Patents
Literature
553 results about "Spreading factor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
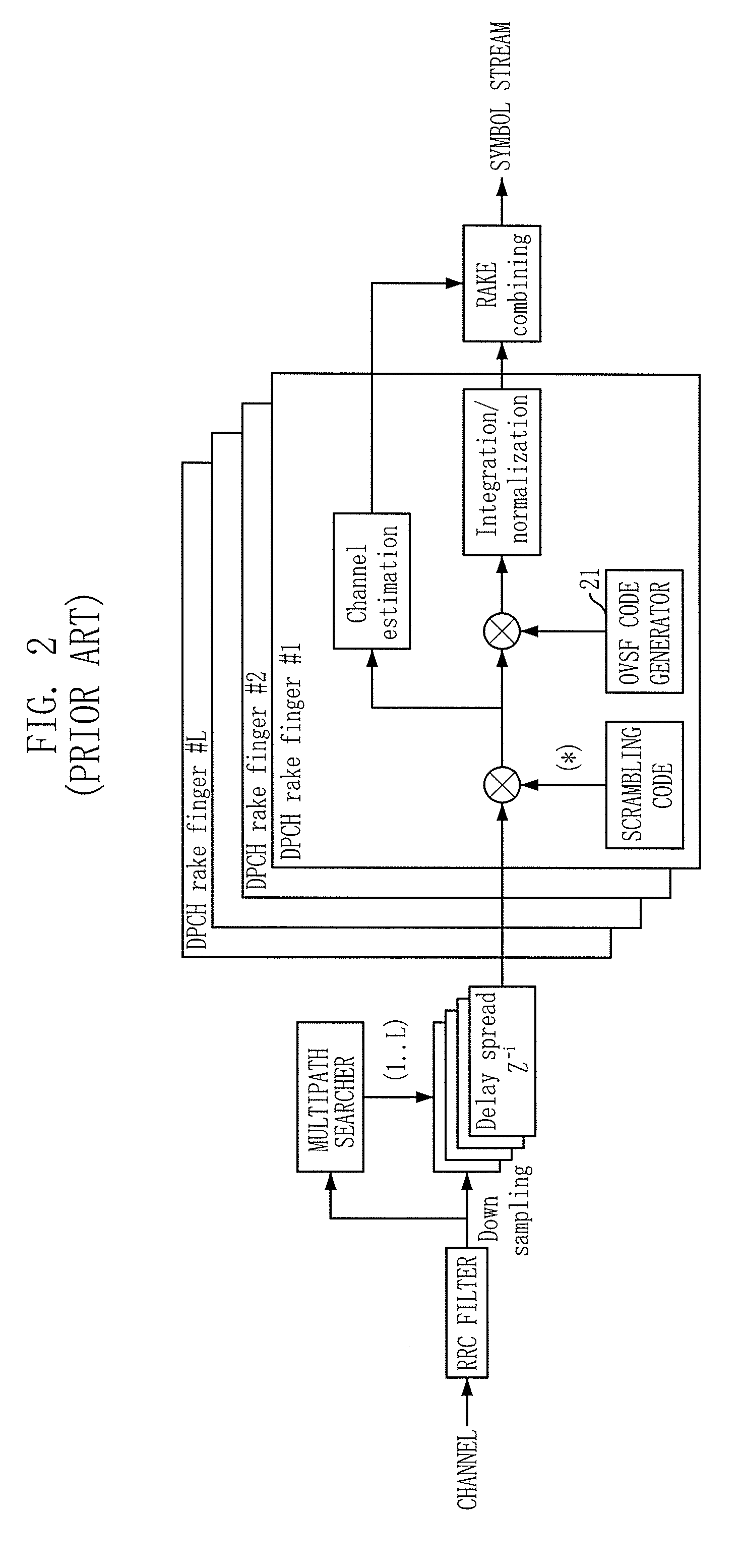
Orthogonal variable spreading factor (OVSF) is an implementation of code division multiple access (CDMA) where before each signal is transmitted, the signal is spread over a wide spectrum range through the use of a user's code. Users' codes are carefully chosen to be mutually orthogonal to each other.
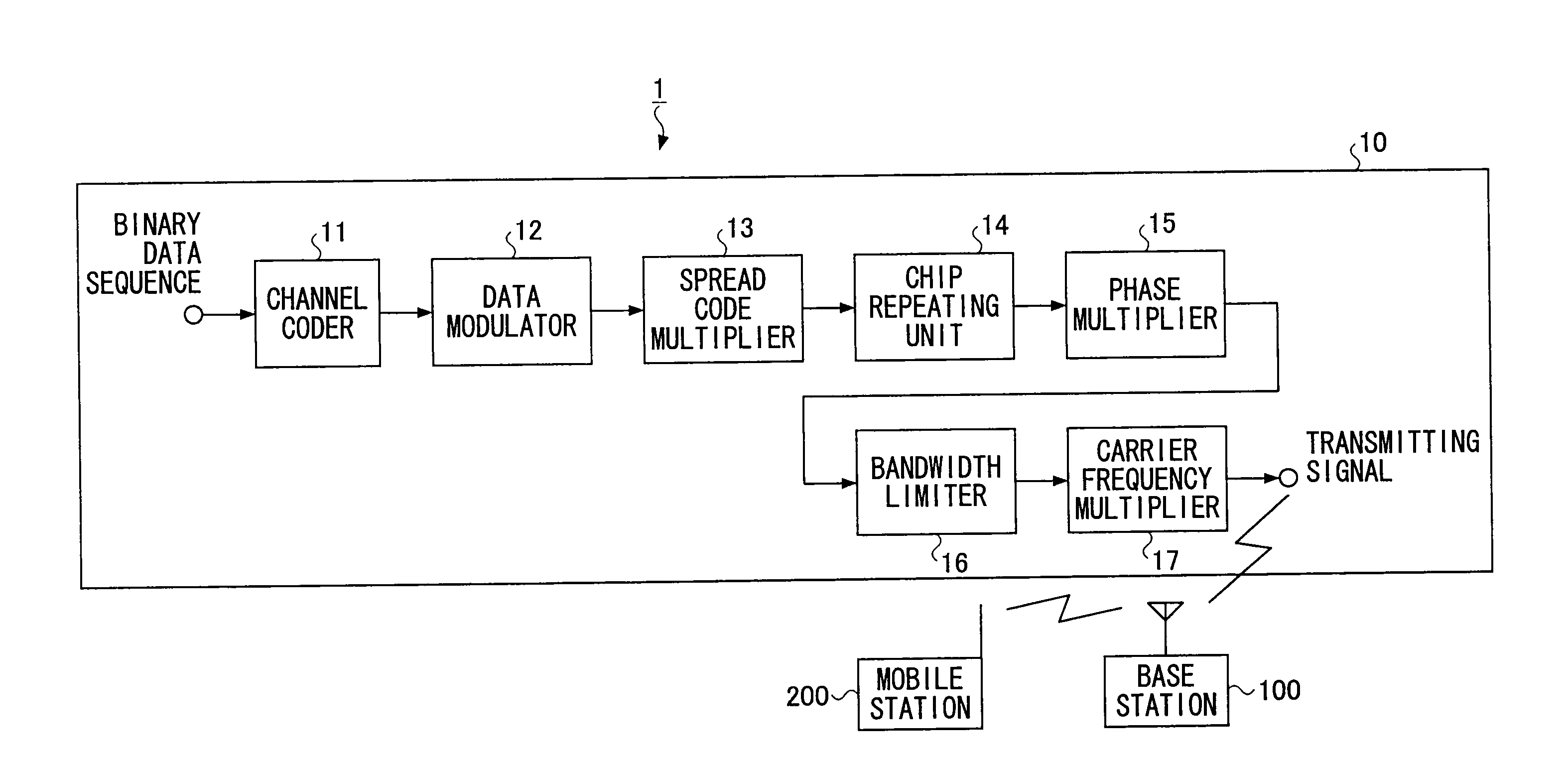
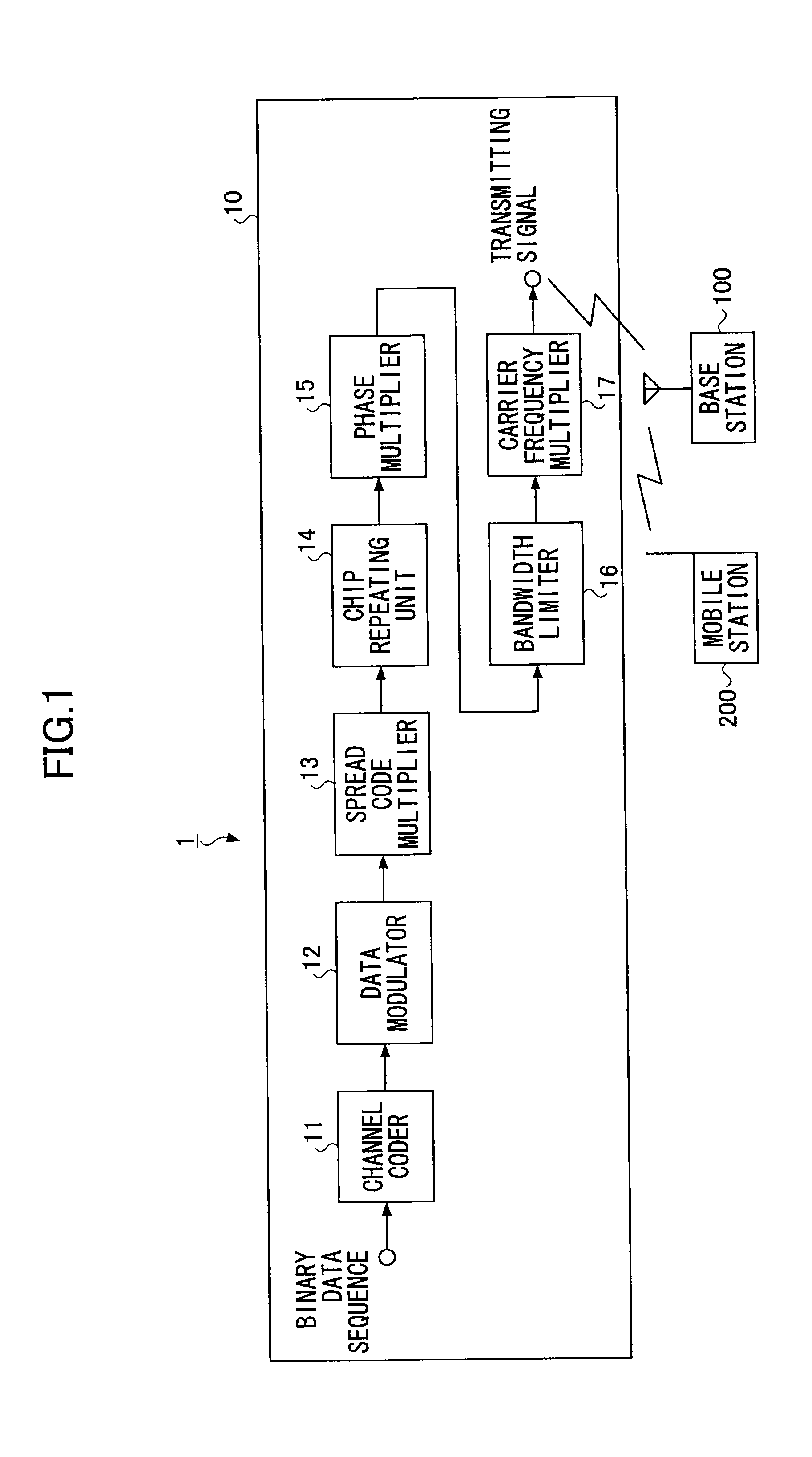
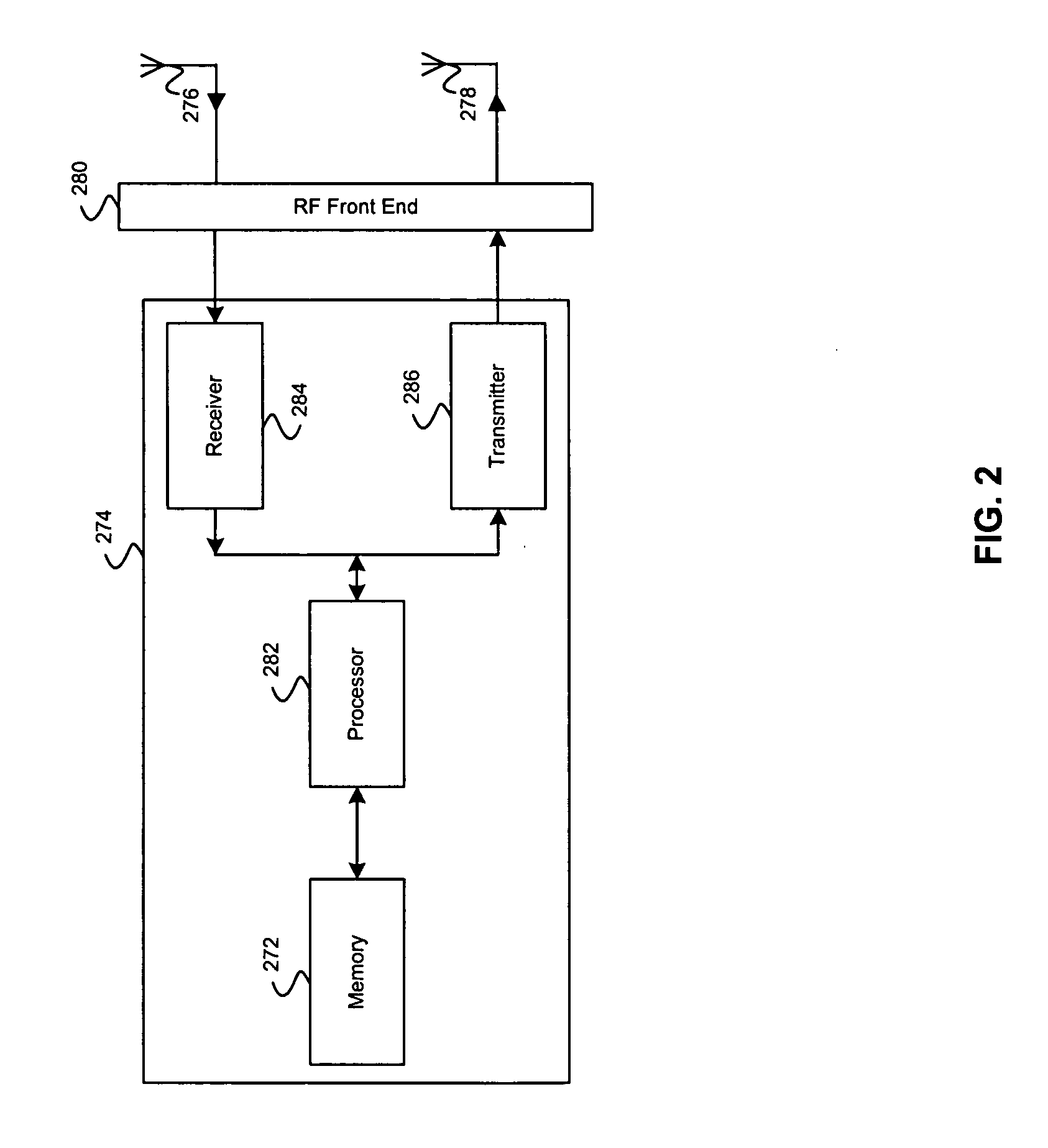
Mobile station and a base station
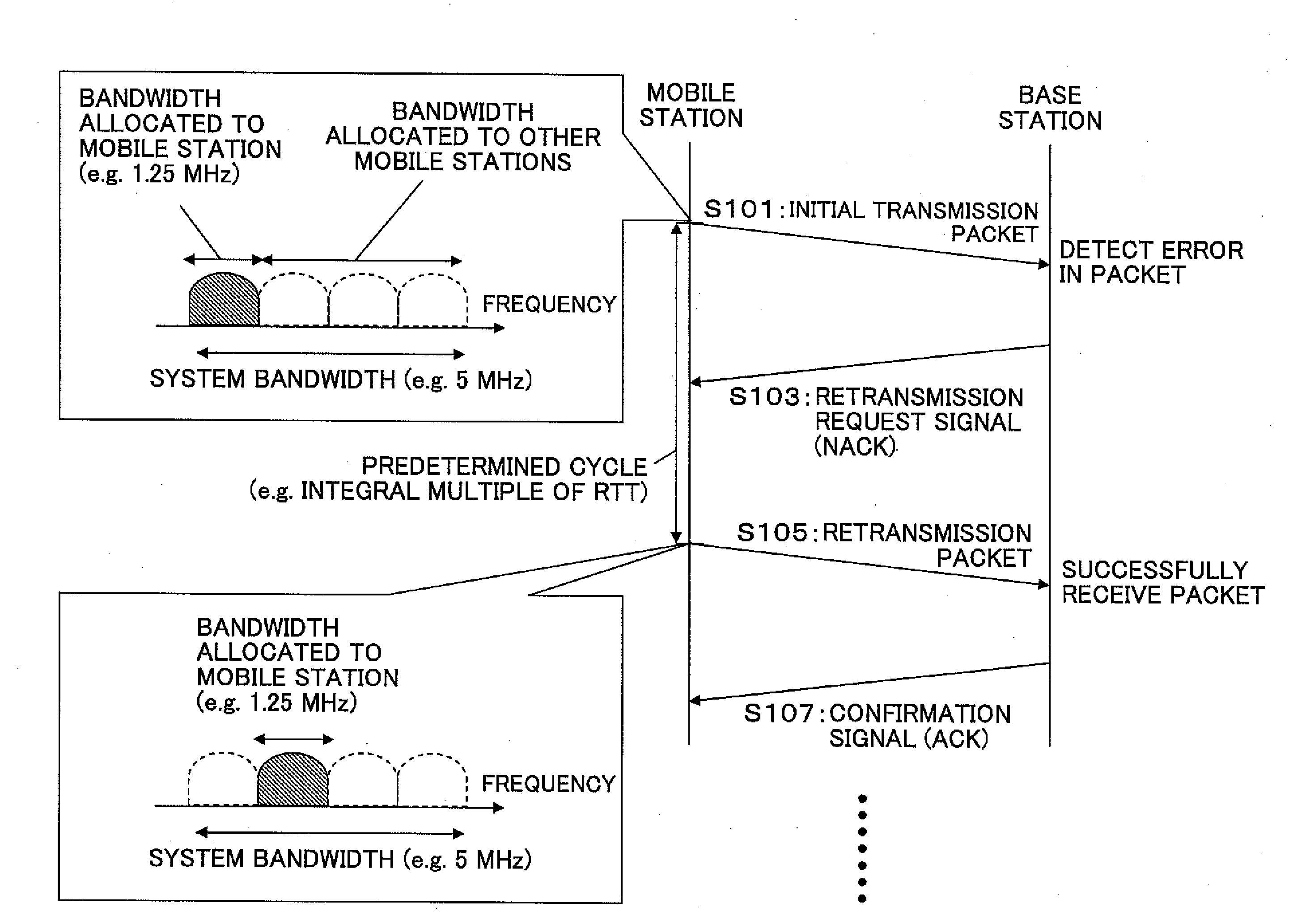
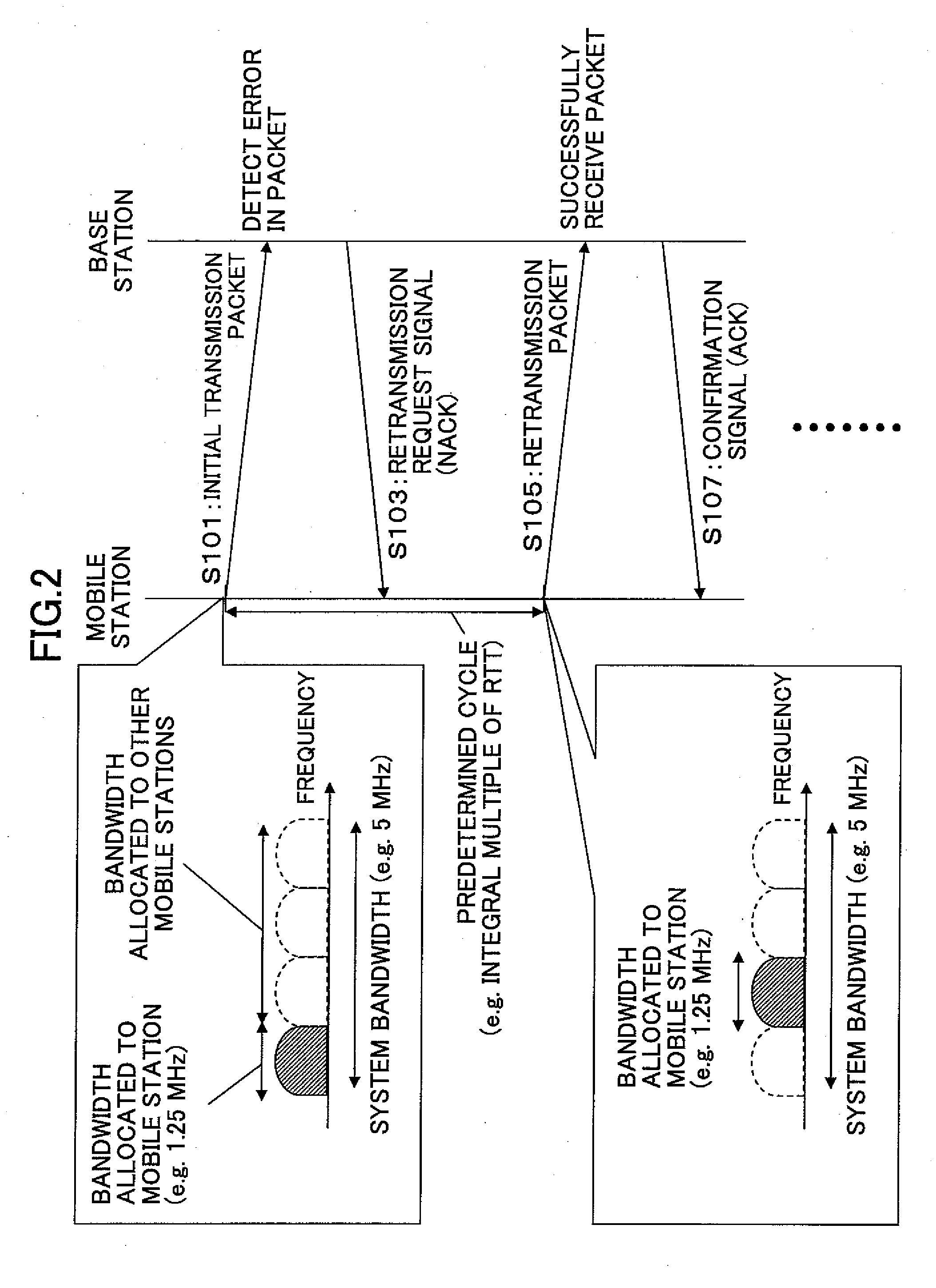
ActiveUS20090175369A1Improve reception qualityError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission path divisionControl signalMobile station
A mobile station includes a control unit configured to change at least one parameter for a retransmission packet from that of a transmission packet, where the at least one parameter is selected from a data modulation scheme; a channel coding rate; a puncturing pattern; a spreading factor; a frequency bandwidth; a frequency allocation position; and transmission power. A base station includes a retransmission format determining unit configured to determine a pattern used for changing at least one parameter for a retransmission packet from that of a transmission packet to determine a format for the retransmission packet, where the at least one parameter is selected from a data modulation scheme; a channel coding rate; a puncturing pattern; a spreading factor; a frequency bandwidth; a frequency allocation position; and transmission power; and a control signal generating unit configured to generate a control signal based on the format for the retransmission packet determined by the retransmission format determining unit.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Mobile station capable of and a method for generating chip patterns for transmission
InactiveUS20080214222A1Easy to useIncrease link capacityDwelling equipmentConnection managementSpread factorEngineering
A base station configured to communicate with a mobile station includes a controlling-information transmitting unit and a receiving unit. The controlling-information transmitting unit is configured to transmit to the mobile station as a set of controlling information, an information set indicating an environment of a cell which is resided by the mobile station, or an information set indicating power of interference from surrounding cells, or an information set indicating a condition of propagation channel. The receiving unit is configured to receive a signal transmitted from the mobile station, based on said set of controlling information, via a variably-controlling process of a spreading factor and a number of chip repetitions.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Method of managing processing resources in a mobile radio system
InactiveUS20020119784A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMobile radioSpreading factor
A method of managing processing resources in a mobile radio system, in which a first entity manages radio resources and corresponding processing resources, the latter being provided in a second entity separate from the first entity, in which method: the second entity signals to the first entity its global processing capacity, or capacity credit, and the consumption law, or quantity of said global processing capacity, or cost, for different spreading factor values, the first entity updates the capacity credit on the basis of the consumption law, and in the case of multicode transmission using N spreading codes, said updating is effected on the basis of the cost for at least one of the N spreading codes.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method of adaptive Walsh code allocation
InactiveUS7280581B2Increase voice capacityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMultiplex code allocationCommunications systemSpread factor
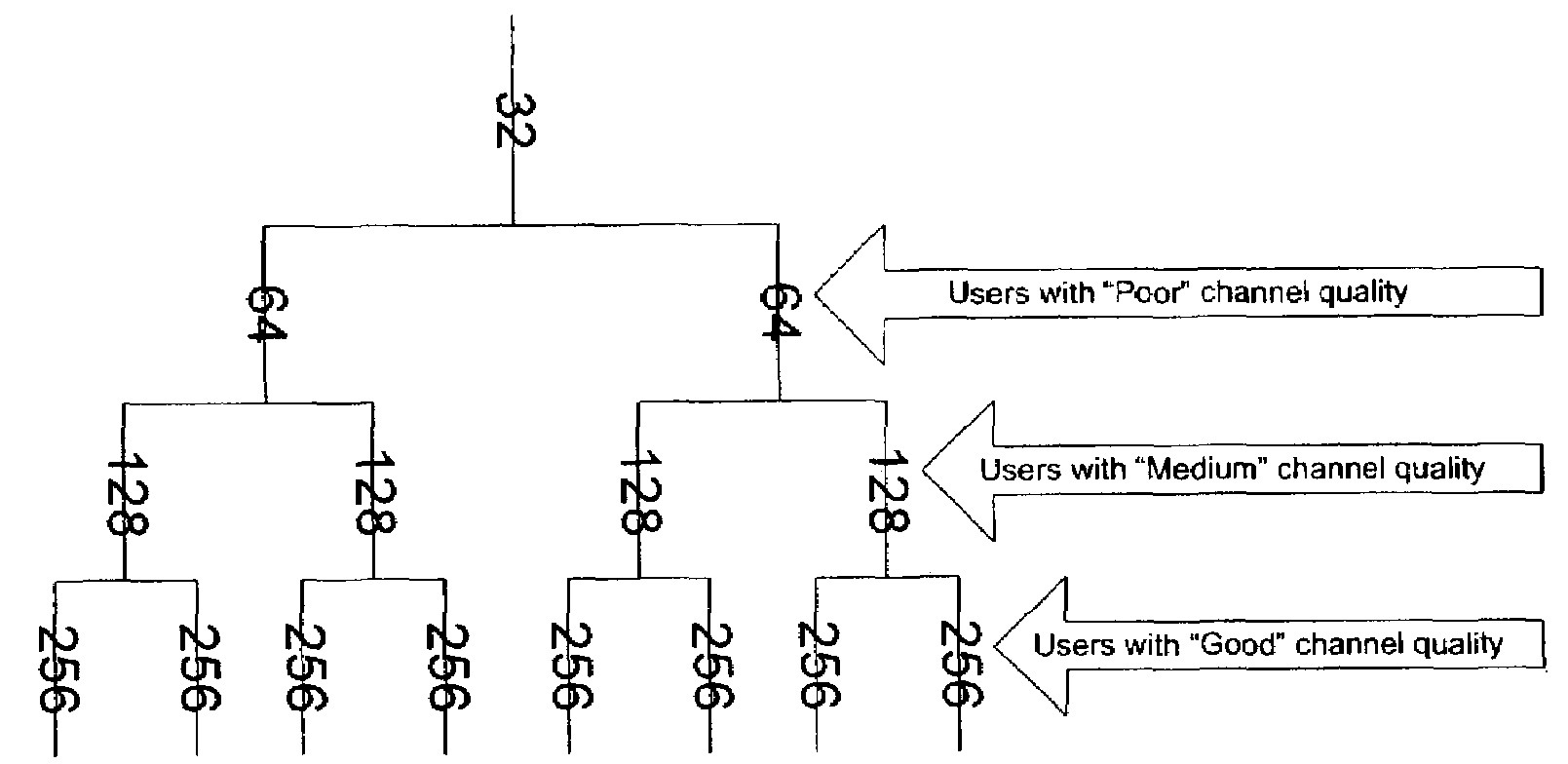
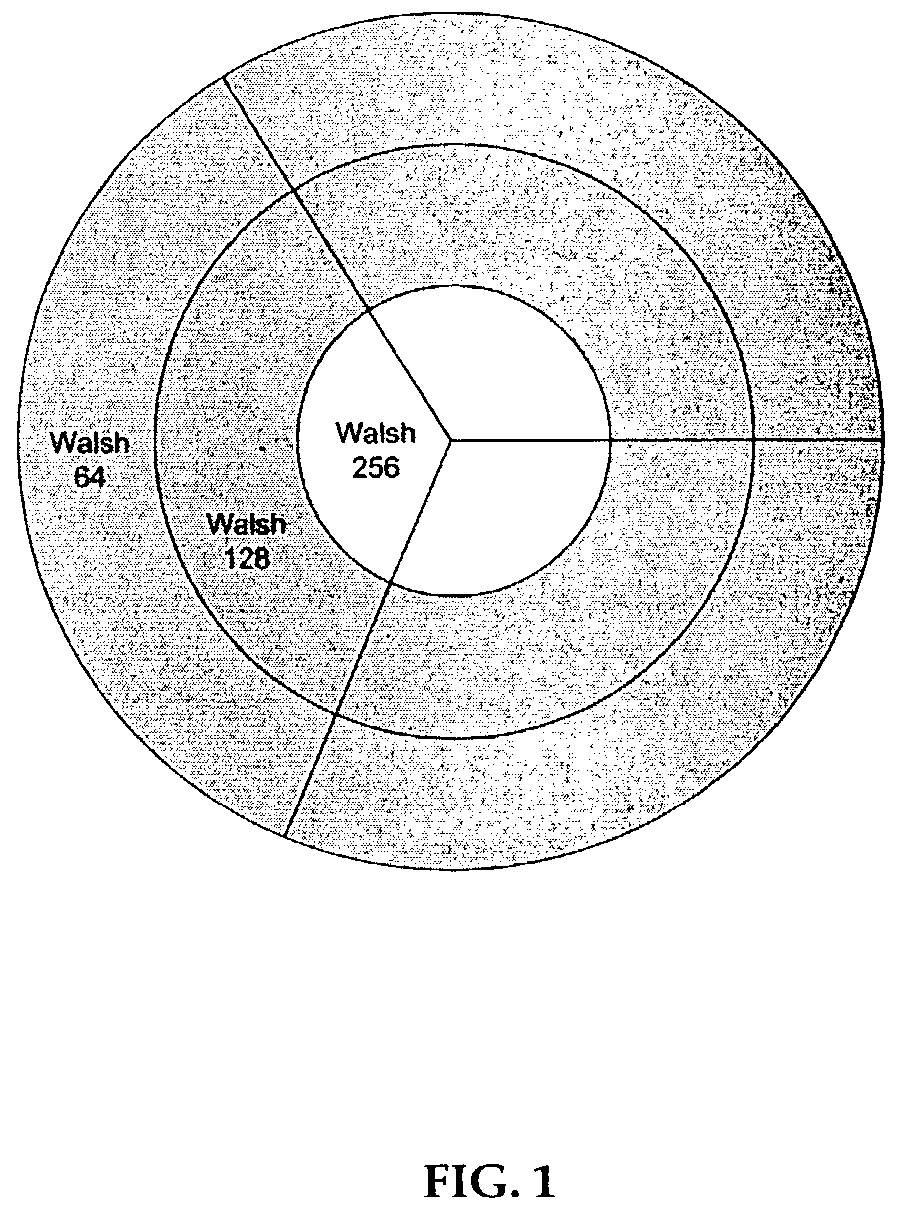
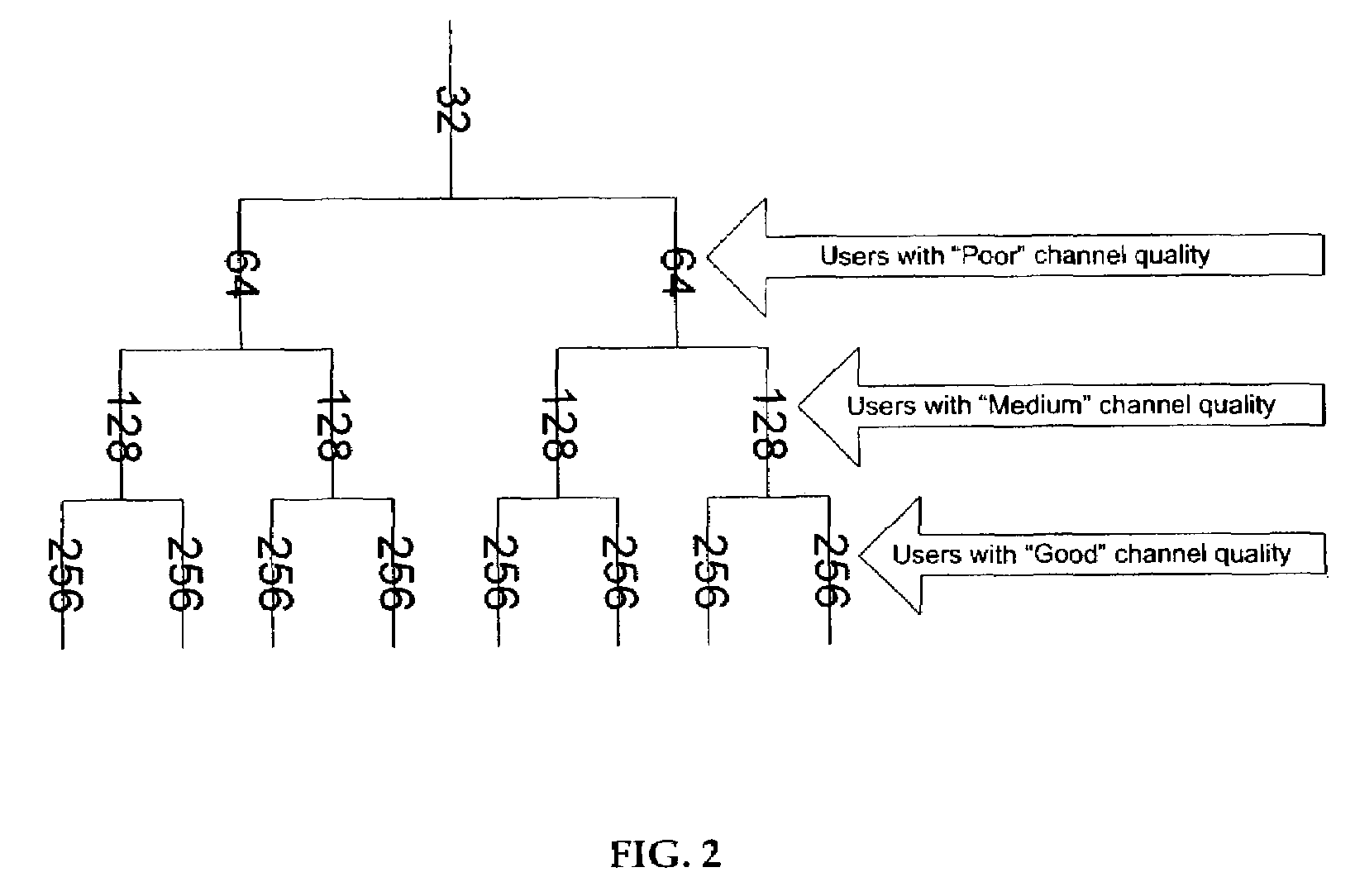
A method of adaptive Walsh code allocation in a wireless communication system. The method includes the step of each voice user transmitting quality condition signal, such as a pilot signal strength measurement to a corresponding base station. Upon receiving each quality condition signal, the method includes determining a spreading factor for each voice user in response to its quality condition signal. A Walsh code is thereafter allocated to each voice user in response to the determined corresponding spreading factor. Thus, for example, if the quality condition signal of a first voice user is relatively higher than the quality condition signal of a second voice user, the spreading factor allocated to the first voice user should be longer than the spreading factor of the second voice user.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
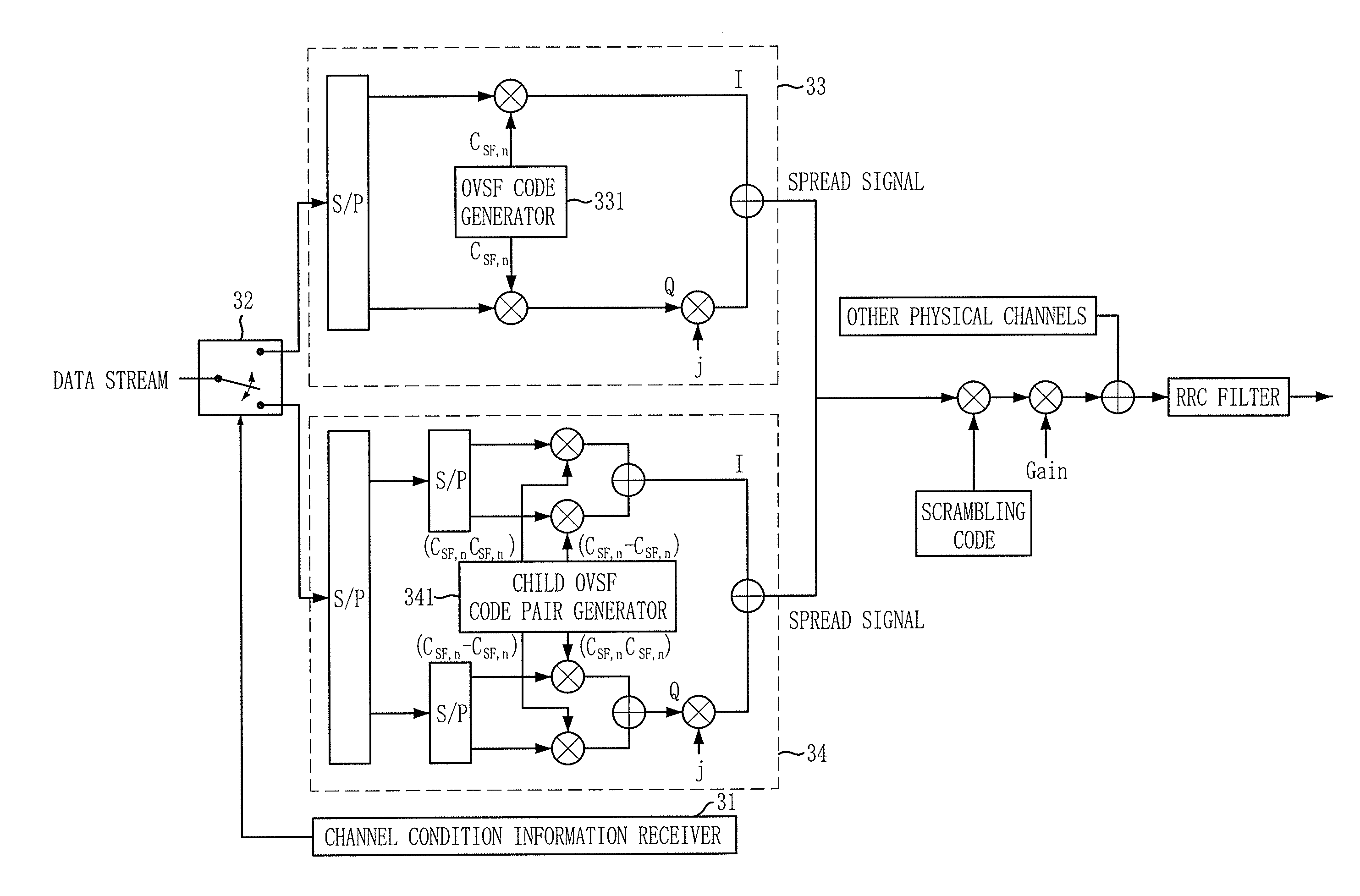
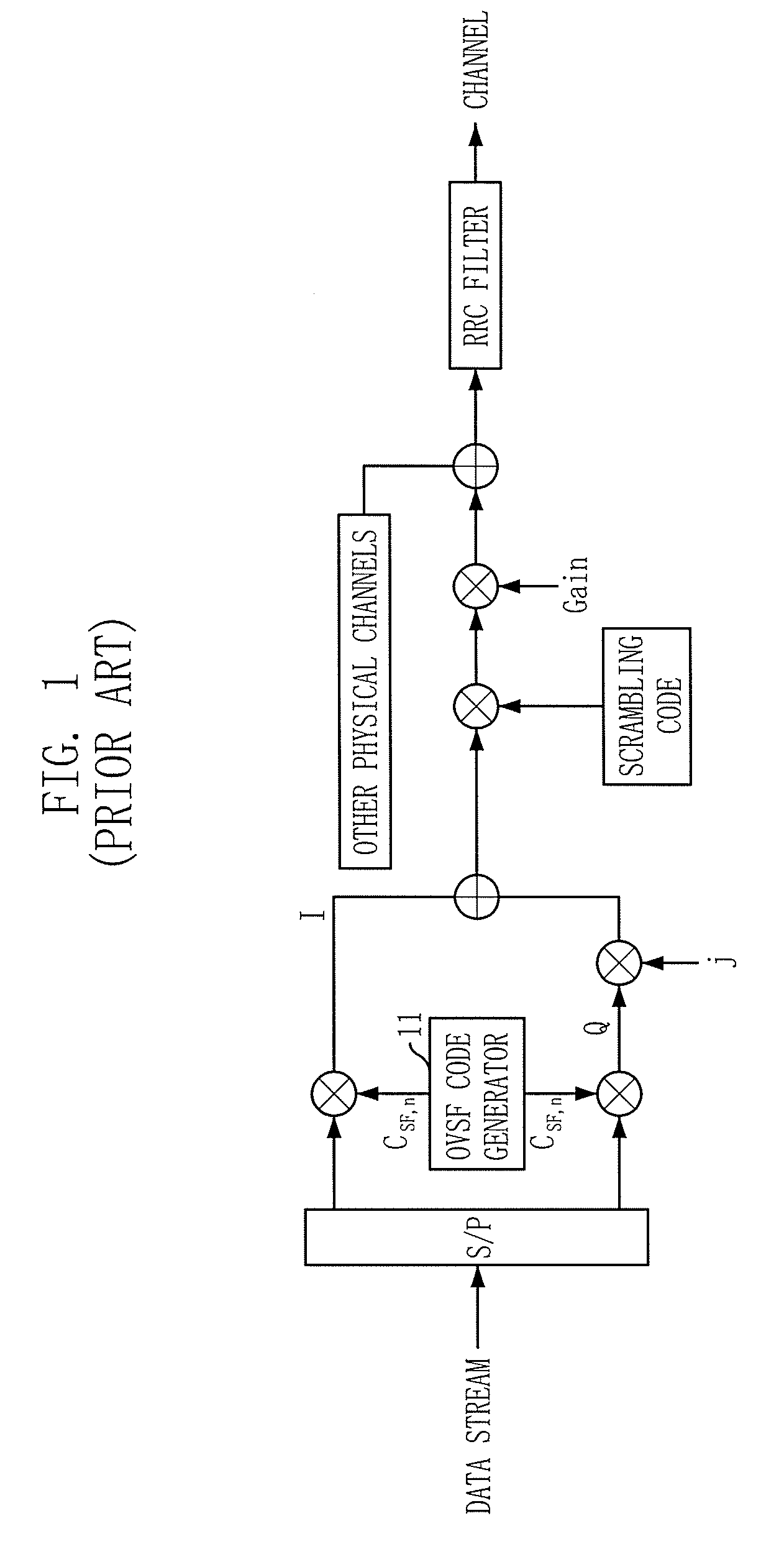
Apparatus and method for spreading/despreading data using pair of child orthogonal variable spreading factor codes
InactiveUS20080130716A1Enhanced signalReduce Intersymbol InterferenceAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAngle modulationData streamEngineering
there is provided a spreading apparatus using a child orthogonal variable spreading factor (OVSF) code pair, including: a channel condition information receiving unit for receiving channel condition information including a channel condition metric; a switch controlling unit for receiving the channel condition information from the channel condition information receiving unit and transferring data stream according to the received channel station information; a first spreading unit for receiving the data stream from the switching controlling unit, and spreading the data stream using a single OVSF code; and a second spreading unit for receiving the data stream from the switching controlling unit, and spreading the data stream using a child OVSF code pair.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
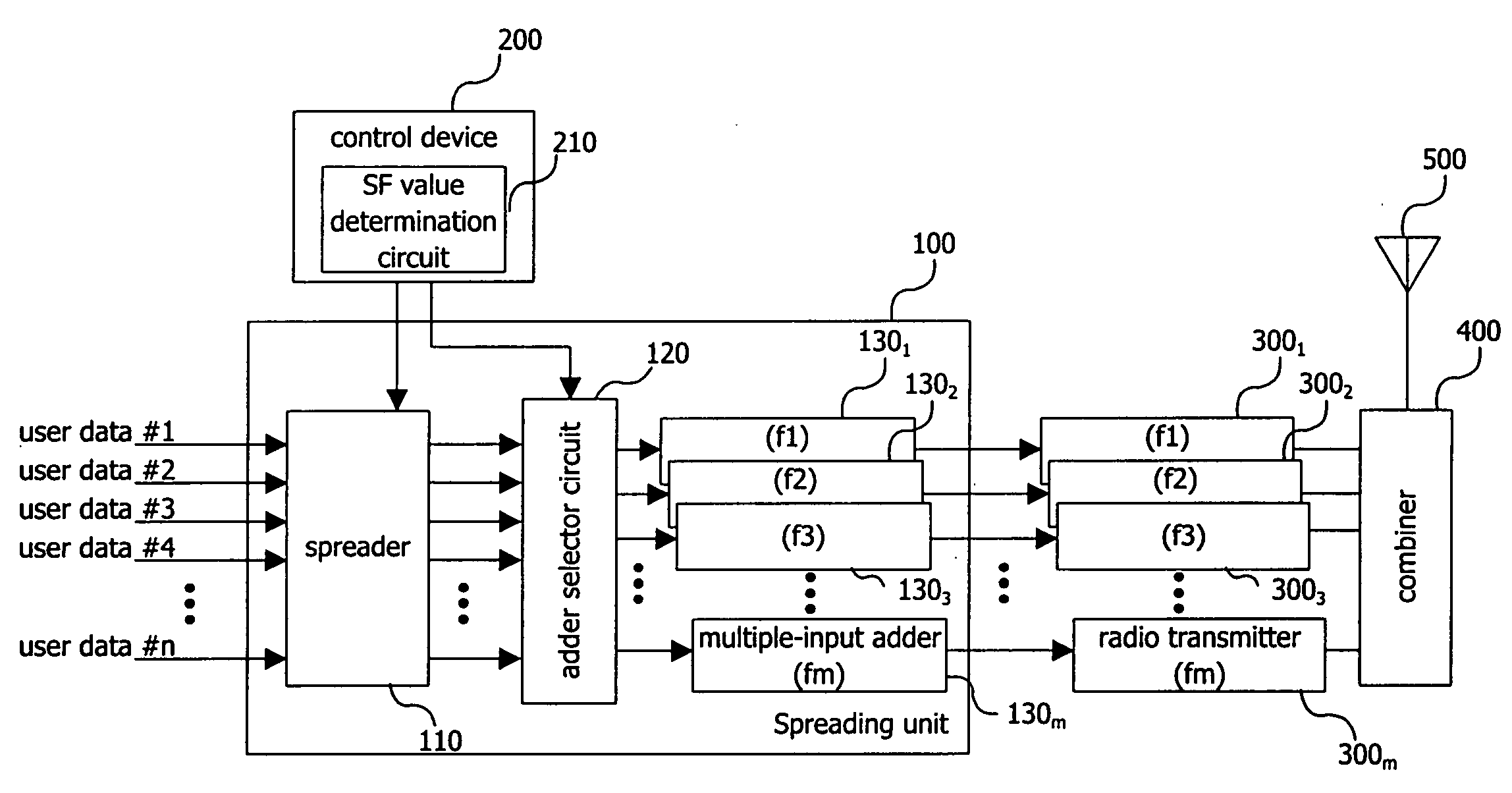
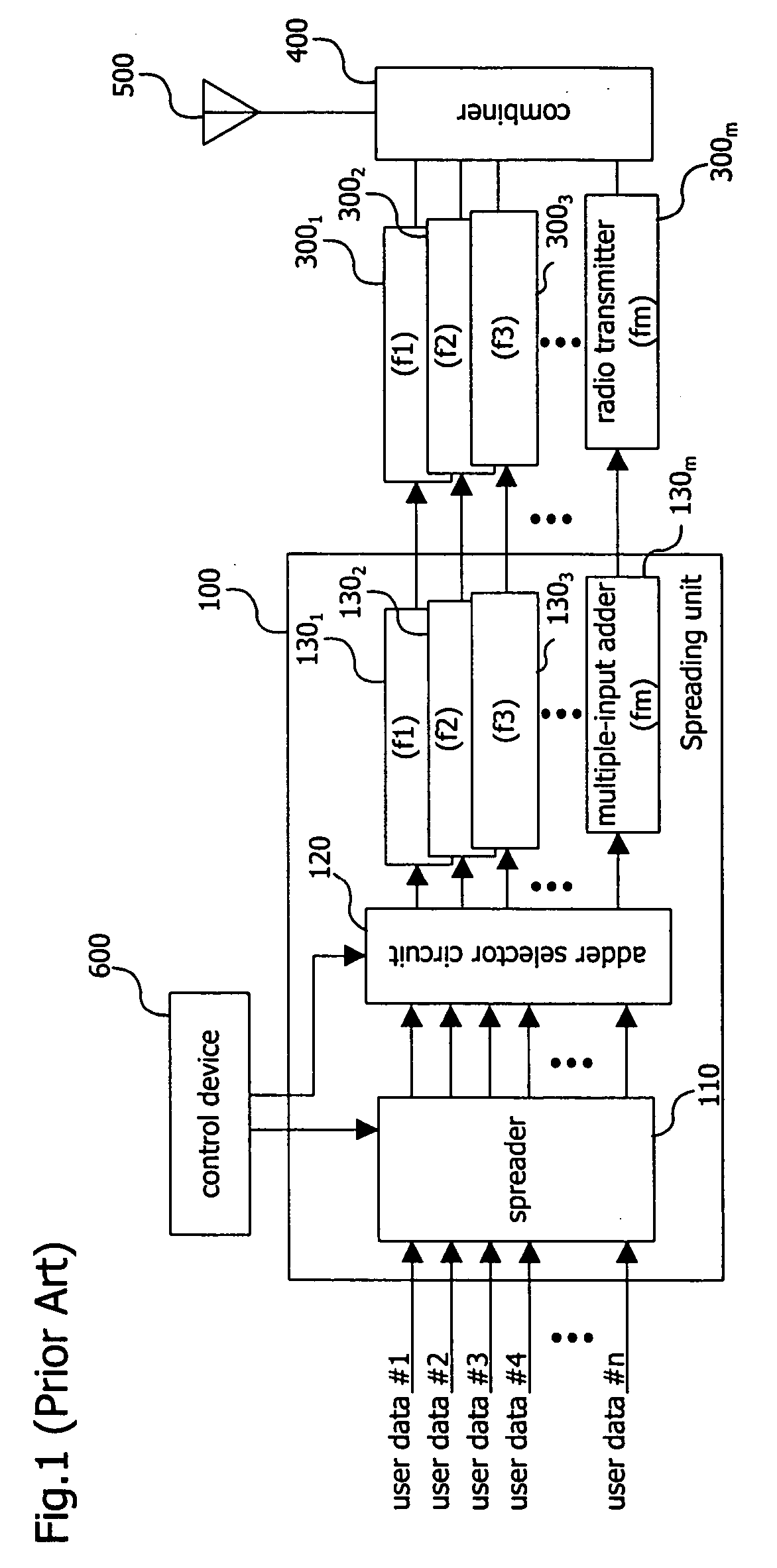
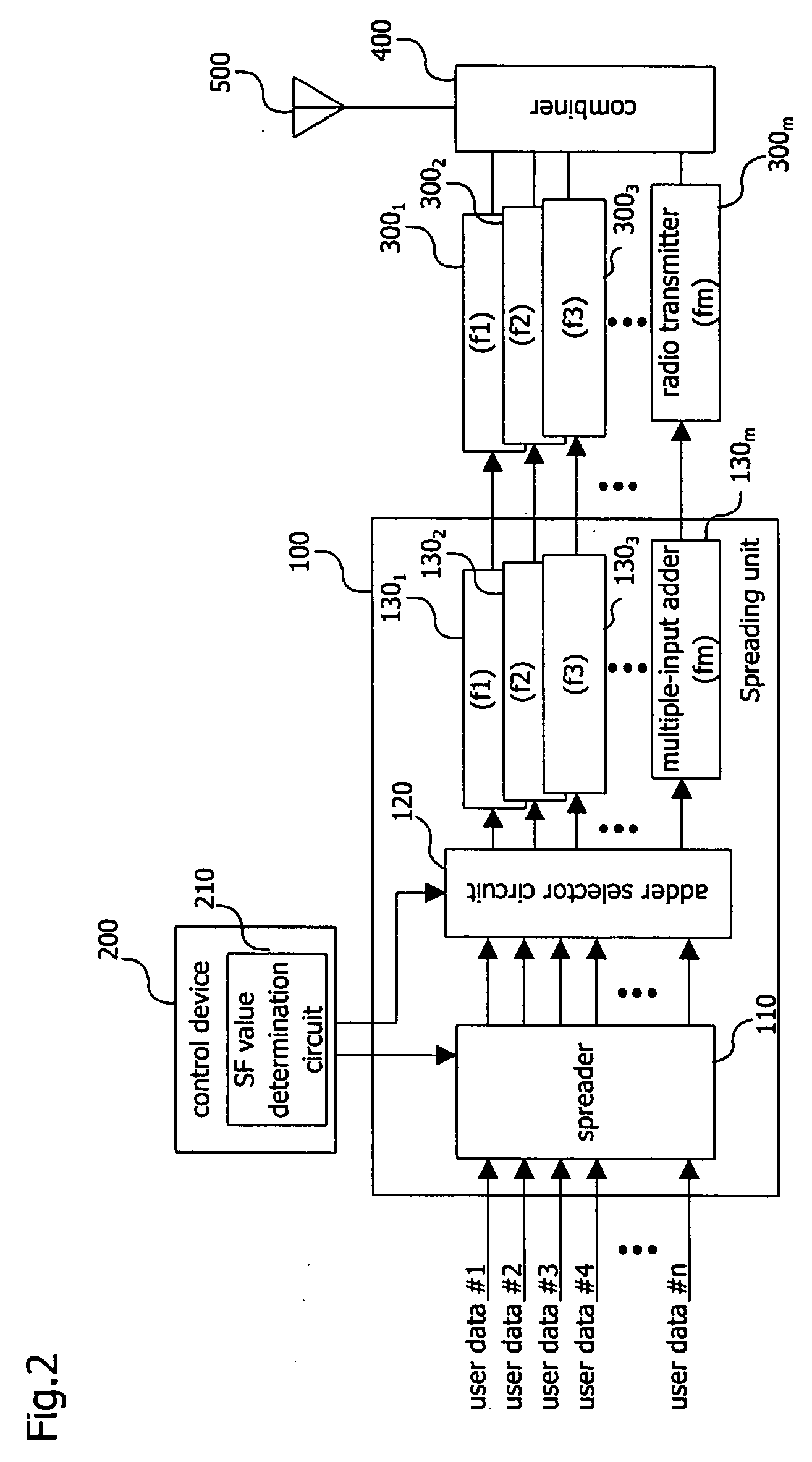
CDMA communication device for improving the usability of frequencies and suppressing the occurrence of call loss
InactiveUS20050025111A1InhibitionImprove usabilityTime-division multiplexConnection managementSpread factorRadiotransmitter
The CDMA communication device of the present invention includes a spreading unit, radio transmitters, and a control device that includes a setting unit and a determination unit. The spreading unit spreads and multiplexes user data of users. The radio transmitters are provided correspondingly to each of a plurality of frequencies, and modulate with the corresponding frequencies the user data that are supplied from the spreading unit. The determination unit determines the working frequency of users based on the spread factor value of the user data. The setting unit sets the spread factor of the user data in the spreading unit. The setting unit further performs setting of the spreading unit such that user data that have undergone spreading are supplied to the radio transmitter that has been provided correspondingly to the frequency determined by the determination unit.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
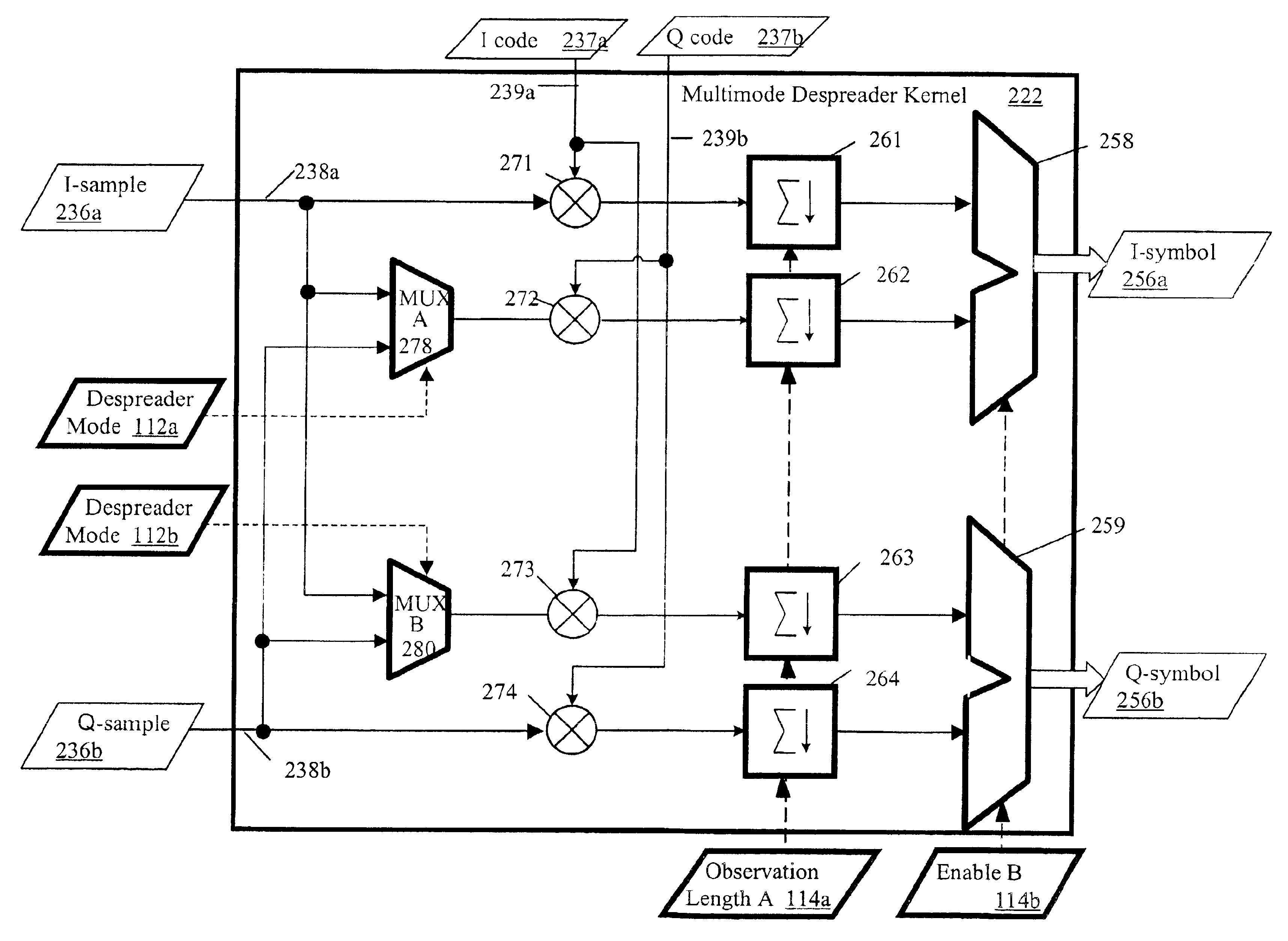
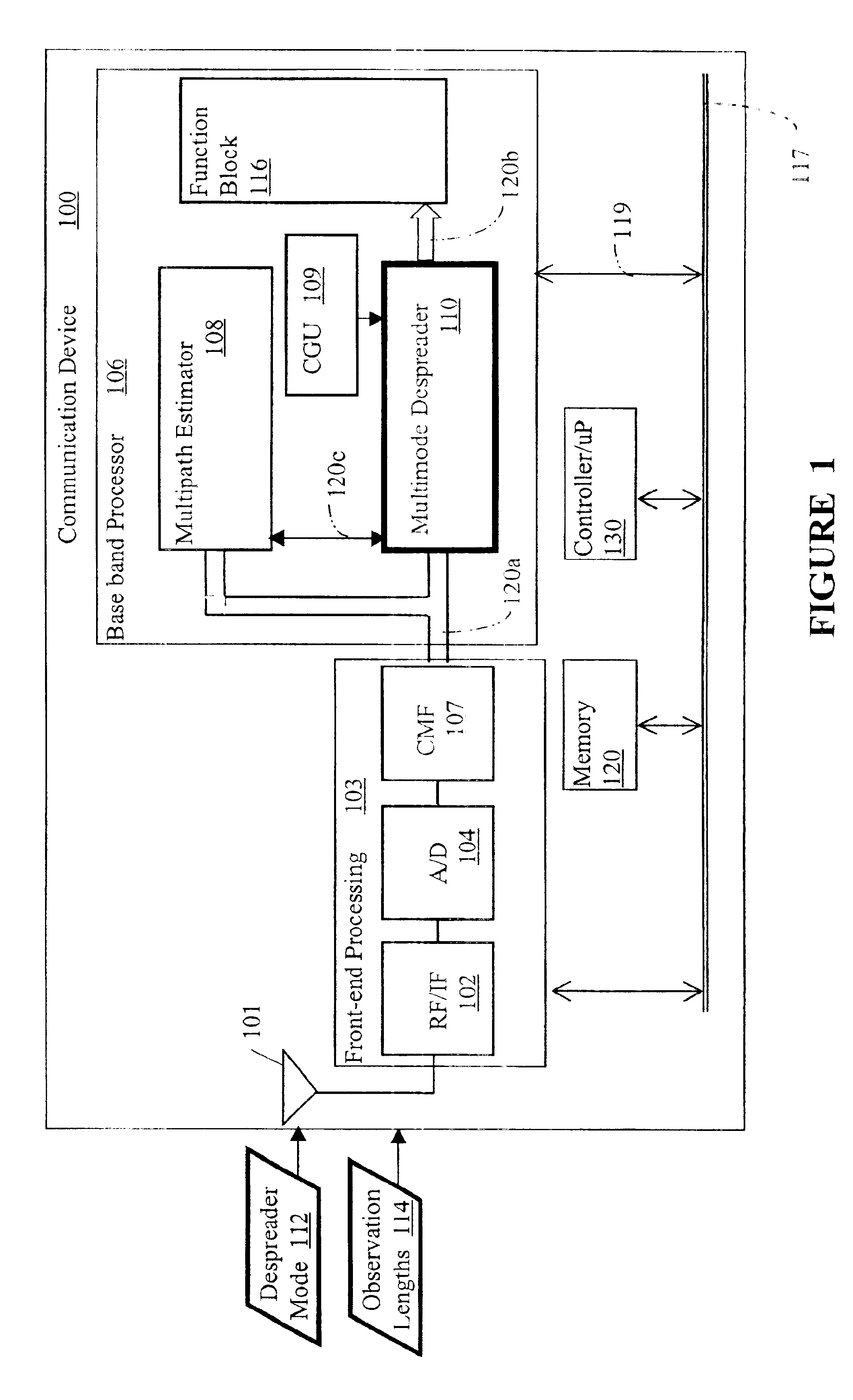
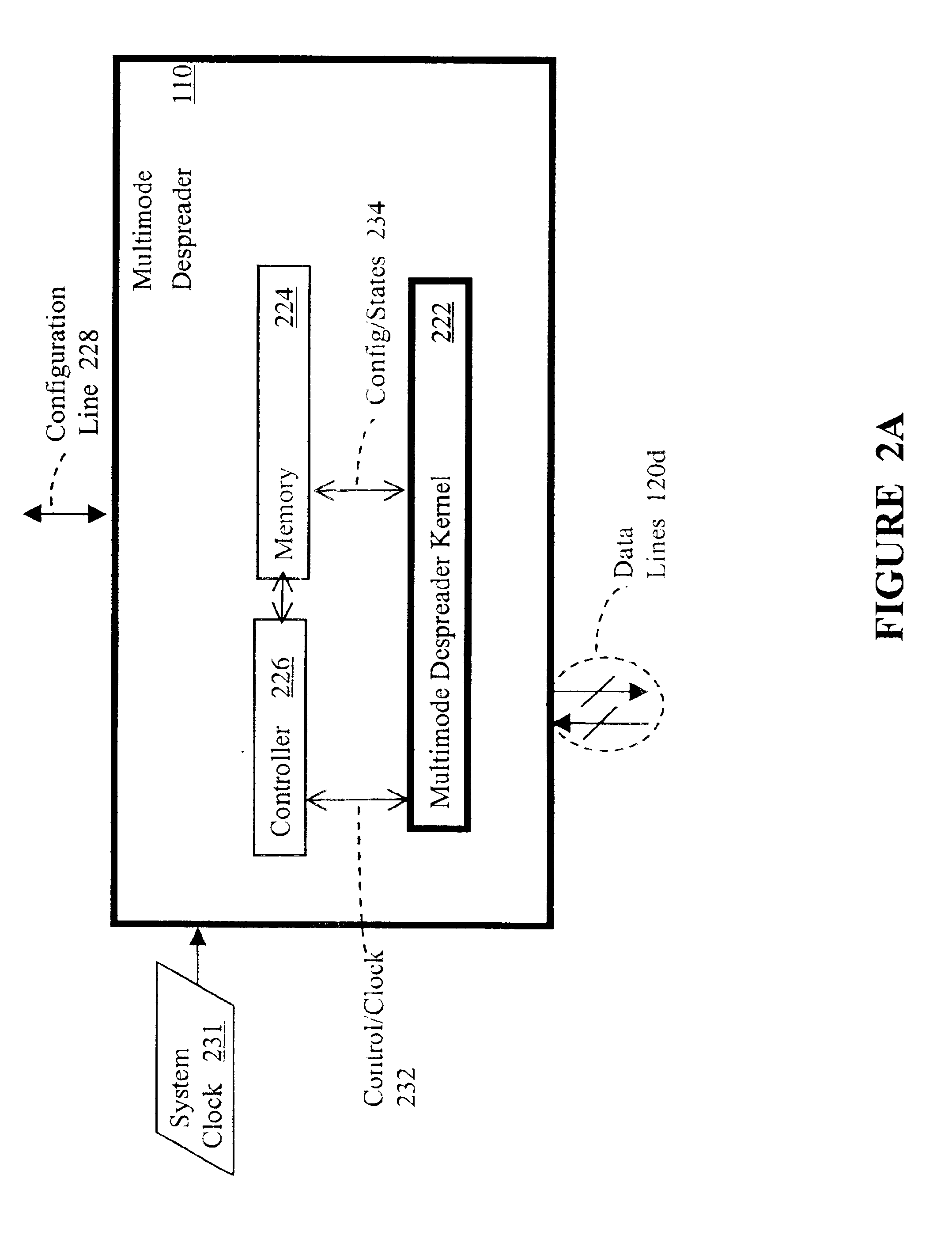
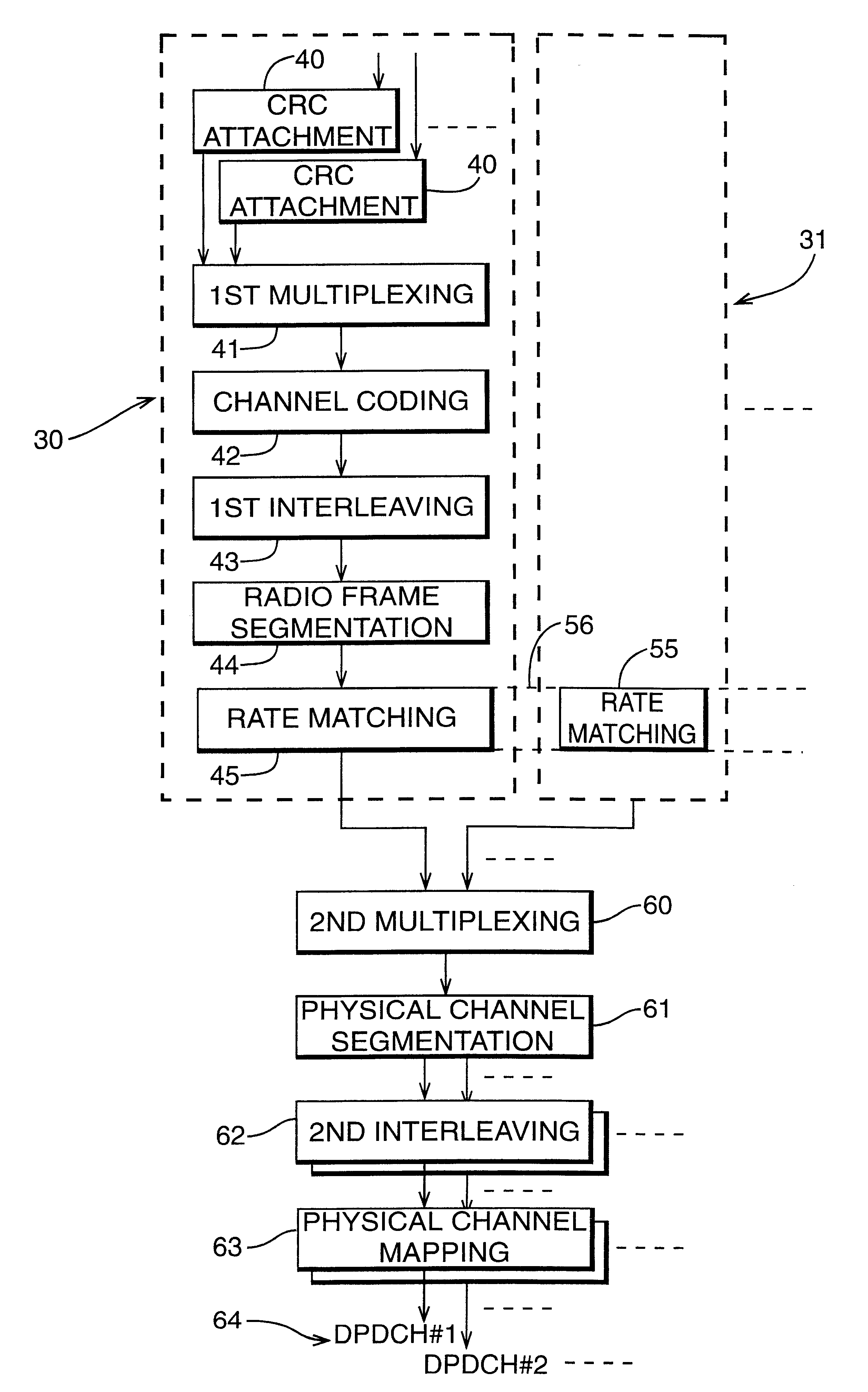
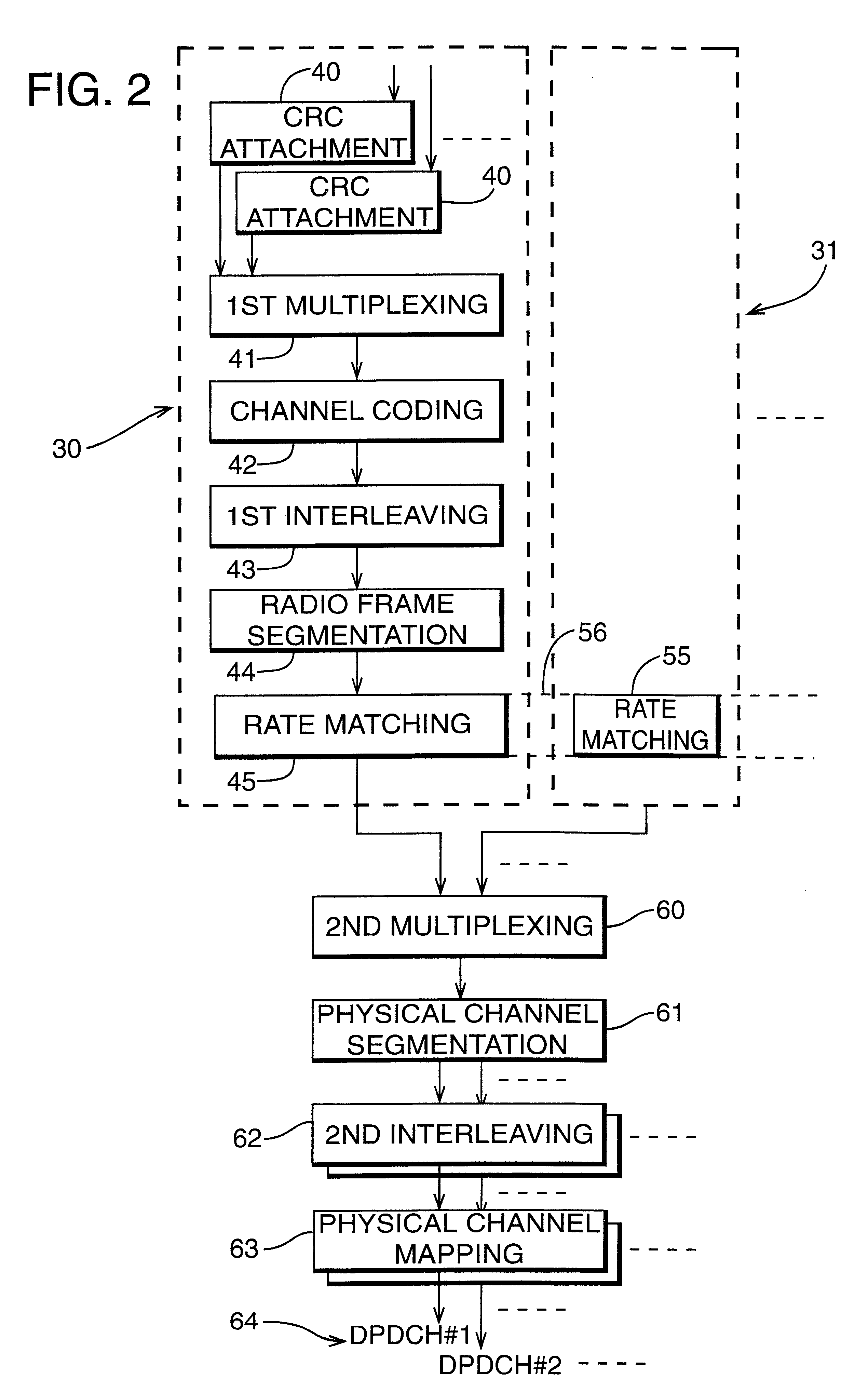
Configurable multimode despreader for spread spectrum applications
InactiveUS6934319B2Overcome limitationsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationBinary multiplierData type
A configurable multimode despreader for spread spectrum applications is disclosed herein. The despreader includes a plurality of data lines, at least one selective coupler coupled to the plurality of data lines, at least one multiplier coupled to the selective coupler, and a code input line coupled to the multiplier. The selective coupler selectively couples one of the plurality of data lines with the multiplier per any one of a plurality of despreading protocols. The multiplier then multiplies a desired input data type received from the selective coupler with a despreading code chip received from the code input line to produce an observation. The programmable multimode despreader supports variable code and data modulation schemes and variable spreading factors.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG +1
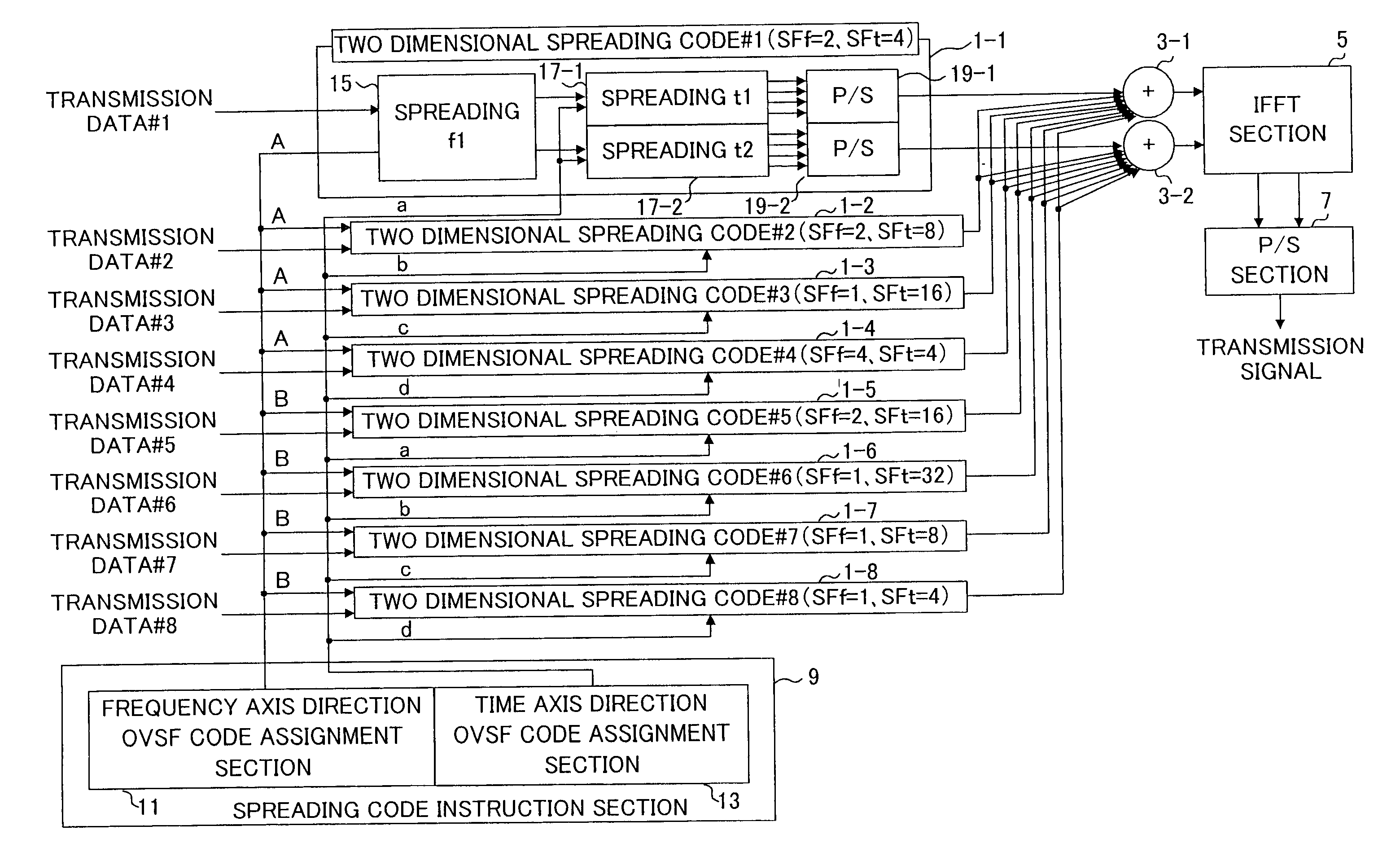
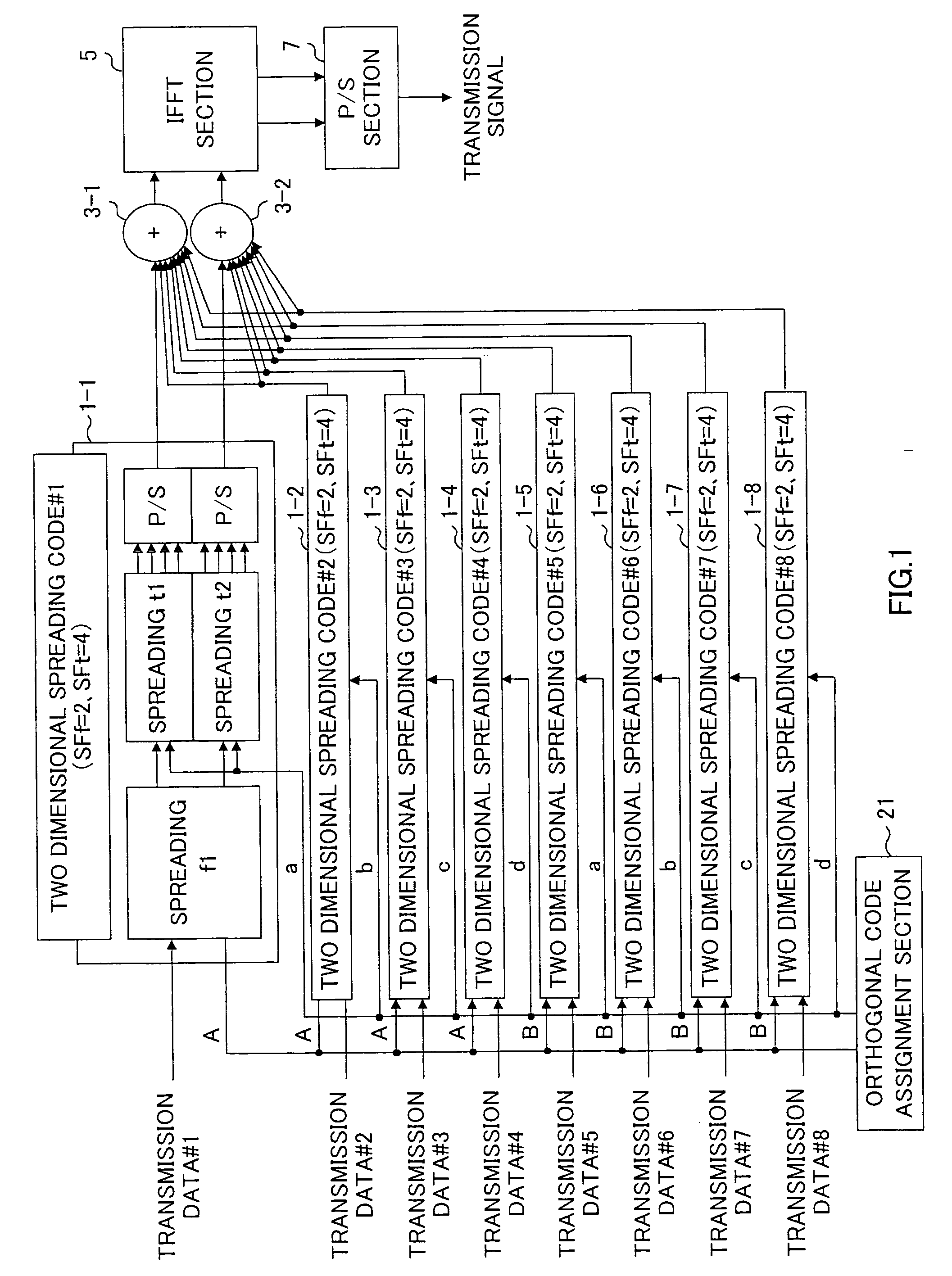
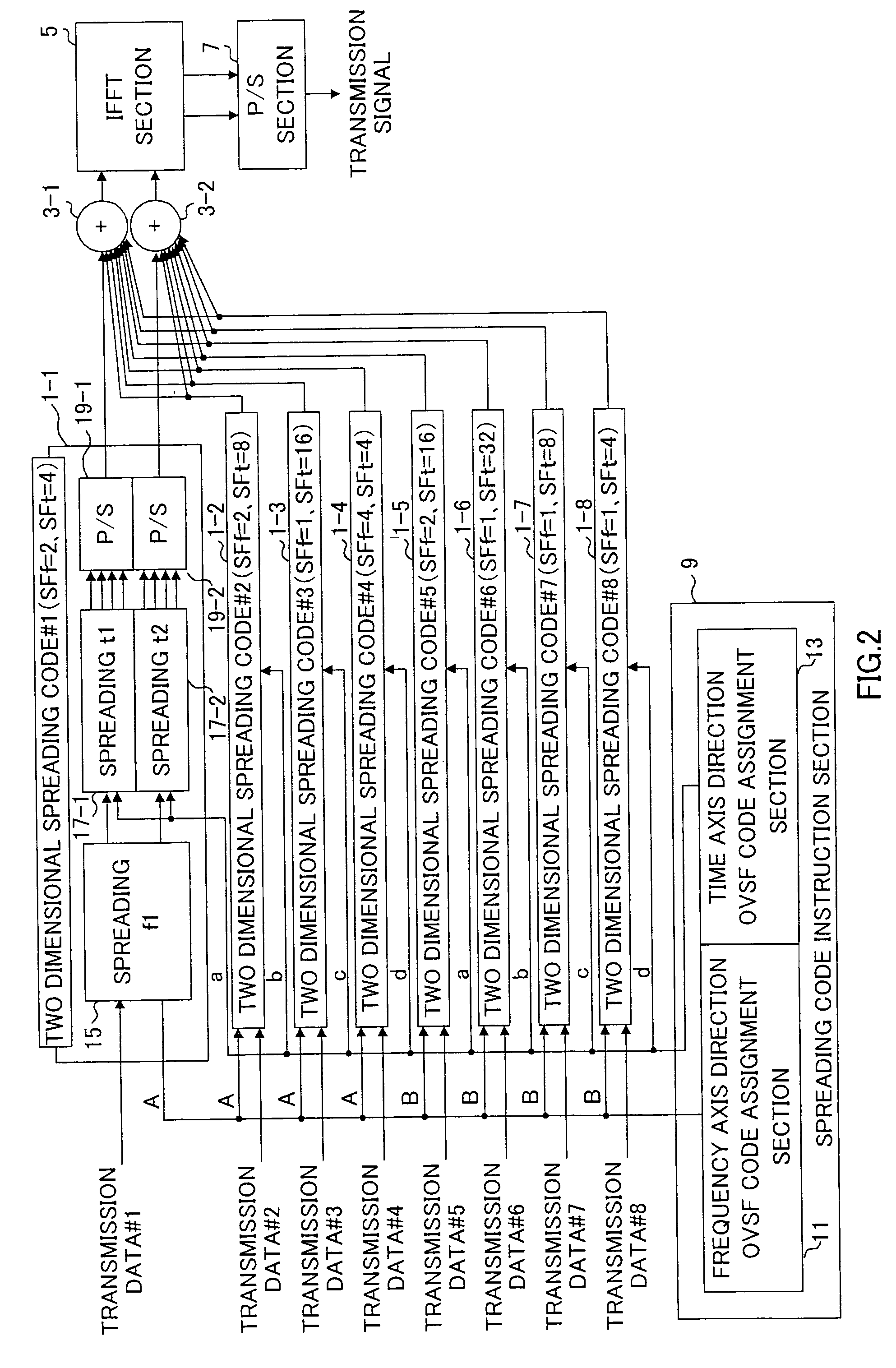
Data transmission apparatus and data transmission method
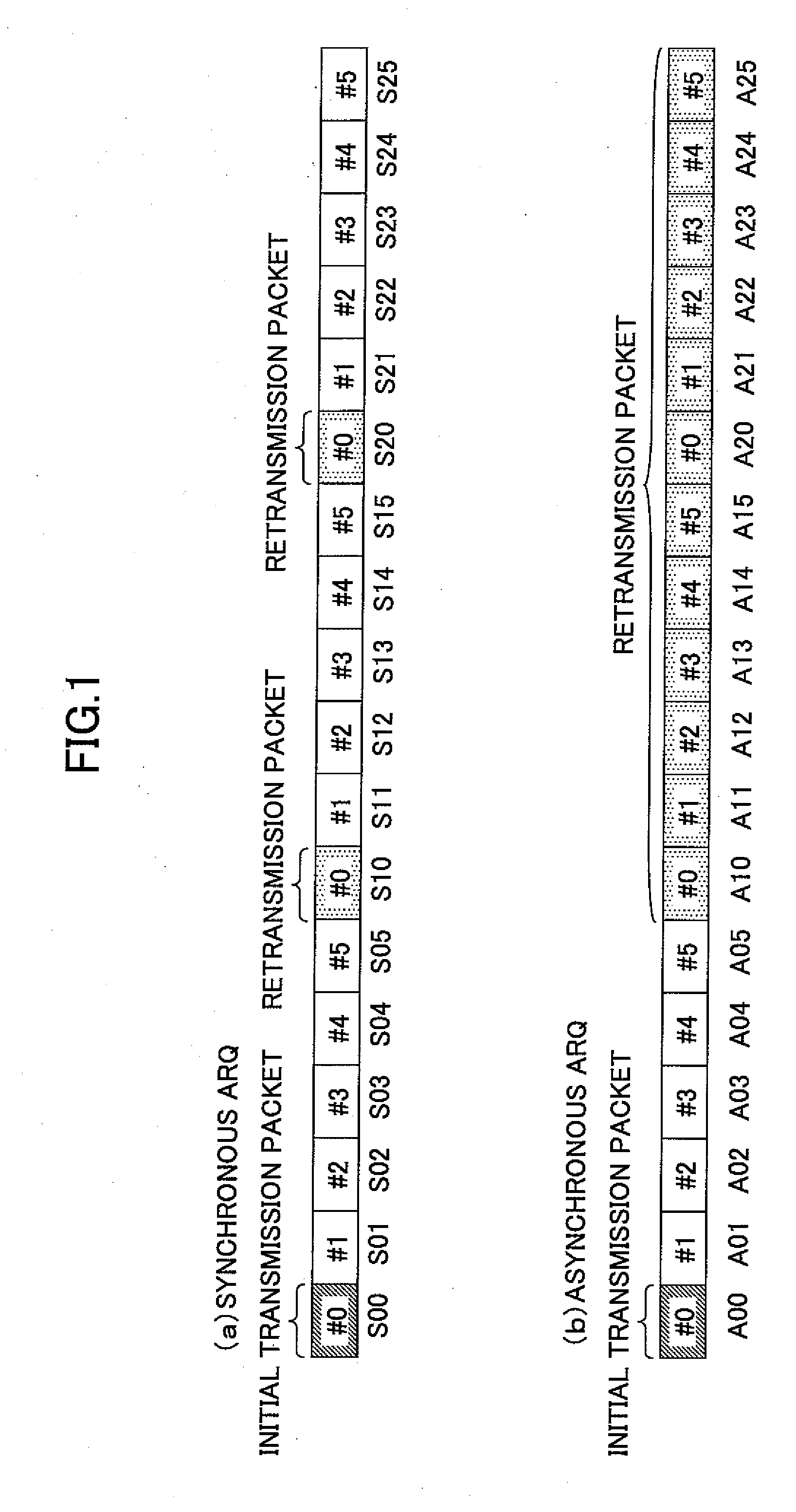
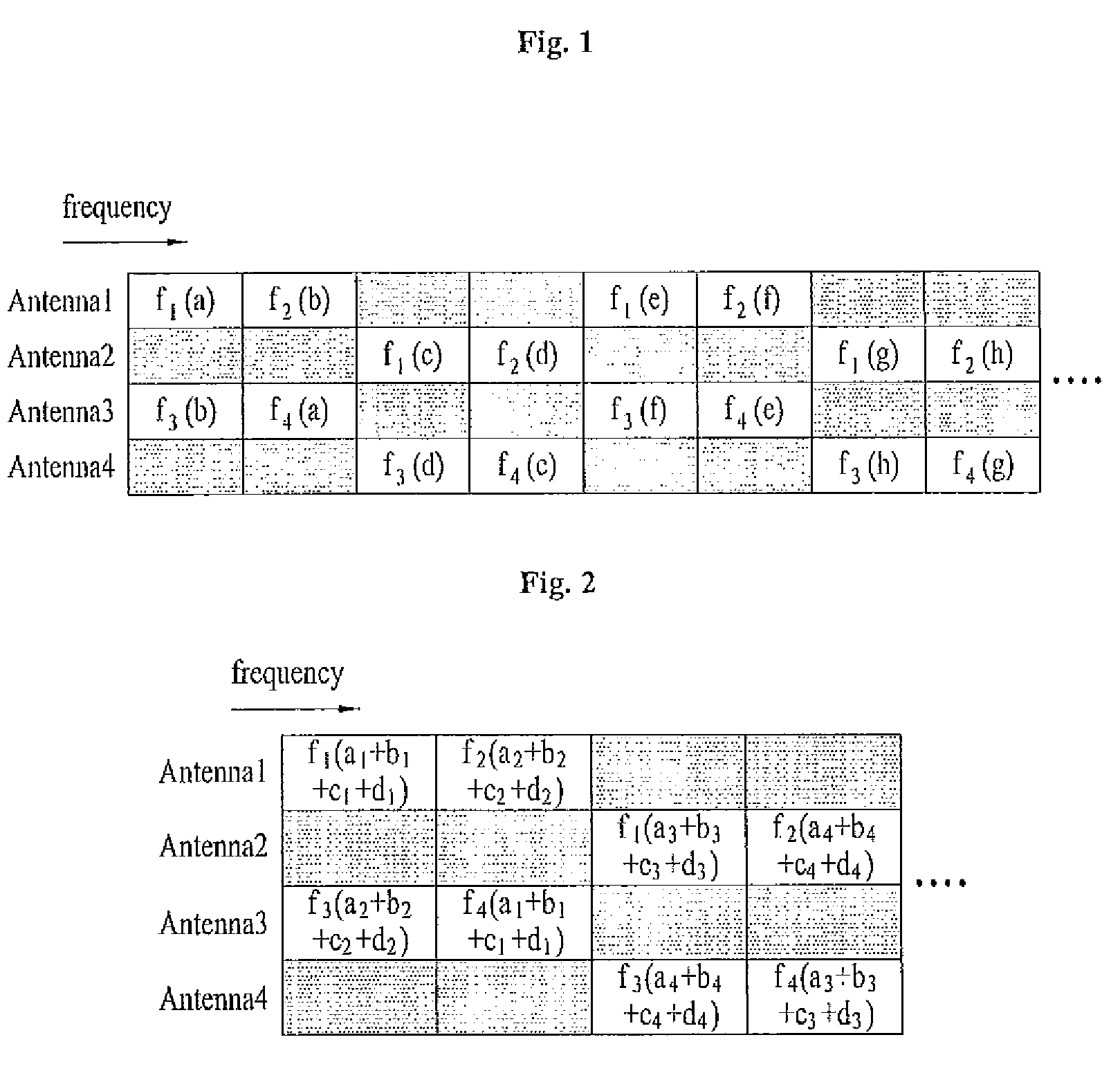
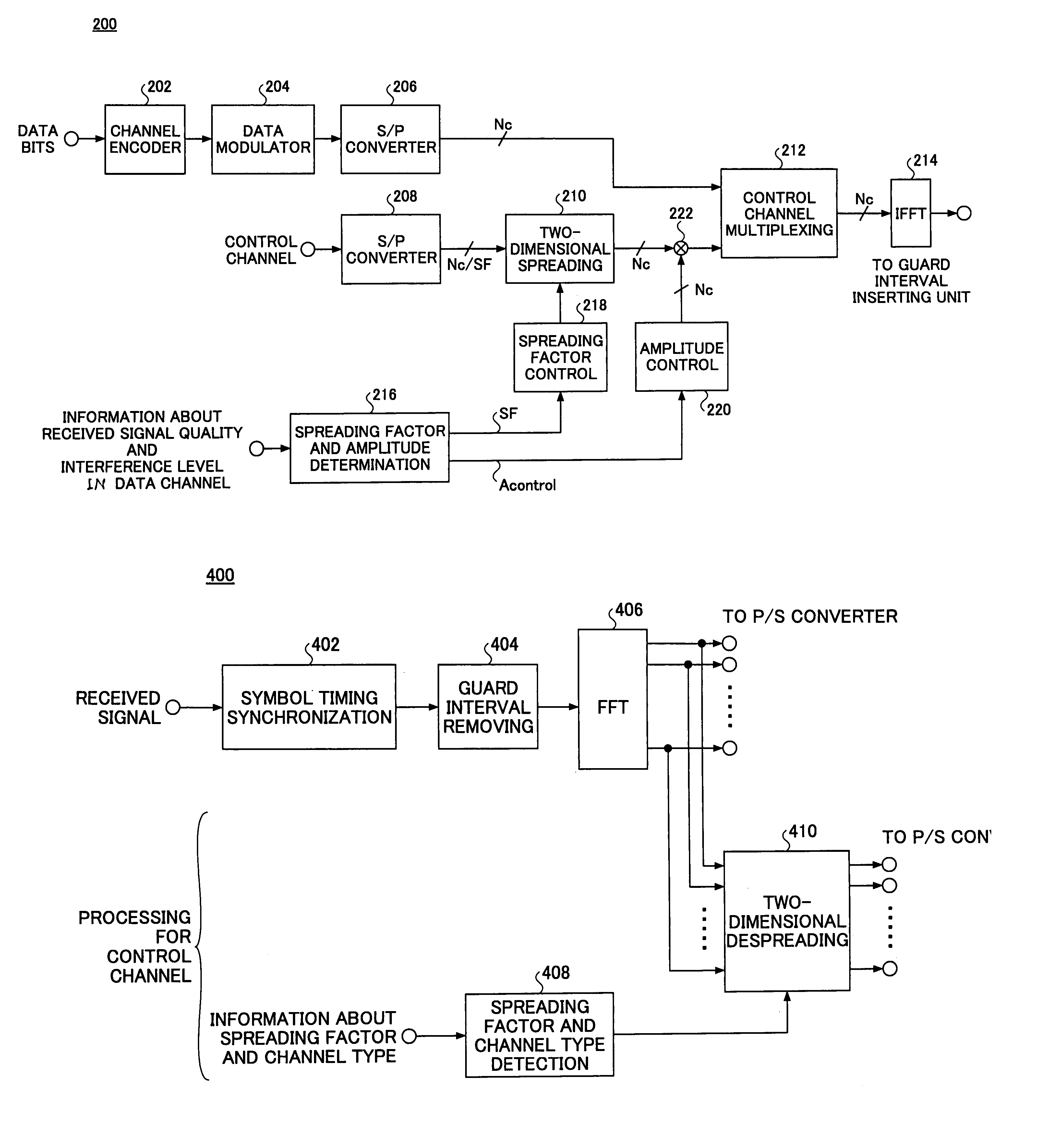
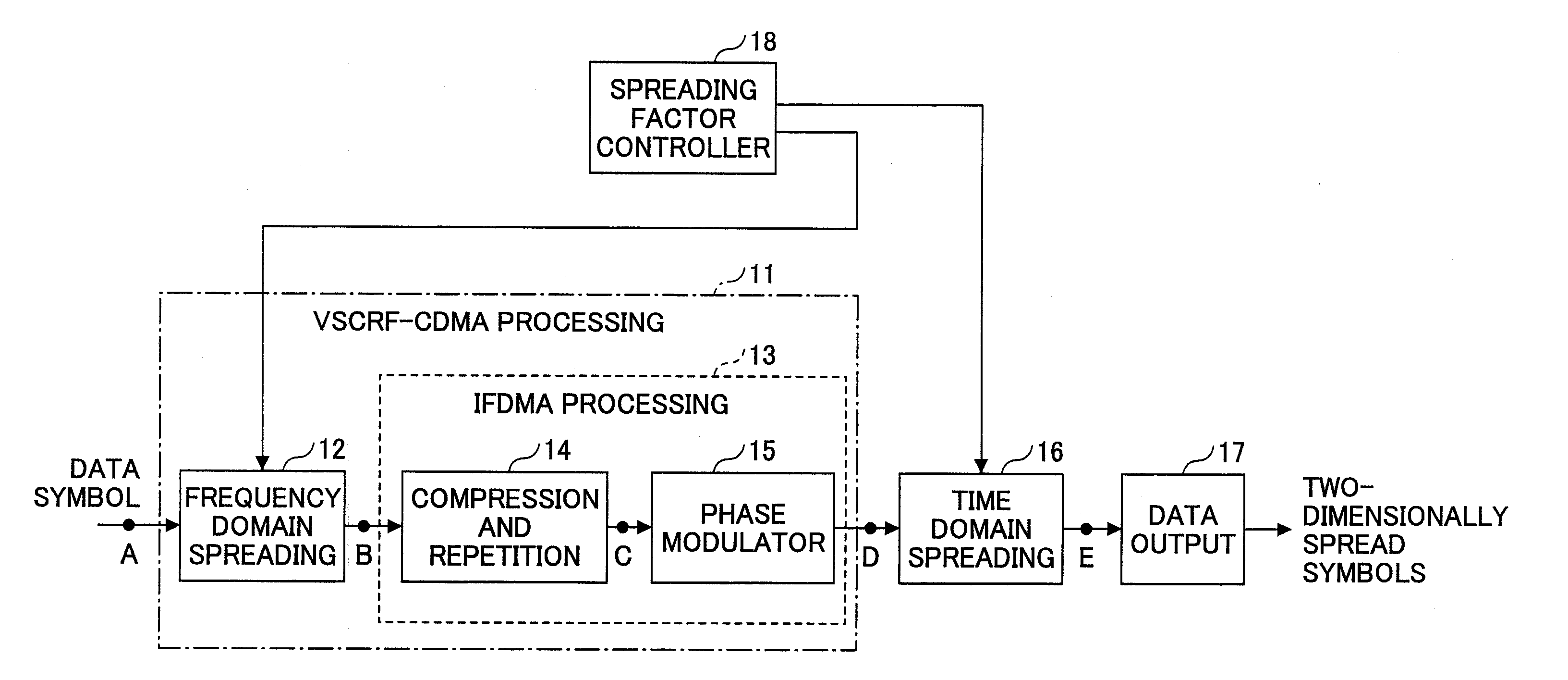
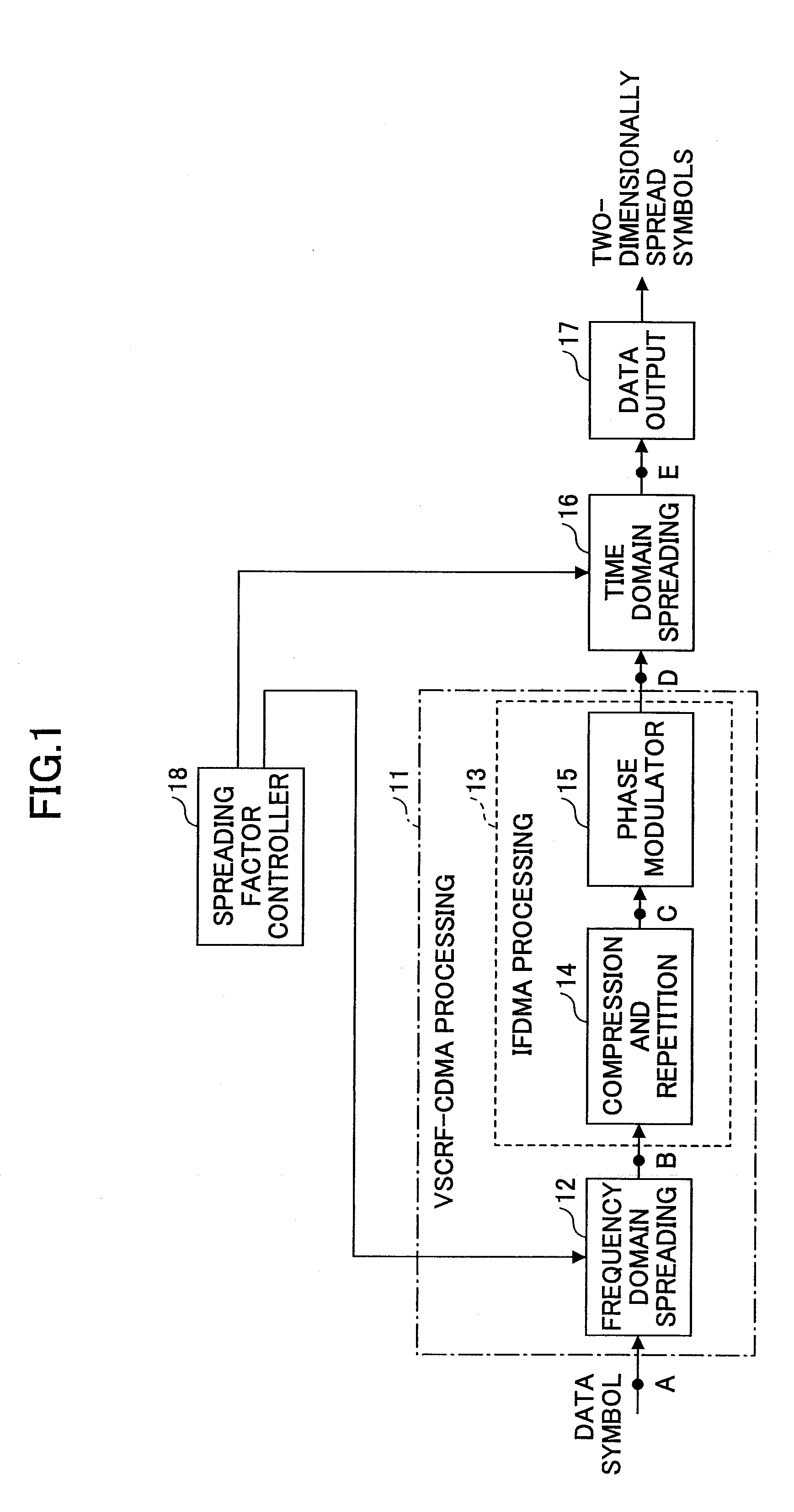
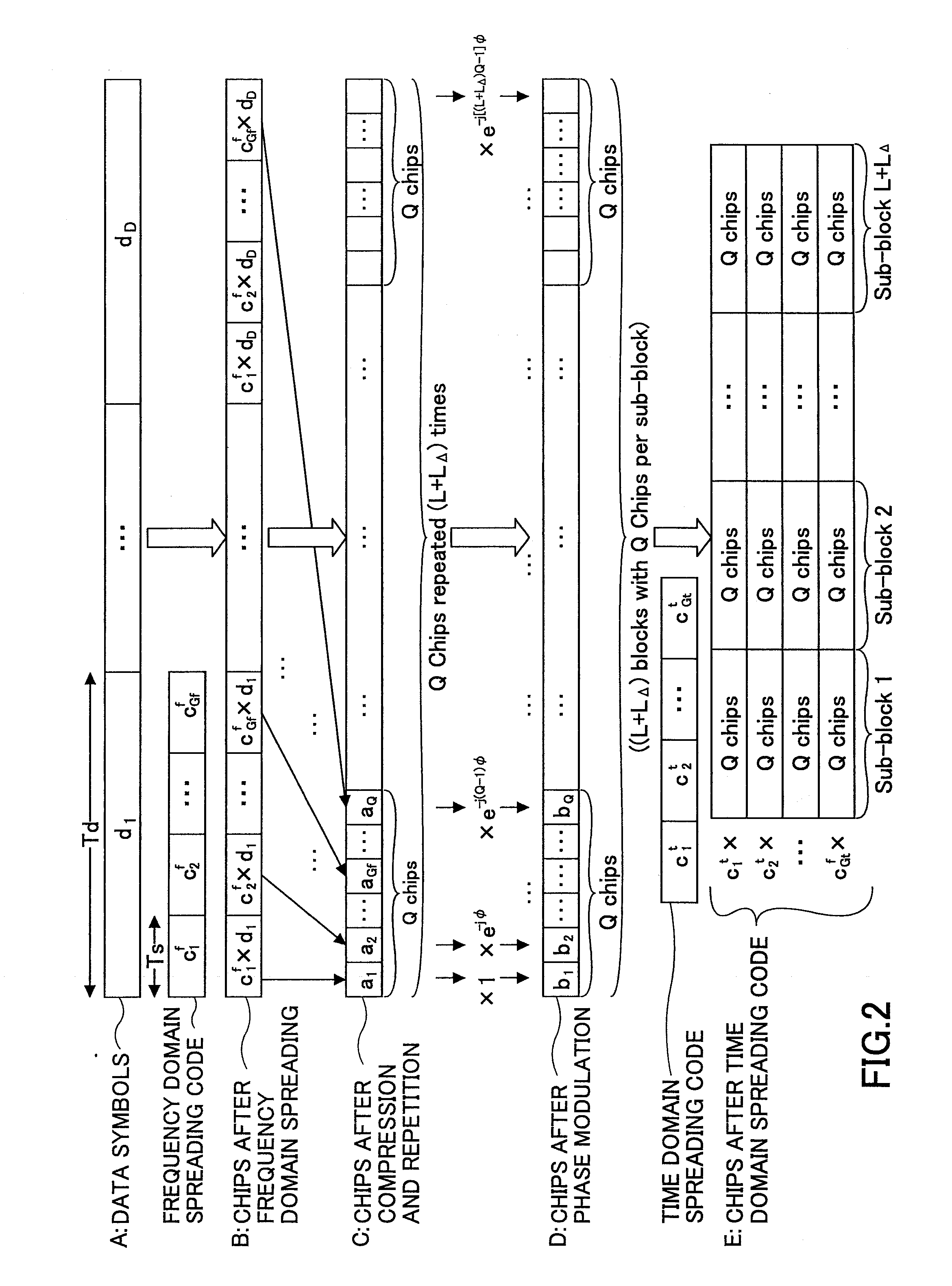
An orthogonal variable spreading factor (OVSF) of one dimension represented by coding tree is extended into two dimensions and applied simultaneously in both directions, frequency axis direction and time axis direction when carrying out spreading of two dimensions of frequency axis direction and time axis direction. For example, the transmission data is first spread by OVSF code of one dimension in the frequency axis direction (obtained from frequency axis direction OVSF code assignment section 11), and the result is spread by OVSF code of one dimension in time axis direction (obtained from time axis direction OVSF code assignment section 13, which is selected independent of frequency axis direction) in each of two-dimensional spreading sections 1-1 to 1-8.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
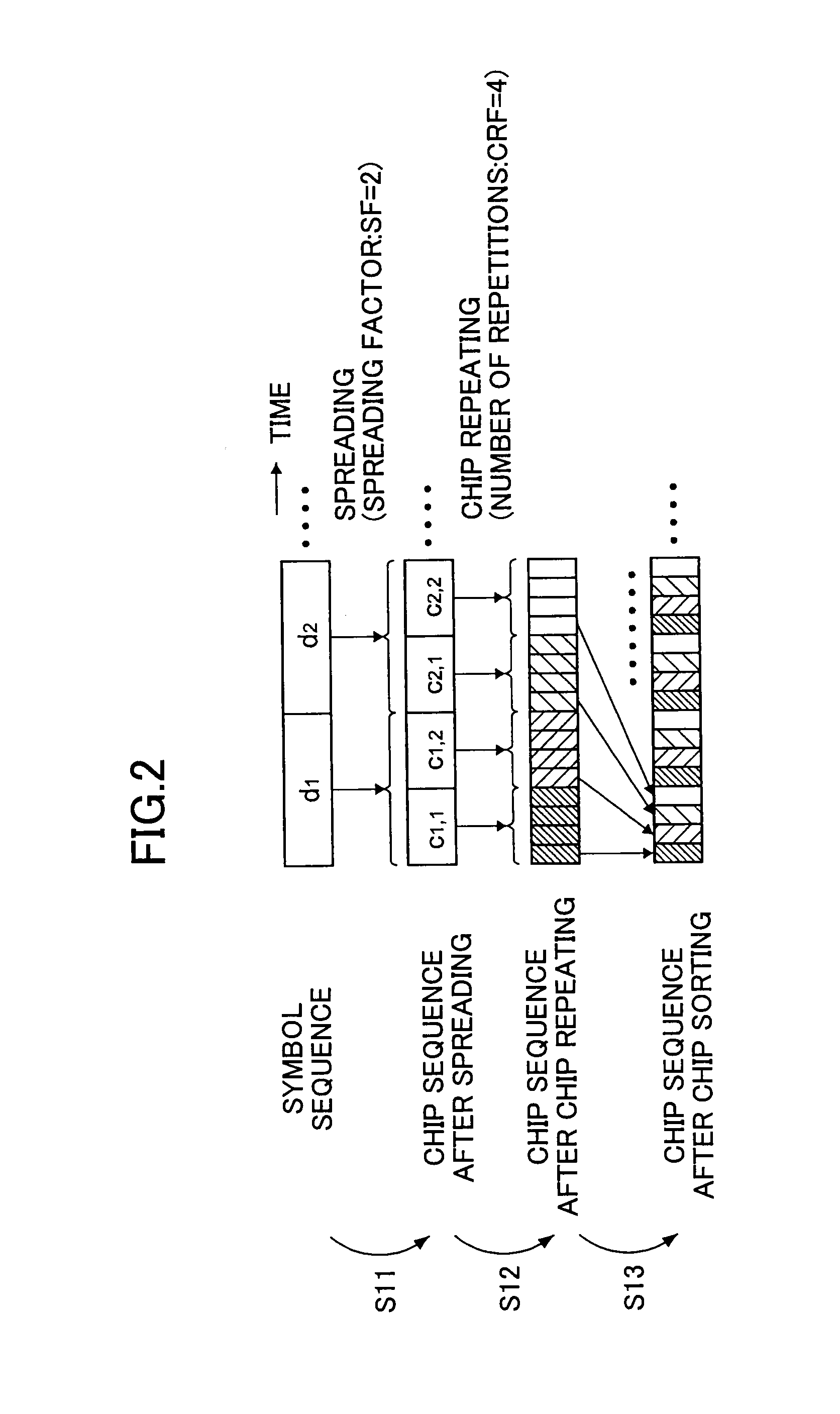
Base station, a mobile station, a radio communications system, and a radio transmission method using spread spectrum and chip repetition
ActiveUS20050276242A1Improve efficiencyWing accessoriesConnection managementCommunications systemSpread factor
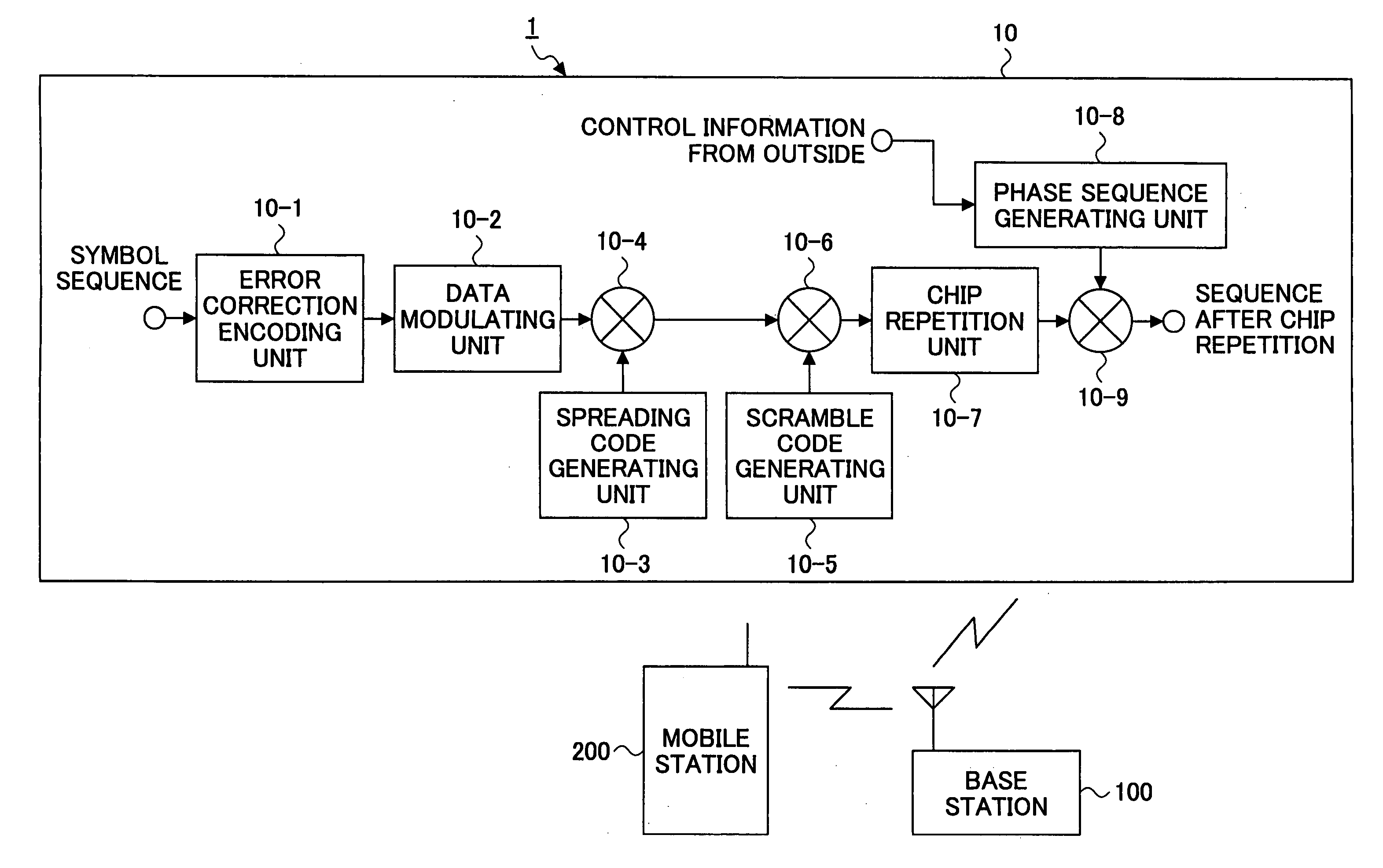
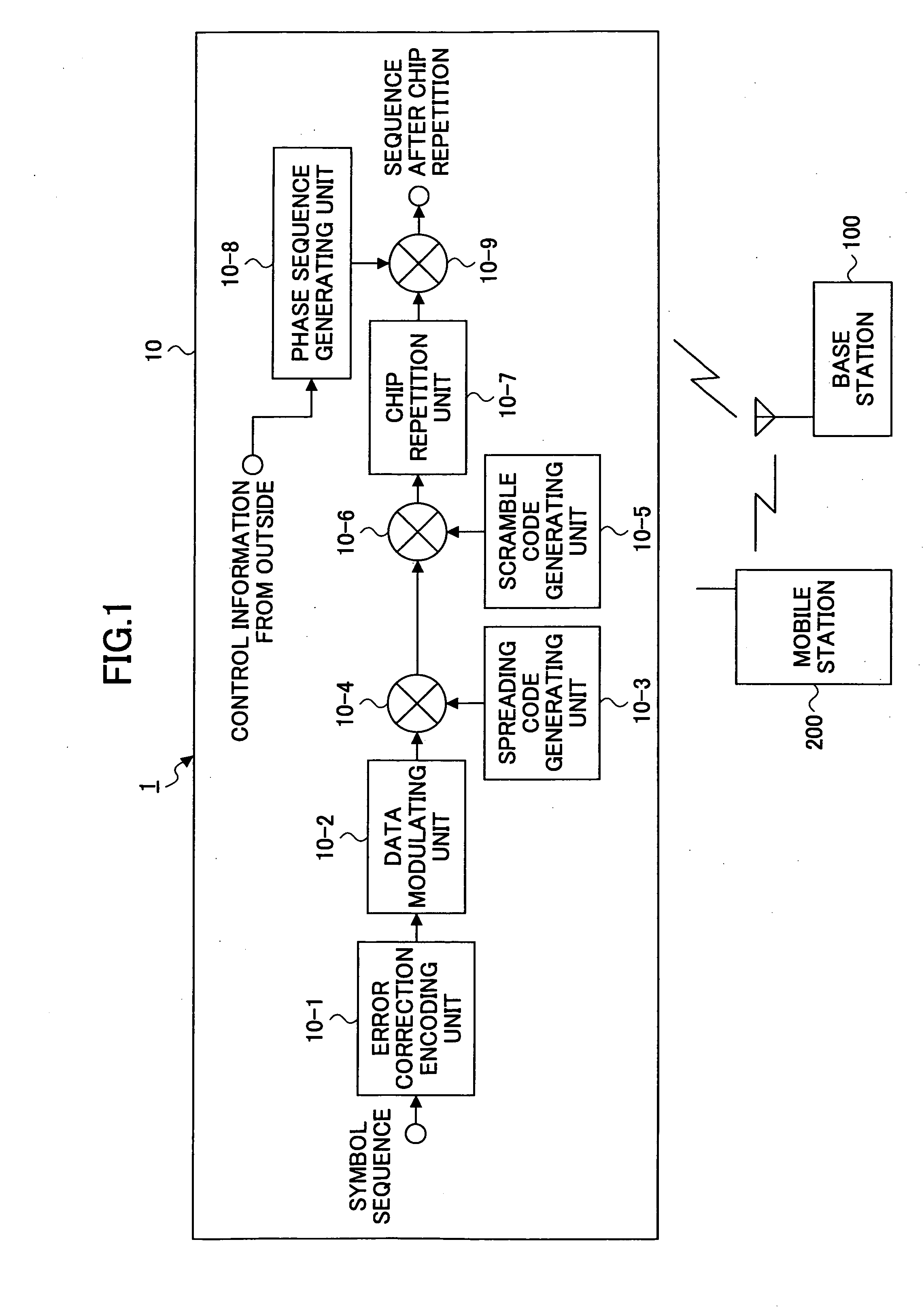
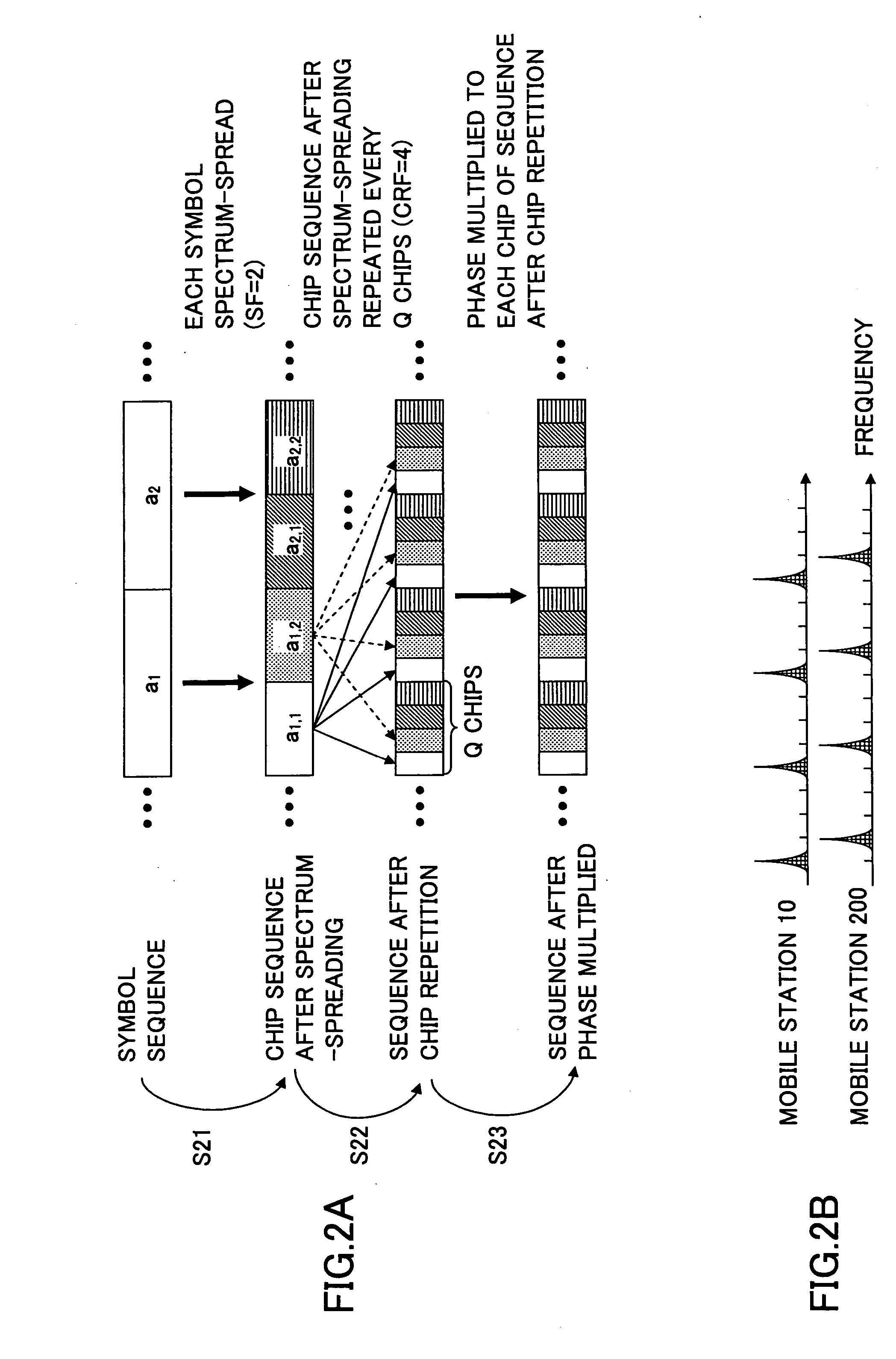
A base station, a mobile station, a radio communications system, and a radio transmission method are disclosed. The base station includes a control information determining unit configured to determine control information that includes a spreading factor, the number of chip repetitions, and a phase unique to the mobile station, based on at least one of information about the type of cell environments in which the mobile station is present, information about the number of mobile stations that are present in the cell, information about information rate required by the mobile station, information about a type of traffic, information about a radio parameter of the mobile station, information about a propagation path condition, and information about interference from an adjacent cell, and configured to transmit the spreading factor, the number of chip repetitions, and the unique phase of the mobile station that is determined to the mobile station.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Method and apparatus for providing uplink packet data service in asynchronous WCDMA system
ActiveUS20050157687A1Efficiently determiningGuaranteed normal transmissionNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementChannel dataUplink transmission
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for providing uplink packet data services through an E-DCH in an asynchronous WCDMA system. A transport block size (TBS) for transmitting uplink transport channel data is determined. A combination of a spreading factor and a modulation scheme for uplink channel data transmission, corresponding to the determined TBS, is selected according to transmittable physical channel data bit sizes and puncturing limit values. The TBS is transmitted by incorporating it into control information of the uplink transport channel data. The modulation scheme and spreading factor combination is determined based on a physical channel data bit size that maximizes transmission efficiency and minimizes the number of punctured bits, without requiring an additional physical channel in transmitting the uplink data having the TBS. This method maximizes uplink transmission efficiency to save transmission resources and reduces signaling overhead required to transmit E-DCH control information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transmission power control method and transmission power control apparatus in OFDM-CDMA
InactiveUS20050105593A1Reduce communicationQuality improvementPower managementTransmission control/equalisingSpread factorCarrier signal
In power control in an OFDM-CDMA system for creating a number of subcarrier components by multiplying a plurality of symbols by channelization codes of a length that conforms to a spreading factor, and transmitting each of the subcarrier components by a corresponding subcarrier, a subcarrier band is divided into a plural subcarrier blocks, the number of the subcarriers in each block is a whole-number multiple of the spreading factor, an identical transmission power is assigned to each subcarrier in each subcarrier block obtained by such division, and transmission power is controlled from one subcarrier block to another.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
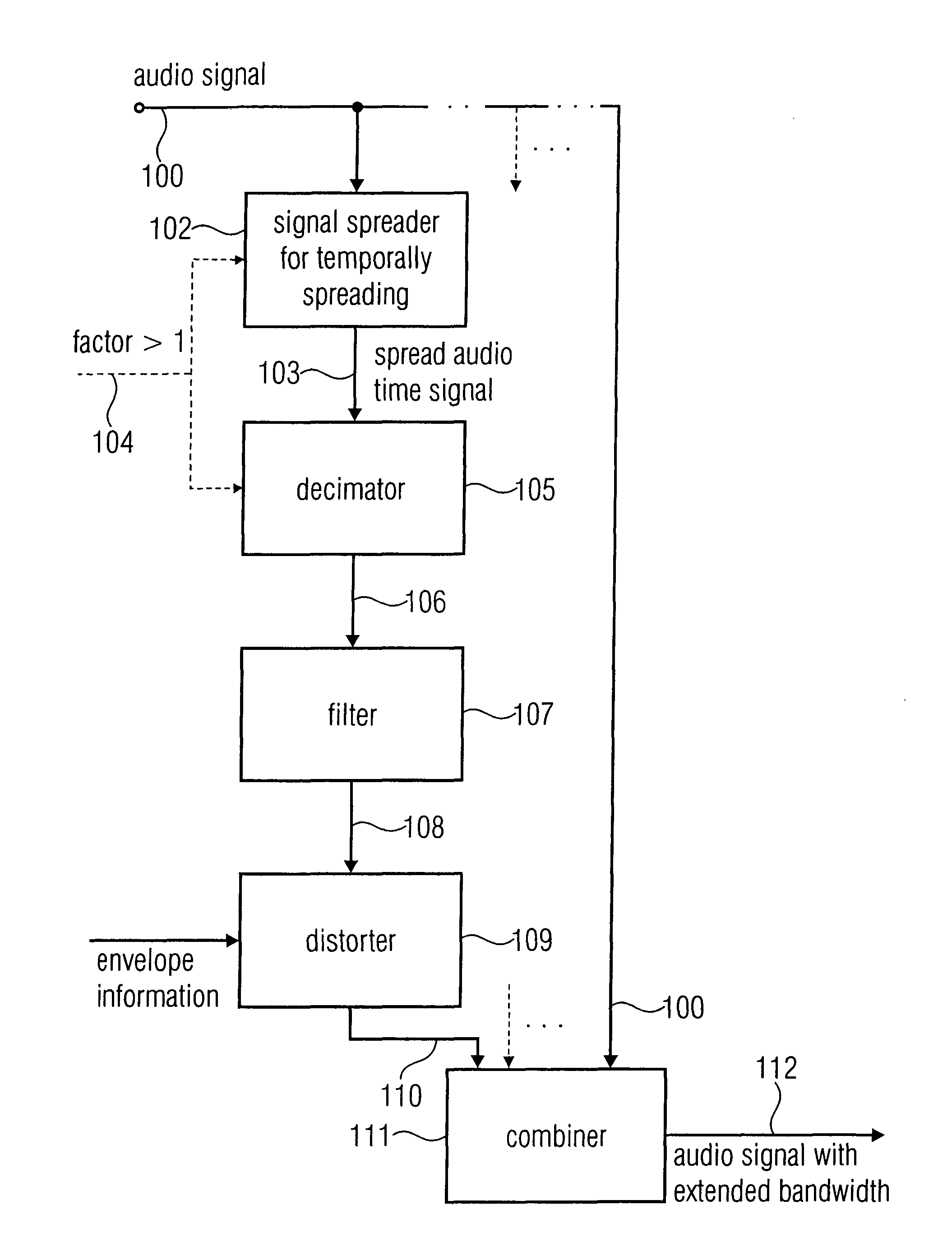
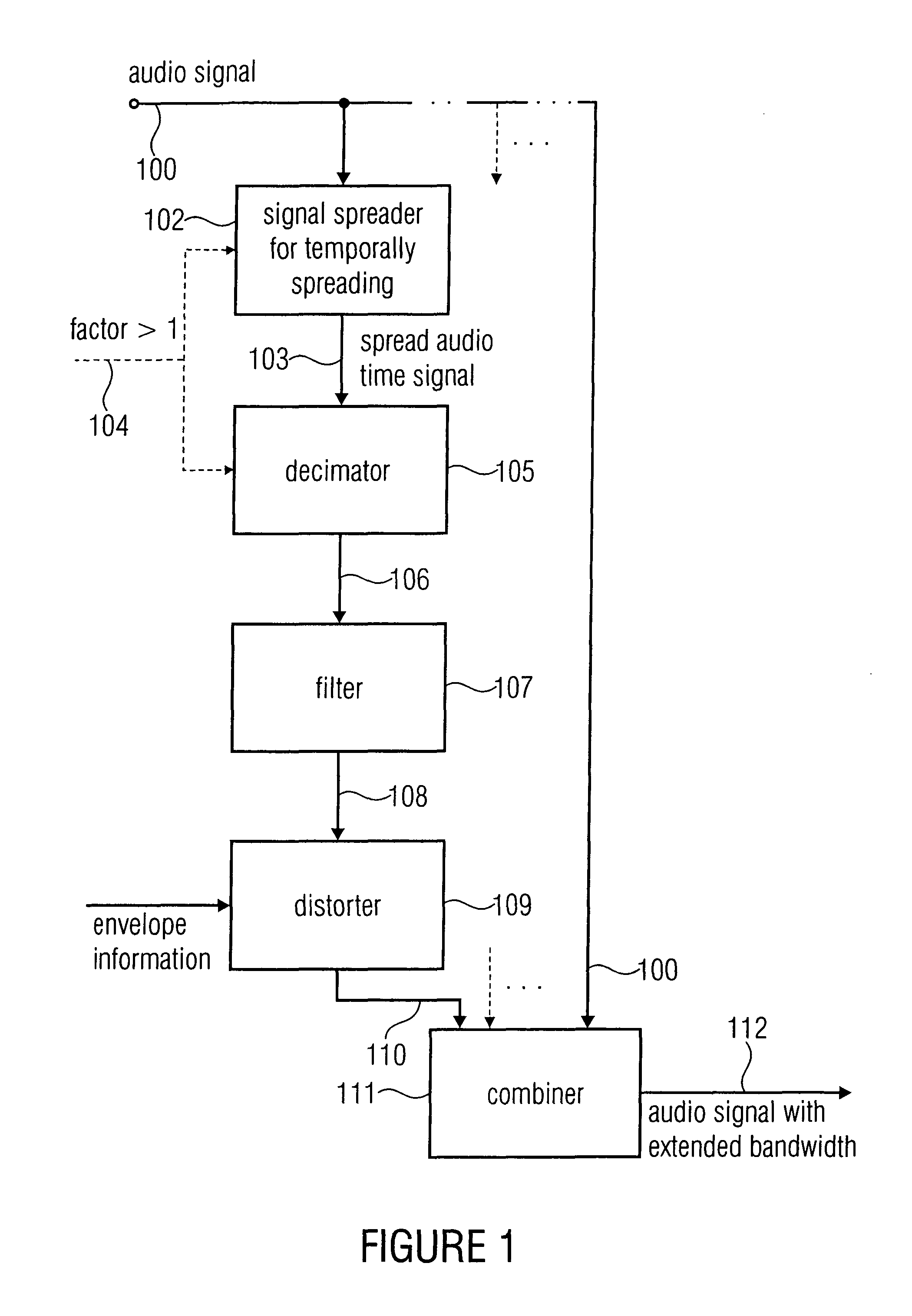
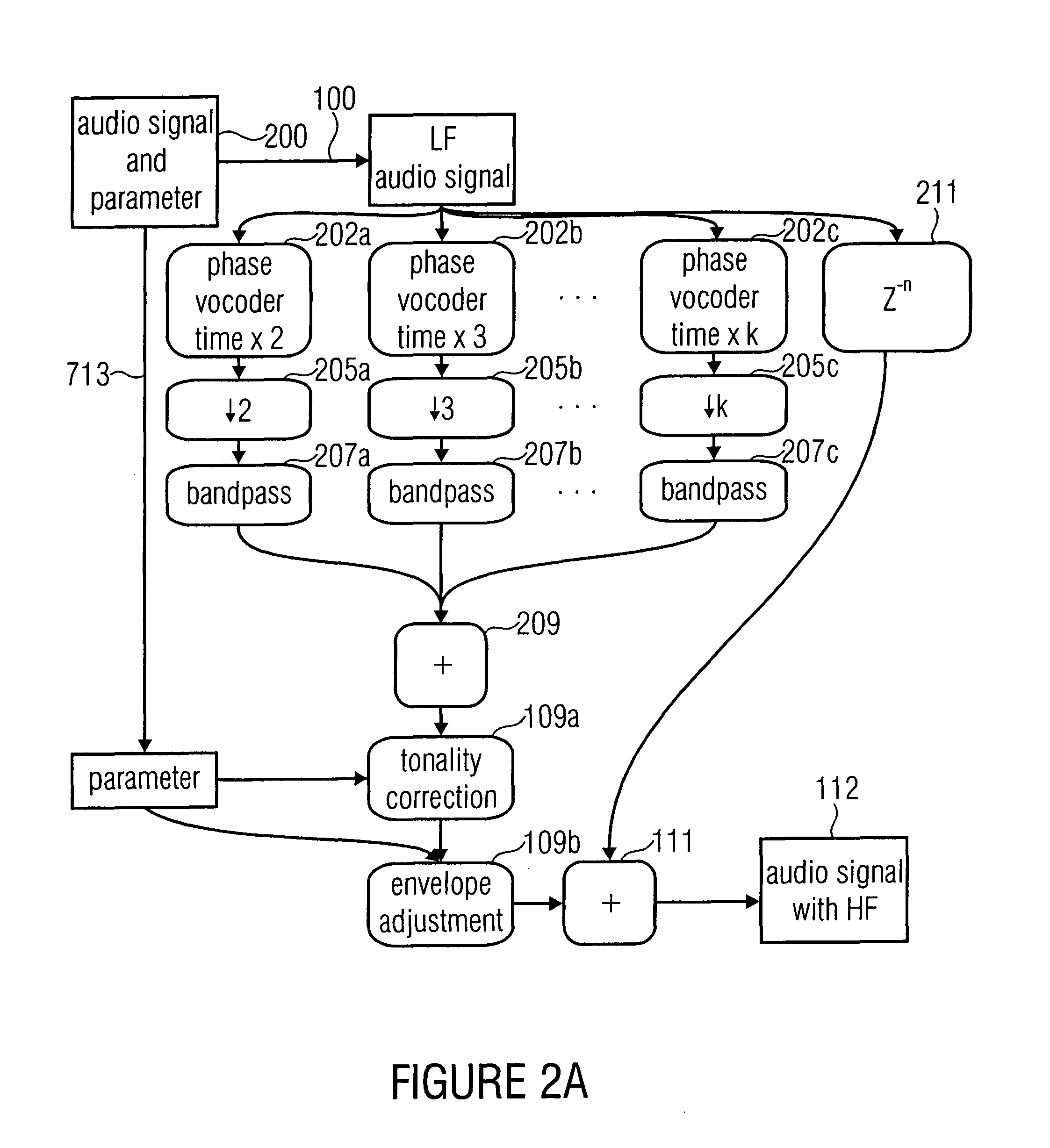
Device and Method for a Bandwidth Extension of an Audio Signal
For a bandwidth extension of an audio signal, in a signal spreader the audio signal is temporally spread by a spread factor greater than 1. The temporally spread audio signal is then supplied to a demicator to decimate the temporally spread version by a decimation factor matched to the spread factor. The band generated by this decimation operation is extracted and distorted, and finally combined with the audio signal to obtain a bandwidth extended audio signal. A phase vocoder in the filterbank implementation or transformation implementation may be used for signal spreading.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
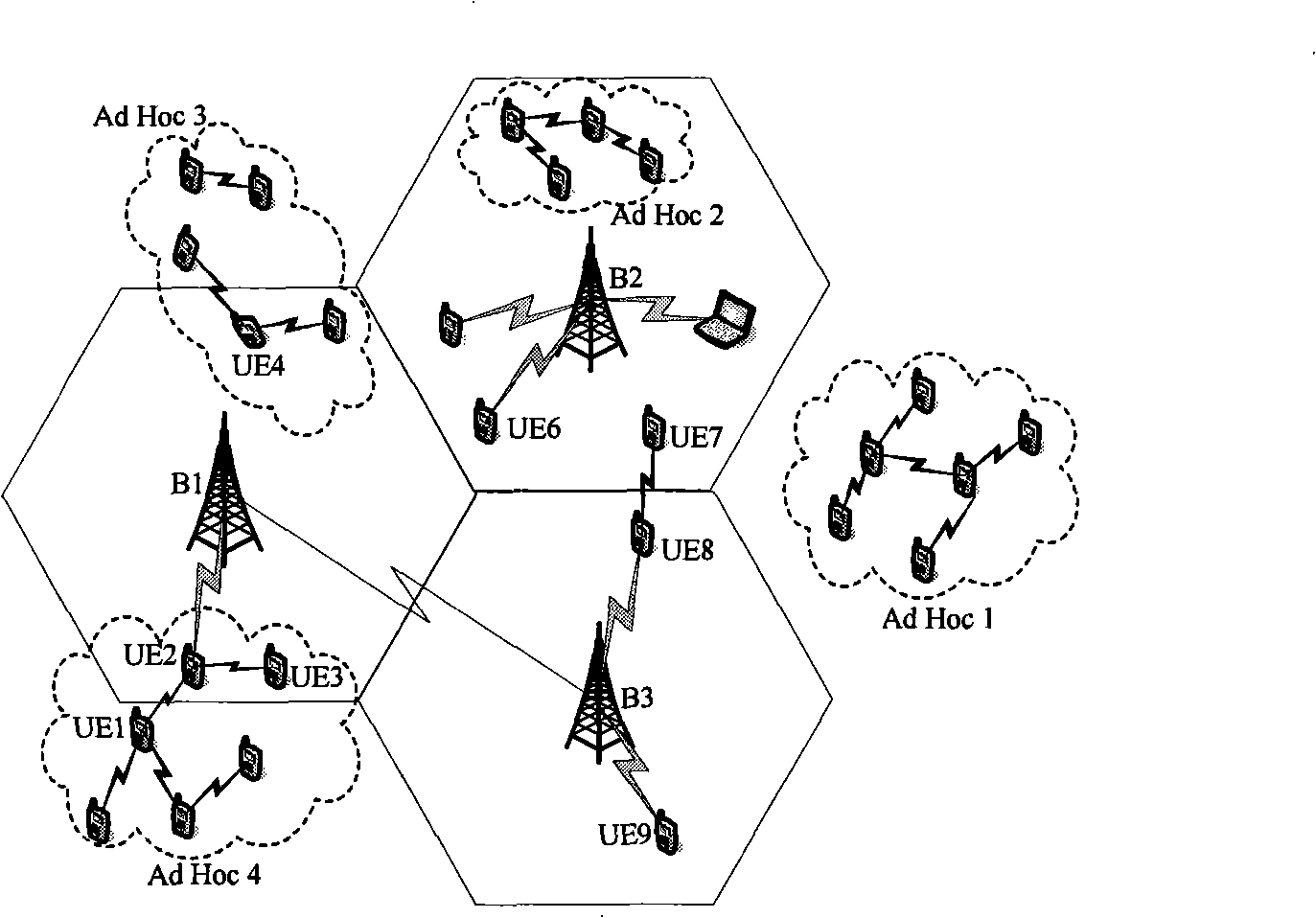
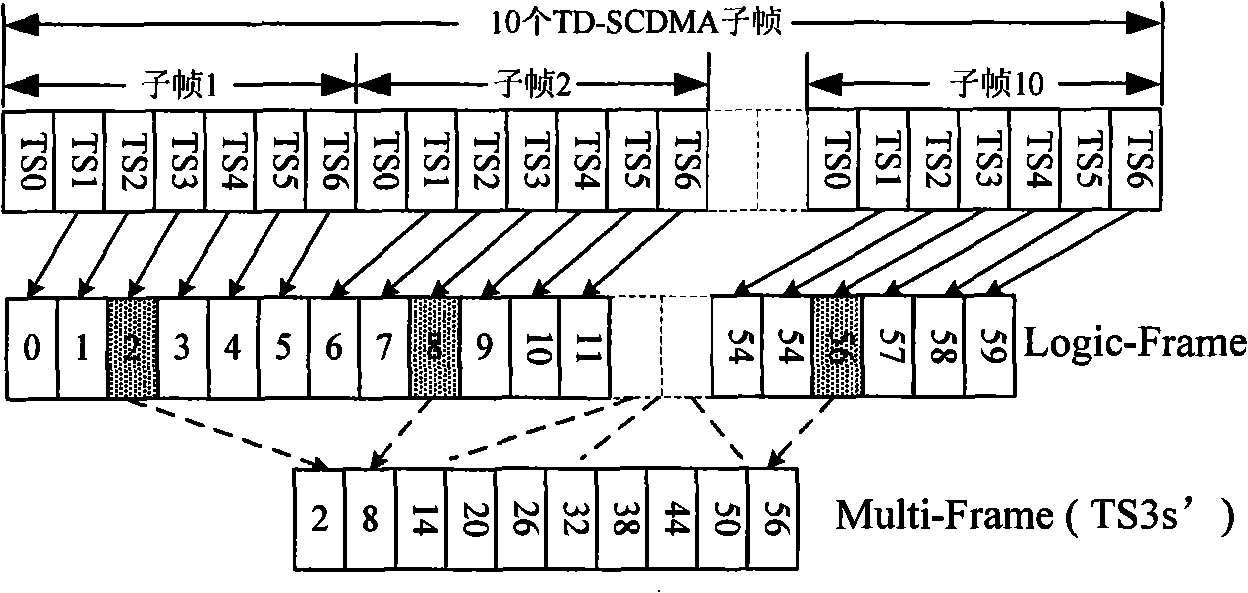
Access control method fusing TD-SCDMA cell phone network and self-organizing network
InactiveCN101360339AAchieve conflict-free wireless accessFast decodingConnection managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsAir interfaceEngineering
A connection controlling method of integrating a time synchronous code division multiple access with a automatic-organizing network belongs to the mobile communication field of the communication technology, based on keeping the unitive air interface of TD-SCDMA honeycomb network physic frame invariable construction, the method is a multi-channel synchronization connecting control method based on the preset pattern and distributing pattern control, the time span resource is divided into the control channel and the data channel by the OVSF (Orthogonal Variable Spreading Factor), thus improving the time span reusability through terminal to terminal status to expose the terminal problem, the method maintains the time span status of node within two jumps time span, and realizes the conflict-free wireless connection within two jumps time span; thereby solving the problems of realizing the conflict-free visit time span and performing the reliable alternation communication under integrating network and multi-communication modes.
Owner:PANDA ELECTRONICS GROUP +3
Method for allocating physical hybrid automatic repeat request indicator channel
ActiveUS20090201904A1Guaranteed normal transmissionMaintain structureError prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityMultiplexingSpread factor
A method for allocating a physical hybrid ARQ indicator channel (PHICH) is disclosed. The method includes allocating a CDM group according to a cyclic prefix type in consideration of a ratio of the numbers of necessary CDM groups according to spreading factors, and allocating a PHICH to the allocated CDM group. The PHICH includes an ACK / NACK signal multiplexed by code division multiplexing (CDM). Therefore, resources for PHICH transmission are efficiently allocated and a transmission structure can be maintained irrespective of a spreading factor.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
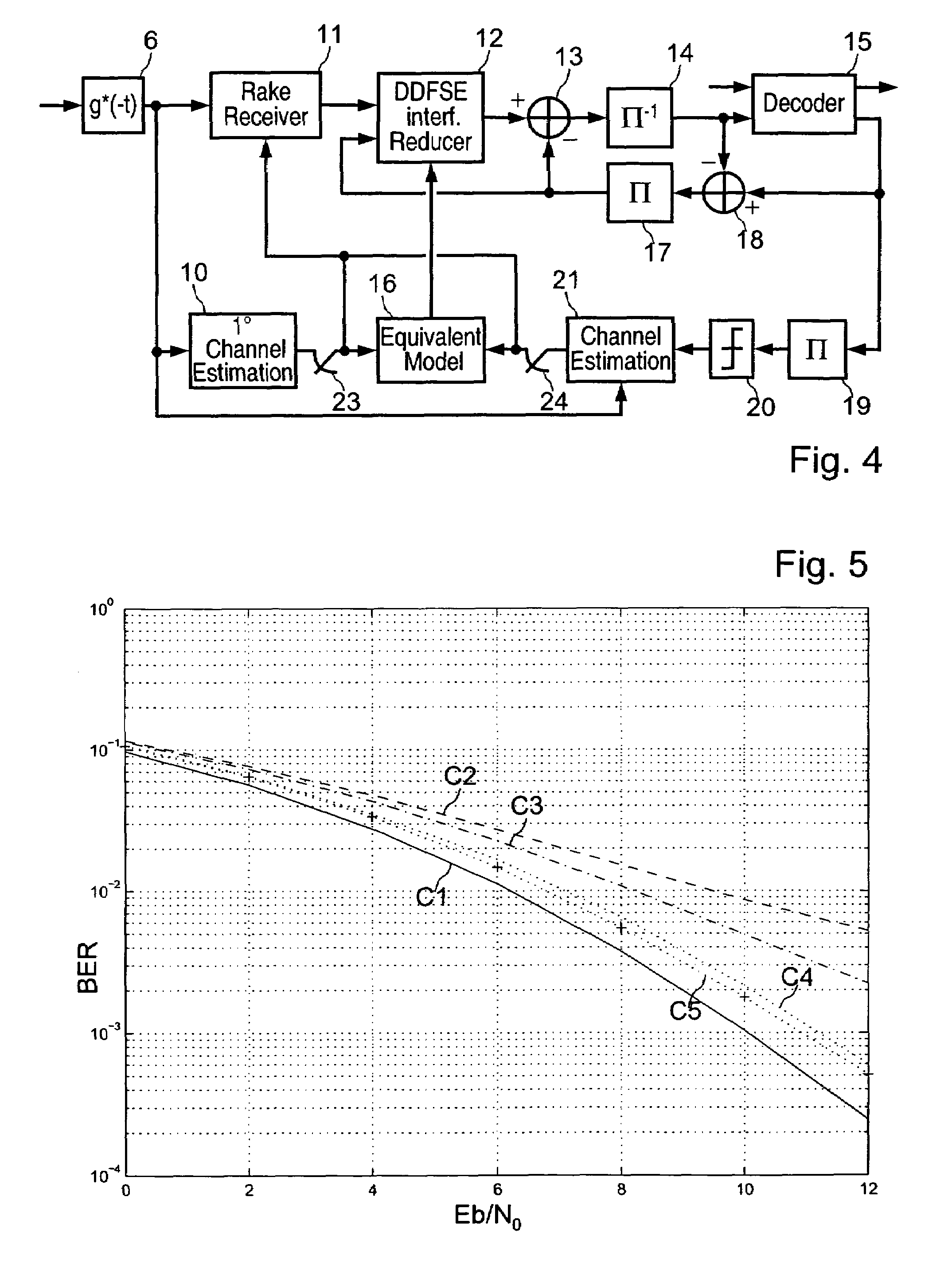
Sub-optimal iterative receiver method and system for a high-bit-rate CDMA transmission system
ActiveUS7298778B2Close to optimum performanceHigh order modulationError preventionOther decoding techniquesSpread factorSpreading factor
A reception method and receiver structure that are relatively simple, that have close to optimum performance, and that use high order modulation combined with a low spreading factor are disclosed. The method receives a signal transmittal in the form of sequences of coded binary symbols comprising both predefined pilot symbols and date symbols multiplied by a spreading sequence. The method also includes a step of determining a channel estimate using received predefined pilot symbols. A system for receiving a signal transmitted on a multipath transmission channel using a spread spectrum technique and low spreading factor is also disclosed.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
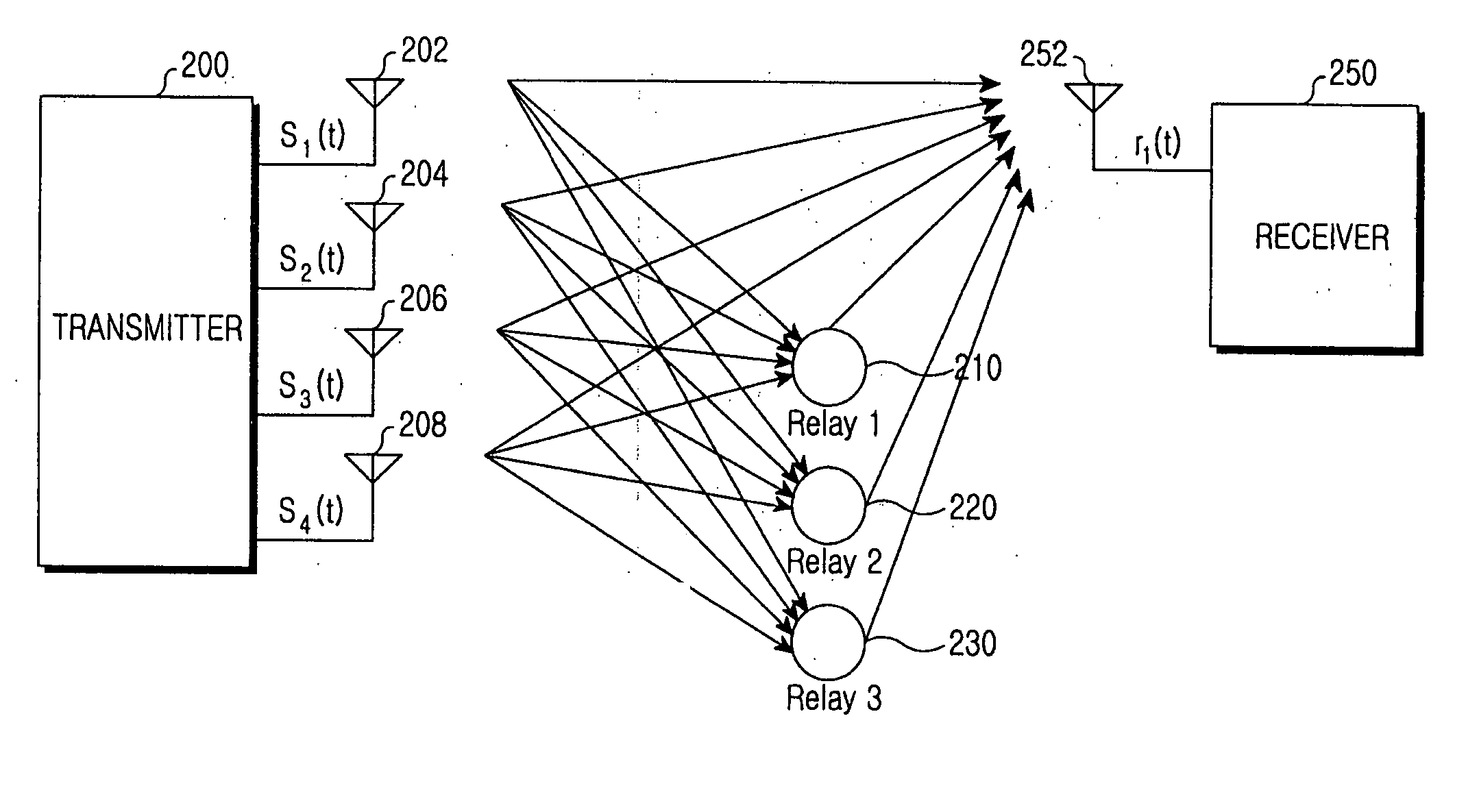
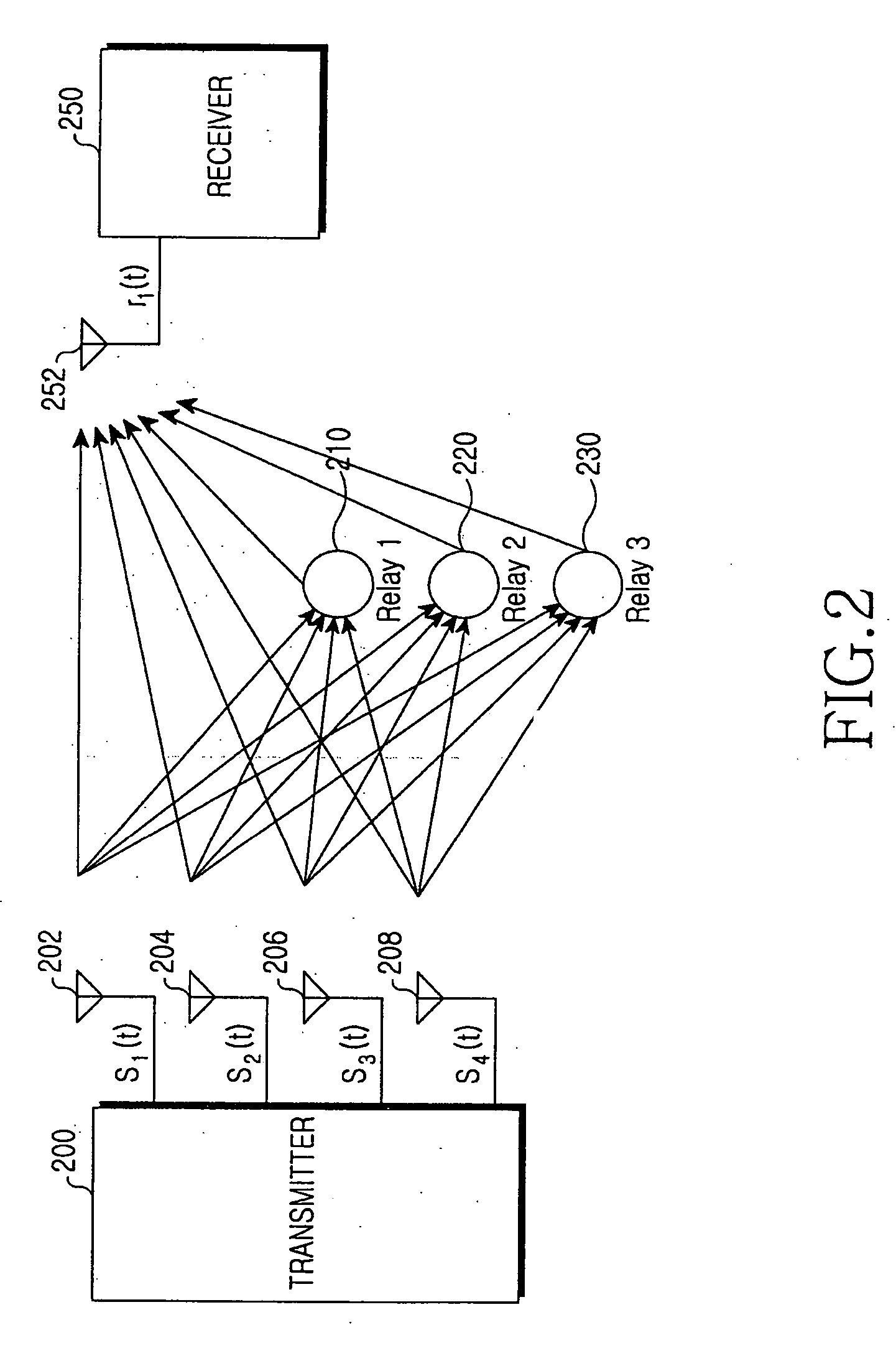
Transmitter and receiver for use in a relay network, and system and method for performing transmission and reception using the same
ActiveUS20060115015A1Polarisation/directional diversitySignalling characterisationData signalEngineering
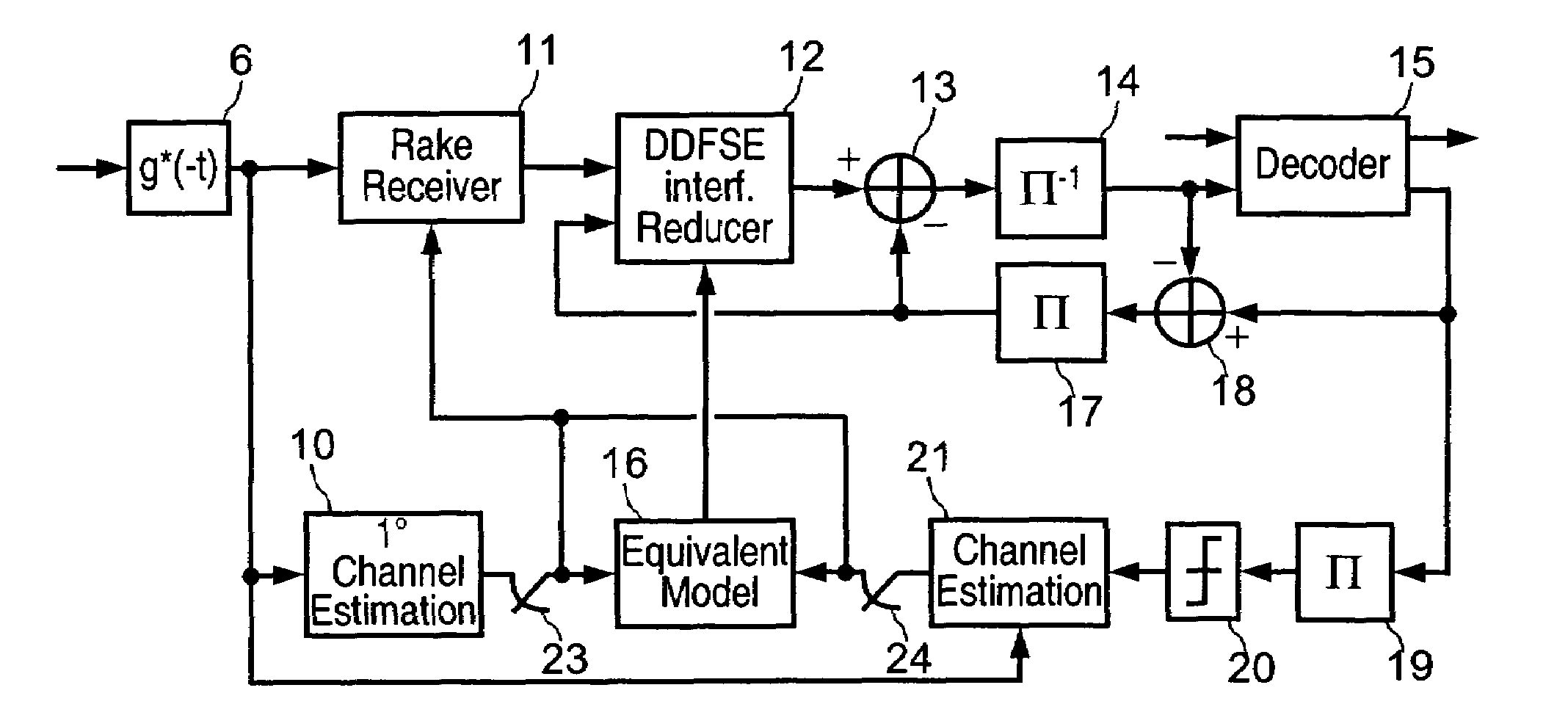
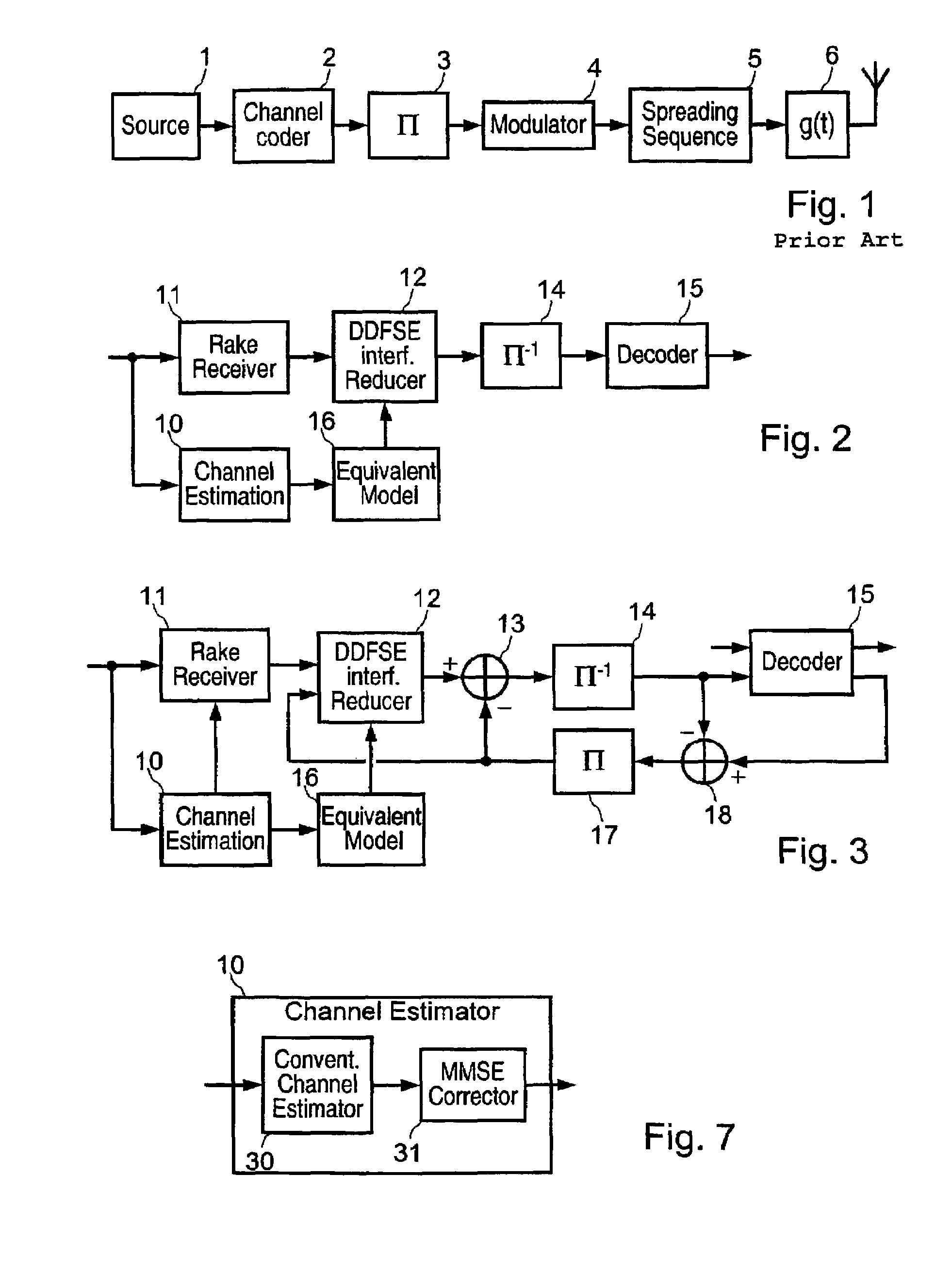
An apparatus and method are provided for transmitting high-speed data through a plurality of transmitter antennas using a relay network, receiving signals transmitted from the plurality of transmitter antennas, and removing interference in a mobile communication system. The received signals are despread on a transmitter antenna-by-transmitter antenna basis according to a preset spreading factor. The despread signals are divided into data signals and noise. The signals transmitted through the plurality of transmitter antennas are regenerated from recovered data signals. Data components and interference signal components are identified. The interference signal components are removed from the signals transmitted on the transmitter antenna-by-transmitter antenna basis.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
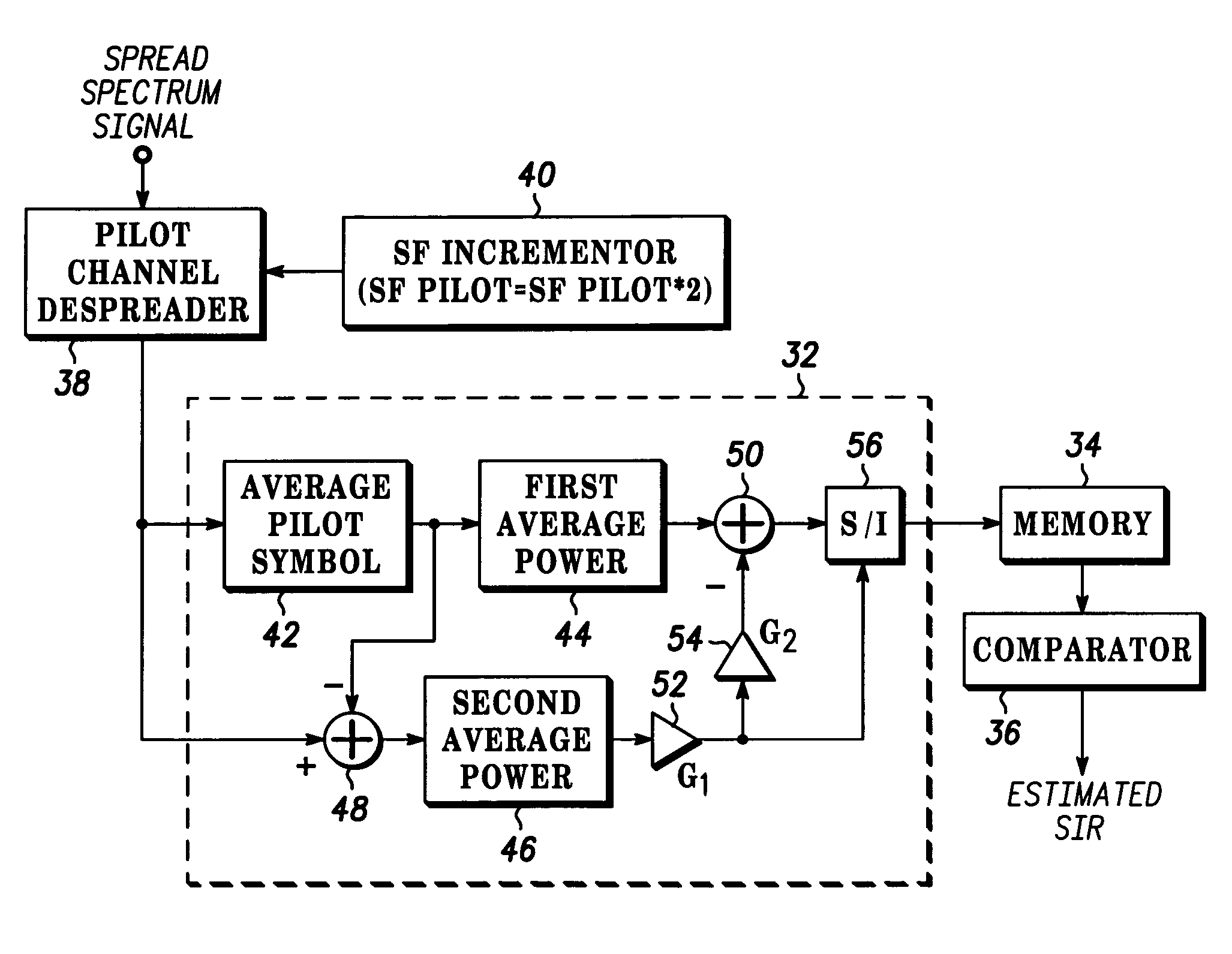
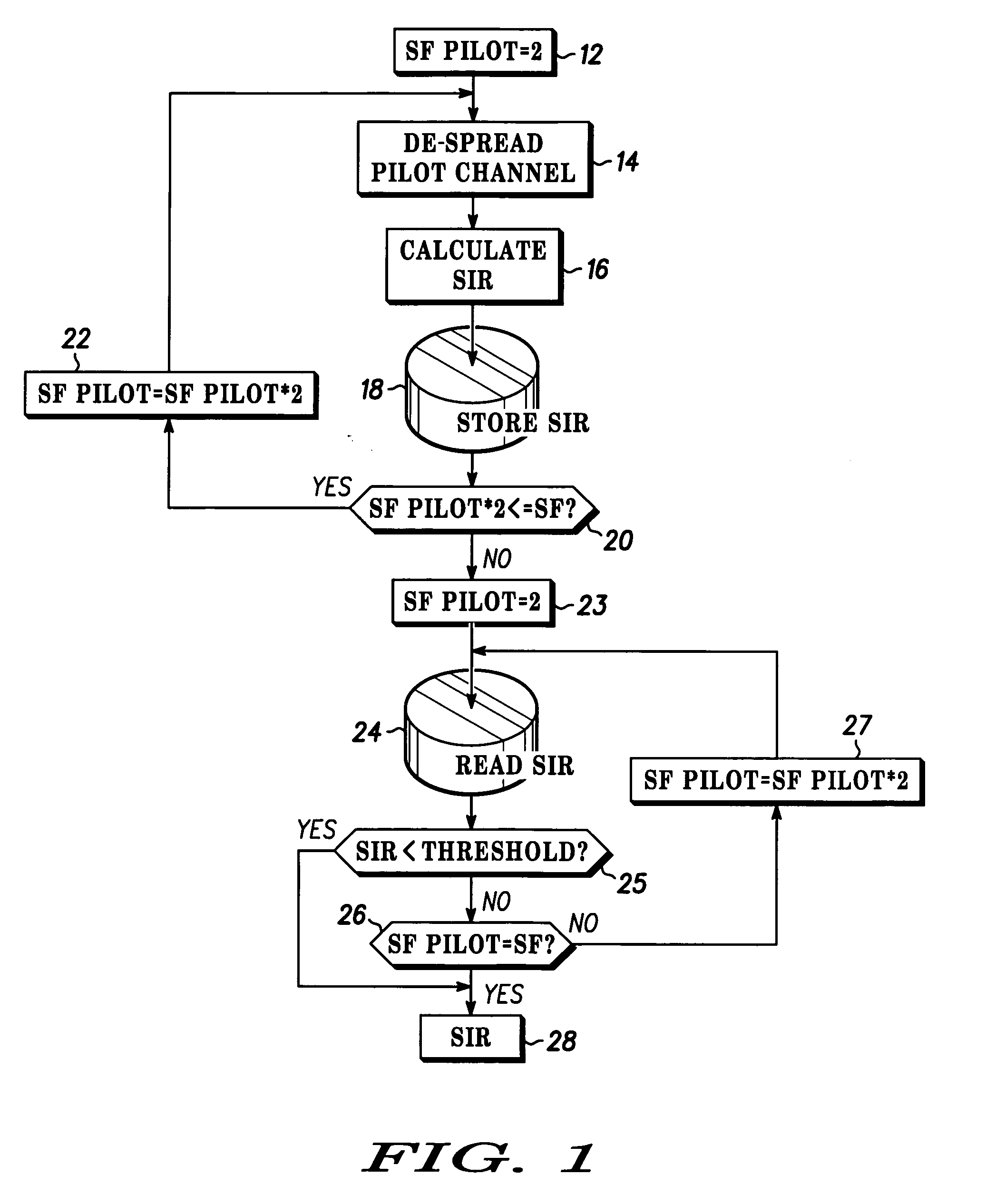
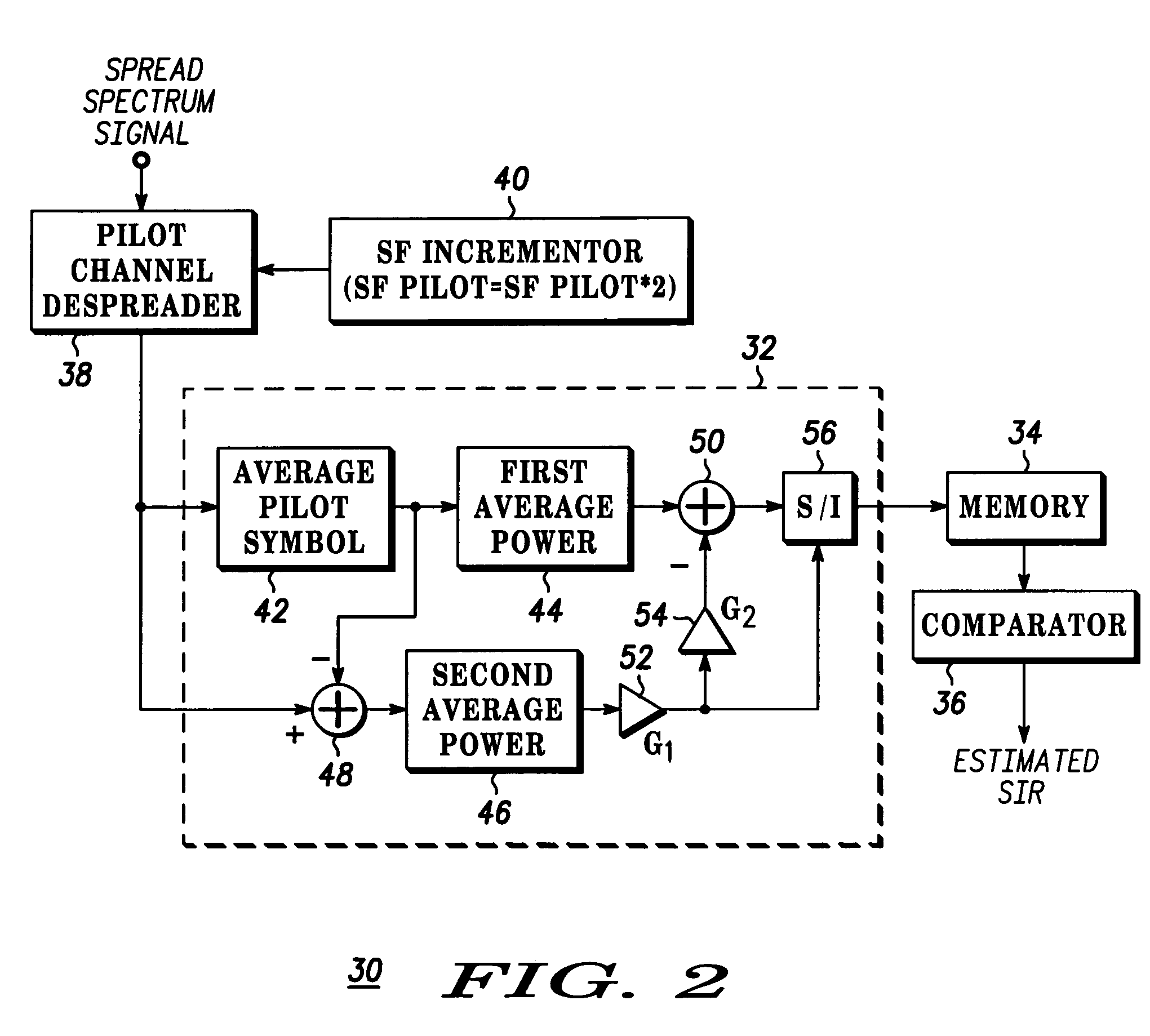
Method and apparatus for estimating a SIR of a pilot channel in a MC-CDMA system
InactiveUS20050141598A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission monitoringSpread factorSpread spectrum
A MC-CDMA handset has a receiver (30) that estimates SIR based on a spread factor of a pilot channel. More particularly, a spread spectrum signal including a pilot channel and multiple data channels is received. The pilot channel is despread using a spread factor (SF). The SIR for the despread pilot channel is calculated and stored in a memory (34). The SF is then incremented and used to despread the pilot channel again, and this process is repeated for all of SF. The stored SIRs are compared to a threshold value in ascending order of the SFs. The first SIR value to fall below the threshold value is used as the estimated SIR result.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
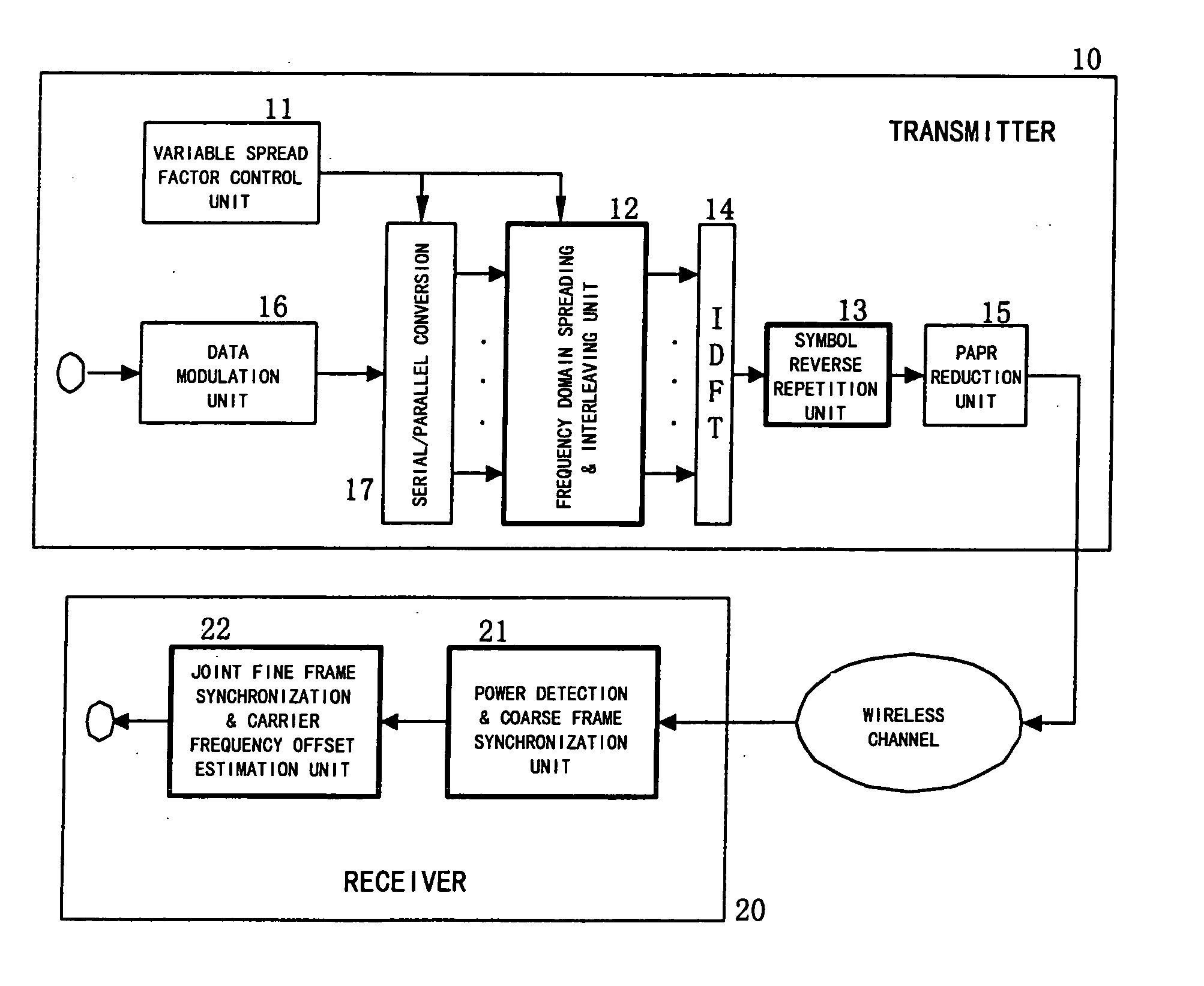
Method for joint time synchronization and frequency offset estimation in OFDM system and apparatus of the same
InactiveUS20060133526A1Improve accuracyReduce loss rateAmplitude-modulated pulse demodulationSecret communicationCarrier frequency offsetSpreading factor
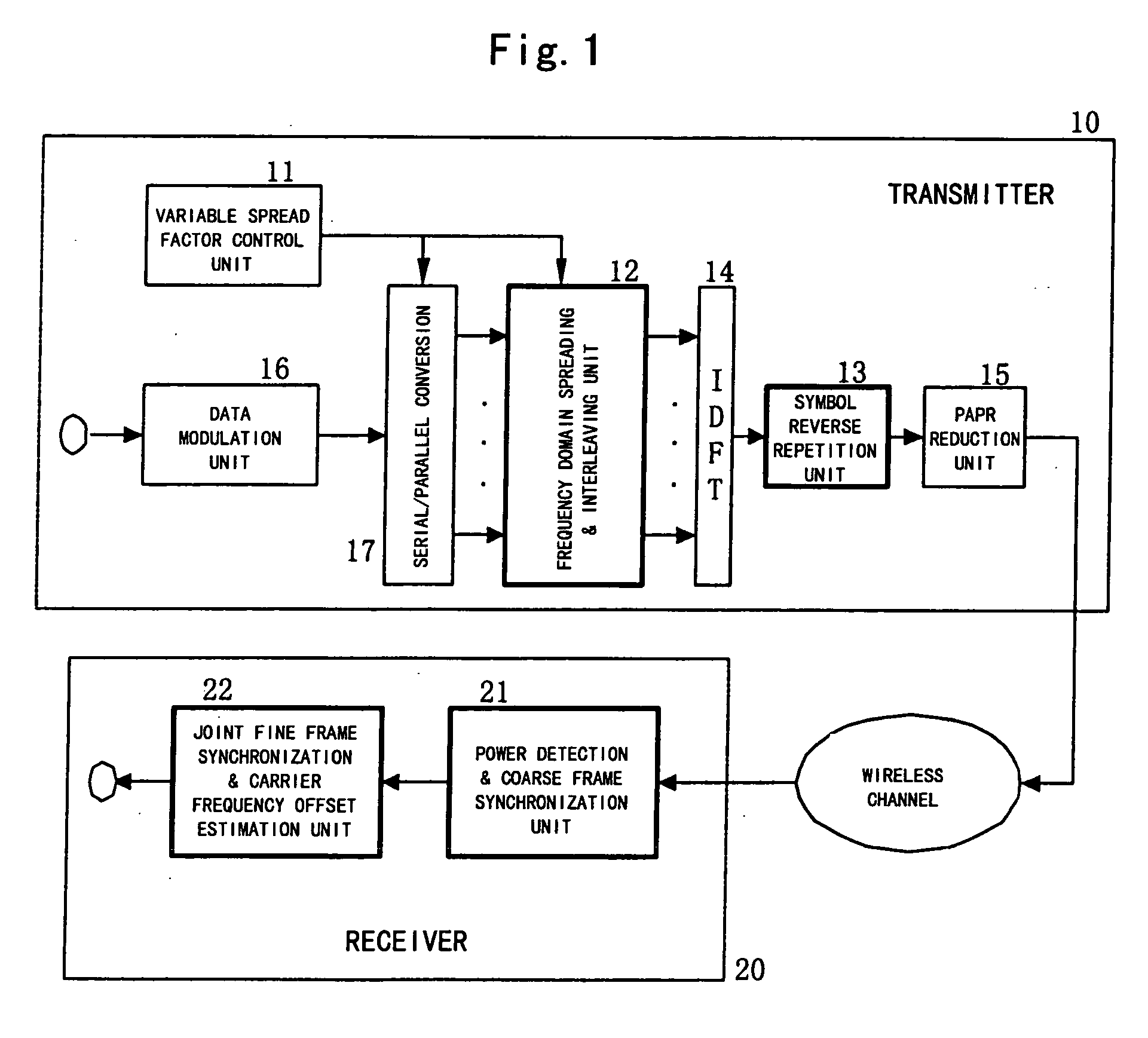
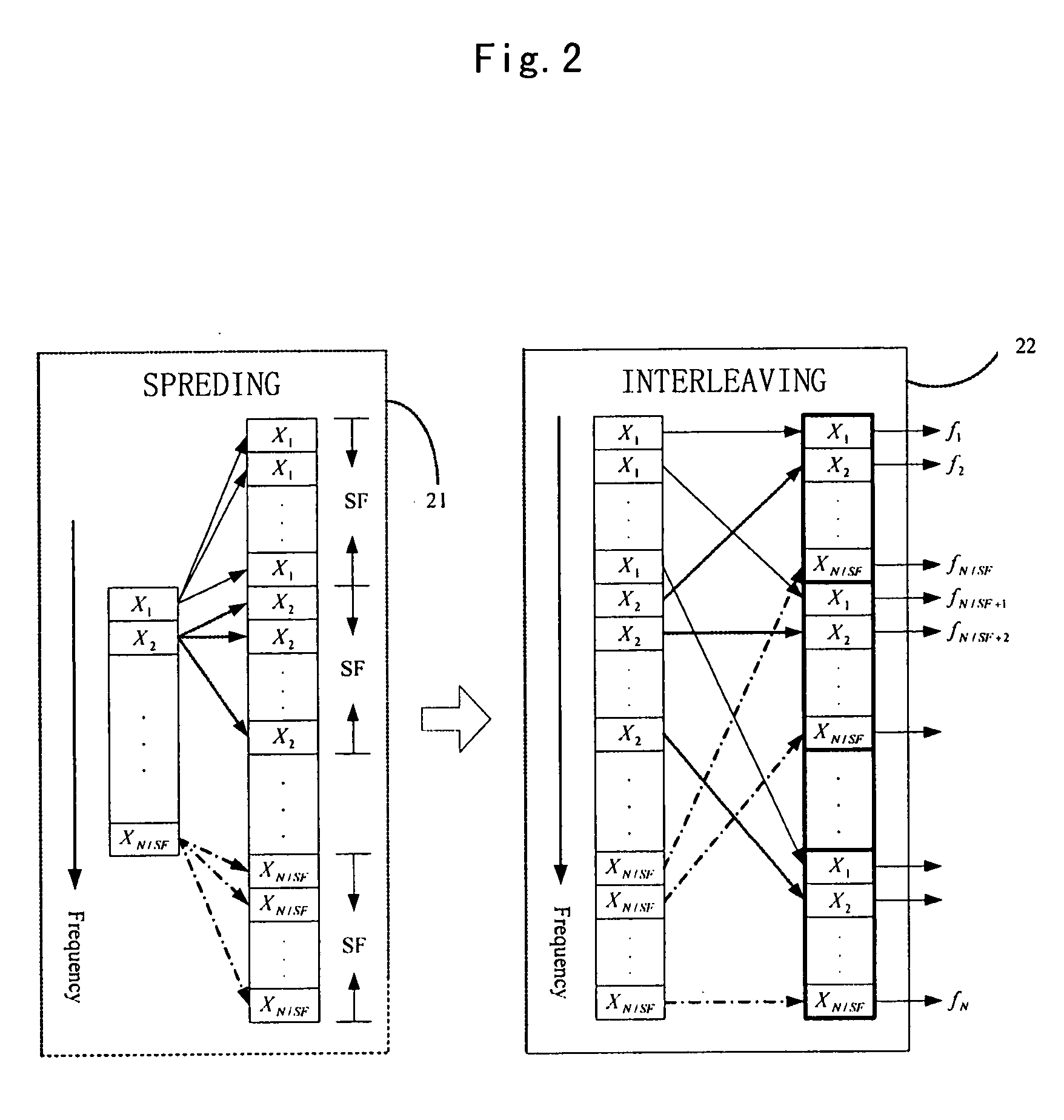
Embodiments of the present invention include a method for performing joint time synchronization and carrier frequency offset estimation in a wireless communication system, comprising steps of: on a transmitter: performing frequency domain spreading and interleaving on input data by using a predetermined spreading factor (SF) to generate a frequency domain training symbol; performing Inverse Discrete Fourier Transformation (IDFT) on the generated frequency domain training symbol to generate a first time domain training symbol; reversely copying the generated first time domain training symbol to a second time domain training symbol such that a complete training sequence is formed; and on a receiver: detecting an average power of received signals to judge the coming of a training sequence, and performing coarse frame synchronization; performing joint fine frame synchronization and carrier frequency offset estimation based on a received training sequence; and compensating for the carrier frequency offset based on the carrier frequency offset estimation result so as to eliminate the carrier frequency offset. In addition, embodiments of the present invention also include an apparatus for performing joint time synchronization and carrier frequency offset estimation and a method for generating a training sequence.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY +1
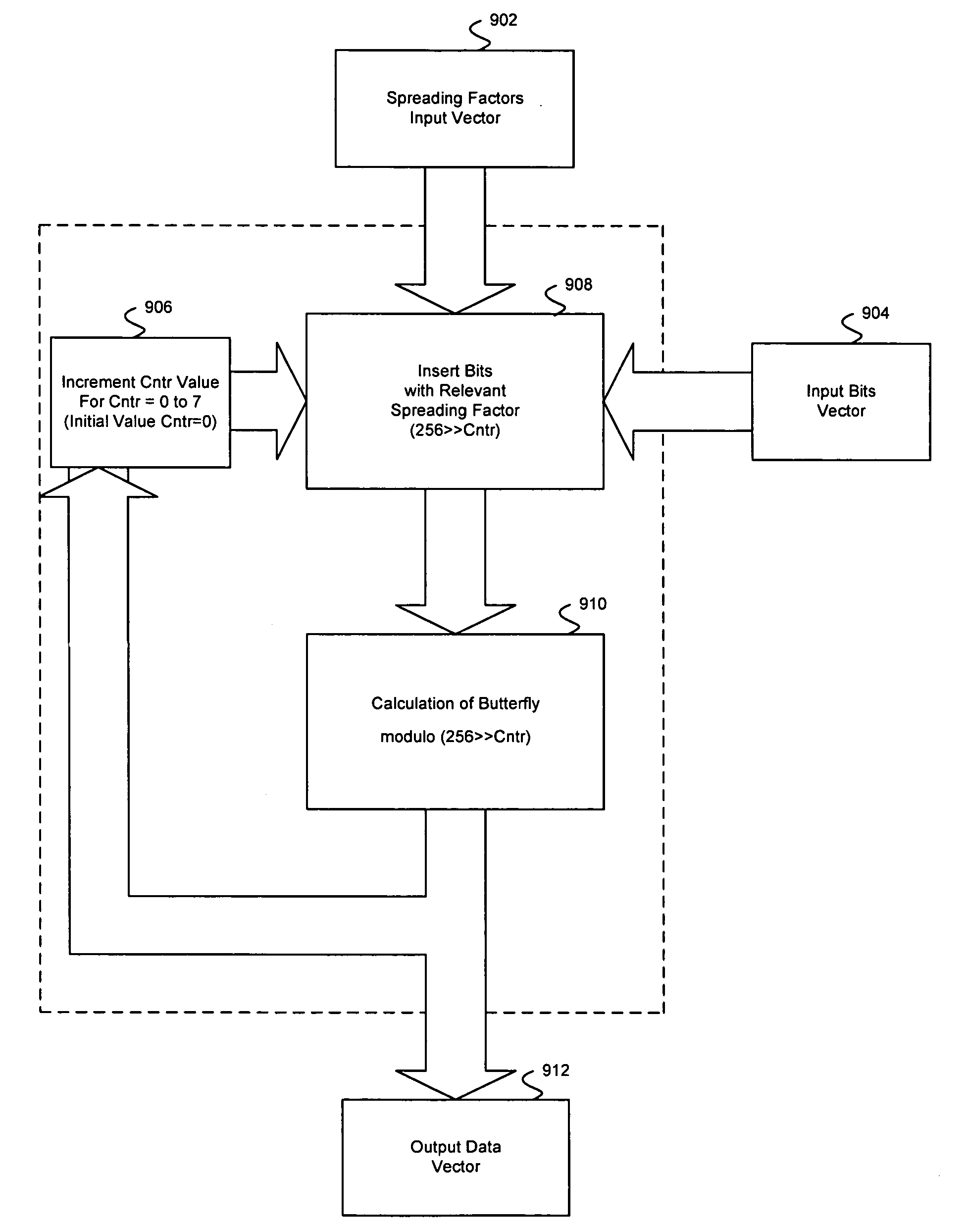
Method and system for a variable spreading factor Walsh Hadamard transform engine
Aspects of a method and system for a variable spreading factor Walsh Hadamard Transform engine are presented. Aspects of the system may include a variable spreading factor Fast Walsh Hadamard Transform engine that enables spread spectrum encoding of data from each of a plurality of data sources. A plurality of spreading factors may be utilized wherein at least 2 of the plurality of spreading factors differ. The variable spreading factor Fast Walsh Hadamard Transform engine may enable combination of a plurality of spread spectrum encoded data to form a data vector.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
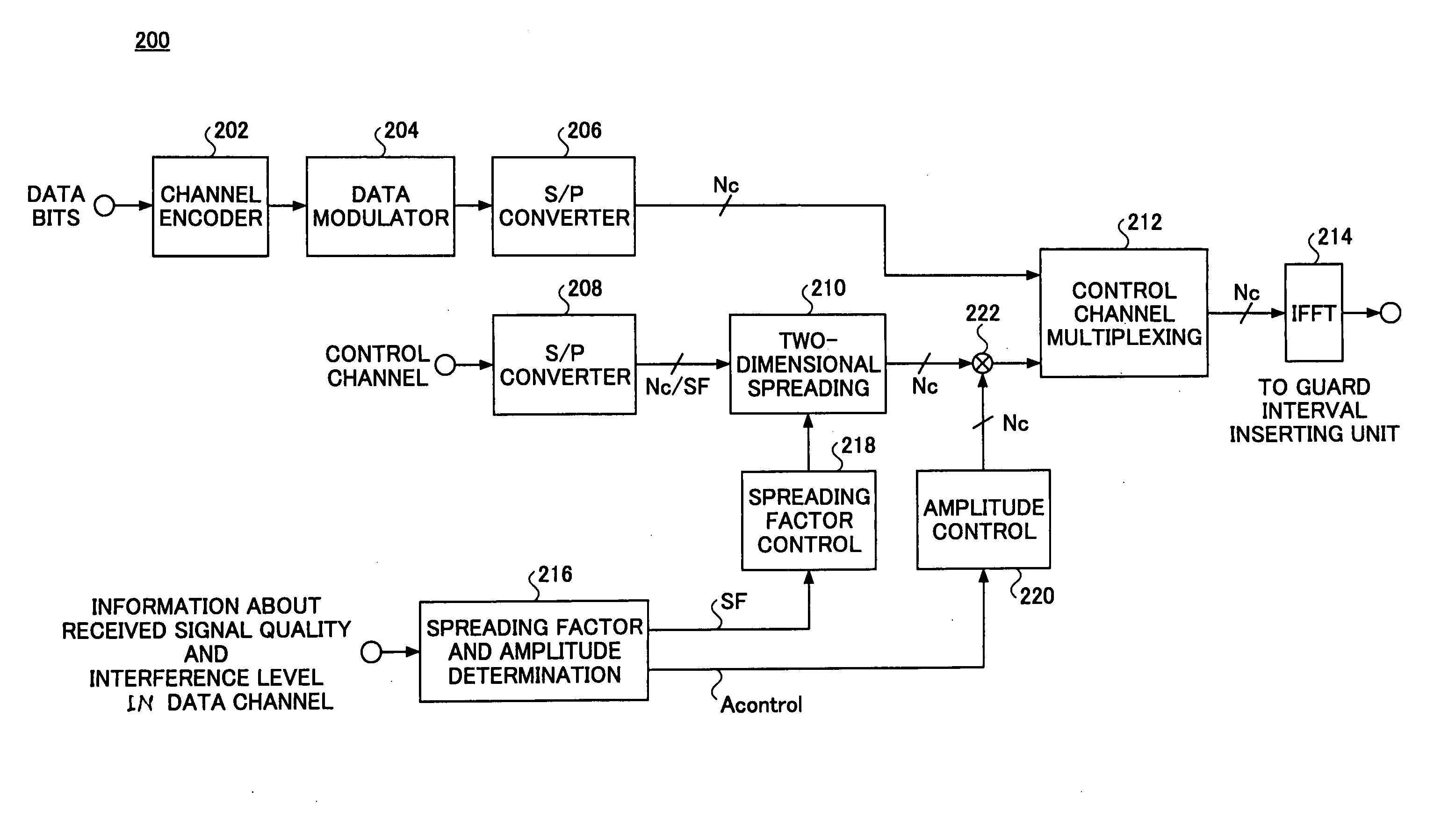
OFDM communication system and method
InactiveUS20050185725A1Easy to useEnsure correct executionSecret communicationTransmission monitoringMultiplexingSignal quality
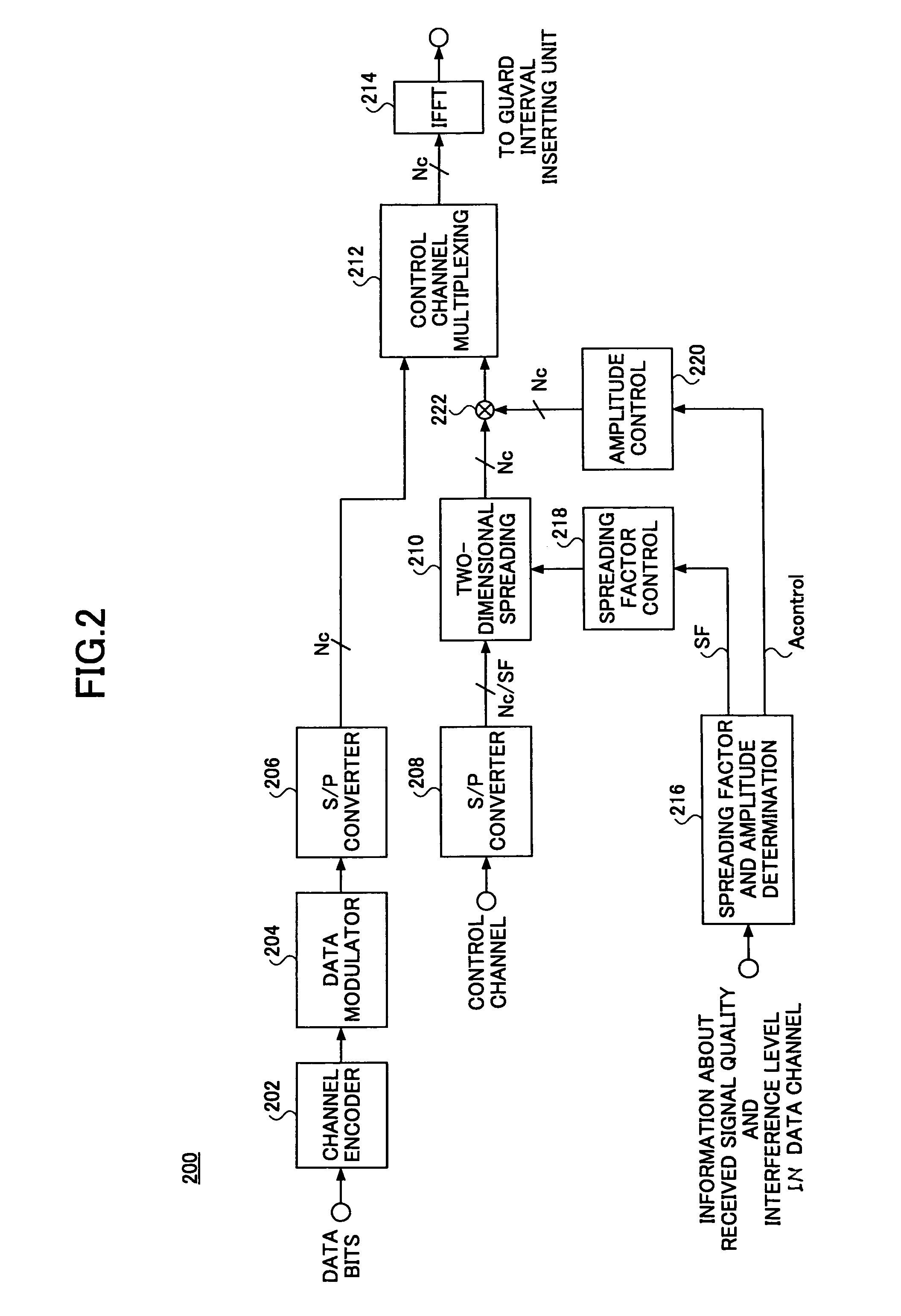
A transmitter (200) used in a wireless communication system based on an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) scheme includes a determination unit (216) configured to determine a spreading factor and an amplitude for a control channel based on at least one of signal quality information and interference information in data transmission, a multiplexing unit (212) configured to multiplex a data channel with the control channel having been code-spread based on the spreading factor and the amplitude, and means (214) configured to modulate the multiplexed signal in the OFDM scheme and transmit the modulated signal as OFDM symbols.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Universal mobile telephone system network with improved rate matching method
InactiveUS6788657B1Power managementNetwork traffic/resource managementMultiplexingMobile Telephone Service
In a UMTS network in which a single user can transmit or receive a number of services having different transmission power requirements over a single channel, a method of determining for each service the number of bits to be punctured or repeated to provide rate matching by the steps of deriving for each service the Energy per Bit per Noise density EB / NO required to achieve a desired Bit Error Rate; from each EB / MO deriving a value of the Energy per coded Symbol per Noise density ES / NO; and from ES / NO deriving a rate matching factor by which that ES / NO can be matched to the minimum Energy per coded Symbol per Noise density applicable to the channel in which to the services are multiplexed. The values of EB / NO are stored in a look up table in the BTS and each mobile; the BSC generates values of semi static rate matching factors and spreading factors for each service and transmits them to the BTS and mobiles so that the mobile can calculate from the received values and the values stored in the look up table the number of bits to be punctured or repeated.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
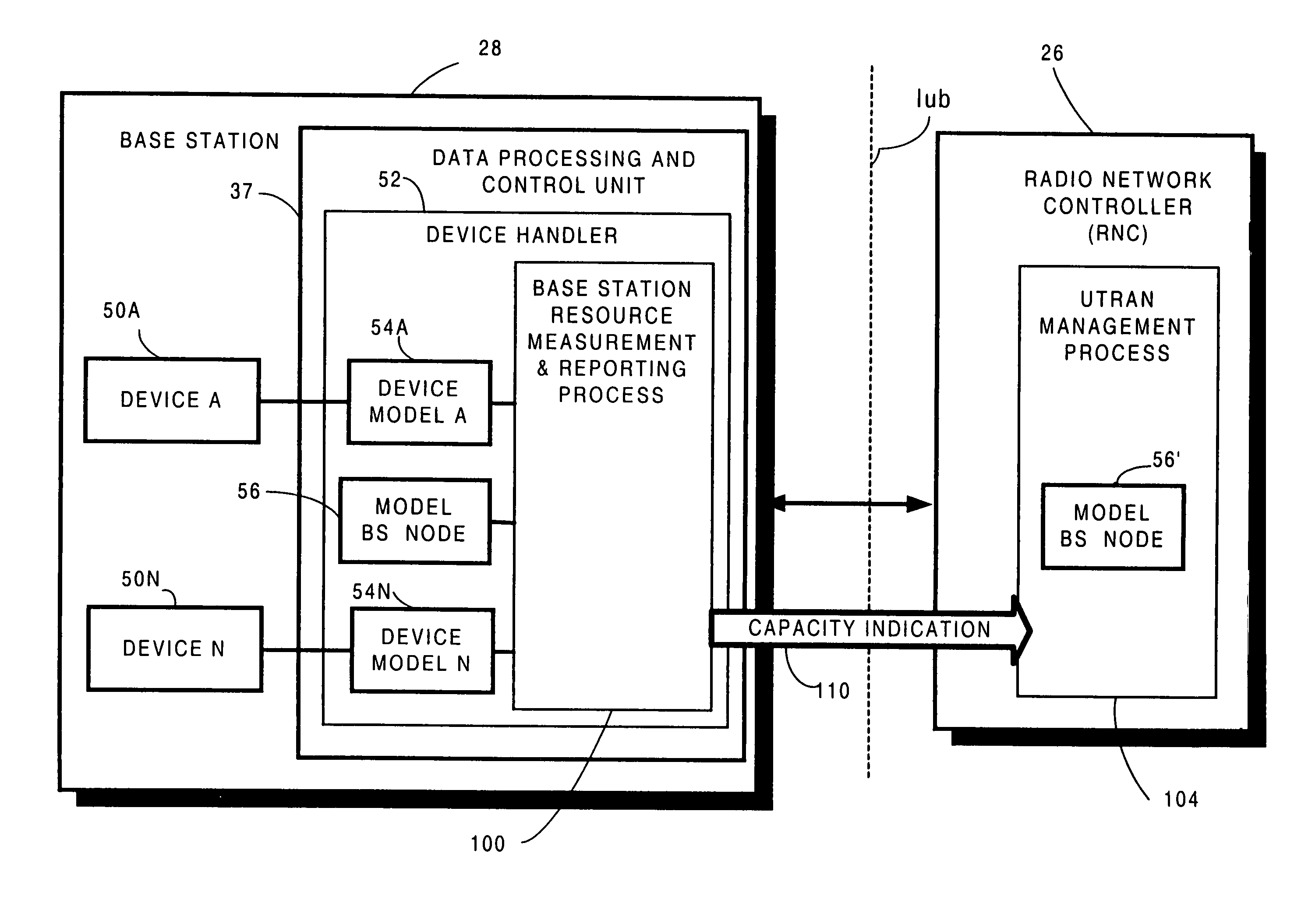
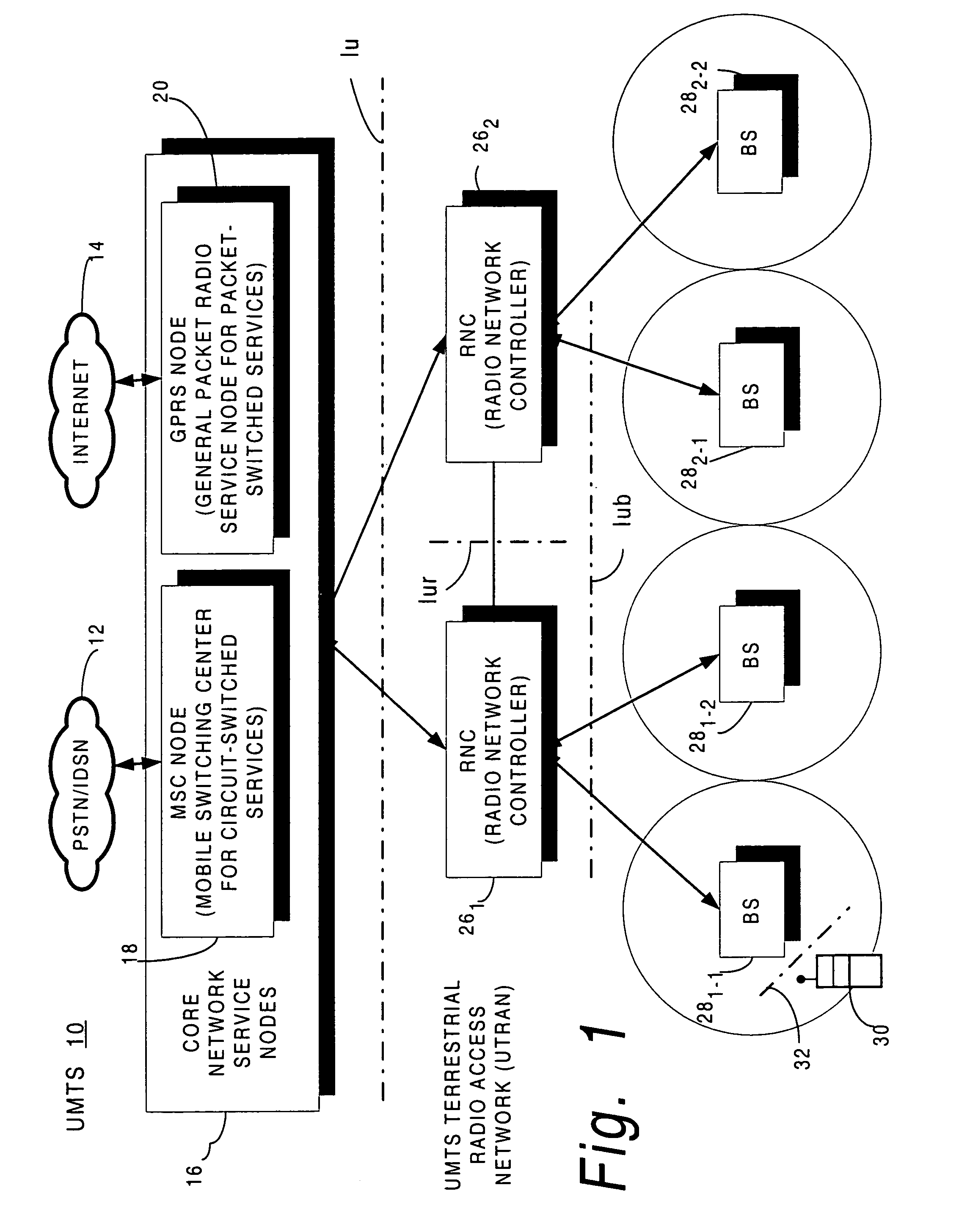
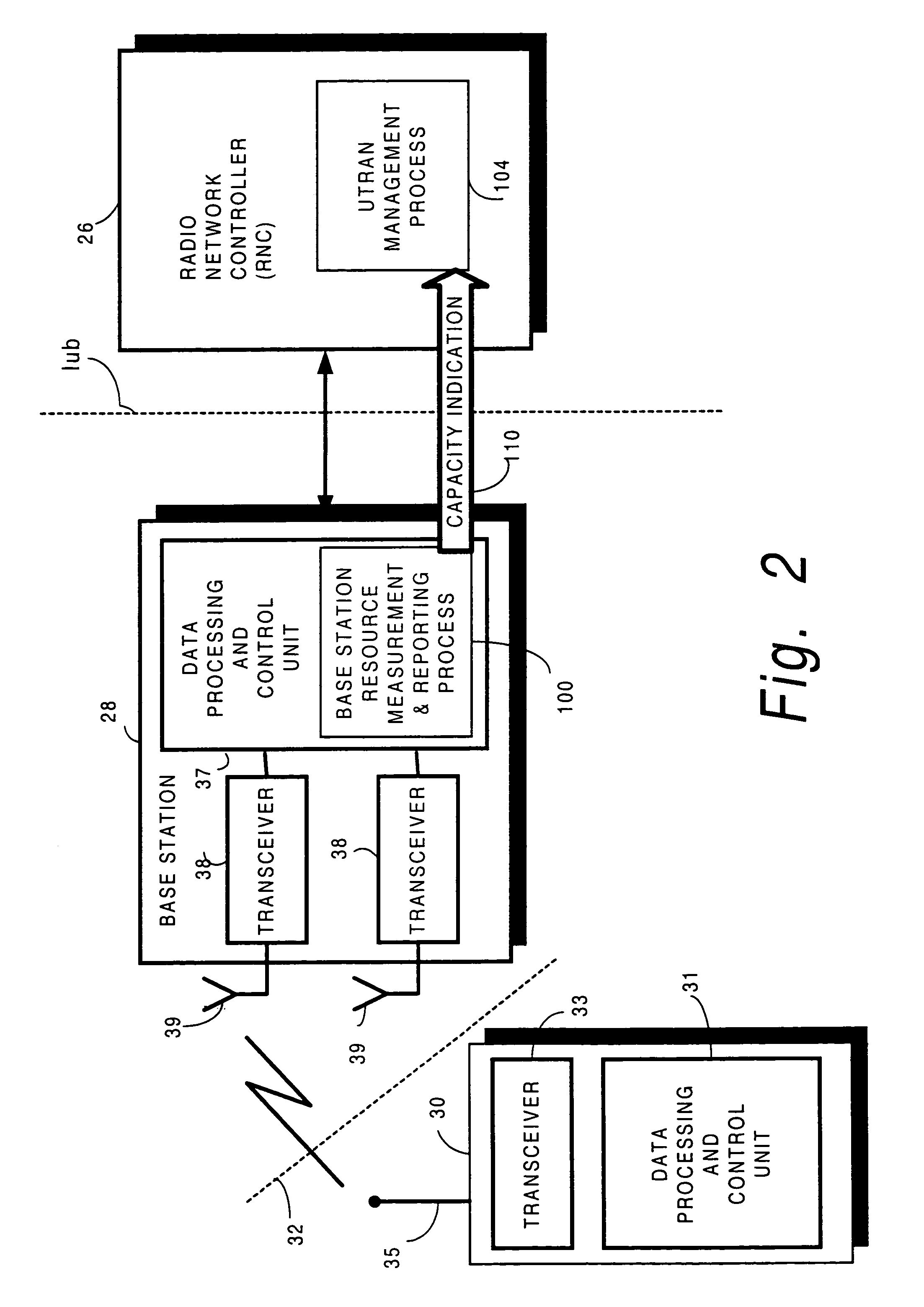
Resource capacity reporting to control node of radio access network
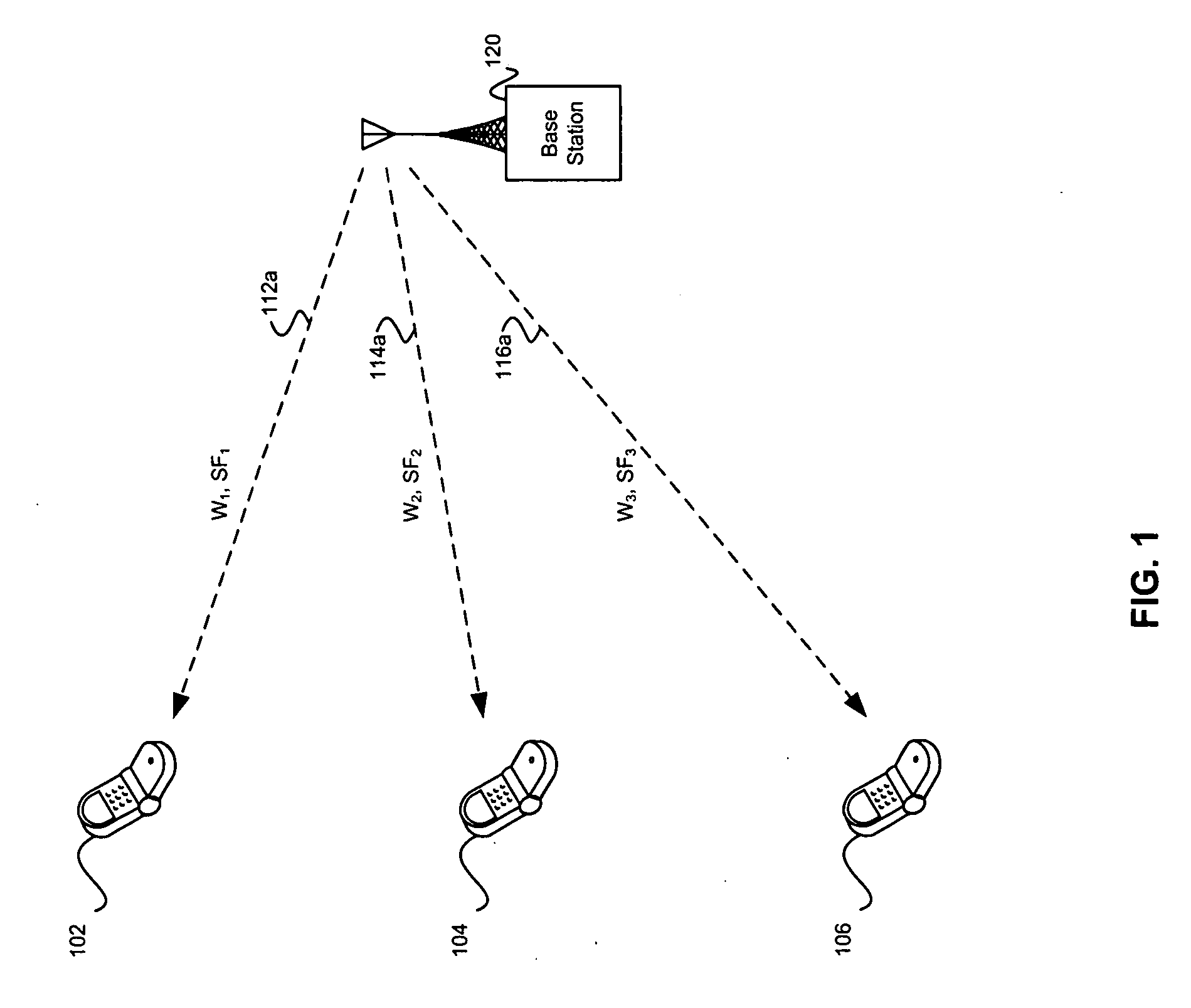
A base station node (28) of a radio access network determines a number of connections that can be added for each of plural spreading factors to the base station node, and sends to a radio network controller (RNC) node (26) a capacity indication (110) including the determined number of connections. In a first message mode of the invention, the capacity indication is included in a conventional 3GPP “Resource Status Indication” message, while in a second message mode the capacity indication is included in a separate supplemental message known as the capacity message. To prepare the capacity indication, the base station tracks actual usage of base station resources for determining the number of connections that can be added to the base station node, and assesses the capability of the base station node to add new connections.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
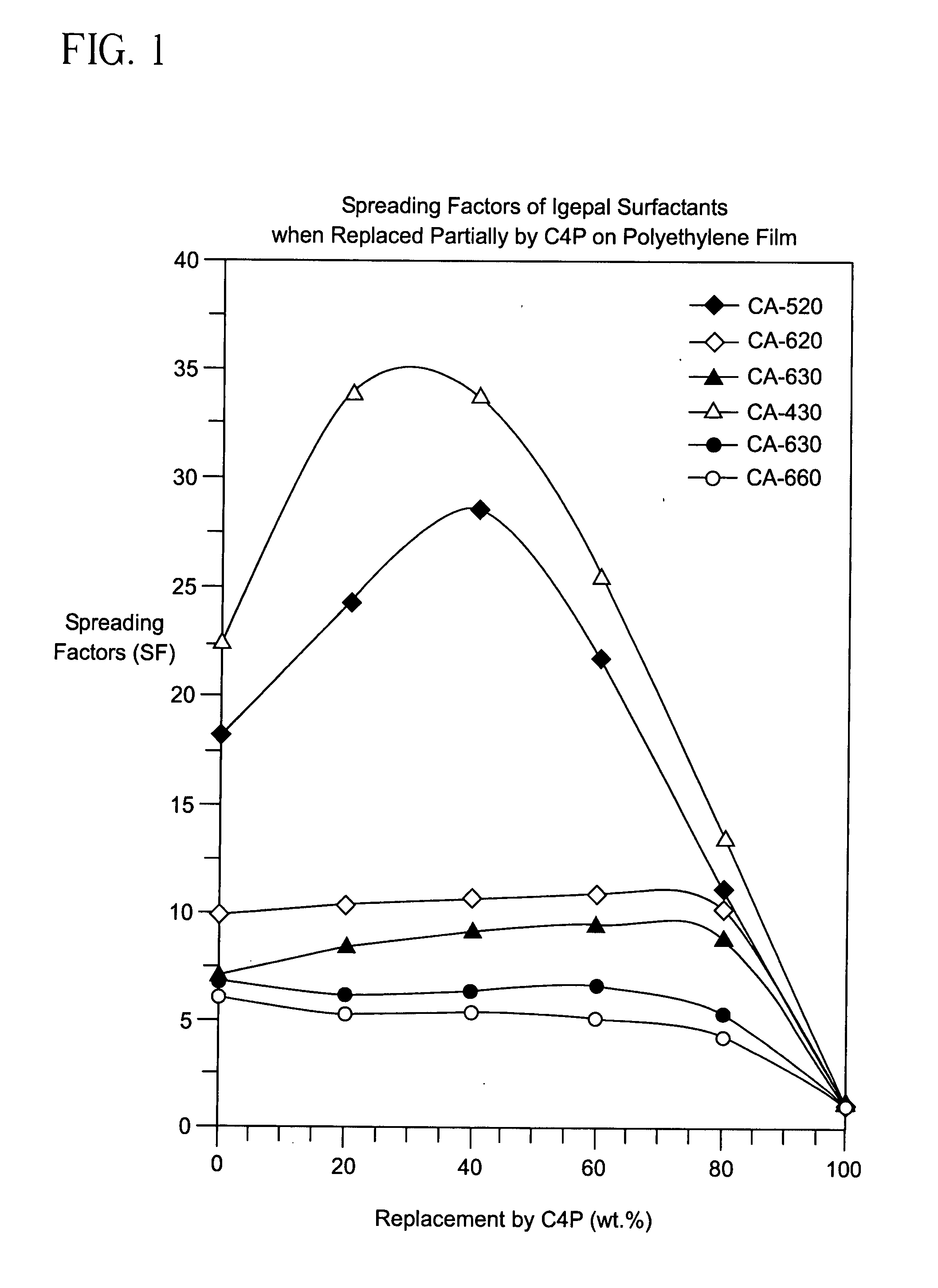
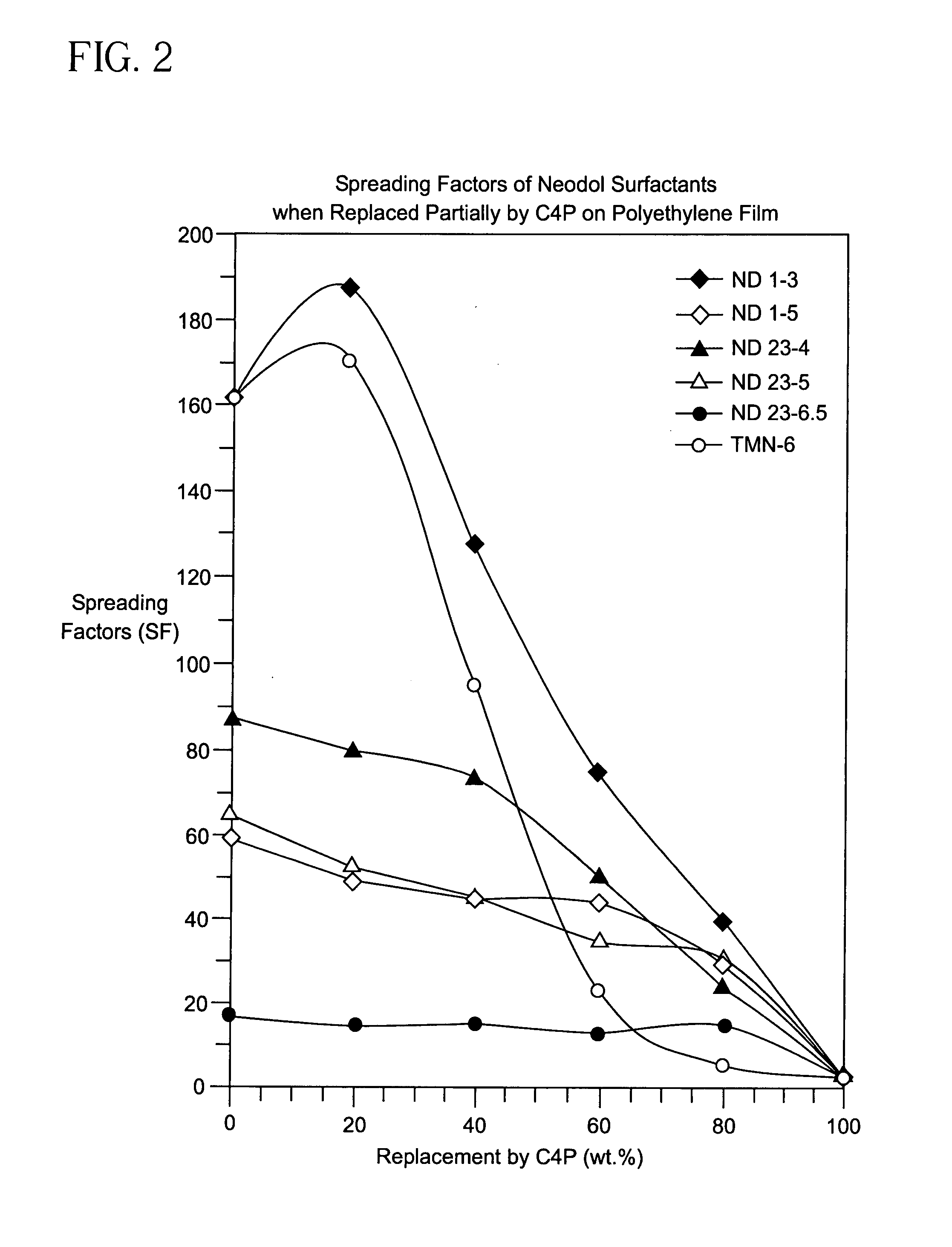
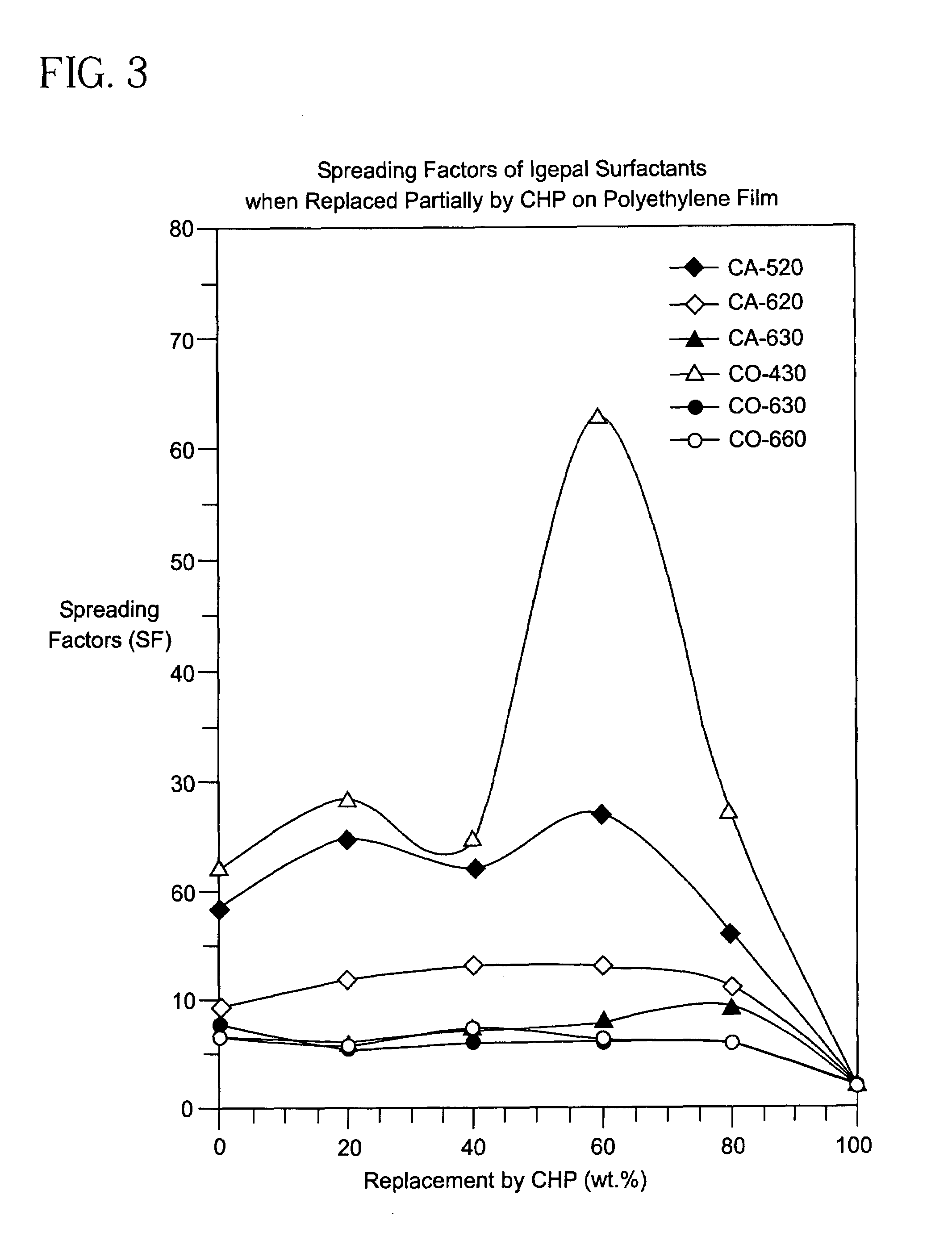
Enhancement of the wetting of hydrophobic surfaces by aqueous surfactant solutions
InactiveUS7264885B2Synthetic resin layered productsGlass/slag layered productsSURFACTANT BLENDPolymer chemistry
A solid hydrophobic surface wetted with an aqueous solution that includes a first and second surfactant. The first surfactant includes a first straight-chain, branched chain or cyclic hydrocarbon chain and a first hydrophilic moiety. The second surfactant includes a second straight-chain, branched chain or cyclic hydrocarbon chain and a second hydrophilic moiety. The first and second straight-chain, branched chain or cyclic hydrocarbon chains may or may not be the same; the first and second hydrophilic moieties are not the same; and the first surfactant is added to the second surfactant in an amount that causes a synergistic increase in the spreading factor on the hydrophobic surface.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method for distributing resource in downward grouped data transmission
ActiveCN1852073AMeet real-time requirementsIncrease profitError preventionPacket data transmissionData transmission
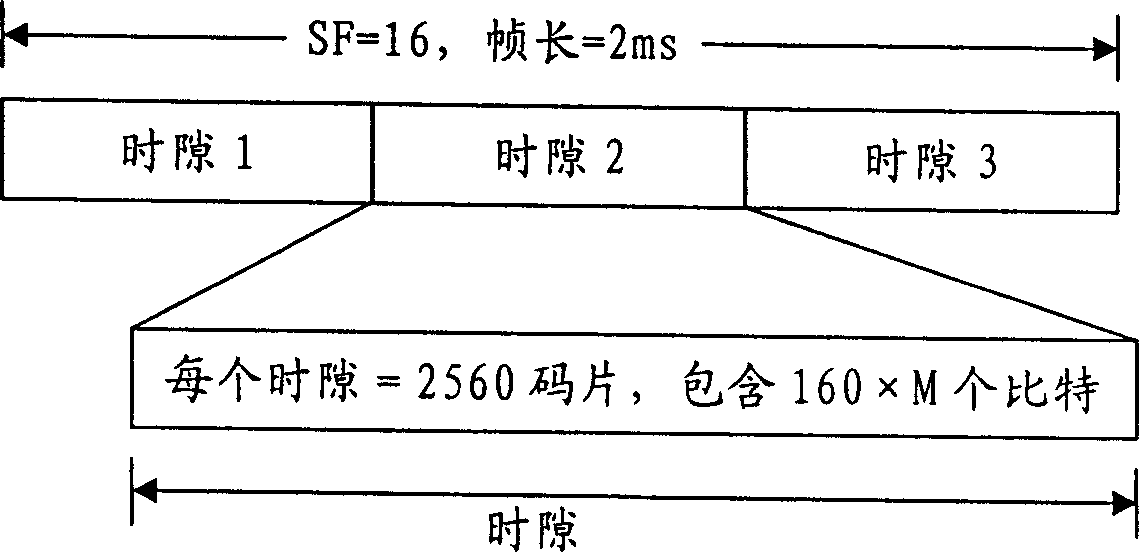
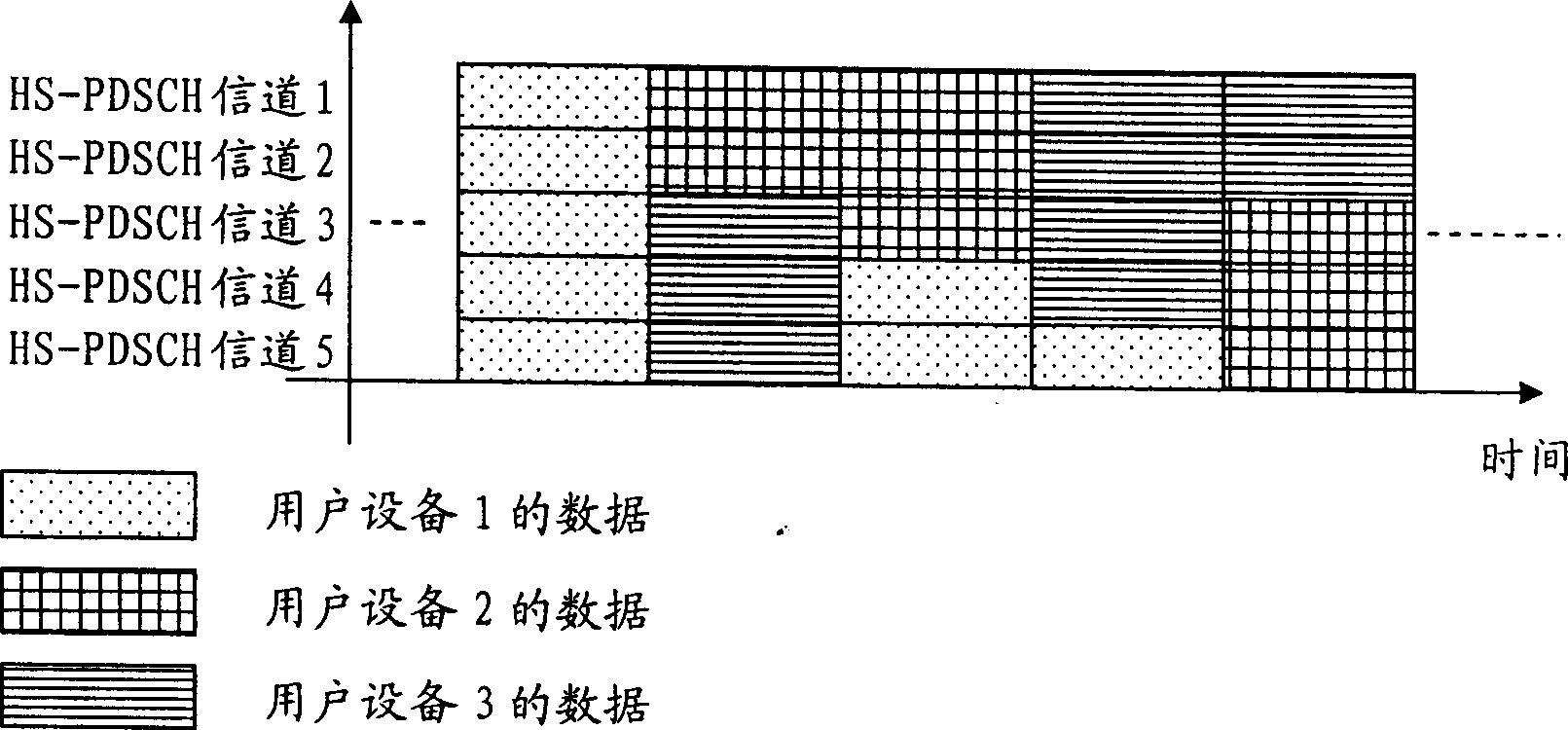
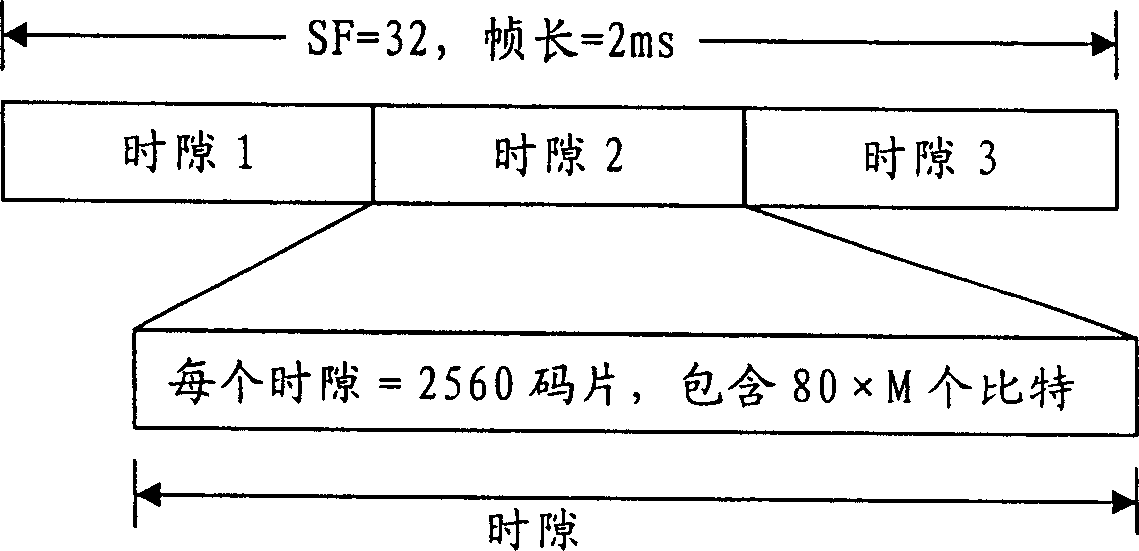
This invention discloses a method for distributing resources in down packet data transmission by increasing HS-PDSCH with the spread-spectrum factors greater than 16 and setting up a corresponding relation between the CQI value corresponding to the increased HS-PDSCH and the transmission block, numbers of the HS-PDSCH channels and a modulation mode including: the base station searches for all corresponding relations based on the CQI value fed back by the UE and the due sent data volume to configure the transmission block, HS-PDSCH channel numbers and a modulation mode for the UE.
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
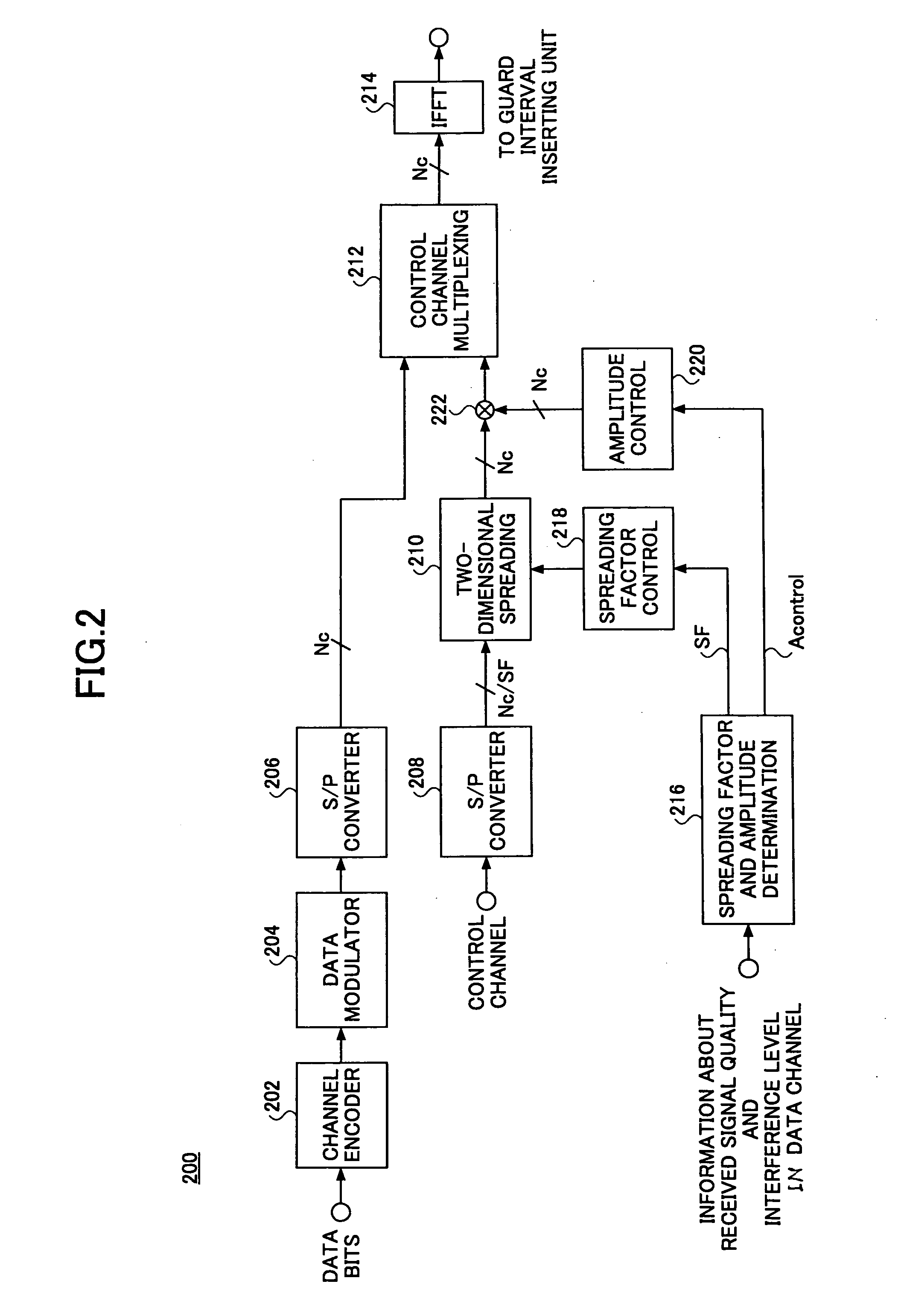
OFDM communication system and method
InactiveUS7397839B2Easy to useEnsure correct executionSecret communicationTransmission monitoringMultiplexingSignal quality
A transmitter used in a wireless communication system based on an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) scheme includes a determination unit that determines a spreading factor and an amplitude for a control channel based on at least one of signal quality information and interference information in data transmission. The transmitter also includes a multiplexing unit that multiplexes a data channel with the control channel having been code-spread based on the spreading factor and the amplitude. A modulator then modulates the multiplexed signal in the OFDM scheme for transmission as OFDM symbols.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Detection method and device
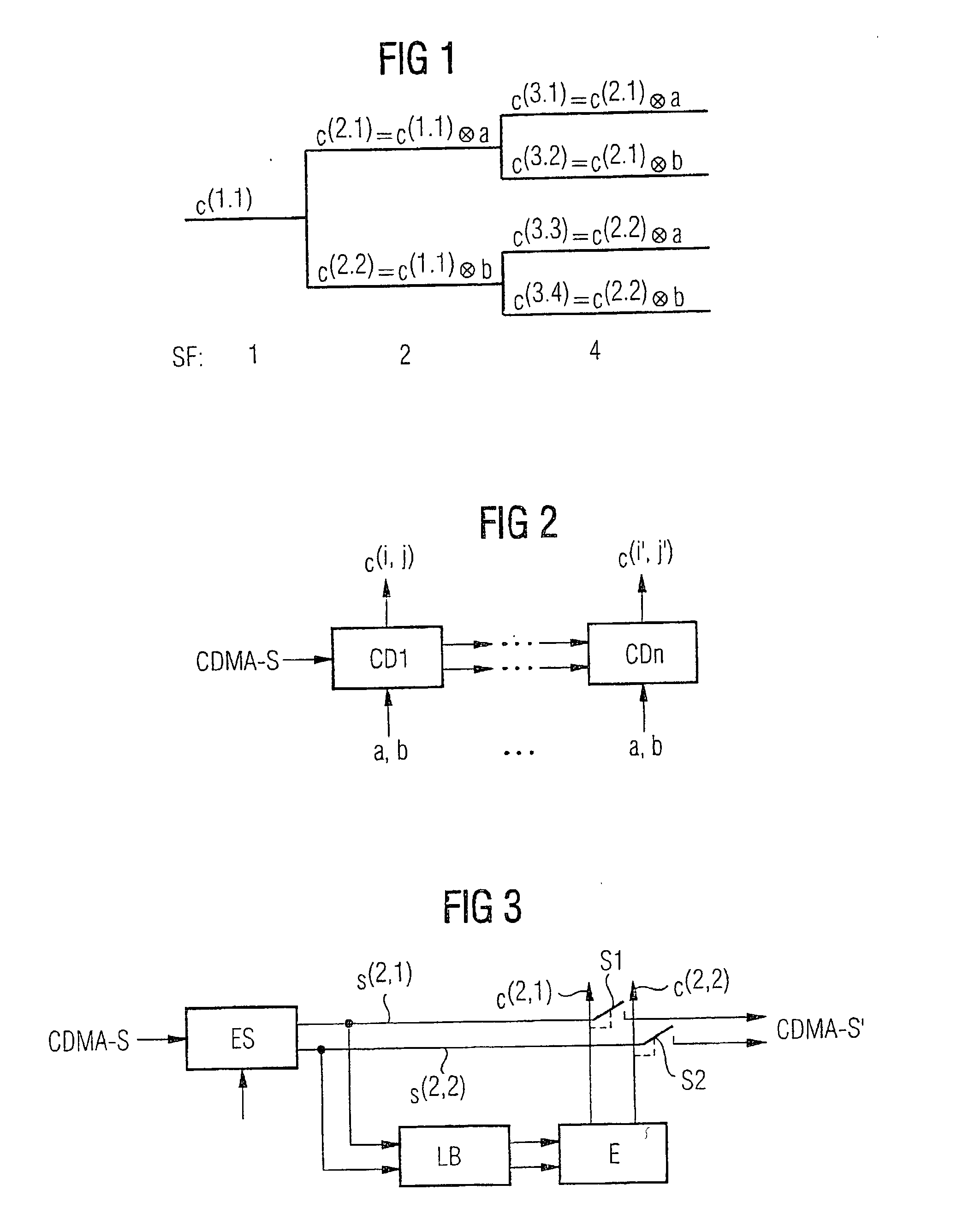
The present invention provides a detection method in which a CDMA-coded data signal is transmitted in the form of a data stream of spread data bursts between a transmitter and a receiver, hierarchical CDMA codes being used for the transmission. In a first step, codes having a smaller spreading factor than a maximally to be detected spreading factor (SF) are detected. In a second step, codes having a larger spreading factor than in the previous step are detected, the detection results of the first step being taken into account. In a third step, the detection process is broken off if all codes are detected, or otherwise the second step is repeated with the detection results last obtained in each instance, until all codes are detected.
Owner:IPCOM GMBH & CO KG
Apparatus and method for performing adaptive channel estimation in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS7376210B2Avoid performanceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLow speedNoise level
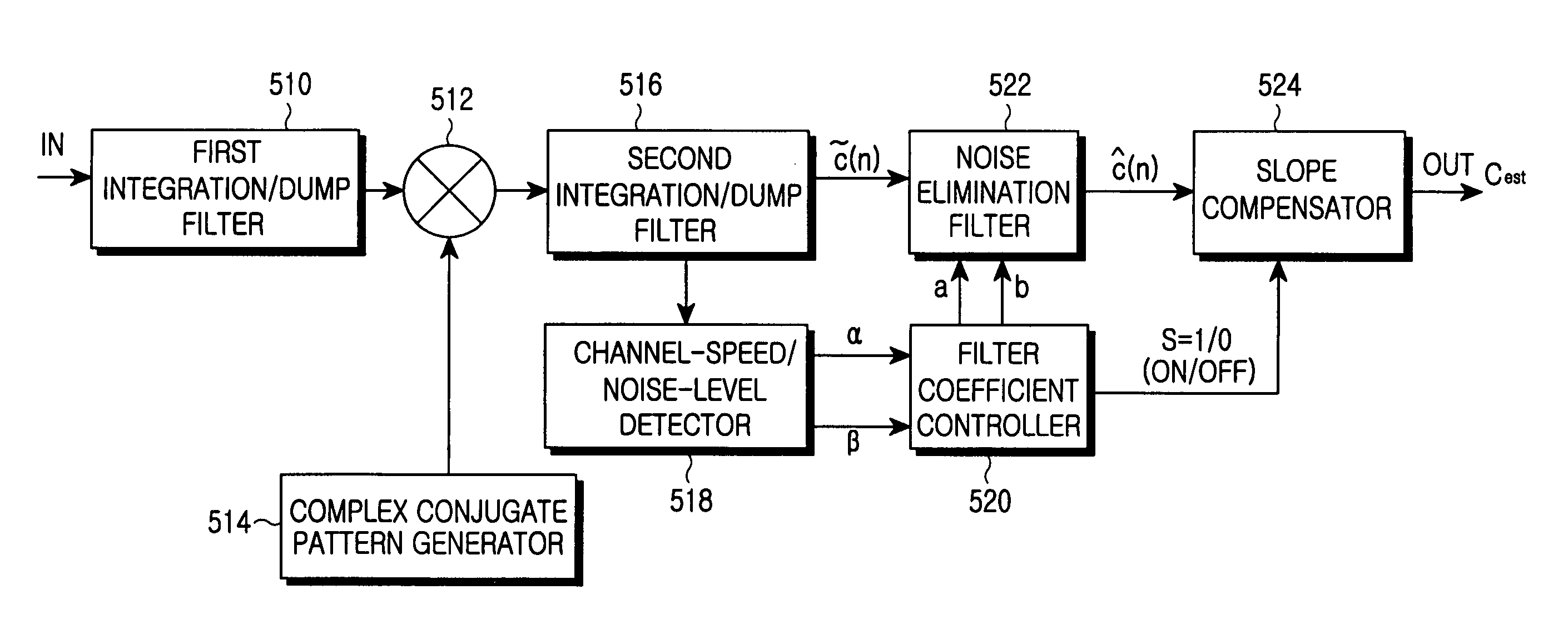
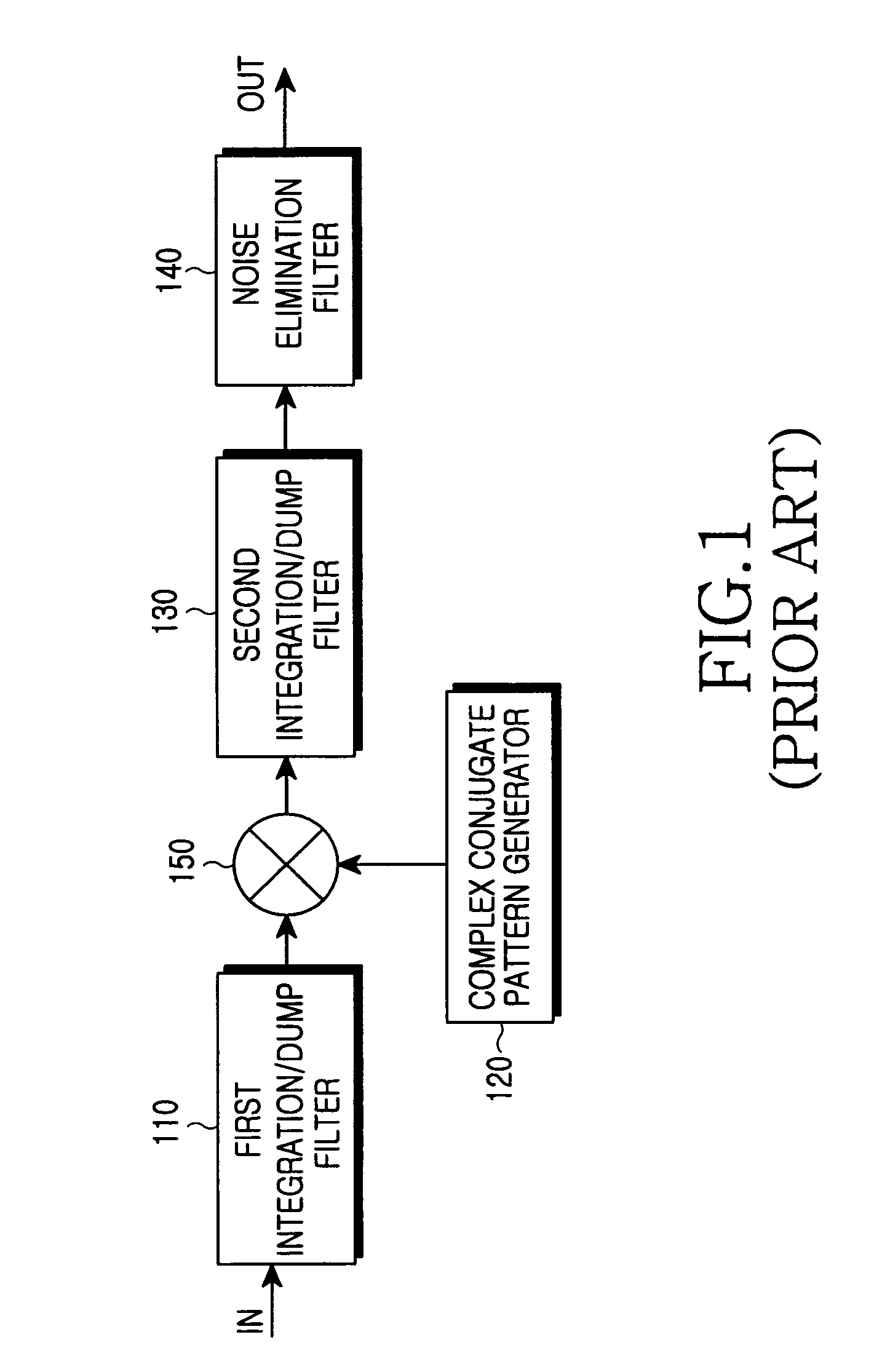
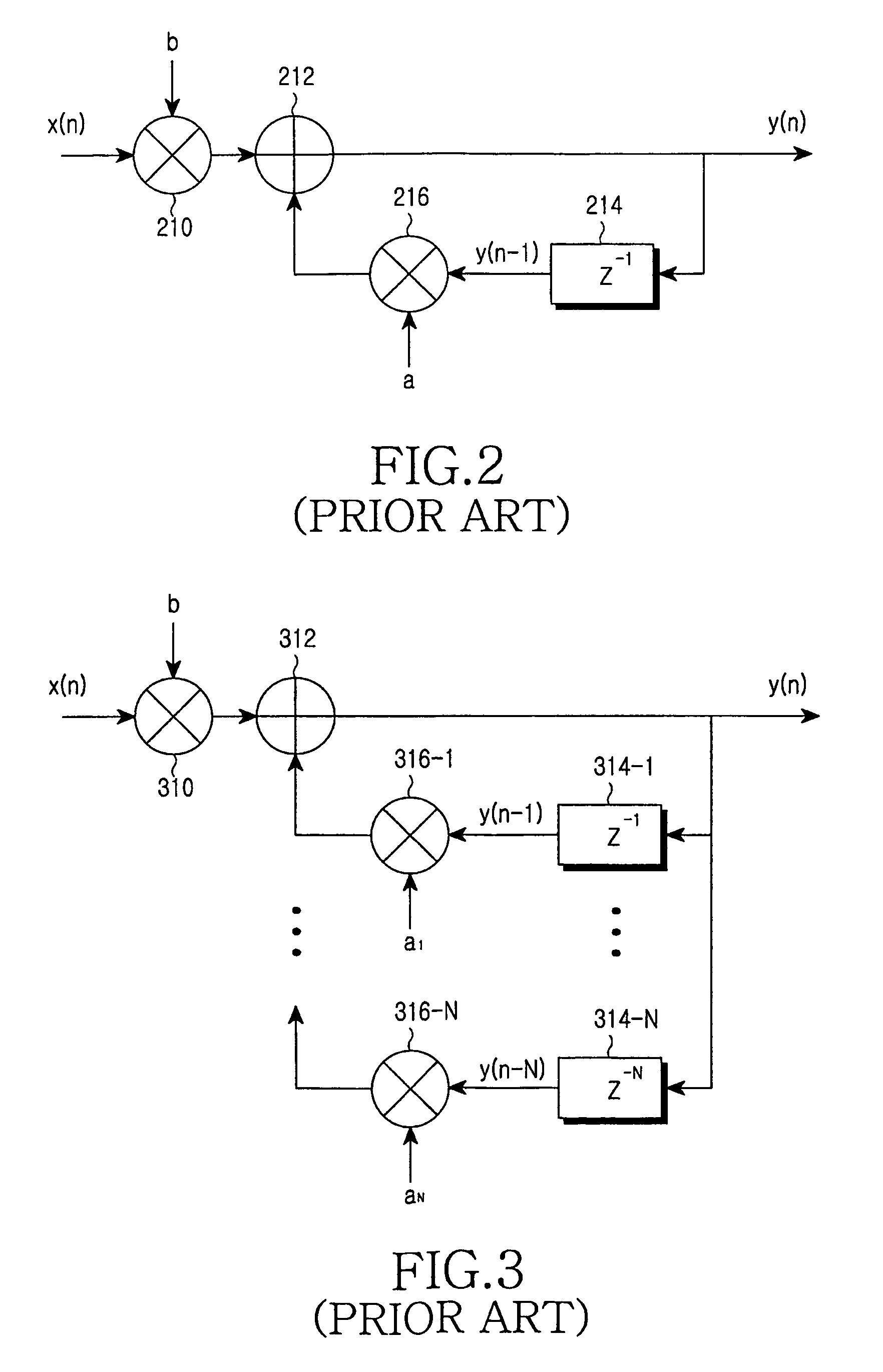
Disclosed is an adaptive channel estimator for improving a performance of a general channel estimator in a mobile communication system, and a method for controlling the same. The adaptive channel estimator further detects a noise level of a channel and a channel speed, and implements an optimum noise elimination filter on the basis of the detected noise level and channel speed. A comparison between mapping degrees predetermined by the detected noise level and channel speed allows an optimum noise elimination filter to be implemented, If such a channel estimator is implemented, then optimum packet data transmission is available for not only a low-speed channel but also a high-speed channel. A channel compensation caused by a difference between a spreading factor (SF) of a pilot channel and a spreading factor (SF) of a data channel can be compensated on the condition that a slope compensator executed by a SF ratio is controlled by a filter coefficient controller.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Two-dimensional code spreading for interleaved fdma system
InactiveUS20110243197A1Reduce distractionsComplex structureError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionTime domainWireless transmission
A transmitter comprises a first spreading unit configured to multiply each of multiple data symbols with a first spreading code sequence of a first spreading factor; a compression and repetition unit configured to compress output signals of the first spreading unit in time domain and repeat the compressed signal L times (where L is a natural number greater than or equal to 2); a phase modulation unit configured to multiply the compressed and repeated signal with a user dependent phase and output a data block consisting of L sub-blocks; a second spreading unit configured to replicate the data block according to a second spreading factor and multiply each set of the replicated sub-blocks with a second spreading code sequence of the second spreading factor to produce a two-dimensionally spread signal; and a wireless transmission unit configured to transmit the two-dimensionally spread signal using a single-carrier transmission scheme.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Method of managing processing resources in a mobile radio system
A method of managing processing resources in a mobile radio system, in which a first entity manages radio resources and corresponding processing resources, the latter being provided in a second entity separate from the first entity. The second entity signals to the first entity its global processing capacity, or capacity credit, and the consumption law, or quantity of the global processing capacity, or cost, for different spreading factor values. The first entity updates the capacity credit on the basis of the consumption law. In the case of multicode transmission using N spreading codes, the updating is effected on the basis of the cost for at least one of the N spreading codes.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
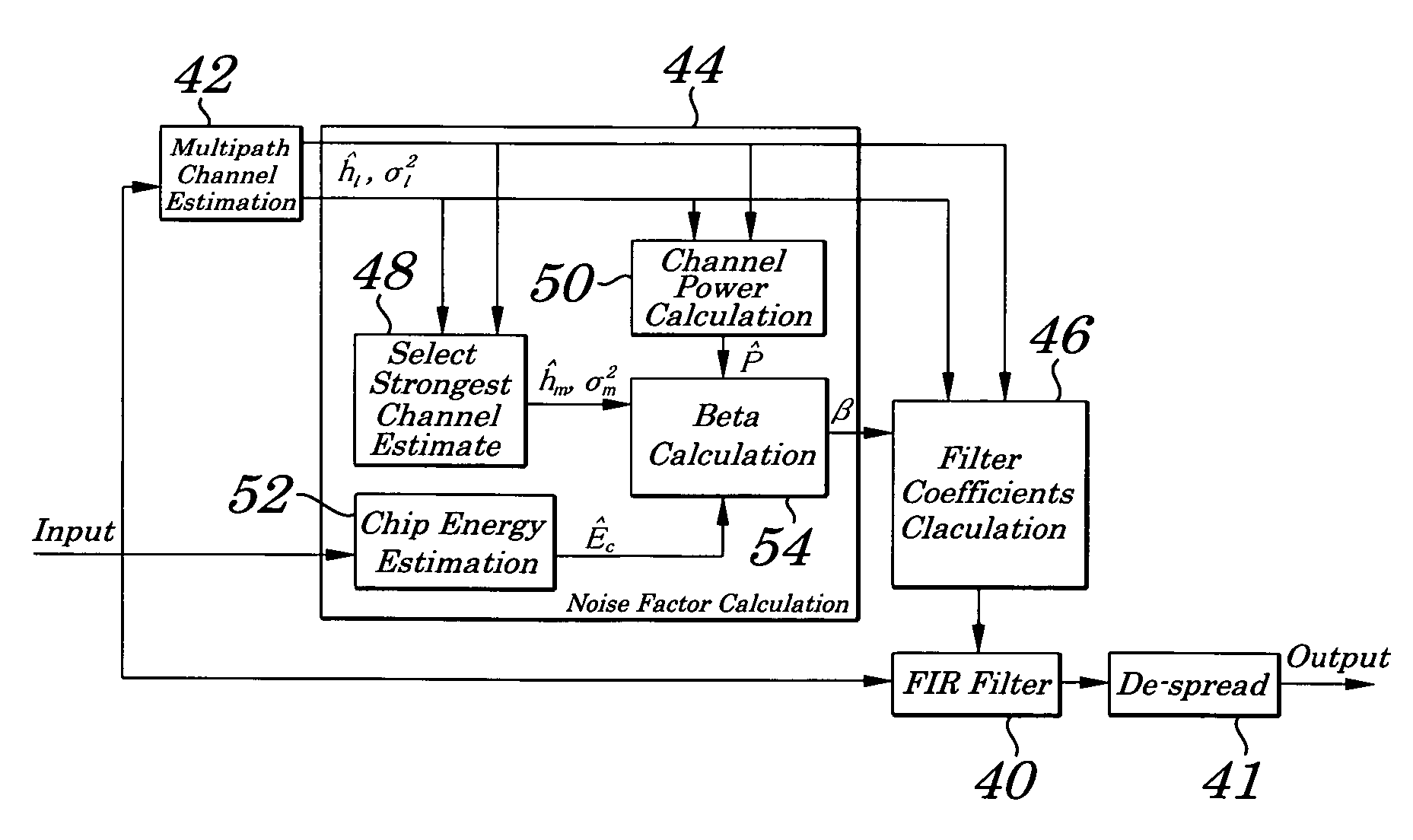
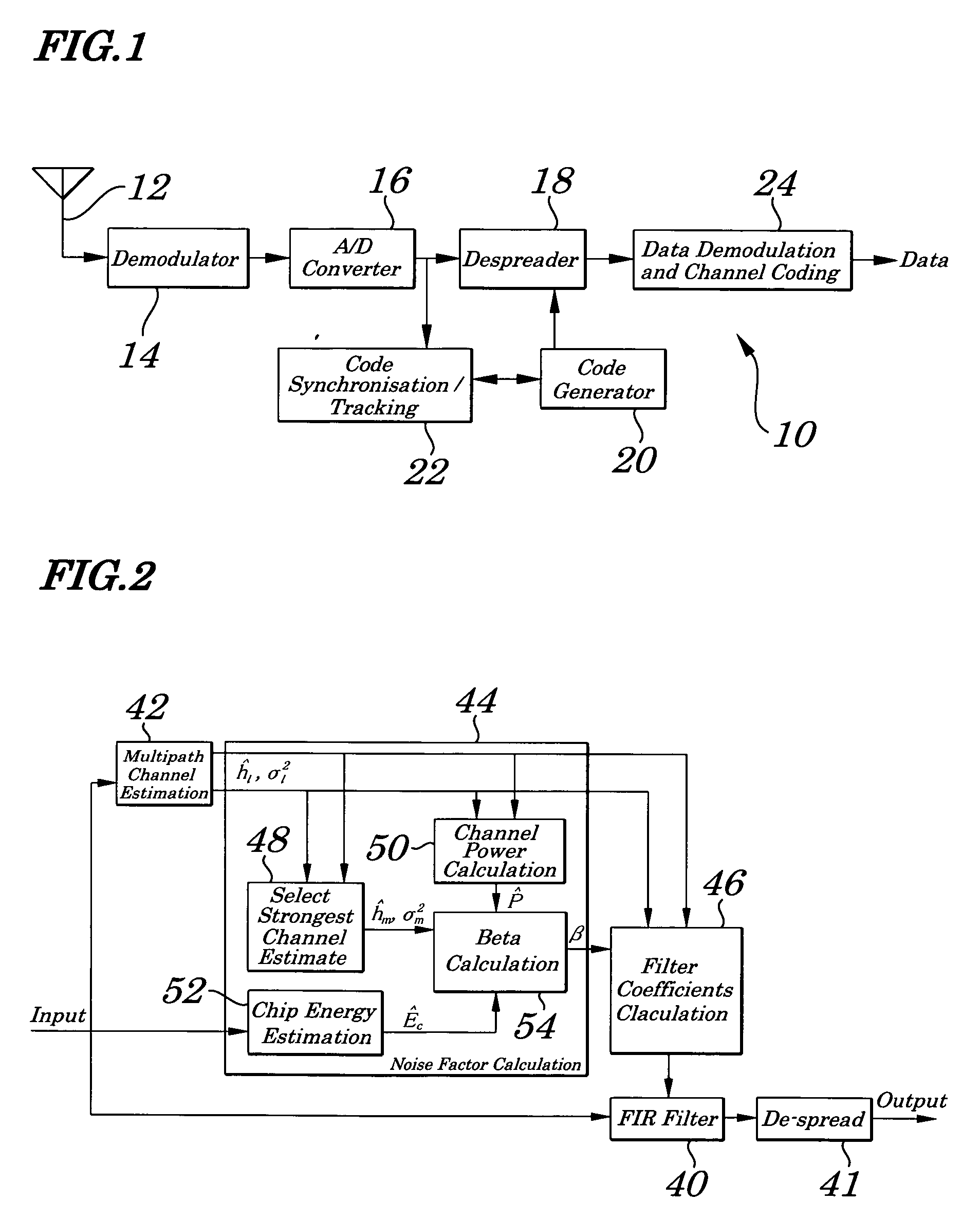
Method of noise factor computation for chip equalizer in spread spectrum receiver
InactiveUS20060018367A1Simple and practical to implementError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorChannel estimationSpread factorEngineering
A method of noise factor computation for a chip equalizer in a spread spectrum receiver, the method including the steps of: computing channel and noise variance estimates for multiple resolvable fading paths of chip signals received at the spread spectrum receiver; computing the sum of power of the channel estimates; estimating the chip energy of the chip signals; and computing the noise factor from the chip energy estimate, channel and noise variance estimates, sum of power of the channel estimates, and spreading factor of the pilot signal.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com