Auxiliary directional access control method of spare nodes in WLAN
An access control and idle node technology, applied in digital transmission systems, electrical components, error prevention and other directions, can solve the problems of wasting channel resources and poor fairness, increase logarithms, avoid hidden node problems, and improve channel utilization. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
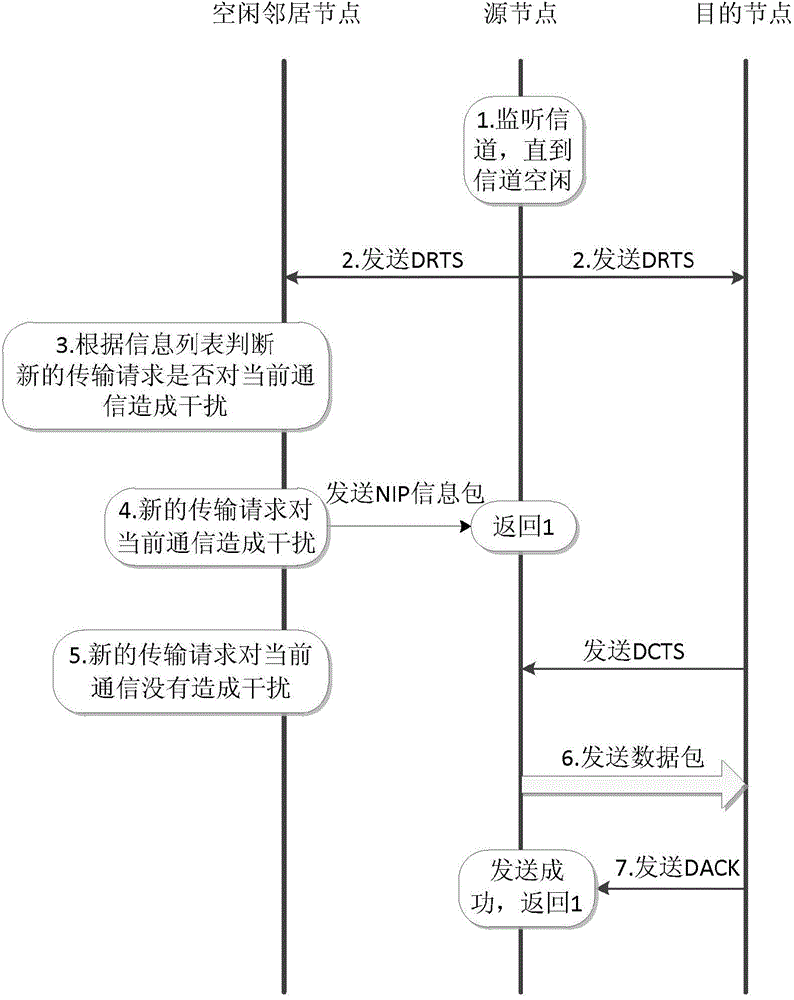
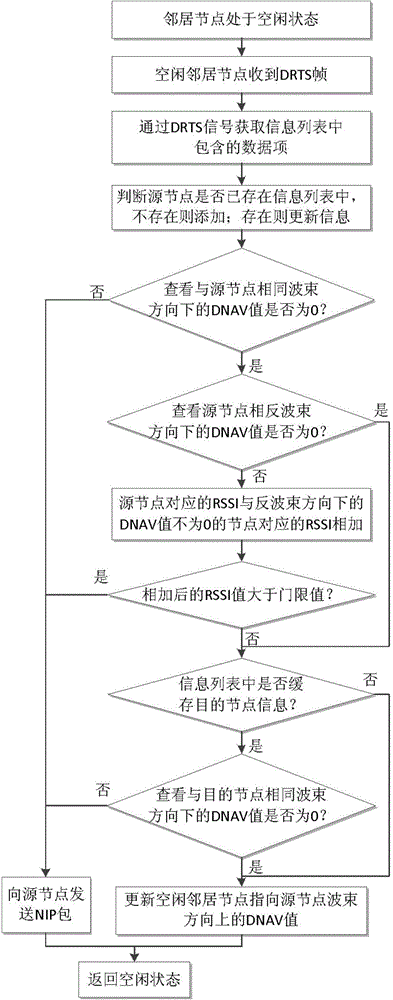
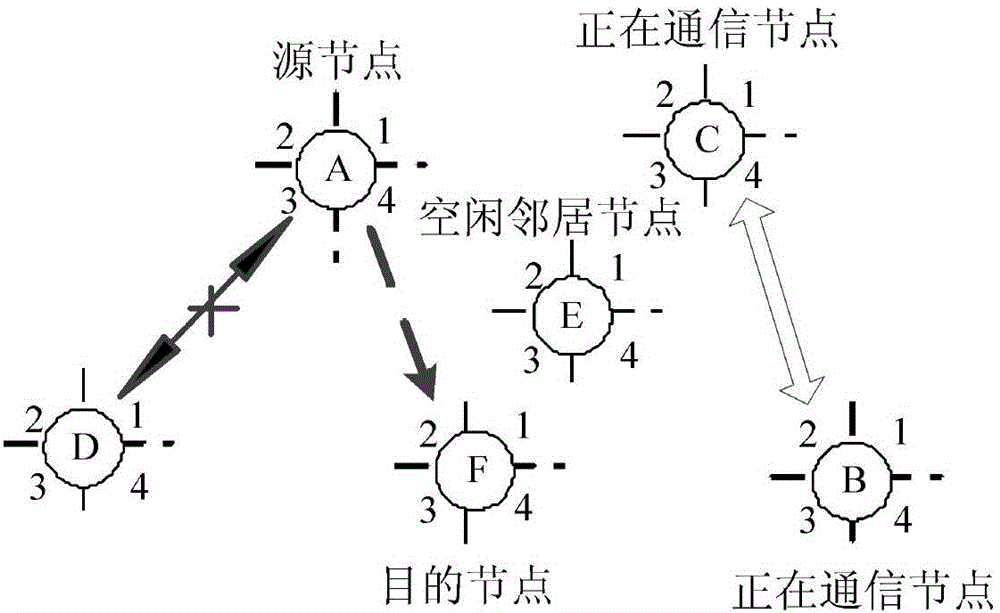
[0039]The traditional DMAC protocol is implemented by requesting to send / allowing to send RTS / CTS signals to reserve channels. When the surrounding nodes hear the handshake signal, DNAV settings are performed, and beams in the direction that will cause interference are blocked to realize distributed beam switching control. However, in a WLAN system using beam switching antennas, handshake signals for channel reservation may be missed during directional transmission / reception, causing hidden node problems. Such as image 3 As shown, nodes A, D communicate with C, B, and the beam of node A locks on beam 3 for directional data transmission and reception, so the DRTS / DCTS handshake signal between B and C is missed. After the transmission between A and D ends, if the new destination node of node A is B, C or F, the DRTS in the direction of beam 4 will interfere with the data transmission between nodes B and C; and A repeats the request until B ends the communication with C Returns...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com