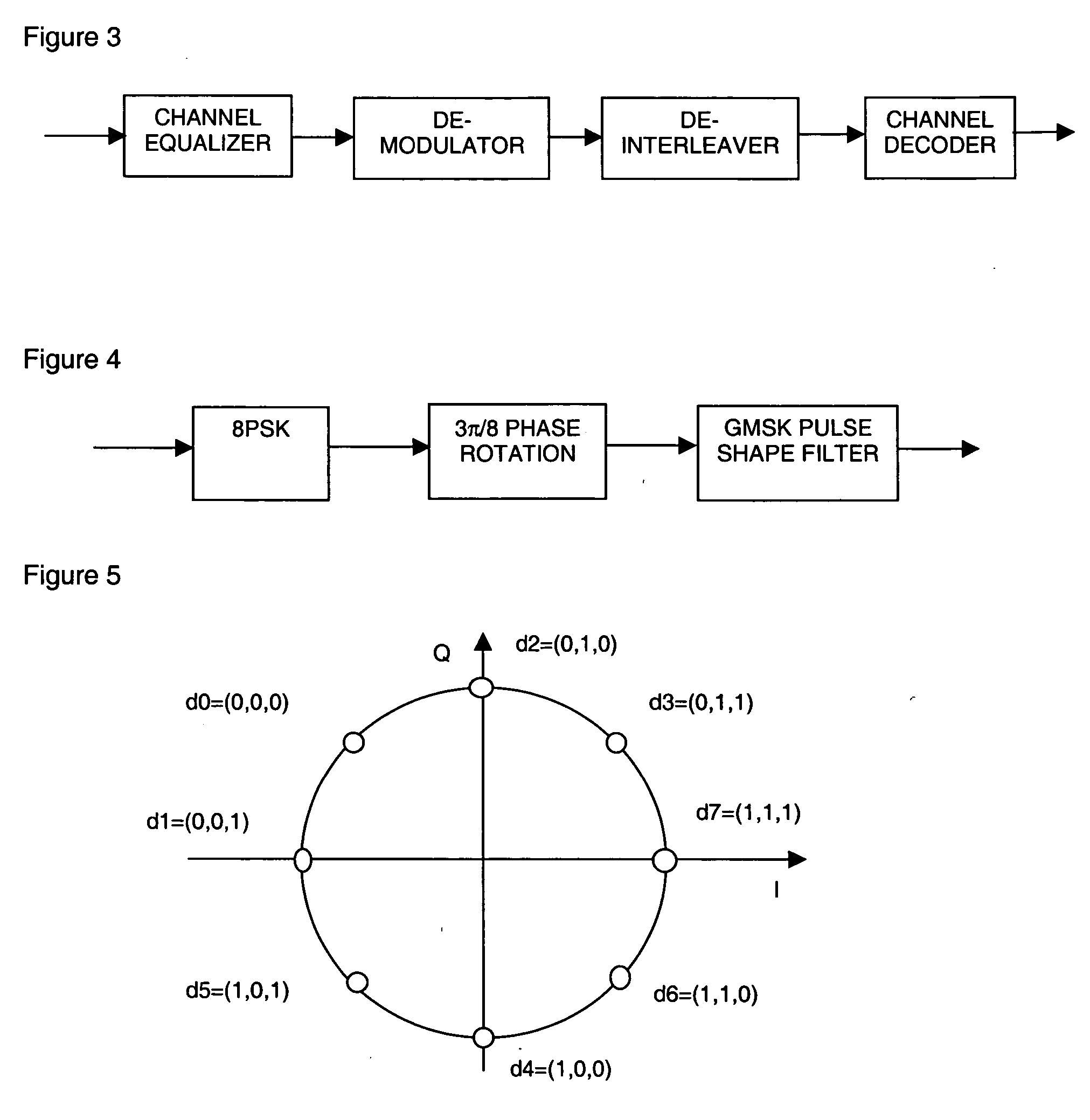
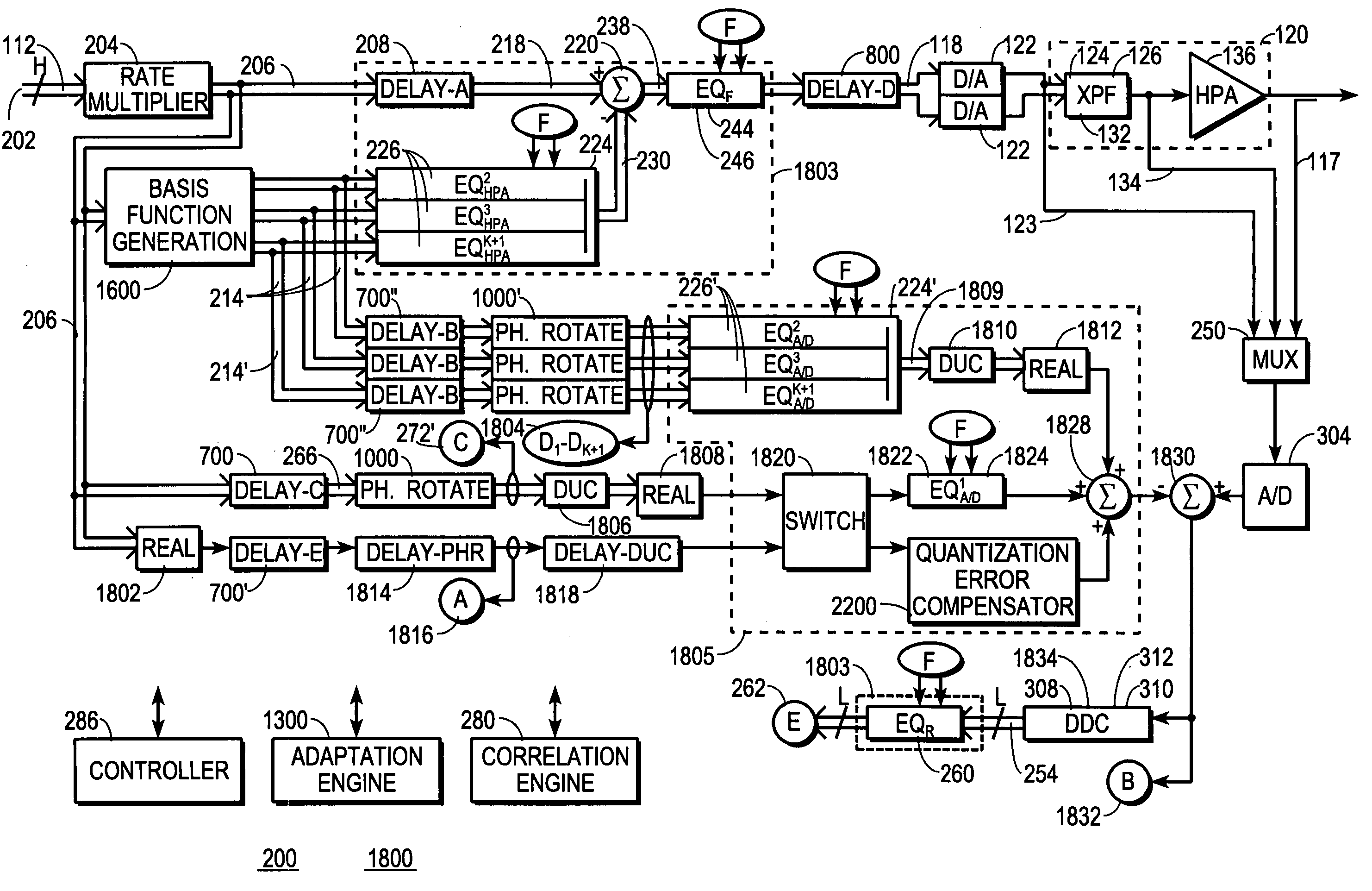
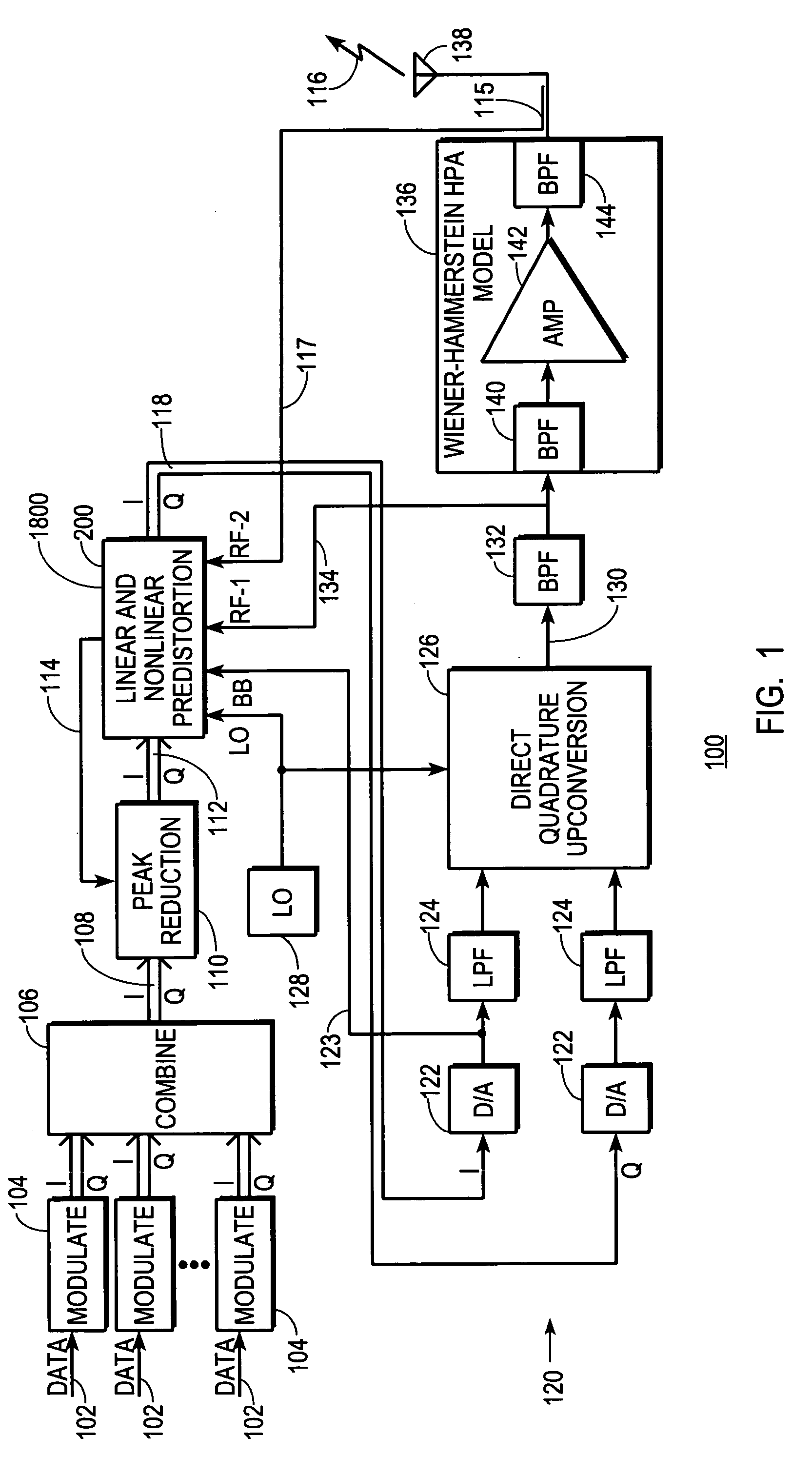
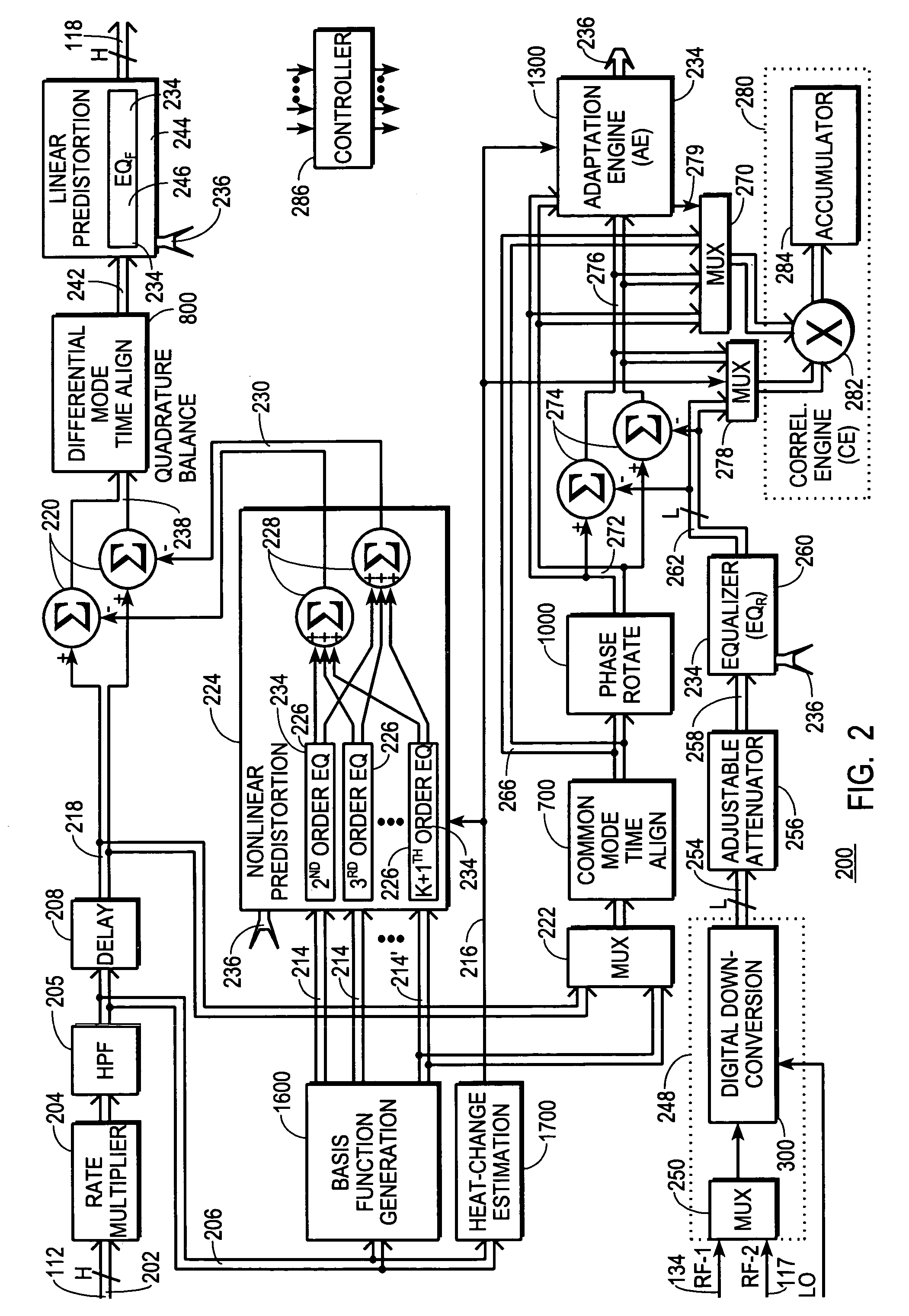
Patents
Literature
937 results about "Equalizer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
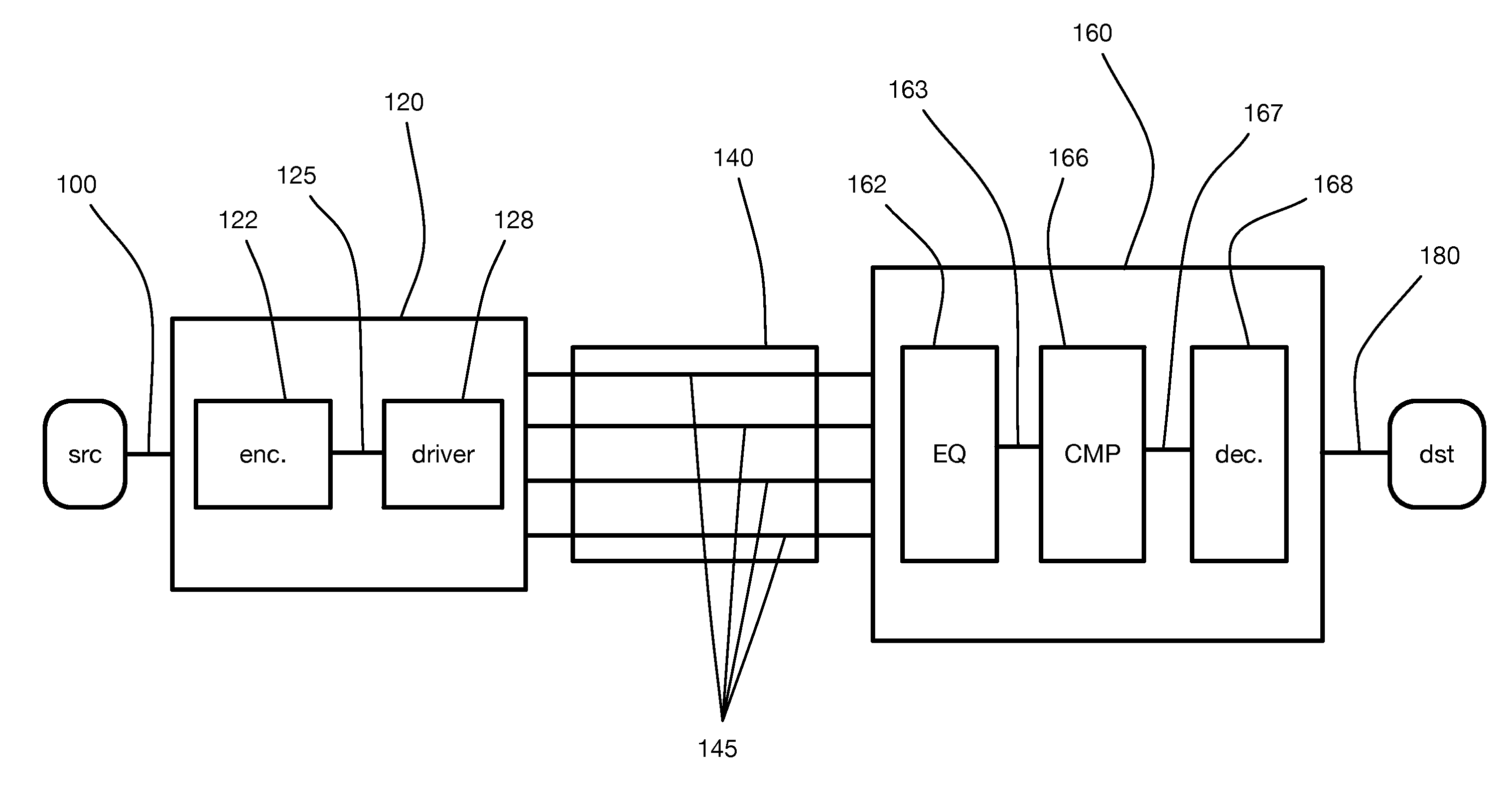
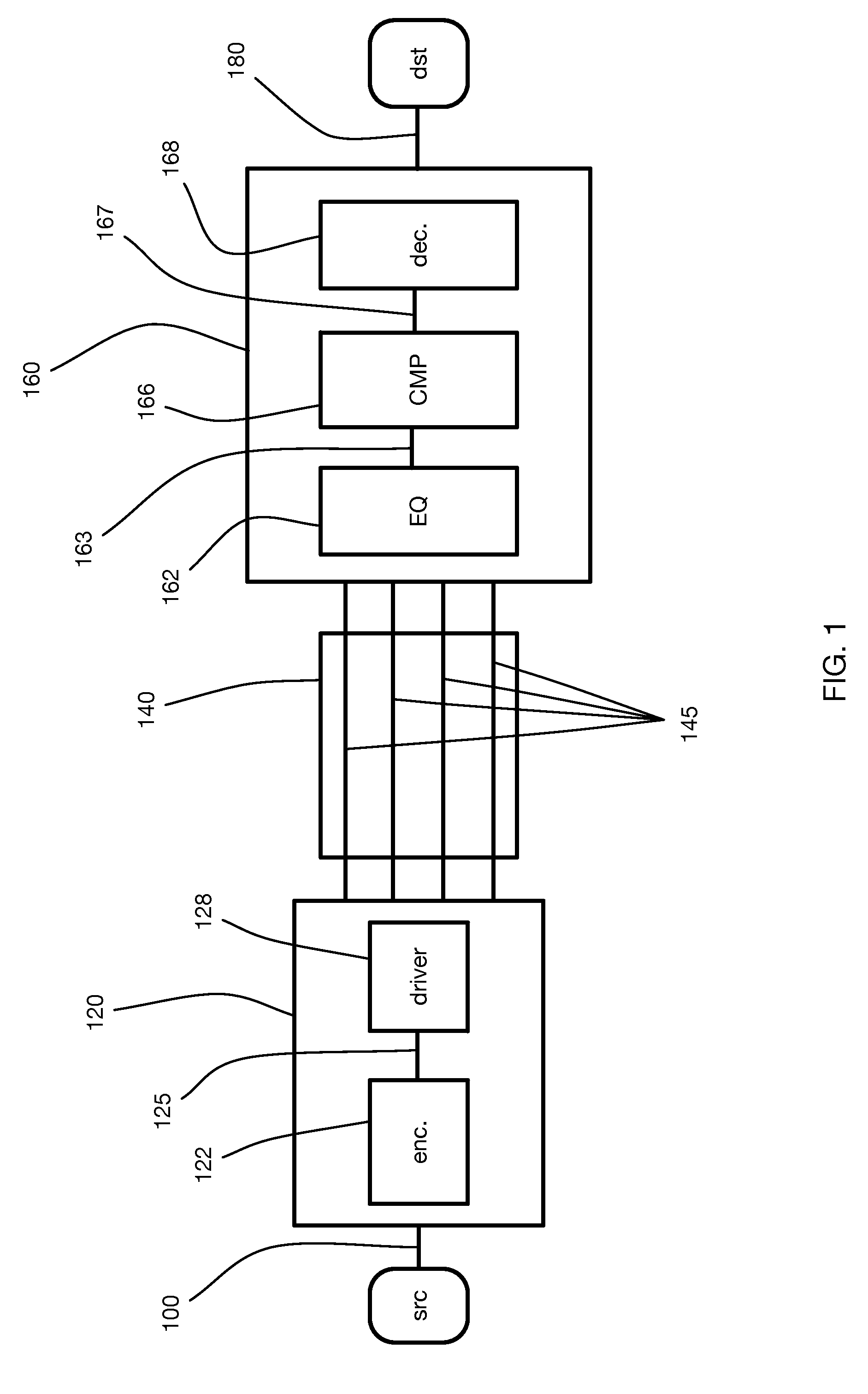
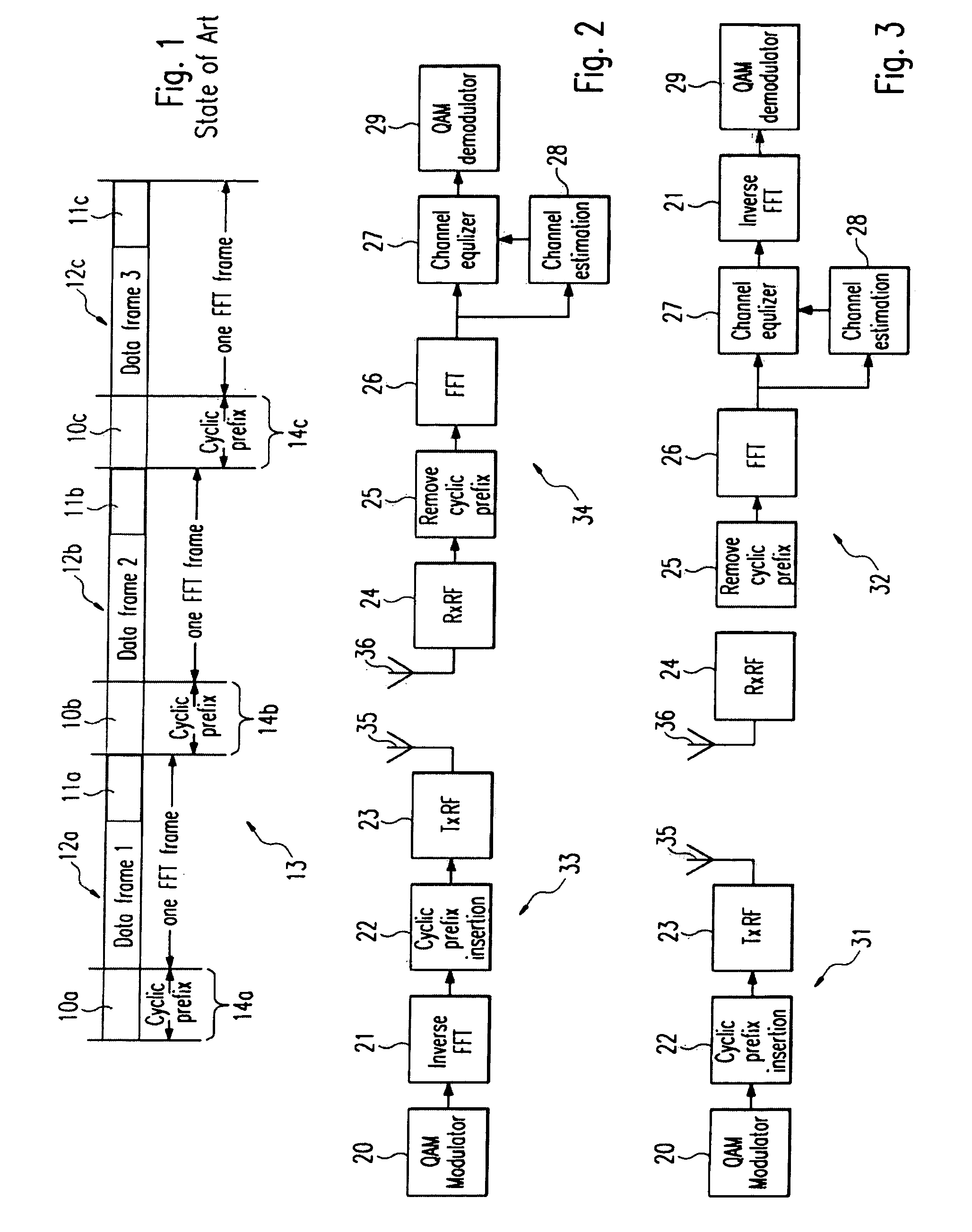
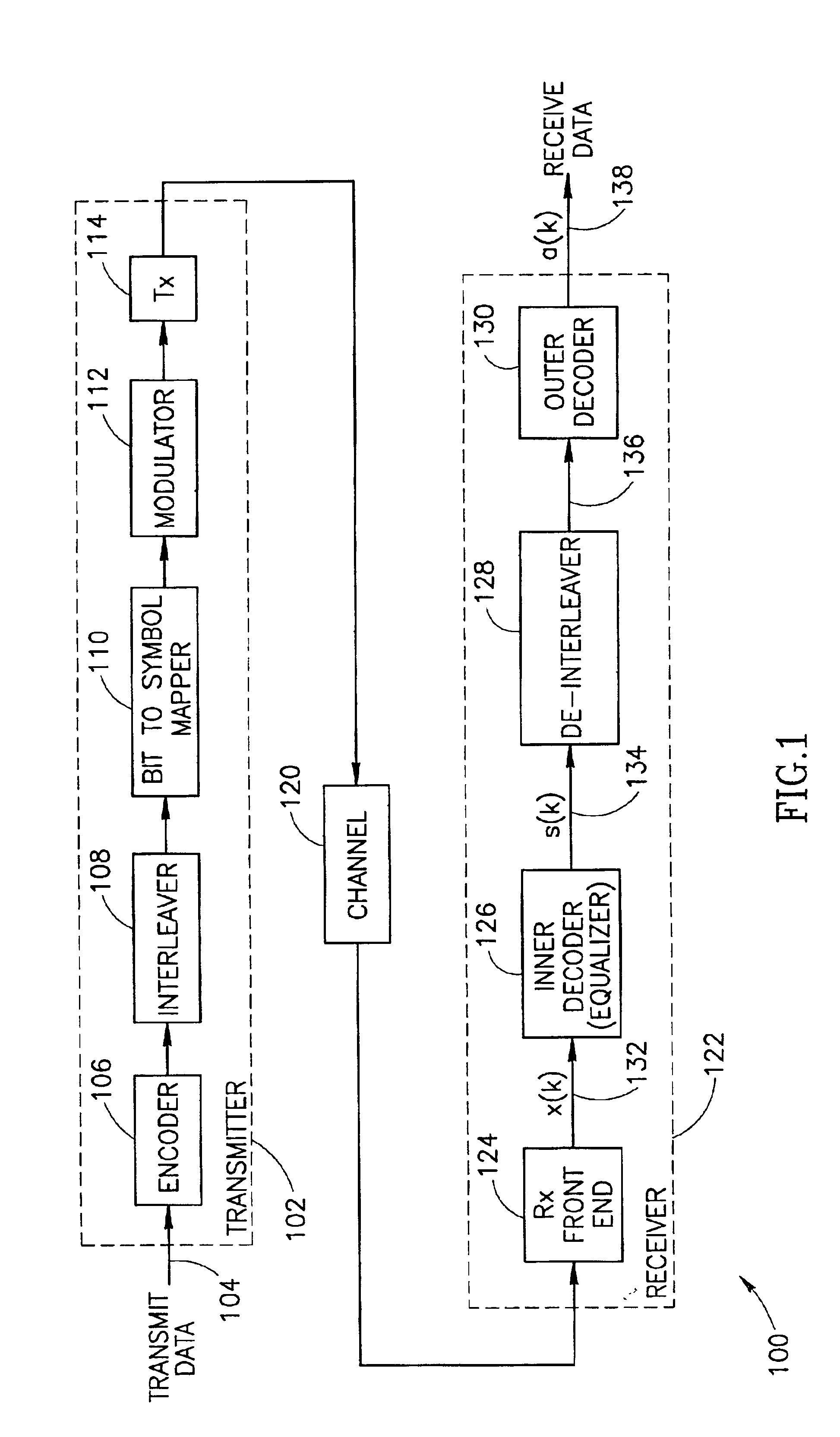
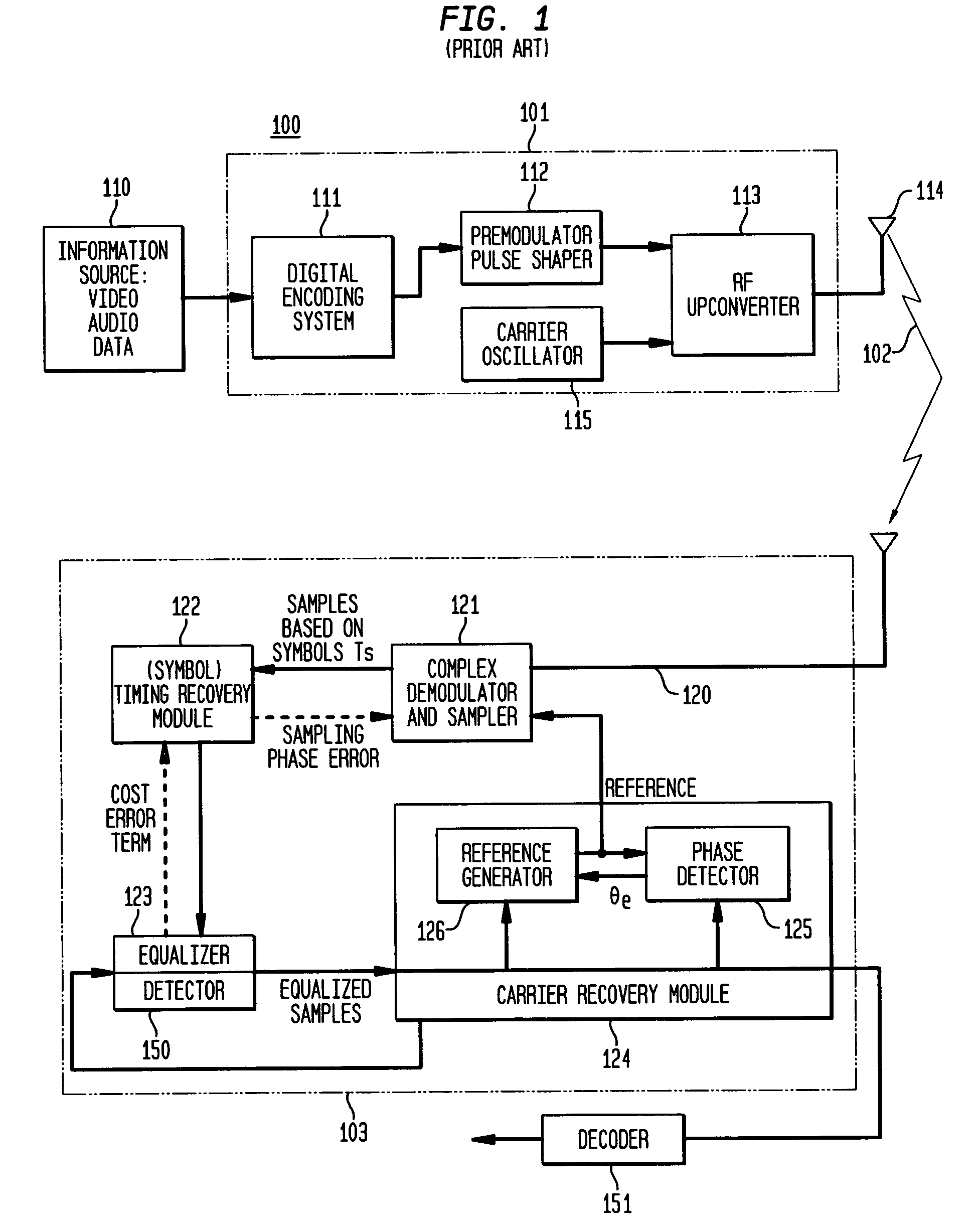
In telecommunication, equalization is the reversal of distortion incurred by a signal transmitted through a channel. Equalizers are used to render the frequency response—for instance of a telephone line—flat from end-to-end. When a channel has been equalized the frequency domain attributes of the signal at the input are faithfully reproduced at the output. Telephones, DSL lines and television cables use equalizers to prepare data signals for transmission.
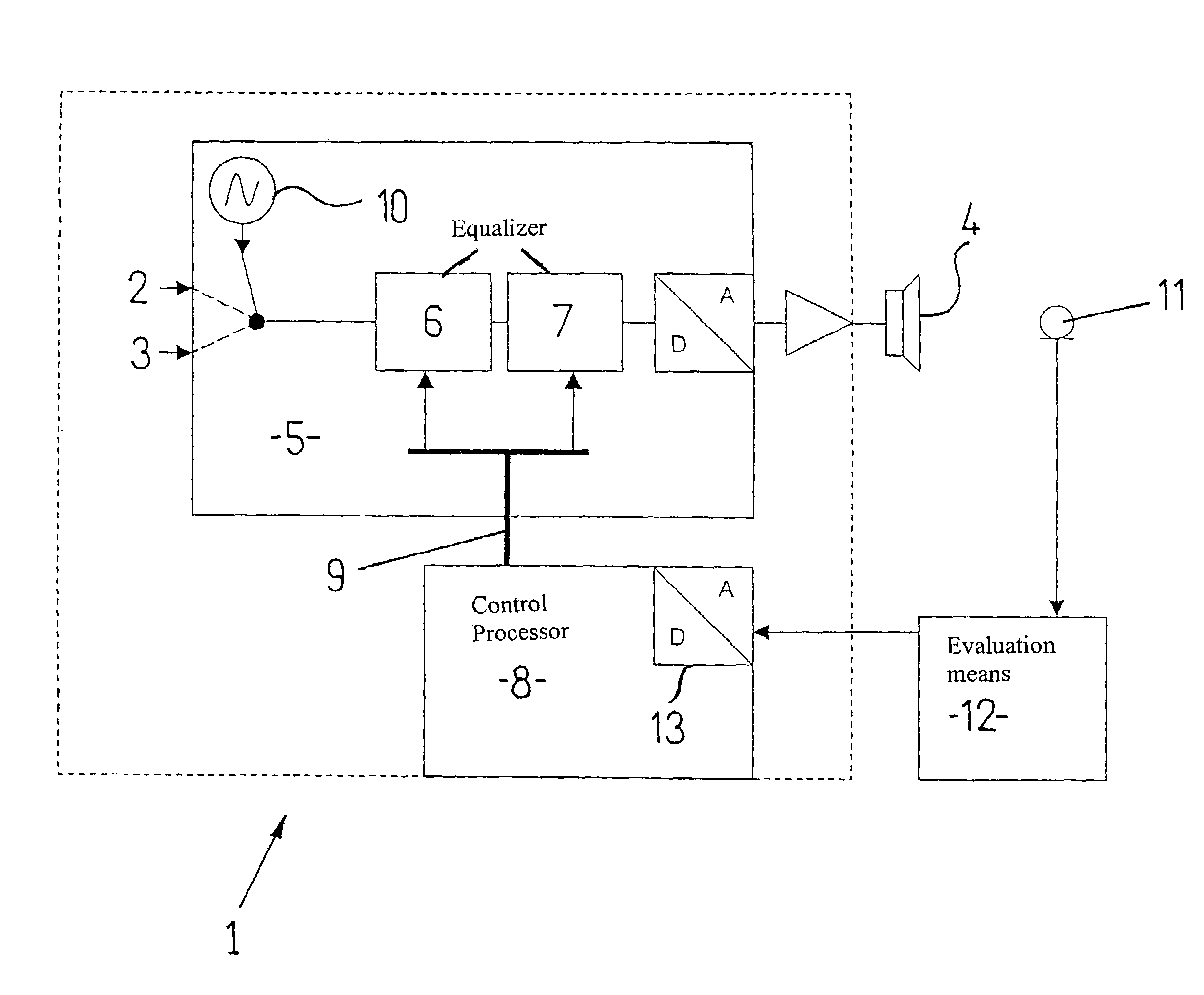
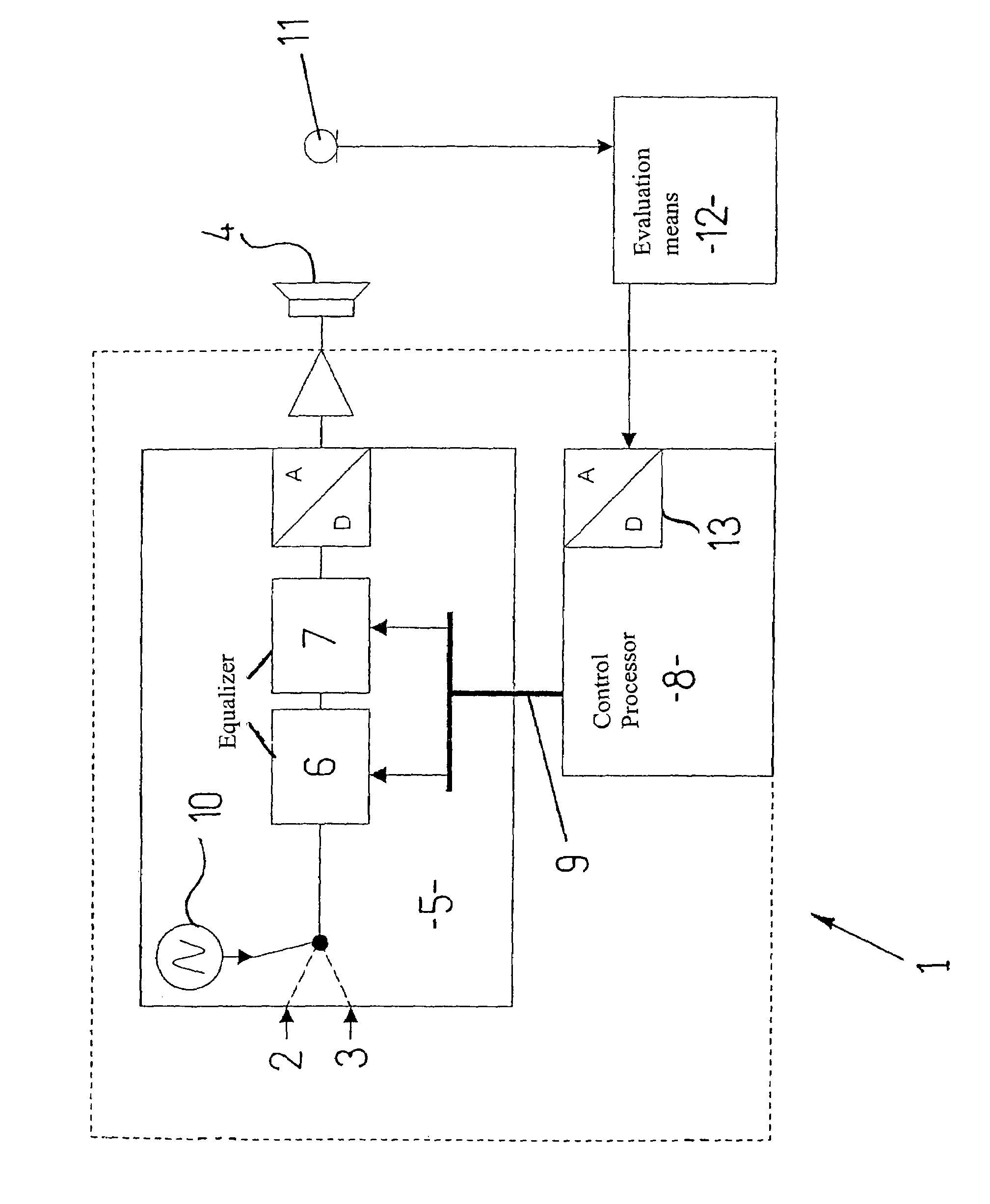
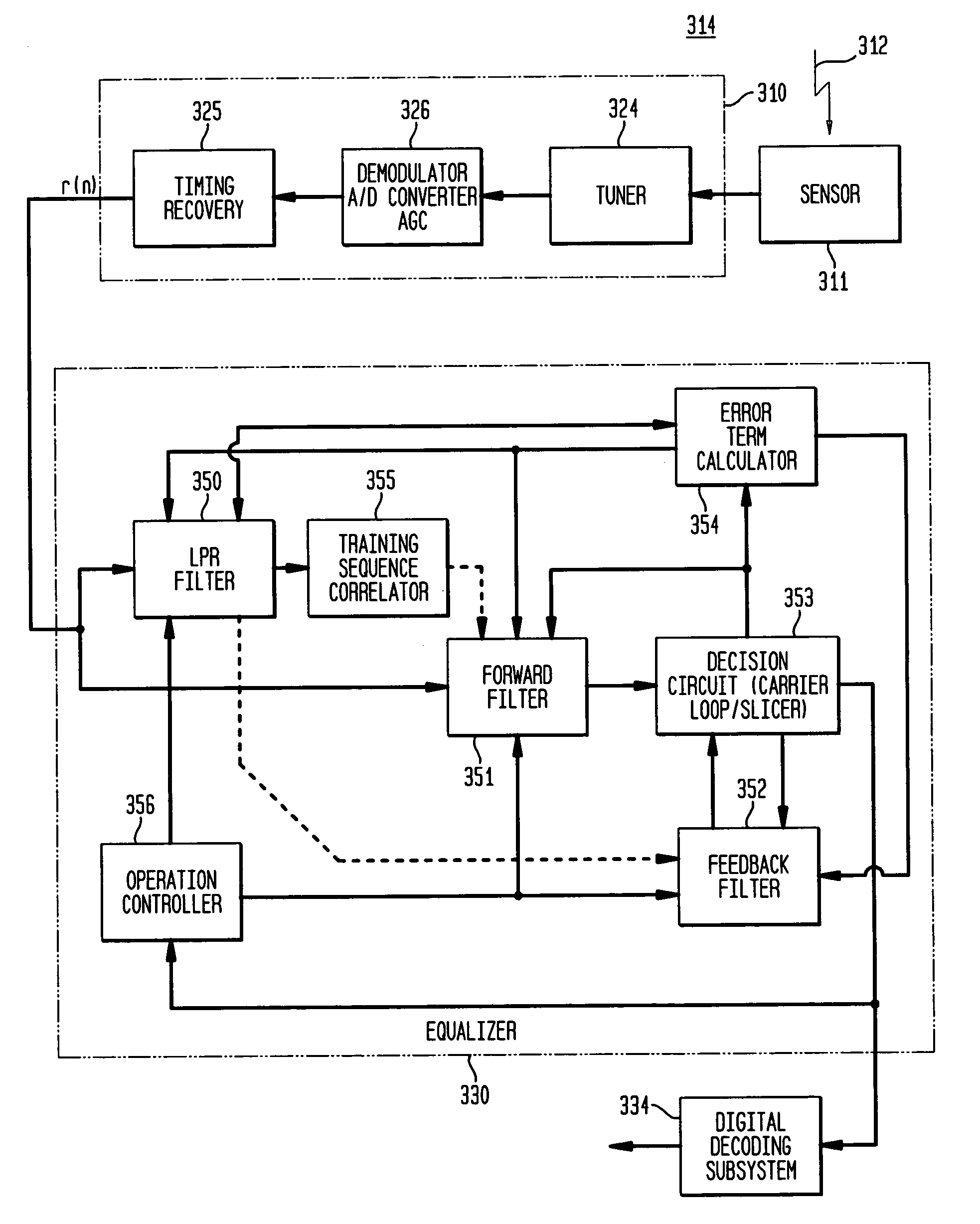
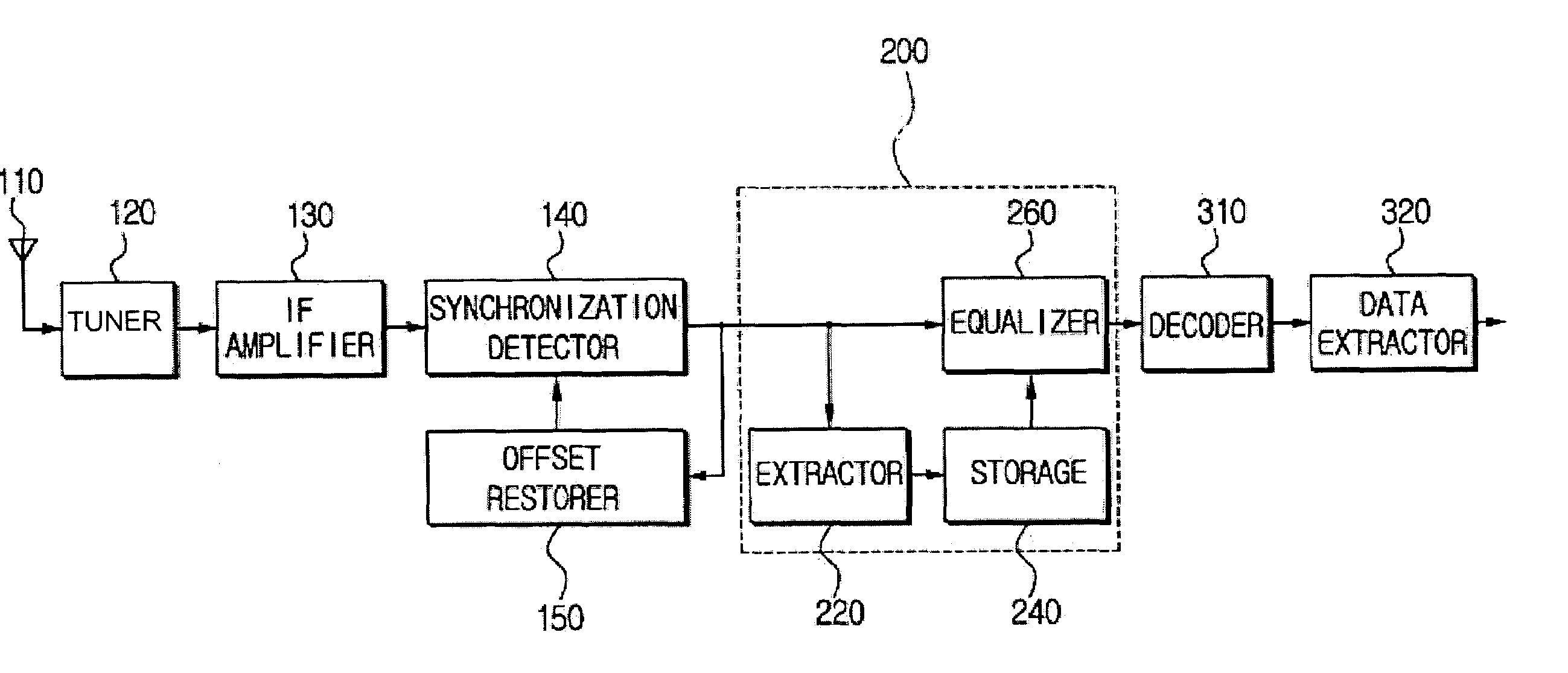
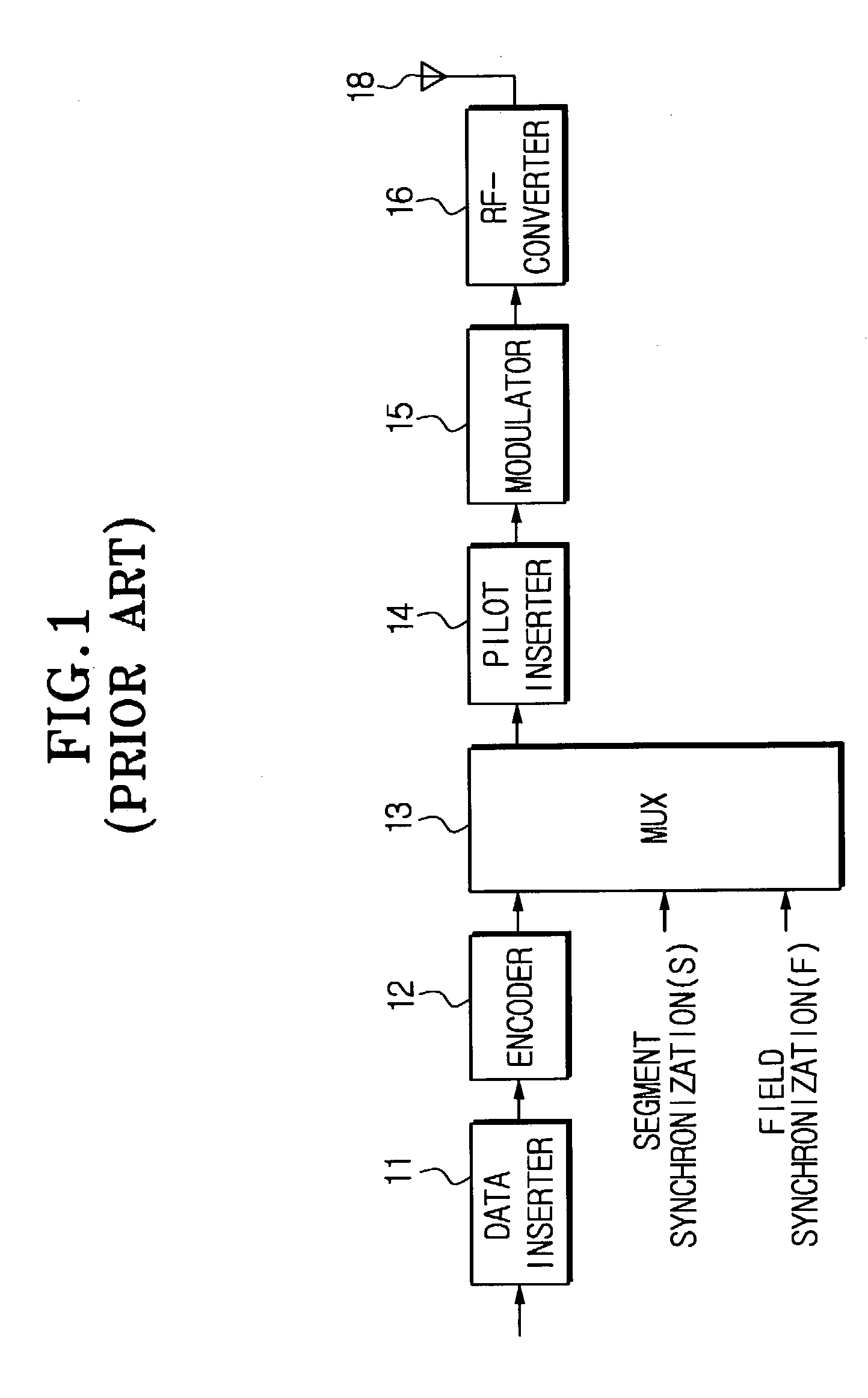
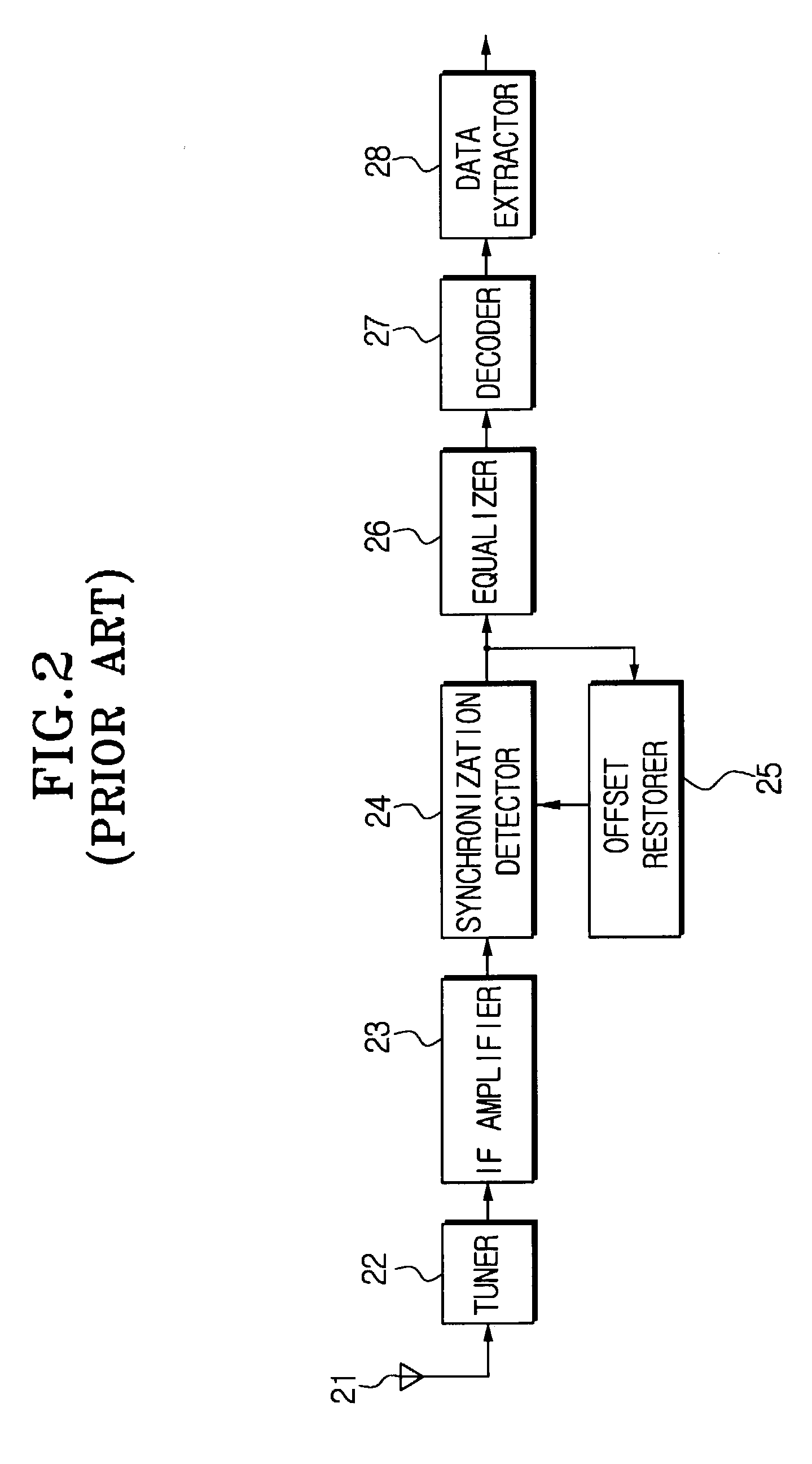
Method and apparatus which compensates for channel distortion
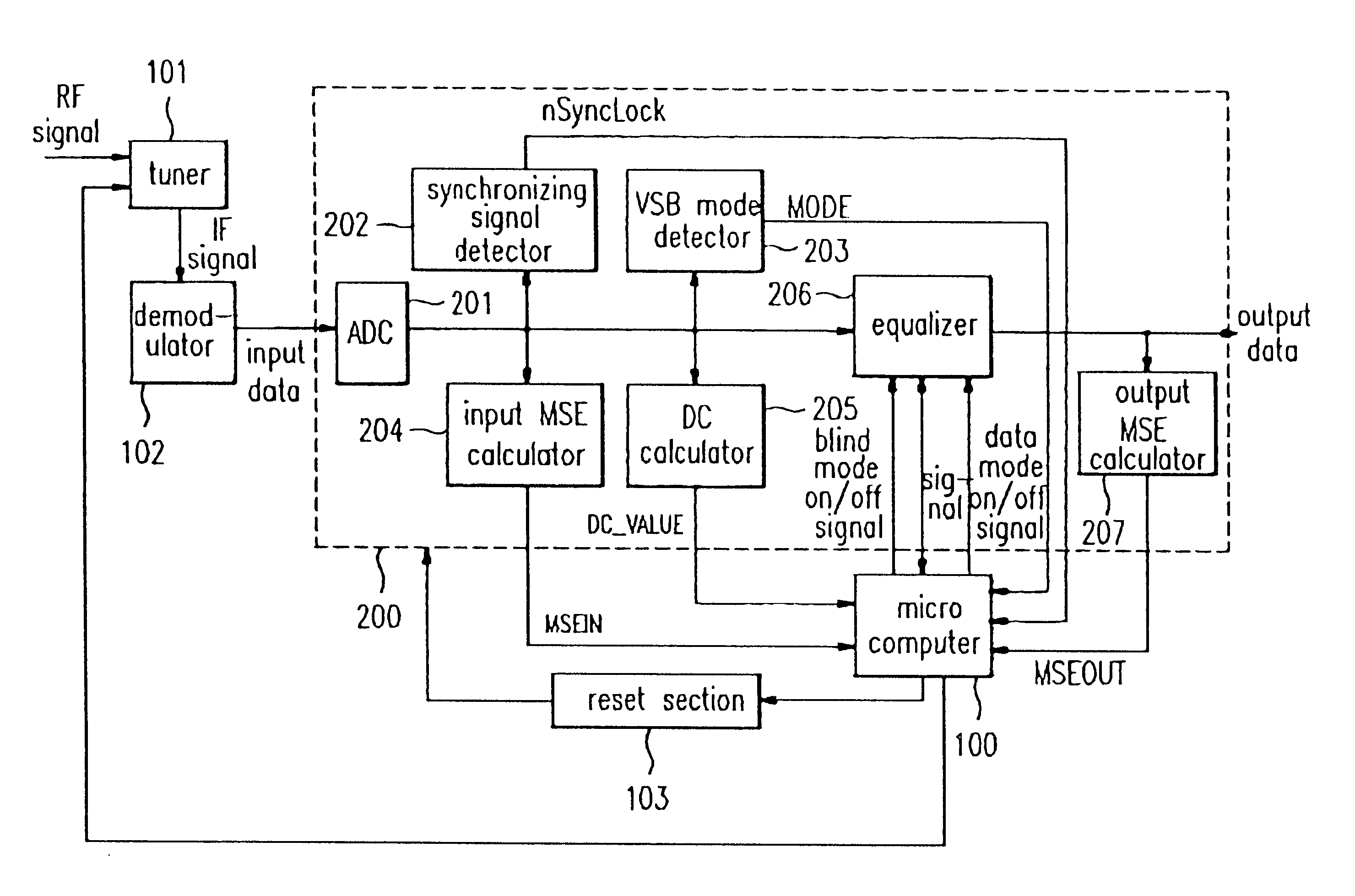
A method and apparatus for compensating for channel distortion is disclosed. In the present invention, equalization is performed in the treating sequence mode when the moving ghost does not exist in the channel and there is no possibility that the equalizer diverges, the data mode is cancelled and the equalization is carried out in the blind mode when the moving ghost does not exist in the channel but there is a possibility that the equalizer diverges, the equalizer is executed in the data mode when there is no possibility that the equalizer diverges but there exists the moving ghost including slowly moving ghosts in the channel, and the equalization is performed in the data mode and blind mode when the moving ghost exists and there is a possibility that the equalizer diverges.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
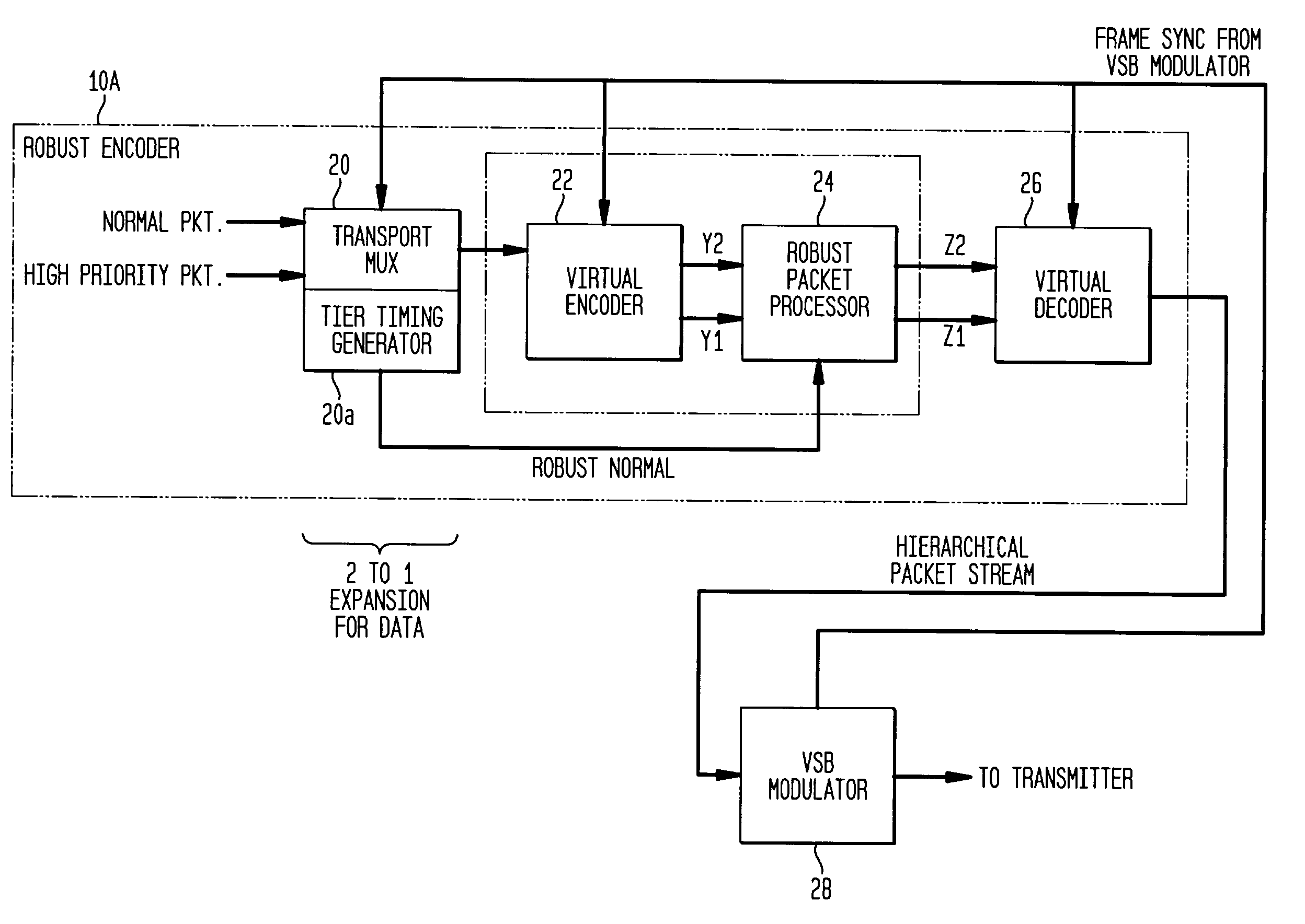
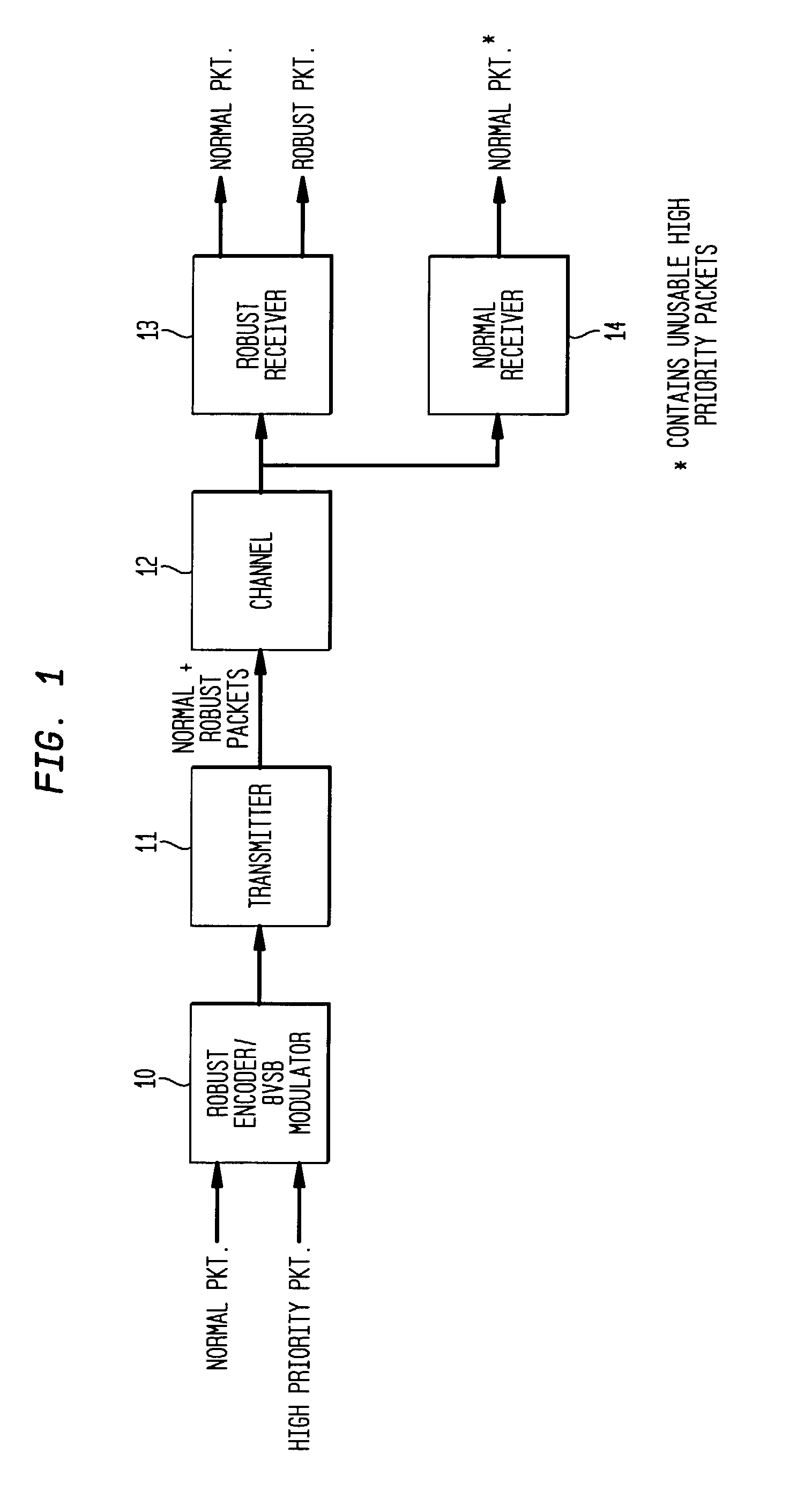
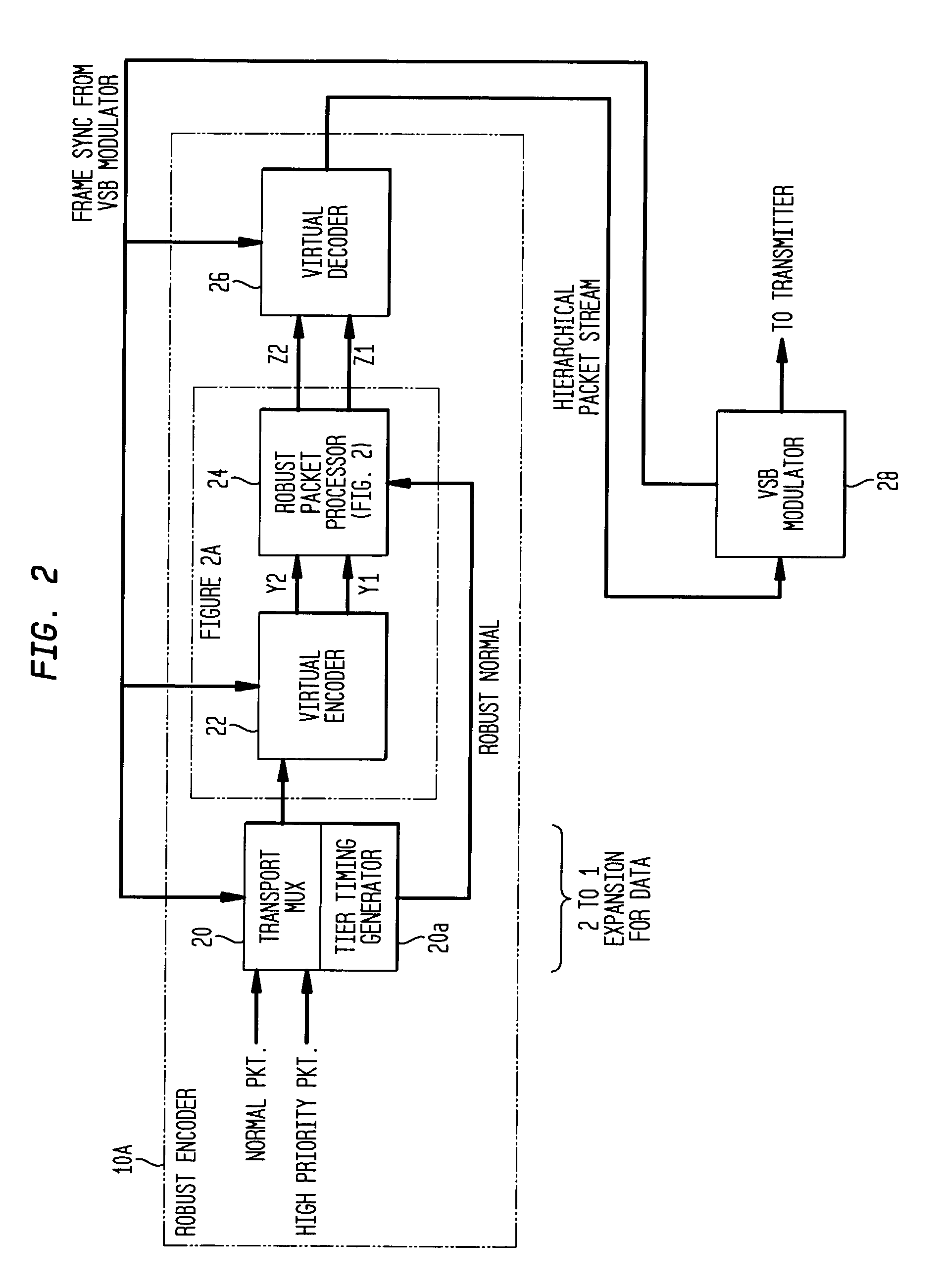
Receiver for robust data extension for 8VSB signaling
InactiveUS7194047B2Robust of serviceImprove performanceData representation error detection/correctionBroadcast specific applicationsDigital televisionCarrier recovery
A robust data extension, added to a standard 8VSB digital television signal, is used to improve the performance of a digital television receiver. Robust data packets are encoded at a 1 / 3-trellis rate as compared to normal data packets that are encoded at a 2 / 3-trellis rate. In addition to delivery of robust data for mobile applications, the redundant robust data packets also improve the performance of the receiver in the normal tier of service. In particular, the robust data packets improve the performance of the receiver equalizer filter in the presence of rapidly changing transient channel conditions such as dynamic multipath for both robust data packets and normal data packets. The robust data packets improve the performance of the carrier recovery loop and the symbol timing recovery loop. Backward compatibility with existing receivers is maintained for 1) 8VSB signaling, 2) trellis encoding and decoding, 3) Reed Solomon encoding and decoding, and 4) MPEG compatibility.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
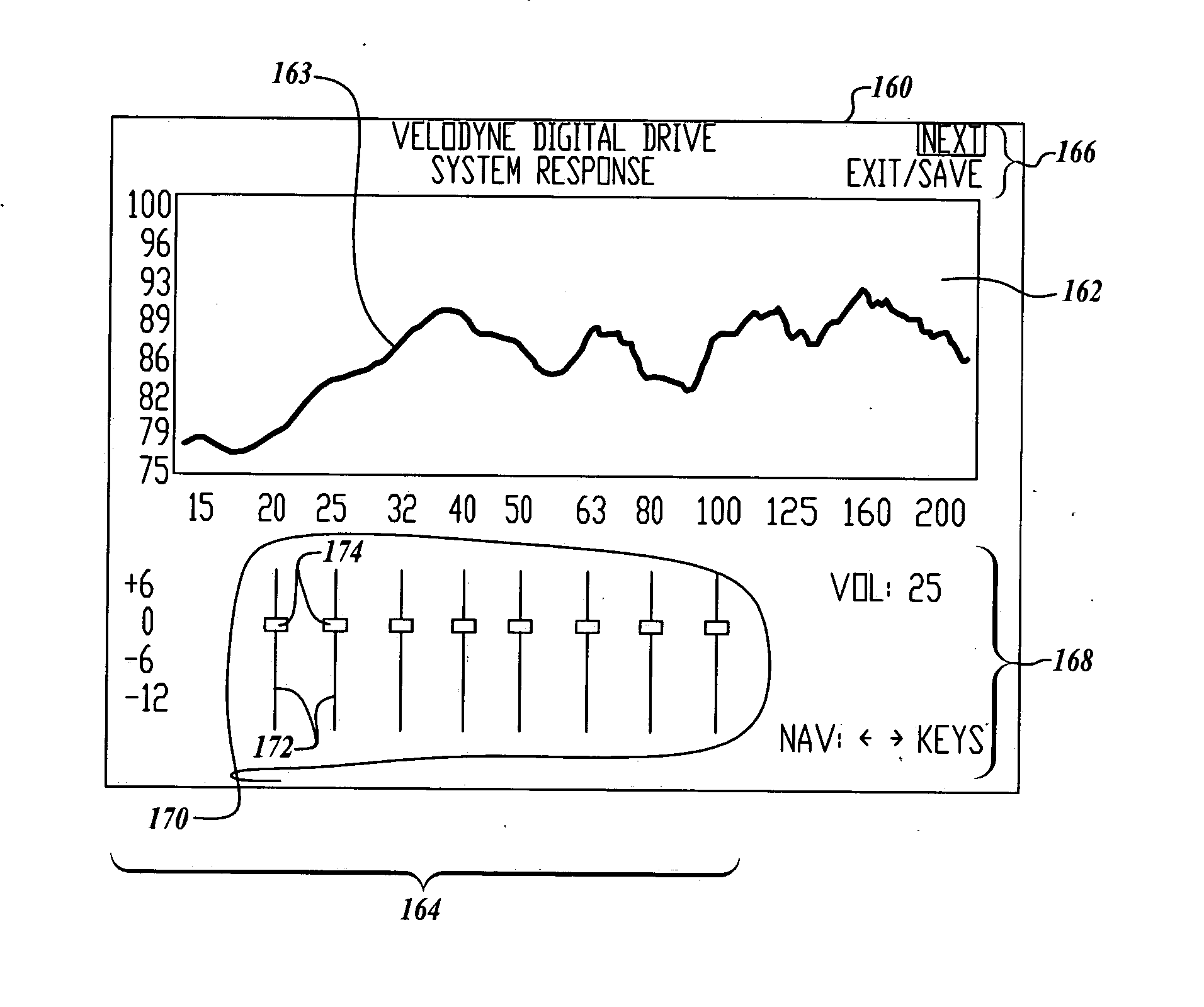
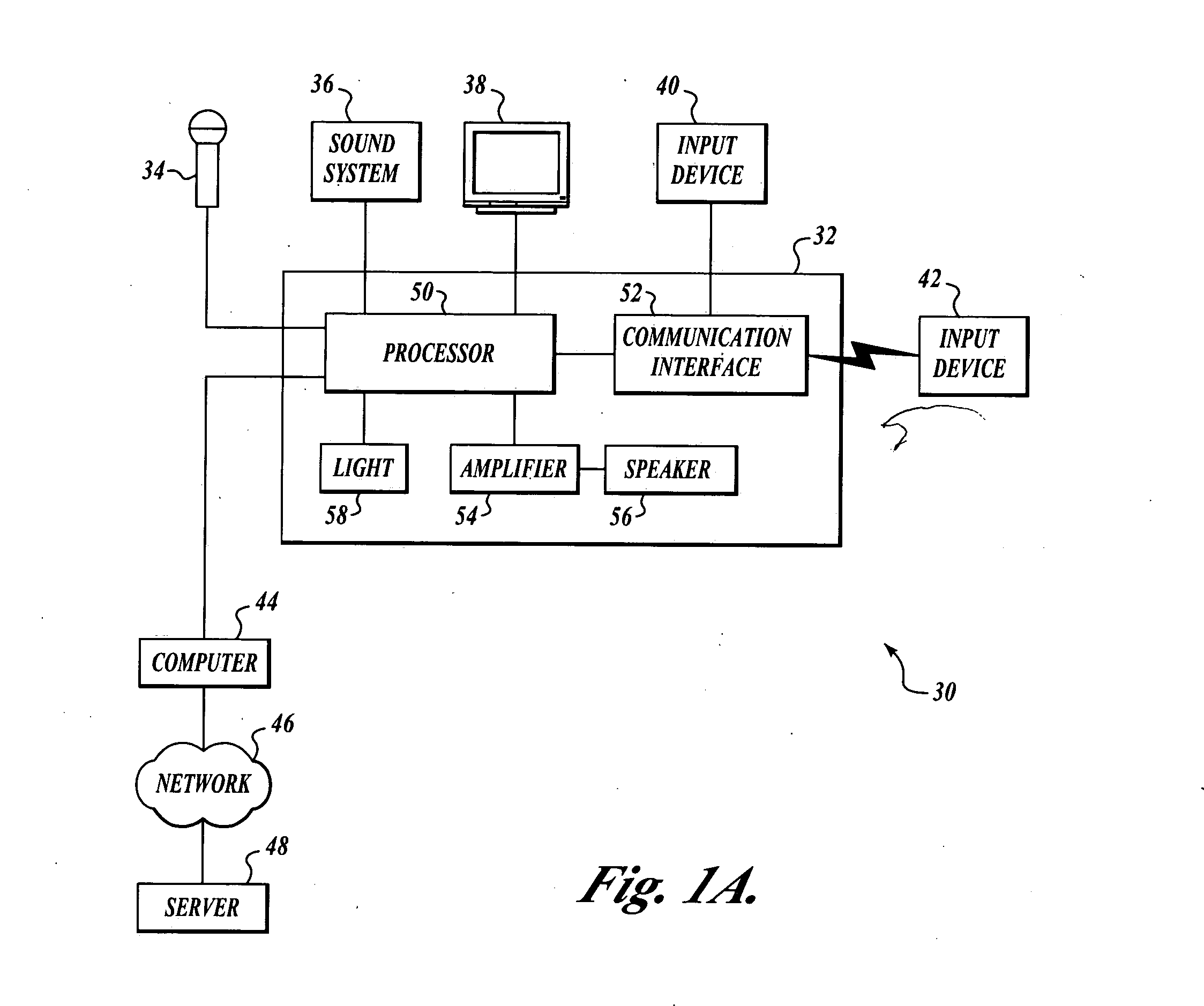
Adjustable speaker systems and methods
InactiveUS20050069153A1Manually operated tone/bandwidth controlStereophonic systemsAudio power amplifierGraphical user interface
Systems and methods for optimizing speaker performance. The system includes a self-contained speaker unit that includes a speaker, an amplifier coupled to the speaker, and a processor coupled to the amplifier. The processor receives a first sound signal from a receiver and a second sound signal from a microphone, processes the first sound signal based on a plurality of parameters, outputs the processed sound signal to the speaker, and generates a video signal based on the second sound signal. A wireless remote control allows a user to manipulate the parameters. The processor generates a test sound signal and outputs it to the receiver. The receiver processes the test sound signal and returns it to the processor for output through the speaker. The video signal includes a graphical user interface having a frequency response graph of the second sound signal and an eight band equalizer.
Owner:VELODYNE ACOUSTICS
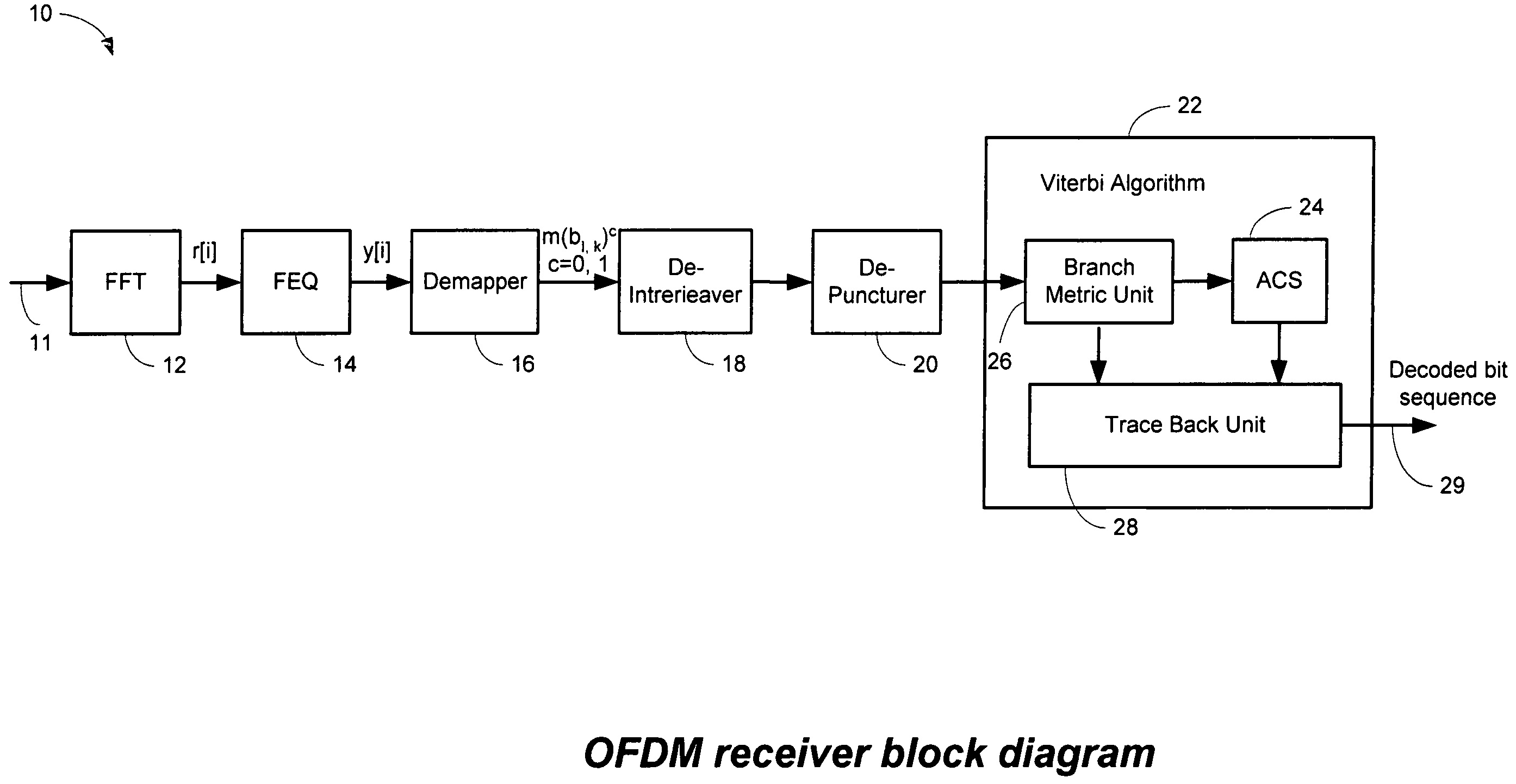
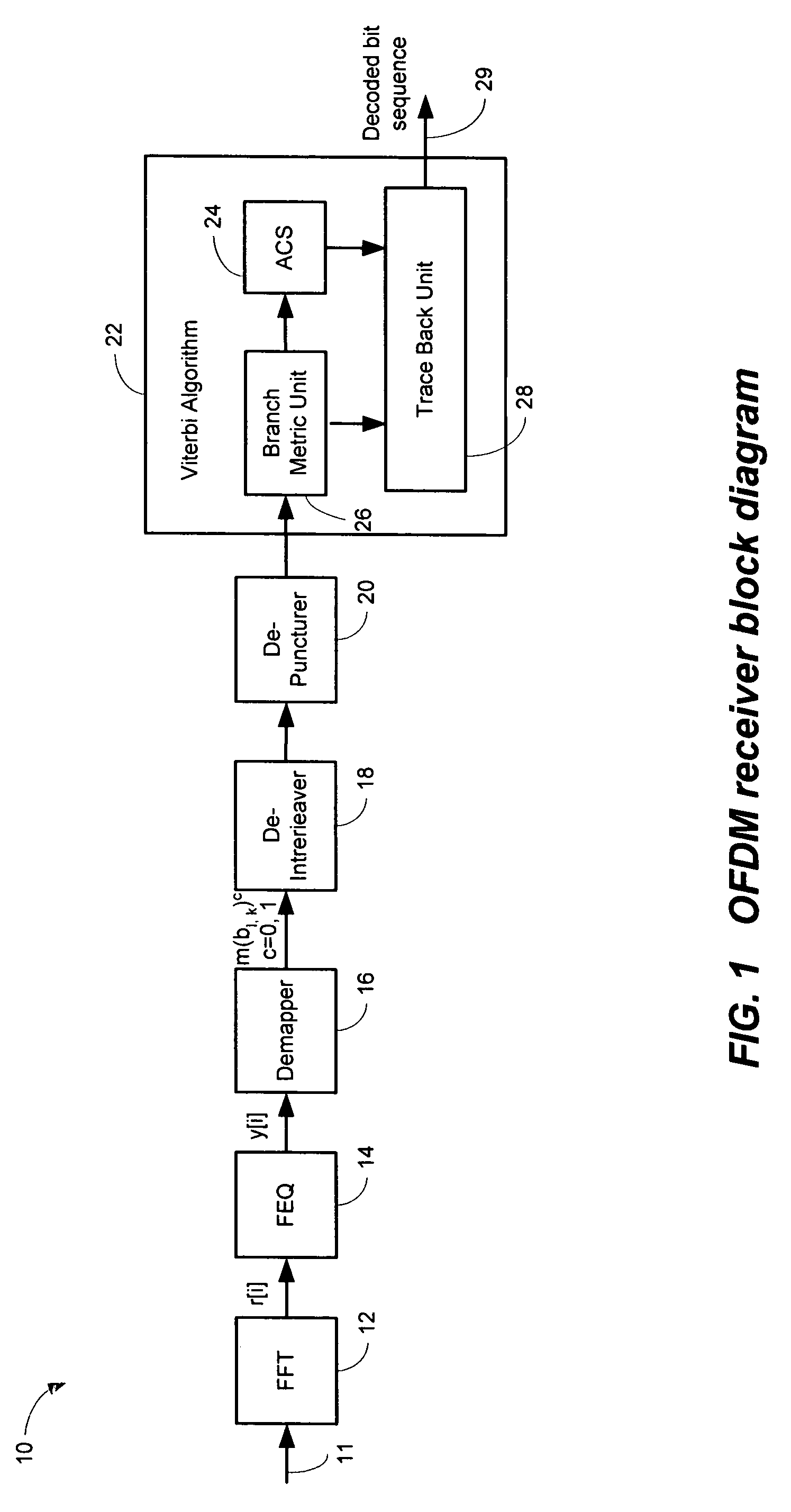
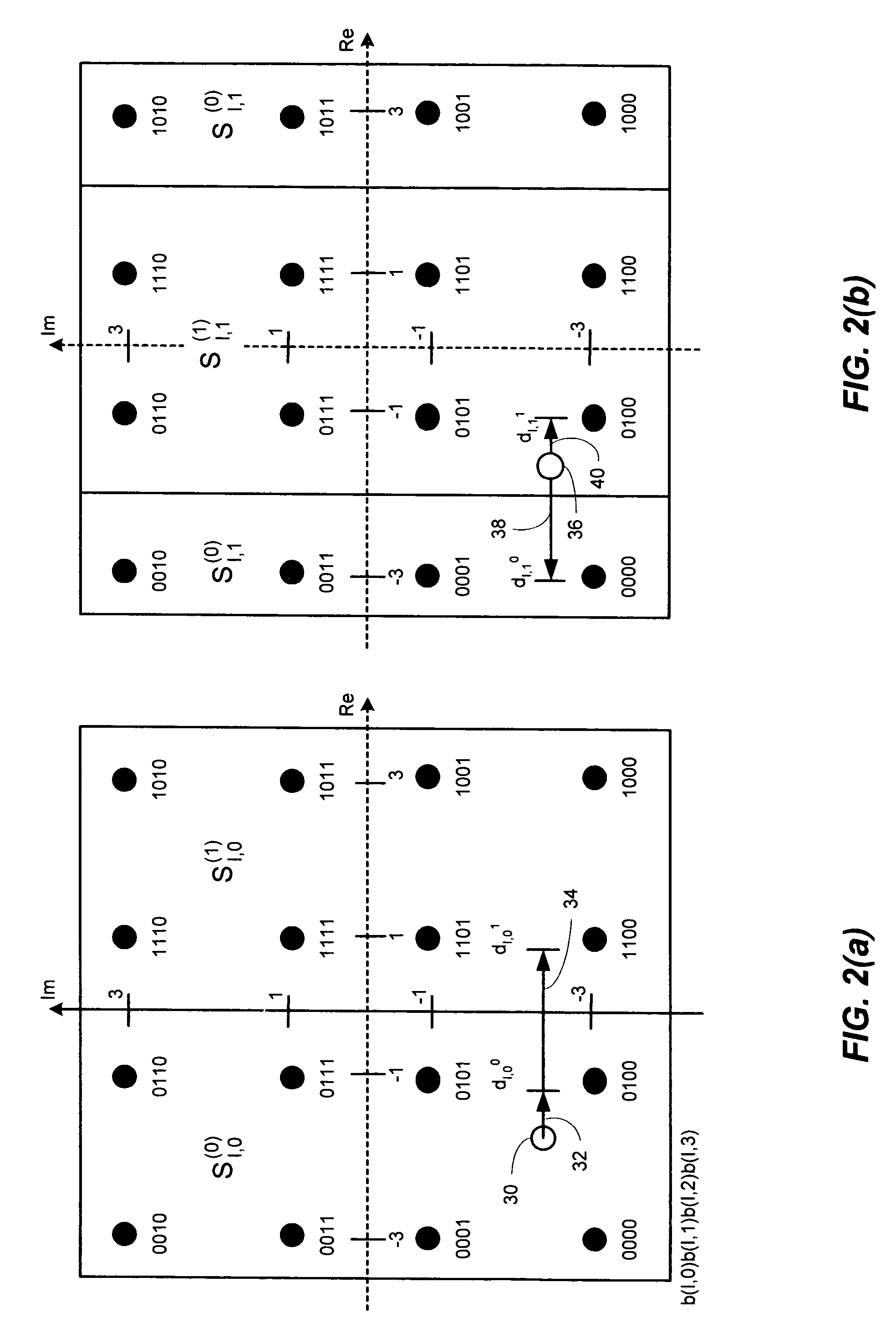
Efficient soft decision demapper to minimize viterbi decoder complexity
InactiveUS7313750B1Improve performanceSmall sizeData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesViterbi decoderComputer science
A receiver system that receives signals and has a demapper device that is responsive to an equalizer output and generates a demapper output including one or more bit metrics. The receiver system also generates equalizer output, and the demapper uses distance measure to calculate bit metrics. The receiver system uses demapper output to generate a processed output. The receiver system further includes a convolutional decoder which is responsive to the processed output, and subsequently generates a decoded bit sequence, as well as uses the processed output to generate one or more path metrics. The convolutional decoder uses bit metrics and path metrics to the decode processed output, to generate a decoded bit sequence. The receiver system uses the distance measure to reduce the size of the bit metrics and the size of the path metrics to improve the performance of said convolutional decoder.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Method for automatically adjusting the filter parameters of a digital equalizer and reproduction device for audio signals for implementing such a method
InactiveUS7289637B2Reduce spendingFrequency response correctionTransmissionUltrasound attenuationEngineering
A method is proposed for automatically adjusting the filter parameters—center frequency, quality and amplification or attenuation—of at least one digital equalizer which is a component of a reproduction device for audio signals in a vehicle passenger compartment. To that end, first of all, the acoustical frequency response of the passenger compartment is ascertained. The inadequacies in the acoustics of the passenger compartment in the form of local maxima and minima in the measured frequency response are then determined. On this basis, the filter parameters are adjusted automatically so that at least a portion of these inadequacies is compensated. A reproduction device for audio signals for implementing this method is also proposed.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
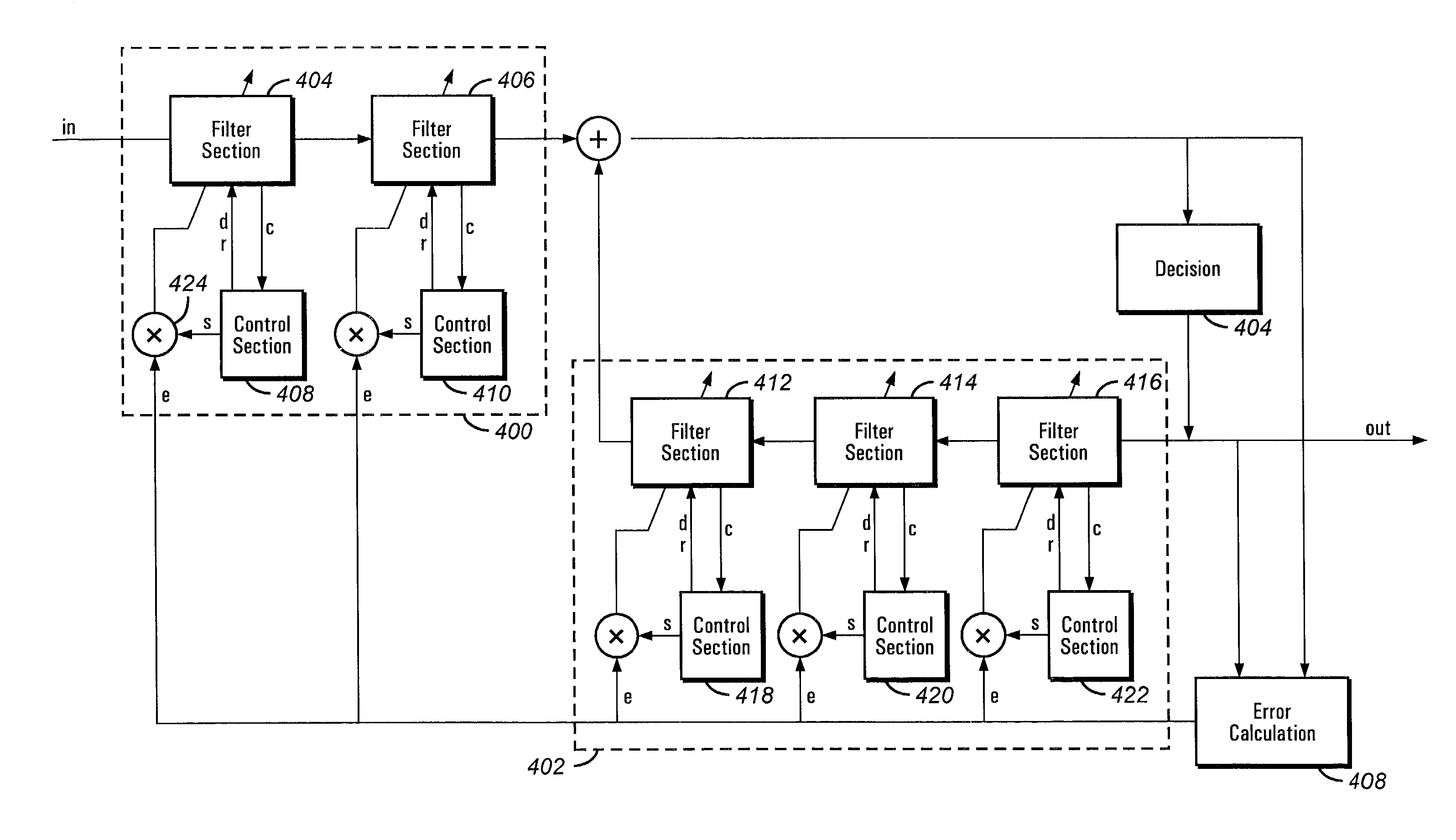
Convergence speed, lowering the excess noise and power consumption of equalizers
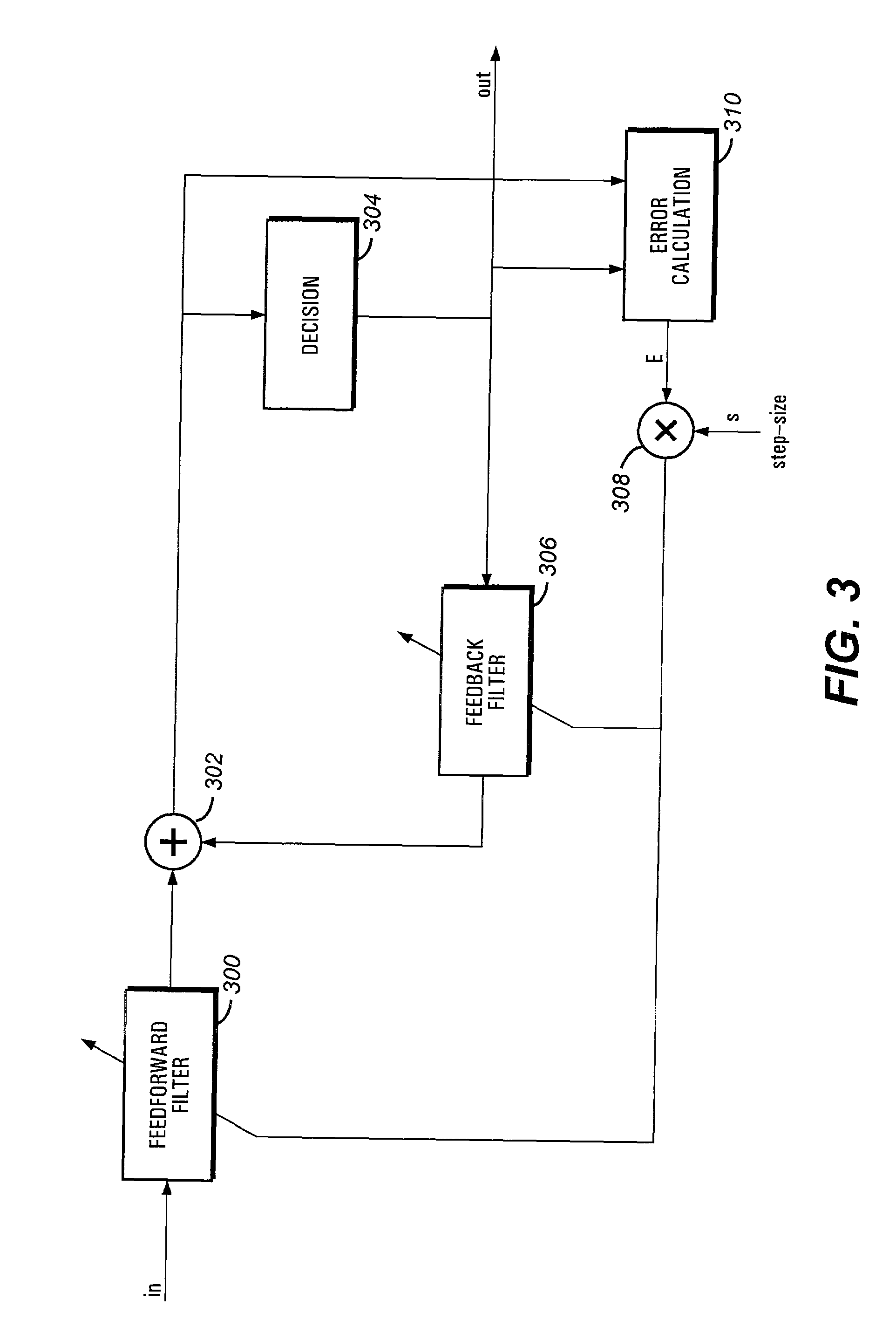
An equalizer for equalizing channel multi-path distortion includes digital filters. To improve the convergence speed and tracking ability of the equalizer while lowering noise and power consumption, the digital filters are divided into sections. Various parameters of the sections, such as step-size, shutdown and update rates can be controlled. Control of the various parameters can be realized either in software on an embedded or external processor or by dedicated hardware.
Owner:CONEXANT SYST INC
Method of channel order selection and channel estimation in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS6907092B1Choose accuratelyLarge energyError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemImpulse response
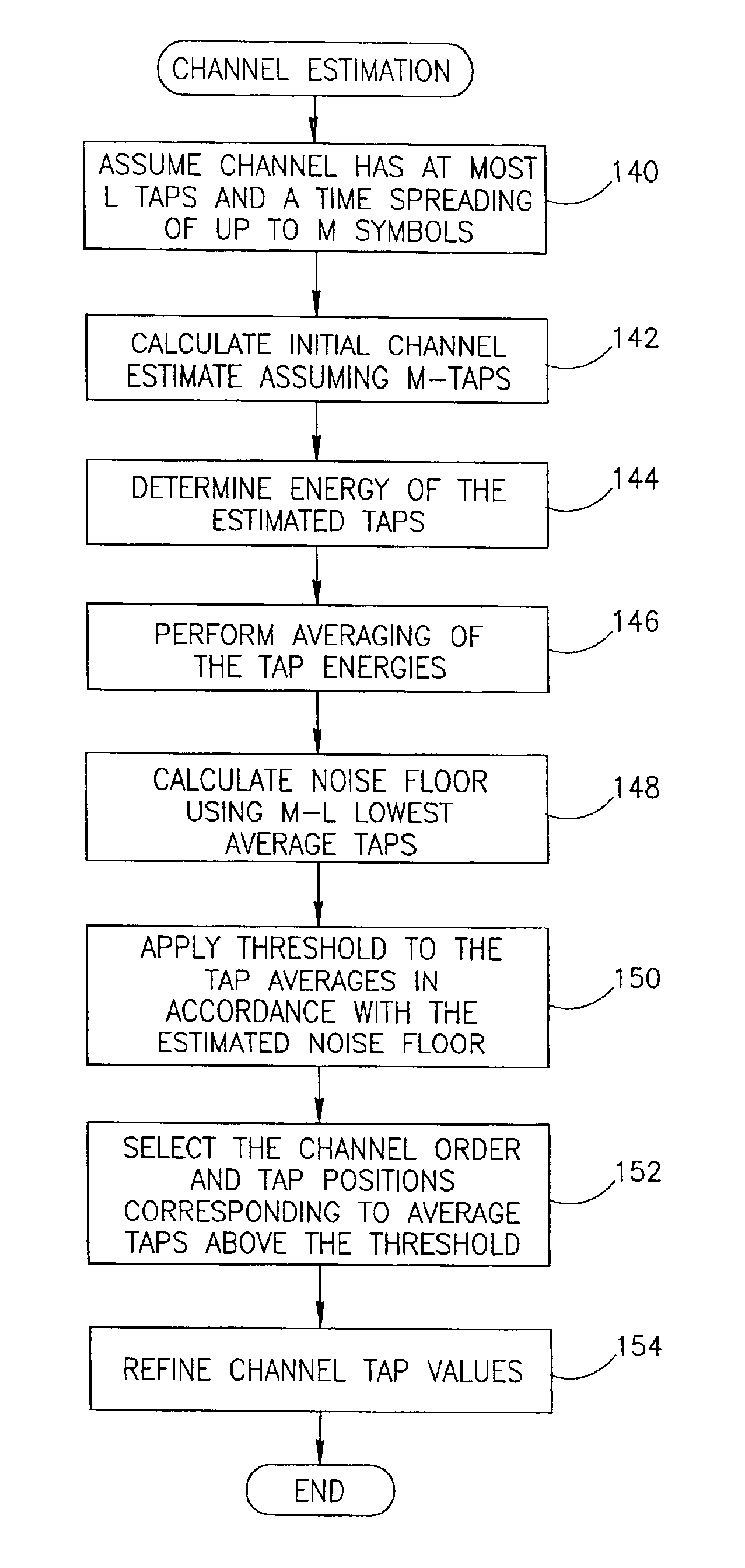
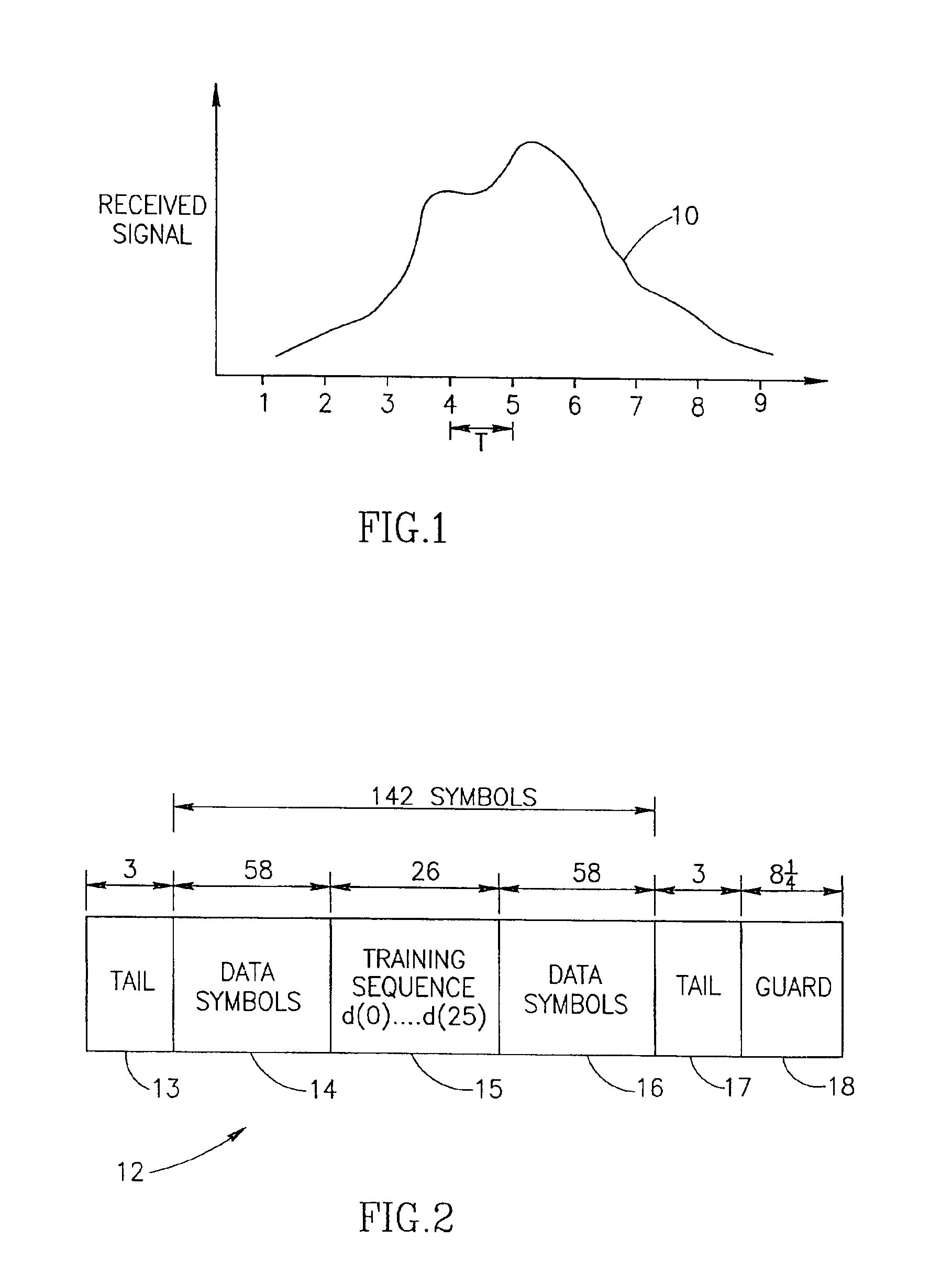
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of determining the channel order and channel estimate in a communications system such as a wireless communication system including cellular and cordless. Such channels are typically characterized by rapidly changing impulse response and their taps can be modeled as zero-mean, complex, Gaussian random processes. A sufficiently long, initial channel estimate of length is performed so as to ensure that the actual channel taps will be contained in the estimated taps thus making certain that the equalizer will effectively eliminate intersymbol interference. Channel estimation is performed during each burst using the training sequence transmitted in the middle of the burst. The tap energies are averaged so as to track slow variations in the pattern of resultant channel taps. A noise floor is calculated using the lowest averaged taps and a threshold is computed based thereon and applied to the average taps. The channel order and the tap positions are then selected in accordance those average taps that are above the threshold.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
Apparatus and method for synchronizing frequency in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing communication system
InactiveUS20020145971A1High precisionAccurate estimateAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationRadio frequencyFourier transform
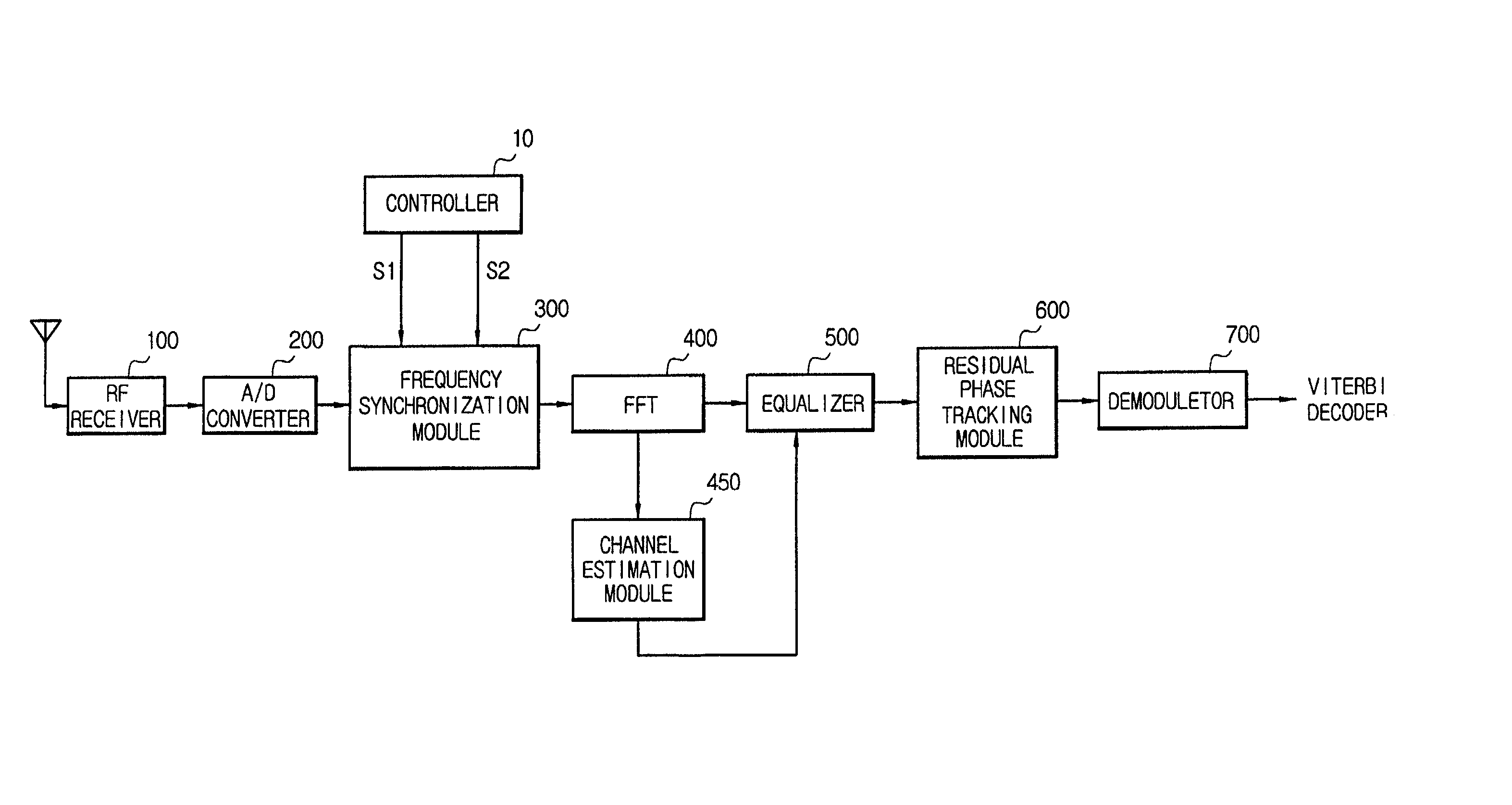
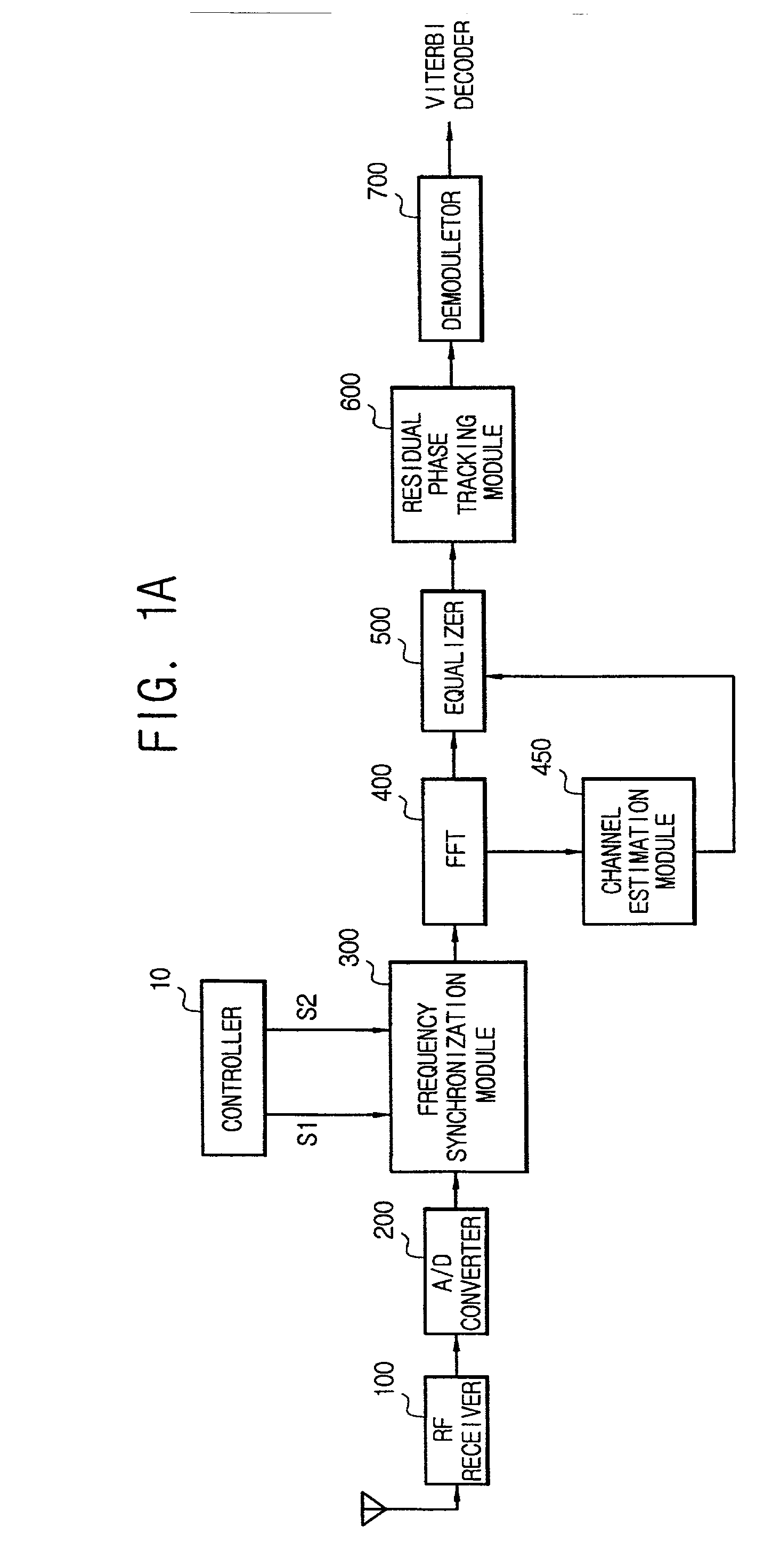
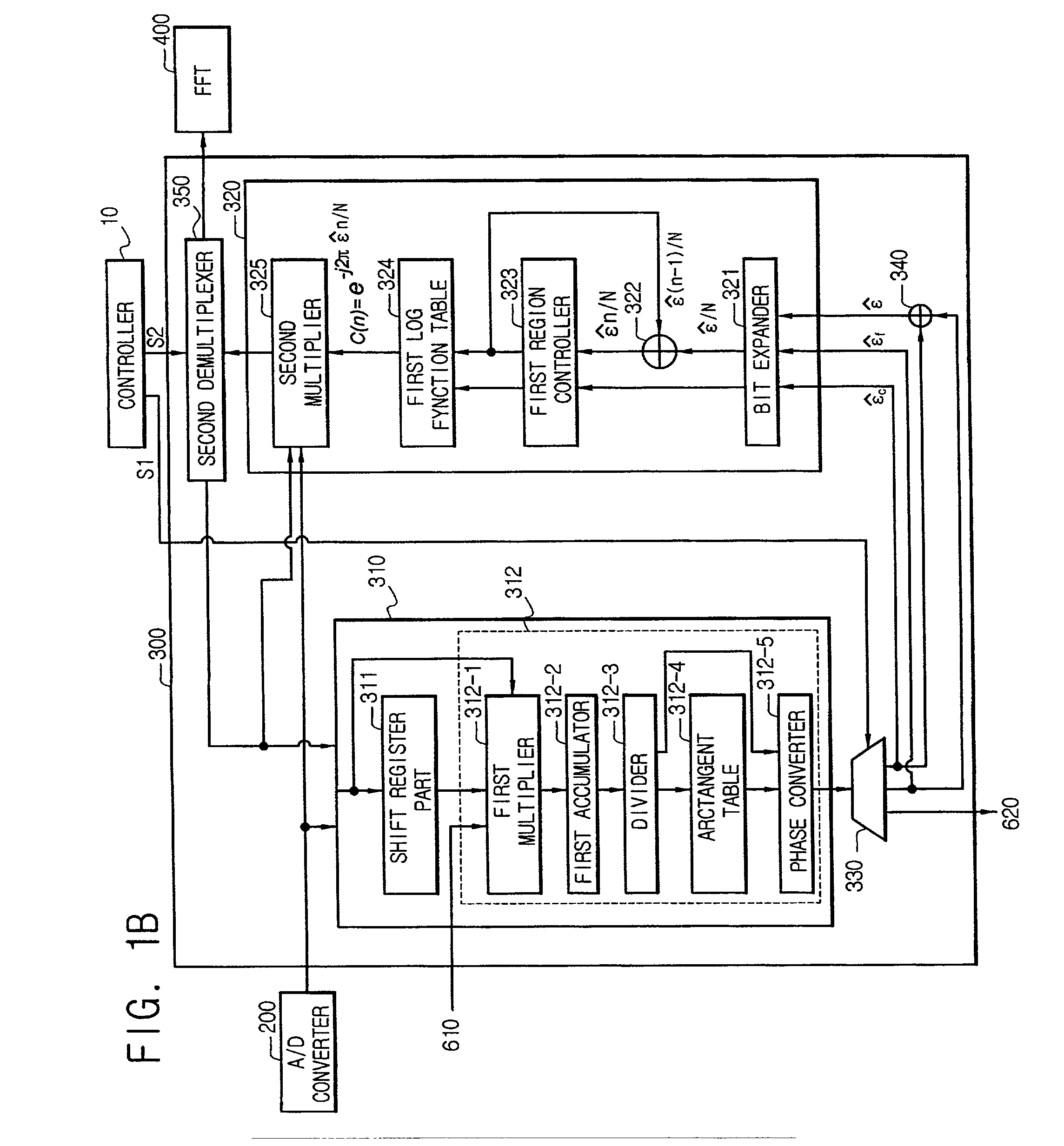
A frequency synchronization apparatus for an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) communication system includes a radio frequency (RF) receiving module for receiving OFDM signal, an analog / digital (A / D) converter connected to the RF receiving module, the A / D converter converting the OFDM signal into a digital signal, a frequency synchronization module connected to the A / D converter, the frequency synchronization module synchronizing carrier frequency, a Fast Fourier Transformer (FFT) connected to the frequency synchronization module, the FFT performing fast Fourier transformation to symbols from the frequency synchronization module, a channel estimation module connected to the FFT, the channel estimation module estimating channel response, an equalizer connected to the FFT and the channel estimation module, the equalizer equalizing channel, a residual phase tracking module connected to the equalizer, the residual phase tracking module tracking residual phase, a demodulator connected to the residual phase tracking module, the demodulator demodulating, and a controller connected to the frequency synchronization module, the controller controlling the frequency synchronization module.
Owner:CHUNG ANG UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
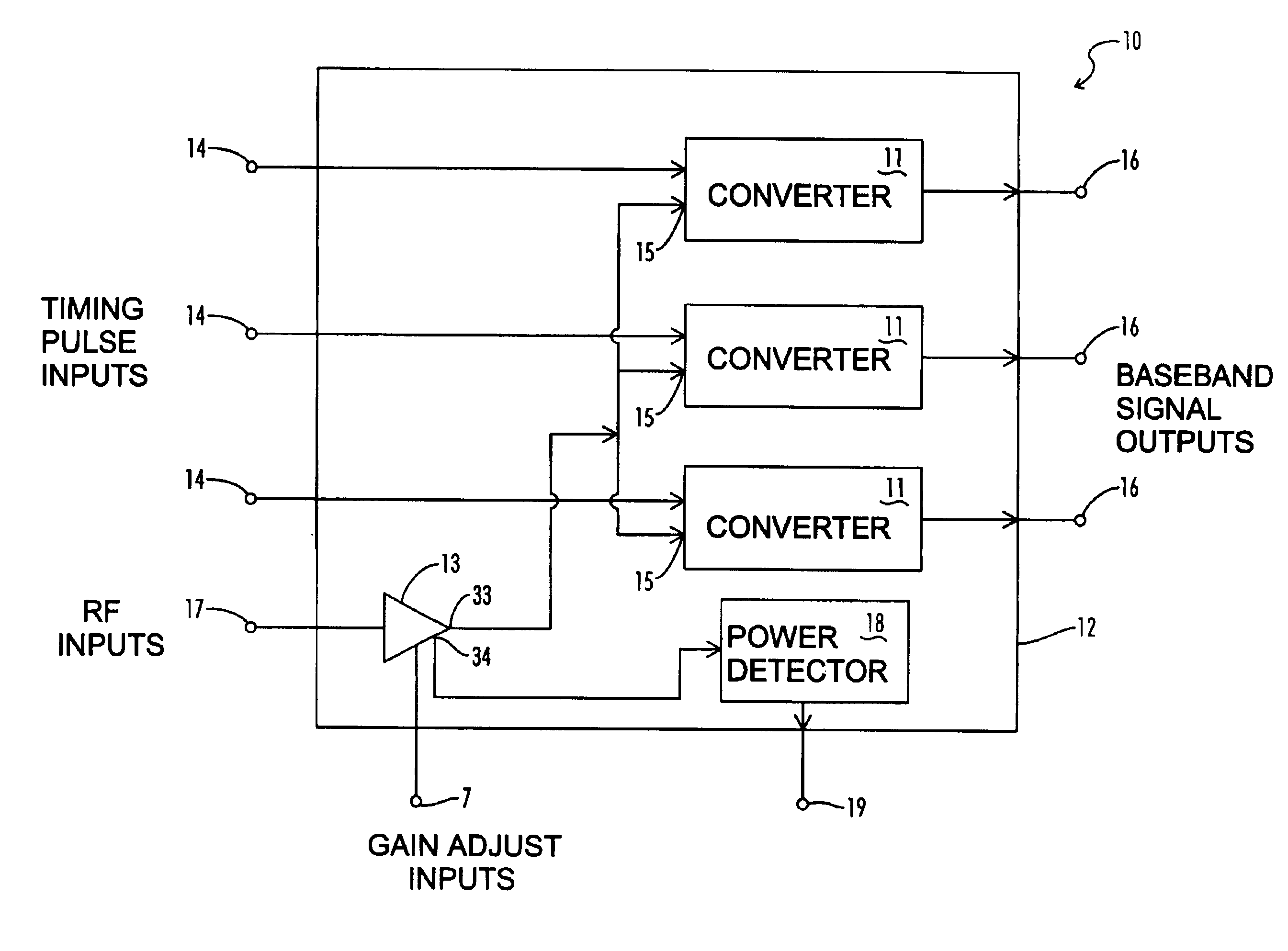
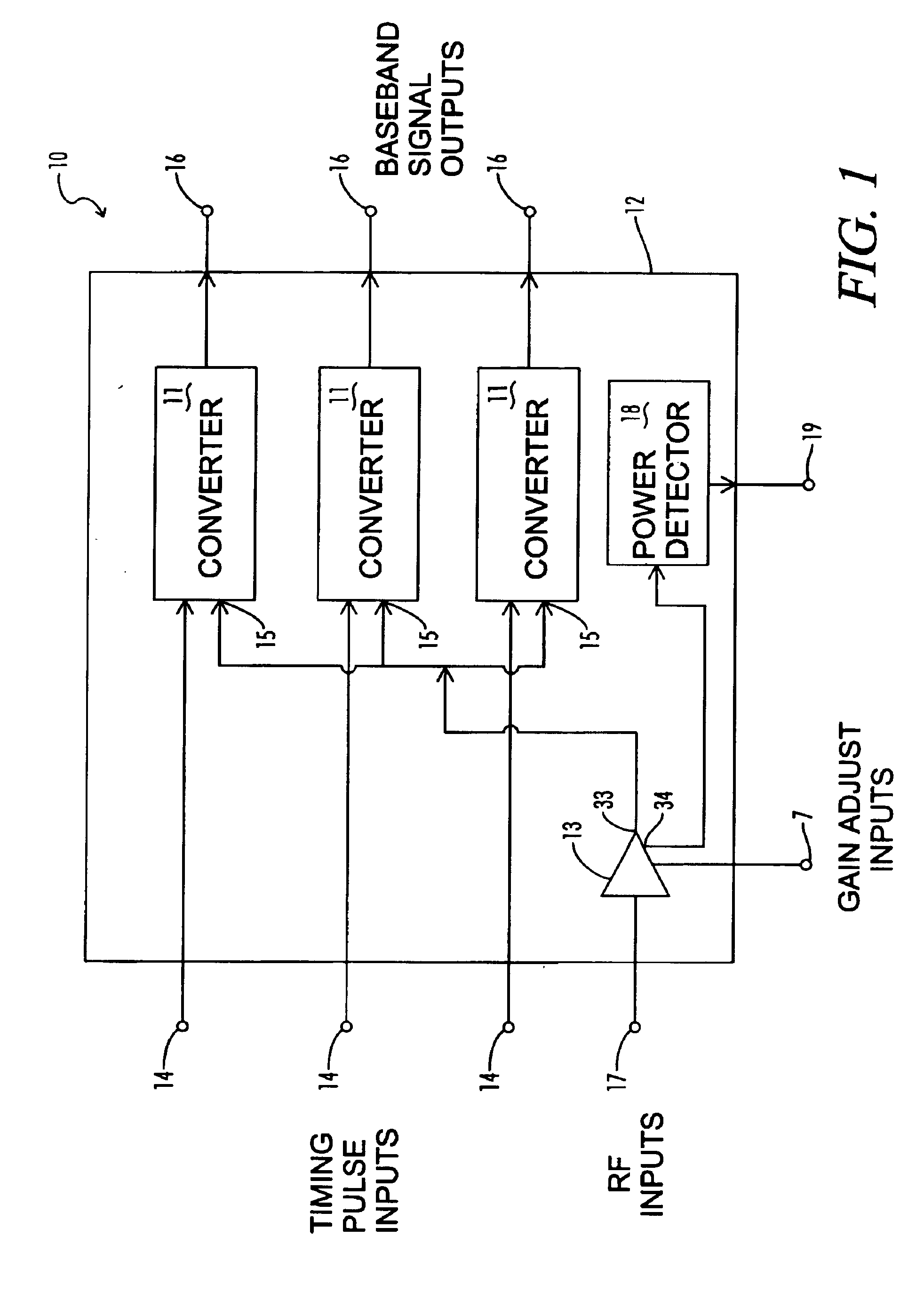
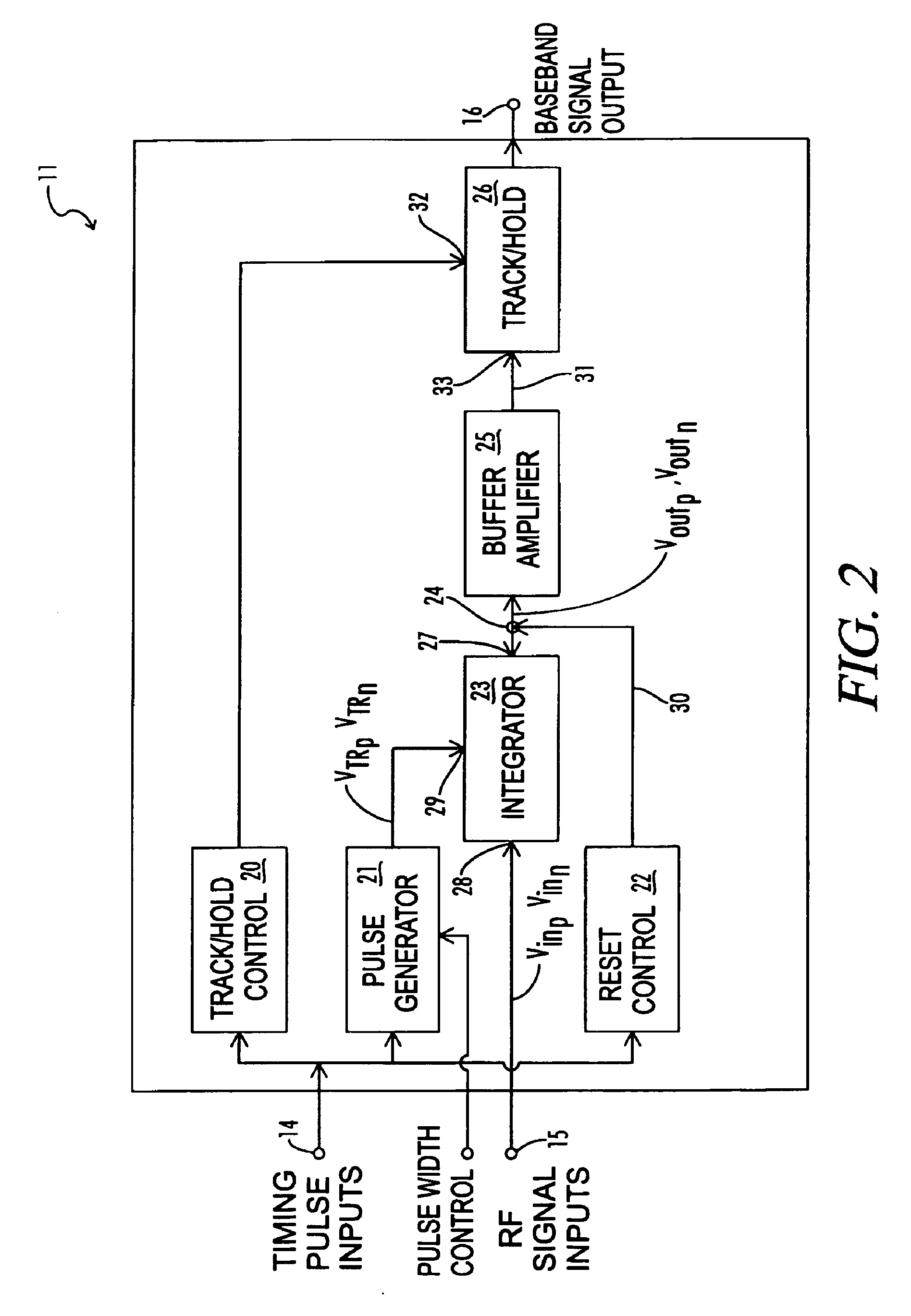
Baseband signal converter for a wideband impulse radio receiver
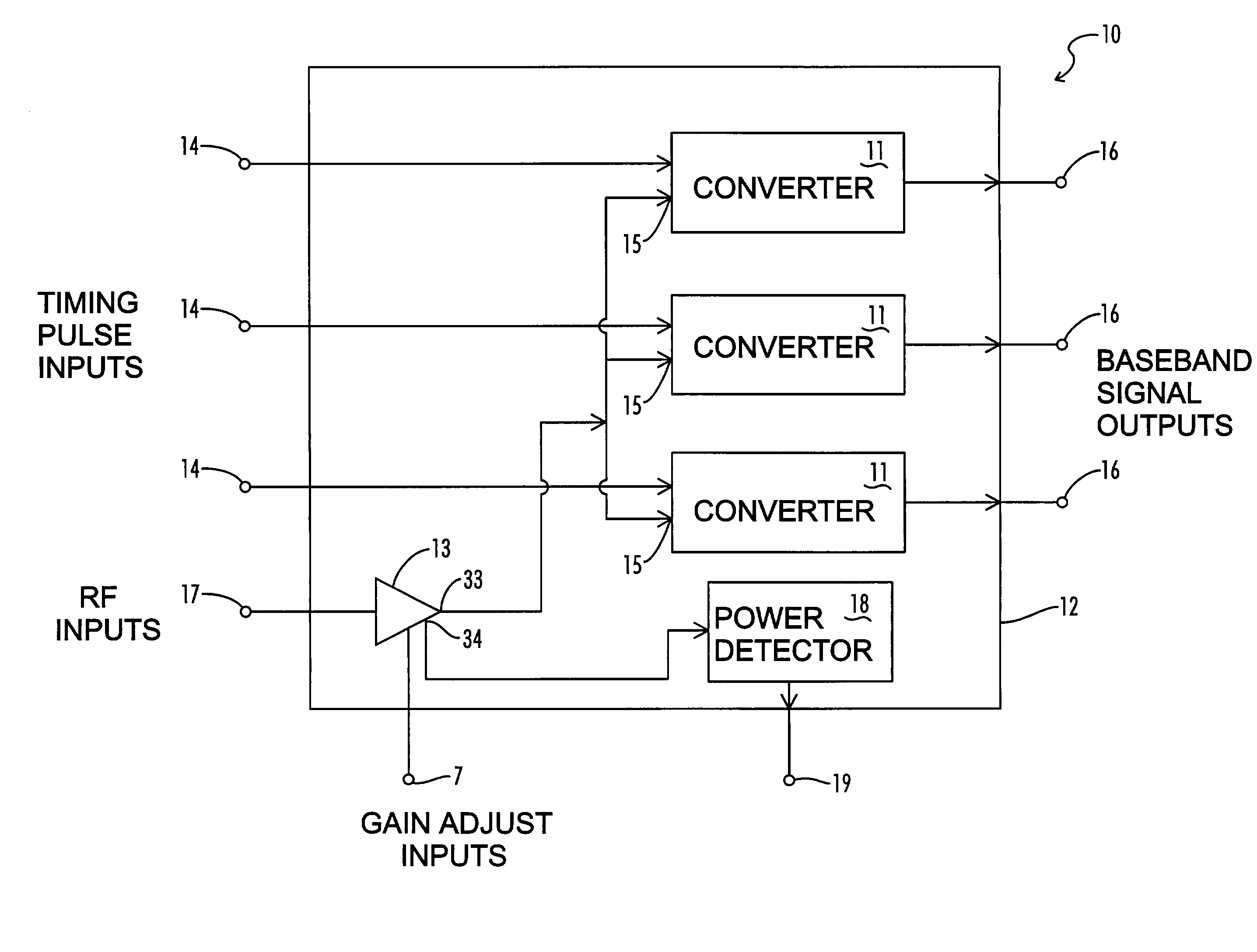
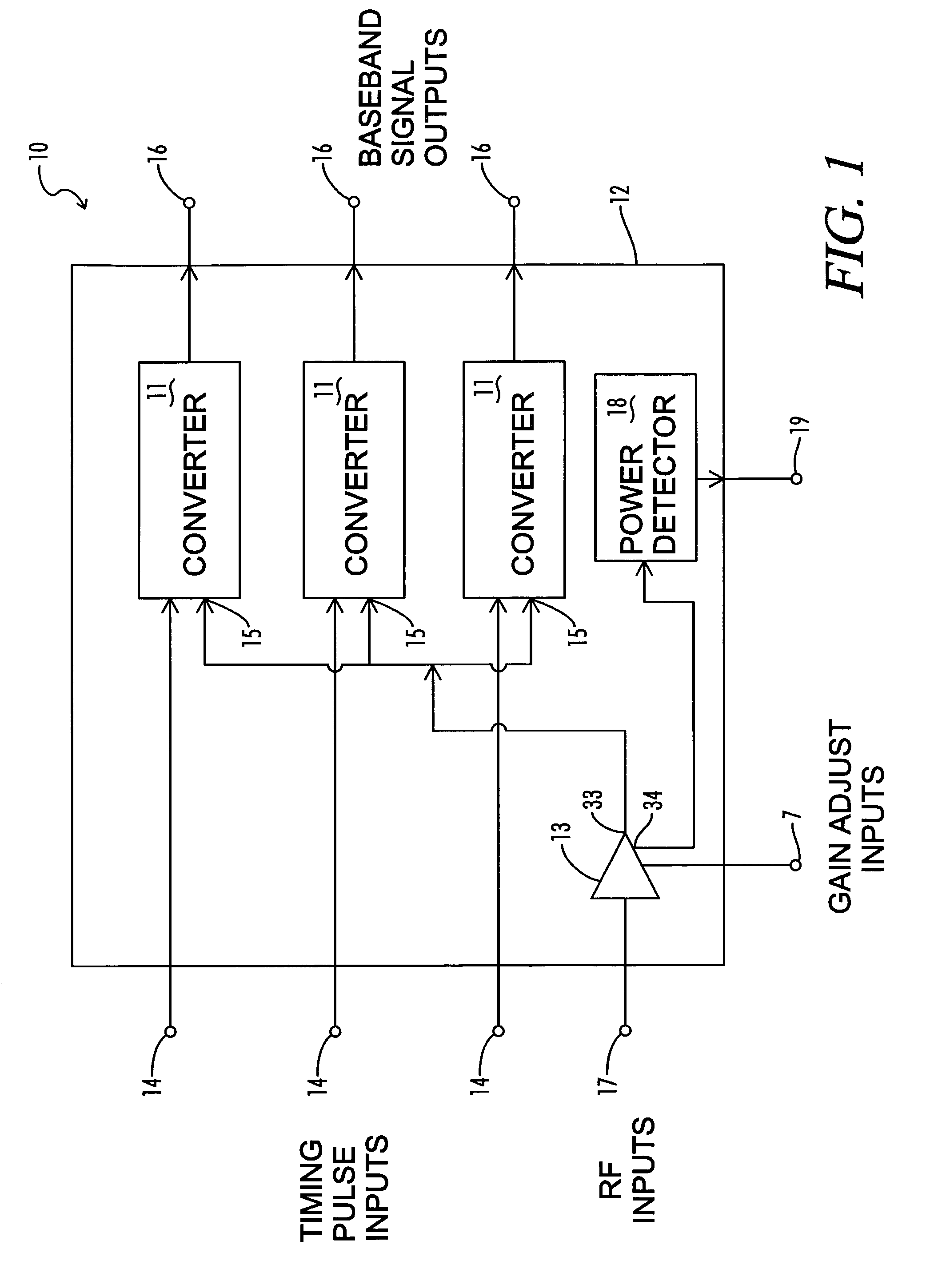
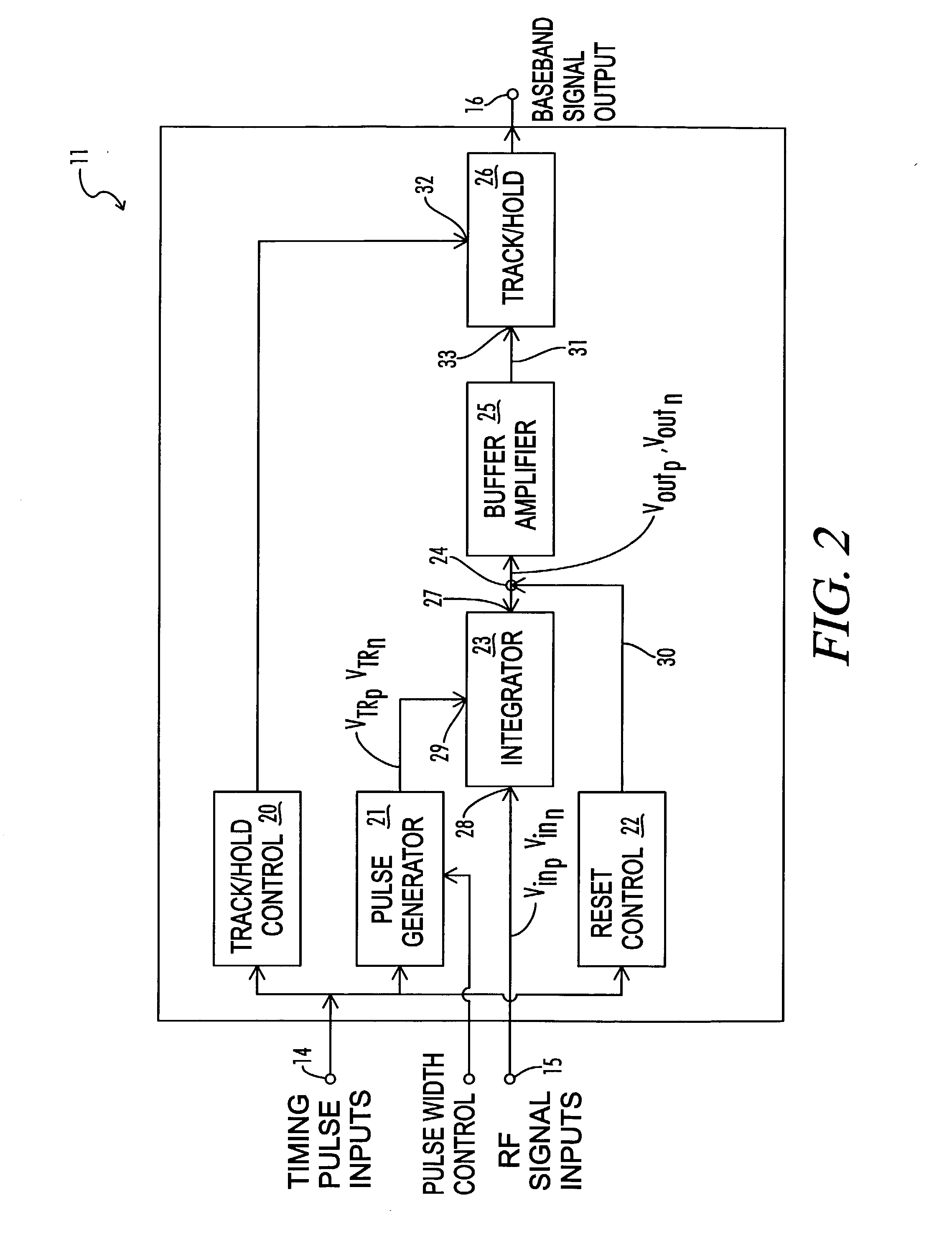
InactiveUS6937663B2Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationBroadband pulseCapacitance
A baseband signal converter device for an impulse radio receiver combines multiple converter circuits and an RF amplifier in a single integrated circuit package. Each converter circuit includes an integrator circuit that integrates a portion of each RF pulse during a sampling period triggered by a timing pulse generator. The integrator capacitor is isolated by a pair of Schottky diodes connected to a pair of load resistors. A current equalizer circuit equalizes the current flowing through the load resistors when the integrator is not sampling. Current steering logic transfers load current between the diodes and a constant bias circuit depending on whether a sampling pulse is present.
Owner:ALEREON
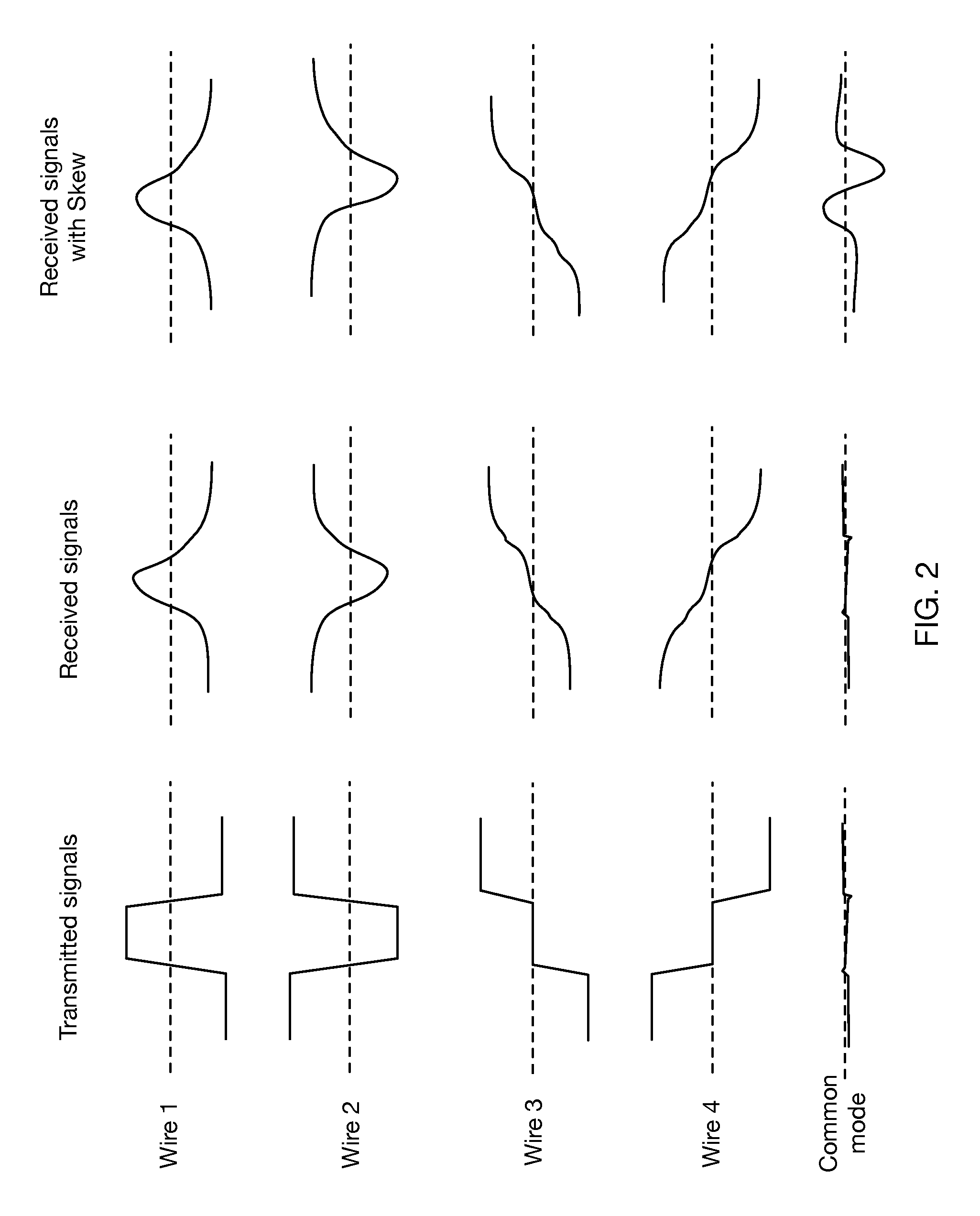
Multiwire linear equalizer for vector signaling code receiver
ActiveUS9106465B2Improve efficiencyReduce power consumptionMultiple-port networksHigh frequency amplifiersSignal onEqualization
Continuous-time linear equalization of received signals on multiple wire channels while maintaining accurate common mode signal values. Multiwire group signaling using vector signaling codes simultaneously transmits encoded values on multiple wires, requiring multiple receive signals to be sampled simultaneously to retrieve the full transmitted code word. By misaligning transitions on multiple wires, skew introduces a transient common mode signal component that is preserved by using frequency-selective common mode feedback at the receiver to obtain accurate sampling results.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
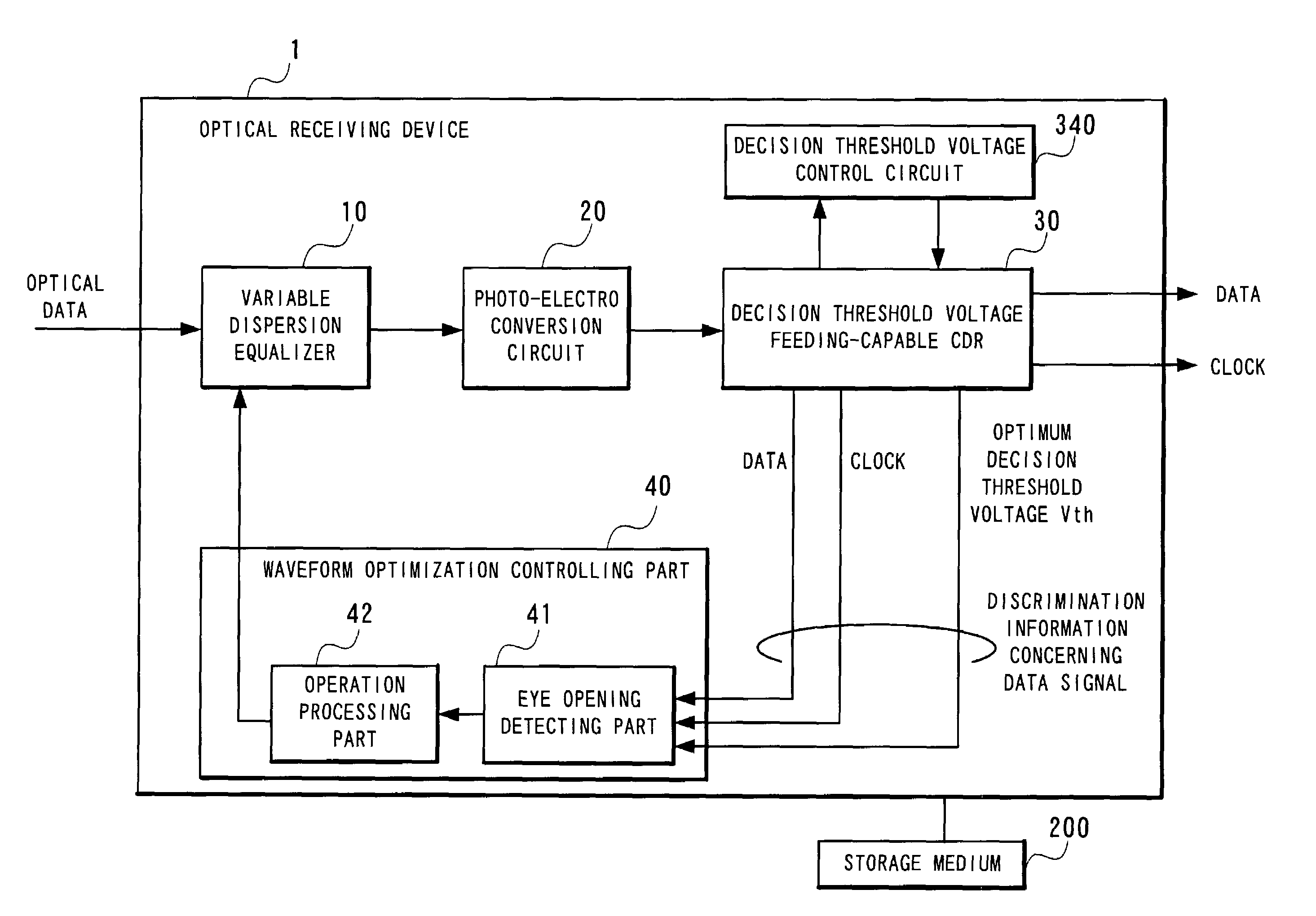
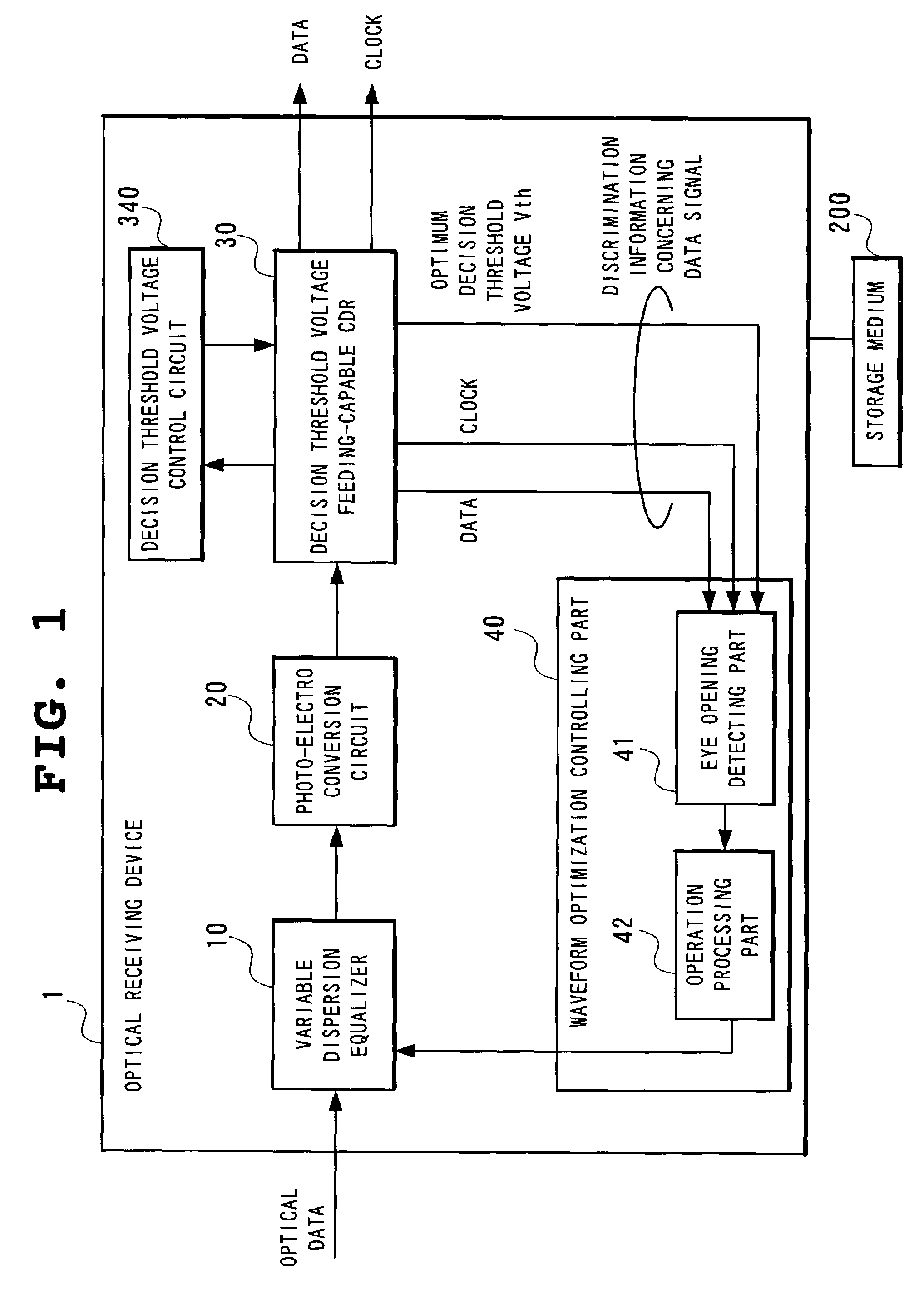
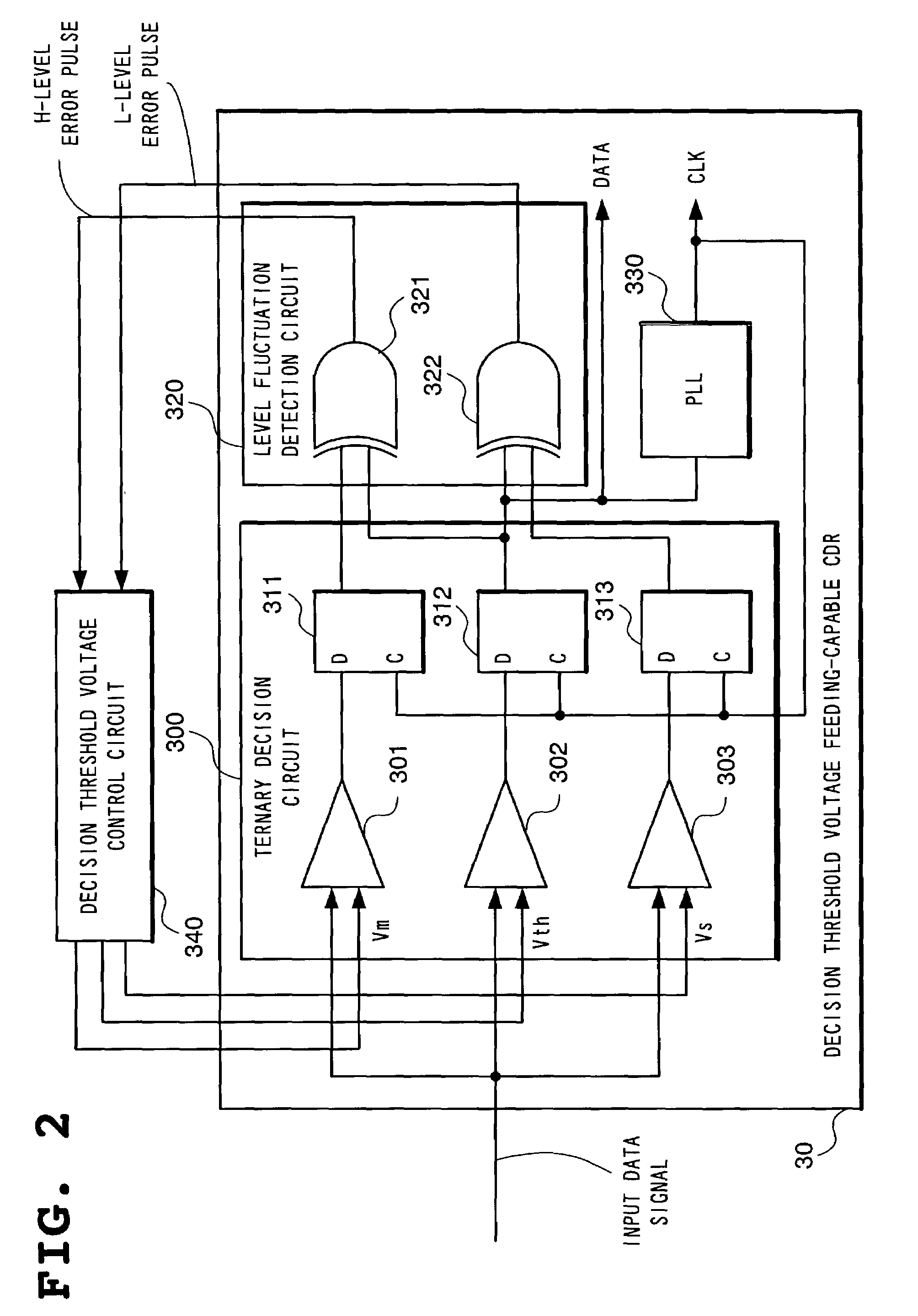
Optical receiving device, waveform optimization method for optical data signals, and waveform optimization program for optical data signals
InactiveUS7123846B2Improve waveformOptimize optical waveformTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersData signalControl data
This optical receiving device for discriminating and recovering a data signal, which results from converting an optical signal input through a dispersion equalizer into an electrical signal and amplifying it to a pre-determined amplitude, by using a clock and data recovery circuit for discriminating a data signal at the decision point controlled to achieve the optimum position controls the dispersion characteristics of a dispersion equalizer so that the error count in the recovered data signal by using a clock and data recovery circuit will be minimized by controlling the eye pattern of the data signal which has been amplified to a pre-determined amplitude.
Owner:NEC CORP
Adjusting sampling phase in a baud-rate CDR using timing skew
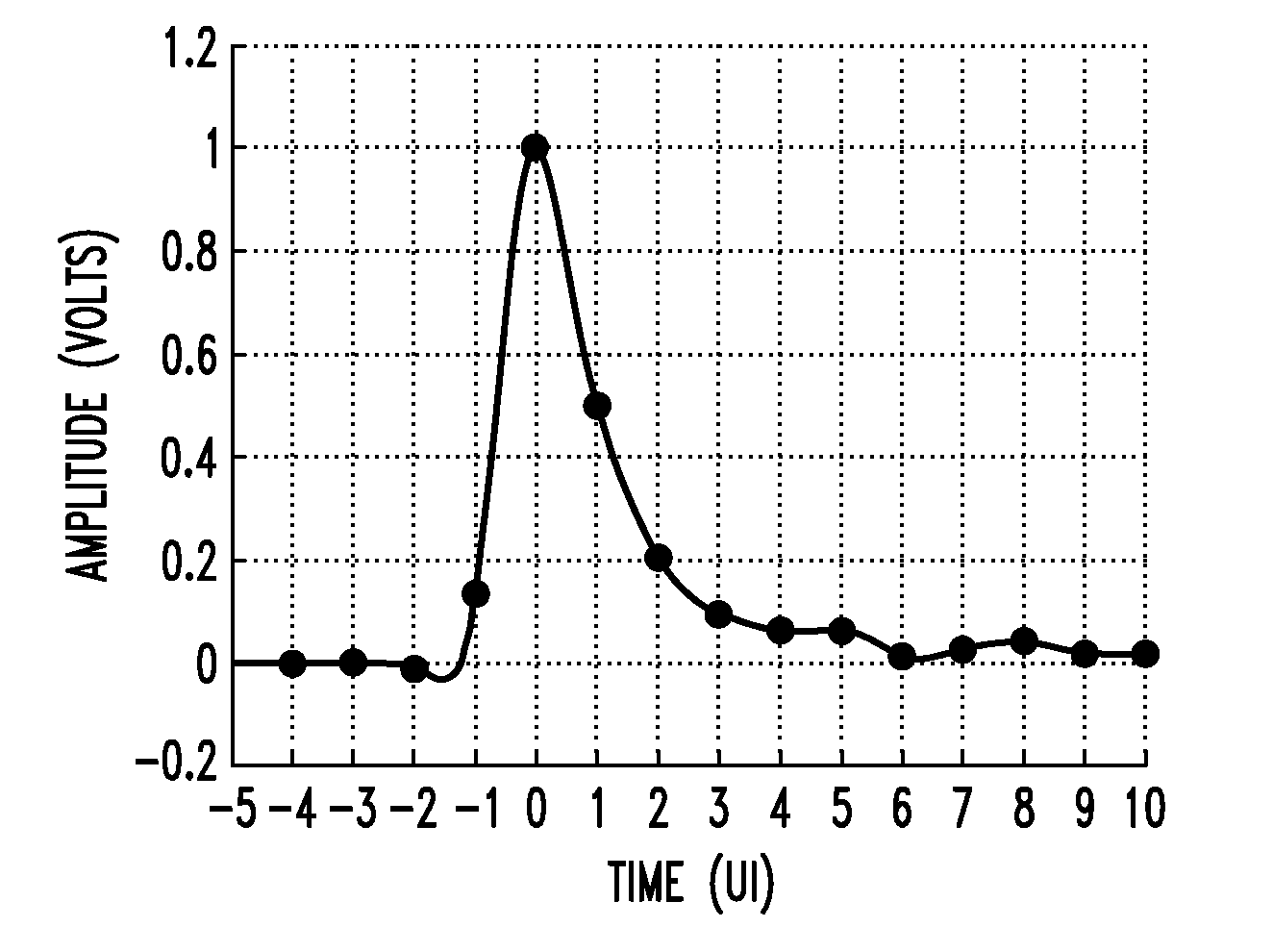
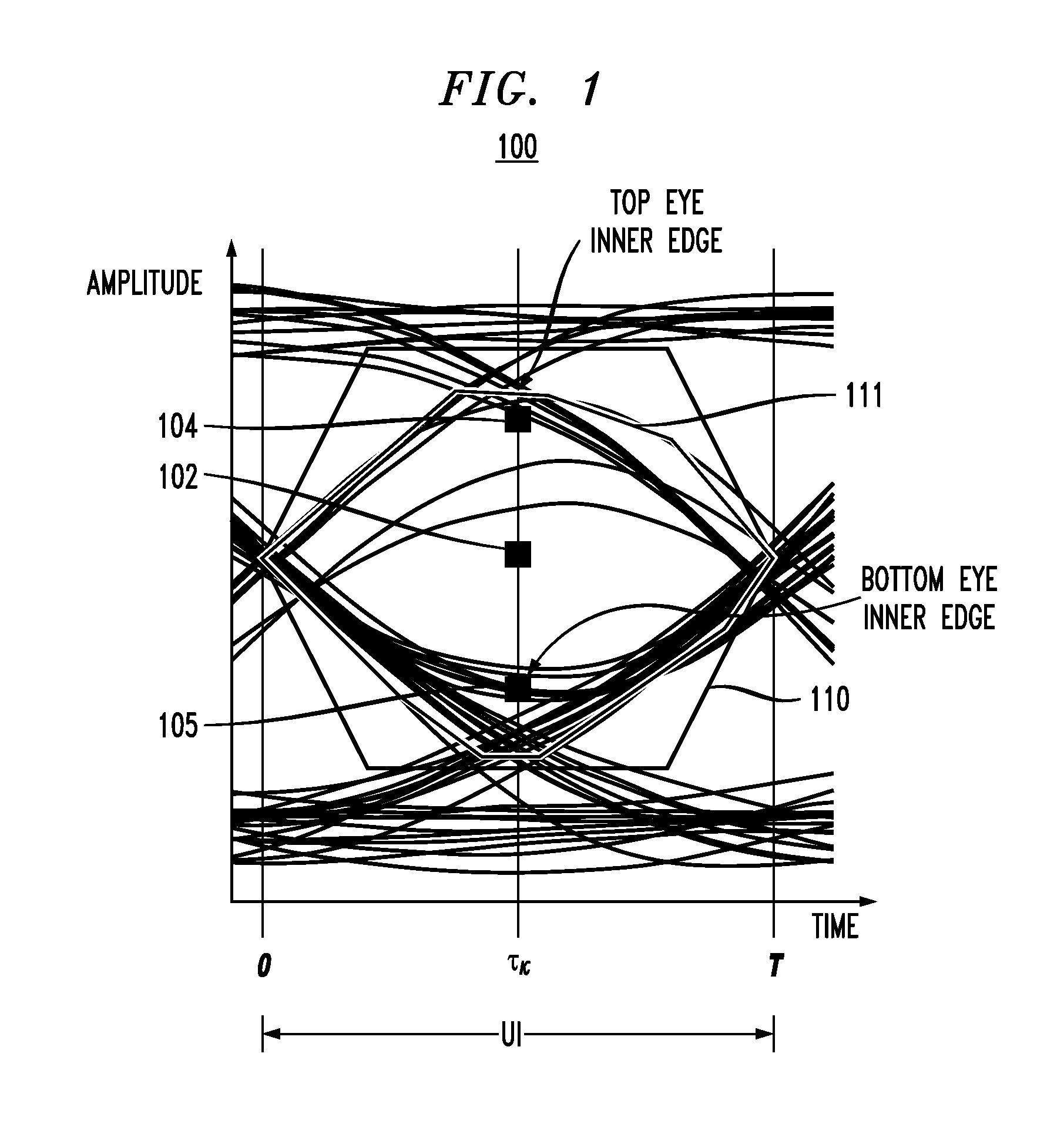
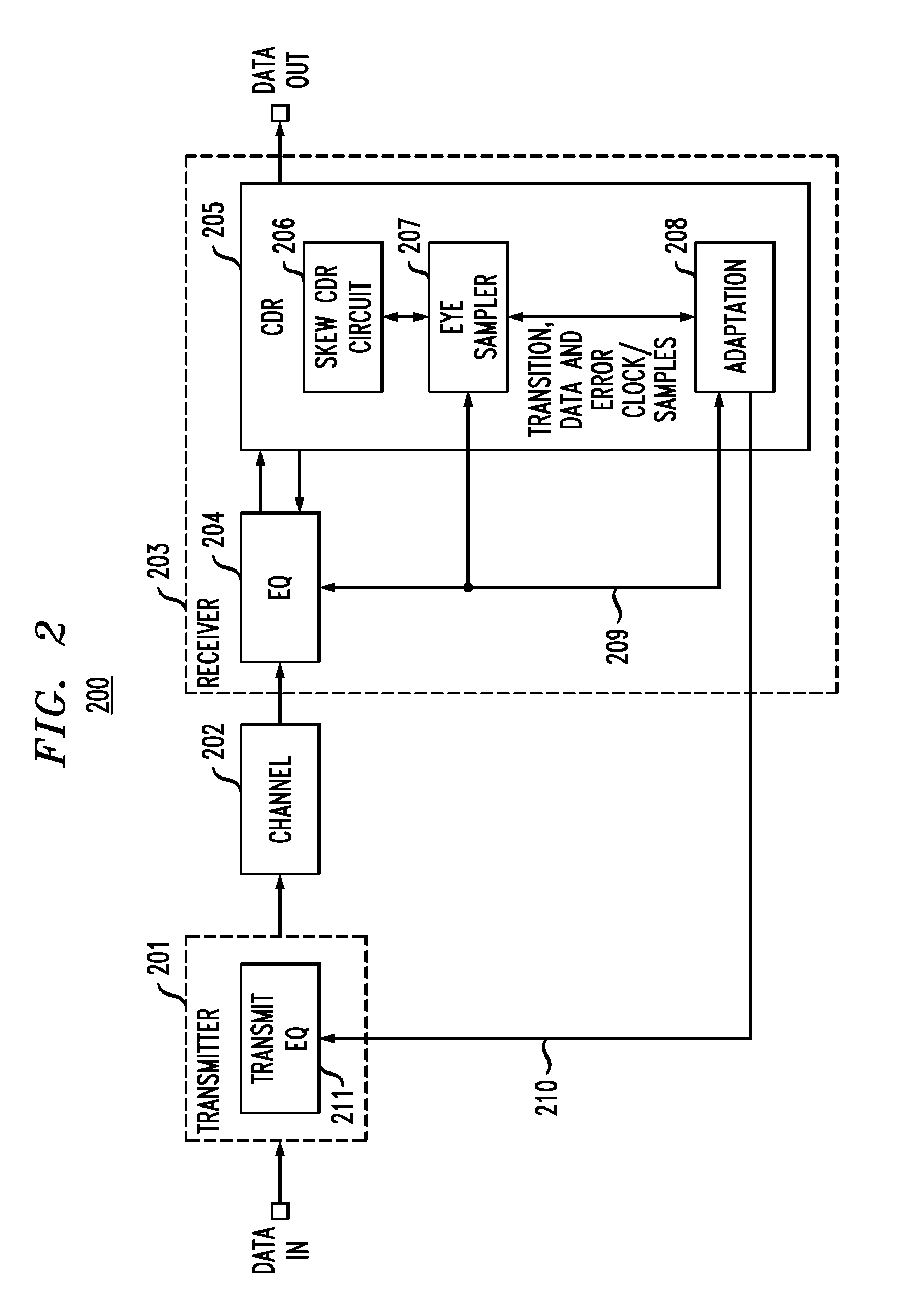
In described embodiments, a transceiver includes a baud-rate clock and data recovery (CDR) module with an eye sampler, and an adaptation module for adaptively setting parameters of various circuit elements, such as timing, equalizer and gain elements. Data sampling clock phase of the CDR module is set for sampling at, for example, near the center of a data eye detected by the eye sampler, and the phase of data error sampling latch(es) is skewed by the CDR module with respect to the phase of the data sampling latch. Since the error signal driving the timing adaptation contains the information of the pulse response that the CDR module encounters, the phase of timing error sampling latch(es) of the CDR module is skewed based on maintaining a relative equivalence of input pulse response residual pre-cursor and residual post-cursor with respect to the timing error sampling clock phase.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Single carrier high rate wireless system
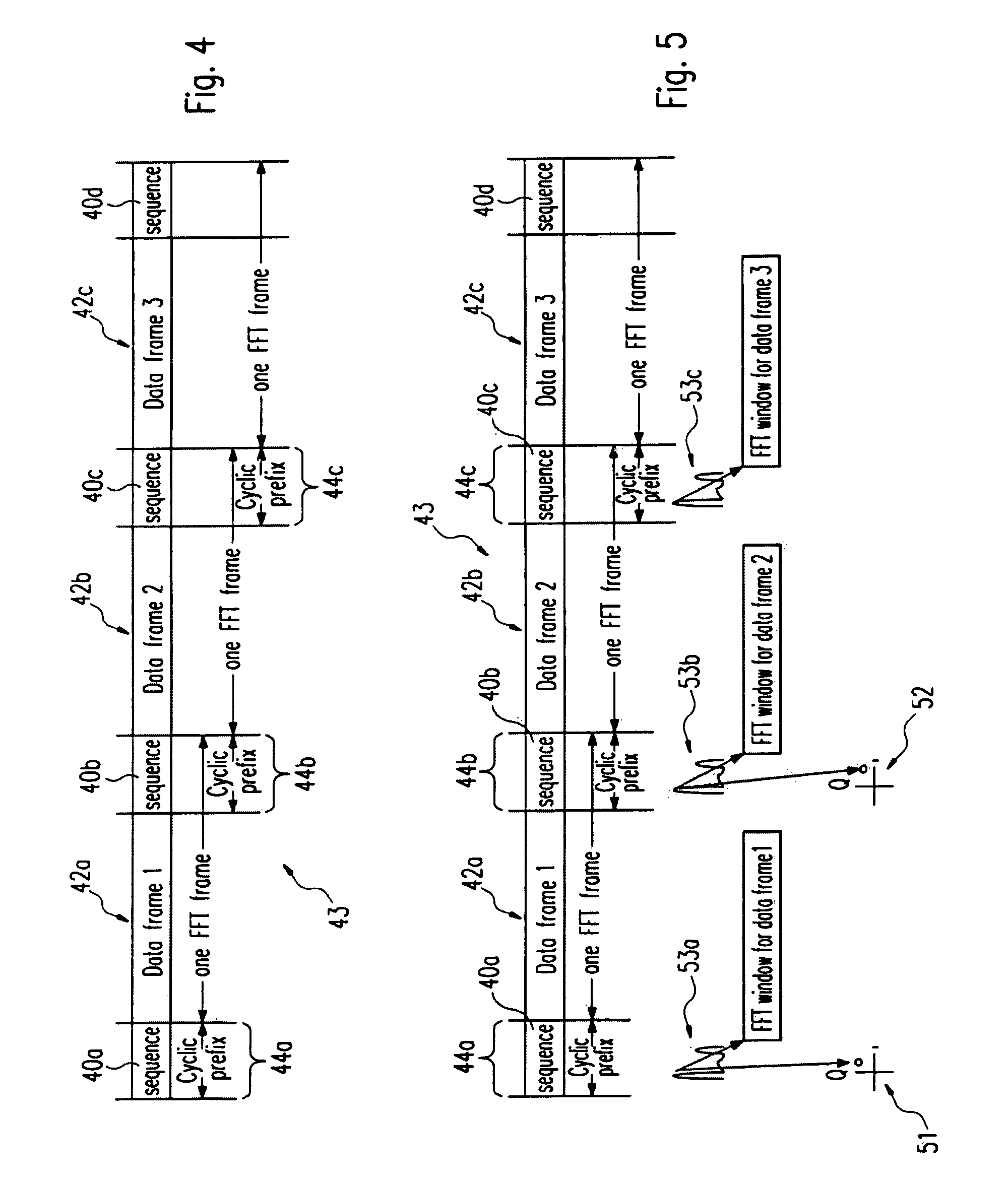
ActiveUS20080240307A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationElectrical and Electronics engineeringCyclic prefix
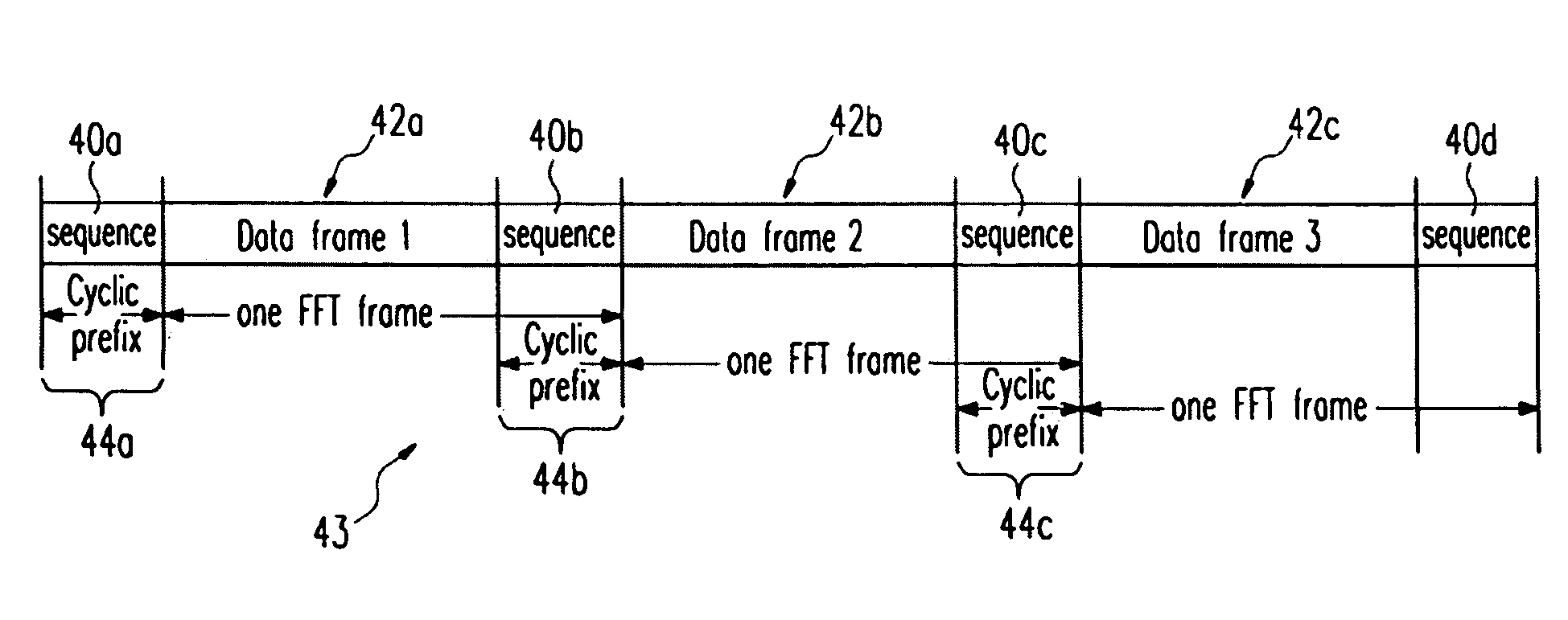
The present invention relates to a signal generator and signal processor for single carrier wireless communication systems with frequency domain equalizer, which are operable to use pseudorandom-noise sequences for cyclic prefix. The different arrangements and examples of said pseudorandom-noise sequences could be used for coarse timing synchronization, channel estimation, carrier synchronization, signal-noise-ration estimation and channel equalization.
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
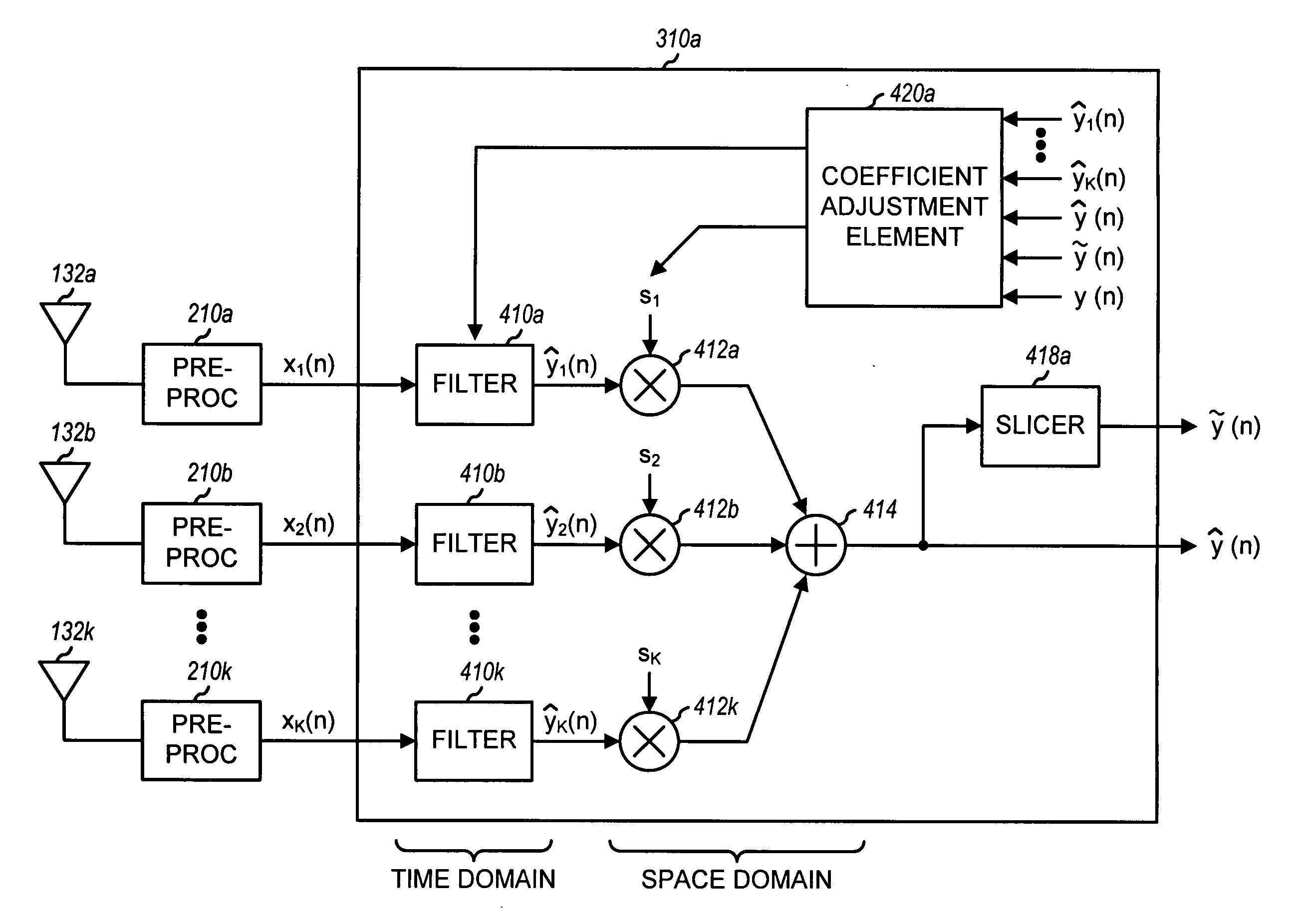
Hybrid time-frequency domain equalization over broadband multi-input multi-output channels
InactiveUS20080304558A1Good flexibilityMore reliabilityMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsMulti inputData stream
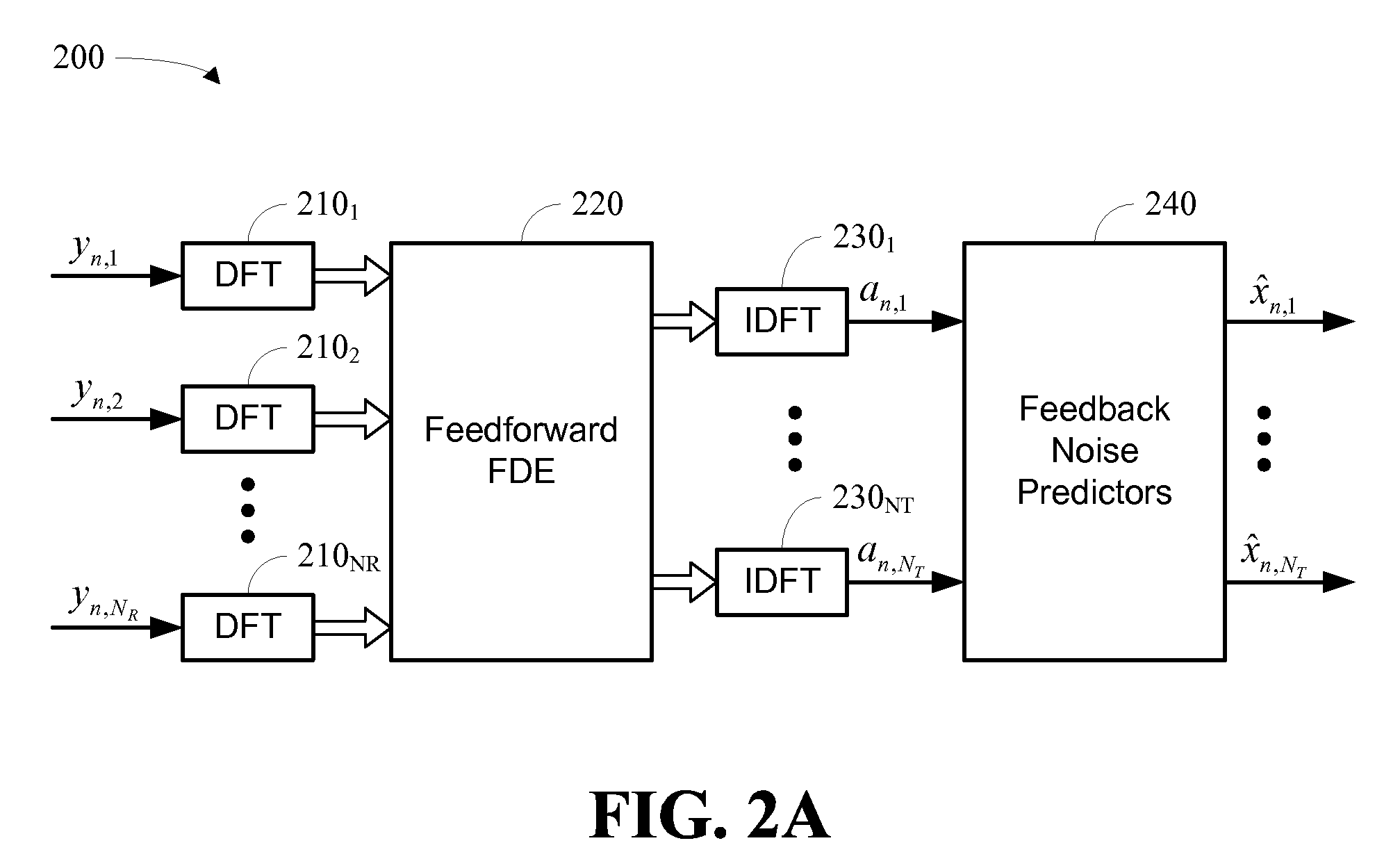
A system and methodology for channel equalization are provided. According to one aspect, a receiver structure for a MIMO system is provided that employs frequency domain equalization (FDE) with noise prediction (FDE-NP). The FDE-NP structure may include a feedforward linear frequency domain equalizer and a group of time domain noise predictors (NPs), which may operate by predicting a distortion corresponding to a given linearly equalized data stream based on previous distortions of all linearly equalized data streams. According to another aspect, a receiver structure for a MIMO system is provided that employs FDE-NP with successive interference cancellation (FDE-NP-SIC), which can extend the functionality of FDE-NP by ordering all linearly equalized data streams according to their minimum mean square errors (MMSEs) and detecting those streams which have a low MMSE first, thereby allowing current decisions of lower-indexed streams to be considered along with previous decisions for all data streams for noise prediction. According to a third aspect, a method for analyzing the performance of a MIMO system with equalization is provided. Pursuant to the method, a general expression of MMSE may first be derived. The MMSE expression may then be related to an error bound by applying the modified Chernoff bounding methodology in a general MIMO system. The parameters in the result may then be varied for applicability to single-input single-output (SISO), multiple-input single-output (MISO), and single-input multiple-output (SIMO) systems with receiver equalization technology.
Owner:YIM TU INVESTMENTS
Baseband signal converter for a wideband impulse radio receiver
InactiveUS20020126769A1Stable outputAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationBroadband pulseSoftware engineering
A baseband signal converter device for an impulse radio receiver combines multiple converter circuits and an RF amplifier in a single integrated circuit package. Each converter circuit includes an integrator circuit that integrates a portion of each RF pulse during a sampling period triggered by a timing pulse generator. The integrator capacitor is isolated by a pair of Schottky diodes connected to a pair of load resistors. A current equalizer circuit equalizes the current flowing through the load resistors when the integrator is not sampling. Current steering logic transfers load current between the diodes and a constant bias circuit depending on whether a sampling pulse is present.
Owner:ALEREON
MMSE equalizers for DMT systems with cross talk
InactiveUS6097763ABetter signal to noise ratioRaise the ratioSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A improved method for optimally equalizing a multicarrier communications system in the presence of both intersymbol interference (ISI) and colored noise. The method provides a frequency-domain training algorithm to obtain a minimum mean square error (MMSE) equalizer that accounts for both intersymbol interference (ISI) and colored noise, maximizes the signal to noise ratio (SNR) of systems using Discrete Multitone (DMT) modulation, and results in significant performance gains over prior equalization methods.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
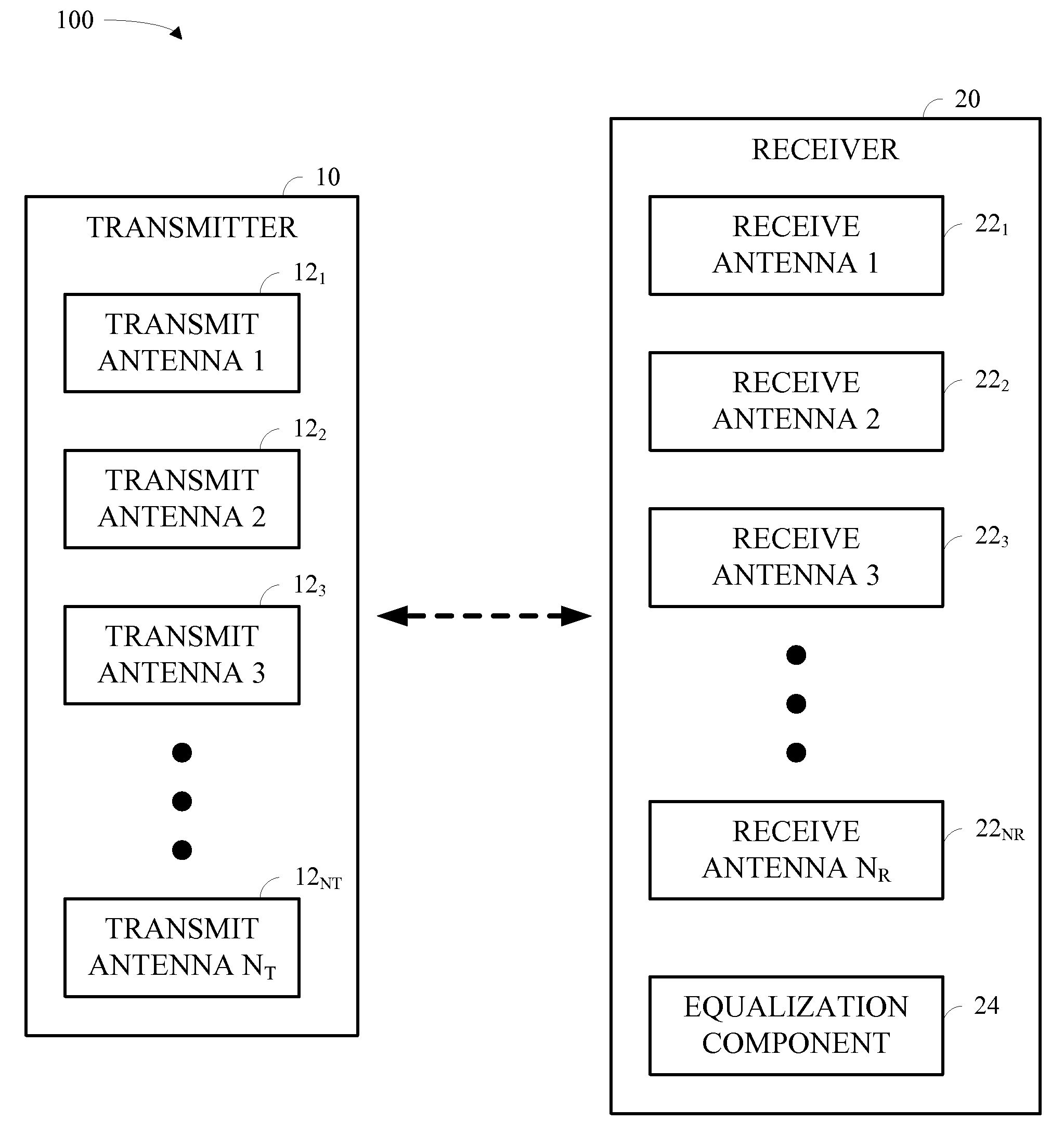
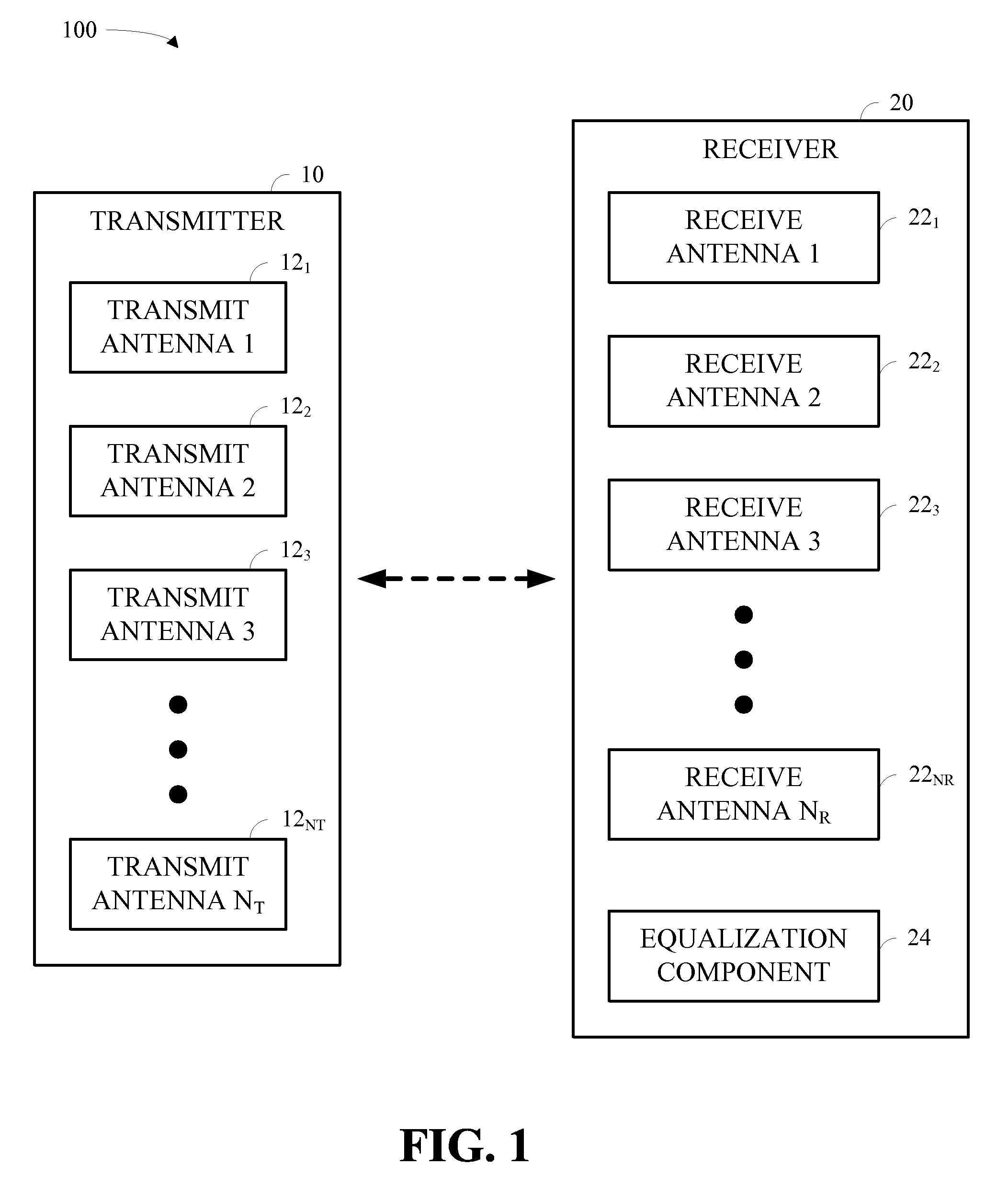
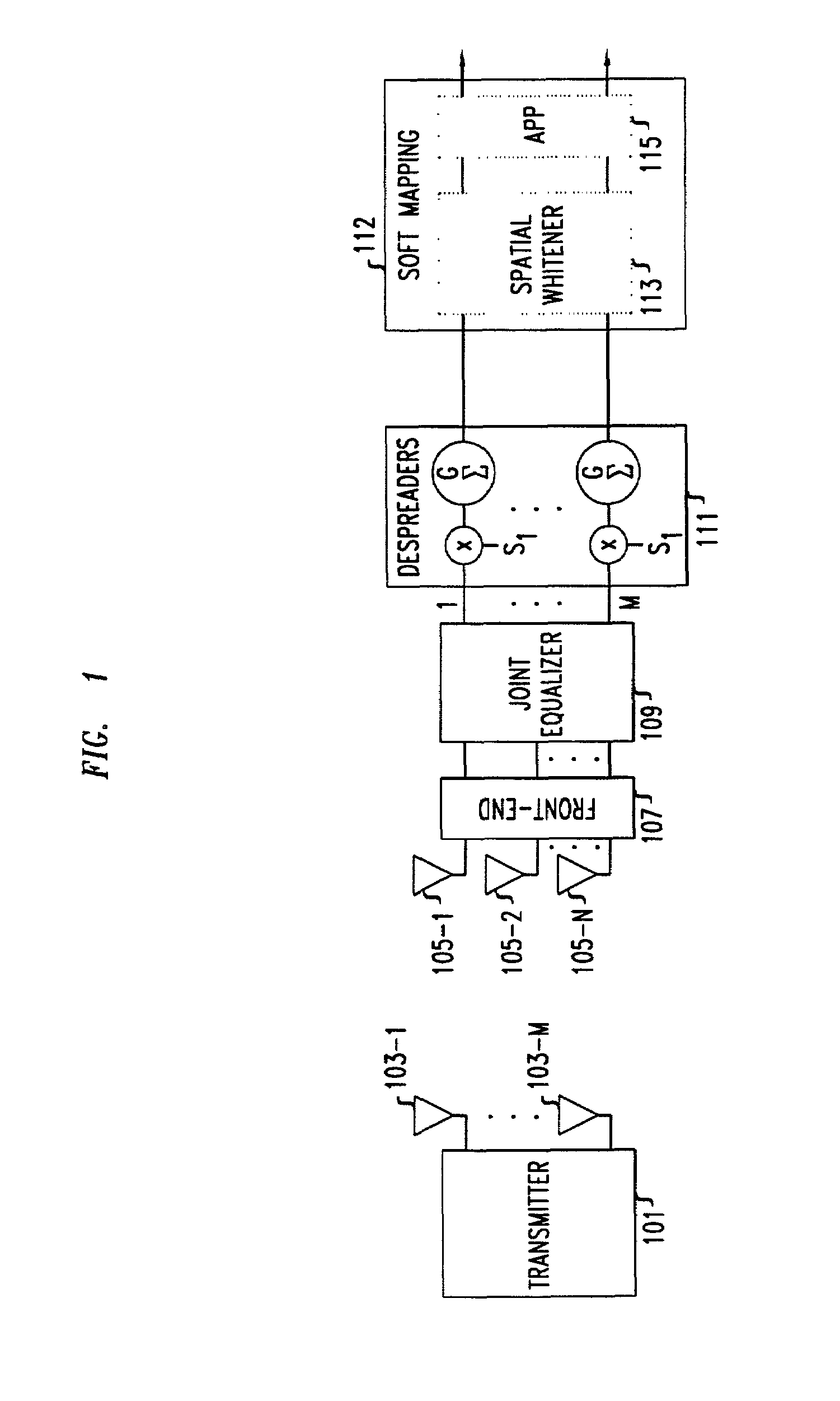
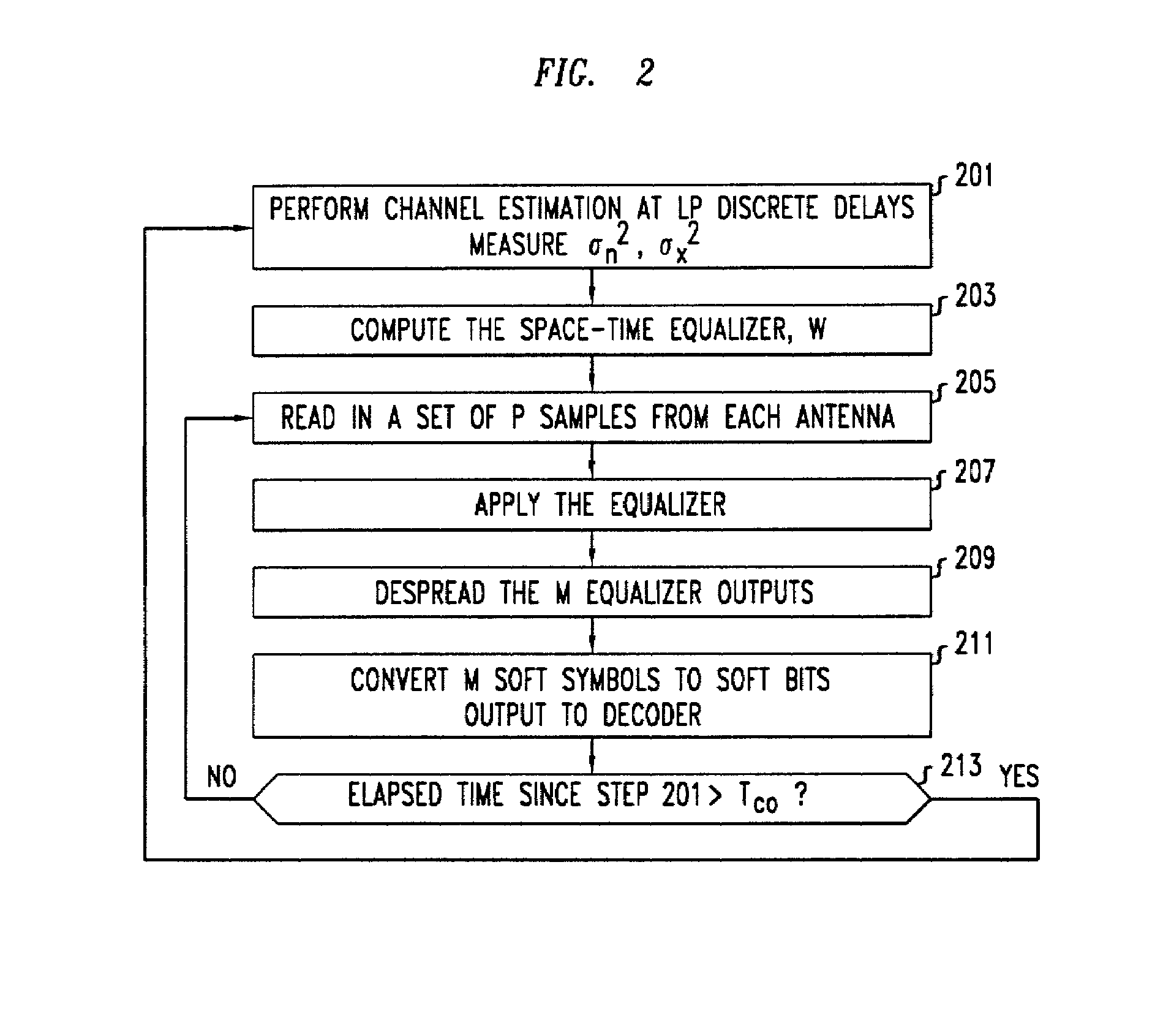
Signal detection by a receiver in a multiple antenna time-dispersive system
In a MIMO system the bit error rate floor caused by time dispersion is reduced by employing a joint minimum mean square error (MMSE) equalizer for all of the respective transmit antenna—receive antenna pairings that are possible in the MIMO system. The resulting joint equalization compensates not only for the impact of the channel on the transmit antenna—receive antenna pairings but also for the interference of the other transmit antennas on any given receive antenna. The joint equalization outperforms simply replicating the prior art minimum mean square error (MMSE) equalizer for each transmit antenna—receive antenna pairings.
Owner:LGS INNOVATIONS
Decoding method and apparatus
ActiveUS7263119B1Improve reception performanceMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsDecoding methodsEqualization
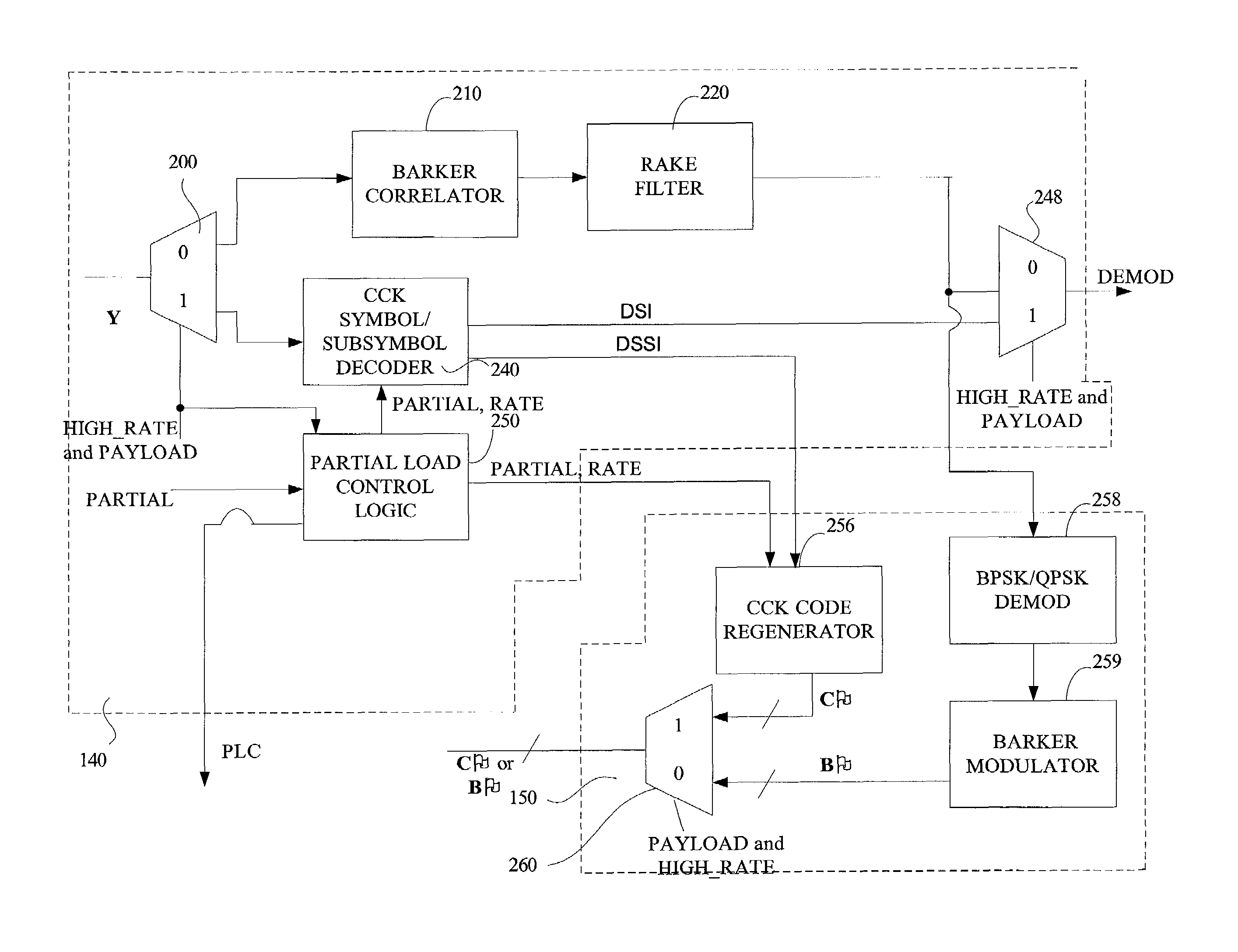
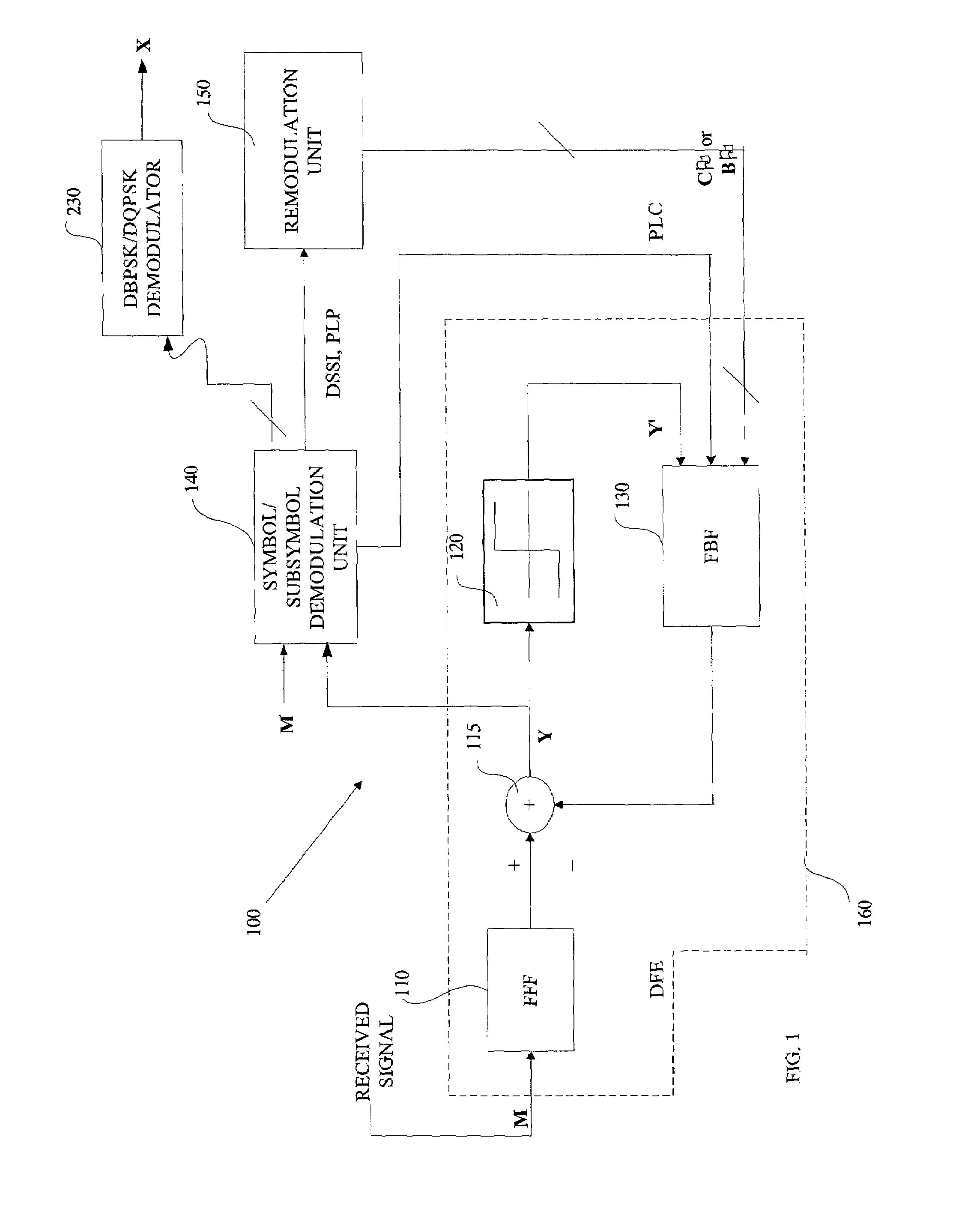
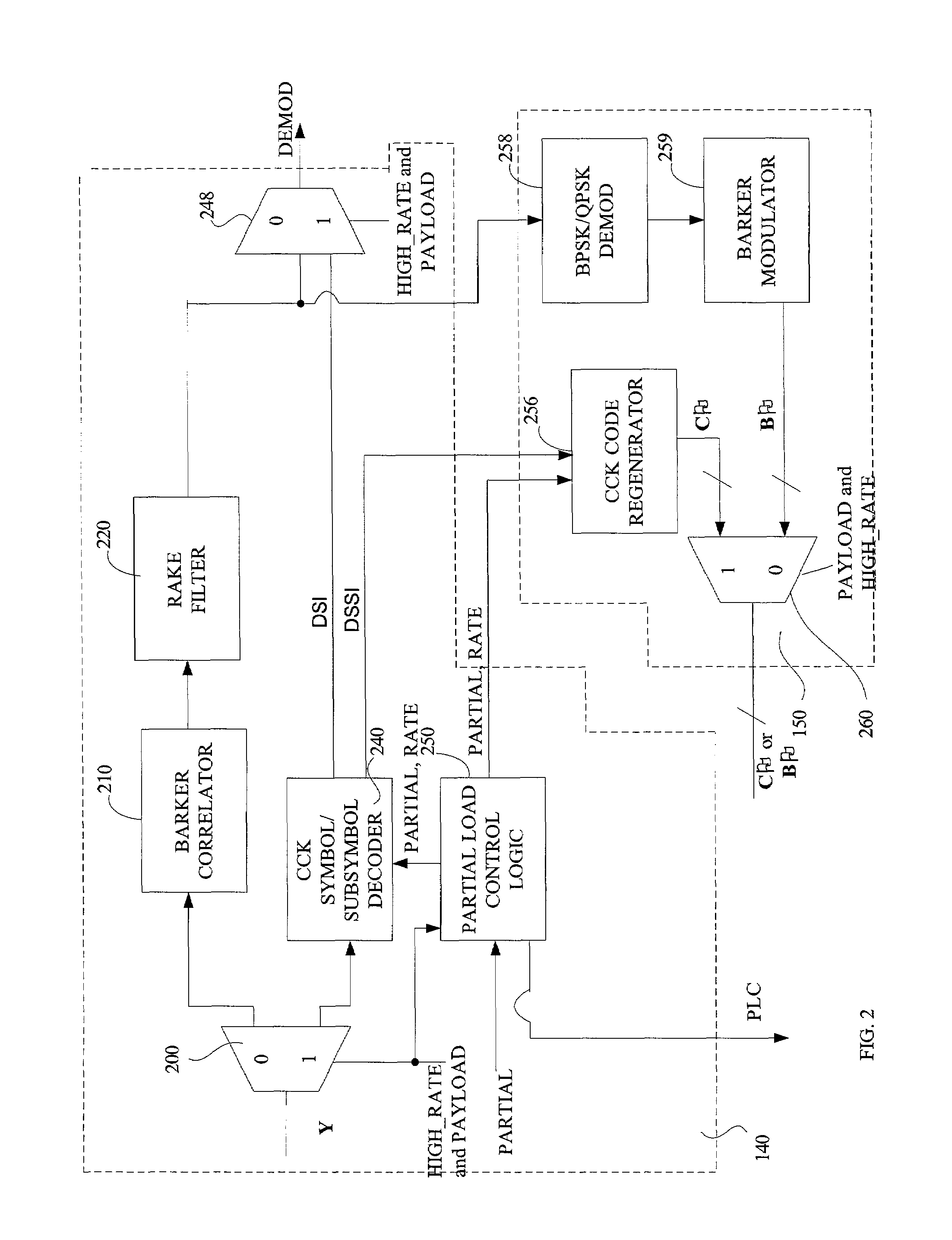
Techniques and instrumentalities to improve ISI and ICI cancellation in reception of modulated symbols by selectively decoding subsymbols of such modulated symbol before they can be completely decided or perceived as well as use of decoded symbol / subsymbol information in the feedback equalization process are disclosed. In particular, a decoder and corresponding method are disclosed which includes a feedback equalizer capable of receiving a modulated signal including a symbol defined by a first number of chips, along with a subsymbol processor to generate a subsymbol waveform upon receipt of a second number, less than the first number, of chips of such symbol and provide the subsymbol waveform to the feedback equalizer in order to equalize the modulated signal using the subsymbol waveform. Other disclosed aspects including techniques and instrumentalities for improving reception performance when symbols encoded by different modulation schemes are encountered, as well as feedback equalization for Barker encoded symbols present in the received signal.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Equalizer for communication over noisy channels
InactiveUS6937648B2Accurate estimateThe result is accurateMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsCommunications systemTransfer matrix
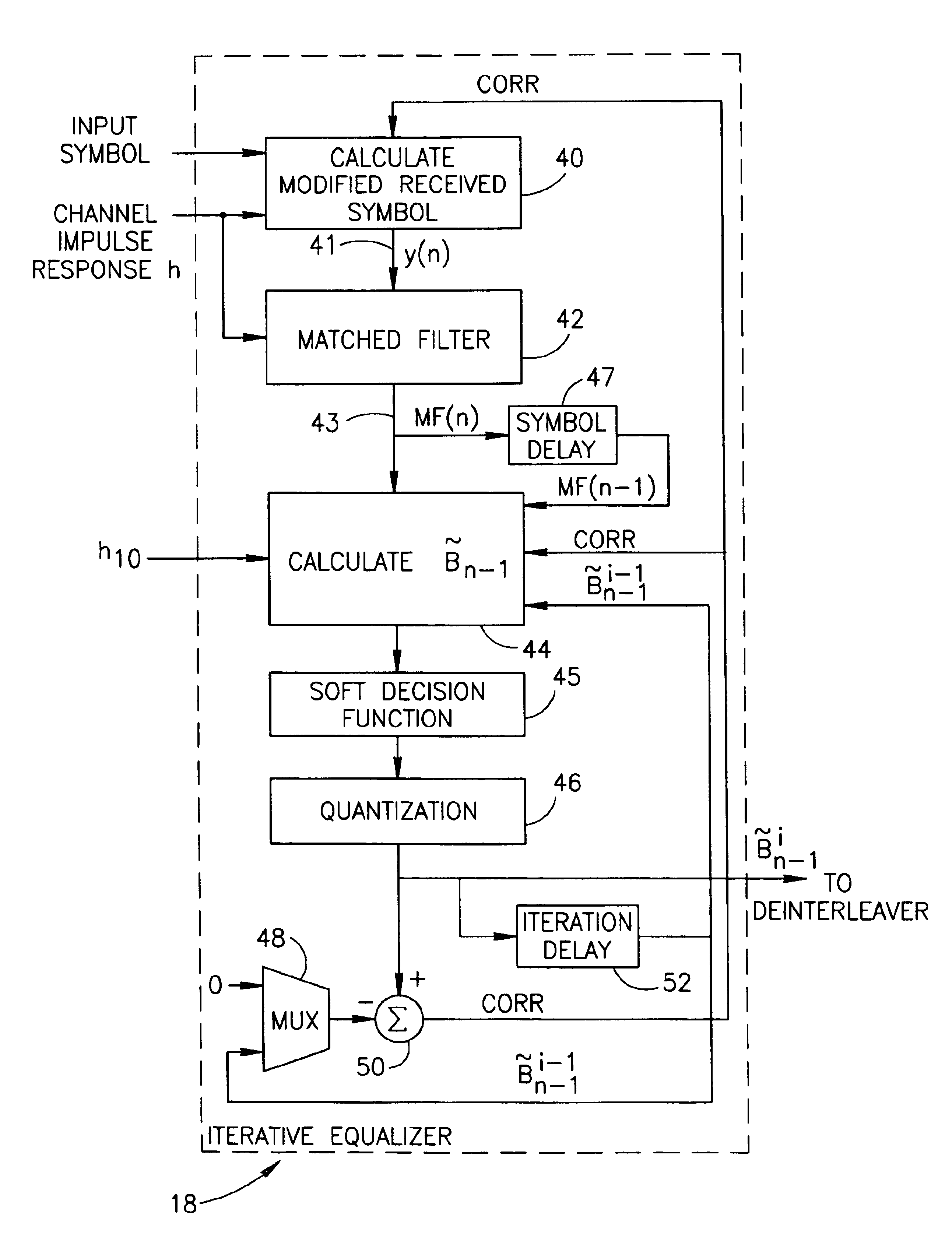
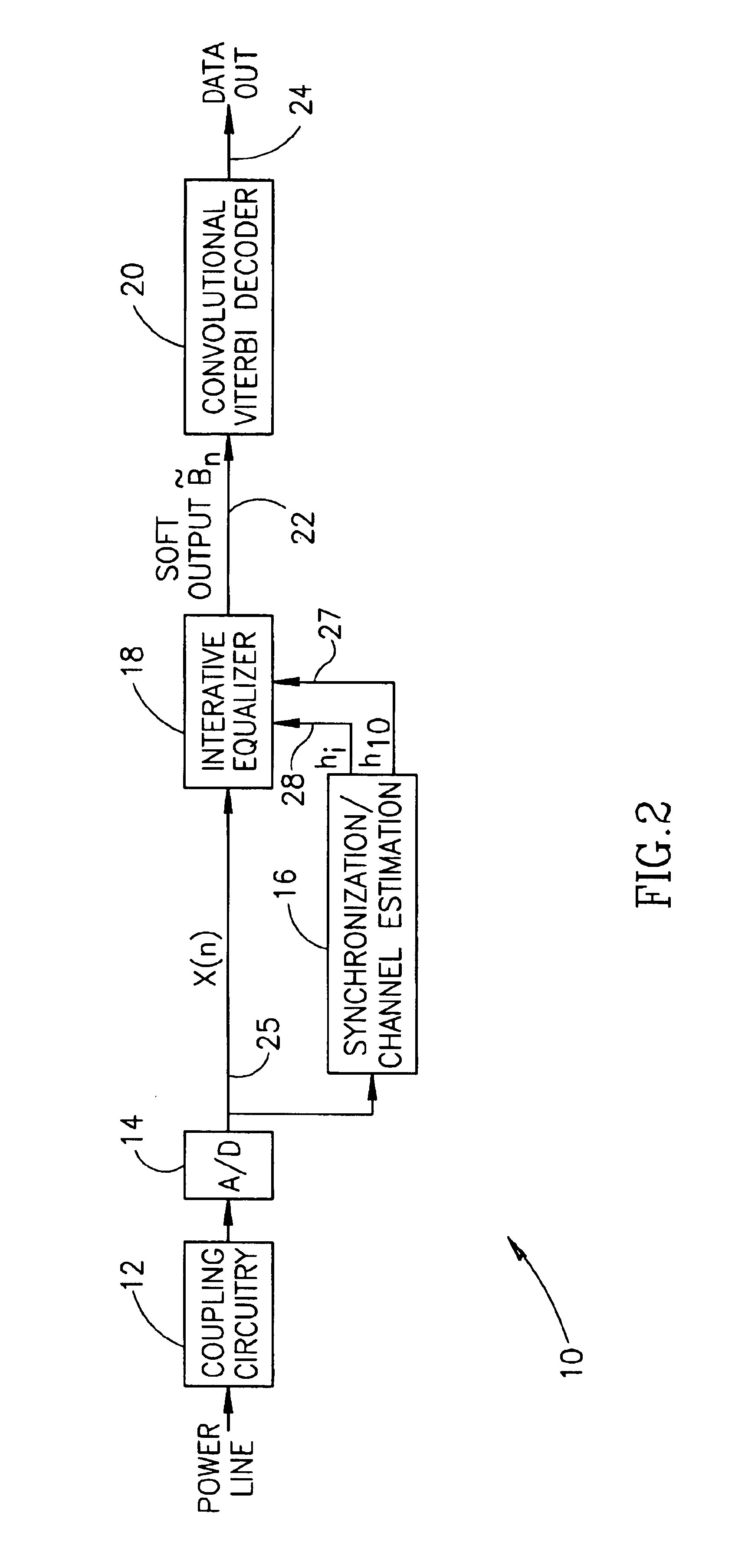
An apparatus for and a method of iterative equalization for communication over noisy channels suitable for use with a wide range of different types of communications systems and channels that is particularly applicable to power line based communication systems. Equalization of received symbols is achieved by iteratively removing the influence of previous symbols dispersed due to channel ISI. Equalization is performed using iterative subtraction in combination with calculations based on the inverse of the transfer matrix. The impulse response of previous symbols is subtracted out to yield the impulse response of the received symbol. The estimate of the current symbol {tilde over (B)}n is then calculated by passing the modified received symbol through a matched filer which functions to remove the effect of channel ISI from the symbol. Multiple iterations are performed to improve the accuracy of the resultant symbol decision.
Owner:ITRAN COMM
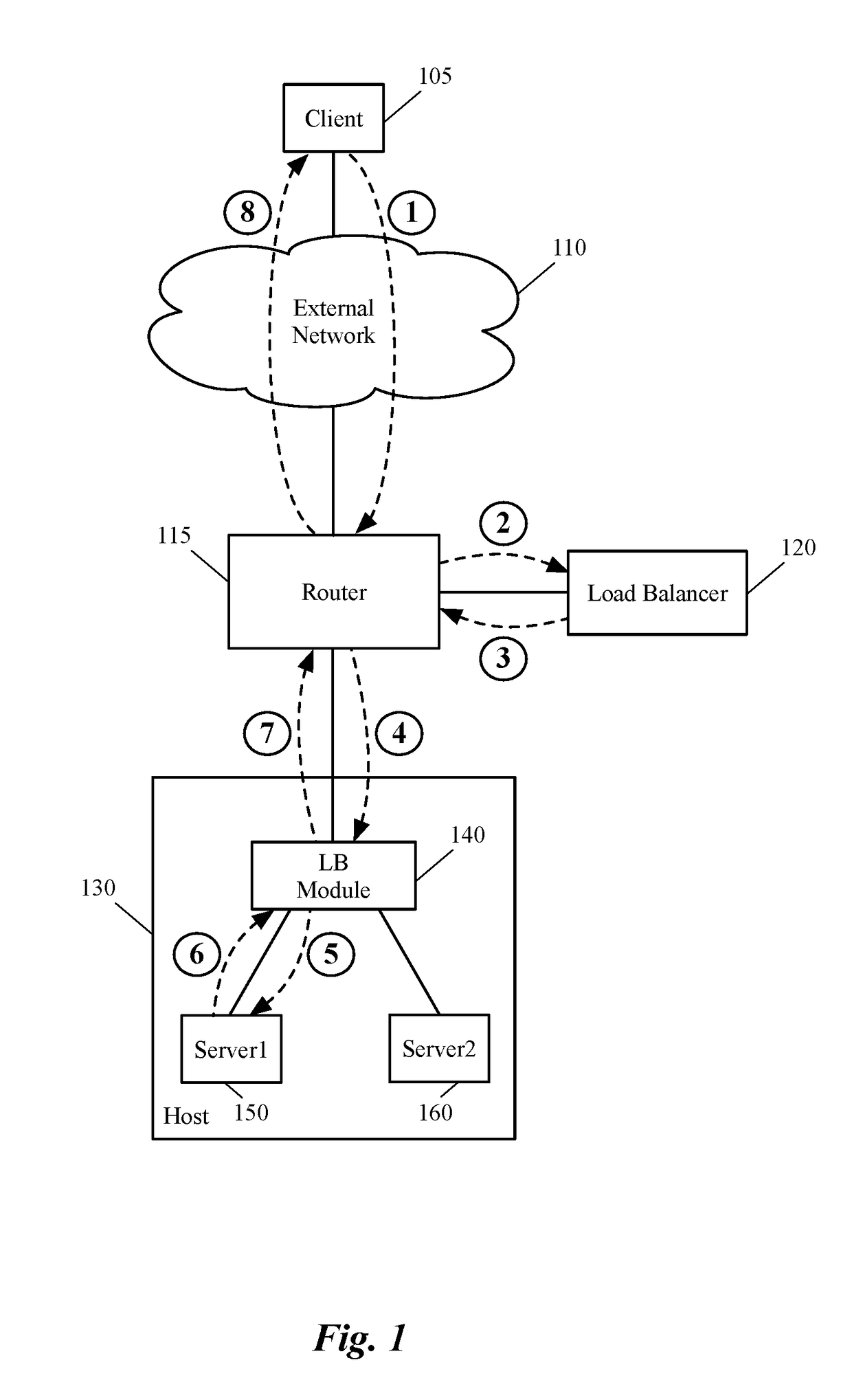
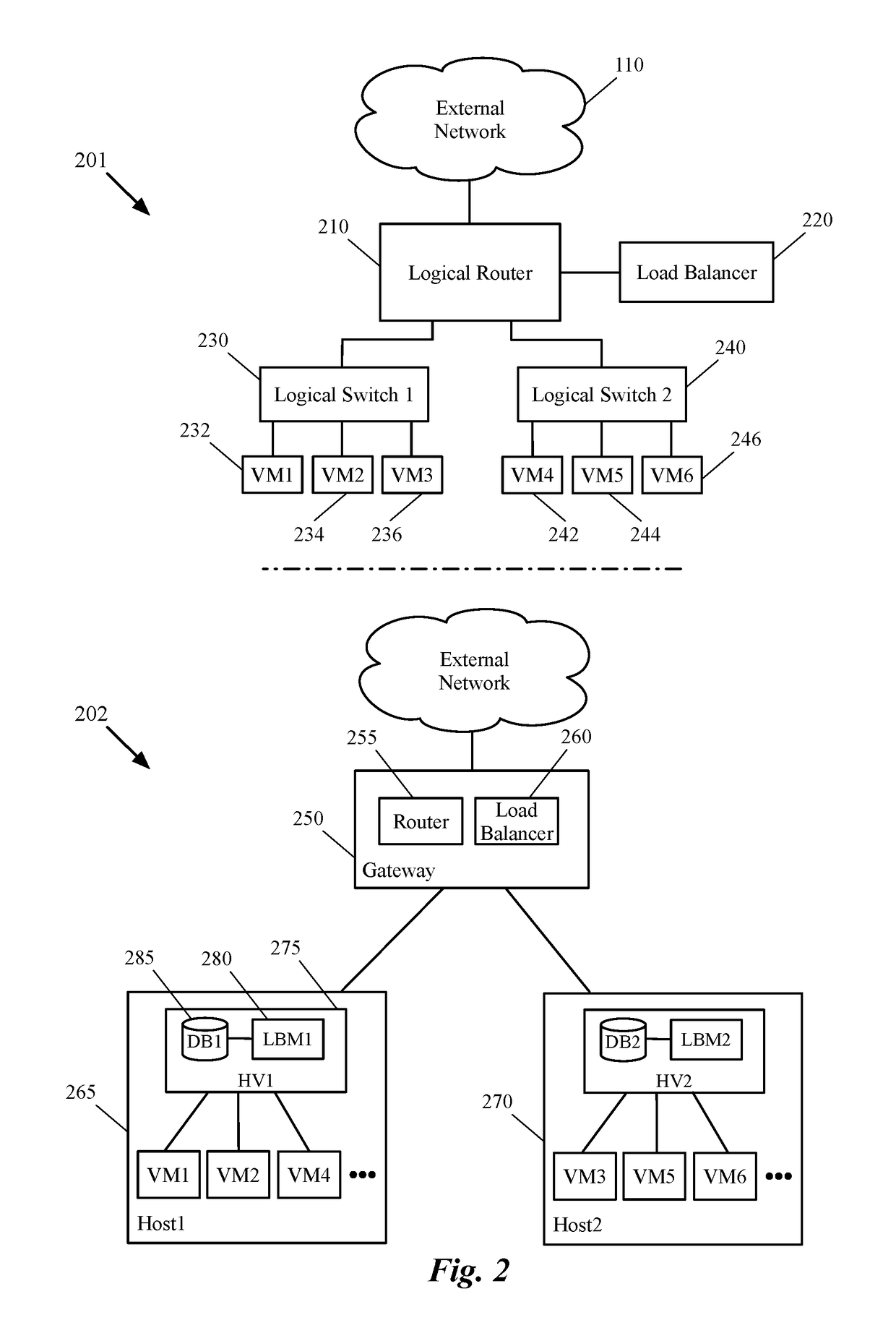
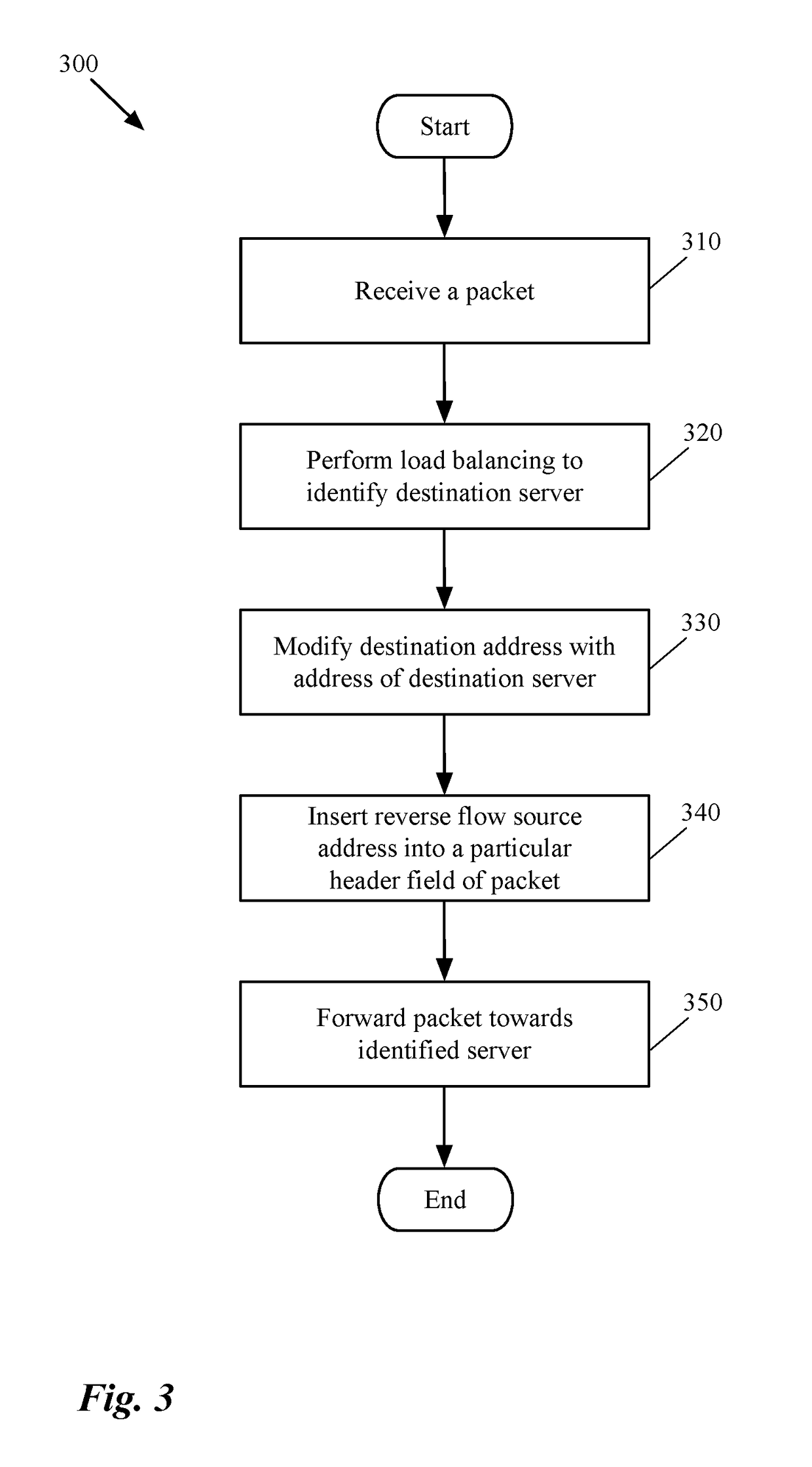
Bypassing a load balancer in a return path of network traffic
Some embodiments provide a method that allows a first data compute node (DCN) to forward outgoing traffic to a second DCN directly in spite of receiving the incoming traffic from the second DCN through a load balancer. That is, the return traffic's network path from the first DCN to the second DCN bypasses the load balancer, even though a request that initiated the return traffic is received through the load balancer. The method receives a first data message from a load balancer to be sent to a DCN. After identifying a particular address embedded in the data message by the load balancer, the method generates a table entry, based on source and destination addresses of the data message and the identified address. This entry is used for modifying a source address of a subsequent data message received from the DCN in response to the data message.
Owner:NICIRA
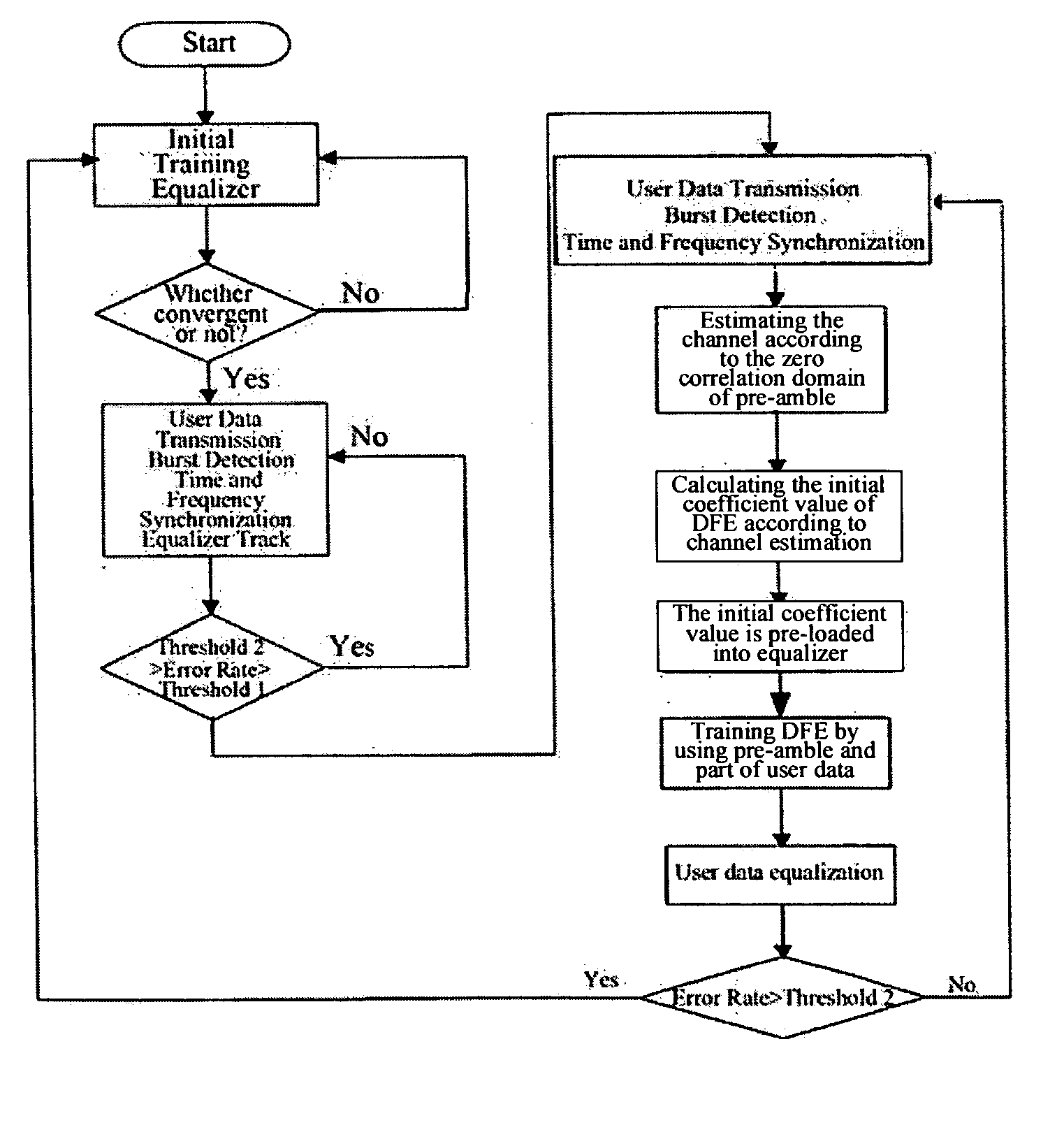
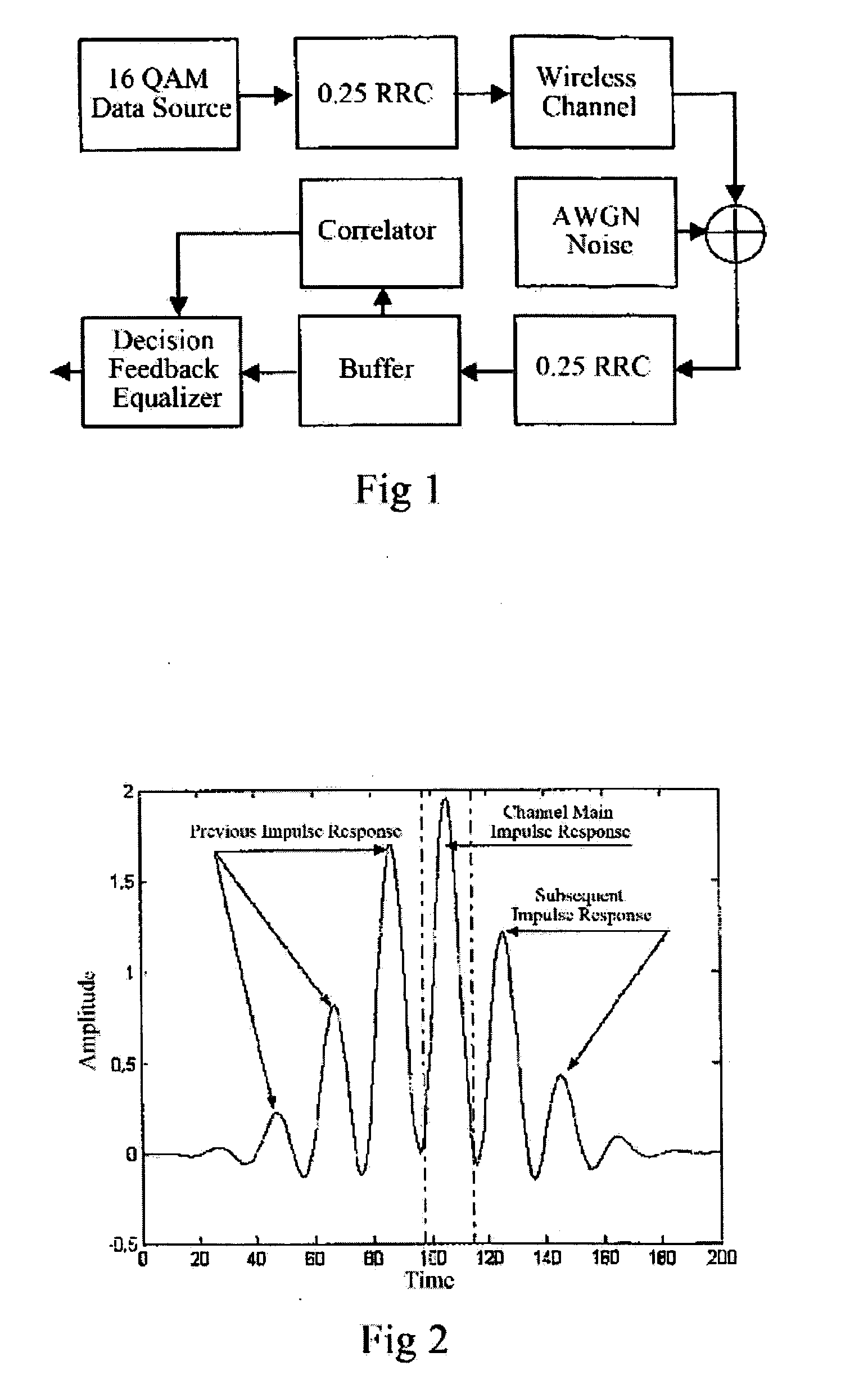
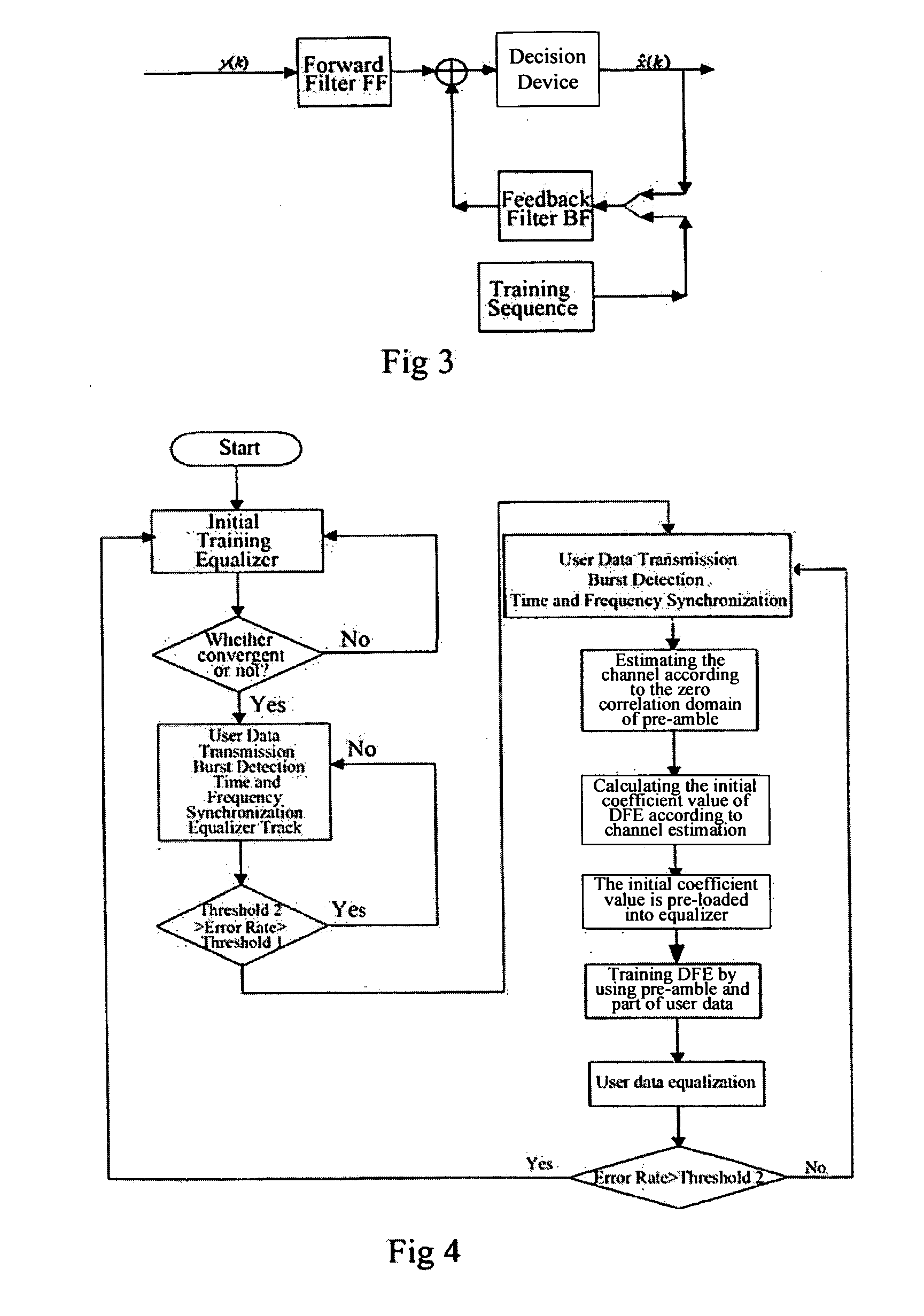
Uplink burst equalizing method in broad wide access system
InactiveUS20070147489A1Shorten the timeIncrease effective bandwidthMultiple-port networksError preventionTelecommunicationsEqualization
A method for uplink burst equalization in broad wide access system, using the form of combining pre-training and burst equalization, that is, before transmitting user data, training the equalizer, then starting transmitting user data, in which, the equalizer uses decision user data as reference to track the changed wireless channel; if the change of channel exceeds the tracking region of equalizer, for example, the error rate exceeds threshold 1 but doesn't exceed threshold 2, the burst equalization will be performed; if the channel change exceeds the equalization region of equalizer, for example, the error rate exceeds threshold 2, the training will be performed again. By using the form of combining pre-training and burst equalization, setting different thresholds for handoff, the present invention greatly prolongs the intervals of subsequent pre-training process, thereby reducing the times of pre-training and increasing the effective bandwidth; By introducing burst equalization process, the present invention also decreases the requirement of system on operation occasion (for example, the static channel or the interval of bursts should be short), thereby increasing the application occasions of product.
Owner:ZTE CORP
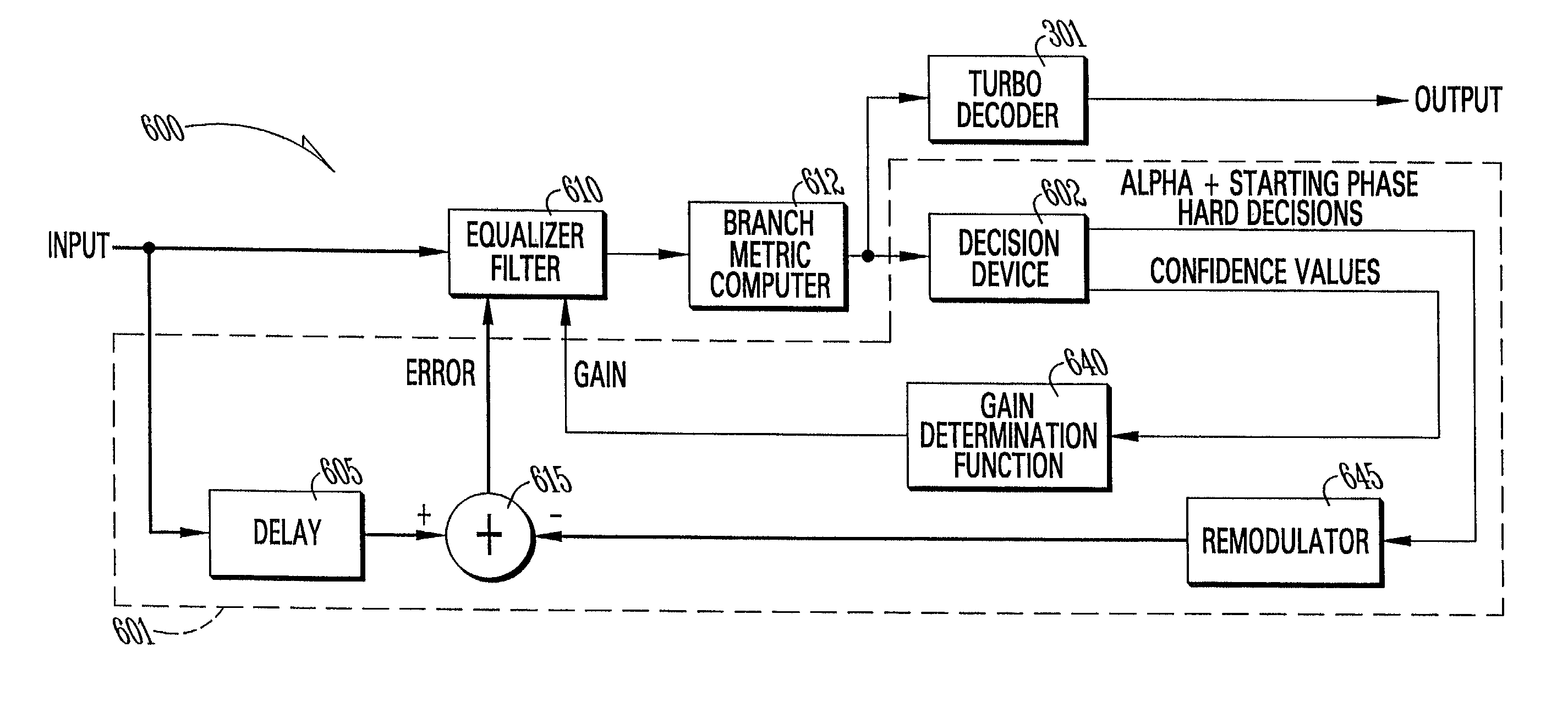
Equalizer for complex modulations in very noisy environments
ActiveUS7088793B1Supply softMultiple-port networksData representation error detection/correctionIntersymbol interferenceSelf adaptive
An equalizer is used with complex modulation modems to reduce intersymbol interference. The equalizer includes an equalizer filter that receives an input data signal and adapts to compensate for the noisy communications channels to reduce intersymbol interference to the input signal. A branch metric computer demodulates the equalizer filter adapted input data signal. A decision device delivers an alpha value, starting phase information and confidence values from the demodulated input data signal. A gain determination function receives the confidence values and determines adaptation gain for the equalizer filter. A remodulator receives the alpha value and starting phase information and remodulates the alpha value and starting phase information into a remodulated data signal. A summing function compares the remodulated data signal to a delayed version of the input signal to generate an error signal for the equalizer filter to adjust the equalizer filter.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
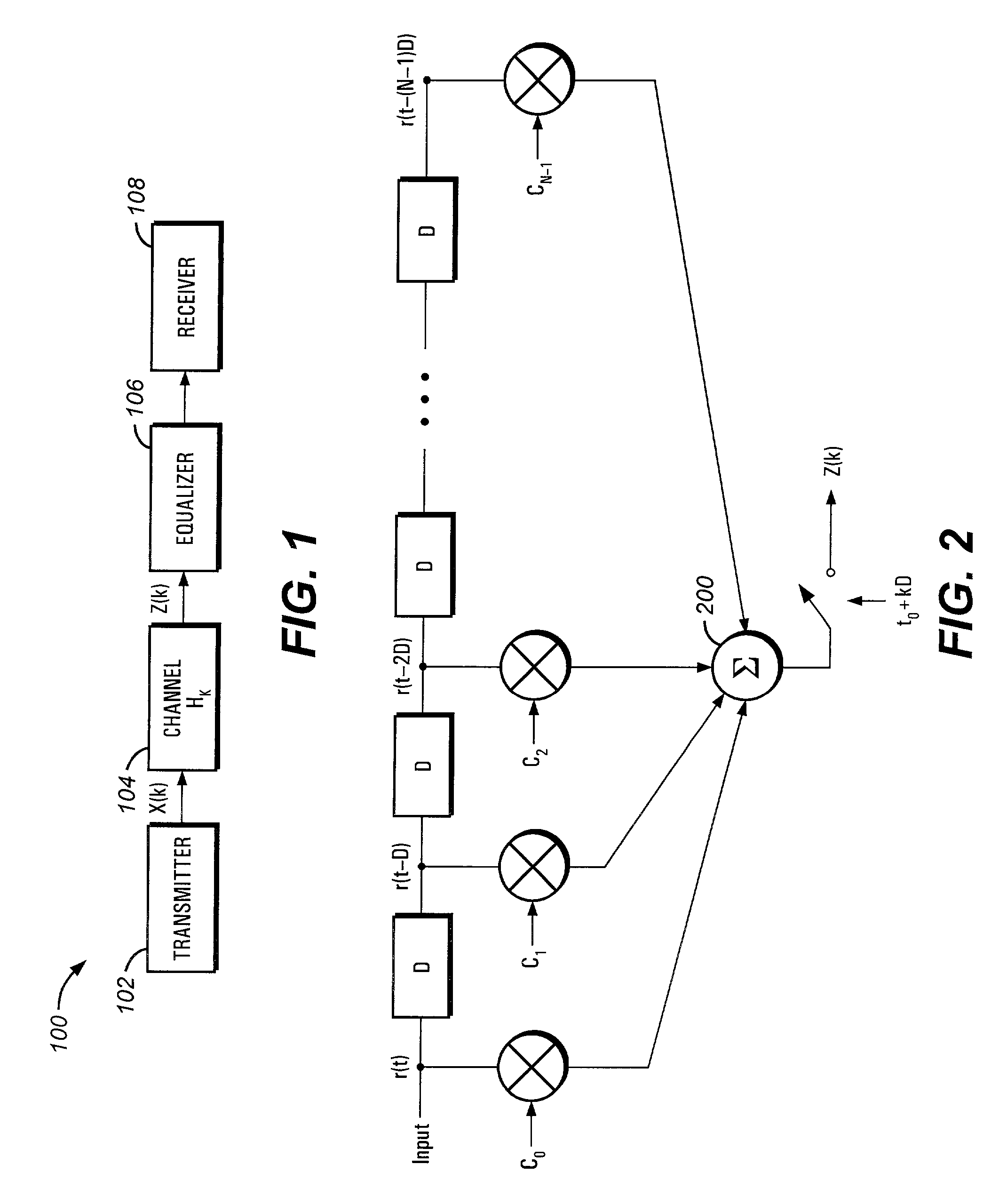
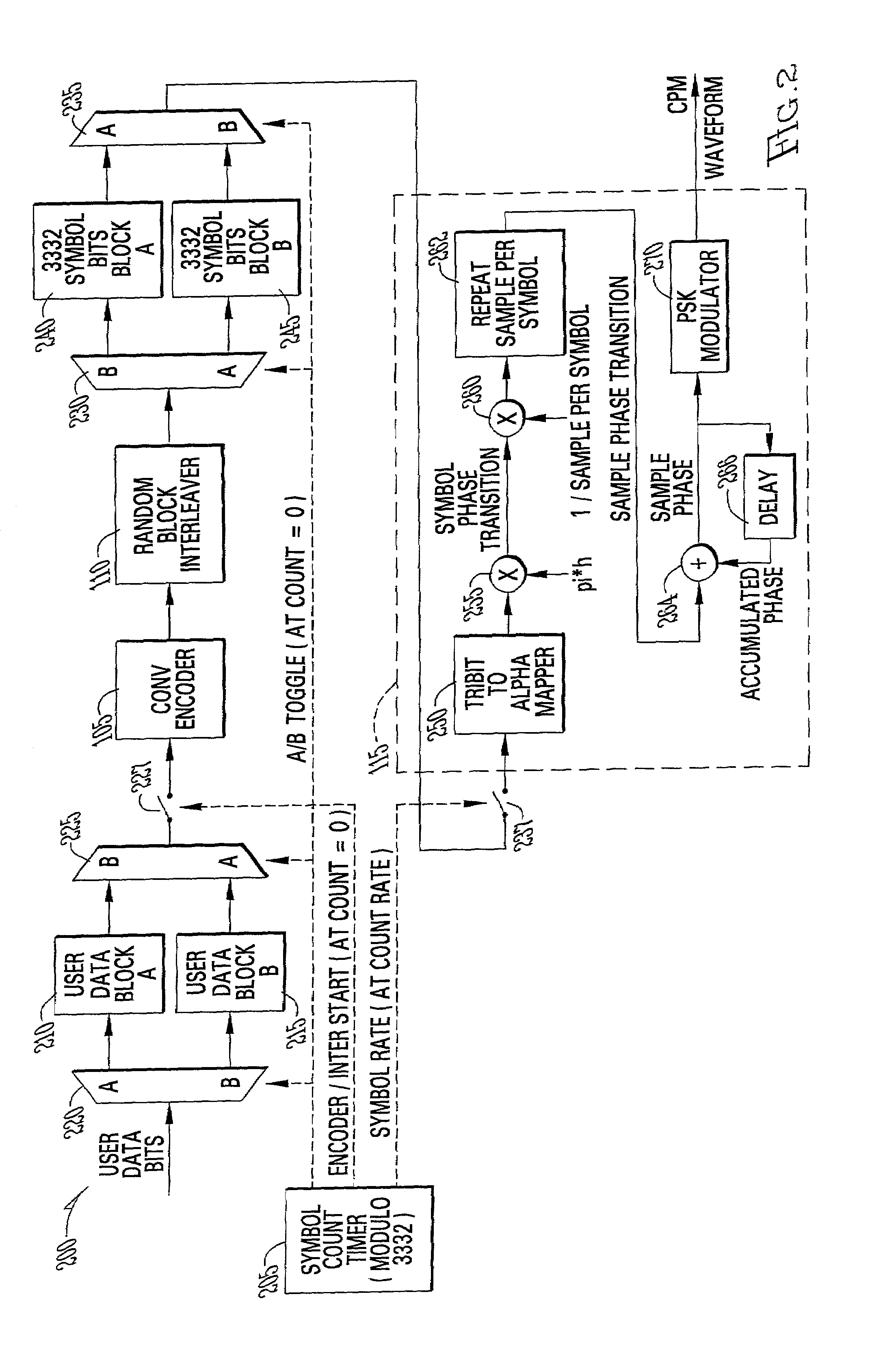
Linear prediction based initialization of a single-axis blind equalizer for VSB signals
ActiveUS7027500B1Minimize output powerMultiple-port networksTelevision system detailsImpulse frequencyEqualization
A single-axis receiver processing, for example, complex vestigial sideband modulated signals with an equalizer with forward and feedback filters. Forward and feedback filters have parameters that are initialized and adapted to steady state operation. Adaptive equalization employs linear predictive filtering and error term generation based on various cost criteria. Adaptive equalization includes recursive update of parameters for forward and feedback filtering as operation changes between linear and decision-feedback equalization of either single or multi-channel signals. An adaptive, linear predictive filter generates real-valued parameters that are employed to set the parameters of the feedback filter. In an initialization mode, filter parameters are set via a linear prediction filter to approximate the inverse of the channel's impulse / frequency response and a constant modulus error term for adaptation of the filter parameters. In an acquisition mode, equalization is as linear equalization with a constant modulus error term, and possibly other error terms in combination, for adaptation of the filter parameters. In a tracking mode, equalization is as decision feedback equalization with decision-directed error terms for adaptation of the filter parameters. For some equalizer configurations, feedback filtering is applied to real-valued decisions corresponding to complex-valued received data, and includes real-part extraction of the error term employed for recursive update of filtering parameters. Where a training sequence is available to the receiver, initial parameters for forward filtering are estimated by correlation of the received signal with the training sequence.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
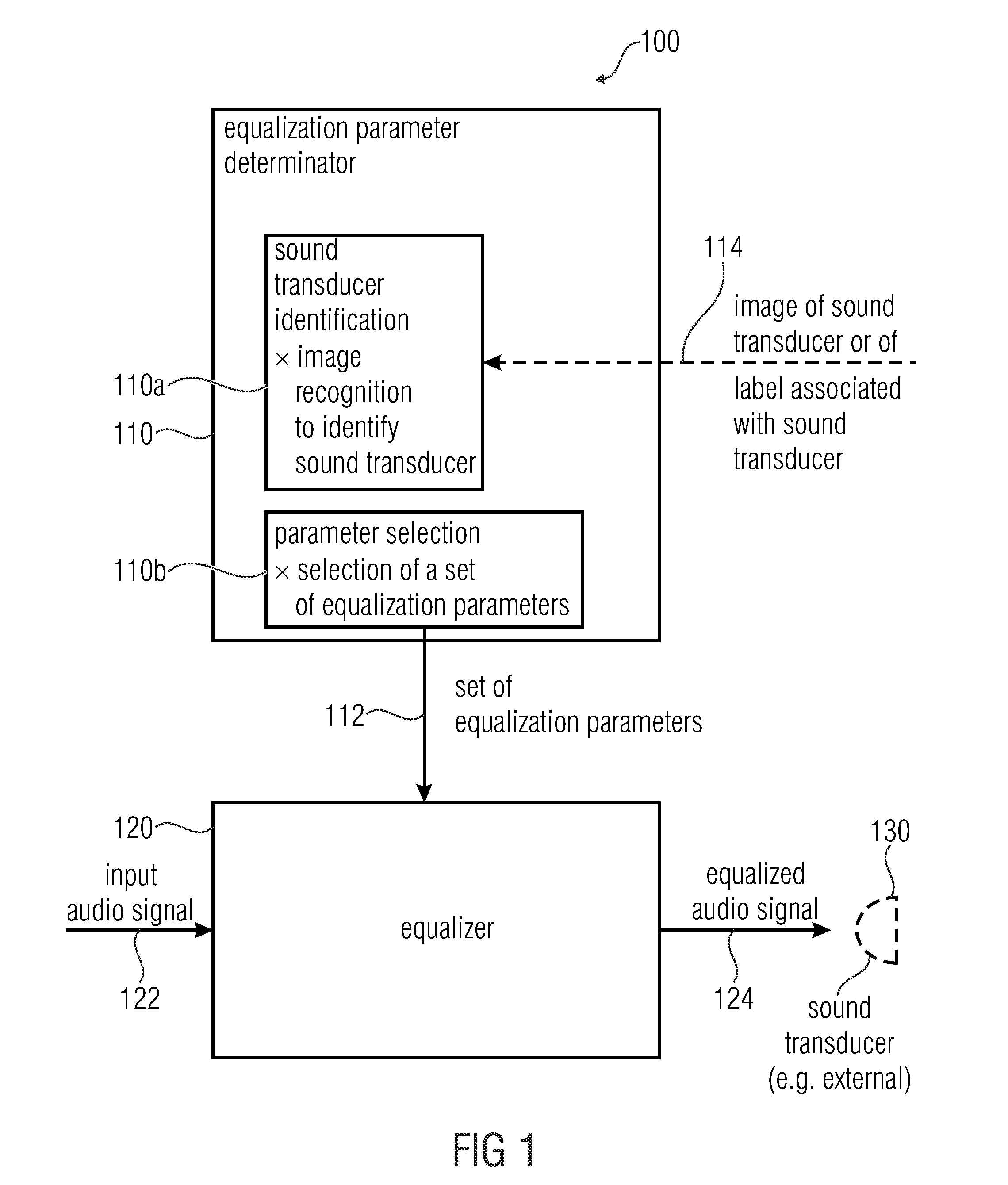
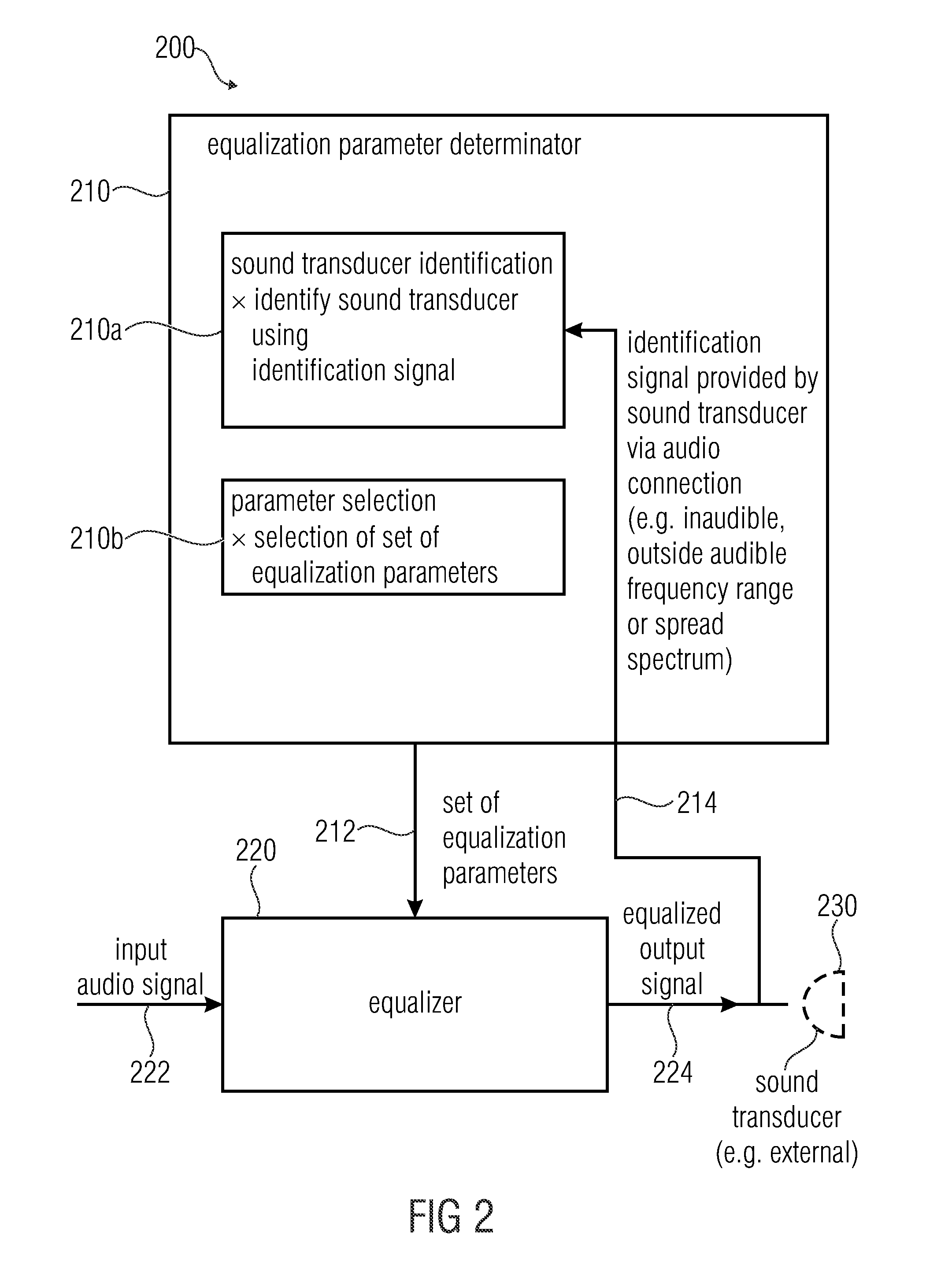
Apparatus for providing an audio signal for reproduction by a sound transducer, system, method and computer program
InactiveUS20140369519A1Improve user satisfactionConvenient lifeDigital data information retrievalEarpiece/earphone attachmentsTransducerEqualization
An apparatus for processing an audio signal for reproduction by a sound transducer includes an equalization parameter determinator for determining a set of equalization parameters and an equalizer configured to equalize an input audio signal, to obtain an equalized audio signal. Different concepts for the determination of the set of equalization parameters include an image recognition, an evaluation of an identification signal which is provided by the sound transducer via an audio connection, and a measurement of the impedance of the sound transducer over frequency. Also, an upload functionality and a download functionality are provided.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
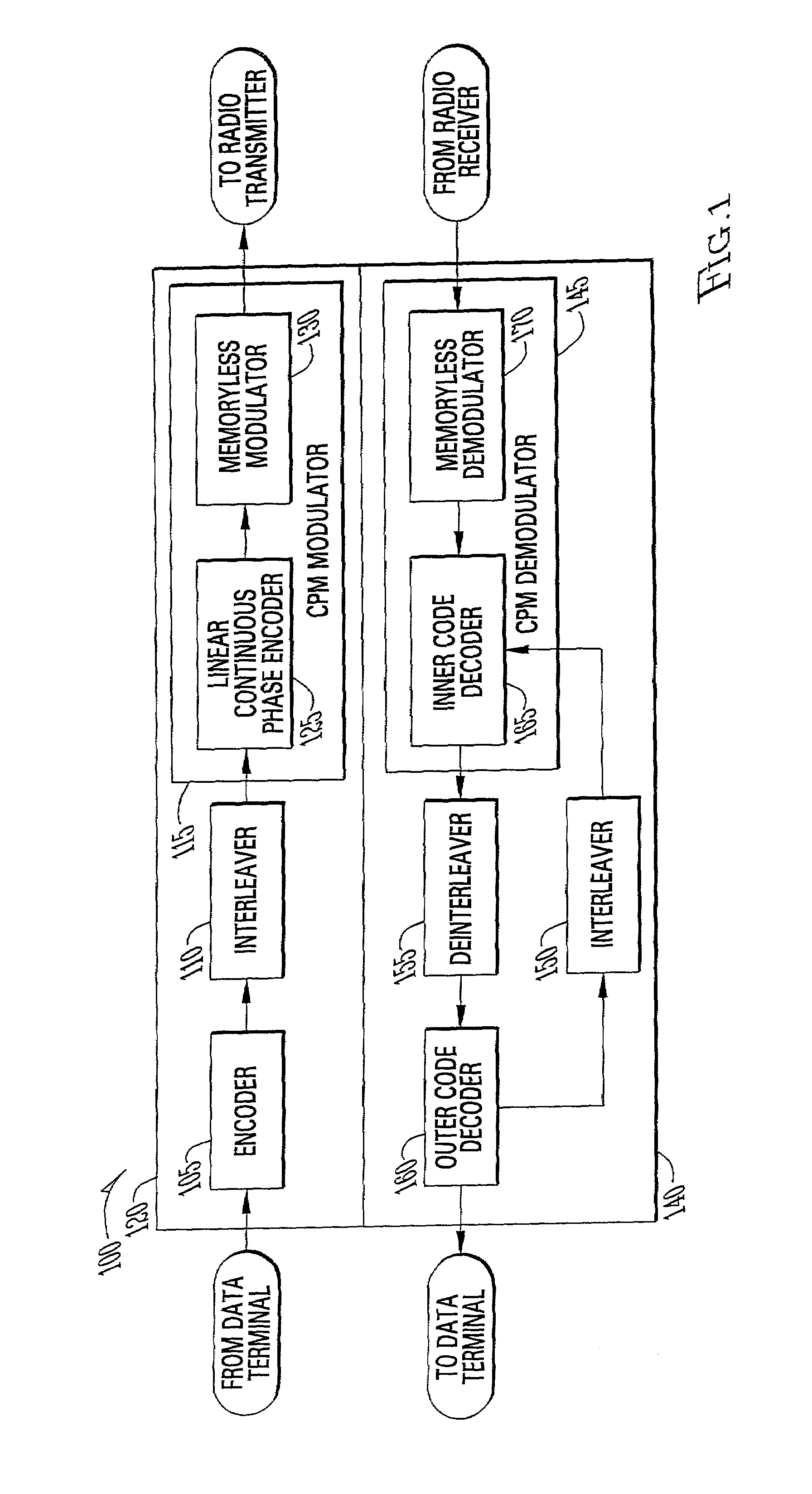
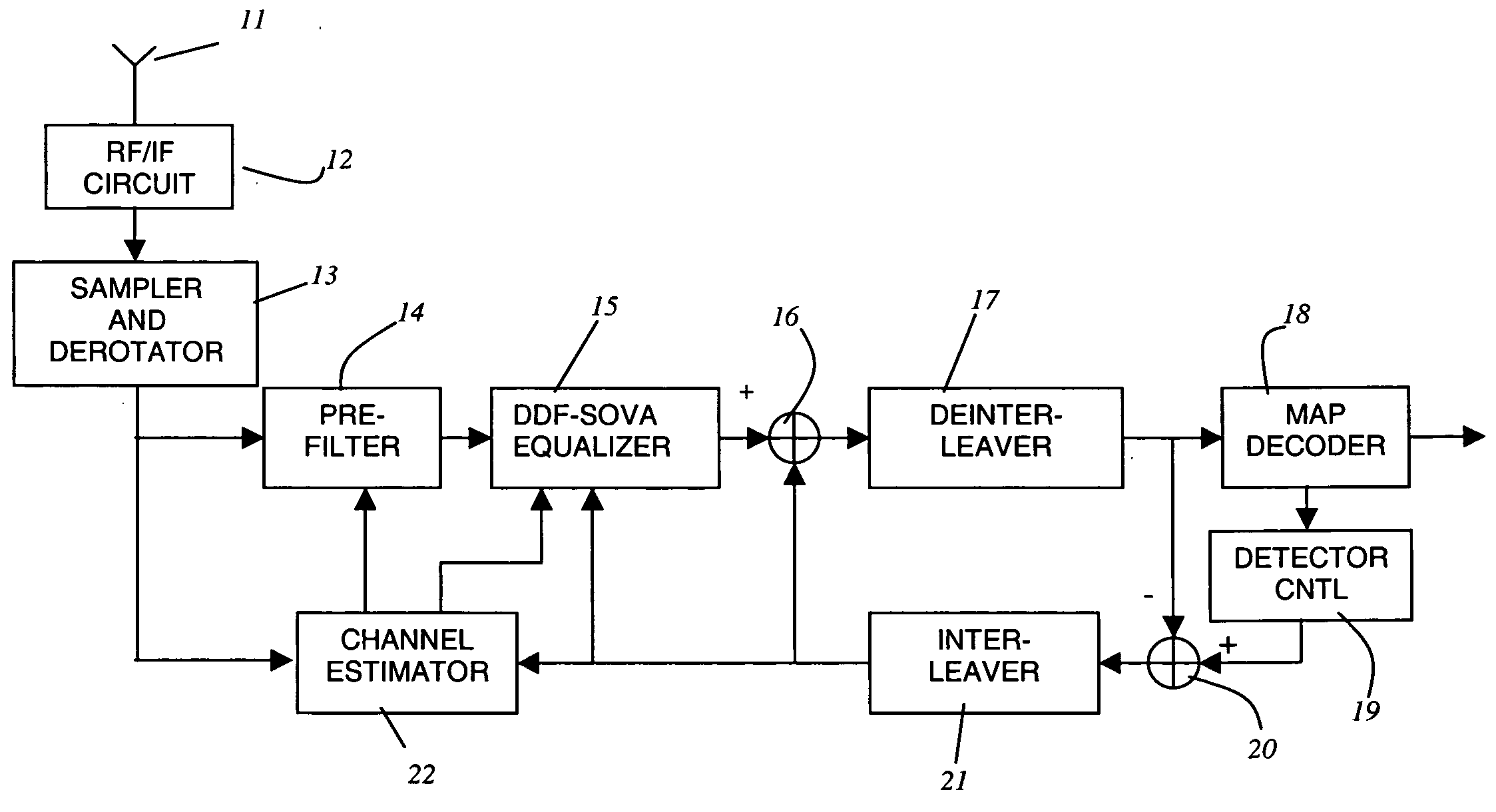
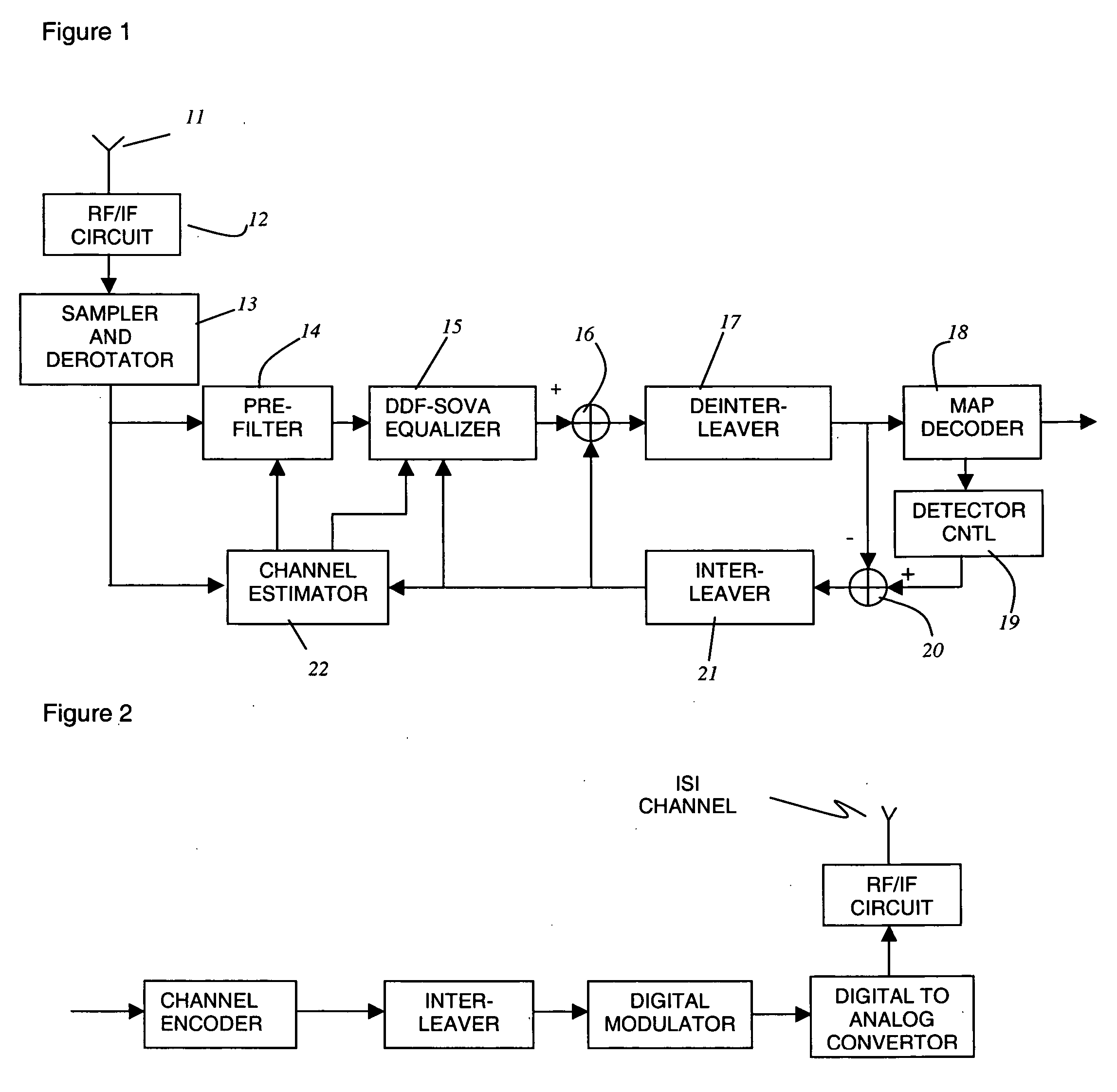
High speed, low-cost process for the demodulation and detection in EDGE wireless cellular systems
InactiveUS20050018794A1Low costEasy to detectAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase-modulated carrier systemsReverse orderForward error correction
A process for signal detection in EDGE cellular systems is presented with the step of wireless channel estimation, a time-reversed signal processor, a soft-output Viterbi signal detector consisting of forward and reverse block processing, a MAP decoder that exchange soft information with the equalizer. Claim 1. A signal detection mechanism to demodulate received data frame that includes an accurate estimator to obtain channel responses, a forward filter and a FIR decision feedback filter to be used in soft-output equalizer, a time-reversal device storing received data in a time-reversed order for reverse block processing, an interference removal apparatus in both forward and reverse processing blocks, and a soft-input soft-output reduced state equalizer that utilizes the forward processing and reversed time processing blocks to generate iterative soft-output signals to the forward error correction decoder within the receiver system.
Owner:TANG XIANGGUO +2
Predistortion circuit and method for compensating A/D and other distortion in a digital RF communications transmitter
InactiveUS20050163251A1Compensation DistortionReduce errorsPower amplifiersCombined modulated pulse demodulationNonlinear distortionData stream
A digital communications transmitter (100) includes a digital linear-and-nonlinear predistortion section (200, 1800) to compensate for linear and nonlinear distortion introduced by transmitter-analog components (120). A direct-digital-downconversion section (300) generates a complex digital return-data stream (254) from the analog components (120) without introducing quadrature imbalance. A relatively low resolution exhibited by the return-data stream (254) is effectively increased through arithmetic processing. Distortion introduced by an analog-to-digital converter (304) may be compensated using a variety of adaptive techniques. Linear distortion is compensated using adaptive techniques with an equalizer (246) positioned in the forward-data stream (112). Nonlinear distortion is then compensated using adaptive techniques with a plurality of equalizers (226) that filter a plurality of orthogonal, higher-ordered-basis functions (214) generated from the forward-data stream (112). The filtered-basis functions are combined together and subtracted from the forward-data stream (112).
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
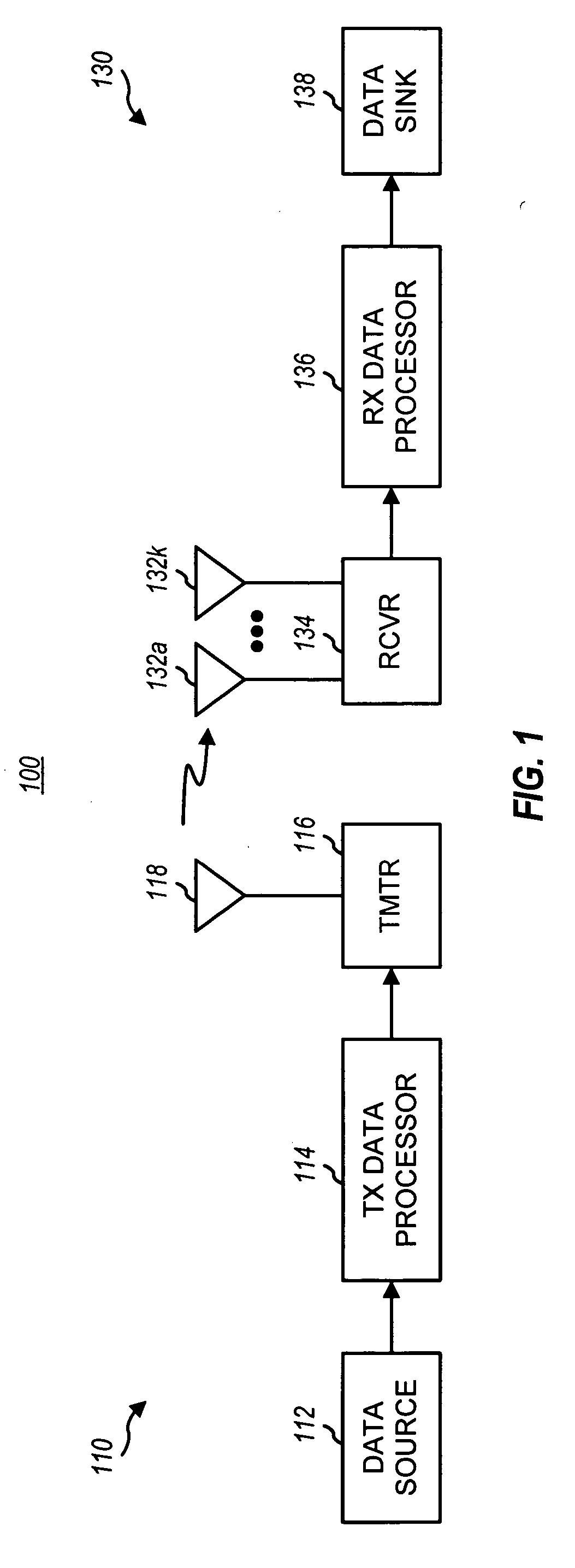
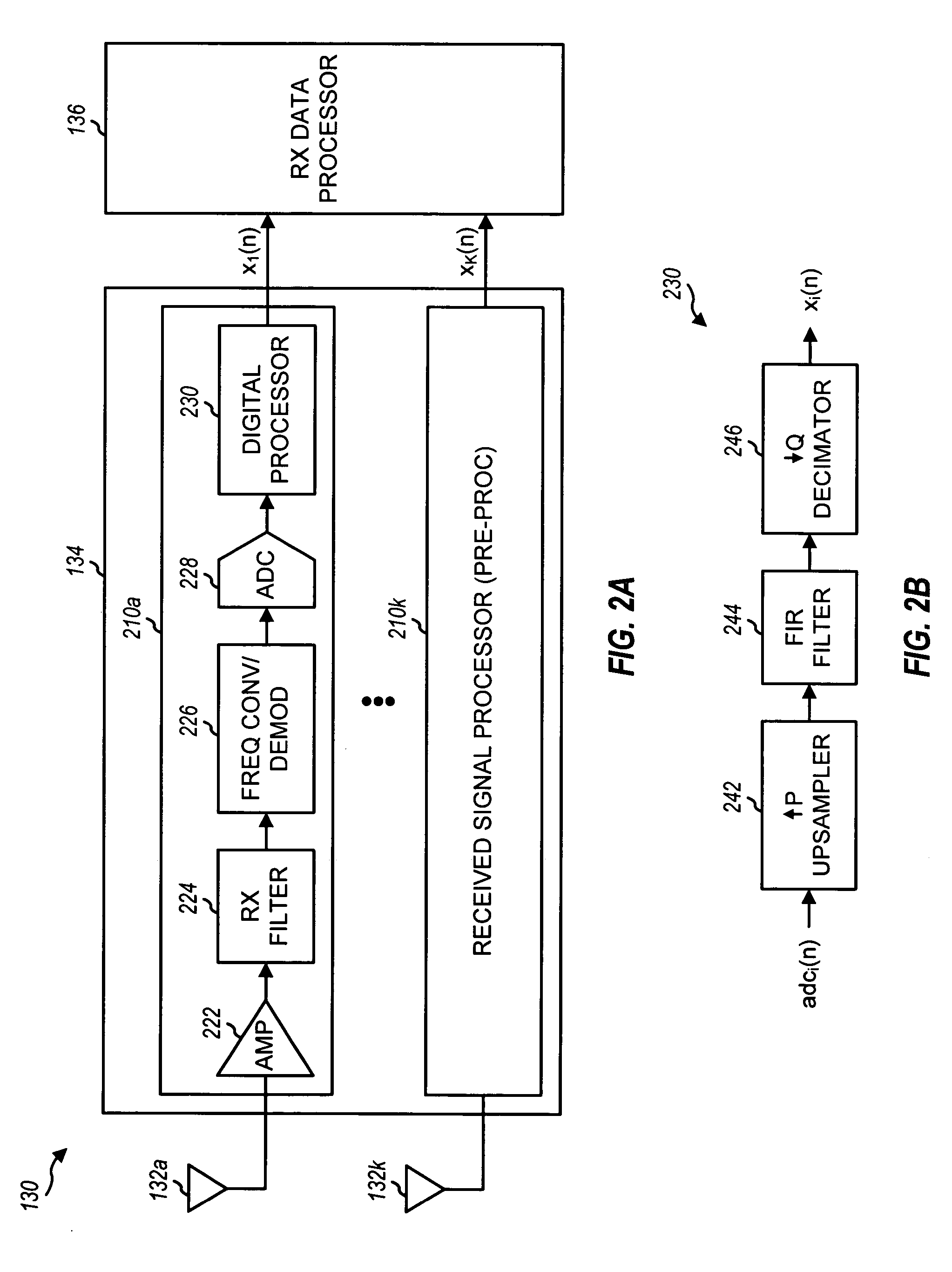
Multiple access system and method for multibeam digital radio systems
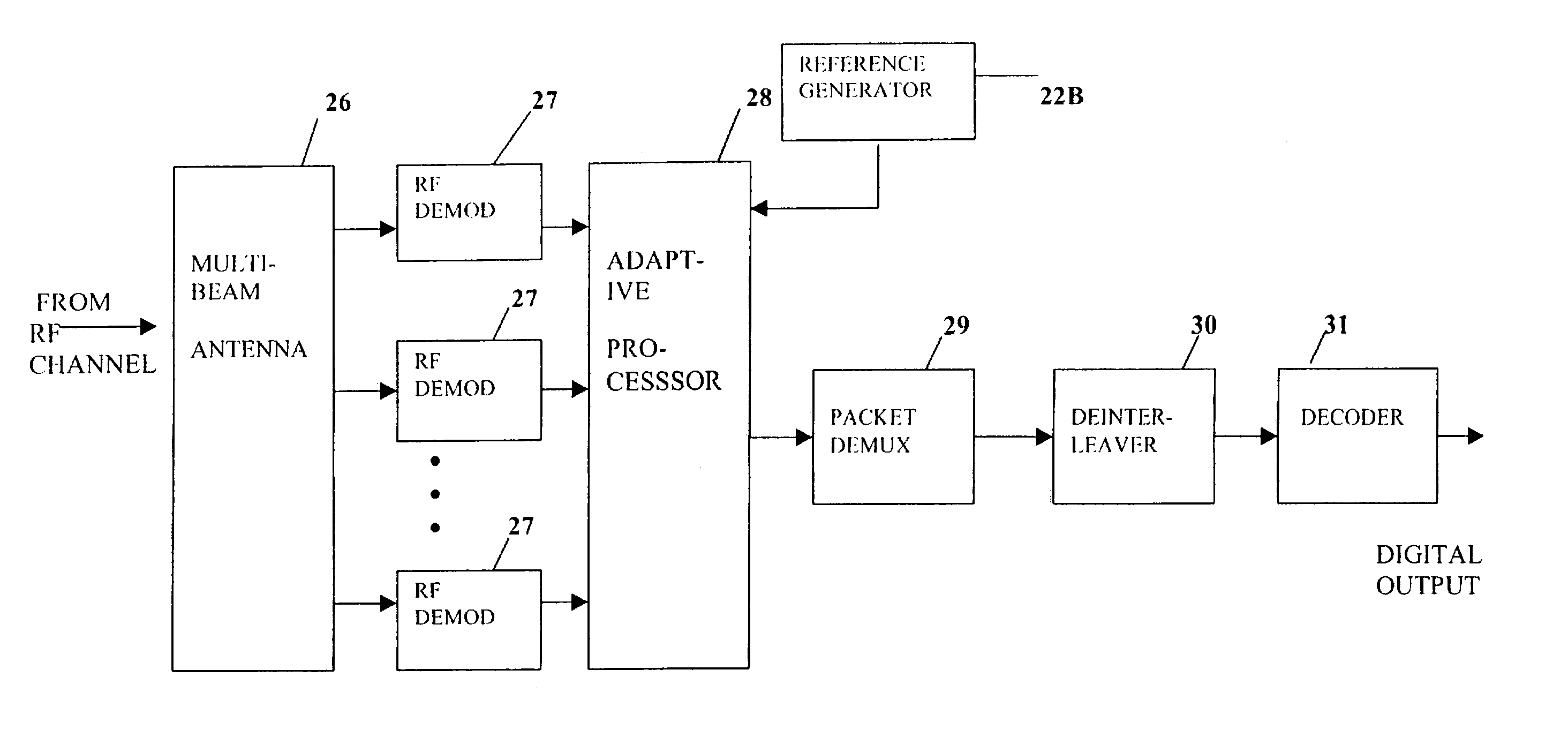
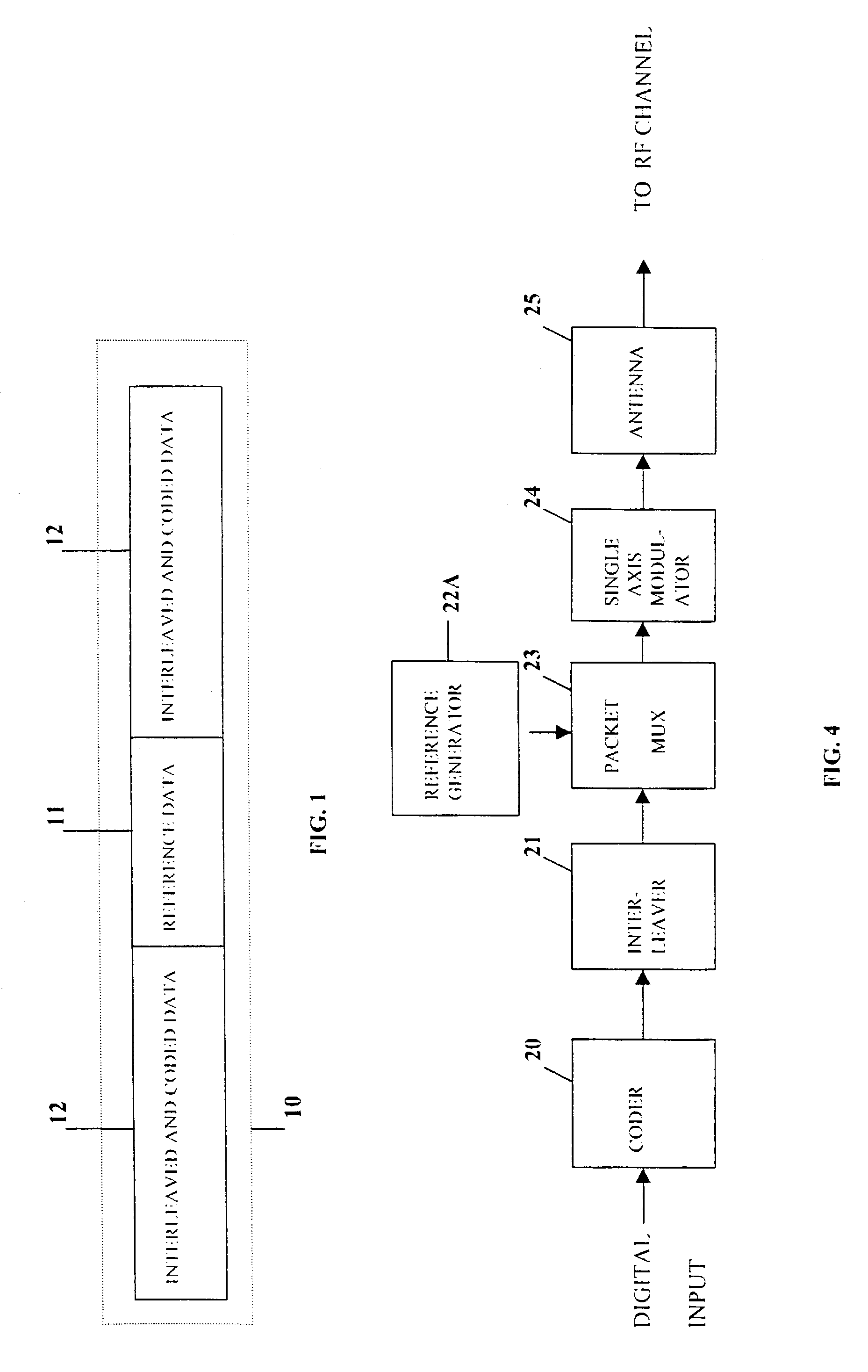
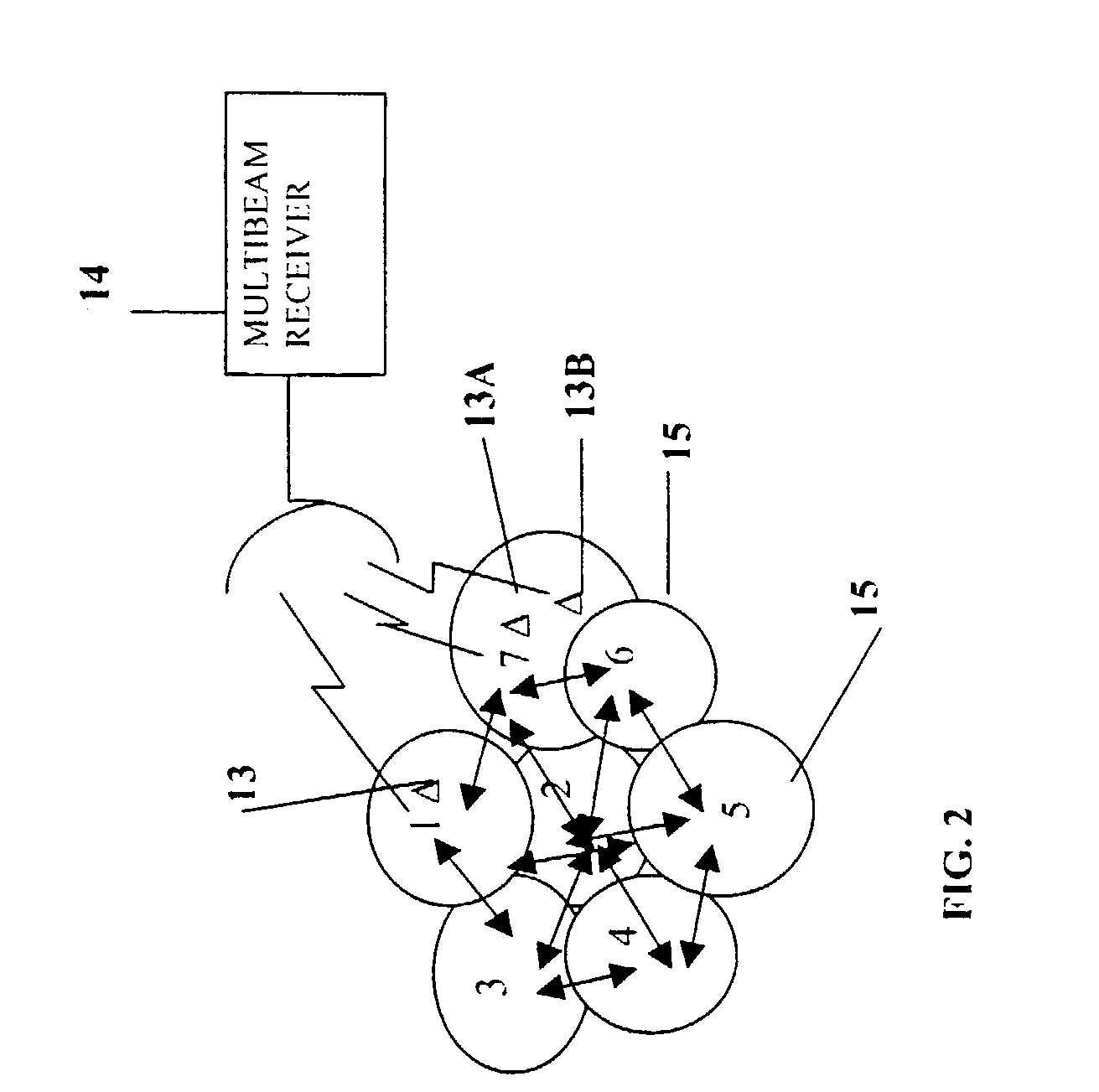
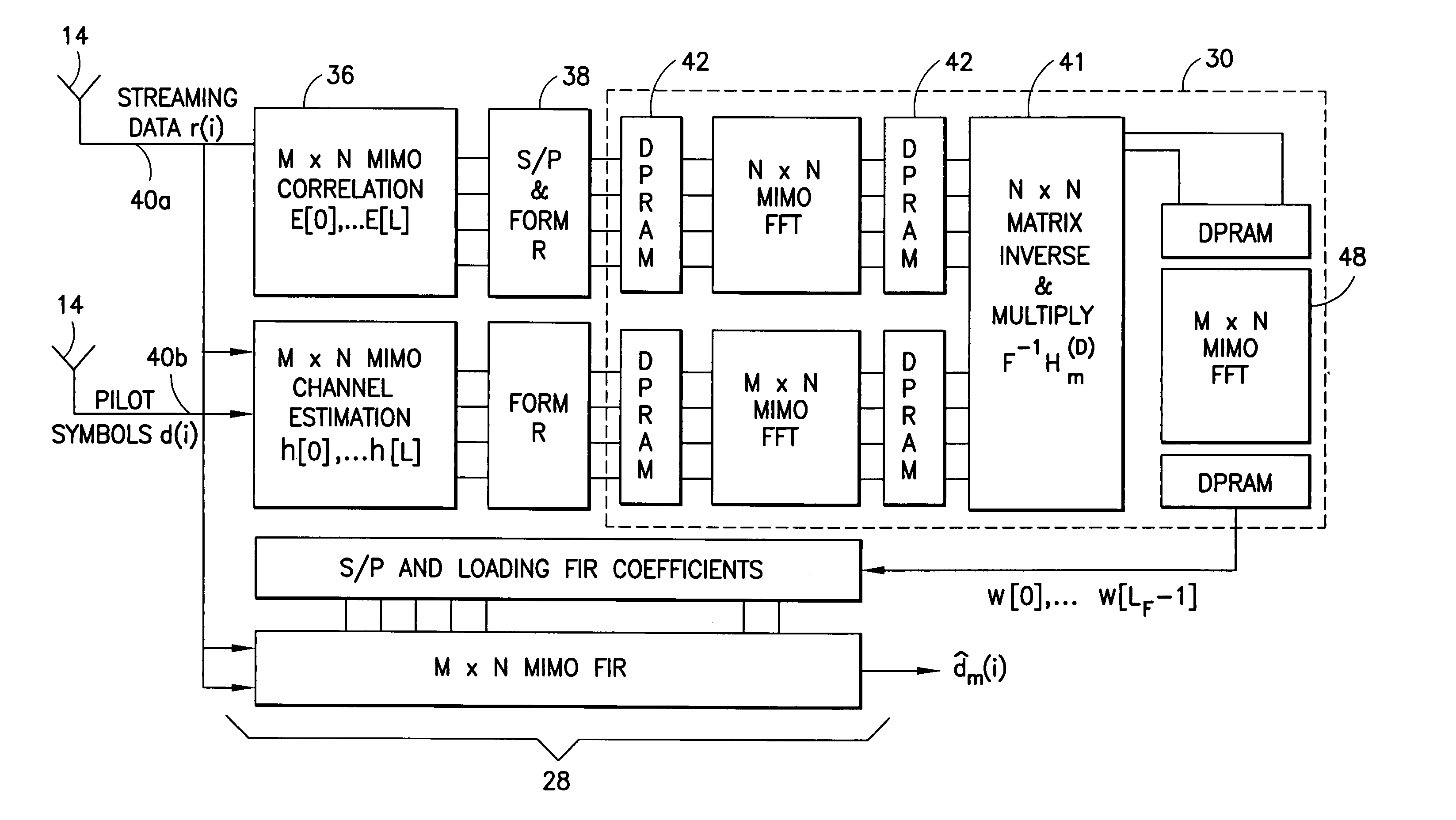
InactiveUS7072410B1Increase channel capacityImprove qualityDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationMultiple antennaTelecommunications link
A multiple-access digital radio communication system and method with communication links between user terminal transmitters and central node with a receiver system including a multibeam antenna. User terminal transmitters assigned to one beam coverage region use mltiple access channels that are mutually orthogonal for transmitting digital message information. These multiple access channels are reused in adjacent and other beam coverage regions. Error-correction coding (20), interleaving (21), and a single-axis modulator (24) are used in the user transmitter to increase resistance to potential interference from user terminal transmitters in other coverage regions. At the receiver, an adaptive processor (28) such as an equalizer or sequence estimator is used to combine multiple antenna beam signals (27) to produce a combined signal associated with each user. Deinterleaving (30) and error-correction decoding (31) of the combined signal is used to complete the recovery of the digital message information.
Owner:MONSEN PETER
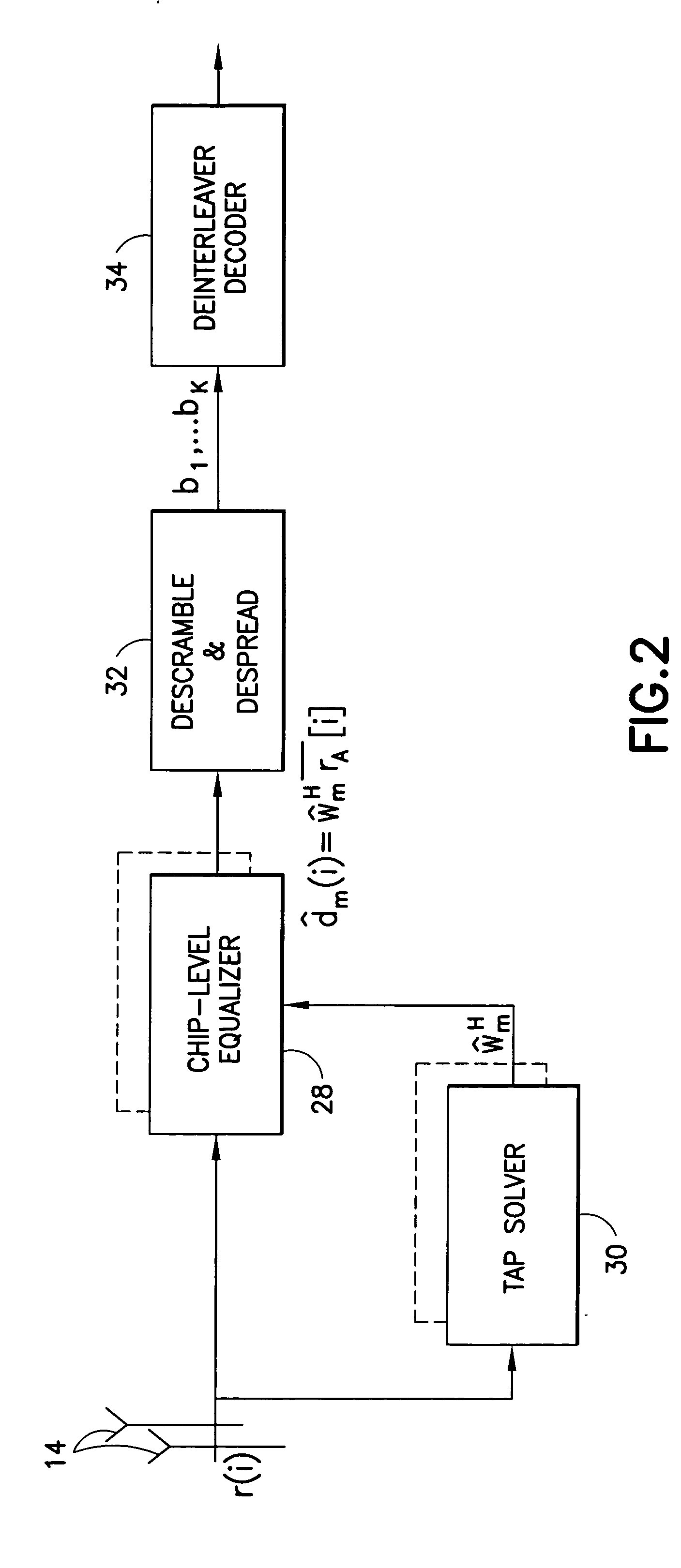
Reduced parallel and pipelined high-order MIMO LMMSE receiver architecture
ActiveUS20060109891A1Reduce complexityReduce the numberMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsFast Fourier transformRound complexity
Disclosed is a LMMSE receiver that restores orthogonality of spreading codes in the downlink channel for a spread spectrum signal received over N receive antennas. The FFT-based chip equalizer tap solver reduces the direct matrix inverse of the prior art to the inverse of some submatrices of size N×N with the dimension of the receive antennas, and most efficiently reduces matrix inverses to no larger than 2×2. Complexity is further reduced over a conventional Fast Fourier Transform approach by Hermitian optimization to the inverse of submatrices and tree pruning. For a receiver with N=4 or N=2 with double oversampling, the resulting 4×4 matrices are partitioned into 2×2 block sub-matrices, inverted, and rebuilt into a 4×4 matrix. Common computations are found and repeated computations are eliminated to improve efficiency. Generic design architecture is derived from the special design blocks to eliminate redundancies in complex operations. Optimally, the architecture is parallel and pipelined.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
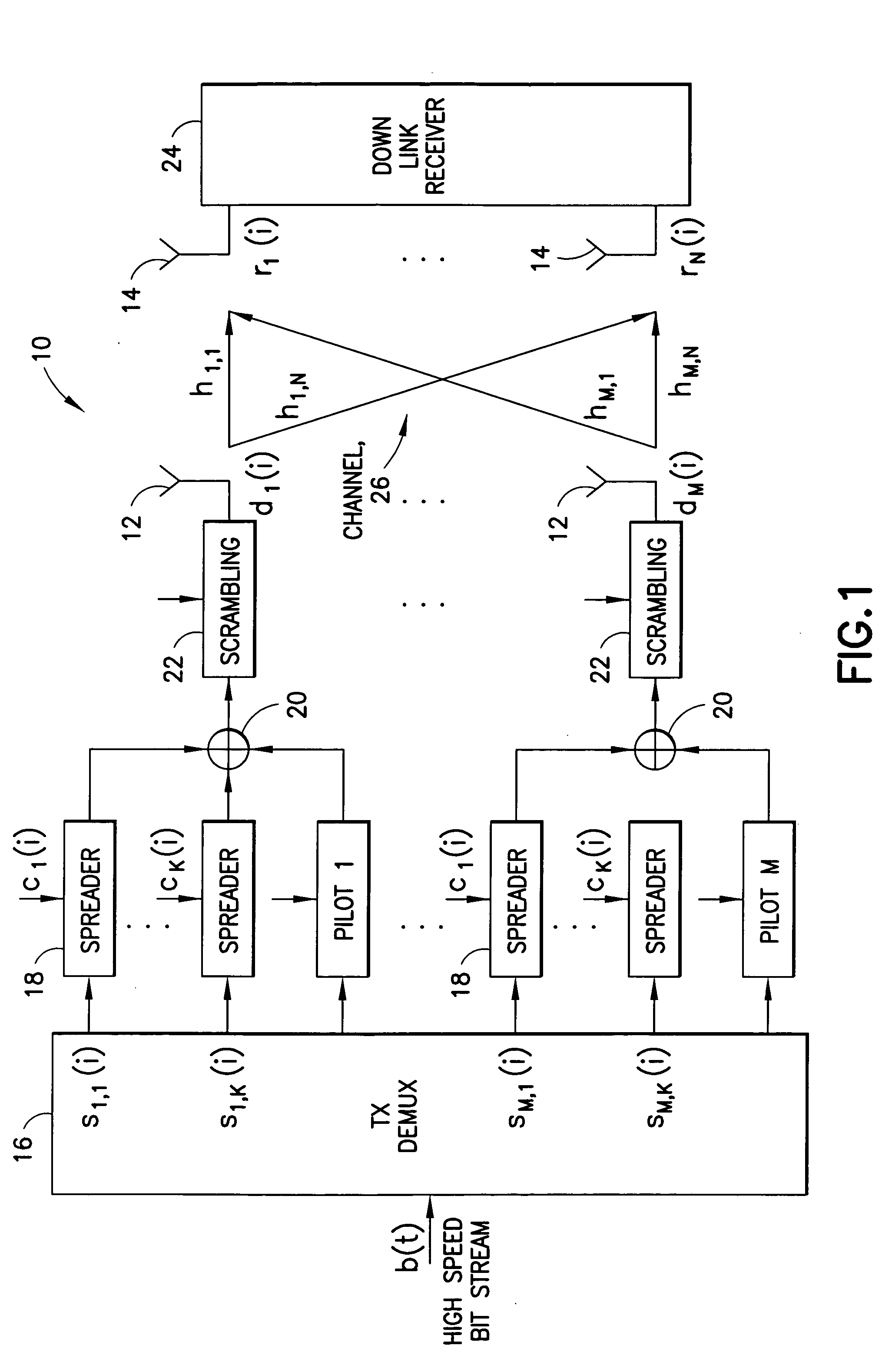
Equalizer for a VSB receiver enabling equalizations using segment synchronization information
InactiveUS7218671B2Improve uniformityTelevision system detailsMultiple-port networksData segmentEqualization
An equalizer for a VSB receiver, which enables equalizations using segment synchronization information, has an extraction unit extracting the segment synchronization information included in the VSB broadcast signal, a storage unit storing the extracted segment synchronization information, and an equalization unit equalizing the VSB broadcast signal based on the segment synchronization information stored in the storage unit. The storage unit stores the segment synchronization information extracted from the extraction unit by field unit or by unit of N data segments within the field according to a channel state. More stable equalizations can be carried out in channel environment changes by storing segment synchronization information by the predetermined number of data segments and equalizing data within a corresponding data segment in a training mode while using the segment synchronization information every matching number of data segments.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for processing a modulated signal using an equalizer and a rake receiver
InactiveUS20060056496A1Improve performanceImprove signal-to-noise ratioMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationSignal qualityEngineering
In a method for achieving higher S / N, one or more signals are received and processed to provide one or more streams of samples. In a first processing scheme, the sample stream(s) are equalized within an equalizer to generate symbol estimates, which may be subsequently processed (e.g., despread and decovered) to provide a first stream of recovered symbols. Each sample stream is filtered with a set of coefficients and may be scaled with a scaling factor. The scaled samples for all streams are then combined to generate the symbol estimates. The sample stream(s) may also be processed by a second processing scheme with one or more rake receivers to provide a second stream of recovered symbols. The signal quality for each processing scheme can be estimated and used to select either the first or second processing scheme.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com