Patents
Literature
957 results about "Status register" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
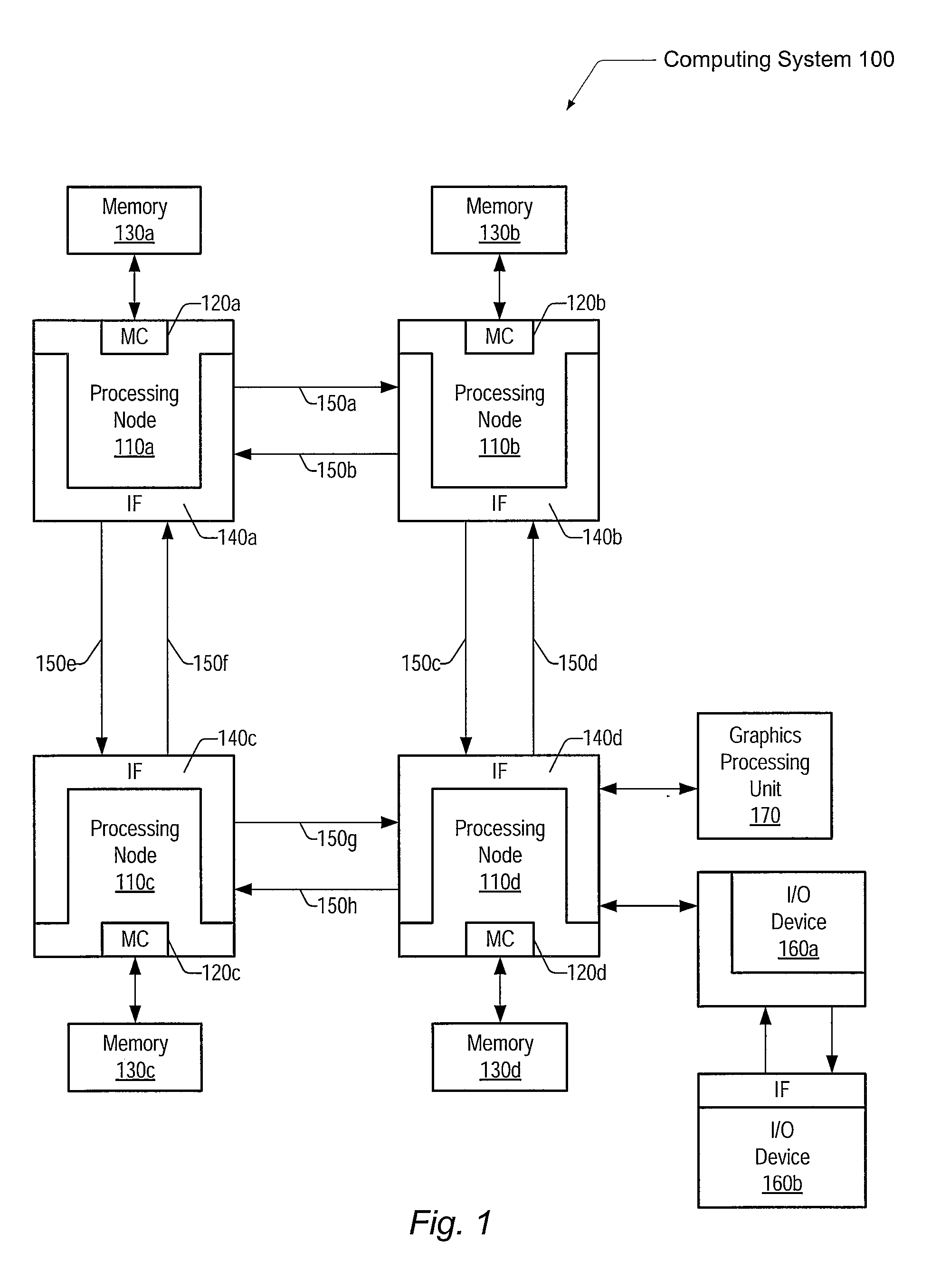
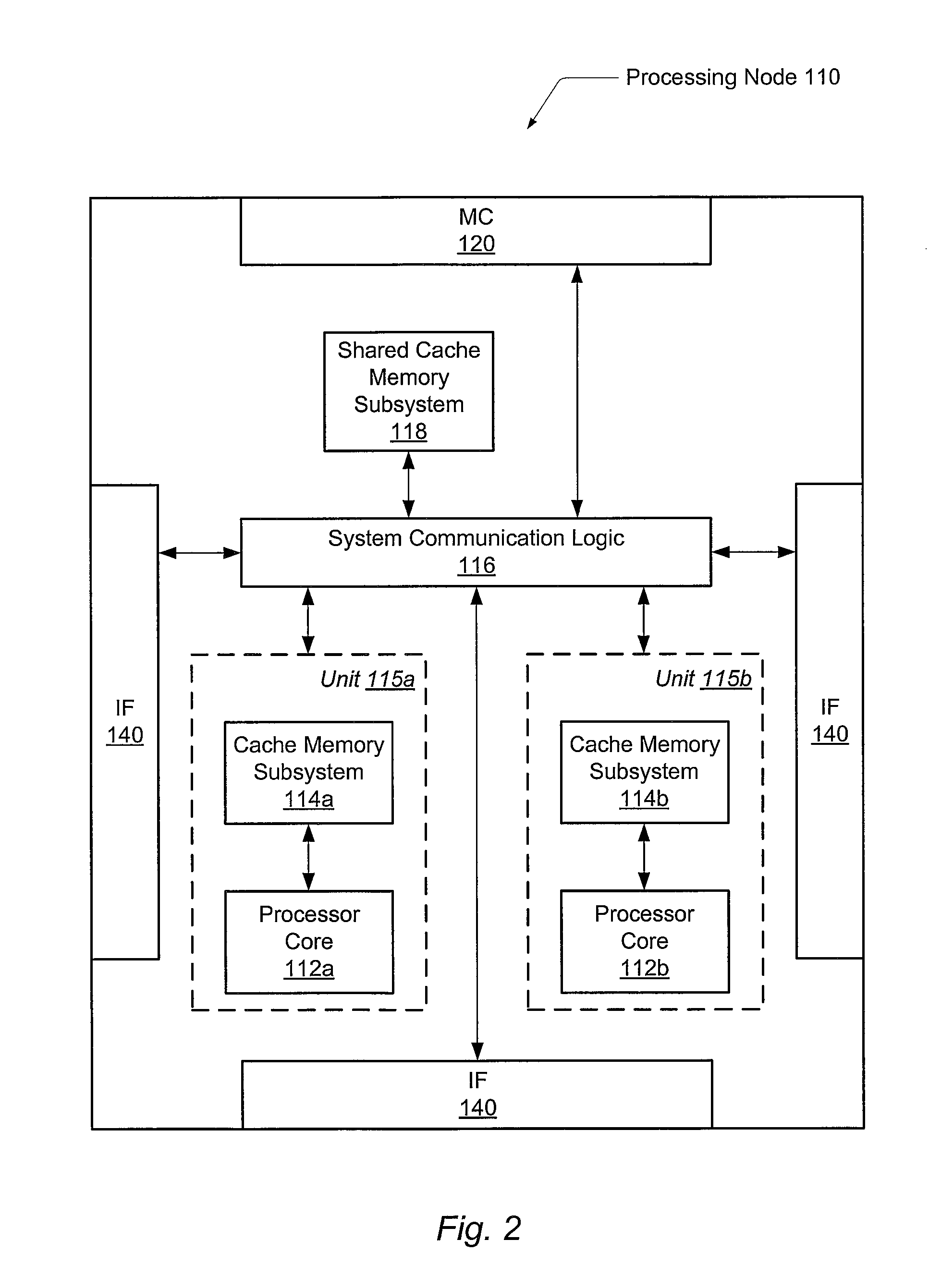
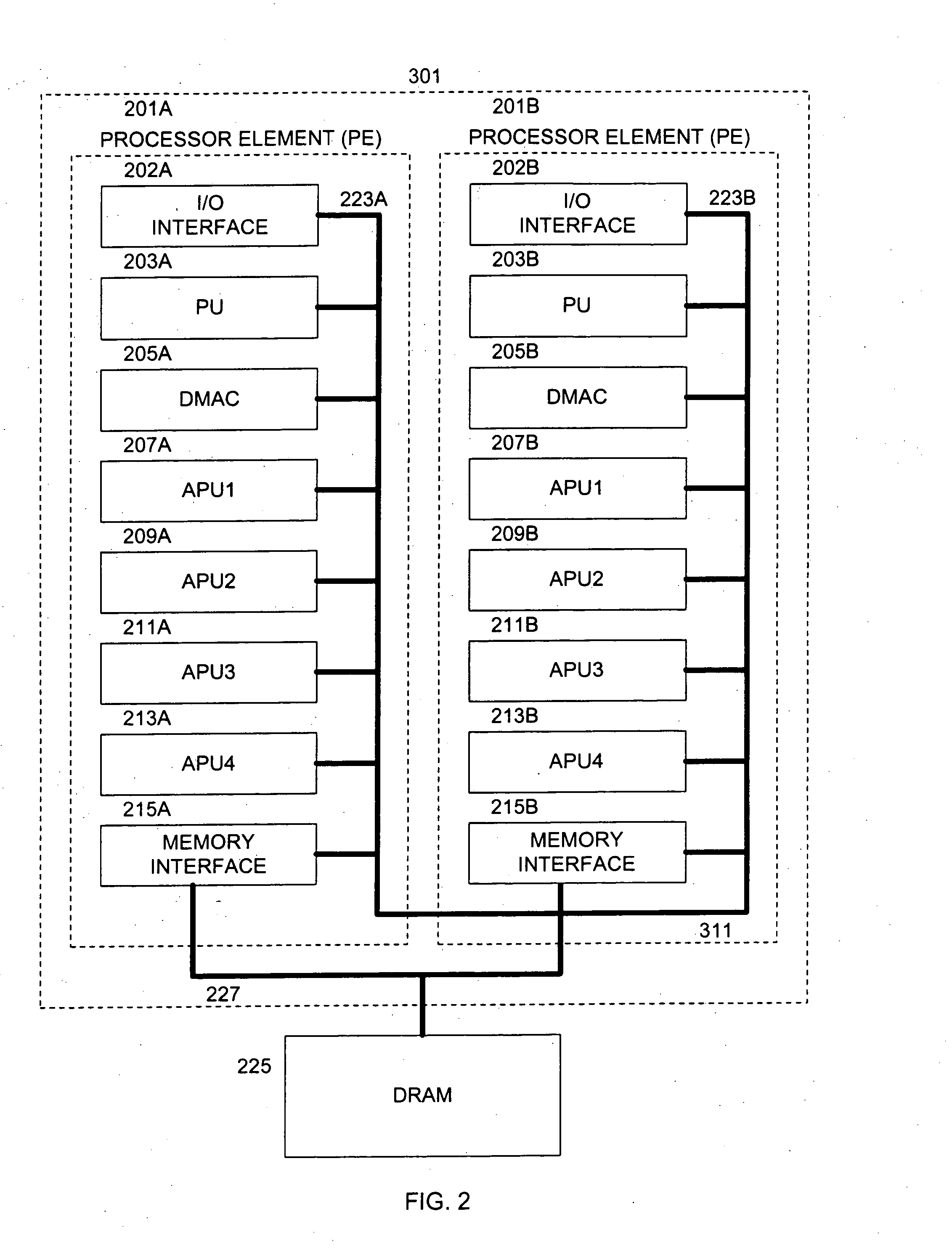
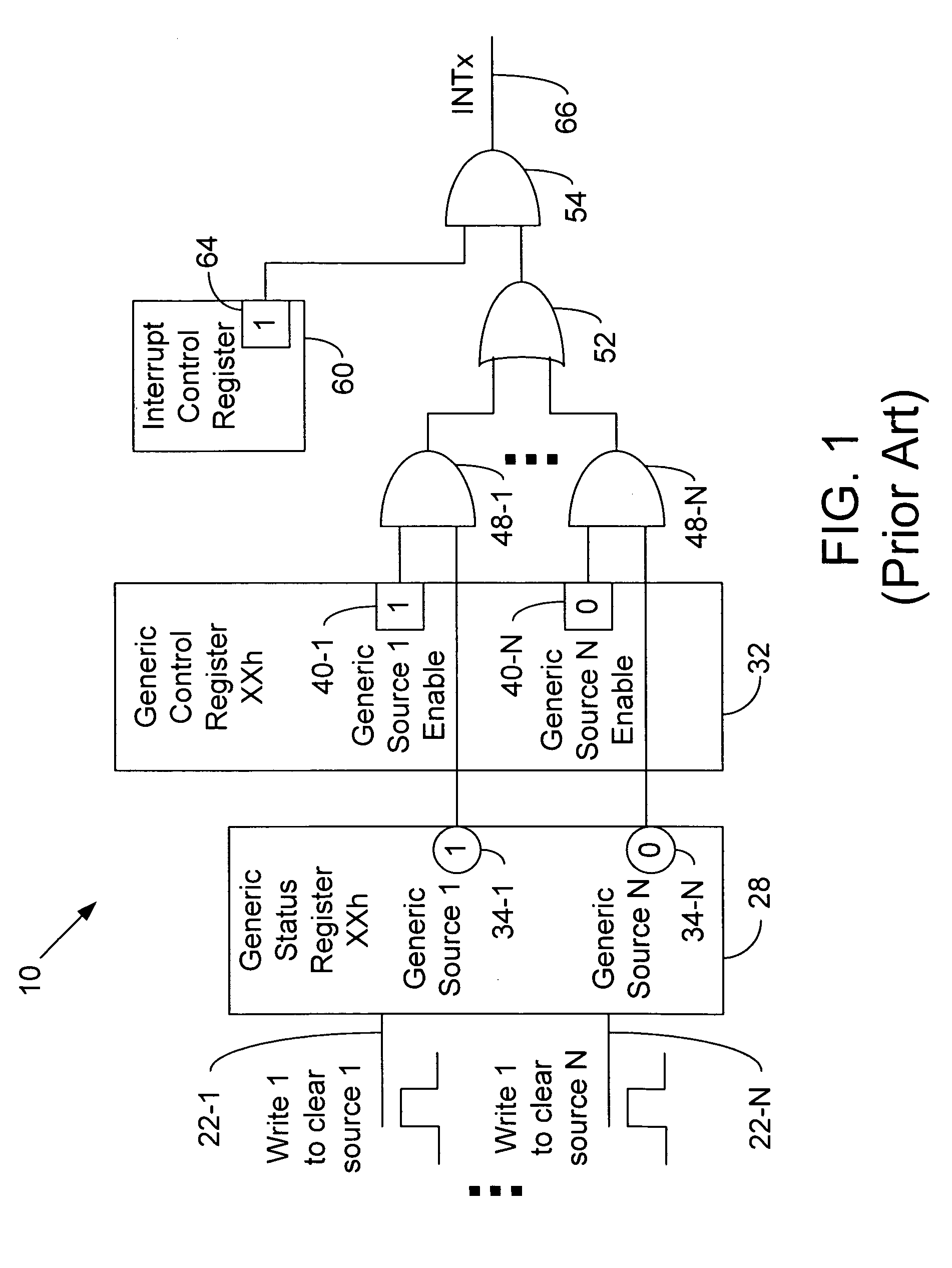
A status register, flag register, or condition code register (CCR) is a collection of status flag bits for a processor. Examples of such registers include FLAGS register in the x86 architecture, flags in the program status word (PSW) register in the IBM System/360 architecture through z/Architecture, and the application program status register (APSR) in the ARM Cortex-A architecture.
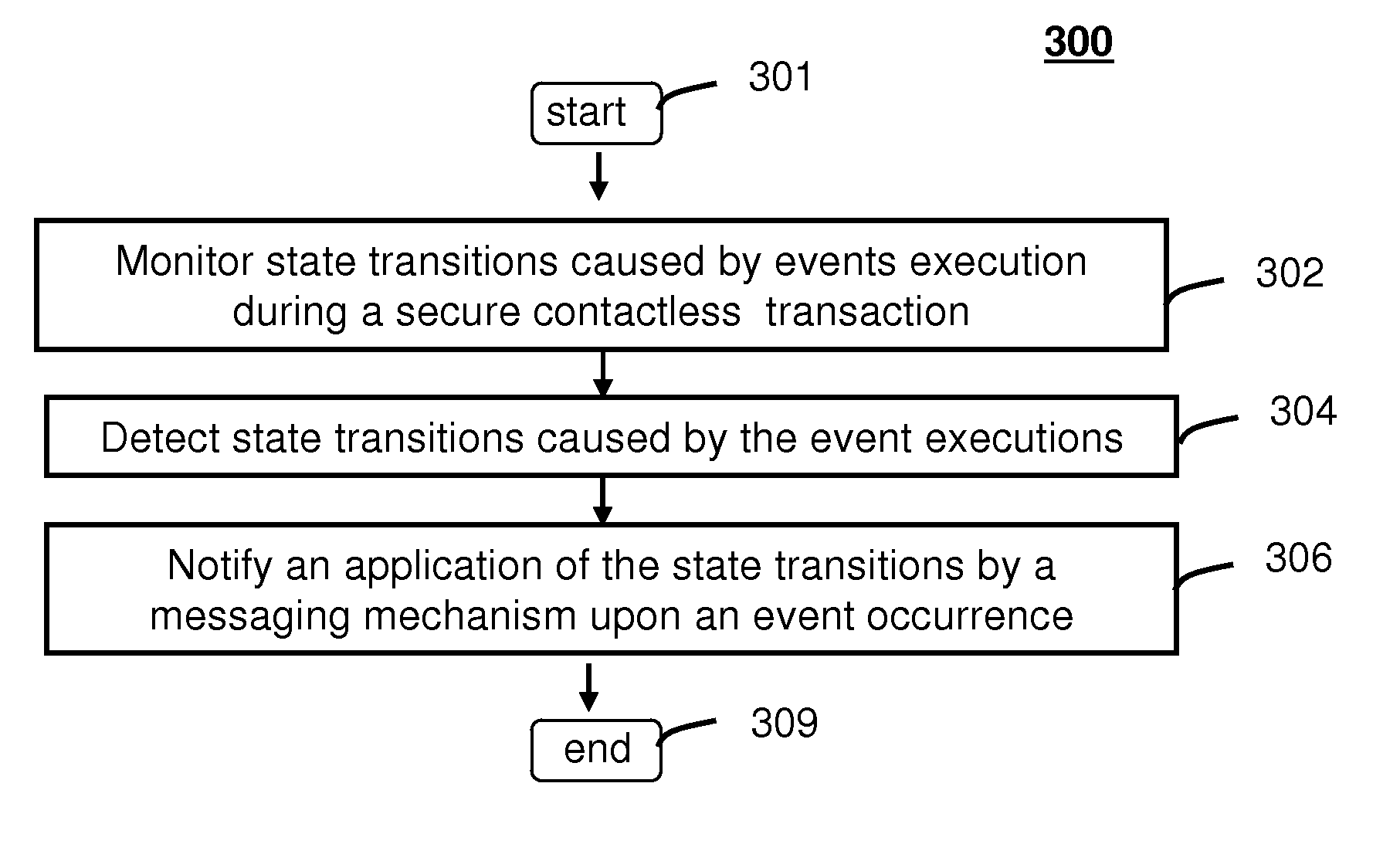
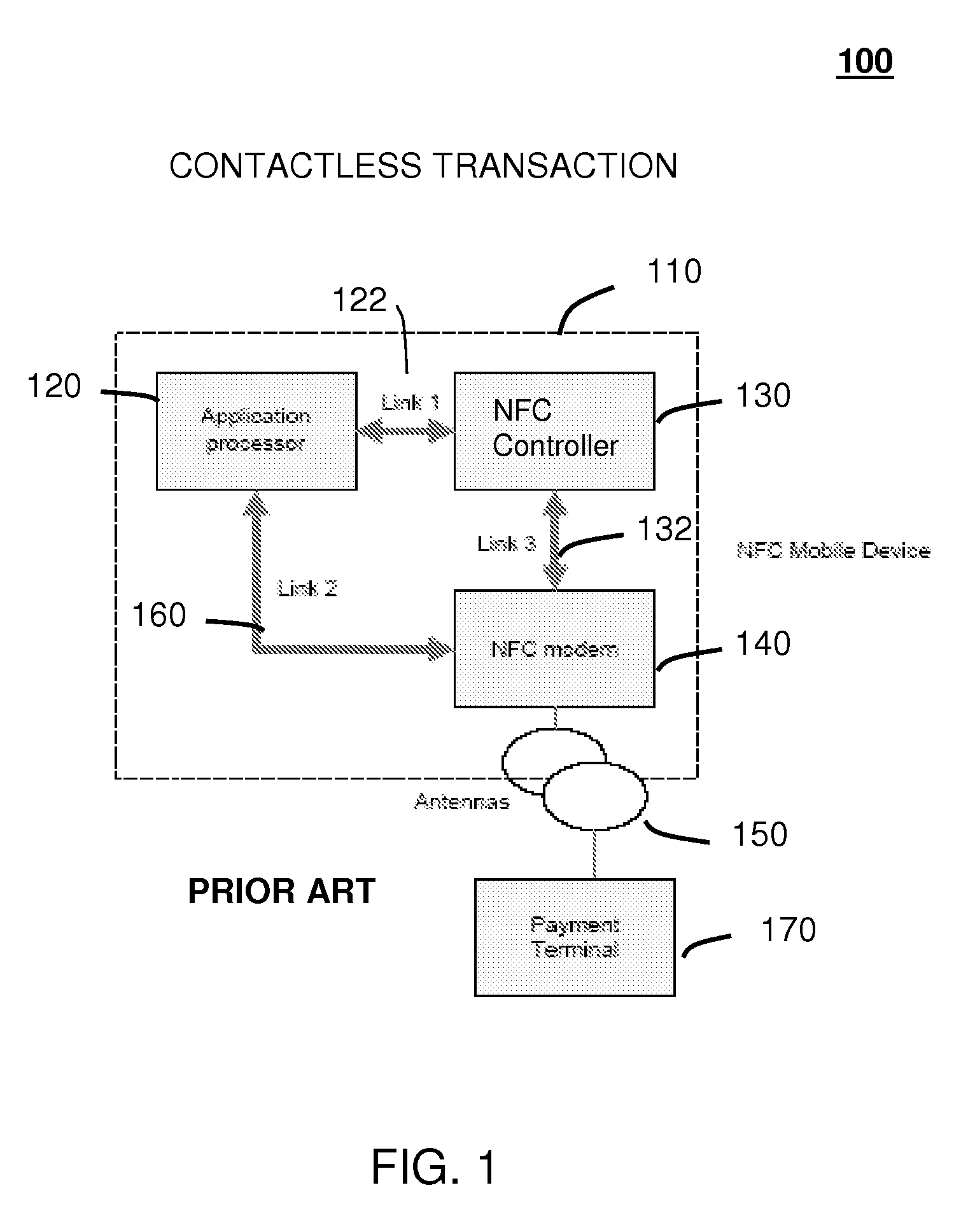
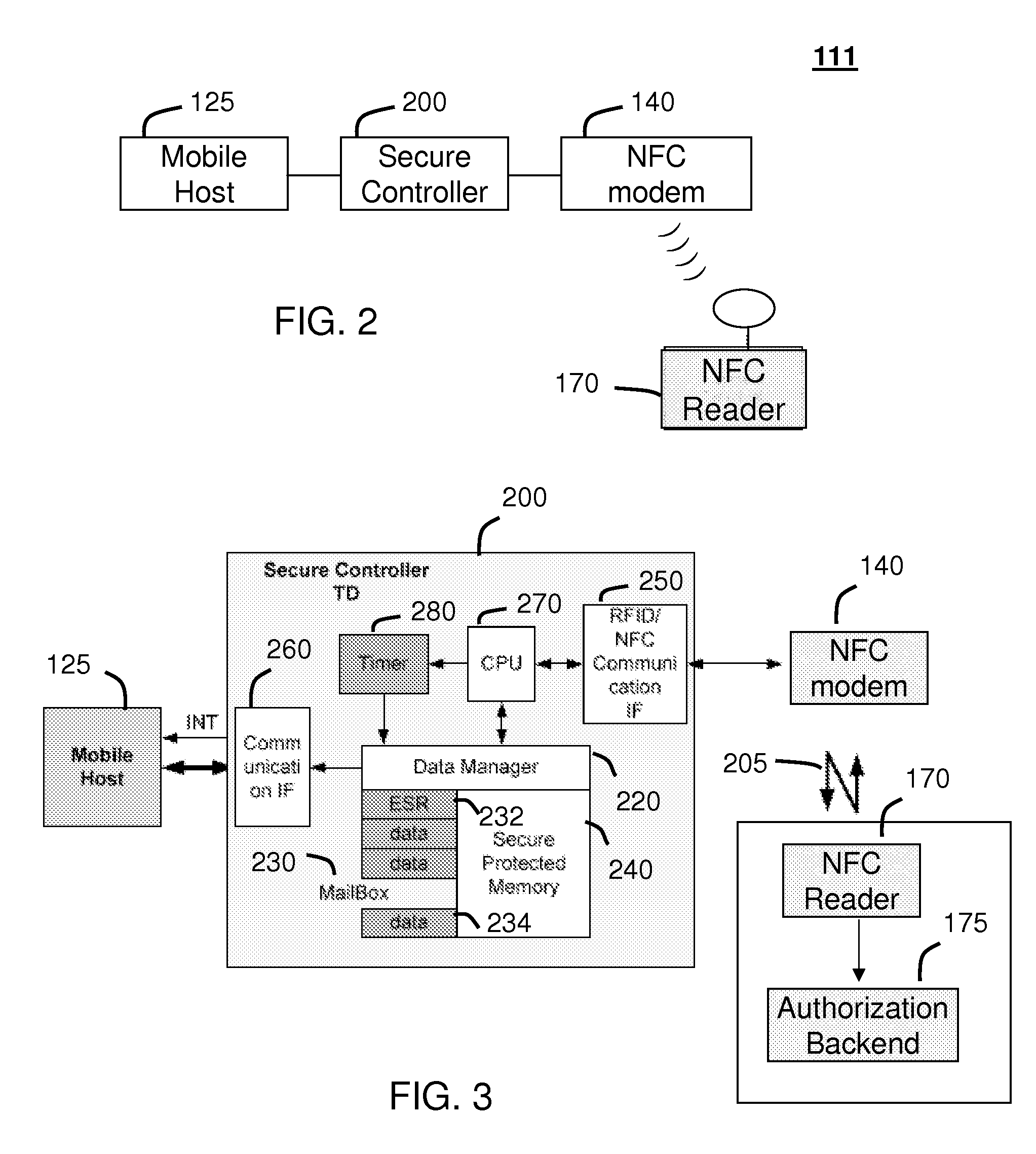
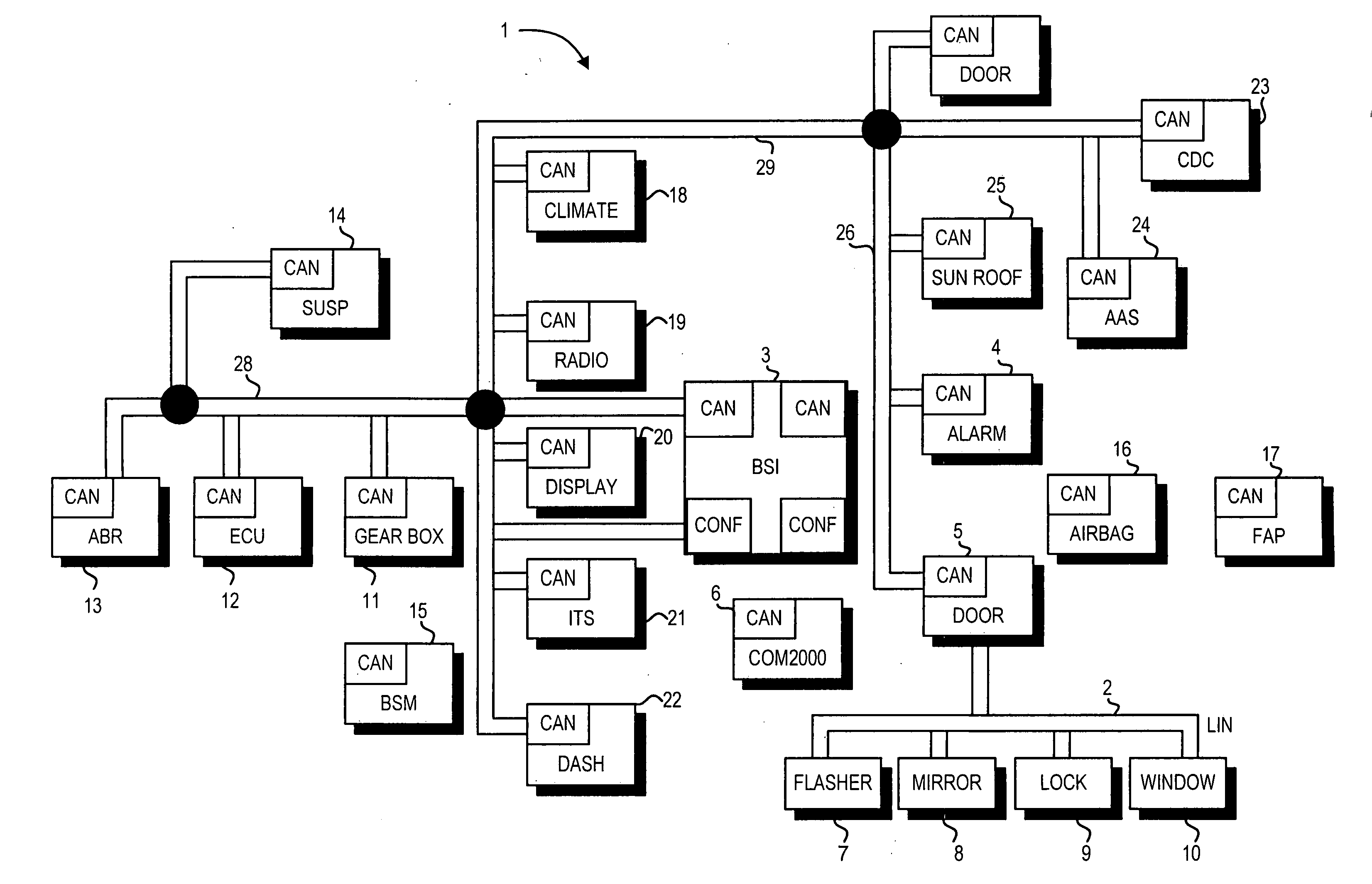
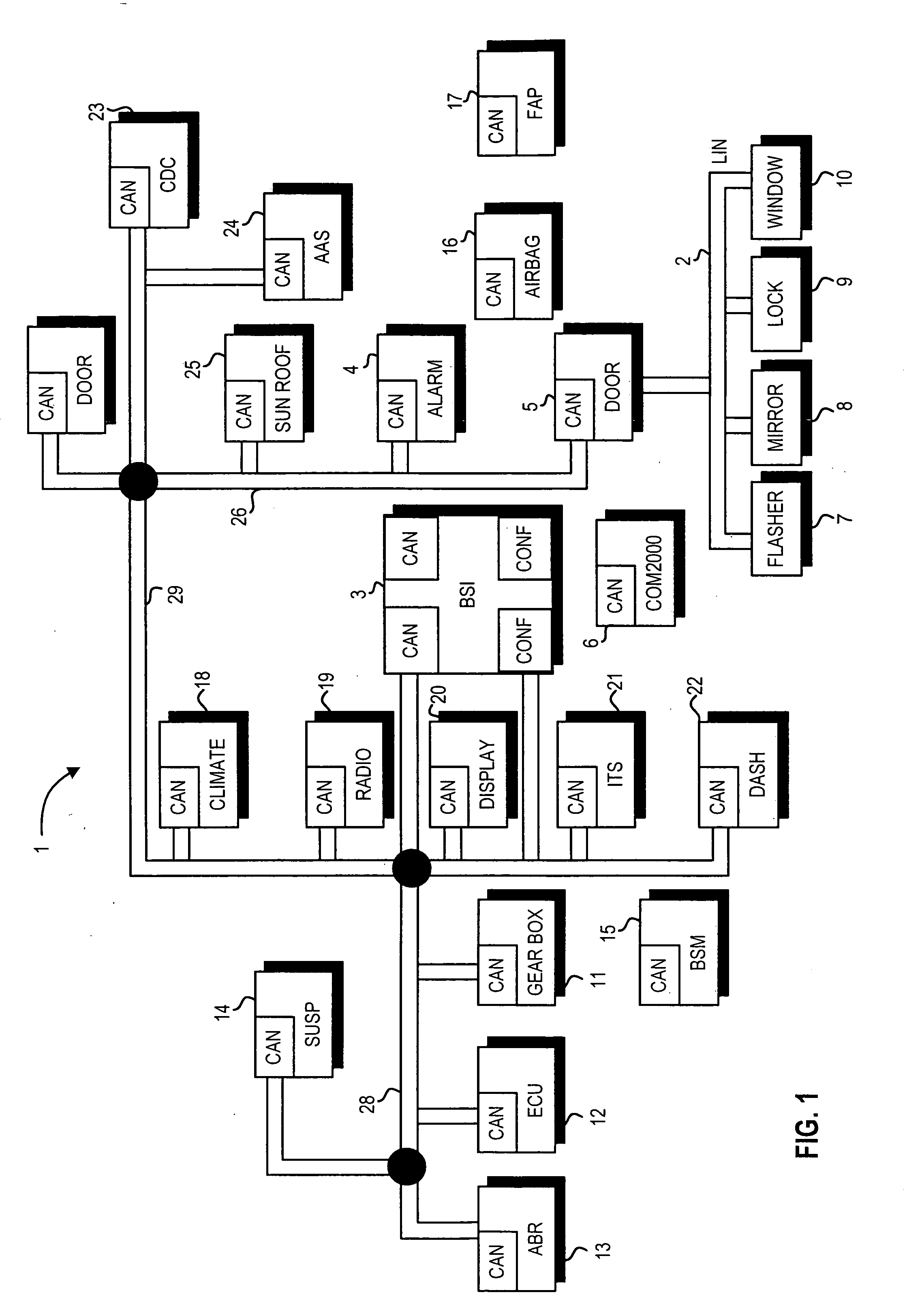
Method and system for monitoring secure application execution events during contactless rfid/nfc communication
ActiveUS20080162361A1Radio transmissionSecuring communicationCommunications securityTechnical communication
A system (211) and method (300) for reliable monitoring of secure application execution events is provided. The system can include a Near Field Communication (NFC) modem (140) for communicating transaction events of a secure contactless transaction (358) with a NFC reader (170), a secure controller (200) for monitoring state transitions caused by the transaction events, and a mobile host communicatively coupled to the secure controller for receiving hardware event notifications of the state transitions. The secure controller can generate message using a hardware interrupt to a mobile host based on secure applet state transition monitoring by setting up the events flag such as a Transaction Completion Flag (TCF) (372) into an Events Status Register (232) to identify a status of a secure contactless transactions
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
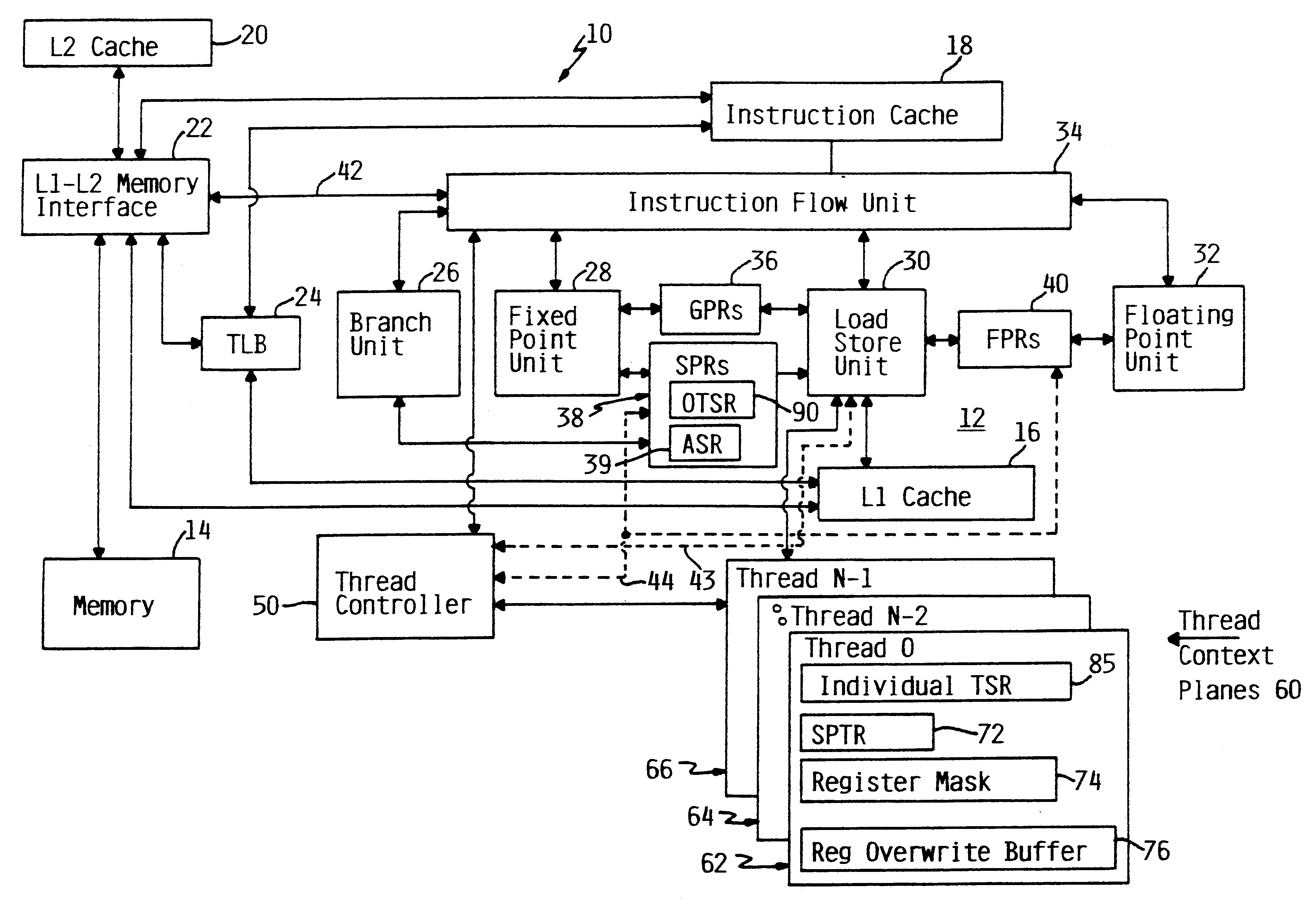
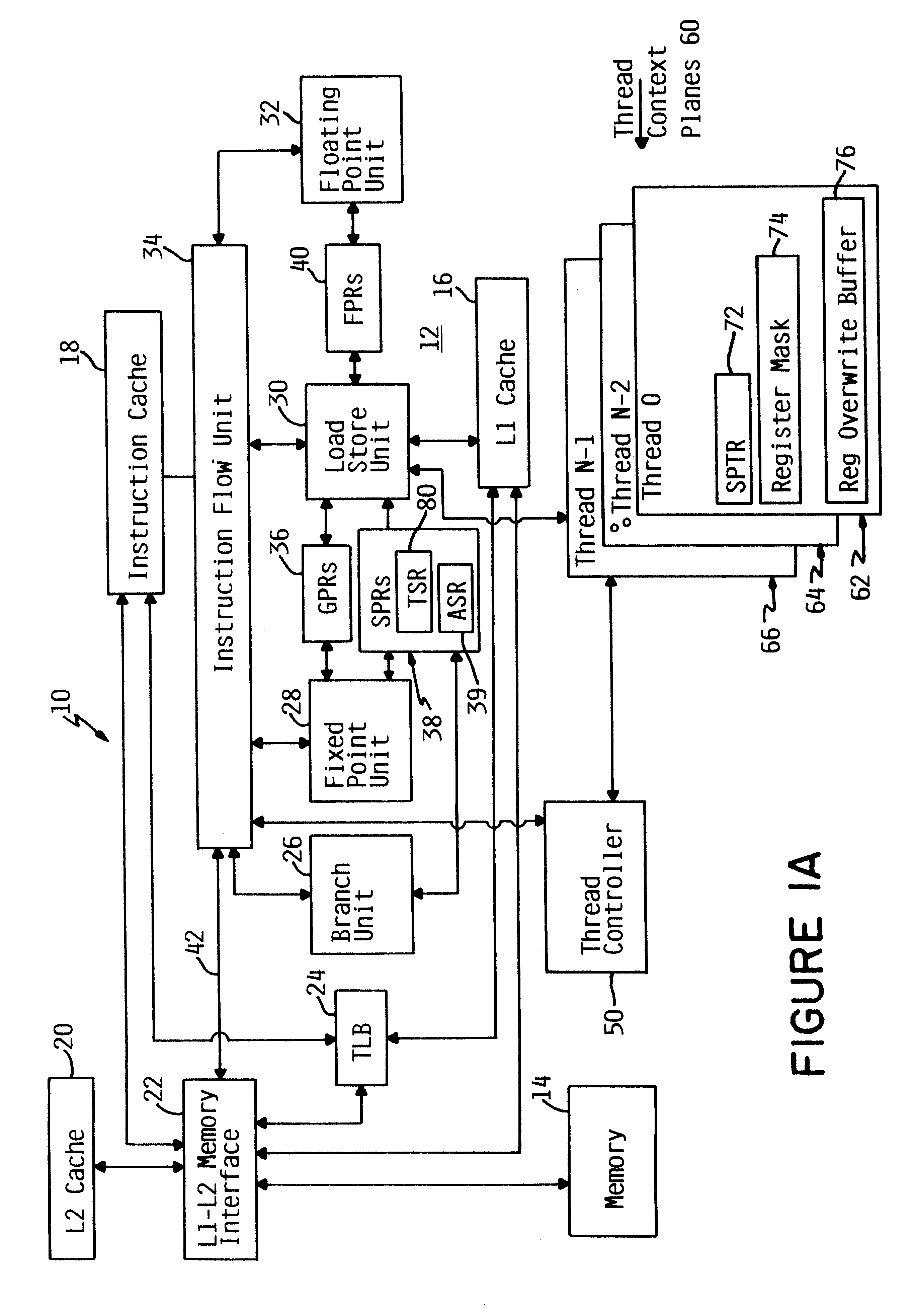
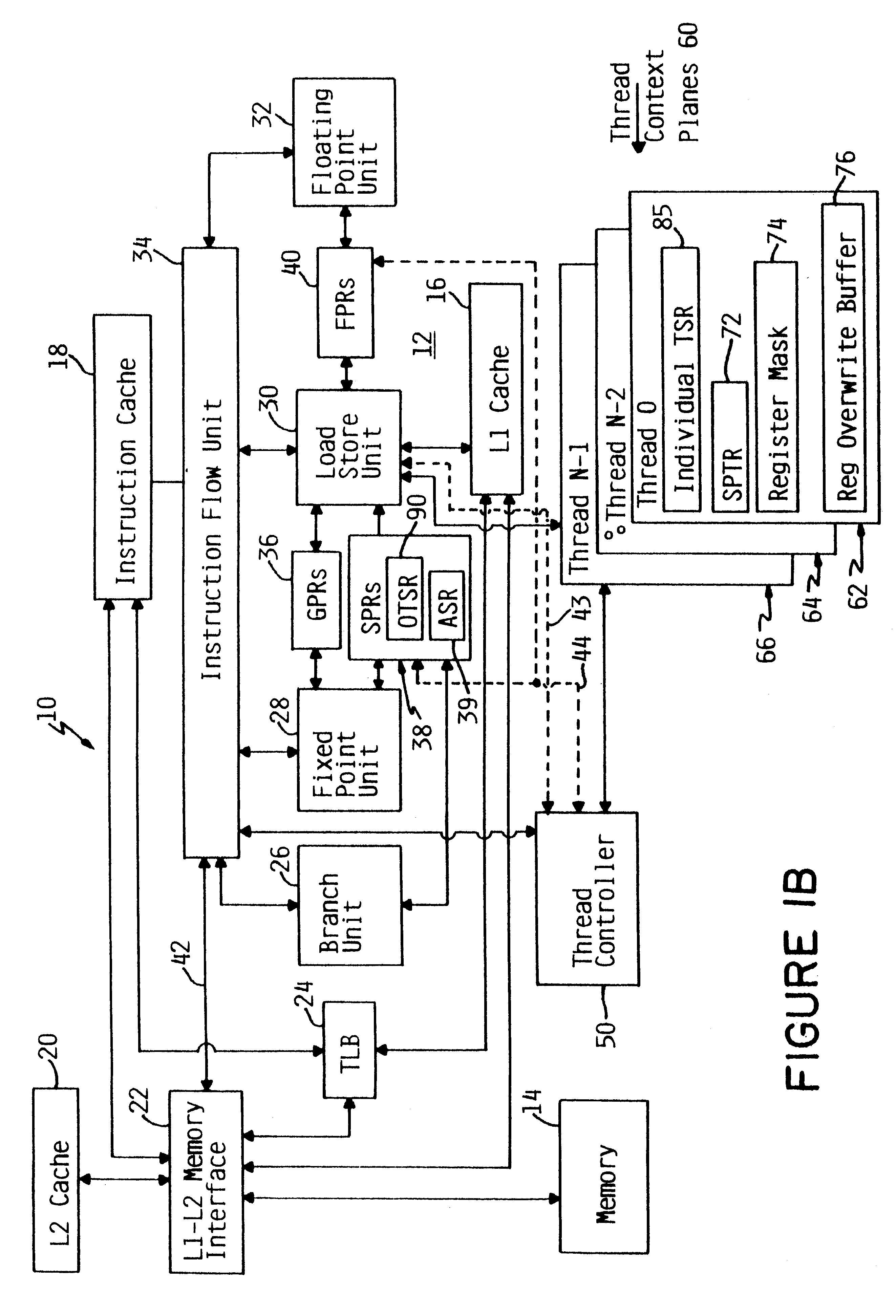
Apparatus and method for retrofitting multi-threaded operations on a computer by partitioning and overlapping registers
InactiveUS6233599B1Improve multithreading performance of processorImprove performanceResource allocationDigital computer detailsGeneral purposeProcessor register
An apparatus and method for performing multithreaded operations includes partitioning the general purpose and / or floating point processor registers into register subsets, including overlapping register subsets, allocating the register subsets to the threads, and managing the register subsets during thread switching. Register overwrite buffers preserve thread resources in overlapping registers during the thread switching process. Thread resources are loaded into the corresponding register subsets or, when overlapping register subsets are employed, into either the corresponding register subset or the corresponding register overwrite buffer. A thread status register is utilized by a thread controller to keep track of READY / NOT-READY threads, the active thread, and whether single-thread or multithread operations are permitted. Furthermore, the registers in the register subsets include a thread identifier field to identify the corresponding thread. Register masks may also be used to identify which registers belong to the various register subsets.
Owner:IBM CORP
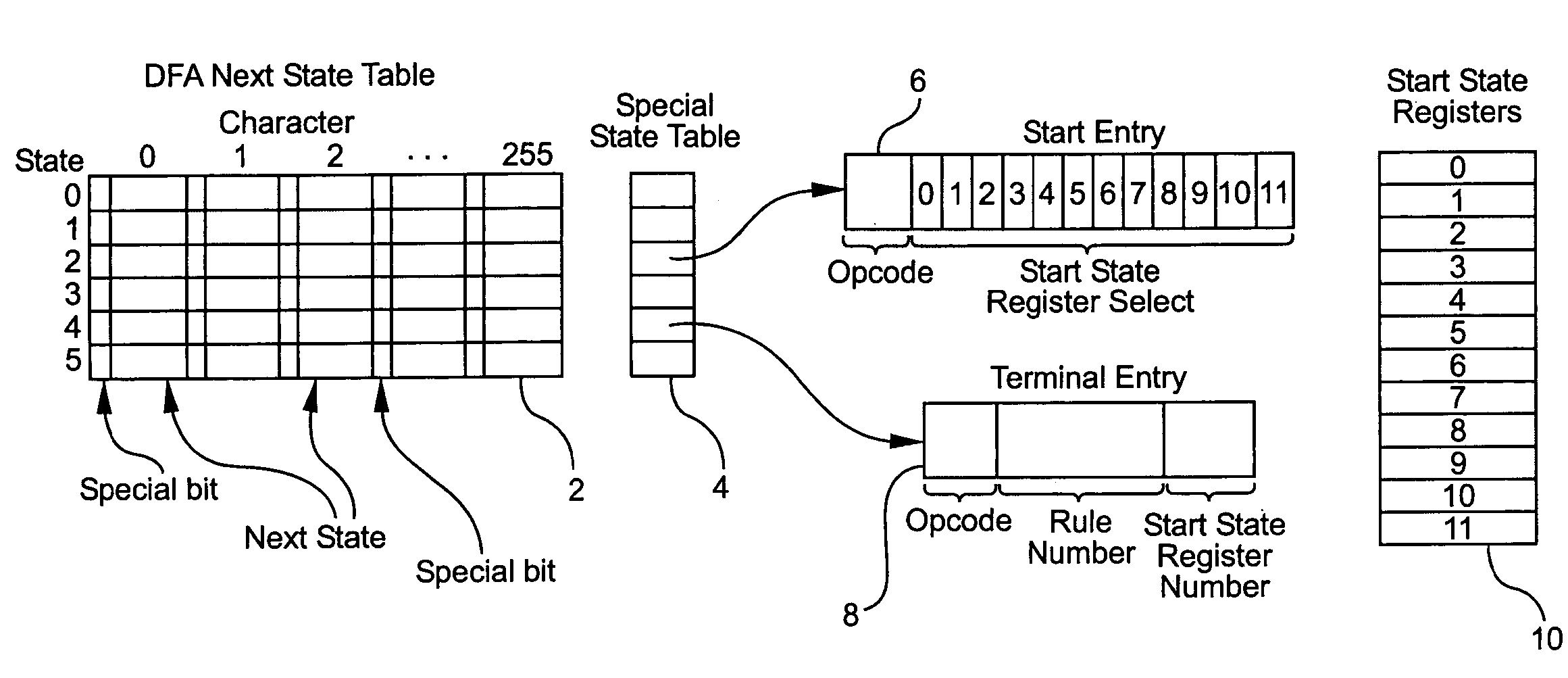
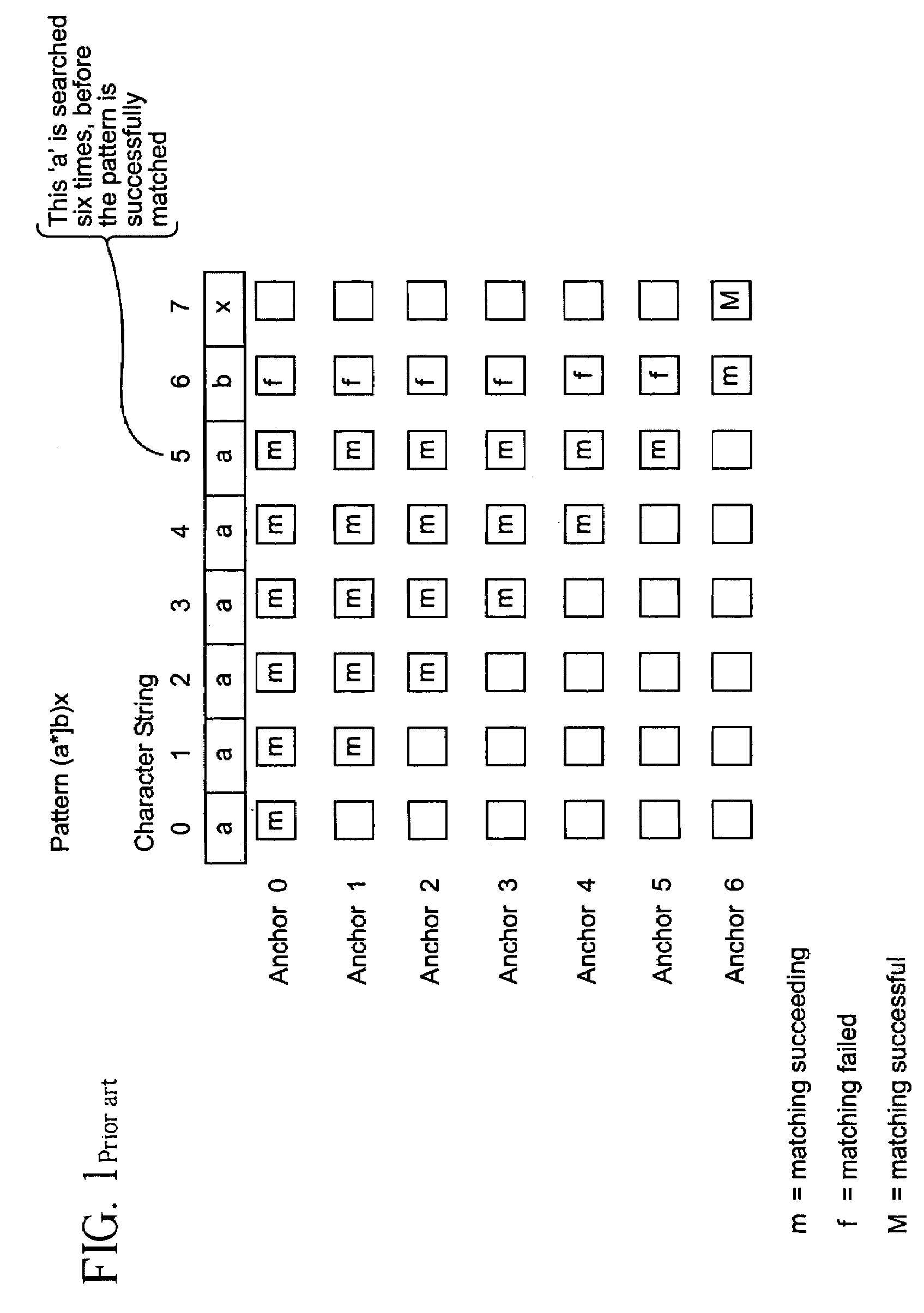
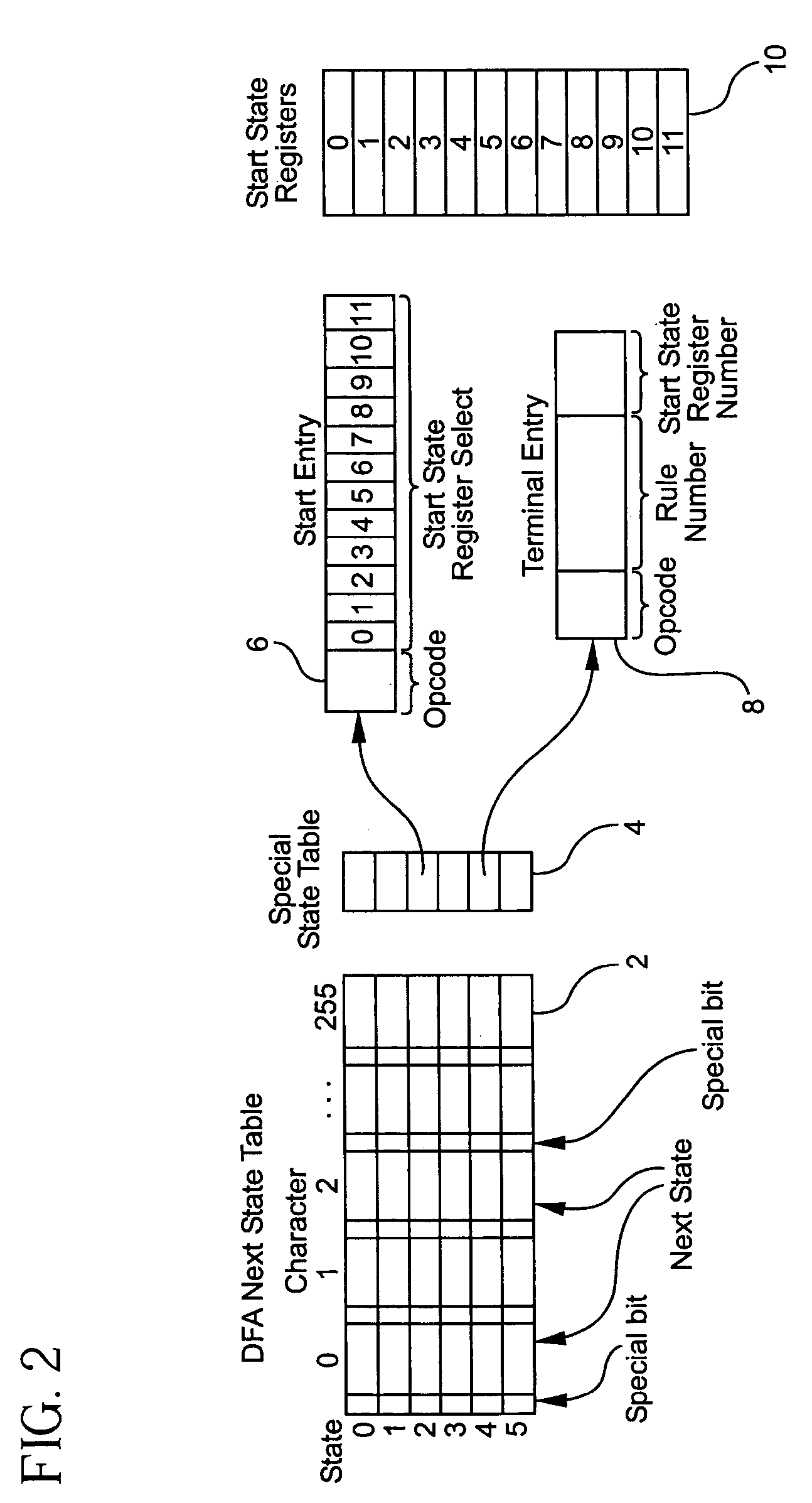
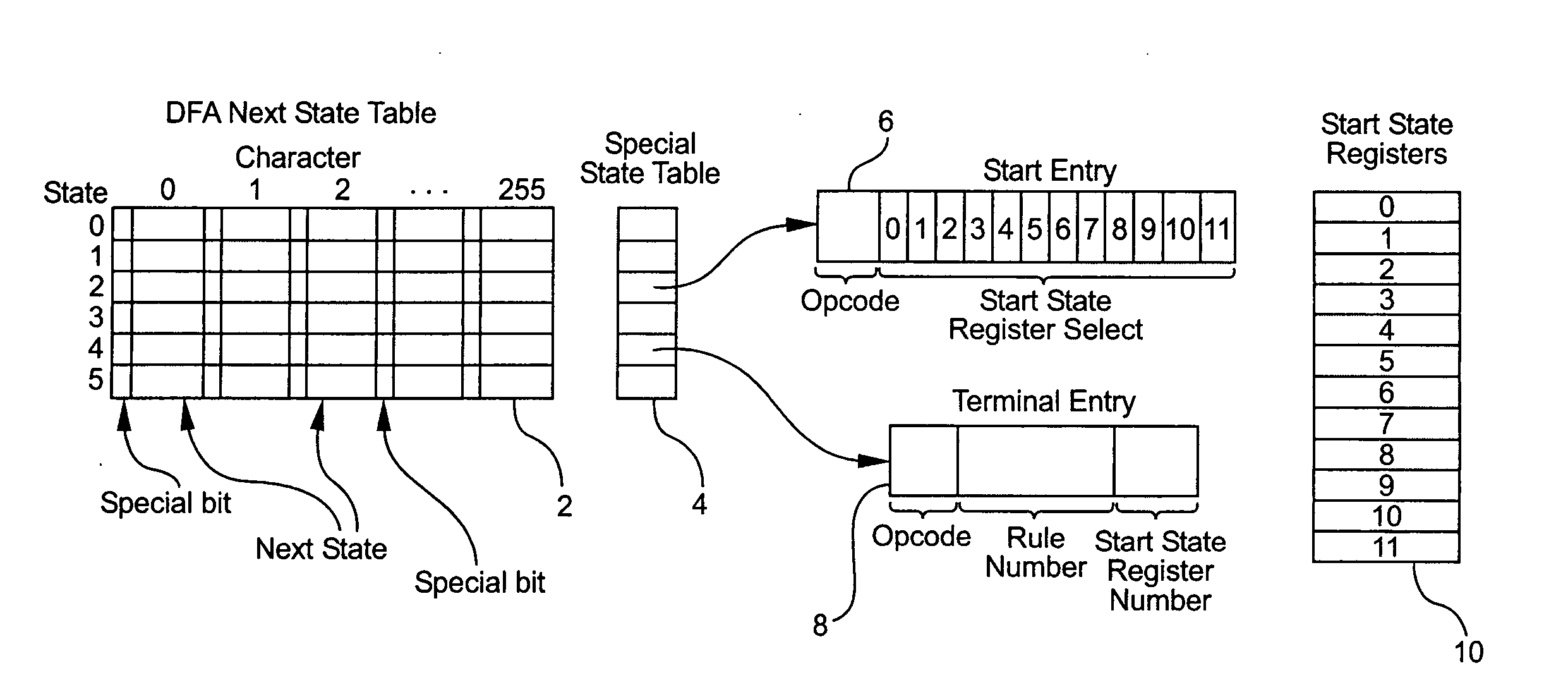
System and method for determining the start of a match of a regular expression
InactiveUS7305391B2Overcome disadvantagesDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsProcessor registerTheoretical computer science
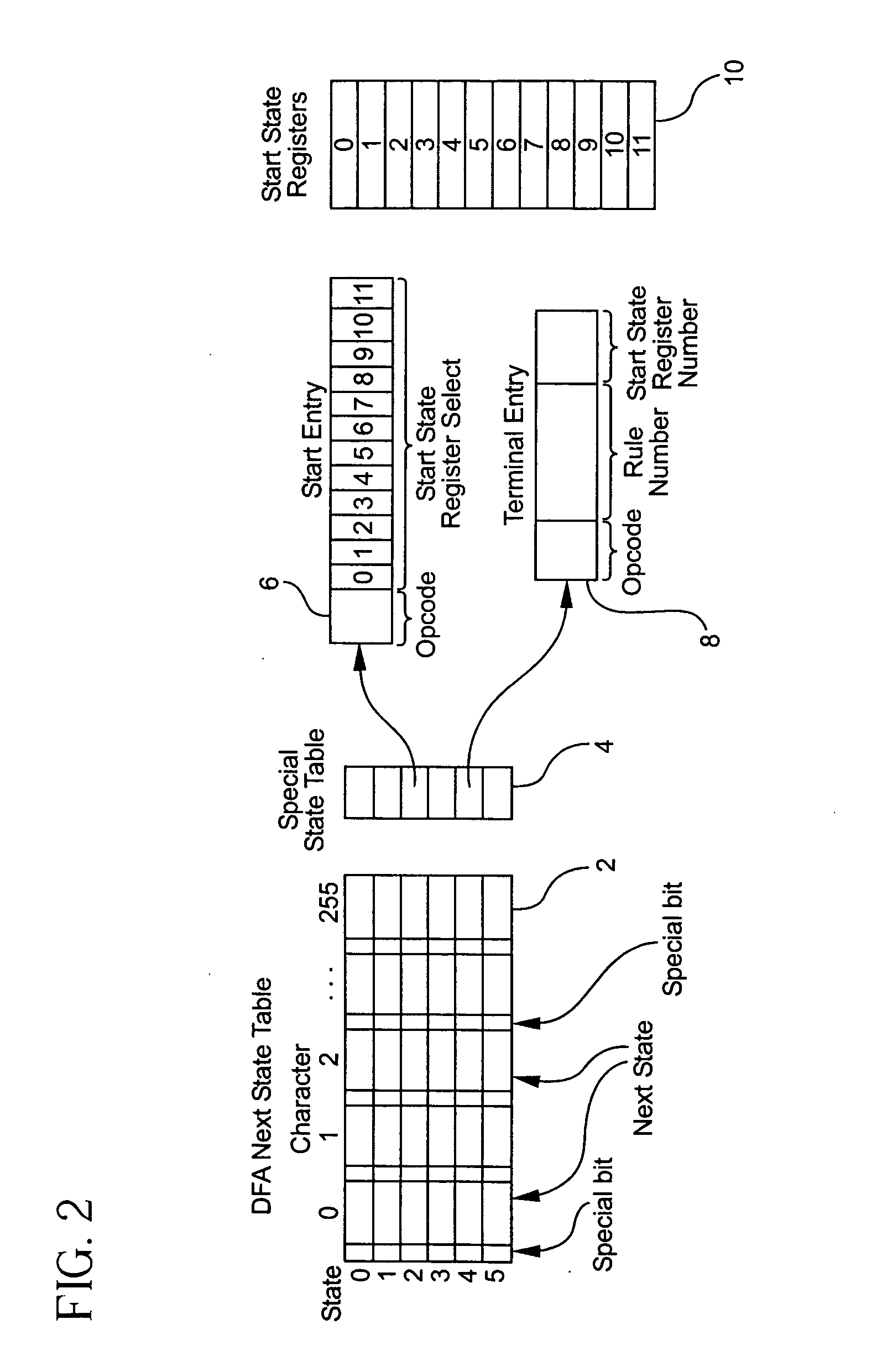
A method for determining the start of a match of a regular expression using the special state table, the set of start state registers and the DFA next state table, includes the step of determining from the regular expression each start-of-match start state and each end-of-match terminal state. For each start state, a start state entry is loaded into the special state table. For each terminal state, a terminal state entry is loaded into each special state table. The next state table is used to return the next state from the current state and an input character. When a start state is encountered, the current offset from the beginning of the input character string is loaded into the start state register. When a terminal state is encountered, the terminal state entry is retrieved from the special state table, and the value of the start state register corresponding to the rule number of the terminal entry in the special state table is further retrieved. The value of the start state register which is retrieved indicates the location in the character string where the start-of-match occurred for a particular rule.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
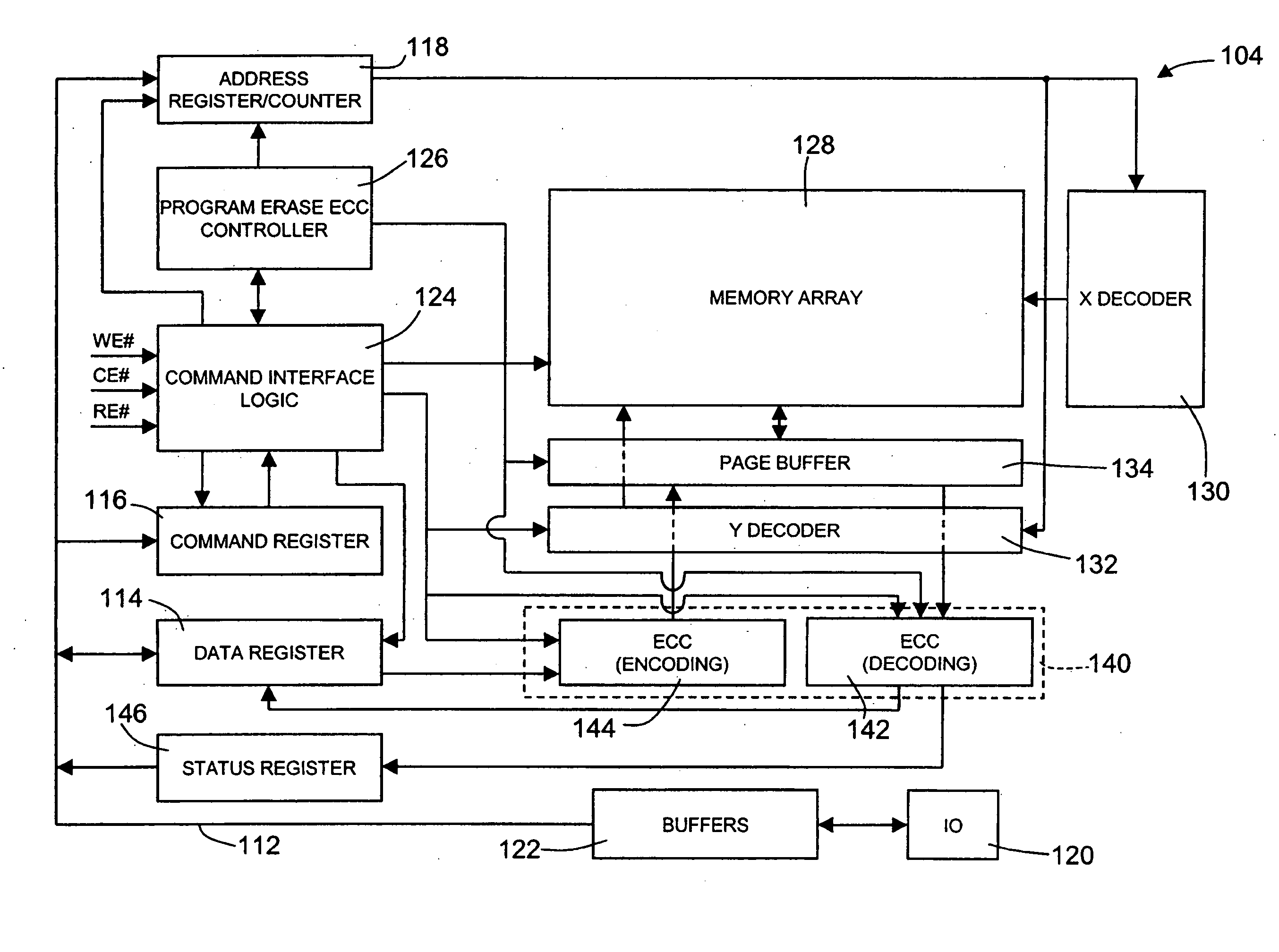
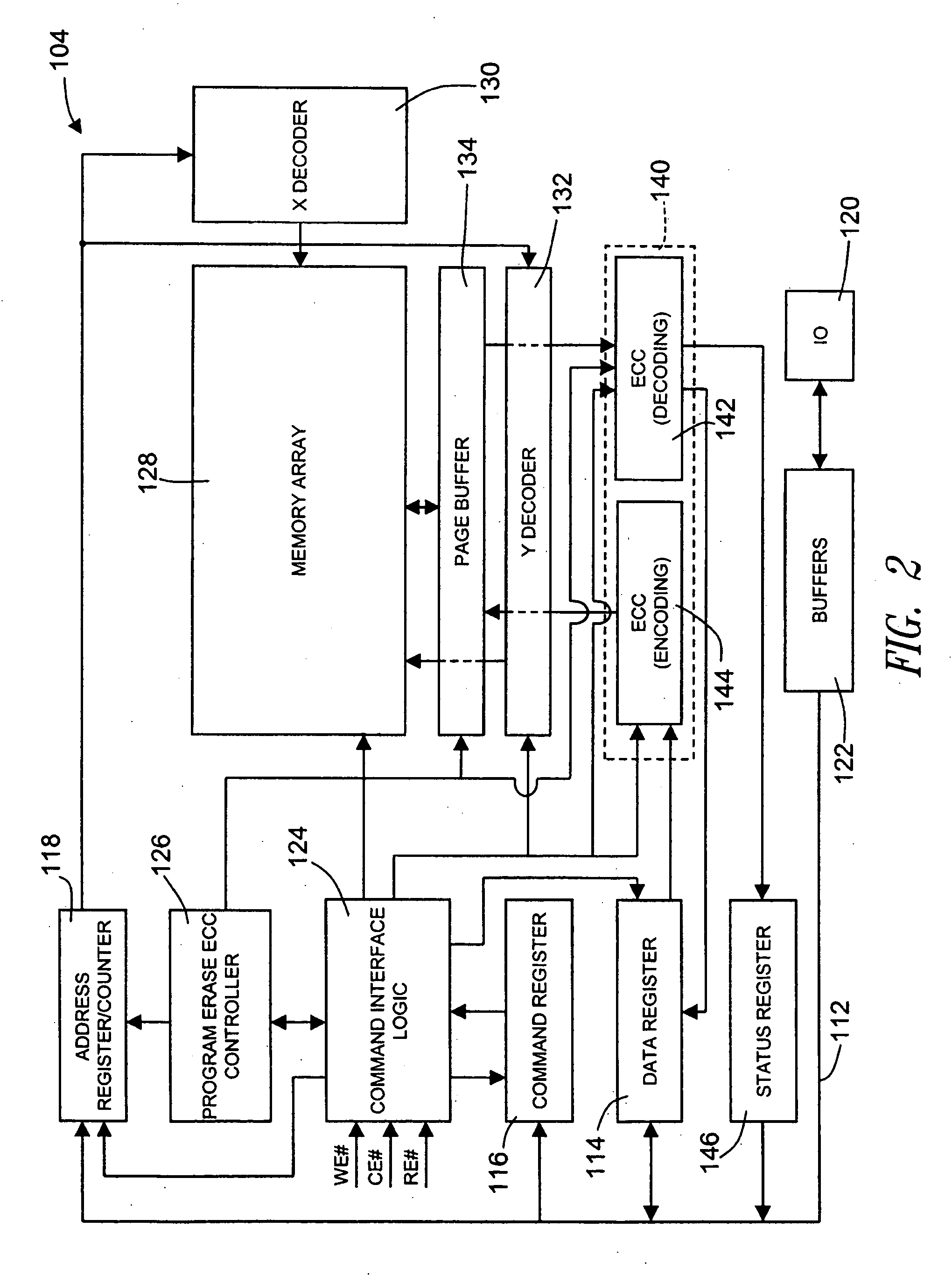
Memory with embedded error correction codes
A memory has one bus for data, addresses, and commands. A data register is coupled to the bus to store the data written to and read from the memory, a command register is coupled to the bus for receiving memory commands, and an address register is coupled to the bus to address the memory. The memory also includes an Error Correction Code circuit for calculating an ECC. The memory is configured to be responsive to external commands for controlling the operation of the ECC circuit for reading or writing of the ECC that are separate from external commands controlling reads or writes of the memory data. The memory may also include a status register that stores information regarding the passing or failing of the ECC.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
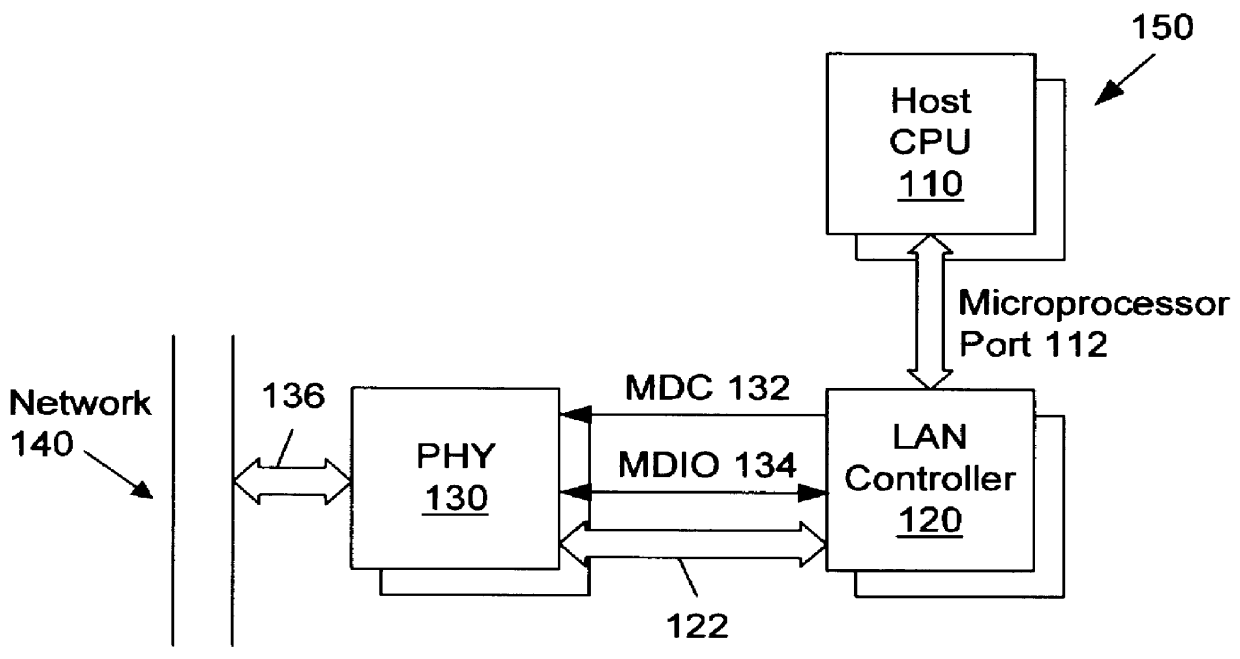
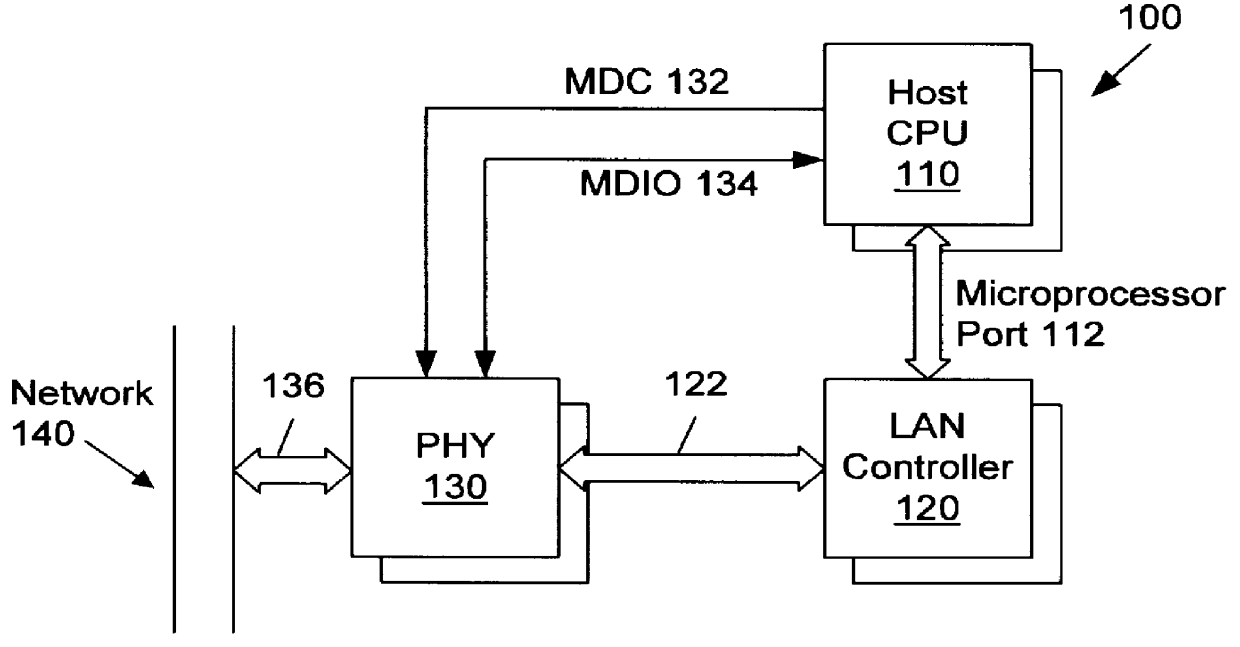
Auto-polling unit for interrupt generation in a network interface device
A system and method for auto-polling a status register within a physical layer (PHY) interface to a local area network (LAN). The system includes a host CPU which needs to detect and service interrupts generated by a PHY device on the LAN which is coupled between a first transmission medium (such as copper or fiber cable) and a management interface to the system. The system further includes an auto-polling unit which monitors activity on the management interface of the PHY device. When the auto-polling unit detects a lack of activity on the management interface of the PHY for a predetermined interval, the auto-polling unit reads a first value from the PHY status register. This first status value is then compared to a previously stored value which corresponds to the last PHY status value read by the host CPU. If a mismatch is detected between these two values, an interrupt is generated to the CPU. In response to receiving the interrupt, auto-polling is suspended (to avoid changing the status data that caused the interrupt) and the CPU requests a read of the status value in the first register. In this manner, the CPU is able to access the status value which caused the interrupt and determine the appropriate course of action. This status read by the CPU also has the effect of clearing the interrupt. This system frees the CPU from having to continually poll the PHY status register to determine if a change in status has occurred.
Owner:JATO TECH
Method of self-synchronization of configurable elements of a programmable module
InactiveUS6542998B1Generating/distributing signalsTransmission path multiple useIndependent elementComputer architecture
A method which permits self-synchronization of elements to be synchronized. Synchronization is neither implemented nor managed by a central entity. By shifting synchronization into each element, more synchronization tasks can also be performed simultaneously, because independent elements no longer interfere with one another when accessing the central synchronization entity. In a module with a two- or multi-dimensionally arranged programmable cell structure, each configurable element can access the configuration and status register of other configurable elements over an interconnecting structure and thus can have an active influence on their function and operation. The configuration can thus be accomplished by a load logic from a processing array.
Owner:SCIENTIA SOL MENTIS AG
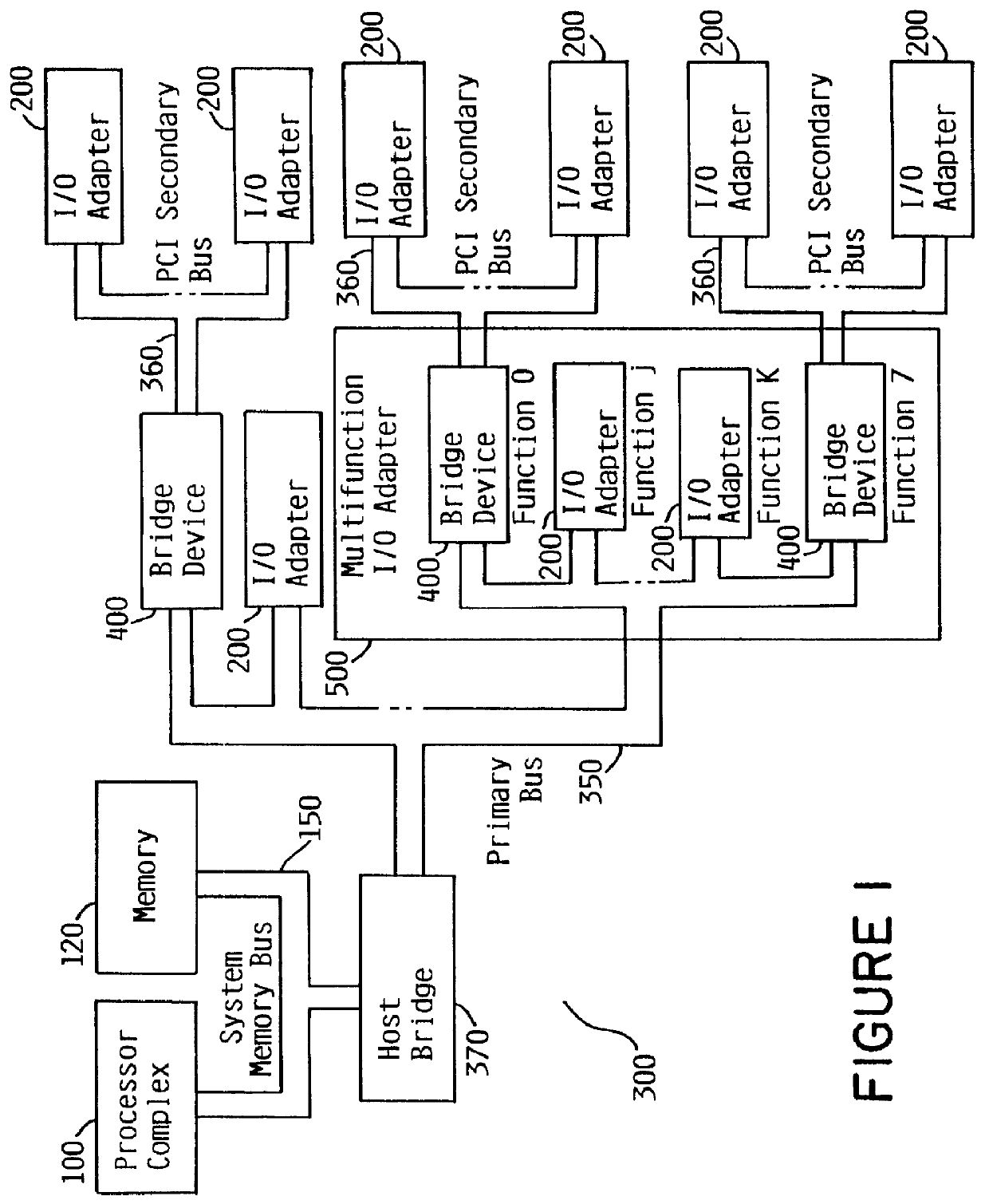
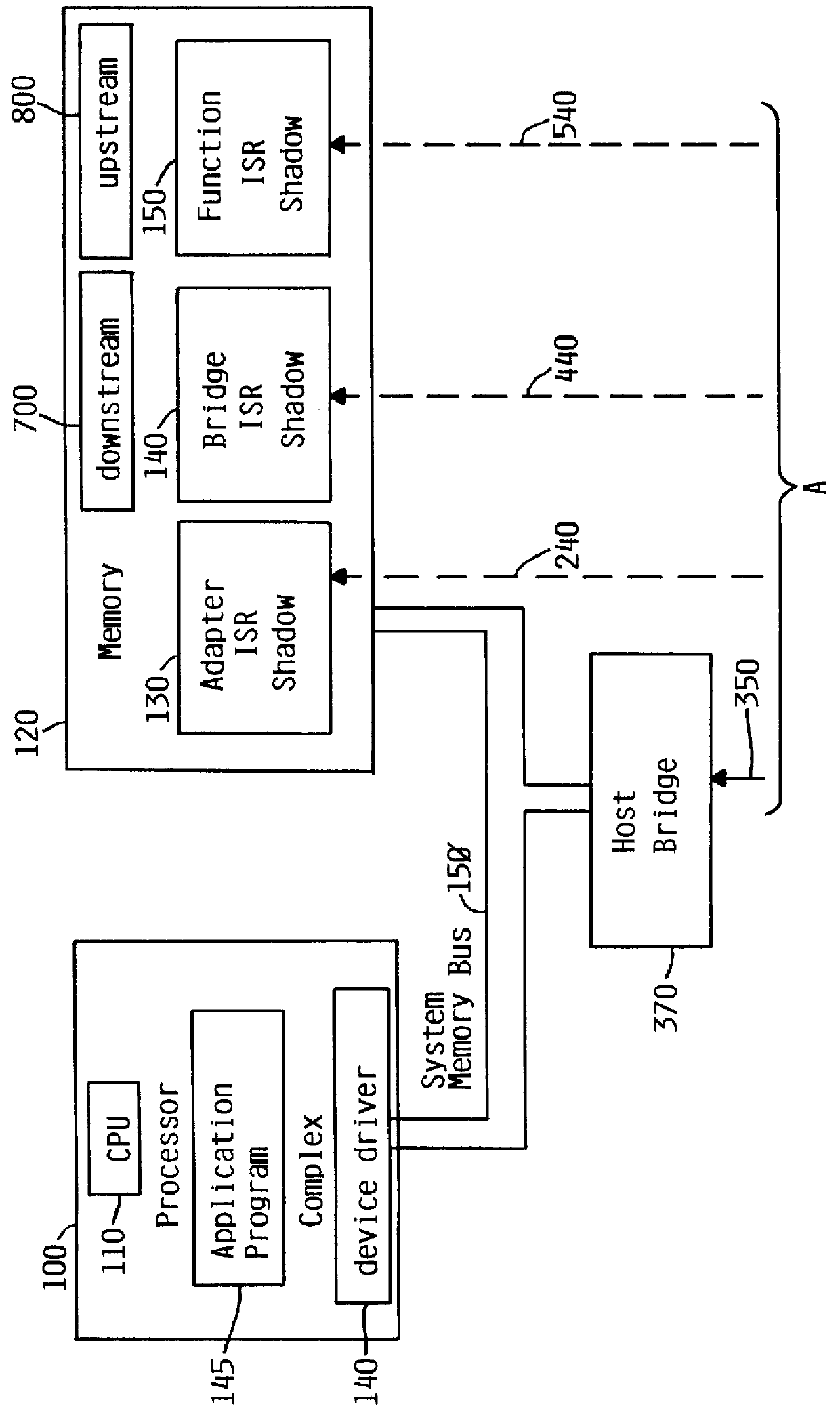
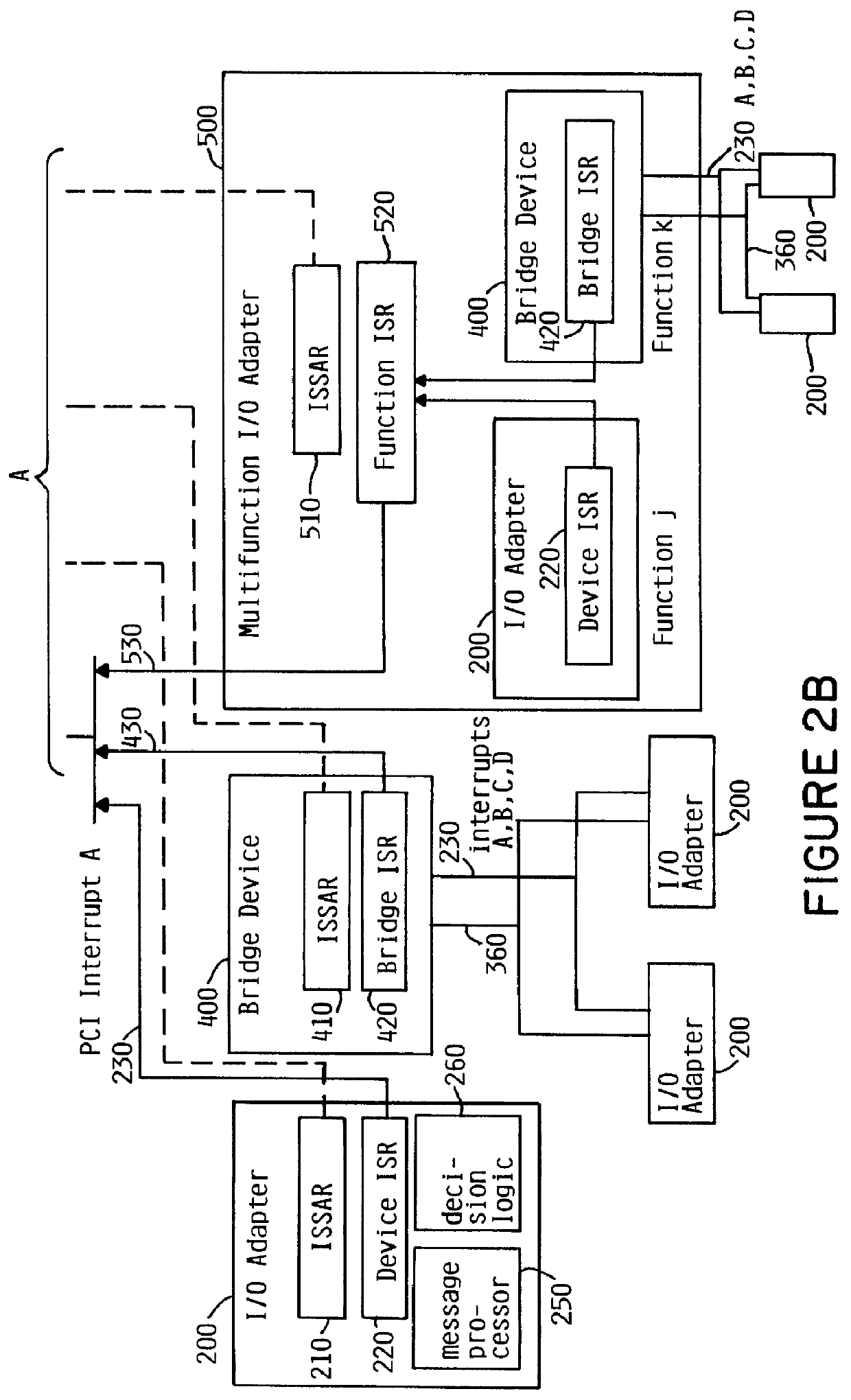
System for determining adapter interrupt status where interrupt is sent to host after operating status stored in register is shadowed to host memory
InactiveUS6078970AMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsProcessor registerHost memory
An I / O adapter connects an I / O adapter to an I / O bus and includes a device interrupt status register and an interrupt status shadow address register. The device interrupt status register stores the interrupt status of the I / O adapter. The I / O adapter accesses the interrupt status shadow address register to determine an address of main memory at which the device interrupt status register is shadowed. After shadowing the interrupt status, the I / O adapter interrupts the processor complex which may then access local, main memory to determine the interrupt status. A multifunction I / O adapter permits a plurality of I / O adapters to be connected thereto and includes a function interrupt status register to summarize the interrupt status of all the I / O adapters attached thereto. After shadowing the summarized interrupt status, the multifunction I / O adapter interrupts the processor complex which may then access local, main memory to determine the interrupt status.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
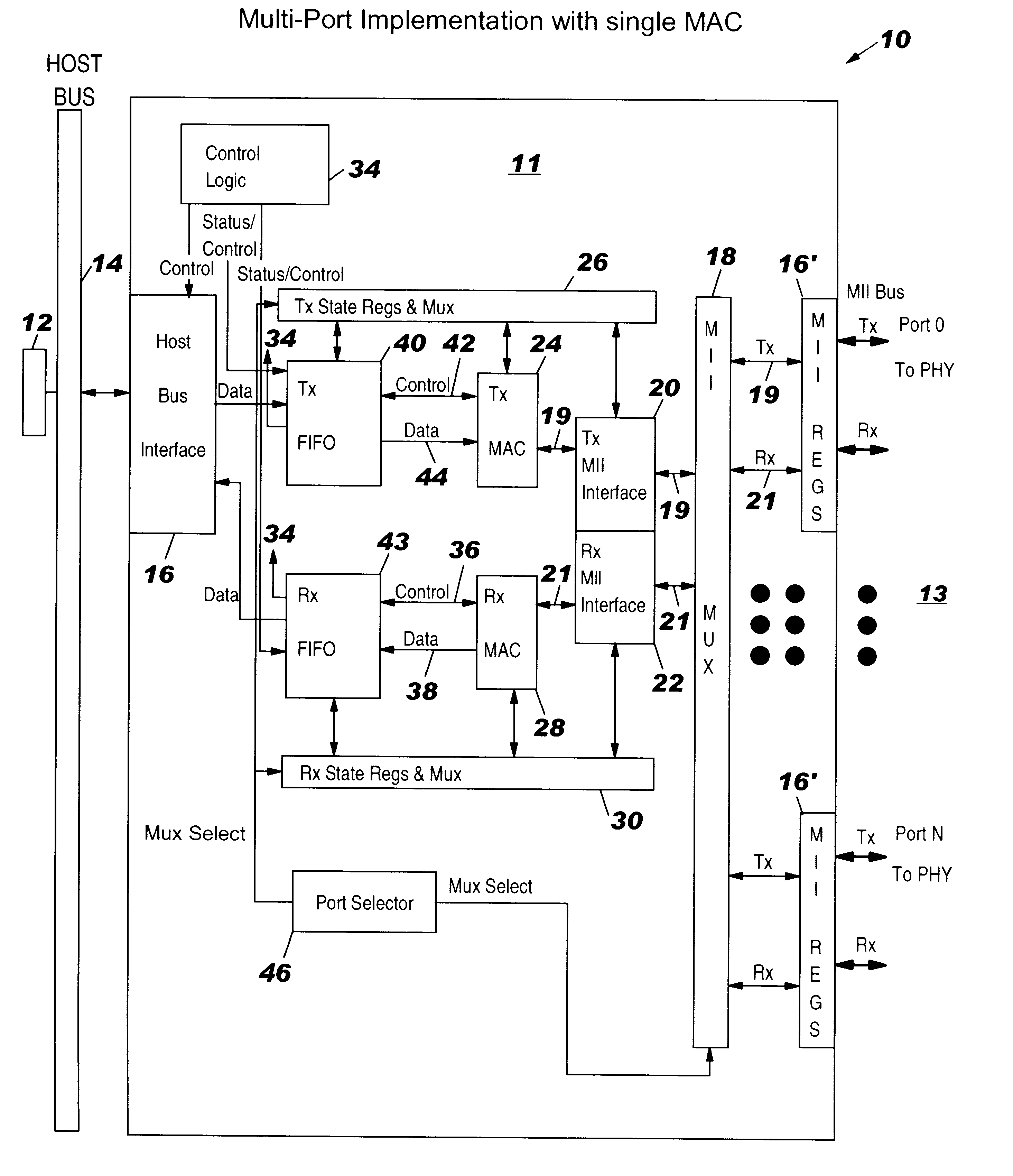
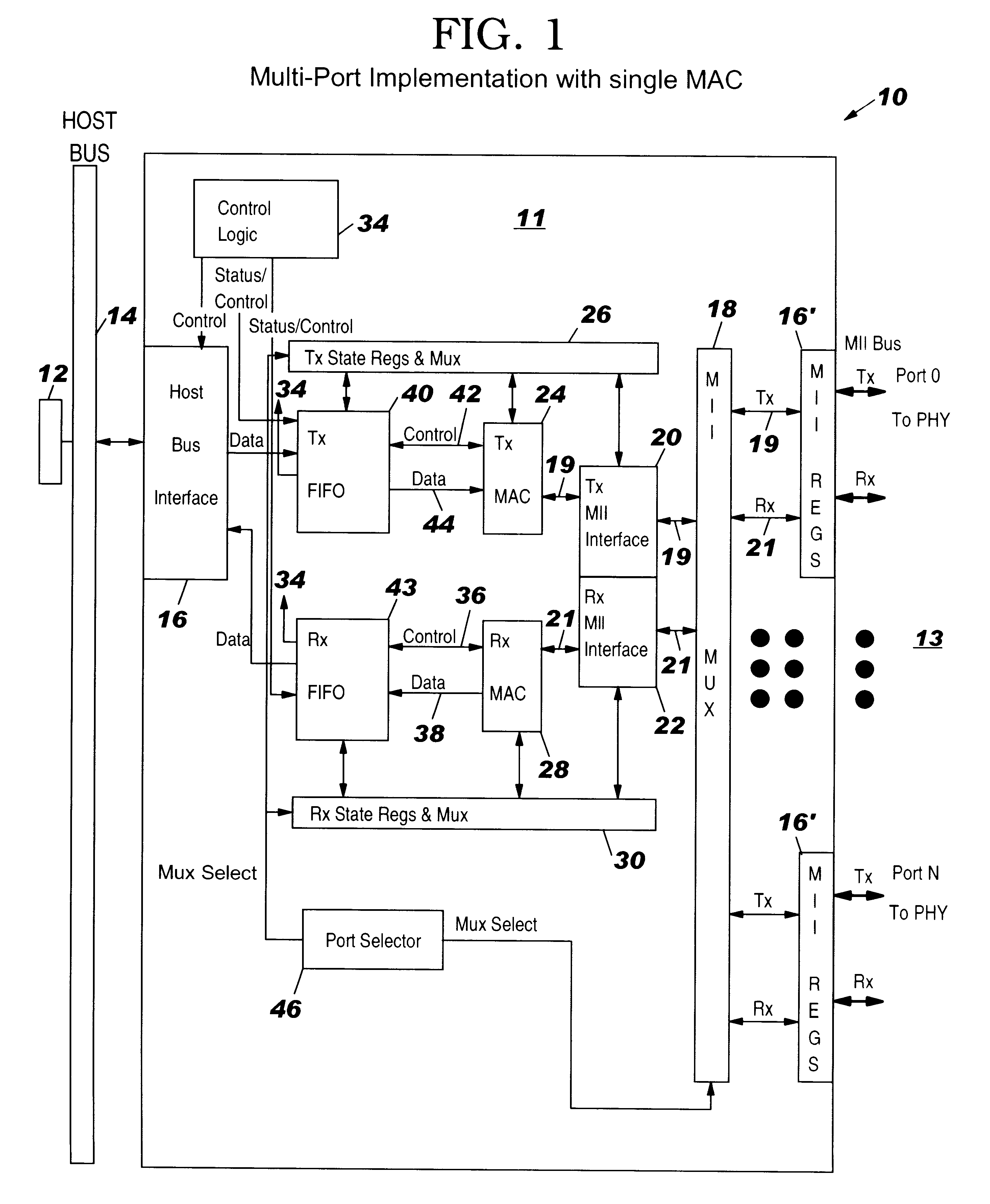
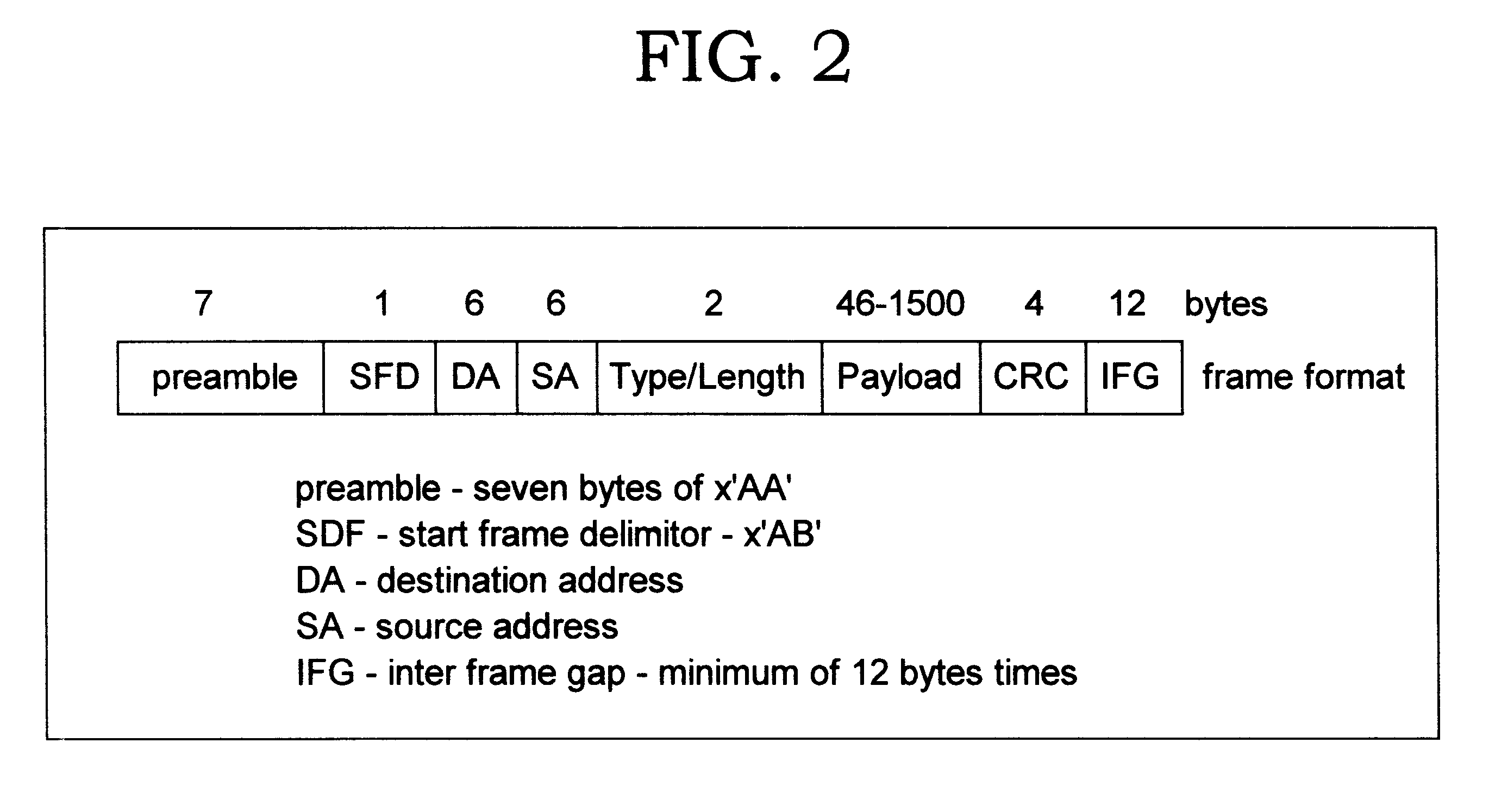
Architecture for a multi-port adapter with a single media access control (MAC)
InactiveUS6373848B1Data switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsBus interfaceMulti port
A multi-port adapter having a single MAC chip has reduced logic circuits for transferring data between a host system and a TDM communication system. The MAC chip includes a transmit MAC and a receive MAC, each coupled at one end to a port multiplexer through an interface and at the other end to respective storage registers. The port multiplexer is coupled to the Physical Layer of each port. Transmit and receive state registers track the state of each port in the transfer of data in the transmit and receive directions. The storage registers are coupled through a host bus interface to a host bus and to the host system. Control logic is coupled to the storage register to control the transfer of data between the system and the storage registers. A port selector coupled between the multiplexer and the transmit and receive state registers selects ports for transfer of data in succession. On each chip clock cycle, the port selector selects a state machine register to determine the state of the MACs for processing the data and a section of the FIFO's to write or read data for the selected port. At the end of the cycle, the state registers are set and stay set until selected again. The process repeats for each port in a cyclic manner. Once data is accumulated in the receive storage register, control logic reads the data of the host bus. Once space is available in the transmit storage register, the control logic writes data from the host system to the transmit storage register.
Owner:IBM CORP
Protocol for Transitioning In and Out of Zero-Power State
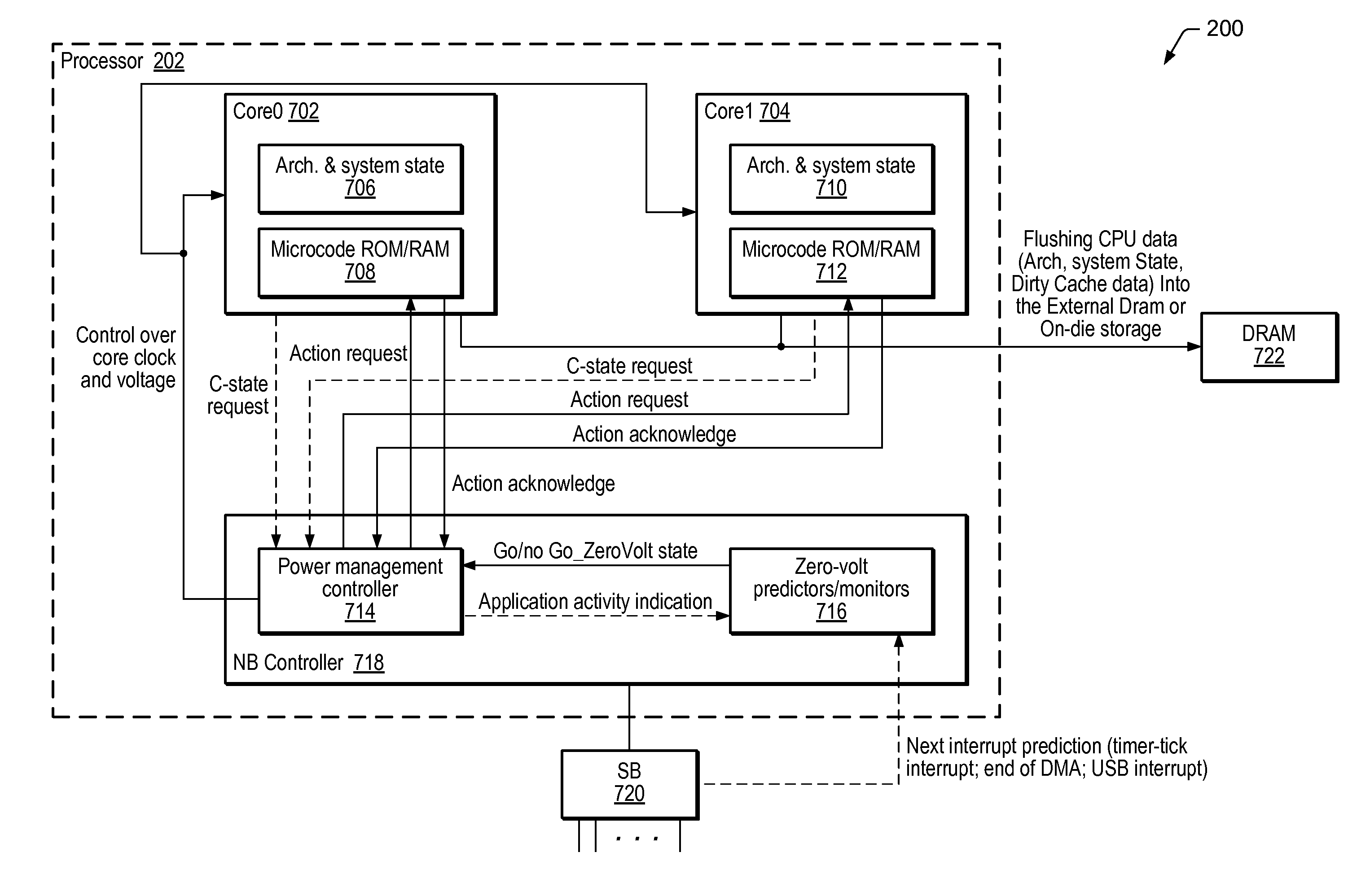
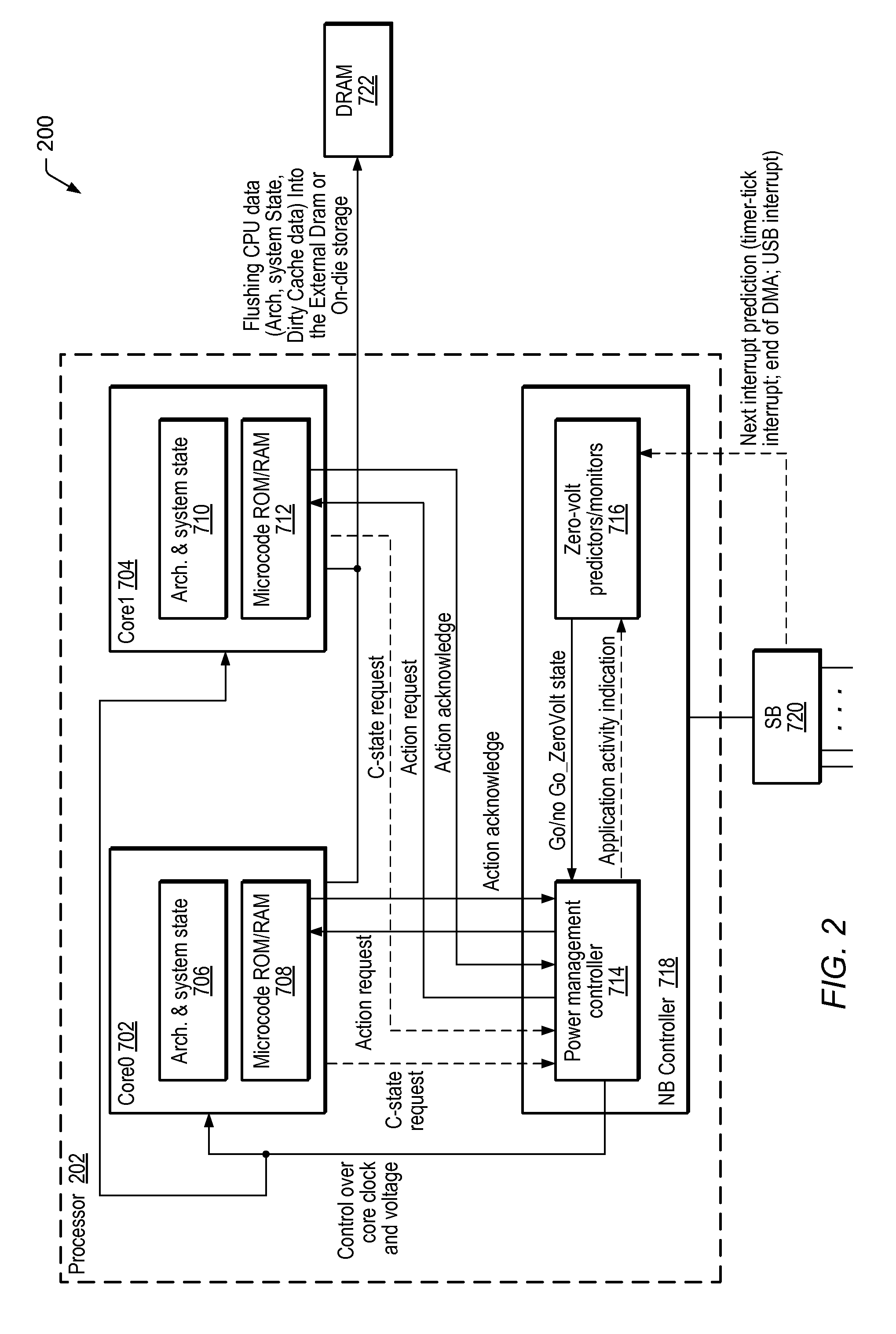
A processor may comprise one or more cores, where each respective core may comprise one or more state registers, and non-volatile memory configured to store microcode instructions executed by the respective processor core. The processor may further comprise a power management controller (PMC) interfacing with each respective core, and a state monitor (SM) interfacing with the PMC. The PMC may be configured to communicate with each respective core, such that microcode executed by the respective processor core may recognize when a request is made to transition the respective core to a low-power state. The microcode may communicate the request to the PMC, which may in turn determine if the request is for the respective core to transition to a zero-power state. If it is, the PMC may communicate with the SM to determine whether to transition the respective processor core to the zero-power state, and initiate transition to the zero-power state if a determination to transition to the zero-power state is made.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Method for way allocation and way locking in a cache
ActiveUS20100250856A1Small sizeEnergy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGraphicsGraphics processing unit
A system and method for data allocation in a shared cache memory of a computing system are contemplated. Each cache way of a shared set-associative cache is accessible to multiple sources, such as one or more processor cores, a graphics processing unit (GPU), an input / output (I / O) device, or multiple different software threads. A shared cache controller enables or disables access separately to each of the cache ways based upon the corresponding source of a received memory request. One or more configuration and status registers (CSRs) store encoded values used to alter accessibility to each of the shared cache ways. The control of the accessibility of the shared cache ways via altering stored values in the CSRs may be used to create a pseudo-RAM structure within the shared cache and to progressively reduce the size of the shared cache during a power-down sequence while the shared cache continues operation.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
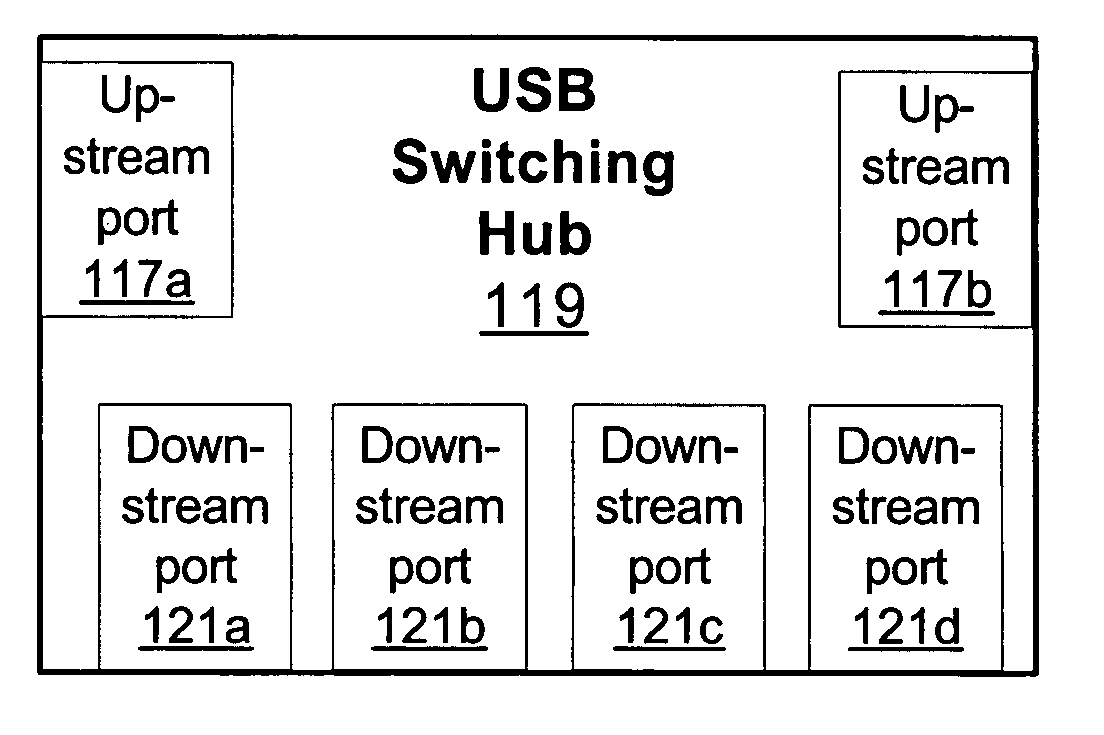
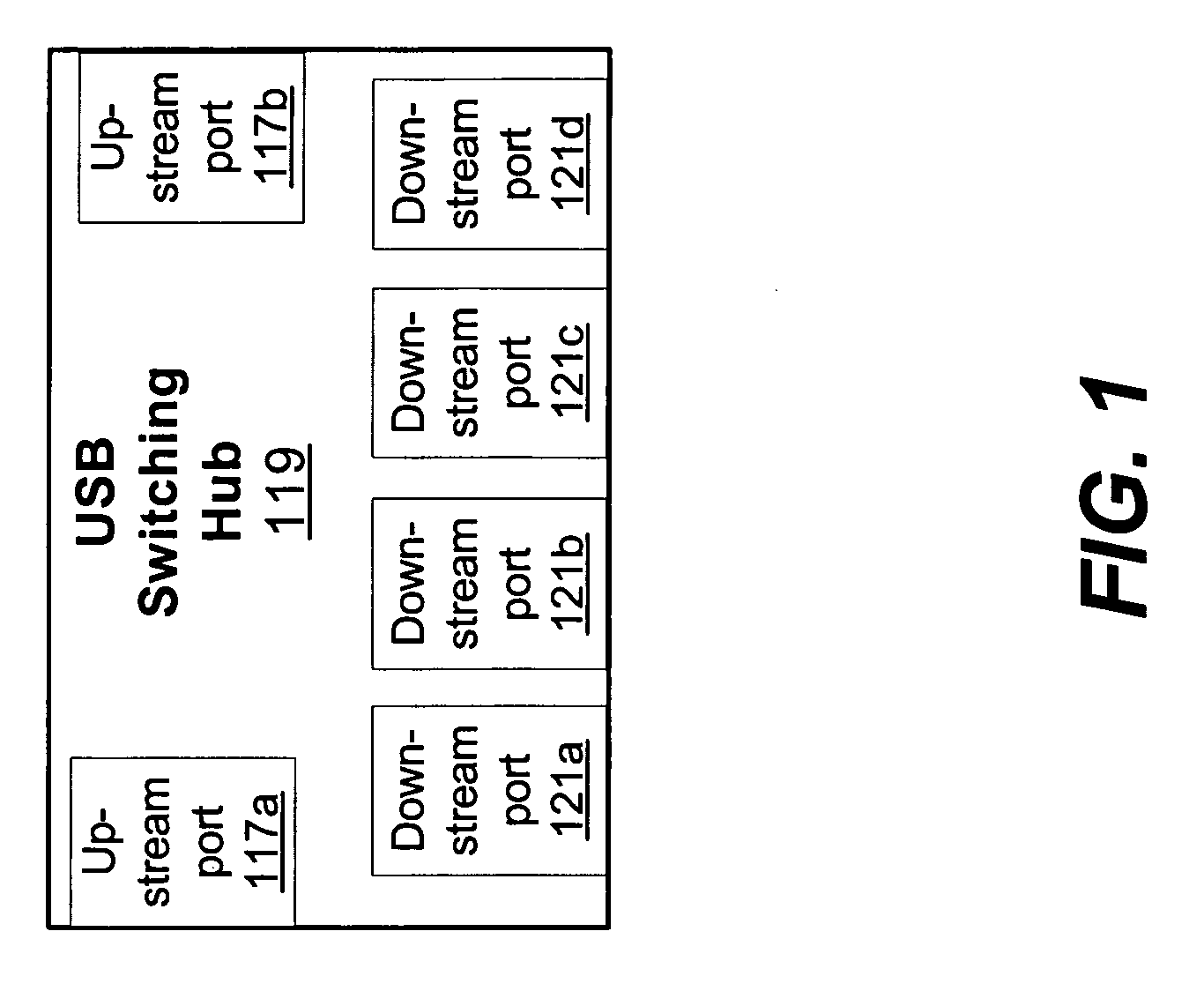
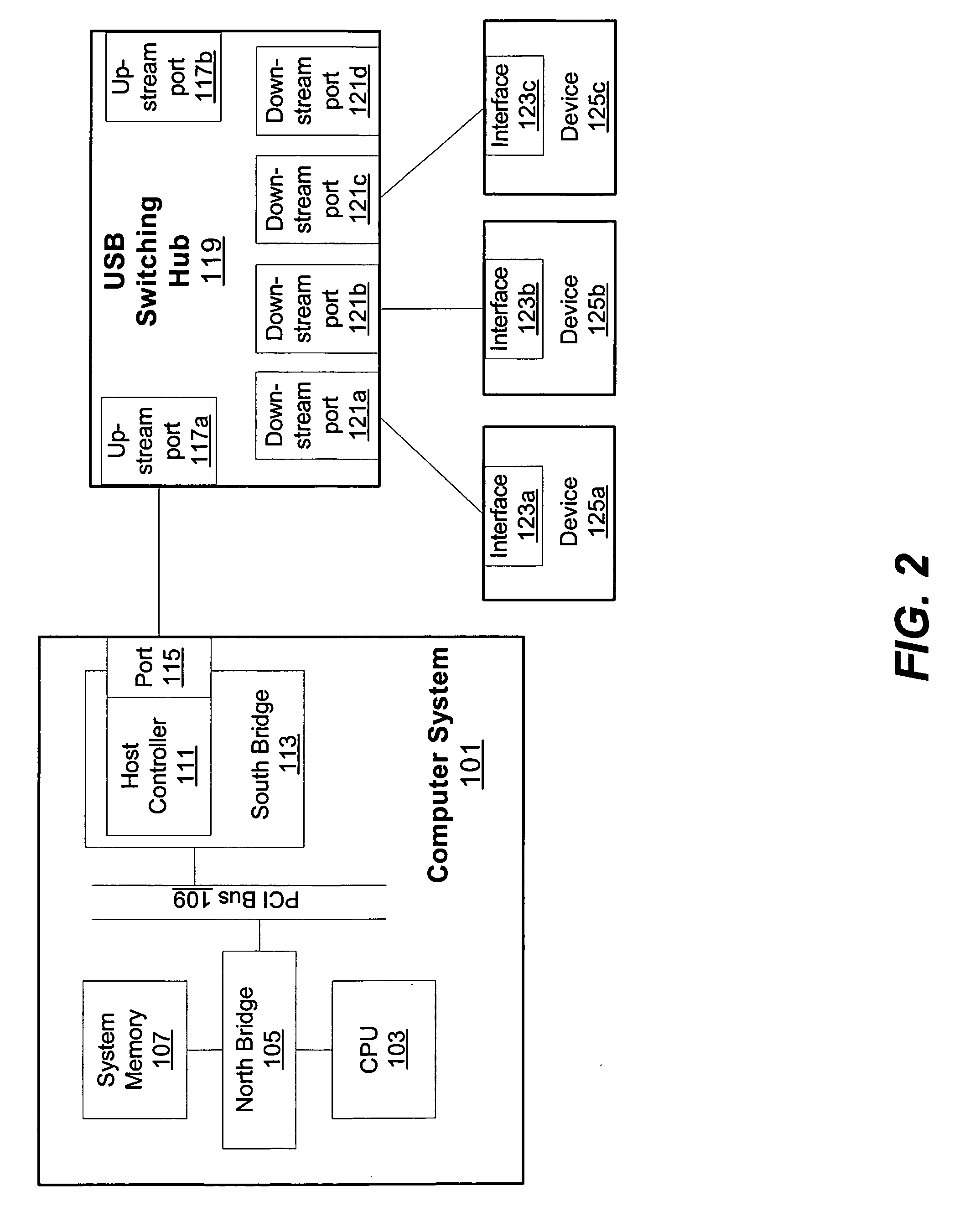
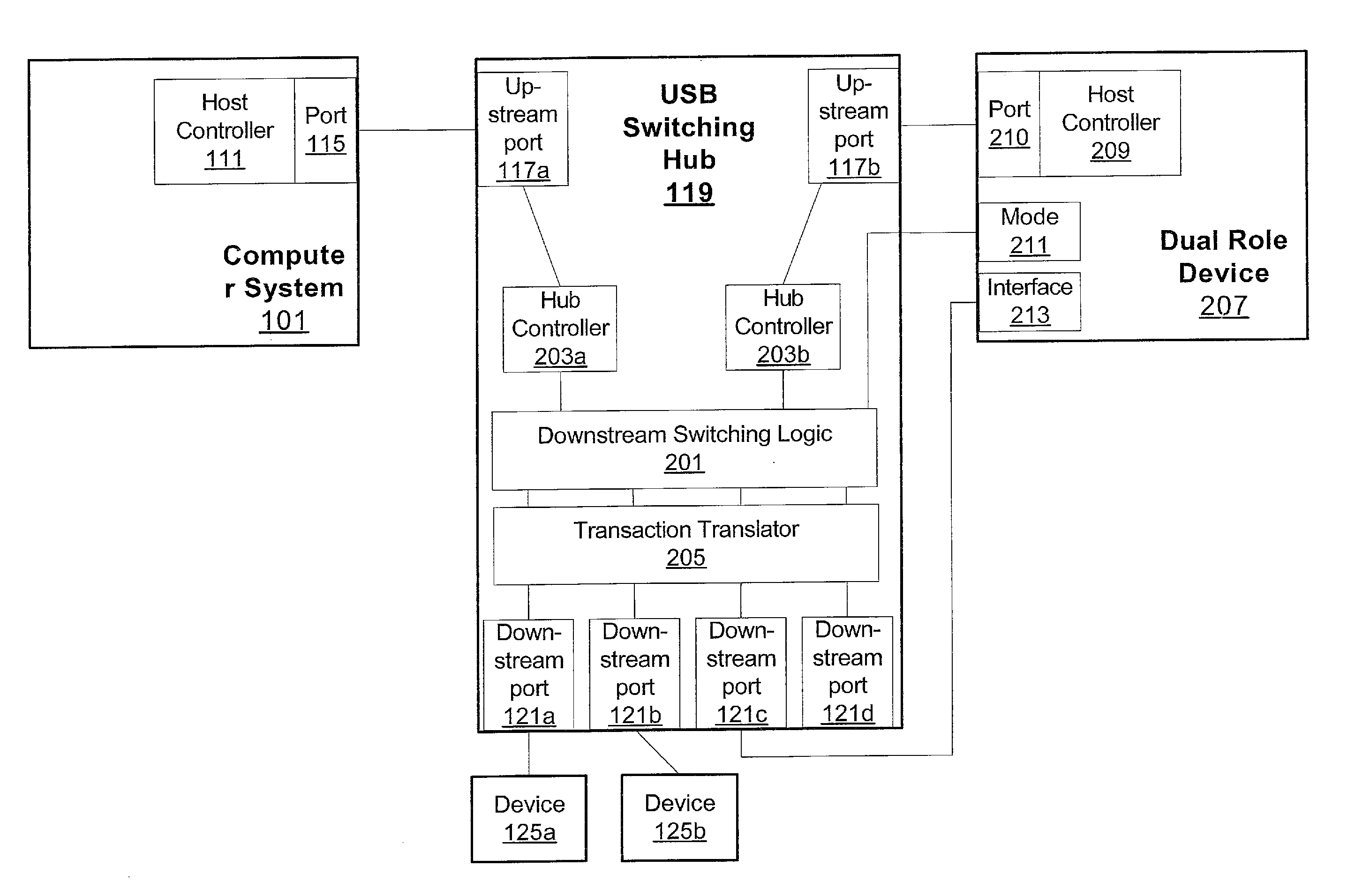
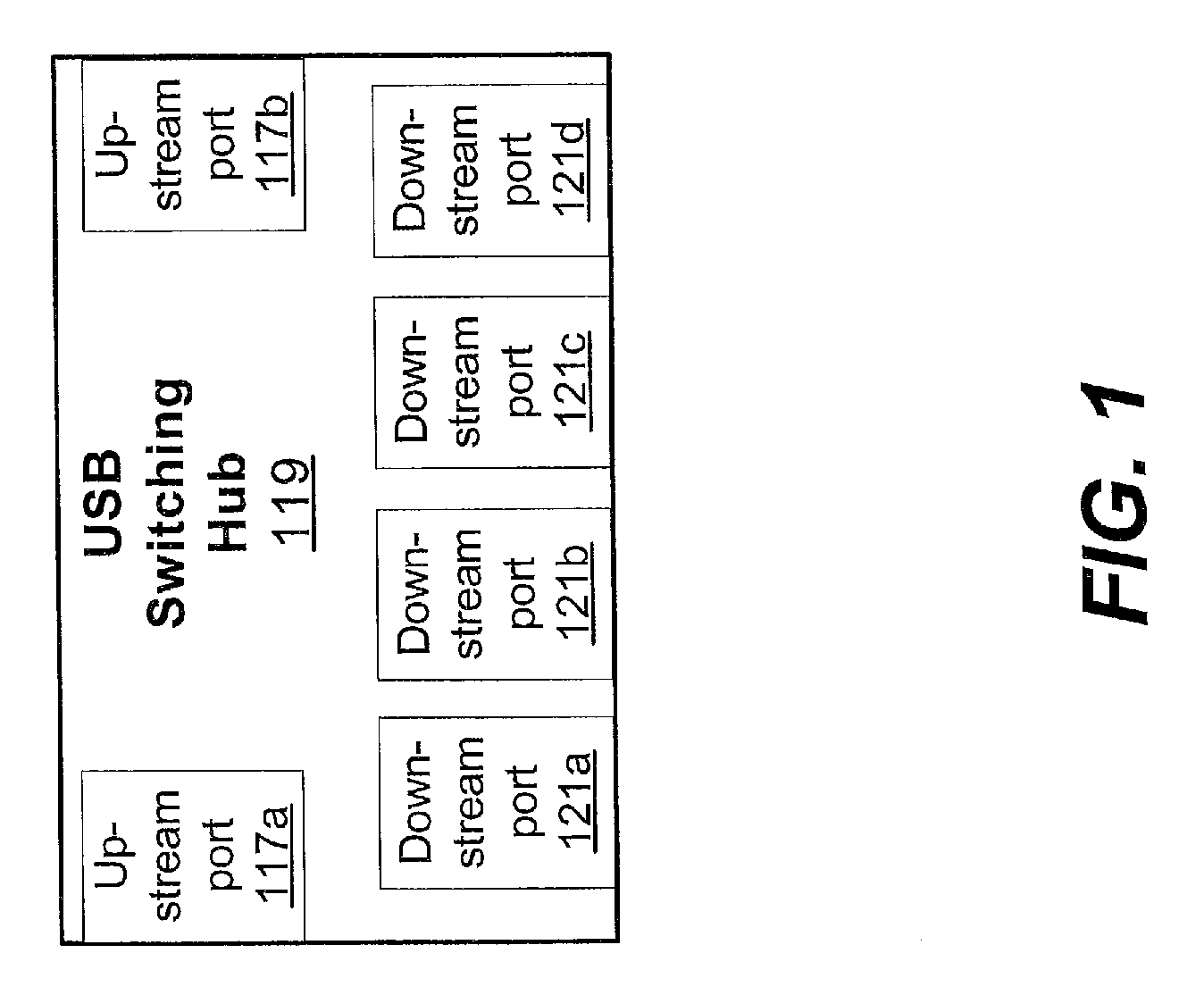
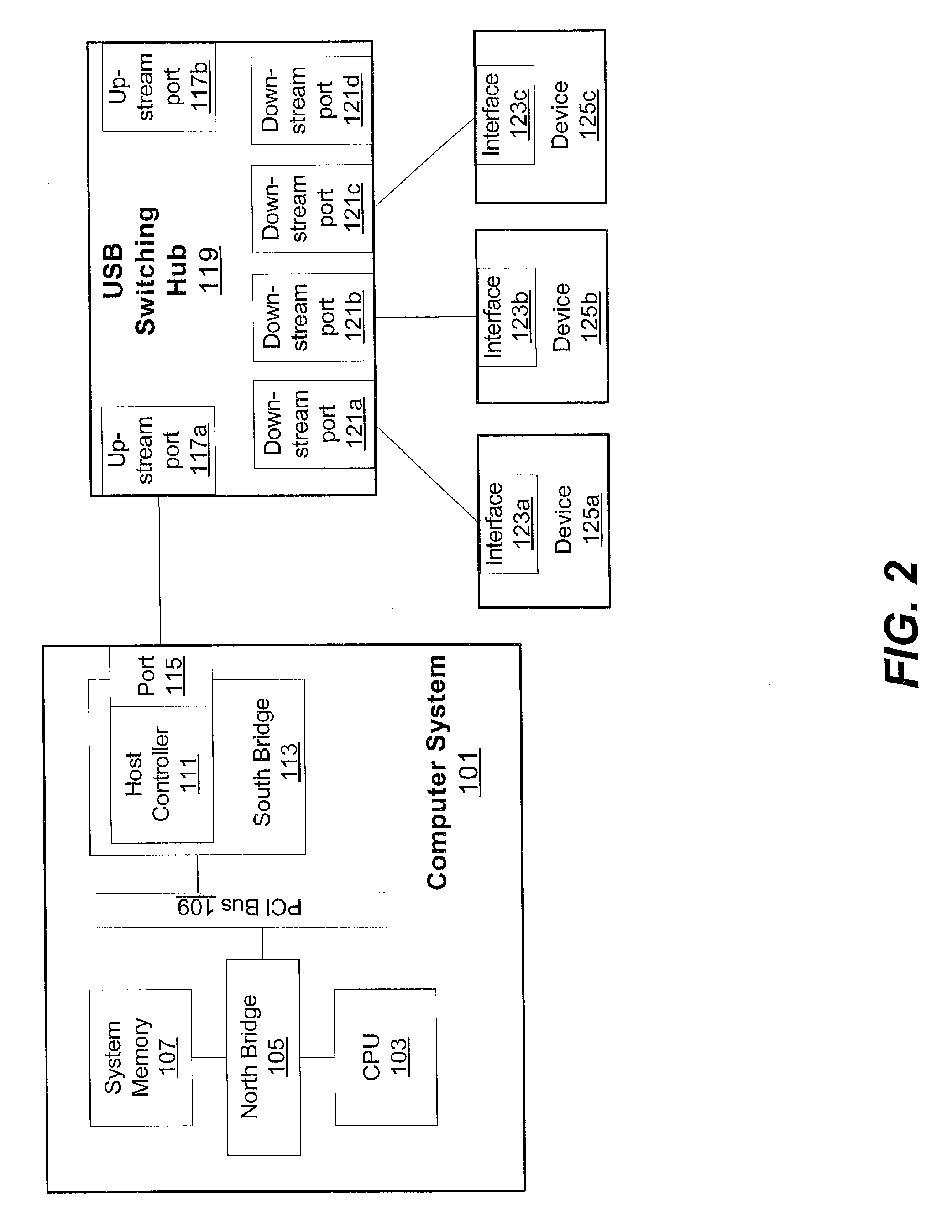
Peripheral sharing USB hub
InactiveUS20060056401A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationUSB hubEmbedded system
In various embodiments, devices coupled to upstream ports may enumerate the USB switching hub according to the total number of downstream ports on the USB switching hub. In some embodiments, when a first upstream port is communicating with a first downstream port, status registers coupled to the second upstream port may indicate to the second upstream device that the first downstream port is disconnected. By enumerating the USB switching hub according to the total number of downstream ports, the upstream devices may not have to reenumerate the hub (and correspondingly each device coupled to the hub) each time a downstream device is switched. In some embodiments, an intelligent port routing switch may delay switching communications for the downstream port if there is an active transfer in progress between a related downstream port and an upstream port.
Owner:STANDRD MICROSYSTEMS CORPORATION
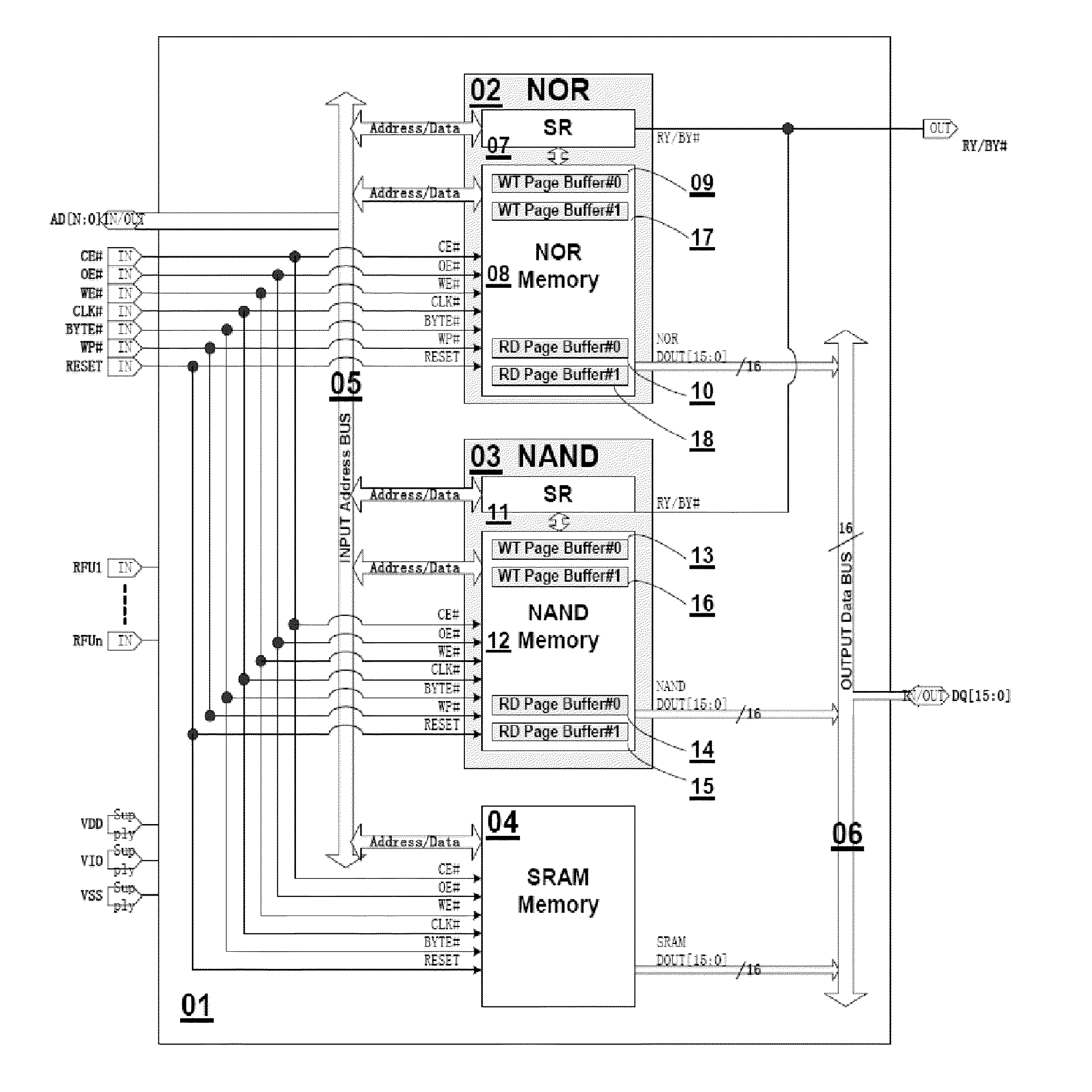
Memory system having NAND-based nor and NAND flashes and SRAM integrated in one chip for hybrid data, code and cache storage
InactiveUS20100329011A1Faster and improved read and write operation of memoryEasy to operateMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRead-only memoriesAddress busMemory map
A memory system includes a NAND flash memory, a NOR flash memory and a SRAM manufactured on a single chip. Both NAND and NOR memories are manufactured by the same NAND manufacturing process and NAND cells. The three memories share the same address bus, data bus, and pins of the single chip. The address bus is bi-directional for receiving codes, data and addresses and transmitting output. The data bus is also bi-directional for receiving and transmitting data. One external chip enable pin and one external output enable pin are shared by the three memories to reduce the number of pins required for the single chip. Both NAND and NOR memories have dual read page buffers and dual write page buffers for Read-While-Load and Write-While-Program operations to accelerate the read and write operations respectively. A memory-mapped method is used to select different memories, status registers and dual read or write page buffers.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
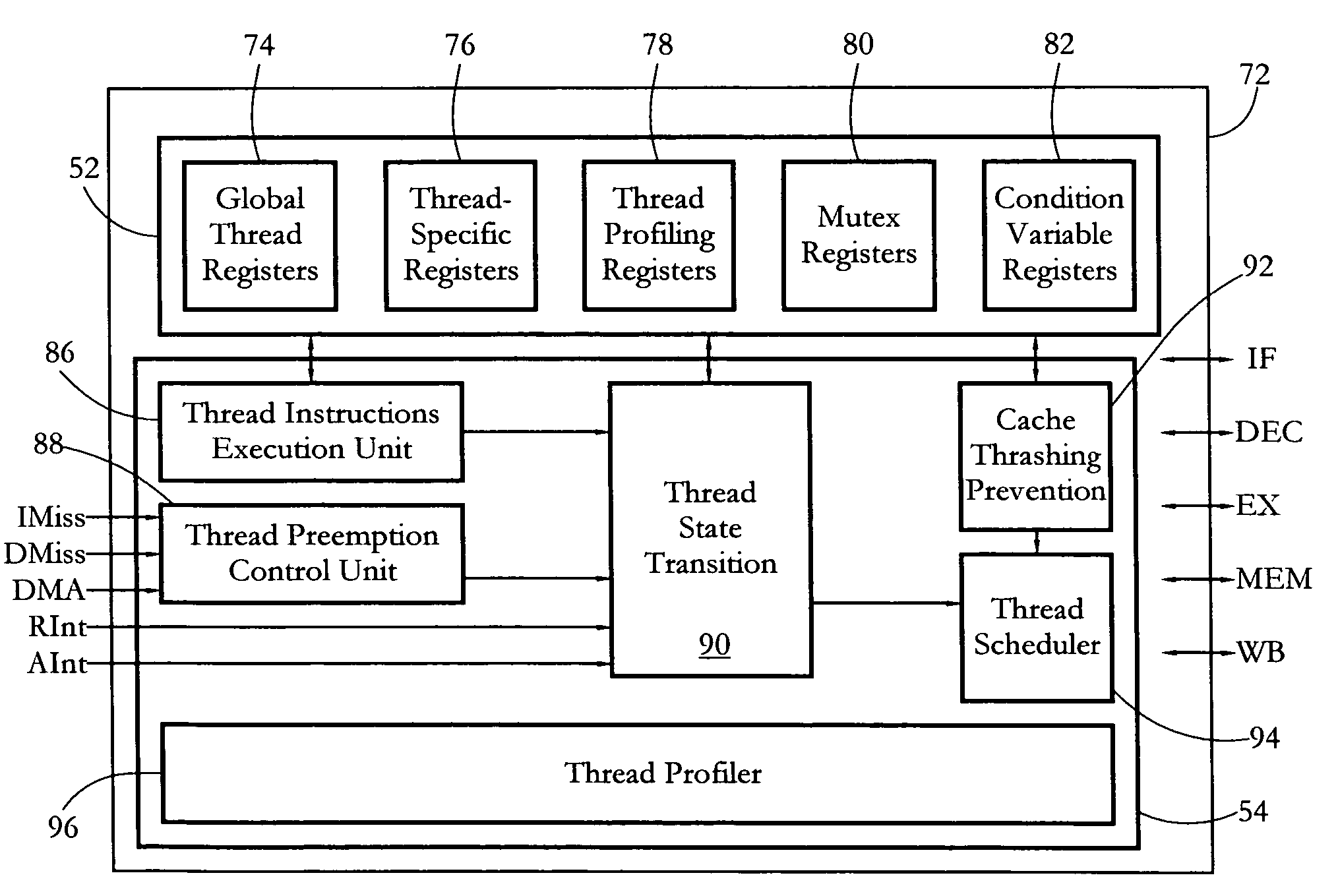
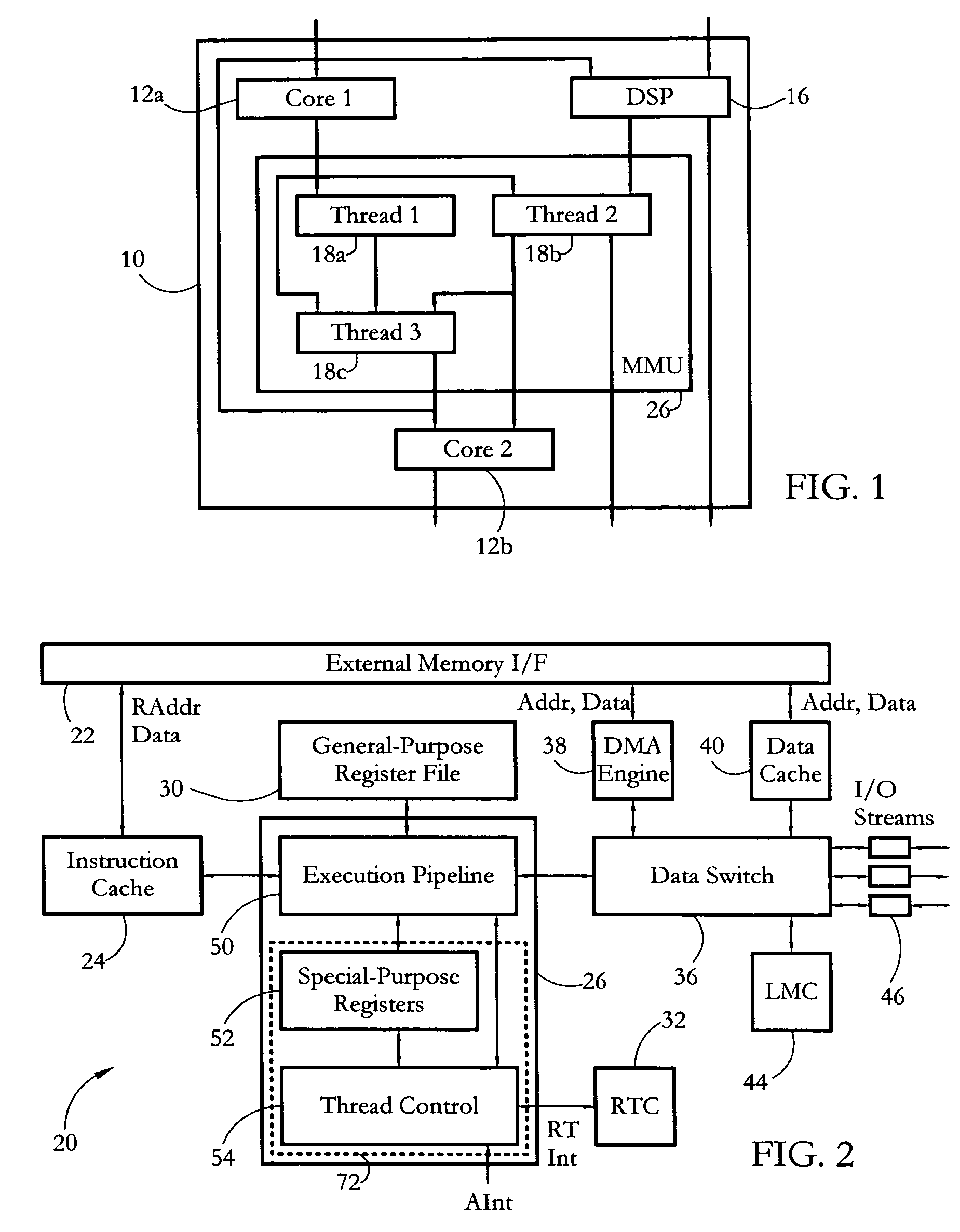
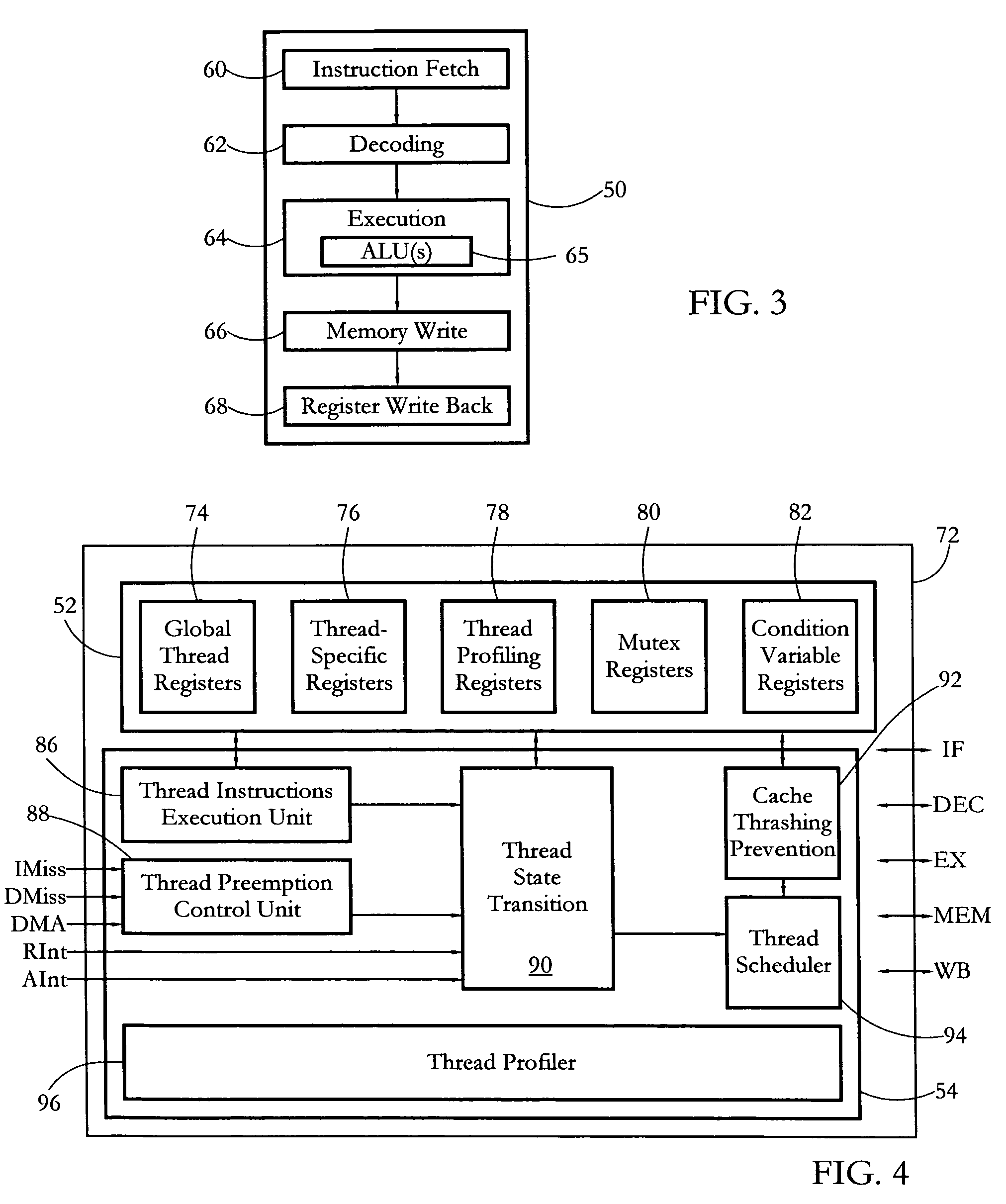
Hardware multithreading systems with state registers having thread profiling data
According to some embodiments, a multithreaded microcontroller includes a thread control unit comprising thread control hardware (logic) configured to perform a number of multithreading system calls essentially in real time, e.g. in one or a few clock cycles. System calls can include mutex lock, wait condition, and signal instructions. The thread controller includes a number of thread state, mutex, and condition variable registers used for executing the multithreading system calls. Threads can transition between several states including free, run, ready and wait. The wait state includes interrupt, condition, mutex, I-cache, and memory substates. A thread state transition controller controls thread states, while a thread instructions execution unit executes multithreading system calls and manages thread priorities to avoid priority inversion. A thread scheduler schedules threads according to their priorities. A hardware thread profiler including global, run and wait profiler registers is used to monitor thread performance to facilitate software development.
Owner:GEO SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Peripheral Sharing USB Hub
InactiveUS20060227759A1Avoid connectionData switching by path configurationElectric digital data processingUSB hubEmbedded system
In various embodiments, devices coupled to upstream ports may enumerate the USB switching hub according to the total number of downstream ports on the USB switching hub. In some embodiments, when a first upstream port is communicating with a first downstream port, status registers coupled to the second upstream port may indicate to the second upstream device that the first downstream port is disconnected. By enumerating the USB switching hub according to the total number of downstream ports, the upstream devices may not have to re-enumerate the hub (and correspondingly each device coupled to the hub) each time a downstream device is switched. In some embodiments, an intelligent port routing switch may delay switching communications for the downstream port if there is an active transfer in progress between a related downstream port and an upstream port.
Owner:STANDRD MICROSYSTEMS CORPORATION
System and method for determining the start of a match of a regular expression
InactiveUS20080077587A1Overcome disadvantagesData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalAutomatonRegular expression
A system for determining the start of a match of a regular expression has a special state table which contains start state entries and terminal state entries; a plurality of start state registers for storing offset information indicative of the start of a match of the regular expression; a deterministic finite state automaton (DFA) next state table which, given the current state and an input character, returns the next state. The DFA next state table includes a settable indicator for any next state table entry which indicates whether to perform a lookup into the special state table. A compiler loads values into the special state table based on the regular expression.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Method and apparatus for managing registers in a binary translator
ActiveUS7260815B1Specific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsProcessor registerParallel computing
The invention relates to managing registers during a binary translation mode in a virtual computing system. A set of registers is saved to memory before beginning to execute a series of blocks of translated code, and the contents of the set of registers are restored from memory later. A status register is maintained for tracking the status of each register within the set, the status indicating whether the contents are valid and whether the contents are saved in memory. Before the execution of each block, a determination is made as to whether the actions taken within the block relative to the registers are compatible with the current status of the registers. If the actions are not compatible, additional registers are saved to memory or restored from memory, so that the translation block can be executed.
Owner:VMWARE INC
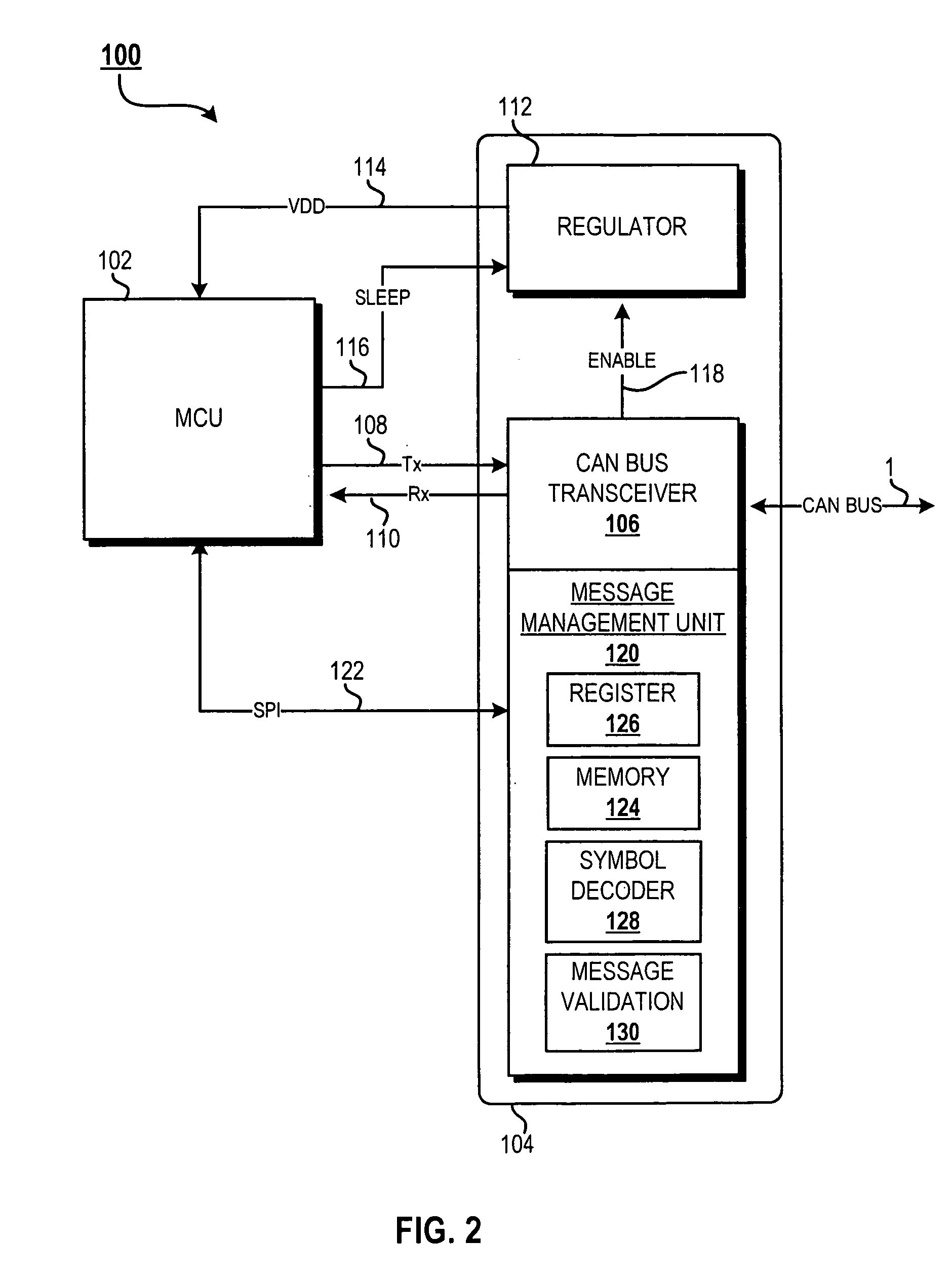
Message buffer for a receiver apparatus on a communications bus
InactiveUS20070230484A1Volume/mass flow measurementData switching by path configurationMicrocontrollerTransceiver
A Controller Area Network (CAN) node consists of a high-powered microcontroller, a low standby power regulator, a CAN bus transceiver, and a minimal CAN message buffer for storing received messages. Low power standby operation allows for the controller to power off, while the transceiver and regulator are operated in standby. The transceiver / regulator will enter run mode after the first symbol of a received CAN message is validated off the bus. As the original CAN message is received, it is buffered in the message buffer and, after stored, a status register is set to indicate the full message has been received. Once the controller has stabilized out of a wake-up mode, it retrieves the stored message and acts accordingly. The CAN message buffer is coupled to the controller by an system packet interface (SPI) interface for transmission of a controller wake-up command and retrieval of a buffered message.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
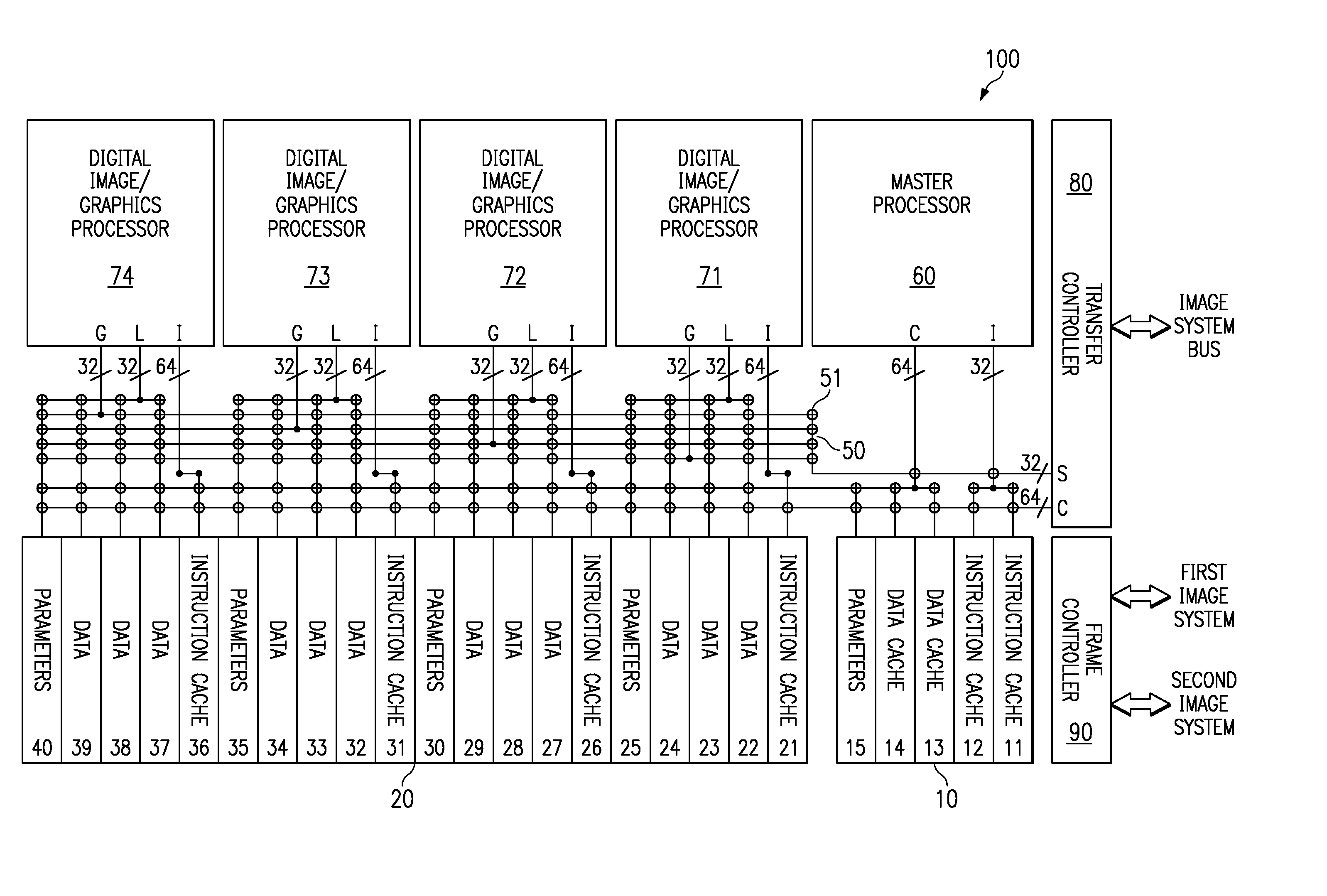
Long Instruction Word Controlling Plural Independent Processor Operations
InactiveUS20080077771A1Instruction analysisComputation using non-contact making devicesIntegrated circuitStatus register
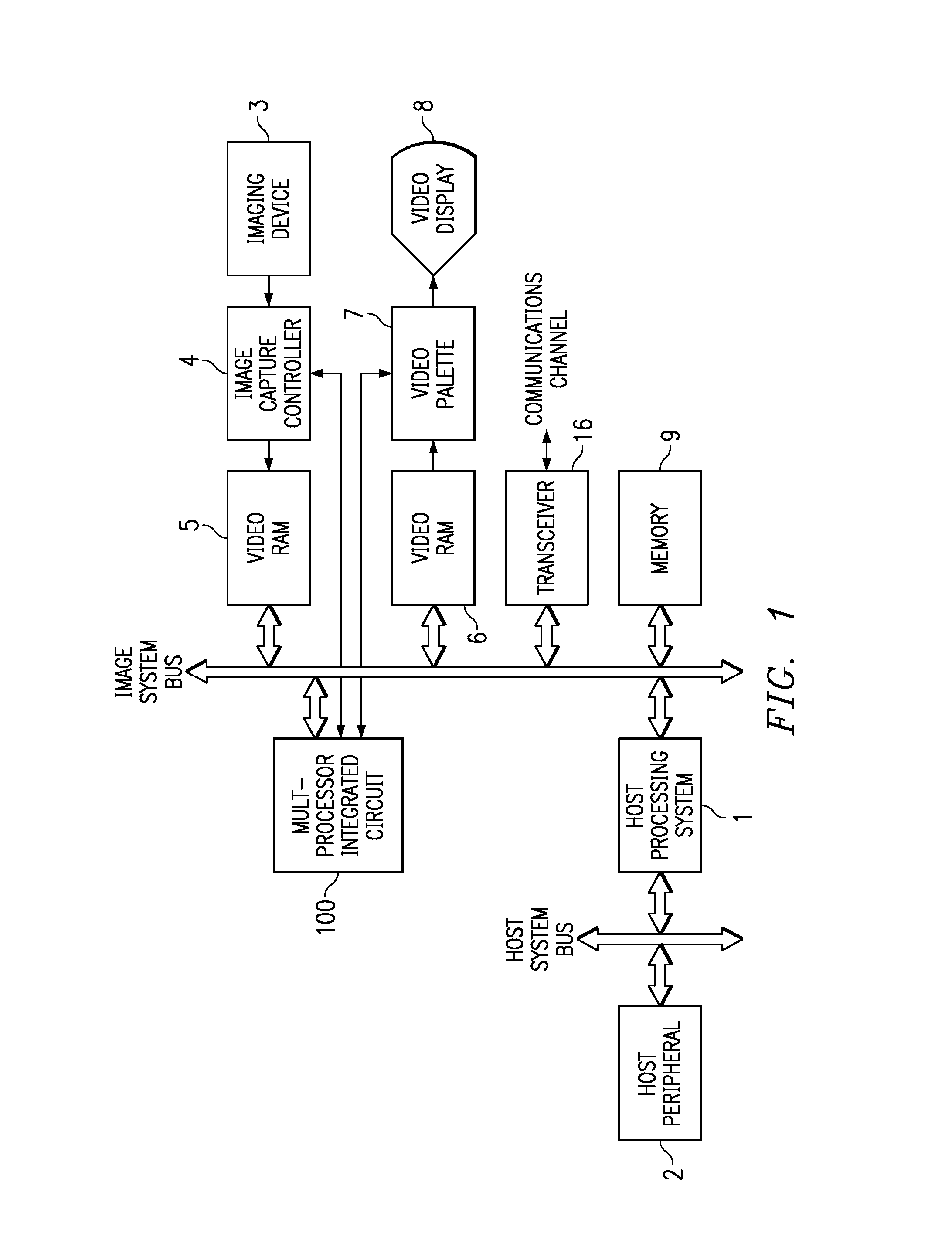
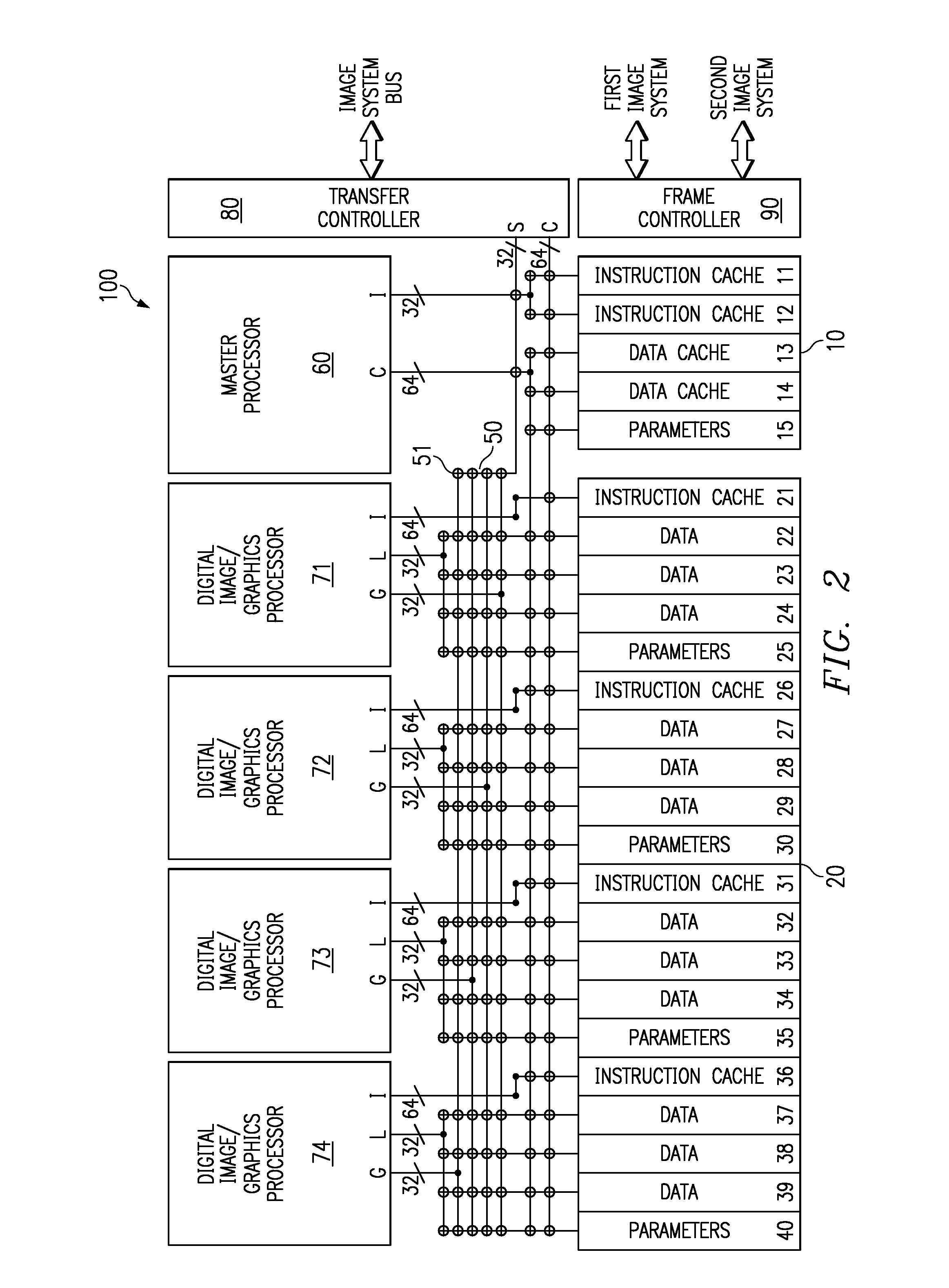
This invention is a data processing apparatus which operates on instruction controlling plural processor actions. Each instruction includes a data unit section and a data transfer section. These instruction sections are independent and may include differing options. In the preferred embodiment, each instruction is 64 bits. The data unit section includes a data operation field that indicates the type of arithmetic logic unit operation and six operand fields. The six operand fields include four source data register fields and two destination register fields. The data unit (110) includes a multiplication unit (220) and an arithmetic logic unit (230). The data unit (110) may include a barrel rotator (235) for one input of the arithmetic logic unit (230). The rotated data may be stored in the first destination register instead of the multiply result. The address unit (120) operations according to the data transfer operation field. This could be a load, a store or a register to register move. Operations may be conditional based upon conditions stored in a status register (210). The status register (210) is set by a prior output of the arithmetic logic unit (230) and the instruction may specify some of the status bits protect from change. The address unit (120) preferably includes a plurality of base address registers (611), a full adder (615) and a left shifter (614). The full adder (615) may add an index as scaled by the left shifter to the base address or subtract the scaled index from the base address. The full adder (615) output may update the base address register (611), either before supply of the address or following supply of the address. The index may be recalled from an index register (612) or an immediate value. In the preferred embodiment of this invention, the data unit (110) including the data registers (200), the multiplication unit (220) and the arithmetic logic unit (230), the address unit (120) and the instruction decode logic (250, 660) are embodied in at least one digital image / graphics processor (71, 72, 73, 74) as a part of a multiprocessor (100) formed in a single integrated circuit used in image processing.
Owner:GUTTAG KARLM +2
Methods and apparatus for efficient multi-tasking
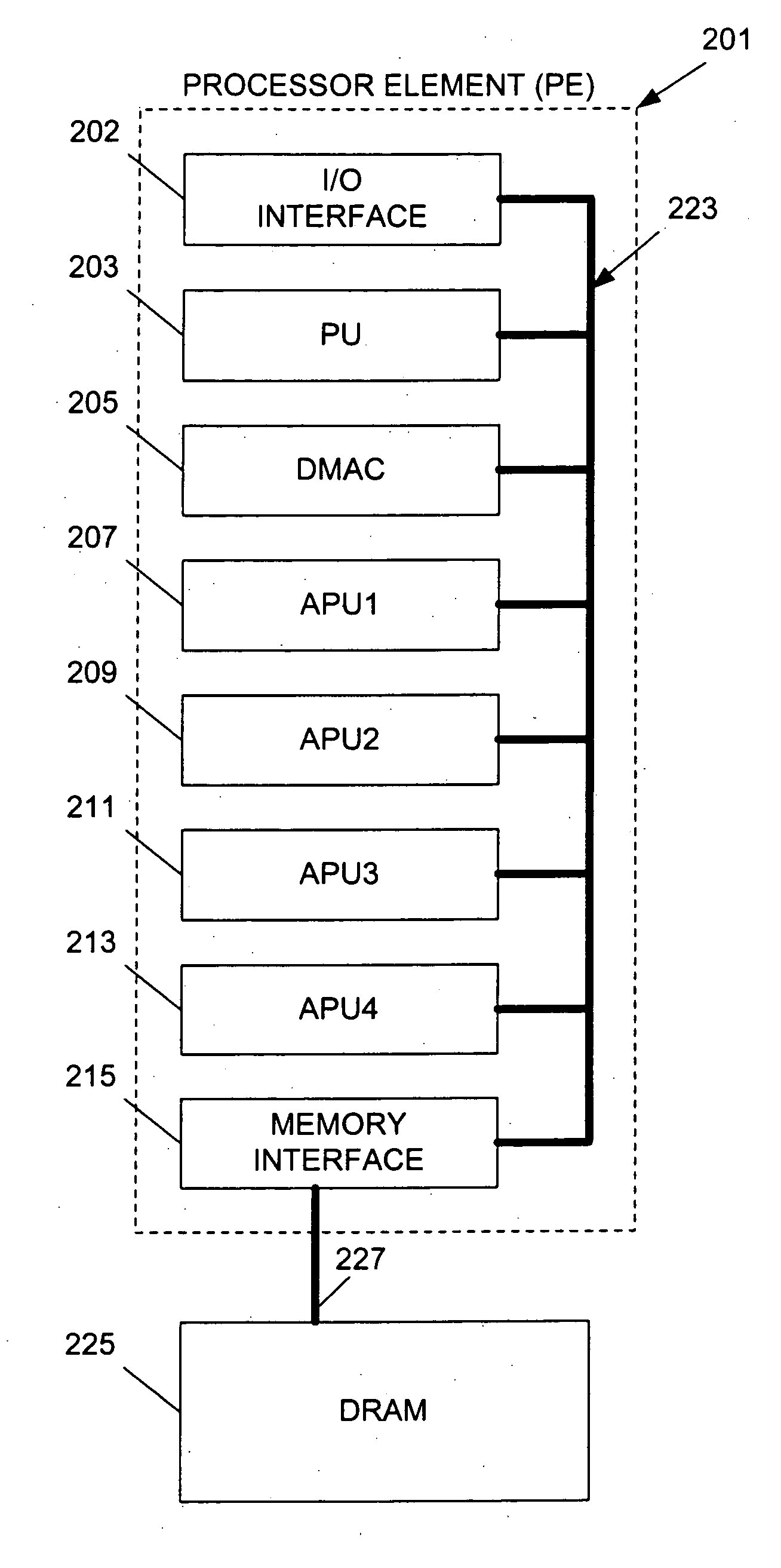
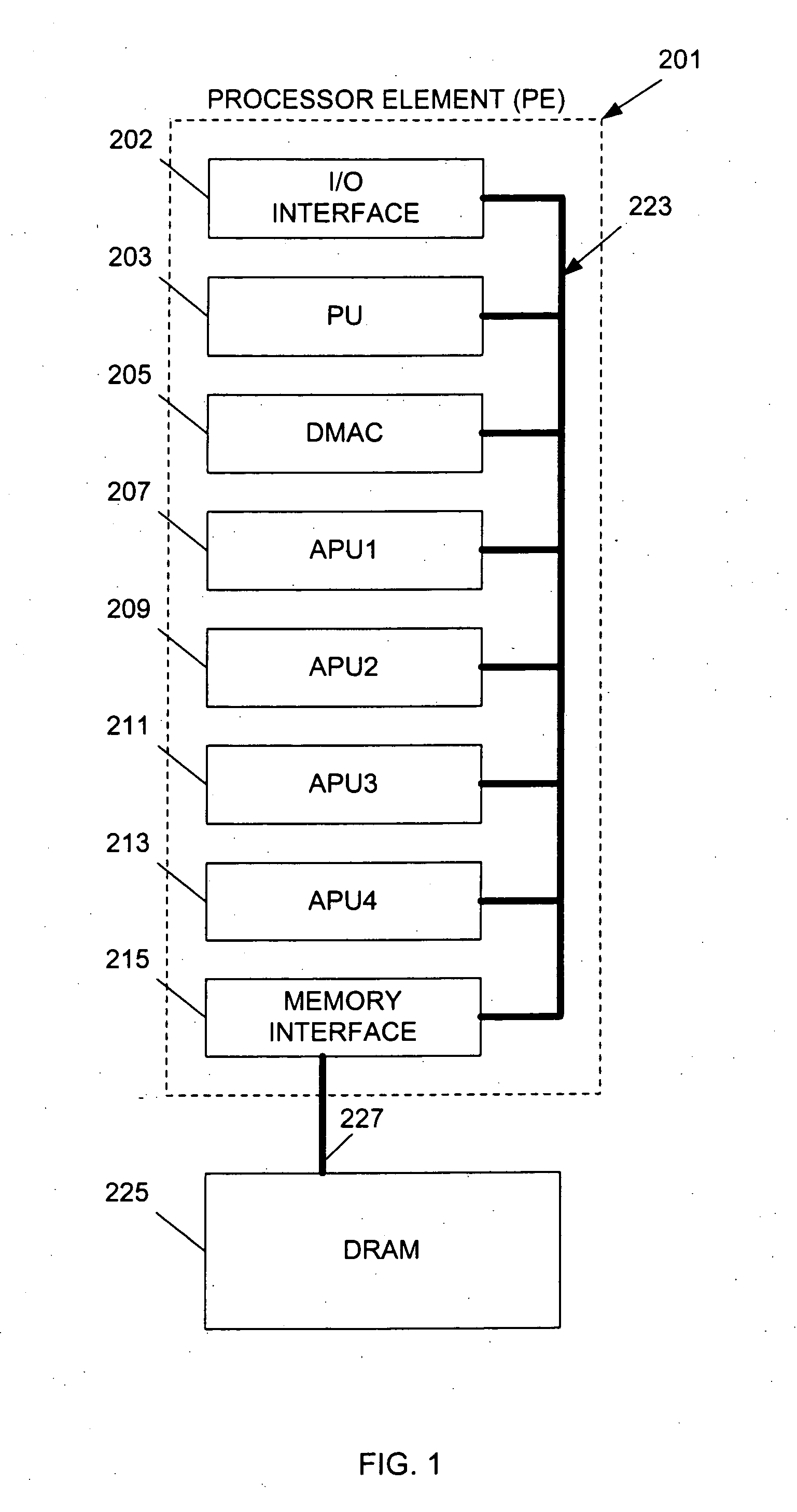
InactiveUS20050120185A1Efficient high speed processingEasy to buildMemory loss protectionProgram synchronisationMemory interfaceData store
A system includes a shared memory; a memory interface unit coupled to the shared memory and operable to retrieve data from the shared memory at requested addresses, and to write data to the shared memory at requested addresses; and a plurality of processing units in communication with the memory interface and operable to (i) instruct the memory interface unit that data be loaded with reservation from the shared memory at a specified address such that any operations may be performed on the data, and (ii) instruct the memory interface unit that the data be stored in the shared memory at the specified address, wherein at least one of the processing units includes a status register having one or more bits indicating whether a reservation was lost: whether the data at the specified address in shared memory was modified.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Method to detect IEEE overflow and underflow conditions
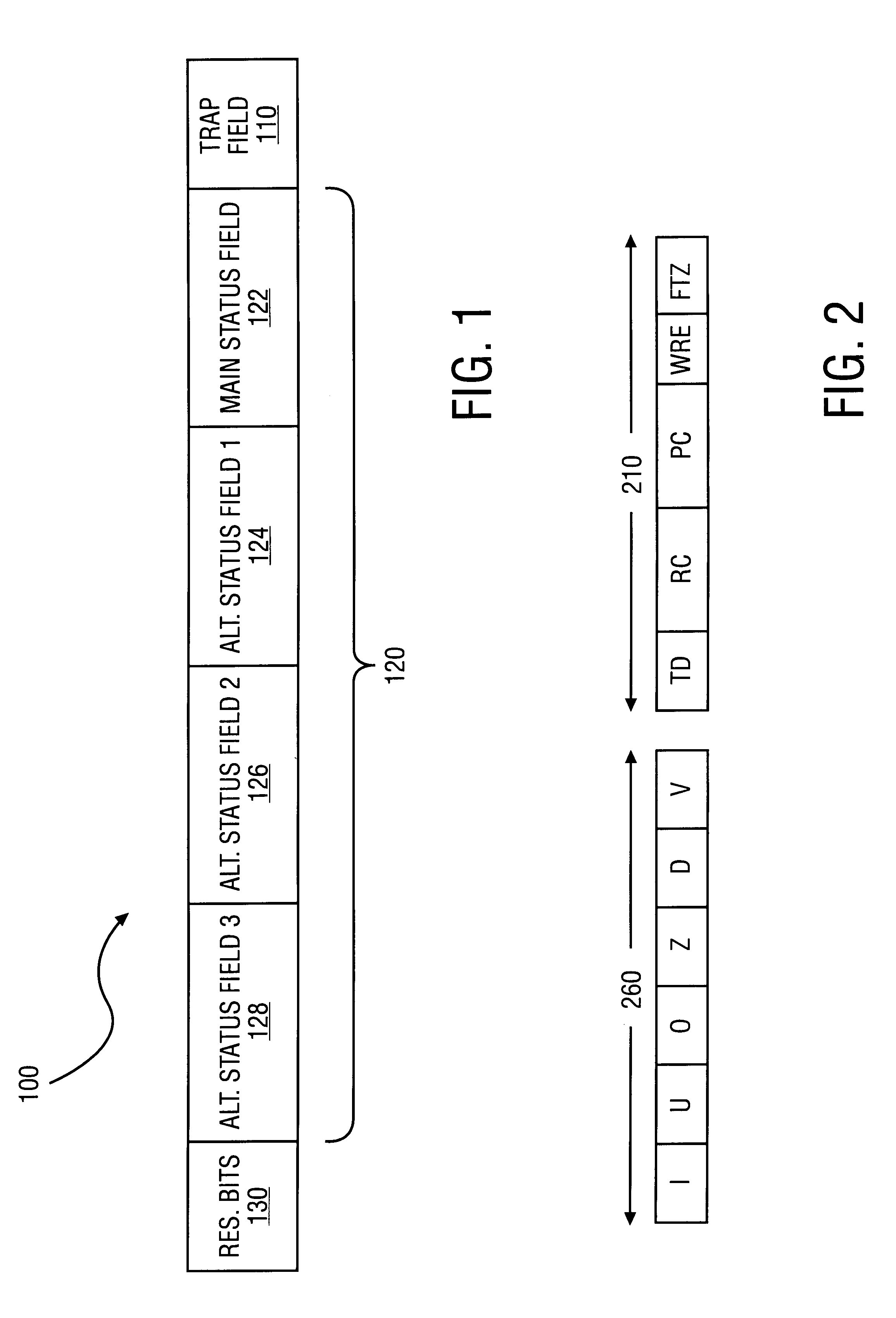
InactiveUS6219685B1Conditional code generationNext instruction address formationStatus registerComputer science
A method is disclosed for detecting overflow and underflow conditions using a status register having a main status field and first and second alternate status fields. The first and second alternate status fields are set to chop and wre modes, respectively, and chop and wre results are determined for an arithmetic operation using the first and second alternate status fields. The chop and wre results are tested against test values to determine whether an overflow or underflow condition exists.
Owner:INTEL CORP
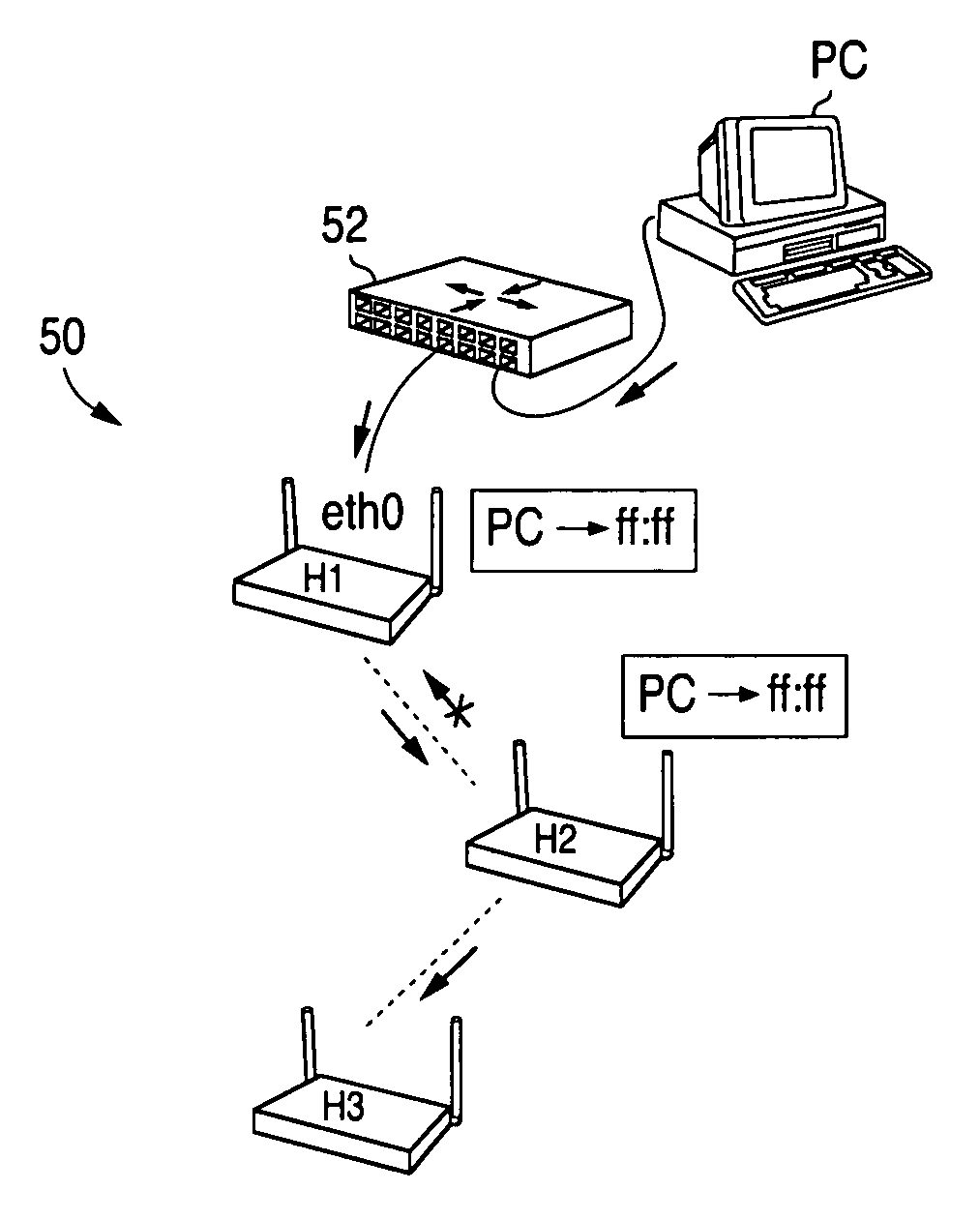
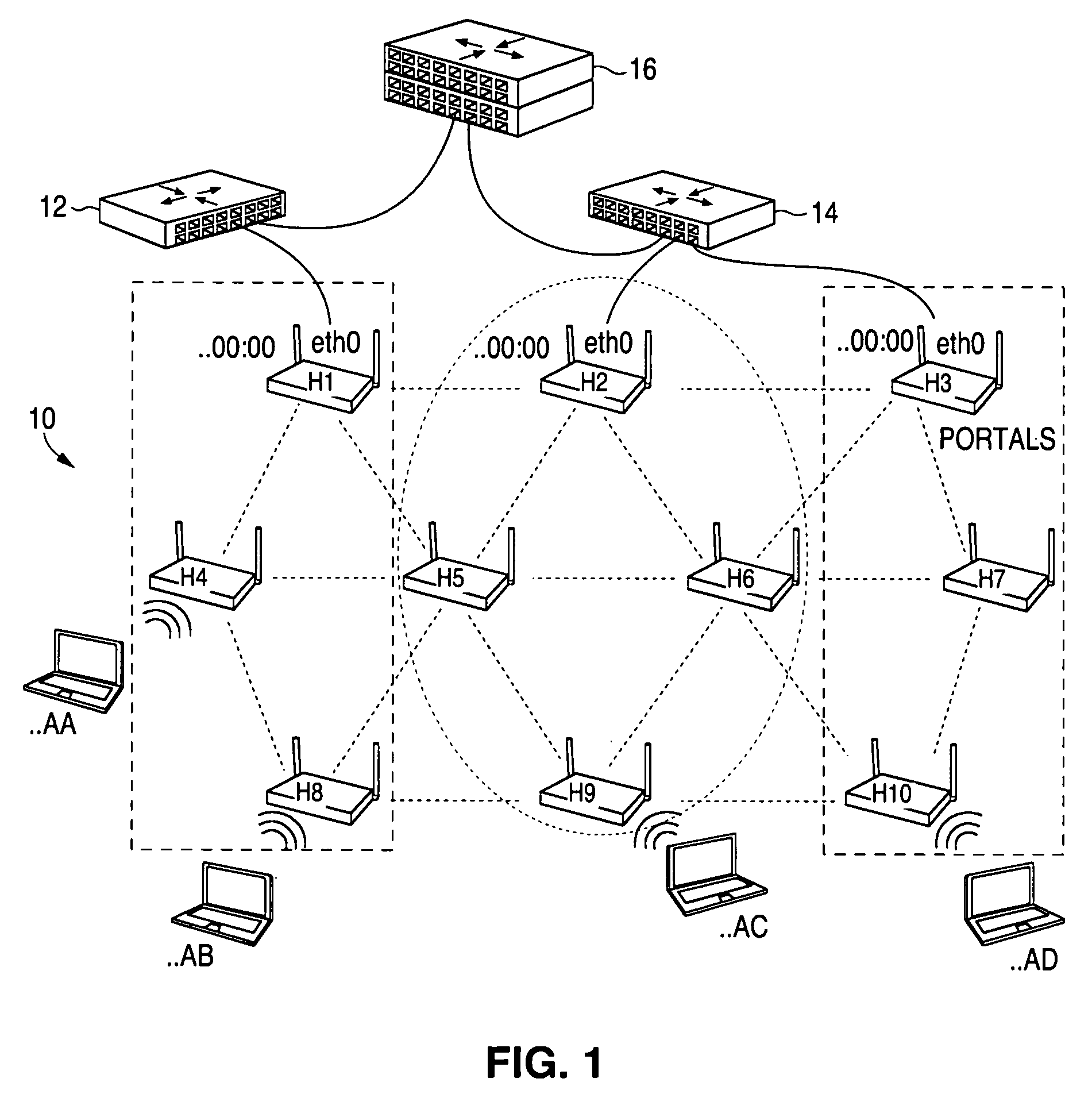
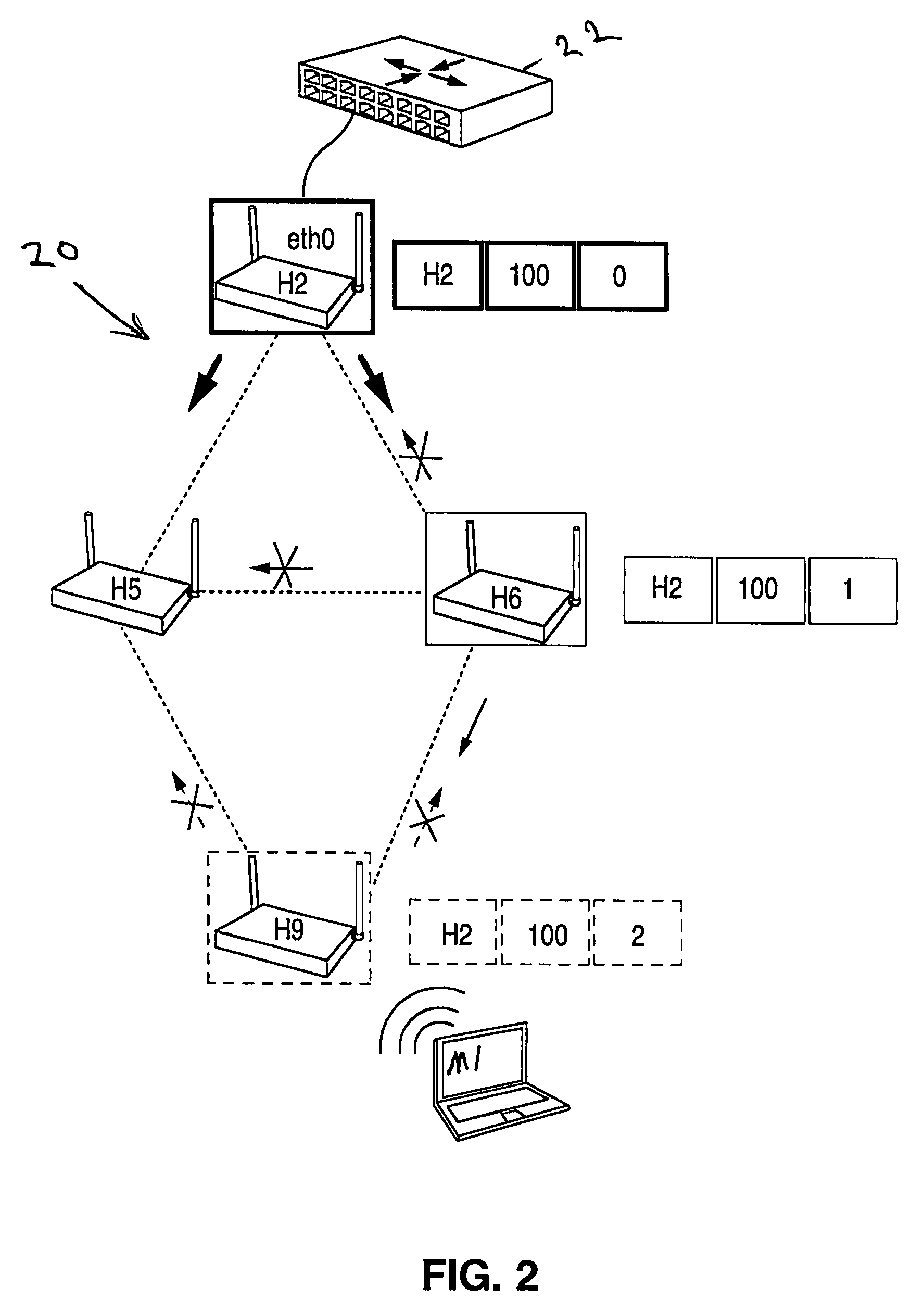
Routing method and system for a wireless network
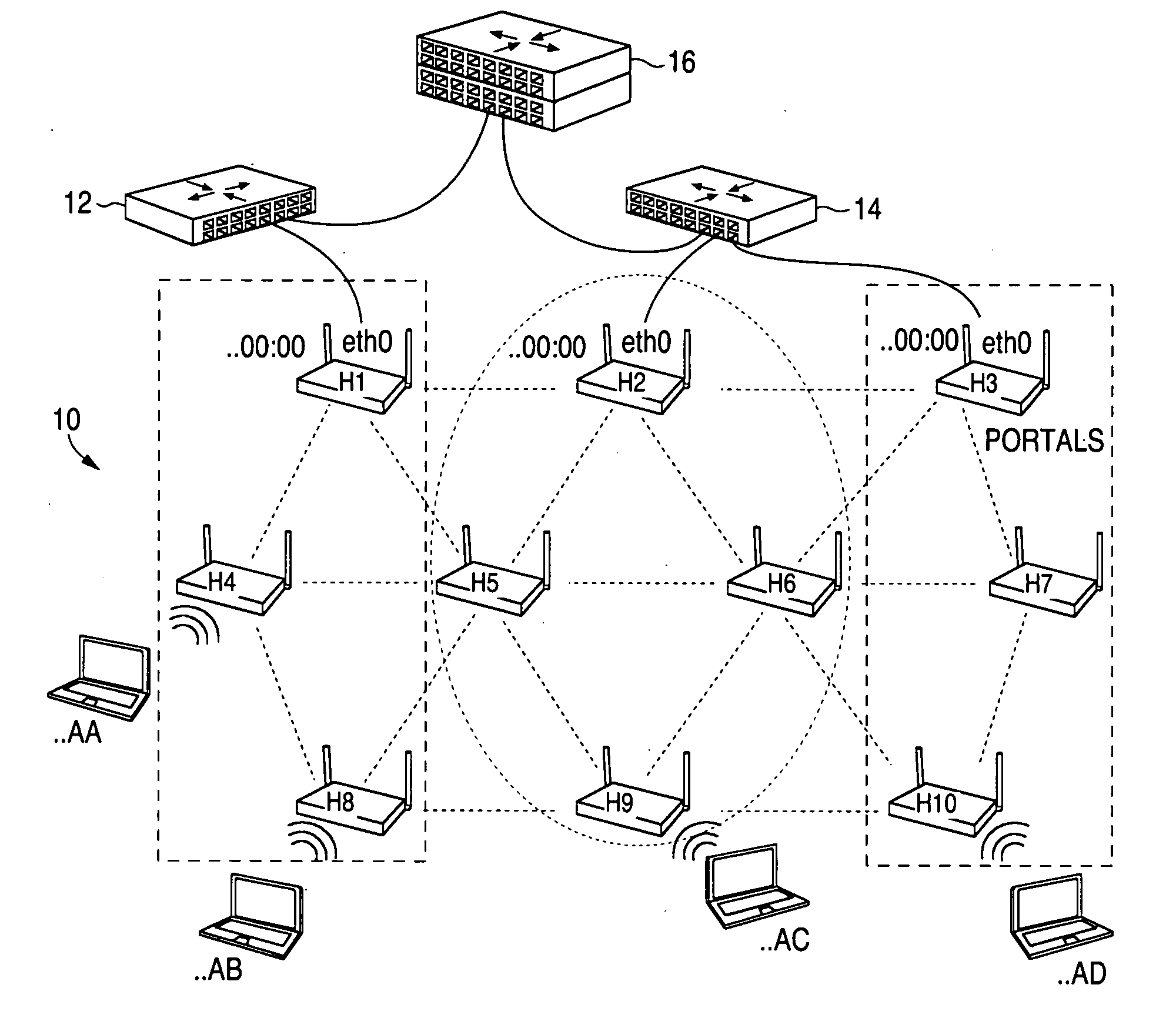
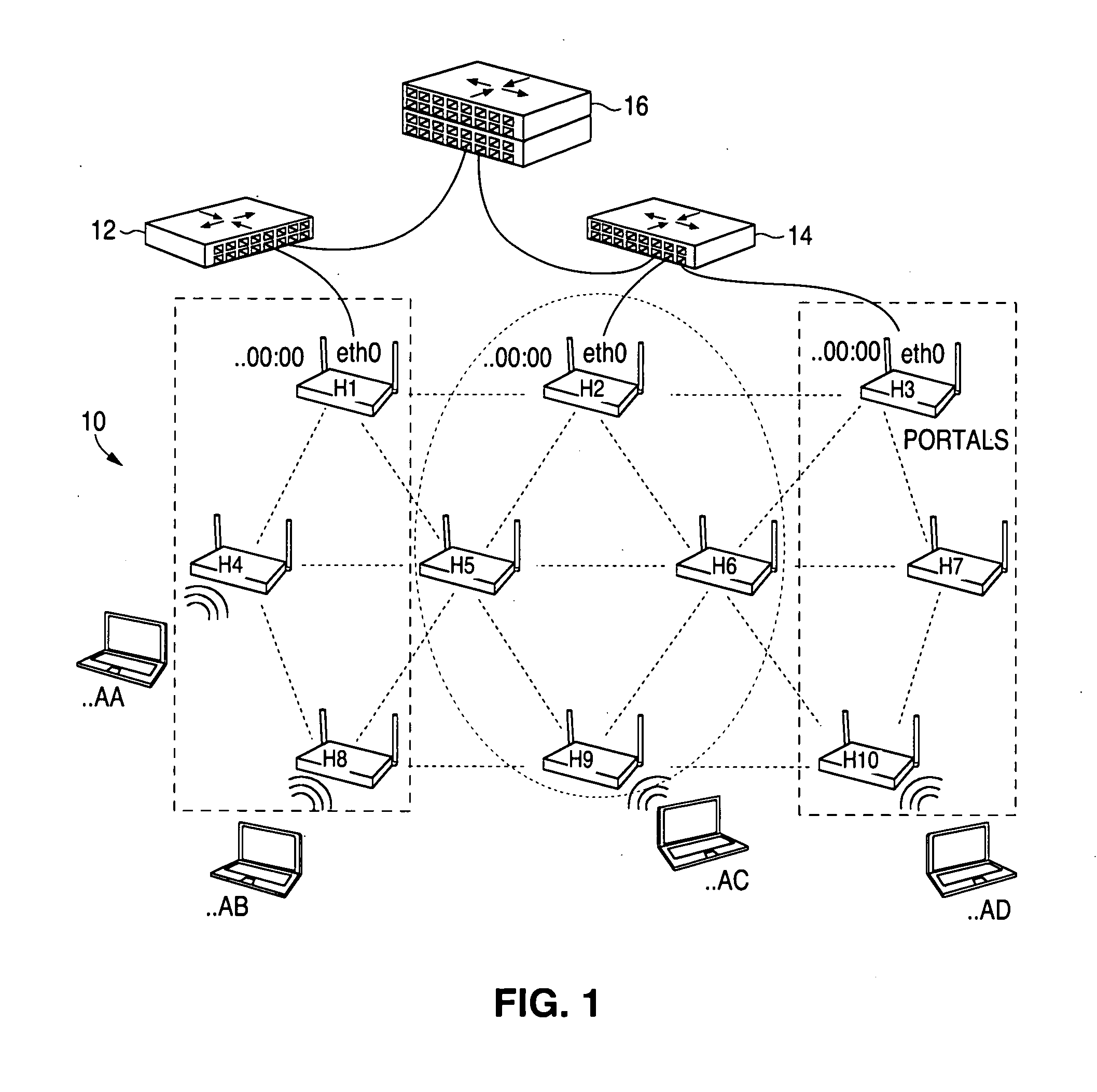
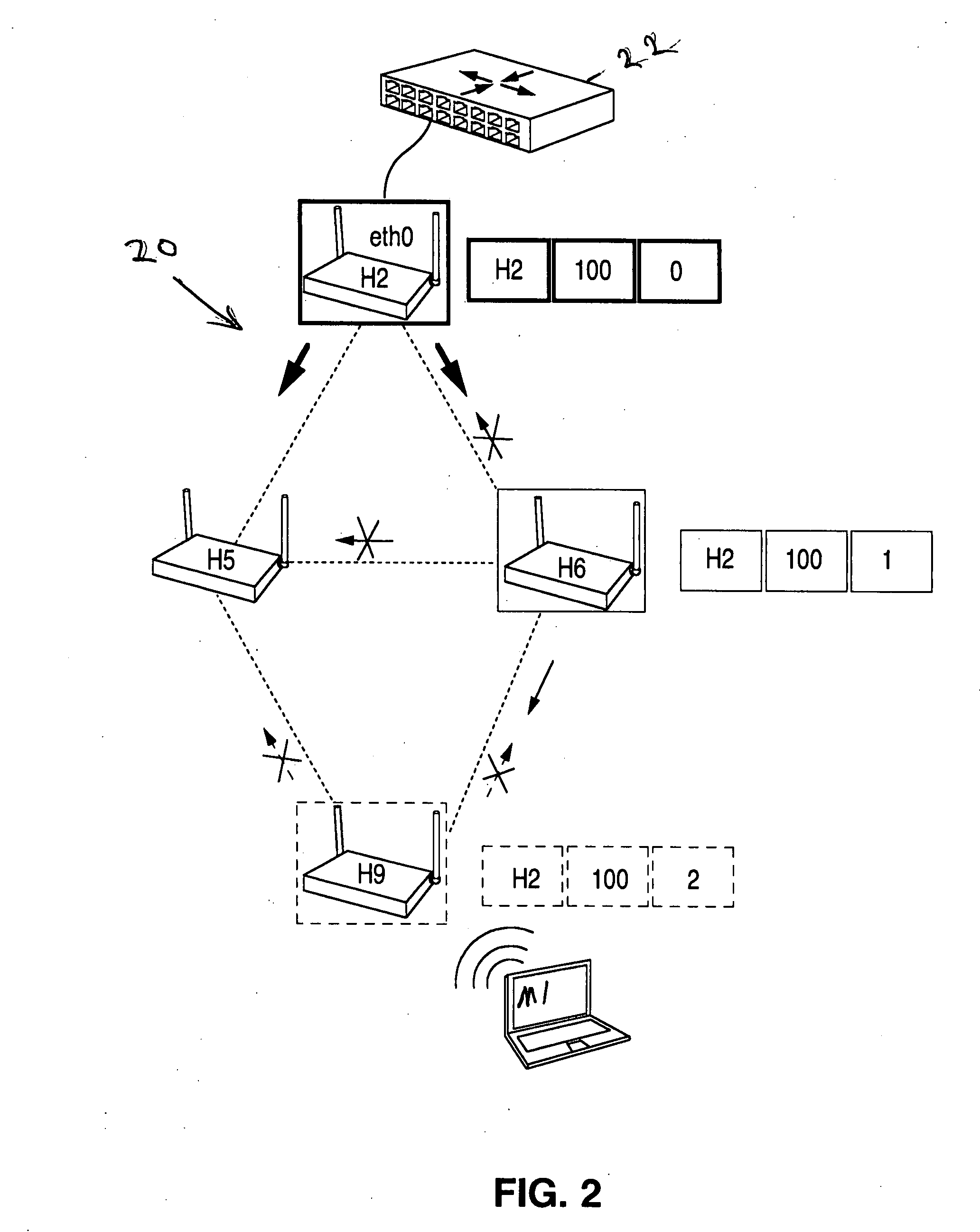
ActiveUS20080267116A1Easy to extendPromote reductionNetwork topologiesBroadcast service distributionWireless mesh networkProcessor register
A method and system for selecting a route in a wireless network for the transmission of a data packet between wireless nodes in said network using a modified link-state routing algorithm wherein only a limited number of broadcast messages are generated to synchronize the link-state database throughout the wireless network. A subset of nodes called portal nodes within the network are elected to do the broadcasting for the entire network. Each portal node broadcasts an announcement of its identity to all of the wireless nodes. Each wireless node responds to these broadcasts to select one of the portal nodes as its root portal node. It then identifies a unicast route back to its root portal node, and sends a link-state register message to this portal node. These link-state register messages received by each portal node are aggregated by them and are broadcast to each of the wireless nodes for storage. When a data packet is thereafter received by a wireless node from a neighboring node, it detects if the data packet satisfies one of a plurality of predetermined conditions and rebroadcasts the data packet to neighboring wireless nodes if none of the conditions is satisfied.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
Circuitry to selectively produce MSI signals
InactiveUS20050289271A1Electric digital data processingElectrical conductorMessage Signaled Interrupts
In some embodiments, the inventions include a chip having a status register circuit coupled to conductors to receive interrupt event signals to provide source signals corresponding to the interrupt event signals. The chip also includes a control register circuit to provide source enable signals for selective ones of the interrupt sources, and a re-arming logic circuit coupled to the conductors to receive the interrupt event signals and provide a re-arming signal. The chip further includes first logic circuit to receive the source signals, the source enable signals, and the re-arming signal to provide an initial interrupt signal, and message signaled interrupt (MSI) signal pulse generation logic to receive the initial interrupt signal and provide an MSI signal in response thereto. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
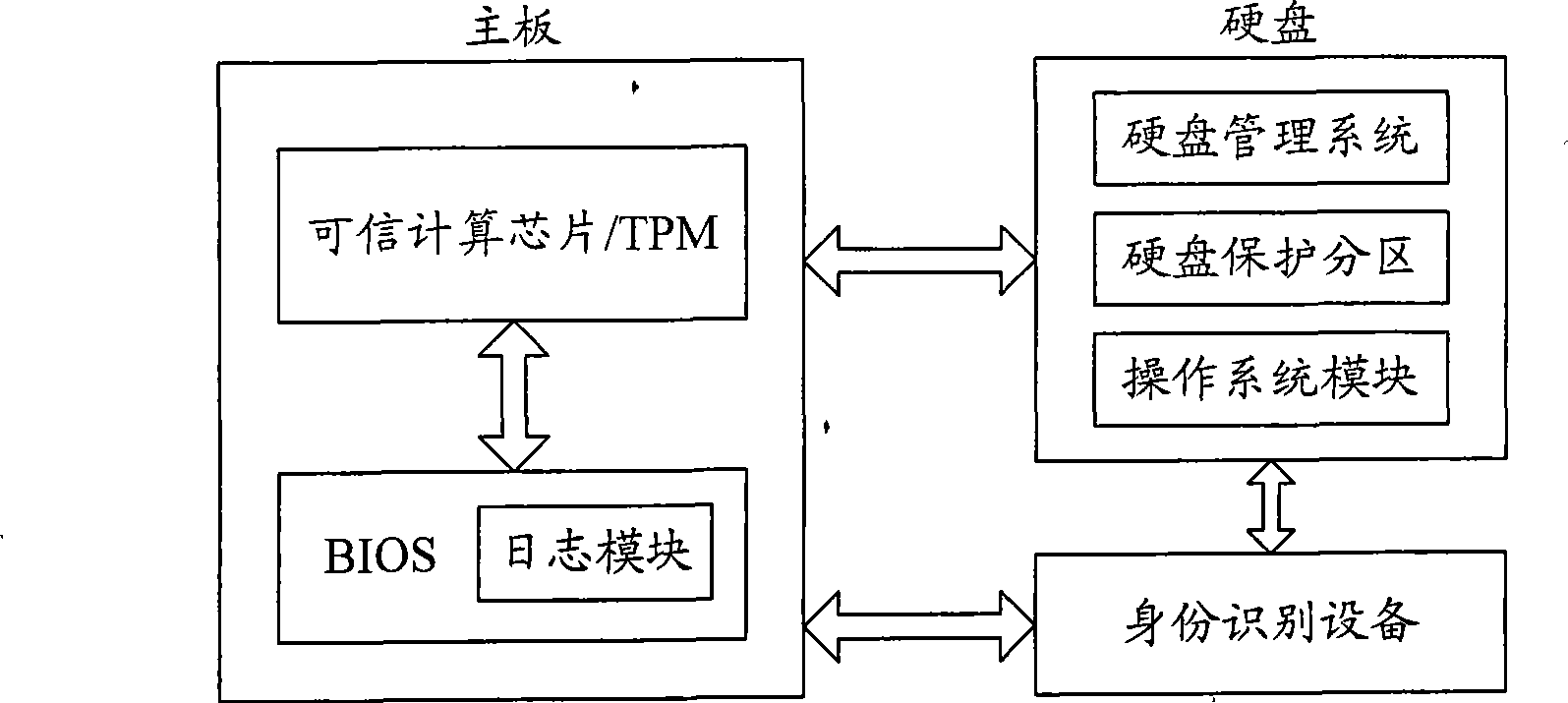
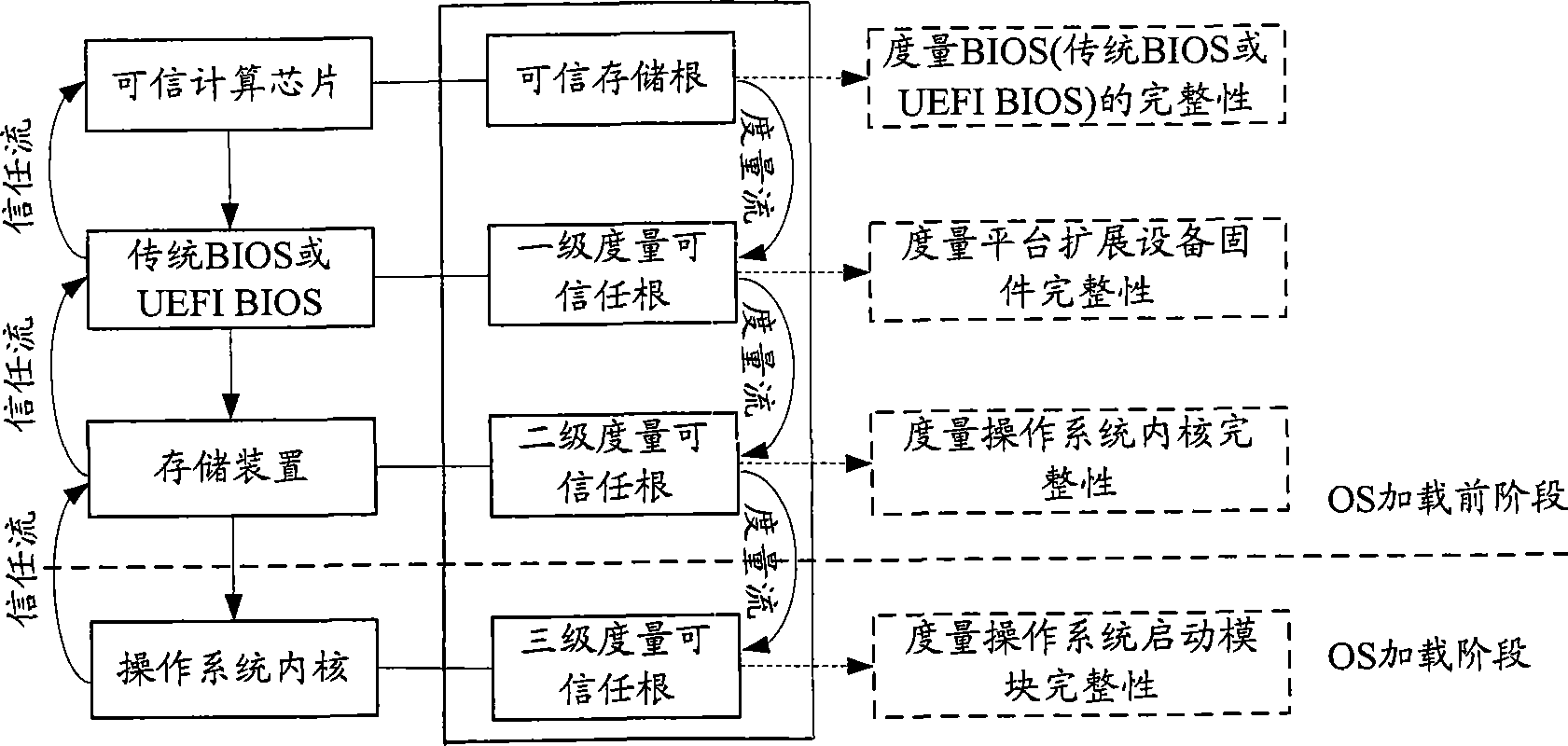
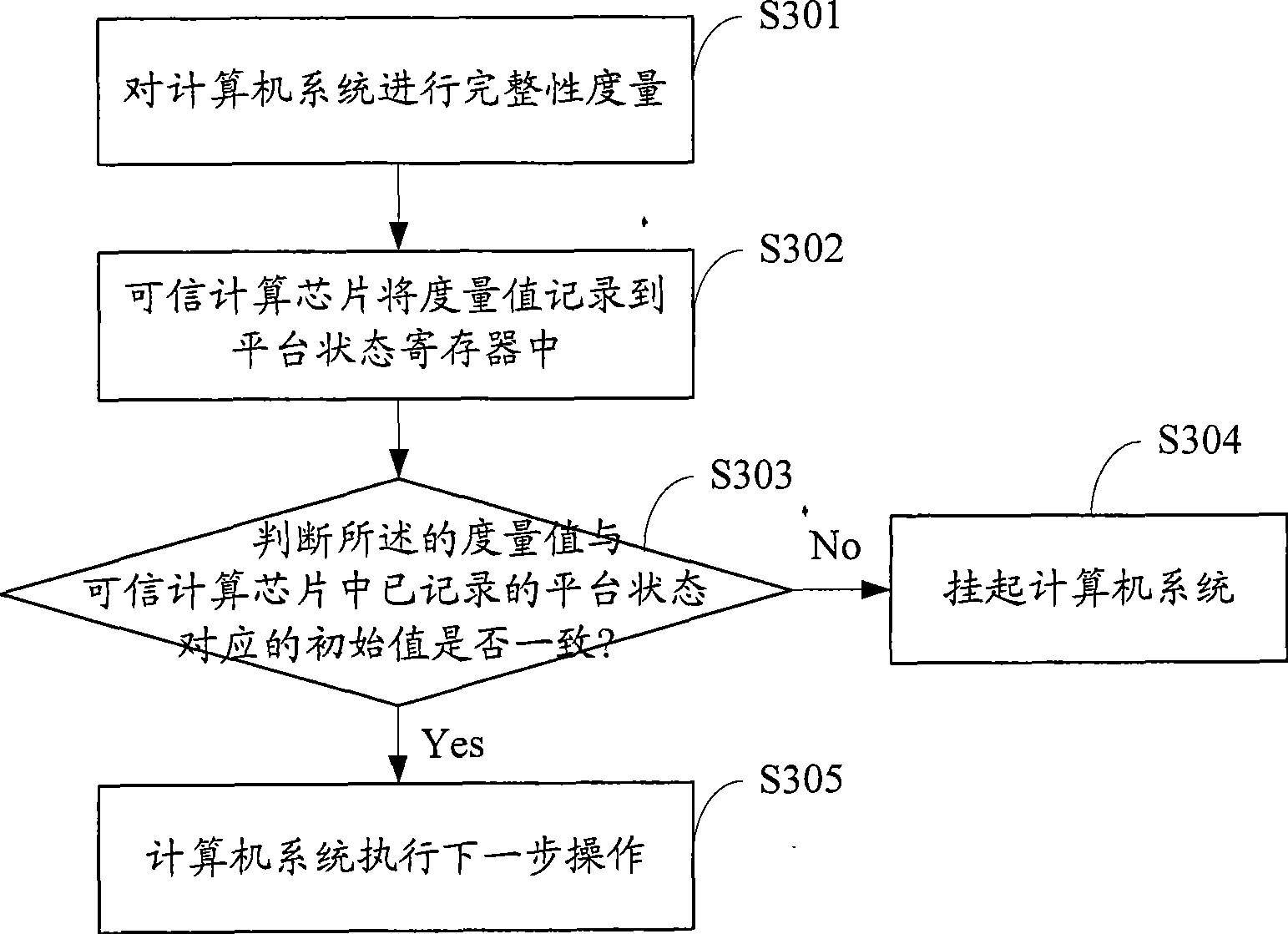
Method for protecting computer system
The invention provides a method for protecting compute system, belonging to the computer security technical field, which comprises: processing attestation of integrity on a computer system; recording the metric value via a credit calculation chip into a platform state register; judging the consistence between the metric value and an initial metric value corresponding to the platform state recorded in the credit calculation chip, when they are consistent, allowing the execution, or else, hanging the computer system. The computer system generates a credit root via embedding a hardware chip on a main board, utilizes password mechanism to build a credit chain from bottom components to superior application, and calculates and adds discrete values into a platform configuration register of a credit calculation chip. When the value is inconsistent to the one stored in the credit calculation chip, the computer system recovers or hangs, thereby confirming the safety of the computer system.
Owner:CHINA GREATWALL TECH GRP CO LTD
Memory-controller-embedded apparatus and procedure for achieving system-directed checkpointing without operating-system kernel support
InactiveUS20060150010A1Eliminate needMemory controllerError detection/correctionSupporting systemImage Inspection
System-directed checkpointing is enabled in otherwise standard computers through relatively straightforward enhancements to the computer's memory controller. Different embodiments of the invention can be used to support: local and remote post-image checkpointing using a memory-resident address buffer for storing the addresses of modified data blocks, either with or without requiring the processor caches to be flushed at each checkpoint; local and remote post-image checkpointing using either memory- or I / O-resident buffers for both the addresses and the data associated with blocks modified since the last checkpoint and supporting background buffer-to-shadow copying; remote and local post-image checkpointing using bit-map memories thereby avoiding the need for either address or data buffers while still supporting background data copying and either with or without requiring caches to be flushed to effect a checkpoint; local post-image checkpointing using a two-bit-per-memory-block state memory that eliminates the need for any data to be copied from one memory location to another; and pre-image local checkpointing again either with or without requiring caches to be flushed for checkpointing purposes. Since most of these implementations have advantages and disadvantages over the others and since similar mechanisms are used in the memory controller for all of these options, the controller can be implemented to support all of them with a hardwired or settable status register defining which is to be supported in a given situation. Alternatively, since some of these implementations require somewhat less extensive memory controller enhancements, the controller can be designed to support only one or a small subset of these embodiments with a correspondingly smaller perturbation to its more standard implementation.
Owner:OSHANTEL SOFTWARE
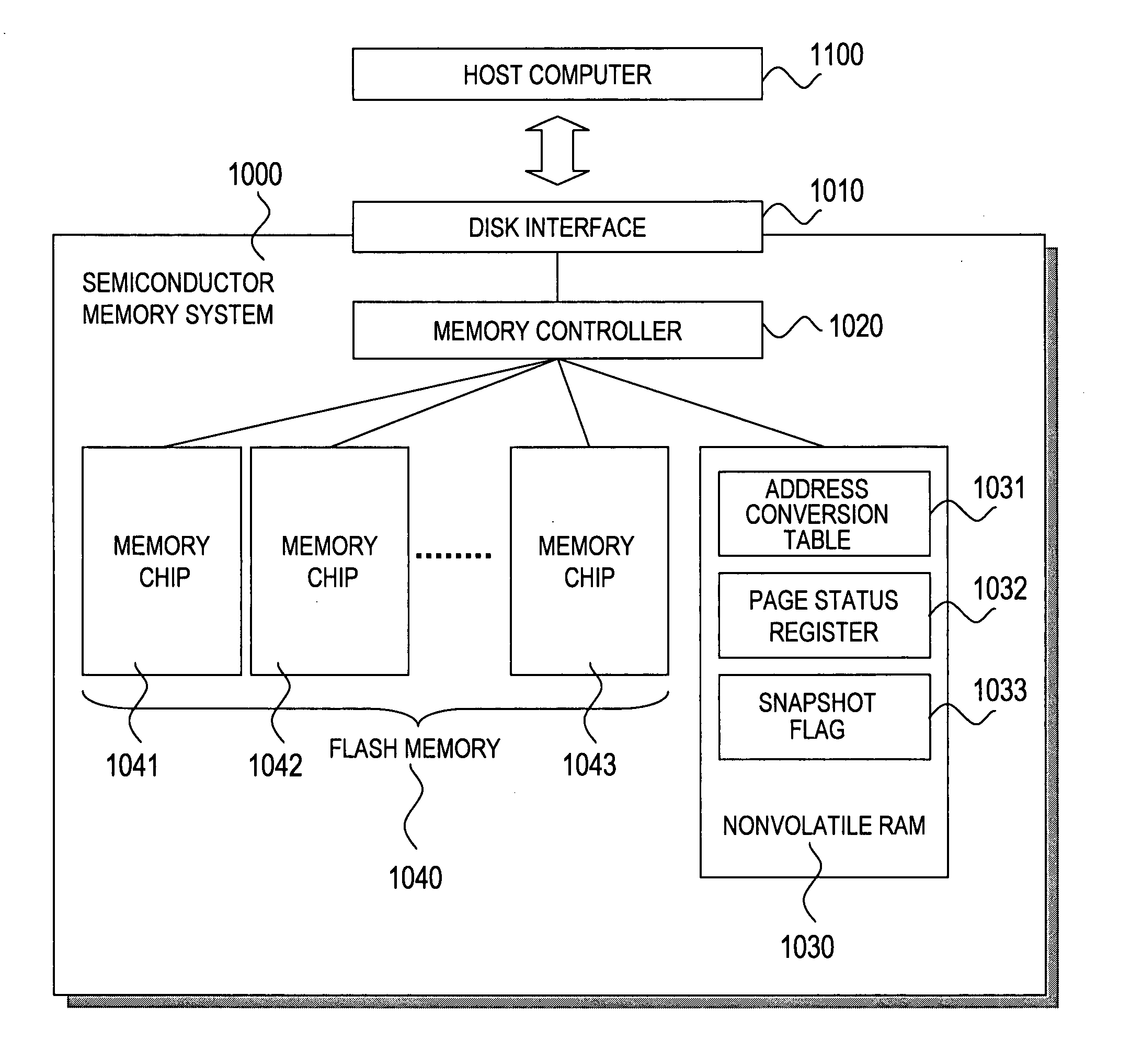
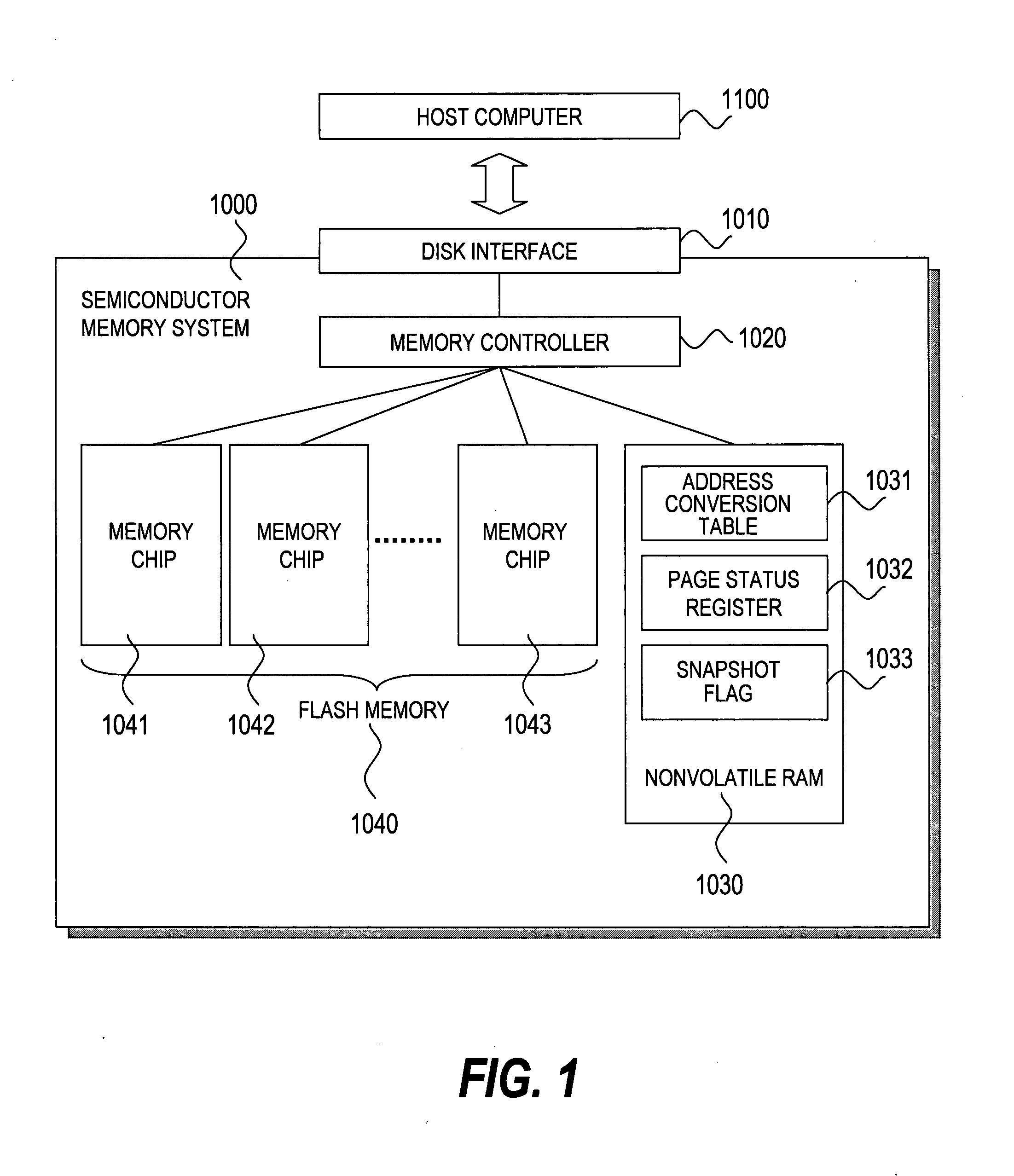
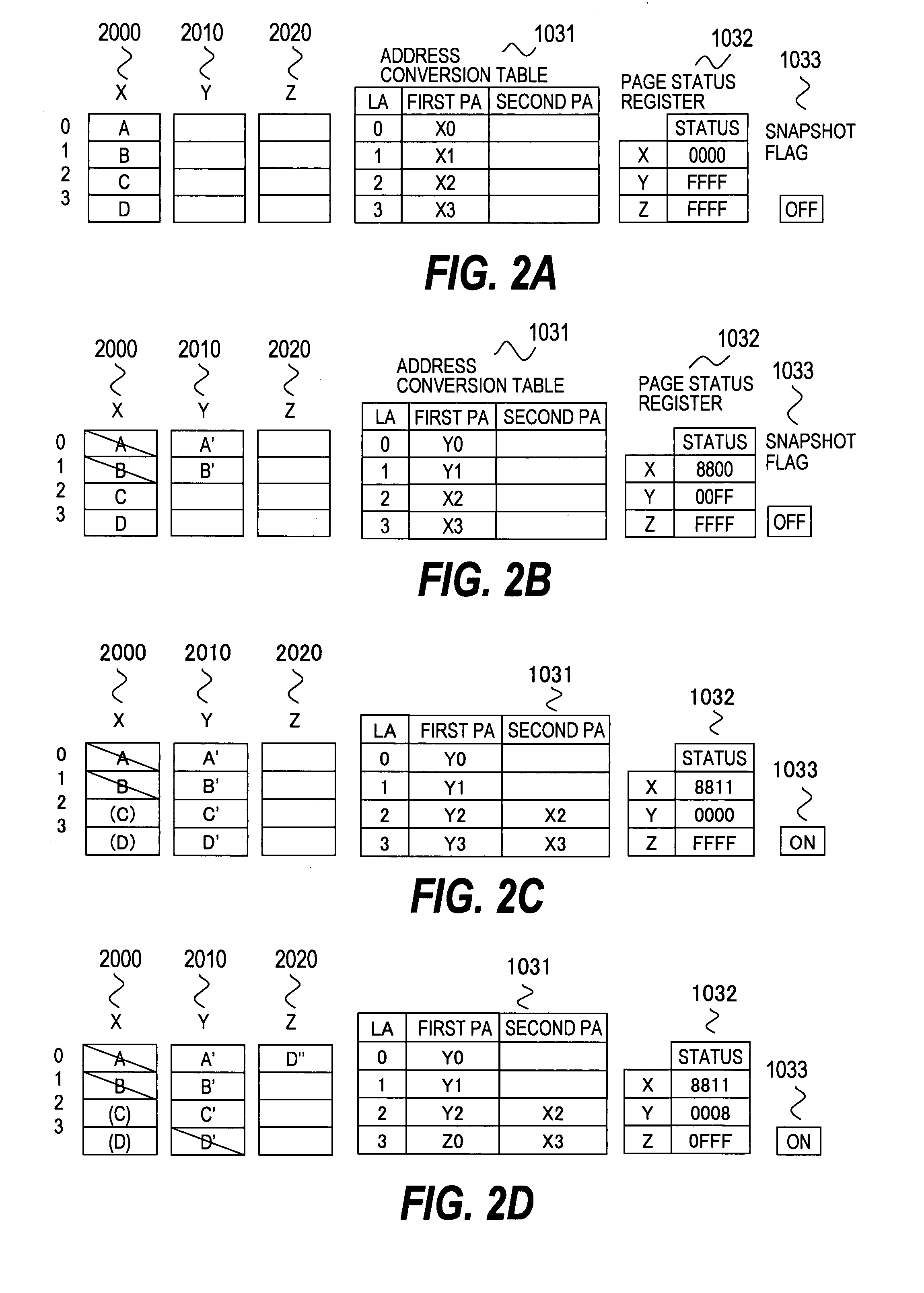
Semiconductor memory system having a snapshot function
ActiveUS20080126712A1Reduce loadImprove usabilityError detection/correctionMemory systemsInvalid DataData store
In a semiconductor memory computer equipped with a flash memory, use of backed-up data is enabled. The semiconductor memory computer includes an address conversion table for detecting physical addresses of at least two pages storing data by designating a logical address from one of logical addresses to be designated by a reading request. The semiconductor memory computer includes a page status register for detecting one page status allocated to each page, and page statuses to be detected include the at least following four statuses: (1) a latest data storage status, (2) a not latest data storage status, (3) an invalid data storage status, and (4) an unwritten status. By using the address conversion table and the page status register, at least two data s (latest data and past data) can be read for one designated logical address from a host computer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
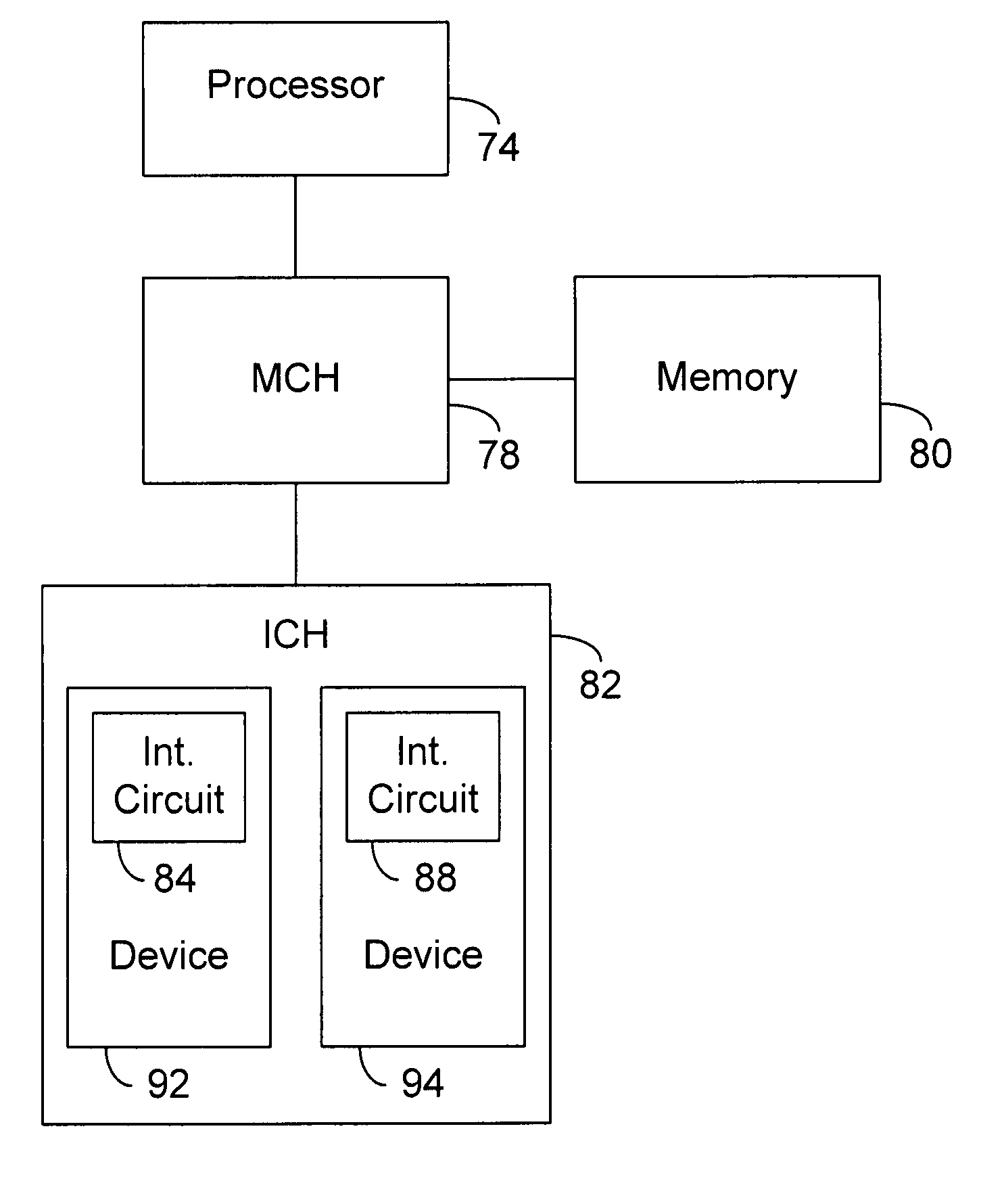
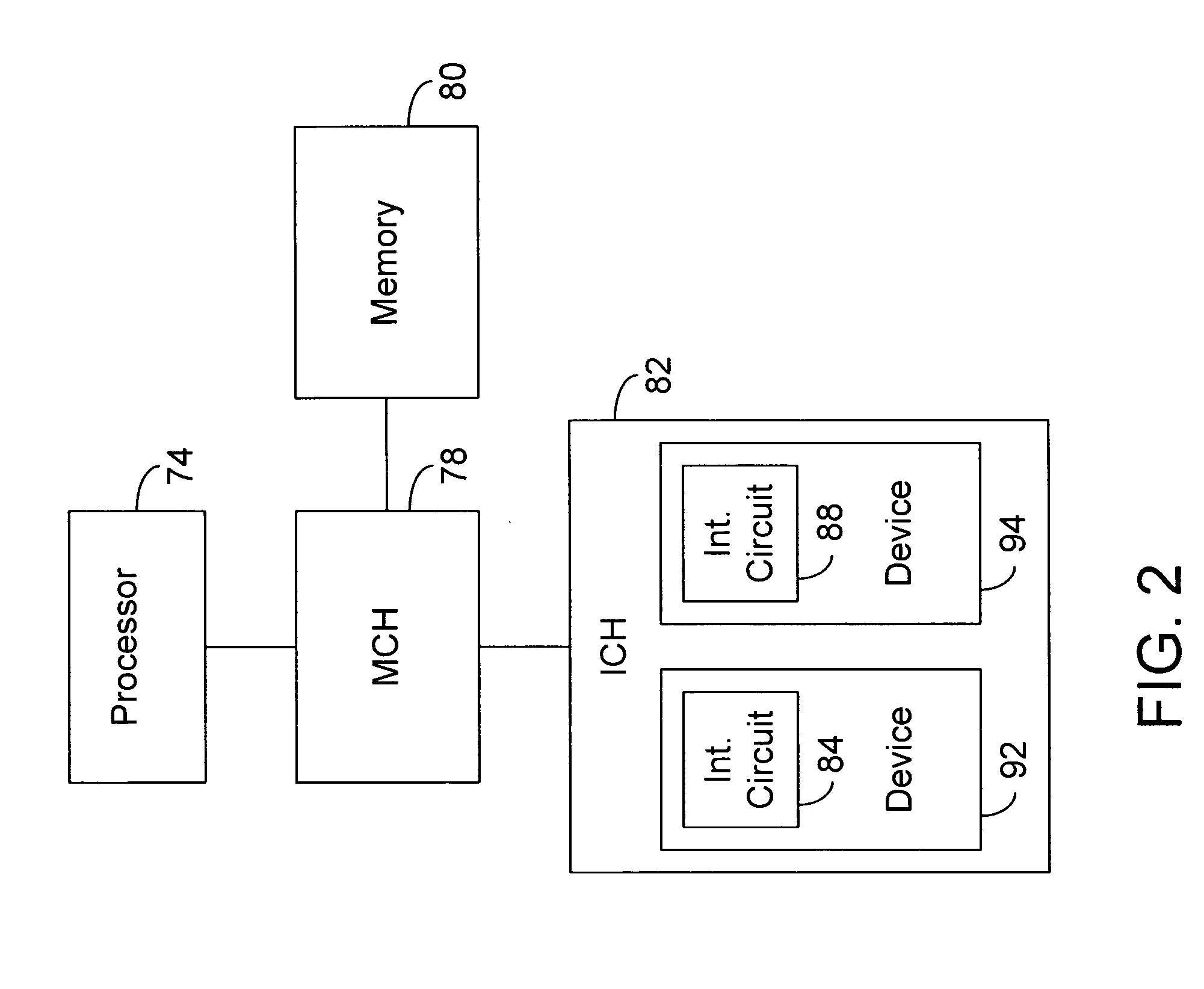
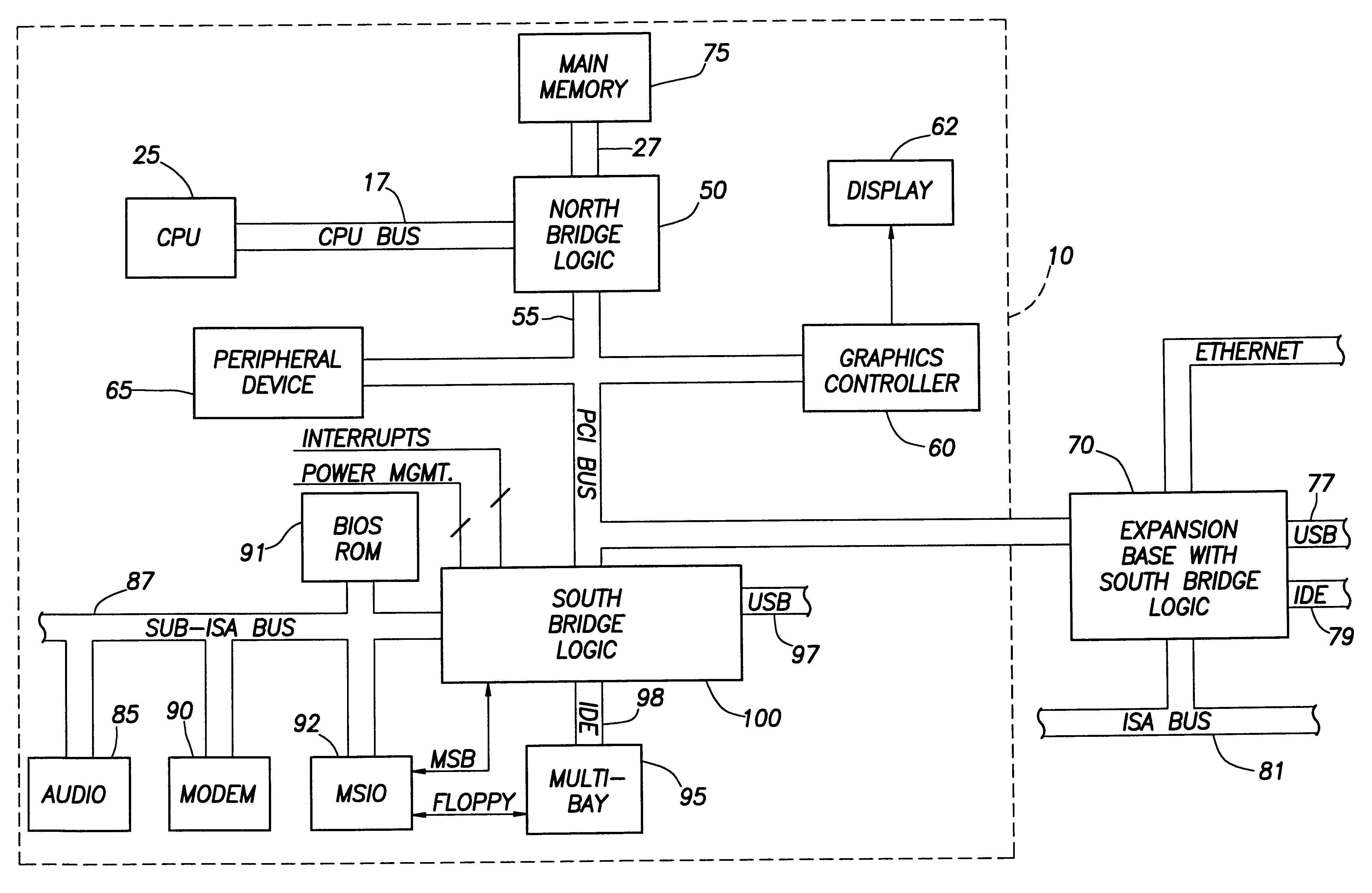
Computer system with bridge logic that asserts a system management interrupt signal when an address is made to a trapped address and which also completes the cycle to the target address
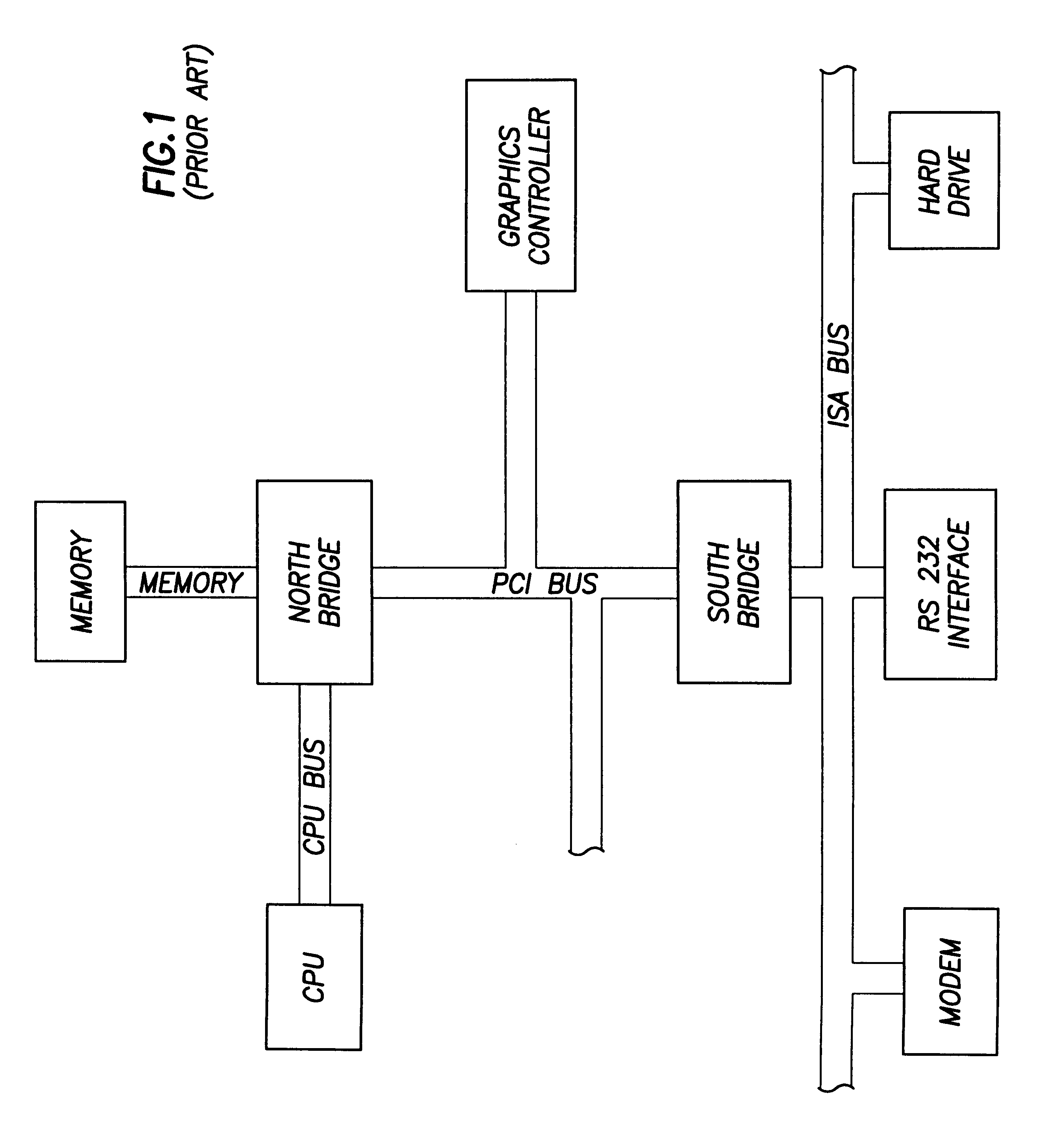
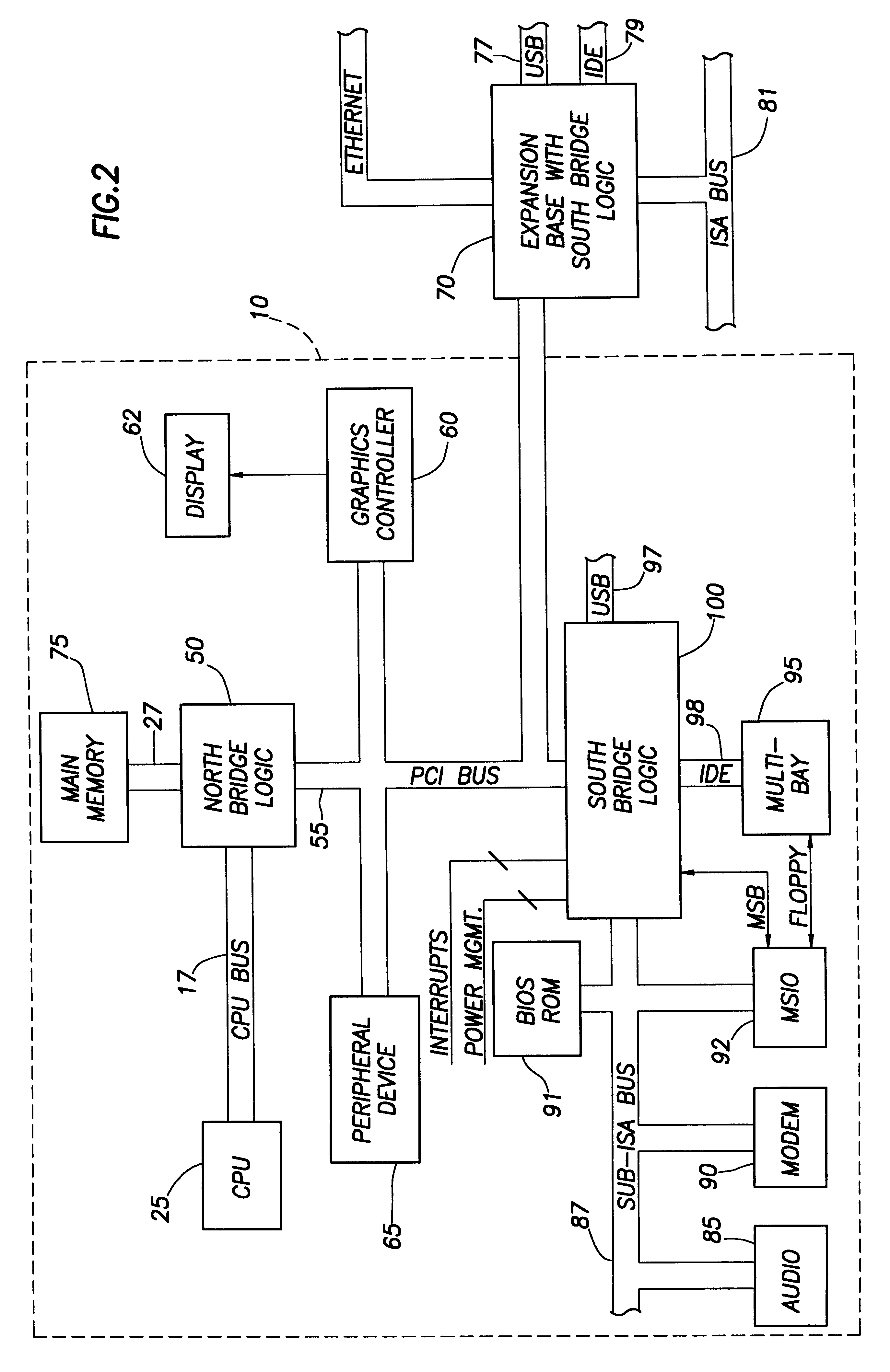
A computer system includes a South bridge logic that connects an expansion bus to one or more secondary expansion busses and peripheral devices. The South bridge logic includes internal control devices that are targets for masters on the expansion bus. The target devices couple to the expansion bus through a common expansion target interface, which monitors and translates master cycles on the expansion bus on behalf of the target devices. The South bridge includes an ACPI / power management logic capable of supporting a Device Idle mode in which selected I / O device may be placed in a low power state. To prevent cycles from being run to a device in a low power state, the ACPI / power management includes status registers that are used to determine when a device in low power mode is the target of an expansion bus cycle. If such a cycle occurs, the cycle is intercepted and an SMI signal is transmitted to the CPU. In addition, the target interface responds to the master by asserting a retry signal. When the transaction is retried, the cycle is passed to the target, which responds with an invalid data signal. The CPU by this time, or at some subsequent time realizes that the target was asleep based upon processing of the SMI signal. The CPU then either re-executes the cycle when the device is removed form the low power state, or else simply rejects the invalid data.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method and system for a result code for a single-instruction multiple-data predicate compare operation
InactiveUS6282628B1Concurrent instruction executionSpecific program execution arrangementsAcceptance testingStatus register
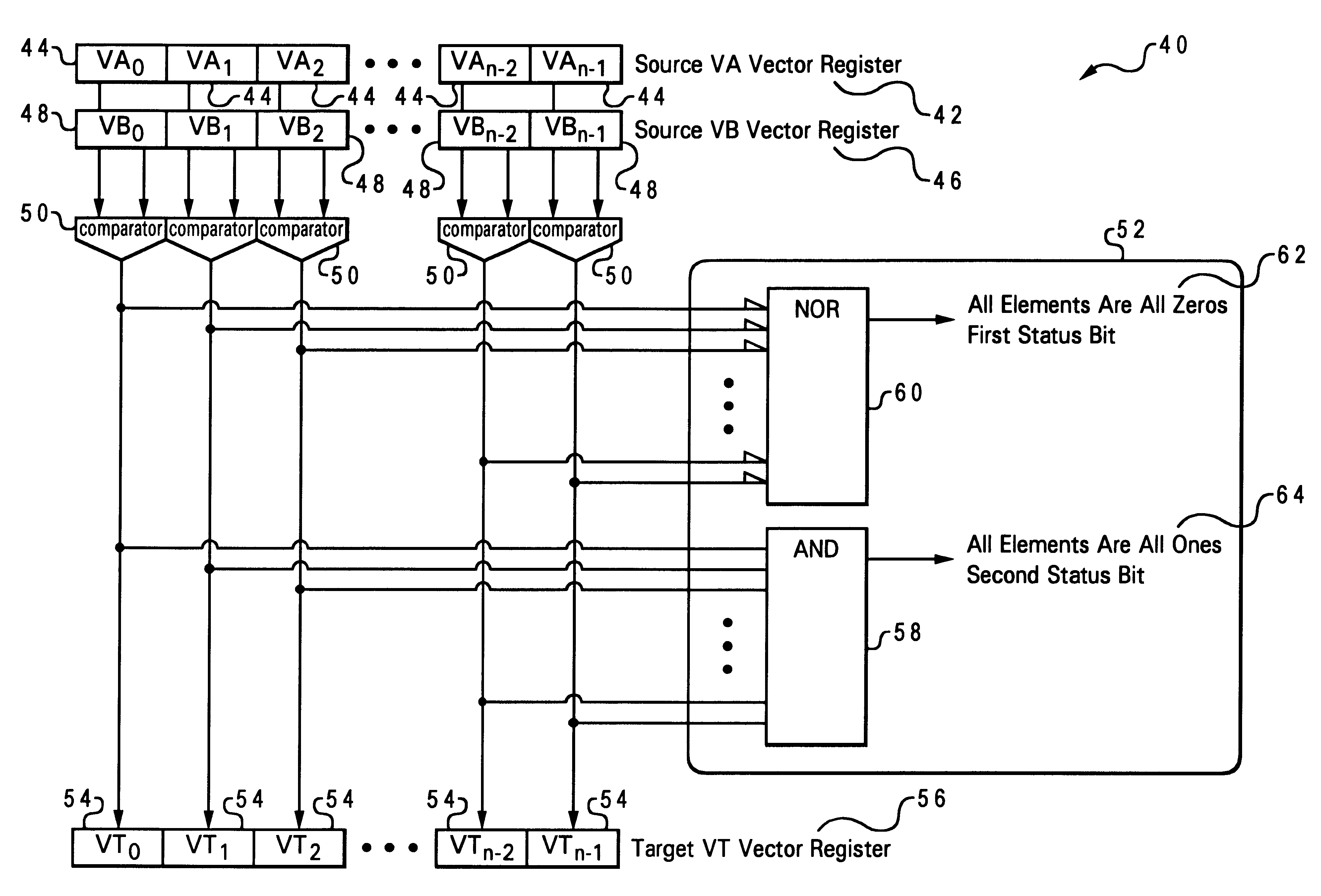
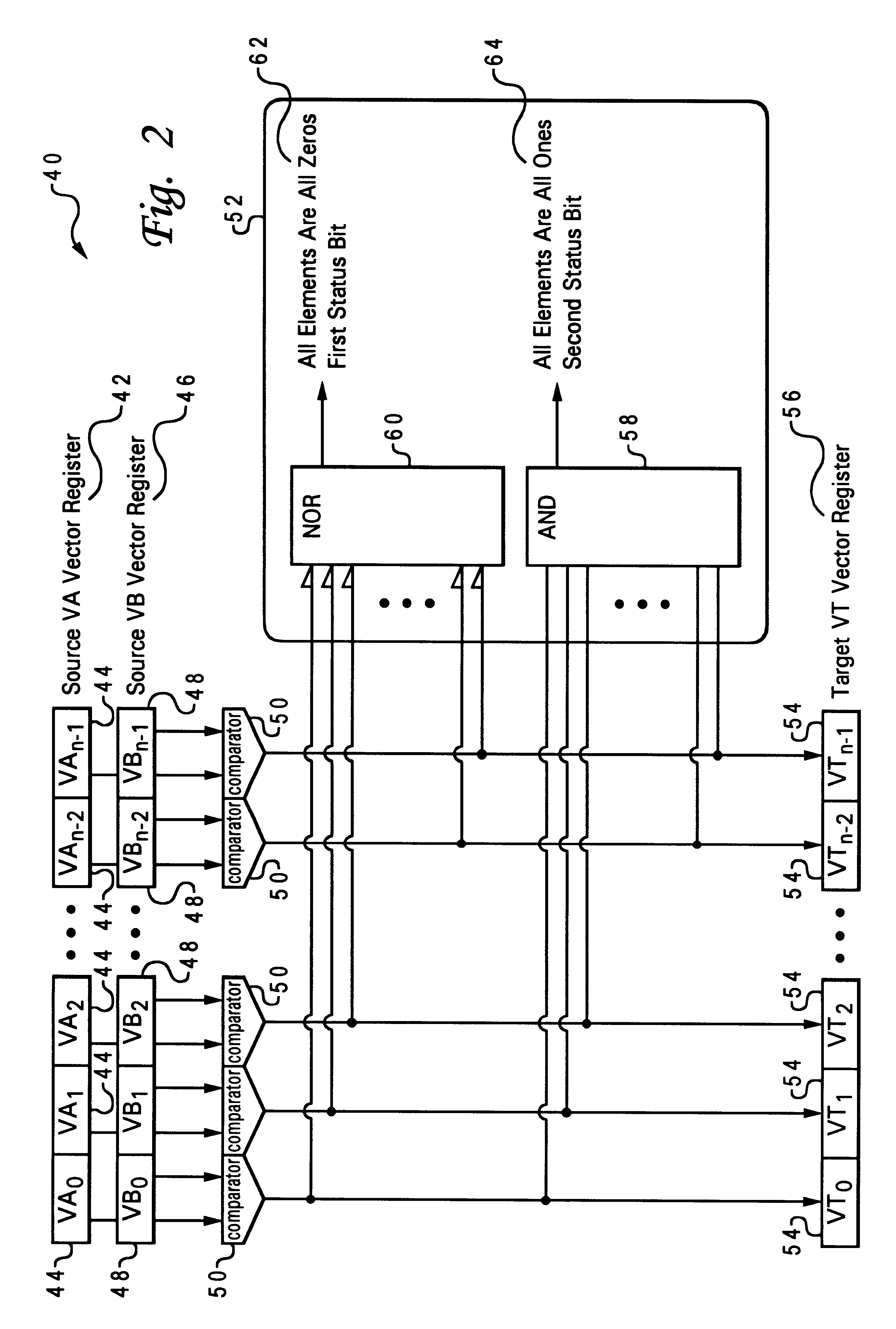
A method and system is disclosed which summarizes the results of a classical single-instruction multiple-data SIMD predicate comparison operation, signaling whether all comparisons resulted in a false result or true result, and placing that status into a separate status register, such as the Power PC Condition Register. The method and system utilizes first and second status bits to support the signaling whether all element comparisons resulted in true or false. The first status bit is set when all element comparisons resulted in false (i.e. a NOR of all predicate comparison results), and the second status bit is set when all element comparisons resulted in true (i.e. an AND of all predicate comparison results). This capability allows control flow using conditional branching on the event when all comparison results are false or when all comparison results are true. The method and system of the present invention is useful in 3-D graphics such as lighting and trivial acceptance testing where executing down both paths of a branch and then selecting the correct result is not tolerable.
Owner:IBM CORP +2
Fly height control for a read/write head in a hard disk drive
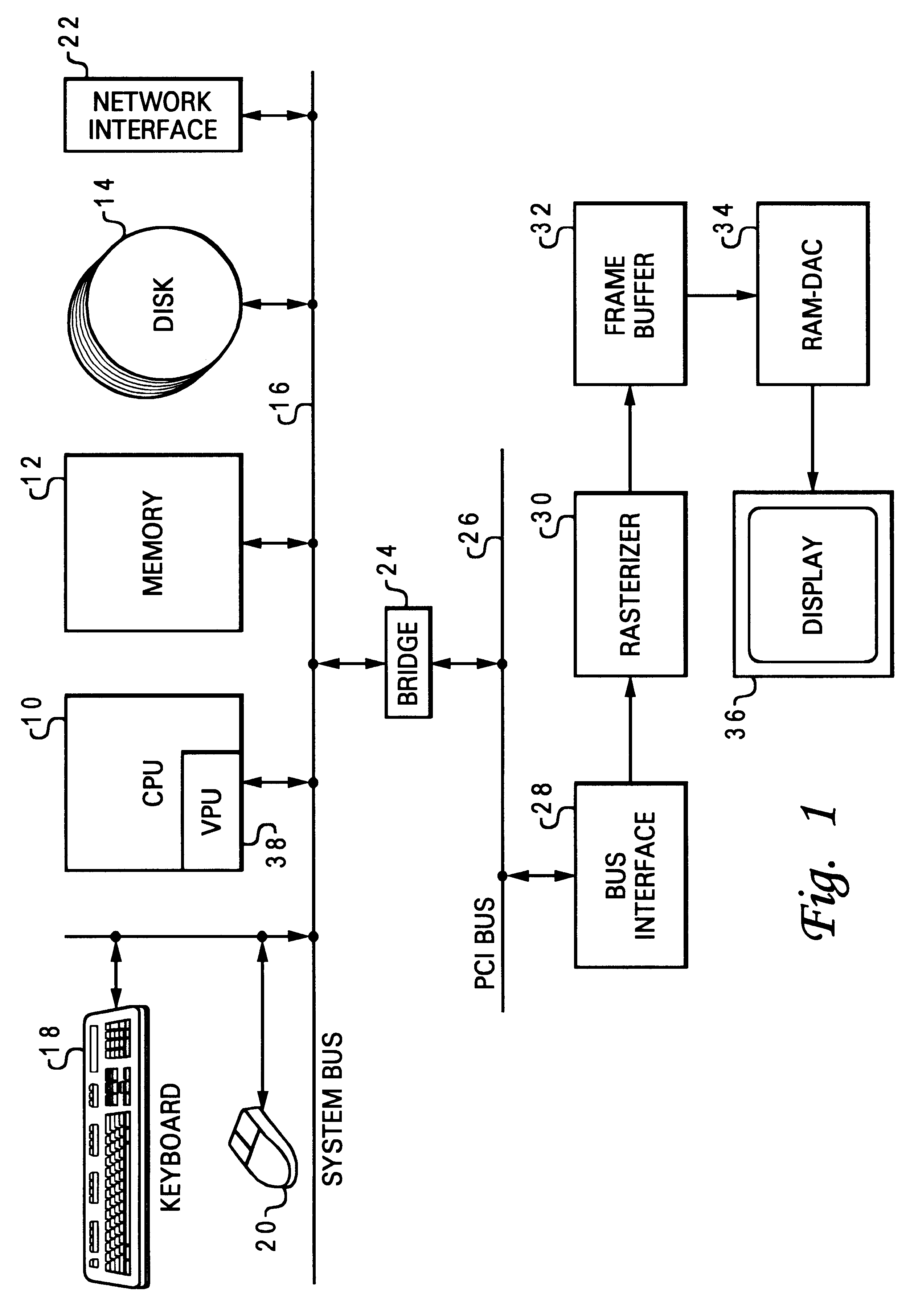
InactiveUS7023647B2Improve heat resistanceDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageHard disc driveDigital data
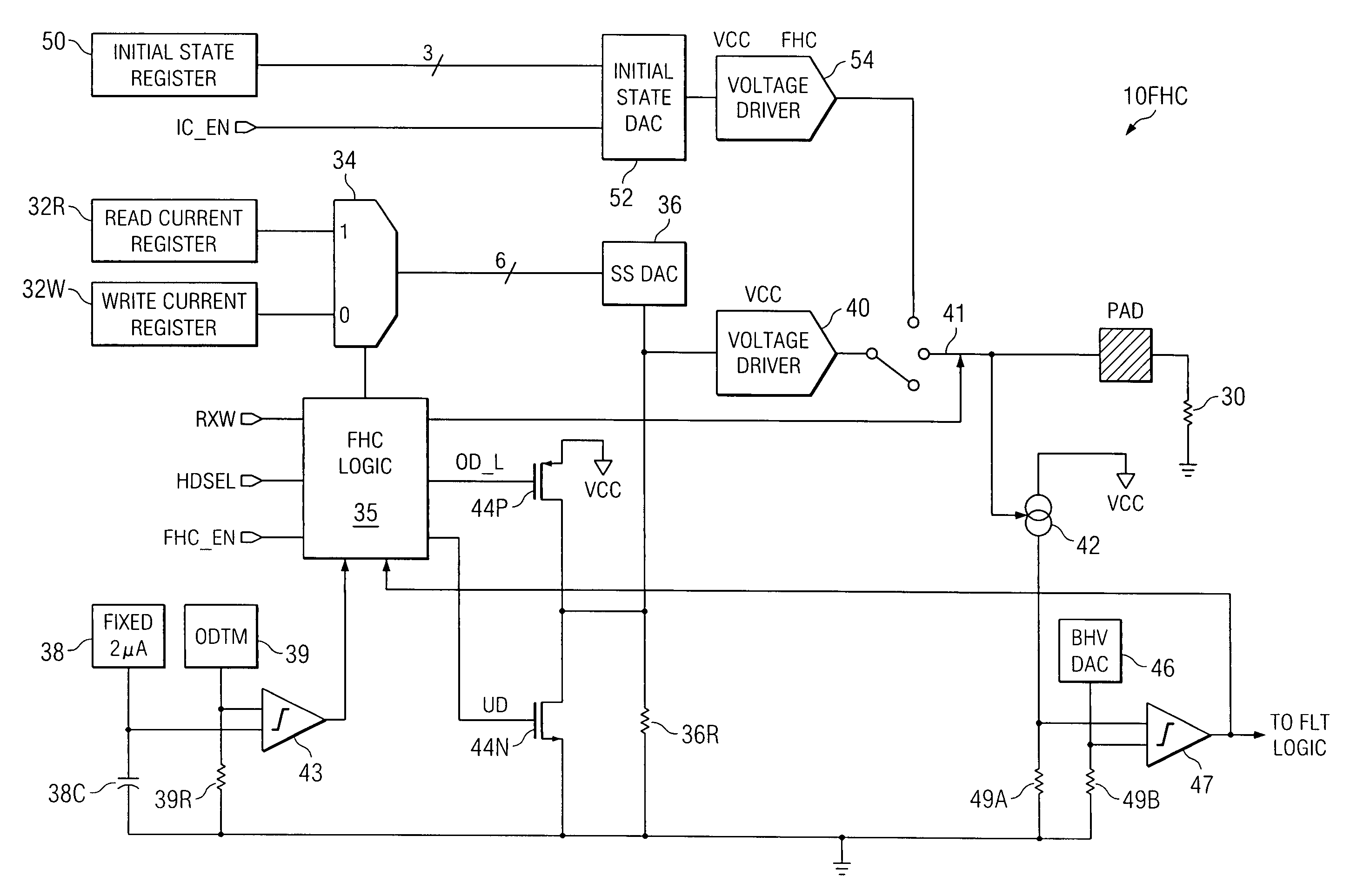
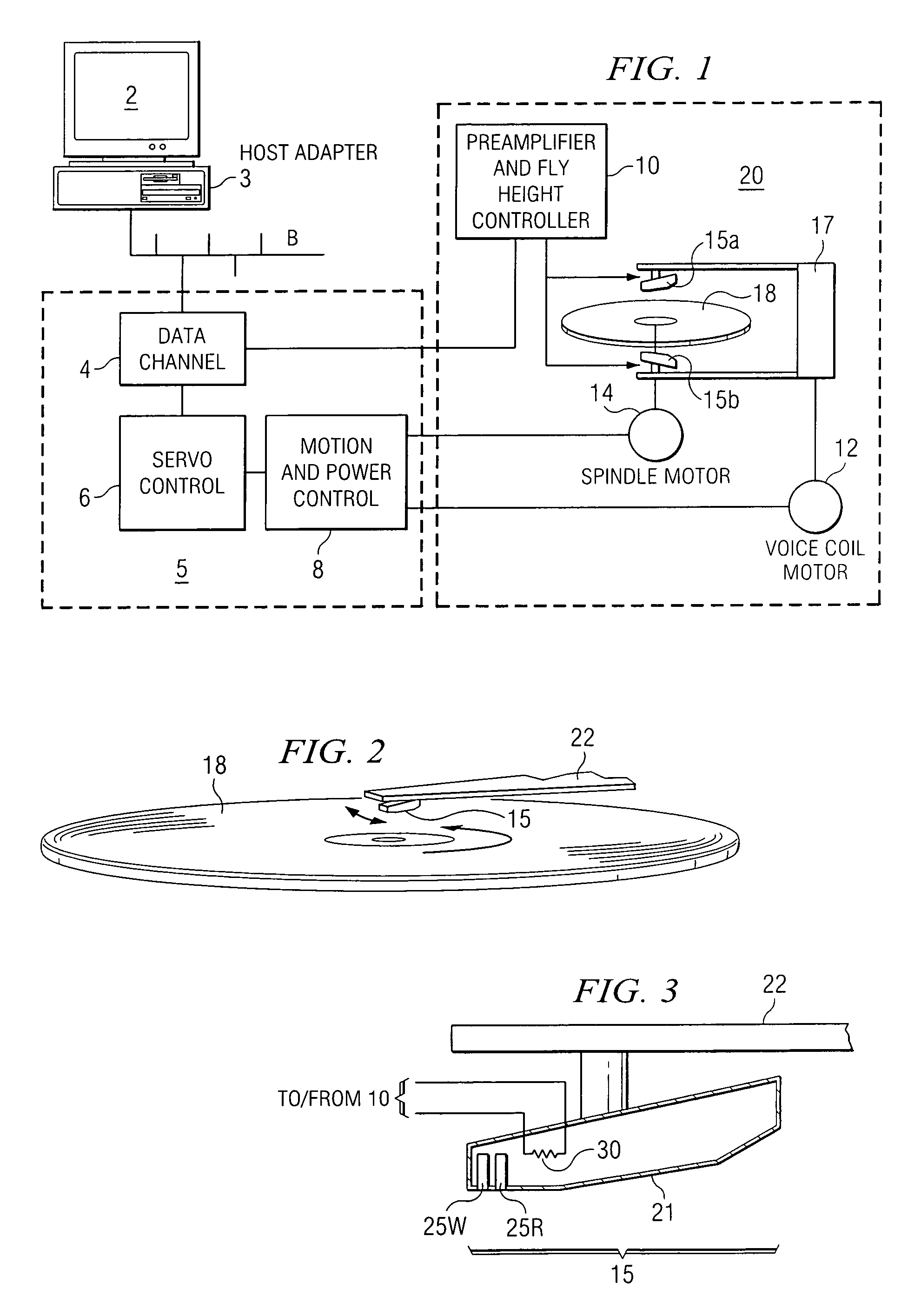
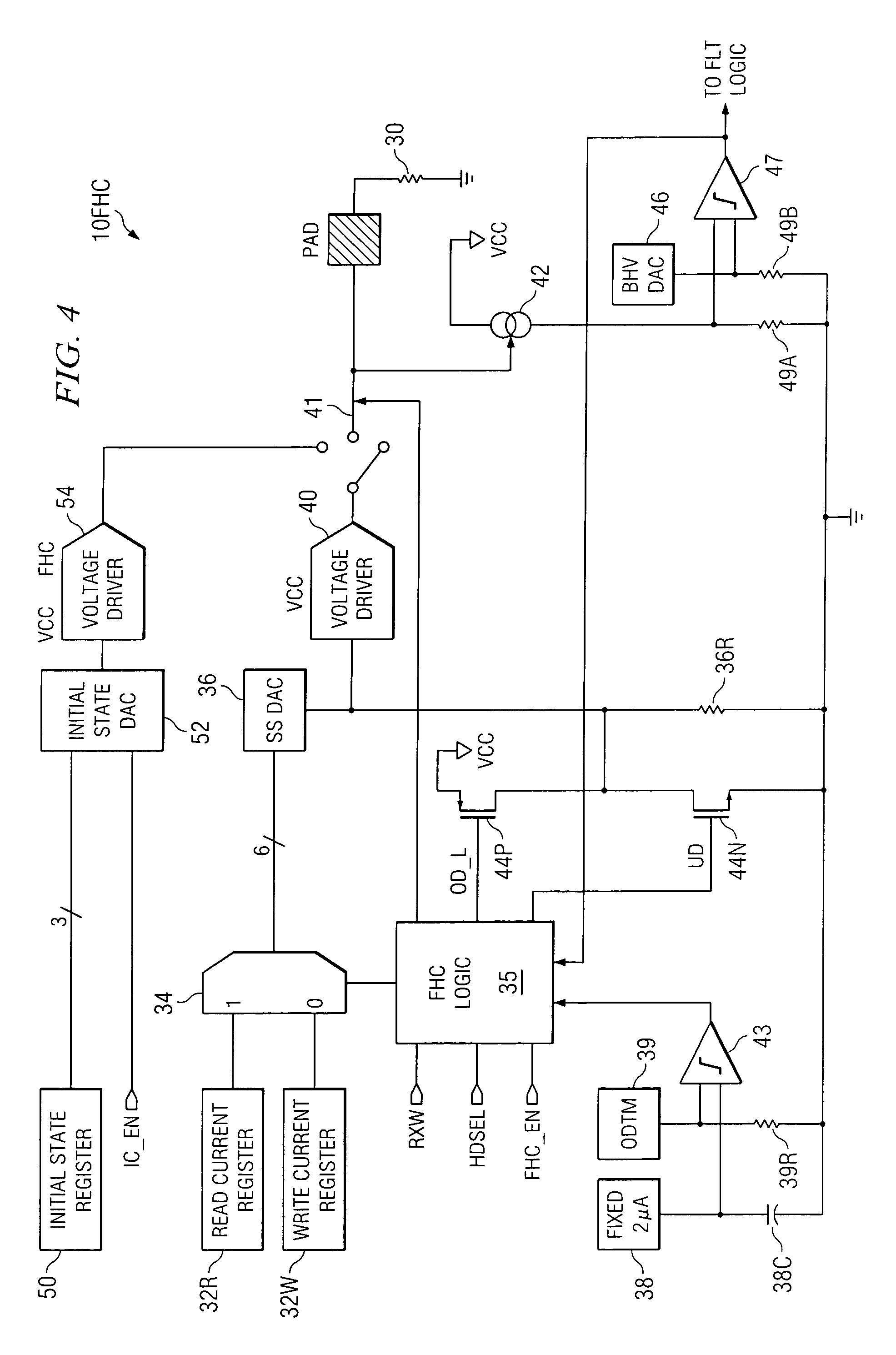
A fly height controller (10FHC; 10FHC′) for controlling the fly height of a read / write head assembly (15) in a disk drive (20) is disclosed. A heat element resistor (30) is disposed within the read / write head assembly (15). The fly height controller (10FHC; 10FHC′) includes registers (32R, 32W) for storing digital data words corresponding to the desired drive levels to be applied to the heat element resistor (30) during read and write operations. The registers (32R, 32W) are selectively coupled to a steady-state digital-to-analog converter (DAC) (36), depending upon whether a read or write operation is occurring; the output of the steady-state DAC (36) is applied to a voltage driver (40), which in turn drives current into the heat element resistor (30). Overdrive and underdrive transistors (44P, 44N) are provided to overdrive and underdrive the input to the voltage driver (40) in transitions between read and write operations. An initial state register (50) receives a digital word indicating the desired current for the heat element resistor (30) when unselected; the output of the initial state register (50) is applied to an initial state DAC (52), which drives an initial state voltage driver (54). Control logic (35; 35′) controls whether the steady-state voltage driver (40) or initial state voltage driver (54) drives the heat element resistor (30). The fly height controller (10FHC′) may also be adapted to control the fly height of multiple read / write head assemblies (15) in a disk drive.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Routing method and system for a wireless network
ActiveUS8948046B2Easy to handleEliminate the broadcast forwarding loopError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsBroadcastingRouting algorithm
A method and system for selecting a route in a wireless network for the transmission of a data packet between wireless nodes in said network using a modified link-state routing algorithm wherein only a limited number of broadcast messages are generated to synchronize the link-state database throughout the wireless network. A subset of nodes called portal nodes within the network are elected to do the broadcasting for the entire network. Each portal node broadcasts an announcement of its identity to all of the wireless nodes. Each wireless node responds to these broadcasts to select one of the portal nodes as its root portal node. It then identifies a unicast route back to its root portal node, and sends a link-state register message to this portal node. These link-state register messages received by each portal node are aggregated by them and are broadcast to each of the wireless nodes for storage. When a data packet is thereafter received by a wireless node from a neighboring node, it detects if the data packet satisfies one of a plurality of predetermined conditions and rebroadcasts the data packet to neighboring wireless nodes if none of the conditions is satisfied.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
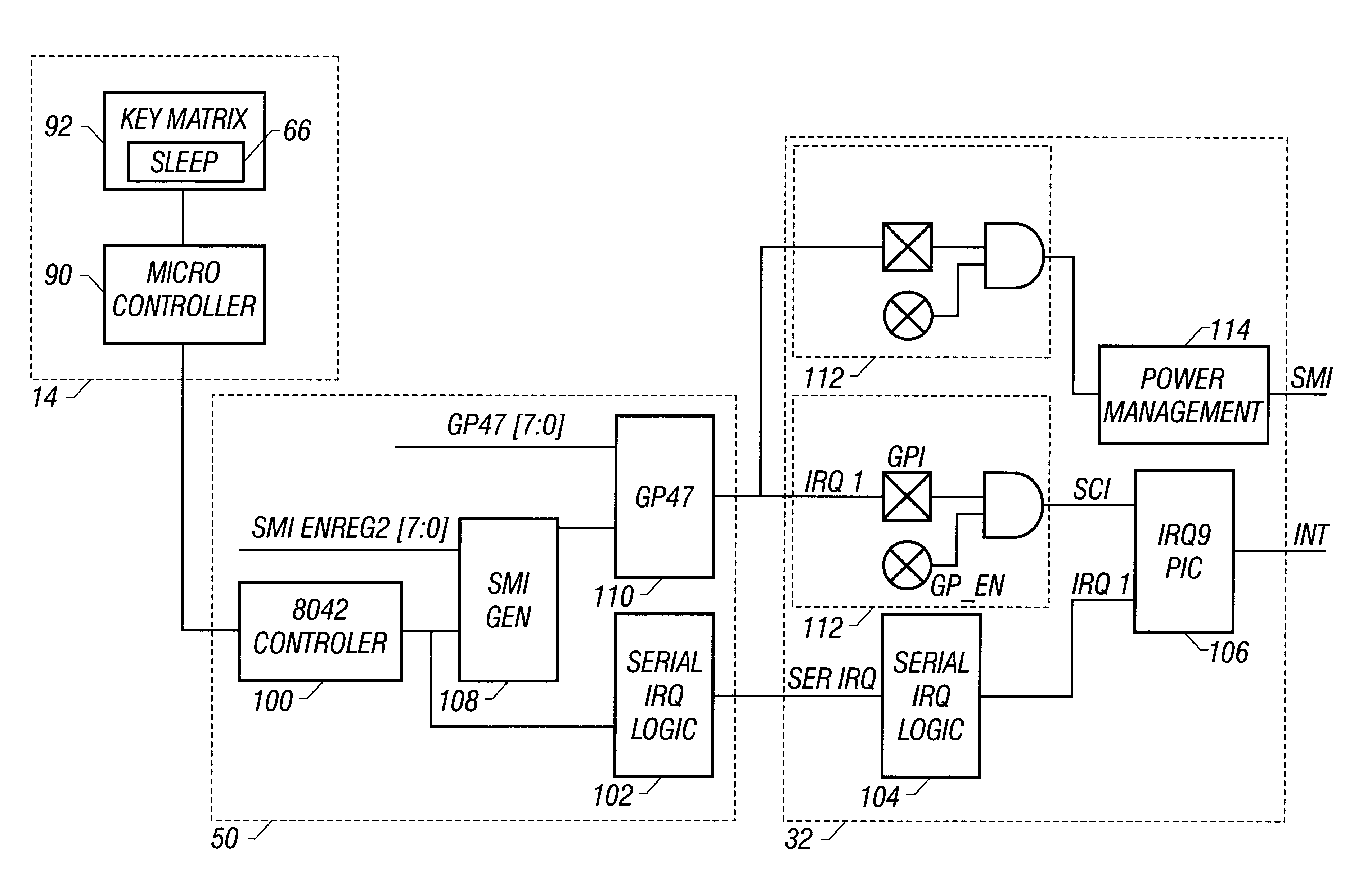
Method and apparatus for an ACPI compliant keyboard sleep key
InactiveUS6678830B1Input/output for user-computer interactionVolume/mass flow measurementPower modeEmbedded system
A computer system includes a status register for receiving events which cause the computer system to change to a low power mode or back to a normal power mode. The status register is selectively coupled to a keyboard controller to receive an interrupt from the keyboard controller when a sleep / wake key is actuated on a keyboard. When the computer system is normally powered, the keyboard interrupt is not routed to the status register. If the computer system is powered down, the keyboard interrupt is routed so that actuation of the sleep / wake key will awake the computer system.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com