Powerline communications (PLC) network routing method and system
A technology of power line carrier and communication network, which is applied in distribution line transmission system, wired transmission system, transmission system, etc. It can solve the problem of low communication reliability in the power consumption information collection system, reduce the amount of signaling messages, and reduce loss Packet rate, the effect of improving forwarding efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
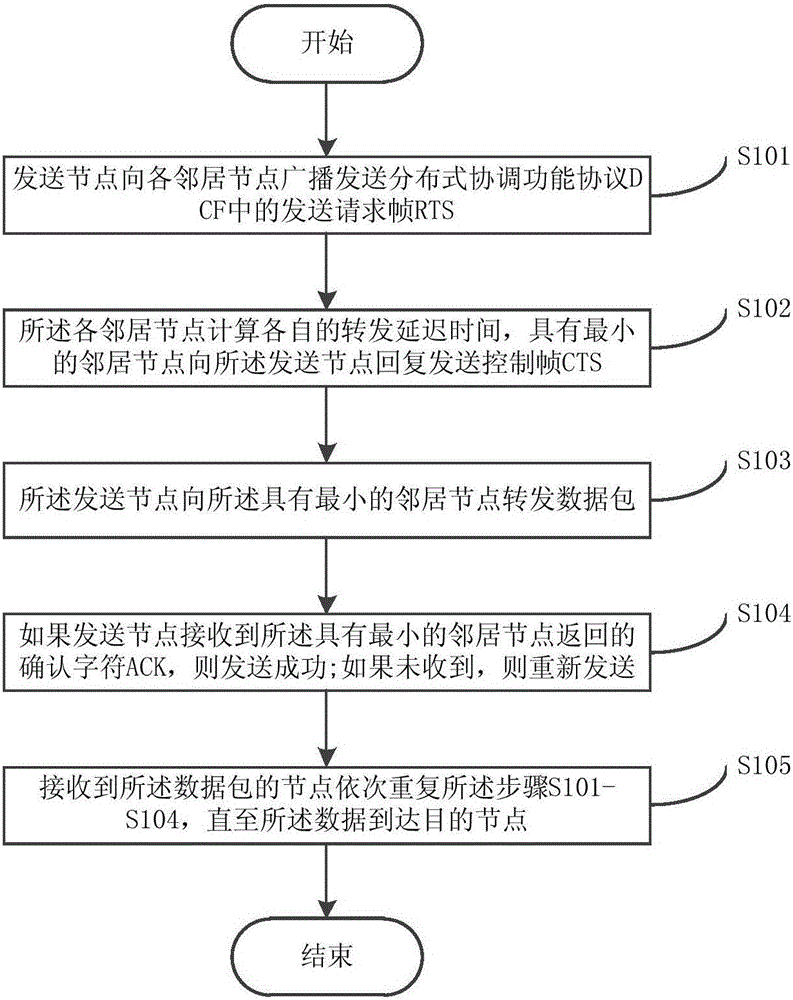
[0031] Such as figure 1 As shown, the power line carrier communication network routing method of the present invention includes:
[0032] Step S101: the sending node broadcasts the sending request frame RTS in the distributed coordination function protocol DCF to each neighboring node;
[0033] The sending node (including the source node or the intermediate forwarding node) broadcasts the RTS frame in the DCF protocol, and waits for the reply of the neighbor node.
[0034] Step S102: each neighbor node calculates its own forwarding delay time T CTS_REQ , with minimum T CTS_REQ The neighbor node of the said sending node replies to send the control frame CTS;
[0035] The node with the minimum forwarding delay time replies the CTS frame to the sending node first, that is, wins the routing competition, and the other neighbor nodes receive the CTS frame sent by the node with the minimum forwarding delay time, cancel their own timers, and give up the routing competition .
[0...
Embodiment 2
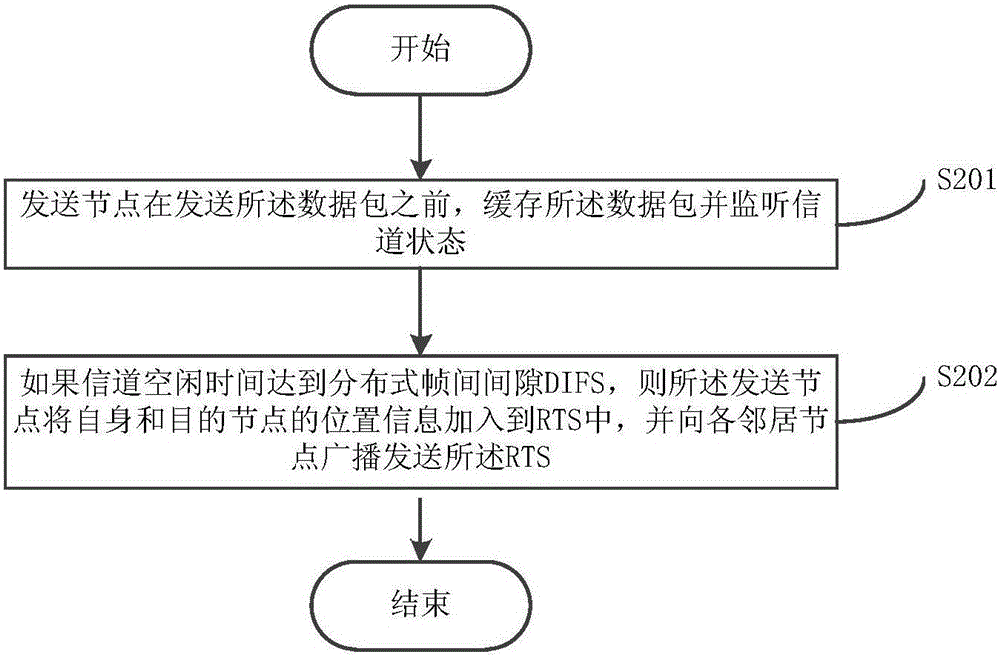
[0046] This embodiment describes the process of step S101 in detail, as figure 2 shown, including:
[0047]Step S201: Before sending the data packet, the sending node buffers the data packet and monitors the channel state;
[0048] Step S202: If the channel idle time reaches the distributed interframe space DIFS, the sending node adds the location information of itself and the destination node into the RTS, and broadcasts the RTS to each neighbor node.
[0049] If the channel idle time reaches DIFS, the sending node puts the location information of itself and the destination node into the header of the RTS frame, and broadcasts it to each neighbor node.
Embodiment 3
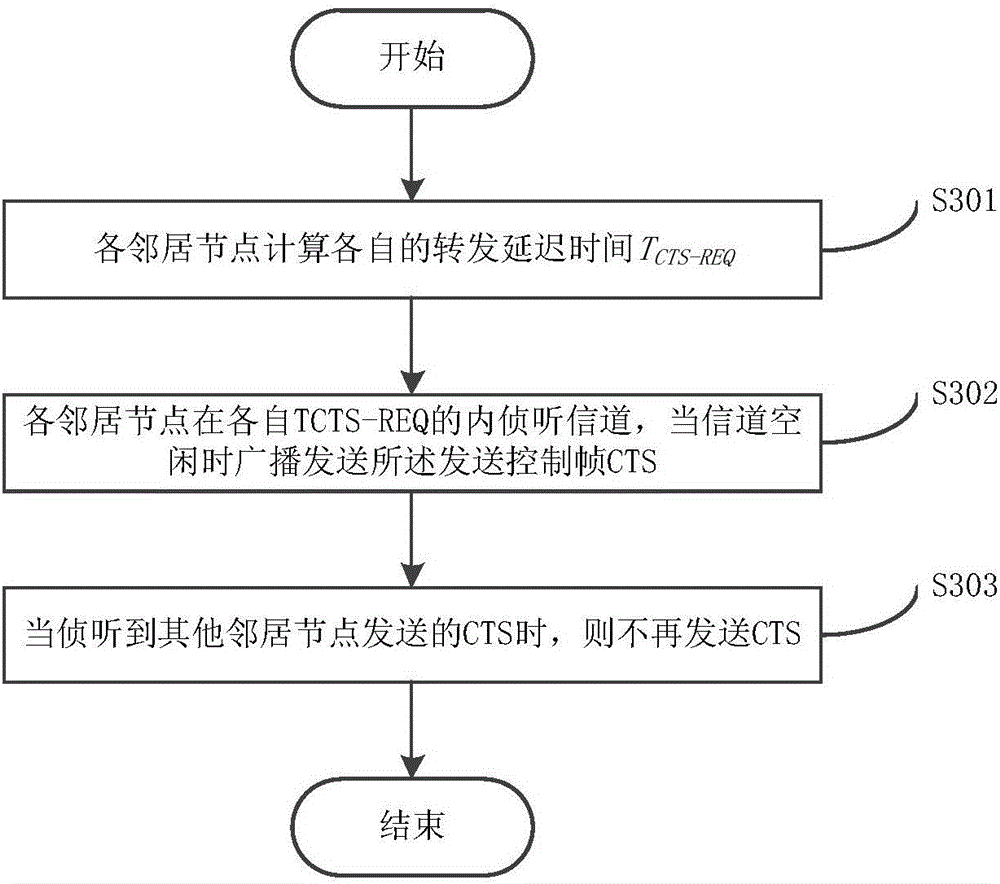
[0051] This embodiment describes the process of step S102 in detail, as image 3 shown, including:
[0052] Step S301: Each neighbor node calculates its own forwarding delay time T CTS_REQ ,
[0053] T C T S _ R E Q = T S I F S + T M A X × P , P = ω 1 × V S N R V S N R _ M A X ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com