Patents
Literature
941 results about "Address Resolution Protocol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
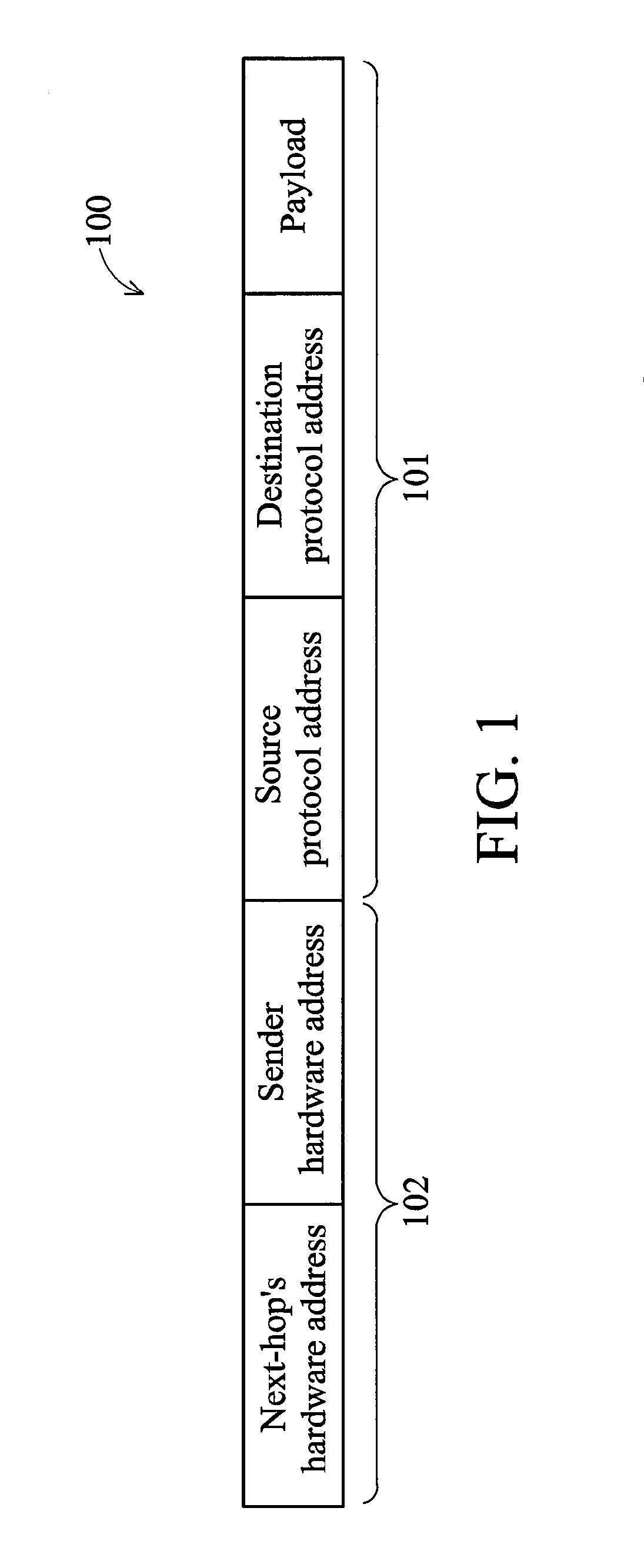
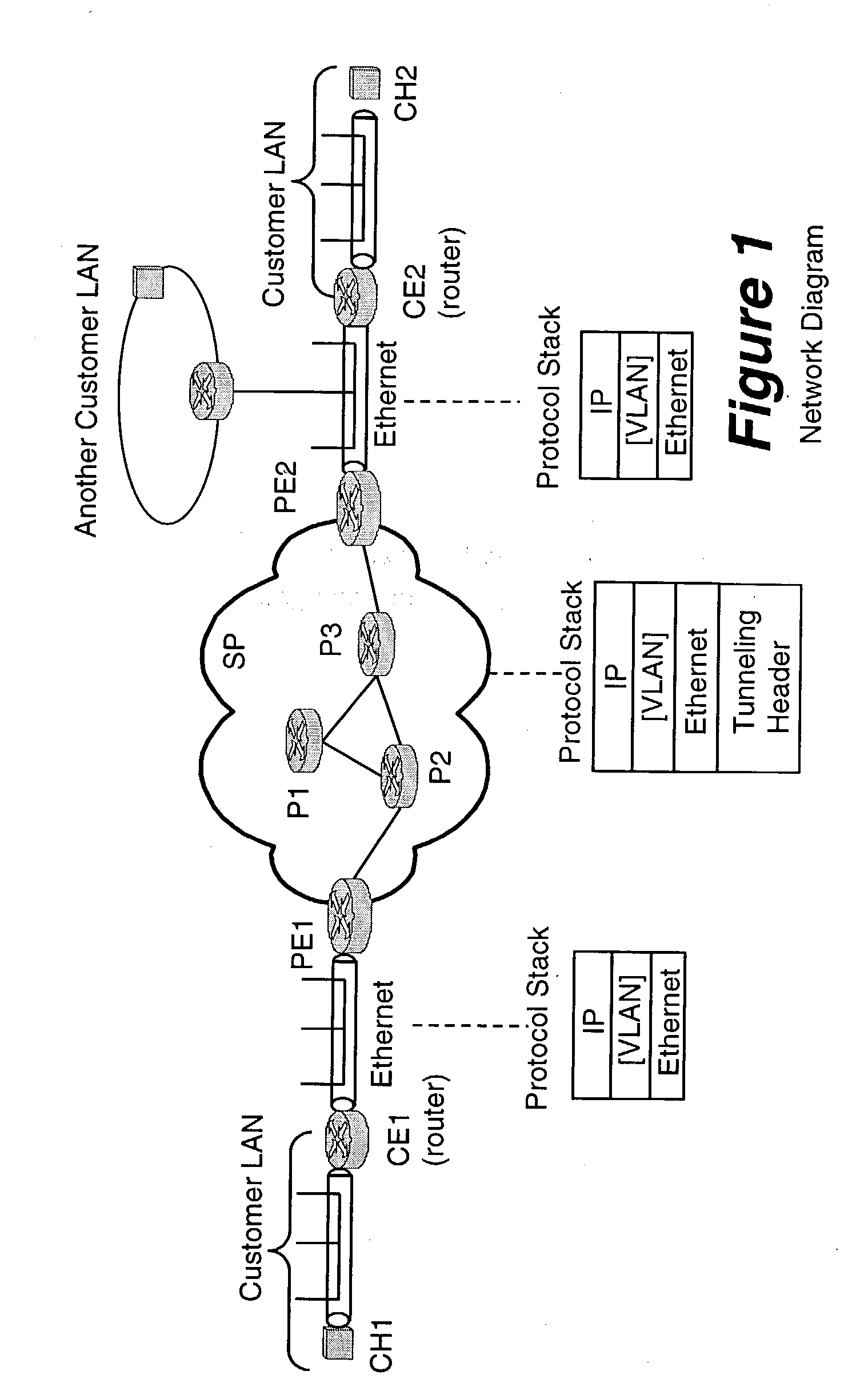
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a communication protocol used for discovering the link layer address, such as a MAC address, associated with a given internet layer address, typically an IPv4 address. This mapping is a critical function in the Internet protocol suite. ARP was defined in 1982 by RFC 826, which is Internet Standard STD 37.
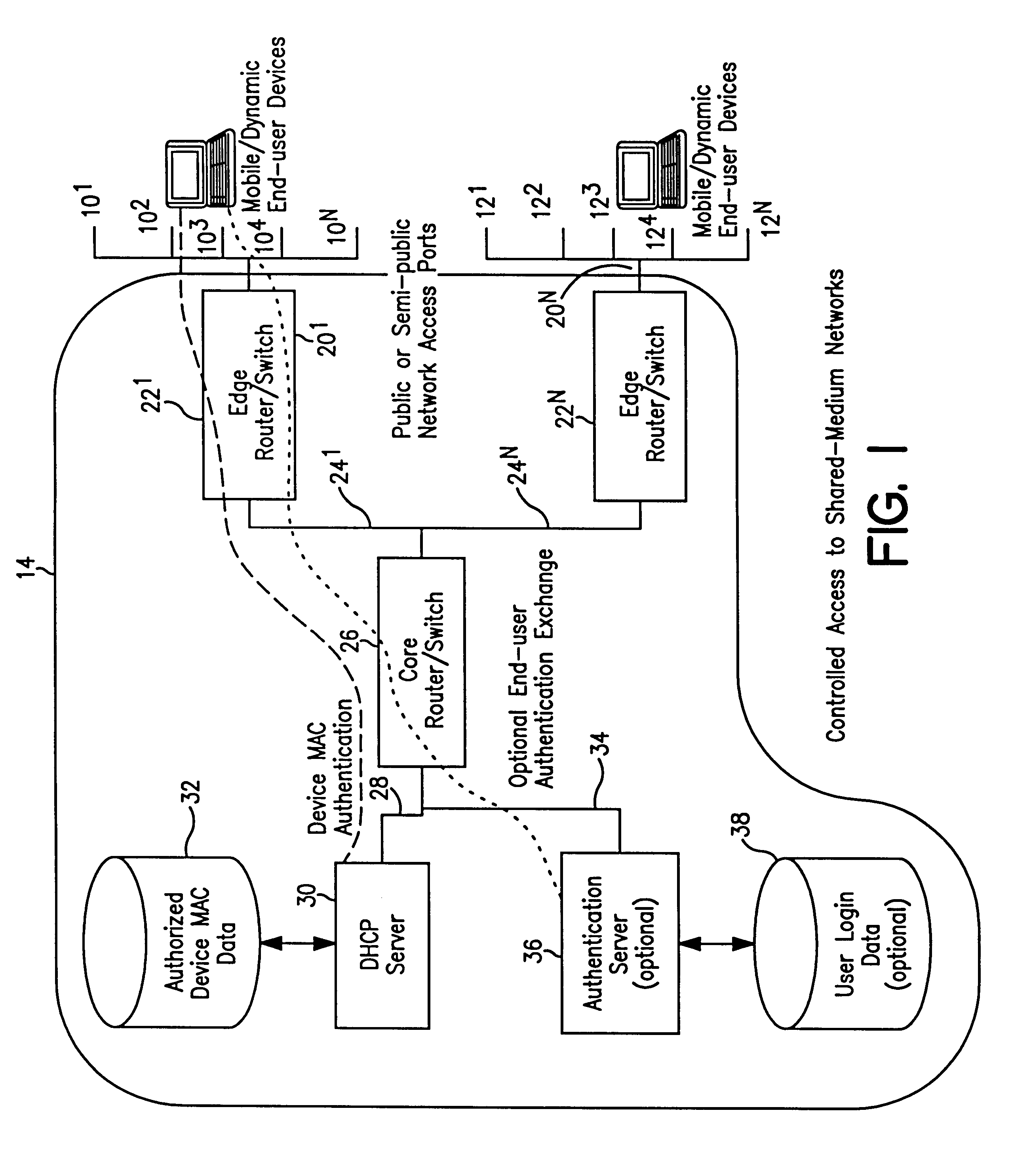
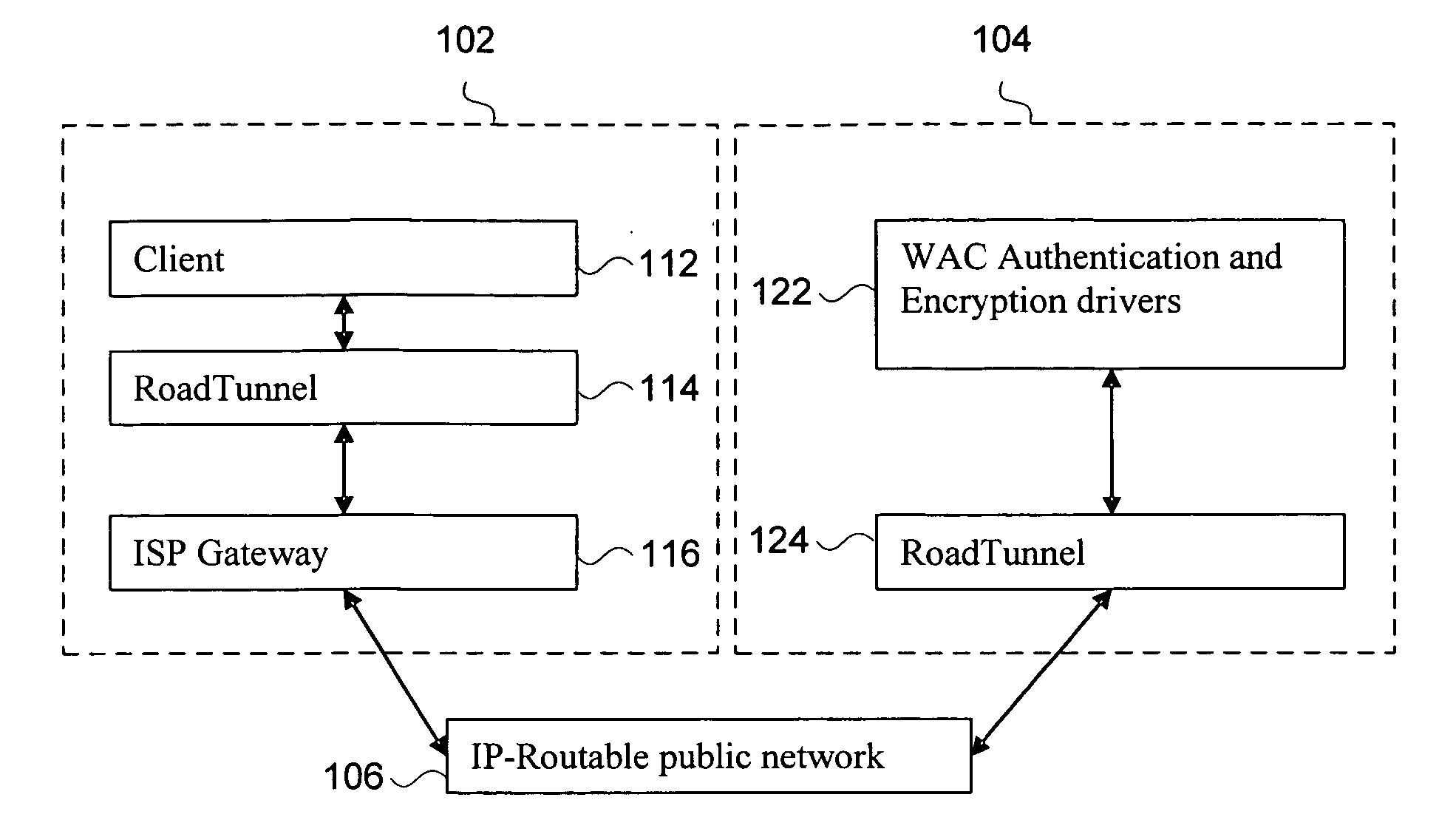
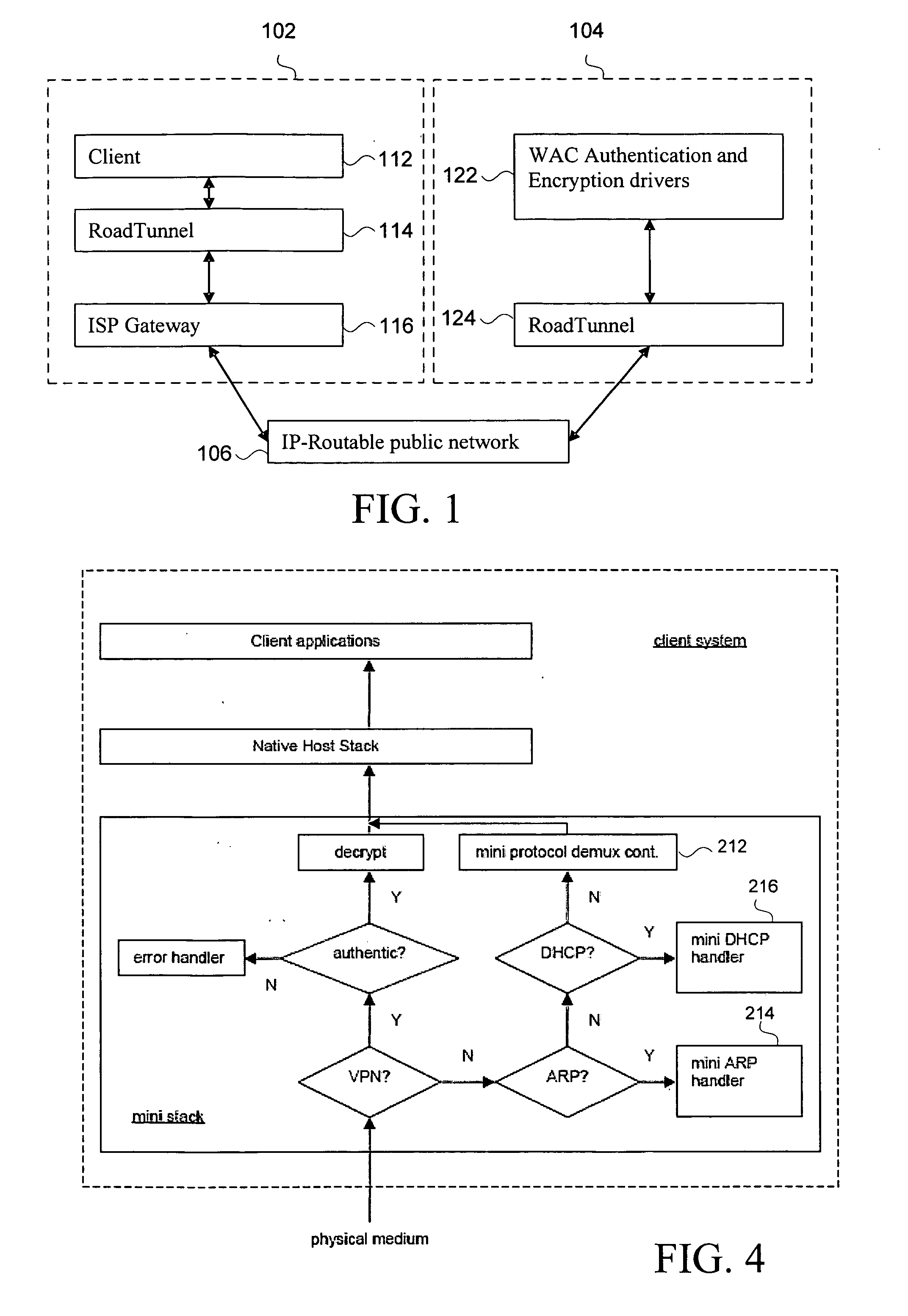
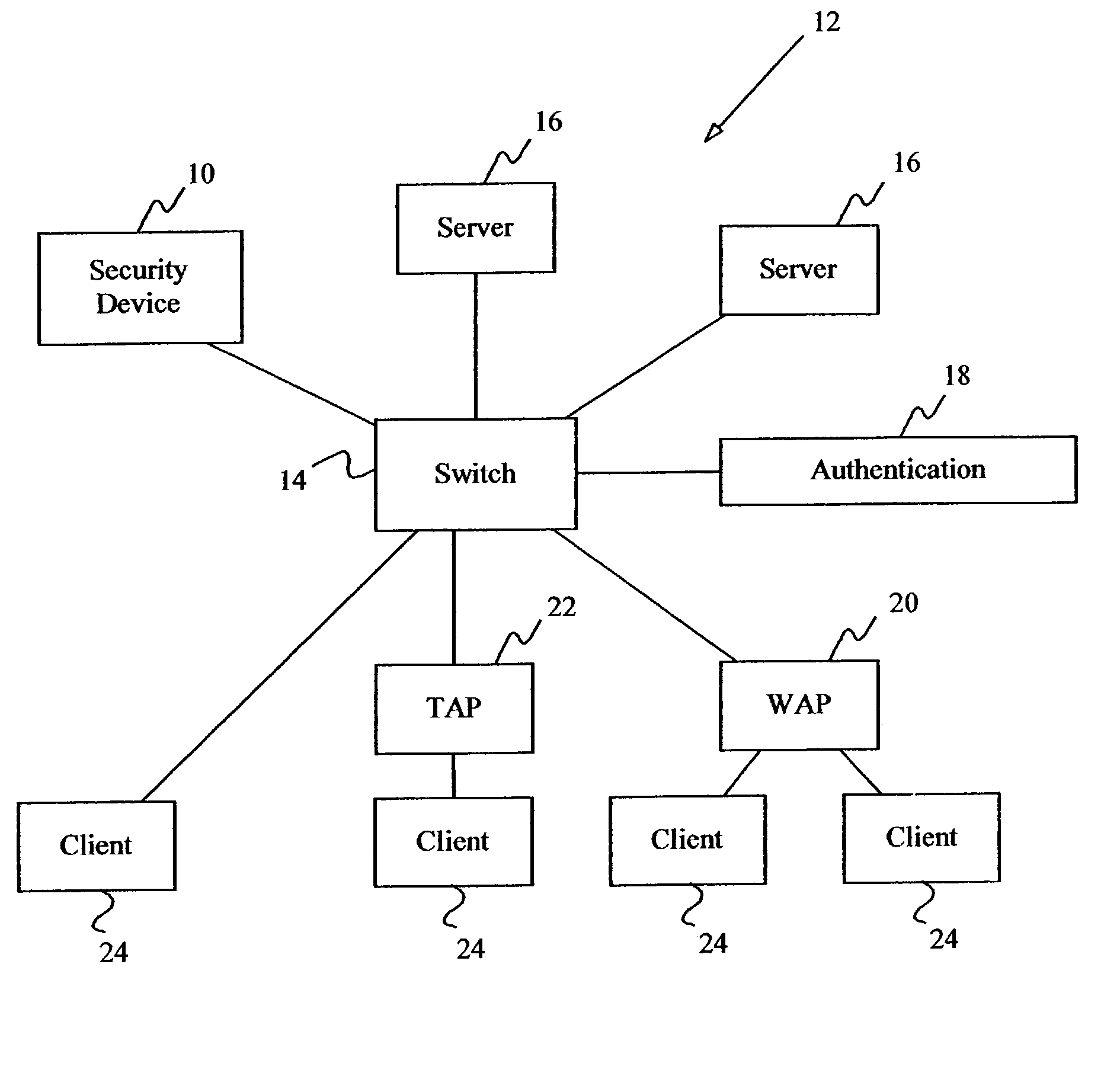
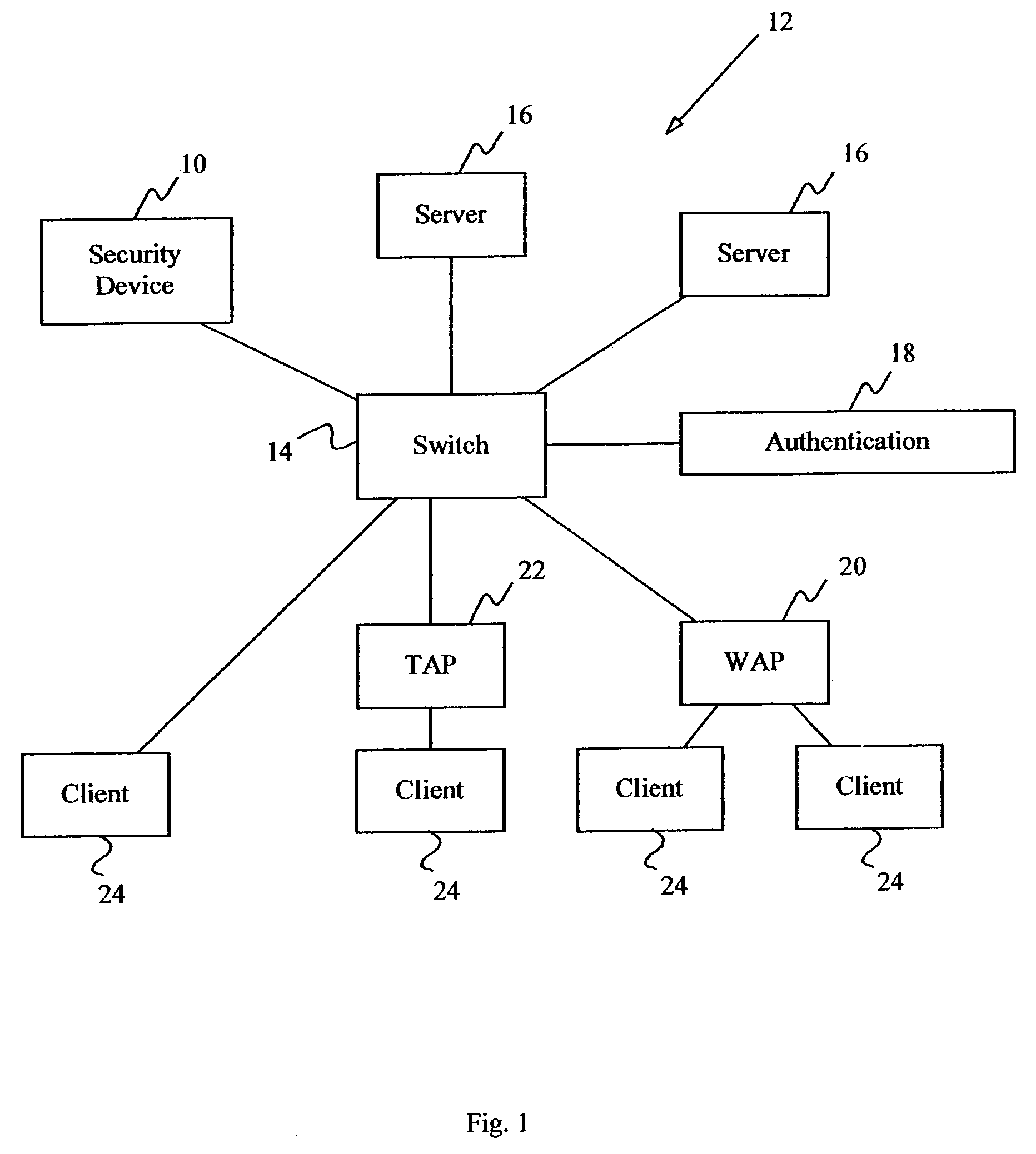
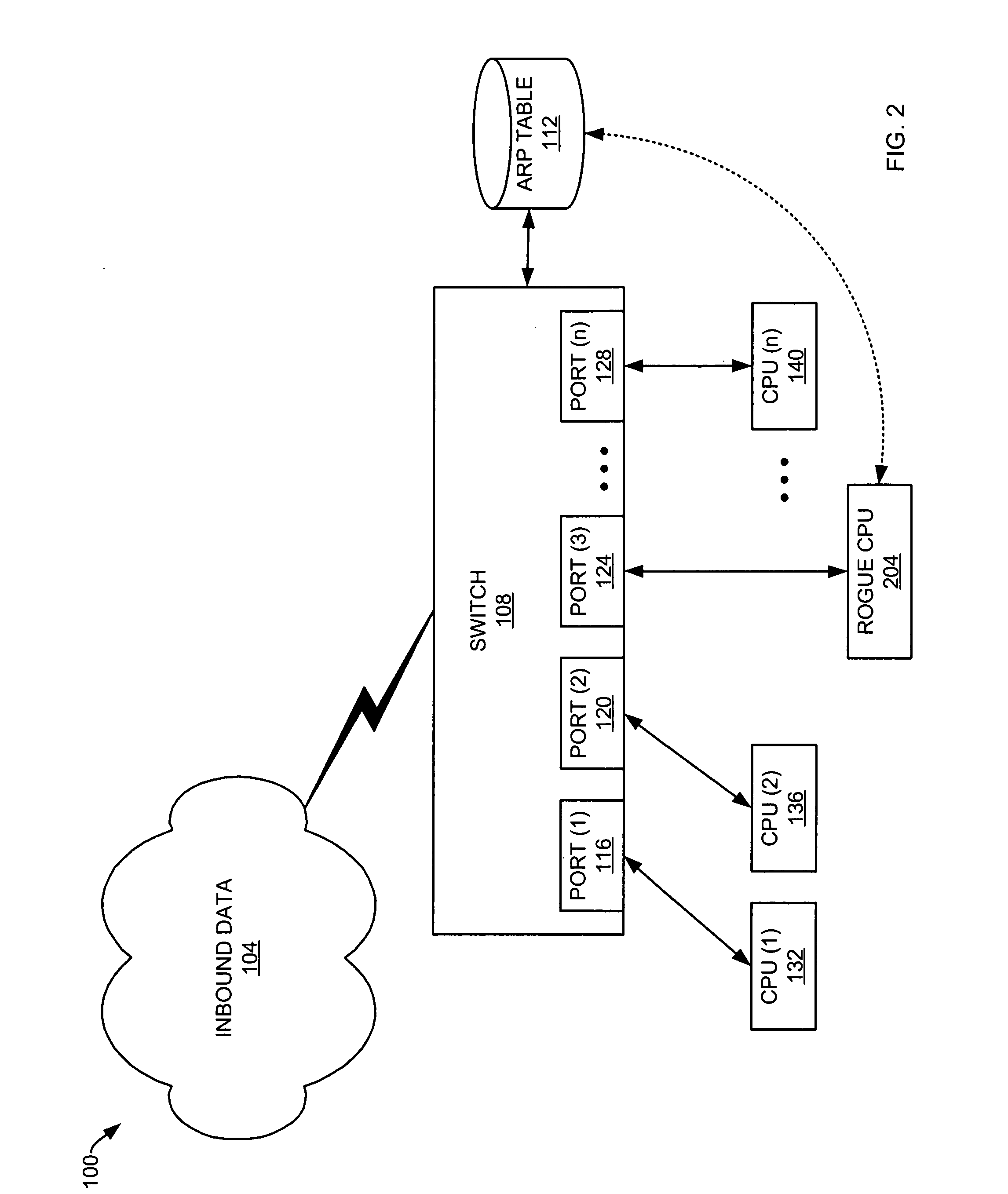
System and method for controlled access to shared-medium public and semi-public internet protocol (IP) networks
InactiveUS6393484B1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionAddress Resolution ProtocolDevice register
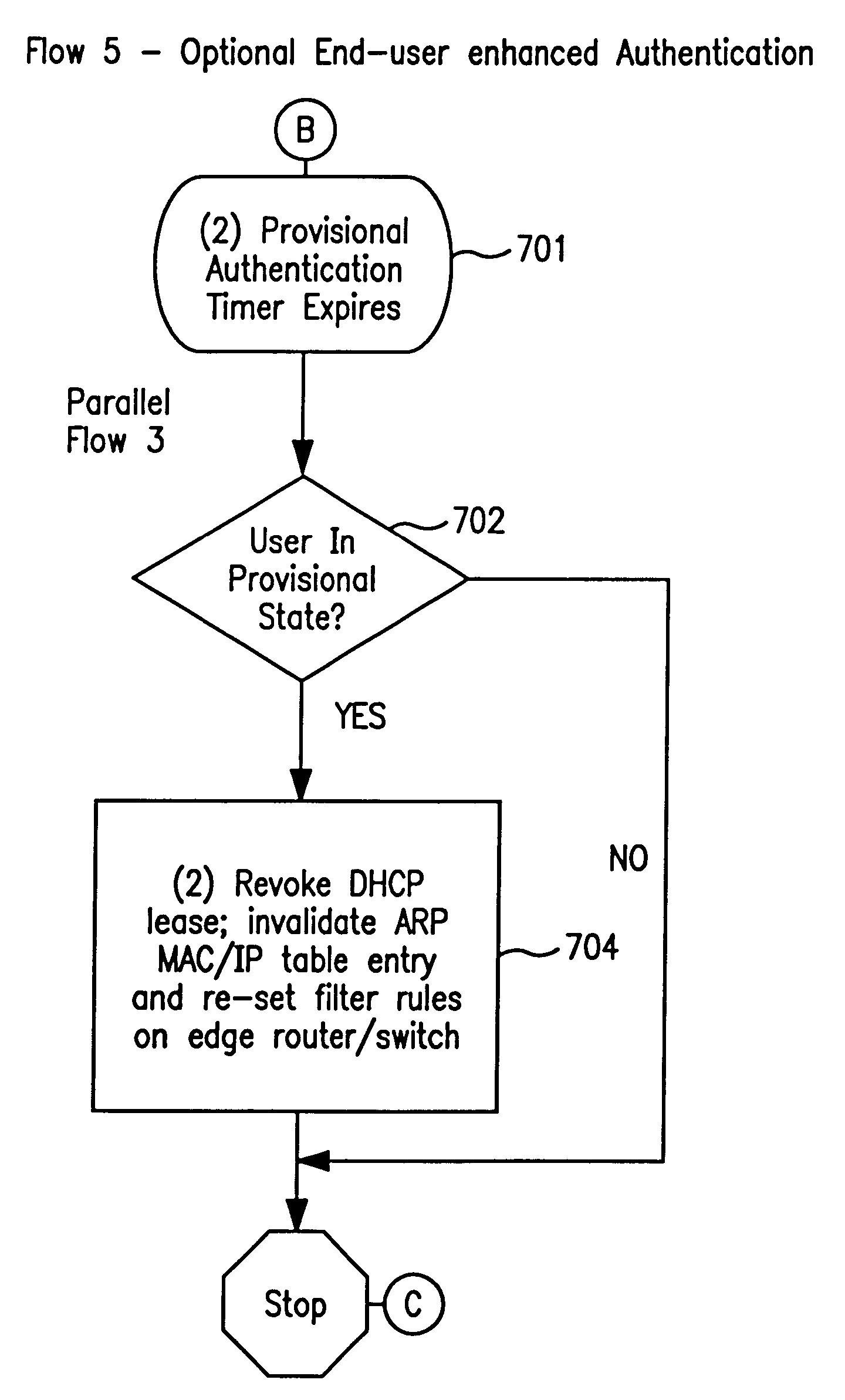
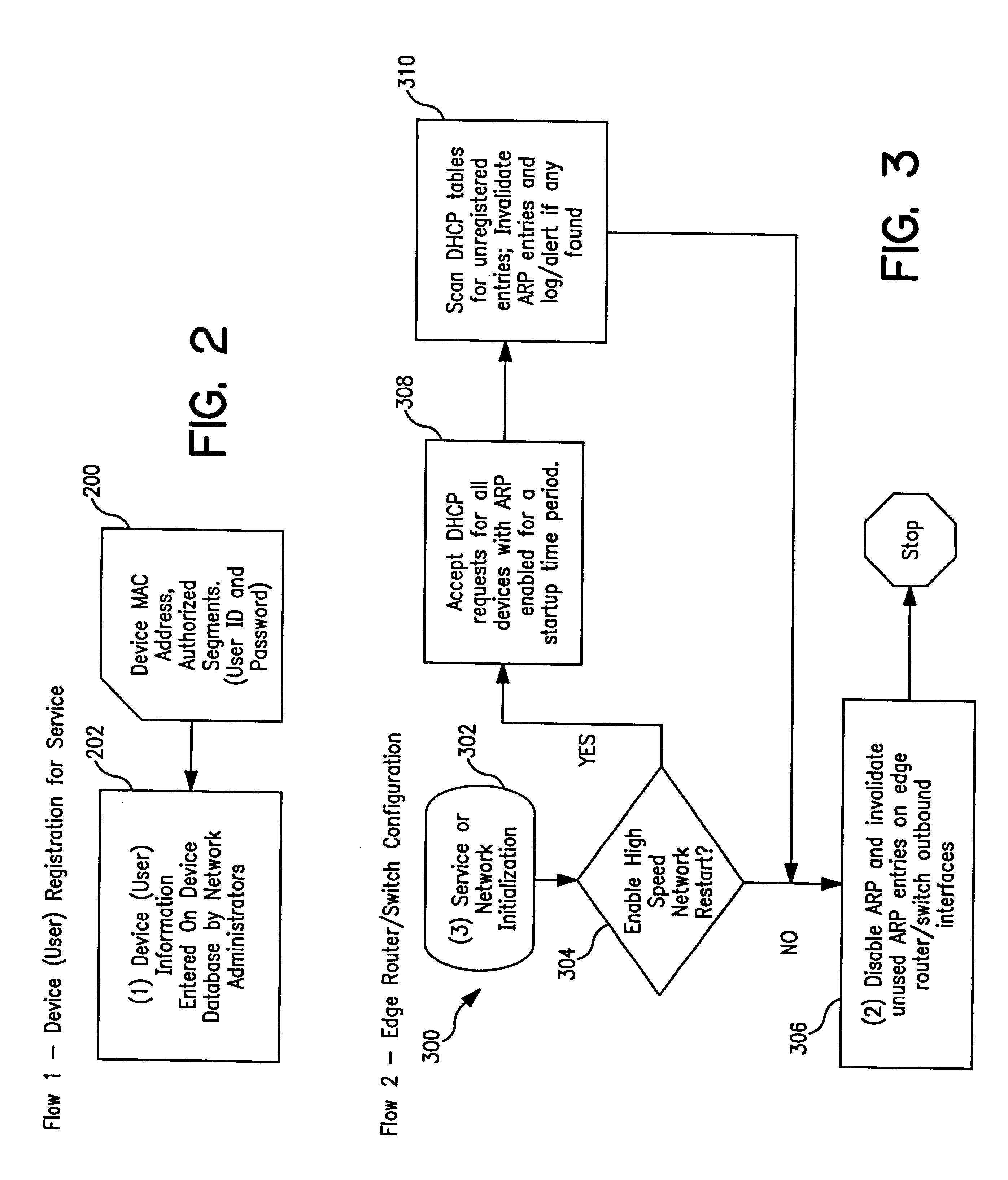
A system and method prevent unauthorized users and devices, in a dynamic user / device environment, from obtaining access to shared-medium public and semi-public IP networks. A network includes a layered communication system and routers / switches for coupling users and devices to a Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) server and an authentication server. Databases support the servers. The network incorporates Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). Authorized users and devices register for service by providing the DHCP with user identification for log-in, passwords, MAC addresses, etc. When users connect to the network access point, a DHCP exchange is initiated to obtain a valid IP address and other associated parameters. The DHCP client initiates a MAC broadcast for IP addresses which contain in the request the end user's device MAC address. The associated router switch will pick up and forward to a DHCP server the end user's device request. The DHCP server will process the end user's request and extract the end user's device MAC address. With the end user's MAC address, the DHCP server accesses its device and / or user information in the database. If the MAC address is not registered, the DHCP server refuses to handle the request and logs the attempt, potentially alerting network operators of a security breach. If the MAC address is registered, a DHCP server selects an appropriate IP address and associated parameters to be returned to the requesting end user and connects via programming or command interface to the router switch that is forwarding the DHCP request on behalf of the end user device. The server adds an ARP IP to the MAC address table entry with the selected IP address and end user's MAC address. End user device authentication and IP lease are marked as provisional. A timer is started for a suggested duration. Optionally, the DHCP dynamically sets up filter rules in the router switch limiting access to a subset of IP addresses such as the address of a log-in server. Initial DHCP processing is completed and an IP address is assigned to the requesting end user's device by DHCP. When the timer expires, if the DHCP server finds the authenticating user state is provisional, it will revoke the IP lease, invalidate the corresponding ARP to MAC table entry in the associated router switch, and reset any IP-permissive filtering for that device. If the user is in the full authenticated state, it will simply remove the restrictive filtering.
Owner:IBM CORP
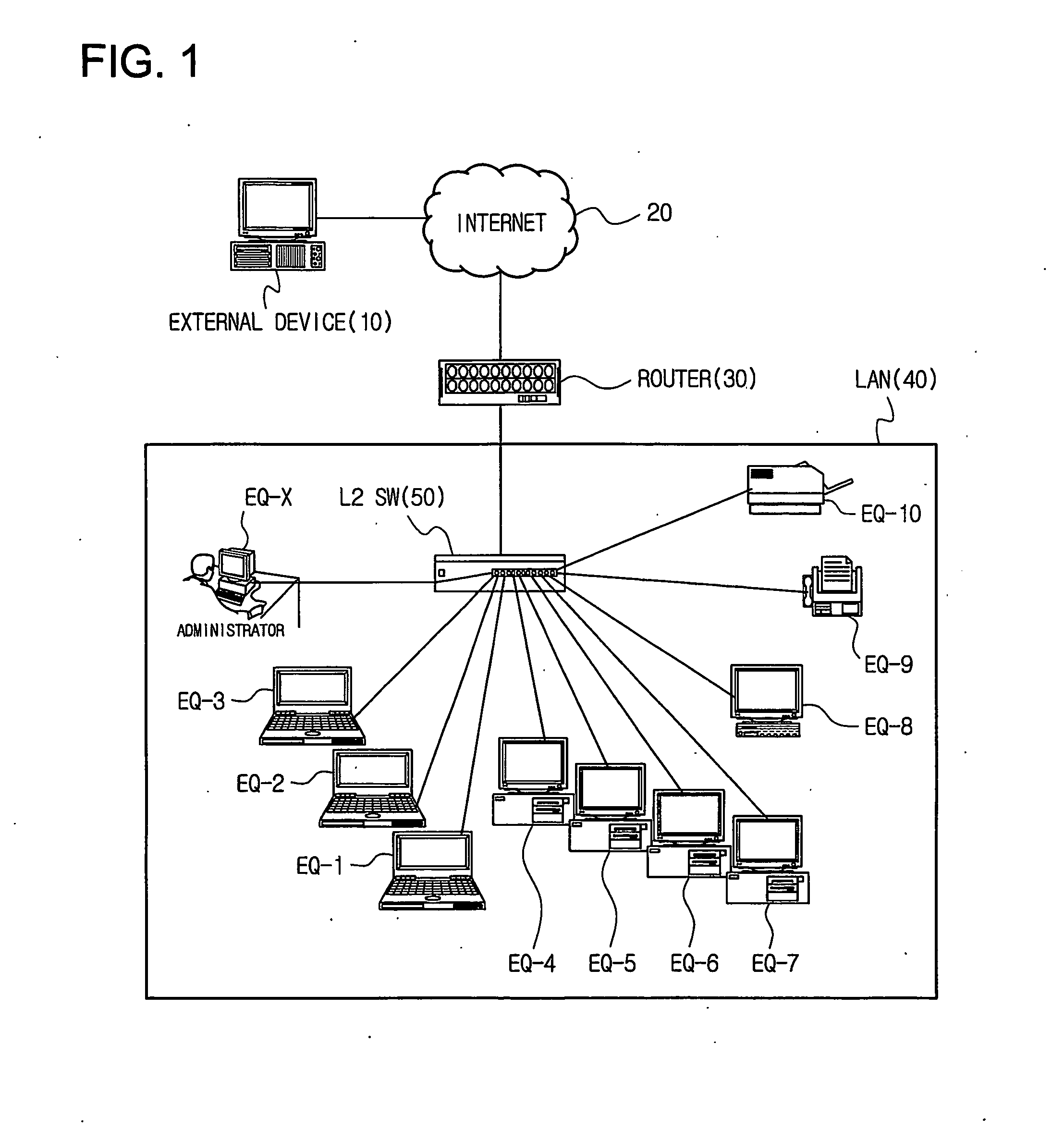
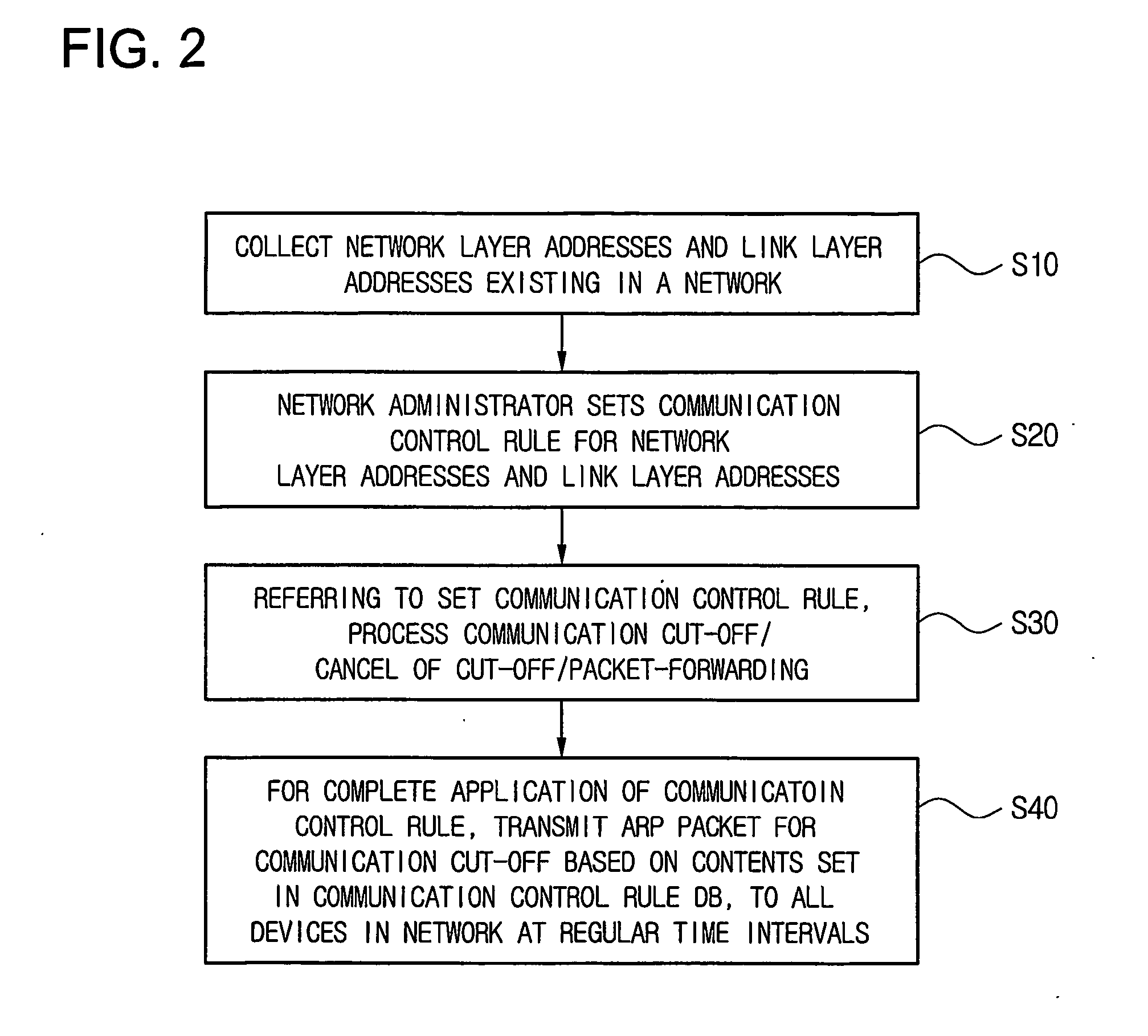
Method of controlling communication between devices in a network and apparatus for the same
InactiveUS20070064689A1Avoid collisionReduce communicationSpecial service provision for substationNetworks interconnectionAddress Resolution ProtocolVirtual firewall
Disclosed is a technology by which rules on communication permission or control are enforced to network internal devices such that an environment which looks as if to have a virtual firewall existing between network internal devices can be established. A communication control apparatus for this is located on the same level in the network as other devices are located. By using this communication control apparatus, an address resolution protocol (ARP) packet in which a data link layer address is manipulated is provided to devices that are the objects of communication cut-off, such that data packets transmitted by the communication cut-off object devices are transmitted to manipulated abnormal addresses. By doing so, communication with the communication cut-off object devices is cut off. For a device which is in a communication cut-off state although the device is not an object of communication cut-off any more, the communication control apparatus transmits an ARP packet including normal address information to the device such that the communication cut-off state is canceled.
Owner:INIMAX
Peer-to-peer name resolution protocol (PNRP) and multilevel cache for use therewith
InactiveUS7065587B2Fast convergenceError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDomain nameAddress Resolution Protocol
A serverless name resolution protocol ensures convergence despite the size of the network, without requiring an ever-increasing cache and with a reasonable numbers of hops. This convergence is ensured through a multi-level cache and a proactive cache initialization strategy. The multi-level cache is built based on a circular number space. Each level contains information from different levels of slivers of the circular space. A mechanism is included to add a level to the multi-level cache when the node determines that the last level is full. A peer-to-peer name resolution protocol (PNRP) includes a mechanism to allow resolution of names which are mapped onto the circular number space through a hash function. Further, the PNRP may also operate with the domain name system by providing each node with an identification consisting of a domain name service (DNS) component and a unique number.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Isolation of hosts connected to an access network
InactiveUS20060062187A1Effective trafficEfficiently broadcastedRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesAccess networkAddress Resolution Protocol
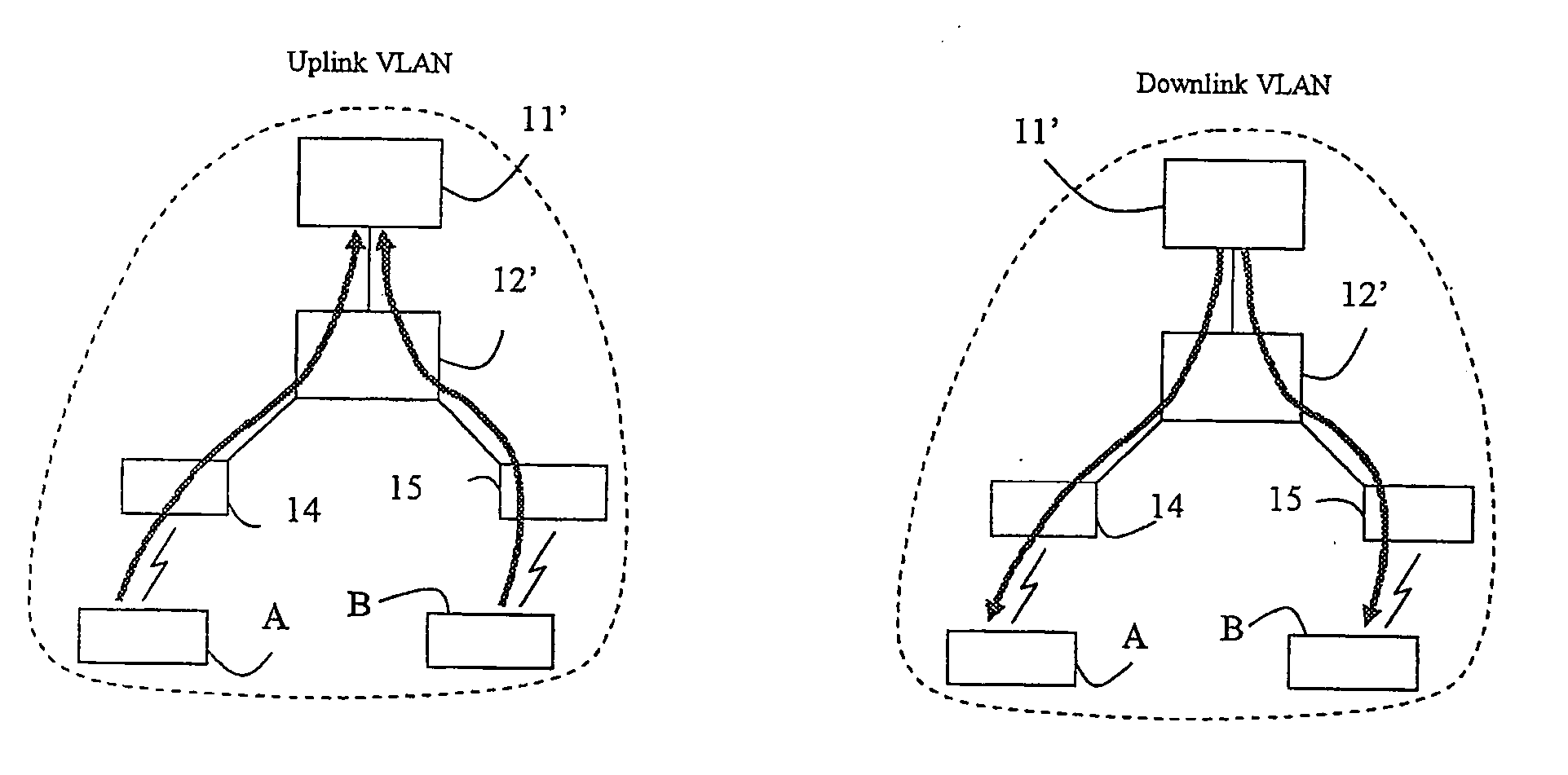
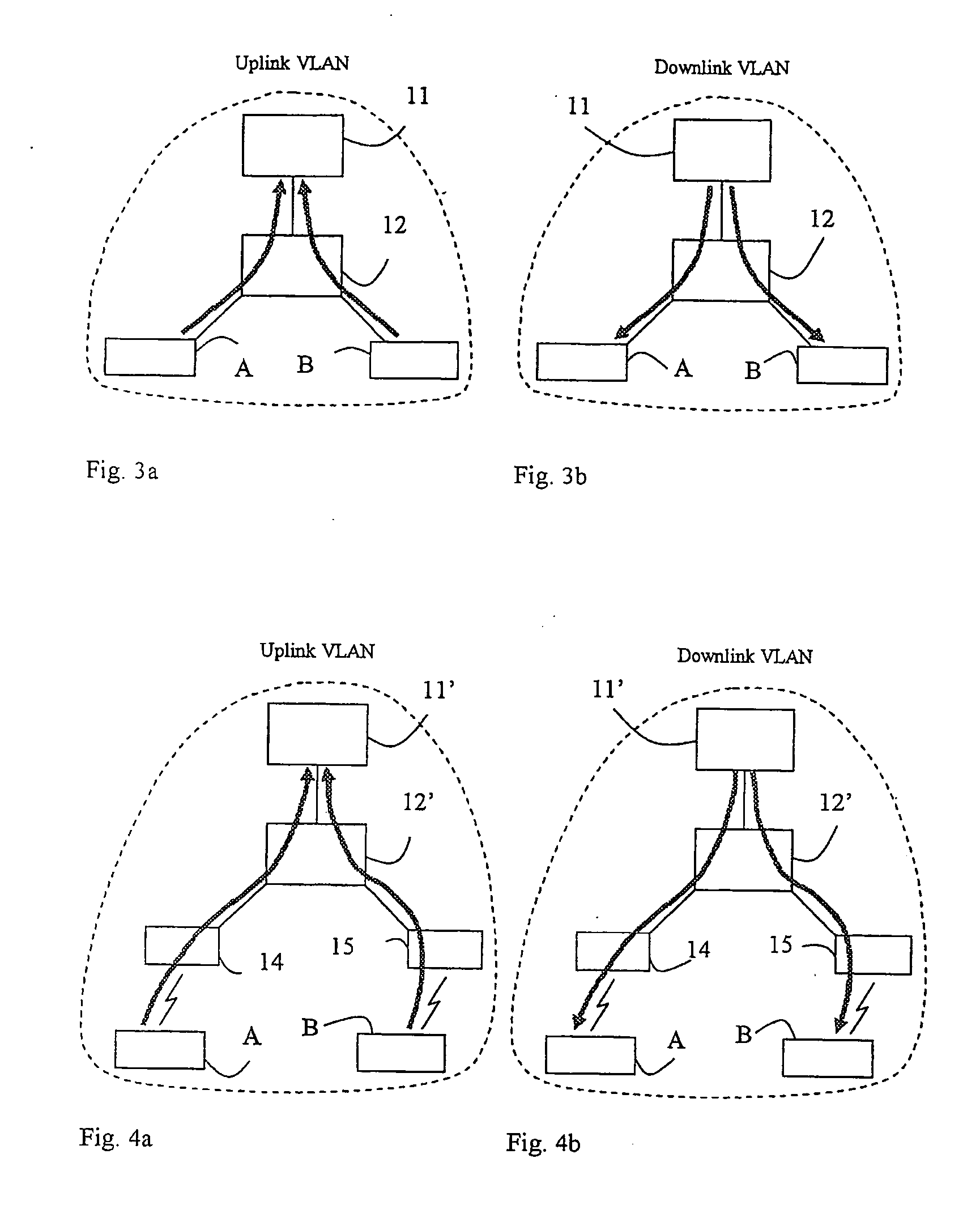
A method and an arrangement in an access network for preventing hosts (5;A,B) connected to the access network from communicating directly with each other. Said method comprises the steps of defining Virtual Local Area Networks, VLANs, in switches (3;12;12′;35,36,37;83) such that traffic arriving in the switches from said hosts is forced to an access router (1;11;11′;11″;81) and defining in the switches one asymmetrical downlink VLAN for downlink traffic from the access router to the hosts, said downlink VLAN being common to said hosts. According to the invention the method comprises the further steps of configuring the VLANs such that said hosts connected to the access network belong to the same IP subnet and configuring the access router to perform intra-subnet routing and to be an Address Resolution Protocol proxy.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
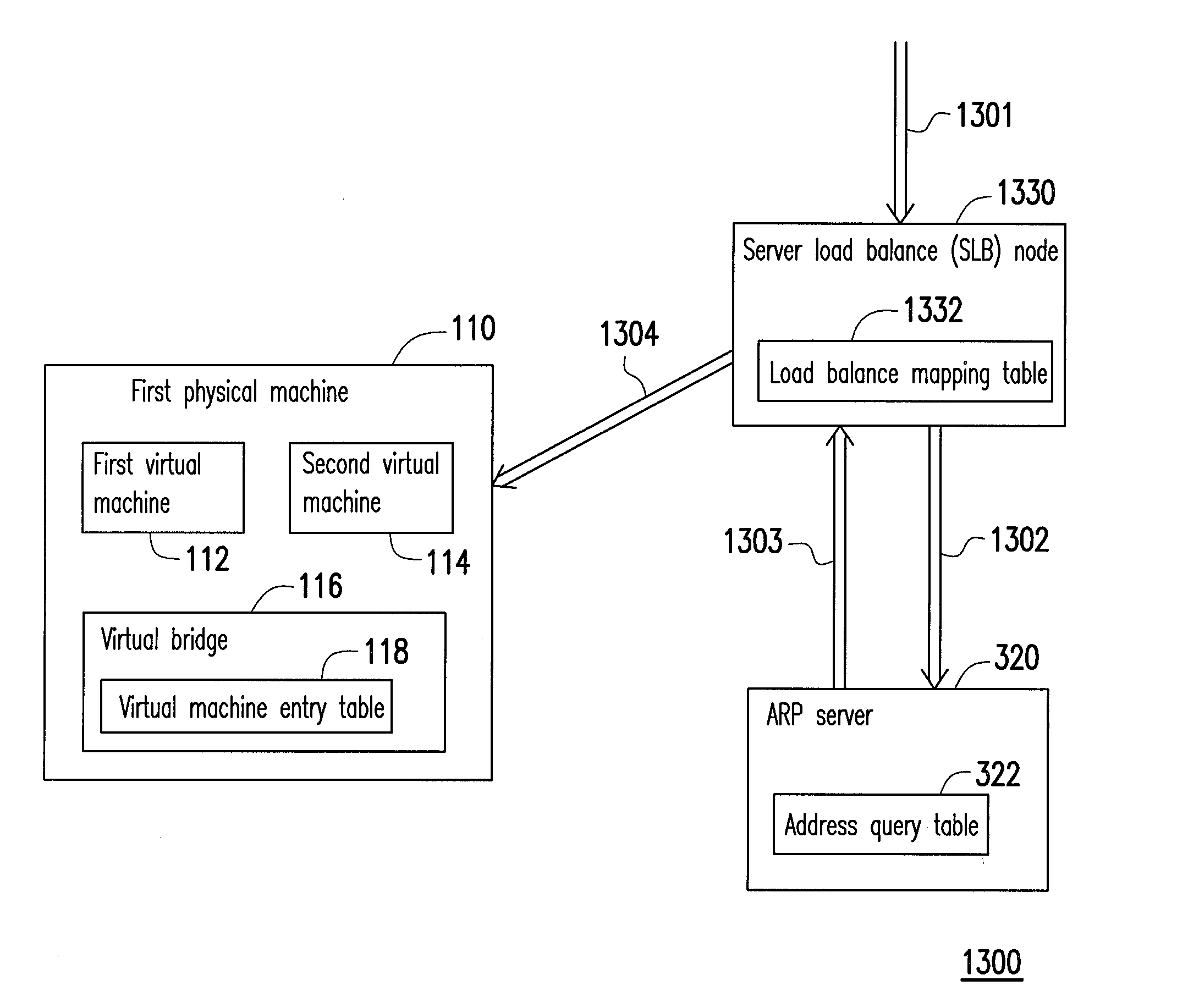
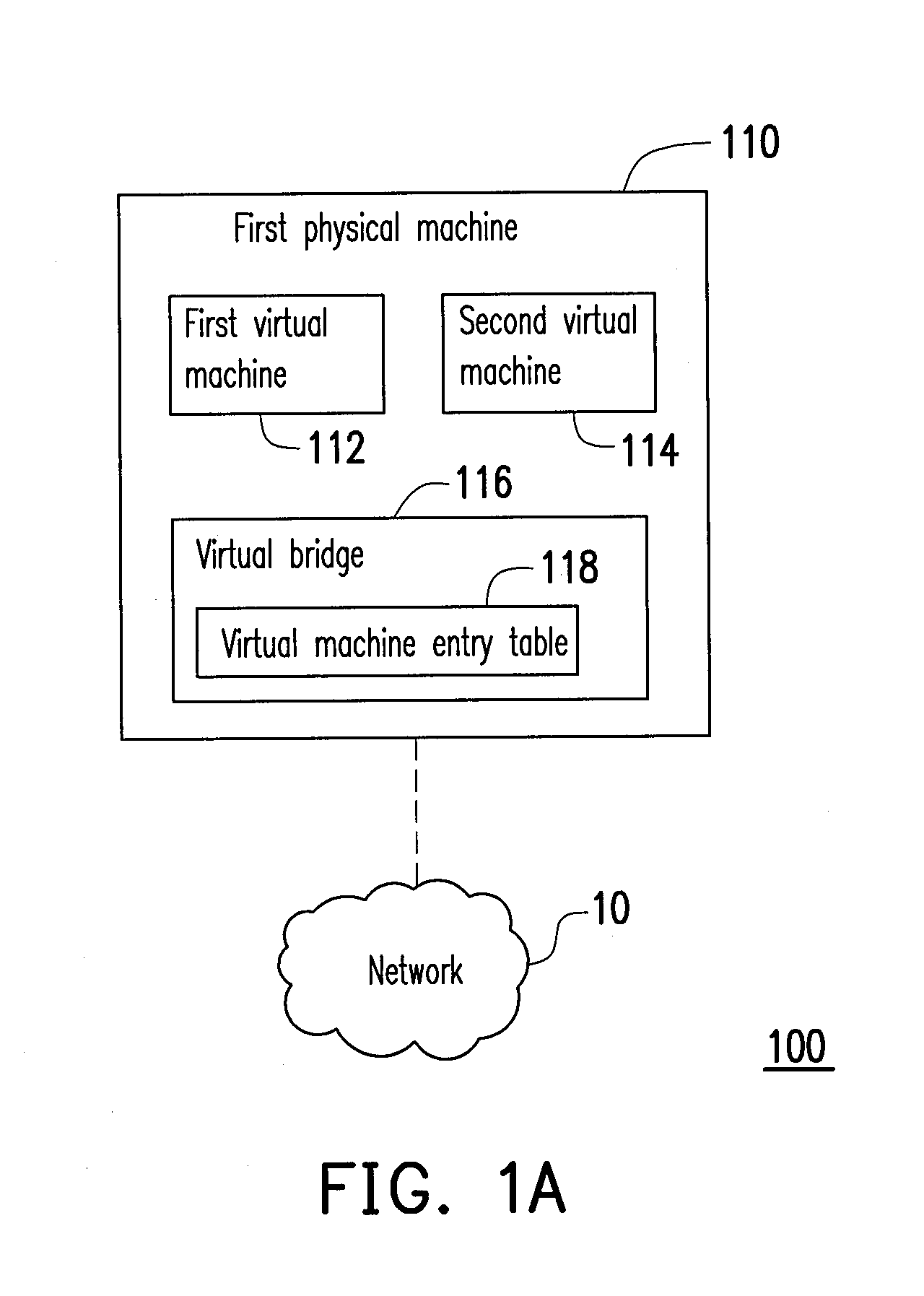
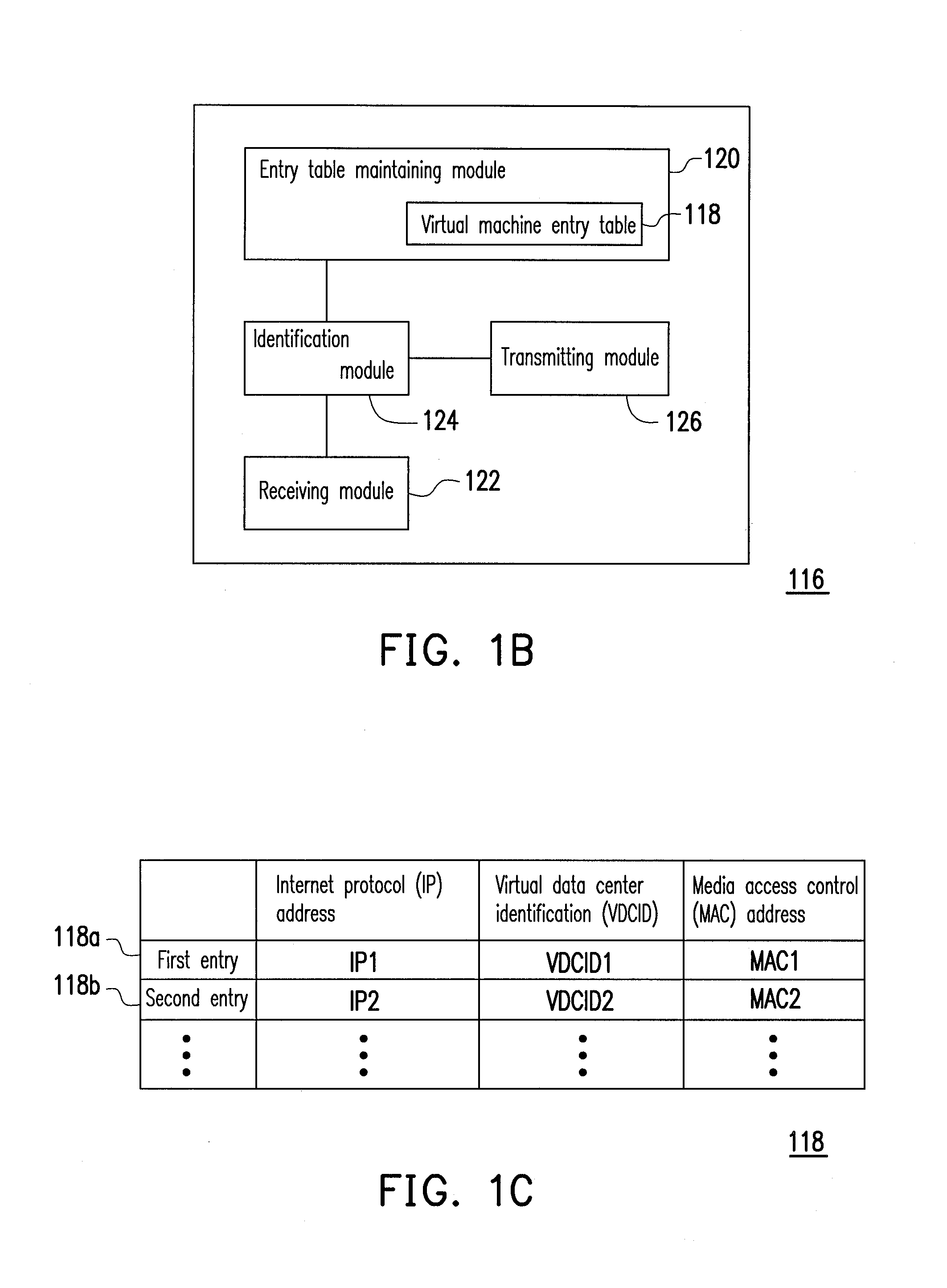
Data center network system and packet forwarding method thereof
ActiveUS20130136126A1Efficient solutionData switching by path configurationProgram controlPrivate IPAddress Resolution Protocol
A data center network system and a packet forwarding method thereof are provided. The data center network system includes a virtual bridge and an address resolution protocol (ARP) server. The virtual bridge intercepts an ARP request having an identification field and a destination IP address field and adds a corresponding virtual data center identification to the identification field of the ARP request and redirecting the ARP request to the ARP server. Additionally, the ARP server queries a corresponding MAC address according to an IP address recorded in the destination IP address field of the ARP request and the corresponding VDCID recorded in the identification field of the ARP request, and transmits the corresponding MAC address in response to the ARP request. Accordingly, the same private IP address can be reused in the data center network system.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
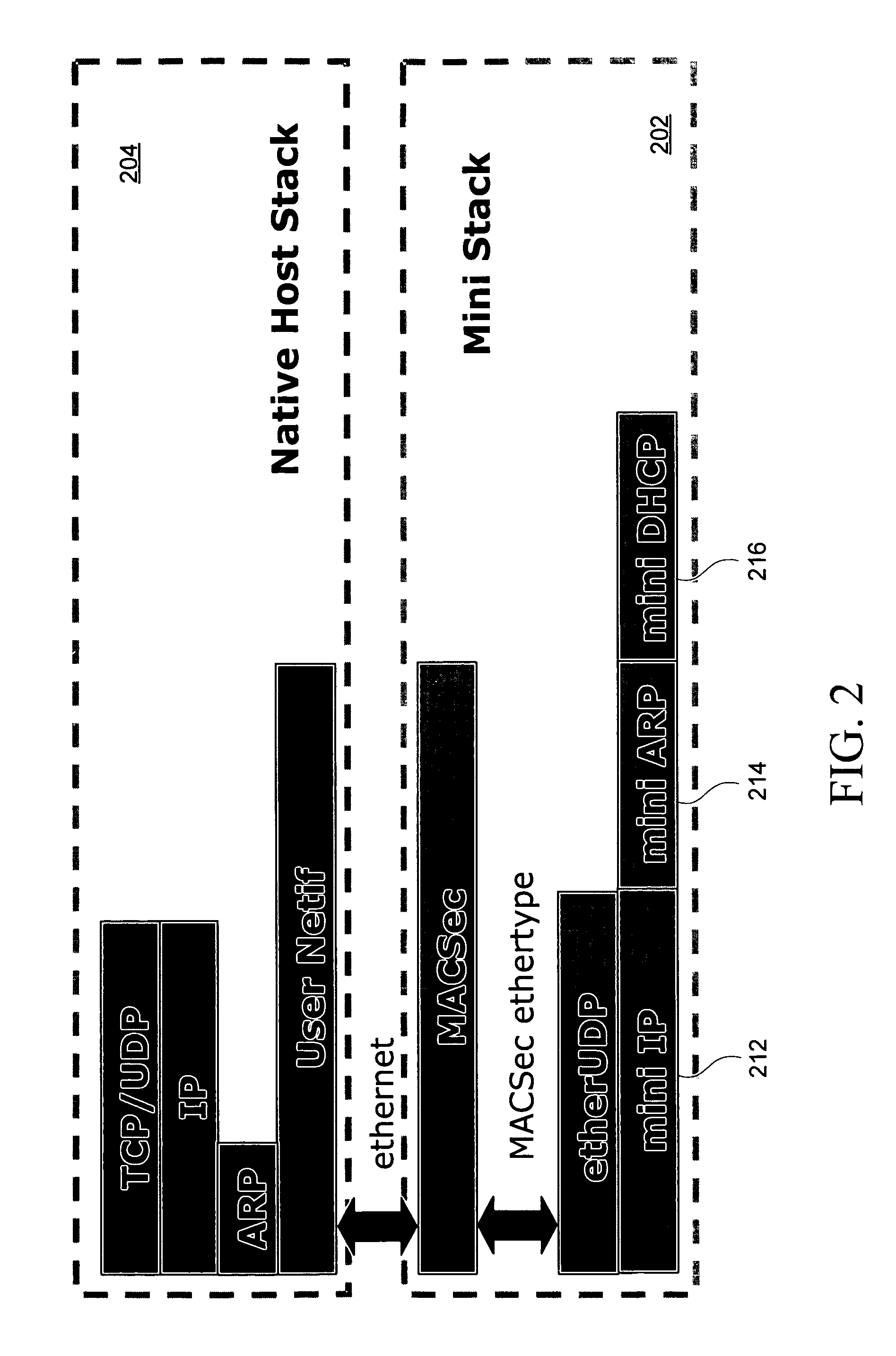
Method and apparatus for managing hardware address resolution
InactiveUS20070248085A1Data switching by path configurationAddress Resolution ProtocolAddress resolution
Disclosed herein is a network device, such as a host computer, that simultaneously has two IP identities: a local IP identity on a local network (e.g., a non-virtual private network) to which the host computer is connected; and a remote IP identity on a second network (e.g., virtual private network) that is remote to the host. Only the remote IP identity is visible to the host operating system's network stack. Each IP identity has its own ARP cache and Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). The local ARP cache is managed with respect to a connection of the host to a local subnet (e.g., an Internet Service Provider (ISP) subnet) and the remote ARP cache is managed with respect to a remote subnet reachable through a gateway on the local subnet.
Owner:E COLT SYST INC
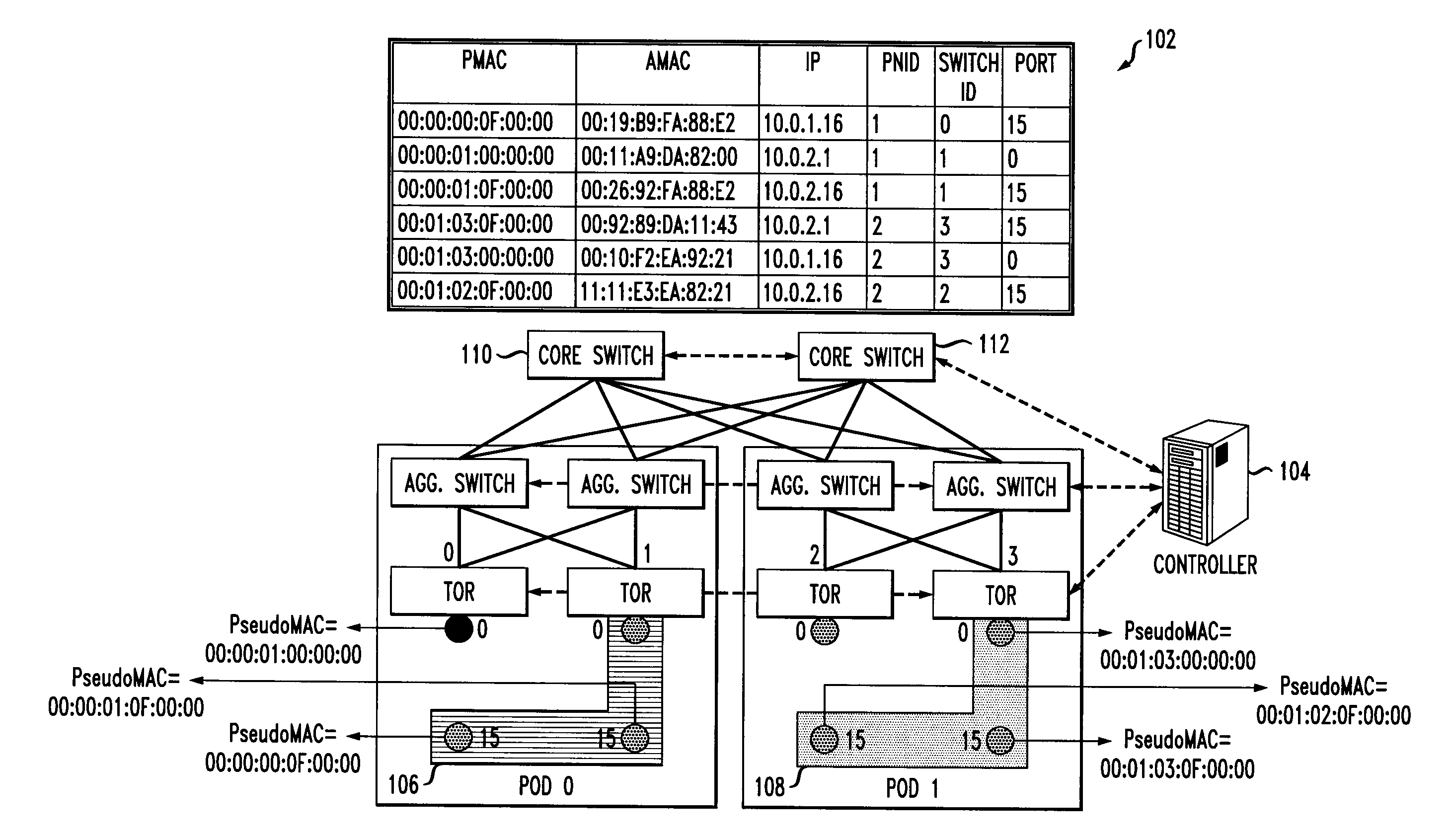
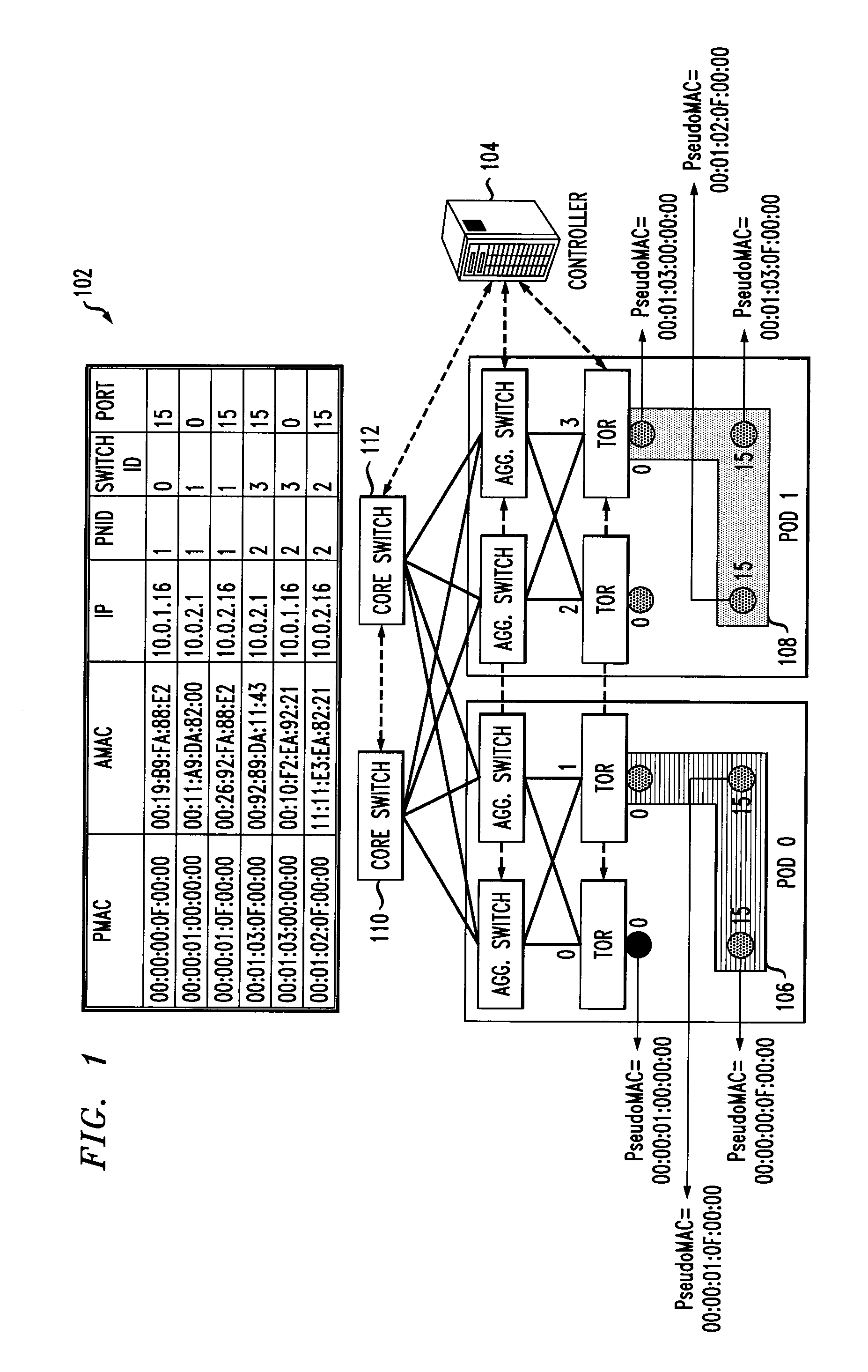
Enabling Co-Existence of Hosts or Virtual Machines with Identical Addresses
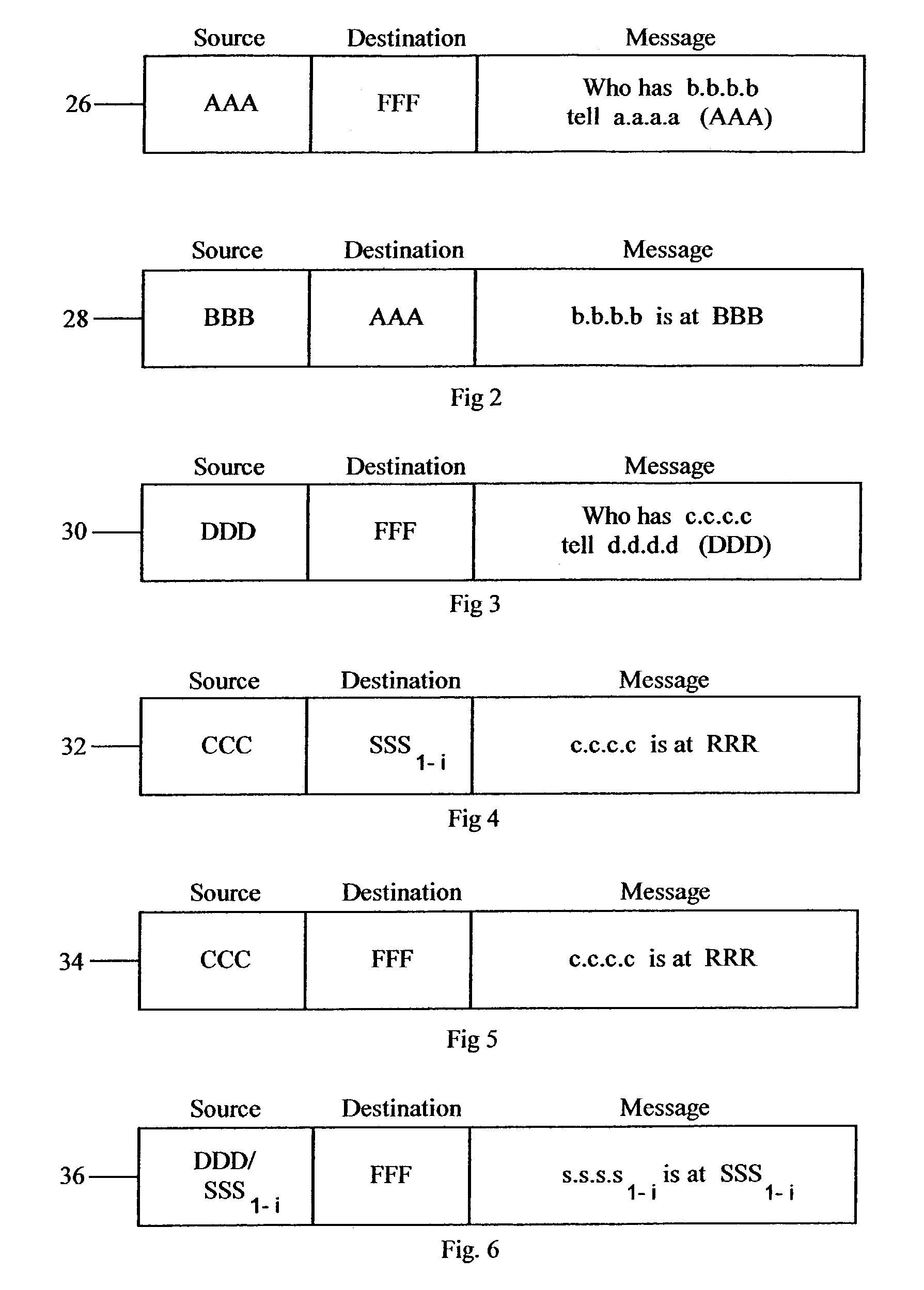
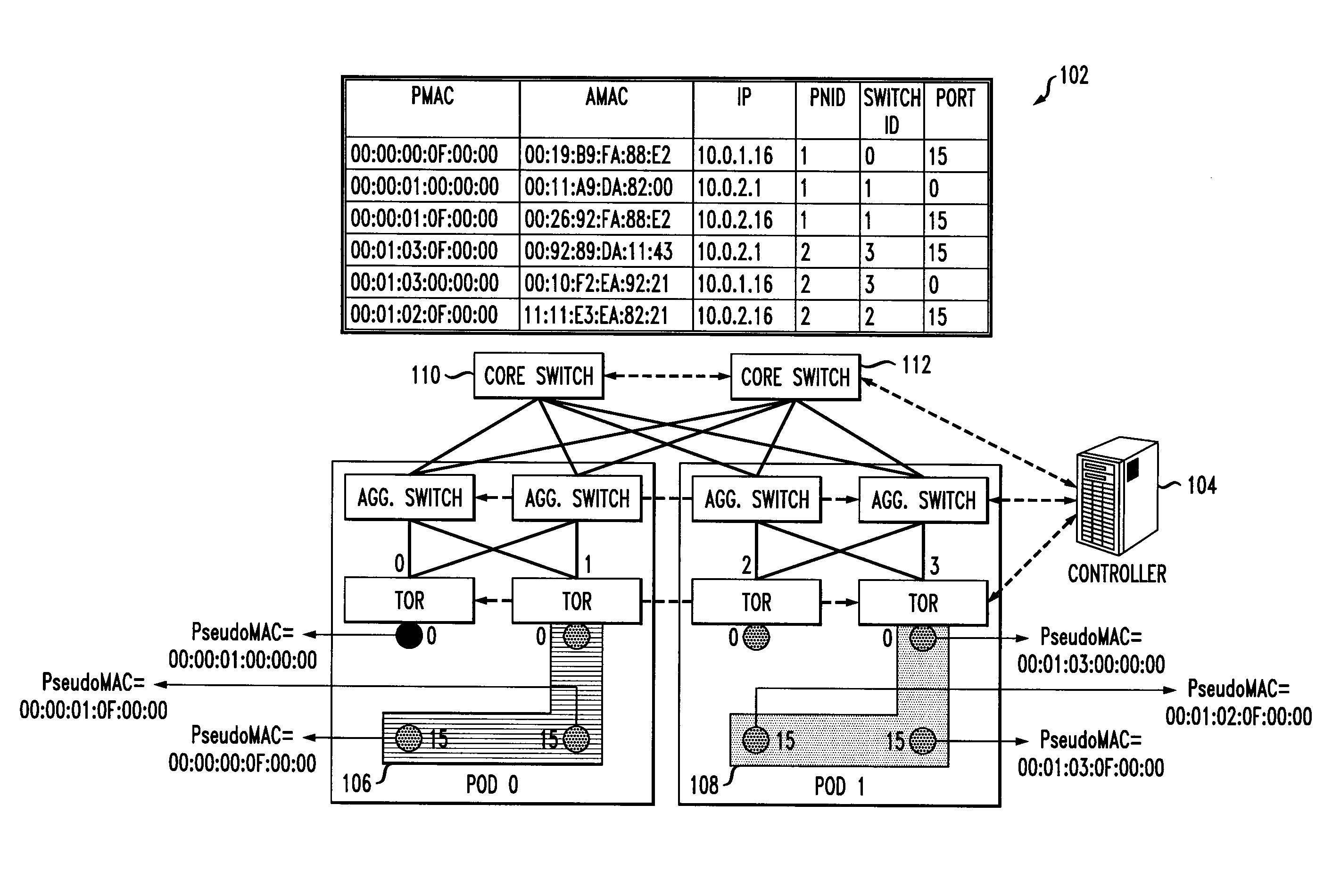
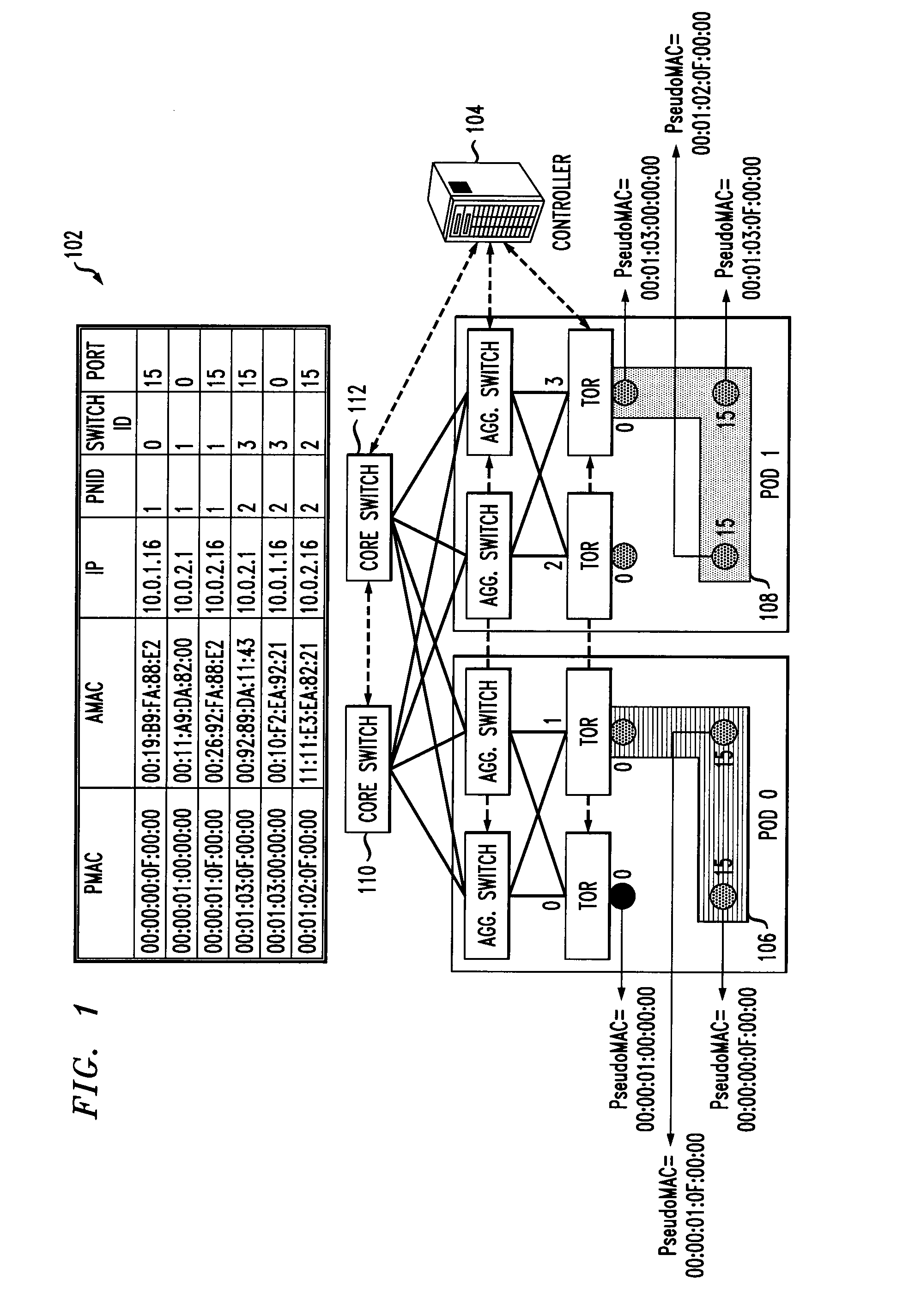
A method for enabling co-existence of multiple machines with identical addresses within a single data center network. The method includes assigning a unique pseudo identifier to each machine in the network that can be used for routing a packet to a destination machine, replacing a sender media access control address on an address resolution protocol request with a pseudo identifier of the sender at an edge network switch, retrieving a private network identifier from a mapping table based on the sender pseudo identifier and returning a pseudo identifier for the destination address based on the private network identifier, and replacing the pseudo identifier of the destination address with an actual identifier at a destination edge network switch for routing the packet to the destination machine.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for preventing spoofing of network addresses
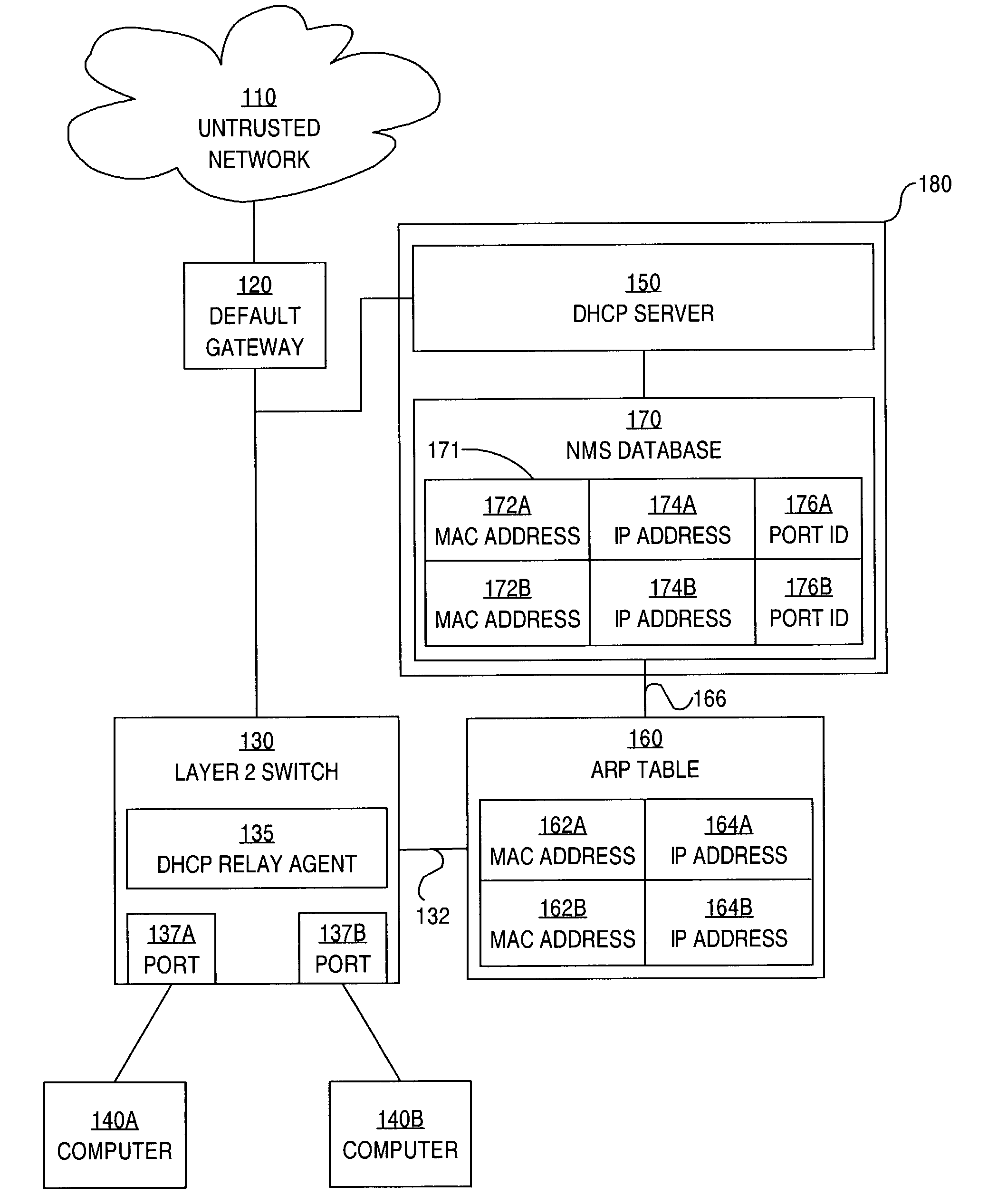
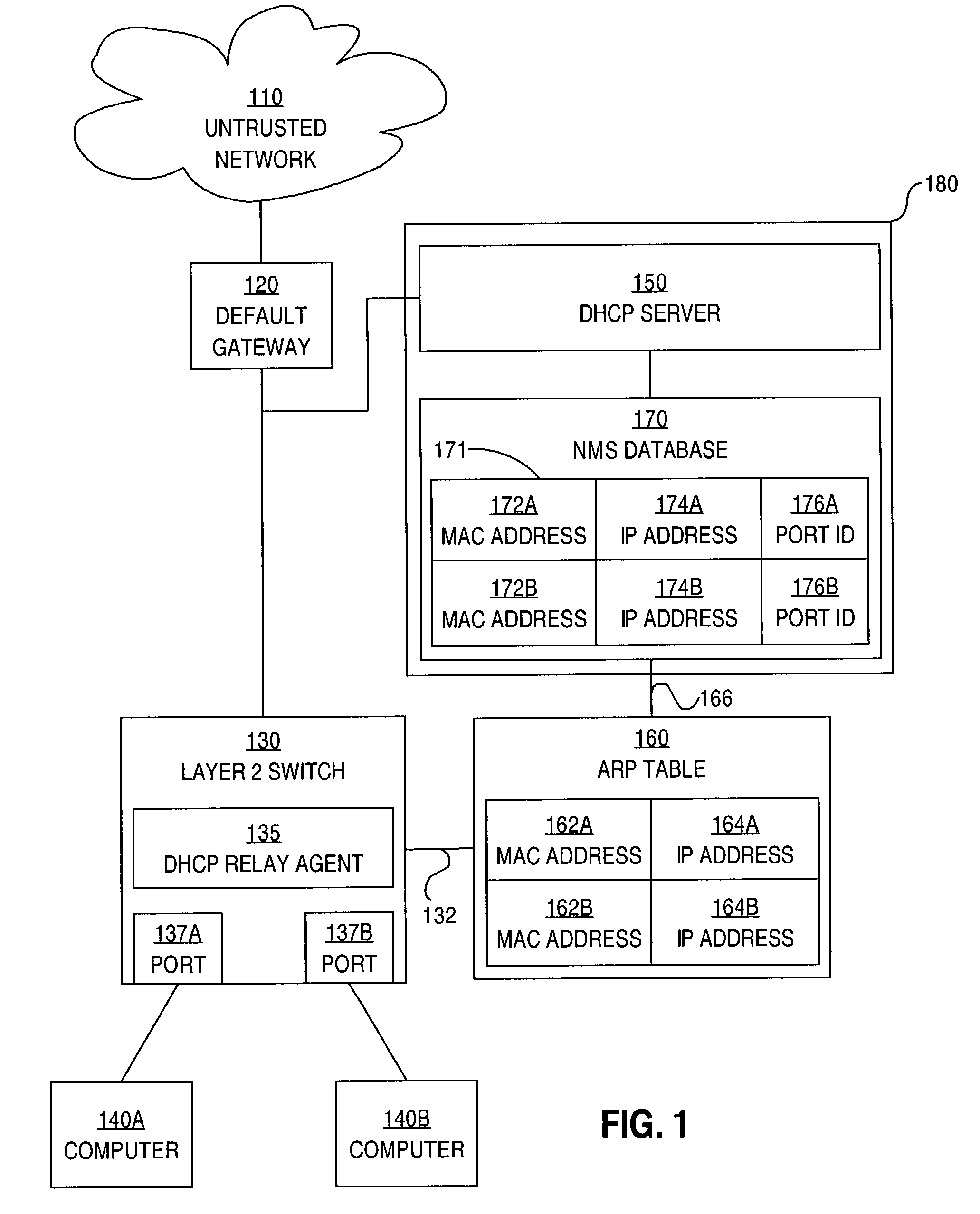
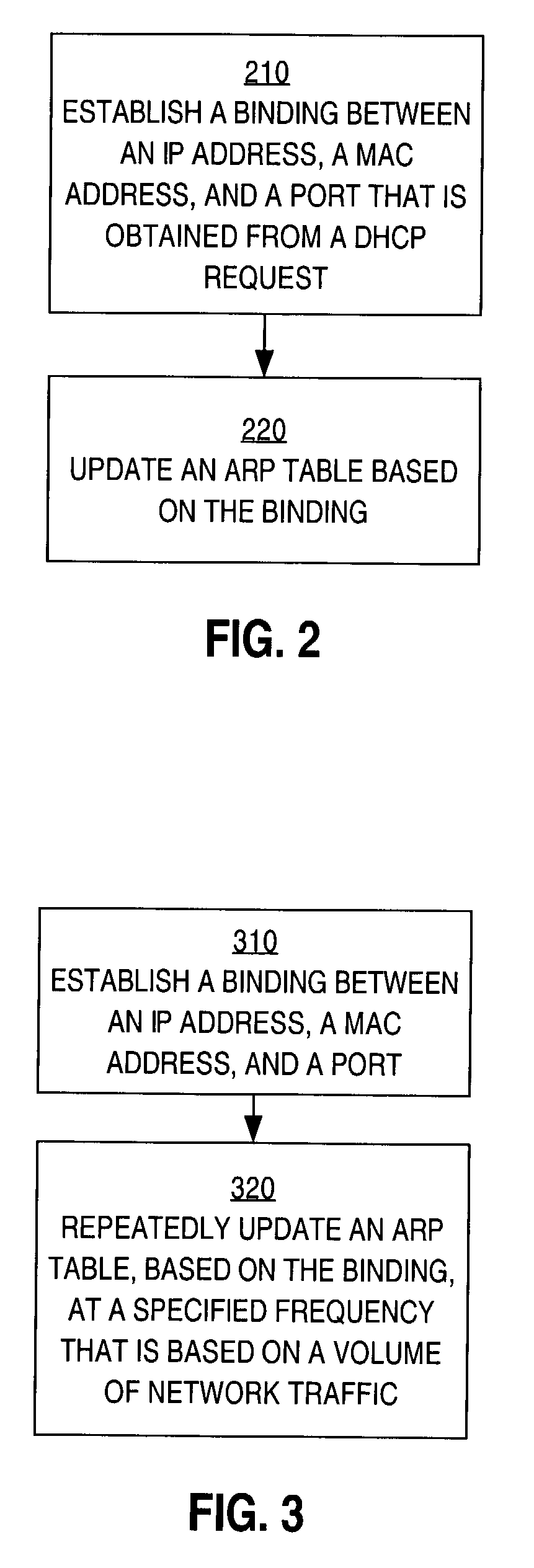
ActiveUS7234163B1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionAddress Resolution ProtocolNetwork addressing
A method is disclosed for preventing spoofing of network addresses. A binding is established between an Internet Protocol (IP) address, a Media Access Control (MAC) address, and a port. An Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) table is updated based on the binding.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Extending sso for DHCP snooping to two box redundancy
InactiveUS20070121617A1OptimizationData switching by path configurationAddress Resolution ProtocolIp address
Disclosed are mechanisms for facilitating the use of DHCP (dynamic host configuration protocol) binding data. In general, certain applications include mechanisms for intercepting data being sent from a node and then determining whether the data corresponds to a valid IP address and MAC address binding. Embodiments of the present invention provide mechanisms for sharing such DHCP binding data between routers (or other type of network devices) in a redundancy group so that any of the routers may take over the data inspection to validate DHCP bindings. In particular aspects of the invention, the DHCP binding data is validated in procedures related to DHCP snooping, dynamic ARP (address resolution protocol) inspection, and the like.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method for address resolution in internet protocol (IP) -based networks
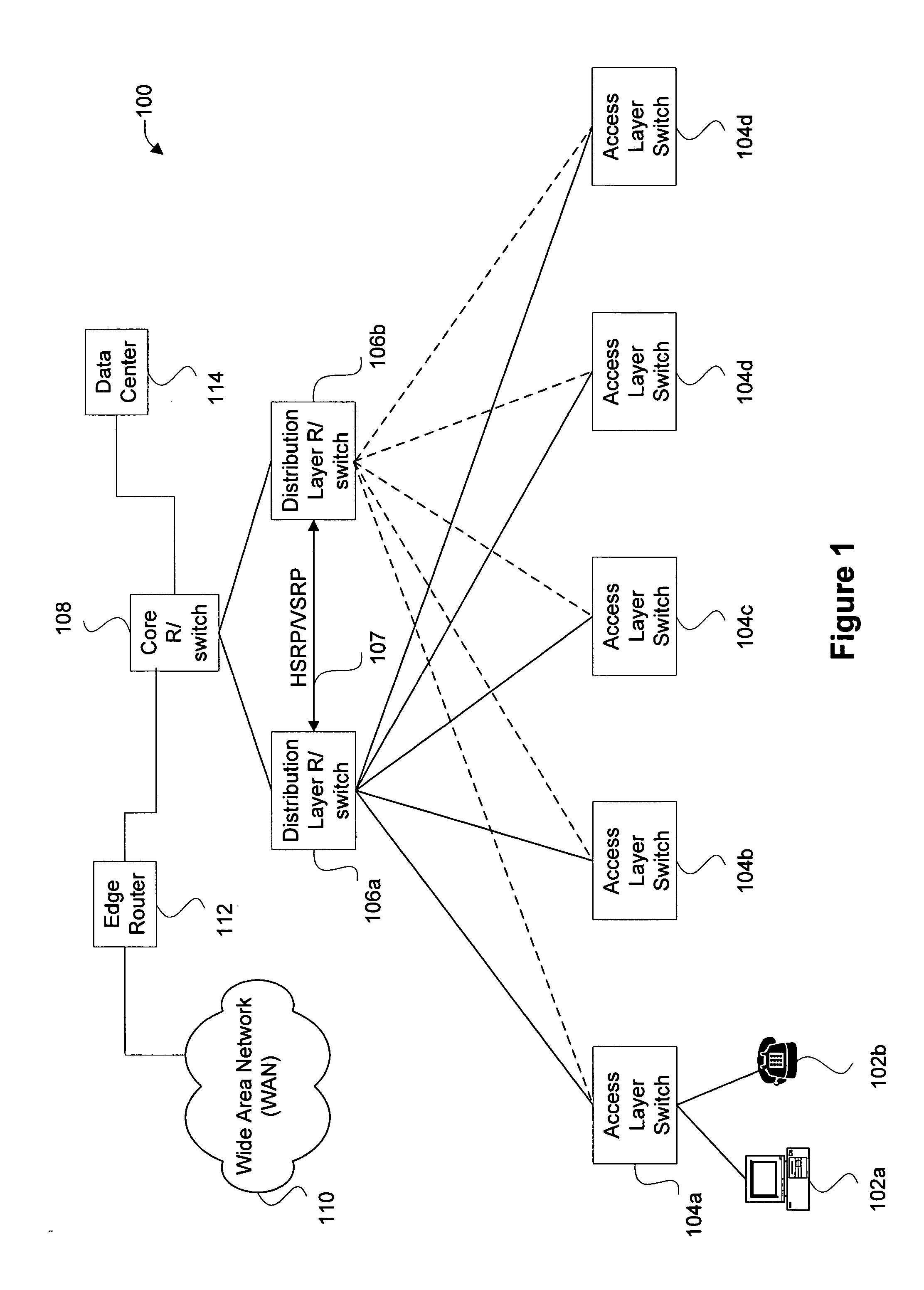
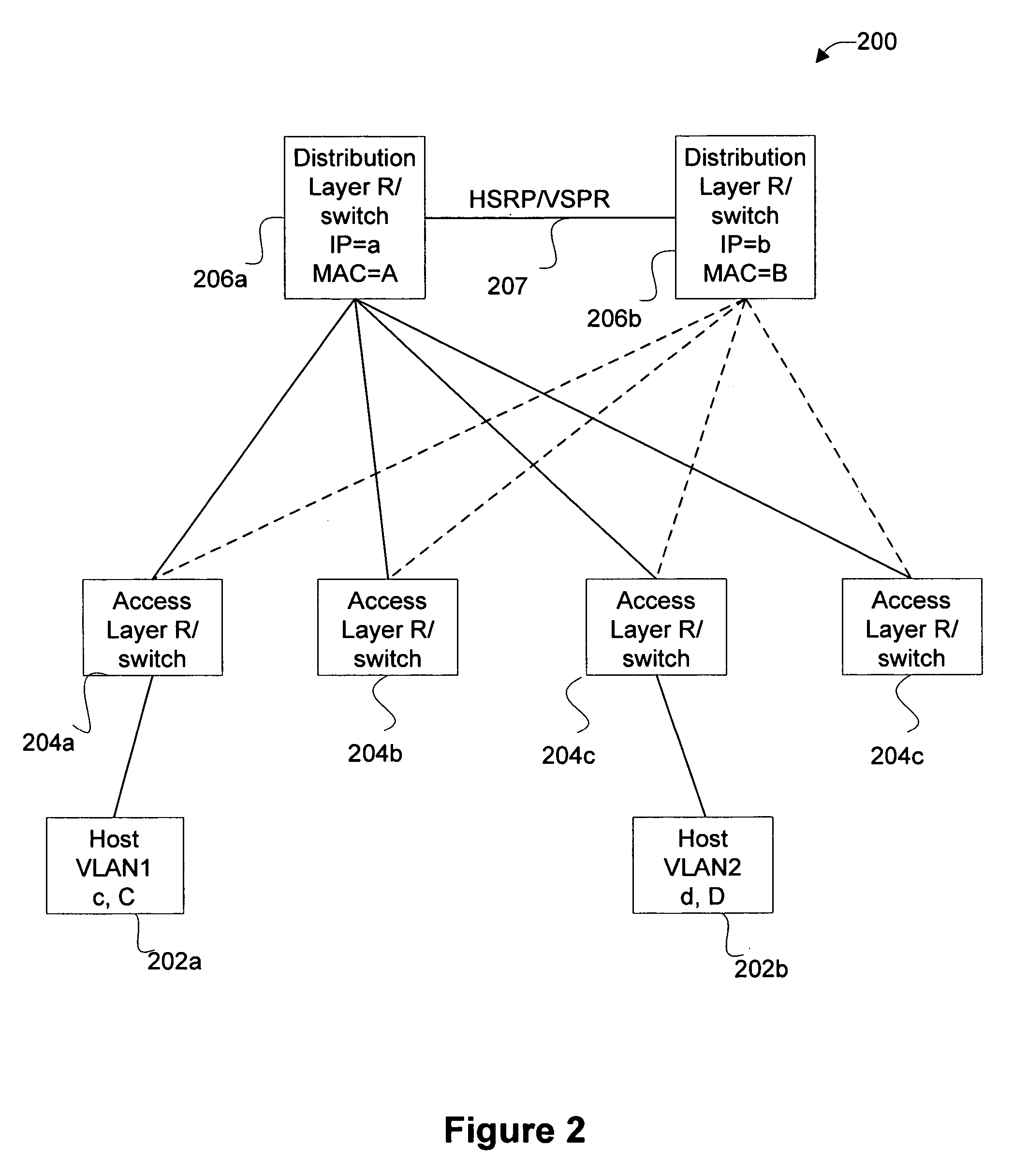
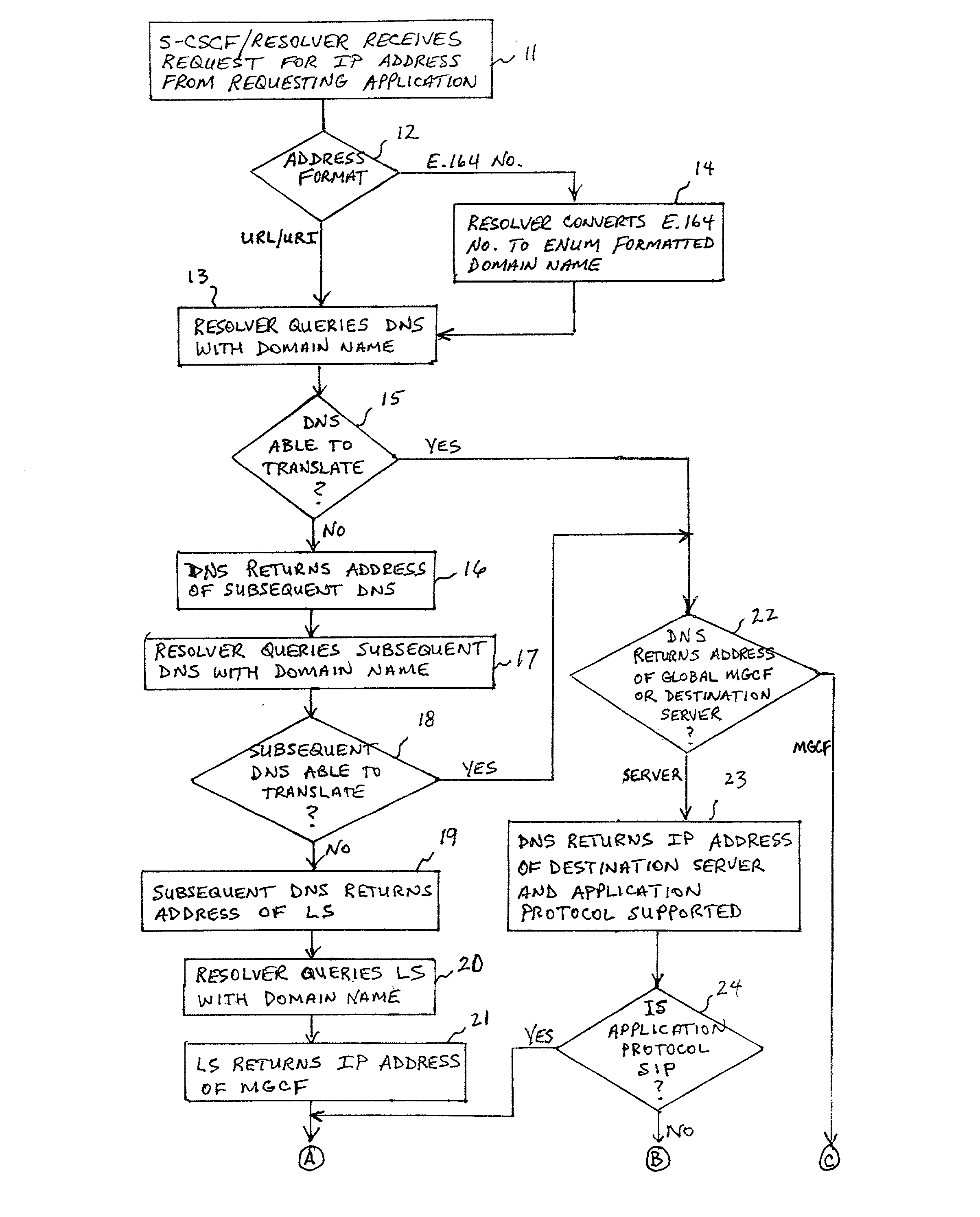
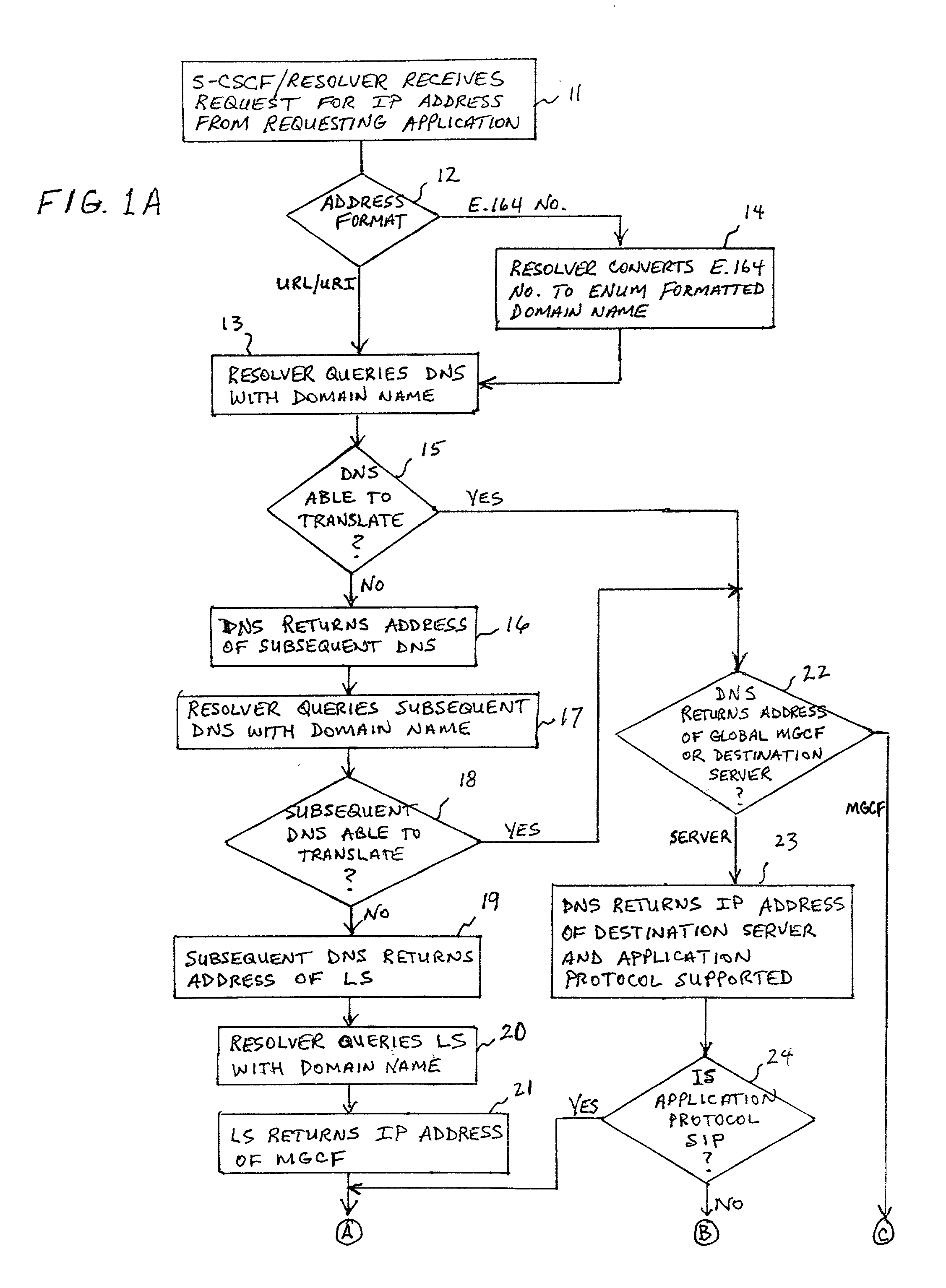
ActiveUS20020027915A1Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsInternet protocol suiteDomain name
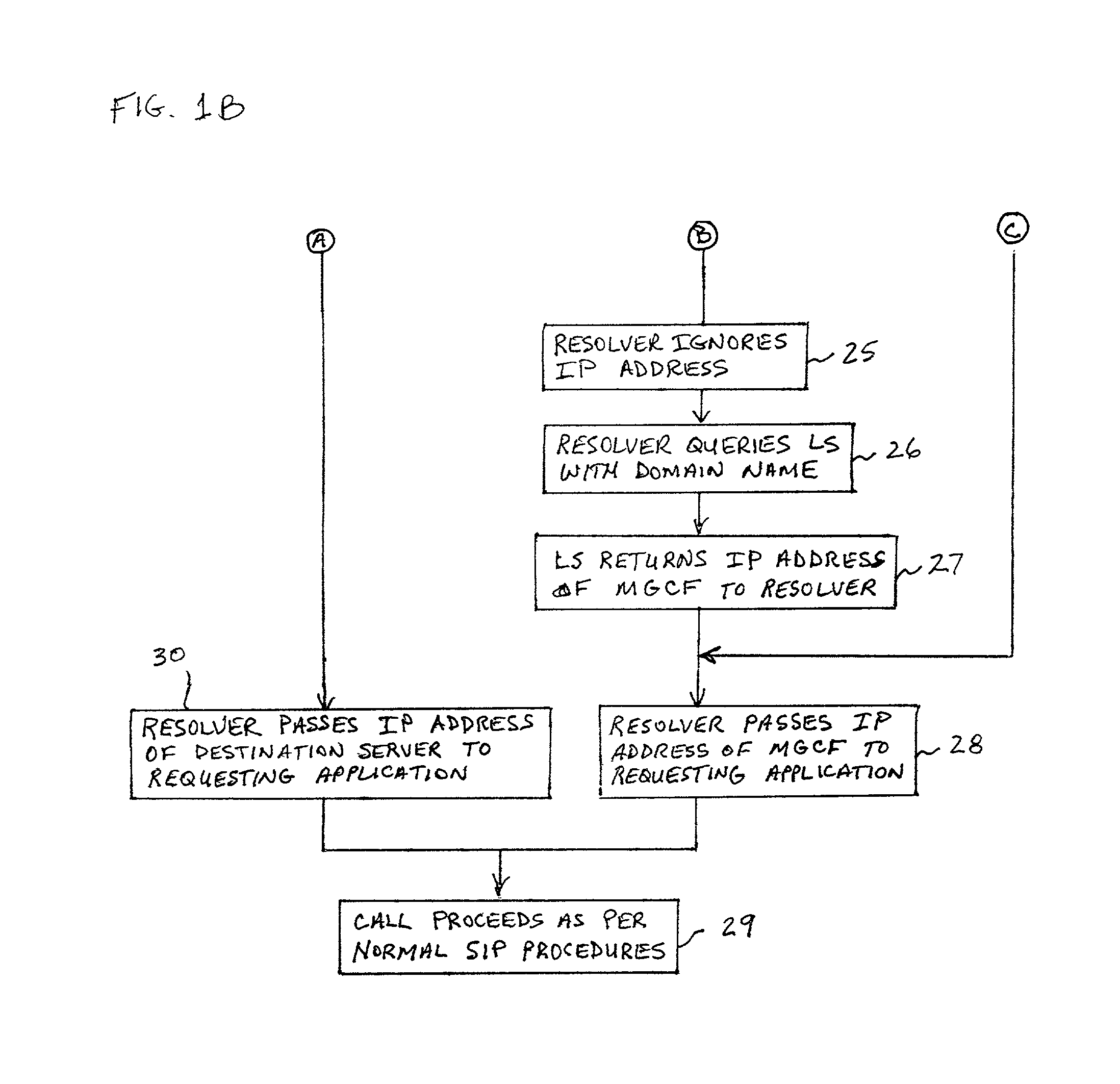
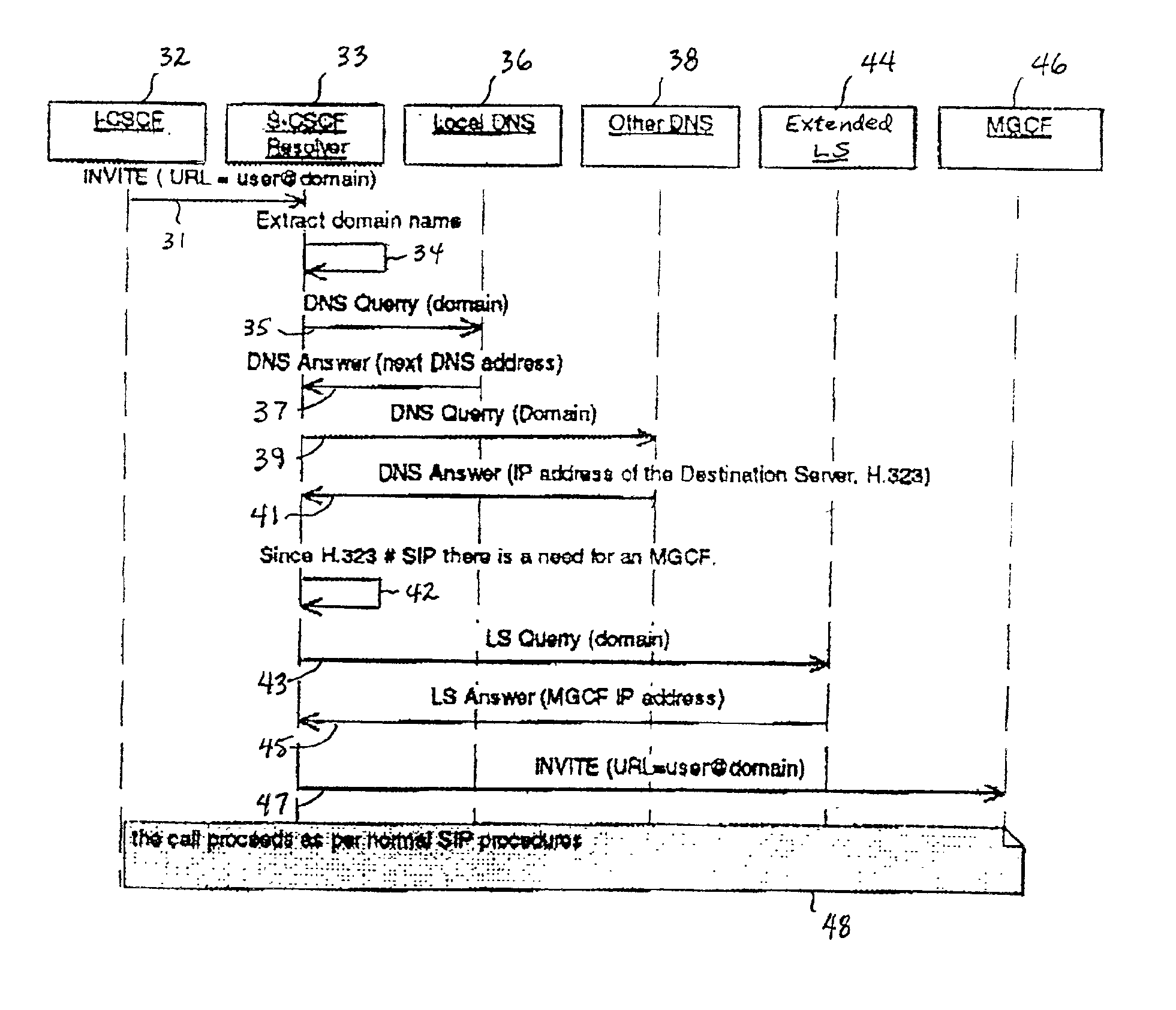
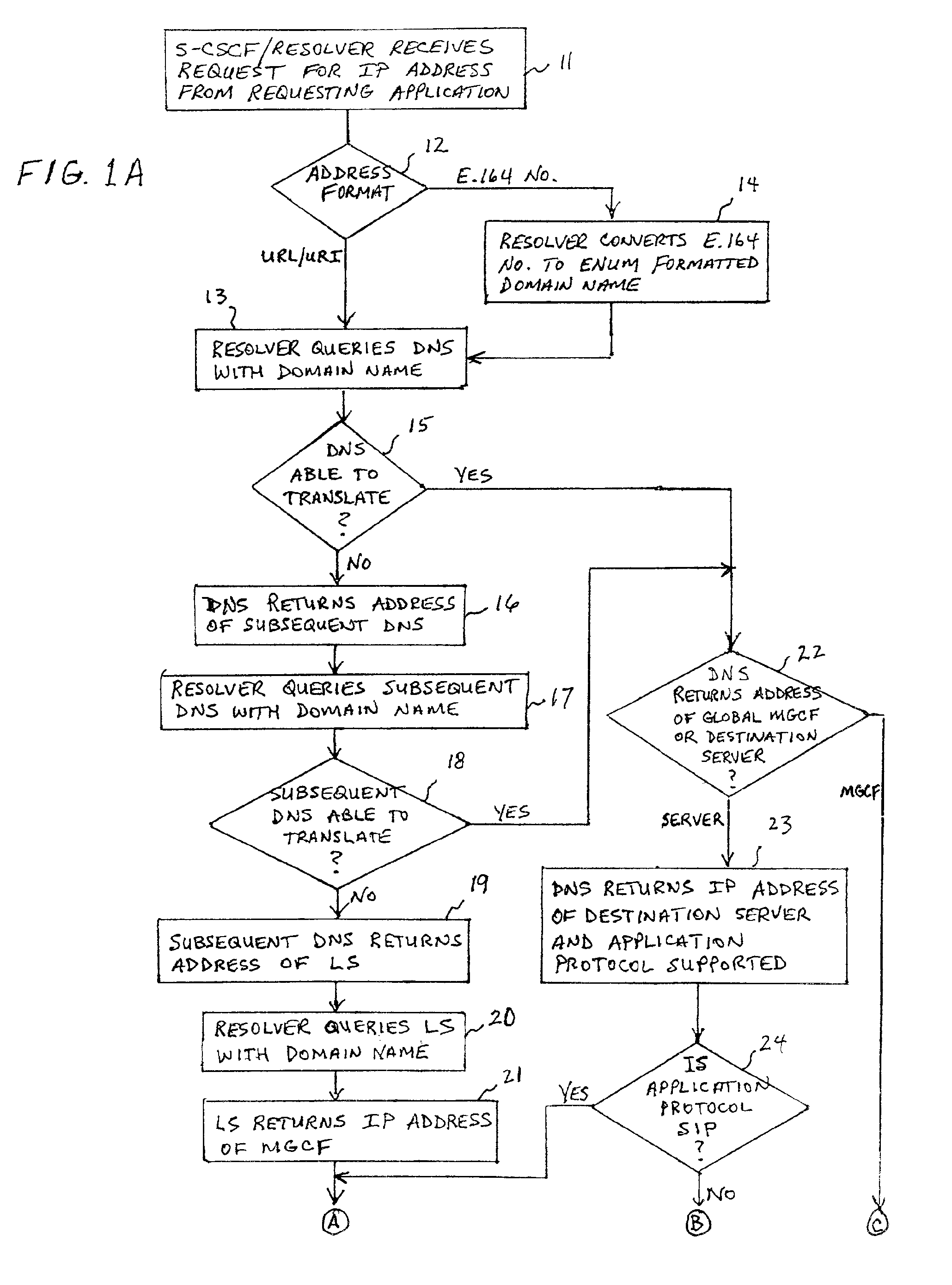
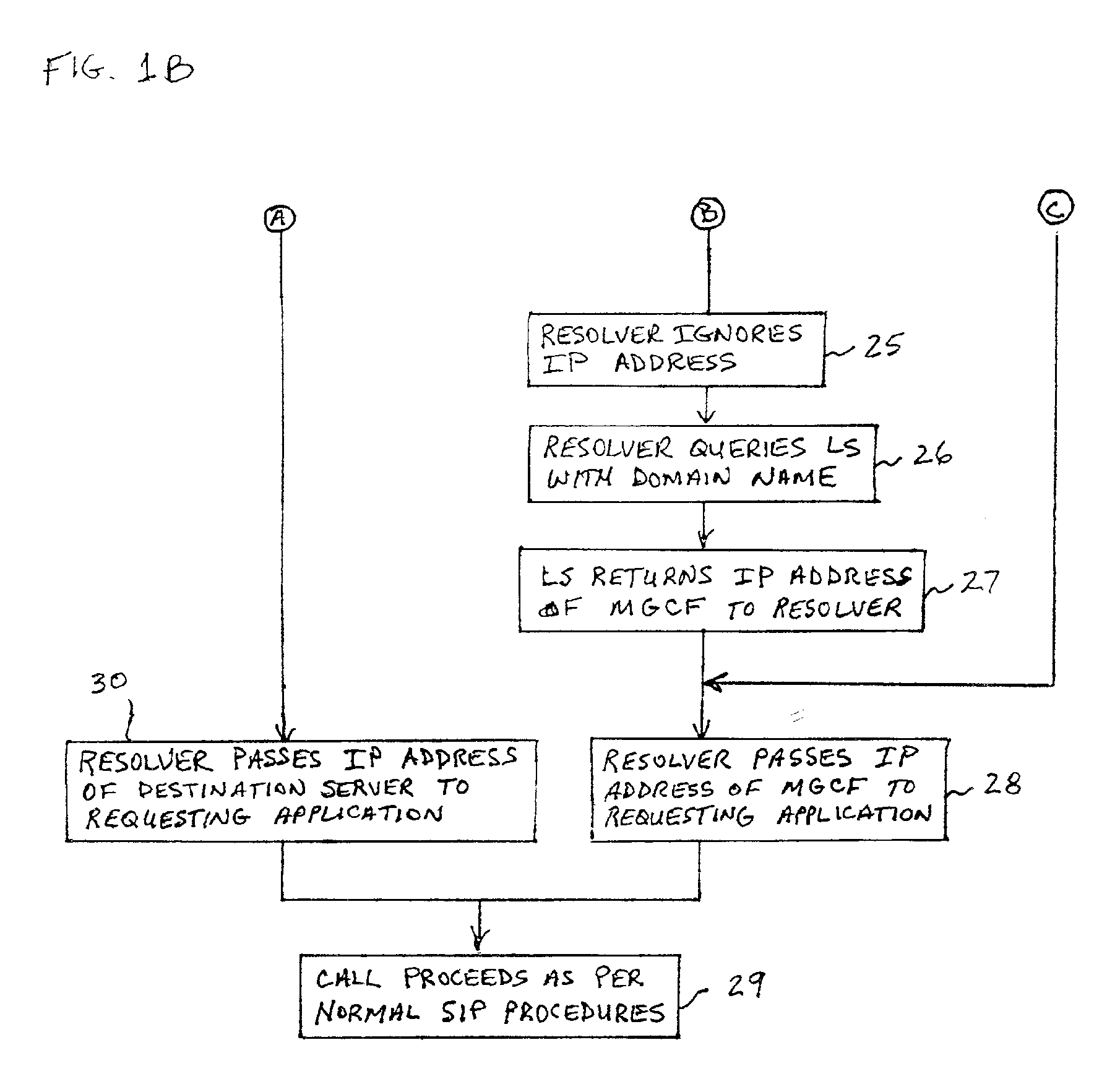
A system and unified method of address resolution in an IP-based network. A Resolver determines whether an input address is a URL / URI, and if so, extracts a domain name. If the input address is an E.164 number, the Resolver converts the E.164 number into a domain name in ENUM format. The Resolver then sends a domain name query to a DNS which, if able, returns the IP address for either a Global MGCF or a destination server along with a supported Application protocol. If the DNS is unable to perform the translation, or the Application protocol returned is not supported by the requesting application, the Resolver sends a domain name query to an extended Location Server (LS) to obtain an IP address of a gateway function capable of interfacing with the destination server.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method for building MAC (Media Access Control) address table and provider edge device
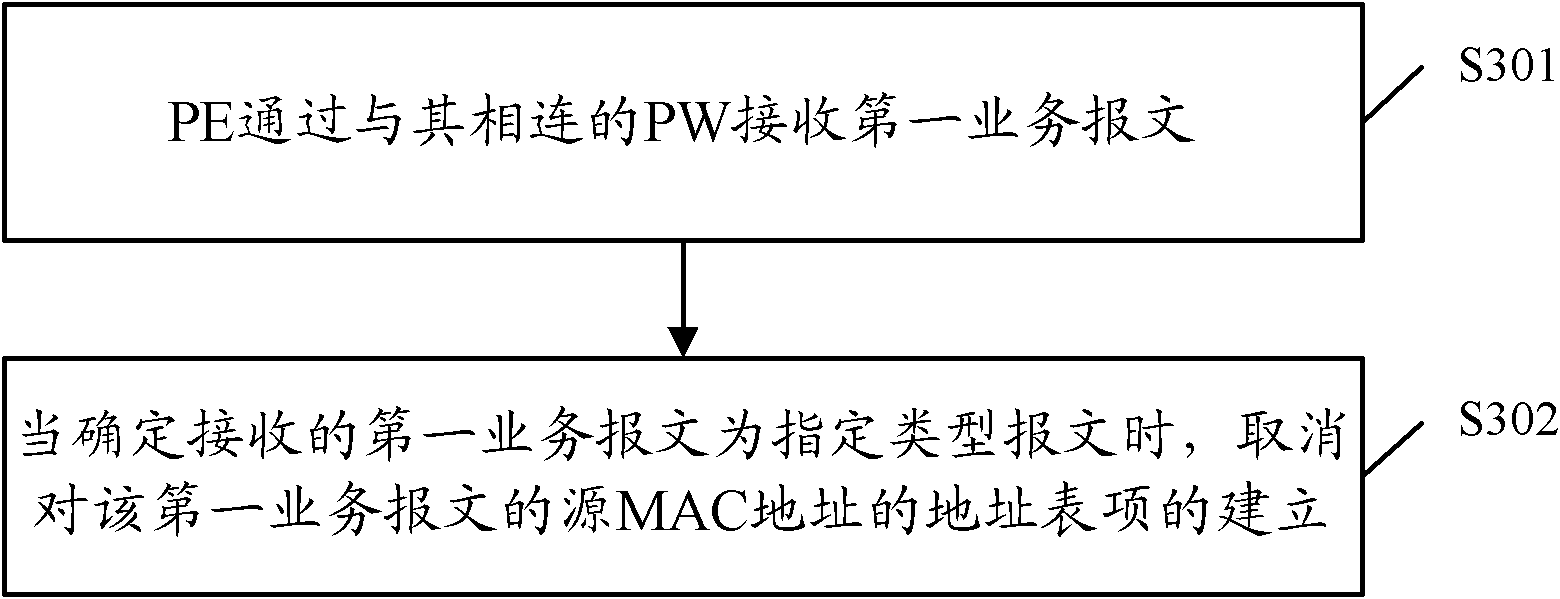
ActiveCN102164091AReduce in quantityReduce capacityData switching networksAddress Resolution ProtocolMedia access control
The invention discloses a method for building an MAC (Media Access Control) address table and a provider edge device. In the method, a PE (Provider Edge Device) receives a first service message by a PW (Pseudo Wire) connected with the PE; when the first received service message is confirmed to be a specific-type message, the building of the address table entry of the source MAC address of the first service message is cancelled, wherein the specific-type message is an unknown unicast message, a multicast message or the broadcasting message of a non-free ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) message. According to the scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, the amount of the address table entries built by the PE is reduced so as to reduce the volume of the MAC address table.
Owner:BEIJING XINWANG RUIJIE NETWORK TECH CO LTD
System and method for address resolution in internet protocol (IP)-based networks
ActiveUS6917612B2Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsInternet protocol suiteDomain name
A system and unified method of address resolution in an IP-based network. A Resolver determines whether an input address is a URL / URI, and if so, extracts a domain name. If the input address is an E.164 number, the Resolver converts the E.164 number into a domain name in ENUM format. The Resolver then sends a domain name query to a DNS which, if able, returns the IP address for either a Global MGCF or a destination server along with a supported Application protocol. If the DNS is unable to perform the translation, or the Application protocol returned is not supported by the requesting application, the Resolver sends a domain name query to an extended Location Server (LS) to obtain an IP address of a gateway function capable of interfacing with the destination server.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Address resolution protocol system and method in a virtual network
InactiveUS7174390B2Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationAddress Resolution ProtocolIp address
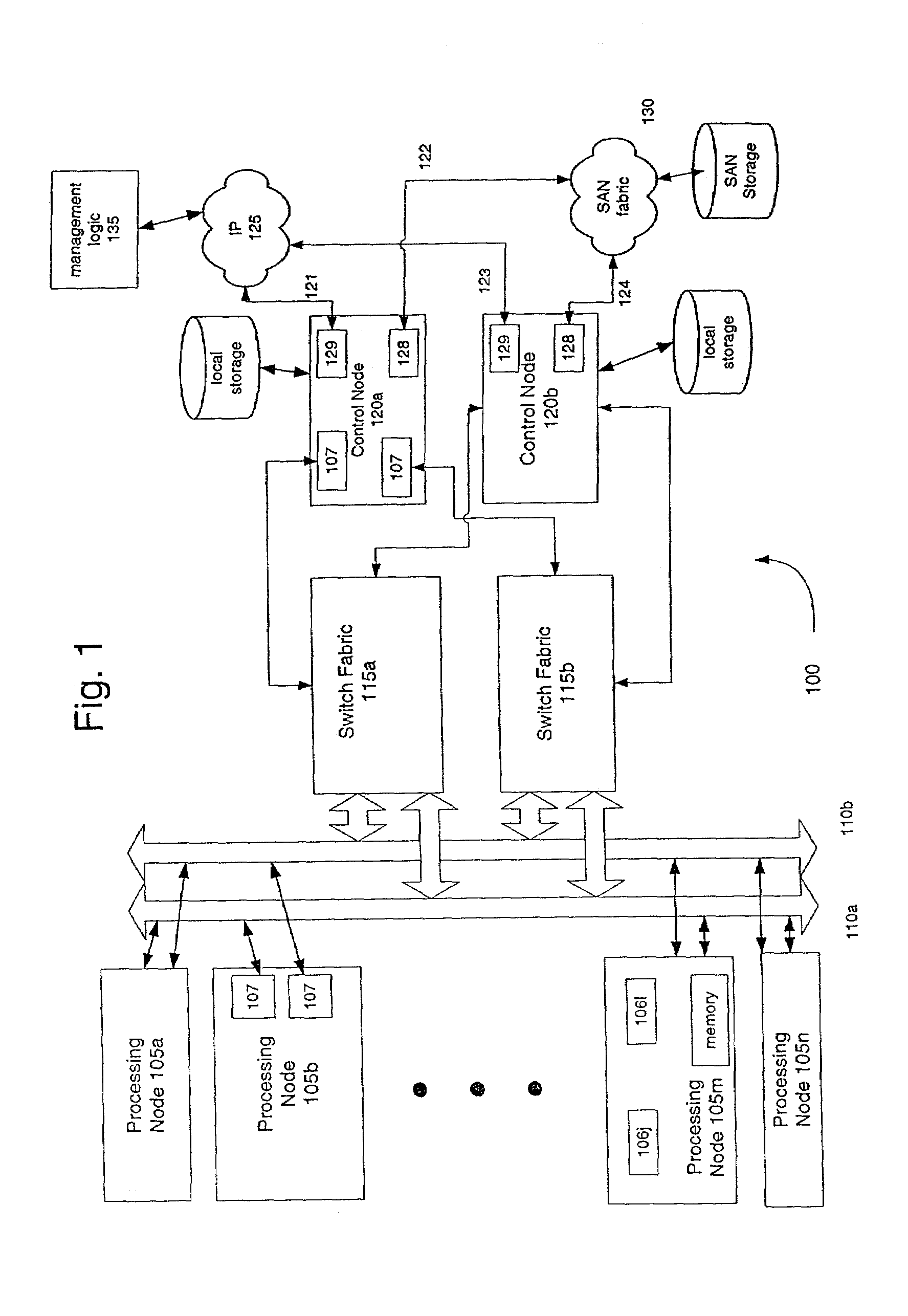
A virtual networking system and method are disclosed. Switched Ethernet local area network semantics are provided over an underlying point to point mesh. Computer processor nodes may directly communicate via virtual interfaces over a switch fabric or they may communicate via an ethernet switch emulation. Address resolution protocol logic helps associate IP addresses with virtual interfaces while allowing computer processors to reply to ARP requests with virtual MAC addresses.
Owner:EGENERA
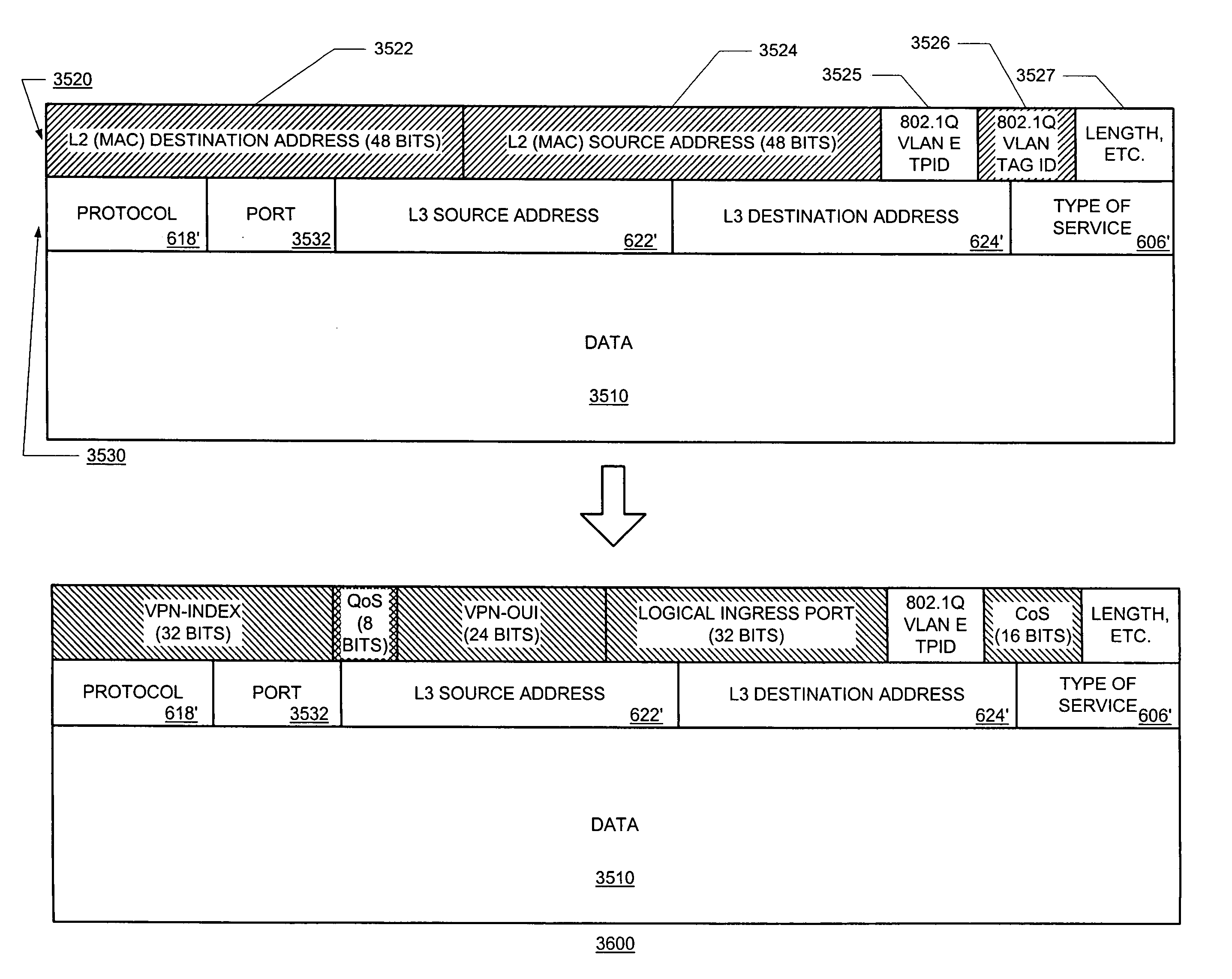
Methods, apparatus and data structures for preserving address and service level information in a virtual private network
InactiveUS6993026B1Energy efficient ICTTime-division multiplexAddress Resolution ProtocolArray data structure
Supporting virtual private networks by using a new layer 3 address to encapsulate a network-bound packet so that its context information, from which a layer 2 (e.g., MAC) address can be derived, is preserved. If this encapsulation was not done, the layer 2 address would change over each segment of the network. Thus, the encapsulation preserves the concept of group identification, using at least a part of the context, over the entire network and not just at the edge of the network. If a packet is received from the network (to be forwarded to a customer), the layer 3 address that was added in the encapsulation is stripped off. The original layer 3 destination address may be used with a client device addressing table to determine a new context information, and a layer 2 (e.g., MAC) address of a destination client device. If the client device addressing table does not include entries corresponding to the layer 3 destination address, an address resolution protocol (or “ARP”) may be broadcast to request such information or contents of inbound packets may be observed (snooping). The packet may then be forwarded to an aggregation device.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Processing method, access device and communication system for address resolution protocol
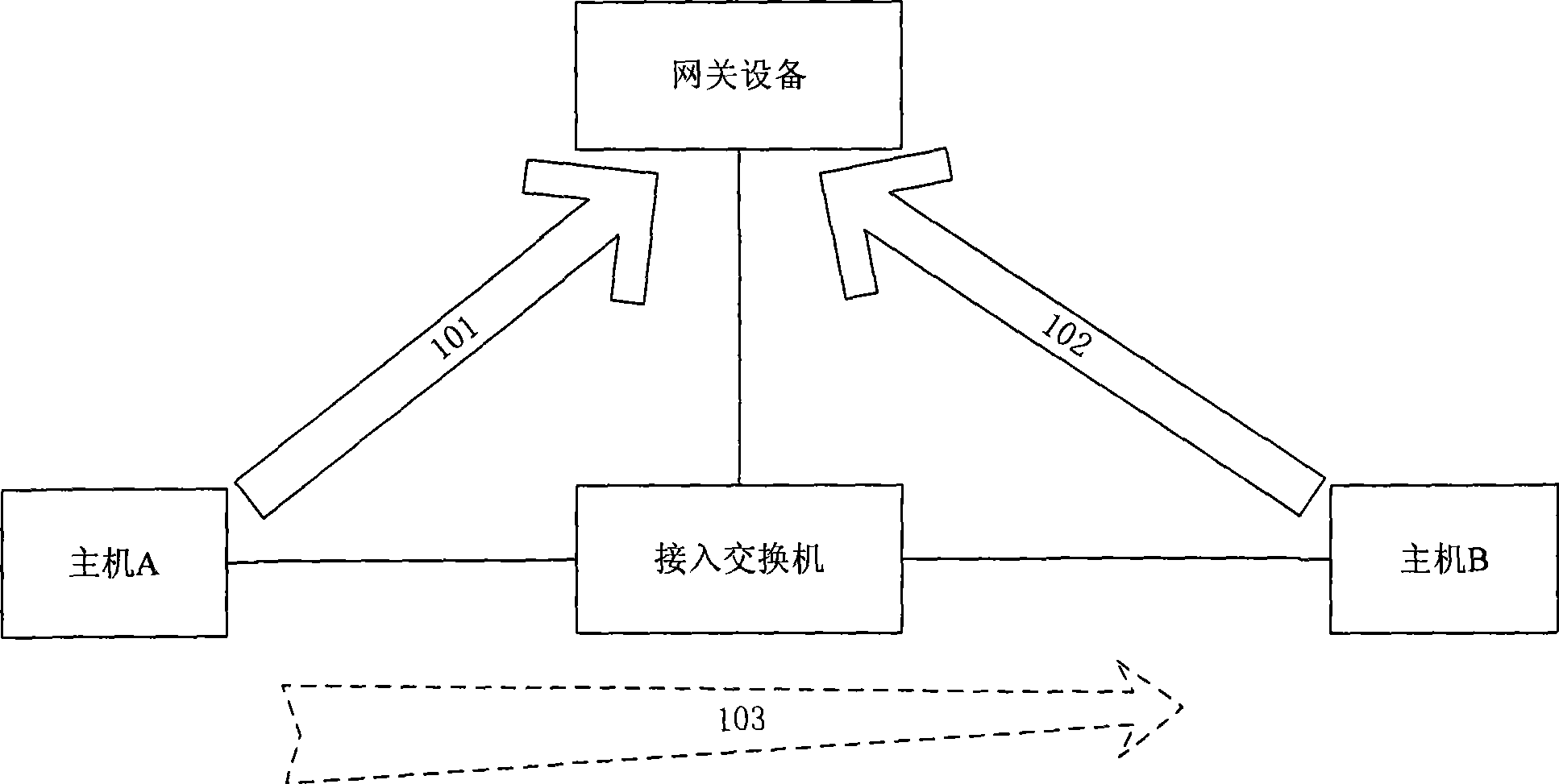
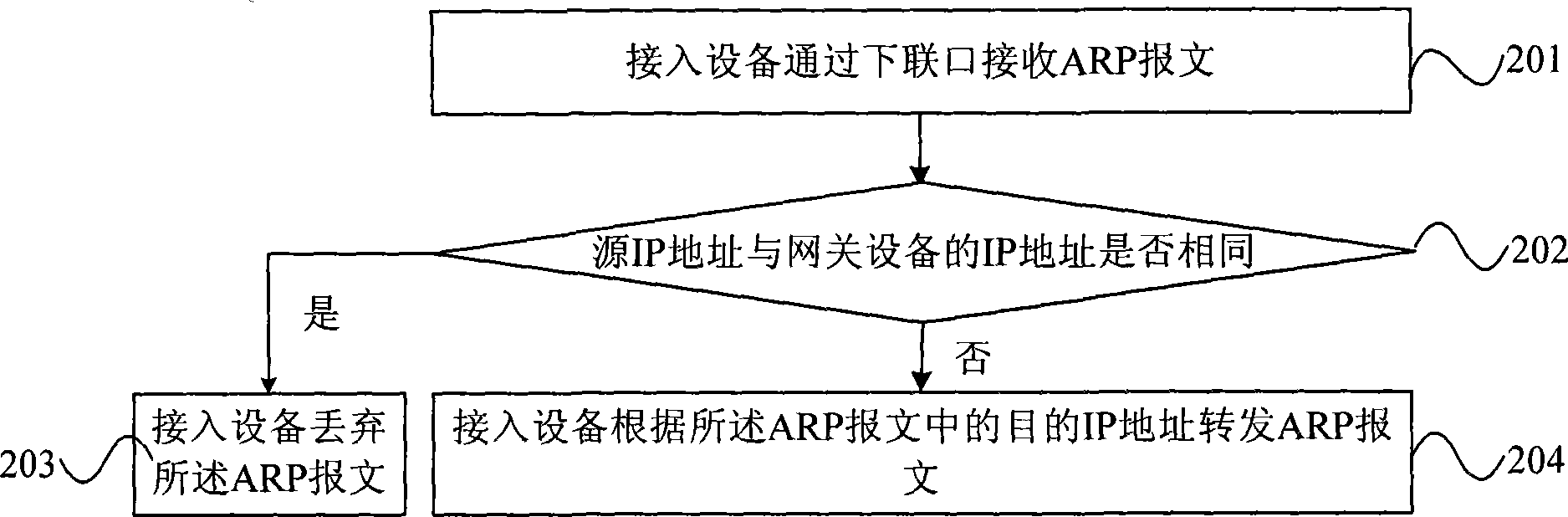
ActiveCN101394360AAvoid vibration and other failuresReduce the burden onData switching networksAddress Resolution ProtocolCommunications system
The invention discloses a method for handling an address resolution protocol (ARP) packet, and access equipment and a communication system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: access equipment receives an ARP packet through a lower interface, which carries an active Internet protocol (IP) address, a source media access control (MAC) address, a destination IP address and a destination MAC address; the access equipment judges whether the source IP address is the same as the IP address of gateway equipment configured on the lower interface, and the upper interface of the access equipment is connected with the gateway equipment; if the source IP address is the same as the IP address of gateway equipment, the access equipment discards the ARP packet; and if the source IP address is different from the IP address of gateway equipment, the access equipment forwards the ARP packet according to the destination IP address in the ARP packet. The embodiment of the invention can prevent the ARP packet which is deceived by an illegal host and passes through the gateway equipment of not performing ARP spoofing with respect to the gateway equipment, without imposing heavier load upon the gateway equipment.
Owner:BEIJING XINWANG RUIJIE NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Tunneling scheme optimized for use in virtual private networks
InactiveUS7379465B2Reduce Layer complexityTime-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionAddress Resolution ProtocolAddress resolution
A tunneling scheme includes the creation of tunnels having a source address and potentially multiple destination addresses. Each tunnel endpoint is divided into two sub-endpoints, where one sub-endpoint has a public network address and the other sub-endpoint has a private network address. Also included in the tunneling scheme is a static Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) table. The static ARP table contains information on virtual private network membership. More particularly, the static ARP table provides address resolution between public network addresses and private network addresses.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
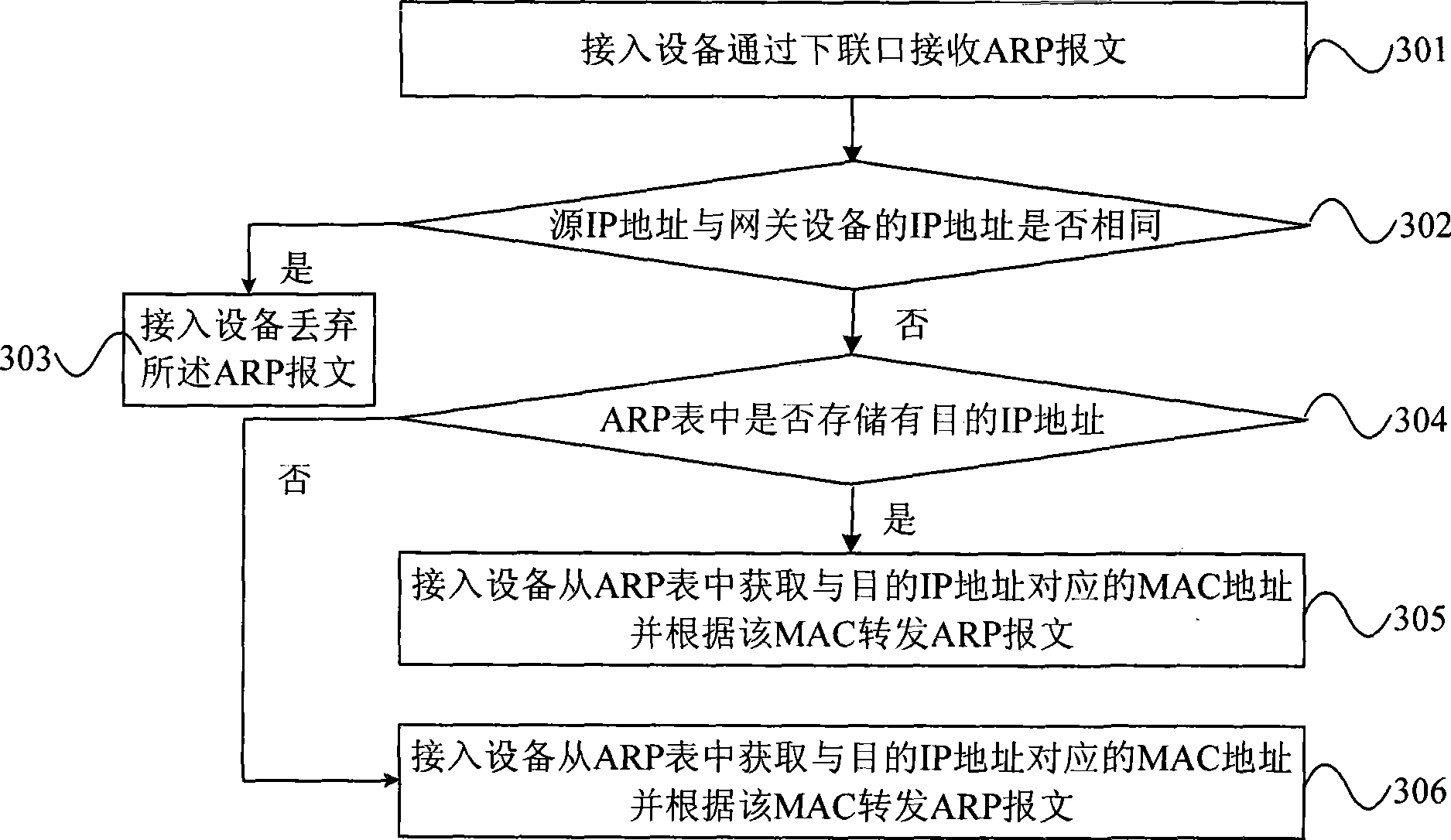
Address resolution protocol (ARP) cache management methods and devices
InactiveUS20080101381A1Reduce the numberData switching by path configurationAddress Resolution ProtocolParallel computing
An address resolution protocol (ARP) cache management method. An ARP cache comprises a plurality of ARP tables. Each ARP table comprises a plurality of updatable entries. The method comprises: receiving an ARP message; looking up the pluralities of ARP tables to find a message-matching entry; choosing an ARP table for storing new entries; creating a new entry to overwrite an existing entry in the chosen ARP table if no message-matching entry is found after looking up the ARP tables.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Peer-to-peer name resolution protocol (PNRP) group security infrastructure and method
InactiveUS7068789B2Improve securityIncrease flexibilityUser identity/authority verificationMultiple digital computer combinationsAddress Resolution ProtocolSecurity domain
A method for ensuring valid and secure peer-to-peer communications in a group structure. Specifically, the system of the present invention presents a method of ensuring secure peer-to-peer group formation, group member addition, group member eviction, group information distribution, etc. Such functionality may be distributed to the individual peers in the group to further enhance the overall security of the group while enhancing flexibility. The P2P group security allows every peer who is a valid member of the group to invite new members. The recipients of these invitations are then able to contact any member of the group to join the group, not only the inviter. Further, groups may function when the group creator is not online. Likewise, the method allows the creation of secure groups with users from different security domains, relying on their security credentials in those domains for initial authentication.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
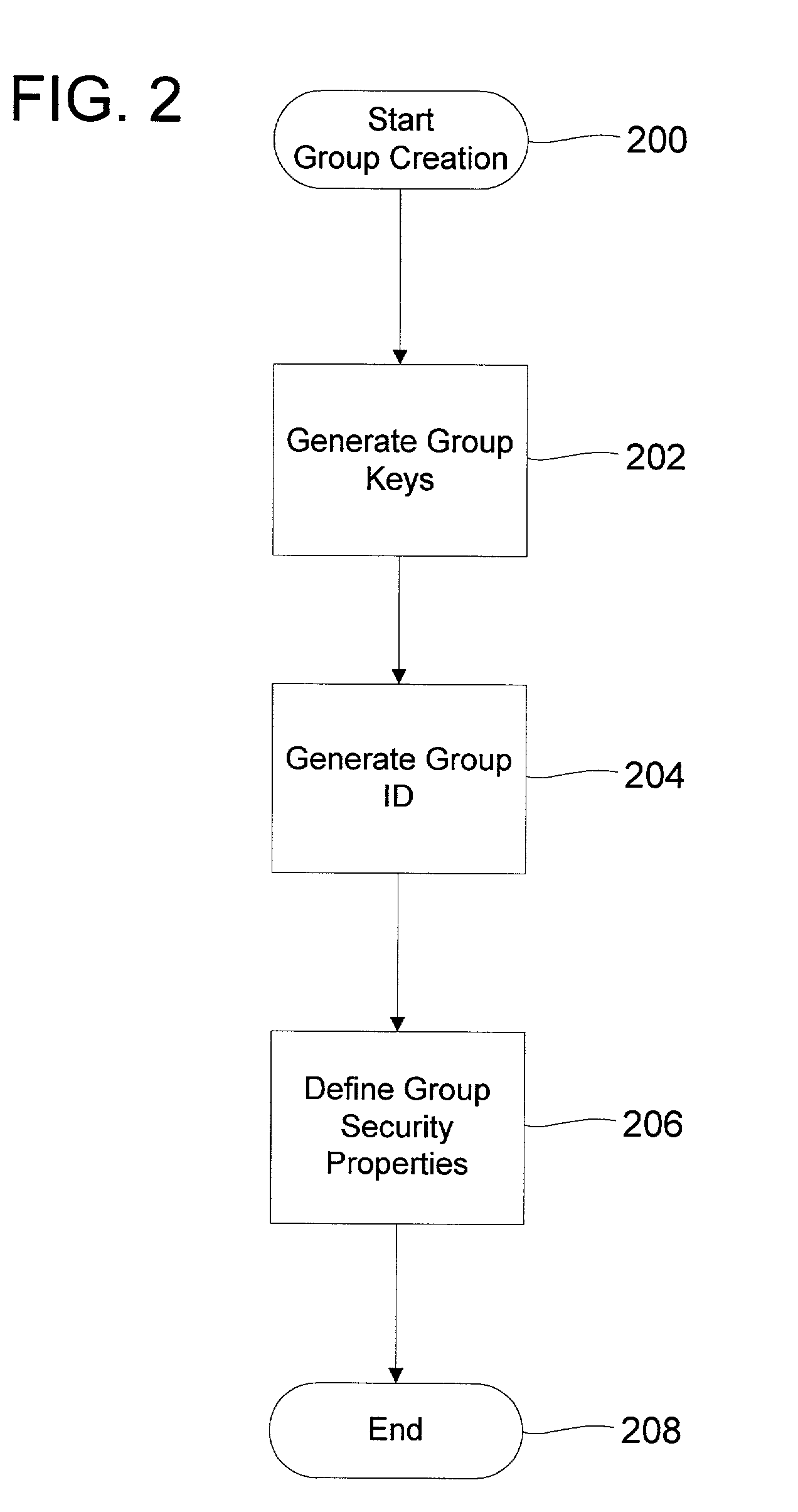
Address resolution protocol (ARP) message forwarding method, exchanger and controller
ActiveCN102938794ASave bandwidthImprove network efficiencyData switching networksAddress Resolution ProtocolAddress resolution
An embodiment of the invention provides an address resolution protocol (ARP) message forwarding method, an exchanger and a controller. The ARP message forwarding method includes: a first exchanger receives ARP messages; the first exchanger sends the ARP messages to the controller in the network to lead the controllers to construct response messages containing forwarding port messages according to the ARP messages; the first exchanger receives the response messages sent by the controller; and the first exchanger forwards the response messages to a corresponding port according to the forwarding port messages. The controller provides ARP service for a main machine of the network managed by the controller, and therefore network efficiency can be improved and network bandwidth can be saved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Security apparatus and method for local area networks
ActiveUS7124197B2Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsAddress Resolution ProtocolAddress resolution
The present invention includes a method and apparatus for controlling data link layer access to protected servers on a computer network by a client device. Address resolution requests broadcast on the network by the client device seeking access to any network device are received and then processed to determine whether the client device is unknown. If the client device is unknown, restriction address resolution replies are transmitted to the protected devices to restrict access by the client device to the protected devices and allow access to an authentication server. The authentication server is monitored to determine if the client device is authorized or unauthorized by the authentication server. If the client device is authorized, access is allowed to the protected devices. If the client device is unauthorized, blocking address resolution replies are transmitted on the computer network to block access by the client device to all other network devices.
Owner:SYSXNET
Enabling Co-Existence of Hosts or Virtual Machines with Identical Addresses
A method, an apparatus and an article of manufacture for enabling co-existence of multiple machines with identical addresses within a single data center network. The method includes assigning a unique pseudo identifier to each machine in the network that can be used for routing a packet to a destination machine, replacing a sender media access control address on an address resolution protocol request with a pseudo identifier of the sender at an edge network switch, retrieving a private network identifier from a mapping table based on the sender pseudo identifier and returning a pseudo identifier for the destination address based on the private network identifier, and replacing the pseudo identifier of the destination address with an actual identifier at a destination edge network switch for routing the packet to the destination machine.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for address resolution
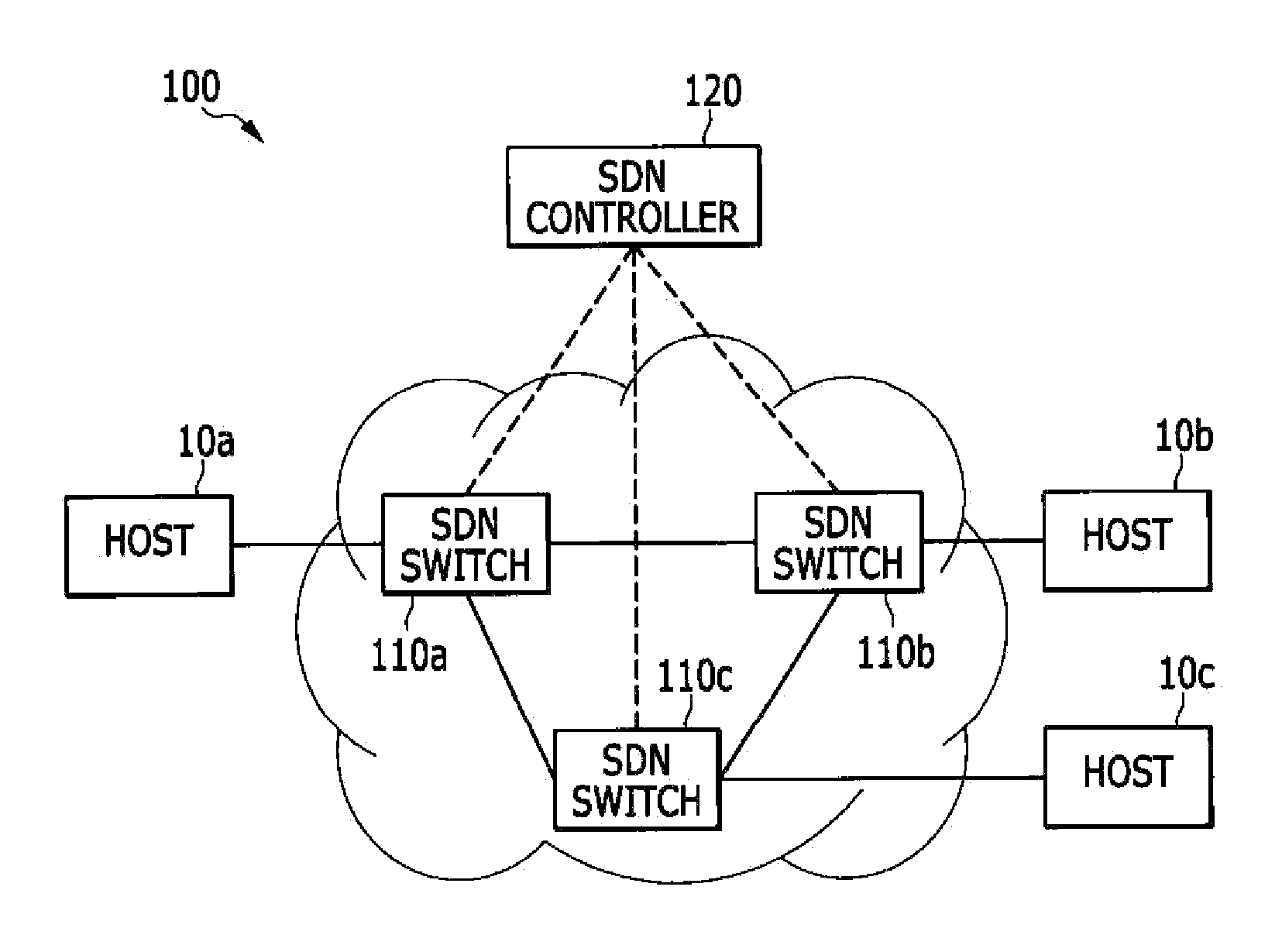
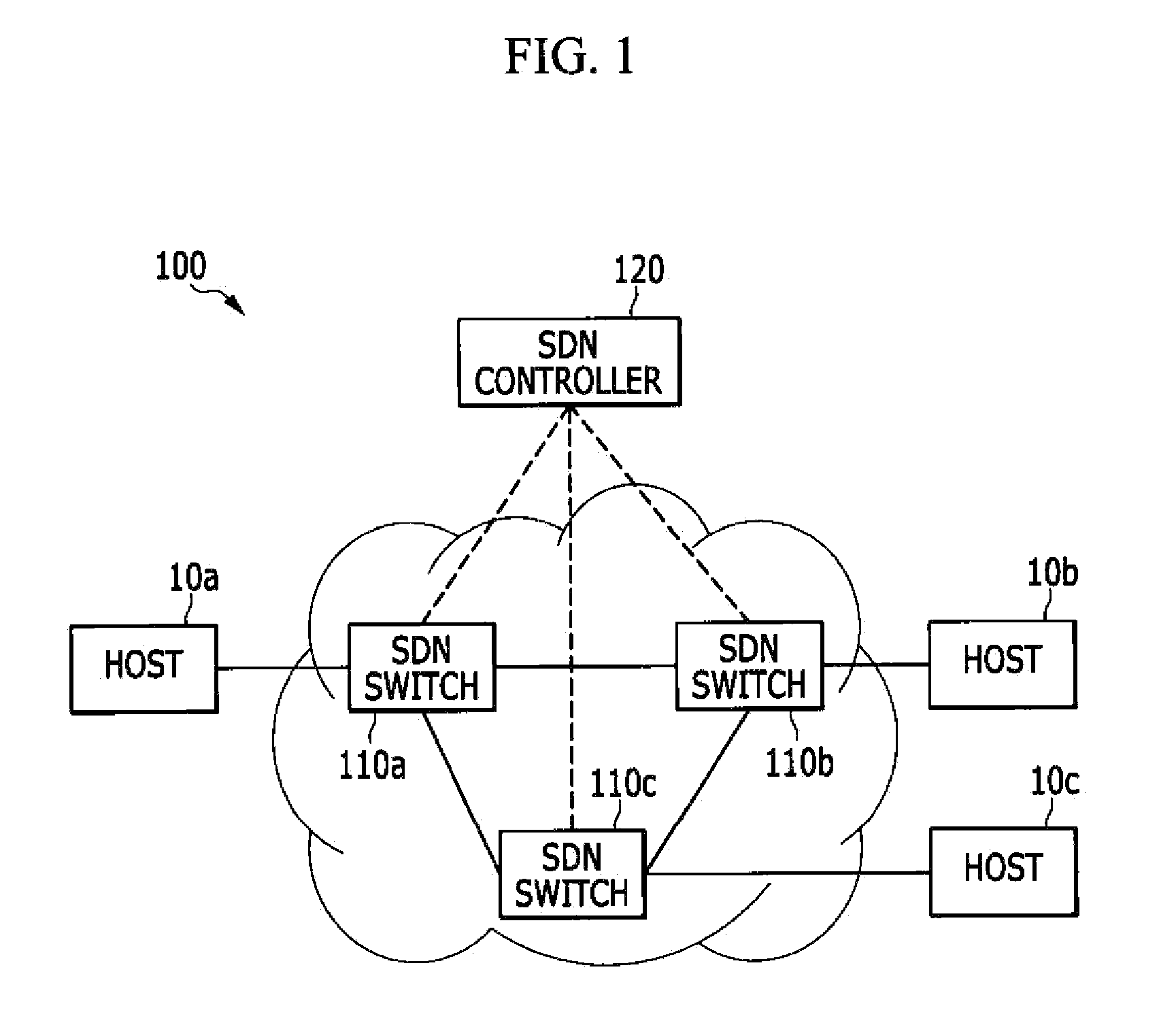
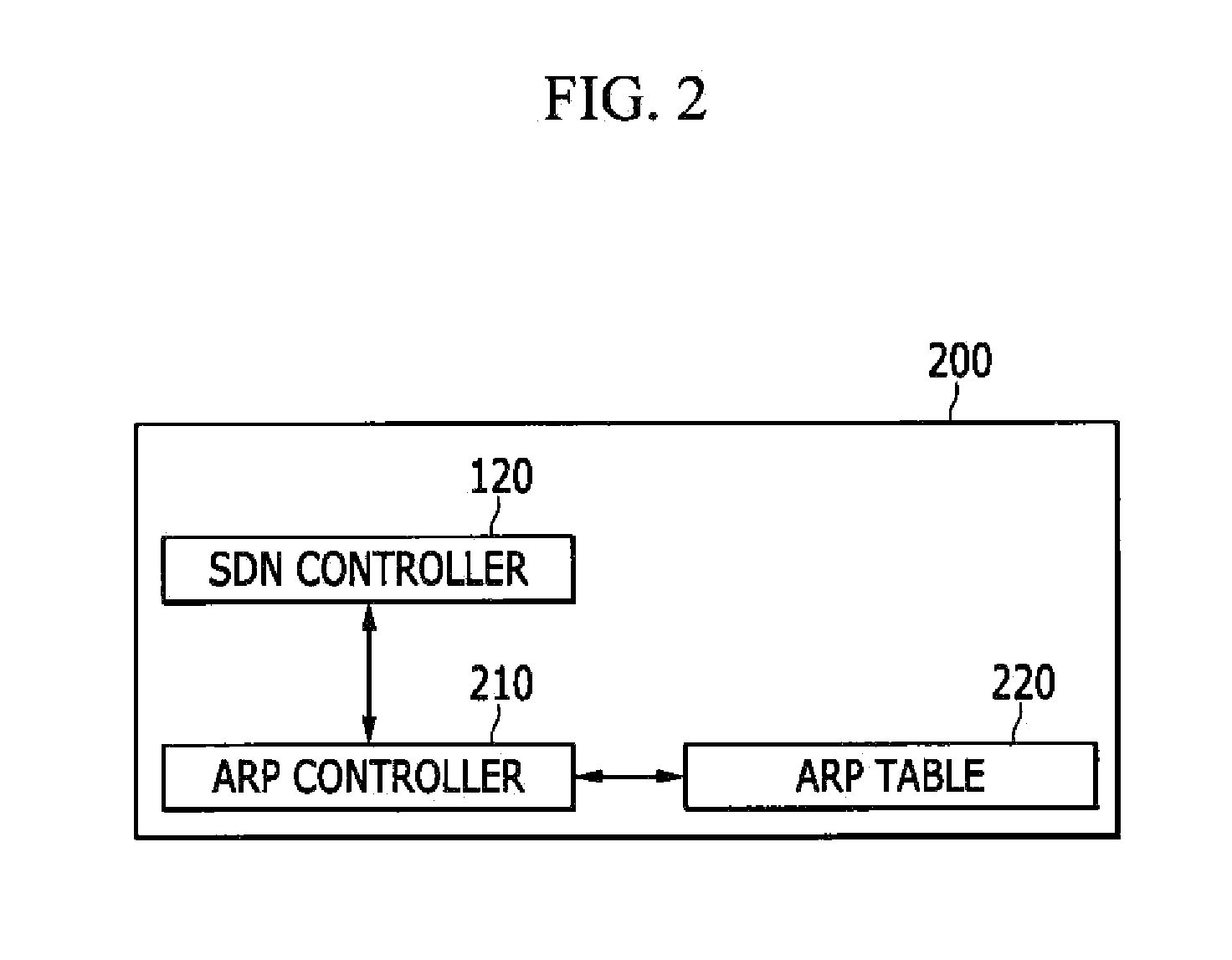
InactiveUS20150071289A1Reduce in quantityData switching by path configurationAddress Resolution ProtocolIp address
In an address resolution system in a centralized network control environment including a plurality of software defined network (SDN) switches, an address resolution protocol (ARP) controller checks whether an ARP table has a MAC address corresponding to the destination IP address of an ARP request packet when the ARP request packet is received from a source host. An SDN controller determines whether to broadcast the ARP request packet according to the existence of the MAC address corresponding to the destination IP address in the ARP table.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Controlling an Apparatus
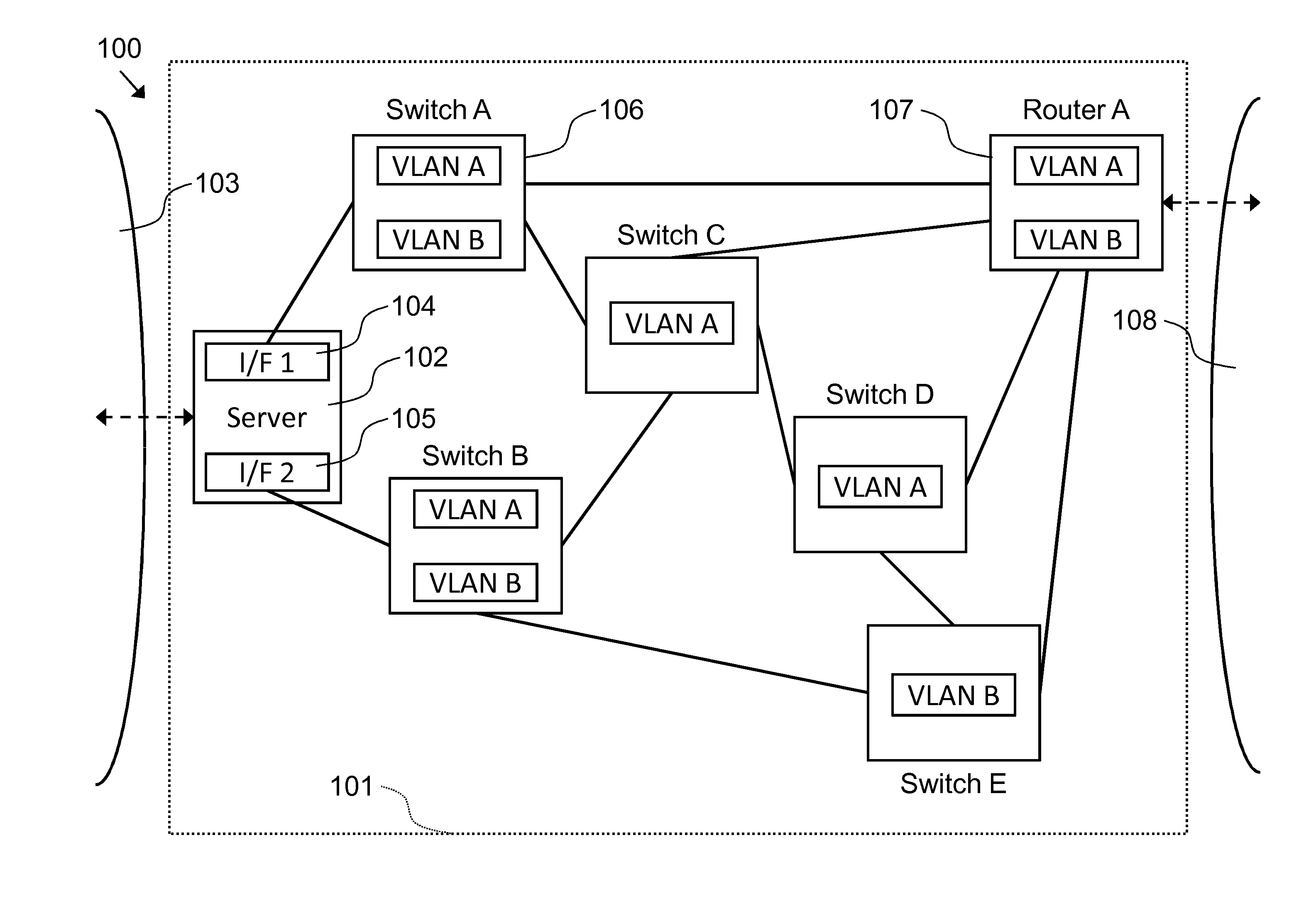
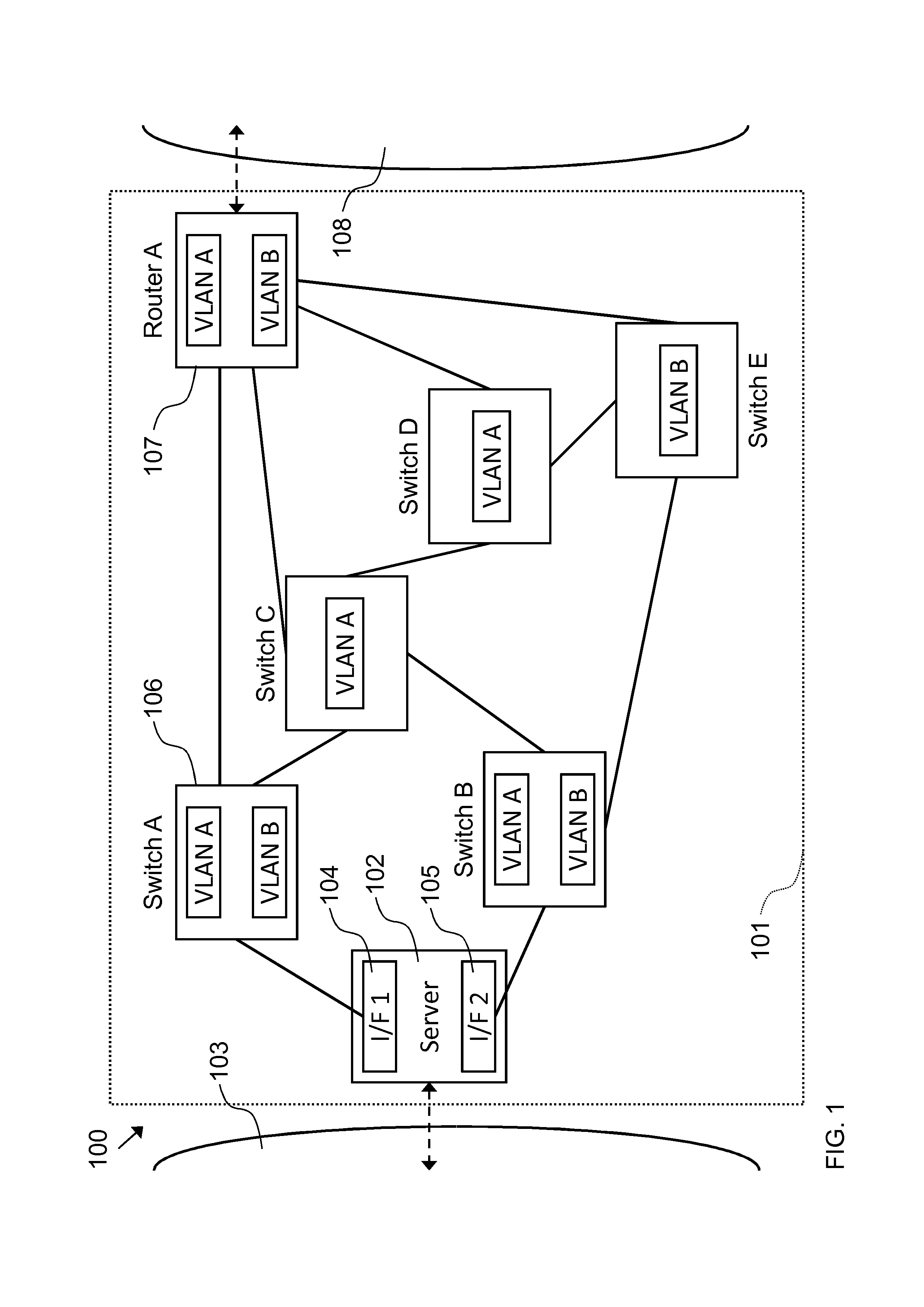
ActiveUS20130185416A1Raise priorityReduce overheadDigital computer detailsData switching networksComputer hardwareAddress Resolution Protocol
An apparatus in a LAN has first and second hardware interfaces to connect to the LAN. First and second monitoring request messages are transmitted to one or more devices in a first VLAN and one or more devices in a second VLAN respectively, via both the first and second hardware interfaces. The monitoring request messages use the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) or the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP). First and second monitoring response messages are received via the first and / or second hardware interfaces in response to the first and second monitoring request messages respectively. A selection is made between the first and second hardware interfaces for performing data communication, based on the first and second monitoring response messages. The selection is performed independently for data communication via the first and second VLANs based on at least one characteristic of the first and second monitoring response messages respectively.
Owner:METASWITCH NETWORKS LTD
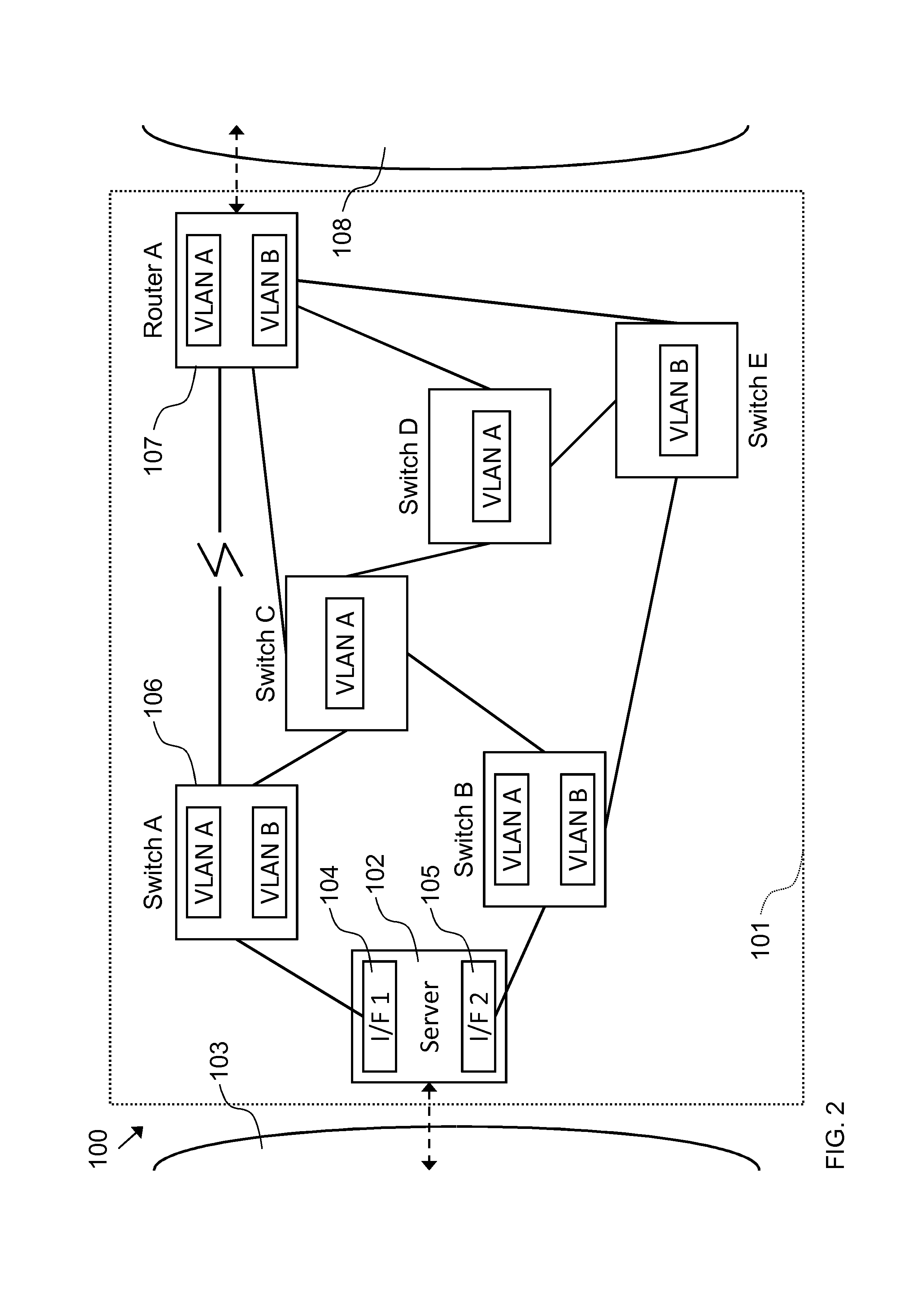
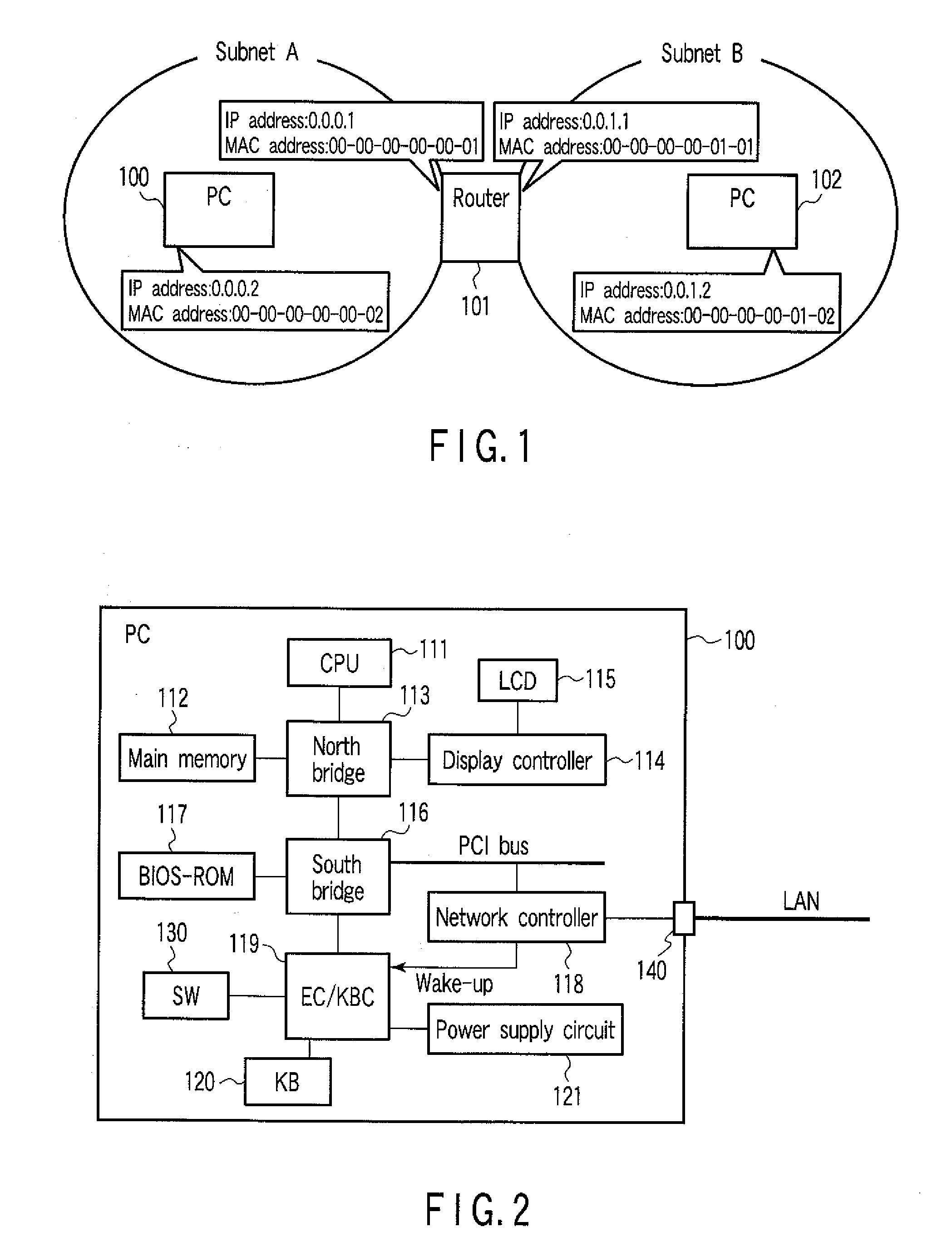
Network controller, information processing apparatus and wake-up control method
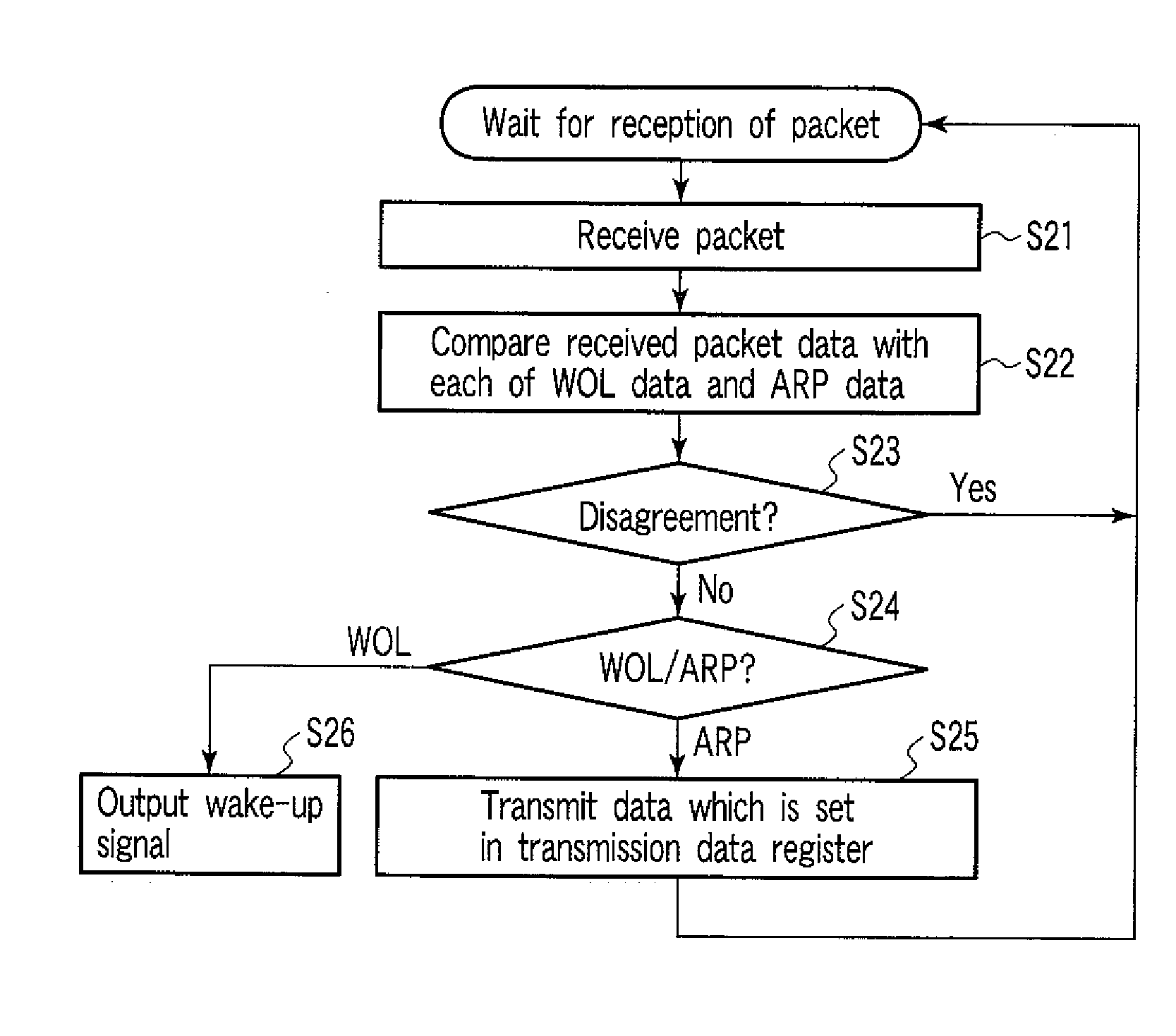
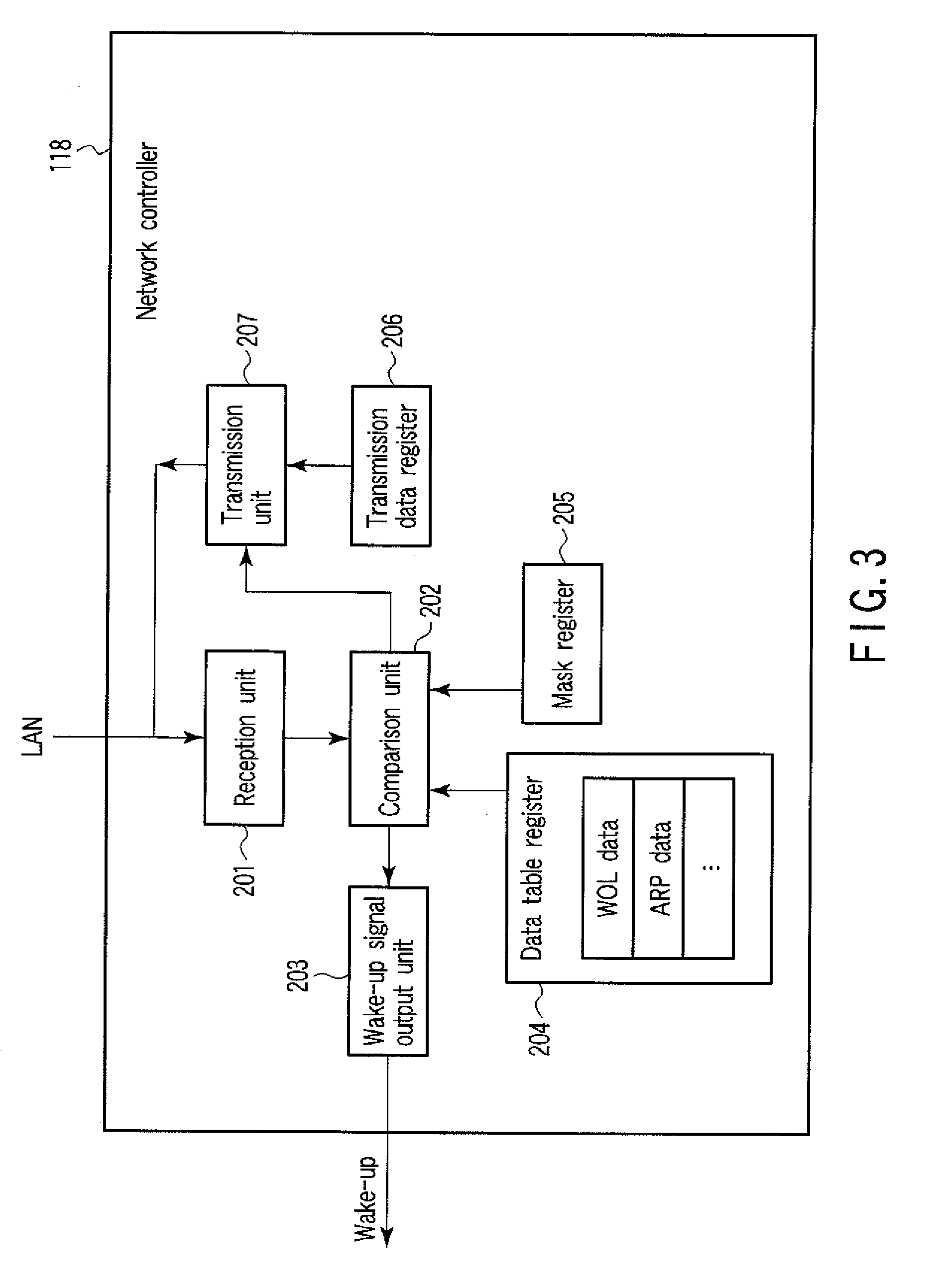
InactiveUS20080301322A1Energy efficient ICTSubstation remote connection/disconnectionAddress Resolution ProtocolData pack
According to one embodiment, a network controller includes a data register which stores first data indicative of a data pattern of an address resolution protocol request packet including a network address of an information processing apparatus, and second data indicative of a data pattern of a wake-up packet for waking up the information processing apparatus, a comparison unit configured to compare a data pattern of an incoming packet with the first data and the second data, while the information processing apparatus is in a sleep state, a transmission unit configured to send, if the data pattern of the incoming packet agrees with the first data, the address resolution protocol reply packet to the network, and a wake-up signal output unit configured to output, if the data pattern of the incoming packet agrees with the second data, a wake-up signal for instructing wake-up to the information processing apparatus.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method for automatic traffic interception
InactiveUS20060050703A1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsAddress Resolution ProtocolIp address
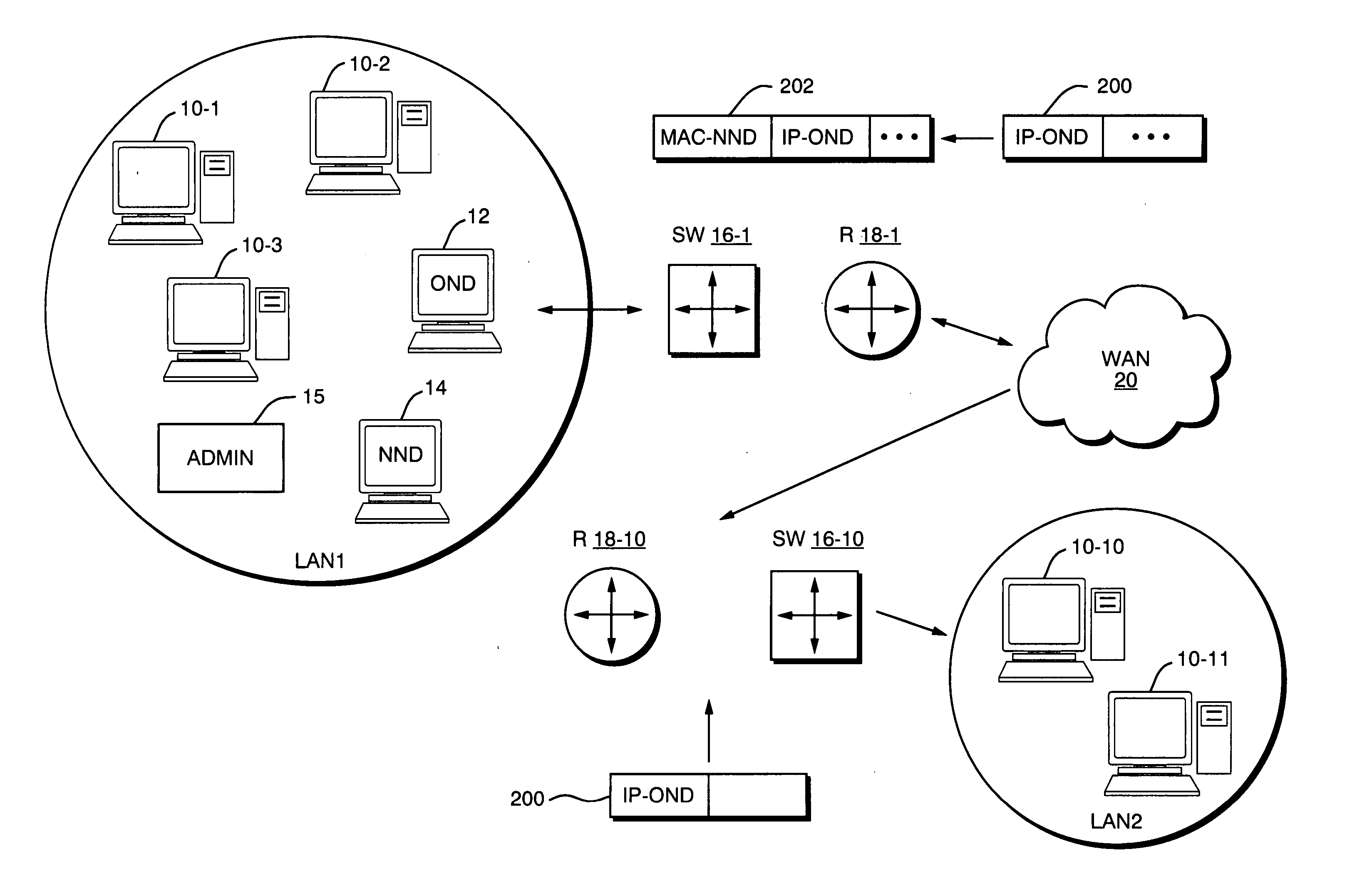
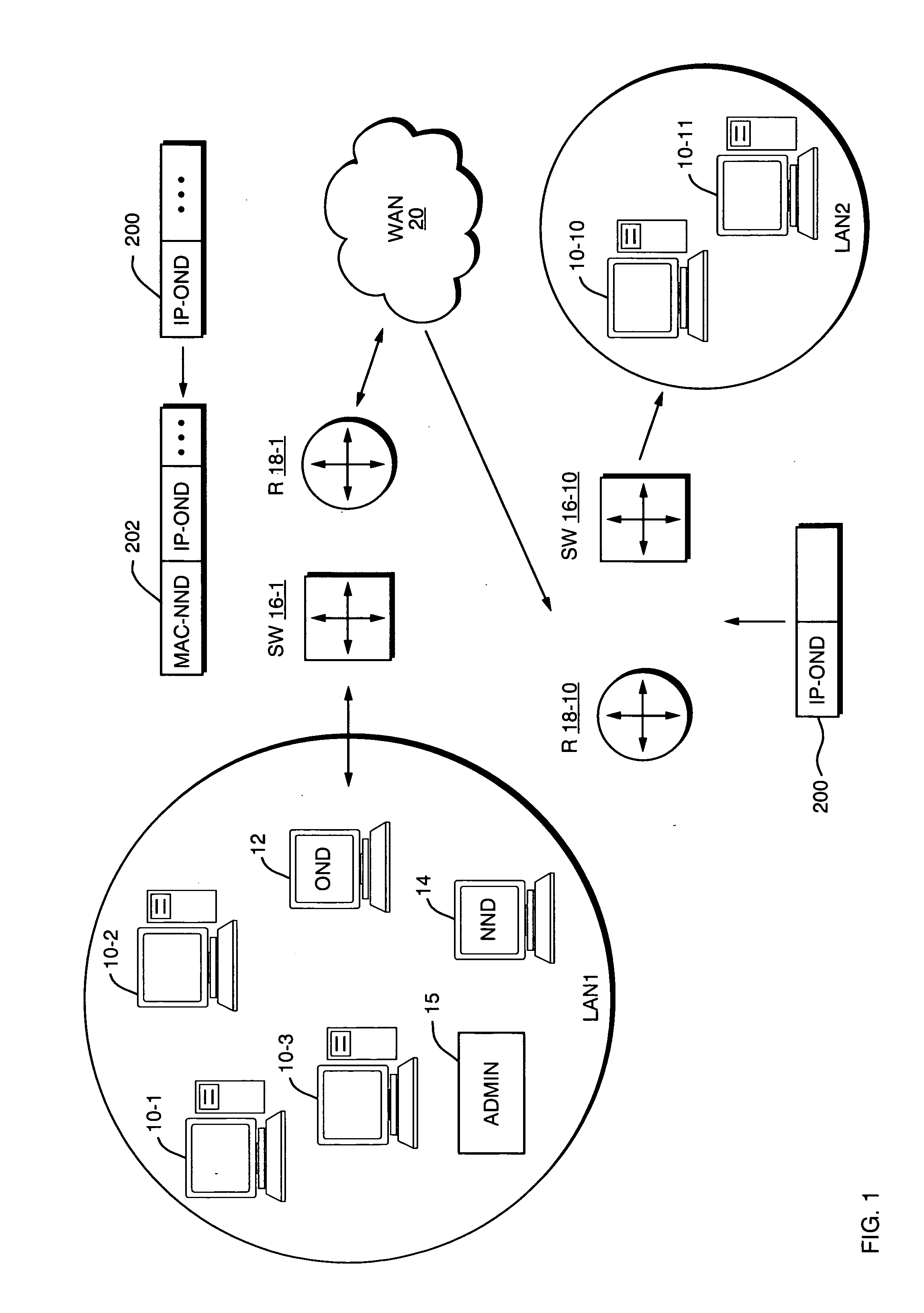
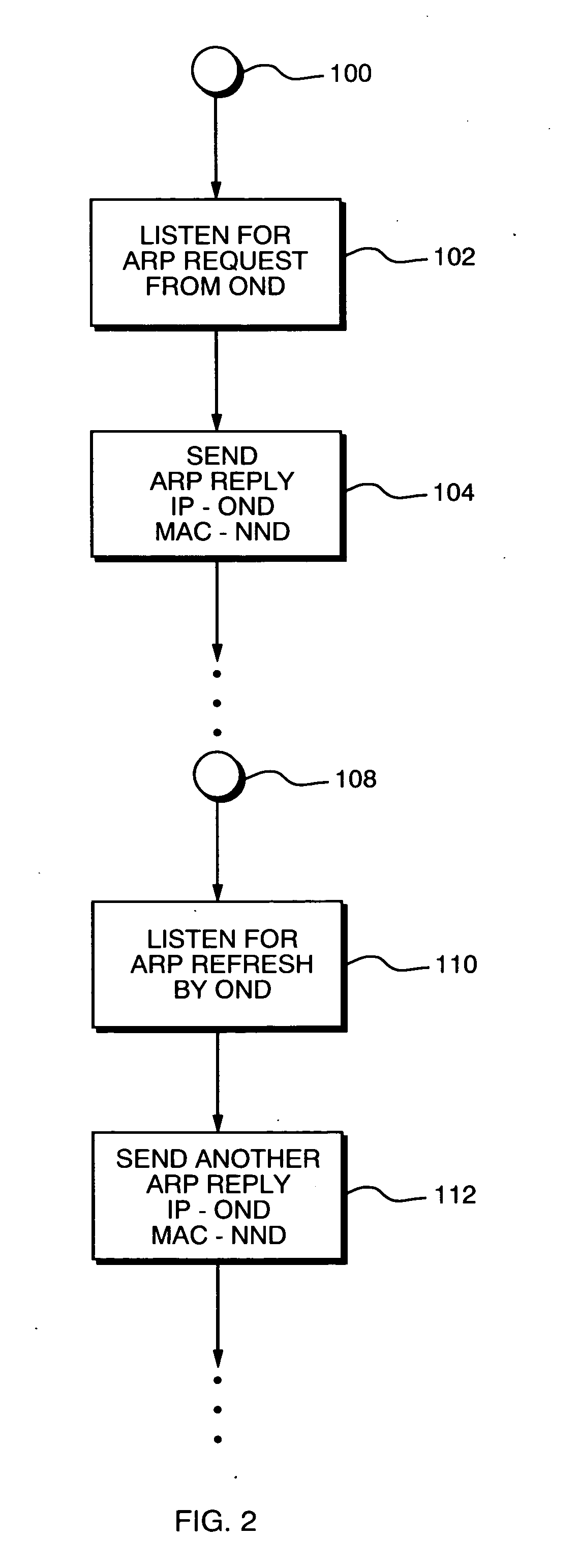
A technique for connecting New Network Devices (NNDs) to an existing communication network. The NND caches the MAC address of an Original (or “Old”) Network Device, then gratuitously transmits Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) responses on behalf of the OND, but pointing to its own MAC address. This, in effect, allows the NND to insert itself in the path of packets originally destined for the OND. After performing its designated operations such as filtering, compression, caching, file serving, virus scanning, etc., any remaining packets can still be forwarded to the OND for further processing. In this event, the packets are forwarded by the NND to the OND as MAC layer frames using the OND's MAC address only and not its IP address. In the event that the NND fails, no special steps need to be taken, as the OND will eventually receive traffic again as it responds to further ARP requests.
Owner:F5 NETWORKS INC +1
IP aliases in logical networks with hardware switches
ActiveUS20170093758A1Reduce decreaseMitigate issueData switching networksIP aliasingAddress Resolution Protocol
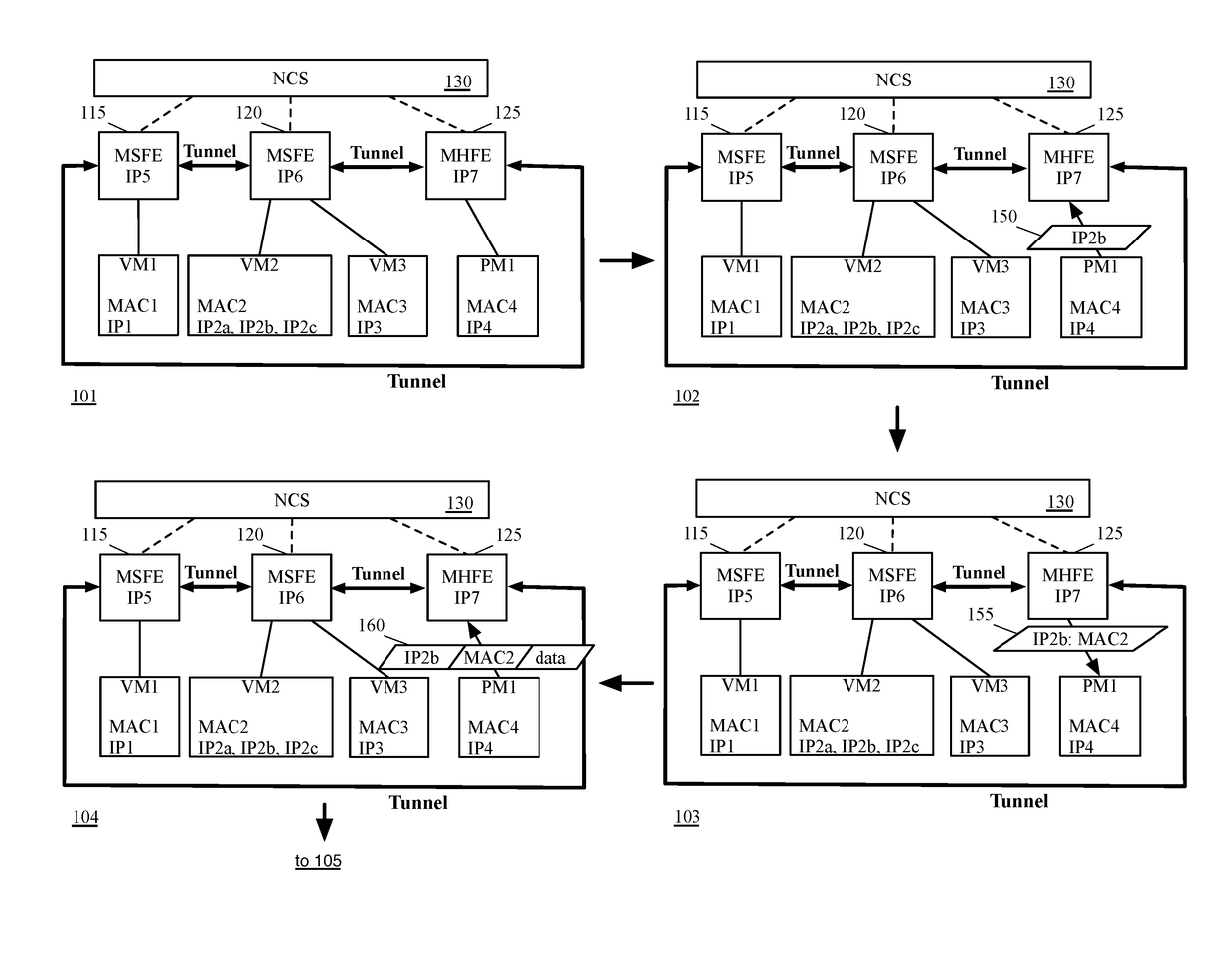
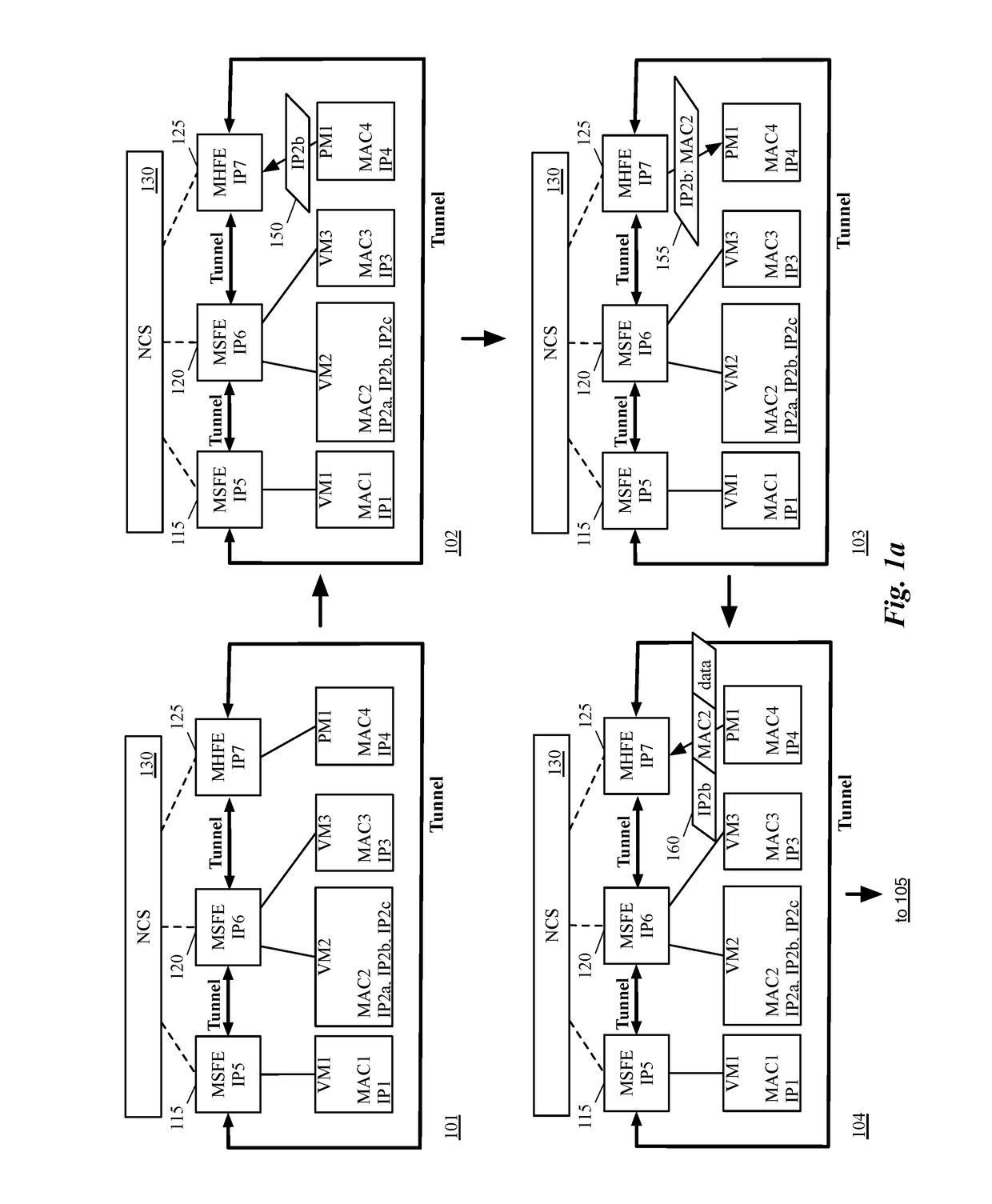
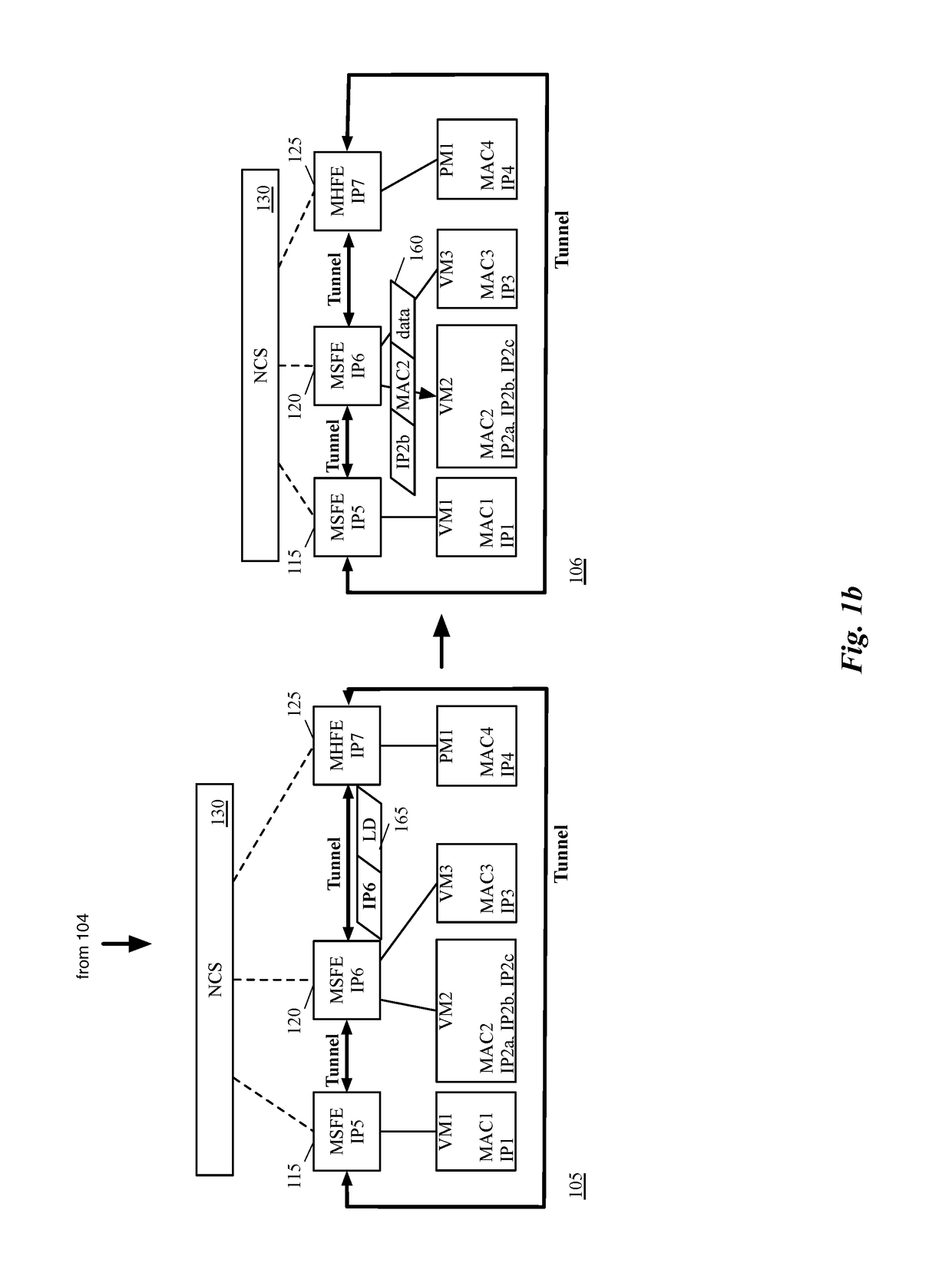
Some embodiments provide a novel method of configuring a managed hardware forwarding element (MHFE) that implements a logical forwarding element (LFE) of a logical network to handle address resolution requests (e.g., Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) requests) for multiple addresses (e.g., IP addresses) associated with a single network interface of the logical network. The method identifies a physical port of the MHFE with which the multiple addresses are to be associated. The physical port is coupled to an end machine (e.g., a virtual machine, server, container, etc.) of the logical network. The method then modifies associations stored at the MHFE to associate the physical port with the multiple addresses.
Owner:NICIRA
Methods and devices for preventing ARP cache poisoning
InactiveUS20060209818A1Improve securityData switching by path configurationAddress Resolution ProtocolIp address
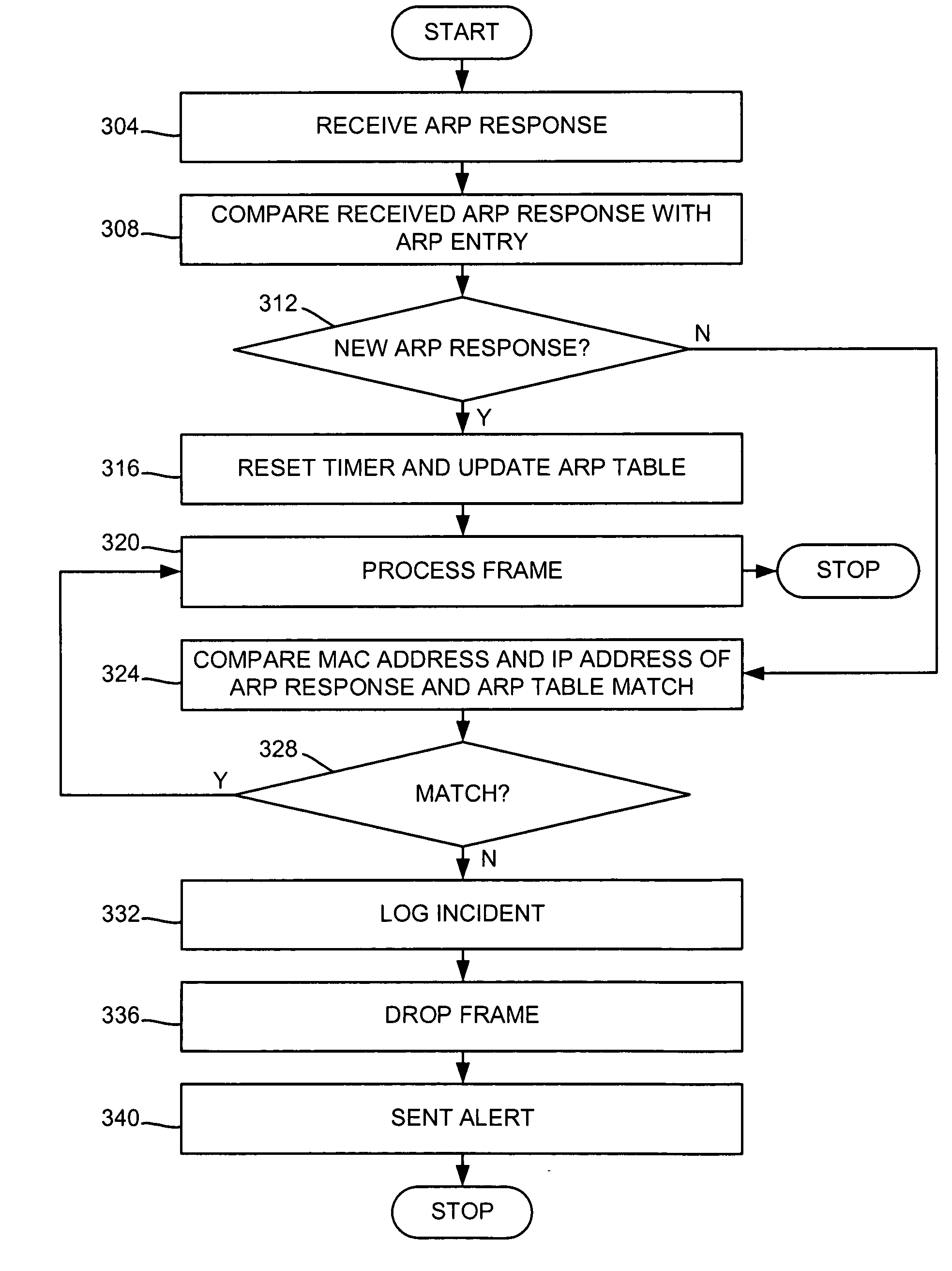
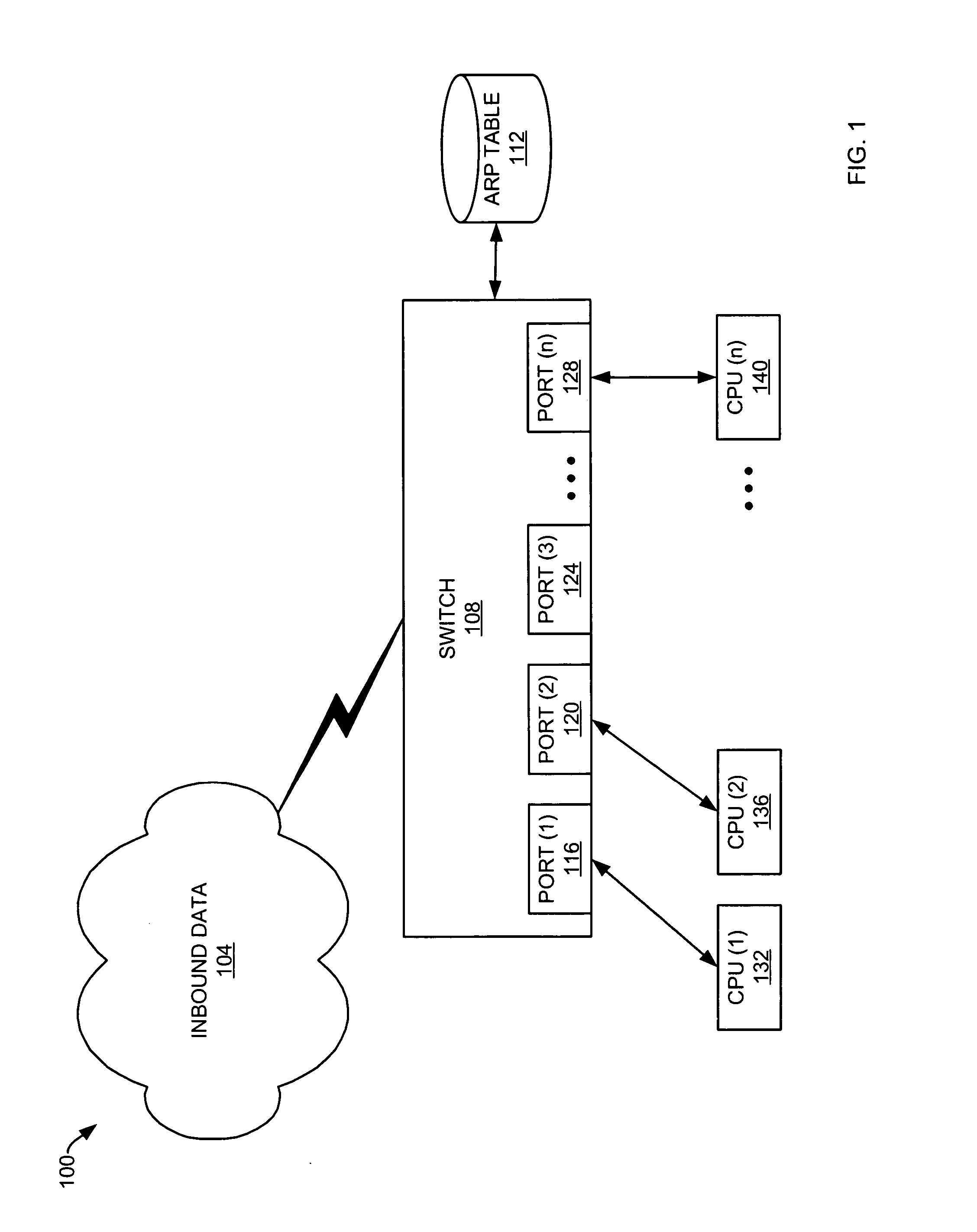
Methods of processing an address resolution protocol (ARP) response in connection with a data control switch are presented including: receiving an ARP response, the ARP response having an ARP response MAC address and a corresponding ARP response IP address; and dropping the ARP response when: the ARP response MAC address matches any of a plurality of ARP entry MAC addresses residing in an ARP table, and the corresponding ARP response IP address does not match a corresponding ARP entry IP address. In some embodiments, methods further include: creating an ARP entry corresponding to the ARP response in the ARP table when: the ARP response MAC address does not match any of the plurality of ARP entry MAC addresses.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
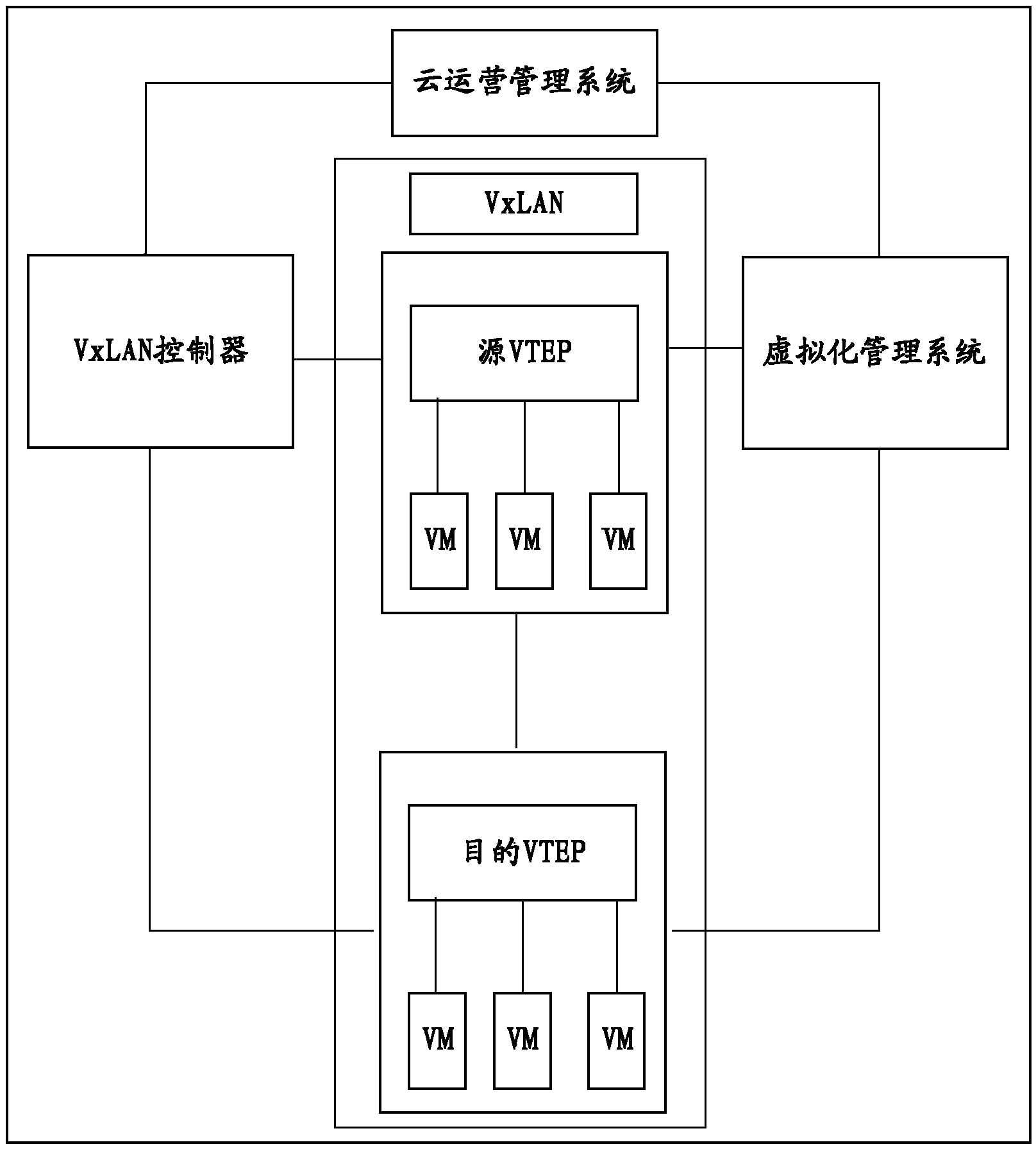
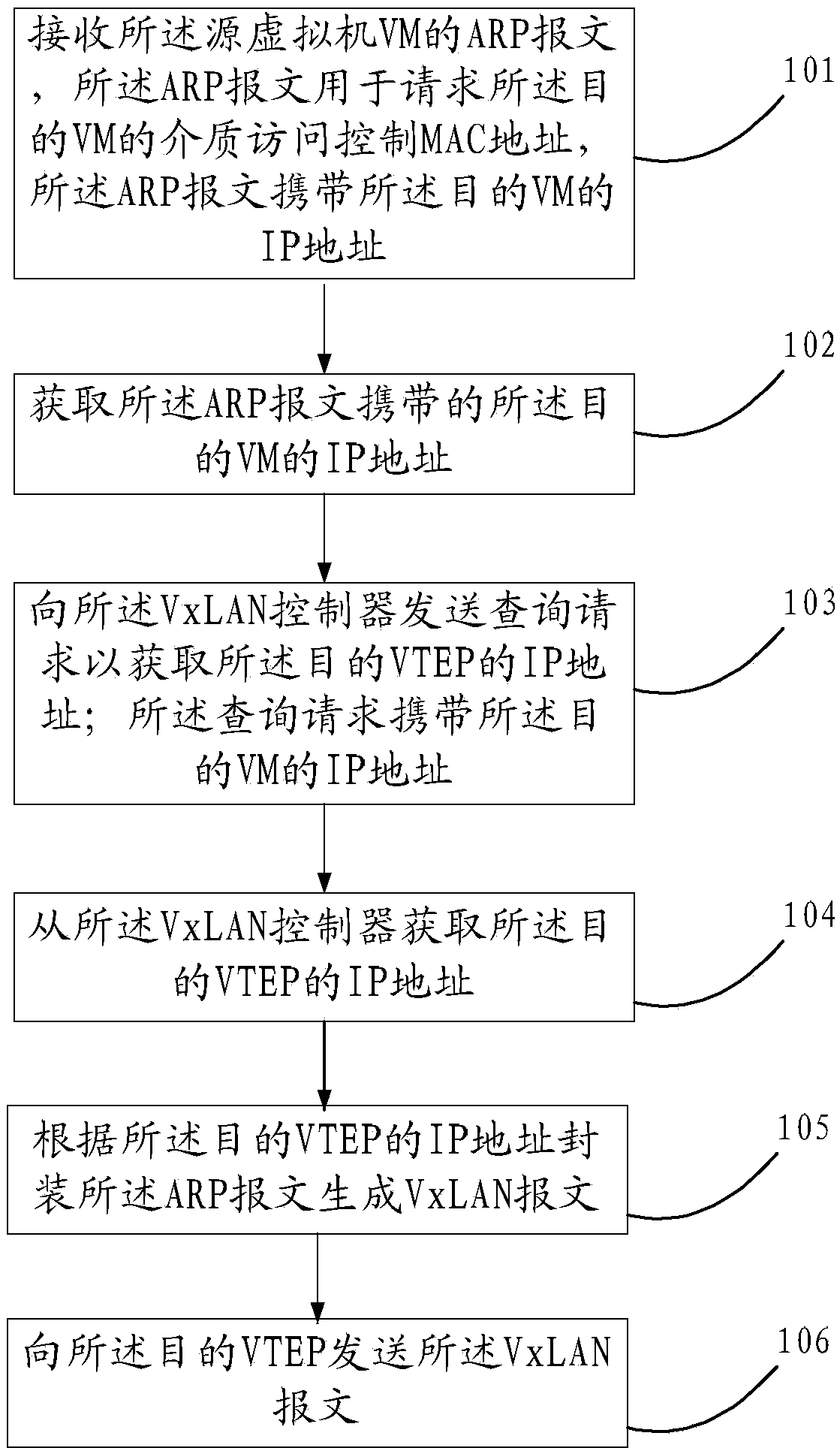
Method for sending ARP message in VxLAN, VTEP and VxLAN controller
ActiveCN103647853AReduce wasteSave bandwidthNetworks interconnectionAddress Resolution ProtocolIp address
The invention discloses a method for sending an ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) message in a VxLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN), a VTEP (VxLAN Tunnel Endpoint) and a VxLAN controller so that a problem that resource waste is generated because messages are sent in a multicast method is eliminated. The method for sending the ARP message mainly includes that: a source VTEP receives an ARP message of a source virtual machine (VM), wherein the APP message is used for requesting a media access control MAC address of a target VM and the ARP message carries the IP address of the target VM; the IP address of the target VM, carried in the APP message is acquired; a query request is sent to the VxLAN controller so as to acquire the IP address of a target VTEP, wherein the query request carries the IP address of the target VM; the IP address of the target VTEP is acquired from the VxLAN controller; the APP message is packaged according to the IP address of the target VTEP so that a VxLAM message is generated; and the VxLAM message is sent to the target VTEP.
Owner:HUAWEI CLOUD COMPUTING TECH CO LTD
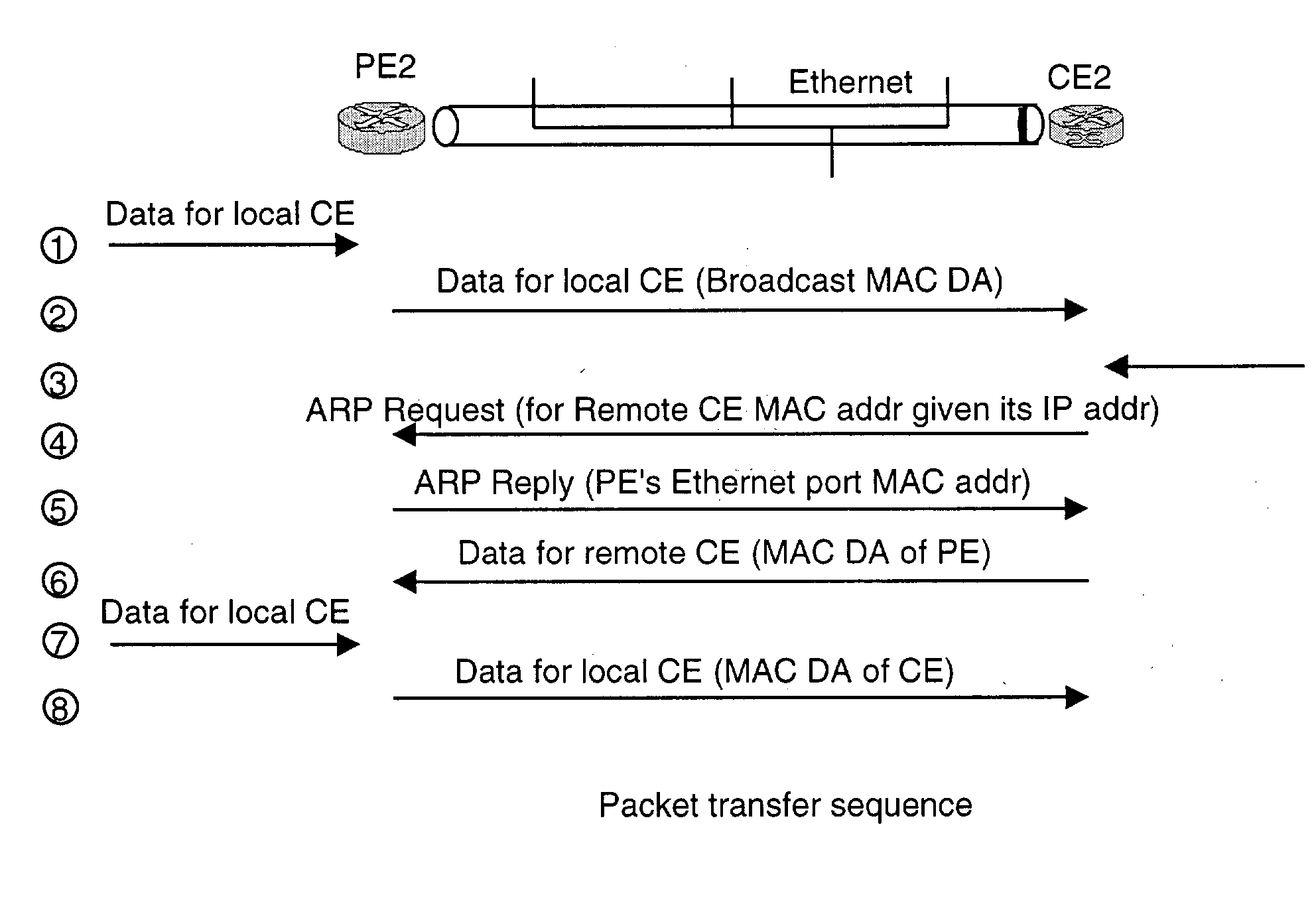
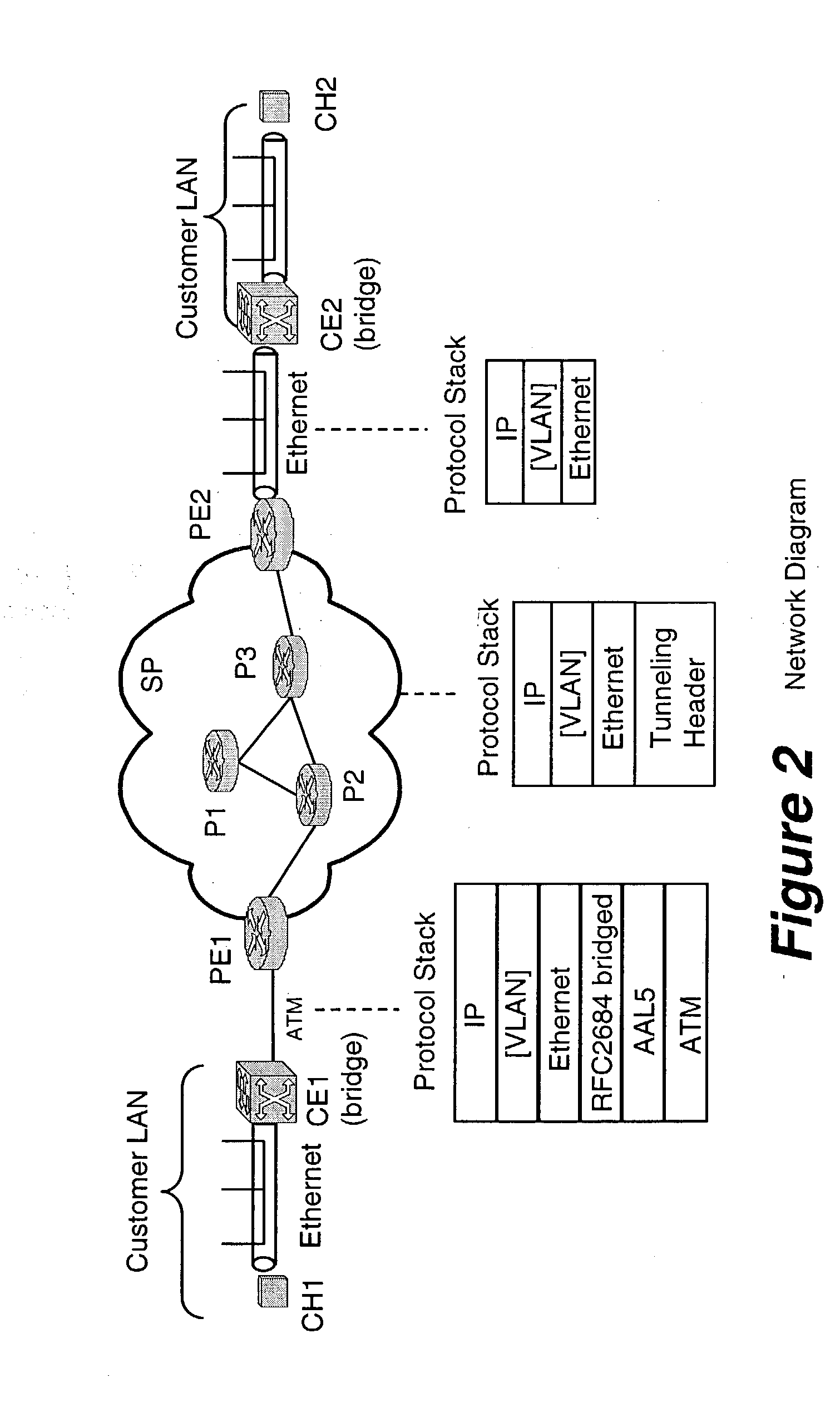
Address resolution in IP interworking layer 2 point-to-point connections
InactiveUS20040202199A1Time-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionAddress Resolution ProtocolFrame Relay
A heterogeneous point-to-point links involves different technologies at it two ends, e.g., Ethernet at one end and ATM or Frame Relay at the other end. If two IP systems are connected via a heterogeneous point-to-point link, each may be using different address learning techniques. It is up to the Provider Edge devices to make these different techniques inter-work. A novel provider edge device and procedures that the edge device it to perform for forwarding packets properly are described. According to the invention, the provider edge device uses a broadcast address to forward the packet in one direction toward a customer edge device. In another direction, the provider edge device responds to an ARP request from the customer edge device with its own MAC address so that it can receive a packet from the customer edge device.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
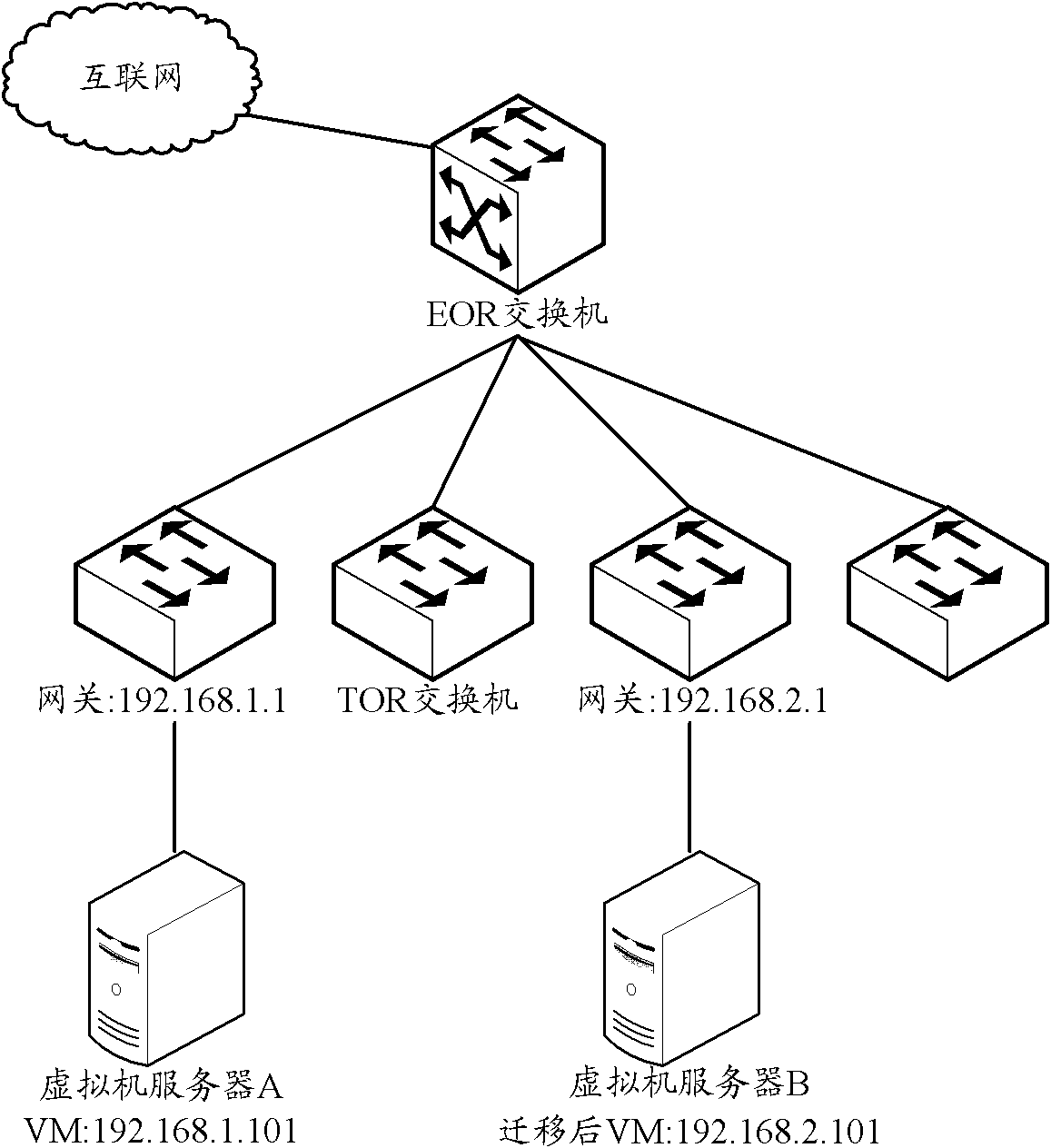
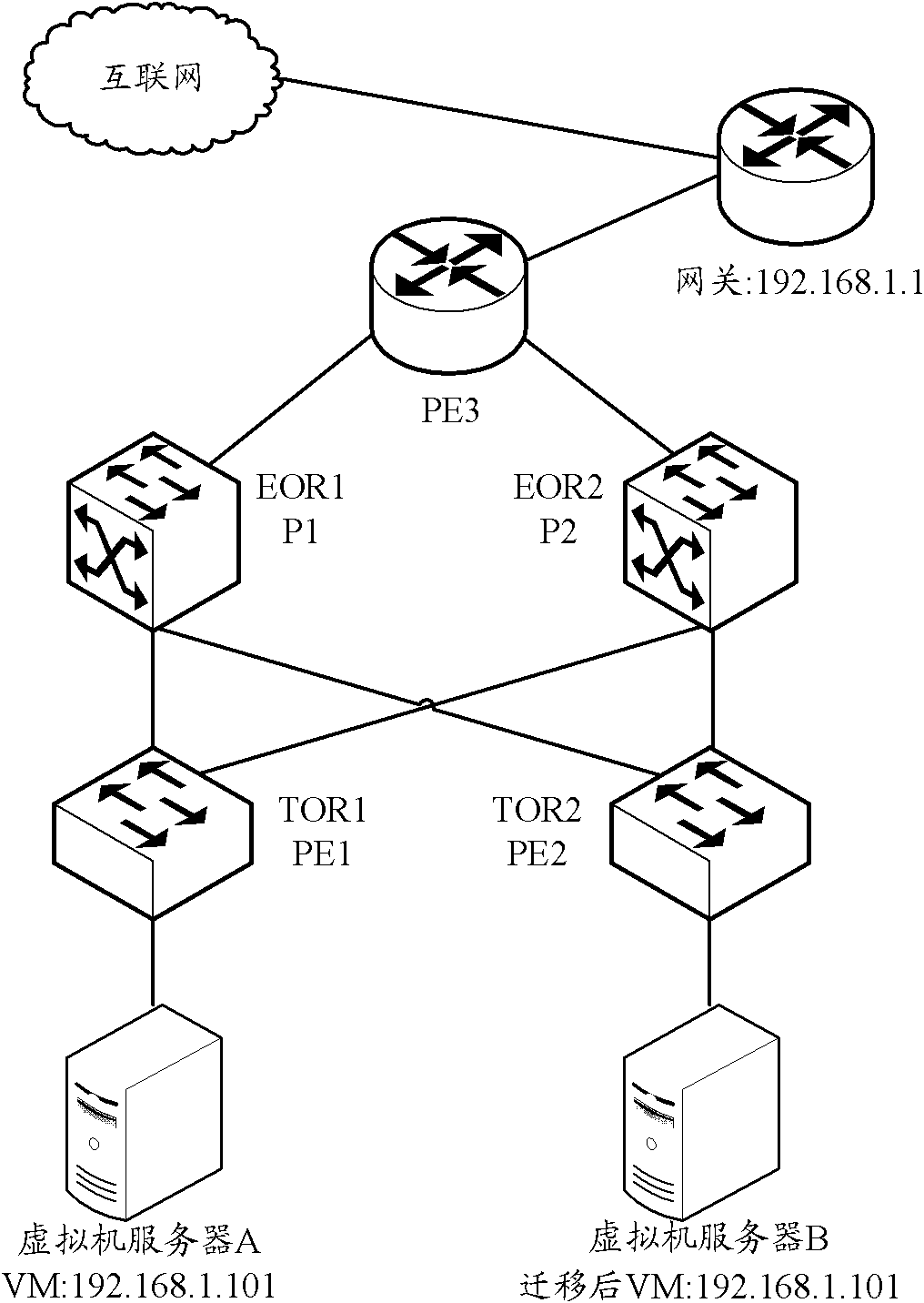
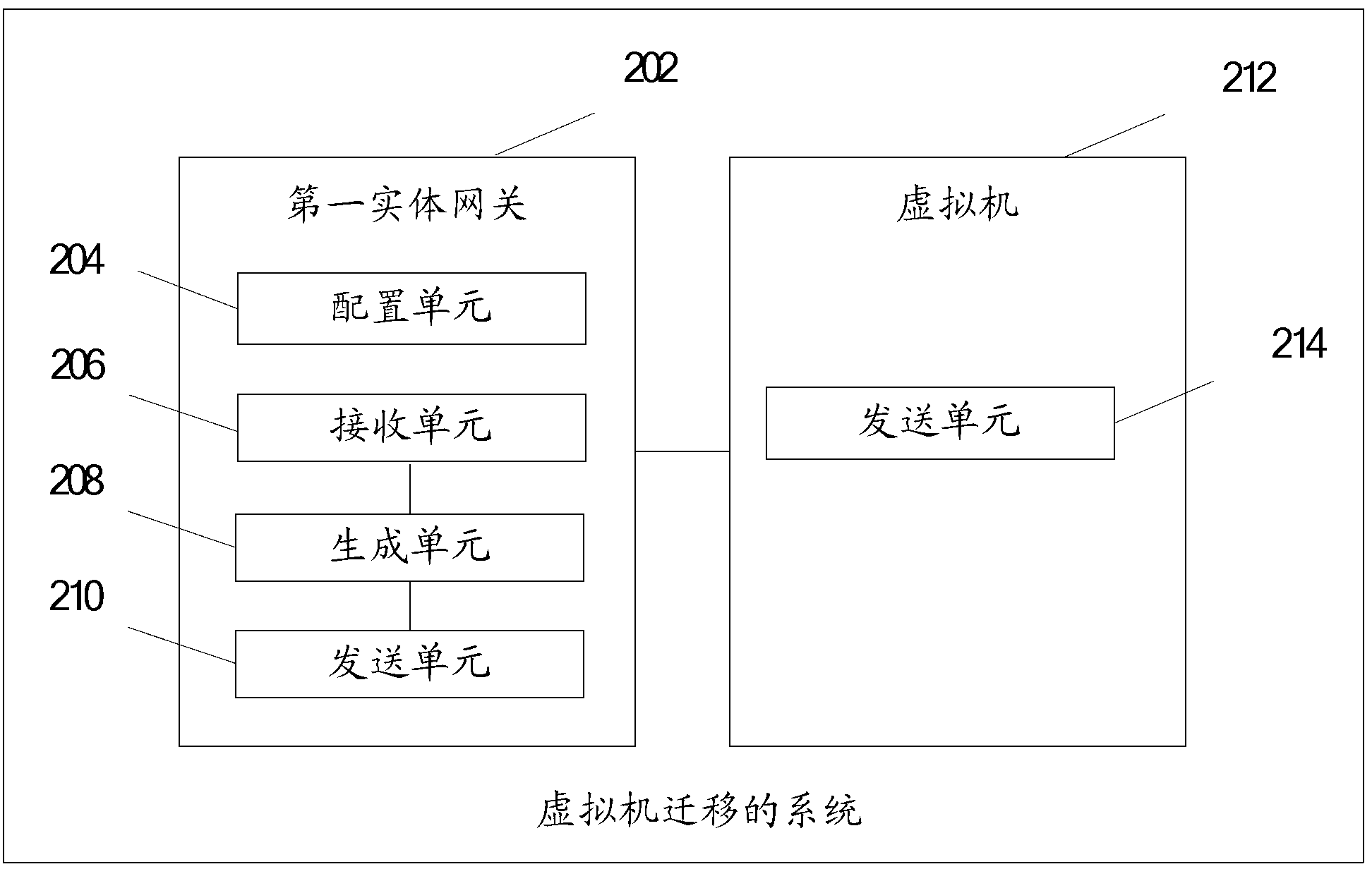
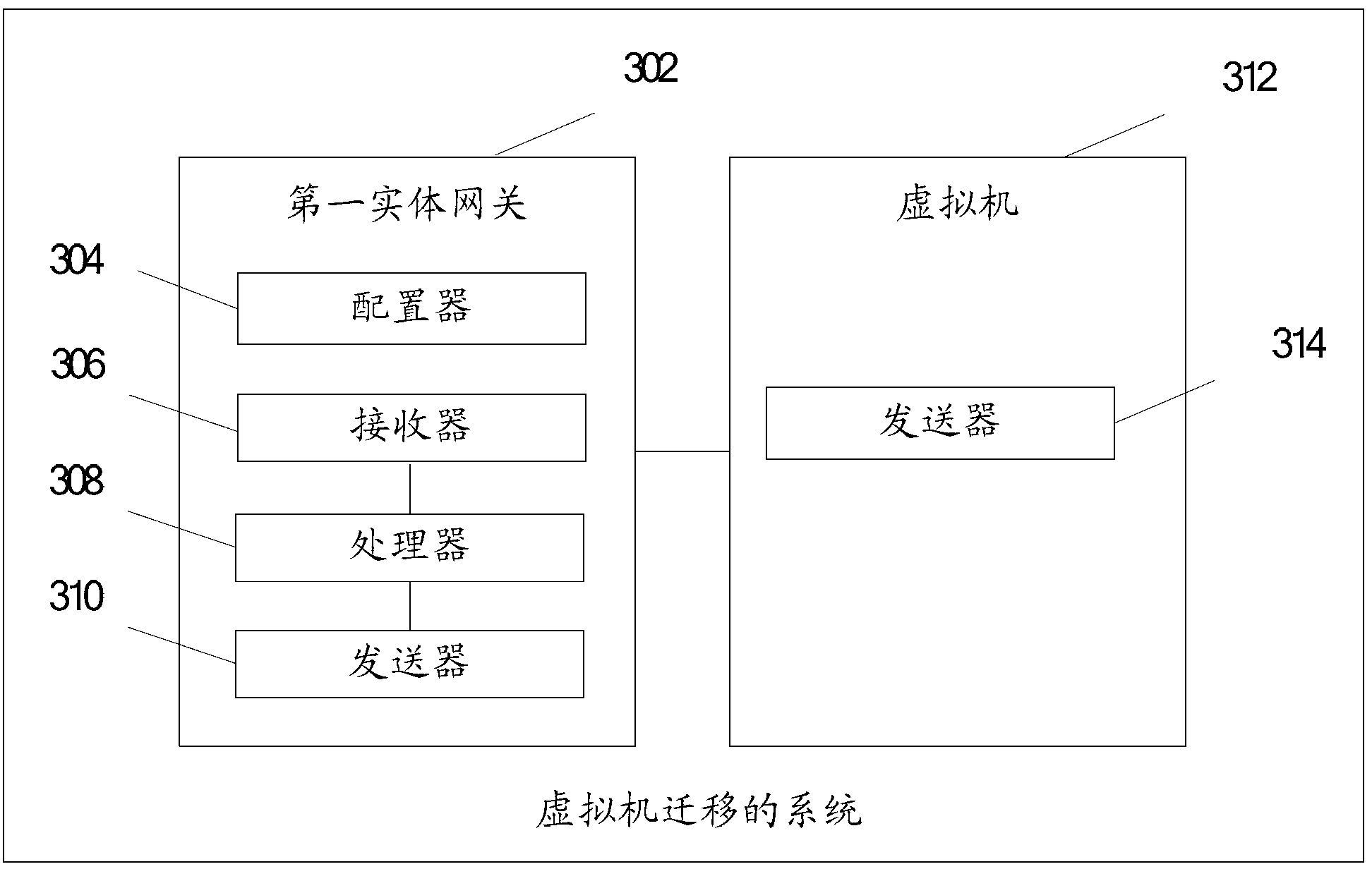
Method for virtual machine migration in network, gateway and system
ActiveCN102801715AAvoid interruptionNetwork connectionsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTraffic capacityAddress Resolution Protocol
An embodiment of the invention provides a method for virtual machine migration in a network. The method comprises: before a virtual machine migrating from a second entity gateway to a first entity gateway, the first entity gateway configuring a virtual gateway IP address; after the virtual machine migrating from a second entity gateway to a first entity gateway, the first entity gateway receiving a free address resolution protocol (ARP) message sent by the virtual machine, the free ARP message comprising an IP address of the virtual machine and an MAC address; the first entity gateway generating routing of the virtual machine according to the IP address of the virtual machine; and the first entity gateway issuing the routing of the virtual machine to a data center. The embodiment of the invention also provides an entity gateway and a system for virtual machine migration. Through the technical scheme provided in the embodiment, when the virtual machine migrates, default gateway configured in the virtual machine does not need reconfiguration. The virtual machine cannot aware changes of the gateway, so that a problem of flow interruption in a process of the virtual machine migration caused by gateway changing is prevented.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com