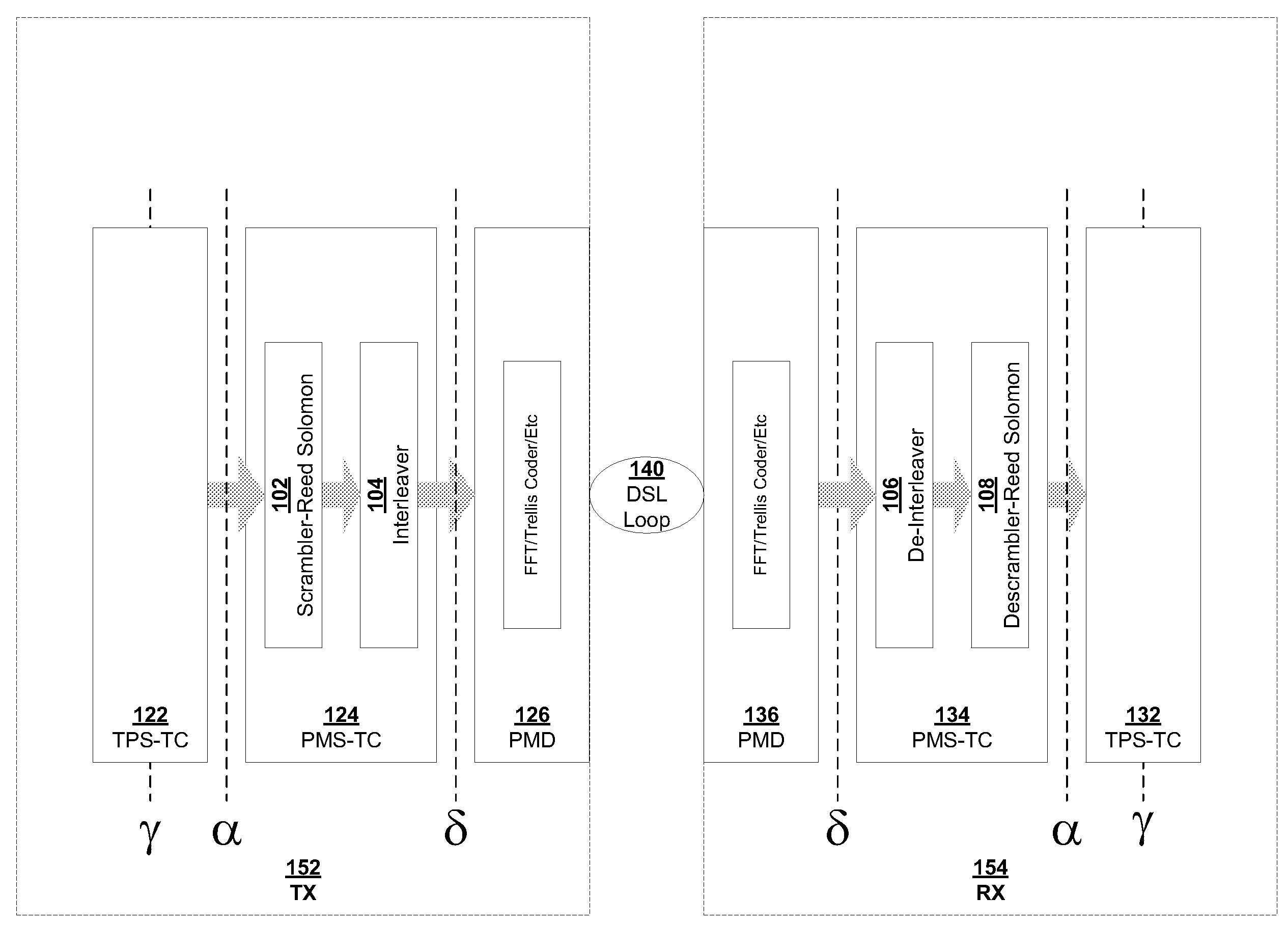
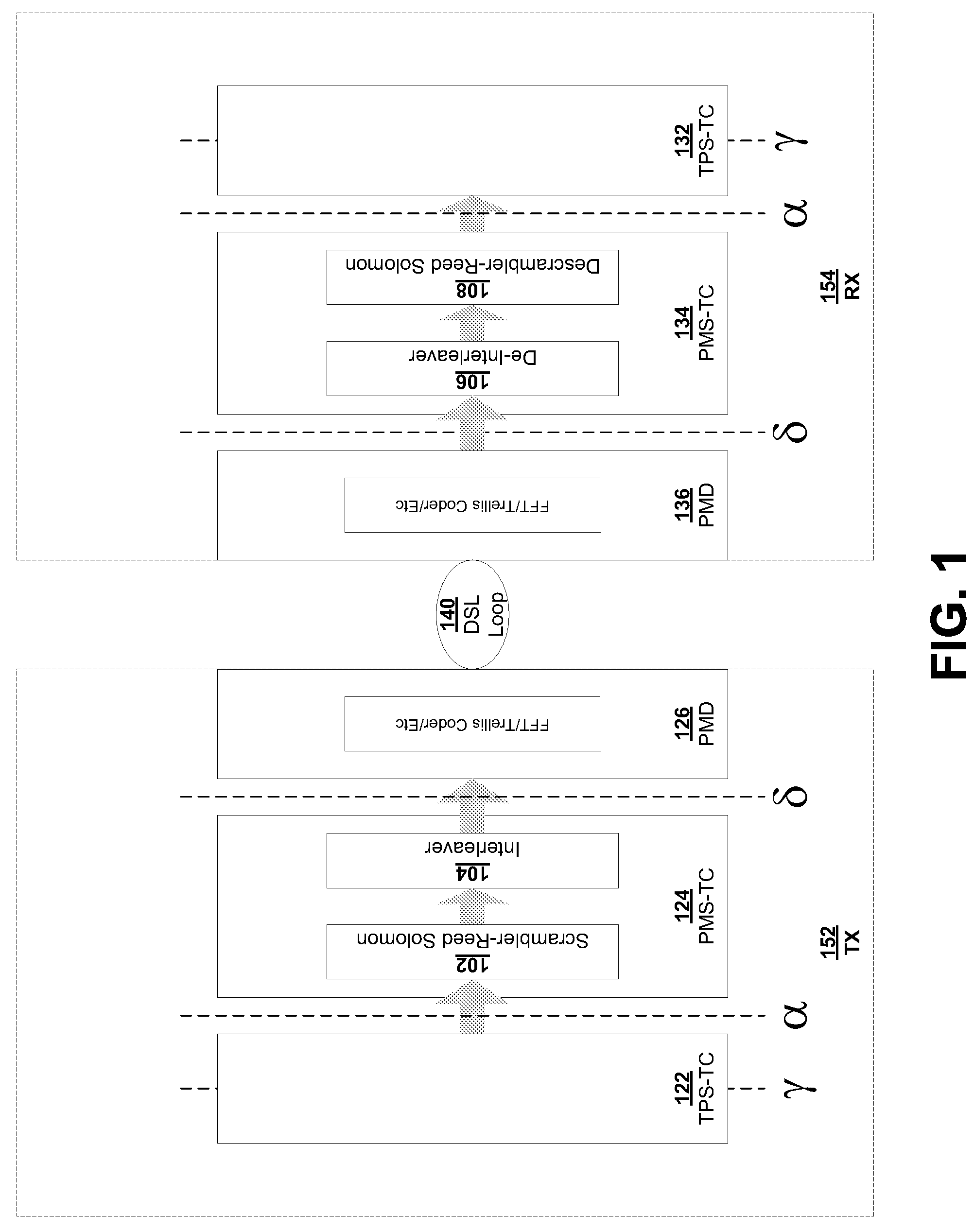
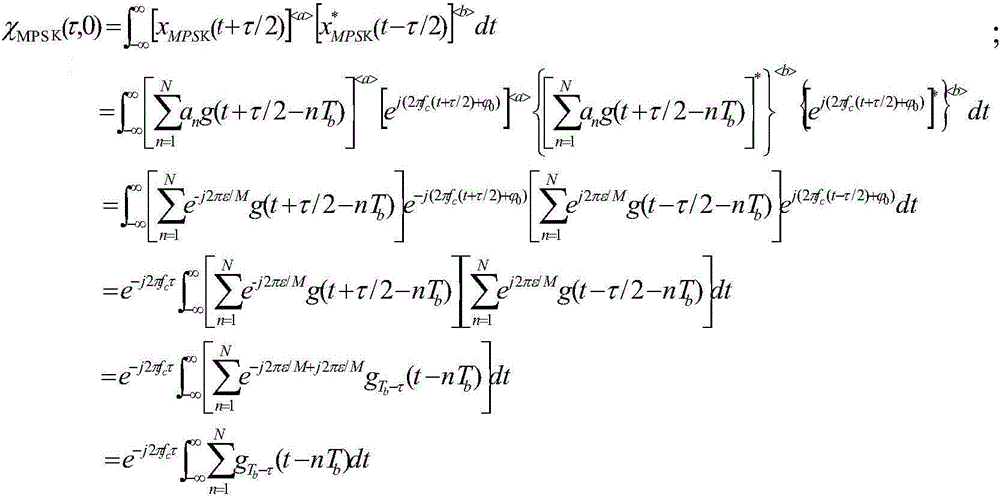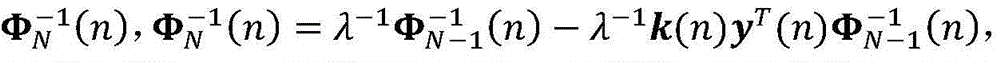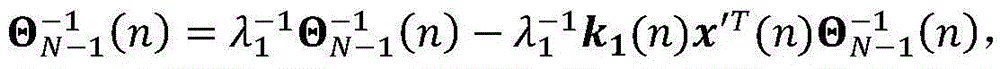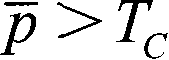Patents
Literature
523 results about "Pulse noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
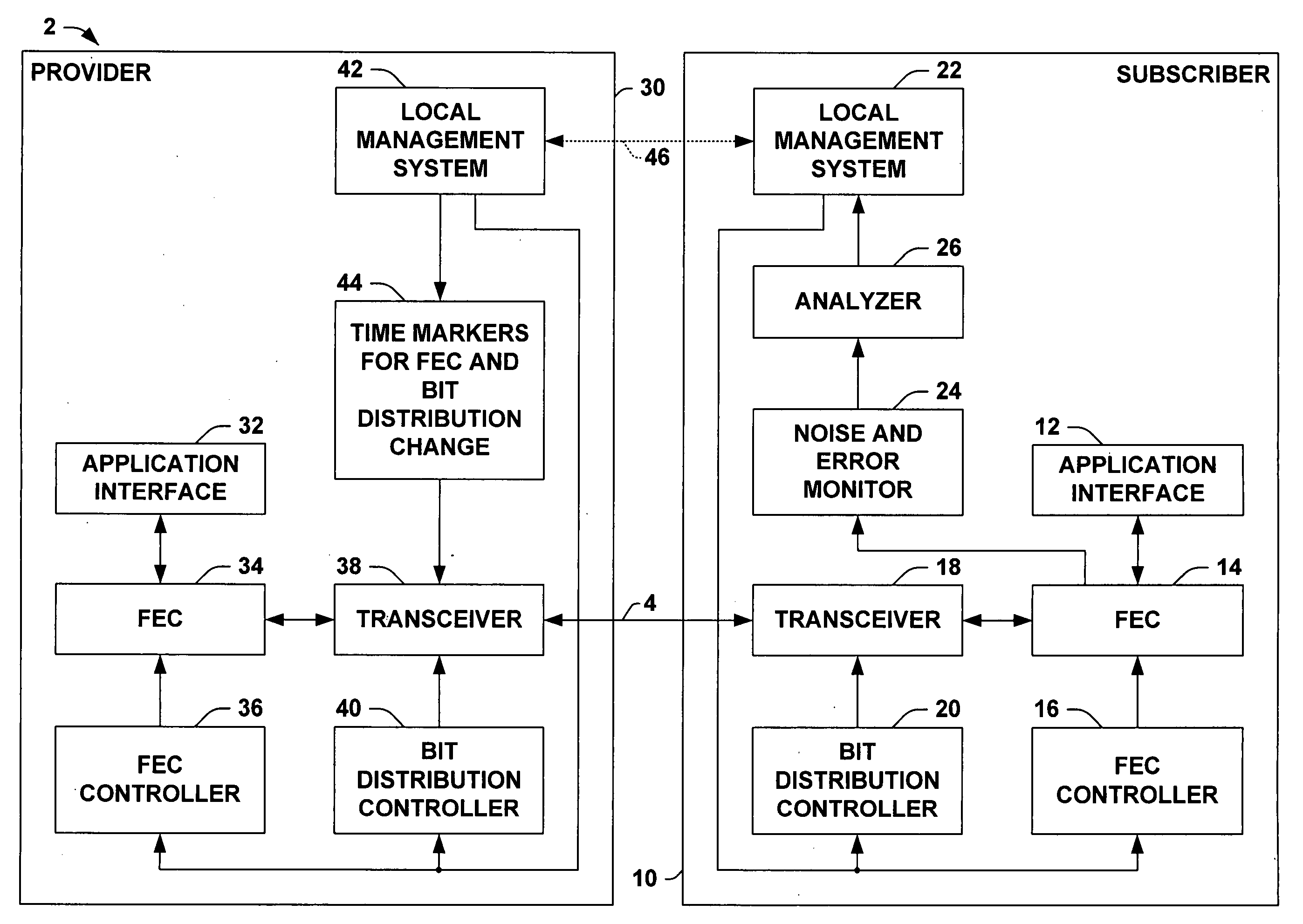
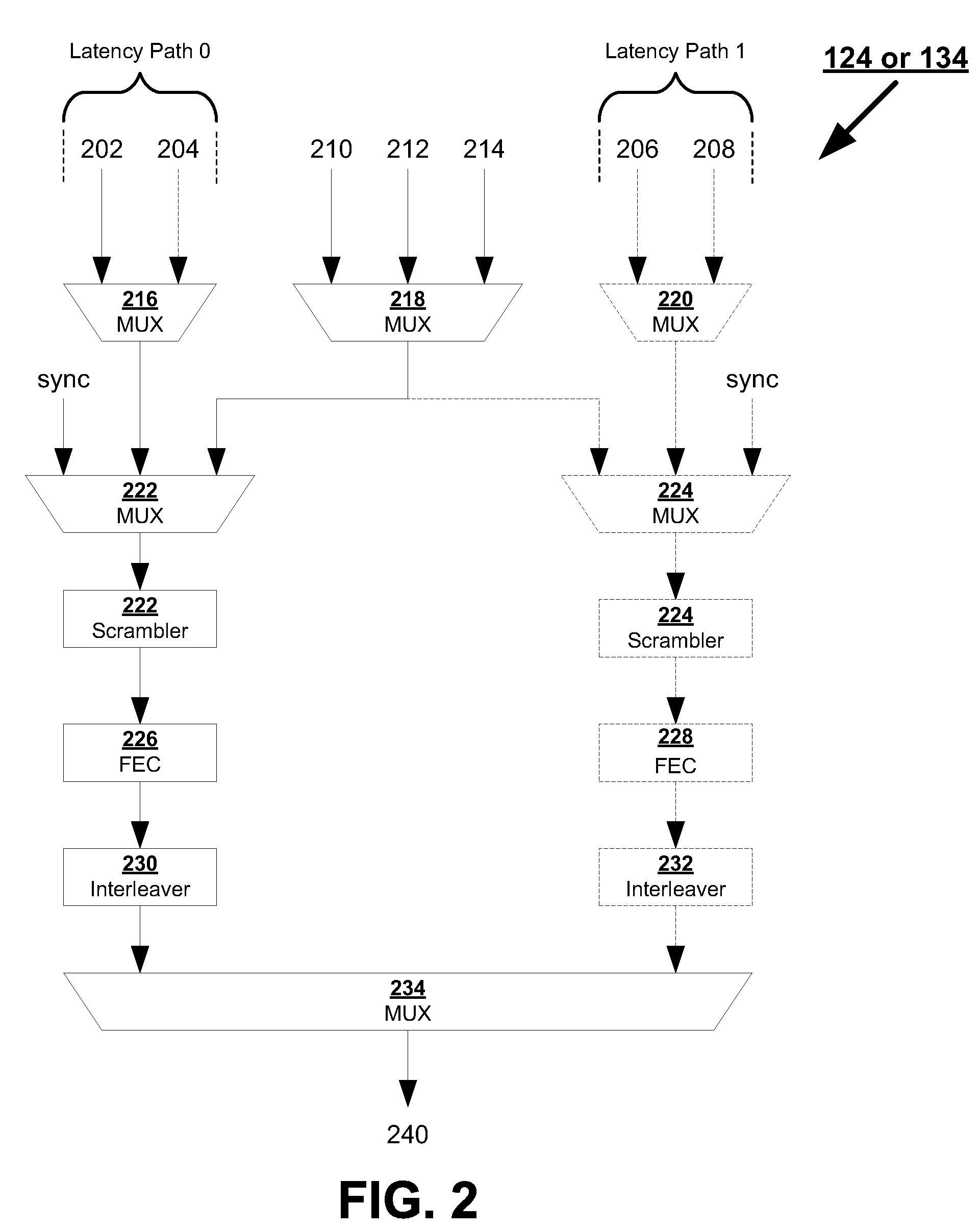
Seamless change of depth of a general convolutional interleaver during transmission without loss of data
InactiveUS20060107174A1Eliminate distractionsEasy to changeError detection/correctionCode conversionCommunications systemComputer science
Methods and communication systems are presented, in which impulse noise is monitored on a communication channel, and an interleaver depth is adjusted according to the monitored impulse noise without interrupting communication service.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
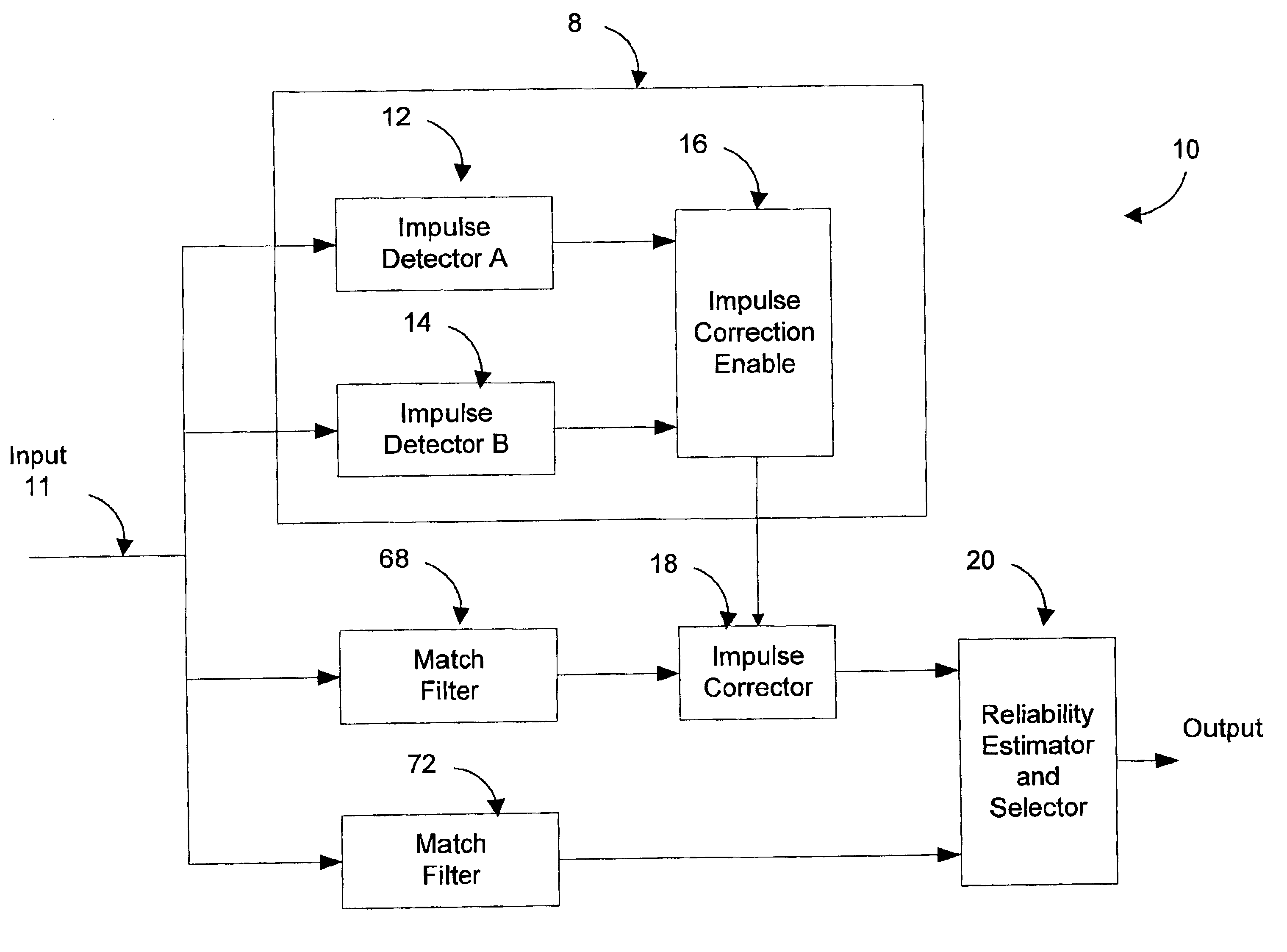
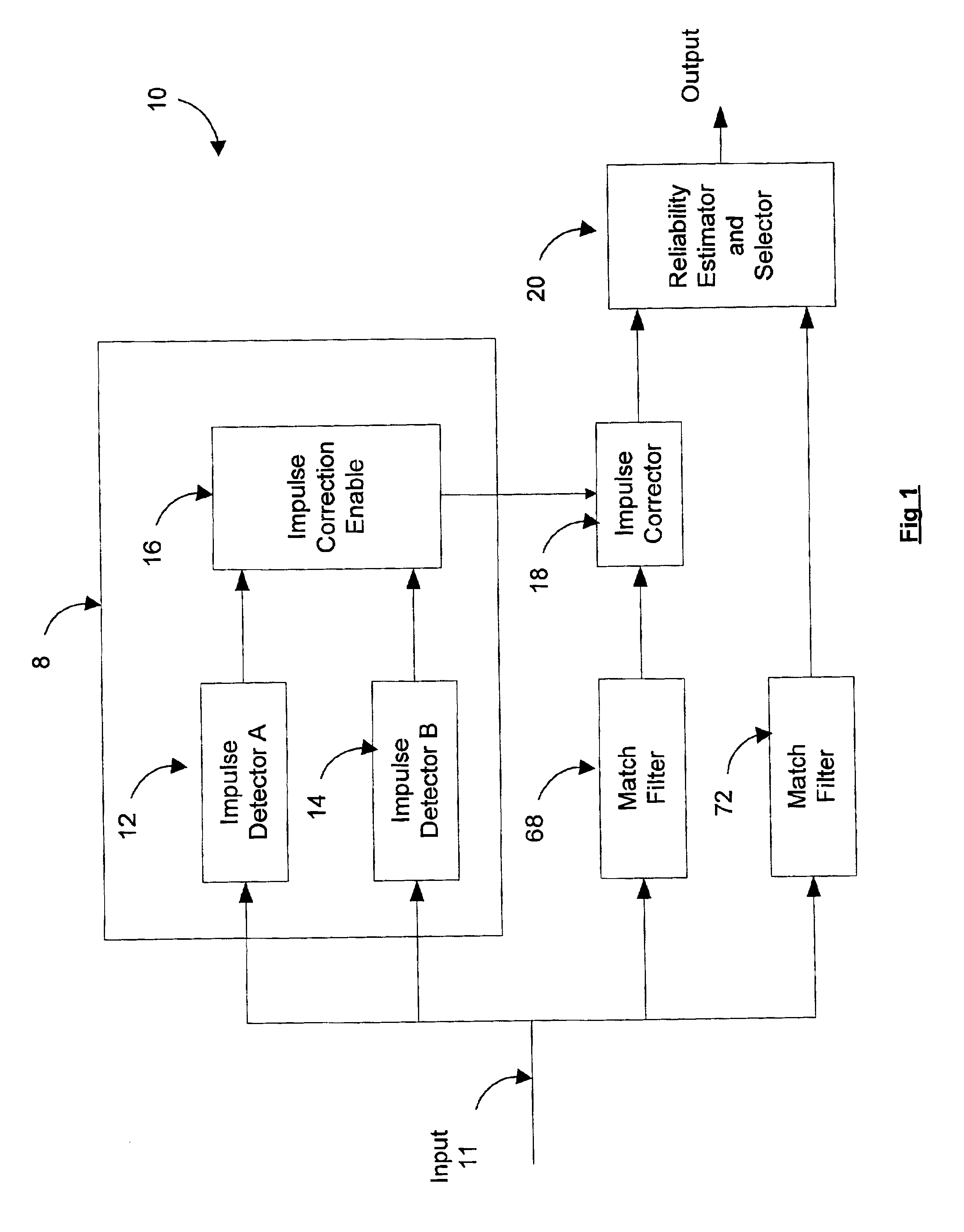
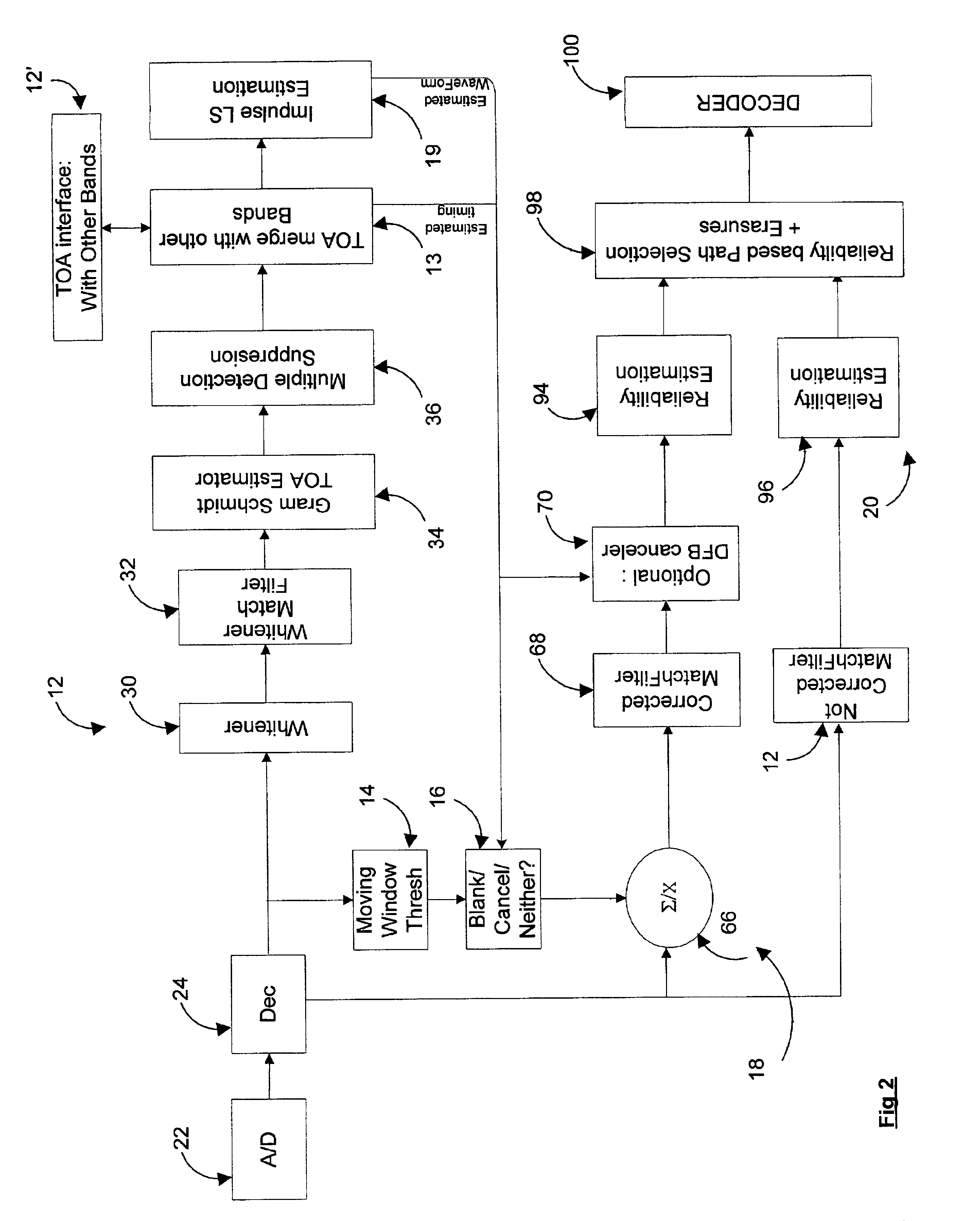
Method and system for detecting, timing, and correcting impulse noise
InactiveUS6920194B2Solve their vulnerability to impulse noiseLess complexDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionMulti-frequency code systemsData signalGram schmidt
A system for detecting and correcting impulse noise present on an input data signal includes an impulse detector module receiving an input data signal and producing as output an correction enable signal indicating when an impulse correction is required. An impulse corrector module receives the input data signal and a correction enable signal and produces a corrected data signal, e.g., having the impulse canceled or blanked, as output. A reliability estimator and selector module receives the corrected data signal and the input data signal and selects as output the input signal which is more reliable. In one embodiment, the impulse detector includes first and second complementary impulse detectors, the outputs of which are analyzed by an enable and correction module to produce an impulse detection signal with improved accuracy. Preferably, the enable and correction module also indicates the most appropriate type of impulse correction in accordance with the detection signals from the complementary detectors. A novel system and method of detecting impulses based on Gram Schmidt techniques is also presented. In this method, one or more channels of a multi-channel data signal are kept free of data. When a whitening filter is applied, impulses on these quiet channels are emphasized. The Gram Schmidt technique exploits this fact to provide for improved impulse detection. The system can be modified to detect other types of low dimensionality noise.
Owner:RPX CORP
Pulse wave detecting device and pulse measurer
PCT No. PCT / JP98 / 01128 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 4, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 4, 1998 PCT Filed Mar. 17, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 41143 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 24, 1998The present invention relates to a pulse wave detecting device for detecting pulse waves, and to a pulse measurer employing this pulse wave detecting device. The present invention addresses the problem of obtaining a pulse wave signal in which the noise components have been suitably removed from a pulse waveform, and of determining the pulse rate with high accuracy based on this pulse wave signal. The method for deriving the pulse wave signal and pulse rate is as follows. The pulse wave signal from pulse wave detecting sensor unit (30) is temporarily stored in buffer (503). When impulse noise is detected in the pulse wave signal in buffer (503) by impulse noise detecting means (505), the band pass for first digital filter (506) becomes a hill-shaped curve centered on the frequency corresponding to the preceding pulse rate, and impulse noise in the pulse wave signal output from buffer (503) is decreased. Thereafter, overall noise and body movement components are decreased in the pulse wave signal by means of second digital filter (507) and third digital filter (508). The signal is then subjected to frequency analysis by frequency analyzer (509), and the pulse rate is calculated from the results of this analysis.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP +1
Suppression of radio frequency interference and impulse noise in communications channels
InactiveUS6546057B1Error preventionUnbalanced current interference reductionDifferential signalingEngineering
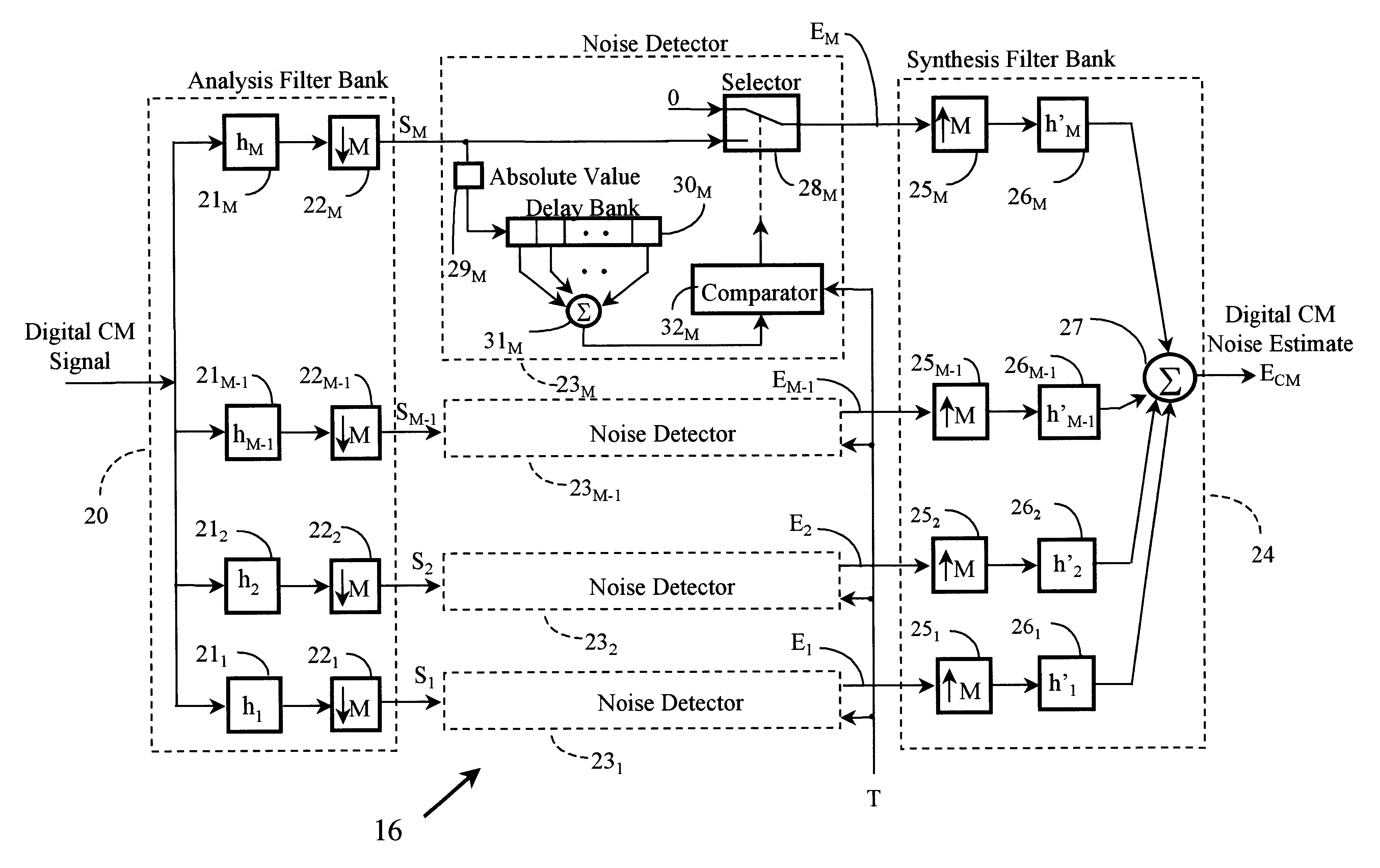
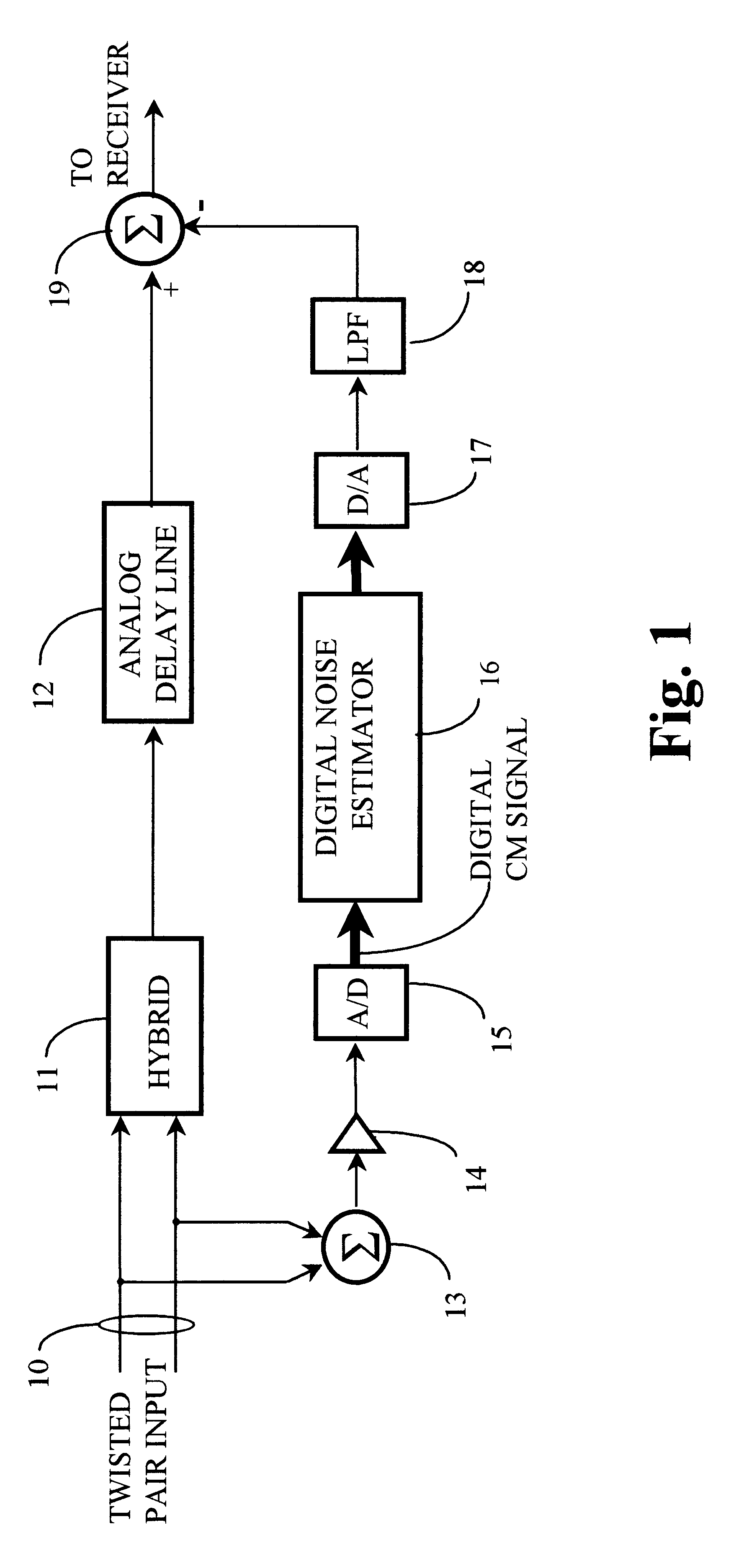
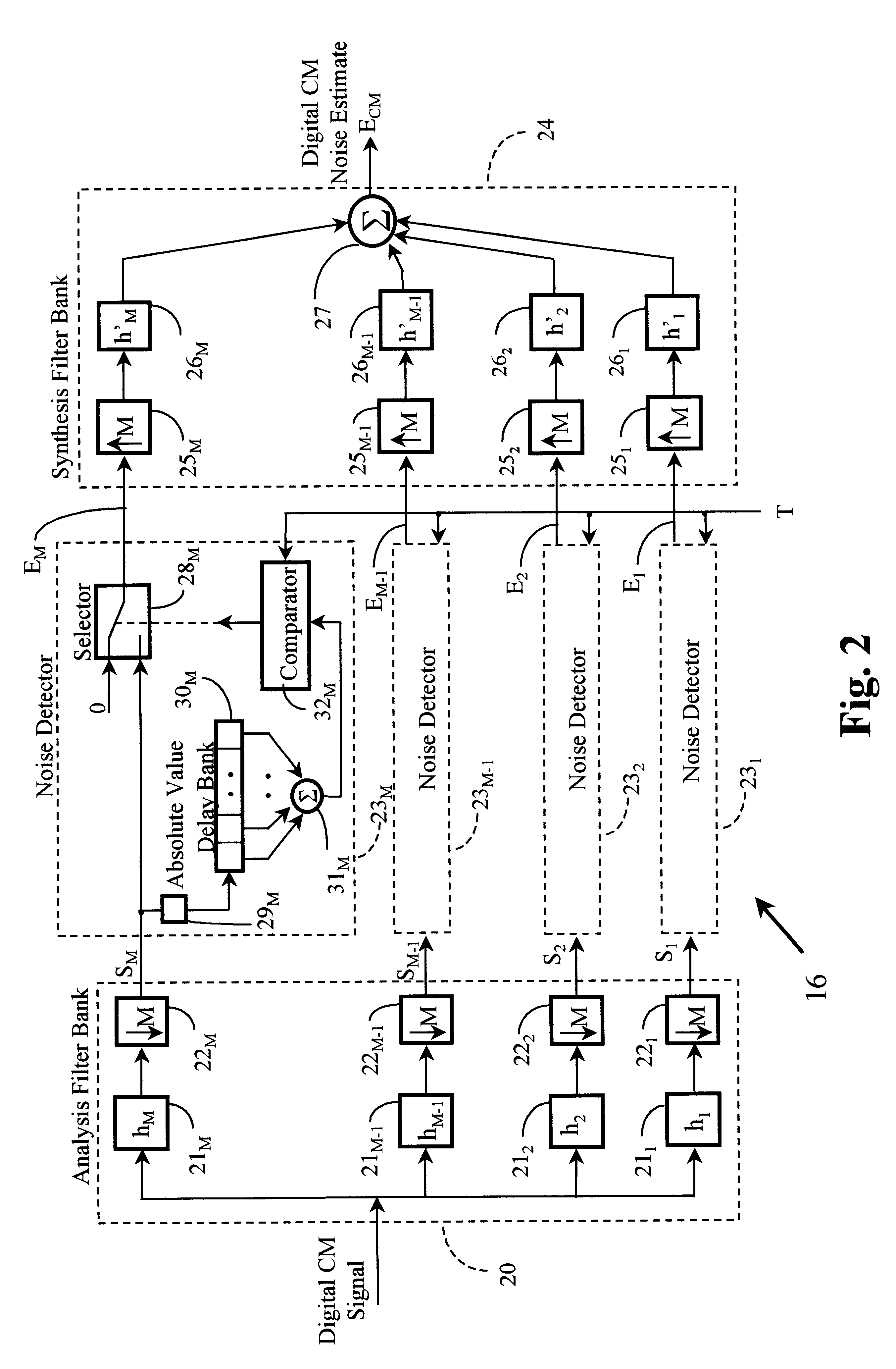
A noise suppression circuit for a communications channel (10) comprises a hybrid device (11) coupled to the channel for providing a differential output signal corresponding to a received signal. A delay unit (12) delays the differential signal by a suitable amount to allow for the generation and subtraction of a noise estimate. A summing device (13) extracts a digital common mode signal from the channel, and a noise estimation unit (16) provides a common mode noise estimate signal in dependence upon a history of the common mode signal over a predetermined period of time and over a plurality of frequency bands. The common mode noise estimate signal is combined subtractively (19) with the delayed differential signal to cancel common mode noise elements of the delayed differential signal. The noise estimation unit may comprise an analysis filter bank (20) for producing a plurality of subband signals (S1-SM), each at a different one of a plurality of different frequencies, a plurality of noise detection circuits (231-23M), each for processing a respective one of the plurality of subband signals to provide a component of the common mode noise estimate signal, and a synthesis filter bank (24) for processing the common mode noise signal components to provide the noise estimate signal.
Owner:BELL CANADA
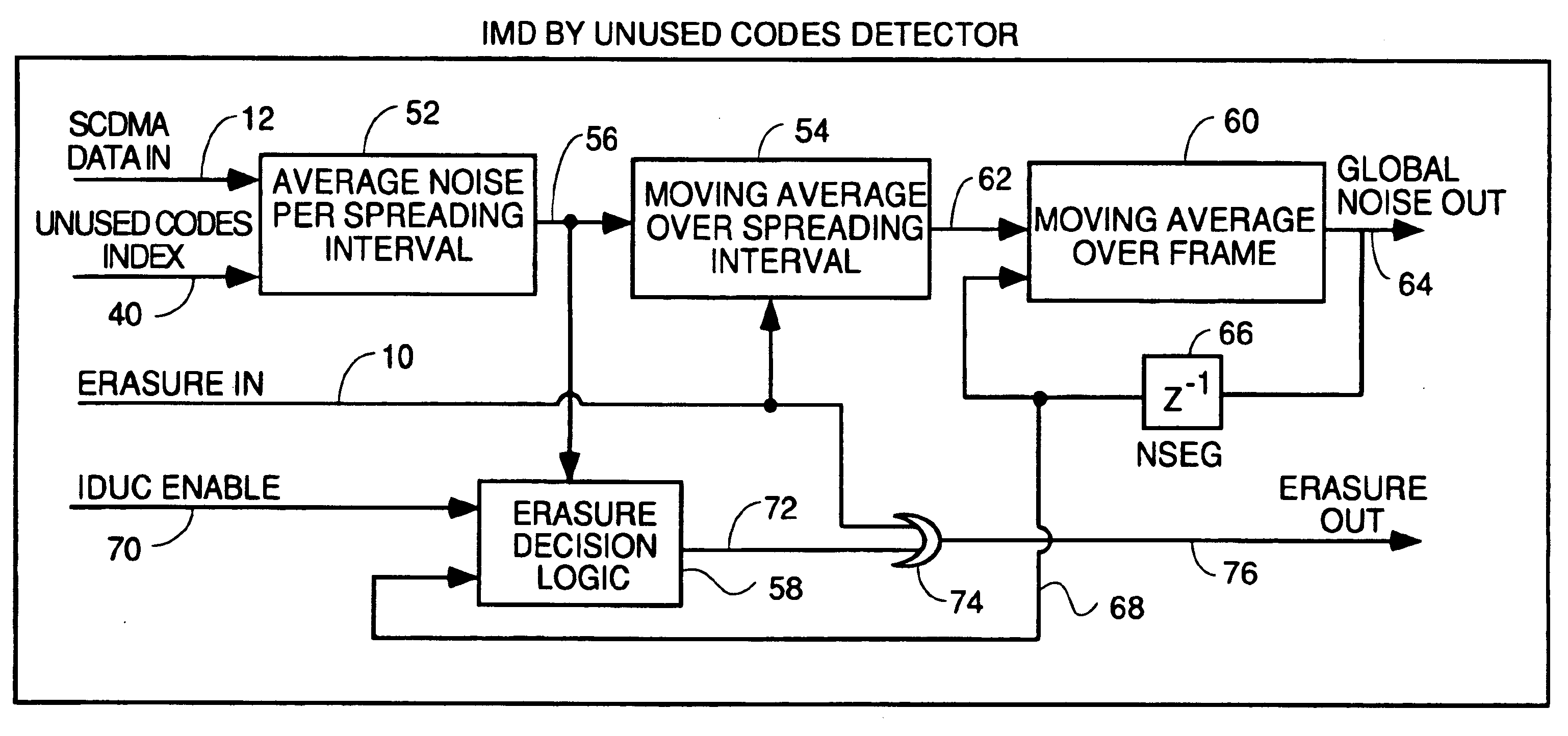
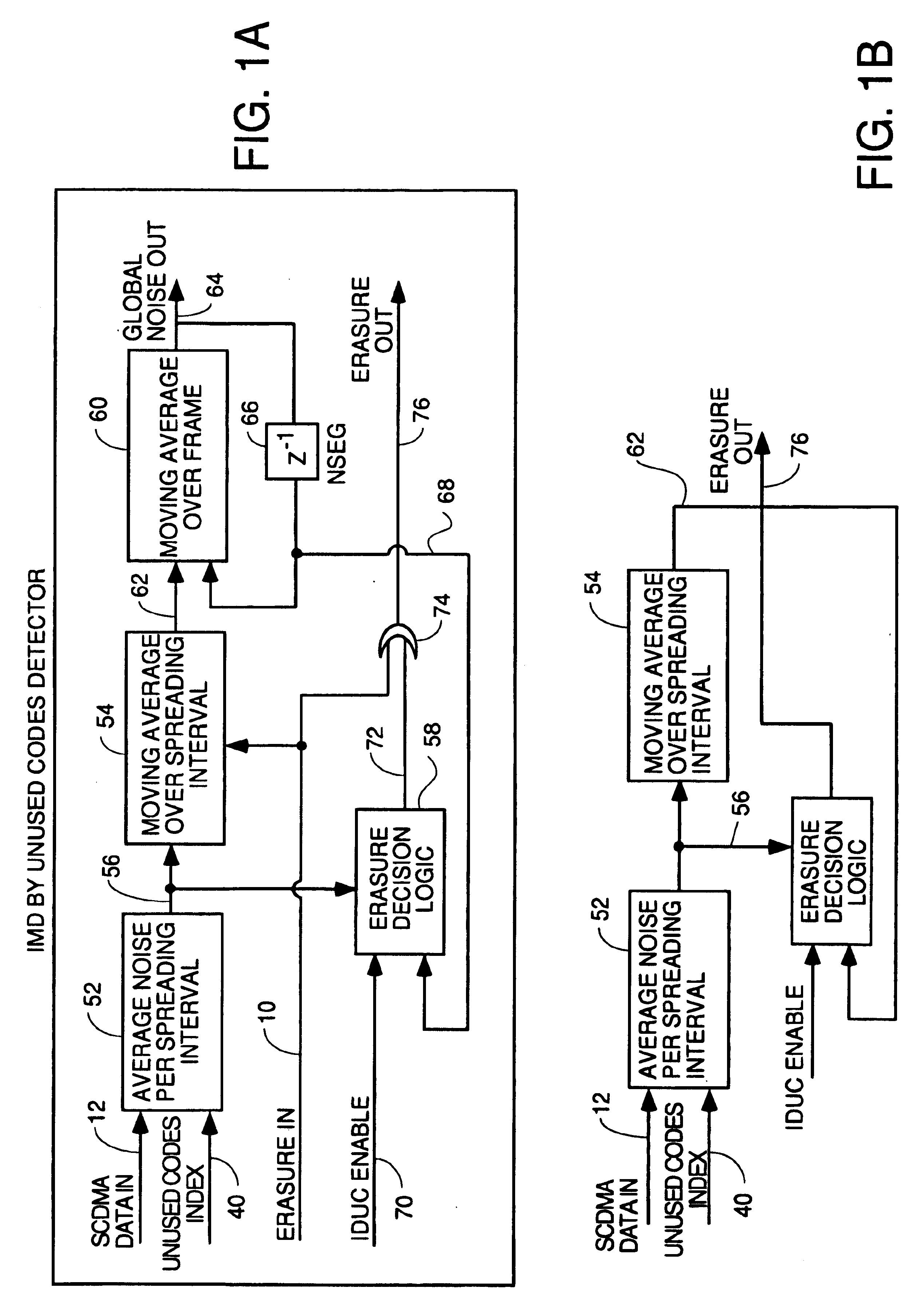
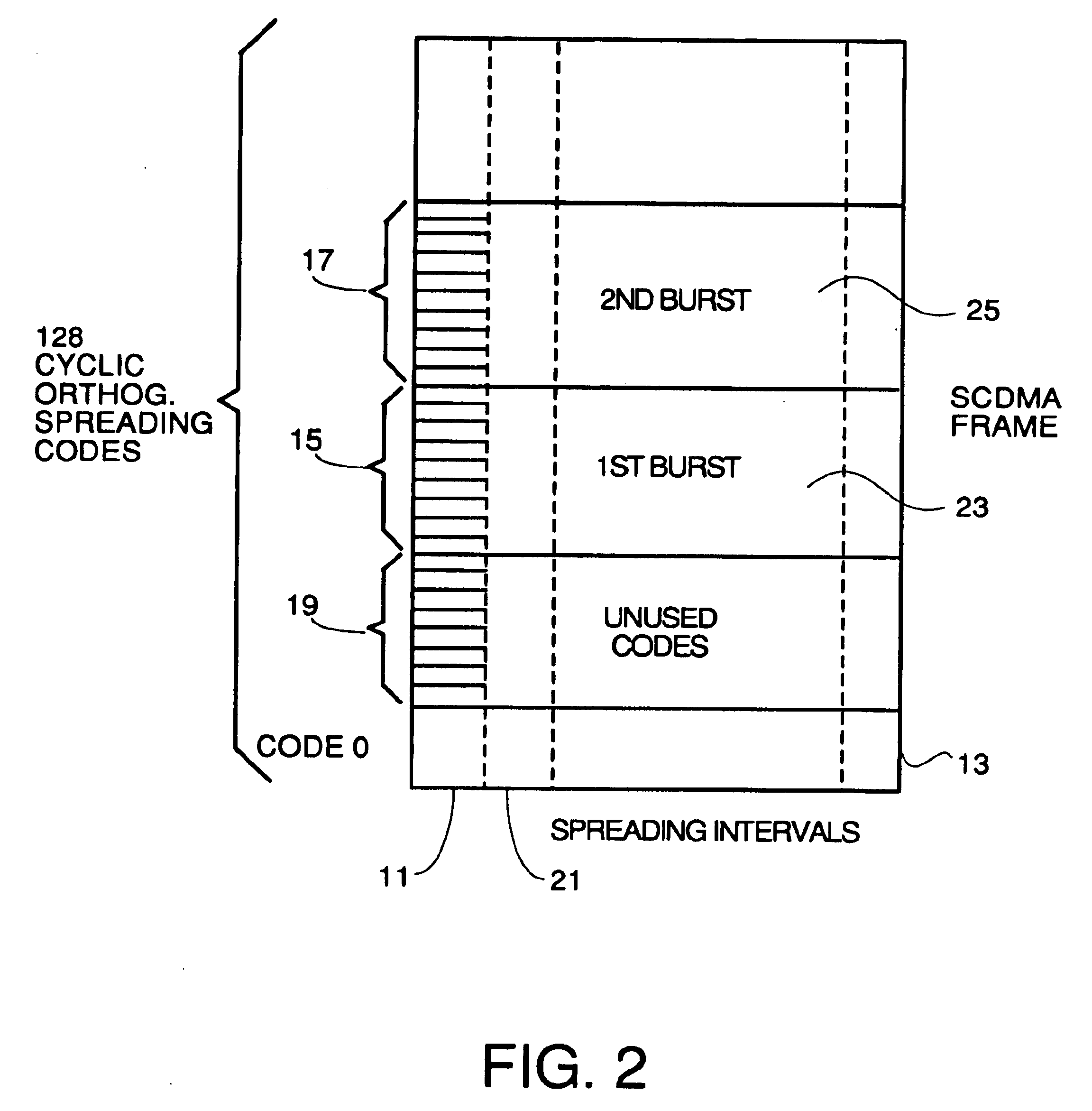
Detection of impulse noise using unused codes in CDMA systems
InactiveUS6859488B2Improving error correction capability of error correctionCancel noiseError preventionSpeech analysisDiscrimination thresholdEngineering
An impulse detector which can detect both low and high levels of impulse noise in a CDMA system is comprised of circuitry to calculate the background noise level in unused codes. Another circuit calculates the average noise power in the unused codes of each spreading interval to output the noise power per spreading interval. This average is continuously averaged over spreading intervals by another circuit which outputs the average background noise power. A comparator compares the noise power in the current spreading interval with the background noise power plus a programmable threshold and generates an erasure indication if the background noise power plus a discrimination threshold is exceeded.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
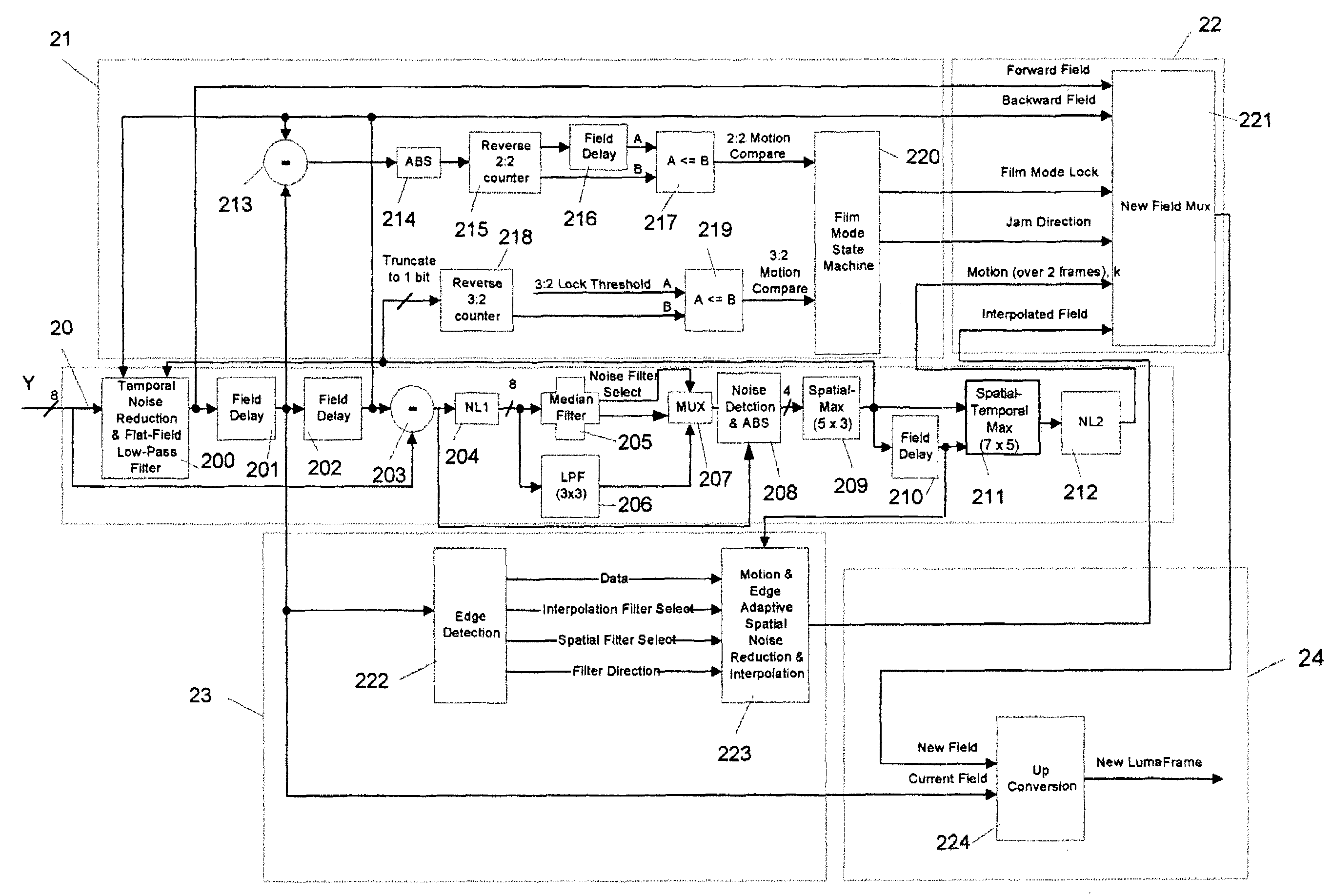
Content-dependent scan rate converter with adaptive noise reduction
ActiveUS7375760B2Quantity minimizationReduce noiseTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionLow-pass filter
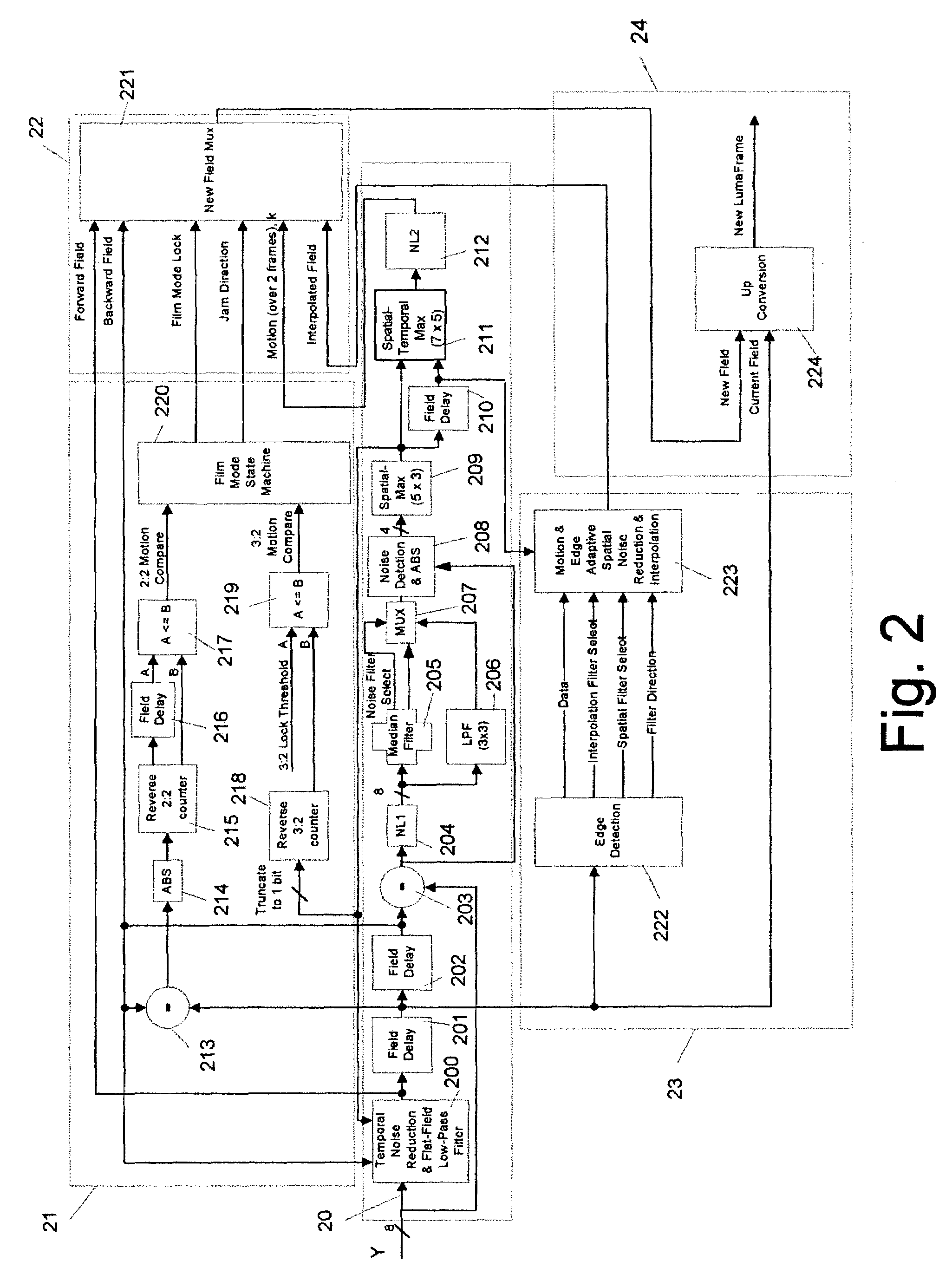
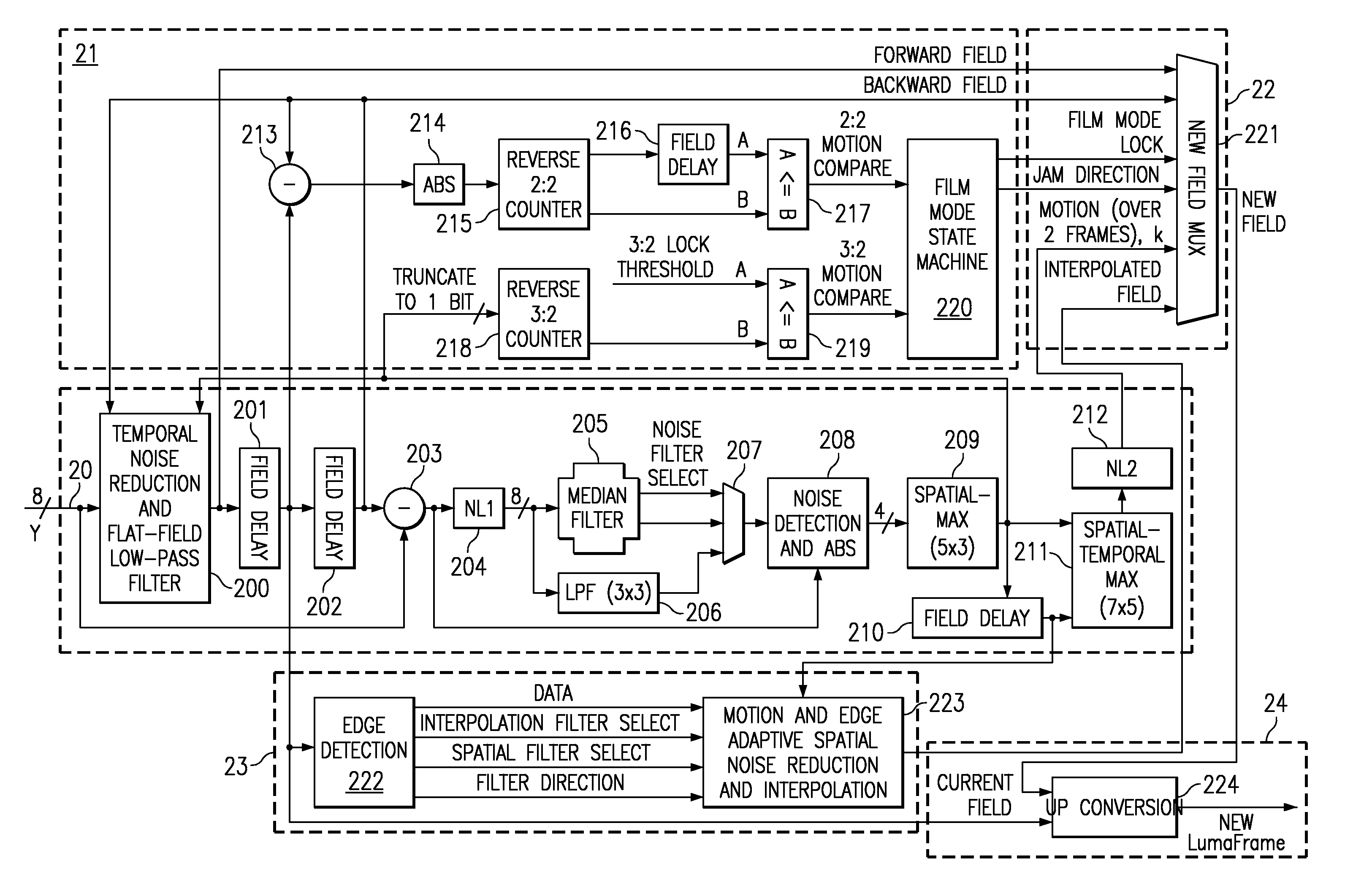
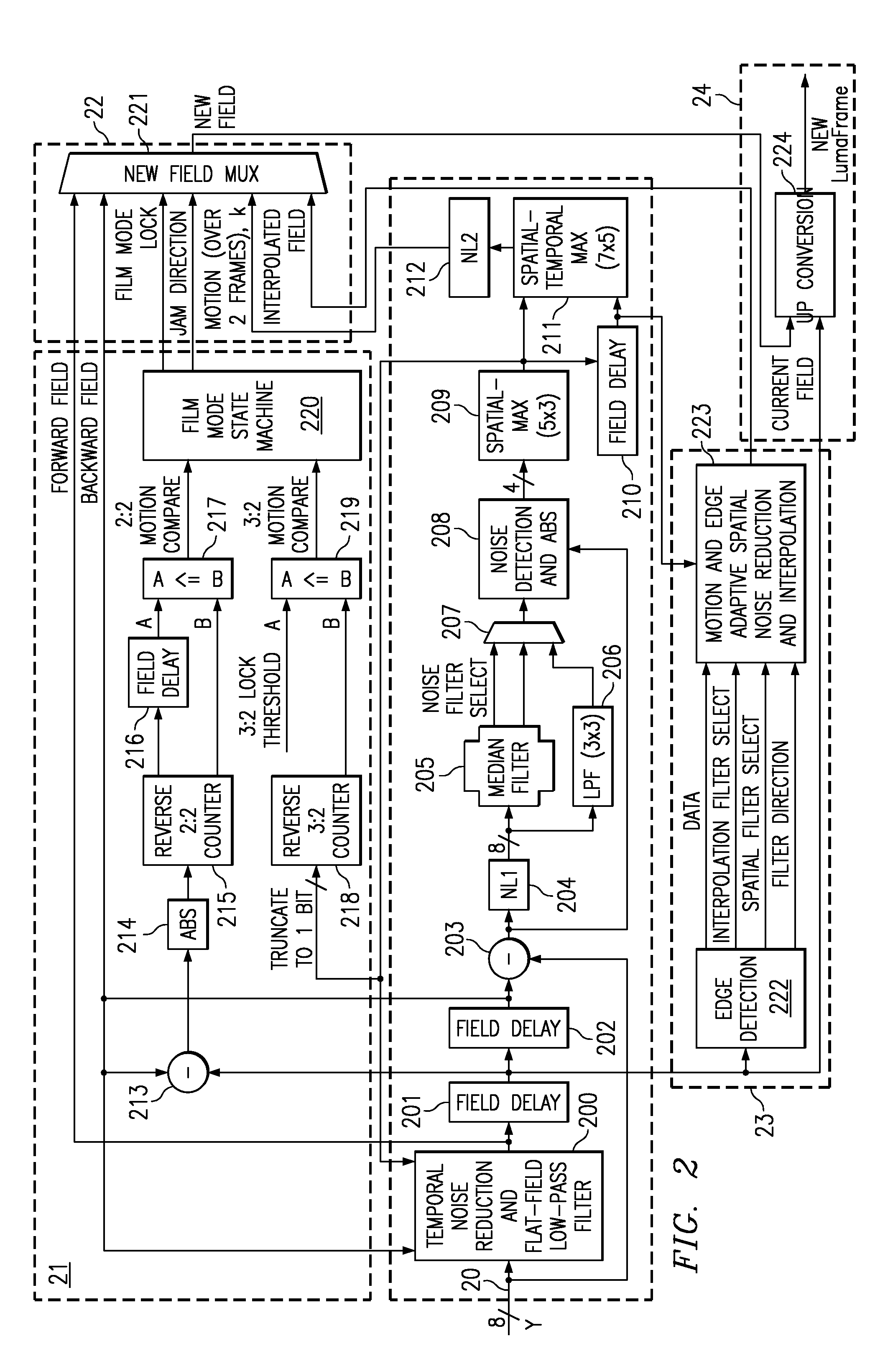
A content-dependent scan rate converter with adaptive noise reduction that provides a highly integrated, implementation efficient de-interlacer. By identifying and using redundant information from the image (motion values and edge directions), this scan rate converter is able to perform the tasks of film-mode detection, motion-adaptive scan rate conversion, and content-dependent video noise reduction. Adaptive video noise reduction is incorporated in the process where temporal noise reduction is performed on the still parts of the image, thus preserving high detail spatial information, and data-adaptive spatial noise reduction is performed on the moving parts of the image. A low-pass filter is used in flat fields to smooth out Gaussian noise and a direction-dependent median filter is used in the presence of impulsive noise or an edge. Therefore, the selected spatial filter is optimized for the particular pixel that is being processed to maintain crisp edges.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
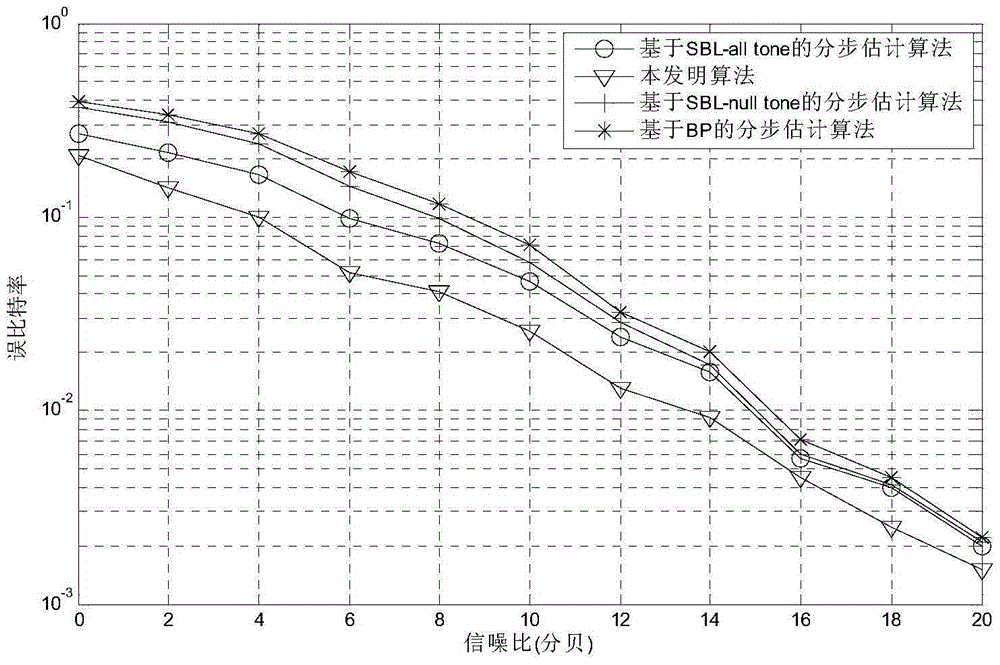
Method for estimating pulse noise in OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Domain Multiplexing) underwater acoustic communication system
ActiveCN105227512AImprove performanceCarrier regulationMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumPhase noise
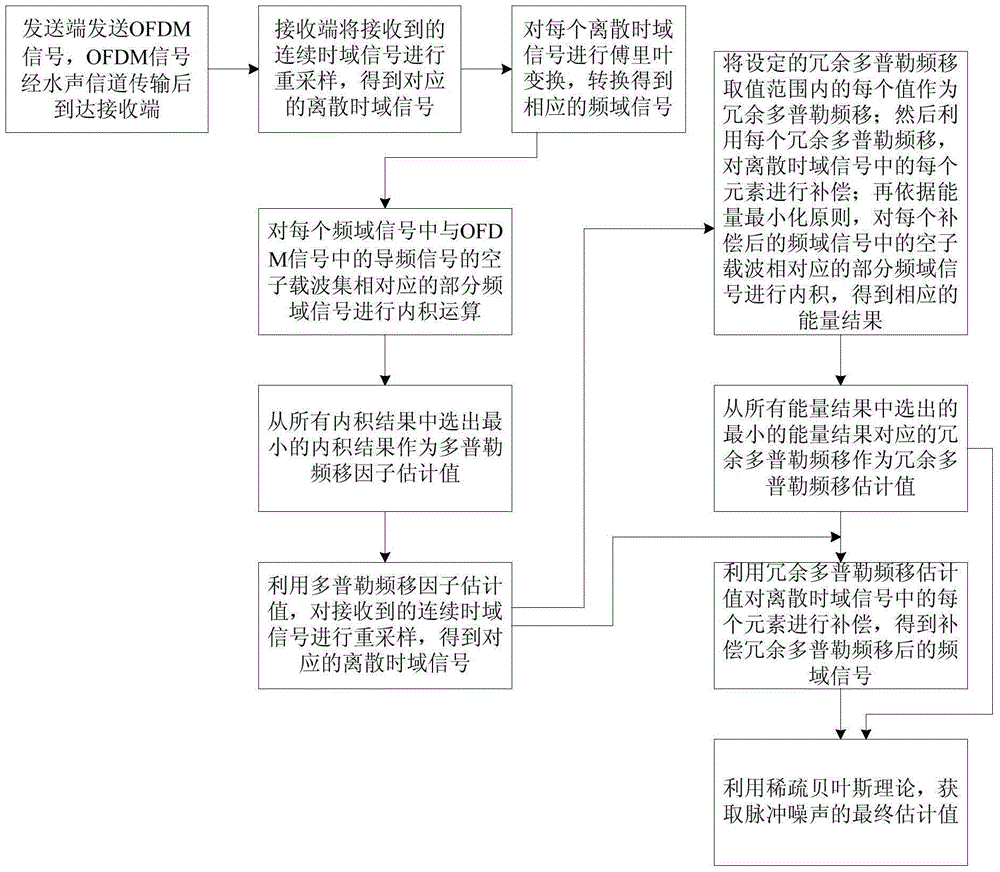
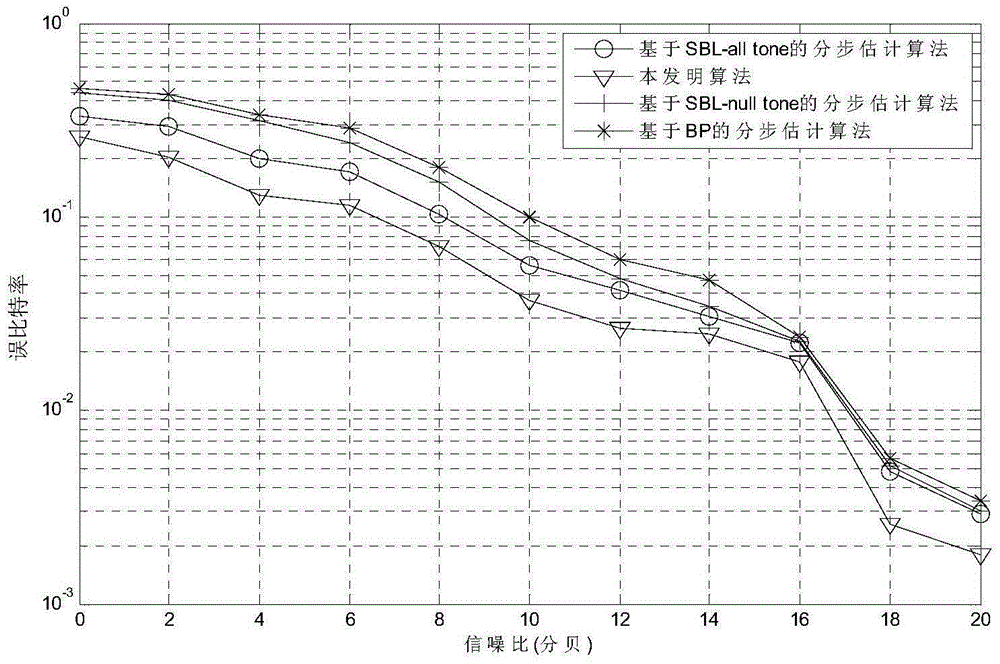
The invention discloses a method for estimating pulse noise in an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Domain Multiplexing) underwater acoustic communication system. At a receiving end, sparse estimation is performed on pulse noise on an OFDM signal in an underwater acoustic channel transmission process according to a frequency domain signal subjected to redundant Doppler frequency shift compensation, and frequency offset compensation is performed on the frequency domain signal subjected to the redundant Doppler frequency shift compensation with void subcarriers. Under the consideration of mutual interference between the pulse noise and a carrier frequency offset in underwater acoustic communication, compensation of the carrier frequency offset is added in an iteration process while the pulse noise is estimated with all subcarriers and a posteriori distribution under a framework of conventional sparse Bayesian learning, and the frequency domain signal subjected to the redundant Doppler frequency shift compensation and a measurement diagonal matrix for estimating the pulse noise are updated continuously in order to lower influences between the two types of interference. Moreover, the pulse noise is estimated by full utilization of all the subcarriers in the method, so that the spectrum efficiency and the performance of the communication system are improved.
Owner:云南保利天同水下装备科技有限公司
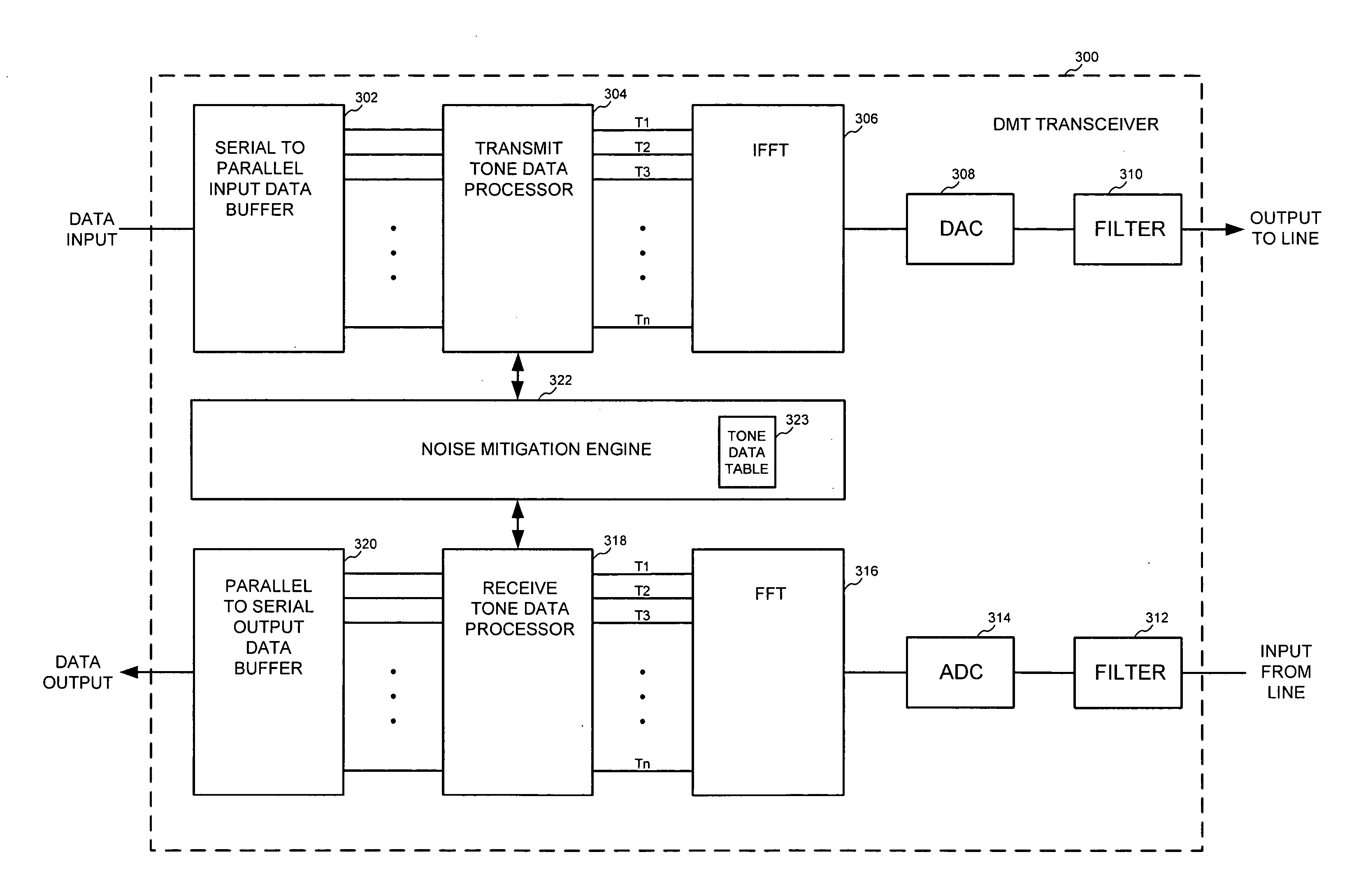
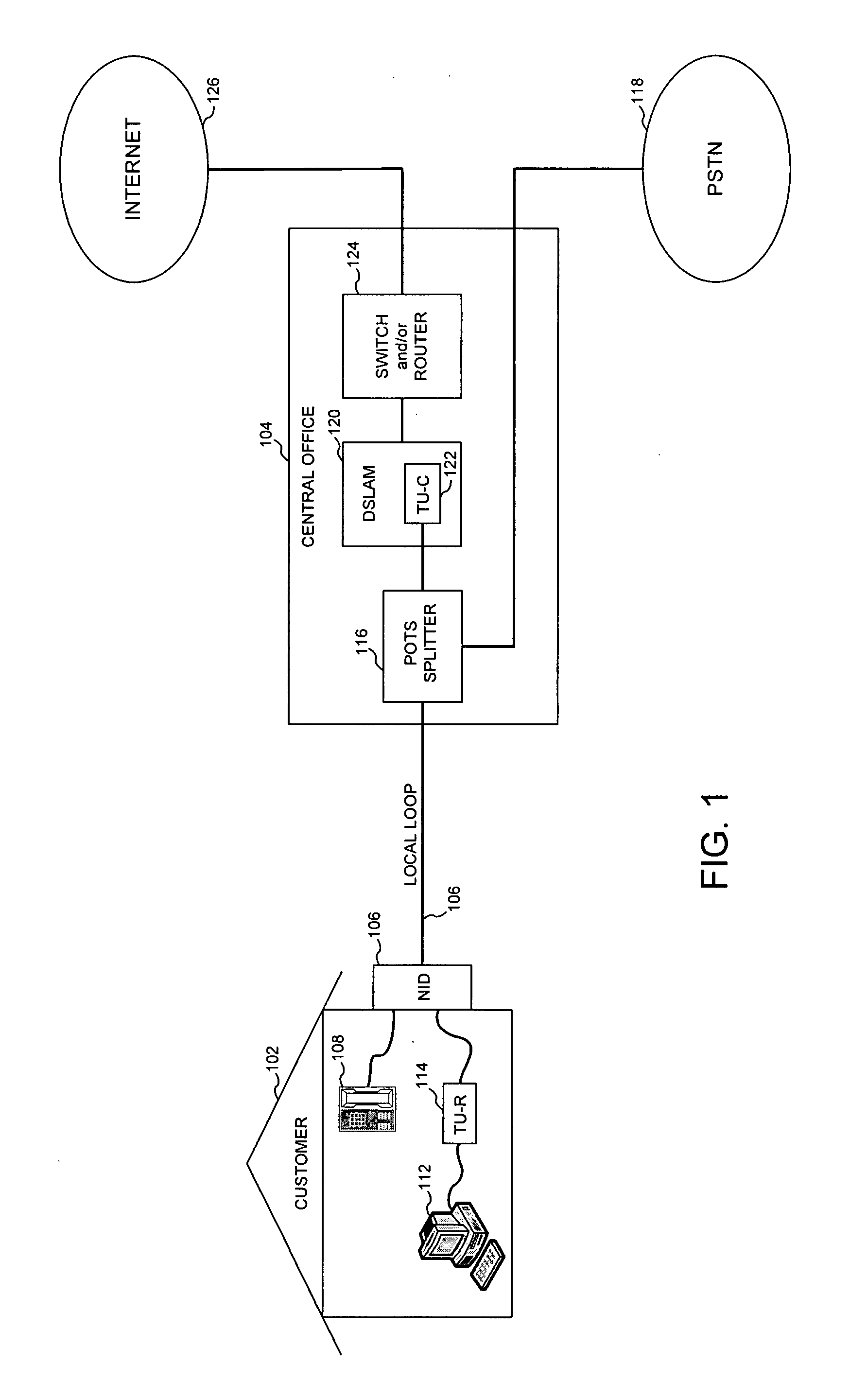
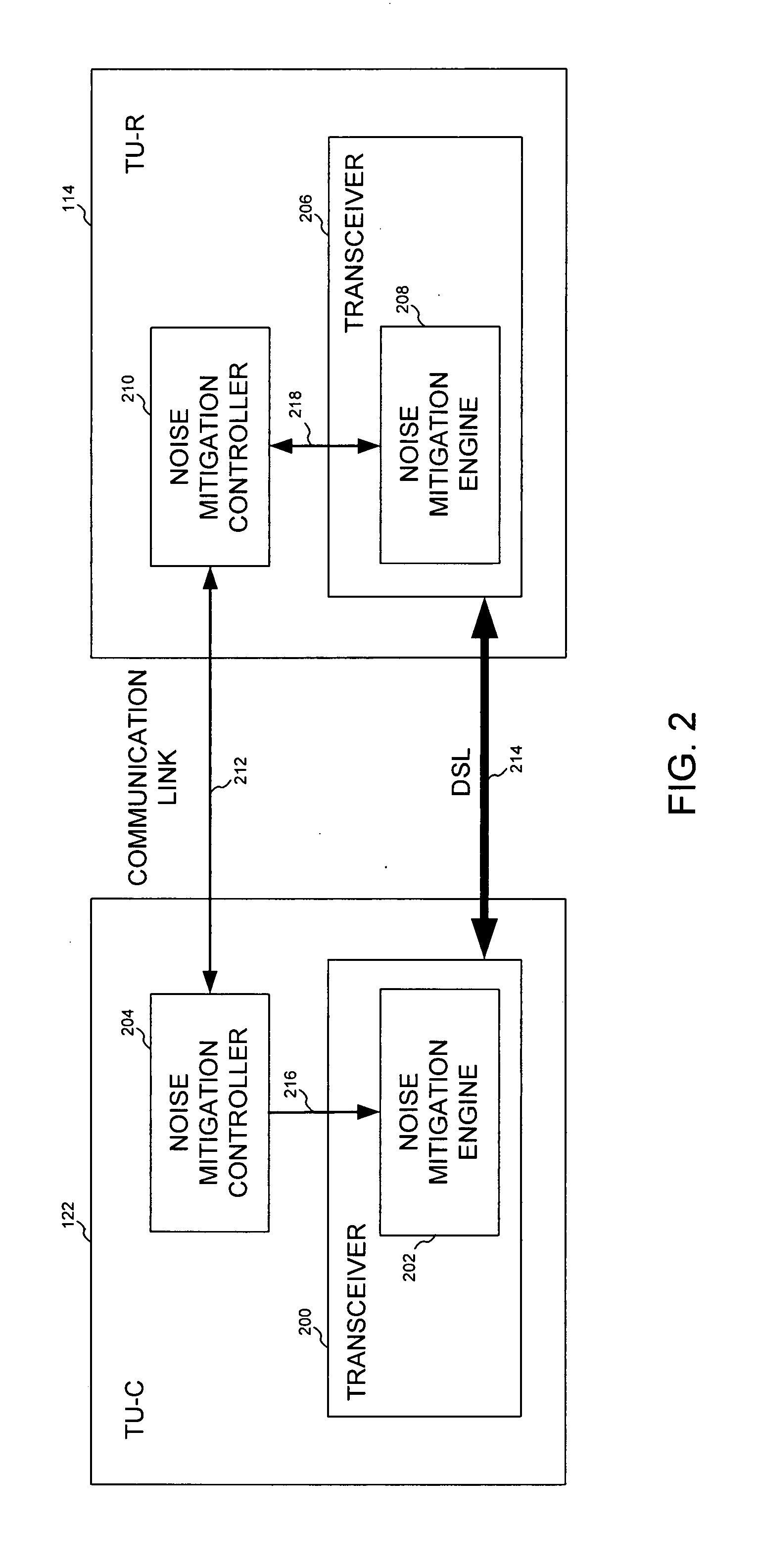
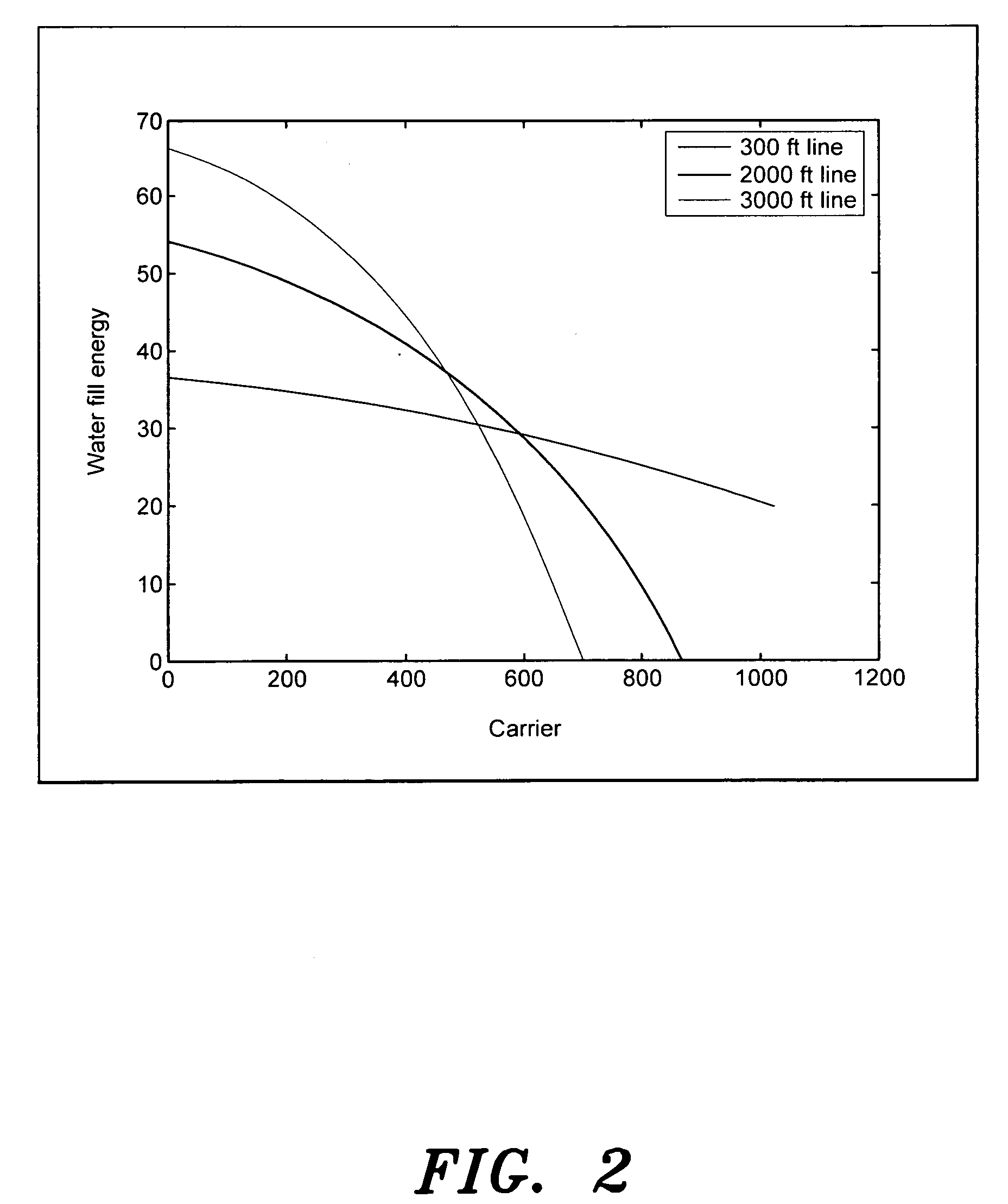
Digital subscriber line noise mitigation techniques, and applications thereof
InactiveUS20070230548A1Reduce the impactImproved noise measurementError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission path divisionNoise monitoringDigital subscriber line
The present invention provides digital subscriber line noise mitigation techniques, and applications thereof. In an embodiment, the present invention provides a toolbox of methods and techniques for mitigating the effects of noise in xDSL systems. These methods and techniques are controllable and locatable at one or both ends of a DSL communication link (e.g., within a central office transceiver unit or a remote transceiver unit). These novel methods and techniques include: (1) per tone noise margin modification, (2) data framer constraints modification, (3) improved noise measurements; (4) more robust on-line reconfiguration processes, (5) worst case noise monitoring, (6) induced bit rate limitations, and (7) distortion noise mitigation. These methods and techniques are particularly useful for mitigating the effects of time-varying noise and impulse noise.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
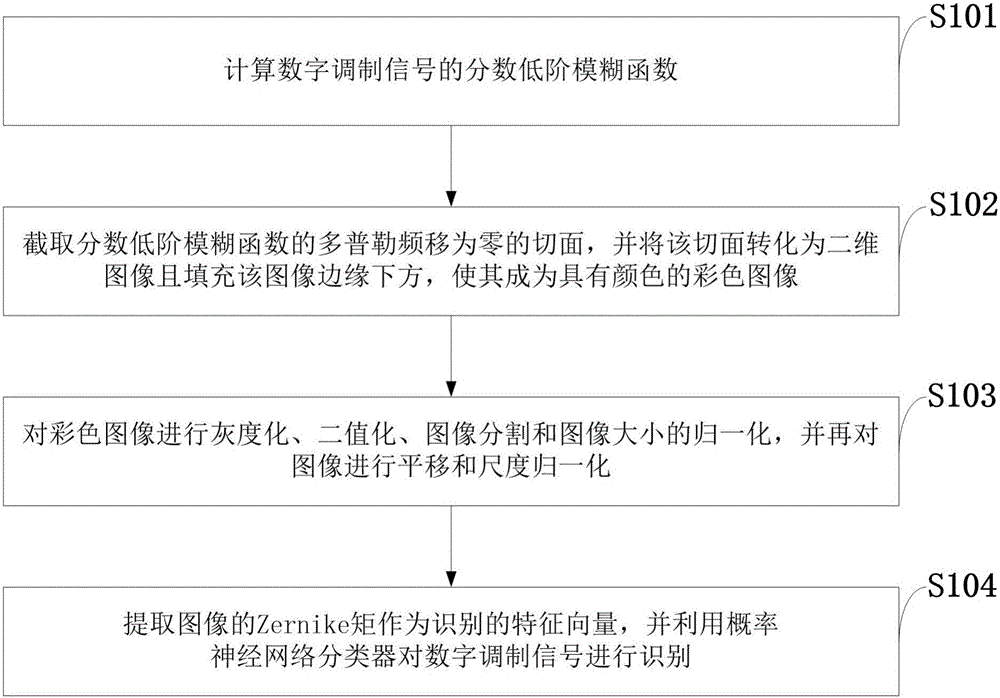
Digital modulation signal identification method under pulse noise
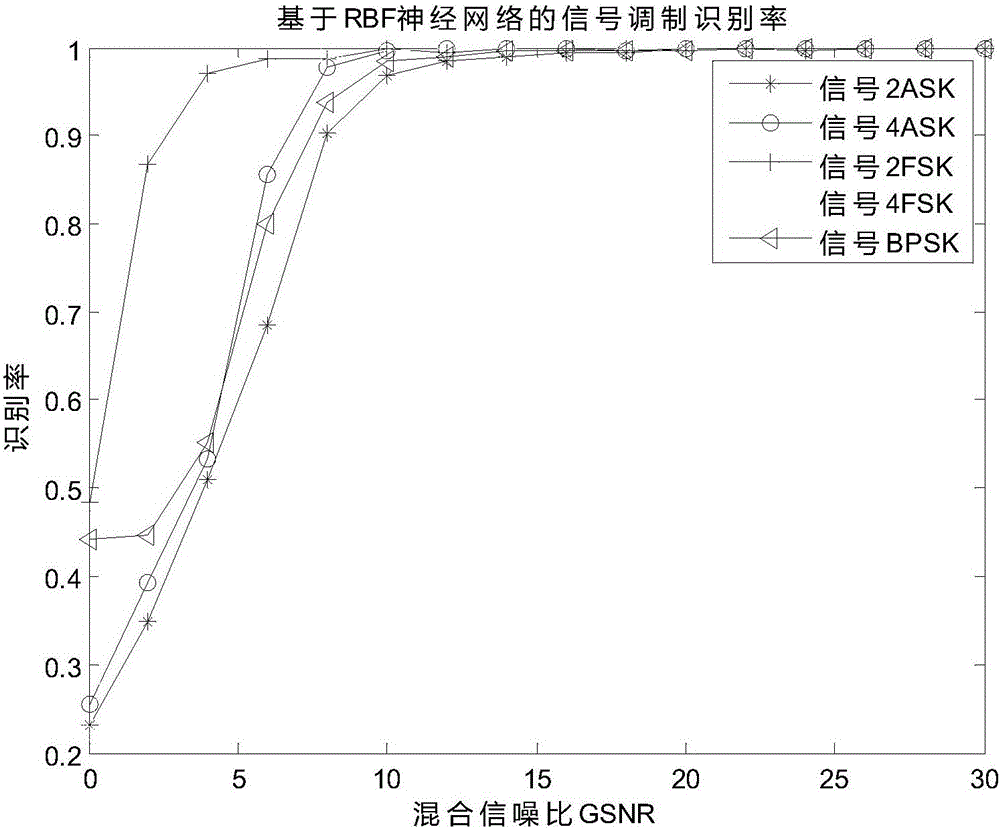
The invention discloses a digital modulation signal identification method under pulse noise. The method comprises the following steps that the fractional low-order fuzzy function of digital modulation signals is calculated; the tangent plane of zero Doppler frequency shift of the fractional low-order fuzzy function is intercepted, and the tangent plane is converted into a two-dimensional image and fills below the edge of the image so as to become a color image with color; graying, binarization, image segmentation and image size normalization are performed on the color image and translation and scale normalization are performed on the image; and the Zernike moment of the image is extracted to act as the characteristic vector of identification, and the digital modulation signals are identified by using a probability neural network classifier. The digital modulation signal identification method has great identification performance on the digital modulation signals 2ASK, 4ASK, 2FSK, 4FSK and BPSK under standard distribution pulse noise.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Active noise reduction method for automobile
ActiveCN104616667AReduce correlationReduced stabilitySpeech analysisSound producing devicesSound sourcesEngineering
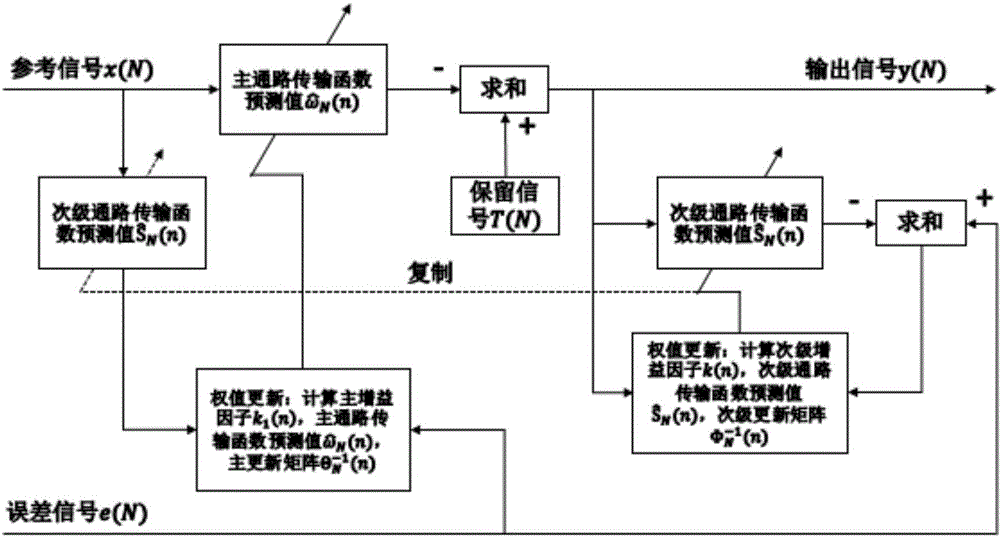
The invention relates to an active noise reduction method for an automobile and belongs to the voice signal processing technical field. The active noise reduction method guides the secondary sound source and adopts the self-adaptive algorithm for controlling the sound signal sent by the secondary sound source, and the outputted secondary sound wave after self-adaptive convergence at the noise reducing point has constant amplitude and reversal phase with the noise at the point for getting the noise reducing target. The algorithm and the method structure are improved based on the original active noise reduction method, the recursive least square method is used for replacing the least mean square algorithm as the core self-adaptive algorithm for the main path transfer function estimation and the secondary path transfer function estimation; the method has strong capability of eliminating the pulse noise and non-stationary noise and has good noise reducing error and noise reducing feed, the stability problem caused by the signal dependency is improved for the retaining signal in the automobile, the useful signal is kept while the noise is reduced and the signal to noise ratio is greatly improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Cognitive and Universal Impulse Noise Protection
InactiveUS20090177938A1Reduced accommodationReduce the amount requiredError prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorDigital subscriber lineForward error correction
Impulse noise from nearby or intense electrical sources can disrupt communications over digital subscriber lines. There are many methods to deal with errors produced by impulse noise sources. Forward error correction (FEC) codes such as Reed Solomon coding along with scrambling and interleaving are used to correct small errors. However, for larger errors, retransmission is favored. Retransmission can be applied at the Discrete Multi-tone symbol level thus eliminating the need to insert sequence identification into data transmission units, furthermore retransmission can also be employed to exploit the error correcting capabilities of the FEC codes. Finally, an impulse noise protection system can exploit impulse noise statistics to configure the redundancy in the FEC codes and to enable the use of blanking. Exemplary embodiments of systems described can cooperatively use impulse noise statistics to utilize retransmission, FEC and blanking to mitigate the effects of impulse noise.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
Noise correlation radar devices and methods for detecting targets with noise correlation radar
InactiveUS8035551B1Instantaneous band widthIncrease the carrier frequencyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsFrequency modulation
A pulsed compression noise correlation radar uses noise modulation and pulse compression technology to scramble recognizable transmit signal characteristics and reduce transmit energy. The pulsed noise correlation radar advantageously uses pulse compression technology, a pulsed linear frequency modulated noise correlation mixer, and a new and innovative noise fused waveform to automatically correlate the pulsed linear frequency modulated (LFM) noise waveform with the received signal. The pulsed noise correlation radar apparatus and system now make it possible to effectively reduce transmitting power, preserve high band widths through oversampling in the receiver, and achieve multi-channel array frequency diversity. A secure pulsed compression noise correlation radar system and methods for undetected target detection with pulsed noise correlation radar and a pulsed LFM fused noise waveform are also provided.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE
Content-Dependent Scan Rate Converter with Adaptive Noise Reduction
InactiveUS20080218630A1Quantity minimizationReduce noiseTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionLow-pass filter
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
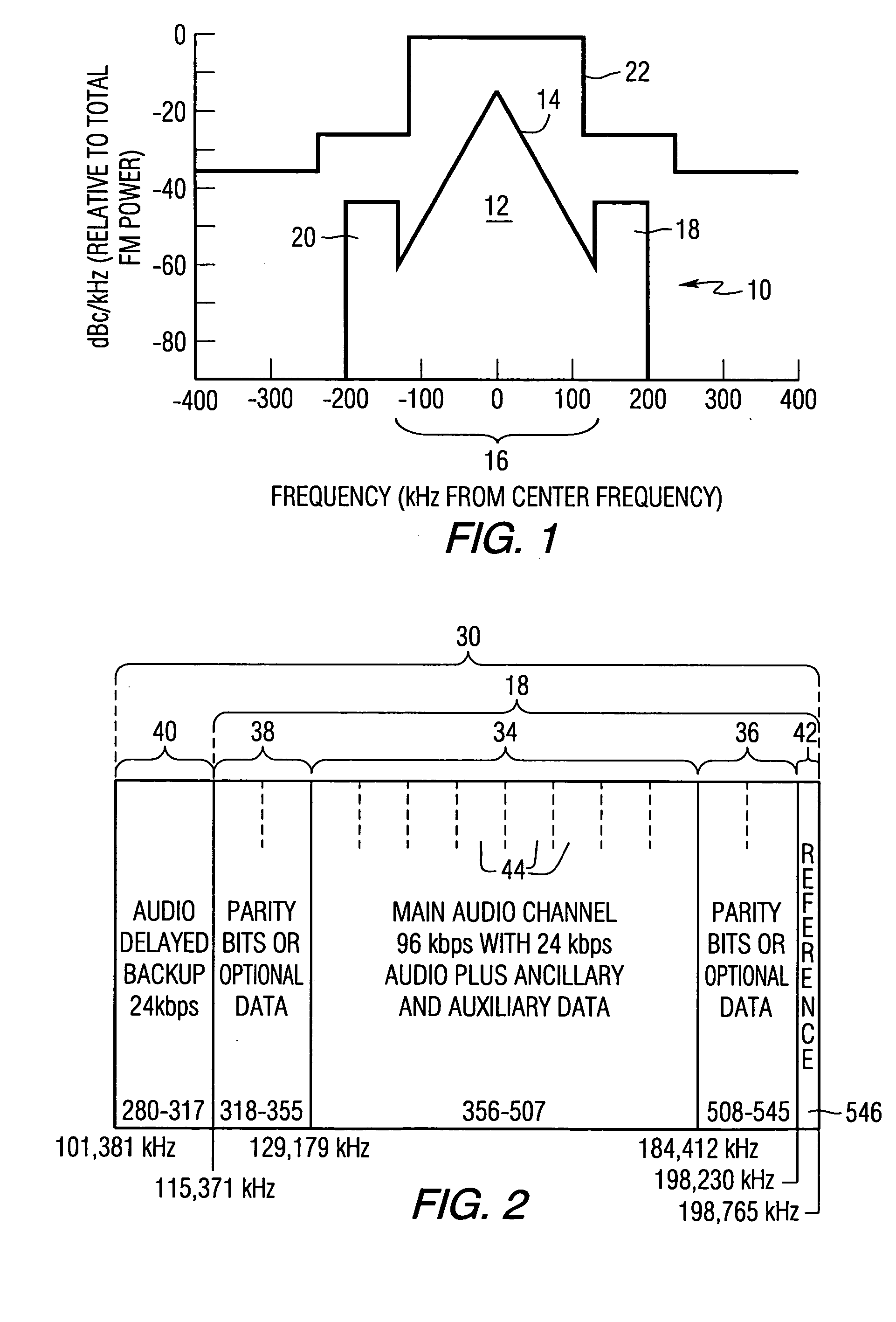
Coherent tracking for FM In-Band On-Channel receivers
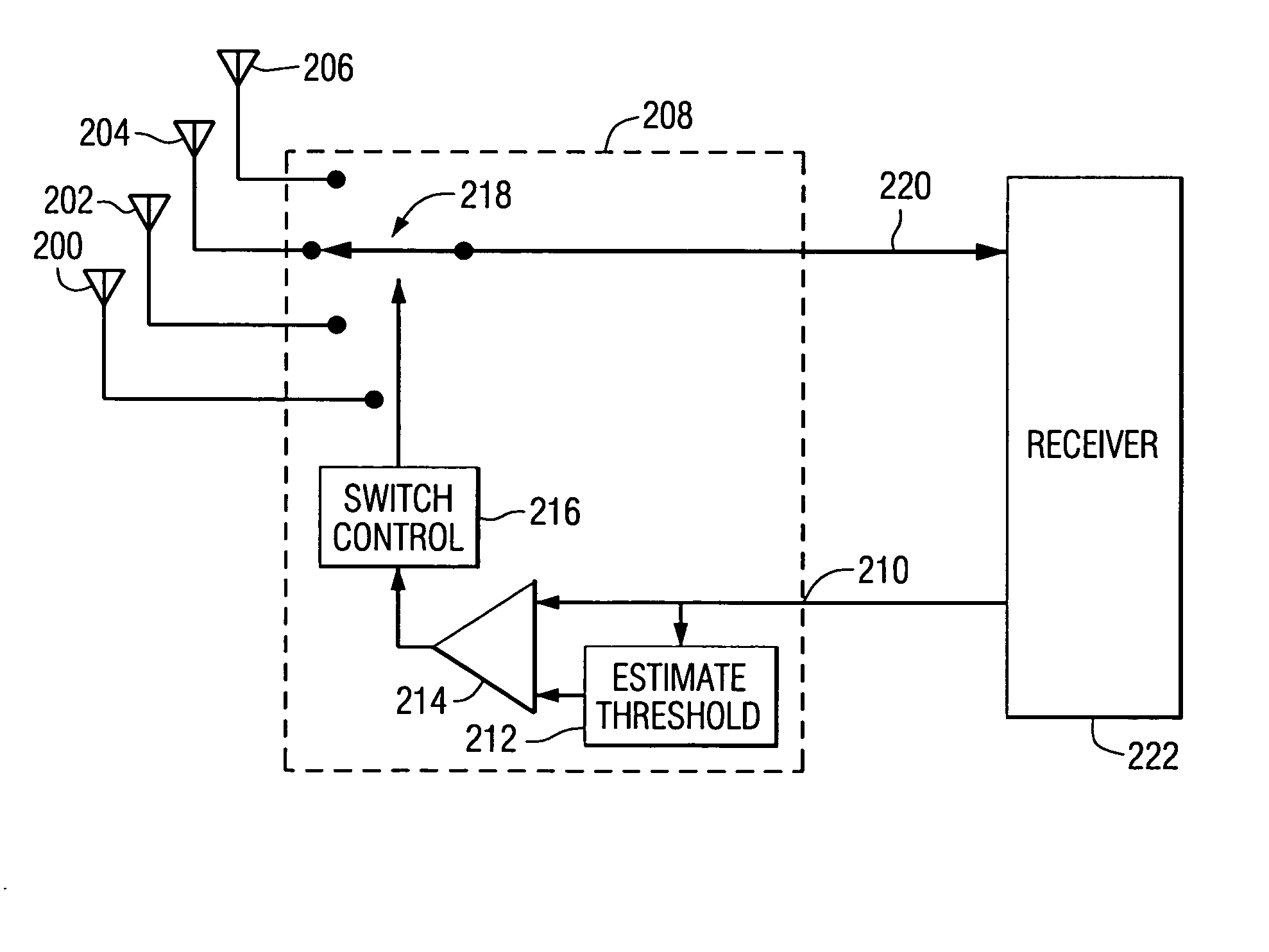
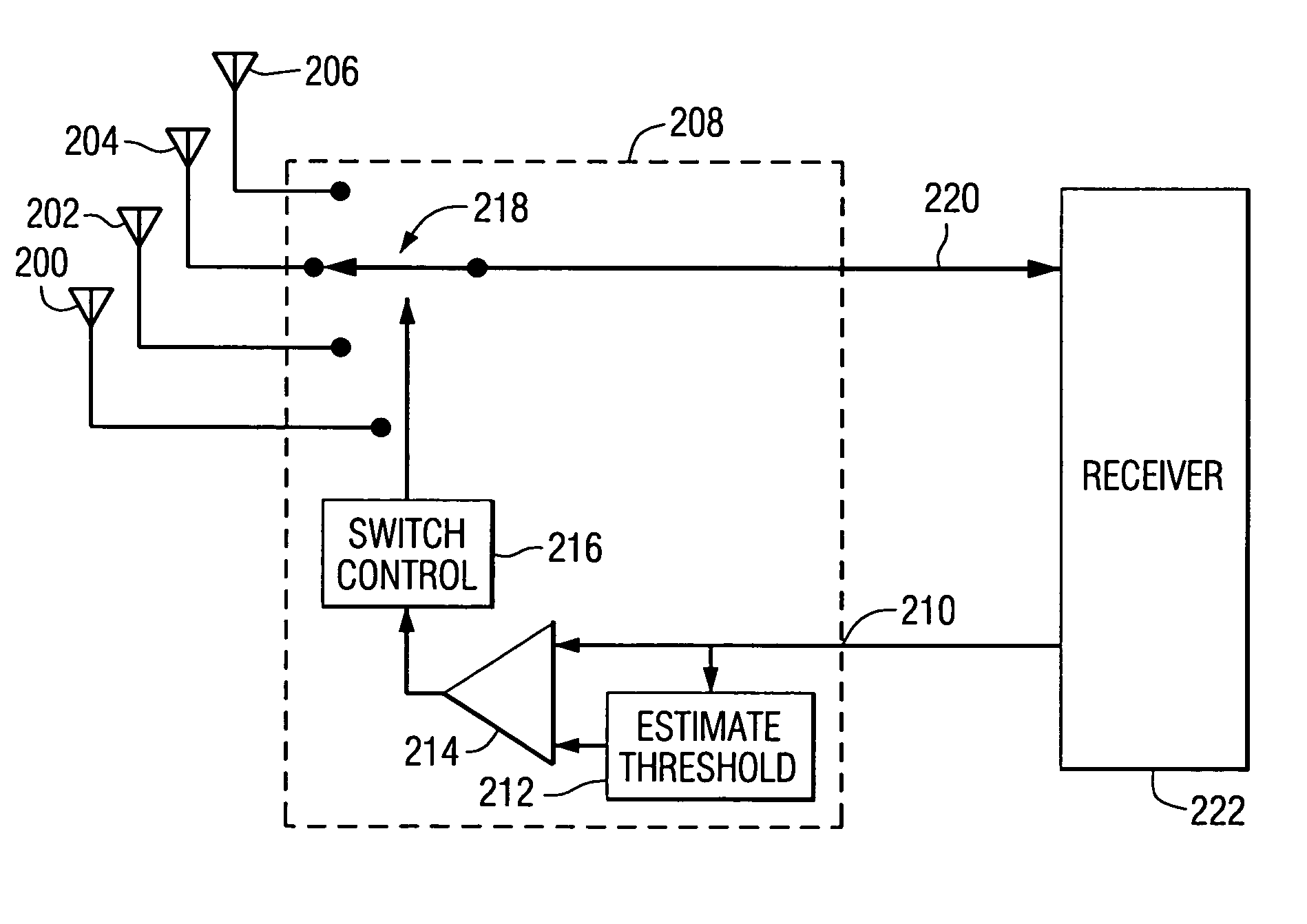
A method for coherently tracking a radio signal including at least one digitally modulated reference carrier is provided, wherein the method comprises the steps of demodulating the reference carrier to produce complex coherent reference gains, detecting a transient that affects the complex coherent reference gains, and adjusting the complex coherent reference gains in the vicinity of the transient to produce adjusted complex coherent reference gains. The transient can be caused by switching among the antenna elements or impulsive noise. Receivers that process signals in accordance with the method, and a method of estimating noise variance of symbols in a radio signal are also provided.
Owner:IBIQUITY DIGITAL CORP
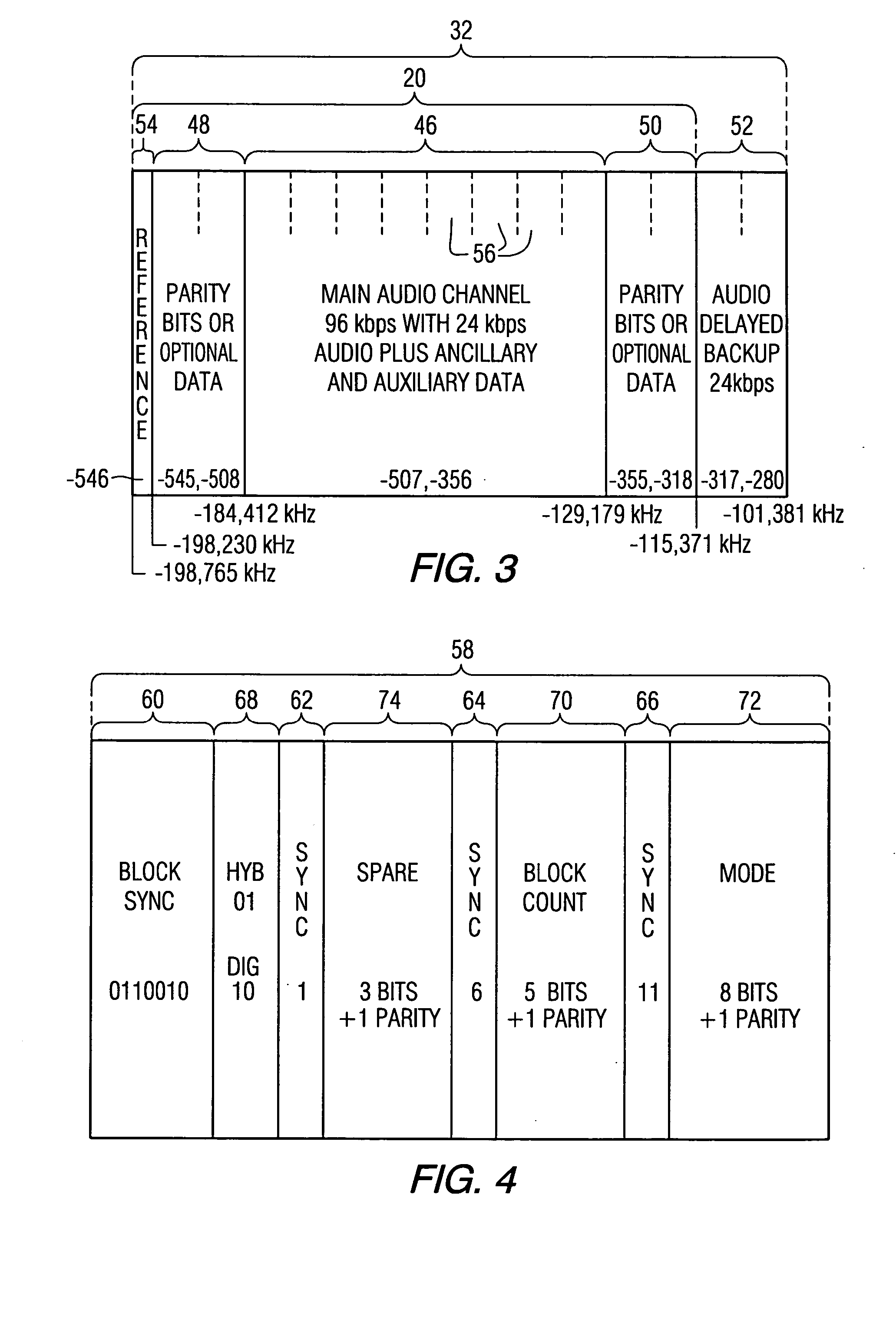
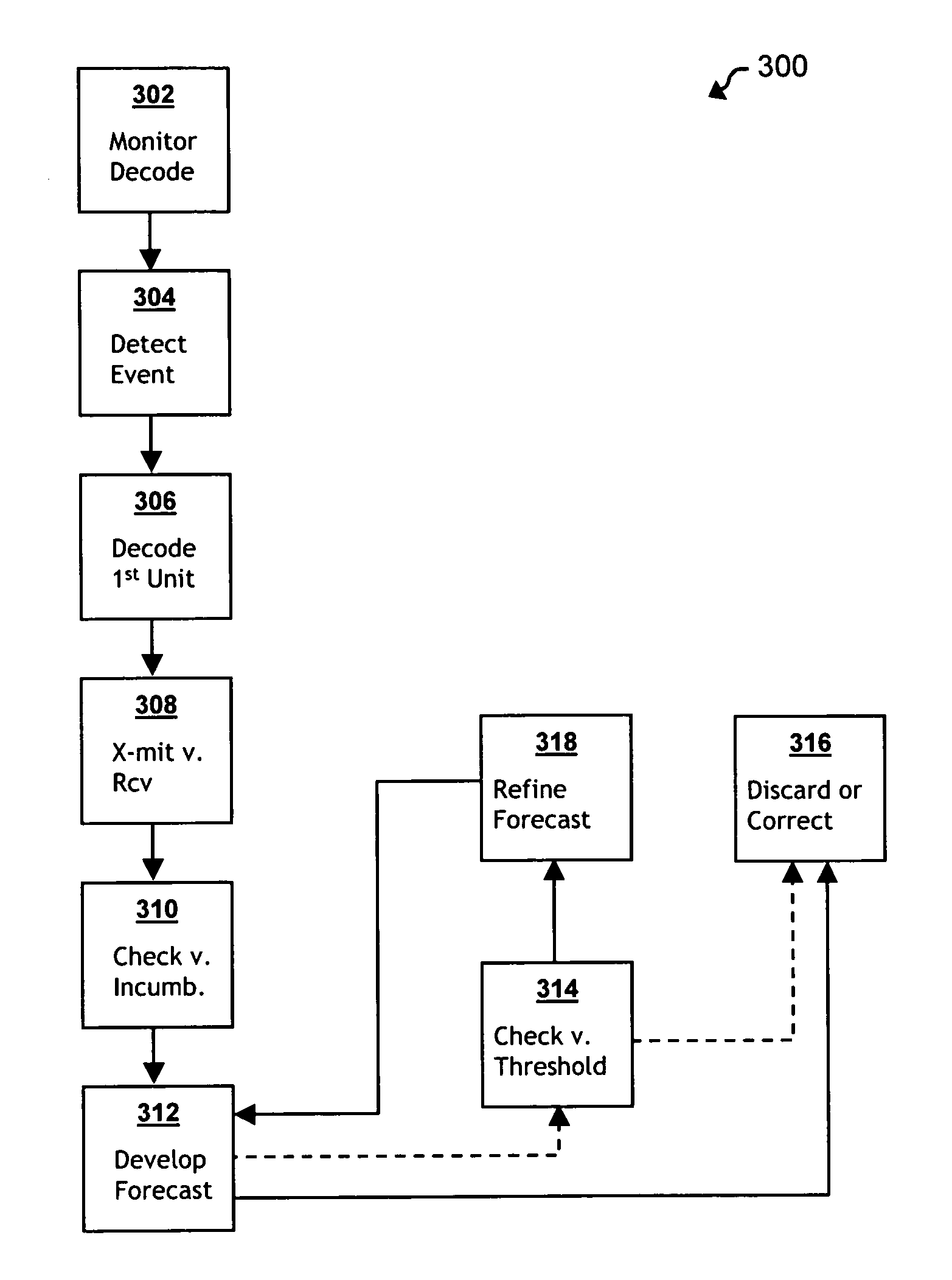
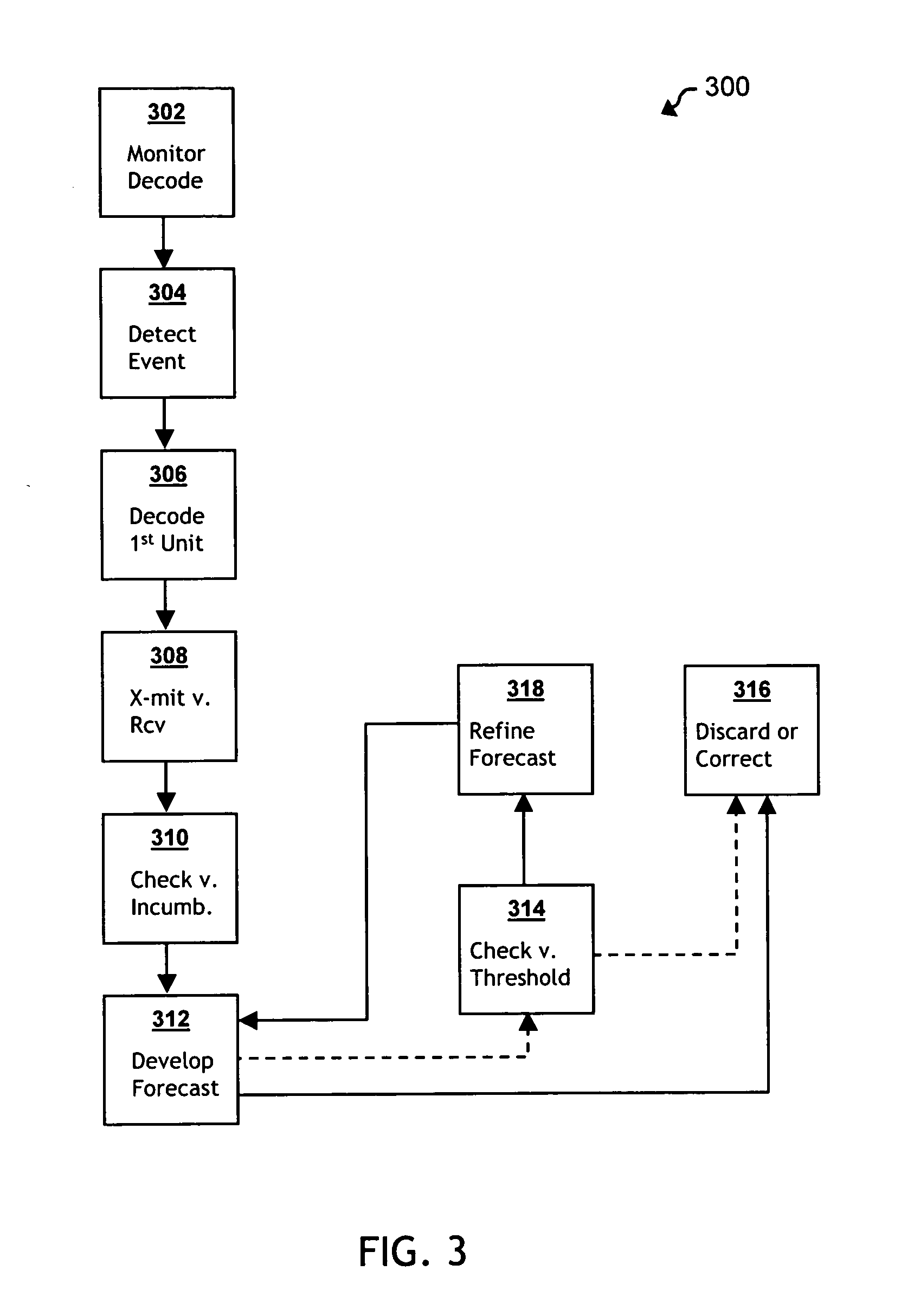
Versatile erasure forecasting system for impulse noise mitigation
InactiveUS20050286566A1Mitigating deleterious impulse noise effectOptimizes data redundancyTime-division multiplexForward error control useDigital dataCommunications system
The present invention provides a system for mitigating impulse noise effects in a digital data transmission system, particularly in a DSL-based communications system (300), by optimizing error correction systems with an erasure forecasting scheme. Within the communications system, encoding and structuring constructs form and permute data transmission units for transmission in a deterministic manner (i.e., having known, fixed characteristics). Once data transmission units have been received over a transmission channel, de-structuring and decoding constructs inversely permute and decode those data transmission units, according to the deterministic manner. Data decoding is monitored (302), and the occurrence of an impulse noise event in the transmission channel is identified (304). A first data transmission unit affected by the impulse noise event is decoded (306). A forecasting construct evaluates the decoded first data transmission unit using known characteristics of the deterministic manner (308, 310), and develops a forecast (312) of locations of an erasure error within a subsequent decoded data transmission unit, which is then utilized to optimize error correction.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Traditional Chinese medicinal material microscopic image noise filtering system and method adopting pulse coupling neural network
InactiveCN104732500AImprove quality inspectionEasy to identifyImage enhancementPattern recognitionMicroscopic image
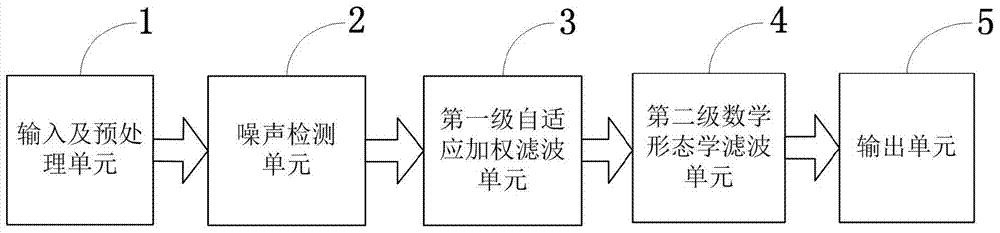
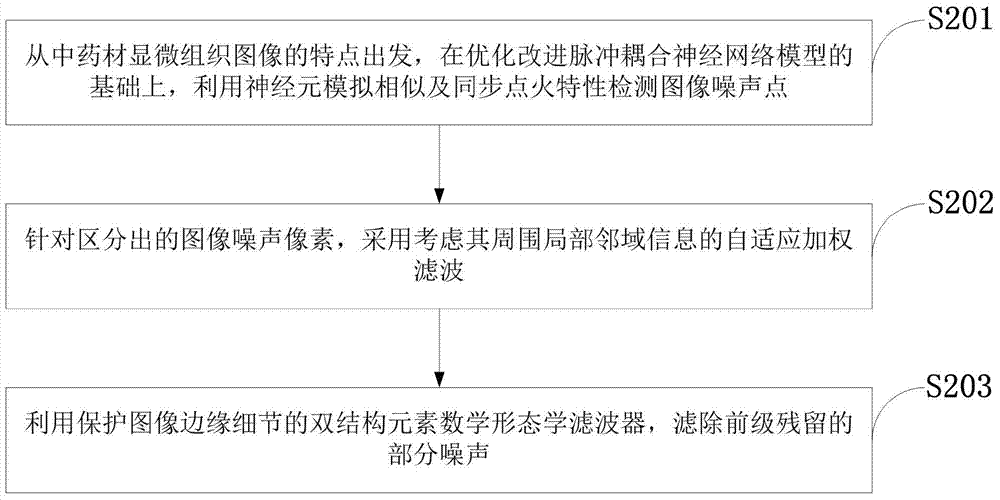
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicinal material microscopic image noise filtering system and method adopting a pulse coupling neural network. A pulse coupling neural network model suitable for processing tissue image information is adopted for detecting traditional Chinese medicinal material microscopic images. When small-density pulse noise pollution happens to the traditional Chinese medicinal material microscopic images, adaptive weighted filtering processing is carried out; when large-density pulse noise pollution happens to the traditional Chinese medicinal material microscopic images, the introduction dual-structure element mathematical morphology with edge detailed information kept is adopted for secondary filtering. Earlier foundations are laid for further improving quality testing, recognition and identification of traditional Chinese medicinal materials; higher noisy point detection performance is achieved, the noise fallout ratio and omission ratio are low, and the noise detection precision is high; detection time is short, and automatism is high; noise is removed, meanwhile, noise interference can be effectively filtered out, and image edge details and other information can be protected well.
Owner:TIANSHUI NORMAL UNIV
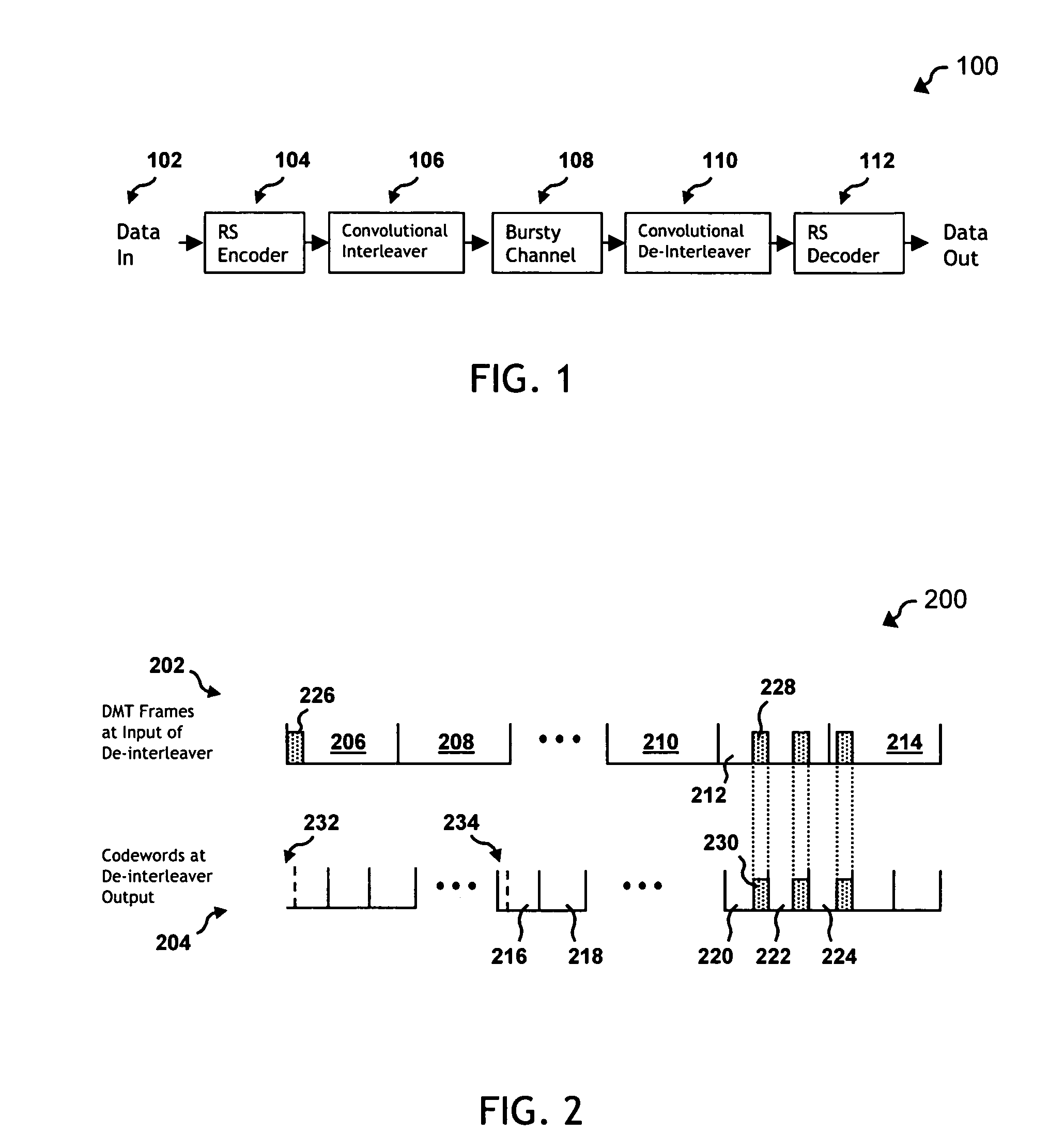
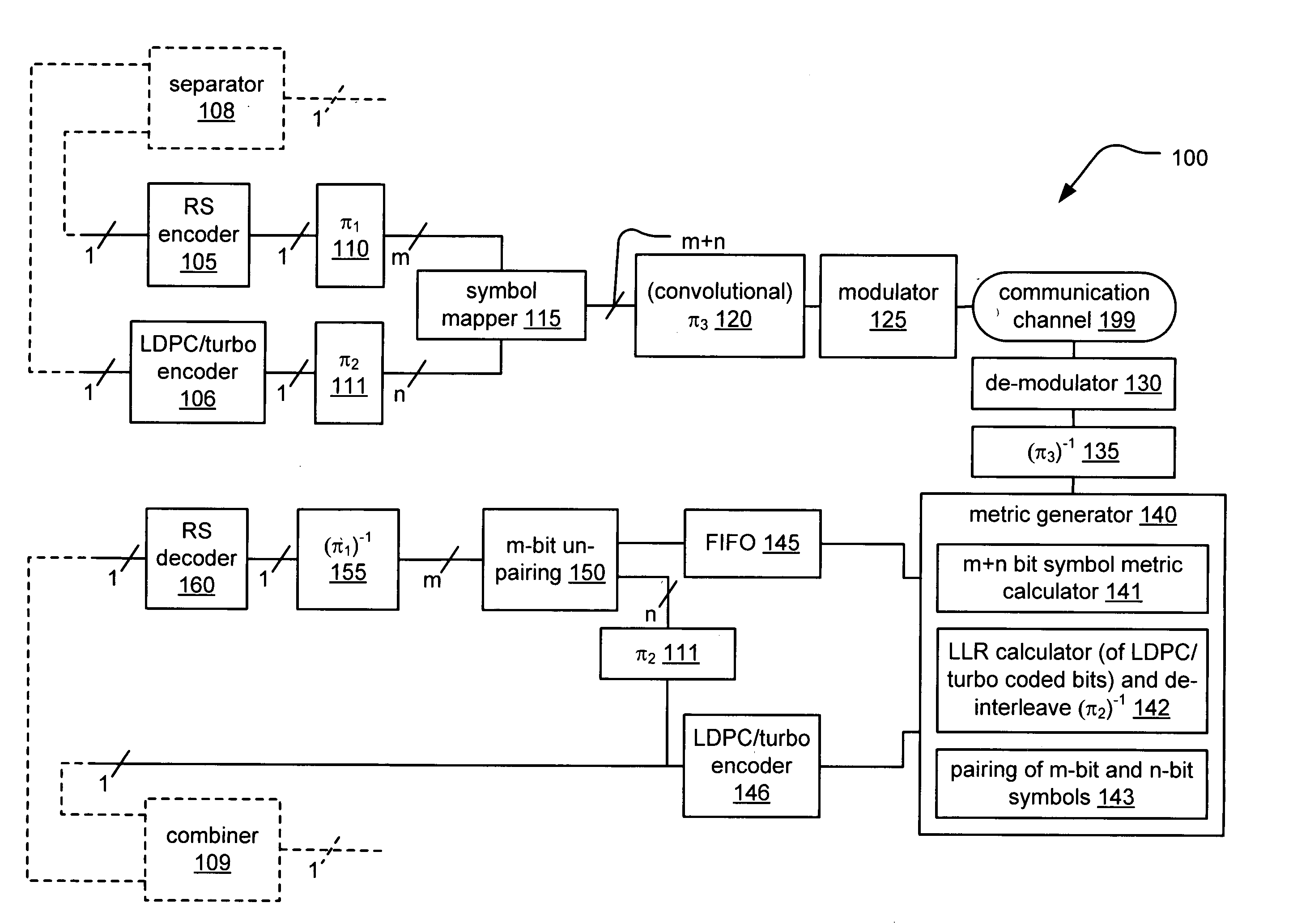
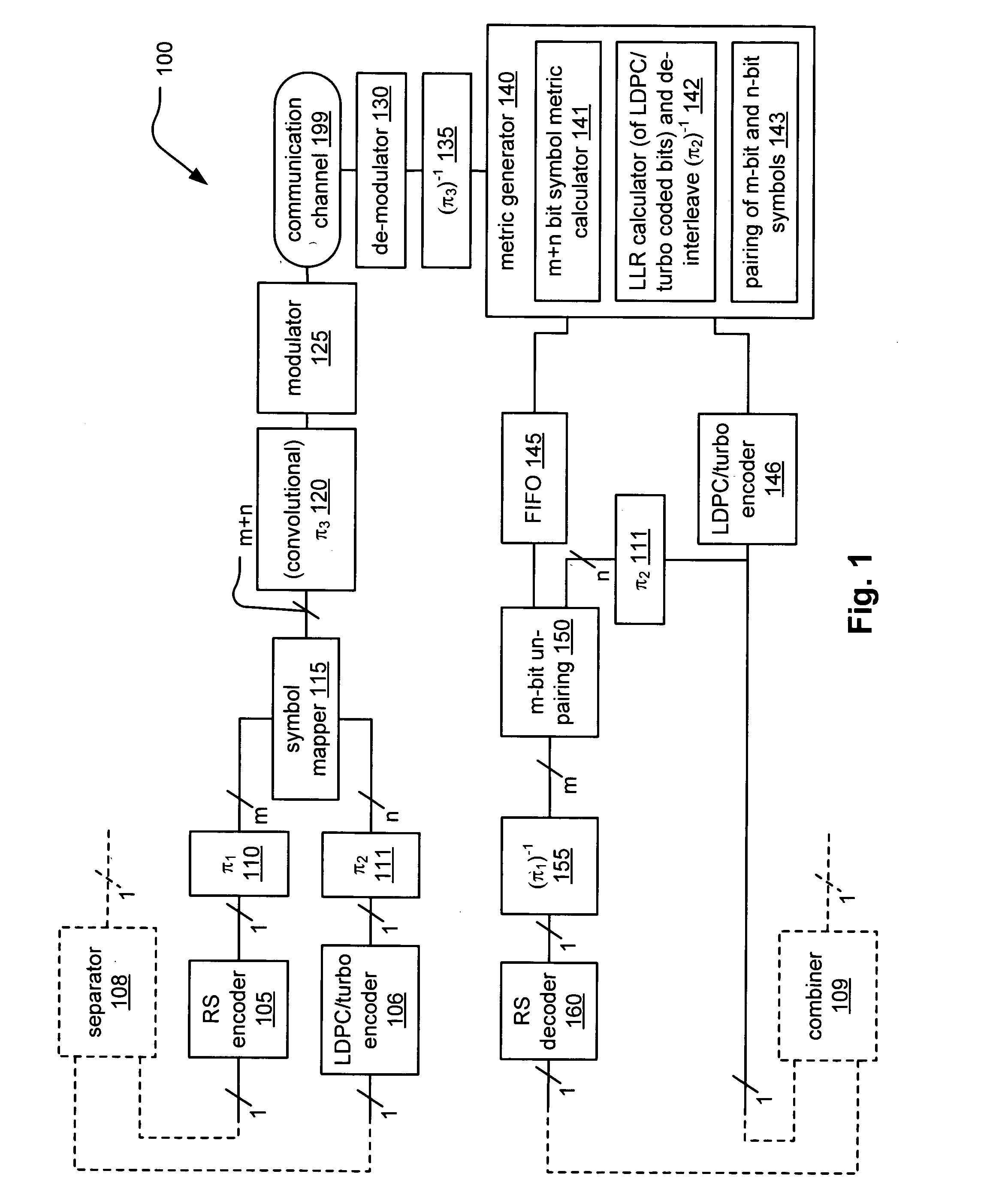
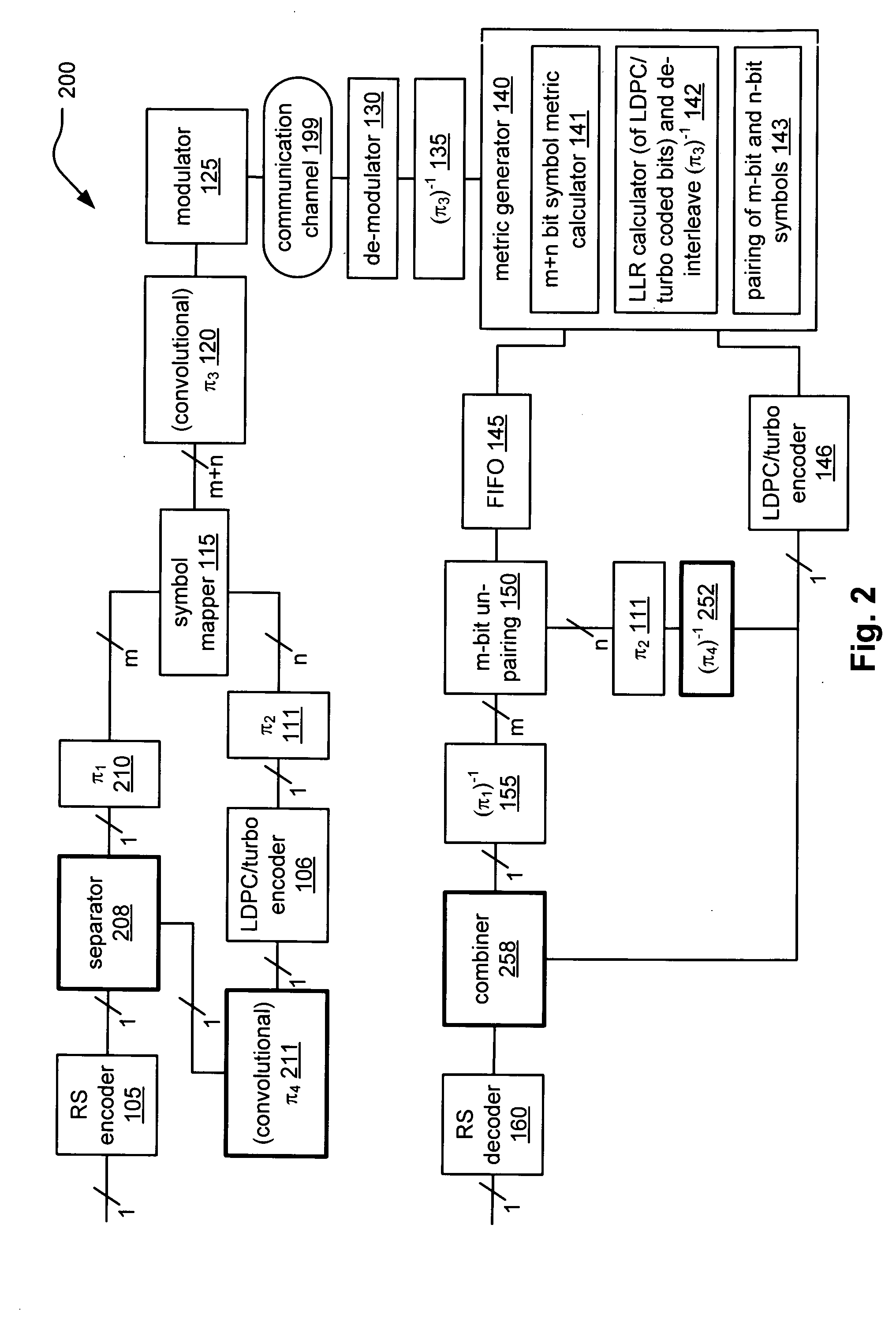
System correcting random and/or burst errors using RS (Reed-Solomon) code, turbo/LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) code and convolutional interleave
InactiveUS20060224935A1Error correction/detection using concatenated codesError detection/correctionComputer hardwareBurst error
System correcting random and / or burst errors using RS (Reed-Solomon) code, turbo / LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) code and convolutional interleave. A novel approach is presented that combines different coding types within a communication system to perform various types of error correction. This combination of accommodating different coding types may be employed at either end of a communication channel (e.g., at a transmitter end when performing encoding and / or at a receiver end when performing decoding). By combining different coding types within a communication system, the error correcting capabilities of the overall system is significantly improved. The appropriate combination of turbo code and / or LDPC code along with RS code allows for error correction or various error types including random error and burst error (or impulse noise).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Coherent tracking for FM in-band on-channel receivers
A method for coherently tracking a radio signal including at least one digitally modulated reference carrier is provided, wherein the method comprises the steps of demodulating the reference carrier to produce complex coherent reference gains, detecting a transient that affects the complex coherent reference gains, and adjusting the complex coherent reference gains in the vicinity of the transient to produce adjusted complex coherent reference gains. The transient can be caused by switching among the antenna elements or impulsive noise. Receivers that process signals in accordance with the method, and a method of estimating noise variance of symbols in a radio signal are also provided.
Owner:IBIQUITY DIGITAL CORP
Receiver and method of receiving
InactiveUS20100246726A1Computationally effectiveComputationally efficientError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionNoise levelFourier transform on finite groups
A receiver recovers data from Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexed (OFDM) symbols, the OFDM symbols including sub-carrier symbols carrying data symbols and sub-carrier signals carrying pilot symbols. The receiver includes a Fourier transform processor arranged in operation to receive a time domain digital version of the OFDM symbols and to form a frequency domain version of the OFDM symbols, from which the pilot symbol sub-carriers and the data symbol bearing sub-carriers can be recovered, and a detector arranged in operation to recover the data symbols from the data bearing sub-carriers of the OFDM symbols. The receiver includes a noise estimator arranged in operation to generate a long term estimate of noise power in the frequency domain version of the OFDM symbols at a plurality of frequencies, by accumulating an average noise power at the plurality of frequencies from a plurality of the OFDM symbols, and for generating an estimate of a current level of the noise power in the frequency domain version of a current one of the OFDM symbols at the plurality of frequencies. An impulsive noise detector detects the presence of an impulse of noise in the current OFDM symbol, by comparing the noise power in the current OFDM symbol with the long term noise power at the plurality of frequencies, and to generate an impulse noise flag to indicate that the current OFDM symbol is affected by an impulse of noise if the comparison indicates the presence of an impulse of noise. Impulsive noise in the time domain will generate an increase in noise level across the frequency bandwidth of the OFDM symbols. If all frequencies experience an increase then an impulse of noise can be detected. Thereafter the detector can conceal the effect of the impulse noise on the recovering of the data symbols from the data bearing sub-carriers, for example by adapting channel state information for use in de-mapping modulated symbols into data symbols.
Owner:SONY CORP
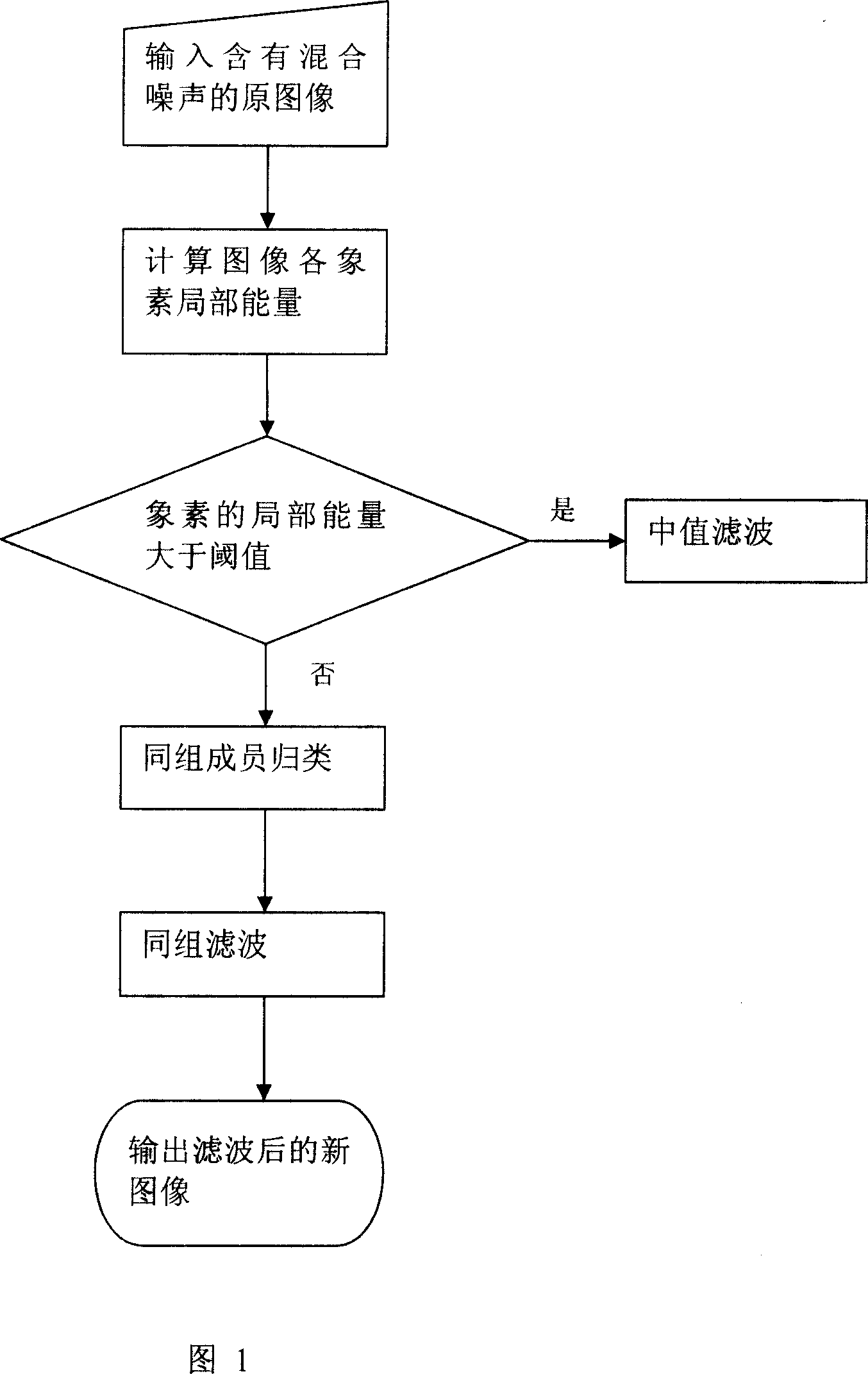
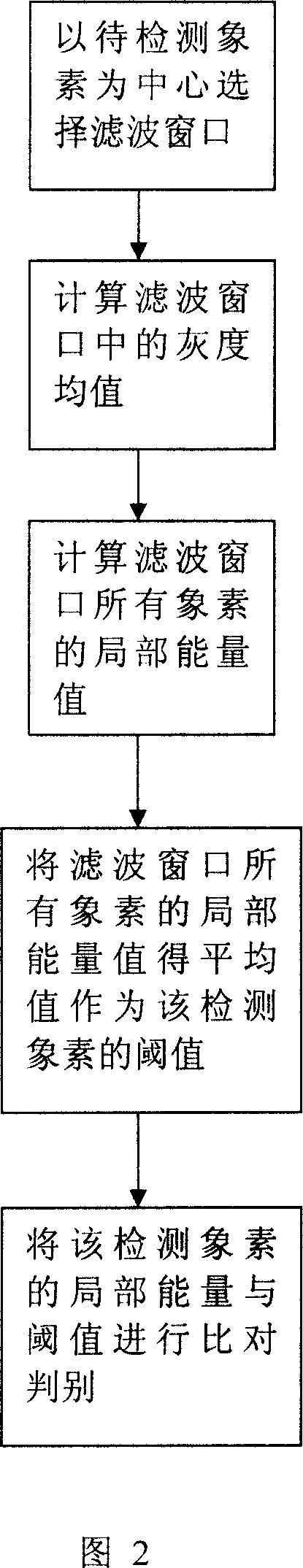
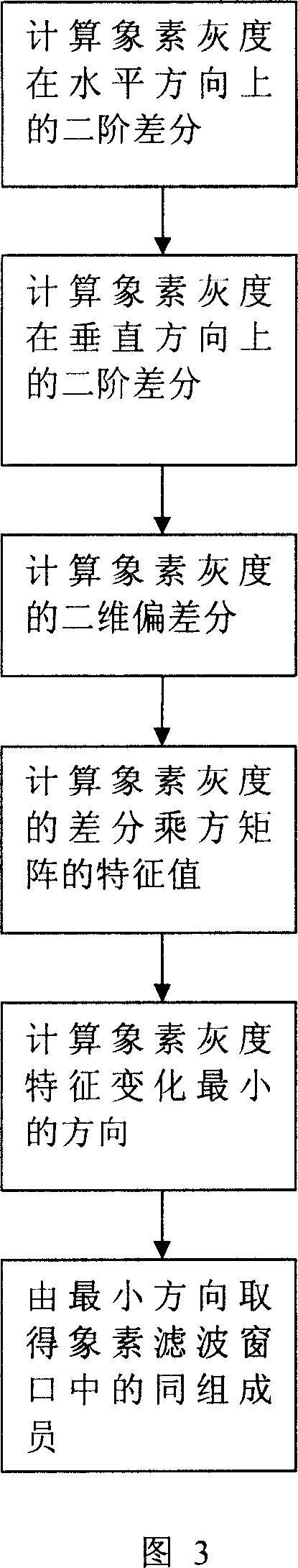
A method for filtering image mixed noise
InactiveCN101087365AProtection edgeProtection detailsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMixed noisePulse noise
The invention discloses a method of filtering image mixed noise, it includes step 1: selecting input first pixel in original image which includes mixed noise; step 2: judging whether the pixel belongs to pulse noise, if it is, enter step 3. if else enter step 4; step 3: the pixel is median filter processed to filter the pulse noise, then enter step 6; step 4: ensuring the members of the un-pulse noise pixel; step 5: gauss noise is filtered by filter; step 6: checking whether the all pixels are processed, if it is not, the next pixel is fetched, then turn to step 2; if it is, new image whose mixed noise is filtered is output. The method can filter mixed noise in image, at the same time edge and detail information of image can be protected well, and calculation speed is high.
Owner:程桂花
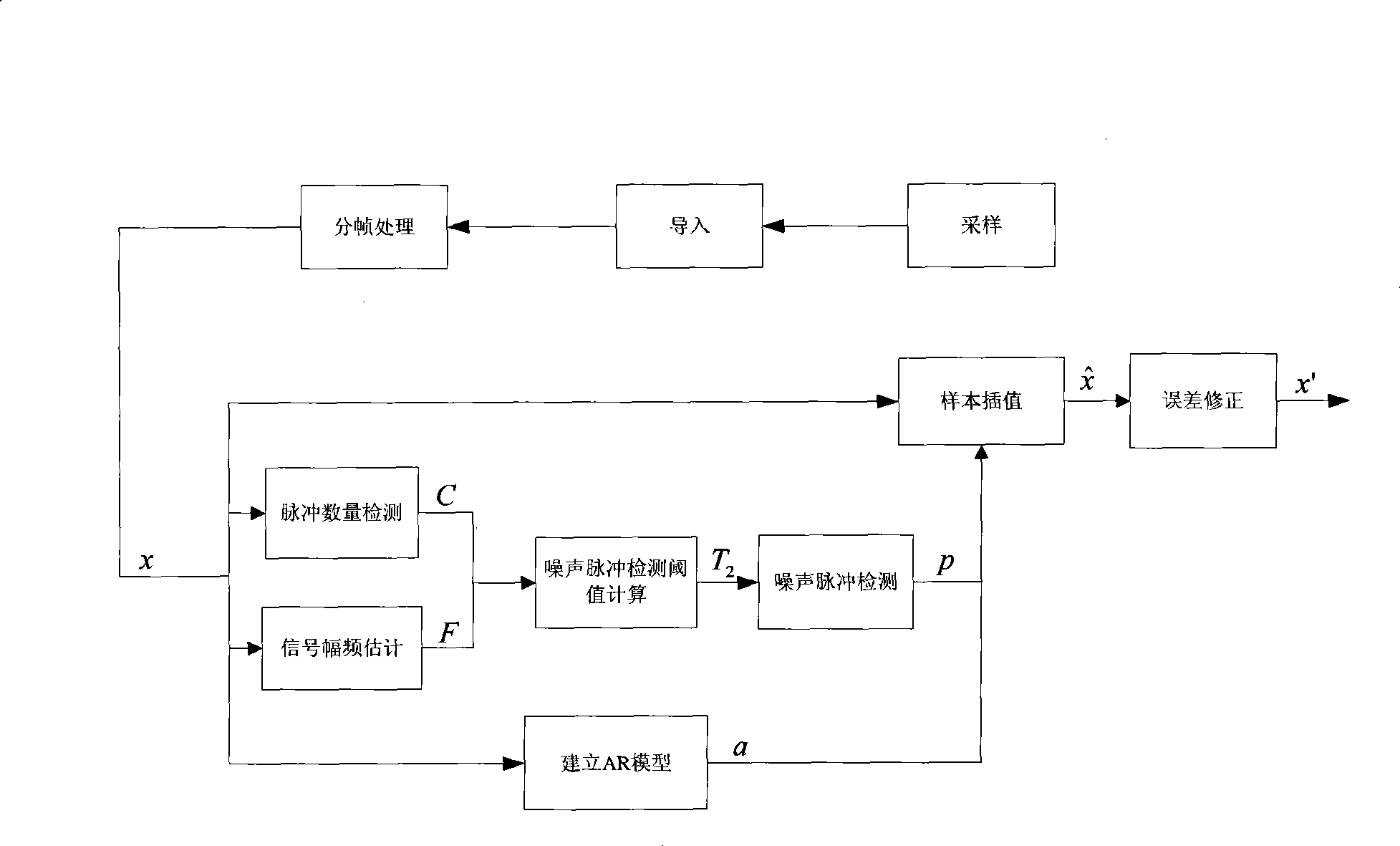
Method for detecting and eliminating pulse noise in digital audio signal
The invention provides a method for detecting and removing pulse noise in a digital audio signal, which comprises the following steps: utilizing weighted difference vectors of adjacent signal samples in a certain neighbor in the signals to detect pulse number and determine detection thresholds of the noise pulse according to the estimation value of the change degree of the amplitude and frequency of the signal; utilizing the envelope based on the weighted difference vectors of the signal samples to evaluate the width of the noise pulse and establish an autoregressive model of the signal; according to the correlation of voice frequency signals, utilizing adjacent signal samples which are repaired or not contaminated to repair a signal section which is contaminated by the pulse noise and recover original signals. The invention has the advantages that a normal signal which is changed abruptly and the noise pulse can be separated, and the width of the pulse can be calculated; and meanwhile, by adopting the envelop which is formed by the weighted difference vectors of the signal, the position and the width of the noise pulse are detected, so that a single noise pulse, a plurality of contiguous noise pulses or a plurality of overlapping noise pulses can be processed.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
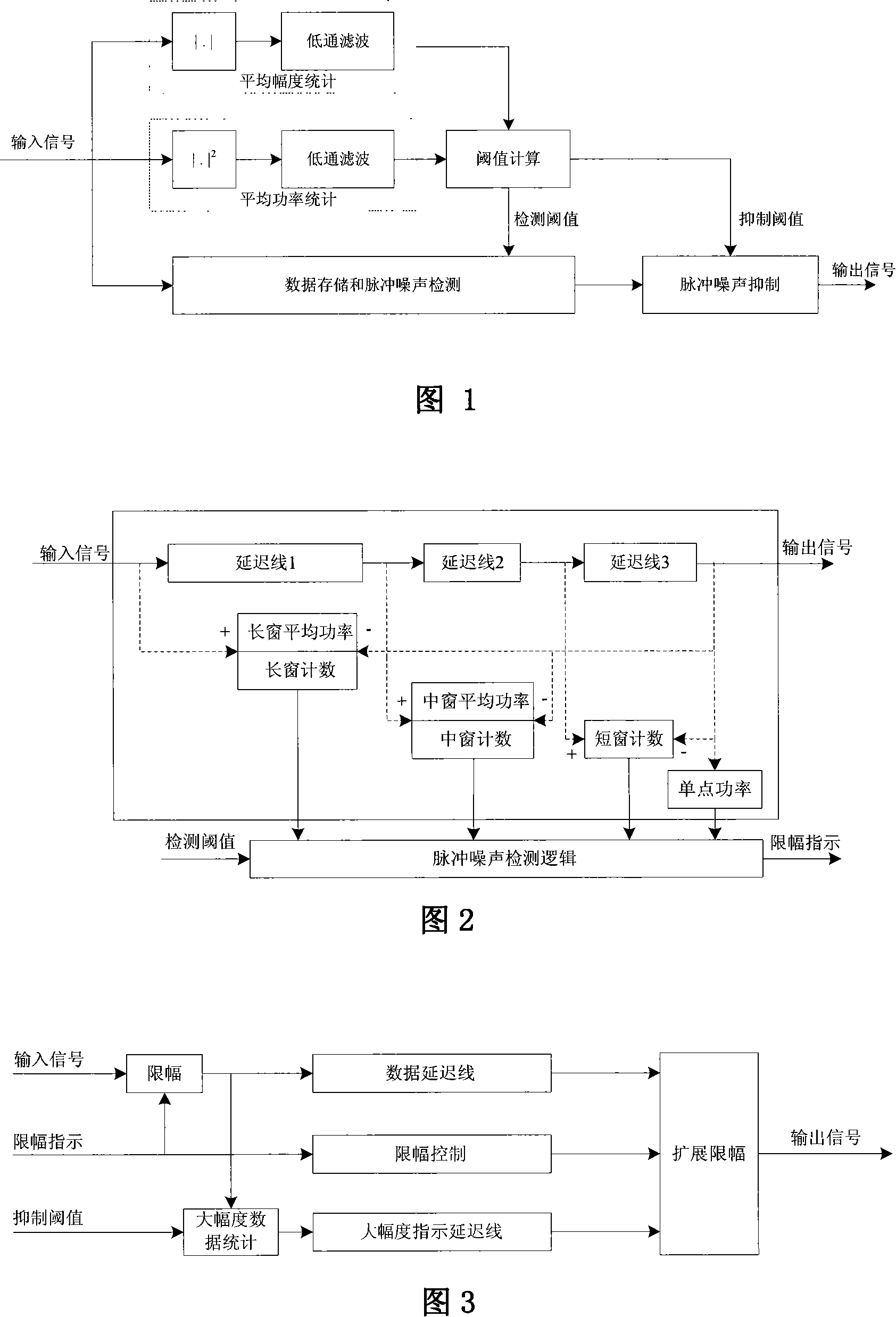
Method of detecting and suppressing pulse noise
The invention relates to a method for detecting and restraining impulse noise interference in received digital signals. The existing method can only handle the impulse noise with a short burst time and work inefficient in restraining the impulse noise with a long and persistent burst time. The invention obtains an average power and an average extent through smooth filtering in a time domain by applying power and extent of received signals, so as to generate detecting threshold values and limiting threshold values for different detecting methods; then a plurality of methods are used for detecting the generating position and type of the impulse noise; lastly, different limiting threshold values are used according to the method for detecting the impulse noise to restrain the impulse noise. The method of the invention can detect the generating position of the impulse noise from the received signals and determine the type of the impulse noise, then select different restraining methods to restrain the impulse noise in different types and perform effective restraint.
Owner:HANGZHOU NATCHIP SCI & TECH
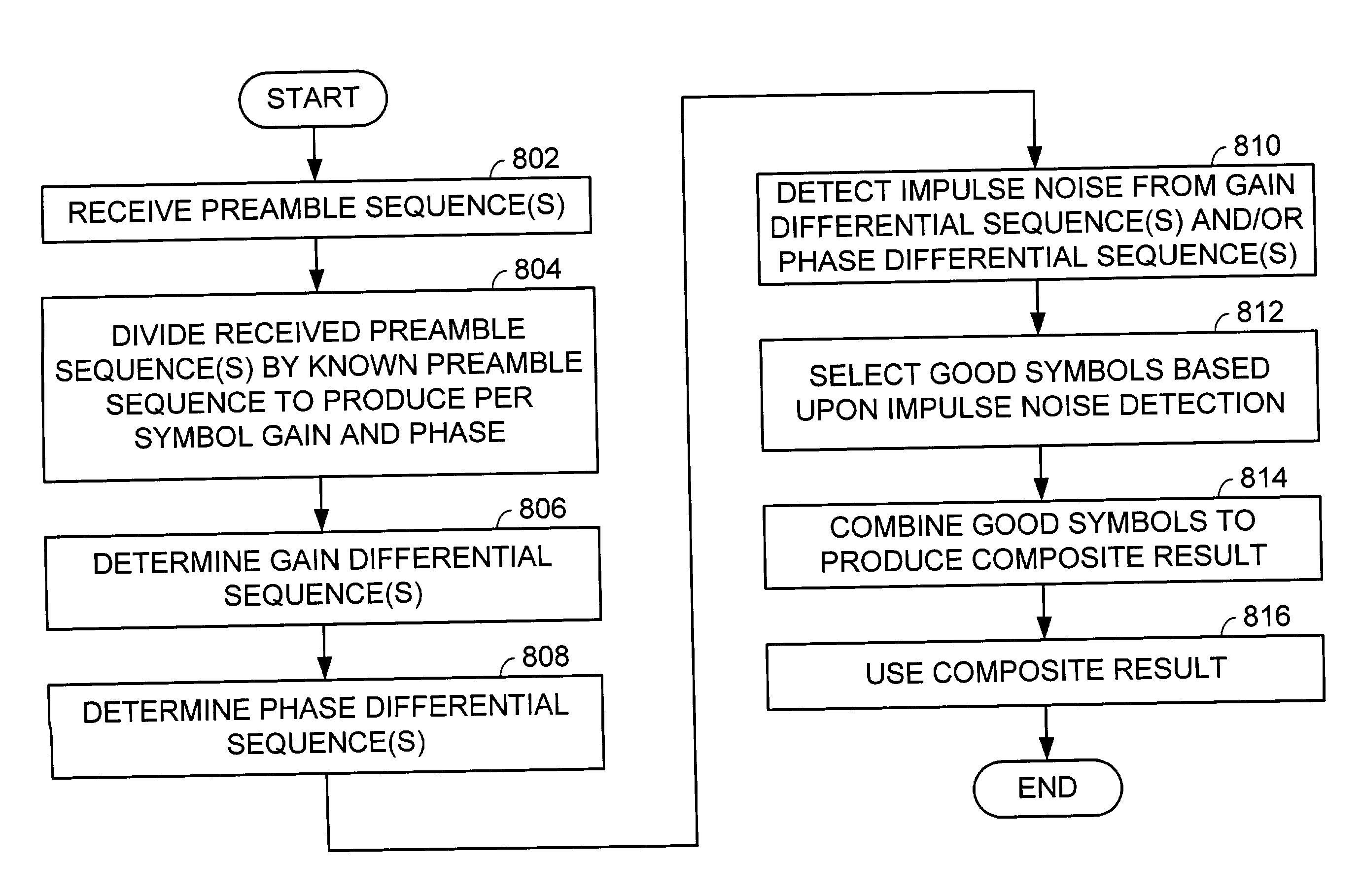
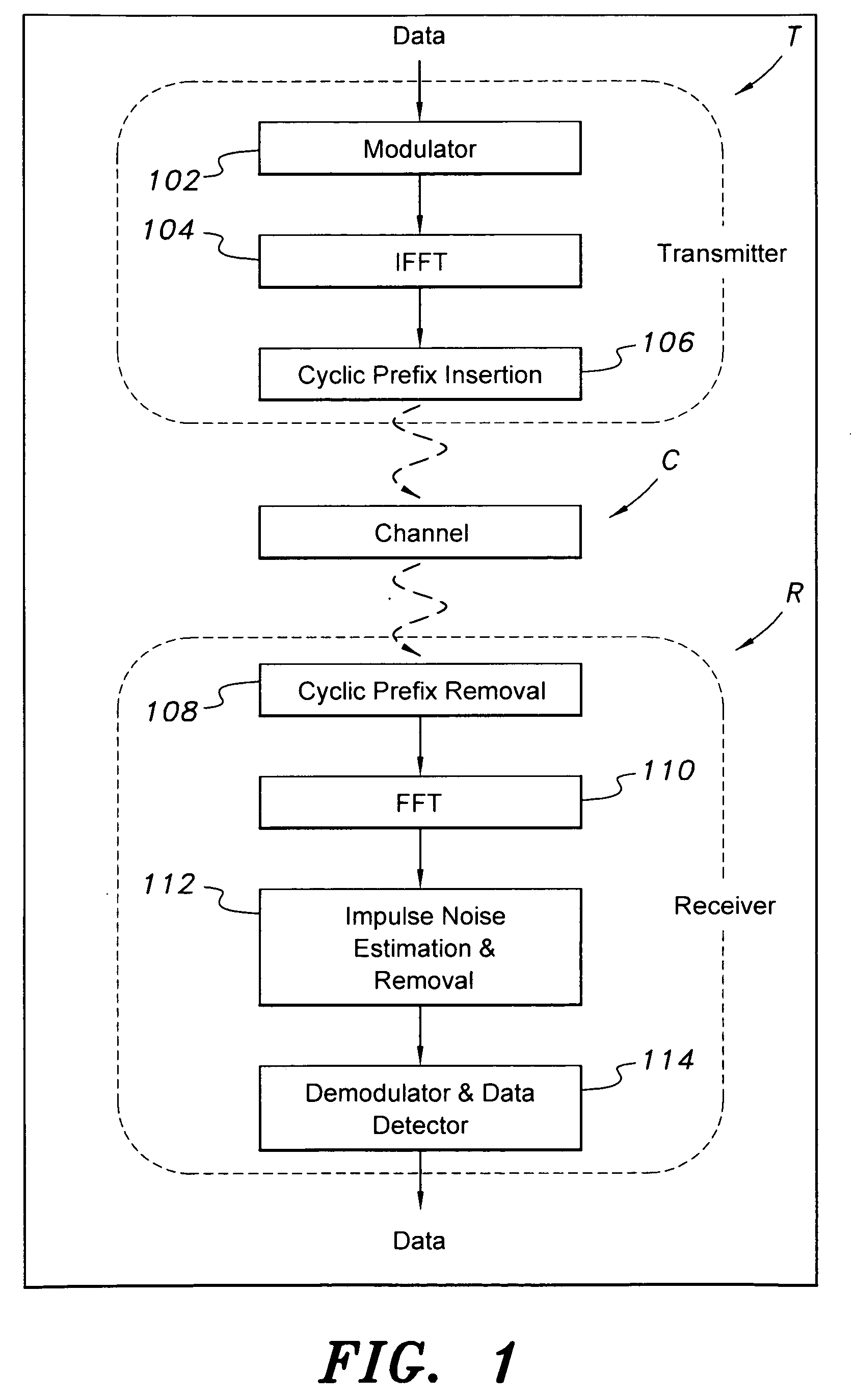
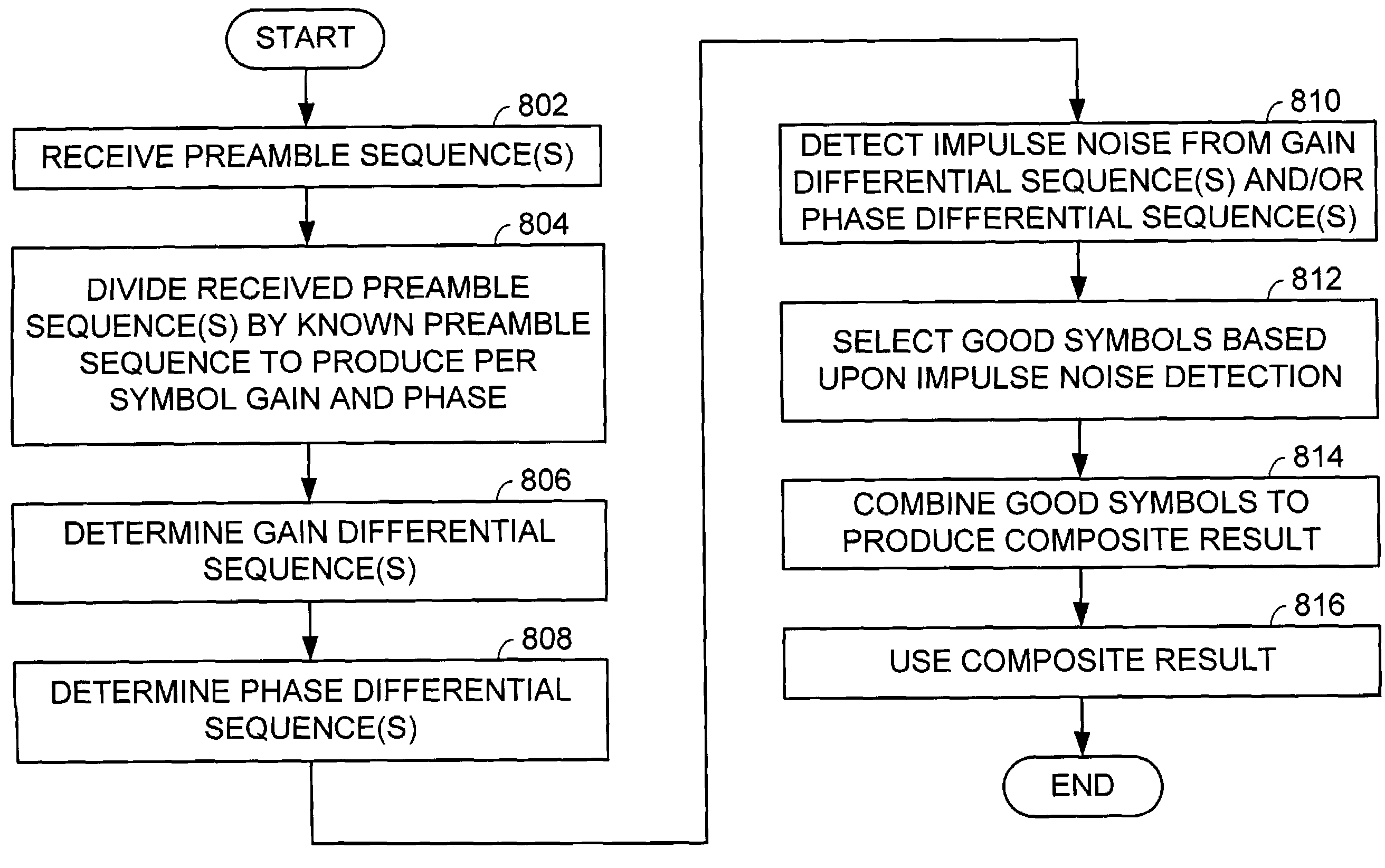
Impulse noise detection from preamble symbols
InactiveUS20040066865A1Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionTelecommunicationsCommunication device
A communication device constructed according to the present invention detects impulse noise in a preamble sequence. In detecting impulse noise in the preamble sequence the communication device first receive a preamble sequence that includes a plurality of preamble symbols. The communication device then divides the plurality of preamble symbols by at least one known preamble symbol to produce a plurality of preamble gains and / or a plurality of preamble phases corresponding to the plurality of preamble symbols. Finally, the communication device determines, based upon the plurality of preamble gains and / or the plurality of preamble phases, that at least one preamble symbol has been adversely affected by impulse noise. The communication device may discard at least one preamble symbol that has been adversely affected by impulse noise from the plurality of preamble symbols. The communication device may combine non-discarded preamble symbols of the plurality of preamble symbols of the preamble sequence to produce a composite result.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
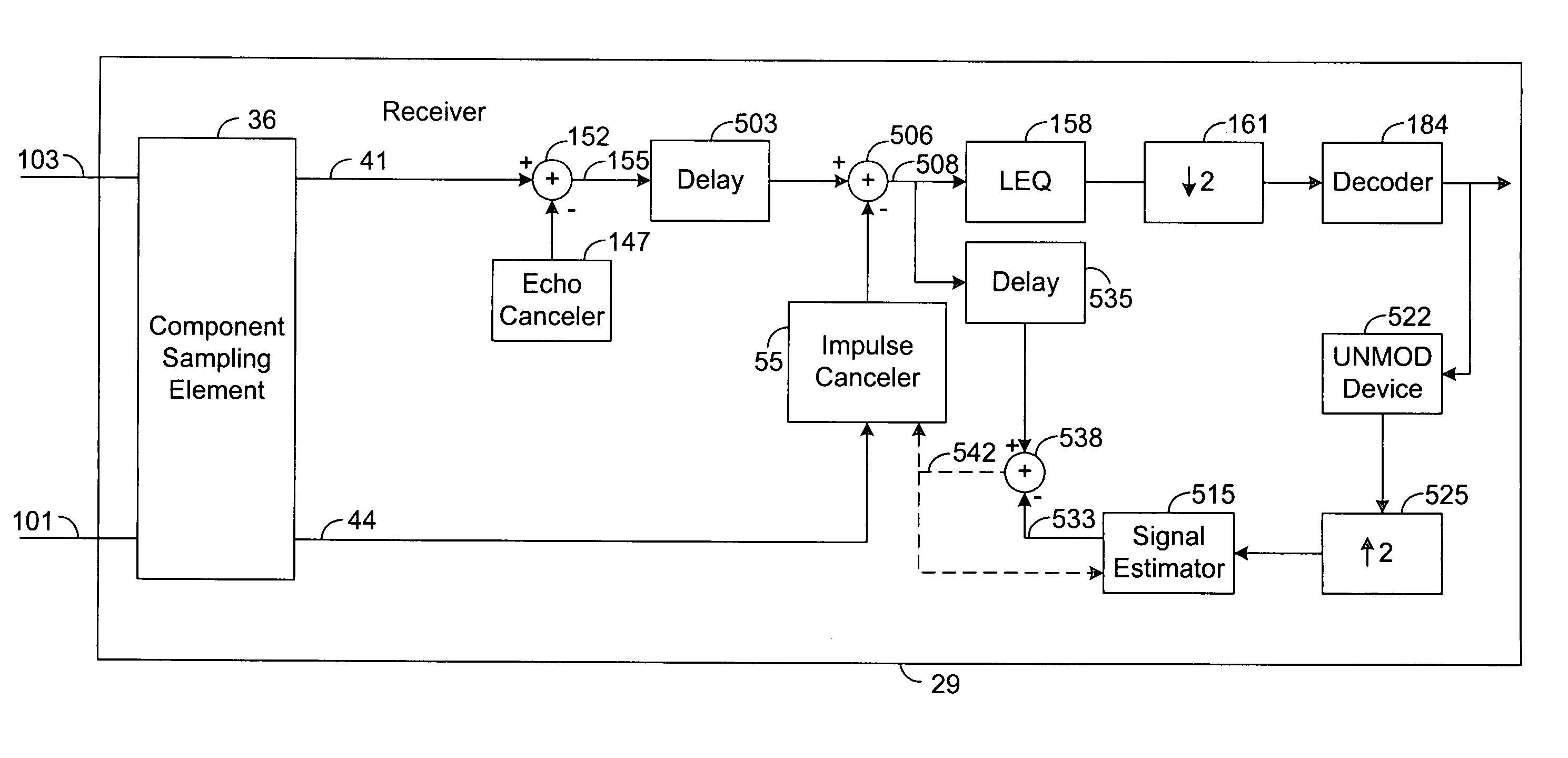
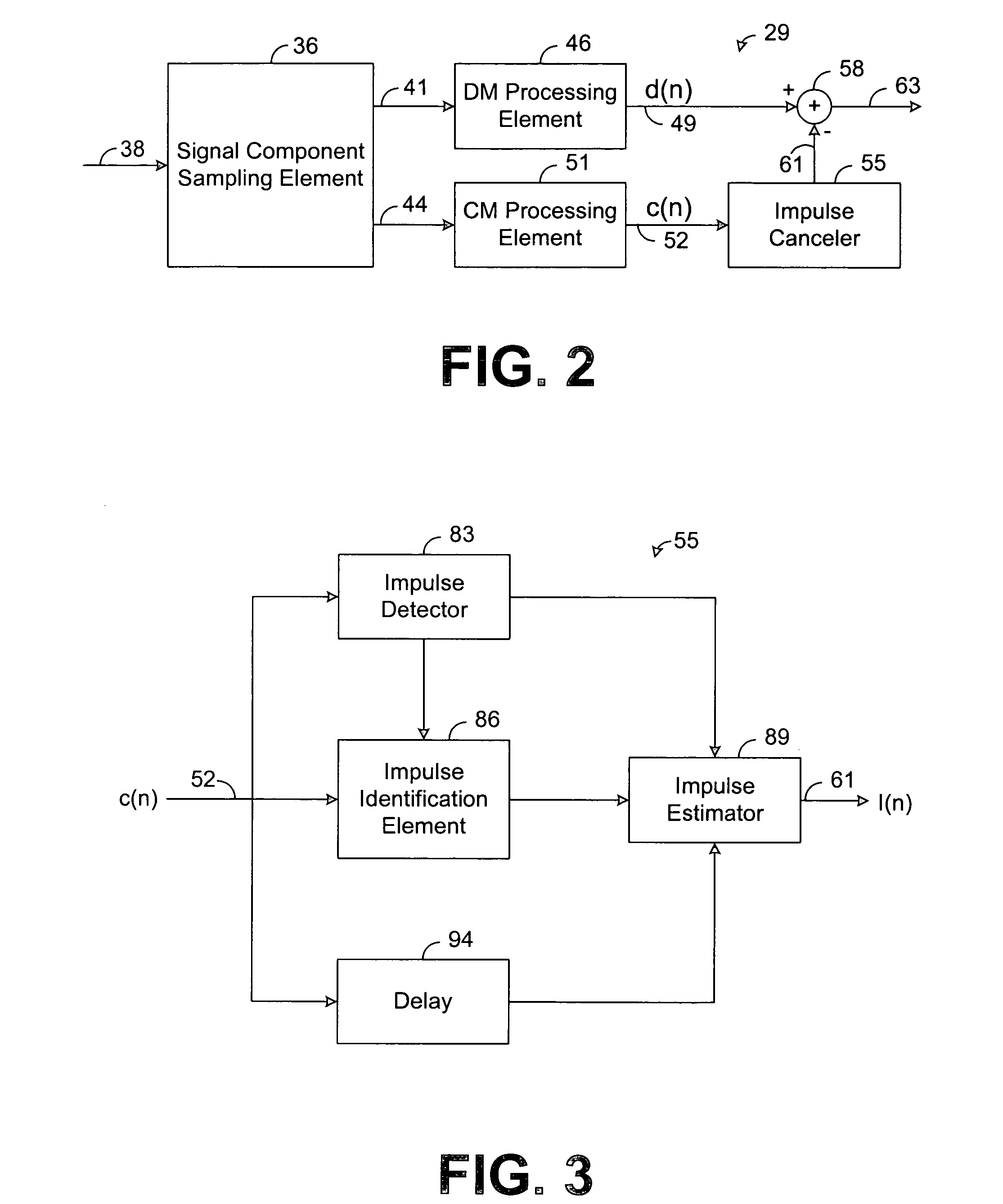
System and method for canceling impulse noise
ActiveUS7593494B1Polarisation/directional diversityUnbalanced current interference reductionSelf adaptivePulse noise
A system for canceling impulse noise comprises an adaptive impulse canceler and a combiner. The adaptive impulse canceler is configured to receive a common mode component of a received signal and to detect a noise impulse in the common mode component. The impulse canceler is further configured to provide, based on the noise impulse in the common mode component, an impulse noise estimation for a differential mode component of the received signal. The combiner is configured to receive the differential mode component and the impulse noise estimation and to subtract the impulse noise estimation from the differential mode component.
Owner:ADTRAN
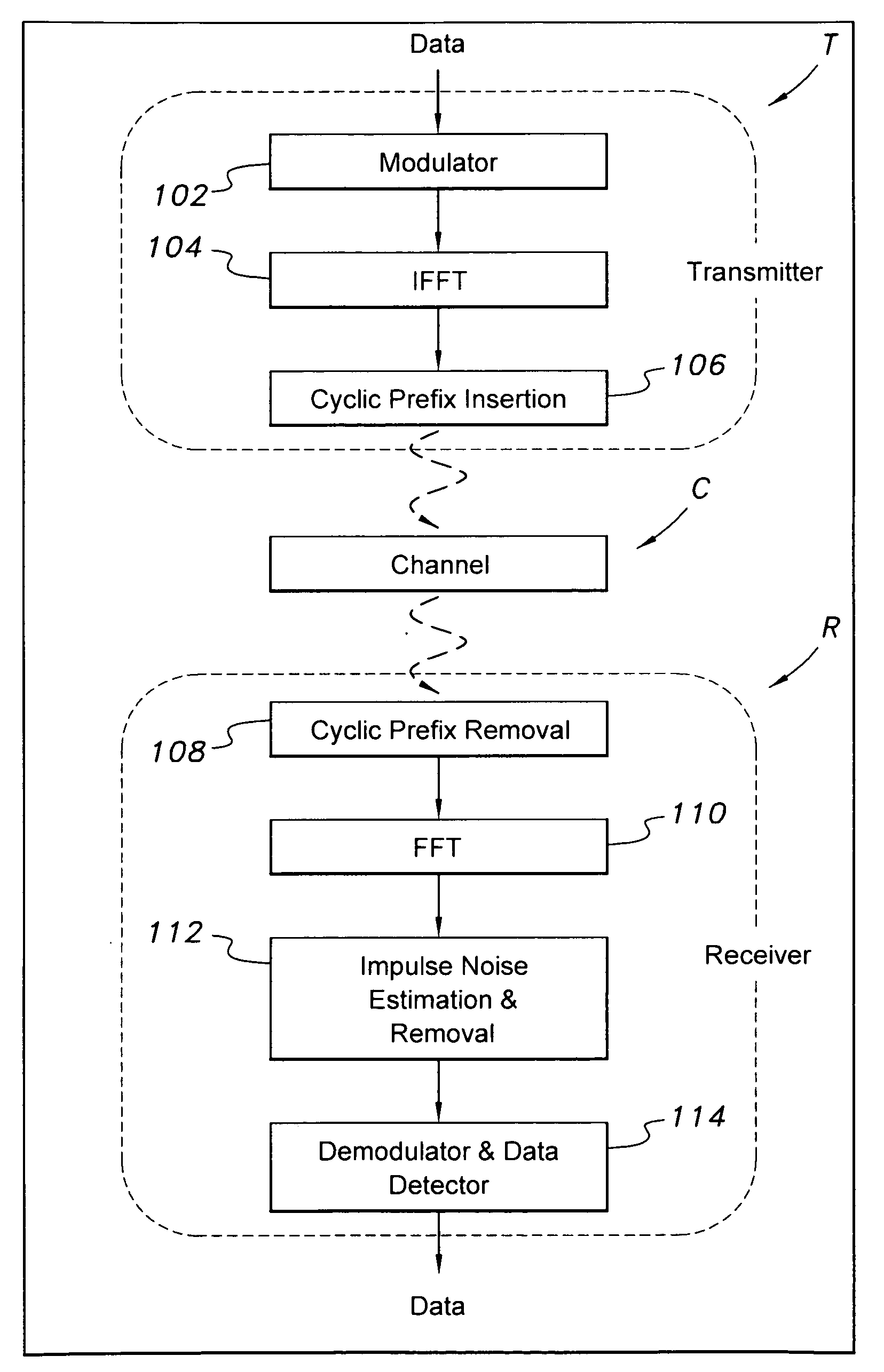
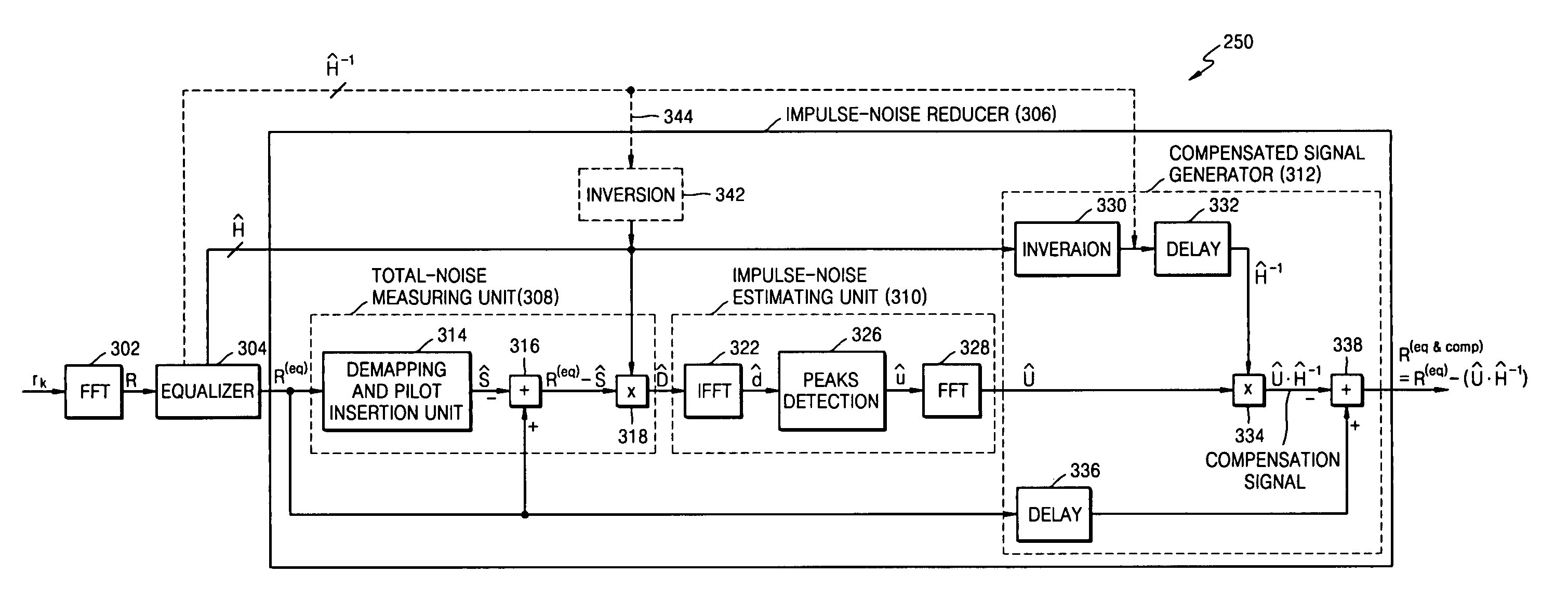
Method of estimating and removing noise in OFDM systems
InactiveUS20100322327A1Readily apparentTransmission/receiving by adding signal to wavePolarisation/directional diversityDigital subscriber lineCyclic prefix
The present invention relates to impulse noise estimation and removal in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) transmissions, and particularly to transmissions in power line communications and digital subscriber line (DSL) transmissions. The method includes the steps of: modulating data to be transmitted; performing an inverse fast Fourier transform; inserting a cyclic prefix into the data; transmitting the data as a set of OFDM symbols via a channel; receiving the set of OFDM symbols; removing the cyclic prefix; performing a fast Fourier transform; estimating impulse noise; canceling the impulse noise based upon the estimated impulse noise to produce a set of impulse noise-free data; estimating the channel; and demodulating and detecting the data transmitted based upon the estimated channel and the set of impulse noise-free data.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Impulse noise detection from preamble symbols
A communication device constructed according to the present invention detects impulse noise in a preamble sequence. In detecting impulse noise in the preamble sequence the communication device first receive a preamble sequence that includes a plurality of preamble symbols. The communication device then divides the plurality of preamble symbols by at least one known preamble symbol to produce a plurality of preamble gains and / or a plurality of preamble phases corresponding to the plurality of preamble symbols. Finally, the communication device determines, based upon the plurality of preamble gains and / or the plurality of preamble phases, that at least one preamble symbol has been adversely affected by impulse noise. The communication device may discard at least one preamble symbol that has been adversely affected by impulse noise from the plurality of preamble symbols. The communication device may combine non-discarded preamble symbols of the plurality of preamble symbols of the preamble sequence to produce a composite result.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
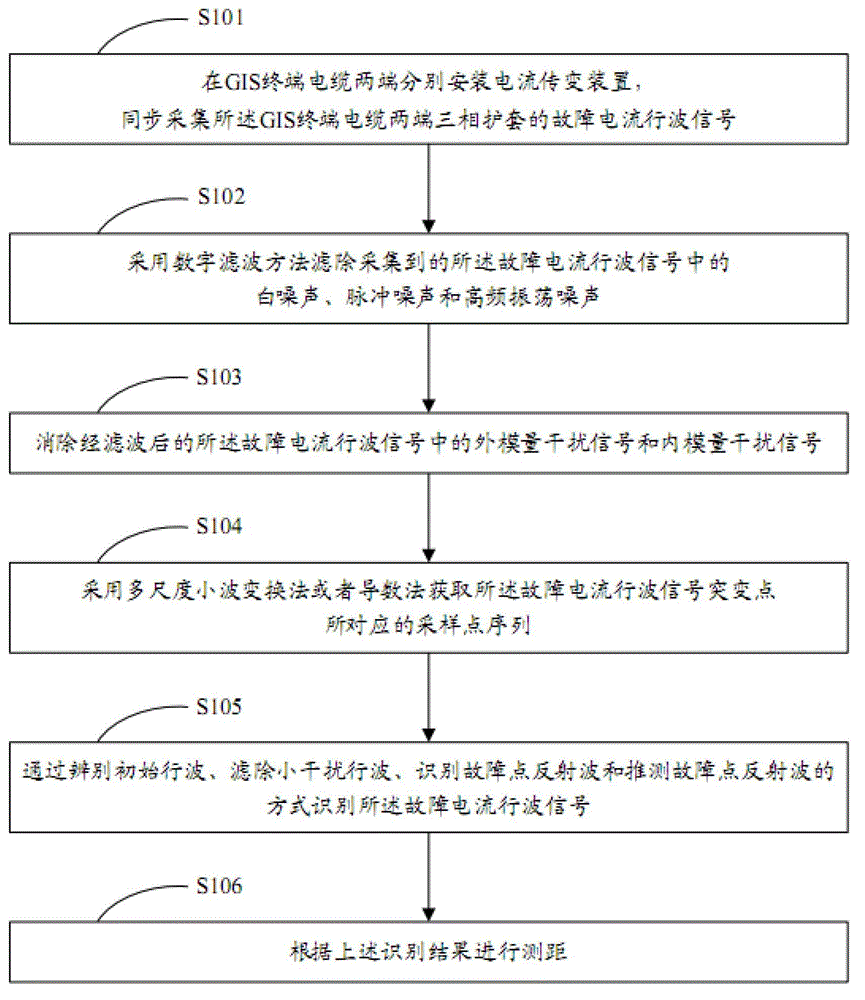
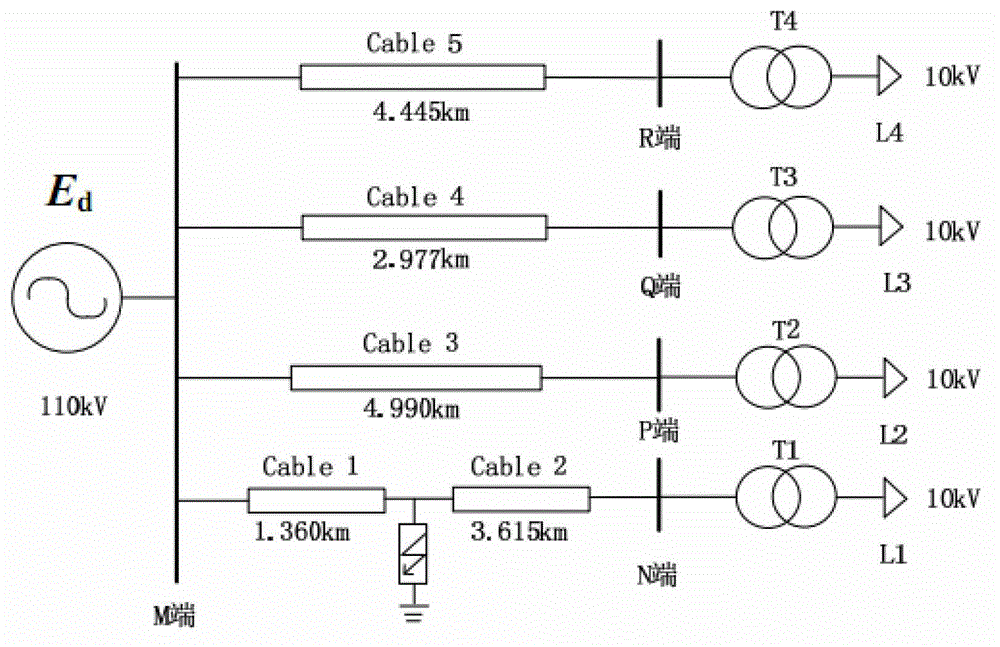
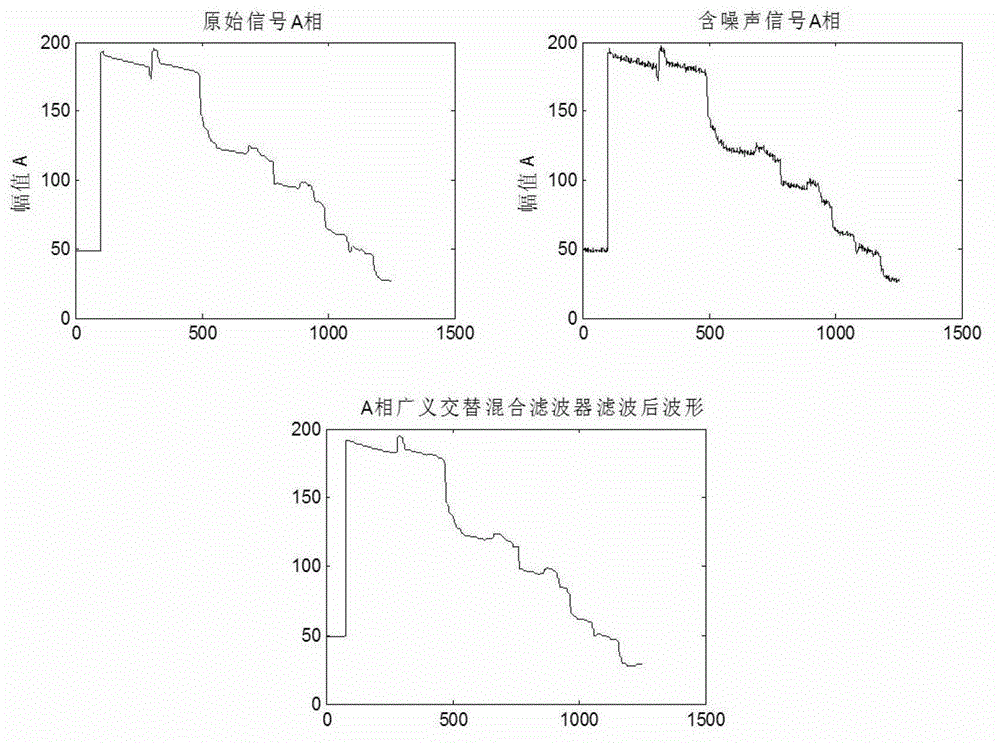
Geographic information system (GIS) terminal cable fault on-line location method
ActiveCN102944818AMeet the requirements of fault locationEliminate noise distractionsFault location by pulse reflection methodsCable fault locationEngineering
The invention discloses a geographic information system (GIS) terminal cable fault on-line location method. The GIS terminal cable fault on-line location method comprises the steps of synchronously acquiring fault current travelling wave signals of three-phase sheaths at two ends of a GIS terminal cable, filtering white noise, pulse noise and high-frequency oscillation noise which are acquired in the fault current travelling wave signals, eliminating outer modulus interference signals and inner modulus interference signals in filtered fault current travelling wave signals, obtaining sampling point sequences corresponding to catastrophe points of the fault current travelling wave signals, identifying the fault current travelling wave signals and performing location according to identified results. The GIS terminal cable fault on-line location method has high applicability, reliability, practical applicability and automation level, and the accuracy of fault location can meet the requirement of underground power cable system fault location.
Owner:FOSHAN POWER SUPPLY BUREAU GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Single photon detector in the near infrared using an ingaas/inp avalanche photodiode operated with a bipolar rectangular gating signal
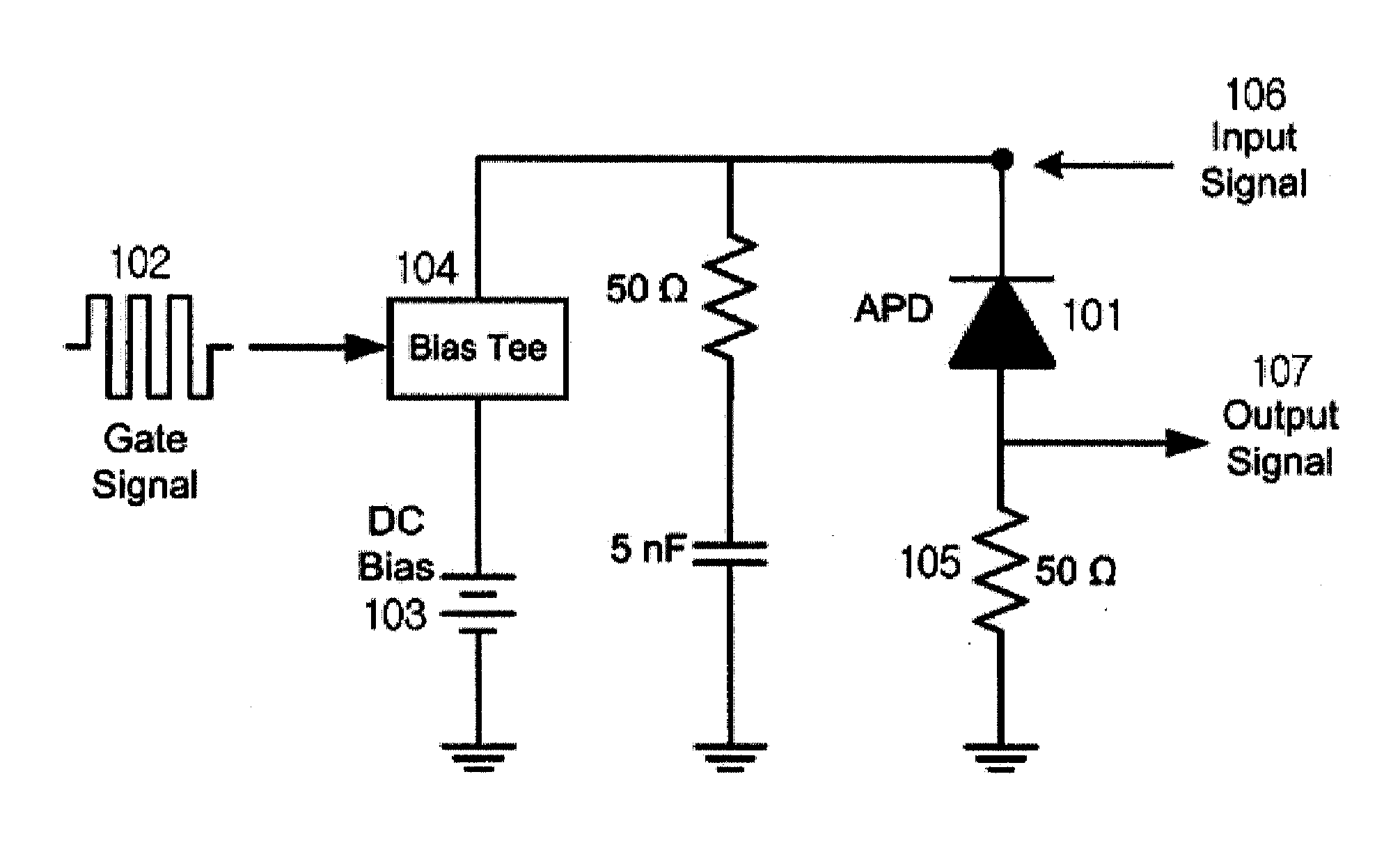
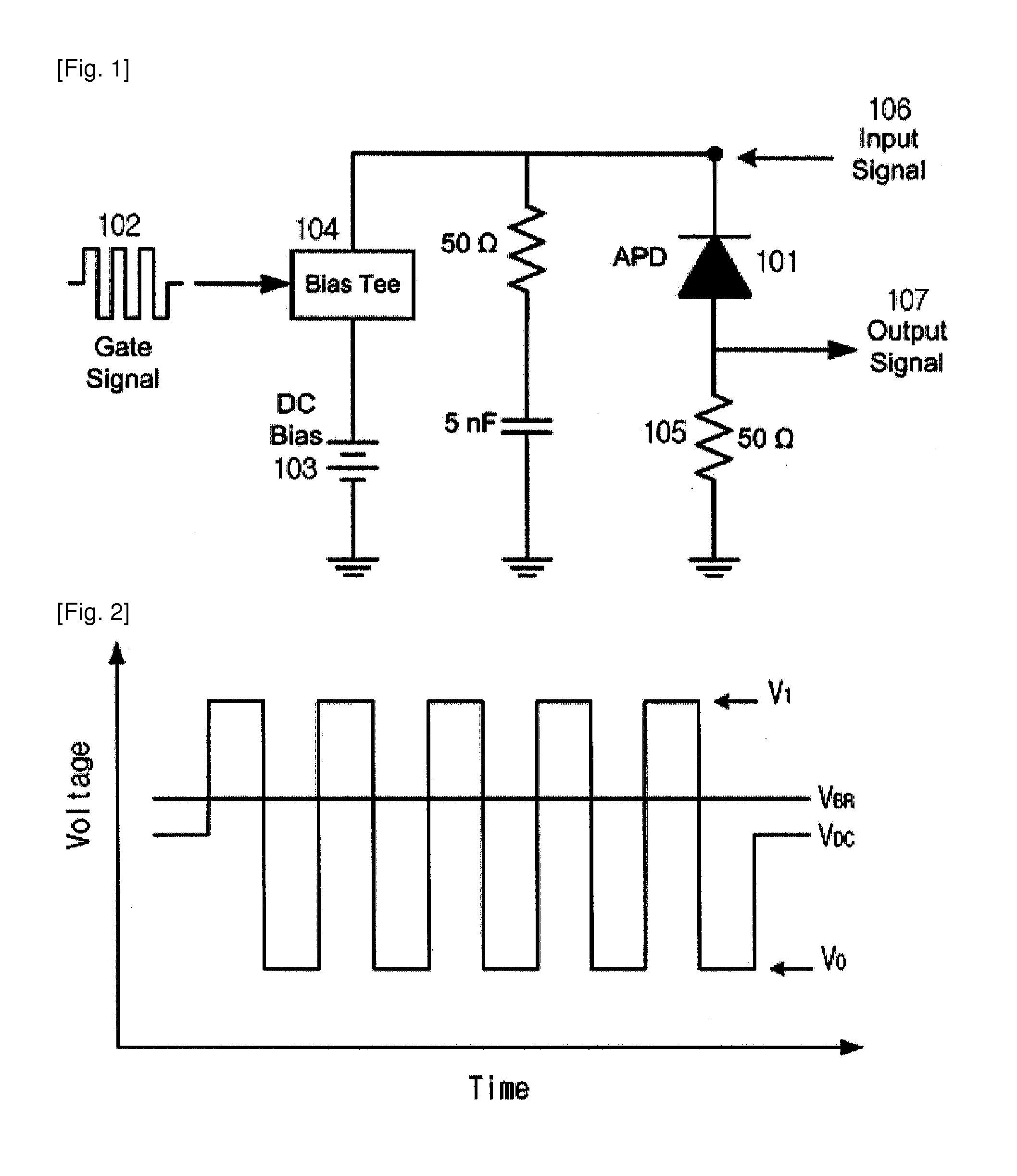
ActiveUS20130221221A1Reduced life-timeReduce intensitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansCharge carrierLength wave
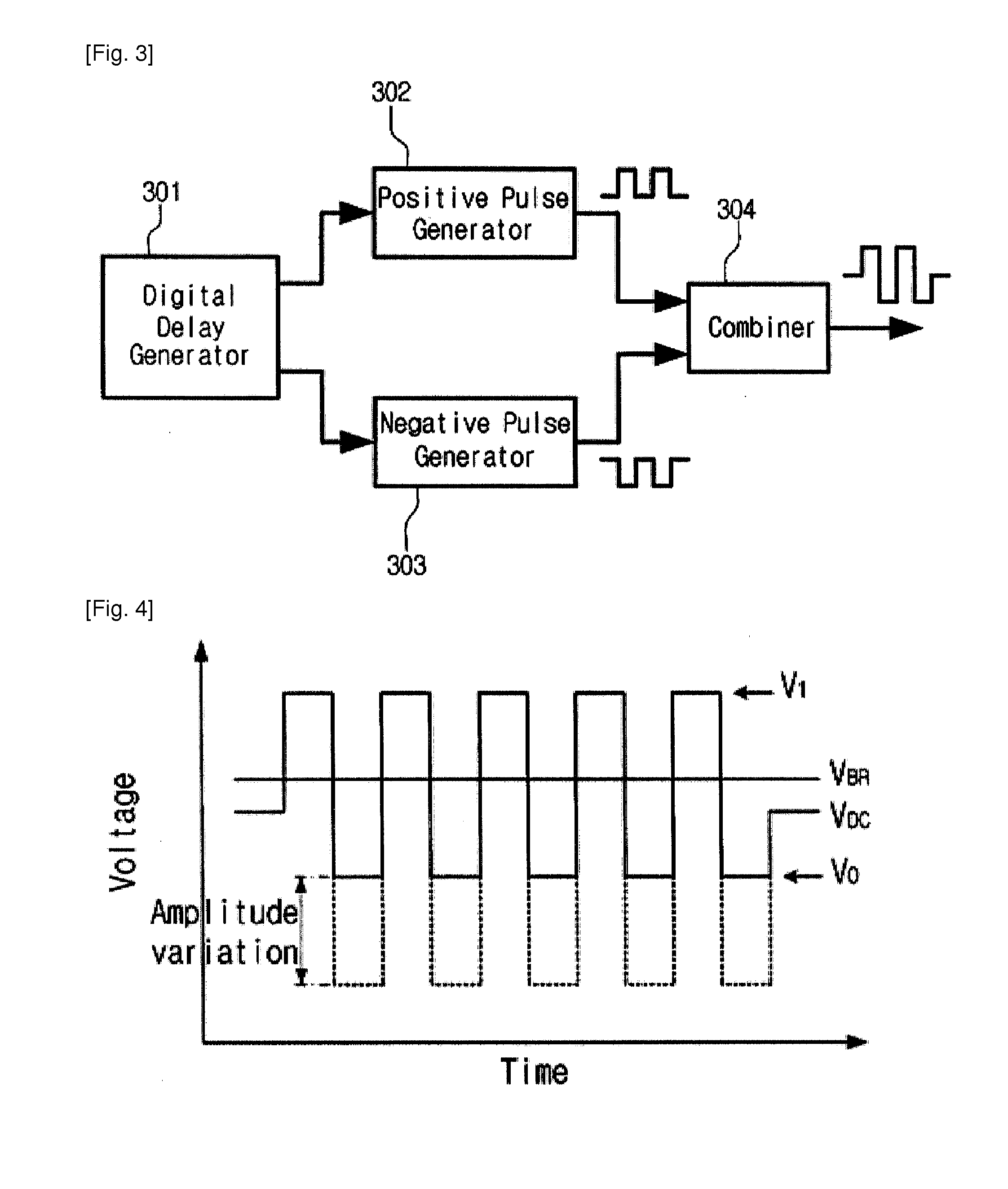
The present invention relates to a single photon detector (SPD) at telecom wavelength of 1.55 μm based on InGaAs / InP avalanche photodiode (APD). In order to operate the SPD at a low after-pulse noise, a DC bias voltage lower than the breakdown voltage is applied to an InGaAs / InP APD. A bipolar rectangular gating signal is superimposed with the DC bias voltage and applied to the APD so as to exceed the breakdown voltage during the gate-on time of each period of the gate signal. The use of the bipolar rectangular gating signal enabling us to operate the APD well below the breakdown voltage during the gate-off time, thereby make the release of the trapped charge carriers faster and then reduces the after-pulse noise. As a result, it permits to increase the repetition rate of the SPD.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Impulse noise reduction to an MCM signal
ActiveUS20050213692A1Reduce noiseError preventionTransmission control/equalisingFrequency changerGuard interval
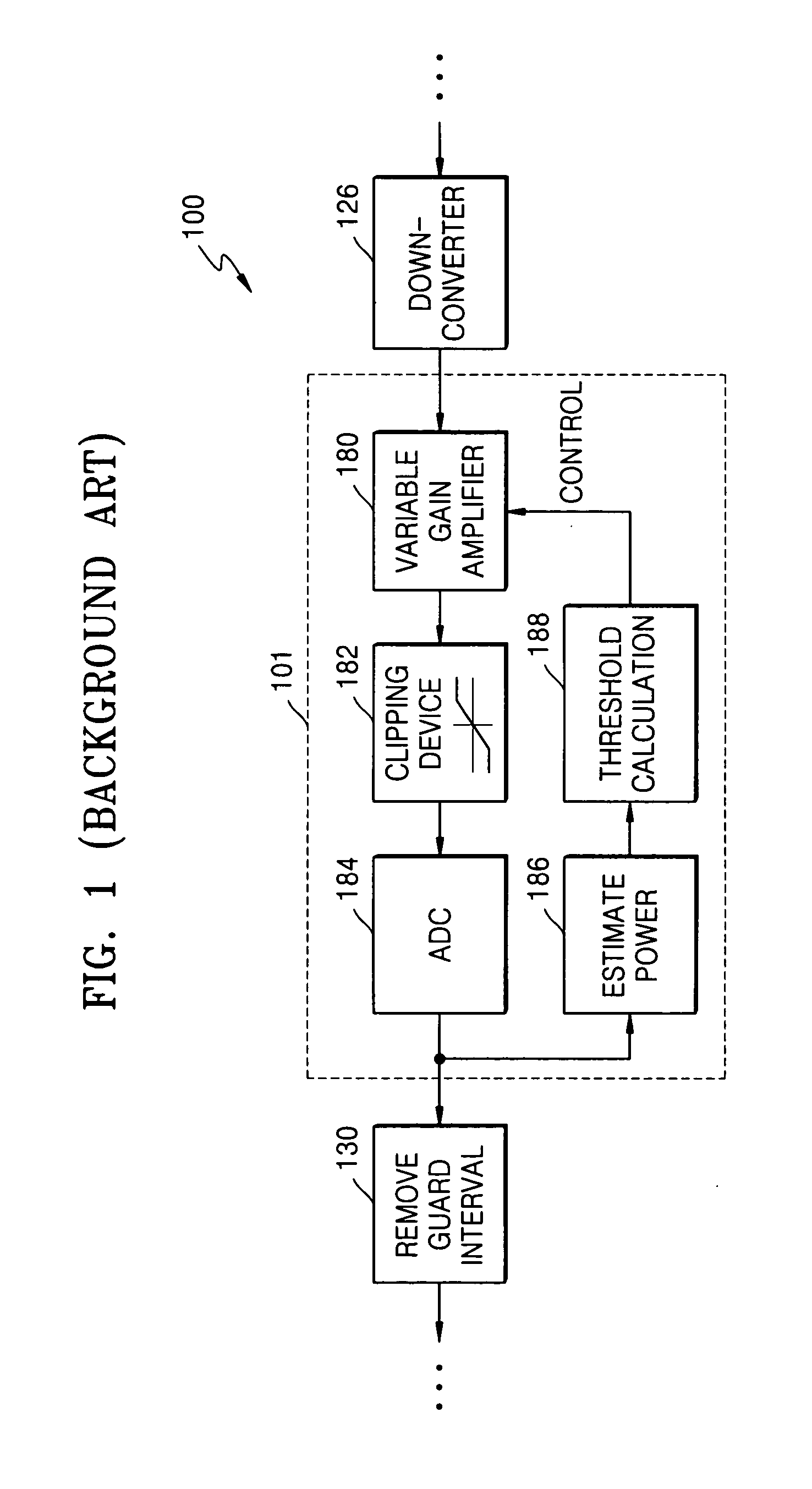
A method reduces noise in a multiple carrier modulated (MCM) signal. Such a method may include: estimating impulse noise based in the equalized signal; and removing a portion of the noise in the equalized signal as a function of the estimated impulse noise. An apparatus reduces noise in the MCM. Such an apparatus may include: a down-converter; an analog to digital converter to digitize the output of the down-converter; a guard-interval removing unit operable upon the digitized output of the down-converter; and a combined FFT, equalization and impulse-noise-compensation unit operable upon a signal from the guard-interval-removing unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Timing synchronization method and system for power line carrier communication
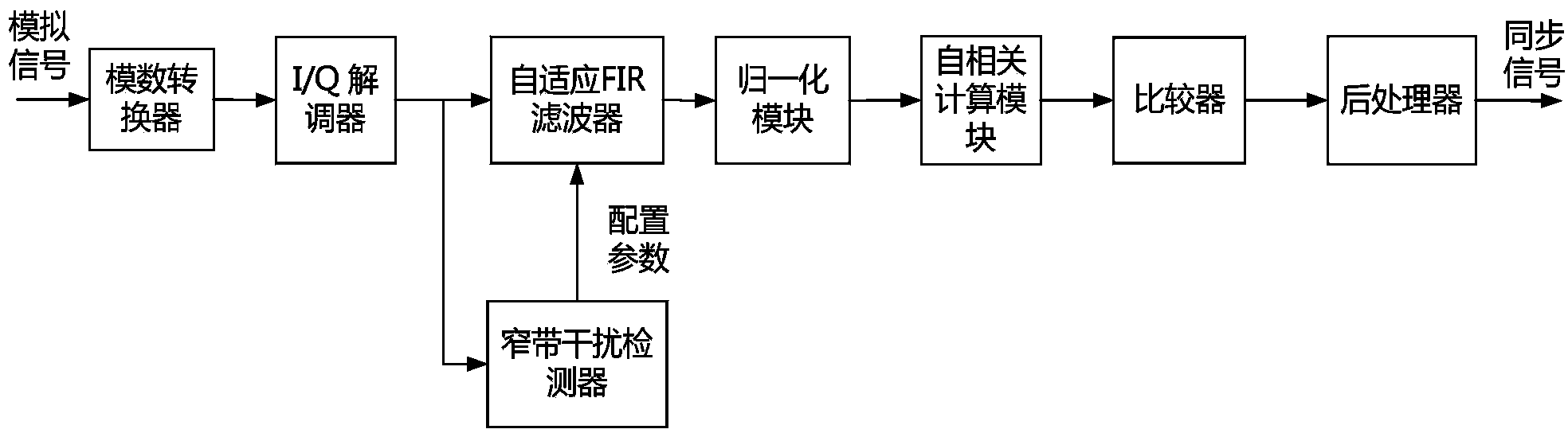
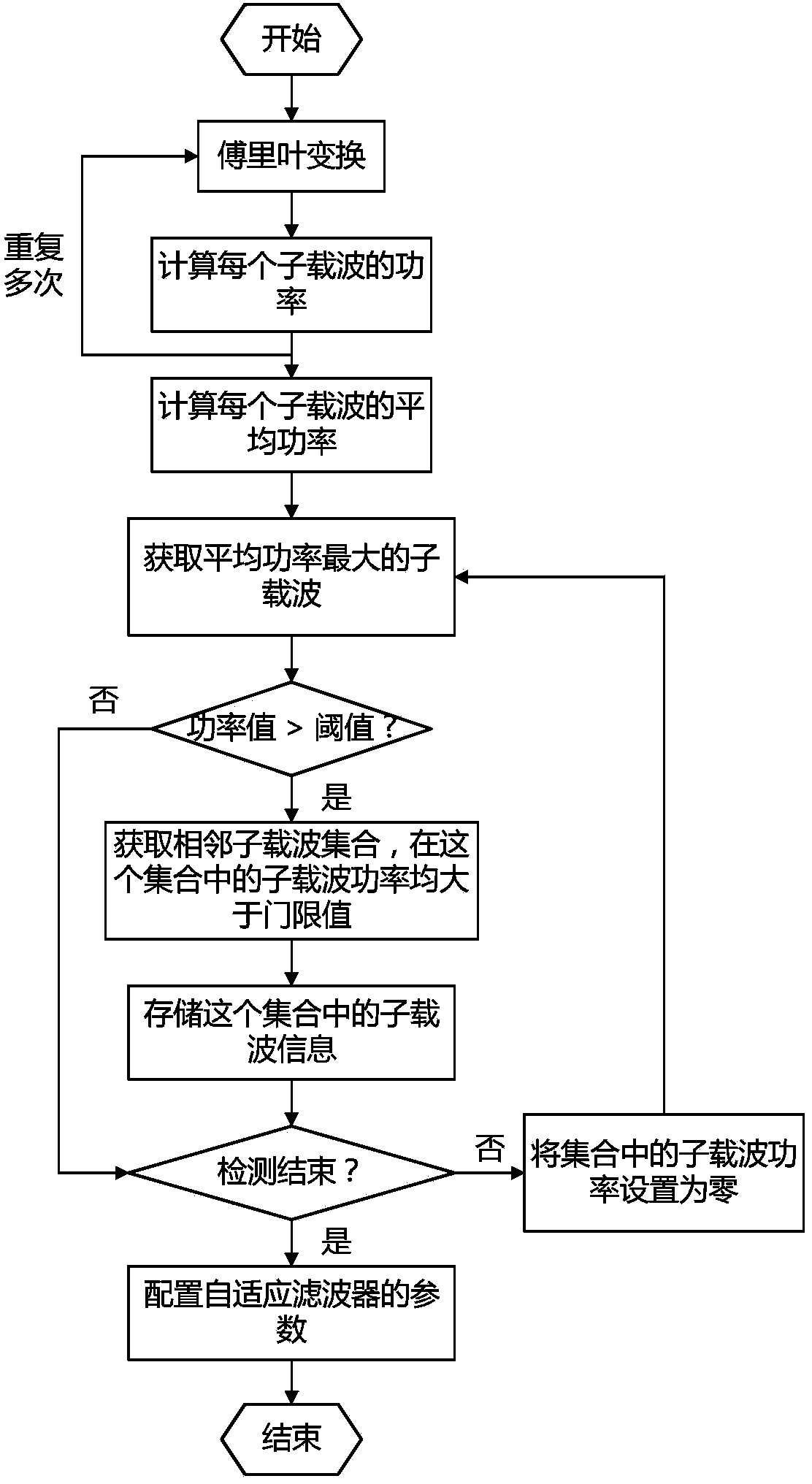
ActiveCN103532901AGood effectReduce consumptionPower distribution line transmissionMulti-frequency code systemsAdaptive filterStart time
The invention provides a timing synchronization method and a timing synchronization system for power line carrier communication. The system comprises an analog-to-digital converter, an I / O (Input / Output) demodulator, a narrowband interference detector, an adaptive filter, a normalization module, an auto-correlation calculation module, a comparator and a postprocessor, wherein an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) carrier signal is converted into an OFDM carrier frequency domain signal by the analog-to-digital converter, the I / O demodulator and the narrowband interference detector. The method comprises the following steps: 1, acquiring average power P of each OFDM subcarrier f; 2, performing narrowband interference detection on the OFDM subcarrier f; 3, filtering the OFDM signal and then performing normalization processing; 4, acquiring start time of the OFDM carrier signal and outputting an OFDM carrier synchronization signal. Compared with the prior art, the timing synchronization method and the timing synchronization system for power line carrier communication have the advantage of higher robustness under various different channel environments of narrowband interference, pulse noise, multi-path propagation and violent change or nonlinear input signal amplitude.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com