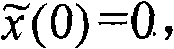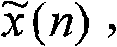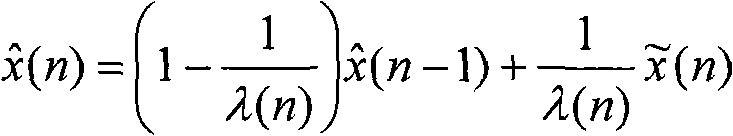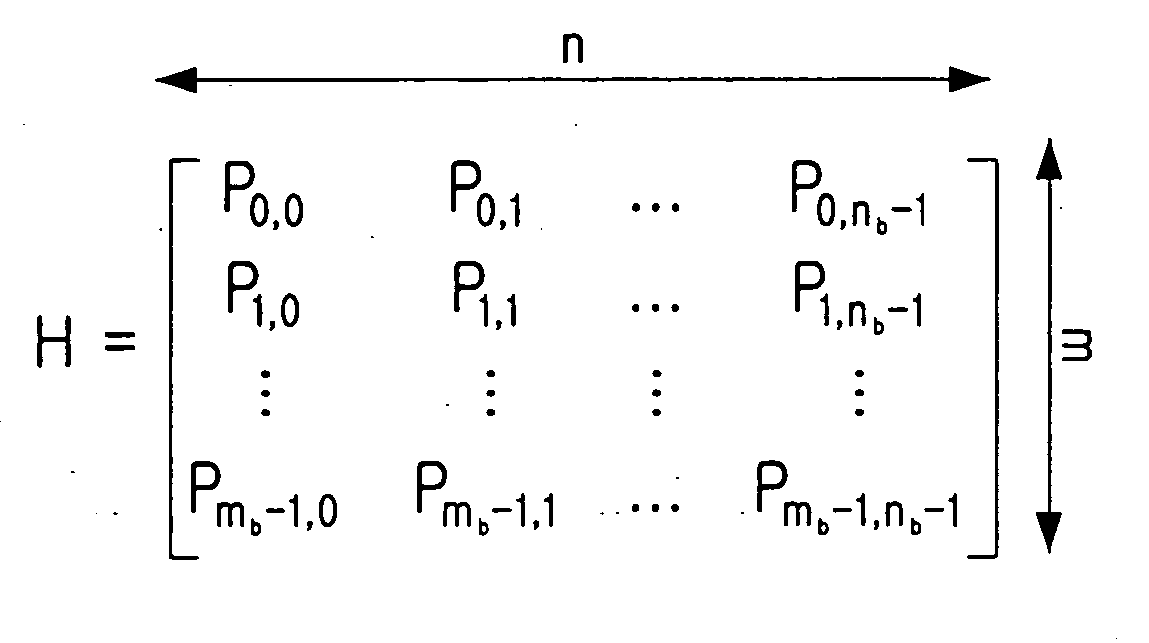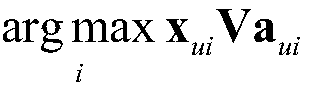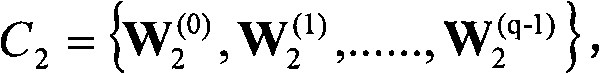Patents
Literature
670 results about "Diagonal matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
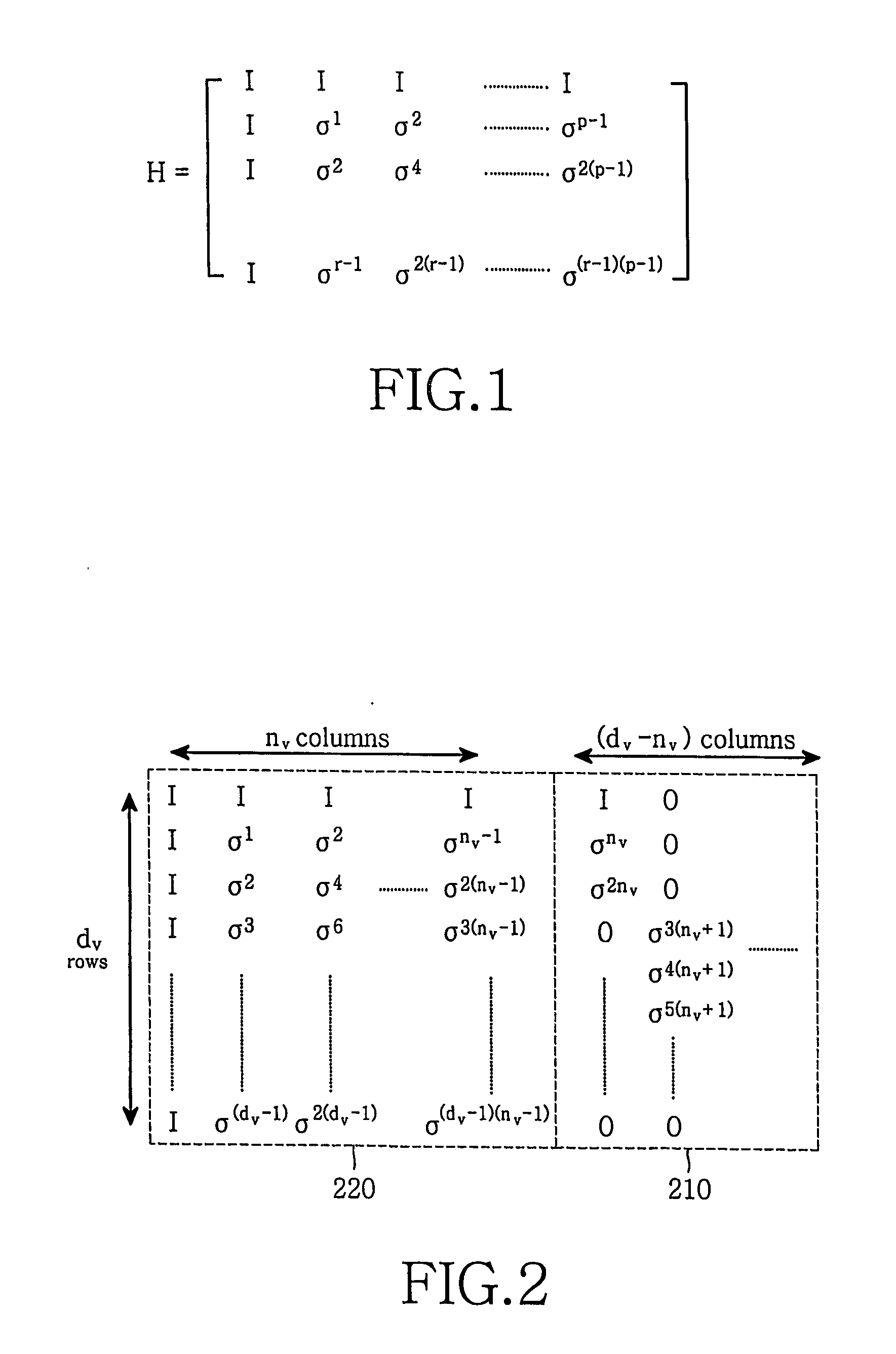
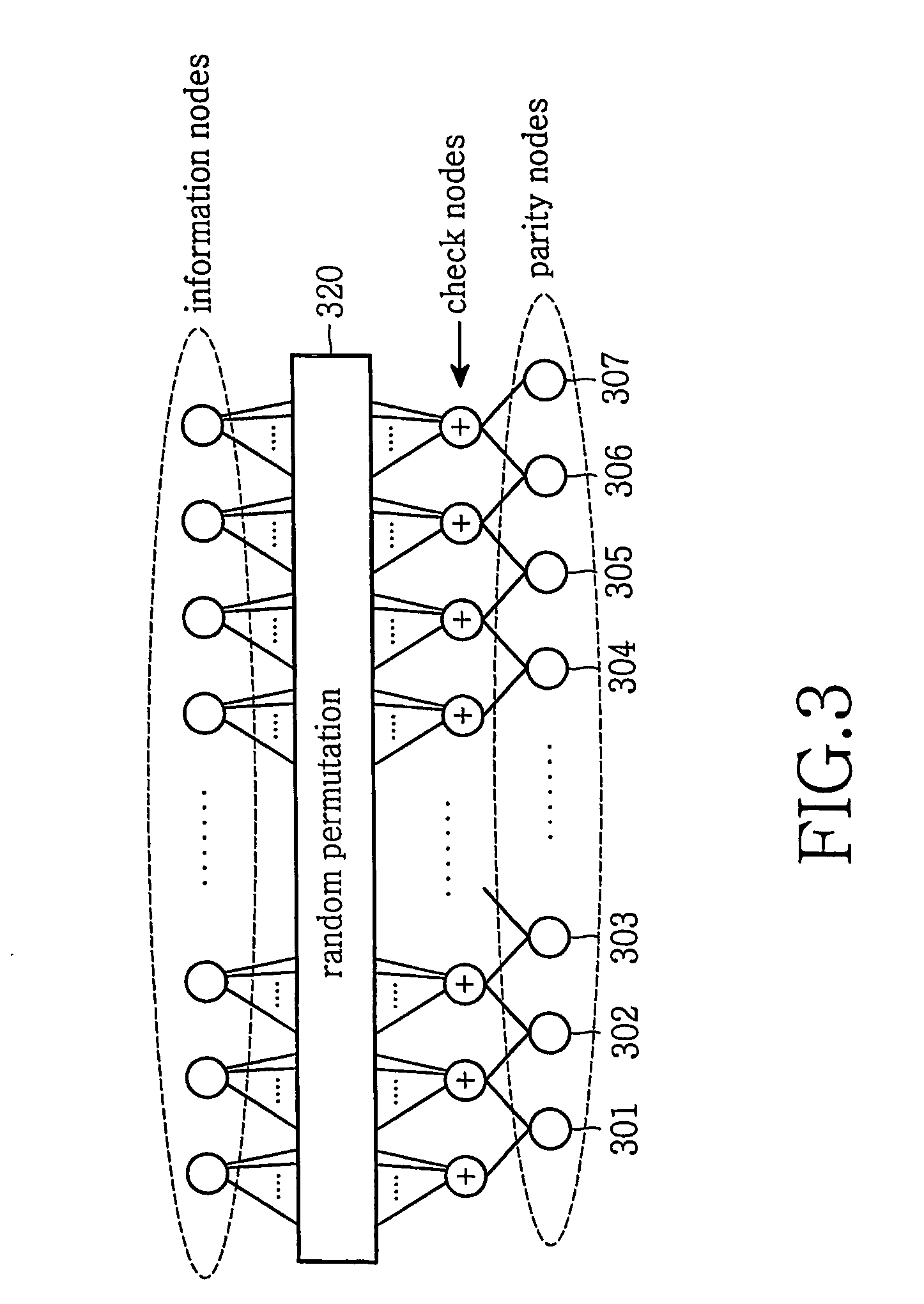
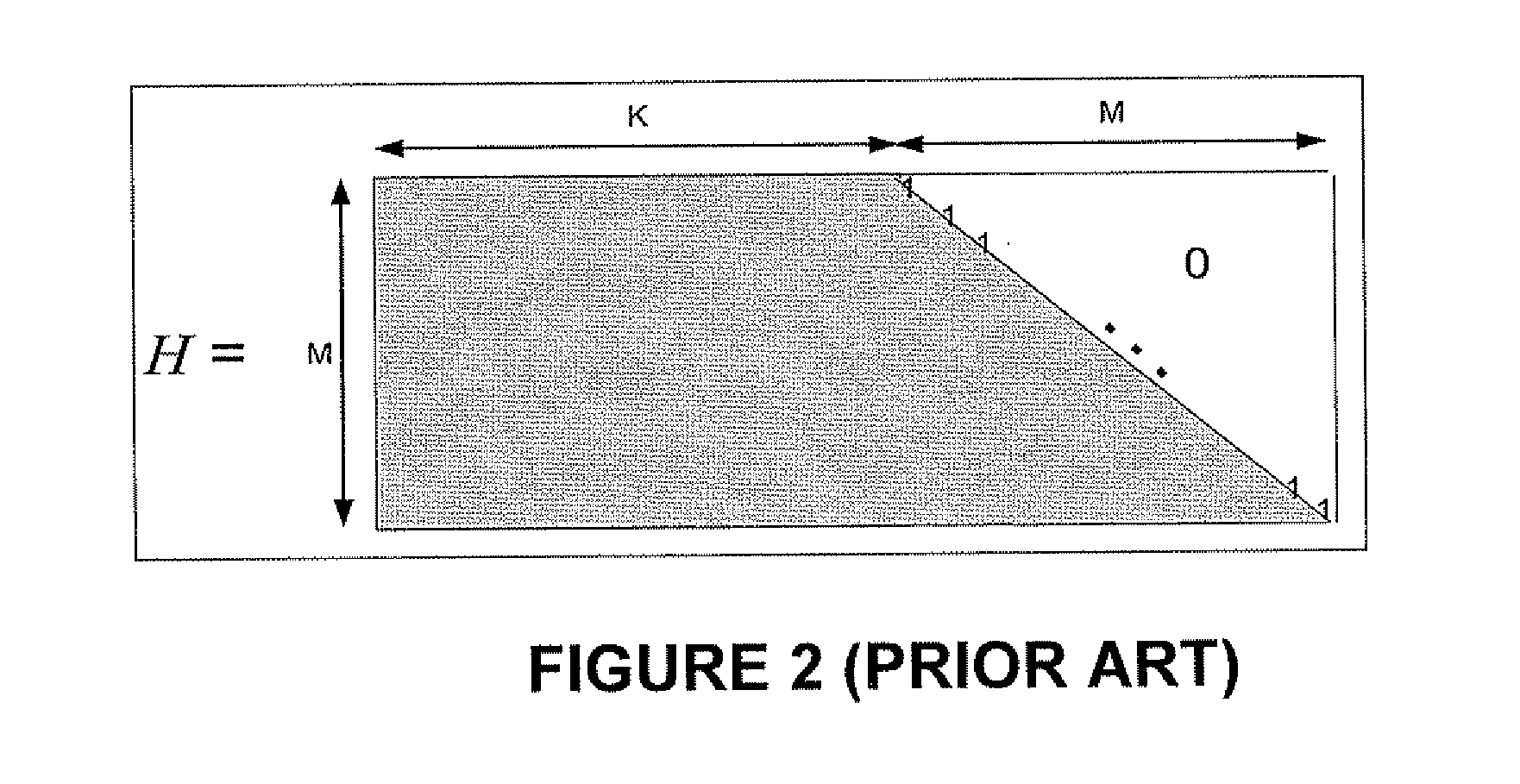
In linear algebra, a diagonal matrix is a matrix in which the entries outside the main diagonal are all zero. The term usually refers to square matrices. An example of a 2-by-2 diagonal matrix is ; the following matrix is a 3-by-3 diagonal matrix:. An identity matrix of any size, or any multiple of it, will be a diagonal matrix.
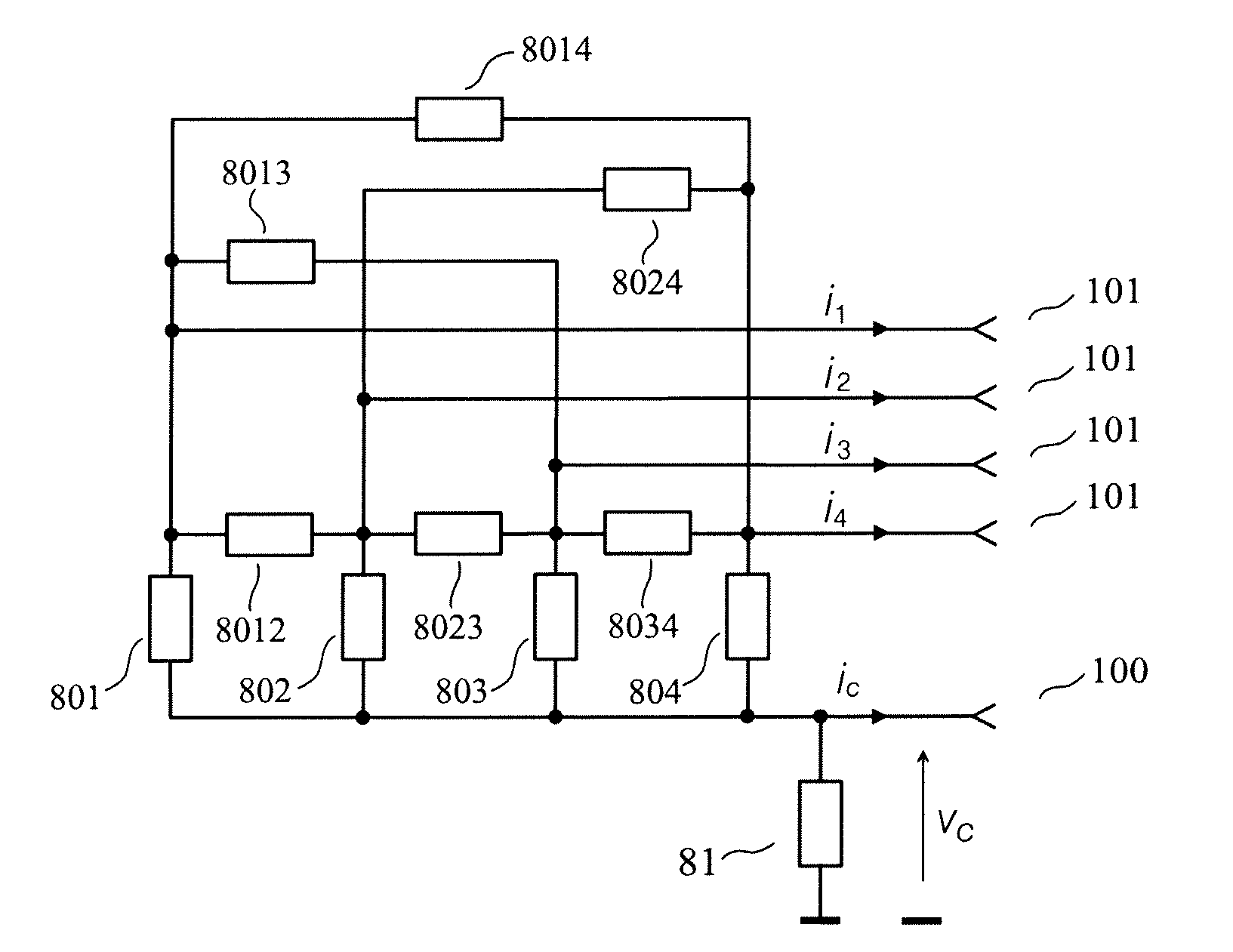
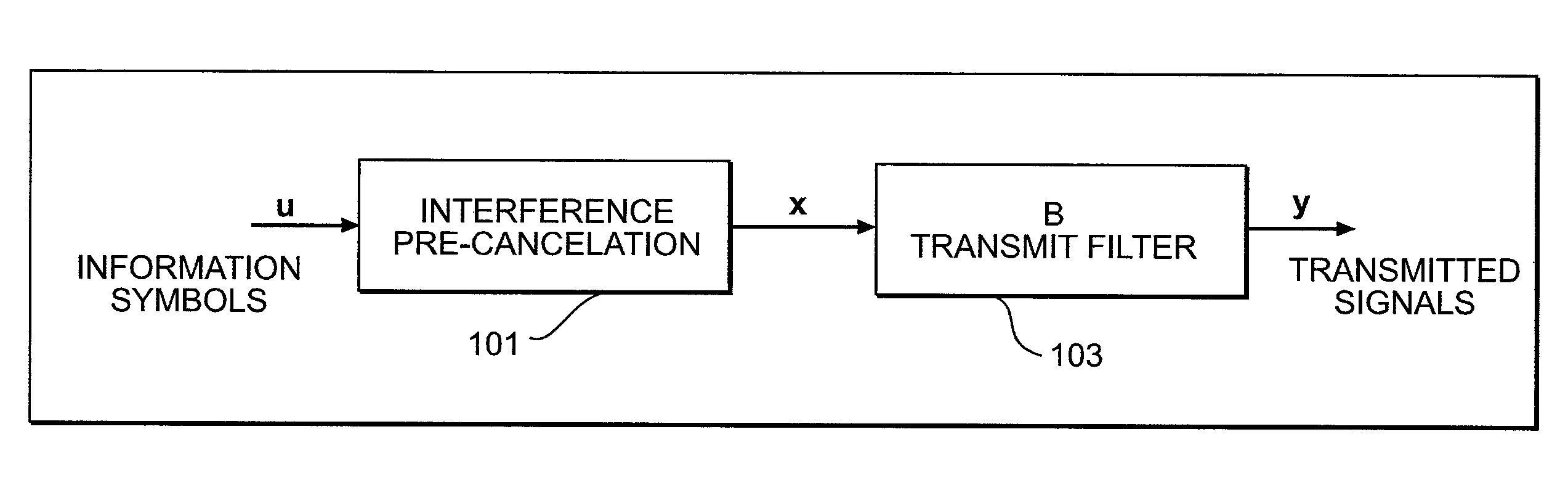
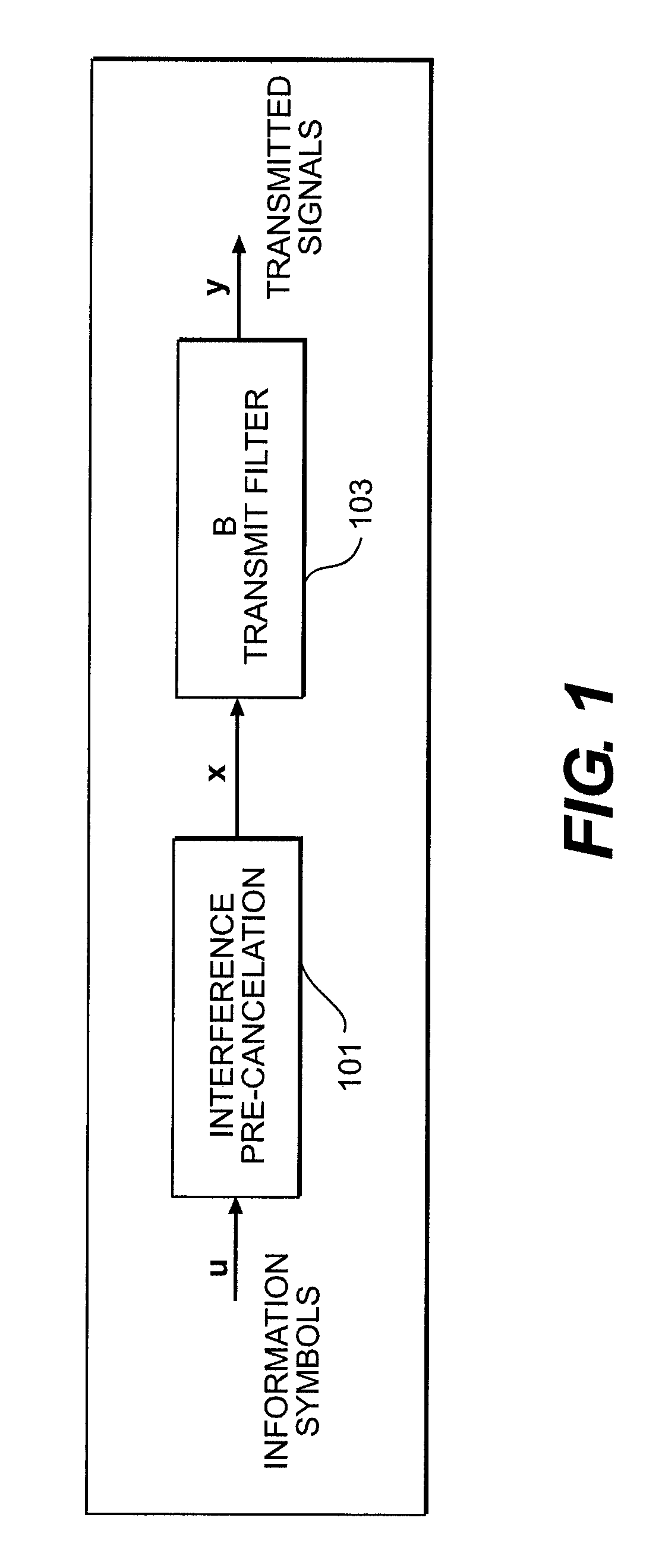
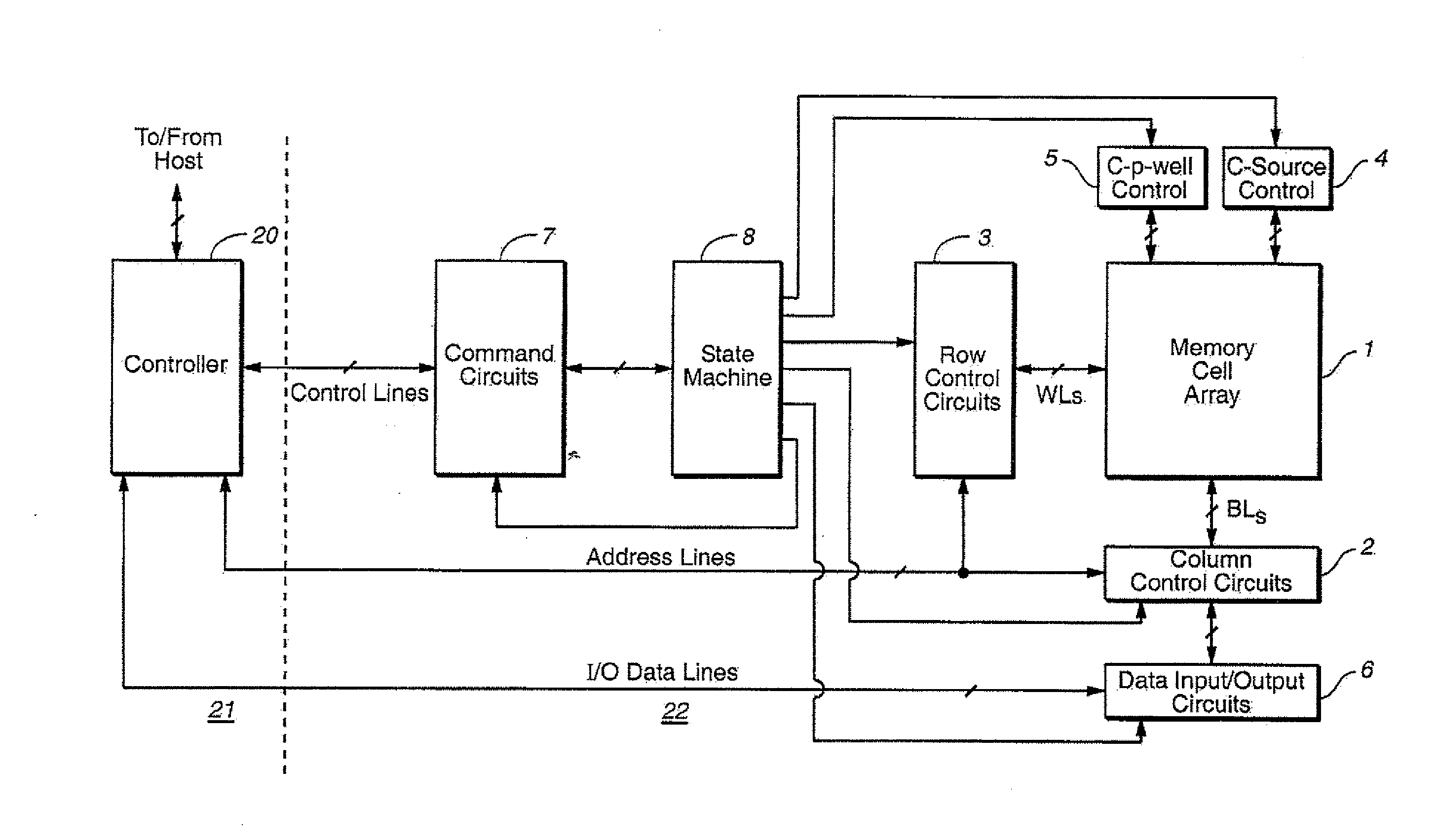
Multichannel interfacing device having a termination circuit
InactiveUS8222919B2Reduce reflectionReduce inductanceMultiple-port networksReliability increasing modificationsDiagonal matrixInterconnection
The invention relates to an interfacing device for transmission through interconnections used for sending a plurality of electrical signals.The interfacing device of the invention comprises signal terminals and a common terminal. A receiving circuit delivers, when the receiving circuit is in the activated state, “output signals of the receiving circuit” determined each by a linear combination of the voltages between one of the signal terminals and the common terminal, to the destination. A termination circuit is such that, when it is in the activated state, it is approximately equivalent, for the signal terminals and the common terminal, to a (m+1)-terminal network such that, for small signals, the impedance matrix, with respect to the common terminal, of the (m+1)-terminal network is equal to a wanted non-diagonal matrix of size m×m.
Owner:ZXNOISE LLC
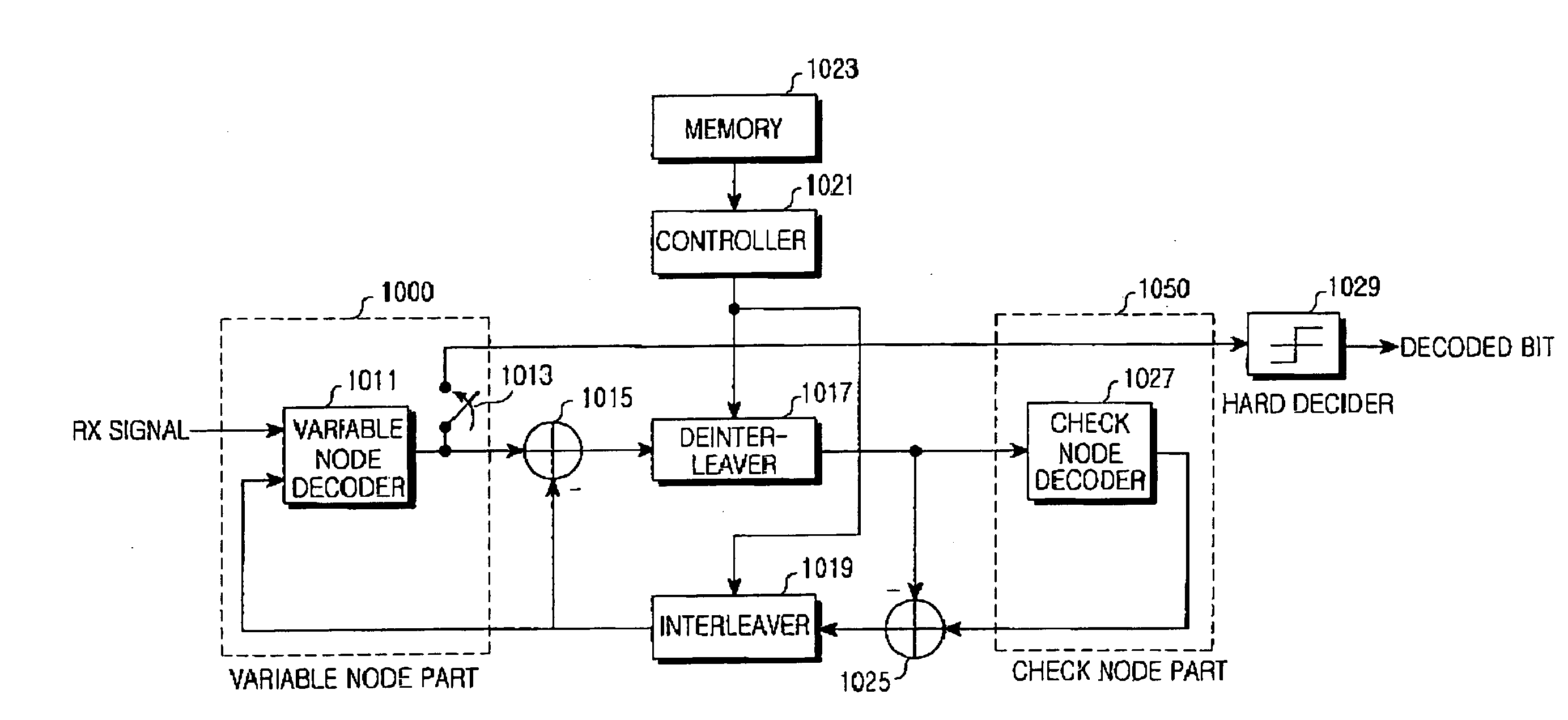
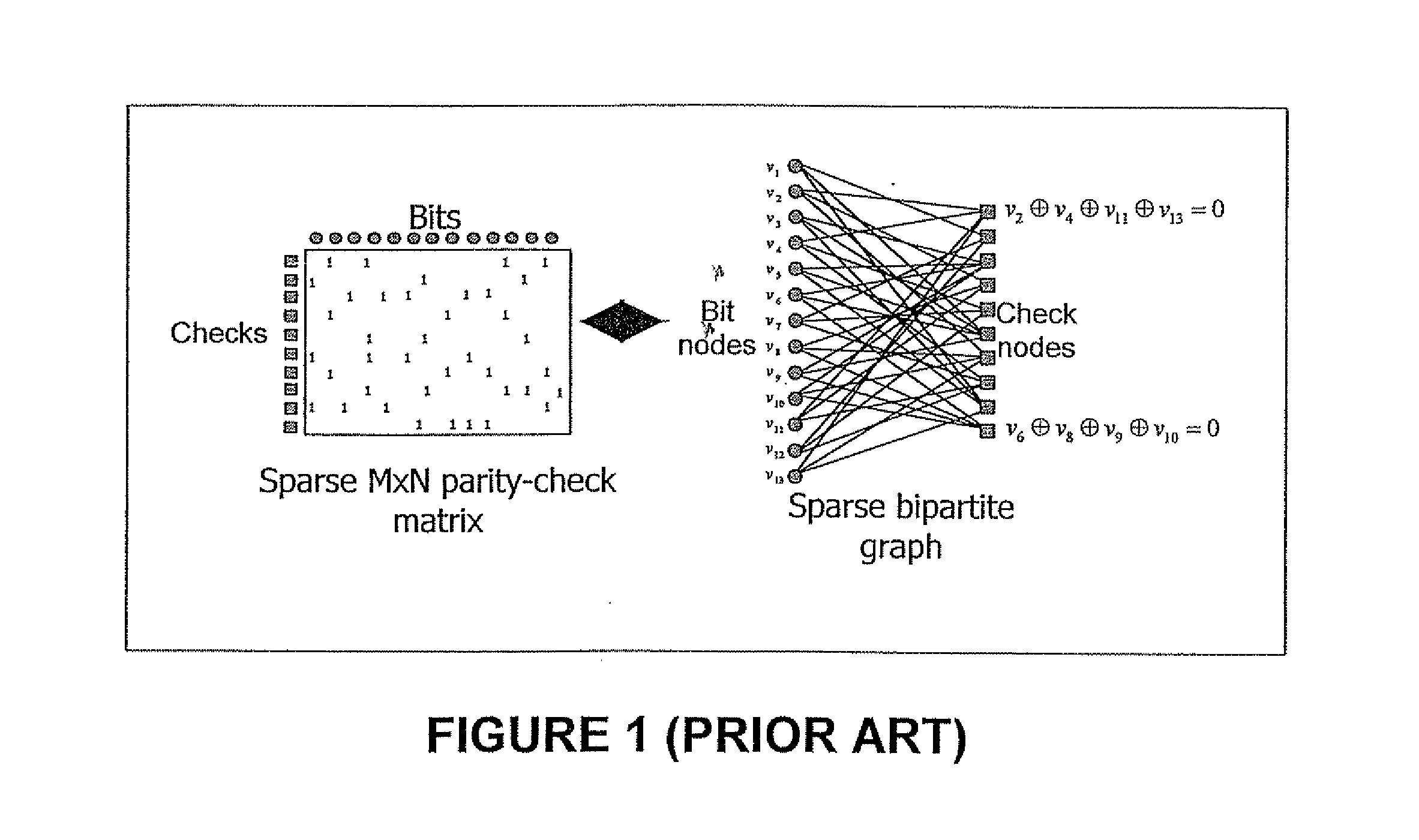
Apparatus and method for encoding a low density parity check code
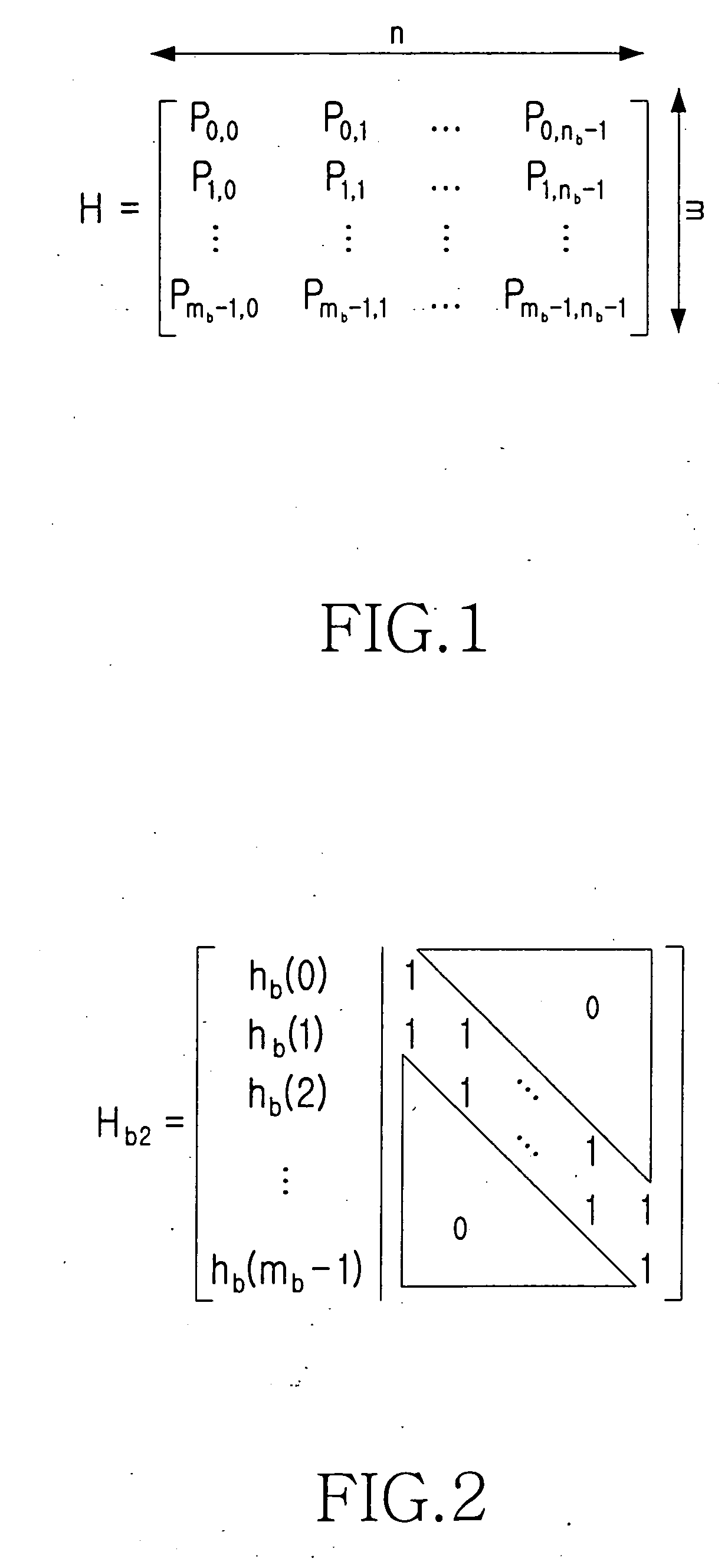
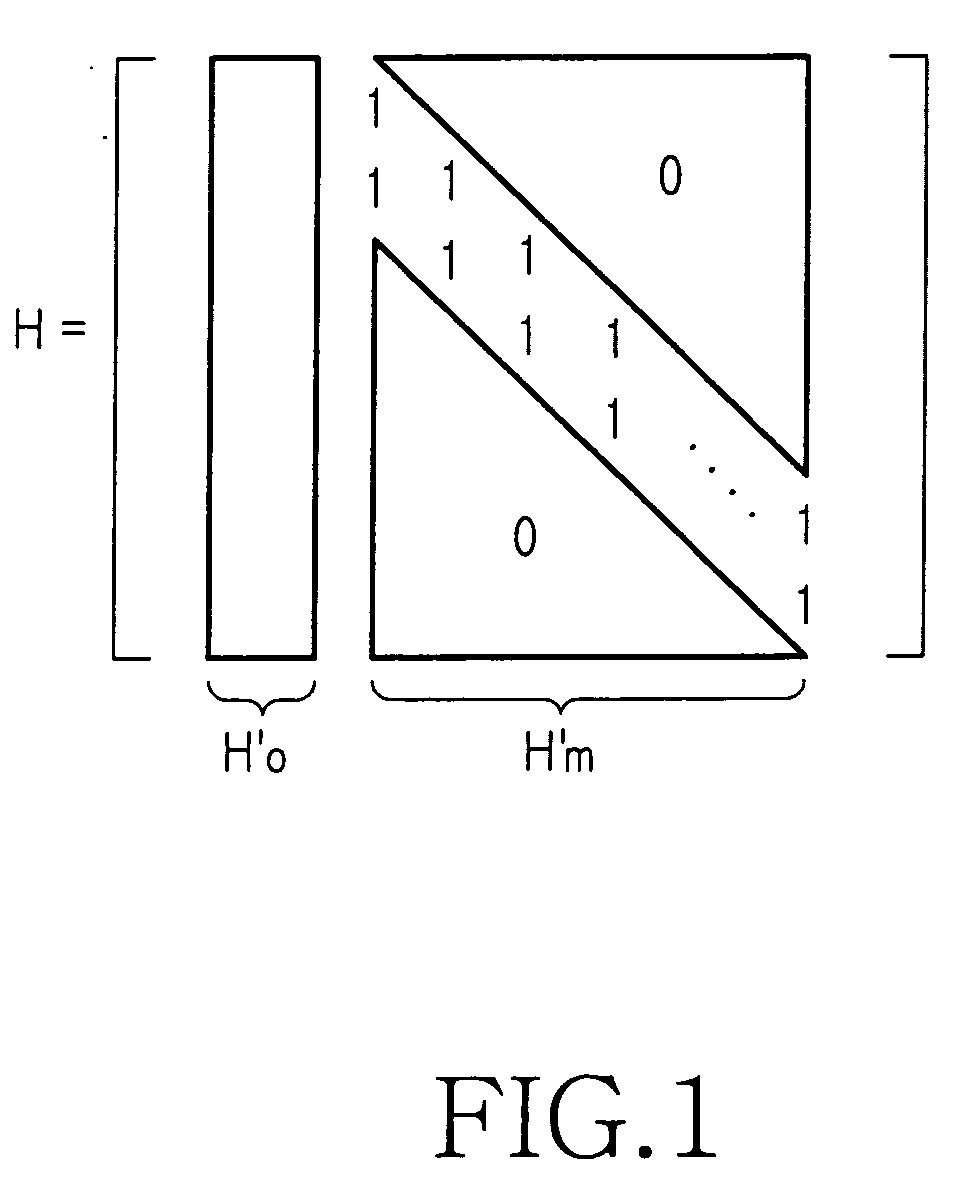
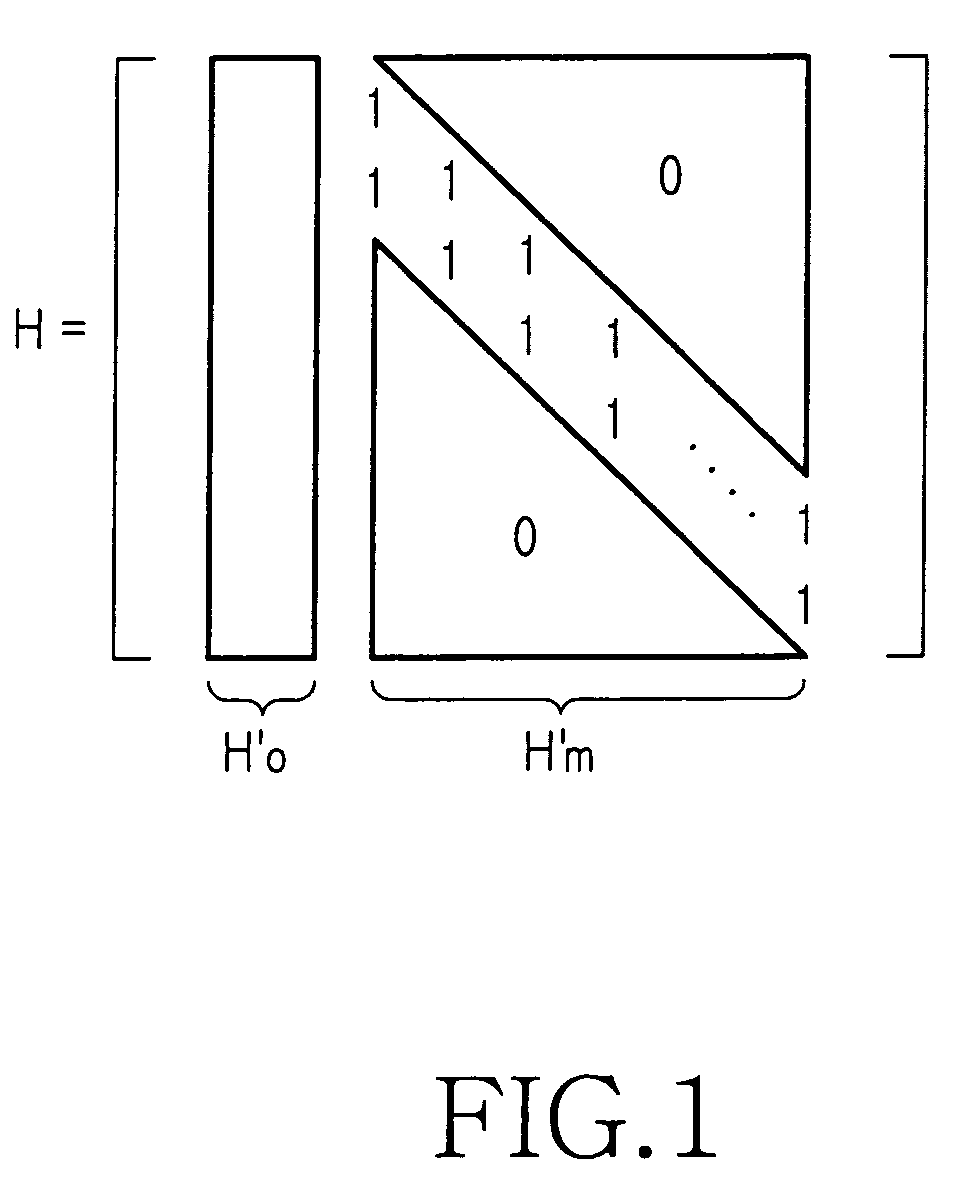
ActiveUS7178082B2Low Density Parity CheckEasy to calculateError detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTheoretical computer scienceDiagonal matrix
An apparatus and method for generating an encoding matrix for a low density parity check (LDPC) code having a dual-diagonal matrix as a parity check matrix are disclosed. The apparatus and method construct an information sub-matrix of the encoding matrix with a predetermined number of square matrixes according to a predetermined code rate such that each of the square matrixes has columns and rows with a weight of 1 and has a different offset value, combine the square matrixes with the dual-diagonal matrix, and perform inter-row permutation on the information sub-matrix.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
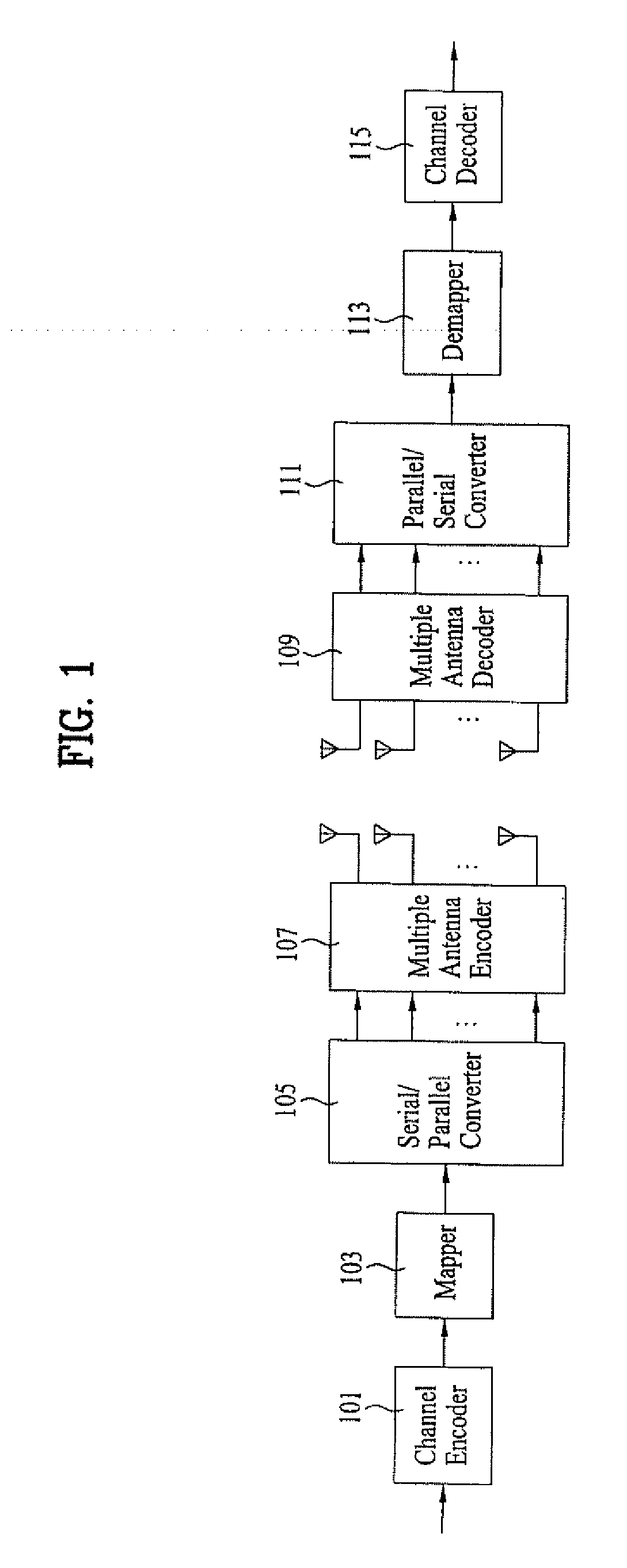
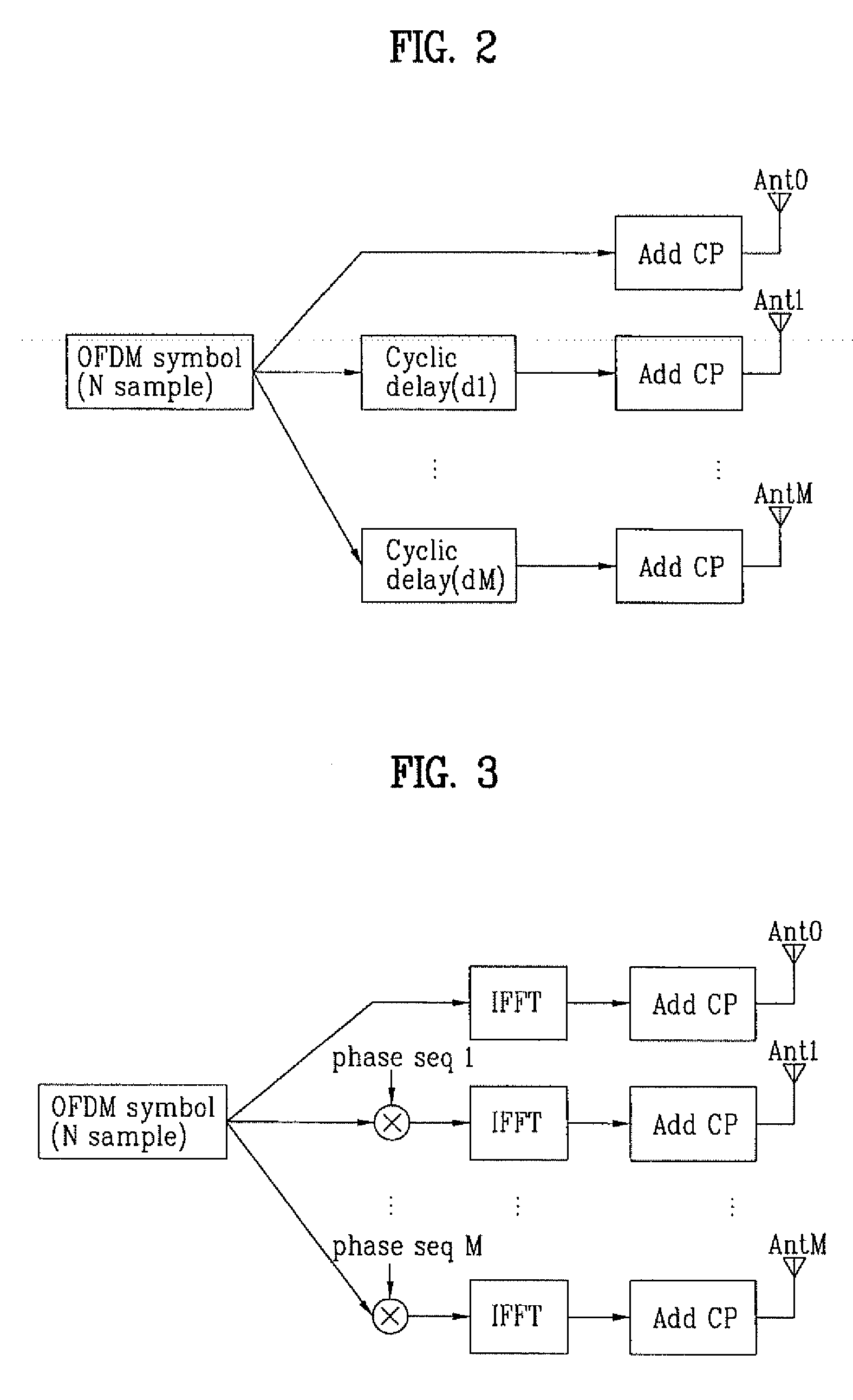
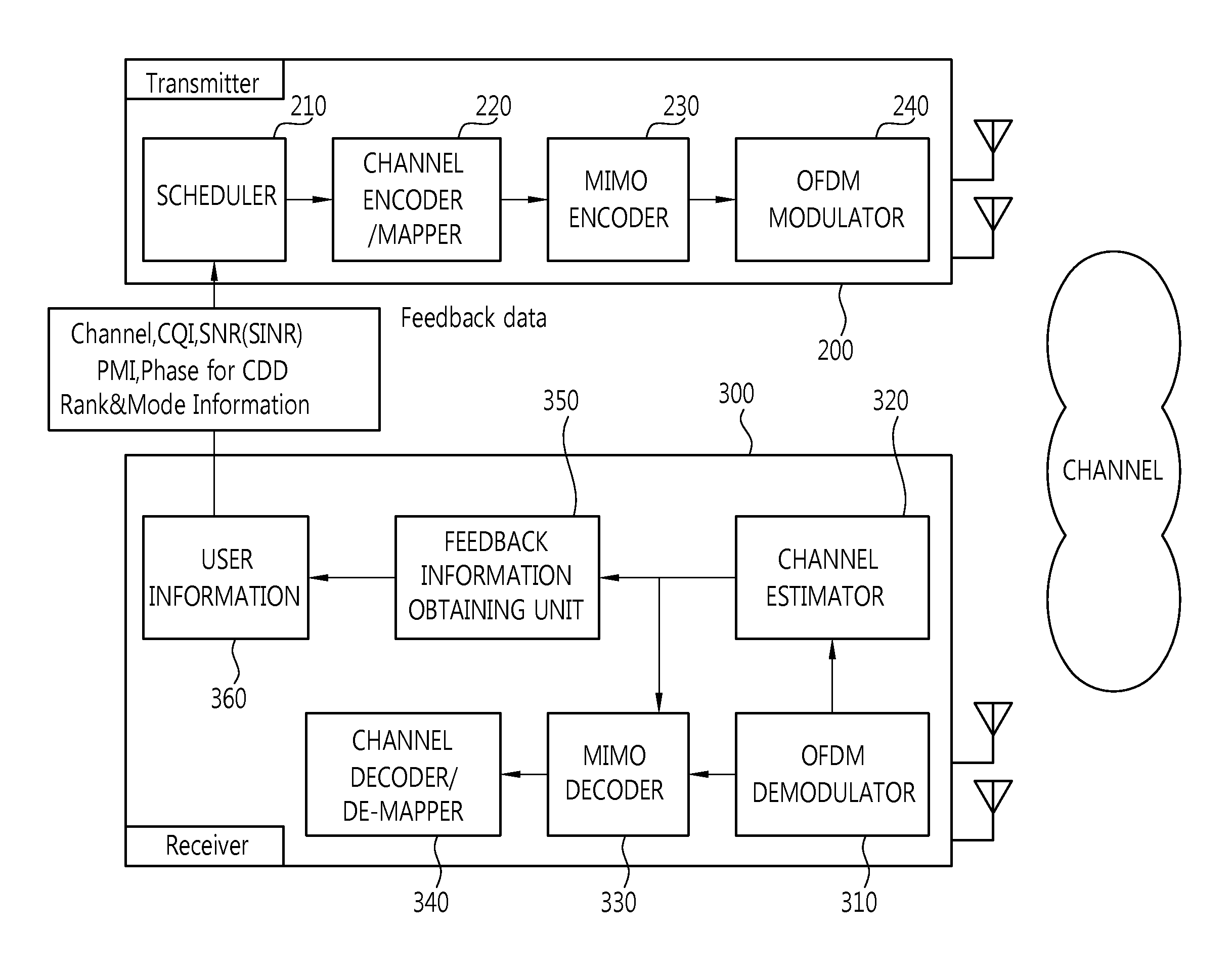
Control method of wireless communication system, wireless communication system, transmitting apparatus, and receiving apparatus
ActiveUS20110105032A1Improve communication qualityShort timeSpatial transmit diversityRadio transmission for post communicationSingular value decompositionCommunications system
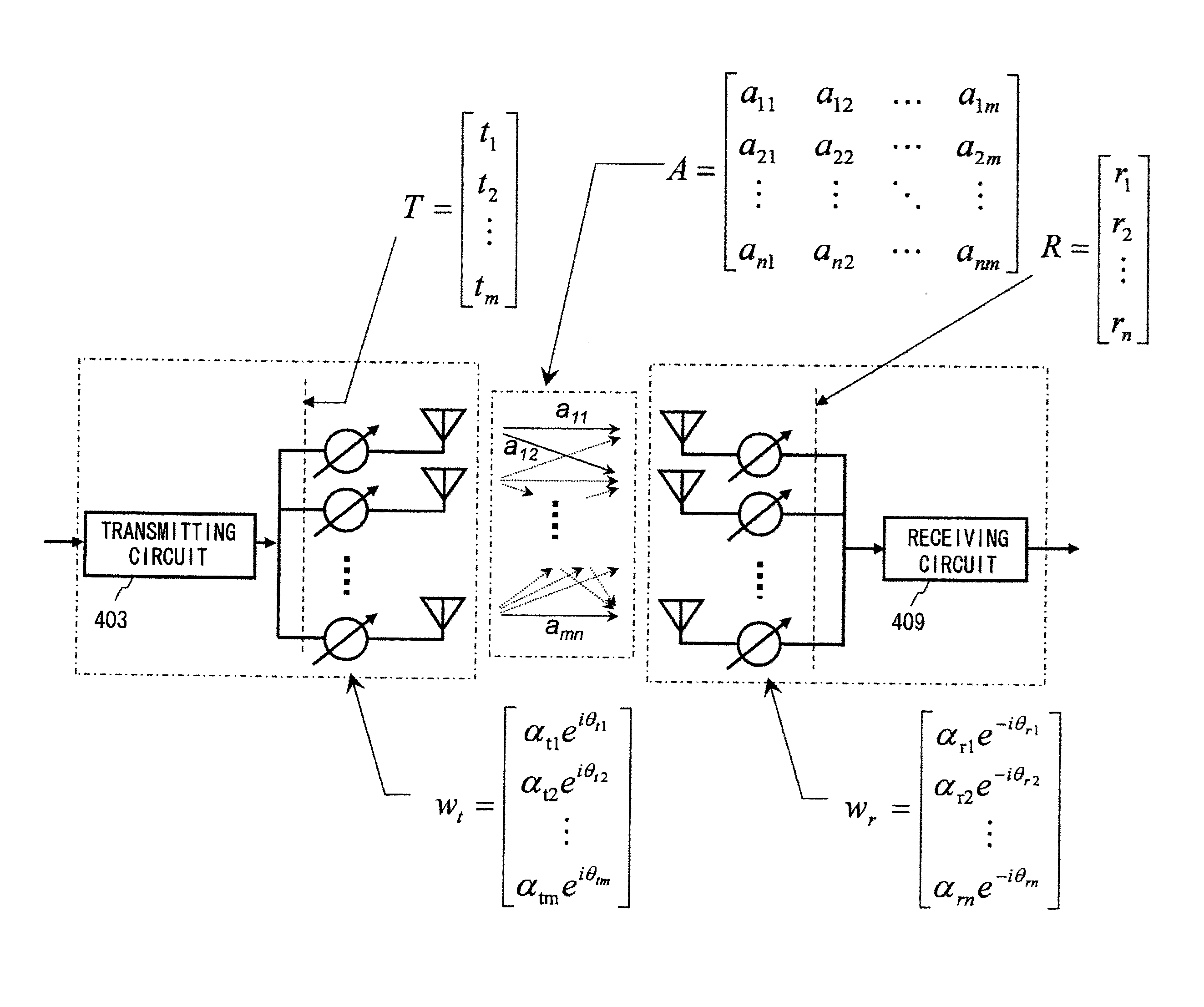
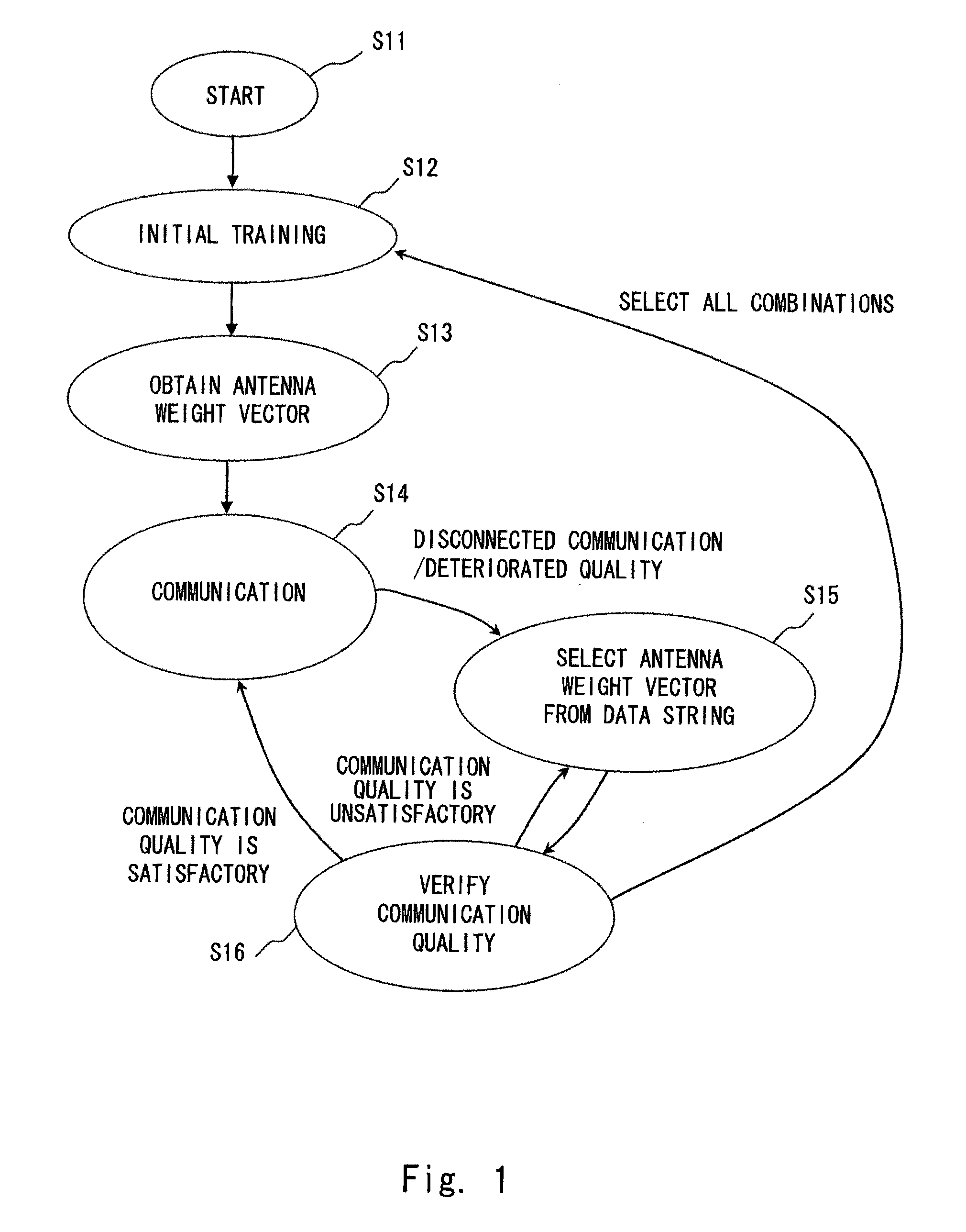
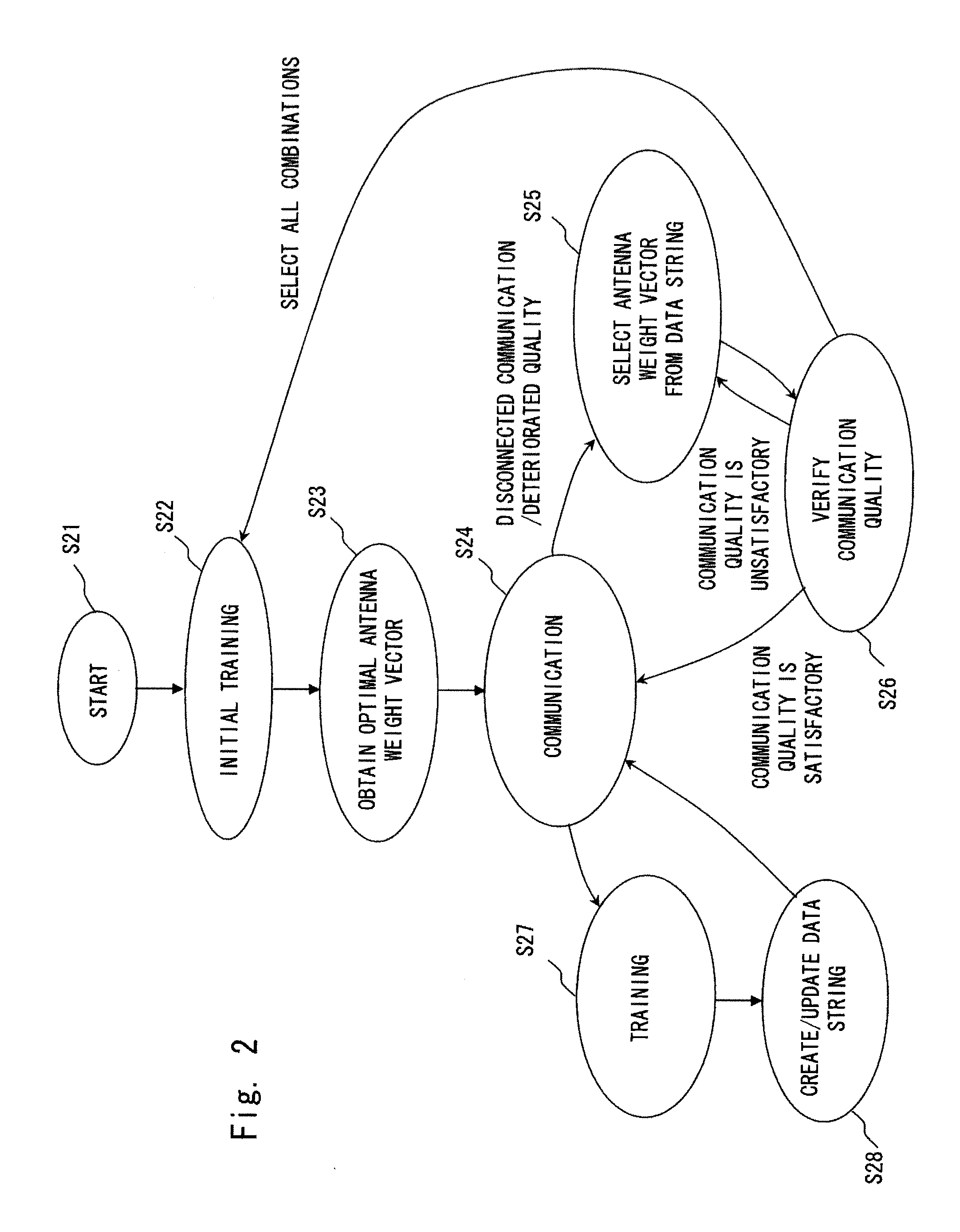
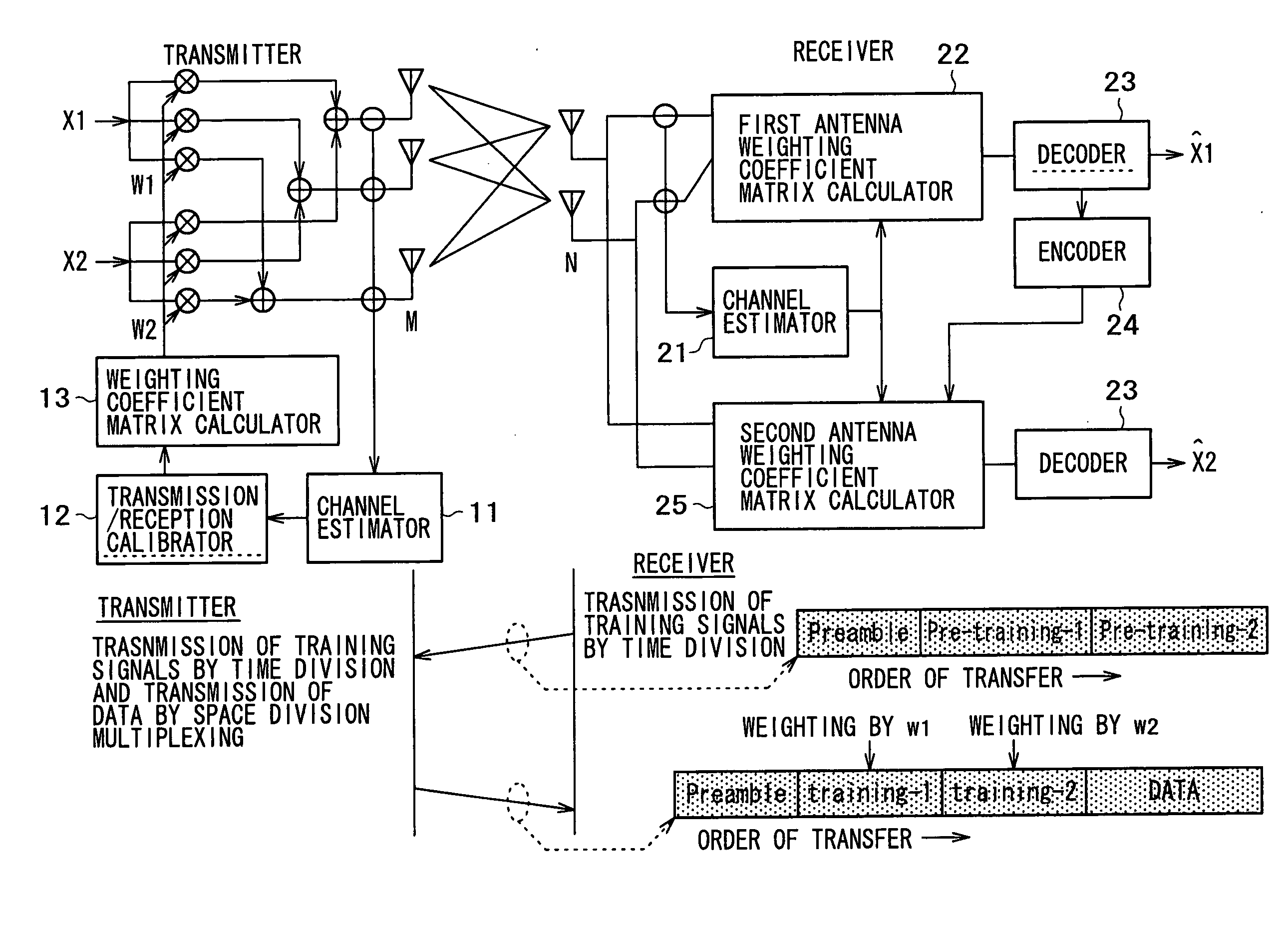
A channel response matrix is obtained by performing a training process between a transmitter 401 and a receiver 402 to obtain optimal signal phases of the antenna array. Next, a singular-value decomposition (SVD) process is performed to decompose the channel response matrix into a correlation matrix and eigenvalues. Next, a diagonal matrix having square roots of the eigenvalues as its components is obtained. Next, all but one of diagonal components included in the diagonal matrix are replaced with zeros, and optimal setting of the amplitudes and phases of signals to be applied to the antenna array (antenna weight vector) for use in wireless communication between the transmitter and the receiver is obtained based on a channel response matrix that is reconstructed by using the component-replaced diagonal matrix. In this way, when wireless communication is implemented by performing beam forming, the time necessary to find and set a beam direction can be reduced.
Owner:NEC CORP
Wireless communication system, wireless communication device and wireless communication method, and computer program thereof
InactiveUS20050141631A1Improve transmission performanceFacilitate communicationSpatial transmit diversityRadio transmission for post communicationSingular value decompositionCommunications system
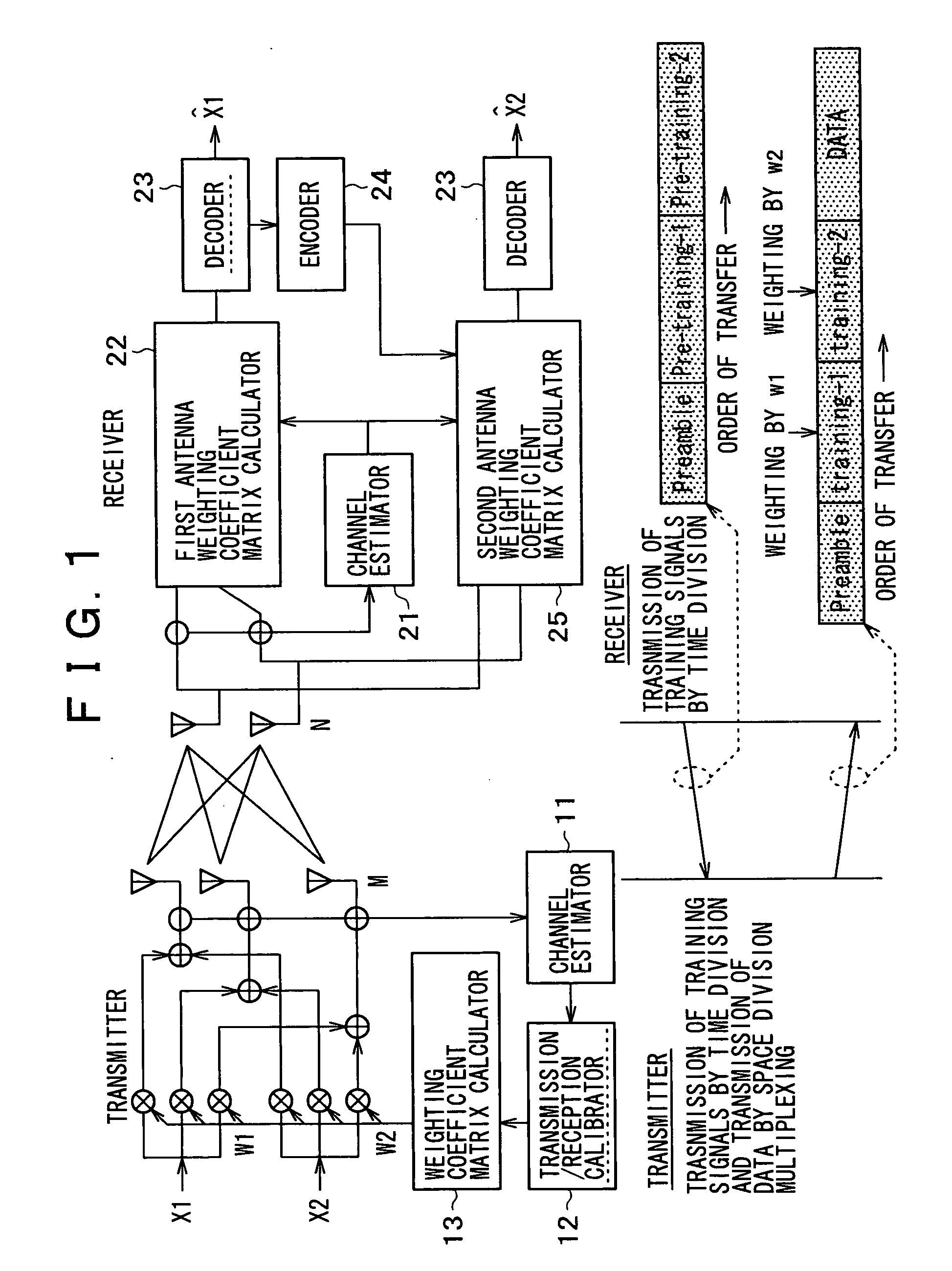
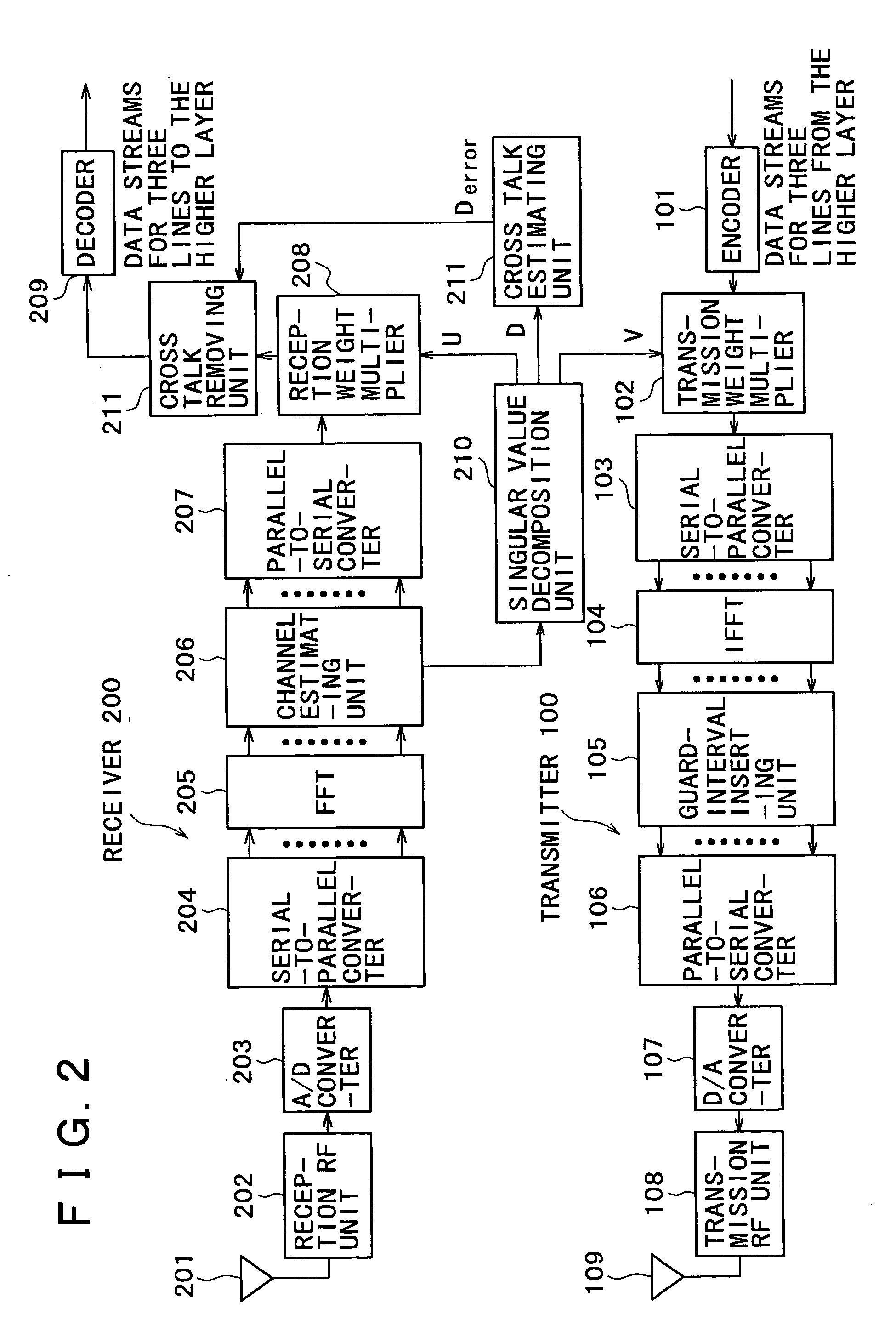
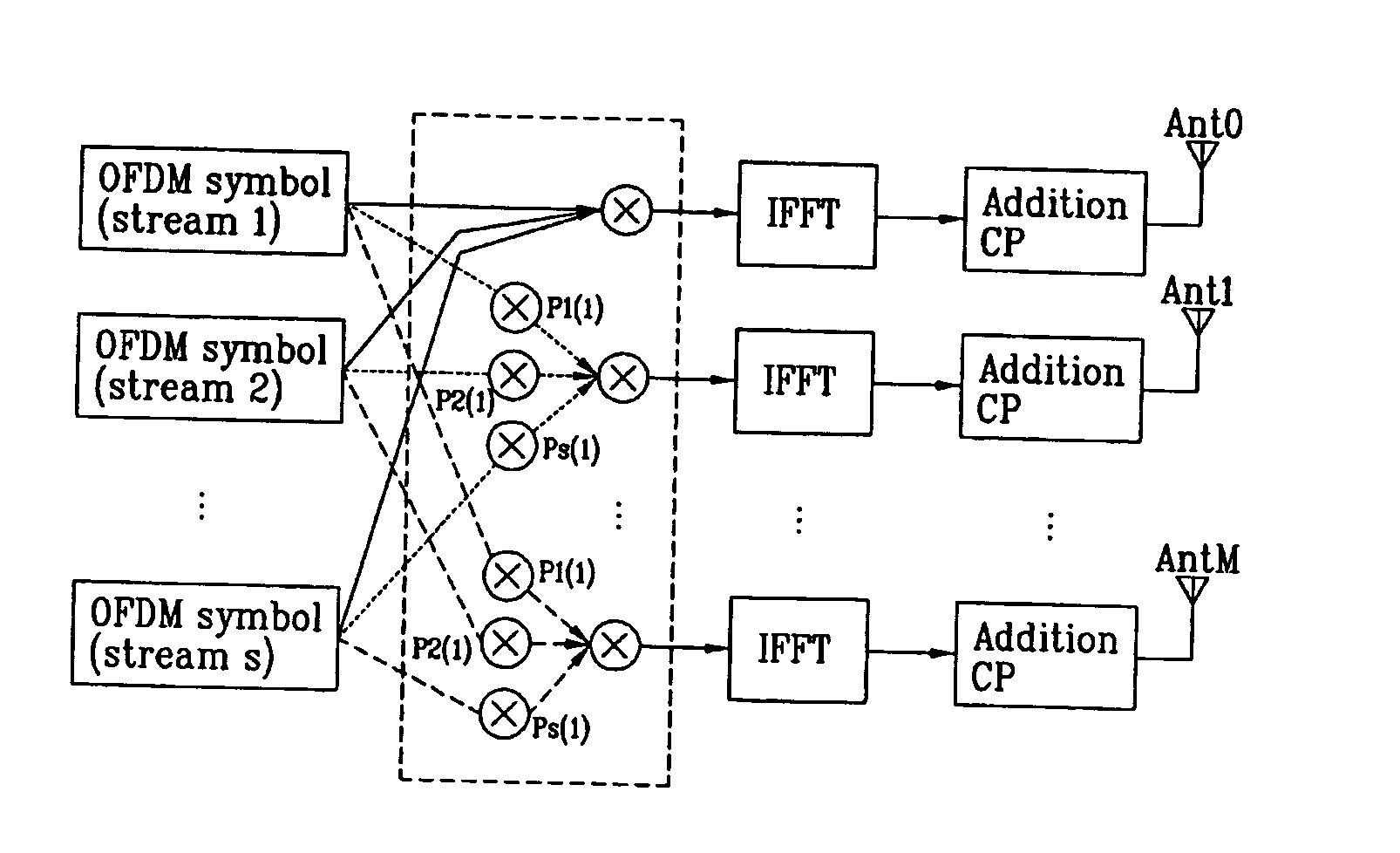
The invention realizes an SVD-MIMO transmission having resistance to the variations in the channel characteristic, which saves the feedback from the receiver to the transmitter. The receiver updates the current one into a new channel matrix Hnew every 100 OFDM symbols, and performs the reception processing by updating the current one into a new decoding weight matrix Unew acquired by the singular value decomposition of the channel matrix Hnew. On the other hand, the transmitter continues to use the original transmission weight matrix V. The diagonal matrix D is turned into a non-diagonal matrix because of the variations in the channel characteristic, where the elements except for the diagonal elements take the values except for zero. This shows that cross talks are generated at this moment. The receiver acquires the cross talk gains, and cancels the cross talk signals of the reception signal to thereby realize the signal transmission without cross talks in consequence.
Owner:SONY CORP
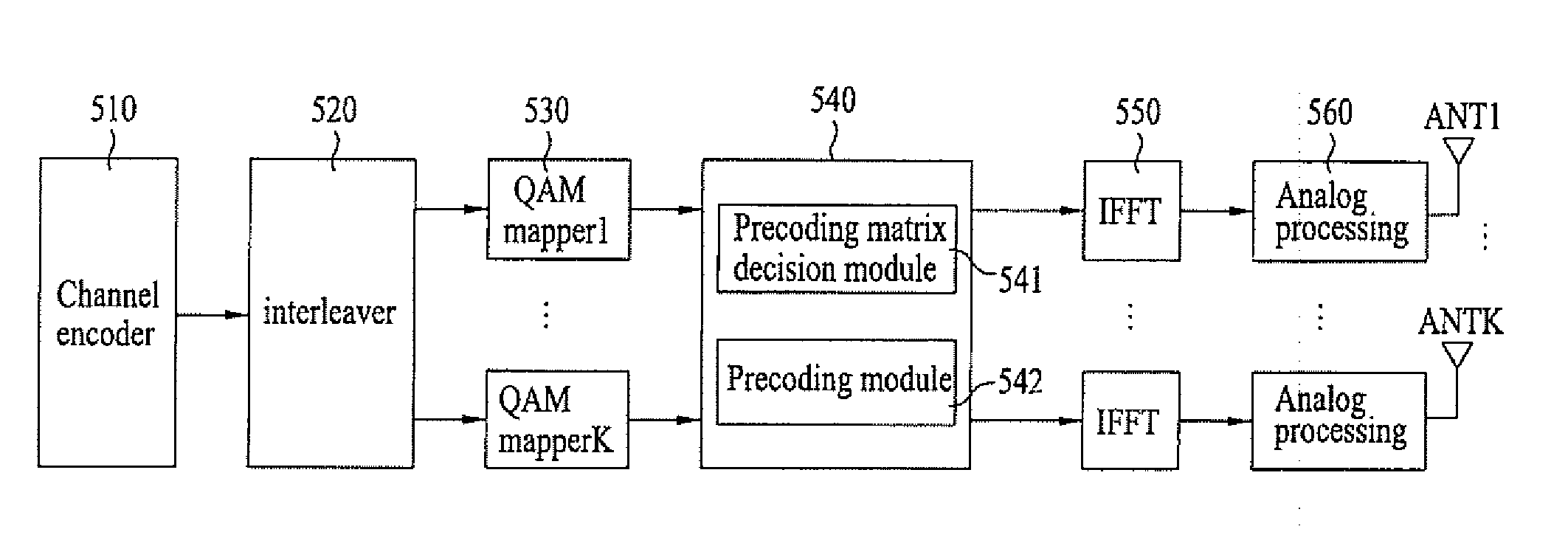
Phase shift based precoding method and transceiver for supporting the same
ActiveUS20070280373A1Solution has disadvantageNear-field transmissionSpatial transmit diversityChannel powerTransceiver
A method of transmitting data using a generalized phase shift based proceding or an extended phase shift precoding scheme in a multiple-antenna system using a plurality of subcarrier and a transceiver for supporting the same are disclosed. A phase shift based precoding matrix may be generalized and determined by a product of a diagonal matrix for phase shift and a unitary matrix for maintaining orthogonality in spatial domain. The diagonal matrix may be extended by a product of a proceding matrix for increasing channel power and the diagonal matrix for phase shift. The design of the transceiver can be simplified or communication efficiency can be improved by generalizing and extending the phase shift based proceding.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method for transmitting data in multiple antenna system
InactiveUS20110128917A1Spatial transmit diversityBroadcast transmission systemsPrecodingDiagonal matrix
A method for transmitting data in a multiple antenna system comprises the steps of: generating a transmission signal in plural antennas through the application of a precoding eight matrix to first and second antenna clusters including the plural antennas, and transmitting the transmission signal. The precoding weight matrix is a block diagonal matrix that is configured in a precoding weight corresponding to first and second antenna clusters respectively. The precoding weight of the first antenna cluster is selected according to a channel condition, and the precoding weight of the second antenna cluster is selected regardless of the channel condition but according to a rule.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
System, method, apparatus, and computer program for wireless communication
ActiveUS20050249151A1Improve transmission performanceEfficient executionSpatial transmit diversityMultiplex communicationSingular value decompositionUnitary matrix
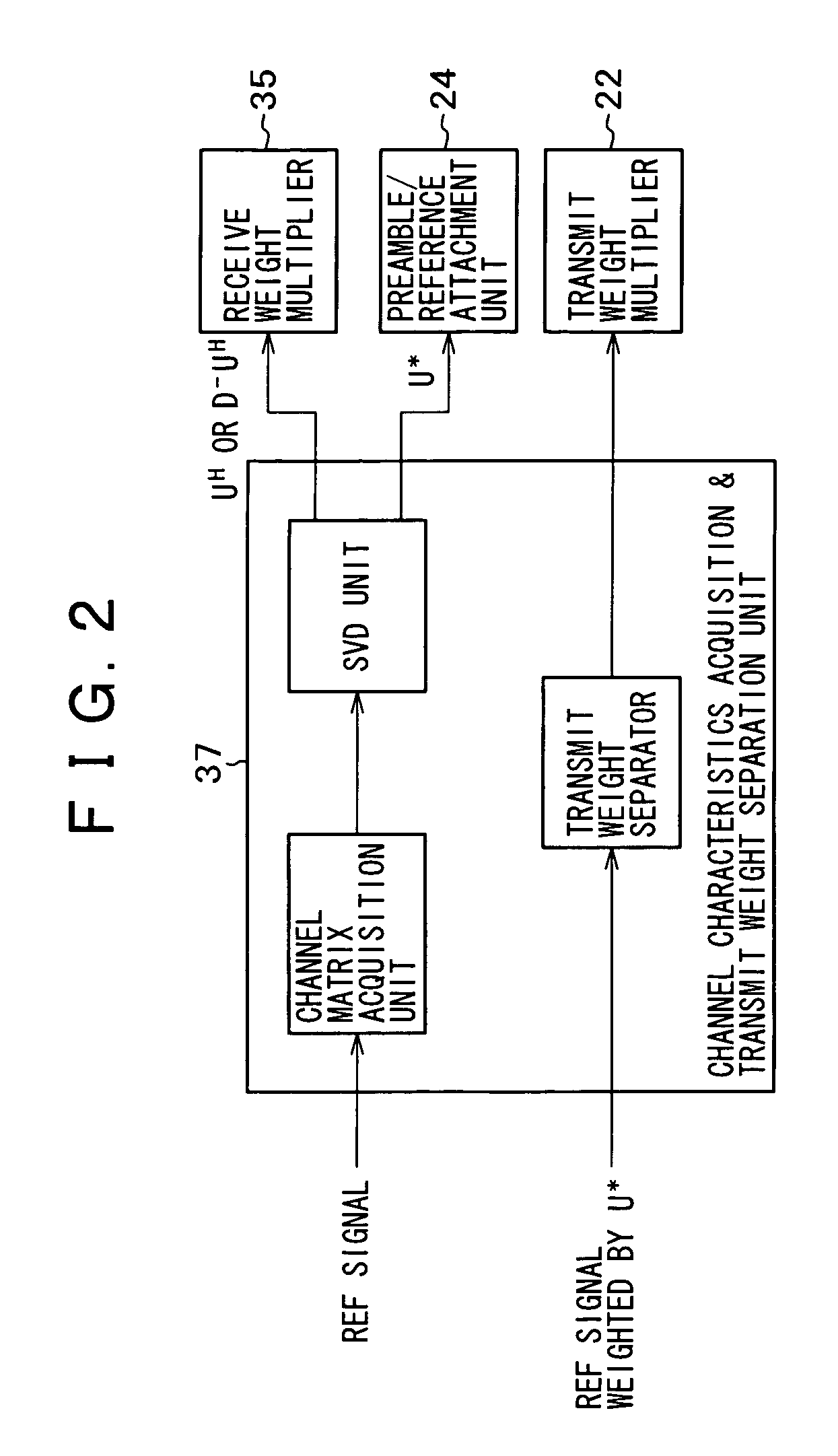
The disclosed invention implements SVD-MIMO communication efficiently with a less number of high-load calculation required for singular value decomposition (SVD) processing for a channel matrix. A receiver derives a channel matrix H from a reference signal from a transmitter and acquires downlink transmit weights V and receive weights UH by SVD of the channel matrix H. The receiver transmits a reference signal weighted with U* to the transmitter, where U* is a conjugate matrix for U as uplink transmit weights. The transmitter receives the reference signal weighted with U* and separates the signal into downlink transmit weights V and a diagonal matrix D, based on unitary matrix properties.
Owner:REDWOOD TECHNOLOGIES LLC
Method for transmitting/receiving data in a multiple-input multiple-output system using multi-carrier
InactiveUS20110274200A1Efficiently establishedSimple designPolarisation/directional diversitySecret communicationCommunications systemPhase shifted
A method for transmitting / receiving data in a Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) communication system is disclosed. The data transmission method includes determining a precoding matrix to be a part of a phase-shift-based precoding matrix, determining a first diagonal matrix for phase shift to be a part of the phase-shift-based precoding matrix, determining a unitary matrix to be a part of the phase-shift-based precoding matrix, precoding a transmission symbol for each resource using the phase-shift-based precoding matrix to produce precoded data, and transmitting the precoded data, wherein the phase-shift-based precoding matrix is determined by the product of the precoding matrix, a Hermitian matrix of the unitary matrix, the first diagonal matrix, and the unitary matrix.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Calibrating method and apparatus for radio frequency circuit of time division duplexing MIMO multi-antenna communicating system
ActiveCN101291503AFix transpose relationshipTransmitters monitoringSpatial transmit diversityTransceiverCommunications system
The invention discloses a calibrating device for a time division duplexing MIMO multi-antenna communication system radio frequency circuit, a method for the same, and a transceiver of the calibrating device. The technical proposal is that: the device comprises: a calibration factor computation module which receives a downlink channel estimation matrix Hdown (k)' and an uplink channel estimation matrix Hup (k)' fed back from the other party, and calculates and outputs the calibration factors AAP (k) and AUE (k) according to Hup (k)'=AAP (k)x(Hdown (k)') <T>x(AUE (k)) -1, wherein the calibration factors AAP (k) and AUE (k) being both diagonal matrixes; a calibration factor memory module which receives and stores the two calibration factors AAP (k) and AUE (k); and a calibration receiving channel estimation matrix module which receives the downlink estimation matrix Hdown (k) requiring calibration, picks up the two calibration factors AAP (k) and AUE (k) from the calibration factor memory module, and works out and outputs a calibrated uplink estimation matrix Hup (k) according to Hup (k)=AAP (k)x(Hdown (k))<T>x(AUE (k)) -1. The invention is applicable to the wireless communication field.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
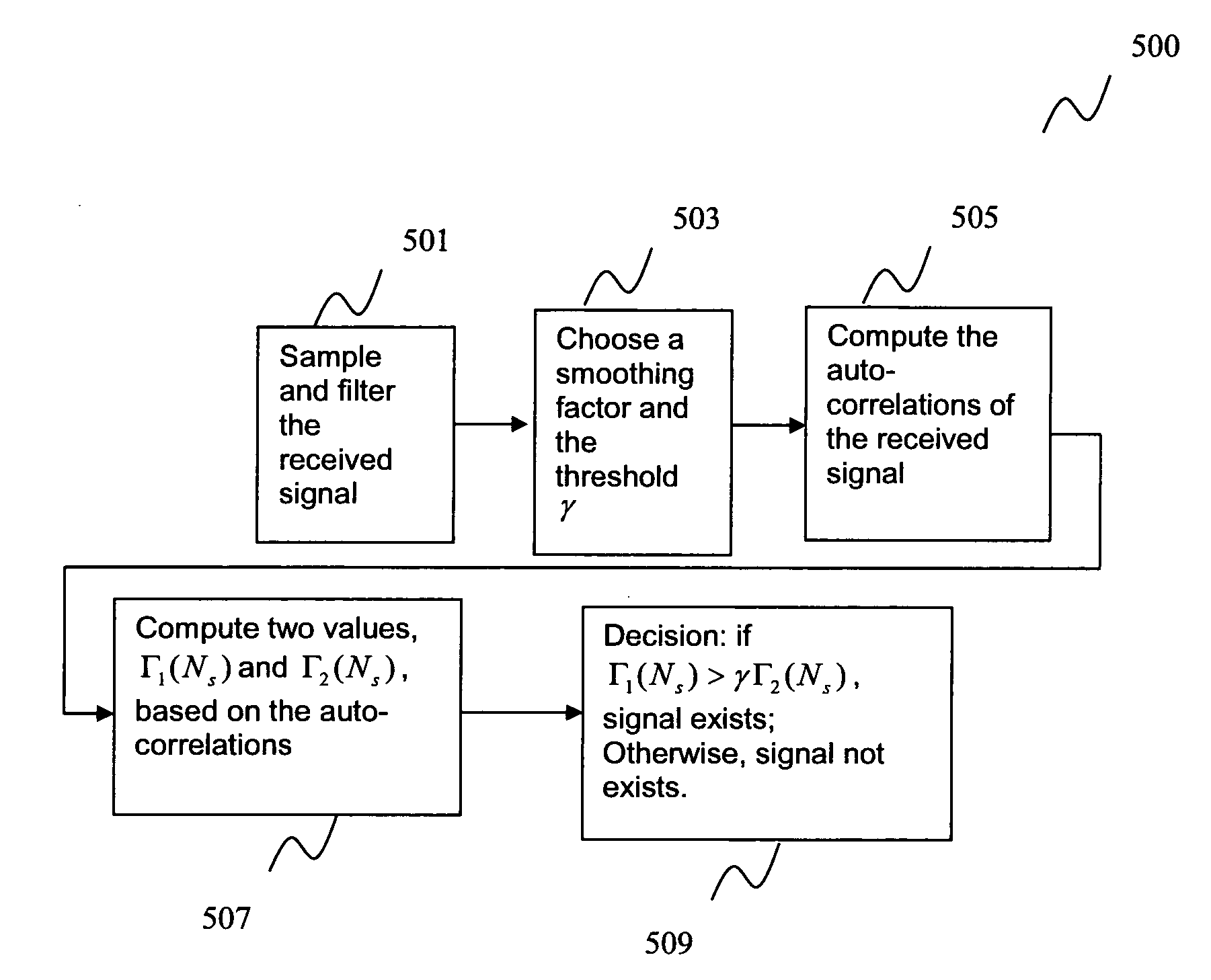
Apparatus and method for coding and decoding irregular repeat accumulate codes
ActiveUS20050132260A1Minimize complexityError prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsParity-check matrixDiagonal matrix
An apparatus and method for coding an irregular Repeat Accumulate (RA) code. A repeater repeats a received information word such that the information word corresponds to weights of a first information part and a second information part of a parity check matrix in which permutation matrixes are arranged in the first information part and the second information part corresponding to the information word such that a minimum length of a cycle on a factor graph of the irregular RA code becomes a predetermined length and weights are irregular, and a dual diagonal matrix is arranged in a parity part corresponding to a parity. An interleaver interleaves a signal output from the repeater using an interleaving scheme predefined for the parity check matrix. An accumulator generates the irregular RA code by accumulating a signal output from the interleaver according to a weight of the parity part.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for estimating pulse noise in OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Domain Multiplexing) underwater acoustic communication system
ActiveCN105227512AImprove performanceCarrier regulationMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumPhase noise
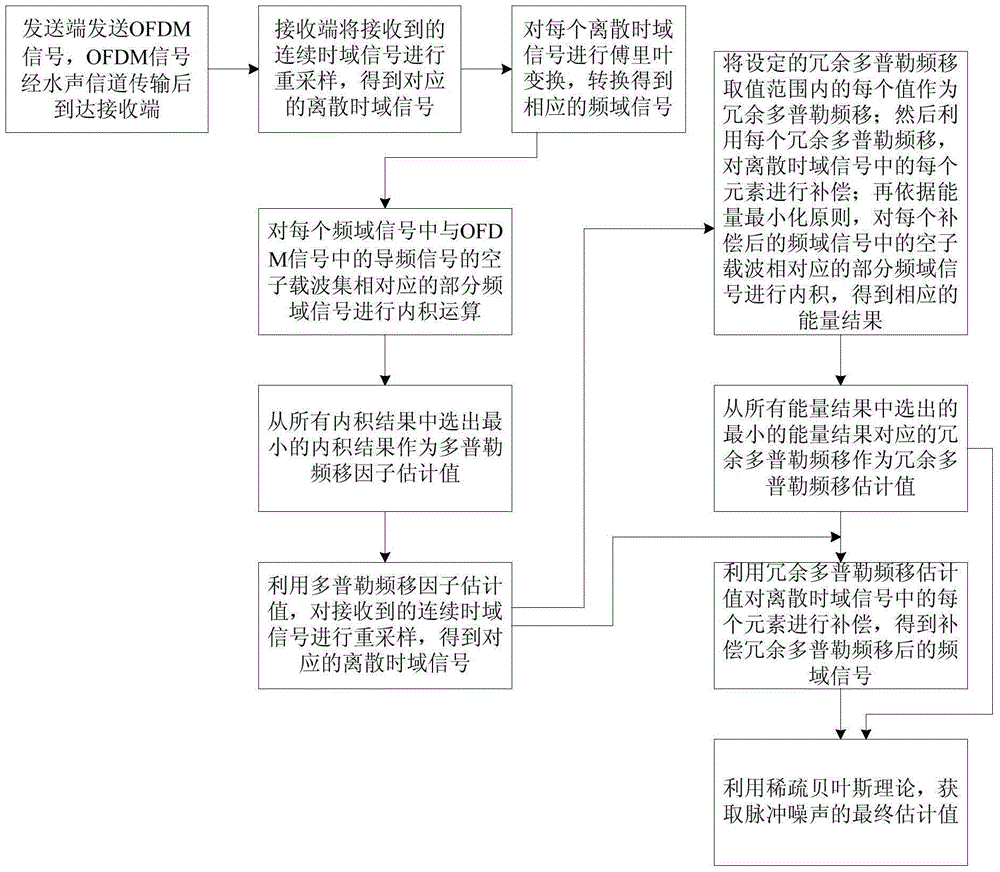
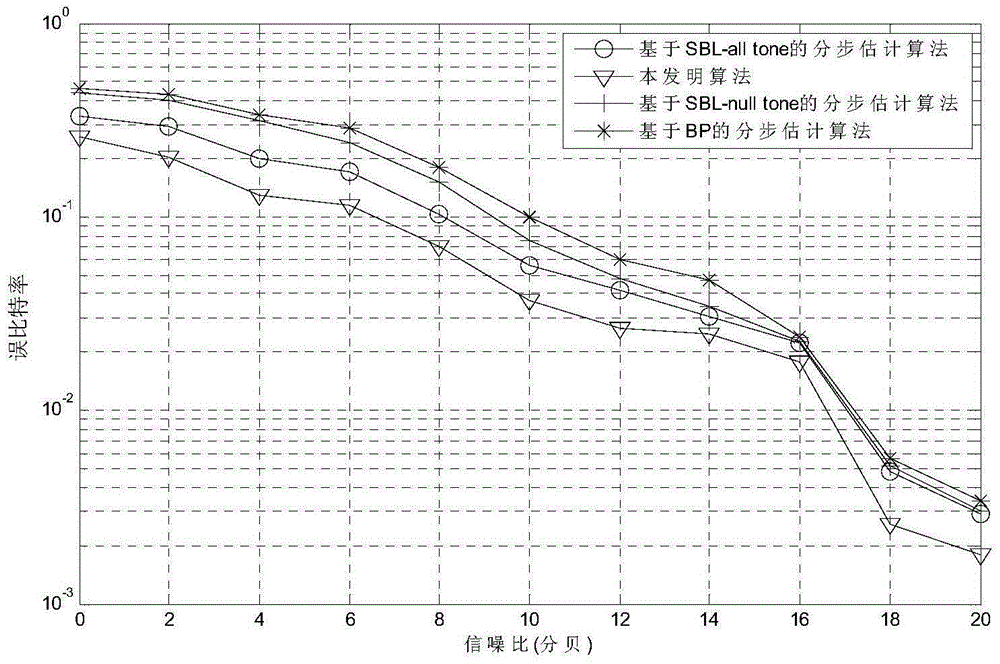
The invention discloses a method for estimating pulse noise in an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Domain Multiplexing) underwater acoustic communication system. At a receiving end, sparse estimation is performed on pulse noise on an OFDM signal in an underwater acoustic channel transmission process according to a frequency domain signal subjected to redundant Doppler frequency shift compensation, and frequency offset compensation is performed on the frequency domain signal subjected to the redundant Doppler frequency shift compensation with void subcarriers. Under the consideration of mutual interference between the pulse noise and a carrier frequency offset in underwater acoustic communication, compensation of the carrier frequency offset is added in an iteration process while the pulse noise is estimated with all subcarriers and a posteriori distribution under a framework of conventional sparse Bayesian learning, and the frequency domain signal subjected to the redundant Doppler frequency shift compensation and a measurement diagonal matrix for estimating the pulse noise are updated continuously in order to lower influences between the two types of interference. Moreover, the pulse noise is estimated by full utilization of all the subcarriers in the method, so that the spectrum efficiency and the performance of the communication system are improved.
Owner:云南保利天同水下装备科技有限公司
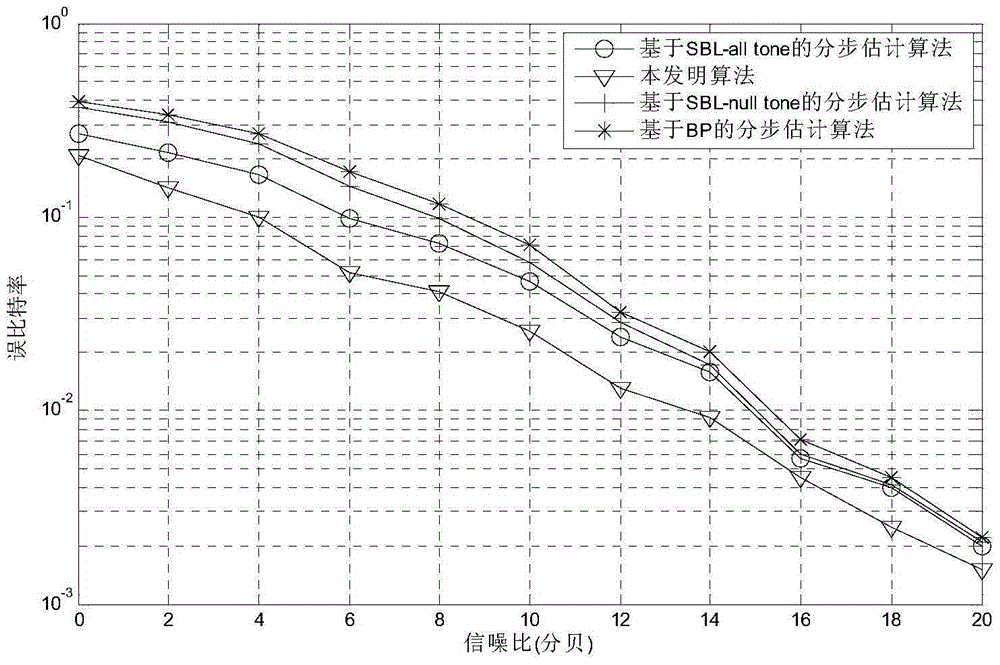
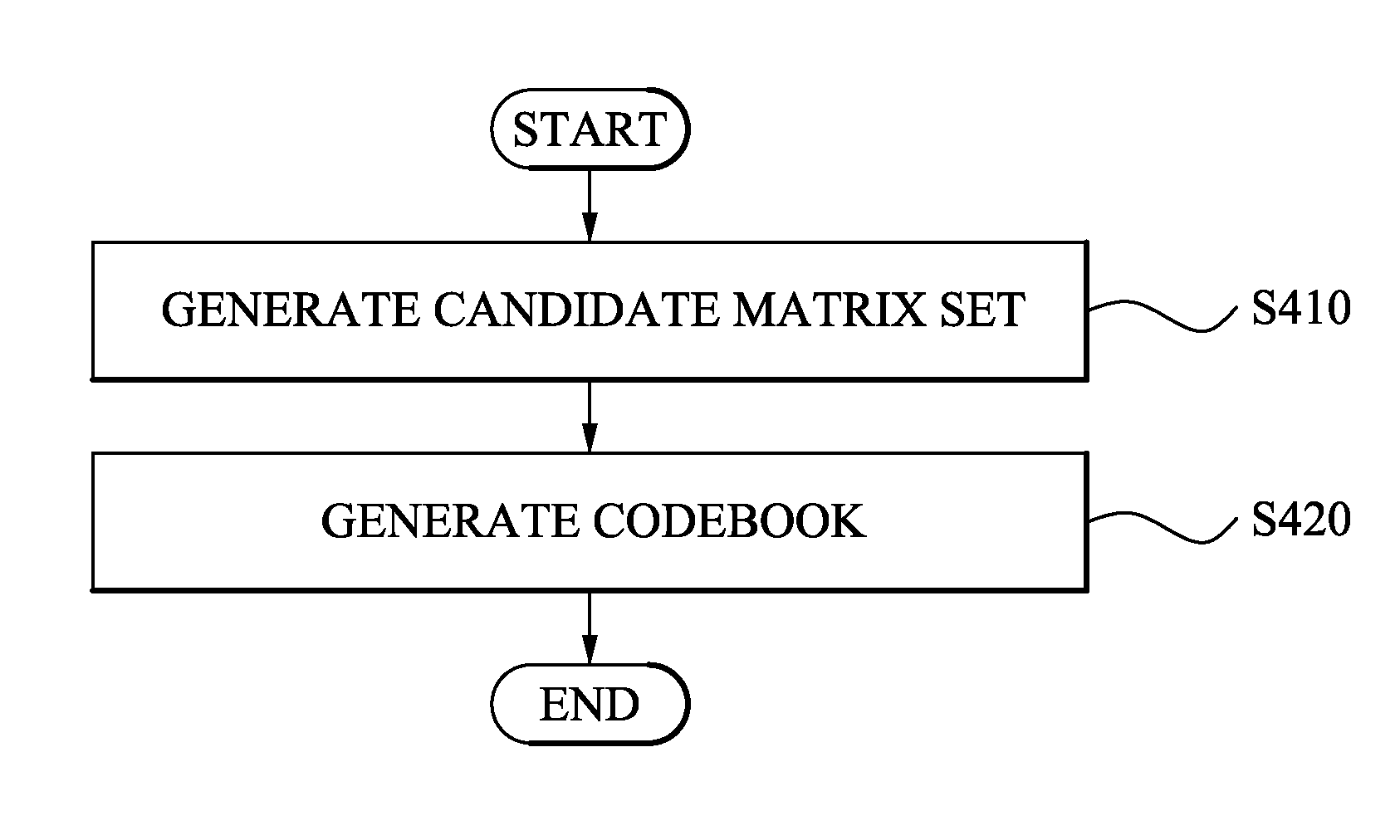
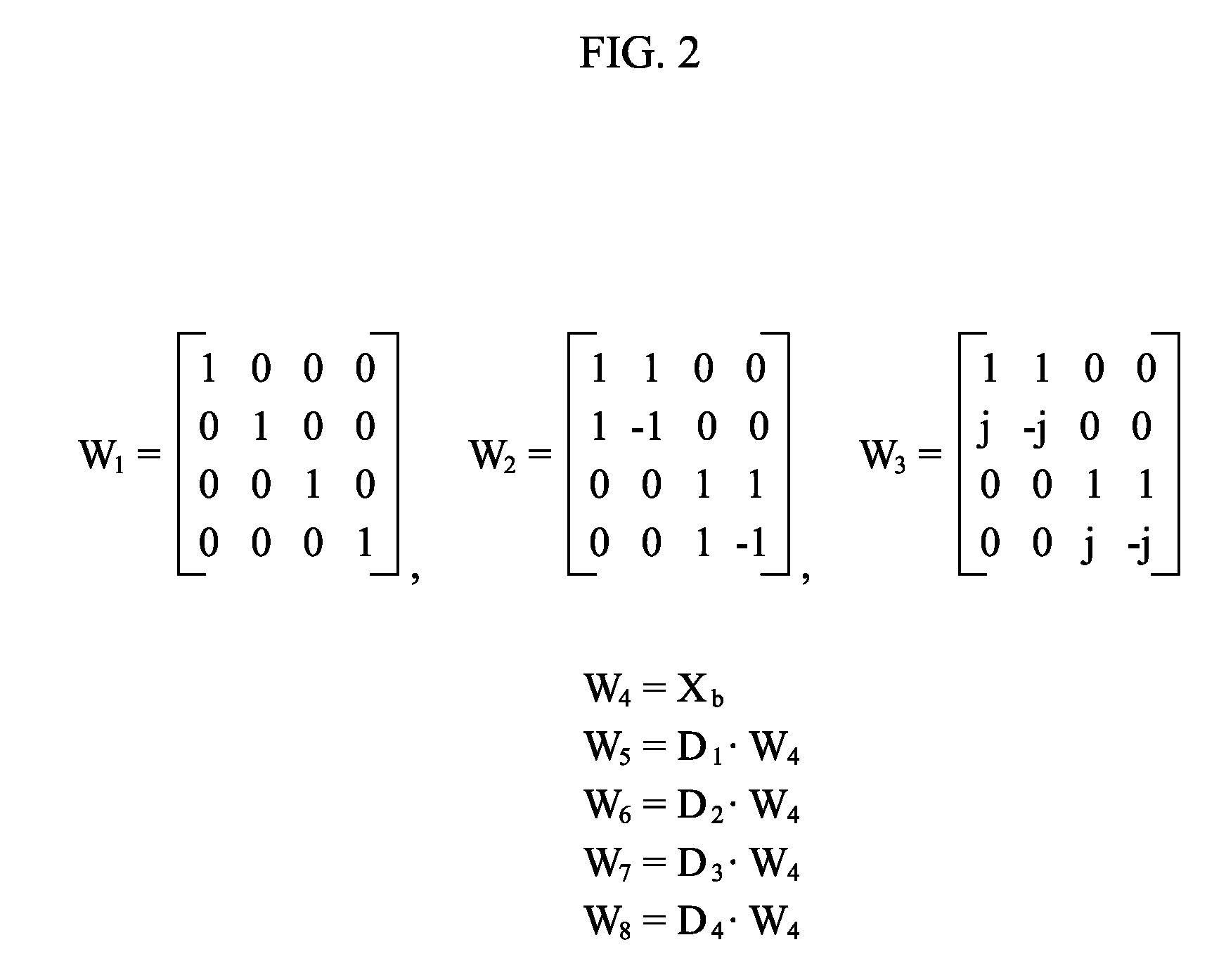
Apparatus and method of generating codebook for multiple input multiple output communication system
InactiveUS20080256163A1Easily realizedEfficient data transferComputation using non-contact making devicesRadio transmissionCommunications systemDiagonal matrix
An apparatus and method of generating a codebook. The codebook generation apparatus includes a matrix extender to generate a candidate matrix set by multiplying a base matrix and at least one diagonal matrix, wherein the at least one diagonal matrix includes elements of a constrained set as diagonal elements; and a codebook generator to generate the codebook where a minimum distance between the elements is maximized, based on the candidate matrix set. According to aspects of the present invention, it is possible to provide a precoding codebook that can reduce an amount of feedback from a terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Parametric Compression of Rank-1 Analog Feedback
InactiveUS20100272014A1Radio transmissionWireless commuication servicesSingular value decompositionCarrier signal
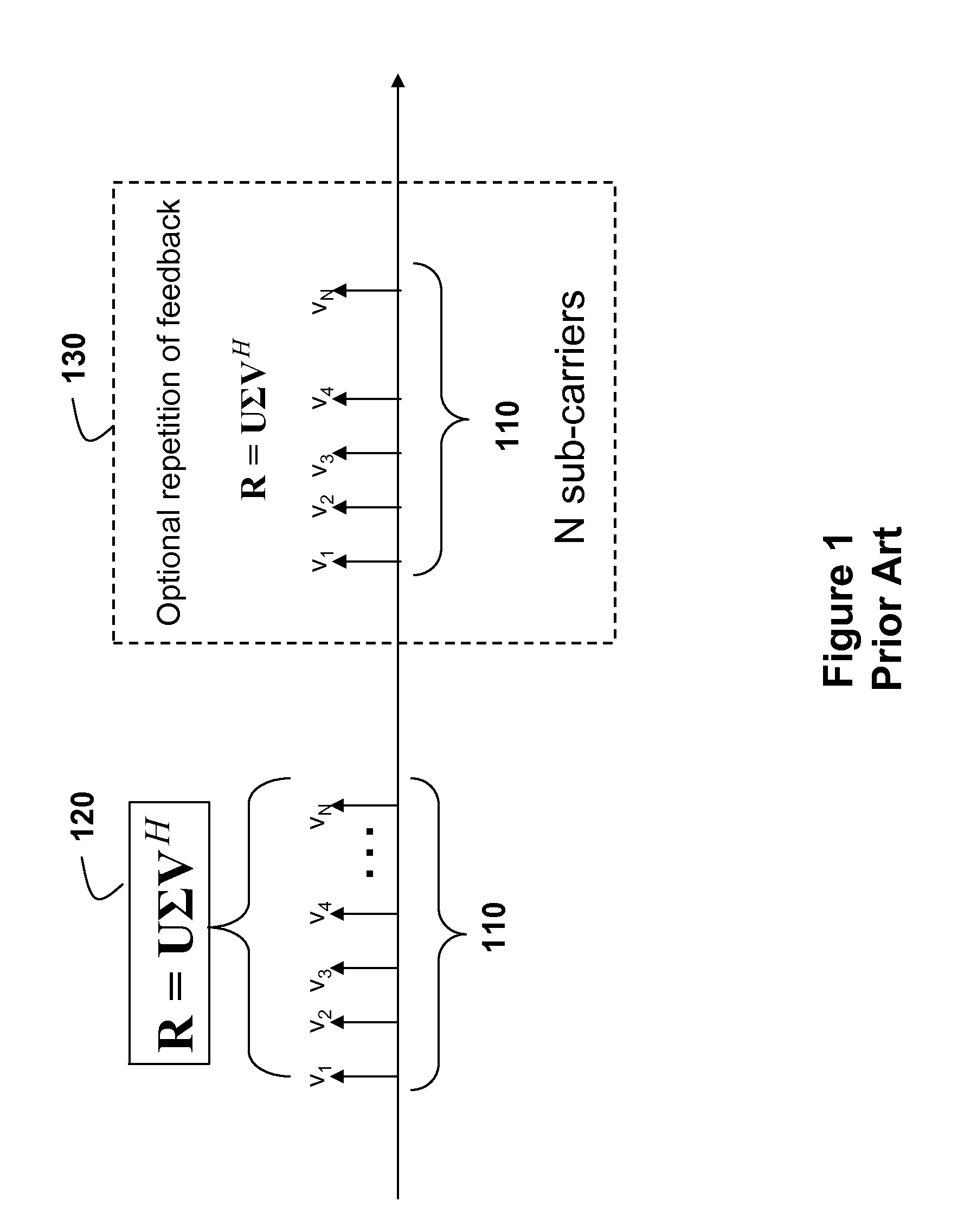
Channel state information in a closed-loop, multiple-input, multiple-output wireless networks is fed back from each mobile station to a base station by first determining a transmit covariance matrix R, and applying a singular value decomposition (SVD) R=UΣVH, where U, V are left and right singular vector matrices, Σ is a diagonal matrix with singular values. The matrix V includes column vectors V. A beamforming vector vmax=[1 exp(jΦ)exp(j2Φ) . . . exp(jΦ)] / √{square root over (N)}] is approximated by the column vector V having a maximum magnitude, where Φ is a real number. Then, only the angle Φ is fed back using a phase modulation mapping of the components exp(jΦ) onto the associated subcarrier.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method for encoding low-density parity check code
ActiveUS20070022354A1Simplify the coding processImprove performanceError detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTheoretical computer scienceDiagonal matrix
An apparatus and method for encoding low-density parity check (LDPC) codes. The method for generating a low-density parity check code formed of an information-part matrix and a parity-part matrix comprises the steps of converting the information-part matrix into an array code structure and assigning a degree sequence to each submatrix column; extending a dual-diagonal matrix corresponding to the parity-part matrix such that an offset value between diagonals has a random value; lifting the normalized dual-diagonal matrix; determining an offset value for cyclic column shift for each submatrix of the lifted normalized dual-diagonal matrix; and determining a parity symbol corresponding to a column of the parity-part matrix.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
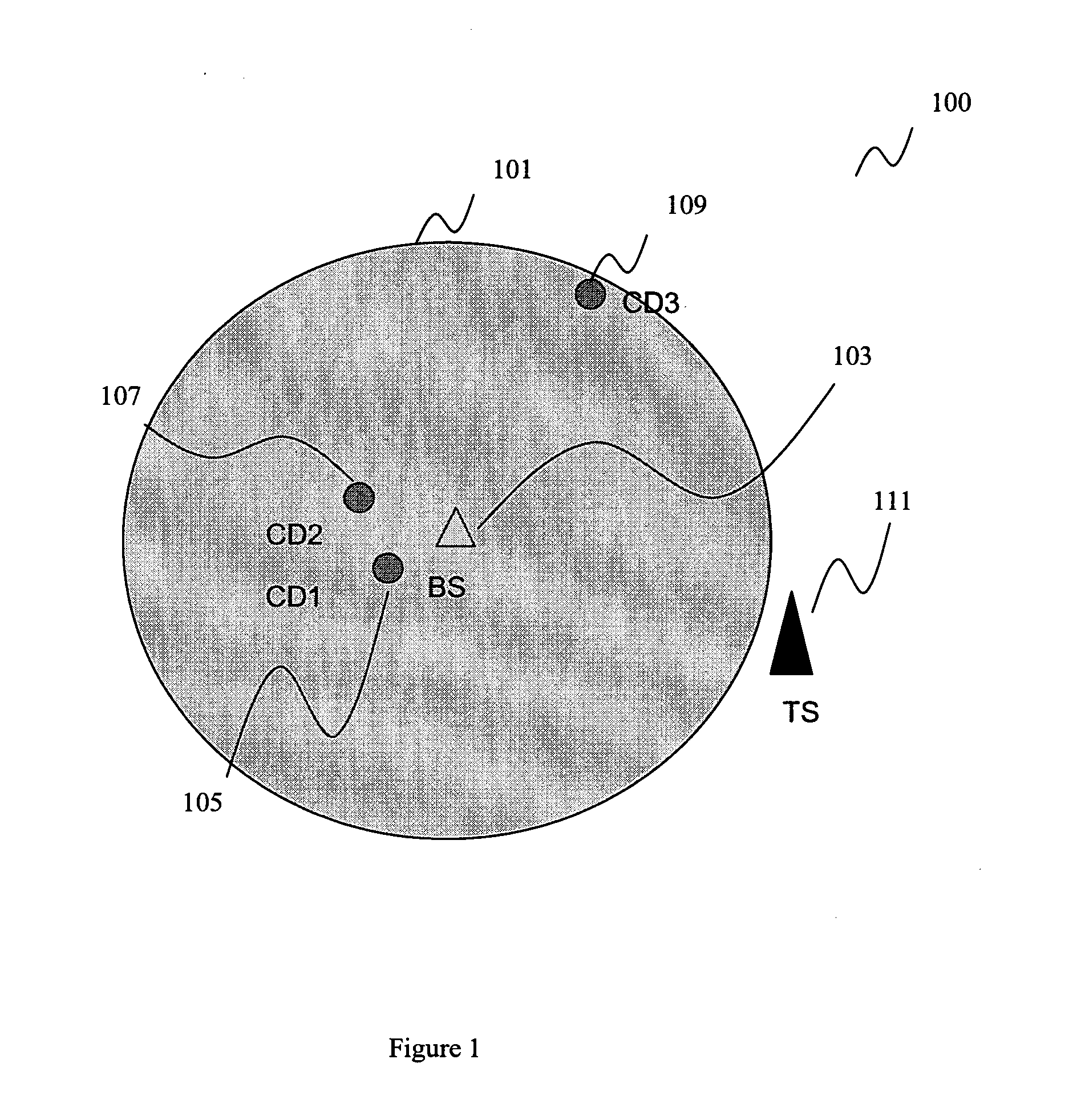
Method of determining as to whether a received signal includes an information signal
A method of determining as to whether a received signal includes an information signal is provided. The method provided includes determining a covariance matrix from a received signal and transforming the covariance matrix into a transformed covariance matrix, wherein the transformation is configured such that the transformed covariance matrix is a non-diagonal matrix in case the received signal includes the information signal, wherein the non-diagonal matrix includes non-zero non-diagonal matrix elements. The method provided further includes determining a first function using at least one of the non-zero non-diagonal matrix elements of the transformed covariance matrix, determining a second function using at least one matrix element of the transformed covariance matrix, wherein the second function is different from the first function, and determining as to whether a received signal includes an information signal based on a comparison of a value of the first function and a value of the second function.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Phase shift based precoding method and transceiver for supporting the same
ActiveUS20100074309A1Solution has disadvantageNear-field transmissionSpatial transmit diversityTransceiverChannel power
A method of transmitting data using a generalized phase shift based precoding or an extended phase shift precoding scheme in a multiple-antenna system using a plurality of subcarrier and a transceiver for supporting the same are disclosed. A phase shift based precoding matrix may be generalized and determined by a product of a diagonal matrix for phase shift and a unitary matrix for maintaining orthogonality in spatial domain. The diagonal matrix may be extended by a product of a precoding matrix for increasing channel power and the diagonal matrix for phase shift. The design of the transceiver can be simplified or communication efficiency can be improved by generalizing and extending the phase shift based precoding.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method for puncturing low density parity check code
InactiveUS20060206781A1Avoid performanceError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionTheoretical computer scienceDiagonal matrix
Owner:K2M +1
Method for padding and puncturing low density parity check code
InactiveUS20070011567A1Simple calculationReduce latencyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionTheoretical computer scienceDiagonal matrix
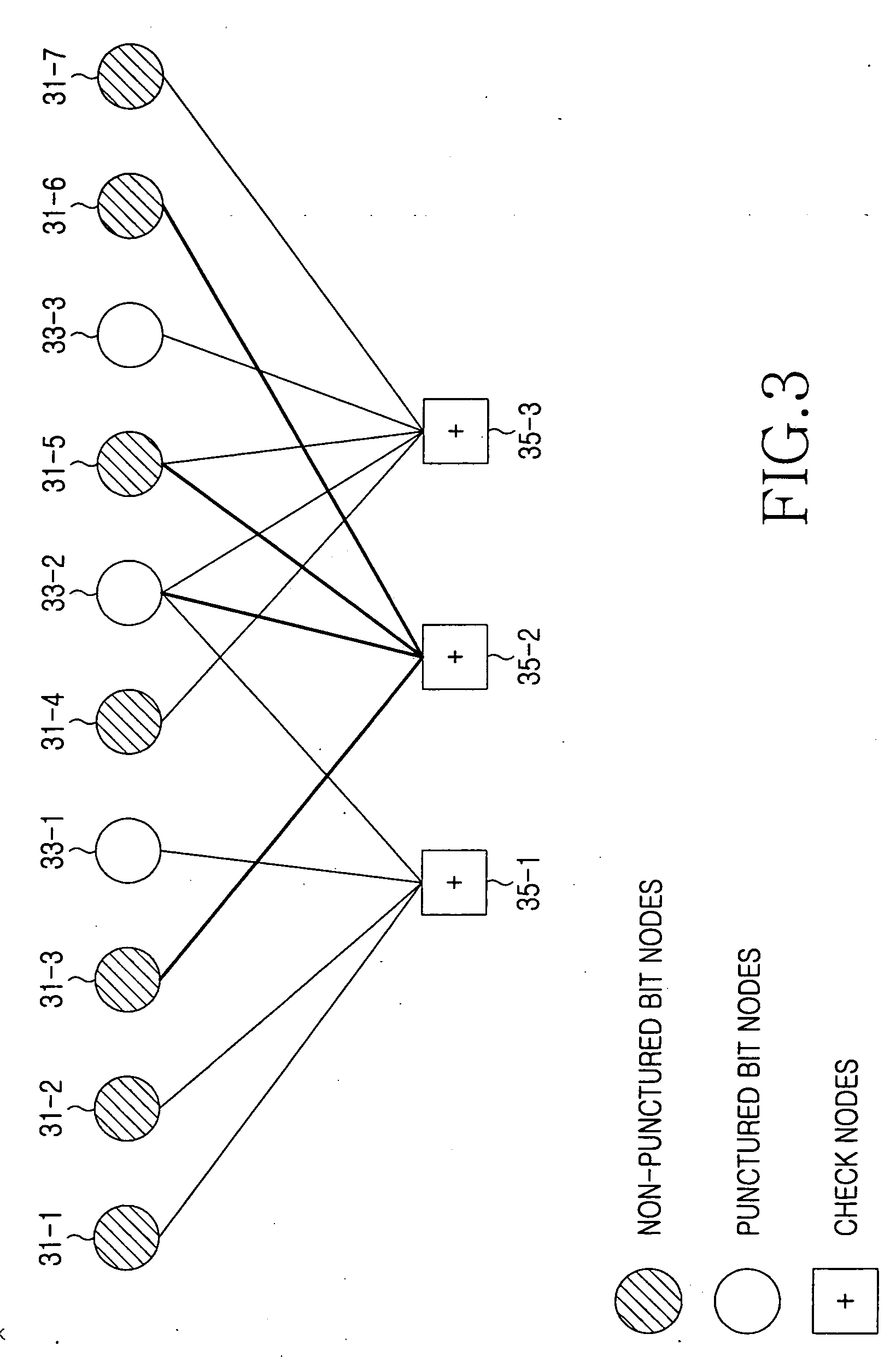
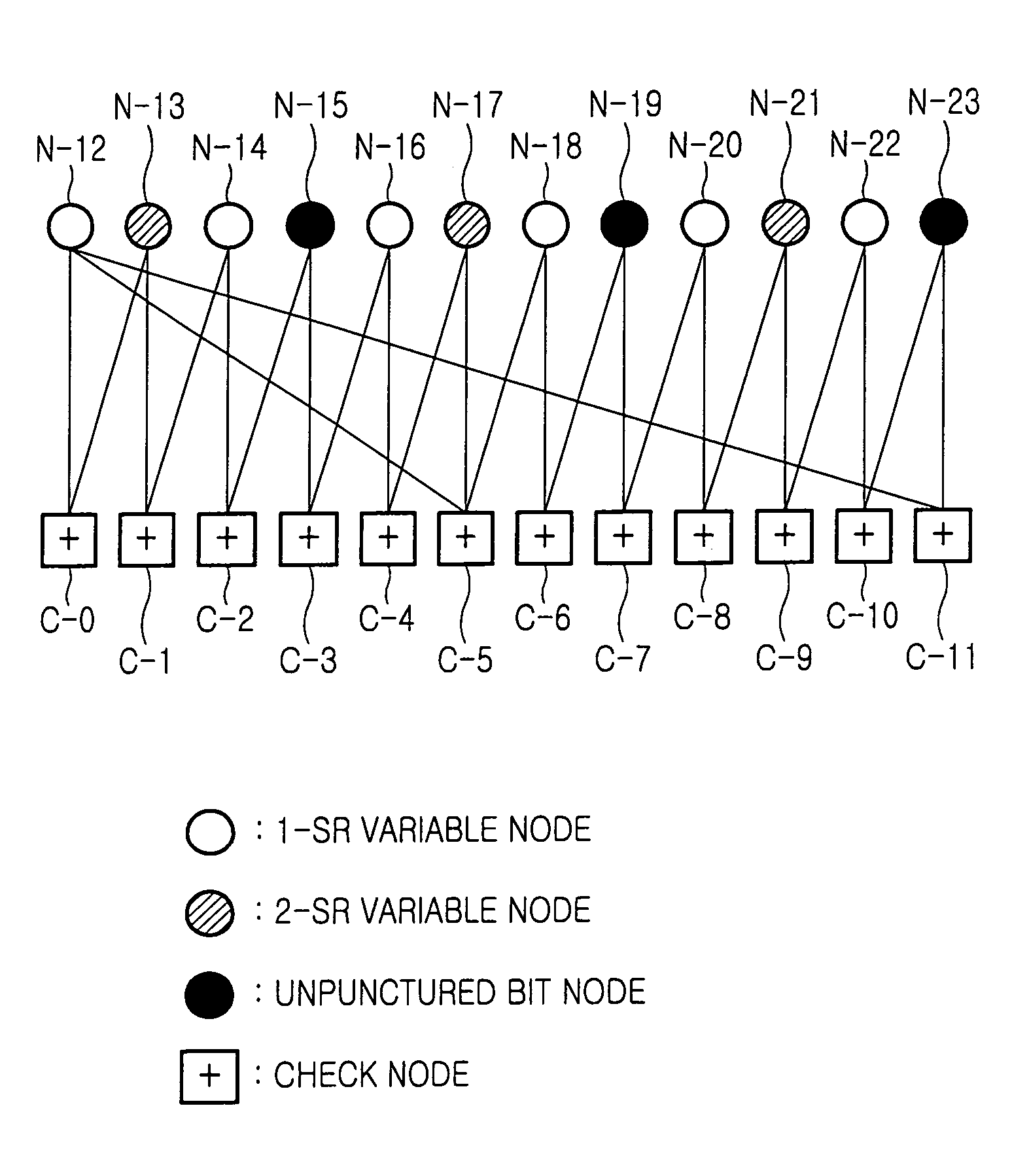
Disclosed is a method for puncturing a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) code that is expressed by a factor graph having a check node and a variable node, connected to each other by an edge, and is decoded by a parity check matrix including a parity part having a single weight-3 column and a dual-diagonal matrix. The method includes selecting 1-step recoverable (1-SR) variable nodes with the highest quality including a variable node mapped to a weight-3 column, and setting a first puncturing priority group using the selected 1-SR variable nodes, selecting k-step recoverable (k-SR) variable nodes with the highest quality in the next step k taking into account the variable nodes selected in the current step, and setting a priority group for each individual step, puncturing an LDPC code mapped to a variable node belonging to a corresponding group according to priority of each group obtained in the preceding steps.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for Estimating Time-Varying and Frequency-Selective Channels
InactiveUS20120082252A1Transmission path divisionSecret communicationTime domainChannel impulse response
Time-varying and frequency-selective channels in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) network are estimated by first storing, in a buffer at a receiver, a received signal corresponding to a set of pilot tones of a set of OFDM symbols, wherein the pilot tones are predetermined and inserted in frequency subcarriers and time slots of the OFDM symbol. A covariance matrix of the received signal is estimated. A diagonal matrix is estimated based on the covariance matrix and a variance of noise in the received signal. The diagonal matrix indicates delays of non-zero paths in a time domain. A channel impulse response (CIR) for each OFDM symbol is estimated using the diagonal matrix, and the received signal. Then, the CIR is transformed to the frequency domain to obtain the channel frequency response (CFR).
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
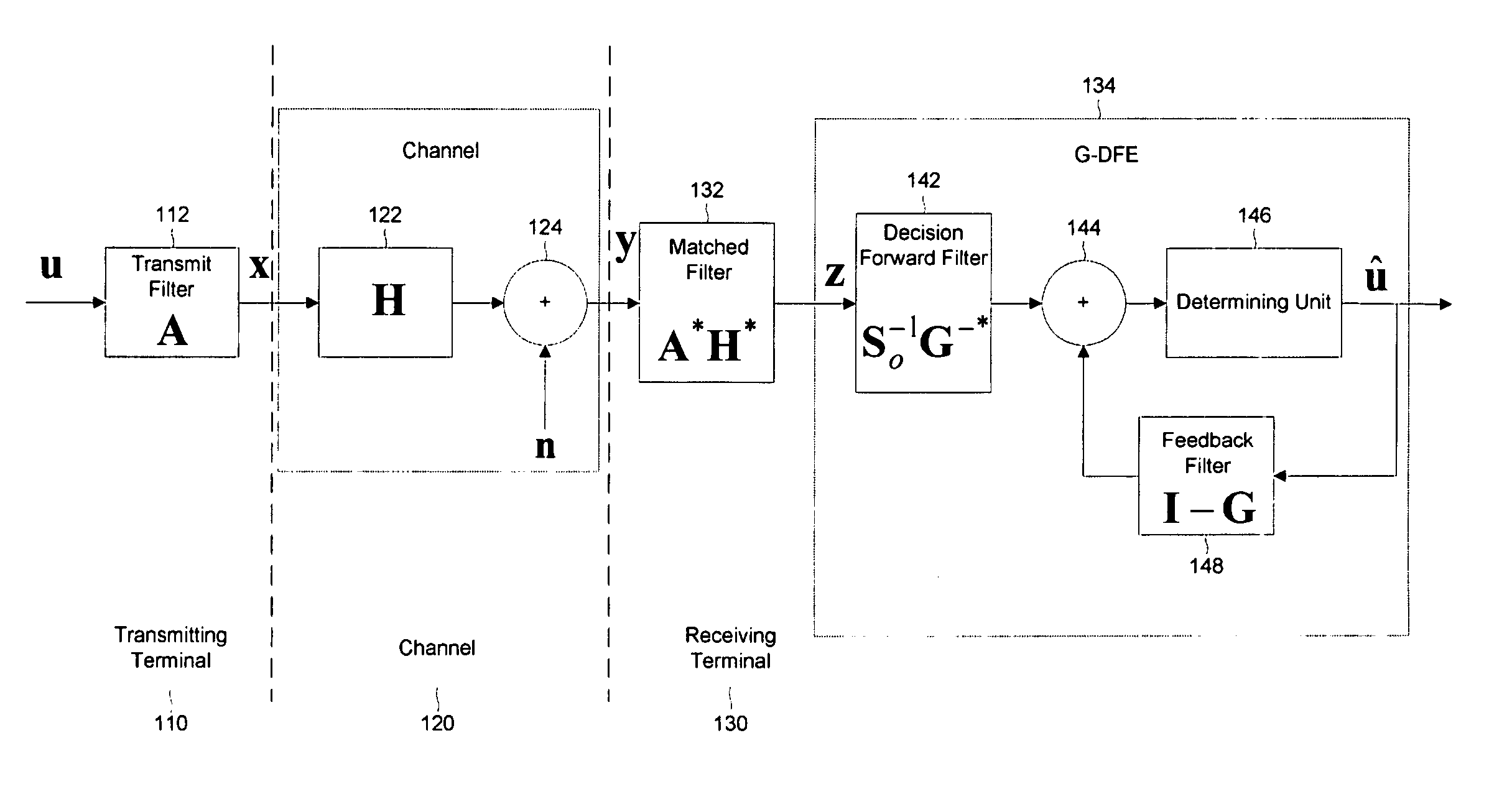
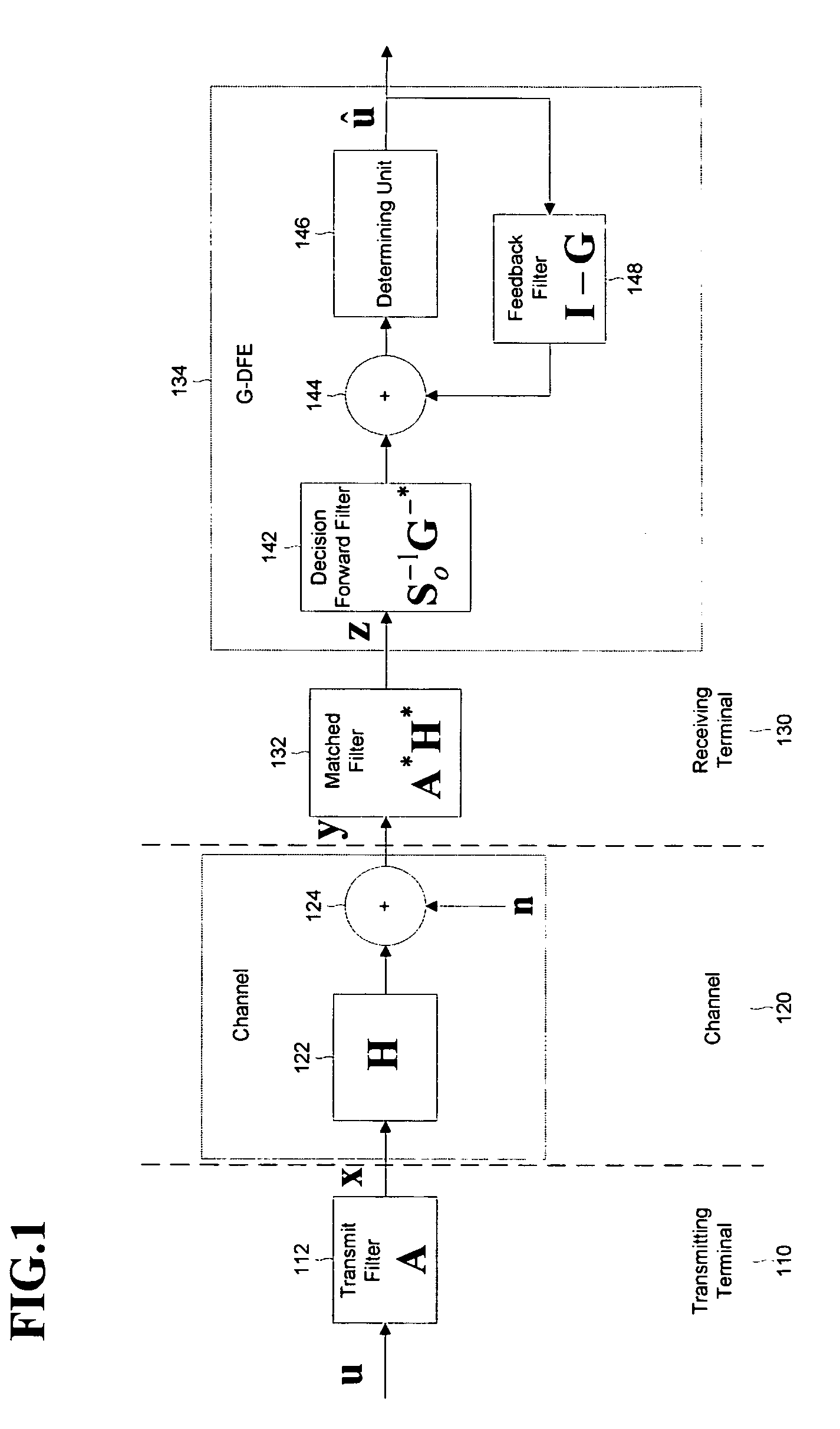
Generalized decision feedback equalizer precoder with input covariance matrix calculation for multi-user multiple-input multiple-output wireless transmission systems
InactiveUS20110058598A1Reduce computing costImprove performanceMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsSingular value decompositionWireless transmission
To realize a GDFE precoder for multi-user MIMO systems, which significantly reduces the computational cost while resulting in no capacity loss, one method comprises computing an effective UL channel matrix HUL using one of two methods HUL=HDLH, or HUL=[(Pt / Nt)HDLHHDL+I]−1 / 2HDLH; extracting Hk from HUL; computing a singular value decomposition of the DL channel between the BS and kth UT, Hk, for all K UTs, Hk=UkSkVkH; extracting all singular values as s=[diag(S1), . . . , diag(SK)]; extracting a vector ŝ from s by choosing first utmost Nt largest non-zero singular values of s; sorting elements in ŝ in decreasing order; performing water-filling to allocate power and obtain a diagonal matrix Γk representing power allocations corresponding to the singular values of the kth UT; computing an UL covariance matrix for each UT as Φk=UkΓkUkH; and obtaining an overall input covariance matrix D for the equivalent UL channel.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
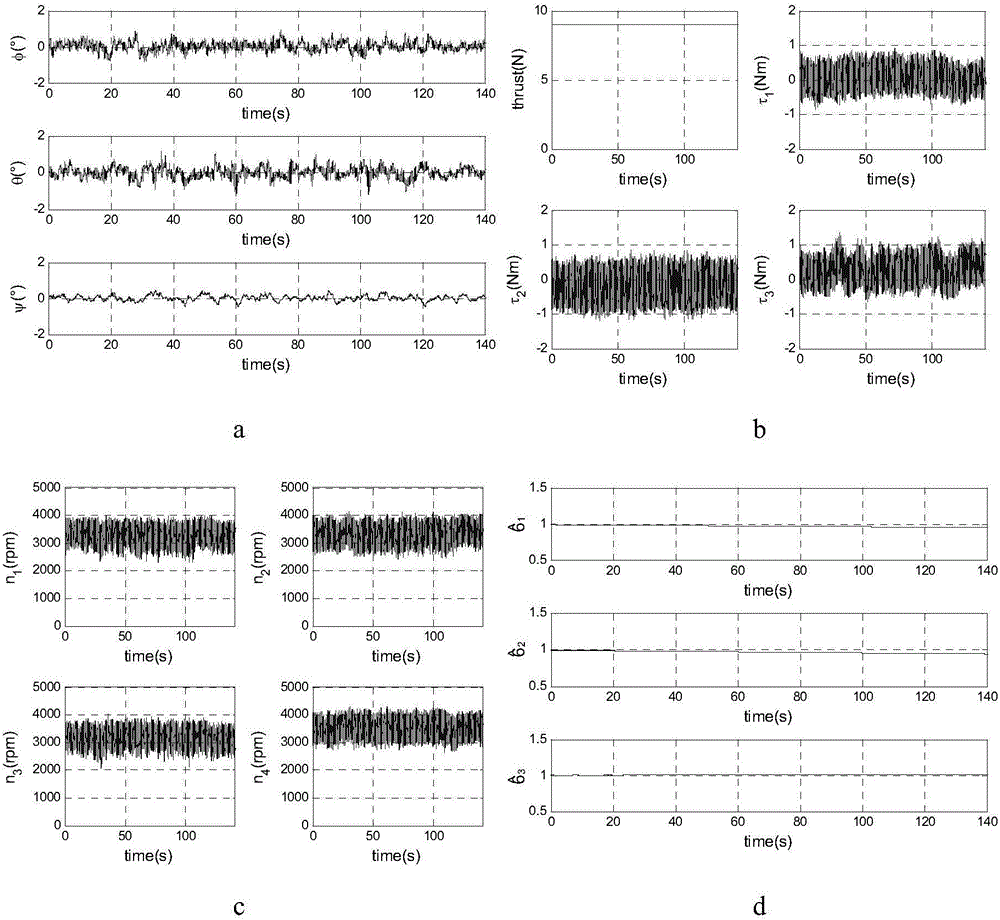
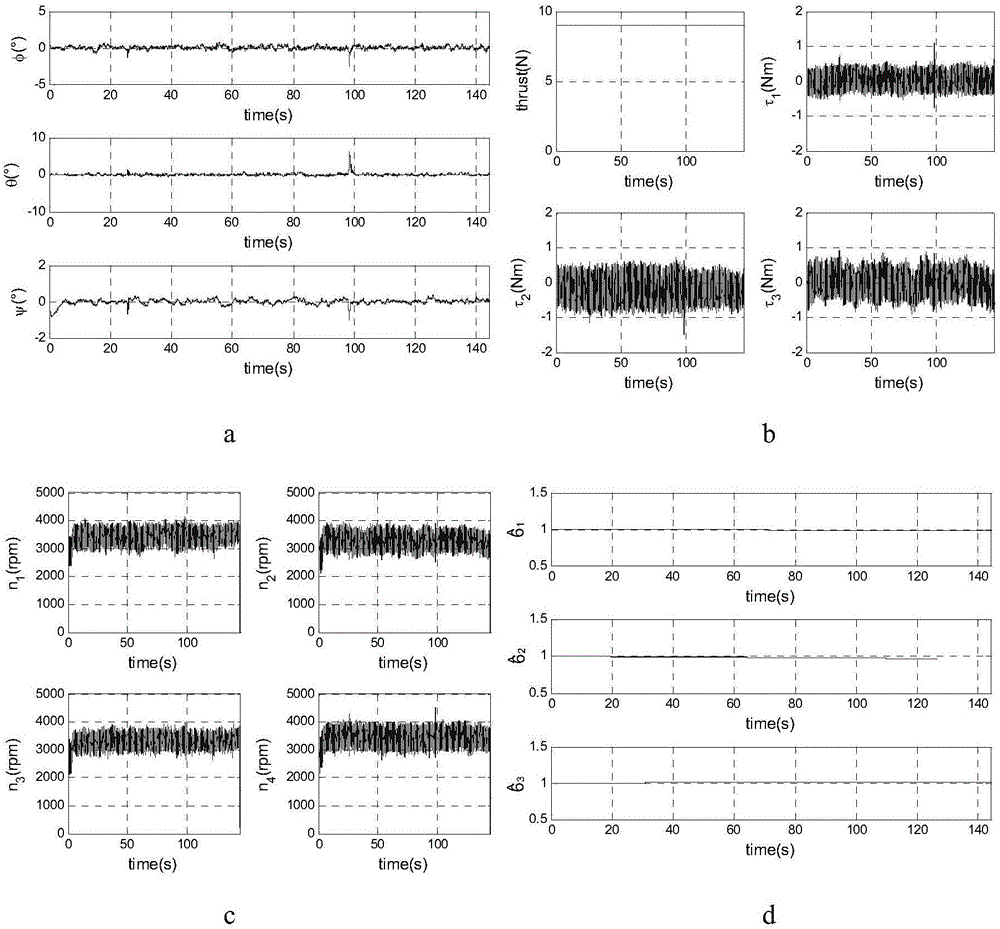
Tolerant control method for partial failure of four-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle actuator
The invention relates to a four-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle tolerant control method, and provides a tolerant controller. When an actuator is partially failed, a four-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle is still stable. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, a tolerant control method for partial failure of the four-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle actuator comprises the steps that the principle of the action of the actuator on the four-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle is analyzed; an unknown diagonal matrix is used to represent the influence of the failed actuator on the dynamics characteristic; by taking into account the disturbance of external unknown disturbance torque, a nonlinear dynamics model of the partially failed four-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle actuator is acquired; and an analysis method based on Lyapunov is used to prove that the whole closed-loop system shown by a formula (12) is asymptotically stable, namely when time tends to be infinite, an attitude angle eta tends to a target attitude angle eta d. The method provided by the invention is mainly used for four-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle tolerant control.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Zero-sample classifying method based on class transfer
ActiveCN108376267ASimple structureEasy to implementCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmTest phase
A zero-sample classifying method based on class transfer comprises the steps of acquiring a vision characteristic of C kinds of training samples, a class semantic characteristic of the training sampleand a true label matrix; calculating a semantic similarity matrix by means of cosine similarity or Gaussian similarity through the class semantic characteristic; calculating a diagonal matrix of a class semantic similarity matrix; calling a Sylvester equation in an MATLAB toolset for obtaining a mapping matrix; inputting the vision characteristic of the training sample, the corresponding class semantic characteristic and the true label matrix into a target function, continuously adjusting the value of a model regularization parameter, calculating the least value of the target function, and finishing model training; and in a testing period, inputting the vision characteristic of the testing sample and the corresponding semantic characteristic, calculating scores of the classes, and determining the class with highest score as the predicated class of the testing sample. The zero-sample classifying method based on class transfer has advantages of sufficiently digging the semantic relationbetween different classes, realizing knowledge transfer between a known class classifier and an unknown class classifier, and realizing high convenience in application in image classification.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
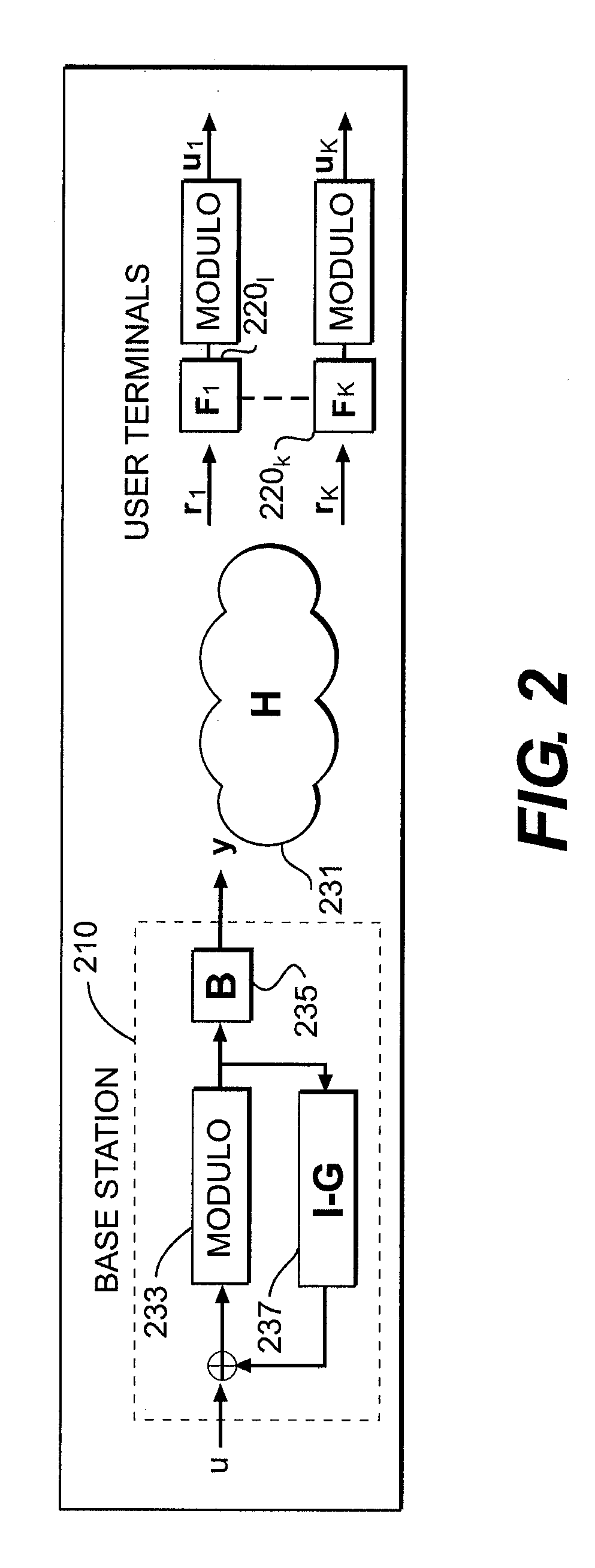
Method and apparatus for cancellation of cross-talk signals using multi-dimensional coordination and vectored transmission
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for cancellation of crosstalk signals using multi-dimensional coordination and vectored transmission. A method of canceling crosstalk signals in a receiver includes a step of multi-dimensionally decomposing the received signals into a user domain and a time domain, a step of calculating a transposed matrix and a diagonal matrix of a unit matrix from the received signals, a step of decoding the received signals with respect to symbols taking the user domain using the transposed matrix and the diagonal matrix of the unit matrix, and a step of decoding the signal decoded in the user domain with respect to symbols taking the time domain so as to calculate the data vectors from which the crosstalk signals are cancelled. Further, a method of canceling crosstalk signals in a transmitter includes a step of multiplying the data vectors to be transmitted from a pre-distortion matrix so as to calculate transmission signals, a step of multi-dimensionally decomposing the transmission signals into a time domain and a user domain, a step of precoding the transmission signals in the time domain and precoding the transmission signals in the user domain, a step of multiplying the signals precoded in the time domain and the user domain by the pre-distortion matrix so as to calculate second transmission signals, and a step of multiplying the second transmission signals by the unit matrix and transmitting the result to the receiver. According to the present invention, near-end crosstalk (NEXT) and far-end crosstalk (FEXT) can be cancelled, computer work in a central system managing cable lines can be reduced, and cable capacity for data transmission can be increased.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method, system and device for transmitting coding instruction information and determining precoding matrixes
ActiveCN103780331AImprove performanceError preventionRadio transmissionComputer architectureDiagonal matrix
The invention relates to the technical field of wireless communication and specifically relates to a method, system and device for transmitting coding instruction information and determining precoding matrixes to solve a problem that decreased performance is caused when a codebook is applied directly to a three-dimension beam forming / precoding technology at present. The method includes: UE determining and sending first precoding instruction information, second precoding instruction information and third precoding instruction information, wherein the first precoding instruction information, the second precoding instruction information and the third precoding instruction information are corresponding to the precoding matrixes. A first component precoding matrix is a block diagonal matrix. A third component precoding matrix is comprised of weighted column selection vectors which include P non-zero elements, the other all being zero. Through adoption of the method, system and device for transmitting the coding instruction information and determining the precoding matrixes, performance of the three-dimension beam forming / precoding technology can be improved.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Method for padding and puncturing low density parity check code
InactiveUS8006162B2Error correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionAlgorithmParity-check matrix
Disclosed is a method for puncturing a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) code that is expressed by a factor graph having a check node and a variable node, connected to each other by an edge, and is decoded by a parity check matrix including a parity part having a single weight-3 column and a dual-diagonal matrix. The method includes selecting 1-step recoverable (1-SR) variable nodes with the highest quality including a variable node mapped to a weight-3 column, and setting a first puncturing priority group using the selected 1-SR variable nodes, selecting k-step recoverable (k-SR) variable nodes with the highest quality in the next step k taking into account the variable nodes selected in the current step, and setting a priority group for each individual step, puncturing an LDPC code mapped to a variable node belonging to a corresponding group according to priority of each group obtained in the preceding steps.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for encoding low-density parity check code
ActiveUS7458009B2Simplify the coding processImprove performanceError detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsAlgorithmDiagonal matrix
An apparatus and method for encoding low-density parity check (LDPC) codes. The method for generating a low-density parity check code formed of an information-part matrix and a parity-part matrix comprises the steps of converting the information-part matrix into an array code structure and assigning a degree sequence to each submatrix column; extending a dual-diagonal matrix corresponding to the parity-part matrix such that an offset value between diagonals has a random value; lifting the normalized dual-diagonal matrix; determining an offset value for cyclic column shift for each submatrix of the lifted normalized dual-diagonal matrix; and determining a parity symbol corresponding to a column of the parity-part matrix.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and device for estimating rank indication and precoding matrix indication in precoding system
InactiveCN101626266AReduce complexityImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionSingular value decompositionAlgorithm
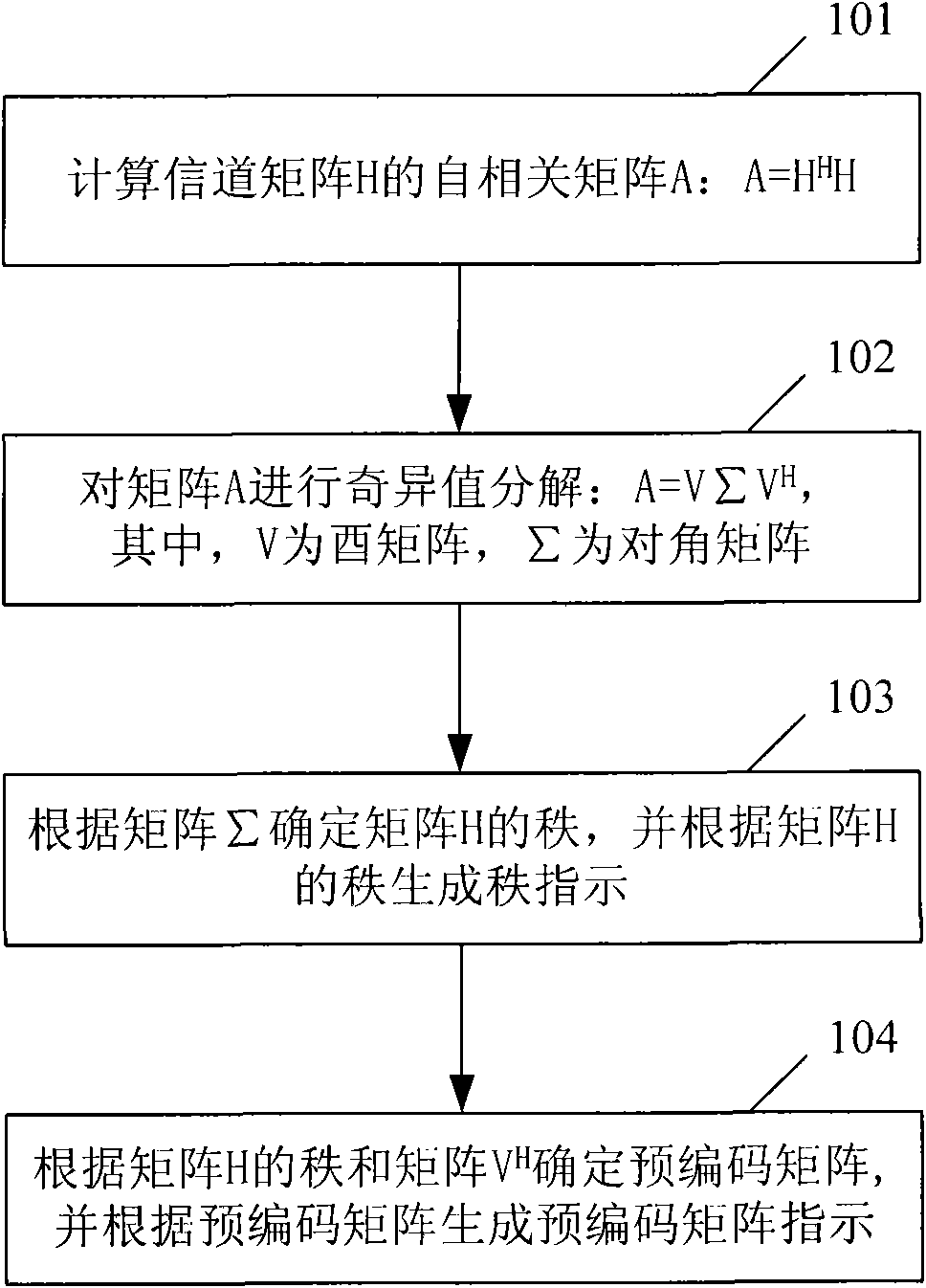
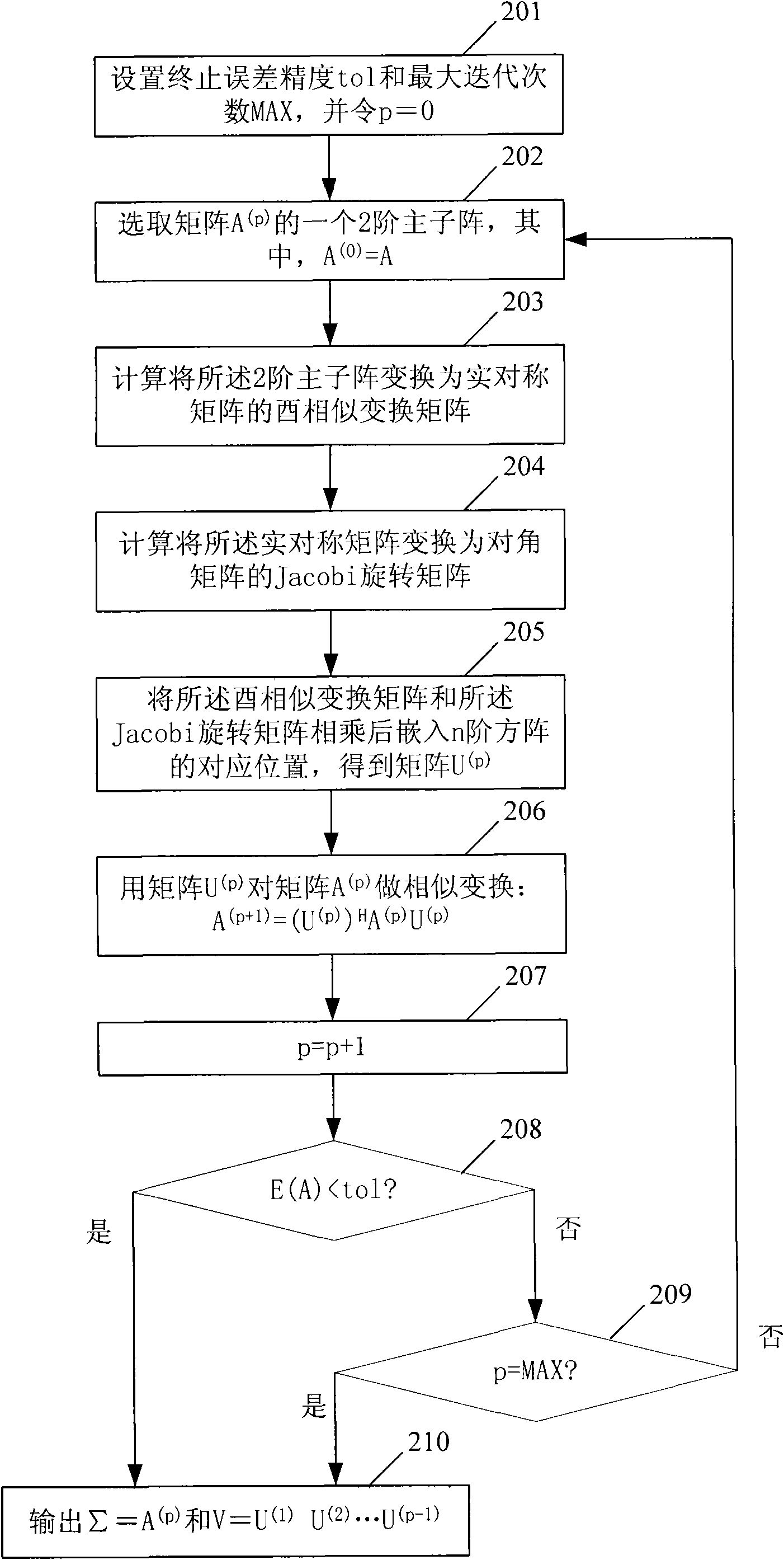
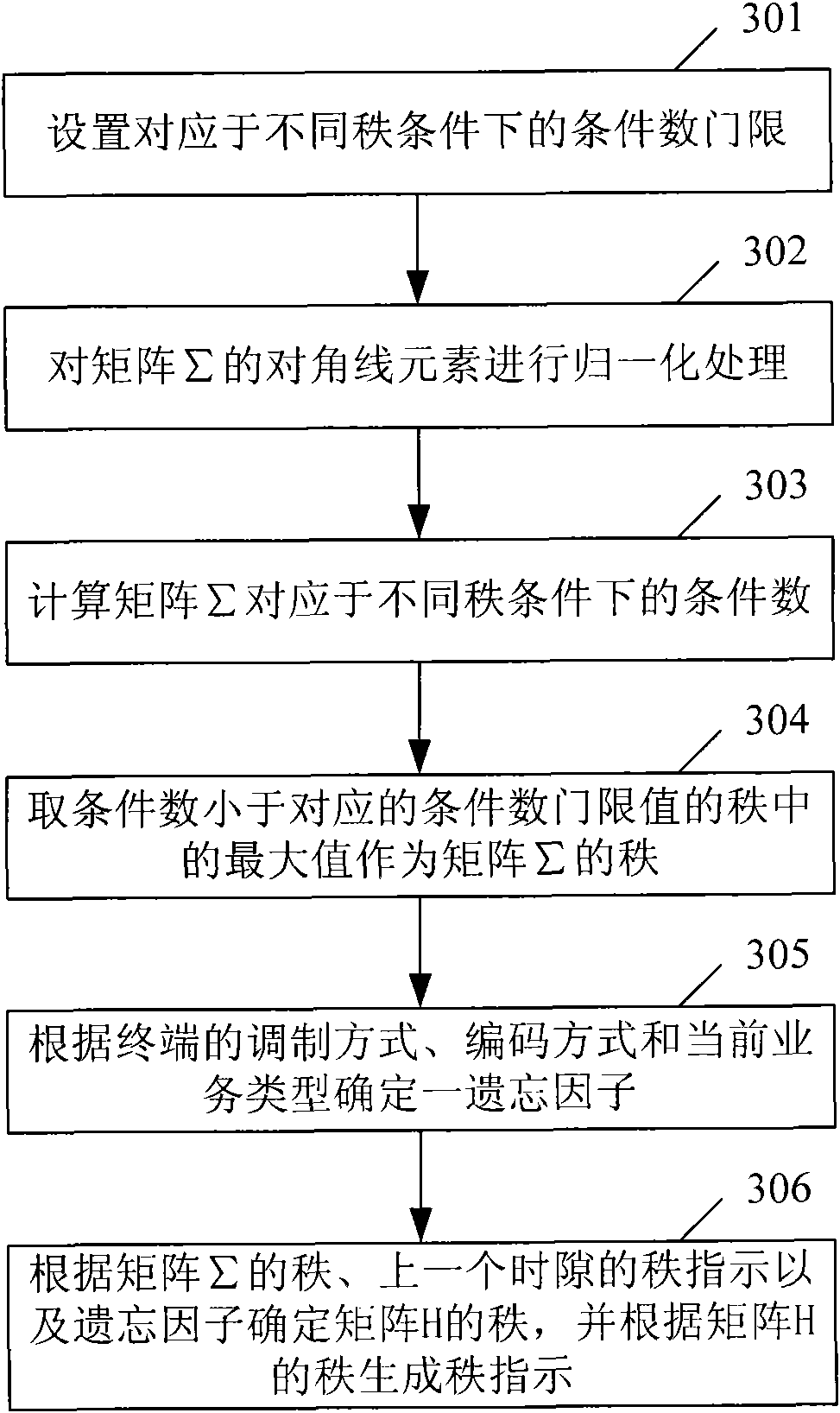
The invention provides a method and a device for estimating rank indication and precoding matrix indication in a precoding system. The method comprises the following steps: A. calculating a self-correlation matrix A of a channel matrix H: A=H<H>H; B. carrying out singular value decomposition on the matrix A: A=VsigmaV<H>, wherein V is a unitary matrix, and sigma is a diagonal matrix; C. confirming a rank of the matrix H according to a matrix sigma and generating rank indication according to the rank of the matrix H; D. confirming a precoding matrix according to the rank of the matrix H and a matrix V<H> and generating precoding matrix indication according to the precoding matrix. The invention can effectively reduce the complexity of an algorithm for estimating the rank indication and the recoding matrix indication by a terminal and improve the performance of the precoding system.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SEMICON BEIJING
Method for determining pre-coding matrix and corresponding communication method and equipment
The invention relates to a method for determining a pre-coding matrix for sub-band pre-coding of a transmitter, wherein the transmitter is provided with M transmitting antennas. The method comprises the steps of: a. determining a first optimal matrix W1 according to the relevant information of a broadband and / or a longtime information channel, wherein the first matrix W1 corresponds to the characteristics of the broadband and / or the longtime information channel; b. multiplying the first optimal matrix W1 and each second matrix W2 in a second codebook so as to obtain a plurality of alternative pre-coding matrixes, wherein the second matrix W2 corresponds to the frequency choice and / or the characteristics of a short-time information channel; and c. selecting the optimal matrix from the plurality of alternative pre-coding matrixes according to the frequency choice and / or the status information of the short-time information channel for pre-coding the data to be transmitted. The method is characterized in that the number of DFT (Discrete Fourier Transform) wave beams is increased, thereby improving the spatial resolution; a diagonal matrix is introduced into the first matrix W1; the phase adjustment is introduced into the second matrix W2; and adjusted phases are ensured to be uniformly distributed in the whole phase space.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SHANGHAI BELL CO LTD
Differentially expressed gene identification method based on combined constraint non-negative matrix factorization
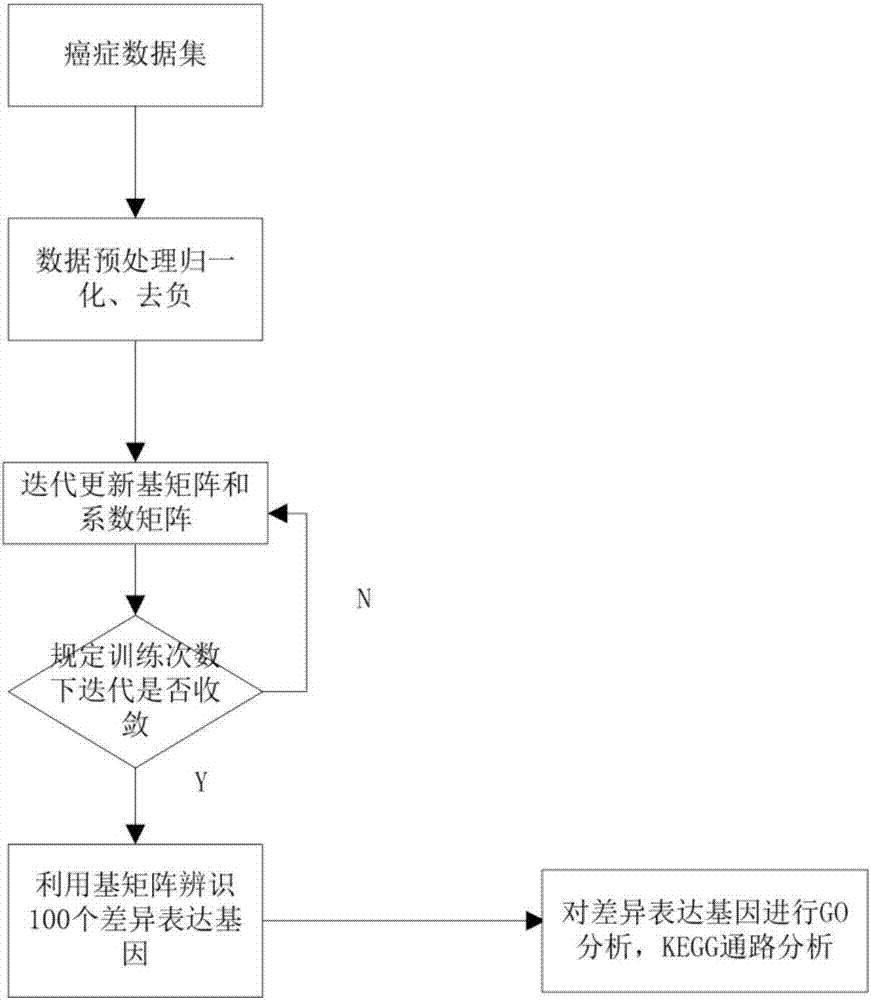
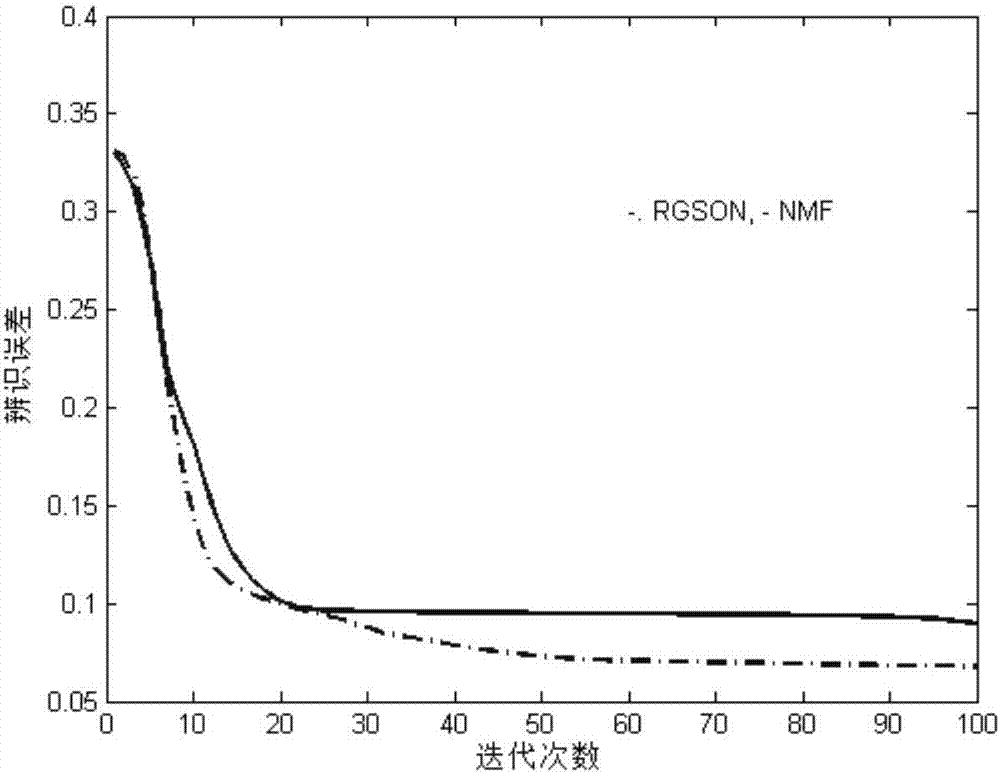
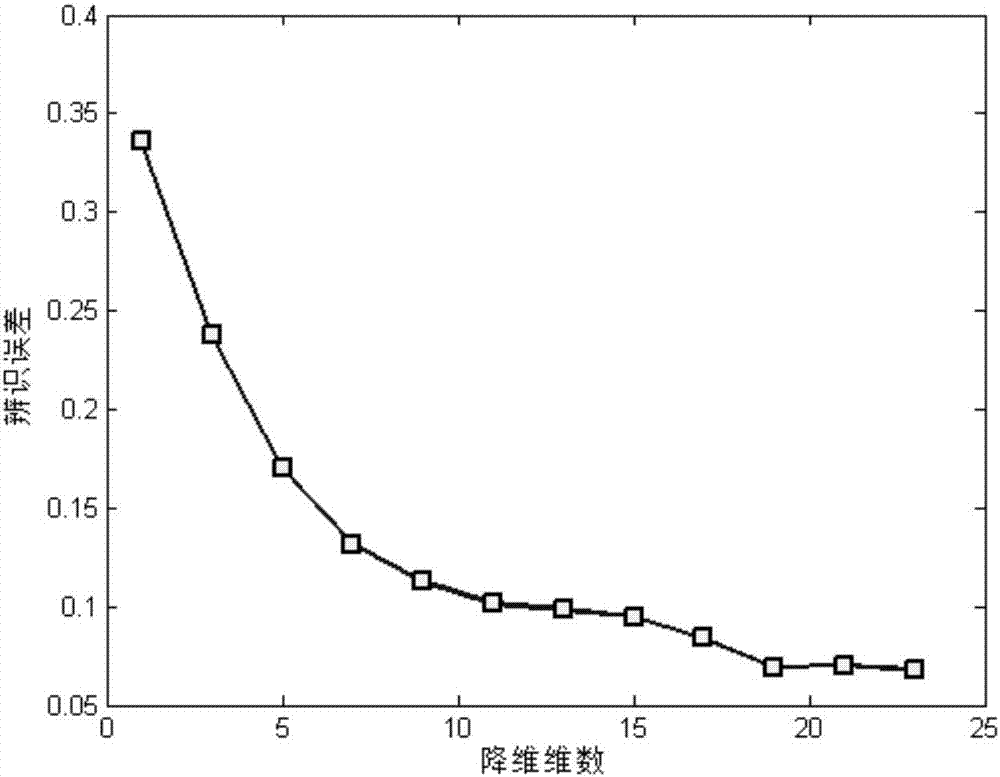
ActiveCN107016261AEffective decomposition resultsEfficient Sparse Decomposition ResultsSpecial data processing applicationsData setAlgorithm
The invention discloses a differentially expressed gene identification method based on combined constraint non-negative matrix factorization. The method comprises the following steps of 1, representing a cancer-gene expression data set with a non-negative matrix X, 2, constructing a diagonal matrix Q and an element-full matrix E, 3, introducing manifold learning in the classical non-negative matrix factorization method, conducting orthogonal-constraint sparseness and constraint on a coefficient matrix G, and obtaining a combined constraint non-negative matrix factorization target function, 4, calculating the target function, and obtaining iterative formulas of a basis matrix F and the coefficient matrix G, 5, conducting semi-supervision non-negative matrix factorization on the non-negative data set X, and obtaining the basis matrix F and the coefficient matrix G after iteration convergence, 6, obtaining an evaluation vector (the formula is shown in the description), sorting elements in the evaluation vector (the formula is shown in the description) from large to small according to the basis matrix F, and obtaining differentially expressed genes, 7, testing and analyzing the identified differentially expressed genes through a GO tool. The identification method can effectively extract the differentially expressed genes where cancer data is concentrated, and be applied in discovering differential features in a human disease gene database. The identification method has important clinical significance for early diagnosis and target treatment of diseases.
Owner:HANGZHOU HANGENE BIOTECH CO LTD
Matrix structure for block encoding
InactiveUS20100287440A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsParity-check matrixTheoretical computer science
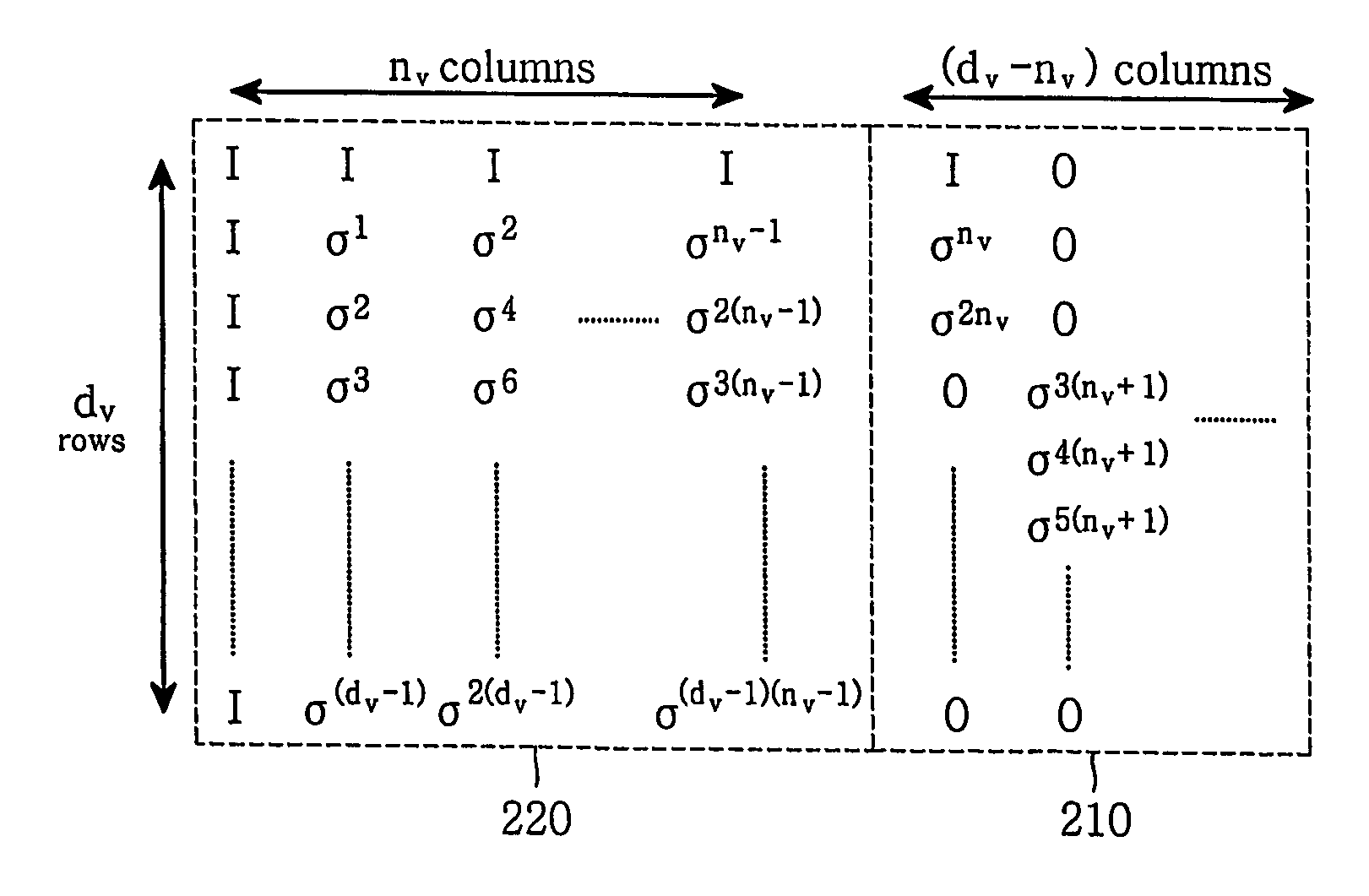
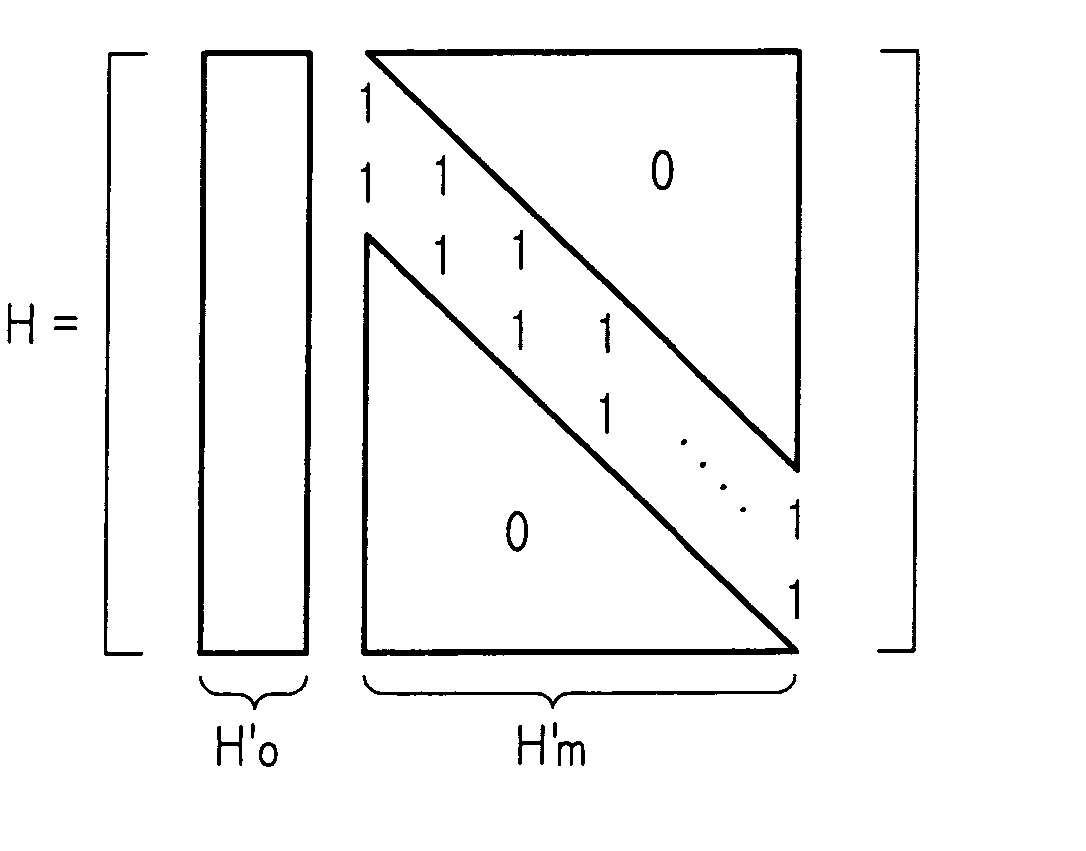
A plurality of information bits are encoded using a parity-check matrix that is equivalent to a modular code matrix. The modular code matrix is a diagonal sub-matrix structure immediately above a connection layer that includes a plurality of diverse connection layer sub-matrices, all but at most one of which are below corresponding diagonal matrix structure sub-matrices. The information bits are assembled with a plurality of parity bits produced by the encoding to provide a codeword that is exported to a medium. Preferably, all the diagonal matrix structure sub-matrices are identical. Preferably, some of the parity bits are computed using only diagonal matrix structure sub-matrices.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com