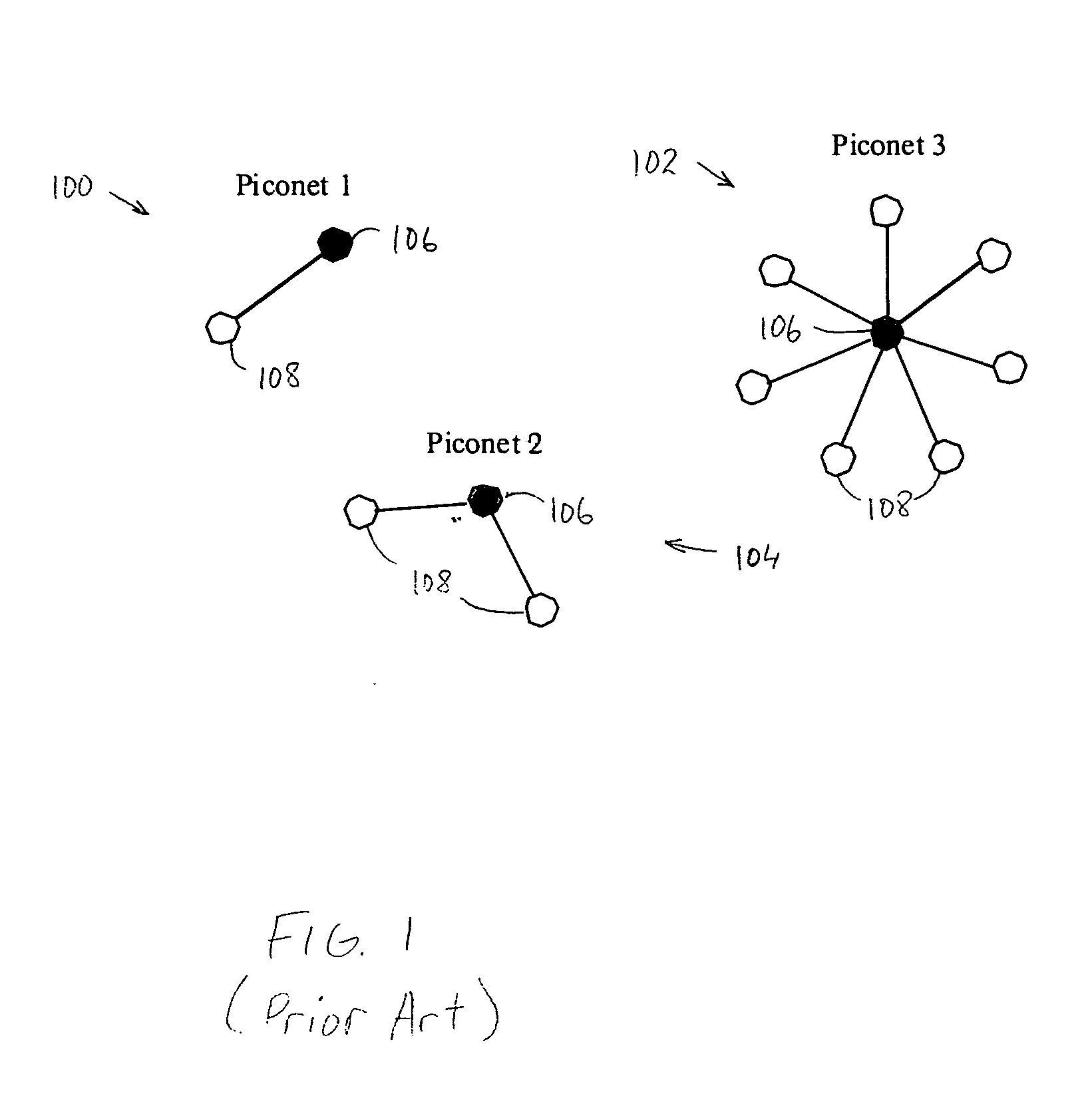
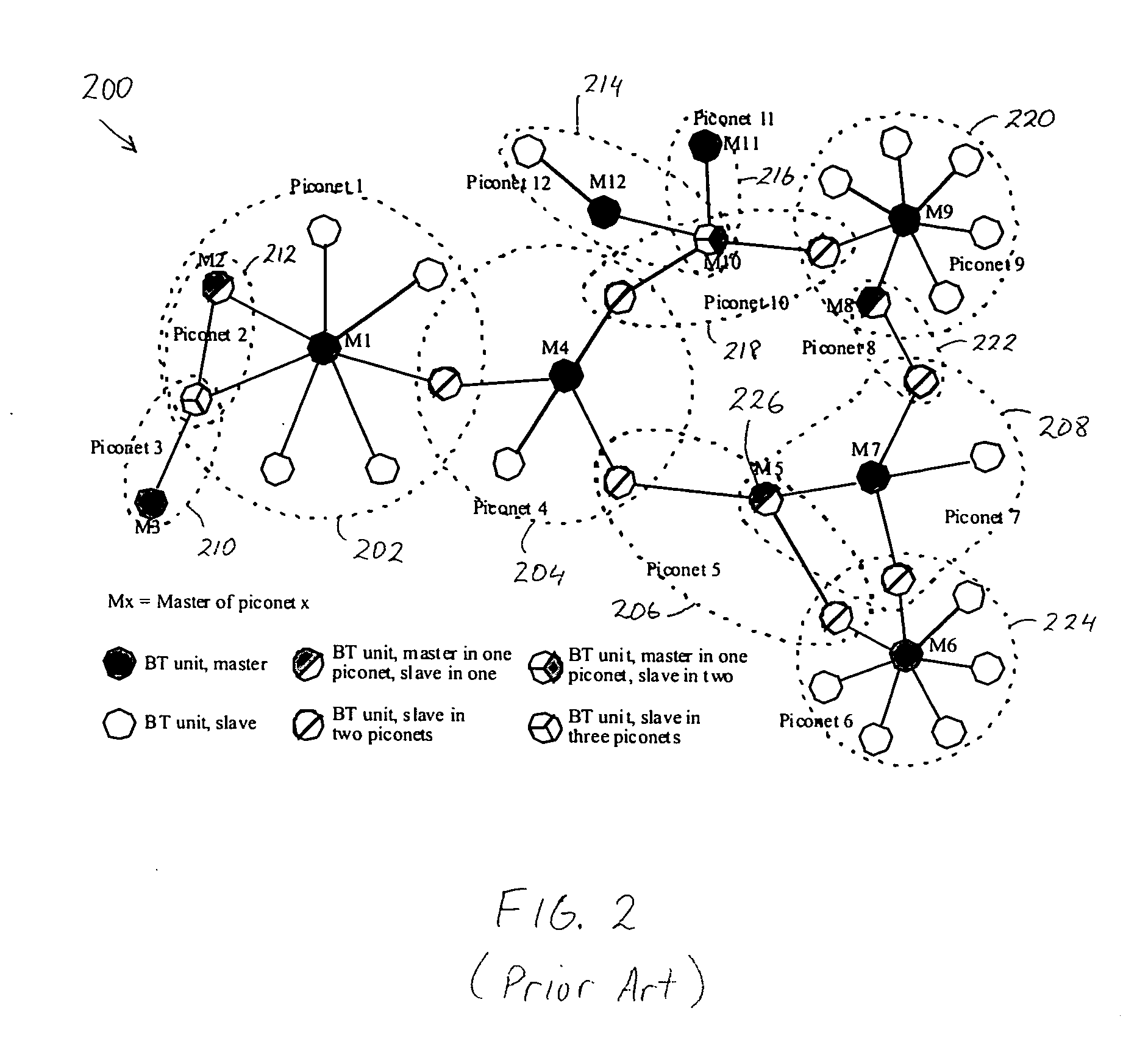
Patents
Literature
450 results about "Shared medium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
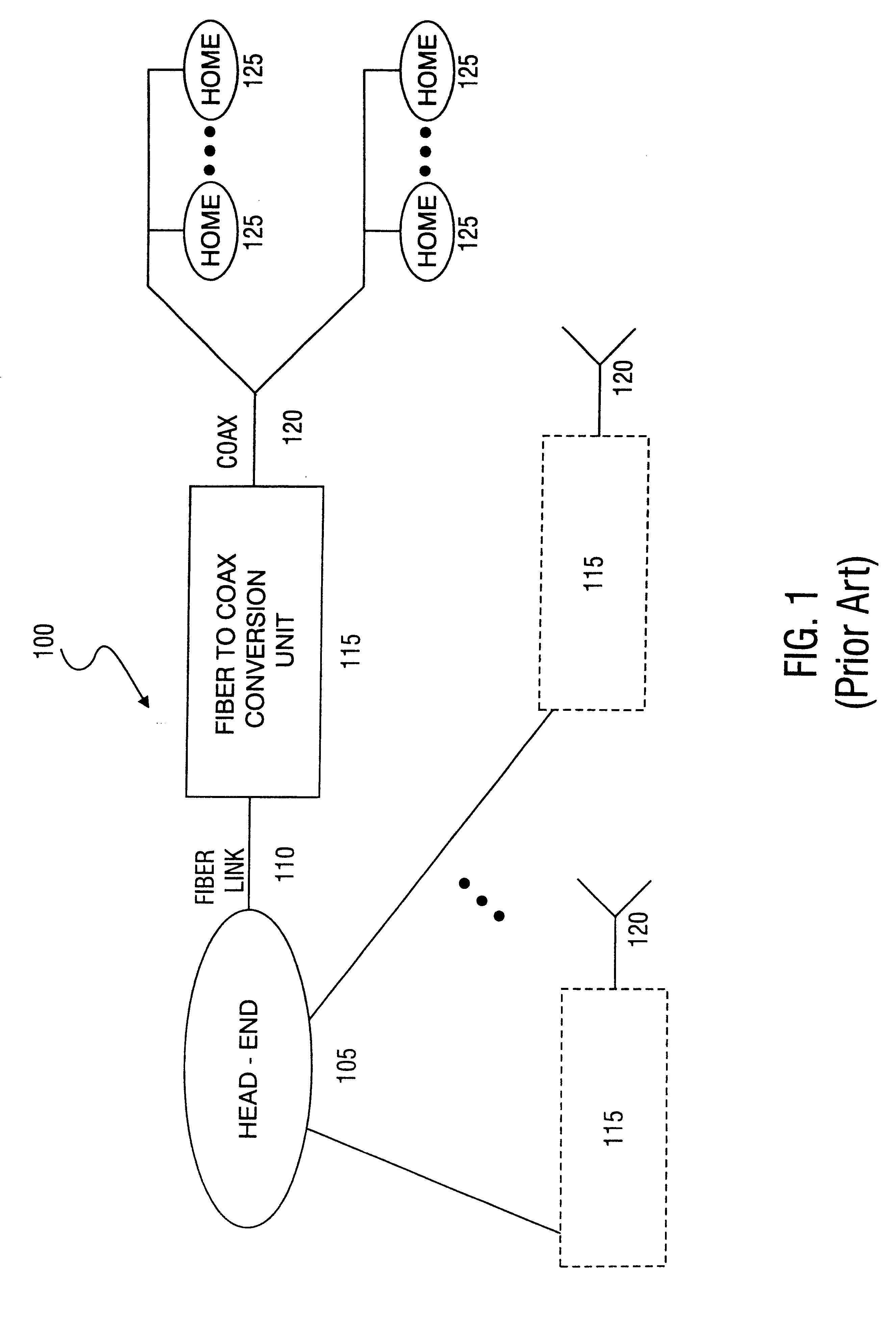
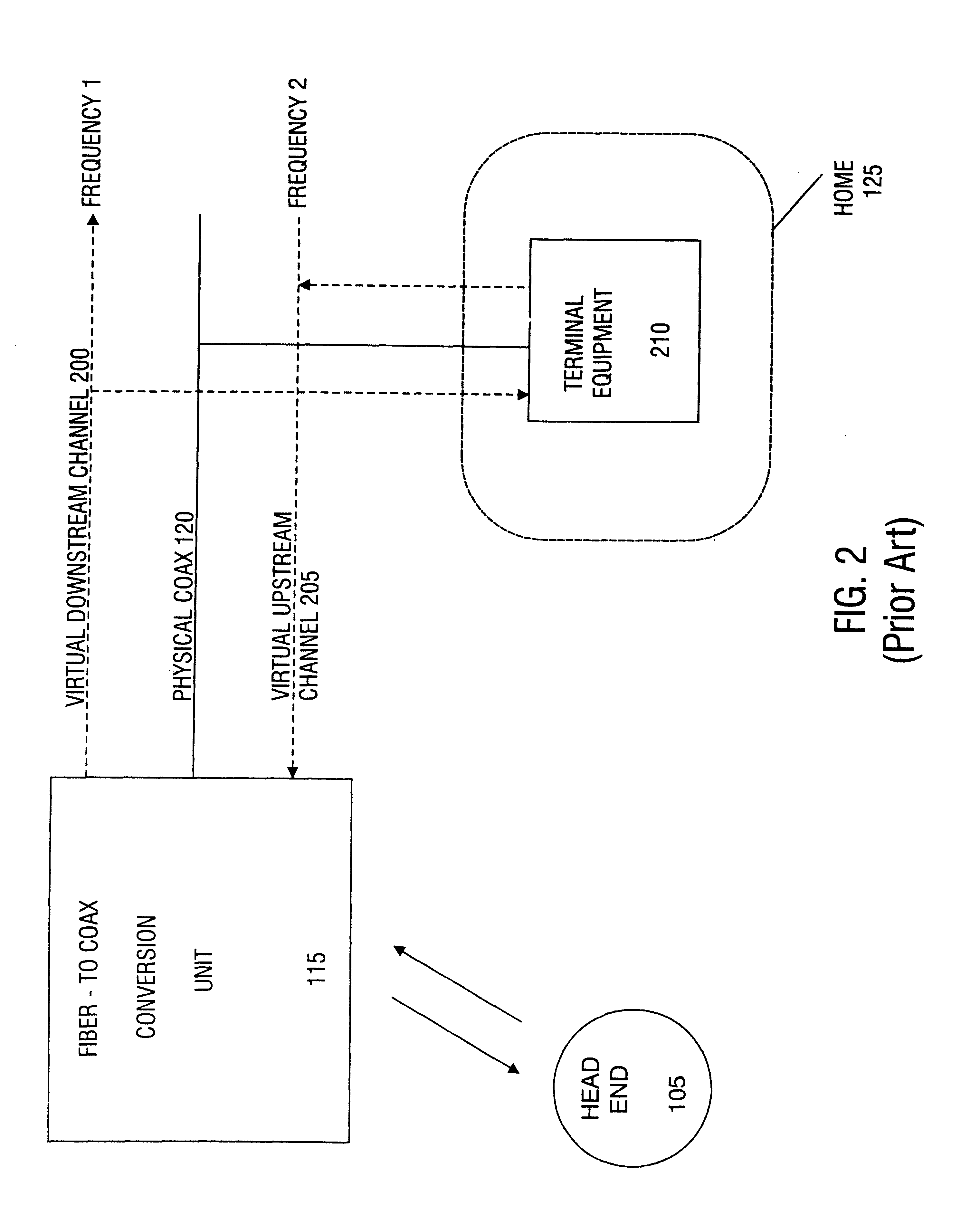
In telecommunication, a shared medium is a medium or channel of information transfer that serves more than one user at the same time. Most channels only function correctly when one user is transmitting, so a channel access method is always in effect.
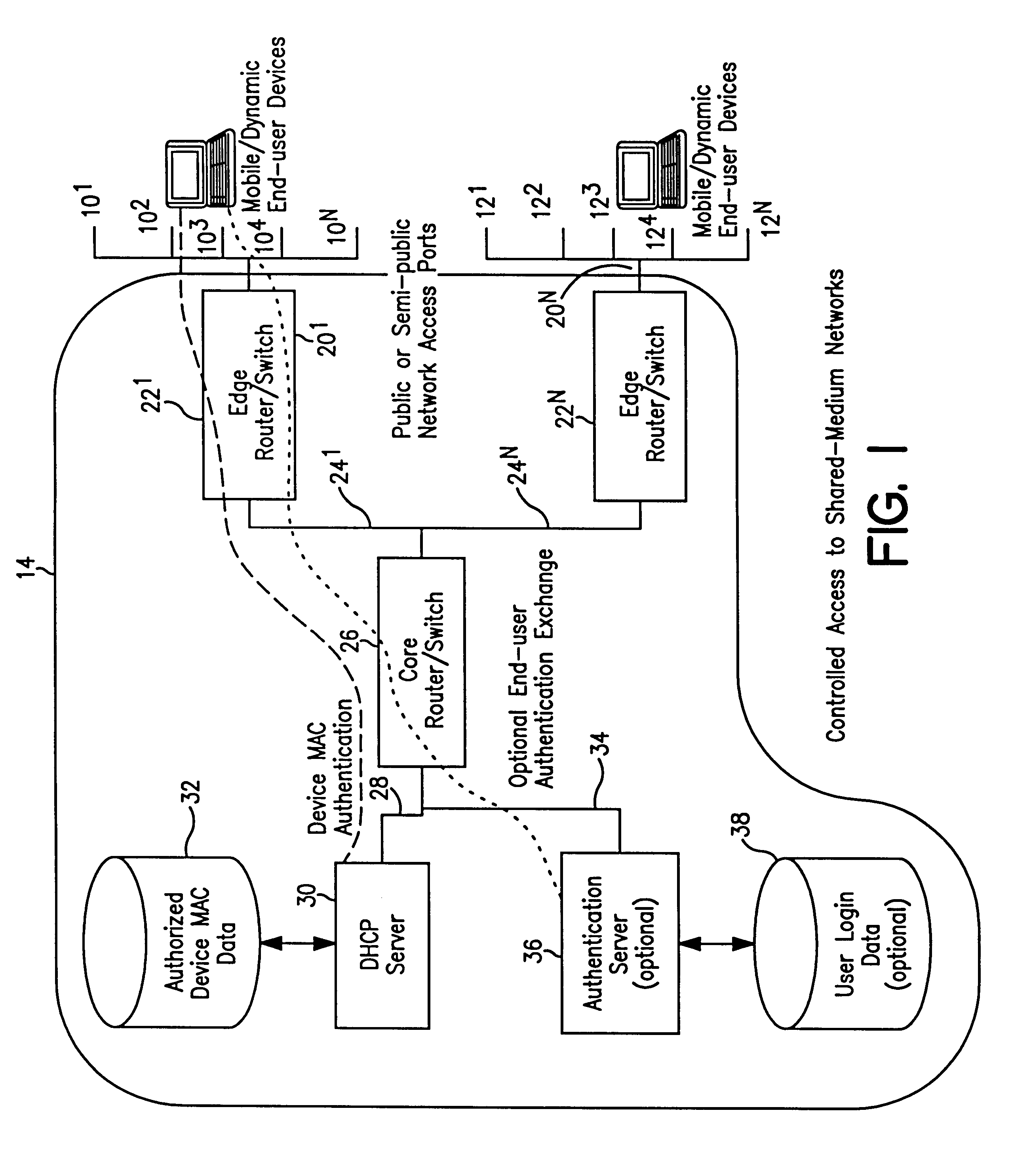
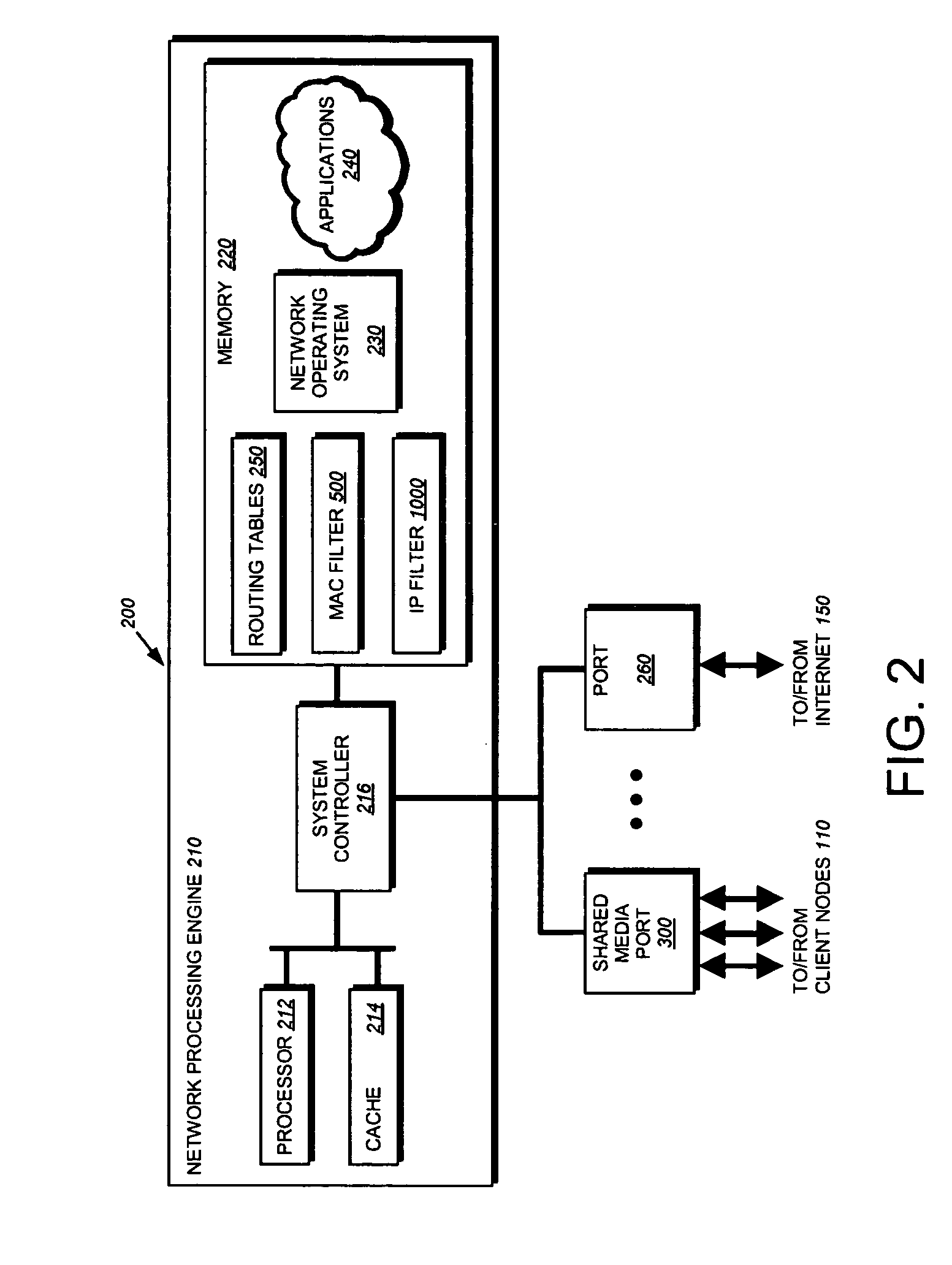
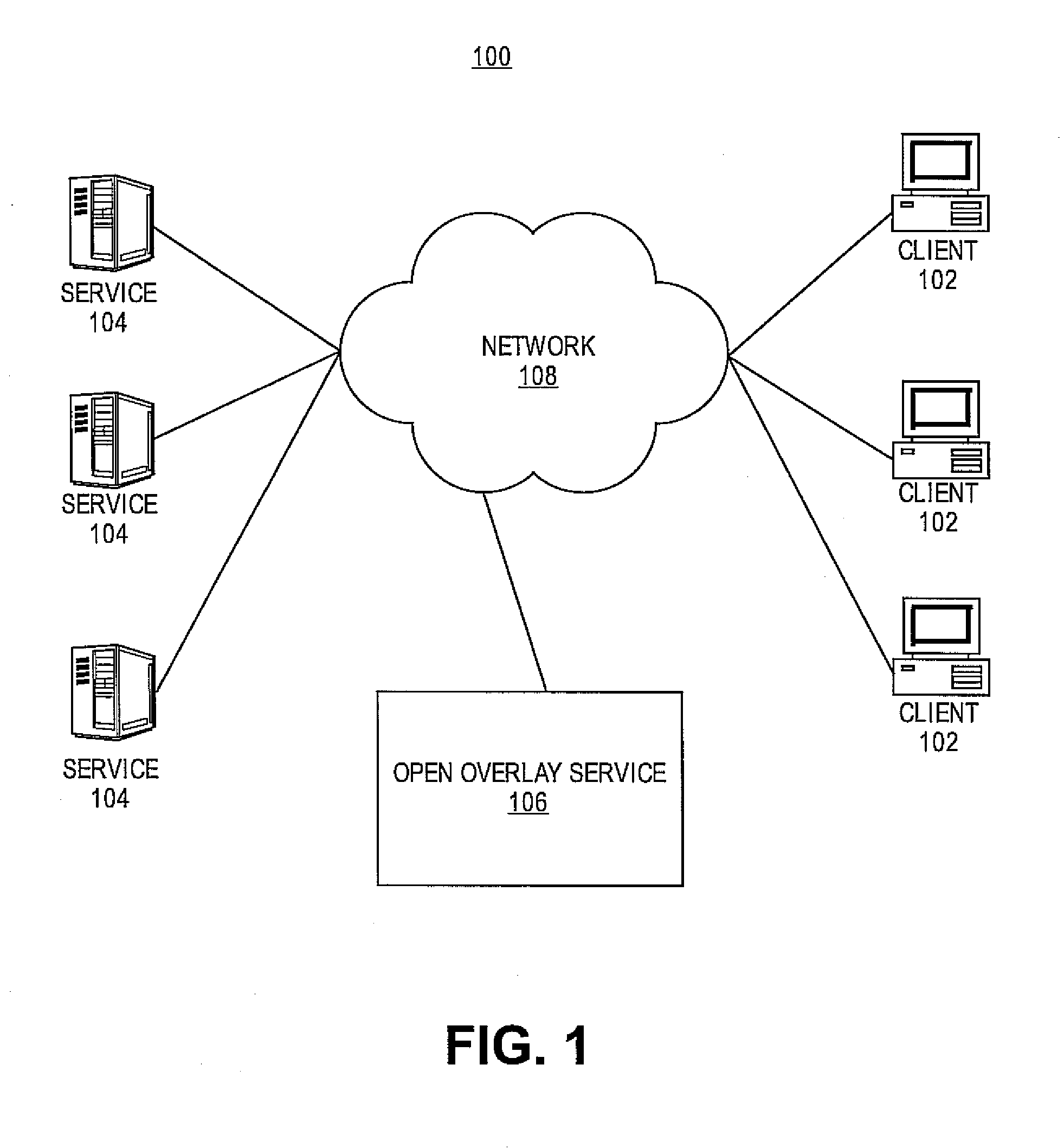
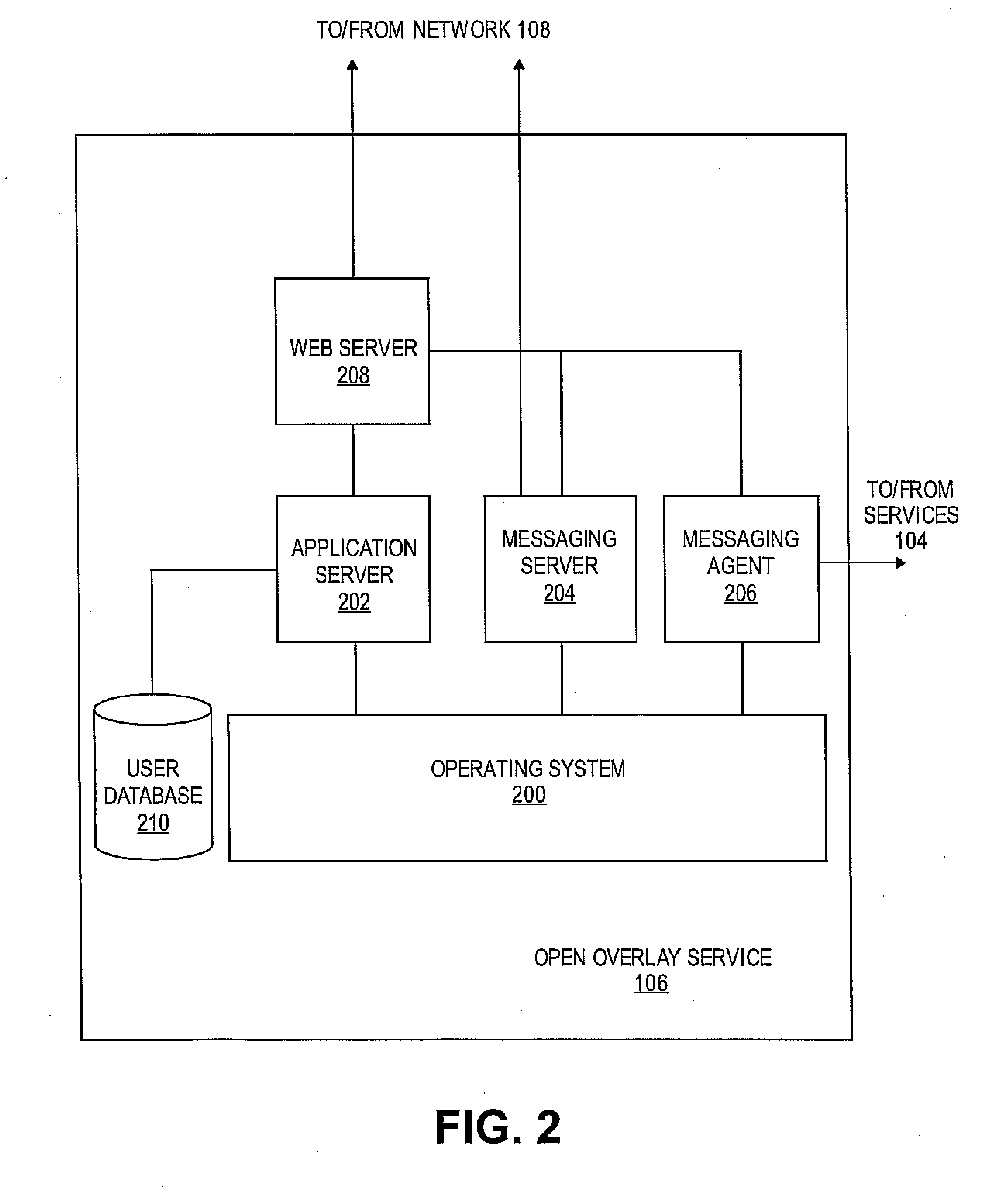
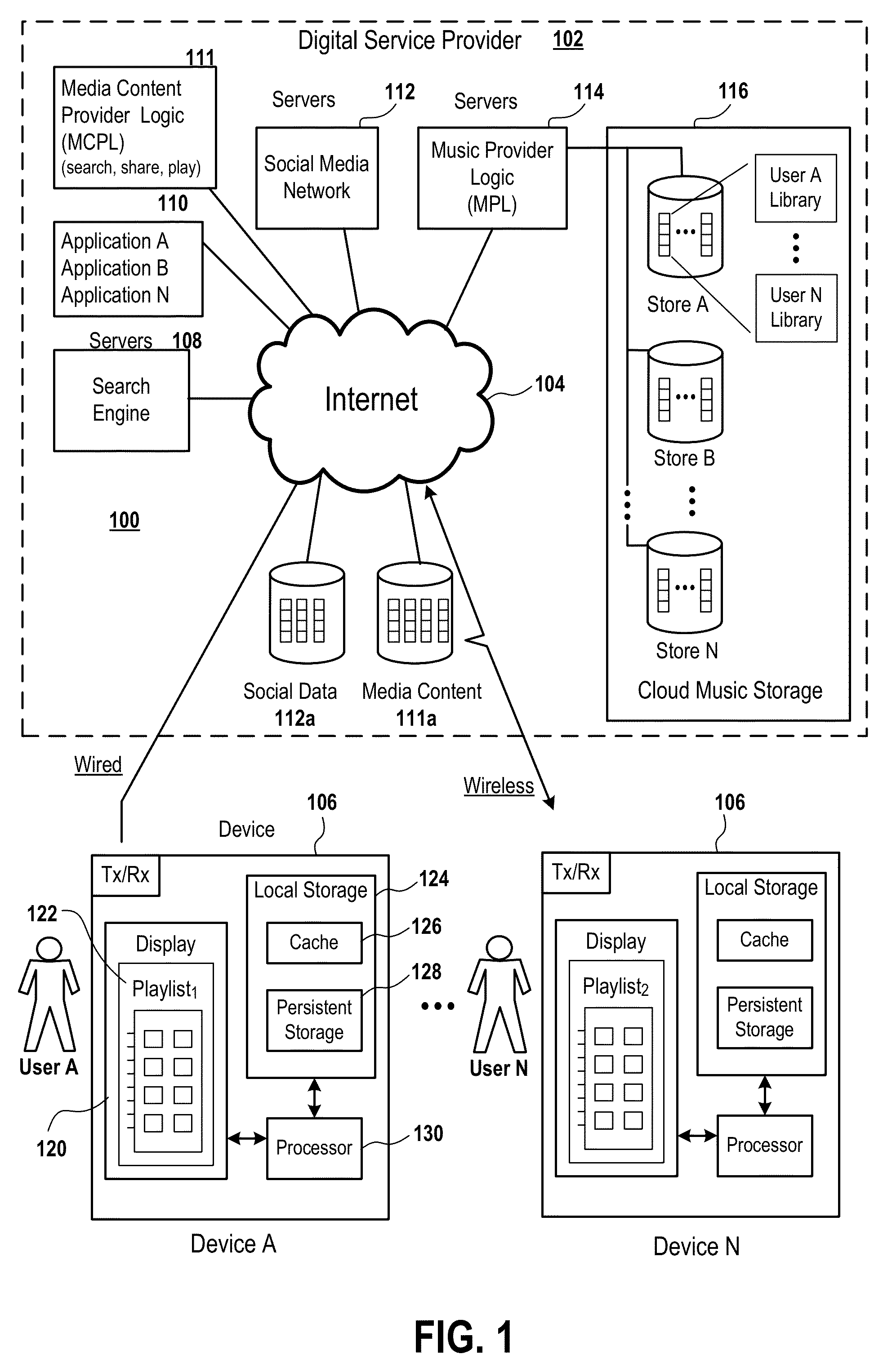
System and method for controlled access to shared-medium public and semi-public internet protocol (IP) networks
InactiveUS6393484B1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionAddress Resolution ProtocolDevice register
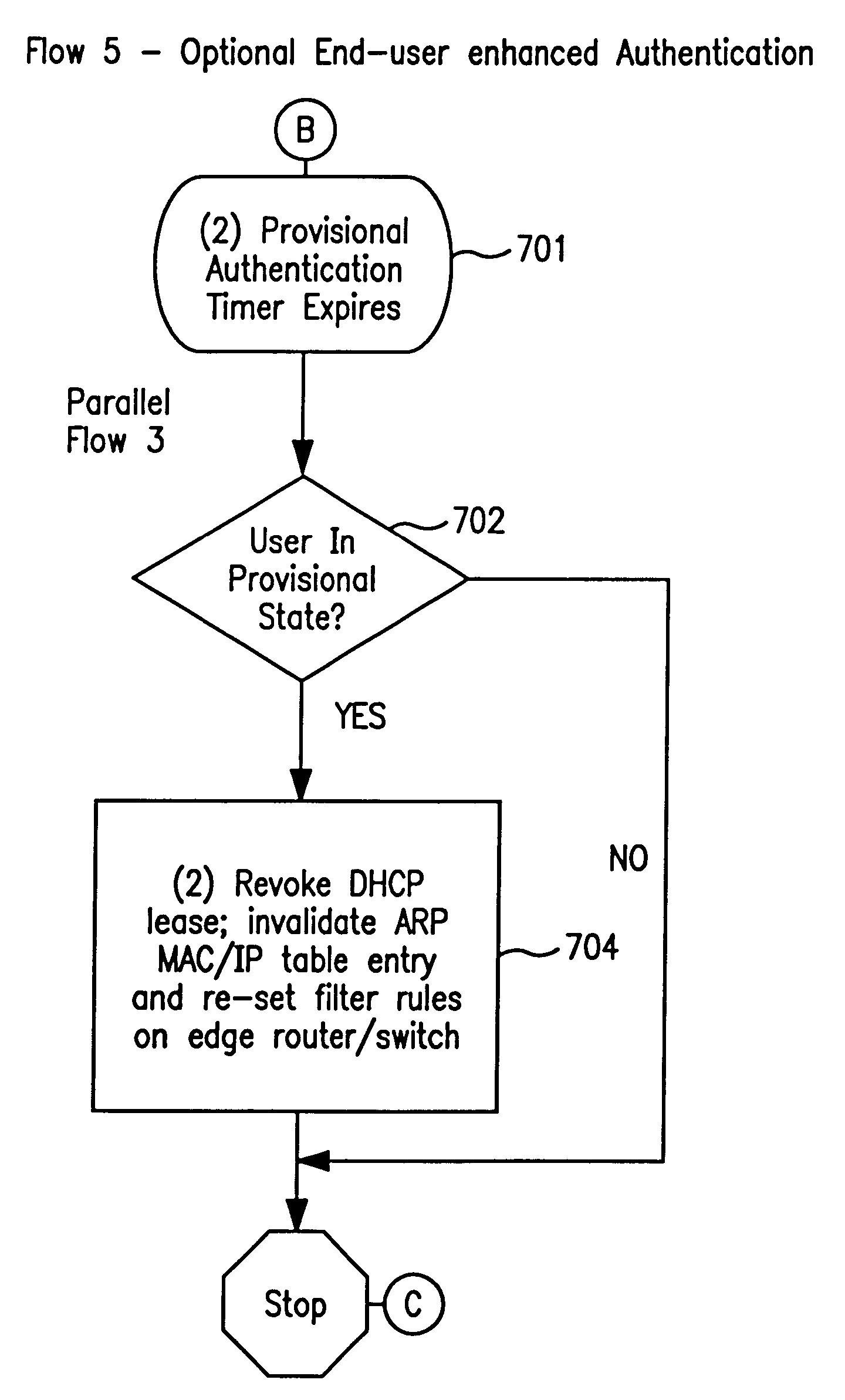
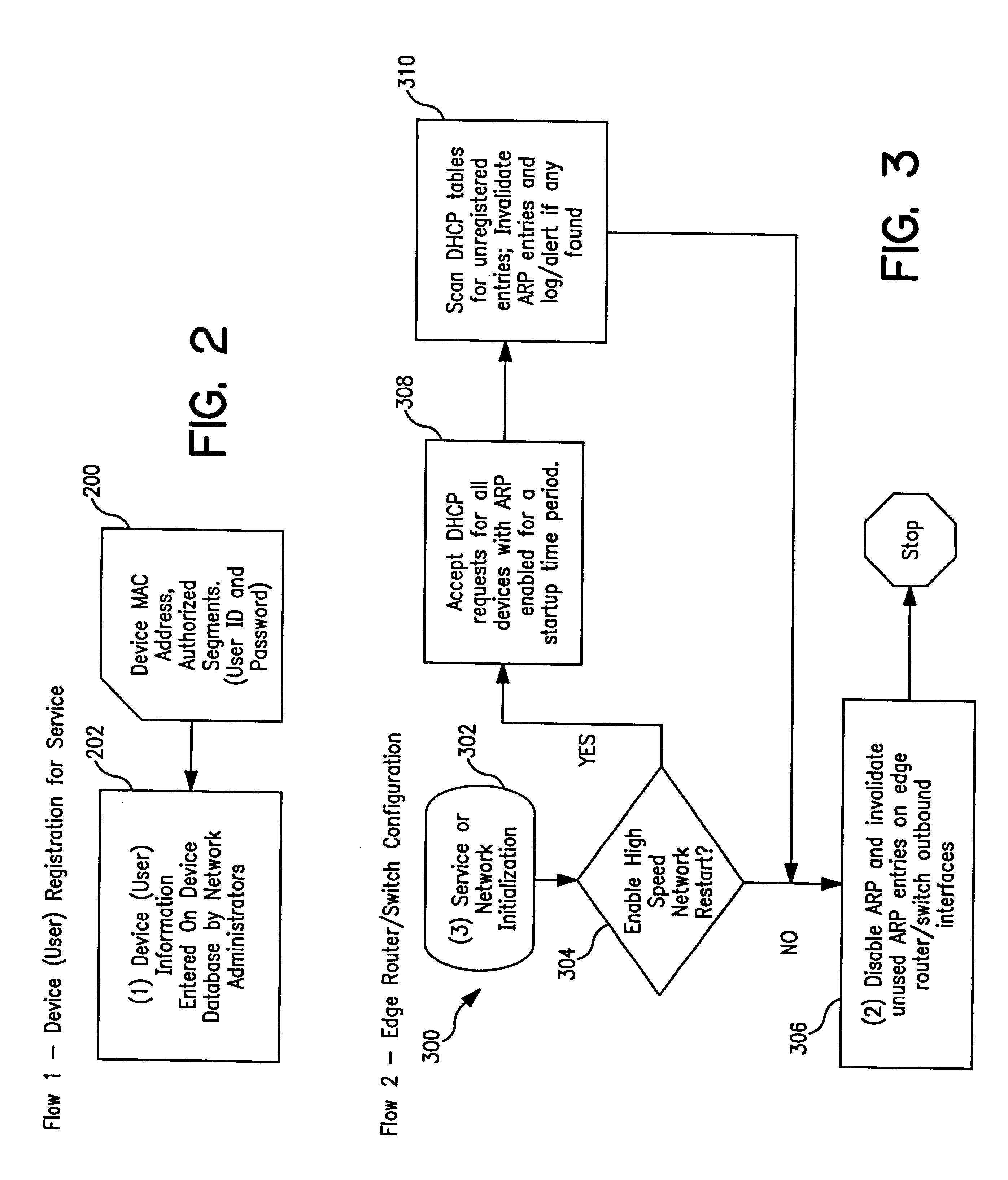
A system and method prevent unauthorized users and devices, in a dynamic user / device environment, from obtaining access to shared-medium public and semi-public IP networks. A network includes a layered communication system and routers / switches for coupling users and devices to a Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) server and an authentication server. Databases support the servers. The network incorporates Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). Authorized users and devices register for service by providing the DHCP with user identification for log-in, passwords, MAC addresses, etc. When users connect to the network access point, a DHCP exchange is initiated to obtain a valid IP address and other associated parameters. The DHCP client initiates a MAC broadcast for IP addresses which contain in the request the end user's device MAC address. The associated router switch will pick up and forward to a DHCP server the end user's device request. The DHCP server will process the end user's request and extract the end user's device MAC address. With the end user's MAC address, the DHCP server accesses its device and / or user information in the database. If the MAC address is not registered, the DHCP server refuses to handle the request and logs the attempt, potentially alerting network operators of a security breach. If the MAC address is registered, a DHCP server selects an appropriate IP address and associated parameters to be returned to the requesting end user and connects via programming or command interface to the router switch that is forwarding the DHCP request on behalf of the end user device. The server adds an ARP IP to the MAC address table entry with the selected IP address and end user's MAC address. End user device authentication and IP lease are marked as provisional. A timer is started for a suggested duration. Optionally, the DHCP dynamically sets up filter rules in the router switch limiting access to a subset of IP addresses such as the address of a log-in server. Initial DHCP processing is completed and an IP address is assigned to the requesting end user's device by DHCP. When the timer expires, if the DHCP server finds the authenticating user state is provisional, it will revoke the IP lease, invalidate the corresponding ARP to MAC table entry in the associated router switch, and reset any IP-permissive filtering for that device. If the user is in the full authenticated state, it will simply remove the restrictive filtering.
Owner:IBM CORP
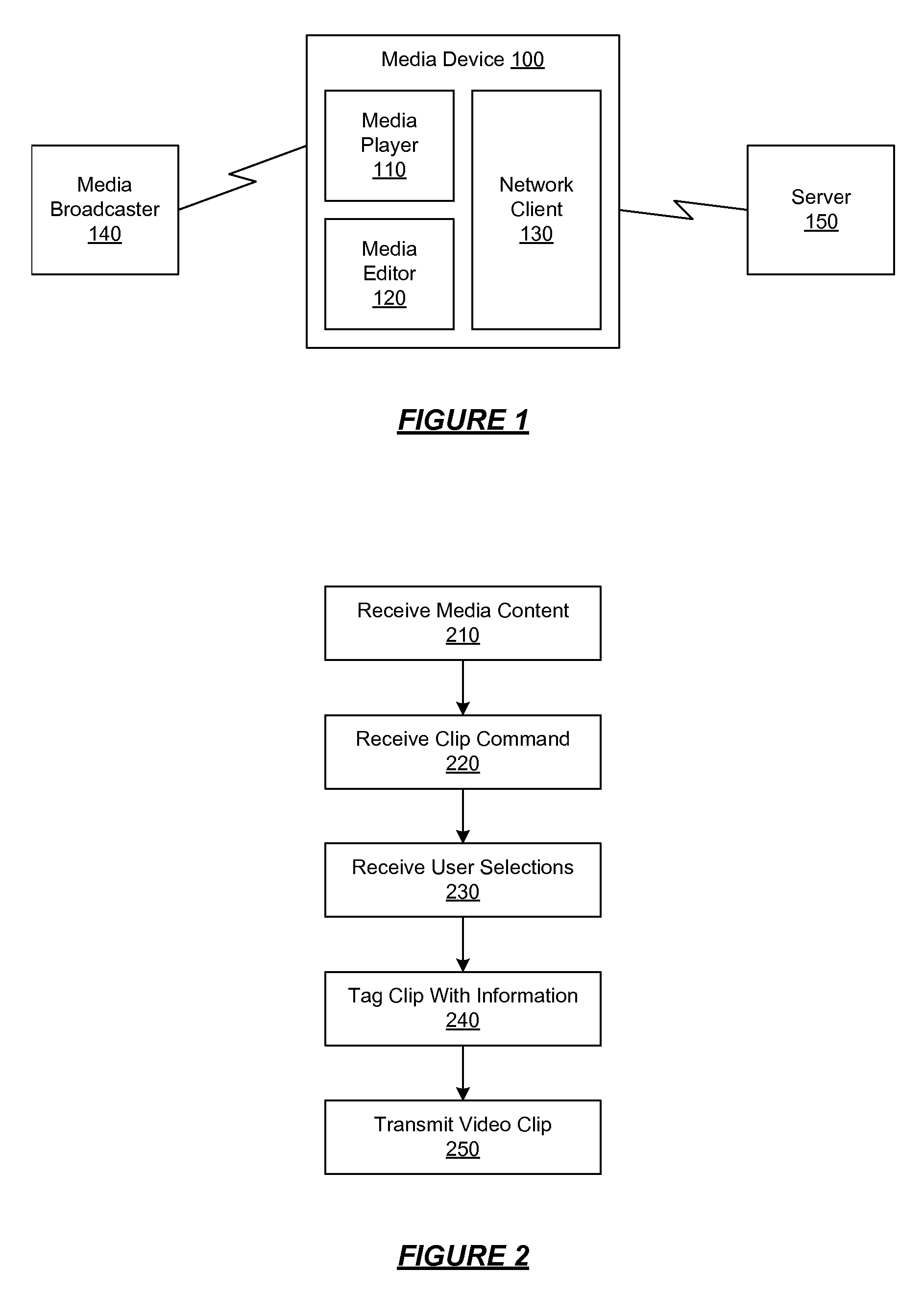
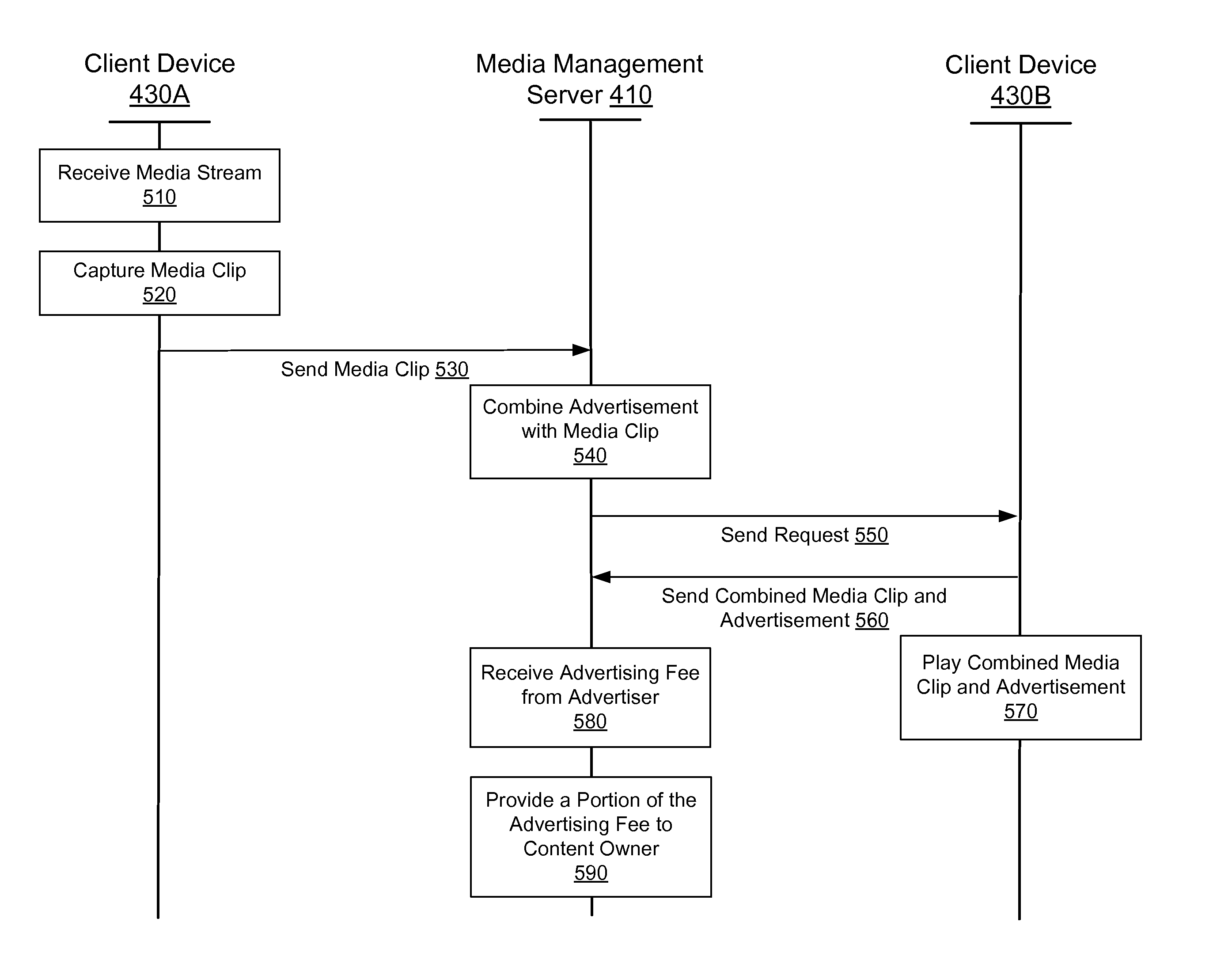
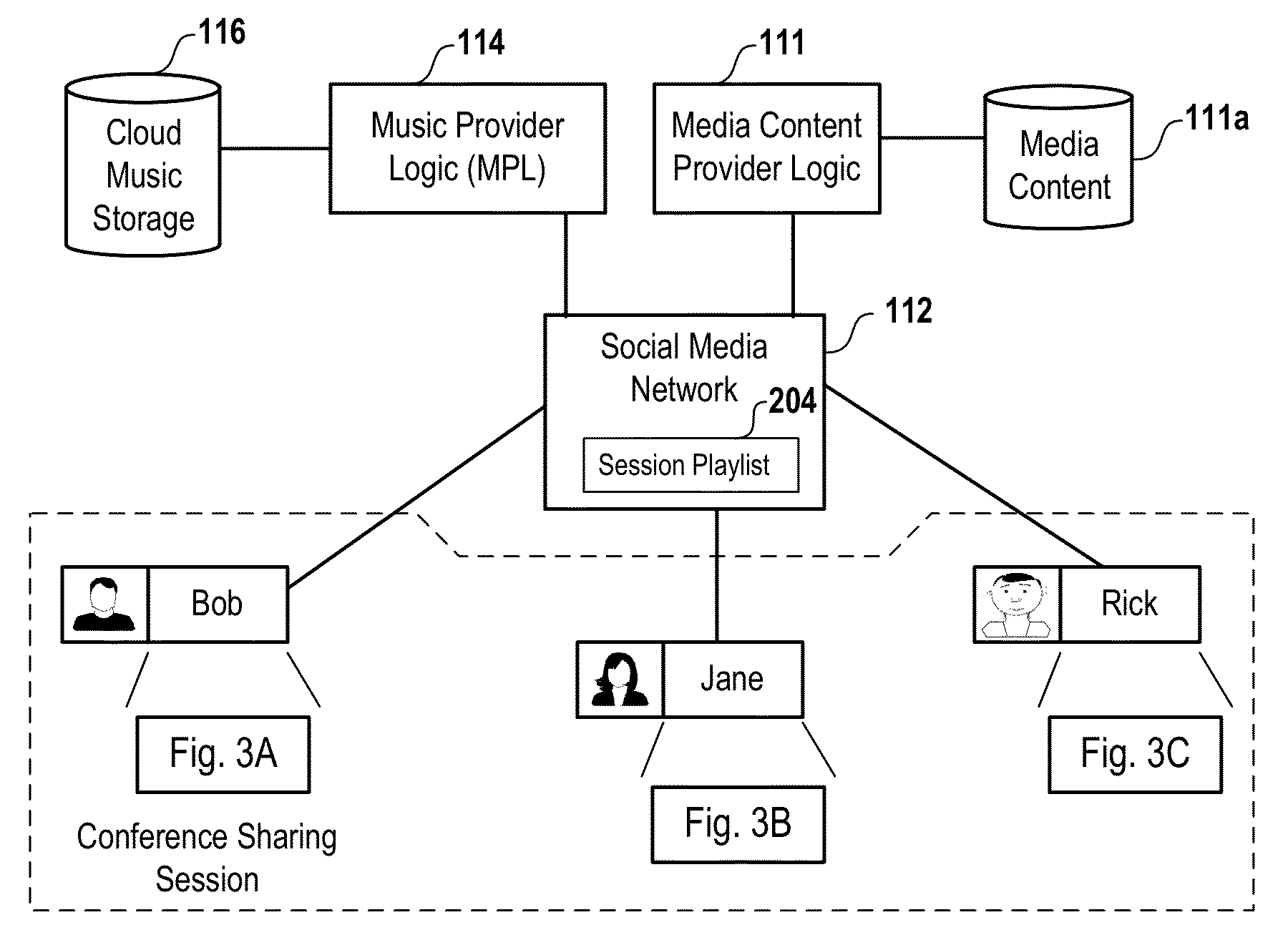
Management of Shared Media Content
ActiveUS20070198532A1GenerateGenerate advertising revenueFinanceAdvertisementsShared mediumMedia content
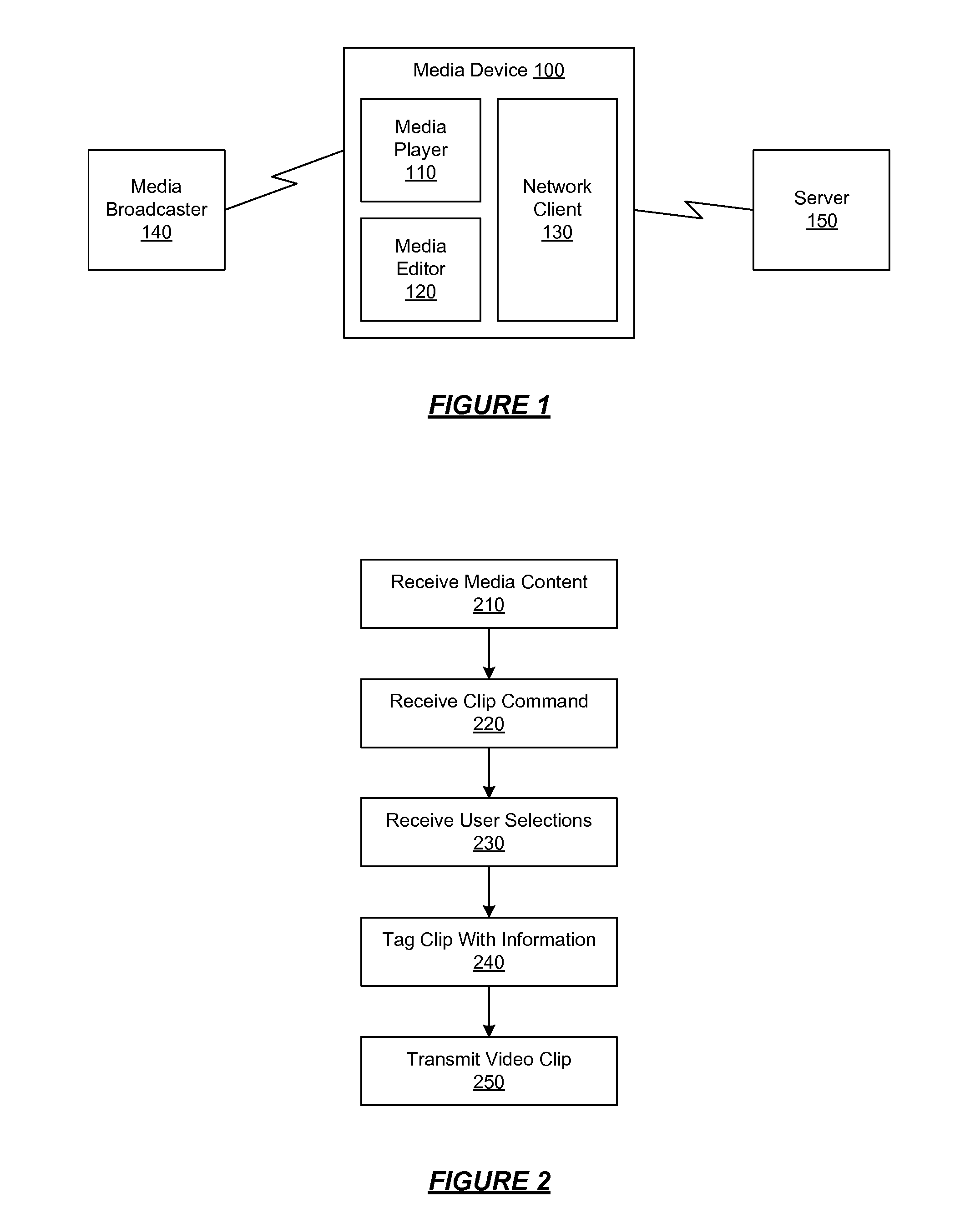
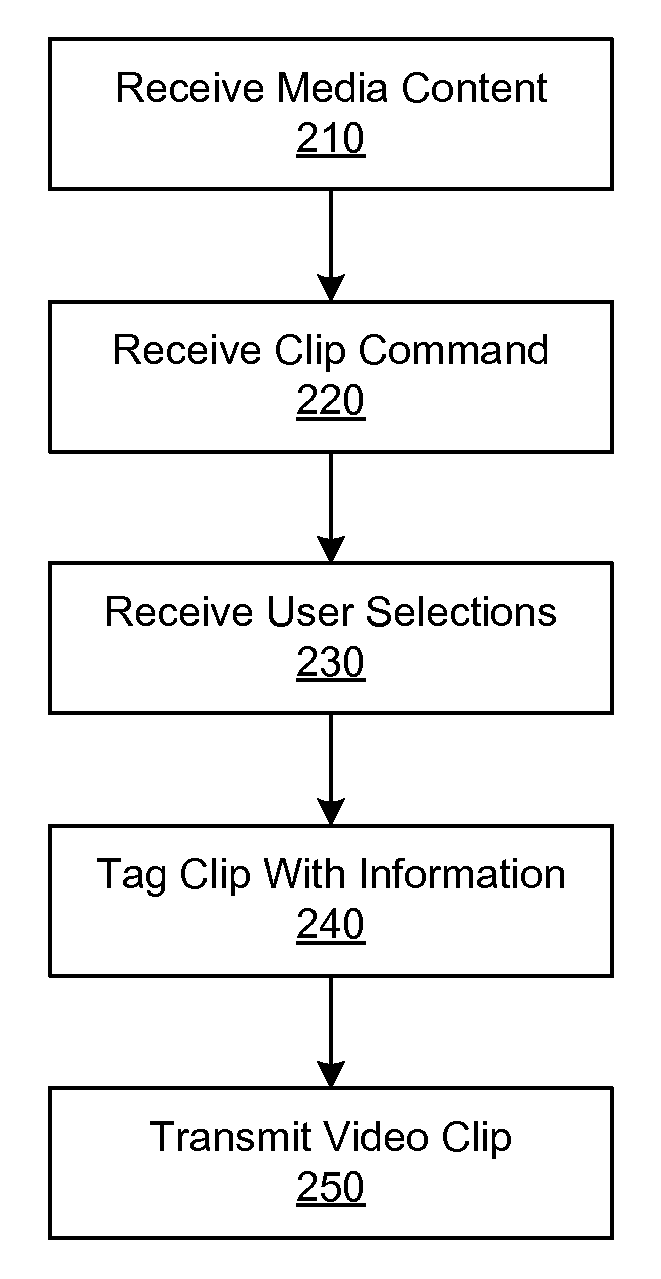
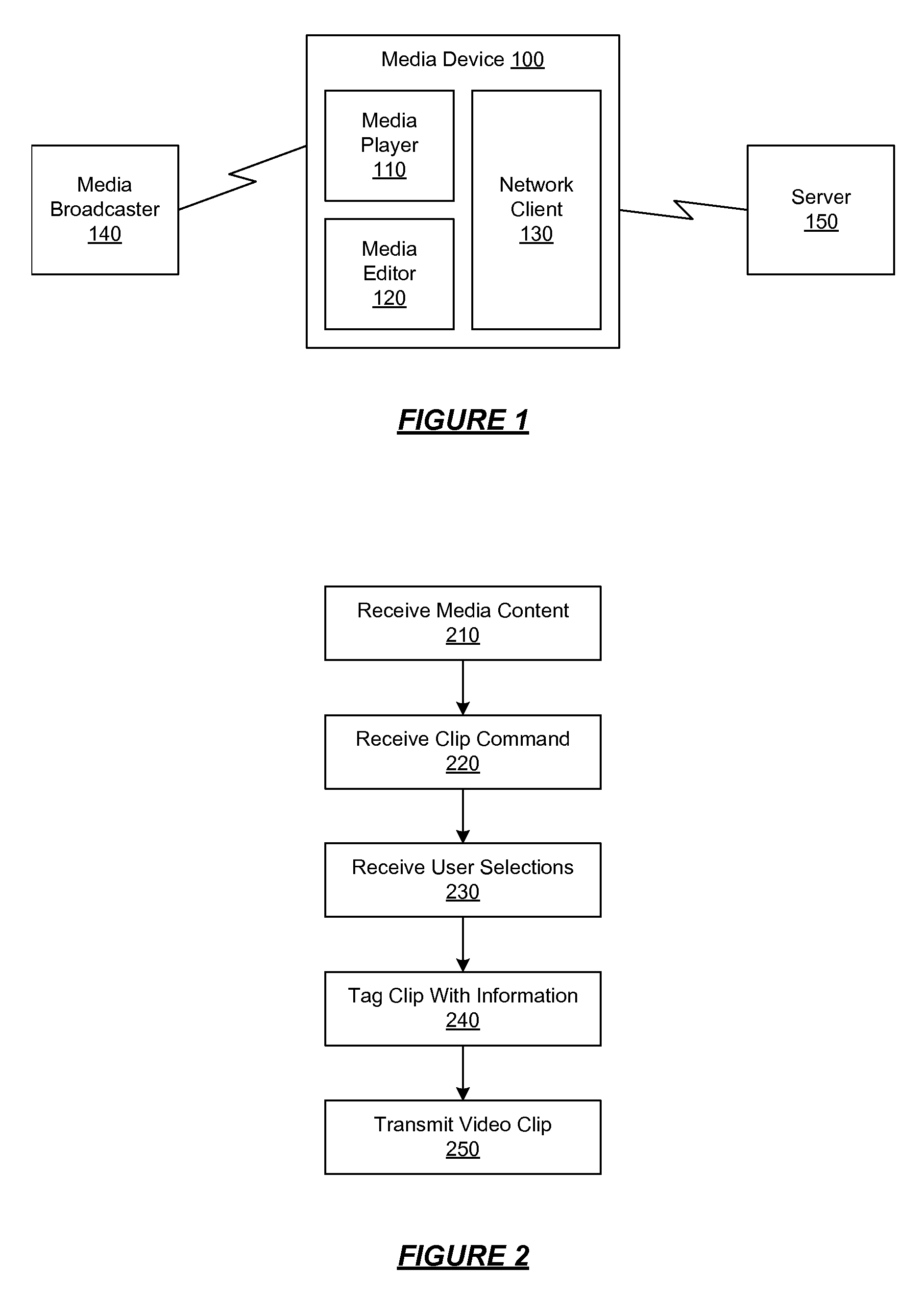
A media device allows users to watch and capture portions from a media broadcast. Users may then share the captured media content items with other users, for example, by uploading the items to a community website. Before providing requested media content items to other users, the website may combine advertisements with the media content items. The website may receive advertising revenue from advertisers and may share the advertising revenue with owners of the media content items in exchange for their permission to provide the media content items. The advertisers may provide restrictions on how the advertisements are combined with the media content items, and the content owners may provide restrictions on how the media content items are provided to the users.
Owner:SLING MEDIA LLC
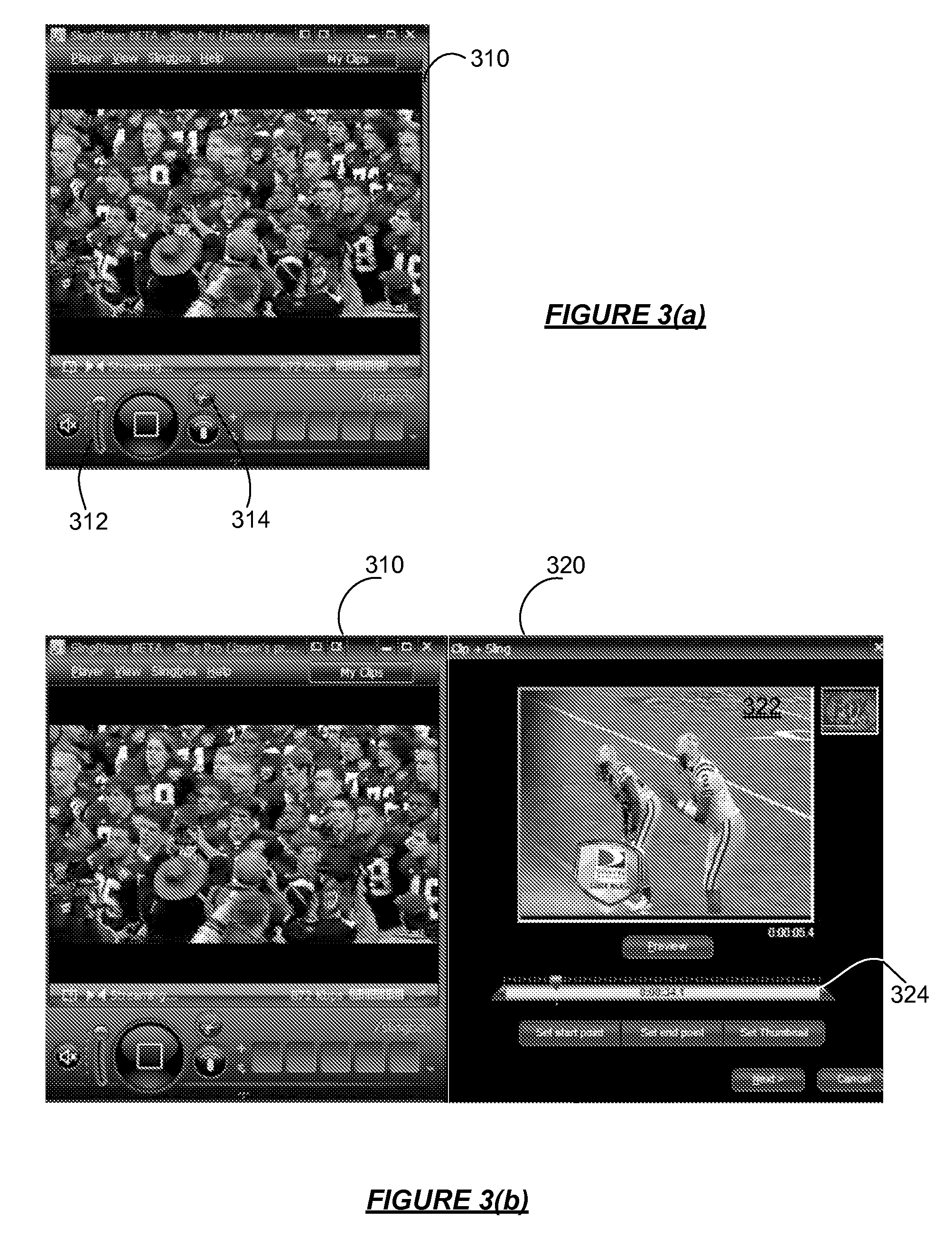
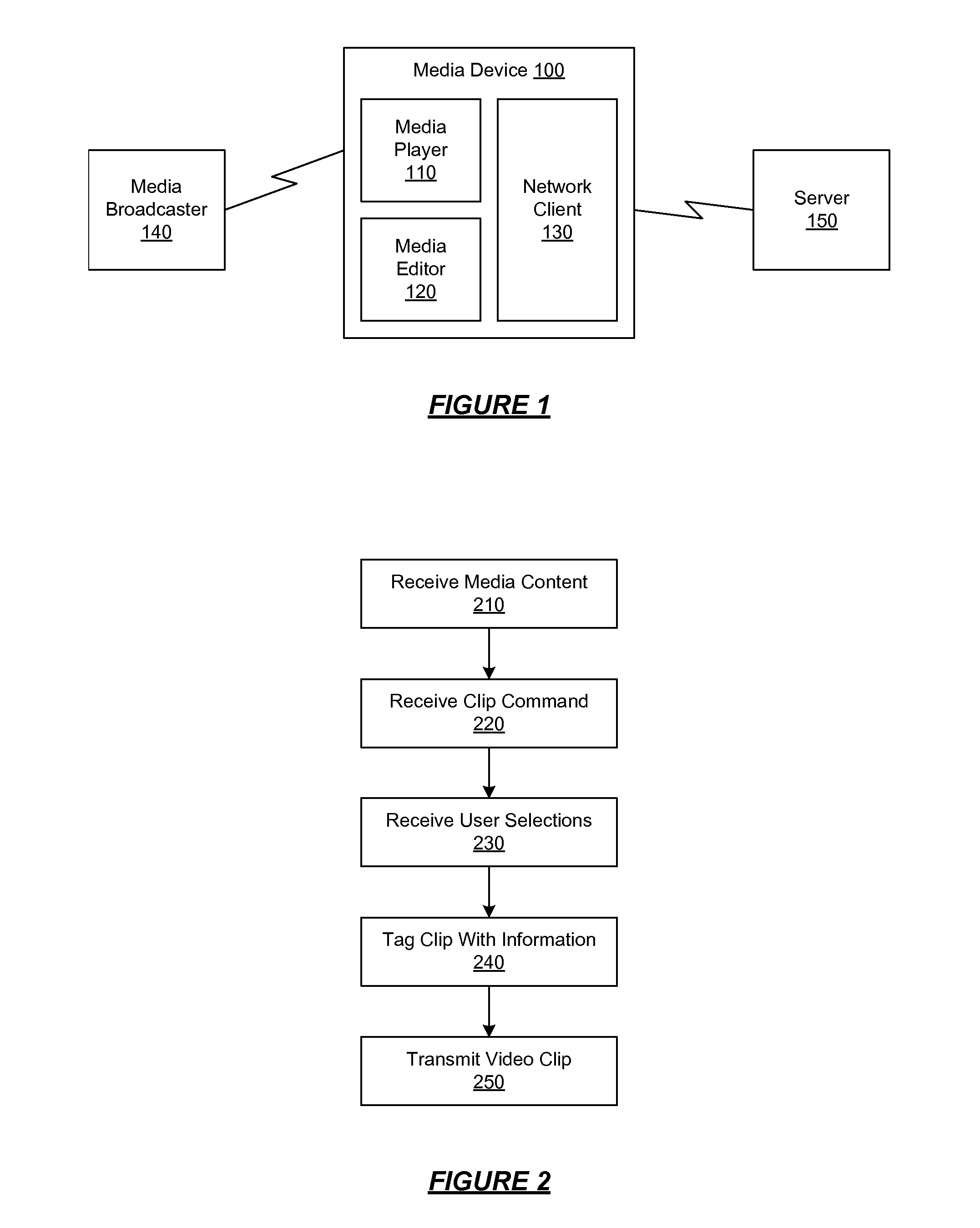
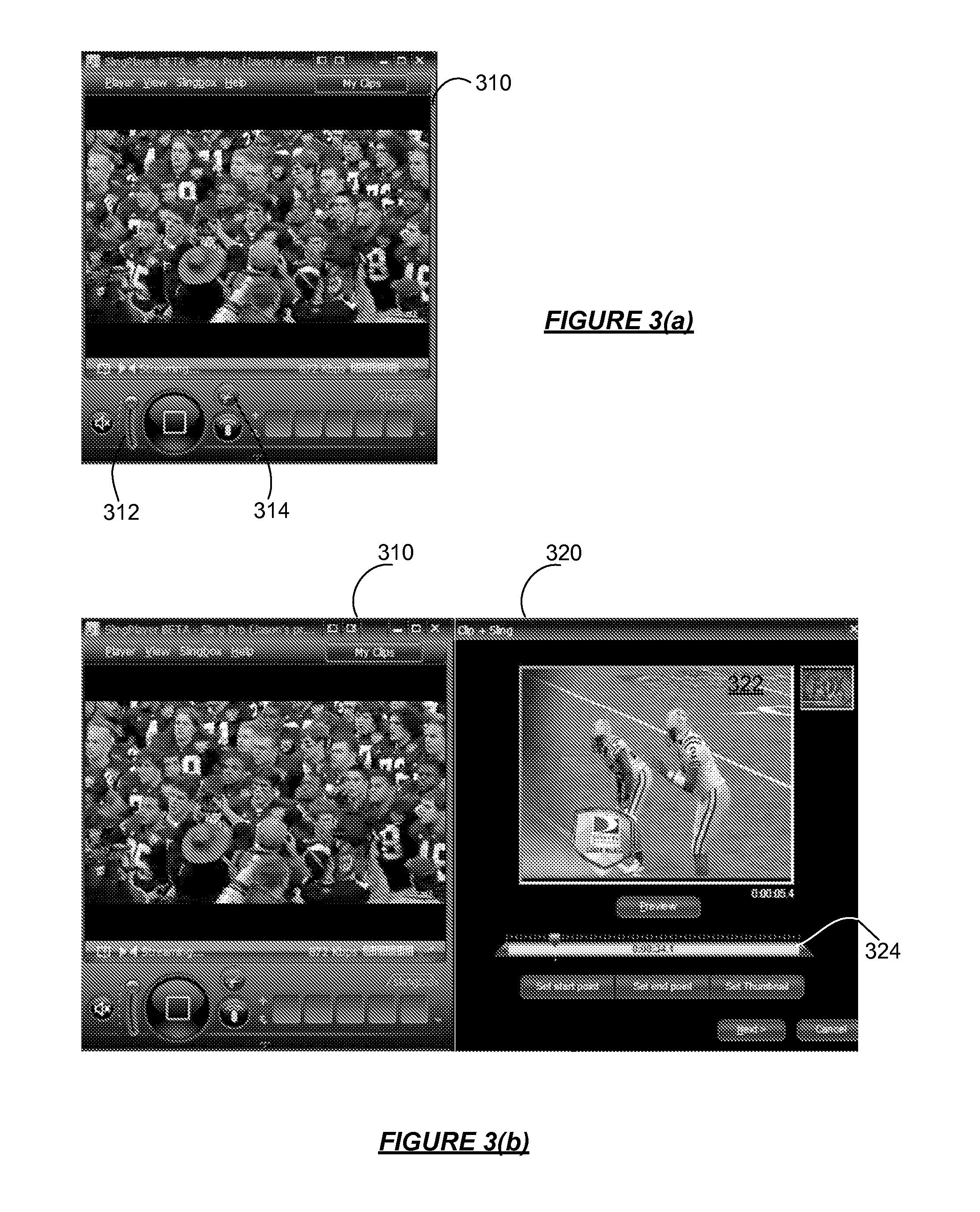
Capturing and Sharing Media Content
ActiveUS20070168543A1Electronic editing digitised analogue information signalsBroadcast-related systemsWeb siteShared medium
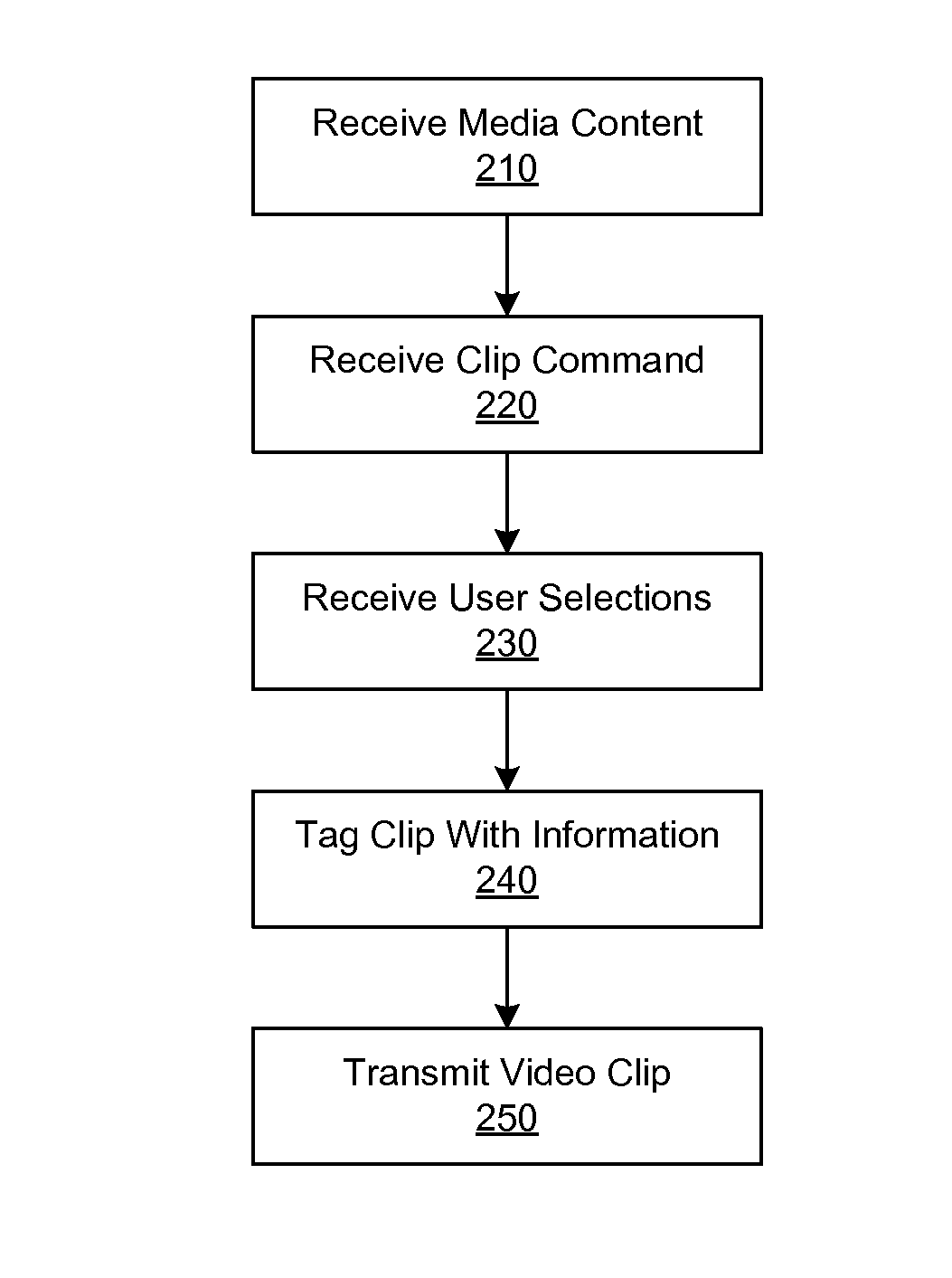
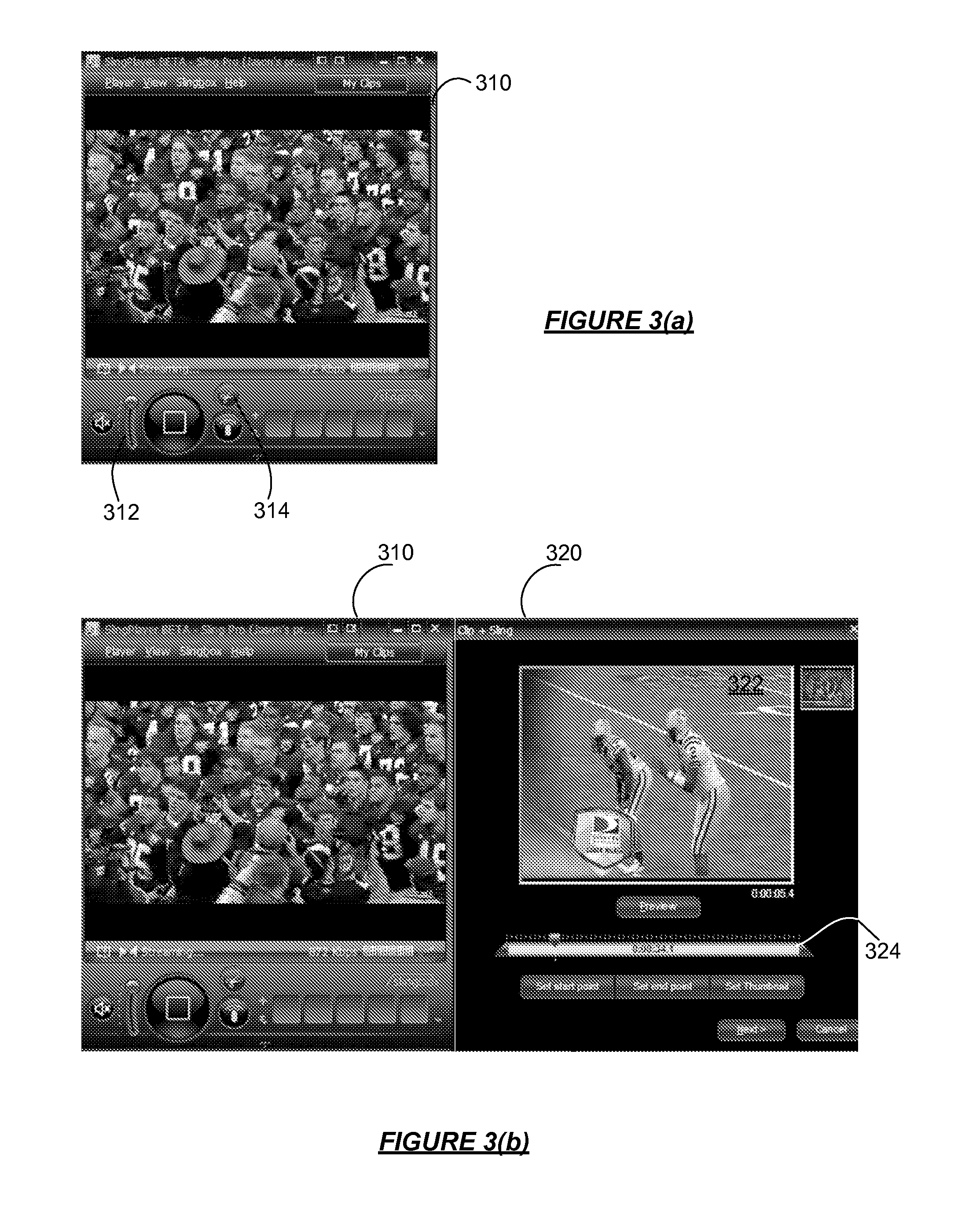
A media device allows users to watch and capture portions from a media stream. Users may then share the captured media content with other users. In one embodiment, the media device receives a media stream, plays the media stream, and caches a portion of the media stream as it is being played. A user can define a media clip by selecting its boundaries in the cached portion of the media stream. The media device creates the media clip based on the user's input and enables the user to transmit the media clip to another system, such as a community website for sharing it with other users.
Owner:SLING MEDIA LLC
Apparatus and methods for incorporating bandwidth forecasting and dynamic bandwidth allocation into a broadband communication system
InactiveUS20060120282A1Energy efficient ICTError preventionDynamic bandwidth allocationComputer network
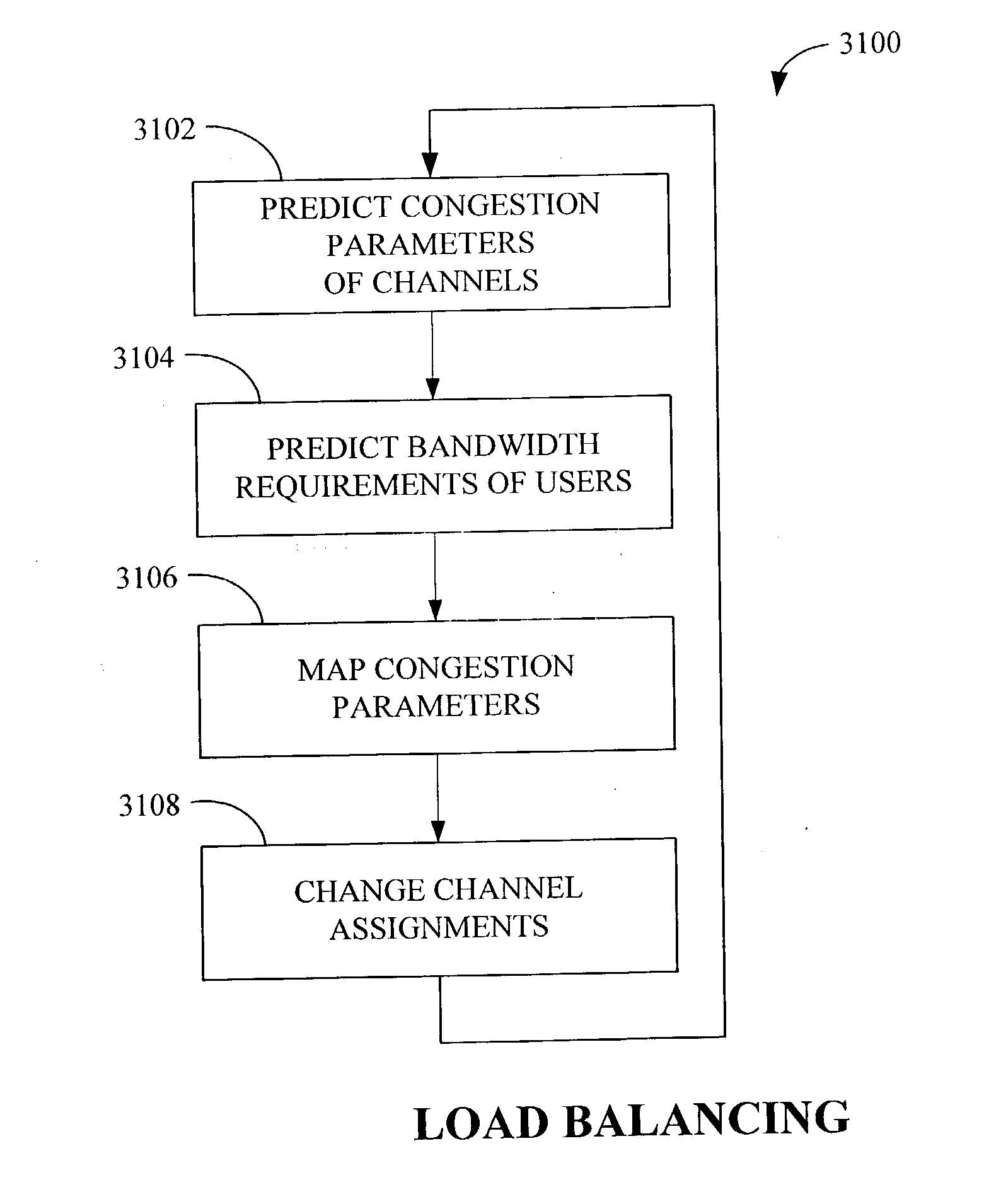
A method for providing network access to a shared access communications medium for a plurality of users includes the steps of conducting predictive admission control by arbitrating user requests for access to the shared medium based on predicted aggregate demands, conducting lookahead scheduling for use in making user channel assignments by forecasting schedule transmission opportunities one or more channels of the shared medium, and balancing load by making channel assignments such that a plurality users are each assigned a respective channel of the shared medium based upon a predicted need. Congestion parameters can predicted for each channel of the shared medium and mapped to a congestion measure using a mathematical function that takes into account packet loss rate, packet delay, packet delay jitter, and available capacity.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
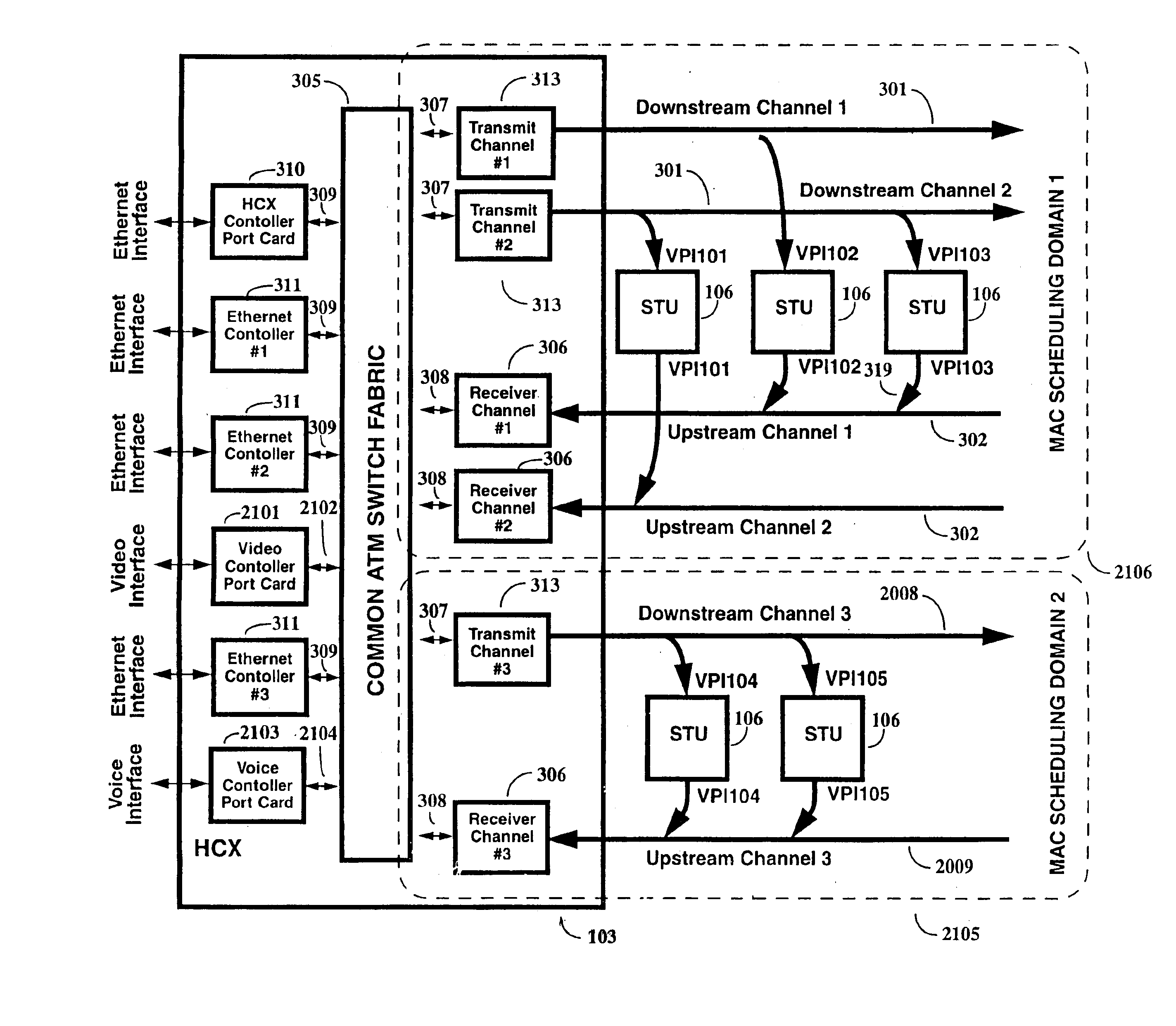
Multi-channel support for virtual private networks in a packet to ATM cell cable system
InactiveUS6917614B1Avoid compromiseExtension of timeBroadband local area networksFrequency-division multiplexQuality of serviceScheduling function
A two-way cable network offering high-speed broadband communications delivered via virtual private networks over a multi-channel shared media system. Bi-directional transmission of packet to ATM cell based communications is established between a head end communication controller and a number of subscriber terminal units, whereby individual cells are prioritized and routed according to a virtual connection. Virtual connections are organized to support multiple virtual private networks in a shared media CATV system. The virtual private network to which a particular STU belongs is user selectable and has the flexibility of handling multi up / downstream channels with different MAC domains. The present invention can also handle non-ATM MAC domains via the same common ATM switch. To overcome the limited number of addresses inherent to common ATM switches, a mapping / remapping function is implemented in the port cards. Furthermore, downstream as well as upstream traffic are filtered at each STU. In one embodiment, information pertaining to downstream traffic is used to implement predictive scheduling in order to improve the timing associated with the request / grant cycle. In another embodiment, a user has the ability to select a quality of service that best suits the needs of the current application. In a further embodiment, the scheduling function is associated with each of the receivers in order to provide improved scalability.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Method enabling multiple communication nodes to access a transmission means on an electrical grid
InactiveUS20060120399A1Low signal noiseFair coexistencePower distribution line transmissionData switching by path configurationShared mediumPower grid
Method enabling multiple communication nodes to access a transmission means on an electrical grid, which permits access in a fair manner by nodes on a shared medium such as the electrical network, achieving the maximum access speed when there are no collisions between reservation requests and the detection of coexistence signals in a robust way in noisy environments. It is characterized by the use of signals for reservation (5) and release (10) of the communication and by the random waiting prior to a reservation of the electrical network with minimum and maximum values fixed in advance.
Owner:DISENO DE SYST & SILICIO SA
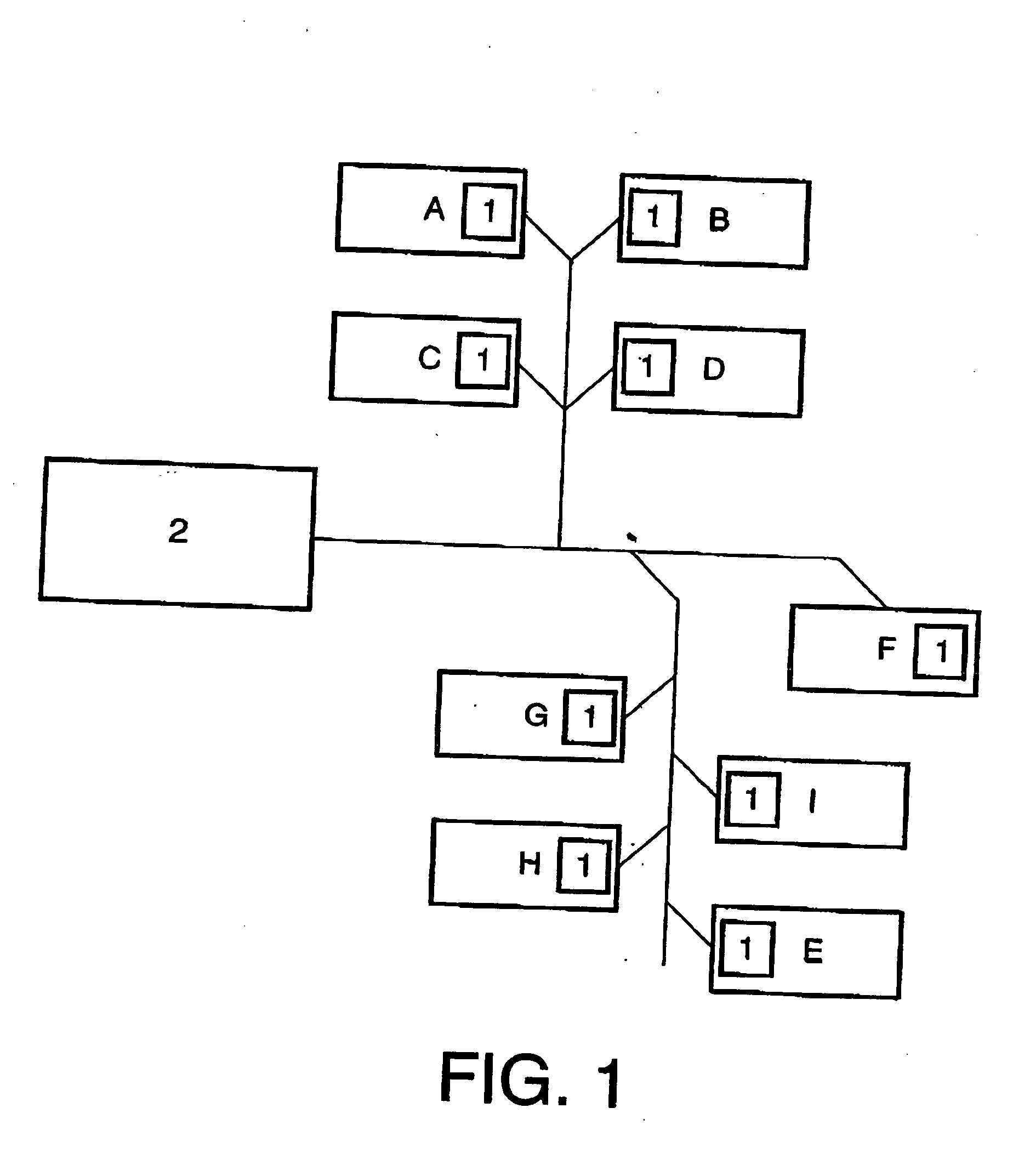
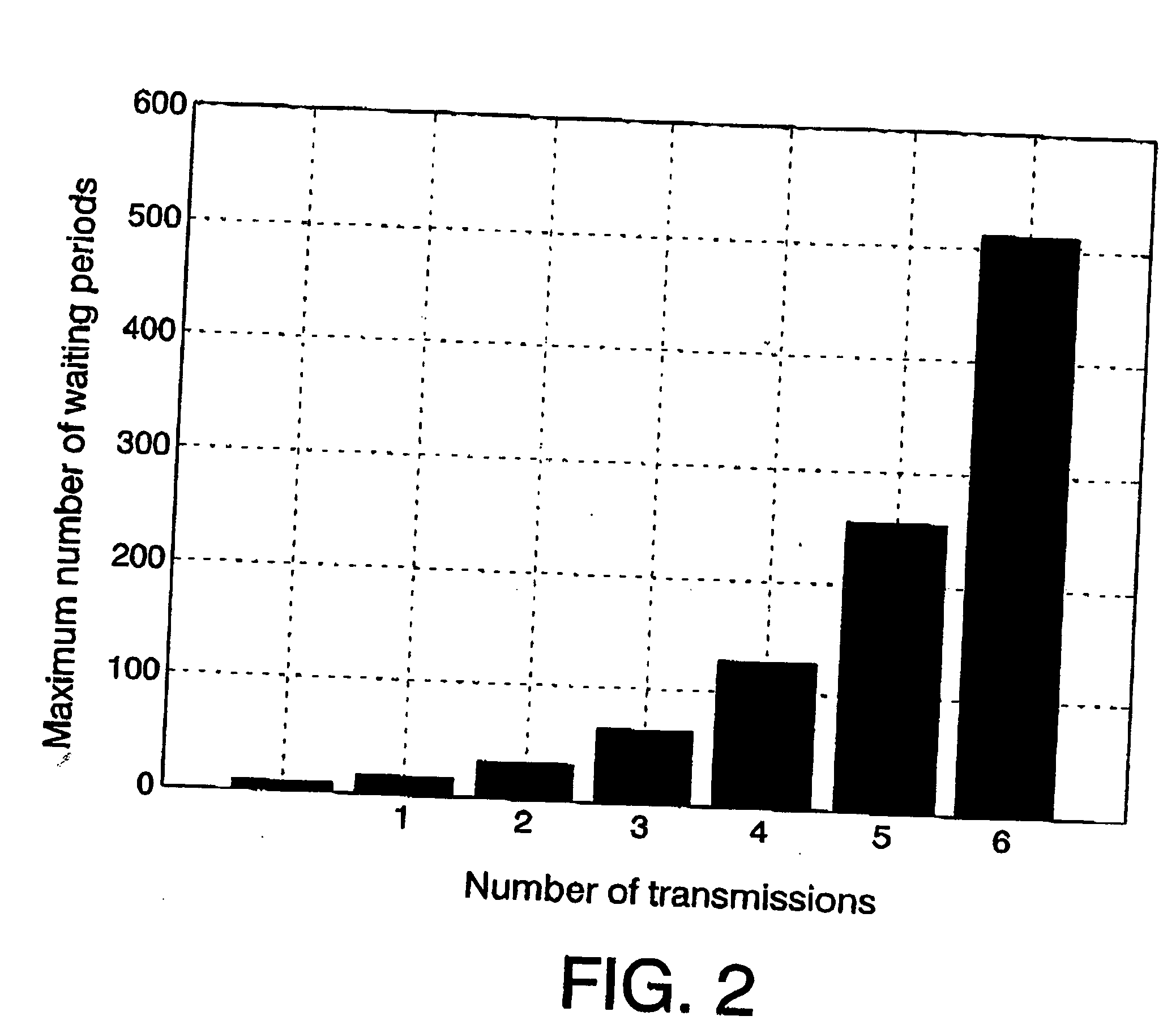
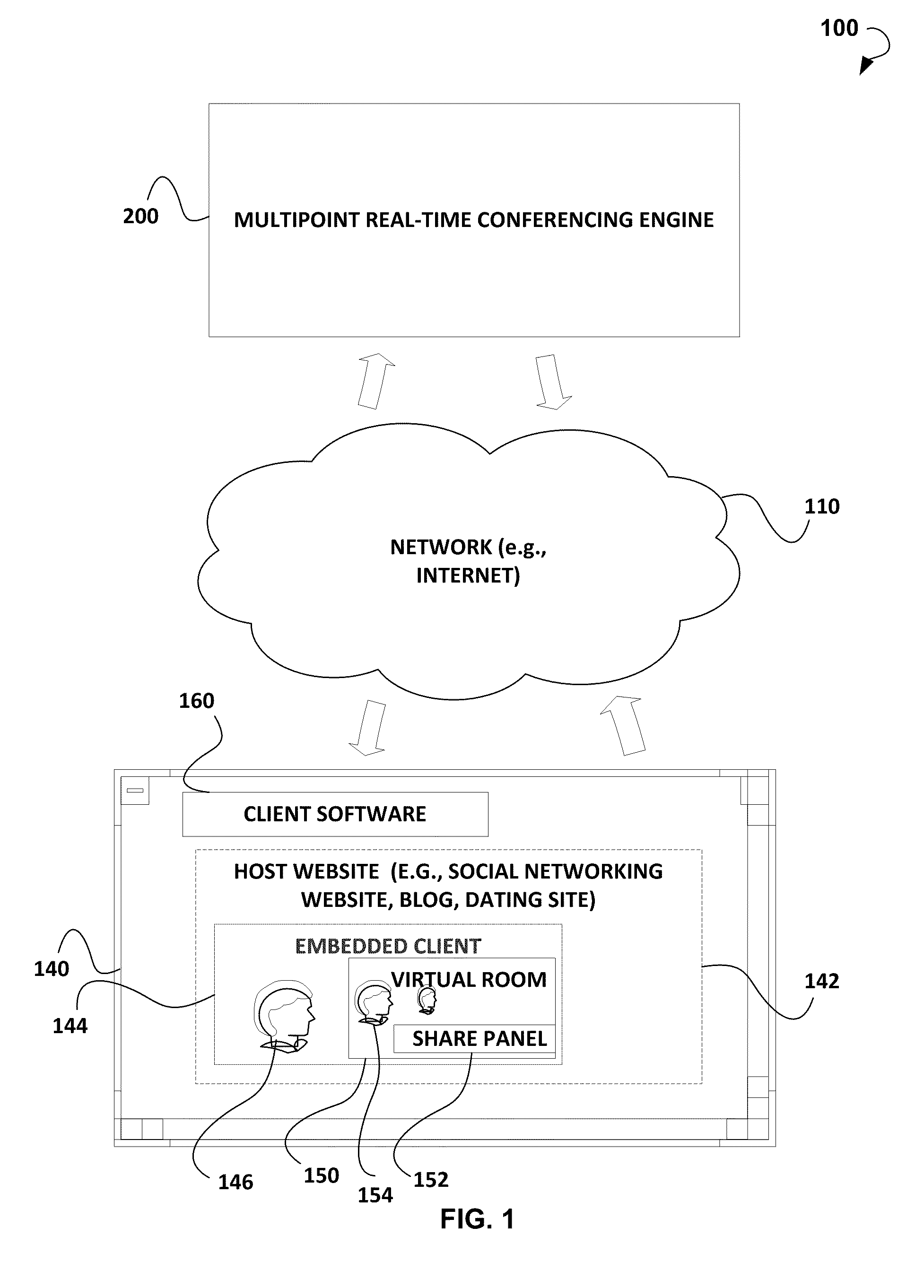
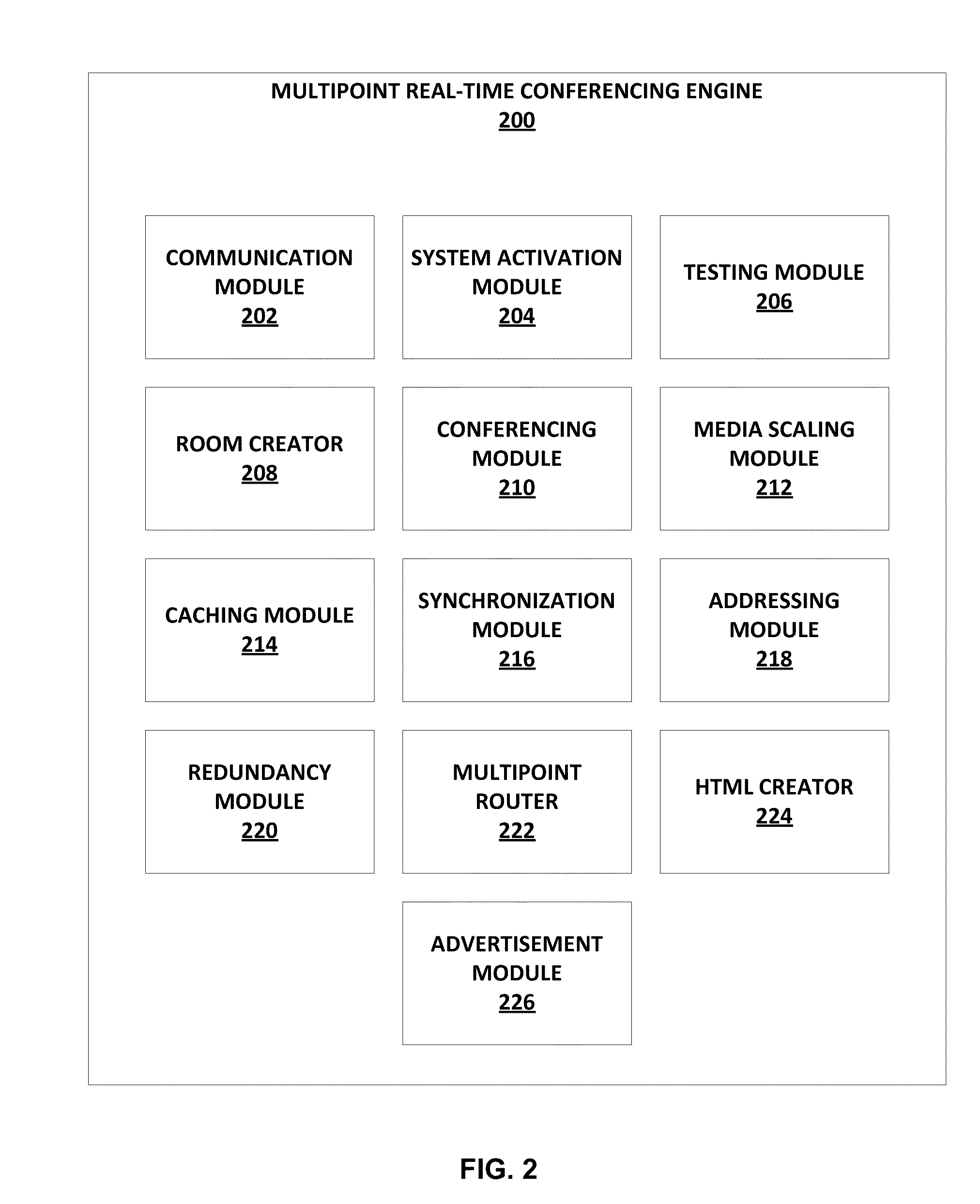
Systems and methods for multimedia multipoint real-time conferencing
A system is disclosed for multimedia multipoint real-time conferencing that includes a communication module to receive via a transport protocol, from a client embedded in a host website (such as a social networking website, a blog, or a dating website), a request to share media content in a real-time group conference associated with users of a virtual room. The content may include an audio, a video, a text, or a HyperText Markup Language (HTML) code referencing a third-party resource. The request may be associated with routing requirements and transport characteristics. The system may further include a content encoder at the host website to create a data packet encapsulating the transport characteristics and the routing requirements. The system may further include a multipoint router to share the content via the transport protocol in the real-time group conference associated with the users of the virtual room. The shared content may include implicit and explicit recommendations.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
Marking and/or sharing media stream in the cellular network terminal
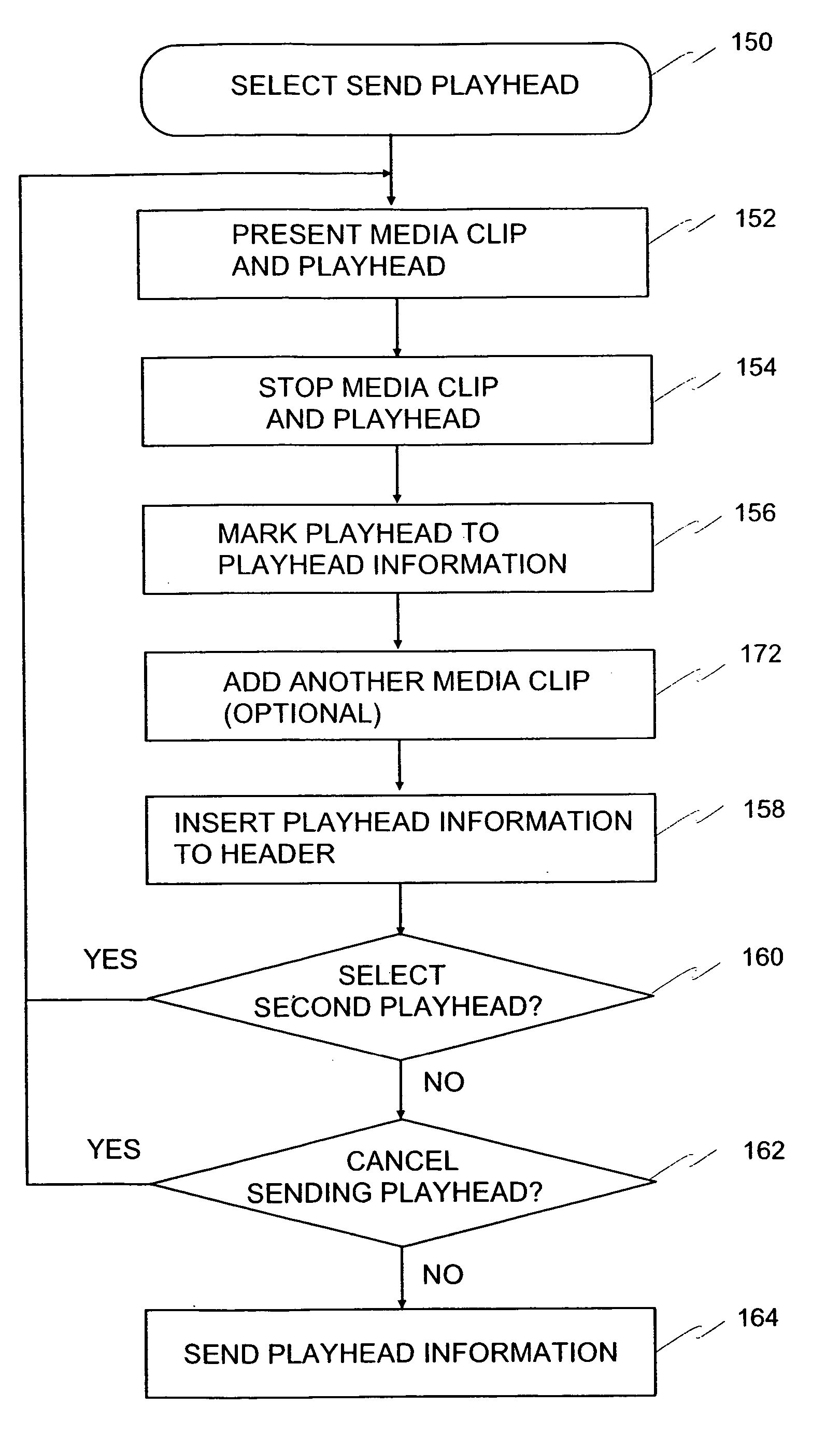
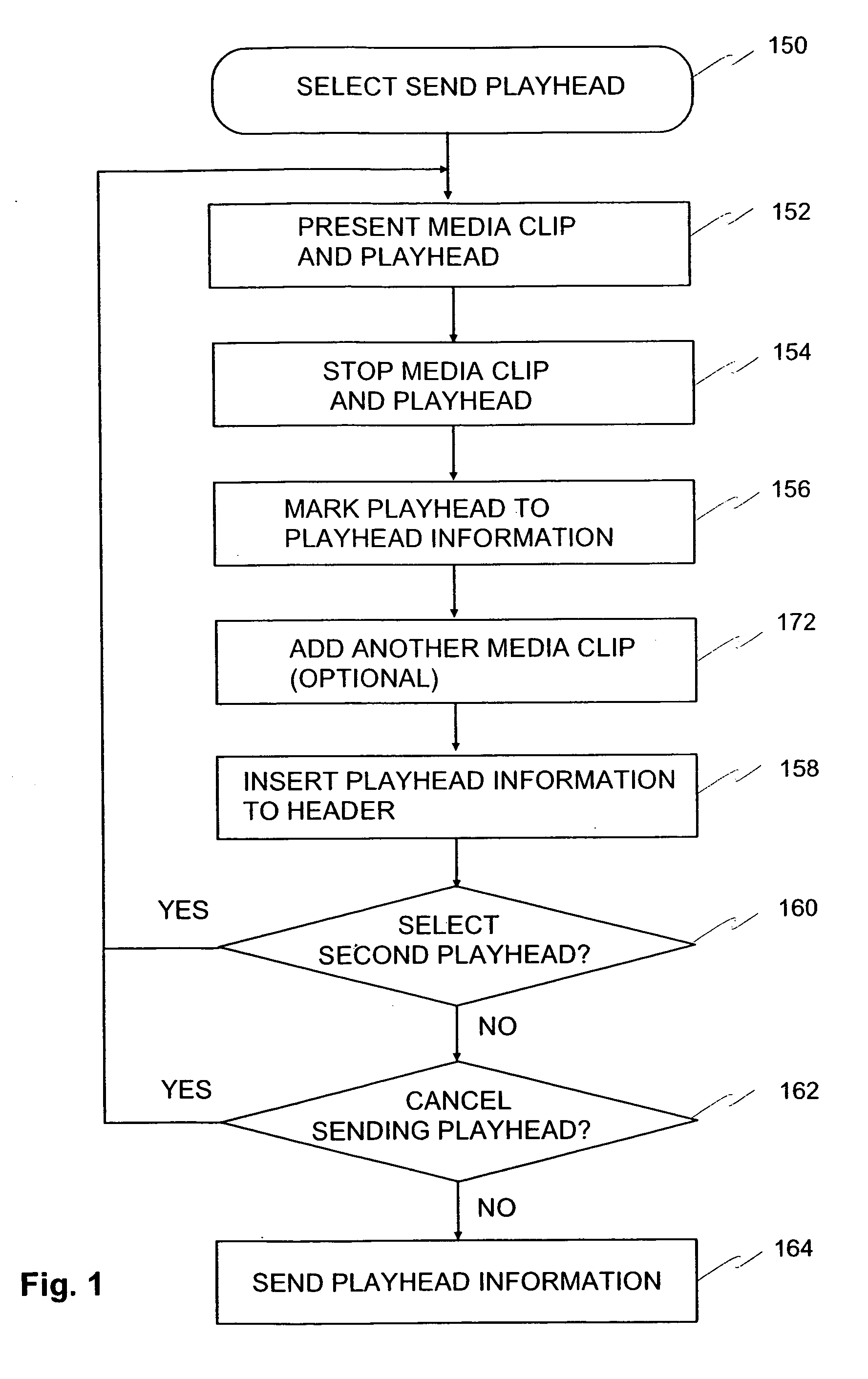
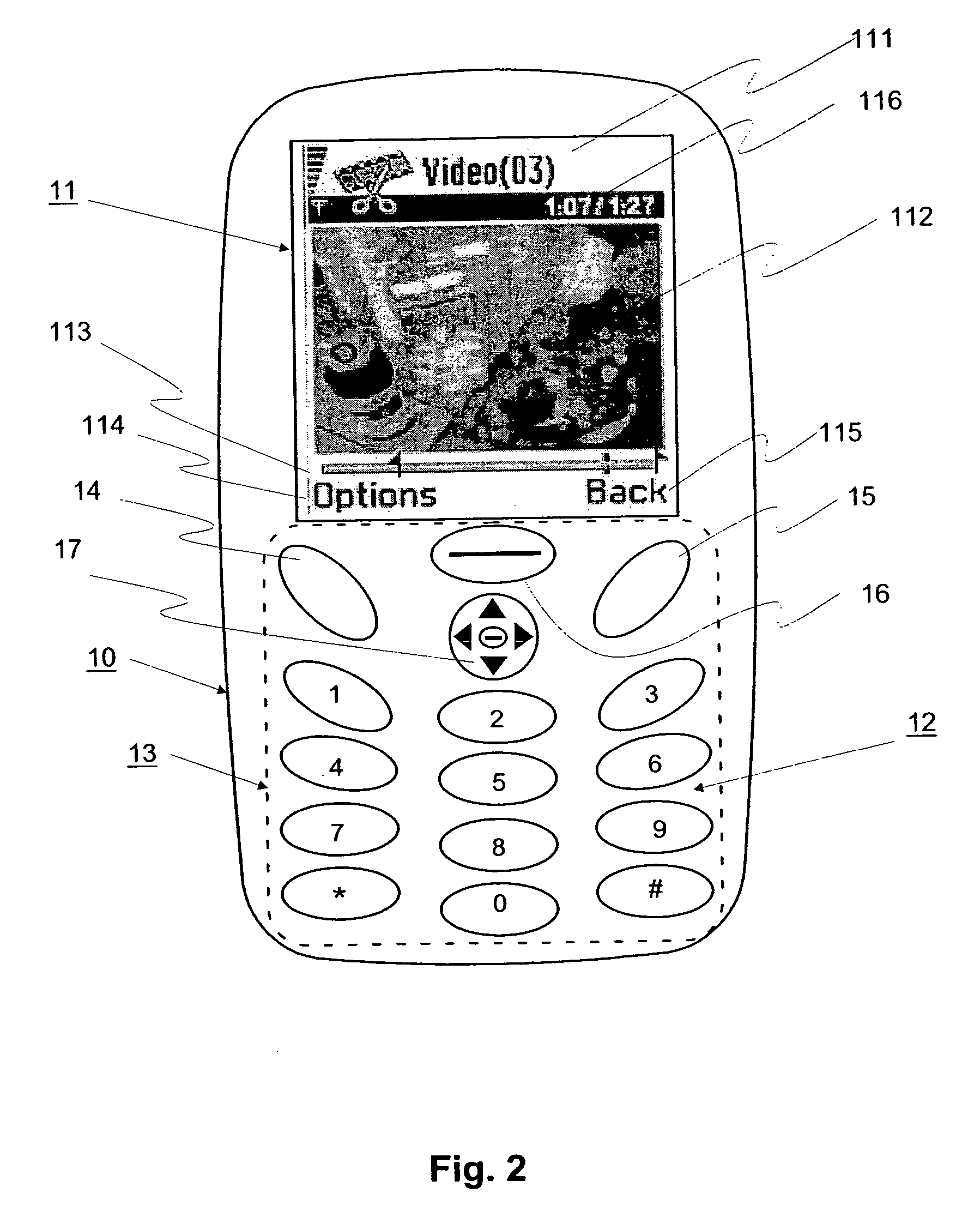
InactiveUS20060161872A1Fast and effective searchingQuickly and conveniently reproduceNetwork traffic/resource managementSubstation equipmentDisplay deviceWireless network
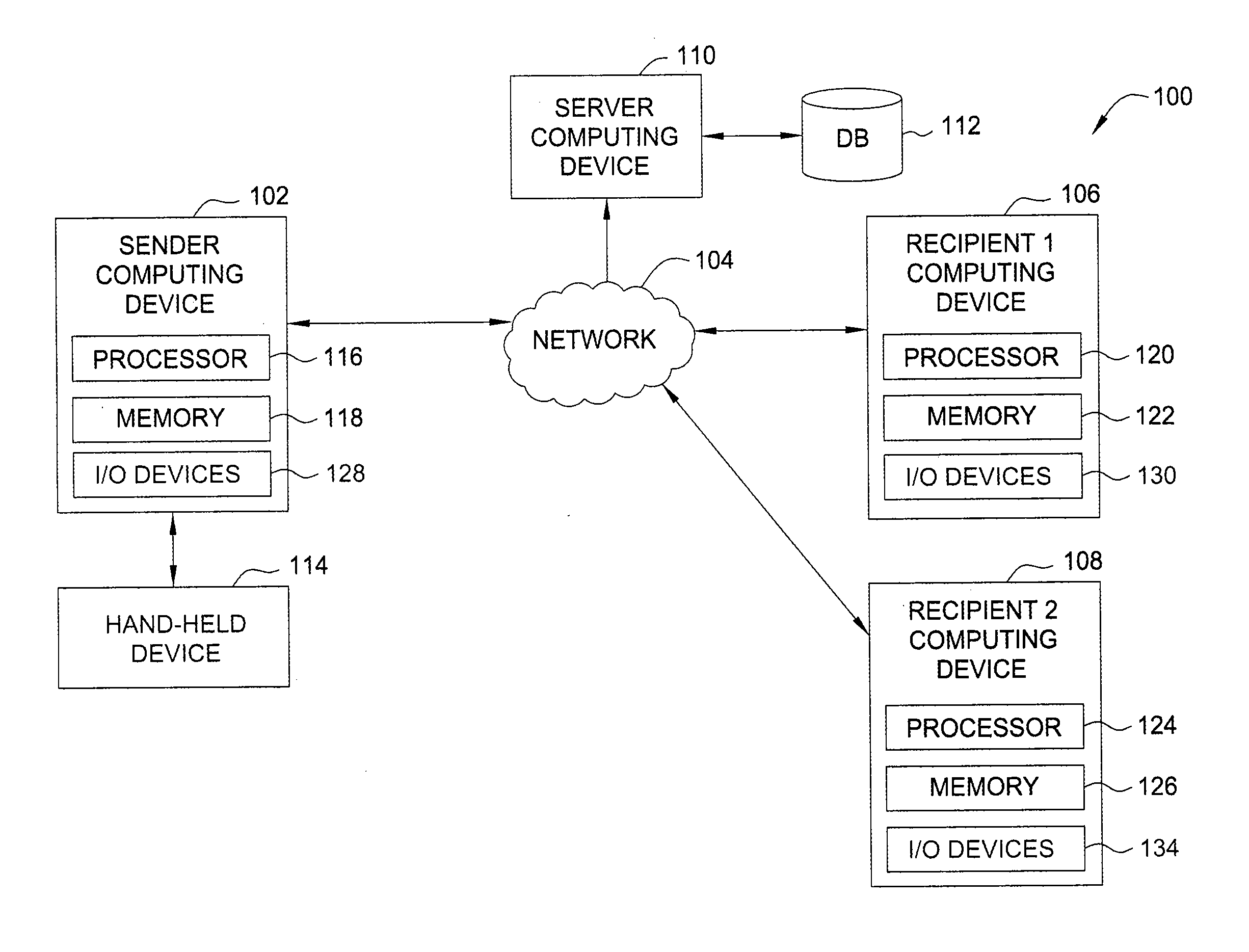
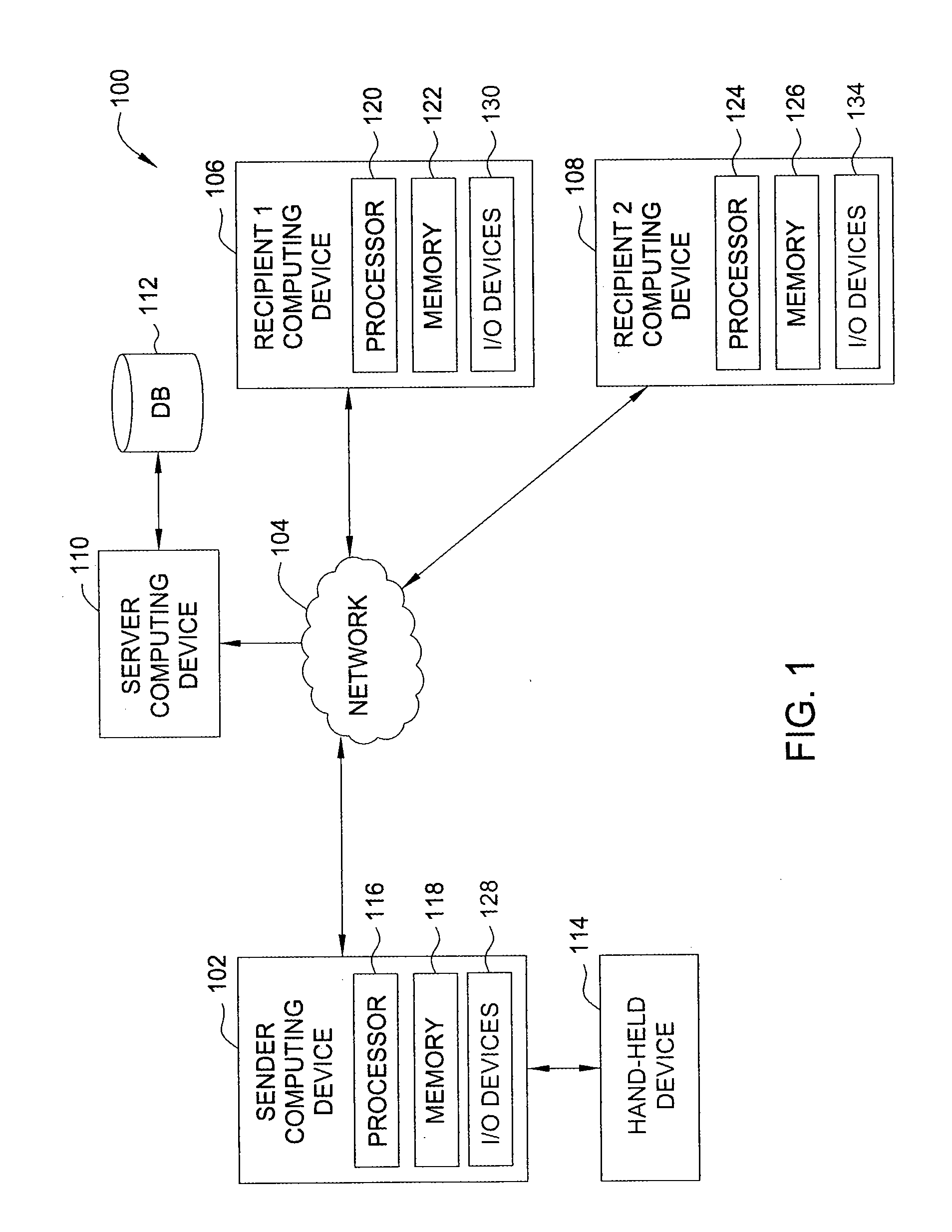
A media clip is marked (156) in a wireless terminal (10) and transmitted further (164) to another wireless terminal (10) in which the marked media stream is received (182) and presented (194) according to the marking (156). A wireless network terminal (10) is shown applying the method, and a programmable means (14, 15, 16, 34, 35) usukkystrated in the wireless network terminal (10) to implement the method. A basis for marking (156) is a playhead position (23, 23a, 23b) which indicates progress of a media clip on a display (11) of the wireless terminal (10), and an end moment of the media clip when the media clip was stopped. This information is associated to playhead information which forms the basis for the marking (156) and reassemblying (184) a media data message (41) before sending it and after receiving it over a wireless network (50).
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method for providing integrated packet services over a shared-media network
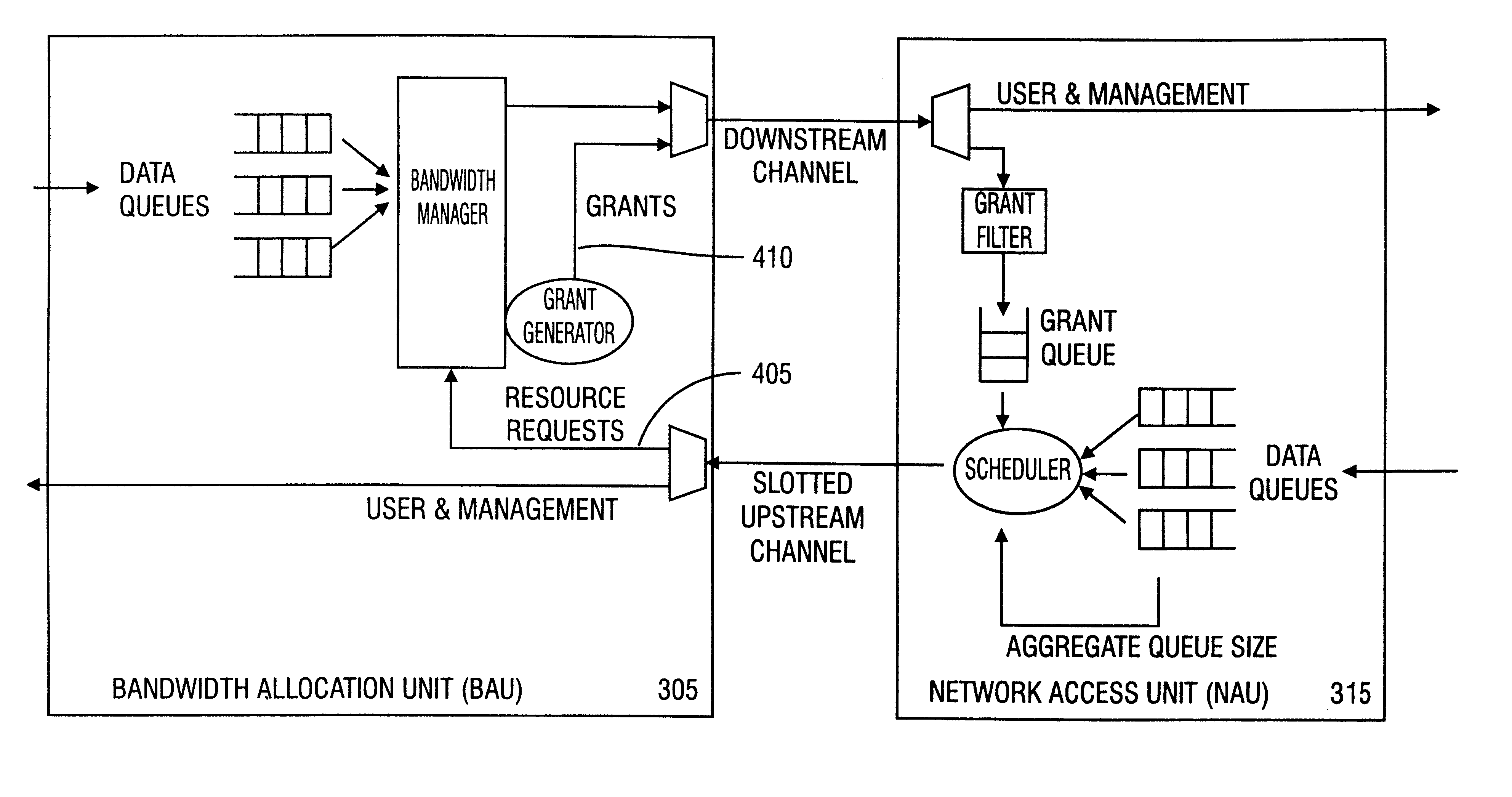
InactiveUS6563829B1Good serviceError preventionTransmission systemsQos quality of serviceExchange network
A method in accordance with the invention allocates bandwidth, fairly and dynamically, in a shared-media packet switched network to accommodate both elastic and inelastic applications. The method, executed by or in a head-end controller, allocates bandwidth transmission slots, converting requests for bandwidth into virtual scheduling times for granting access to the shared media. The method can use a weighted fair queuing algorithm or a virtual clock algorithm to generate a sequence of upstream slot / transmission assignment grants. The method supports multiple quality of service (QoS) classes via mechanisms which give highest priority to the service class with the most stringent QoS requirements.
Owner:AMERICAN CAPITAL FINANCIAL SERVICES
Automatic Media Sharing Via Shutter Click
InactiveUS20120027256A1Still image data retrievalData processing applicationsShared mediumGroup based
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and system for aggregating media collections between participants of a sharing network
InactiveUS20090265426A1Digital data information retrievalRecord information storageCollections dataShared medium
Owner:CONCERT TECH
Super share
ActiveUS20080109852A1Increase incomePrecise managementDistributed storage methodsNetwork topologiesComputer networkShared medium
A method and apparatus for sharing media content between electronic equipment includes transferring session data from a first electronic equipment to a second electronic equipment, said session data including a queue of media content executing or executable on the first electronic equipment, and transferring media content identified in the session data to the second electronic equipment.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Capturing and sharing media content
ActiveUS7975062B2Electronic editing digitised analogue information signalsBroadcast-related systemsWeb siteMediaFLO
A media device allows users to watch and capture portions from a media stream. Users may then share the captured media content with other users. In one embodiment, the media device receives a media stream, plays the media stream, and caches a portion of the media stream as it is being played. A user can define a media clip by selecting its boundaries in the cached portion of the media stream. The media device creates the media clip based on the user's input and enables the user to transmit the media clip to another system, such as a community website for sharing it with other users.
Owner:SLING MEDIA LLC
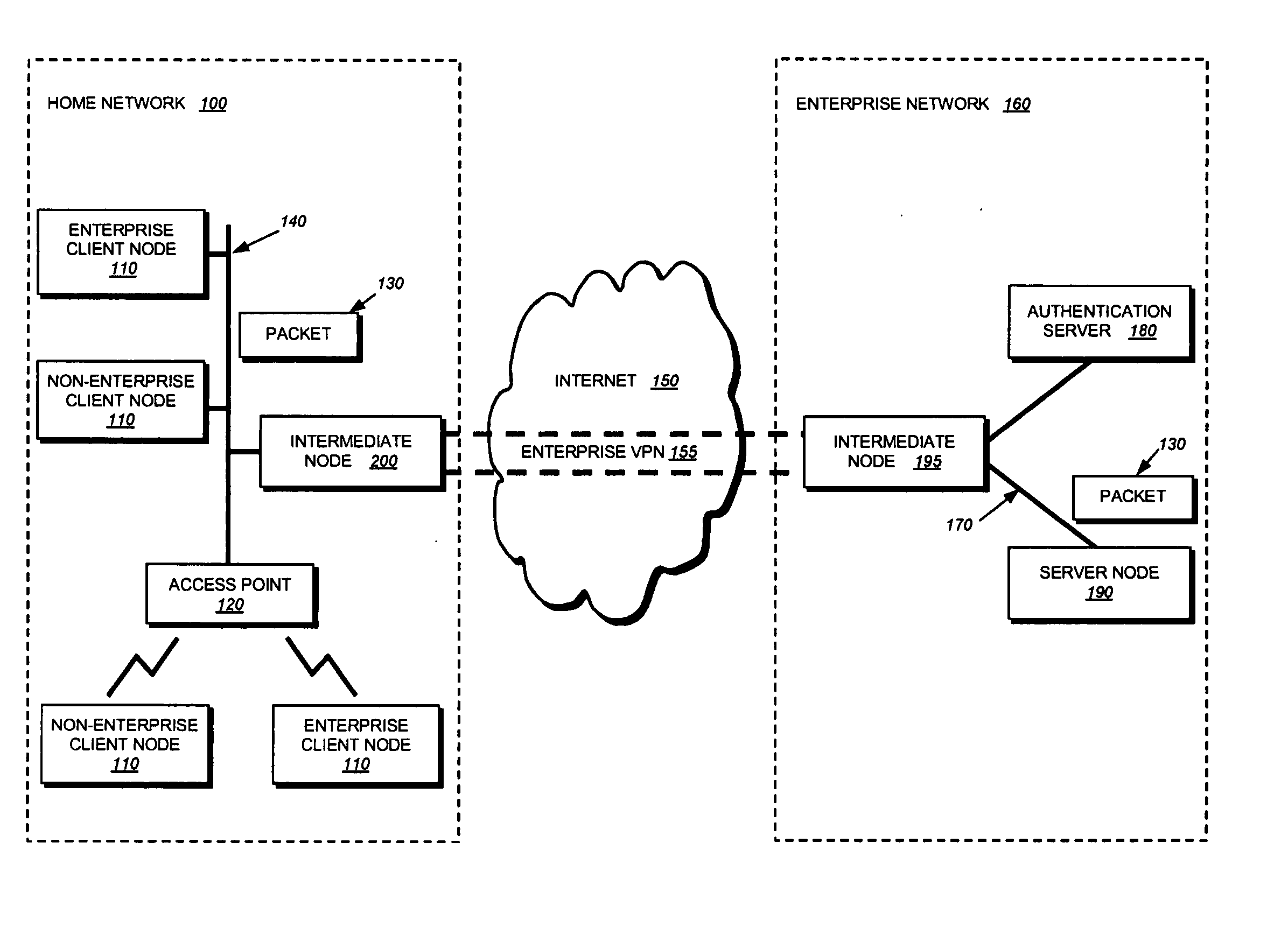
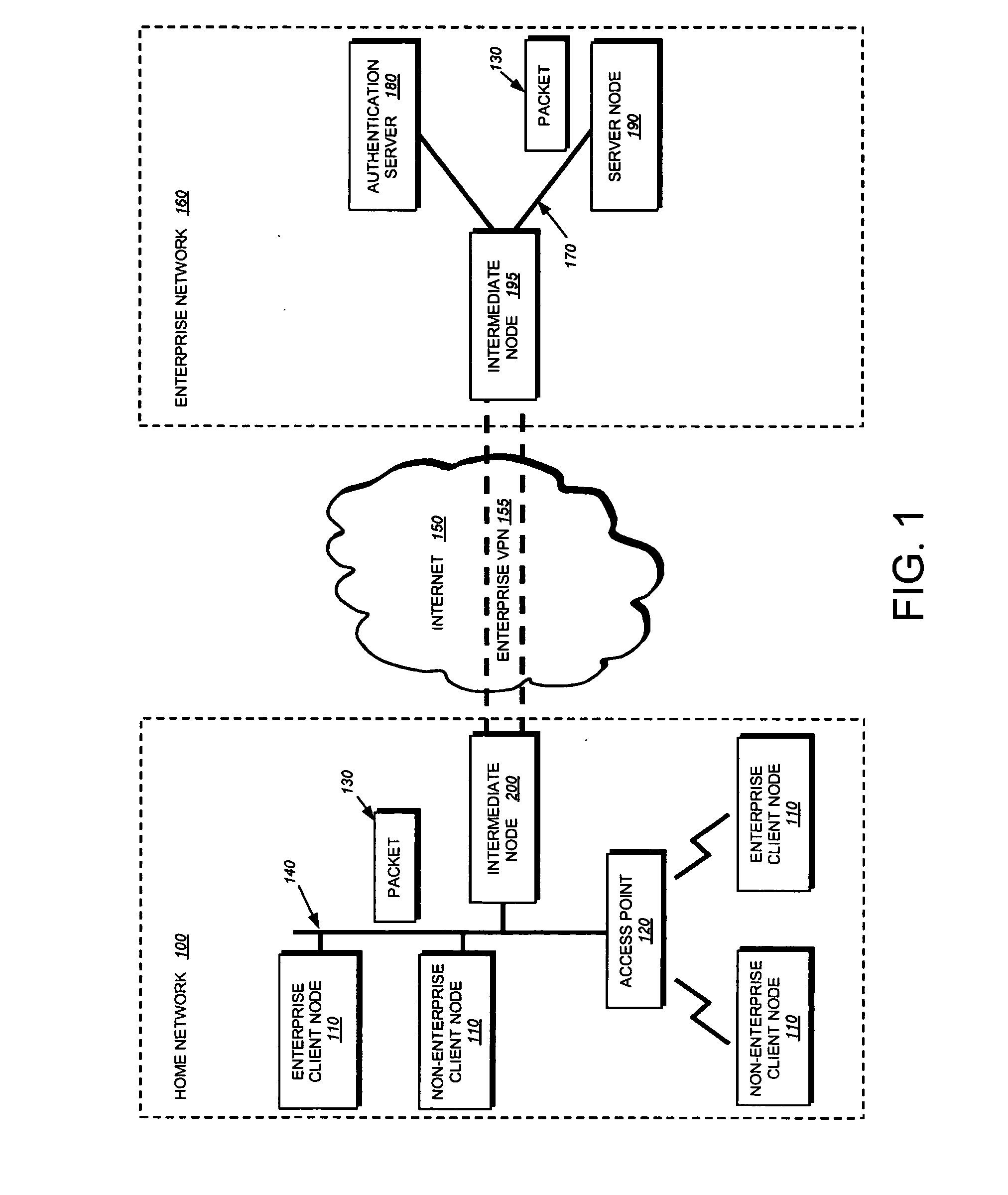
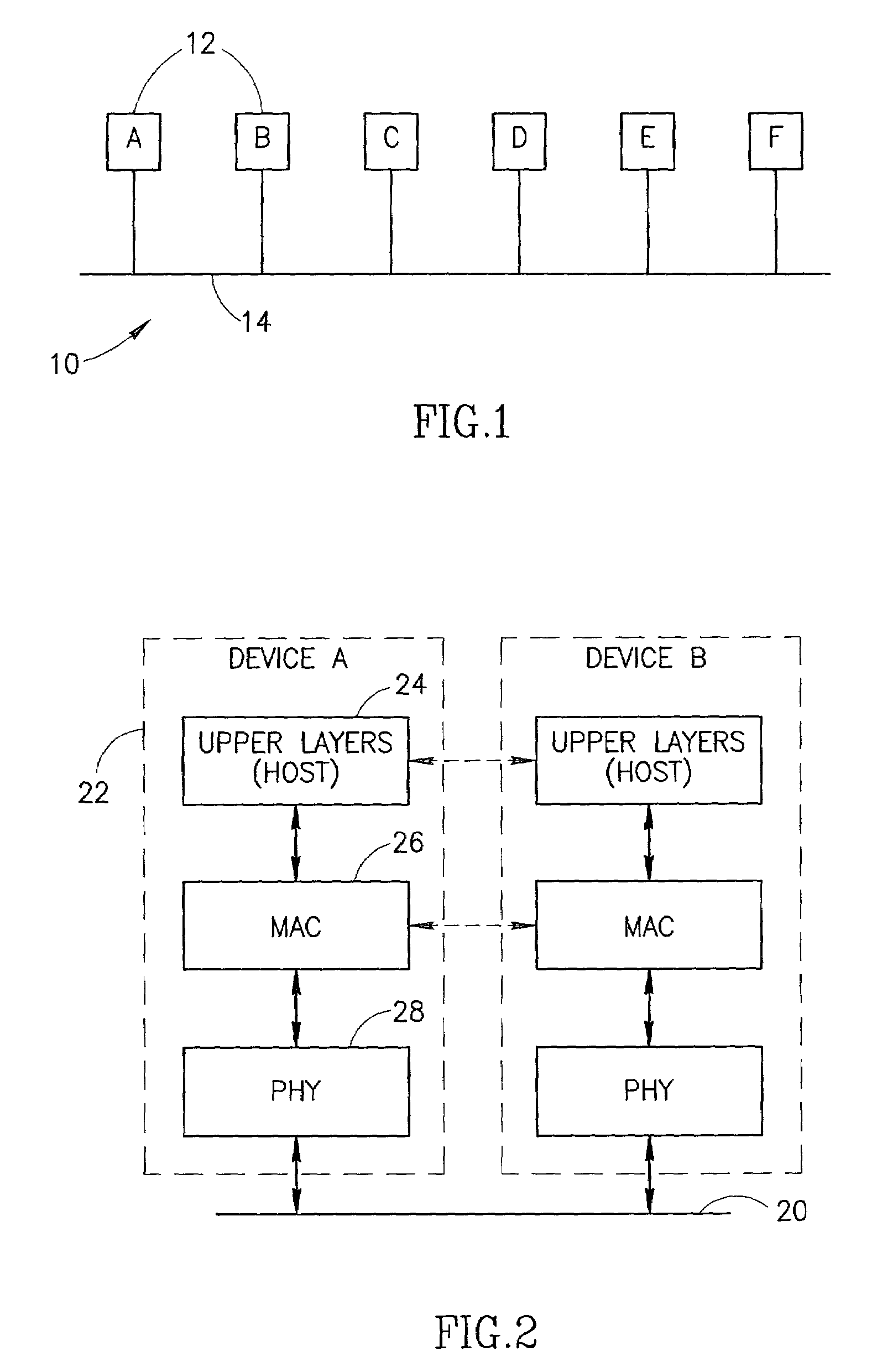
802.1X authentication technique for shared media
ActiveUS20050125692A1Increase network-access securityConvenient access controlDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationClient-sideNetwork Access Control
The present invention provides a technique for securely implementing port-based authentication on a shared media port in an intermediate node, such as a router. To that end, the invention provides enhanced port-based network access control that includes client-based control at the shared media port. Unlike previous implementations, the port does not permit multiple client nodes to access a trusted subnetwork as soon as a user at any one of those nodes is authenticated by the subnetwork. Instead, port-based authentication is performed for every client node that attempts to access the trusted subnetwork through the shared media port. As such, access to the trusted subnetwork is not compromised by unauthenticated client nodes that “piggy-back” over the shared media port after a user at another client node has been authenticated by the trusted subnetwork.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
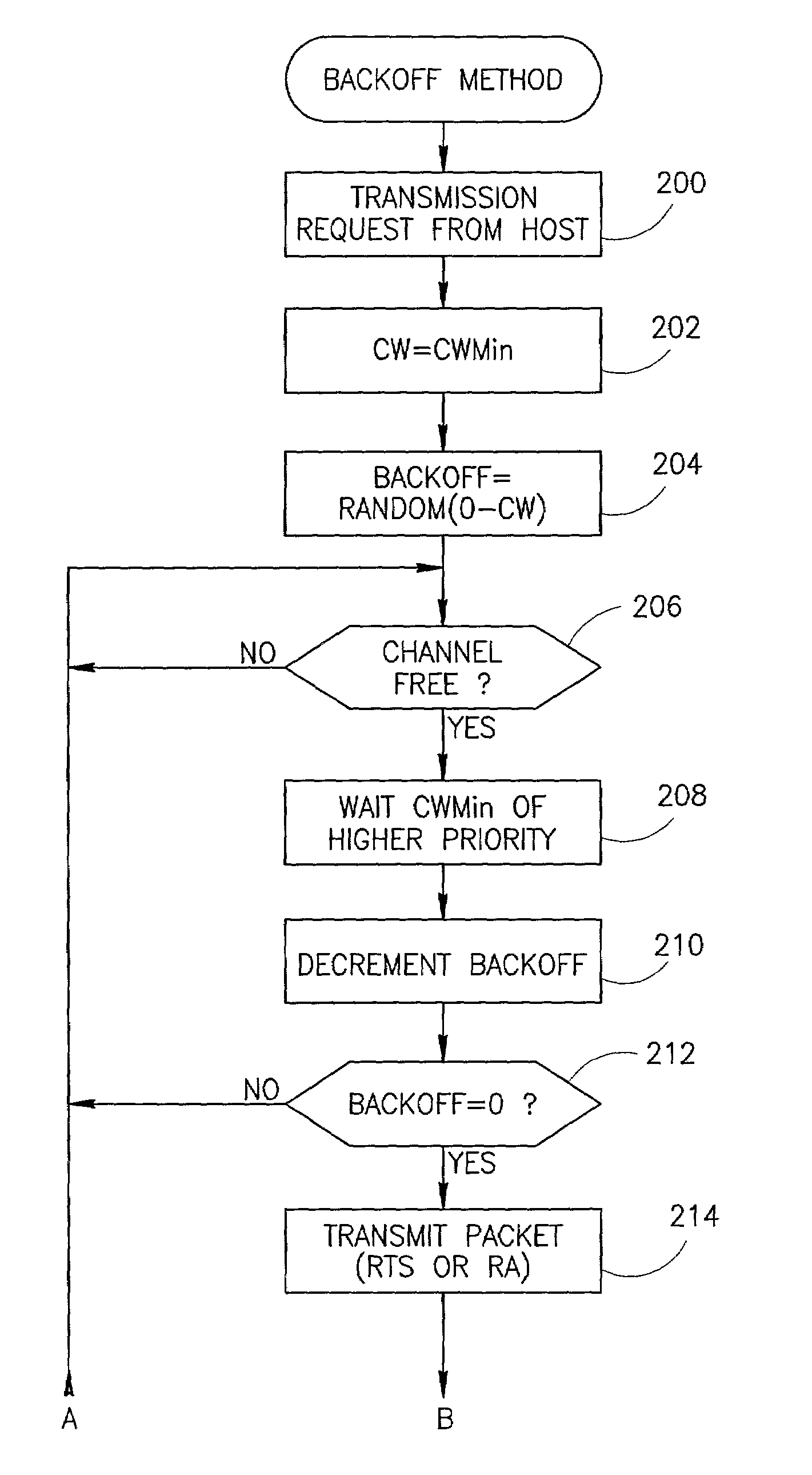
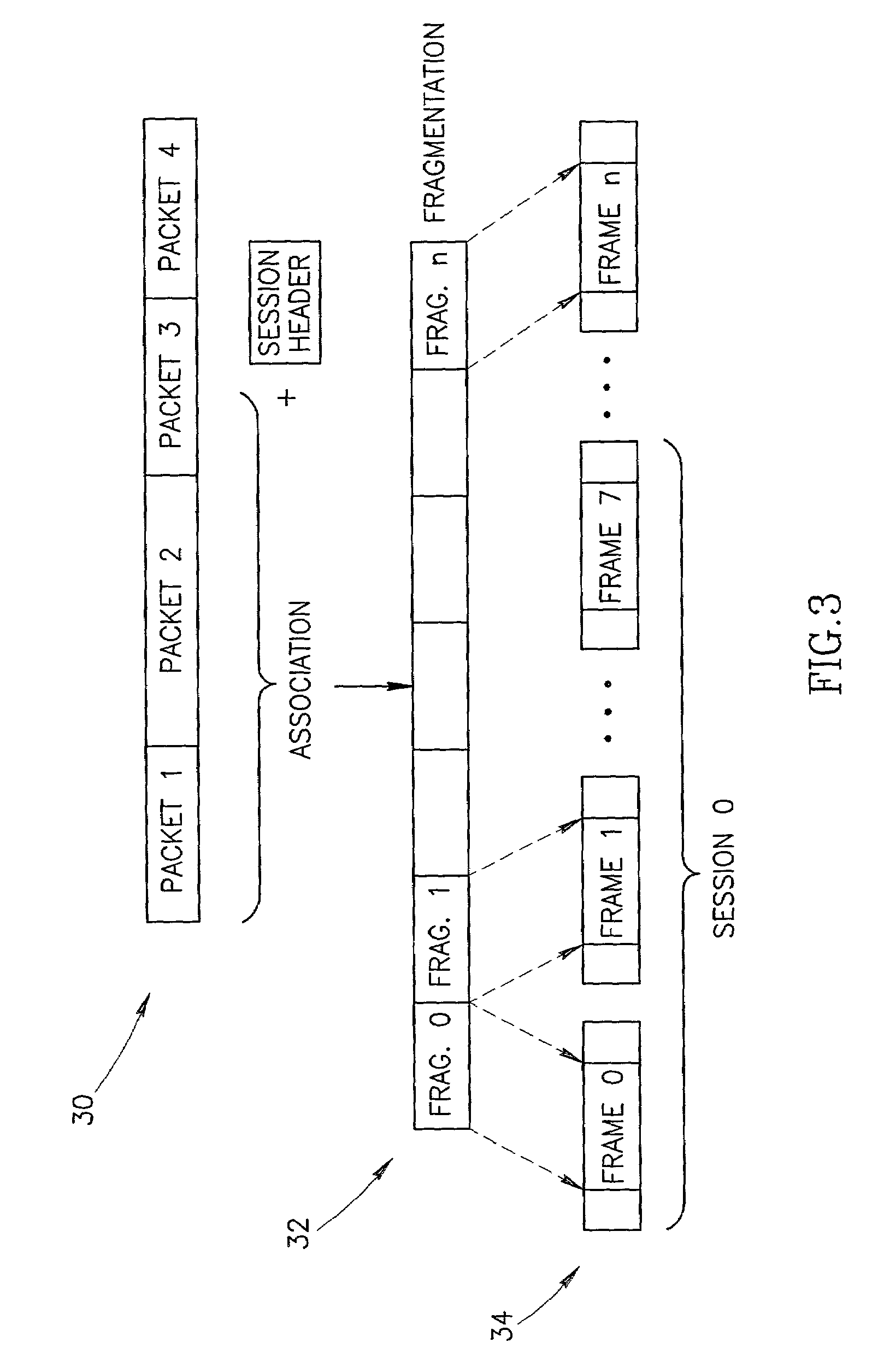
Channel access method for powerline carrier based media access control protocol
InactiveUS7570656B2Efficient and reliableEfficient mechanismError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementCarrier signalMulticast transmission
A novel and useful media access control (MAC) protocol that is intended for use over noisy shared media channels. The MAC protocol provides layer 2 functionality over a network using a shared medium including a backoff mechanism for CSMA / CA channel access, link addressing that reduces the overhead of long MAC addresses, a flooding scheme having controlled exposure for broadcast transmissions, multicast transmissions using selective ACKs, implementation of traffic prioritization using an adaptive backoff scheme, a second layer repeater establishment process and multi-packet transport for short packets and fragmentation for long packet transport.
Owner:ITRAN COMM
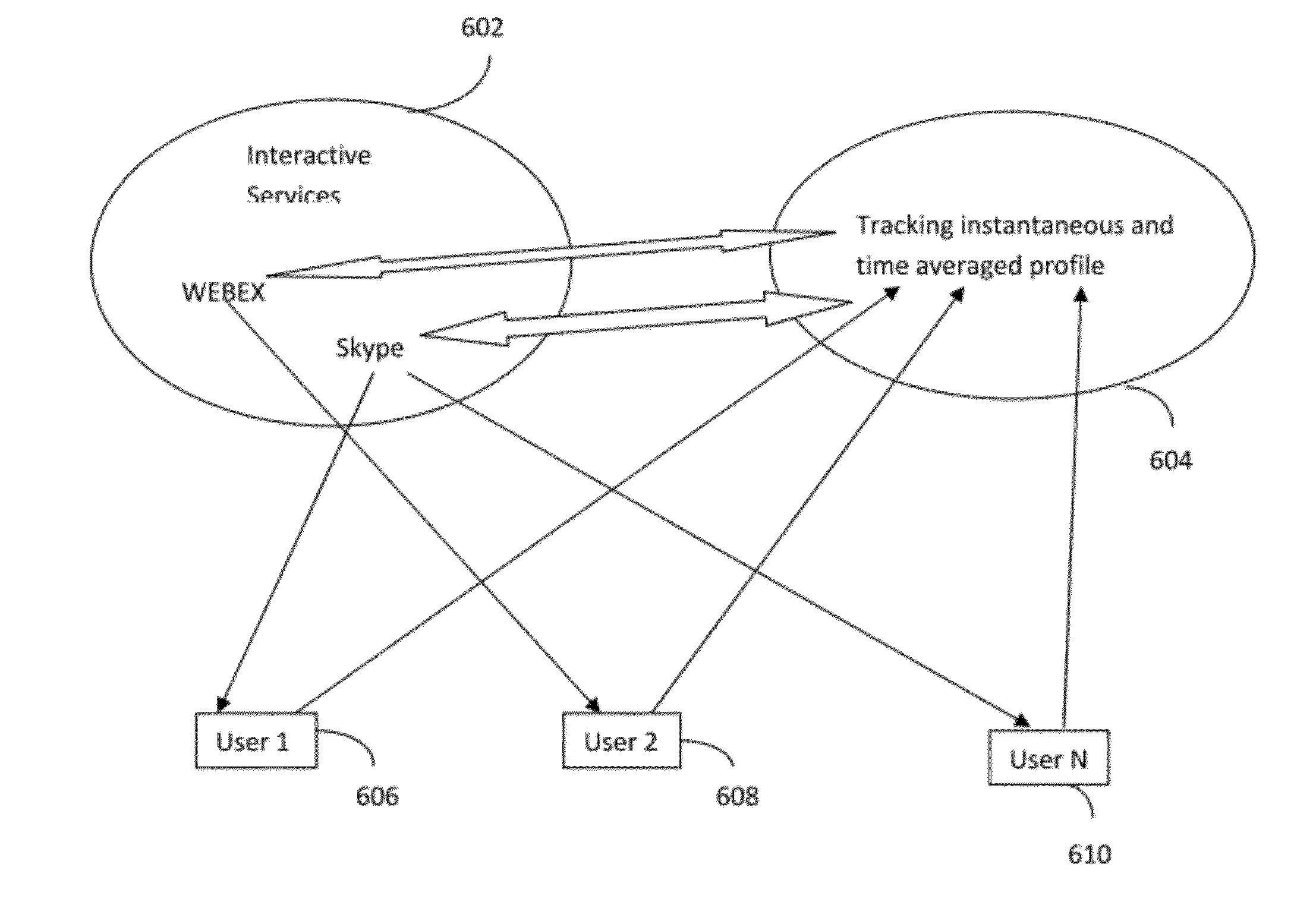
System and Method for Personalized Media Rating and Related Emotional Profile Analytics
ActiveUS20120290508A1Digital computer detailsMetadata multimedia retrievalPersonalizationComputer science
A system and a method for generating an emotional profile of the user and deriving inference from the analytics of generated emotional profile is provided. The method involves sharing media content or online event in a connected environment; capturing user's reaction to the said content or event; generating an emotional score of the user to rate the media content or event; and sharing the emotional score within the connected environment.
Owner:BIST ANURAG
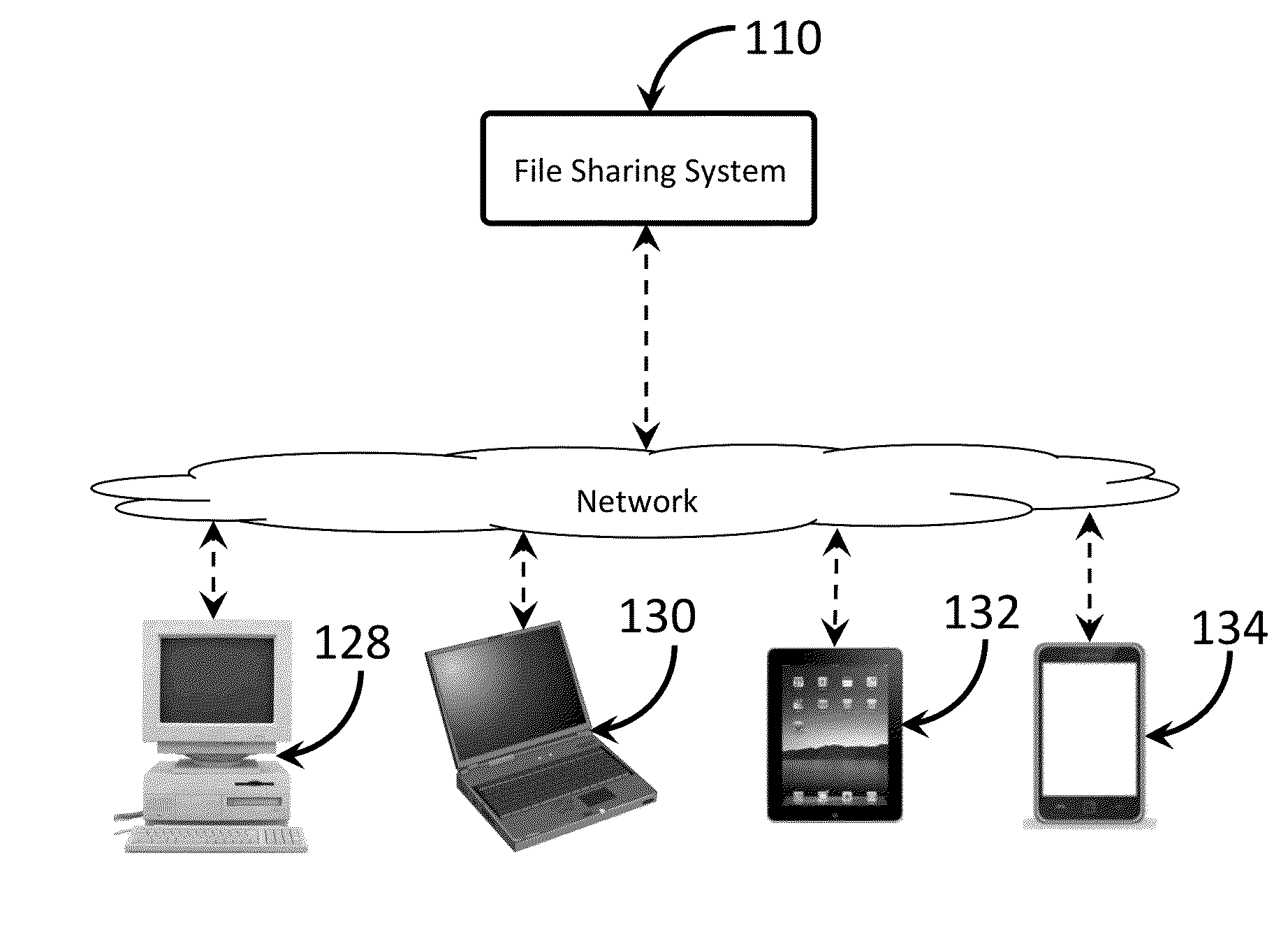
File sharing system and method
ActiveUS20140165176A1More securityControl moreDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsOperating systemShared medium
According to the present application, systems, devices and methods for sharing media files may promote sharing of media without permitting the media to be downloaded. Such systems, devices and methods for sharing media may further enable lists of files to be shared and responses to be delivered to the media owner during playback by a user. A local device may be utilized to enable the storing and sharing of media that is hosted off the cloud. Streaming from the file sharing system or the local device is facilitated through the system.
Owner:DUVON
Simultaneous sharing communication interface
ActiveUS20080168154A1Geometric image transformationNatural language data processingCommunication interfaceGraphics
A user can share (show) multimedia information while simultaneously communicating (telling) with one or more other users over a network. Multimedia information is received from at least one source. The multimedia information may be manually and / or automatically annotated and shared with other users. The multimedia information may be displayed in an integrated live view simultaneously with other modes of communication, such as video, voice, or text. A simultaneous sharing communication interface provides an immersive experience that lets a user communicate via text, voice, video, sounds, music, or the like, with one or more other users while also simultaneously sharing media such as photos, videos, movies, images, graphics, illustrations, animations, presentations, narratives, music, sounds, applications, files, and the like. The simultaneous sharing interface enables a user to experience a higher level of intimacy in their communication with others over a network.
Owner:SNAPCHAT
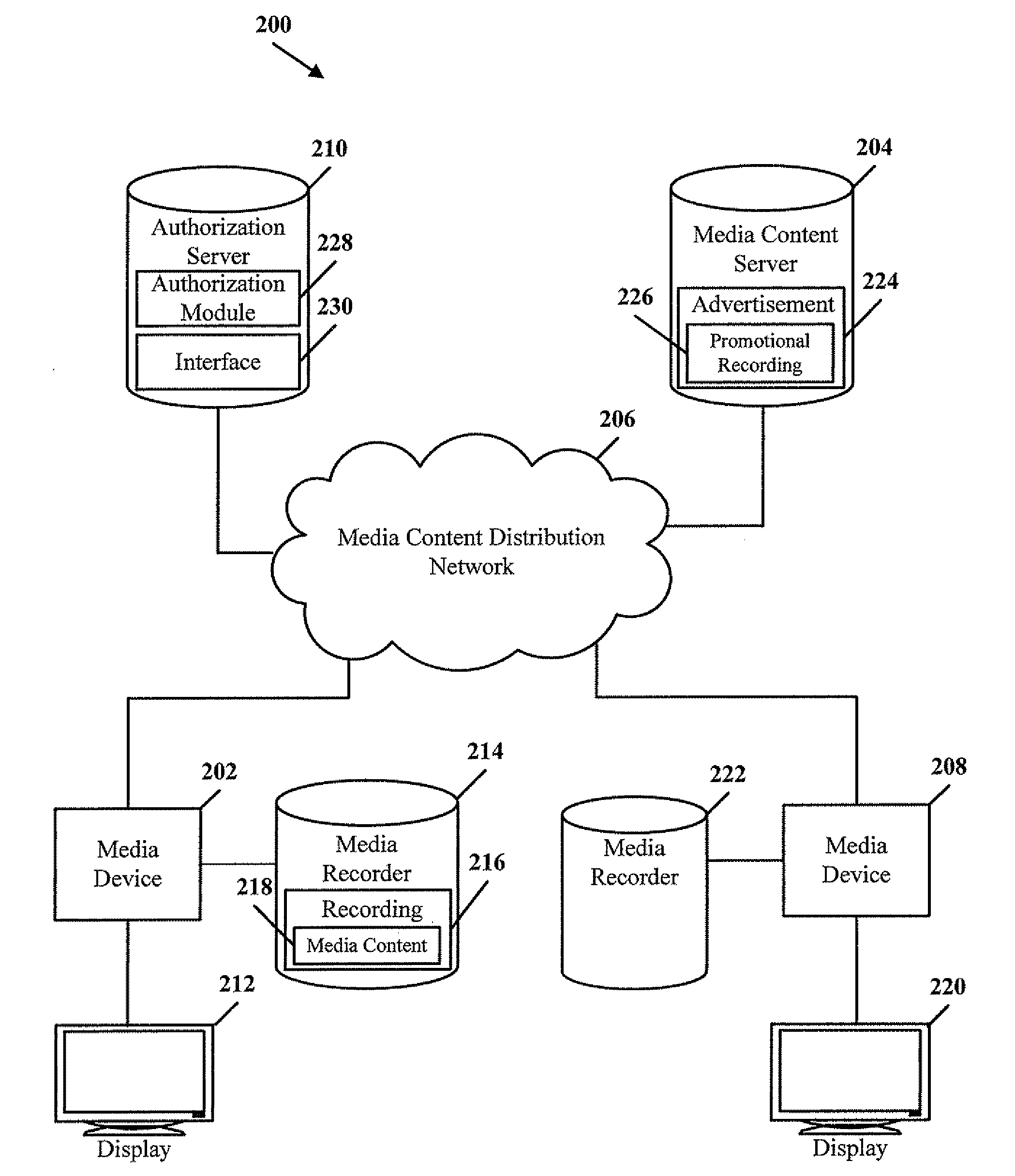
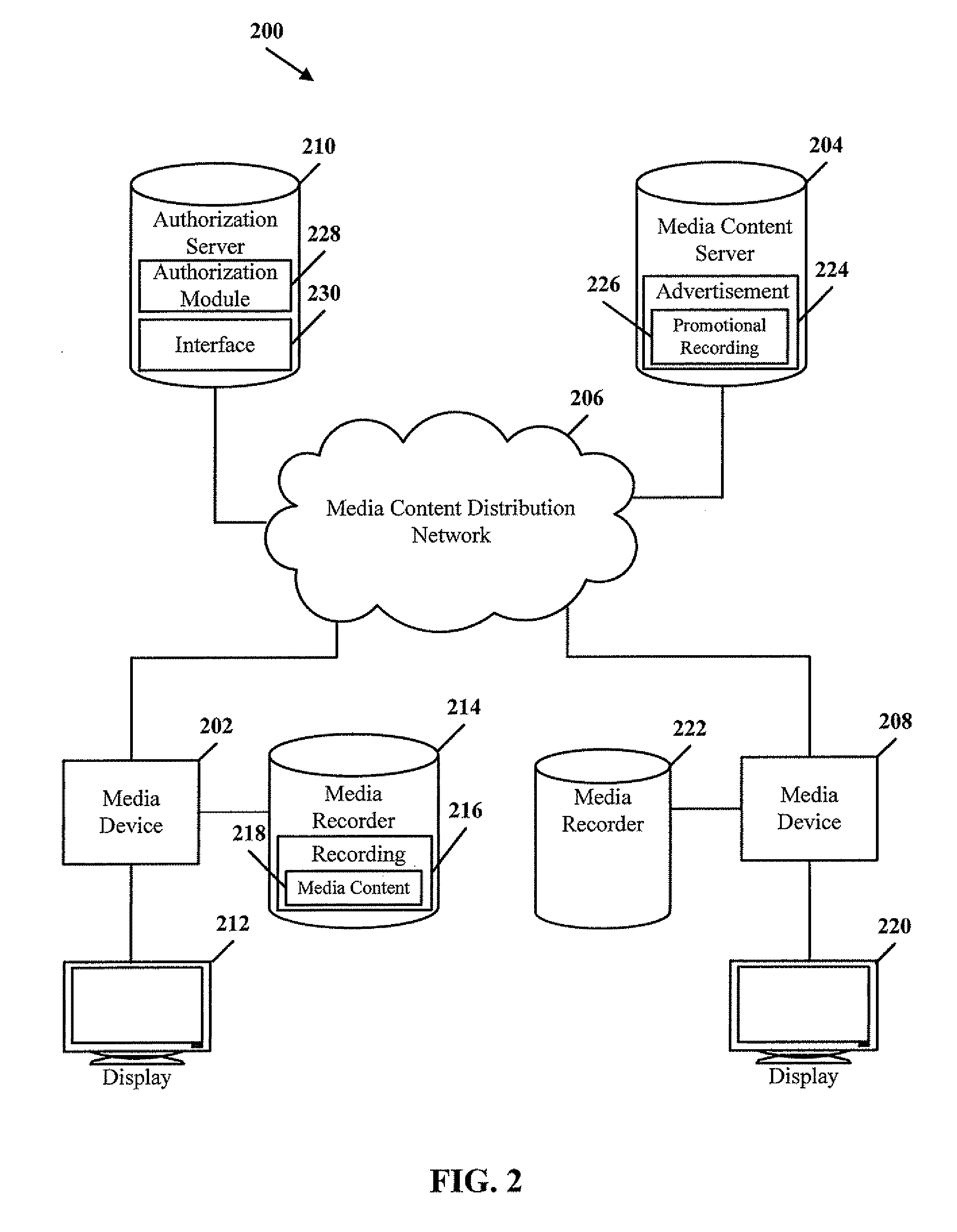
System and method of sharing media content
ActiveUS20090228938A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsTwo-way working systemsNetwork connectionWorld Wide Web
A method of sharing media content is disclosed. A request is received at a network-connected media recorder to send a recording including media content to one or more users. At least one subscriber in the one or more users is identified, where the at least one subscriber is authorized to display the media content. At least one media device associated with the at least one subscriber is determined. The recording is sent to the at least one media device associated with the authorized subscriber.
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
Management of shared media content
A media device allows users to watch and capture portions from a media broadcast. Users may then share the captured media content items with other users, for example, by uploading the items to a community website. Before providing requested media content items to other users, the website may combine advertisements with the media content items. The website may receive advertising revenue from advertisers and may share the advertising revenue with owners of the media content items in exchange for their permission to provide the media content items. The advertisers may provide restrictions on how the advertisements are combined with the media content items, and the content owners may provide restrictions on how the media content items are provided to the users.
Owner:SLING MEDIA LLC
Automated screen saver with shared media
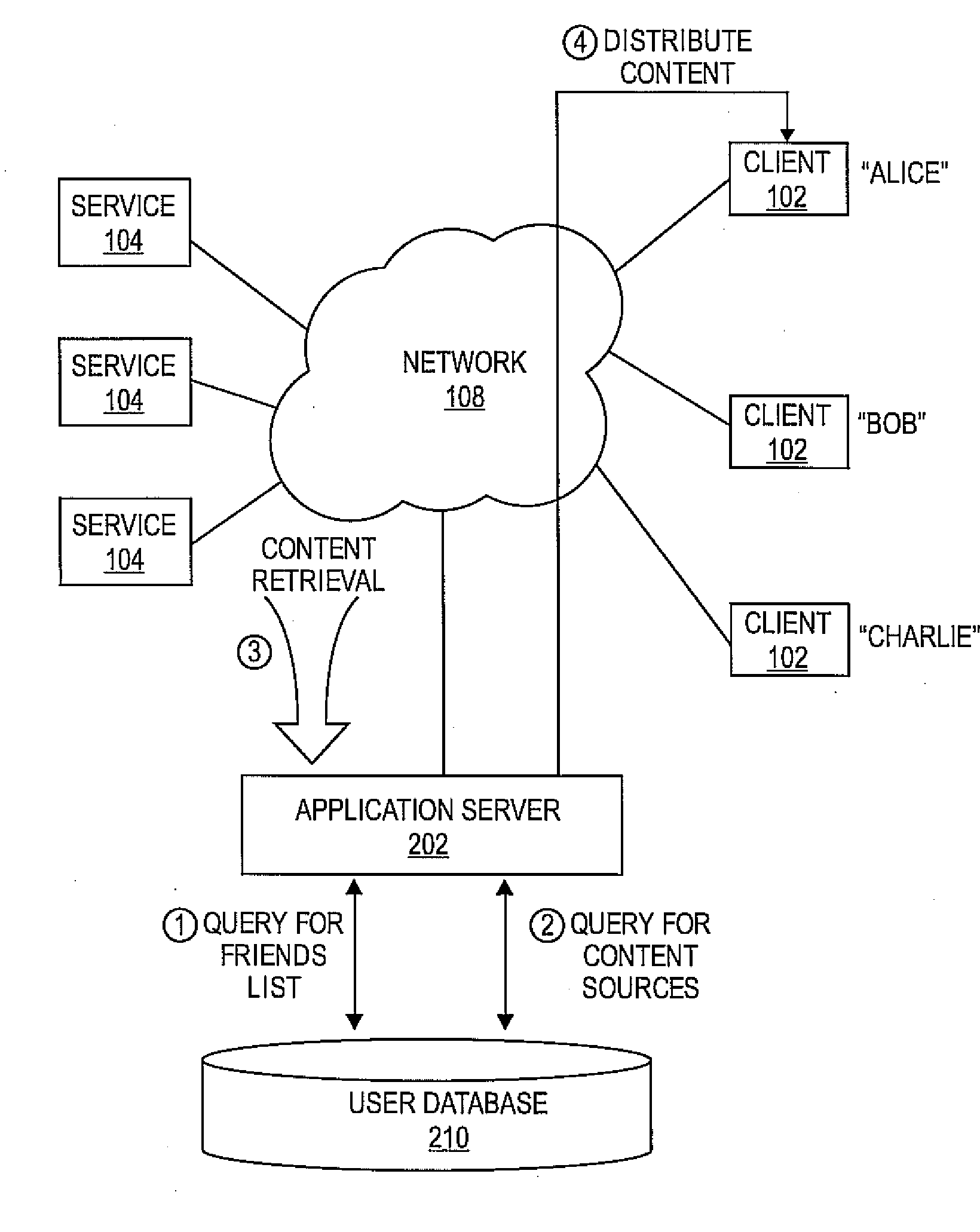
ActiveUS20080133649A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsHard disc driveImage sharing
Embodiments of the present invention provide users in a social network with a screen saver constructed by media shared by their contacts and groups in a social network. The present invention provides a shared photo album that displays images from a user's own photo collection, and that of their social network automatically. For a user, the social network service queries its database to retrieve a list of photo sources. The sources of images may be online photo sharing services, other computers with photos on their local hard drives, and public peer-to-peer storage services. The images may be displayed to the user and optionally may be accompanied with information, such as the owner of the photo or descriptive phrases or comments about the photo. The social network service may be configured to continuously or periodically request photos to update the screen saver.
Owner:RED HAT
Configuring channels for sharing media
A user interface for sharing media items with others. From a sender's perspective, embodiments of the invention allow for an easy-to-use drag-and-drop technique that is more user-friendly than conventional techniques. From the recipient's perspective, embodiments of the invention allow media items from multiple sources to be aggregated into a single viewport, providing a cohesive and unified approach to media items received from others.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
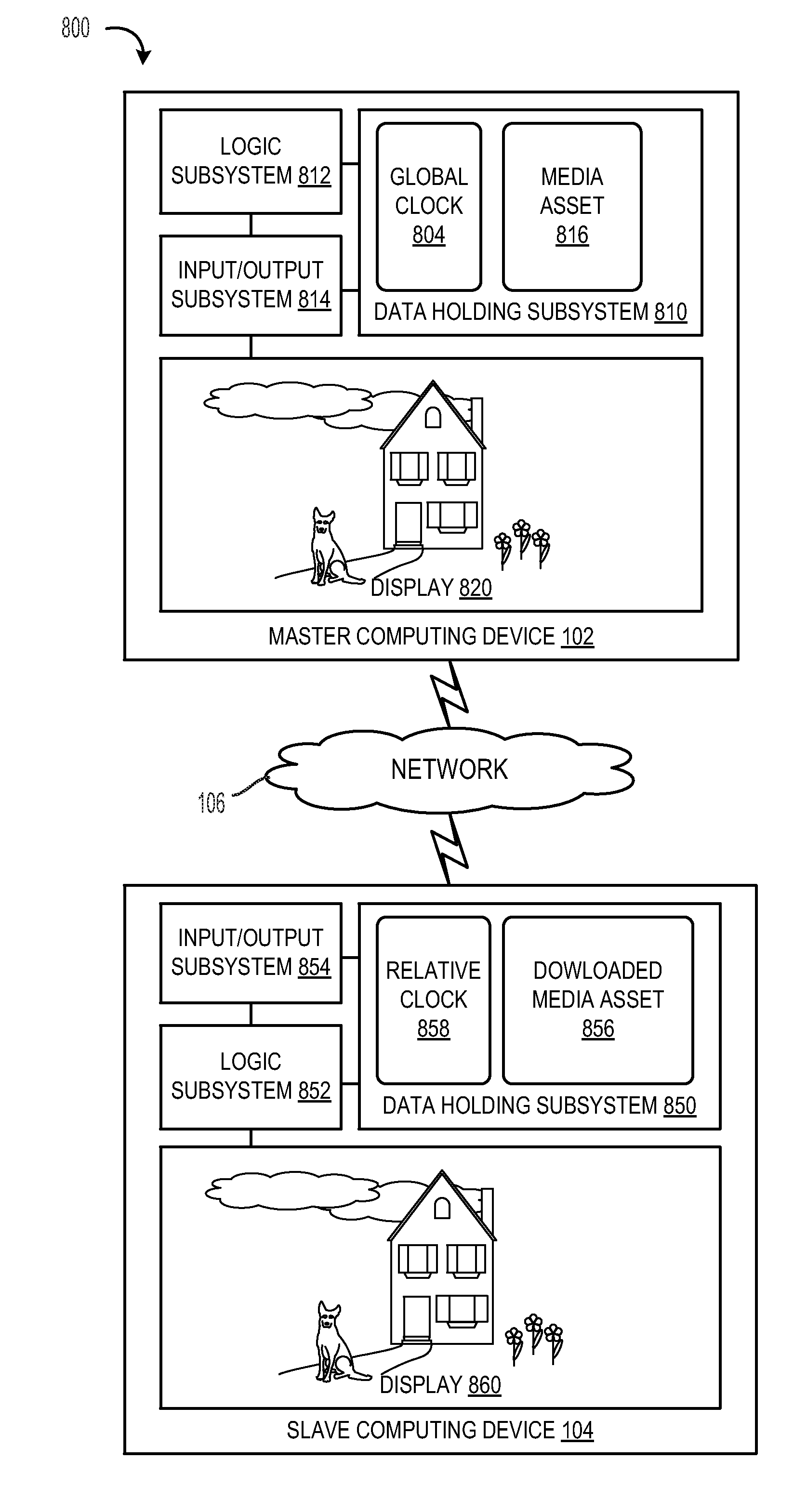
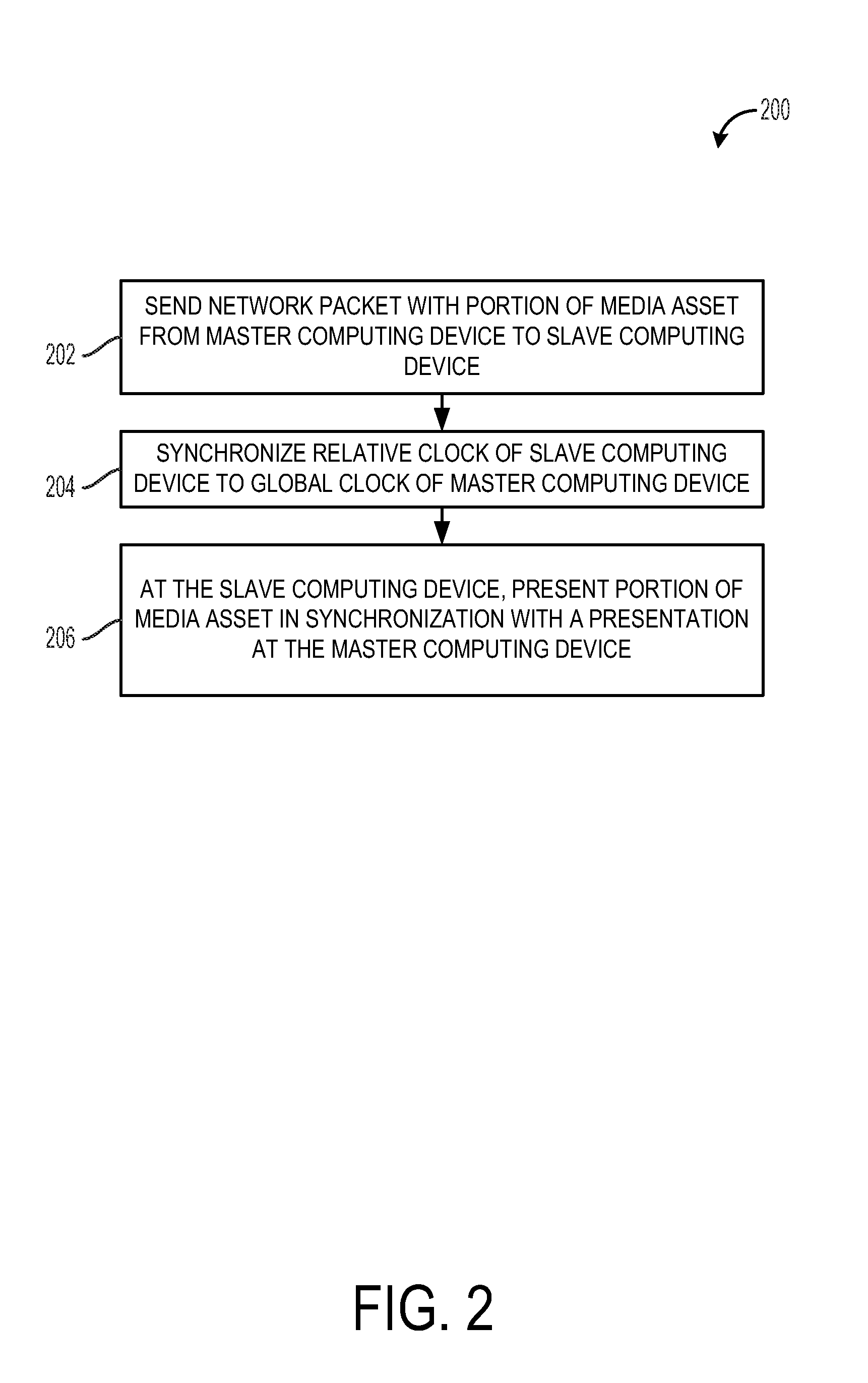
Clock synchronization for shared media playback
Various embodiments are provided that relate to clock synchronization. In one embodiment, a method for synchronizing a relative clock to a global clock comprises receiving a network packet from a master computing device, the network packet including a network packet time stamp indicating a system time of the global clock when the network packet was transmitted; determining a receipt time offset between a receipt time of the network packet and the network packet time stamp, the receipt time indicating a time at which the network packet is received as measured by the relative clock; and adjusting a system time of the relative clock toward the system time of the global clock by updating a system time offset to the receipt time offset if the receipt time offset is smaller than the system time offset.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
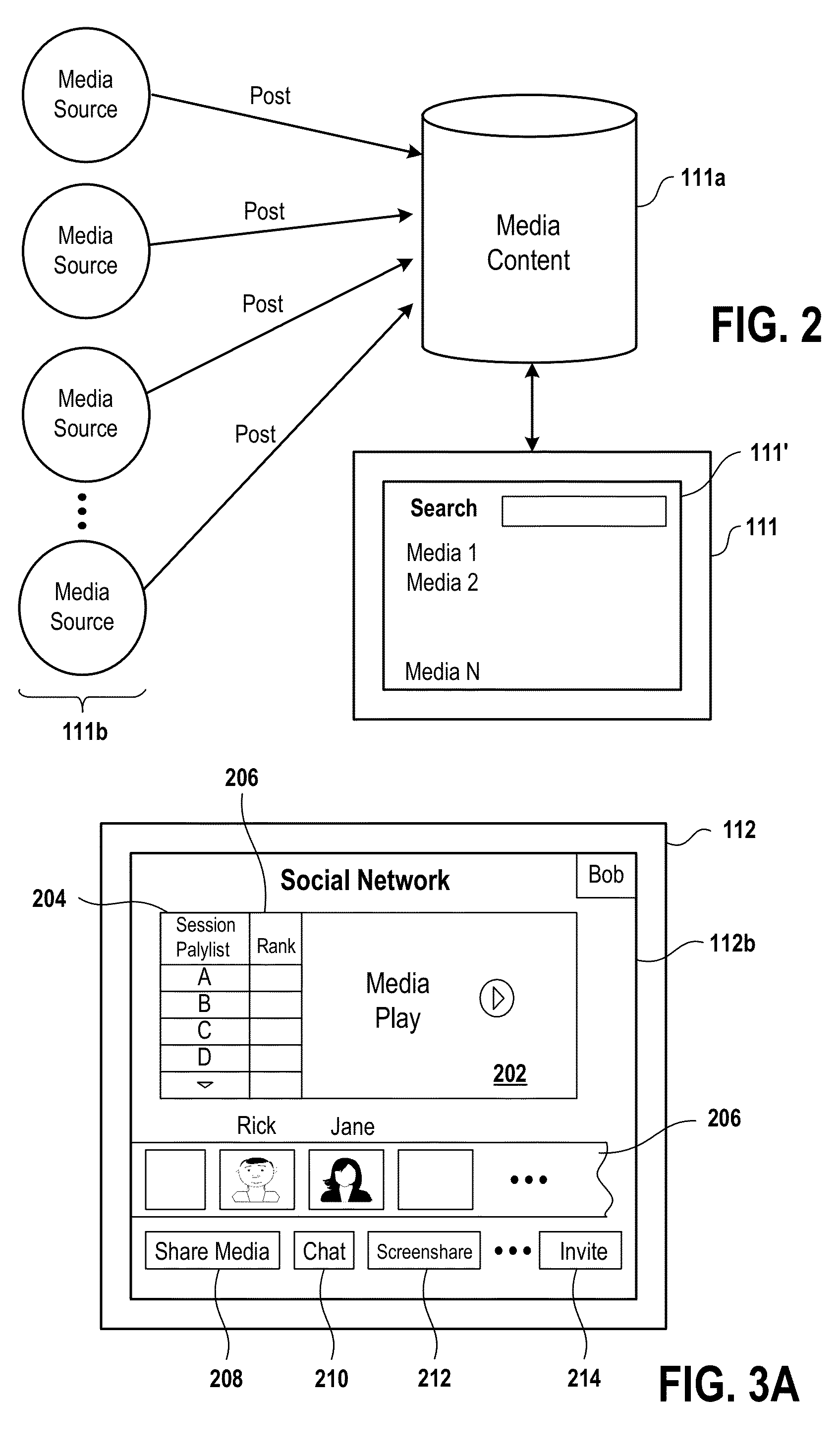
Methods and systems for ordering and voting on shared media playlists
ActiveUS20130246522A1Multiple digital computer combinationsSelective content distributionConnected deviceWorld Wide Web
Methods and systems for managing ordering of media items for play is provided. The method includes establishing a session between two or more connected devices, and receiving a request from one of the connected device to create a shared media playlist. The shared media playlist accepting addition of a plurality of media items from at least one of the connected devices. Then, collecting vote input from one or more of the connected devices. The vote input is applied to selected ones of the plurality of media items in the shared media playlist. The method processes the collected vote input to set a score for at least one of the plurality of media items. The method orders the plurality of media items in the shared media playlist, such that playing of the plurality of media items during the session follow the ordering.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
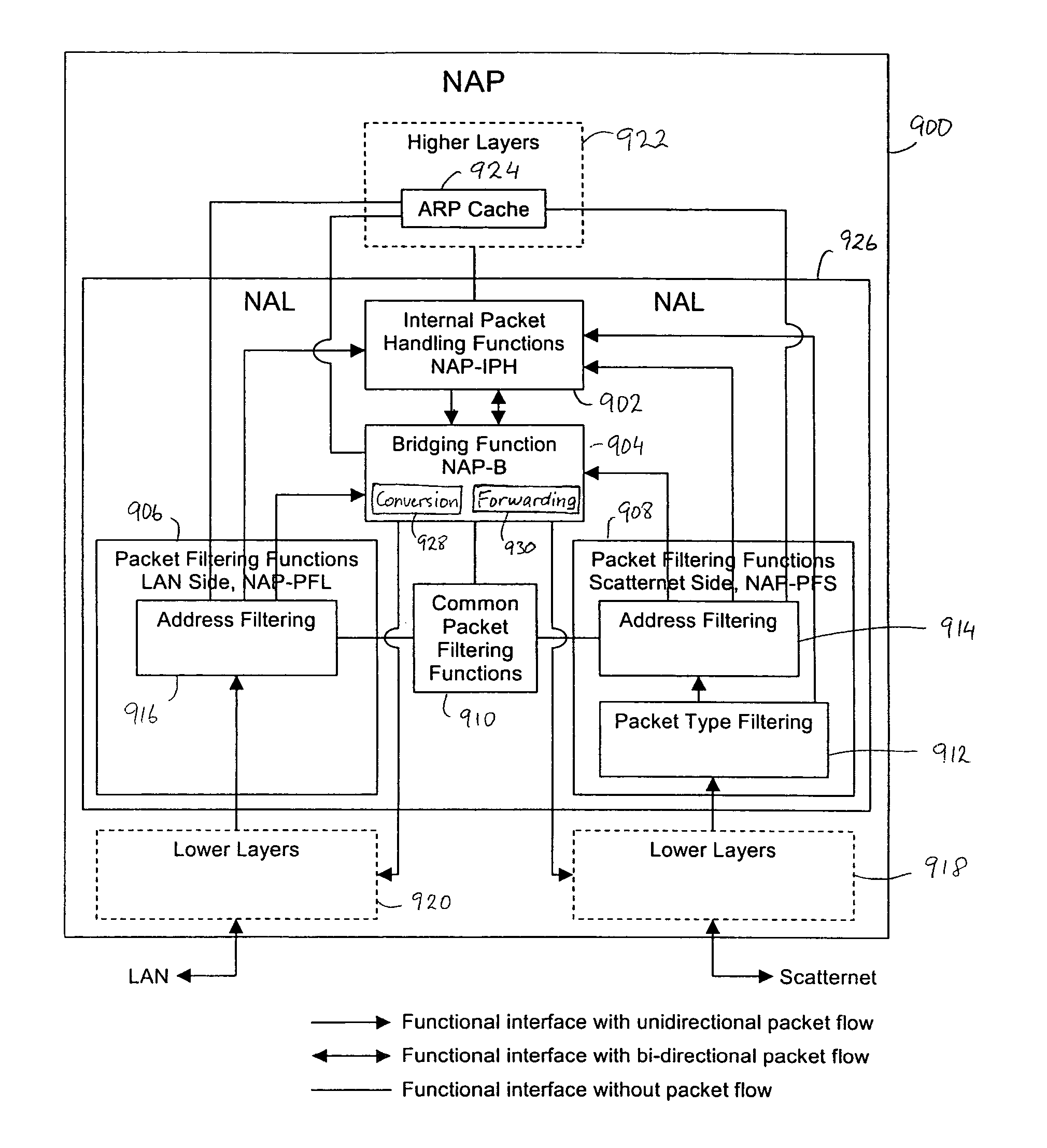
Bridging between a Bluetooth scatternet and an Ethernet LAN
InactiveUS20040167988A1Multiple digital computer combinationsNetworks interconnectionNetwork packetAdministrative domain
System and method are disclosed for bridging a point-to-point network such as a Bluetooth scatternet with a shared medium network such as an Ethernet LAN. The scatternet is connected to the LAN via a network access point (NAP). Data packets sent from the LAN to the scatternet are filtered at the NAP to eliminate unnecessary data packets from being sent to the scatternet. Only certain ones of the data packets are forwarded between the LAN and the scatternet. An inter-NAP protocol is used to exchange messages where two or more NAPs are connected to the LAN. Broadcast loops are prevented from occurring in the scatternet and the LAN by defining Administrative domains and NAP service areas (NAPSAs), and controlling the borders thereof according to a broadcast type of the data packets.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
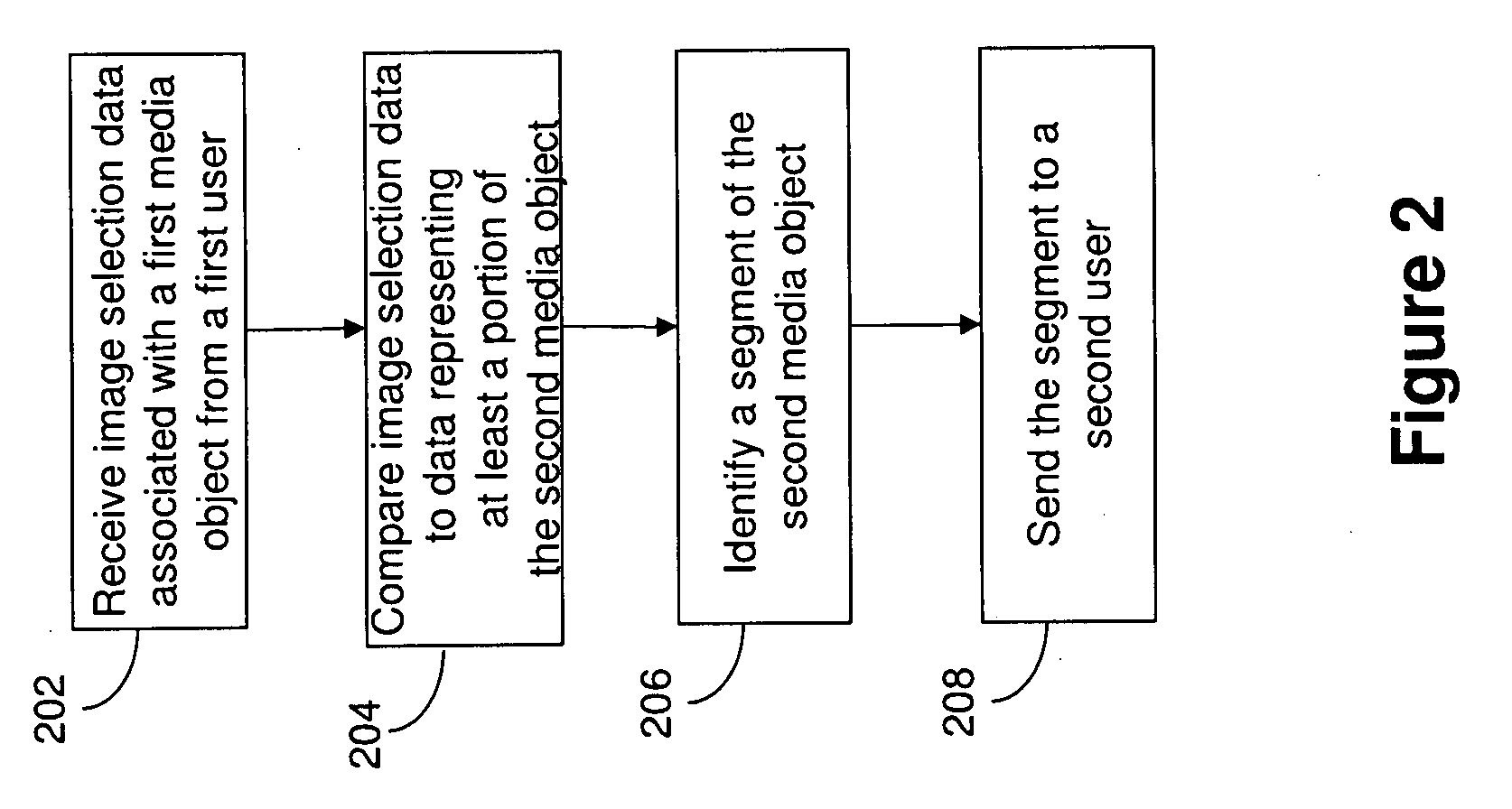
Identification and transfer of a media object segment from one communications network to another
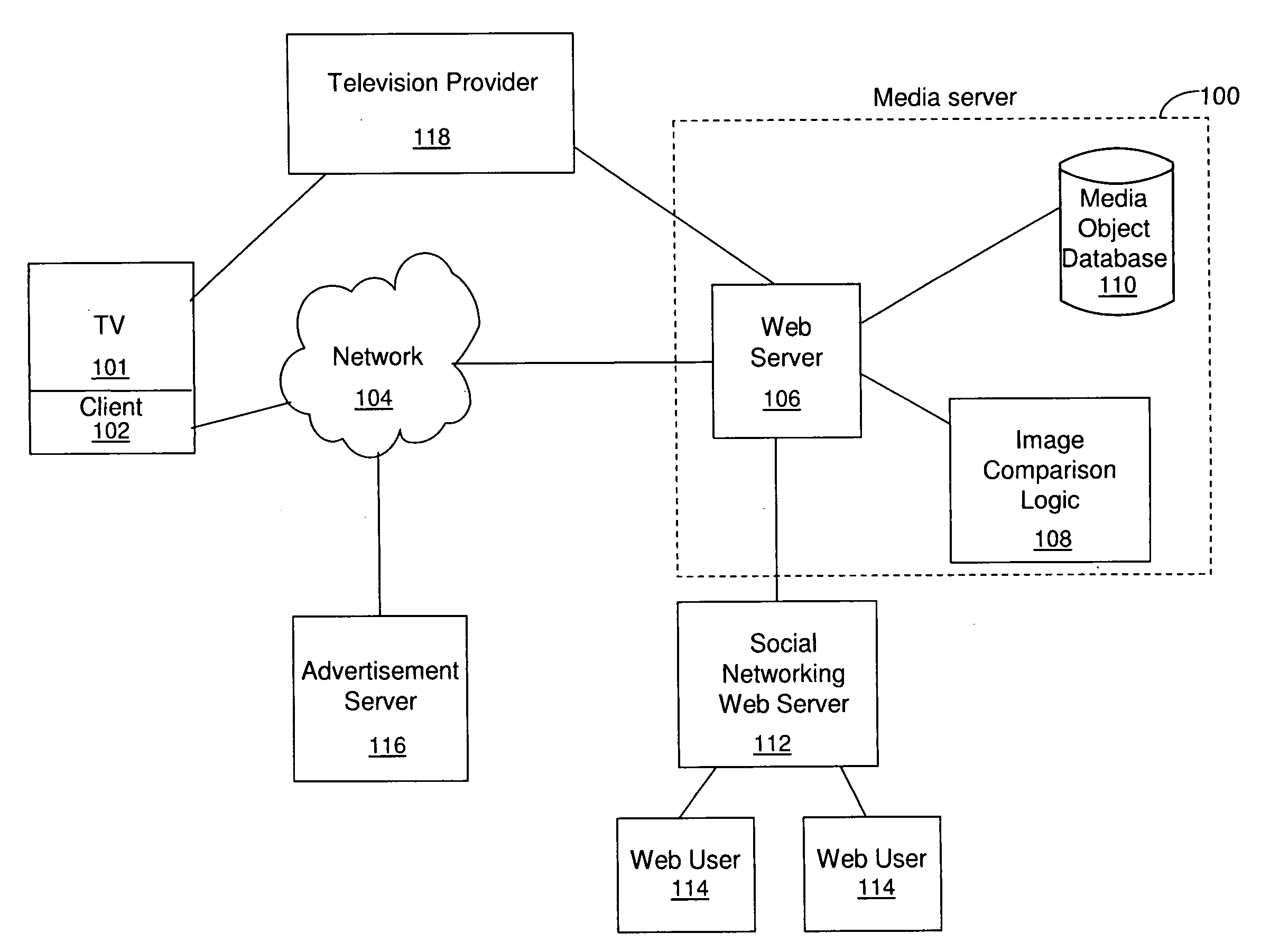
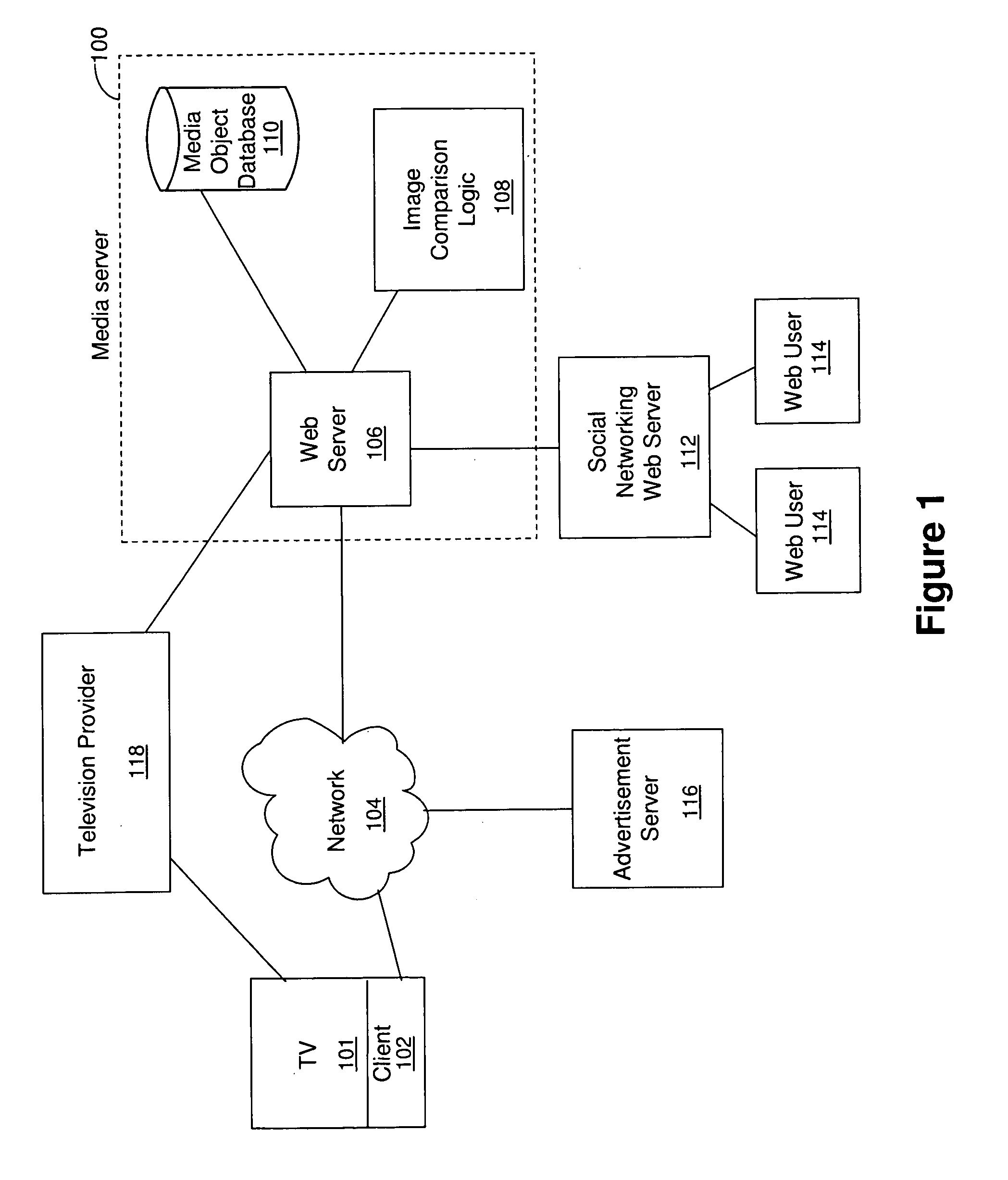
InactiveUS20100158391A1Digital data information retrievalElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsMedia serverShared medium
Technology for sharing media objects includes receiving image selection data associated with a first media object, where the first media object is a television broadcast video. A media server maybe included for storing a second media object. In one embodiment, the second media object is a recording of the broadcast of the first media object. In another embodiment, the second media object may be loaded into a media object database within the media server separate from the television broadcast. The media server may then identify a segment of the second media object by comparing the image selection data with data representing at least a portion of the second media object. The media server may then send the segment to a second user. In one embodiment, sending the segment to a second user may include sending a web-link reference to the segment. The media server may also send or cause the transmission of advertising data related to the image selection data.
Owner:OATH INC
Remote interface optical network
InactiveUS20050044186A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision conference systemsEncoder decoderTransport medium
A remote interface network in which multiple remote HID encoder / decoder units share a common physical transport medium for connecting to one or more processing unit encoder / decoders is described. In one embodiment, the physical transport medium includes an optical shared media transport network. Each remote HID encoder / decoder unit can support one or more remote HIDs. The processing unit encoder / decoder can support one or more Pus. The network can be used, for example, in office, hospital, dense seat (e.g., aircraft, bus, etc.) and content provider networks.
Owner:GLOBAL EAGLE ENTERTAINMENT
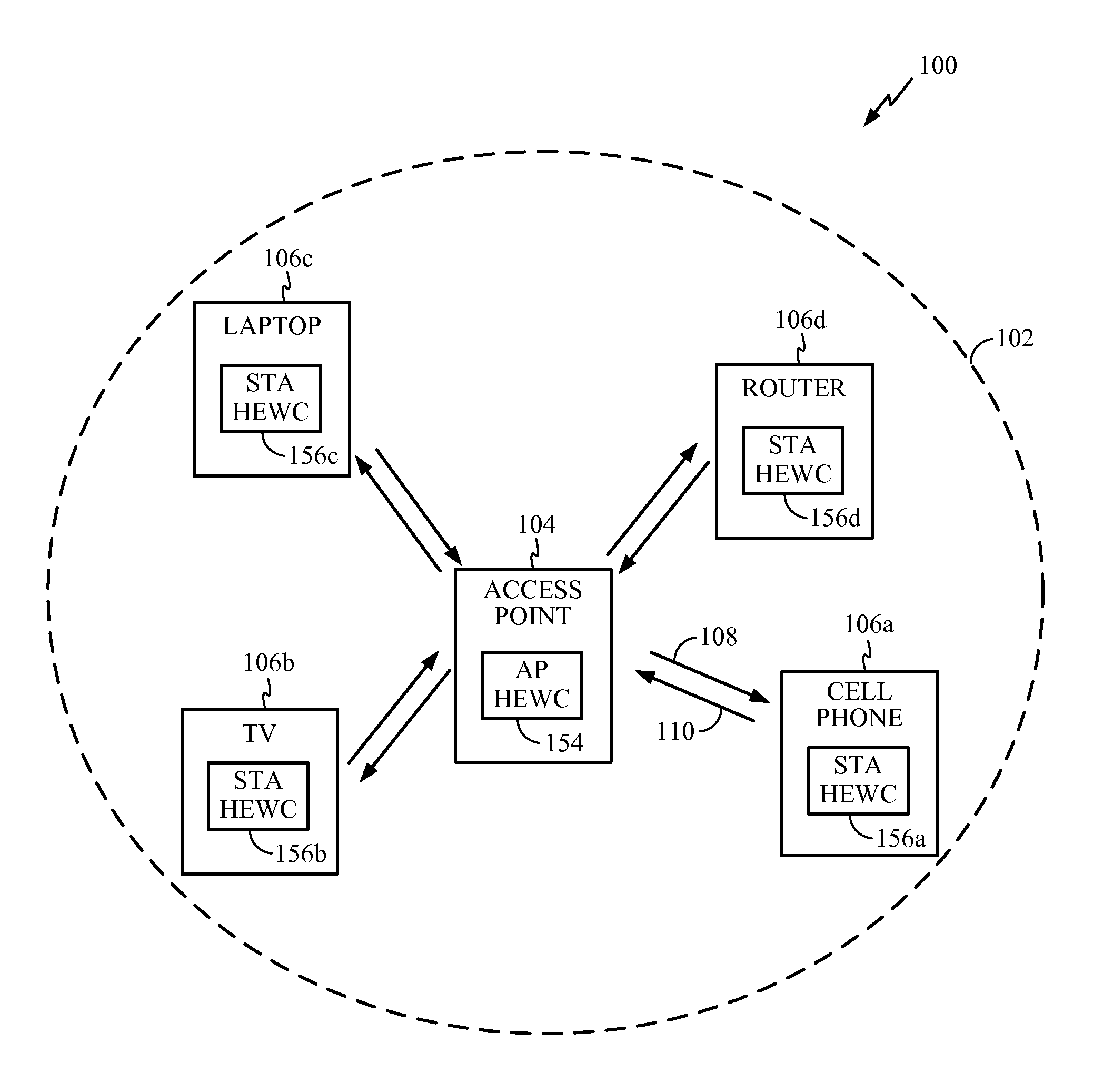
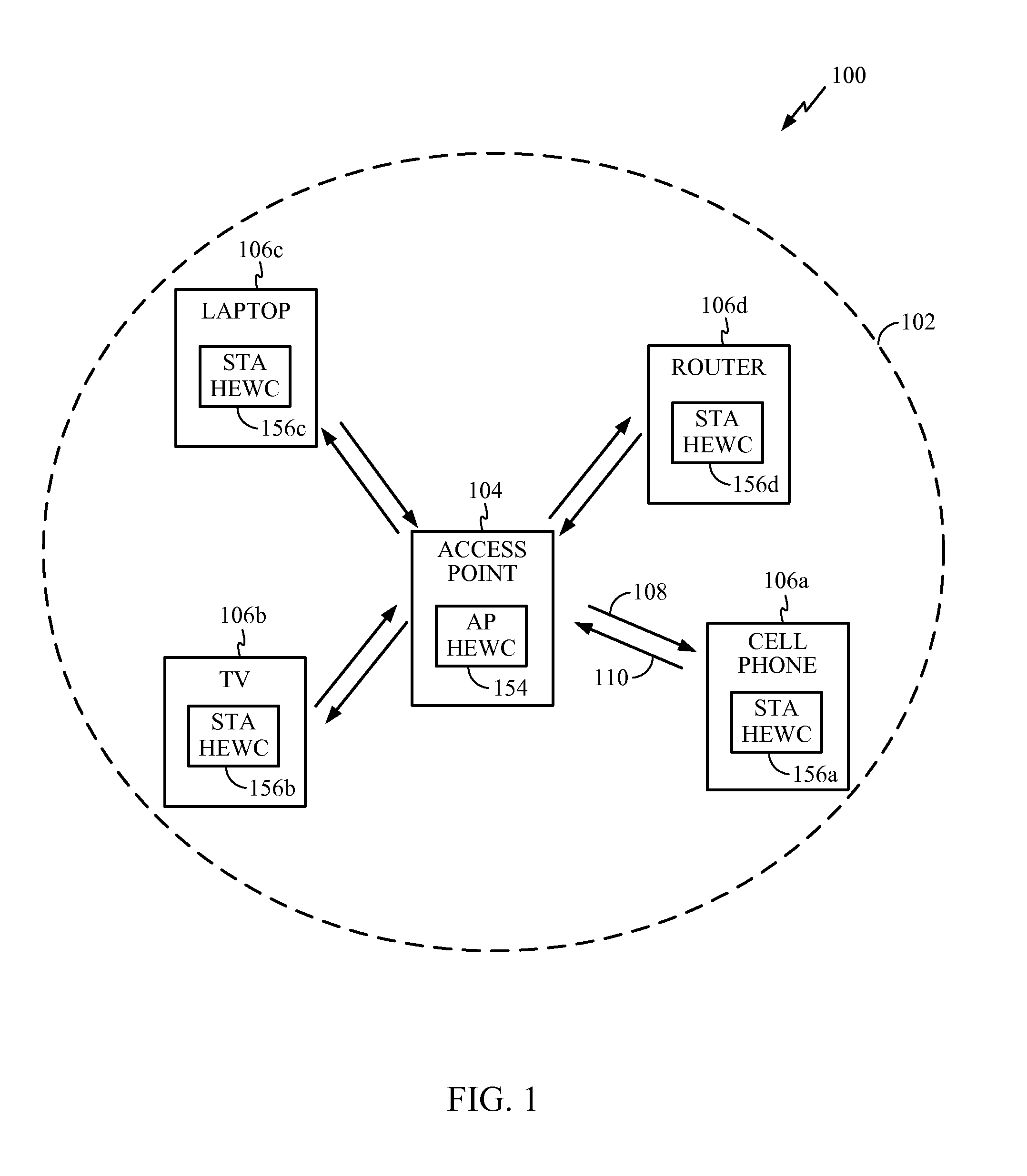
High efficiency wireless (HEW) access point (AP) coordination protocol
InactiveUS20150063327A1Facilitate communicationSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexComputer scienceShared medium
Systems, methods, and devices for high efficiency wireless (HEW) access point (AP) coordination protocol are described herein. According to certain aspects, a method for coordinating access to a shared medium by an access point (AP) is provided. The method generally synchronizing with one or more peer apparatuses based on synchronization messages detected during a listening time, outputting, for transmission, scheduling information to the one or more peer apparatuses, the scheduling information indicating one or more time periods during which coordinated access to the shared medium is desired, and outputting, for transmission, at least some of the scheduling information to devices served by the apparatus.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
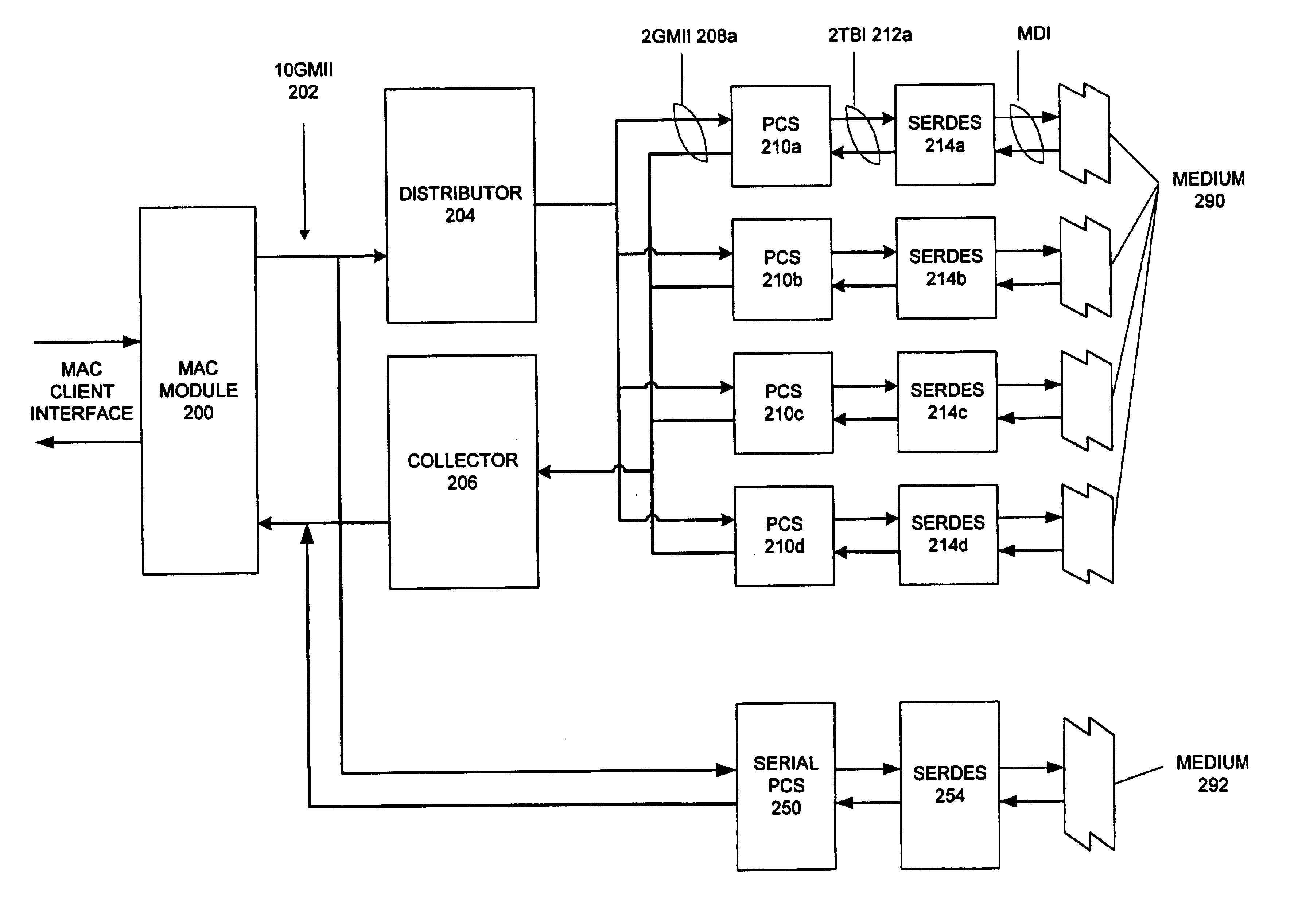
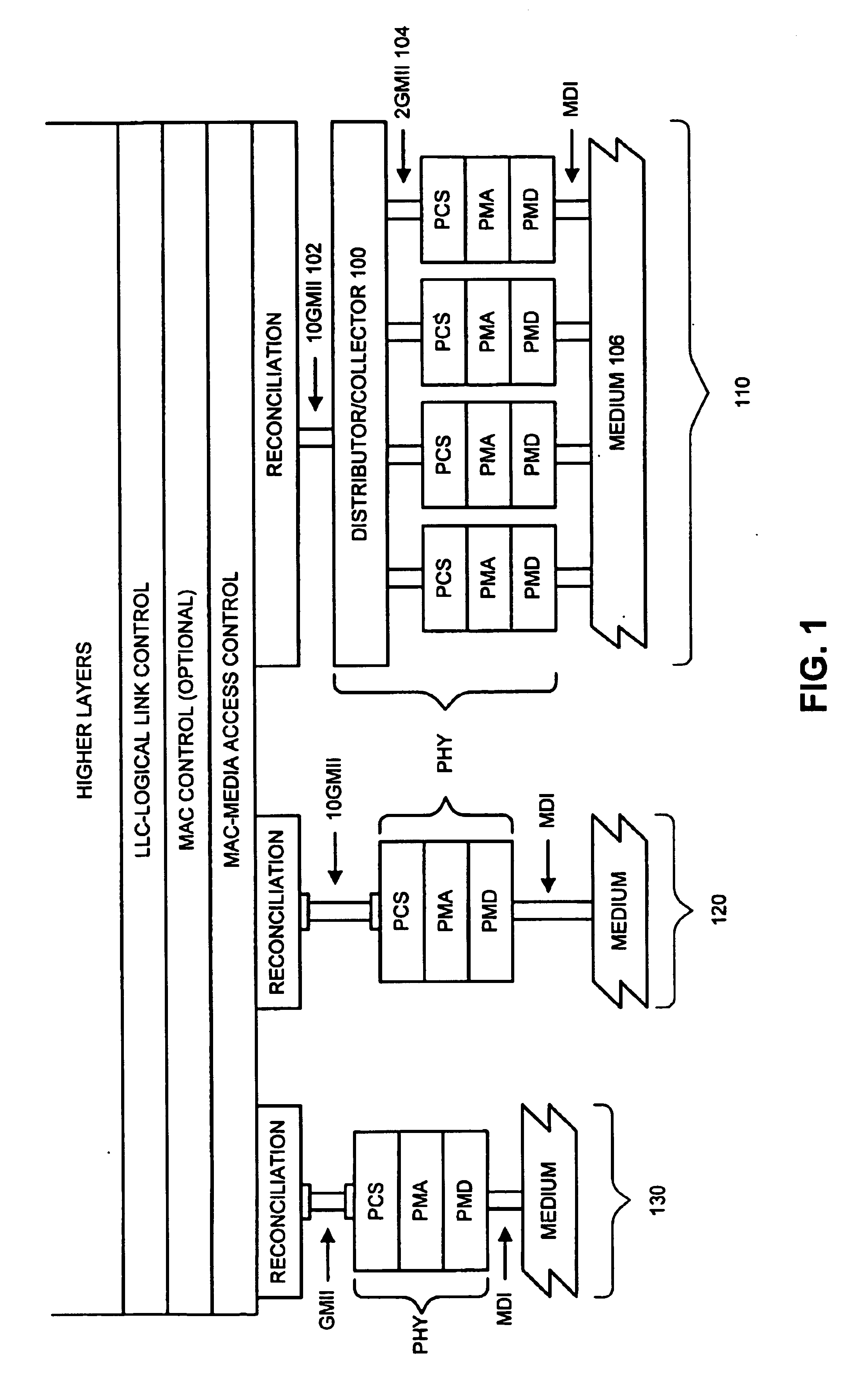
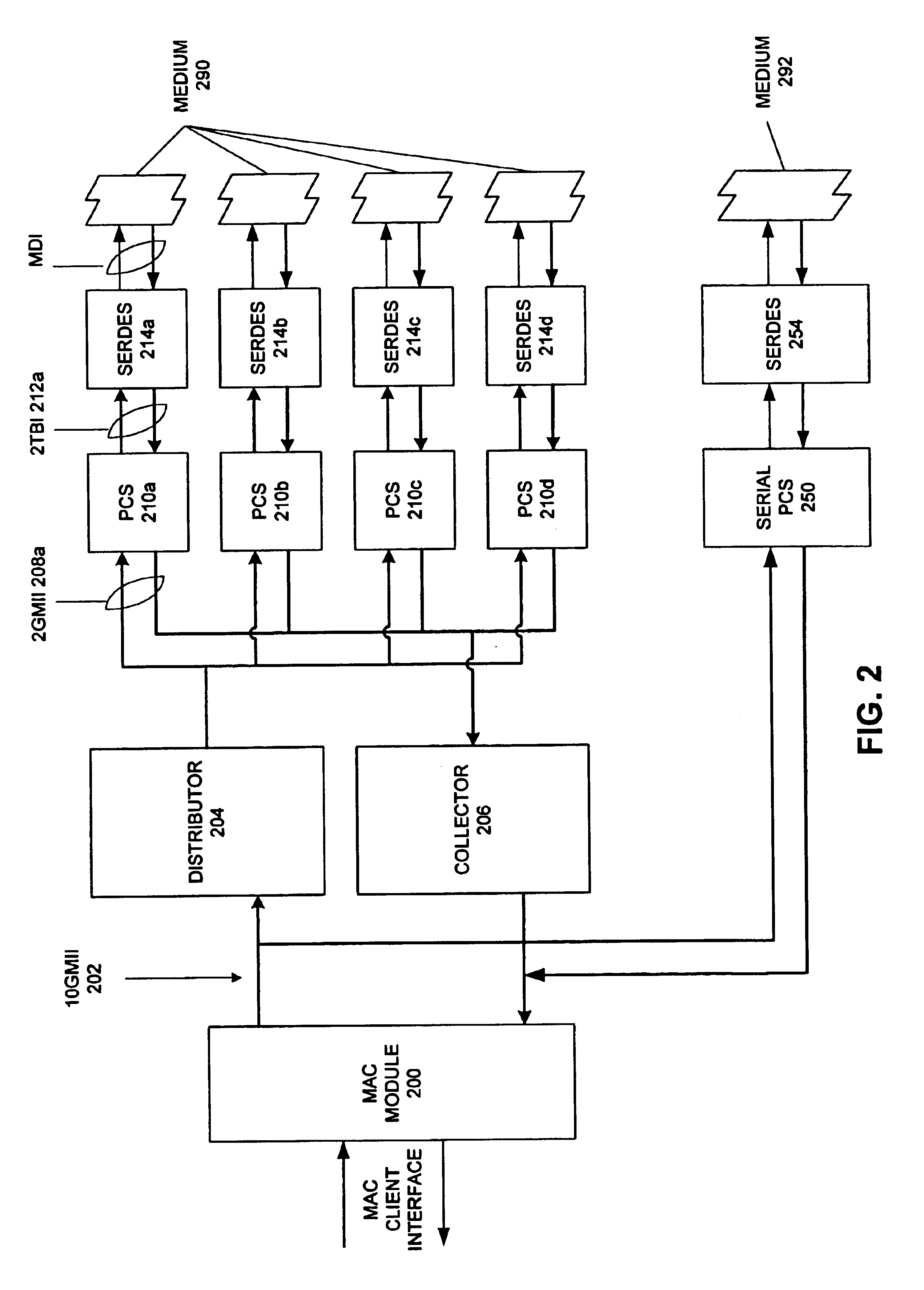
Method and apparatus for a multi-gigabit ethernet architecture
InactiveUS6873630B1Communication speed be lowerTime-division multiplexNetwork connectionsMultiplexingPropagation delay
An Ethernet architecture is provided for connecting a computer system or other network entity to a dedicated Ethernet network medium. The network interface enables the transmission and receipt of data by striping individual Ethernet frames across a plurality of logical channels and may thus operate at substantially the sum of the individual channel rates. Each channel may be conveyed by a separate conductor (e.g., in a bundle) or the channels may be carried simultaneously on a shared medium (e.g., an electrical or optical conductor that employs a form of multiplexing). On a sending station, a distributor within the sender's network interface receives Ethernet frames (e.g., from a MAC) and distributes frame bytes in a round-robin fashion on the plurality of channels. Each “mini-frame” is separately framed and encoded for transmission across its channel. On a receiving station, the receiver's network interface includes a collector for collecting the multiple mini-frames (e.g., after decoding) and reconstructing the frame's byte stream (e.g., for transfer to the receiver's MAC). The first and last bytes of each frame and mini-frame are marked for ease of recognition. Multiple unique idle symbols may be employed for transmission during inter-packet gaps to facilitate the collector's synchronization of the multiple channels and / or enhance error detection. A maximum channel skew is specified, and each received channel may be buffered with an elasticity that is proportional to the maximum skew so that significant propagation delay may be encountered between channels without disrupting communications.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
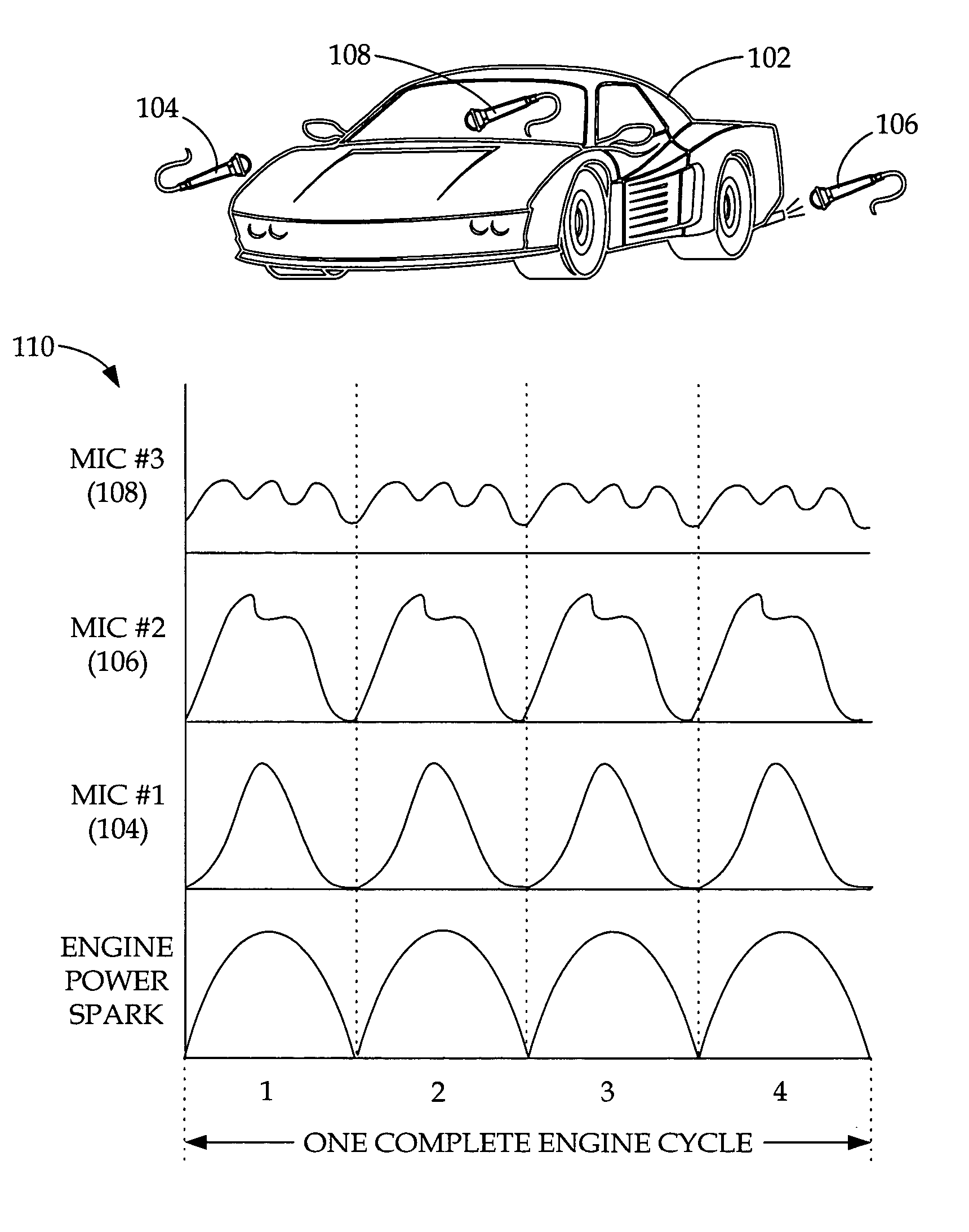
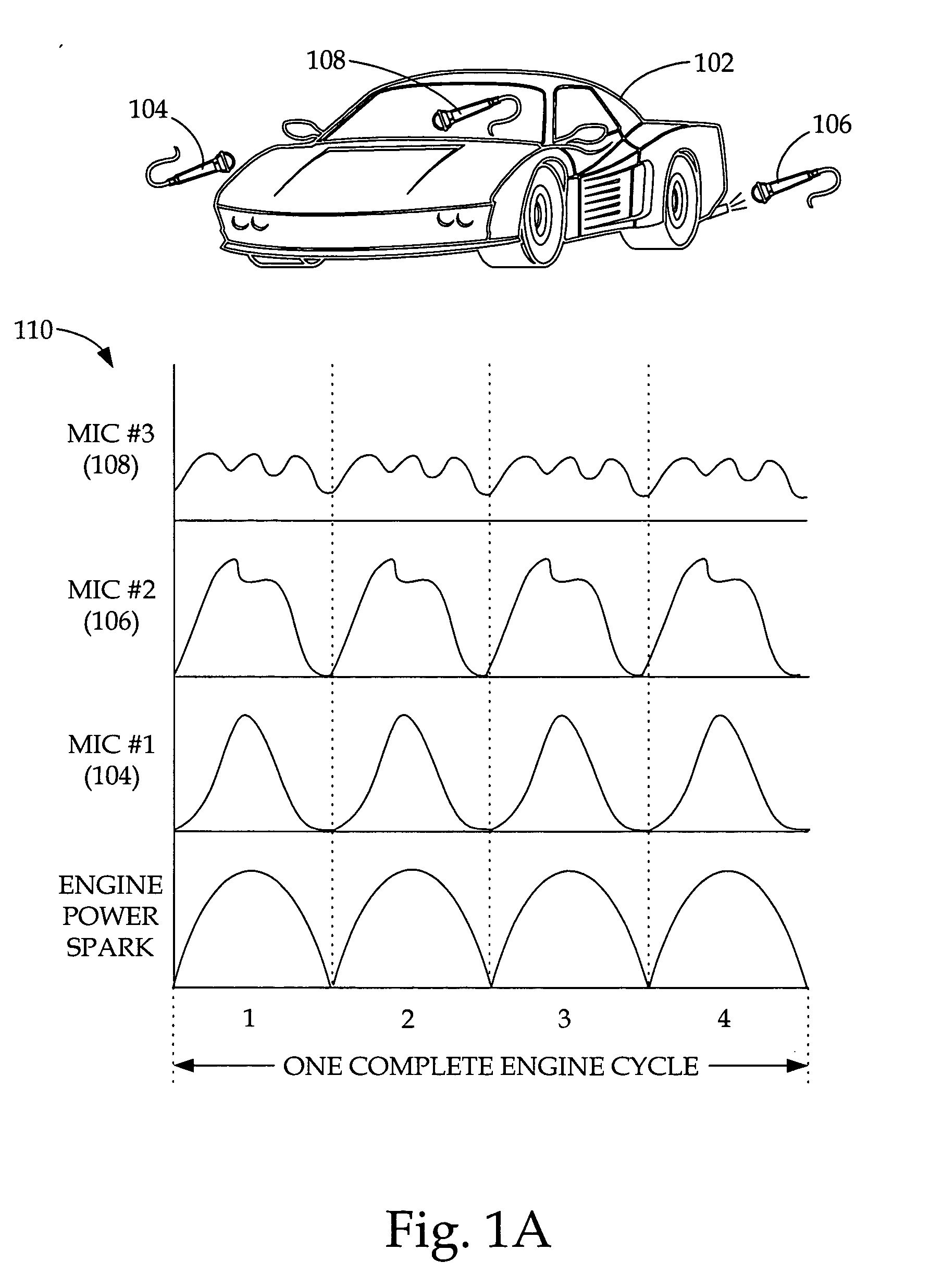
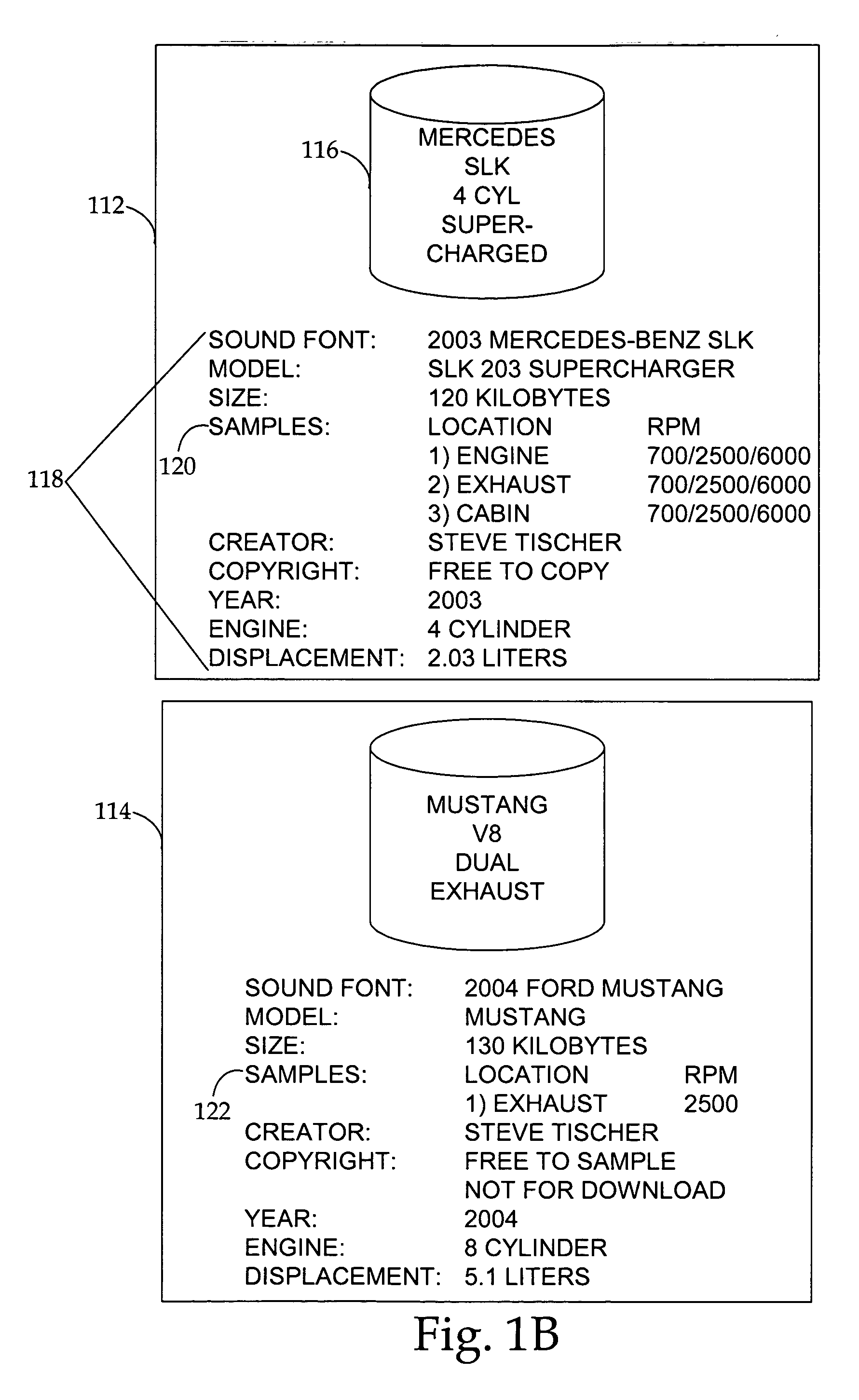
System and methods for vehicle sound font creation, playback, and networking
InactiveUS20060074645A1Augment the engine sounds of a vehicleSimulate the realGain controlPublic address systemsControl mannerShared medium
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com