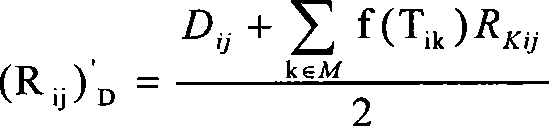Patents
Literature
51 results about "Hidden node problem" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
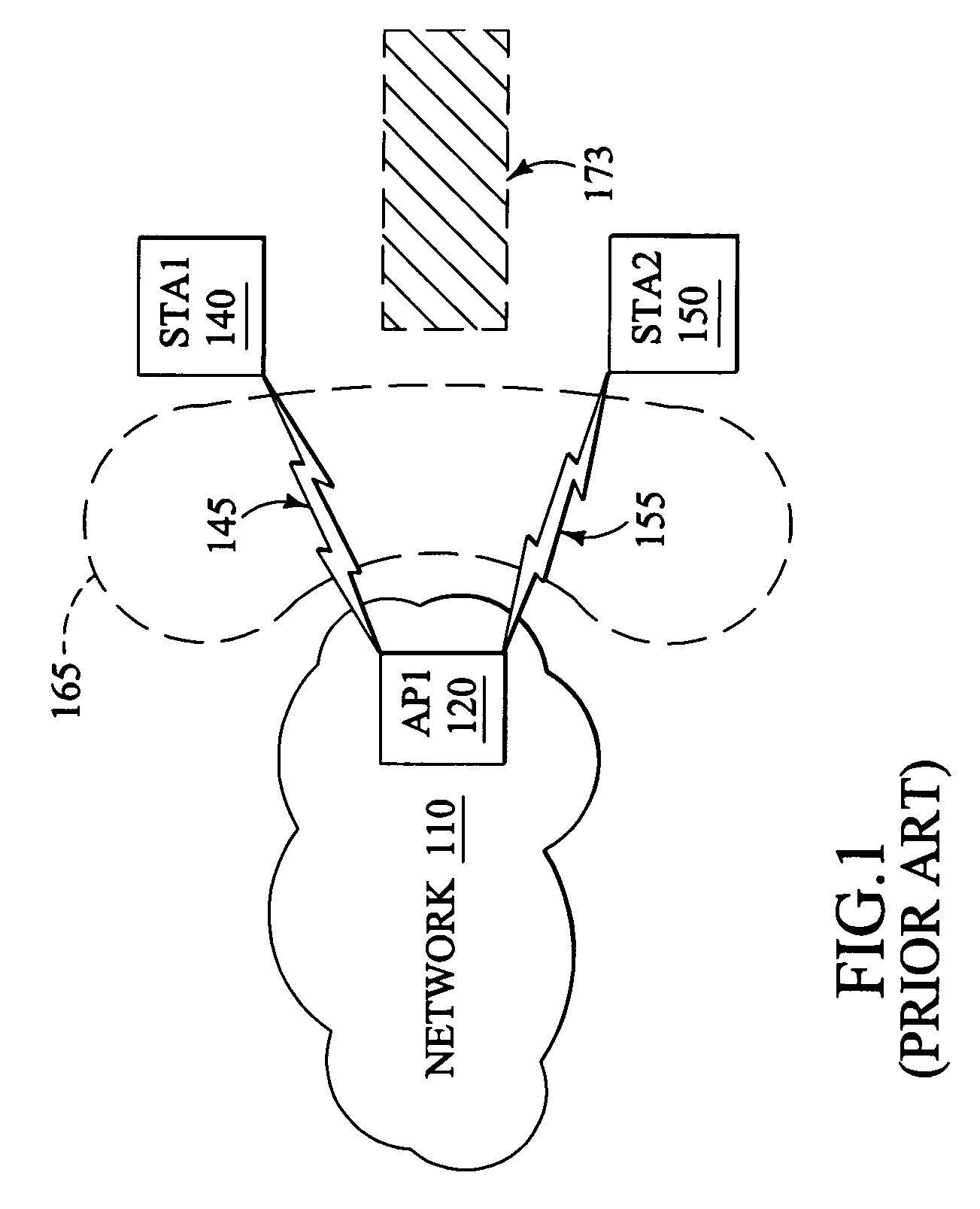
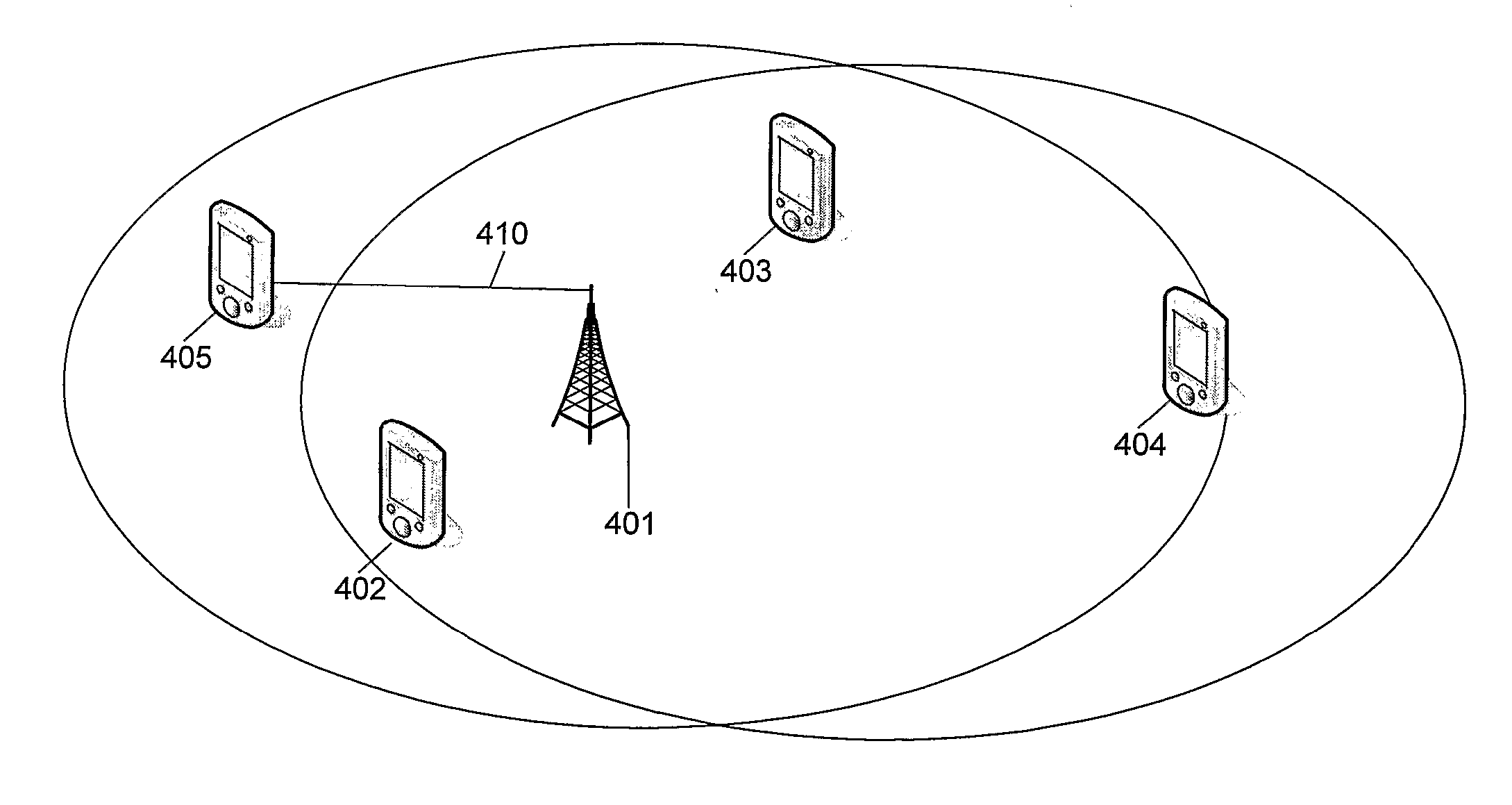
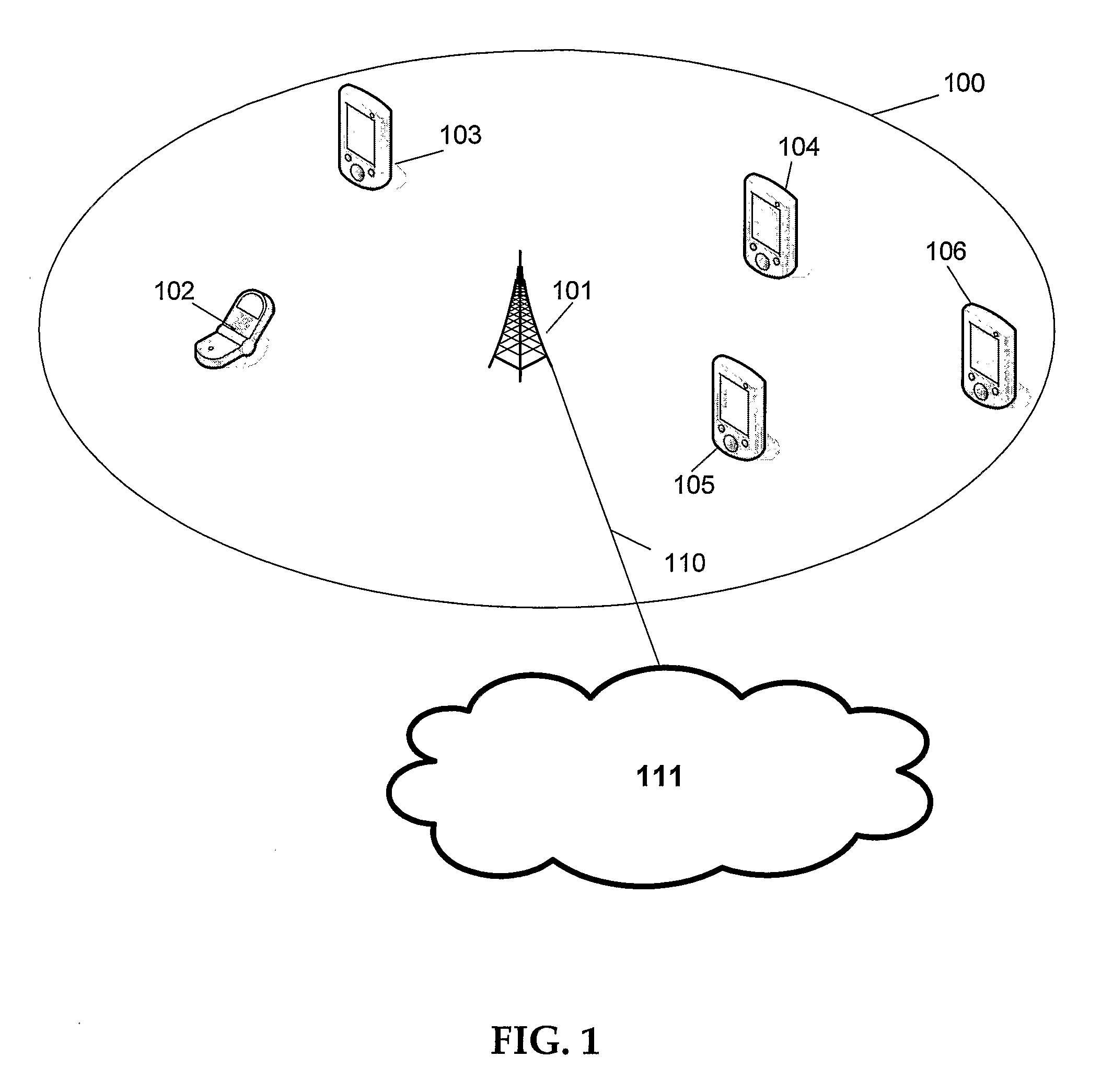
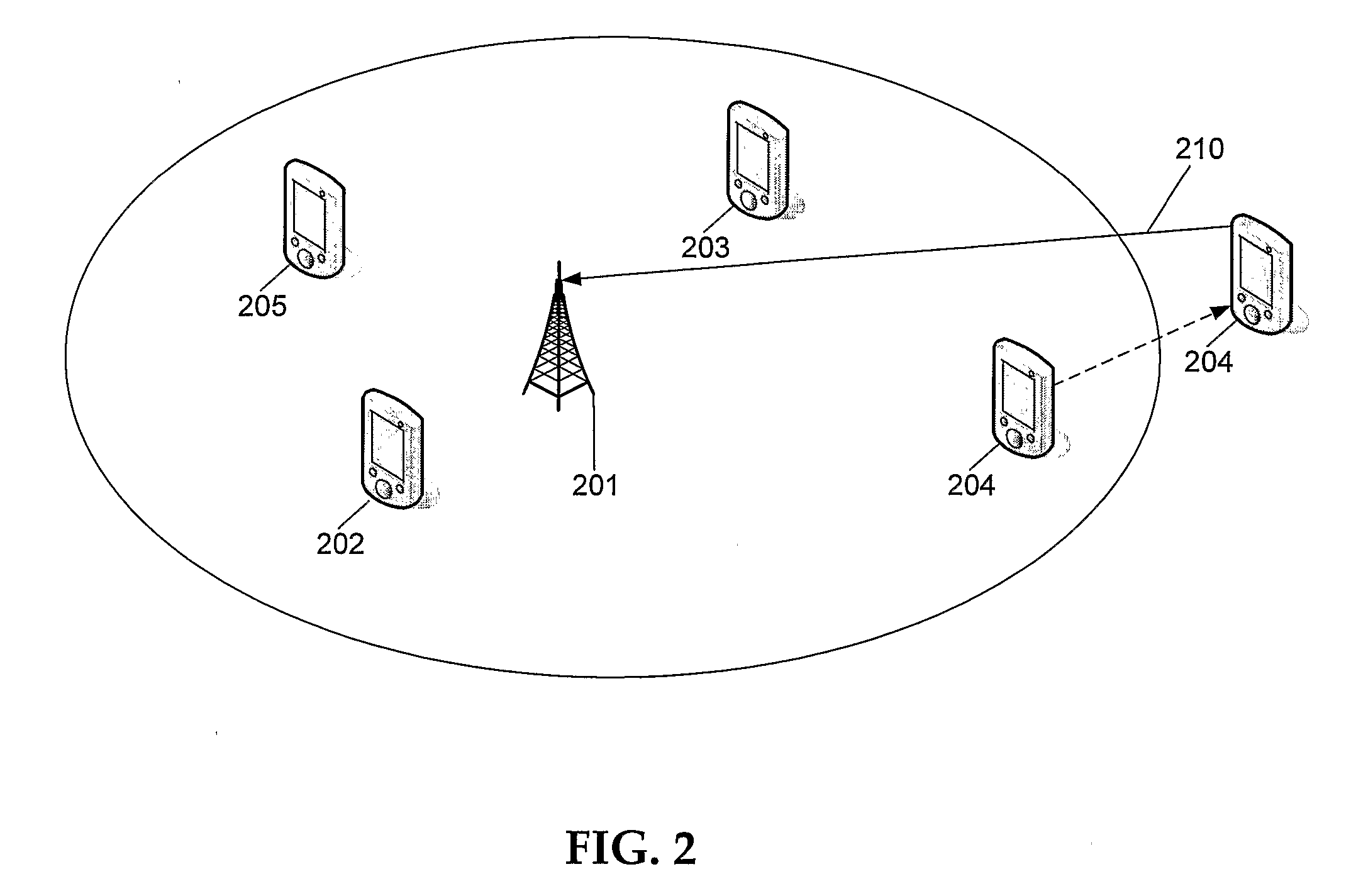
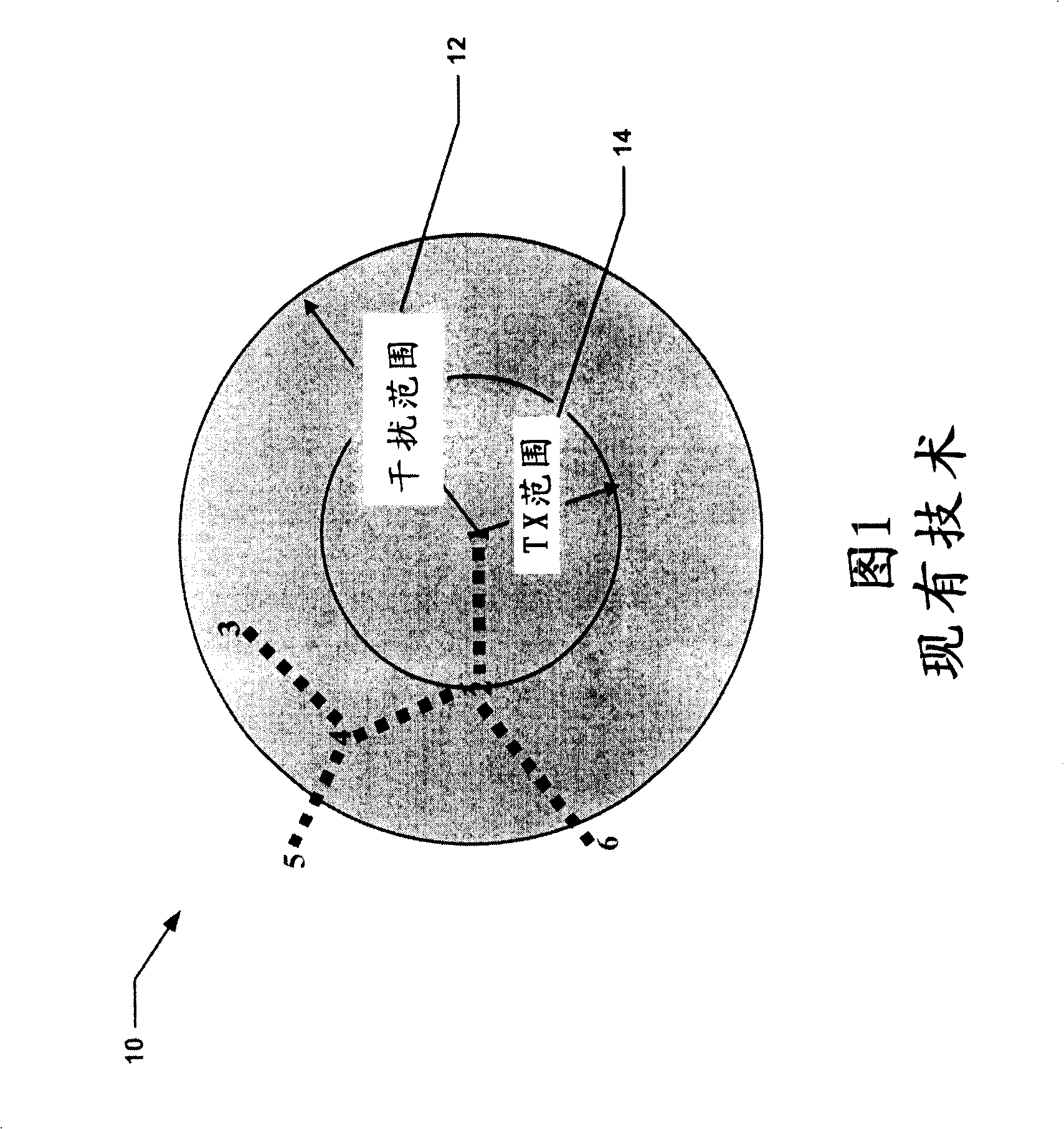
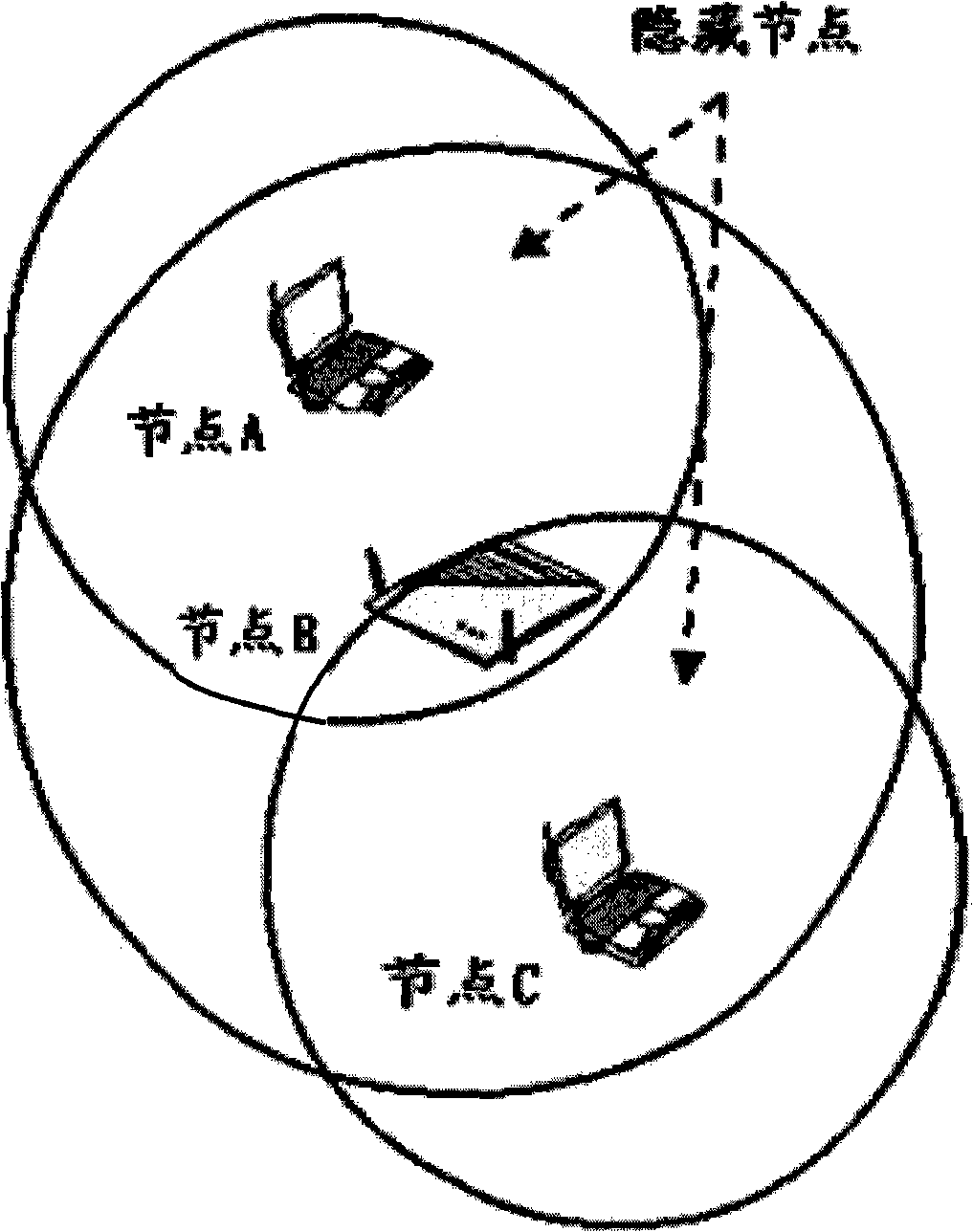
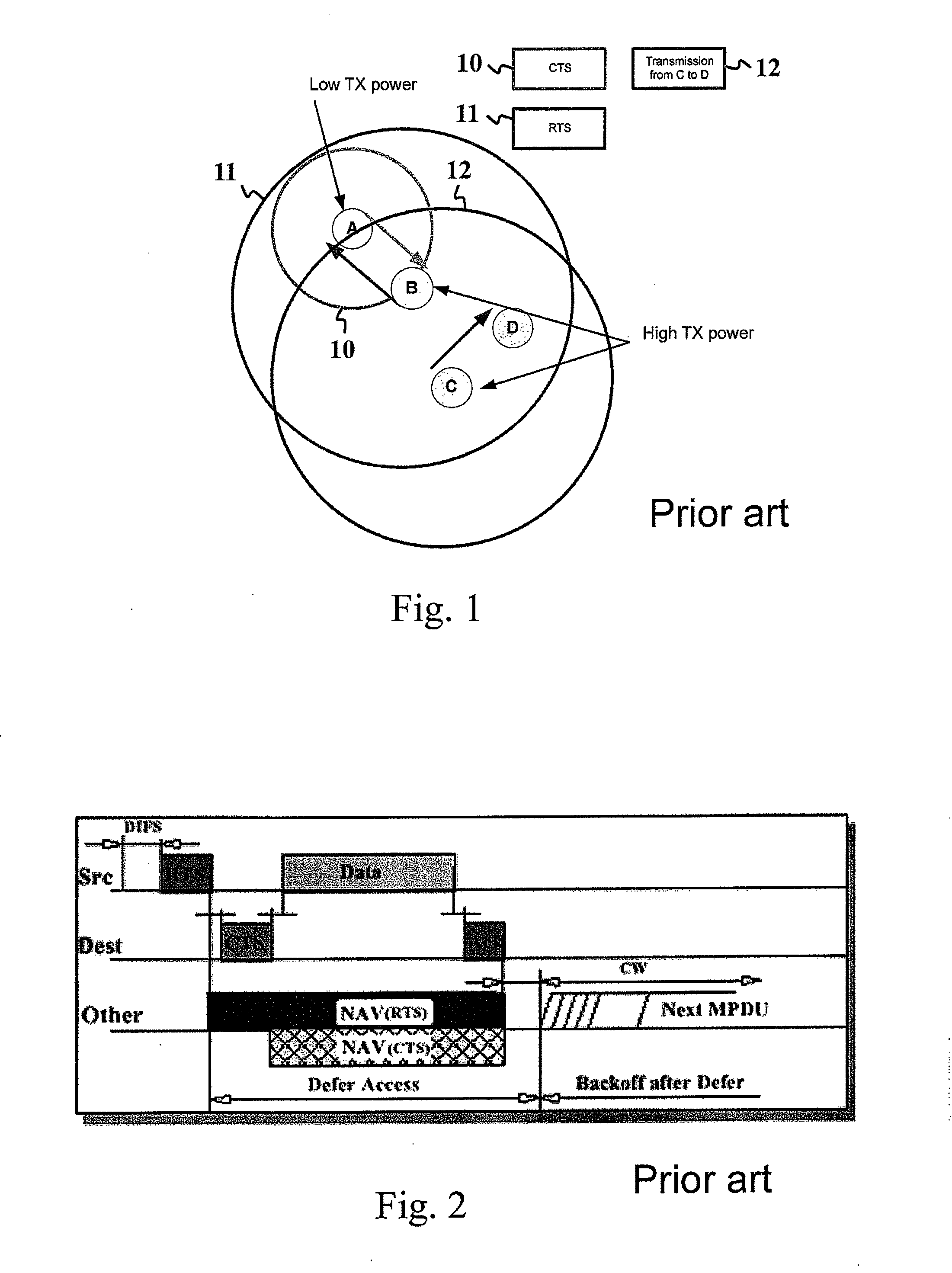
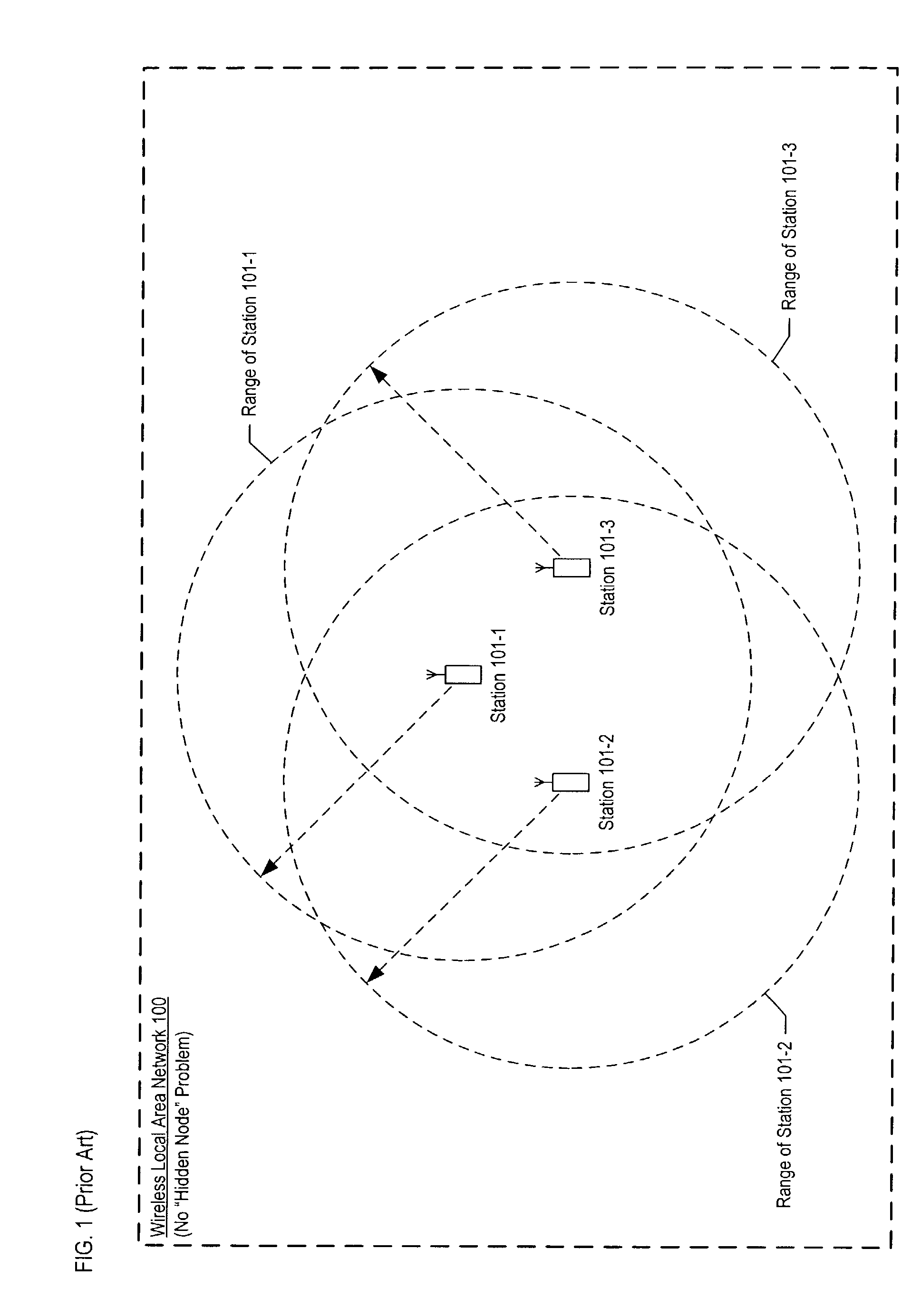
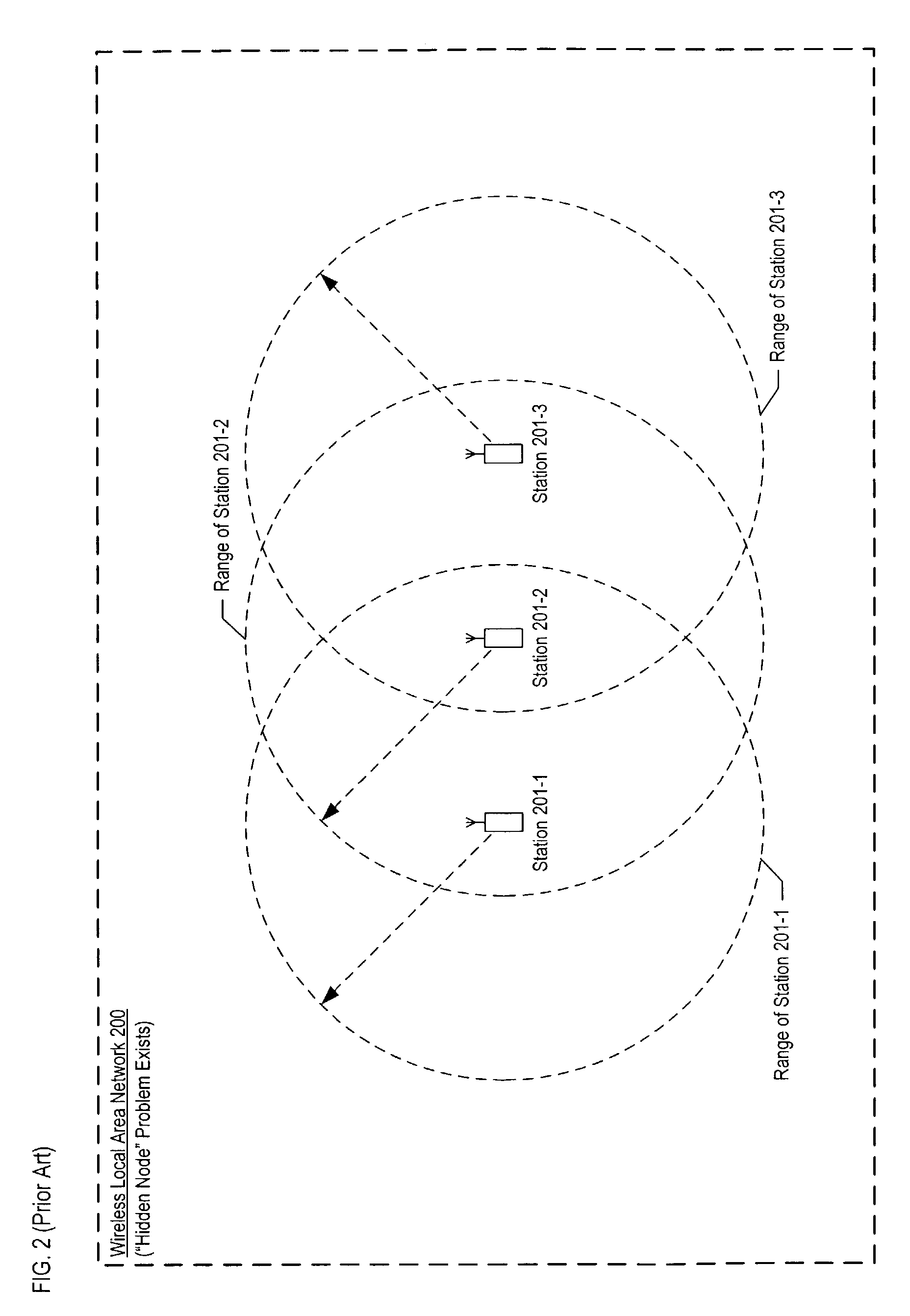
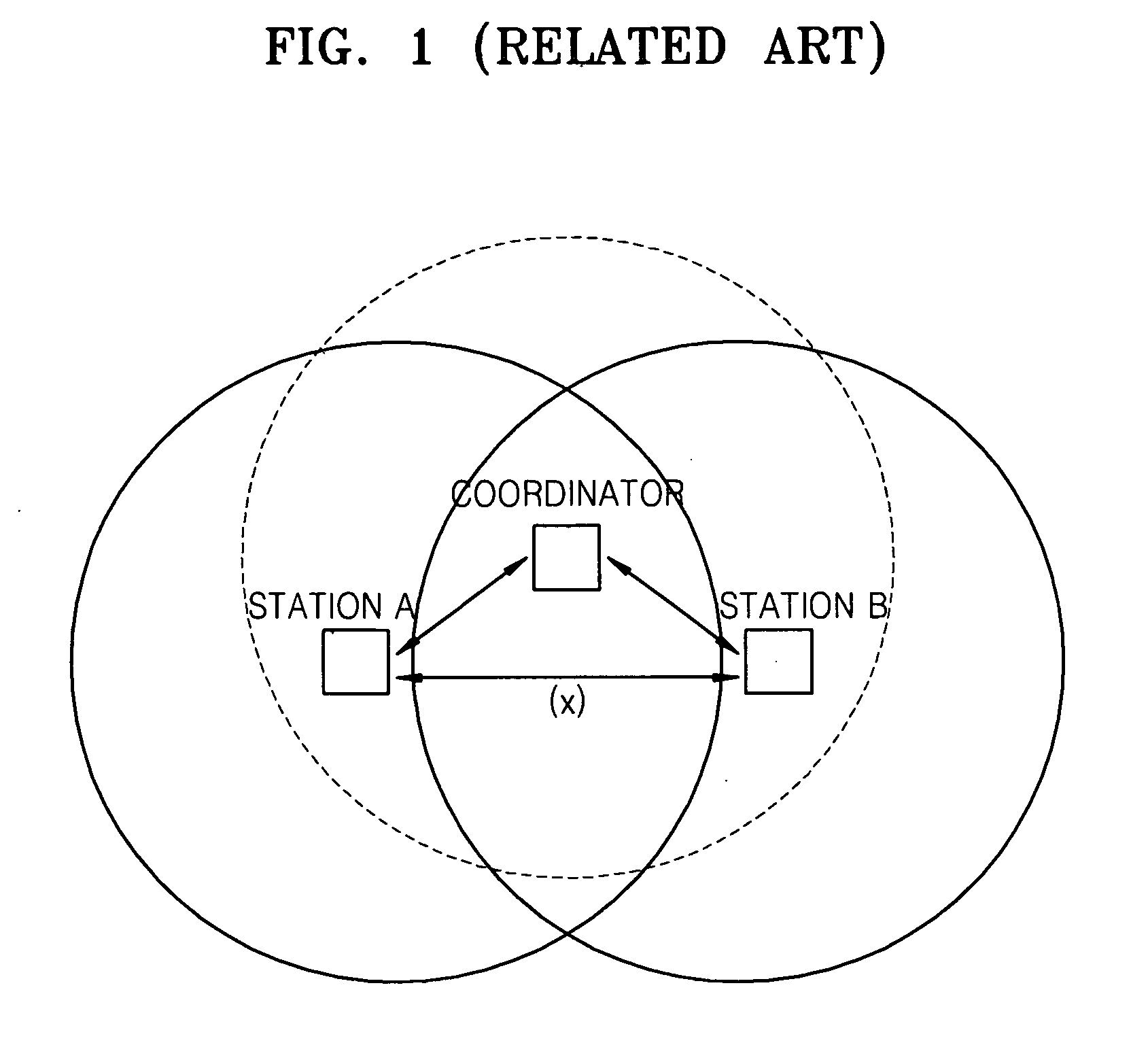
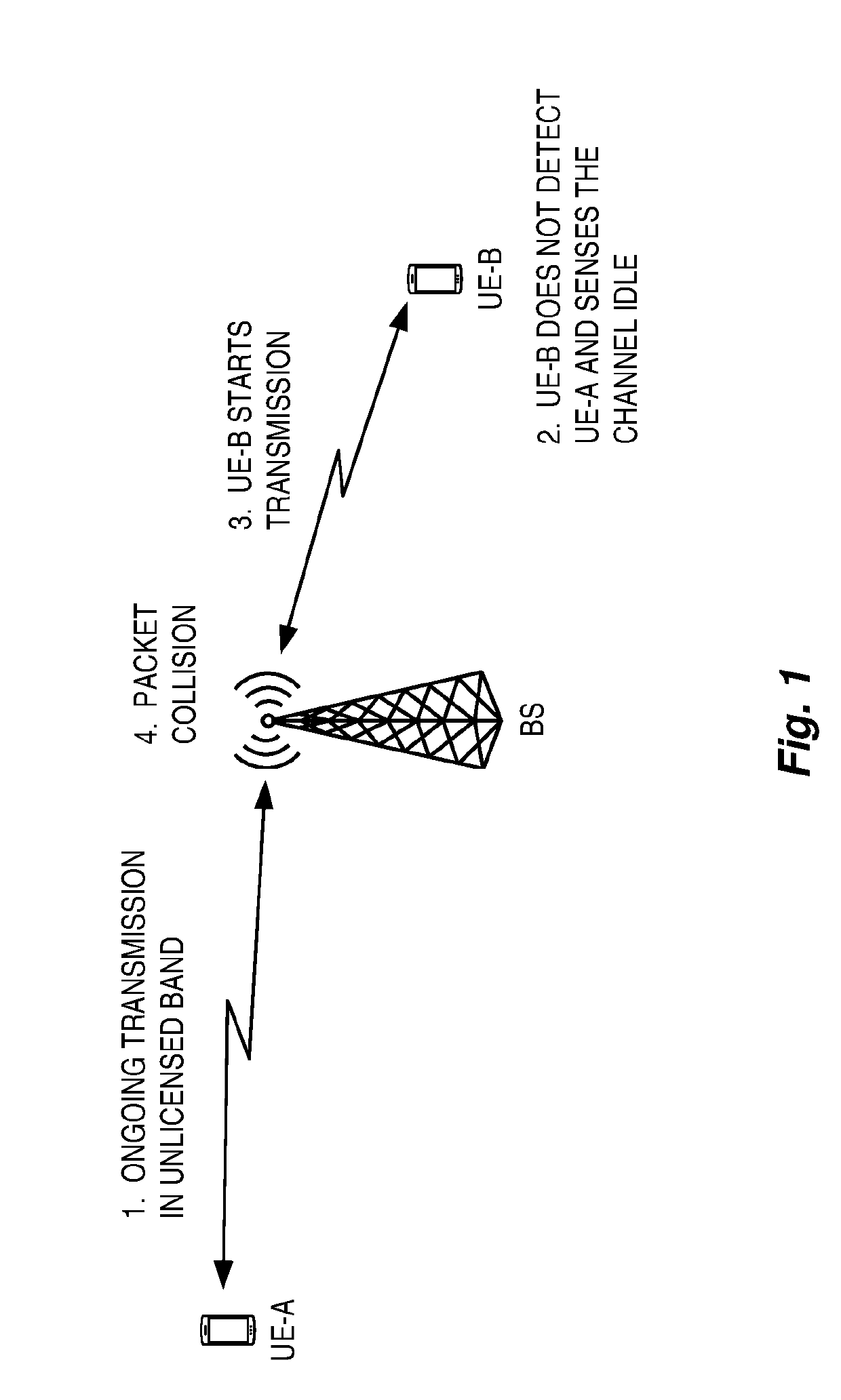
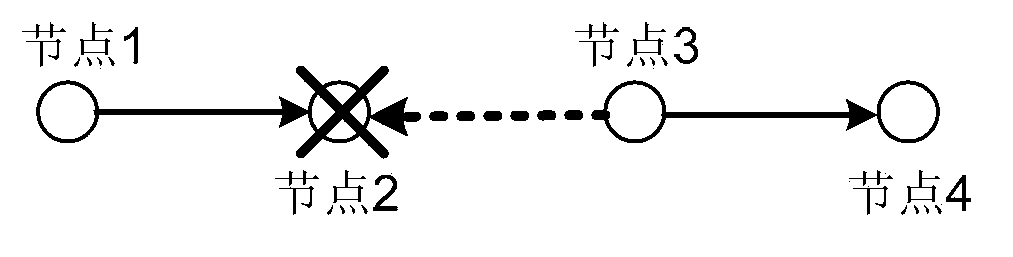
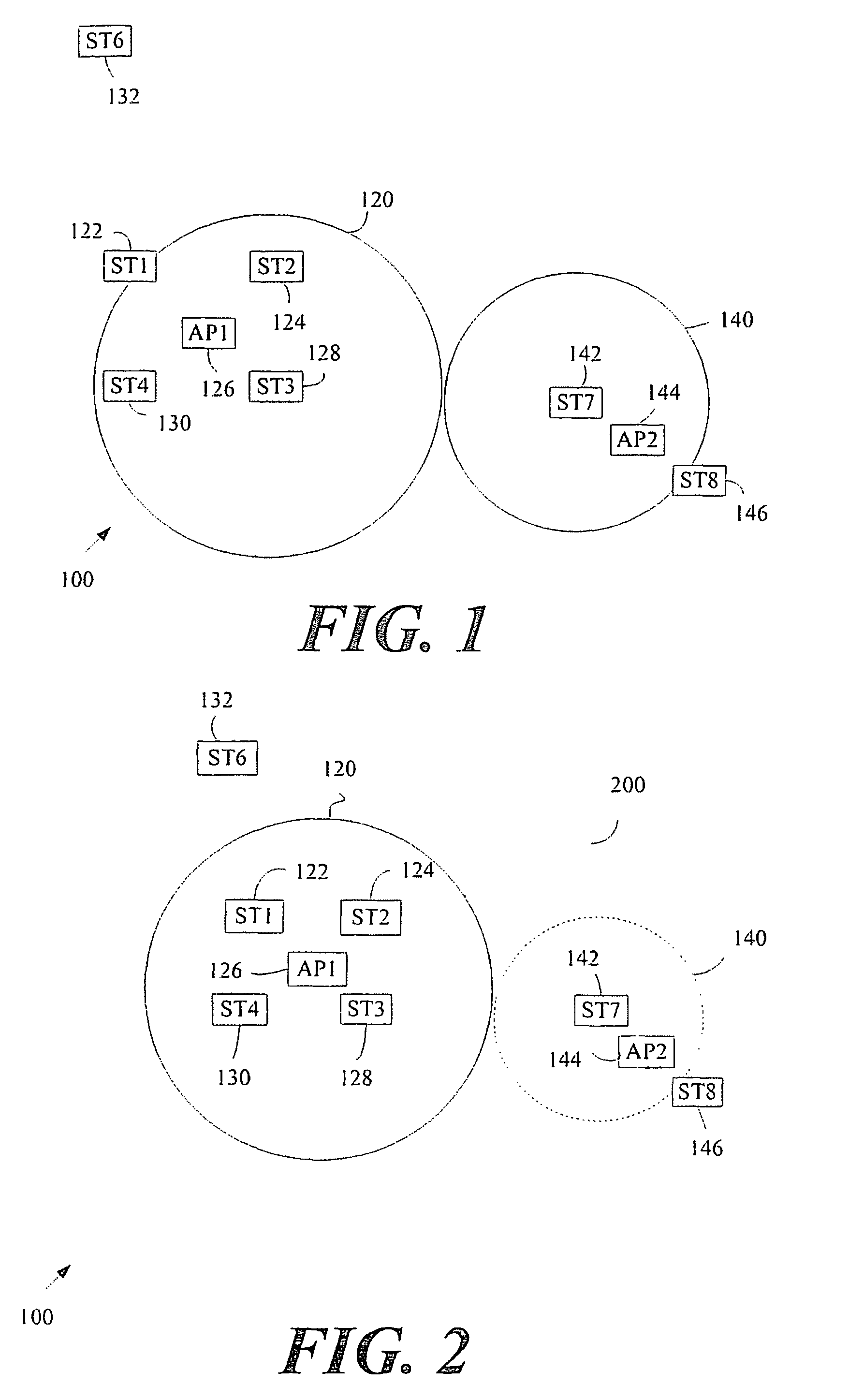
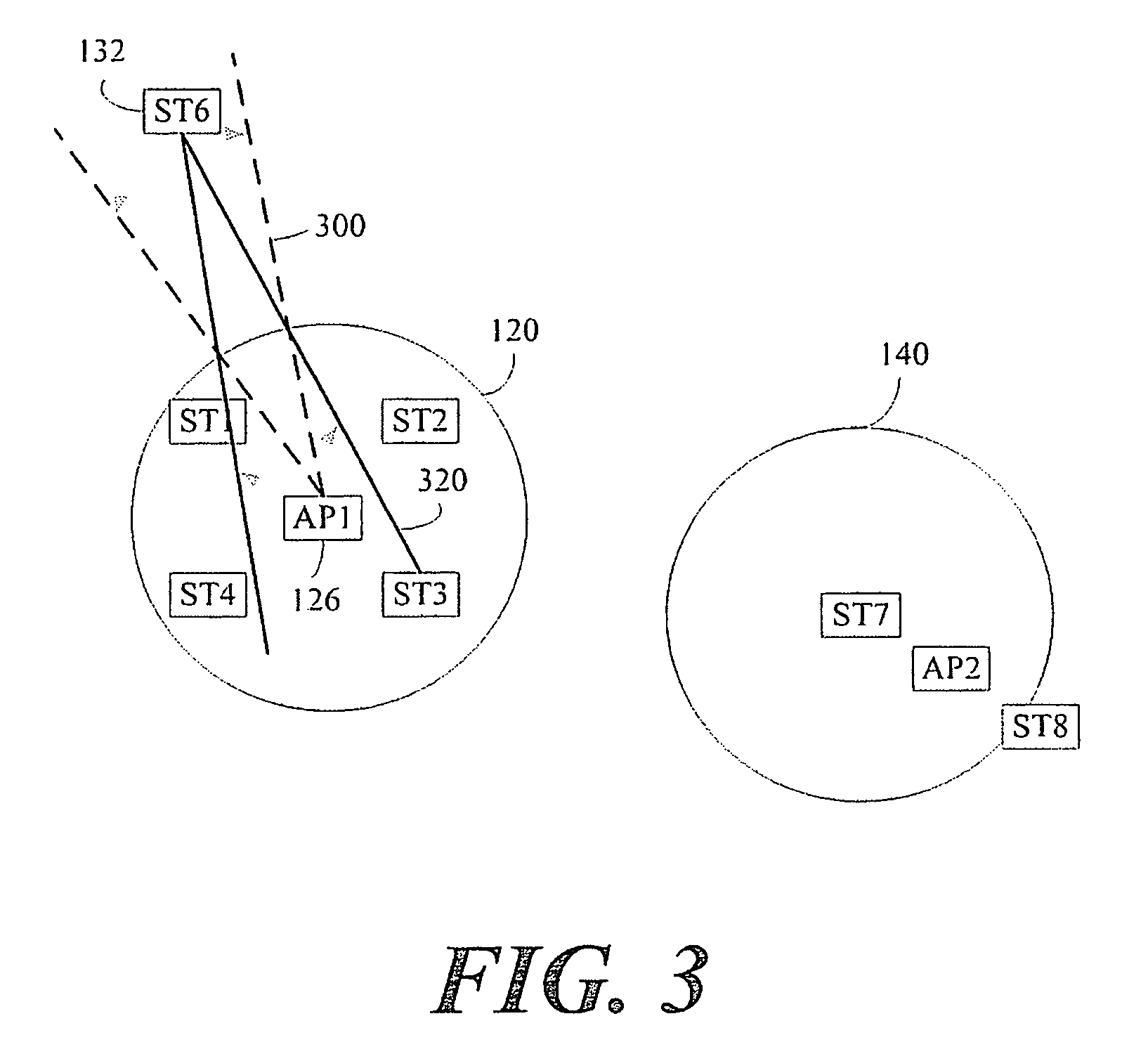
In wireless networking, the hidden node problem or hidden terminal problem occurs when a node can communicate with a wireless access point (AP), but cannot directly communicate with other nodes that are communicating with that AP. This leads to difficulties in medium access control sublayer since multiple nodes can send data packets to the AP simultaneously, which creates interference at the AP resulting in neither packet getting through.
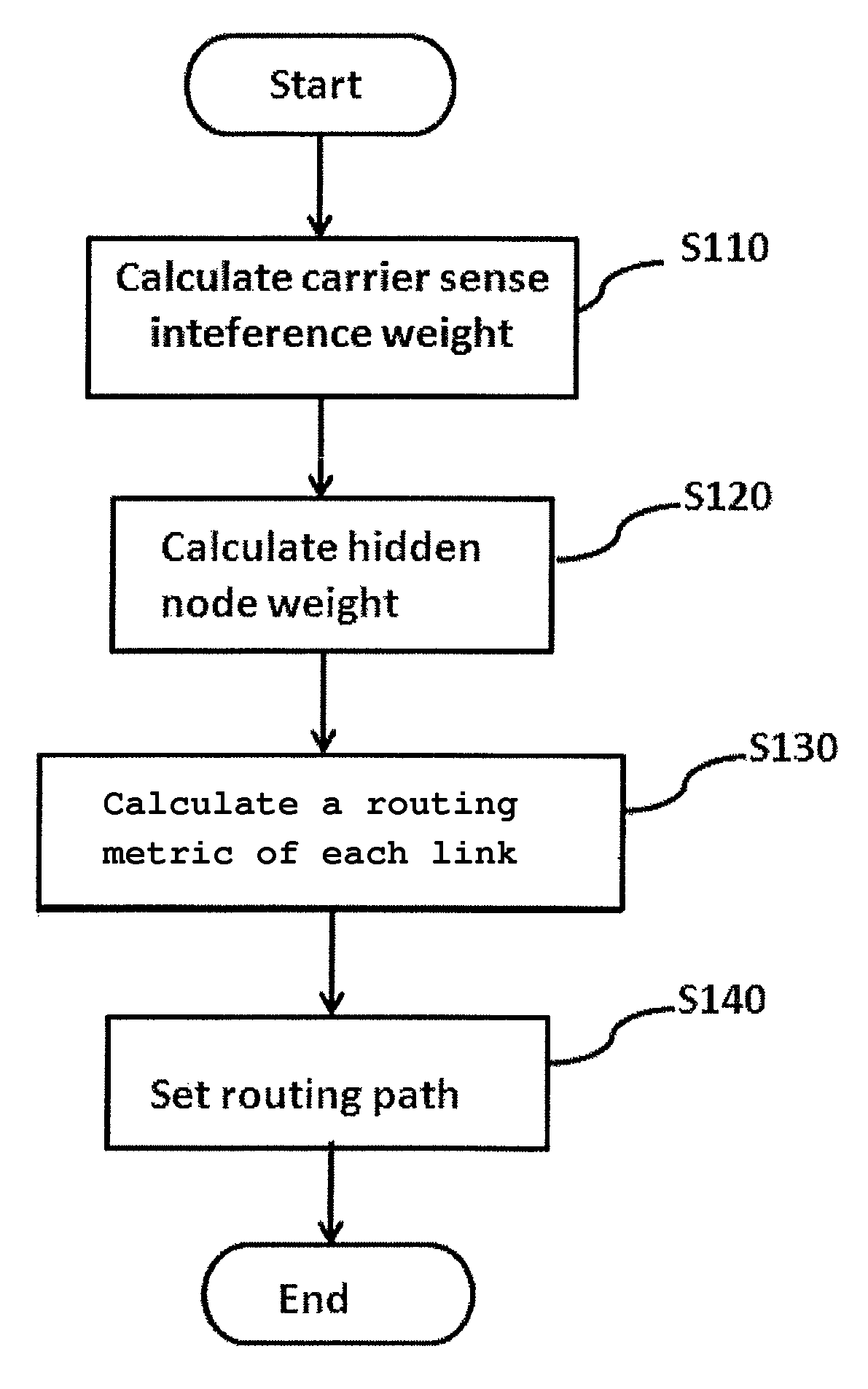
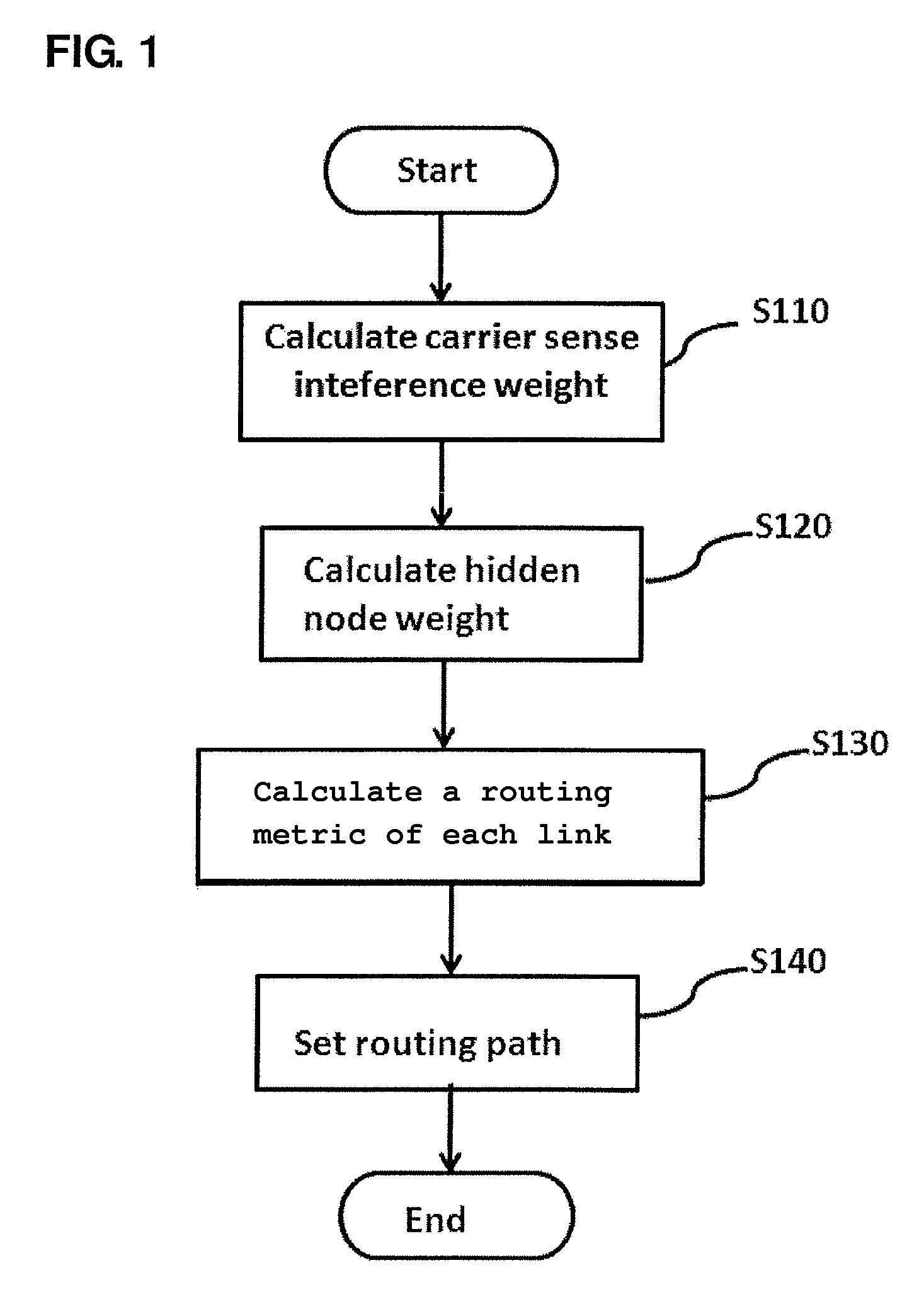
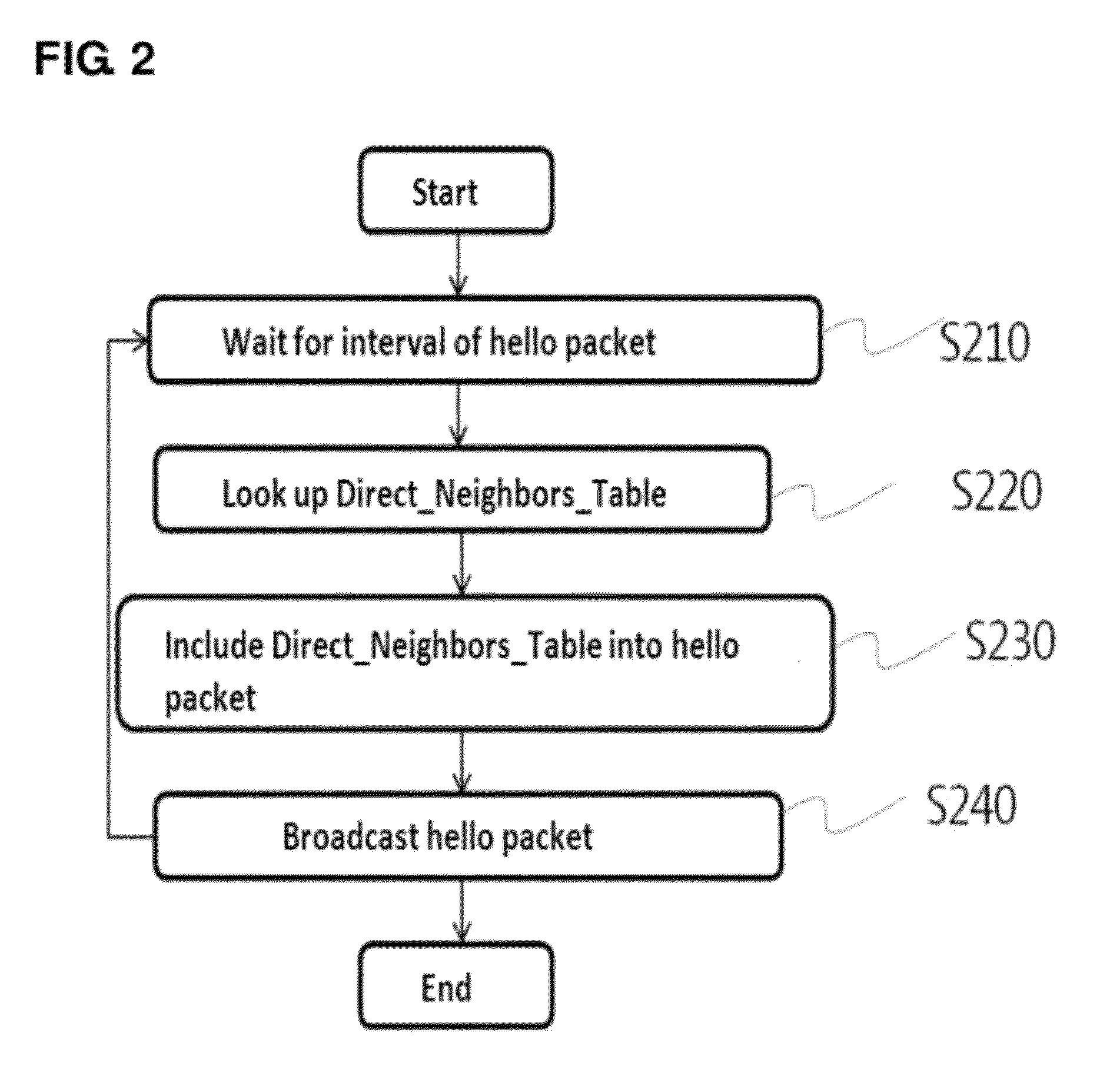
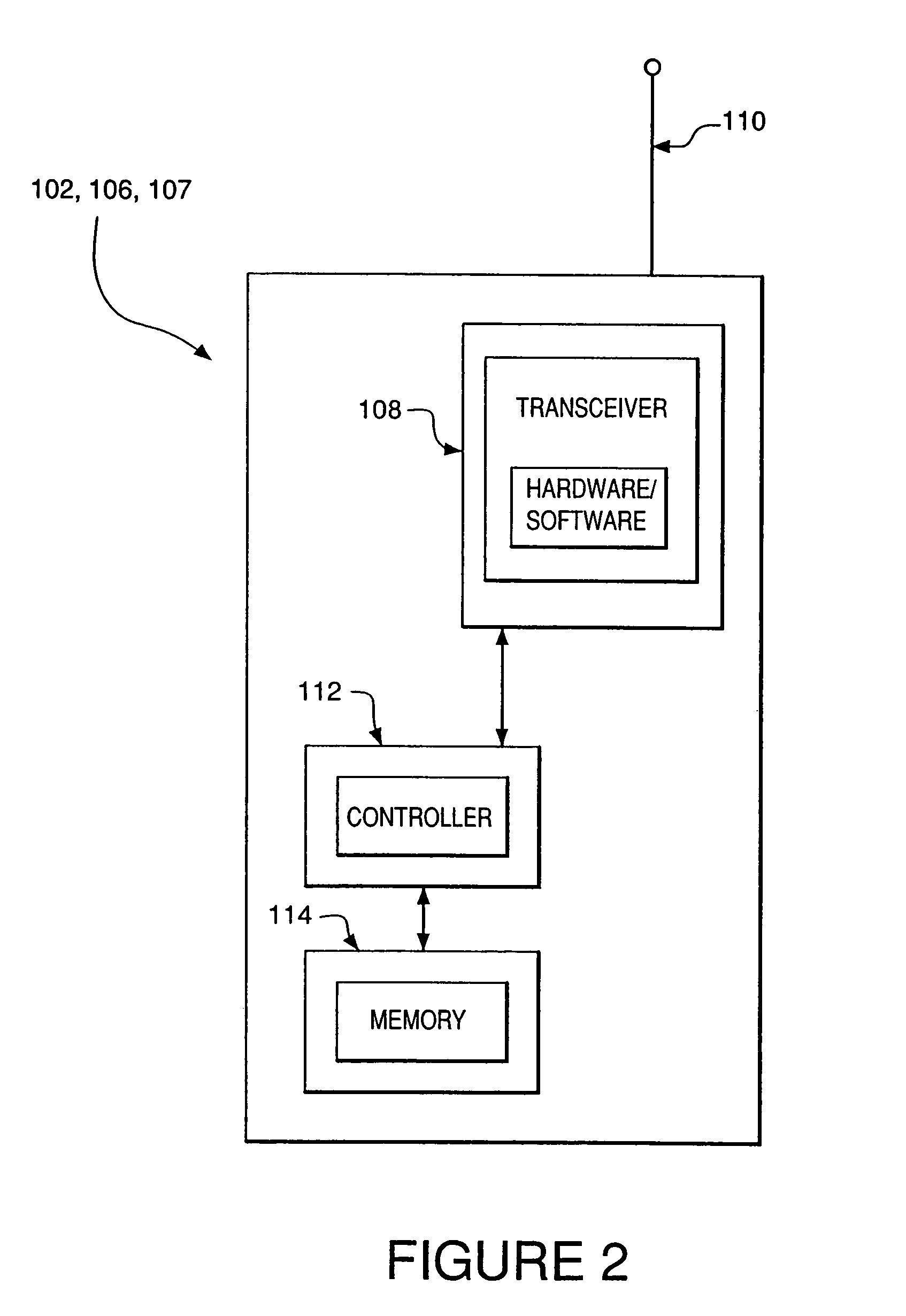
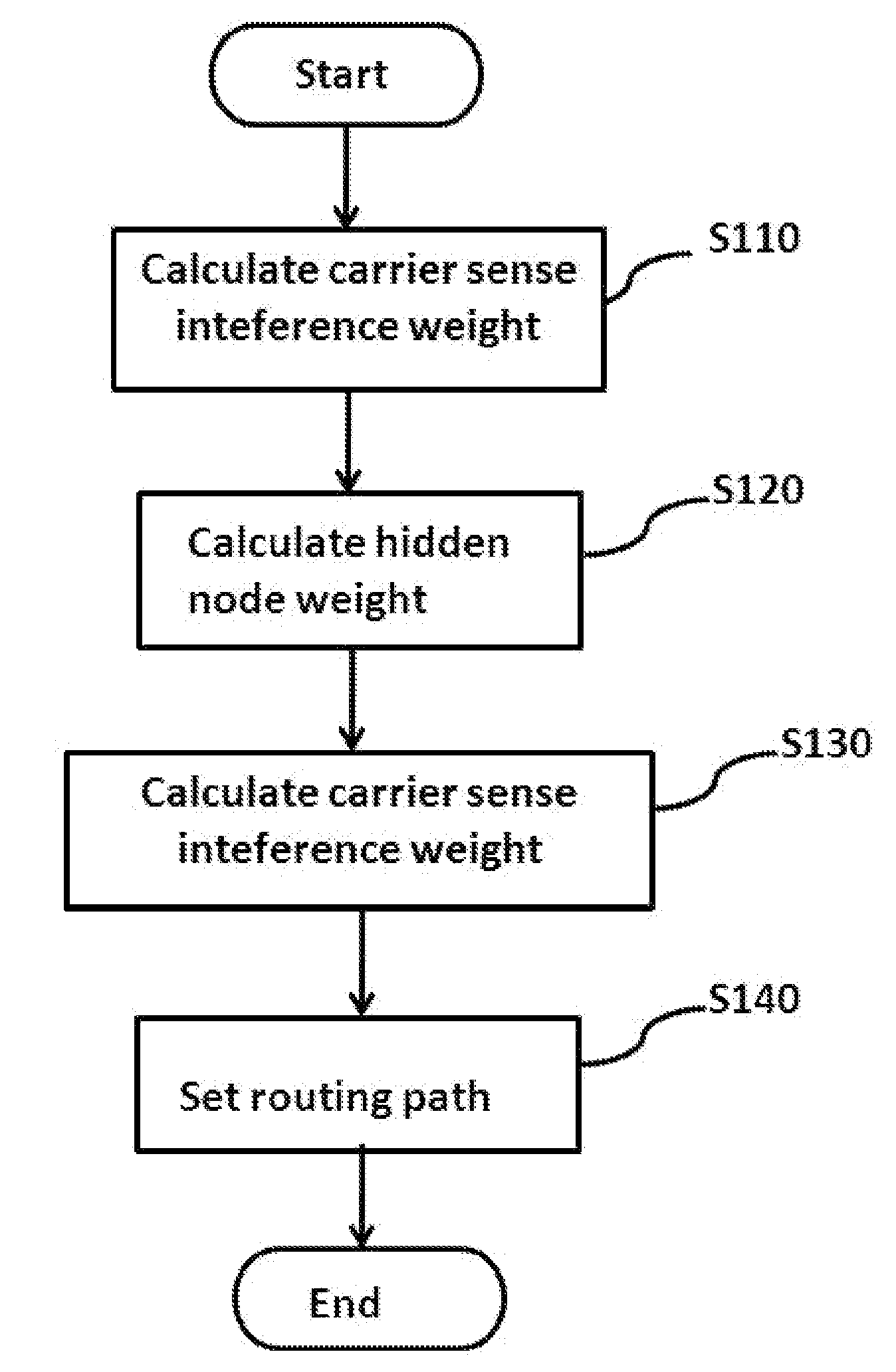
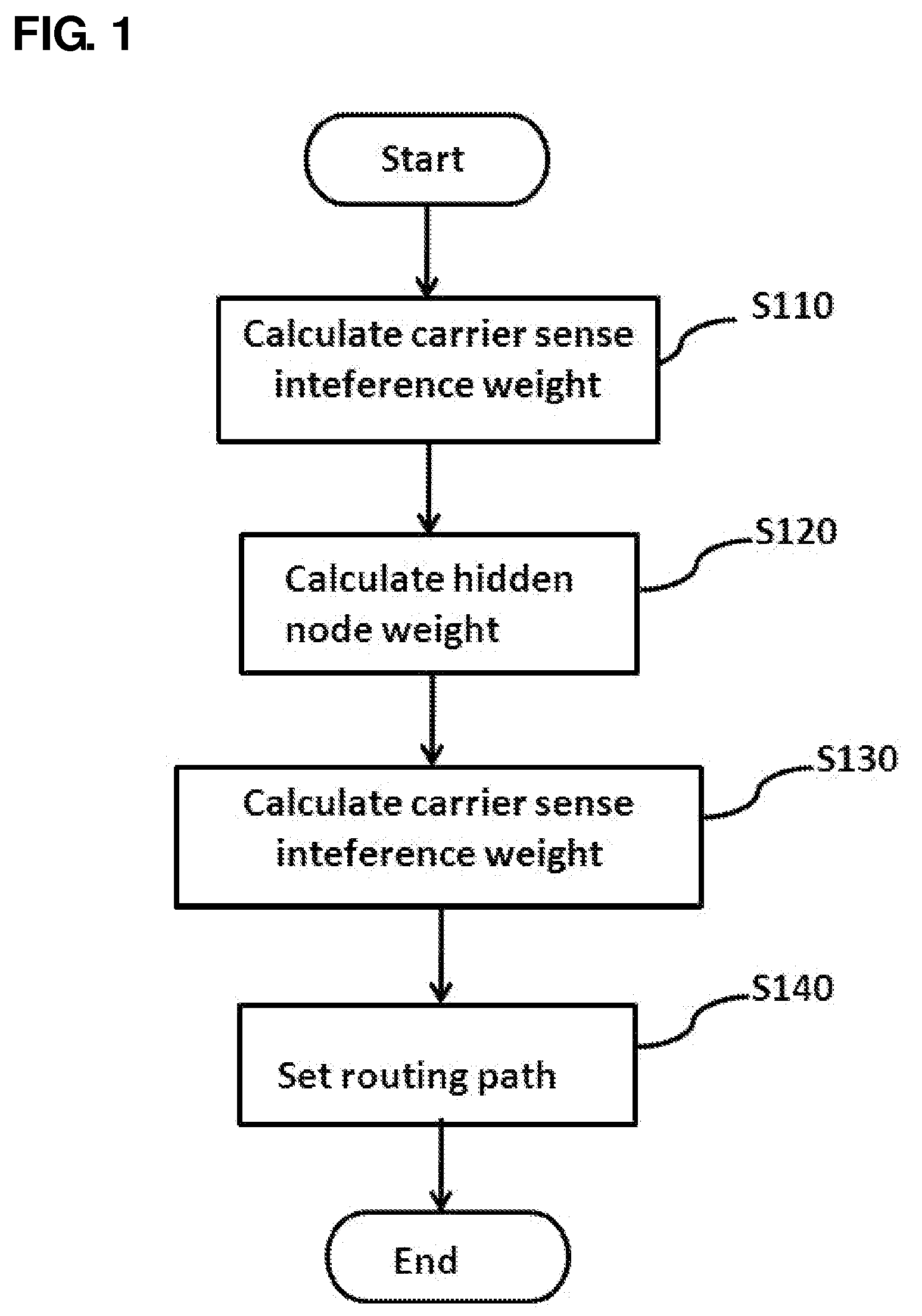
Method and system for setting routing path considering hidden node and carrier sense interference, and recording medium thereof
ActiveUS8300538B2Improve routing performanceImprove network performanceError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsHidden node problemCarrier signal
A method of setting a routing path for transmitting a packet from a source node to a destination node in a wireless multi-hop network including plural nodes and plural links for connecting two nodes with each other. The method includes calculating carrier sense interference weights representing carrier sense interference related to the respective links and combining the carrier sense interference weights of the links included in at least one specific path connecting the source node with the destination node. The method further includes calculating hidden node weights representing hidden node problems related to the respective links and accumulating the hidden node weights of the links included in the path. The method further includes calculating a metric value for the specific path by combining the carrier sense interference weights and the hidden node weights, and determining the specific path with the least metric value as the routing path.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Devices, softwares and methods for rescheduling multi-party sessions upon premature termination of session
InactiveUS7330877B2Readily apparentConnection managementData switching by path configurationHidden node problemTime efficient
Devices, softwares and methods reschedule multi-party sessions upon premature termination of a wireless communication session. Upon sensing a premature termination, an access point transmits a rescheduling frame. All sessions are advanced in time, which saves time in the end, without leaving quiet times. In addition, the invention avoids a hidden node problem.
Owner:SHARP KK
System and method for identifying potential hidden node problems in multi-hop wireless ad-hoc networks for the purpose of avoiding such potentially problem nodes in route selection
InactiveUS7200149B1Effective and efficient identificationHigh degreeNetwork topologiesBroadcast transmission systemsHidden node problemAd hoc communication
A system and method for identifying potential hidden node problems in a multi-hop wireless ad-hoc communication network, such as an 802.11 network. The system and method evaluates the relationship between the neighbors of each respective node to identify nodes of a wireless ad-hoc communication network whose capabilities of receiving data packets can be adversely affected by hidden node problems in order to avoid selecting paths containing those potentially problem nodes for routing data packets. Specifically, for each node, the system and method generates a node metric identifying the relationship between the neighbors of a node. Each node can then transmit its respective metric with its routing advertisement data, so that other nodes can assess the degree of potential hidden node problem that may be experienced by that node, and can choose to avoid using that potentially problem node for routing data packets to other nodes.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Method and system for setting routing path considering hidden node and carrier sense interference, and recording medium thereof
ActiveUS20110075578A1Improve network performanceReduce network overheadError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsHidden node problemWireless mesh network
Disclosed are a method and a system for setting a routing path in consideration of hidden nodes and carrier sense interference.The method of setting a routing path for transmitting a packet from a source node to a destination node in a wireless multi-hop network consisting of plural nodes and plural links for connecting two nodes with each other, comprises: calculating carrier sense interference weights representing carrier sense interference related to the respective links and combining the carrier sense interference weights of the links included in at least one specific path connecting the source node with the destination node; calculating hidden node weights representing hidden node problems related to the respective links and accumulating the hidden node weights of the links included in the path; and calculating a metric value for the specific path by combining the carrier sense interference weights and the hidden node weights, and determining the specific path with the least metric value as the routing path.Accordingly, in the multi-channel multi-radio wireless mesh network, the path with minimized hidden node problem and carrier sense interference can be selected to improve network performance
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Power Control In a Communication Network and Method
ActiveUS20070223403A1Reduce power consumptionInterference minimizationEnergy efficient ICTPower managementHidden node problemCarrier signal
In a wireless network using a carrier sense multiple access (CSMA) scheme is provided a method, system, devices and instruction sets for detecting transmission levels and adjusting the transmission levels for both a connection point and mobile stations within the network in order to reduce power consumption in network devices and minimize interference problems while keeping hidden node problems on a controlled level.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Avoiding exposed node problems in wireless local area networks
ActiveCN101356775AAvoid the need to cancelData switching networksHidden node problemTransmission response
A method, apparatus and computer program product for preventing occurrences of the hidden node problem are presented. A transmission request (CC-RTS) is received from a source node, the CC-RTS frame including a reservation duration value indicating the length of time needed for a transmission reservation. A timer is adjusted for the period other nodes must refrain from transmitting on the channel (NAV) equal to a duration of a transmission request / transmission response (CC-RTS / CC-CTS) handshake. When the CC-RTS has been denied, then a second CC-RTS frame is received having a reservation duration value of zero, and when the CC-RTS is accepted then the NAV is extended to remainder of the reservation duration value of the original CC-RTS frame. The CC-RTS and CC-CTS are sent at a more robust PHY mode than traffic frames.
Owner:AVAYA TECH LLC
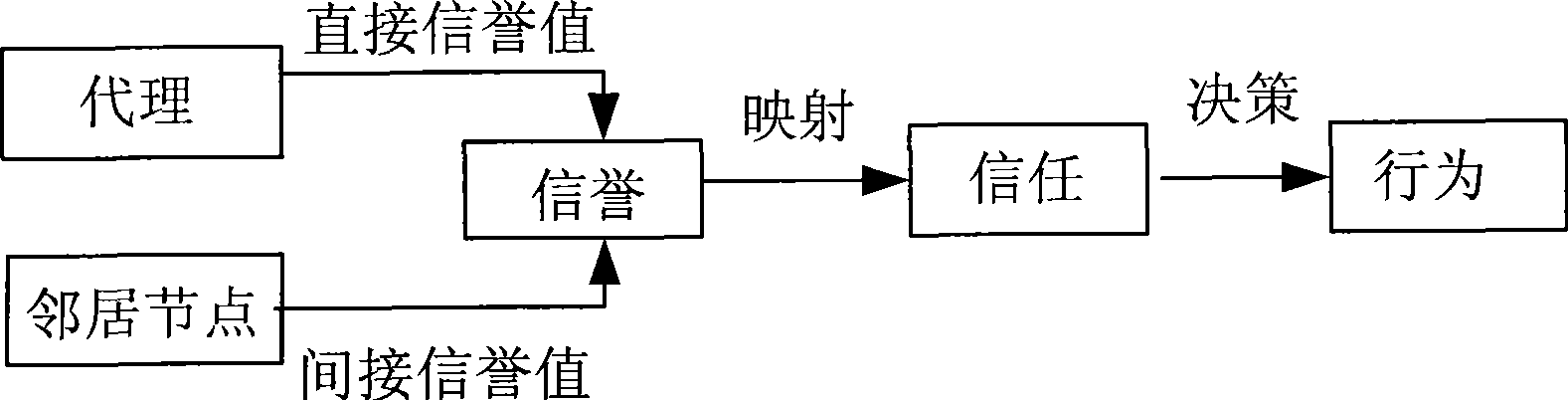
Method for calculating wireless sensor network credit value based on unreliable channel
InactiveCN101442824AReliable direct reputation valueReliable reputation valueNetwork topologiesHidden node problemPacket loss
The invention relates to a trust value calculation method for wireless sensor network based on unreliable channel and trusted management scheme, especially for unreliable channel condition as high packet loss and severe hidden nodes. The method proposes a trust structure HRFSN based on Heider's balance theory and public nodes of interacted two parties directly participates in observation activity for observing the nodes to optimize direct trust value calculation under unreliable channel so as to increase reliability of trust value. The method changes direct trust value observation style and calculation method of trust management scheme of known wireless sensor network, can acquire more accurate direct trust value and further more reliable trust value. The method, with relatively high scientificity and higher application value, can provide more accurate trust foundation during cooperation of sensor node.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
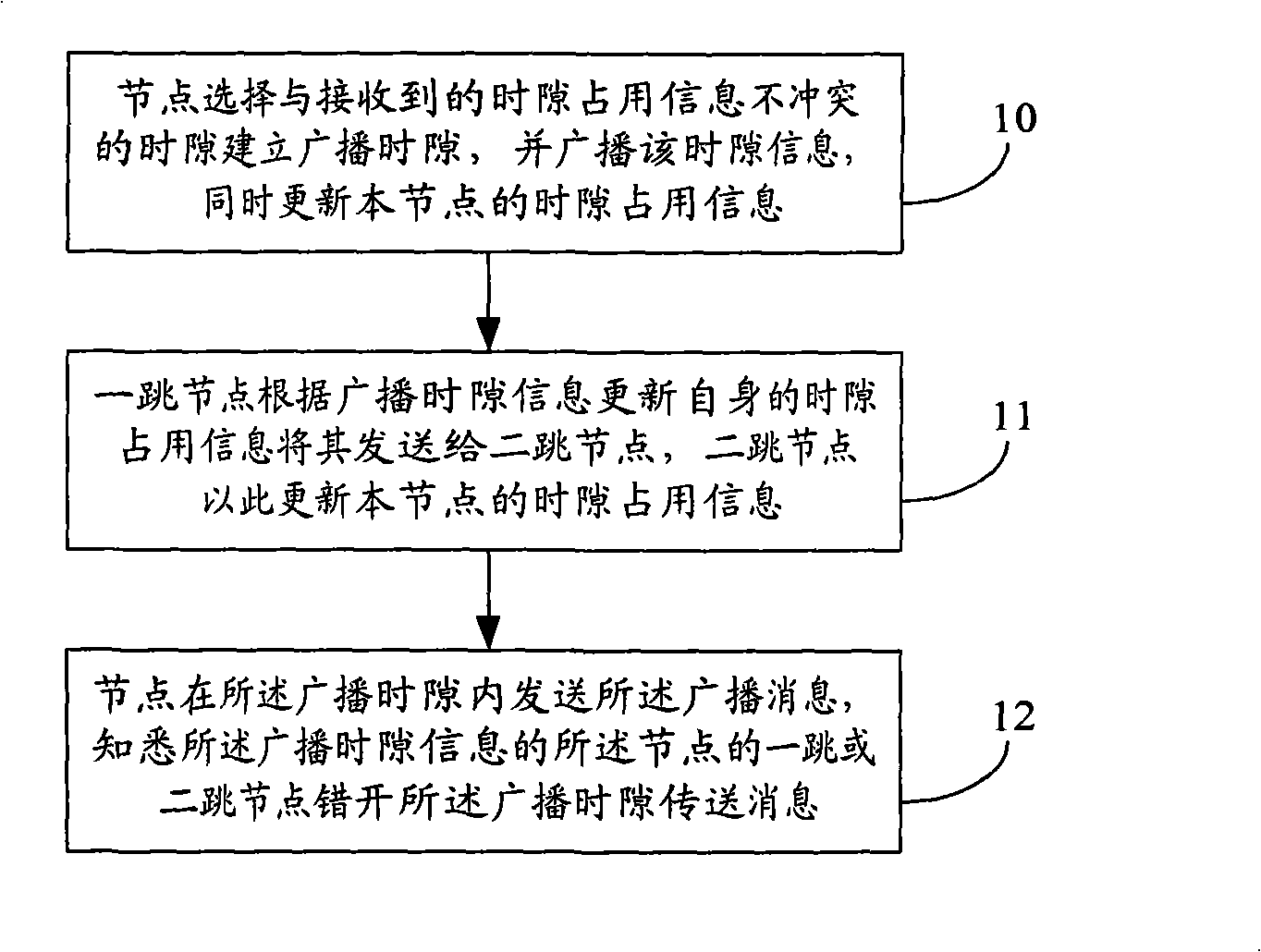
Method and node for establishing time slot in wireless mesh network
InactiveCN101282256ASolve conflictsAvoid conflictTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationHidden node problemWireless mesh network
The invention discloses a method for establishing broadcast time slots in a wireless netlike network and a node, the method comprises the steps that: the node collects acquires time slot occupation information of a first-leap and a second-leap nodes by collecting time slot notification message of the first-leap node thereof, the node selects a time slot which is conflict-free with the time slot occupation information to establish the broadcast time slot; the node comprises an time slot occupation information receiving module and a broadcast time slot establishing module, the invention solves the problem about conflict of the broadcast messages resulted by existence of the hidden nodes in current wireless netlike network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
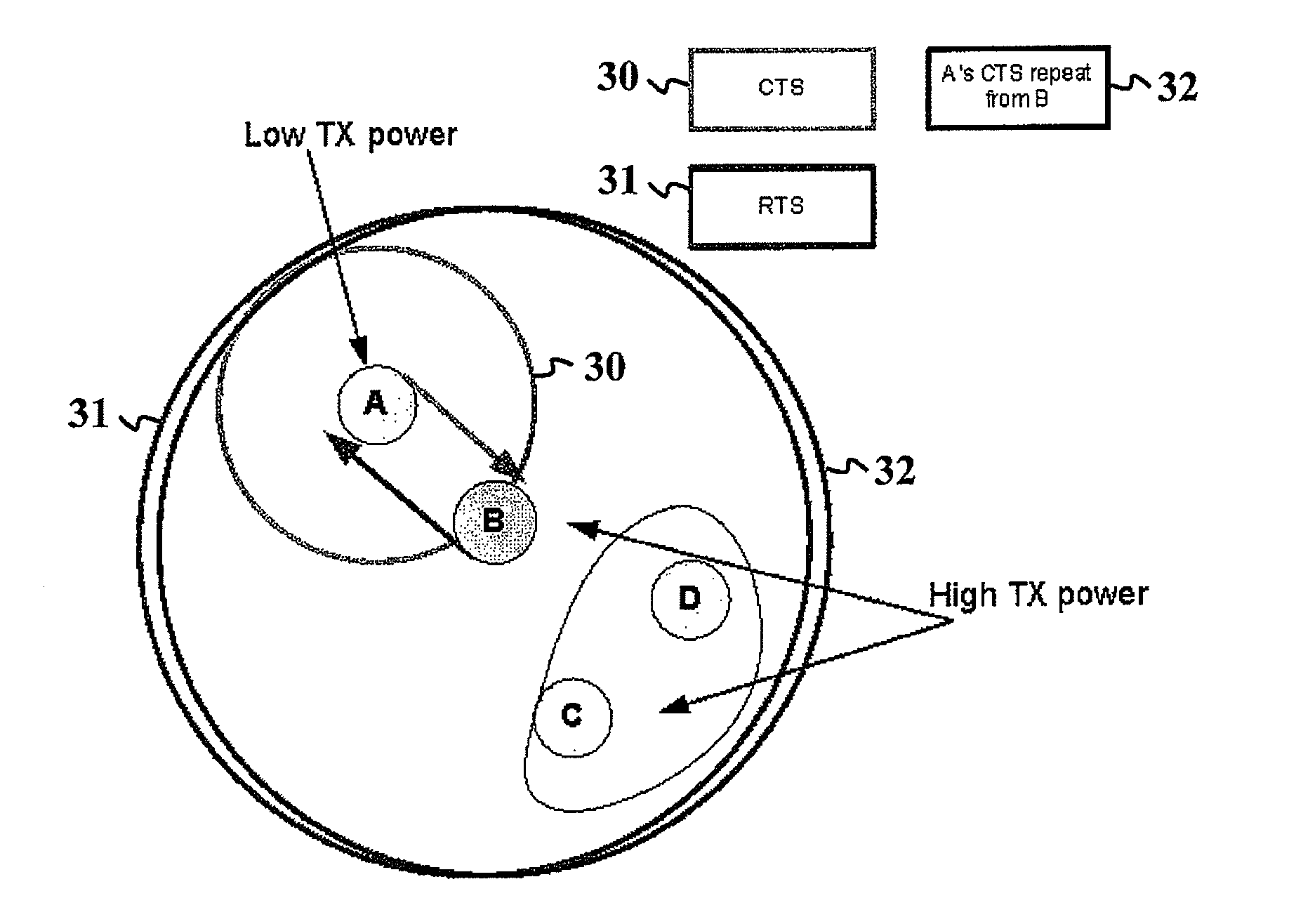
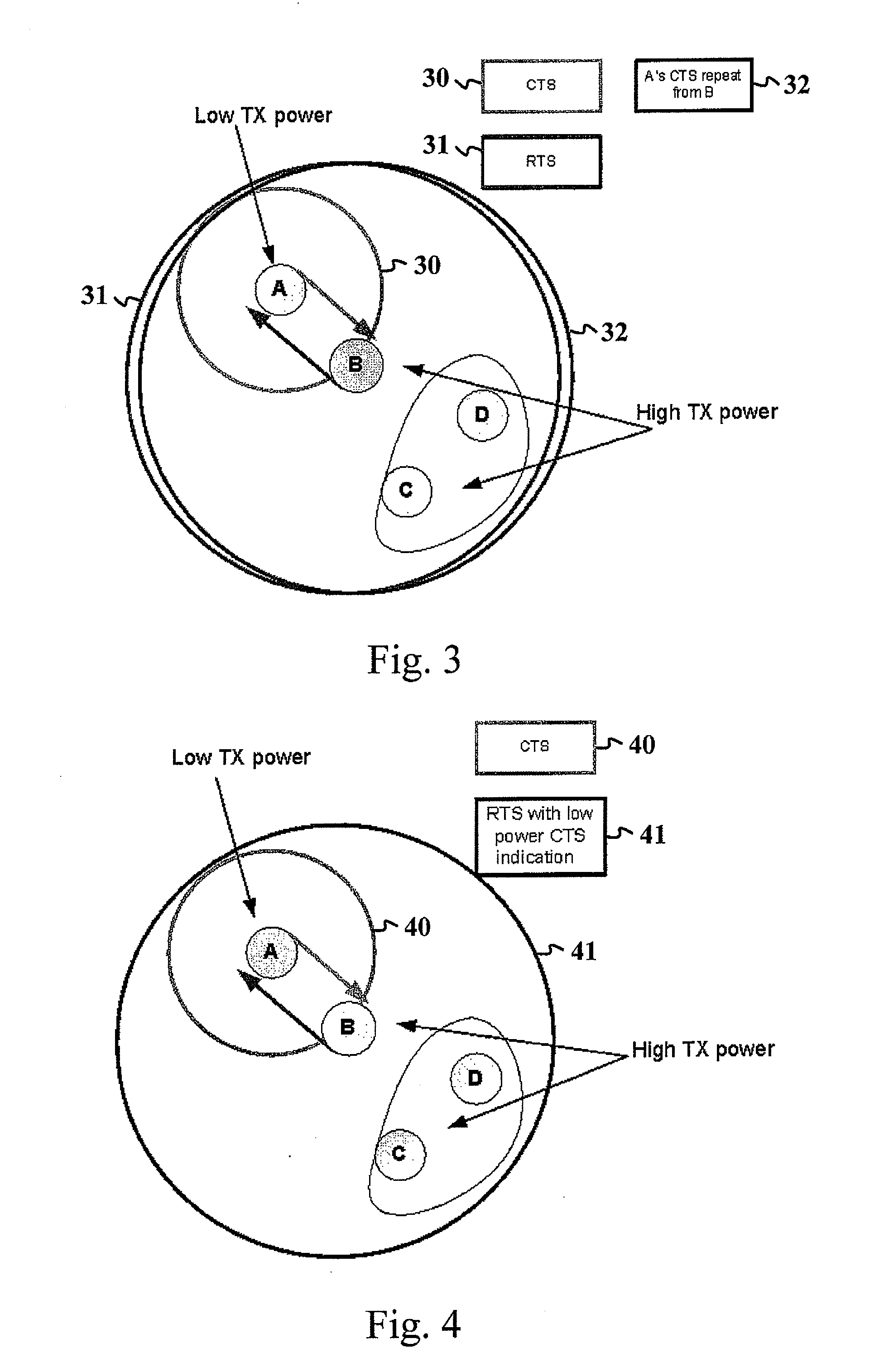
Solving a hidden node problem due to transmission power imbalance
InactiveUS20120243519A1Network topologiesWireless commuication servicesClear to sendHidden node problem
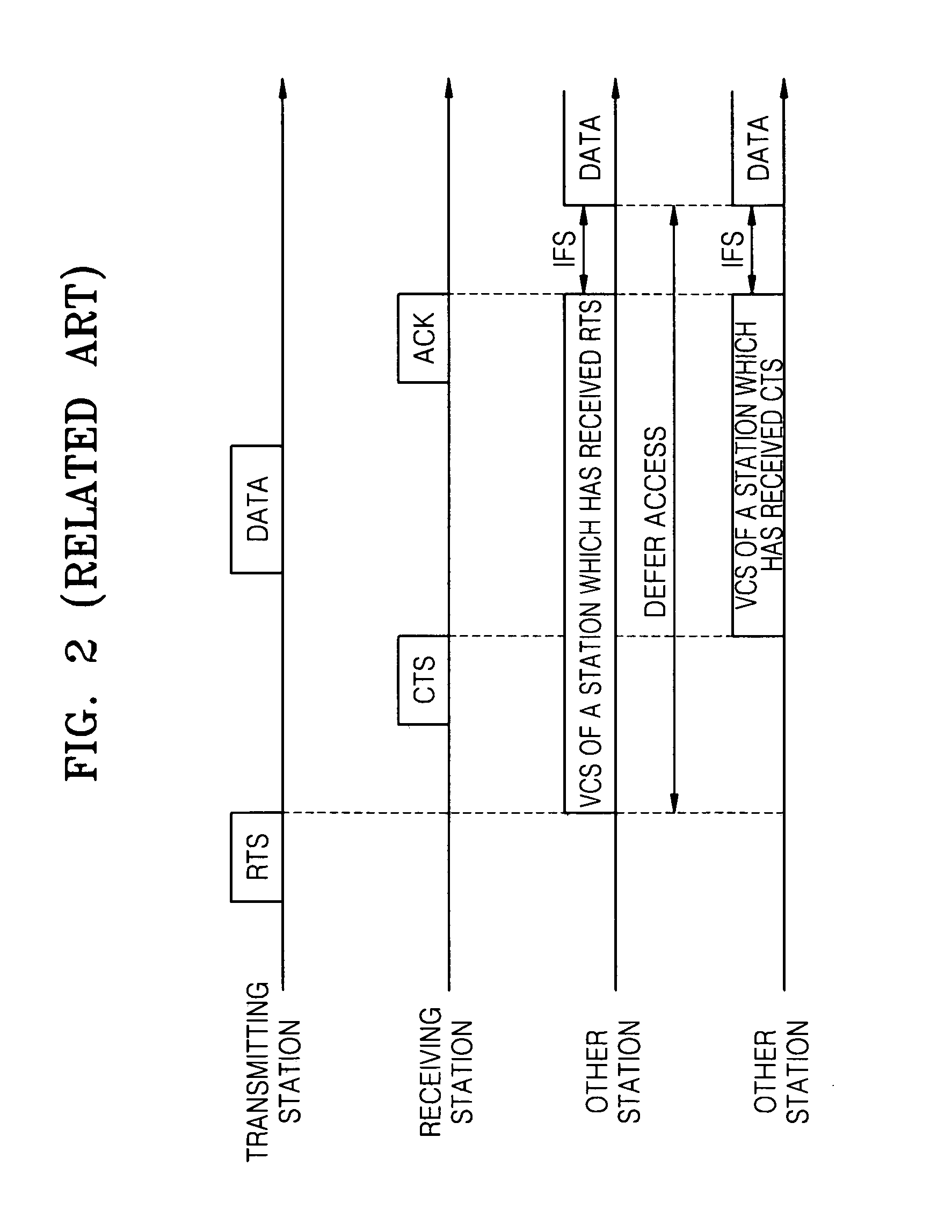
The present invention discloses an apparatus, a method and a computer program for resolving a hidden node problem in relation to handshake message transferring e.g. in WLAN networks. In one embodiment of the invention, the apparatus receiving a Clear to Send (CTS) message repeats the message after a Short Interframe Space (SIFS) time period. Stations not directly hearing the original CTS due to a low power are able to receive the repeated CTS and defer their transmissions accordingly. In another embodiment, the apparatus receiving the CTS message indicates in its Ready to Send (RTS) message that the CTS sender station has a low transmitting power. With this knowledge, the other present stations can defer their transmissions until they are sure that the data transfer between the first two stations having the RTS-CTS messaging has not been initiated or is already completed.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Resolving hidden node problem in synchronized dcf based channel access in wlan
ActiveCN104412690AAvoid confictHigh level techniquesWireless communicationHidden node problemTerminal equipment
Embodiments of the invention provide signaling mechanisms for wireless networks composed of a large number of stations. An example method embodiment comprises: receiving by a wireless terminal device, a first message from an access point, the first message comprising information indicating a plurality of restricted access windows, each allocated for a different group of terminal devices associated to a wireless network managed by the access point; receiving by the terminal device, a second message from the access point, within a restricted access window of the plurality of restricted access windows, the restricted access window allocated to a group of terminal devices of which the terminal device is a member, the second message comprising information indicating that a communications channel is available; and determining by the terminal device, based on the second message, that the communications channel is not occupied by hidden ones of the terminal devices associated to the network.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
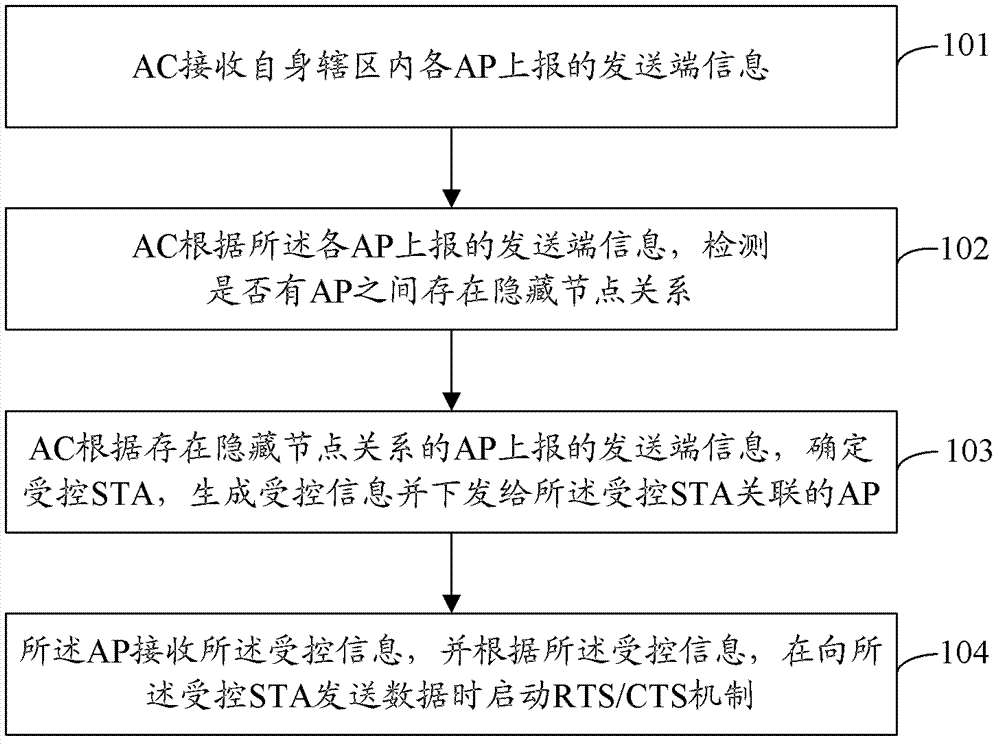
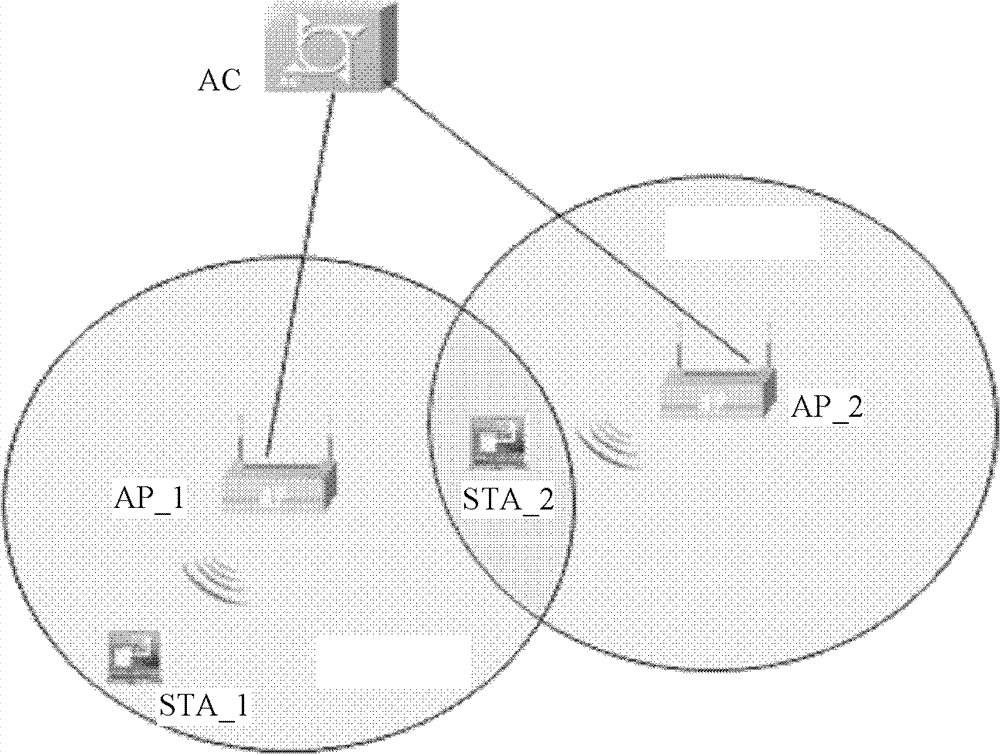
Method and device and system for starting RTS/CTS mechanism
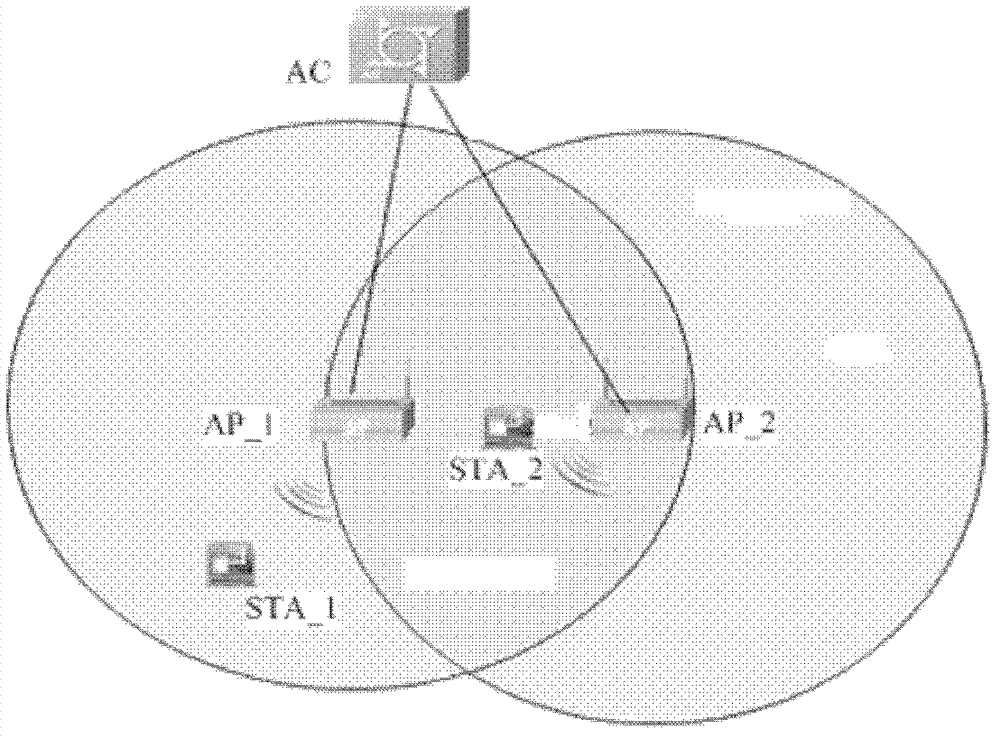
ActiveCN103249166AReduce distractionsAvoid blindnessTransmissionWireless communicationHidden node problemAir interface
The invention discloses a method for starting an RTS / CTS mechanism, which comprises the following steps: an AC (AP (Access Point) Controller) receives transmitting terminal information reported by APs in the self district; the AC detects whether hidden nodes exist between APs or not according to the transmitting terminal information reported by the APs; the AC determines STAs (Station) influenced by the hidden nodes according to the transmitting terminal information reported by APs between which the hidden nodes exist, so as to generate controlled information and issue the controlled information to the APs related with the STA; and the APs receive the controlled information, and start the RTS / CTS mechanism when sending data to the STAs according to the controlled information. Accordingly, the invention further discloses a device and system for starting the RTS / CTS mechanism. The method, the device and the system reduce the interference caused by the hidden nodes existing between the APs in the system, the RTS / CTS mechanism is not abused, and the air interface utilization rate and the system access capability are improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Visible light full duplex continuous transmission random access method based on channel reservation mechanism
ActiveCN107046733AResolve hidden nodesFix performance issuesClose-range type systemsWireless communicationCA protocolHidden node problem
The invention discloses a visible light full duplex continuous transmission random access method based on a channel reservation mechanism. Different from the CSMA / CA protocol in the existing IEEE802.15.7 standard, after a user executes idle channel estimation and detects that the channel is in an idle state, the user does not directly send a data frame, but firstly sends a RTS frame to reserve the channel, and sends the data frame after successfully reserving the channel. A full duplex visual light access point needs to broadcast busy tone to eliminate the hidden nodes when receiving the RTS frame or the data frame. Moreover, the user can directly execute CCA without executing random evasion again after successfully transmitting the data frame, therefore the conflict of the data frame is prevented, the time slot resources consumed by the random evasion mechanism are reduced, and the throughput and delay performance are improved. By adoption of the visible light full duplex continuous transmission random access method, the visible light hidden node problem is effectively solved, and meanwhile, the throughput and the delay performance of the visible light CSMA / CA protocol is optimized at the same time.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Transmit power management in shared-communications channel networks
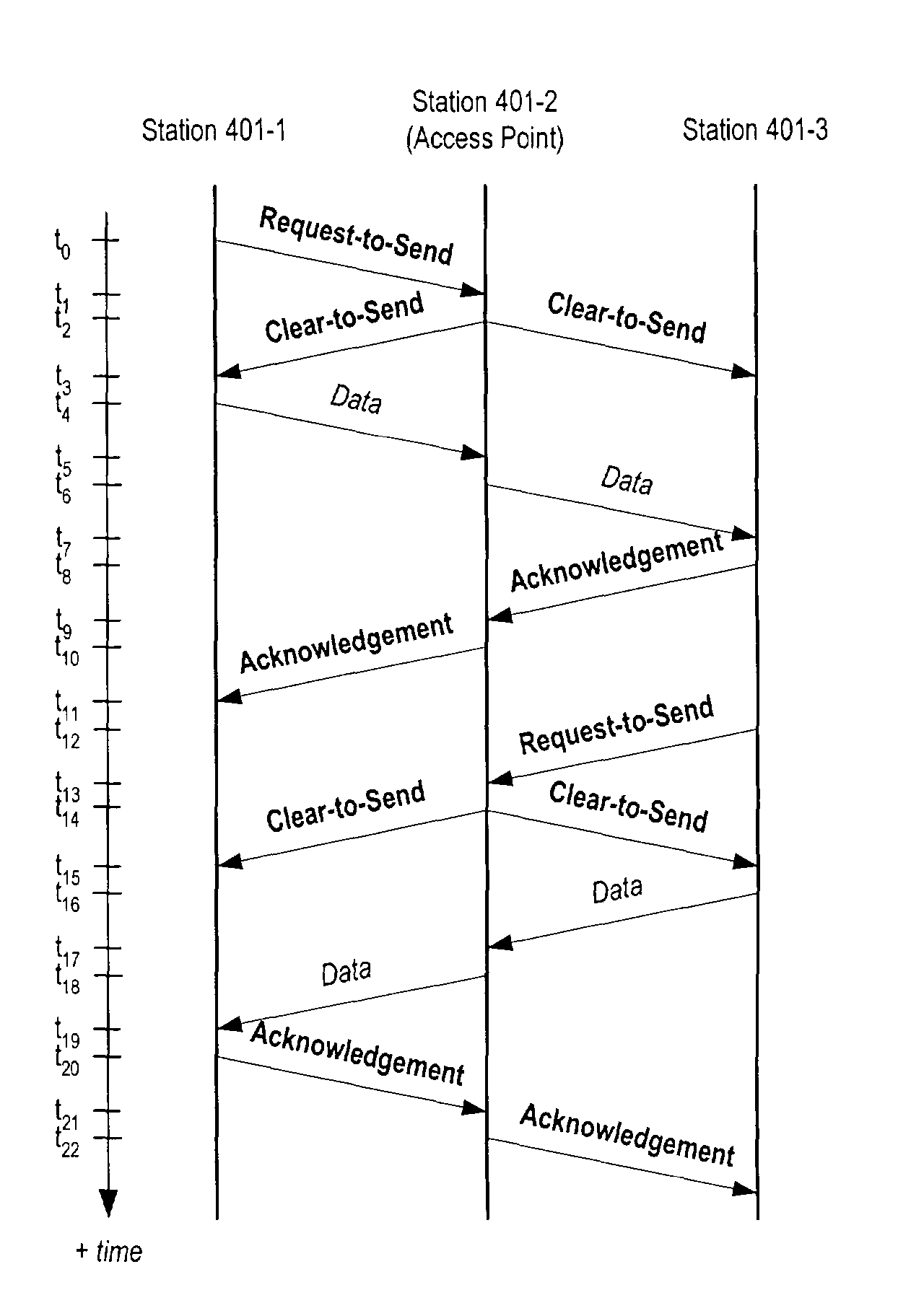
InactiveUS7742443B2Save energyKeep properlyError prevention/detection by using return channelPower managementHidden node problemClear to send
A method of ameliorating the hidden node problem in wireless local area networks employing power control is disclosed. The illustrative embodiments function in a variety of ways that have a common theme: while the Data Frames are transmitted at lesser potency, at least one of the control frames—Request-to-Send, Clear-to-Send, and Acknowledgement—associated with the Data Frame are sent at a greater potency. This causes at least one of the “loud” control frames to be heard and decoded by all of the potentially contending stations. And because the control frames carry duration information for the virtual carrier sense mechanism, their reception suppresses transmissions by potentially-contending stations that cannot sense the “quiet” Data Frames.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Methods and apparatus for media access control in TV white space
InactiveUS20120314681A1Power managementNetwork traffic/resource managementHidden node problemFrequency spectrum
Methods and apparatus for using 802.11 Wireless LANs in TV white space that allow networks with overlapping wireless regions to coexist. The methods and apparatus offer a solution to the mutated hidden node problem. Wireless devices communicate with a coexistence manager over a backhaul connection. Signals are sent by a low power station indicating a request to use a portion of spectrum. The coexistence manager communicates with a plurality of second stations that transmit at a higher power level. The plurality of second stations either send a signal to the first station indicating that it can transmit, or send signals so that the first station can determine which interference it is receiving, after which the coexistence manager tells the interfering station to transmit a signal to the first station indicating when it can transmit.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Power control in a communication network and method
ActiveUS7835384B2Reduce power consumptionMinimizes problemEnergy efficient ICTPower managementHidden node problemInterference problem
In a wireless network using a carrier sense multiple access (CSMA) scheme is provided a method, system, devices and instruction sets for detecting transmission levels and adjusting the transmission levels for both a connection point and mobile stations within the network in order to reduce power consumption in network devices and minimize interference problems while keeping hidden node problems on a controlled level.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Auxiliary directional access control method of spare nodes in WLAN
ActiveCN104639289ATransport blockingHidden node problem avoidanceError preventionHidden node problemClear to send
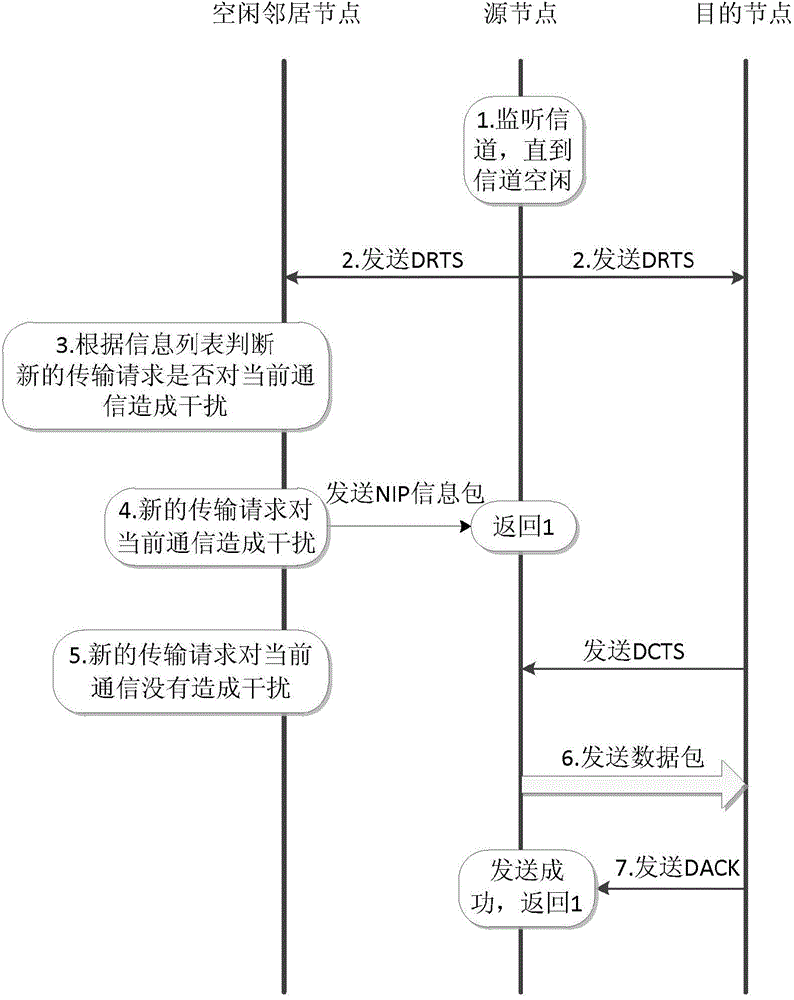
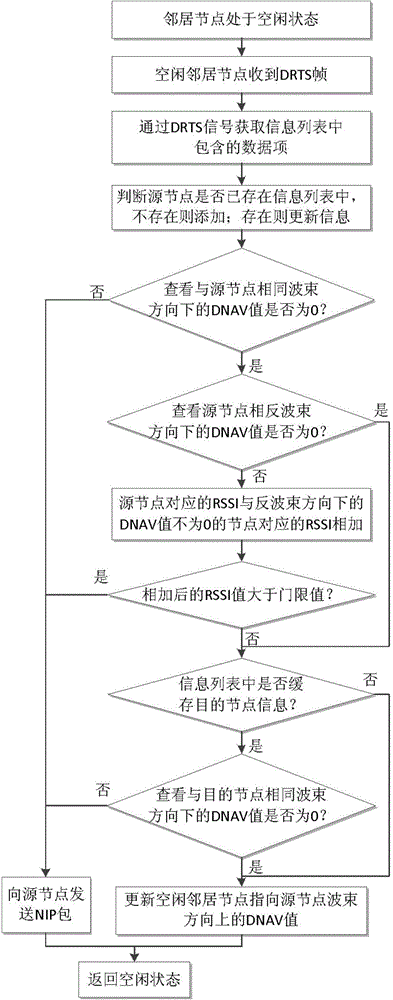
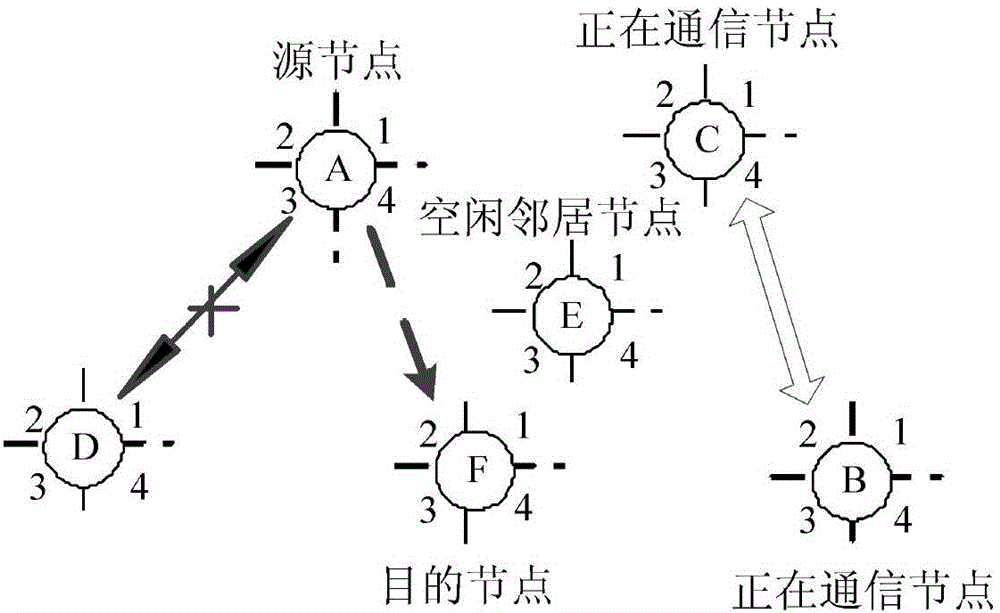
The invention provides an auxiliary directional access control method of idle nodes in WLAN. The method comprises the following steps: firstly monitoring a channel by a source node, after the channel is idle, sending a Directional Request To Send (DRTS) information; after an idle neighbor node receives the DRTS, judging whether the DRTS causes interference on communication among other nodes according to an information list, if interference is caused, sending a Neighbor Information Package (NIP) to the source node by the idle neighbor node, and blocking the transmission of the source node; if interference is not caused, updating a Directional Network Allocation Vector (DNAV) value in the DRTS information list according to the DRTS, sending Directional Clear To Send (DCTS) information to the source node by a destination node by using a wave beam in the DRTS direction of a receiving source node, beginning to send data by the source node and confirming successful transmission after the response of the destination node is received, and returning to a monitoring state. The problem of hidden nodes caused by handshaking signal listening missing is avoided, the pair number of parallel transmission nodes is increased, and the channel utilization rate is improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for transmitting data in power line communication network while preventing hidden node problem
InactiveUS20070195812A1Avoid problemsIncrease transmit powerError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsHidden node problemClear to send
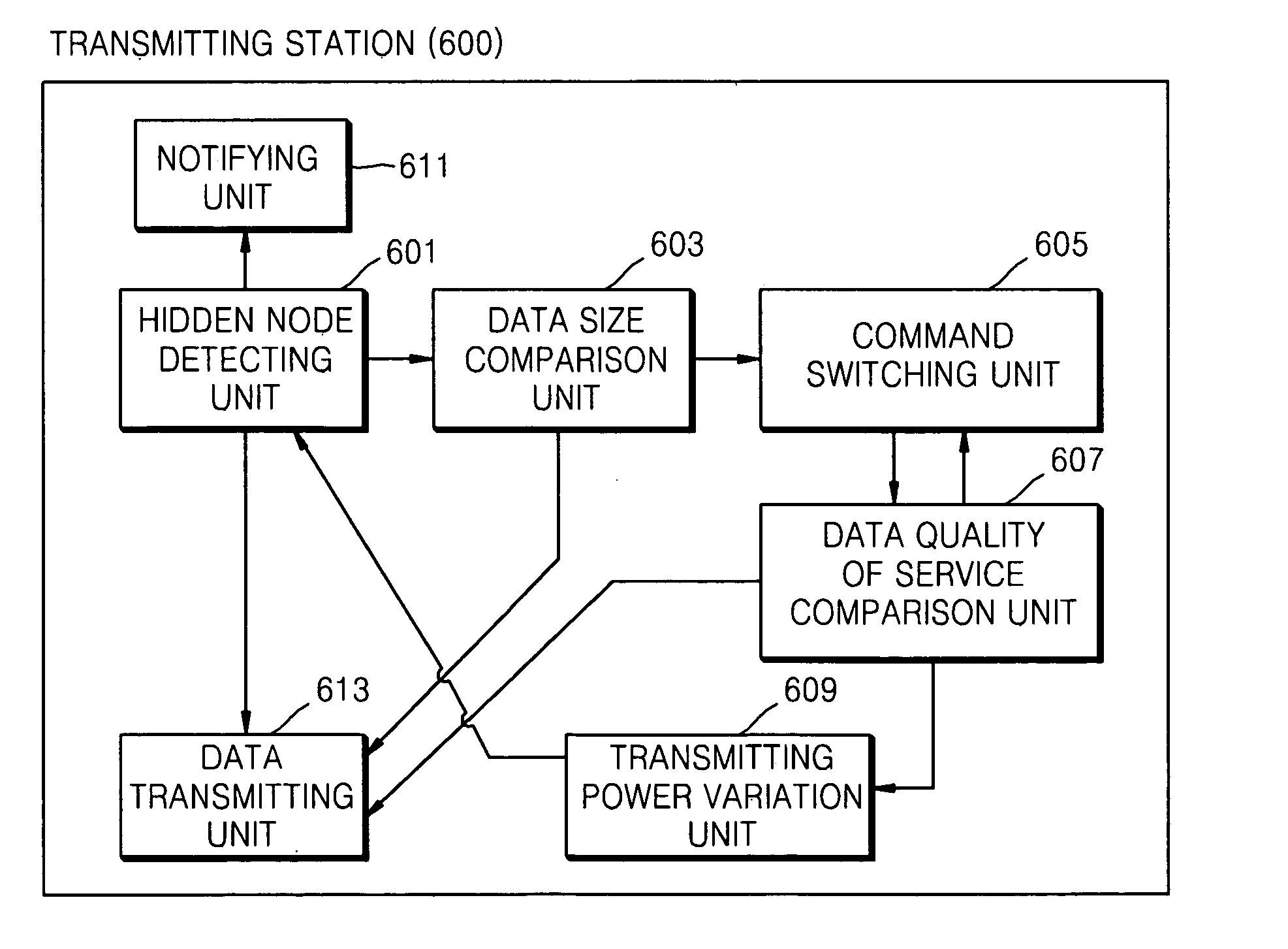
A method and apparatus are provided for transmitting data more efficiently between stations in a power line communication (PLC) network while preventing a hidden node problem. The method of transmitting data includes: detecting a hidden node in a network; and transmitting at least one of a request to send (RTS) command and a clear to send command (CTS) to the network before transmitting the data, if a hidden node is detected and a transmitting station a data packet having a size which is larger than a predetermined size. Using the method, interference of data transmissions and a low data throughput caused by the hidden node problem should be prevented.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
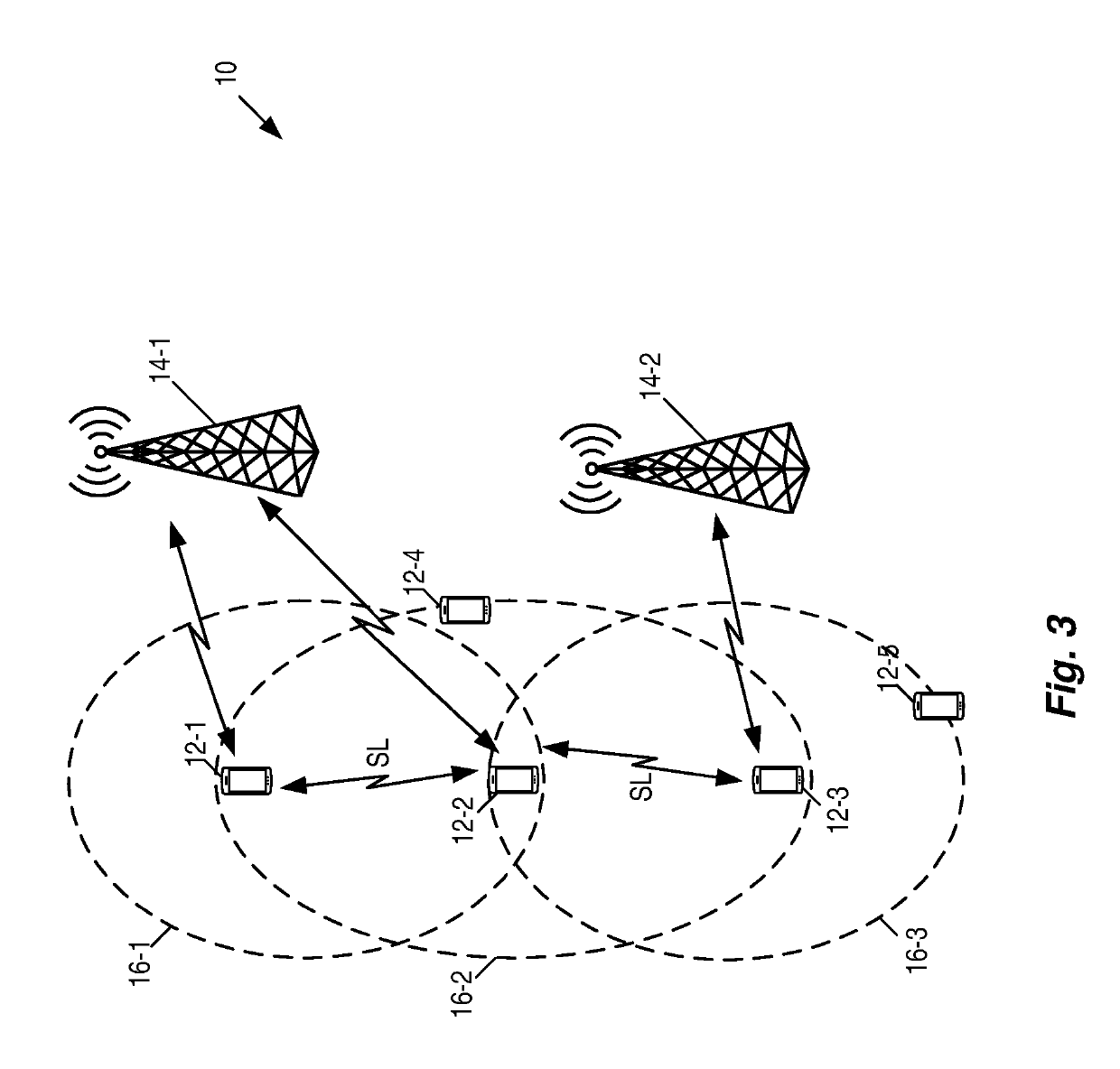
Sidelink Assisted Cooperative Listen-Before-Talk
Systems and methods are disclosed herein that relate to the use of a Device-to-Device (D2D) sidelink, e.g., in a licensed spectrum, to assist with clear channel assessment in an unlicensed spectrum. In doing so, the hidden node problem and / or the exposed node problem can be mitigated. In some embodiments, a method of operation of a wireless device in a cellular communications network comprises performing a sidelink-assisted clear channel assessment (SLA-CCA) procedure to determine whether to transmit on an unlicensed channel. The SLA-CCA procedure is a Clear Channel Assessment (CCA) procedure that is assisted by information received by the wireless device from one or more other wireless devices over a D2D sidelink in a licensed spectrum. The method further comprises, upon determining to transmit on the unlicensed channel as a result of performing the SLA-CCA procedure, transmitting a transmission on the unlicensed channel.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Channel multiplexing method and system, channel multiplexing device and access point
The embodiment of the invention relates to the field of wireless communication, and particularly relates to a channel multiplexing method and system, a channel multiplexing device and an access point, and aims at solving a hidden node problem and an exposed node problem existing in the prior art. The channel multiplexing method provided by the embodiment of the invention comprises that: aiming at one target access point, the access point which is adjacent to the logic of the target access point is confirmed, and the access point which is not adjacent to the logic of the target access point is confirmed; the target access point and the access point which is adjacent to the logic of the target access point are arranged to use a same channel to perform data transmission within different time ranges; and the target access point and the access point which is not adjacent to the logic of the target access point are arranged to use the same channel to perform data transmission. The hidden node problem and the exposed node problem existing in the prior art are solved by the embodiment of the invention so that interference is avoided and efficiency in channel multiplexing is enhanced.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GRP BEIJING
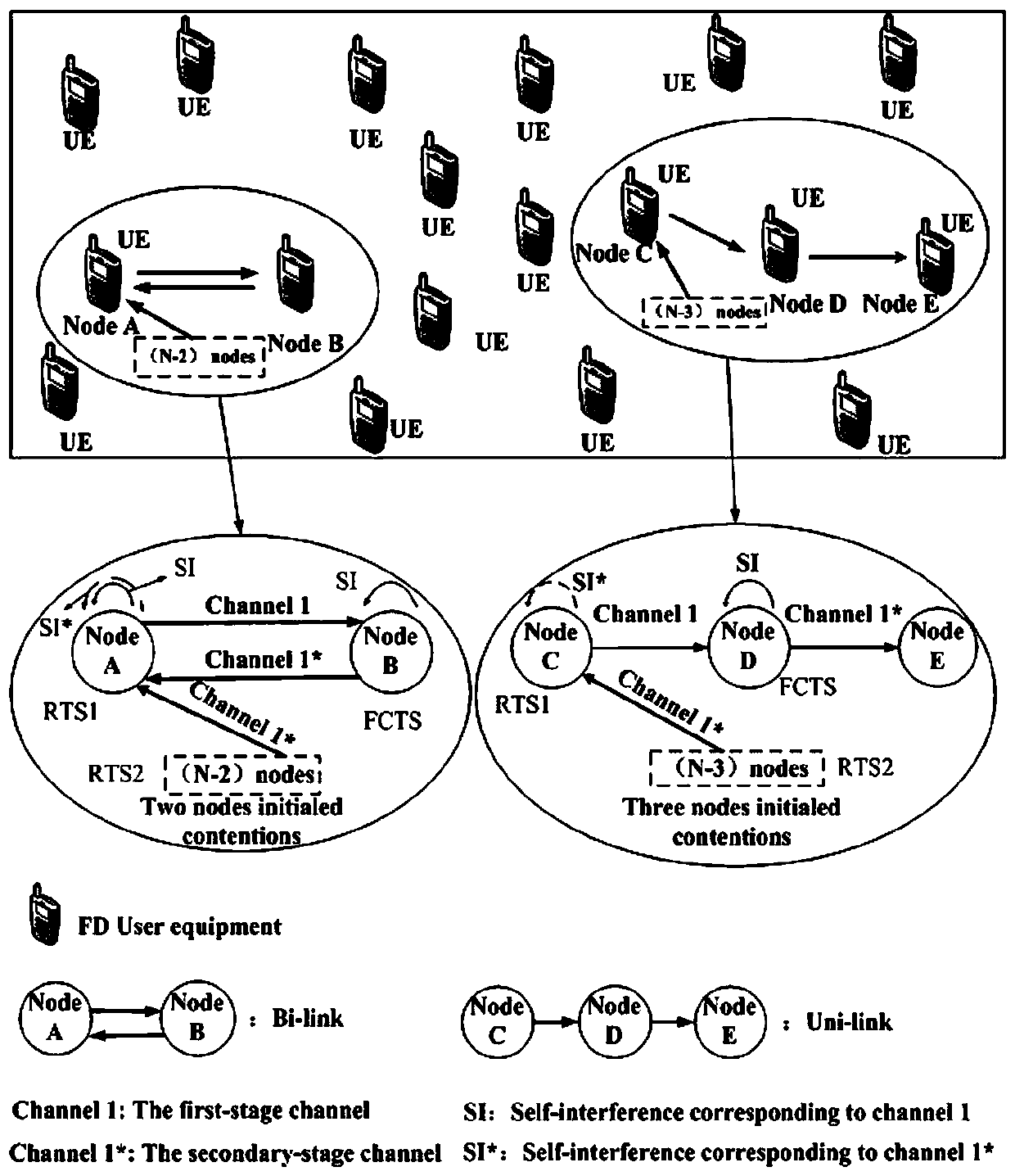
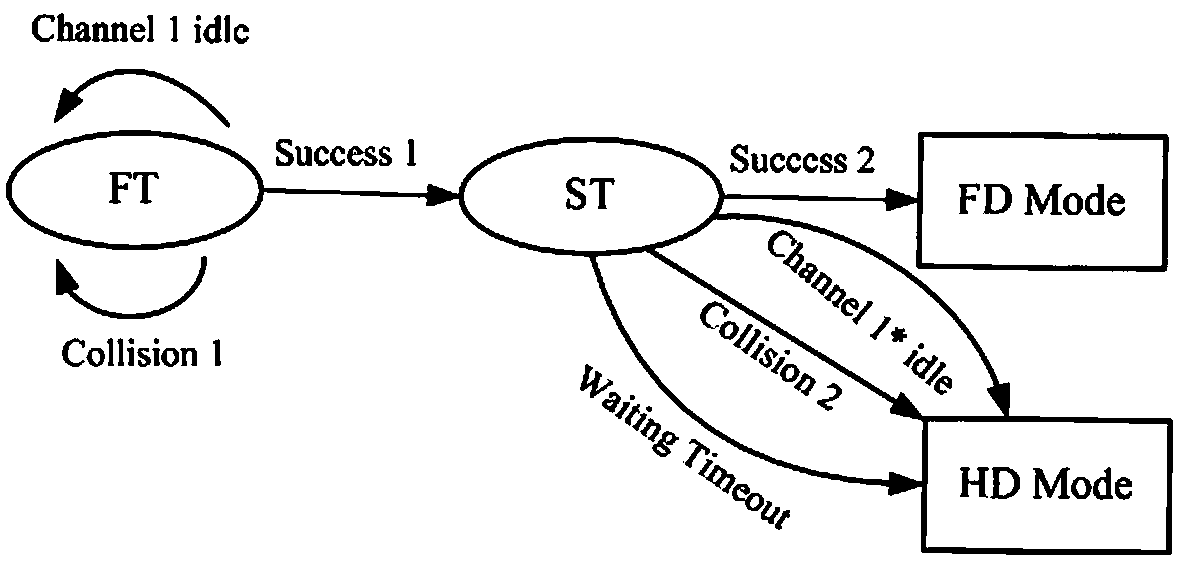
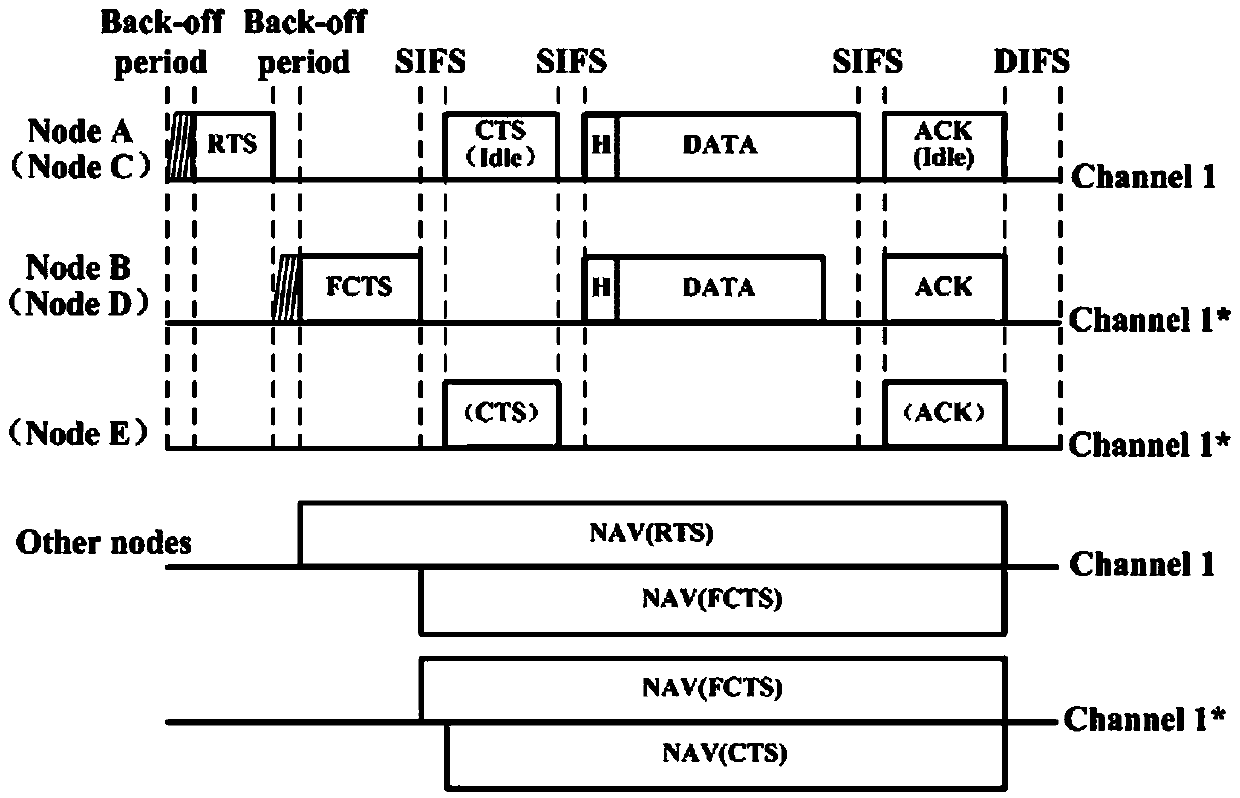
Two-stage competition-based MAC (media access control) protocol method in full duplex wireless network
ActiveCN107666489ASolve the problem of hidden nodesExcellent throughputDuplex signal operationMarkov chainHidden node problem
The invention discloses a two-stage competition-based MAC (media access control) protocol method in a full duplex wireless network, and proposes a method using a two-stage competition-based TF-MAC protocol to optimize the full duplex wireless network throughput; the control protocol comprises a RTS / FCTS / CTS handshake mechanism and a full duplex back off algorithm, thus solving the hidden node problems in the full duplex network, and reducing data frame bumping in the first stage transmission and the second node transmission; the method is suitable for a two-node symmetrical full duplex link and a three-node asymmetric full duplex link; the method can select three types of competition node transmission probabilities so as to obtain the optical throughput of the full duplex wireless network;the method uses a cascade two dimensional Markov chain model to analyze the performance of the full duplex wireless network employing the TF-MAC protocol, thus obtaining a full duplex wireless network throughput enclosed expression, and using the simulation result to verify the validity of the proposed TF-MAC protocol.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
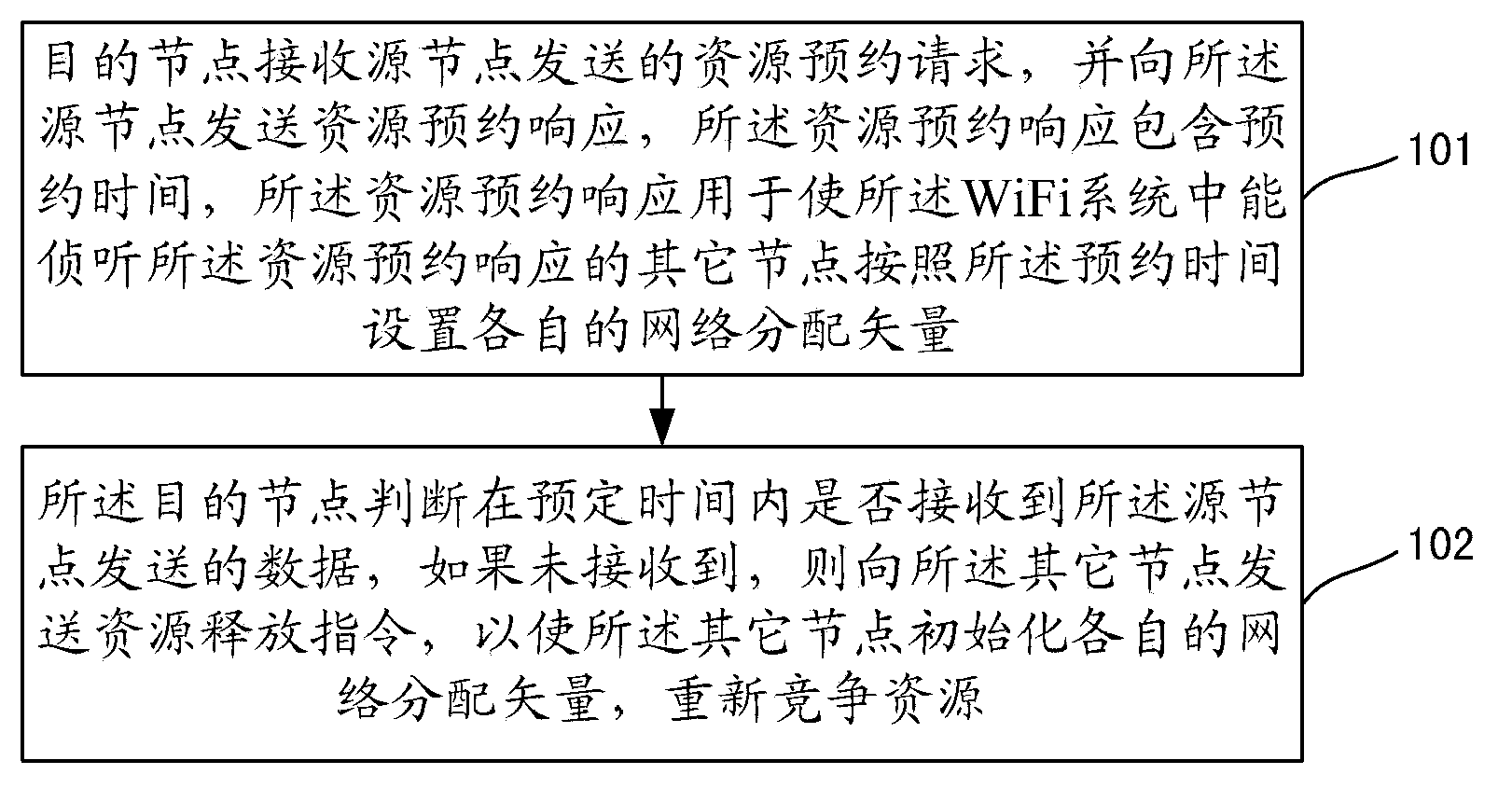
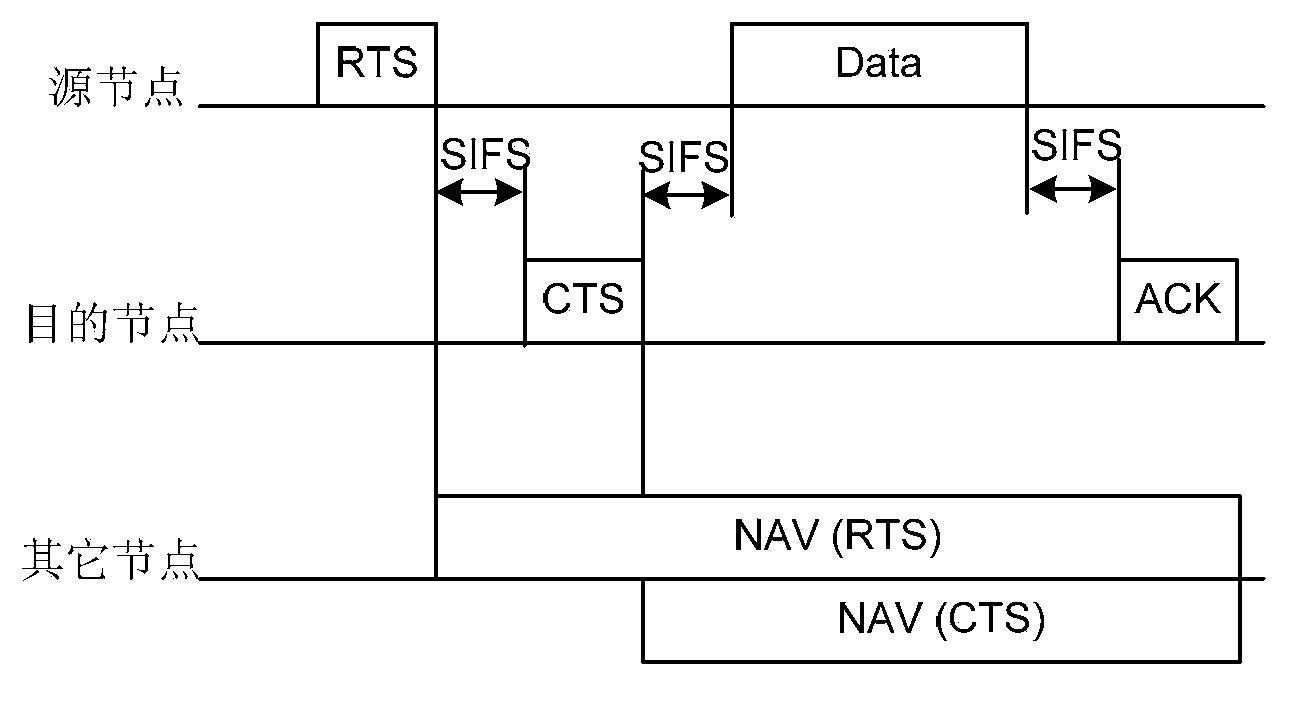
Resource reservation method and device
InactiveCN104105216AImprove resource utilizationMake full use ofNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesHidden node problemComputer network
Disclosed are a resource reservation method and device, which are applied to a WiFi system. The method includes the following steps: a target node receives a resource reservation request sent by a source node and sends a resource reservation response to the source node, wherein the resource reservation response includes a reservation time, and the resource reservation response is used for enabling other nodes which are capable of monitoring the resource reservation response in the WiFi system to set respective network allocation vectors according to the reservation time; and the target node judges whether data sent by the source node is received in a preset time and if not so, a resource release instruction is sent to the other nodes so as to enable the other nodes to initialize the respective network allocation vectors and re-compete for resources. Therefore, a hidden node problem is solved and at the same time, sufficient and reasonable utilization of network resources are ensured.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
Method and apparatus to provide hidden node protection
A method and a wireless communication device to overcome a hidden node problem in a BSS The method includes detecting that transmitting one or more data frames causing one or more nodes of an unsynchronized wireless communication network to become hidden nodes. The wireless communication device that causes the hidden node problem requests a time allocation for transmitting one or more data frames to at least one node of the unsynchronized wireless communication network and to transmit the one or more data frames using an antenna beam forming technique at the allocated time frame.
Owner:INTEL CORP
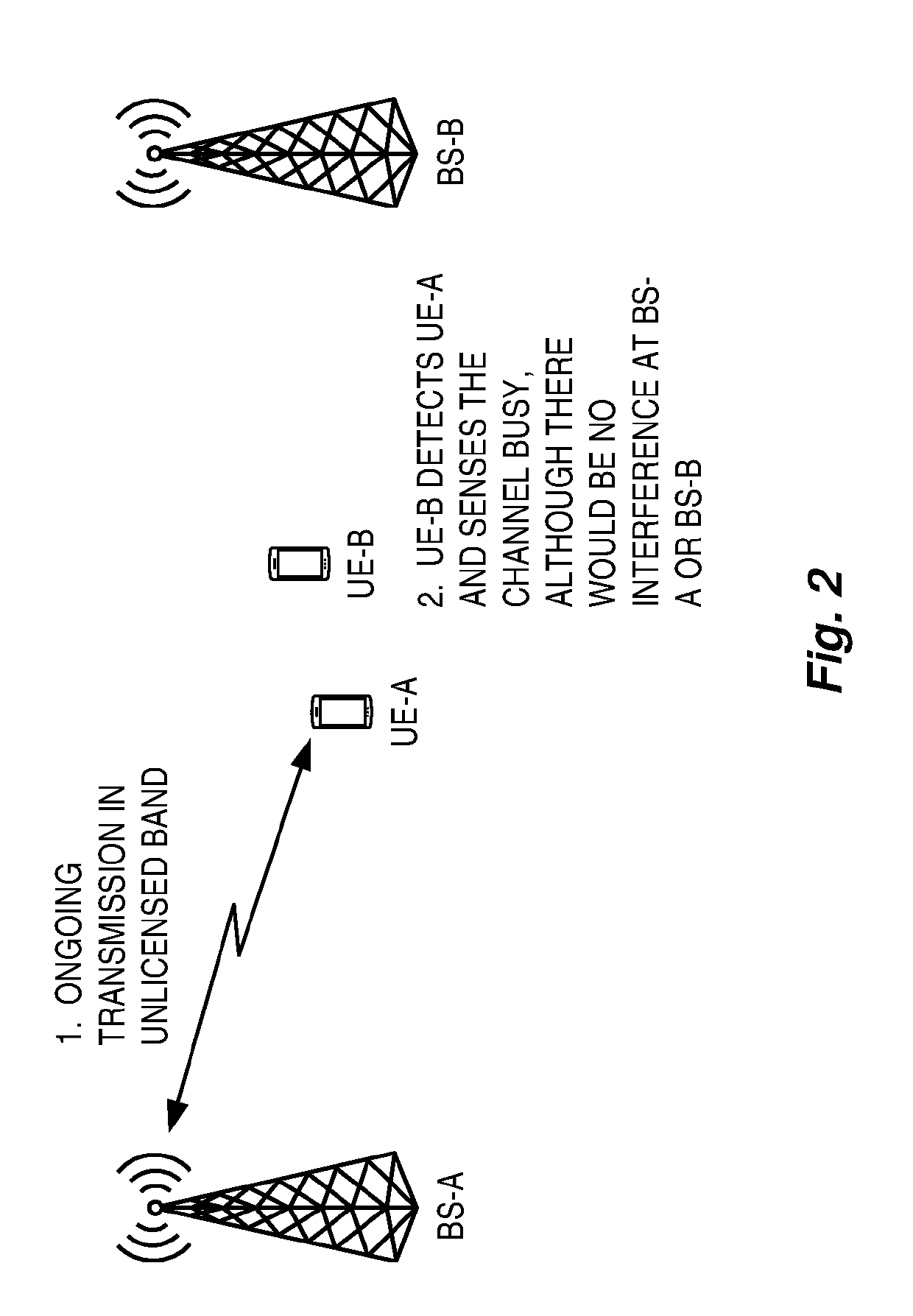
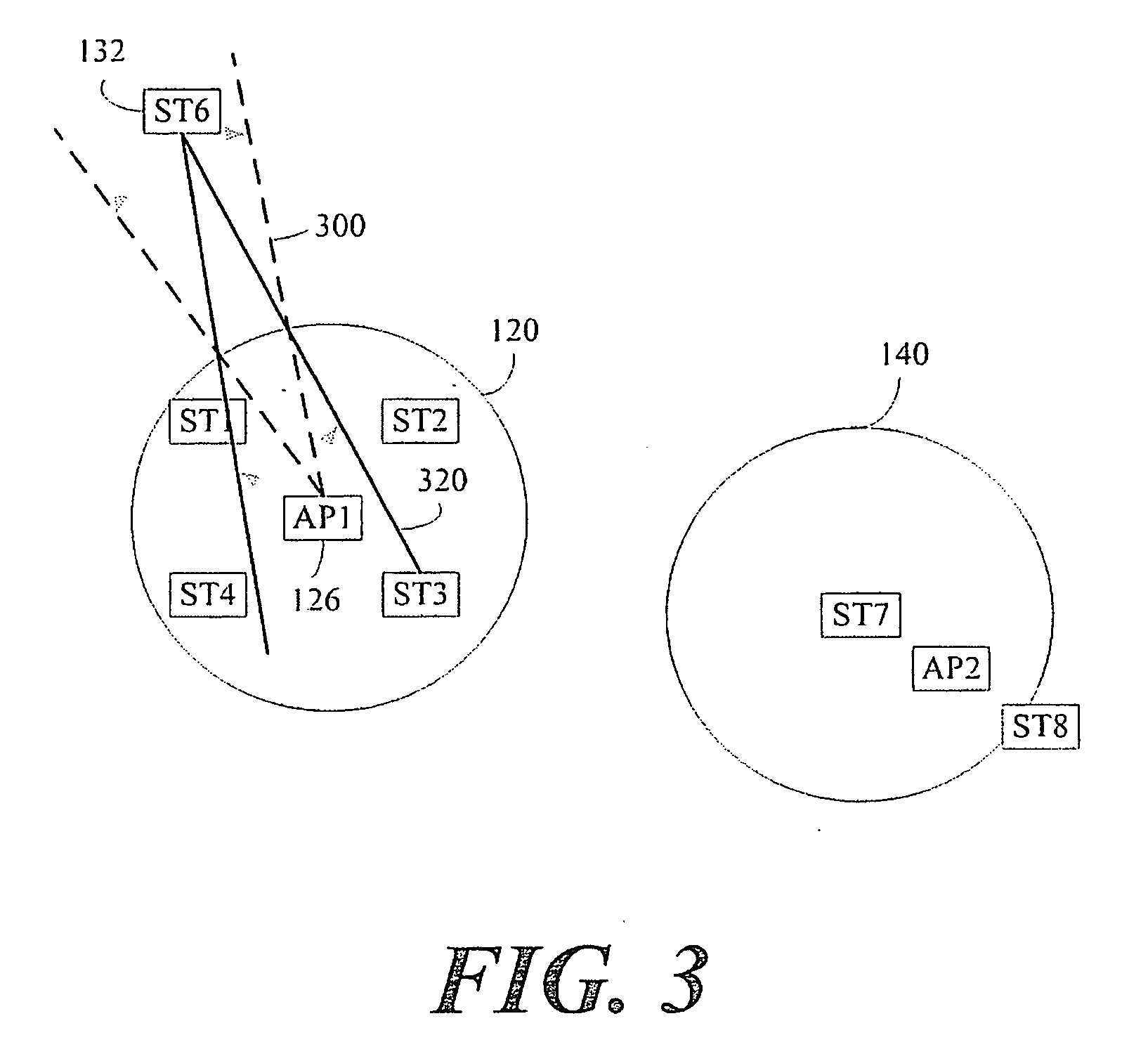
System and methods for detection of hidden nodes in cellular systems on unlicensed bands
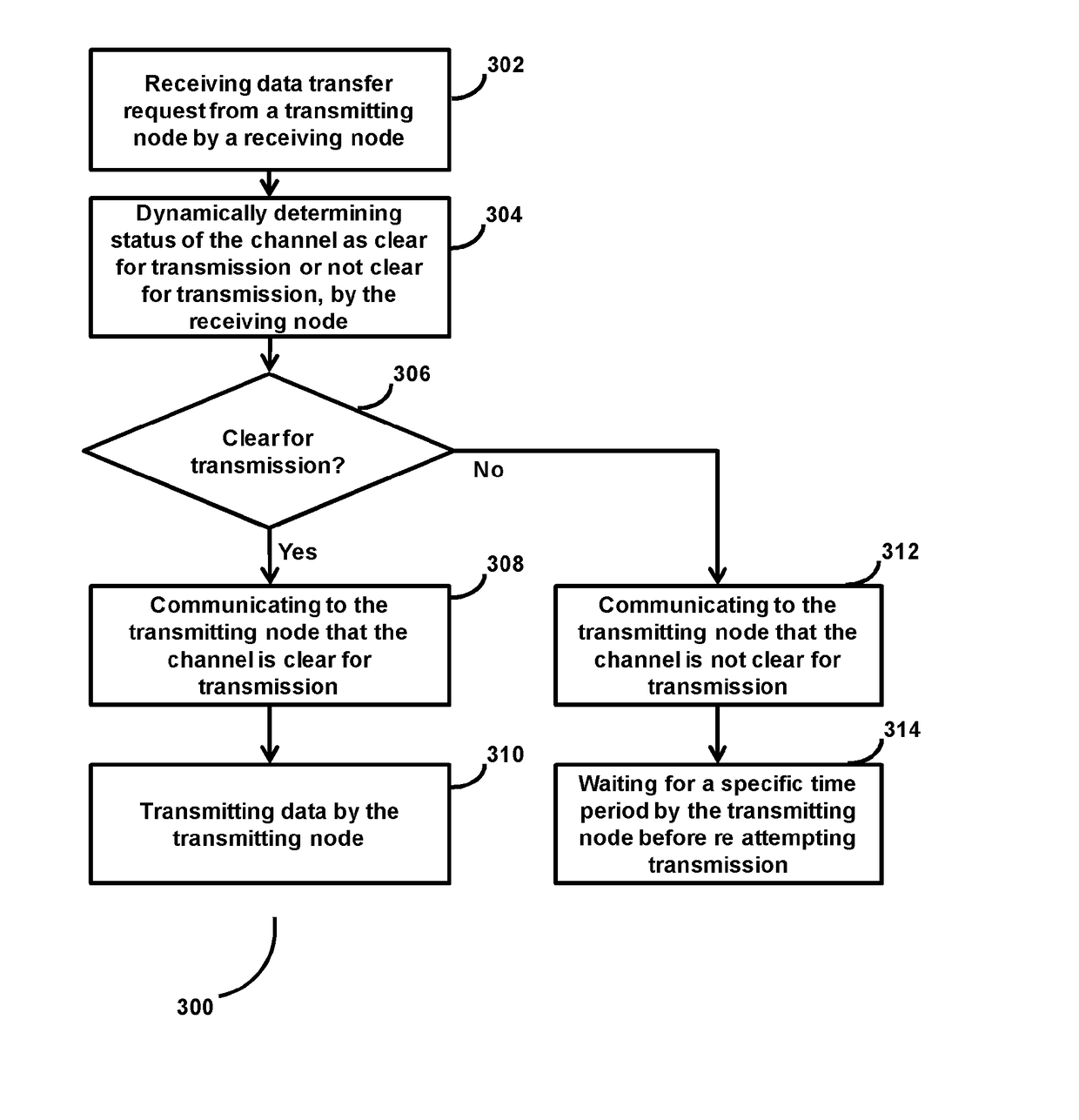
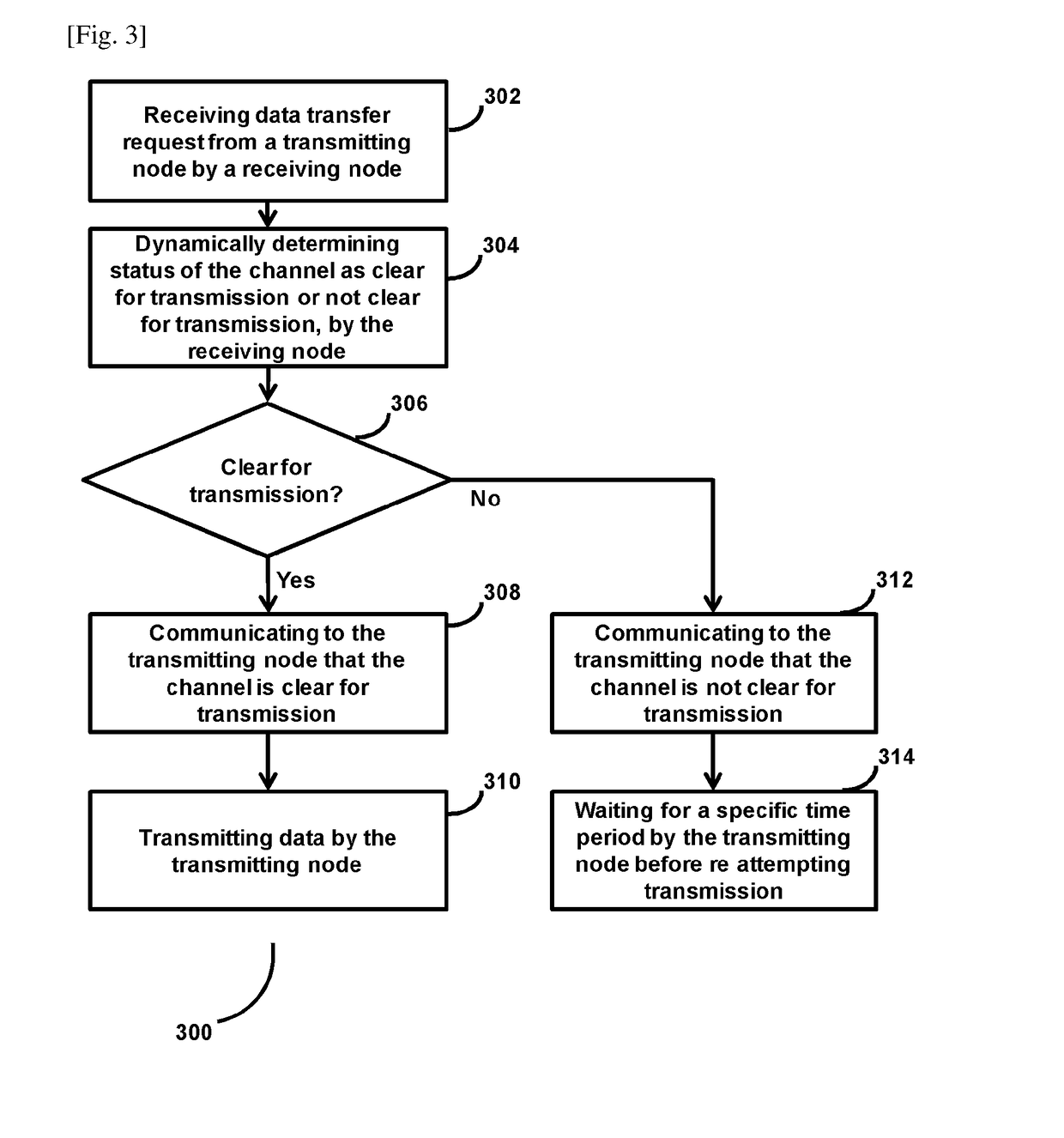
Method and system for managing hidden node problem in a communication network. A receiving node in the system, upon receiving a data transmission request from at least one transmitting node, dynamically checks status of the channel between the transmitting node and the receiving node. If the channel is found to be clear for transmission, then the receiving node sends a message that indicates that the channel is clear, to the transmitting node, and the transmitting node starts transmitting the data. Upon receiving a message from the receiving node that the channel is not clear for transmission, then the transmitting node waits for a particular time period and attempts the connection again.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for expanding capacity of Ad Hoc network through mitigating interference using multiple antennas MAC (MIMO-MAC) optimization
InactiveCN102137506AReduce interaction timeIncrease capacityError prevention/detection by using return channelWireless communicationHidden node problemClear to send
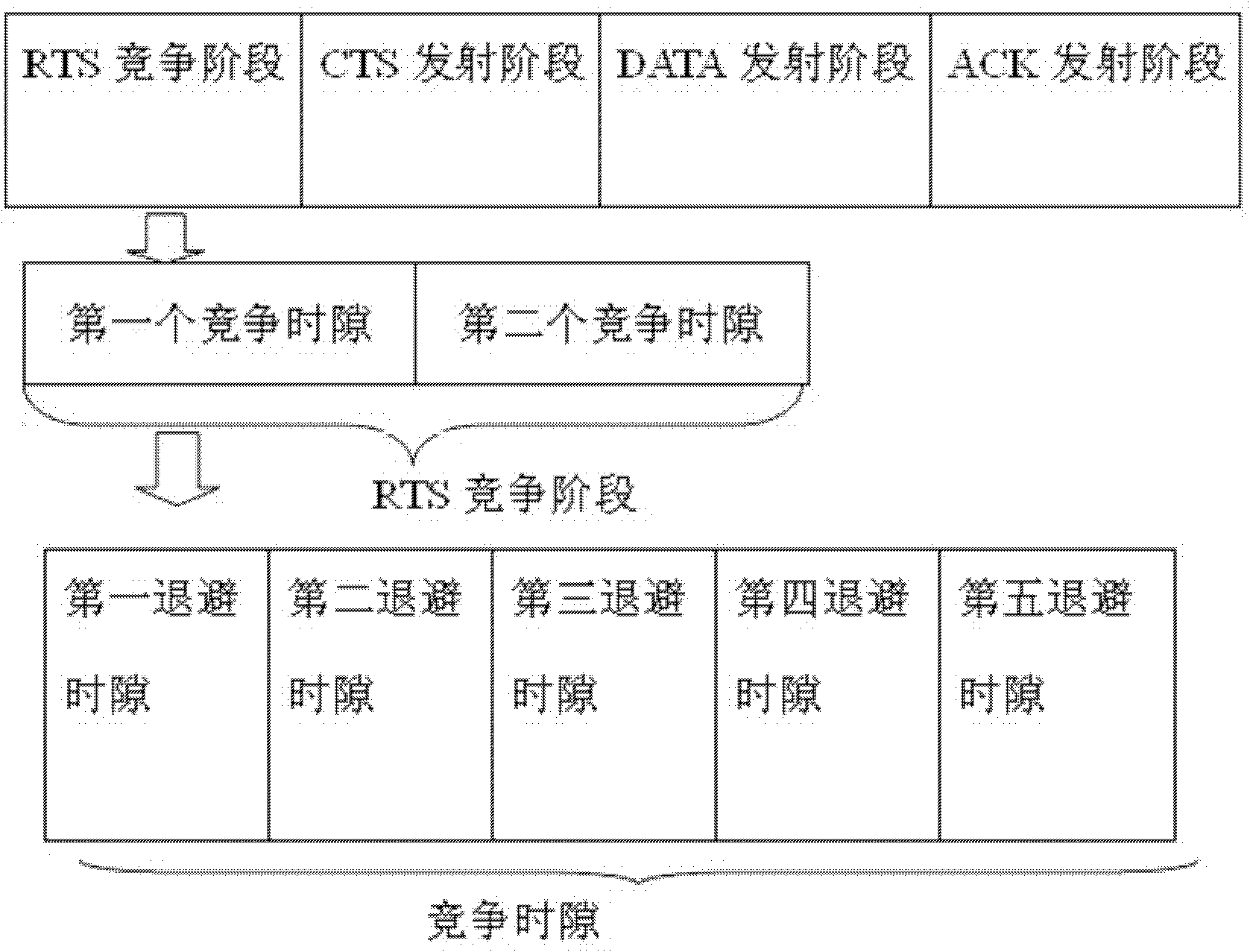
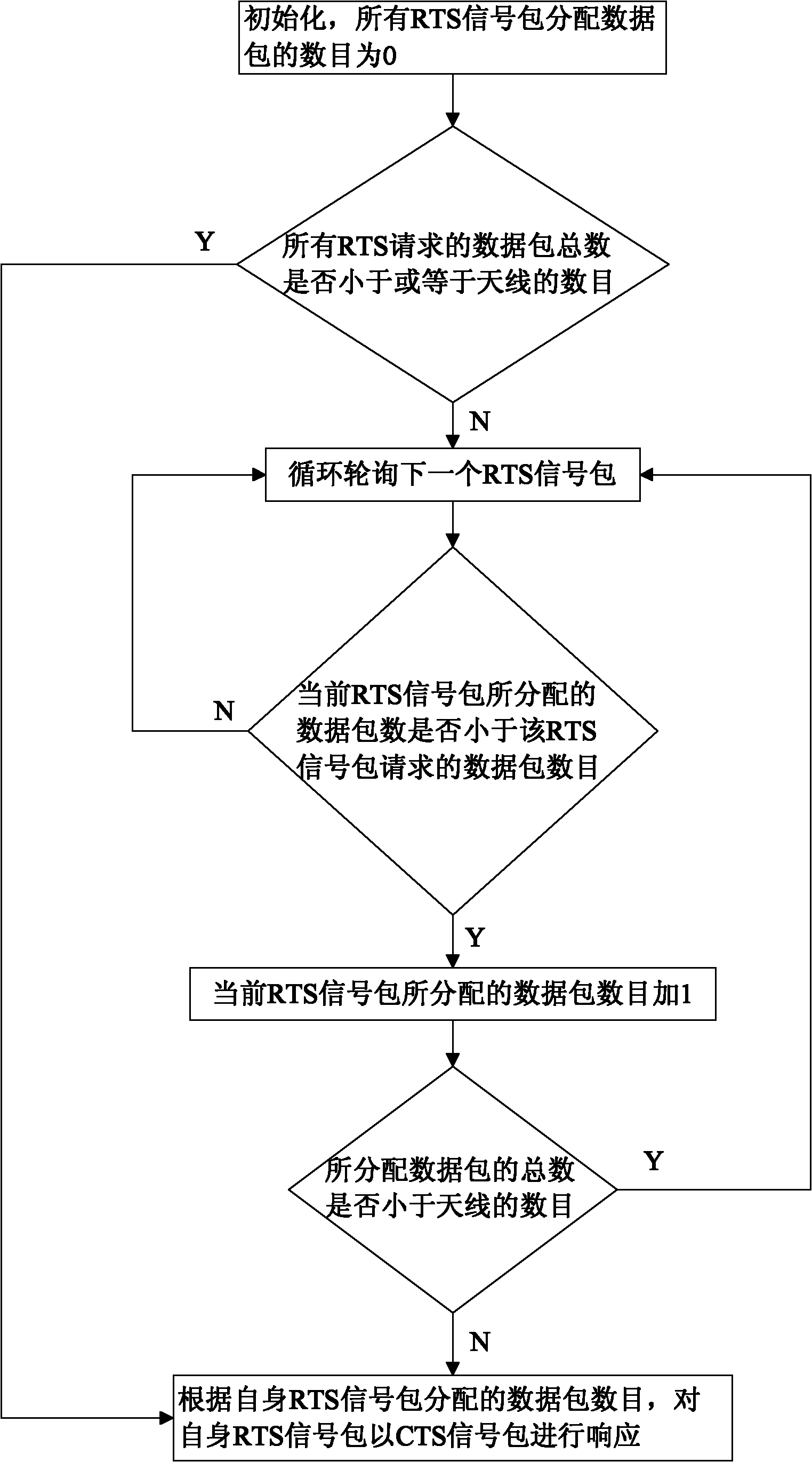
The invention discloses a method for expanding capacity of Ad Hoc network through mitigating interference using multiple antennas MAC (MIMO-MAC) optimization. The method comprises the following step that: each node is provided with a plurality of antennas, and the number of the antennas on each node is the same. Data frames of the MAC layer are synchronized and have four stages: namely a request to send (RTS) competing stage, a clear to send (CTS) emitting stage, a data (DATA) emitting stage and an acknowledgement (ACK) emitting stage, which are closely associated and cannot be separated. RTS signal packets in the method are emitted in a competition manner and CTS signal packets are synchronously emitted so as to shorten interactive time for RTS and CTS. The number of the data packets which can be emitted by each node is derived by a method for bilaterally allocating the data packets, so the problem of node hiding is solved and the capacity of the network is greatly expanded.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Zigbee hidden conflict resolution method for wireless sensor network
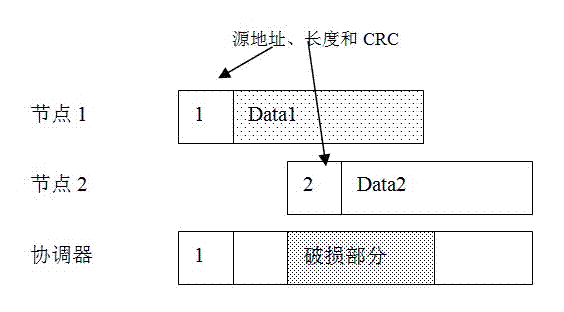
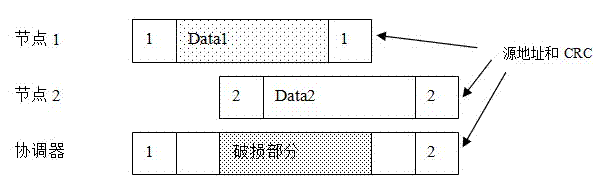
InactiveCN102572892AReduce overheadLow message complexityEnergy efficient ICTNetwork topologiesHidden node problemLine sensor
The invention discloses a Zigbee hidden conflict resolution method for a wireless sensor network. A hidden node problem is an important factor for the performance degradation of an IEEE802.15.4 protocol. According to the method, a contention free period (CFP) of the IEEE802.15.4 is equally divided into a plurality of timeslots, the address information of hidden nodes is extracted from a partially-damaged frame caused by a hidden conflict, the nodes are dynamically regulated into different competition groups according to a currently acquired hidden relationship, the nodes in the same competition groups competitively transmit messages according to a binary backoff method in the same period, and the nodes in different competition groups transmit the messages in different timeslots, so that the problem of hidden conflict is completely solved. Compared with other hidden conflict resolution methods, a conflict-identification-and-grouping-based hidden conflict avoidance method has the advantages of low additional overhead, dynamic regulation and the like, and a data transmission rate, throughput and an energy utilization rate are remarkably increased.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
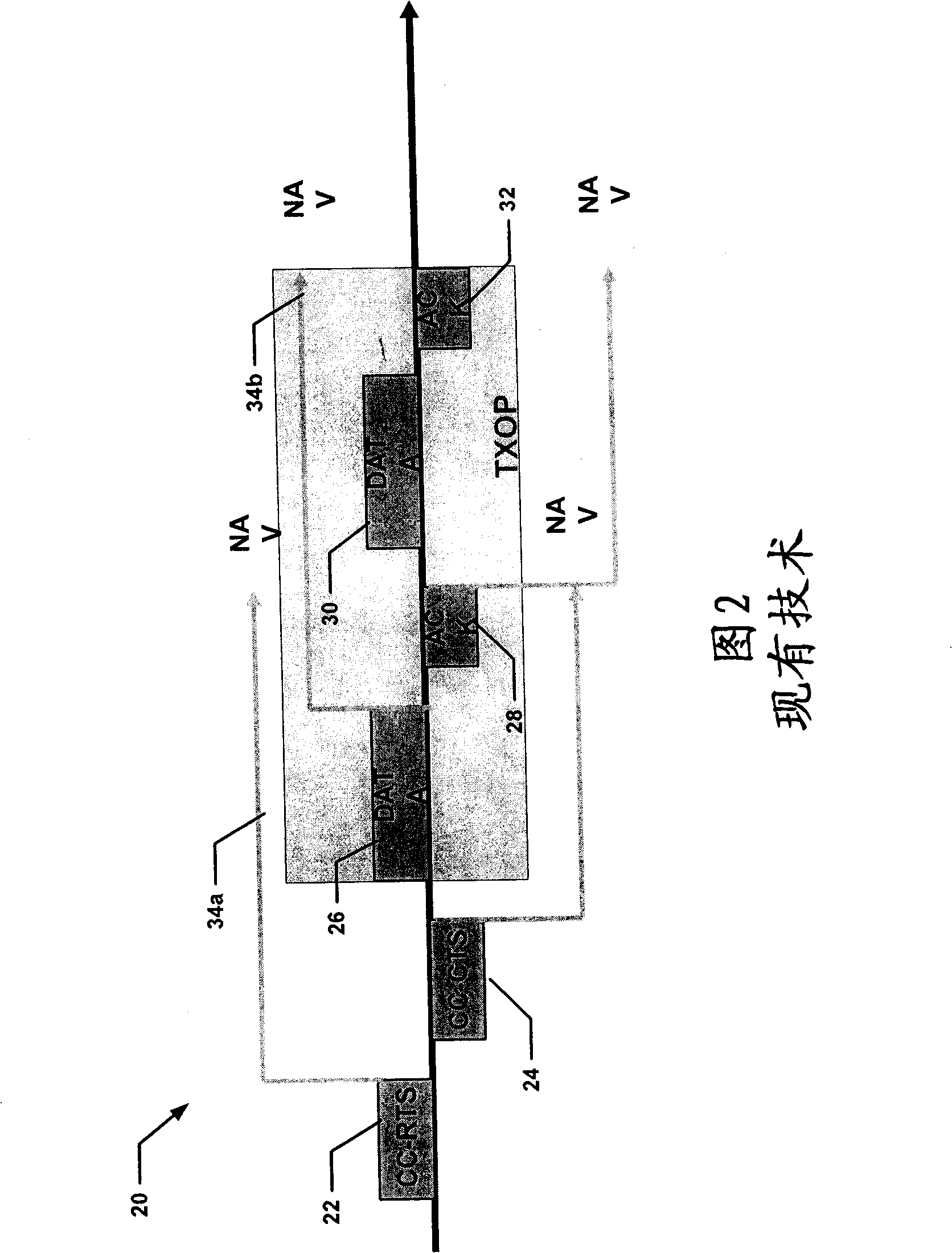
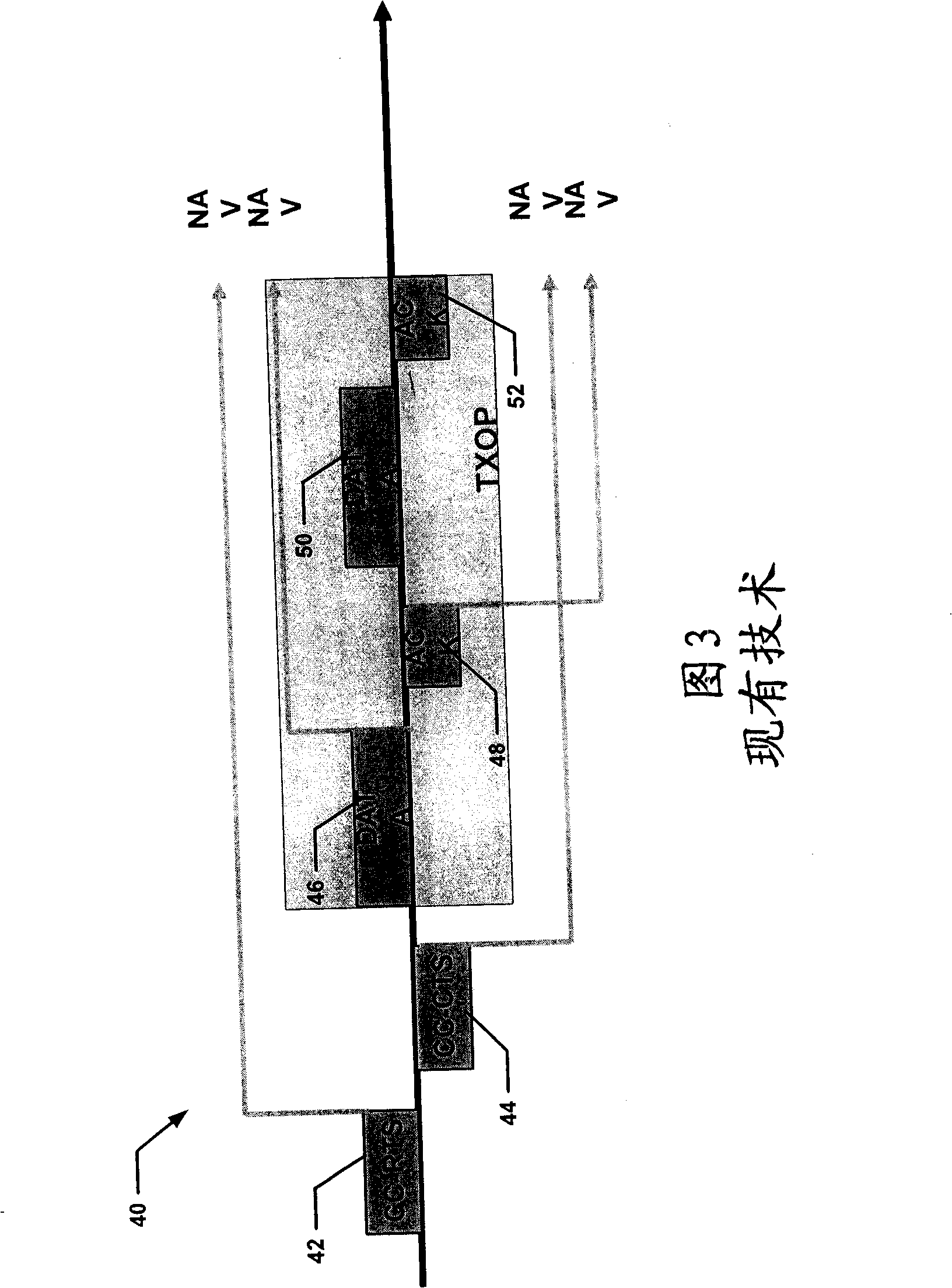
Symmetric transmit opportunity (TXOP) truncation
ActiveUS8031661B2Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesHidden node problemTelecommunications
Symmetric transmit opportunity (TXOP) truncation (STT) including receiving a frame that truncates a TXOP around a first station, and responsive to receiving the frame, sending a second frame that truncates the TXOP around a second station. By transmitting a second frame that repeats the truncation of the TXOP transmitted from the first station, a hidden node problem can be avoided and equitable access to the medium provided by ensuring that stations that may be outside the broadcast range of the first station also receive the frame truncating the TXOP. Also disclosed is an access point (AP) that receives an extended interframe space (EIFS) set frame responsively transmits a second frame having a completed transmission corresponding to time based on an interval of EIFS less DIFS, the interval commencing from an end of the EIFS set frame.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
MAC protocol based on instant forwarding
InactiveCN104065720AImprove performanceSolve the hidden node problemTransmissionHidden node problemNetwork packet
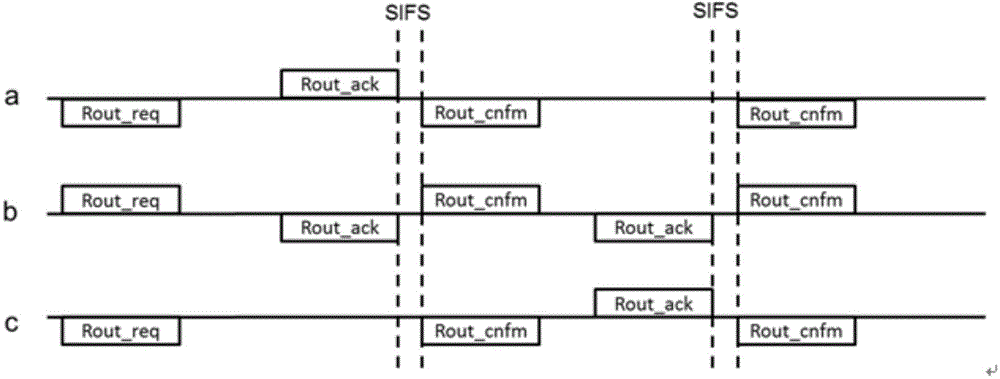
The invention provides an MAC protocol based on instant forwarding. The protocol is achieved through the self-organization router step and the transmission step. According to the self-organization router step, nodes generate a self-organization router according to a ROUT_REQ frame, a response frame ROUT_ACK and an acknowledgement frame ROUT_CNFM. According to the transmission step, the nodes are classified, the classified nodes acquire target addresses according to the self-organization router, and data packets are sent or received according to the target addresses. According to the MAC protocol based on instant forwarding, through the self-organization router and the improvement of a handshaking mechanism, synchronous check can be carried out through forwarded signals in the forwarding process, dual-way contralateral routing and single-way instant forwarding are supported at the same time, the problem of hidden nodes can be solved, end-to-end delay is lowered, and the throughput rate and full-duplex network performance are improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
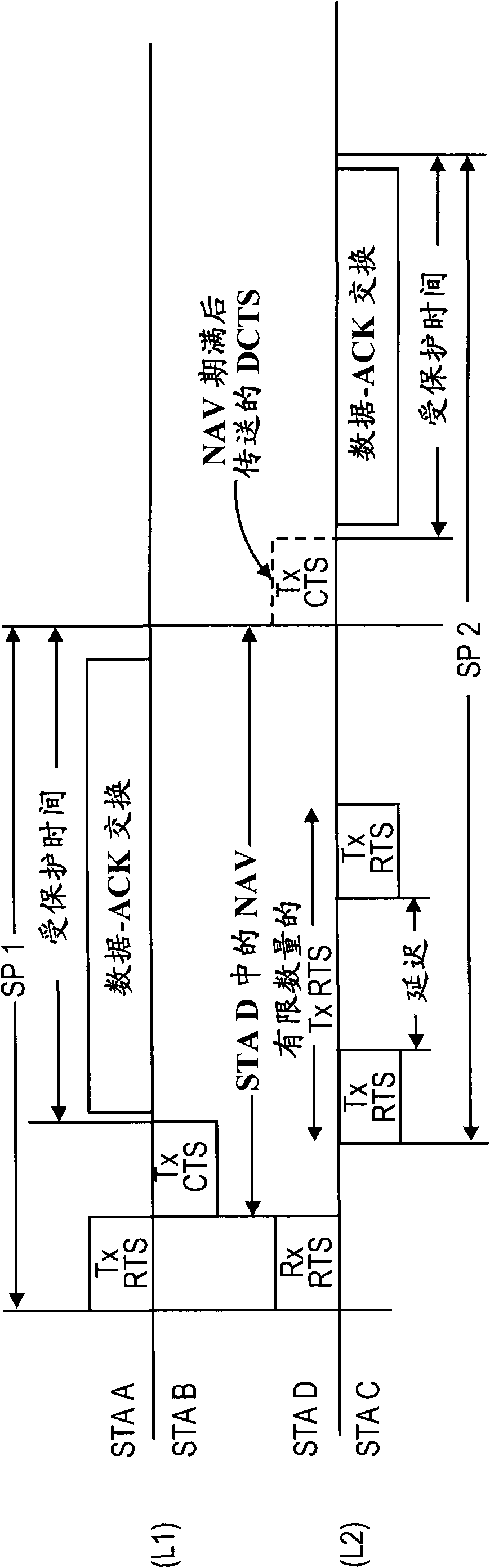
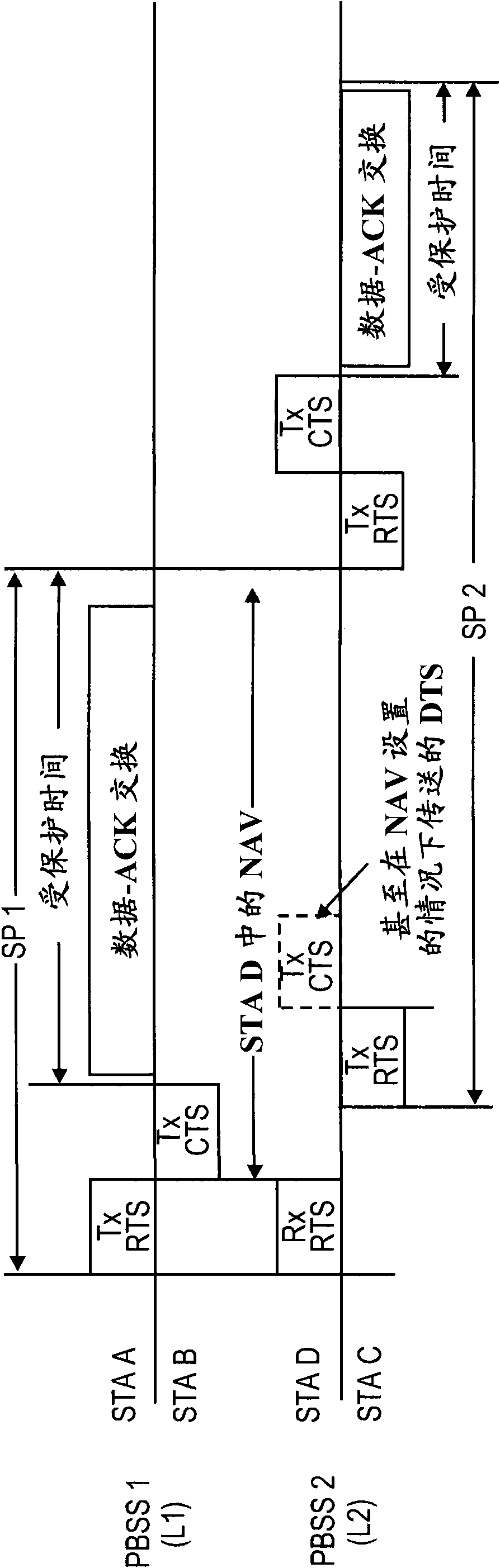
Use of delayed clear-to-send and denial-to-send in directional wireless networks
For directional wireless communications, at least one new response to a Request-to-Send (RTS) message has been created to avoid a hidden-node problem that is particular to directional networks. In response to an RTS received during a NAV period, a Denial-to-Send (DTS) may be transmitted to indicate that the responding device cannot currently communicate further because its NAV is currently set, but it will be ready to communicate after expiration of the time period specified in the DTS.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus in node used for wireless communication
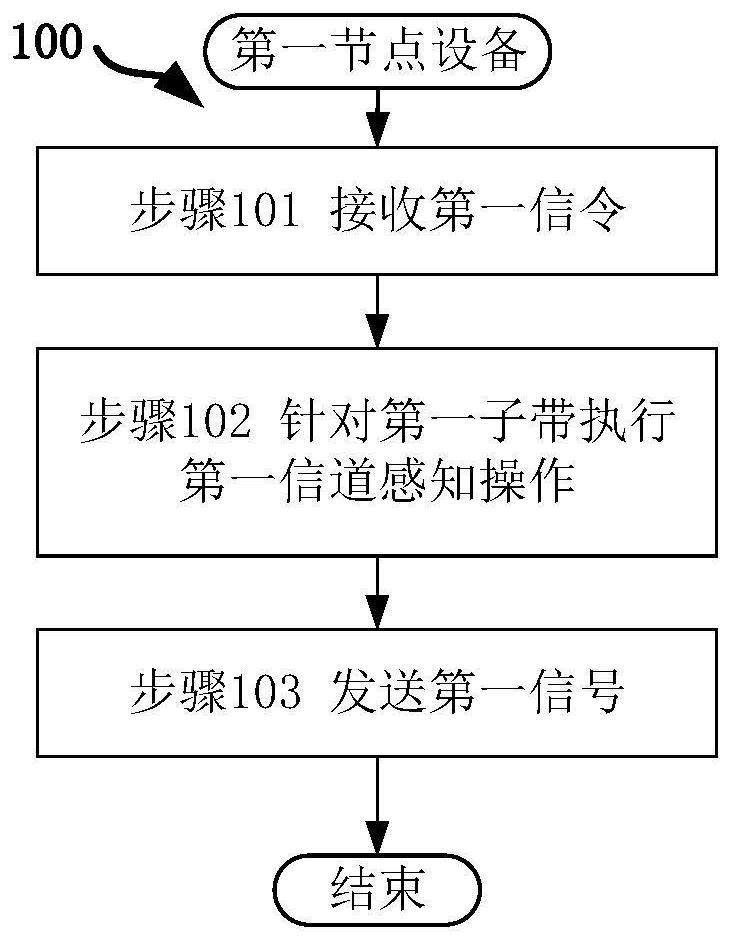
ActiveCN113225814AAvoid or mitigate the hidden node problemAvoid interferenceWireless communicationHidden node problemTelecommunications
The invention discloses a method and an apparatus in a node used for wireless communication. The first node receives the first signaling; performing a first channel sensing operation on the first sub-band; and sending the first signal. Wherein the first signaling comprises first indication information, and the first indication information is used for indicating a receiving parameter of the first channel sensing operation; the first channel sensing operation is used for determining channel occupation information, and the channel occupation information is used for determining whether the first sub-band can be used for signal transmission by a sender of the first signaling; the first signal is used for indicating the channel occupation information; the first signaling is used for determining Q1 candidate resource groups, a first resource group is one of the Q1 candidate resource groups, and the first signal occupies the first resource group. According to the method, the receiving party of communication can execute the channel sensing operation and feed back the result, and interference caused by the hidden node problem is relieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI LANGBO COMM TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus to provide hidden node protection
InactiveUS8774140B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsHidden node problemComputer science
A method and a wireless communication device to overcome a hidden node problem in a BSS The method includes detecting that transmitting one or more data frames causing one or more nodes of an unsynchronized wireless communication network to become hidden nodes. The wireless communication device that causes the hidden node problem requests a time allocation for transmitting one or more data frames to at least one node of the unsynchronized wireless communication network and to transmit the one or more data frames using an antenna beam forming technique at the allocated time frame.
Owner:INTEL CORP
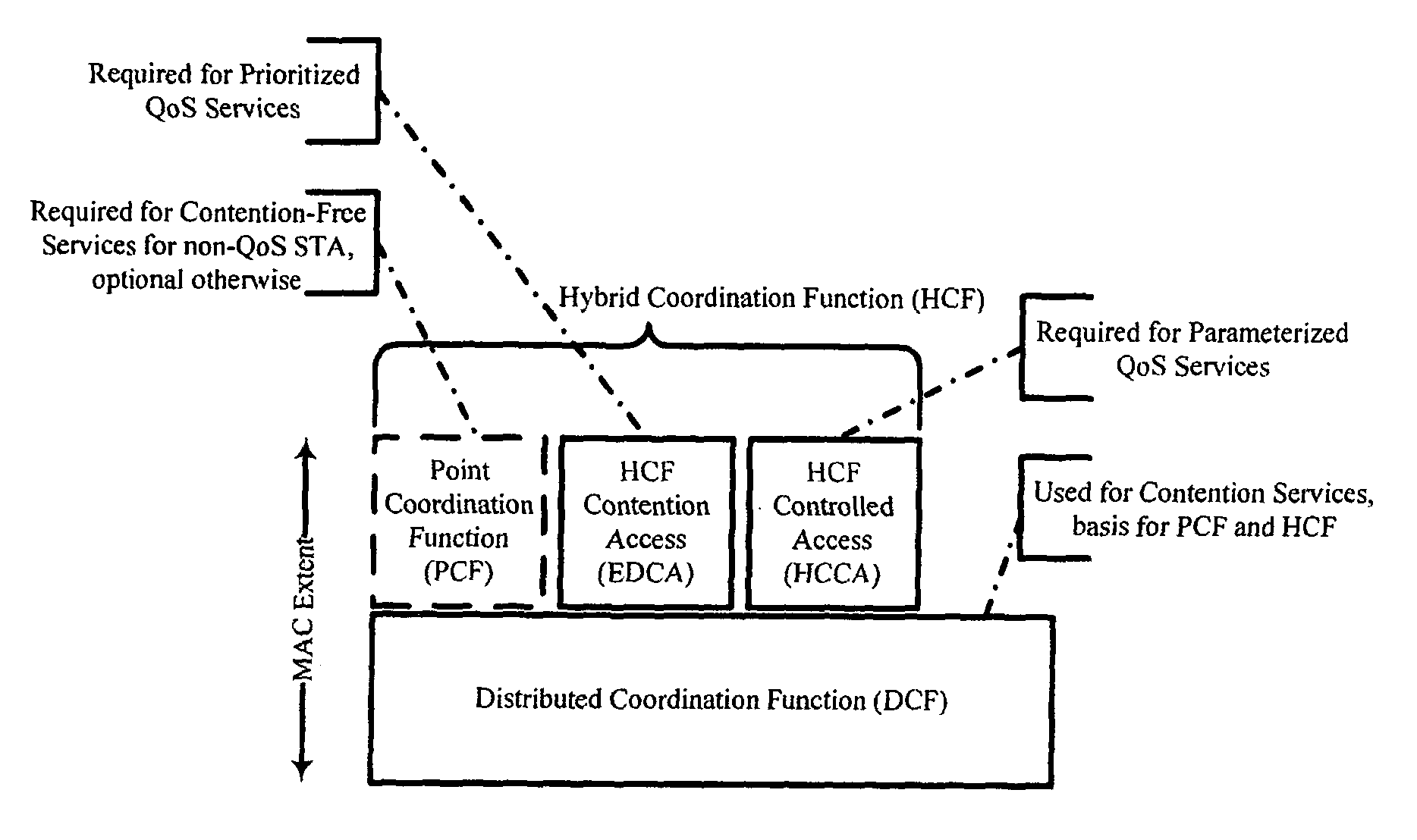
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com