Patents
Literature
388results about How to "Improve network efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
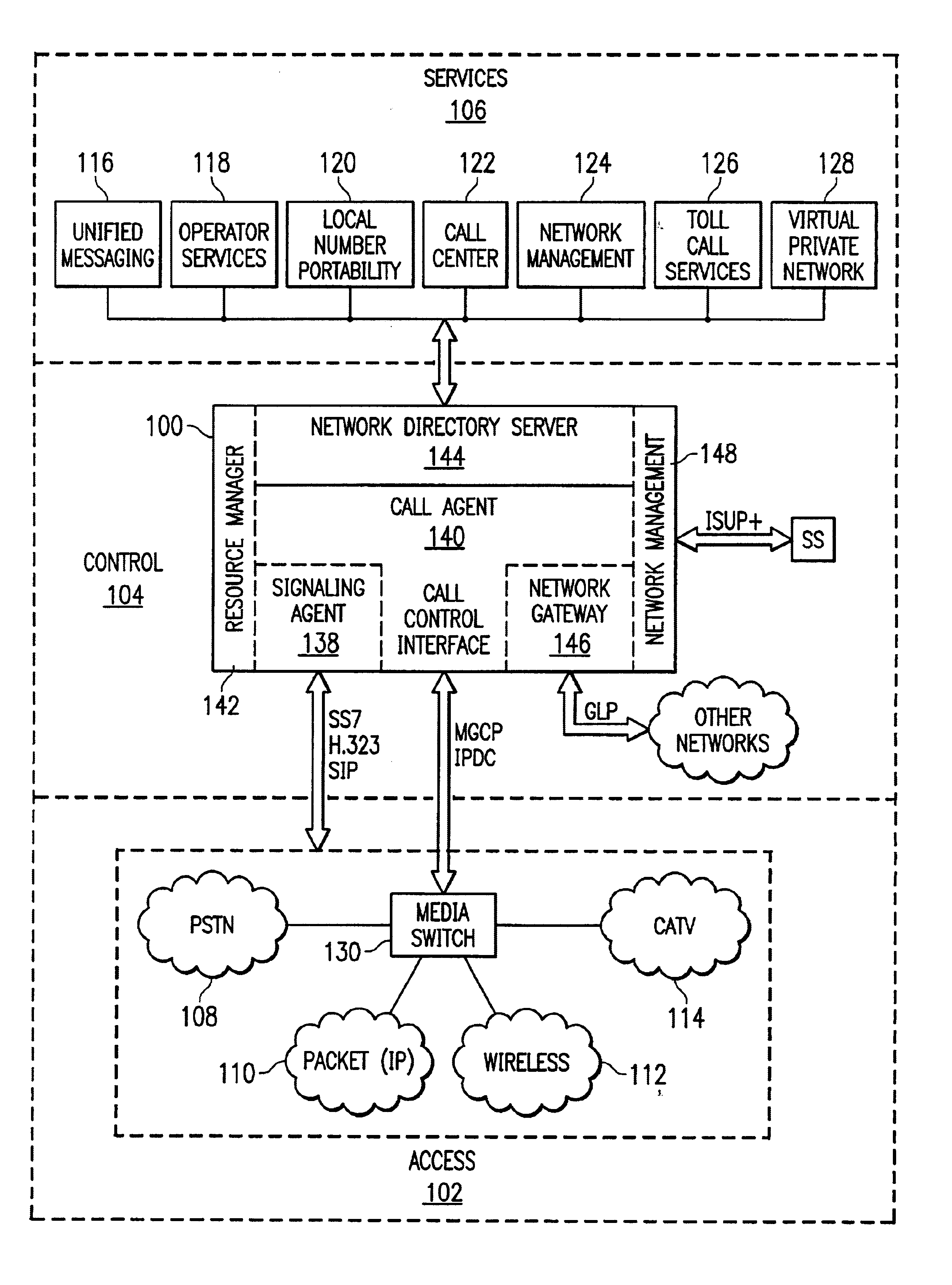
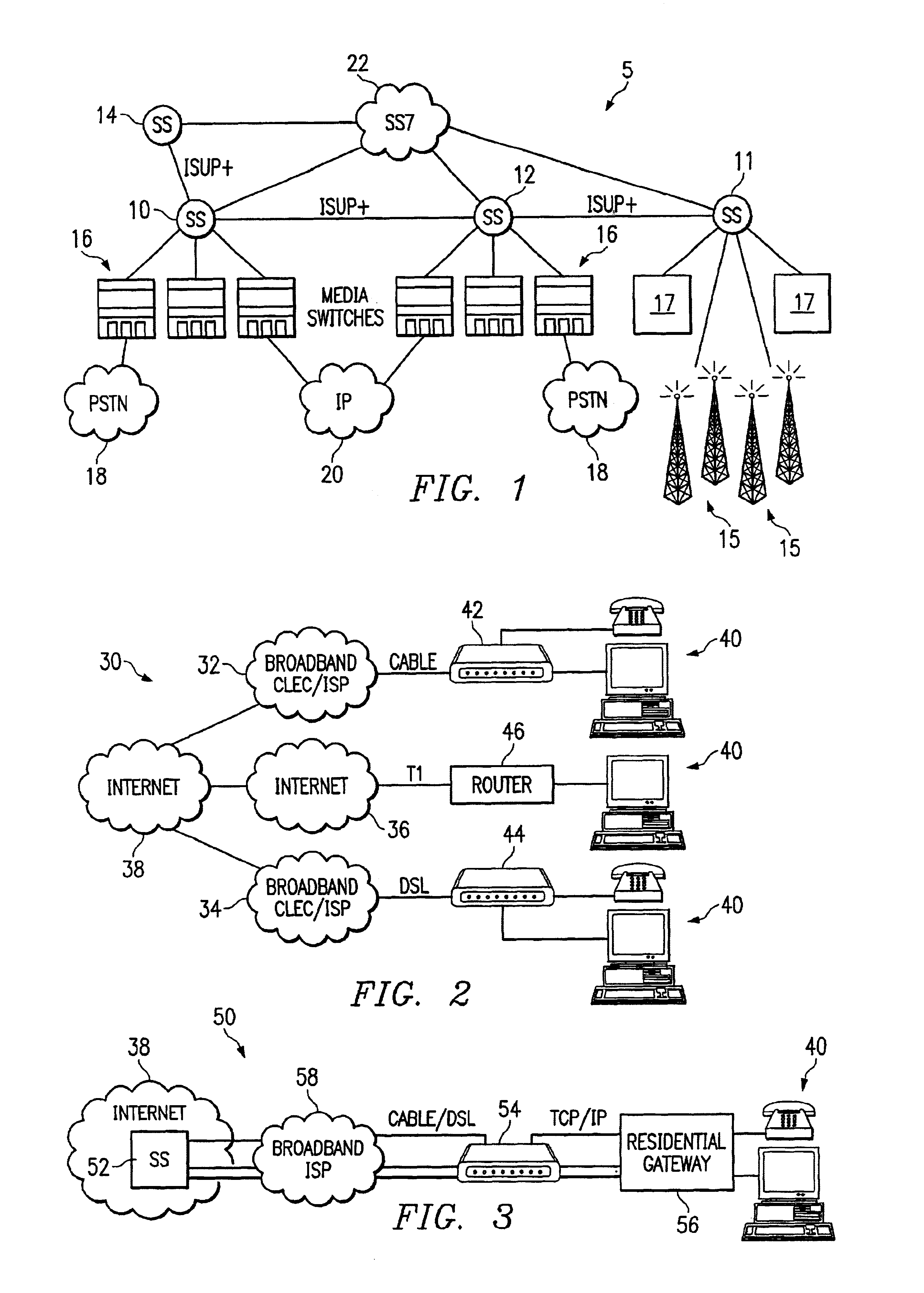
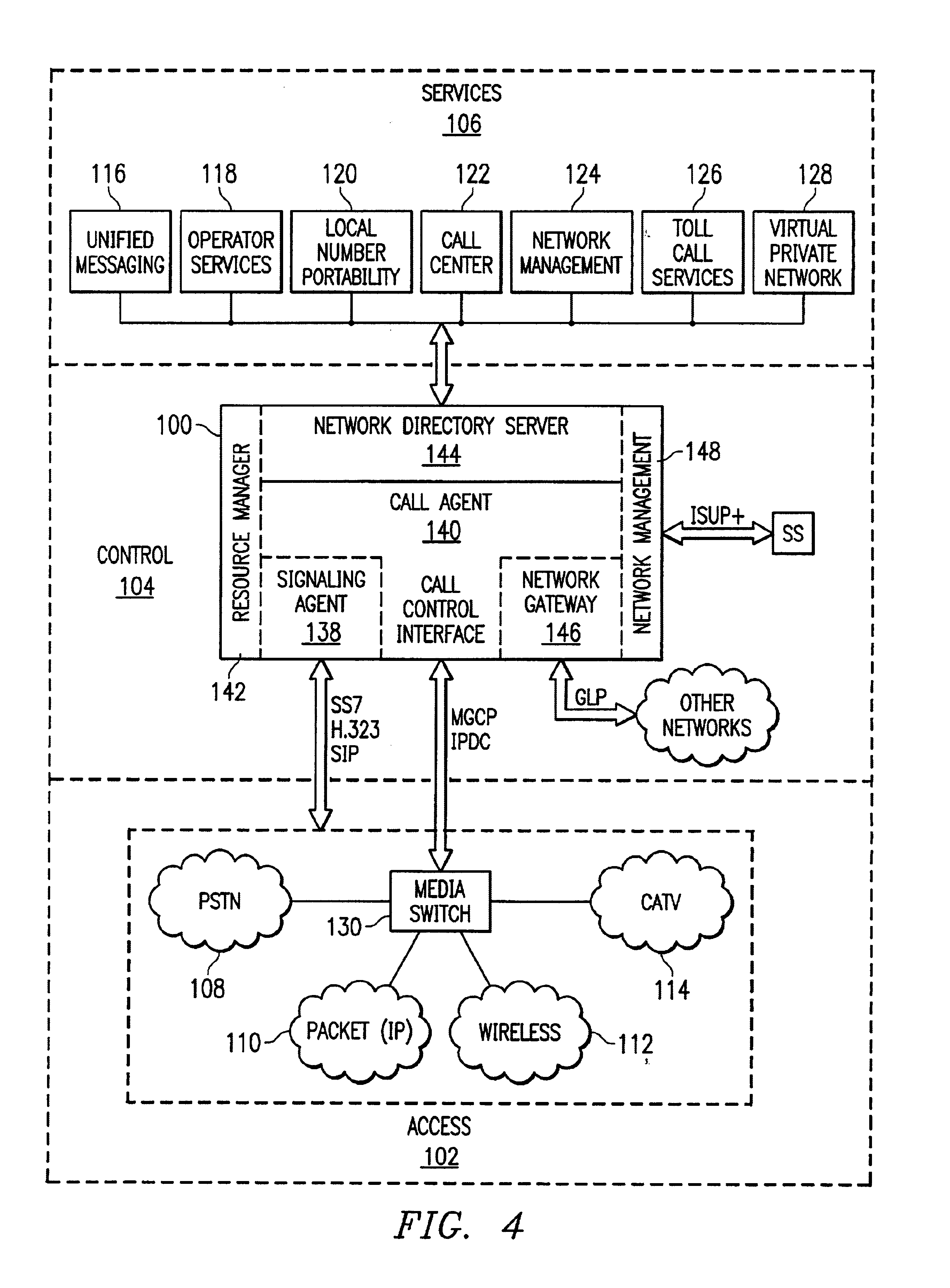
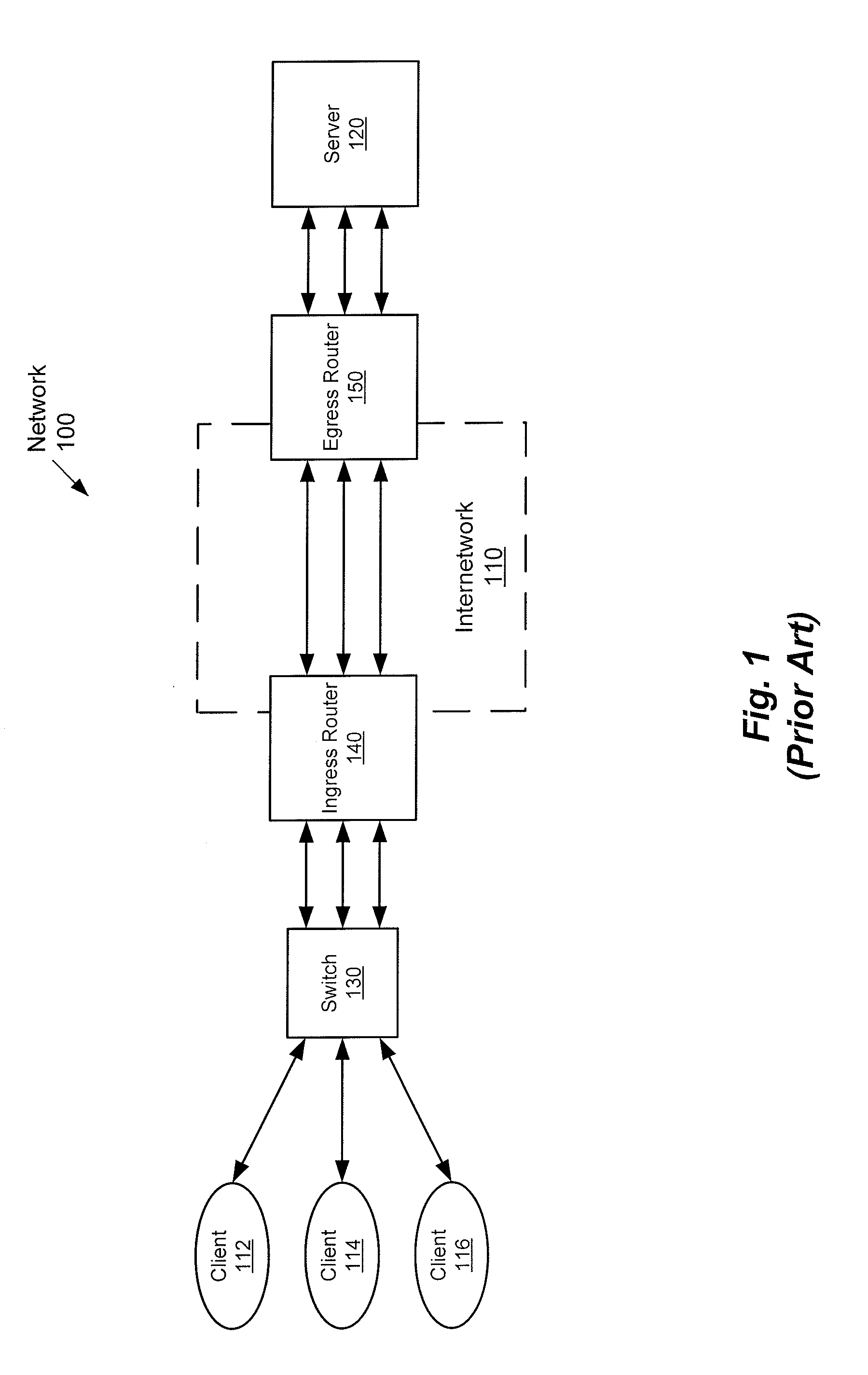
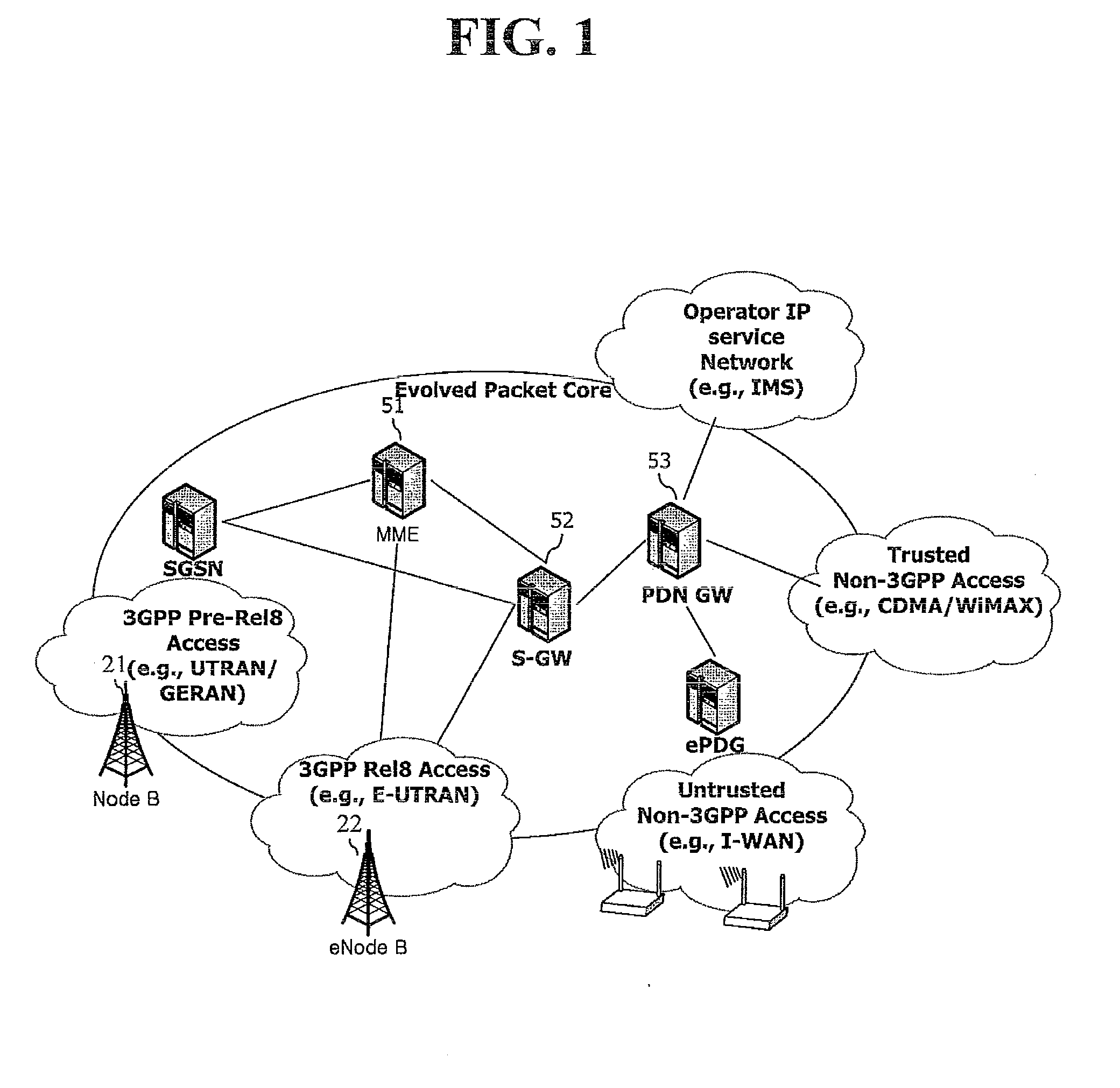
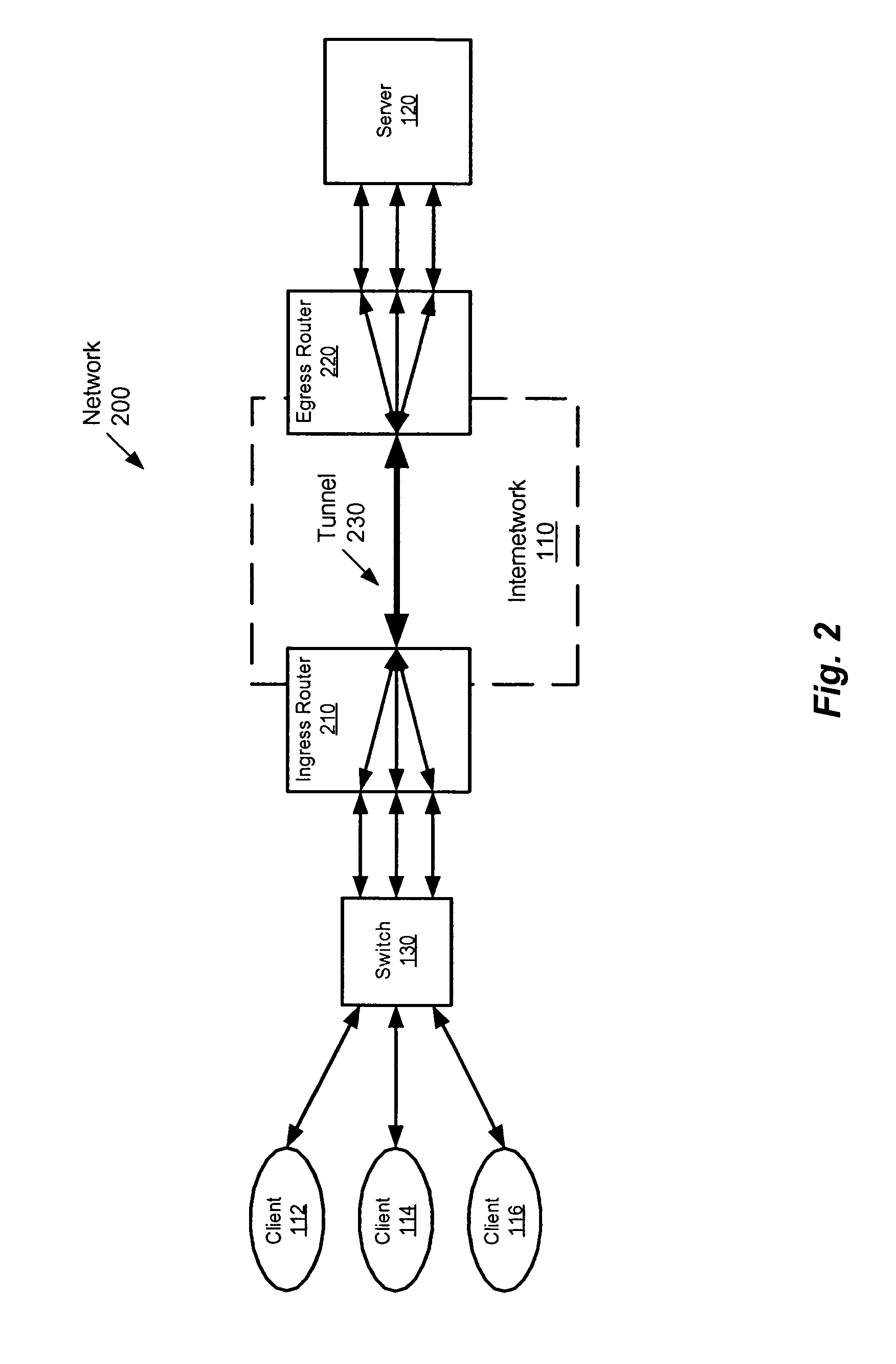
System and method to internetwork wireless telecommunication networks
ActiveUS6996076B1Improve network efficiencyAdditional drawbackTime-division multiplexConnection managementCommon logicLogic Control
One aspect of the invention is a method for wireless call processing. The method includes downloading at least one function-specific logic control program into each of a plurality of generic logic control state machines and receiving a message at a wireless protocol-specific codec, parsing the message, and routing the message to a first logic control state machine associated with the protocol-specific codec. The method also includes executing the function-specific logic control program of a first logic control state machine and generating a call event and routing the call event to an event codec. The method also includes executing the function-specific logic control program of a second logic control state machine and processing the call event. In a particular embodiment, the method also includes allocating an RF channel that may be used for the call event without seizing the RF channel. In another embodiment, the method also includes accessing a database that includes routing and verification information related to the call event, and routing the call event in response to the information.
Owner:RIBBON COMM OPERATING CO INC
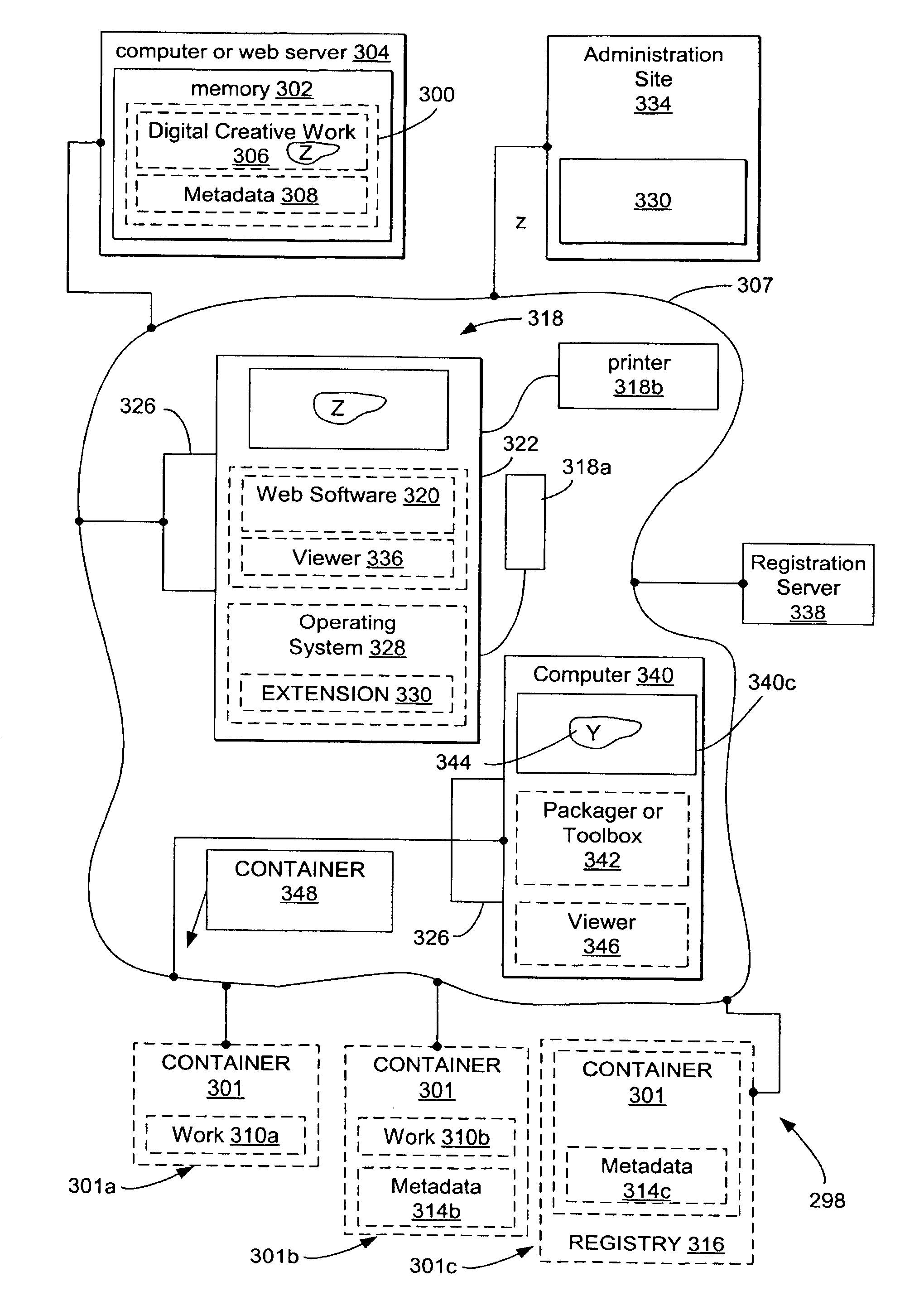
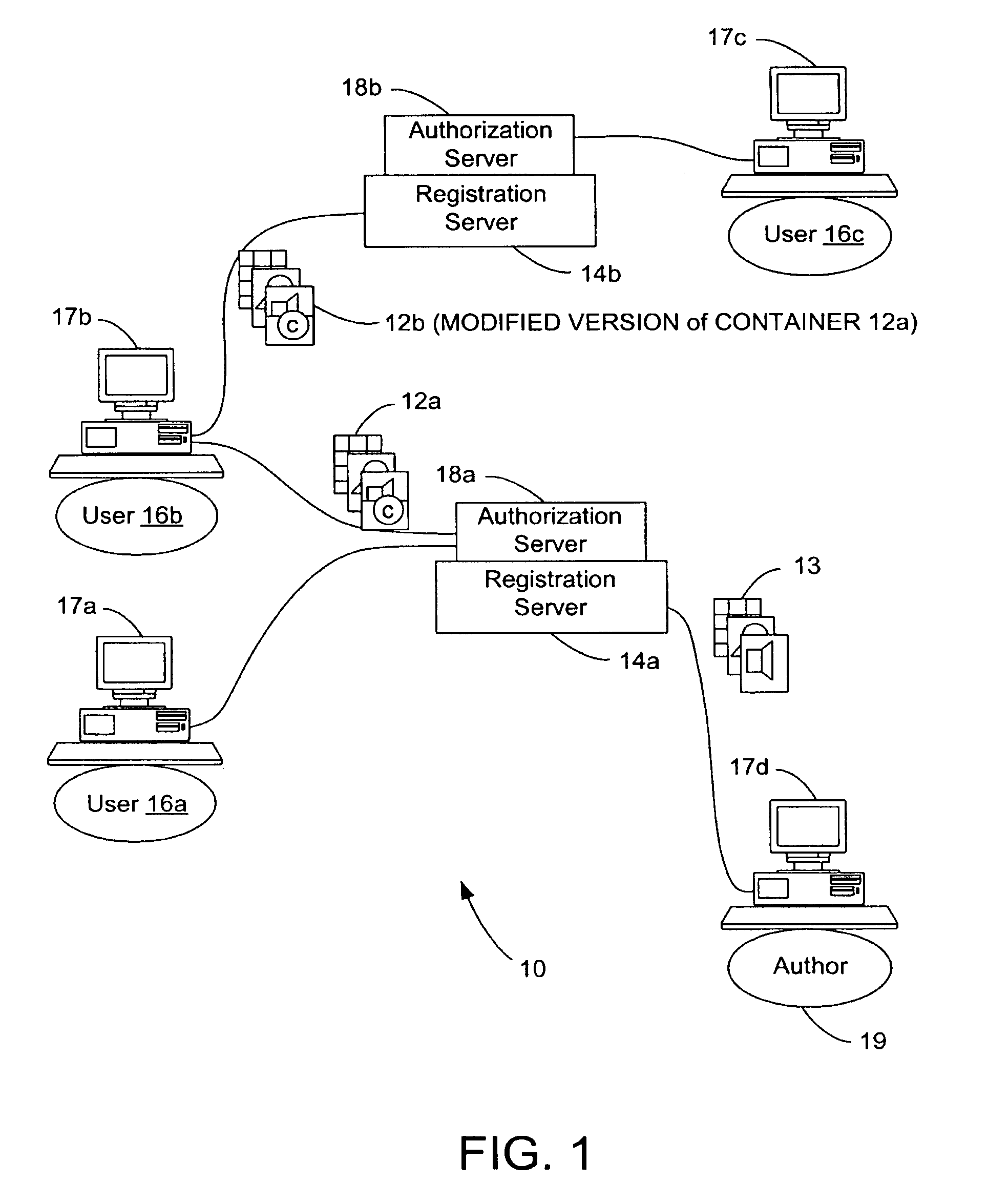
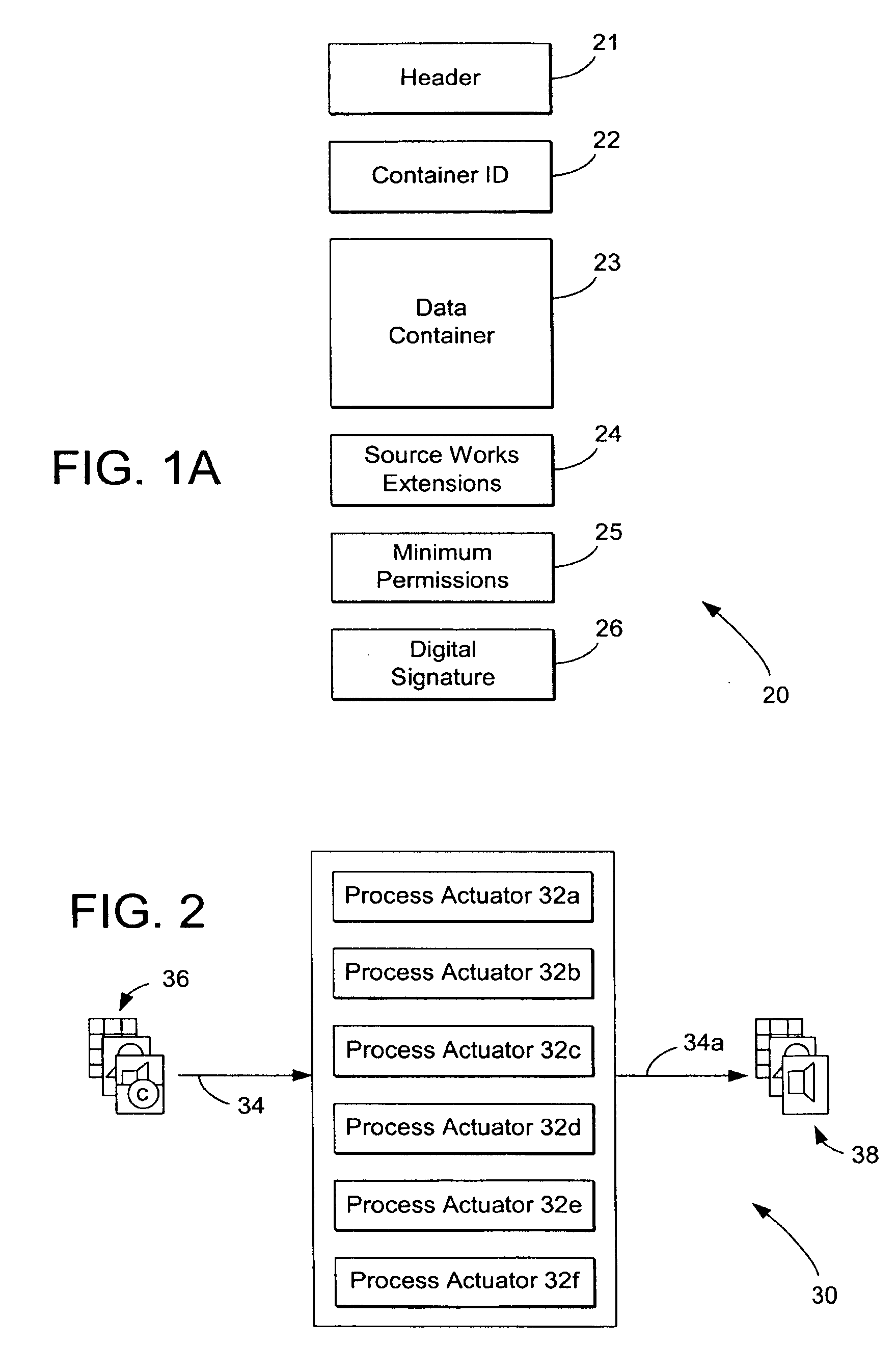
System and methods for managing digital creative works
InactiveUS7047241B1Improve network efficiencyEliminate needKey distribution for secure communicationData processing applicationsData setDigital signature
Digital Creative Works such as copyrighted electronic media are packaged in a secure electronic format, or CONTAINER, and registered on associated registration server, which serves to provide on-line licensing and copyright management for that Work. Users are connected to the registration server through a computer network or the Internet to enable data transfers and to transact licenses to utilize the media. Packaged electronic media are typically created by an author or derivative user of the work. Once the packaged media is registered on the server, the media is made available for limited use and possible license through an authorization server. This limited use is specified within the minimum permissions data set assigned to each packaged media. Without a license, users are typically permitted to view the packaged media—through a system which unpackages the media—but cannot save, print or otherwise transfer the media without obtaining auxiliary permissions to do so from the authorization server. The electronic media is authenticated through digital signatures and optional encryption.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
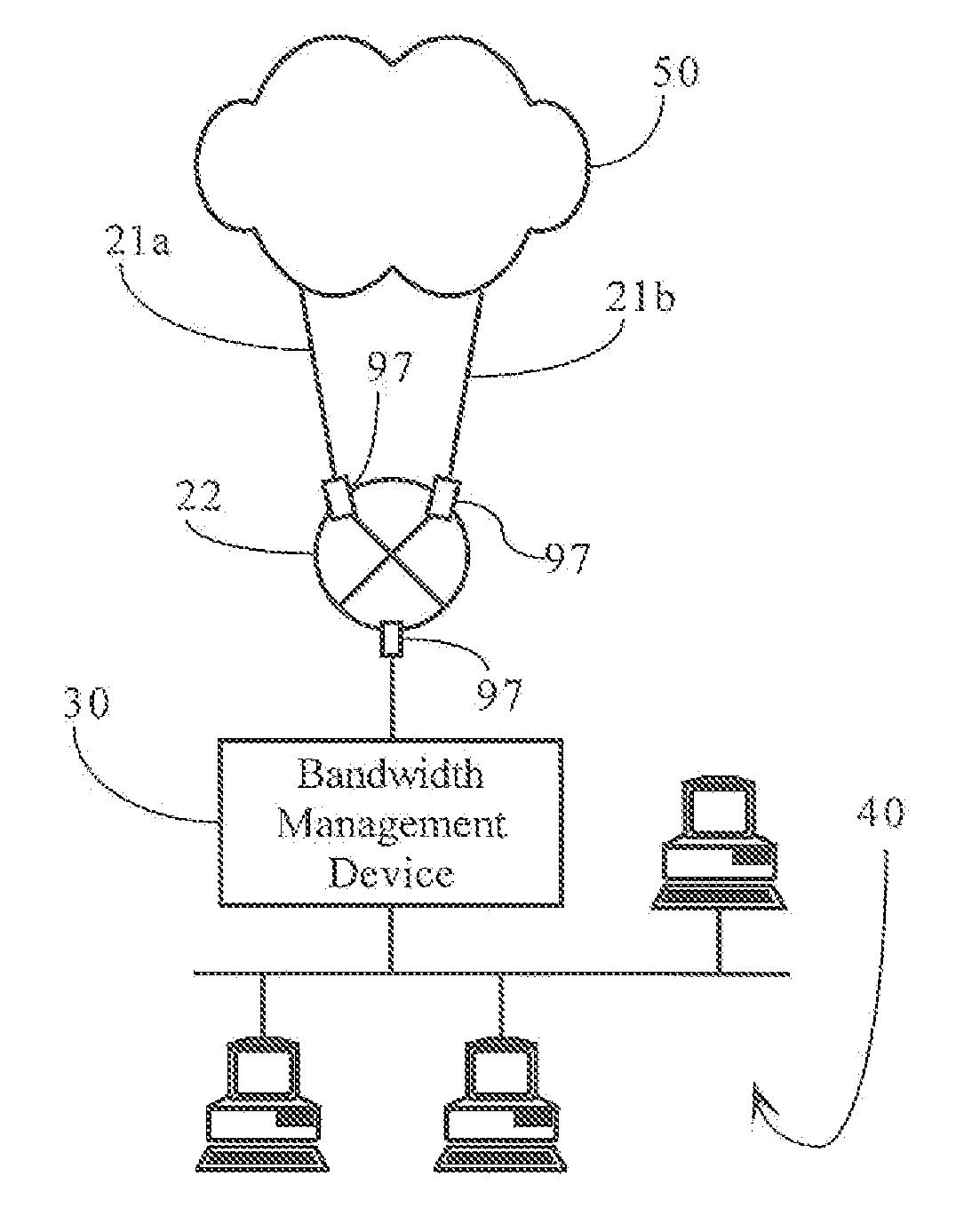
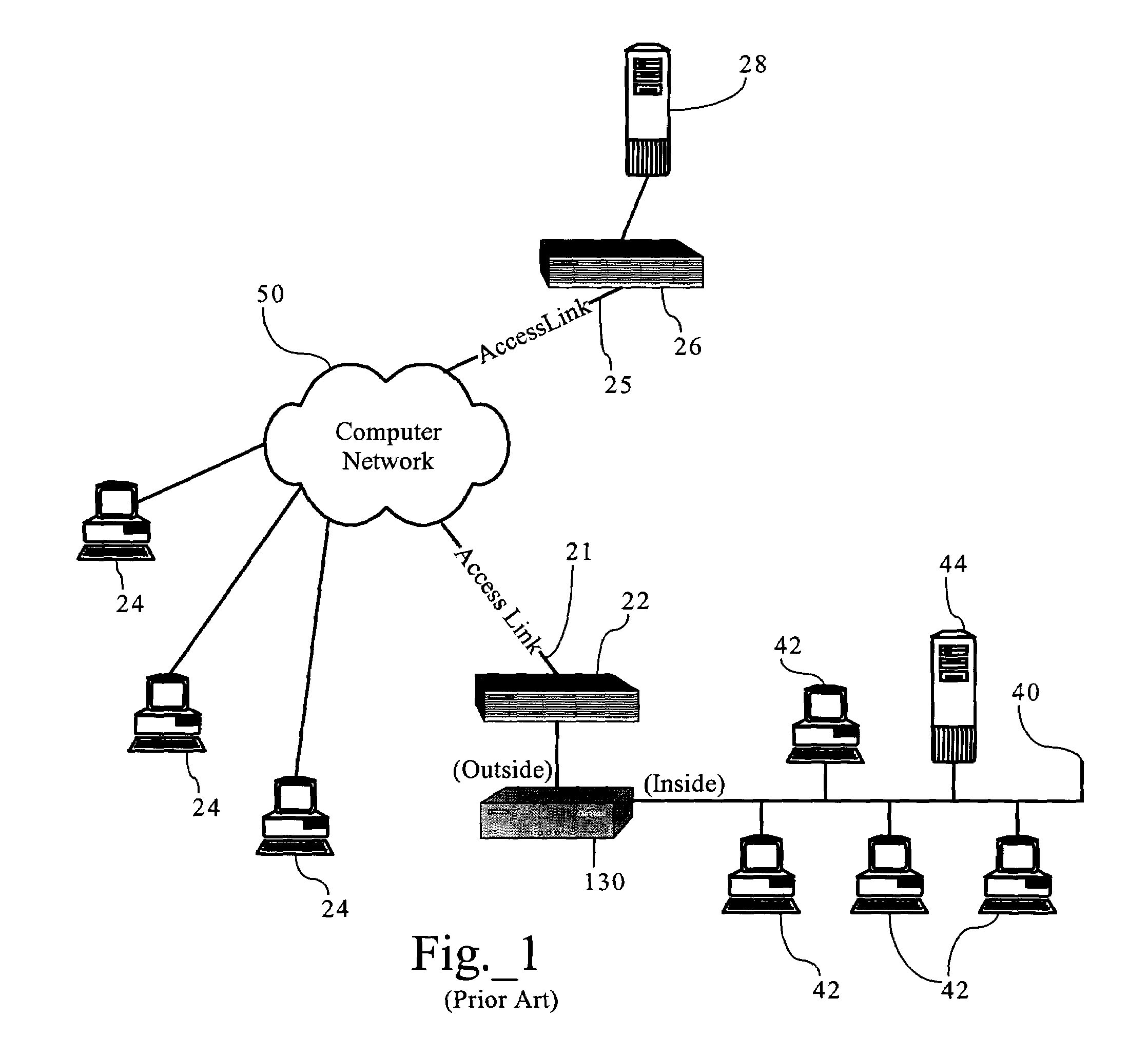
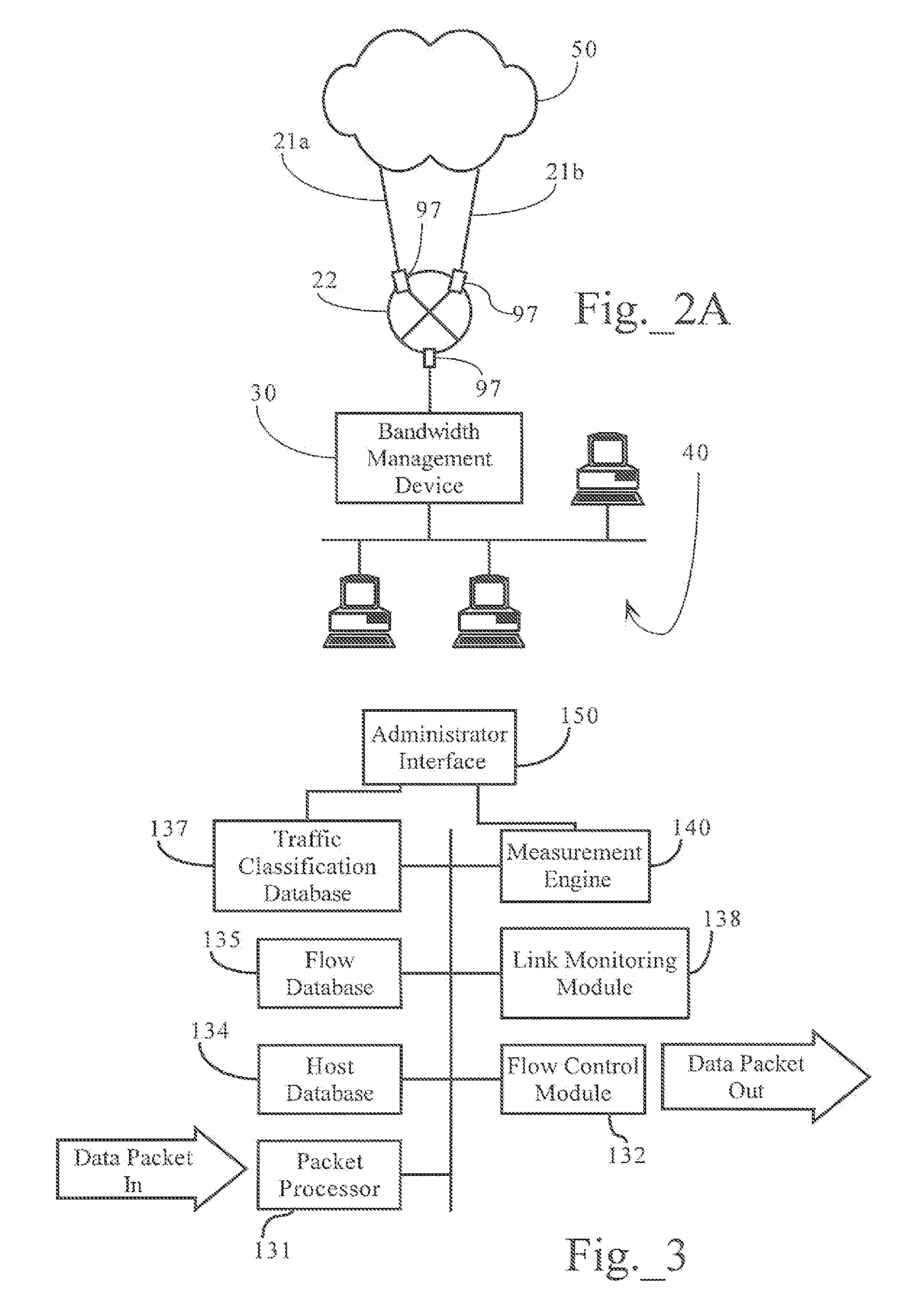
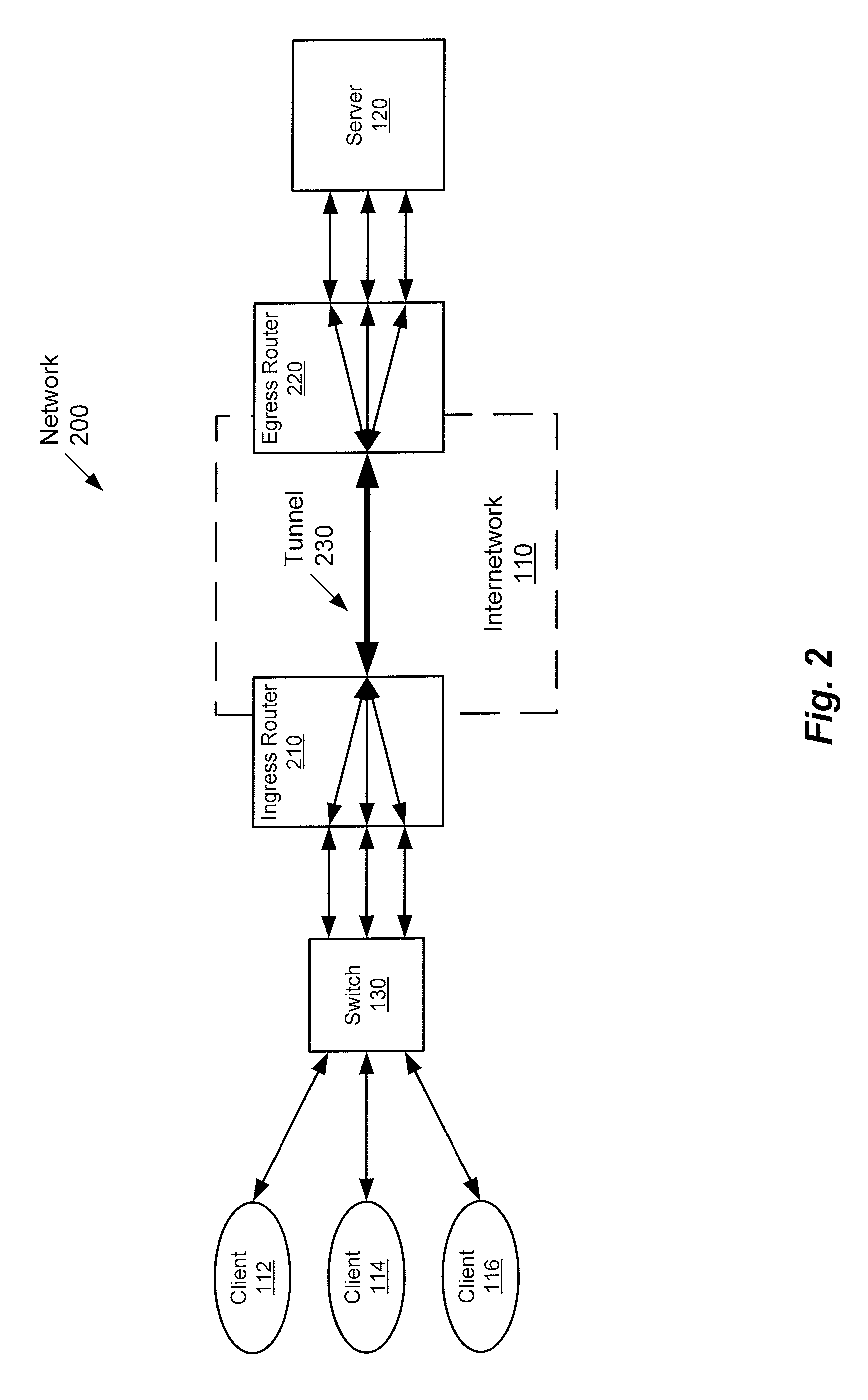
Dynamic bandwidth management responsive to access link state in redundant network topologies
ActiveUS7324553B1Improve network efficiencyEnsure smooth networkError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityBandwidth management
Methods, apparatuses and systems allowing for dynamic bandwidth management schemes responsive to the state of a plurality of access links in redundant network topologies. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a bandwidth management device that periodically queries routing systems associated with access links, conceptually grouped into a virtual access link, to monitor that load of the access links and, depending on the detected load, adjust the configuration of the bandwidth management device to avoid overloading one or more of the access links. Embodiments of the present invention increases network efficiency and help network traffic to flow more smoothly with higher throughput. In one embodiment, the dynamic link control functionality is invoked when any given access link reaches a threshold capacity level. Assuming that network traffic will scale in the same ratio as presently observed, the present invention calculates the maximum traffic that can be let through so that no network interface or access link is overloaded.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Quality of service network and method
InactiveUS20060250959A1Improve network efficiencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceAdmission controller
A configurable edge device for use in a network, the edge device being adapted and configured to be coupled to at least one other edge device in a network, and including an admission controller for controlling admission of data traffic onto a pre-defined flow over a physical link, and a router for routing the data traffic through the edge device onto the pre-defined flow in accordance with a pre-defined routing scheme, wherein operation of the admission controller and the router is controlled in accordance with data defining all physical and logical links in the network; a telecommunications carrier network for data traffic, the network including at least two such configurable edge devices, and a method for transmitting data traffic through such an edge device.
Owner:TEJAS NETWORKS
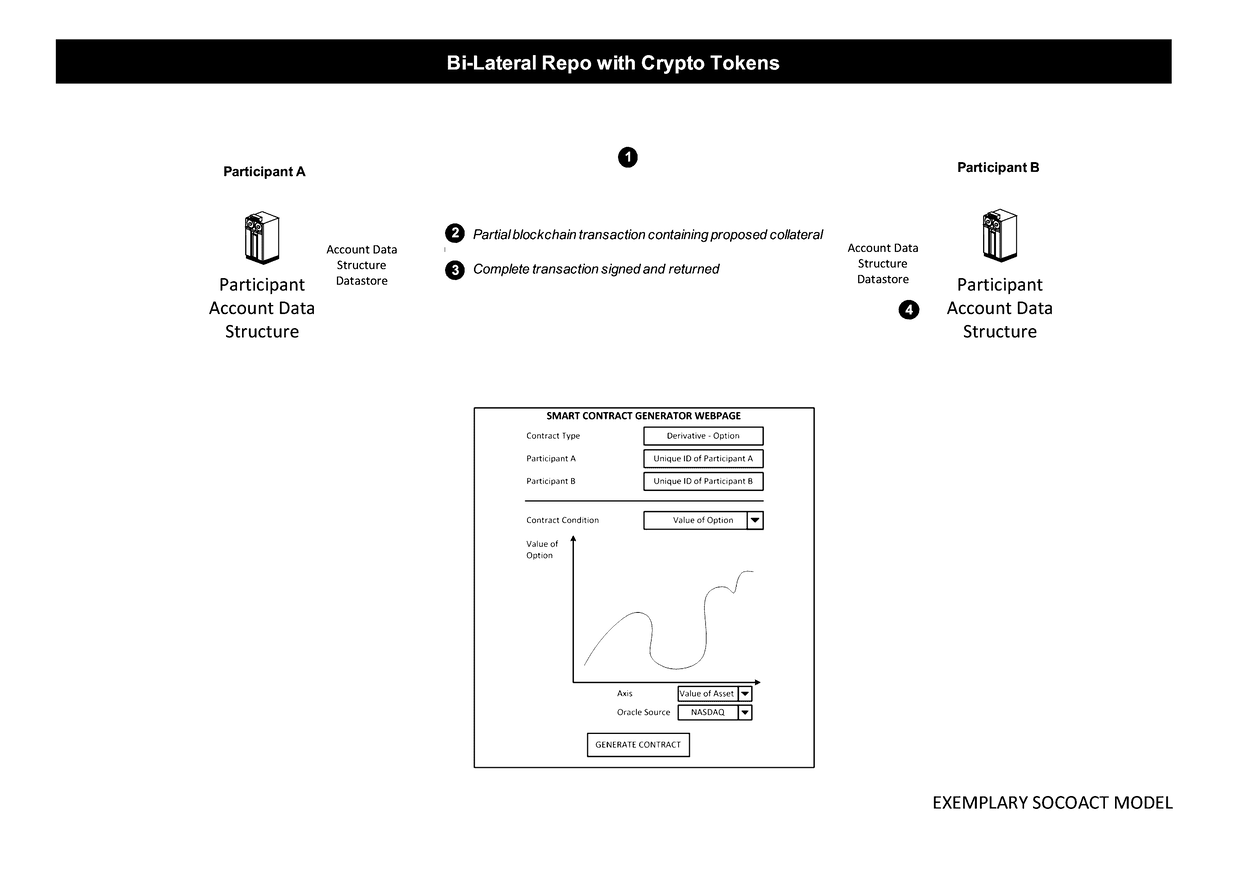
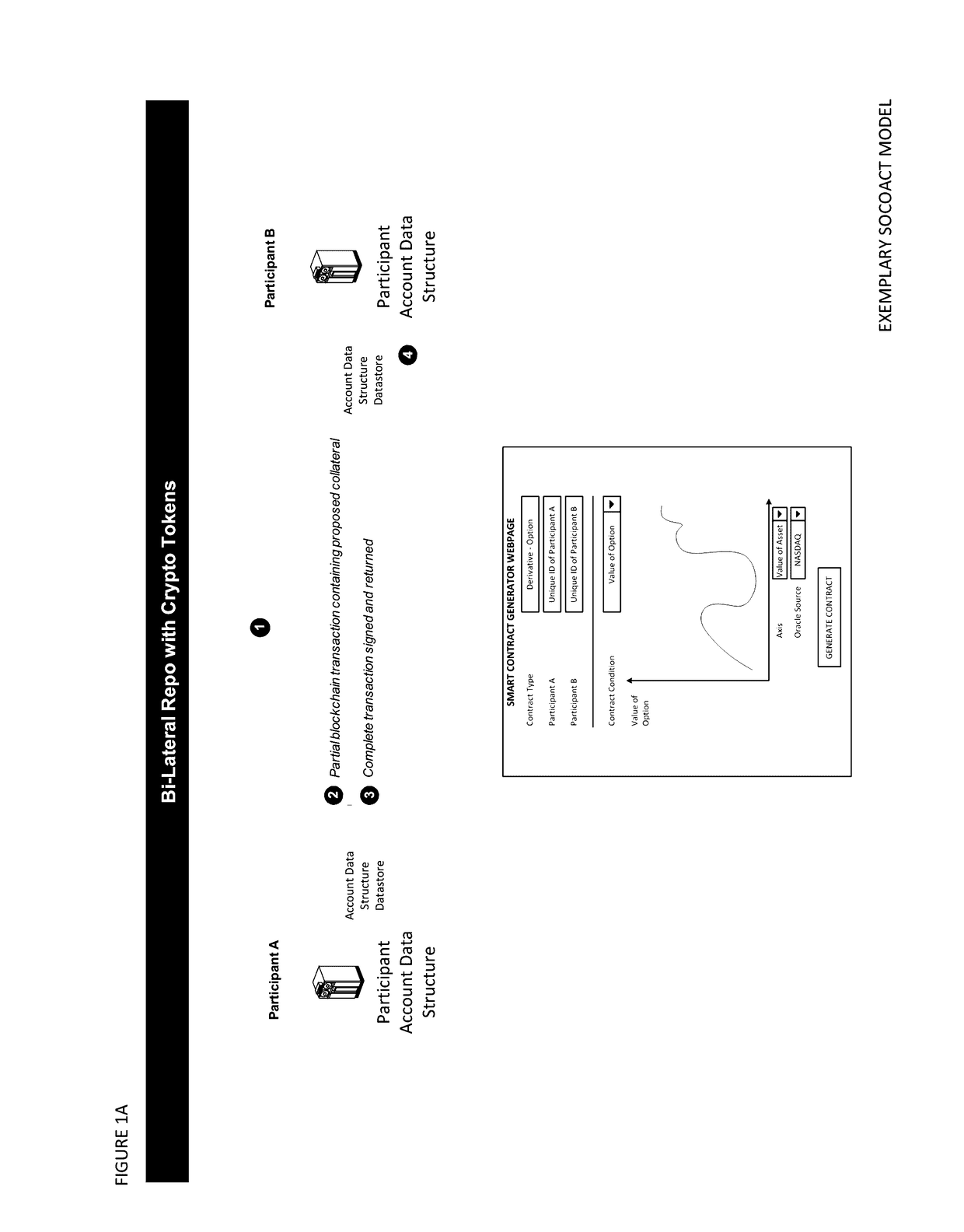
Point-to-Point Transaction Guidance Apparatuses, Methods and Systems
InactiveUS20170085555A1Prolong lifeEasy accessInput/output to record carriersDigital data information retrievalProcessing InstructionSmart contract
The Point-to-Point Transaction Guidance Apparatuses, Methods and Systems (“SOCOACT”) transforms smart contract request, crypto currency deposit request, crypto collateral deposit request, crypto currency transfer request, crypto collateral transfer request inputs via SOCOACT components into transaction confirmation outputs. Also, SOCOACT transforms virtual wallet address inputs via SOCOACT (e.g., P2PTG) components into transaction confirmation outputs. In one embodiment, the SOCOACT includes a point-to-point payment guidance apparatus, comprising, a memory and processor disposed in communication with the memory, and configured to issue a plurality of processing instructions from the component collection stored in the memory, to: obtain a target wallet identifier registration at a beacon. The SOCOACT then may register the target wallet identifier with the beacon and obtain a unique wallet identifier from a migrant wallet source associated with a user at the beacon. The SOCOACT may then obtain a target transaction request at the beacon from the migrant wallet source and commit the target transaction request for the amount specified in the target transaction request to a distributed block chain database configured to propagate the target transaction request across a distributed block chain database network for payment targeted to the target wallet identifier registered at the beacon.
Owner:FMR CORP
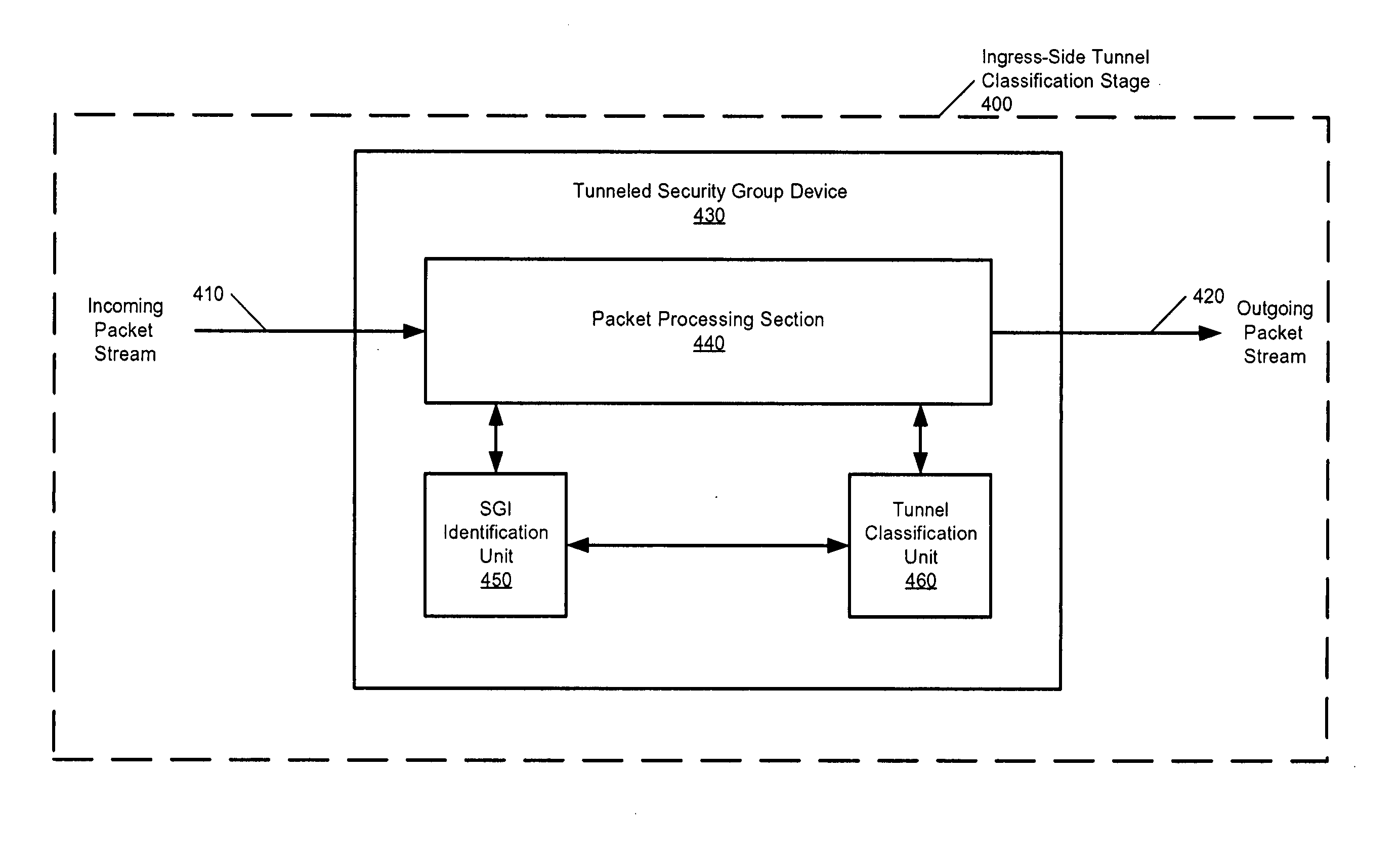
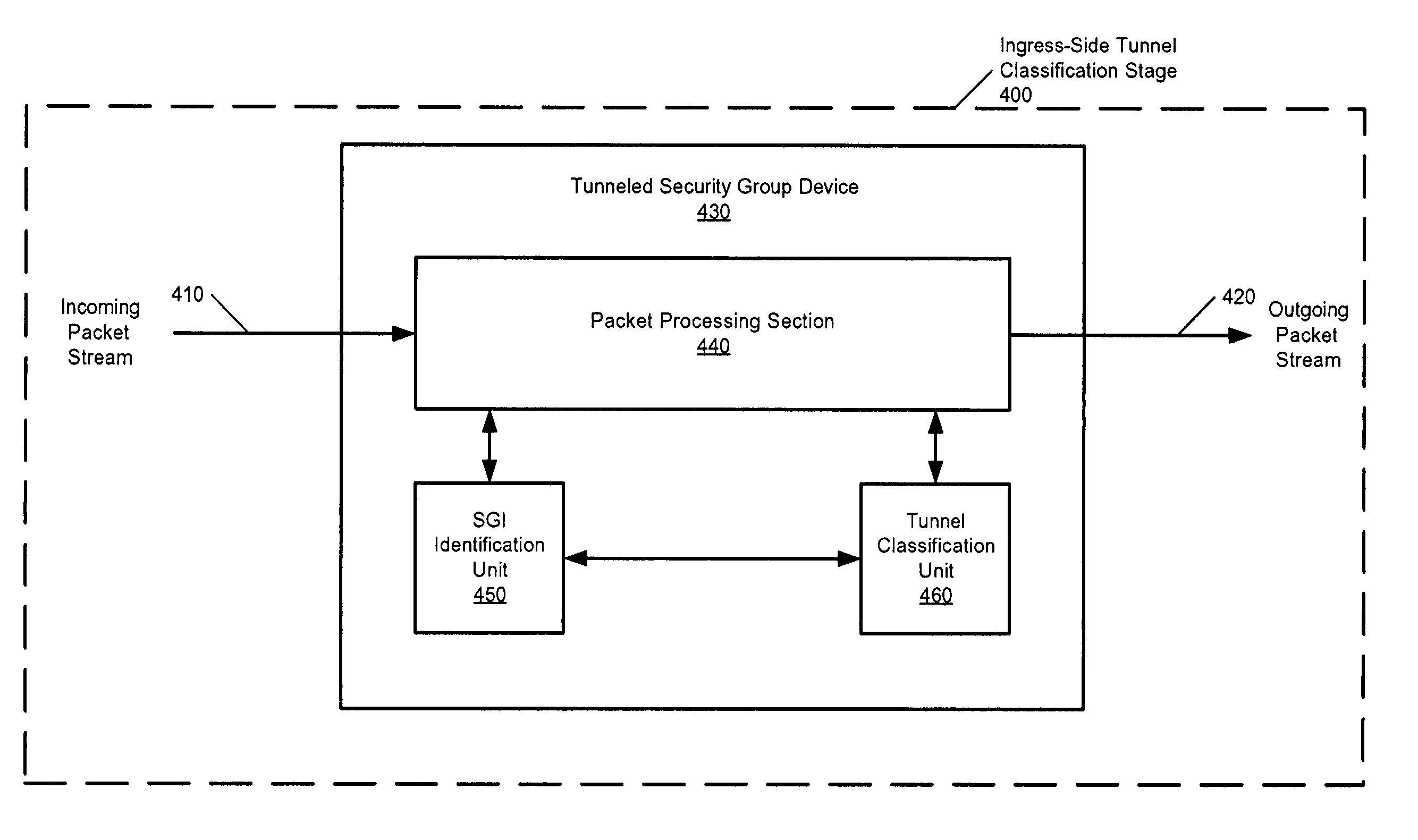
Tunneled Security Groups
InactiveUS20120131643A1Reduce in quantityImprove network efficiencyDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsGroup identifierComputer security
A method for providing security groups based on the use of tunneling is disclosed. The method includes assigning a security group identifier (SGI) to a packet and classifying the packet based on the packet's SGI.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
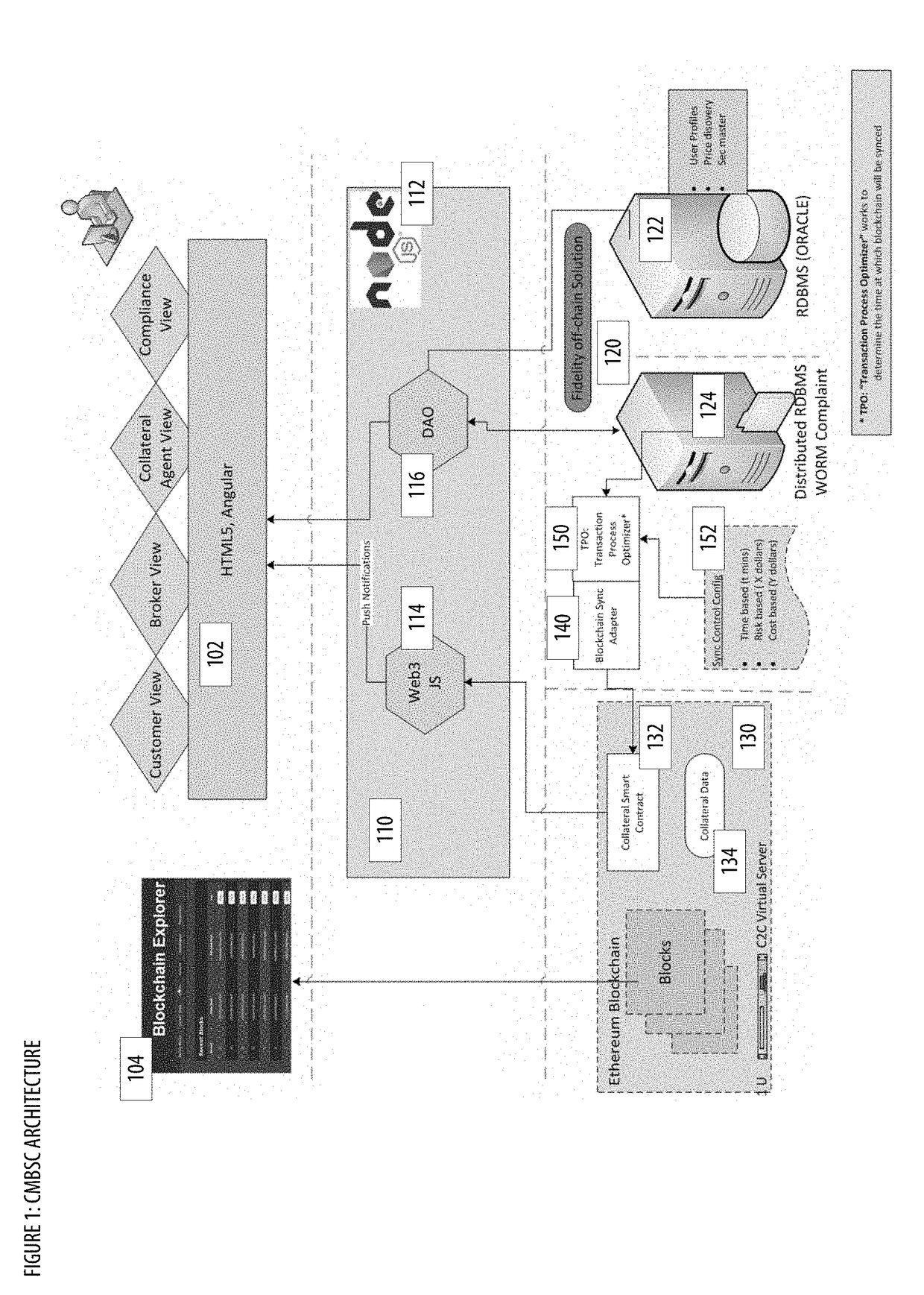
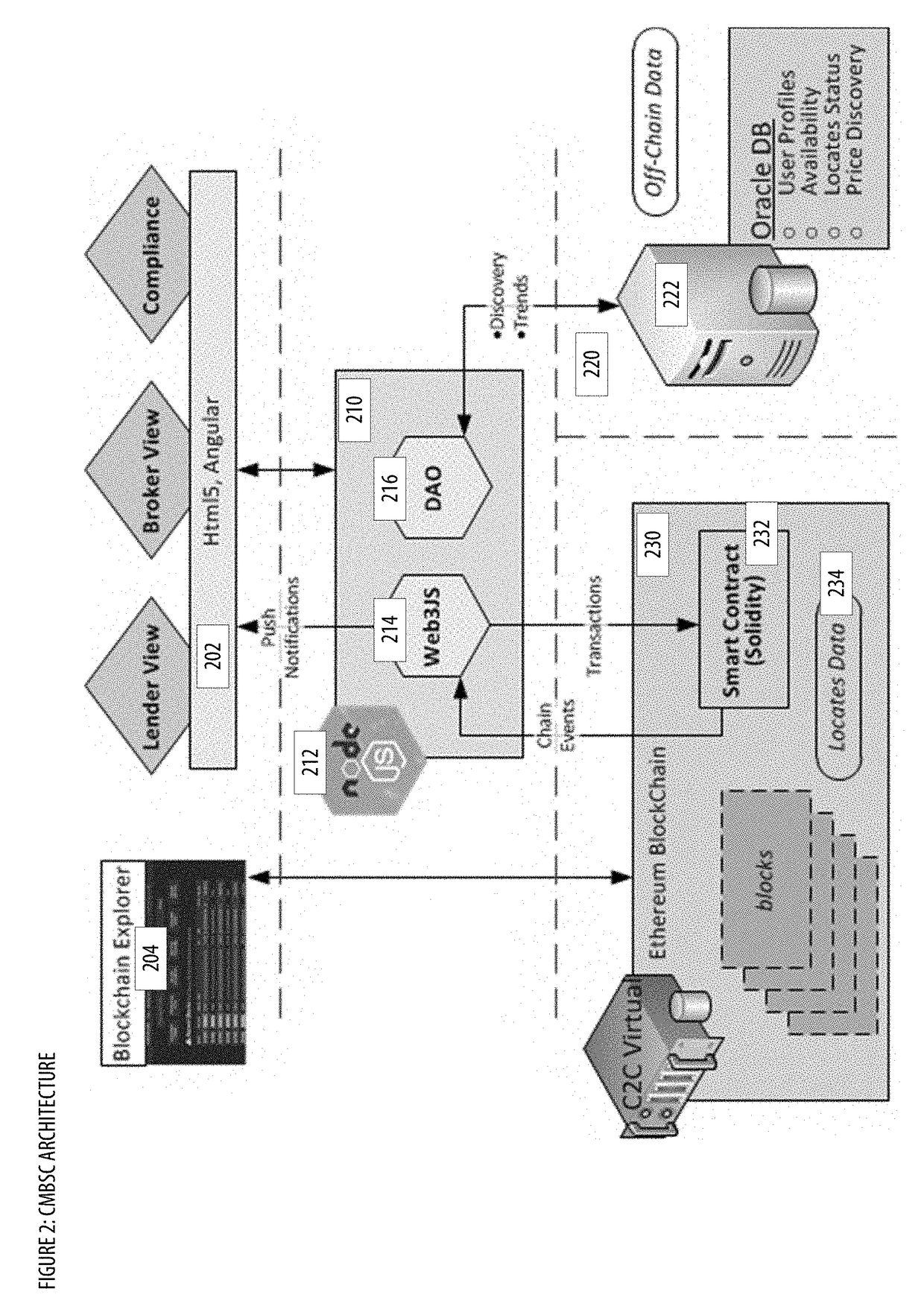
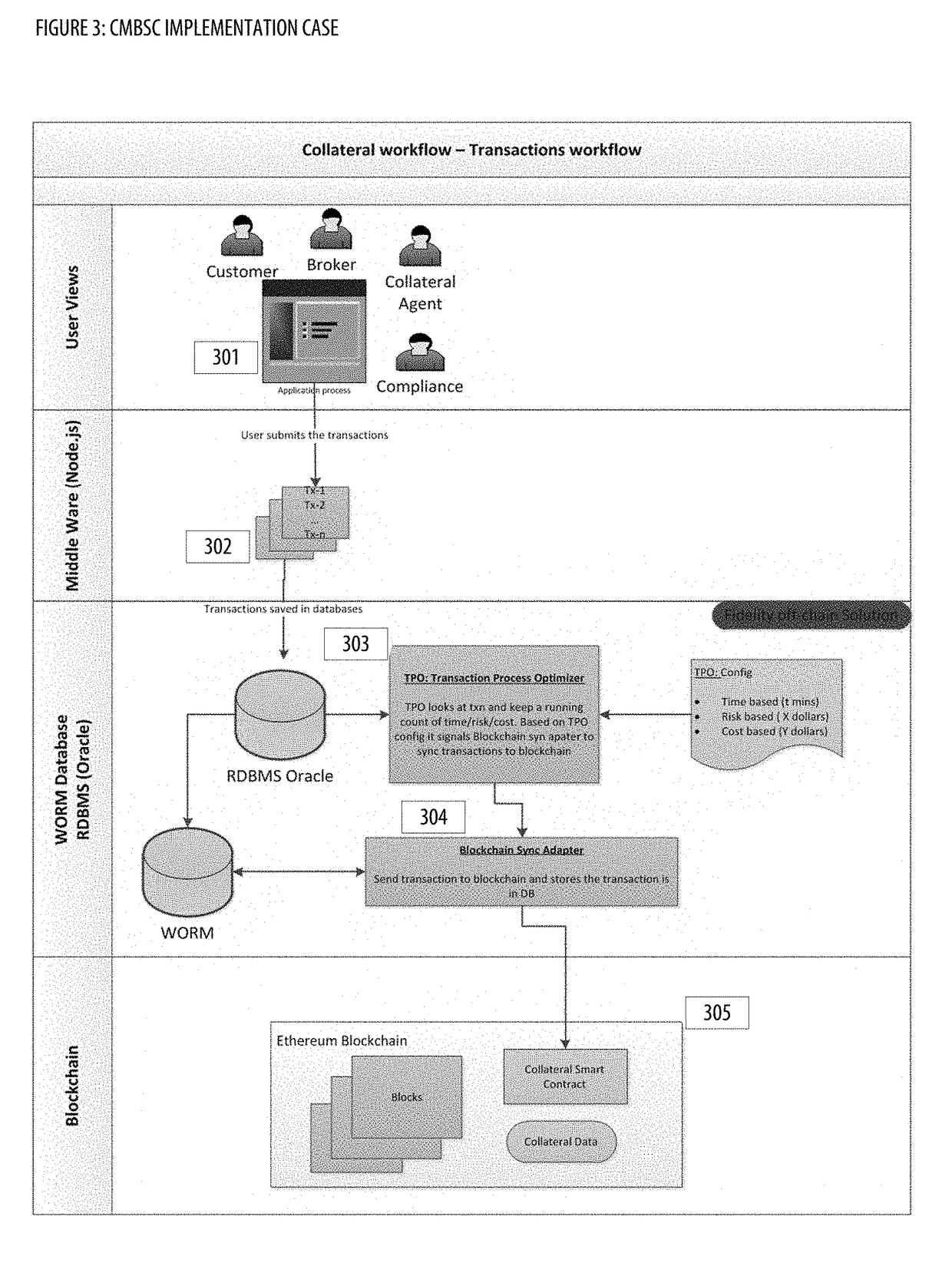
Collateral Management With Blockchain and Smart Contracts Apparatuses, Methods and Systems
PendingUS20190005469A1Borrowing and/or returning assets (e.g., stocks) may be facilitatedFacilitate actionFinanceEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesCollateral managementInit
The Collateral Management with Blockchain and Smart Contracts Apparatuses, Methods and Systems (“CMBSC”) transforms borrow transaction request inputs via CMBSC components into borrow transaction init notification, borrow transaction sync notification outputs. A borrow transaction request associated with a borrow transaction is obtained. Transaction attributes associated with the borrow transaction are stored in a database. The transaction process optimizer component is notified regarding the borrow transaction. A blockchain sync notification associated with the borrow transaction is obtained from the transaction process optimizer component. The stored transaction attributes associated with the borrow transaction are filtered. A smart contract associated with the borrow transaction is generated. The generated smart contract is sent to a blockchain node of a blockchain network. A smart contract notification associated with the smart contract is received. A push notification regarding the smart contract notification is provided to a user interface component of a user's client.
Owner:FMR CORP
Tunneled security groups
ActiveUS20050129019A1Reduce in quantityImprove network efficiencyMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlGroup identifierComputer security
A method for providing security groups based on the use of tunneling is disclosed. The method includes assigning a security group identifier (SGI) to a packet and classifying the packet based on the packet's SGI.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
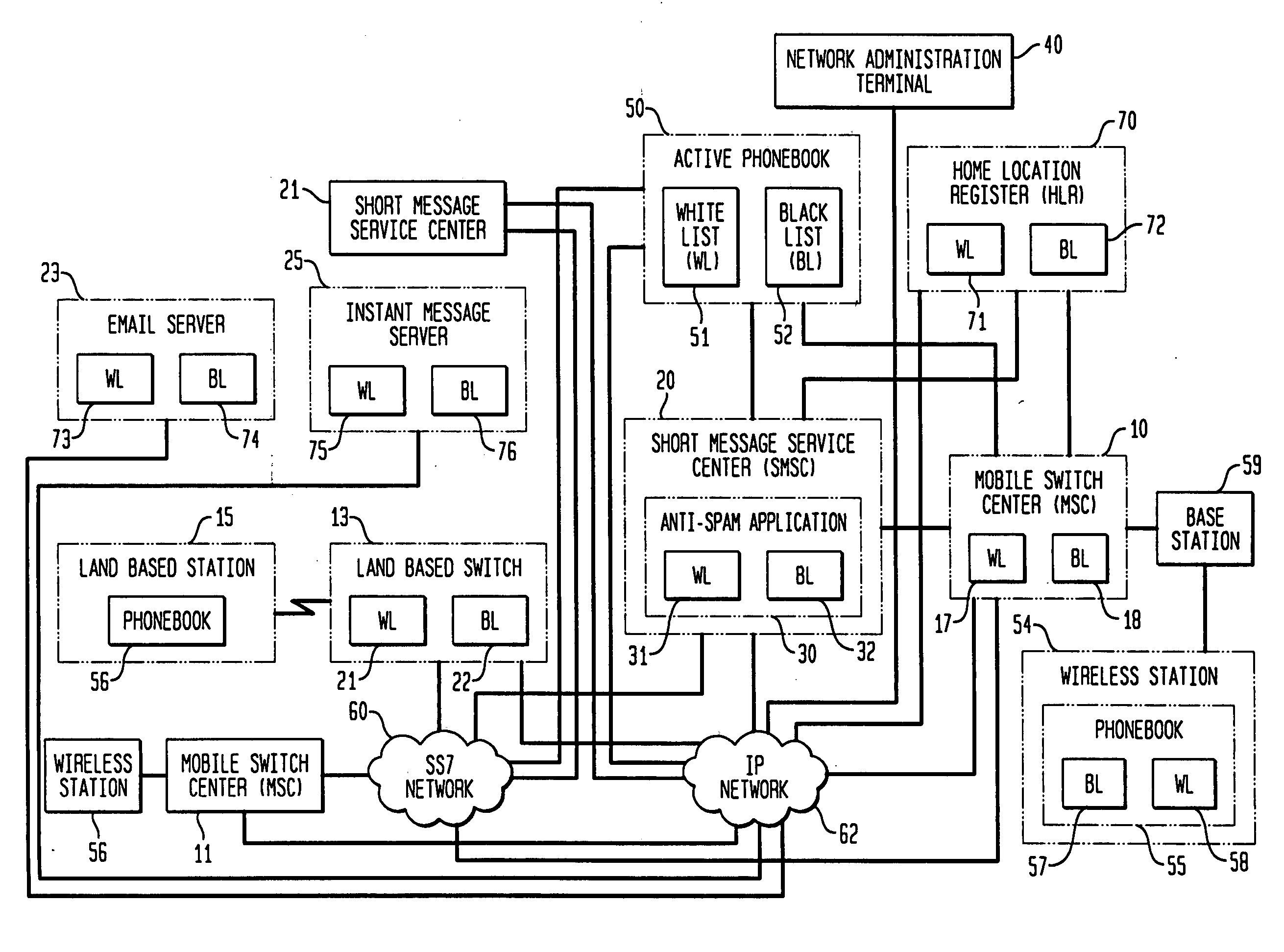
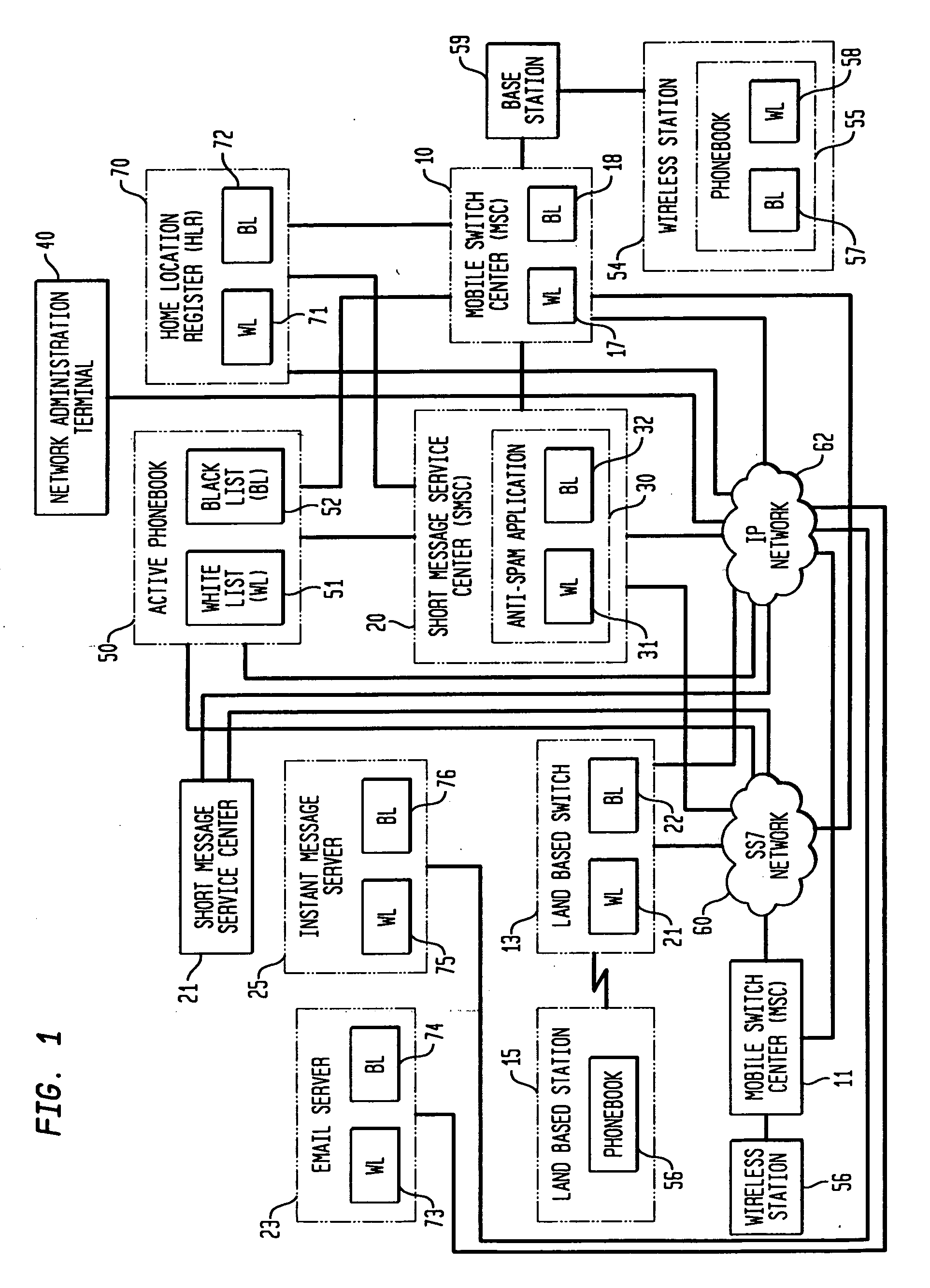
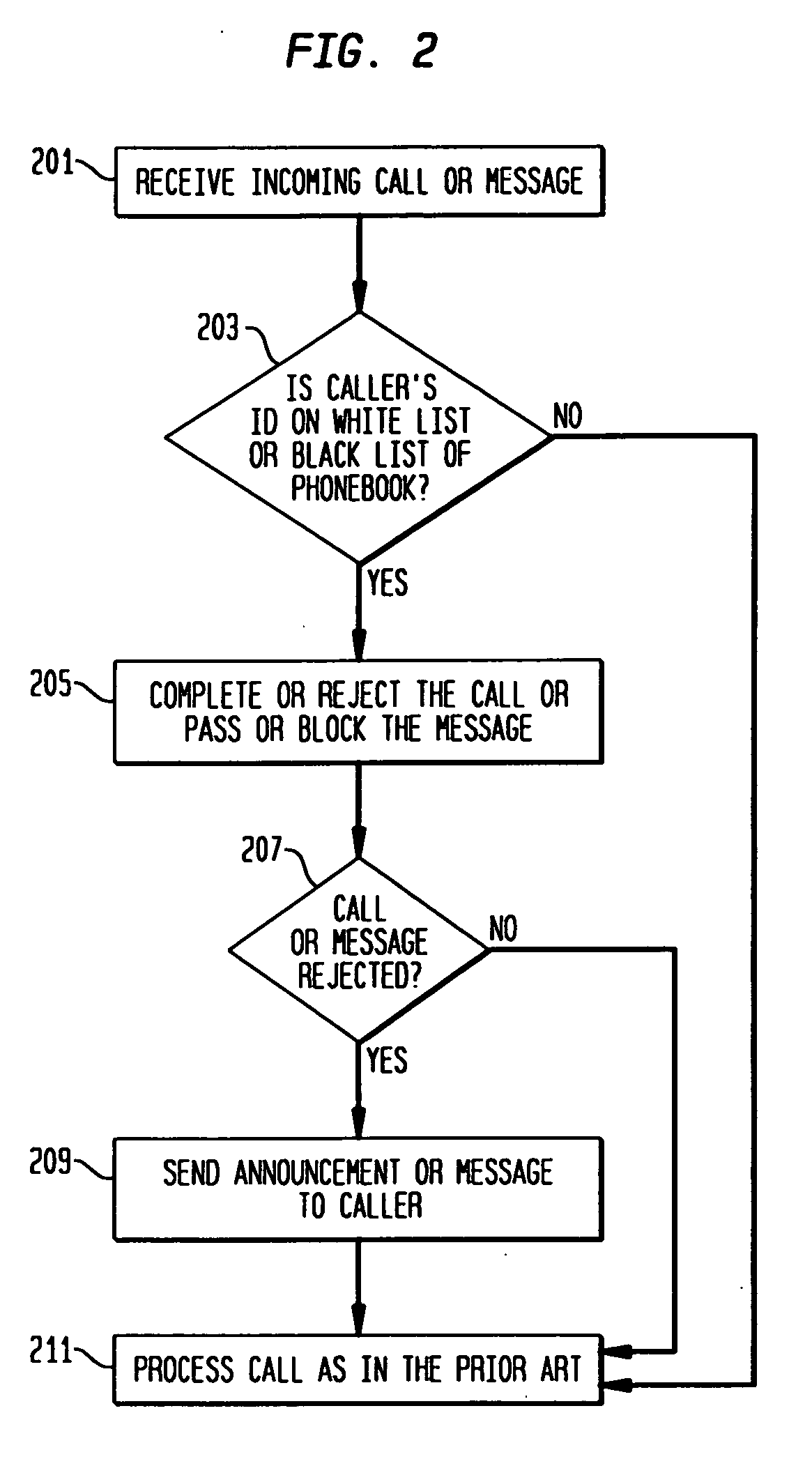
Phonebook use to filter unwanted telecommunications calls and messages
InactiveUS20070143422A1Minimizes and eliminates processingImprove network efficiencyMultiple digital computer combinationsSubstation equipmentTelecommunicationsWhitelist
This invention relates to the use of a customer phonebook feature for storing white lists and black lists for filtering unwanted voice calls or data messages. It also relates to the automatic population of a customer phonebook of identifications of a destination of outgoing calls. Advantageously, the phonebook can be rapidly and effortlessly populated with white lists and black lists to reduce processing for determining whether incoming calls or messages should be blocked or passed to the called destination.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
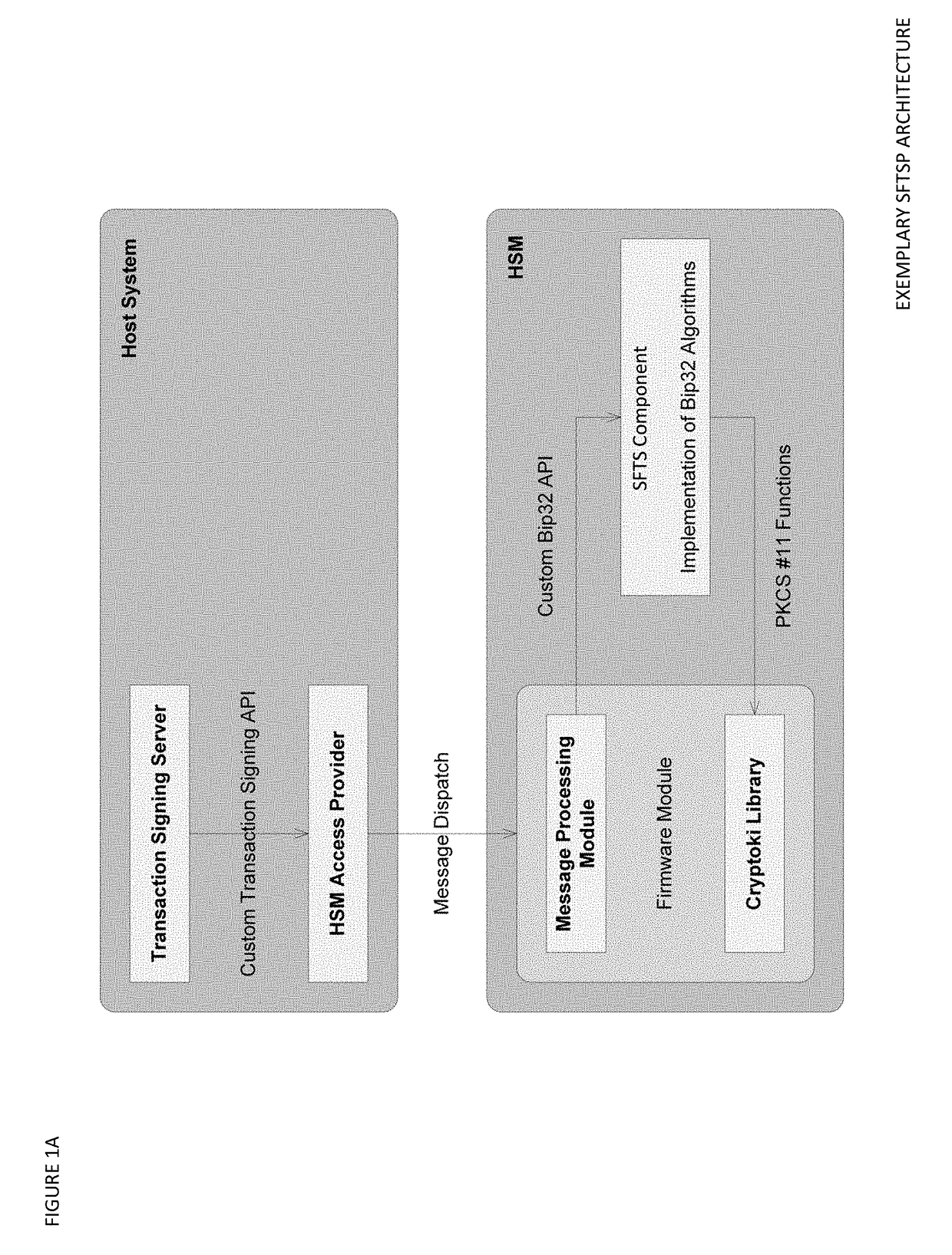
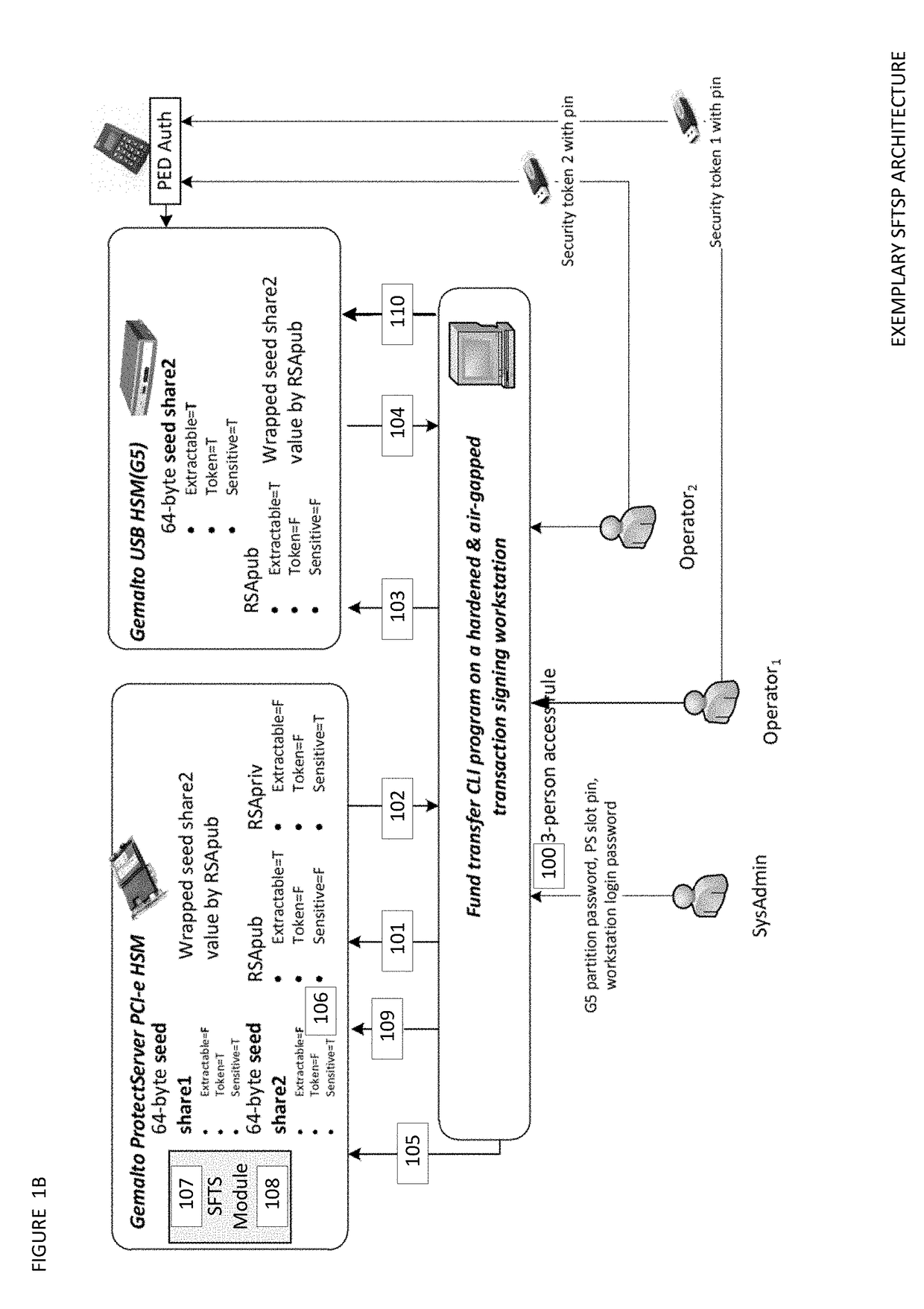
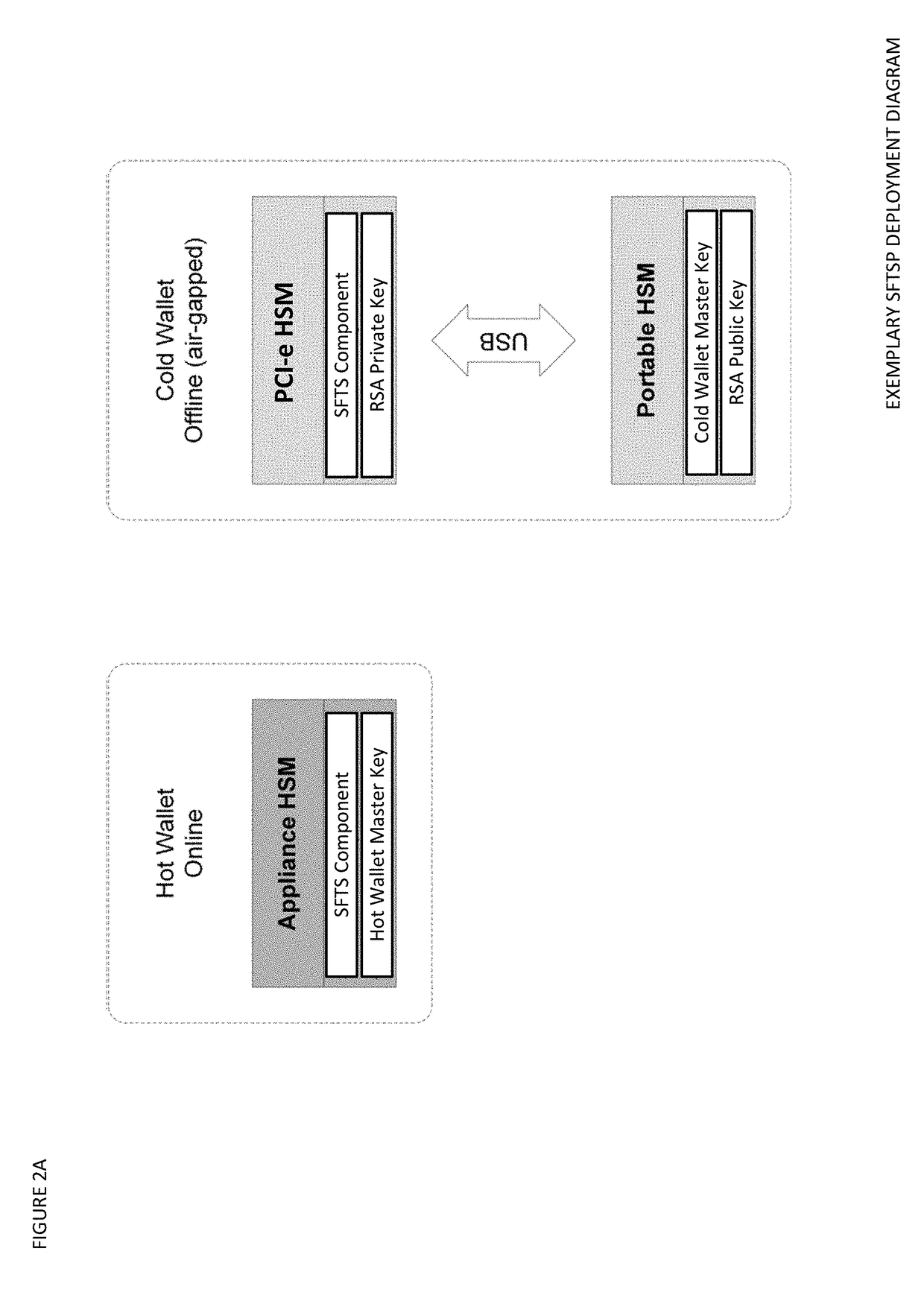
Seed splitting and firmware extension for secure cryptocurrency key backup, restore, and transaction signing platform apparatuses, methods and systems
ActiveUS20180367316A1Improve network efficiencyProlong lifeKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesMaster keyKey sharing
The Seed Splitting and Firmware Extension for Secure Cryptocurrency Key Backup, Restore, and Transaction Signing Platform Apparatuses, Methods and Systems (“SFTSP”) transforms transaction signing request, key backup request, key recovery request inputs via SFTSP components into transaction signing response, key backup response, key recovery response outputs. A transaction signing request message for a transaction is received by a first HSM and includes an encrypted second master key share from a second HSM whose access is controlled by M-of-N authentication policy. The encrypted second master key share is decrypted. A first master key share is retrieved. A master private key is recovered from the master key shares. A transaction hash and a keychain path is determined. A signing private key for the keychain path is generated using the recovered master private key. The transaction hash is signed using the signing private key, and the generated signature is returned.
Owner:FMR CORP
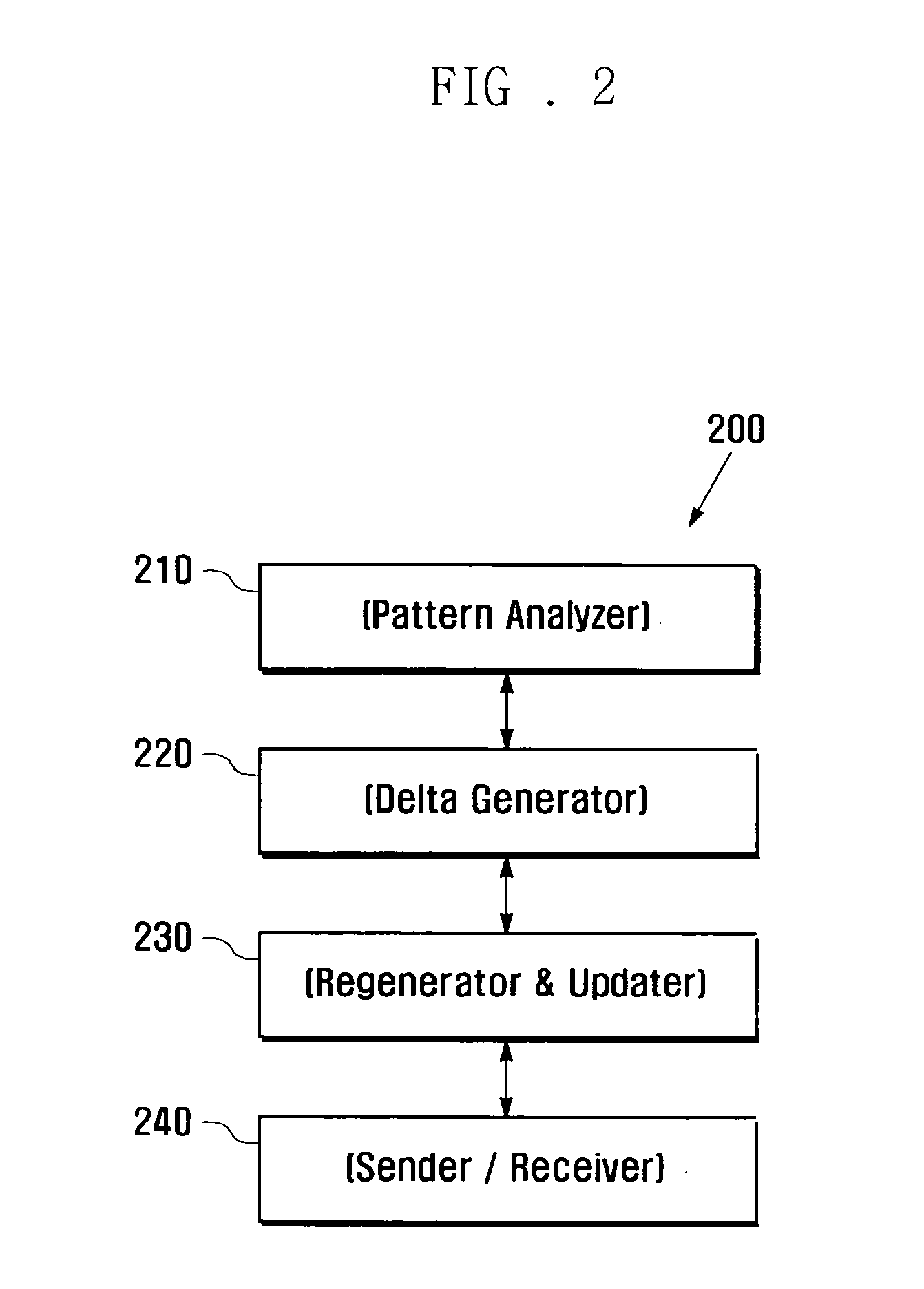
Data compression method and data communication system utilizing the same
InactiveUS20100115137A1Reduce processing loadImprove network efficiencyCode conversionMultiple digital computer combinationsData compressionText-based protocol
A data compression method and data communication system utilizing the same includes: a sender apparatus that compares, in response to input of data to be sent, the input data with the previously sent data in storage. The sender apparatus produces, when a data item repeated in the input data and previously sent data is found, delta data by excluding the repeated data item from the input data. The sender apparatus represents the delta data in a transport format, and transmits the delta data. The system includes a receiver apparatus that receives the data in a transport format. The receiver apparatus adds, when delta data is present in the received data, a repeated data item to the delta data, and recovers the original data. The sender apparatus sends and receives data to and from the receiver apparatus through a text-based protocol.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
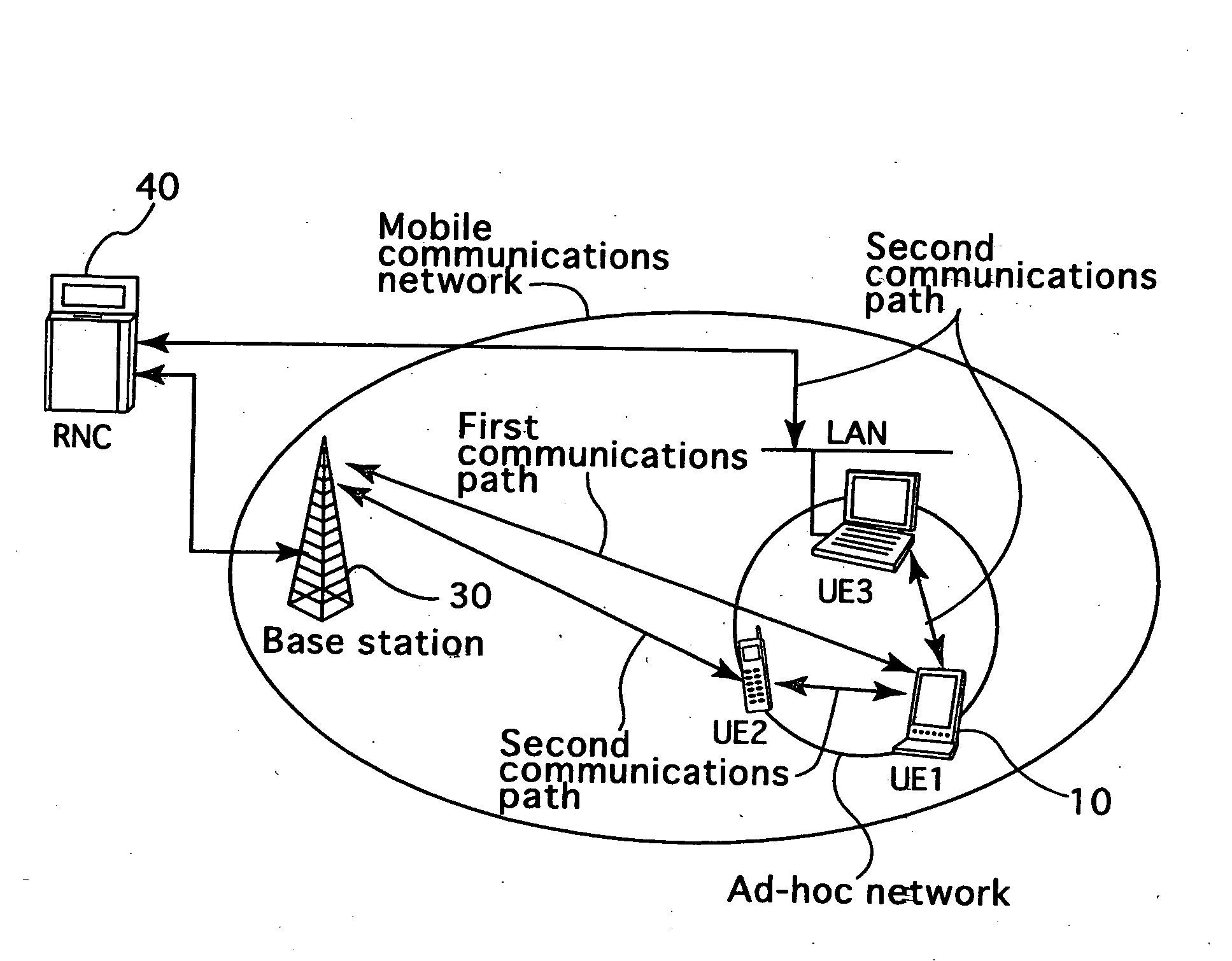
Radio communications apparatus, radio communications system, and base station equipment
InactiveUS20060205408A1Promote network efficiencyEasy to optimizeData switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemRadio communications
Radio communications apparatus, radio communications system, and base station equipment that effectively utilize the network resources of both an ad-hoc network and a mobile communications network to increase the efficiency of and optimize the networks, thereby improving the communication capacity and throughput of the networks as a whole. The radio communications apparatus (UE1) employs TDD-CDMA system for communications with a base station (30) of the mobile communications network, and also employs the TDD-CDMA system, which is common to the base station, for communications with other radio communications apparatuses in the ad-hoc network, while using the same frequency band. Communications paths for communicating with the base station equipment include a first communications path for directly communicating with the base station and a second communications path for communicating with the base station equipment via another radio communications apparatus (UE2, UE3 or the like) in the ad-hoc network. The radio communications apparatus (UE1) uses one of those communications paths, which is designated by the base station equipment, to communicate with the base station equipment.
Owner:KEIO UNIV +1
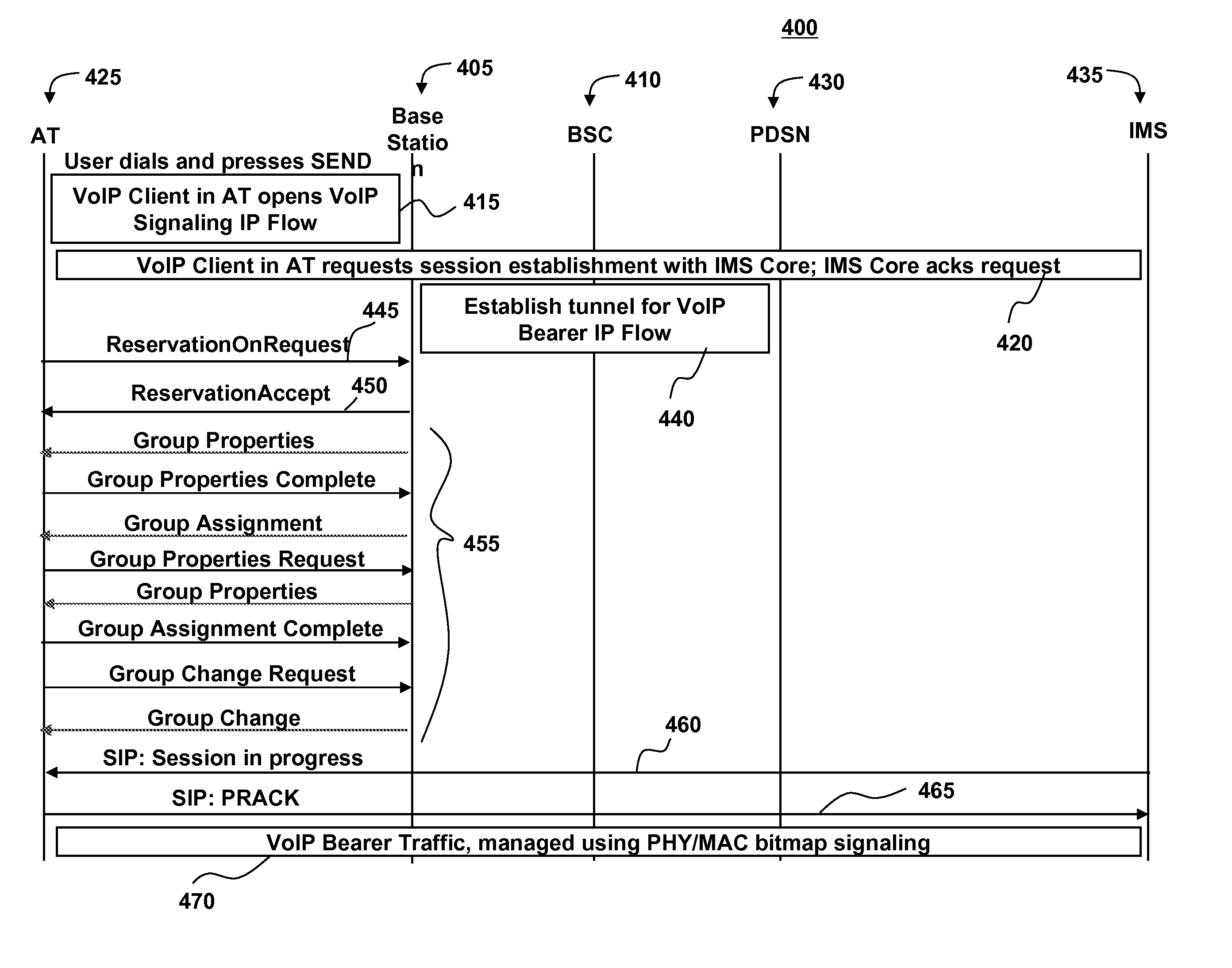
Method and system for processing group resource allocations
InactiveUS20080062936A1Efficient processingEffective distributionBroadcast service distributionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio access networkGroup property
A method and system for processing, in a wireless communication device, data concerning a group resource allocation enables efficient use of radio frequency resources. The method includes processing a group properties message received from a radio access network (block 1410). The group properties message comprises group properties for a scheduling group, and the group properties comprise a group identifier that identifies the scheduling group. A group assignment message received from the radio access network is then processed (block 1425). The group assignment message comprises the group identifier and a position assignment within the scheduling group. The group properties are then associated with the group assignment message (block 1430).
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
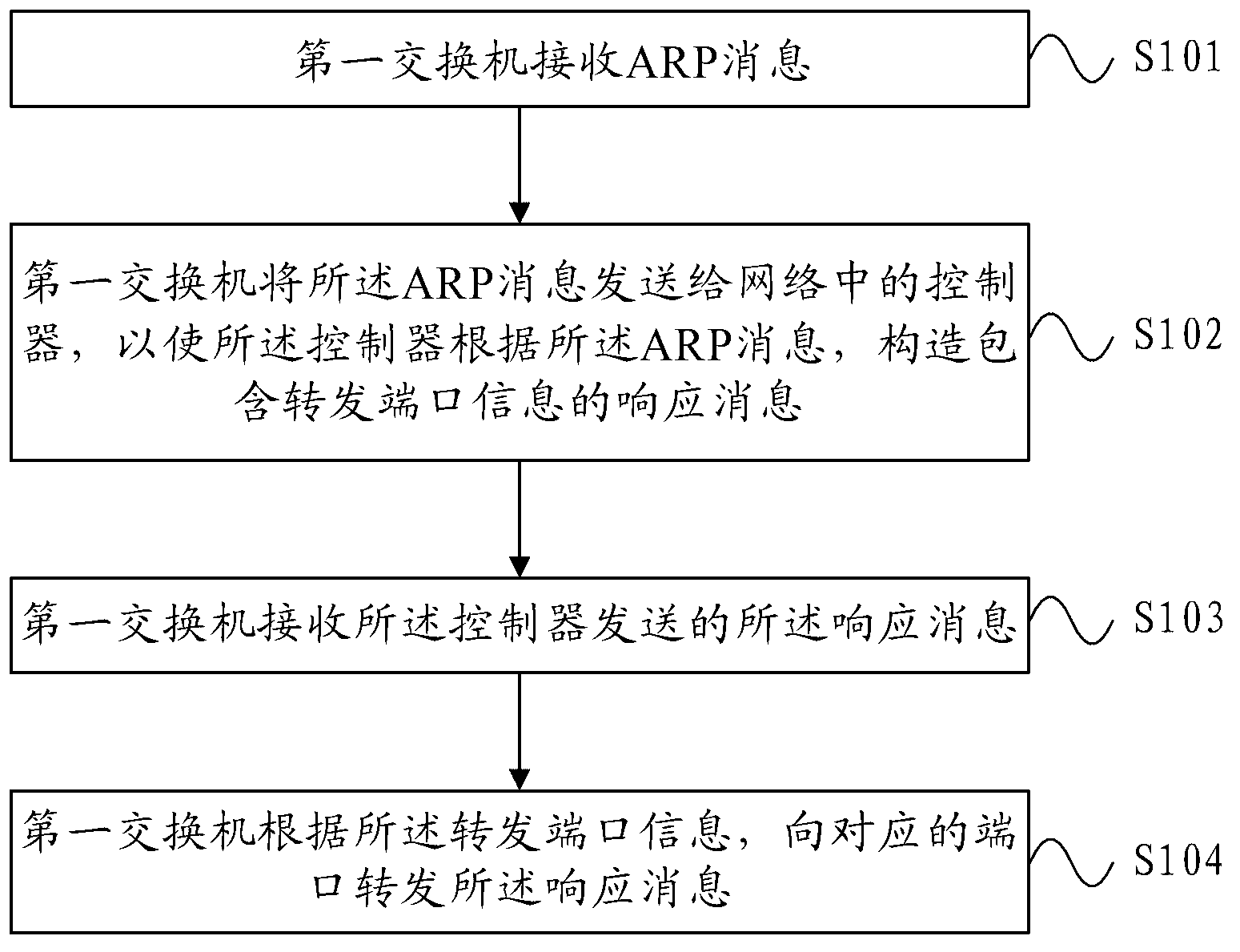
Address resolution protocol (ARP) message forwarding method, exchanger and controller
ActiveCN102938794ASave bandwidthImprove network efficiencyData switching networksAddress Resolution ProtocolAddress resolution
An embodiment of the invention provides an address resolution protocol (ARP) message forwarding method, an exchanger and a controller. The ARP message forwarding method includes: a first exchanger receives ARP messages; the first exchanger sends the ARP messages to the controller in the network to lead the controllers to construct response messages containing forwarding port messages according to the ARP messages; the first exchanger receives the response messages sent by the controller; and the first exchanger forwards the response messages to a corresponding port according to the forwarding port messages. The controller provides ARP service for a main machine of the network managed by the controller, and therefore network efficiency can be improved and network bandwidth can be saved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
System and method for optimizing network capacity in a cellular wireless network
InactiveUS7573862B2Improve efficiencyReduce operating costsNetwork traffic/resource managementPower distribution line transmissionQuality of serviceFiber
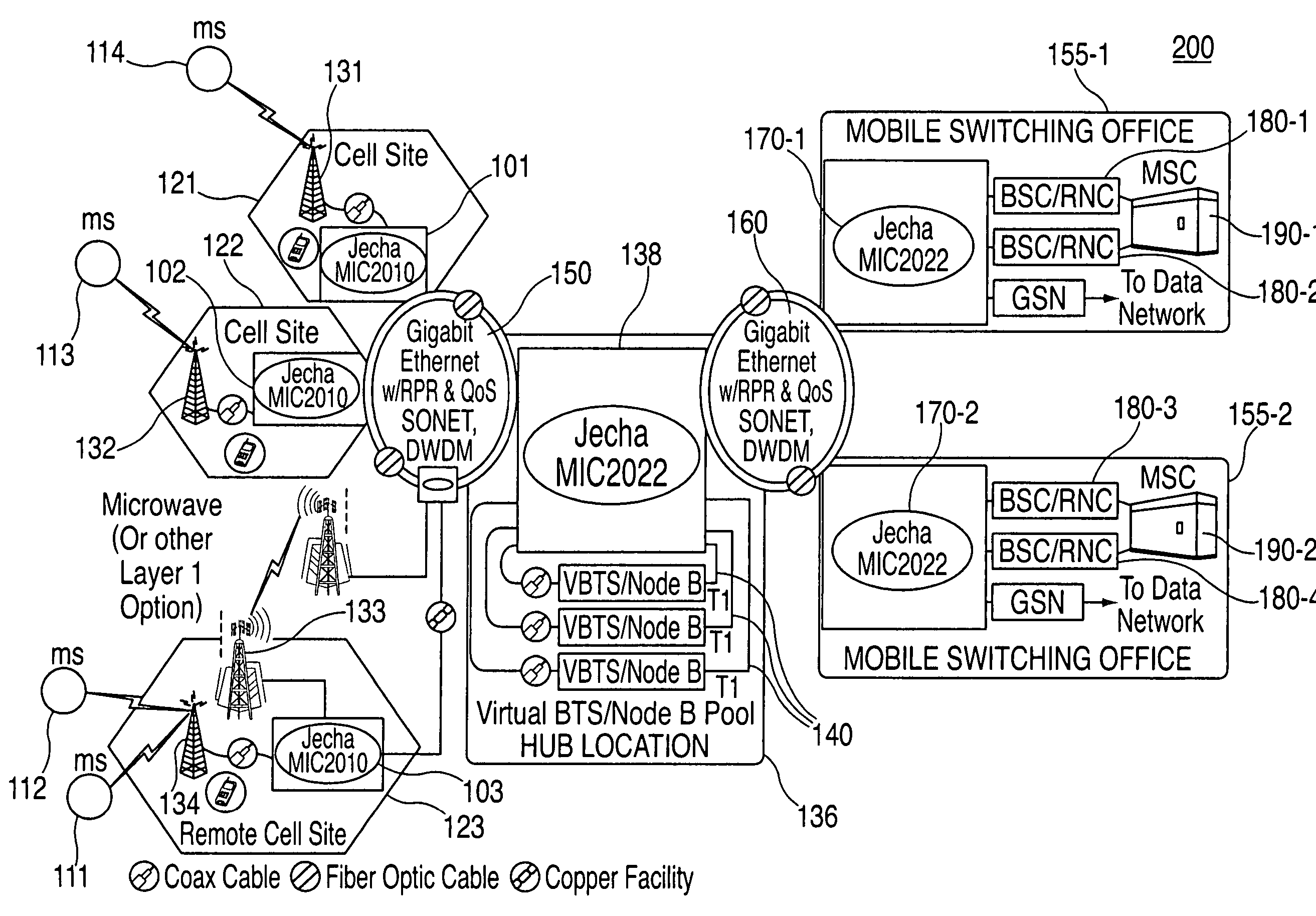
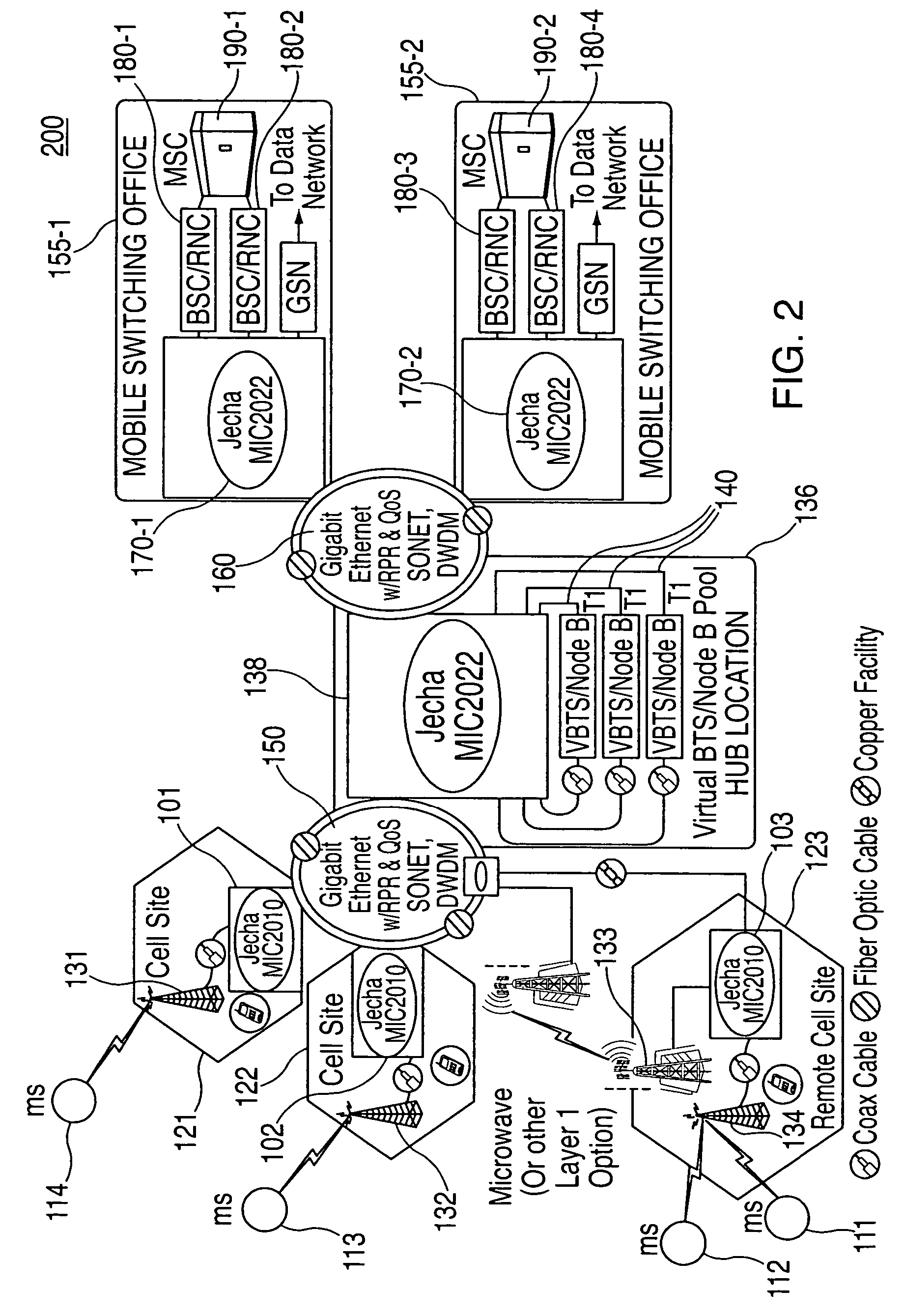
A system and method is disclosed for increasing the efficiency of a cellular communication network, reduce ongoing operating costs and increase revenue. According to one aspect, a method is disclosed for increasing the efficiency of a cellular communication network whereby network capacity in the radio access network (RAN) and baseband processing for wireless connections are dynamically adjusted to automatically provision sufficient bandwidth and baseband processing capacity in response to changes in the network. The method is further extended by implementing policy management which allows wireless carriers to develop and implement network based policies to automatically increase or decrease the amount of processing resources and network bandwidth required from any cell site, hub or mobile switching office. According to another aspect, network efficiency is enhanced by utilizing a novel cellular network infrastructure. RF signals from cell site antennas of various technology types are demodulated, digital bit information is extracted from the RF signals, processed, and groomed into Gigabit Ethernet / Resilient Packet Ring (GigE / RPR) or Ethernet over copper traffic flows using specific Quality of Service (QoS) priorities. The GigE / RPR traffic flows are routed to hub sites or mobile switching offices, at which point the packetized information is extracted and converted to RF signals that are equivalent to the signals that were received at the antenna. The RF signals are sent over coaxial cable to a network hub including a pool of Base Transceiver Stations (BTSs) (or Node Bs). The hub is coupled to one or more mobile switching offices via a second fiber optic ring.
Owner:CHAMBERS MAHDI +1
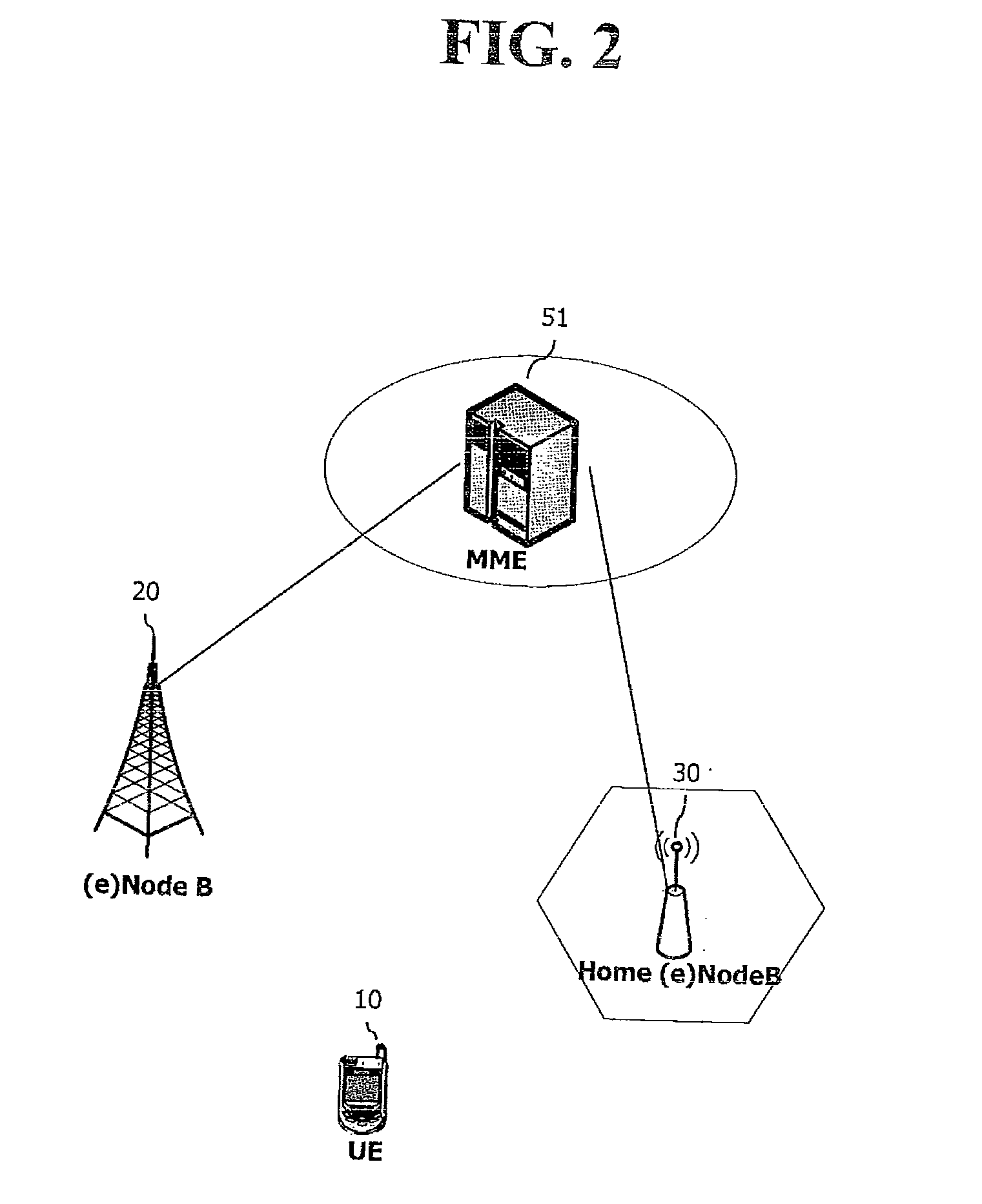
Optimized paging method for home (e)nodeb system
InactiveUS20100210288A1Efficiently determinedAvoid wastingNetwork topologiesPagingClosed subscriber groups
An optimized paging method for a Home (e)NodeB system comprises: receiving, by a network entity, a notification message indicating whether downlink data for a terminal exists or not; determining, by the network entity, one or more Home (e)NodeBs to which a paging message is to be transmitted among one or more base stations included in a base station list for the terminal, based on an access mode of the Home (e)NodeB, and based on whether the terminal is a member of a Closed Subscriber Group (CSG) supported by the Home (e)NodeB; to transmitting, by the network, a paging message to the determined one or more Home (e)NodeBs or (e)NodeBs included in the base station list; and receiving, by the network, a paging response message from a specific (e)NodeB or Home (e)NodeB among the one or more (e)NodeBs or Home (e)NodeBs to which the paging message has been transmitted.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Tunneled security groups
ActiveUS8146148B2Reduce in quantityImprove network efficiencyMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlGroup identifierComputer security
A method for providing security groups based on the use of tunneling is disclosed. The method includes assigning a security group identifier (SGI) to a packet and classifying the packet based on the packet's SGI.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for caching secure web content
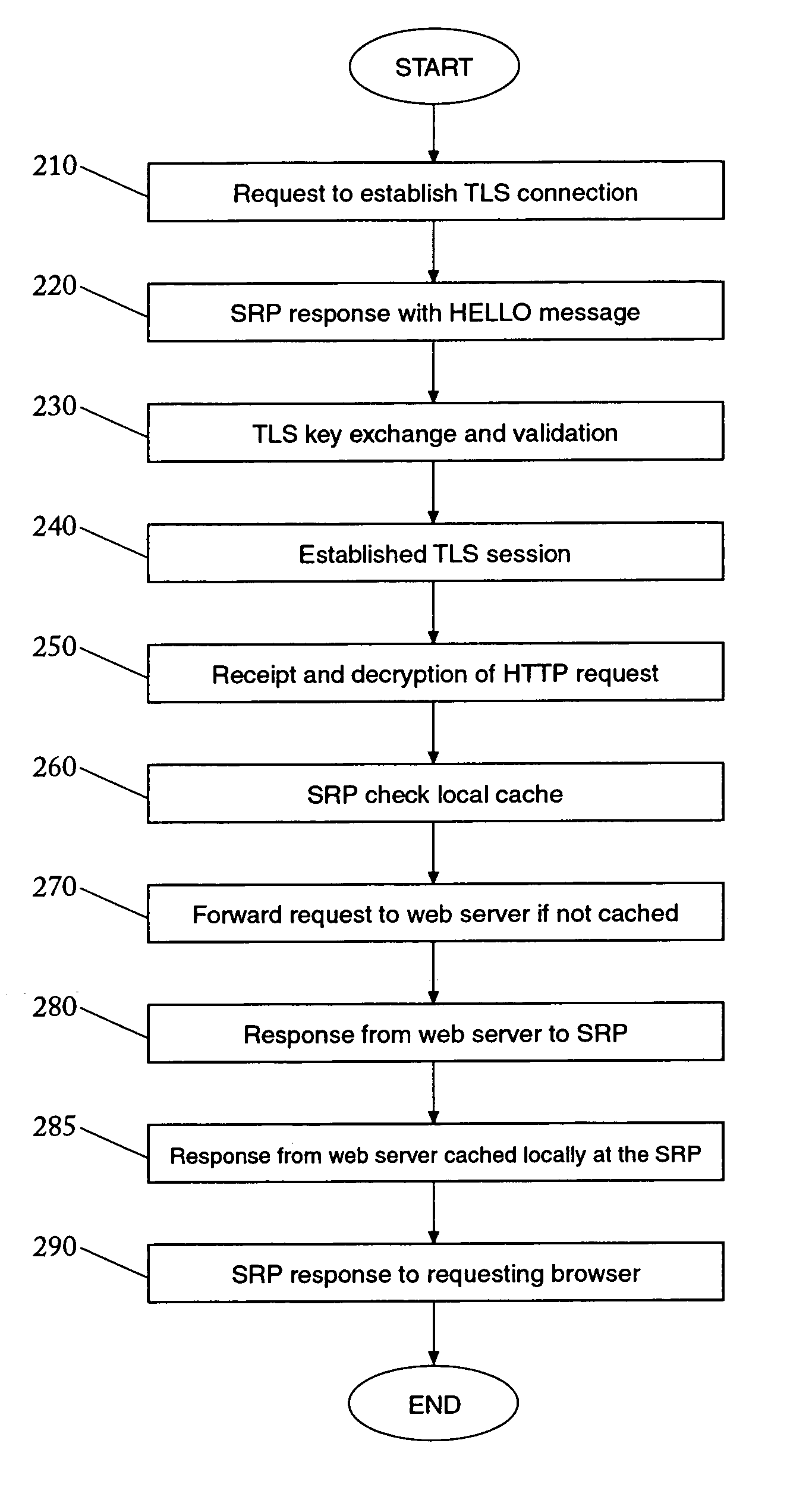
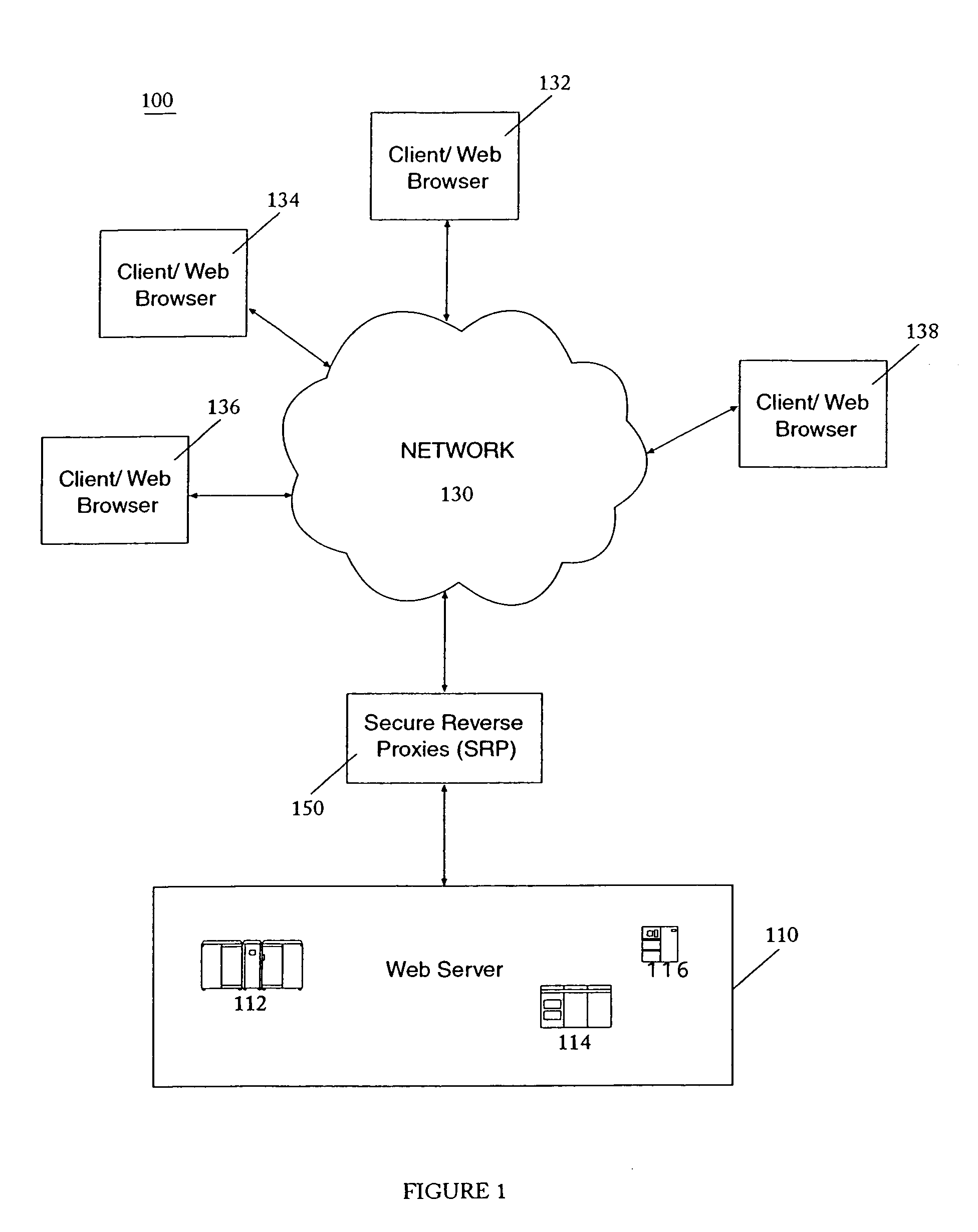
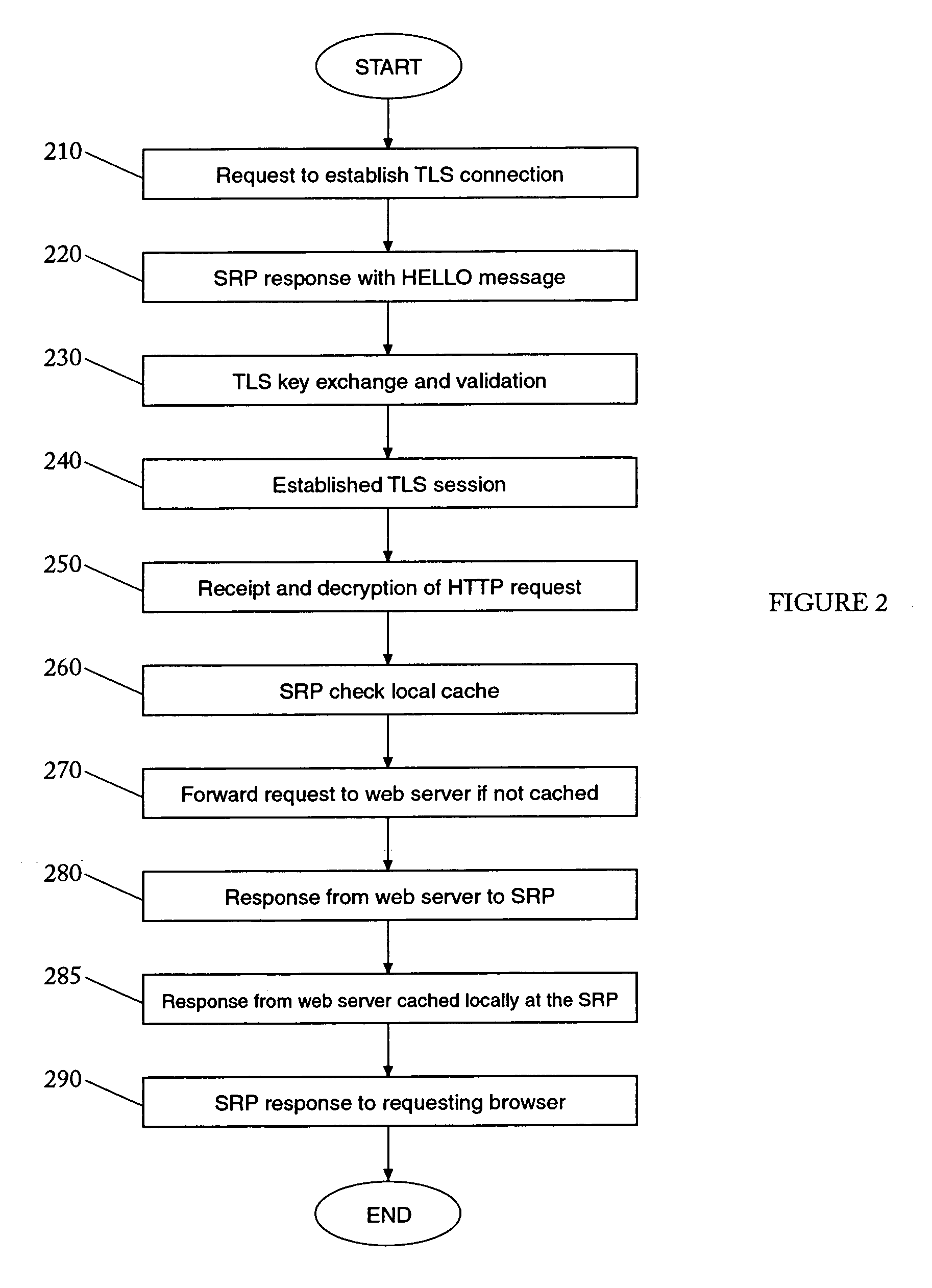
InactiveUS7137143B2Increase network efficiencyLoading be diminishDigital data information retrievalComputer security arrangementsProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network AccessClient-side
A method and system for securing network communications are provided. In a network a Secure Reverse Proxy (“SRP”) is placed among a server and a client where the client and SRP establish a secure connection using TLS protocol. Upon receiving a request from the client for a secure HTTP page, the SRP determines if the secure page is maintained in its cache. If the page is present, the SRP responds to the client by sending the requested secure HTTP page without contacting the server. If the page is not contained within the SRP's cache, the SRP establishes secure TLS connection with the server and forwards the request for the HTTP page. Receiving the HTTP page from the server, the SRP places it in its cache for future use. Having the page in its cache the SRP retrieves the page, encrypts it, and sends it to the requesting client. Subsequent requests for the same page do not involve the server enhancing the efficiency of network operations.
Owner:SAFENET
User equipment capability determination for multiple radio capability groups
InactiveUS20180084539A1Effective serviceBetter support mobile broadband Internet accessConnection managementNetwork data managementData transmissionUser equipment
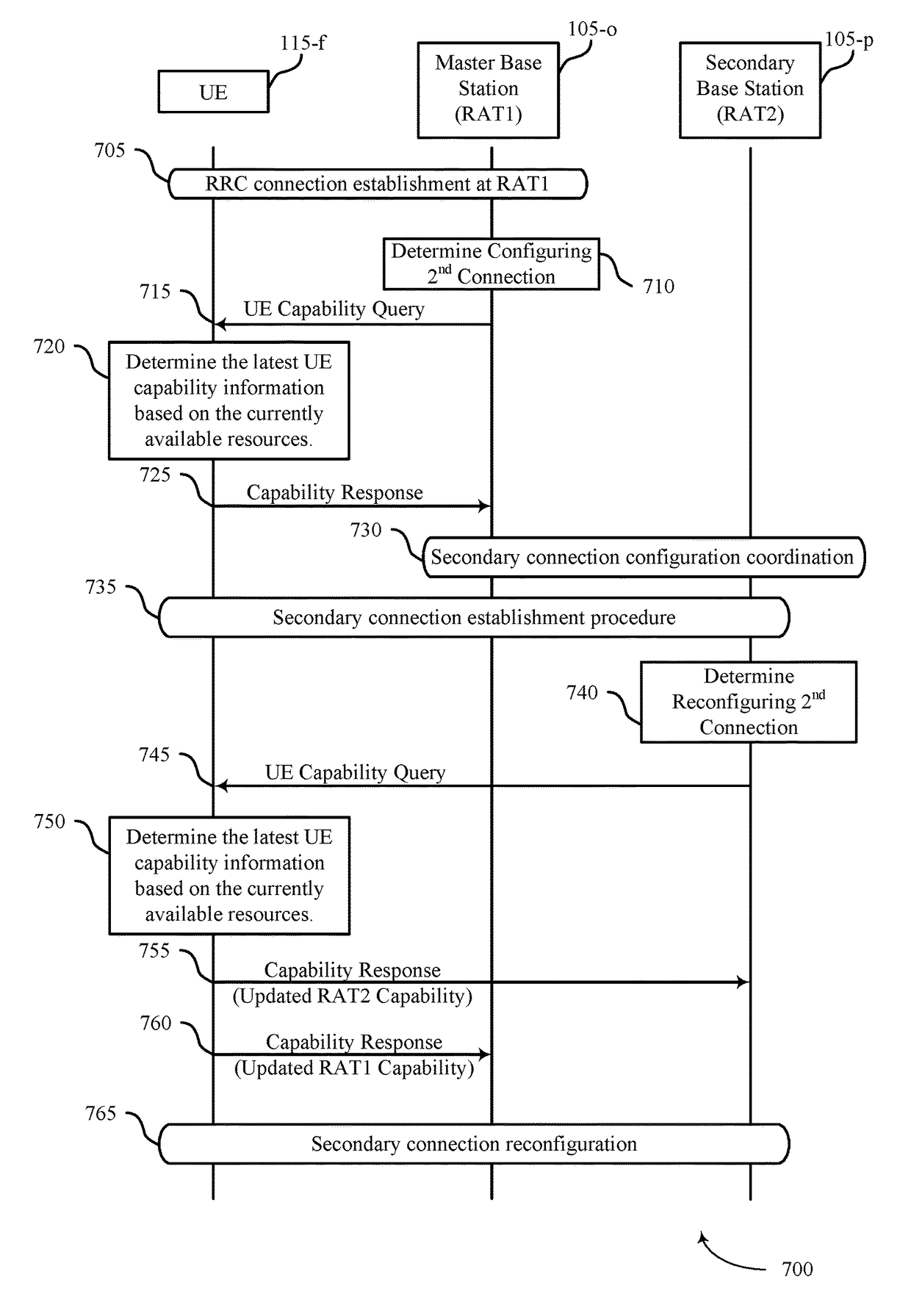
LUE capability information is provided for coordination across multiple RATs or for single-RAT connectivity where UE capabilities may change or be reported according to capability groups. A base station may establish a first connection with a UE using a first RAT, and determine that the first connection is to be reconfigured, such as due to data transmission requirements exceeding the capacity of the currently configured connection. The base station may receive UE capability information, such as in response to a capability query transmitted to the UE. The base station may reconfigure the connection with the UE based on the UE capability response through initiating a second connection with a second base station using a second RAT, through reconfiguring the first connection, or combinations thereof.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
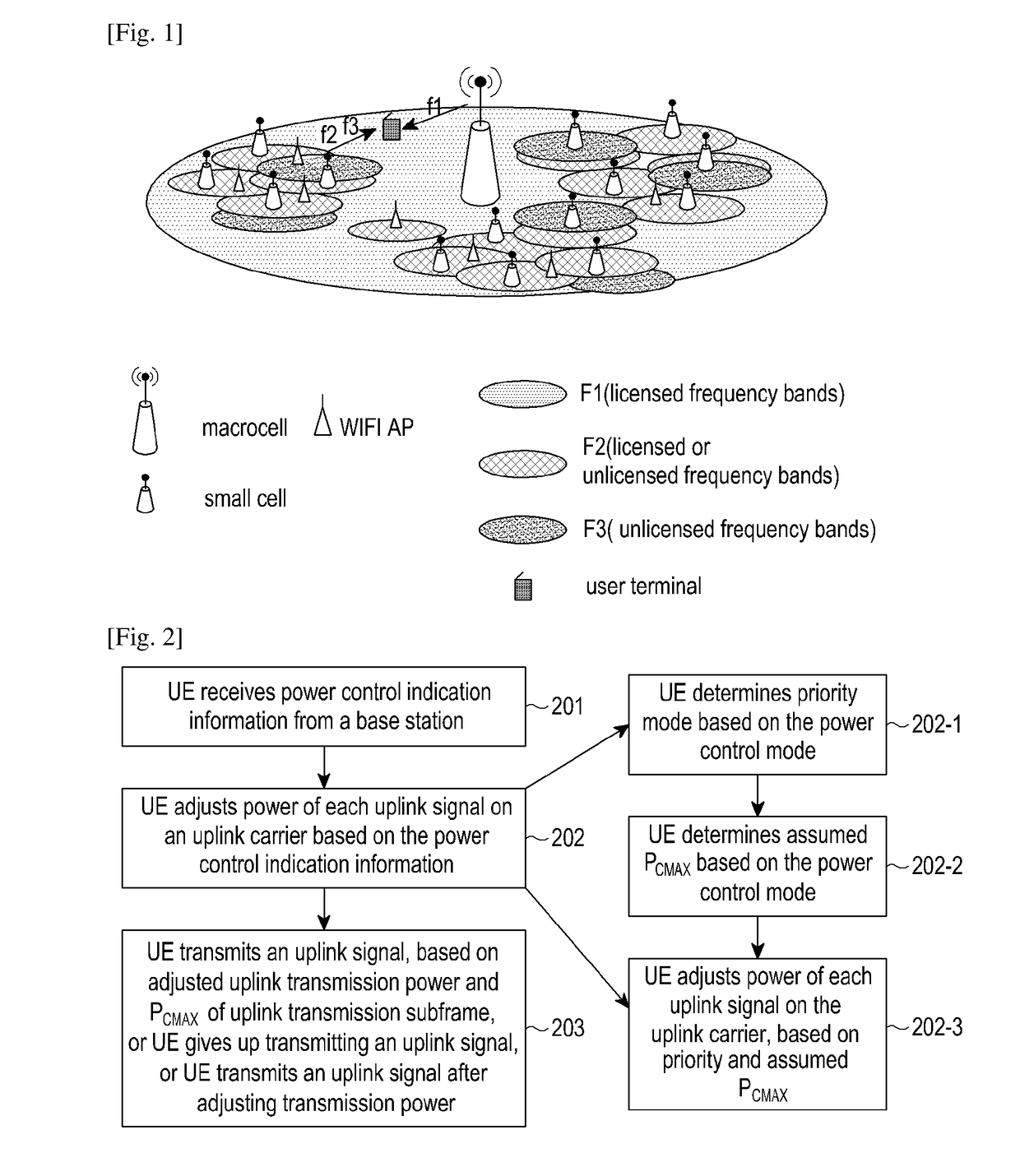
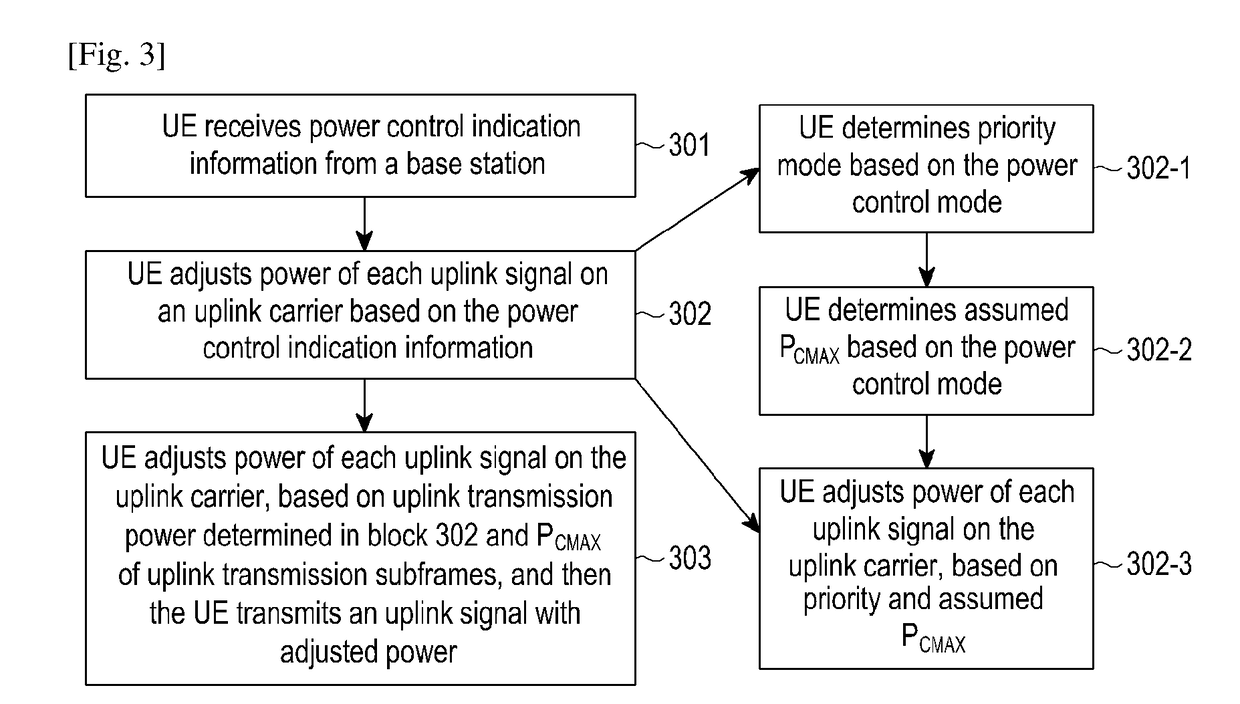
Method and user equipment for allocating uplink power in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20180139701A1Power is wastedImprove Uplink Scheduling EfficiencyPower managementCommunications systemUplink transmission
The present disclosure relates to a pre-5th-Generation (5G) or 5G communication system to be provided for supporting higher data rates Beyond 4th-Generation (4G) communication system such as Long Term Evolution (LTE). The present disclosure provides a power allocating method. A User Equipment (UE) receives power control indication information from a control node, obtains a power control mode, and / or, uplink transmission power configuration information. The UE allocates power for each uplink carrier, based on the power control mode, and / or, the uplink transmission power configuration information. By applying the present disclosure, power waste generated in the following scene may be reduced. A scheduled uplink signal cannot be transmitted in a corresponding carrier due to a busy channel. Subsequently, uplink scheduling efficiency of the UE may be improved, and the whole network efficiency may also be enhanced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
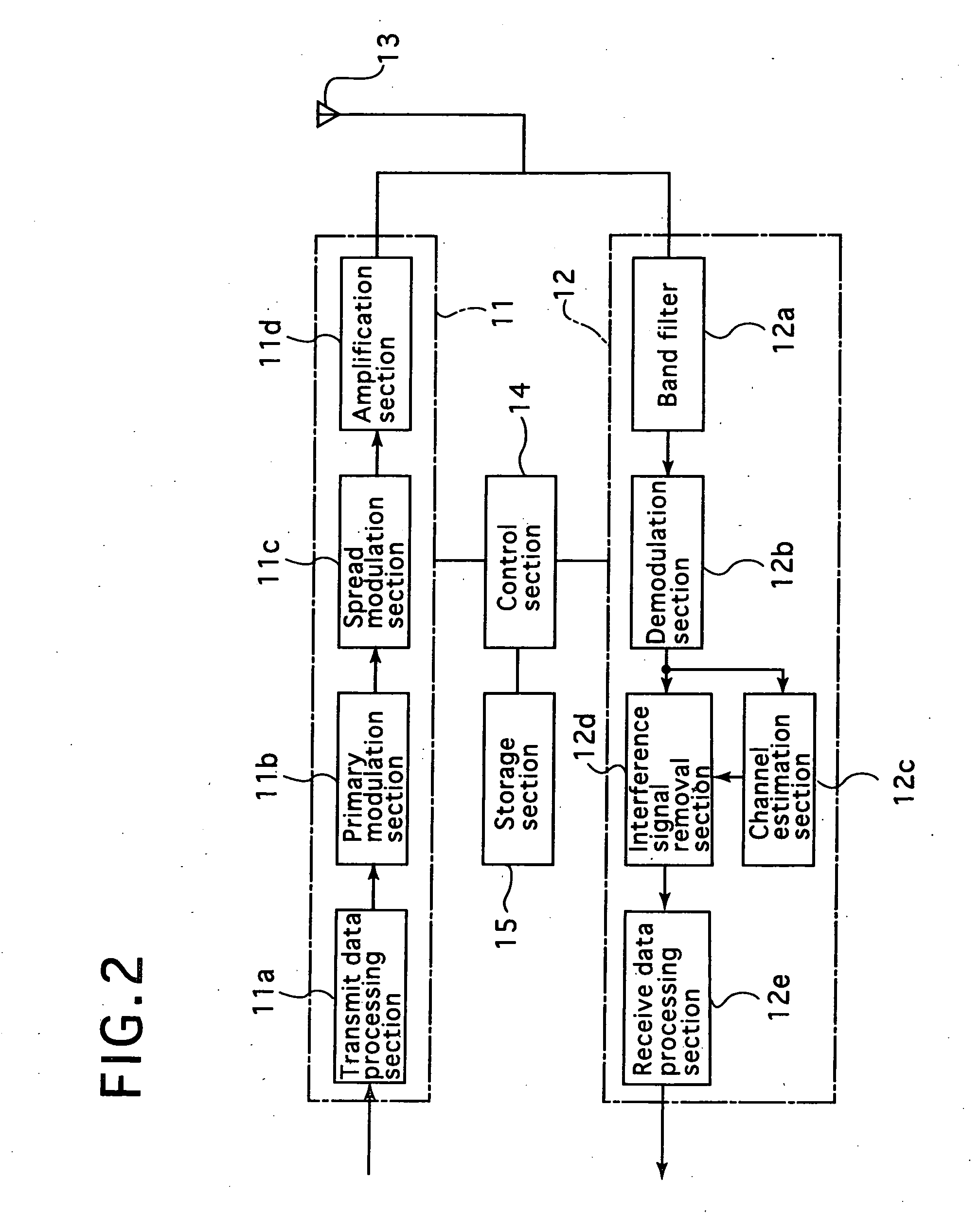
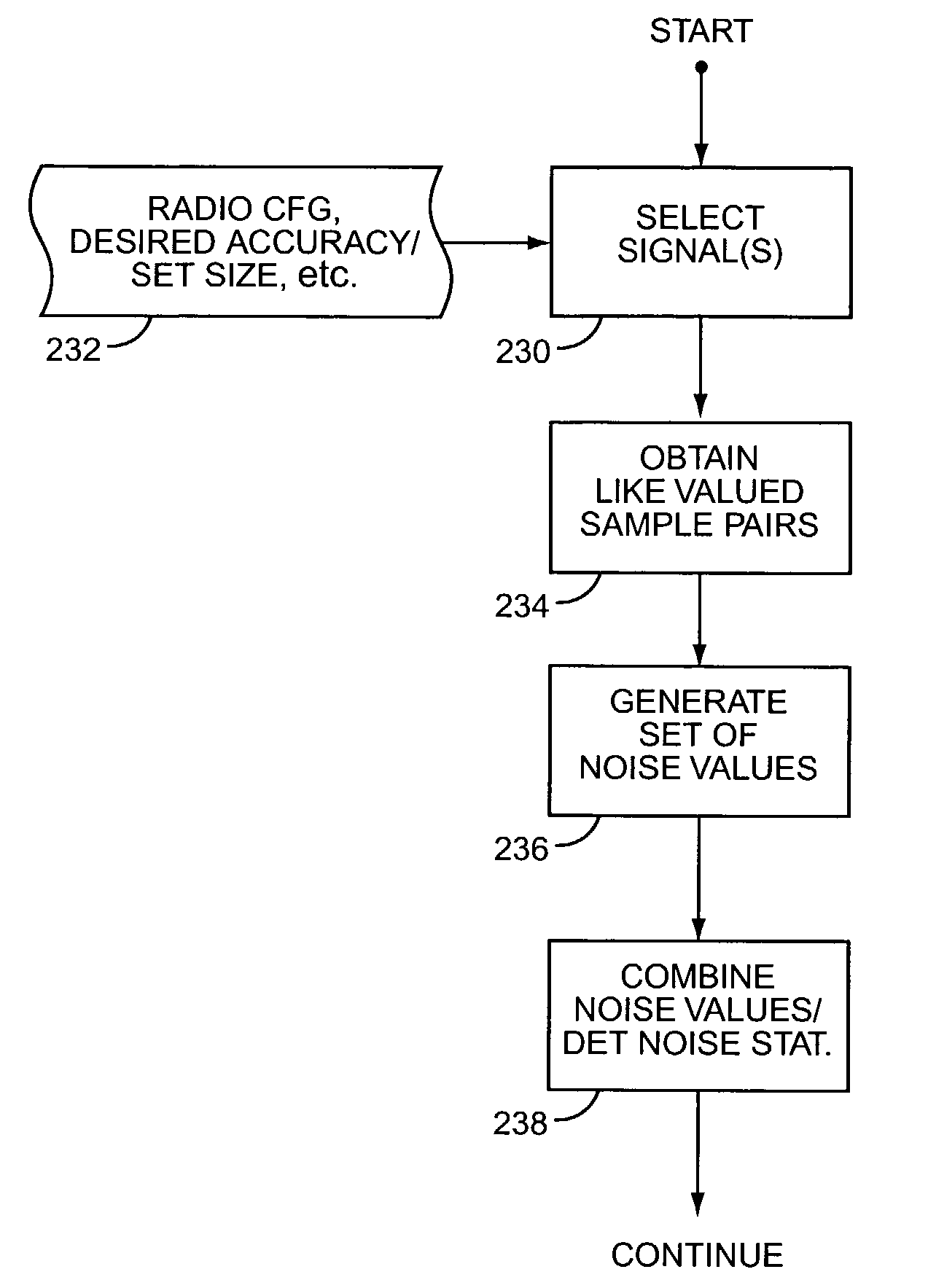
Signal-to-noise ratio estimation of CDMA signals
ActiveUS7313167B2Cancel improvementMinimize timePower managementEnergy efficient ICTSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Deterministic noise
An improved approach to noise estimation permits, for example, tighter closed-loop power control in a wireless communication network with attendant improvements in transmit power efficiency and network capacity. In an exemplary embodiment, the received signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of a data signal is estimated based on noise samples obtained from one or more other signals received in association with the data signal. In general, these associated signals are characterized by the receiver's ability to extract like valued samples from them, such that pairs of these like valued signal samples may be subtracted, thereby canceling their deterministic signal components and leaving only difference values representative of the non-deterministic noise components of the signal samples. Obtaining difference values from more than one associated signal increases the sample size of difference values used in noise estimation, thereby improving the statistical basis for noise estimation and, therefore, the accuracy of SNR estimation.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and apparatus for media access in contention-based networks
InactiveUS20100135319A1Improve performanceEnsure fairnessData switching networksTime-division multiplexing selectionTraffic capacityComputer science
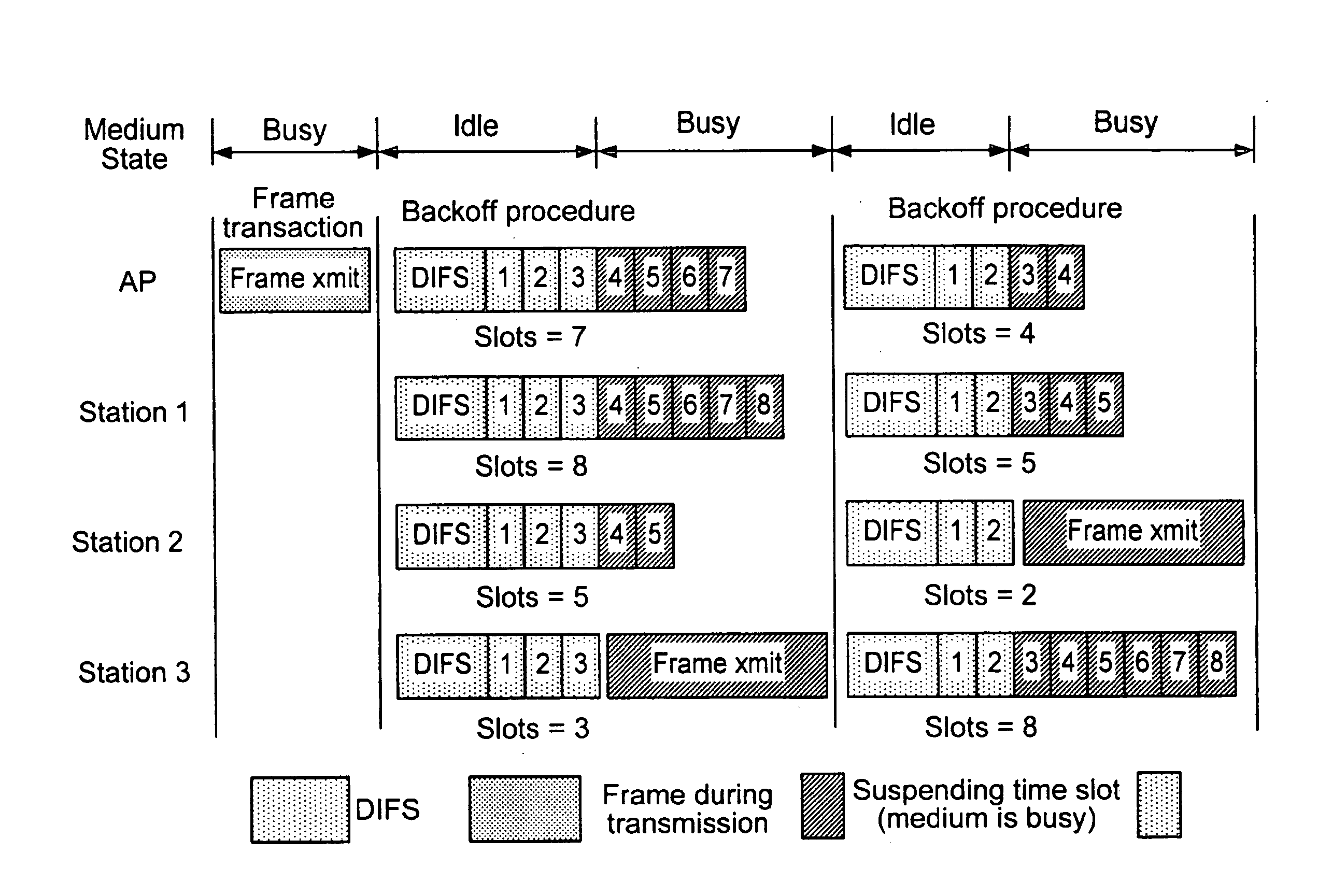
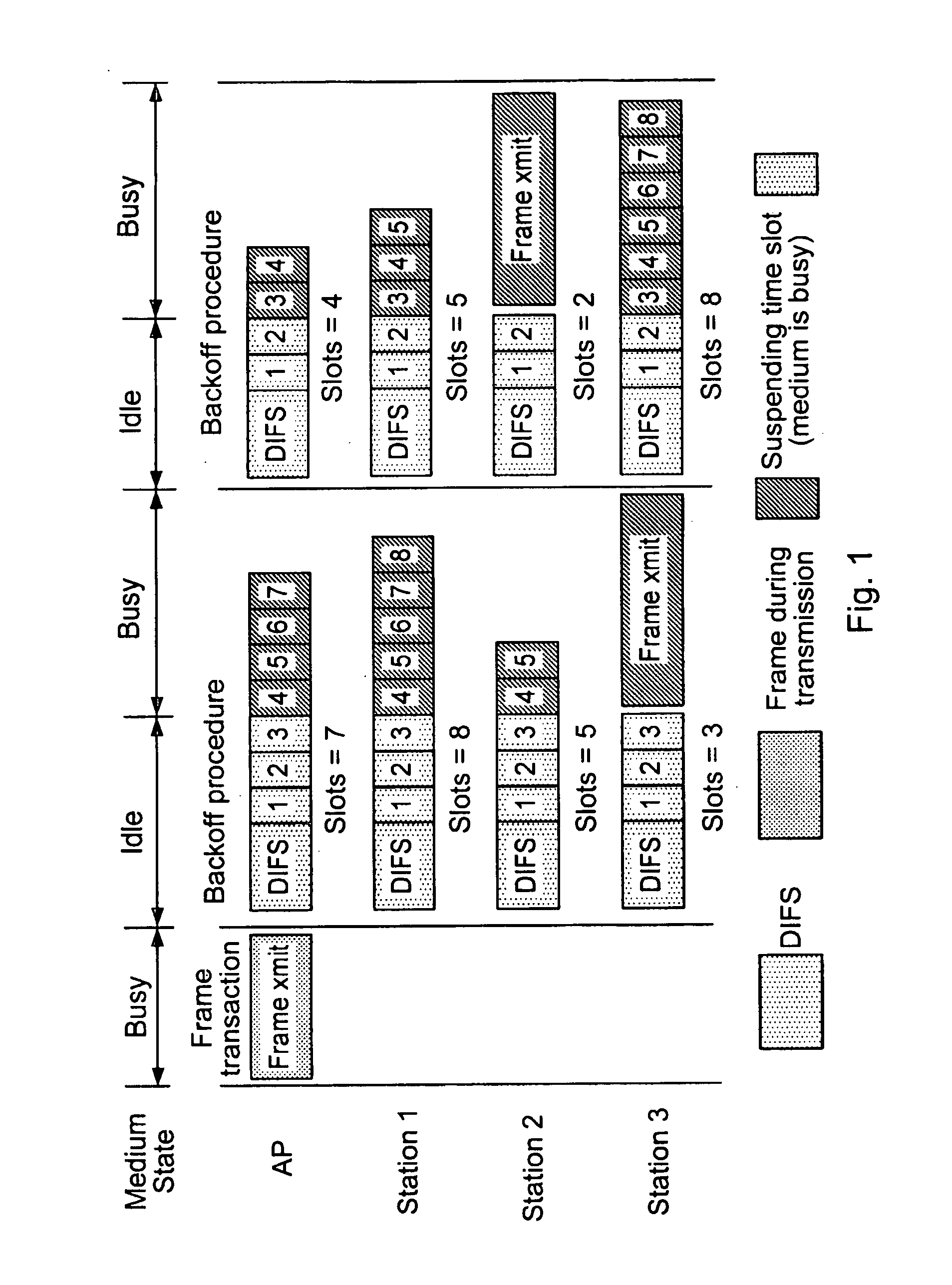
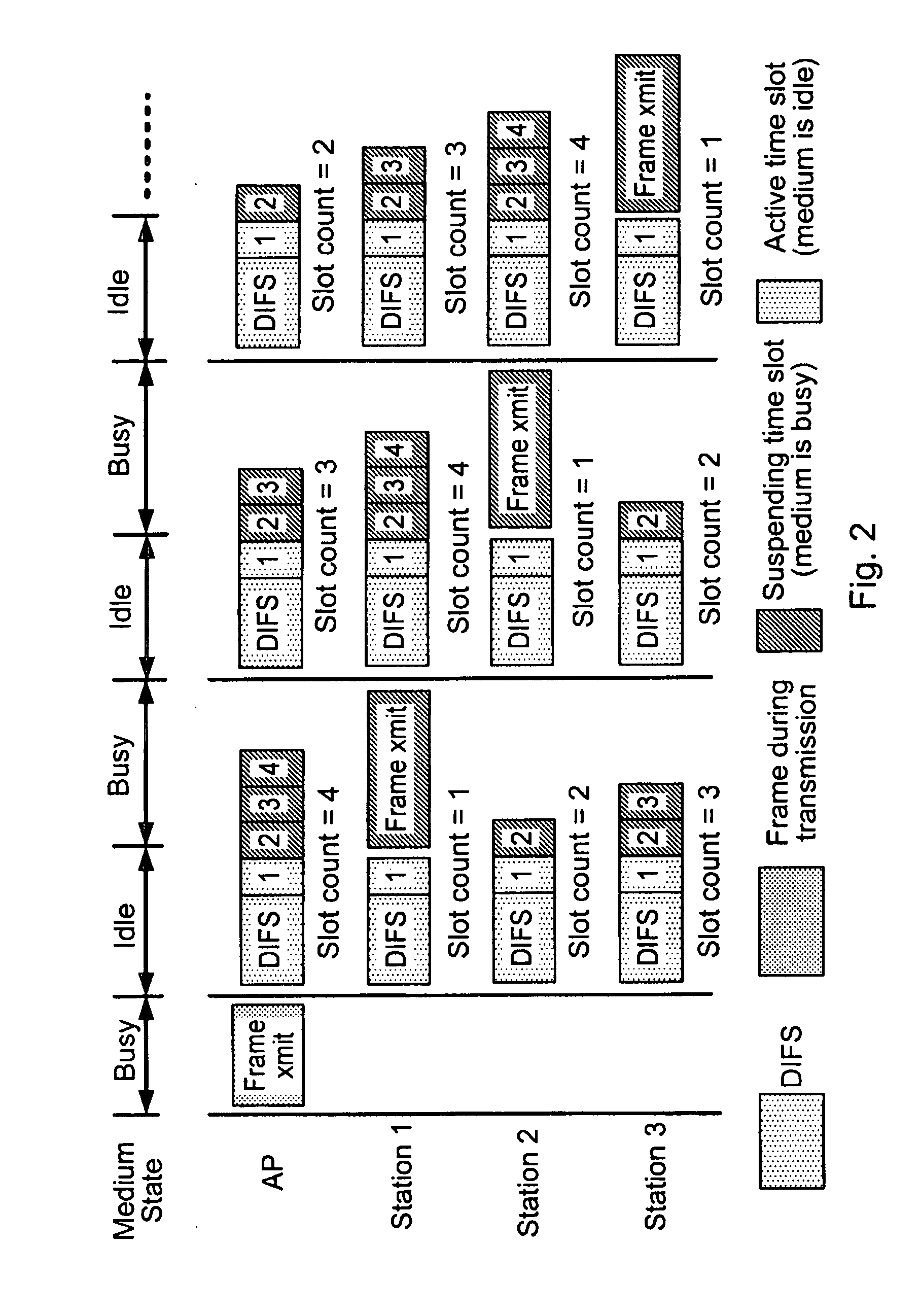
A method and apparatus are described for gaining access to a communication medium in a contention-based network, including determining a slot count based on a number of stations in the contention-based network, adjusting the slot count, initiating a frame transmission when the slot count reaches a predetermined value and wherein said number of stations and an address queue are adjusted to reflect one of a priority and traffic patterns. Further, a method and apparatus are described for gaining access to a communication medium in a contention-based network, including receiving a slot count based on a number of stations in the contention-based network, adjusting the slot count, initiating a frame transmission when the slot count reaches a predetermined value and wherein said number of stations and an address queue are adjusted to reflect a priority.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Signing-in to software applications having secured features
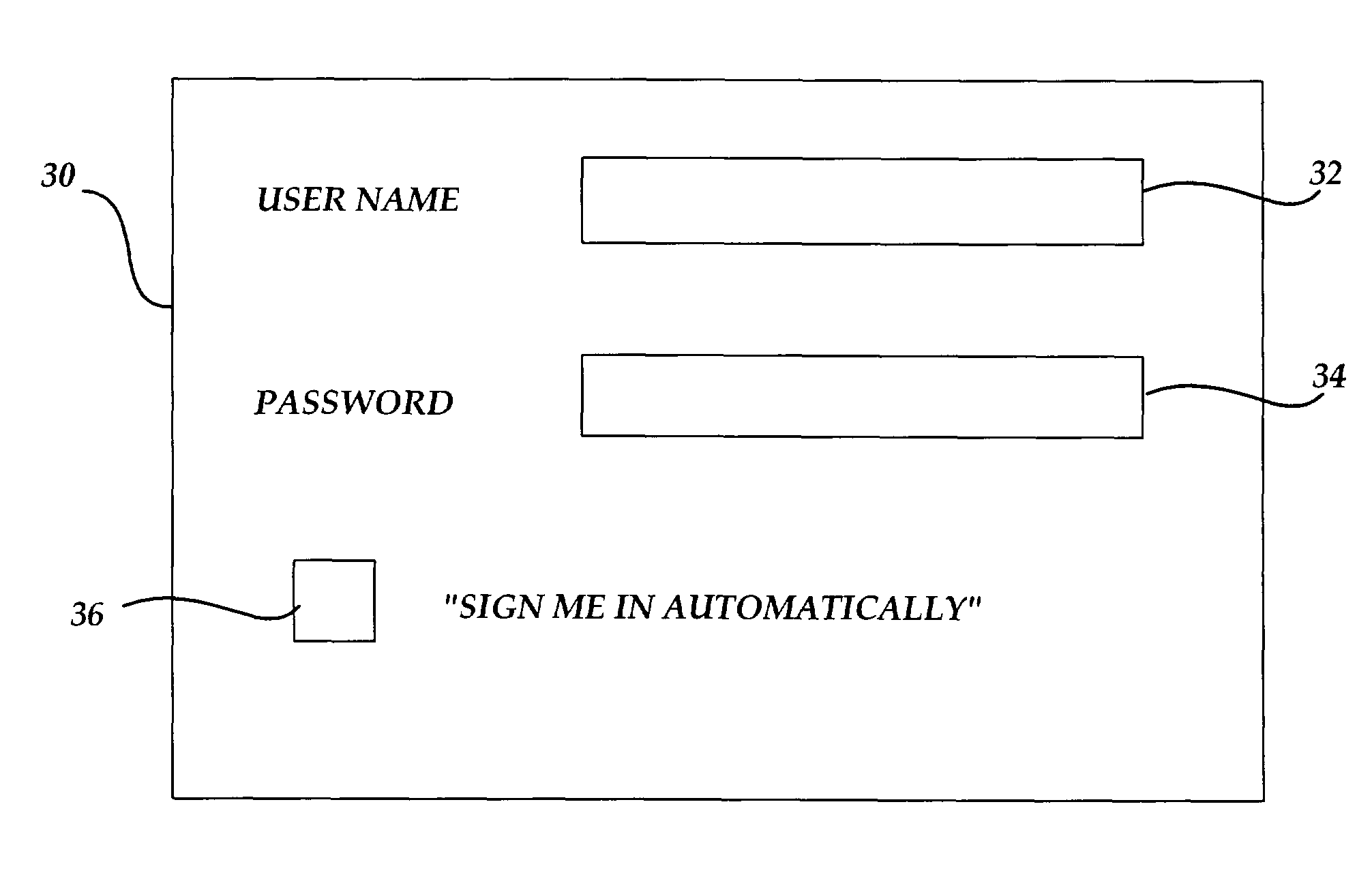
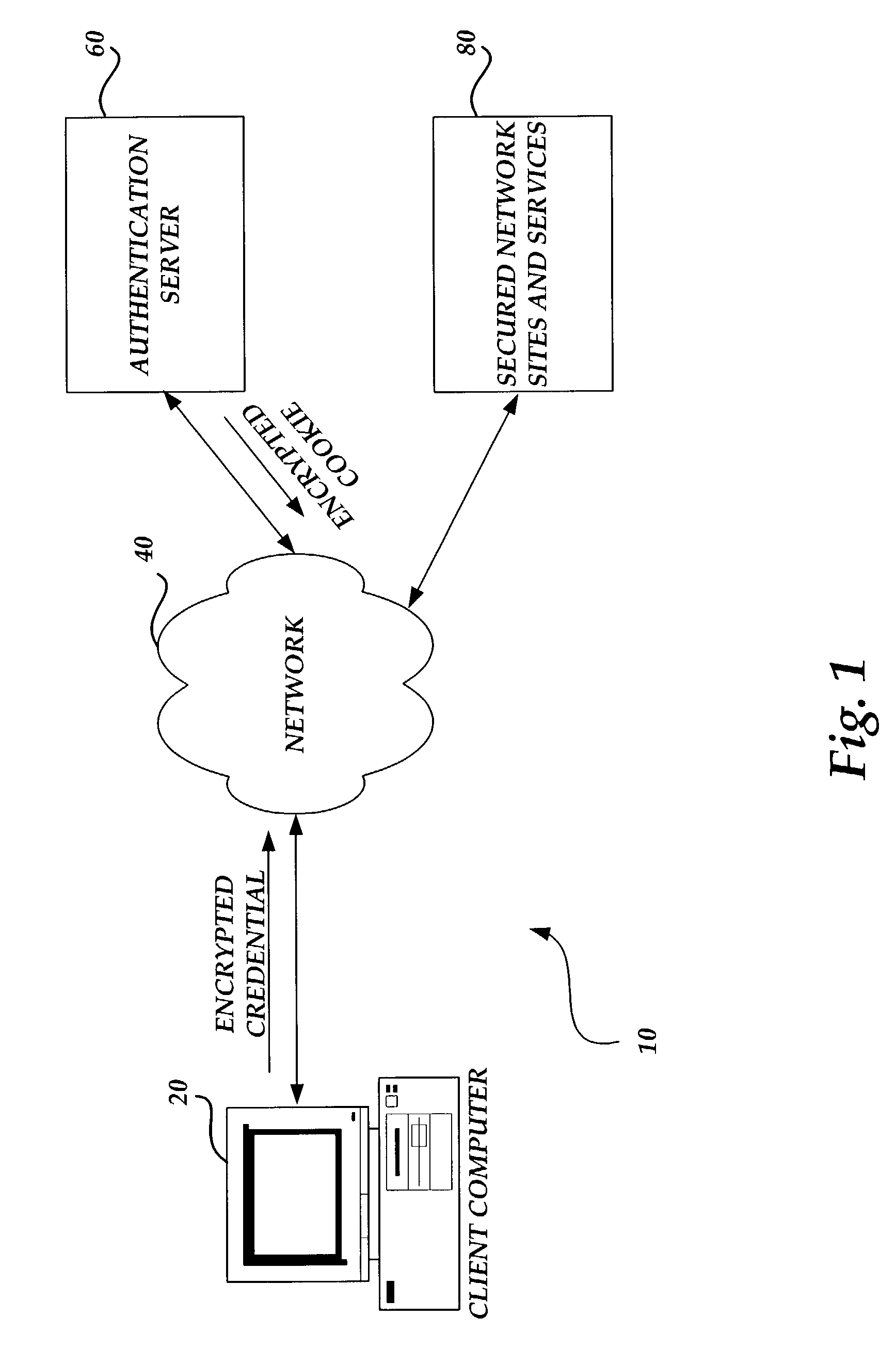
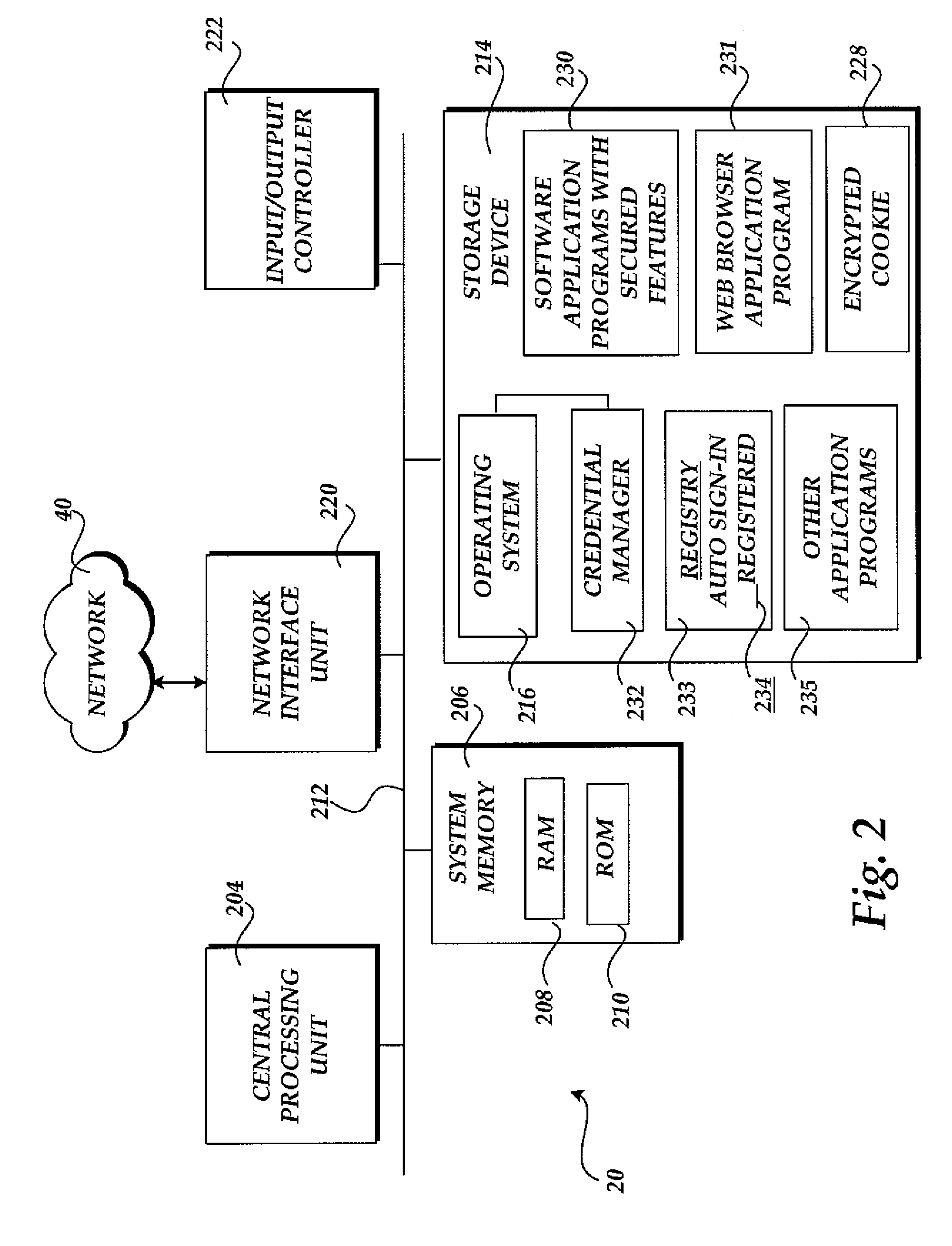
InactiveUS8024781B2Improve network efficiencyReduce network trafficDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork managementApplication software
The present invention automatically signs or logs a user in to access secured features within a software application without prompting manual intervention when a user starts the software application having secured features. When the software application is started and an automatic sign-in condition is enabled, the software application transitions to a signed-in or logged-in state as long as security criteria are met. As a result, unnecessary and repetitive steps are avoided when signing-in. The automatic sign-in condition may be enabled through initial system setup, from a prompt to enter a credential, or through a service options menu. The present invention improves network efficiency by limiting network transmissions to an as needed basis. The automatic sign-in condition is capable of roaming to other computers within a network, thereby following mobile users. Further, the automatic sign-in condition is controllable by network administrative policy, giving network administrators the ability to disable its functionality when desired.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
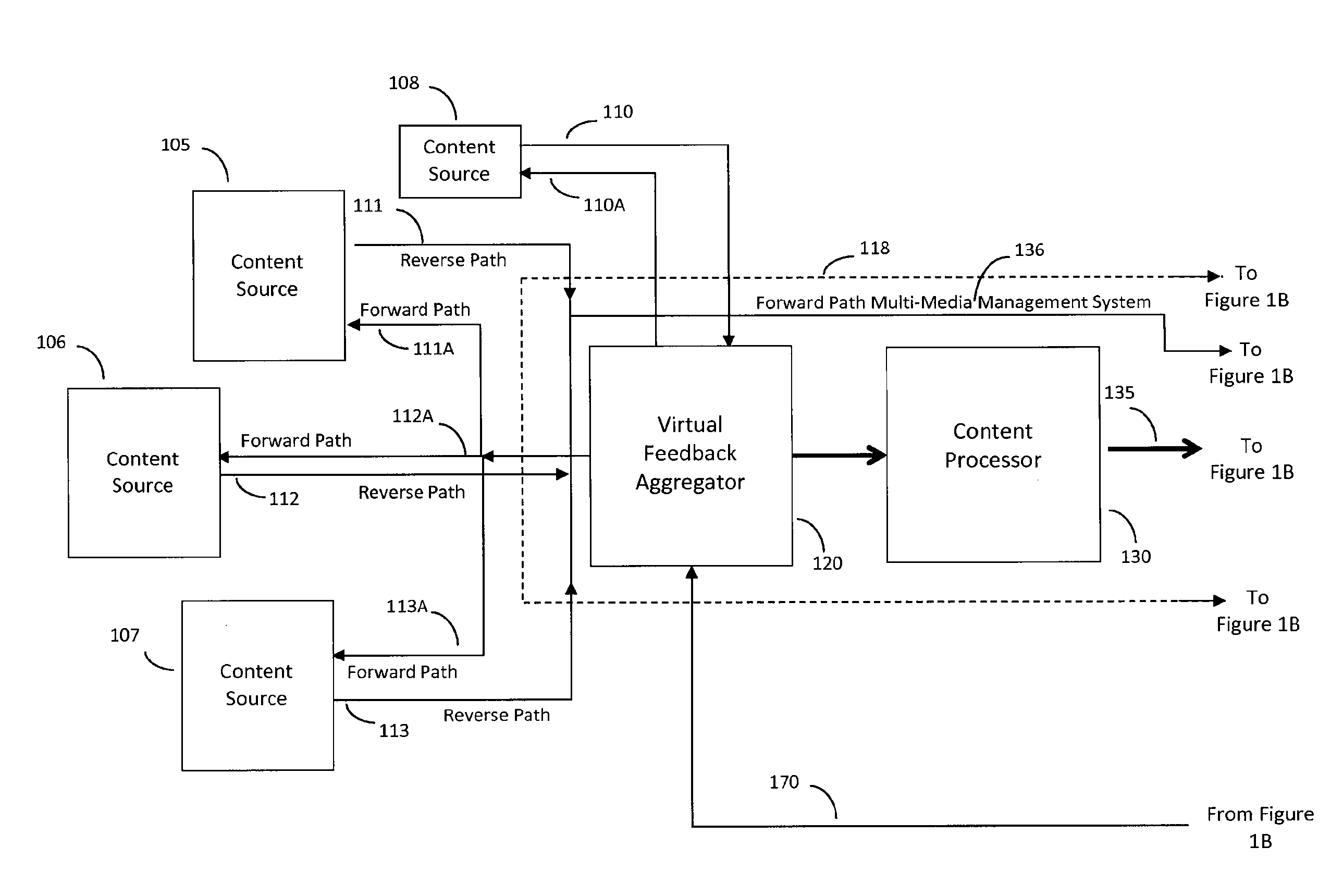
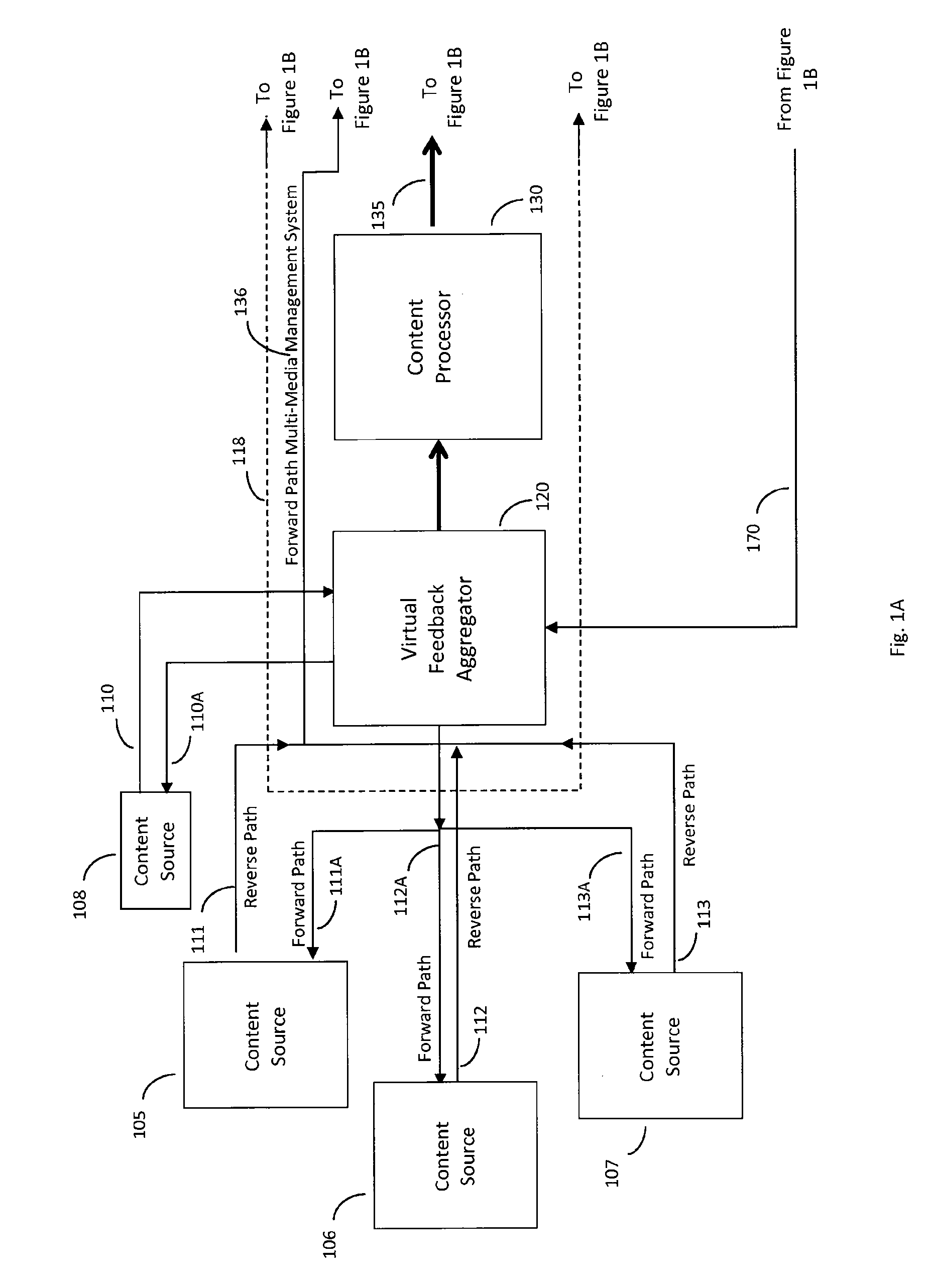
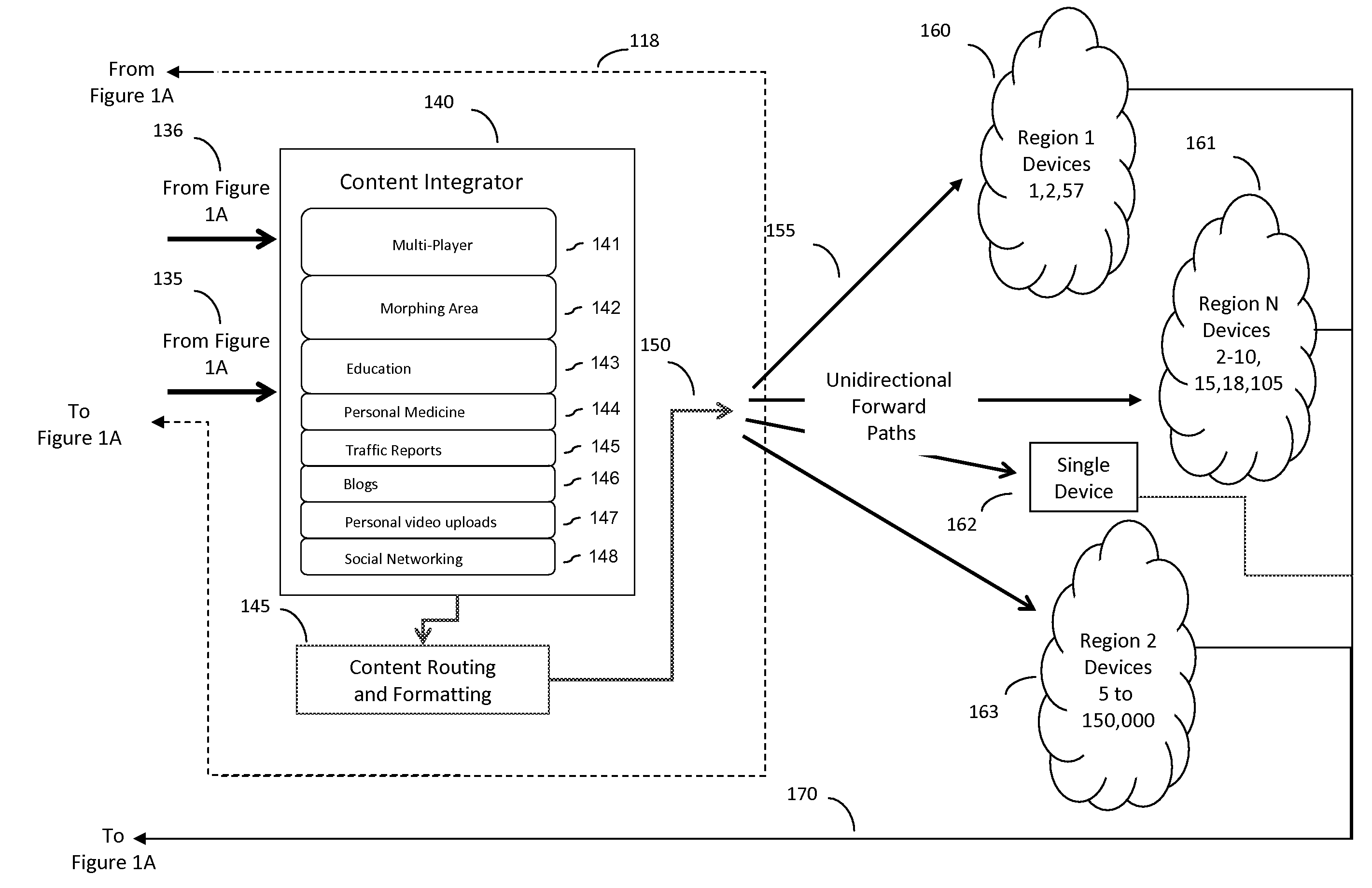
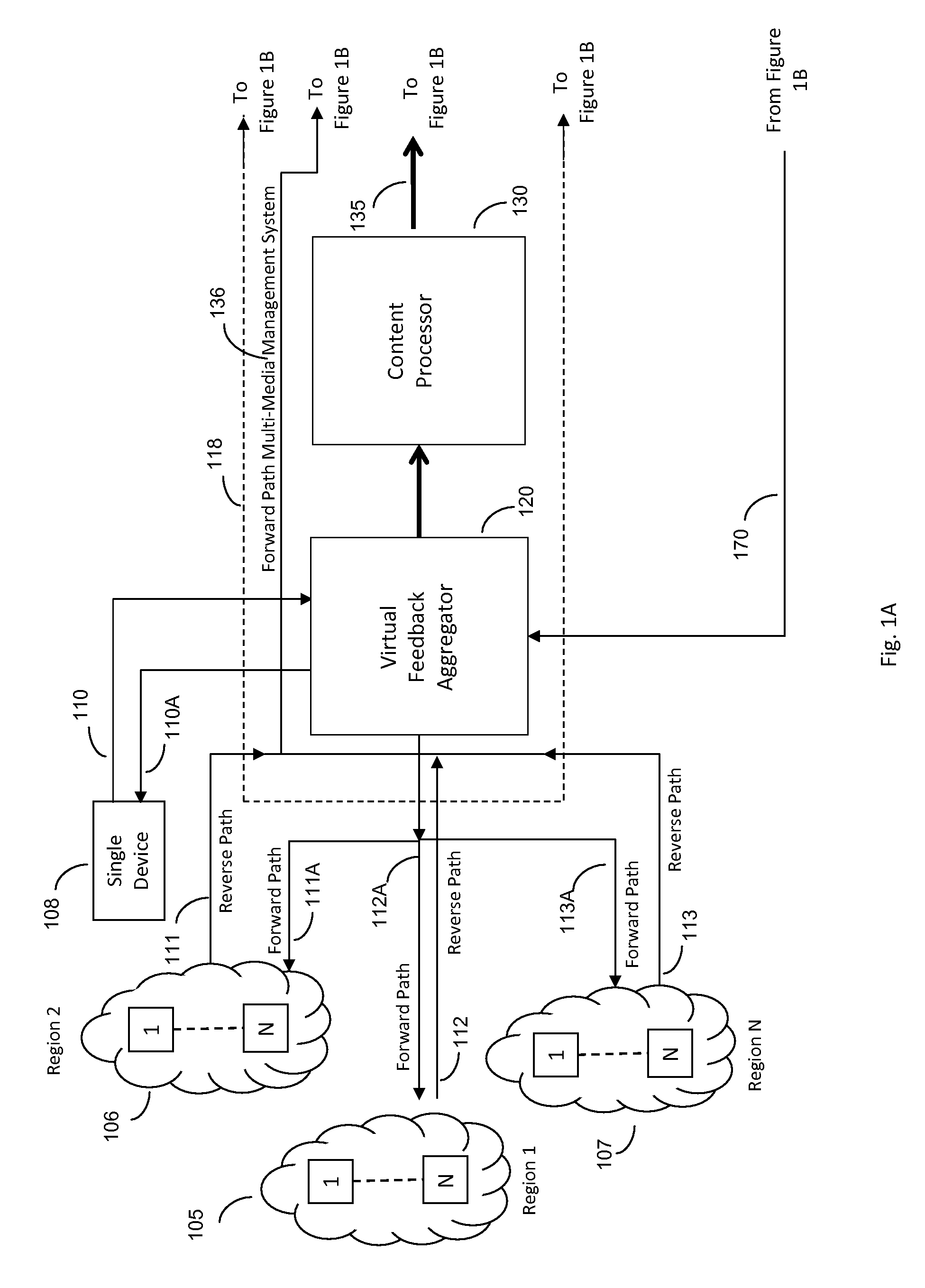
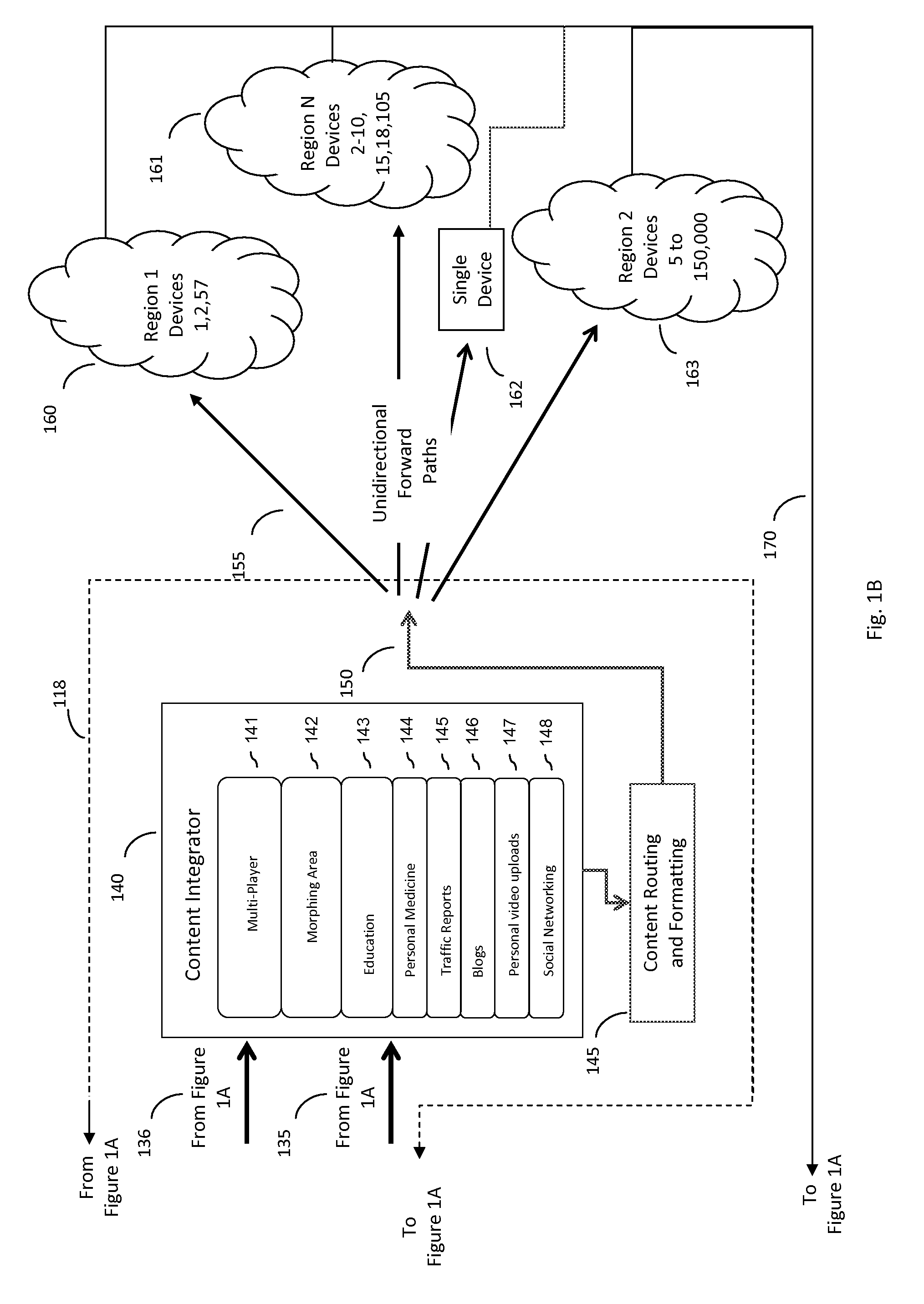
Forward path multi-media management system with end user feedback to central content sources
ActiveUS20110188415A1Improve efficiencyImproves takenTelevision systemsBilling/invoicingClosed loopMulticast communication
The Forward Path Multi-Media Management System architecture enables end user devices to share a common wireless forward path of a multicast communication architecture in which the forward path delivered content is dynamically changed or modified based on a real-time, near-real-time, or delay-time basis via aggregated reverse path feedback from at least one of a plurality of end user devices. The Forward Path Multi-Media Management System periodically or continuously aggregates the feedback input received via the reverse path (having wired and / or wireless connectivity), modifies the forward path multi-media content, and delivers this dynamically modified multi-media content to the then connected population of end user devices via a wireless forward path multicast in a repetitive closed loop fashion.
Owner:LAVA TWO
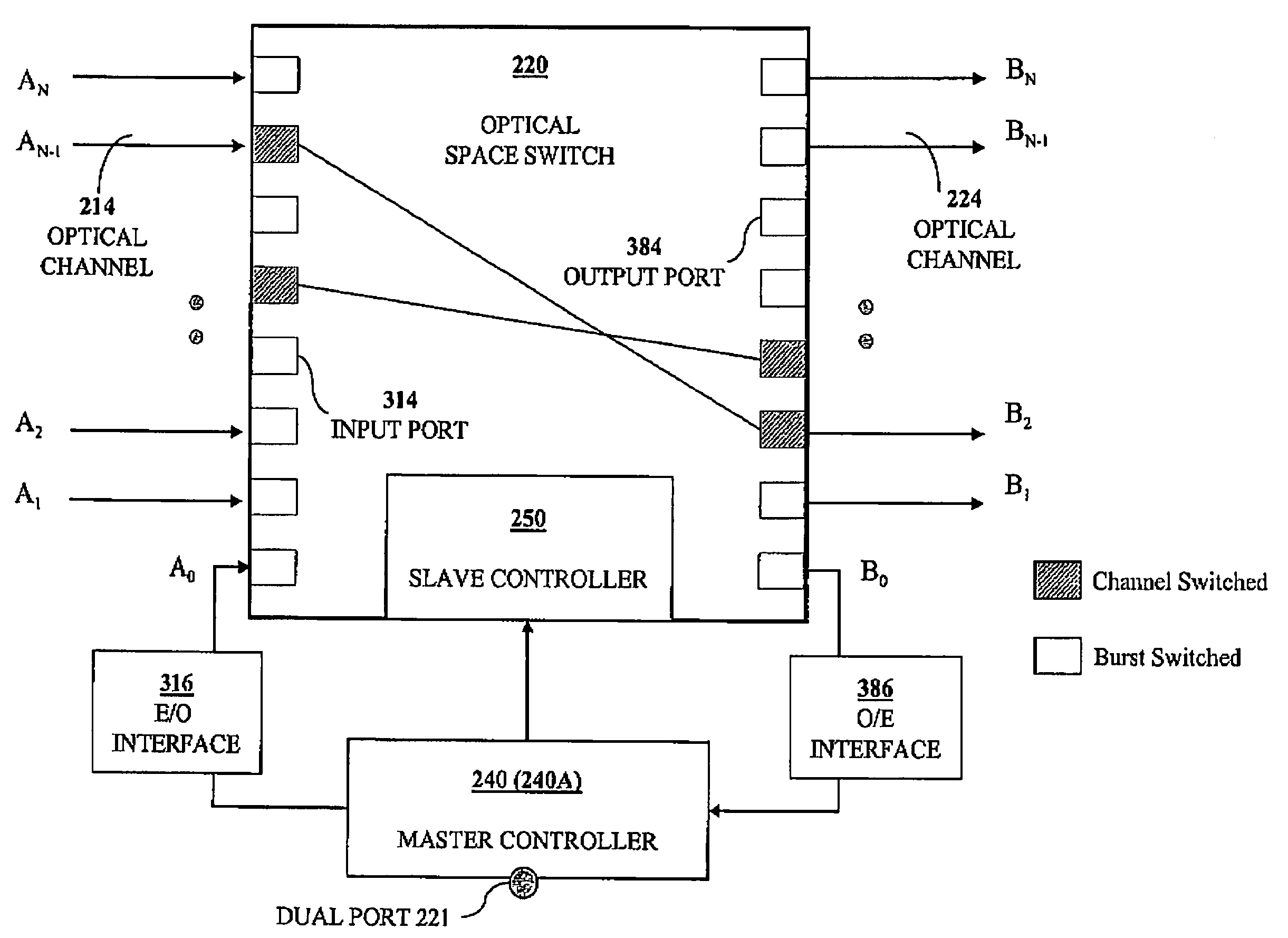
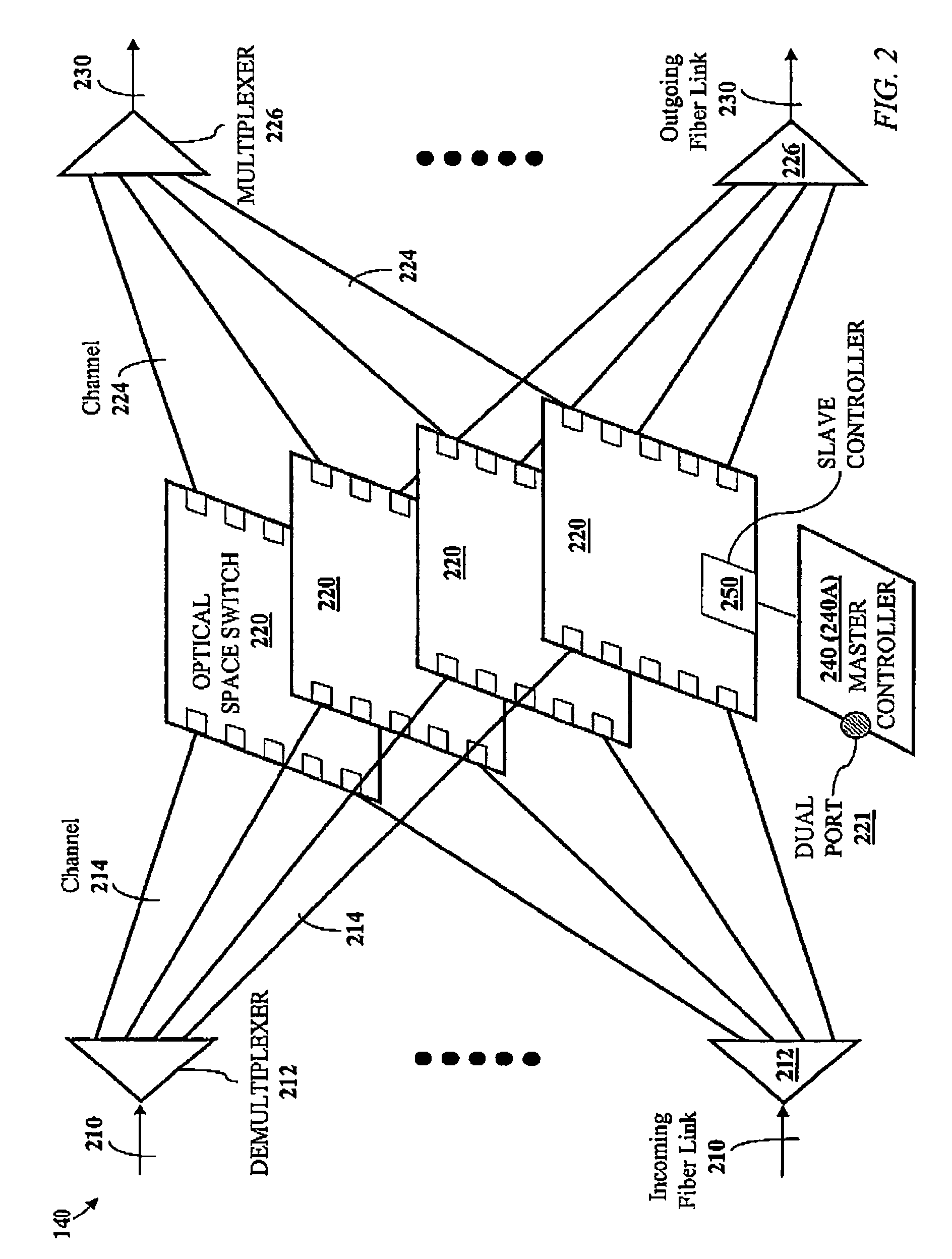
Data burst scheduling
InactiveUS7215666B1Reduce in quantityReduce effortMultiplex system selection arrangementsCircuit switching systemsBurst transmissionPhotonics
A method and apparatus for scheduling the transfer of data bursts in a network comprising electronic edge nodes interconnected by bufferless core nodes are disclosed. Each edge node comprises a source node and a sink node, and each core node comprises several bufferless space switches operated in parallel. Each source node is connected to at least one core node by an upstream link that includes multiple upstream channels. Each core node is connected to at least one sink node by a downstream link that includes multiple downstream channels. Any of the space switches can have either an electronic fabric or a photonic fabric. Each space switch has a master controller, and one of the master controllers in a core node is designed to function as a core-node controller in addition to its function as a master controller. Each master controller has a burst scheduler operable to compute a schedule for the transfer of data bursts, received from source nodes, to destination sink nodes.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
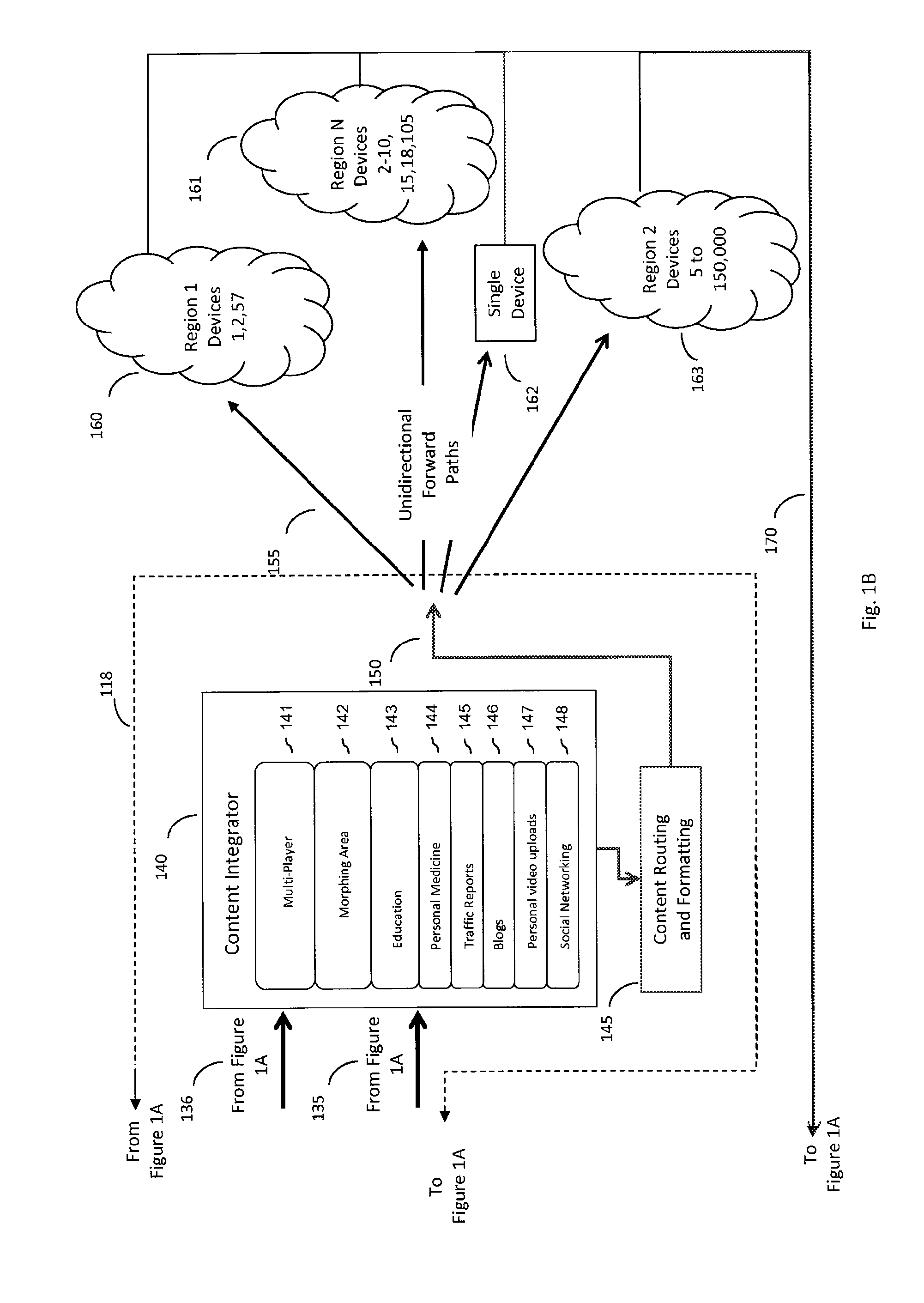
Forward path multi-media management system with end user feedback to distributed content sources
ActiveUS20100228814A1Improve network efficiencyEfficient deliveryIndoor gamesMultiple digital computer combinationsDelayed timeClosed loop
The Forward Path Multi-Media Management System architecture enables end user devices to share a common wireless forward path of a multicast communication architecture in which the forward path delivered content is dynamically changed or modified based on a real-time, near-real-time, or delay-time basis via aggregated reverse path feedback from at least one of a plurality of end user devices. The Forward Path Multi-Media Management System periodically or continuously aggregates the feedback input received via the reverse path (having wired and / or wireless connectivity), modifies the forward path multi-media content, and delivers this dynamically modified multi-media content to the then connected population of end user devices via a wireless forward path multicast in a repetitive closed loop fashion.
Owner:LAVA TWO
Channel allocation for access point in mesh network
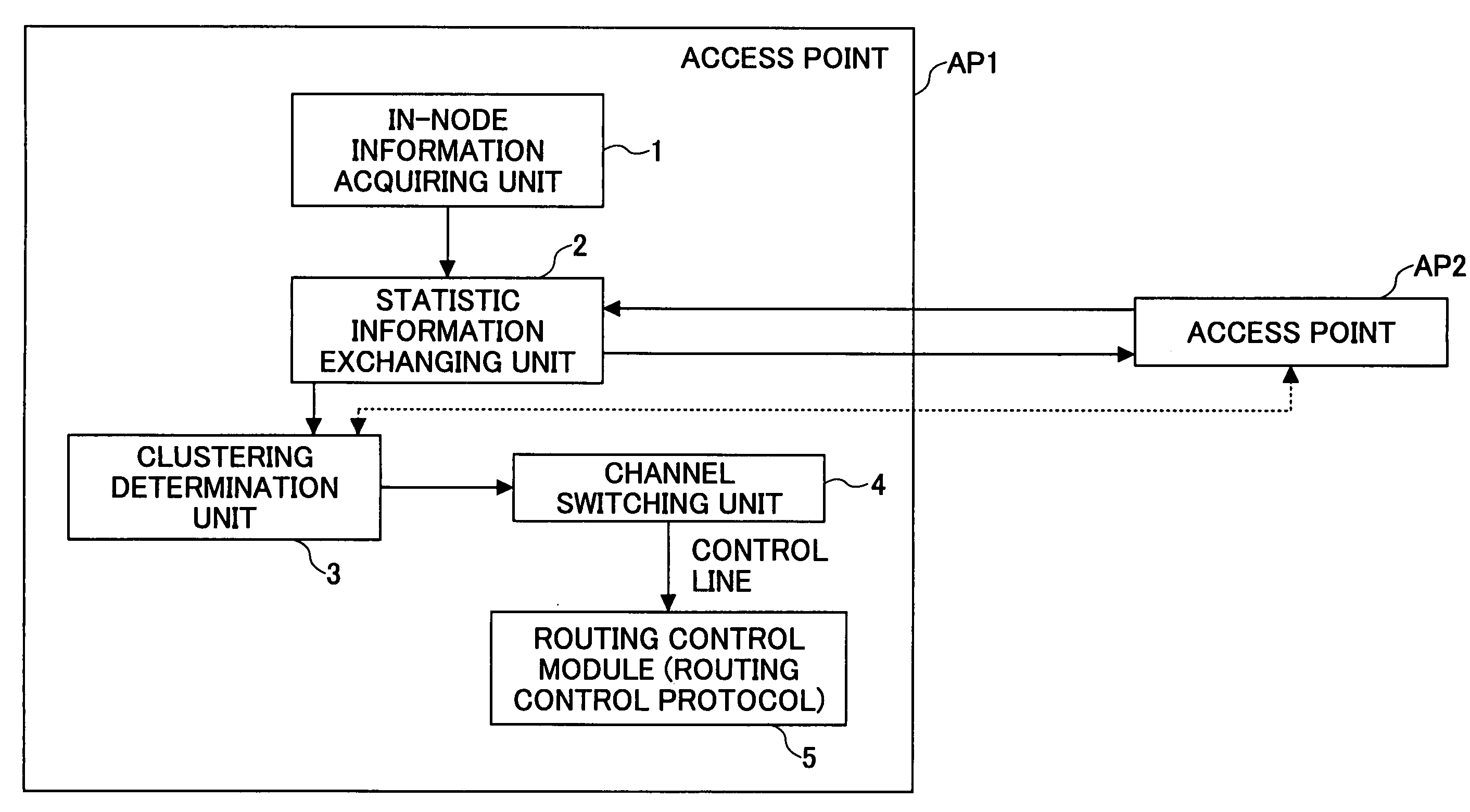
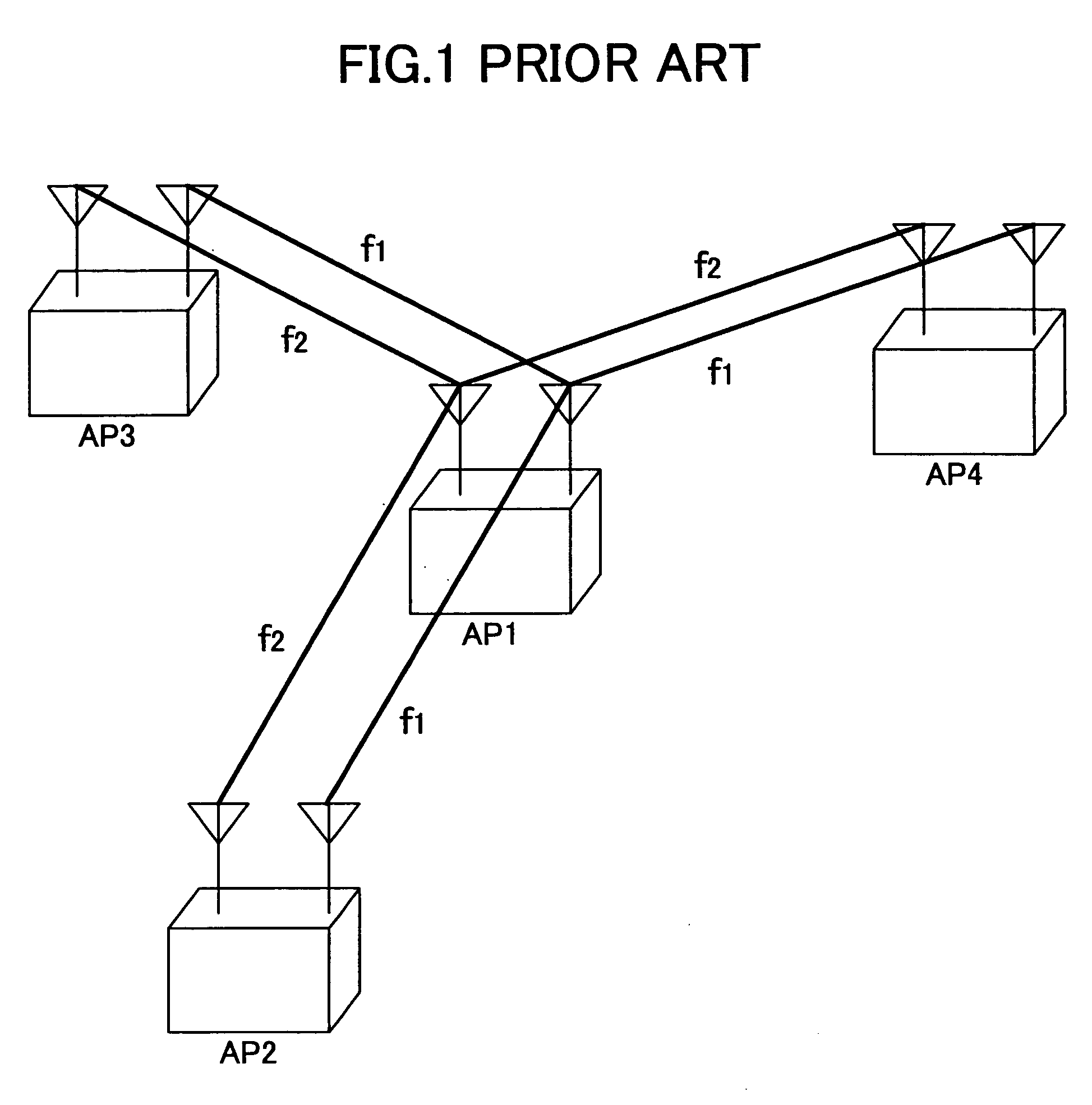
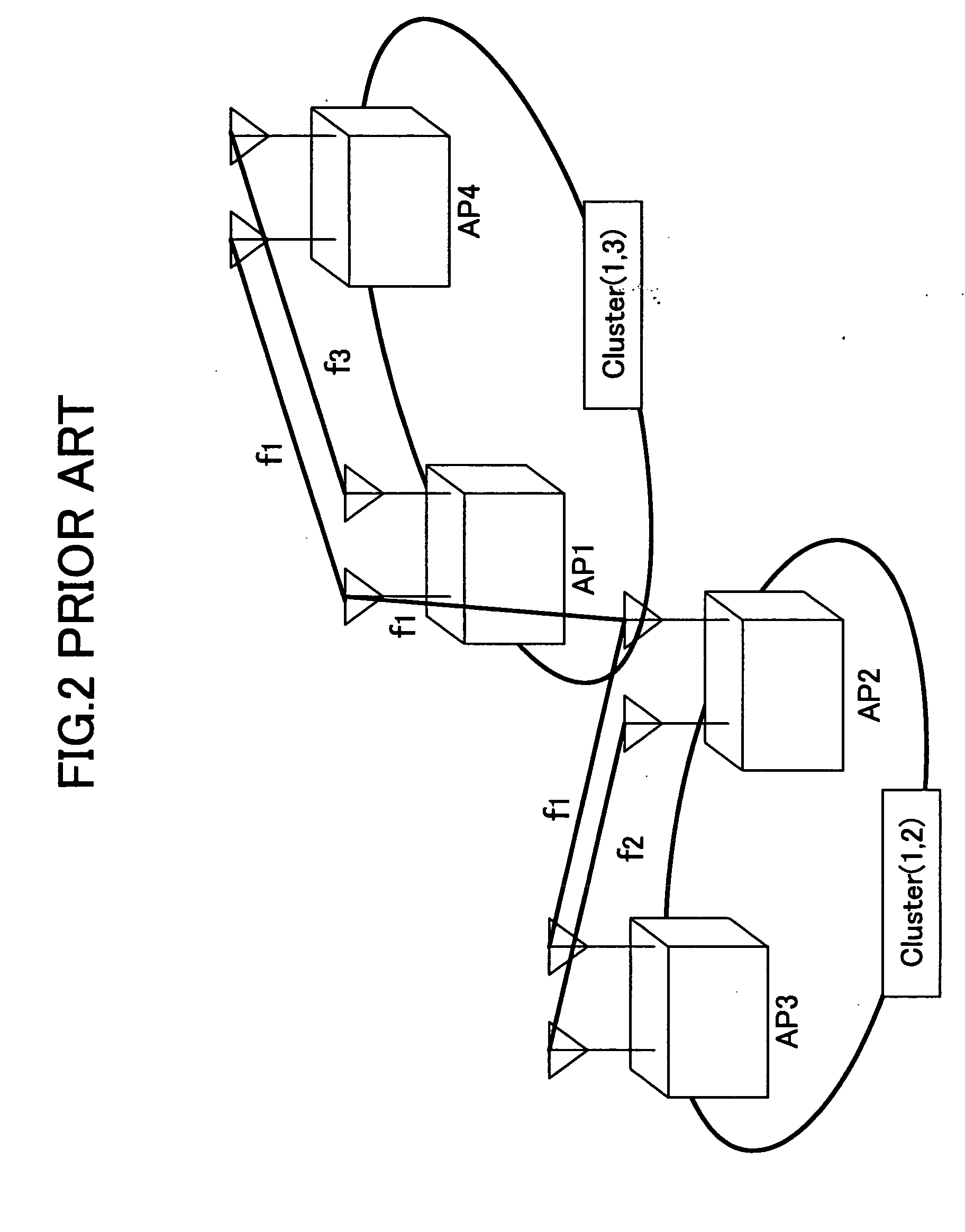
InactiveUS20060019673A1Improve throughputImprove network efficiencyAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsAllocation method
A channel allocation method for dynamically allocating channels of a plurality of radio interfaces at each access point included in a mesh network is provided. The method includes the steps of (a) acquiring, at each access point, in-node information about the access point itself, and (b) grouping high-traffic access points in a cluster using a same channel set based on the acquired information.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
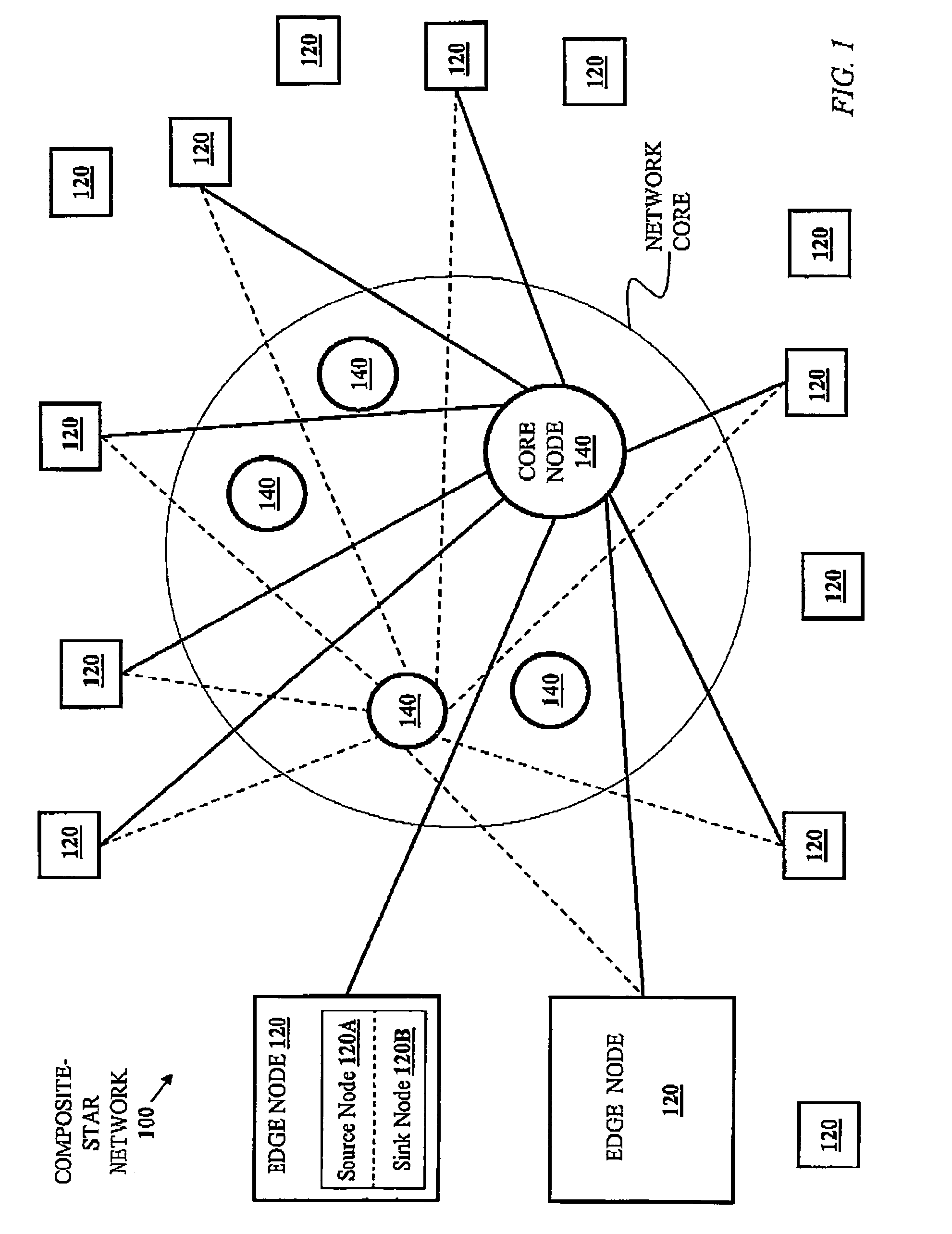
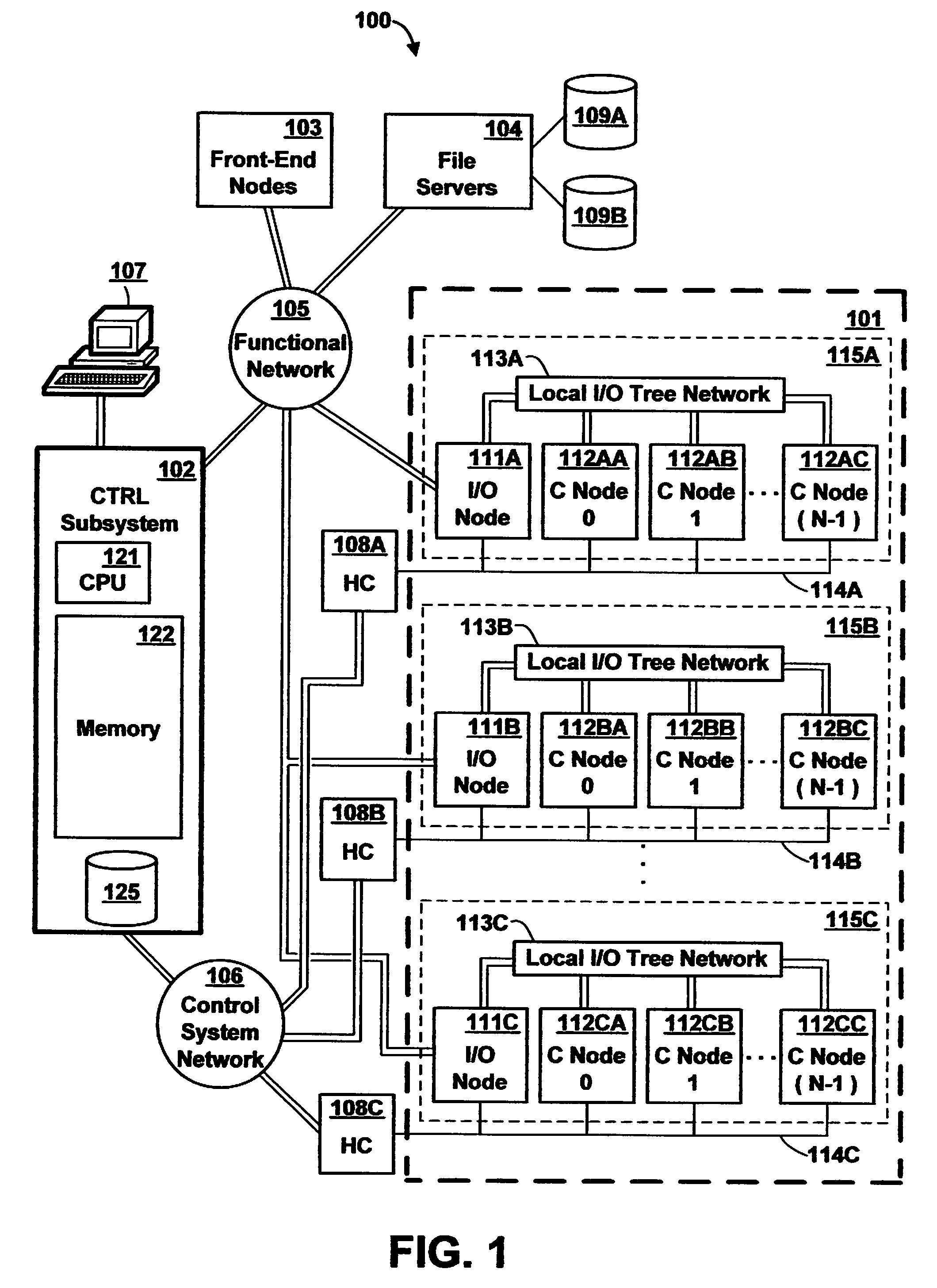
Method and Apparatus for Routing Data in an Inter-Nodal Communications Lattice of a Massively Parallel Computer System by Dynamically Adjusting Local Routing Strategies
InactiveUS20080084889A1Improve network performanceImprove network efficiencyData switching by path configurationWorkloadDistributed computing
A massively parallel computer system contains an inter-nodal communications network of node-to-node links. Each node implements a respective routing strategy for routing data through the network, the routing strategies not necessarily being the same in every node. The routing strategies implemented in the nodes are dynamically adjusted during application execution to shift network workload as required. Preferably, adjustment of routing policies in selective nodes is performed at synchronization points. The network may be dynamically monitored, and routing strategies adjusted according to detected network conditions.
Owner:IBM CORP
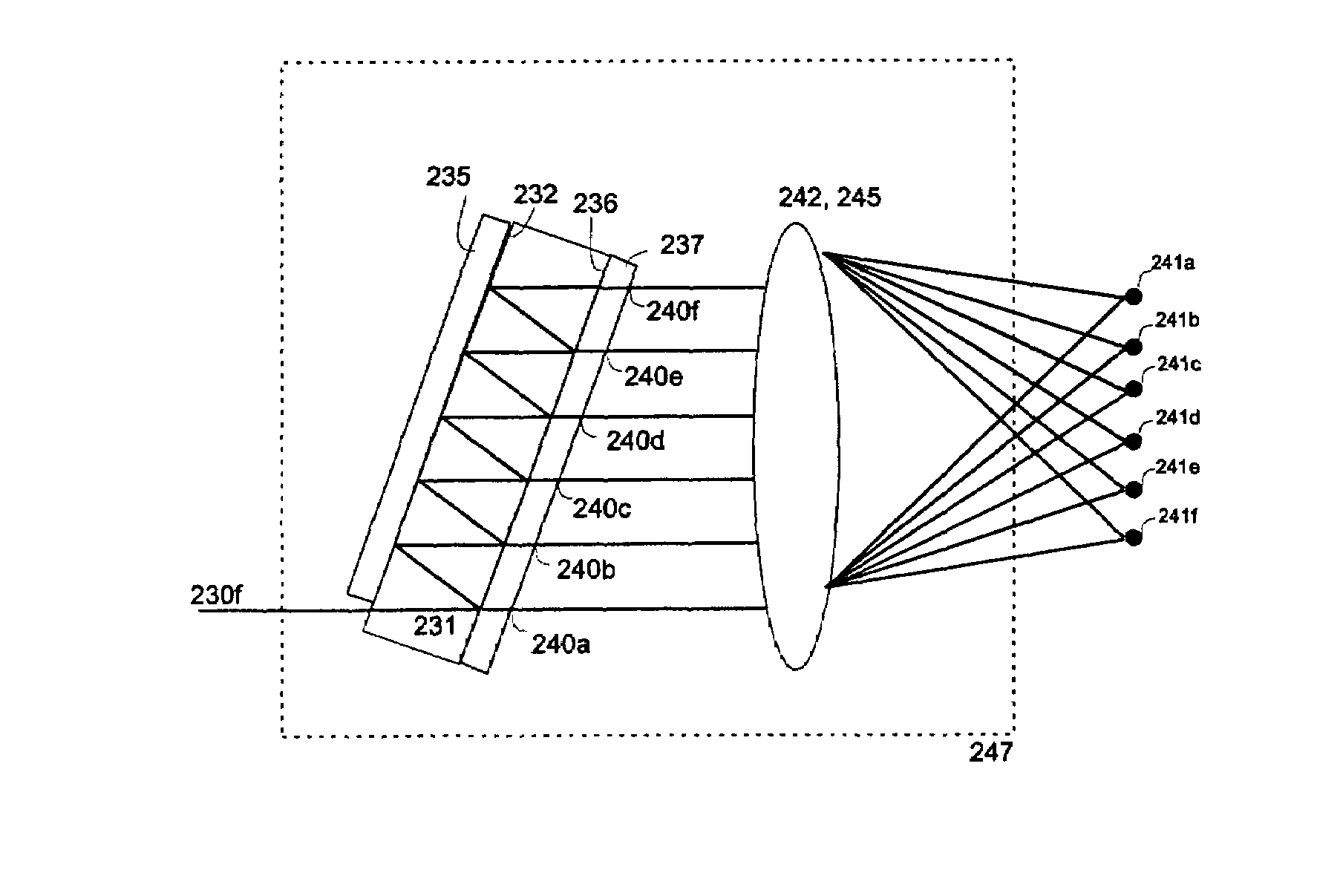
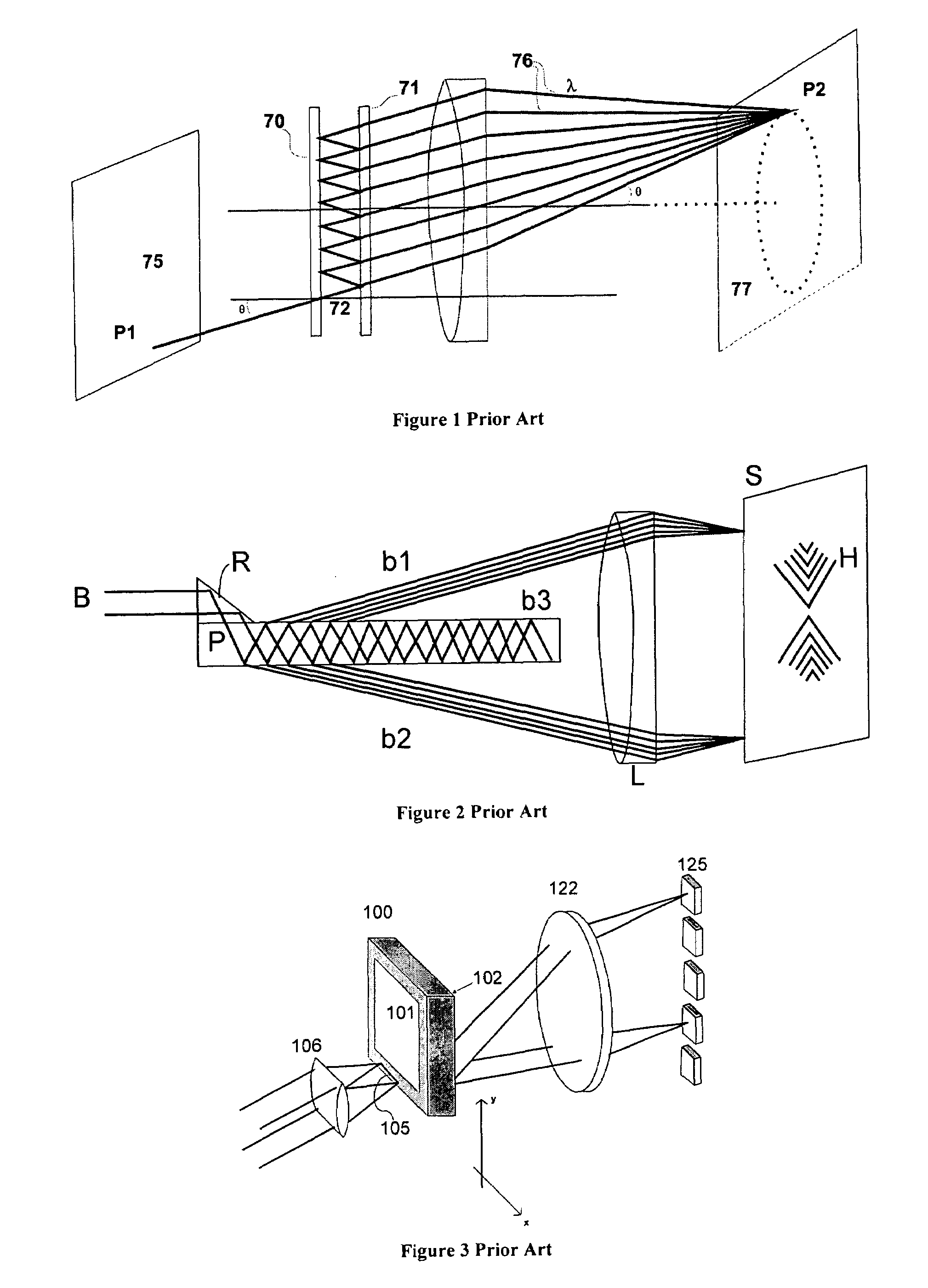
Method and apparatus for optical signal processing using an optical tapped delay line
ActiveUS7509048B2Small component sizeSmall device sizeWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesMultiplexingFrequency spectrum
An Optical Tapped Delay Line (OTDL), which resolves multiple wavelength signals having extremely narrow wavelength spacing, is combined with other known optical devices to provide a wide variety of optical signal processing applications, including: multiplexing and de-multiplexing a multi-channel signal; adding a signal to, or dropping a signal from, a multi-channel optical signal; specialized coding processing such as generating code division multiple access signals; wavelength locking (stabilizing) a signal; filtering a signal; and analyzing and monitoring a signal spectrum. The OTDL spatially separates individual channels to allow separate processing on each channel. Fixed and tunable embodiments are identified in appropriate cases. Bulk, hybrid, and integrated optical embodiment and methods of fabrication are described, as are curved self-focusing and evanescent embodiments of OTDL devices. The devices and processes disclosed have particular application to dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) and permit a significant improvement in the quantity of information that can be carried on DWDM signals while enhancing signal quality.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
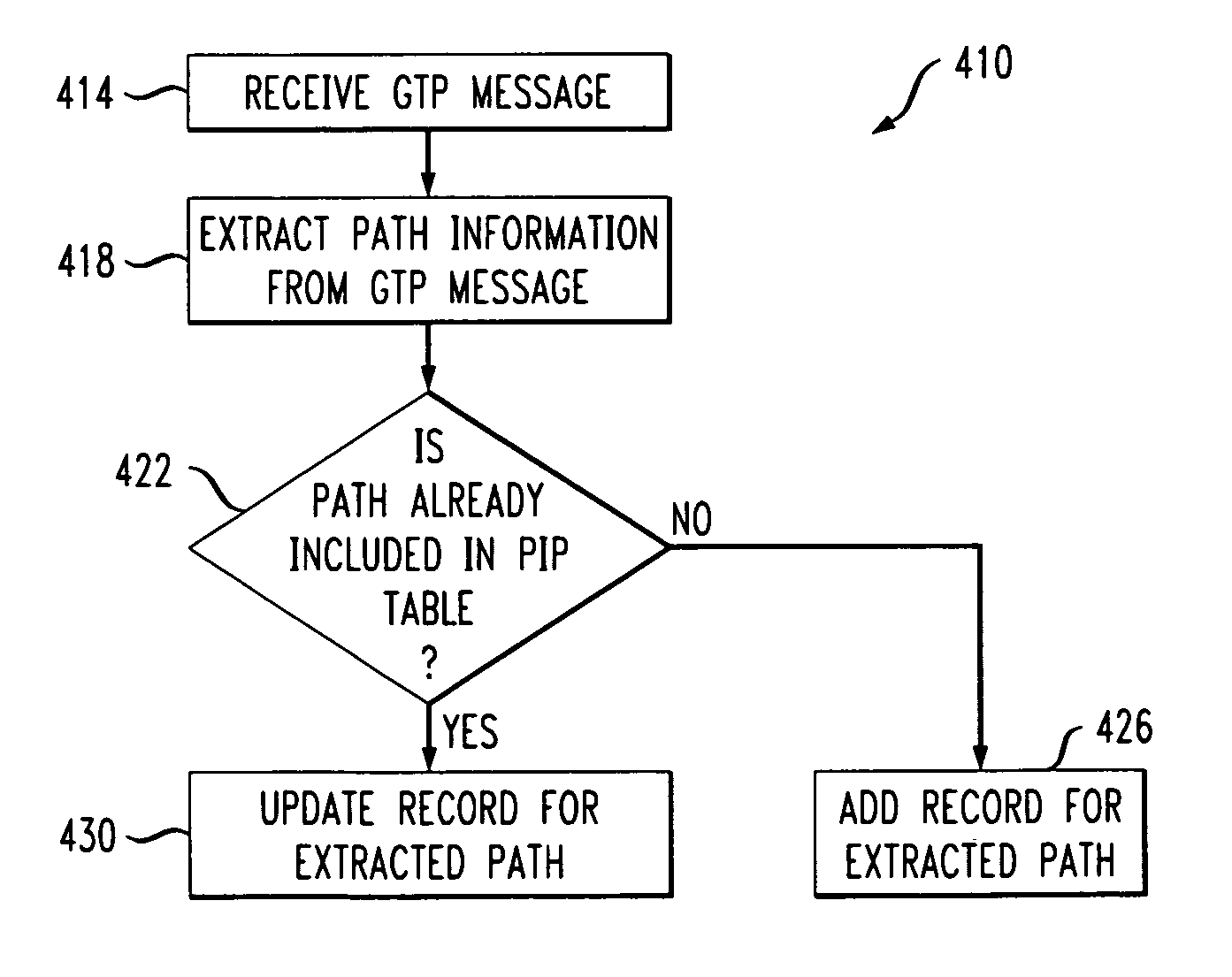
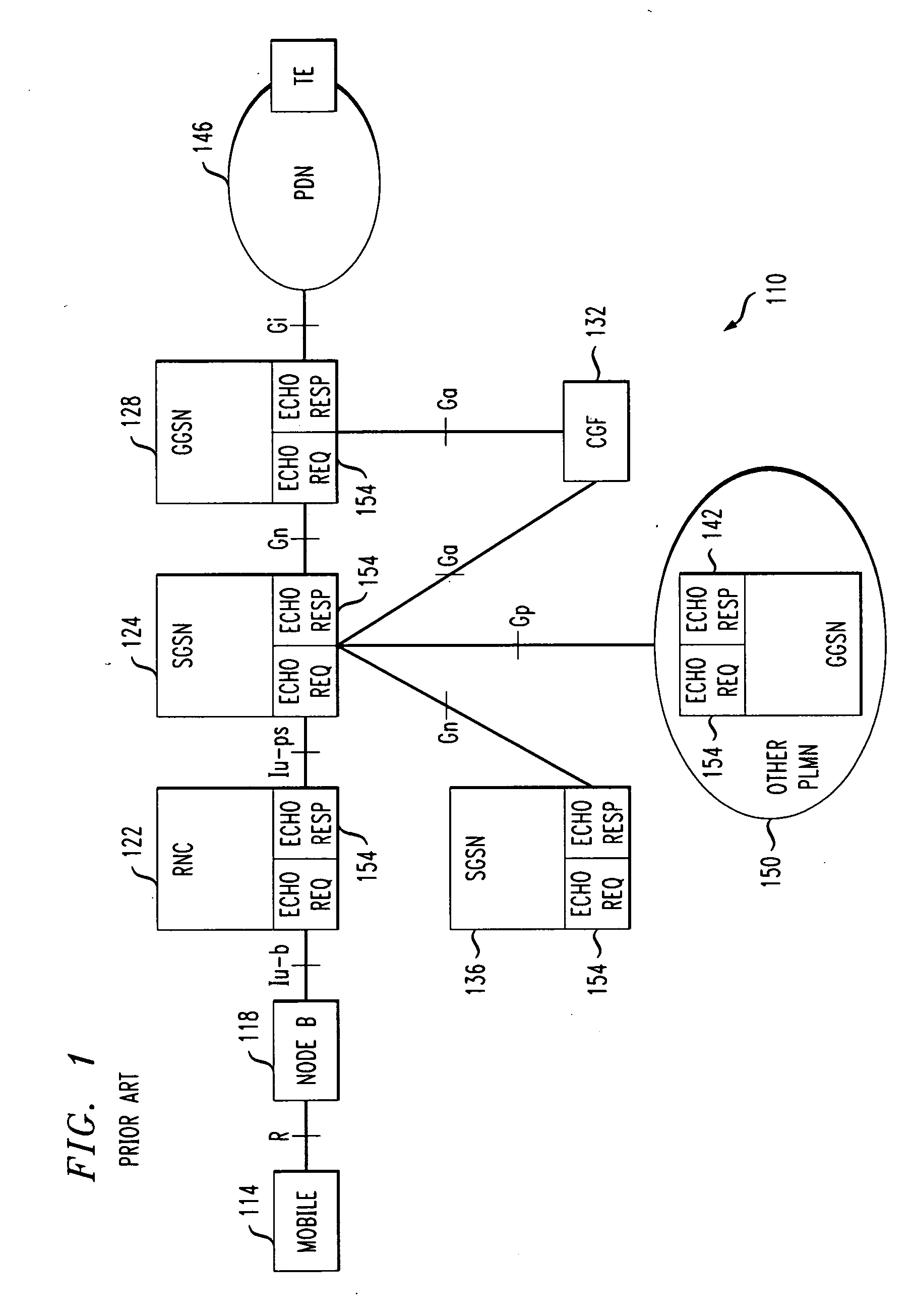
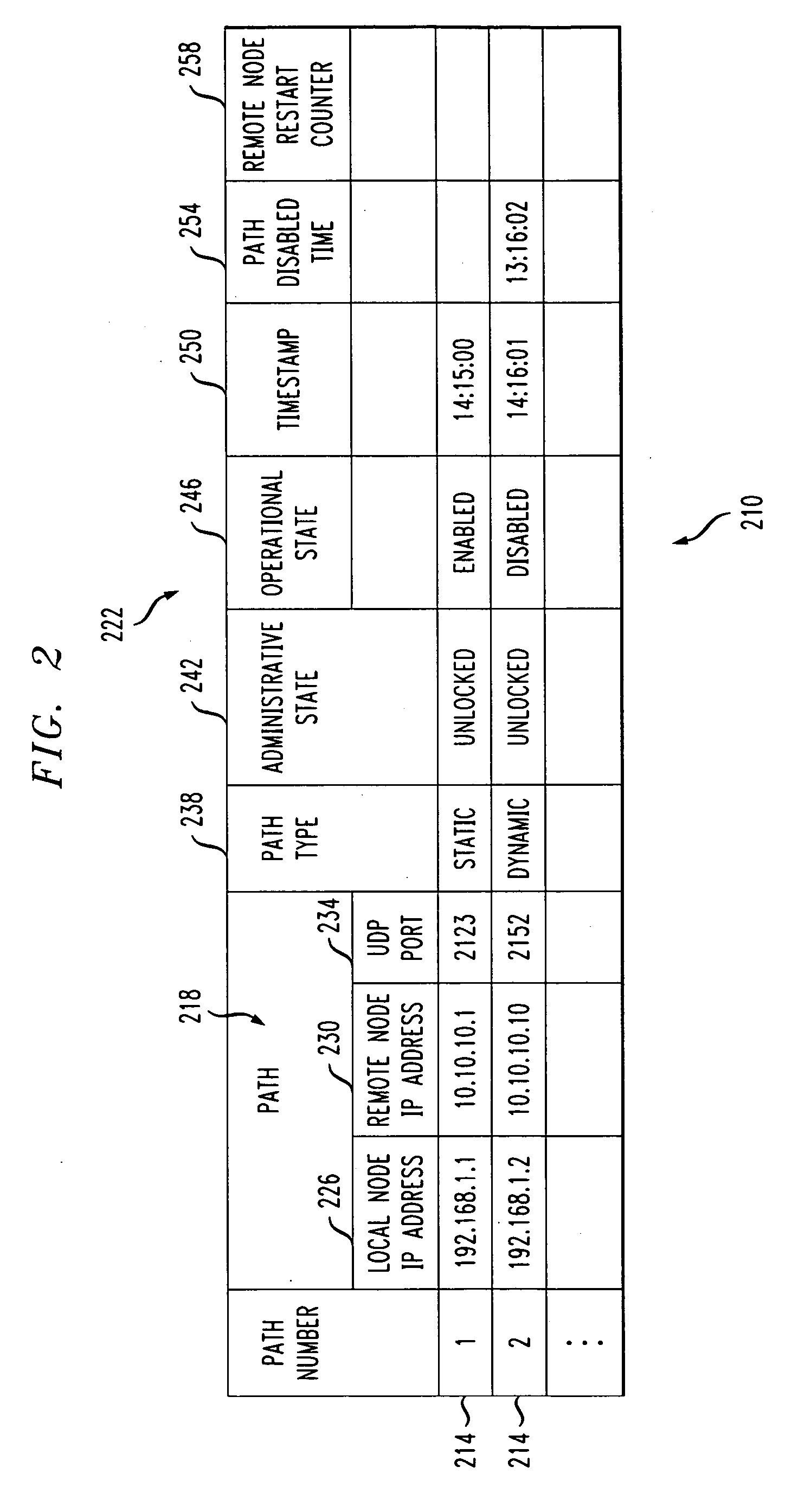
GPRS tunneling protocol path integrity protocol
ActiveUS20050201371A1Improved GTP path integrity assuranceImprove network efficiencyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPathPingProcess information
Network efficiency is improved by building and maintaining path integrity tables in nodes of a network. The tables include path integrity information for paths associated with the nodes. A path is defined by a source address, a destination address and a port or version number. Once a node is made aware of a path, either by handling network message traffic associated with the path or through manual entry, the node maintains path status information with information provided by normal network message traffic, or absent the normal network message traffic, by transmitting Echo Request messages and processing information related to Echo Response messages or the lack thereof. Information related to paths that are disabled for longer than a disabled path duration limit is deleted from the tables. A Gratuitous GTP Echo Response message can notify other nodes of an administrative state change in a node.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com