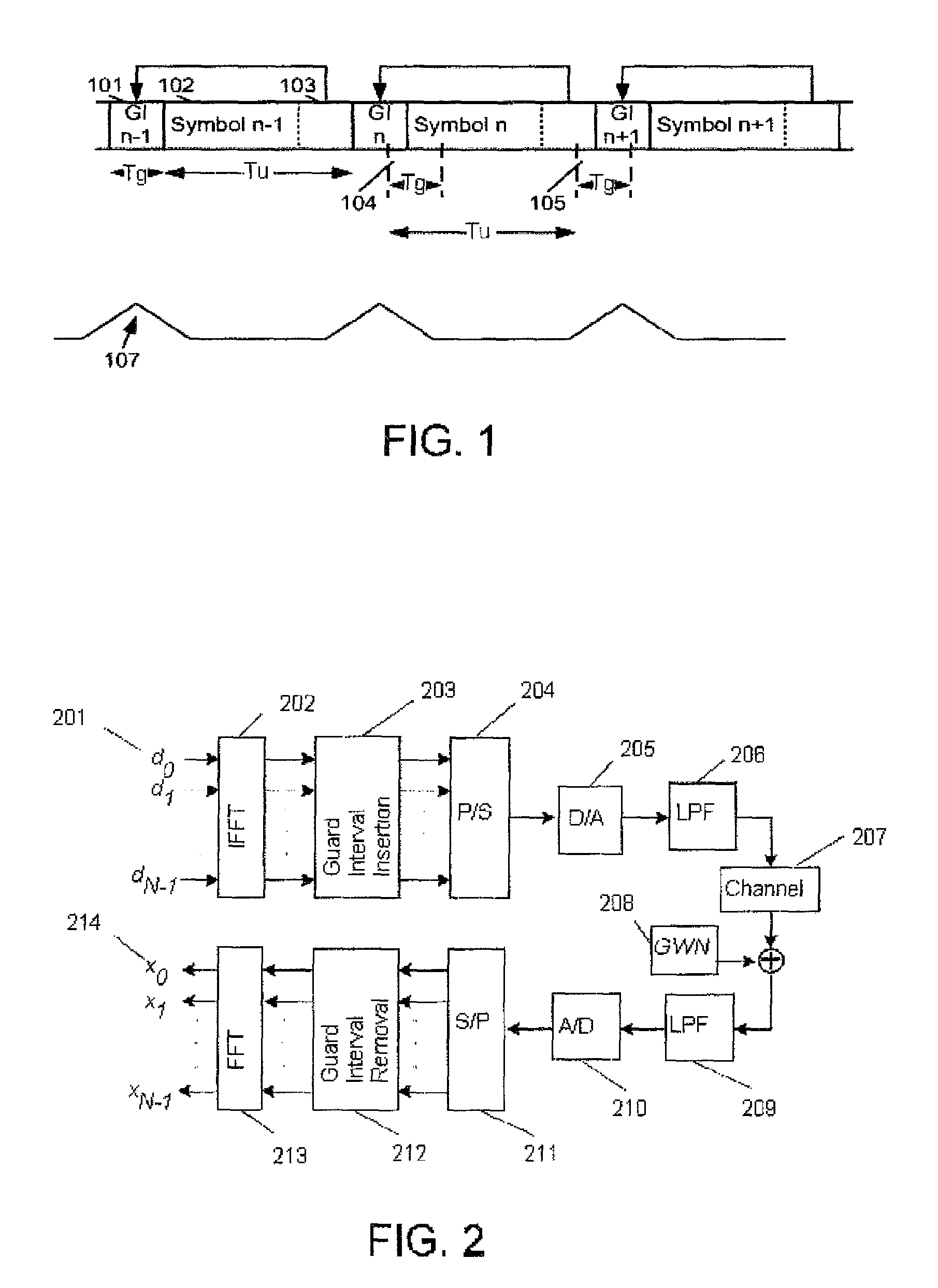
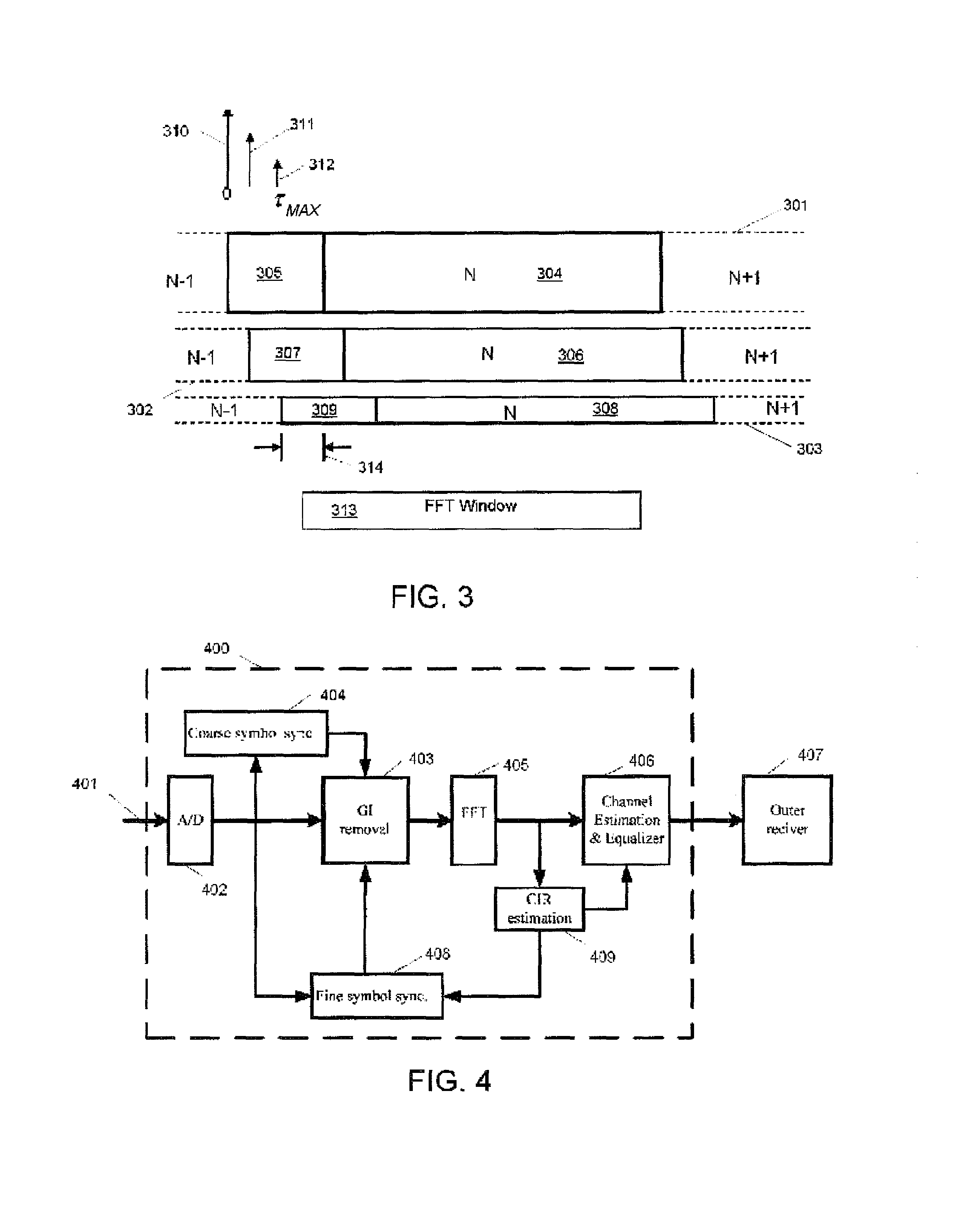
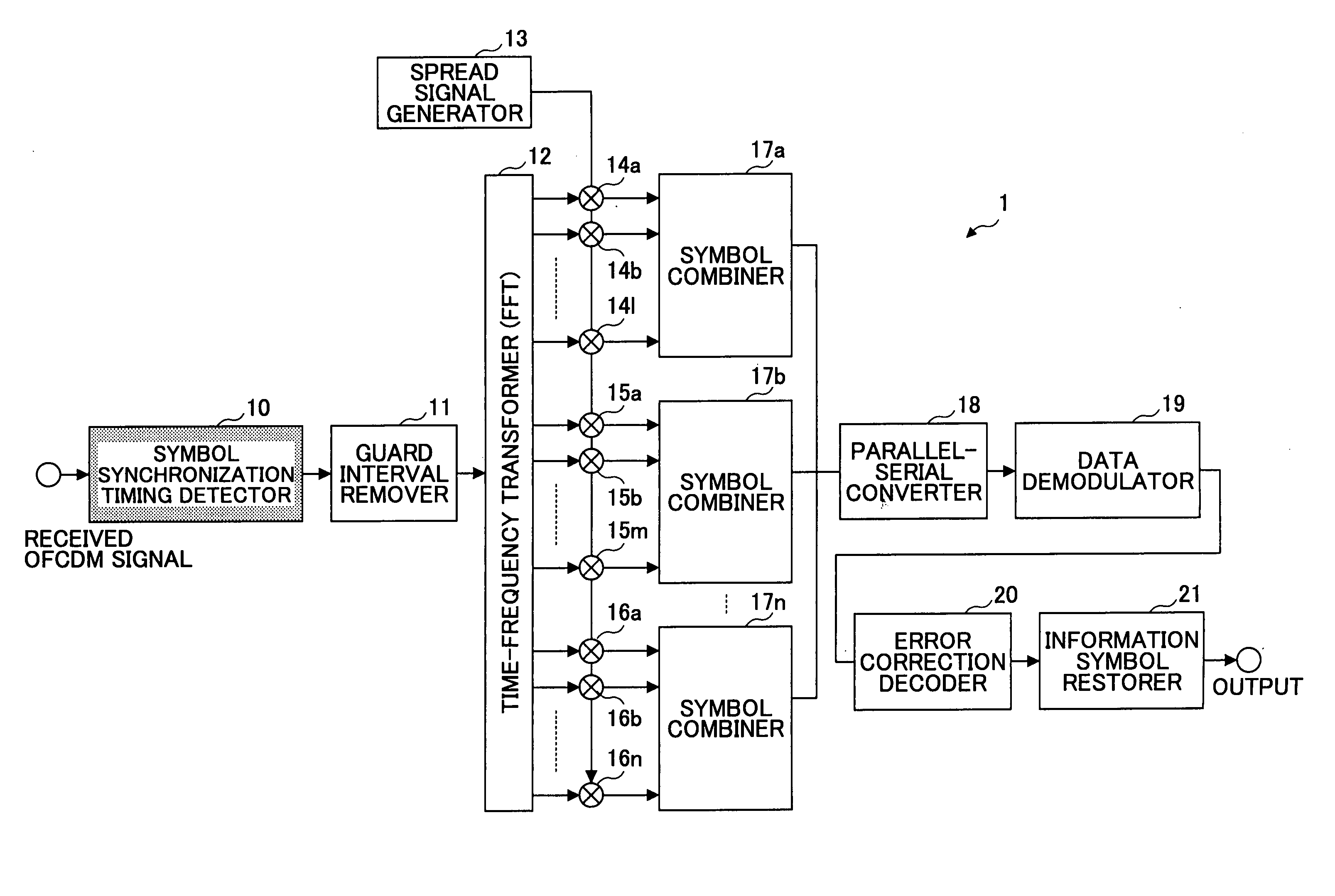
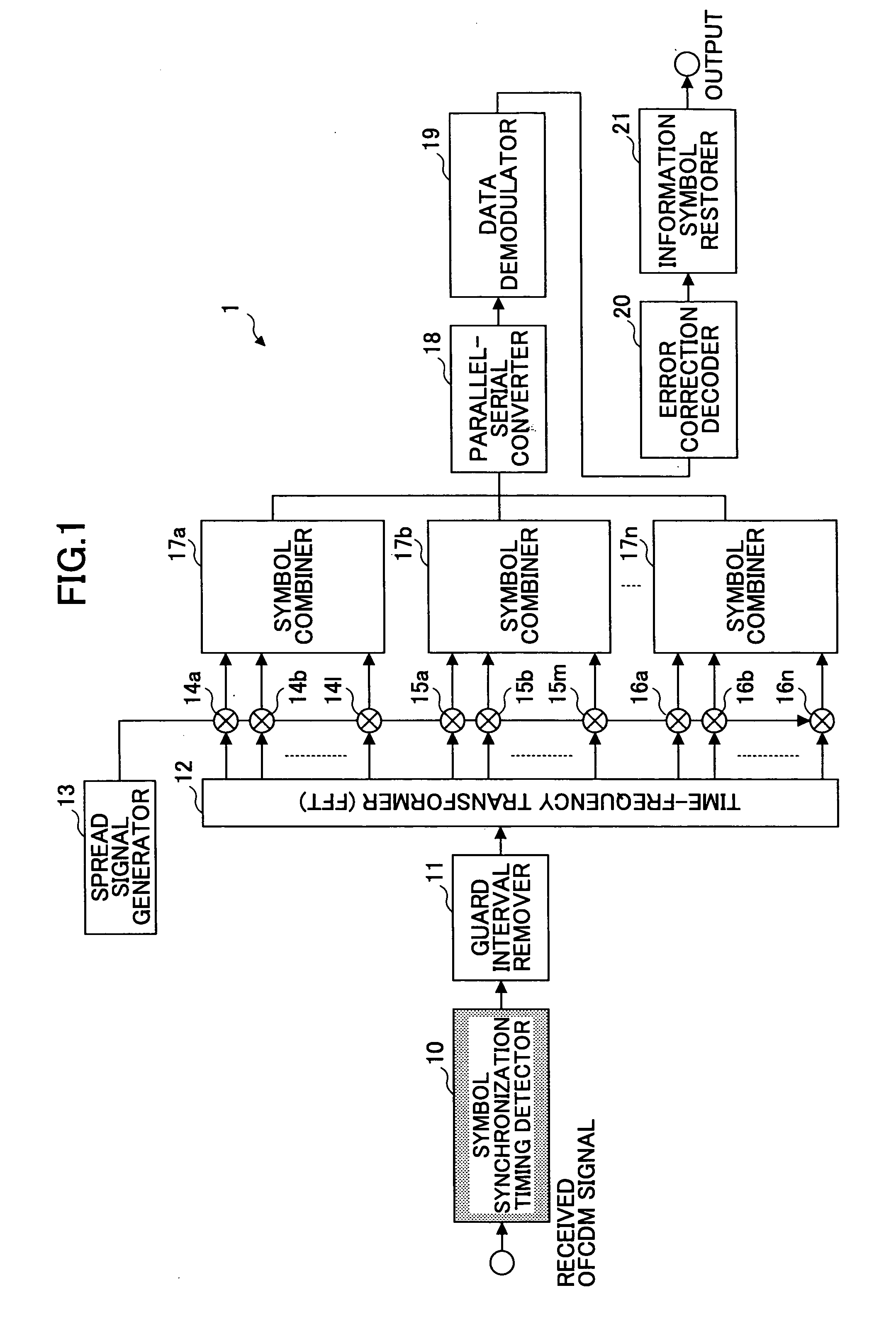
Patents
Literature
110results about How to "Reduce Intersymbol Interference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
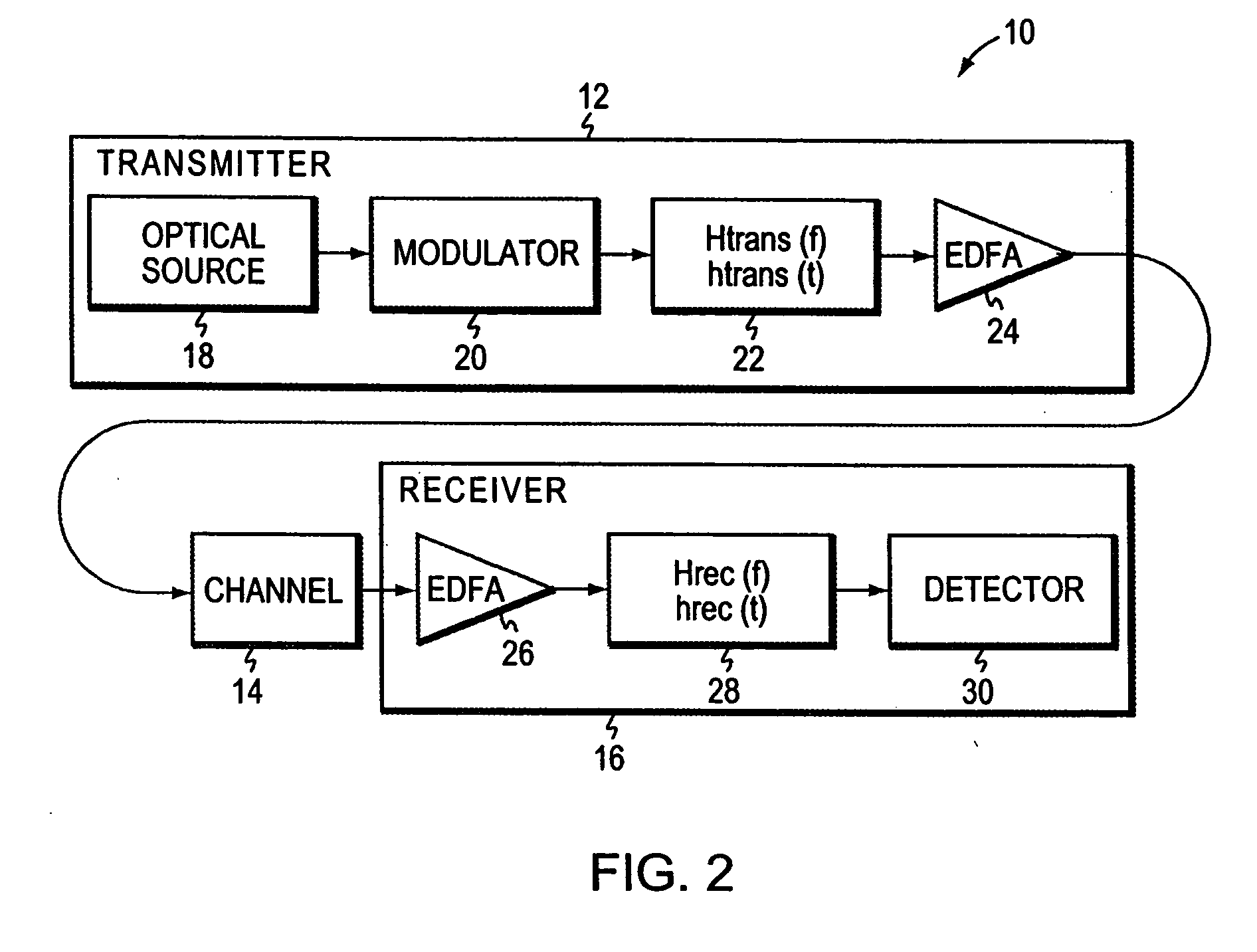
System and Method for Acoustic Data Transmission
InactiveUS20080112885A1Reduce Intersymbol InterferenceImprove system performanceSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionEndoscopesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Transducer
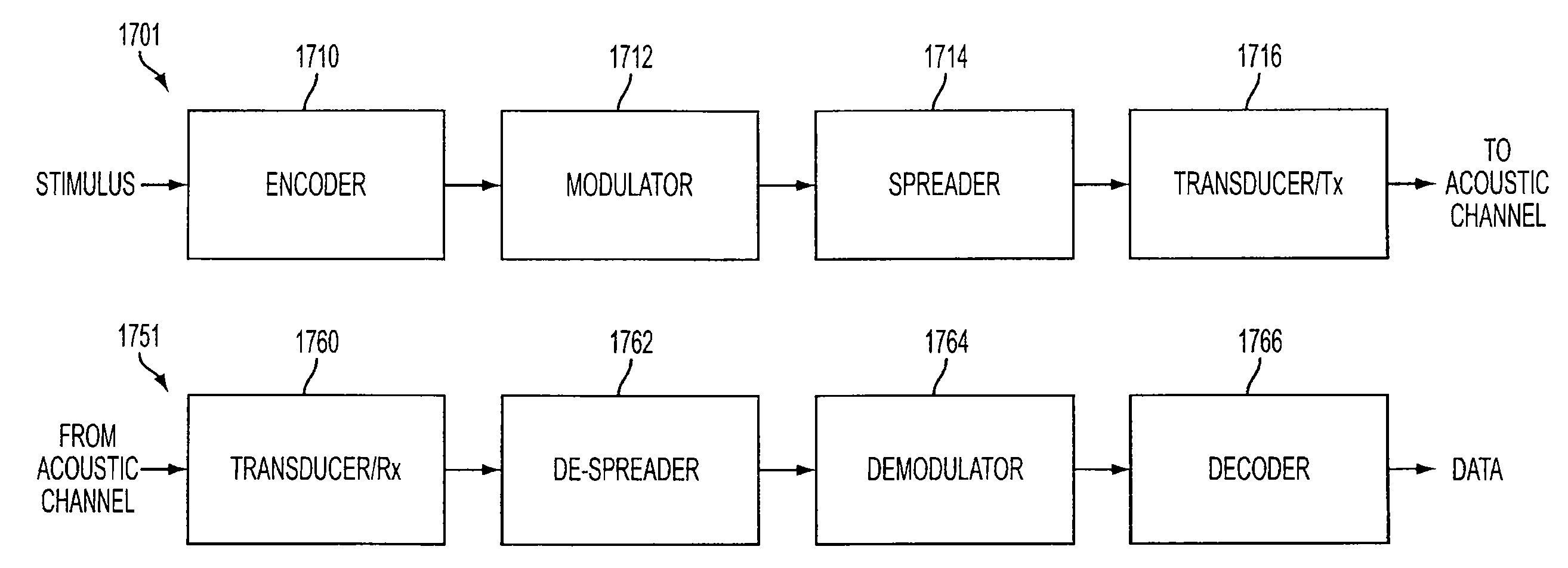
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to acoustic data transmission using a spreading code. A system for acoustic data transmission includes an ingestible capsule and an acoustic receiver. The ingestible capsule includes a modulator, a spreader, and an acoustic transmitter. The modulator modulates data according to a modulation scheme. The spreader spreads the modulated data according to a spreading code. The acoustic transmitter acoustically transmits the modulated and spread data through a body of an animal. The acoustic receiver includes an acoustic transducer a de-spreader and a demodulator. The acoustic transducer receives the acoustically transmitted signal and forms an electrical signal therefrom. The de-spreader de-spreads the received signal in accordance with the spreading code. The demodulator demodulates the received and de-spread signal in accordance with the modulation scheme, wherein a phase of the spreading code is synchronized with the received signal whereby a signal-to-noise ratio of the received signal is increased.
Owner:INNURVATION
High-speed multi-channel communications transceiver with inter-channel interference filter
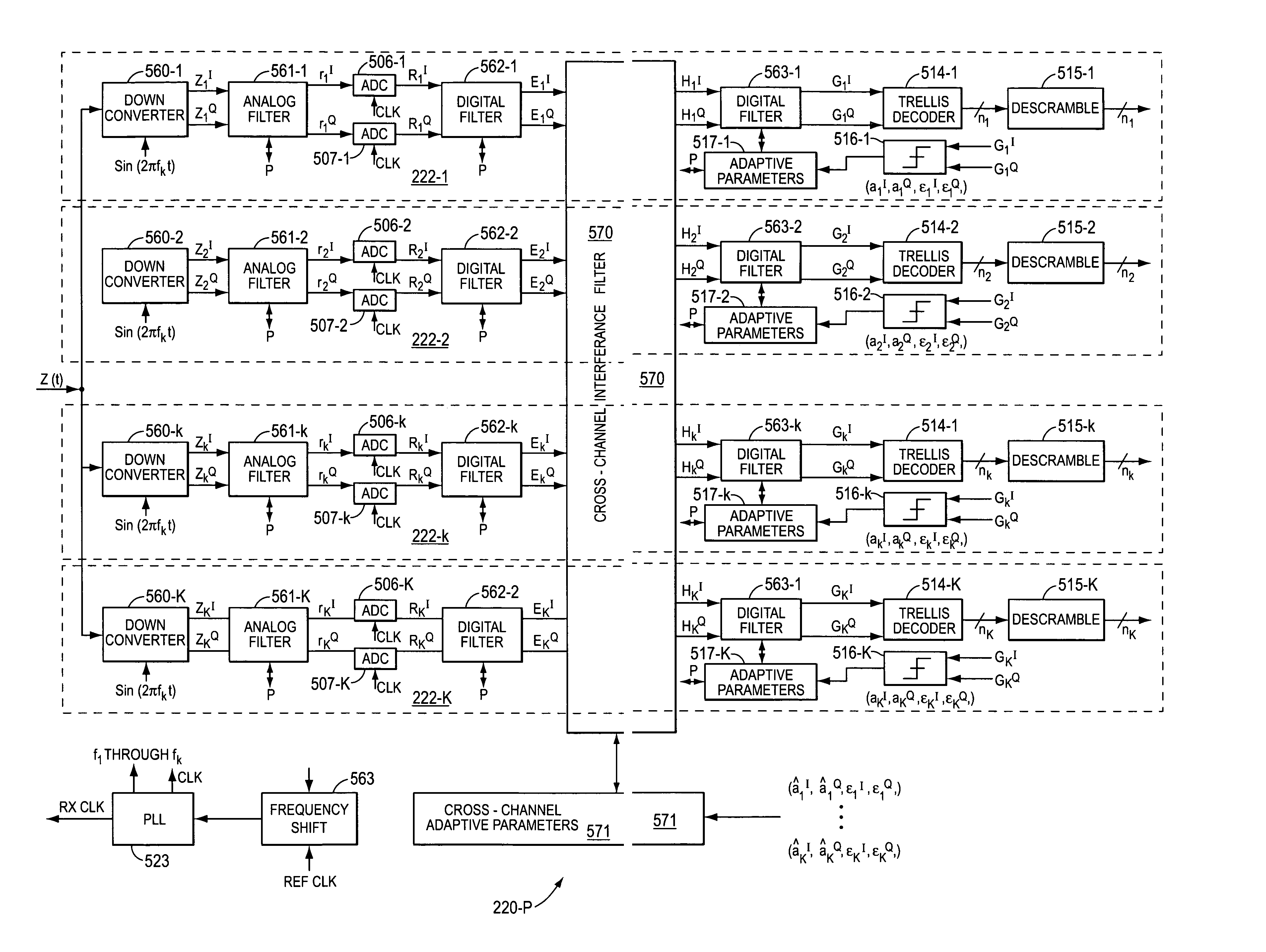
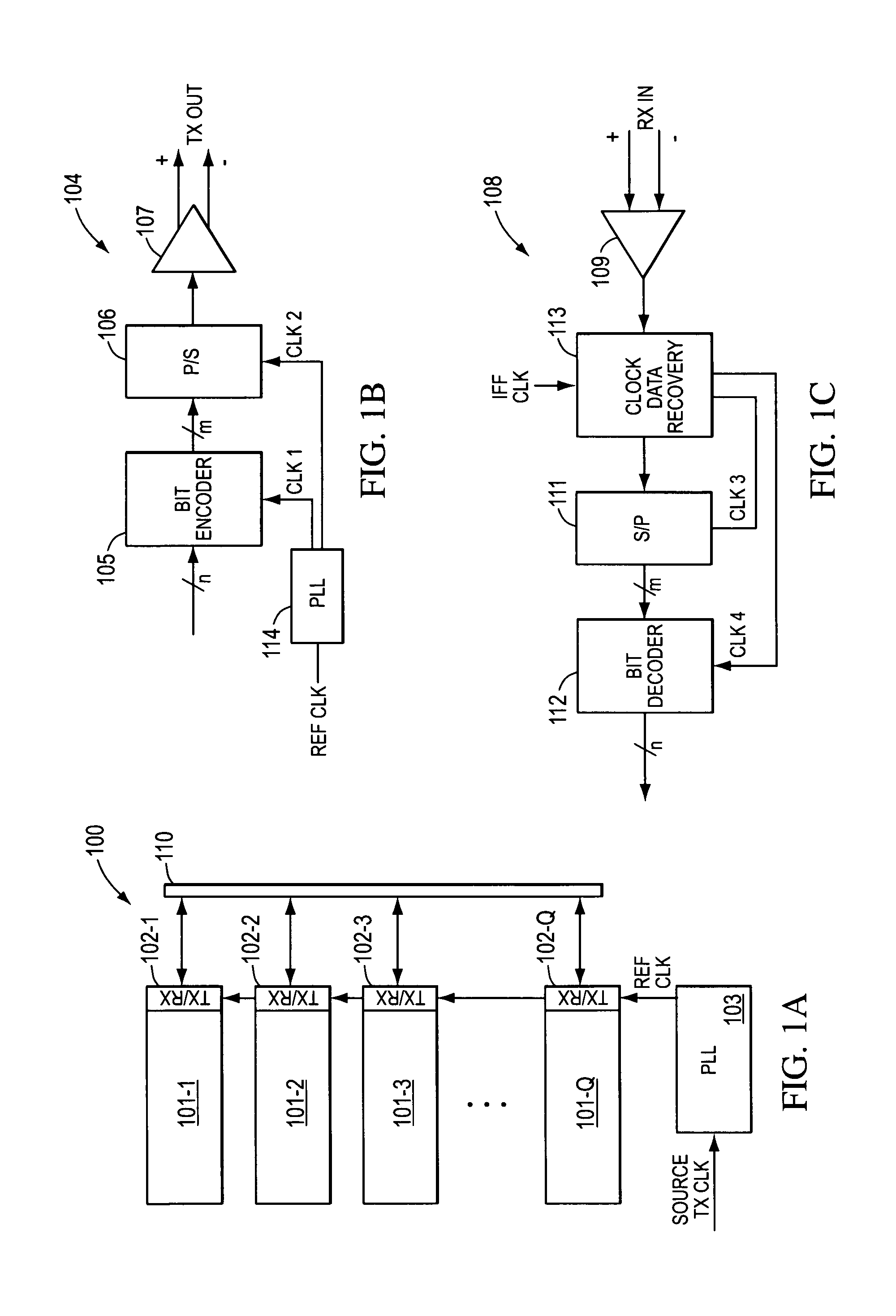
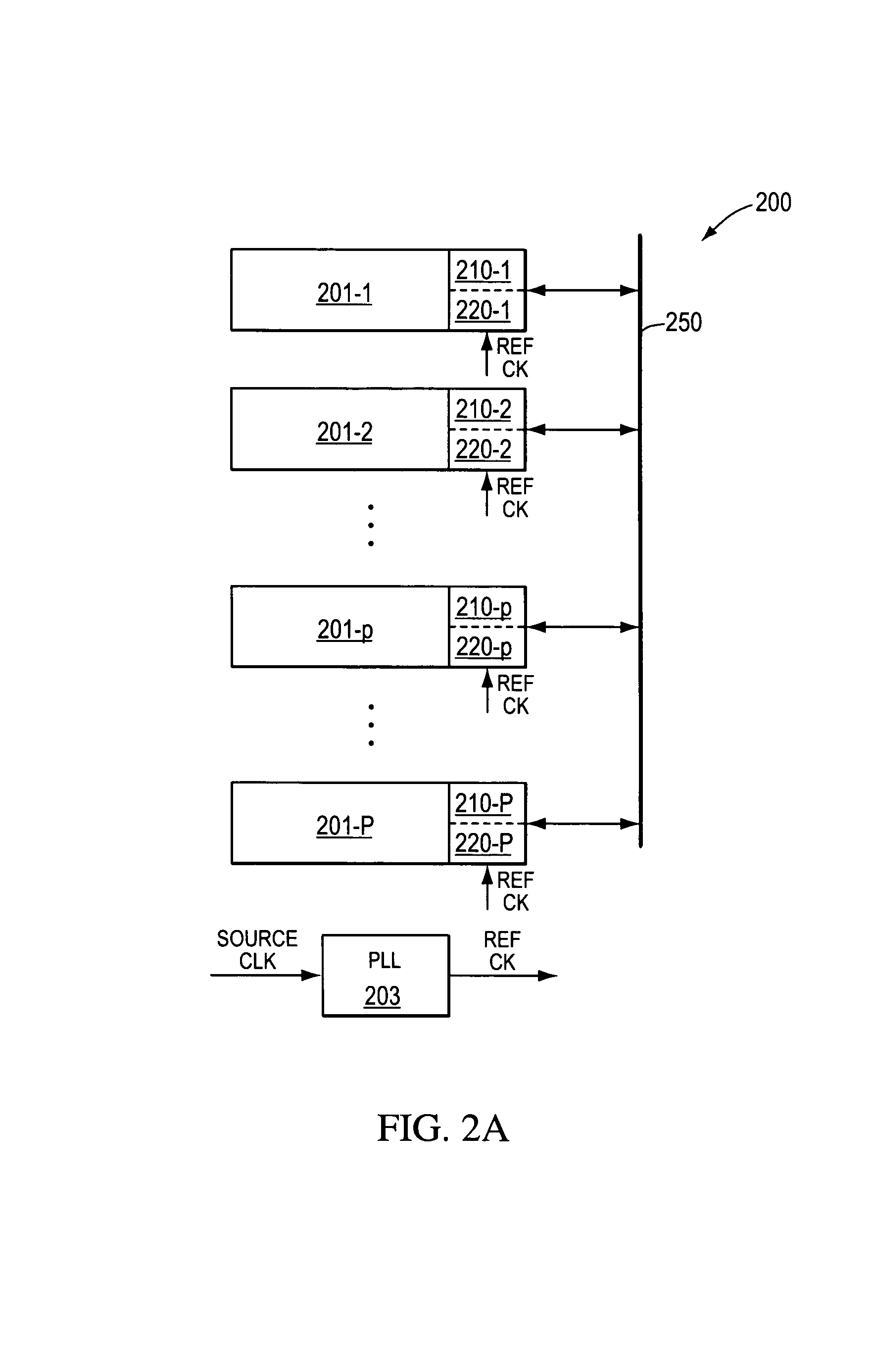
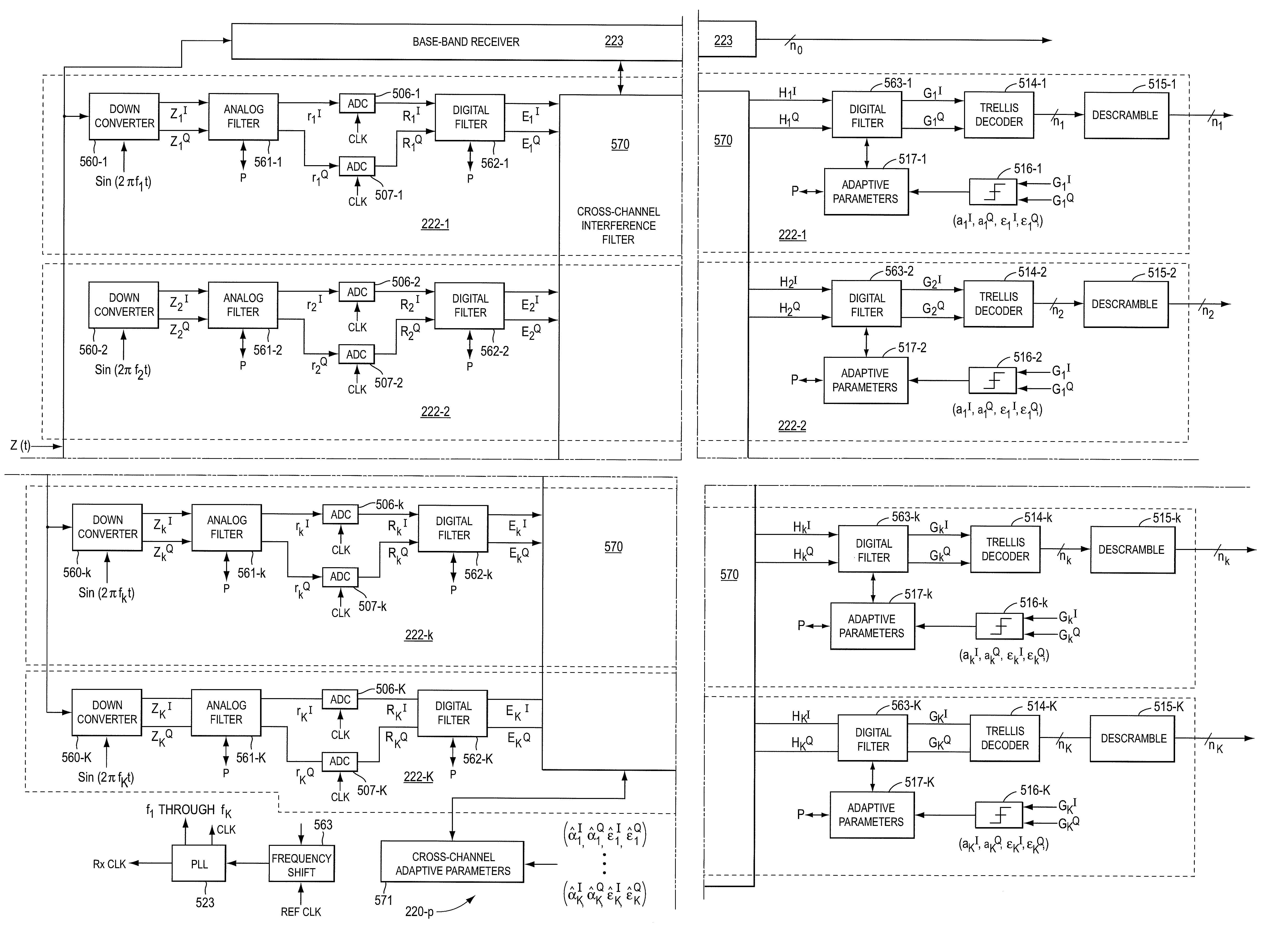
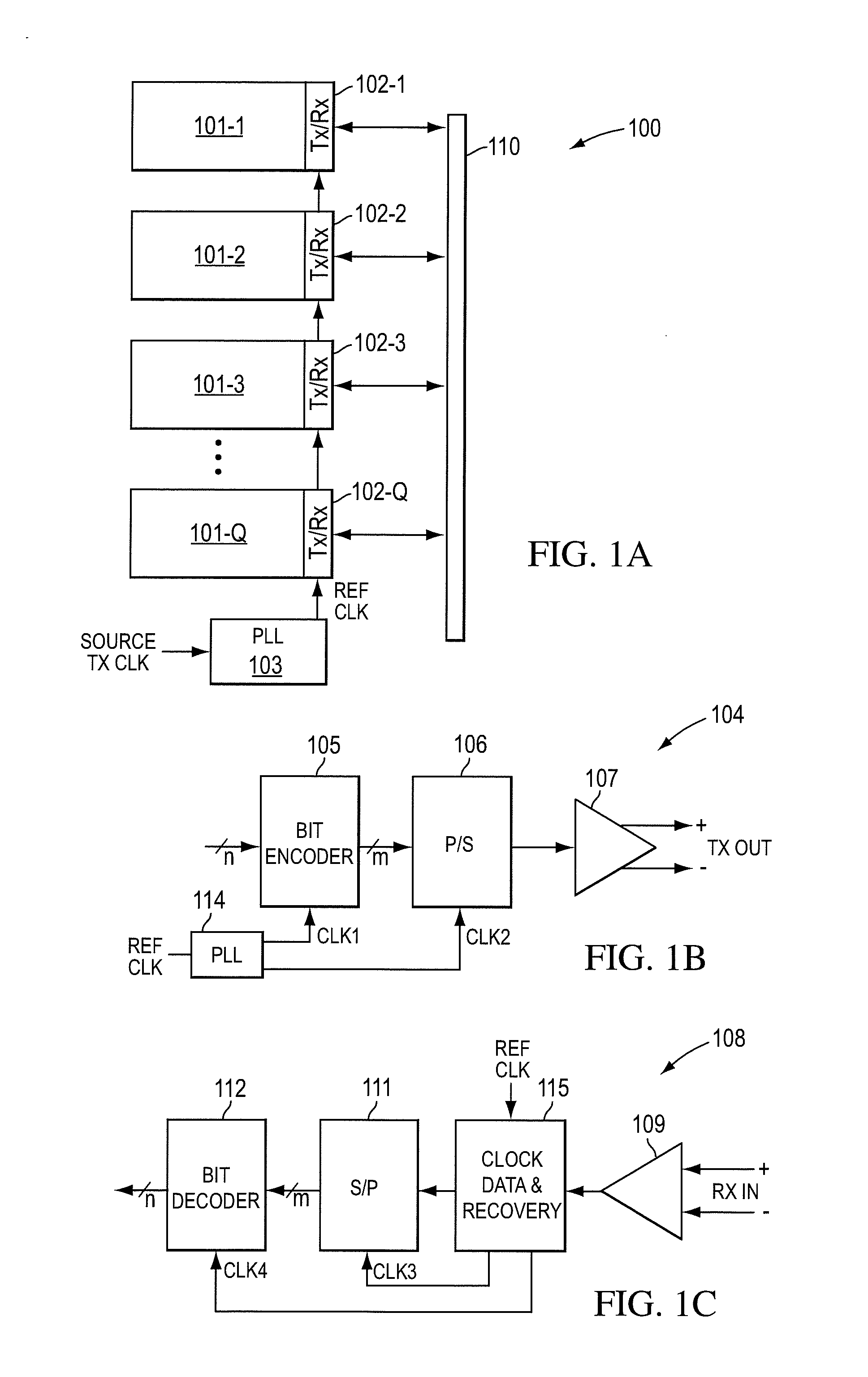
InactiveUS7236757B2Reduce Intersymbol InterferenceImprove data transfer rateSpatial transmit diversitySecret communicationCommunications systemTransceiver
A communication system is disclosed that allows high data-rate transmission of data between components. N-bit parallel data is transmitted in K-frequency separated channels on the transmission medium so as to fully take advantage of the overall bandwidth of the transmission medium. Additionally, a cross-channel interference filter in a receiver section corrects for cross-channel interference in the communication system. As a result, a very high data-rate transmission can be accomplished with low data-bit transmission on individual channels. A transmitter system and a receiver system are described for the communication system.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
Multi-channel communications transceiver
InactiveUS7403752B2Reduce Intersymbol InterferenceImprove data transfer rateResonant long antennasSpatial transmit diversityBaseband receiverEngineering
A transceiver system according to the present invention transmits data utilizing the baseband and one or more frequency separated transmission bands. A baseband transmitter is combined with one or more transmitters that transmit data into one of the frequency separated transmission bands. A baseband receiver is combined with one or more receivers that receive data from the frequency separated transmission bands. Any combination of modulation systems can be utilized (e.g. PAM for the baseband and QAM for the frequency separated bands). A transceiver circuit or chip according to the present invention includes a transmitter and a receiver and communicates with a corresponding transceiver chip. In some embodiments, one baseband PAM transmitter is combined with one frequency separated QAM transmitter.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
Non-linear equalizer system and method
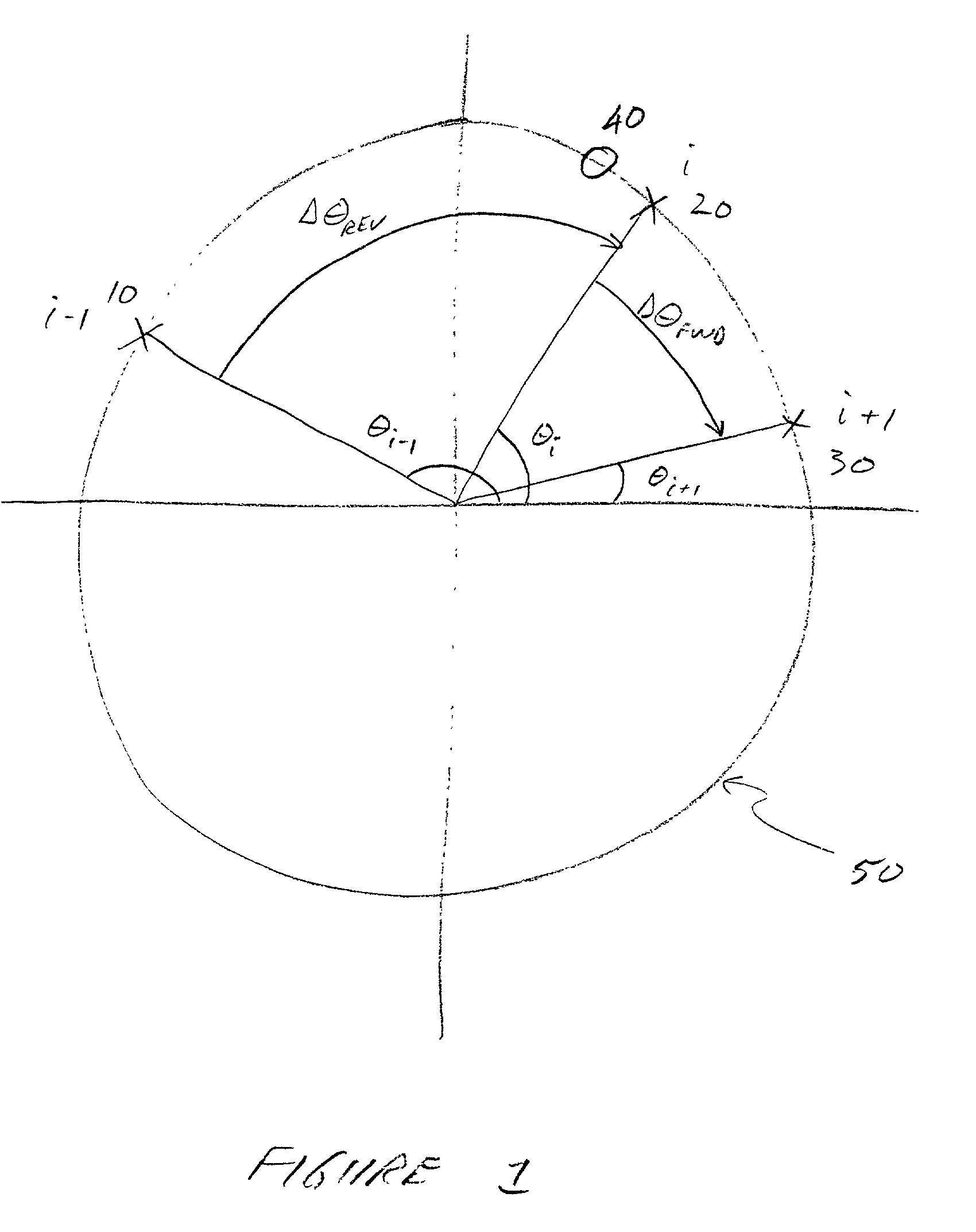
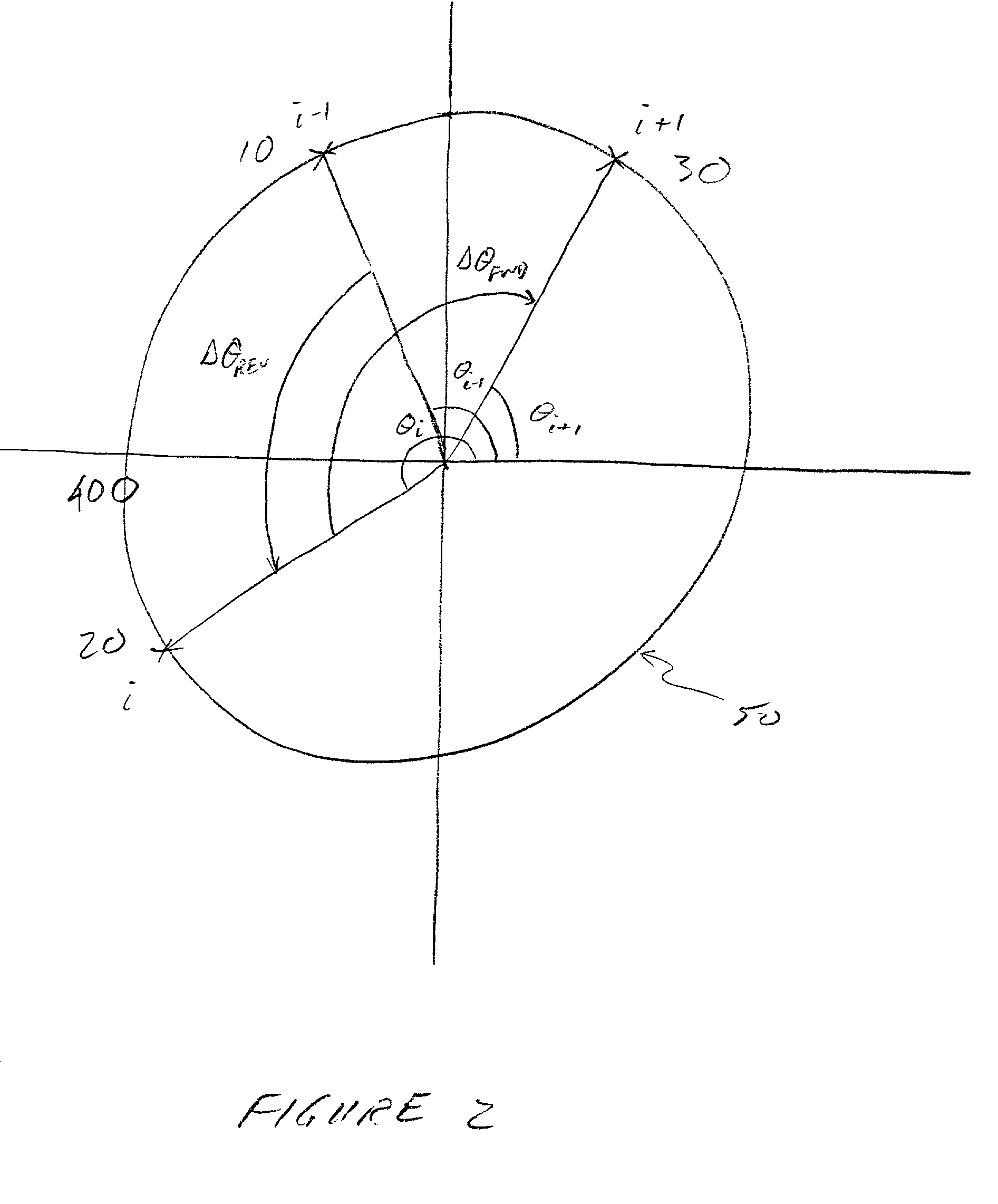
ActiveUS7031382B2Reduce distortionReduce Intersymbol InterferenceMultiple-port networksError preventionPhysicsPhase shifted
A system and method for compensating for angular distortion of a received waveform is disclosed. One embodiment measures the angular position of a current symbol, the preceding symbol and the succeeding symbol, calculates the phase shift between the current symbol and a preceding symbol and the phase shift between the current symbol and a succeeding symbol, uses the phase shifts to enter a 2-D lookup table to extract a phase correction factor, then uses the phase correction factor to modify the angular position of the current symbol.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMMUNICATIONS INC
Time error estimation for data symbols
ActiveUS20100166050A1Reduce Intersymbol InterferencePromote resultsError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionTime errorTransport system
The invention relates to a method and a system for estimating a symbol time error in a broadband transmission system, comprising: determination a timing error signal of an input-signal of a discrete Fourier-transformation block (5) in a data symbol stream on the basis of intersymbol correlation using a predetermined period in each received symbol, selecting as a predetermined period a number of samples of different useful data parts of a symbol, determining the time error value (ε) based on the intersymbol interference of the selected samples of the different parts of said symbol.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
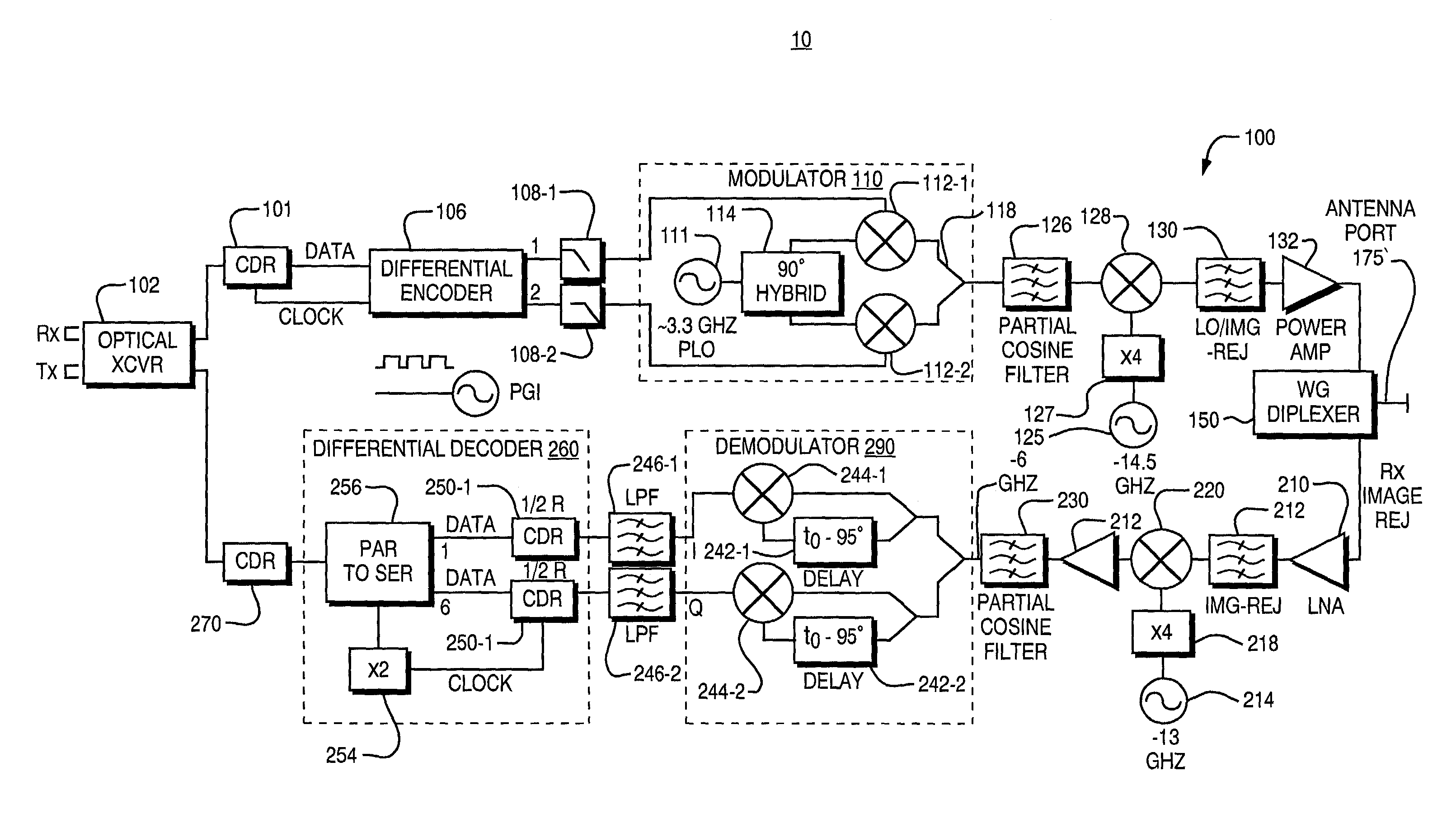
Architecture for wireless transmission of high rate optical signals
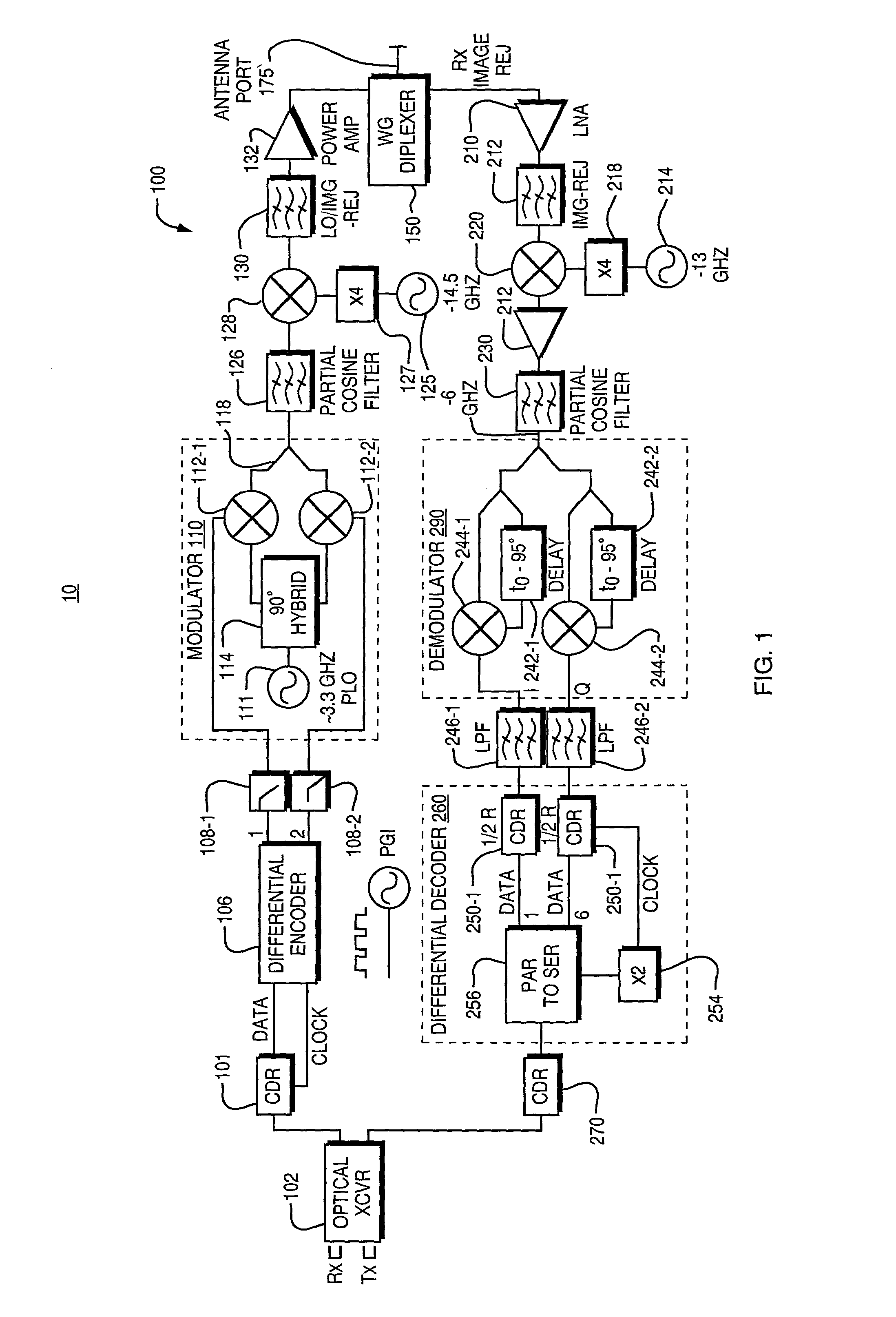
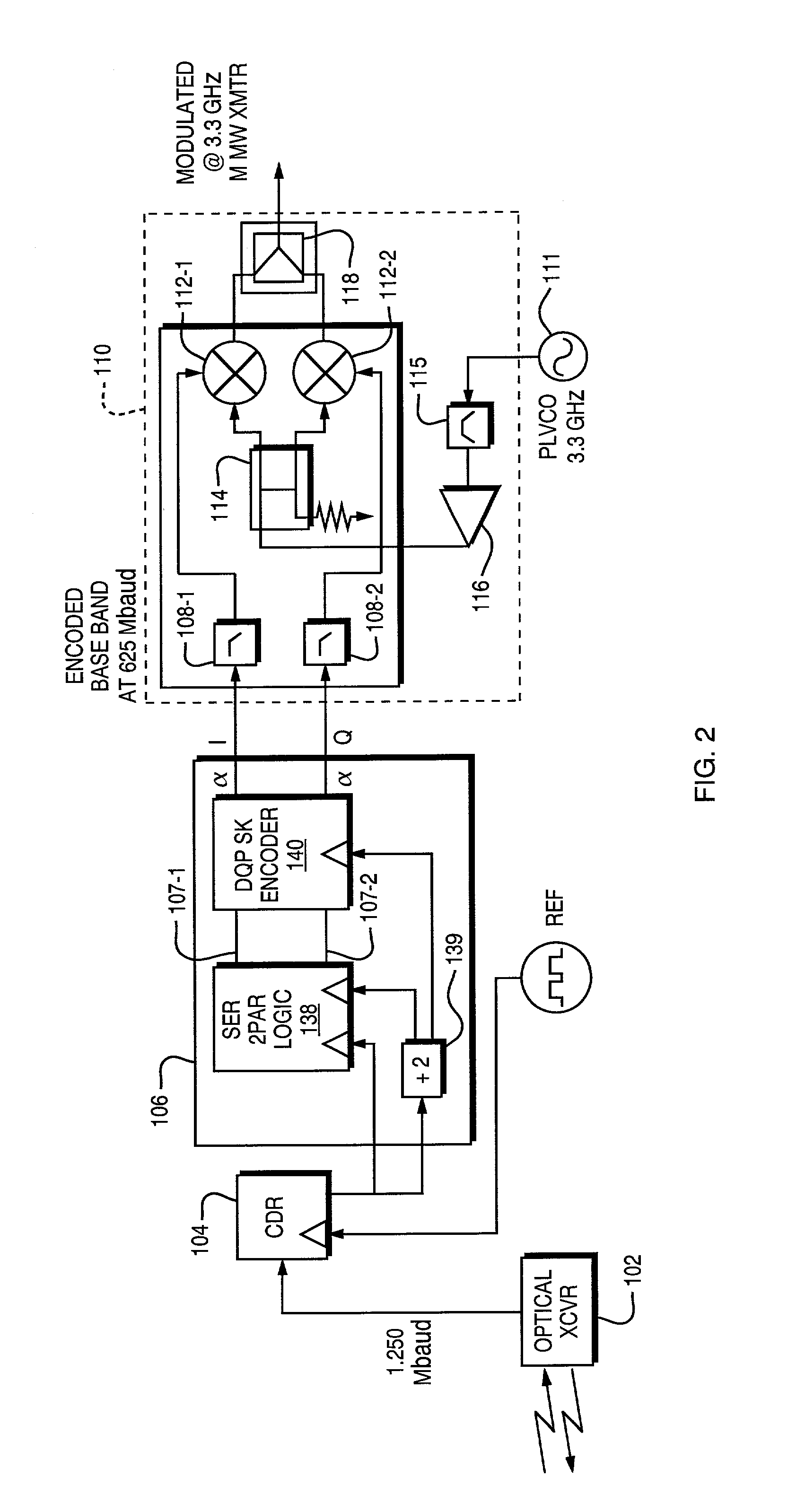
InactiveUS7103279B1Minimize intersymbol interferenceReduce noiseLine-of-sight transmissionElectromagnetic transmittersFiberHigh rate
An apparatus for a wireless transmission of high data rate signals such as received from an optical interface including gigabit fiber channel or a sonet. The architecture combines direct detection of the optical signal with clock and data recovery circuit and a differential signal encoder which is preferably a differential quadrature phase shift encoder and modulator pair. A millimeter wave, local oscillator and up conversion chain converts the optical input signal to a microwave carrier. In the opposite direction, the down converted signal is non-coherently phase detected and fed to a pair of synchronized clock and data recovery circuits to recover I and Q channel signals. These recovered signals are then combined prior to re-timing before they are fed back to the optical transceiver.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO
Neural network equalization method used for indoor visible light communication system
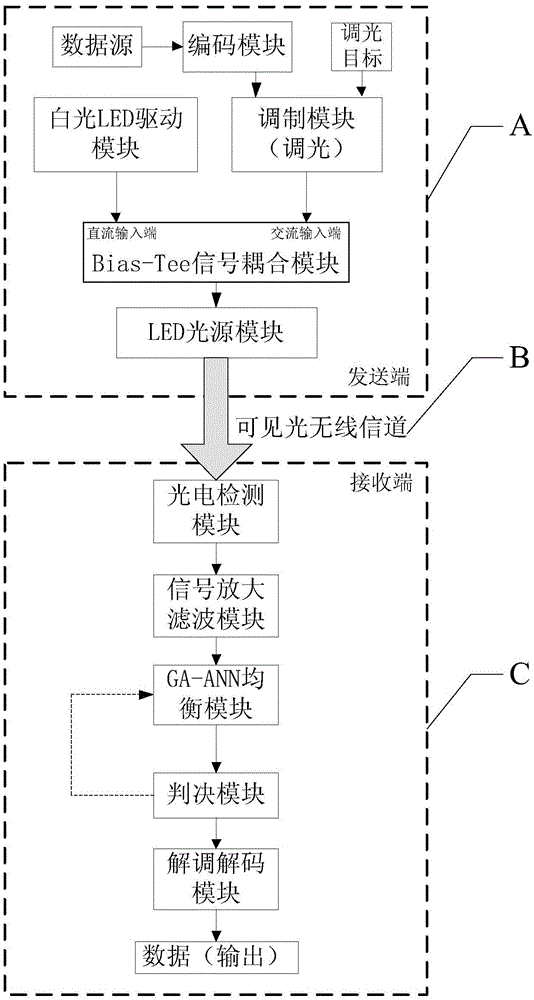
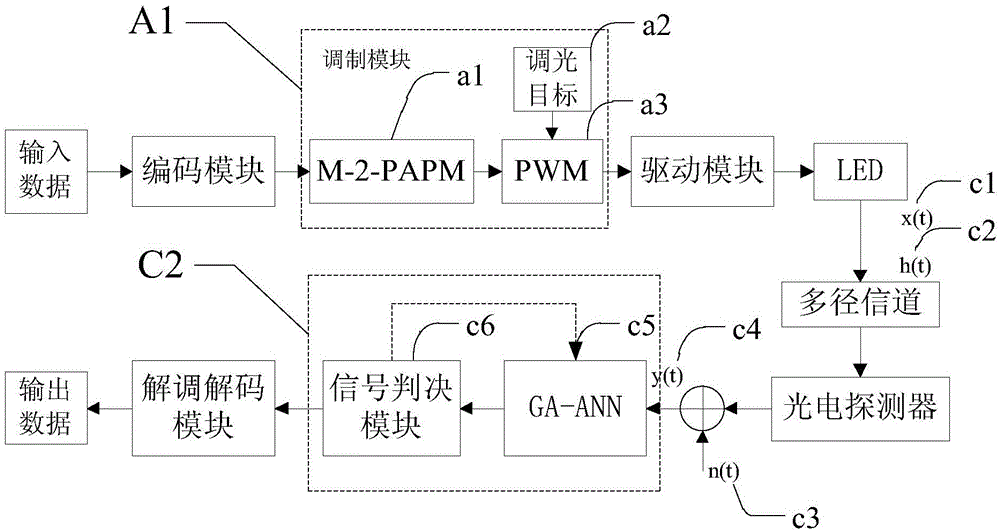
ActiveCN105007118AReduce Intersymbol InterferenceReduce bit error rateClose-range type systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksError functionVisible light communication
The invention provides a neural network equalization method used for an indoor visible light communication system, and belongs to the visible light wireless communication technology field. The method includes the steps: utilizing a ceiling bounce model to calculate a VLC channel impulse response, carrying out photoelectric conversion for a visible light power signal received by a receiving end, and sending a sequence to a neutral network channel equalizer after amplification sampling; utilizing a heredity algorithm to optimize initialization weights and thresholds among neurons, establishing a neural network for training, and minimizing an error function; and judging an output, restoring the sent sequence, and finally achieving an equalization purpose. According to the scheme, interference among codes is obvious minimized, an error rate is reduced, the communication quality is further improved, a transmission rate that the system can reach is increased, the training time is shortened, and the system complexity is reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Apparatus and method for spreading/despreading data using pair of child orthogonal variable spreading factor codes
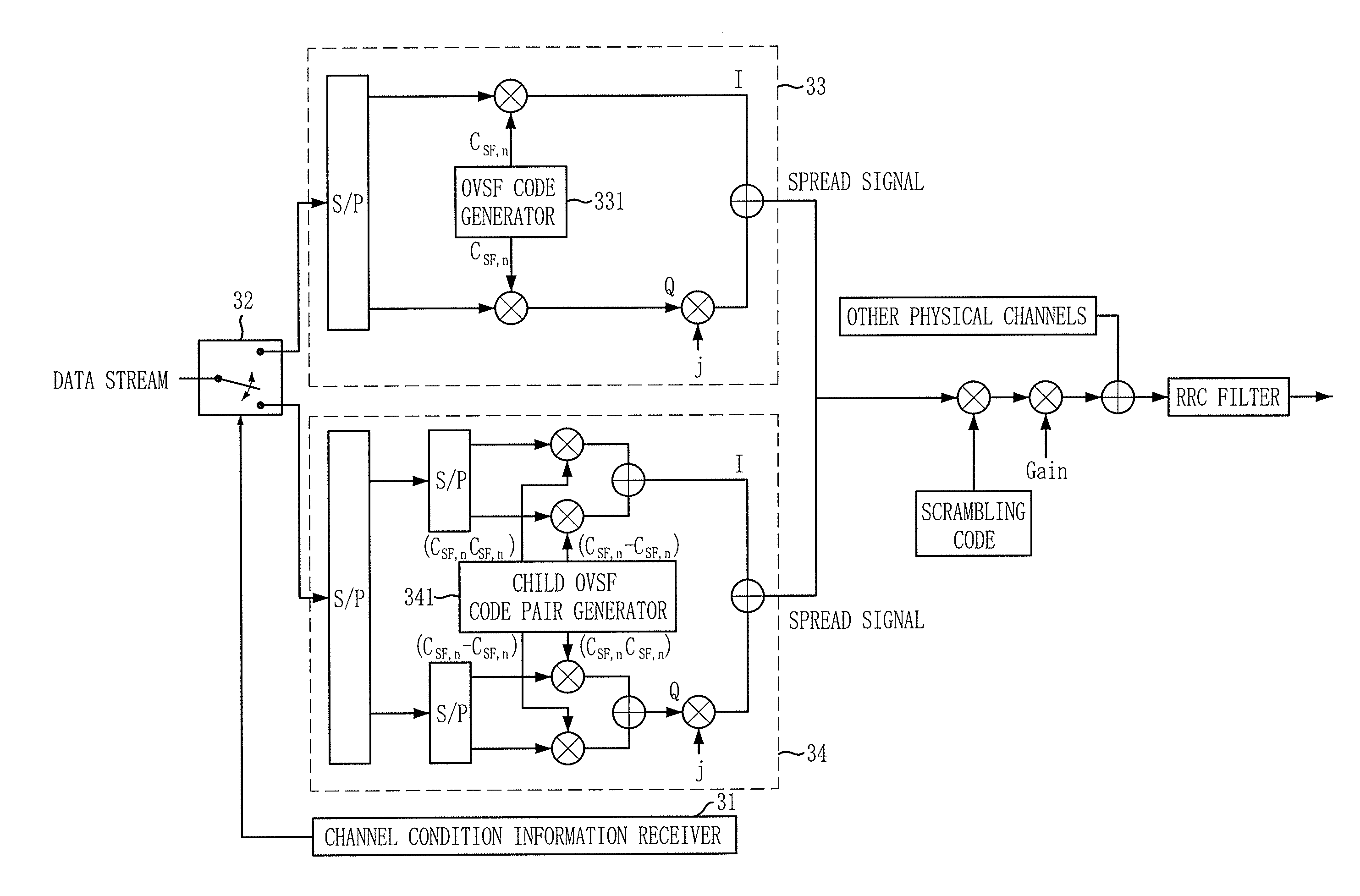
InactiveUS20080130716A1Enhanced signalReduce Intersymbol InterferenceAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAngle modulationData streamEngineering
there is provided a spreading apparatus using a child orthogonal variable spreading factor (OVSF) code pair, including: a channel condition information receiving unit for receiving channel condition information including a channel condition metric; a switch controlling unit for receiving the channel condition information from the channel condition information receiving unit and transferring data stream according to the received channel station information; a first spreading unit for receiving the data stream from the switching controlling unit, and spreading the data stream using a single OVSF code; and a second spreading unit for receiving the data stream from the switching controlling unit, and spreading the data stream using a child OVSF code pair.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Sub-optimal iterative receiver method and system for a high-bit-rate CDMA transmission system
ActiveUS7298778B2Close to optimum performanceHigh order modulationError preventionOther decoding techniquesSpread factorSpreading factor
A reception method and receiver structure that are relatively simple, that have close to optimum performance, and that use high order modulation combined with a low spreading factor are disclosed. The method receives a signal transmittal in the form of sequences of coded binary symbols comprising both predefined pilot symbols and date symbols multiplied by a spreading sequence. The method also includes a step of determining a channel estimate using received predefined pilot symbols. A system for receiving a signal transmitted on a multipath transmission channel using a spread spectrum technique and low spreading factor is also disclosed.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
Technique for adaptive multiuser equalization in code division multiple access systems
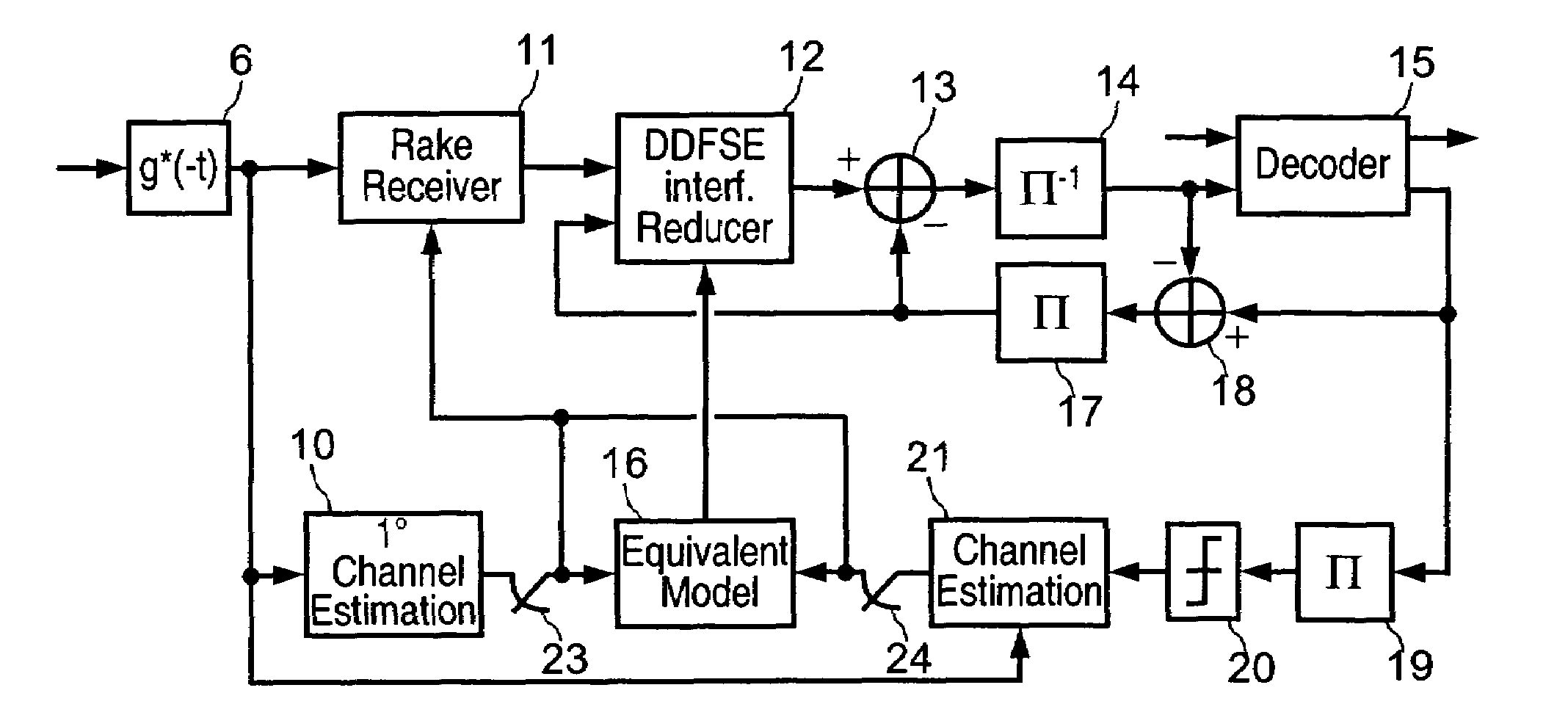
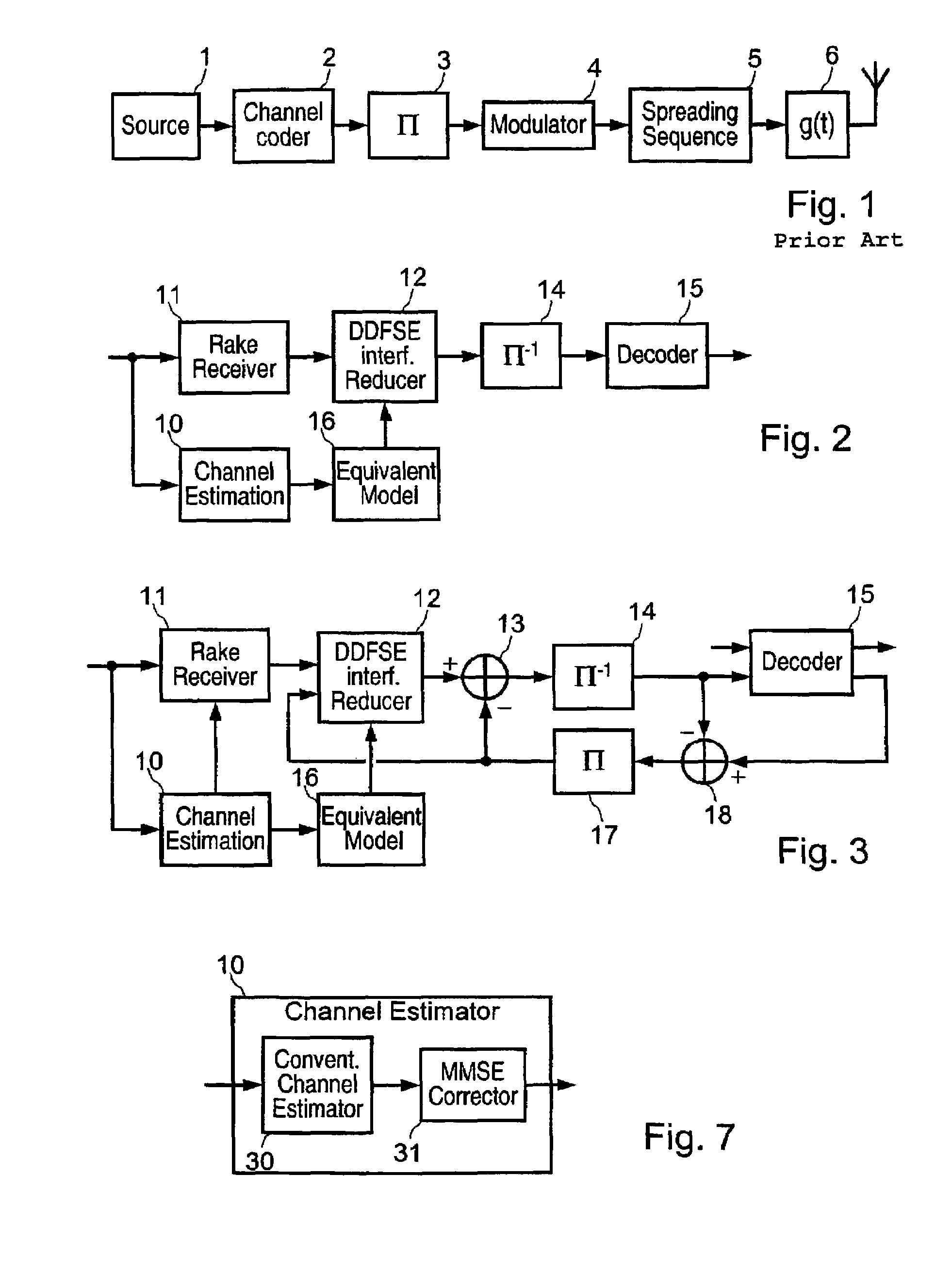
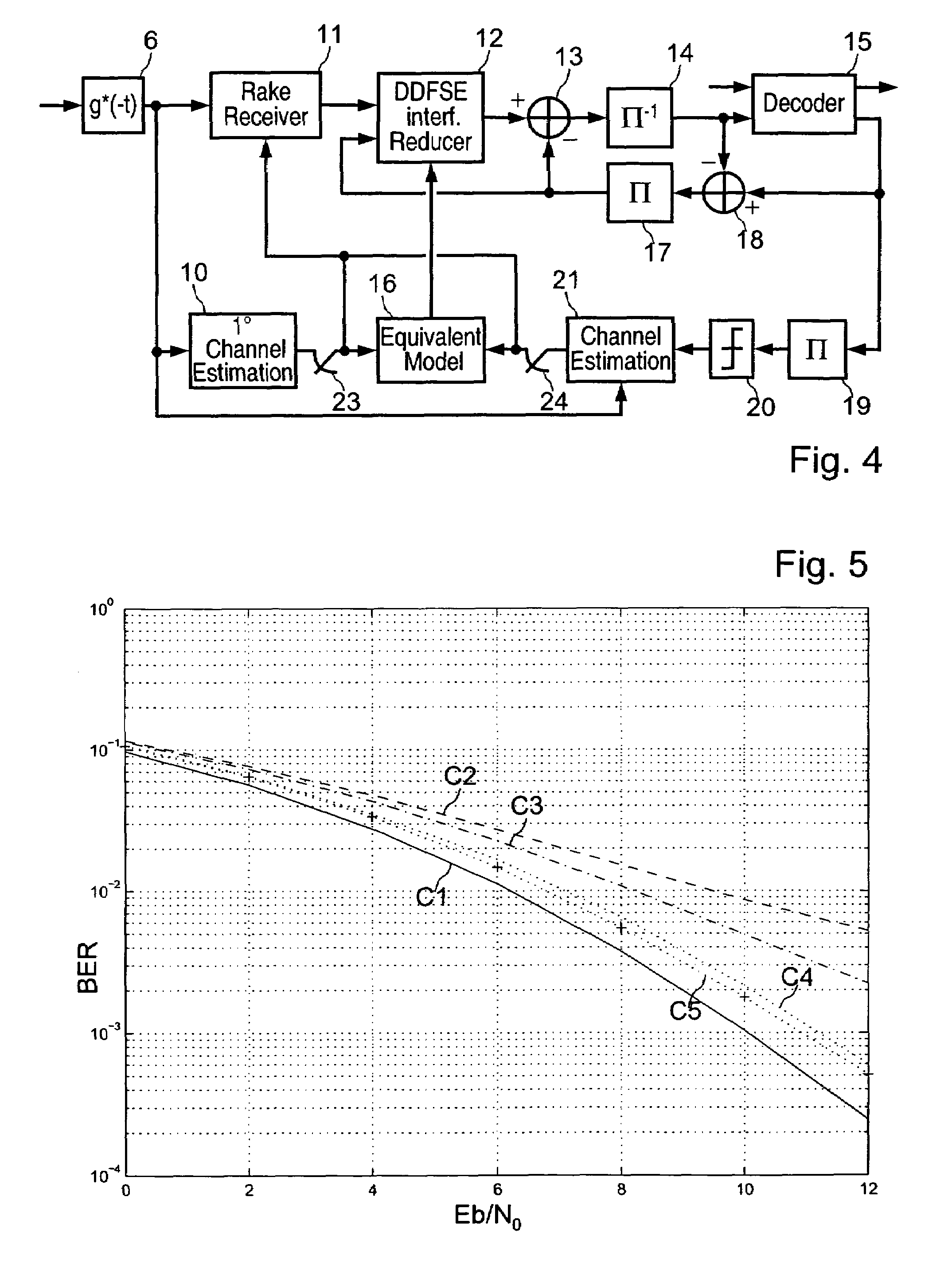
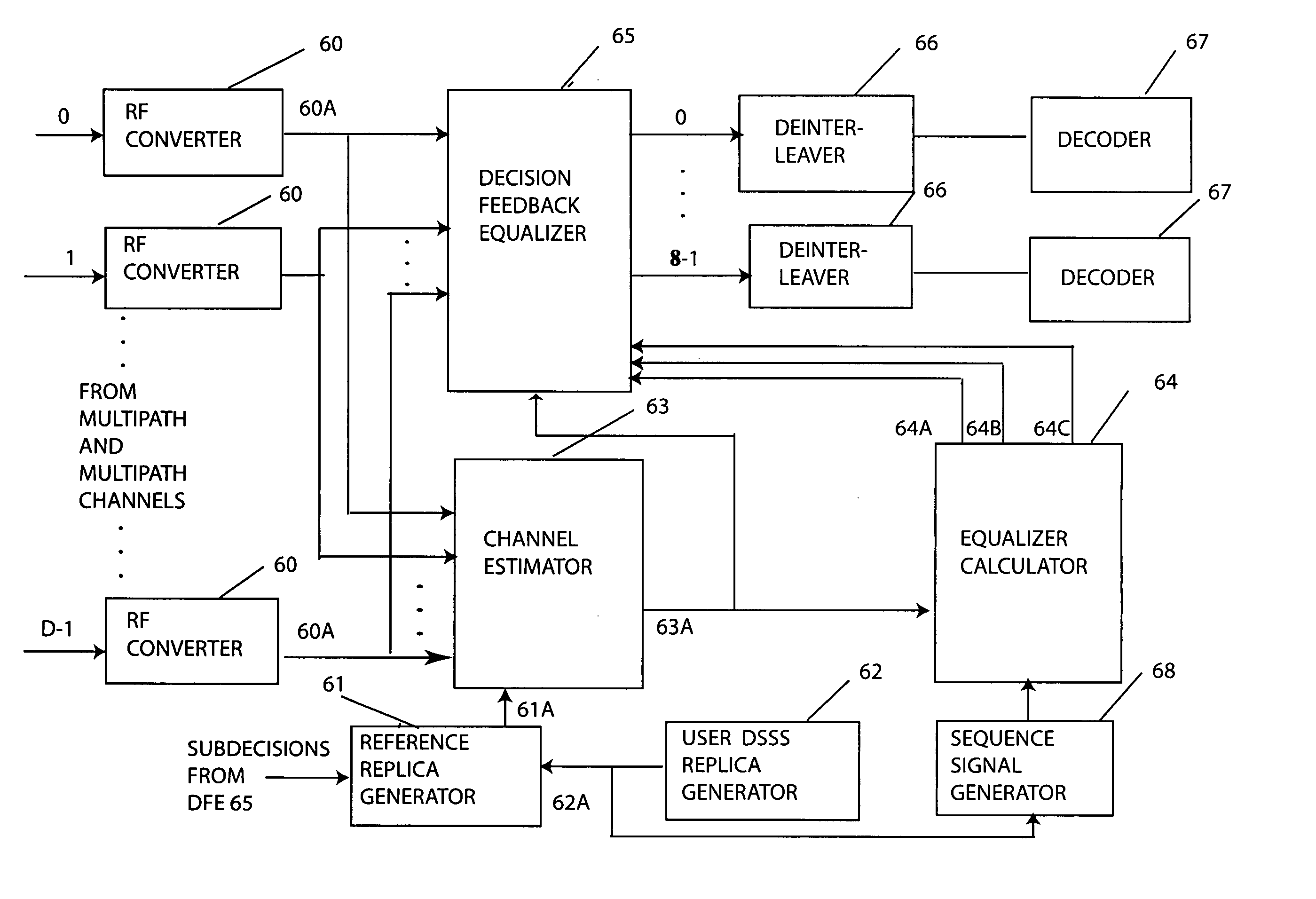
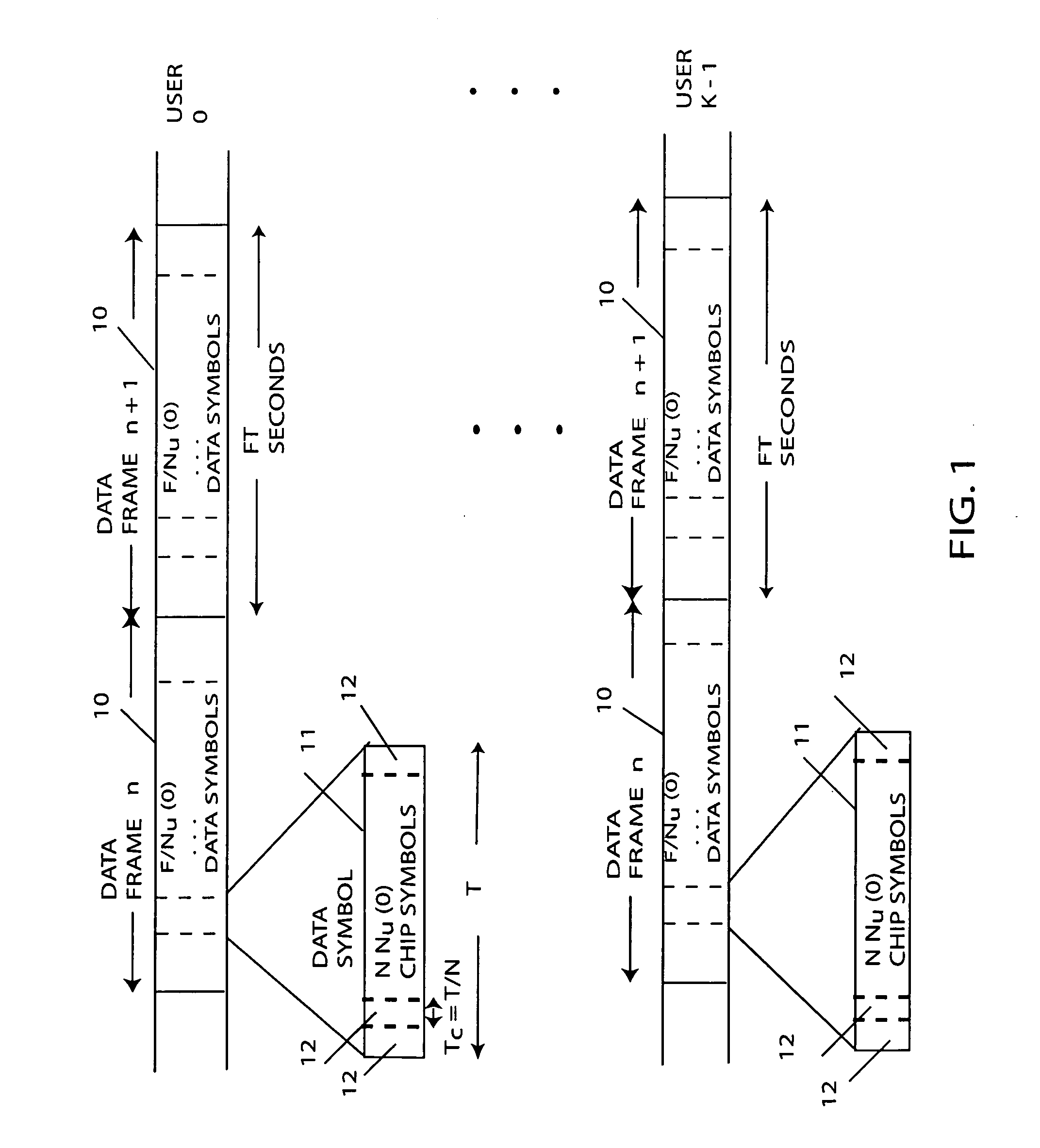
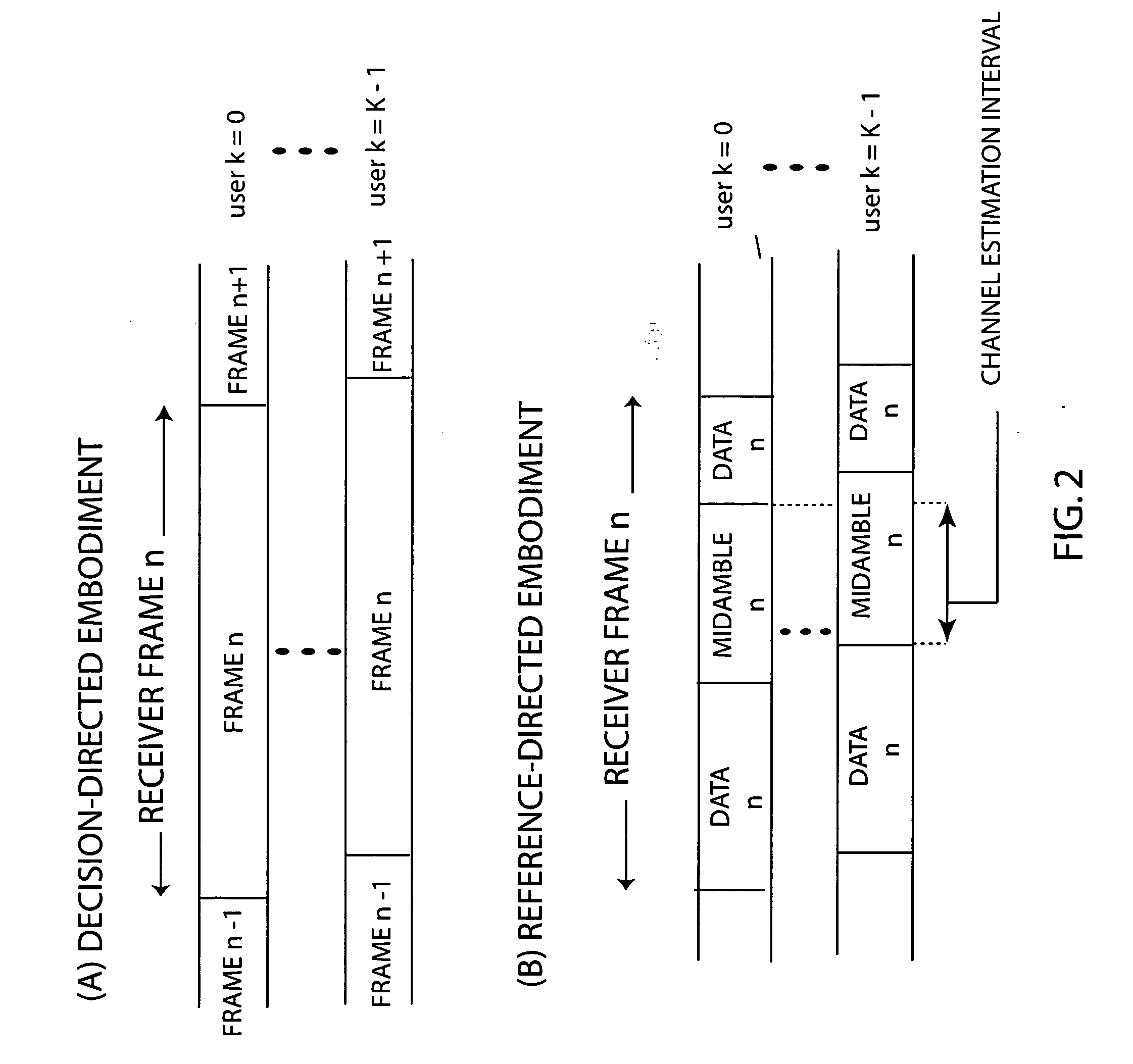
InactiveUS20050207477A1Quality improvementFast convergenceSpatial transmit diversityWireless commuication servicesDigital dataSequence signal
A radio communication method and system for transmitting multiple-user digital data information in a Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) format over multipath and mutual-interfering channels to a receiving terminal with diversity antennas and equalization signal processing. At the receiving terminal, diversity antenna signals are grouped into time blocks and replicas are generated of the user-unique CDMA sequence signals for a set of K mutually interfering users. Within each time block the multiuser channel is estimated, equalization parameters are calculated, and decision-feedback equalization is used to produce multiuser estimates associated with a subset λ of the K users. These estimates are deinterleaved and error-correction decoded to recover transmitted digital data information for the subset of λ users. The invention includes embodiments for a CDMA sequence period that is equal to or longer than the transmitted data symbol interval with applications to current CDMA reverse link and forward link standards. Also embodiments for both decision-directed and reference-directed channel estimation are given.
Owner:MONSEN PETER
Automatic gain control method and control circuit suitable for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFM) system
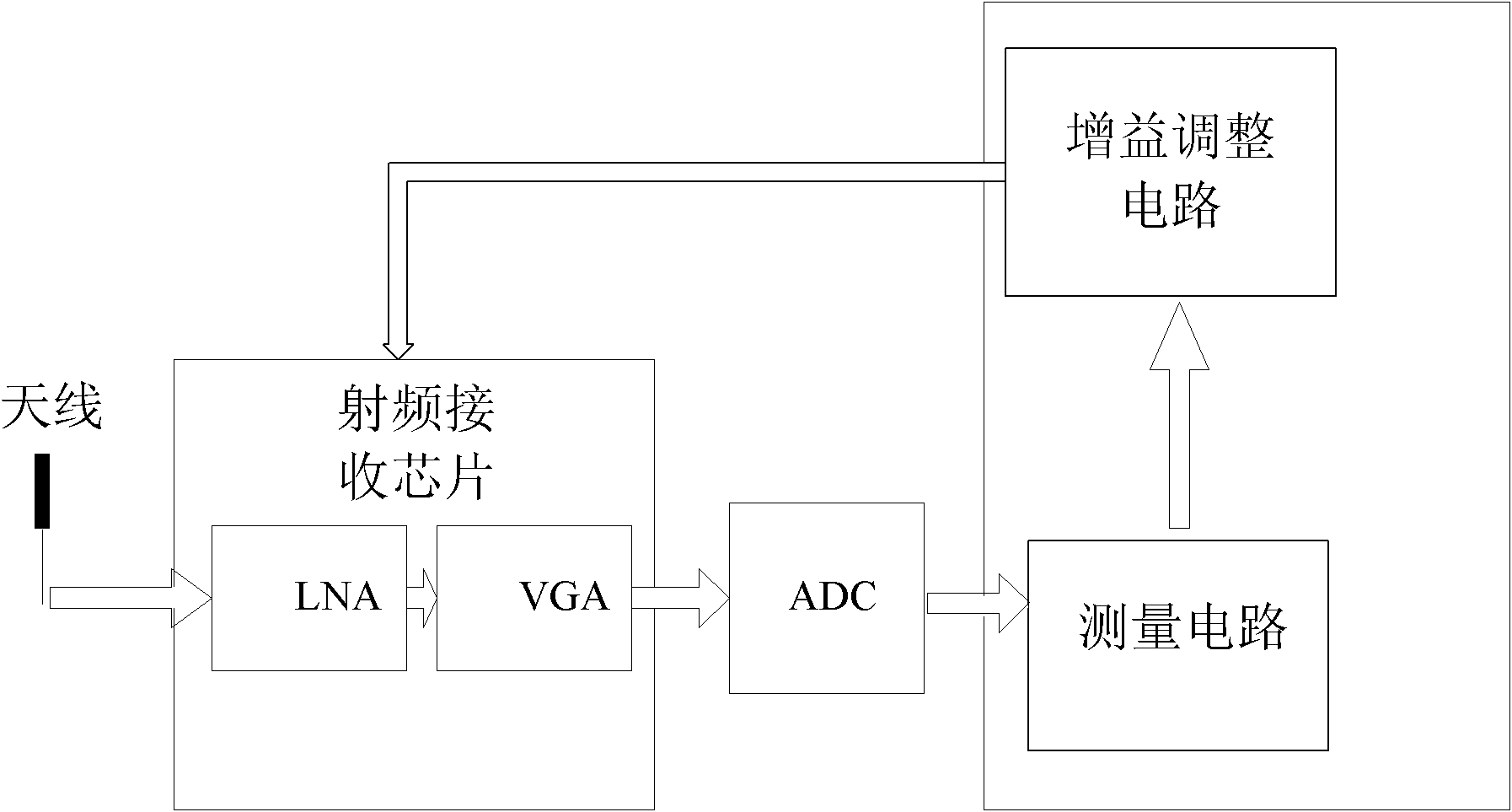
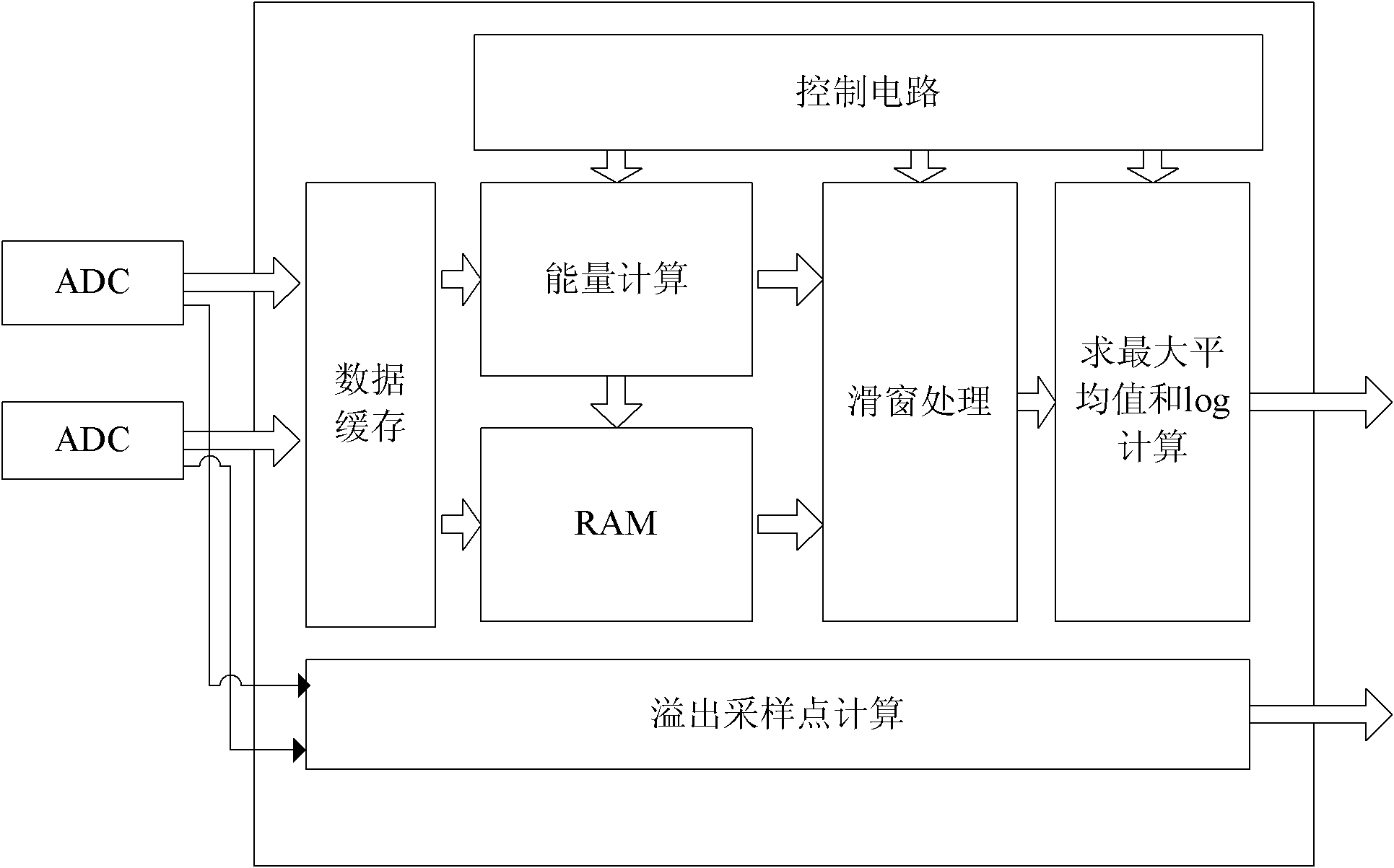
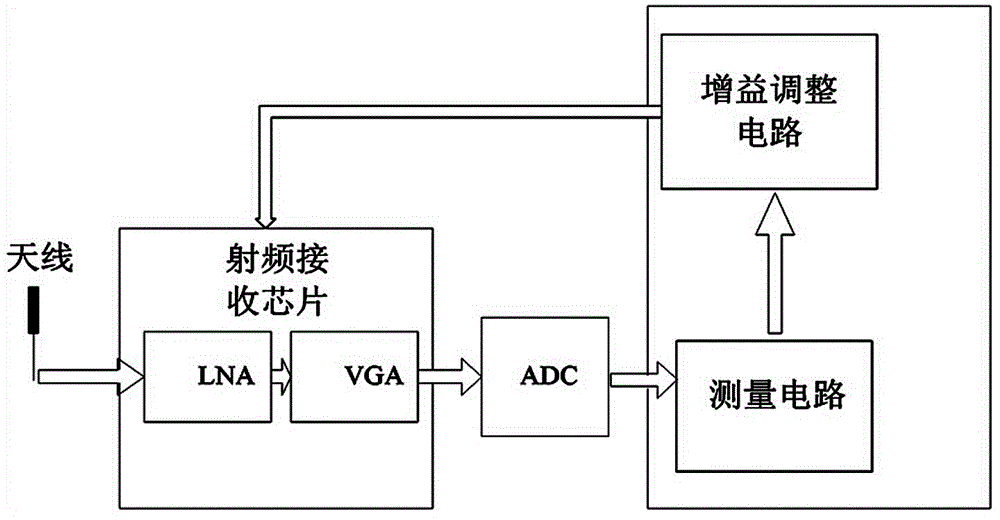
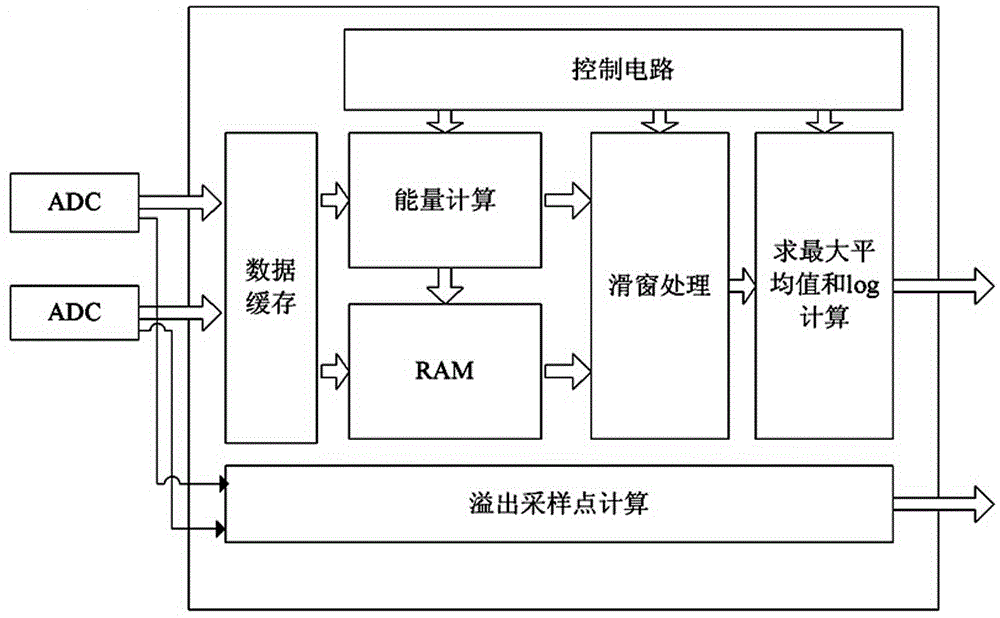
InactiveCN101964774ASimplified Computational ComplexityStrong lockPower managementMulti-frequency code systemsSlide windowReceived signal strength indication
The invention discloses an automatic gain control method and an automatic gain control circuit which are suitable for an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFM) system. The method comprises the following steps of: measuring a baseband signal; and adjusting gain. Slide window processing is performed during signal measuring so as to average signal energy in a window. A gain adjustment algorithm determines reasonable gain of the next adjustment period through conditions such as the gain of an upper frame, a measured value of the upper frame, the number of overflow sampling points, the receiving signal intensity indication on the current antenna and the like. Simultaneously, the gain of a radio frequency receiving chip is changed by circulating prefix time so as to track an OFDM symbol level.
Owner:江西开昂教育股份有限公司
Receiver which demodulates OFDM symbol
InactiveUS7313189B2Reduce Intersymbol InterferenceError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionCarrier signalLatency distribution
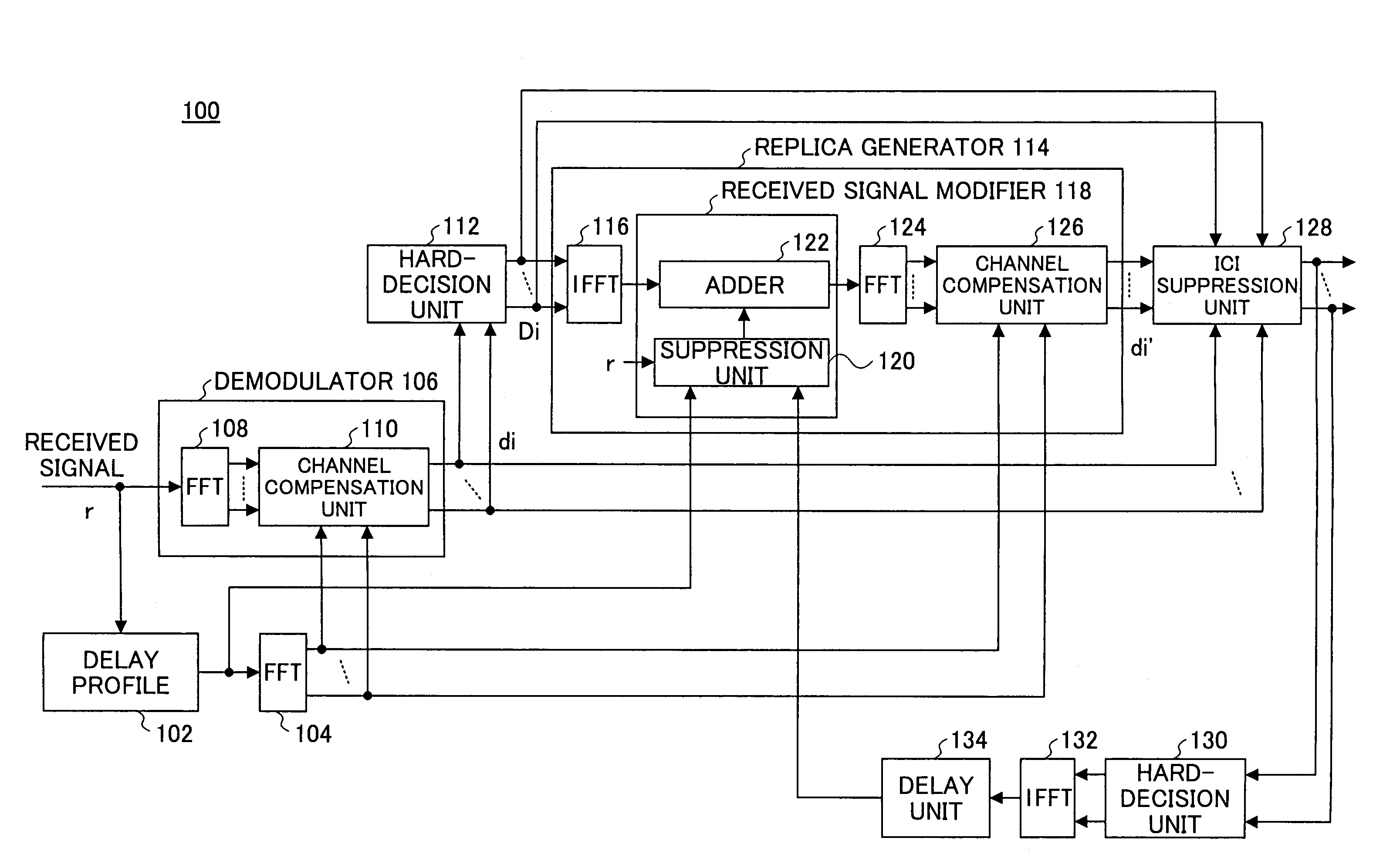
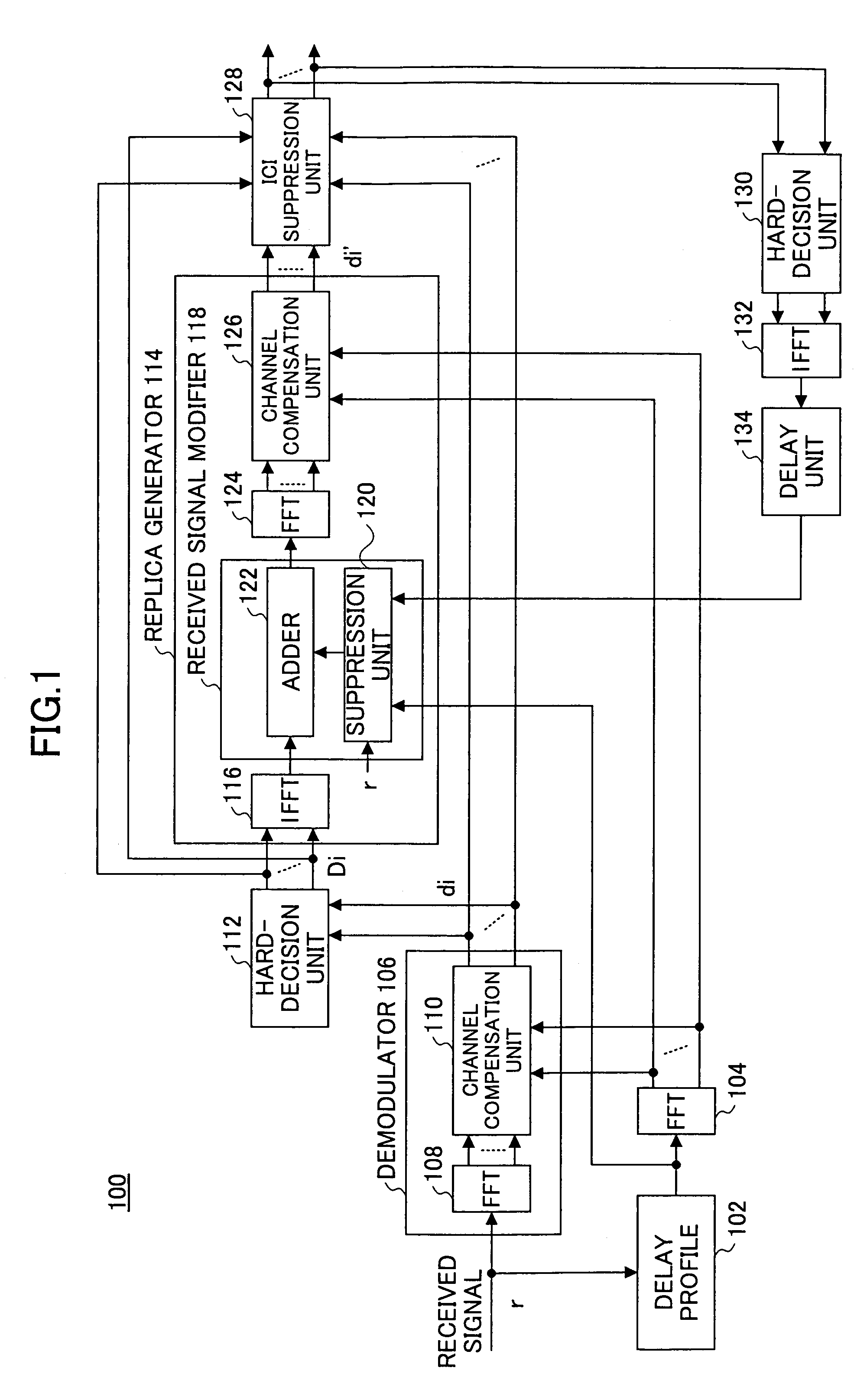
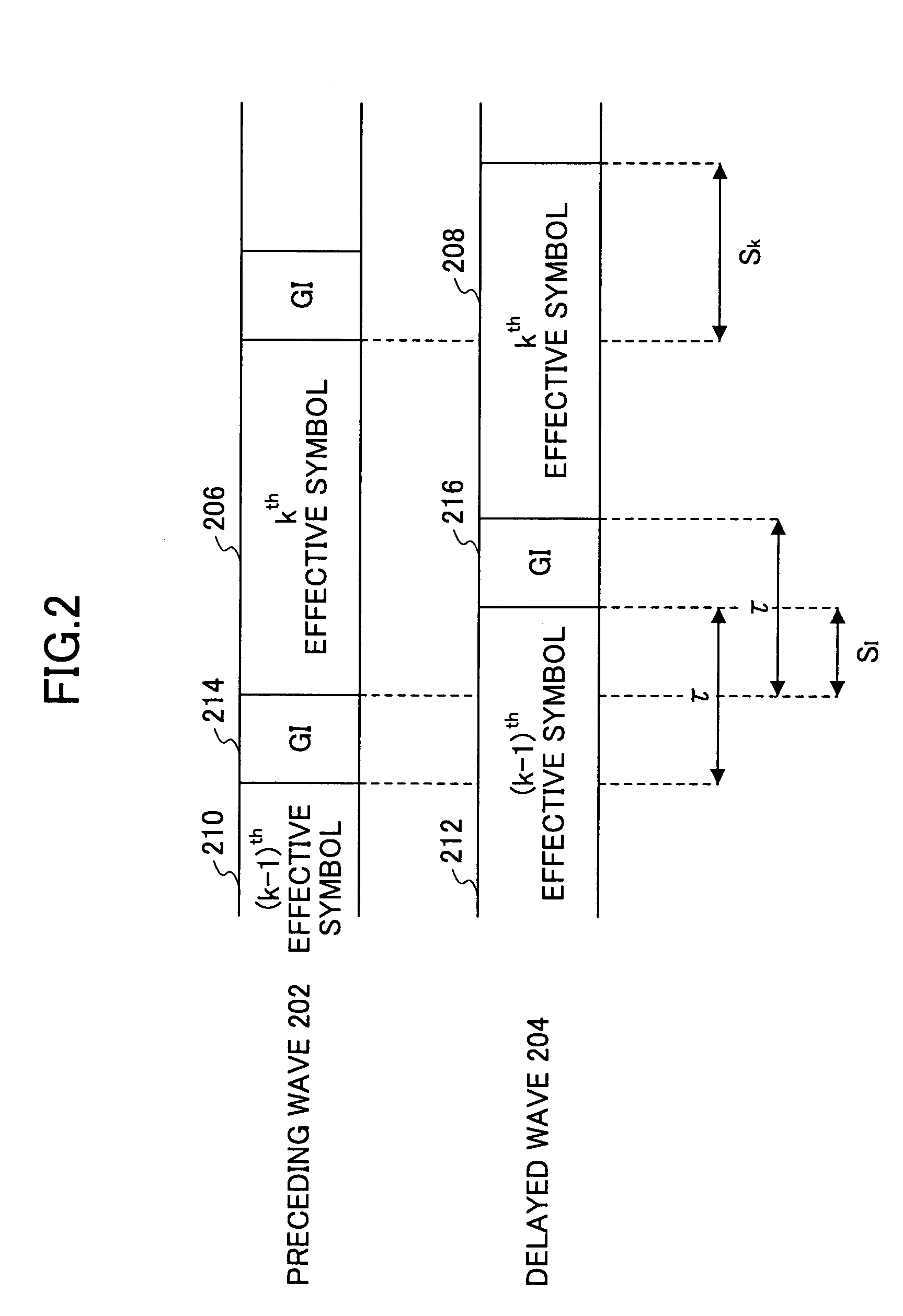
A receiver is disclosed that demodulates an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) symbol transmitted by an OFDM method. The receiver includes a delay profile generation unit that generates a delay profile regarding a preceding wave and a delayed wave included in a received signal, a demodulation unit that demodulates the received signal so as to output a demodulated signal per sub-carrier, a hard-decision unit that makes a hard decision per sub-carrier on a signal point based on the demodulated signal so as to output a hard-decision signal, a replica generation unit that uses the hard-decision signal to generate a replica signal per sub-carrier, and an inter-carrier interference suppression unit that adds a difference between the hard-decision signal and the replica signal to the demodulated signal so as to suppress an inter-carrier interference.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Hybrid adaptive equalizer for optical communications systems
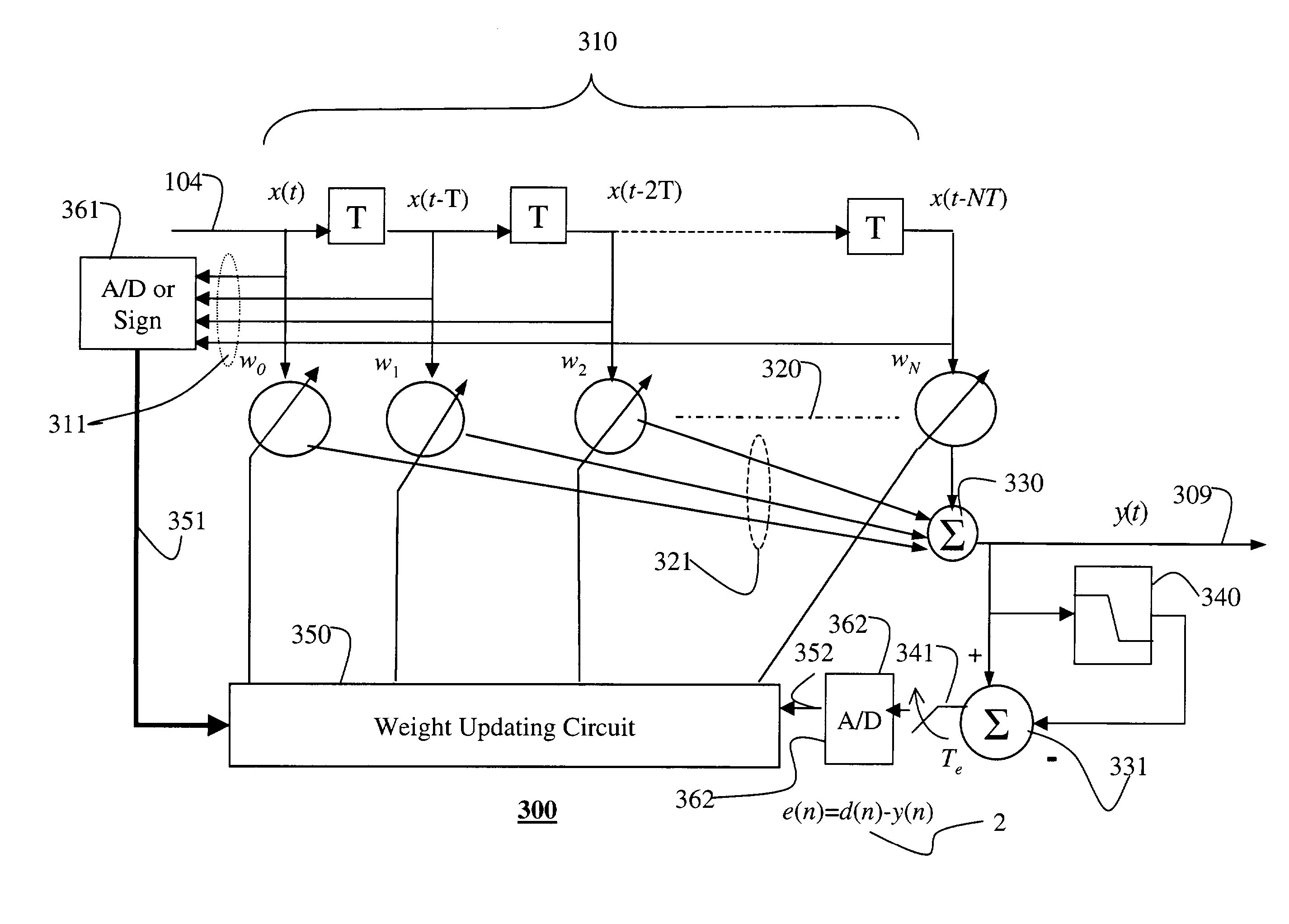
InactiveUS7023912B2Reduce Intersymbol InterferenceEliminate needMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationCommunications systemAnalog delay line
A method equalizes a received signal in an optical communications system. The received signal is passed through an analog delay line where it is tapped to generate a set of delayed copies of the received signal. In a set of analog multipliers, each delayed copy of the received signal is multiplied by a corresponding weight to generate a set of weighted signals that are then summed to produce an output signal. The output signal is thresholded and subtracted from the output signal to produce an error signal, which is periodically sampled. In a digital weight updating circuit, the weights are produced from digitized versions of the sampled error signal and samples of the delayed copies of the received signal.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
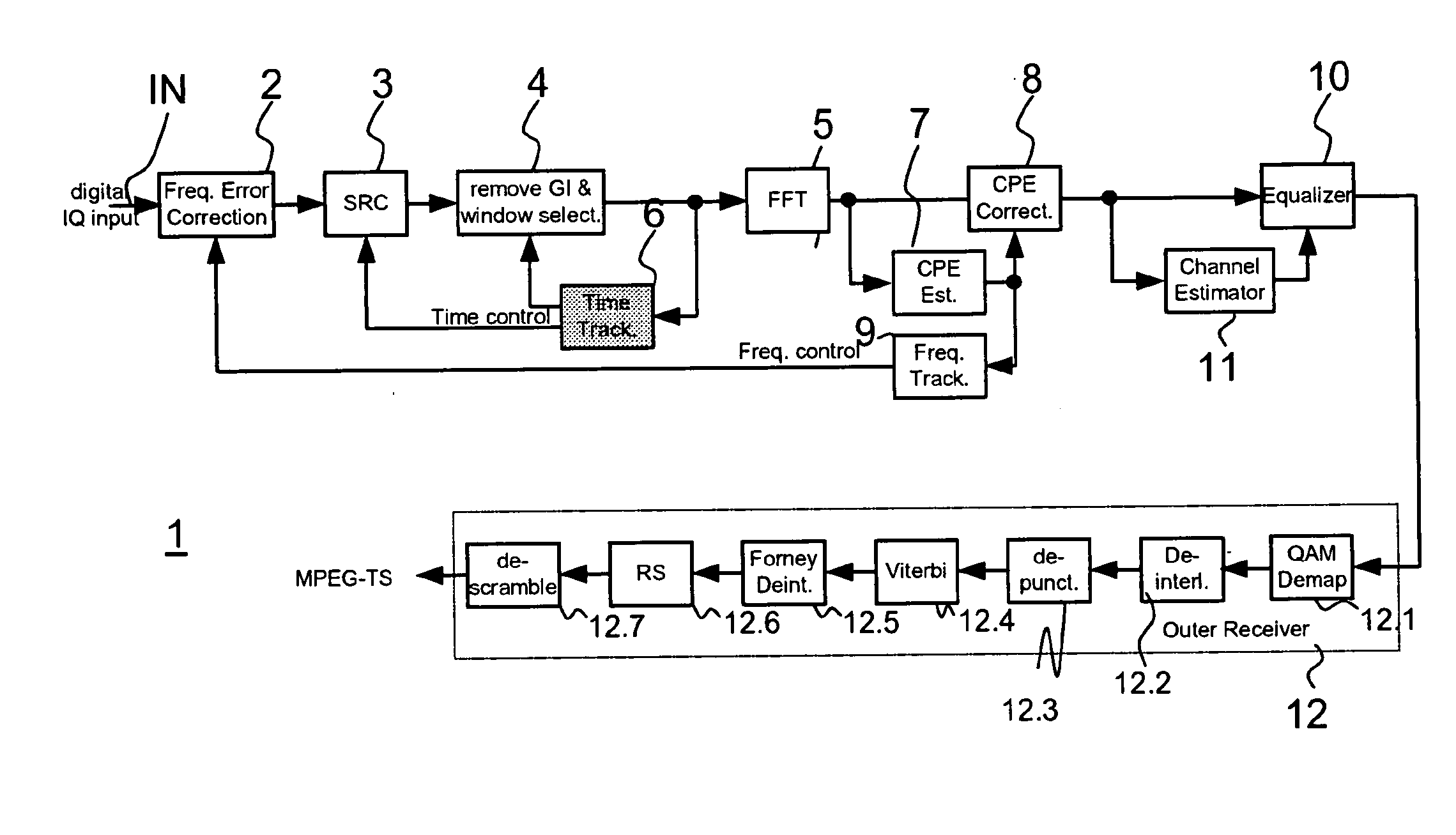
System and method for ISI based adaptive window synchronization
InactiveUS8340234B1Reduce Intersymbol InterferenceReduce transmissionError preventionModulated-carrier systemsSelf adaptiveComputer science
This disclosure is directed to systems and methods for positioning a FFT window using the noise power that is related to ISI By selecting a FFT window position that minimizes the noise power, ISI is reduced or eliminated The techniques can be used in coherent and non-coherent systems Further, noise associated with the Doppler effect is compensated for, allowing the use of these system and methods in time-varying environments, such as mobile applications.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
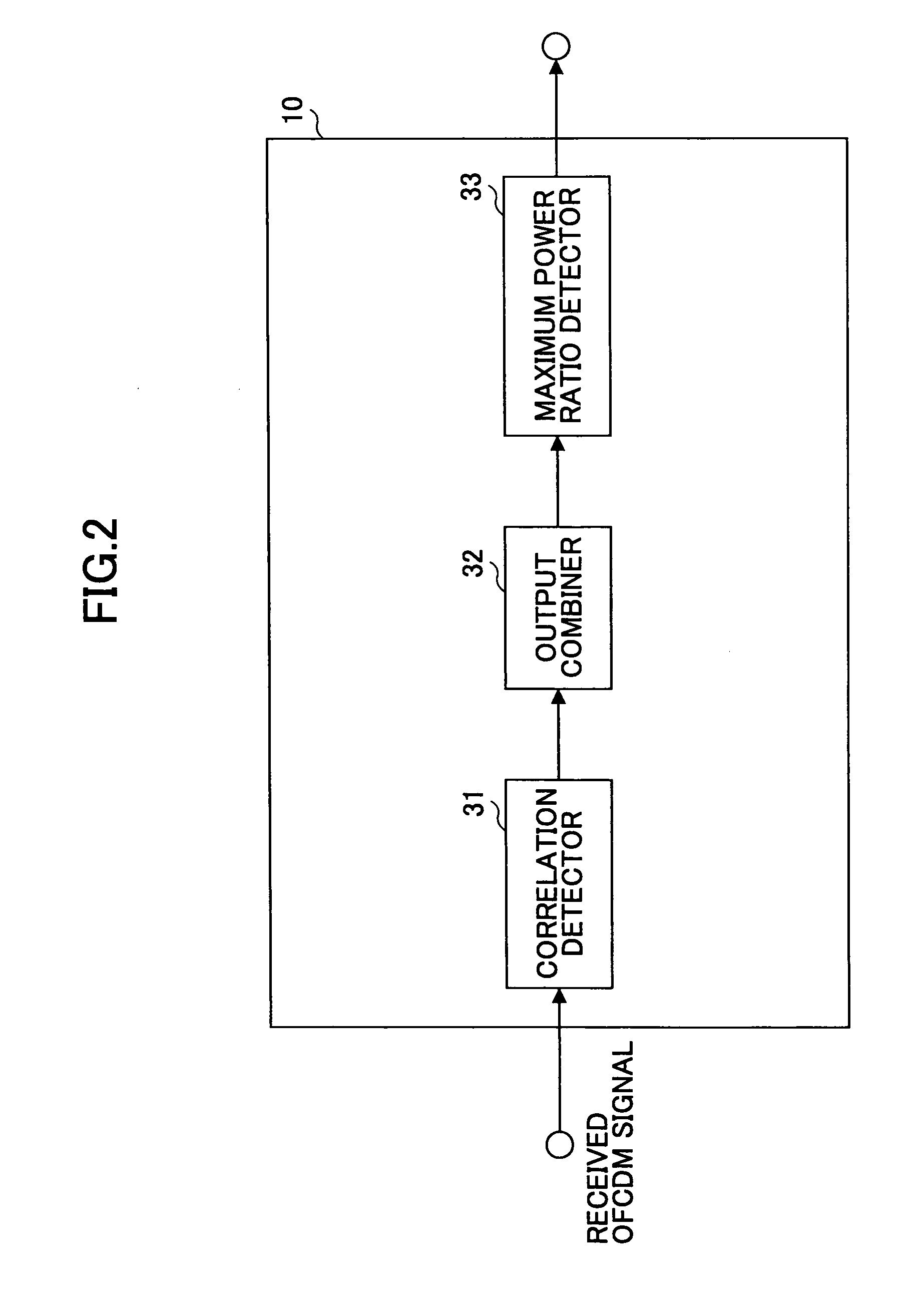
Signal reception device and method of signal reception timing detection
InactiveUS20050100109A1Reduce Intersymbol InterferenceImprove signal transmission performanceElectric pulse generator circuitsSecret communicationCarrier signalEngineering
A signal reception device is disclosed that is capable of detecting symbol synchronization timing with high precision in accordance with a condition of a propagation path even in an environment involving multi-path interference. The signal reception device adopts an OFCDM transmission scheme or a multi-carrier transmission scheme. The signal reception device includes a received signal information calculation unit to calculate received signal information representing a signal reception condition of a received signal; an output combination unit to combine correlation values in a predetermined section obtained by correlation detection based on the received signal information; and a symbol timing detection unit to detect a symbol synchronization timing based on the combined value.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
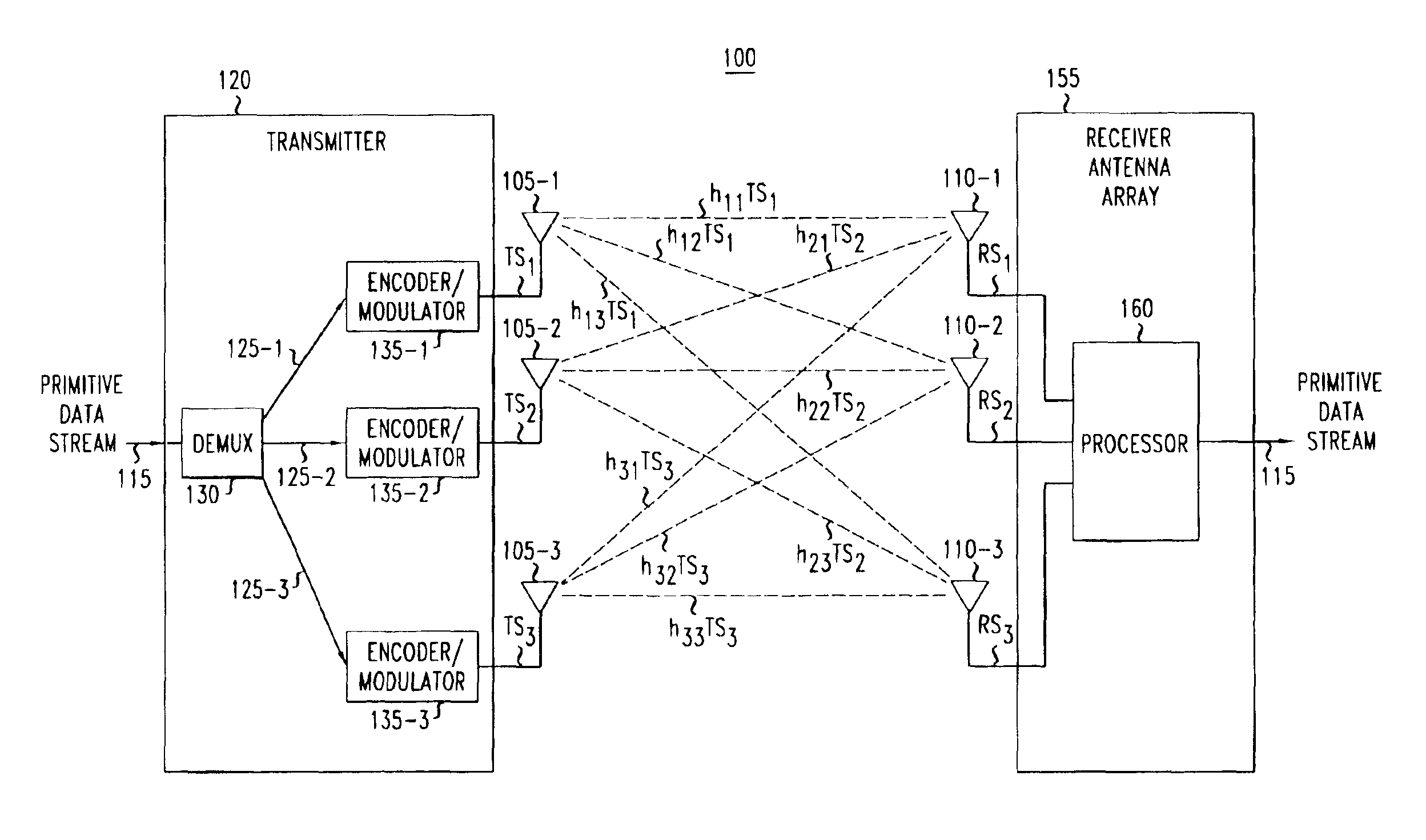
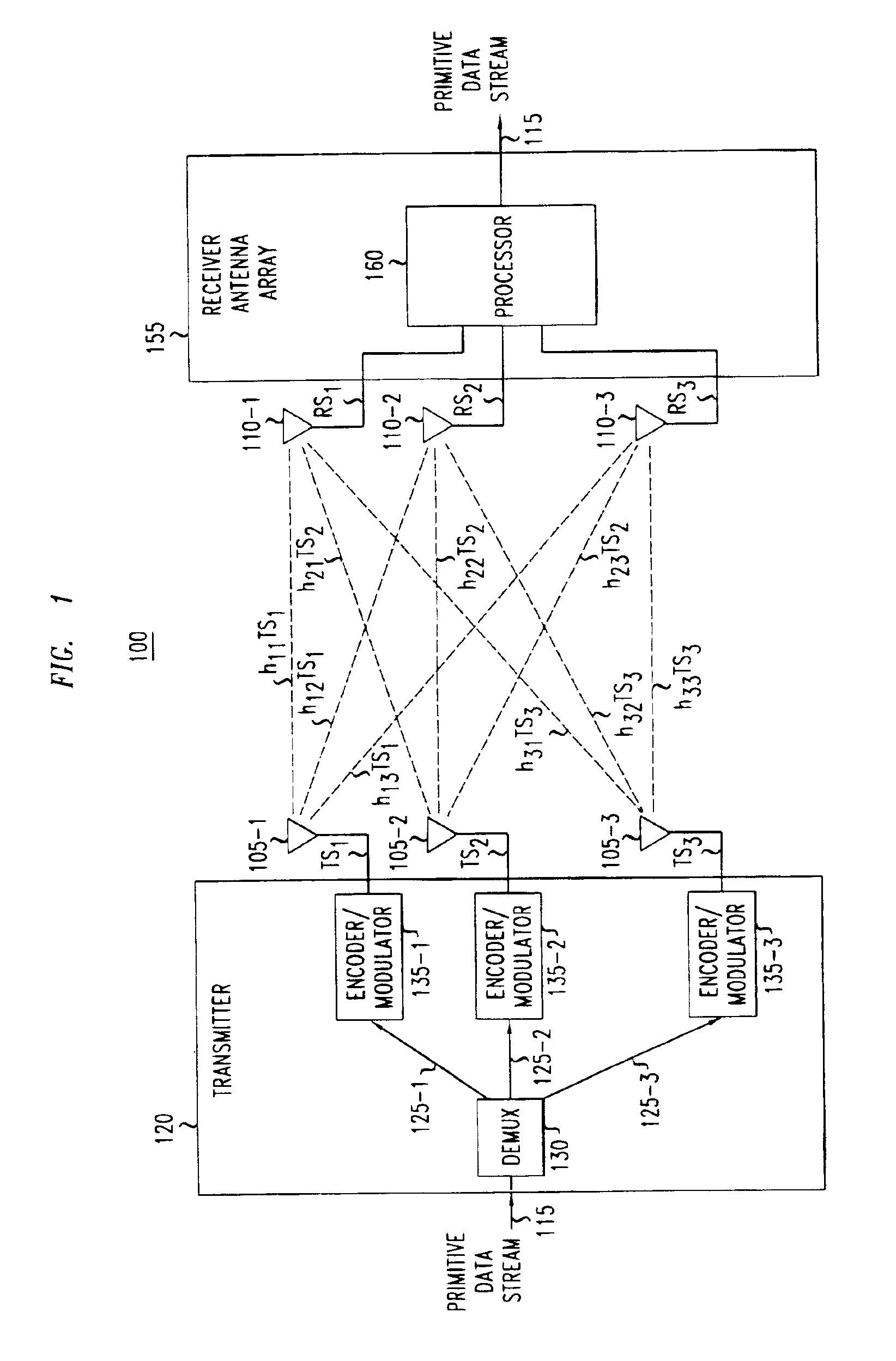
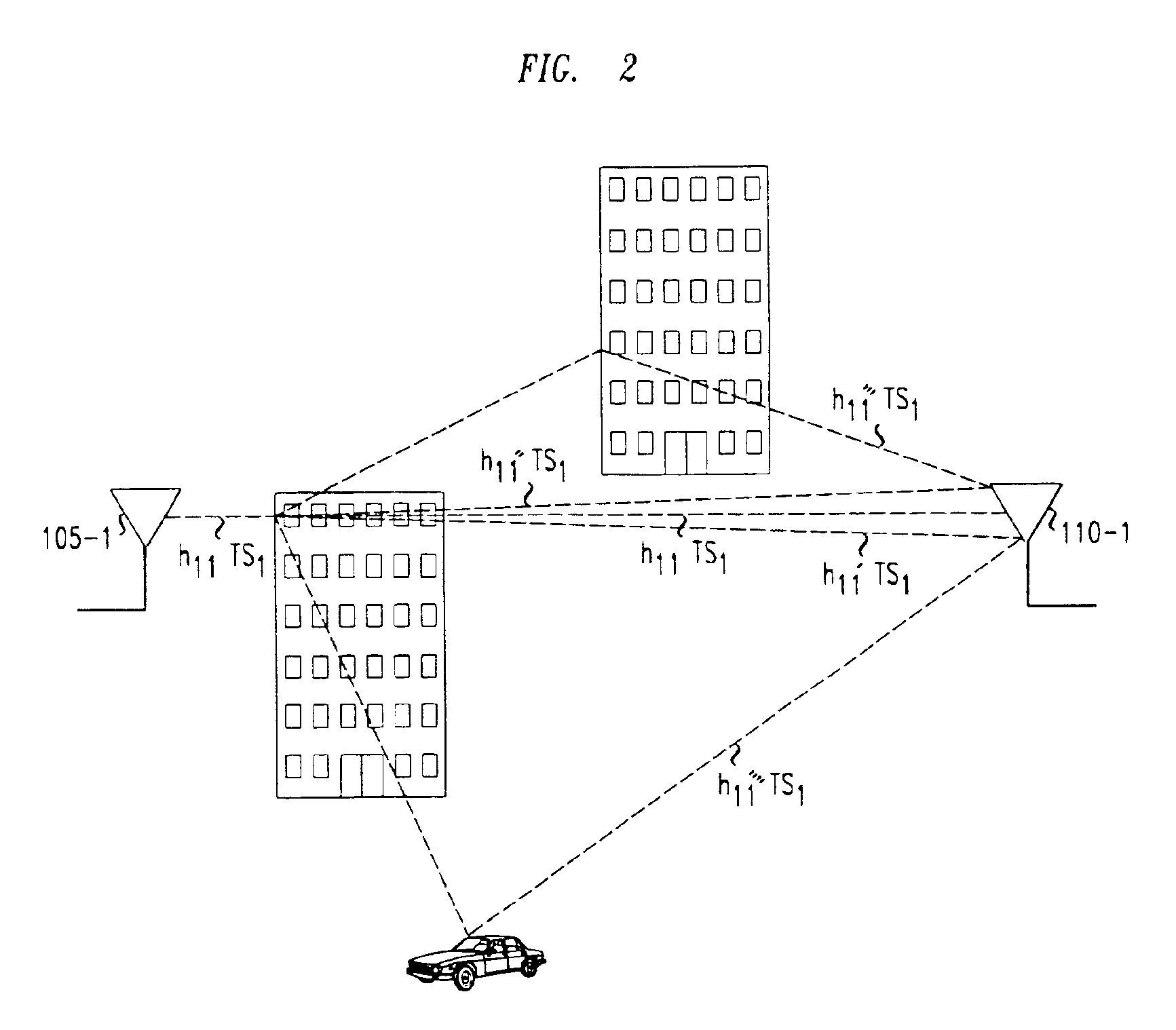
Determining channel characteristics in a wireless communication system that uses multi-element antenna
InactiveUS6925131B2High data rateReduce Intersymbol InterferenceSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsConjugate transposeCommunications system
A method and apparatus for increasing in the data rate of a multiple-input and / or multiple-output system that has frequency selective fading by using training sequences with both low normalized auto-correlation and low normalized cross-correlation. Both 1) the sum of the square of the normalized auto-correlation of each training sequence over an auto-correlation window and 2) the sum of the square of the normalized cross-correlation of each pair of the training sequences over a cross-correlation window, are significantly less than unity. In one embodiment of the invention the training sequences are shifted versions of each other, and the low normalized cyclic-auto-correlation of cyclic sequences is significantly less than unity, with each cyclic sequence being N′, N′=N−L+1, symbols of one of the at least two training sequences. In another embodiment, the training sequences are ones where the trace of the inverse of the product of the matrix of training sequences' symbols and the conjugate transpose of this matrix is low. The matrix is a function of the number of symbols over which multipaths of significant power can arrive, the number of training sequences, and the number of symbols in a training sequence. More particularly the matrix is a block-toeplitzmatrix composed of the training symbols.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
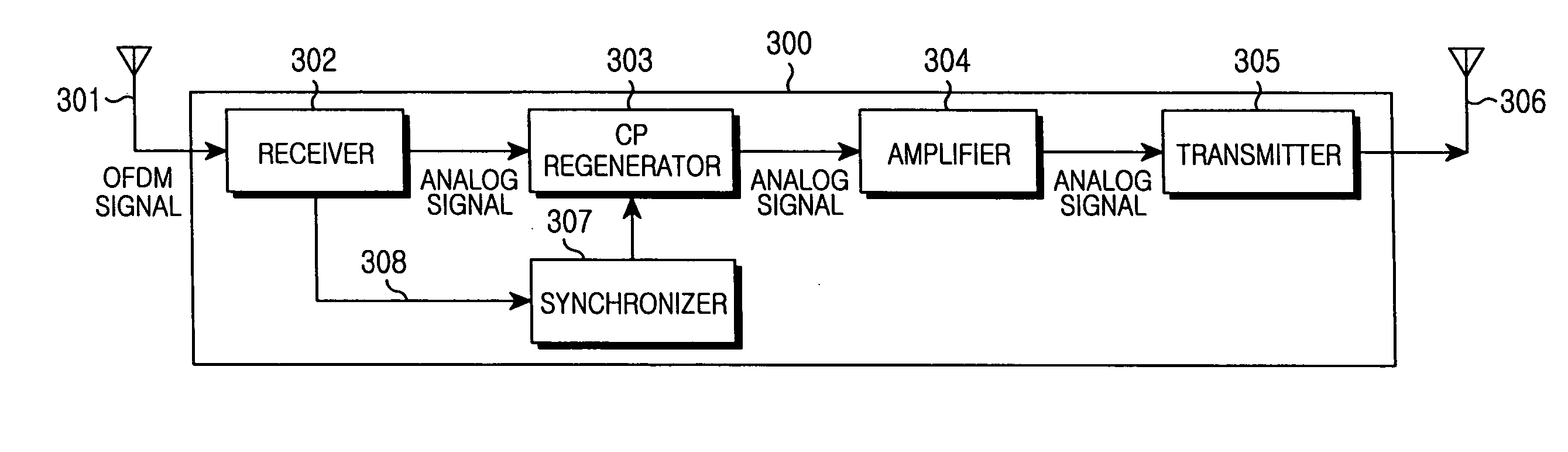
Apparatus and method for providing relay service in an OFDM mobile communication system
InactiveUS20080112497A1Reduce Intersymbol InterferencePreventing propagation of time dispersionRepeater/relay circuitsSecret communicationCommunications systemCyclic prefix
An apparatus and method for providing a relay service in an OFDM mobile communication system are provided, in which symbol synchronization is acquired from a received OFDM signal, an OFDM signal is acquired using the symbol synchronization, and a relay signal is reconfigured by removing a cyclic prefix from the acquired OFDM signal, amplifying the relay signal, and transmitting the relay signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
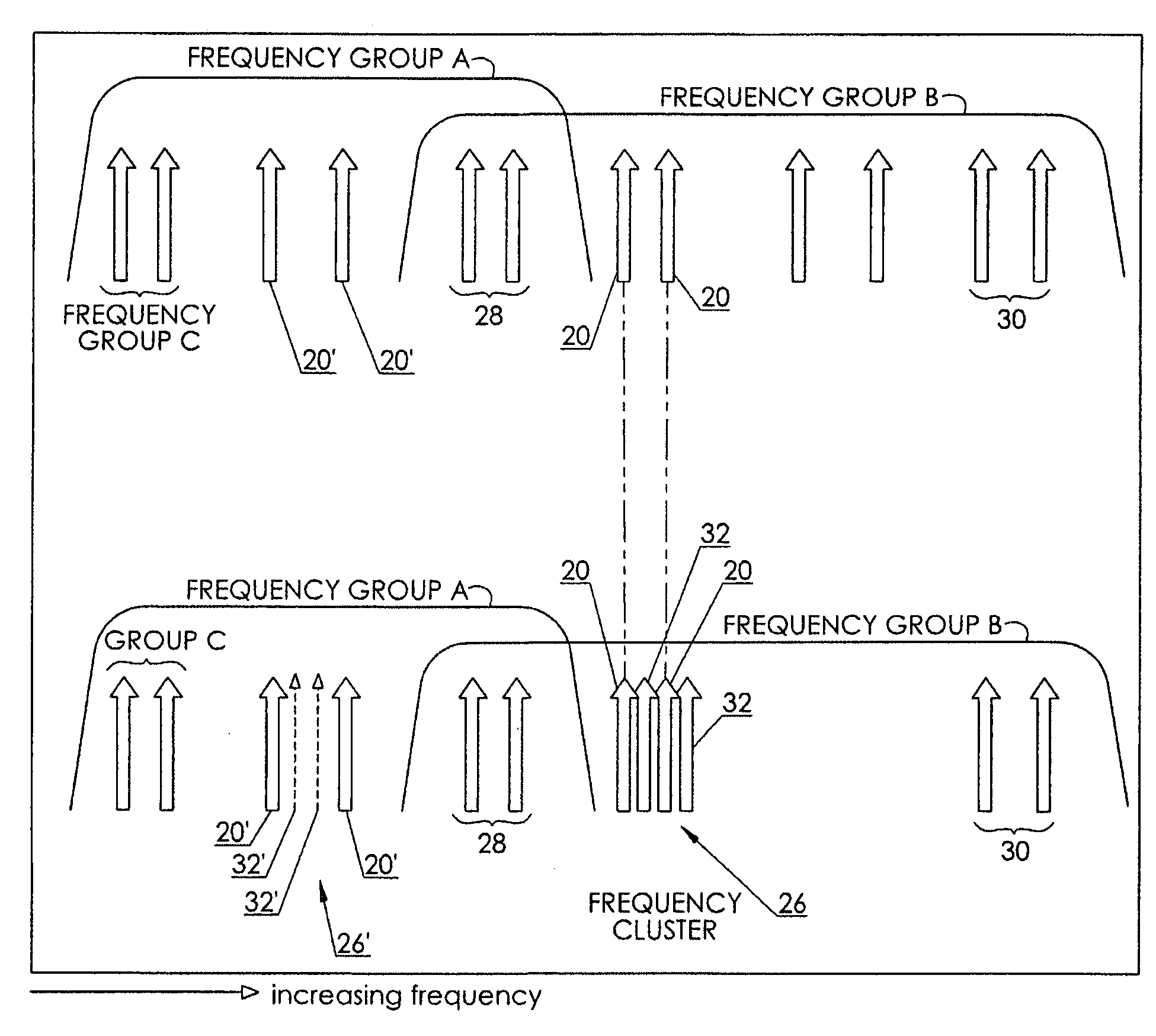
Non-orthogonal frequency-division multiplexed communication through a non-linear transmission medium
InactiveUS20080253400A1Reduce noise disturbanceMinimize distortionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMulti-frequency code systemsEngineeringBase frequency
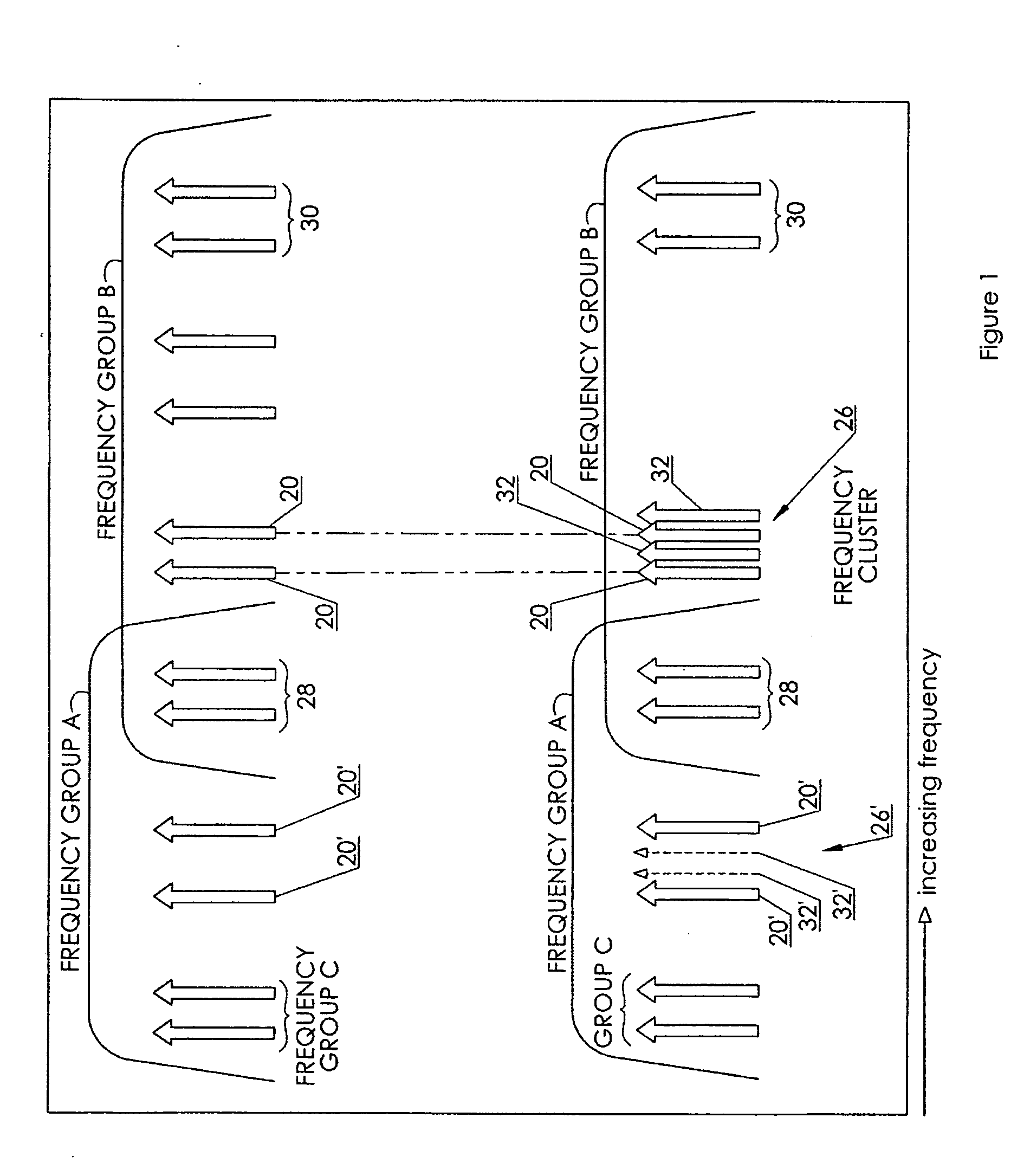
A method for non-orthogonal frequency division multiplexed communication through a non-linear transmission medium includes the steps of selecting at least one desired bandwidth, selecting a non-orthogonal pair of base frequencies within a first bandwidth of the at least one desired bandwidth, identifying where primary intermodulation products formed as a result of signal transmission on the pair of base frequencies fall within the first bandwidth. The method may also include the step of selecting a plurality of non-orthogonal interleaved frequencies adjacent at least one of the pair of base frequencies so as to be interleaved between the primary intermodulation products to form a frequency cluster which includes the at least one of the pair of base frequencies and the interleaved frequencies.
Owner:SIGNALINK TECH
Variable-rate communication system with optimal filtering
InactiveUS20050084270A1Efficient implementationMulti-rate communicationElectromagnetic transmissionTransmission rate adaptationVariable bit rate vbrDigital data
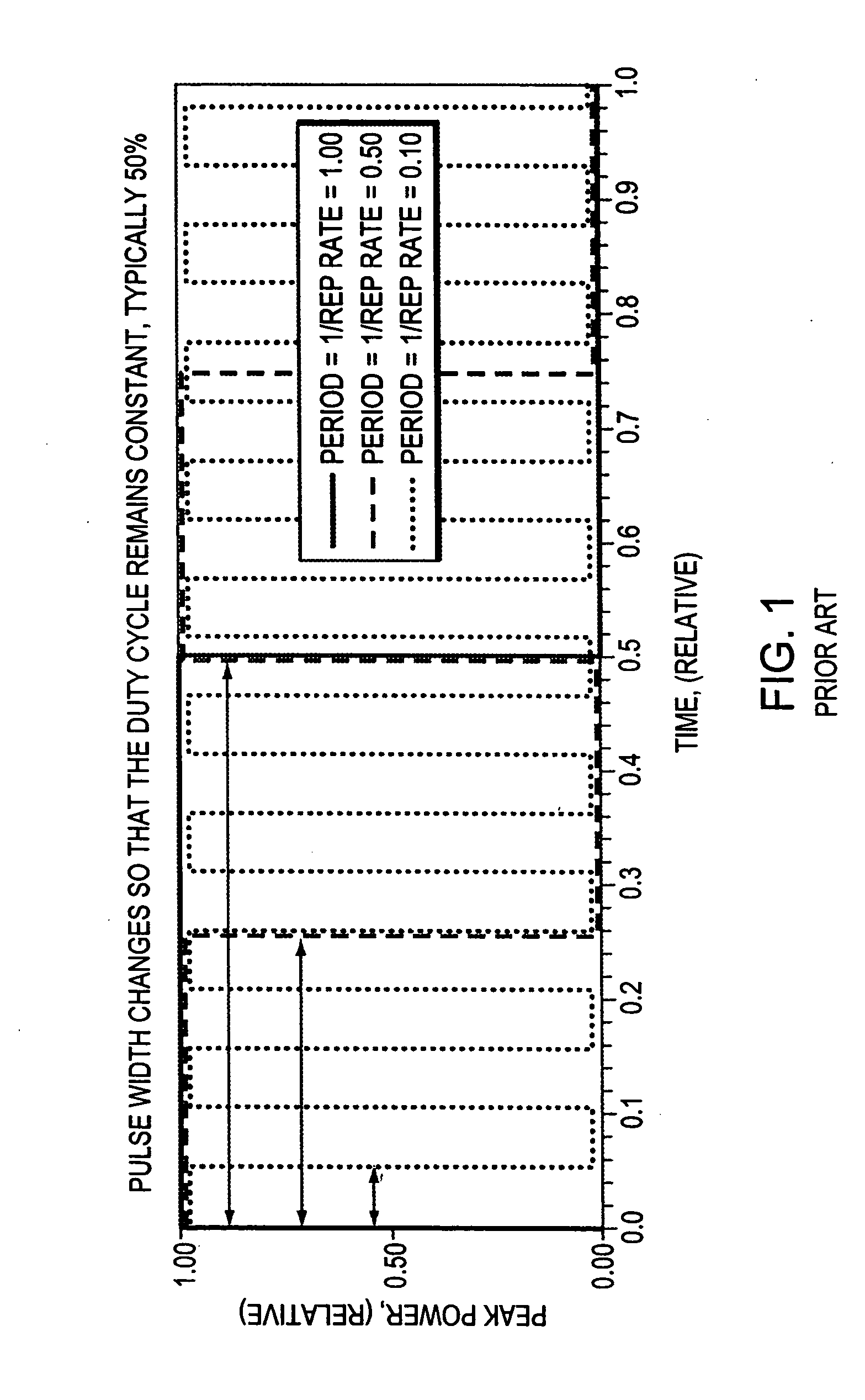
A variable-bit-rate communication system is described. The communication system includes a variable-bit-rate transmitter that generates digital data at a first or a second bit rate and a variable-bit-rate receiver that receives the digital data. The digital data comprises a sequence of signaling waveforms having a first or a second duty cycle, respectively, wherein each signaling waveform has the same shape.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Pi/4DQPSK demodulator and its method
InactiveCN1585503ADownsamplingSimple structureRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPhase-modulated carrier systemsPhase detectorDiscriminator
The method includes following steps: through software, a radiotechnics is introduced into demodulator based on structure of limiter coupling with discriminator to make the angle resolution of demodulator is not limited by sampling rate; the reception matched filter adopts root raised cosine filter (RRCF) to make problem of which demodulator with structure of hardware limiter is sensitive to roll-off factor of root raised cosine filter is solved. The invention can be applied in PHS and PCS system, signal demodulation based on PSK modulation technology like satellite communication system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Semiconductor device
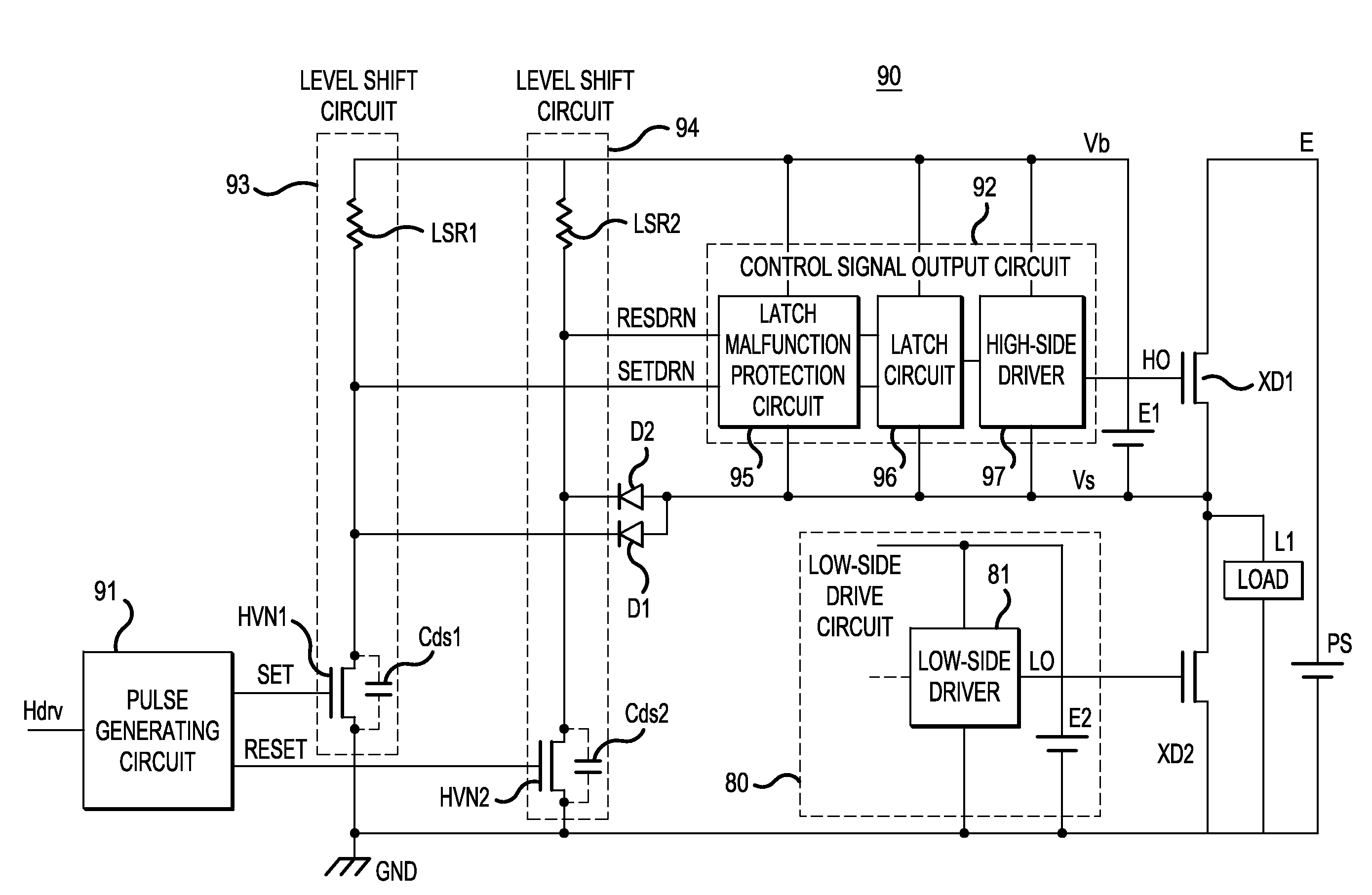
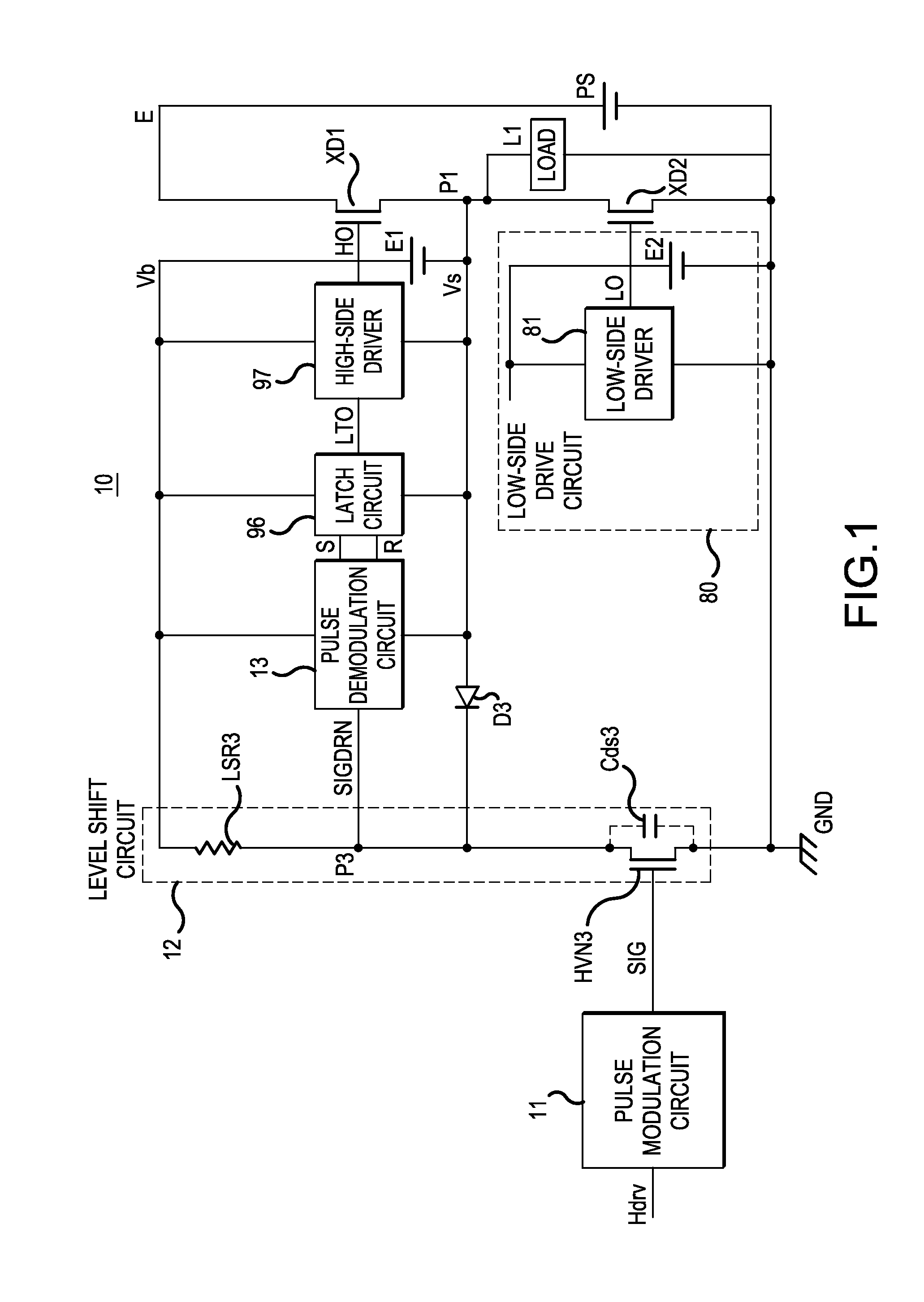
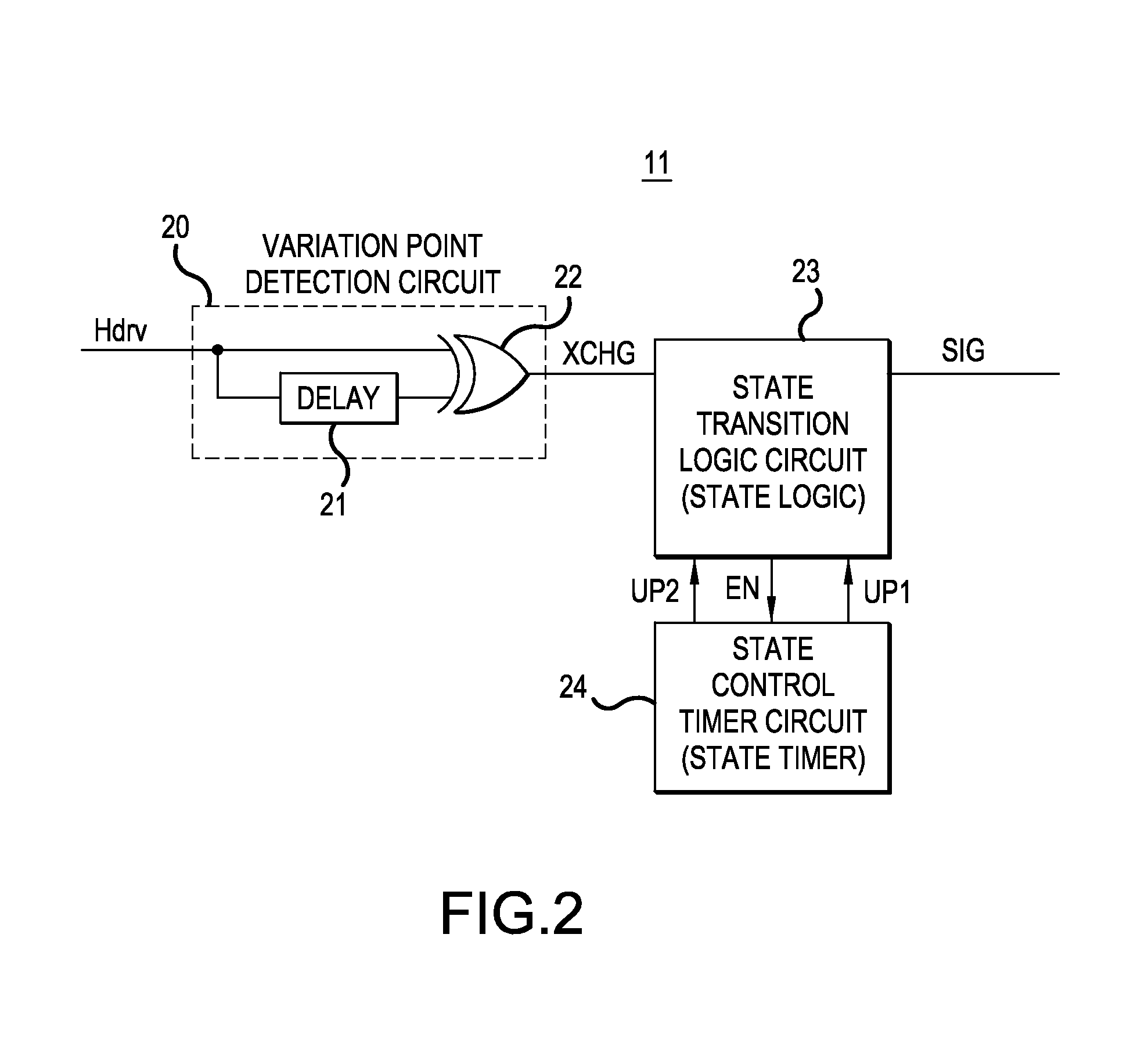
ActiveUS20140320180A1Reduce effectCost reductionTransistorPulse automatic controlHigh potentialVIT signals
In aspects of the invention, a semiconductor device can include one level shift circuit that outputs a low-side input signal as a high-side signal upon raising a signal level, a pulse modulation circuit that operates in a low-side region, generates a data symbol constituted by or more bits and representing a set signal or a reset signal, where bit is defined as a combination of codes forming a pair. The pulse generation circuit can output the generated data symbol as an input signal of the level shift circuit. Also included can be a pulse demodulation circuit that operates in a high-side region, demodulates the data symbol outputted from the level shift circuit and generates a level-shifted set signal or reset signal; and a control circuit that controls conduction / non-conduction of the high-potential-side switching element on the basis of the level-shifted set signal or reset signal outputted from the pulse demodulation circuit.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Heterogeneous weighted overlap-add windowing and filtering for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing waveforms
ActiveUS20170331647A1Enhanced out-of-band (OOB) suppressionReduce Intersymbol InterferenceRadio transmission for post communicationMulti-frequency code systemsCarrier signalFrequency-division multiple access
Techniques for processing of symbols (e.g., orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) or single carrier-frequency division multiple access (SC-FDMA) symbols) provide enhanced out-of-band (OOB) suppression of the symbols and also provide reduced inter-symbol interference (ISI) between a symbol and a subsequent symbol. Multiple frequency tones of a symbol may be divided into two or more subsets of tones. For example, subsets of tones associated with a head portion or a tail portion of an OFDM symbol may be processed with a relatively long weighted overlap-add (WOLA) weighting length or filtering length, and a subset of tones associated with a center portion of the OFDM symbol may be processed with a relatively short WOLA weighting length or filtering length. Such heterogeneous processing of tones within a symbol may provide enhanced inter-channel interference (ICI) and improved OOB suppression and also provide reduced ISI for the center tones of the symbol.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
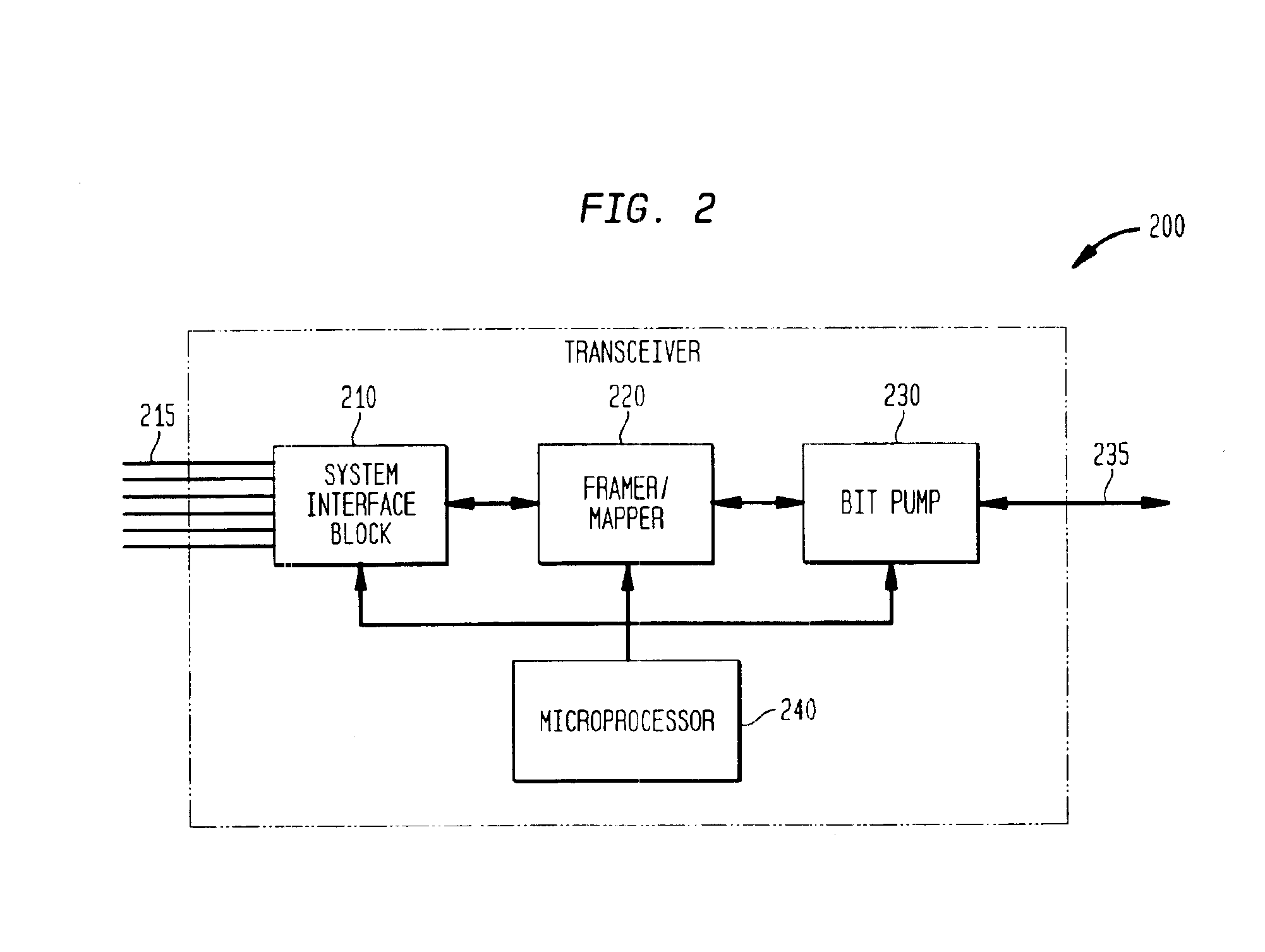
Filter circuit for a bit pump and method of configuring the same
InactiveUS6876699B1Improve system performanceReduce Intersymbol InterferenceMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTransceiverSignal correlation
A filter circuit, method of configuring the filter circuit, and a bit pump and transceiver employing the circuit and method. In one embodiment, the filter circuit includes a noise prediction equalizer that generates a noise prediction equalizer coefficient during activation of the bit pump to reduce an intersymbol interference associated with a receive signal propagating along a receive path of the bit pump. The filter circuit also includes a decision feedback equalizer that generates a decision feedback equalizer coefficient during the activation of the bit pump to reduce the intersymbol interference associated with the receive signal. The noise prediction equalizer is concatenated with the decision feedback equalizer during showtime of the bit pump to form a precoder associated with a transmit path of the bit pump.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Radio transmitting apparatus and radio transmitting method
InactiveUS20100002671A1Reduce Intersymbol InterferenceInhibit deteriorationSynchronisation arrangementAssess restrictionEngineeringWindow Width
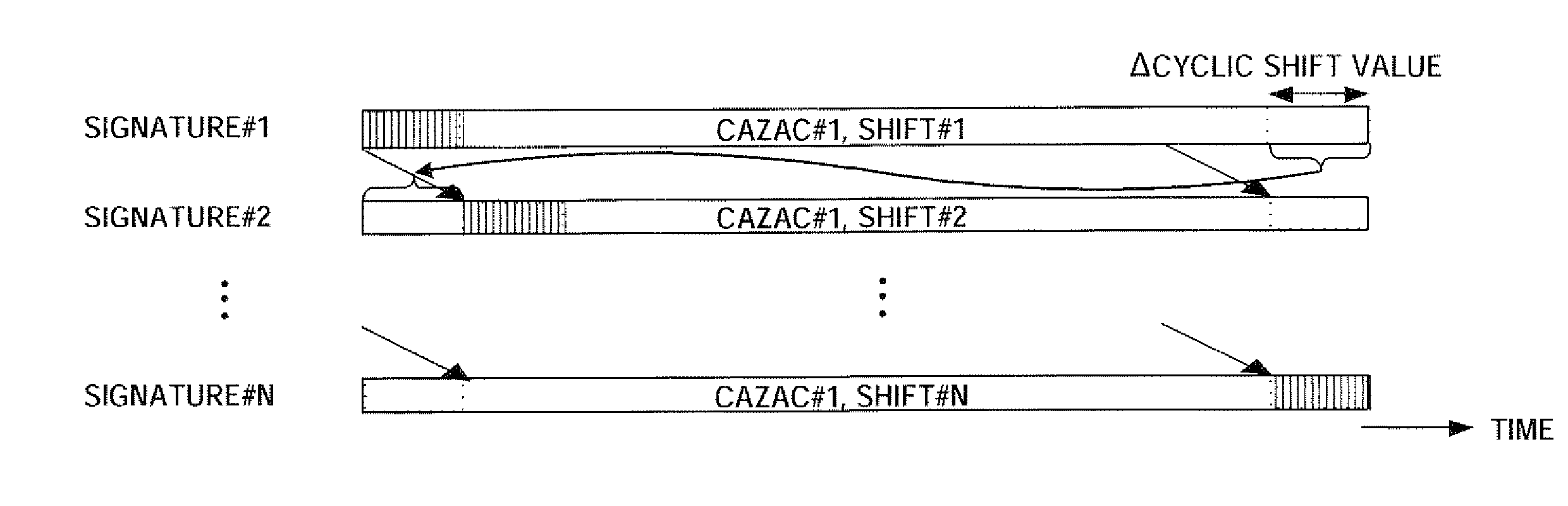
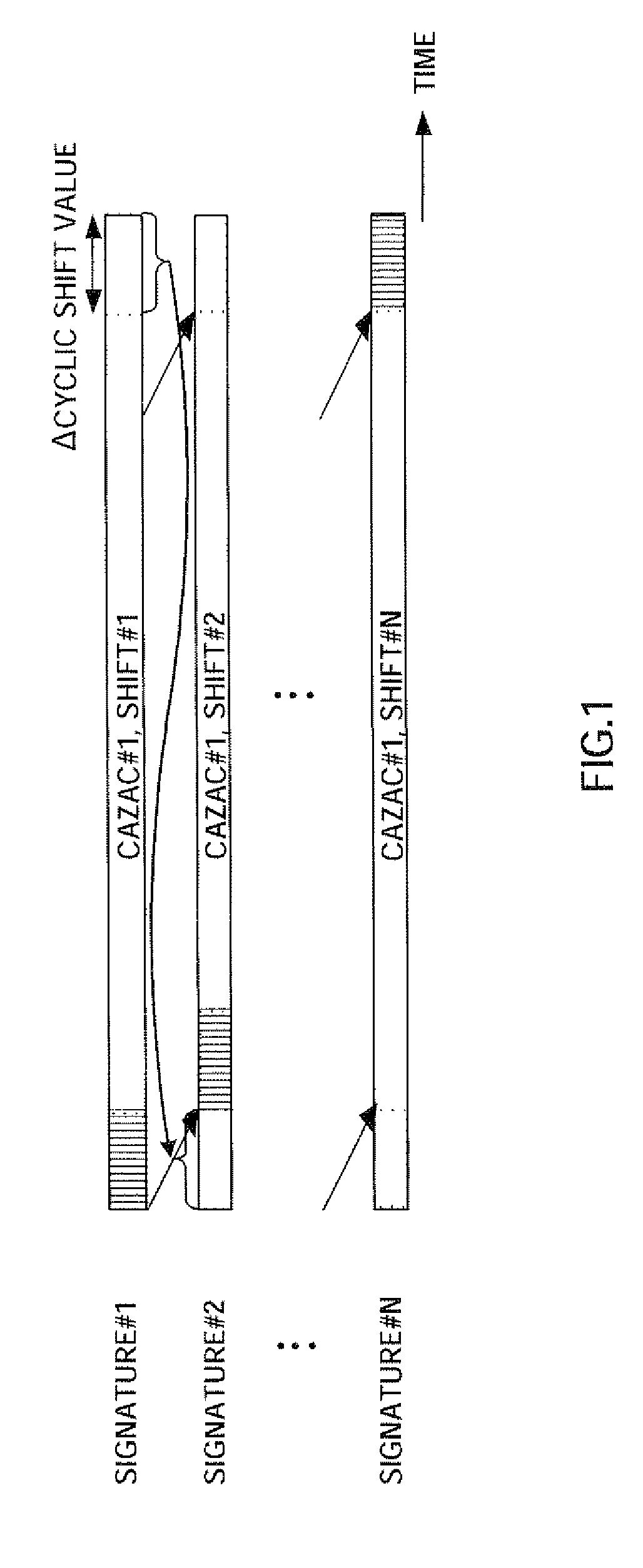
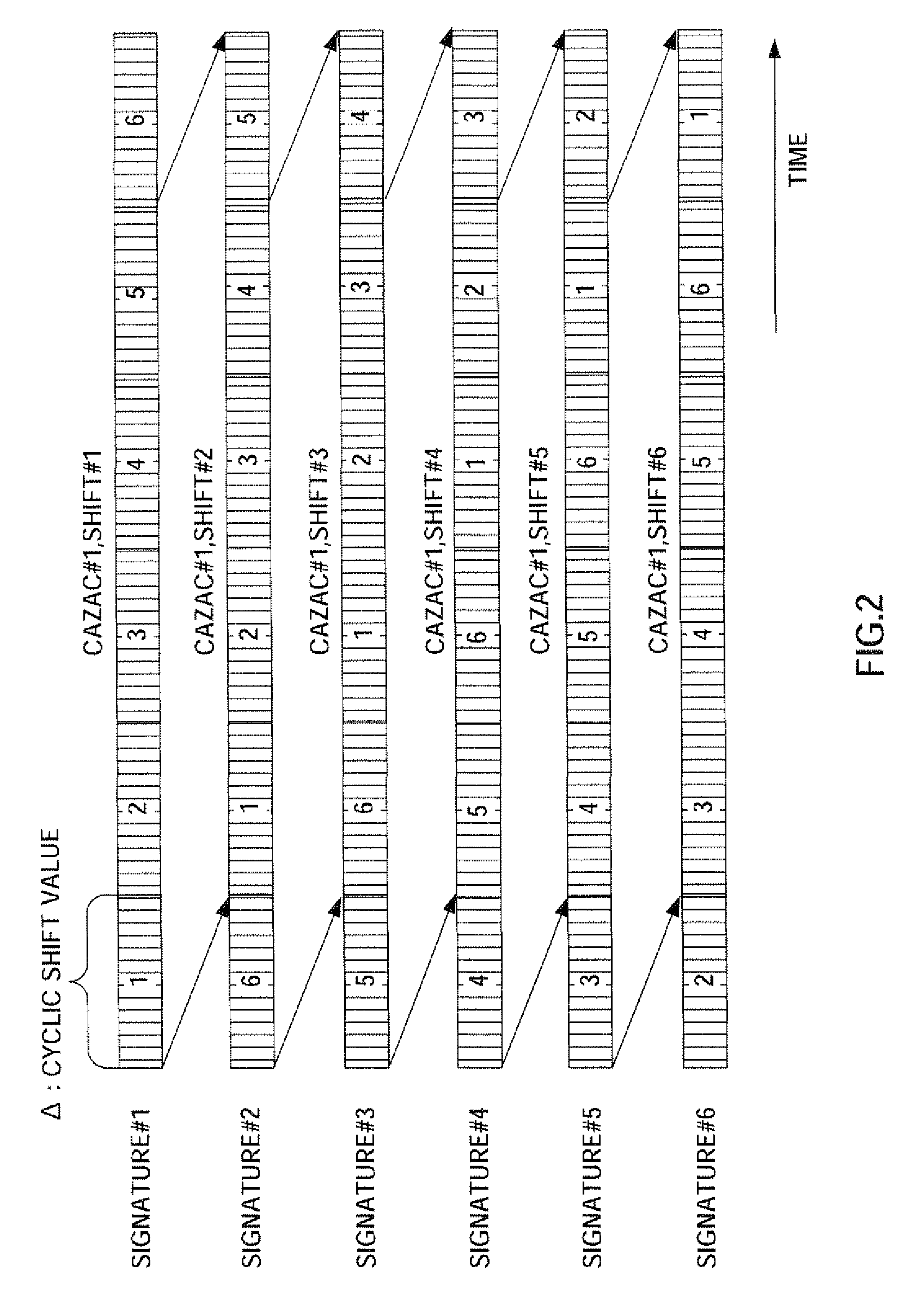
A radio transmitting apparatus and a radio transmitting method wherein the interference between codes can be reduced and the degradation of preamble detection capability can be prevented. According to these apparatus and method, a signature table storing part (103) that stores a table including a plurality of signatures obtained by classifying the magnitudes of propagation loss levels into levels in accordance with the distances from a base station, associating preamble detection window widths with those levels as classified, and by circularly shifting the pattern of a detection window signature #n corresponding to a signature #n to generate a signature #n+1. A signature selecting part (104) selects, based on the magnitude of a propagation loss level outputted by a propagation loss level determining part (102), one of the corresponding signatures from the signature table storing part (103) at random. A RACH signal generating part (105) uses the selected signature to generate a RACH signal.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
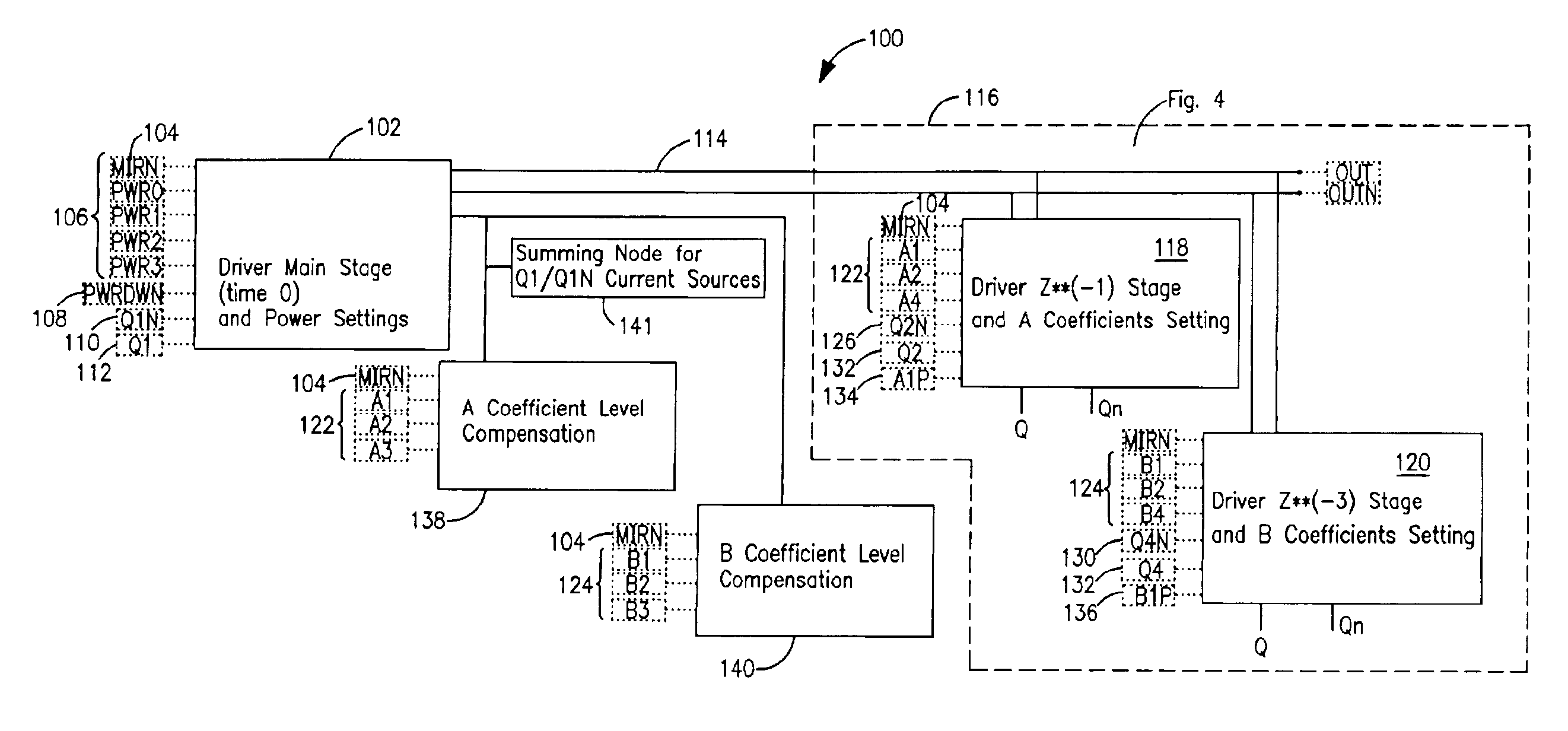
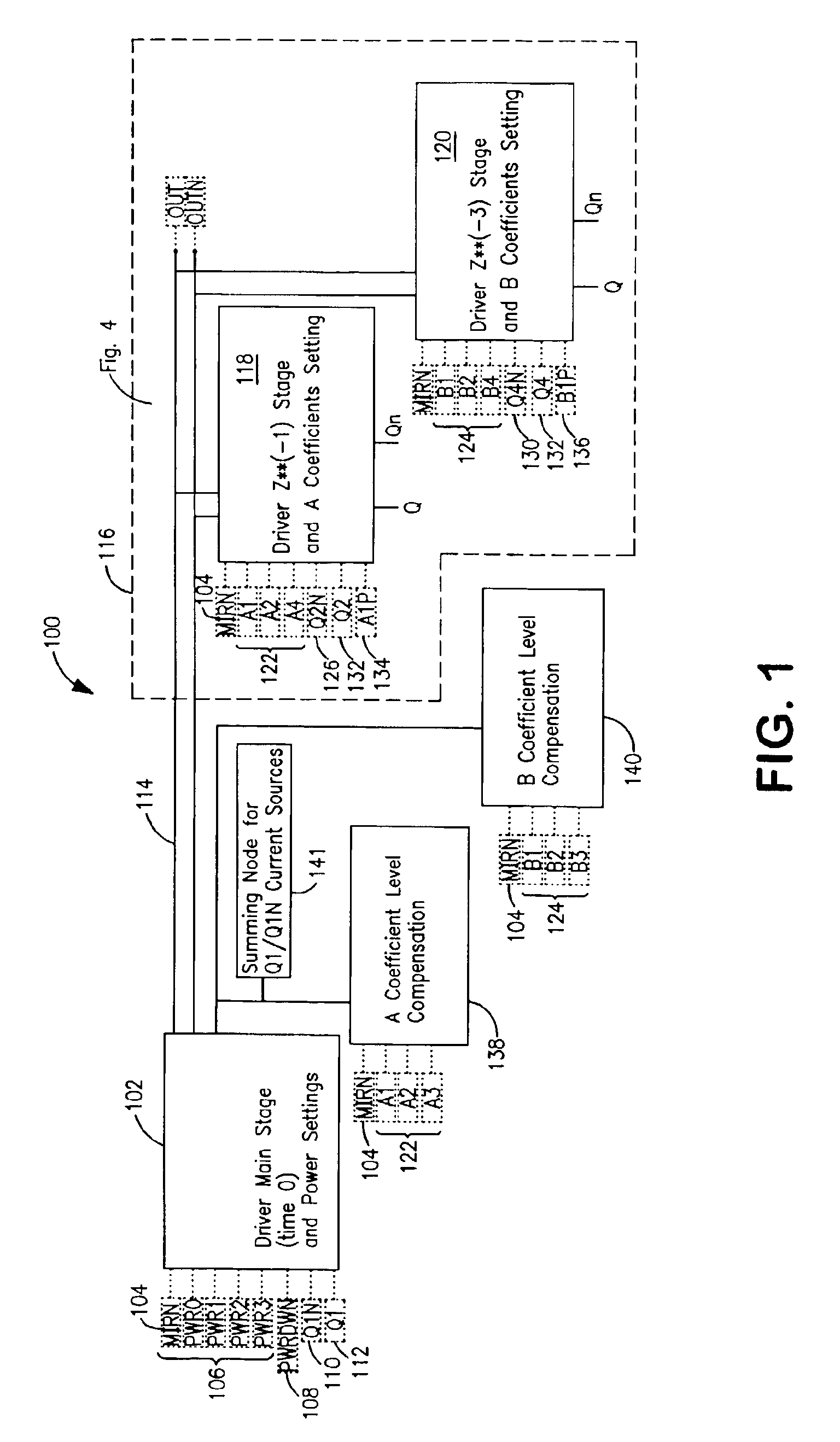
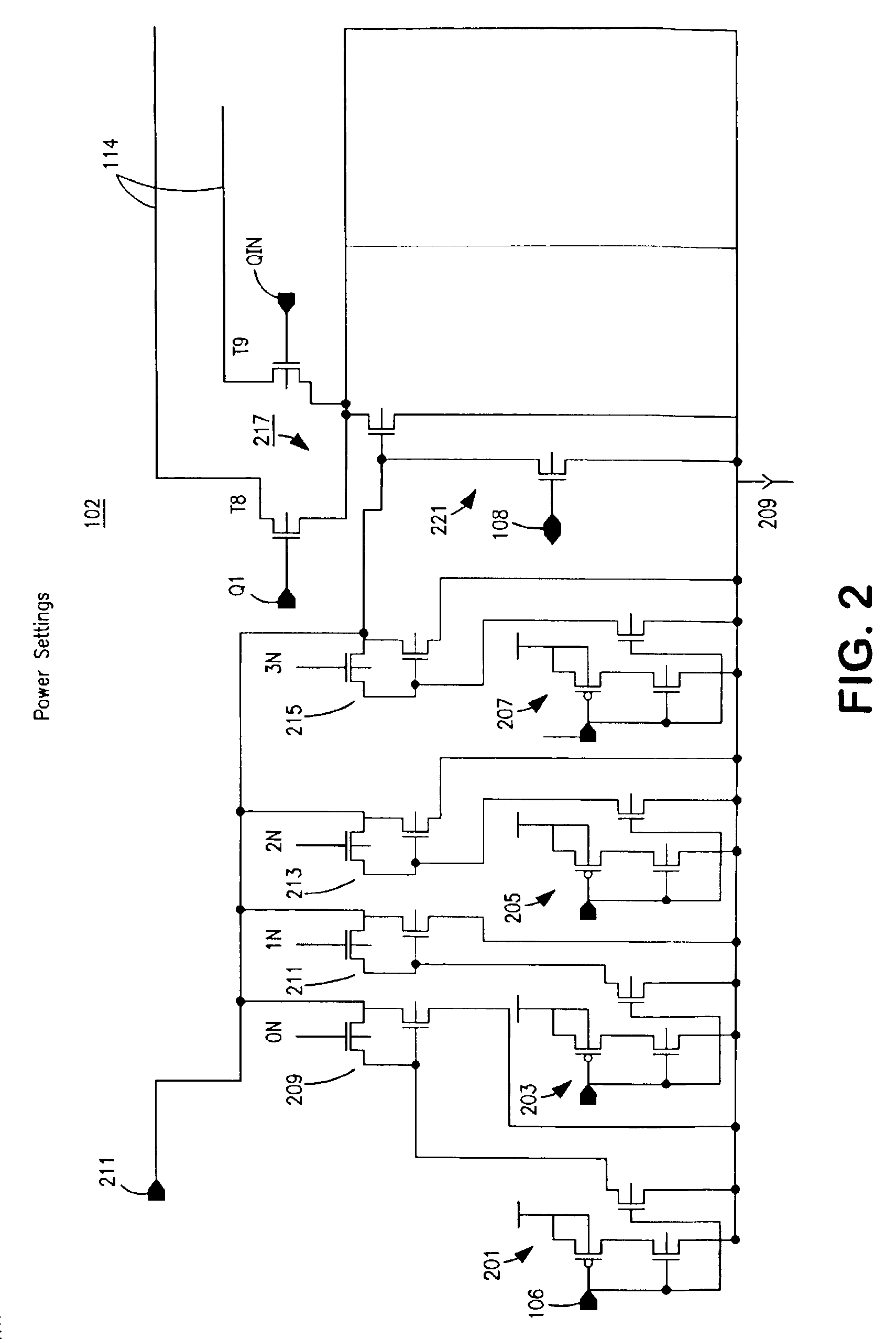
Programmable driver/equalizer with alterable analog finite impulse response (FIR) filter having low intersymbol interference and constant peak amplitude independent of coefficient settings
InactiveUS6999540B2Reduce Intersymbol InterferenceConstant peak amplitudeMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsFinite impulse responseDriver circuit
Owner:TWITTER INC
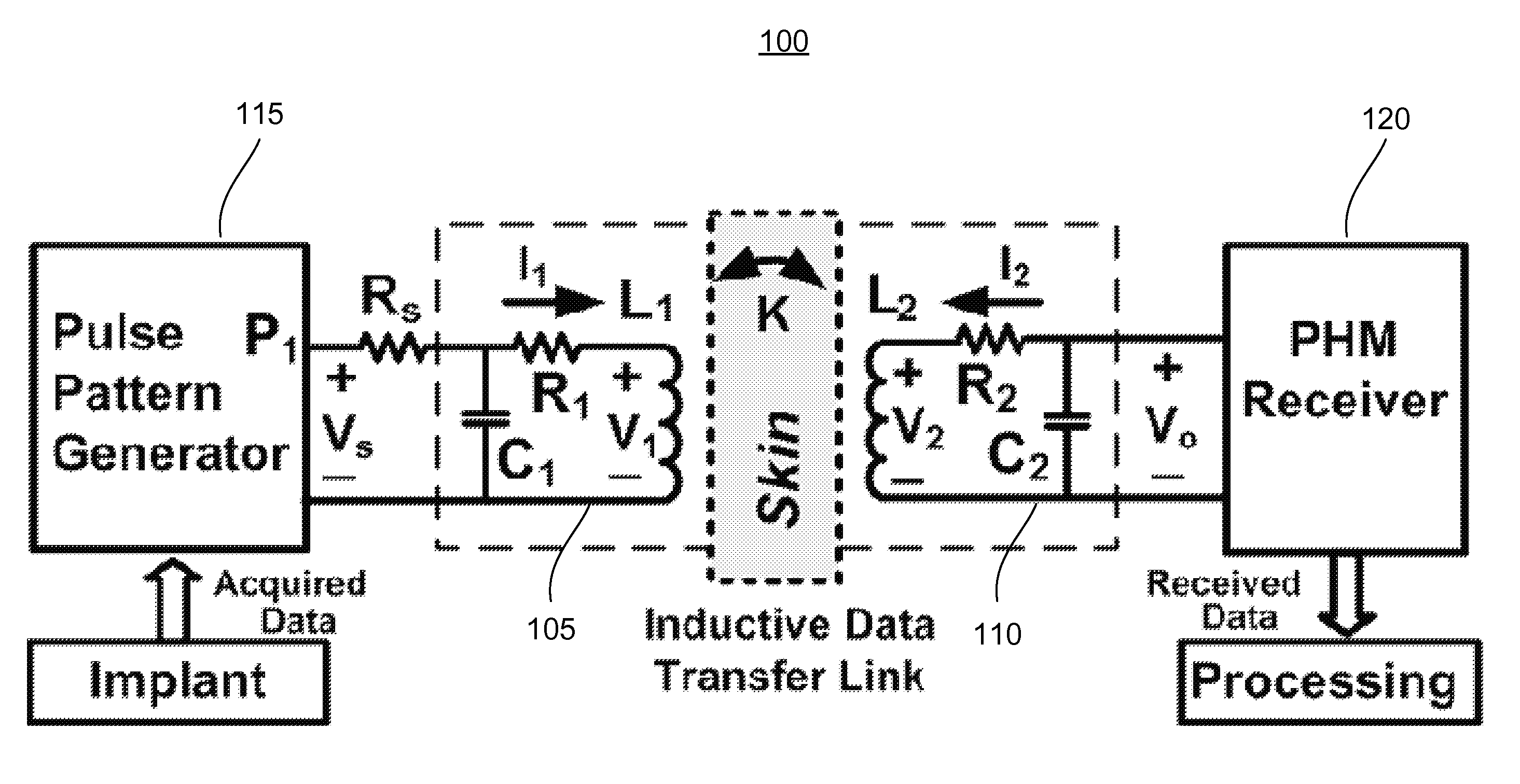
Pulse Harmonic Modulation Systems And Methods
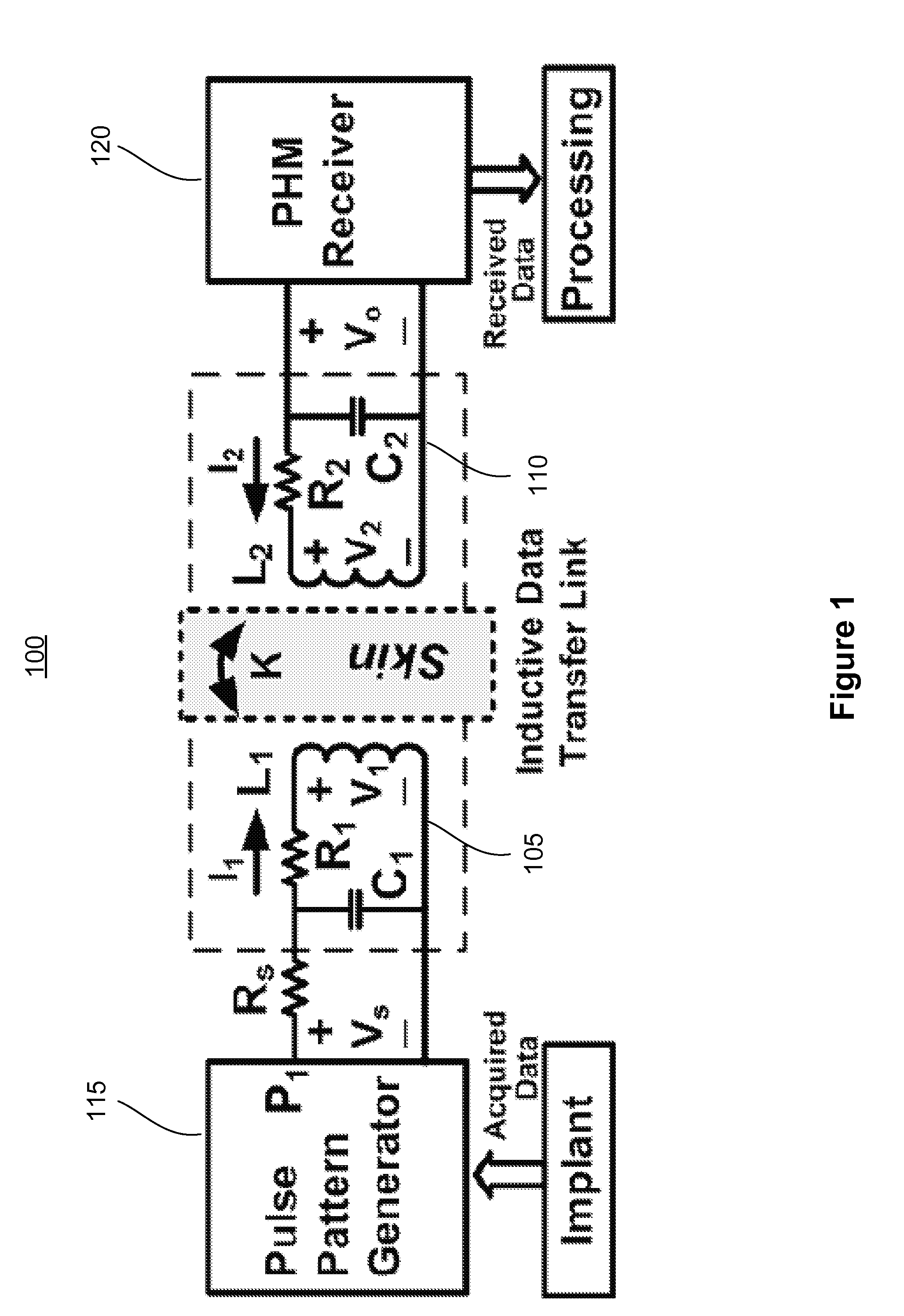
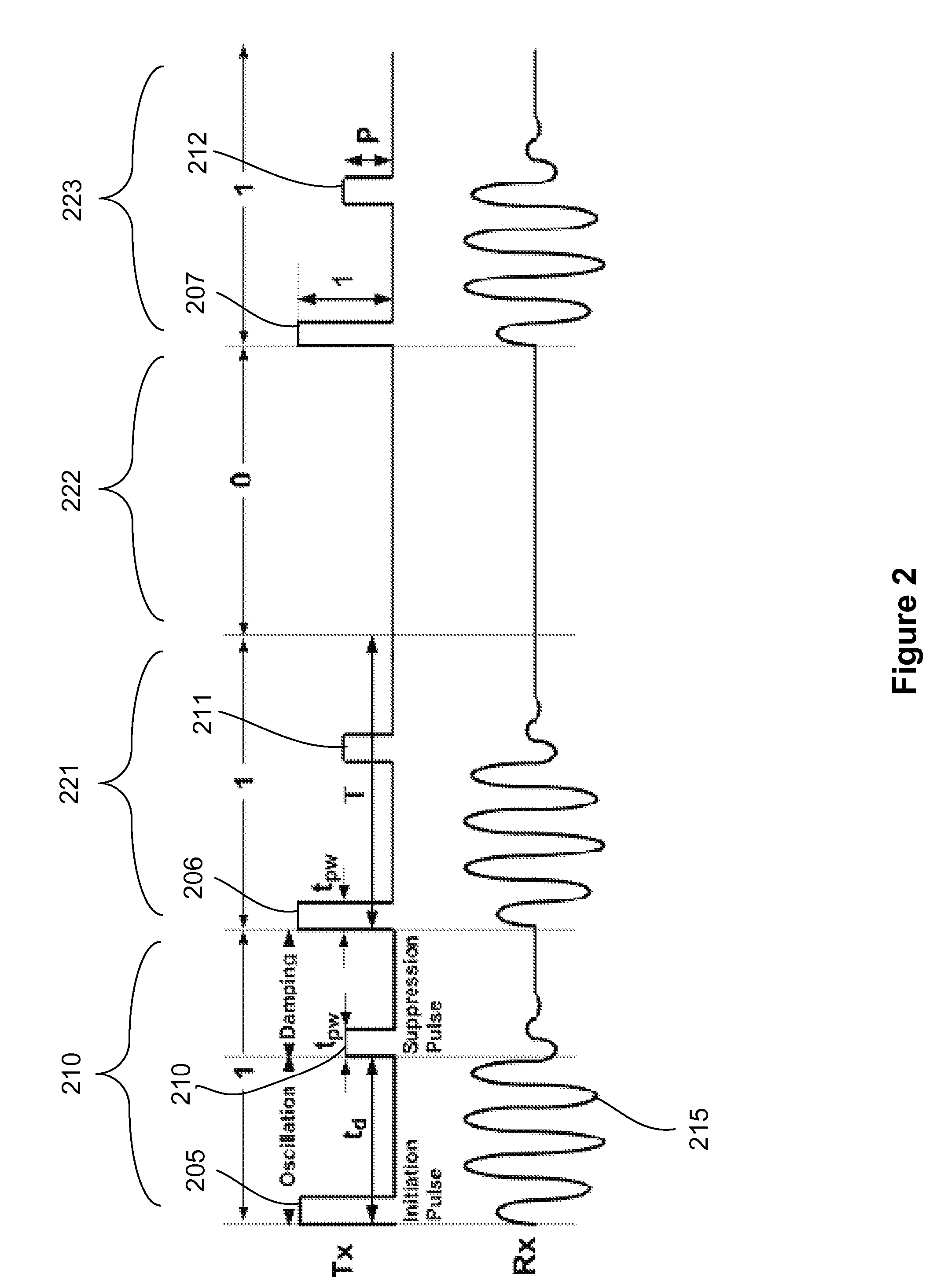
InactiveUS20120294386A1Reduce Intersymbol InterferenceNear-field transmissionElectrotherapyHarmonicPhysics
The various embodiments of the present disclosure relate generally to pulse harmonic modulation systems and methods. An embodiment of the present invention provides a pulse harmonic modulation method comprising transmitting a first data initiation pulse to an input of a first resonant circuit thereby creating an oscillating waveform at an output of a second resonant circuit and transmitting a first modifying pulse to the input of the first resonant circuit. The first modifying pulse can modify a first portion of the oscillating waveform.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Channel capacity optimization method for molecular communication model based on diffusion
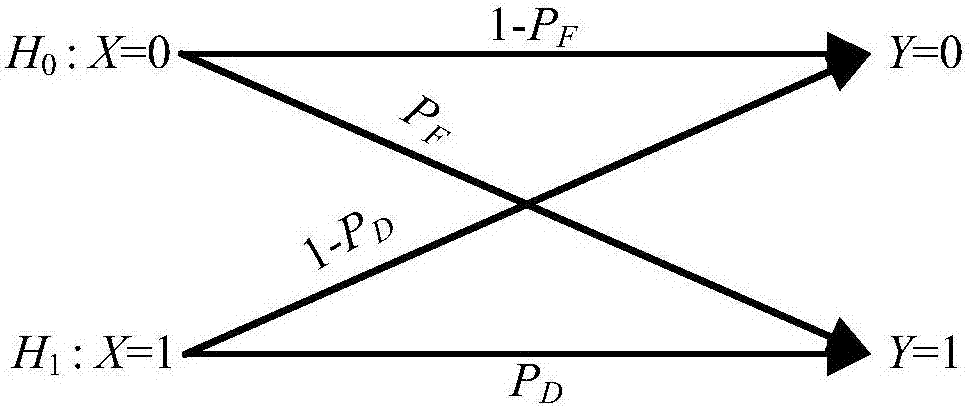
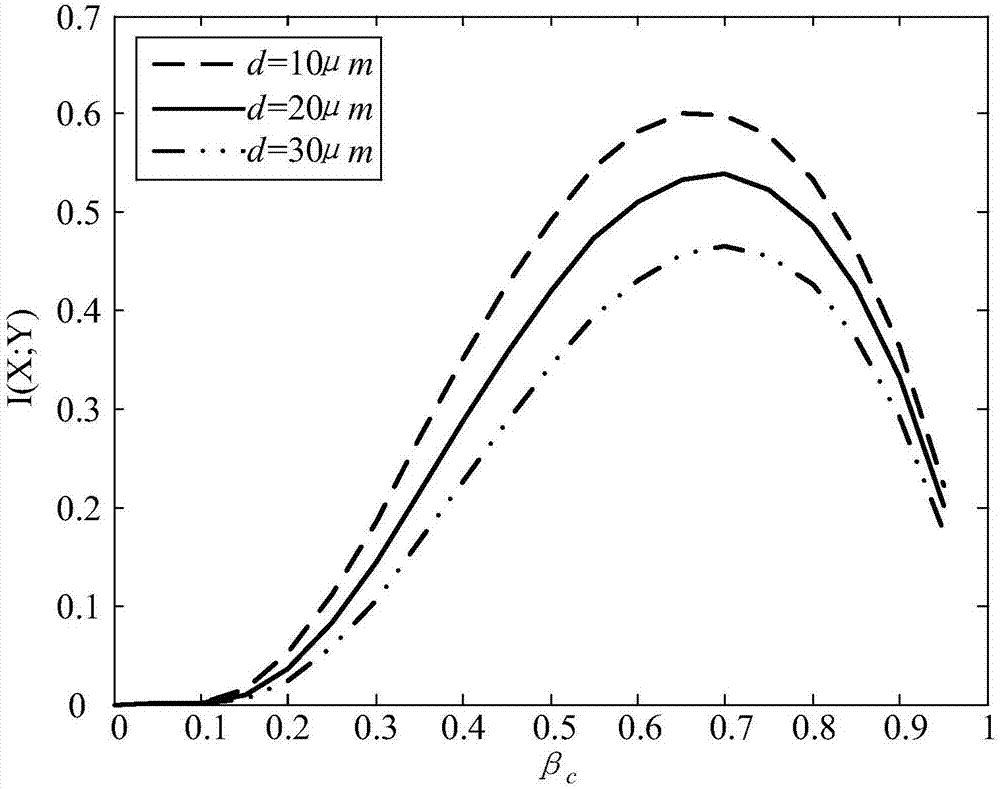
ActiveCN106972902AImprove transmission efficiencyReduce Intersymbol InterferenceTransmission monitoringWireless communicationChannel capacityCurrent time
A channel capacity optimization method for a molecular communication model based on diffusion comprises the following steps: step 1, obtaining the number of molecules received at the current time slot RN by approximating the binomial distribution through the Poisson distribution; step 2, establishing a hypothetical detection channel model of the molecular communication model based on diffusion; step 3, acquiring a mathematical expression of an optimal decision threshold by using the Skellam distribution, and further obtaining the optimal decision threshold theta; and step 4, obtaining an optimal channel capacity value based on the optimal decision threshold theta. According to the channel capacity optimization method for the molecular communication model based on diffusion provided by the invention, the channel capacity can be effectively increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Inverse signal transformation
InactiveUS9077315B2Reduce Intersymbol InterferenceDigital technique networkSecret communicationTransmission channelTreatment error
Owner:BOGDAN JOHN W
Automatic gain control method suitable for OFDM system
InactiveCN104703272ASimplified Computational ComplexityStrong lockPower managementMulti-frequency code systemsCyclic prefixRadio frequency
The invention relates to an automatic gain control method suitable for an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) system. The method comprises the following steps of measuring baseband signals and adjusting gains, and the method is realized by a measuring circuit and a gain adjustment circuit. In the method, an AGC (Automatic Gain Control) technology is executed by the OFDM system; the AGC includes two parts: measuring signals and calculating next used gains according to the measured value. The gain of a radio frequency receiver chip is adjusted by the cyclic prefix (CP) time of the OFDM system, gains in one frame can be repeatedly adjusted, convergence time is shortened, the OFDM symbol of the received signal can be tracked, the AGC locking is greatly quickened, and signals in one frame can be tracked. The reception of the effective data cannot be affected when the convergence time is shortened.
Owner:SUZHOU SIYUANTONG TECH
Multiplexer with low parasitic capacitance effects
InactiveUS20050035810A1Reduce Intersymbol InterferenceElectric signal transmission systemsElectronic switchingMultiplexingMultiplexer
A differential multiplexer includes a plurality of multiplexing circuits. Each multiplexing circuit inputs a corresponding differential input signal including a positive input signal and a negative input signal, and outputs positive and negative output signals. Each multiplexing circuit includes first, second, third and fourth transistors. The first and second transistors input the positive input signal. The third and fourth transistors input the negative input signal. Outputs of the first and third transistors are connected to the positive output signal. Outputs of the second and fourth transistors are connected to the negative output signal. The positive and negative output signals are controlled using gate voltages on the first and fourth transistors. The second and third transistors are turned off when the differential multiplexer is in use. The transistors are cross-coupled to make leakage between the positive and negative input signals common mode in the positive and negative output signals.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com