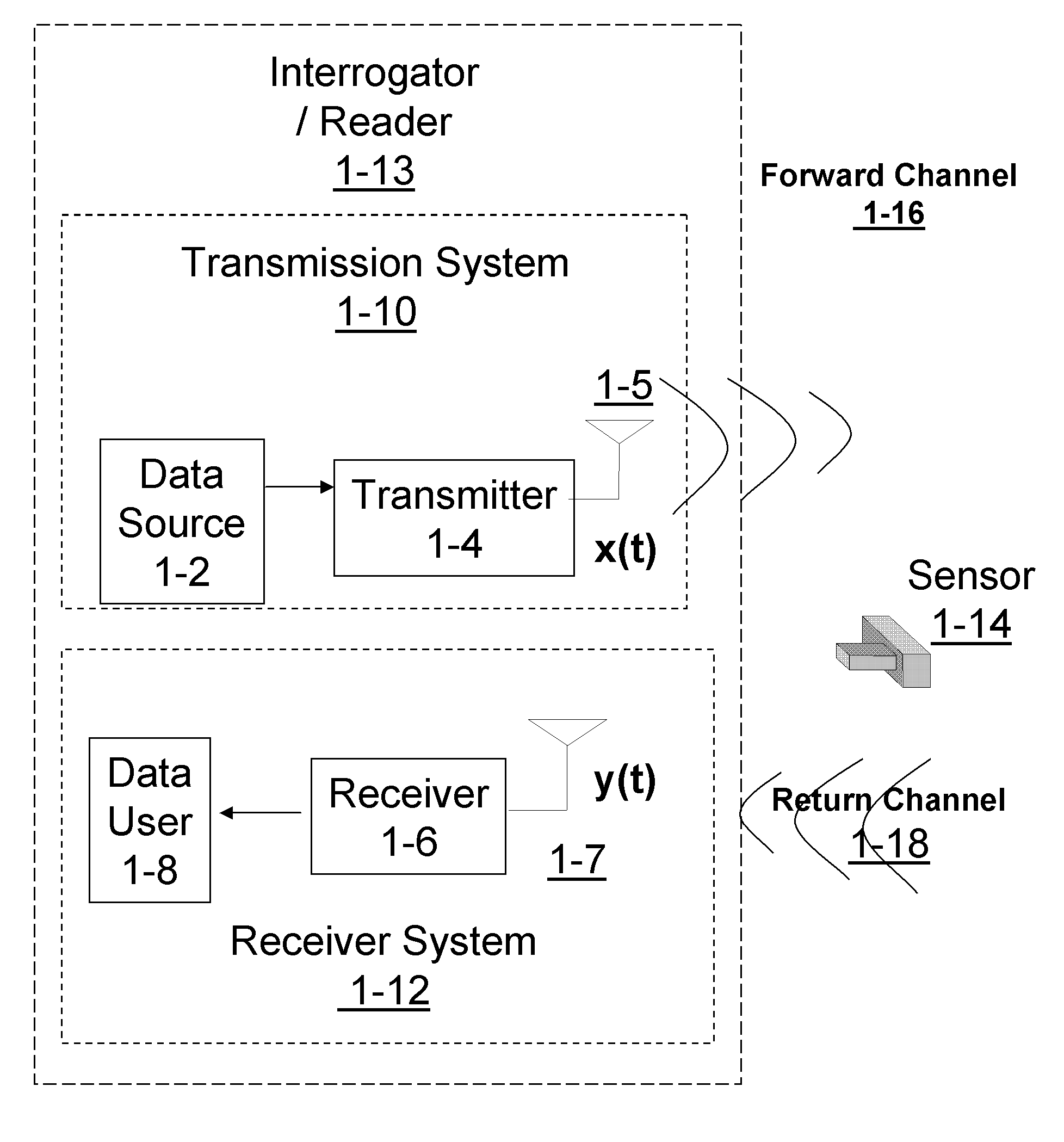
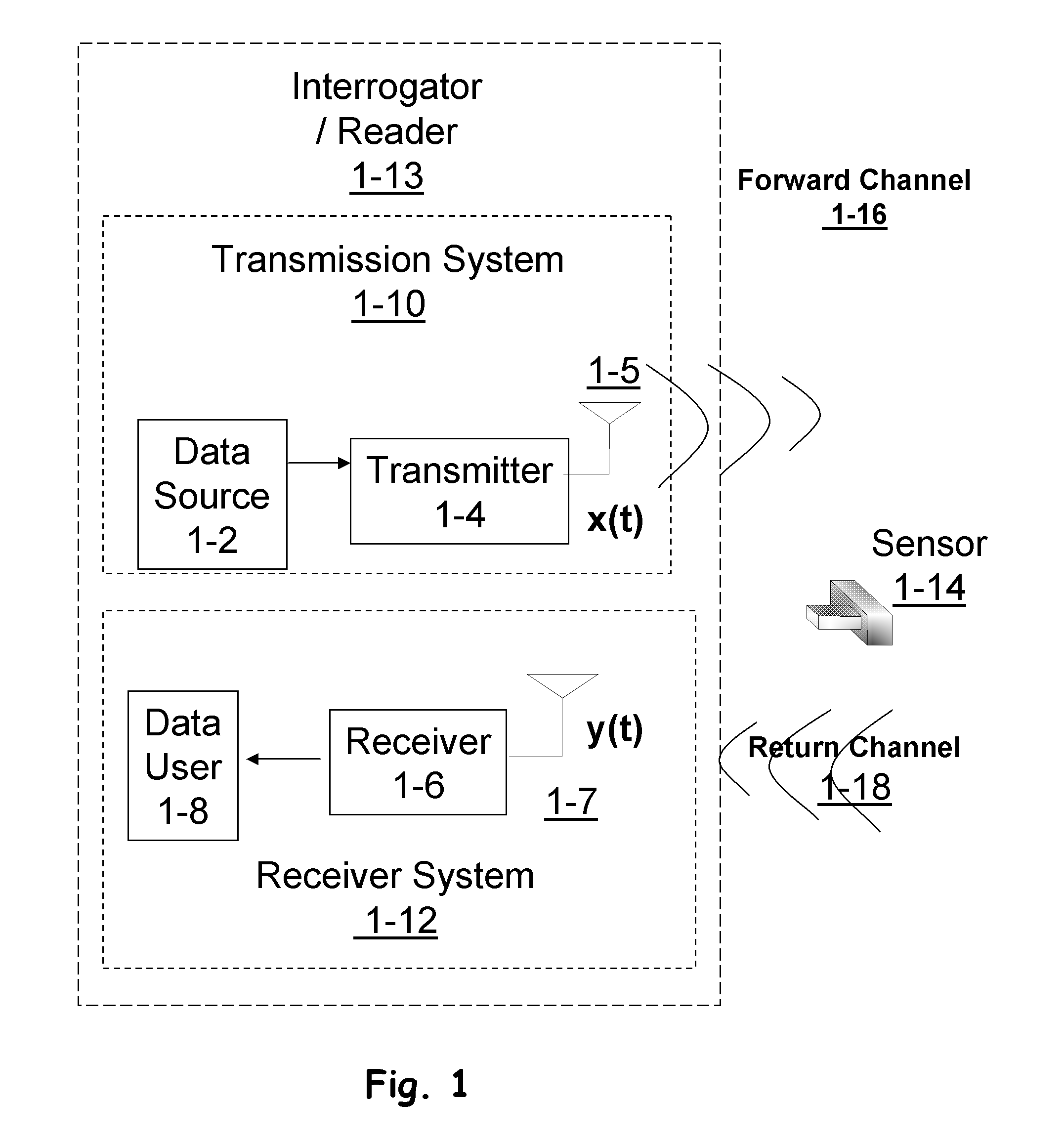
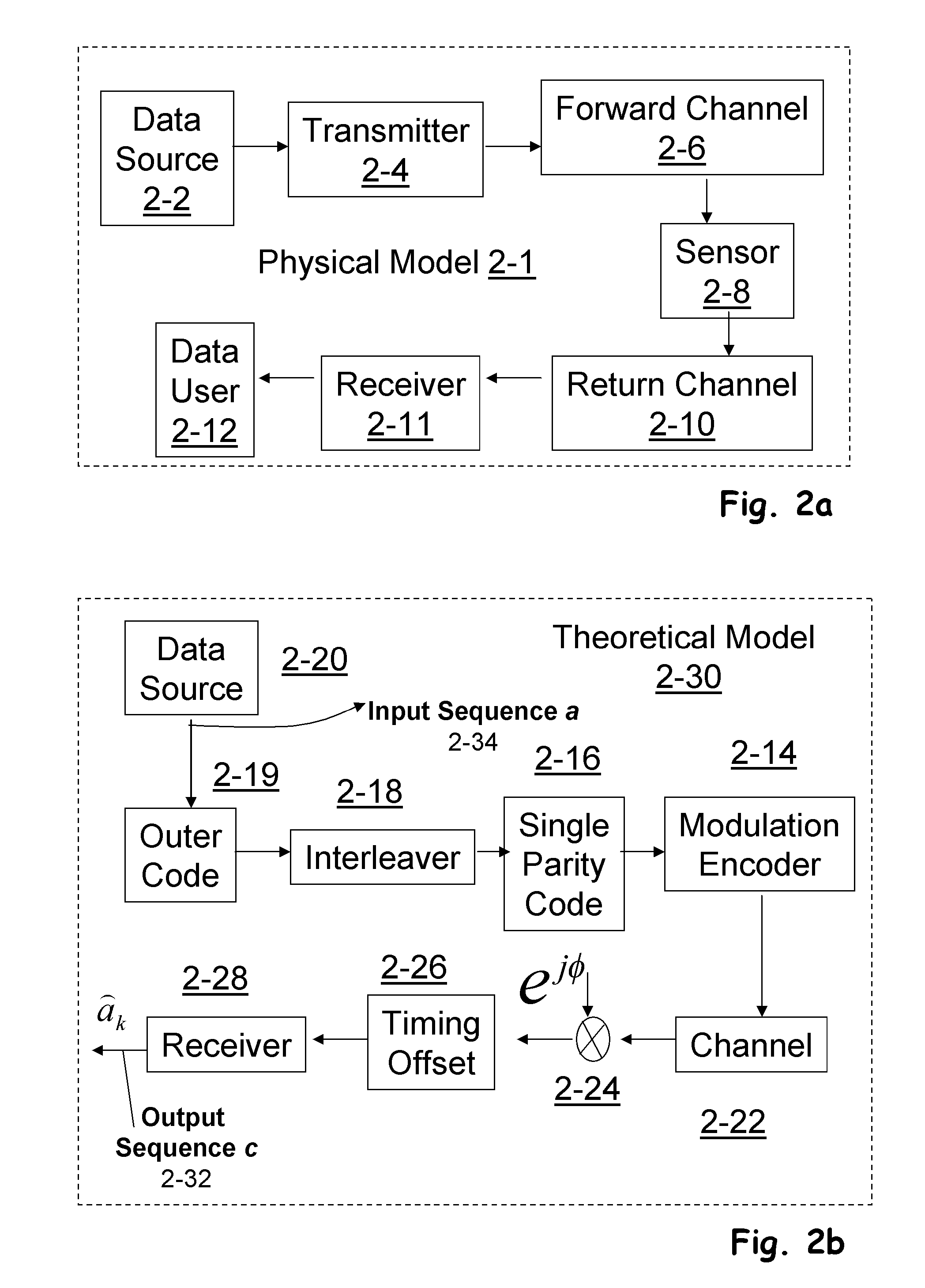
Patents
Literature
1038 results about "Baud" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
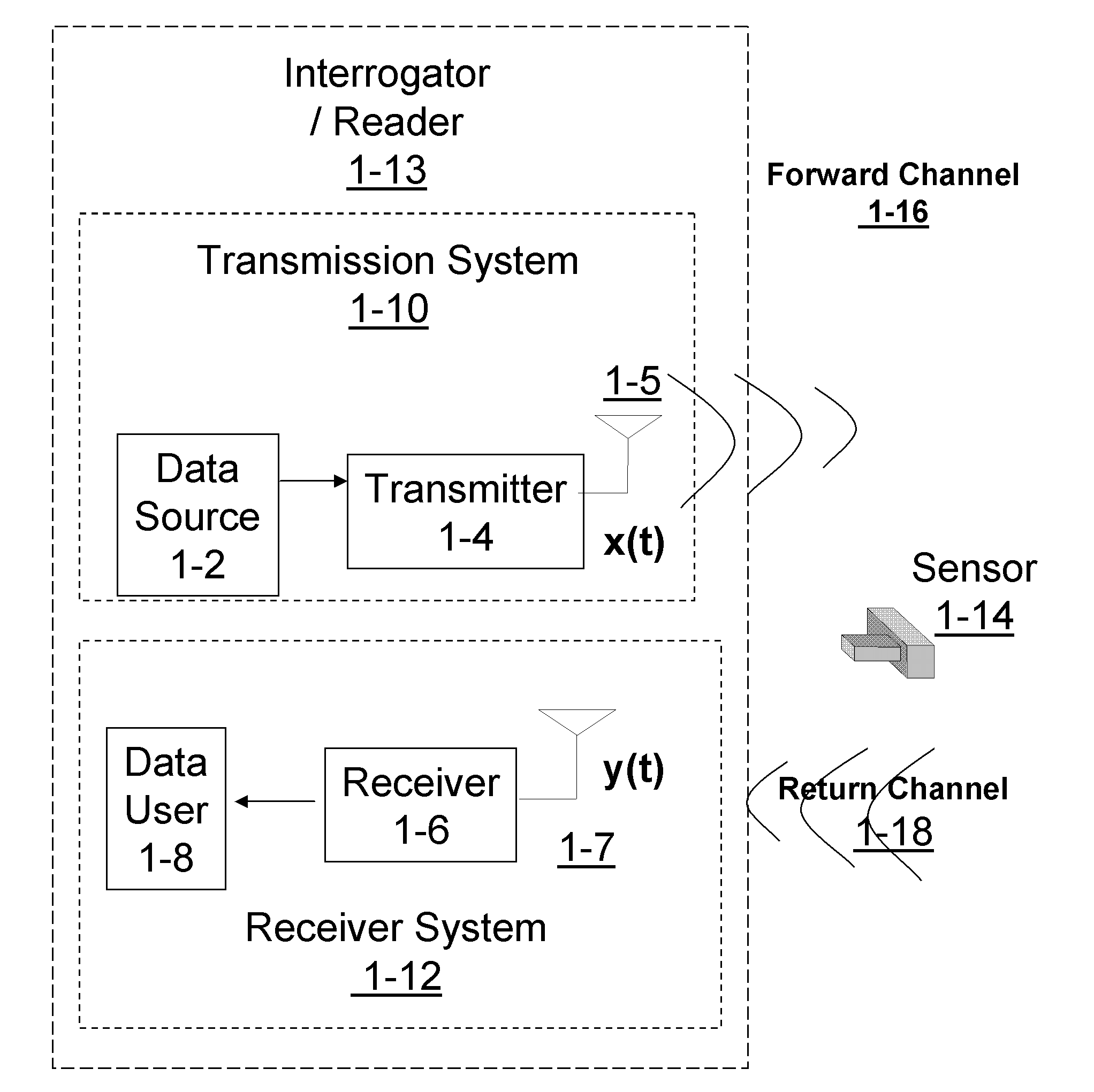
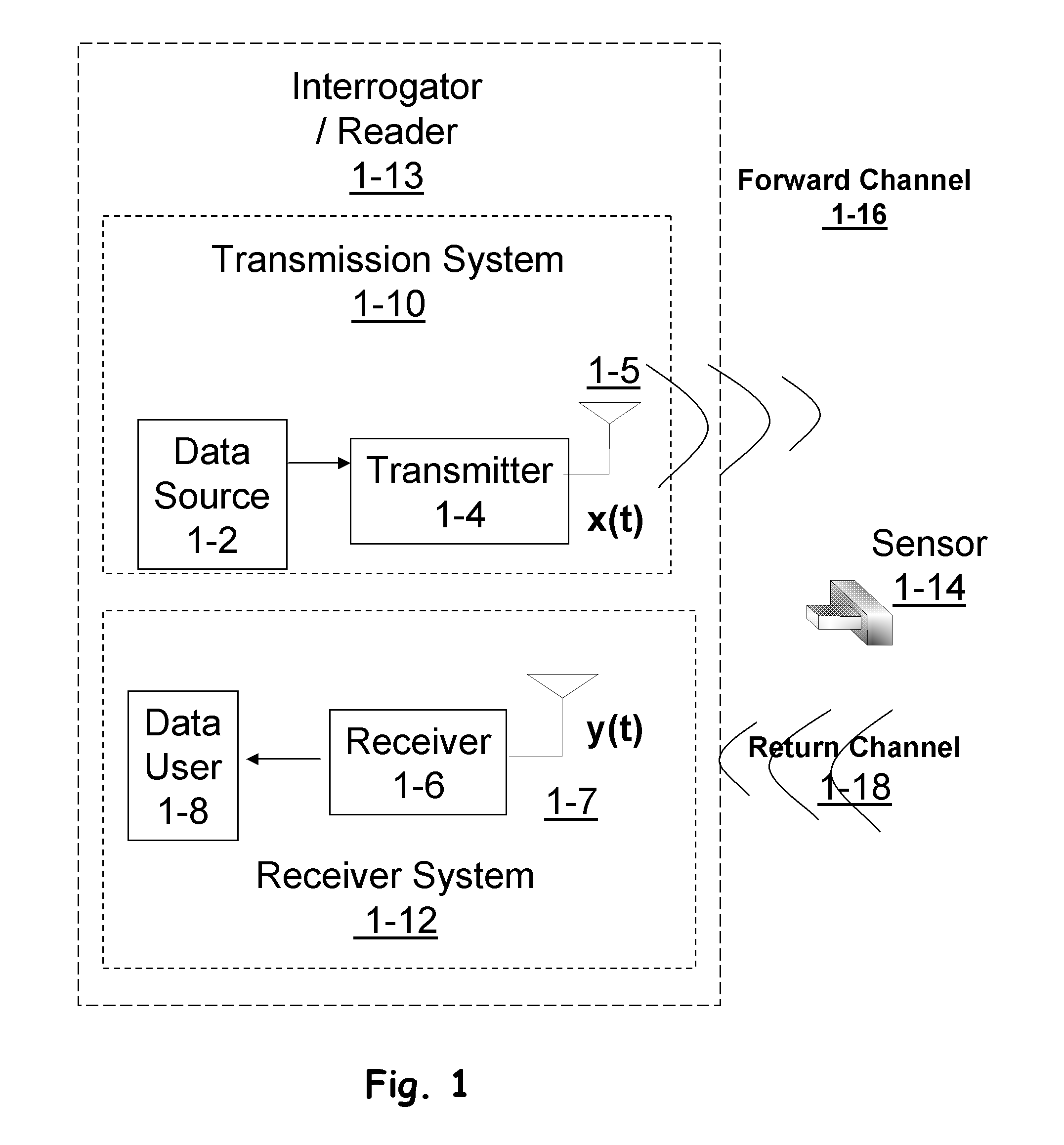
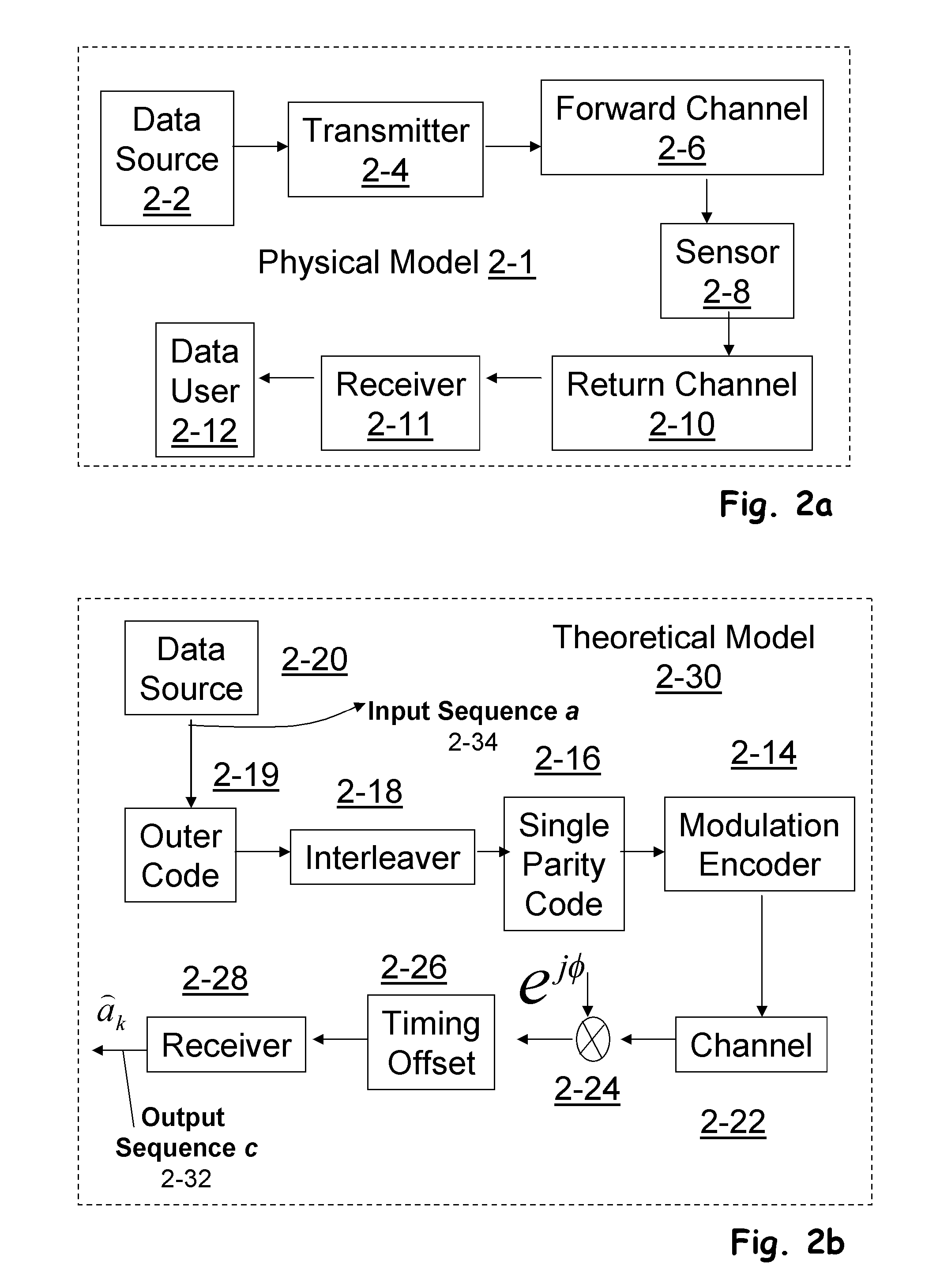
In telecommunication and electronics, baud (/bɔːd/; symbol: Bd) is a common measure of symbol rate, one of the components that determine the speed of communication over a data channel. It is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second or pulses per second. It is the number of distinct symbol changes (signaling events) made to the transmission medium per second in a digitally modulated signal or a bd rate line code.
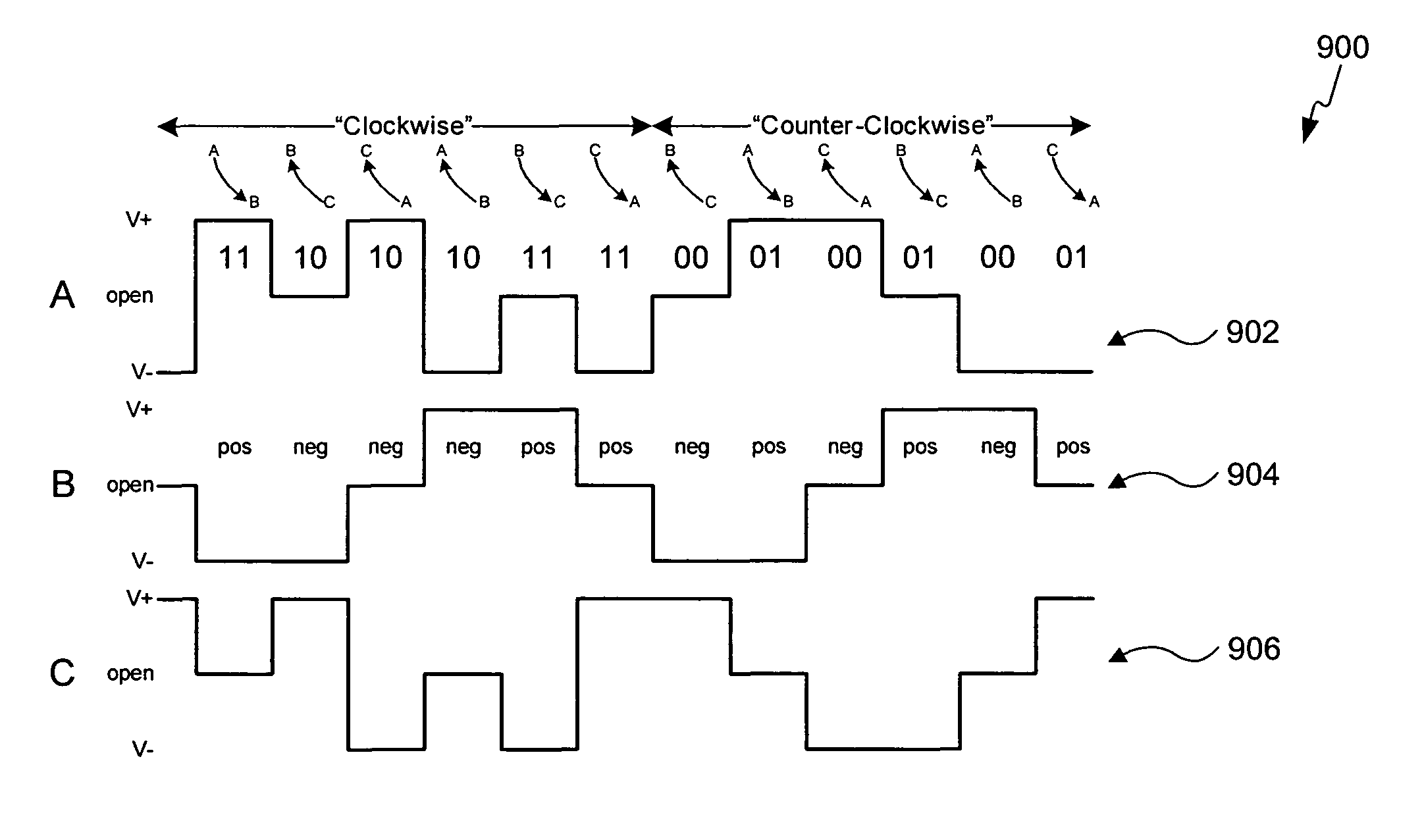
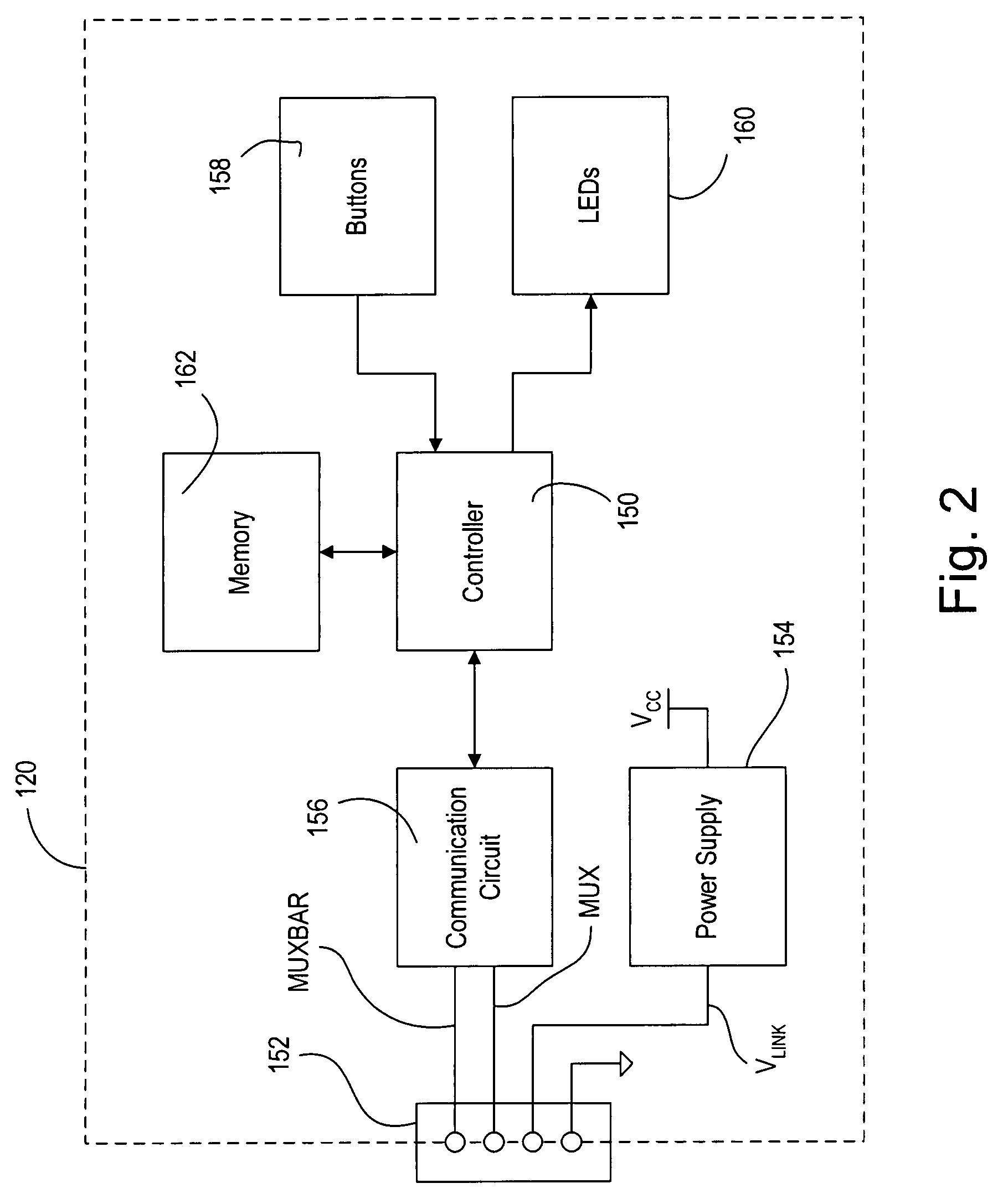
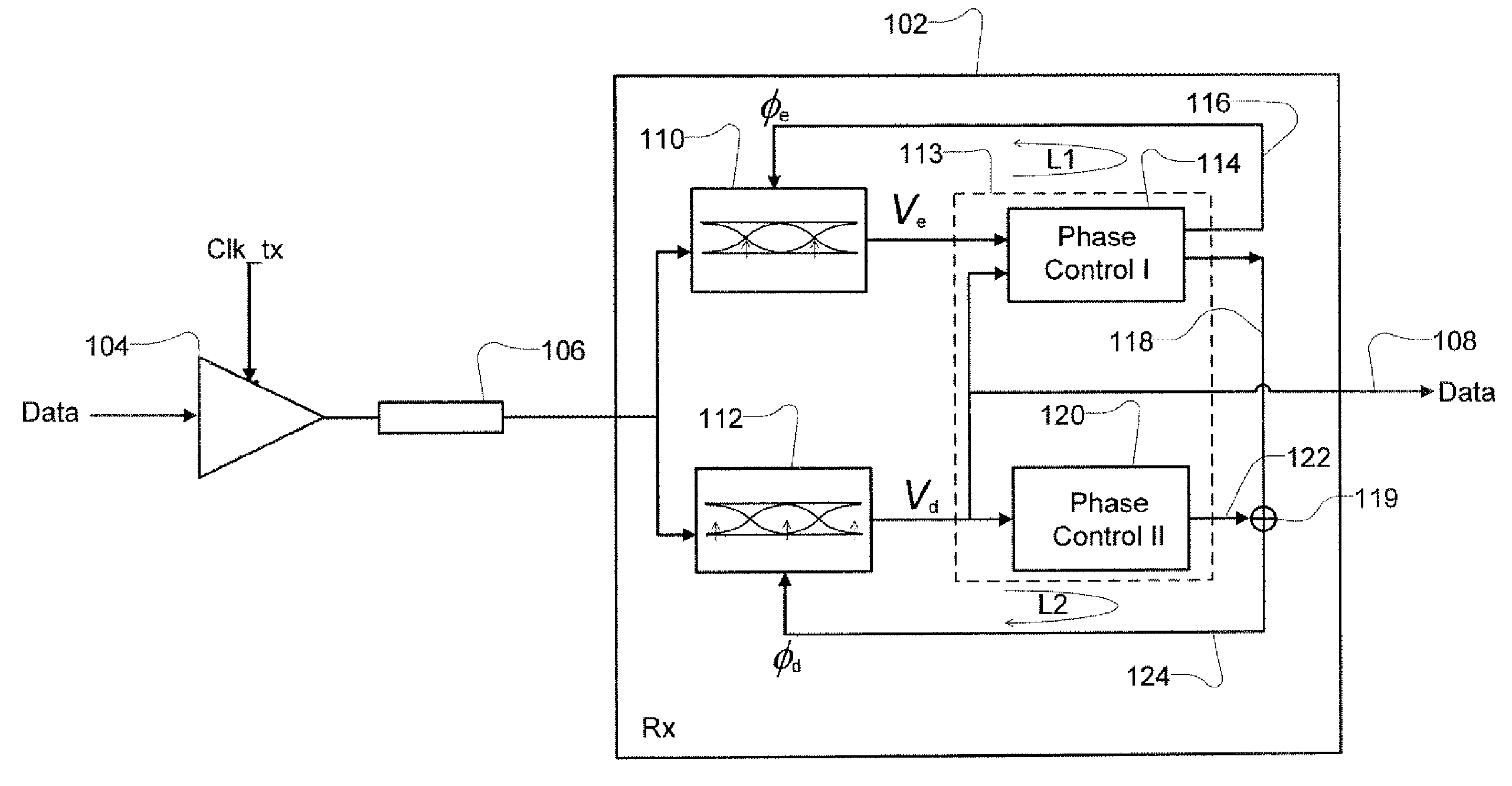
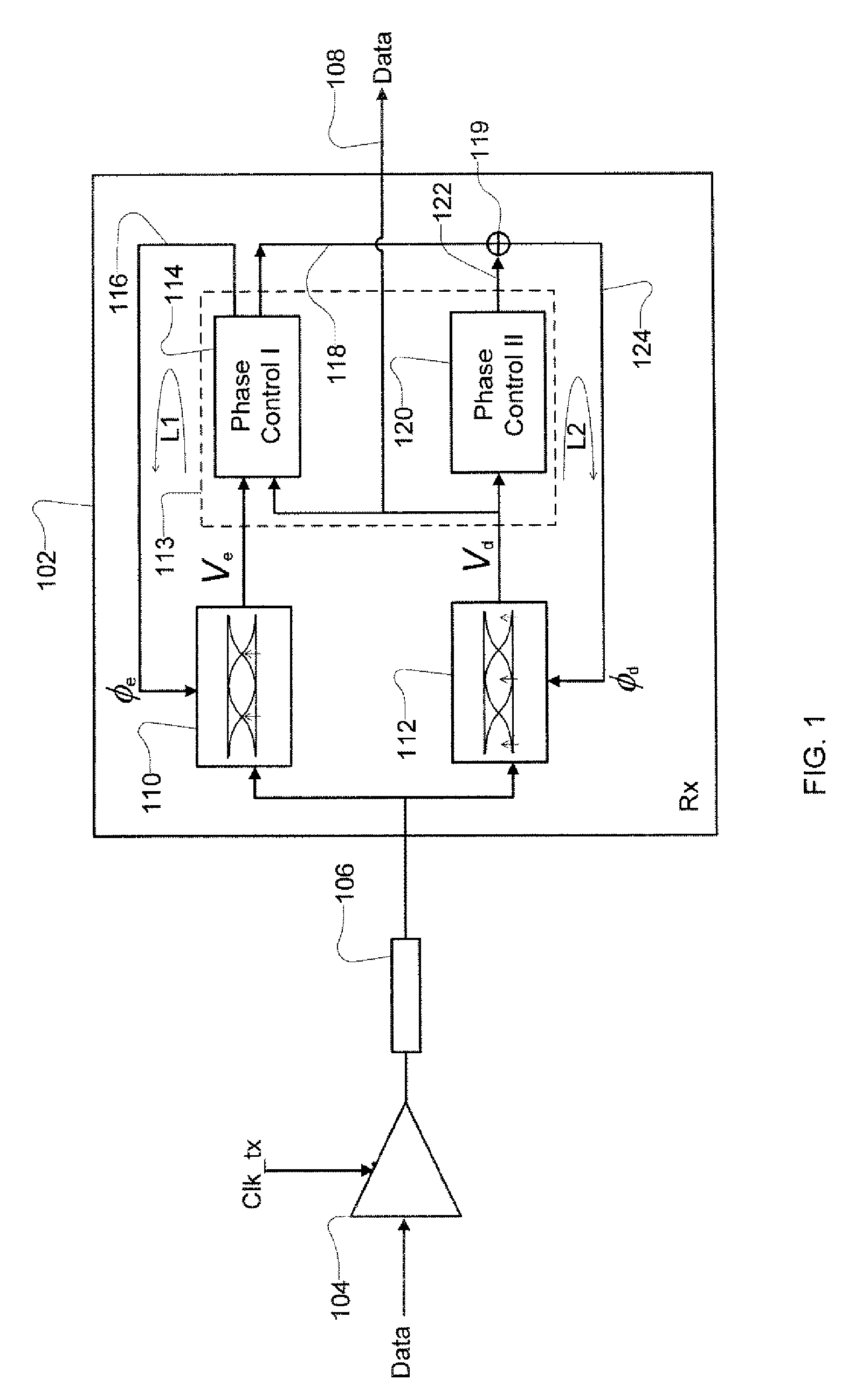
Three phase and polarity encoded serial interface
ActiveUS8064535B2Shorten the timeImprove efficiencyIndividual digits conversionPhase-modulated carrier systemsSerial digital interfaceElectrical conductor
A high speed serial interface is provided. In one aspect, the high speed serial interface uses three phase modulation for jointly encoding data and clock information. Accordingly, the need for de-skewing circuitry at the receiving end of the interface is eliminated, resulting in reduced link start-up time and improved link efficiency and power consumption. In one embodiment, the high speed serial interface uses fewer signal conductors than conventional systems having separate conductors for data and clock information. In another embodiment, the serial interface allows for data to be transmitted at any speed without the receiving end having prior knowledge of the transmission data rate. In another aspect, the high speed serial interface uses polarity encoded three phase modulation for jointly encoding data and clock information. This further increases the link capacity of the serial interface by allowing for more than one bit to be transmitted in any single baud interval.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
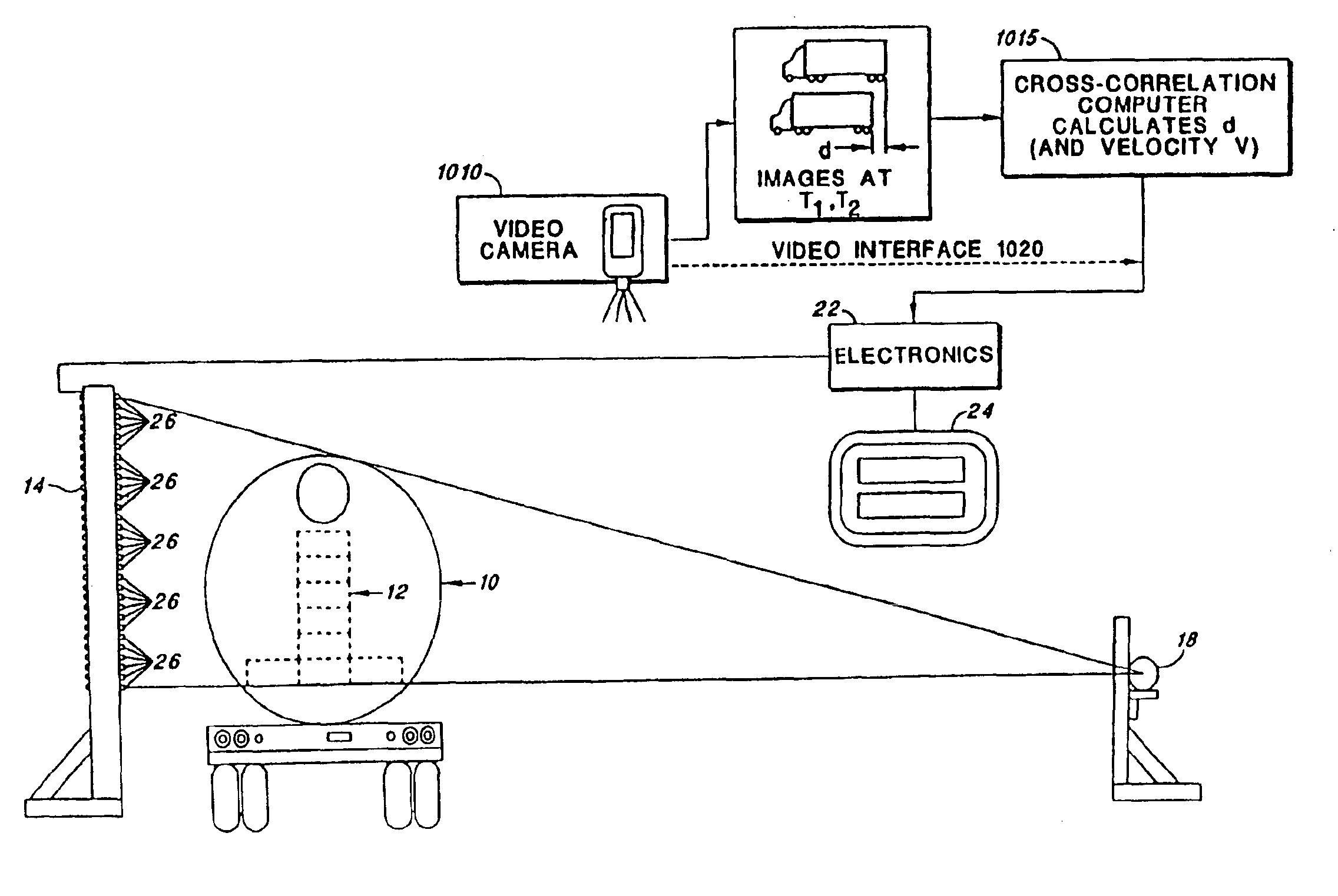
Density detection using real time discrete photon counting for fast moving targets
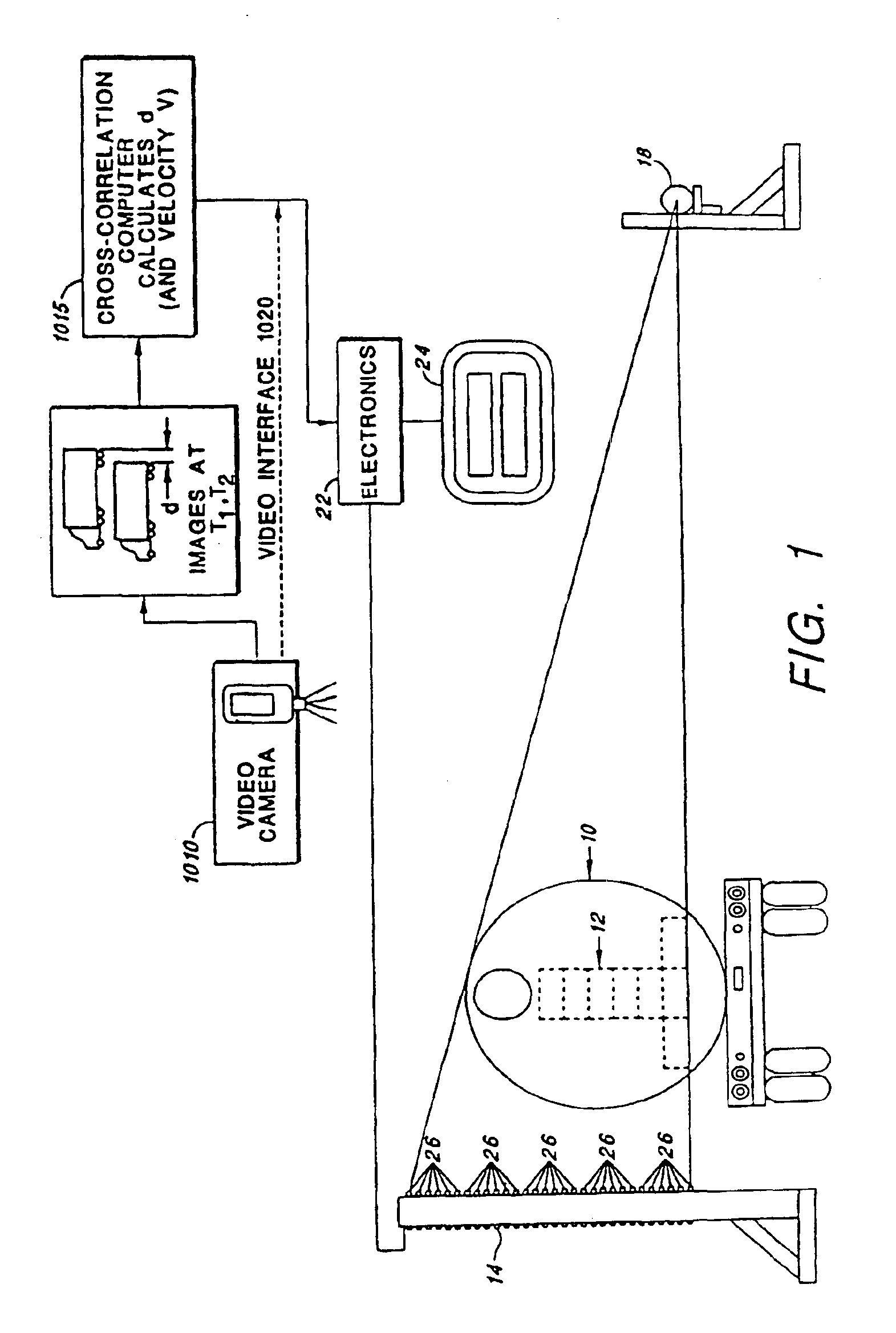
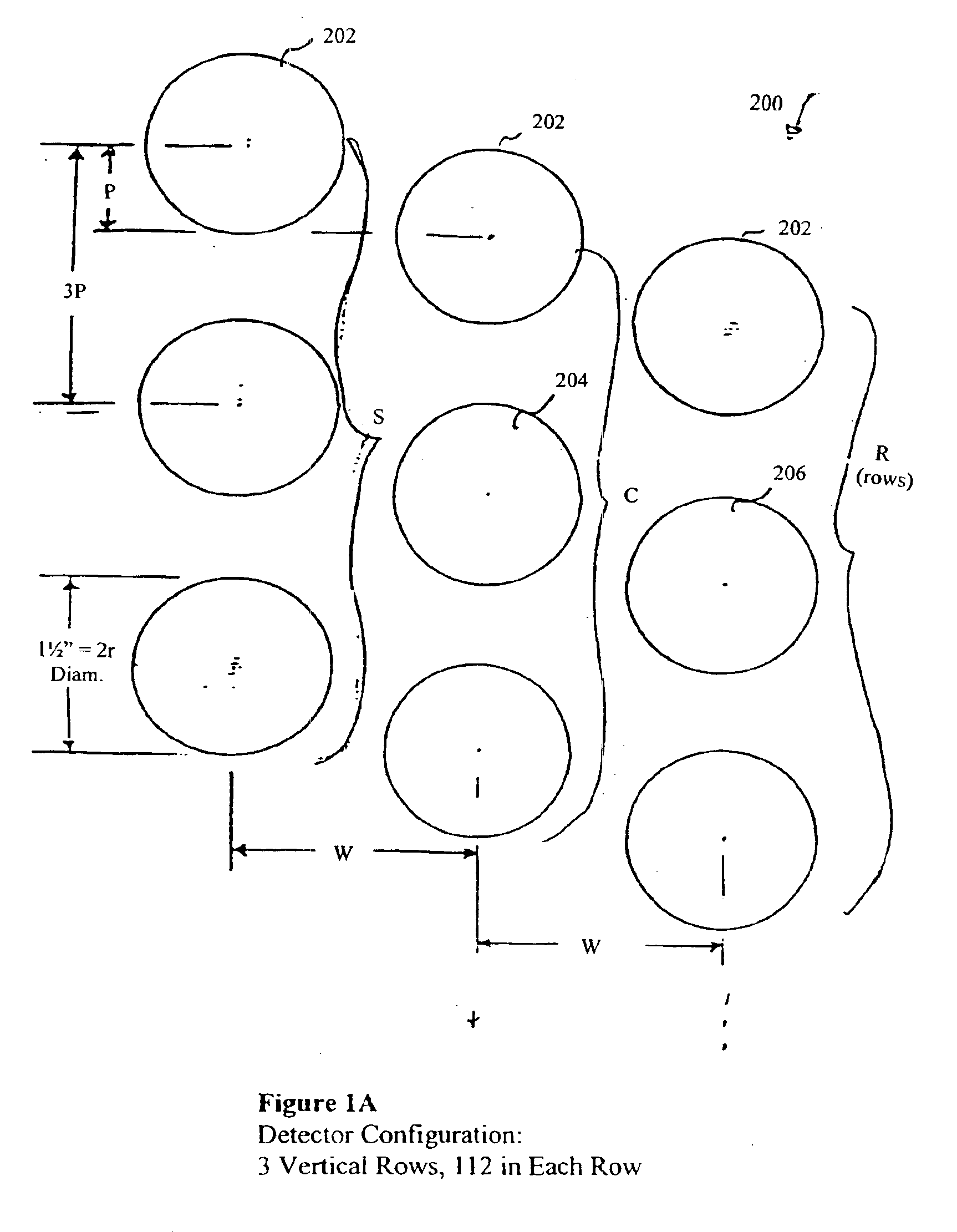
A system for detecting and graphically displaying a contents of a fast-moving target object comprises: a radiation source, having a position such that at least a portion of radiation emitted from the radiation source passes through the fast-moving target object, the fast-moving target object having a variable velocity and acceleration while maintaining a substantially constant distance from the radiation source and being selected from the group consisting of: a vehicle, a cargo container and a railroad car; a velocity measuring device configured to measure the variable velocity of the fast-moving target object; a detector array comprising a plurality of photon detectors, having a position such that at least some of the at least a portion of the radiation passing through the target object is received thereby, the detector array having a variable count time according to the variable velocity and a grid unit size; a counter circuit coupled to the detector array for discretely counting a number of photons entering individual photon detectors, the counter circuit measuring a count rate according to a contents within the fast-moving target object; a high baud-rate interface coupled to the counter circuit for sending count information from the counter circuit at a rate fast enough to support real-time data transfer therethrough; and a processor coupled to the velocity measuring device and to the high-baud-rate interface, receiving count information from the high baud-rate interface and generating distortion-free image data in real time as a function of the count information and the variable velocity. A method for using the system is also disclosed.
Owner:LEIDOS
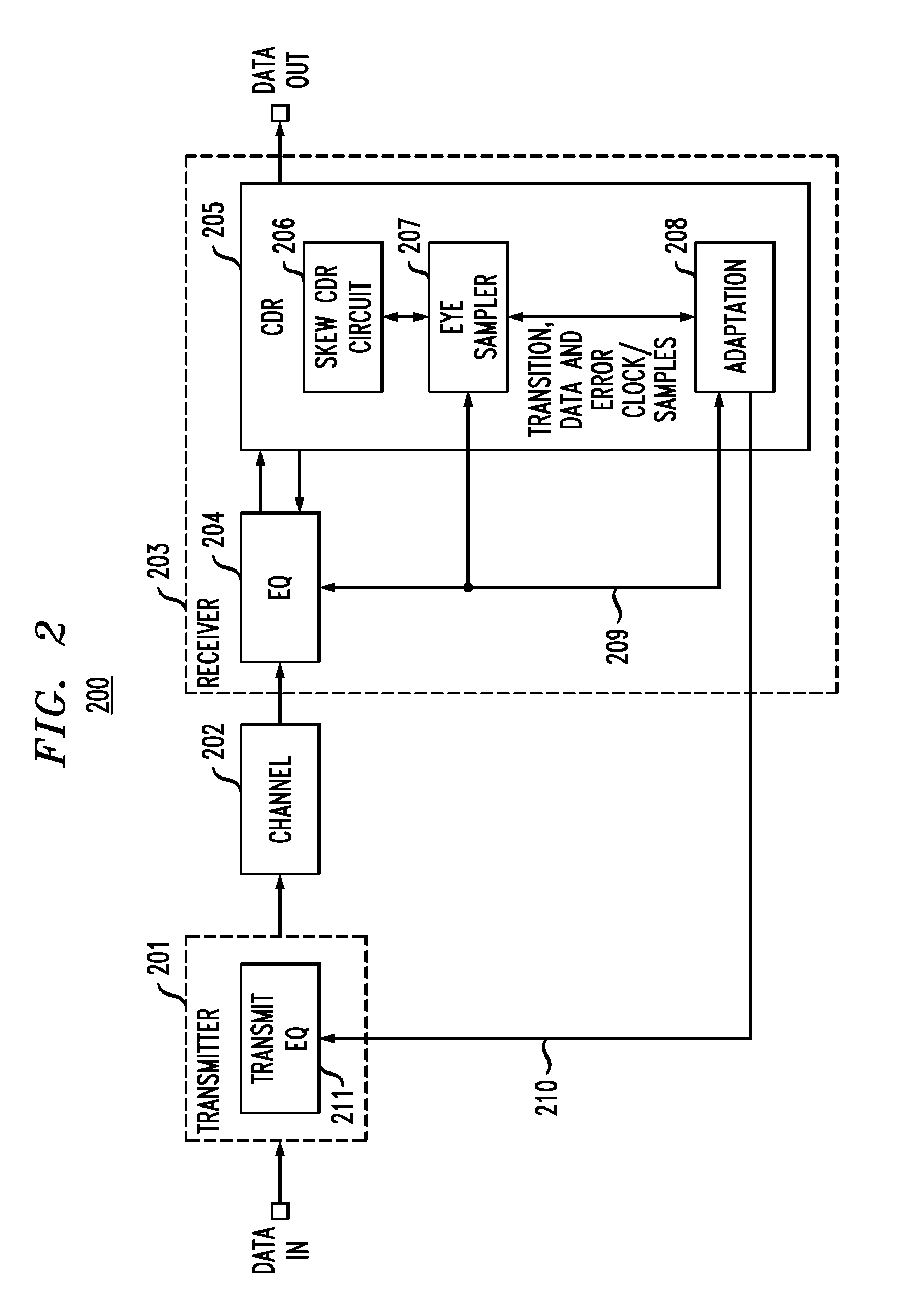
Adjusting sampling phase in a baud-rate CDR using timing skew
In described embodiments, a transceiver includes a baud-rate clock and data recovery (CDR) module with an eye sampler, and an adaptation module for adaptively setting parameters of various circuit elements, such as timing, equalizer and gain elements. Data sampling clock phase of the CDR module is set for sampling at, for example, near the center of a data eye detected by the eye sampler, and the phase of data error sampling latch(es) is skewed by the CDR module with respect to the phase of the data sampling latch. Since the error signal driving the timing adaptation contains the information of the pulse response that the CDR module encounters, the phase of timing error sampling latch(es) of the CDR module is skewed based on maintaining a relative equivalence of input pulse response residual pre-cursor and residual post-cursor with respect to the timing error sampling clock phase.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
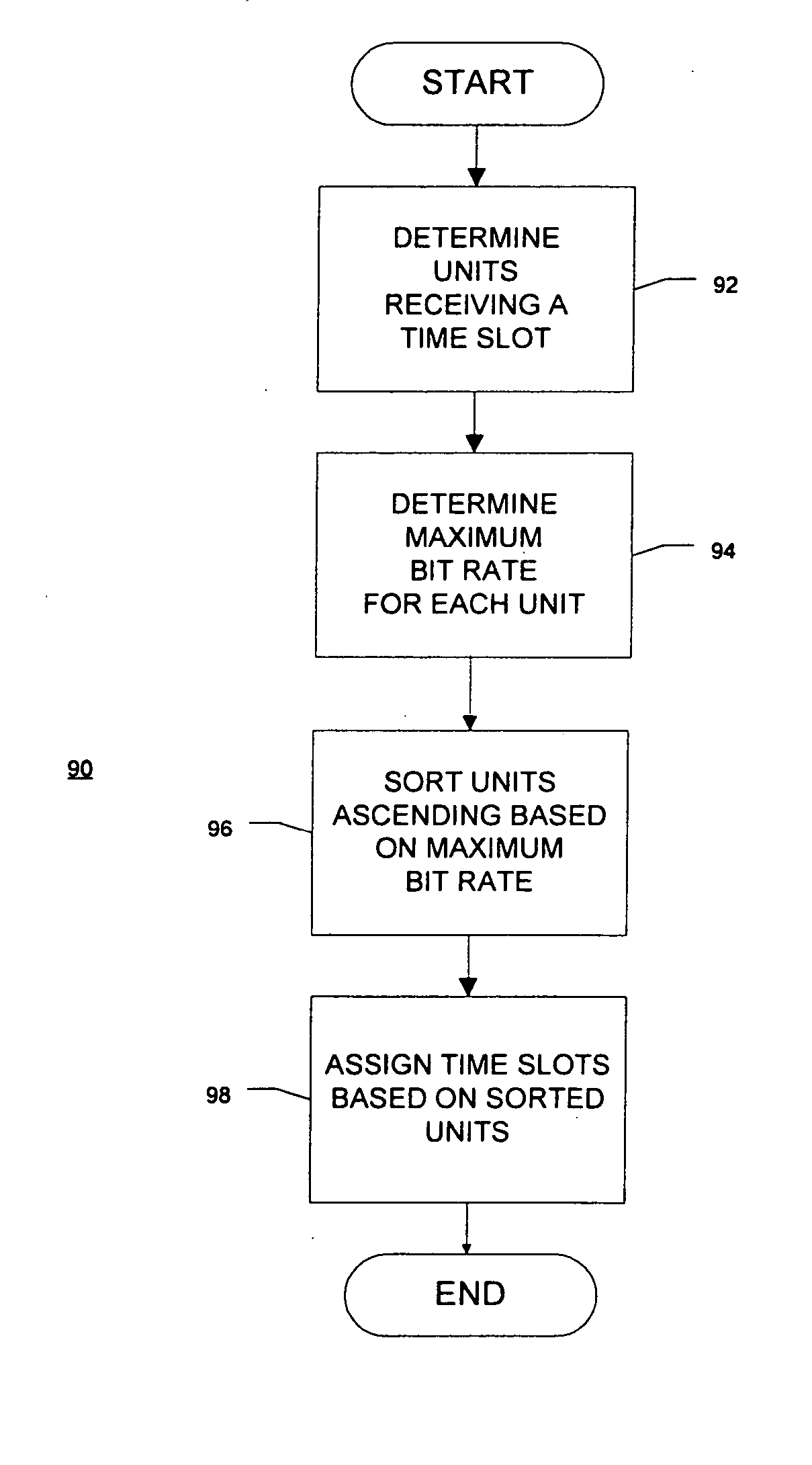
Frame structure for an adaptive modulation wireless communication system
InactiveUS20050058098A1Significant complexityReduce complexityEnergy efficient ICTMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsCommunications systemFrame time
A method of assigning downlink time slots to receive units where the units may generate data using different modulation schemes. The method preferably assigns the downlink time slots as a function of the complexity of modulation schemes employed by the units. Further, the method preferably assigns the time slots from the least complex modulation scheme to the most complex scheme. The method may further assign uplink time slots to transmit units where the transmit units may generate data using different modulation schemes. The method preferably assigns the uplink time slots as a function of the complexity of modulation schemes employed by the uplink units. Further, the method preferably assigns the uplink time slots from the least complex modulation scheme to the most complex scheme. In other embodiments, the downlink time slots are assigned as a function of the bit per symbol rate employed by the receive units, preferably from the lowest bit per symbol rate to the highest bit per symbol rate. Further, the uplink time slots are assigned as a function of the bit per symbol rate employed by the transmit units, preferably from the lowest bit per symbol rate to the highest bit per symbol rate. The present invention is also a method of simplifying the encoding of a predetermined number of bits of data into frames. The method adds error coding bits so that a ratio of the frame length times the baud rate of the frame times the bit packing ratio of the data divided the total bits of data is always an integer. The method may also convolutionally encode the bits of data so that the same equation is also always an integer. The present invention is also a method of updating the weights of a FIR filter where the filter processes symbols having variable modulation rates. When the modulation rate of the incoming symbols changes, the weights corresponding to the first symbol having the new modulation rate are changed based as the symbol propagates through the filter.
Owner:WI LAN INC
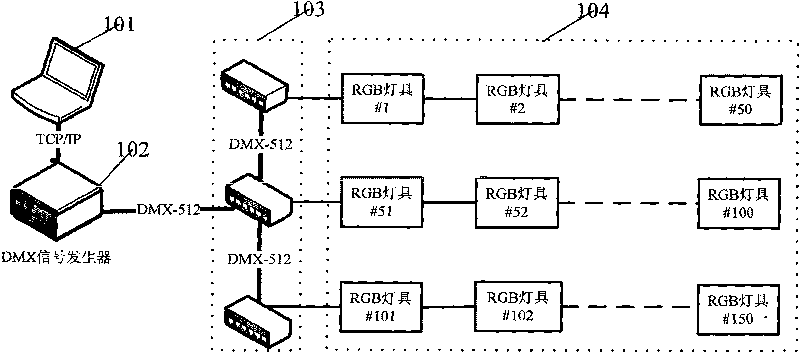
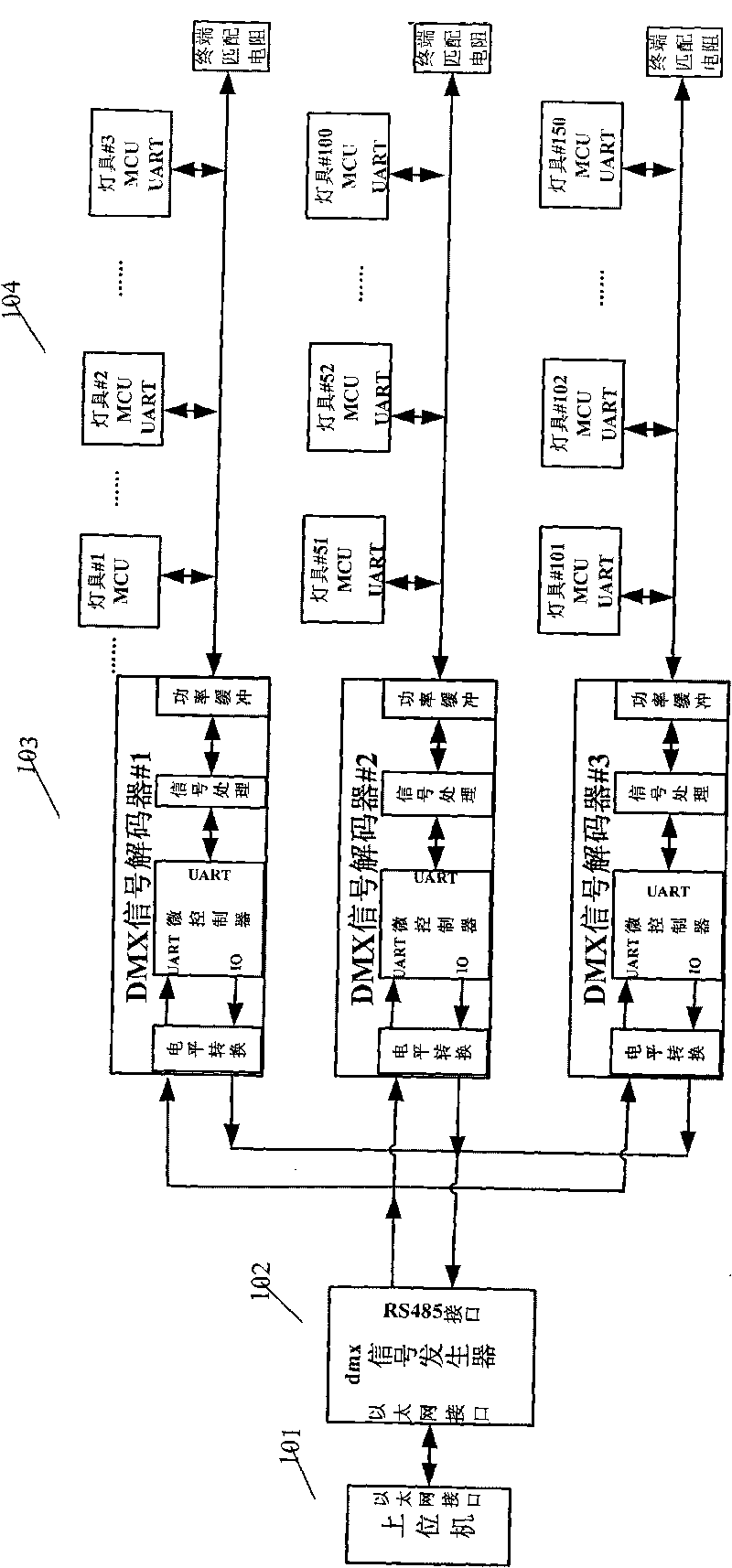
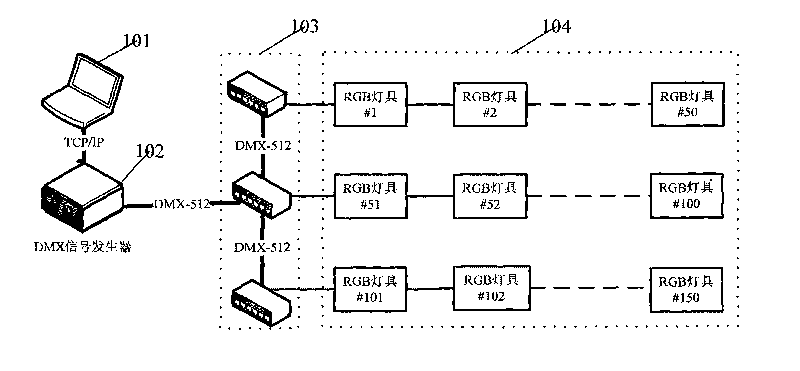
Lighting control system based on DMX512 protocol and method thereof
InactiveCN101699923AReduce wiring costsReduce long-distance transmission interferenceElectric light circuit arrangementNetwork connectionDMX512
The invention discloses a lighting control system based on a DMX512 protocol and a method thereof. The system comprises an upper computer, a DMX signal generator, a DMX signal decoder and lamps, wherein each part is connected in a distribution mode; the upper computer is connected with the DMX signal generator by a network; the DMX signal generator is connected with the DMX signal decoder by an interface; and the DMX signal decoder is communicated with the lamps by a single data bus. The method comprises the following steps: the upper computer controls the DMX signal generator; the signal generator is communicated with the DMX signal decoder; and the signal decoder is connected with the lamps. Baud rate of the communication between the decoder and the lamps can be configured online to synchronize DMX devices with different speeds; the invention is provided with the functions of luminance adjustment for the lamps, temperature detection and open circuit detection and the like; and the invention has an important reference value for the design of the lighting control system.
Owner:广州中大中鸣科技有限公司 +1
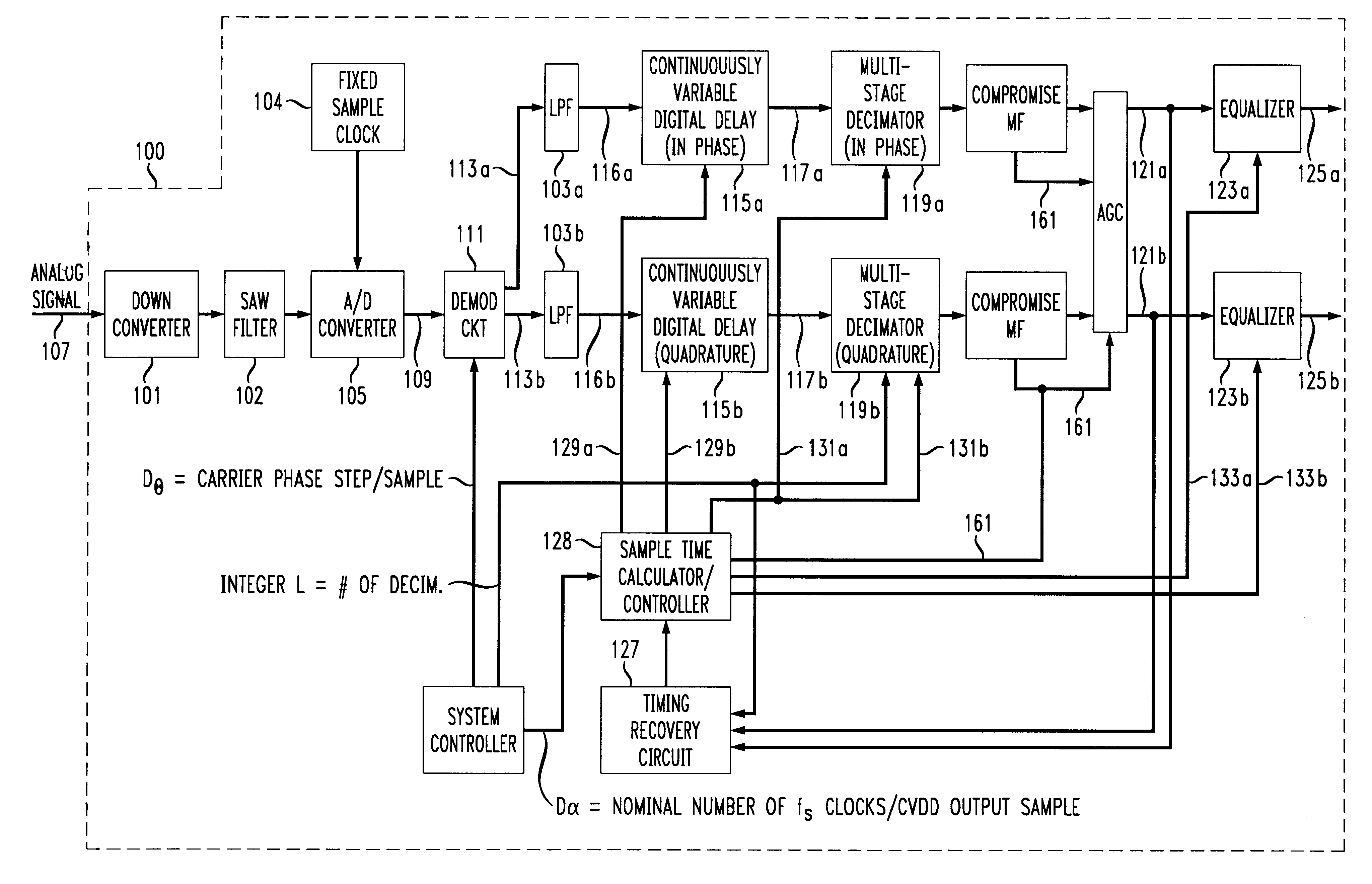
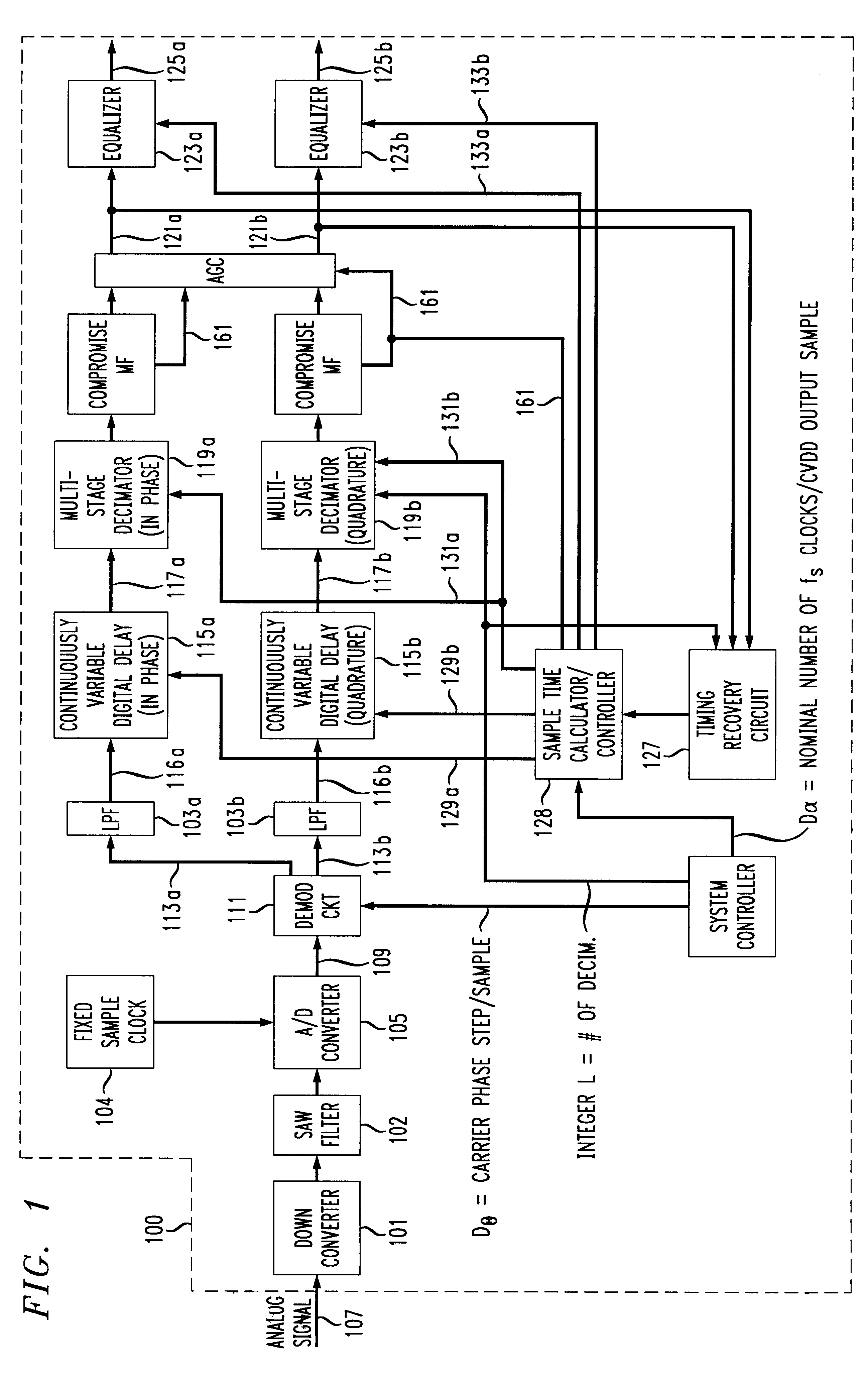
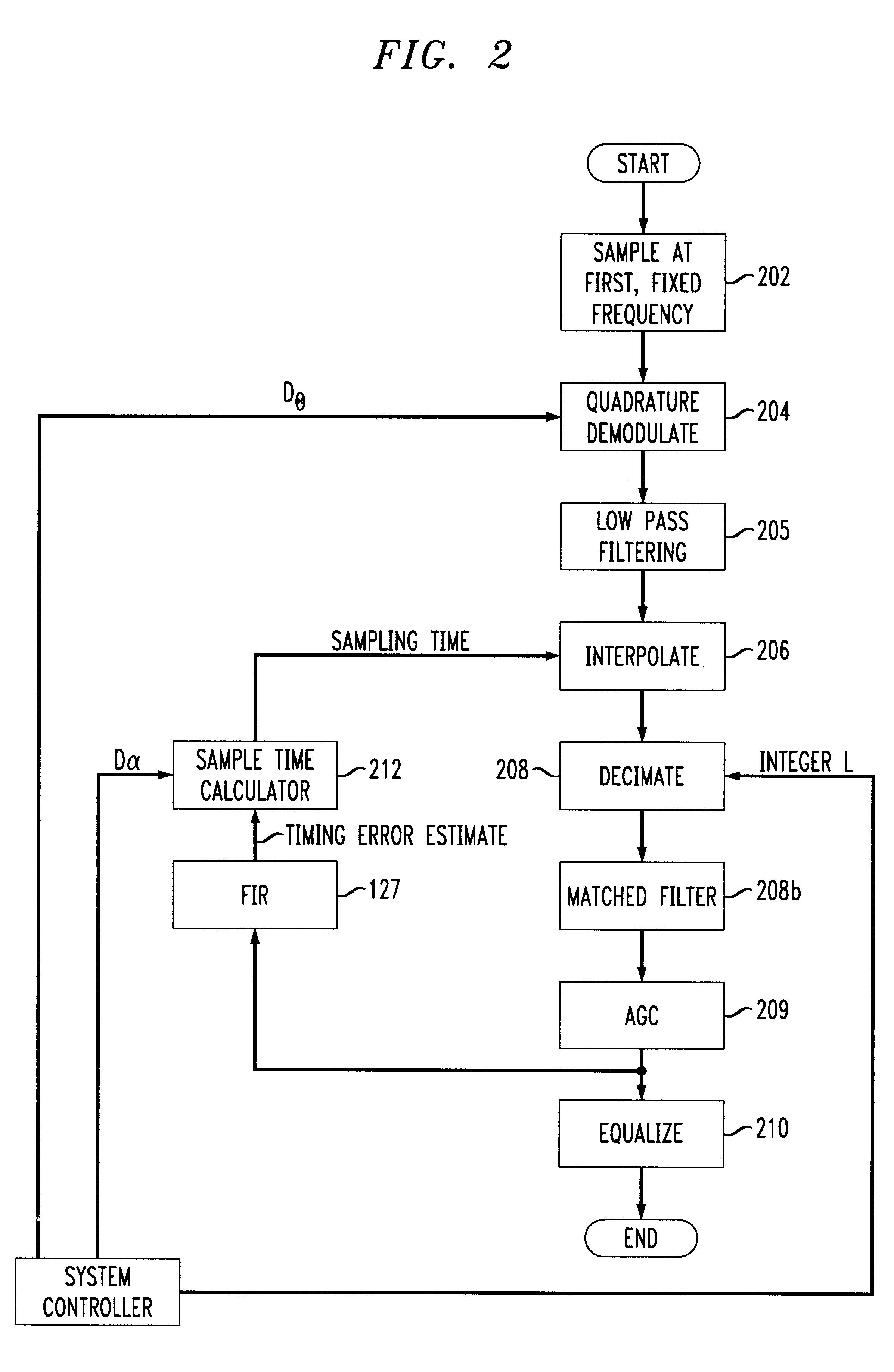
Fixed clock based arbitrary symbol rate timing recovery loop
InactiveUS6295325B1Receiver initialisationAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionData signalSymbol rate
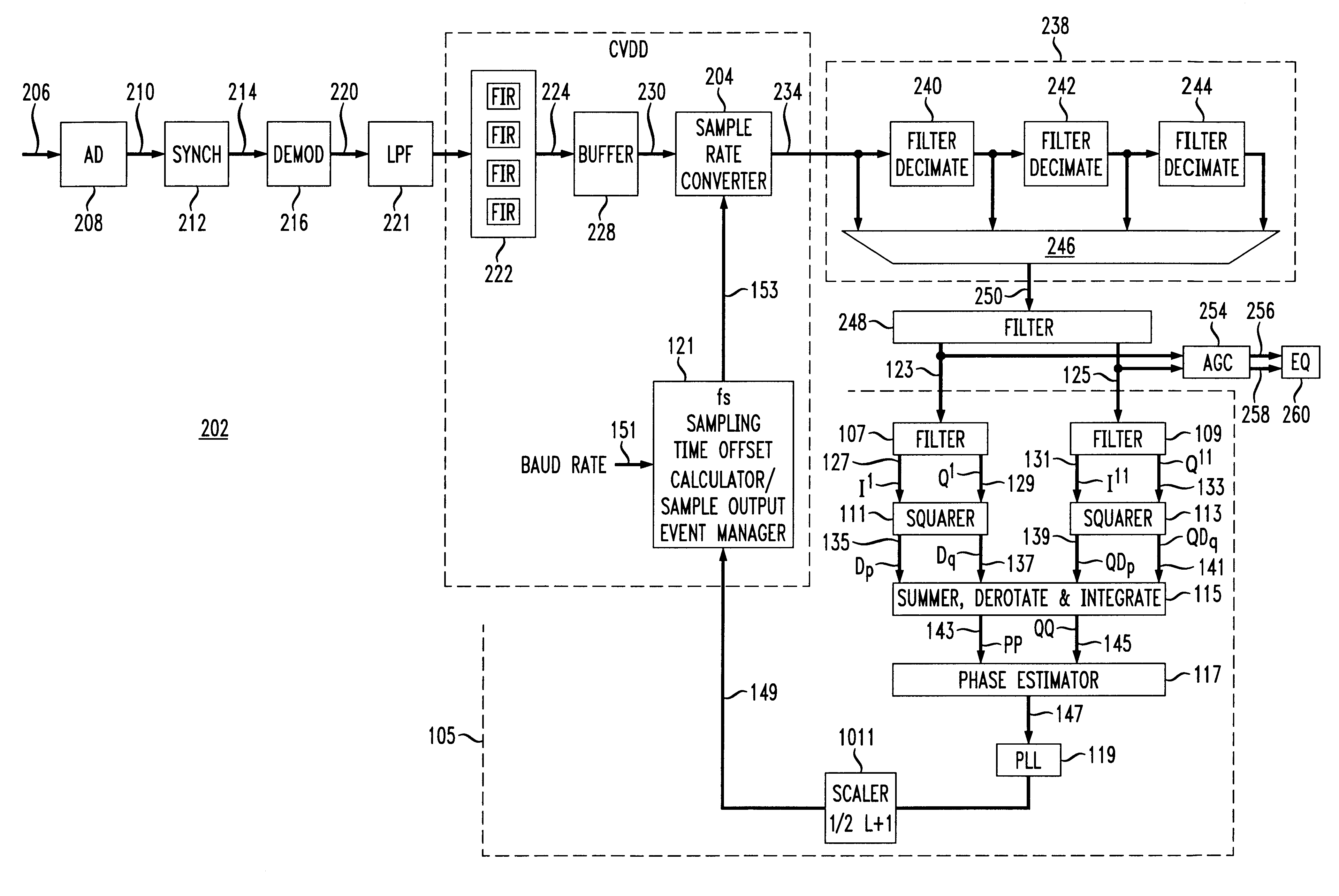
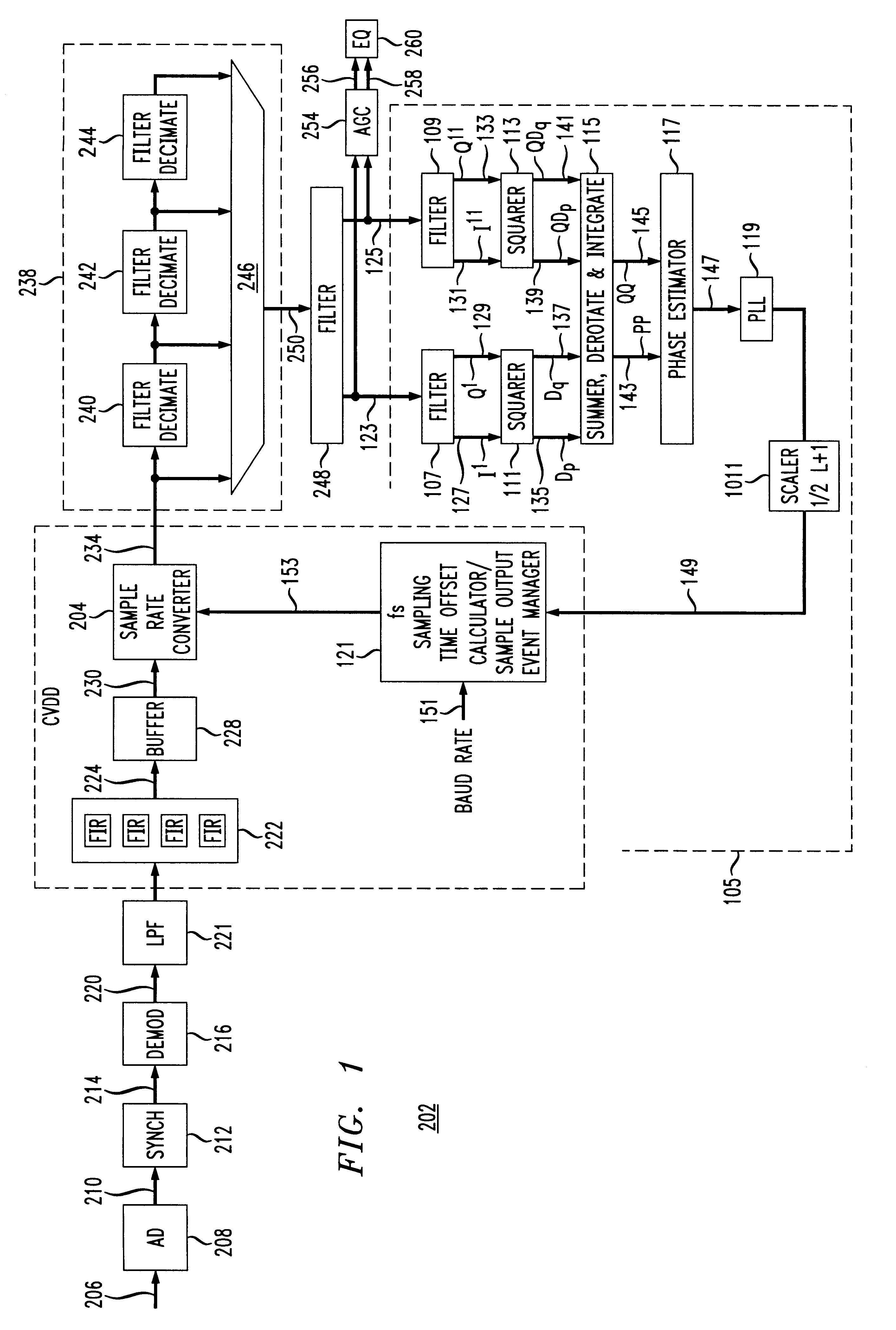
A QAM data signal timing recovery loop feedback element provides a fixed sampling time offset adjustment to two continuously variable digital rate interpolators / decimators to produce a quadrature output stream at a programmed rational rate multiple of the actual baud rate of the received data signal. The continuously variable digital rate interpolators / decimators are configured at startup so as to produce output streams at the same programmed rational rate multiple of the nominal baud rate of the anticipated received data signal, assuming the fs sample timing offset adjustment stream provided by the timing recovery feedback element to be identically 0. The "nominal" fixed sampling rate fs of the received analog input signal need not be rationally related to the nominal baud rate of the anticipated received data signal.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
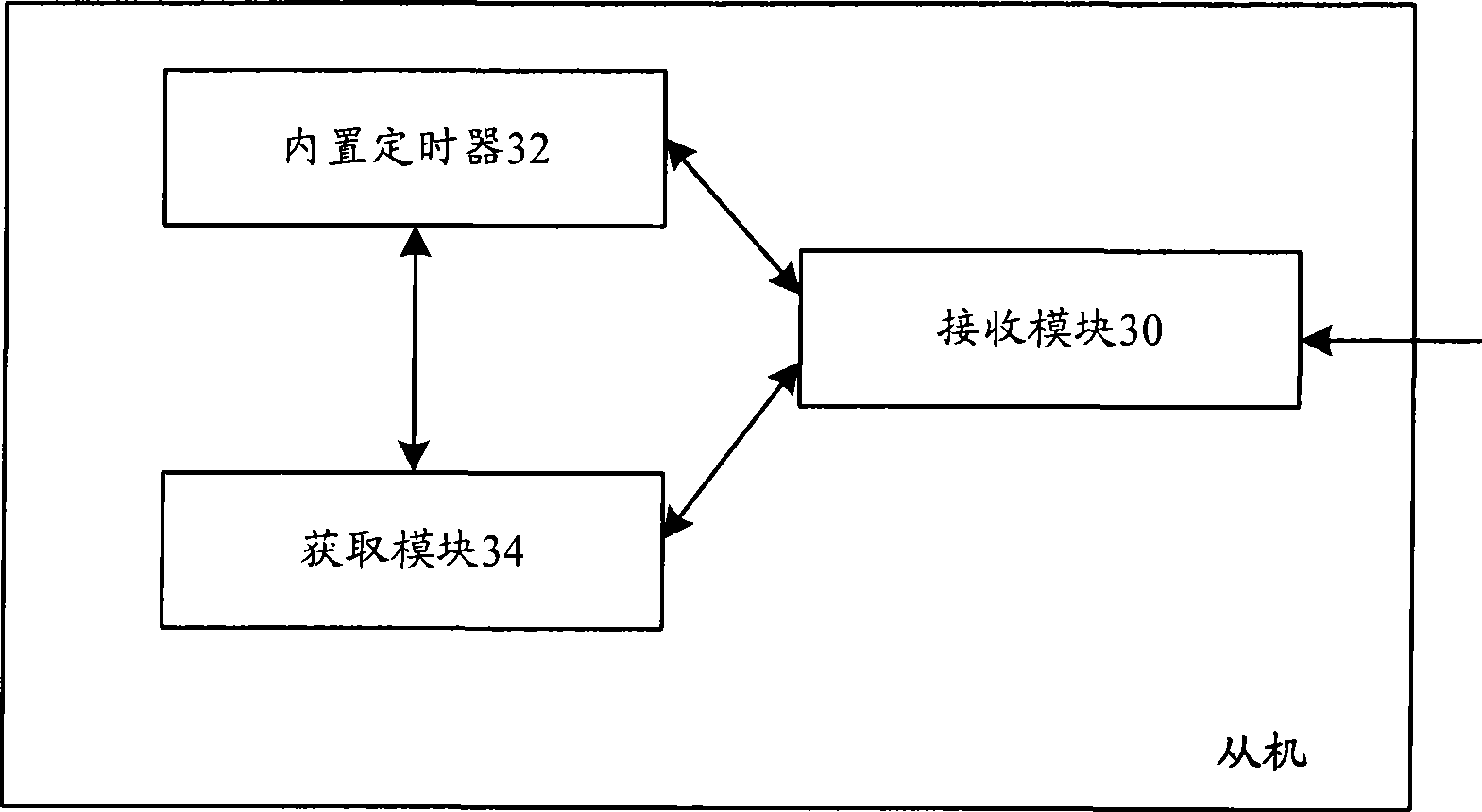
Baud rate adaptation method, apparatus and host for communication
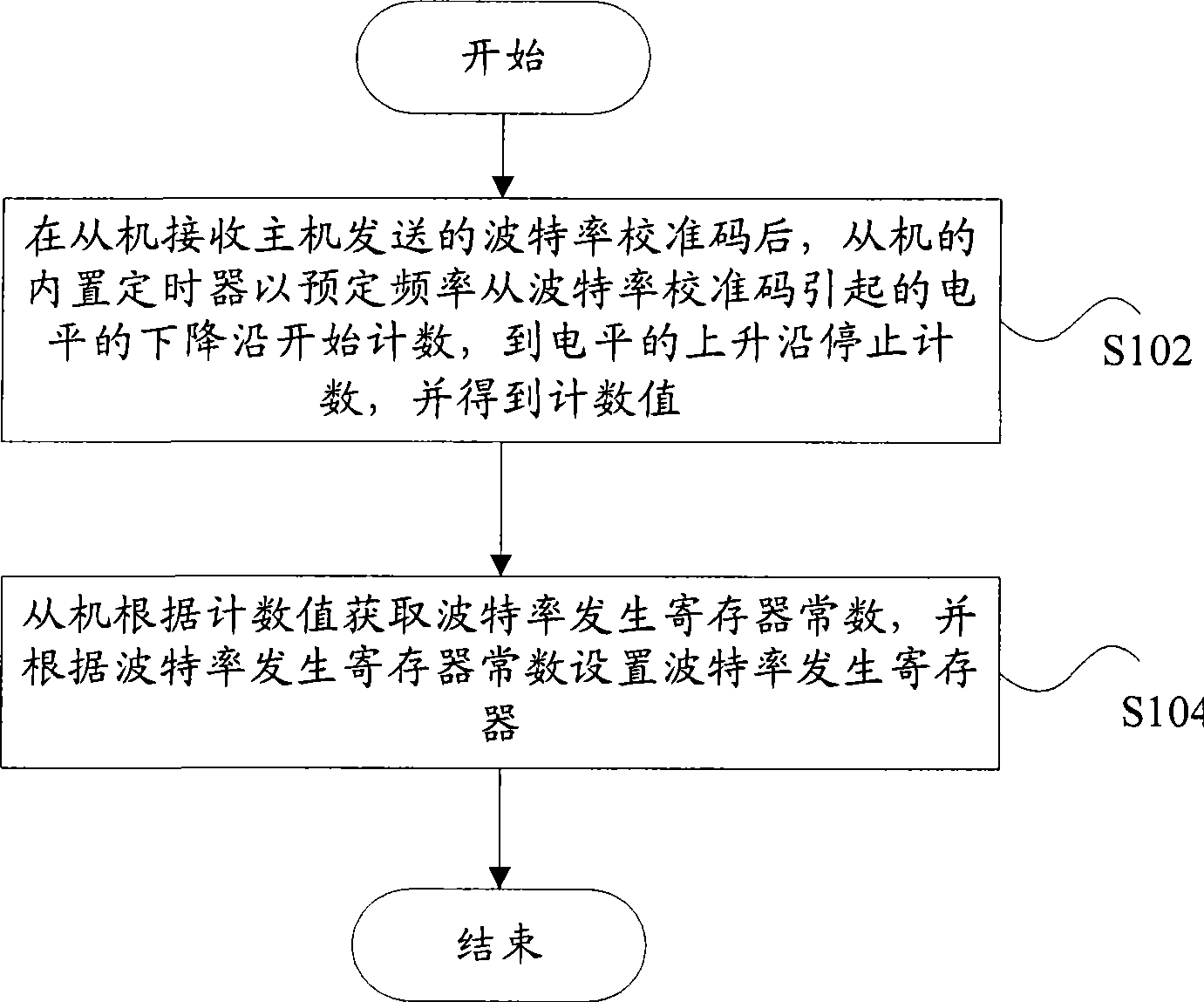
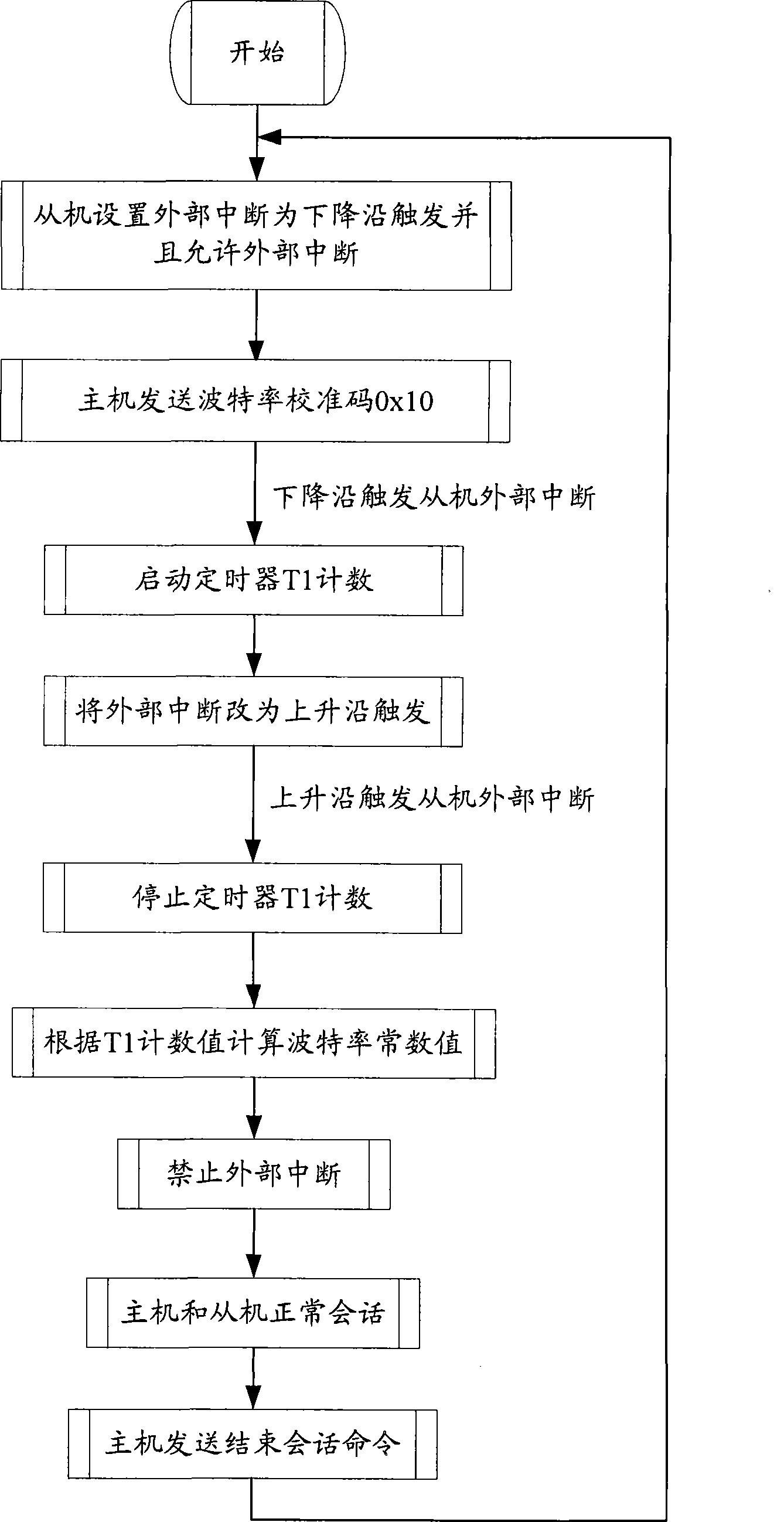
The invention discloses a communication baud rate self-adaptive method, a device and a host computer thereof. The method comprises the following steps: after a slave computer receives a baud rate calibration code sent by the host computer, a built-in timer of the slave computer starts counting from a level falling edge caused by the baud rate calibration code at a preset frequency and stops counting at a level rising edge, and obtains a count value; and the slave computer obtains a baud rate generation register constant according to the count value, and the slave computer sets the baud rate generation register according to the baud rate generation register constant. By adopting the technical proposal, the self-adaptive adjustment of the communication baud rate is realized without adding any hardware, the hardware manufacturing cost is reduced, the method can be applicable to application occasions of any communication baud rates, and is especially applicable to the application occasion that a slave computer crystal oscillator is unstable.
Owner:ZTE CORP
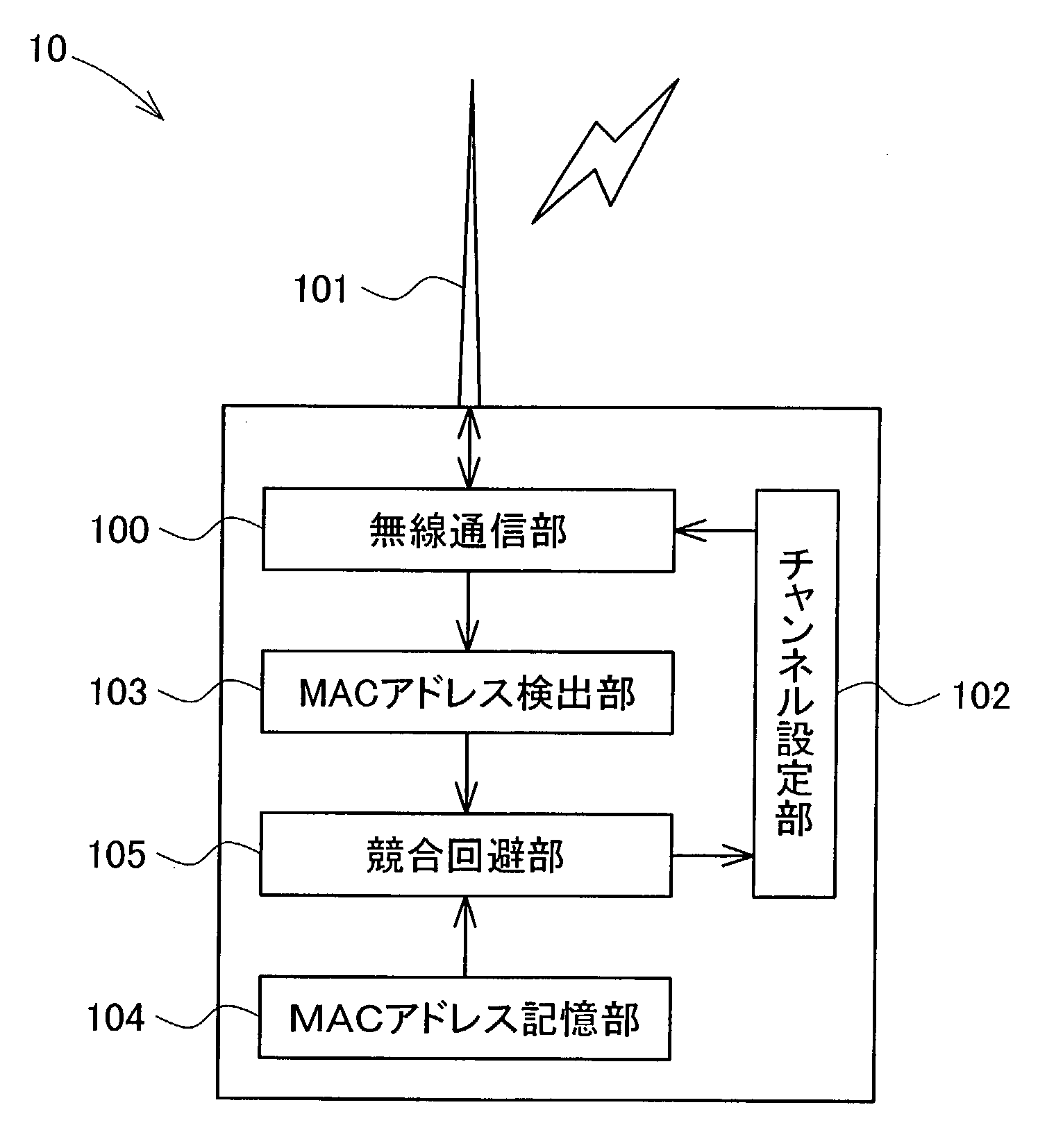
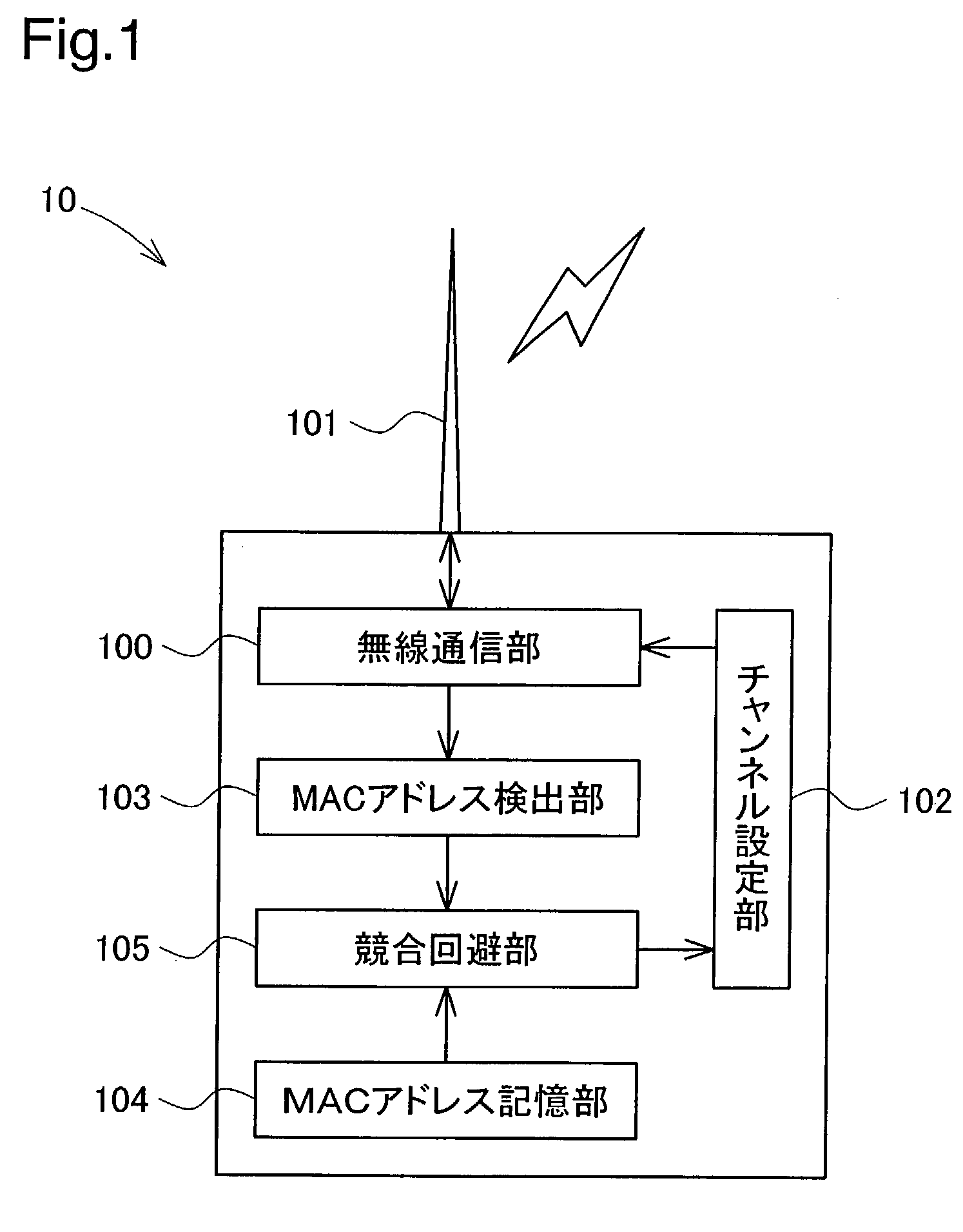
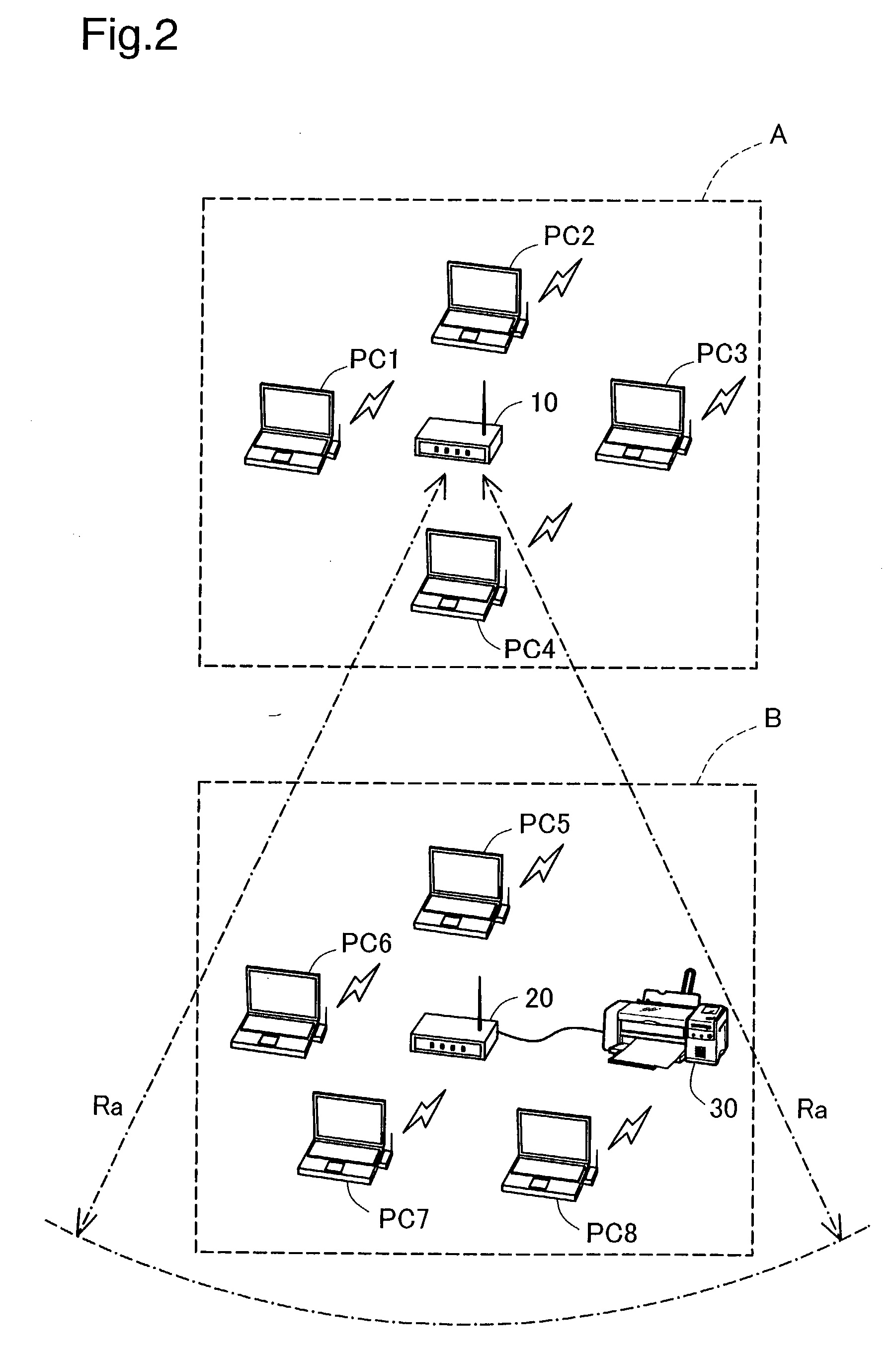
Wireless communication device
InactiveUS20030236064A1Reduce stepsGreat outputSubstation equipmentCommunication jammingMultiple deviceBaud
The technique of the present invention prevents troubles, such as the lowered baud rate, in wireless communication. In a wireless LAN connecting with multiple devices, when a baud rate between two devices is lowered to or below a preset level, the procedure of a first arrangement compares MAC addresses of the two devices and switches over the communication channel of a device having the smaller MAC address, while keeping the communication channel of a device having the greater MAC address. When the baud rate is lowered to or below the preset level, the procedure of a second arrangement temporarily switches over the working communication channel from an original communication channel to another communication channel. When wireless communication in a predetermined unit is completed, the procedure makes a re-switchover to the original communication channel.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Modular electronic sign and method of assigning a unique identifier to common modules of said sign
InactiveUS7495576B2Frees up more time for actual showingMinimally activeRoad vehicles traffic controlElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingData connectionMicrocontroller
A plurality of common, modular panels attach to a support frame carrying power and data connections for an electronic display sign. LEDs are used as the light mechanisms for illumination of said sign. Each modular panel is under separate microcontroller control and includes its own on-board memory. The electronic display sign includes a master control element that connects to a PC or laptop computer for loading data or programs into the memory of each modular board. The master control sends out commands or data that is interrogated by every microcontroller on each modular panel of the entire sign such that only the panel with a unique identification number will process data intended therefore. The on-board memory allows for the creation of a virtual screen such that each modular panel of the entire sign is rendering the entire message being displayed on said sign even though each modular panel may only be actually illuminating a portion of said message on the LEDs of each panel. A novel auto-baud scheme re-sets the baud rate for the sign for each packet of data received. A novel identifier assignment scheme allows the end user to assign serial numbers to each panel after the sign is attached to the support frame.
Owner:MASKENY DONALD D +1
Multi-channel optical transceiver with offset quadrature amplitude modulation
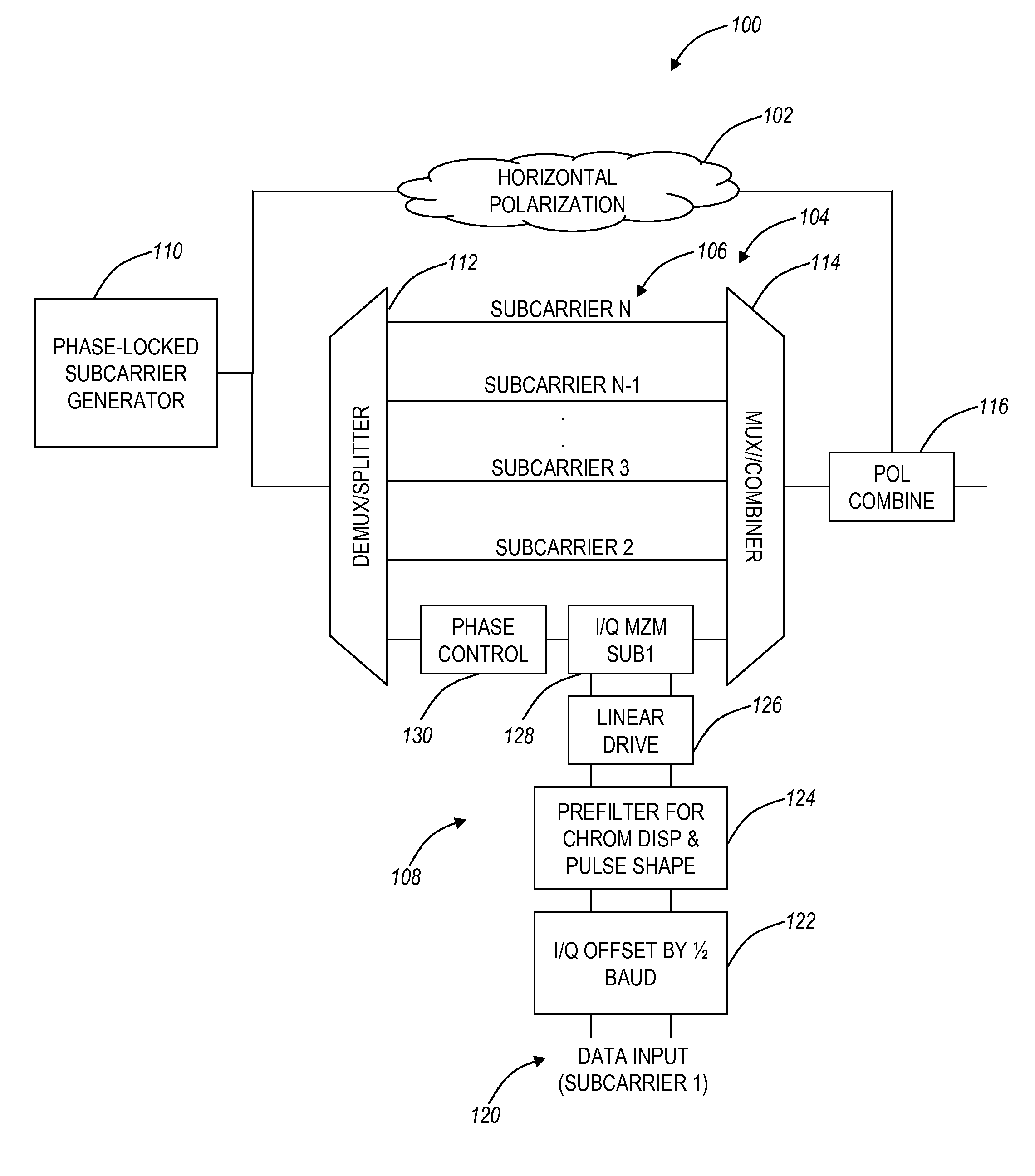
The present disclosure provides a multi-carrier optical transmitter, receiver, transceiver, and associated methods utilizing offset quadrature amplitude modulation thereby achieving significant increases in spectral efficiency, with negligible sensitivity penalties. In an exemplary embodiment, an optical transmitter includes circuitry configured to generate a plurality of optical subcarriers, a plurality of data signals for each of the plurality of subcarriers, and a plurality of modulator circuits for each of the plurality of subcarriers, wherein each of the plurality of modulator circuits includes circuitry configured to offset an in-phase component from a quadrature component of one of the plurality data signals by one-half baud period.
Owner:CIENA
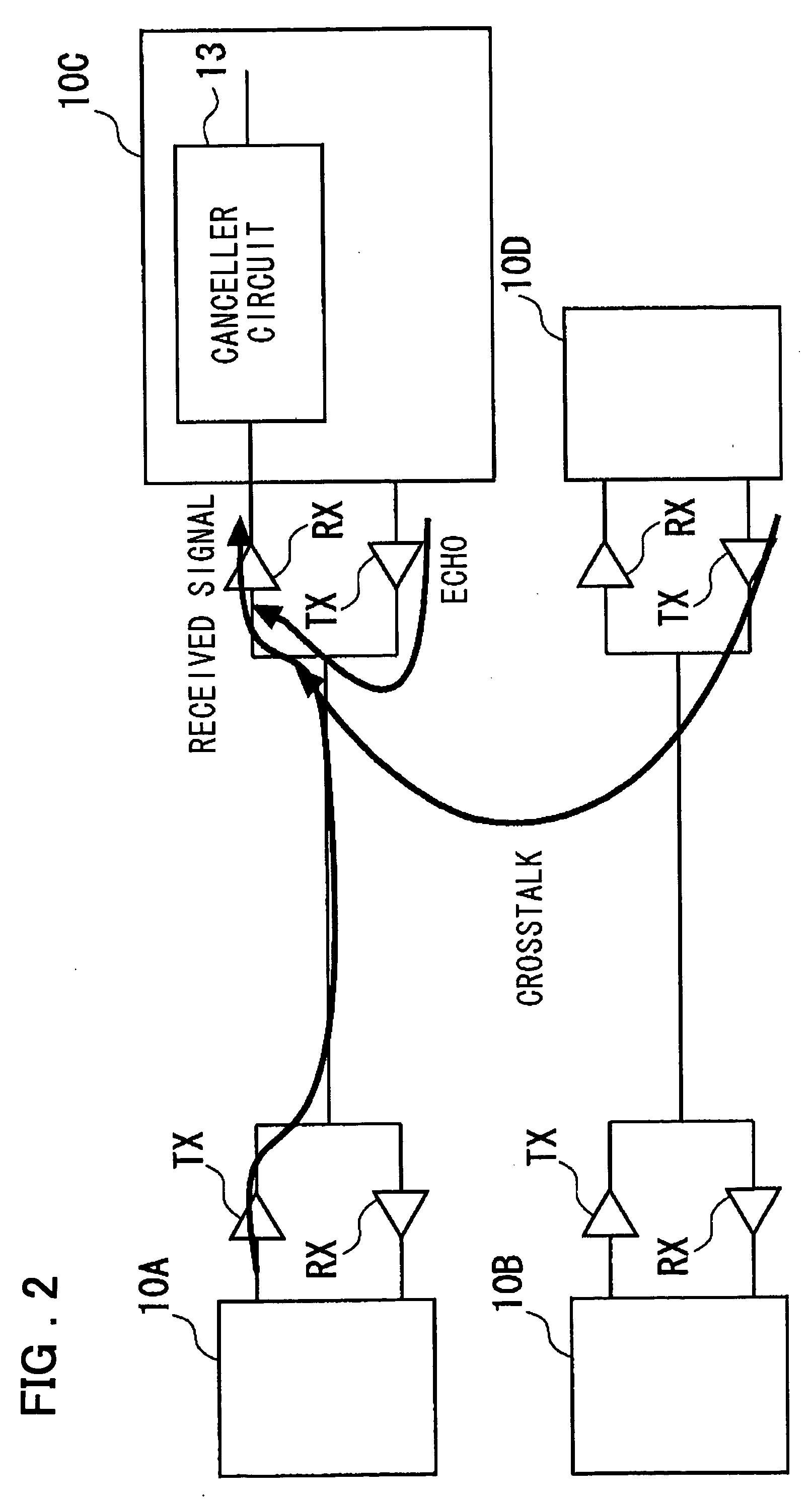
Canceller circuit and controlling method
InactiveUS20050099967A1Easy to integrateAdaptive networkCross-talk reductionAdaptive filterEngineering
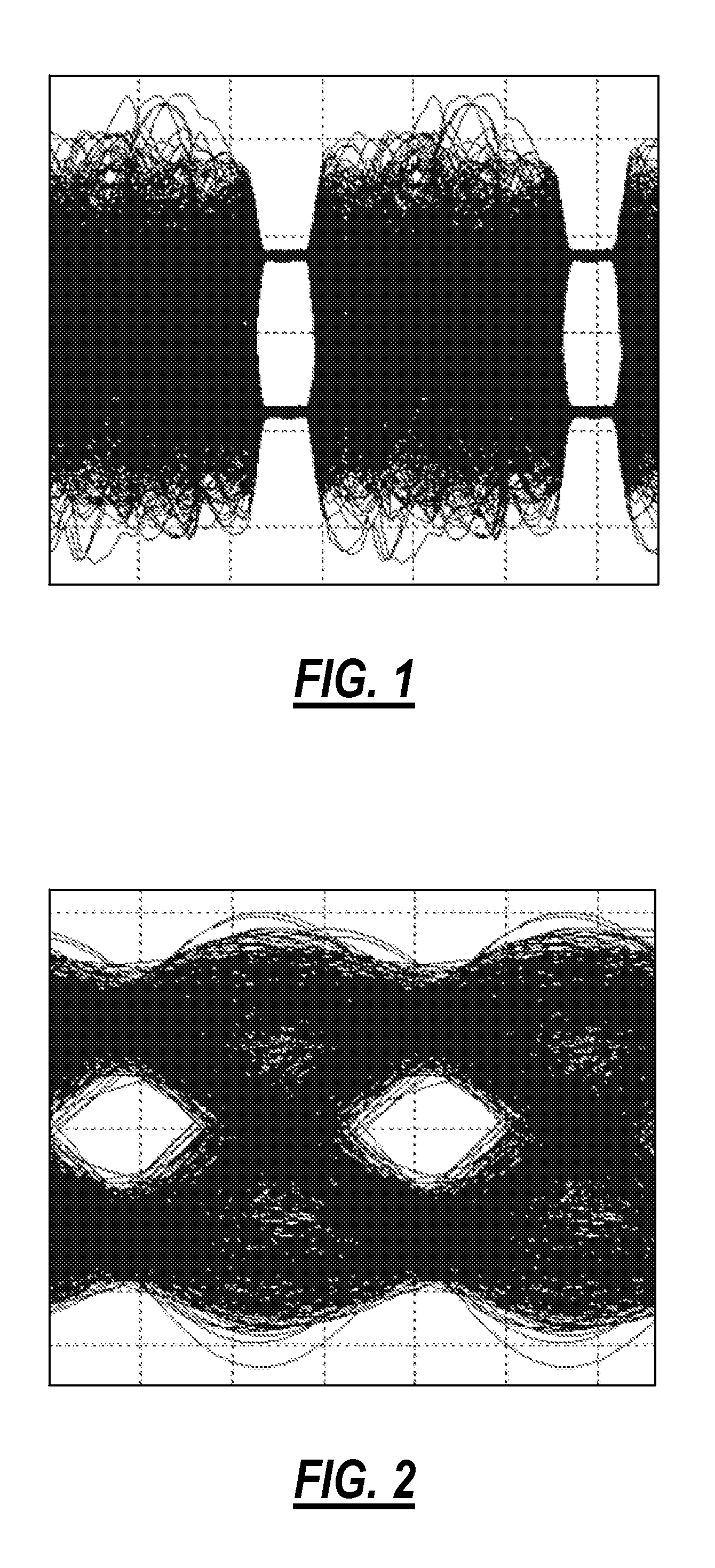
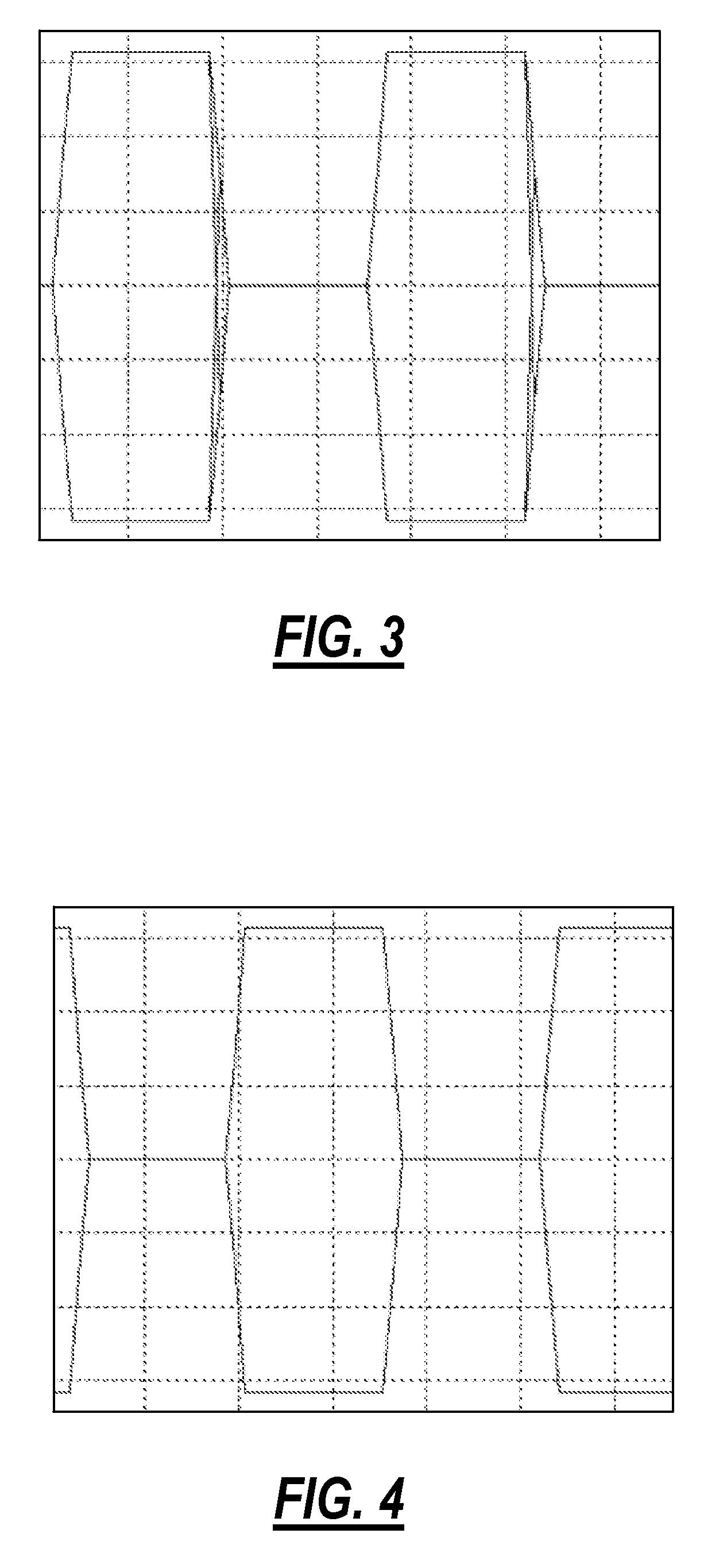
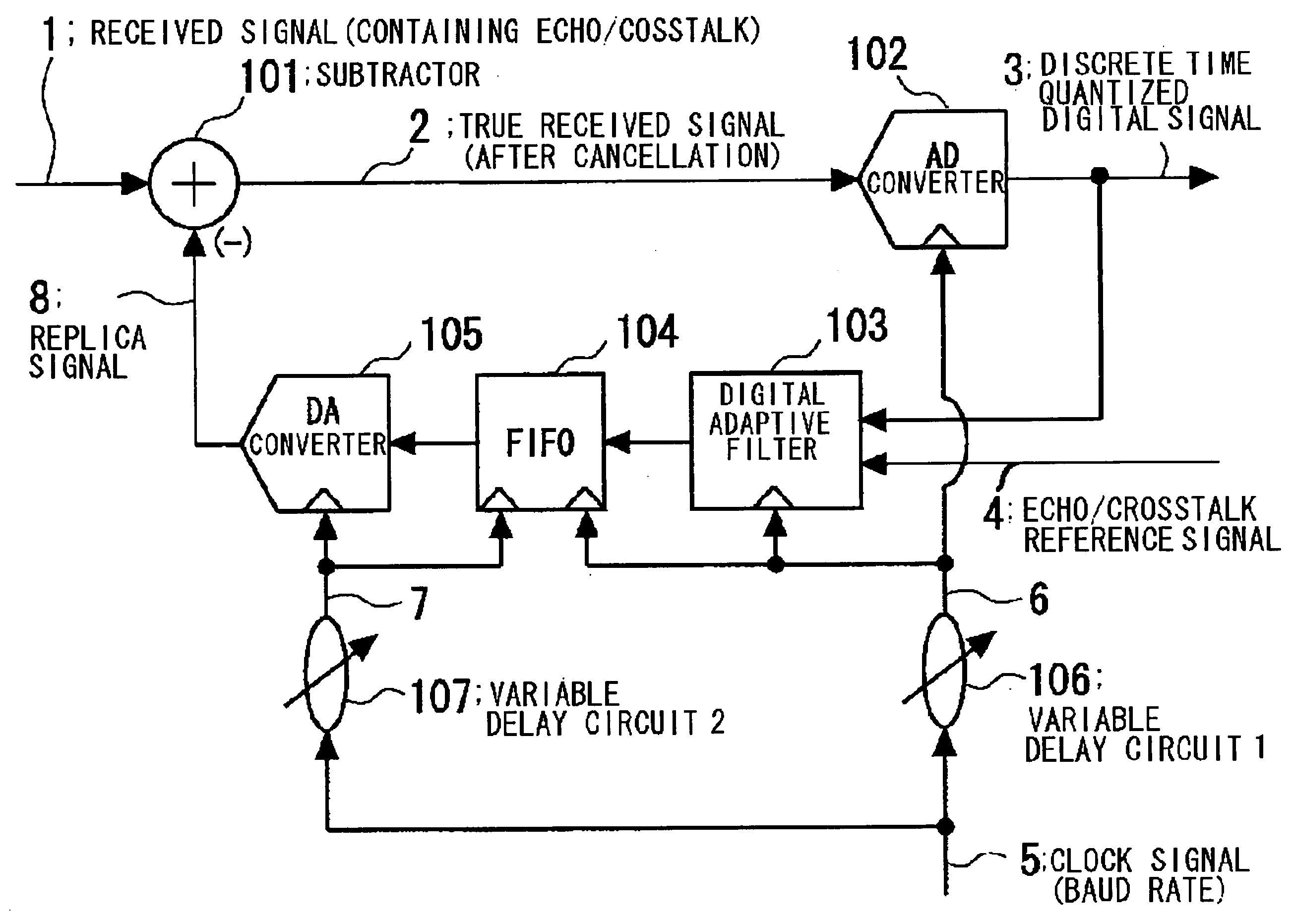
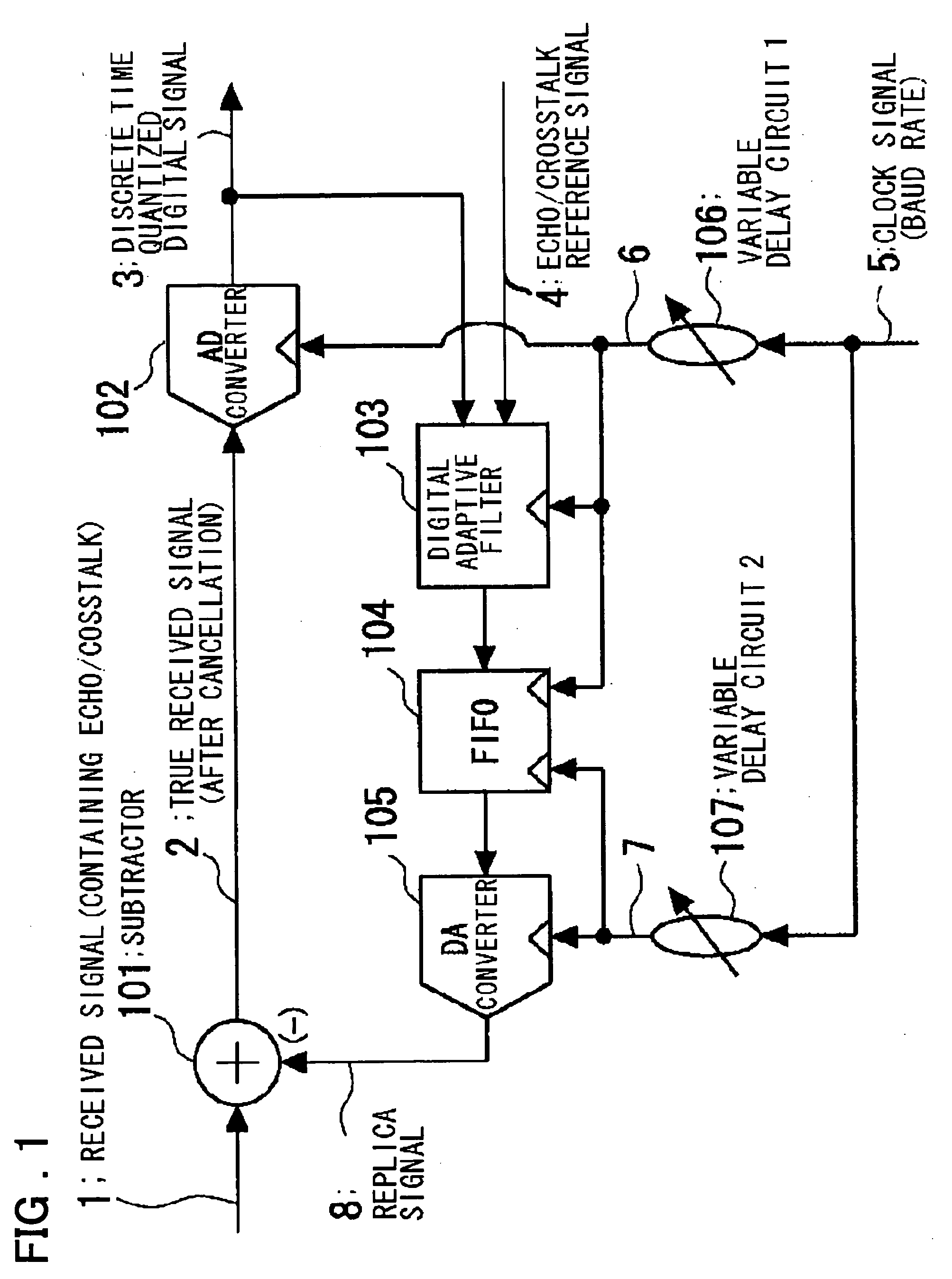
Disclosed is a device in which overasampling is not needed and in which the echo / crosstalk of a continuous time analog waveform may be canceled at a baud rate. There are provided a continuous time analog subtractor, an AD converter for converting an analog signal from a subtractor to a digital signal, an adaptive filter receiving a digital output signal from the AD converter and an echo / crosstalk reference signal and having adaptively variable filter coefficients, a FIFO in which a digital output signal from the FIFO is written in first-in first-out and in which a write and read clocks are interchanged, a D / A converter for converting the digital output signal from the FIFO to an analog signal to output the analog signal, and first and second variable delay circuits for variably delaying an input clock signal to output the delayed signals as first and second clock signals. The first clock signal is supplied to the AD converter, adaptive filter and to the FIFO, while the second clock signal is supplied to the FIFO and to the DA converter as sampling clock. A received signal, containing the echo-crosstalk, and a replica signal of the echo-crosstalk, output from the D / A converter, is supplied to the subtractor. A true received signal, which is the received signal from which the echo / crosstalk has been cancelled, is supplied to the AD converter.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
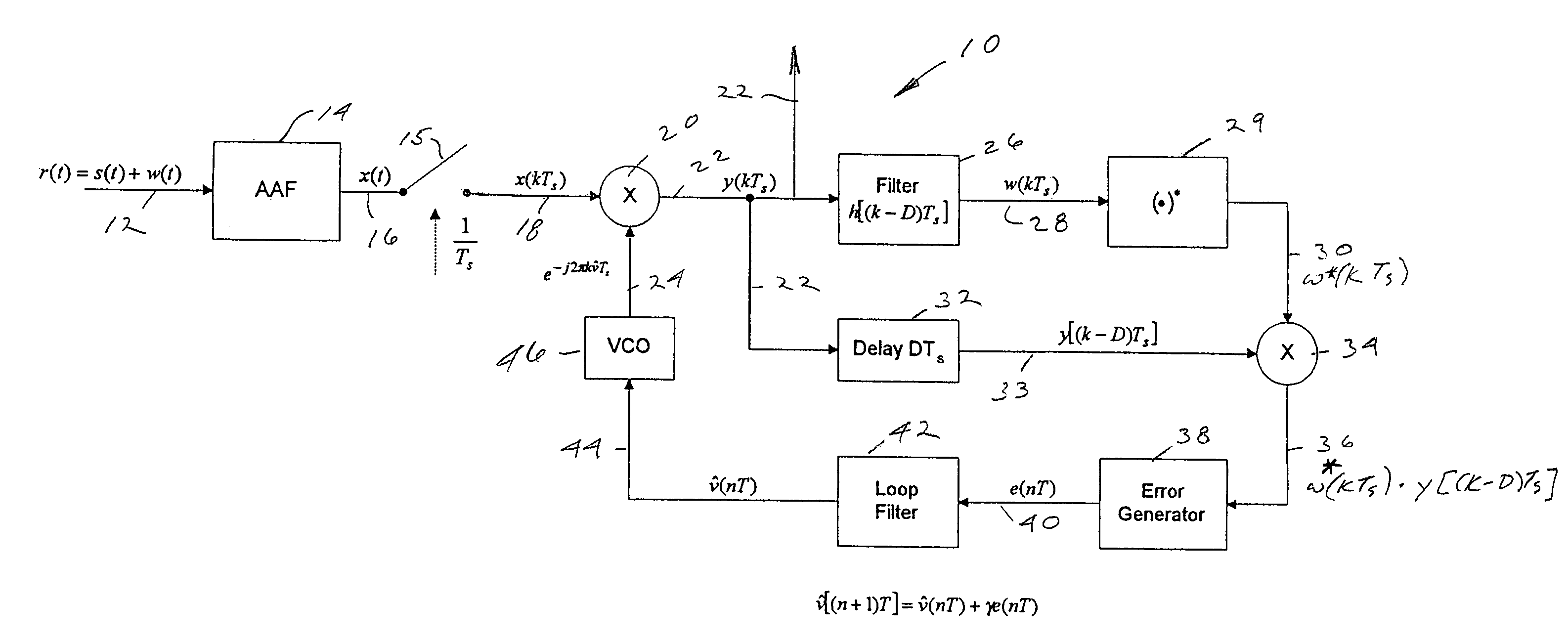
Variable baud rate demodulator
InactiveUS6282248B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsFrequency-modulated carrier systemsFrequency spectrumLow-pass filter
A method of efficiently demodulating and isolating a signal within a fixed possibly wider band spectral region, having any of a wide range of baud rates. The signal is sampled at a fixed, first frequency which remains fixed no matter what the baud rate. Thus, the sample rate does not necessarily correspond to the desired baud rate. The sampled signal is then demodulated and low pass filtered to create baseband samples at the first frequency, which are then subject to user-specified arbitrary rate change in a continuously variable interpolator / decimator (continuously variable digital delay (CVDD) device), and decimated by a programmable power of 2, to produce samples at a second frequency. The second frequency is preferably determined to be a whole number multiple of the desired baud rate, e.g., twice the desired baud rate. The samples are equalized to produce output symbols at the target baud rate. Based on this method, a demodulator can receive signals of varying bandwidth and baud rates at arbitrary spectral locations within a possibly wider bandwidth aggregate channel span, and can adapt its target baud rate for each signal to be the actual baud rate of the derived incoming data signal within the possibly wider bandwidth aggregate channel span.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Baud rate fast self-adaptive method based on field programmable gate array (FPGA), processor and receiving end
InactiveCN103036823AAchieve adaptiveApplicable to occasions where data transmission requires encryptionBaseband system detailsComputer moduleSelf adaptive
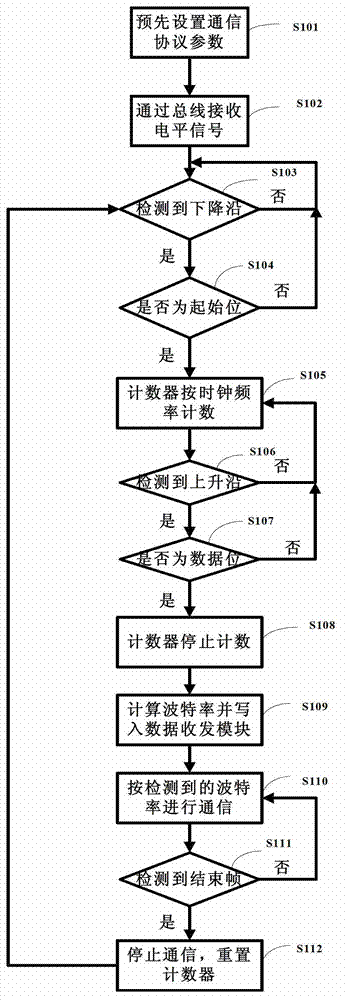
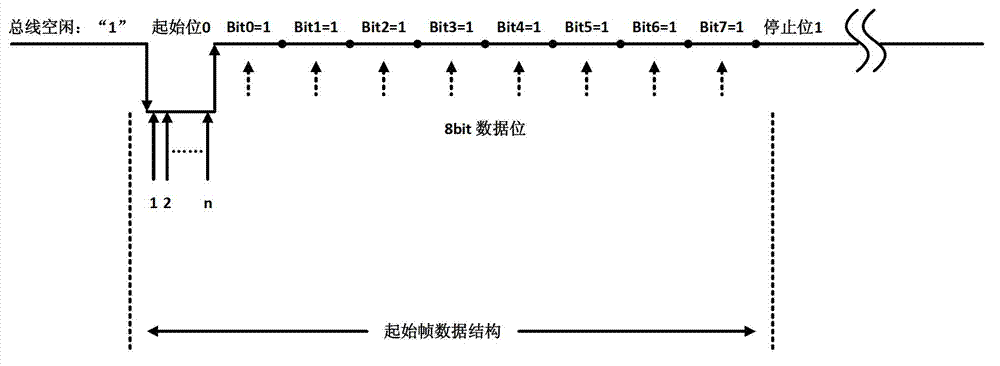
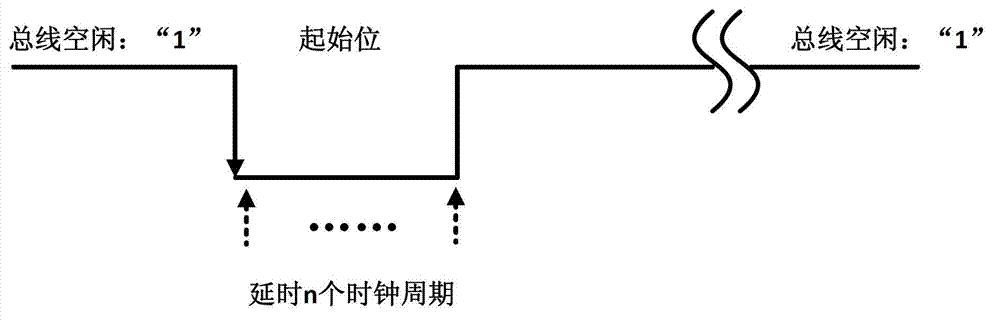
The invention discloses a baud rate fast self-adaptive method based on a field programmable gate array (FPGA), a processor and a receiving end. The method comprises the following steps: an falling edge of a bus enables a spurious triggered detection circuit to be started, the falling edge is judged whether to be a start bit of a pre-set start frame of sending and receiving double-parties, and if the falling edge is judged to be the start bit, a counter is controlled to continue counting; a rising edge of the bus enables a spurious triggered detection circuit to be started again, the rising edge is judged whether to be a data bit, and if the rising edge is judged to be the data bit, the control counter is controlled to stop counting; and when the control counter stops counting, an actual baud rate of a current data frame is calculated according to a counting result of the counter and a frequency of a high precision clock, the baud rate is written into a data sending and receiving module, the data sending and receiving module is enabled to communicate according to the baud rate, and a baud rate fast self-adaptive process is completed. According to the baud rate fast self-adaptive method based on the FPGA, the self-adaption of any baud rate can be achieved, and a baud rate detection error caused by peaks or burrs on the bus is effectively removed by the use of the spurious triggering detection circuit.
Owner:CSIC WUHAN LINCOM ELECTRONICS
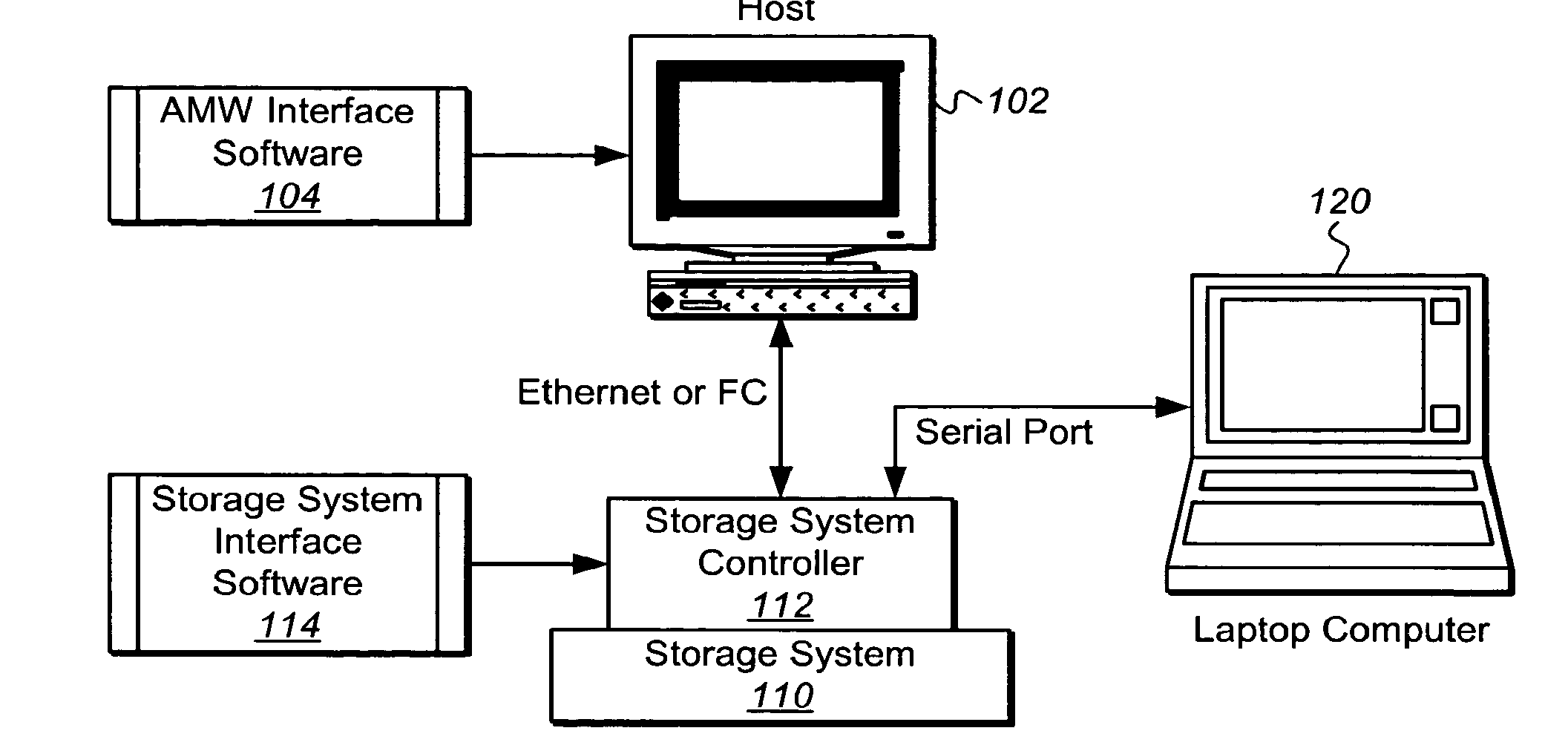
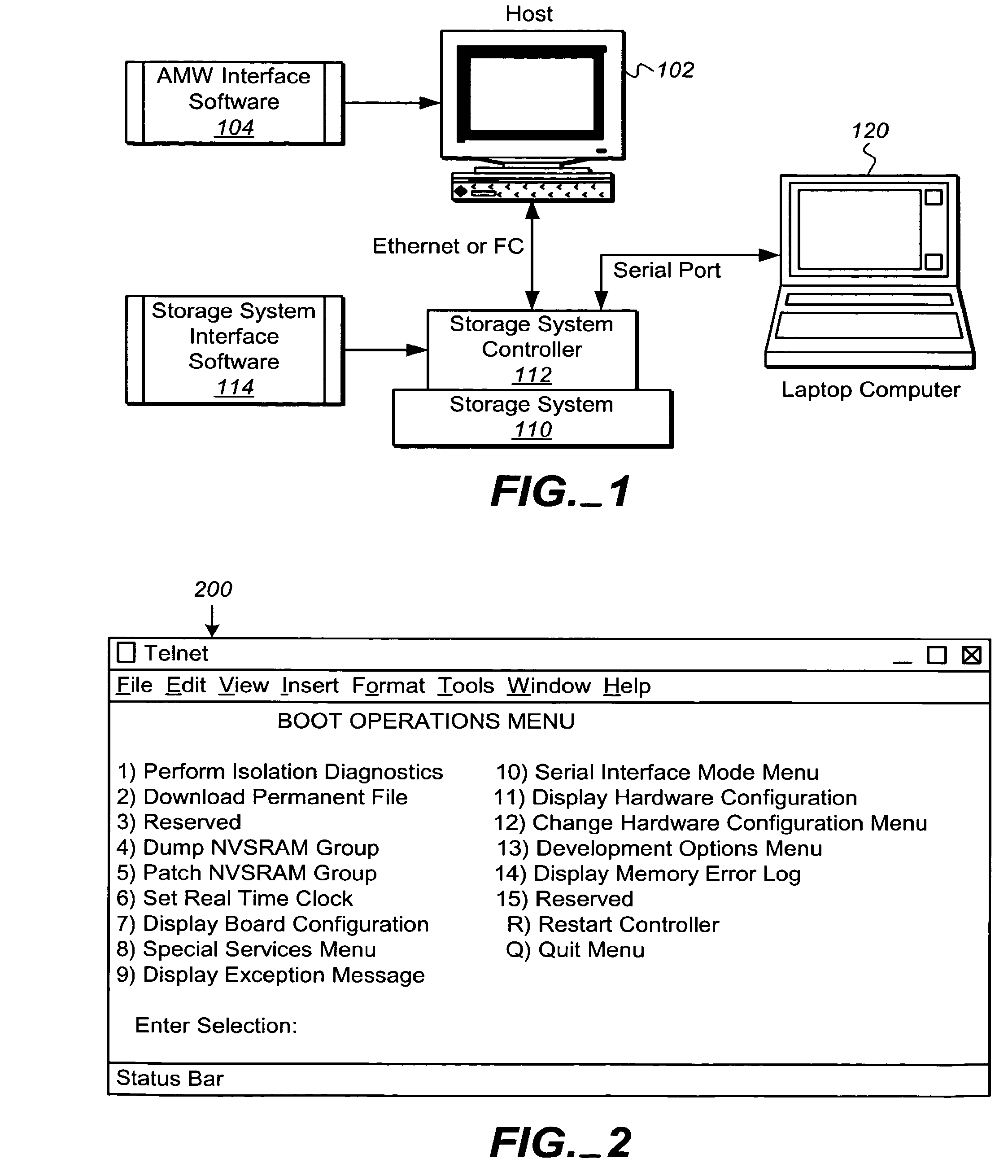
Serial port initialization in storage system controllers
InactiveUS20080288660A1Program controlInput/output processes for data processingInitAdministrative management
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
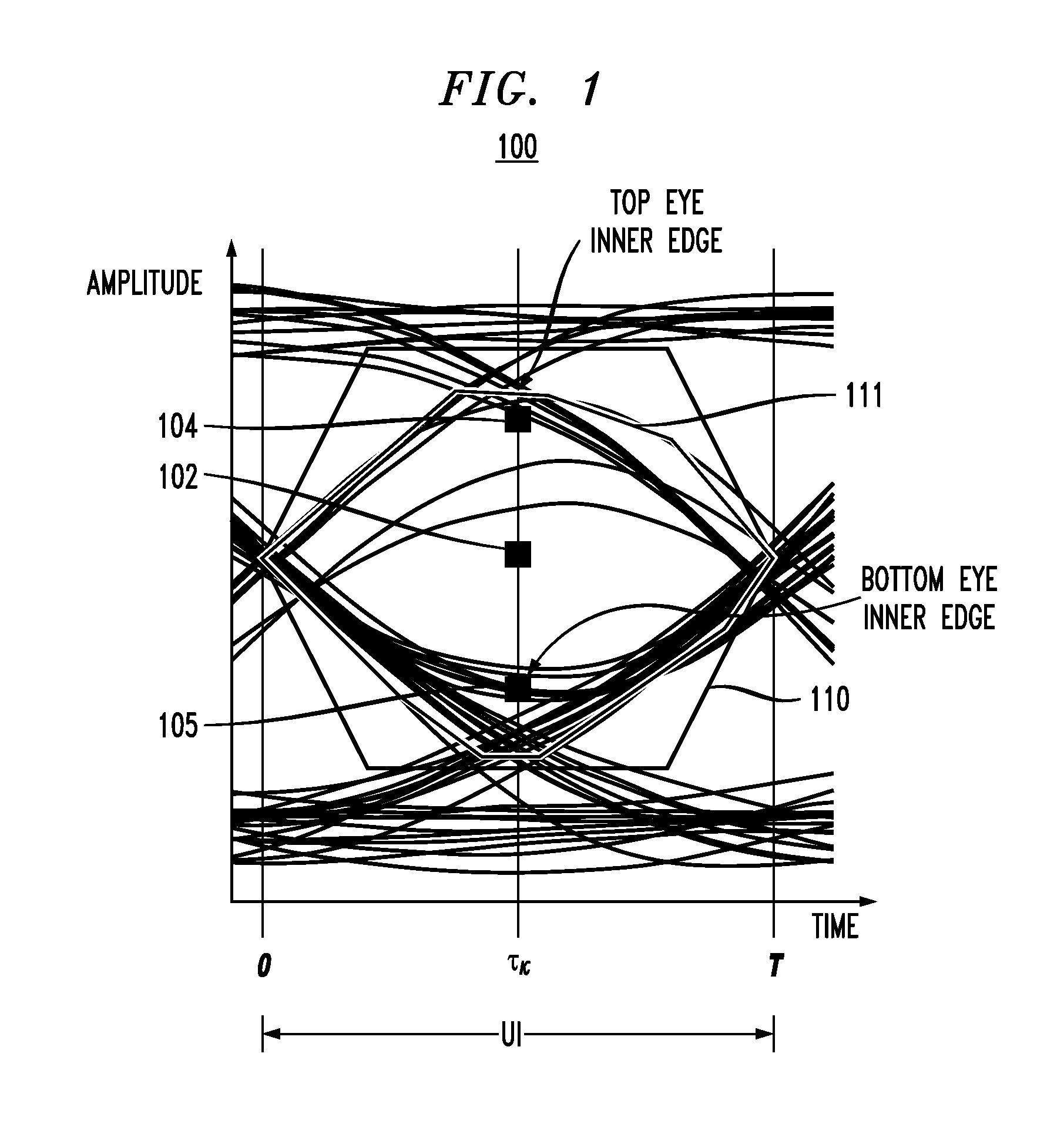
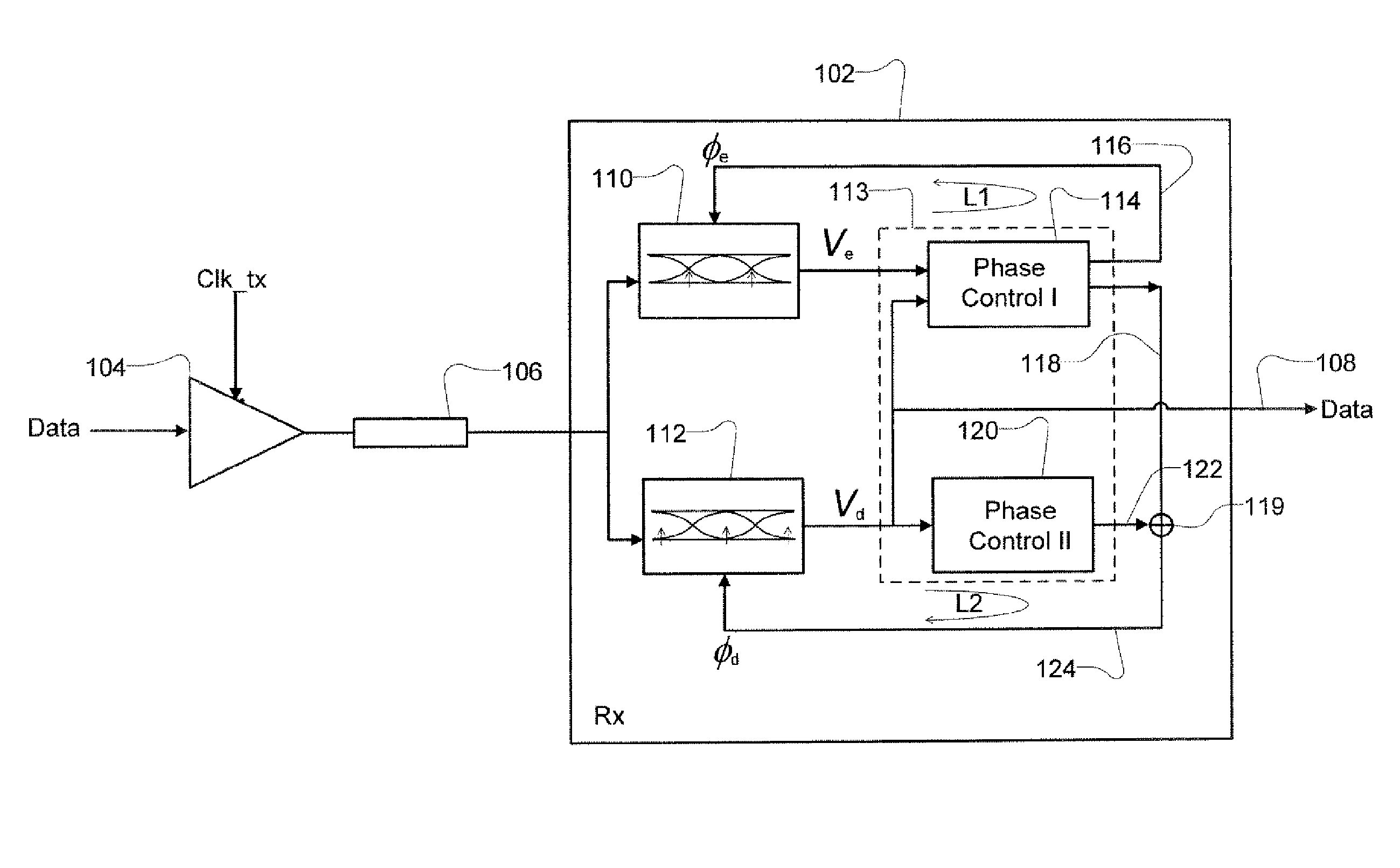
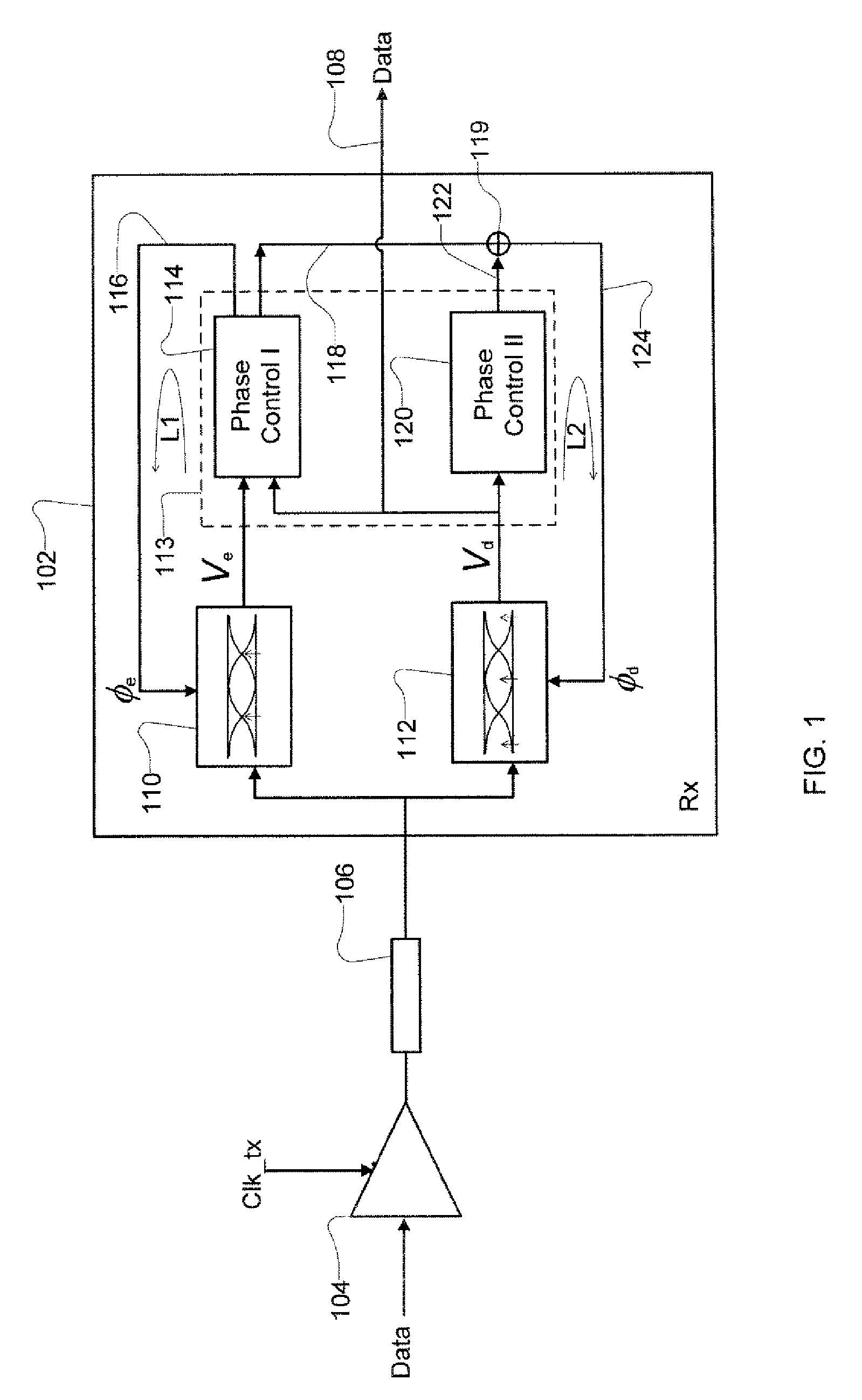
Receiver with enhanced clock and data recovery
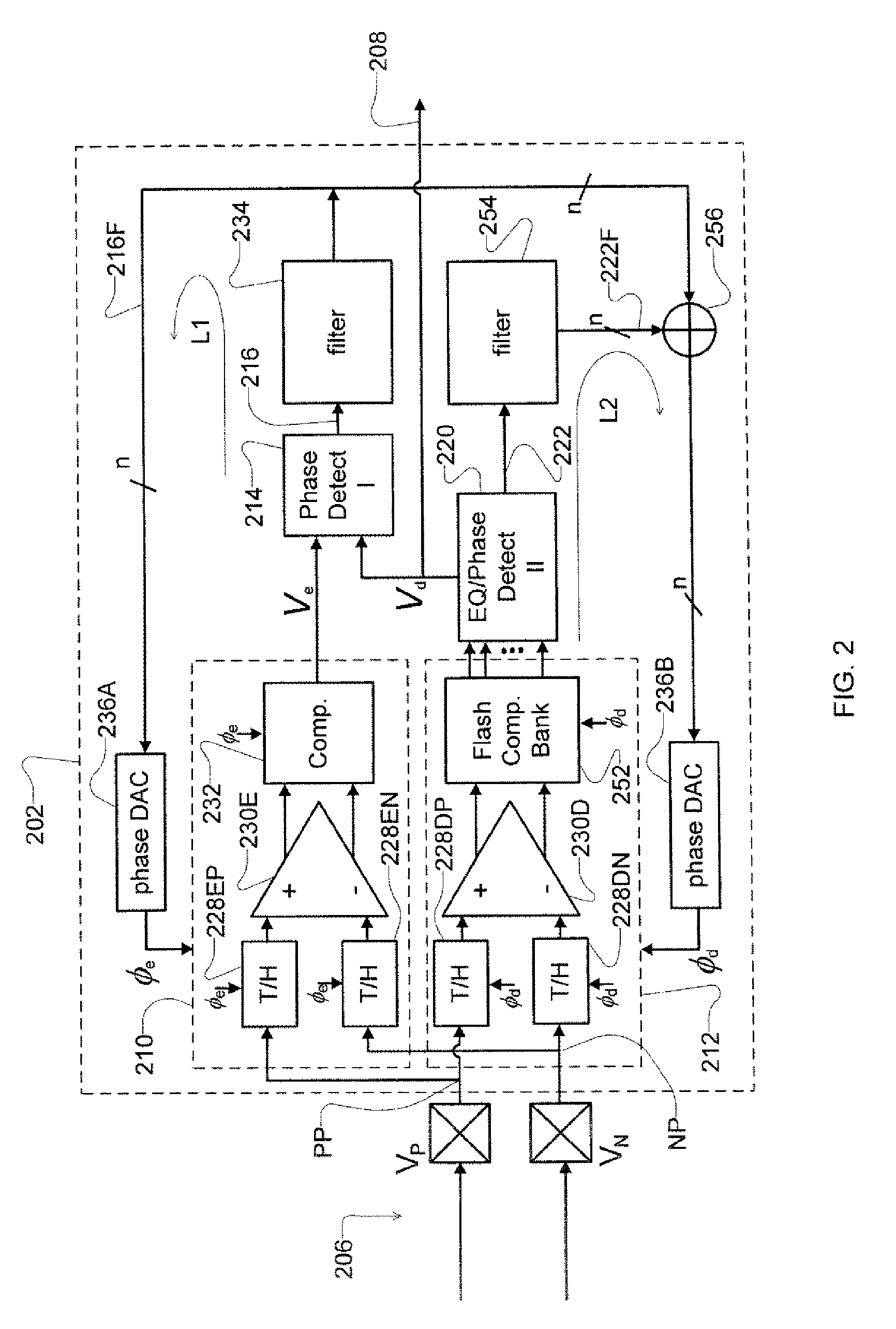
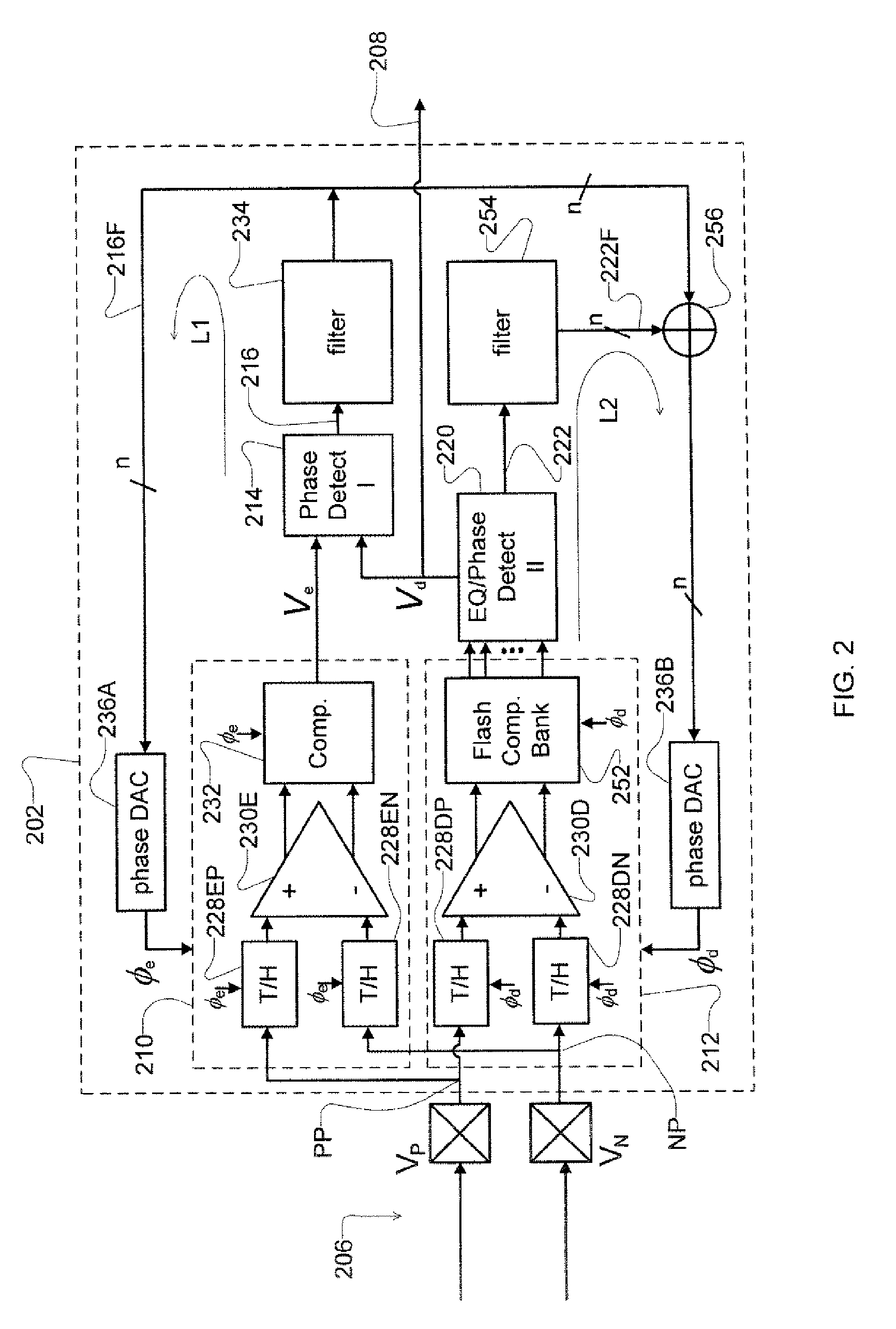
ActiveUS8929496B2Receiver initialisationSynchronisation error correctionData transformationBang bang phase detector
A receiver device implements enhanced data reception with edge-based clock and data recovery such as with a flash analog-to-digital converter architecture. In an example embodiment, the device implements a first phase adjustment control loop, with for example, a bang-bang phase detector, that detects data transitions for adjusting sampling at an optimal edge time with an edge sampler by adjusting a phase of an edge clock of the sampler. This loop may further adjust sampling in received data intervals for optimal data reception by adjusting the phase of a data clock of a data sampler such a flash ADC. The device may also implement a second phase adjustment control loop with, for example, a baud-rate phase detector, that detects data intervals for further adjusting sampling at an optimal data time with the data sampler.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
RFID receiver
Owner:MOJIX
Method and apparatus for synchronizing an OFDM signal
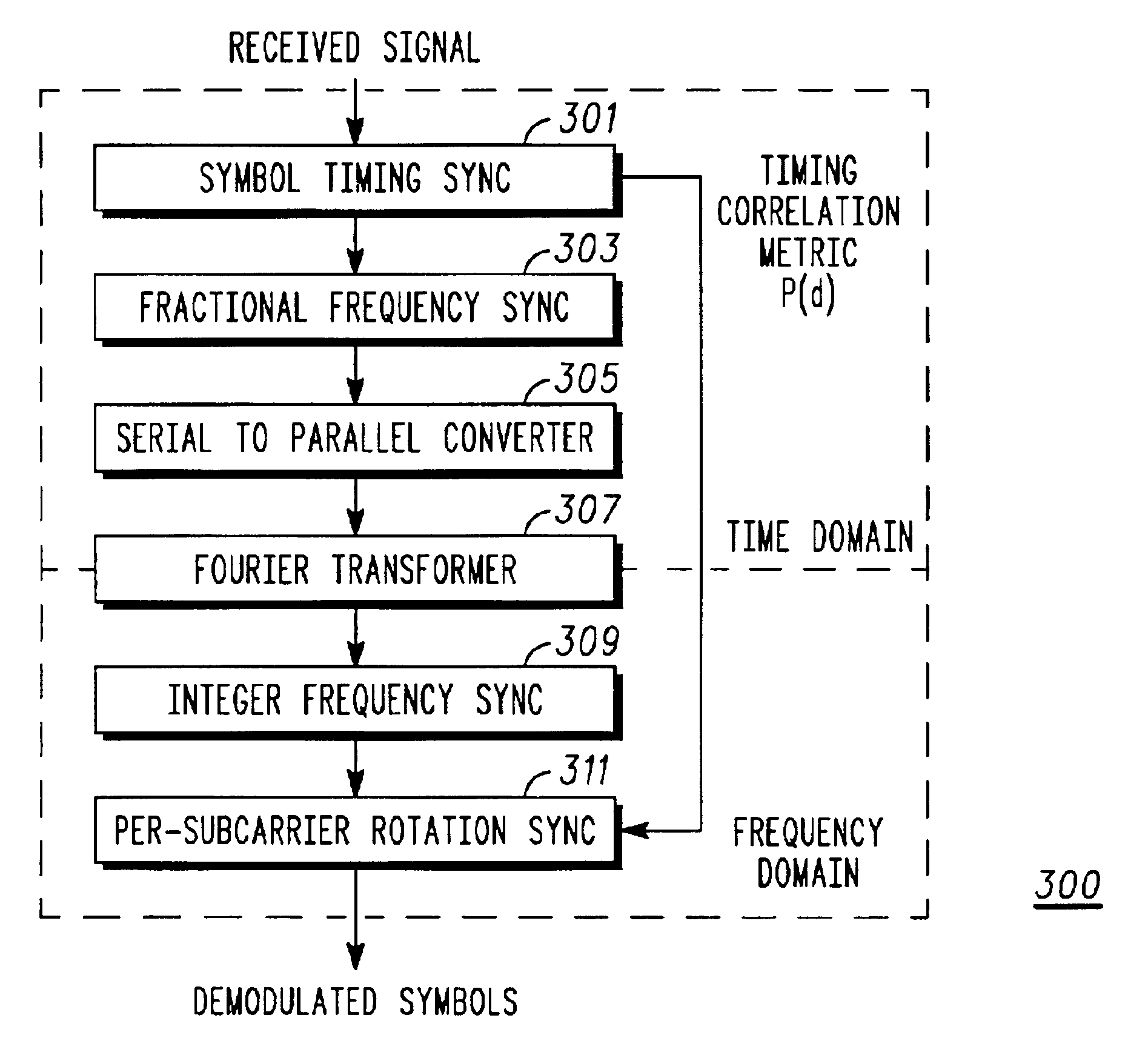
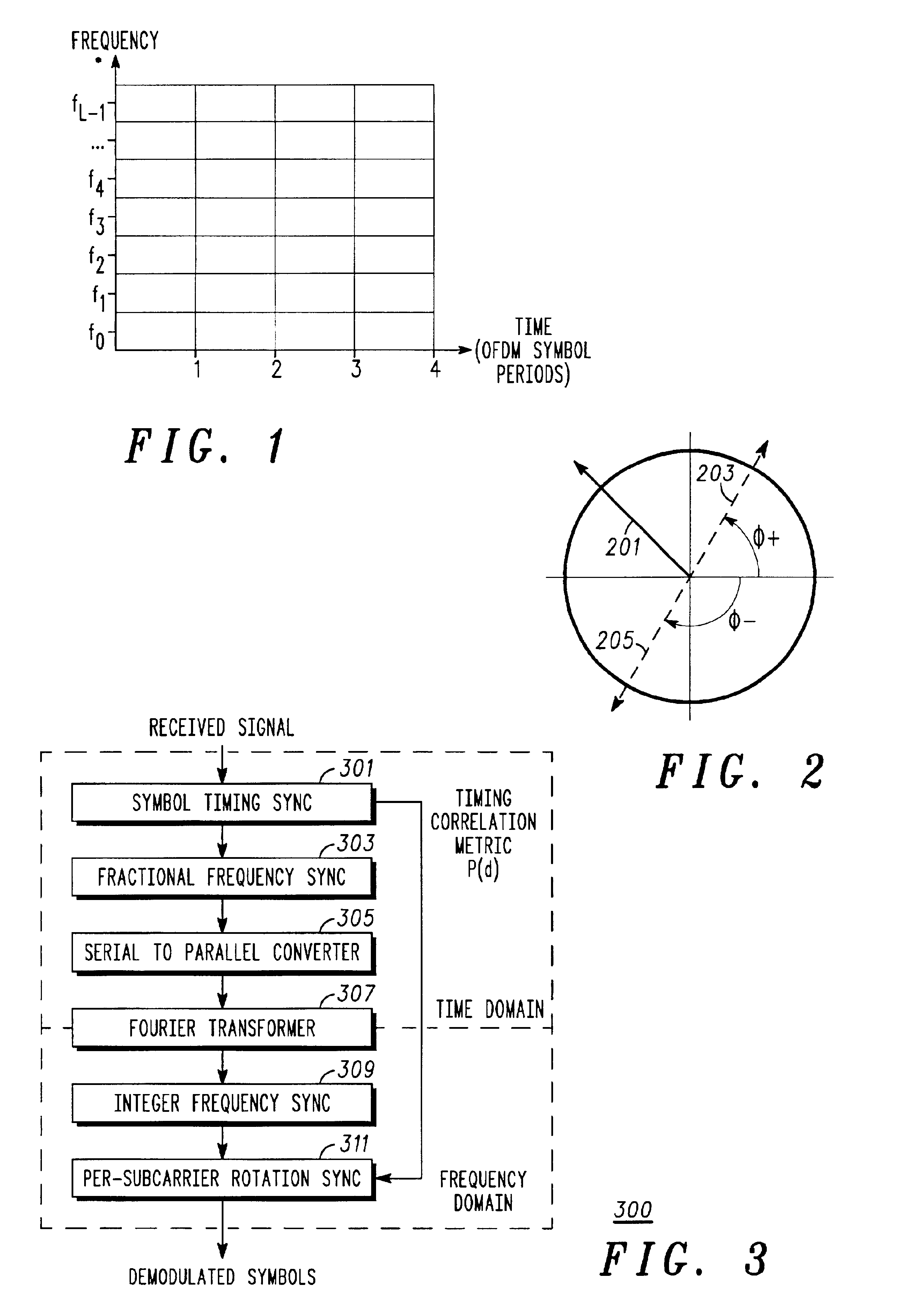
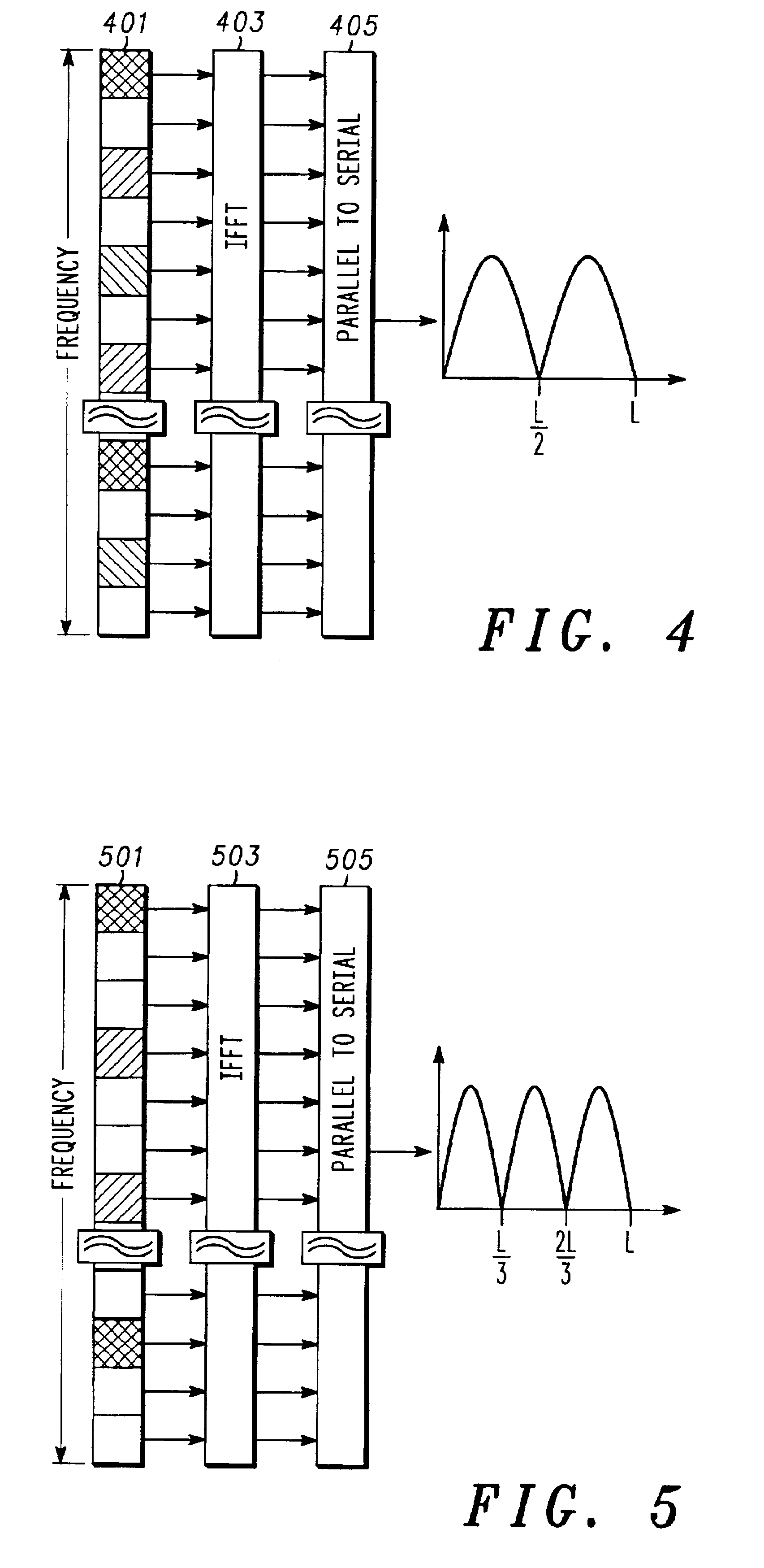
ActiveUS6959050B2Time-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
An apparatus (300) for and method of synchronizing OFDM signals utilizes a single baud to provide synchronization in time, frequency, and per-subcarrier rotation (201). Timing and fractional subcarrier frequency synchronization may be obtained from either a known or unknown (e.g., data symbol) baud having known symmetry properties. Because all three synchronization tasks may be accomplished utilizing a single sync baud, the present invention is spectrally efficient. A differential correlation metric is utilized to efficiently provide integer subcarrier frequency synchronization and per-subcarrier rotation synchronization.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Computerized methods for data loggers
InactiveUS6895347B2Eliminate the problemEnergy efficient ICTSoftware engineeringPower batteryData stream
The present invention provides methods for operating data loggers and in particular, software techniques useful for controlling the critical functions of a low-power-battery-operated data logger. One method initializes various memory locations upon a detection of new firmware. Another method allows a processor system belonging to a data logger to receive a high baud rate data stream while being operated in a sleep mode. Yet another method provides a highly efficient process for estimating the remaining battery capacity of a data logger's primary power source. Finally, a method is provided for protecting volatile variables during a disruption of primary power. The protected variables are written to non-volatile memory using parasitic power only.
Owner:REMOTE DATA SYST
Method of transmitting a high-priority message in a lighting control system
ActiveUS20080192767A1Time-division multiplexElectric light circuit arrangementTelecommunications linkCommunication link
A lighting control system having a plurality of control devices coupled to a communication link operates with a communication protocol that allows the system to expeditiously process high-priority events while operating communicate at a low enough baud rate to allow for a free-wiring topology of the communication link. The transmission of regular-priority messages is suspended if any of the control devices has a high-priority message to transmit. To signal that a control device has a high-priority message to transmit, each control device is operable to transmit a break character in a predetermined time period after the transmission of one of the digital messages. After the transmission of the break character, the transmission of the regular-priority messages on the communication link is suspended to allow the high-priority message to be transmitted quickly.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Method for analyzing and triggering controller area network (CAN) bus
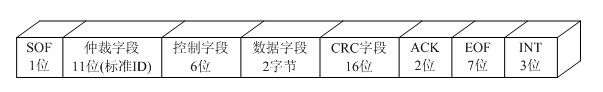
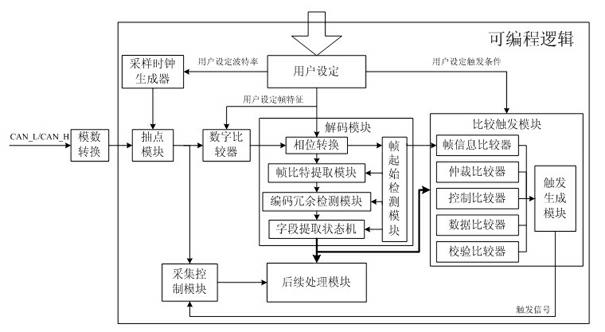
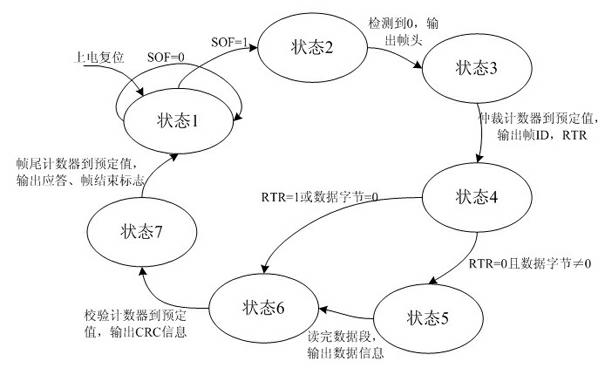
InactiveCN102355382AEasy to readImprove debugging efficiencyBus networksArea networkMeasuring instrument
The invention discloses a method for analyzing and triggering a controller area network (CAN) bus, which can provide a triggering and decoding function of a CAN bus for a measuring instrument. The method comprises the following steps of: converting a CAN bus signal to be measured into a digital signal through an analog-to-digital converter; generating, by a sampling clock generator, sampling clock of corresponding frequency to a snapshot module to snapshot the digital signal according to baud rate set by a user; converting, by a digital comparator, into 0 / 1 value and then transmitting to a decoding module to extract frame information; transmitting to a comparative trigger module to compare with a trigger condition set by the user; and if the trigger condition is met, generating a trigger signal to an acquisition control module to control acquisition and storage of the signal after snapshot. The frame information output by the decoding module can be transmitted to a subsequent processing module together with acquired and stored waveform information so as to be used for further analysis processing. By adopting the method, the acquisition of an interesting CAN bus event of the measuring instrument is facilitated, interruption of the CAN bus information of the user is facilitated, and debugging efficiency of the CAN bus is increased.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Receiver With Enhanced Clock And Data Recovery
ActiveUS20100289544A1Receiver initialisationSynchronisation error correctionBaudAnalog-to-digital converter
A receiver device implements enhanced data reception with edge-based clock and data recovery such as with a flash analog-to-digital converter architecture. In an example embodiment, the device implements a first phase adjustment control loop, with for example, a bang-bang phase detector, that detects data transitions for adjusting sampling at an optimal edge time with an edge sampler by adjusting a phase of an edge clock of the sampler. This loop may further adjust sampling in received data intervals for optimal data reception by adjusting the phase of a data clock of a data sampler such a flash ADC. The device may also implement a second phase adjustment control loop with, for example, a baud-rate phase detector, that detects data intervals for further adjusting sampling at an optimal data time with the data sampler.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
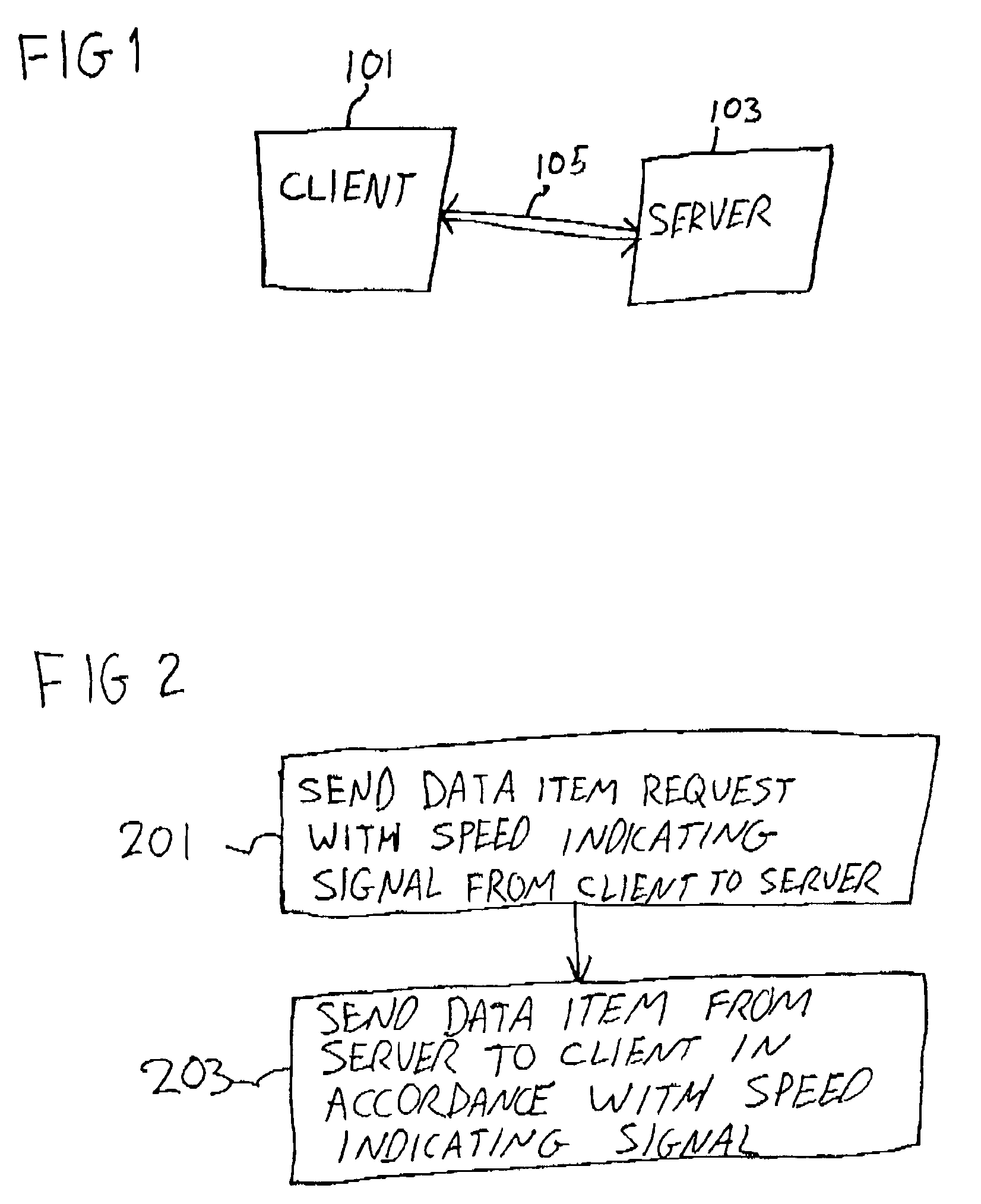
User input based allocation of bandwidth on a data link
InactiveUS7383350B1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksUser inputData source
In a computer network, user input is used to control the bandwidth used by particular applications. Data is sent from either a data source computer or an intermediate computer (e.g. dial-up server) to a client computer according to the user input. The allocation of bandwidth may be managed from the client computer, data source computer, or intermediate computer. The user may set a limit on the baud rate used by particular applications.
Owner:IBM CORP
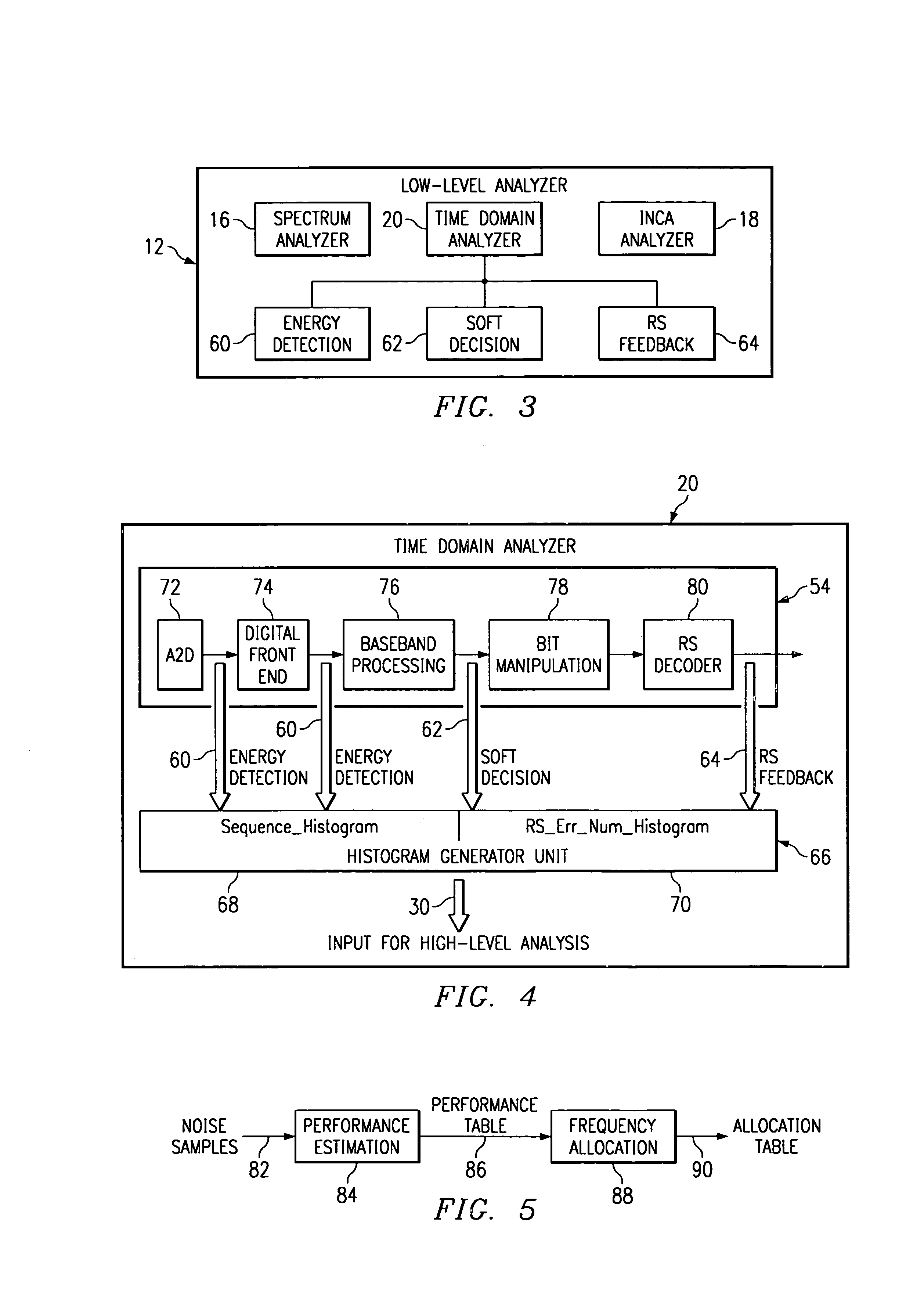
Noise analysis in a communication system
InactiveUS7492703B2Improve noiseError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission systemsCommunications systemEngineering
A system is provided to automatically estimate performance of a receiver for receiving input signals, the input signals having a carrier frequency and a baud rate, from a channel in a communication system and the effect of highly correlated noise cancellation on performance of the receiver, while no active transmission is occurring on the channel, comprising: a digital front end in the receiver for receiving samples of the input signals; a predictor coupled to the digital front end for predicting highly correlated noise in a second sample of the input signal; and a subtraction unit coupled to the predictor for subtracting the predictor output from the second sample to determine residual noise in the second sample. Other systems and methods are disclosed.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
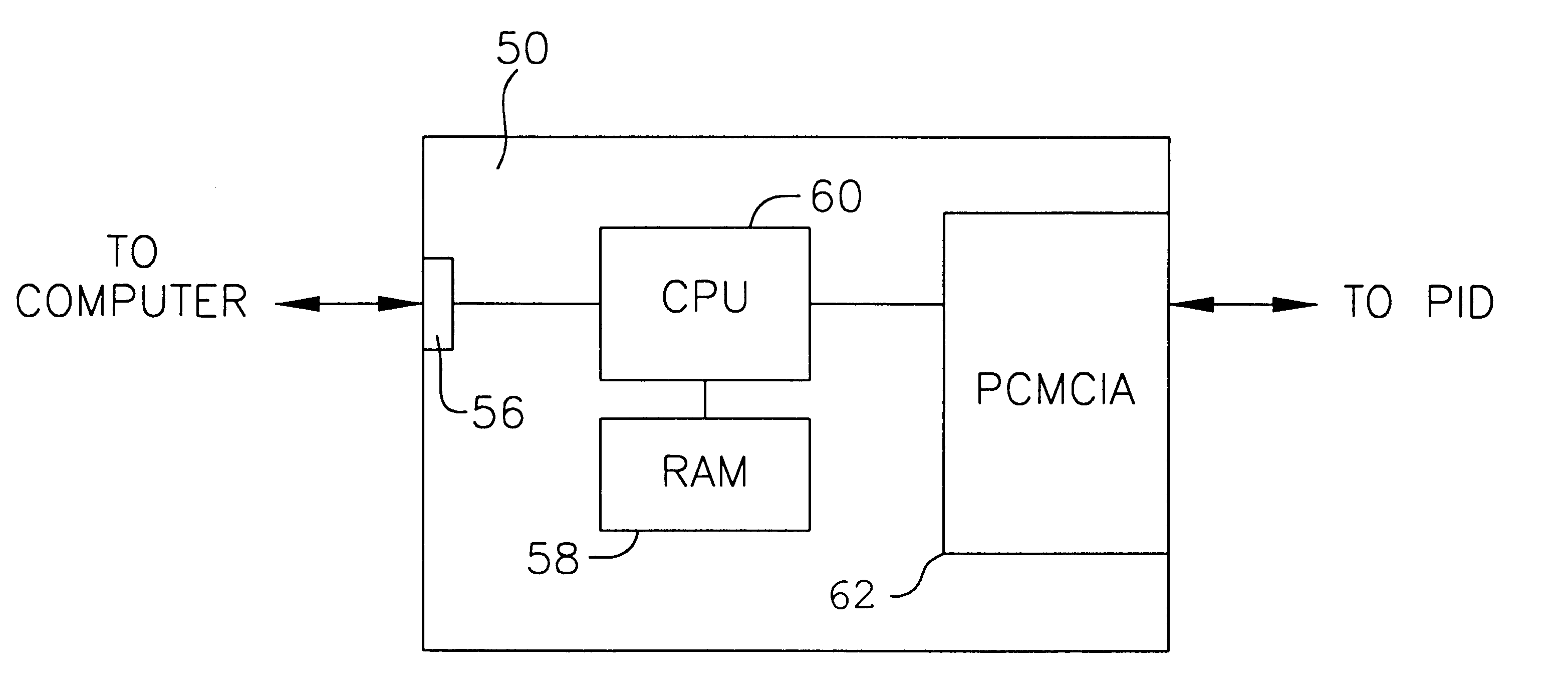
Personal information device and method for downloading reprogramming data from a computer to the personal information device via the PCMCIA port or through a docking station with baud rate conversion means
InactiveUS6202209B1Easily and safely receiveEasily reprogrammedEnergy efficient ICTError detection/correctionDocking stationInformation device
A personal information device is provided in the form of a PCMCIA card and includes a PCMCIA I / O port that is adapted to be coupled to a PCMCIA port of a computer, a first memory that is directly accessible by the computer via the PCMCIA I / O port, second and third memories that are not directly accessible to the computer, and a controller. When the personal information device is inserted into the computer's PCMCIA port, the first memory directly receives and stores therein reprogramming data supplied by the computer. Immediately after the data is downloaded, or alternatively, upon disconnection of the personal information device from the computer, the personal information device's controller transfers to the second memory reprogramming code included in the reprogramming data stored in the first memory, executes the reprogramming code stored in the second memory, and then programs the third memory by utilizing the application code included in the reprogramming data stored in the first memory in accordance with the reprogramming code being executed. The downloaded application code may include organizer application code for the end user, diagnostic code or other types of code. In addition to being able to interface with a computer via the computer's PCMCIA port, the personal information device may communicate with a computer by using a docking station that includes therein a controller and that is capable of changing the baud rate of data serially supplied thereto so as to allow a computer and a personal information device communicating at different baud rates to serially communicate with one another.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC +2
Optical transmitter
InactiveUS20070264028A1Increase powerReliably compensate delay shiftPhase-modulated carrier systemsElectromagnetic transmittersContinuous lightRelative phase
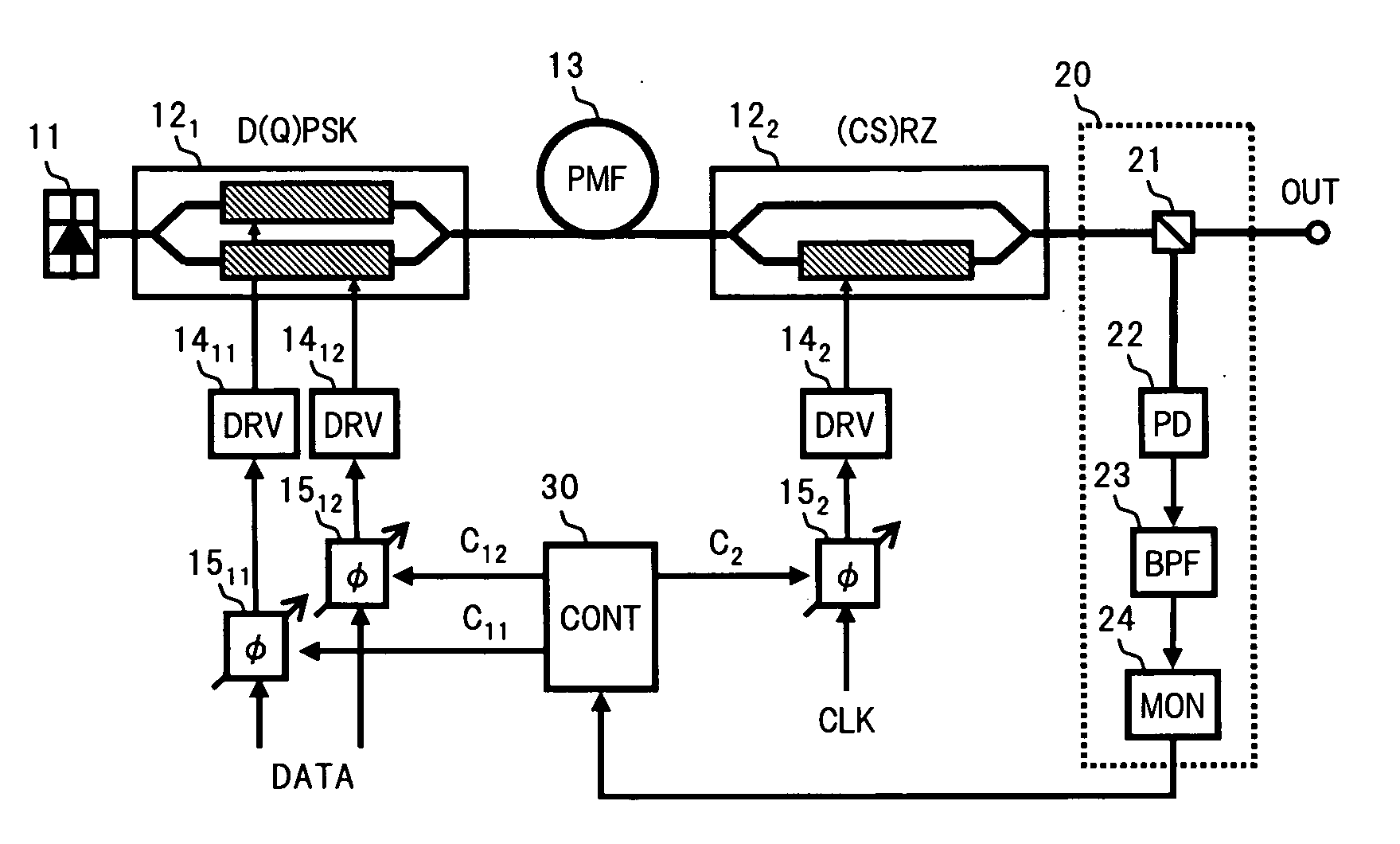
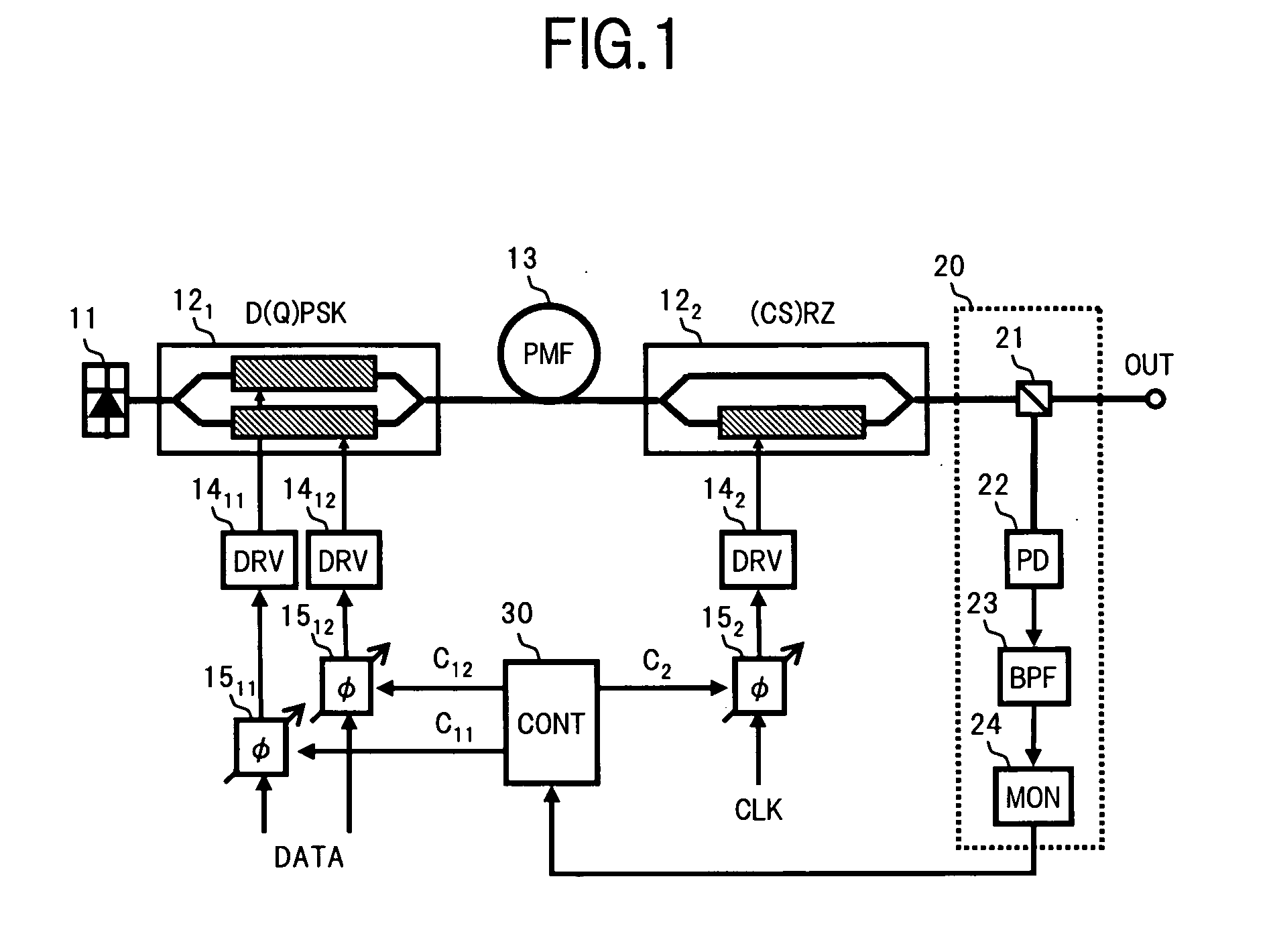
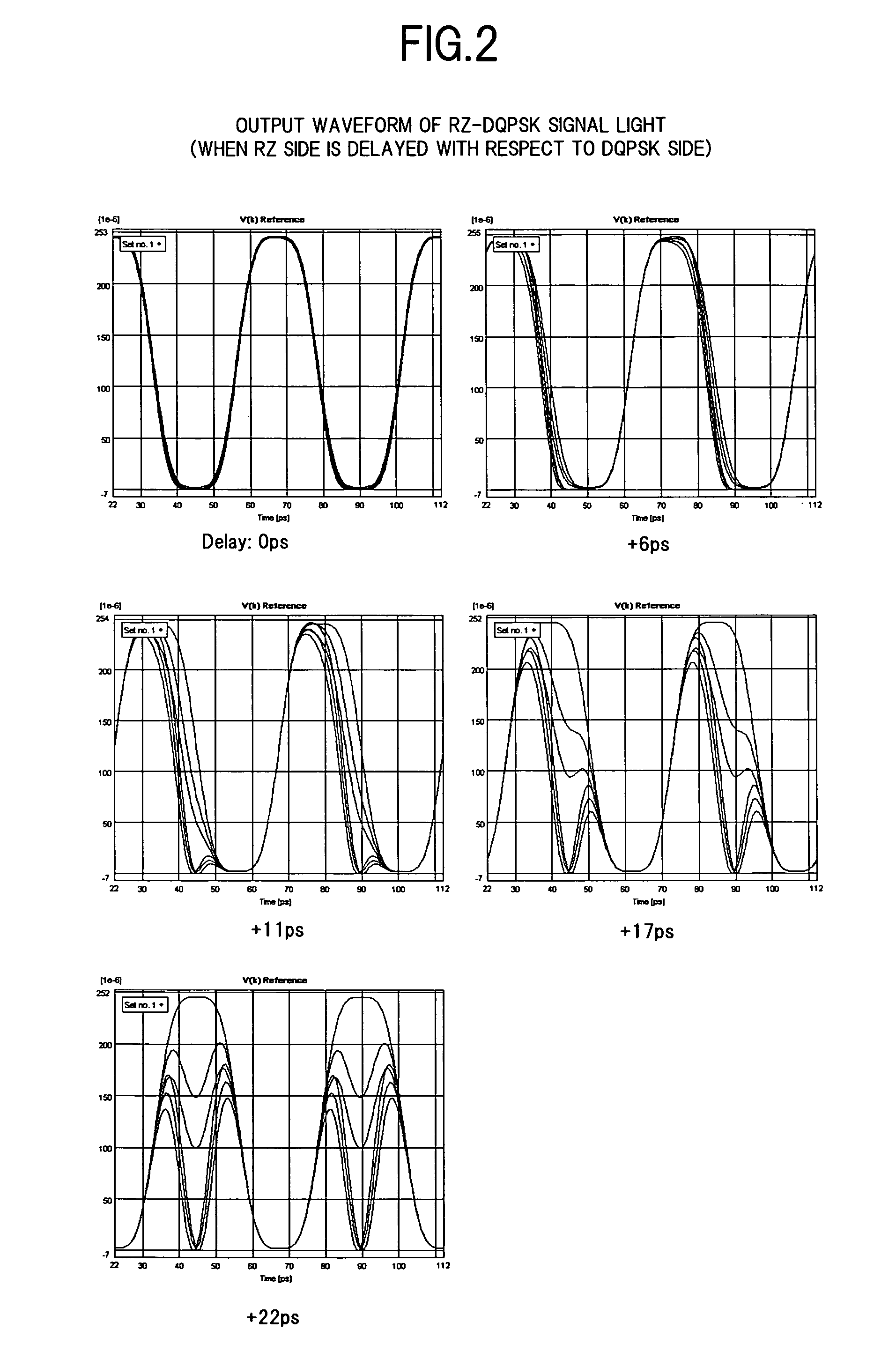
In an optical transmitter of the invention, continuous light from a light source is a (CS)RZ-D(Q)PSK modulated by two optical modulators connected in series, and a part of the optical signal output from a post-stage optical modulator is branched by an output monitor section, and the power of a preset frequency component, excluding a frequency component corresponding to a baud rate, included in an electrical spectrum acquired by photoelectrically converting the branched beams is measured. The relative phase of drive signals applied to the optical modulators is then feed-back controlled so that the power becomes a minimum. As a result, a delay shift due to a temperature change or the like between drive signals applied to respective optical modulators, can be reliably compensated.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
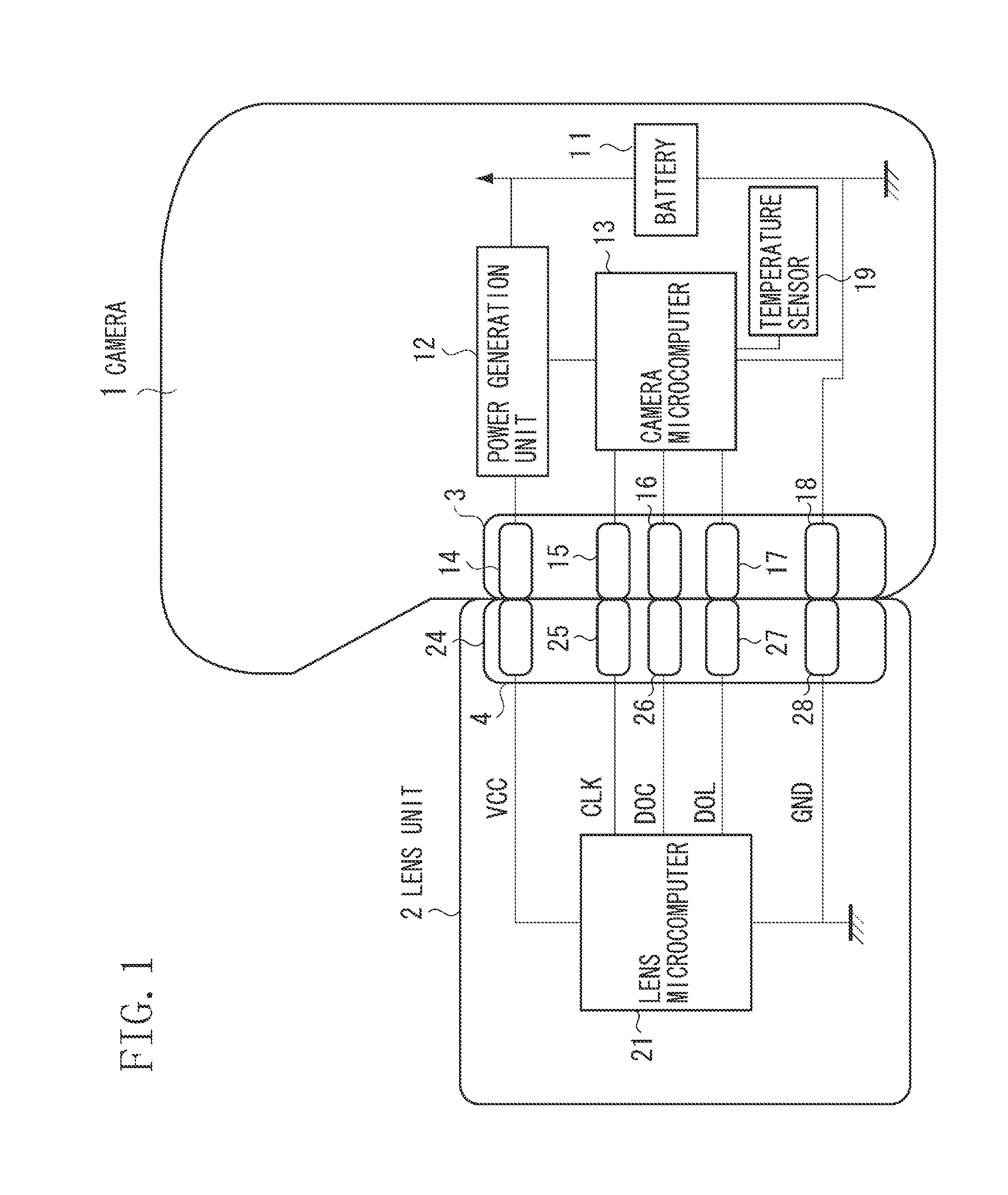
Imaging apparatus and lens unit
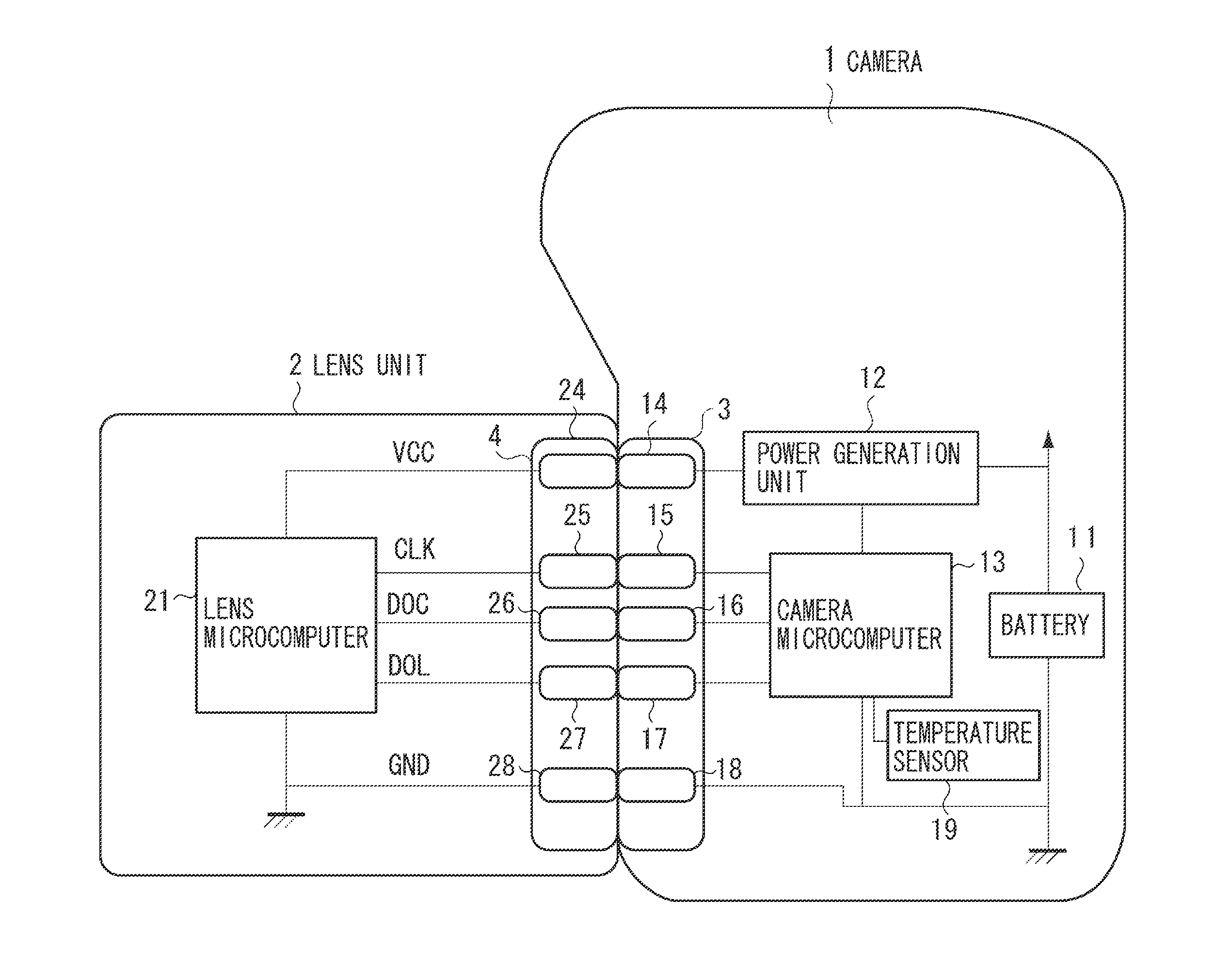
An imaging apparatus includes a first terminal and a second terminal and a control unit configured to perform switching between a first communication mode for outputting a clock signal via the first terminal and communicating with a mounted lens unit via the second terminal based on the clock signal and a second communication mode for communicating with the mounted lens unit via the first terminal or the second terminal without using the clock signal. The control unit continuously sets the first communication mode if the second communication mode is not usable for the mounted lens unit. On the other hand, the control unit sets the second communication mode if the second communication mode is available for the mounted lens unit and sets a baud rate to communicate with the lens unit in the second communication mode to be a baud rate value received from the lens unit.
Owner:CANON KK
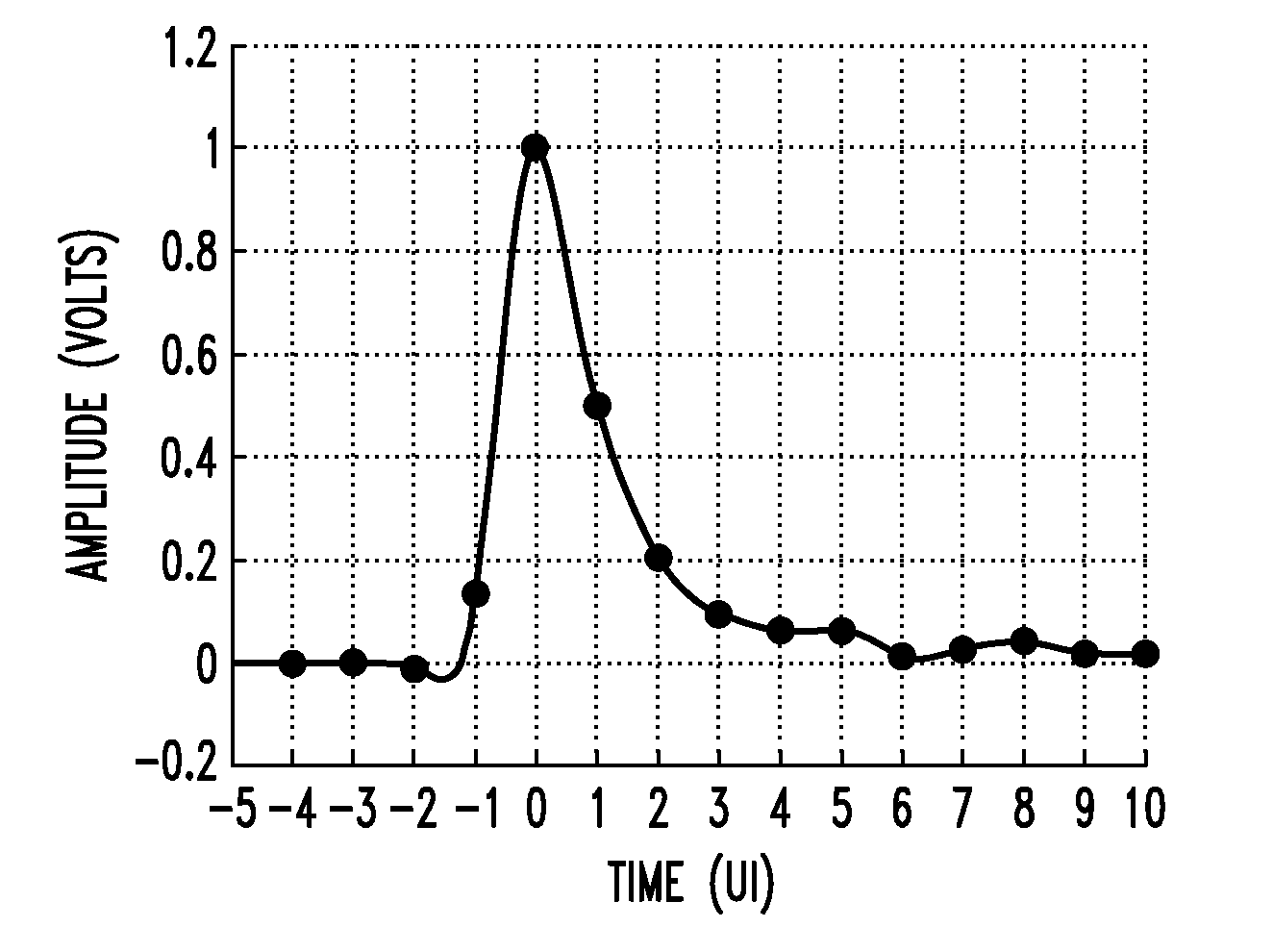
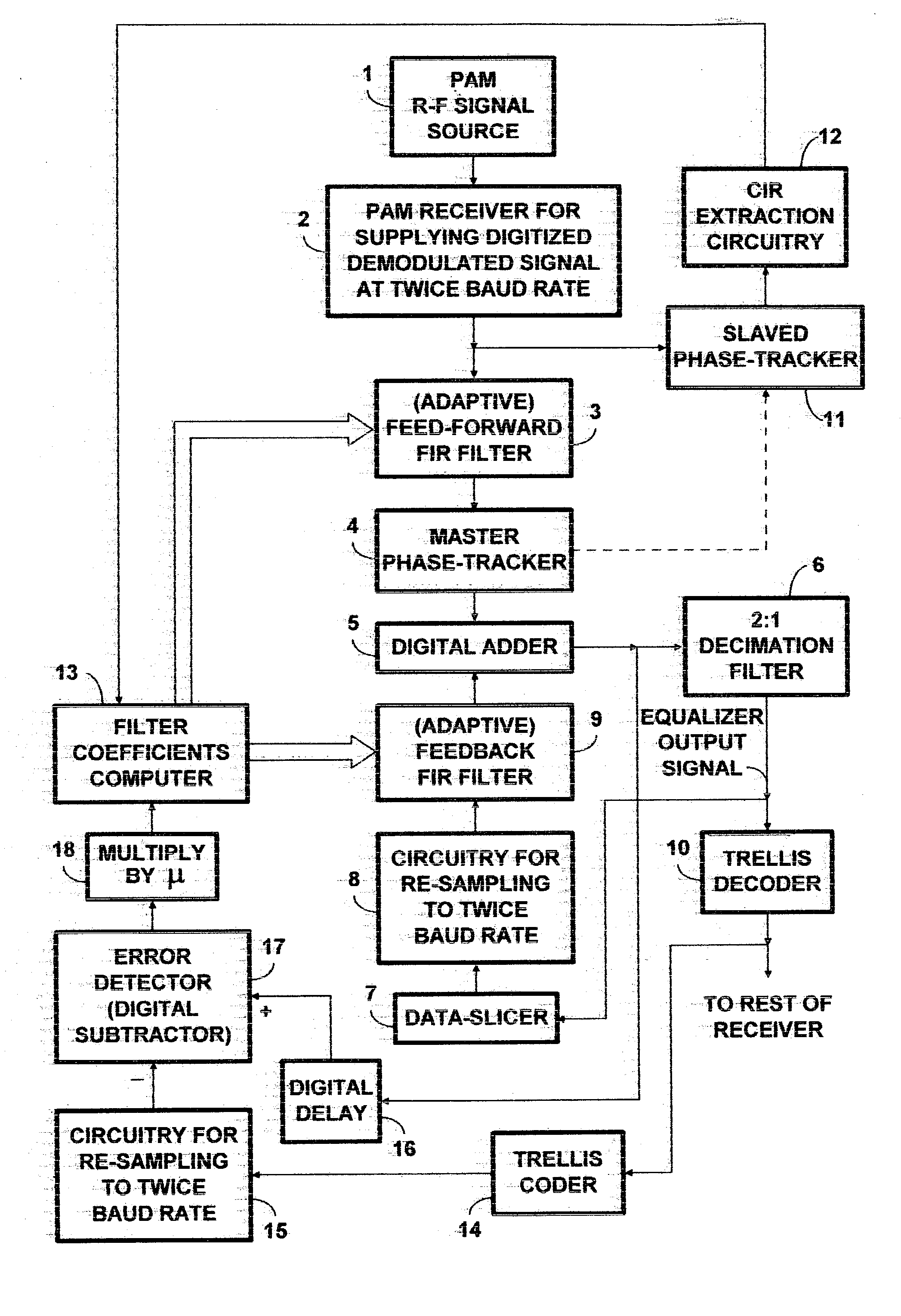
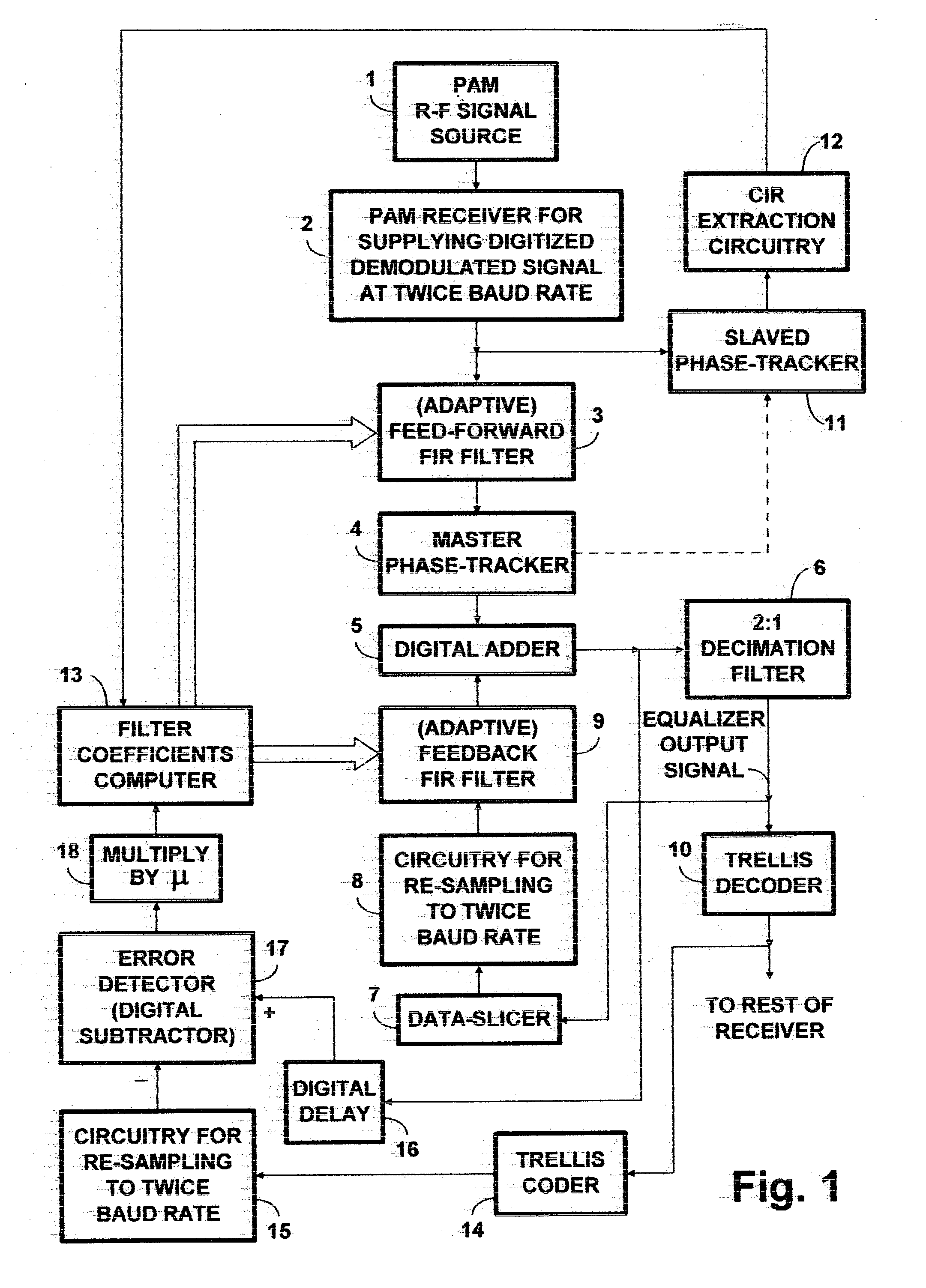
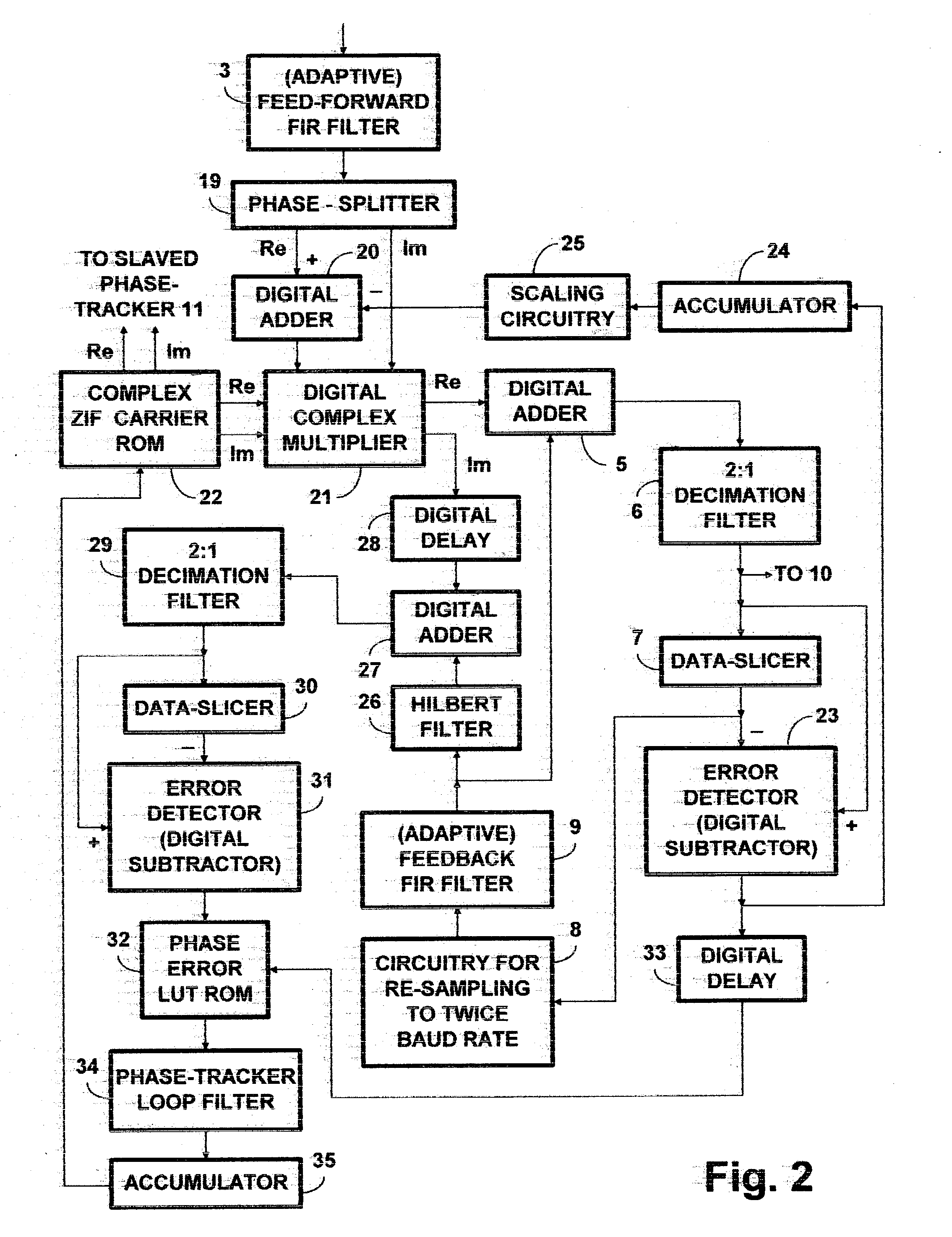
PAM radio signal receiver with phase-tracker succeeding adaptive FIR filtering and preceding adaptive IIR filtering
InactiveUS20050002474A1Reduce Intersymbol InterferenceReduce phase noiseMultiple-port networksTelevision system detailsDigital dataIir filtering
A PAM receiver for reproducing a baseband signal that symbol codes digital data is combined with an decision-feedback equalizer (DFE) incorporating first adaptive digital filtering as a feed-forward element and second adaptive digital filtering as a feedback element. The DFE response is supplied to symbol decoding circuitry for reproducing the digital data. A de-rotator re-samples the first adaptive digital filtering response before it is combined with the second adaptive digital filtering response to generate an equalizer response. The resulting baud-rate equalizer response is sampled at baud rate and quantized to generate baud-rate decisions that applied to the second adaptive digital filtering as input signal, for completing the decision-feedback loop. The re-sampling of the first adaptive digital filtering response by the de-rotator is controlled, so as to provide a phase-tracker that reduces phase noise and intersymbol interference, prior to the making of decisions for decision feedback.
Owner:LIMBERG ALLEN LEROY
RFID receiver
RFID data signals from RFID tags may be recovered by determining the probabilities of transitions between data states between a series of a pairs of signal samples using a set of predetermined probabilities related to data, timing, baud rate and / or phase variables affecting the received signal and processing those determined probabilities to determine the sequence of such transitions that has the highest probability of occurrence. A second set of predetermined probabilities related to transitions in the opposite direction may be used to sequence in a reverse direction. The determination of the sequence representing the RFID tag data may be iterated in both directions until further iterations don't change the determined probabilities.
Owner:MOJIX
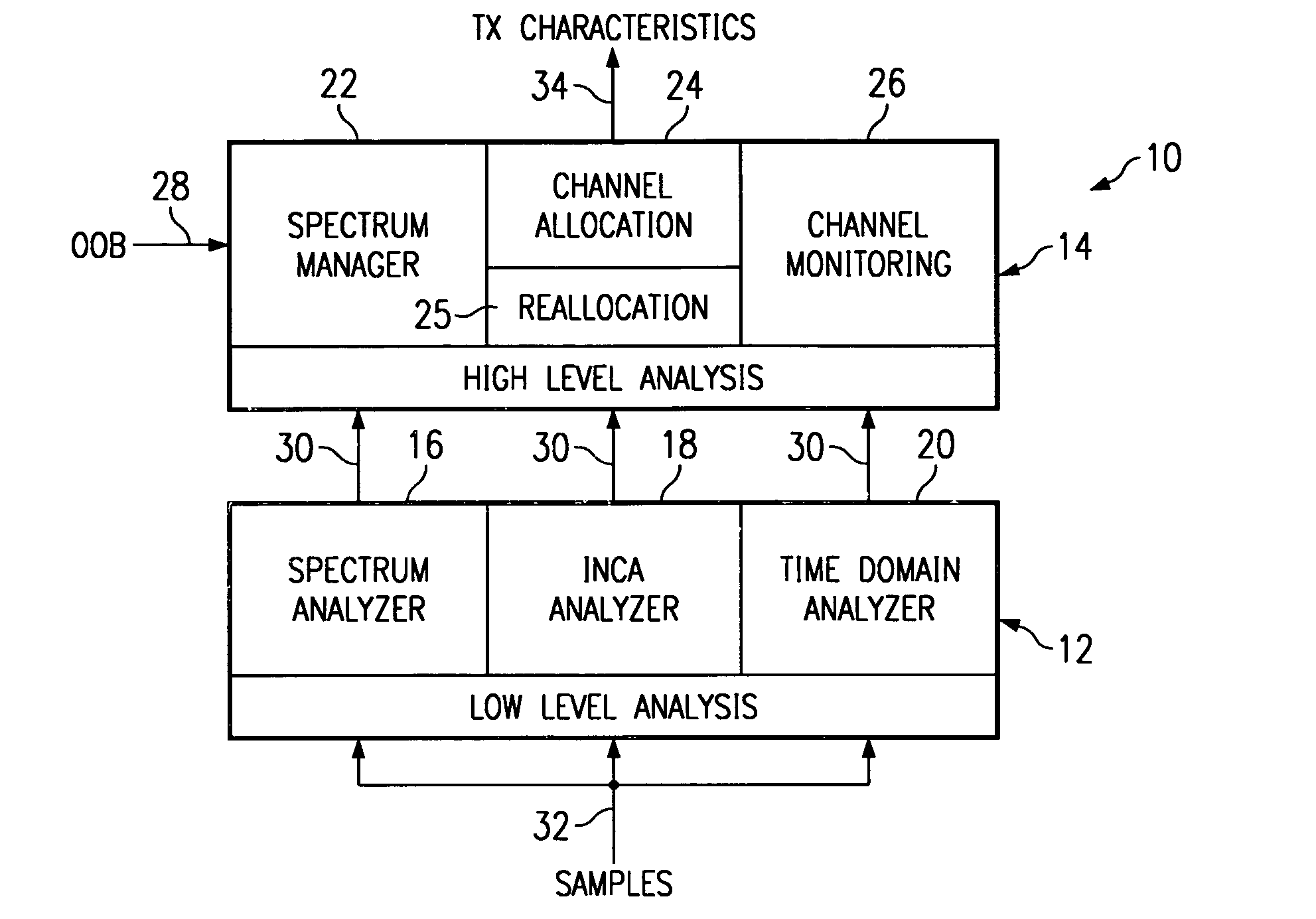
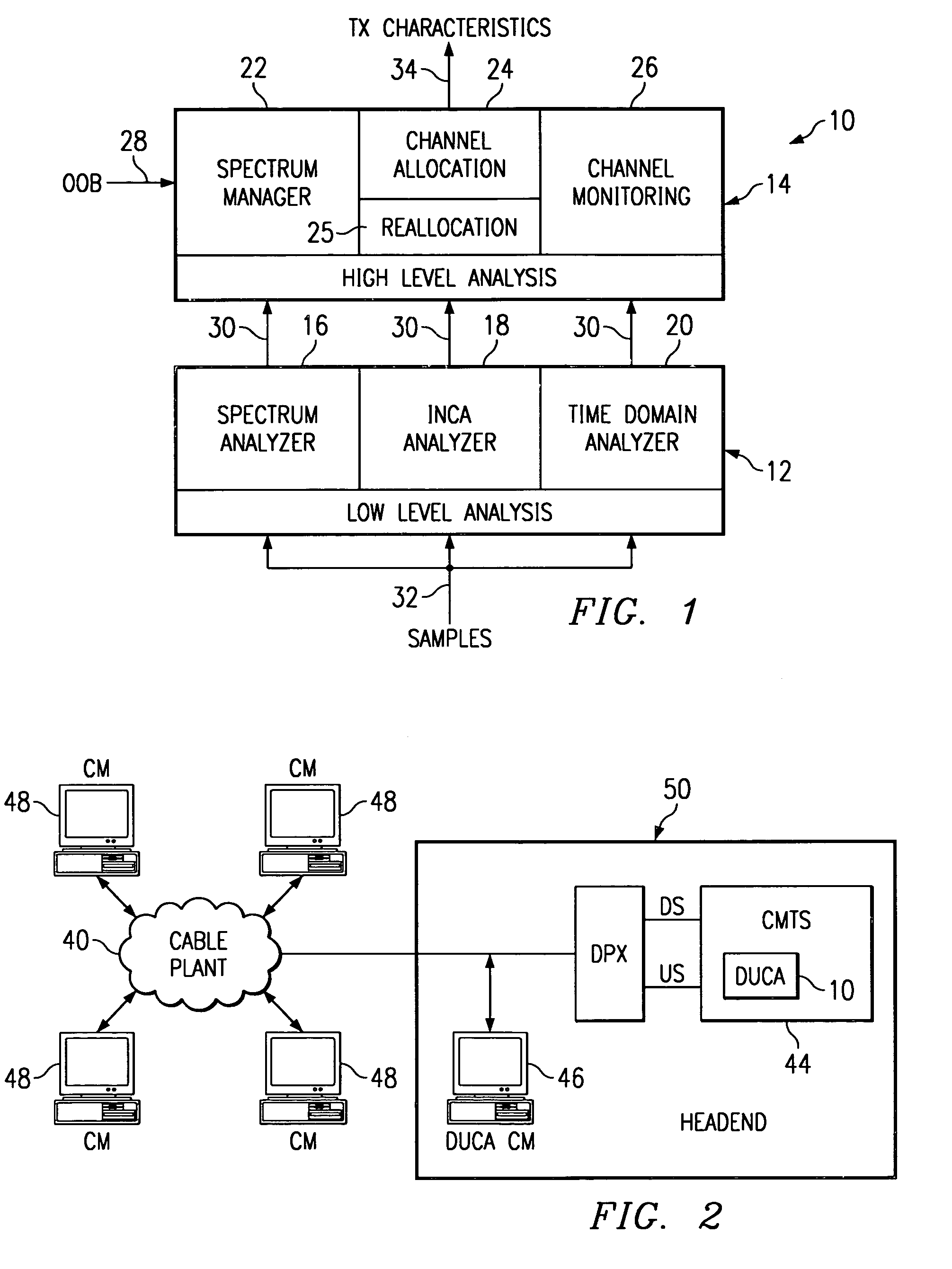
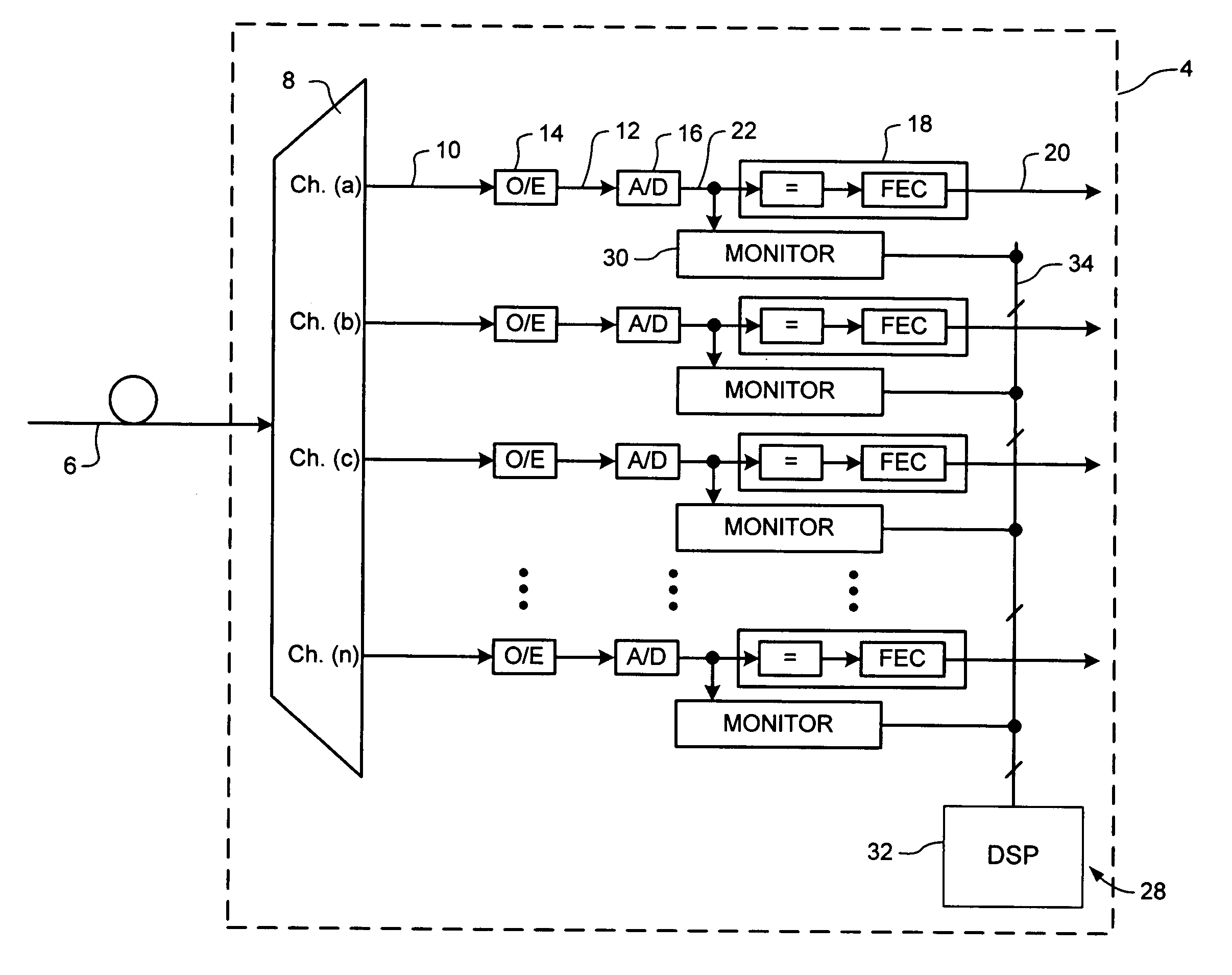
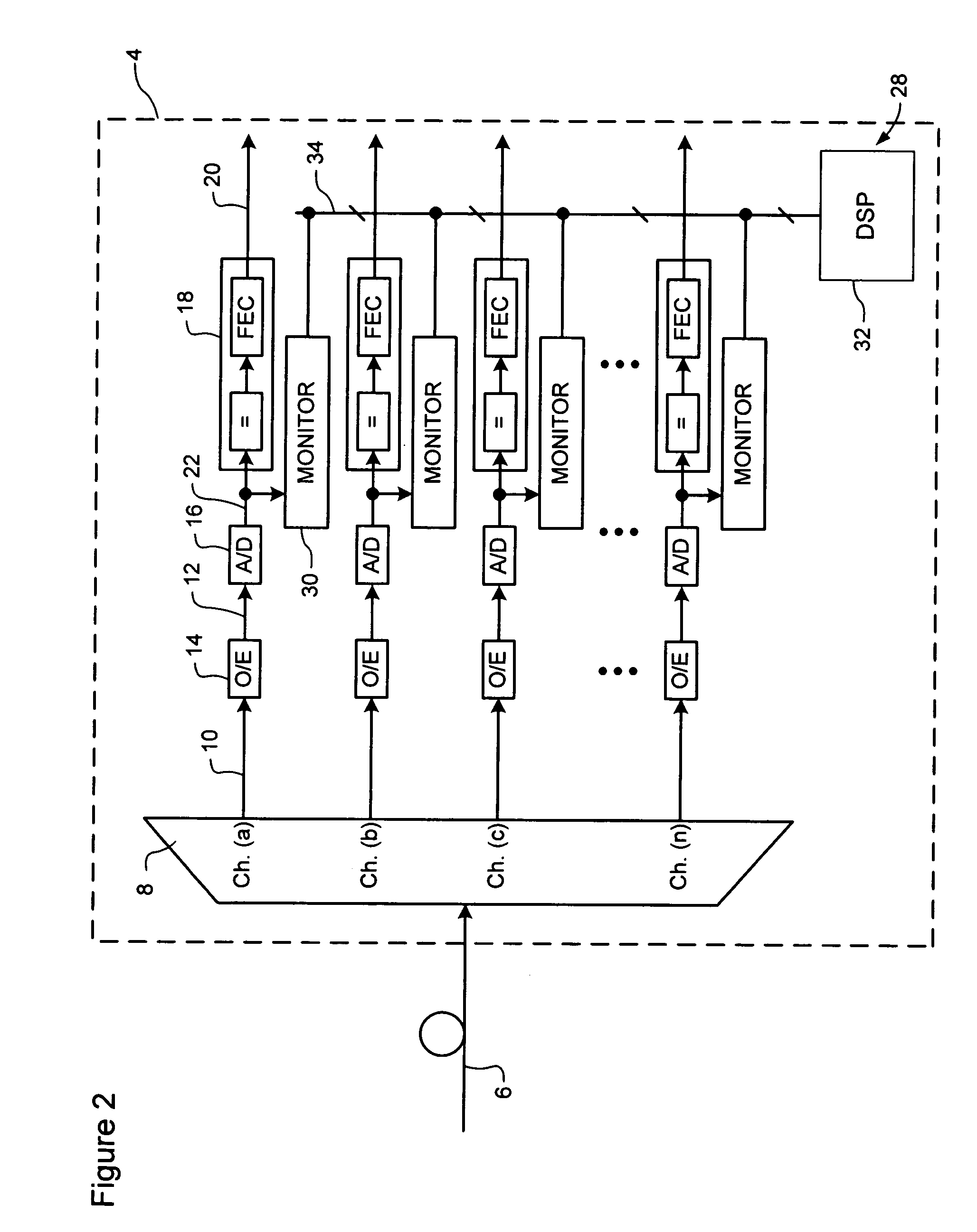
Digital performance monitoring for an optical communications system
ActiveUS7356256B1Highly accurate correlationImprove performanceTransmission monitoringElectromagnetic transmittersDigital signal processingCommunications system
A digital performance monitoring method and system for an optical communications system utilizes a channel monitor and a digital signal processor (DSP). The channel monitor is designed to monitor a respective channel signal of the optical communications system, and includes a sample memory for storing sample data including a set of sequential N-bit (where N>1) samples generated by an Analog-to-Digital (A / D) converter at a predetermined sample rate. The digital signal processor (DSP) is designed to calculate at least one performance parameter of the optical communications system based on the stored sample data. The sample rate of the A / D converter is at least equal to a baud rate of the channel, and preferably satisfies the Nyquist criterion. Multiple A / D converters may be used parallel to sample respective orthogonal components of the channel signal. In this case, the stored sample data may be representative of the complex E-field of the channel signal.
Owner:CIENA
Frequency synchronizer
InactiveUS6947504B1Apparent advantageHigh bandwidthAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationCarrier signalErrors and residuals
A frequency synchronizer system is based on the maximum likelihood criterion from estimation theory and that can achieve both frequency acquisition and frequency tracking without requiring knowledge at the receiver of the carrier's phase angle, baud timing, or a preamble consisting of known signal symbols. The synchronizer includes a processor for executing the following sequence of operations: a) initializing an estimated frequency correction factor; b) determining a corrected frequency offset value from a first product of a sample signal and the estimated frequency correction factor; c) filtering a first sample of the corrected frequency offset value to obtain a filtered corrected frequency offset value; d) imparting a delay to a second sample of the corrected frequency offset value to obtain a delayed corrected frequency offset value; e) determining a conjugate product value from a second product of the filtered corrected frequency offset value and a conjugate of the filtered corrected frequency offset value; f) determining a delay conjugate value from a third product of the delayed corrected frequency offset value and the conjugate product value; g) determining an error signal from the delay conjugate value; h) determining a frequency offset value from the error signal; and i) determining an updated value of the estimated frequency correction factor from the frequency offset value.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com