Patents
Literature
1020 results about "PHY" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
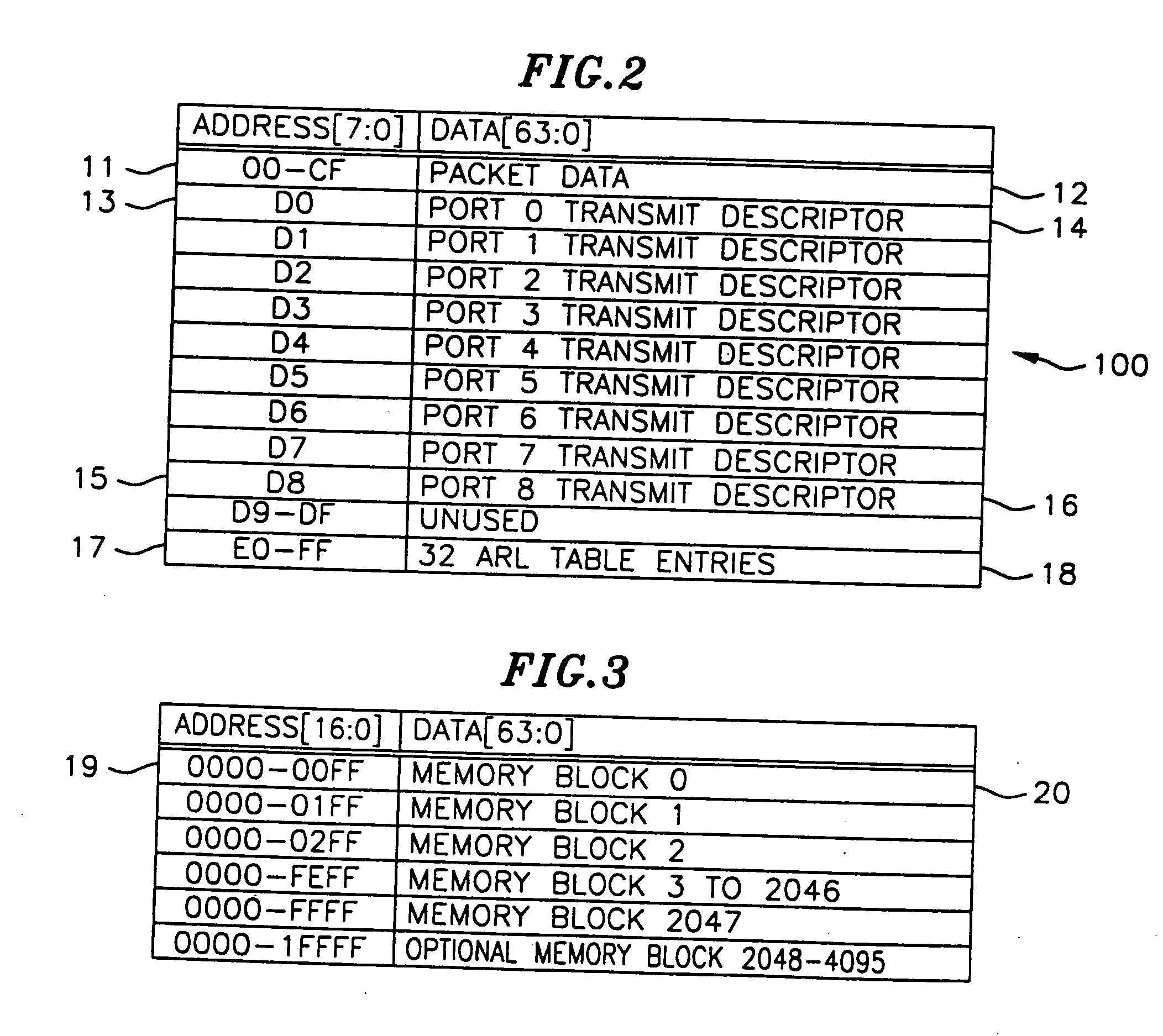
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
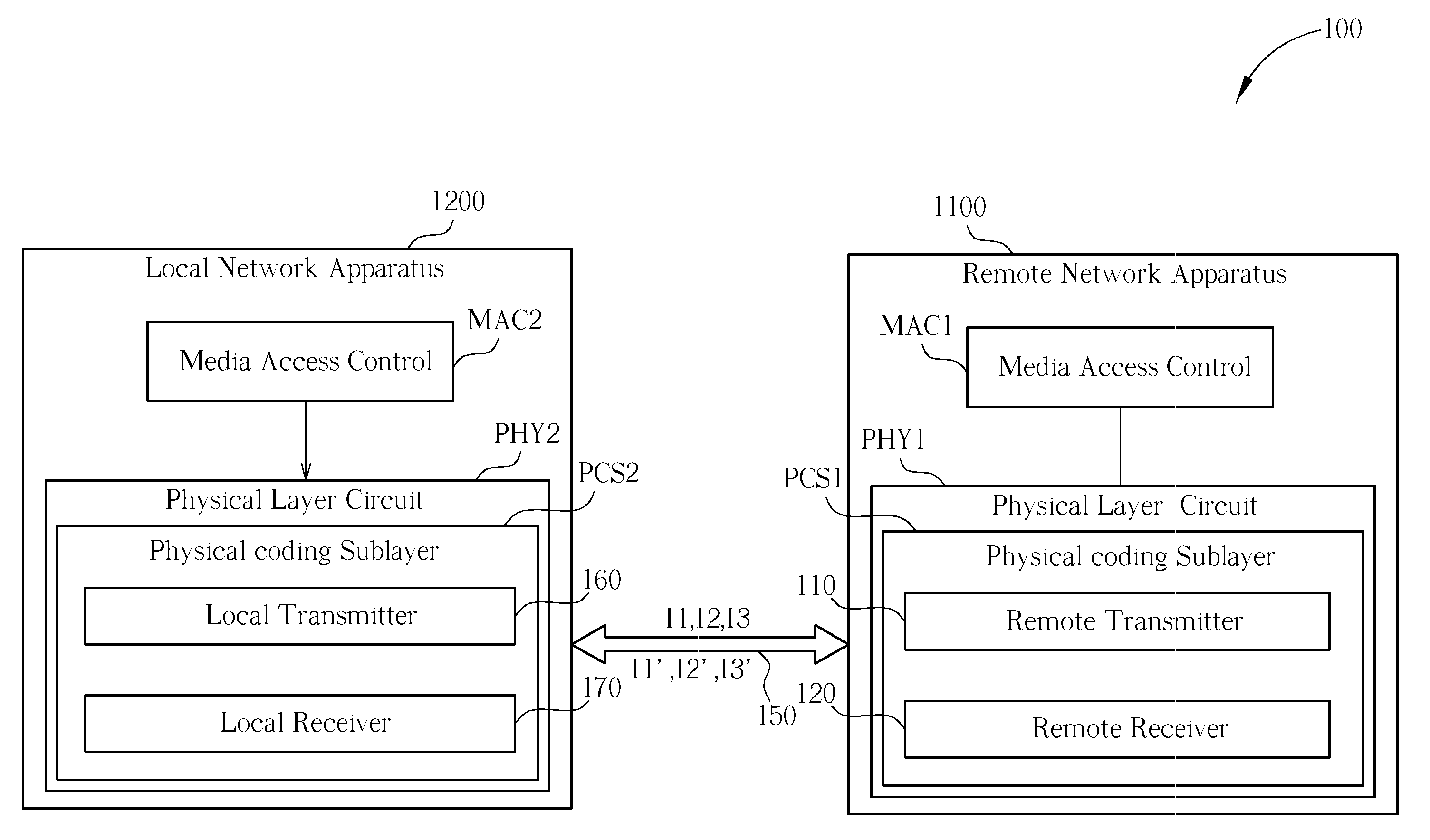
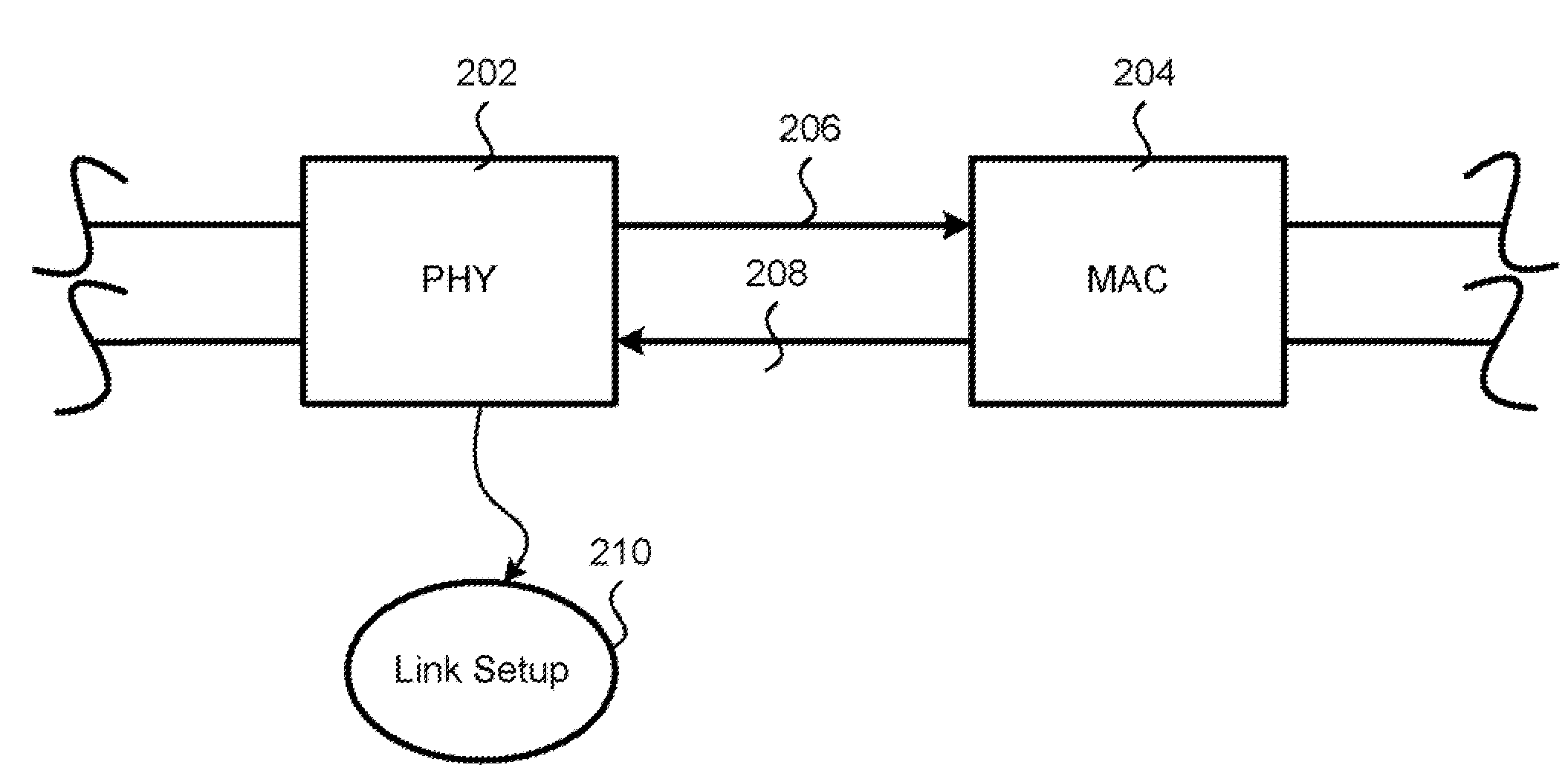
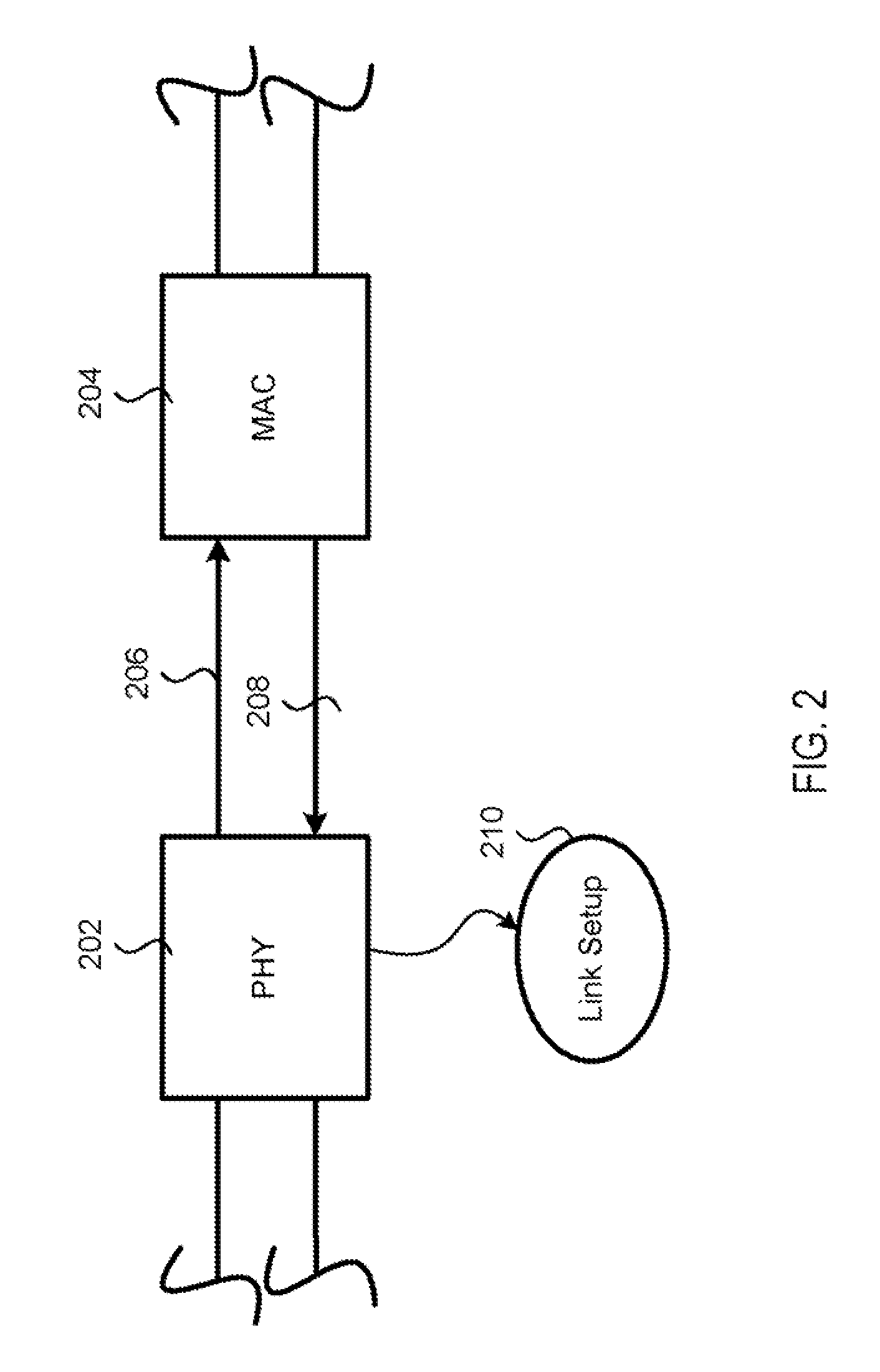
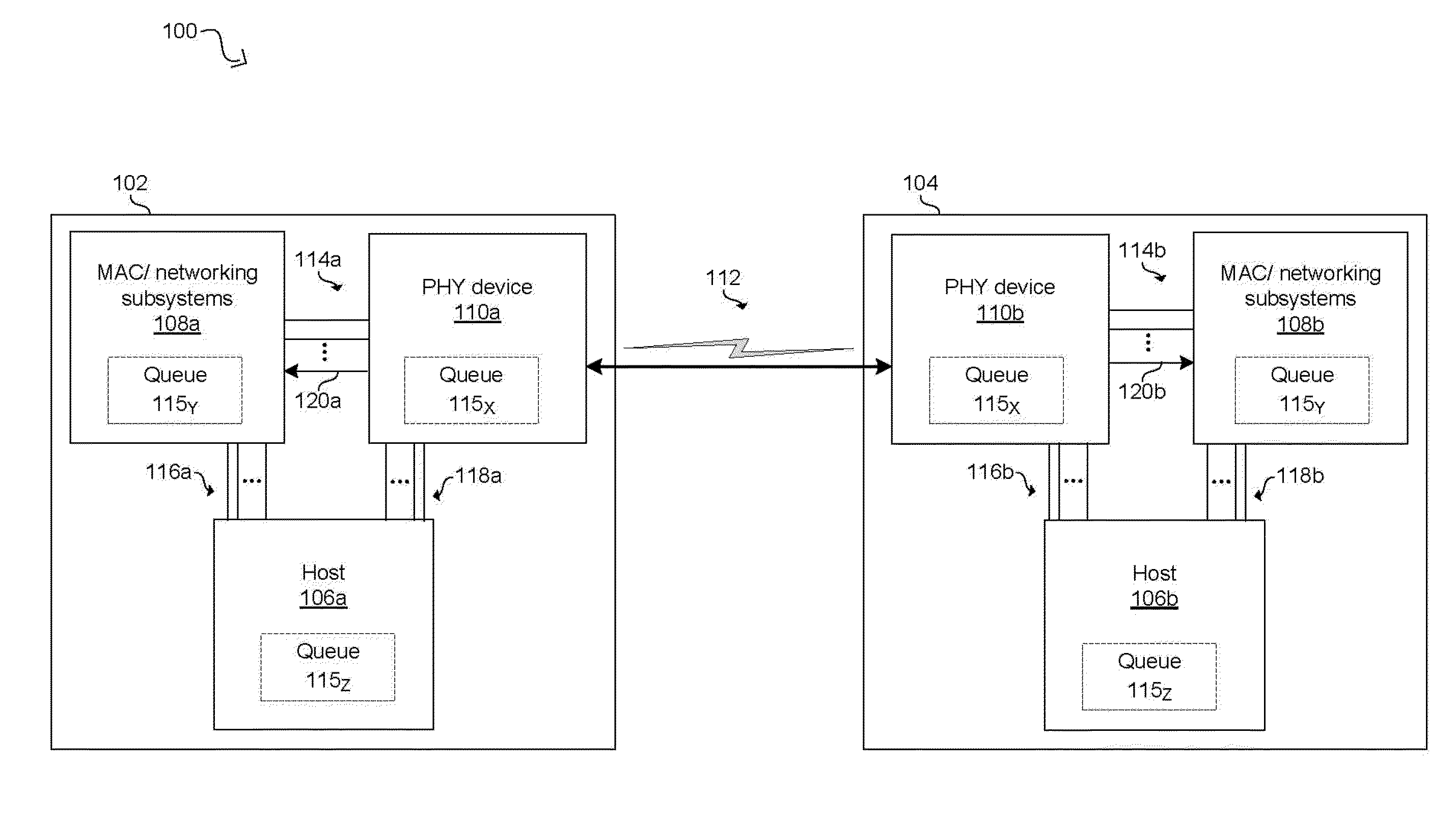
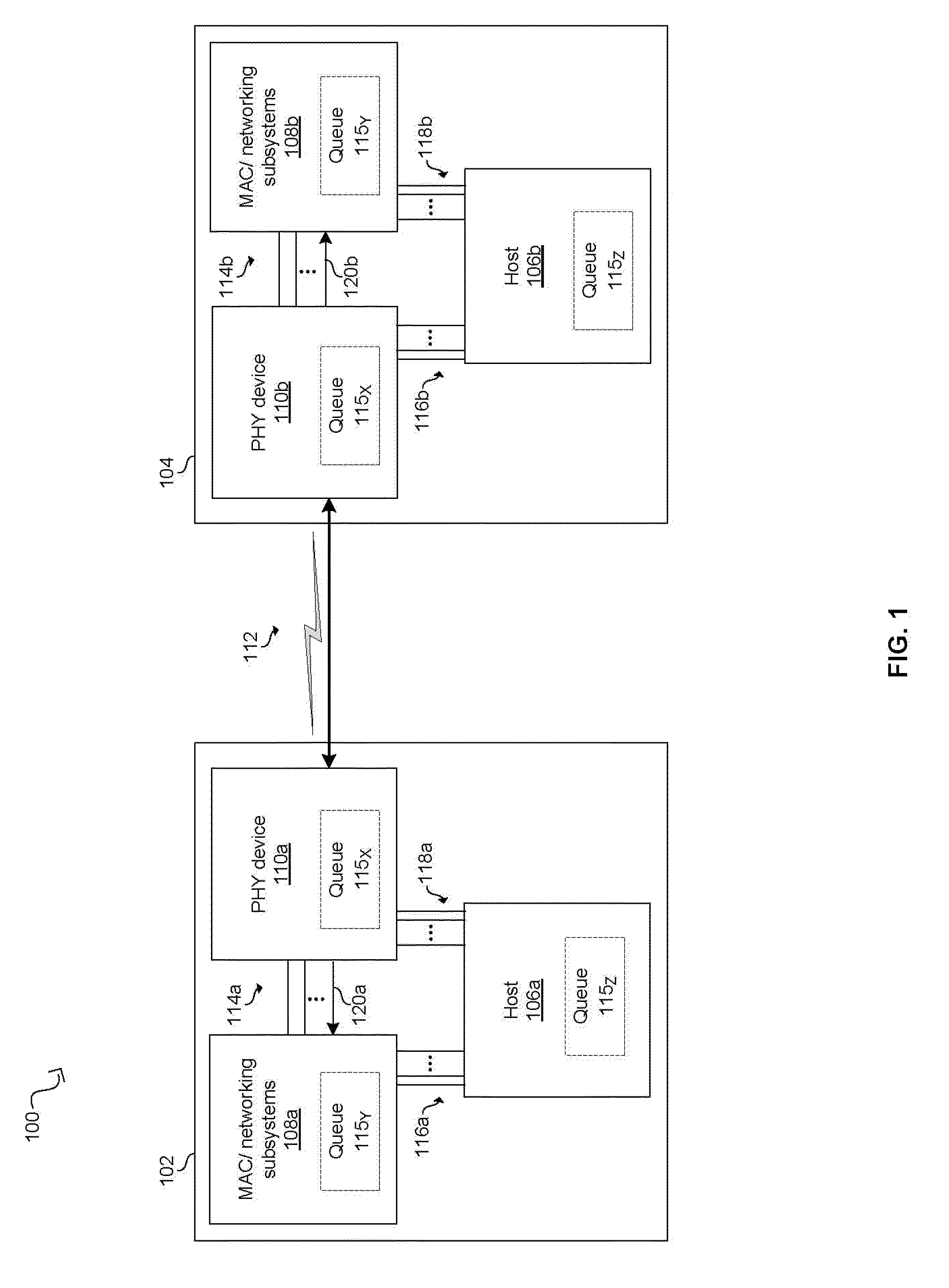
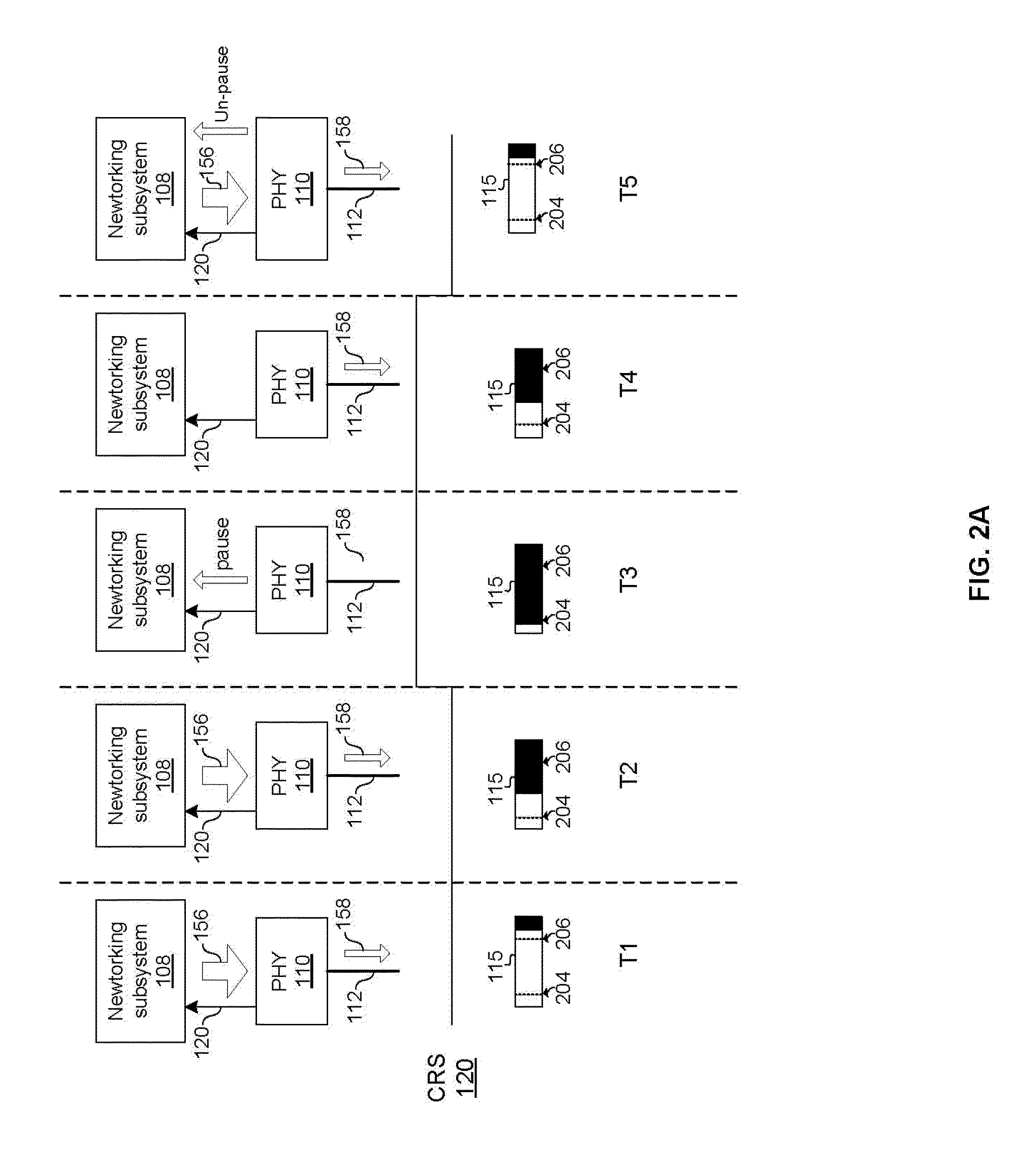
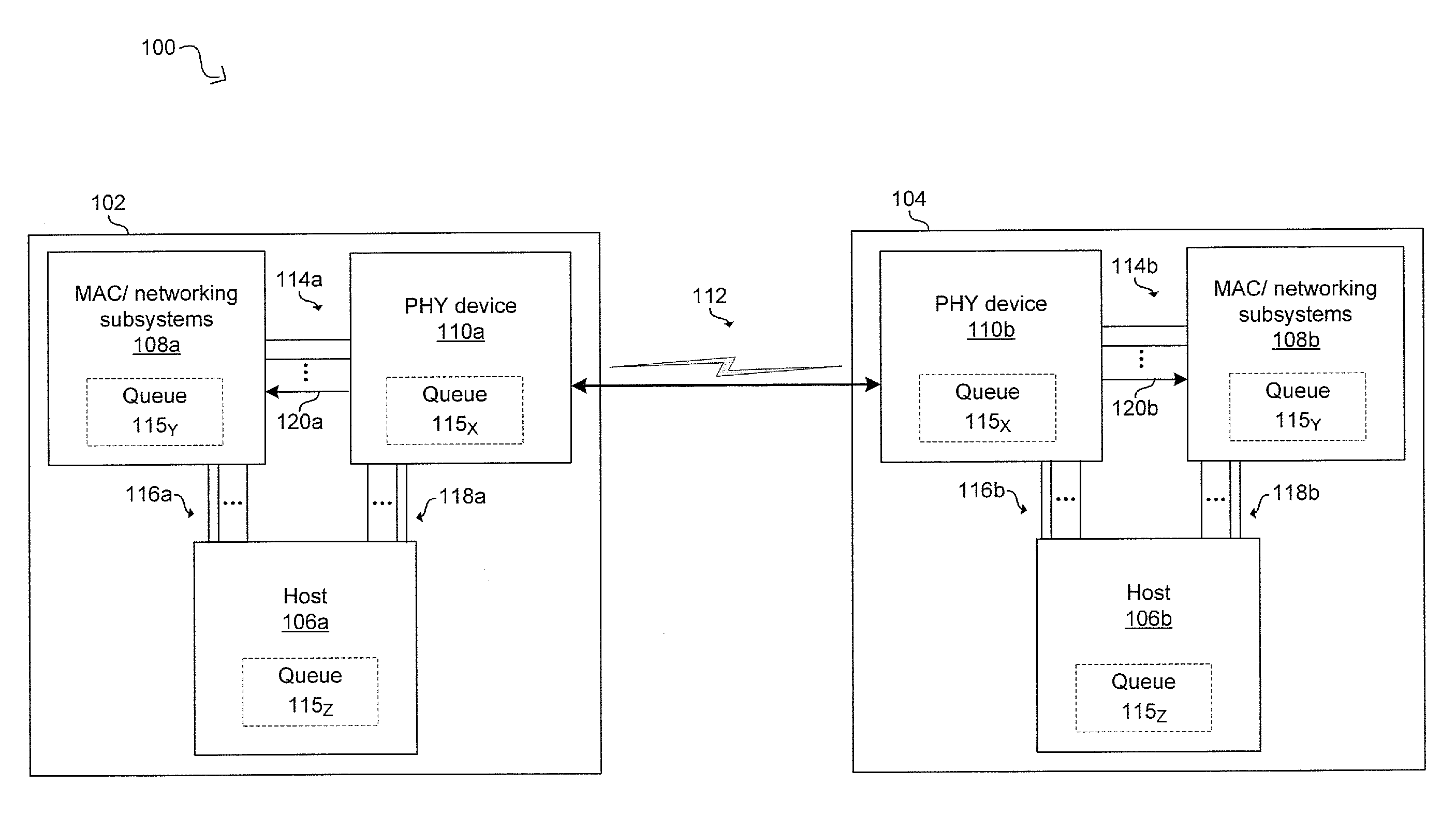
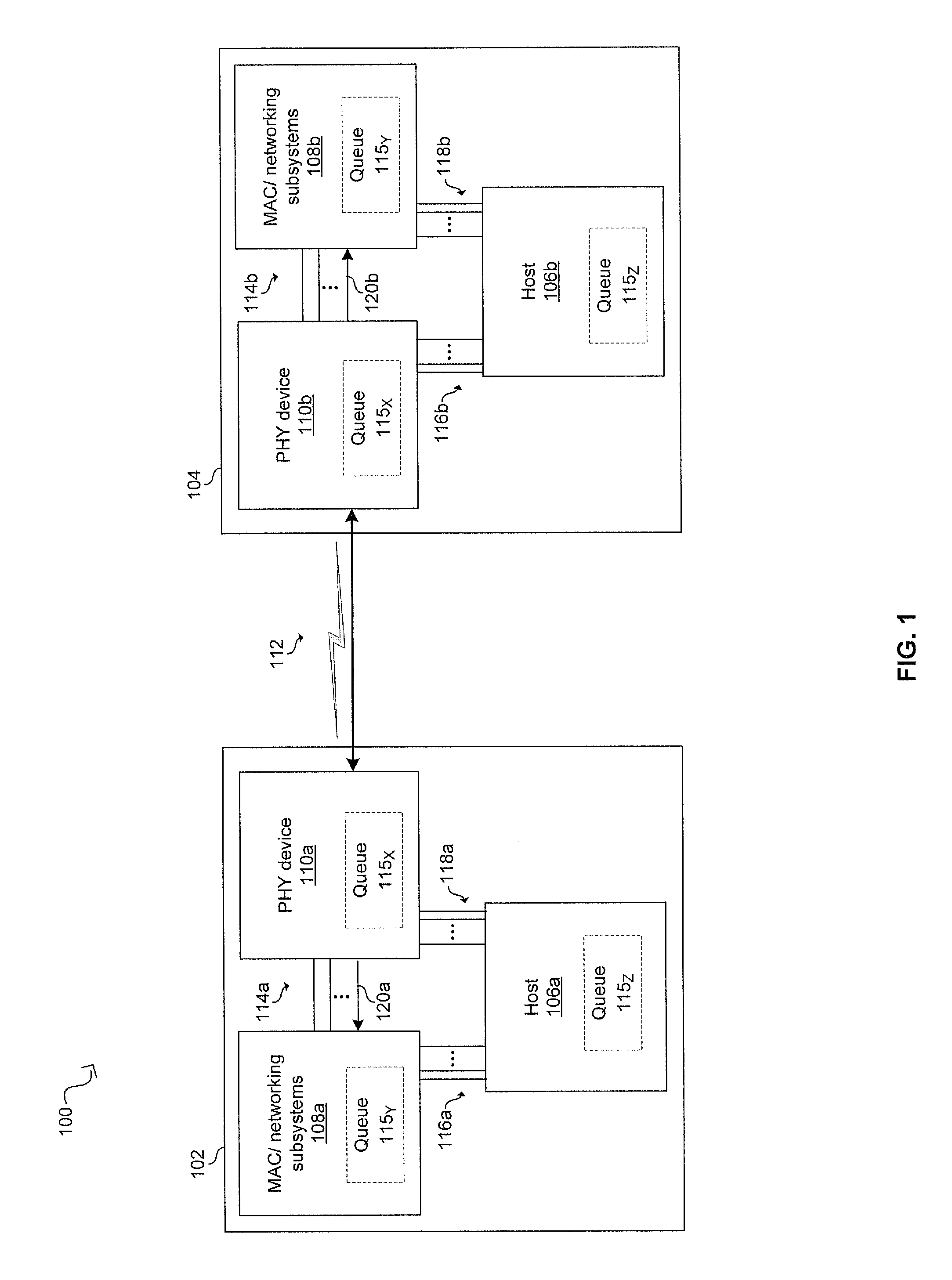
A PHY, an abbreviation for "physical layer", is an electronic circuit, usually implemented as a chip, required to implement physical layer functions of the OSI model. A PHY connects a link layer device (often called MAC as an acronym for medium access control) to a physical medium such as an optical fiber or copper cable. A PHY device typically includes both Physical Coding Sublayer (PCS) and Physical Medium Dependent (PMD) layer functionality.
Dynamic parameter adjustment for LTE coexistence
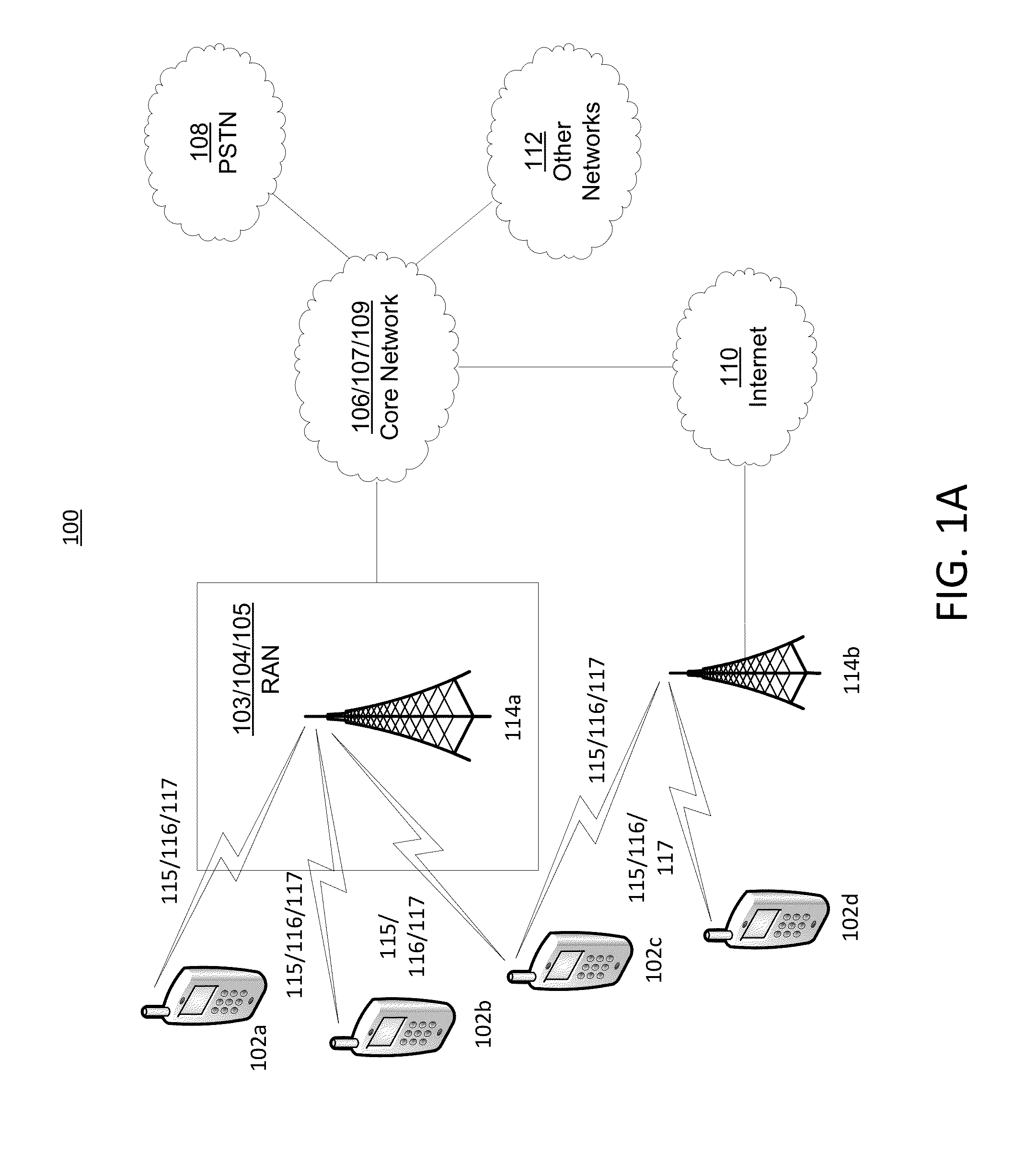
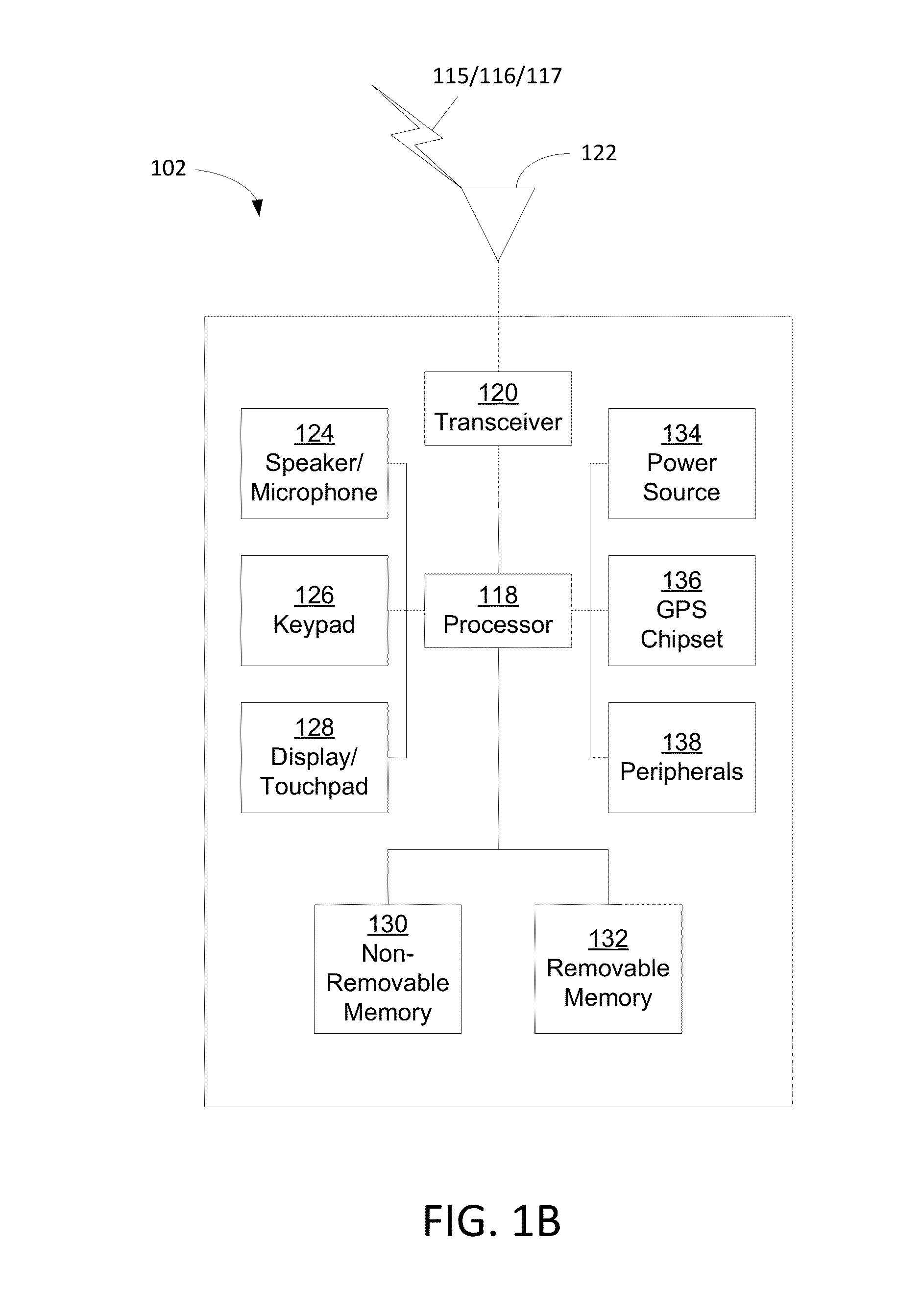
Coexistence gaps may permit one radio access technology (RAT) to coexists with another RAT by providing period in which one RAT may be silent and another may transmit. Methods may account for the RAT traffic and for the presence of other secondary users in a channel. Methods may be provided to dynamically change the parameters of a coexistence gap pattern, such as the duty cycle, to adapt to both the RAT traffic and the presence of other secondary users. Methods may include PHY methods, such as synchronization signal (PSS / SSS) based, MIB based, and PDCCH based, MAC CE based methods, and RRC Methods. Measurements may be provided to detect the presence of secondary users, and may include reporting of interference measured during ON and OFF durations, and detection of secondary users based on interference and RSRP / RSRQ measurements.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
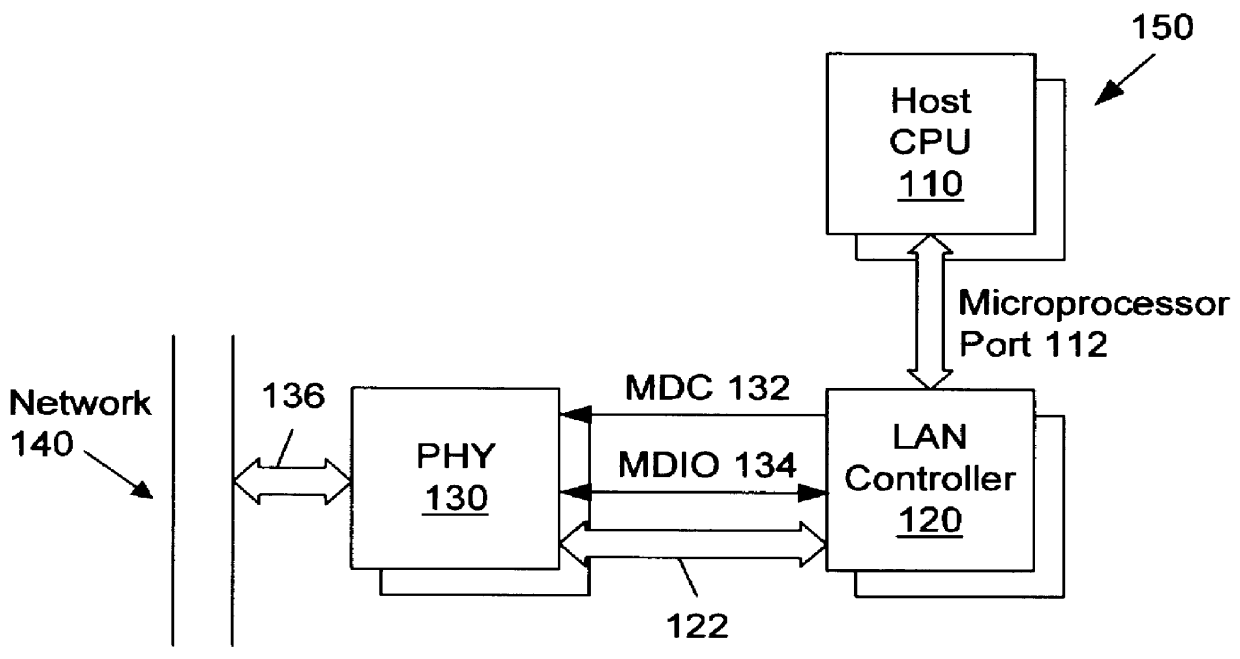
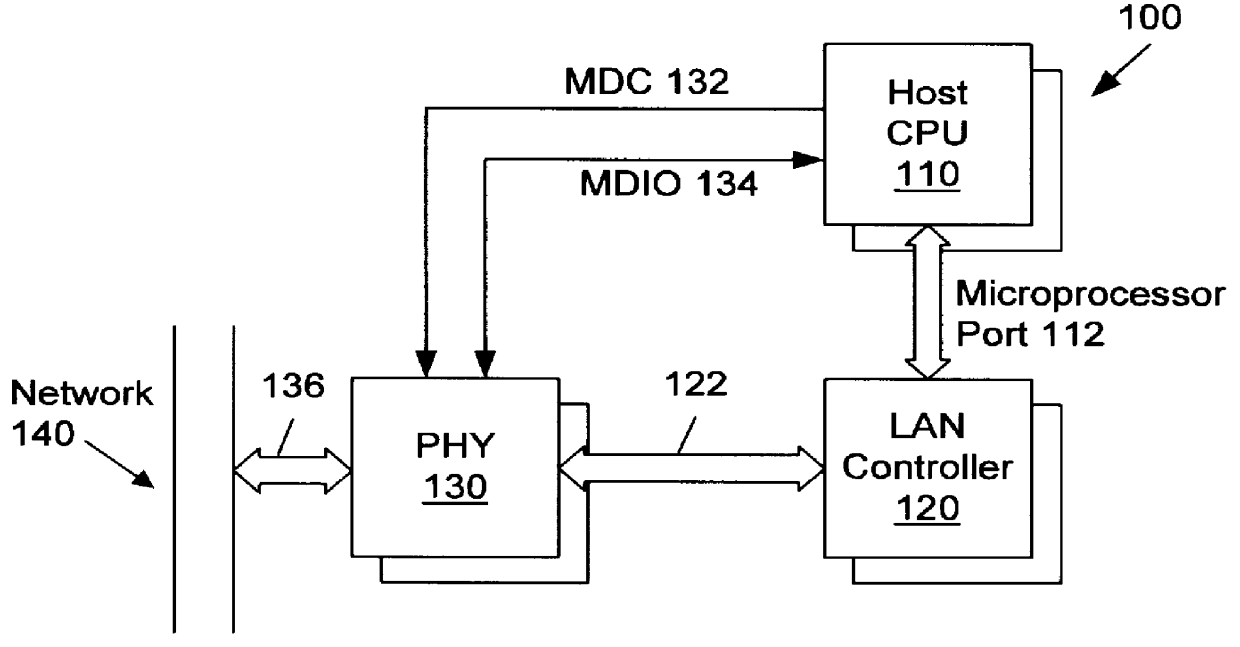
Auto-polling unit for interrupt generation in a network interface device
A system and method for auto-polling a status register within a physical layer (PHY) interface to a local area network (LAN). The system includes a host CPU which needs to detect and service interrupts generated by a PHY device on the LAN which is coupled between a first transmission medium (such as copper or fiber cable) and a management interface to the system. The system further includes an auto-polling unit which monitors activity on the management interface of the PHY device. When the auto-polling unit detects a lack of activity on the management interface of the PHY for a predetermined interval, the auto-polling unit reads a first value from the PHY status register. This first status value is then compared to a previously stored value which corresponds to the last PHY status value read by the host CPU. If a mismatch is detected between these two values, an interrupt is generated to the CPU. In response to receiving the interrupt, auto-polling is suspended (to avoid changing the status data that caused the interrupt) and the CPU requests a read of the status value in the first register. In this manner, the CPU is able to access the status value which caused the interrupt and determine the appropriate course of action. This status read by the CPU also has the effect of clearing the interrupt. This system frees the CPU from having to continually poll the PHY status register to determine if a change in status has occurred.
Owner:JATO TECH
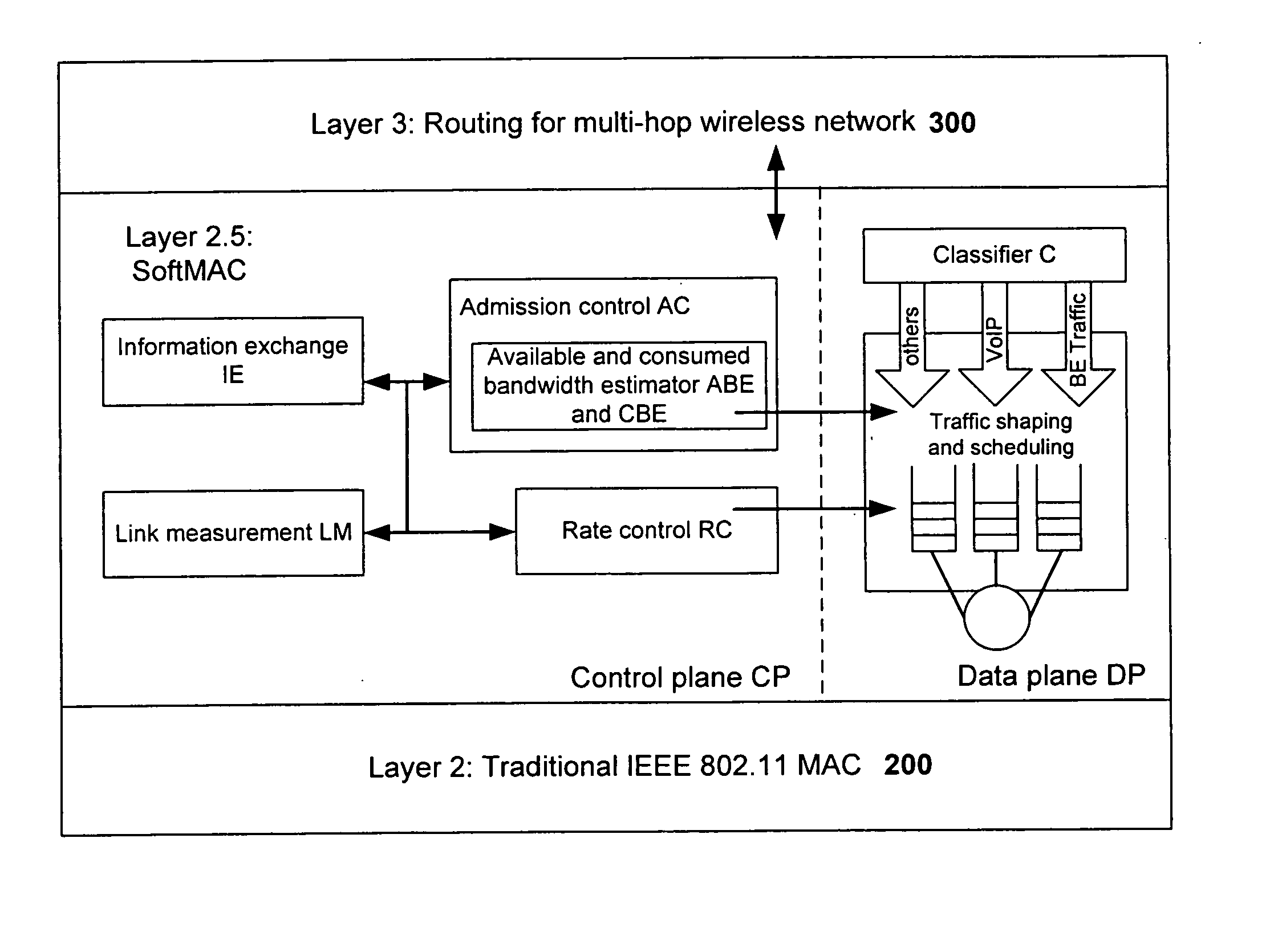
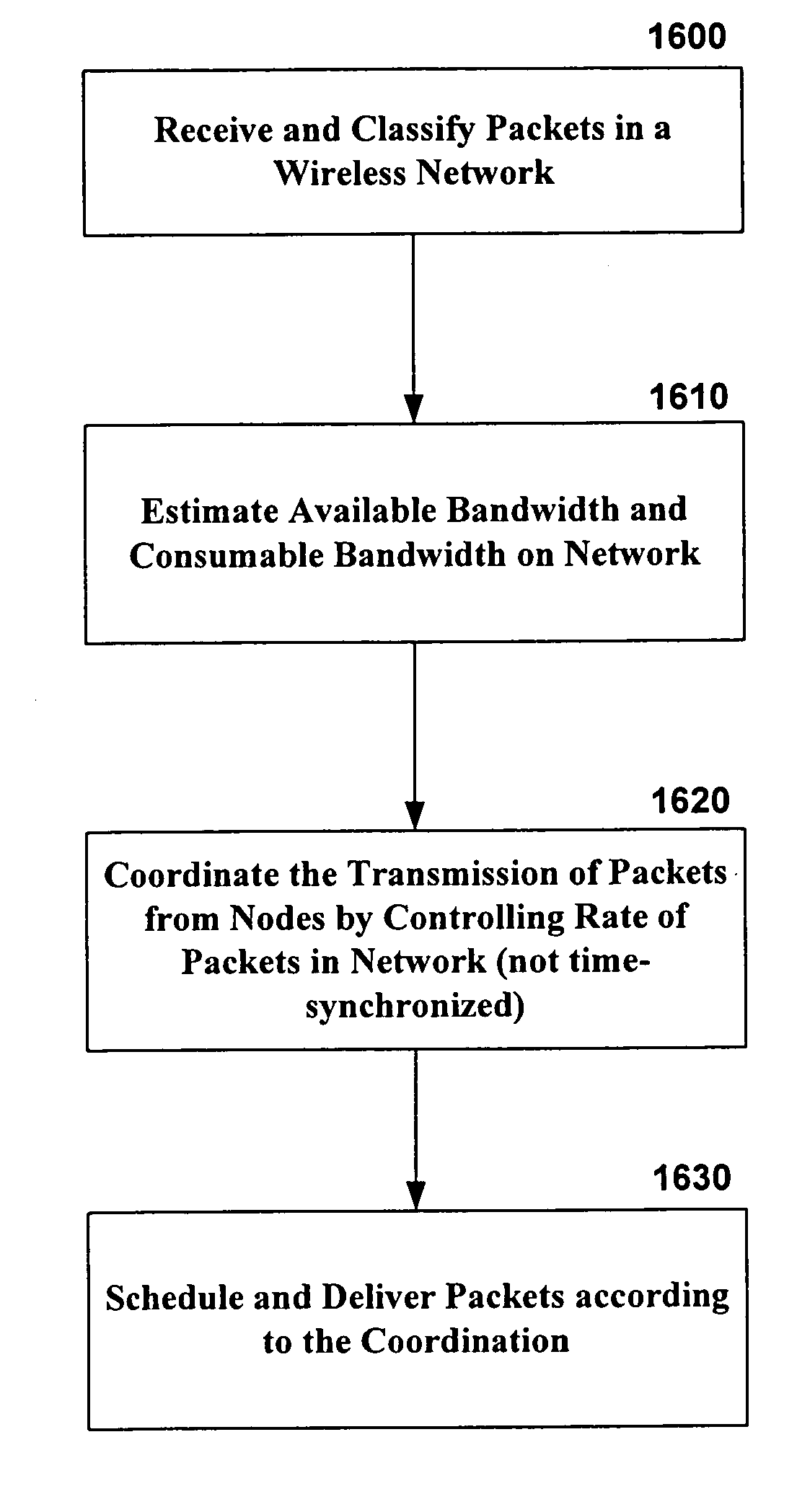
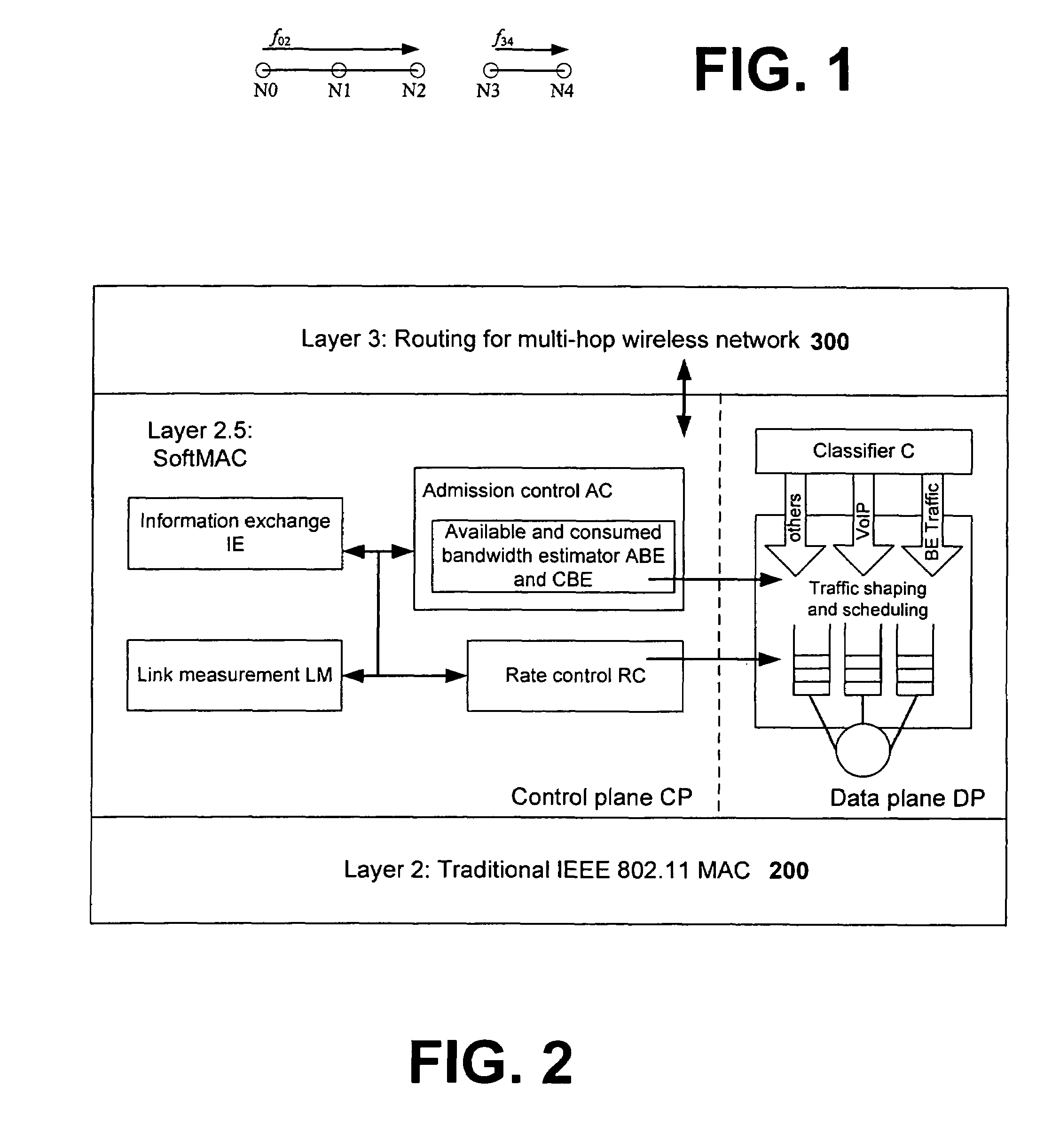
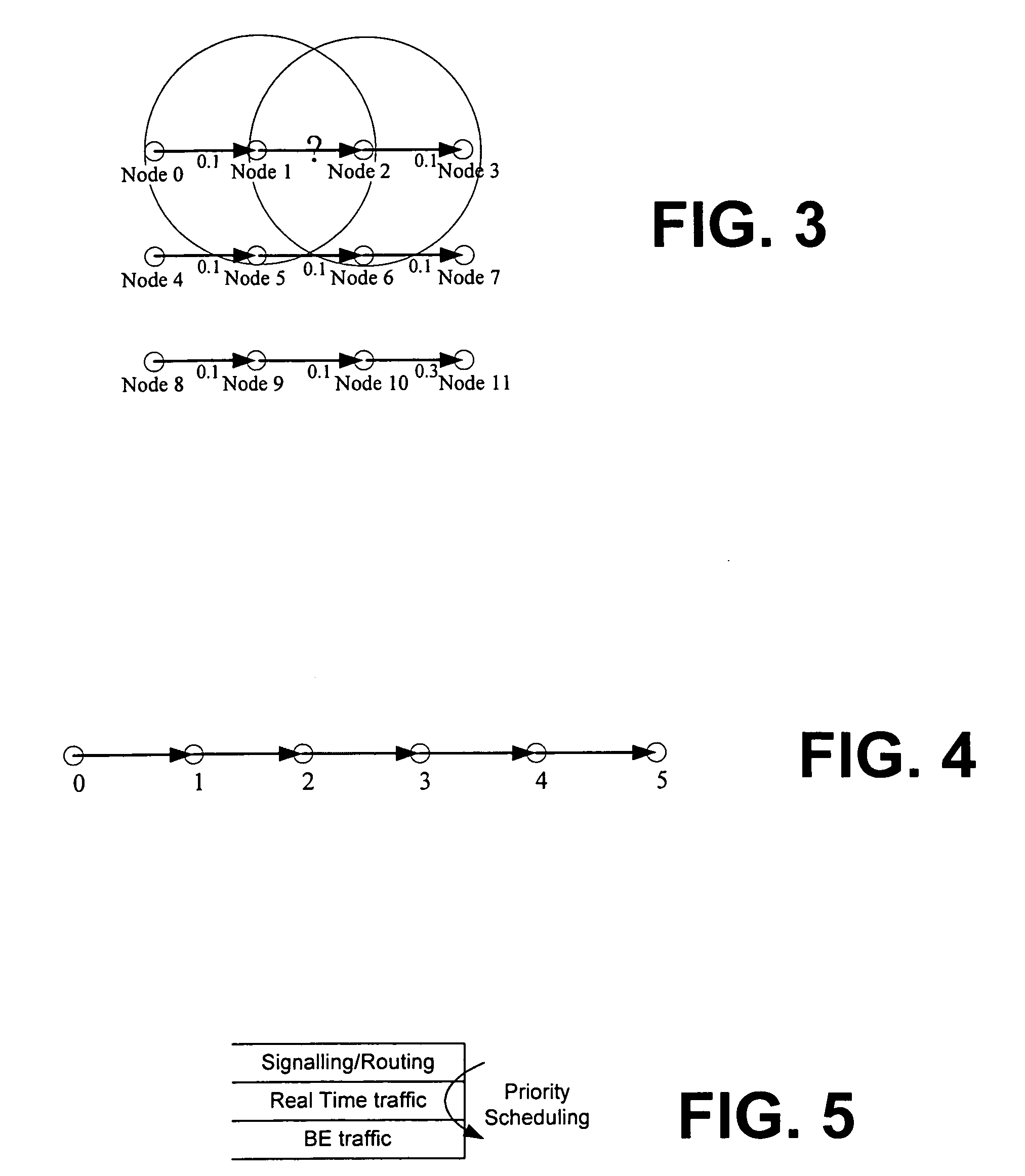
Systems and methods for coordinating wireless traffic for heterogeneous wireless devices
InactiveUS20060215556A1Good effectError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityPHY
In view of the foregoing, the present invention provides a unified software framework or architecture for distributed coordination of wireless devices and radios, referred to as Layer 2.5 Software MAC (or ‘SoftMAC’), which resides between the standard 802.11 MAC layer (Layer 2) and IP layer (Layer 3) to regulate and control the amount of traffic (both real-time and “best effort”) delivered to 802.11 MAC DCF interfaces. The software based design can be ported to different OS platforms and systems and is capable of handling new hardware interfaces and MAC mechanisms (e.g., 802.11e) with only a software upgrade. The invention thus provides a natural way to make end systems support coordination of different radios of device(s), achieving better performance. Advantages of the 2.5 layer software MAC in accordance with the invention include: (a) there are no hardware constraints; (b) heterogeneous wireless / radio support is provided at the 2.5 layer; and (c) an evolutionary and extensible solution with the ability to support future wireless MAC / PHY chip combinations.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
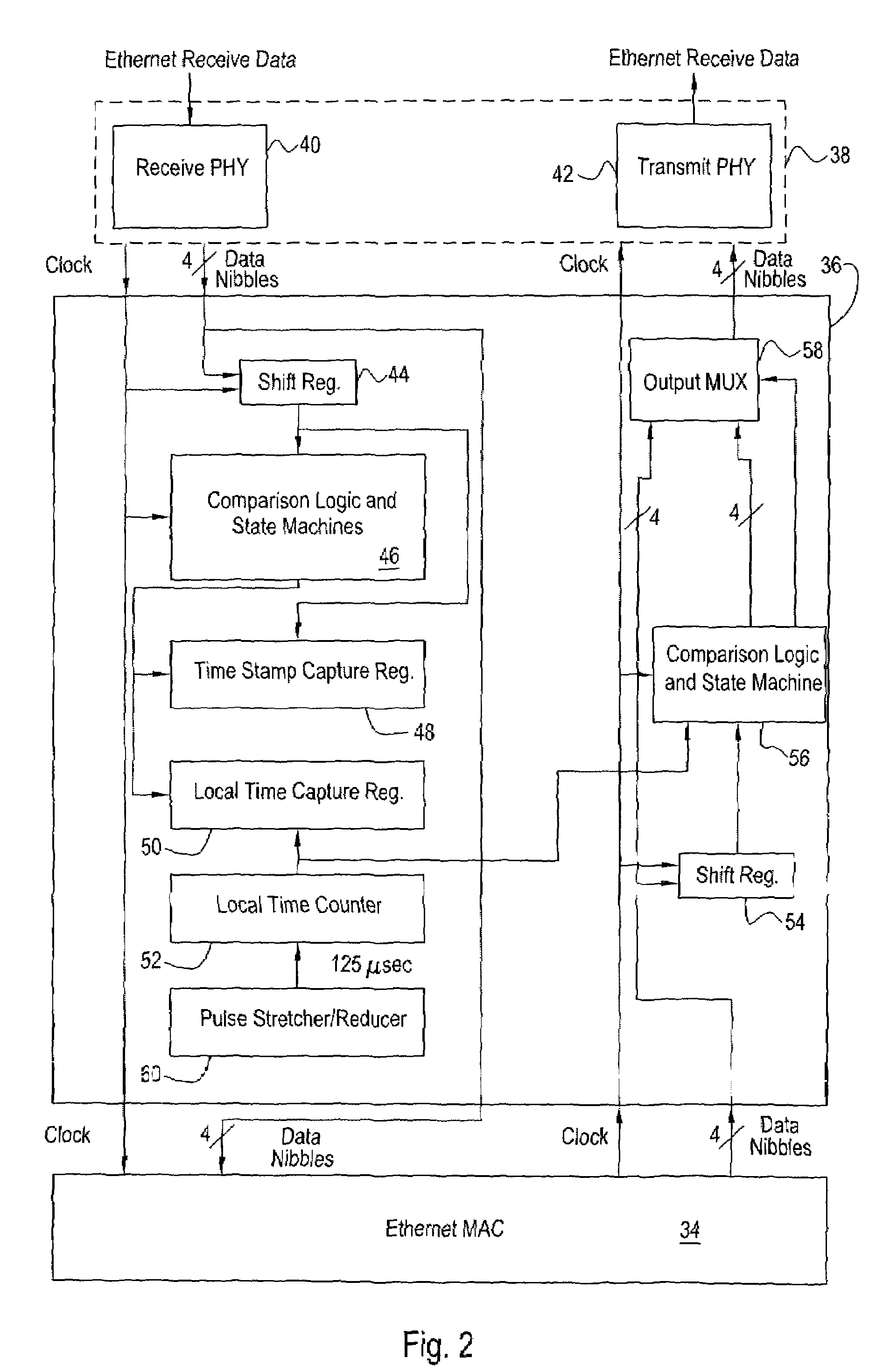
IEEE 1588 time synchronization system and implementation method thereof
ActiveCN101447861ASynchronized High Precision TimeGuaranteed real-timeTime-division multiplexSynchronising arrangementTime informationPHY
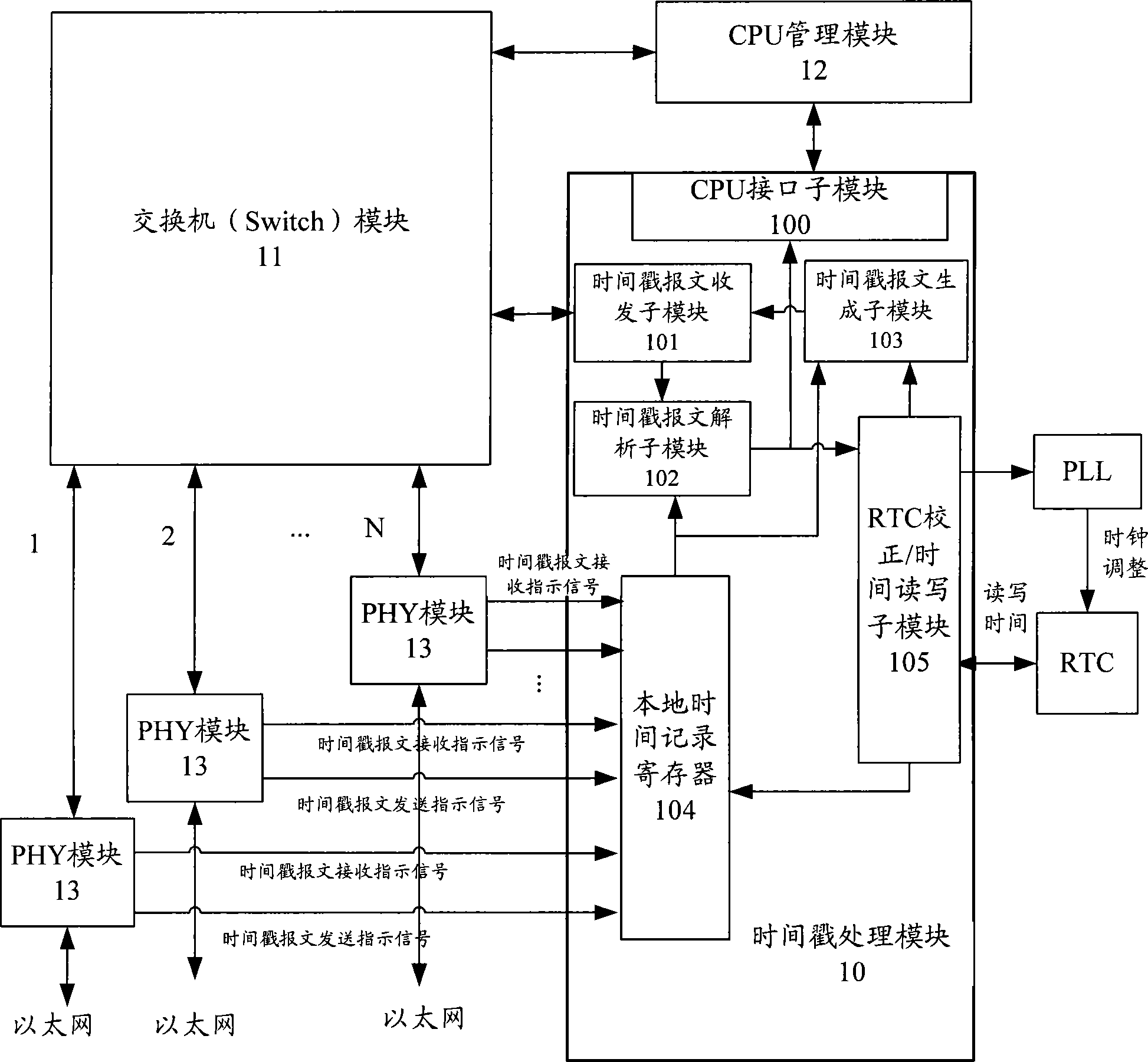
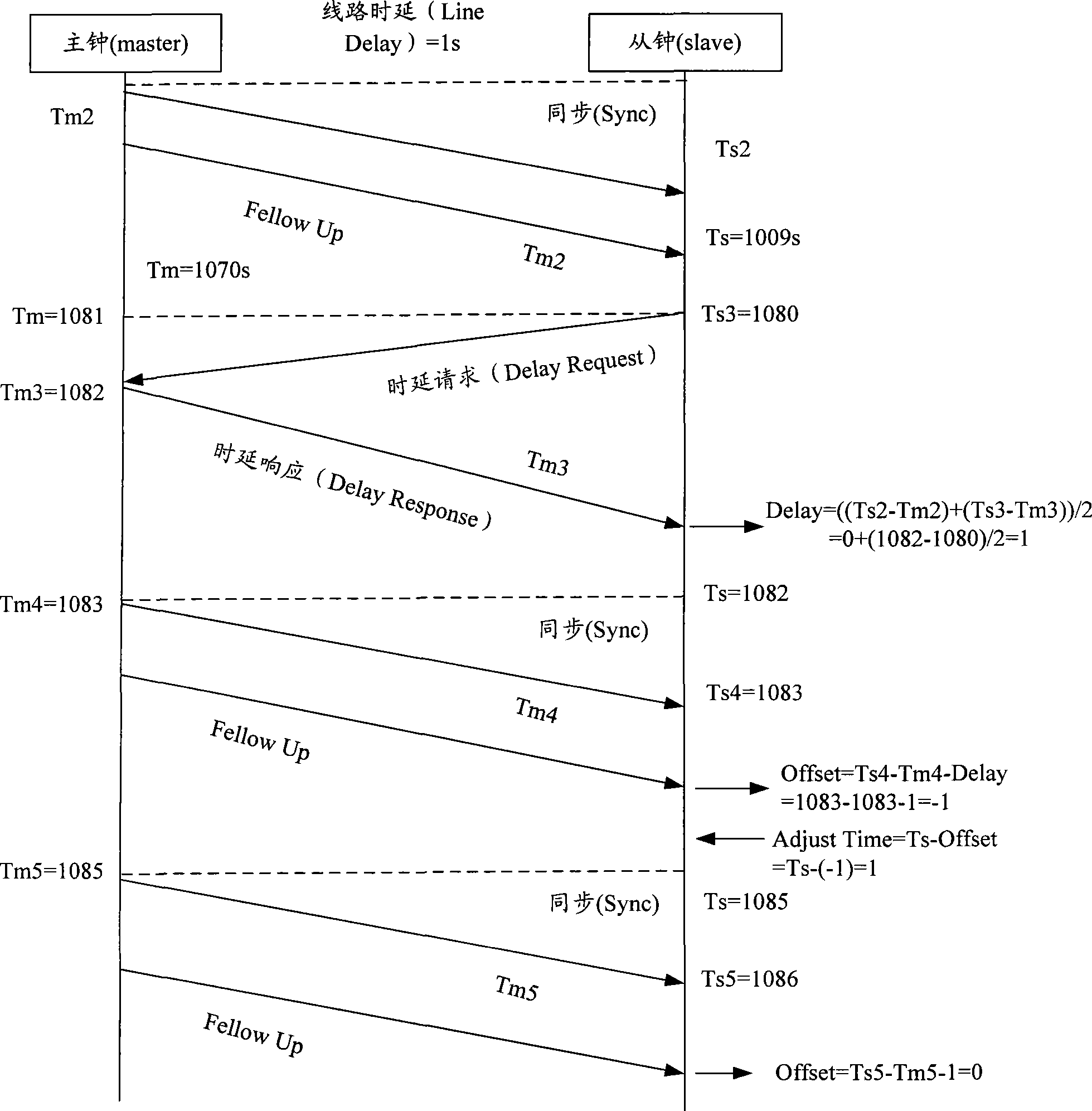
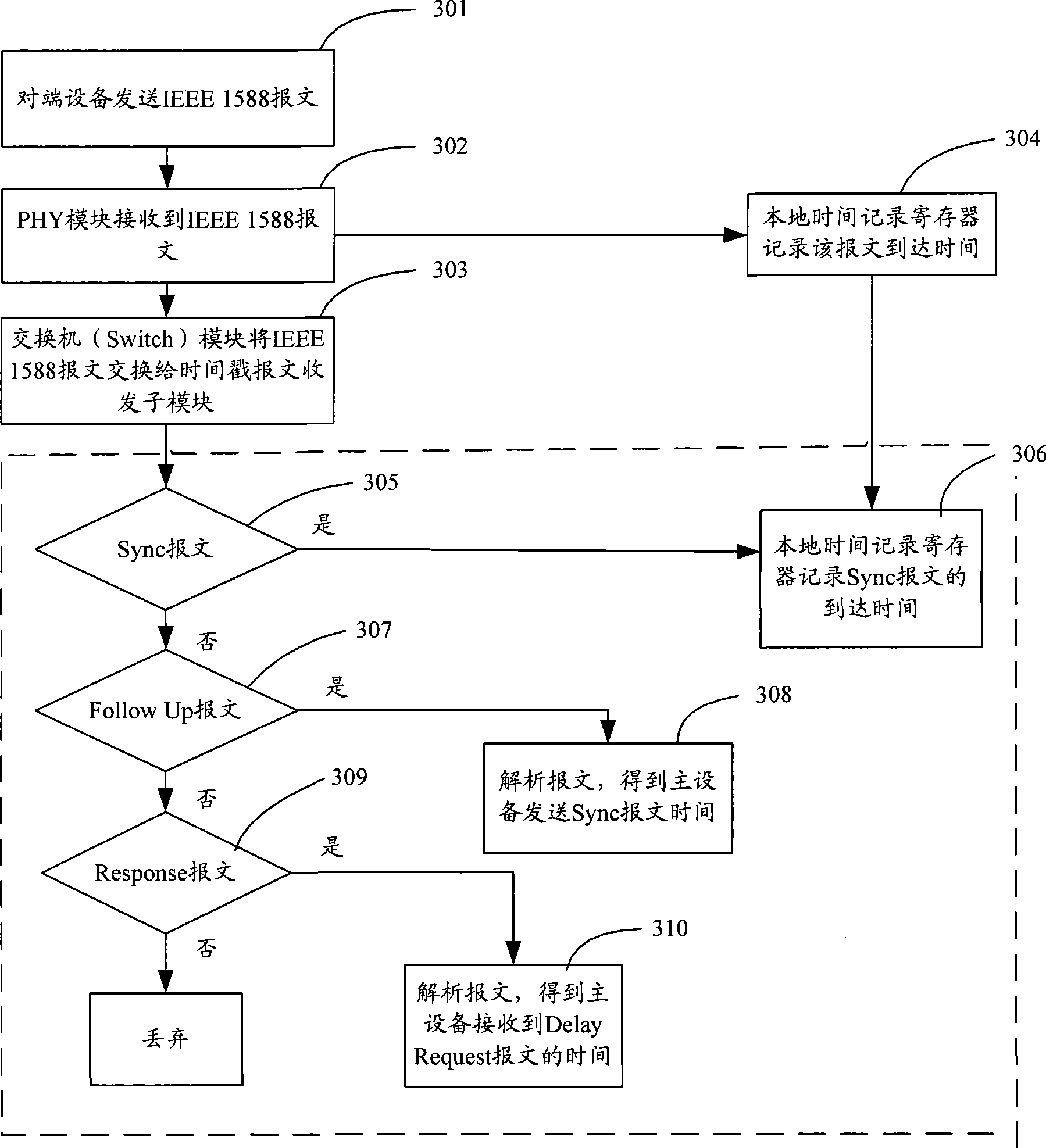
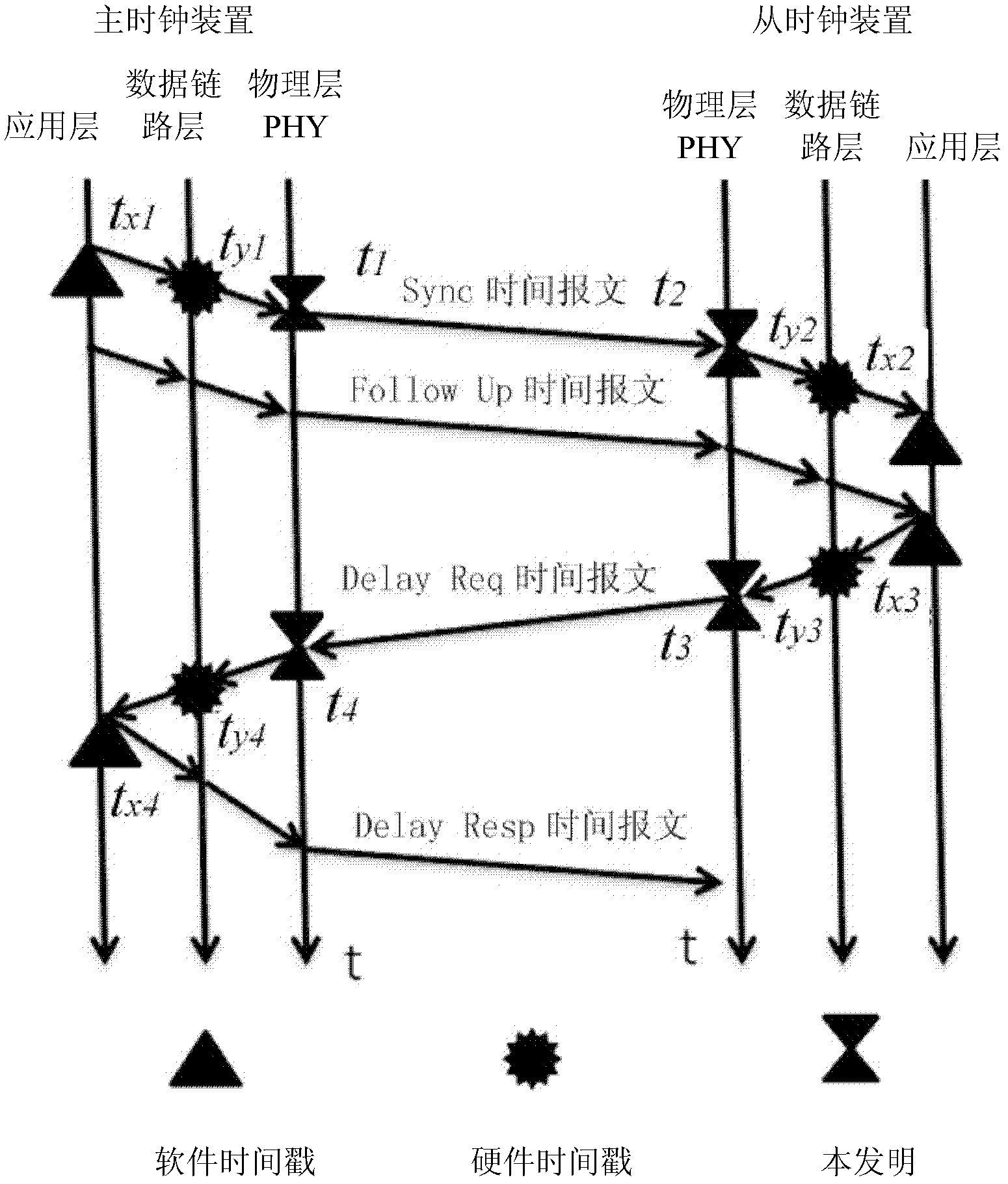
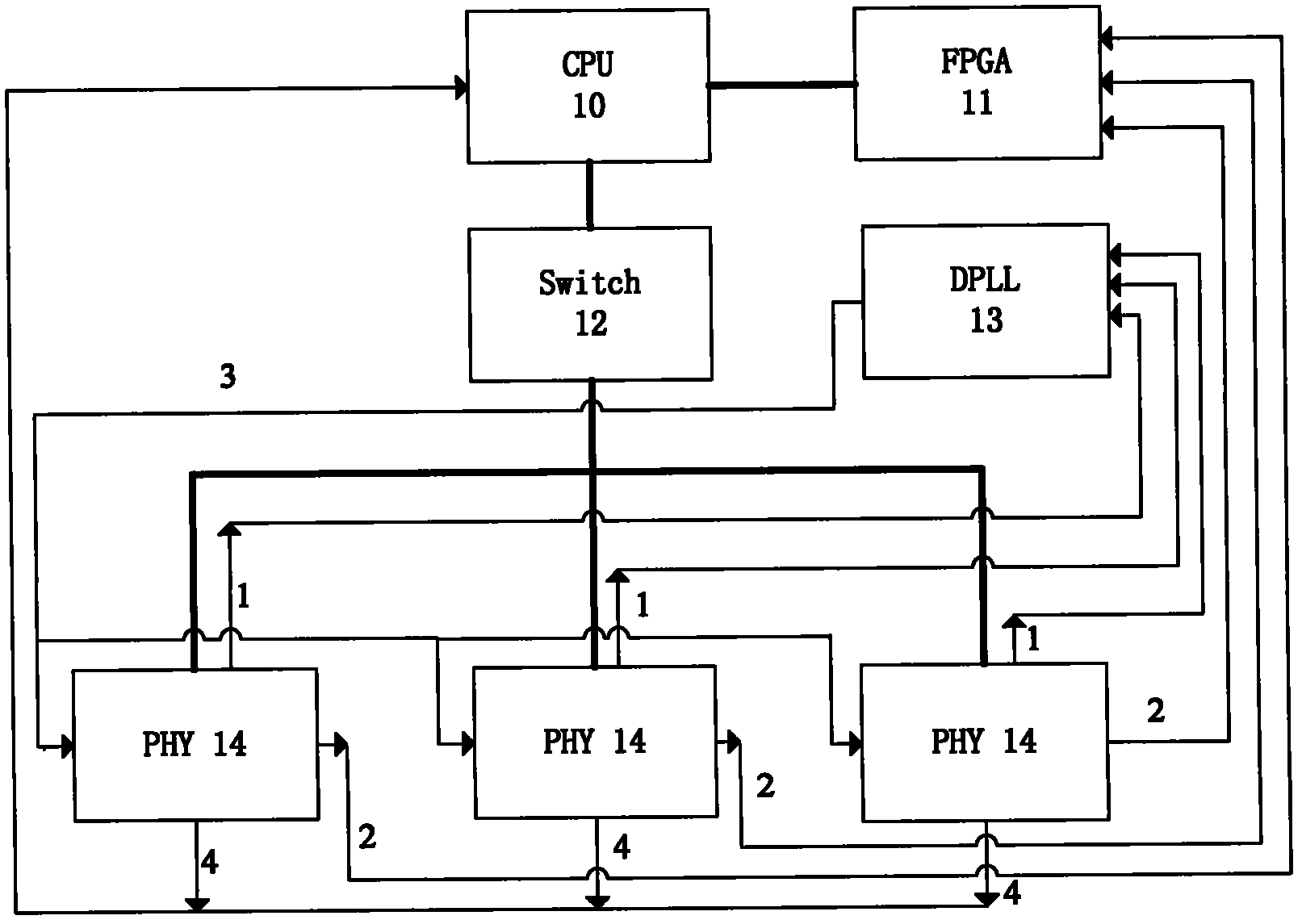
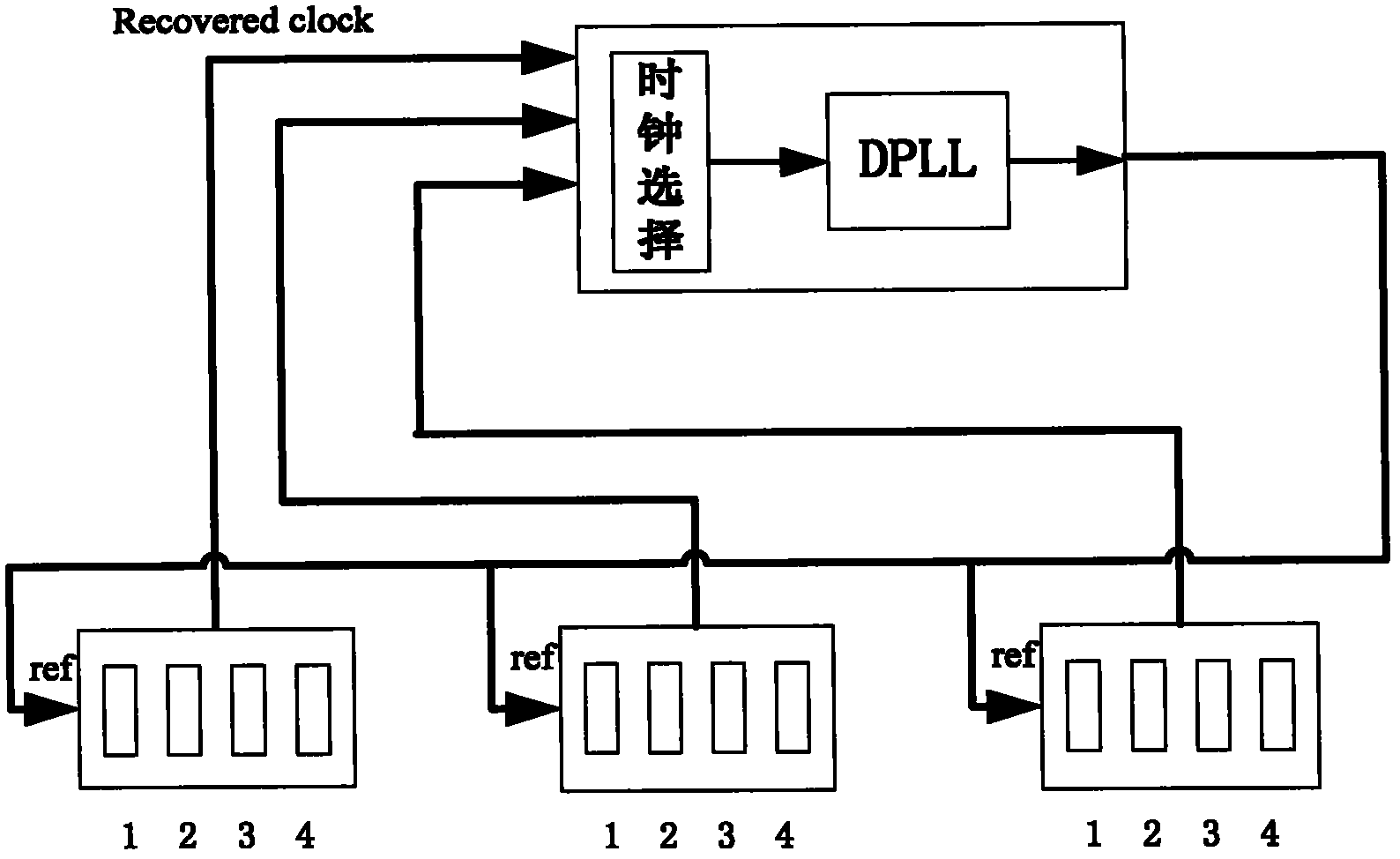
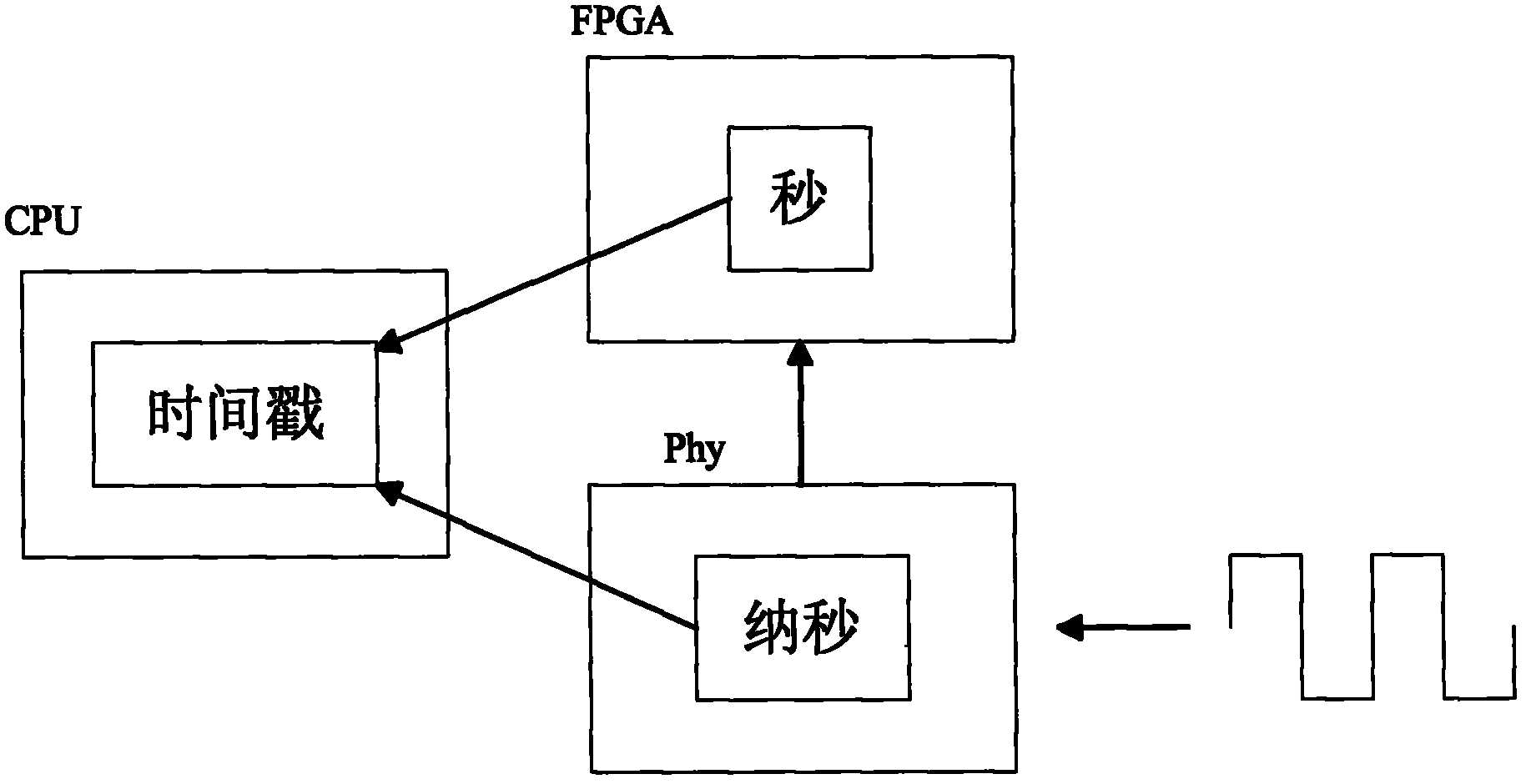
The invention discloses an IEEE 1588 time synchronization system. By adding a time-stamp processing module, a time-stamp message transceiving sub module, a time-stamp message resolving sub module, a time-stamp message generating sub module, a local time recording register, and an RTC correction / time read-write module in the module are used for combining peripheral components such as a switch module, a PHY and a real-time clock (RTC) module to form a hardware system. When in use, the high precision time synchronization requested by an IEEE 1588v2 protocol can be implemented by using the modes of one-to-one or one-to-many of master-slave synchronization. The invention also discloses a method for implementing the IEEE 1588 time synchronization, which can implement the function of the time synchronization system by processing the time information of master-slave devices in real time. The invention plays an active role in promoting Ethernet construction.
Owner:ZTE CORP
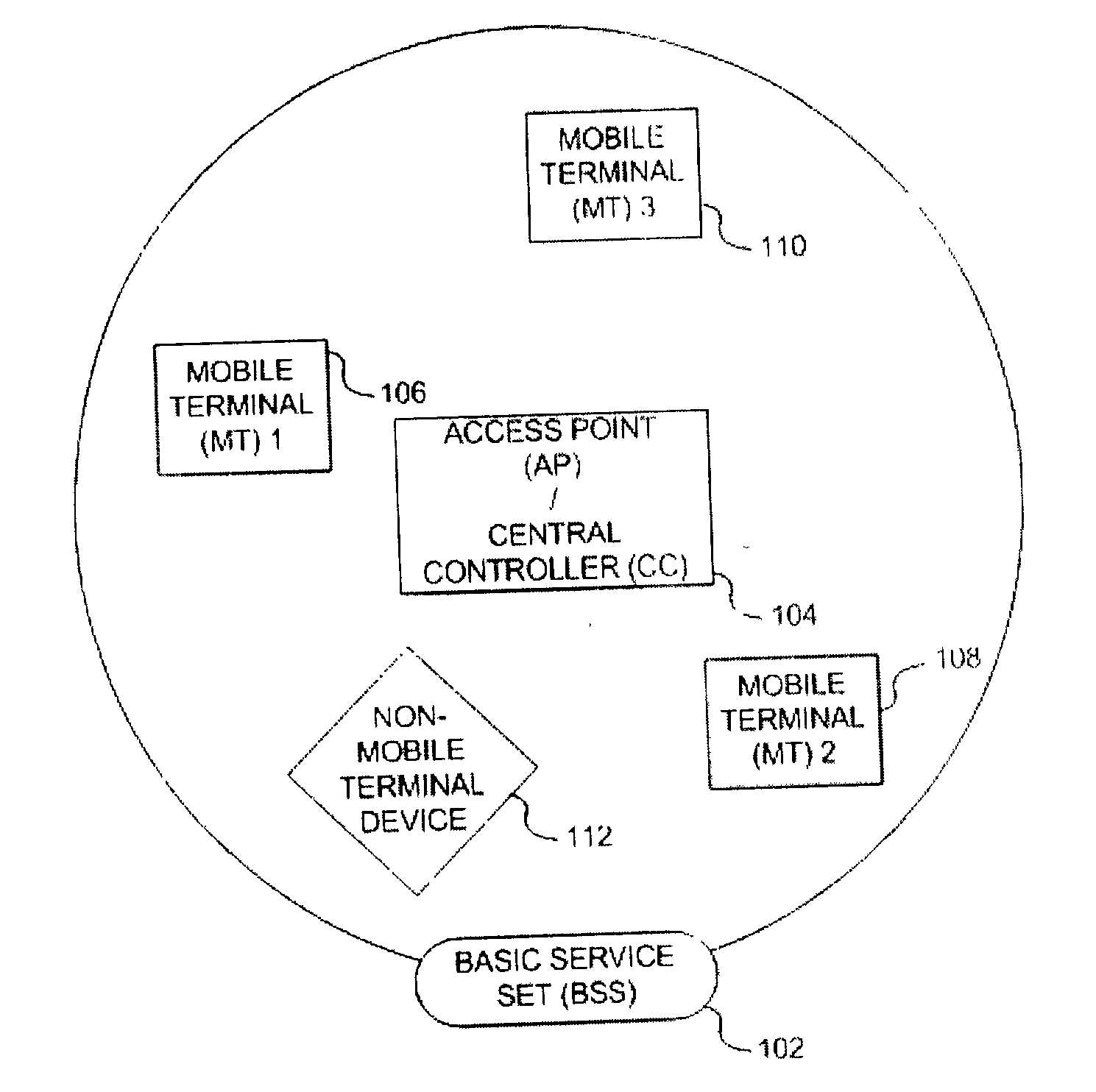
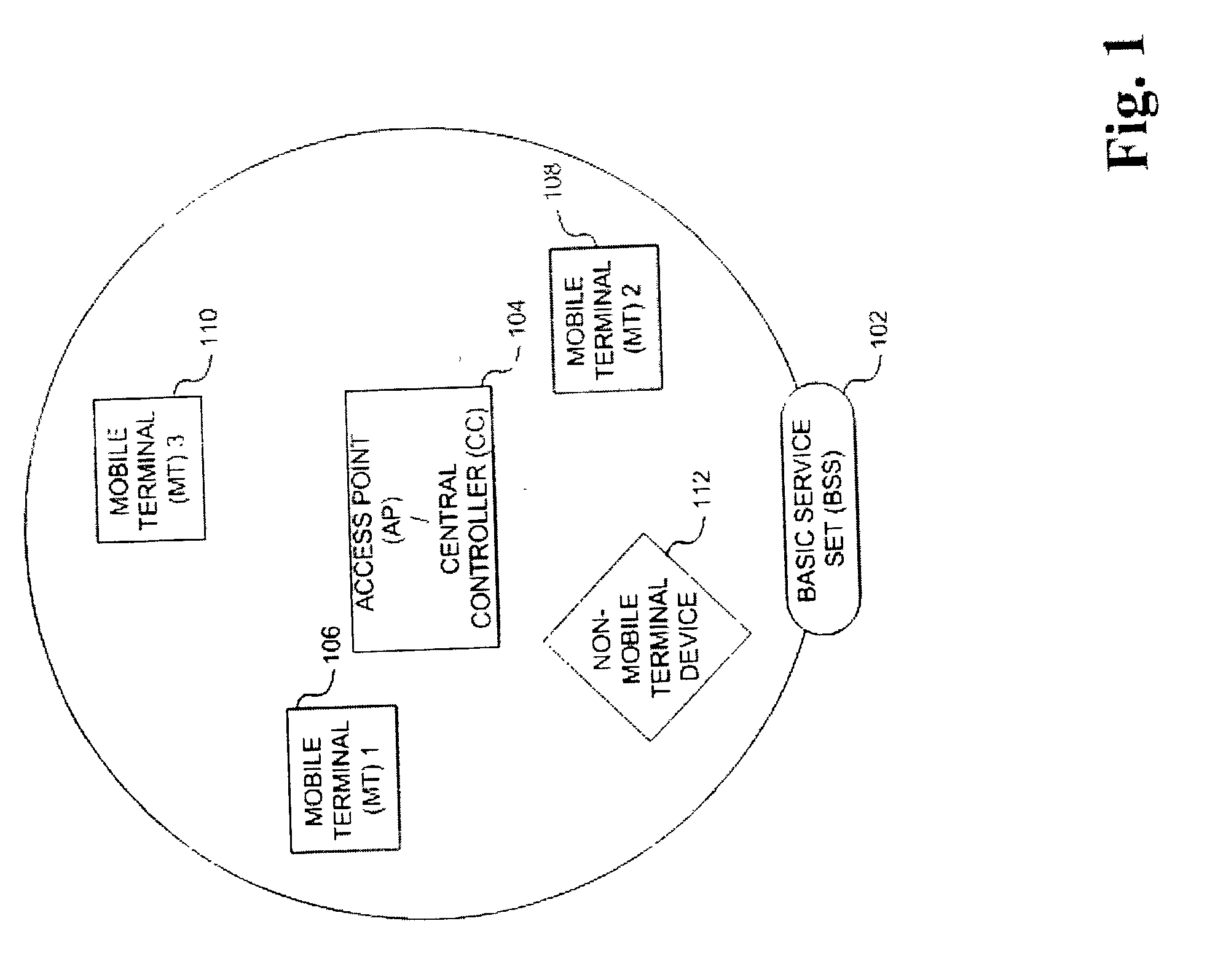
Method and apparatus for assuring quality of service in wireless local area networks
InactiveUS20040037257A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesQuality of serviceReliable transmission
A method and apparatus is described for maintaining quality of service (QoS) between a central controller and a set of mobile terminals (MTs) located within the coverage area of a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless local area network (WLAN). Upon a detection of a connection request by an MT and determining if adequate resources are available, establishing a connection with the MT using the most robust physical layer (PHY) mode with a sufficiently large set of packets to fulfill throughput requirements, if adequate resources are available and additional resources can be allocated. If adequate resources are not available, then attempting to allocate additional resources. In addition, a method is described for providing reliable transmission for a critical packet in a connection, including the steps of transmitting the critical packet at a first PHY mode; determining if adequate resources in the connection are available; and, transmitting a duplicate packet on a second PHY mode if adequate resources are available.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
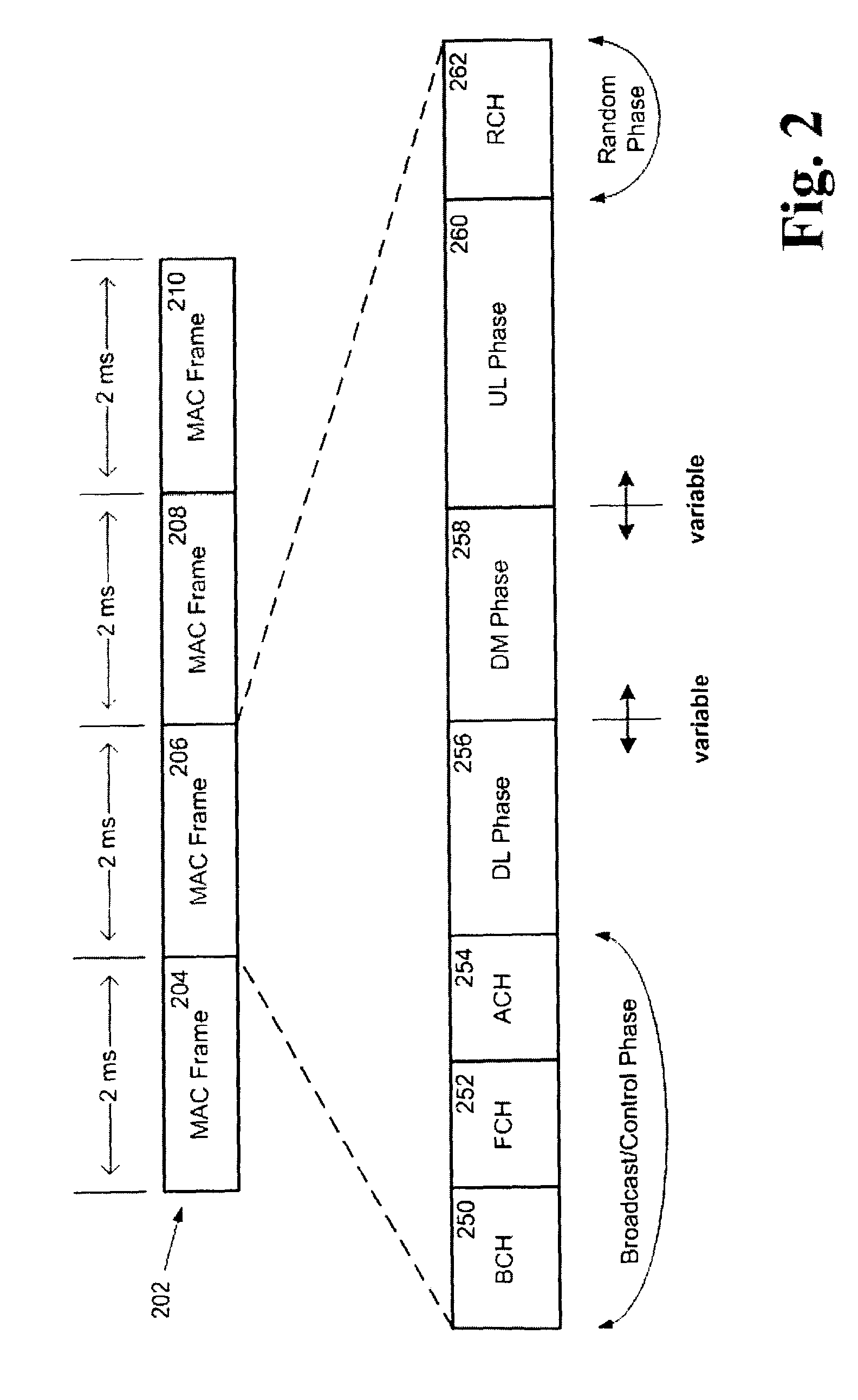
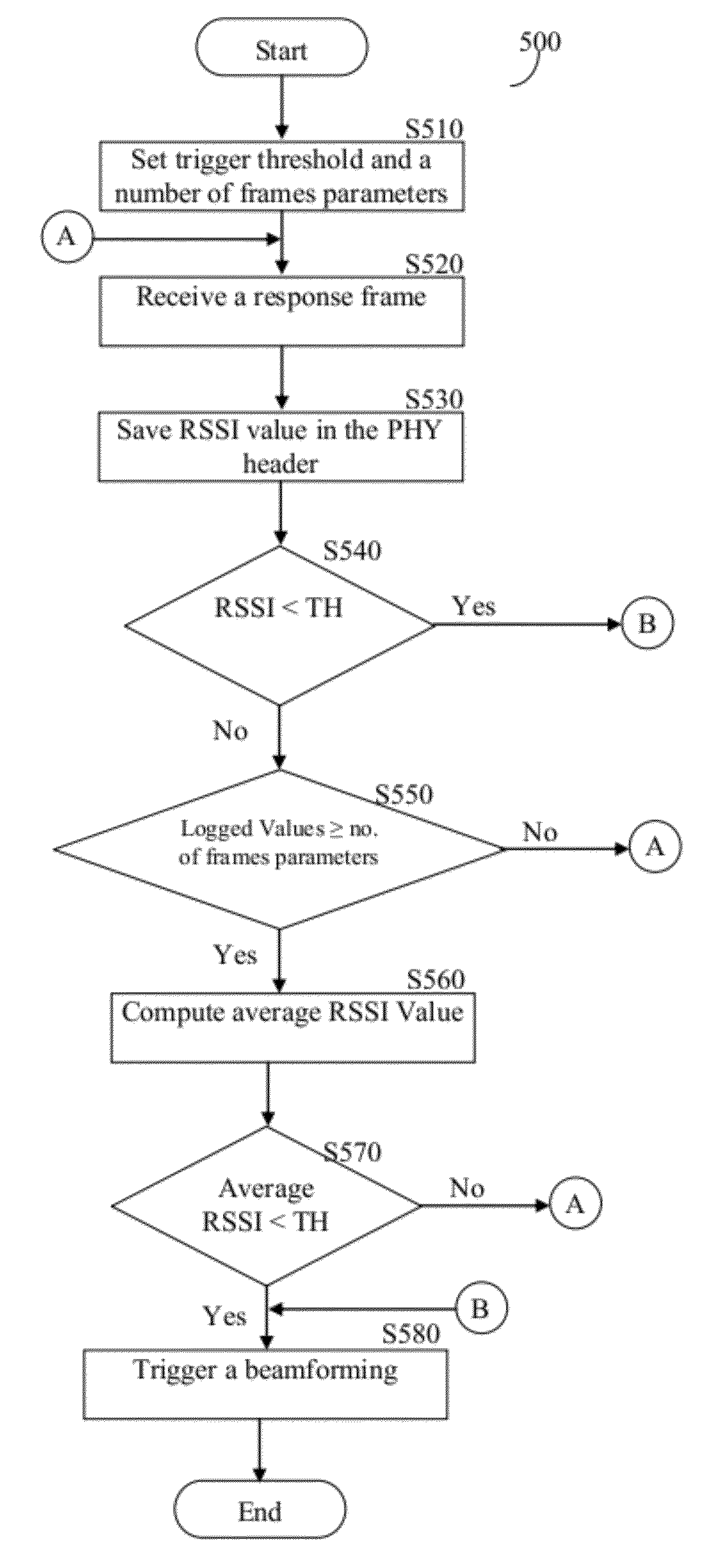
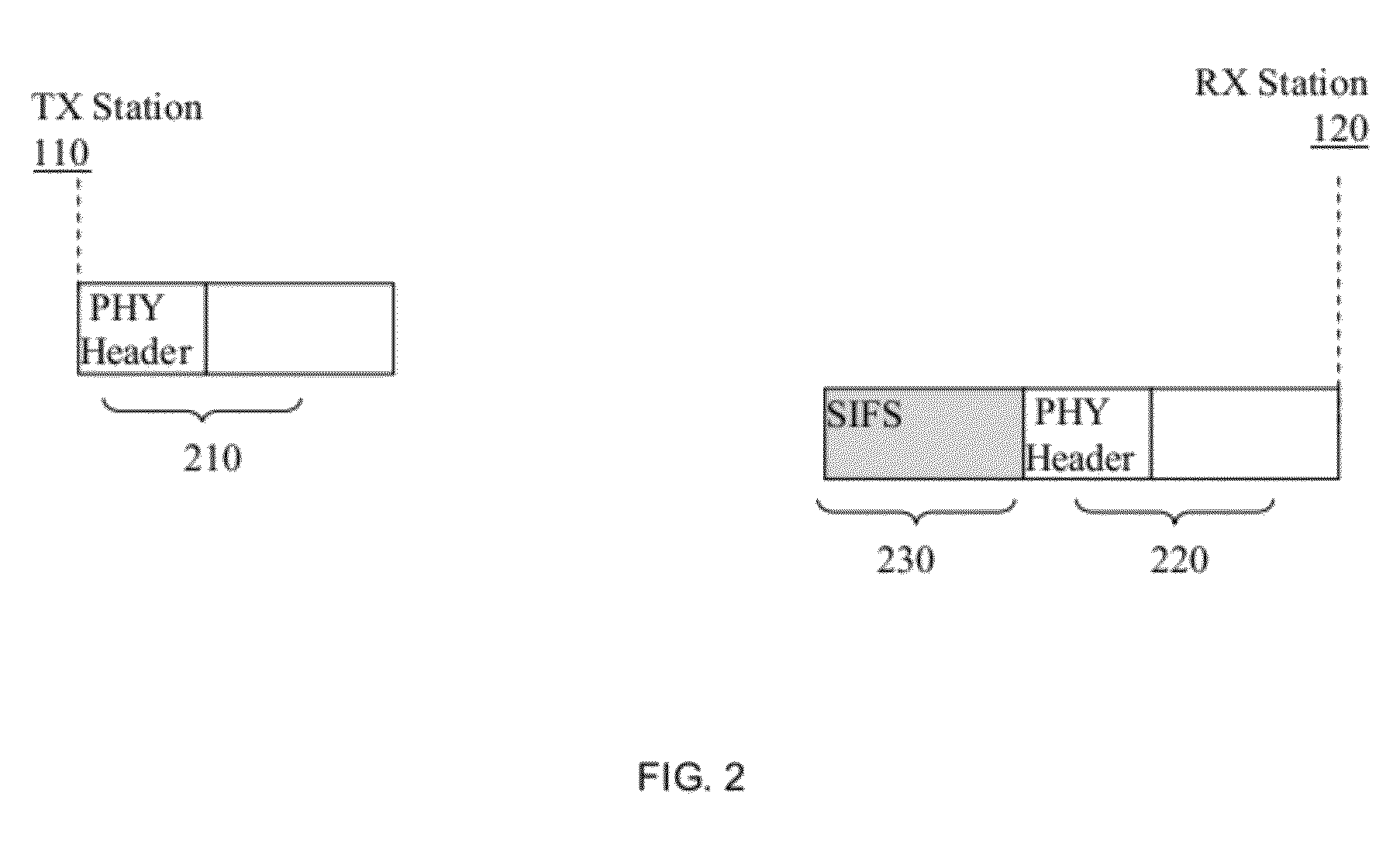
Techniques for minimizing the beam forming time in wireless local area networks
InactiveUS20120287797A1Shorten the timeError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsSignal qualityWireless lan
A method for beamforming in a wireless local area network (WLAN), the method is performed by a receiver wireless station. The method comprises receiving a frame transmitted by a transmitter wireless station over a wireless medium; analyzing a physical (PHY) header of the received frame to determine if a Short Interframe Space (SIFS) response is required; when a SIFS response is required, performing: constructing a response frame including a PHY header, wherein the PHY header includes at least a measured link quality field; inserting a measured signal quality in the measured link quality field; waiting a time equal to a SIFS period; and sending the response frame to the transmitter wireless station after the SIFS period has elapsed, wherein based on received measured values included in response frames the transmitter wireless station predicts a loss link to initiate a beamforming training, thereby reducing the beamforming time.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
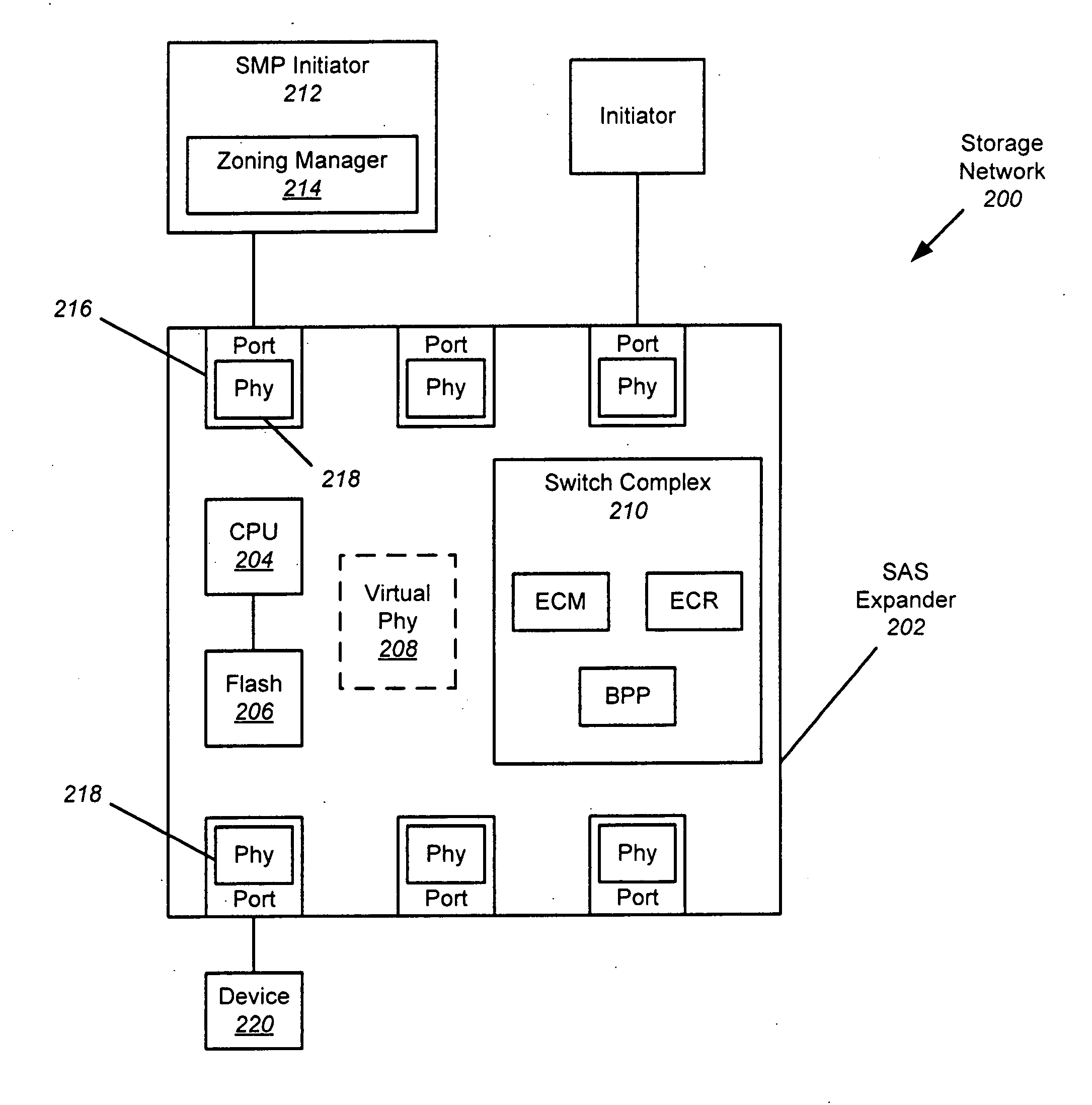
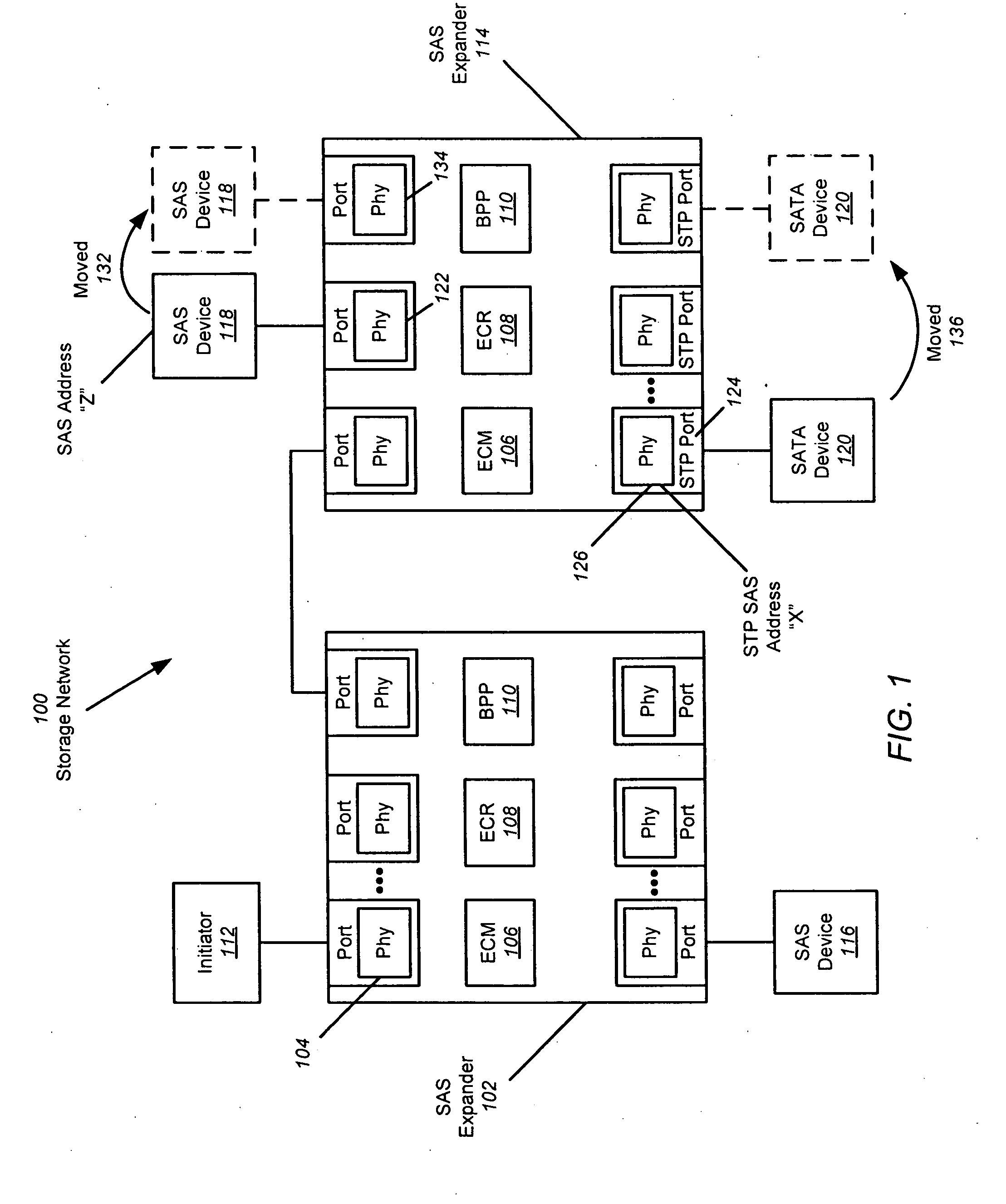
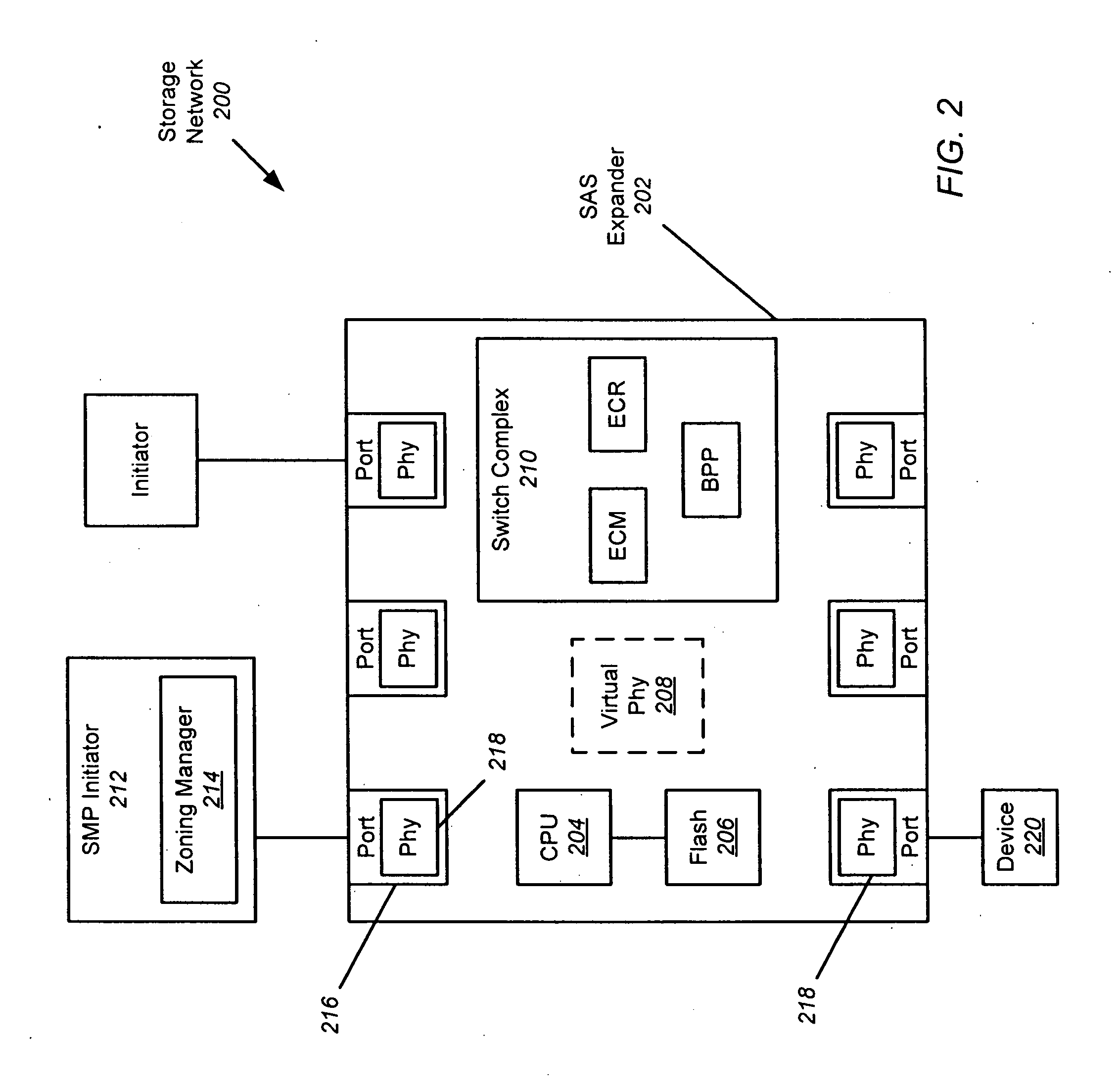
Expander-based solution to the dynamic STP address problem
ActiveUS20090007155A1Simplifying re-discovery processDisabling its PhyTransmissionMemory systemsHash functionPersistent binding
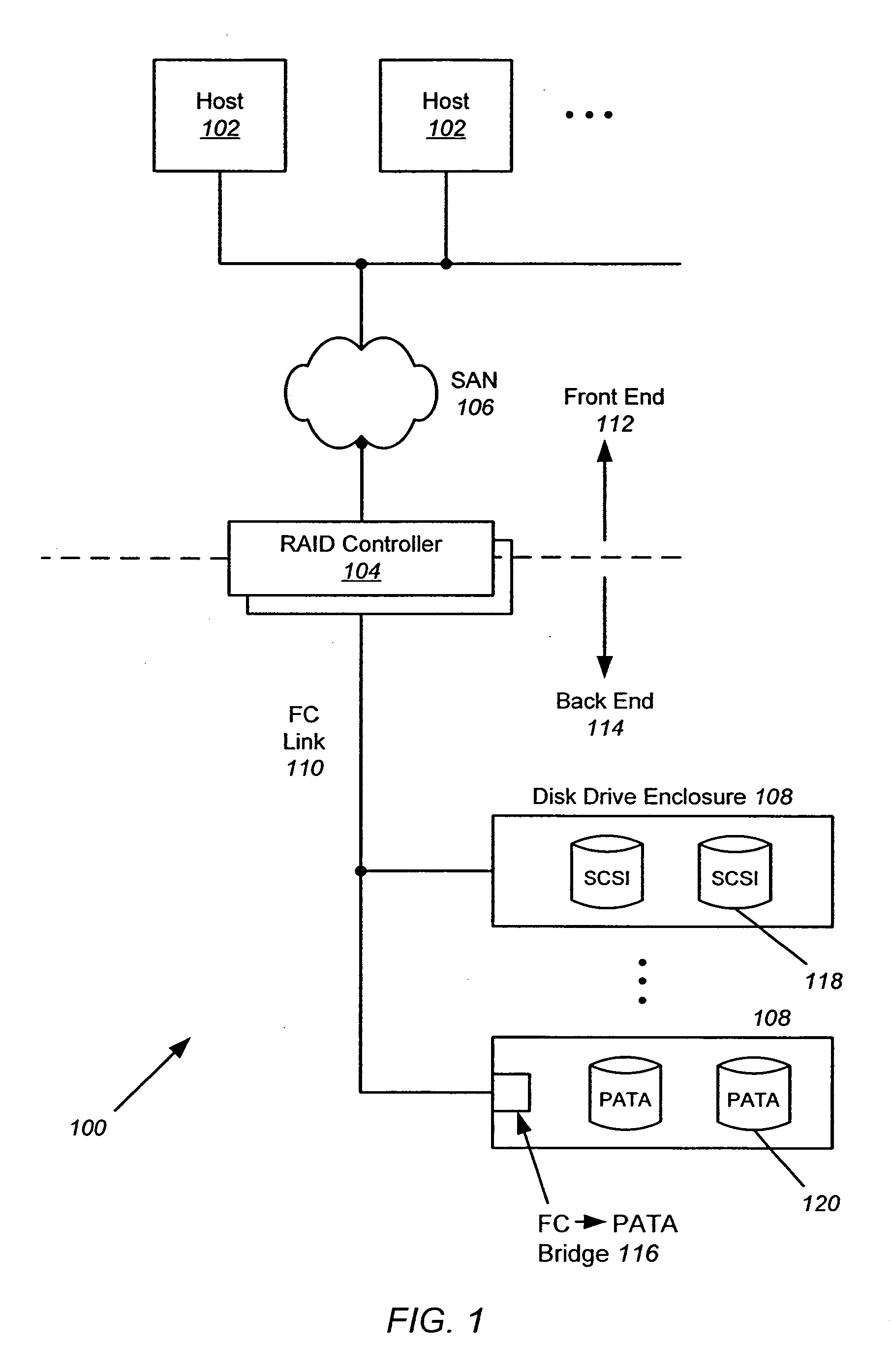
The persistent binding of STP SAS addresses to SATA devices is disclosed so that SATA devices can be moved to different insertion points (ports) within a SAS expander and still properly receive I / O requests. When a SATA device is inserted into the SAS expander, it is interrogated to obtain information about the attached device. This information may be combined using a hashing function to obtain a unique ID for the SATA device. A table can be used to assign a STP SAS address to the Phy connected to the device based in the unique ID. In this manner, the same STP SAS address will be assigned to the Phy connected to a particular SATA device, regardless of where the device is connected to the SAS expander.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
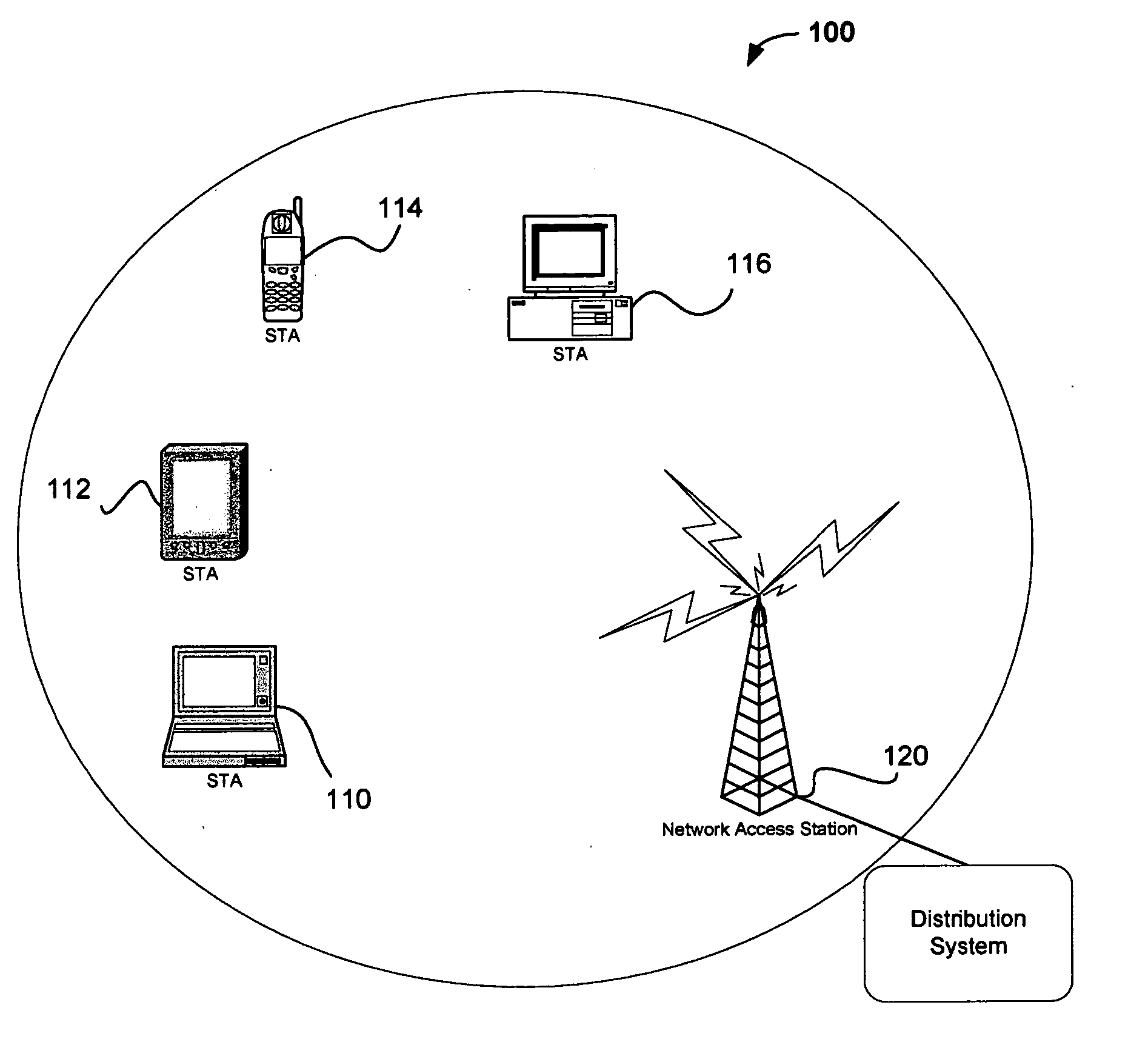
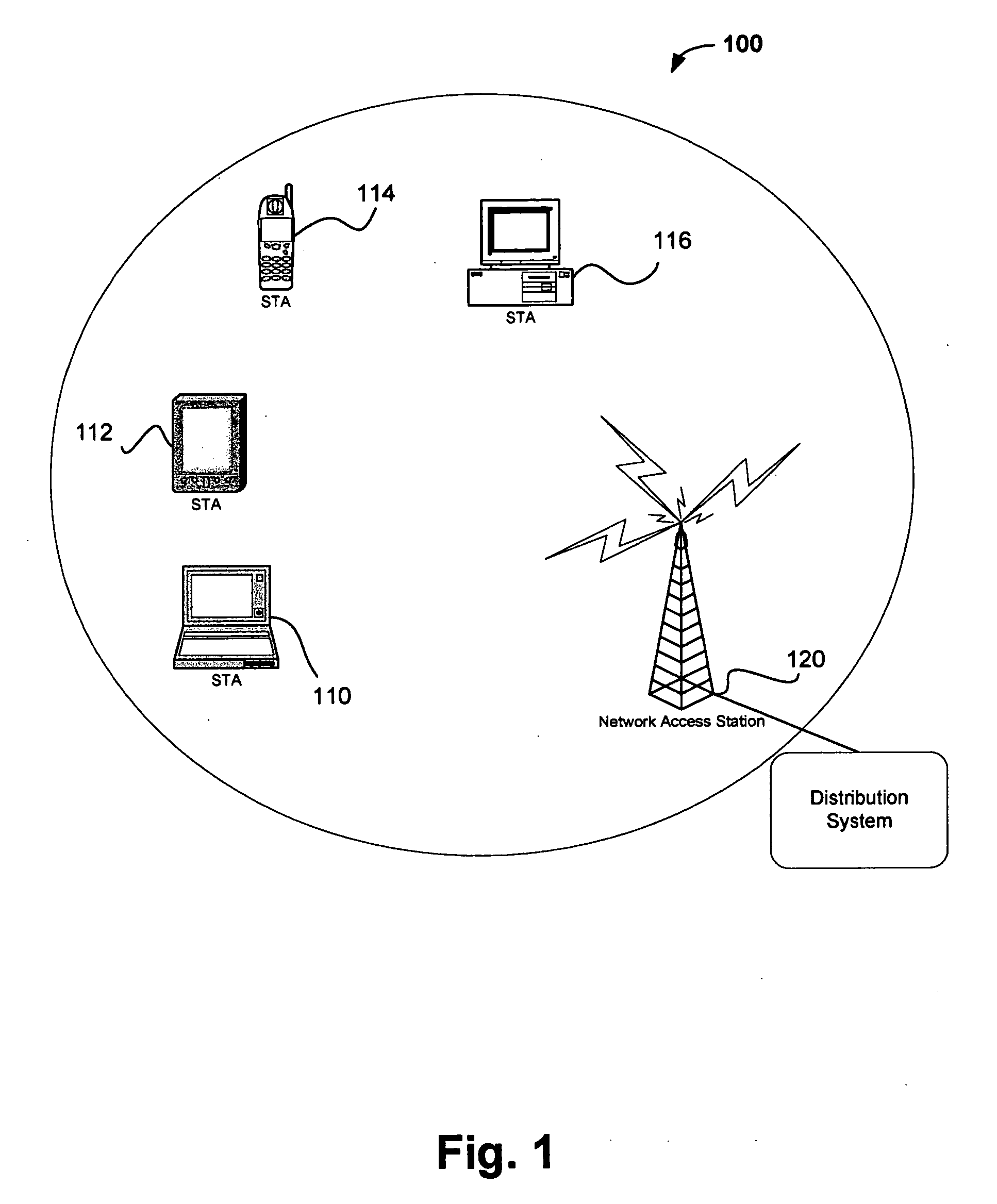
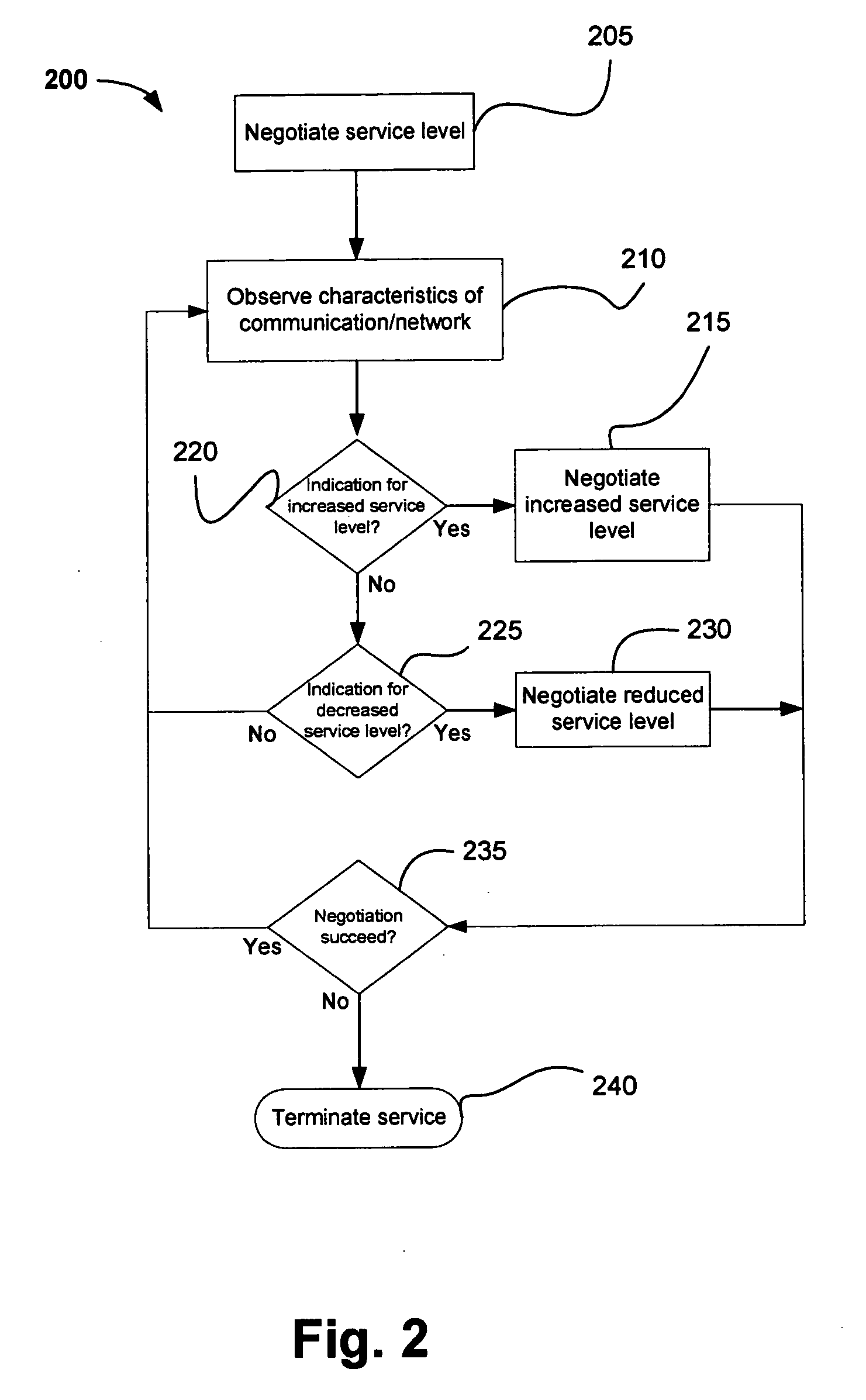
Method and system for adapting wireless network service level
InactiveUS20050243755A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesTelecommunications linkData stream
Methods and systems for communicating in a wireless network negotiate a level of service for a data stream between peers of the wireless network. The level of service may be modified based on one or more characteristics of a communication link or the wireless network such as channel load, channel free time, physical (PHY) link rate, data rate and / or overall channel capacity. Various specific embodiments and variations are also disclosed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
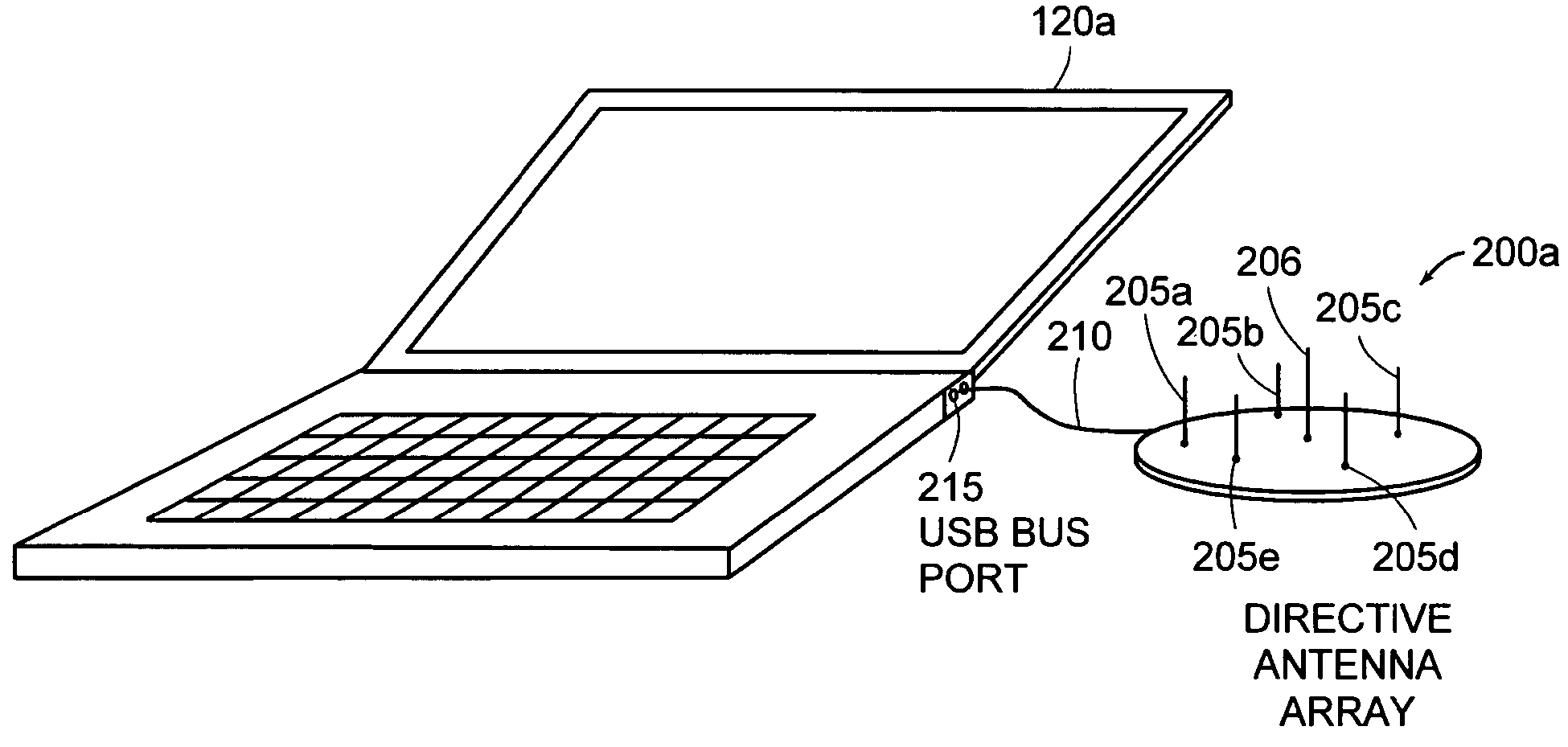
Antenna steering method and apparatus for an 802.11 station
InactiveUS20050037822A1Improves diversityImprove signal qualityAntenna supports/mountingsSubstation equipmentSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Media access control
A method or apparatus steers a directional antenna for a station to communicate with an Access Point (AP) in an 802.11 protocol system. The method or apparatus may include setting the directional antenna in an omni-directional pattern during a Beacon scan. After authentication with a selected AP, the method or apparatus conducts an antenna beam selection process to determine a “best” direction for communicating with the selected AP based on a metric, such as Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), of the Beacon frames received on each of the directional antenna scan angles. The method or apparatus may be integrated into or associated with a Medium Access Control (MAC) layer and receive signal quality metrics from the Physical (PHY) layer.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
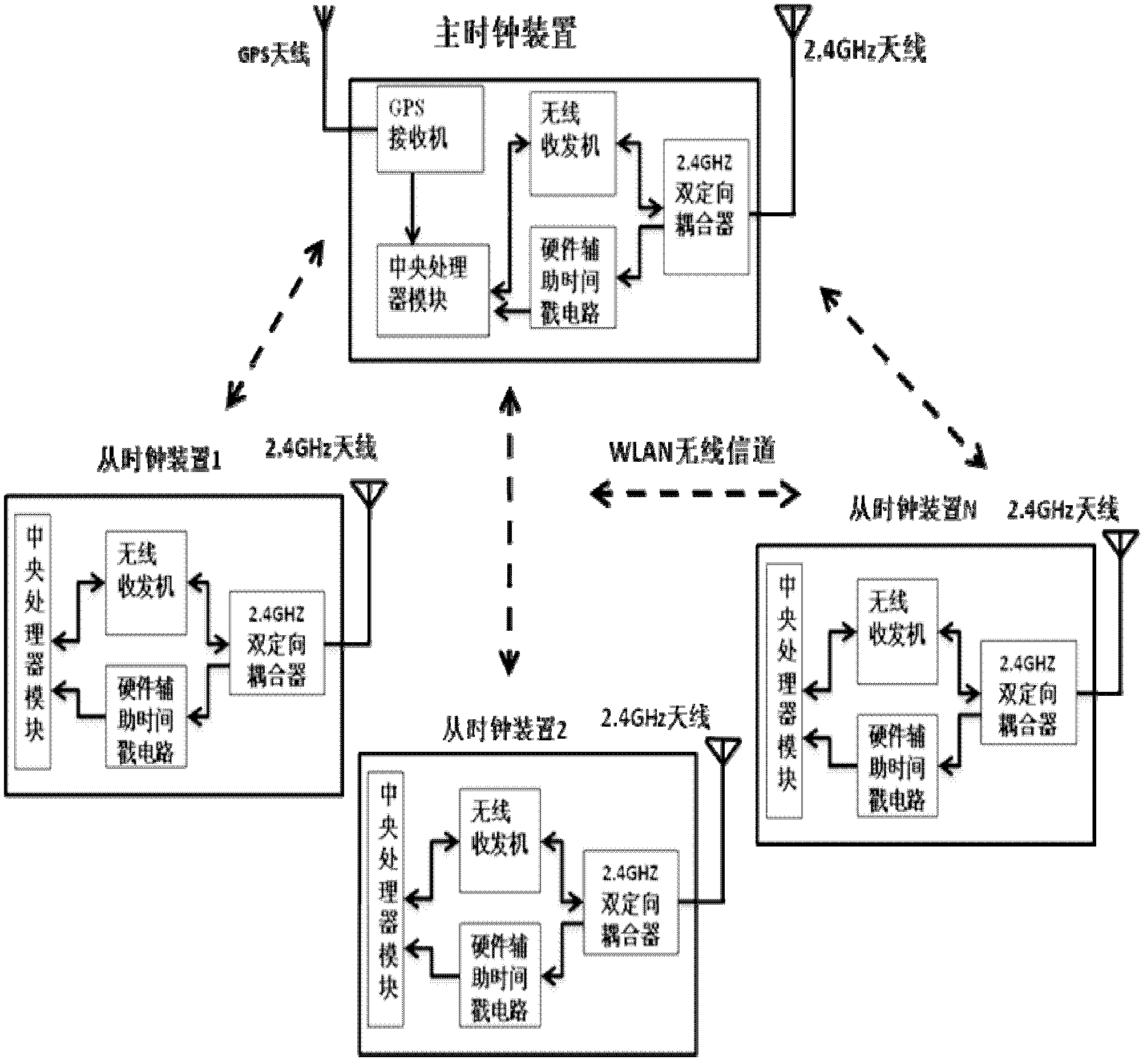
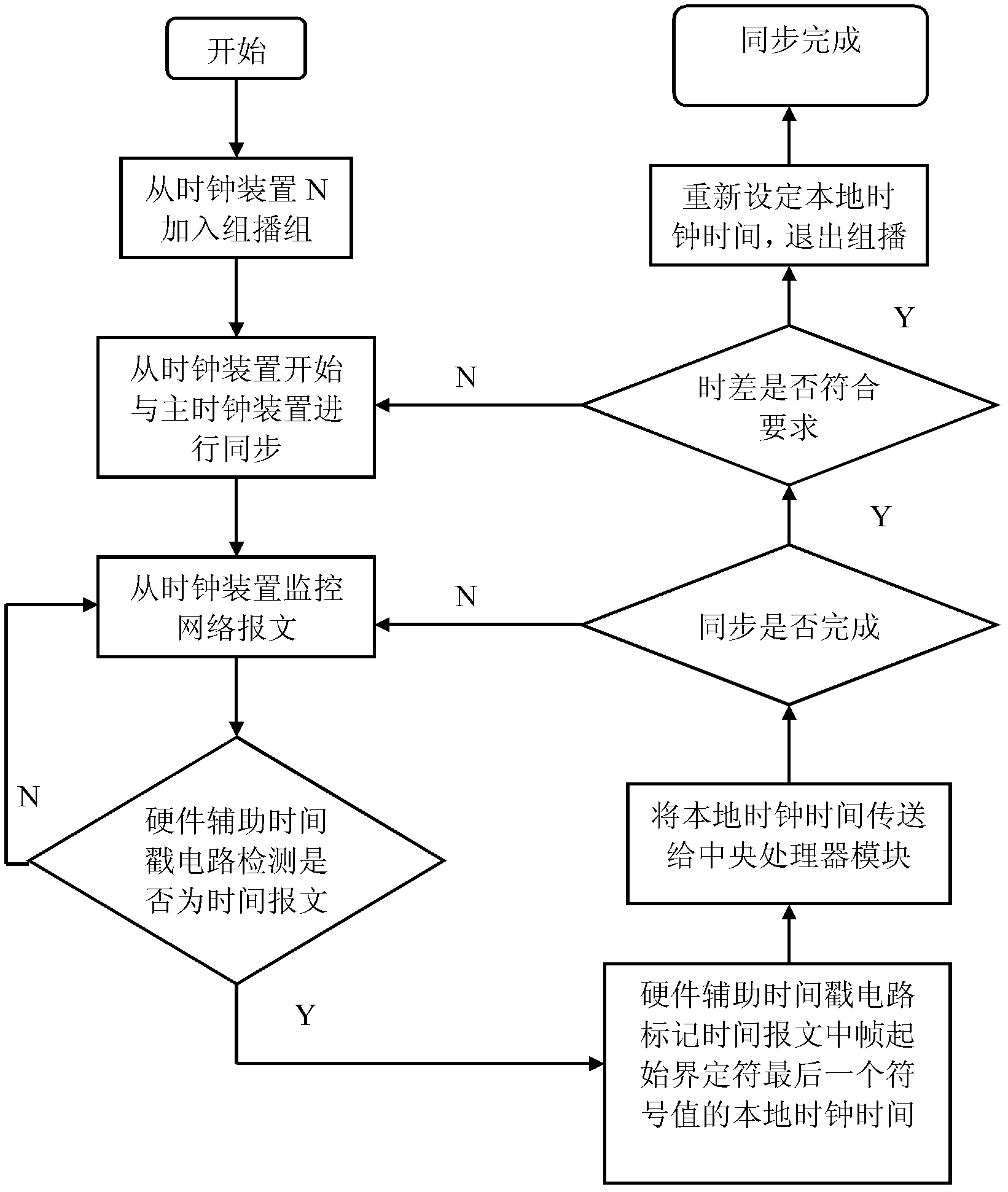
High-accuracy wireless clock synchronization system for power system
InactiveCN102547969AAvoid Uncertain LatencyImprove reliabilitySynchronisation arrangementTransmissionTimestampElectric power system
The invention discloses a high-accuracy wireless clock synchronization system for a power system. A hardware assisting timestamp circuit is added in a physical layer, the identification of the timestamp is transferred from a traditional application layer or a MAC (Medium Access Control) sub-layer of a data link layer to a PHY (physical layer); the timestamp information is transferred to a central processor. Compared with the hardware timestamp method of the prior art, because the driving program of the MAC (Medium Access Control) sub-layer and the uncertain time delay for the interruption response of the driving program are avoided further, the time synchronization accuracy is higher, at the same time, the reliability and the safety are improved further, the requirement that each distribution-type system has high clock synchronization accuracy is met, and the power system oriented high-accuracy wireless clock synchronization system is not suitable for application occasions with laid cables.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Method and apparatus for auto-protocol discrimination between fibre channel, SAS and SATA devices
InactiveUS20070223517A1No wasteQuick serviceError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsAutonegotiationData rate
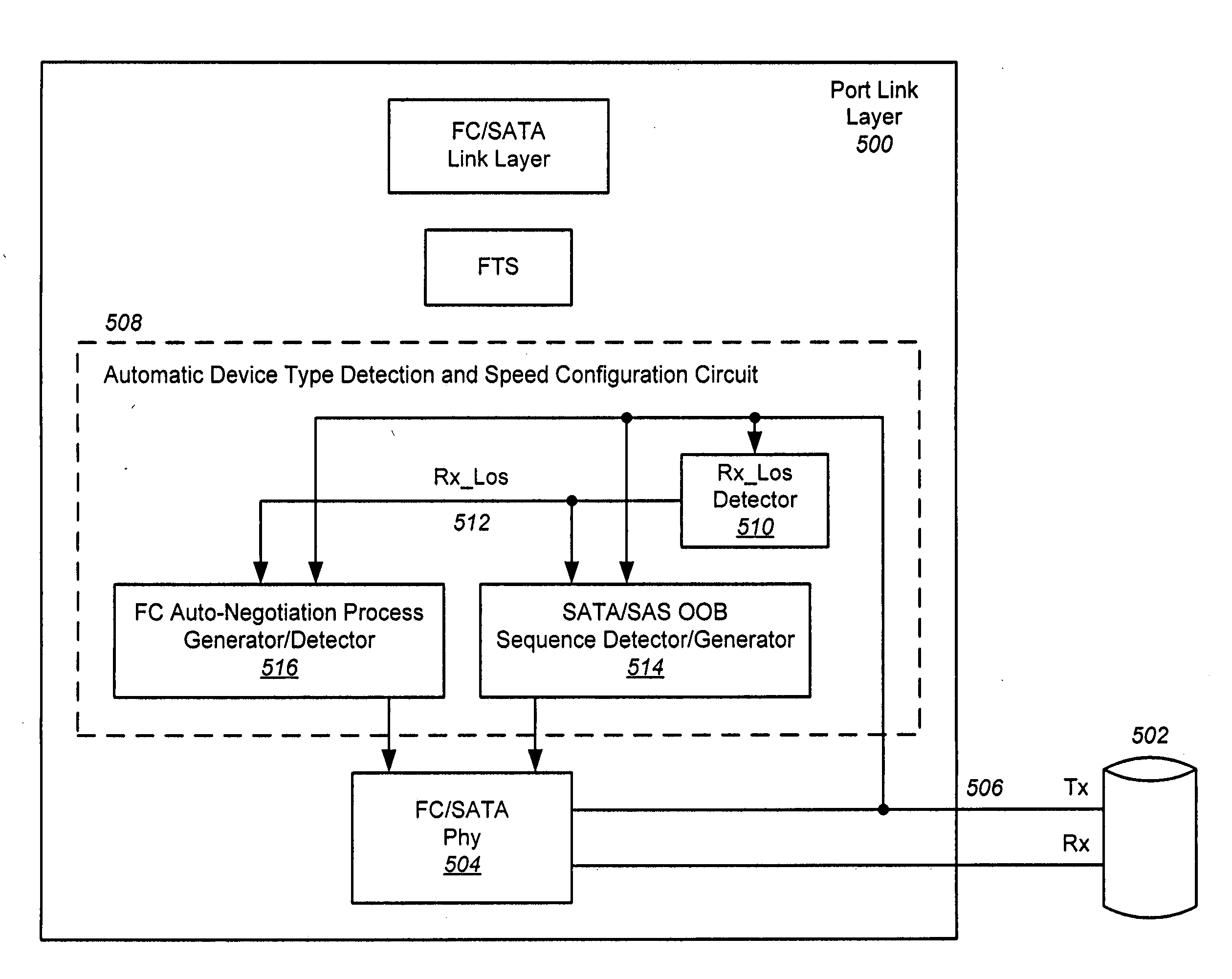
Auto-discrimination between FC and SATA devices upon insertion of a device into a port of a FAST-compatible switch is disclosed. Without user intervention, the port is able to determine the type of device attached, set the appropriate data rate in the Phy or SERDES and, in the case of FC or SATA drives, start the disk insertion process into the active switch zones. The SERDES is first initialized to FC speeds, and the receive path is searched for a receive signal. Upon detecting a receive signal, the detection circuitry then checks to see if a valid SATA Out Of Band (OOB) sequence is received. If a valid SATA OOB sequence is received, the SERDES is configured for SATA speeds and analog settings. If a valid SATA OOB sequence is not received, and instead a FC auto-negotiation process runs to completion, the SERDES remains at FC speeds.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method for realizing precision time protocol (PTP) with nanosecond-level precision
ActiveCN102195768AHigh precisionImprove accuracySynchronising arrangementCommunications systemTimestamp
The invention discloses a method for realizing a precision time protocol (PTP) with nanosecond-level precision. The method comprises the following steps of: identifying a PTP message and recording a leaving or arrival timestamp of the PTP message in a physical layer (PHY) chip; realizing frequency synchronization by using a synchronization Ethernet (SyncE) technology in a physical layer; and managing the timestamp in a way of combining the PHY chip and a field programmable gate array (FPGA), and ensuring the consistency of time in the PHY chip and FPGA maintenance time at the arrival of the PTP message by adopting a software processing method. By the technical scheme provided by the invention, the requirements of a communication system on time synchronization precision can be met, and the synchronization precision of the PTP reaches a nanosecond level.
Owner:北京神州数码云科信息技术有限公司
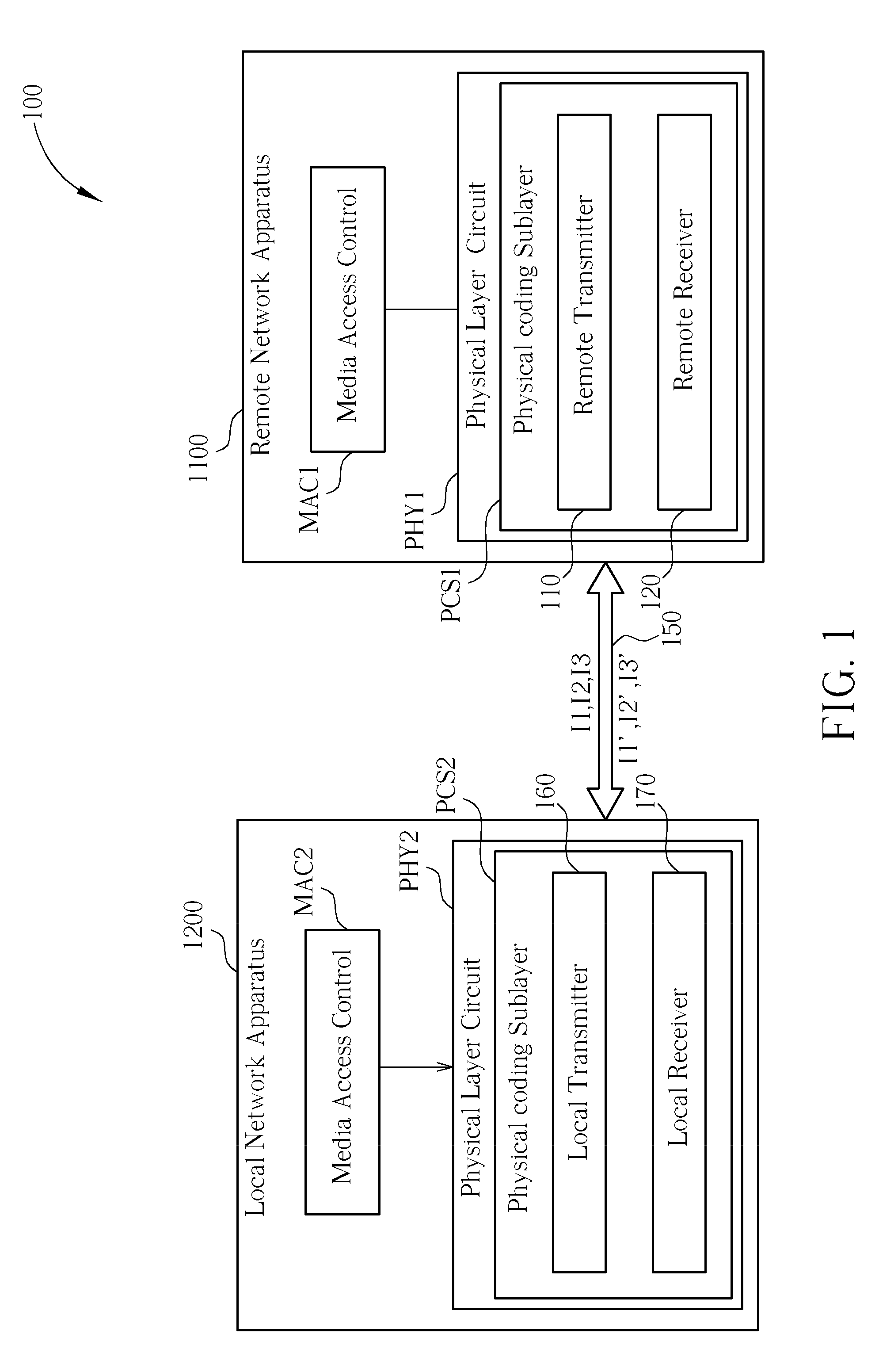
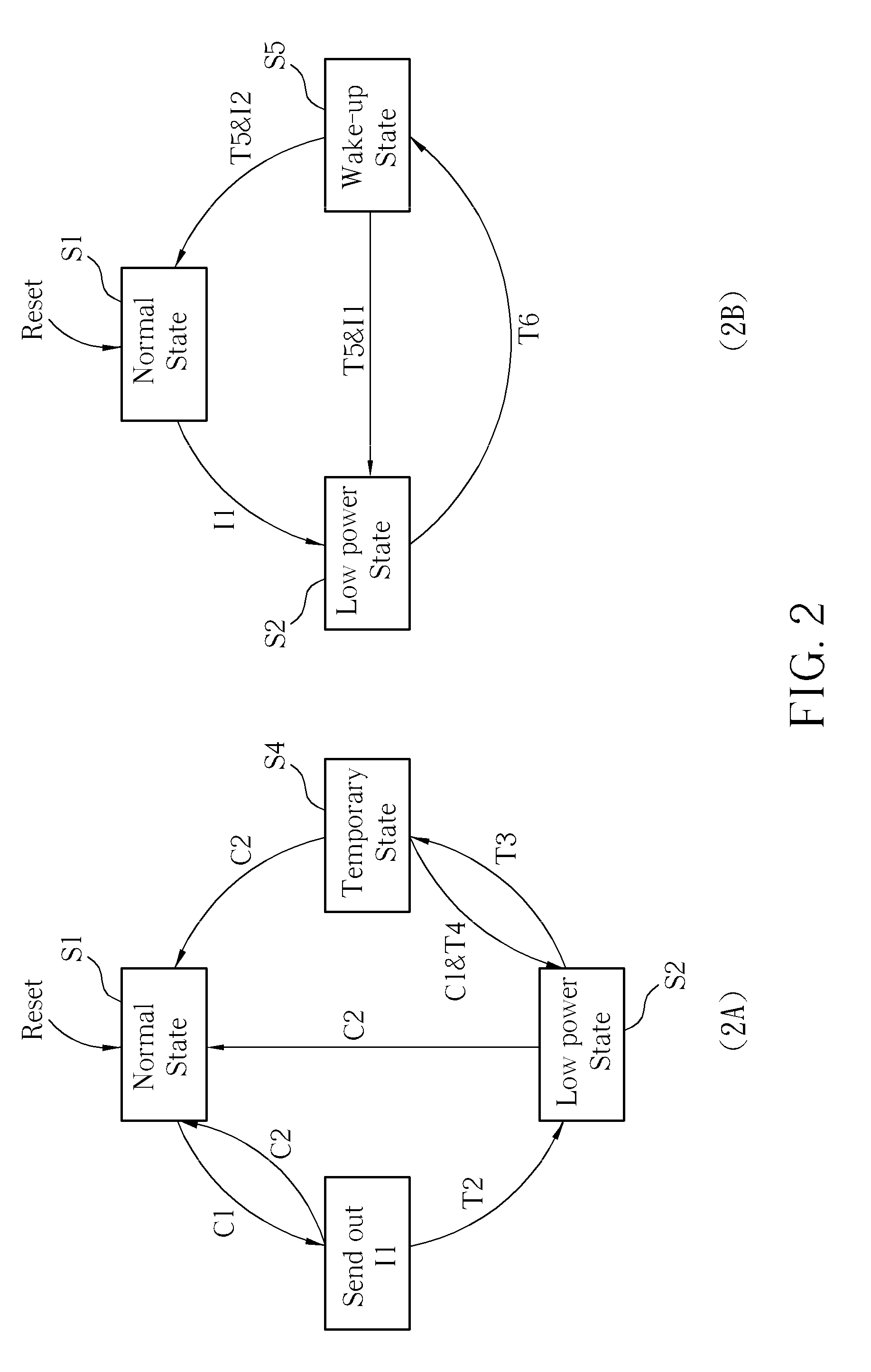
Power-saving network apparatus and method thereof
ActiveUS20090193109A1Volume/mass flow measurementMultiple digital computer combinationsPHYData signal
A power-saving network apparatus includes a MAC and a PHY. The PHY includes a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter executes the operations of: transmitting a data signal to a remote network apparatus according to output packets of the MAC when the transmitter enters a normal state; transmitting an idle signal to the remote network apparatus when the transmitter enters an idle state; transmitting an indication signal to the remote network apparatus to notify it to enter a low power state, wherein the indication signal is different from the idle signal; entering the idle state or the normal state from the low power state in response to at least one of a predetermined period and a transmitting enable signal.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
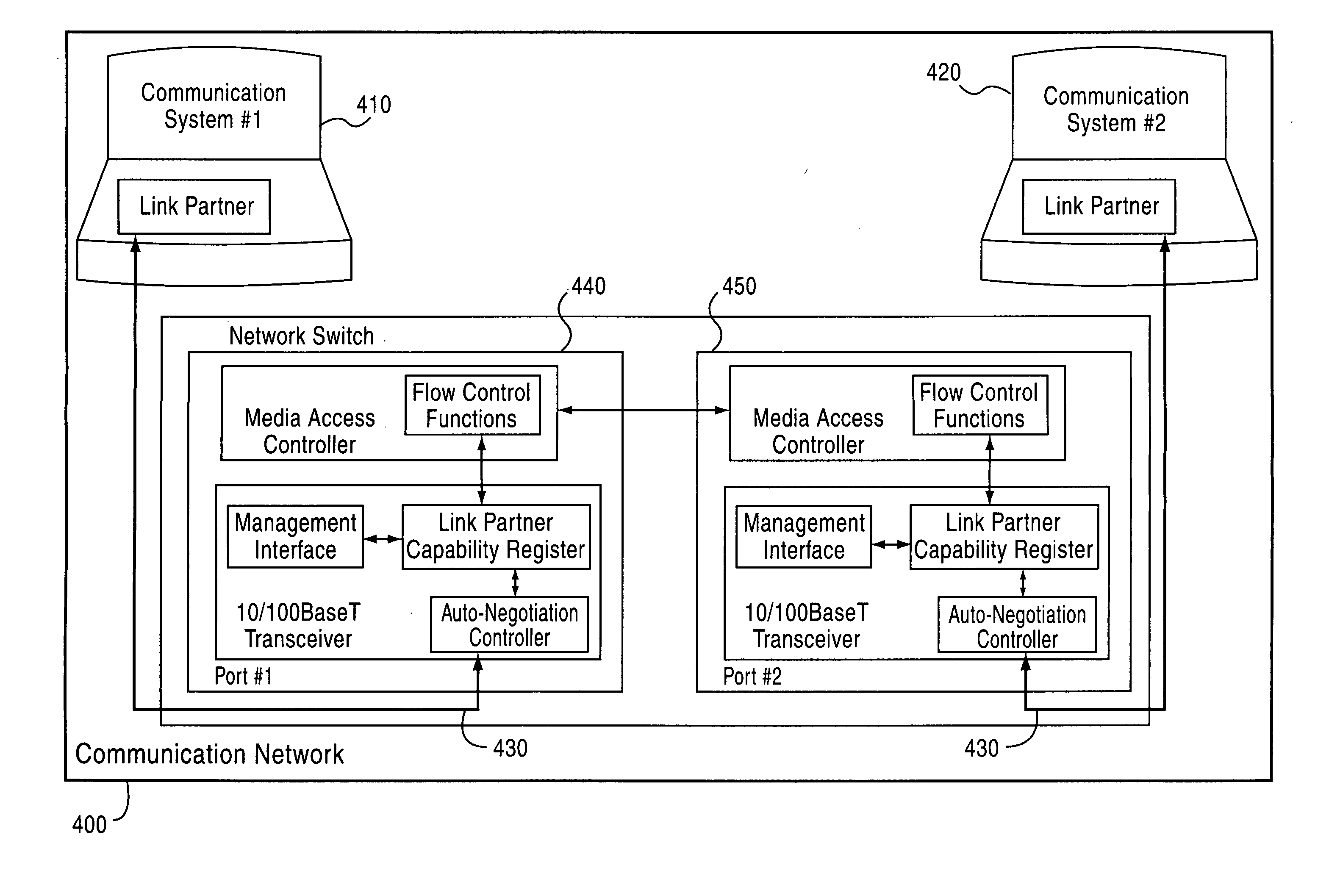
Apparatus for ethernet PHY/MAC communication
InactiveUS20060077995A1Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsProcessor registerMulti port
An integrated Ethernet PHY / MAC apparatus having a single link partner capability register shared between a PHY and a corresponding MAC, which implements IEEE Standard 302.3, including IEEE Standards 802.3u and 802.3x. Apparatus also includes plural PHYs, each having a corresponding MAC integrably coupled therewith such that an integrated multi-port Ethernet device is realized. A network consists of at least one integrated Ethernet PHY / MAC device having a single link partner capability register.
Owner:BROADCOM CORP
Enhanced communication network tap port aggregator arrangement and methods thereof
An arrangement in a network device for facilitating at least one of multiple connection speeds with a network, active response between a monitoring device and an end-device, and power over Ethernet (POE) over a network is provided. As a facilitator of multiple connection speeds, the arrangement includes a plurality of physical layer interface (PHY) and media access controller (MAC) that are configured to support multiple speeds. As a facilitator of active response, the arrangement includes a logic arrangement for multicasting a set of instructions that is sent from a monitoring port. As a facilitator of POE, the arrangement is configured to receive data traffic (e.g., data packets and / or power packets) through a first network port and to send the data traffic out a second network port.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH SINGAPORE (SALES) PTE LTD
Gigabit Ethernet field bus communication device based on FPGA
InactiveCN102594627AReal time monitoringReal-time communicationBus networksCommunication interfaceSignal on
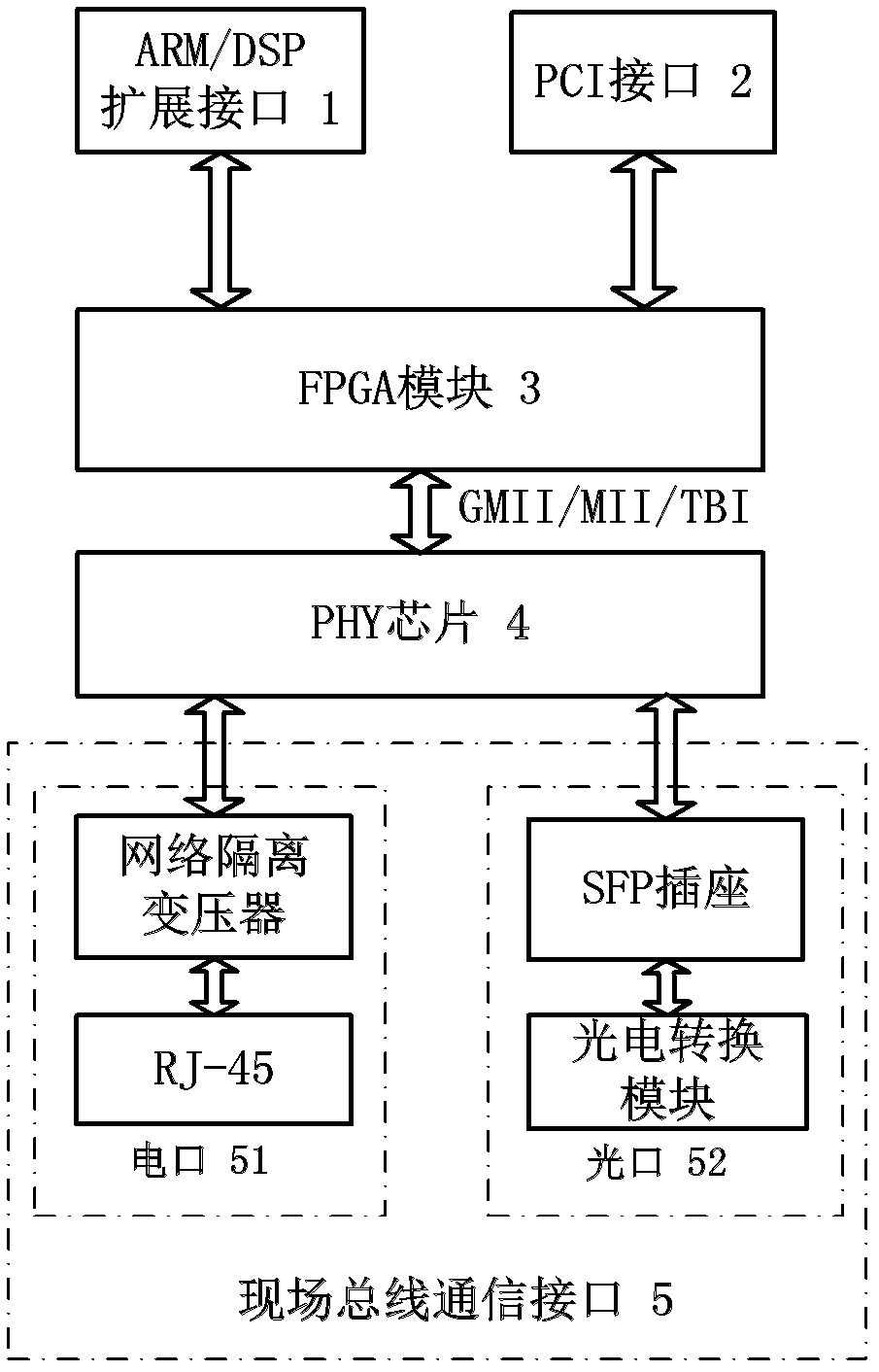
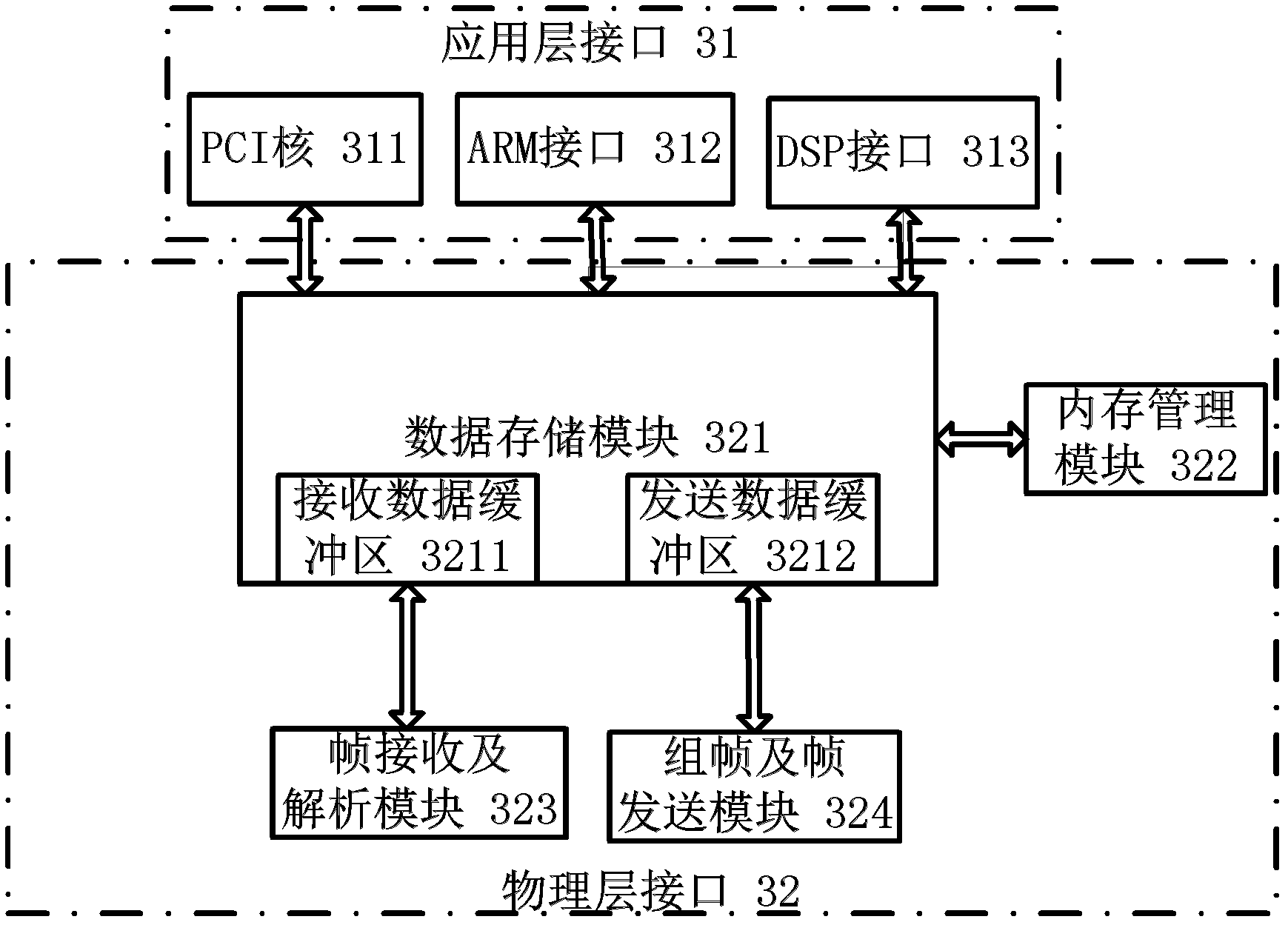
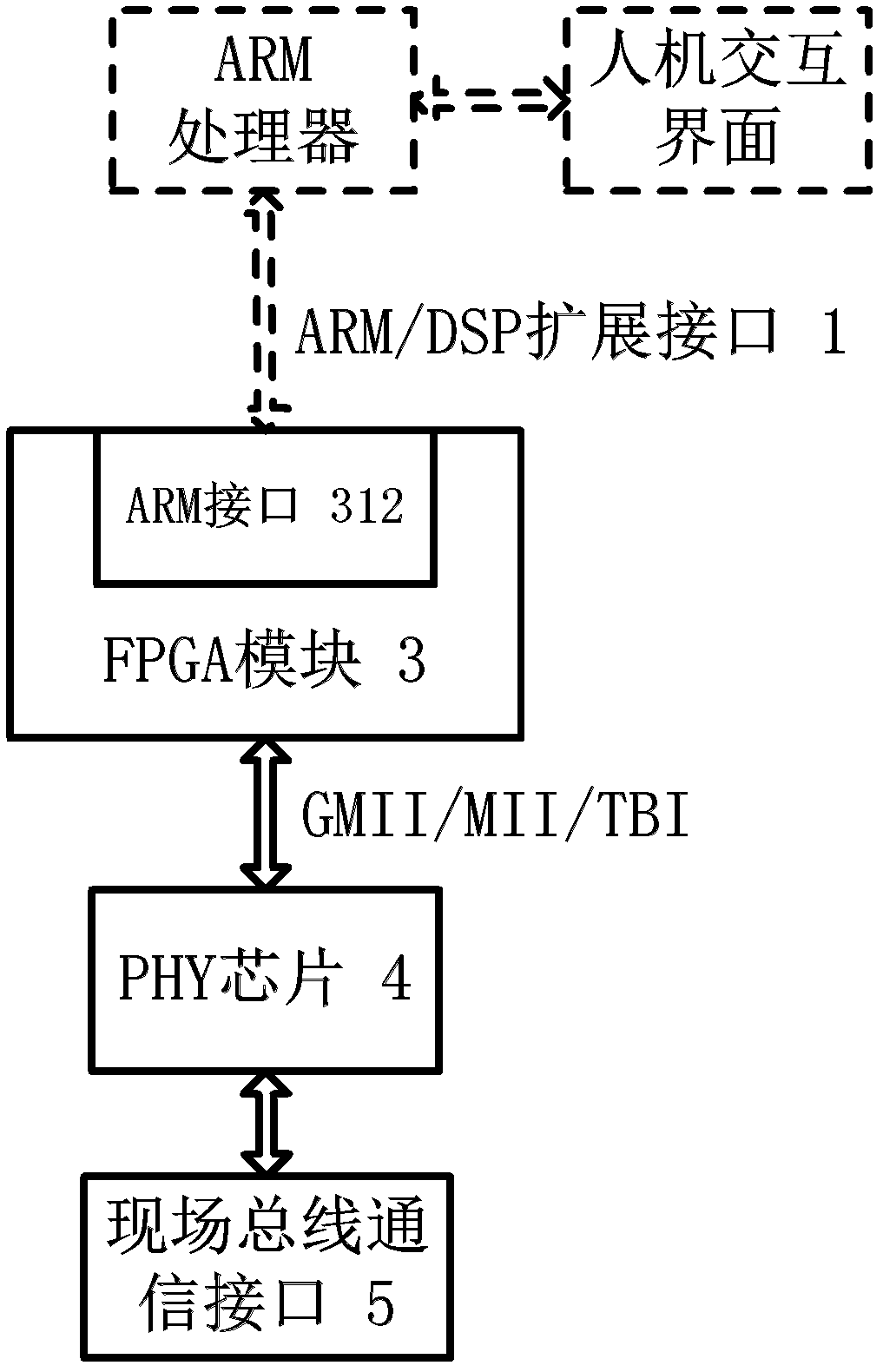
The invention discloses a gigabit Ethernet field bus communication device based on an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array). The device comprises an ARM (Asynchronous Response Mode) / DSP (Digital Signal Processor) expansion interface, an FPGA module, a PHY (Physical Layer) chip and a field bus communication interface and is characterized in that an electrical signal or an optical signal on a field bus is converted into a differential signal through a field bus interface; data is downloaded into the FPGA module through the gigabit PHY chip; and the FPGA module is used for receiving and analyzing the downloaded data and then transmitting the analyzed data to an ARM or a DSP connected with the ARM / DSP expansion interface through the ARM / DSP expansion interface for processing; the data processed by the ARM / DSP is packaged into a data frame by the FPGA module and is then converted into the differential signal through the gigabit PHY chip; and the differential signal is converted into the electrical signal or the optical signal through the field bus communication interface to be transmitted onto a the field bus. The gigabit Ethernet field bus communication device has the beneficial effects that the data transmission rate of 1000 Mbps can be realized, the communication with external equipment with the PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) interface can be realized, and different controllers can be externally connected according to the actual needs, the flexibility is high, and the gigabit Ethernet field bus communication device can be flexibly applied to real-time monitoring and communication of an industrial control field.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Measuring and Displaying Wireless Network Quality
ActiveUS20110243020A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsFrequency spectrumWireless network
Methods of calculating and displaying quality metrics on a wireless digital network such as a network using IEEE 802.11 Wi-Fi standards. The quality metric calculation assigns weights only to factors which are observed above a threshold, combining multiple factors into a scalar result. The quality metric is derived from the weighted sum of two or more parameters such as: noise floor offset, channel busy indication, adjacent and overlapping channel interference, interferer duty-cycle, frame retry-rate, PHY error rate and CRC error rate. Quality spectrograms may be used to display calculated quality metrics across a channel, channel range, or frequency band, plotting calculated quality metric versus frequency or channel range over a configurable time frame. Using known locations of radios, quality ranges are mapped onto visual representations such as contour lines, shading density, or color codes, and overlayed for example over floor plans or other site representations.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
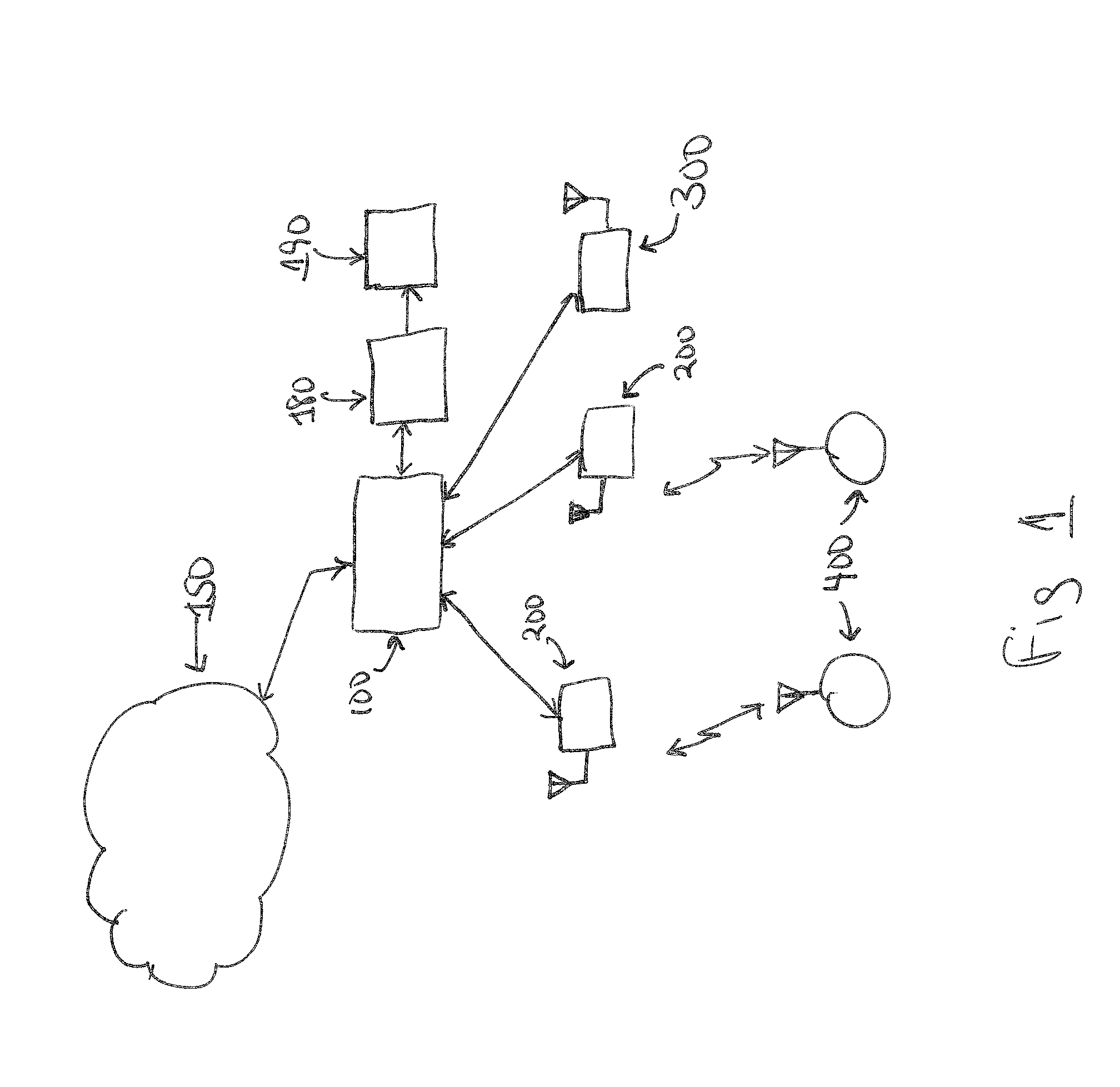
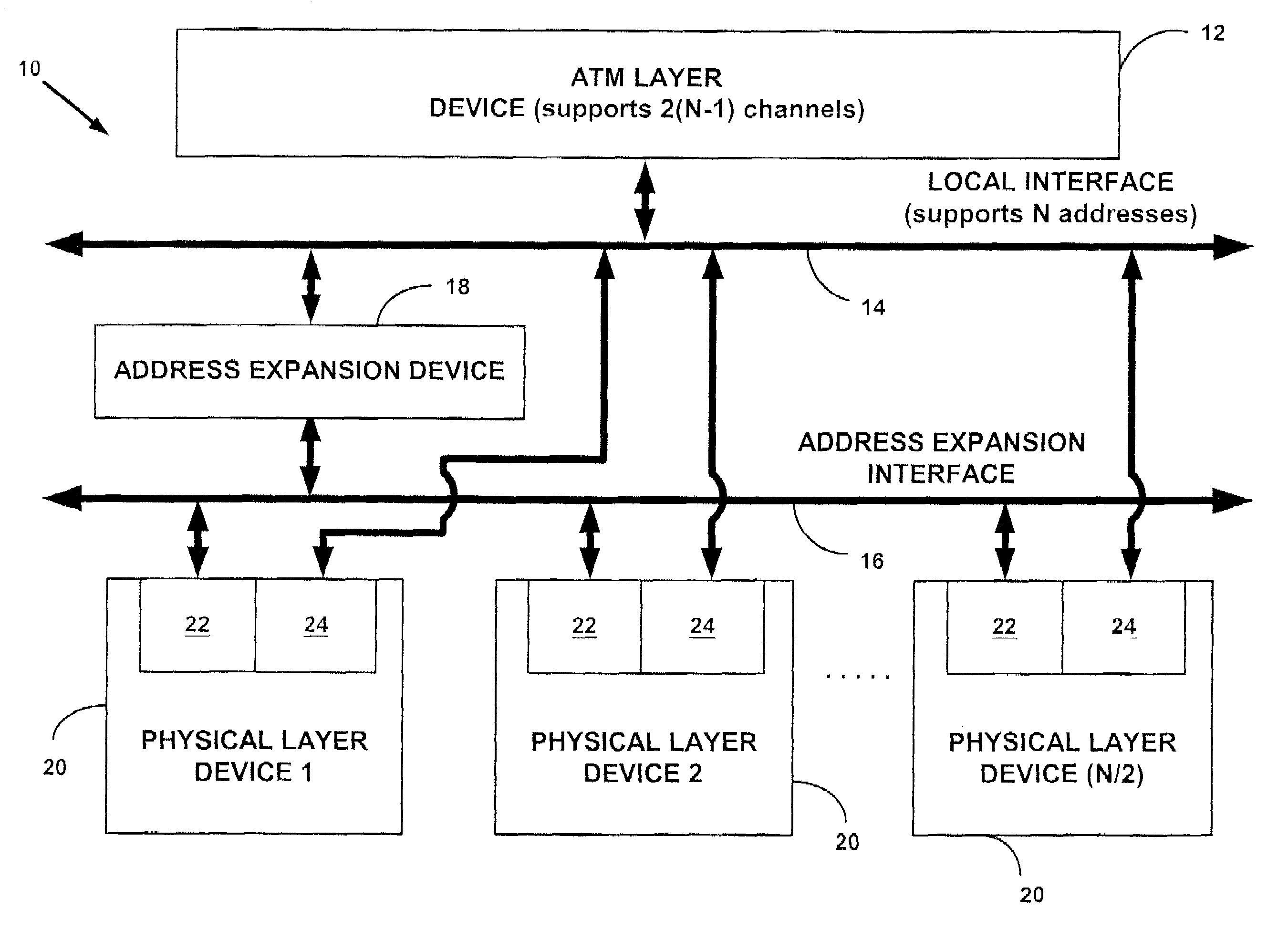
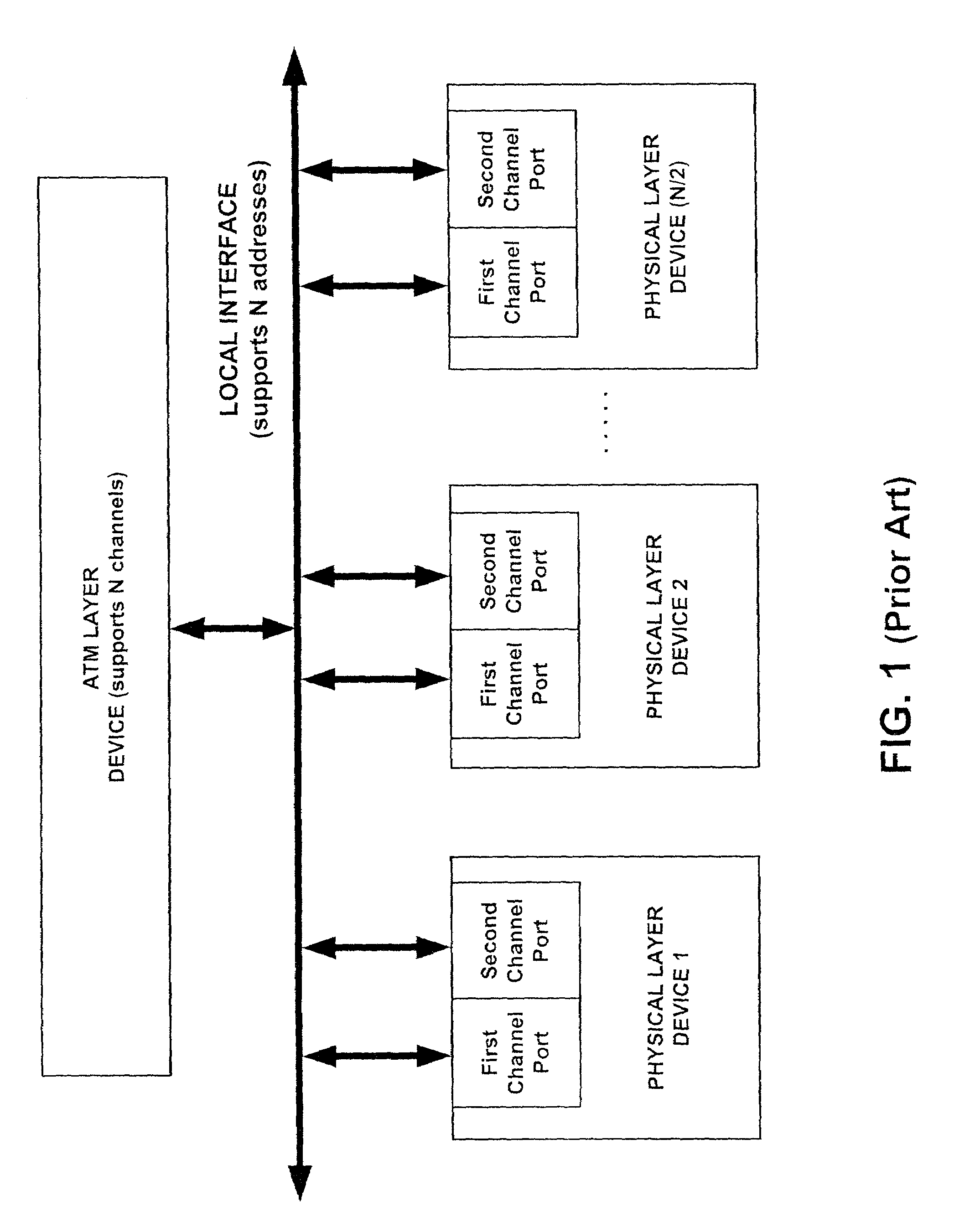
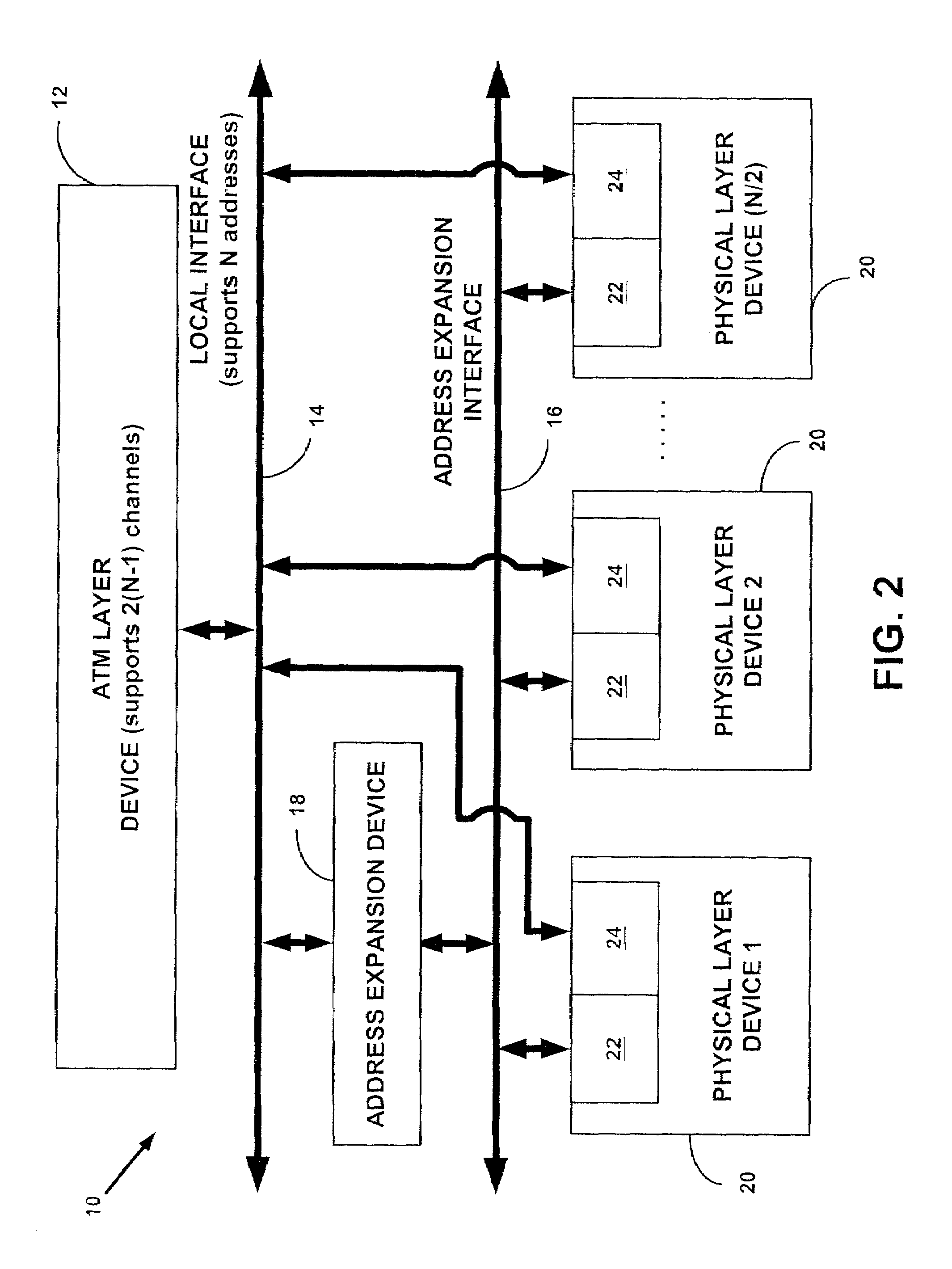
Systems and methods for providing communication between an ATM layer device and multiple multi-channel physical layer devices
InactiveUS7023829B1Increase in numberIncrease the number ofError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsClass of serviceComputer network
Systems and methods are provided for providing communication between an ATM layer device and multiple multi-channel PHY layer devices, which increase the number of multi-channel PHY layer ports supported by the ATM layer device. In general, one such system comprises an ATM layer device that supports a plurality of ATM communication channels in which each of the plurality of ATM communications channels correspond to a first class of service or a second class of service, a plurality of physical layer devices each having a first channel port associated with the first class of service and a second channel port associated with the second class of service, and a local interface in communication with the ATM layer device and the plurality of physical layer devices for establishing a plurality of channel connections between each of the plurality of ATM communication channels and the first channel port and the second channel port in each of the plurality of physical layer devices, the local interface having a plurality of addresses. In the system, each of the plurality of channel connections associated with the plurality of second channel ports is via one of the plurality of addresses and at least two of the plurality of channel connections associated with the plurality of first channel ports is via no more than one of the plurality of addresses. In this manner, the system increases the number of physical layer devices communicating with the ATM layer.
Owner:SOLMIRA COMM
Method and System for Network Communications Via a Configurable Multi-Use Ethernet PHY
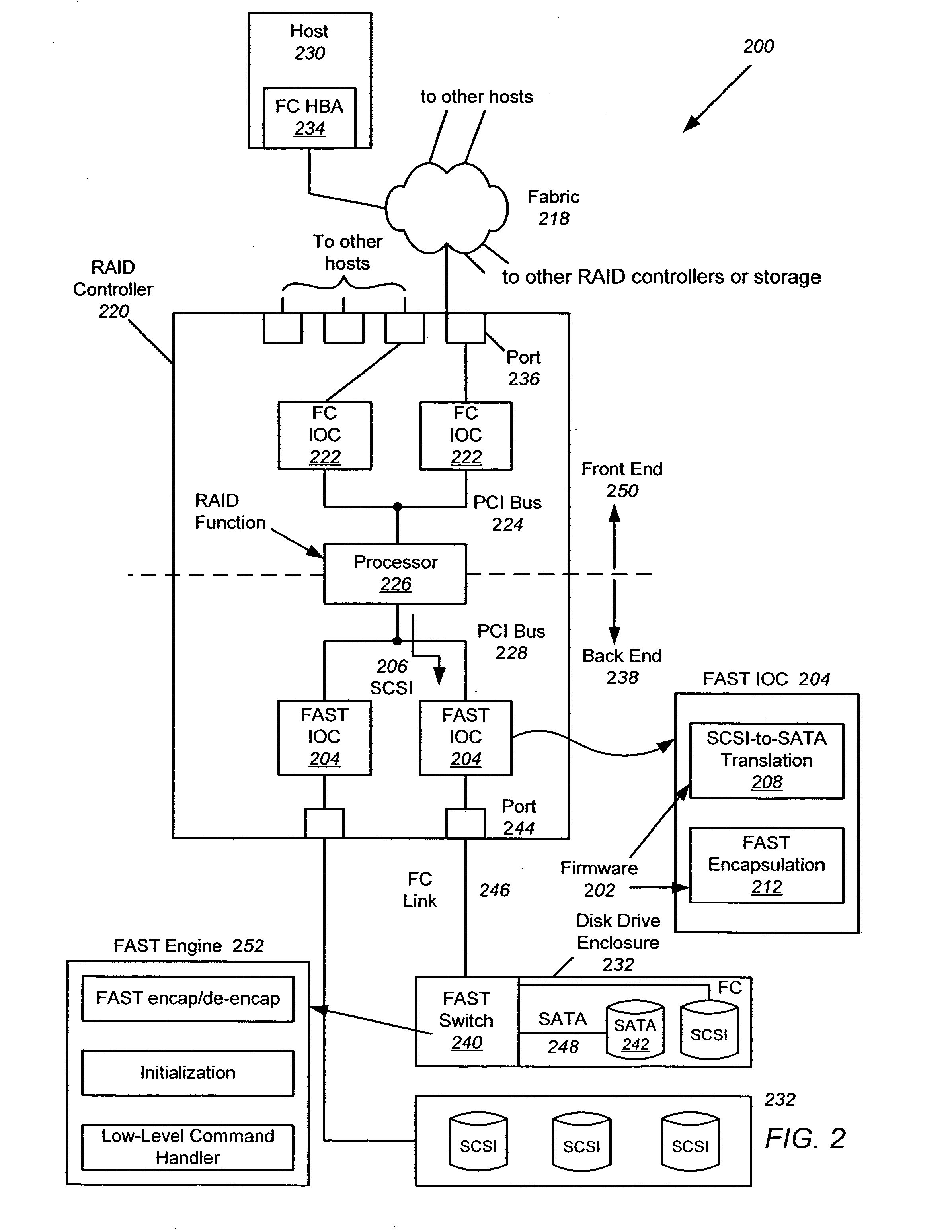
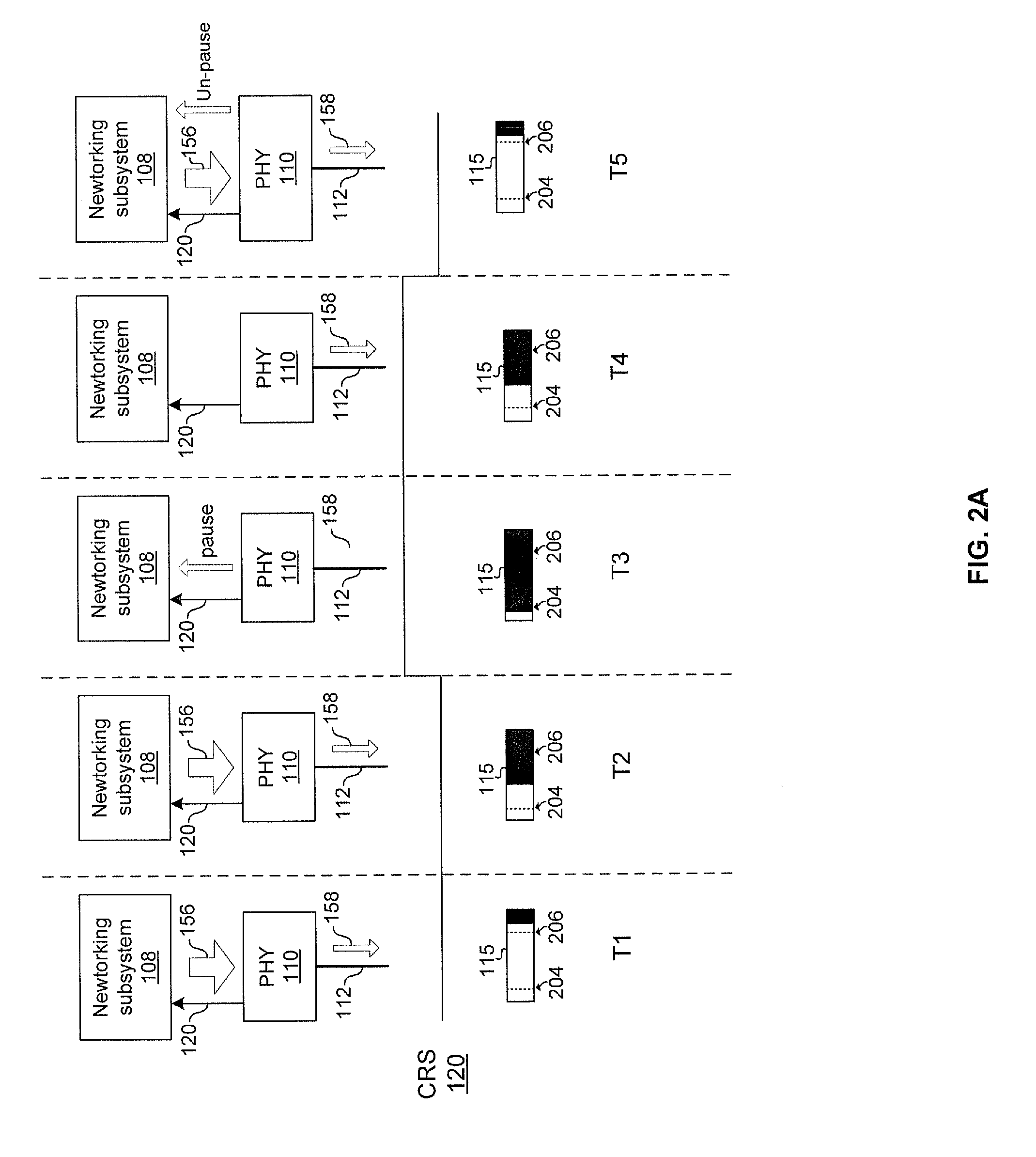
Aspects of a method and system for network communications via a configurable multi-use Ethernet PHY are provided. In this regard, an Ethernet PHY may be configured based on characteristics of a network link over which the Ethernet PHY communicates, energy efficiency considerations, etc. In one embodiment a first Ethernet PHY, a first MAC, a second Ethernet PHY, and a second MAC can be integrated within a network device. Data can be received by the second Ethernet PHY, buffered in a queue, and transmitted by the first Ethernet PHY, where the second Ethernet PHY receives the data at a rate that may be different than the rate at which the first Ethernet PHY transmits the data. In some instances, the second Ethernet PHY may be operable to request that a link partner pause or slow down transmission of data based on a status of the queue.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
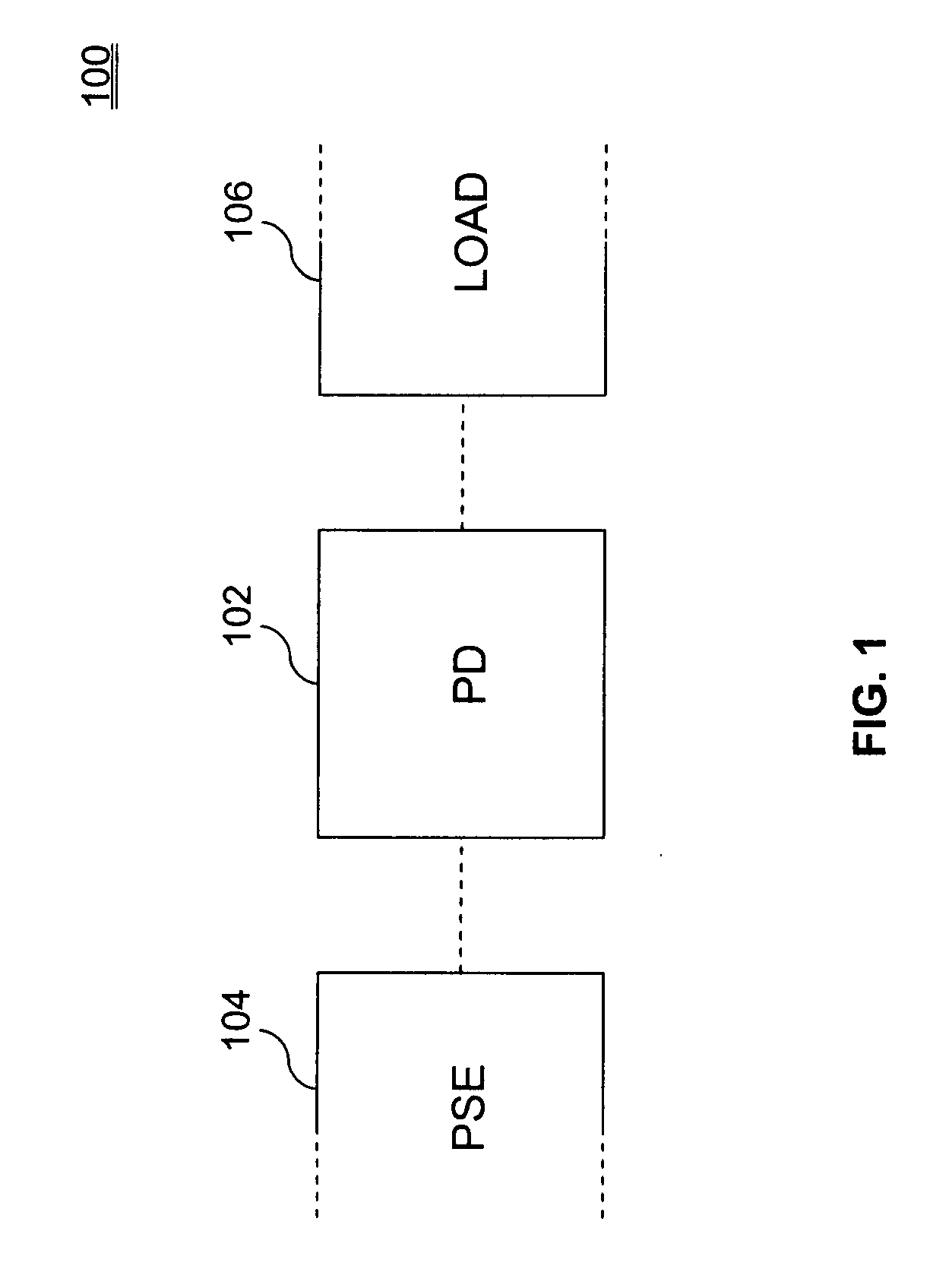
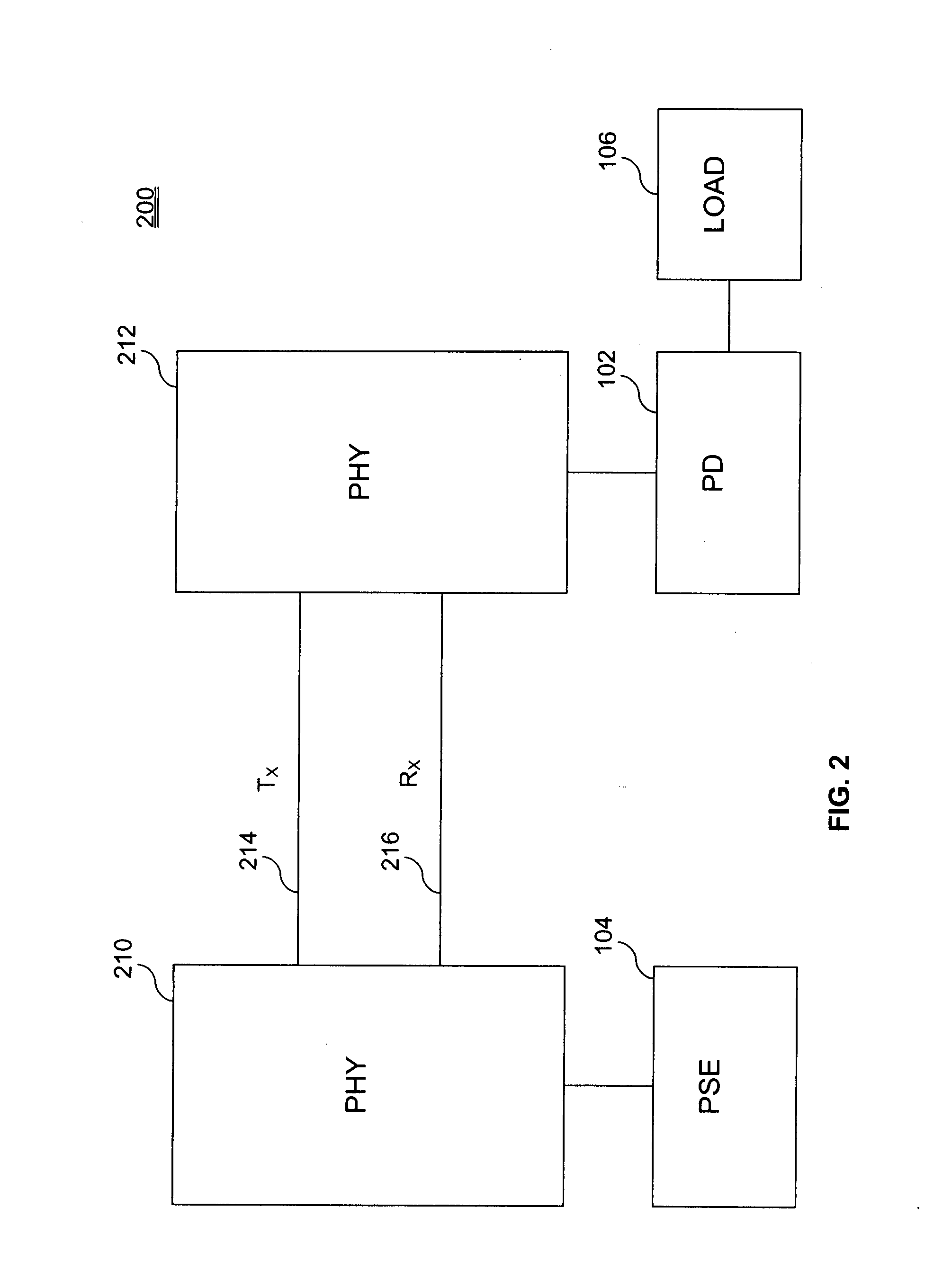
Powered device analysis and power control in a Power-over-Ethernet system
ActiveUS20080175260A1Batteries circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectricityPHY
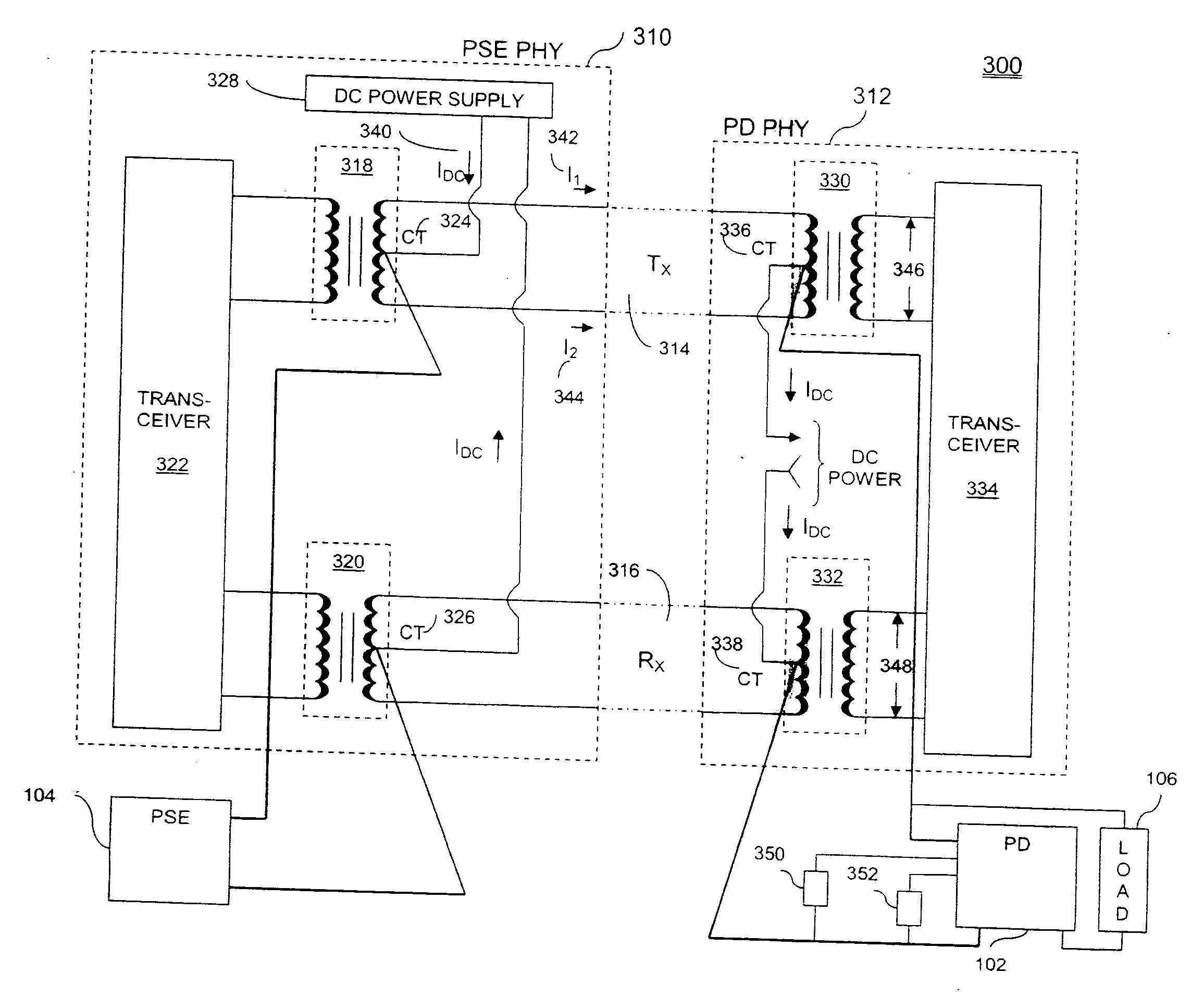
A system and method of analyzing a powered device (PD) in a Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) system are presented. The system includes an Ethernet interface having a physical layer (PHY) chip capable of providing a signal pulse in addition to physical layer 1 functions. The system further includes a pulse transformer, coupled to the PHY chip, capable of relaying the signal pulse provided by the PHY chip to the PD via the transmit line and a second PHY chip. The first PHY chip receives one or more return pulse signals from the PD, analyzes characteristics such as voltage and / or frequency of the return pulse signal(s), and determines attributes of the PD based on those characteristics. The attributes can include powered device validity and power classification. A method of supplying power to a PD is also presented.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
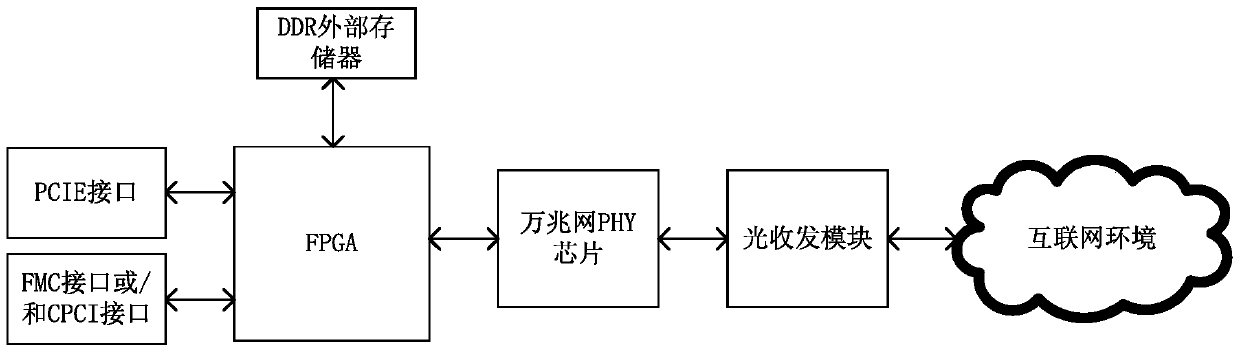
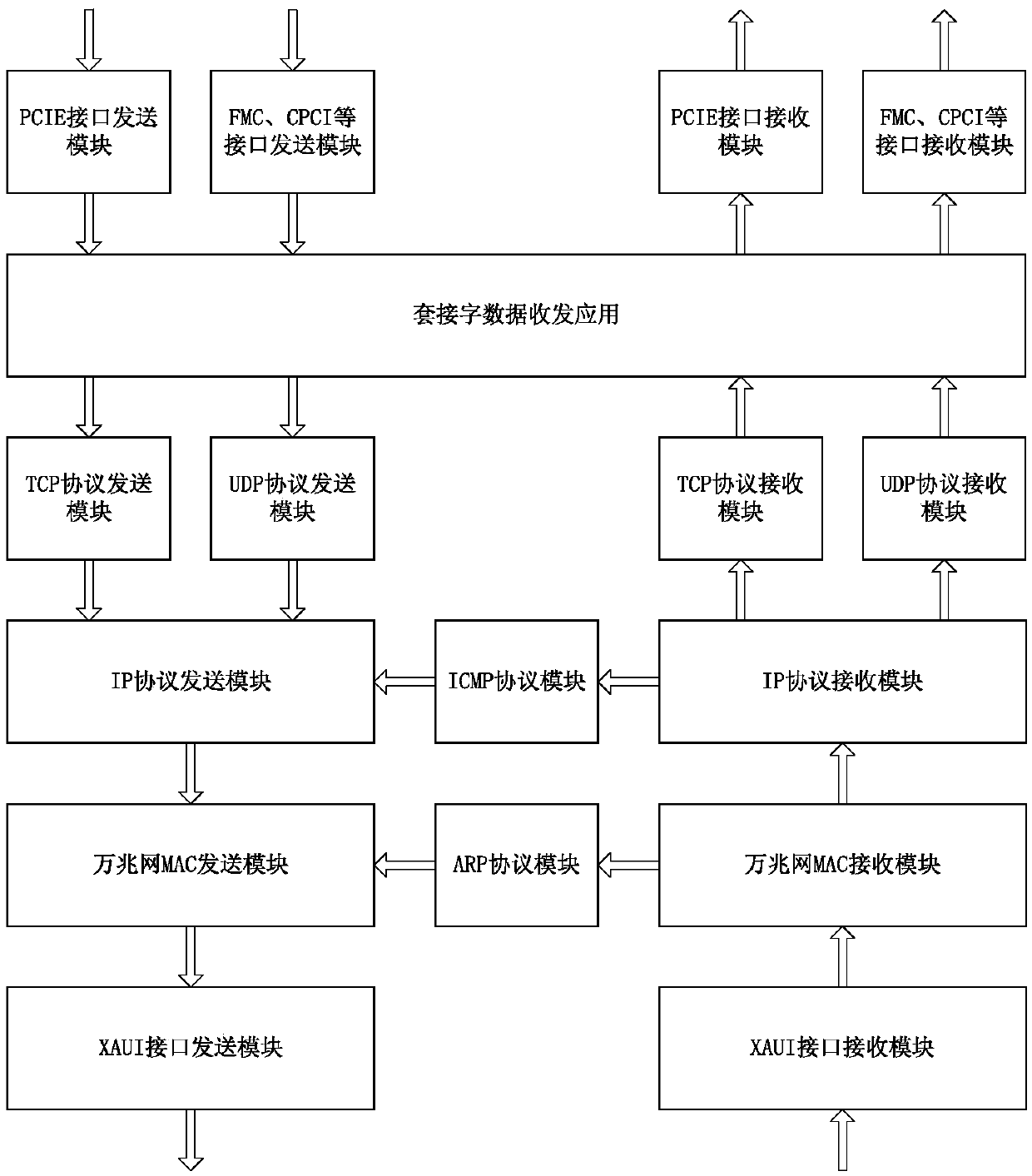
10-gigabit Ethernet TCP offload engine (TOE) system realized based on FPGA
ActiveCN105516191AAvoid homeostasisImprove the status quo of high loadTransmissionTransceiverNetworked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol
The invention discloses a 10-gigabit Ethernet TCP offload engine (TOE) system realized based on an FPGA, comprising the FPGA for realizing a TCP / IP protocol stack and a 10-gigabit Ethernet MAC layer, a 10-gigabit Ethernet PHY chip connected with the FPGA, a 10G optical transceiver module connected with the FPGA and used for serving as a 10-gigabit Ethernet transmission medium, and a DDR external memory connected with the FPGA and used for data caching. The FPGA is creatively adopted to realize the TCP / IP protocol stack, replacing a soft TCP / IP protocol stack realized by a conventional way of using a processor and an operation system with a hardware manner. According to the system, the processing speed of the TCP / IP protocol stack is effectively increased, the smoothness and balance of 10-gigabit Ethernet transmission are realized, and most importantly, computer application and network protocol separation is realized.
Owner:CHENGDU ZHIXUN LIANCHUANG TECH
Method and system for network communications via a configurable multi-use ethernet phy
ActiveUS20100322105A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDigital subscriber lineNetwork link
Aspects of a method and system for network communications via a configurable multi-use Ethernet PHY are provided. In this regard, an Ethernet PHY may be configured based on characteristics of a network link over which the Ethernet PHY communicates, and a rate at which data is conveyed from a MAC to the Ethernet PHY may be controlled via a carrier sense signal of the MII. The carrier sense signal may be controlled based on a rate at which the Ethernet PHY transmits data over the network link. The Ethernet PHY may be configured based on a length of the network link and / or on a grade of the network link, where exemplary grades may comprise Cat-1 through Cat-7a cable. The Ethernet PHY may be configured into one of a plurality of modes comprising an Ethernet over digital subscriber line (DSL) mode, an extended reach mode, and a standard Ethernet mode.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
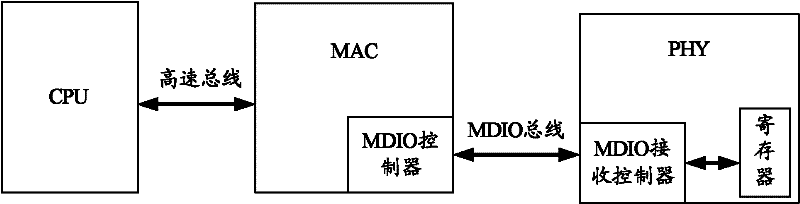
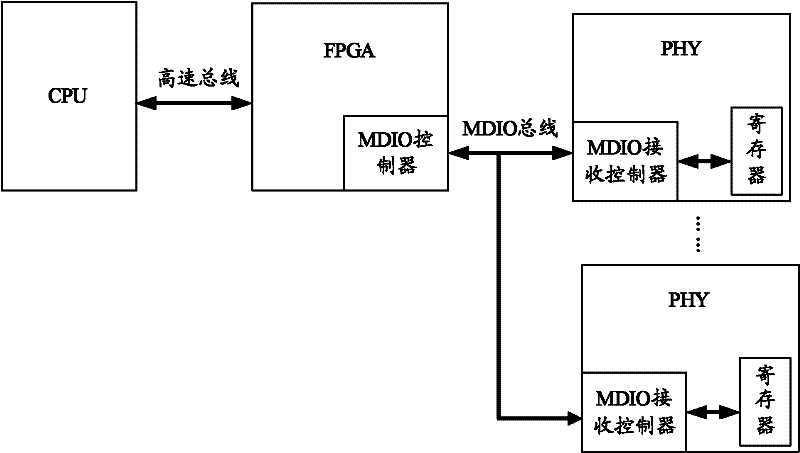
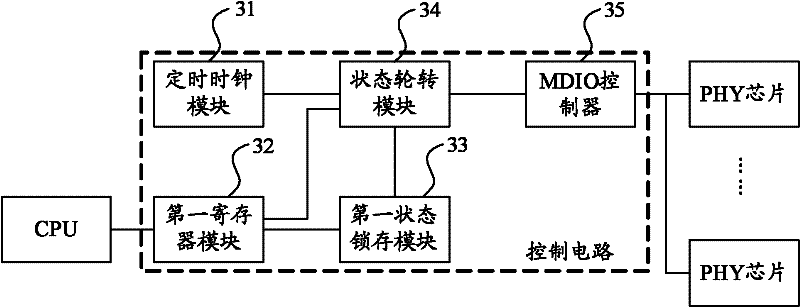
Method and control circuit for controlling physical layer chip
InactiveCN102291423AReduce the burden onEasy to controlTransmissionAutomatic controlData information
The invention provides a method for controlling a physical layer (PHY) chip and a control circuit. The control circuit comprises a timing clock module, a first register module, a first state locking and storing module, a state rotation module and a management data input / output (MDIO) controller, wherein the state rotation module is used for reading the first register module according to a clock signal provided by the timing clock module and change information provided by the first state locking and storing module and providing first address information and control data information for the MDIO controller according to a reading result; and the MDIO controller is used for writing the control data information into a register of a pin of the PHY chip corresponding to the first address information so that the pin state of the PHY chip can be controlled automatically. After the technical scheme disclosed by the invention is adopted, the same MDIO controller can be used for managing multiplePHY chips so that the load of a central processing unit (CPU) is reduced.
Owner:RUIJIE NETWORKS CO LTD
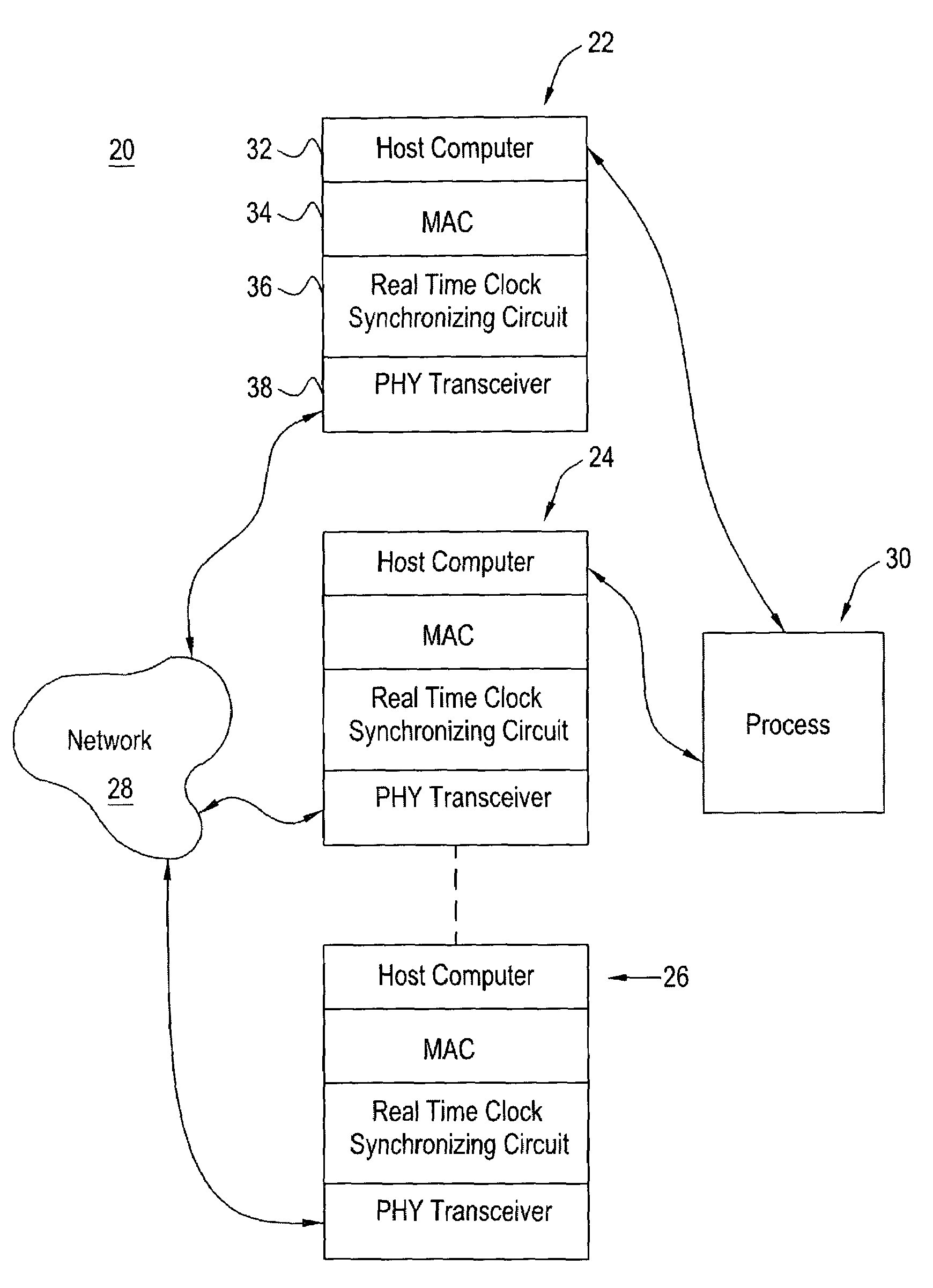
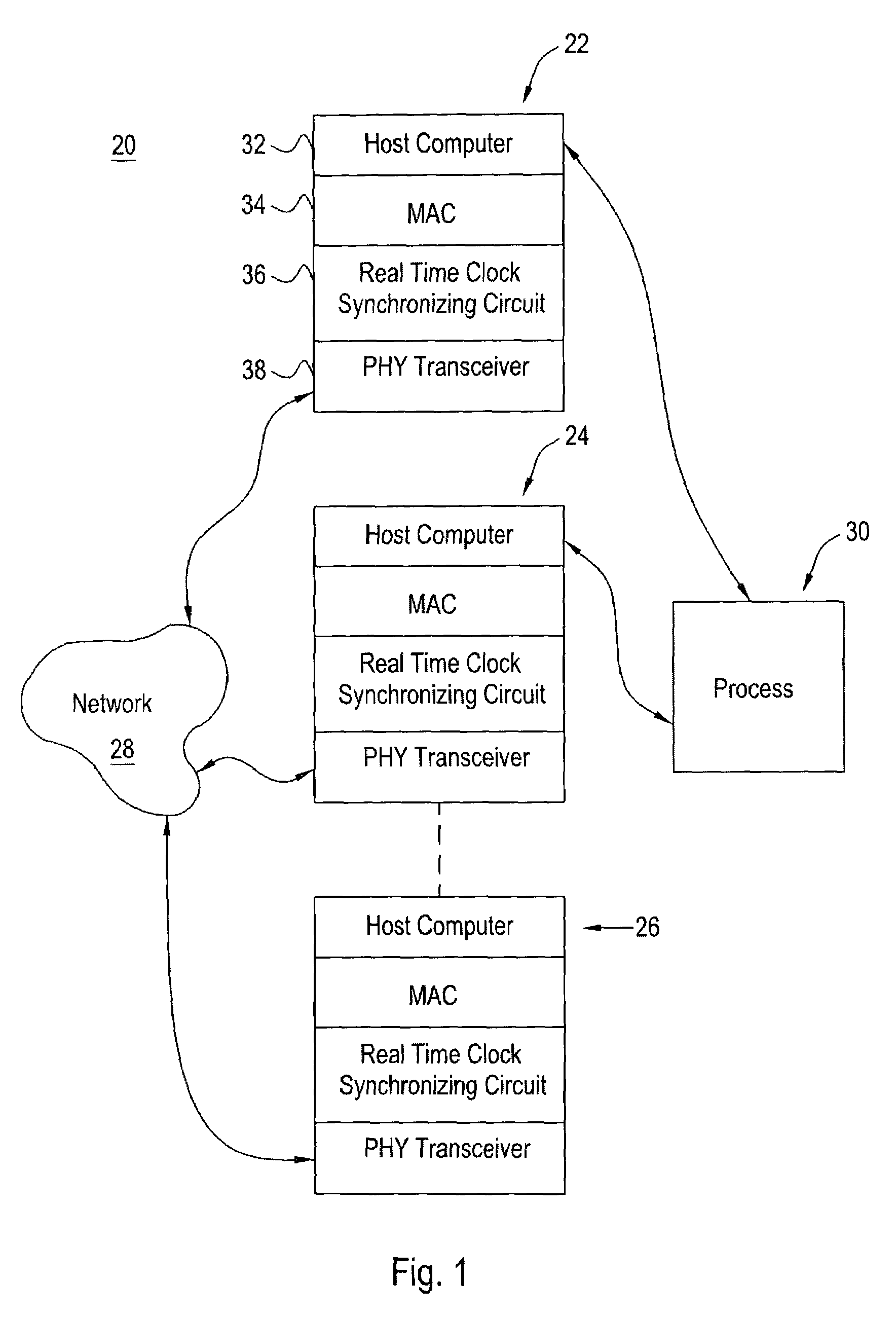
Clock synchronizing method over fault-tolerant Ethernet
ActiveUS7200158B2Compensation delayTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTransceiverMedia access controller
A device that recognizes the time synchronization packet and substitutes a real-time value from the master internal counter into the proper place in a data packet is placed between an Ethernet Media Access Controller (MAC) and a Physical Interface Transceiver (PHY). A second device monitors the packet passing from the MAC to the PHY and determines when it is a time synchronization packet from the time master. Upon recognition of the proper packet, the second device simultaneously captures the master's time value and captures the value of a local real-time clock. The result of these captures are presented to the local host computer which controls the time base clock that increments the local real-time clock to either speed up or slow down this local clock, thereby synchronizing the local clock to the time master clock. The offset and skew of the local clock to the master clock is reduced to only the network latency plus variability due to network congestion.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
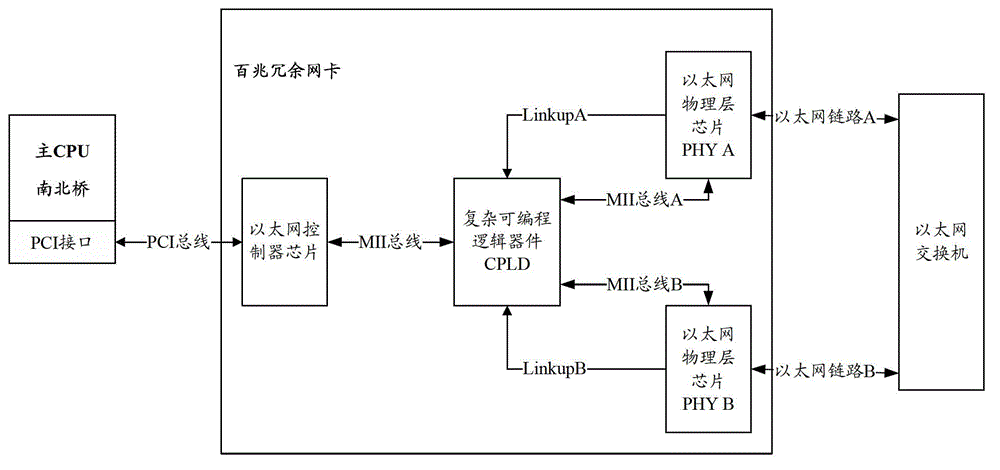
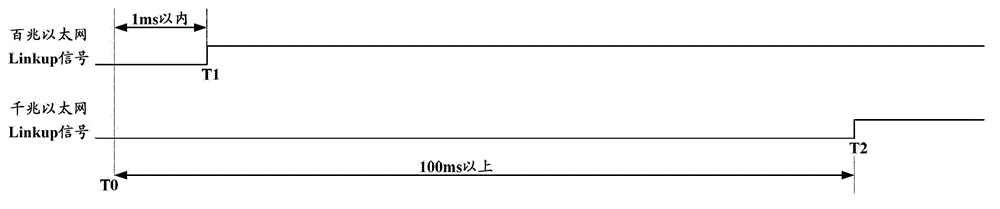
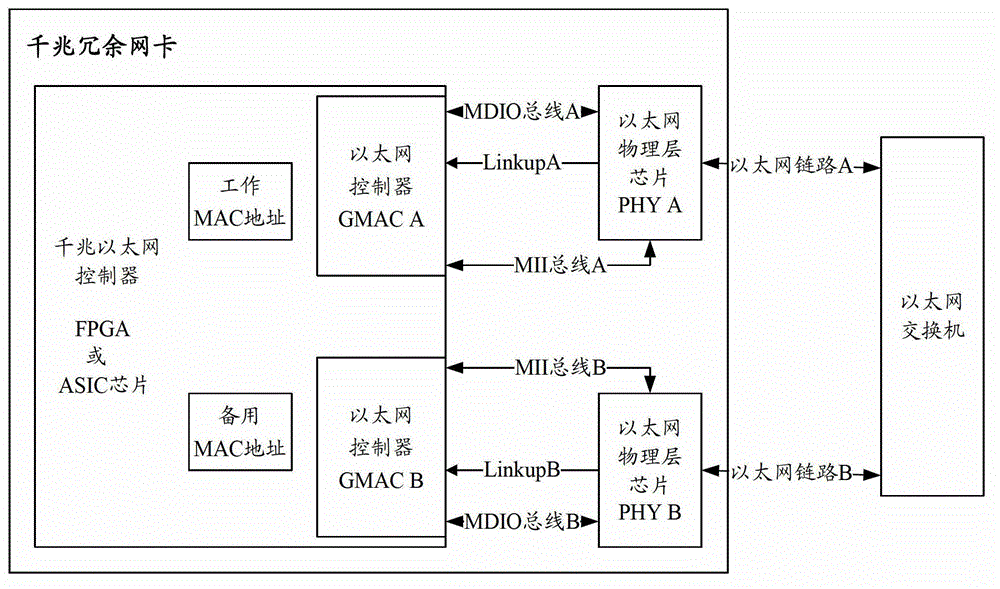
Gigabit Ethernet redundant network card and link switching condition determination result control method thereof
ActiveCN102984059ASimple structureLow application costError preventionData switching by path configurationPHYComputer module
The invention relates to a gigabit Ethernet redundant network card and a link switching condition determination result control method thereof and belongs to the technical field of networks. The network card consists of a gigabit Ethernet controller, a working link Physical Layer (PHY) chip, and a backup link PHY chip, wherein the gigabit Ethernet controller comprises a working link control module and a backup link control module. The working link control module and the backup link control module are connected to a PHY chip of a corresponding link through a corresponding link MII bus and a link Management Data Input Output (MDIO) bus, corresponding working heartbeat frames and backup heartbeat frames are transmitted, the state of the working link and the backup link can be determined through receiving of corresponding working heartbeat frames and backup heartbeat frames, the Ethernet link is determined to be disconnected under the condition that the gigabit Ethernet PHY chip is not modified, the switch of the working link and the backup link is controlled, the response speed of the redundant switching of the card is improved and the use experiment of users is optimized.
Owner:NO 32 RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
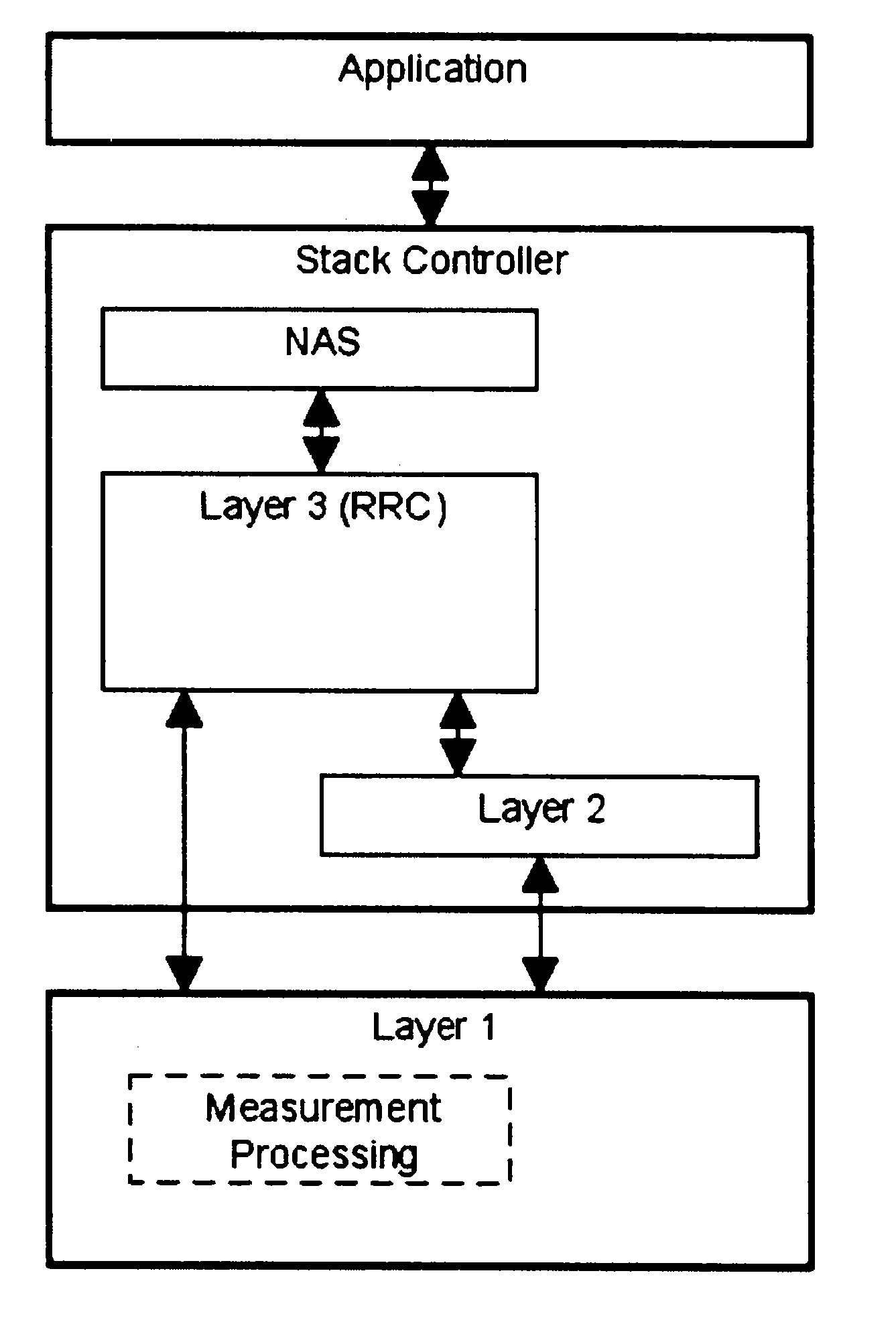
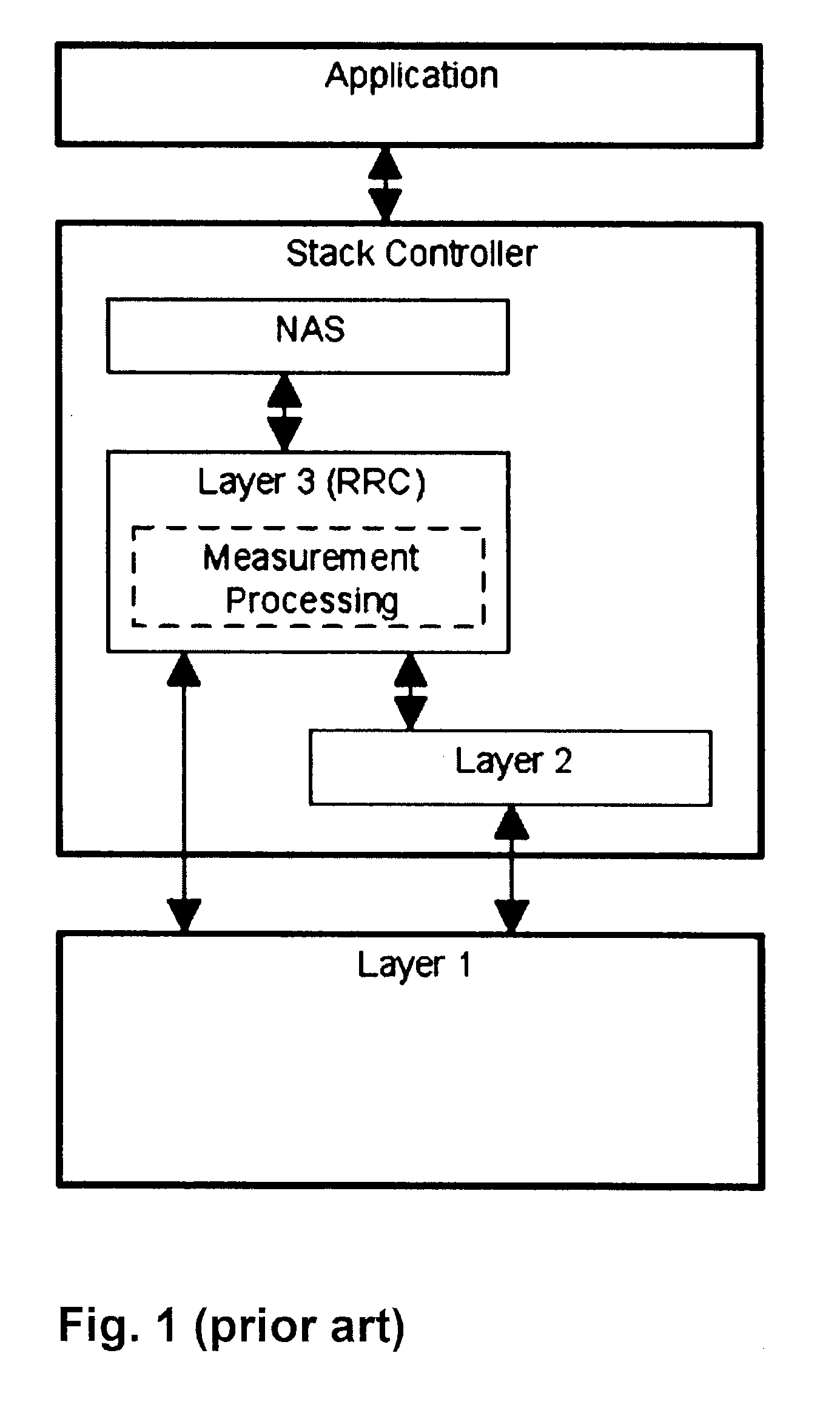
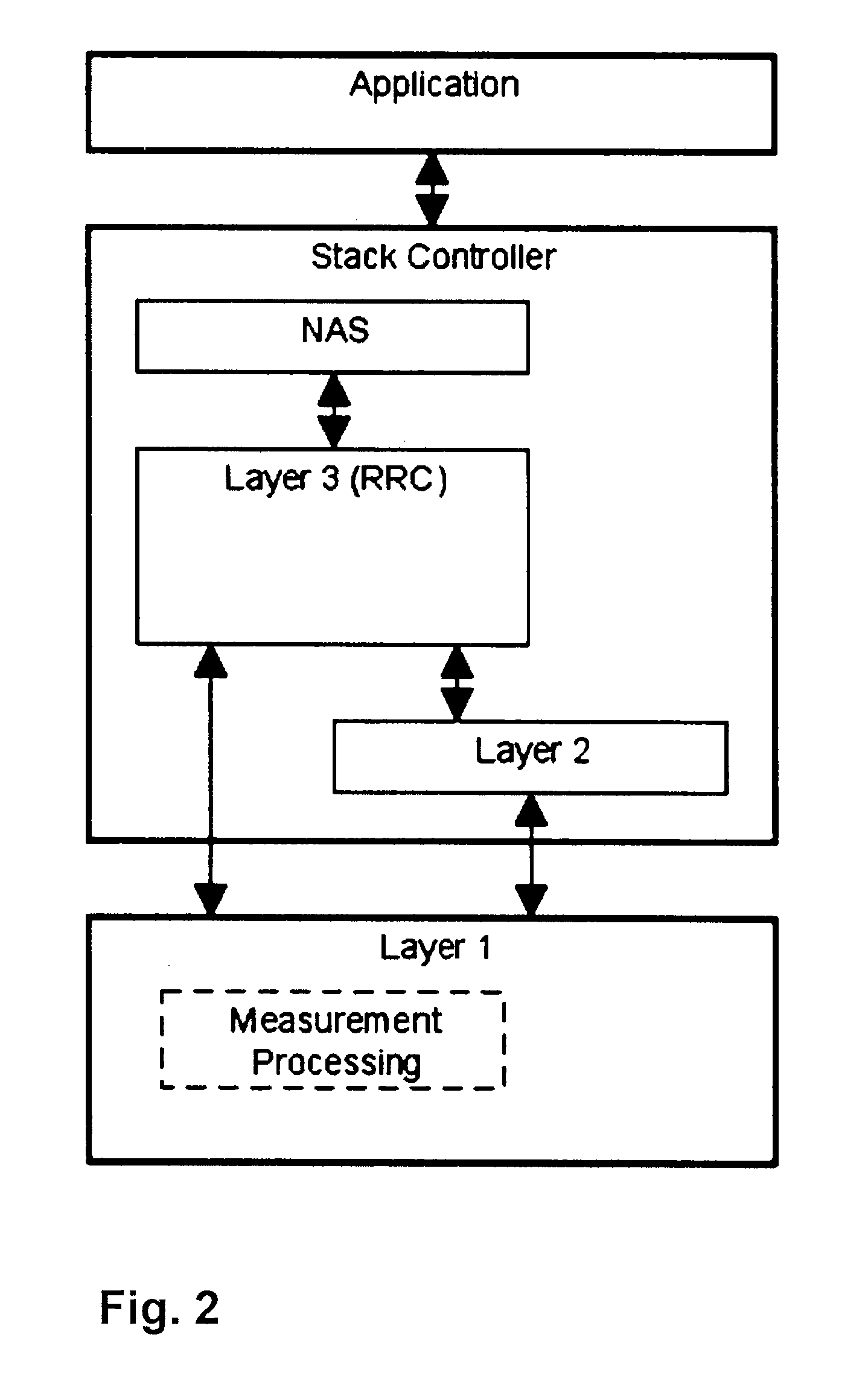
Method for controlling measurements in a wireless telecommunications terminal
ActiveUS20110305159A1Increase power consumptionMinimize timeEnergy efficient ICTPower managementCommunications systemComputer terminal
A method is provided for controlling measurements in a wireless telecommunications terminal. In a Long Term Evolution (LTE) wireless communication system, the network instructs a UE to measure the received power and quality of the reference signals of the serving cell as well as of neighbor cells. The object of improving the system power consumption of user equipment (UE) that has to perform such measurements is solved by distributing the measurement functionality between RRC and PHY layers such that the RRC layer is enabled to rest in a power save mode unless results of the measurements have to be reported to the network, and to be only active for a minimum to ensure that the UE still behaves standard compliant to the network.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Configuration and signaling for ul noma operations
PendingUS20210045181A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission path divisionPHYEngineering
Switching between Orthogonal Multiple Access (OMA) and Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) modes of a user equipment (UE) can be determined and indicated by a gNB to a UE at an RRC connected state using one or more of the following schemes: at an RRC (Radio Resource Control) layer with an RRC configuration message, at a MAC (Medium Access Control) layer with MAC CE (MAC control element) signaling, at a PHY (Physical) layer with DCI (Downlink Control Information) signaling, jointly with RRC configuration and DCI signaling, and / or jointly with RRC configuration and MAC CE signaling. The OMA or NOMA mode that the UE operates after the transition may be requested by the UE, indicated by the gNB, and / or may be based on one or more rules for OMA-NOMA switching.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Method, system, integrated circuit, communication module, and computer-readable medium for achieving resource sharing including space and time reuse within a power line communication system
ActiveUS20090174532A1Reduce mutual interferenceImprove throughputFrequency-division multiplex detailsDigital data processing detailsComputer architectureCommunications system
A communication system includes communication protocols that allow a single network or multiple neighboring networks to increase resource sharing and reduce mutual interference and increase their overall throughput. Various protocols apply to homogenous networks in which all power line communication (PLC) devices of multiple networks are interoperable with respect to full power line communication in a common PHY (specifications, signaling capabilities, modulation scheme, coding scheme, bandwidth, etc.) and to heterogeneous networks in which devices of some PLC networks are not interoperable with PLC devices of other PLC networks with respect to full power line communication given that the devices of the different networks do not employ a common PHY. With respect to heterogeneous networks, a protocol is provided to enable coexistence via a signaling scheme common to all of the devices of the network that allows resource sharing between the devices of the multiple heterogeneous networks. Homogeneous networks are those in which all nodes can communicate with each other using a common PHY, so that information about one PLC network can be transferred to another PLC network. Heterogeneous networks are those in which not all PLC networks can exchange information using their own native PHY, such as where users in different apartments or houses use different devices having different specifications, different signaling capabilities, modulation scheme, coding scheme, bandwidth and the like.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical/electric interface module space multiplexing method and apparatus used for Ethernet SFP interface
InactiveCN1674547ASolving application-specific cost challengesData switching by path configurationMultiplexingElectricity
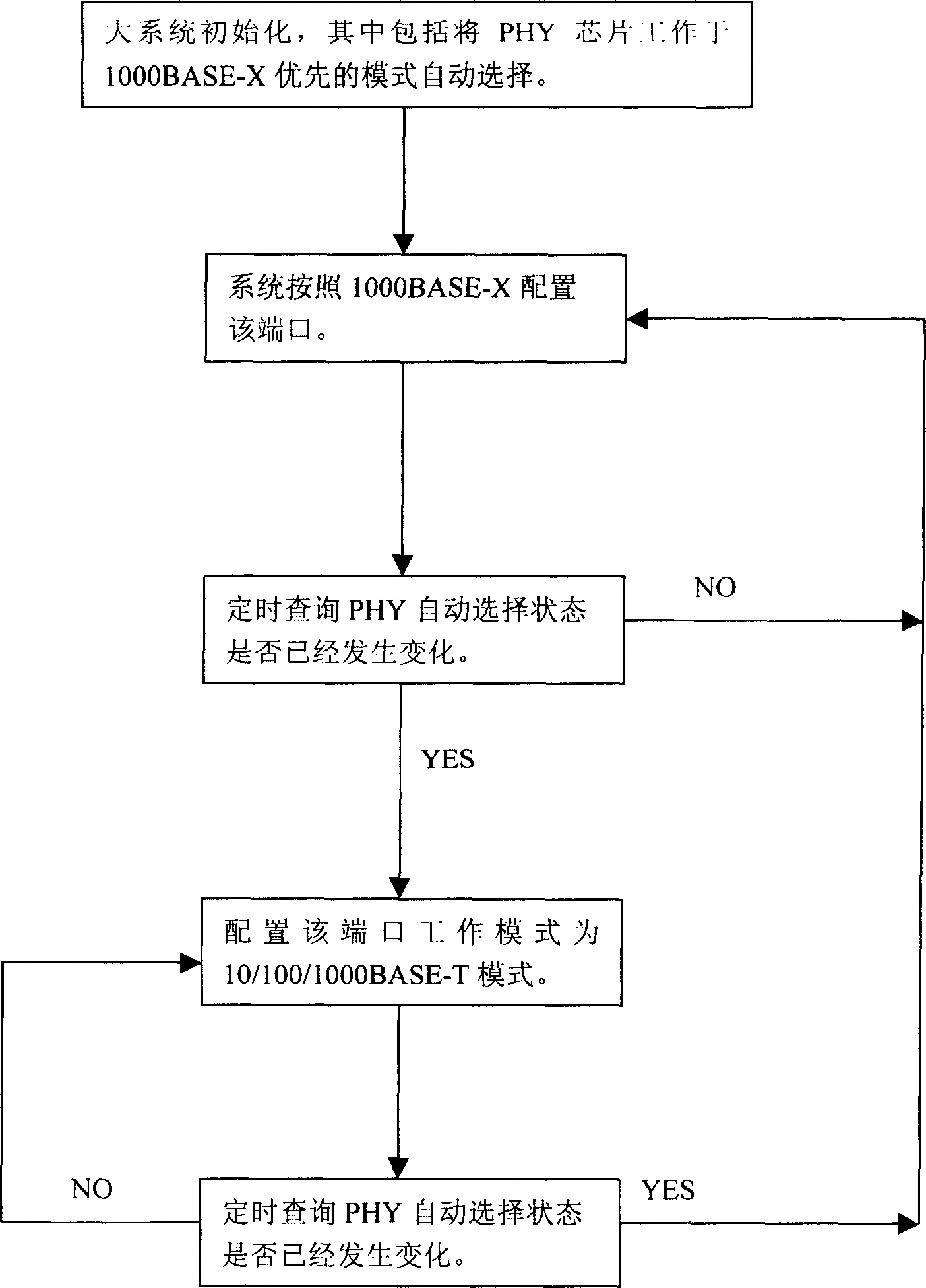
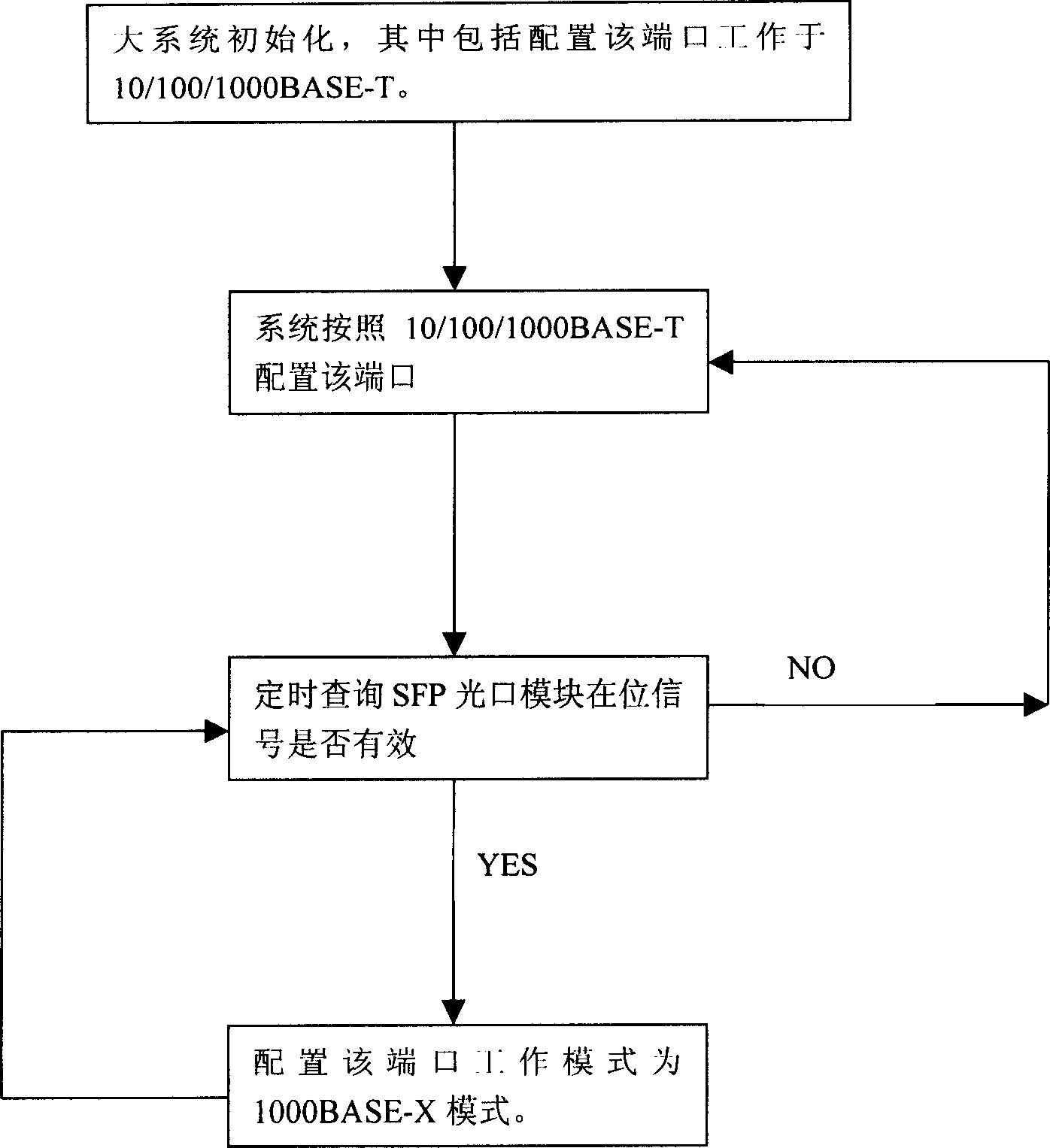
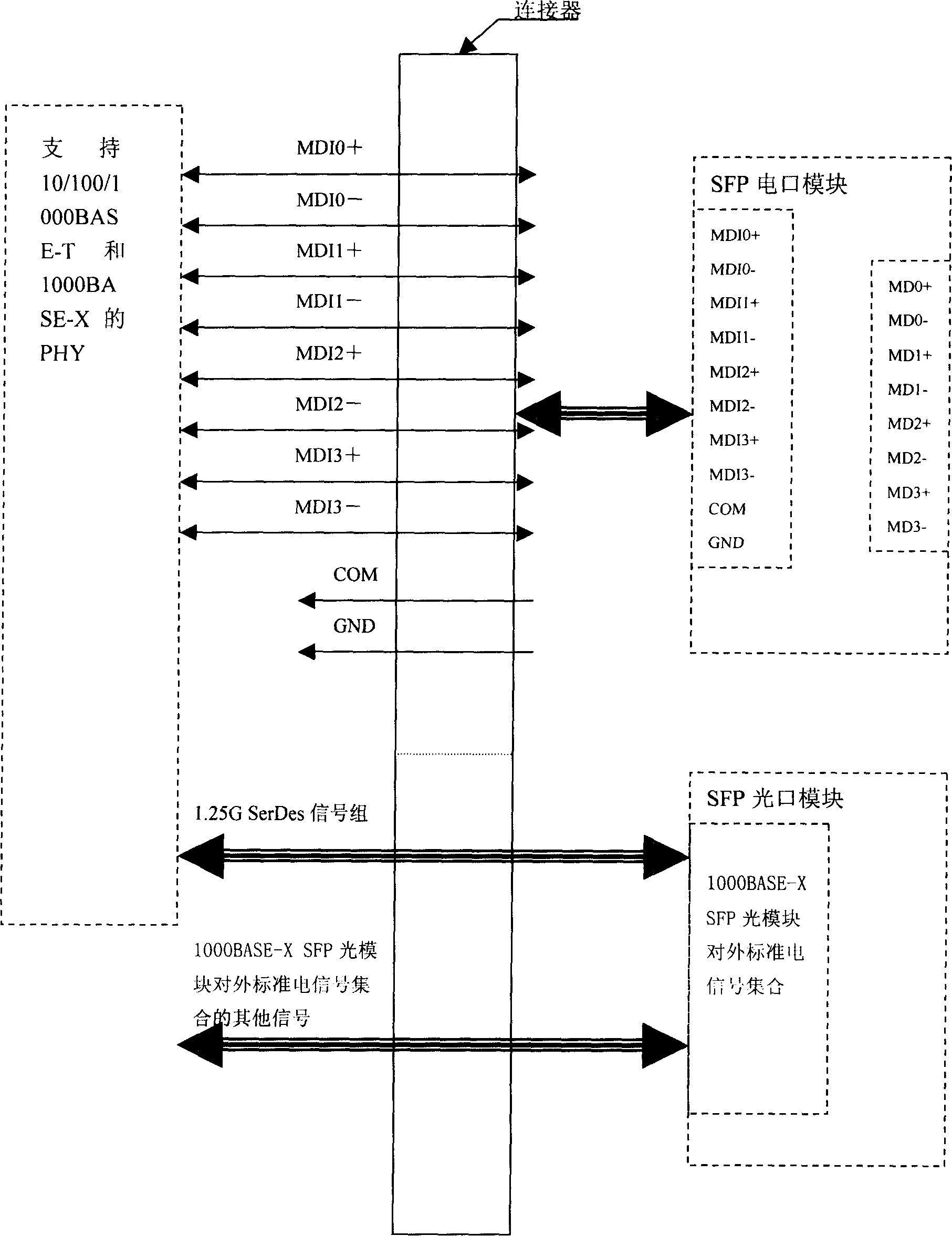
The present invention relates to the field of Ethernet exchange equipment and router equipment, mainly, it is an optical / electric interface module space multiplexing method for Ethernet SFP interface and its device. Said method includes: 1). adopting PHY chip for supporting 10 / 100 / 1000 BASE-T and 1000 BASE-X function; 2). interface of 10 / 100 / 1000 BASE-T adopts special SFP electric interface module; 3). 1000 BASE-X adopts general SFP kilomega optical interface module; 4). at SFP interface side of PHY chip using multiplexer equipment provided by said invention for supporting SFP electric module and SFP optical module and making space multiplex in same SFP CAGE space; 5). according to the detected result large system can make correspondent configuration for said port so as to make said port be worked in electric interface or optical interface module.
Owner:黄炜
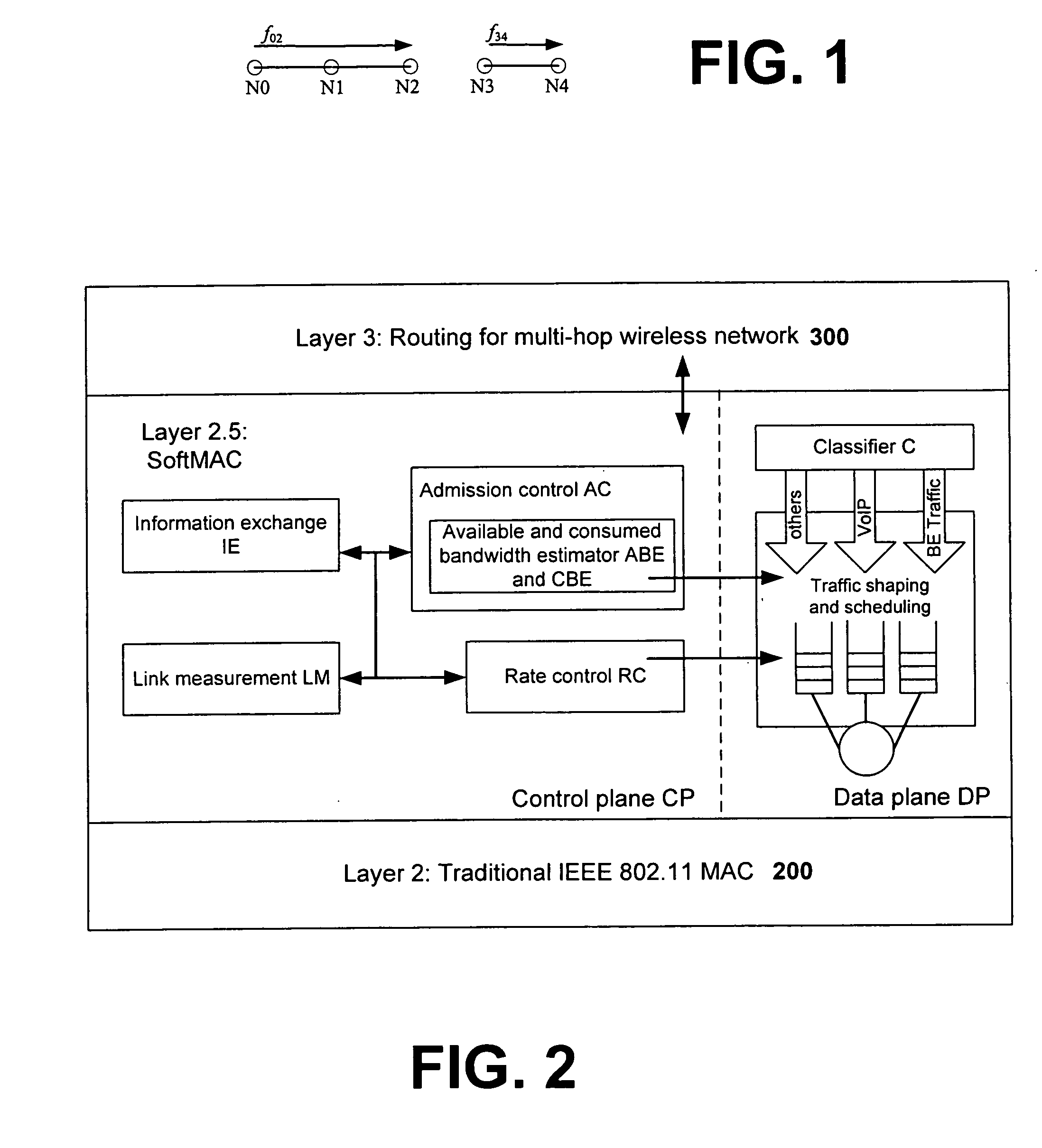
Systems and methods for coordinating wireless traffic for heterogeneous wireless devices
In view of the foregoing, the present invention provides a unified software framework or architecture for distributed coordination of wireless devices and radios, referred to as Layer 2.5 Software MAC (or ‘SoftMAC’), which resides between the standard 802.11 MAC layer (Layer 2) and IP layer (Layer 3) to regulate and control the amount of traffic (both real-time and “best effort”) delivered to 802.11 MAC DCF interfaces. The software based design can be ported to different OS platforms and systems and is capable of handling new hardware interfaces and MAC mechanisms (e.g., 802.11e) with only a software upgrade. The invention thus provides a natural way to make end systems support coordination of different radios of device(s), achieving better performance. Advantages of the 2.5 layer software MAC in accordance with the invention include: (a) there are no hardware constraints; (b) heterogeneous wireless / radio support is provided at the 2.5 layer; and (c) an evolutionary and extensible solution with the ability to support future wireless MAC / PHY chip combinations.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com