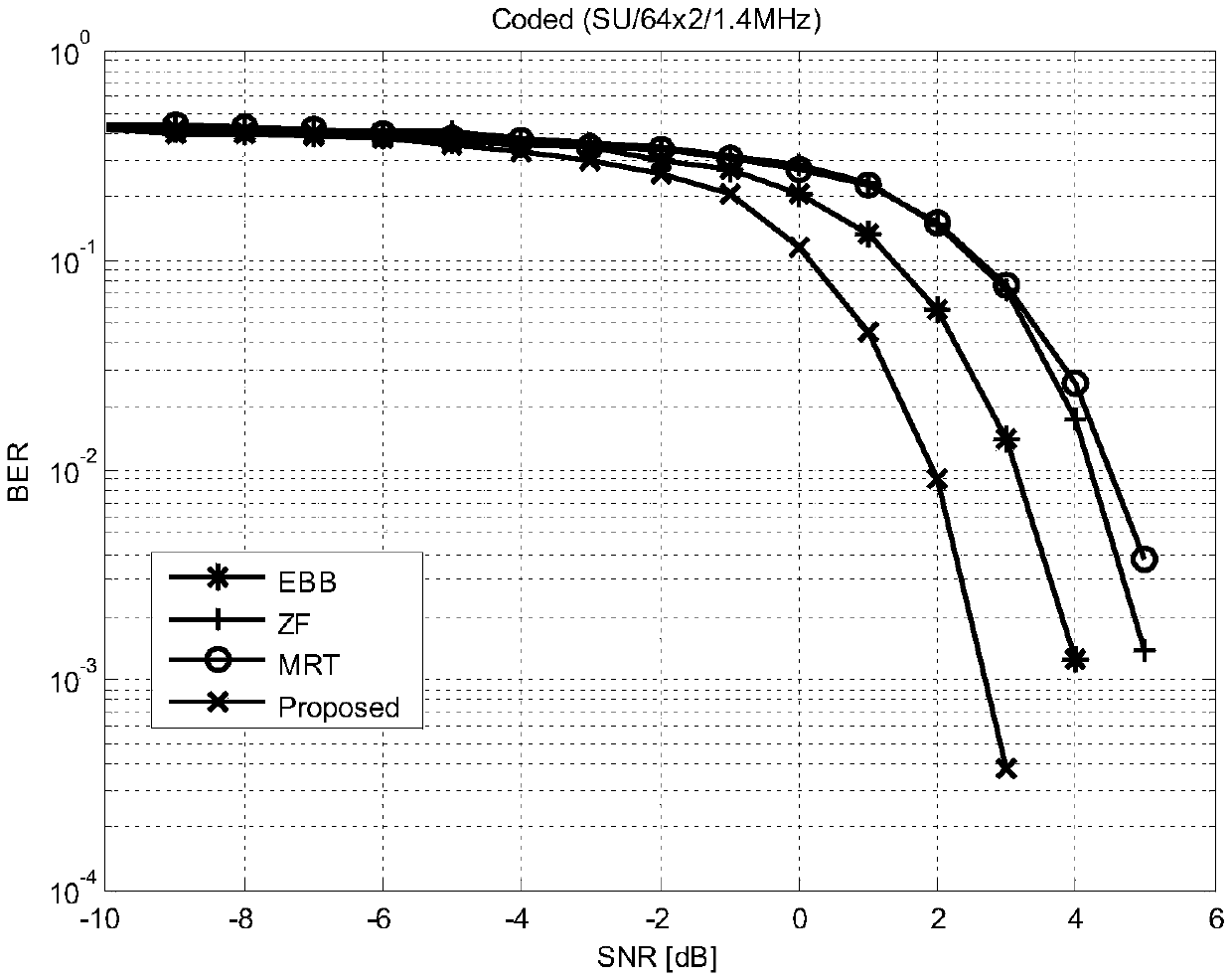
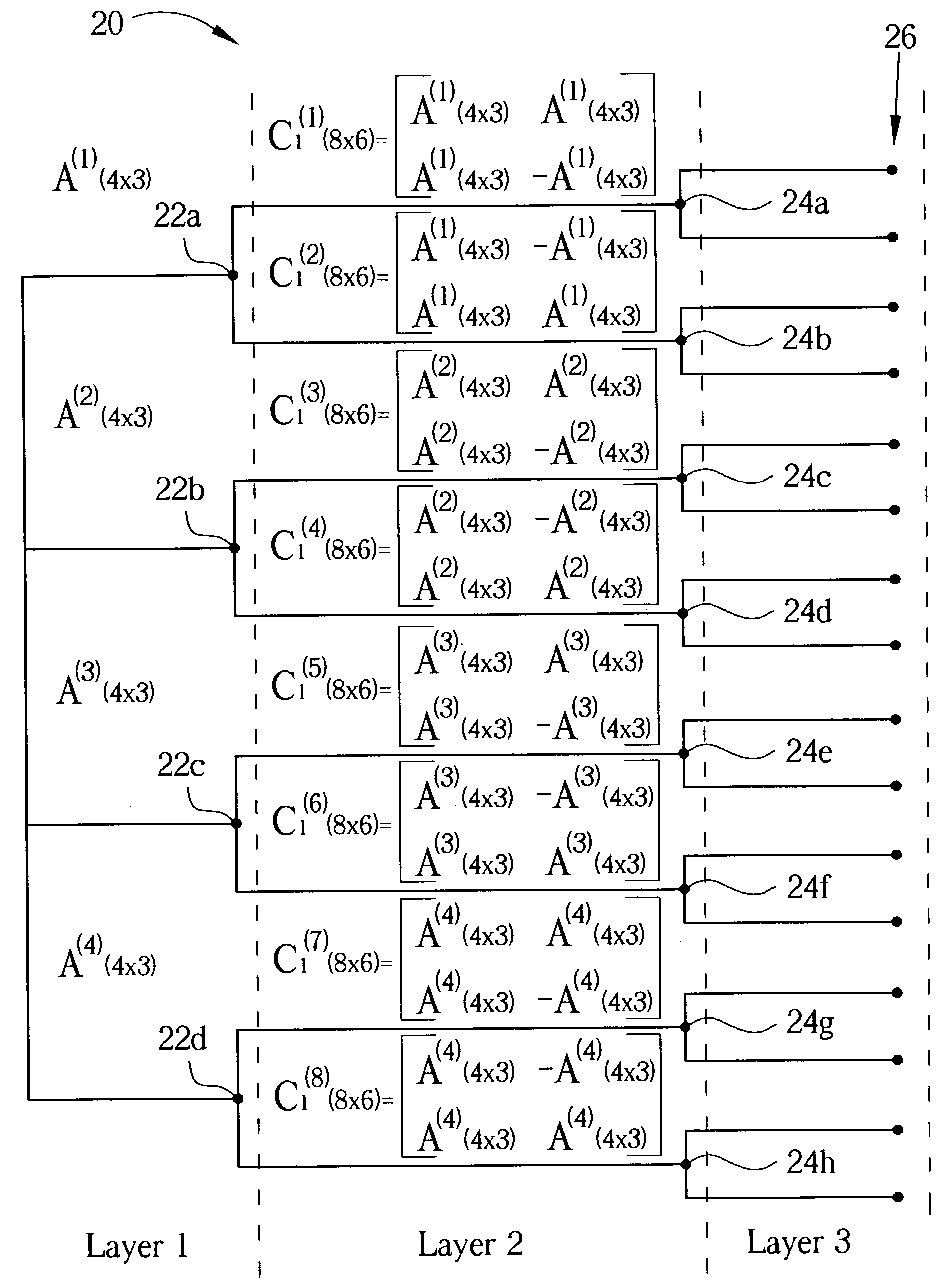
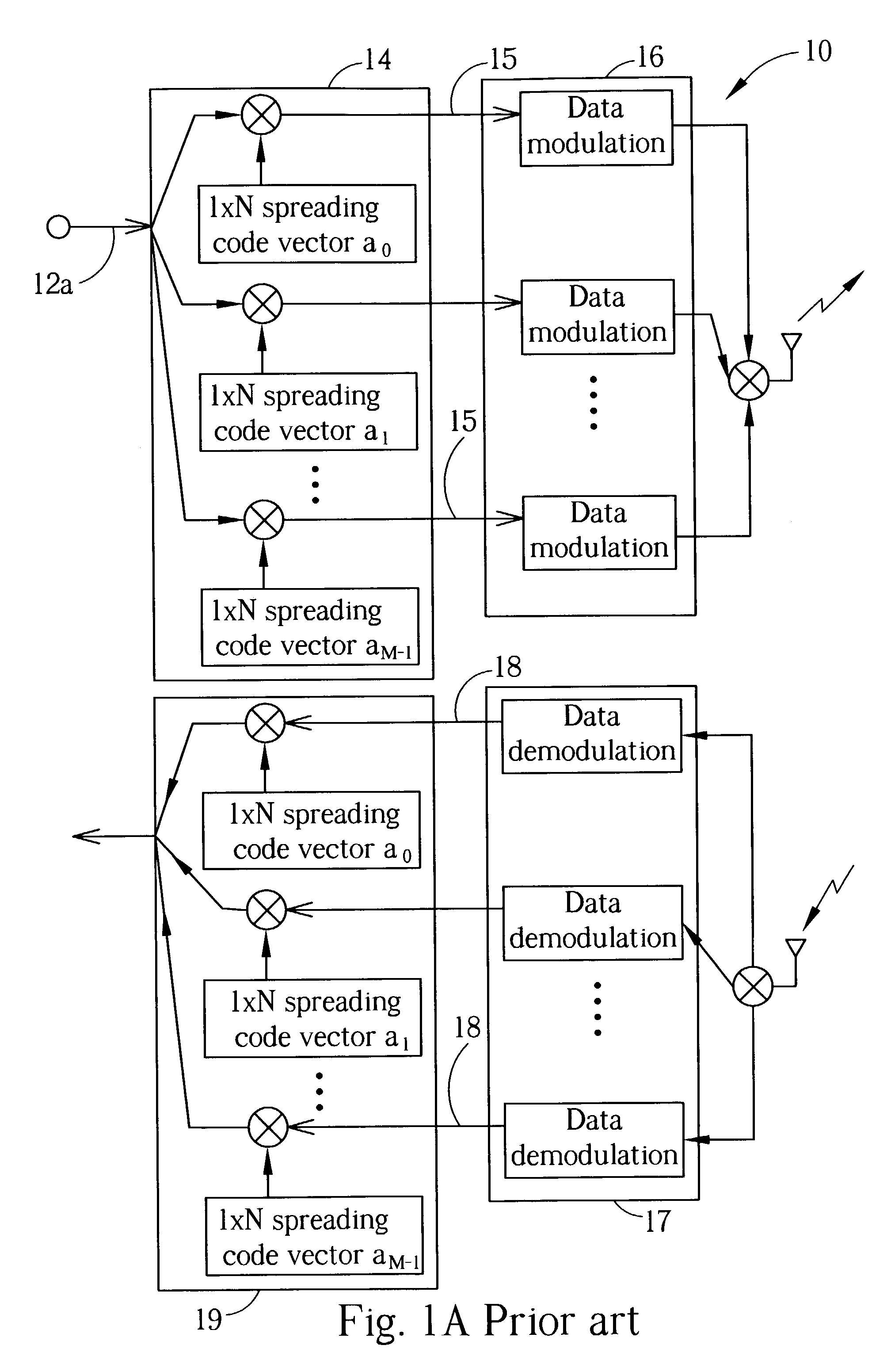
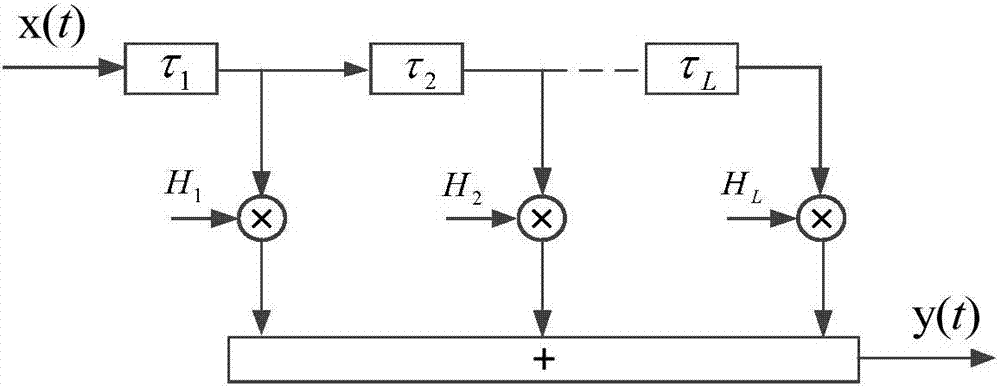
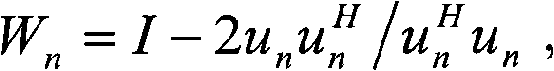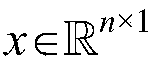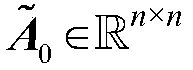Patents
Literature
144 results about "Kronecker product" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, the Kronecker product, denoted by ⊗, is an operation on two matrices of arbitrary size resulting in a block matrix. It is a generalization of the outer product (which is denoted by the same symbol) from vectors to matrices, and gives the matrix of the tensor product with respect to a standard choice of basis. The Kronecker product should not be confused with the usual matrix multiplication, which is an entirely different operation.
Precoding code book constructing method and precoding code book constructing device of multi-input multi-output system
InactiveCN101635612ASatisfy the orthogonality propertyImprove compatibilityRadio transmissionError prevention/detection by diversity receptionPrecodingMulti input
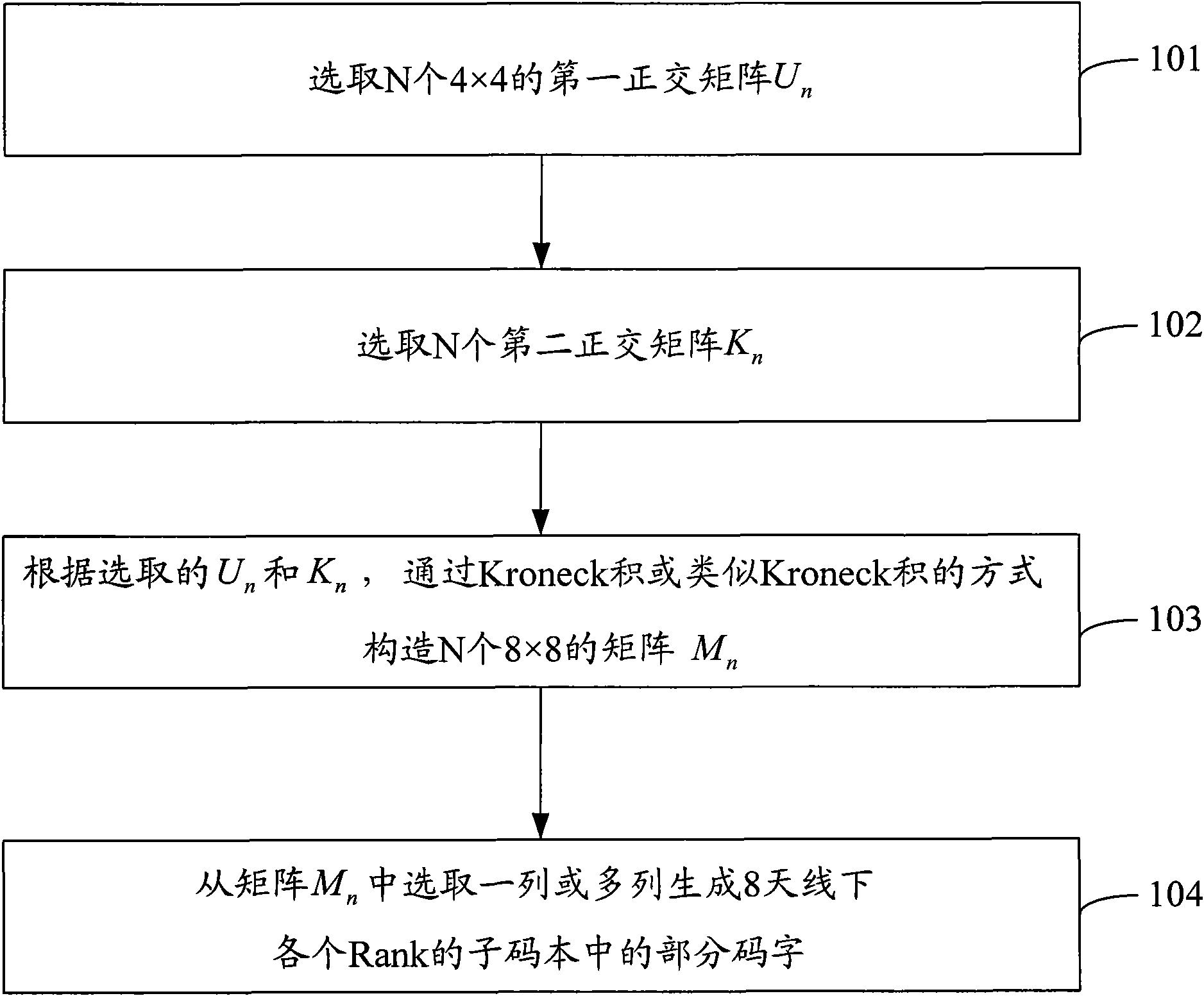
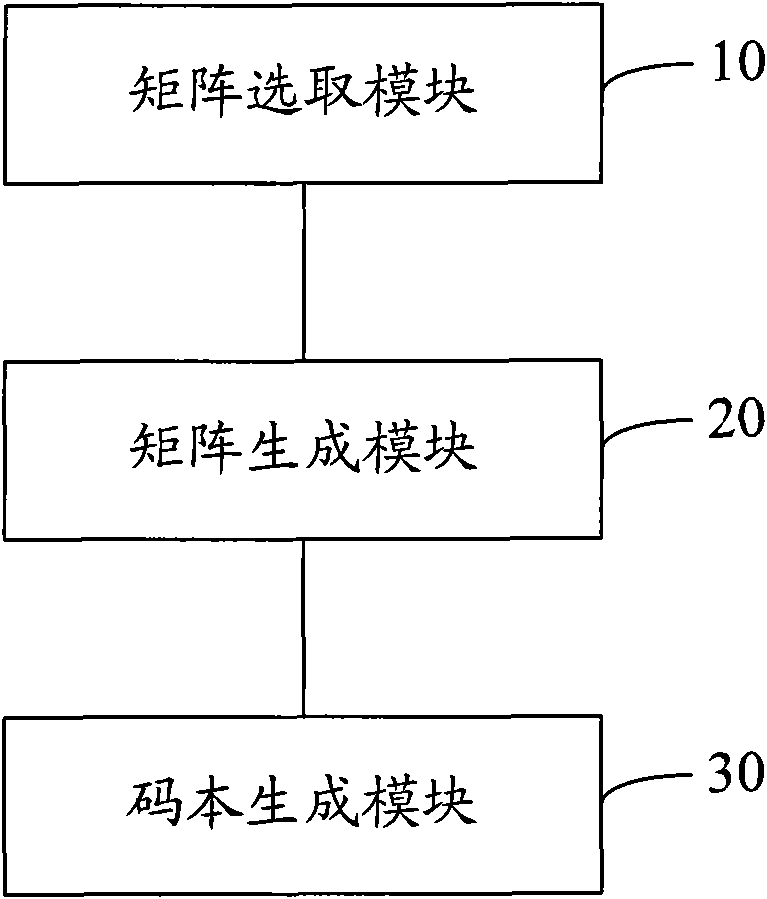
The invention discloses a precoding code book constructing method of a multi-input multi-output system, comprising the following steps: selecting N 4*4 first orthogonal matrixes Un, and selecting N second orthogonal matrixes Kn; generating N 8*8 matrixes Mn according to the selected Un and Kn in a manner of a Kronecker product or analog Kronecker product; and selecting a row or multiple rows of matrixes Mn to construct partial code words in a subcode book of each rank under 8 antennae. The invention also discloses a precoding code book constructing device of a multi-input multi-output system. The method and the device enables the designed code book to satisfy an orthogonal characteristic, a constant modulus characteristic and a 8 PSK characteristic in 8 antennae and have better performance under correlation channels and noncorrelation channels.
Owner:ZTE CORP
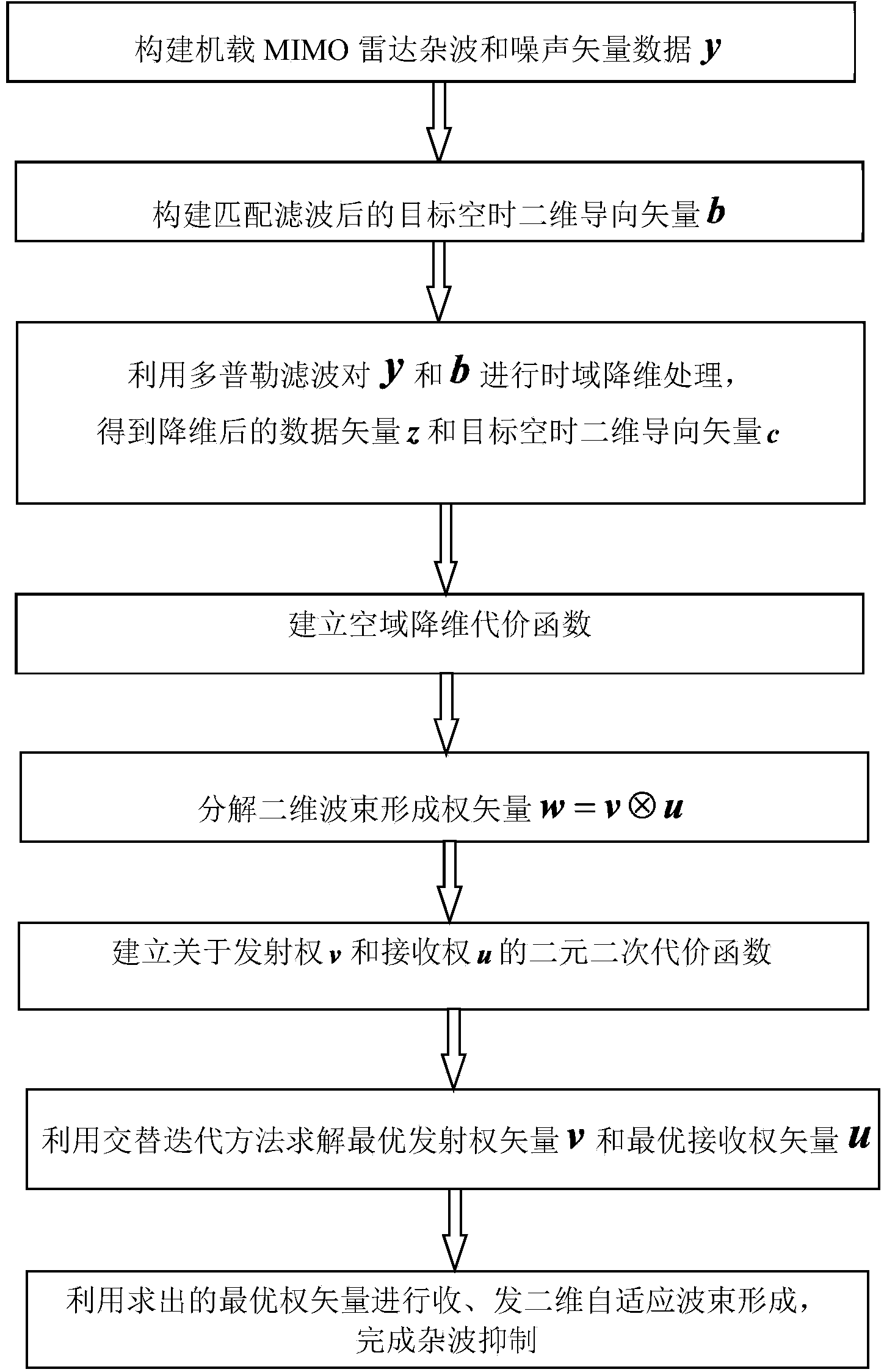
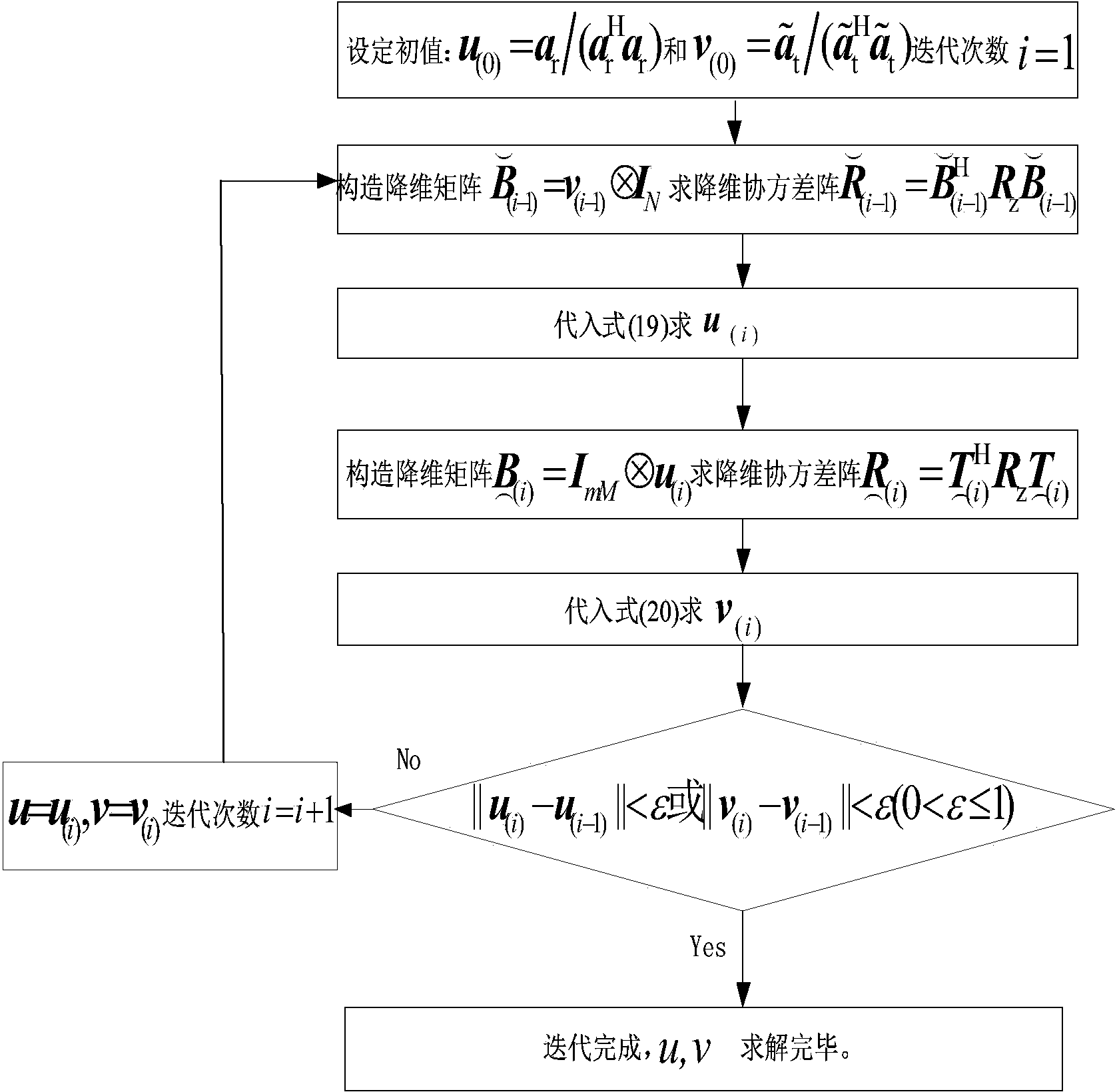
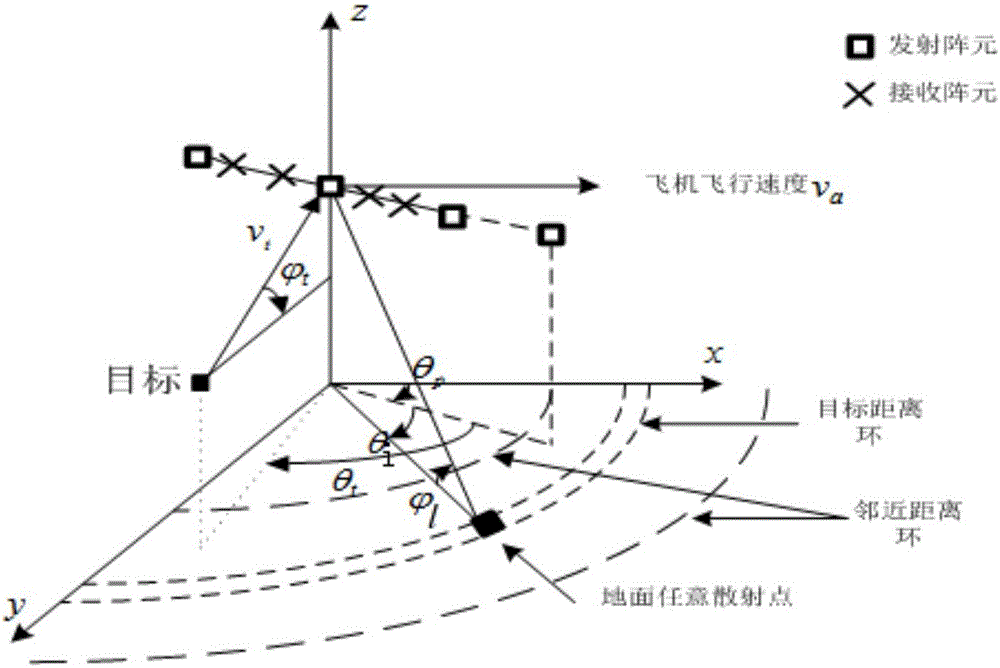
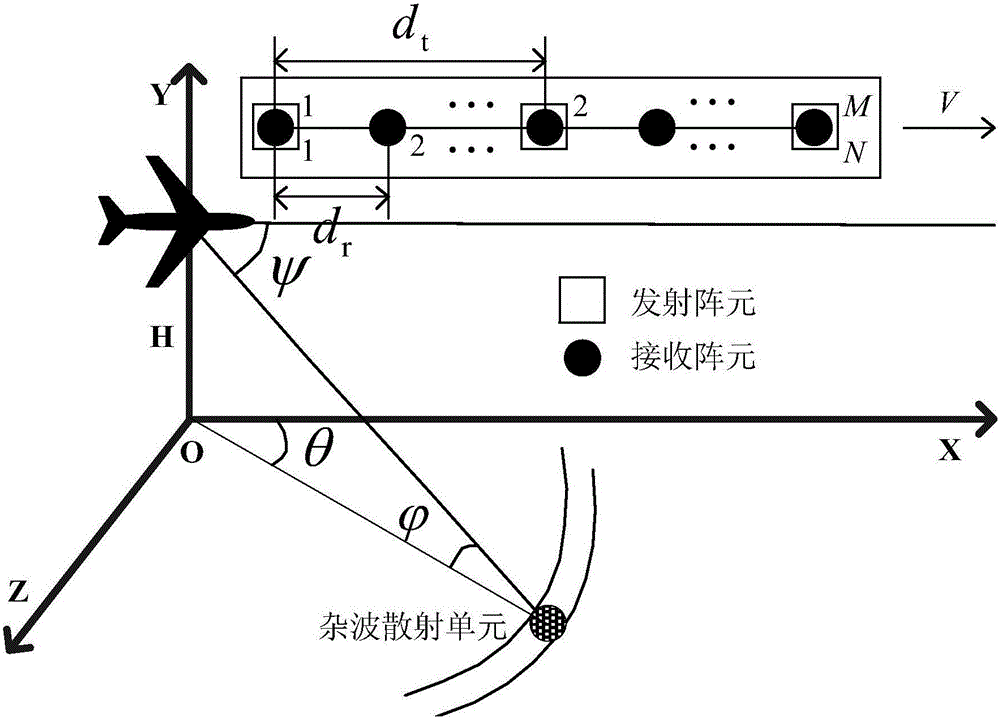
Doppler channel correlation two-stage dimension reduction method for onboard multiple input multiple output (MIMO) radar
InactiveCN103728606AFull rank reversibleFast convergenceWave based measurement systemsSmall sampleNavigation system
The invention discloses a Doppler channel correlation two-stage dimension reduction method for an onboard multiple input multiple output (MIMO) radar. The method includes constructing an onboard MIMO radar clutter signal model and a target space time two-dimensional guide vector; utilizing Doppler filtering to conduct time domain dimension reduction processing on the echo data; resolving weight vectors formed by a space domain transmitting-receiving two-dimensional wave beam into a Kronecker product of a receiving weight and a transmitting weight, building a dyadic and square cost function, utilizing alternative computation to calculate the optimal weight, utilizing the optimal weight to conduct receiving and transmitting two-dimensional self-adaptation wave beam forming and restraining clutter. By means of the method, the dimension of the obtained weight vectors is greatly reduced, optimum covariance matrix estimation can be obtained through less samples, and the clutter restraining performance is greatly improved under small samples. Meanwhile, high-dimensional sampling covariance matrix inversion is avoided, and the calculation quantity is greatly reduced. By means of clutter restraining, further target detection, target location and tracking and flight track forming are facilitated. The method is applied to various actual systems like navigation systems.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
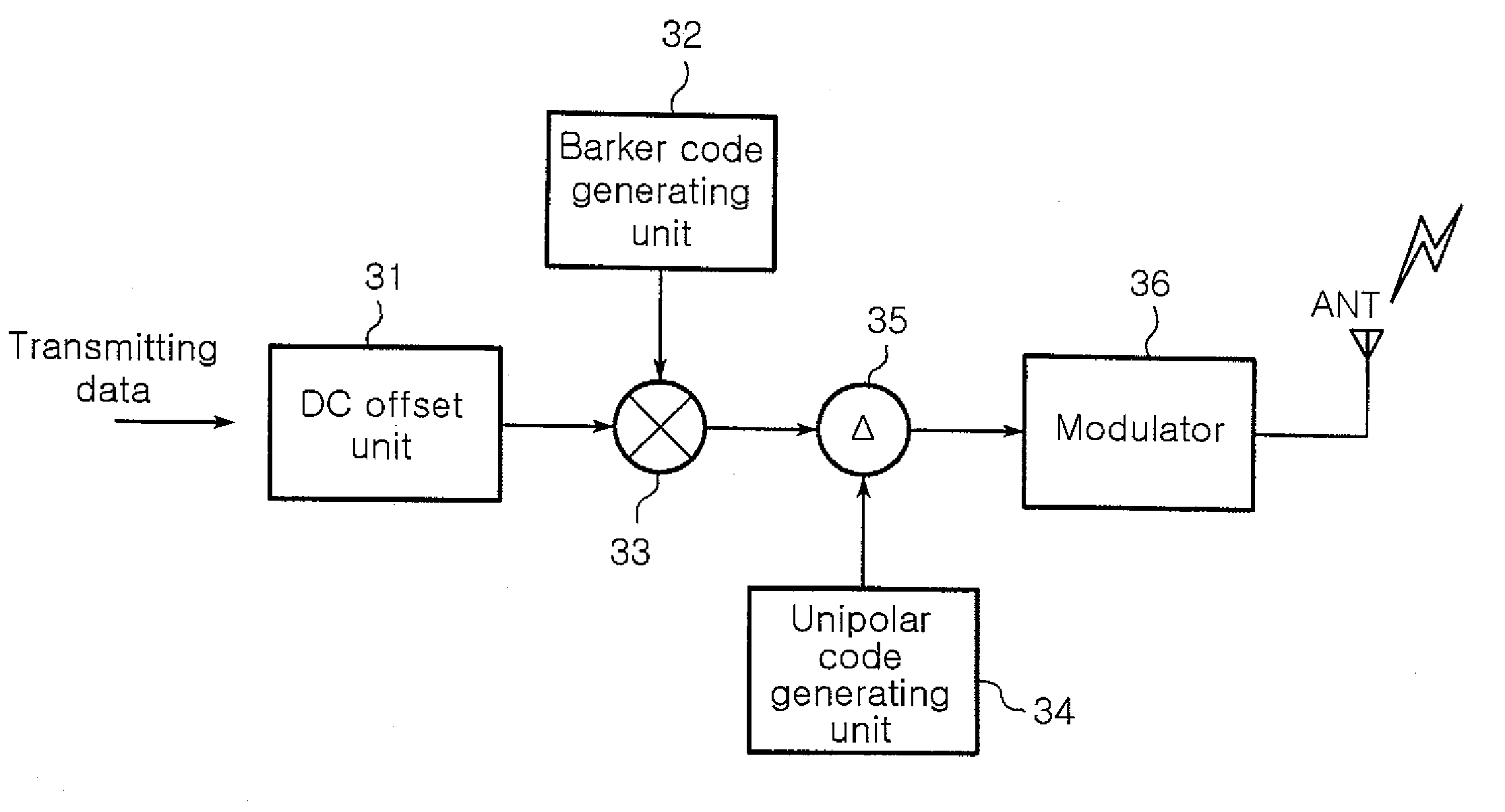
Transmitter and transmitting method of code division multiplexing wireless communication system using on-off keying modulation scheme
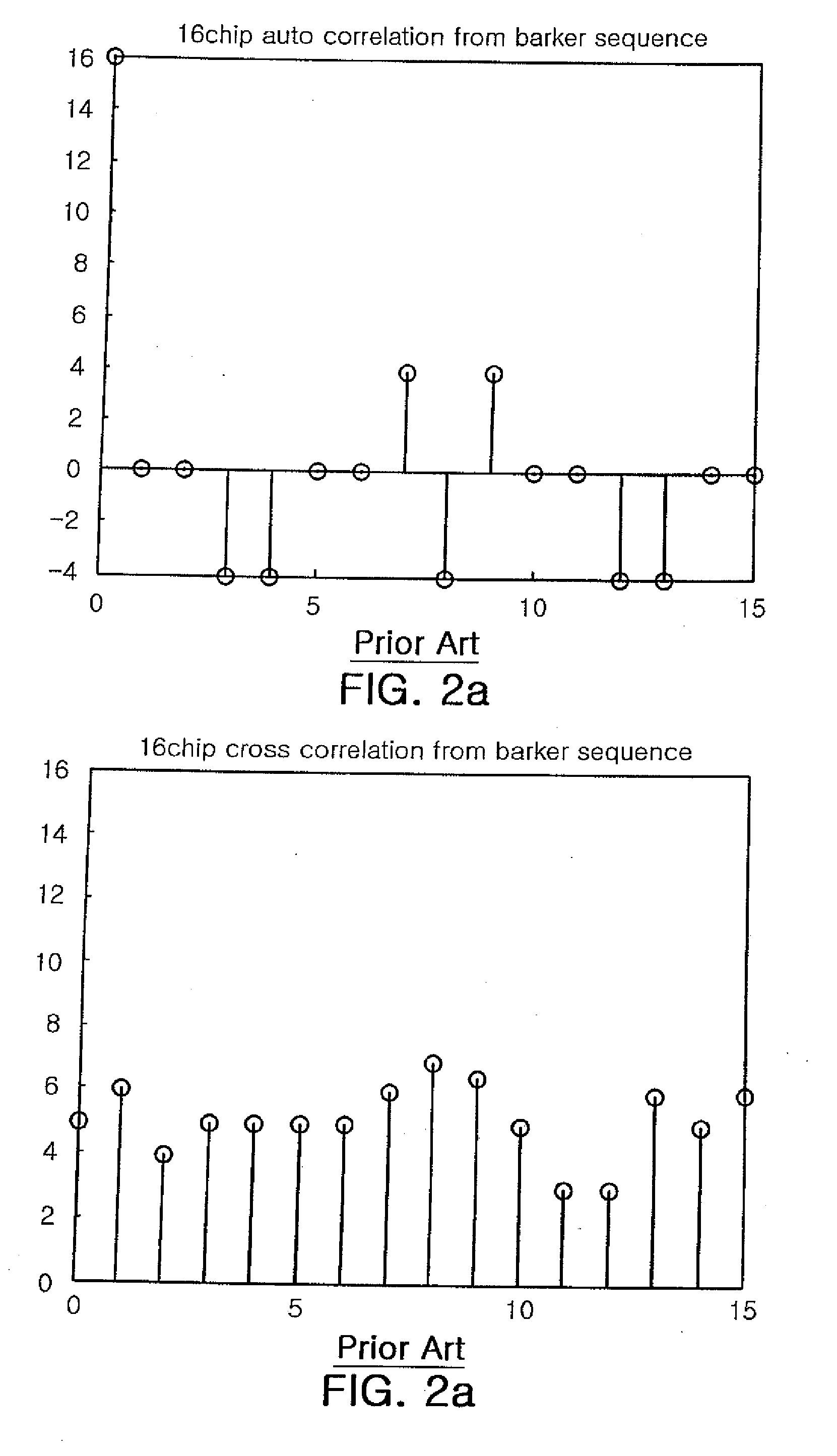
InactiveUS20070133495A1Improving auto correlation characteristicImproving correlation characteristic crossError preventionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMultiplexingOn-off keying
A transmitter and a transmitting method in a code division multiplexing (CDM) wireless communication system are provided. The transmitter includes a DC offset unit, a Barker code generating unit, a multiplier, a unipolar code generating unit, a Kronecker product unit, and a modulator. The DC offset unit transforms digital transmitting data to bipolar data, and the Barker code generating unit generates a Barker code. The multiplier multiplies the bipolar data with the Barker code and outputting the multiplying result, and the unipolar code generating unit generates a predetermined unipolar code. The Kronecker product unit multiplies the multiplying result from the multiplier and the unipolar code based on the Kronecker product, and outputs the result thereof, and the modulator modulates the output of the Kronecker produce unit through the On-Off keying modulation scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Bistatic MIMO radar target sparsity imaging method
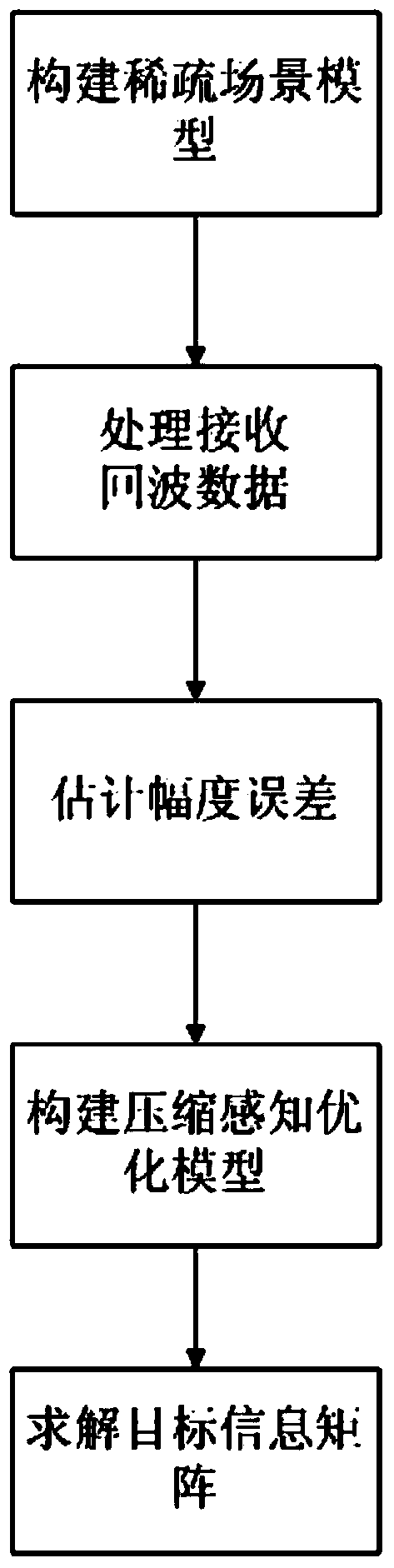
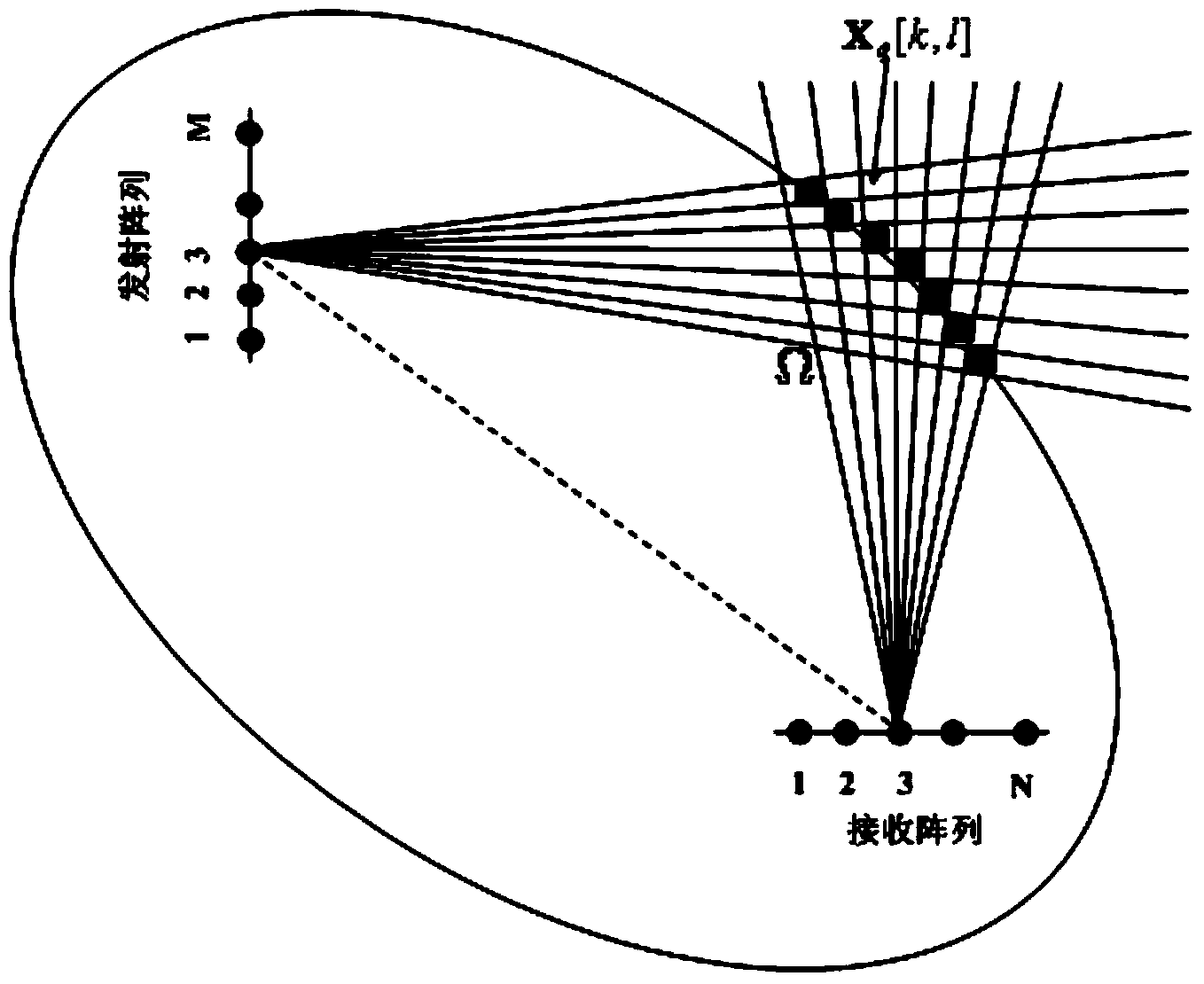
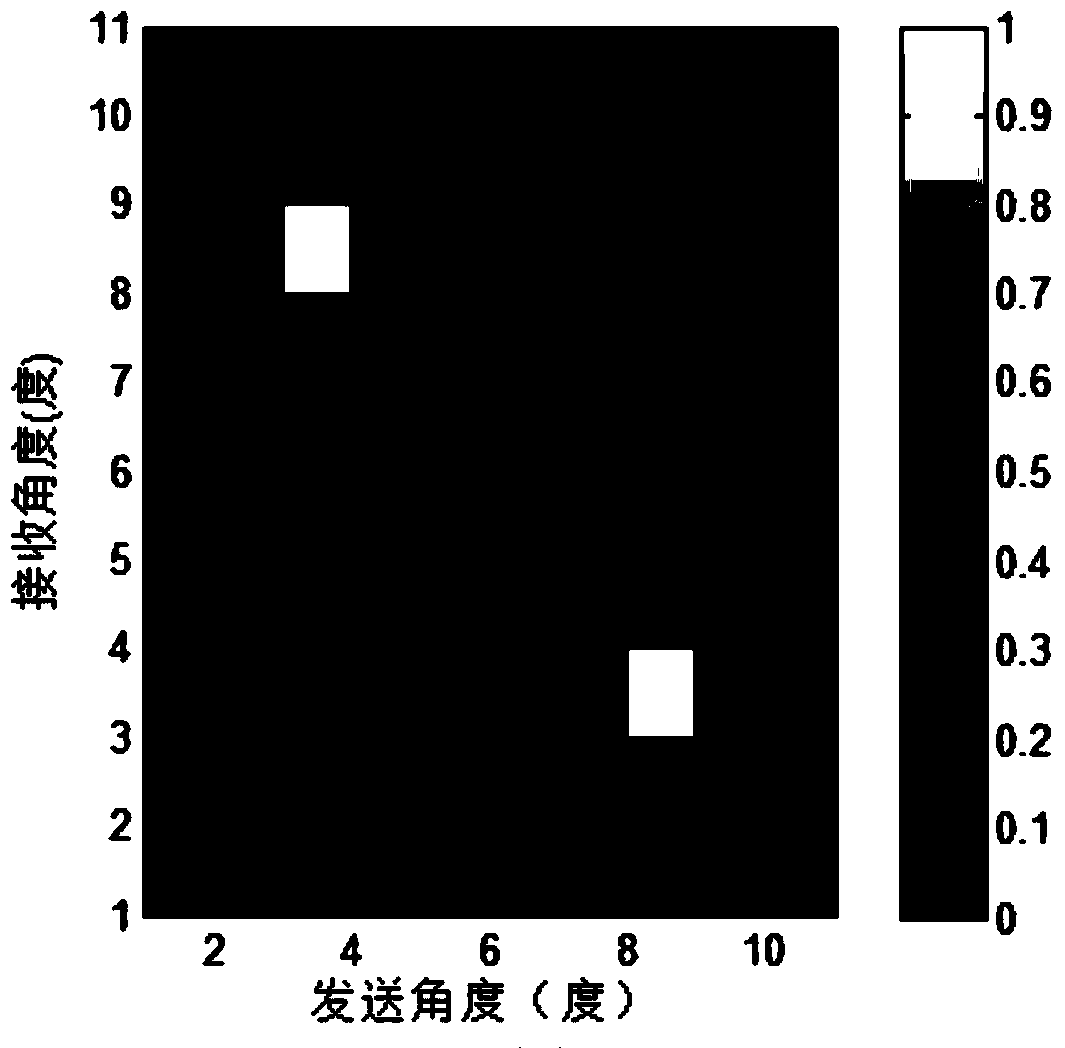
InactiveCN103969640AHigh resolutionFewer snapshotsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging processingImaging technique
The invention belongs to the technical field of bistatic MIMO radar imaging, and particularly relates to a bistatic MIMO radar target sparsity imaging method. The bistatic MIMO radar target sparsity imaging method comprises the following step that target imaging processing is carried out on distance doors of a bistatic MIMO radar in sequence. The target imaging processing carried out on any distance door of the bistatic MIMO radar comprises the steps of constructing a two-dimensional discrete angle space, and converting a target scene into a sparsity scene; then obtaining a receiving signal model obtained after matched filtering in the sparsity scene; setting a transmitting signal amplitude error opposite angle matrix gamma t and receiving a signal amplitude error opposite angle matrix gamma r of the bistatic MIMO radar; according to the receiving signal model obtained after the matched filtering, constructing a compressed sensing optimization model including the gamma trace constraint, wherein gamma=gamma t kronecker product gamma r; solving the compressed sensing optimization model; according to the solved result, obtaining the position where each target is located, and obtaining position imaging diagrams of all the targets.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
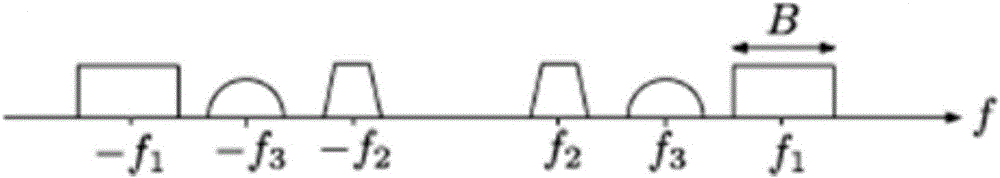
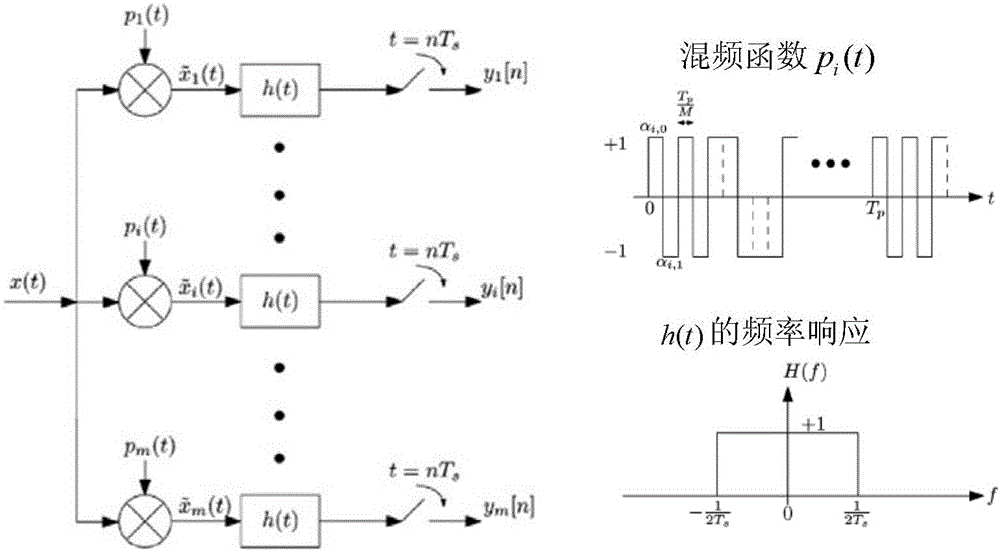
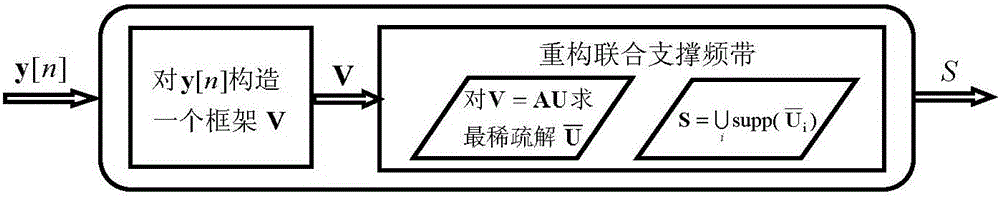
Multiband signal reconstruction method based on clustering sparse regularization orthogonal matching tracking algorithm
ActiveCN105933008AHigh probability of reconstructionCode conversionHigh level techniquesModulation bandwidthObservation matrix
The invention discloses a multiband signal reconstruction method based on a clustering sparse regularization orthogonal matching tracking algorithm, relates to the technical field of information and communication, and aims at solving a problem of restoring an original multiband signal from an unknown-sparseness multi-observation-value vector in a Xampling frame after the conversion through a continuous-finite module and sampling through a modulation bandwidth converter. Because many simulation signals met a multiband signal model in a process of signal processing, the method plays an important role in enabling the compressed sensing theory to be used for simulation signals. The basic idea of the method is to convert an infinite observation value vector problem into a single-observation-value vector problem. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out the column vectorization of observation values; carrying out the extension of an observation matrix through a Kronecker product; estimating a support set of the original signal through employing the above two results and signal sparseness estimation; finally reconstructing the signal, wherein the regularization idea is used in an estimation process of the support set.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
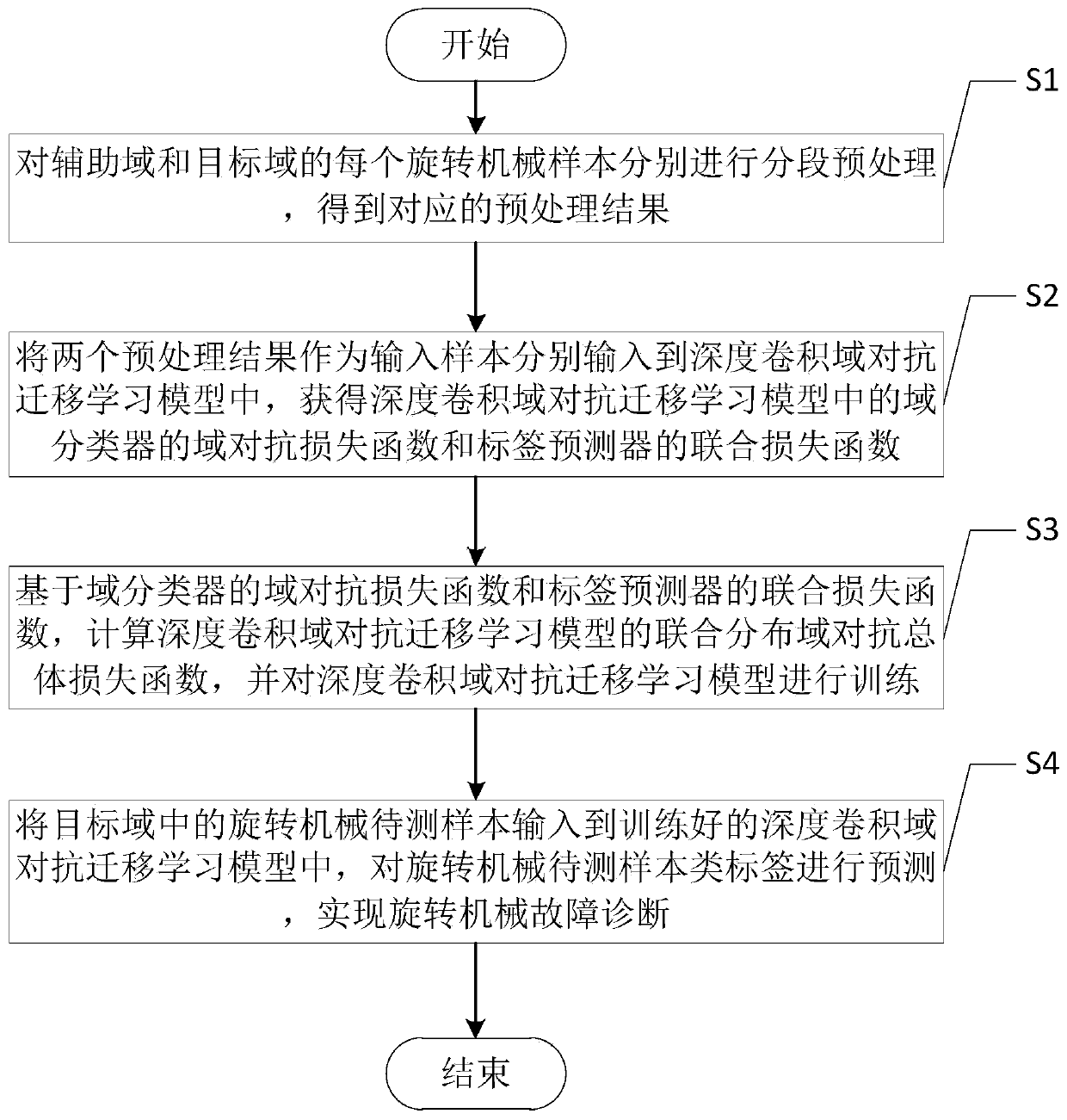
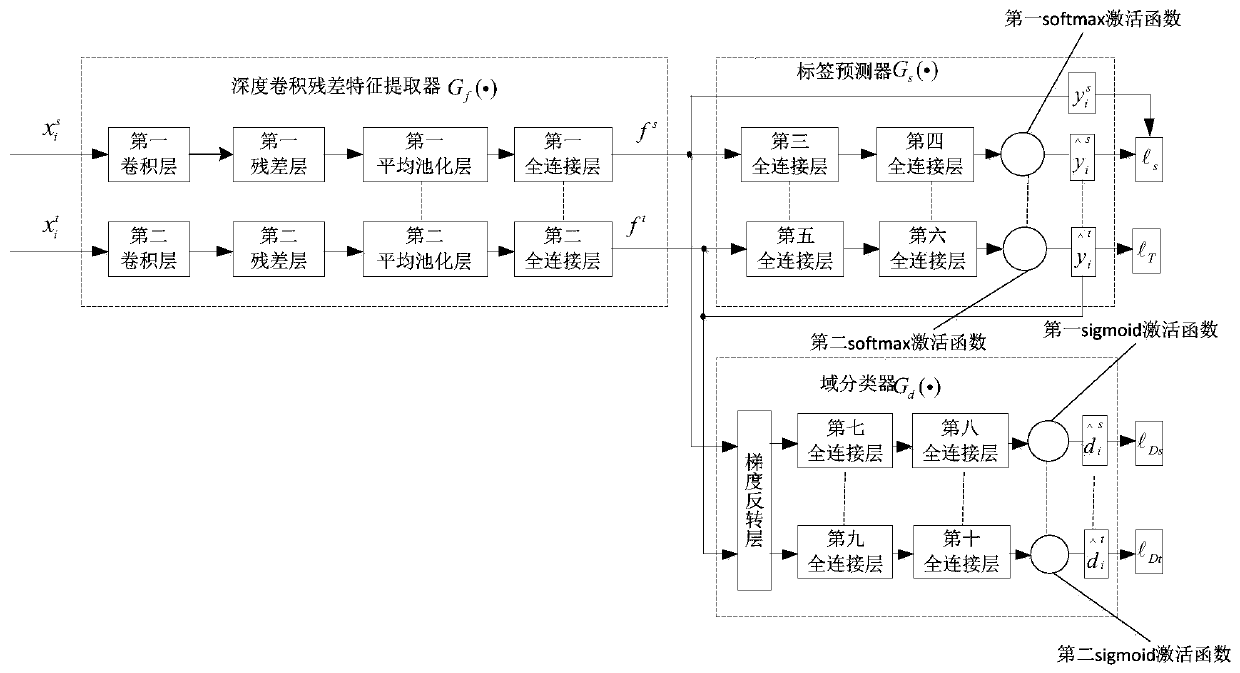
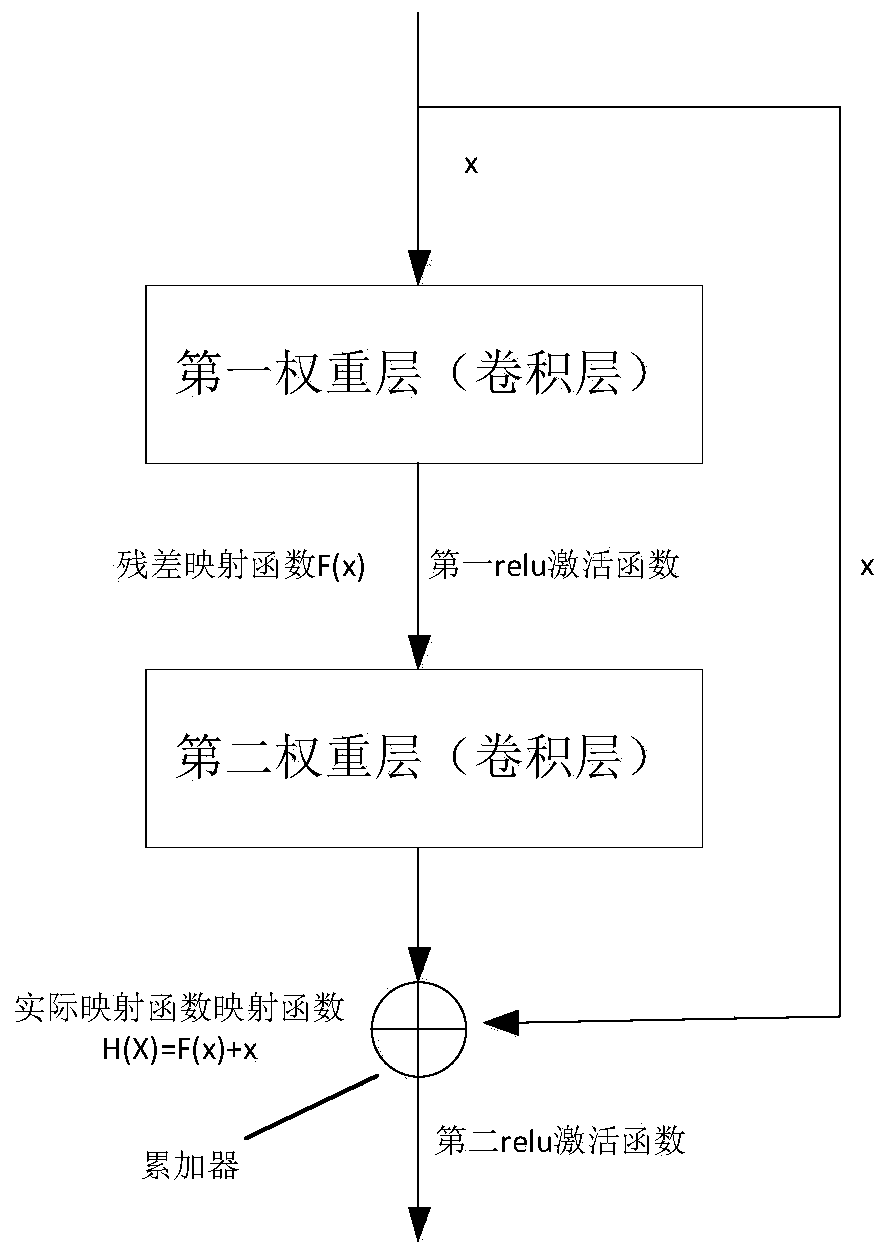
Fault diagnosis method based on deep convolution domain adversarial transfer learning
ActiveCN110751207AFast convergenceImprove migration abilityStructural/machines measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionNonlinear approximationFeature extraction
The invention discloses a fault diagnosis method based on deep convolution domain adversarial transfer learning, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out high-level feature extraction in a DCDATL through employing a deep convolution residual feature extractor, and improving the convergence and nonlinear approximation capability of the DCDATL; acquiring feature joint distribution representation through an obtained Kronecker product of high-level features and label information and is embedded into a domain classifier, and training domain adversarial to improve the migration performance of the DCDATL. The feature migration and classification process of the joint distribution domain confrontation overall loss function based on the minimized DCDATL improves the classification precisionafter migration. Due to the advantages of the DCDATL, the fault diagnosis method based on the DCDATL can perform high-precision fault diagnosis on the current to-be-detected sample of the rotating machine by utilizing the labeled sample under the historical working condition under the condition that the labeled sample under the current working condition of the rotating machine does not exist.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Methods for transmitting coding indication information and determining pre-coding matrix, system and equipment
The invention relates to the technical field of wireless communication and particularly a method for transmitting coding indication information and a method for determining a pre-coding matrix, a system and equipment. The objective of the invention is to solve the problem of performance reduction caused by a situation in which a codebook is directly applied to three-dimensional wave beam shaping / pre-coding technologies at present. The method for transmitting the coding indication information comprises the step that user equipment determines and transmits first pre-coding indication information, second pre-coding indication information and third pre-coding indication information, wherein the indication information is corresponding to the pre-coding matrix, wherein the pre-coding matrix is equal to a function matrix of a first component pre-coding matrix, a second component pre-coding matrix and a third component pre-coding matrix, wherein the first component pre-coding matrix is a diagonal matrix, the second component pre-coding matrix is a diagonal matrix, the third component pre-coding matrix is composed of a wave beam rotating vector, wherein the beam rotation vector is equal to the Kronecker product of two vectors. With the method for transmitting the indication information, the method for determining the pre-coding matrix, the system and the equipment of the invention adopted, the performance of the three-dimensional wave beam shaping / pre-coding technologies can be improved.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Block encoder and encoding method of polarization code
ActiveCN106253913AReduce encoding delayImprove coding efficiencyOther decoding techniquesError correction/detection using linear codesBinary multiplierComputer module
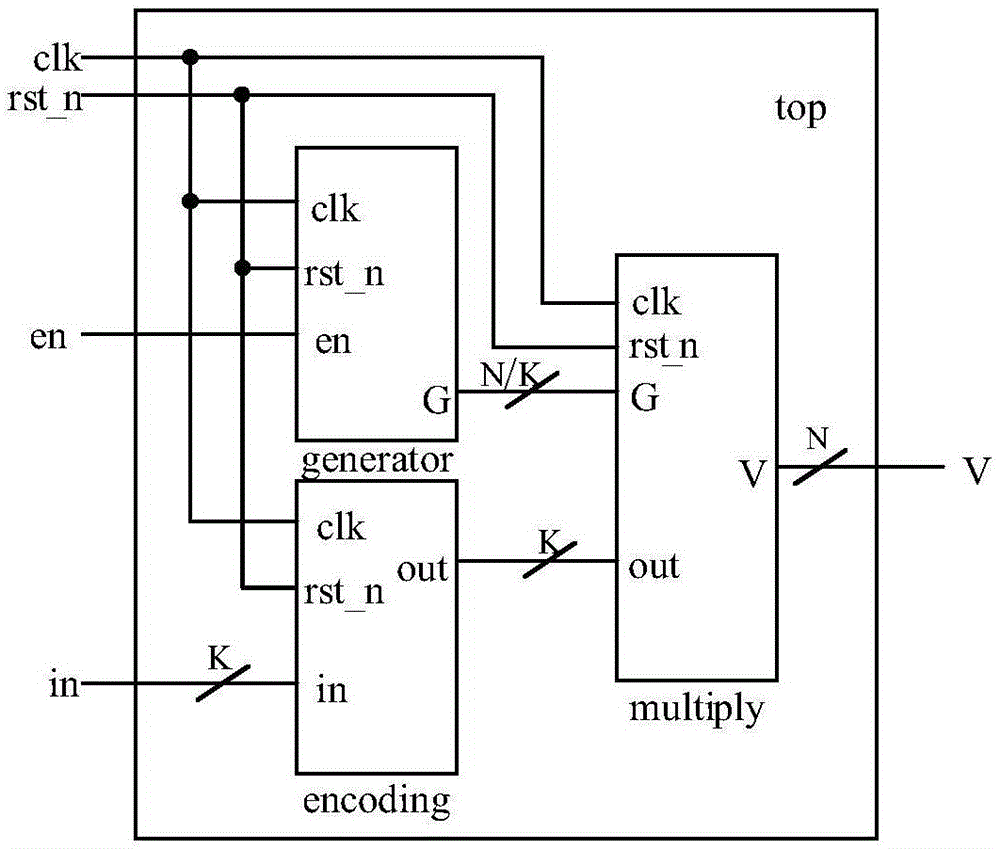
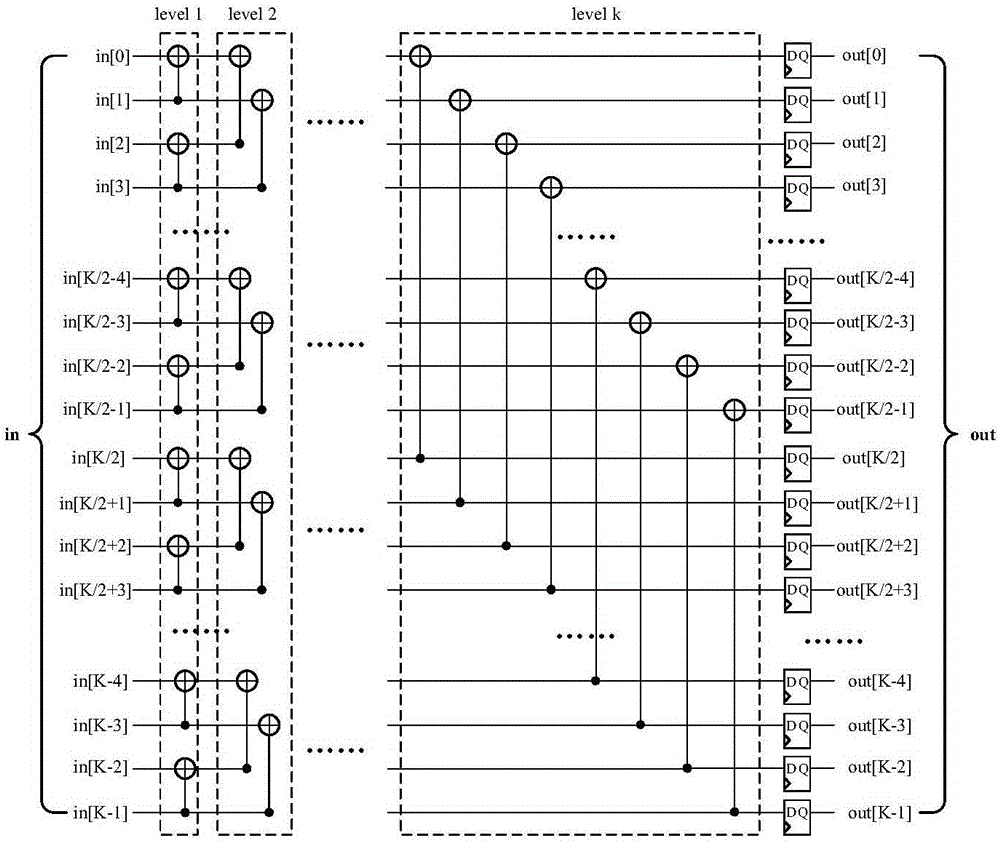
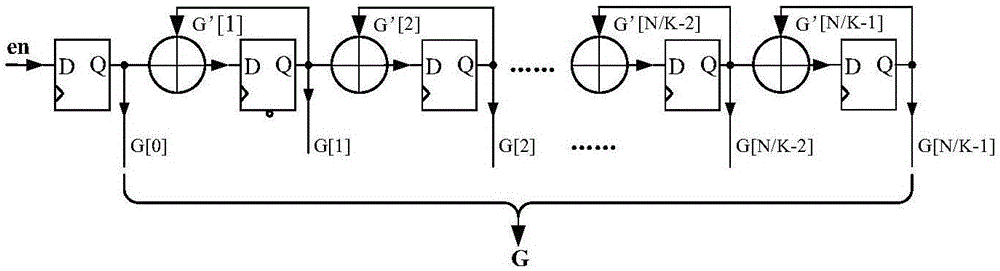
The invention relates to a block encoder and an encoding method of a polarization code, and belongs to the technical field of encoding devices. According to the block encoder and the encoding method of the polarization code, the problems of high algorithm complexity and relatively low processing speed existing in the prior art are solved. The block encoder comprises an input encoding module, a generator matrix module and a multiplier module; and each module is provided with multiple exclusive-OR gates and multiple time delay units. The encoding method comprises the steps of grouping to-be-encoded input information sequences; constructing a generator matrix of the polarization codes; and generating an encoding result. The principle of the block encoder and the encoding method of the polarization code is that a matrix GN is compressed, a position containing F<Kronecker product k> is replaced by 1, a K*K zero matrix is replaced by zero, the compressed matrix is the generator matrix F< Kronecker product (n-k)> of the encoder; K information bits are input to the information sequences per each clock; and a result of corresponding encoding operation for a matrix GK is output after the result is subjected to selection and exclusive-OR operation. According to the block encoder and encoding method of the polarization code, K-bit data can be input at each clock, and N-bit data can be output after 1+N / K clocks, so that encoding delay is reduced, and the encoding efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Large-scale MIMO system limiting feedback method based on compressive sensing
ActiveCN104683074AReduce Feedback OverheadReduce computational complexityError prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityChannel state informationObservation matrix
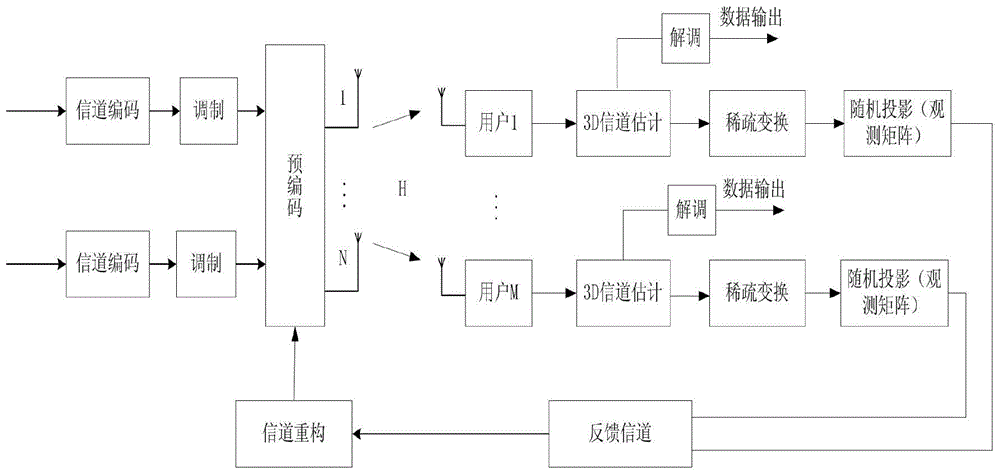
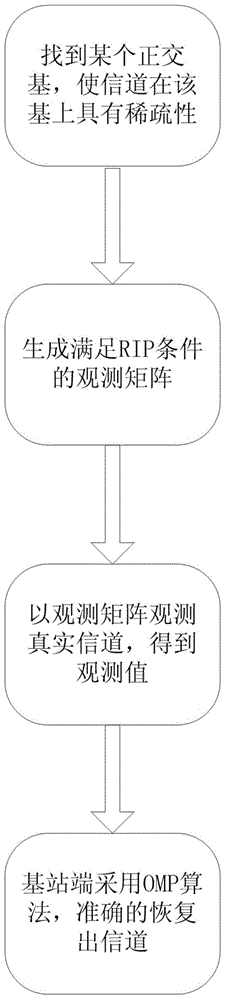
The invention discloses a large-scale MIMO system limiting feedback method based on compressive sensing. In a large-scale MIMO limiting feedback system, an Nh*Nv-dimensional uniform planar array (UPA) is adopted at a base station, and a linear array is adopted at a user terminal. The large-scale MIMO system limiting feedback method comprises the following steps: firstly, seeking a sparse base matched with a large-scale MIMO horizontal-dimensional channel and a vertical-dimensional channel by using a compressive sensing (CS) theory, thereby furthermore obtaining a two-dimensional united sparse base matched with a large-scale MIMO channel according to a Kronecker product; secondly, projecting an observation matrix irrelevant to the sparse base to a low-dimensional space, thereby obtaining an observation signal, quantifying the signal, and feeding the quantified signal back to the base station; finally, reconstructing channel state information at the base station by using an orthogonal matching pursuit (OMP) algorithm. The utility model provides a simple and efficient implementation method for the large-scale MIMO limiting feedback system.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Low-complexity two-dimensional angle and polarization parameter joint estimation method
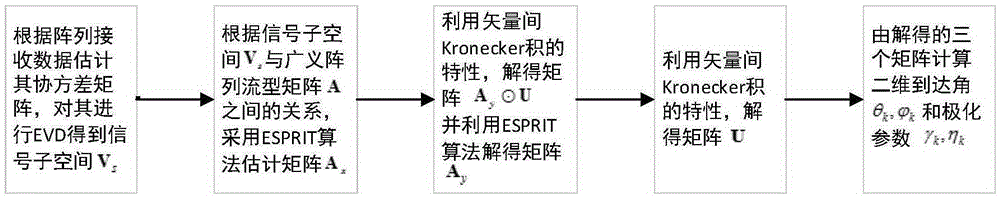
ActiveCN105335615AImprove estimation accuracyAvoid mistakesInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsComputation complexityEstimation methods
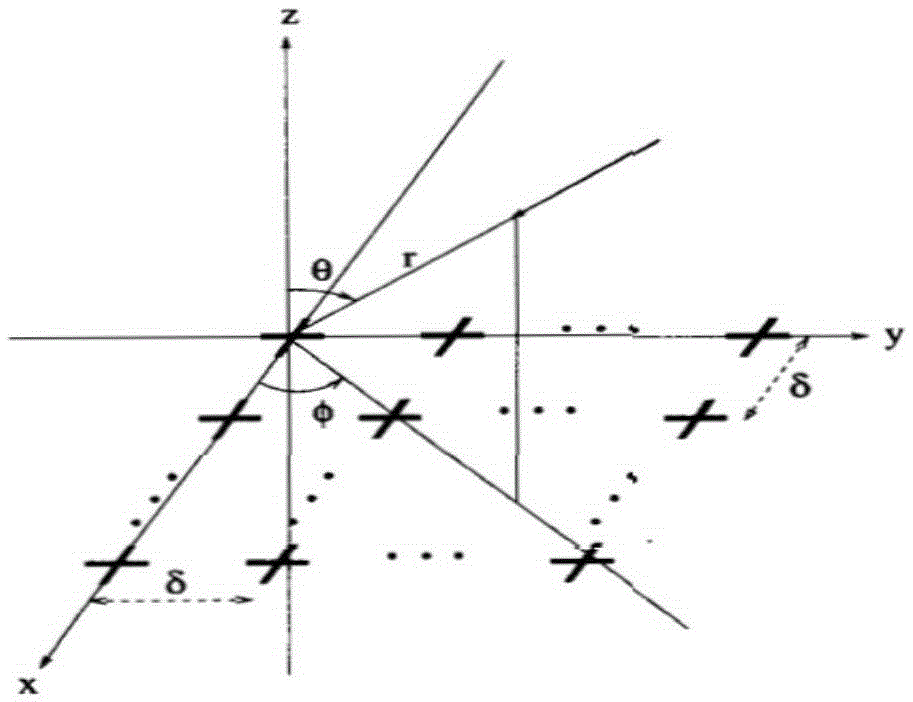
The invention provides a low-complexity two-dimensional angle and polarization parameter joint estimation method. Cross electric dipoles are adopted to form a uniform plane square matrix in an XOY coordinate system to receive signals. Firstly, an array manifold matrix of an X axis is solved from a covariance matrix of received data by fully utilizing the rotation invariant characteristic of a receiving array. Then, an array manifold matrix and a polarization-sensitive matrix of a Y axis are gradually solved by utilizing the characteristic of a Kronecker product between vectors. Finally, a DOA parameter and a polarization parameter are solved by comprehensively considering relationships between internal elements of the three matrixes. In a parameter solution process, the parameters can be automatically paired by utilizing the characteristic of the Kronecker product between the vectors, and an additional algorithm is not needed; since the computation process only relates to the multiply-add operation between the matrixes, relative to other automatic pairing algorithms, the complex operation such as matrix SVD is avoided, the computation complexity is effectively reduced and the quick realization is facilitated.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method, system and device for transmitting coding indication information and determining pre-coding matrix
ActiveCN103780332AImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionDiagonal matrixEuclidean vector
Embodiments of the invention relate to the technical field of wireless communication and particularly relate to a method, system and device for transmitting coding indication information and determining a pre-coding matrix so as to solve the problem that since in the prior art, a conventional codebook is designed based on horizontal beamforming / precoding, when the codebook is applied directly to the three-dimensional beamforming / precoding technology, the performance is reduced. The method in the embodiments of the invention comprises user equipment determines and sends first pre-coding indication information and second pre-coding indication information to a network side, wherein a first component pre-coding matrix is a block diagonal matrix, and submatrixs on the diagonal line is equal to Kronecker product of two matrixes; and a second component pre-coding matrix is formed by weighted column selection vectors, and the weighted column selection vectors are zero except P nonzero elements, the P being positive integer. The scheme adopted in the embodiments of the invention is capable of improving the performance of the three-dimensional beamforming / precoding technology.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Method and system for spatial channel state information feedback based on a kronecker product
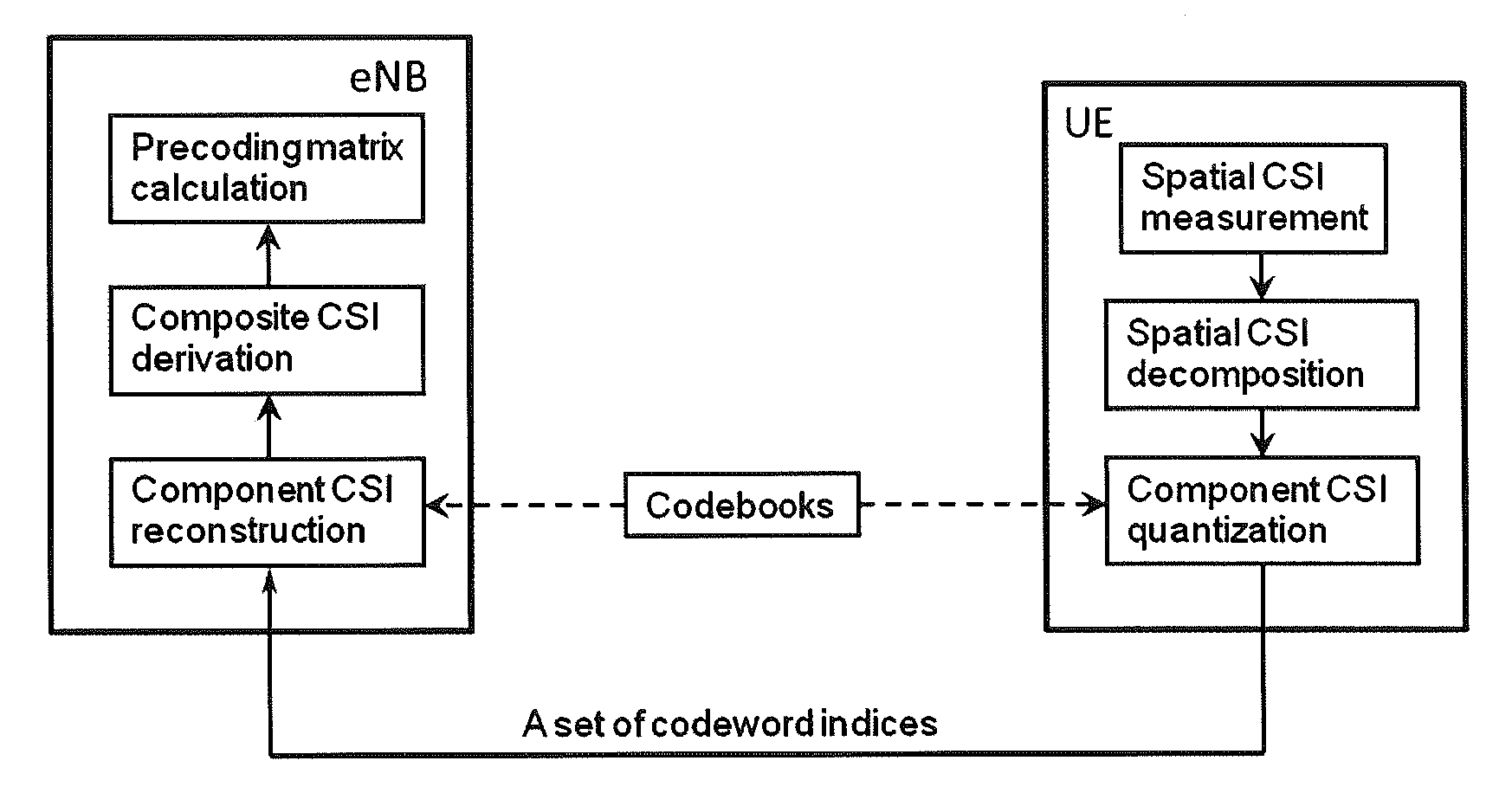
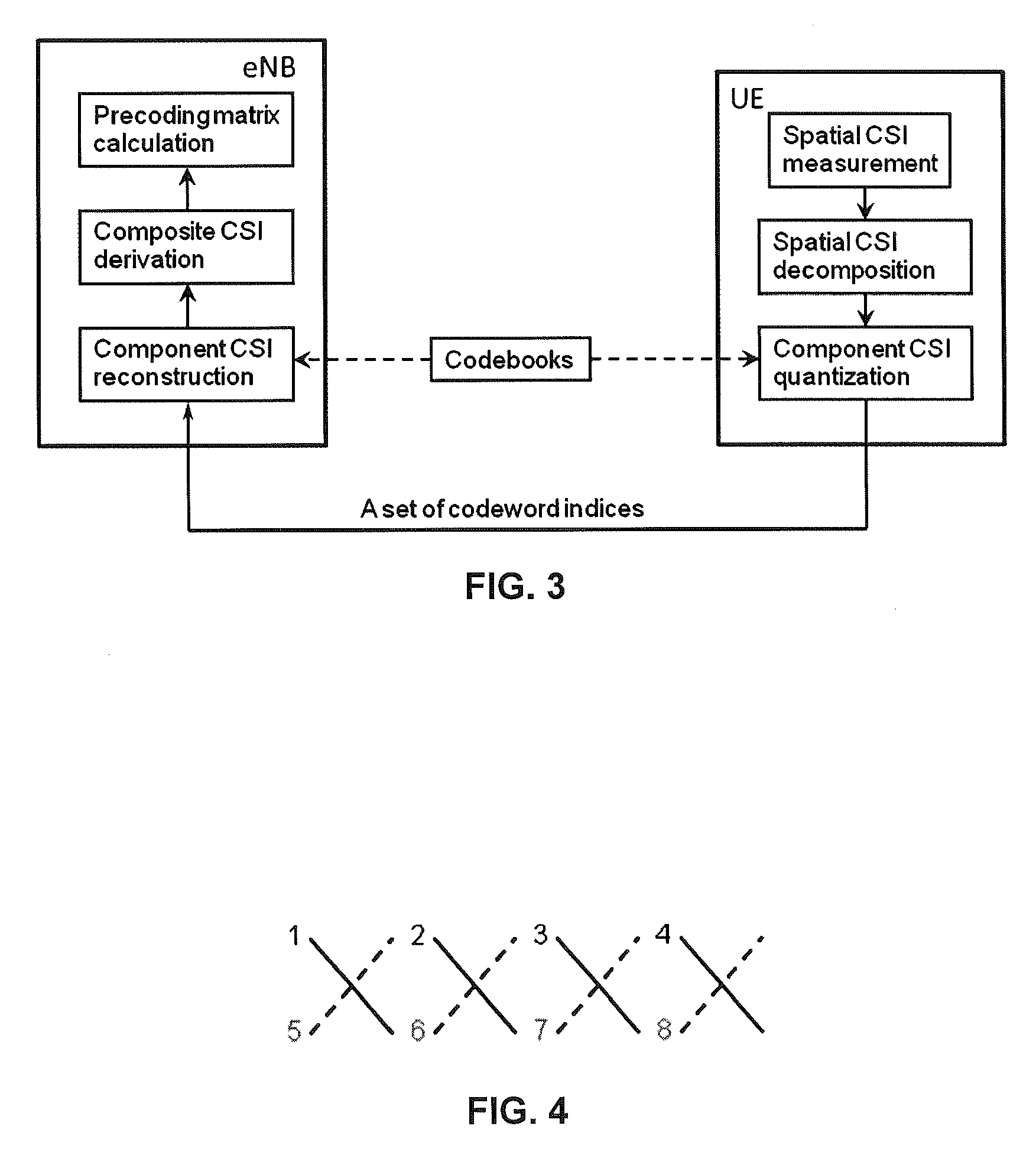
ActiveUS8488725B2Accurate spatial CSI feedbackReduce Feedback OverheadPolarisation/directional diversityLine-faulsts/interference reductionEngineeringChannel state information feedback
A spatial channel state information (CSI) feedback technique is incorporated into multiple-input multiple-output mobile communications technologies. Spatial channel state information is measured at receiving equipment and then decomposed into components. The components are then quantized using codebook(s) and fed back as multiple indices to transmitting equipment.
Owner:ADVANCED STANDARD COMM LLC
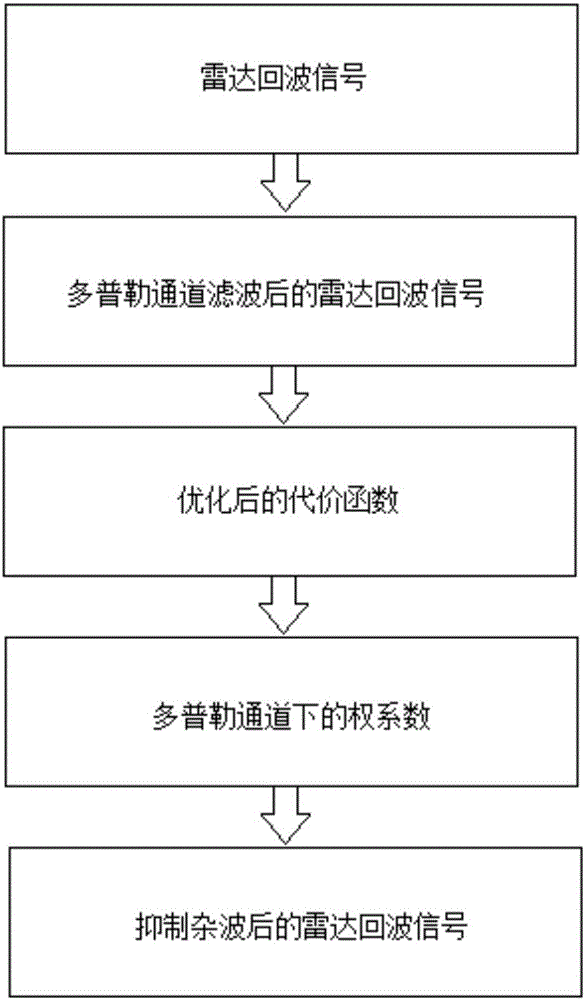
Onboard MIMO radar post Doppler self-adaptive processing method based on airspace multi-grade decomposition
ActiveCN106772304AReduce the amount of calculationReduce demandWave based measurement systemsQR decompositionSmall sample
The invention discloses an onboard MIMO radar post Doppler self-adaptive processing method based on airspace multi-grade decomposition; the method includes steps of performing a Doppler filtering processing on an onboard MIMO radar echo signal; and then performing the self-adaptive treatment at one or more Doppler channel; decomposing the high-dimensional self-adaptive weight vector, and making it become the Kronecker product of several low-dimensional right vector; through loop iteration, acquiring the weight coefficient; processing the radar echo signal by the weight coefficient, and acquiring the radar echo signal for reducing clutters; the invention can effectively reduce the calculated amount and sample demand of onboard MIMO radar space-time Doppler self-adaptive processing; thus under the condition of improving the small sample condition, the onboard MIMO radar inhibits the clutters and detects the performance of the dynamic goal, and saves precious time and resources.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
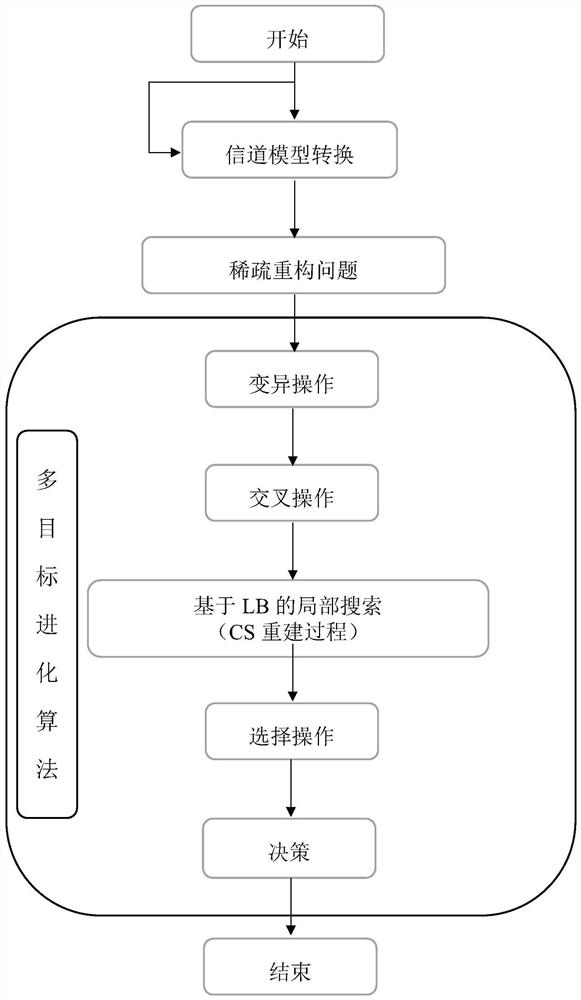
Large-scale antenna channel estimation method based on millimeter wave intelligent reflector communication
ActiveCN112769461AAvoid selectionFast convergenceBaseband system detailsRadio transmissionMillimeter wave communication systemsMillimetre wave
The invention discloses a large-scale antenna channel estimation method based on millimeter wave intelligent reflector communication. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a beam forming vector adopted by a base station; collecting signals received by a user at different moments; a Kronecker product is utilized to convert the channel model into a sparse recovery problem; performing mutation operation and crossover operation on the channel model; performing CS reconstruction by using an LB-based local search algorithm; and carrying out selection operation and obtaining a final decision. The method has the advantages that the IRS technology is utilized, the coverage range of the millimeter wave MIMO communication system is enhanced, compressed sensing is adopted, the hybrid multi-objective evolutionary algorithm is utilized to solve the reconstruction problem of compressed sensing, and therefore the channel estimation precision of the millimeter wave MIMO communication system based on the intelligent reflecting surface technology is improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
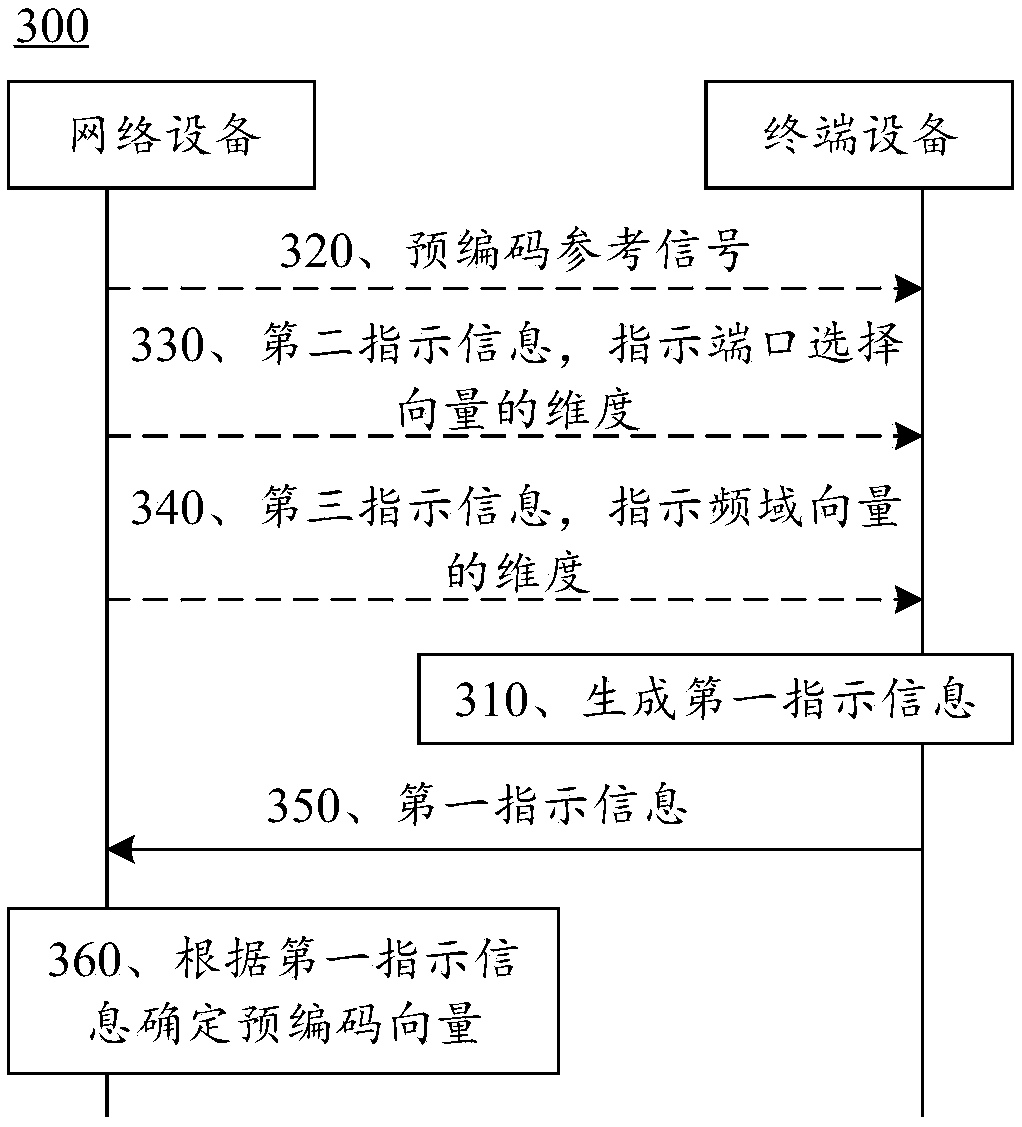
A method of indicating and determining precoding vector and communication device
The invention provides a method for indicating and determining a precoding vector and a communication device. The method comprises the following steps: the terminal equipment generates and sends indication information to the network equipment; wherein the indication information is used for indicating one or more port selection vectors, one or more frequency domain vectors and one or more linear superposition coefficients, and each linear superposition coefficient corresponds to one port selection vector and one frequency domain vector; or the indication information is used for indicating one or more space-frequency vectors and the linear superposition coefficient of each space-frequency vector; wherein the space-frequency vector is a Kronecker product of a port selection vector and a frequency domain vector, each port selection vector indicates a port of a reference signal, the reference signal is a precoding reference signal, and each frequency domain vector indicates a change rule ofa channel in a frequency domain. The network device determines a precoding vector based on the indication information. Change of a channel in a frequency domain is simulated through linear superposition of frequency domain vectors, and feedback overhead can be reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
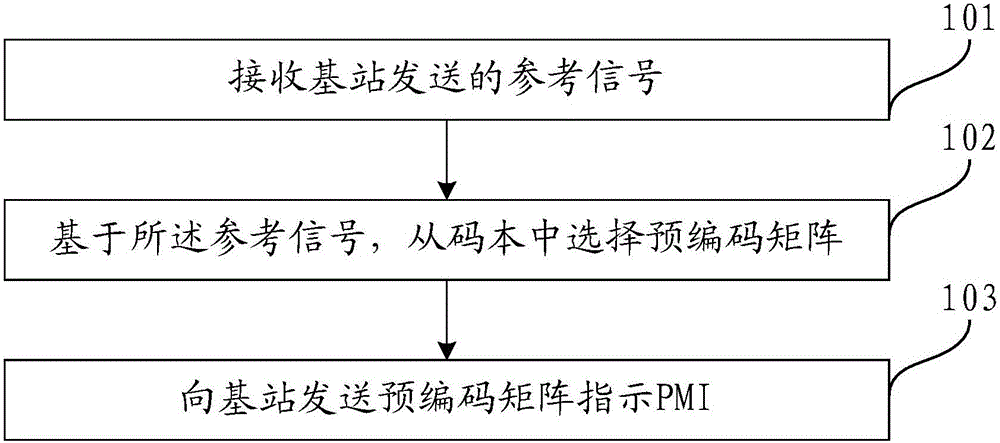
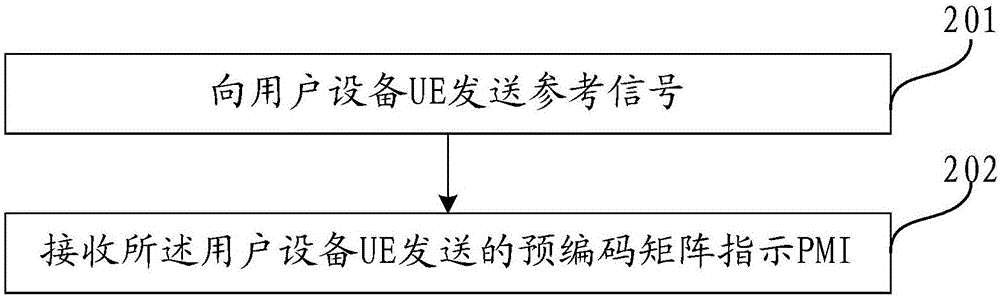
Method determining pre-coding matrix indication, user equipment, and base station evolution node
ActiveCN106603136AImprove Feedback AccuracyImprove system throughputSpatial transmit diversityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksPartition matrixDiagonal matrix
The invention relates to a method determining a pre-coding matrix indication, user equipment UE, and a base station eNB and a system; the method comprises the following steps: receiving a reference signal sent by the base station; selecting a pre-coding matrix from a codebook according to the reference signal, wherein the codebook comprises a pre-coding matrix, the pre-coding matrix W refers to the product of two matrixes W1 and W2, the W1 refers to a partitioning diagonal matrix, and each partitioning matrix refers to the kronecker product of a matrix Ai and a matrix Bi; sending a pre-coding matrix indication PMI to the base station, wherein the PMI is matched with the selected pre-coding matrix, and the base station can obtain the pre-coding matrix according to the PMI. According to the pre-coding matrix formed by the matrix Ai and matrix Bi and supporting vertical direction and horizontal direction quantification, the method and system can fully utilize the degree of freedom in the horizontal direction and vertical direction, thus greatly improving channel state information feedback precision.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
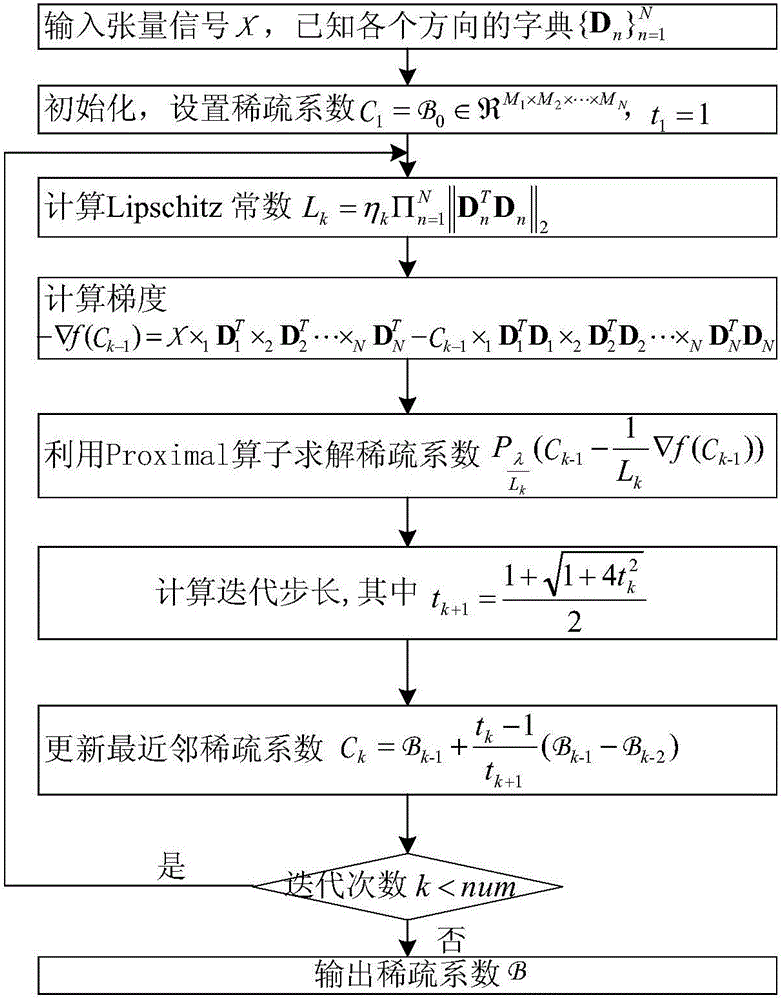
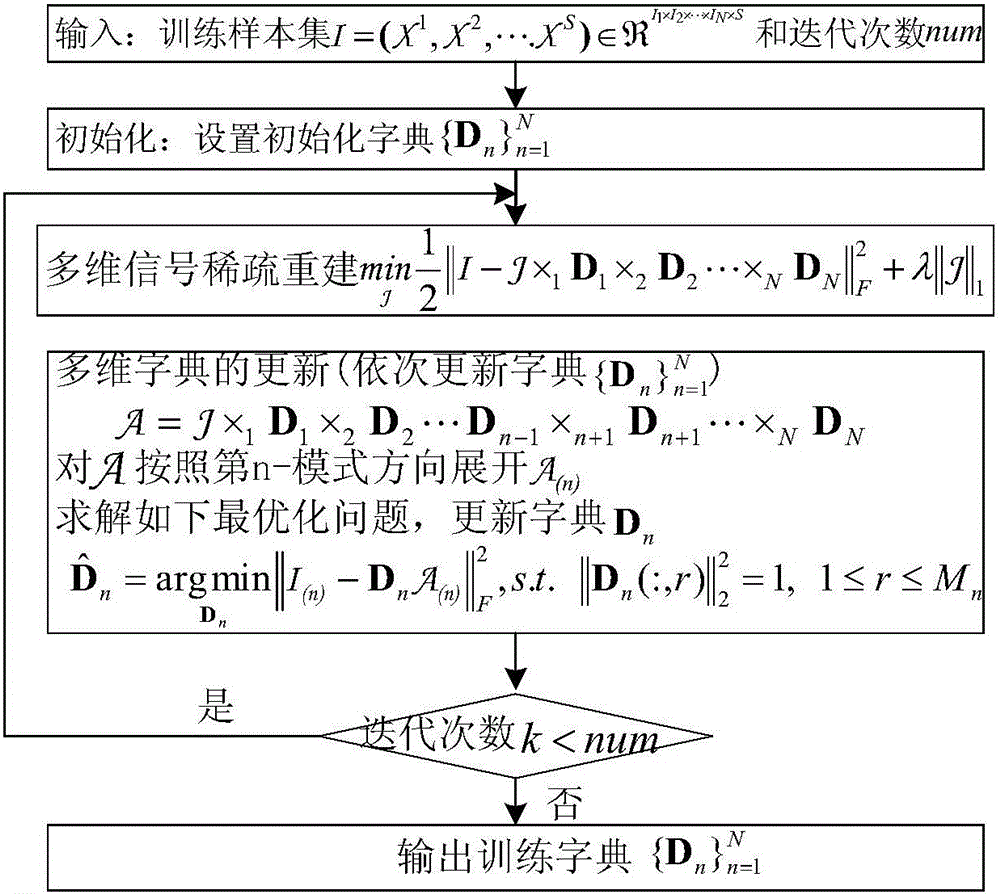
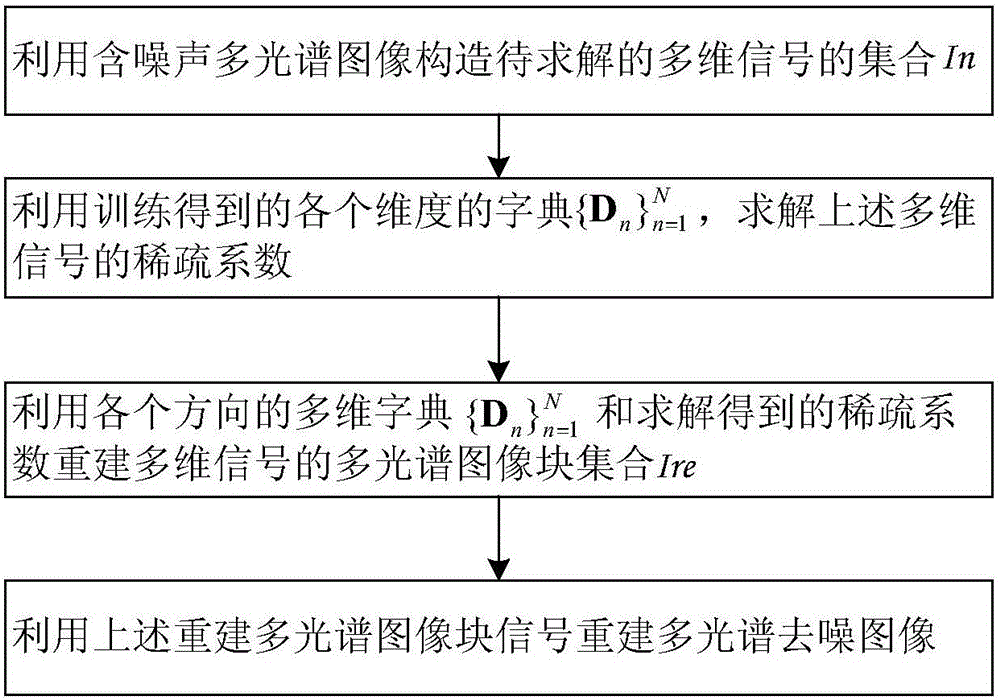
Sparse model of multi-directional signal, reconstruction method of sparse model and dictionary training method of reconstruction method
ActiveCN106097278AReduce complexityReduce storage spaceImage enhancementImage analysisSparse modelReconstruction method
The invention discloses a sparse model of a multi-directional model, wherein the sparse model can ensure remarkable improvement on algorithm complexity and storage space without Kronecker product. The sparse model of the multi-directional model is represented by a formula x=B*1D1*2*D2...NDN, wherein ||B||<=K. In the formula, tension x represents a tension product between an N-directional sparse tension B which belongs to R<M1*M2*...*MN and a series of sparse dictionary Dn which belongs to R<In*Mn>, wherein In<=Mn, Dn is defined as the dictionary in an n-th direction, K is sparsity and is used for representing the number of non-zero elements in a sparse coefficient B. The invention furthermore provides a reconstruction method of the sparse model and a dictionary training method of the reconstruction method.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Building method of complex network
InactiveCN103870691AEasy to buildReduce computational complexitySpecial data processing applicationsScale-free networkComputer science
The invention discloses a building method of a complex network. The building method comprises main steps of generated network determination, adjacent matrix calculation, degree distribution polynomial determination, complex network adjacent matrix calculation and the like. The complex network obtained by adopting the building method simultaneously has the self-similarity and worldlet characteristics, the self-similarity characteristic derives from the fractal matrix form adjacent matrix generated through Kronecker product iteration of the generated network adjacent matrix, and the worldlet characteristic derives from the network with the diameter not exceeding two times of the diameter of the generated network. In addition, the degree distribution of the complex network can be theoretically worked out through the number multiplication and coefficient multiplication operation of the degree distribution polynomial expression form. Studies show that the degree distribution of the complex network does not meet the power-law distribution, i.e., the complex network is not a scale-free network.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
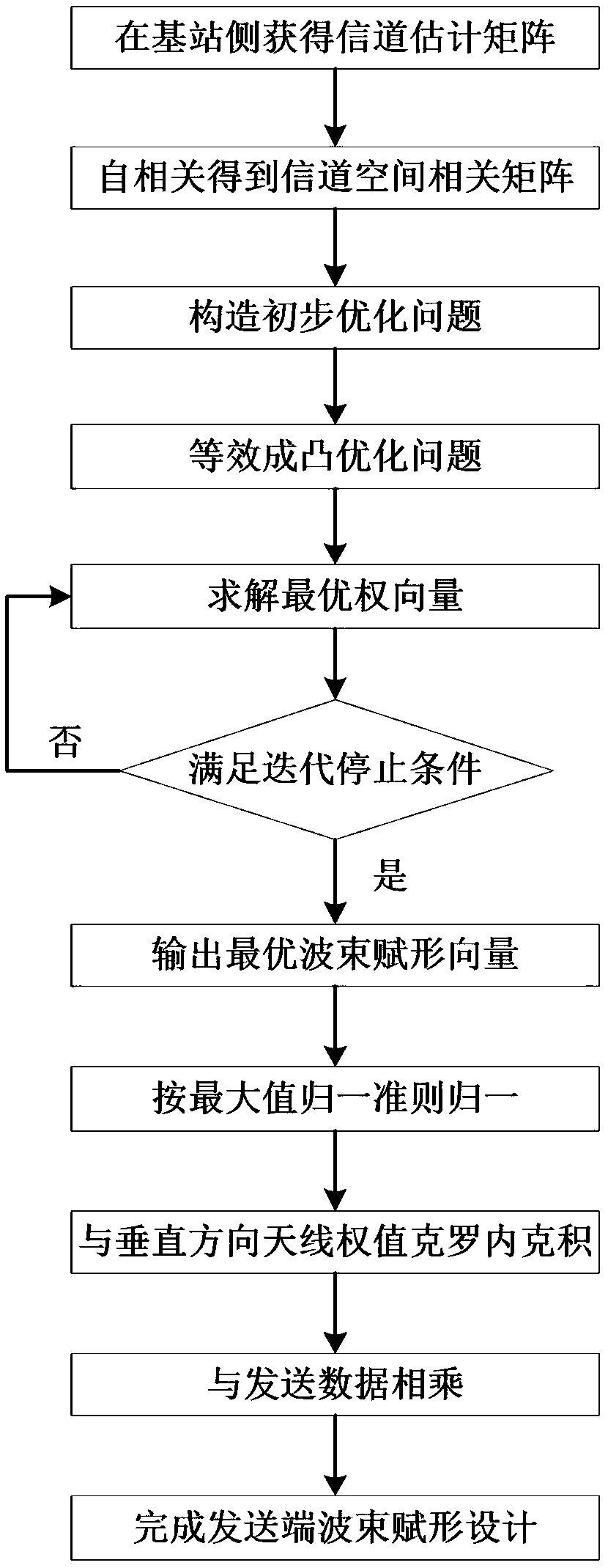
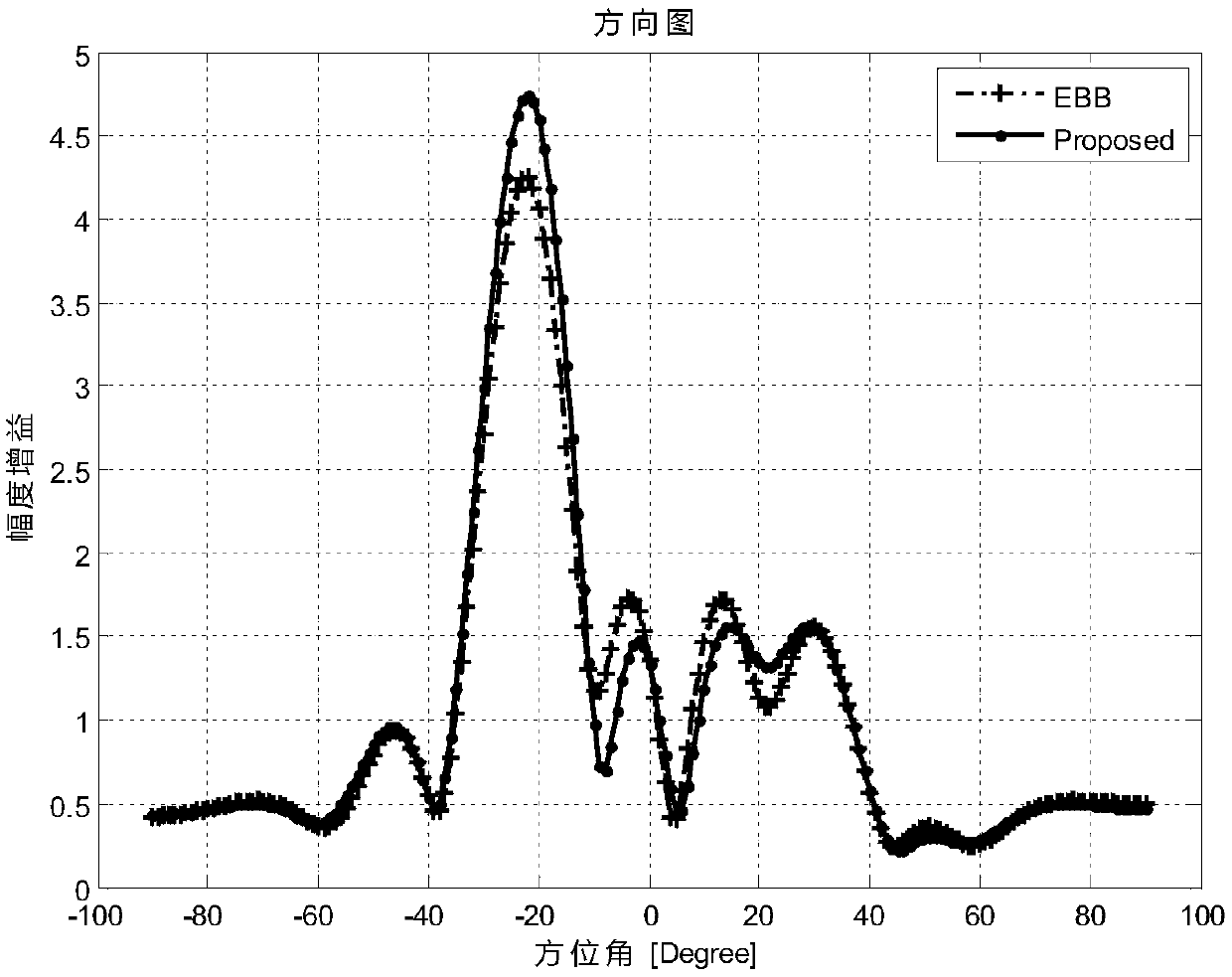
Beam-forming method for NLOS scenarios in massive MIMO
ActiveCN108667493AOvercome the shortcomings of being seriously affected by the time-varying characteristics of the channelMeet the actual communication requirementsSpatial transmit diversityBaseband system detailsSignal-to-quantization-noise ratioOptimization problem
The invention belongs to the technical field of communications, and discloses a beam-forming method for NLOS scenarios in massive MIMO, comprising: obtaining a channel estimation matrix at the base station side; performing autocorrelation on the channel estimation matrix to obtain a spatial correlation matrix; constructing an optimization problem according to a maximum received signal-to-noise ratio criterion; performing equivalent minimization on the optimization problem; solving the optimal weight vector; performing maximum naturalization; performing Crohneck product with vertical antenna weight; and multiplying by transmission data. The invention has the advantages of low sensitivity to channel time-varying characteristics, strong anti-non-line-of-sight NLOS capability, low algorithm complexity and simple implementation, and finally improves the receiving power of the desired user. The invention solves the problems that the beam-forming method of the prior art has weak resistance tochannel time-varying, and cannot effectively improve the received power of the desired user in the case of multipath, and the algorithm has high complexity.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for generating 2D OVSF codes in multicarrier DS-CDMA systems
InactiveUS7346038B2Zero cyclic auto-correlation and cross-correlation propertiesMultiplex code generationRadio transmissionCommunications systemCarrier signal
A multicarrier direct-sequence code-division multiple-access (MC-DS / CDMA) communications system is provided. A code tree of two-dimensional orthogonal variable spreading factor (2D-OVSF) codes is then generated for the system. To generate the code tree, a set of existing M1×N1 2D-OVSF matrices, in the form of A(i)(M<sub2>1< / sub2>×N<sub2>1< / sub2>) for i={1, 2, . . . , K1} is selected as seed matrices. M1 represents the number of available frequency carriers in the MC-DS / CDMA system, and N1 represents a spreading factor code length. Another set of existing M2×N2 2D-OVSF matrices, in the form of B2(i)(M<sub2>2< / sub2>×N<sub2>2< / sub2>) for i={1, 2, . . . , K2} is then selected as mapping matrices. The mapping matrices are used to generate corresponding children matrices. These second layer child matrices are M1M2×N1N2 matrices with cardinality K1K2, which are defined by reiterating the relationship:C(M1M2×N1N2)((i-1)K2+1)=B2(M2×N2)(1)⊕A(M1×N1)(i)C(M1M2×N1N2)((i-1)K2+2)=B2(M2×N2)(2)⊕A(M1×N1)(i)⋯C(M1M2×N1N2)((i-1)K2+K2)=B2(M2×N2)(K2)⊕A(M1×N1)(i)where ⊕ indicates a Kronecker product, and i=1, 2, 3, 4, . . . , K1.
Owner:ACCTON TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Data adaptive compression and data encryption using kronecker products
ActiveUS20170257649A1Digital video signal modificationSelective content distributionSingular value decompositionSoftware
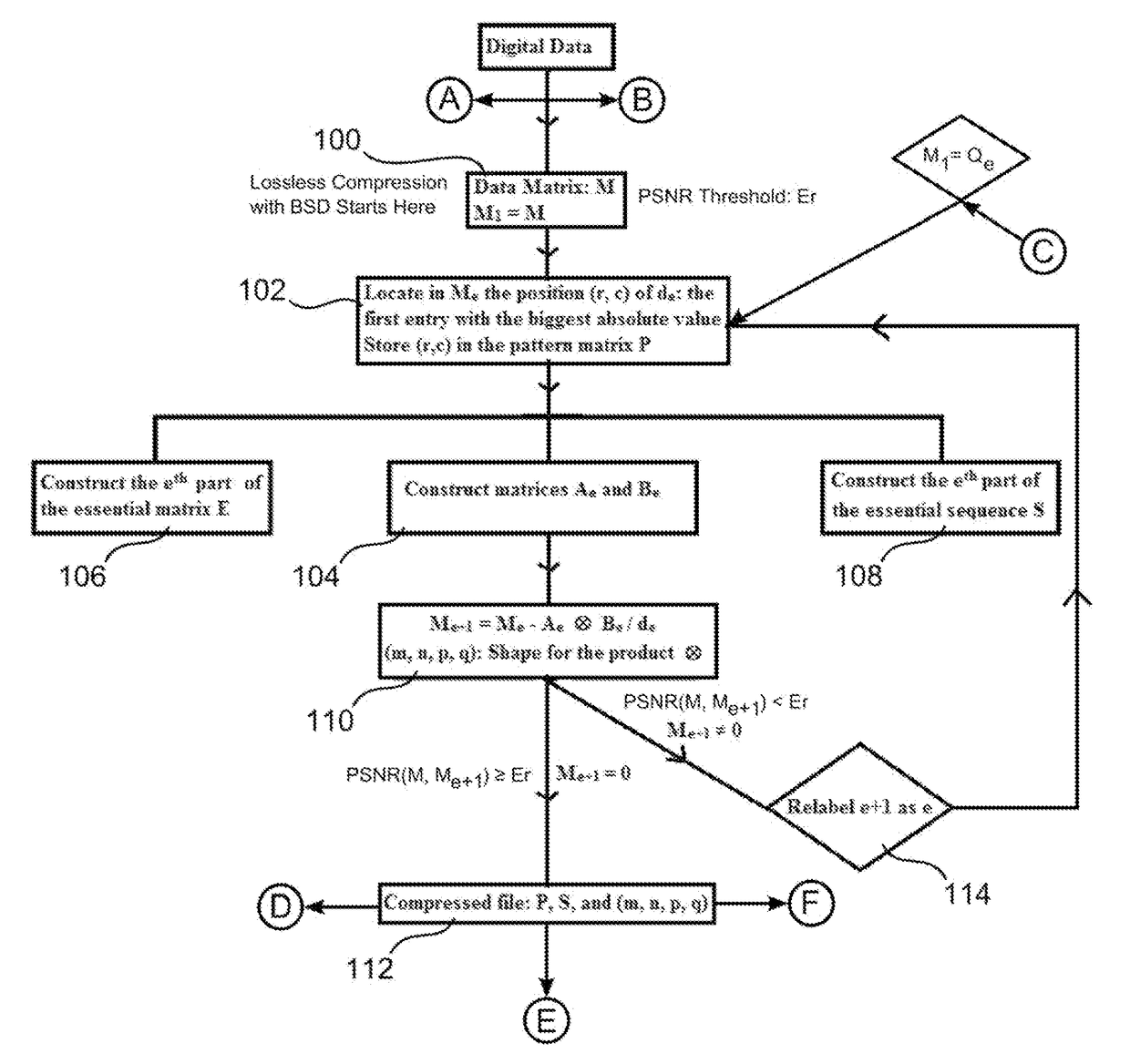
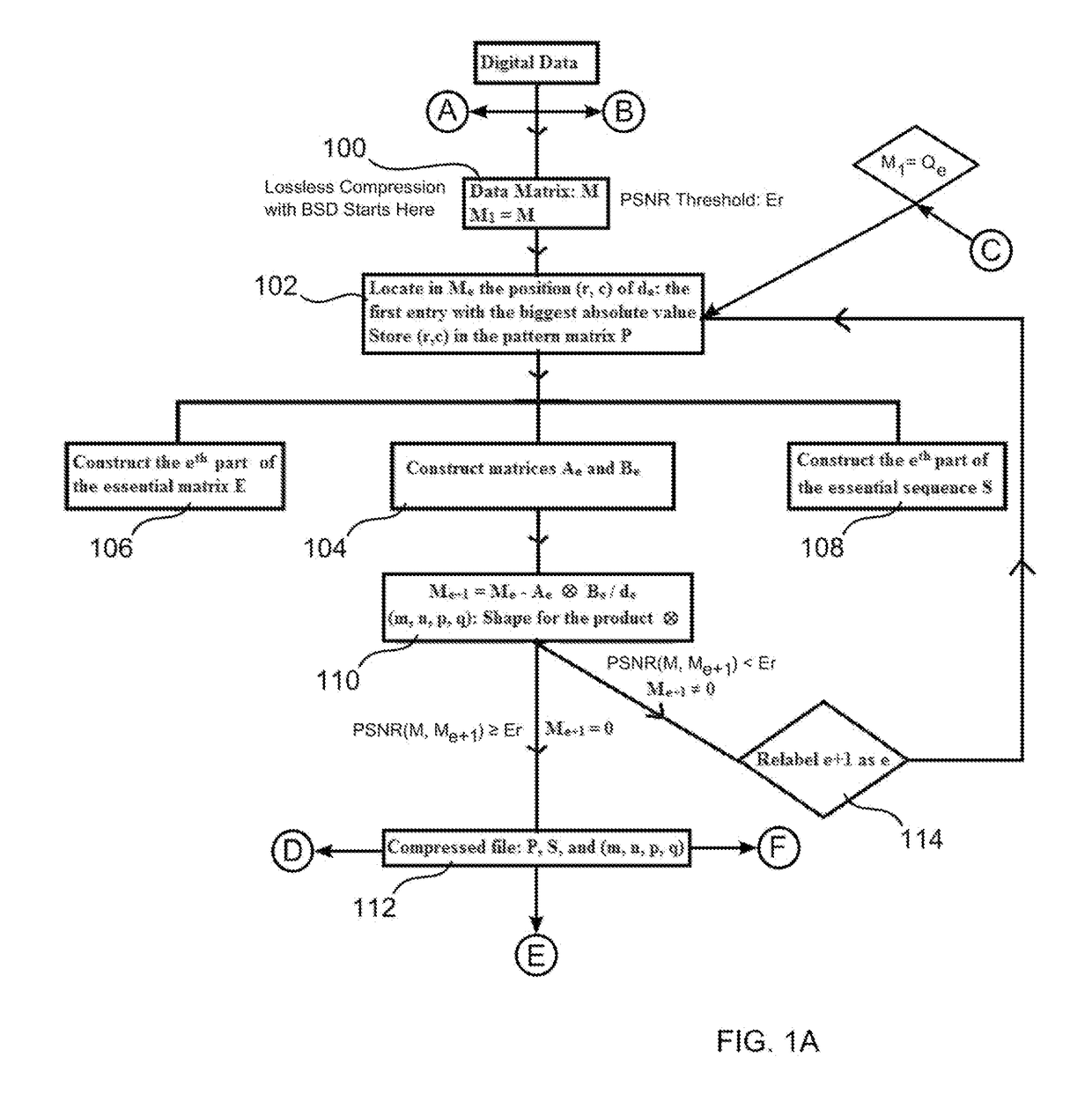
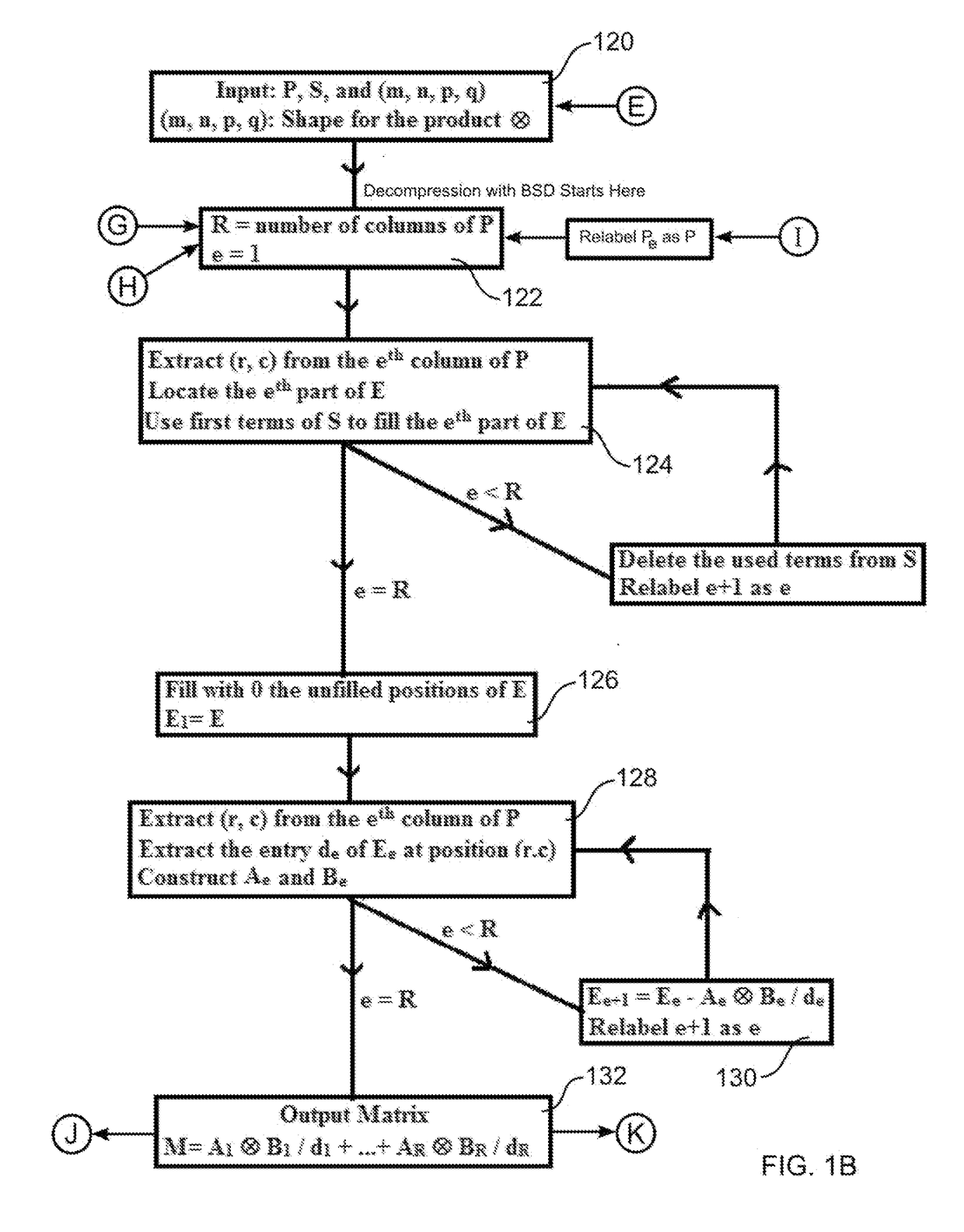
Digital files are compressed using a process including Schmidt decompositions of matrices using an algorithm, termed ‘BSD’ herein, which is based on an algebraic method generalizing QR decomposition. Software analyzes an input file and initially identifies a matrix M, with entries within a predefined set of integers, within the file. Next, essential entries are defined, extracted from M, that contain sufficient information to recover Musing BSD. The compressed file includes the essential entries and their positions within M. To achieve an encryption process, software encrypts the pattern matrix that includes the positions of the essential entries of M. To achieve a lossy compression, software identifies essential entries that contain sufficient information to recover an approximation to M for which the quality is determined by an error threshold. For a more efficient lossy compression, software uses singular value decomposition, BSD, and other signal processing of M.
Owner:NOVA SOUTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY
Novel channel estimation method of multi-user 3D MIMO system
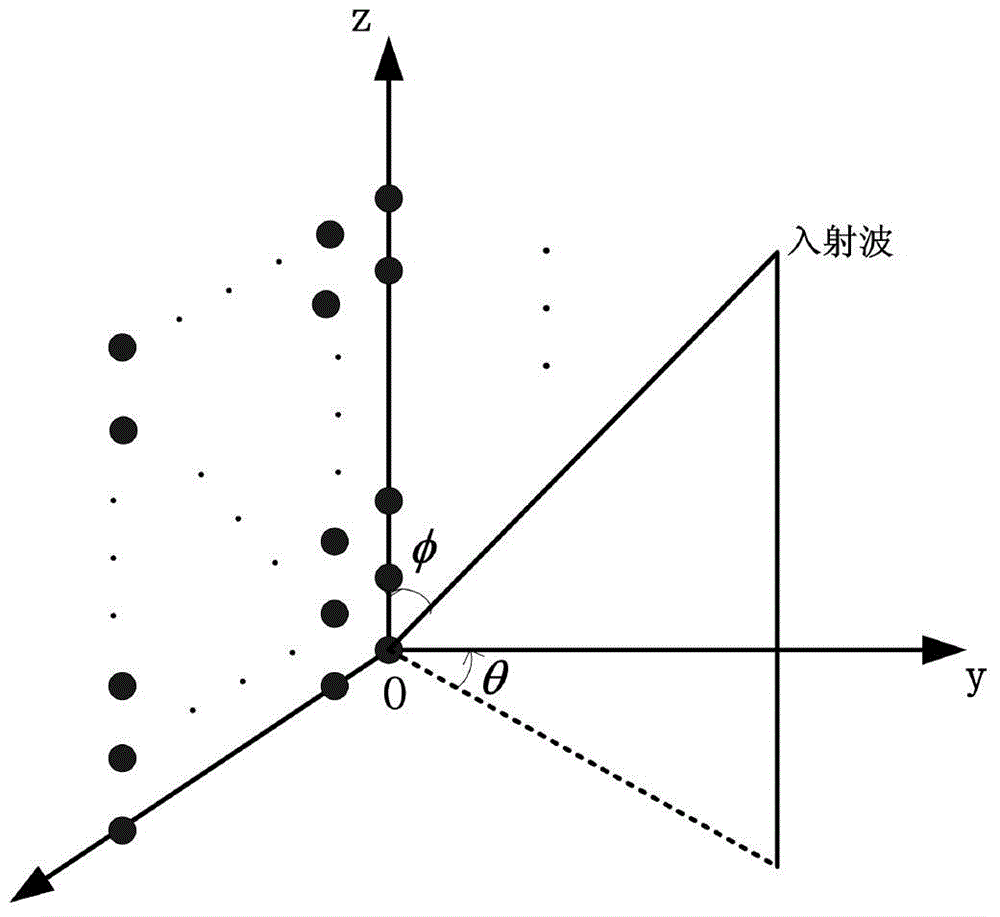
ActiveCN110460549ASimplified Channel ModelingTo achieve the purpose of dimensionality reductionTransmission monitoringRadio transmissionEstimation methodsEngineering
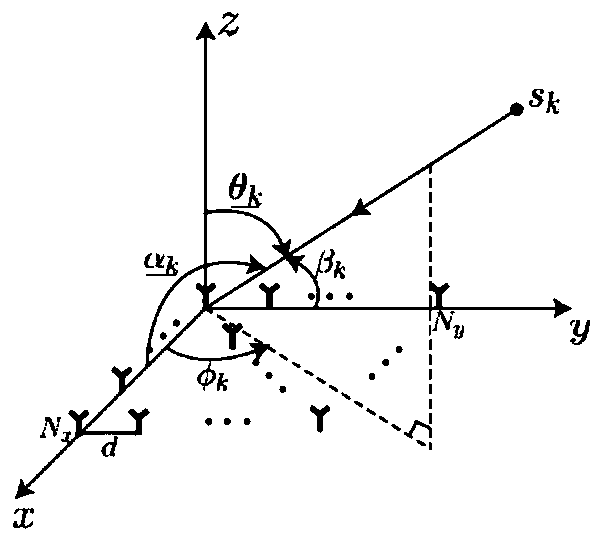
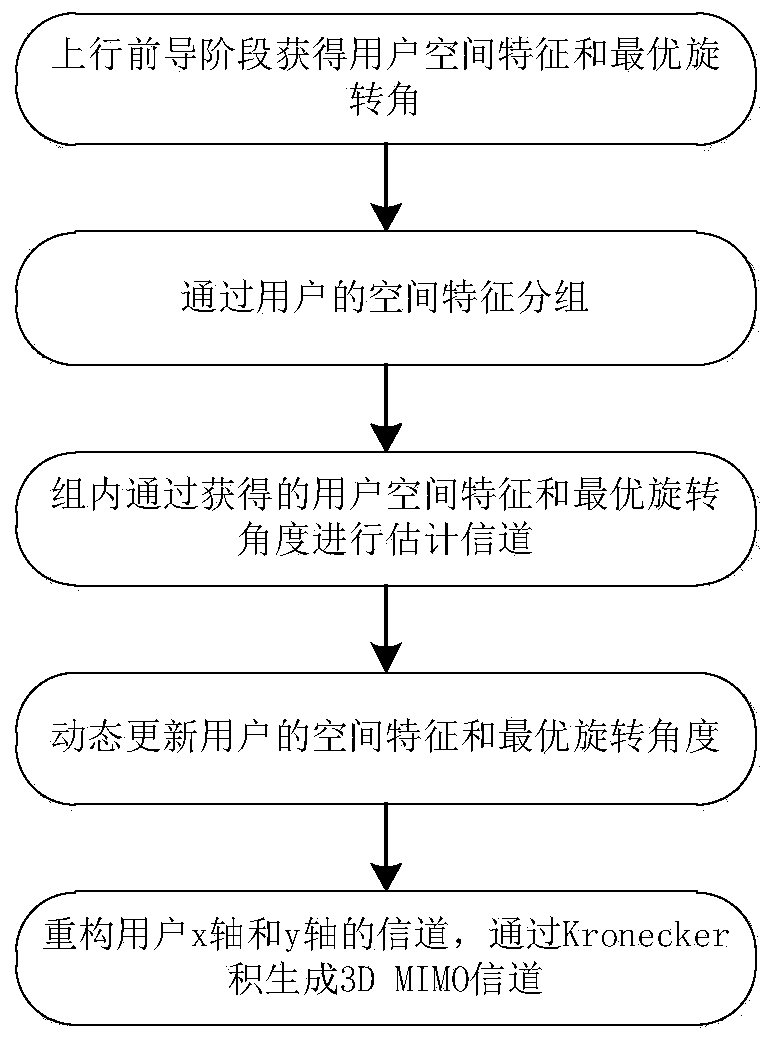
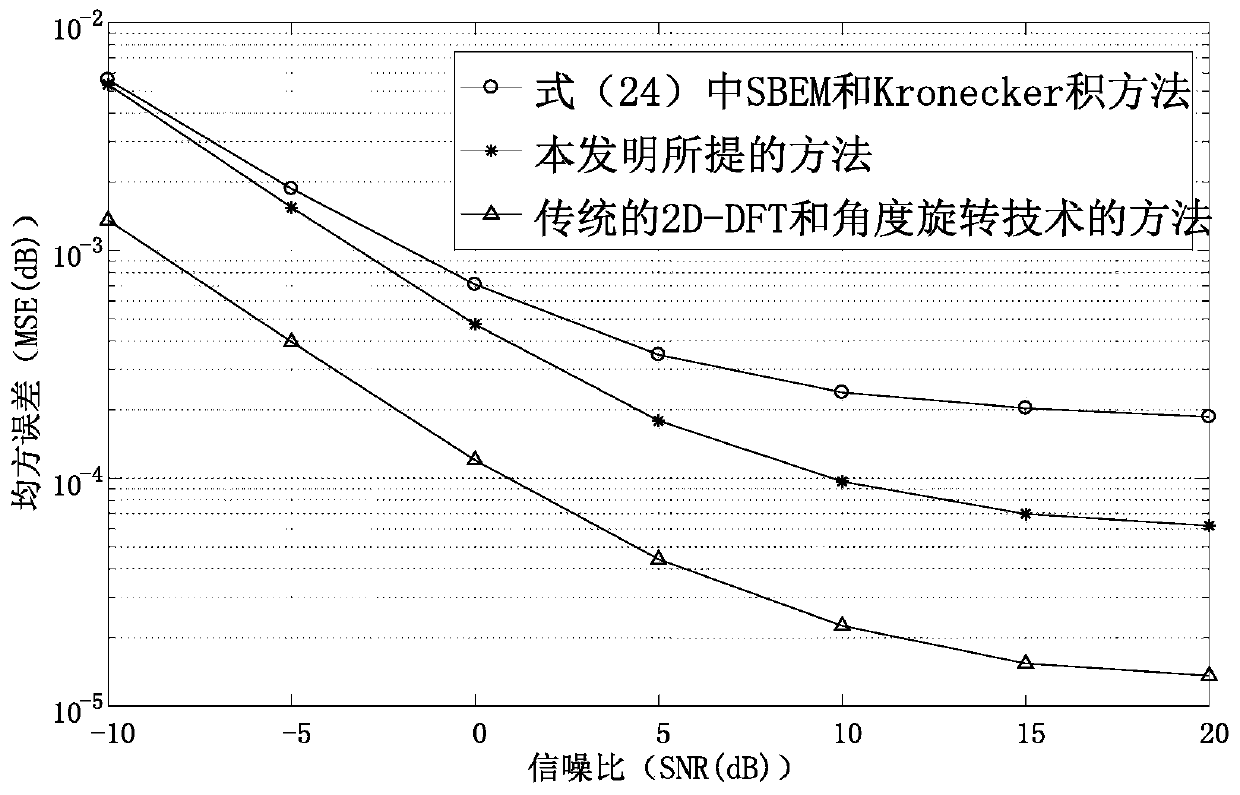
The invention discloses a novel channel estimation method for a multi-user 3D MIMO system, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the modeling through employing an included angle between a direction of arrival and an x axis and an included angle between the direction of arrival and a y axis of a planar array antenna, and projecting a 3D MIMO channel to the x axis and the y axis; in the uplink preamble stage, allocating an orthogonal pilot frequency sequence to each user, and obtaining paired spatial features and optimal rotation angles of channels projected to the x axis and the y axis by each user; grouping the obtained paired spatial features, distributing the same pilot frequency information in the groups, and distributing orthogonal pilot frequency sequences among the groups;carrying out channel estimation through the spatial feature and the optimal rotation angle of the (n-1)th coherence time in the group of the nth coherence time after the leader stage, and then dynamically updating the spatial feature and the optimal rotation angle of the user; and repeating the intra-group channel estimation method to obtain spatial features and optimal rotation angles of all users in the cell, reconstructing channels of an x axis and a y axis of all users in the cell, and generating a 3D MIMO channel through a Kronecker product.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Radar robust space-time adaption processing method based on iterative subspace tracking algorithm
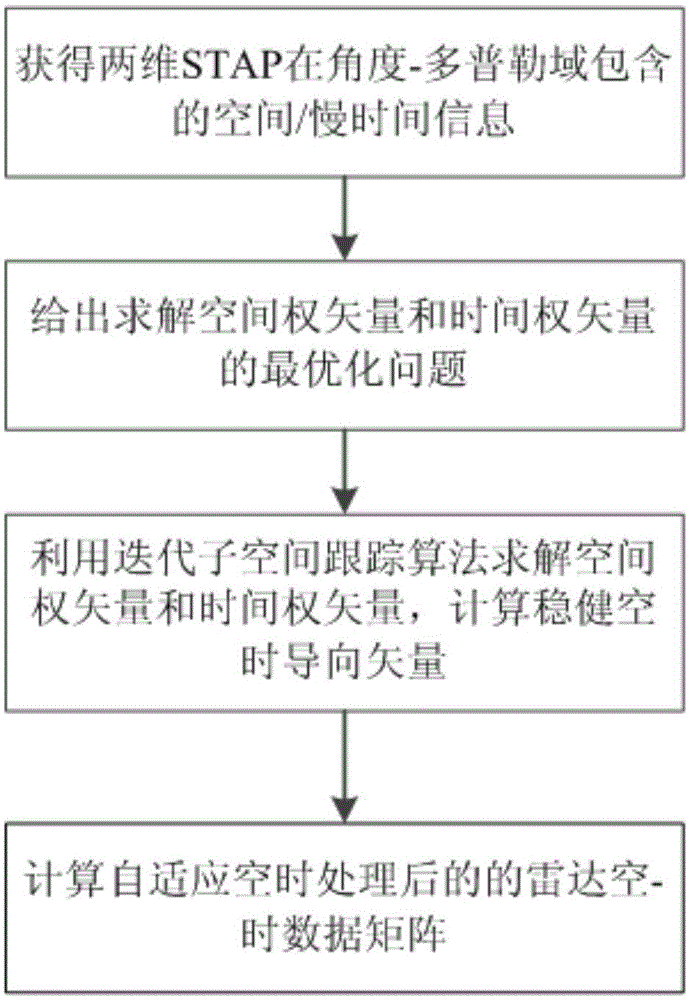
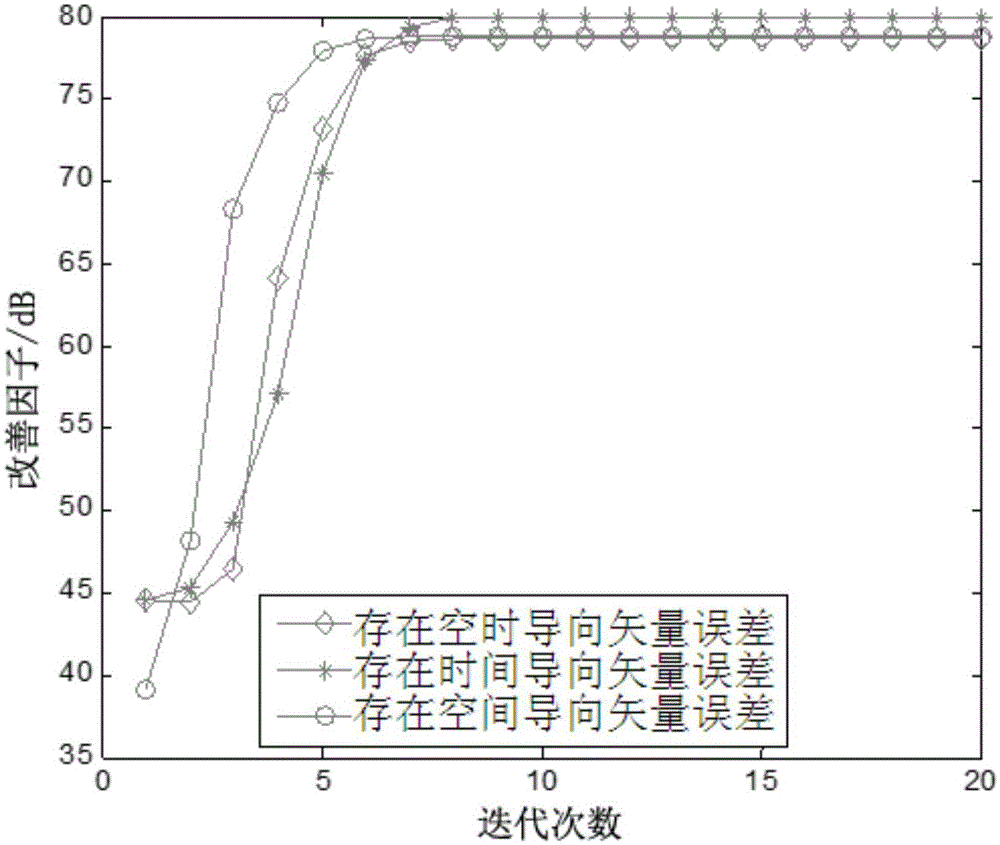
ActiveCN105044688ASpace-time adaptive processing is robustReduce time complexityWave based measurement systemsRadarTarget signal
The invention discloses a radar robust space-time adaption processing method based on an iterative subspace tracking algorithm. The method comprises the following steps of (1) according to a space-time data matrix X received by a known radar, acquiring P space-time data matrixes of a distance unit; (2) according to the space-time data matrix X received by the radar, writing a corresponding space-time adaptive weight matrix W as the following equation: W=uvT, and giving an optimization problem which is used to solve a space weight vector u and a time weight vector v, wherein the optimization problem is defined in the description; (3) using the iterative subspace tracking algorithm to solve and acquire the space weight vector u and the time weight vector v and calculating a robust space-time steering vector s; (4) carrying out Kronecker product on the robust space-time steering vector s and the space-time data matrix X received by the radar so as to obtain a radar space-time data matrix after adaptive space-time processing so that a target signal after the adaptive space-time processing is obtained.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Airborne MIMO radar robust dimension-reduction space-time self-adaptive processing method
InactiveCN105785333AReduce operational complexityRobustWave based measurement systemsTime domainDimensionality reduction
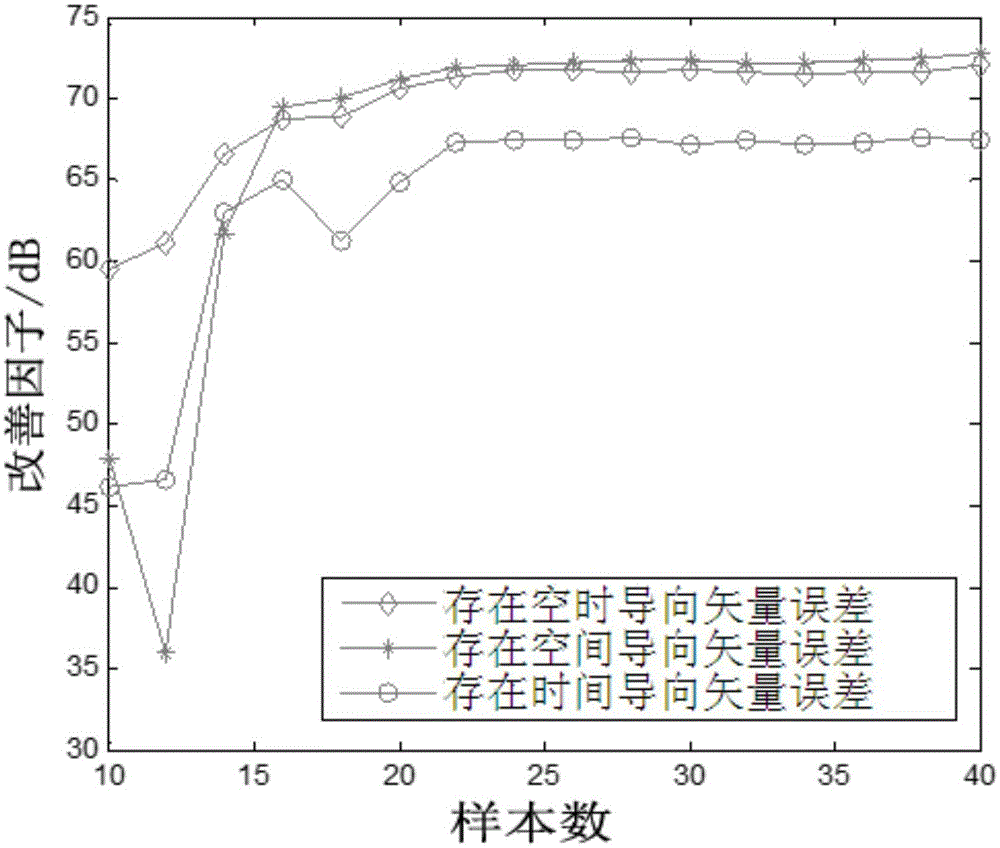
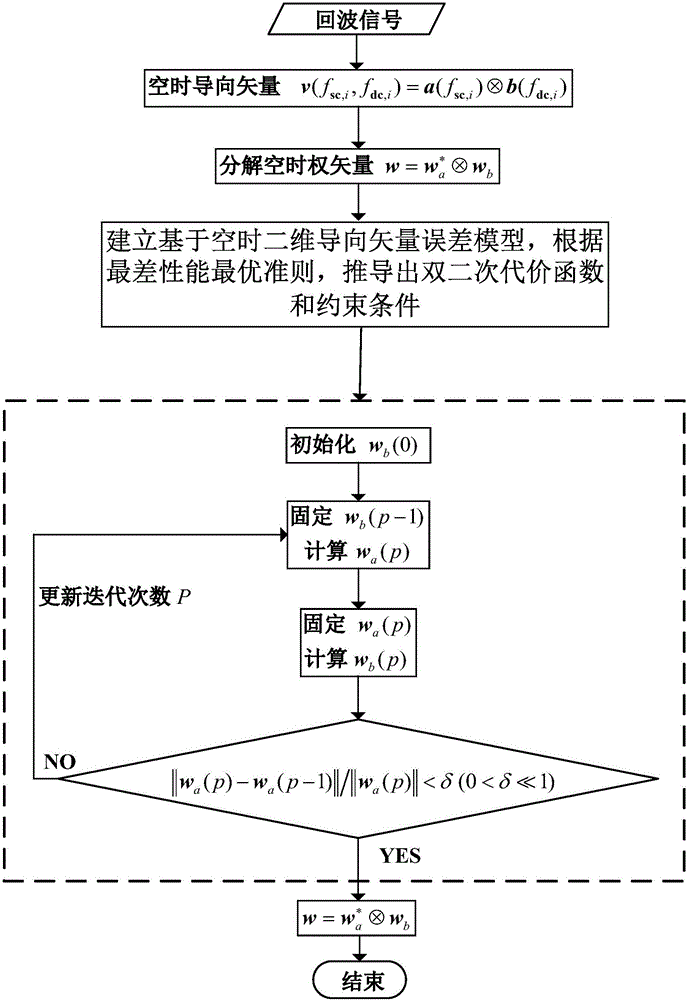
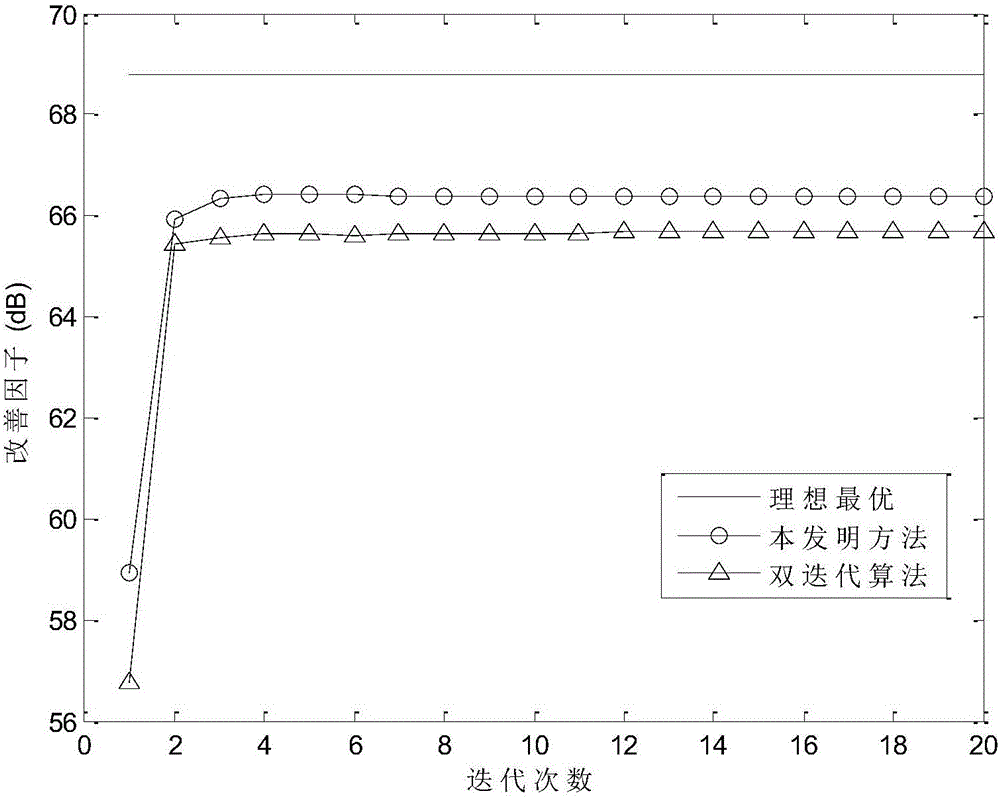
The invention relates to an airborne MIMO radar robust dimension-reduction space-time self-adaptive processing method, which comprises the following steps: to begin with, decomposing MIMO-STAP weight vector into Kronecker product of space and time two low-dimension weight vectors; then, based on an error model of space and time steering vectors, carrying out deduction through a second-order convex optimization algorithm to obtain a bi-quadric cost function and constraint conditions; carrying out cycle optimization solution on the space and time two low-dimension weight vectors through a double iterative algorithm; and finally, enabling the space and time weight vectors obtained through optimization to be synthesized into a full-dimensional MIMO-STAP weight vector. In the dimension-reduction processing, robust processing is carried out on each dimension of solution, so that dimension is reduced, and meanwhile, robustness of the steering vector error is enhanced; and under the condition of same sample number and algorithm complexity, the method has higher robustness.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
SOD-IRK based time-delay power system stability determination method
ActiveCN108321821AFully consider the scaleFully consider the impact of communication time lagPower oscillations reduction/preventionZ eigenvalueComputation process
The invention discloses a SOD-IRK based time-delay power system stability determination method. The SOD-IRK based time-delay power system stability determination method comprises: establishing a time-delay power system model; using different implicit Runge-Kutta methods to discretize solution operators to obtain a discretized matrix of the solution operators; transforming an eigenvalue problem ofinfinite dimension into an eigenvalue problem of finite dimension; using an implicit Arnoldi algorithm to calculate an approximate value of the eigenvalue having the maximum modulus, of the discretized matrix of the solution operators; using a rotation-amplifying method to perform preprocessing during calculation, and performing sparse implementation by using the properties of a Kronecker product;transforming the approximate value of the eigenvalue having the maximum modulus, of the discretized matrix into the approximate eigenvalue of the time-delay power system model according to the spectral mapping relationship; using the Newton iteration method to correct the approximate eigenvalues to obtain the exact eigenvalues of the time-delay power system; and determining the stability of the time-delay power system according to the magnitude of the exact eigenvalue damping ratio.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
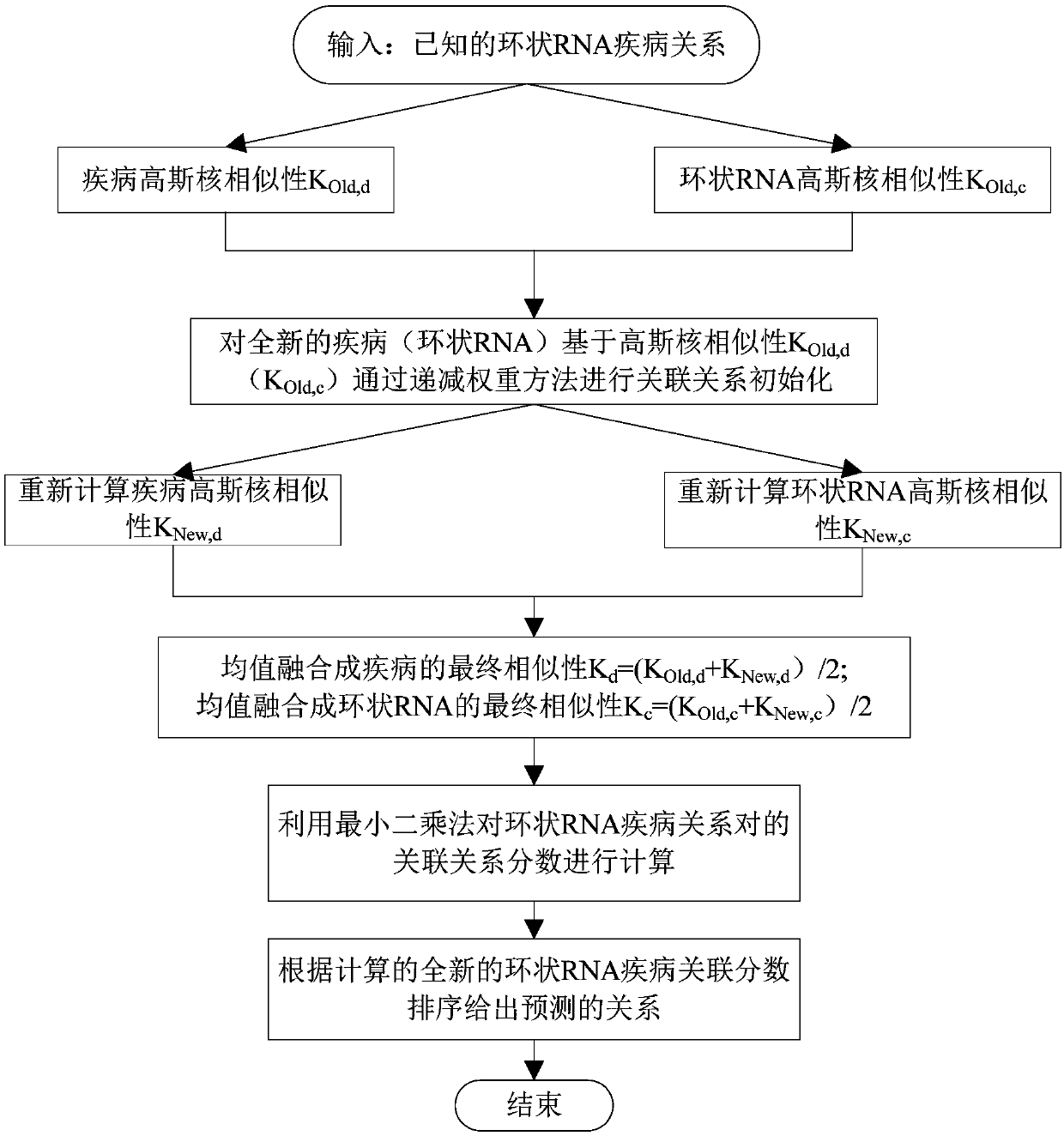
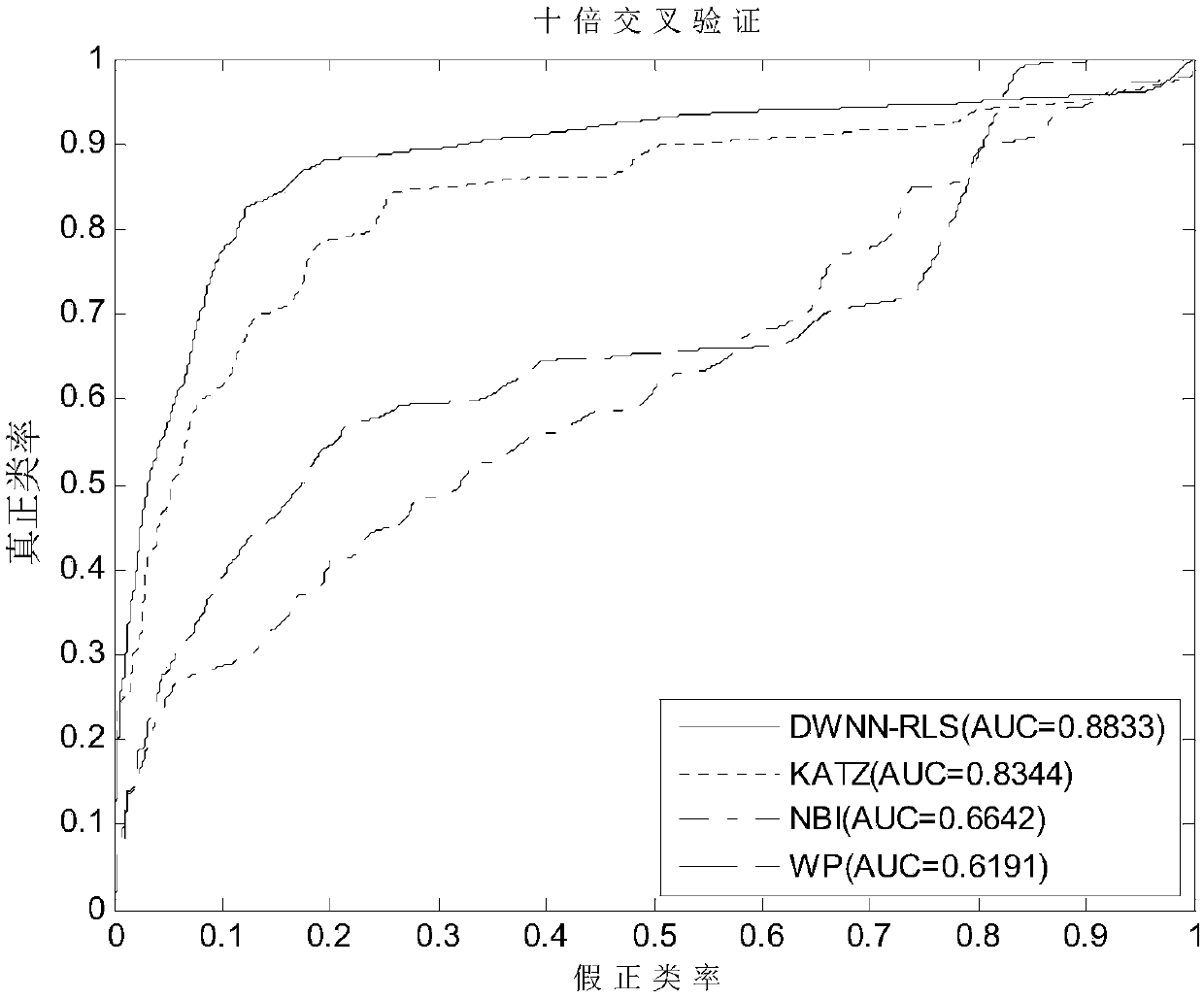
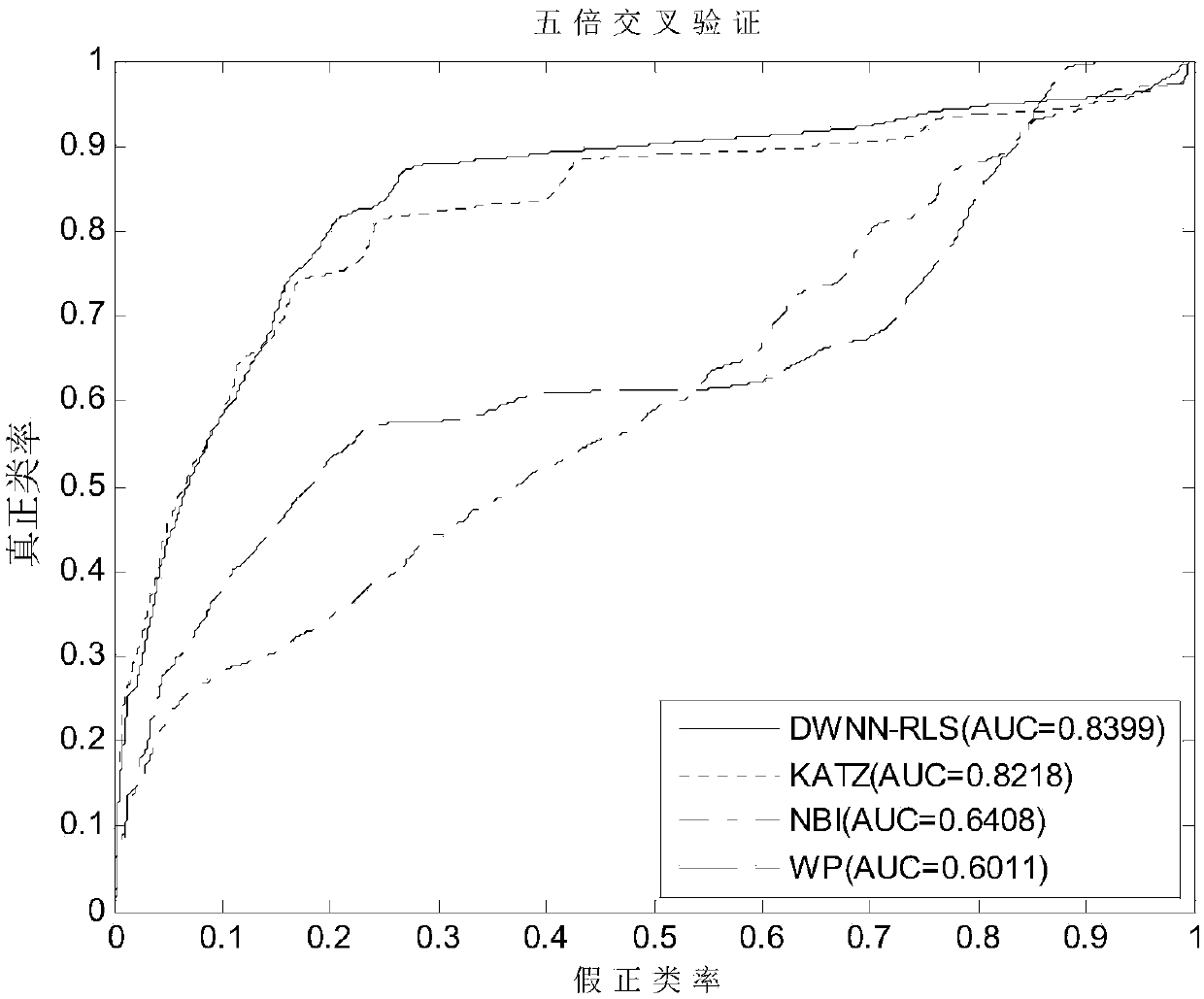
Incidence relation prediction method of circular RNA
ActiveCN108920895AAccurate predictionSave manpower and material costsSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmCircular RNA
The invention discloses an incidence relation prediction method of circular RNA. The method comprises the steps that step one, a circular RNA Gauss kernel similarity first matrix and a disease Gauss kernel similarity first matrix are constructed; step two, the relation initial values between new circular RNA and each disease, a new disease and each circular RNA are calculated based on a decreasingweight method; step three, a circular RNA Gauss kernel similarity second matrix and a disease Gauss kernel similarity second matrix are constructed; step four, a circular RNA similarity matrix and adisease similarity matrix are constructed; step five, a Kronecker product least square method is adopted to calculate a circular RNA and disease relation score matrix, and the relation scores of the new circular RNA and all diseases and the relation scores of the new disease and all circular RNA are obtained. By means of the method, prediction is conducted on incidence relation of circular RNA diseases through a computing prediction model, and the vacant of a computing model used for predicting the relation between circular RNA and disease is filled.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
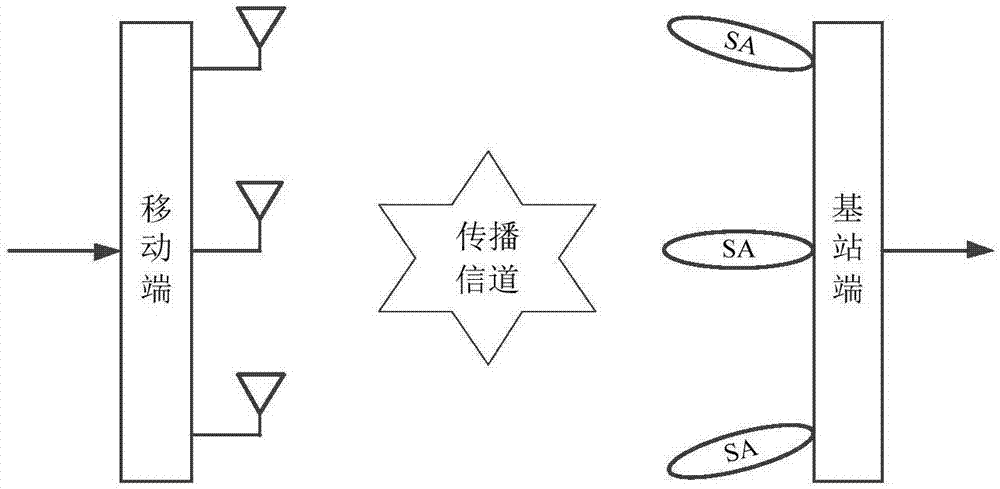
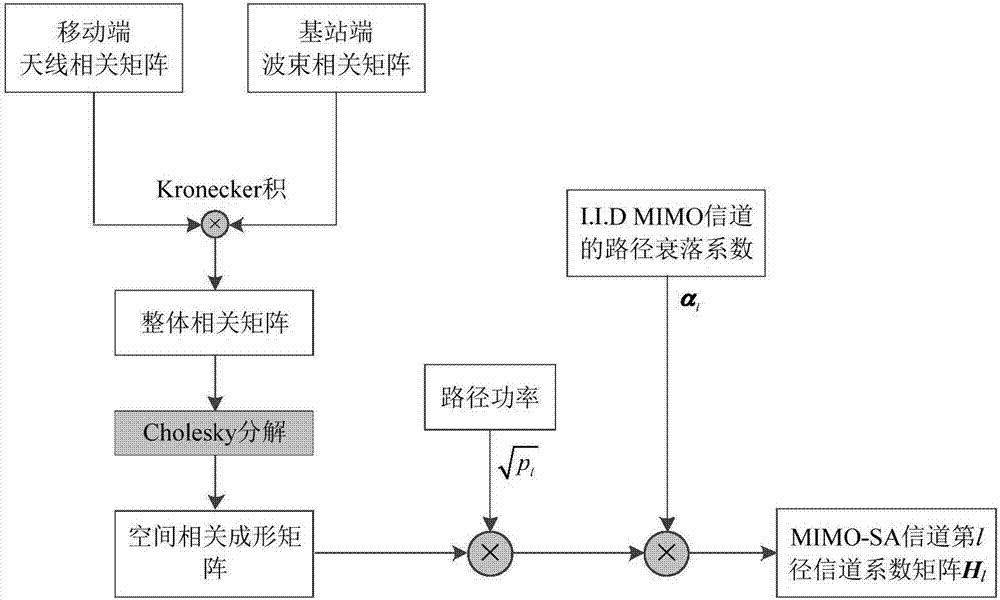
MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) wireless channel modeling method fusing smart antenna
ActiveCN107171757ASimplified channel structureTrue channel characteristicsRadio transmissionTransmission monitoringEngineeringMultiple input
The invention discloses an MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) wireless channel modeling method fusing a smart antenna, and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing a transmitting end antenna correlation matrix and a receiving end wave beam correlation matrix, and taking a Kronecker product of the transmitting end antenna correlation matrix and the receiving end wave beam correlation matrix as an integral correlation matrix; taking a matrix obtained through Cholesky decomposition of the integral correlation matrix as a spatial correlation forming matrix; generating a spatial independent MIMO channel fading coefficient; allocating power to different delay paths according to power delay distribution of a channel; calculating a channel coefficient matrix of all delay paths according to a time-frequency fading characteristic of an MIMO channel and the spatial correlation forming matrix; and lastly, building an MIMO wireless channel matrix fusing the smart antenna according to the channel coefficient matrix and path delays of all the delay paths according to a tapped delay line structure of a frequency selective channel. Through implementation of the method, a propagation channel of an actual MIMO-smart antenna fusion system can be approximated well.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
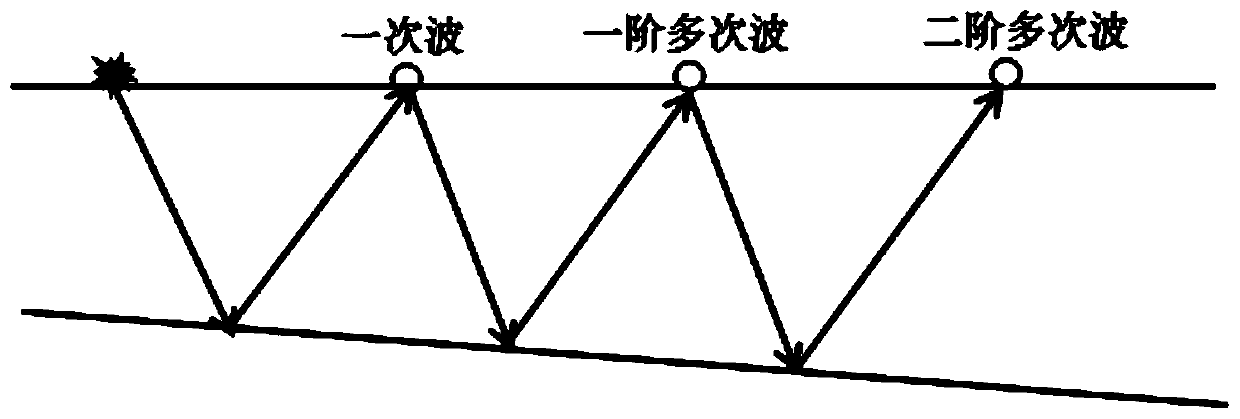
Three-dimensional seismic data multiple suppression method based on local similarity coefficient
The invention belongs to the technical field of geophysical exploration signal processing, and relates to a three-dimensional seismic data multiple suppression method based on a local similarity coefficient. The method is based on a conventional three-dimensional surface related multiple wave pressing technology. The method comprises: calculating a local similarity coefficient spectrum of the multiple contribution gather of the contact survey line and the Radon transformation result; constructing a weighted threshold operator according to the similarity coefficient difference; using the Kronecker product of the original data and a weighted threshold operator, determining stationary phase overlay space, replacing a direct summation process of multiple wave connection measuring lines by superposition of Fresnel spaces, and the high-resolution multiple wave prediction method for the three-dimensional ocean seismic data is realized. The spatial false frequency generated by a conventional method is effectively suppressed, so that multiple wave prediction is more accurate, the precision and accuracy of multiple wave suppression are improved, and much convenience is brought to subsequentprocessing and explanation of seismic data processing.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
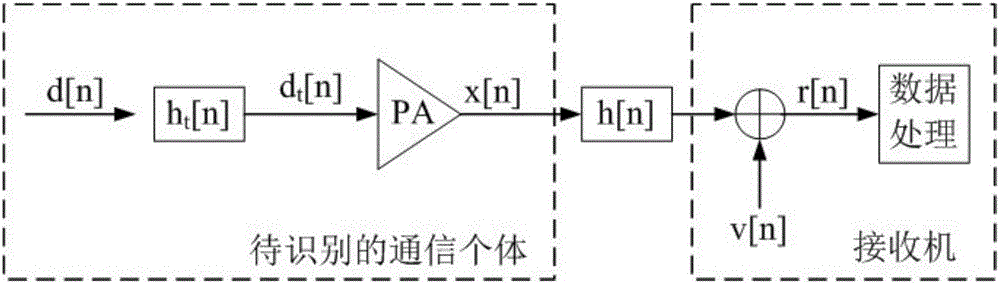
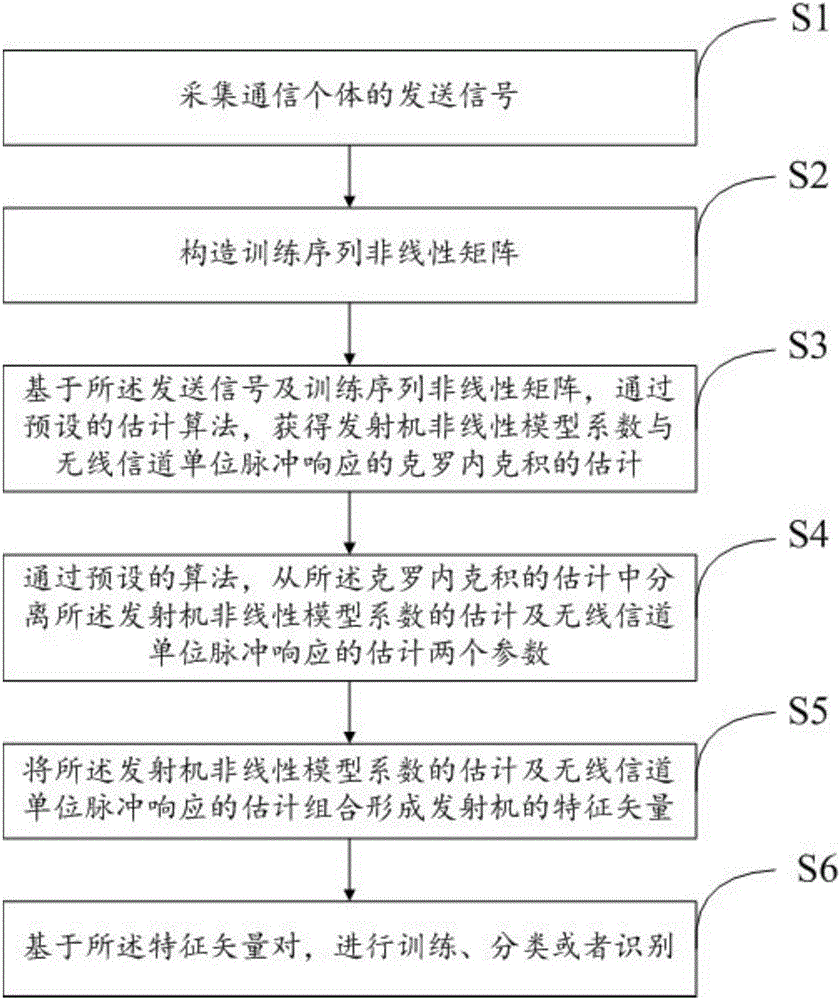
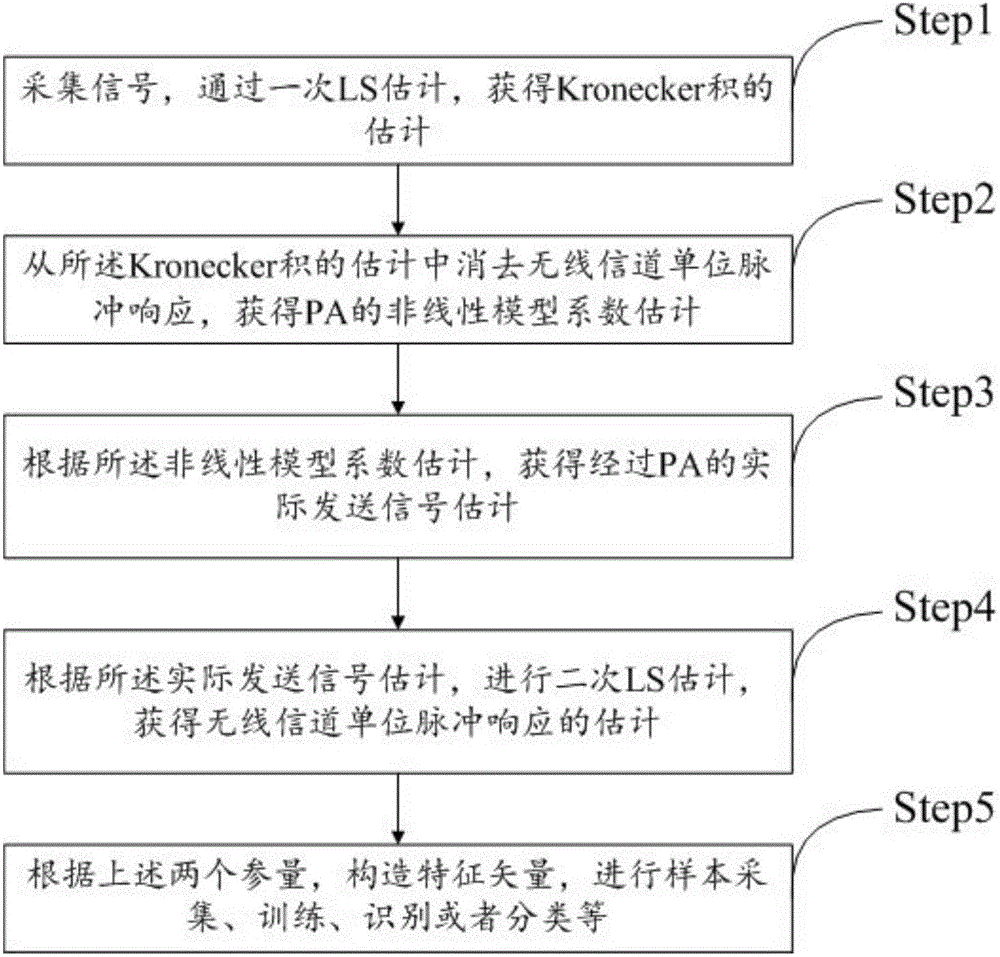
Physical layer parameter separation and individual identification method for single carrier communication system
ActiveCN105743630AImprove recognition accuracyFight against impersonation attacksBaseband system detailsTransmission path divisionRadio equipmentFeature vector
The present invention provides a physical layer parameter separation and individual identification method for a single carrier communication system. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a signal; constructing a nonlinear training sequence matrix; obtaining estimations of a nonlinear transmitter model coefficient and a Kronecker product of wireless channel unit pulse response based on the sending signal and the nonlinear training sequence matrix by a preset estimation algorithm; separating the two estimation parameters of the nonlinear transmitter model coefficient and the wireless channel unit pulse response by the a preset algorithm; combining the estimations of the nonlinear transmitter model coefficient and the wireless channel unit pulse response into a feature vector of the transmitter and a wireless channel pair; and training, classifying or identifying a communication source individual based on a sample of the feature vector. The physical layer parameter separation and individual identification method is applied to the joint estimation and separation of the nonlinear transmitter model coefficient and the wireless channel unit pulse response, and can be applied to parameter separation and individual identification based on communication transmitter hardware and single carrier radio equipment of the position and other fields.
Owner:上海海洋地质勘察设计有限公司
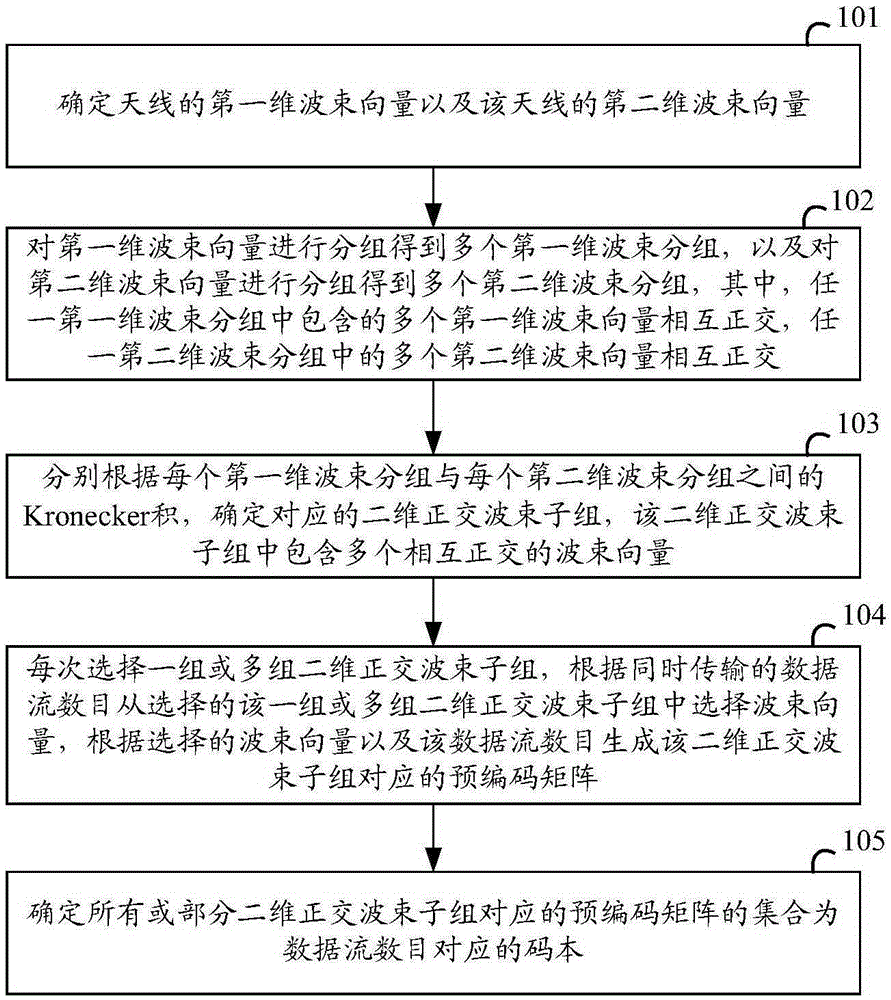
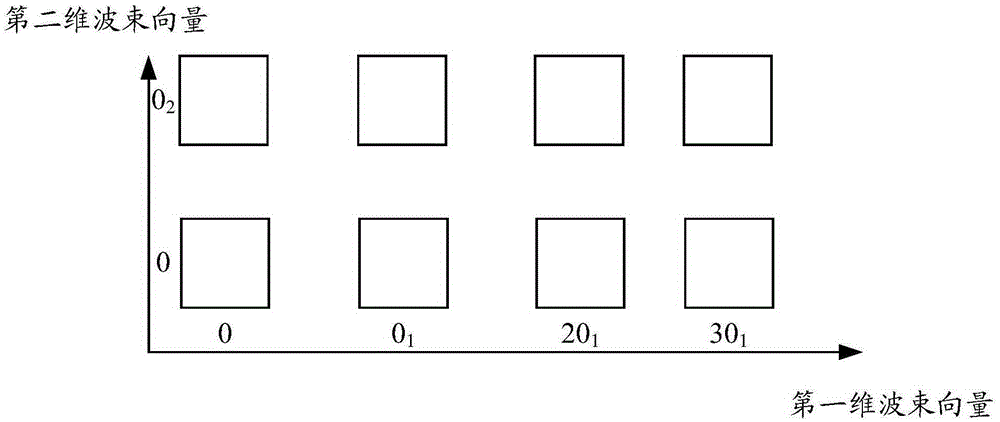
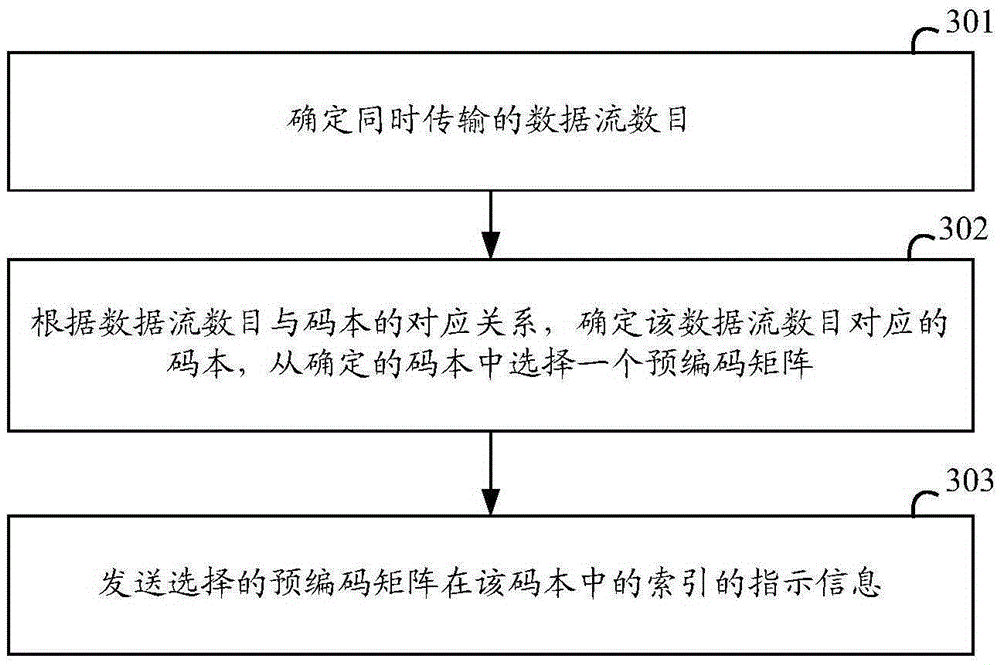
Codebook generation method, precoding matrix determination method and related device
The invention discloses a codebook generation method, a precoding matrix determination method and a related device, so as to provide a codebook design scheme for conditions in which the simultaneously-transmitted data stream number rank is larger than 1. The method comprises steps: first dimension beam vectors and second dimension beam vectors are grouped respectively to obtain multiple first dimension beam subgroups and multiple second dimension beam subgroups, wherein multiple beam vectors in the first dimension beam subgroups or the second dimension beam subgroups are mutually orthogonal; according to the Kronecker product between each first dimension beam subgroup and each second dimension beam subgroup, multiple two-dimension orthogonal beam subgroups are determined; according to the simultaneously-transmitted data stream number, a beam vector is selected from one or multiple two-dimension orthogonal beam subgroups, and according to the selected beam vector and the data stream number, a precoding matrix corresponding to the two-dimension orthogonal beam subgroup is generated; and a precoding matrix set corresponding to all or partial two-dimension orthogonal beam subgroups is determined to be the codebook corresponding to the data stream number.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com