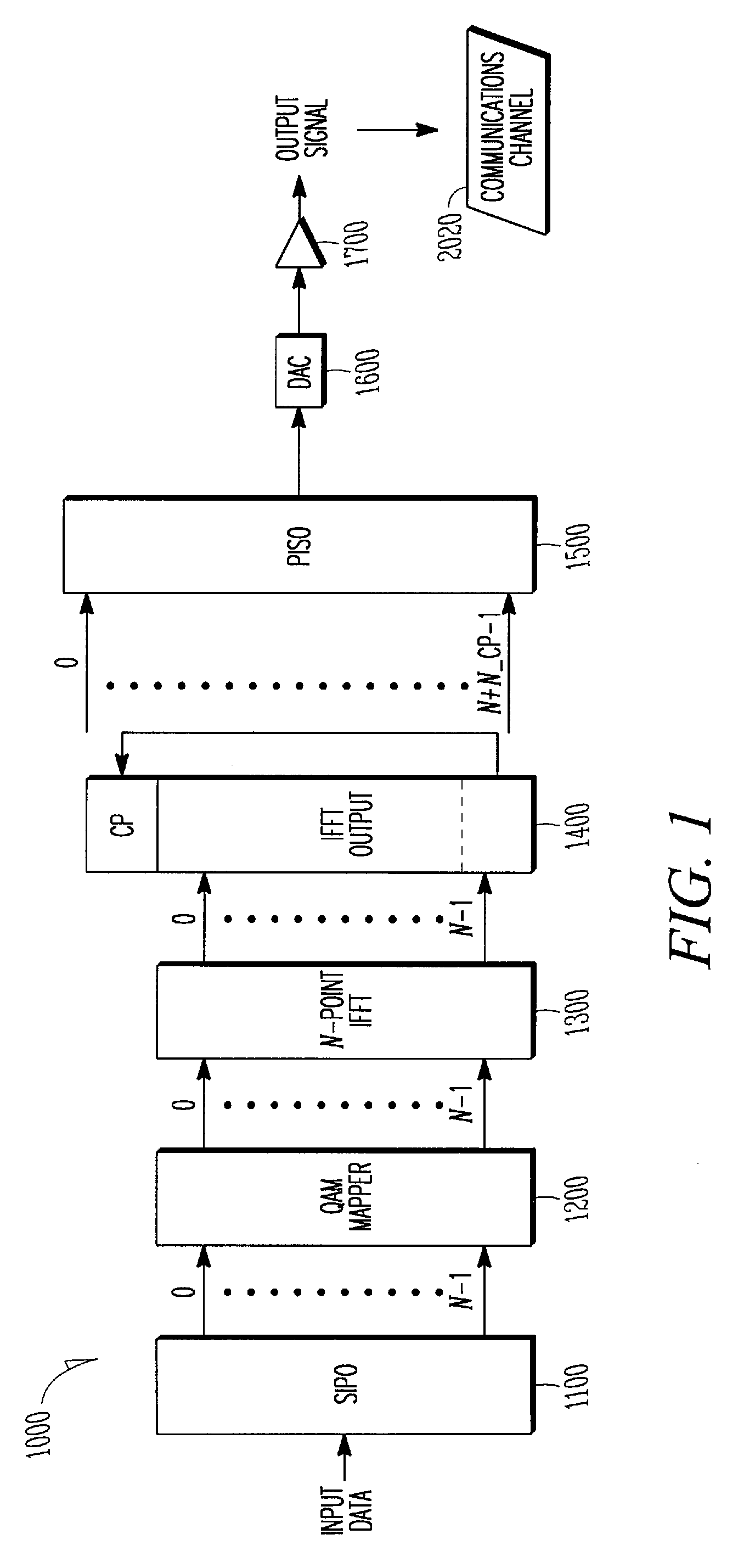
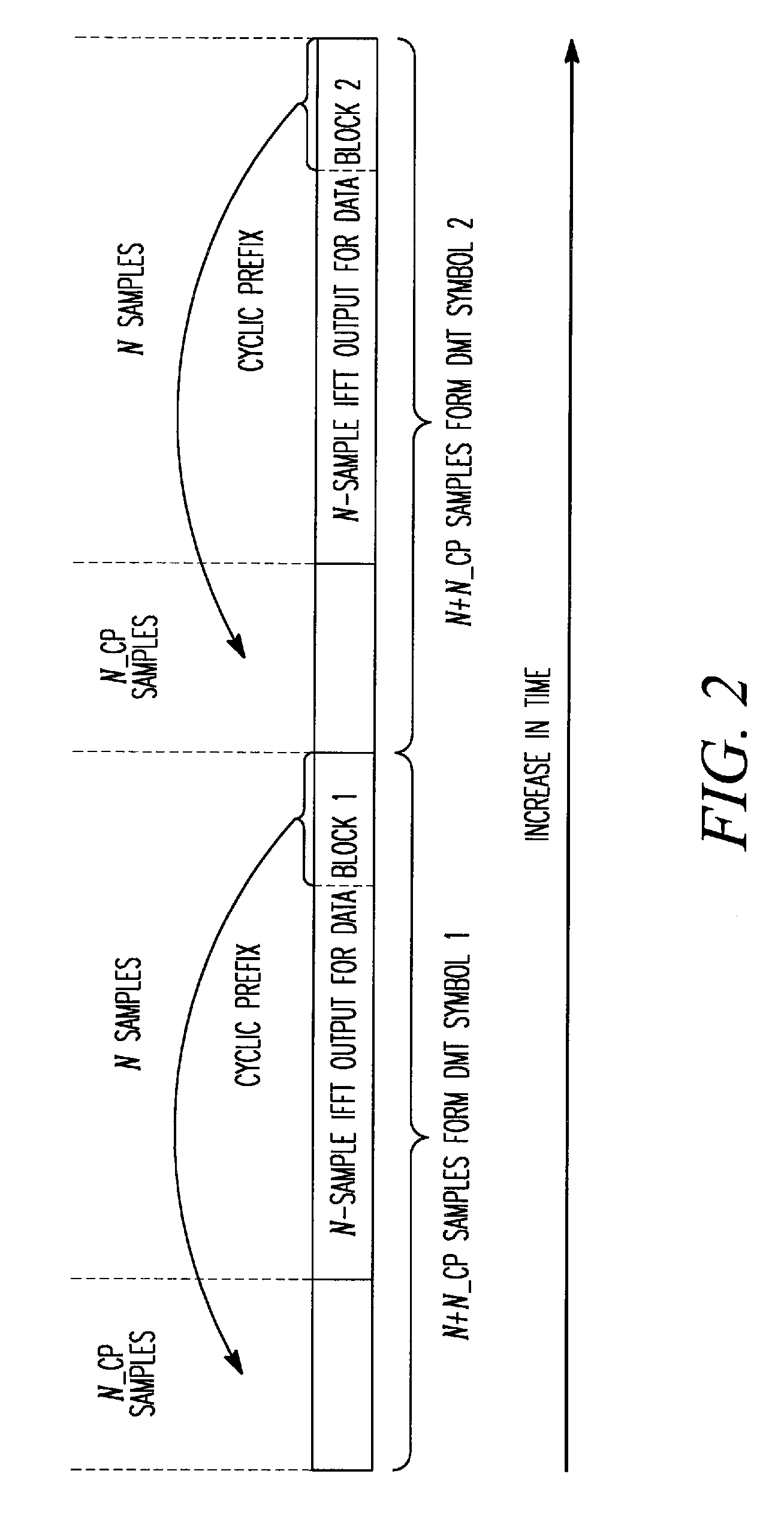
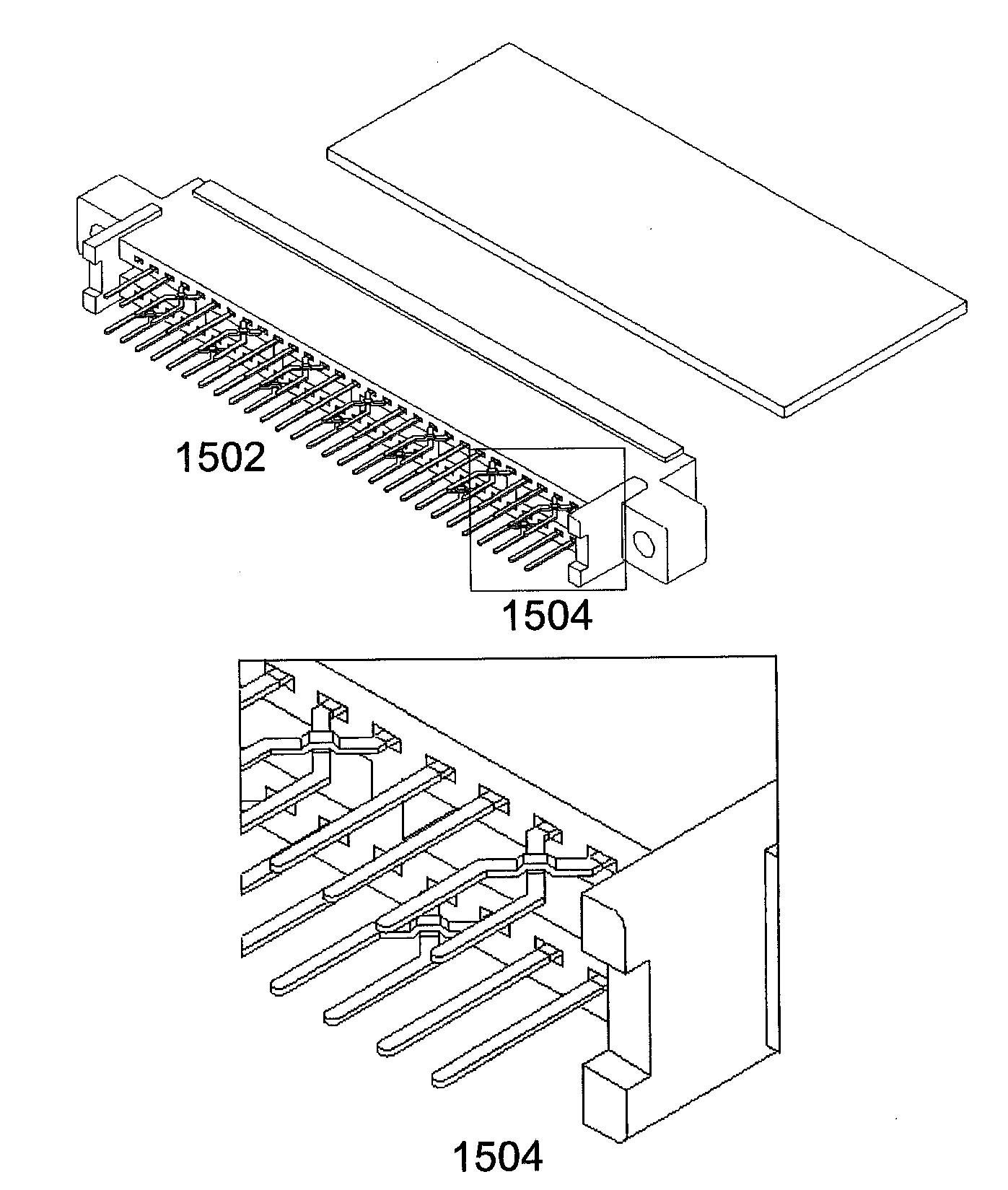
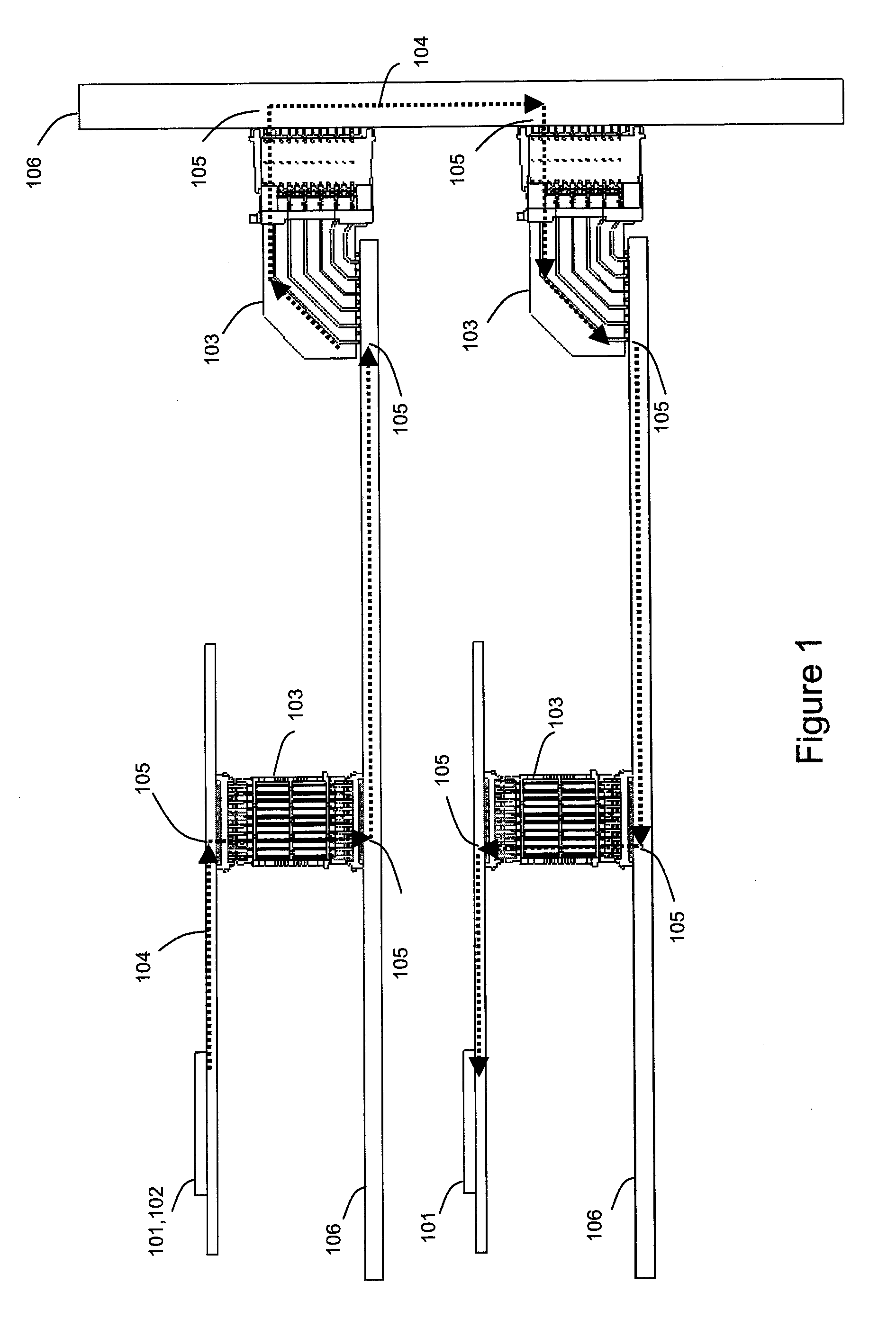
Patents
Literature
37results about How to "Cancel improvement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
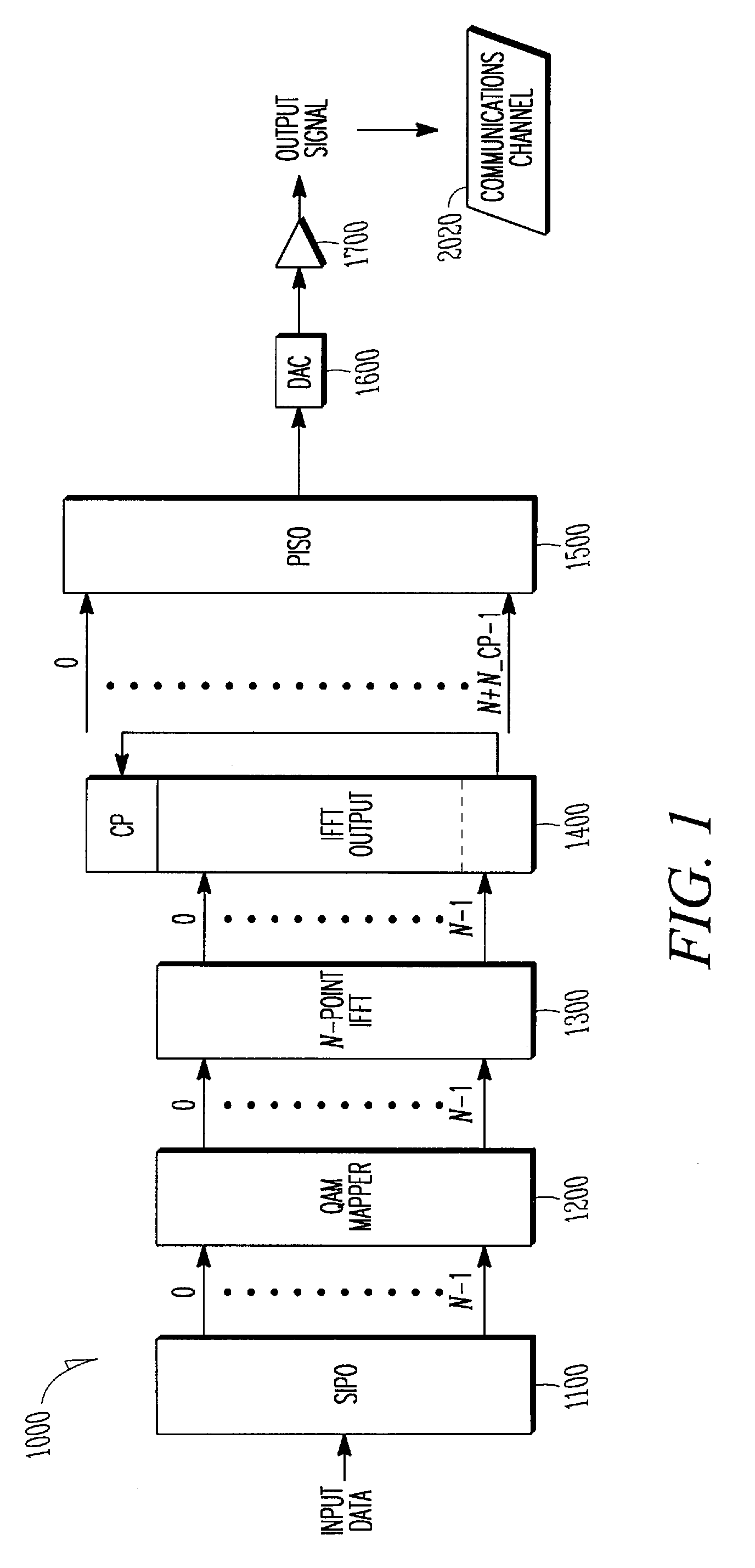
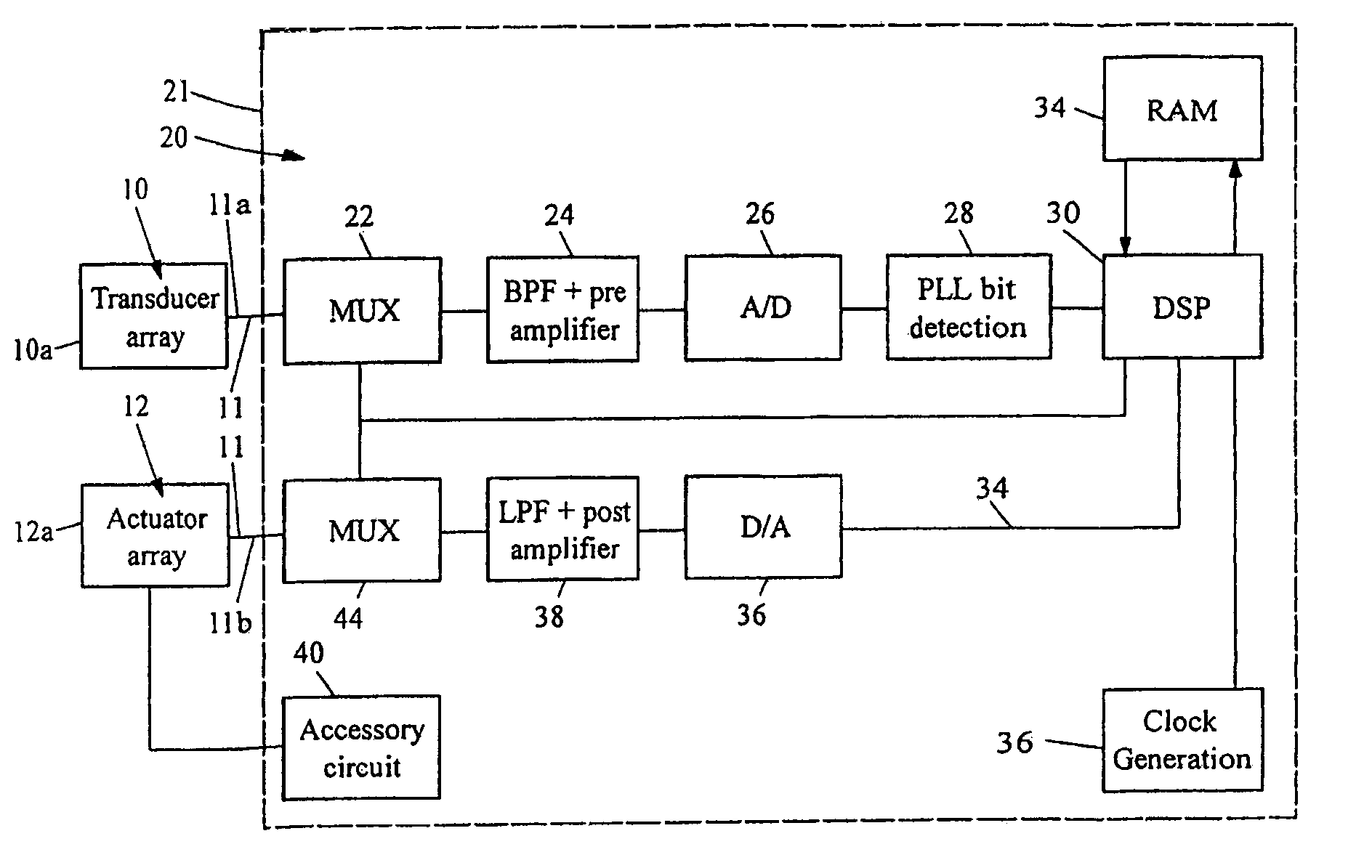
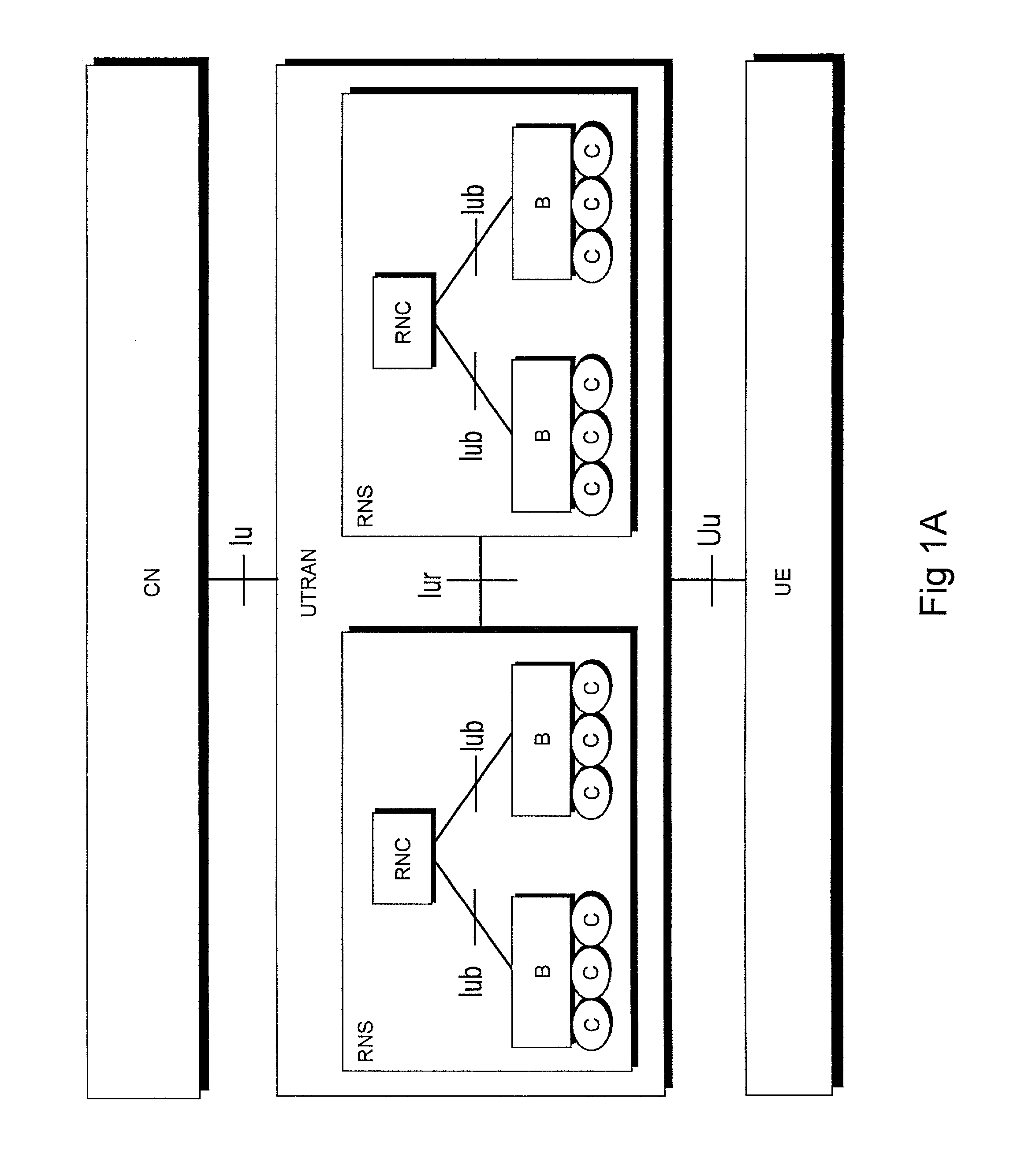
Variable gain active noise cancelling system with improved residual noise sensing
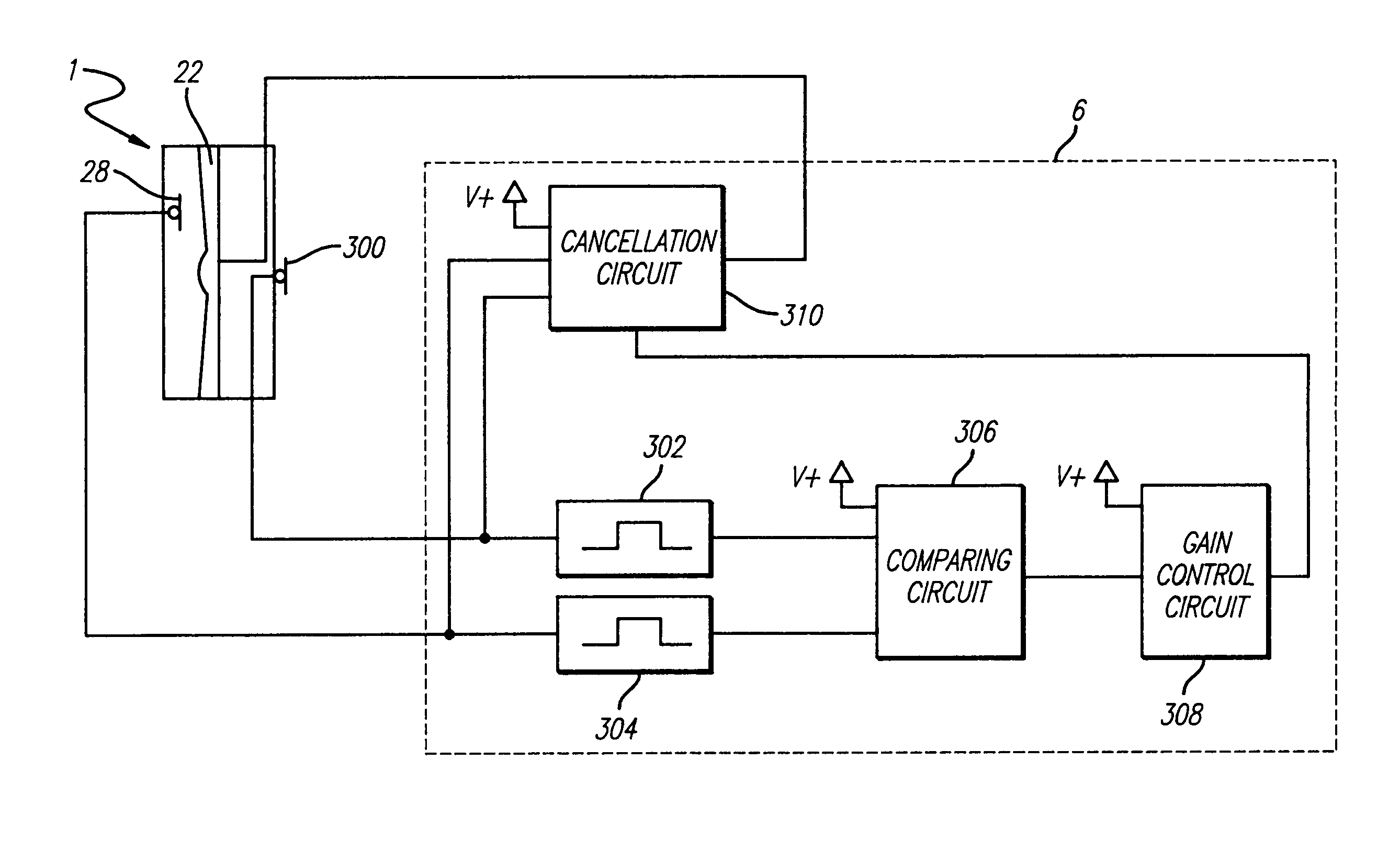
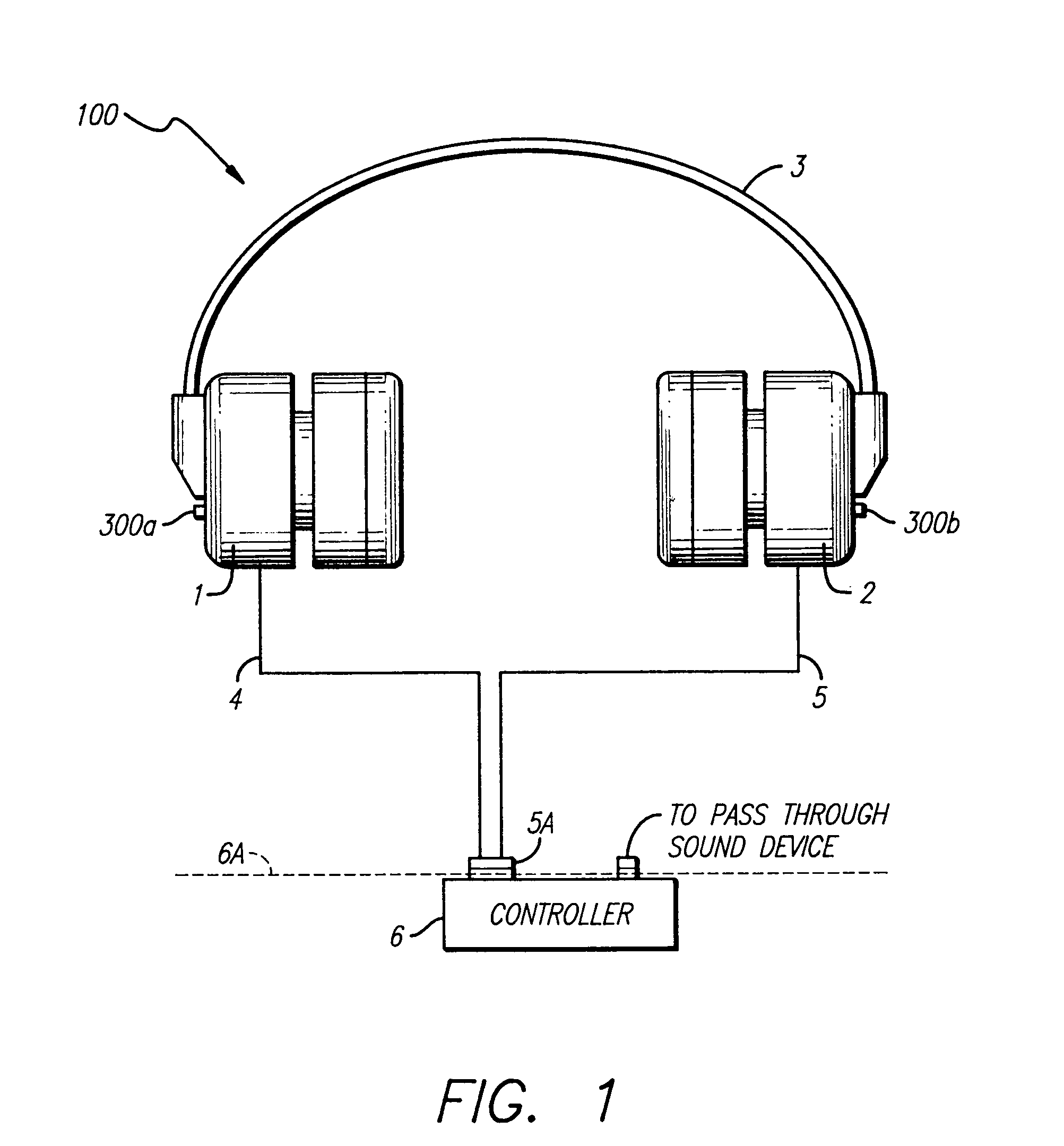
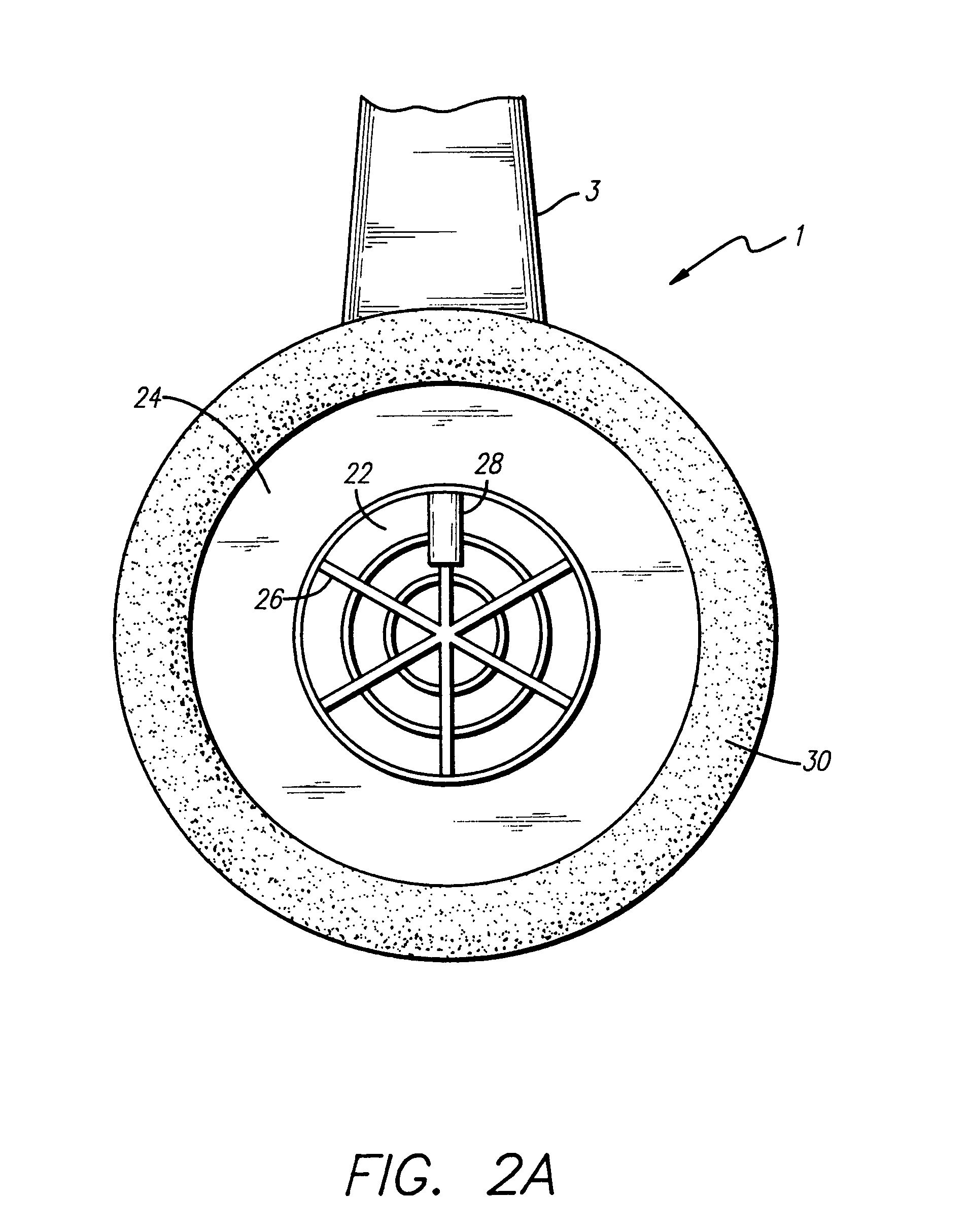
InactiveUS7103188B1Less instabilityImprove Noise CancellationEar treatmentHearing device active noise cancellationInstabilityEngineering
An active noise cancellation system includes a series of features for more effective cancellation, greater reliability, and improved stability. A particular feature adapted for headset systems includes locating a residual microphone radially offset from the center of a sound generator to detect a signal more similar to that incident upon the eardrum of the user. In addition, an open back headset design includes perforations on the side of the headset instead of the back, so that the perforations are less susceptible to inadvertent blockage. The system also includes a mechanism for detecting changes in the acoustic characteristics of the environment that may be caused, for example, by pressure exerted upon the earpieces, and that may destabilize the cancellation system. The system automatically responds to such changes, for example, by reducing the gain or the frequency response of the system to preserve stability. The system further includes other methods for detecting imminent instability and compensating, such as detecting the onset of signals within enhancement frequencies characteristic of the onset of instability, and adjusting the gain or frequency response of the system or suppressing the enhanced signals. The system further includes a mechanism for conserving battery life by turning the system off when sound levels are low, or adjusting the power supply to the system to correspond to the current power requirements of the system.
Owner:NCT GROUP
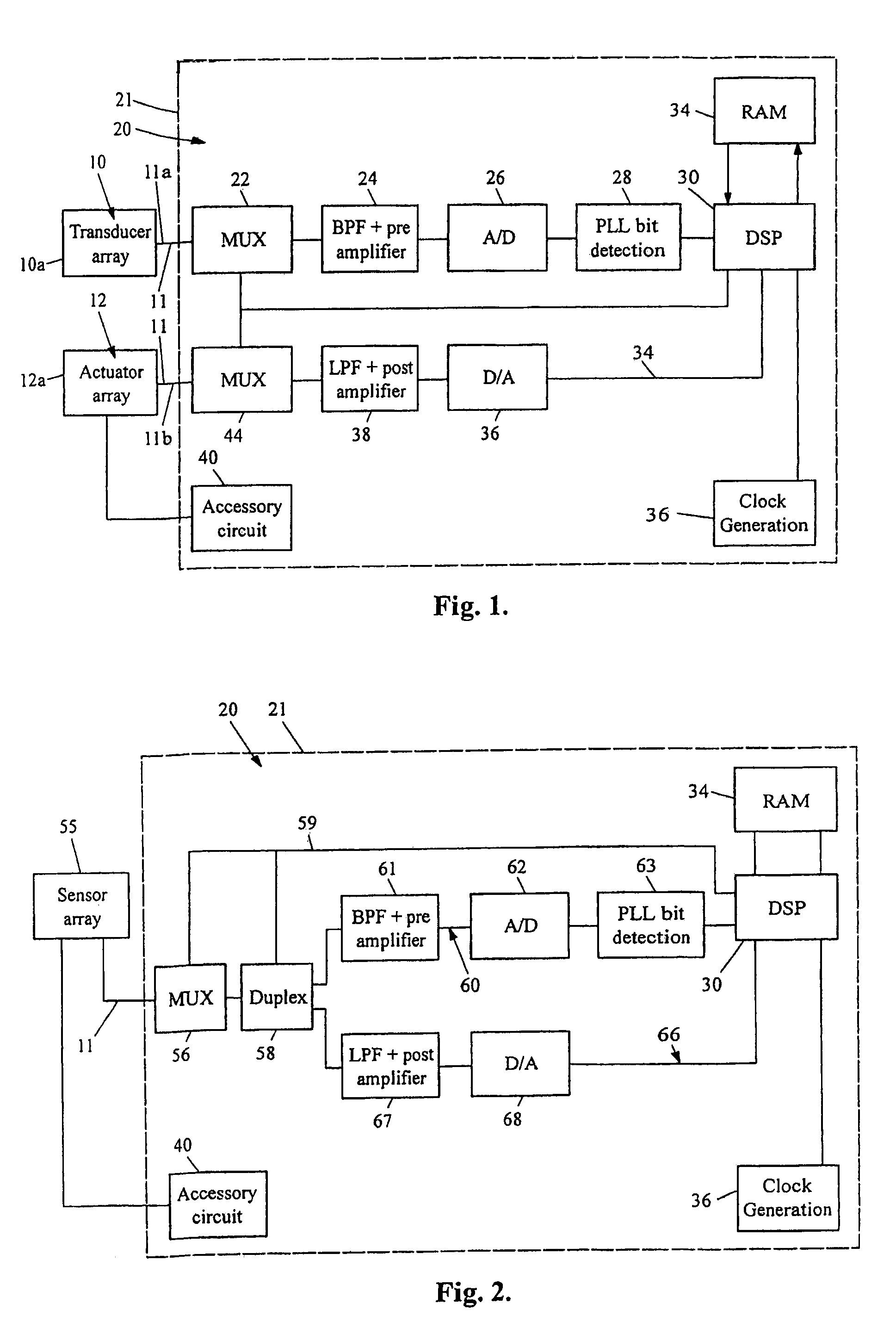
Hearing aid having acoustical feedback protection
InactiveUS7043037B2High cancellationCancel improvementHearing device active noise cancellationDeaf-aid setsHearing aidEngineering
Apparatus for use in a hearing aid wherein a first microphone is connected to the hearing aid case and exposed to free air and a second microphone is connected to the hearing aid case and sealed from free air. The audio inputs from the two microphones are applied to a subtractive circuit so as to cancel any audio signals transmitted through the case of the hearing aid while passing audio signals received by the microphone exposed to free air. In another aspect of the invention, a hearing aid of the behind-the-ear (BTE) type couples sound from the hearing aid loudspeaker through a hollow tube to an inner portion of the ear. A second hollow tube is coupled between a third microphone on the hearing aid case and an outer portion of the ear. Some sound emanating from the tube disposed in the inner ear, exits the ear and is picked up by the second tube and directed to the third microphone. The signal from the third microphone is nulled out by the electronic circuitry of the hearing aid. The gain and phase of the signals picked up by the second tube are automatically adjusted to provide the intended nulling and resulting minimization of acoustical feedback.
Owner:GJL PATENTS
Adaptive cancellation of multi-path interferences
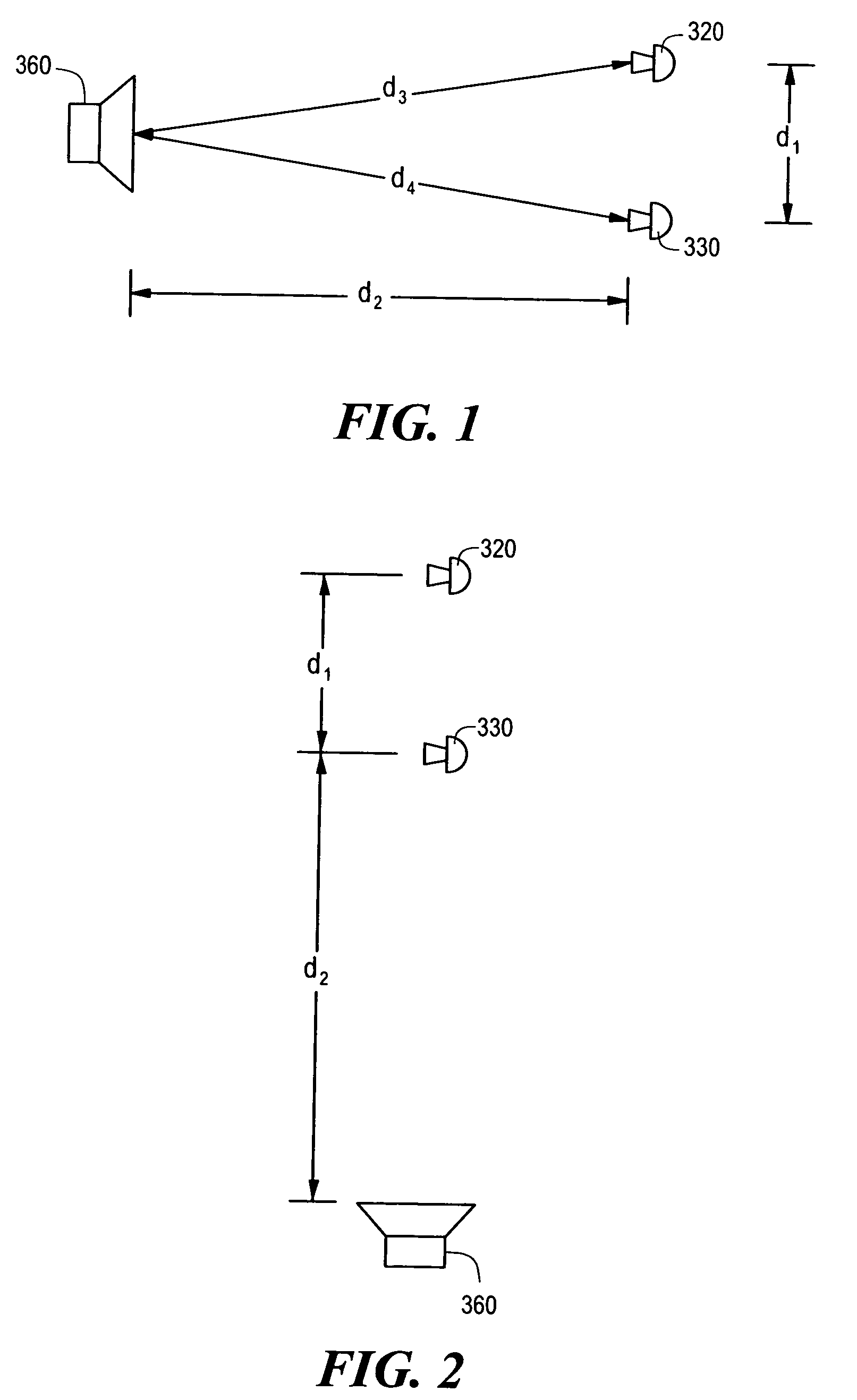
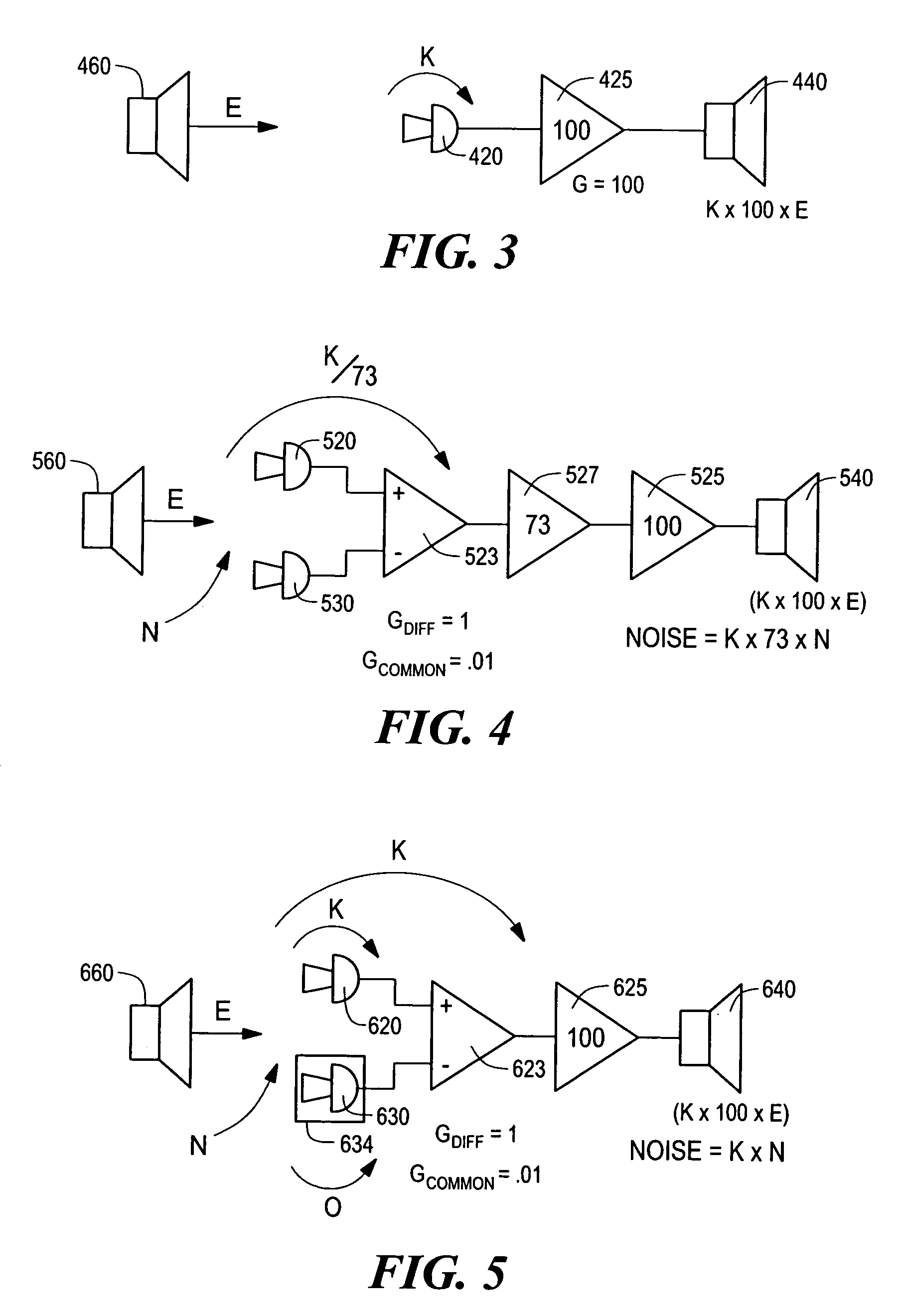
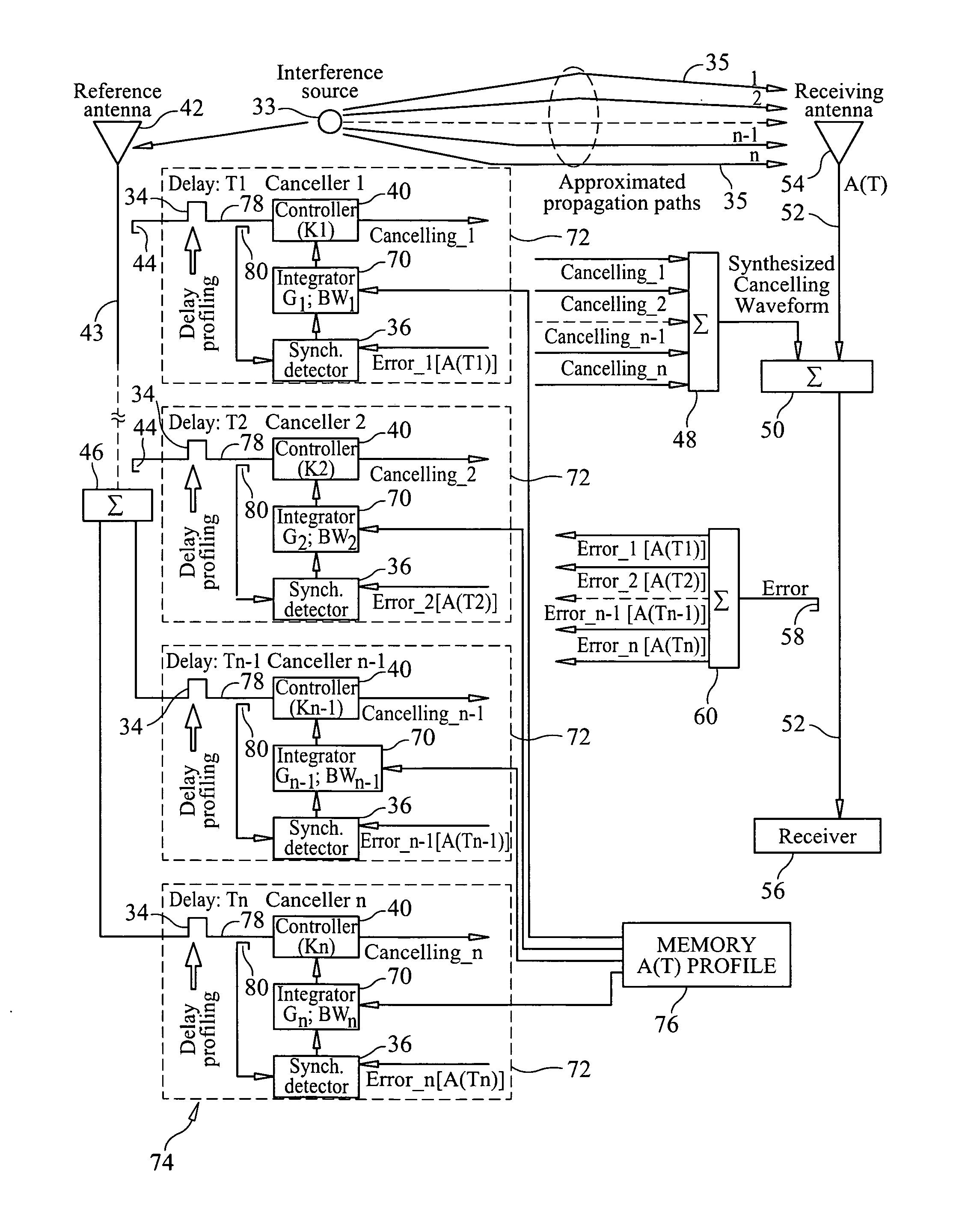
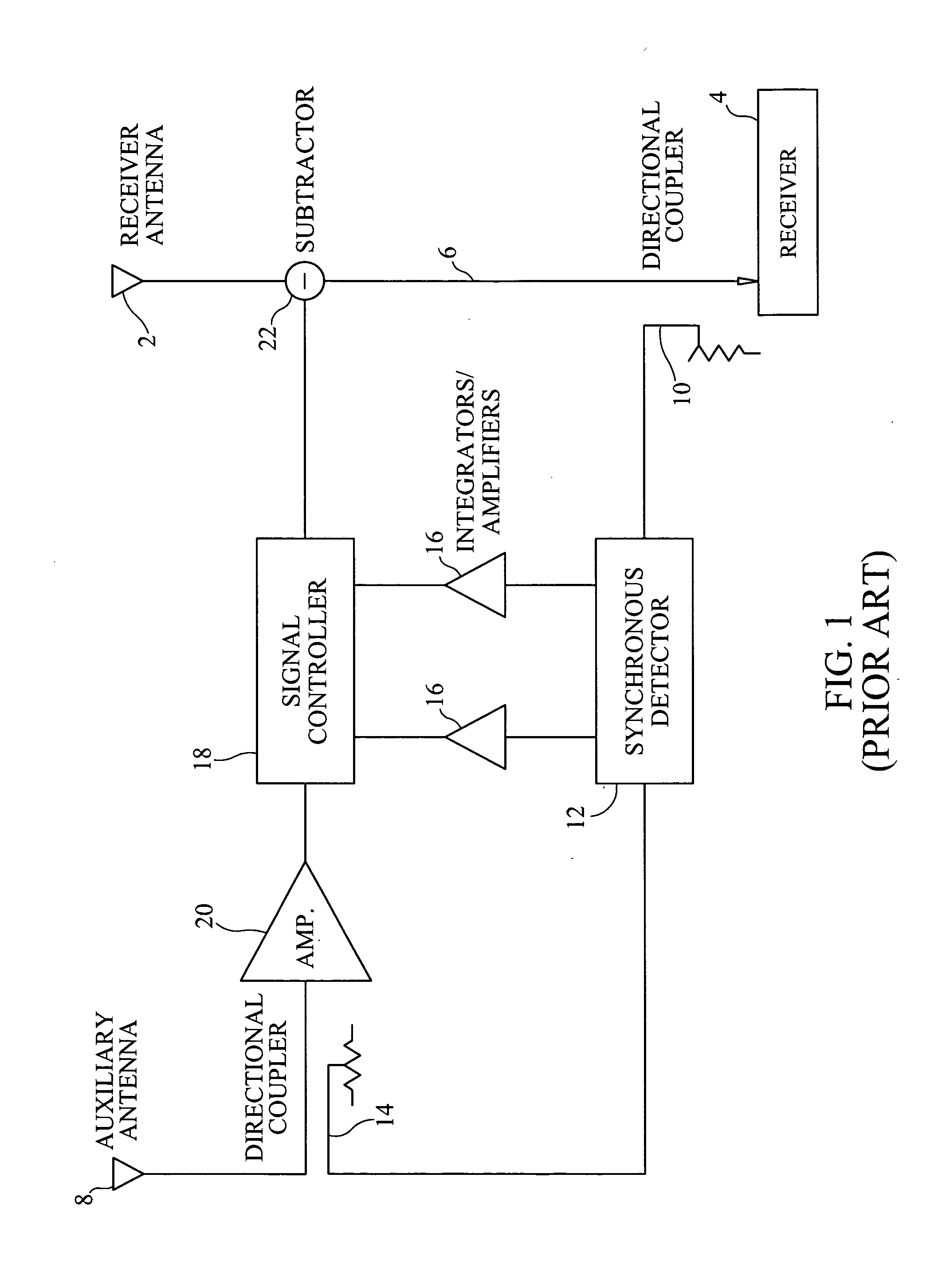
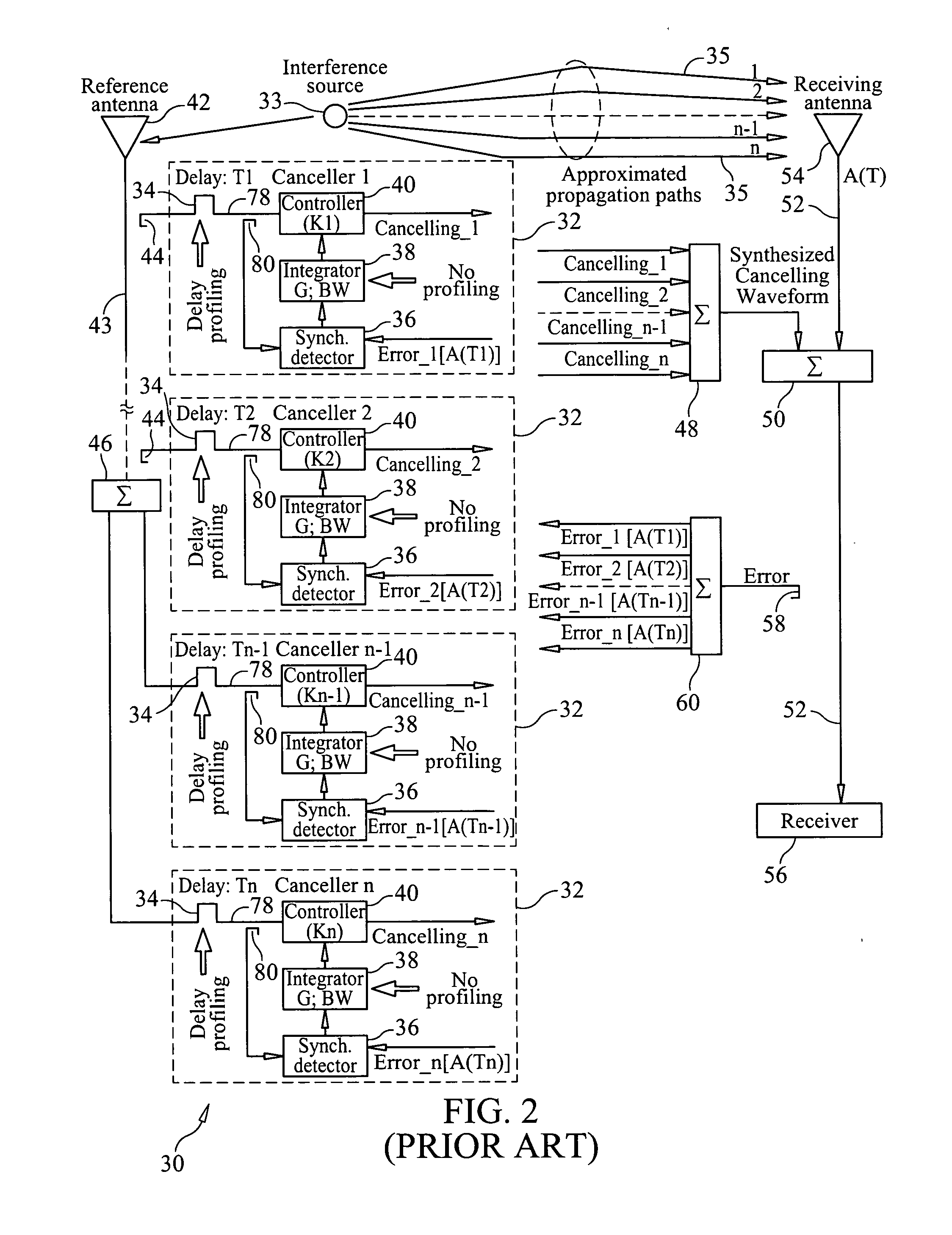
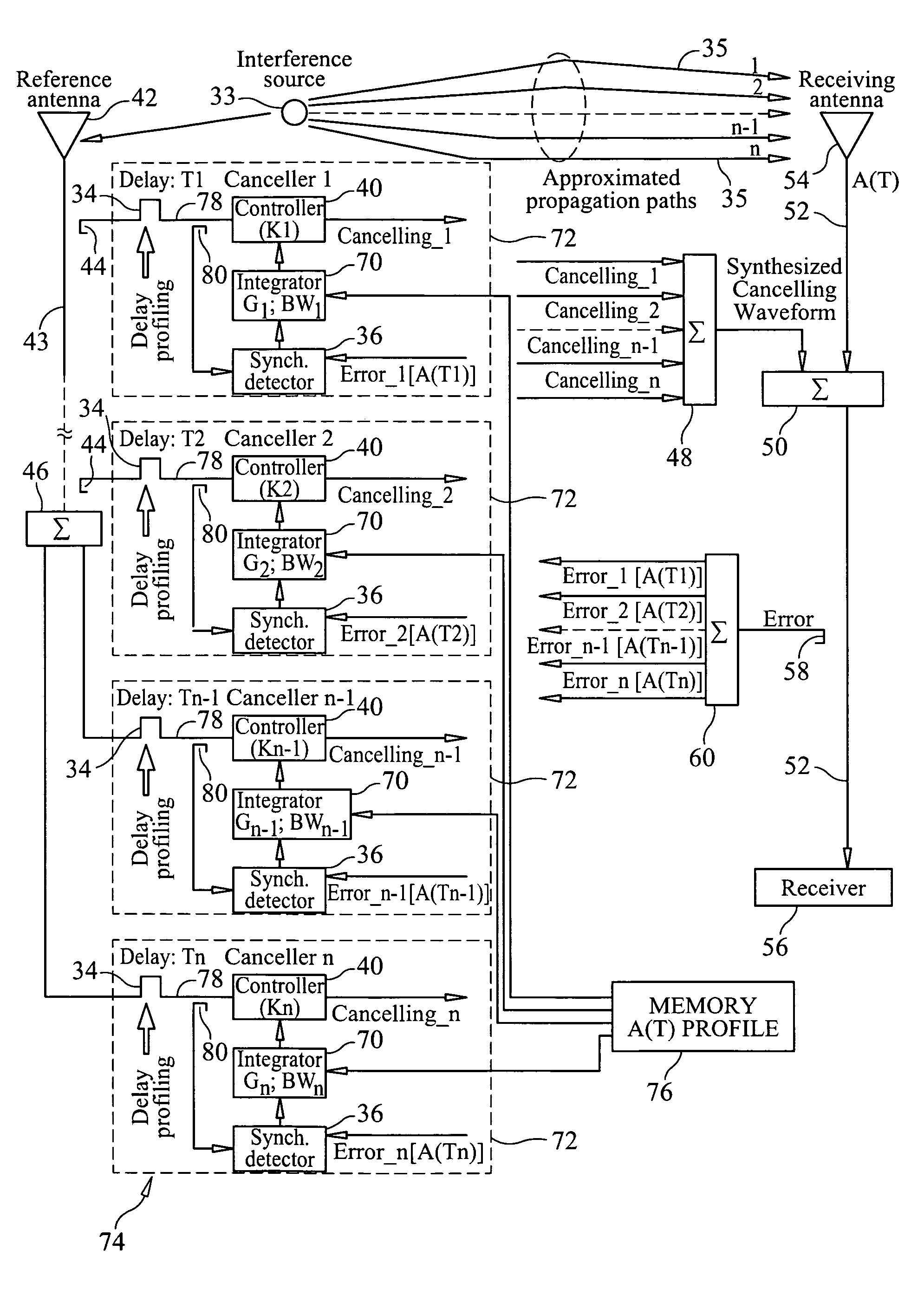
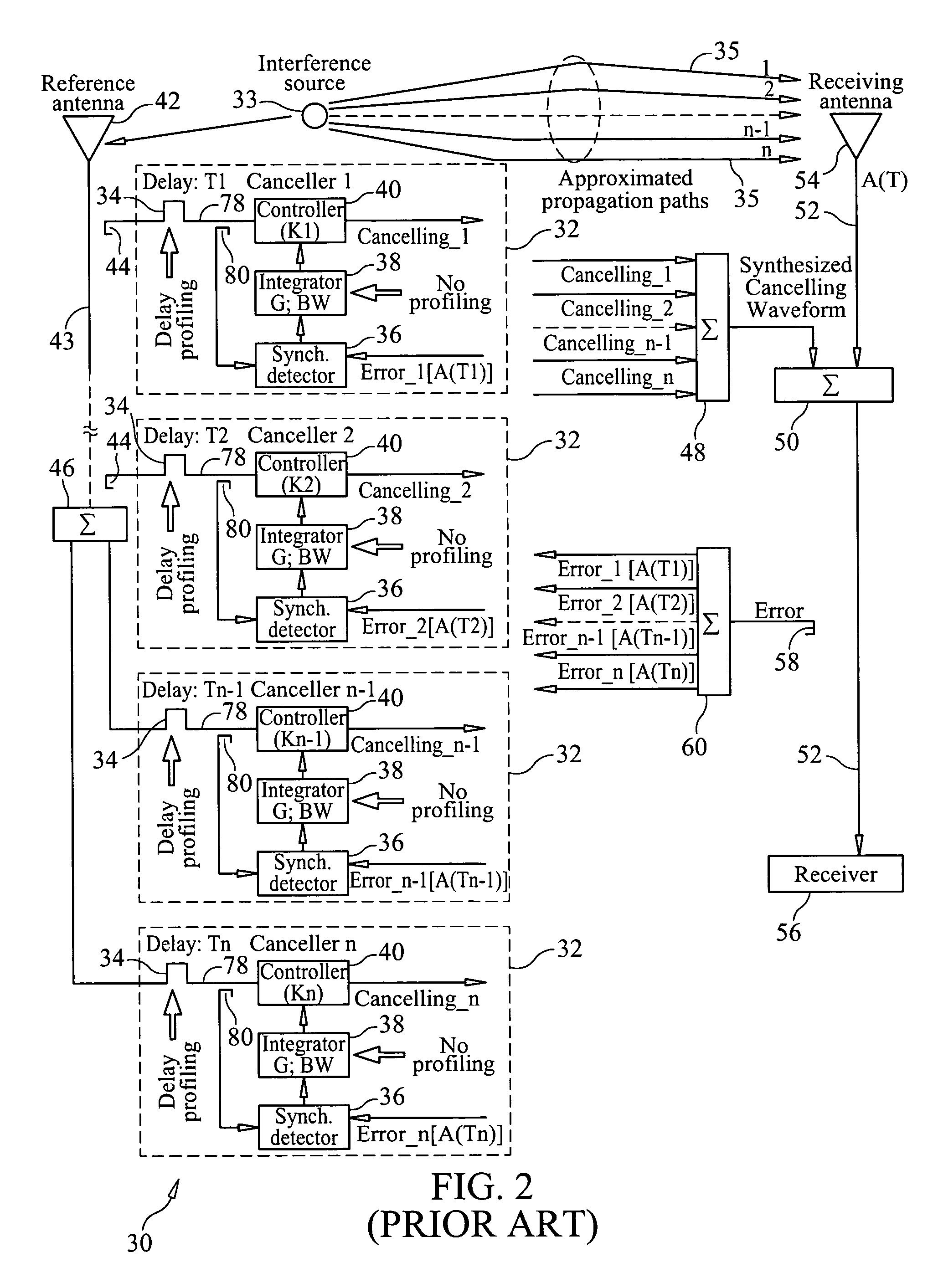
ActiveUS20110319044A1Minimize and eliminate signalMinimize or eliminate unwanted signals arrivingRadio transmissionIntegratorInterference canceller
A multi-path signal interference cancellation system cancels multiple time delayed signal components of a multi-path interference signal received by a receive antenna and carried on a receiver transmission line of a radio receiver system. The interference cancellation system includes a plurality of adaptive interference canceller circuits, each of which has a synchronous detector, a signal controller and an integrator as essential parts of closed control loops defined by the canceller circuits. The integrator has gain and bandwidth characteristics associated therewith which are adjustable to adjust the gain and bandwidth of each closed control loop. An intensity profile of the multi-path interference signal is generated and stored in a memory. An intensity profile signal from the memory is provided to the integrator of each adaptive interference canceller circuit to adjust the gain and bandwidth of the integrator and the loop in which it is situated to maximize the error detection residual signal-to-noise ratio of each adaptive interference canceller circuit. Each adaptive interference canceller circuit generates a cancellation signal from which a synthesized cancellation signal is generated and effectively injected onto the receiver transmission line to cancel the multiple time delayed signal components of the multi-path interference signal carried thereon so that the radio receiver of the radio receiver system only receives a desired signal.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Semiconductor substrate subassembly with alignment and stress relief features
InactiveUS6127727ALow parasitic impedanceEnhance cancellationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSolderingElectrical conductor
A composite conductor for contacting a semiconductor device chip. A durable substrate subassembly for a high power transistor switching modules. The substrate subassembly is durable because wire bonds to the semiconductor device electrodes are replaced with a soldered metal / ceramic composite conductor. The part of the composite conductor contacting the semiconductor device has a coefficient of thermal expansion close to that of the semiconductor device. The substrate in the substrate subassembly has automatic alignment features. The composite conductor also has automatic alignment features, along with stress relief features. Automatic alignment permits concurrent soldering of the chip to the substrate, and the composite conductor to the chip and to a terminal contact.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
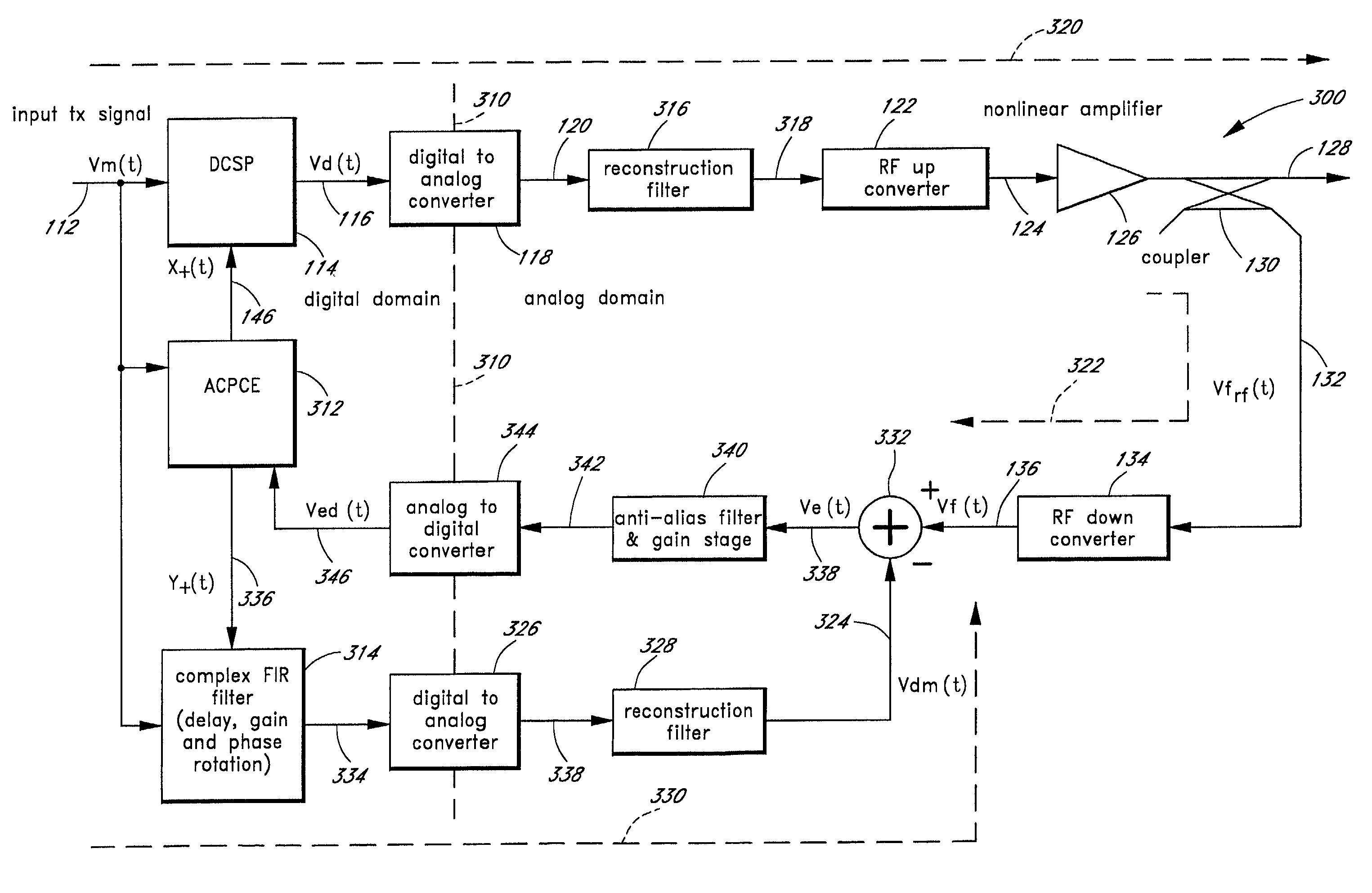
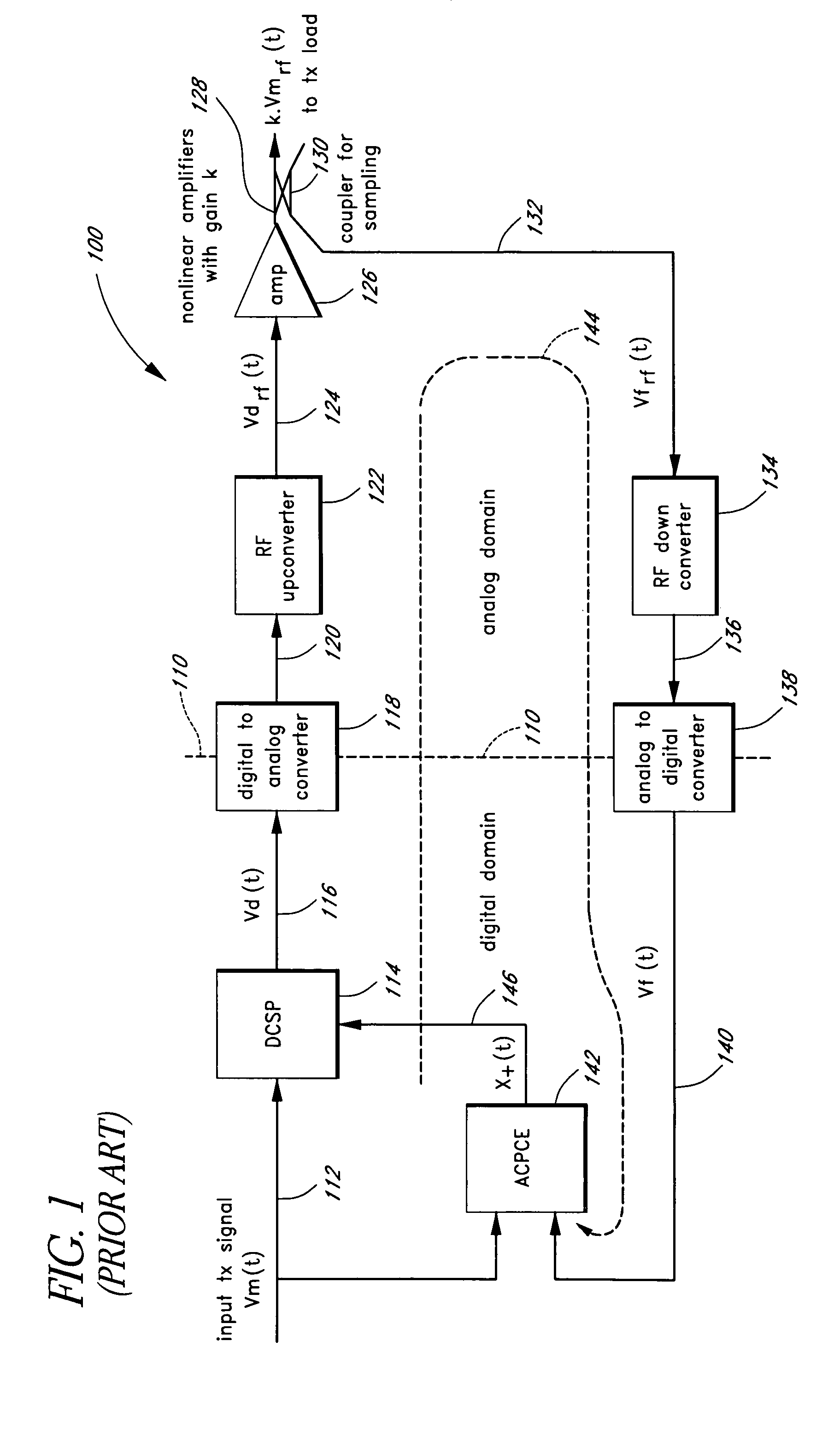
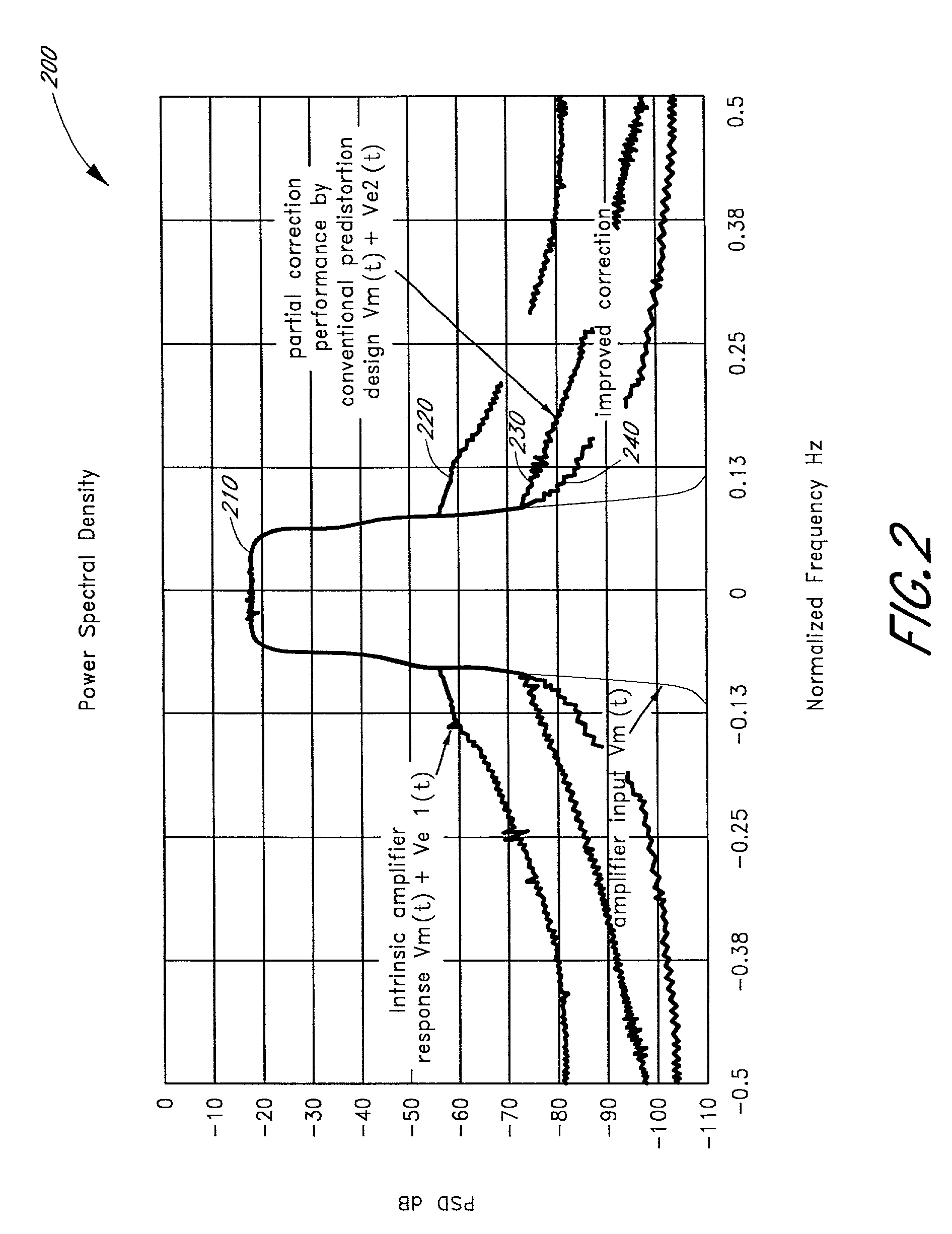
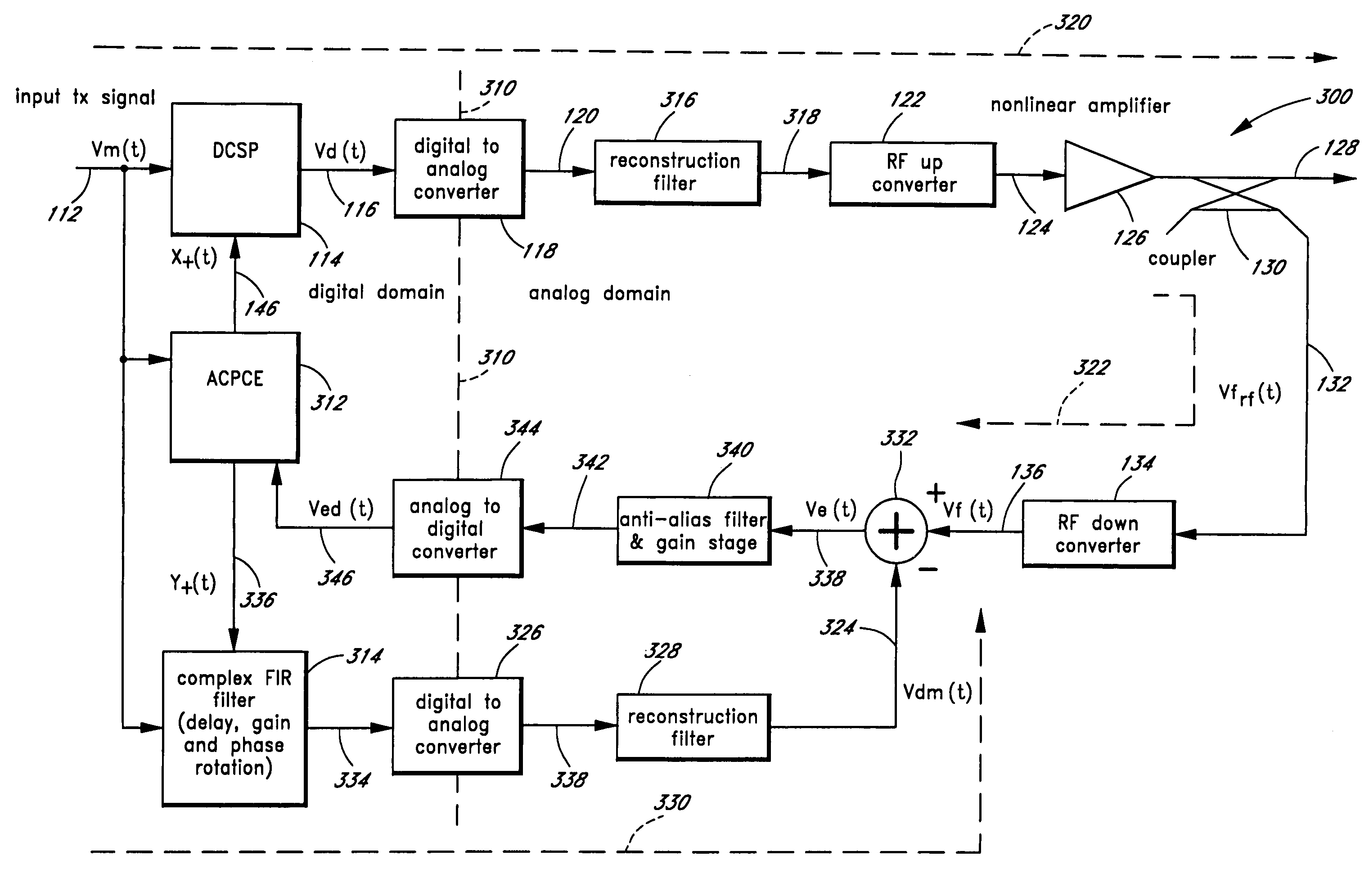
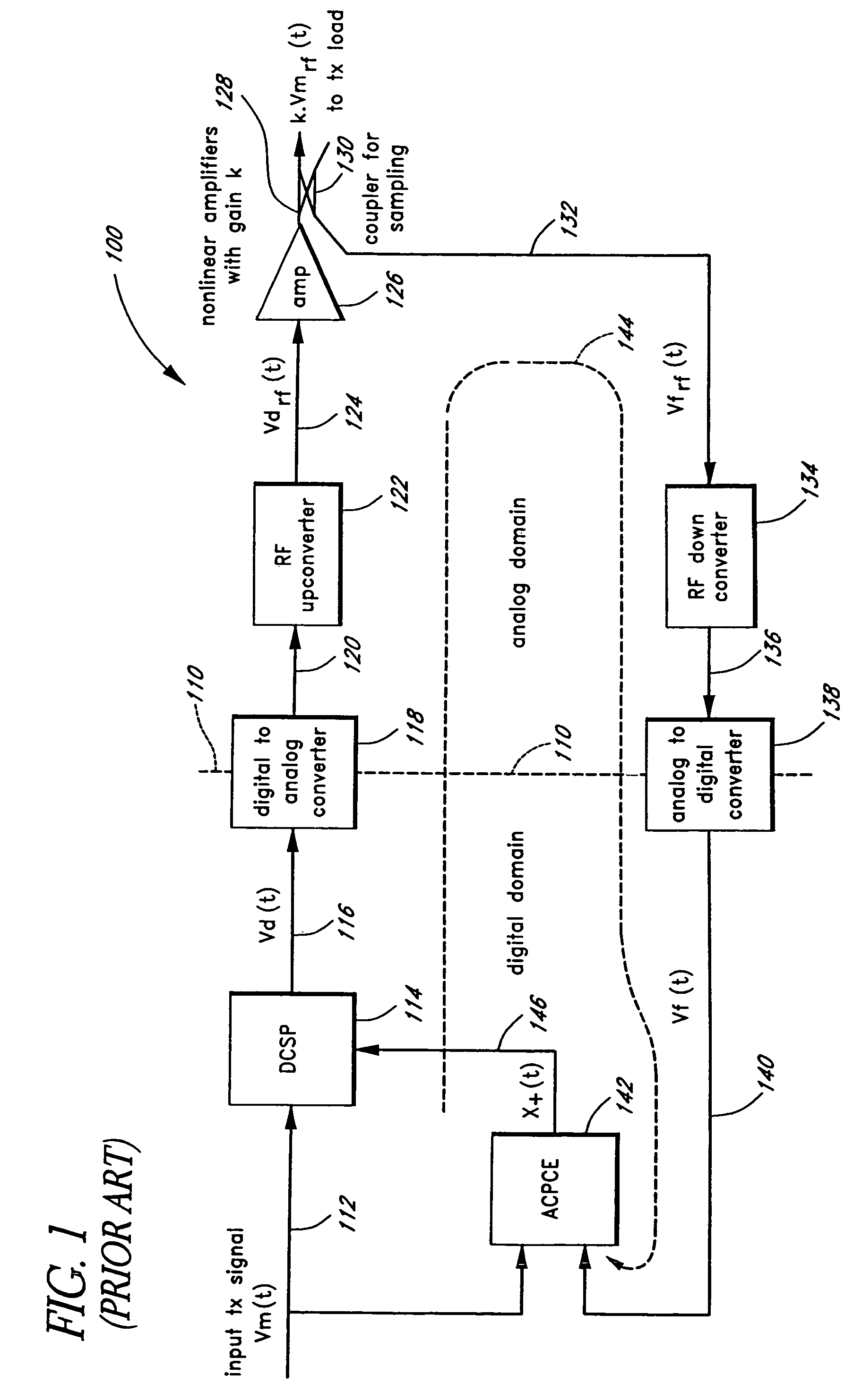
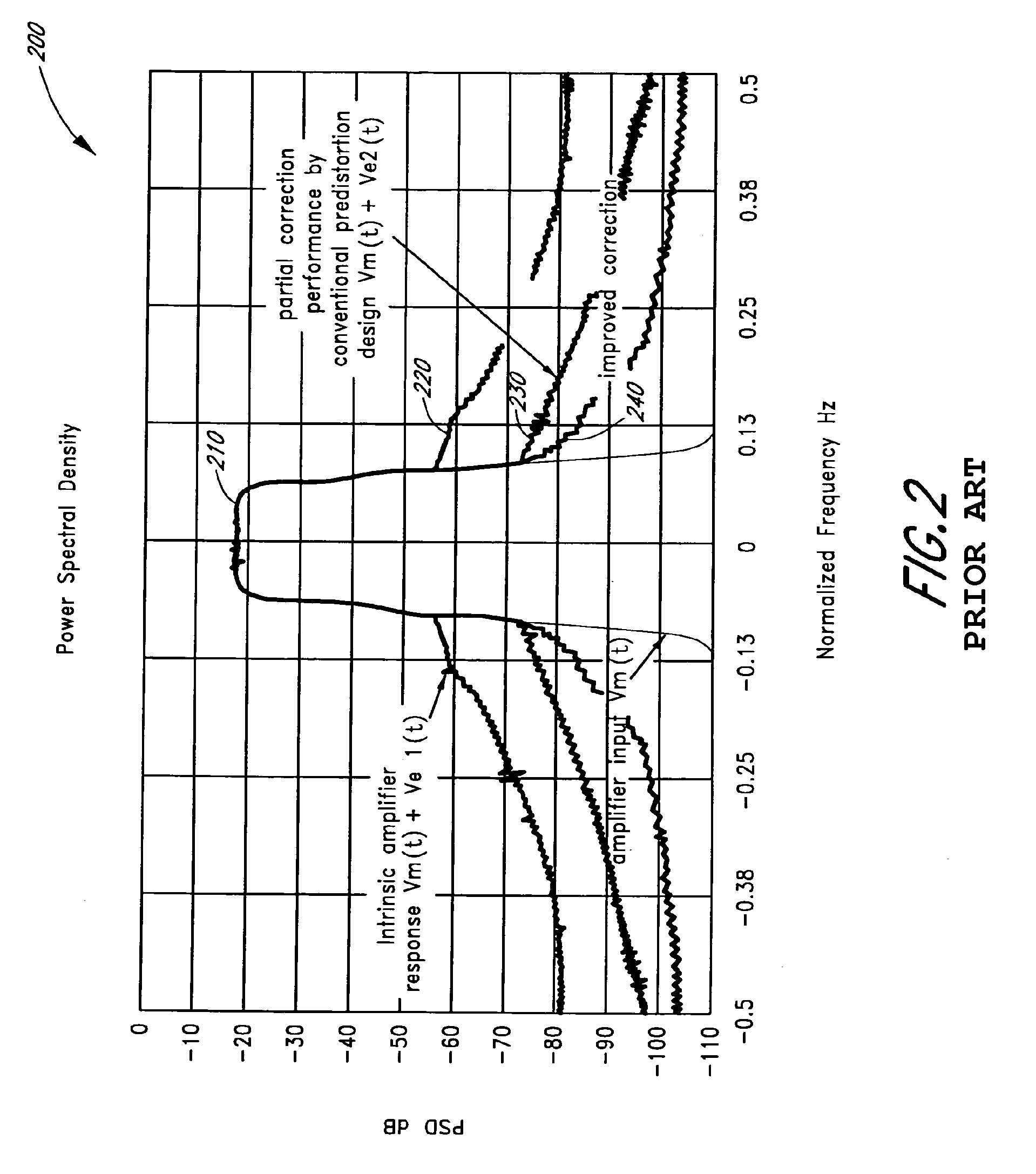
Advanced adaptive pre-distortion in a radio frequency transmitter
ActiveUS6973138B1Improve linearityLow costSecret communicationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksEngineeringLinearity
The present invention is related to methods and apparatus that advantageously permit the more efficient use of an input range of an analog-to-digital converter used by an adaptive predistortion linearized RF transmitter. A main signal component of a down-converted output of an RF transmitter is removed prior to the analog-to-digital conversion of the down-converted output, thereby allowing more of the input range of the analog-to-digital converter to capture an error signal component of the down-converted output. Embodiments of the present invention can thus adaptively tune the predistortion stage to a higher degree of linearity or can use lower cost analog-to-digital converters with fewer quantization steps for the same performance.
Owner:MAXLINEAR ASIA SINGAPORE PTE LTD
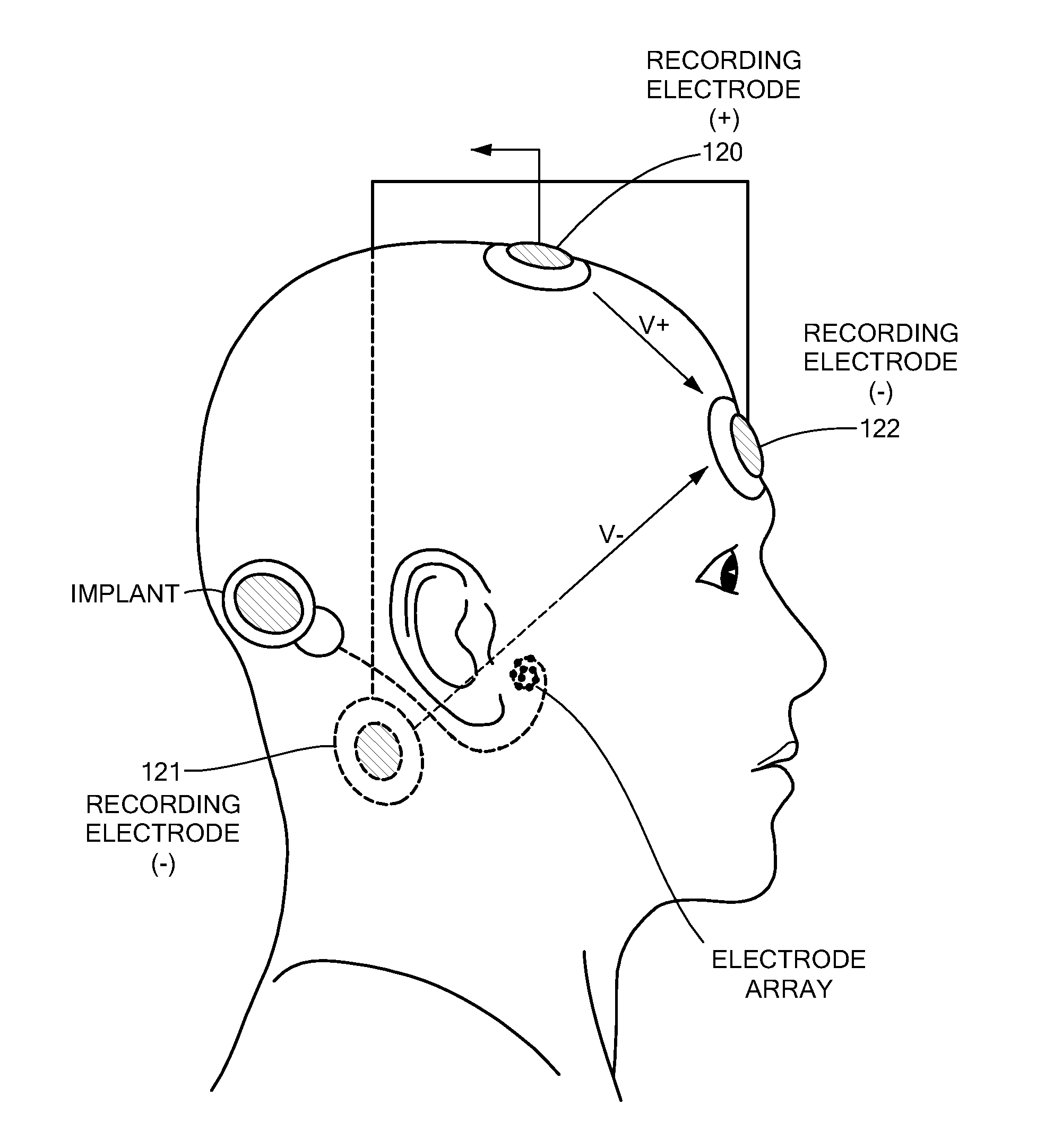
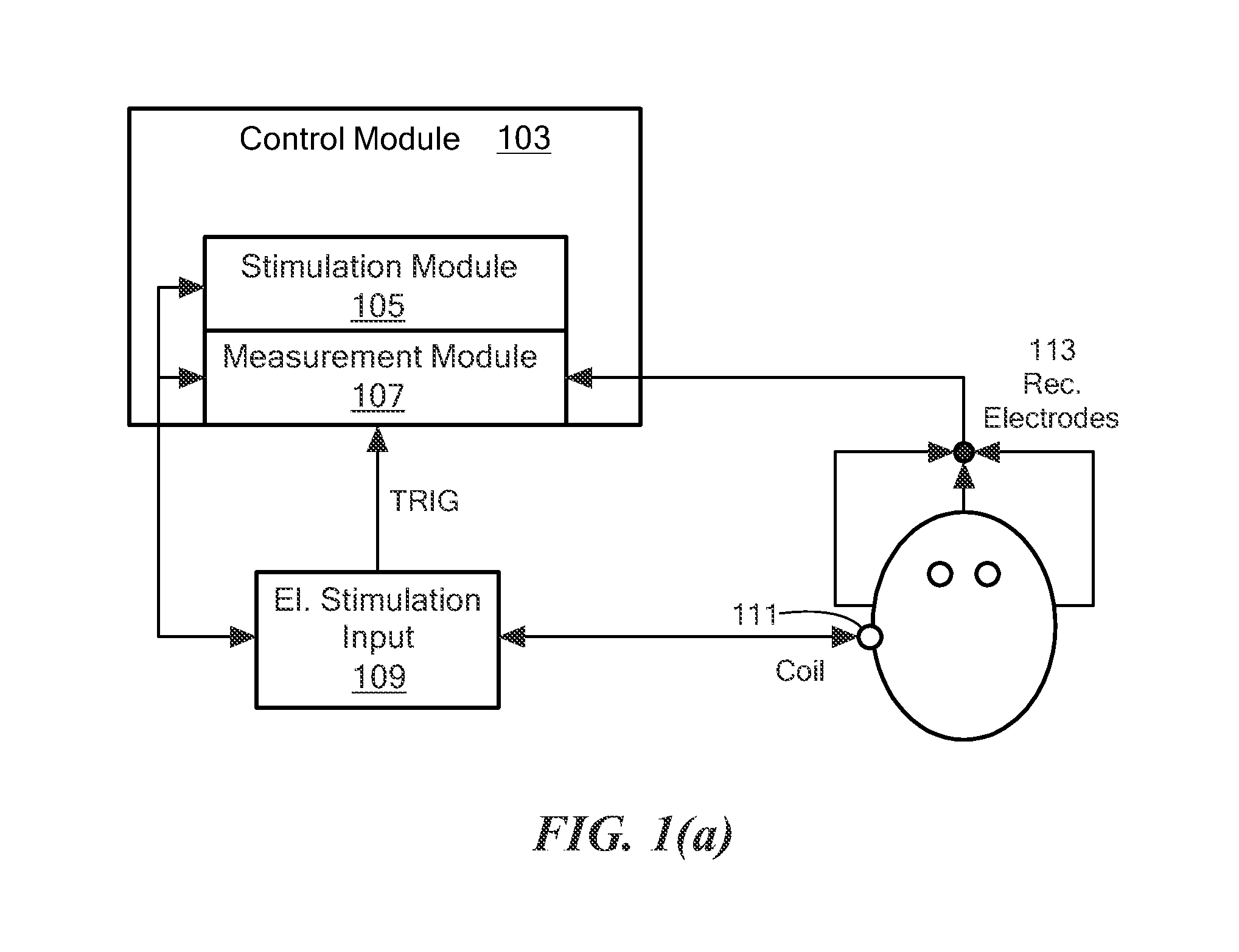
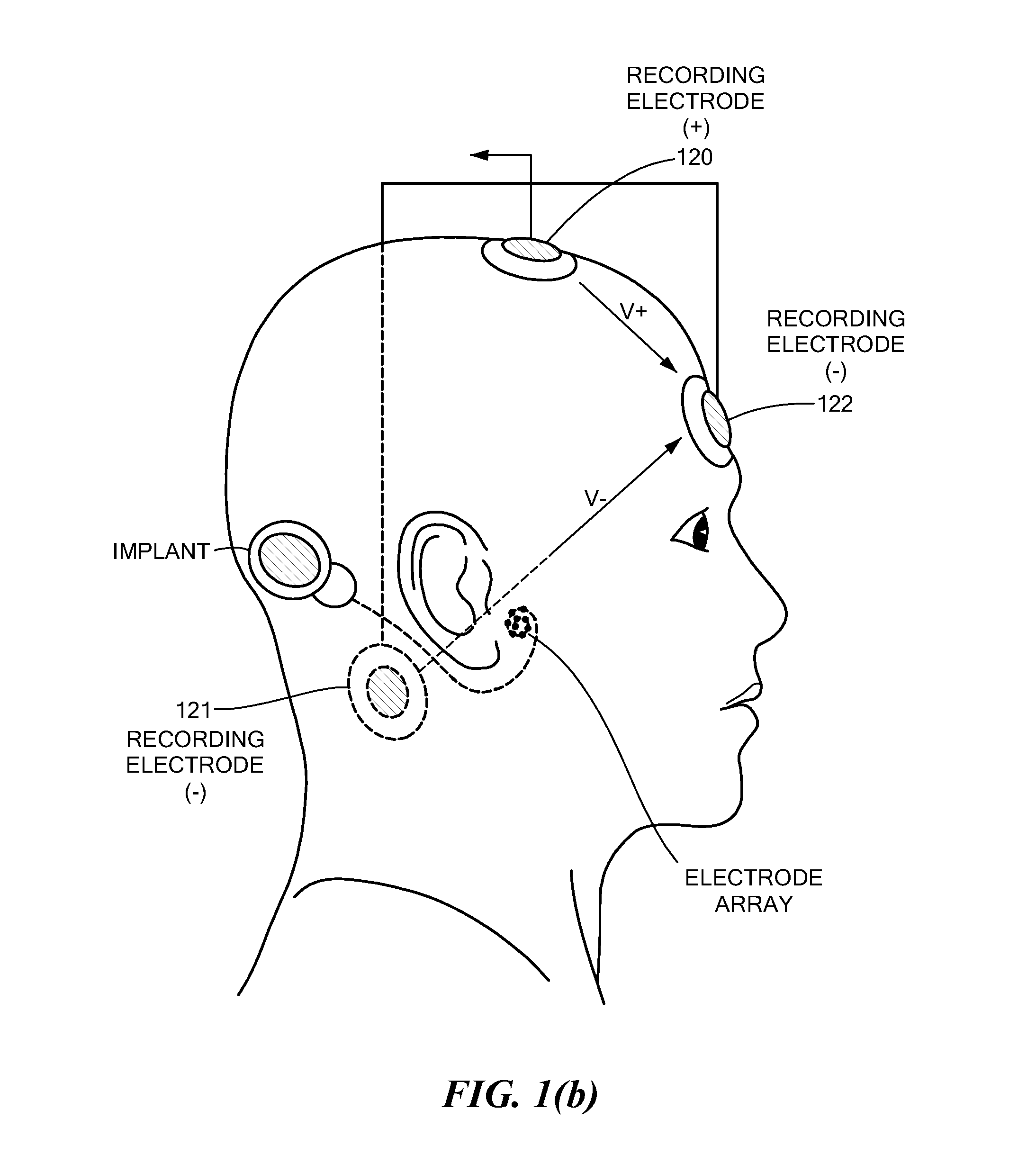
Electrically Evoked Brainstem Response Measurements via Implant Prosthesis
ActiveUS20120029377A1Improved forward masking cancellationCancel improvementElectroencephalographyHead electrodesElectrode arrayCochlea
A method of measuring electrically evoked auditory brainstem responses of a patient or animal body is provided. The method includes surgically implanting an auditory prosthesis having an electrode array, the electrode array positioned either intracochlear or substantially proximate a brainstem of the body. At least one electrode is stimulated in the electrode array. Electrically evoked auditory brainstem responses resulting from said stimulation are recorded using, at least in part, an electrode in the electrode array as a negative electrode, and a positive electrode positioned substantially proximate the vertex of the head of the body.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
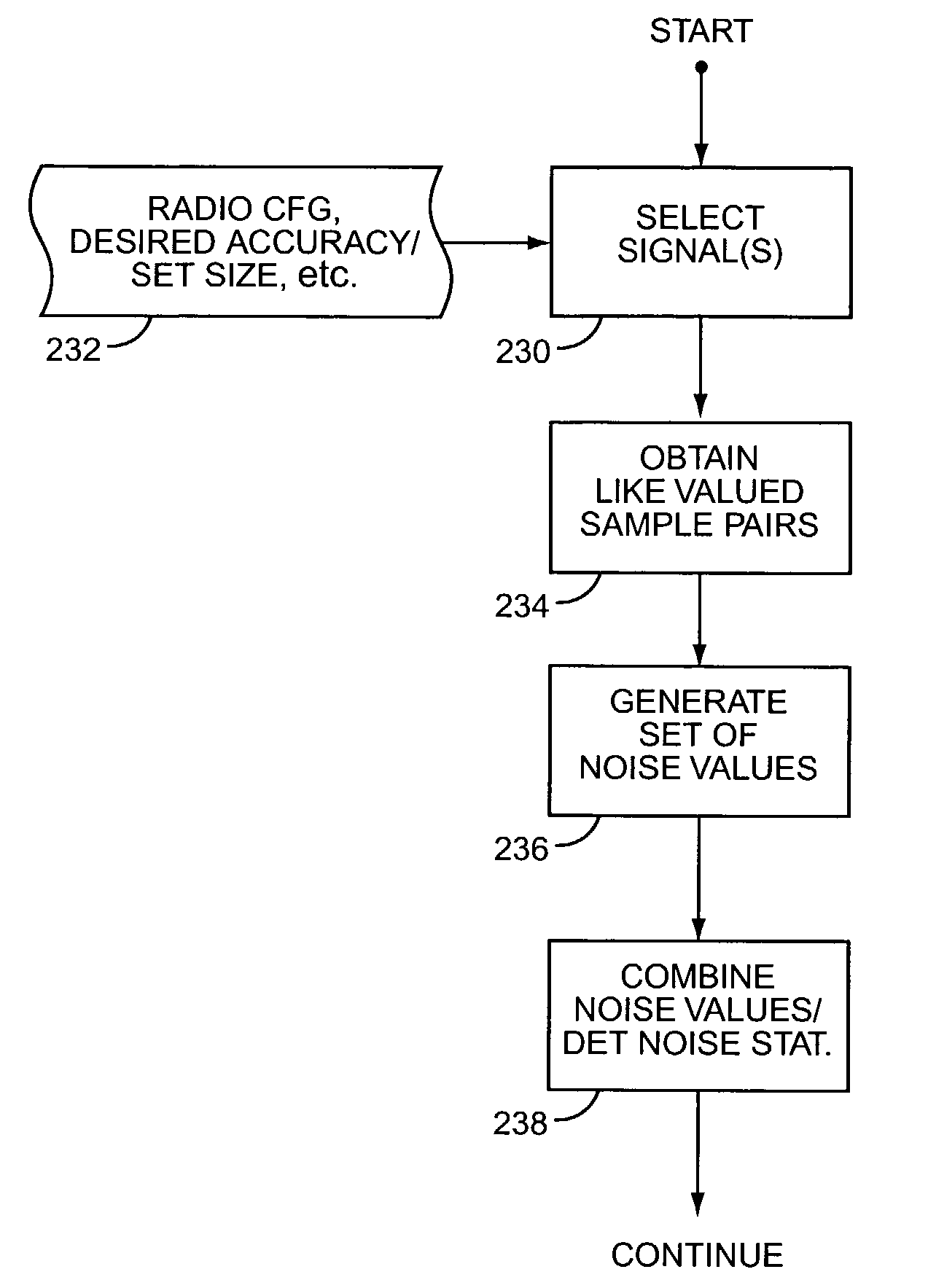
Signal-to-noise ratio estimation of CDMA signals
ActiveUS7313167B2Cancel improvementMinimize timePower managementEnergy efficient ICTSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Deterministic noise
An improved approach to noise estimation permits, for example, tighter closed-loop power control in a wireless communication network with attendant improvements in transmit power efficiency and network capacity. In an exemplary embodiment, the received signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of a data signal is estimated based on noise samples obtained from one or more other signals received in association with the data signal. In general, these associated signals are characterized by the receiver's ability to extract like valued samples from them, such that pairs of these like valued signal samples may be subtracted, thereby canceling their deterministic signal components and leaving only difference values representative of the non-deterministic noise components of the signal samples. Obtaining difference values from more than one associated signal increases the sample size of difference values used in noise estimation, thereby improving the statistical basis for noise estimation and, therefore, the accuracy of SNR estimation.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Interference cancellation and receive diversity for single-valued modulation receivers
InactiveUS20090058728A1Cancel improvementIncrease diversityMultiple-port networksError preventionWeight coefficientEngineering
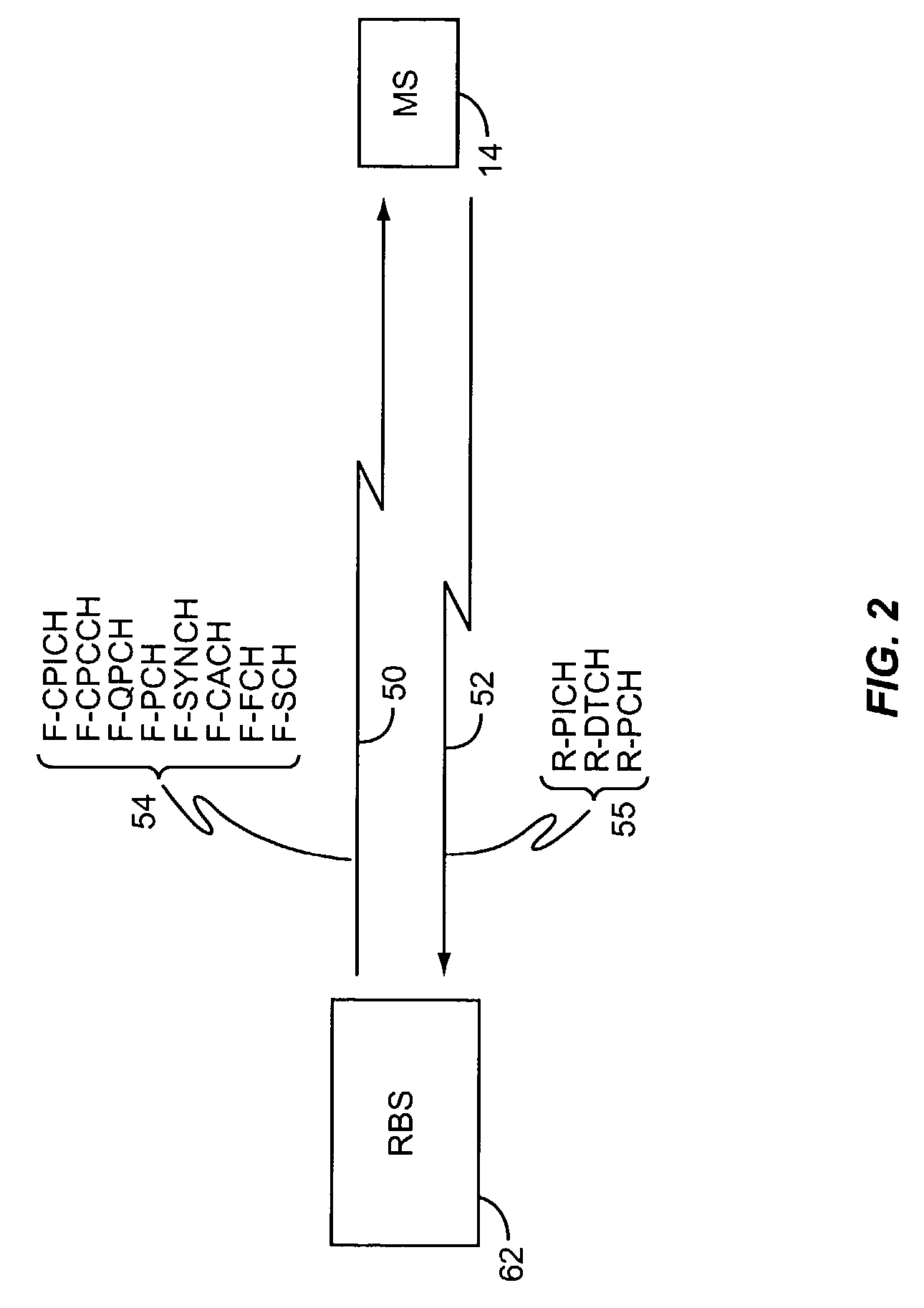
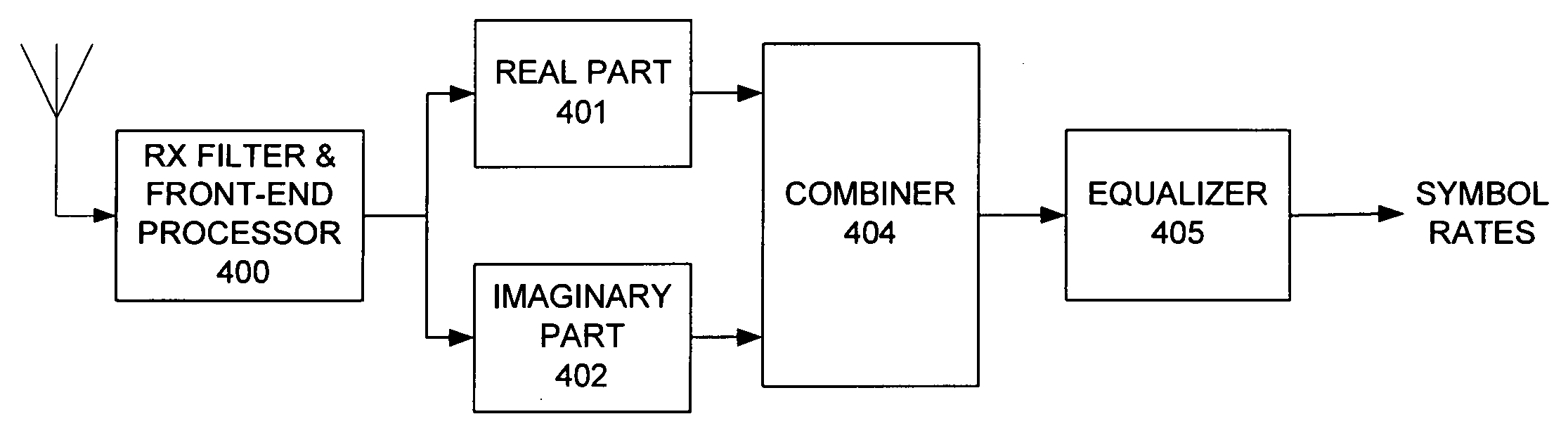
A combined SAIC receiver and a multiple-antenna, receive diversity receiver are employed to reduce interference in a wireless system. The real and imaginary parts of the de-rotated signal for each receive path associated with an antenna are separately filtered and a combined output signal of all receive paths is generated. The weighting coefficients are adjusted based on an error signal produced by comparing the combined output signal with a reference signal. The weighting coefficients are initially set based on an MMSE / LS type of signal processing criteria, where the reference signal is the Training Sequence Code (TSC). Subsequent adjustment / tracking can be accomplished by using known tracking algorithms, e.g. LMS or RLS, or the coefficients can be re-computed using MMSE / LS processing. The reference signal for tracking may be a combination of the TSC and estimated data symbols provided by an equalizer.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC +1
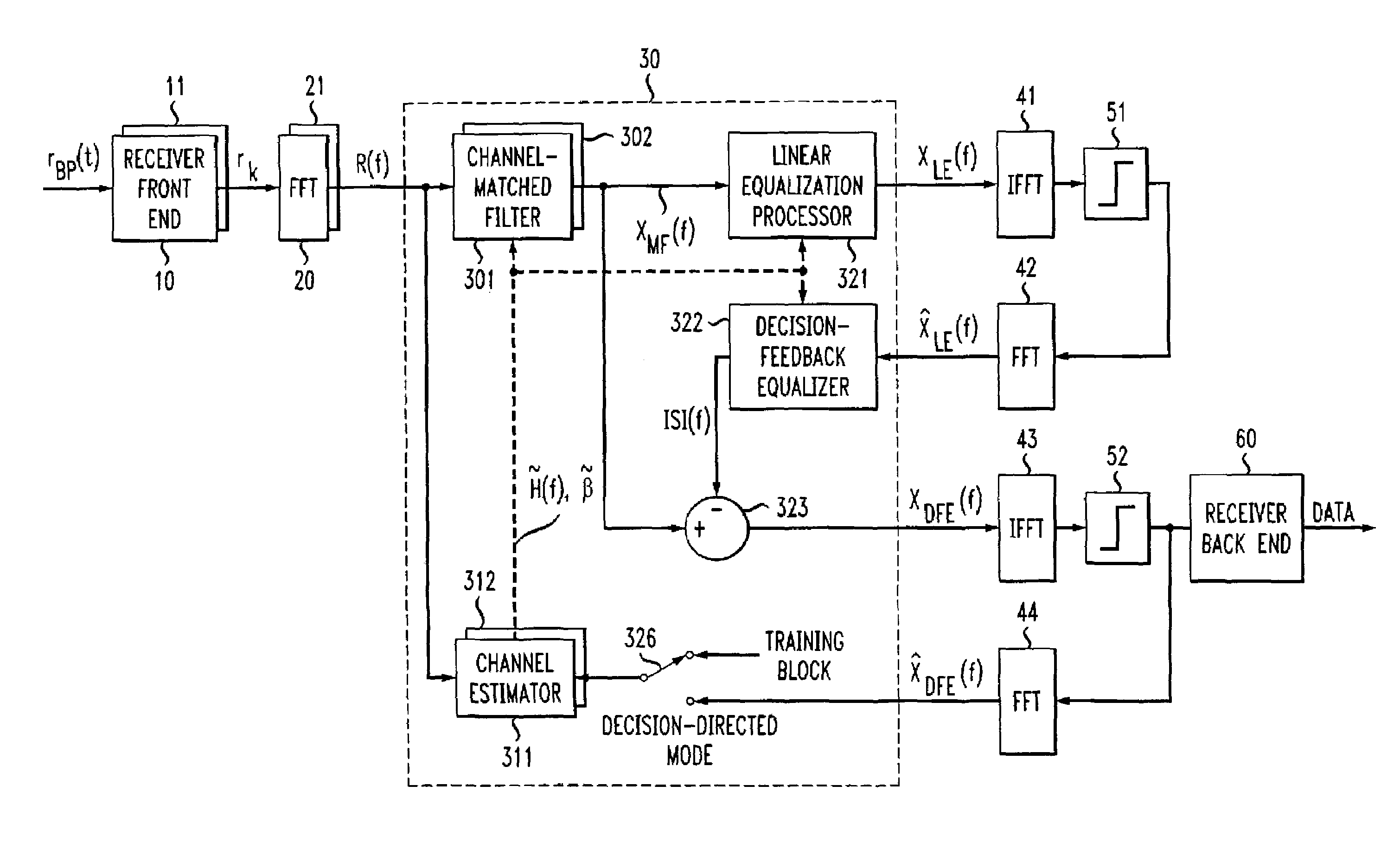
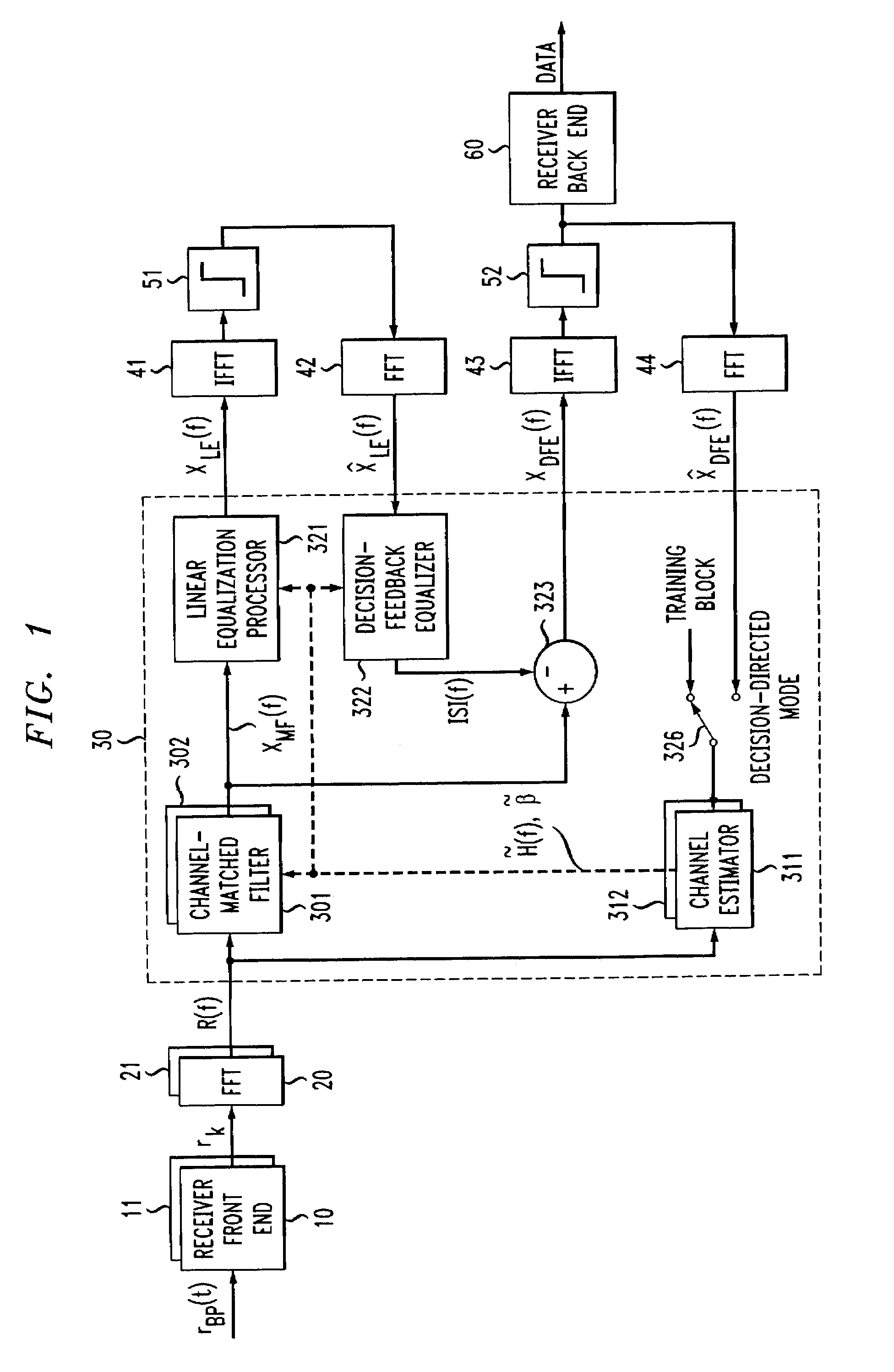
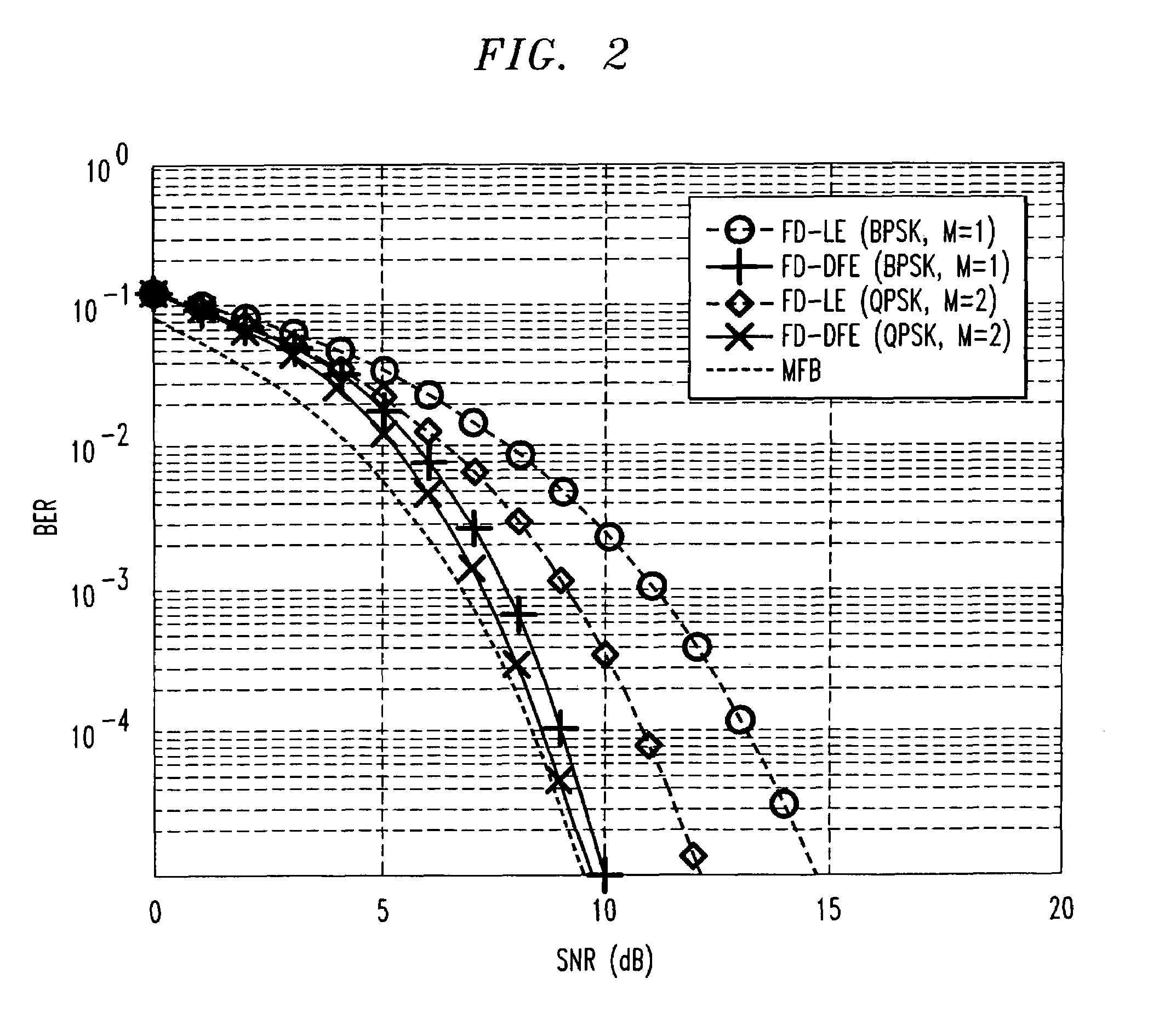
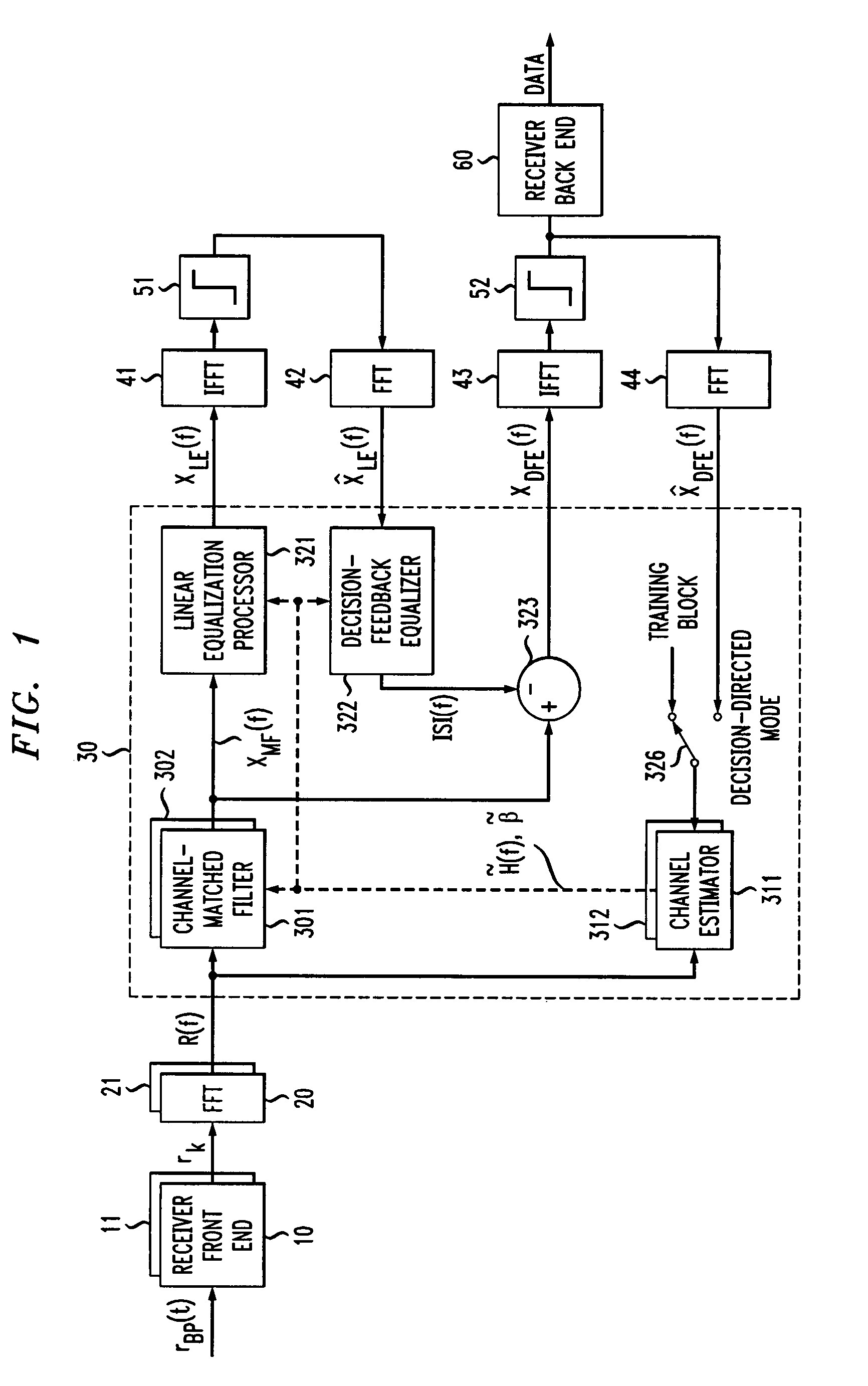
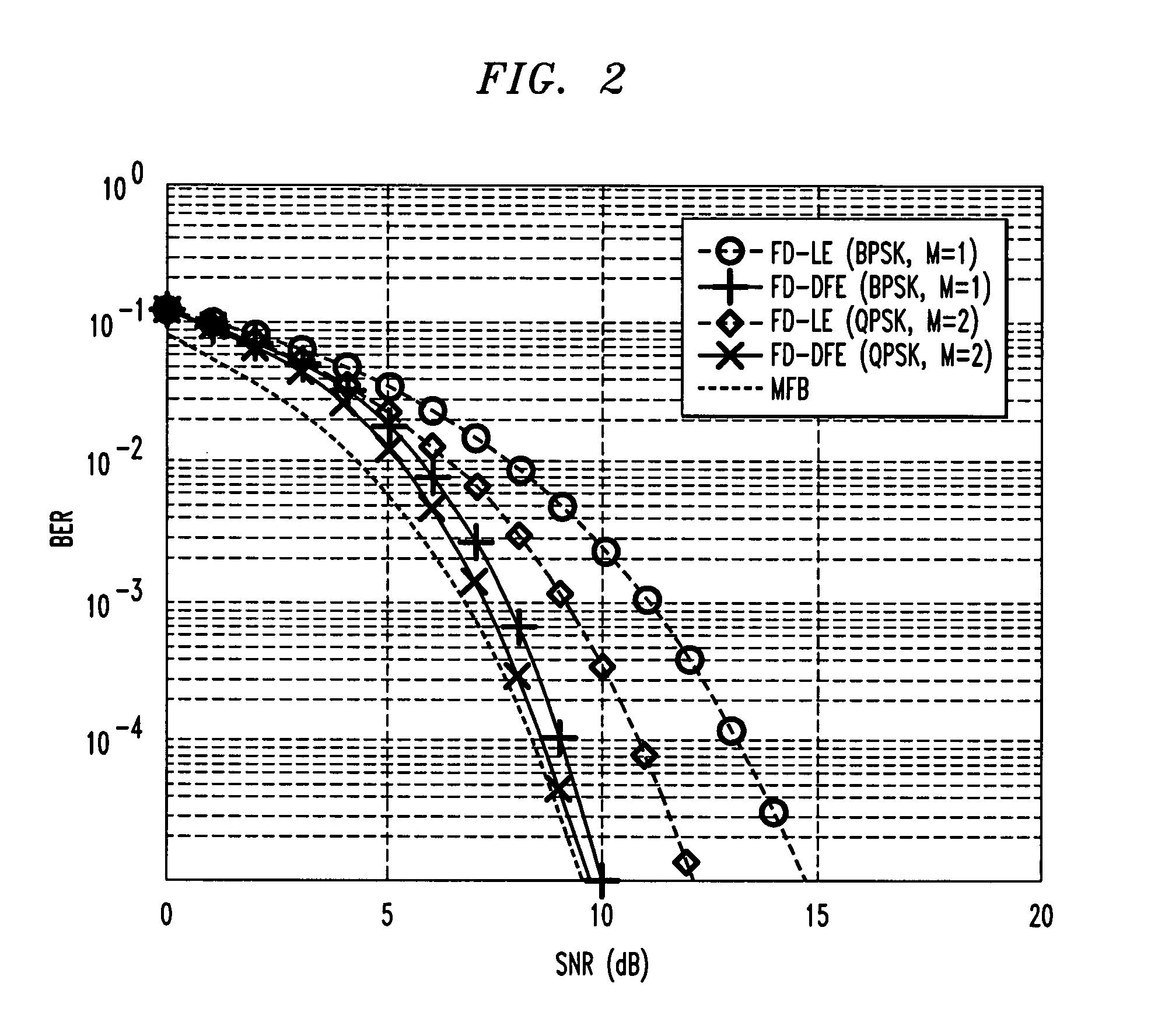
Frequency domain decision feedback equalizer
InactiveUS7212569B1Enhanced ISI cancellationImprove signal-to-noise ratioMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTime domainRound complexity
The feedback structure of a frequency domain decision feedback equalizer is implemented in the frequency domain, rather than in the time domain. Advantageously, this permits the synthesis of long feedback filters with a much smaller increase in receiver complexity than is the case when the feedback structure is illustratively implemented in the time domain. Adaptation of the characteristics of the feedback structure of the frequency domain equalizer (as well as its feedforward structure) is carried out based on tentative symbol decisions that are fed back on a block basis. Although possibly rendering the receiver more susceptible to channel estimation errors, this approach renders the receiver capable not only of the post-cursor intersymbol interference cancellation afforded by a standard DFE, but pre-cursor intersymbol interference cancellation, as well, helping to offset any impact of increased channel estimation errors.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Advanced adaptive pre-distortion in a radio frequency transmitter
InactiveUS7471739B1Low costImprove linearityAmplitude modulation detailsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceLinearitySelf adaptive
The present invention is related to methods and apparatus that advantageously permit the more efficient use of an input range of an analog-to-digital converter used by an adaptive predistortion linearized RF transmitter. A main signal component of a down-converted output of an RF transmitter is removed prior to the analog-to-digital conversion of the down-converted output, thereby allowing more of the input range of the analog-to-digital converter to capture an error signal component of the down-converted output. Embodiments of the present invention can thus adaptively tune the predistortion stage to a higher degree of linearity or can use lower cost analog-to-digital converters with fewer quantization steps for the same performance.
Owner:MAXLINEAR ASIA SINGAPORE PTE LTD
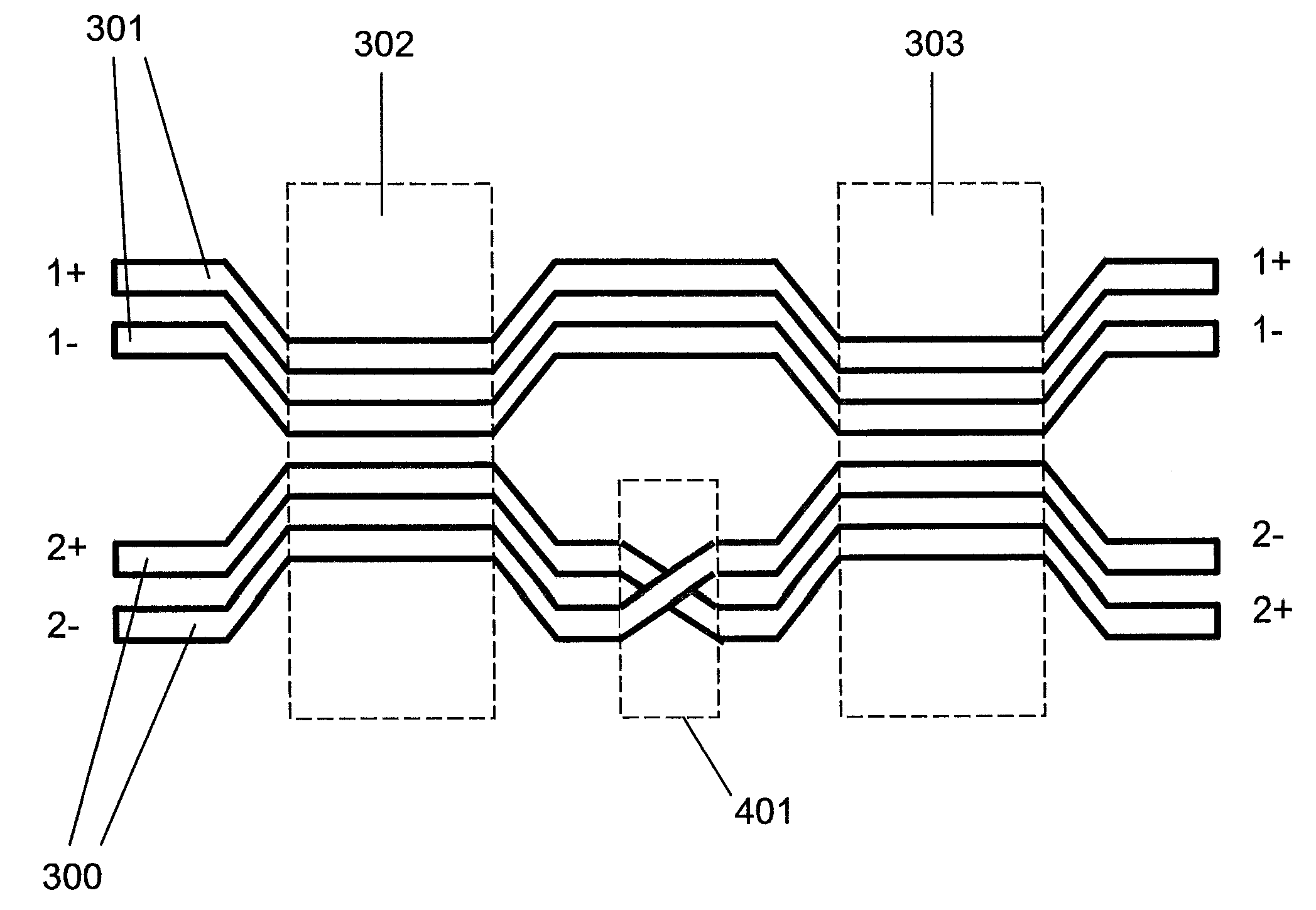
Reducing far-end crosstalk in chip-to-chip communication systems and components
InactiveUS20100183141A1Big improvements in total FEXTCancel improvementSubstations coupling interface circuitsInterconnection arrangementsCommunications systemElectrical polarity
The present invention involves chip-to-chip communication systems for reducing Far-End Crosstalk (FEXT) through the use of novel polarity swapping to negate the cumulative effect of FEXT. Skew adjustment is used to improve the FEXT cancellation from polarity swapping. The polarity reversal location or locations among FEXT sources are optimized to achieve maximum FEXT cancellation. The novelty polarity swapping technique can be applied to a wide variety of systems that can benefit from FEXT reduction.
Owner:HIROSE ELECTRIC GROUP
Reducing far-end crosstalk in electrical connectors
ActiveUS20100184307A1Big improvements in total FEXTCancel improvementInterconnection arrangementsSubstations coupling interface circuitsElectricityElectrical polarity
The present invention involves connectors for reducing Far-End Crosstalk (FEXT) through the use of novel polarity swapping to negate the cumulative effect of FEXT. Skew adjustment is used to improve the FEXT cancellation from polarity swapping. The polarity reversal location or locations among FEXT sources are optimized to achieve maximum FEXT cancellation. The novelty polarity swapping technique can be applied to a wide variety of connectors, such as mezzanine connectors, backplane connectors, and any other connectors that can benefit from FEXT reduction.
Owner:HIROSE ELECTRIC GROUP
Adaptive cancellation of multi-path interferences
ActiveUS8428542B2Minimize or eliminate unwanted signals arrivingEnhance degree of adaptive cancellationRadio transmissionIntegratorInterference canceller
A multi-path signal interference cancellation system cancels multiple time delayed signal components of a multi-path interference signal received by a receive antenna and carried on a receiver transmission line of a radio receiver system. The interference cancellation system includes a plurality of adaptive interference canceller circuits, each of which has a synchronous detector, a signal controller and an integrator as essential parts of closed control loops defined by the canceller circuits. The integrator has gain and bandwidth characteristics associated therewith which are adjustable to adjust the gain and bandwidth of each closed control loop. An intensity profile of the multi-path interference signal is generated and stored in a memory. An intensity profile signal from the memory is provided to the integrator of each adaptive interference canceller circuit to adjust the gain and bandwidth of the integrator and the loop in which it is situated to maximize the error detection residual signal-to-noise ratio of each adaptive interference canceller circuit. Each adaptive interference canceller circuit generates a cancellation signal from which a synthesized cancellation signal is generated and effectively injected onto the receiver transmission line to cancel the multiple time delayed signal components of the multi-path interference signal carried thereon so that the radio receiver of the radio receiver system only receives a desired signal.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
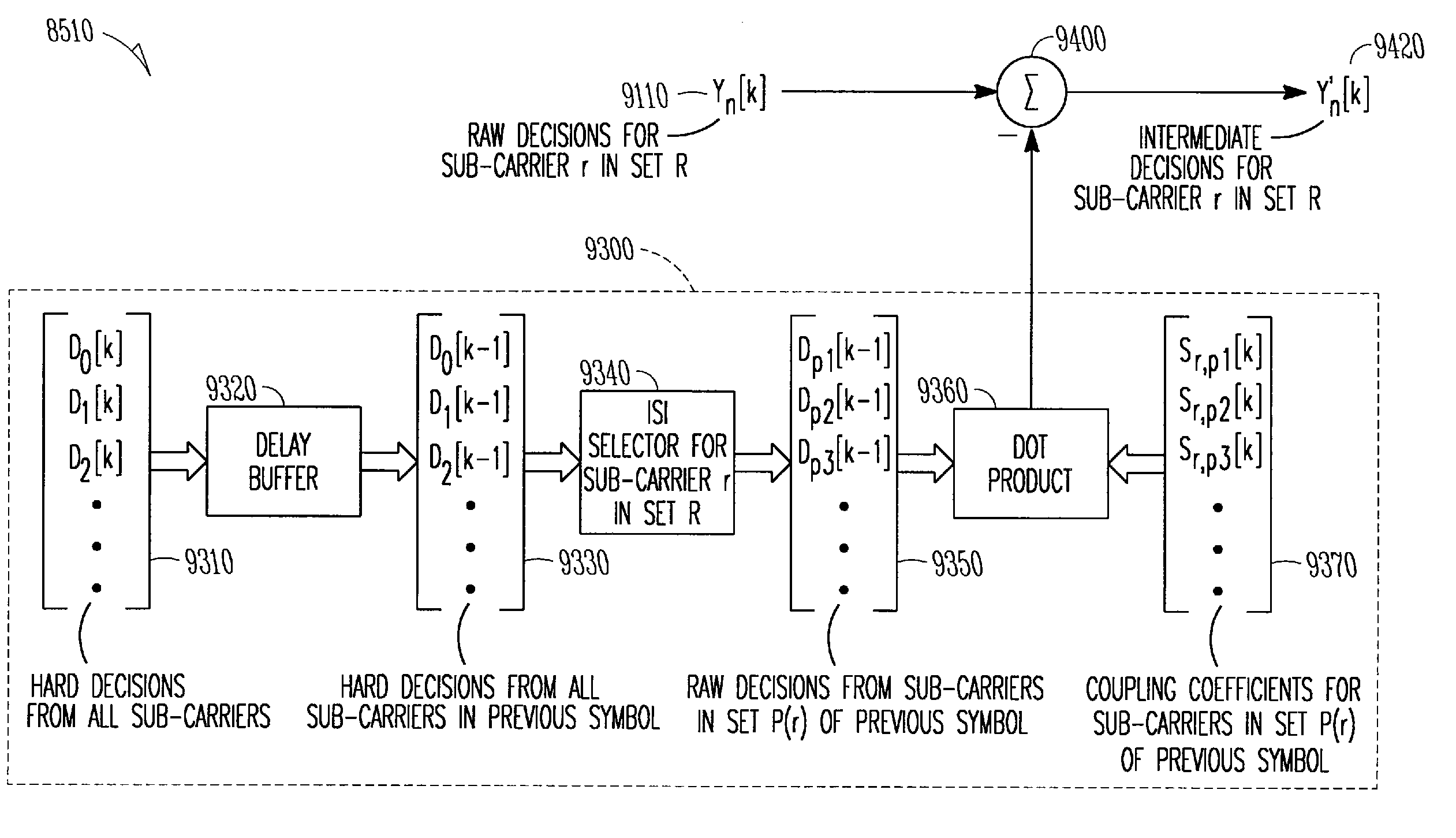
Low noise inter-symbol and inter-carrier interference cancellation for multi-carrier modulation receivers
ActiveUS20070053453A1Minimize cross-couplingEnhance cancellationError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionCarrier signalIntersymbol interference
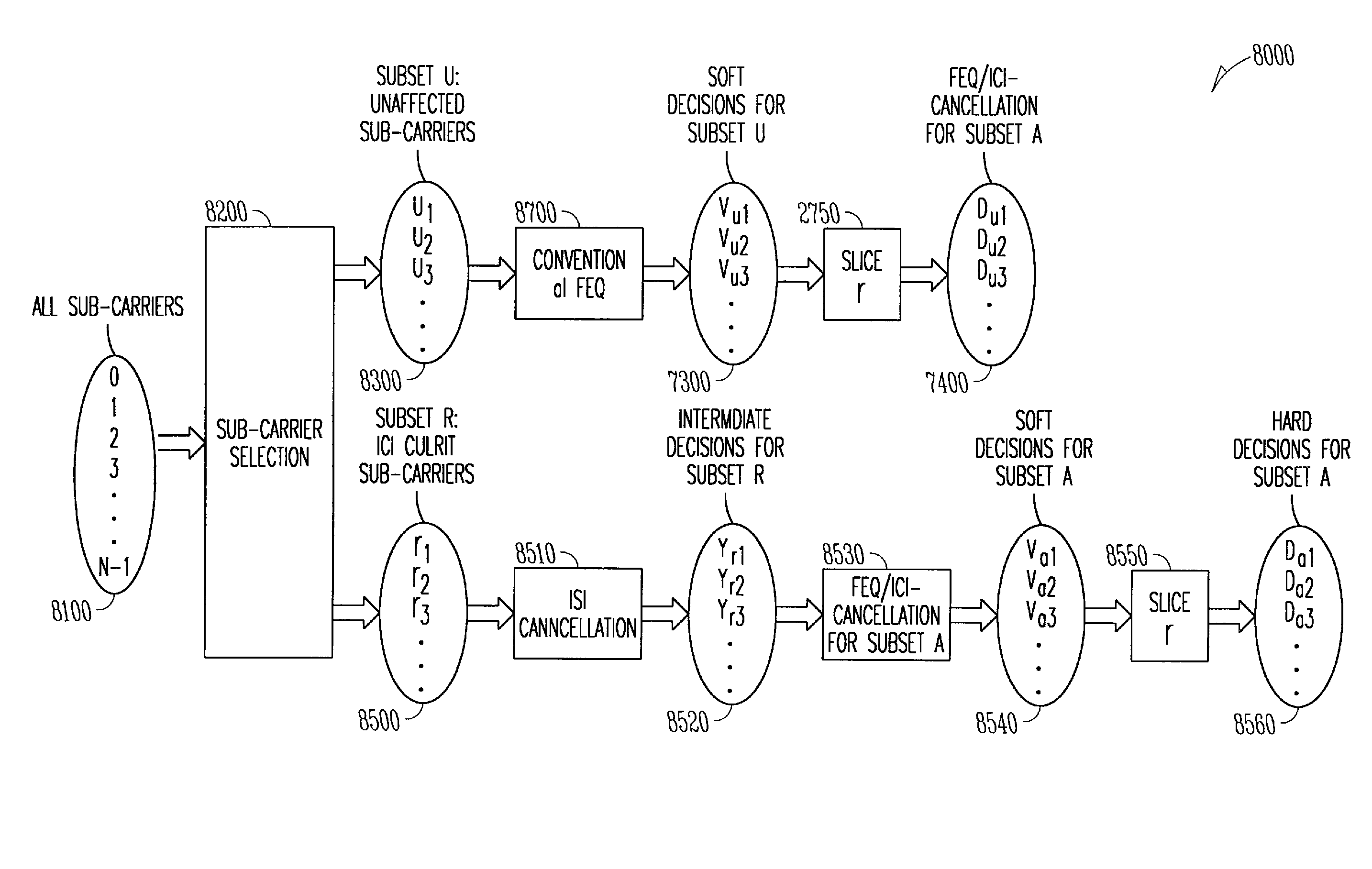
A MCM (multi-carrier modulation) receiver that utilizes a plurality sub-carriers (e.g., tones) to transmit information in a frame-by-frame manner. Identify a first subset of sub-carriers that have negligible ISI (inter-symbol interference) and ICI (inter-carrier interference), and a second subset of sub-carriers that ISI / ICI cancellation is needed to improve the performance. For sub-carriers in the first subset, conventional equalization is performed to obtained soft decisions. For those sub-carriers in the second subset, perform ISI cancellation then ICI cancellation along with equalization. For sub-carriers in the second subset, identify a series of third subsets (one for each of the sub-carriers in the second subset) that cause interference to the sub-carriers in the second set. For sub-carriers in the third subset, identify a series of fourth subsets from a previous frame that cause interference to the sub-carriers in the third set. For each element in the third subset, perform ISI cancellation to eliminate the interference from the elements in the fourth subset from the previous frame to obtain a plurality of intermediate decisions. For each element in the second subset, perform a combined equalization and ICI cancellation using said intermediate decisions. The selection of the first subset, the second subset, the third subset, and the fourth subset are based on examining the frequency response of the communication channel.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
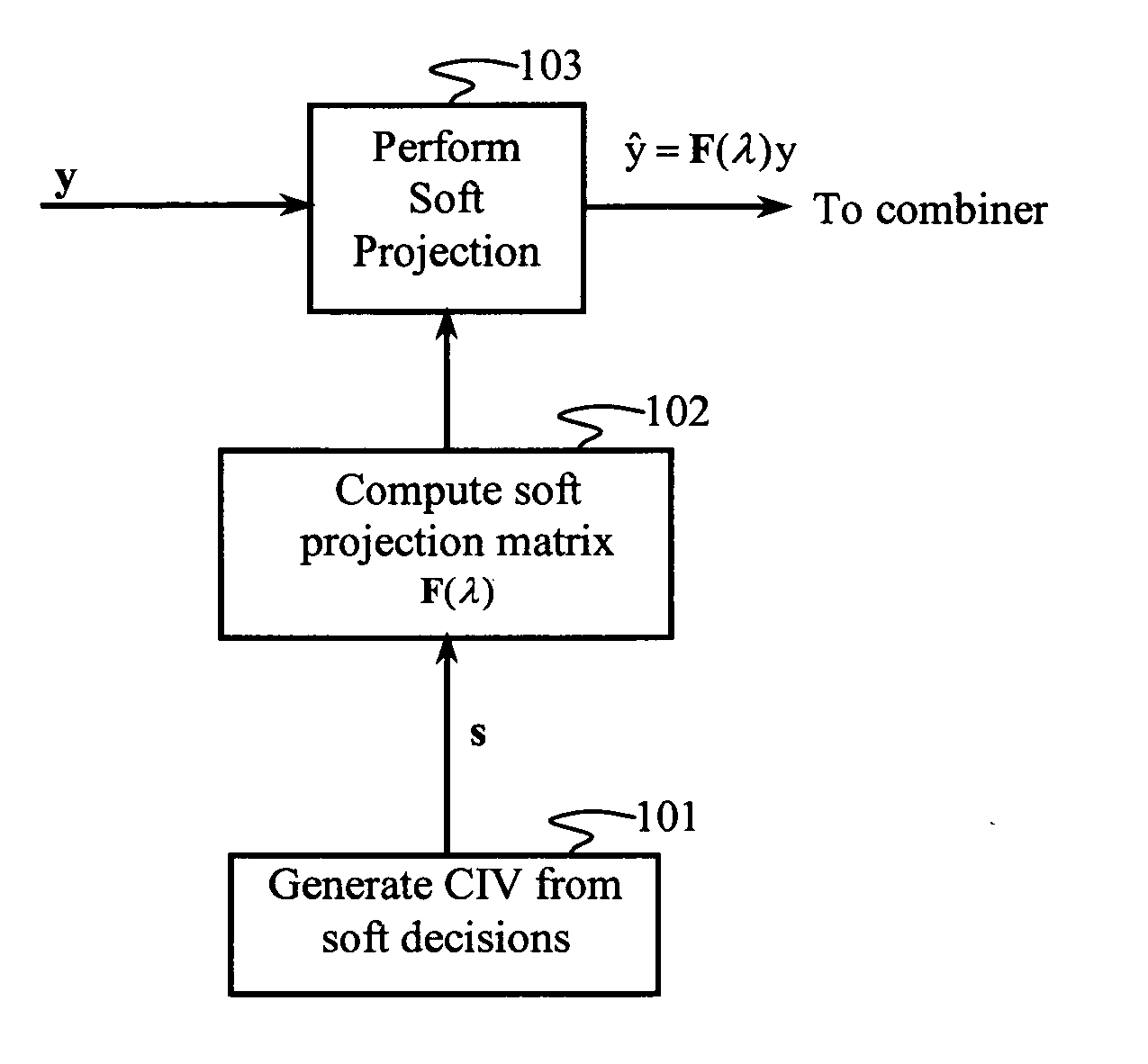
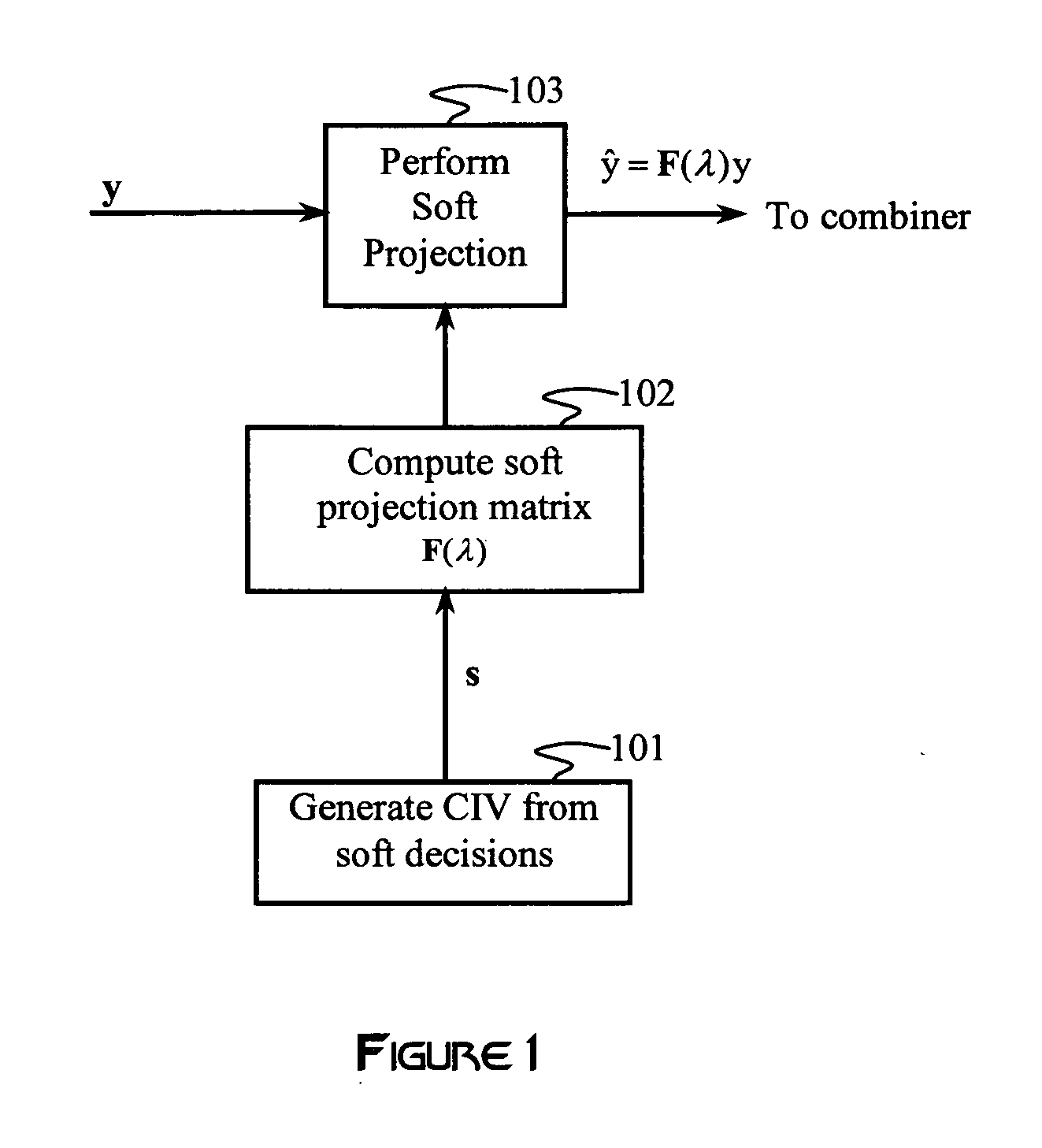
Variable interference cancellation technology for CDMA systems
ActiveUS20060227730A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioCancel improvementAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRadio transmissionInterference cancellerInterference cancelation
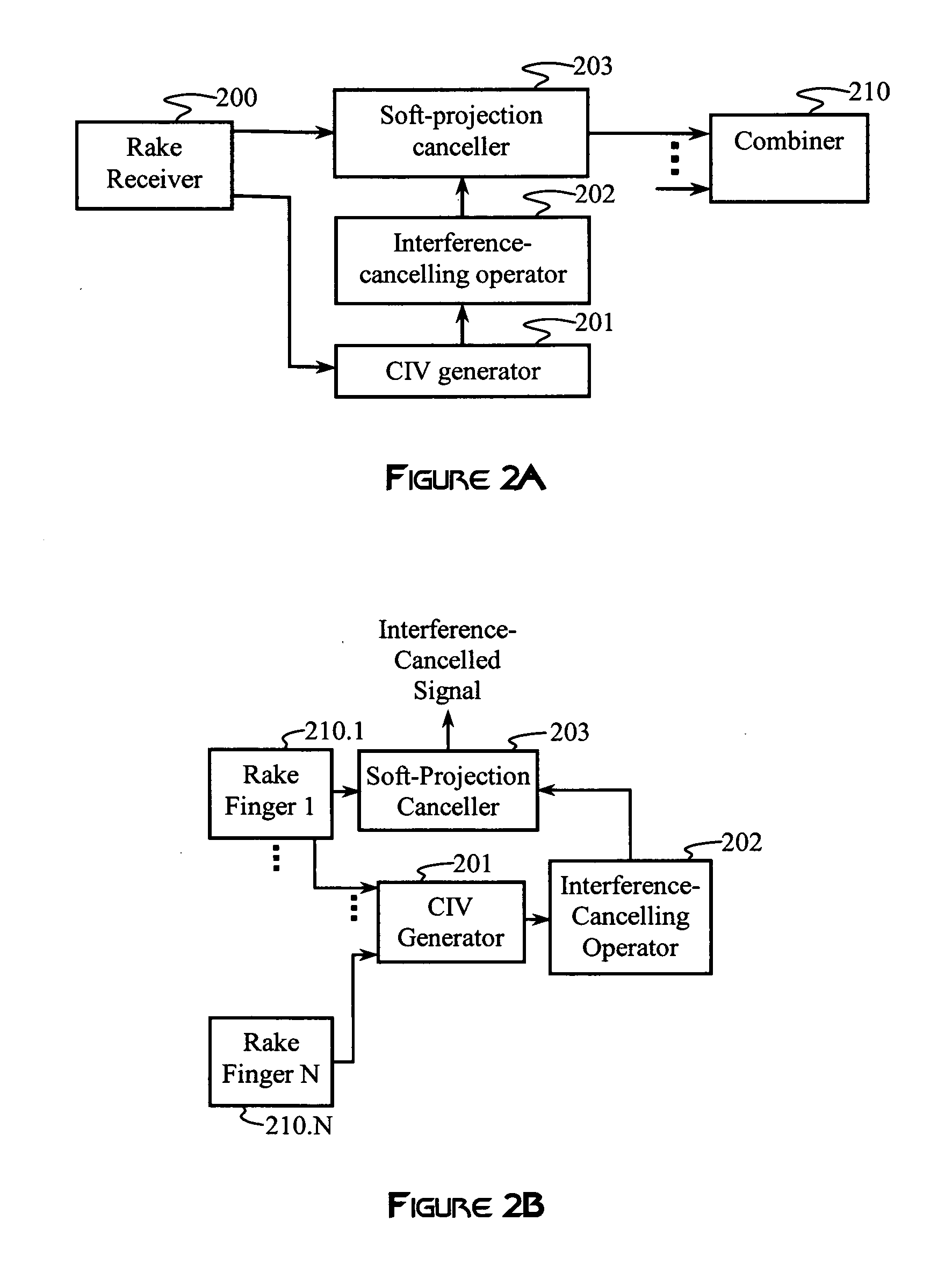
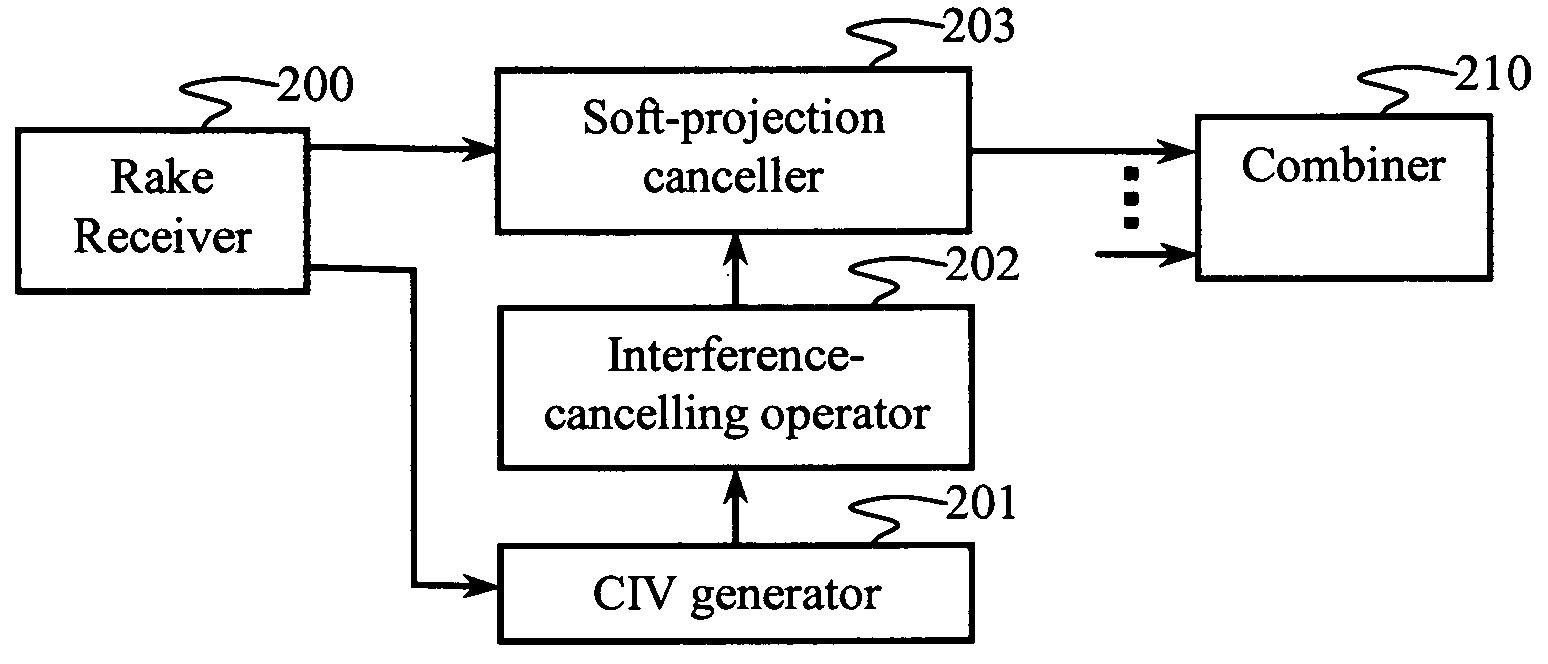
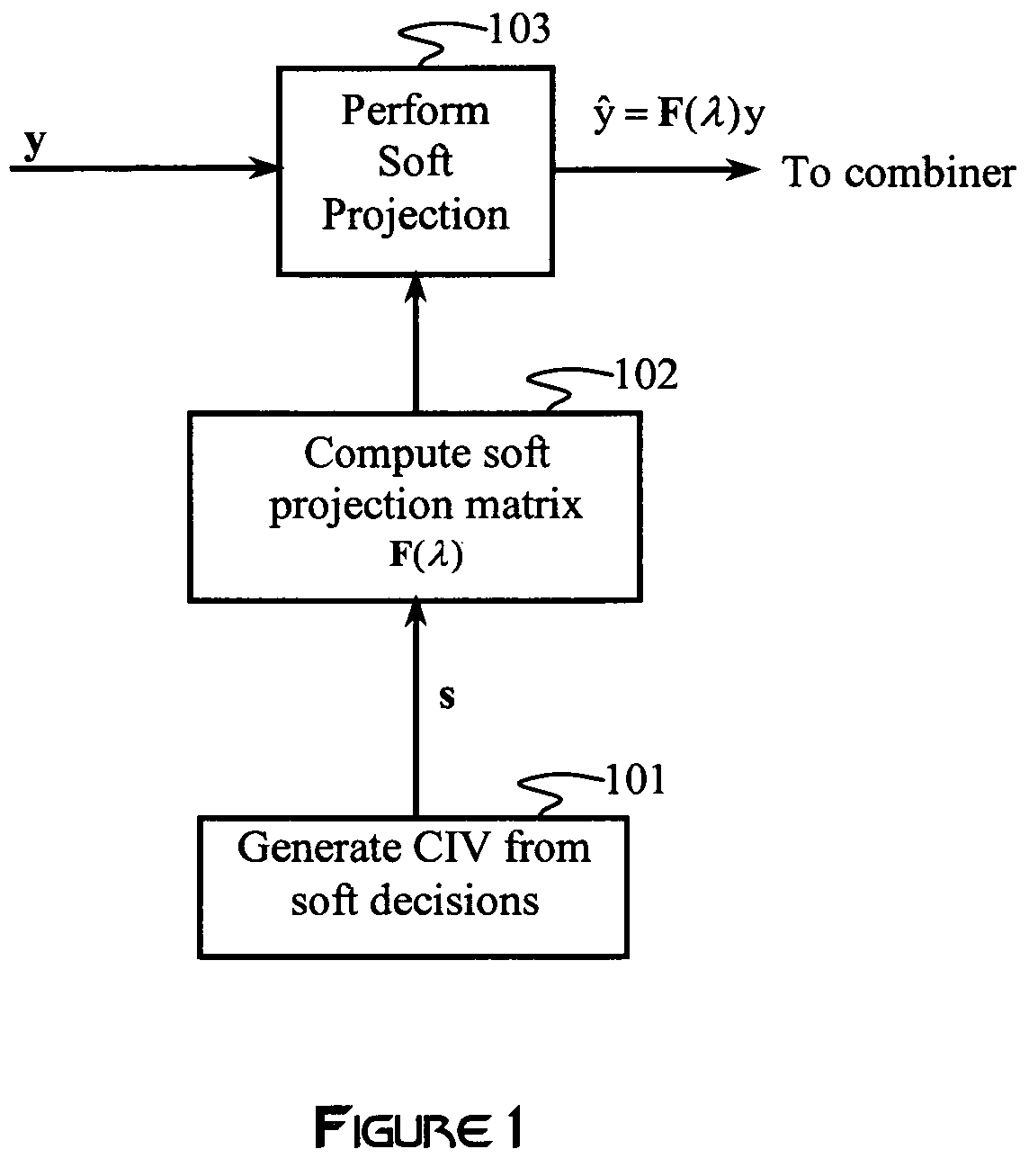
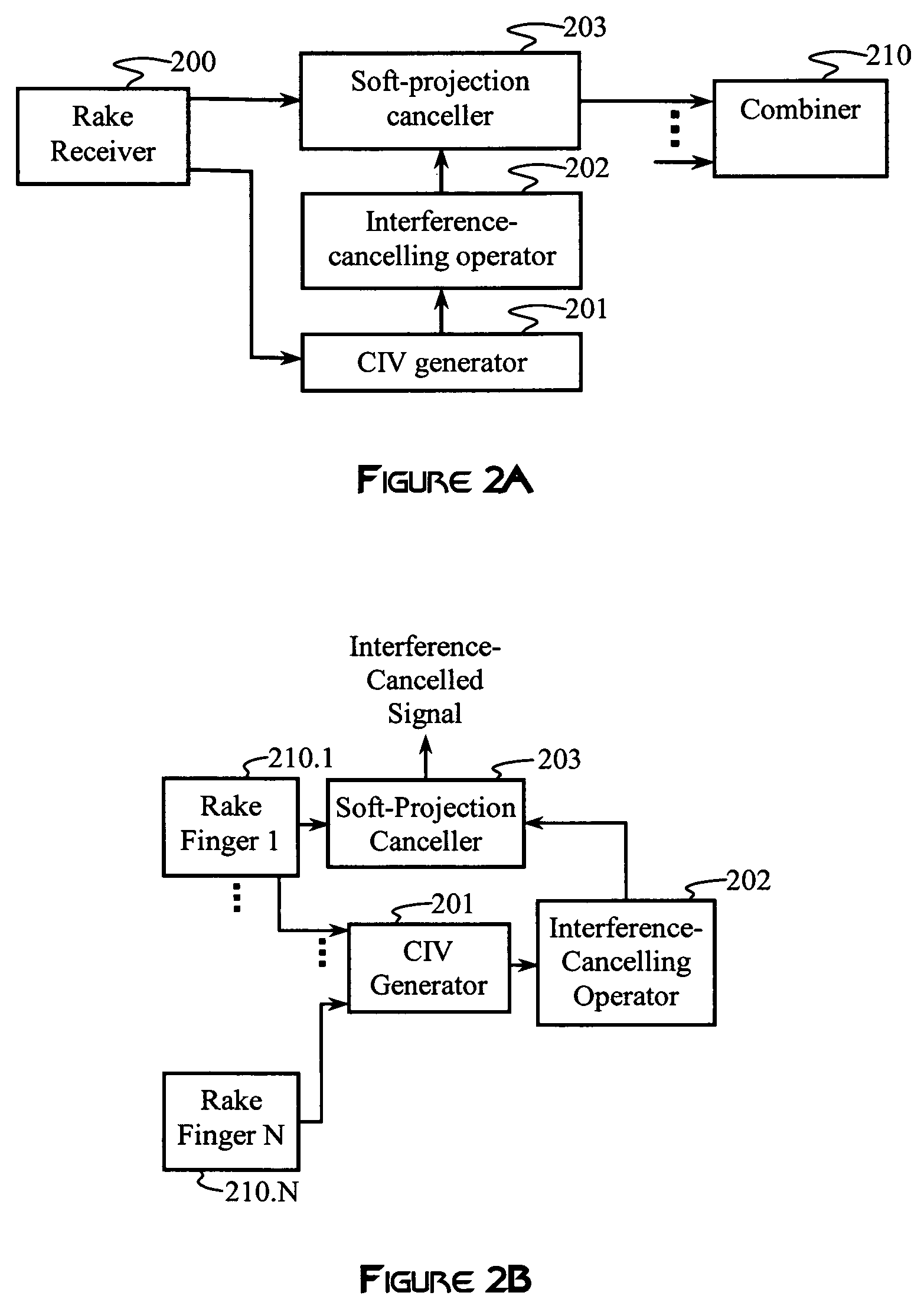
An interference canceller comprises a composite interference vector (CIV) generator configured to produce a CIV by combining soft and / or hard estimates of interference, an interference-cancelling operator configured for generating a soft-projection operator, and a soft-projection canceller configured for performing a soft projection of the received baseband signal to output an interference-cancelled signal. Weights used in the soft-projection operator are selected to maximize a post-processing SINR.
Owner:III HLDG 1
Variable interference cancellation technology for CDMA systems
InactiveUS7808937B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioCancel improvementAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRadio transmissionInterference cancellerInterference cancelation
An interference canceller comprises a composite interference vector (CIV) generator configured to produce a CIV by combining soft and / or hard estimates of interference, an interference-cancelling operator configured for generating a soft-projection operator, and a soft-projection canceller configured for performing a soft projection of the received baseband signal to output an interference-cancelled signal. Weights used in the soft-projection operator are selected to maximize a post-processing SINR.
Owner:III HLDG 1
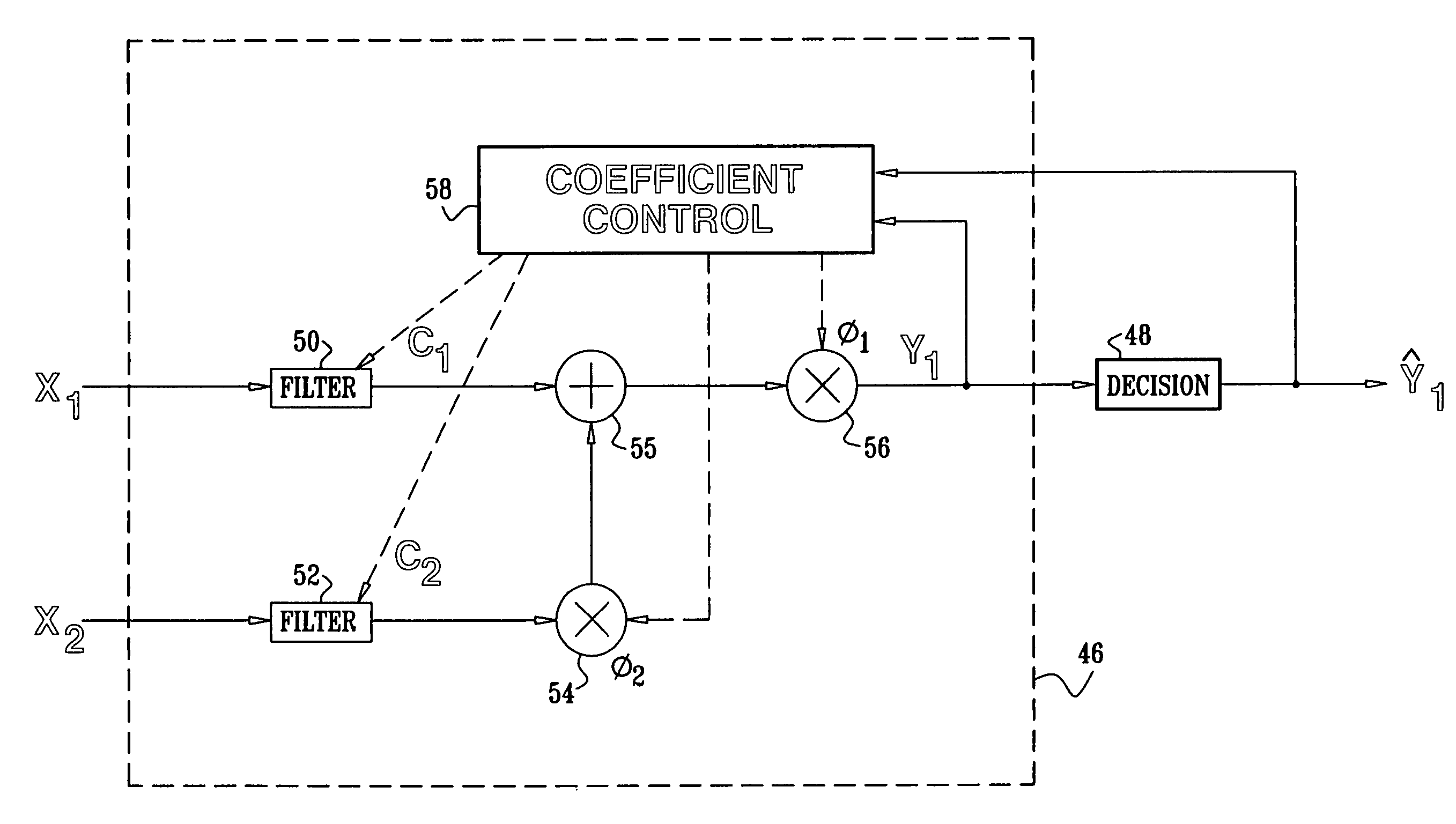
Interference canceller with fast phase adaptation
ActiveUS7046753B2InterferenceReduce distractionsSpatial transmit diversityError preventionInterference cancellerPhase shifted
A receiver includes an input circuit, which is coupled to at least one antenna so as to receive, process and digitize first and second signals, thus generating first and second streams of input samples. An interference cancellation circuit includes first and second processing chains, which are reaspectively coupled to filter the first and second streams of input samples using respective first and second adaptive coefficients to generate respective first and second filter outputs, at least one of the first and second processing chains being further adapted to apply a variable phase shift so as to compensate for a phase deviation between the first and second signals. An adder sums the first and second filter outputs so as to generate a third stream of output samples, which is representative of the first signal. A coefficient controller is operative to set the first and second adaptive coefficients and to separately set the variable phase shift responsively to the output samples.
Owner:MAXLINEAR ISRAEL LTD
Frequency domain decision feedback equalizer
InactiveUS7418035B1Cancel improvementImprove signal-to-noise ratioMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTime domainRound complexity
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
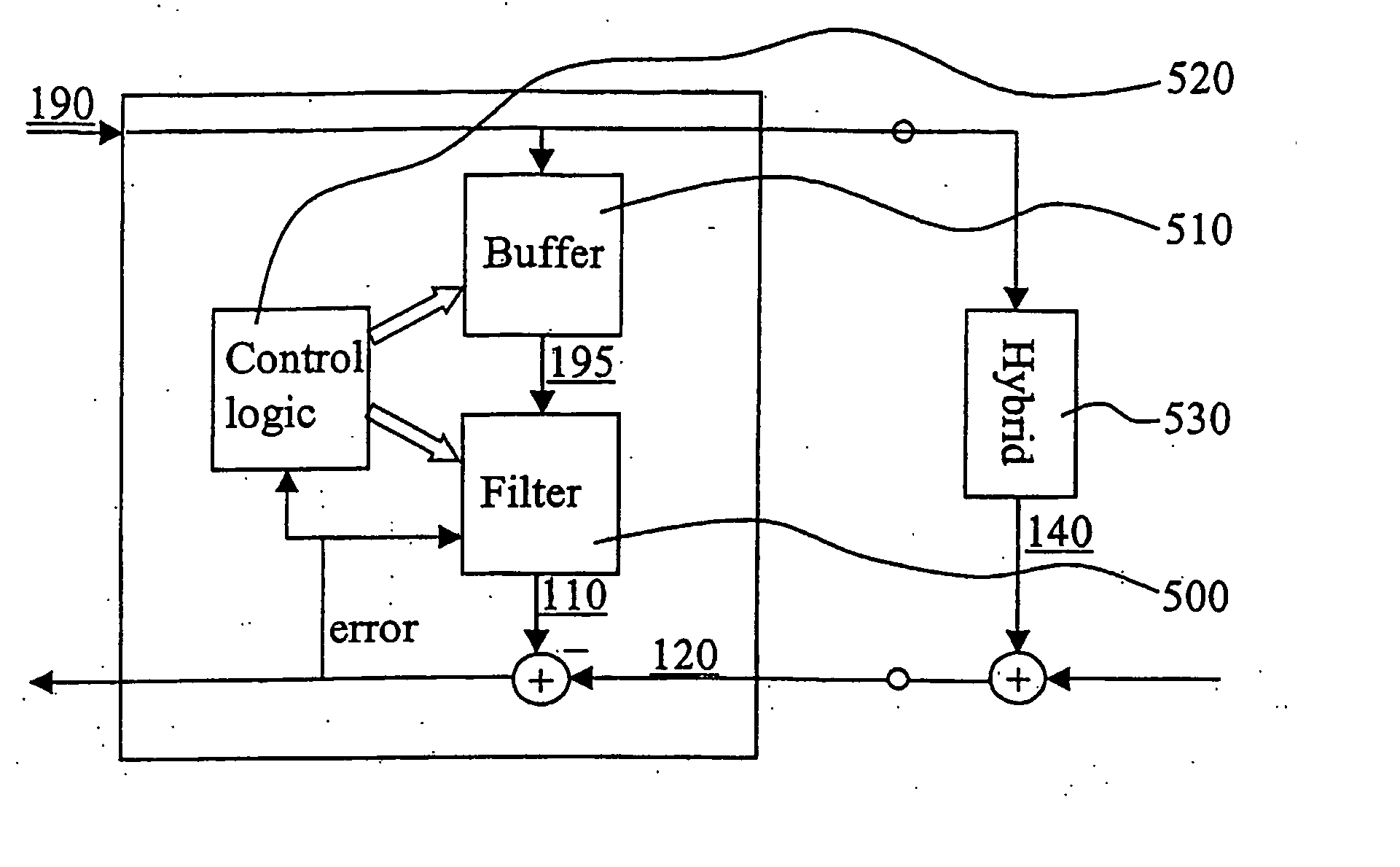
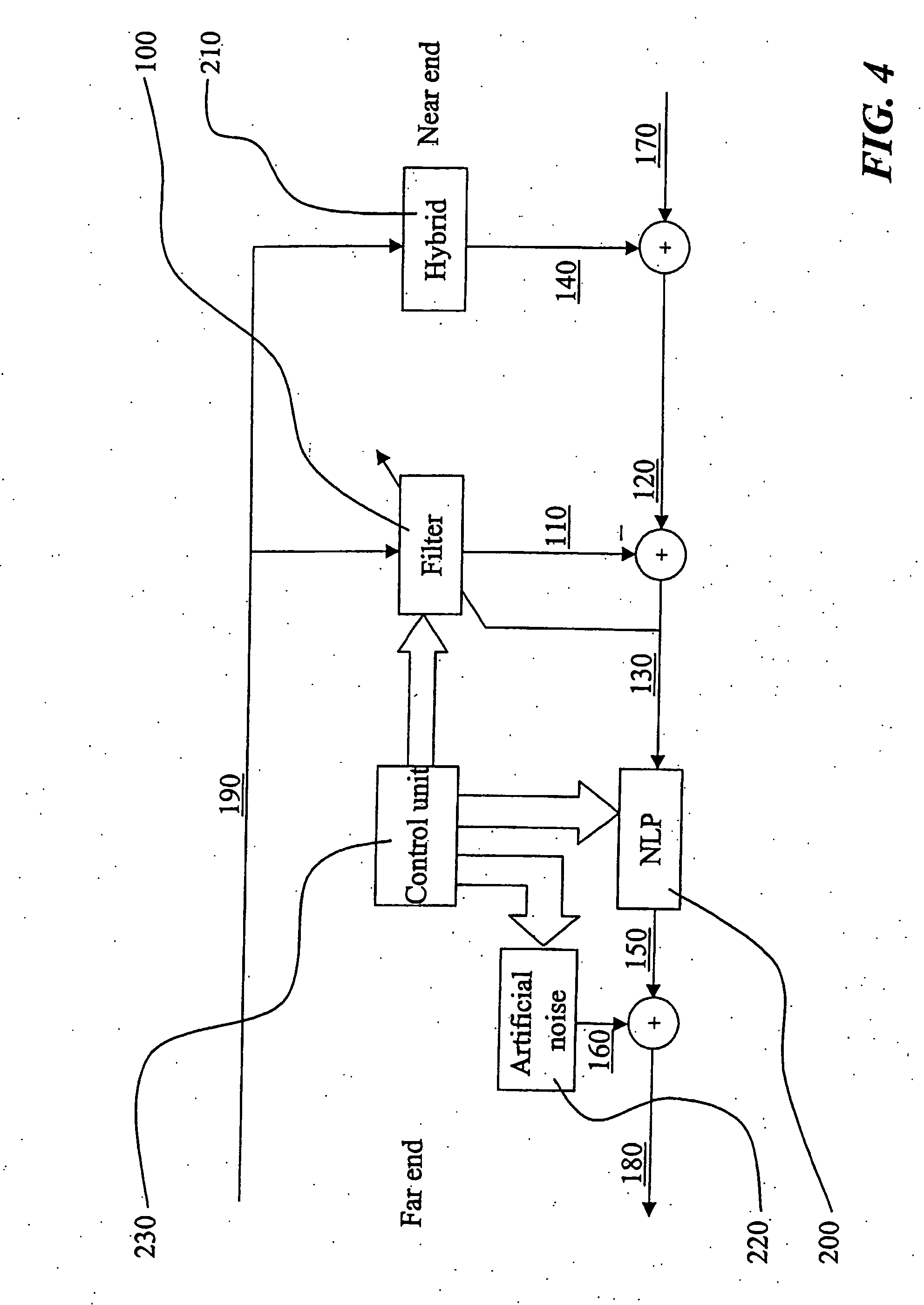
Echo cancellation
ActiveUS20050220043A1Cancel improvementImprove resolutionTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsLine-transmissionPath delayEngineering
The present invention relates to a cancellation of echoes in telecommunications systems, more specifically it relates to adaptive alignment of a linear filter (500) used for echo cancellation. According to the invention, it is continuously determined, by means of control logic (520), if a reflection replica delay included in an echo replica signal (110), which delay is provided by a signal buffer (510), should be attempted to be increased or not. Similarly, it is continuously determined if the reflection replica delay should be attempted to be decreased or not. In this way it is possible to provide a delay of the reflection replica which corresponds to the pure delay of a corresponding reflection included in an echo signal (120) received over an echo path. The invention is advantageous since the filter (500) will continuously and quickly adapt to changes in the echo path delay by continuously increasing or decreasing, in an incremental and smooth manner, a present replica delay.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
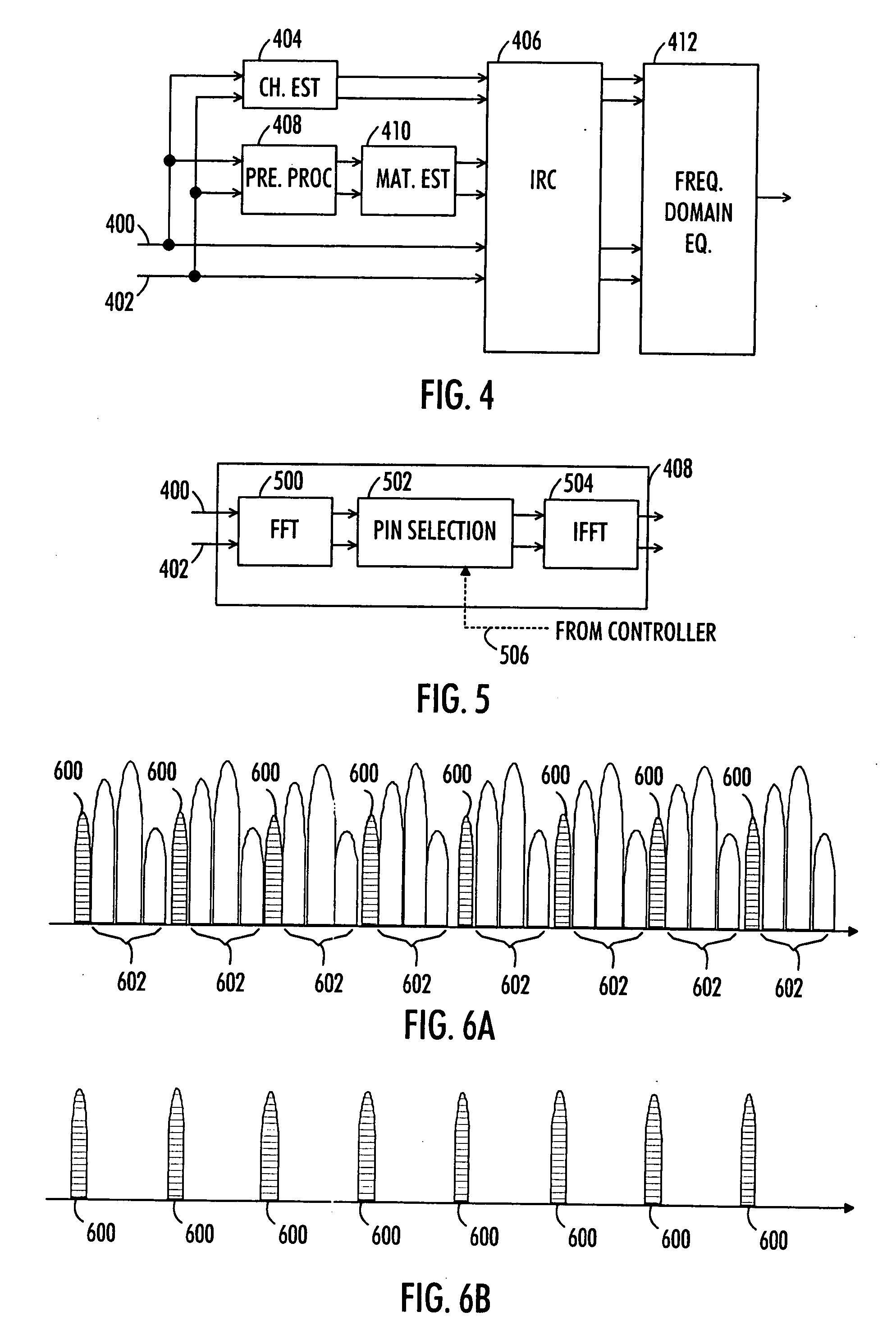
Interference cancellation unit and interference cancellation method
ActiveUS20080025200A1Enhances interference cancellationExtra lossError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionInterference cancelationEngineering
An interference cancellation unit having as an input two or more IFDMA signals comprising a multitude of frequency bins is provided. The unit comprises a channel estimator for determining a channel estimate from the input signals, a matrix calculator for determining an error covariance matrix of the input signals, and an estimator for determining weight factors on the basis of the channel estimate and the error covariance matrix and weighting and combining the input signals. The unit further comprises a preprocessor for removing unwanted frequency bins from the input signals prior to the error covariance calculation.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Interference canceller with fast phase adaptation
ActiveUS20050286665A1InterferenceReduce distractionsSpatial transmit diversityError preventionPhase shiftedInterference canceller
A receiver includes an input circuit, which is coupled to at least one antenna so as to receive, process and digitize first and second signals, thus generating first and second streams of input samples. An interference cancellation circuit includes first and second processing chains, which are reaspectively coupled to filter the first and second streams of input samples using respective first and second adaptive coefficients to generate respective first and second filter outputs, at least one of the first and second processing chains being further adapted to apply a variable phase shift so as to compensate for a phase deviation between the first and second signals. An adder sums the first and second filter outputs so as to generate a third stream of output samples, which is representative of the first signal. A coefficient controller is operative to set the first and second adaptive coefficients and to separately set the variable phase shift responsively to the output samples.
Owner:MAXLINEAR ISRAEL LTD
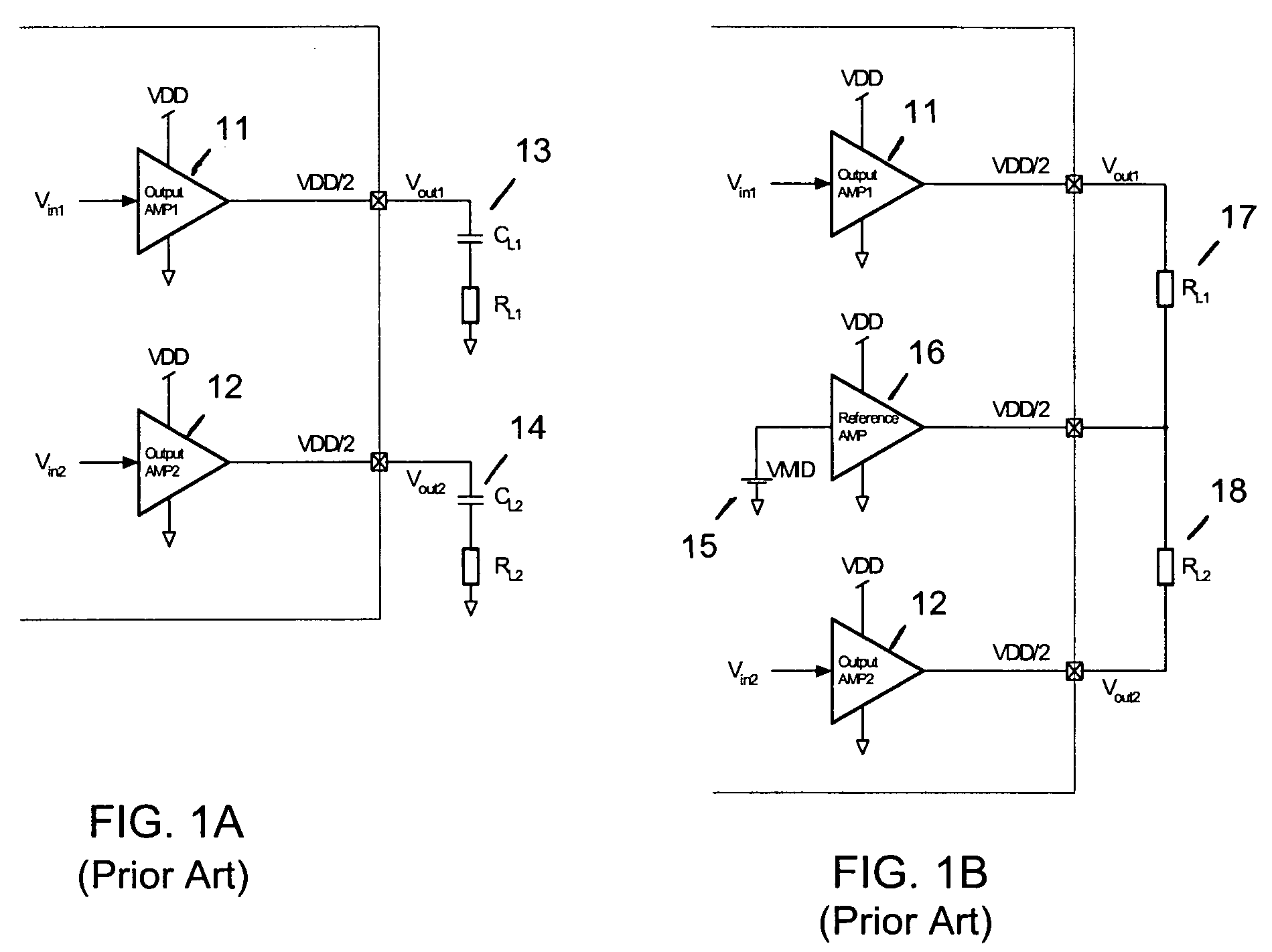
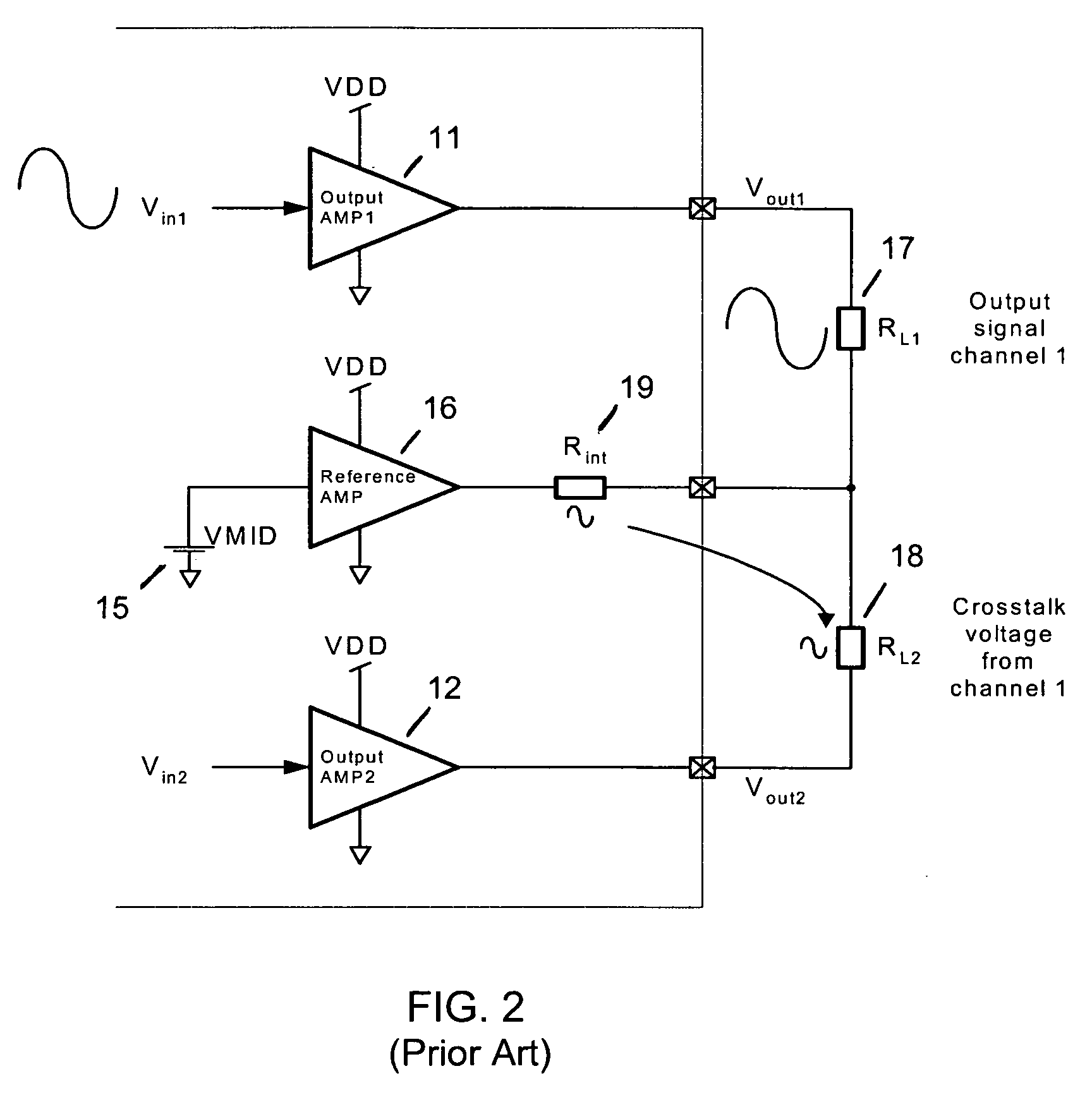
Crosstalk cancellation using load impedence measurements
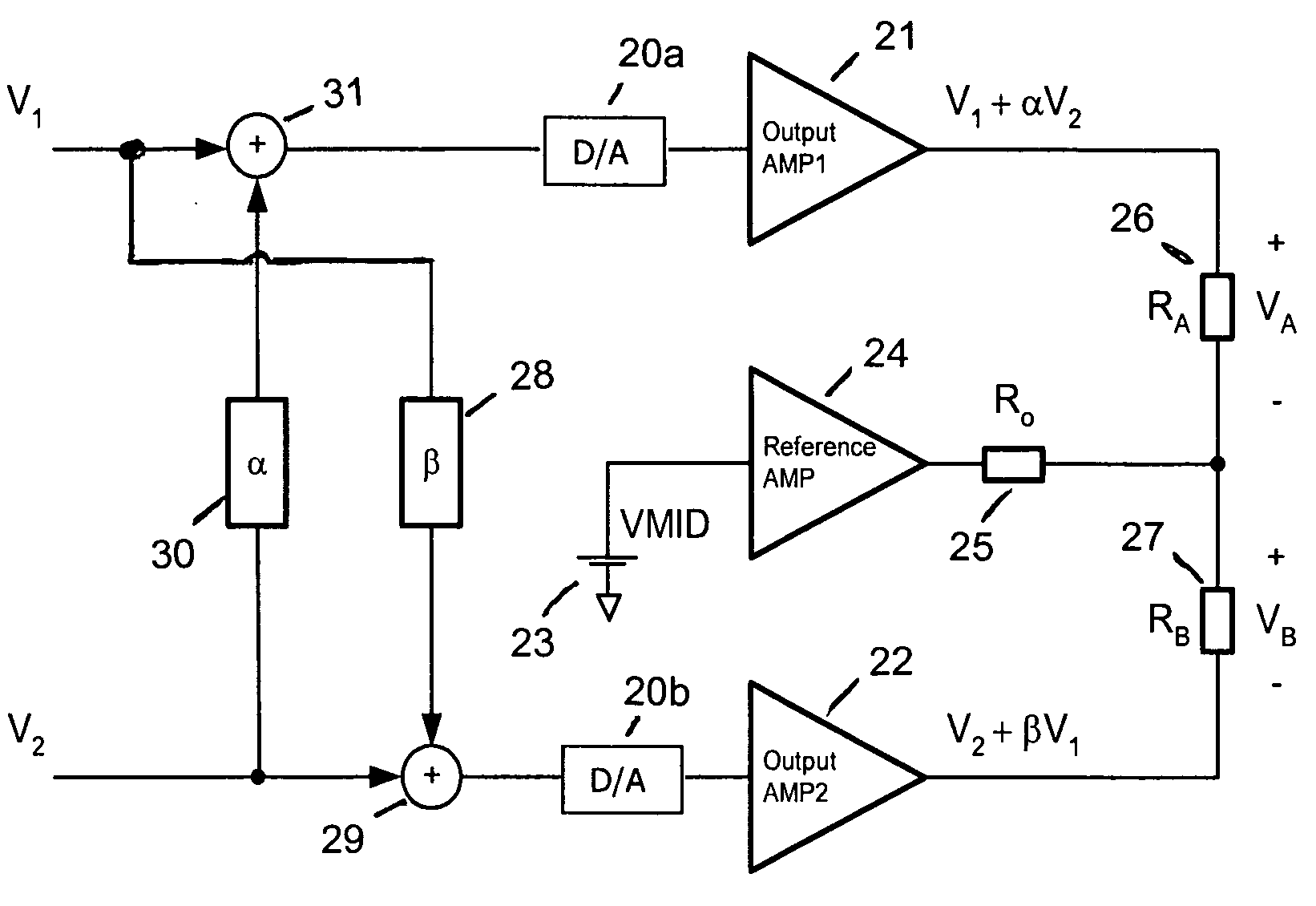
ActiveUS20080008325A1Low costCancel improvementHeadphones for stereophonic communicationBroadcast circuit arrangementsCrosstalk cancellationAudio power amplifier
A method and ASIC for canceling crosstalk between a first stereo channel and a second stereo channel, wherein a first signal is input to a first output amplifier for the first channel, and a second signal is input to a second output amplifier for the second channel, and an output load for each output amplifier is connected between each output amplifier and a reference amplifier. In one embodiment, the first and second signals are split prior to inputting the signals to the first and second output amplifiers, and a gain-adjusted portion of each signal is added to the other signal on the inputs of the output amplifiers. In another embodiment, the first and second input signals are again split into two paths each. While a first path of each signal is inputted to each signal's respective output amplifier, the second paths of the first and second signals are adding together. The resulting sum is adjusted by a gain function, biased by a suitable DC voltage, and input to the reference amplifier.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
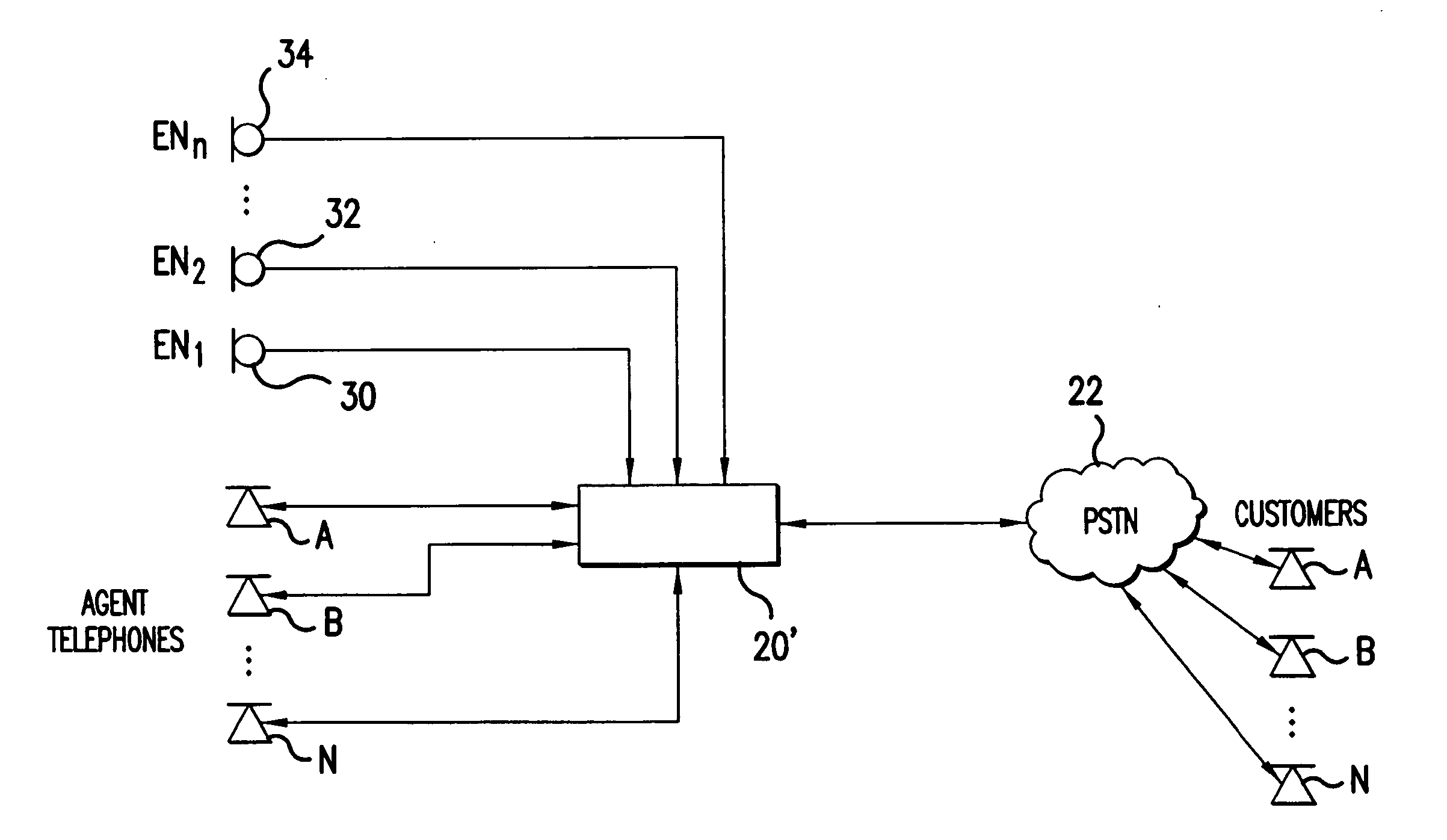
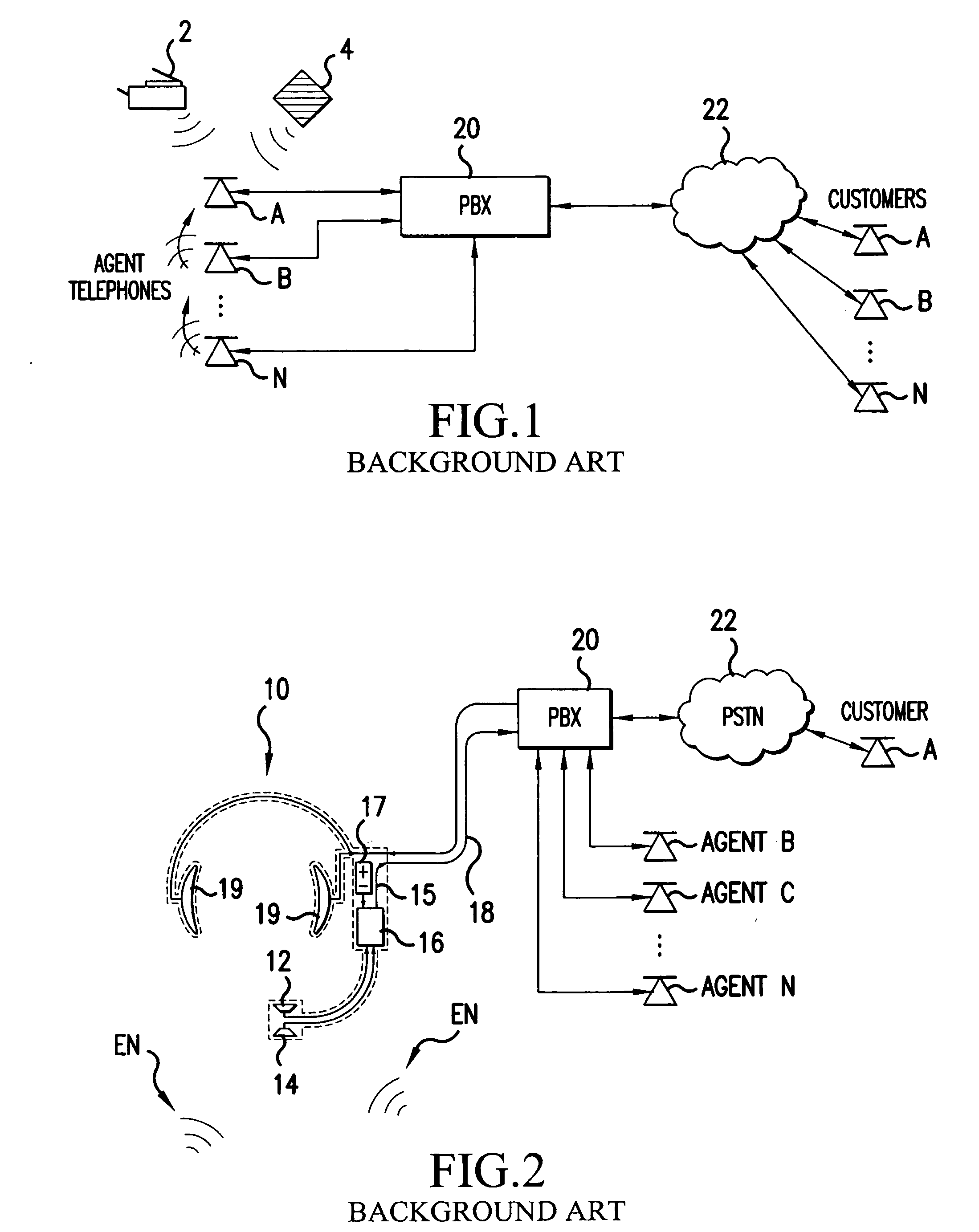
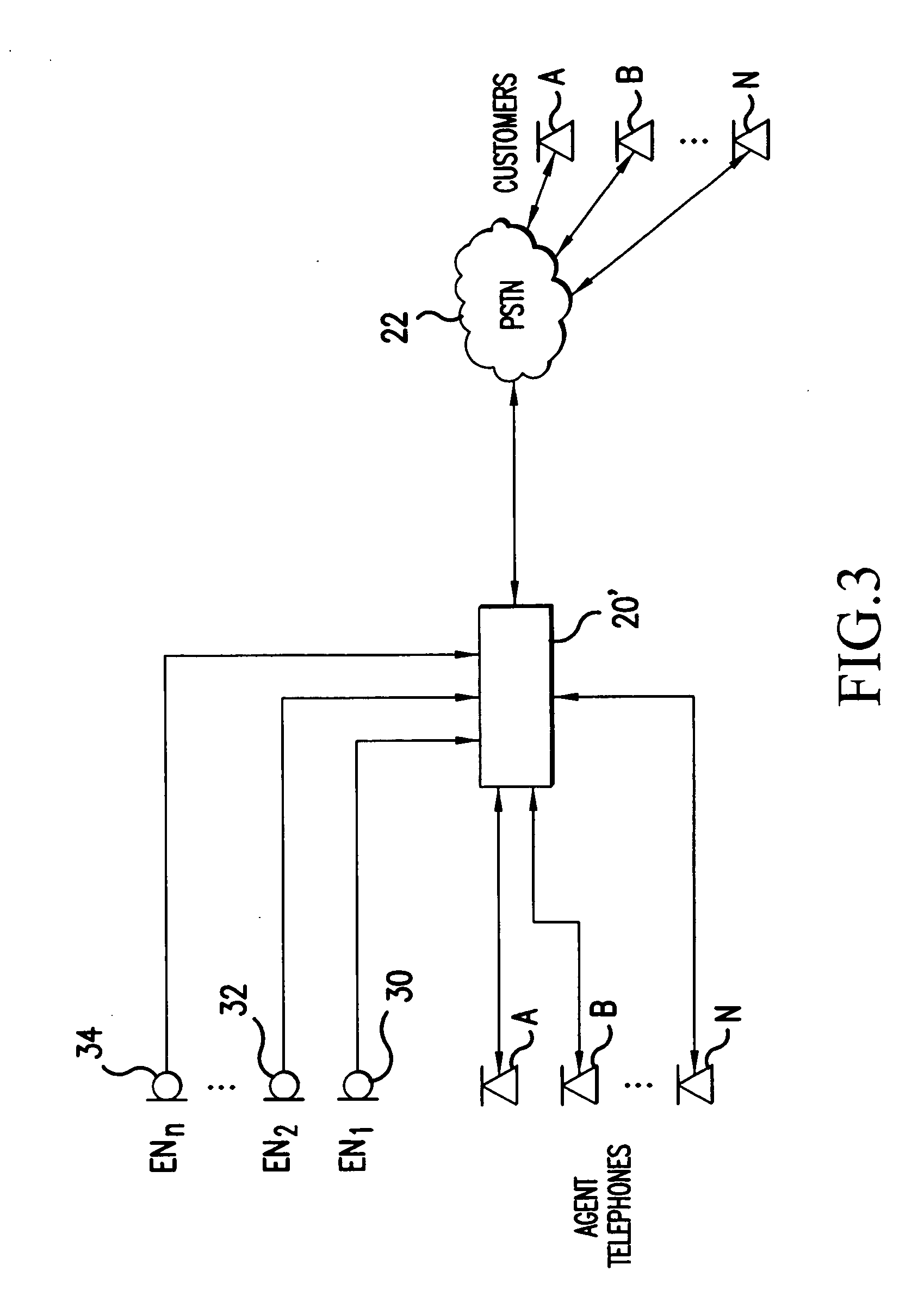
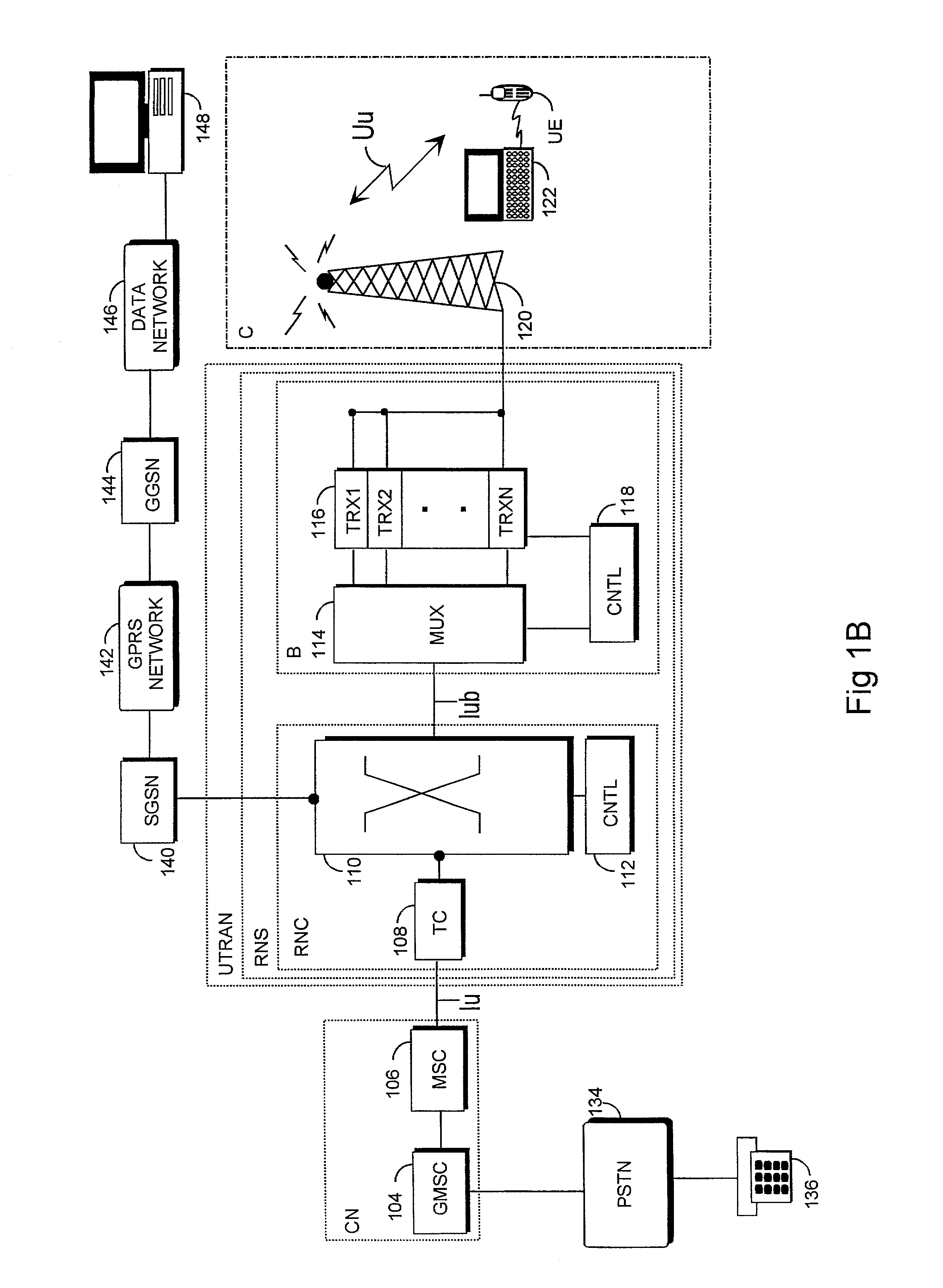
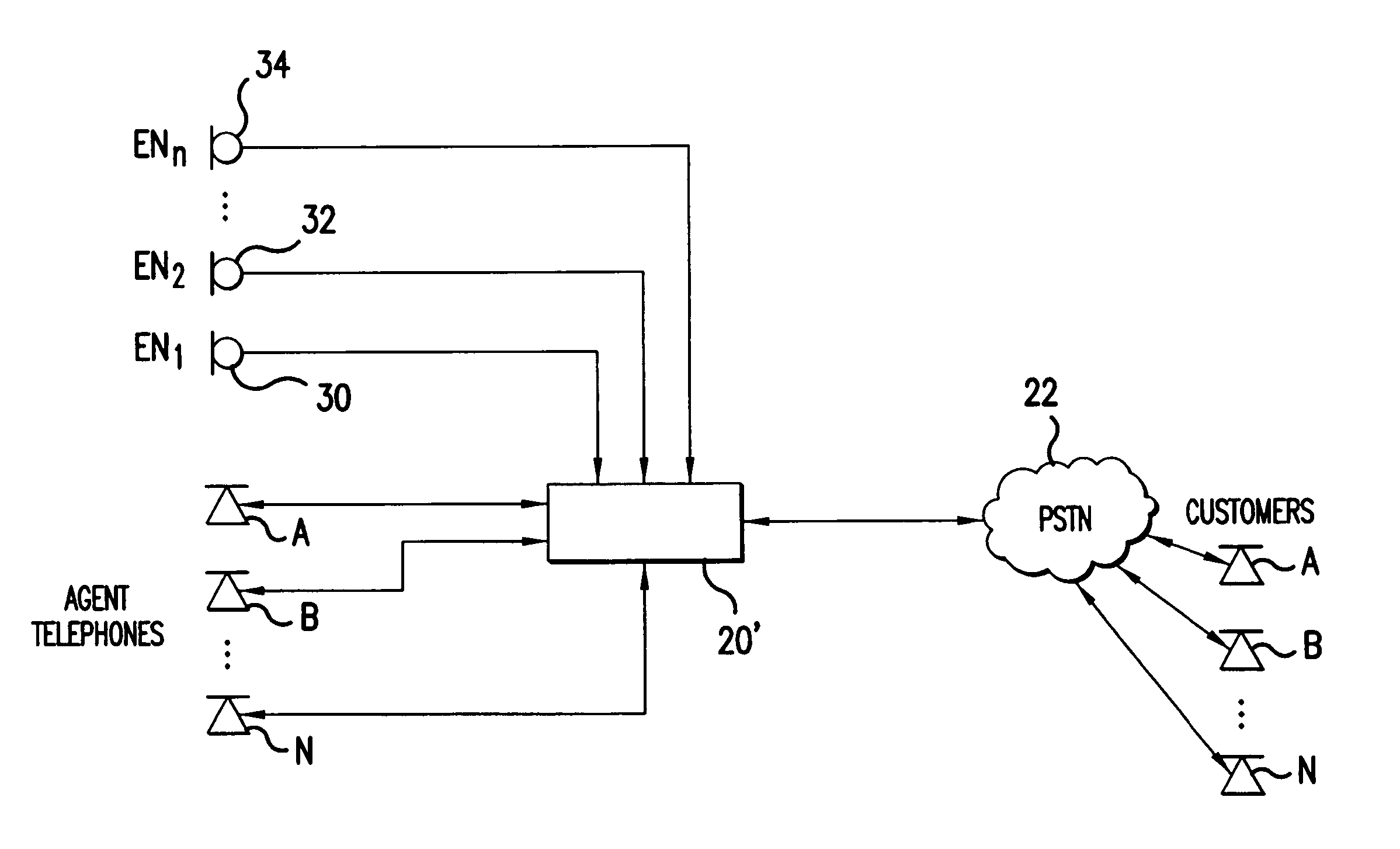
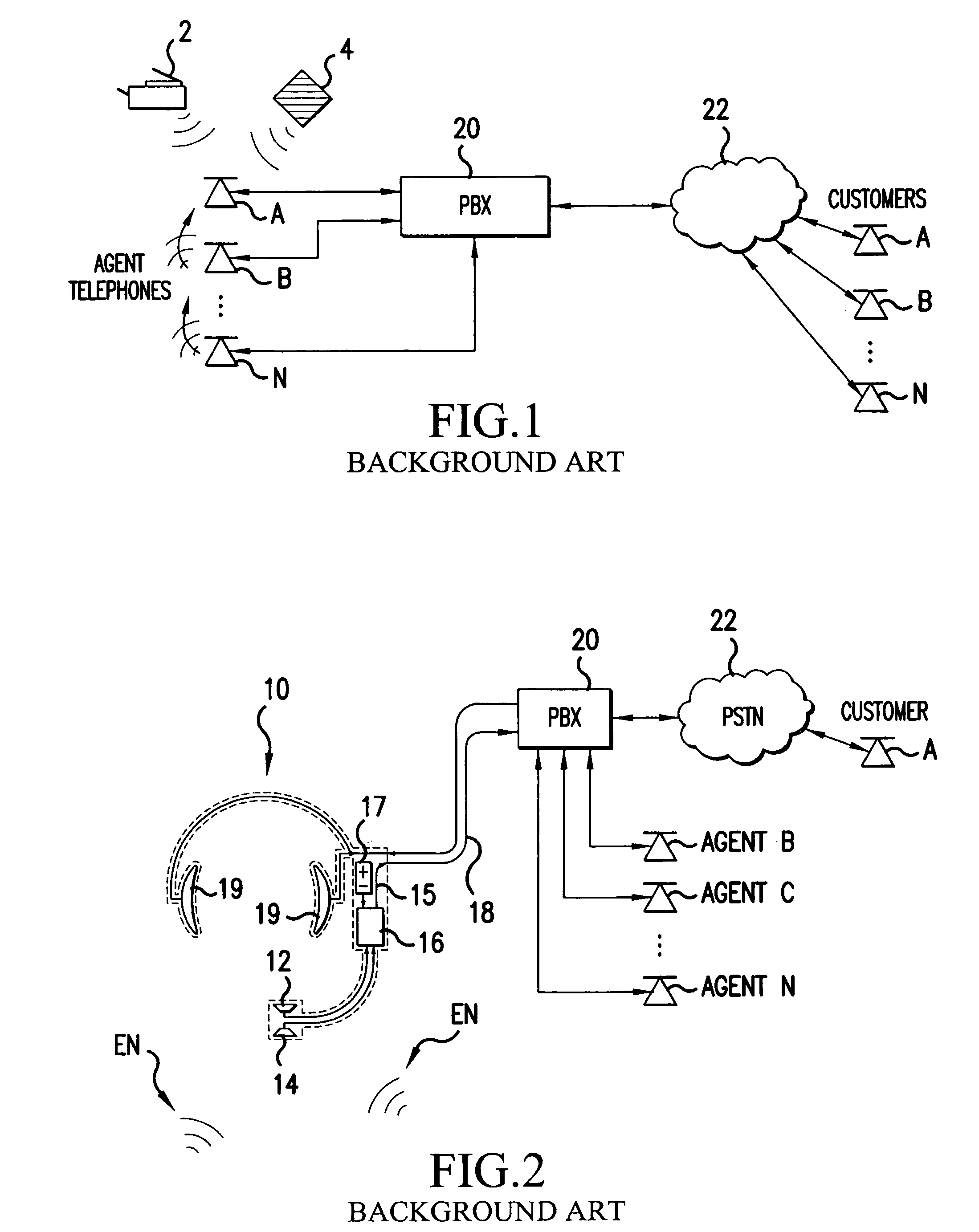
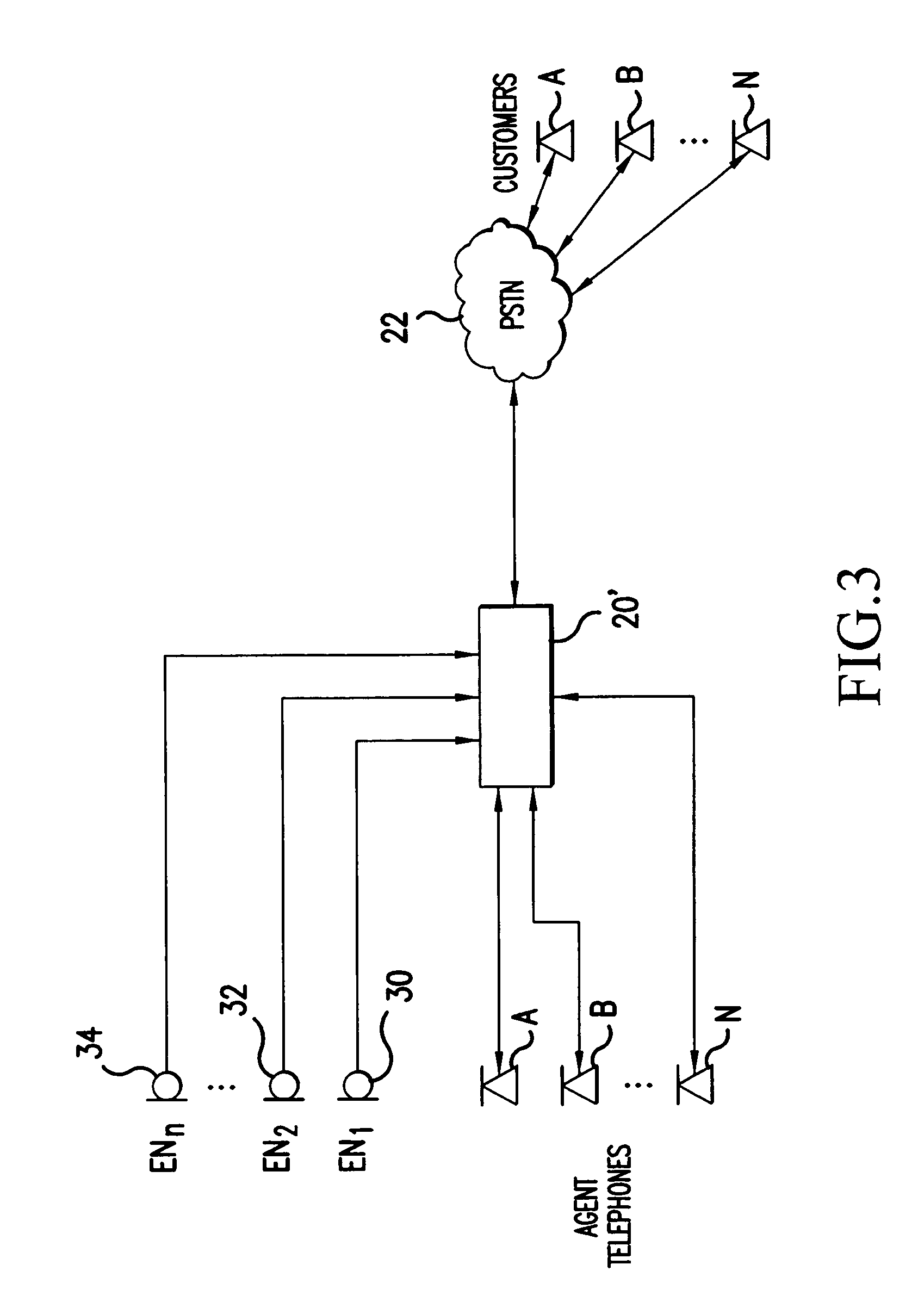
Speech canceler-enhancer system for use in call-center applications
ActiveUS20070237336A1Cancel improvementImprove integrity and qualityMicrophonesEar treatmentHVACMicrophone
A call-center has agents using headsets, which are connected to a private business exchange (PBX). Noise cancellation occurs in a noise filter, within or connected to the PBX. Noise cancellation for a particular agent's conversation is achieved by receiving the voice signals from neighboring agents' headsets and by using adaptive noise cancellation in the noise filter to remove the other agents' conversations from the particular agent's conversation. Microphones may also be placed at other noise sources, such as HVAC equipment, so that offending noises are accurately received at the noise filter and removed from the agents' conversations.
Owner:AVAYA INC
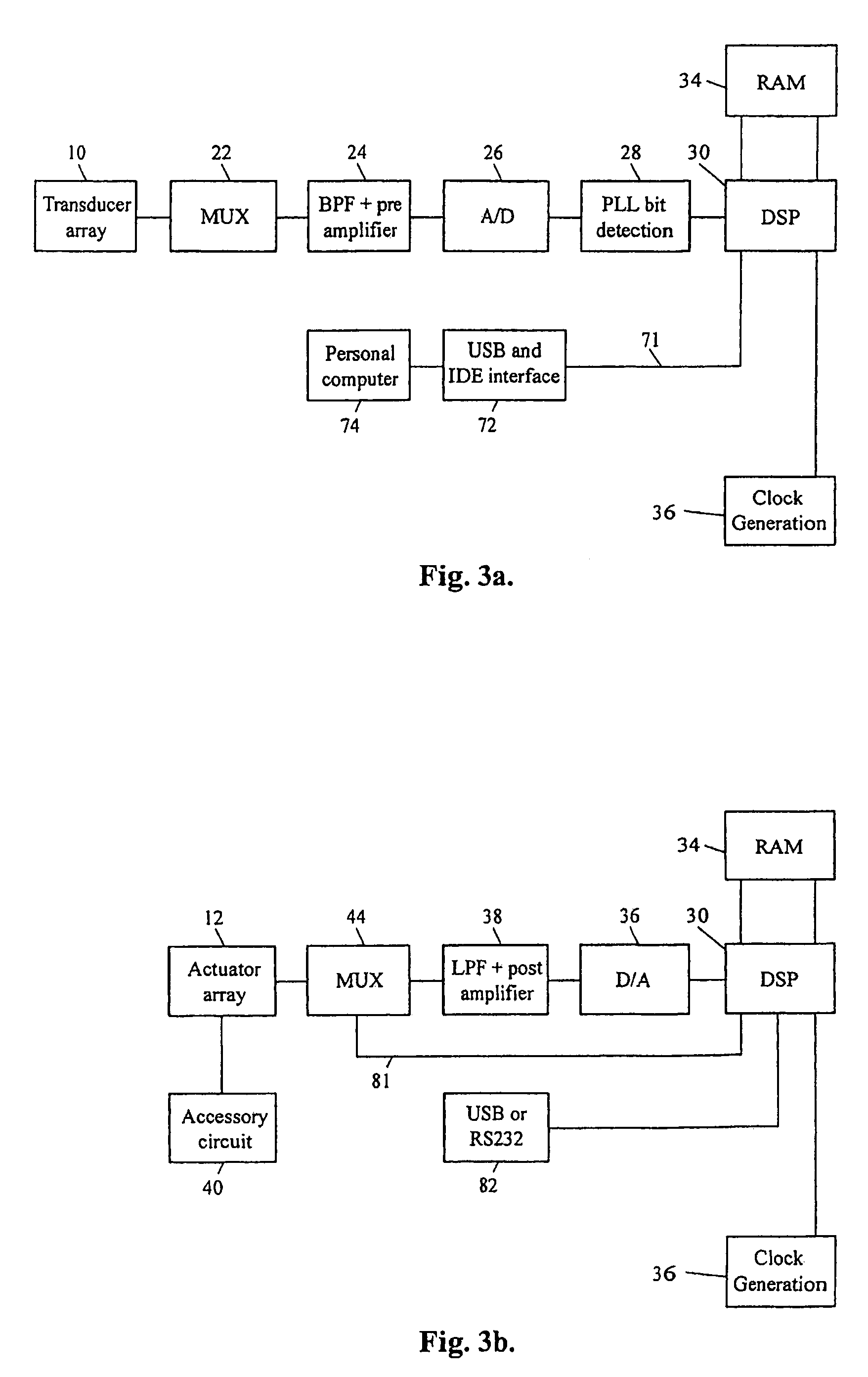
Method and apparatus for controlling repetitive nervous system malfunction
InactiveUS7177694B2Reduce unwanted movementCancel improvementElectrotherapyArtificial respirationDiseaseNervous system
An apparatus and method for controlling the symptoms of repetitive nervous system malfunction in a person such as the symptoms of Parkinson's disease and other ailments which create unwanted movement of a part of the person's body. The apparatus includes a support member to be worn on or in close proximity to a part of a patient's body effected by malfunction. The support member includes an actuator array for applying output signals to the part of the patient's body to cancel out pulse signals caused by the malfunction, to at least reduce unwanted movement of the part of patient's body. The actuator array preferably includes skin contact devices. In one embodiment the apparatus includes a detector for detecting pulses produced by the patient and which create the unwanted movement. Processing means may be used to produce an output signal which cancels those pulses. A method of treating the symptoms of repetitive nervous system malfunction is also provided.
Owner:WONDERTAP
System and method for subband beamforming using adaptive weight normalization
ActiveUS6980614B2Remove distortionCancel improvementSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityFourier transform on finite groupsEngineering
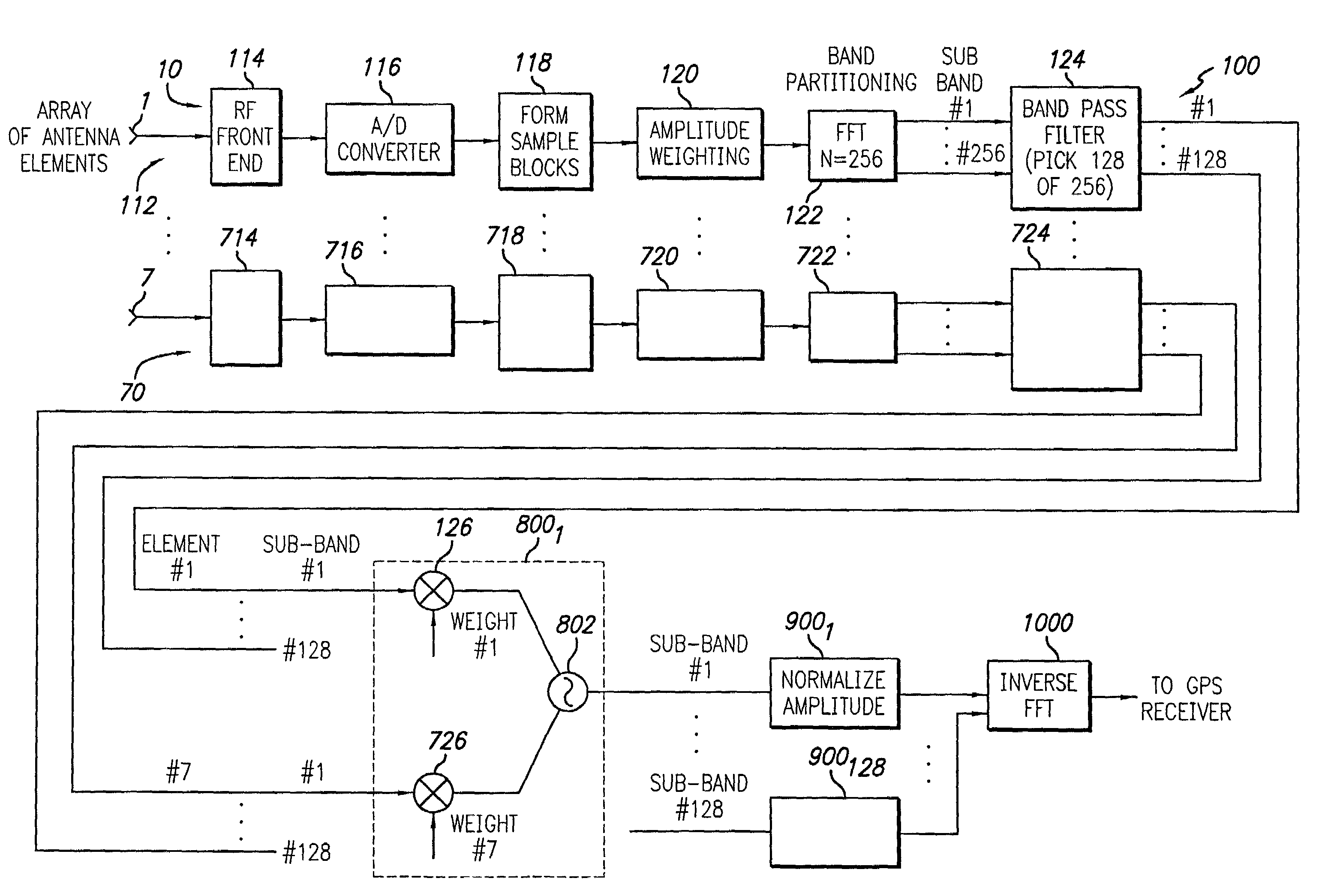
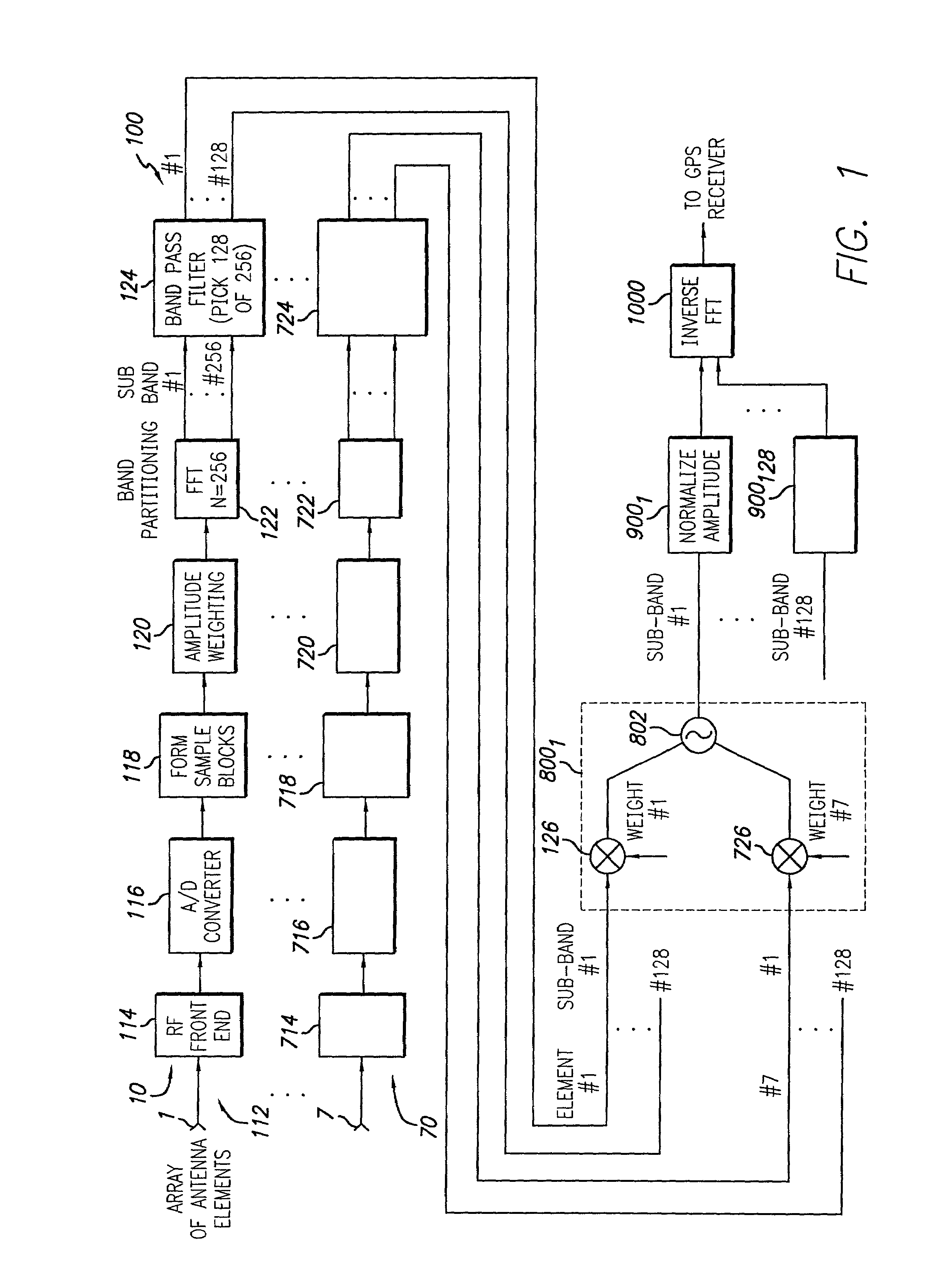
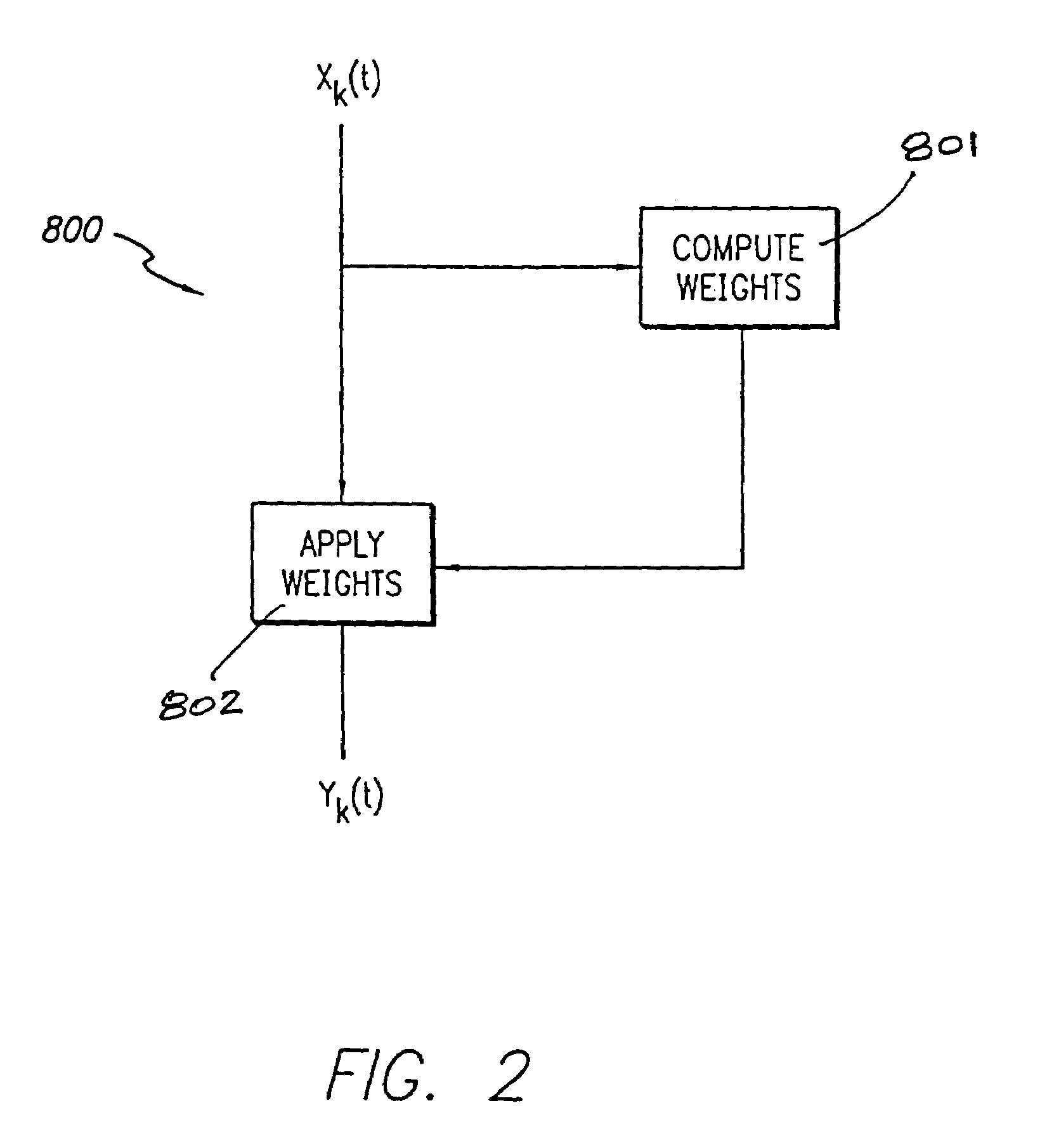
A beamforming system and method. The inventive beamforming system is adapted for use with an array antenna having a plurality of antenna elements and includes a Fast Fourier Transform (EFT) for transforming a signal received by an antenna into a plurality of frequency subbands. A plurality of adaptive processors are included for performing adaptive array processing on each of the subbands and providing a plurality of adaptively processed subbands in response thereto. A normalizing processor is also included for normalizing the adaptively processed subbands. In the illustrative embodiment, the signal is a Global Positioning System (GPS) signal and a digital multiplier for applying a weight to a respective frequency subband for each of the elements of the array. The weights are chosen to steer a beam in a direction of a desired signal. Normalization involves adjusting the amplitude of one or more of the subbands to remove any bias distortion due to the adaptive processing thereof.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Low noise inter-symbol and inter-carrier interference cancellation for multi-carrier modulation receivers
ActiveUS7711059B2Minimize cross-couplingCancel improvementError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionLow noiseCarrier signal
A MCM (multi-carrier modulation) receiver that utilizes a plurality sub-carriers (e.g., tones) to transmit information in a frame-by-frame manner. Identify a first subset of sub-carriers that have negligible ISI (inter-symbol interference) and ICI (inter-carrier interference), and a second subset of sub-carriers that ISI / ICI cancellation is needed to improve the performance. For sub-carriers in the first subset, conventional equalization is performed to obtained soft decisions. For those sub-carriers in the second subset, perform ISI cancellation then ICI cancellation along with equalization. For sub-carriers in the second subset, identify a series of third subsets (one for each of the sub-carriers in the second subset) that cause interference to the sub-carriers in the second set. For sub-carriers in the third subset, identify a series of fourth subsets from a previous frame that cause interference to the sub-carriers in the third set. For each element in the third subset, perform ISI cancellation to eliminate the interference from the elements in the fourth subset from the previous frame to obtain a plurality of intermediate decisions. For each element in the second subset, perform a combined equalization and ICI cancellation using said intermediate decisions. The selection of the first subset, the second subset, the third subset, and the fourth subset are based on examining the frequency response of the communication channel.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Reducing far-end crosstalk in electrical connectors
ActiveUS8357013B2Big improvements in total FEXTCancel improvementInterconnection arrangementsSubstations coupling interface circuitsElectricityElectrical polarity
The present invention involves connectors for reducing Far-End Crosstalk (FEXT) through the use of novel polarity swapping to negate the cumulative effect of FEXT. Skew adjustment is used to improve the FEXT cancellation from polarity swapping. The polarity reversal location or locations among FEXT sources are optimized to achieve maximum FEXT cancellation. The novelty polarity swapping technique can be applied to a wide variety of connectors, such as mezzanine connectors, backplane connectors, and any other connectors that can benefit from FEXT reduction.
Owner:HIROSE ELECTRIC GROUP
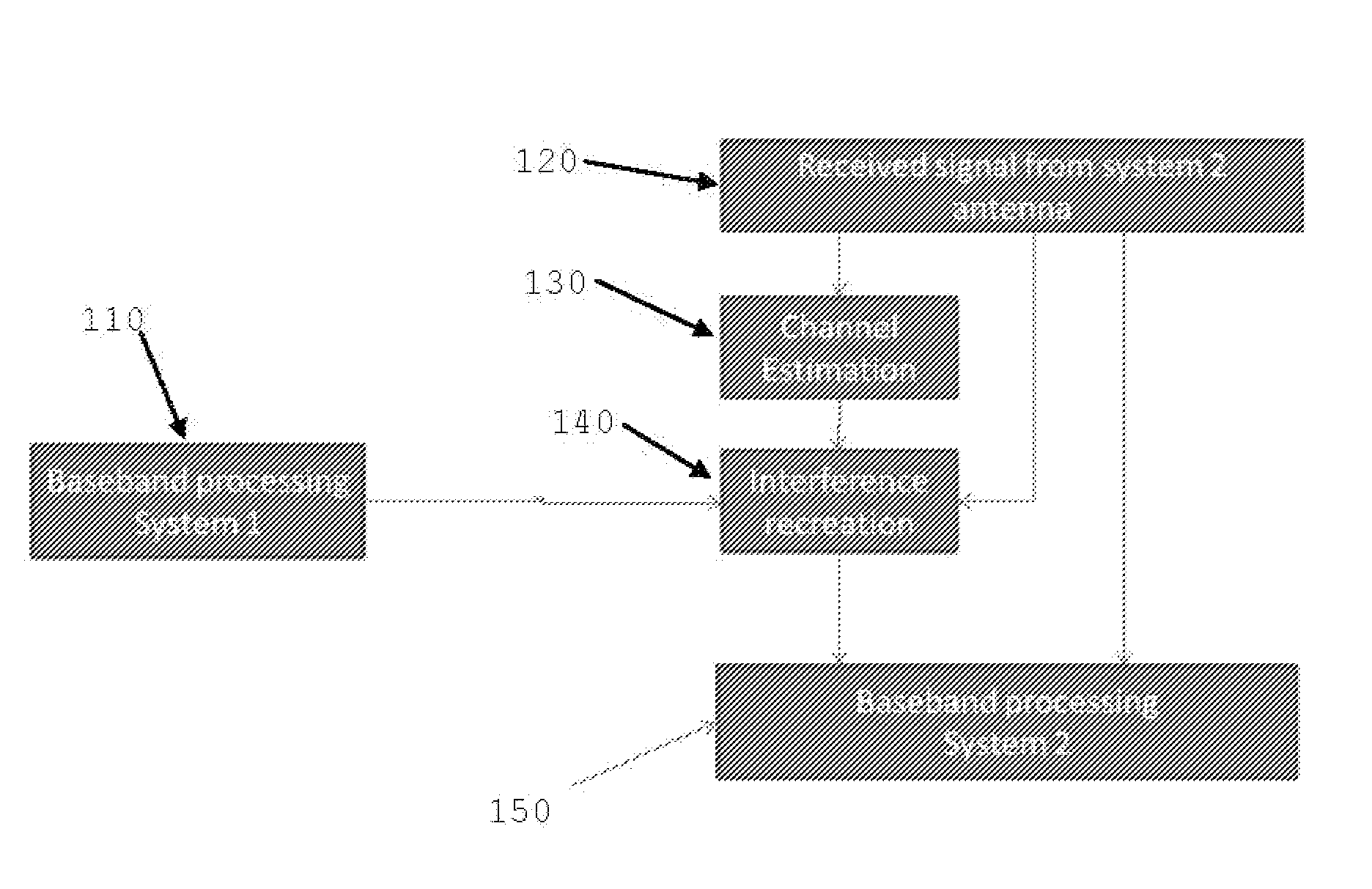
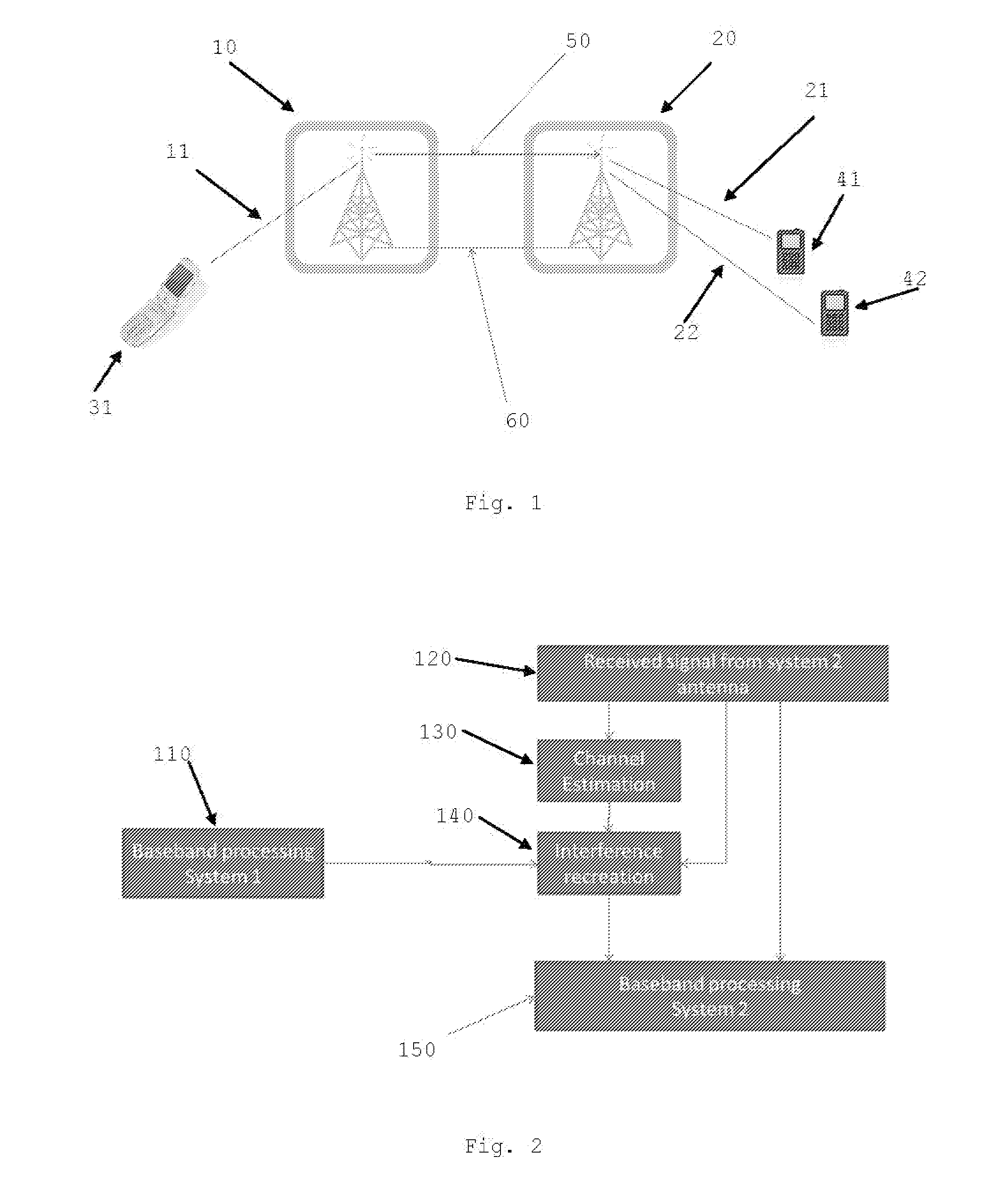
Coexisting wireless systems
InactiveUS20140376423A1Improves interference cancellationIncrease in cost and complexityTime-division multiplexOrthogonal multiplexWireless transmissionTransmitter
The present invention provides a method of cancelling interference caused by a transmitter of a first wireless system to a receiver of a second wireless system, the transmitter and receiver being operative in adjacent frequency bands. The method comprises receiving a signal at the second wireless system that is corrupted by interference caused by a wireless transmission from the first wireless system; providing the second wireless system with transmitted symbols of the wireless transmission from the first wireless system; and processing the signal received at the second wireless system using the transmitted symbols of the wireless transmission in order to cancel the interference.
Owner:VODAFONE IP LICENSING
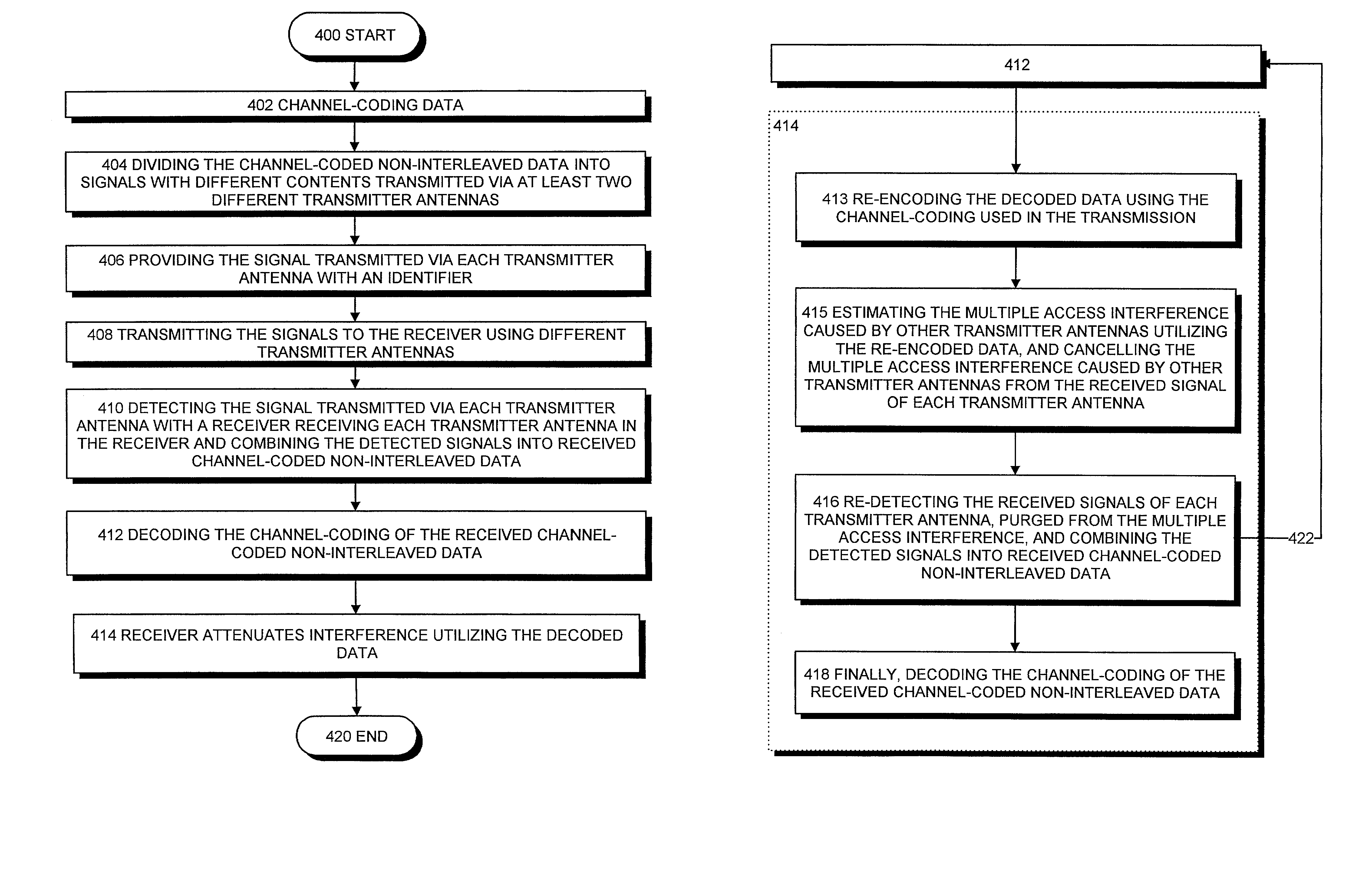
Method of transmitting data from a transmitter to a receiver, and a radio system
InactiveUS7286612B2Reduce distractionsCancel improvementSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsTelecommunicationsTransmitter antenna
The invention relates to a method of transmitting data from a transmitter to a receiver in a radio system, and to a radio system. The method includes the following: channel-coding the data using selected channel-coding; dividing the channel-coded non-interleaved data into signals with different contents, to be transmitted via at least two different transmitter antennas; providing the signal to be transmitted via each transmitter antenna with an identifier, by means of which identifier the signals transmitted via different transmitter antennas are distinguishable from each other in the receiver; transmitting the signals to the receiver using different transmitter antennas; detecting the signal transmitted via each transmitter antenna with a receiver receiving each transmitter antenna in the receiver, and combining the detected signals into received channel-coded non-interleaved data; decoding the channel-coding of the received channel-coded non-interleaved data; and the receiver attenuating interference utilizing the decoded data.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Speech canceler-enhancer system for use in call-center applications
ActiveUS8848901B2Cancel improvementImprove integrityMicrophonesInterconnection arrangementsEngineeringHeadphones
A call-center has agents using headsets, which are connected to a private business exchange (PBX). Noise cancellation occurs in a noise filter, within or connected to the PBX. Noise cancellation for a particular agent's conversation is achieved by receiving the voice signals from neighboring agents' headsets and by using adaptive noise cancellation in the noise filter to remove the other agents' conversations from the particular agent's conversation. Microphones may also be placed at other noise sources, such as HVAC equipment, so that offending noises are accurately received at the noise filter and removed from the agents' conversations.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com