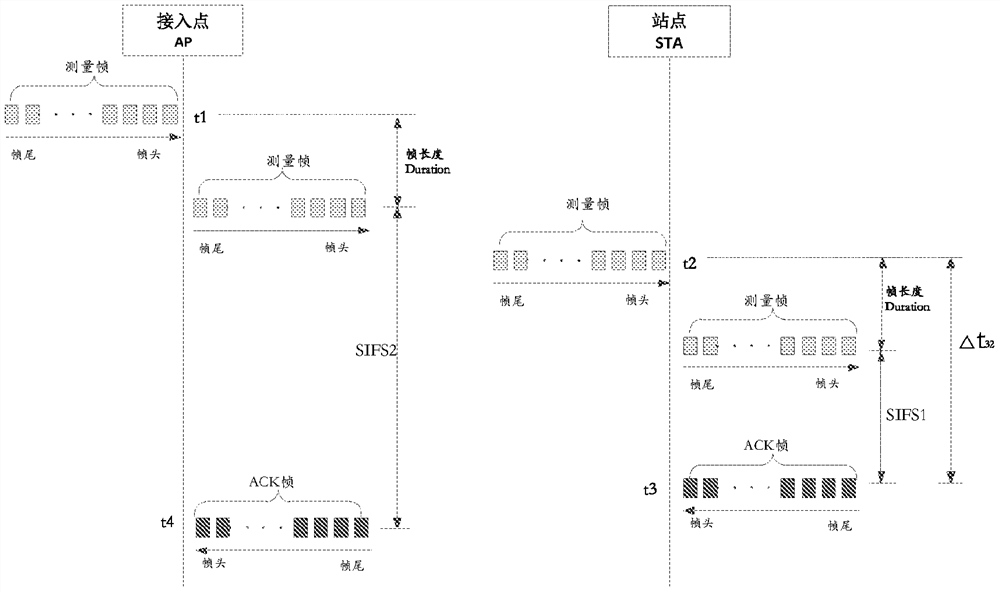
The embodiment of the invention discloses a positioning method, device and system based on time measurement. The method includes: the requesting party performs time measurement with multiple responding parties respectively, and calculates the position of the requesting party according to the measurement results. Among them, the measurement results obtained by the time measurement between the requester and each responder include time tags t1, t2, t3 and t4, t1 is the time when the responder sends the measurement frame, t2 is the time when the requester receives the measurement frame, and t3 is the request t4 is the time when the responder sends the response frame to the measurement frame, and t4 is the time when the responder receives the response frame. Wherein, the response frame is sent by the requesting party after receiving the last symbol of the measurement frame and waiting for a randomly generated short inter-frame interval. The randomly generated short interframe interval is randomly generated within the specified fluctuation range of the standard short interframe interval. The foregoing solution can prevent the location of the station from being known by the access point or the access point system, and improves the privacy of station positioning.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Same-frequency full duplex media access control method in a wireless local area network
ActiveCN109819507AIncrease profitPower managementNetwork topologiesUltrasound attenuationInformation transmission
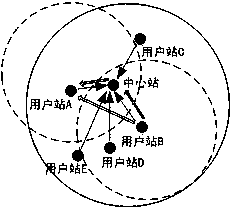
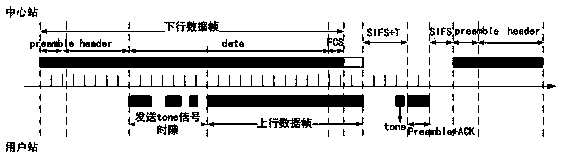
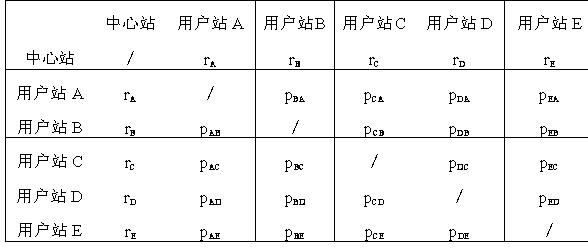
The invention discloses a wireless local area network. The invention discloses a full-duplex media access control method for receiving uplink information at the same frequency while a central stationsends information in a downlink mode at a certain frequency. The method comprises the following steps: when a network is initialized, a central station establishes and maintains a channel attenuationinformation table between each user station and the central station and between each user station and other user stations, so that the central station determines an uplink sending user station and distributes uplink sending power of the user stations during transmission; in the information transmission process, the central station sends and receives data in a co-frequency full-duplex uplink and downlink mode; a blank time slot T is added to the central station after a first short inter-frame interval SIFS, a new user station sends a request to the central station in the blank time slot and reports the attenuation condition of the central station signal received by the new user station and the attenuation condition of interference signals of other user stations, and the central station executes a network maintenance process and updates a channel attenuation information table. According to the method, the same-frequency full-duplex information receiving and transmitting of the central station side is realized, the information interaction efficiency in a wireless local area network is improved, and the influence on the data receiving and transmitting of other user stations when a newuser station joins is reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING JINMEI COMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com