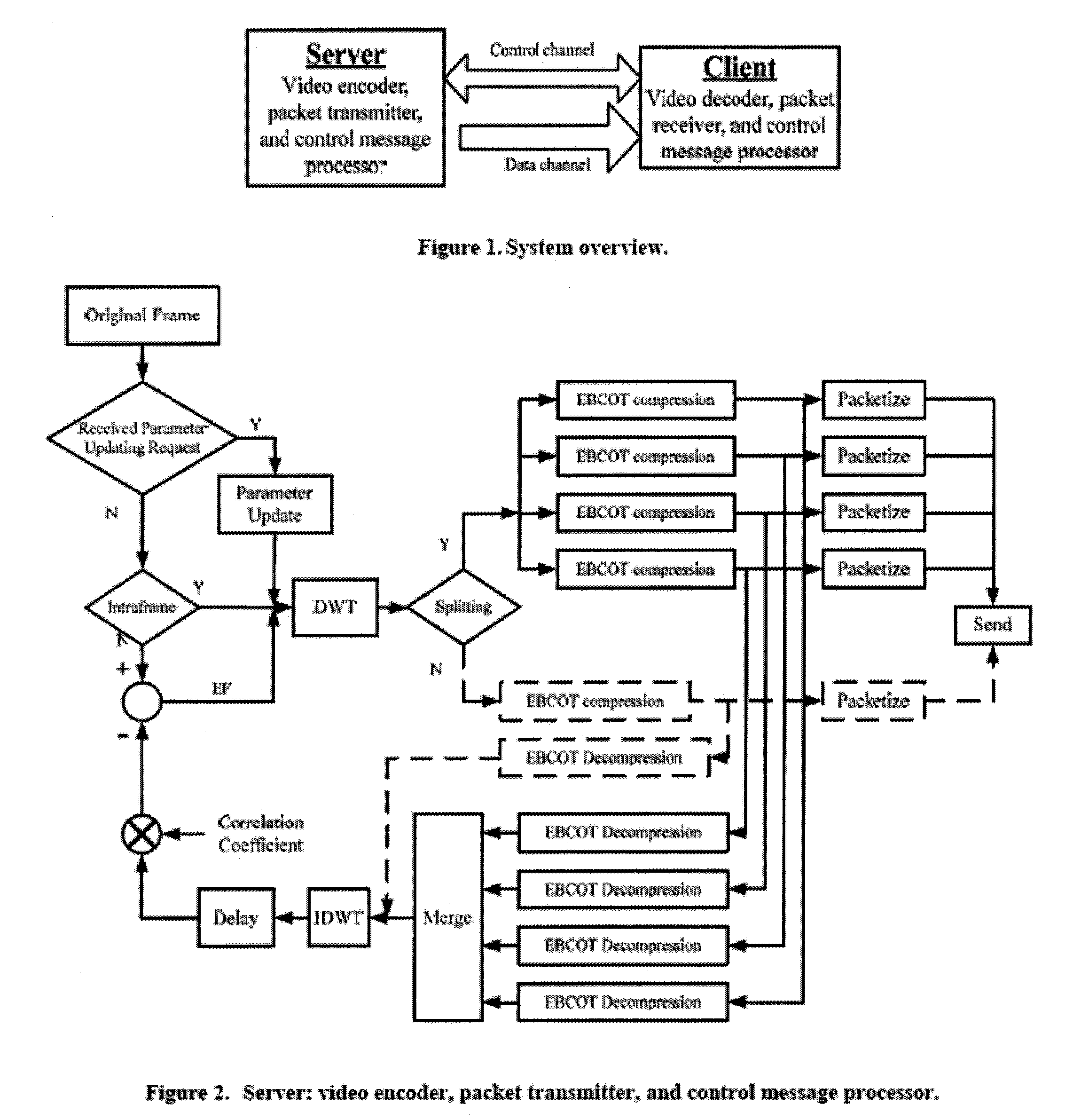
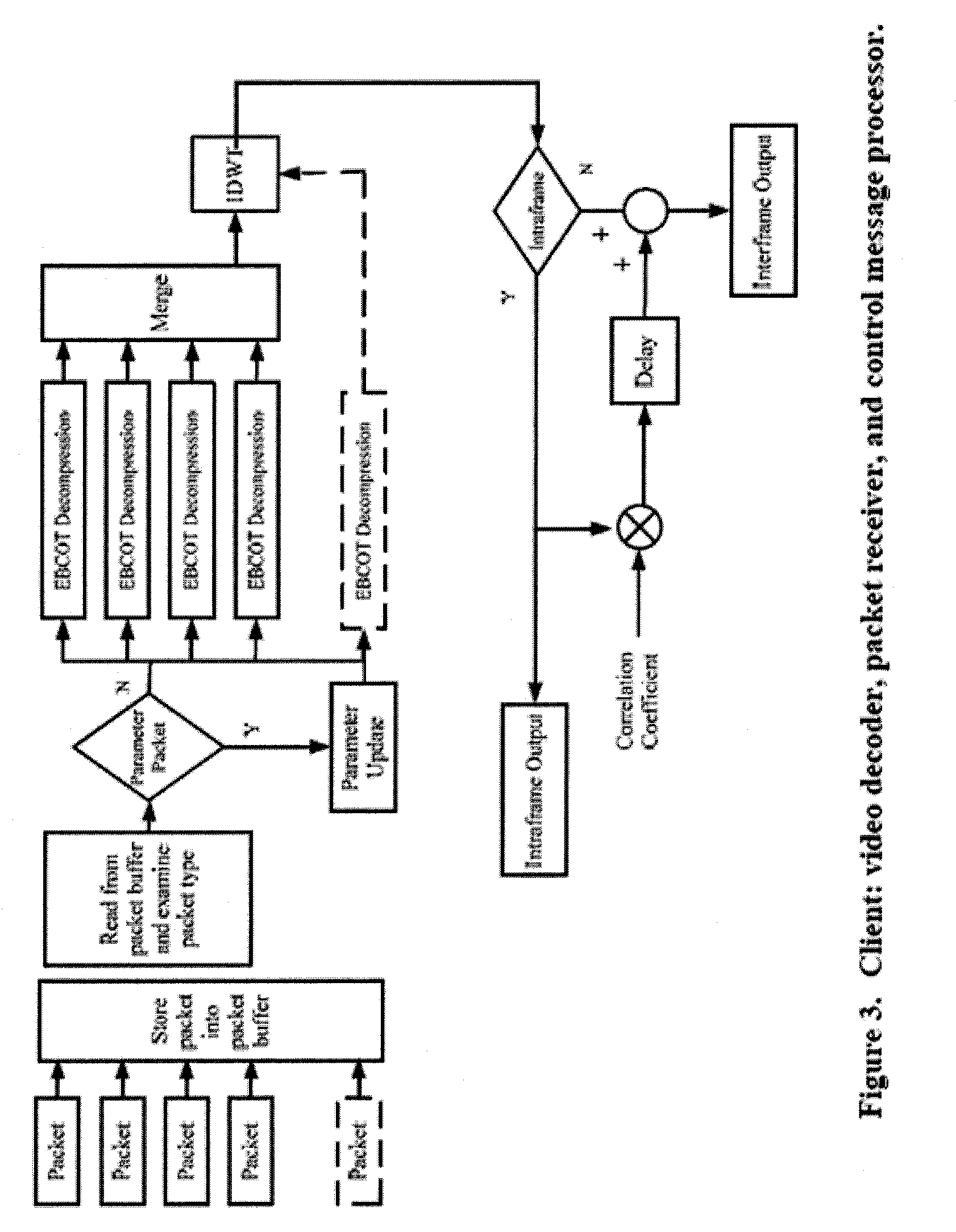
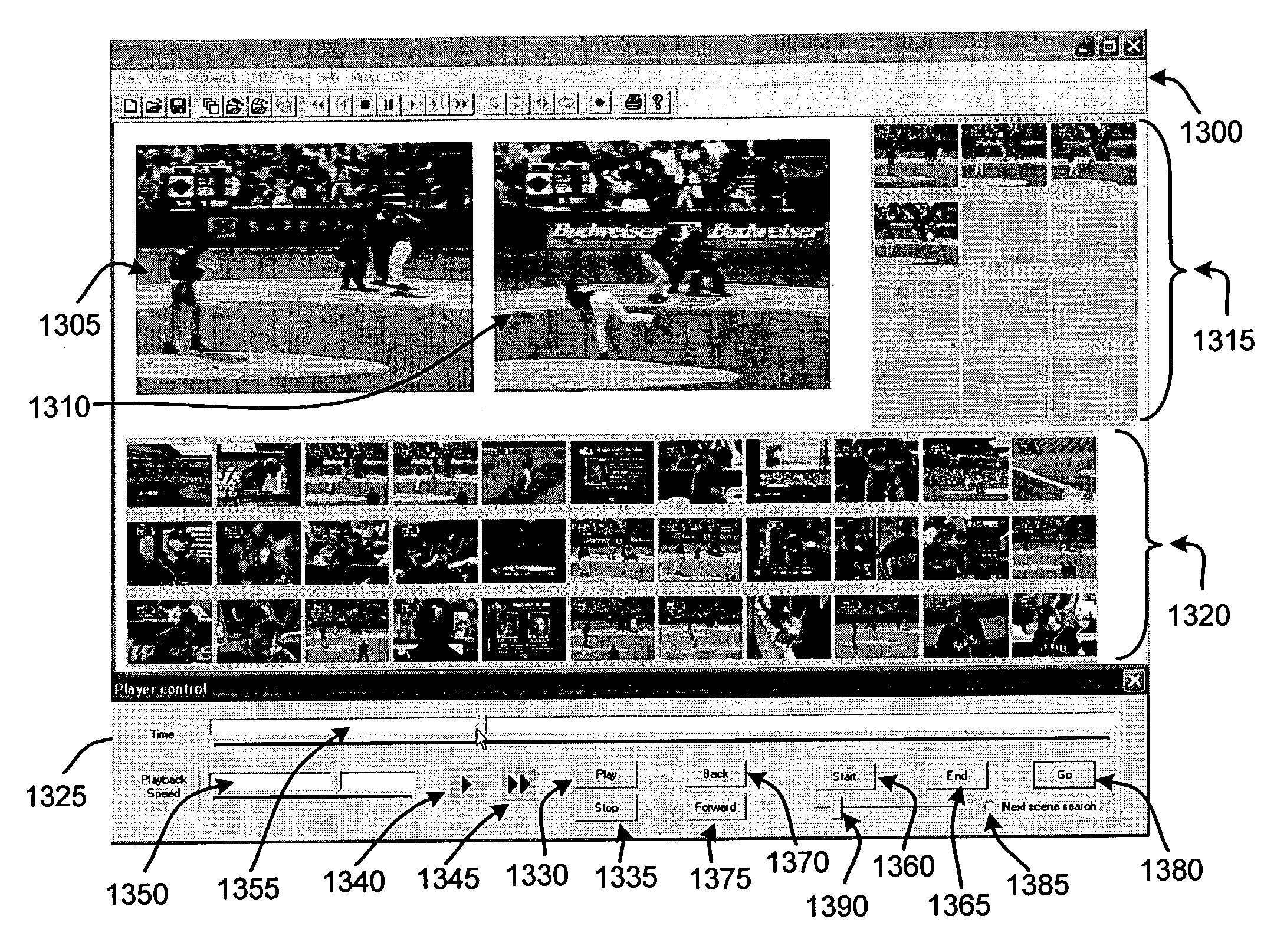
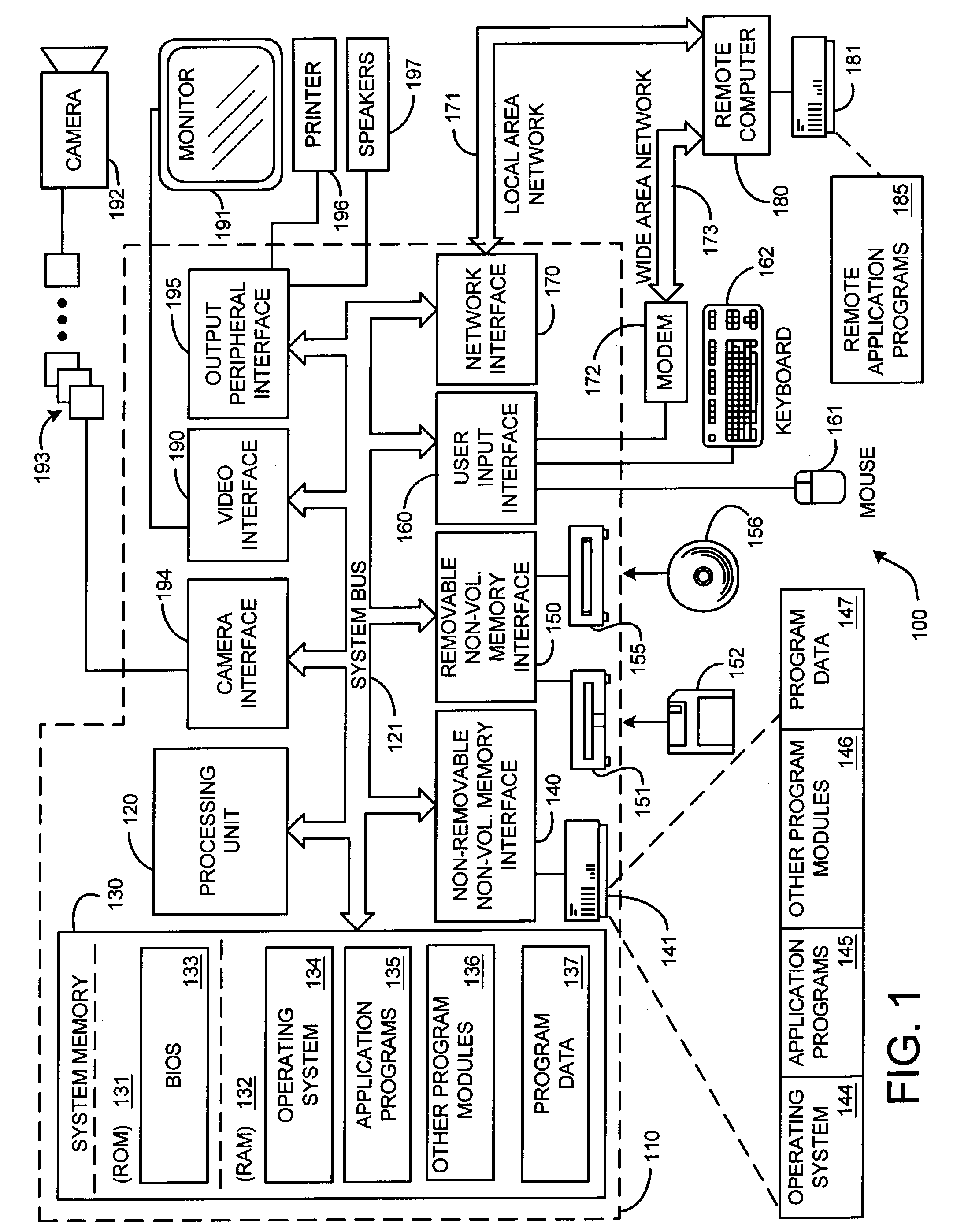
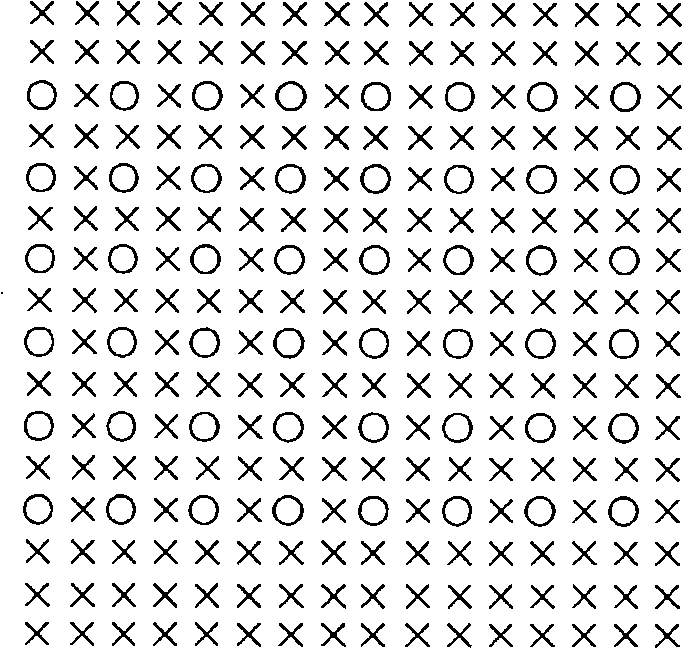Patents
Literature
393 results about "Adaptive video" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
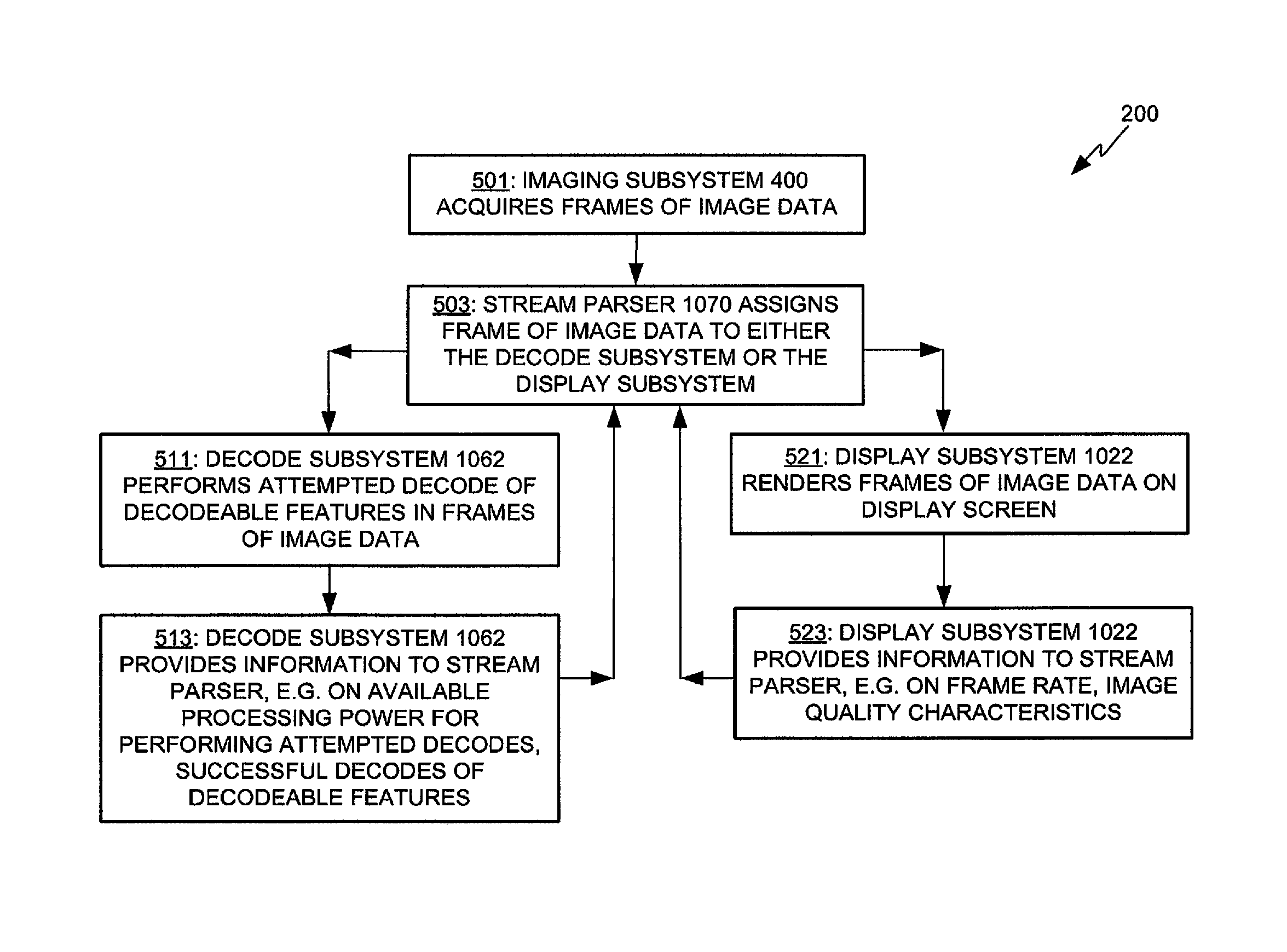
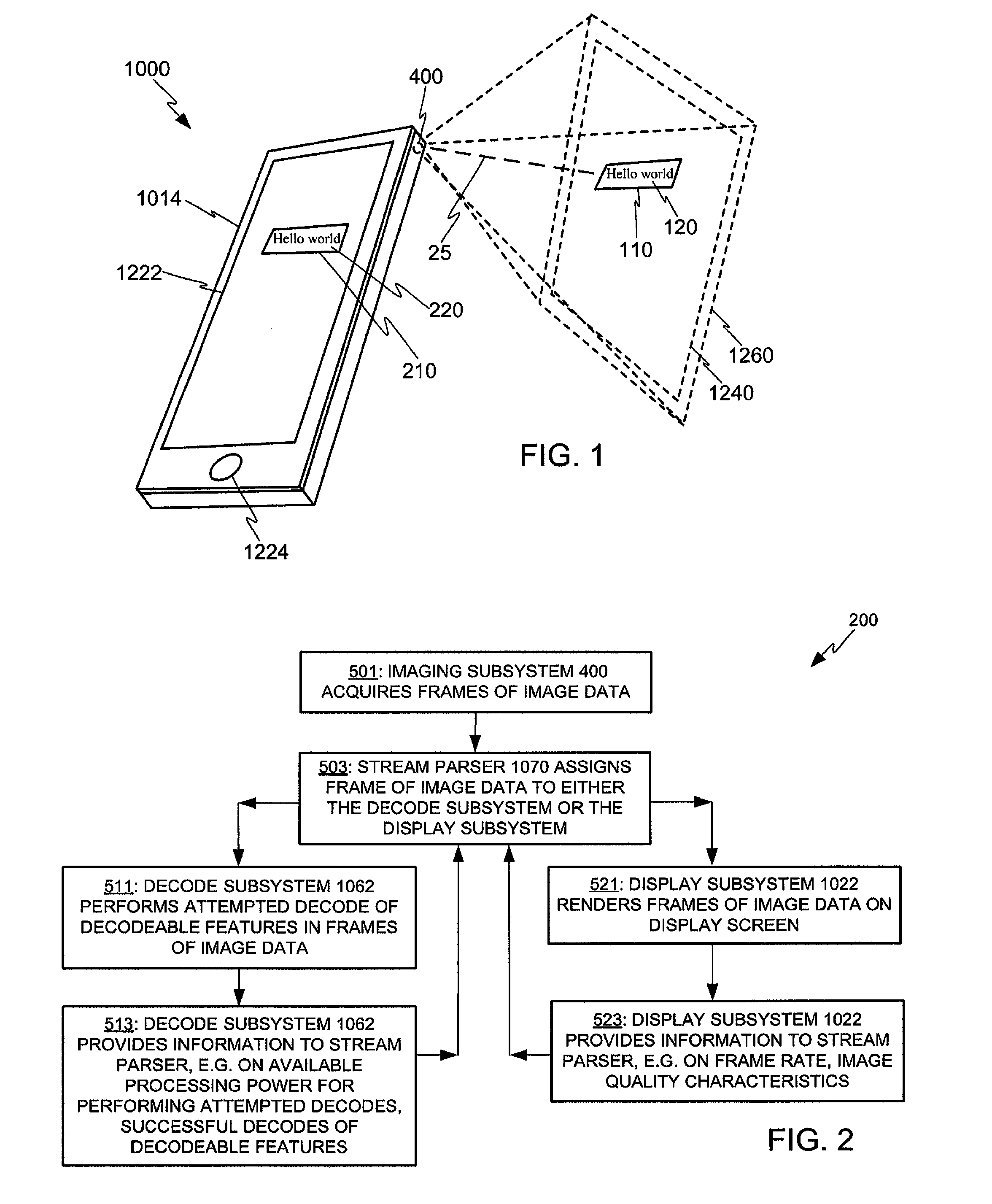
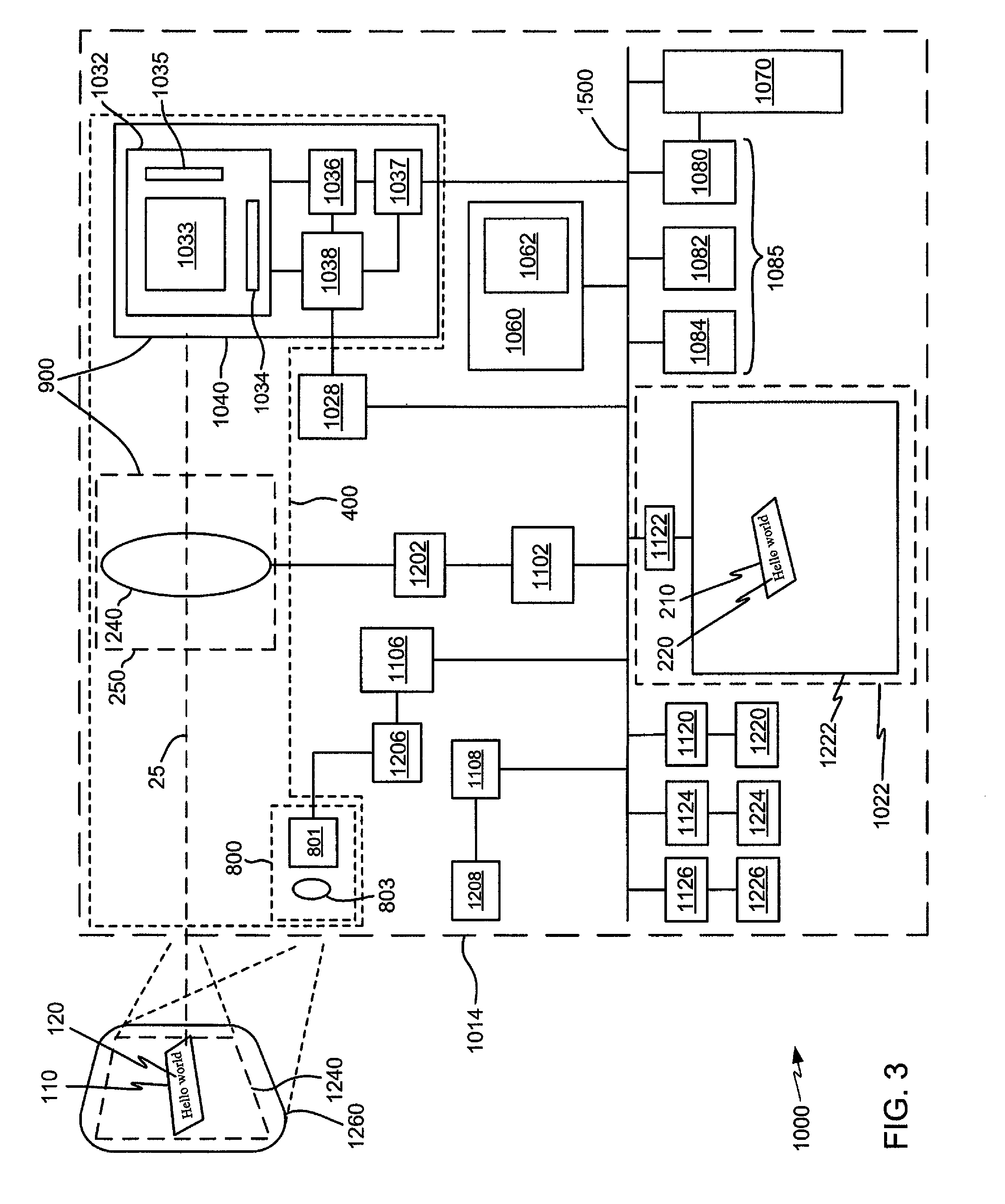
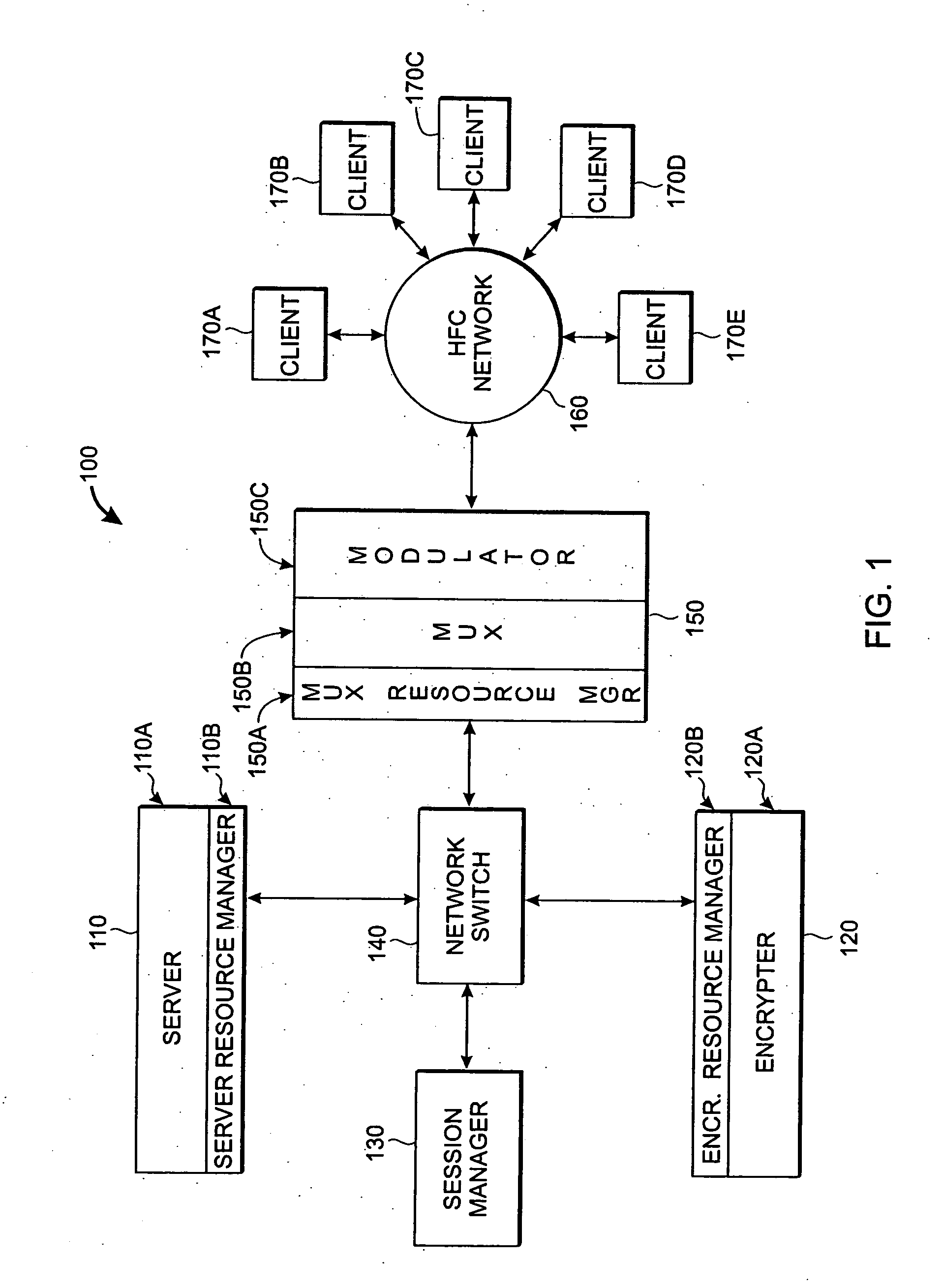
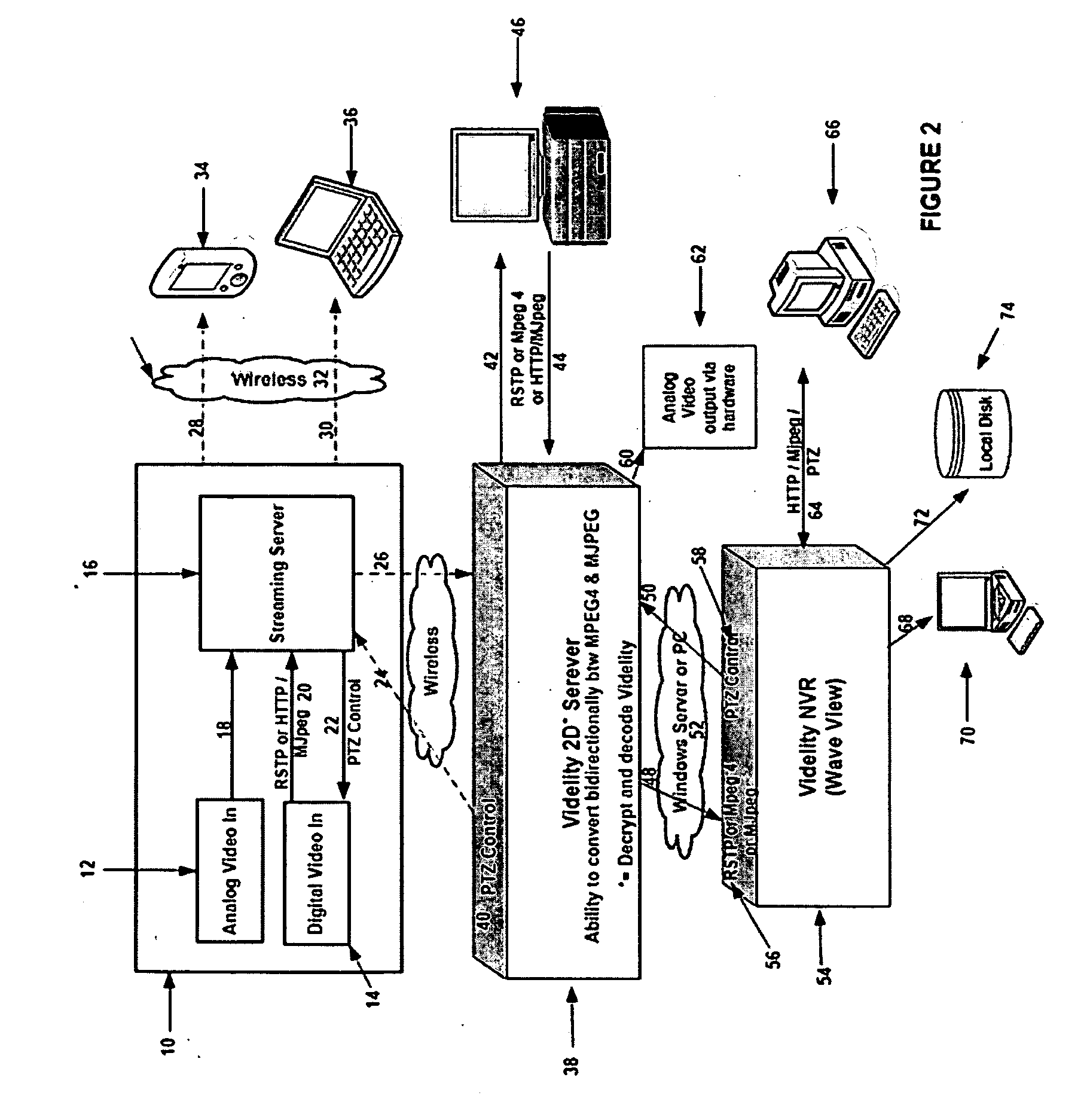
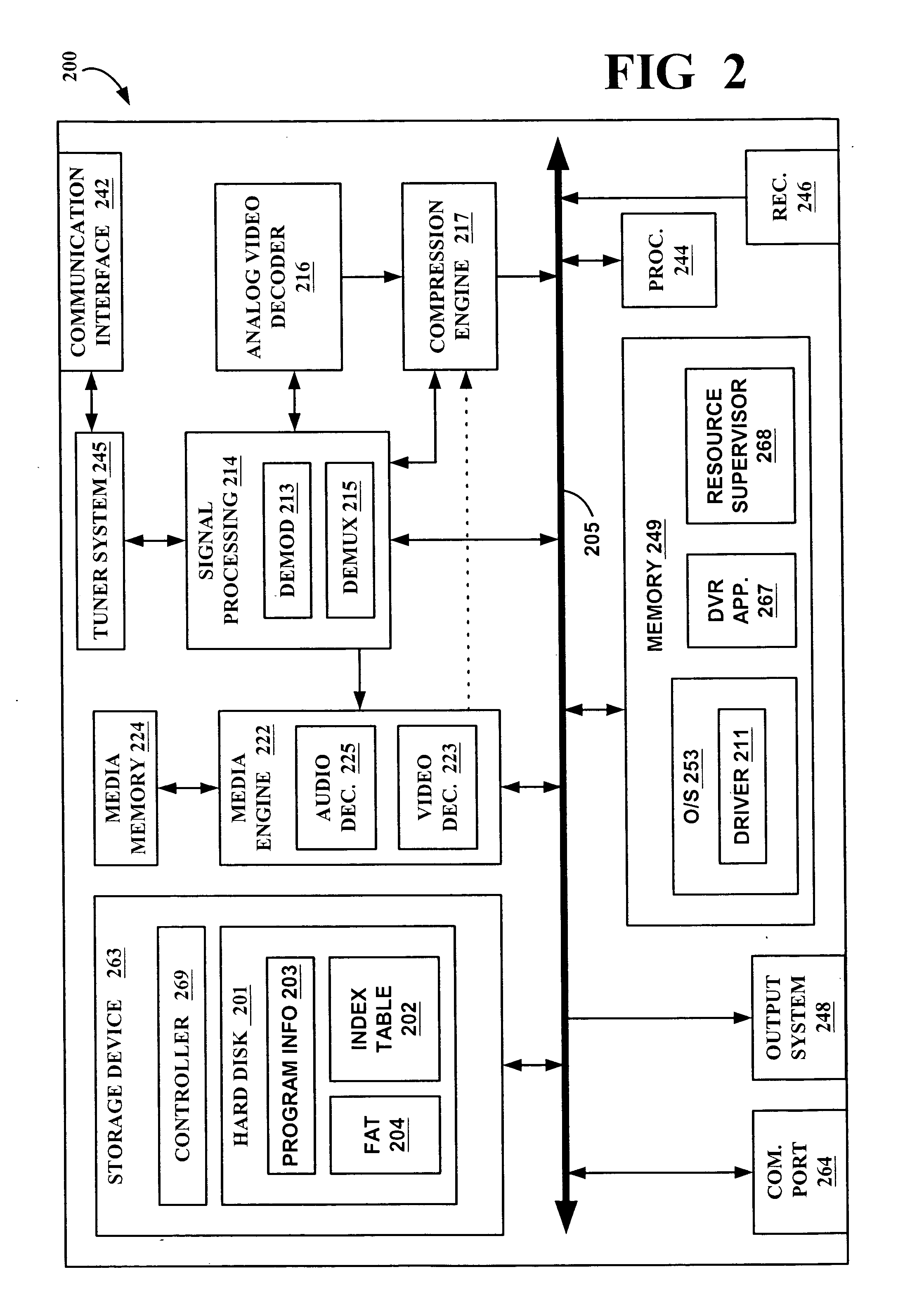
Adaptive video capture decode system
ActiveUS8879639B2Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningComputer graphics (images)Adaptive video
Devices, methods, and software are disclosed for an adaptive video capture decode system that efficiently manages a stream of image frames between a device display screen and a processor performing decode attempts on decodable features in the image frames. In an illustrative embodiment, a device assigns frames of image data from a stream of frames of image data to either a display subsystem or a decode subsystem. The display subsystem is operative for rendering the frames of image data on a display screen. The decode subsystem is operative for receiving frames of image data and performing an attempted decode of a decodable indicia represented in at least one of the frames of image data. None of the frames of data are assigned to both the display subsystem and the decode subsystem.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
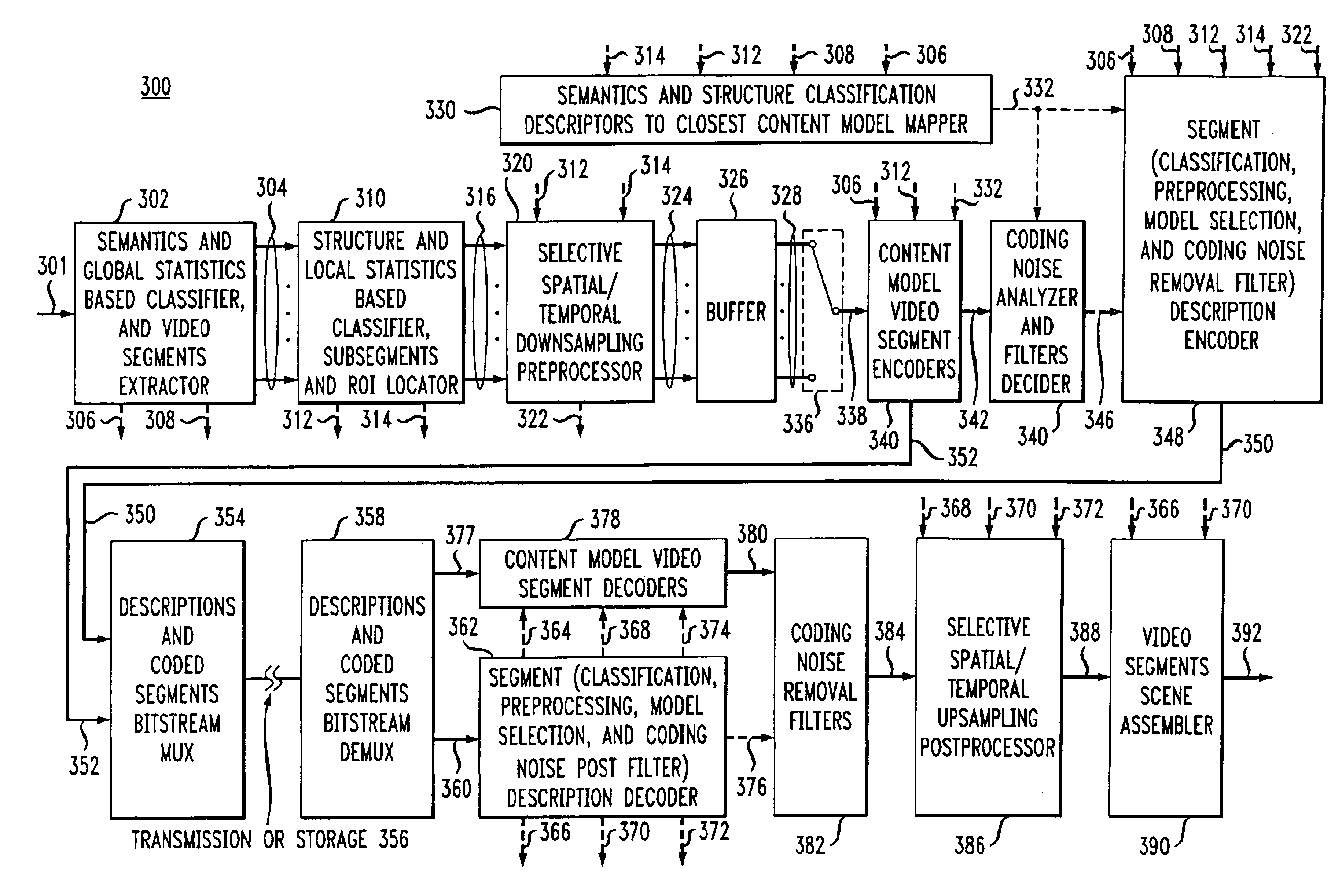
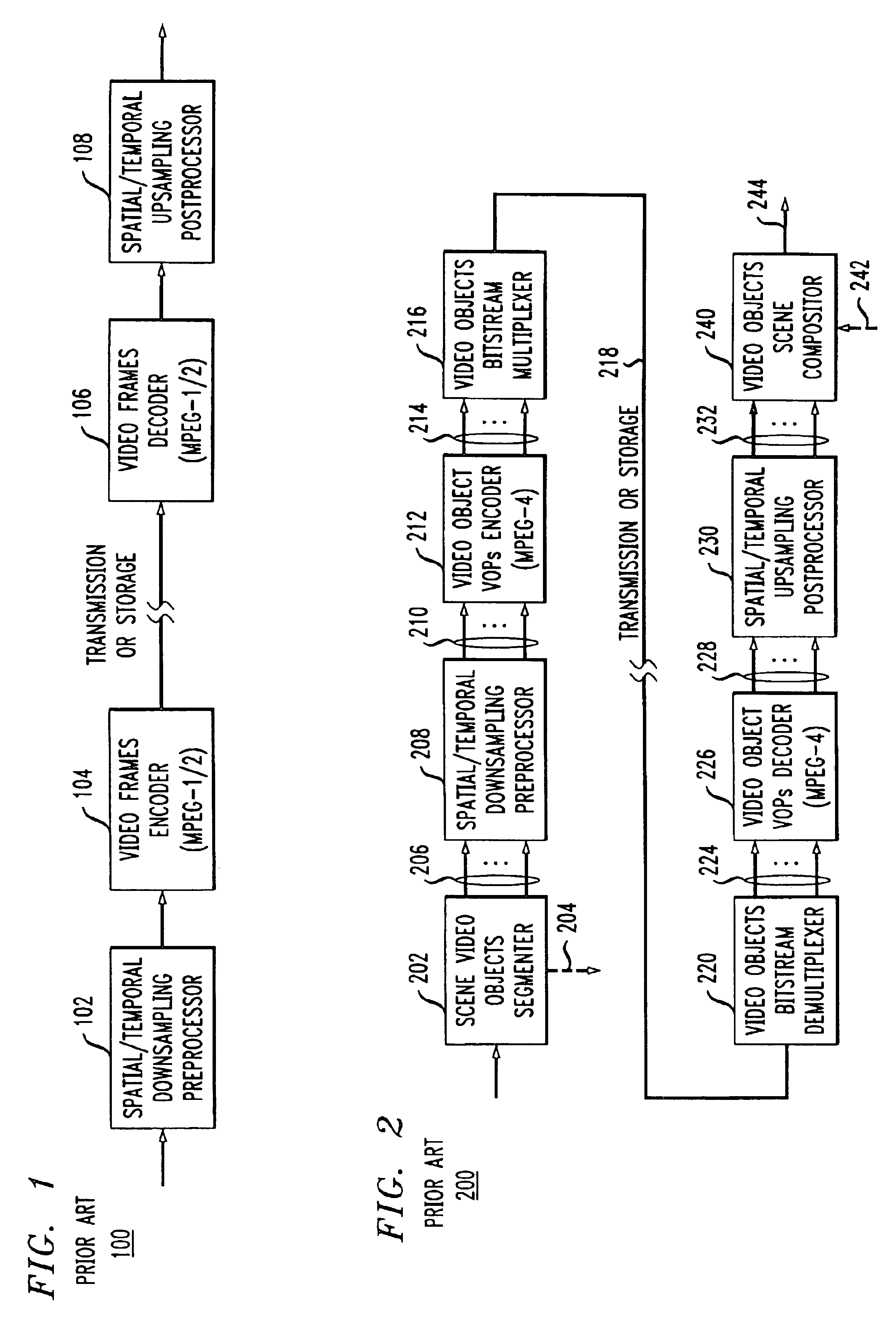
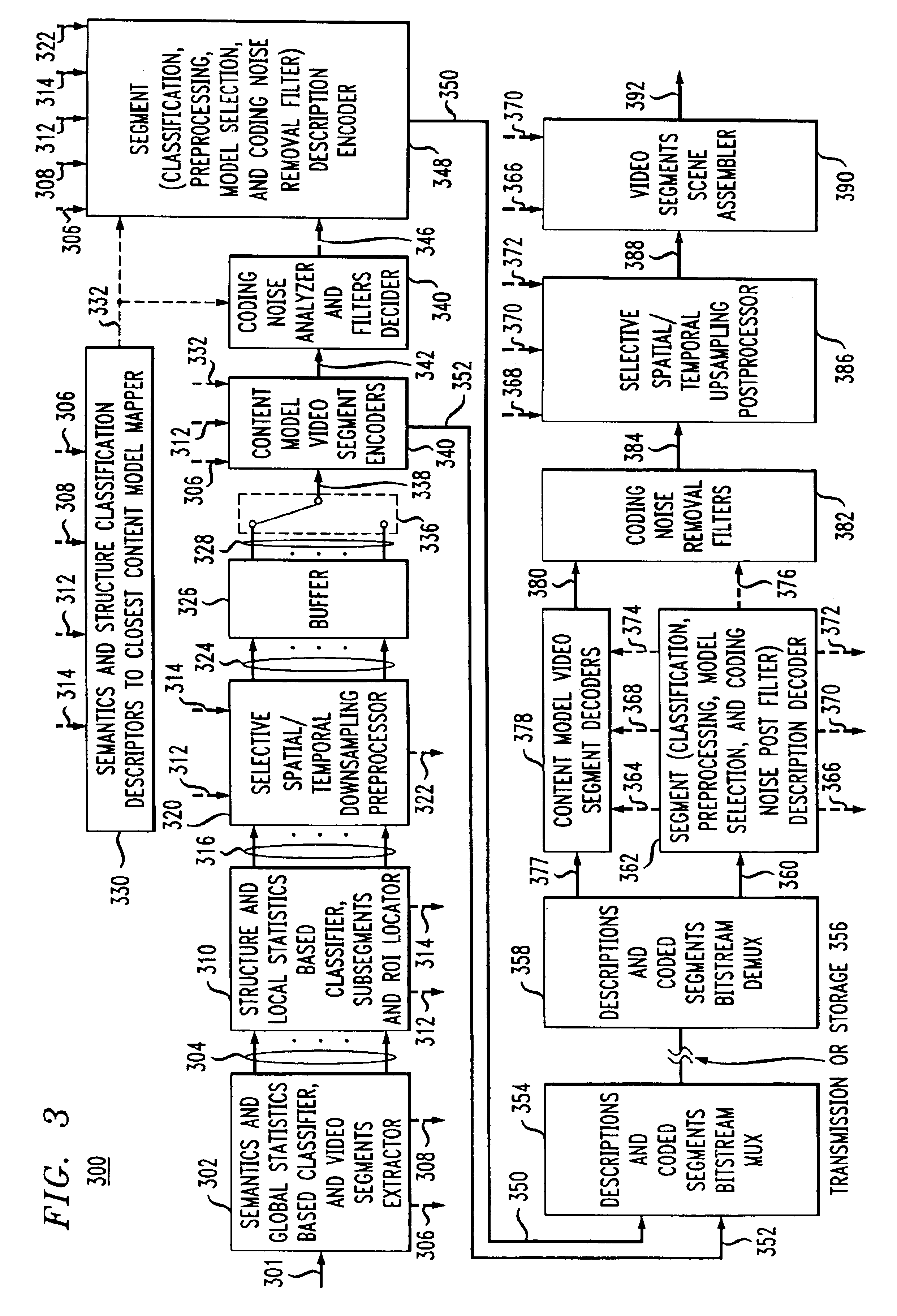
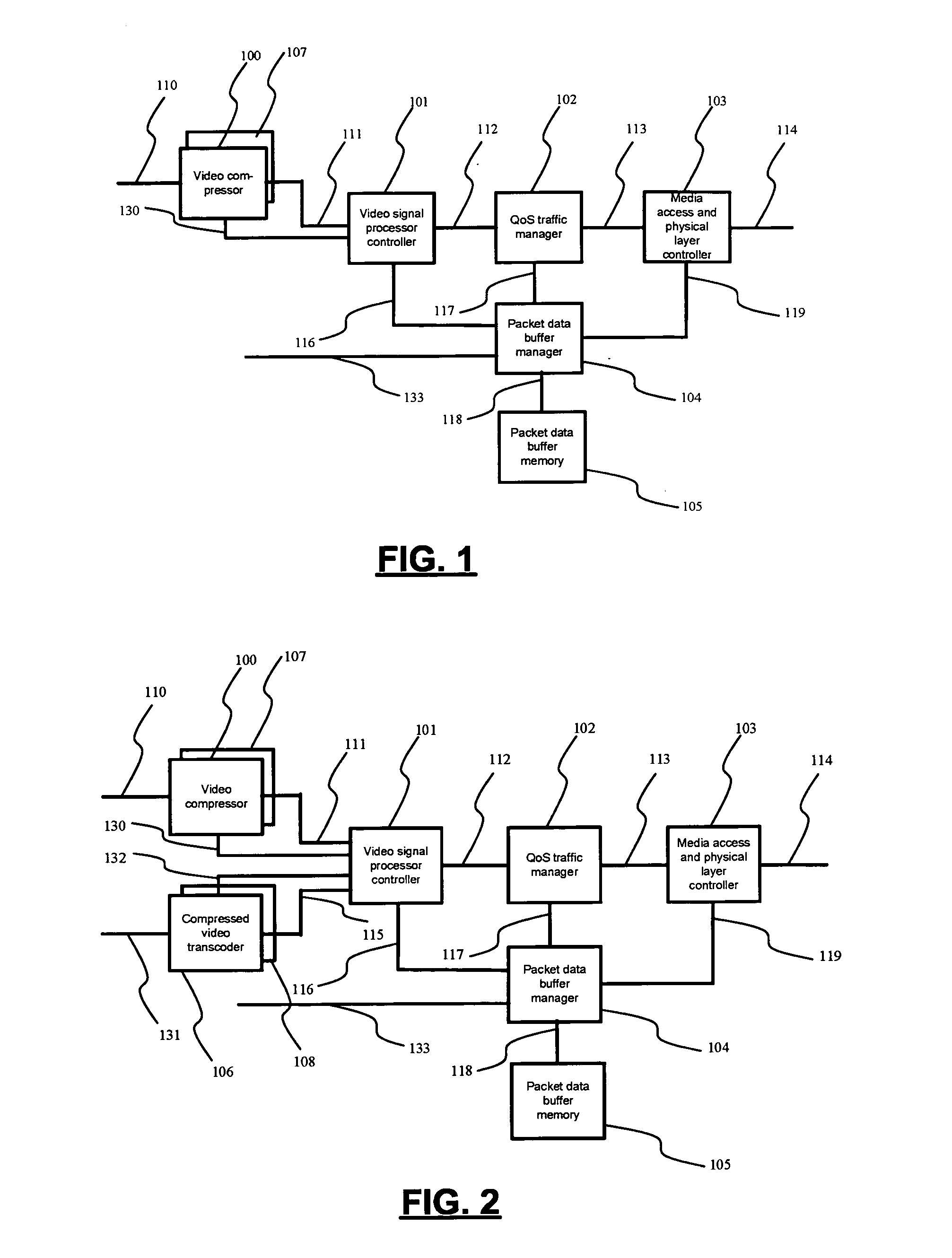
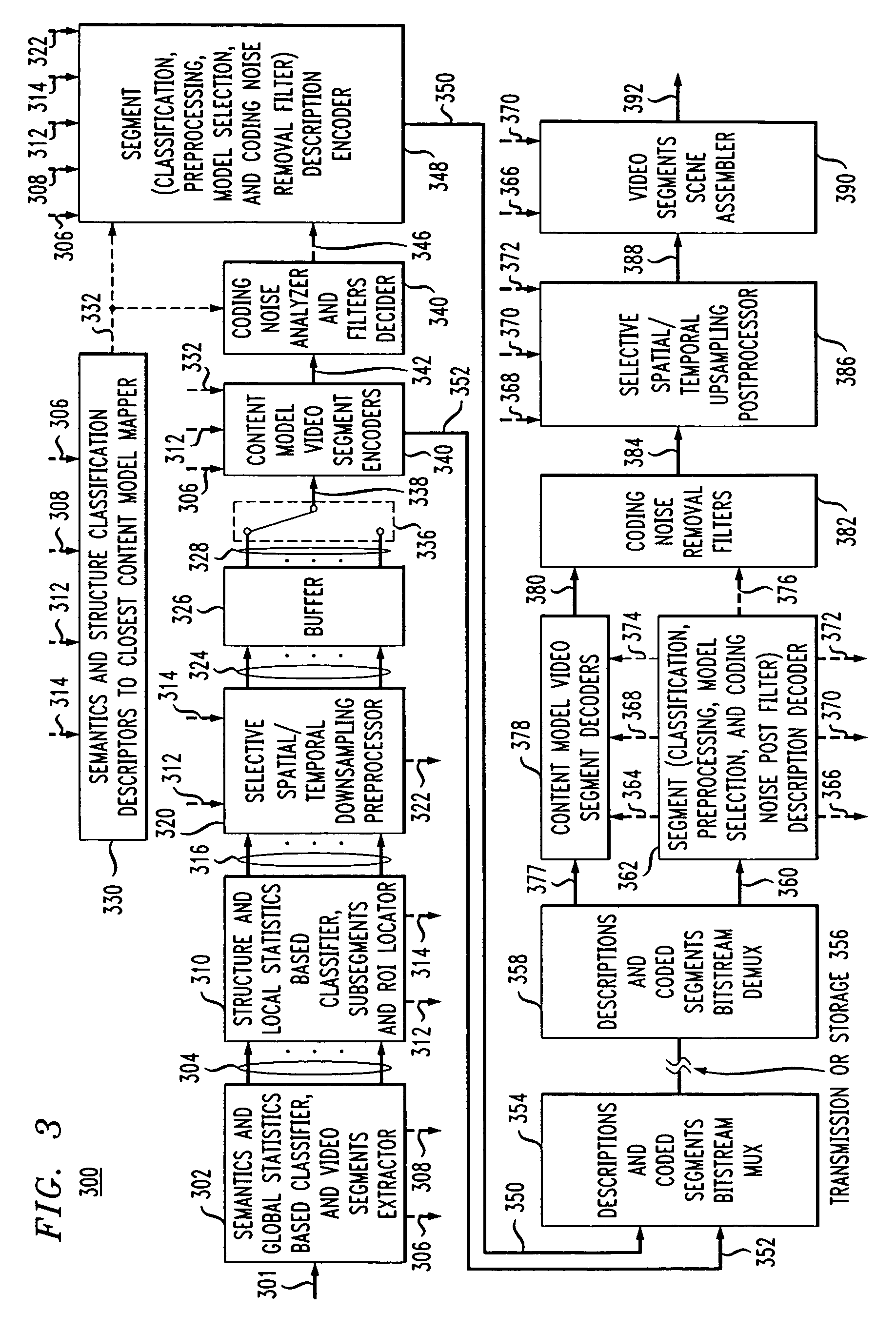
Content adaptive video encoder
InactiveUS6909745B1Improve efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAdaptive encodingSubject matter
A system for content adaptive encoding and decoding video is disclosed. The system comprises modules for segmenting video content into segments based on predefined classifications or models. Examples of such classifications comprise action scenes, slow scenes, low or high detail scenes, and brightness of the scenes. Based on the segment classifications, each segment is encoded with a different encoder chosen from a plurality of encoders. Each encoder is associated with a model. The chosen encoder is particularly suited to encoding the unique subject matter of the segment. The coded bit-stream for each segment includes information regarding which encoder was used to encode that segment. A matching decoder of a plurality of decoders is chosen using the information in the coded bitstream to decode each segment using a decoder suited for the classification or model of the segment. If scenes exist which do not fall in a predefined classification, or where classification is more difficult based on the scene content, these scenes are segmented, coded and decoded using a generic coder and decoder.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
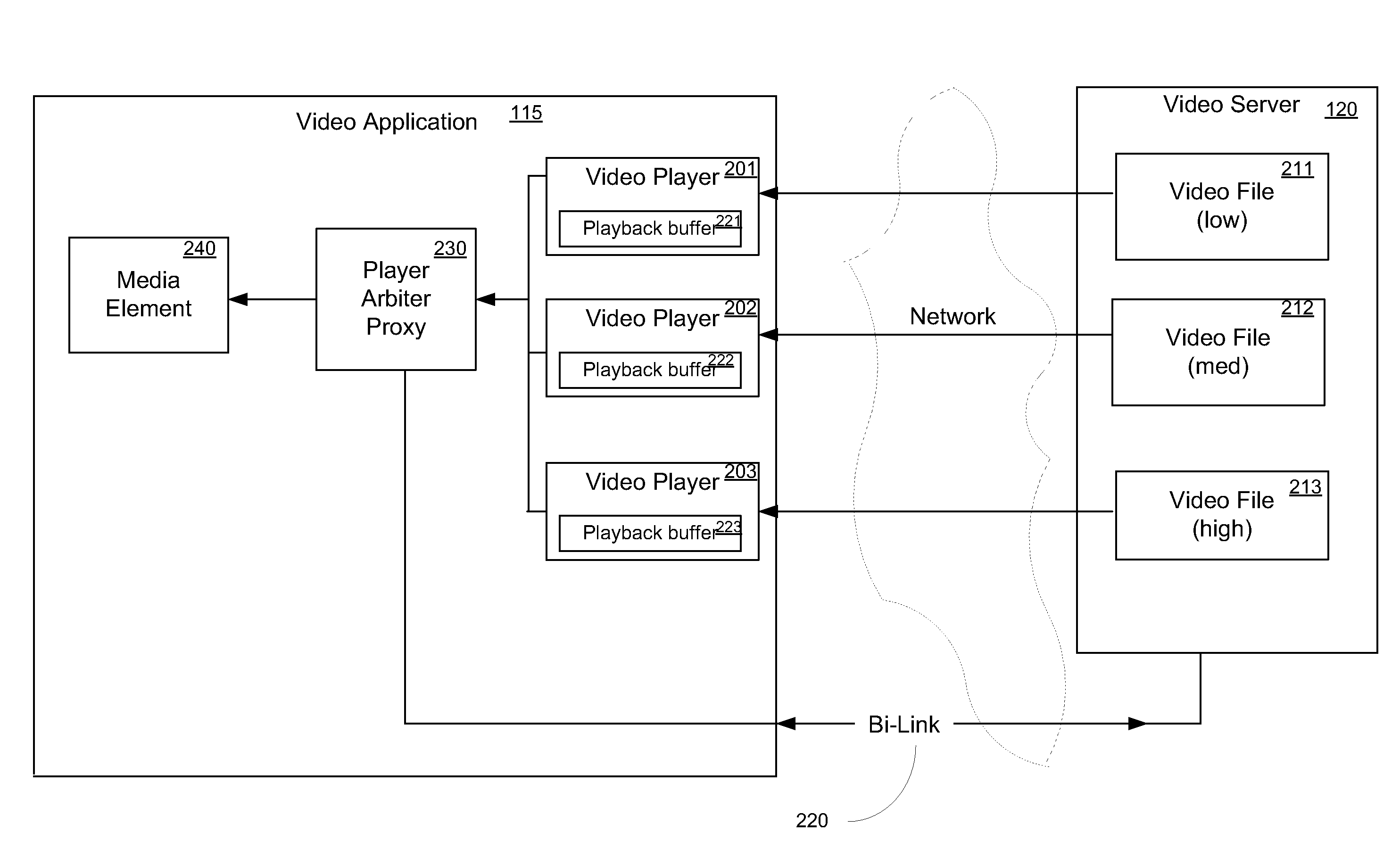
Adaptive video switching for variable network conditions
InactiveUS20090328124A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareNetwork conditions
A method for video playback switching in response to changing network conditions. The method includes accessing a server to retrieve respective index files for a low bit rate version and a high bit rate version of the video file, and instantiating a low bit rate media player and a high bit rate media. Playback of the video file is begun by the high bit rate media player streaming the high bit rate version from the server. Upon an indication of impeded network conditions, a transition point is selected, wherein the transition point indicates where downloading of the high bit rate version stops and where downloading of the low bit rate version begins. The low bit rate media player is then positioned to begin playback at the transition point. Playback of the video file is then switched to the low bit rate player upon encountering the transition point.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
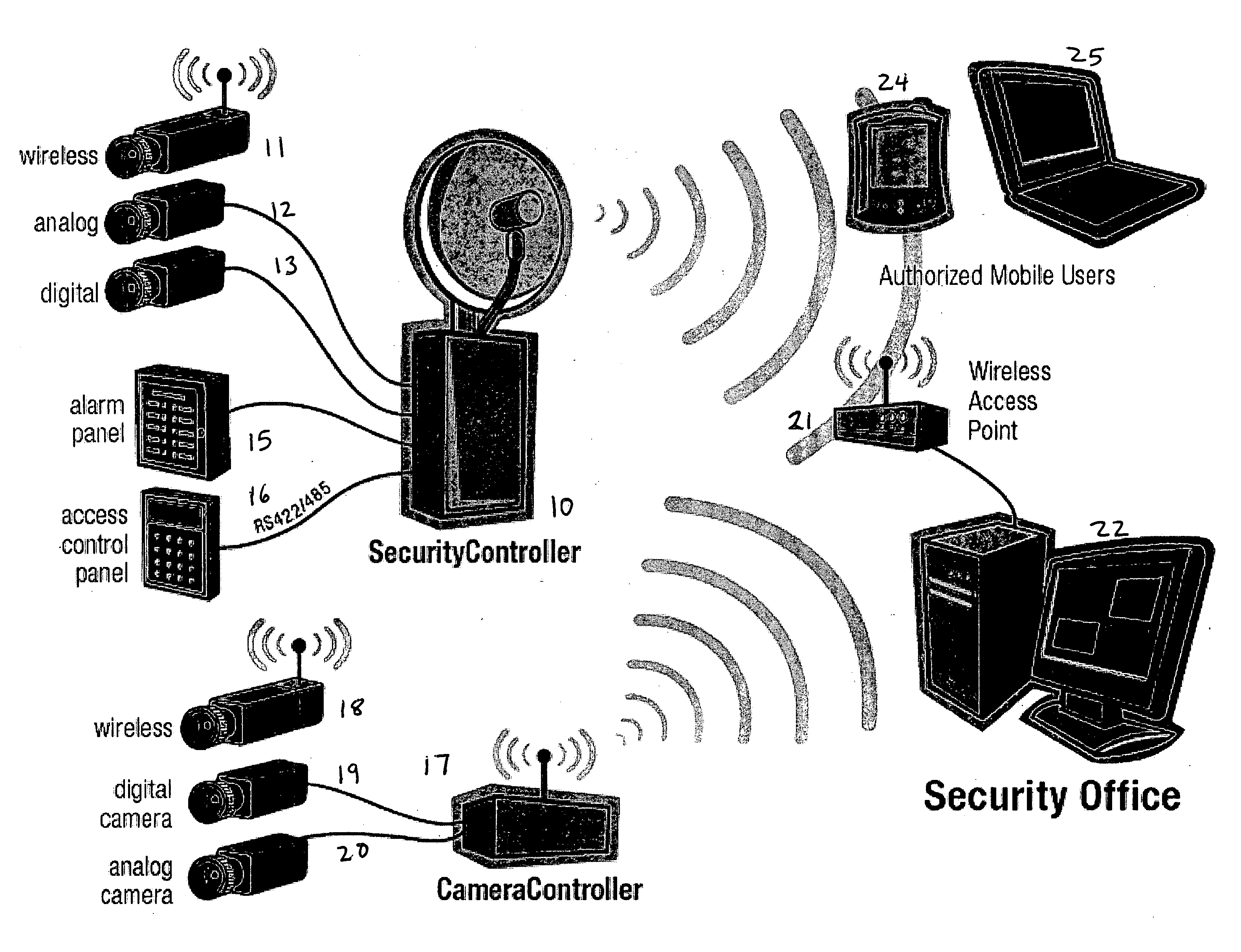
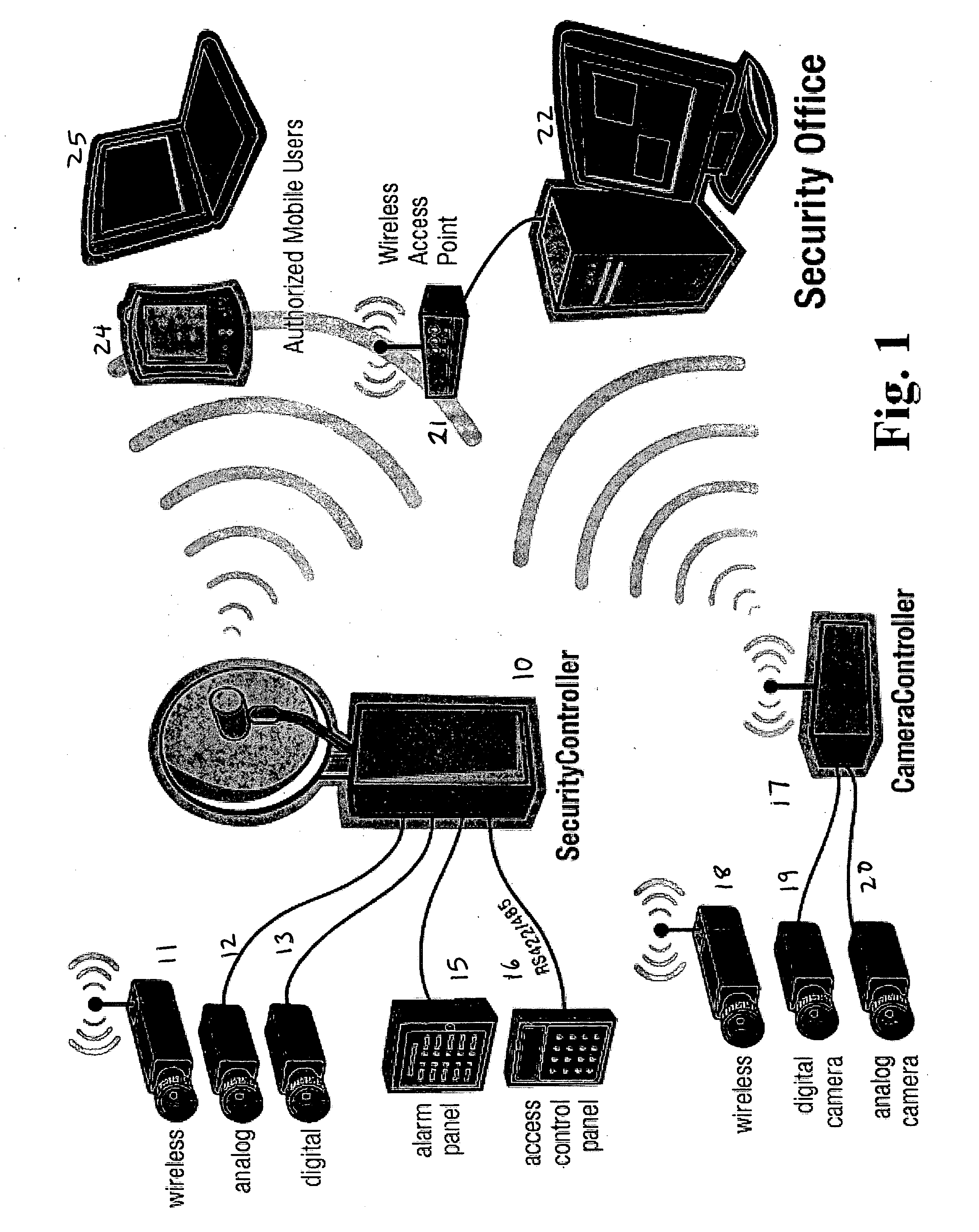
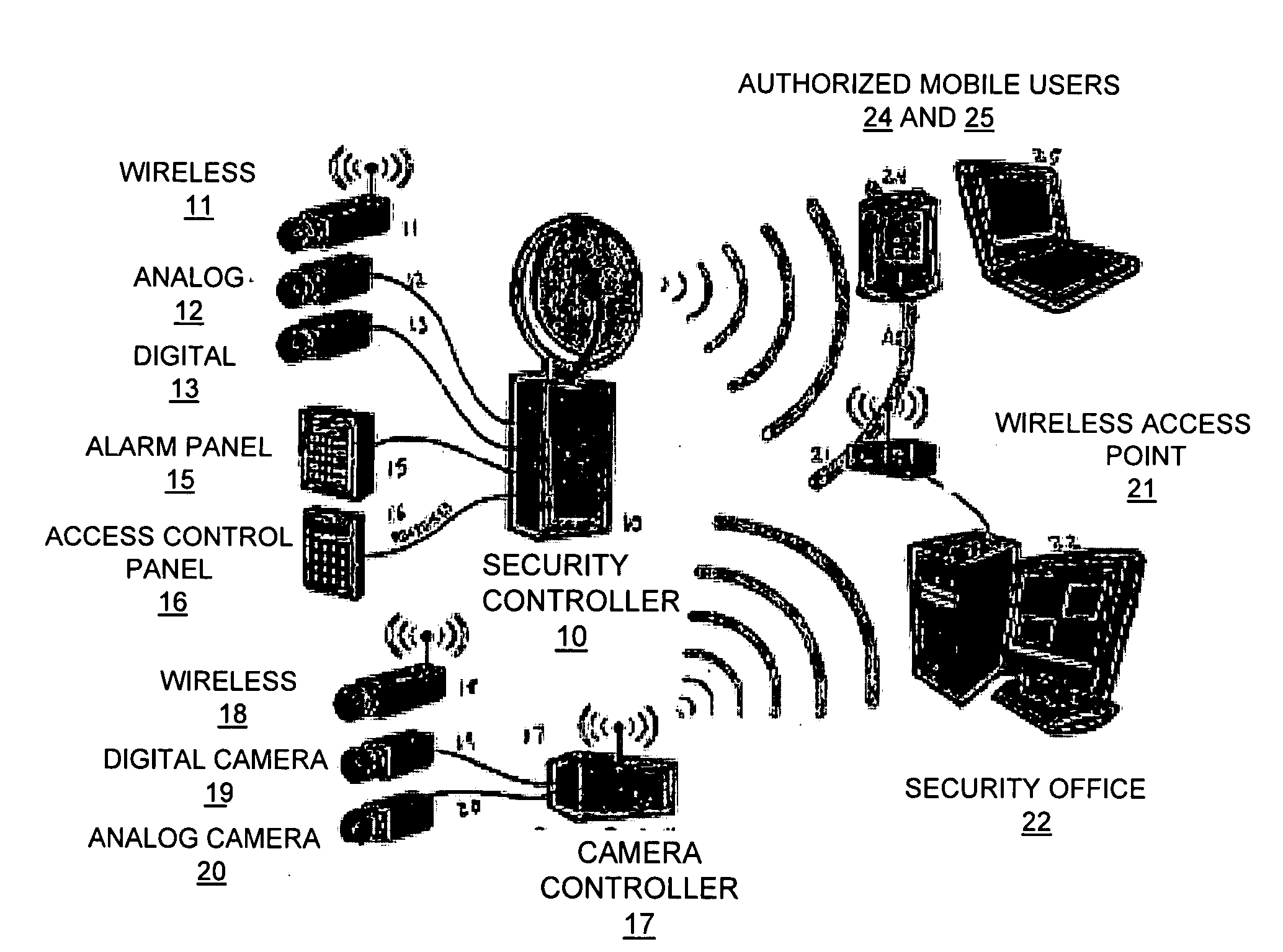
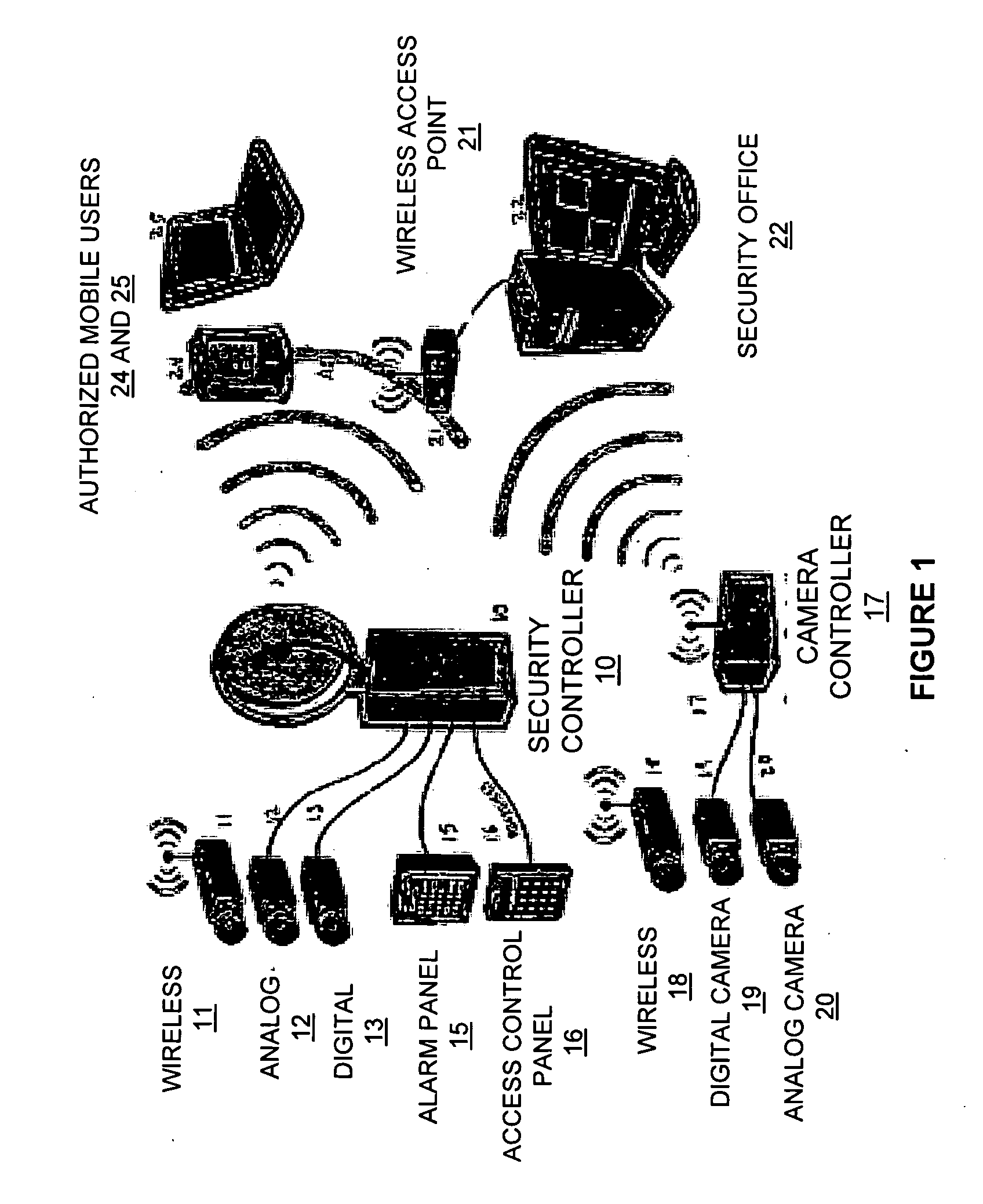
Wireless integrated security controller
InactiveUS20060200845A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsColor television detailsDigital videoMulti camera
A system and method are disclosed for improved video transmission, particularly in security settings. An improved security controller combines the interfaces and functionality for high quality video delivery over often less-than-perfect wireless networks, multi-camera analog / digital video controllers and encoders, multi-frequency wireless camera support, connectivity for serial controllers, network switching, and distributed digital video recording with optional object and motion detection. The video transmission in enhanced using wireless adaptive video encoding, mobile viewing optimization, and wireless bandwidth improvement.
Owner:REEDY CO TRUSTEE OF ARMIDA TECH LIQUIDATING TRUST MATTHEW C +1
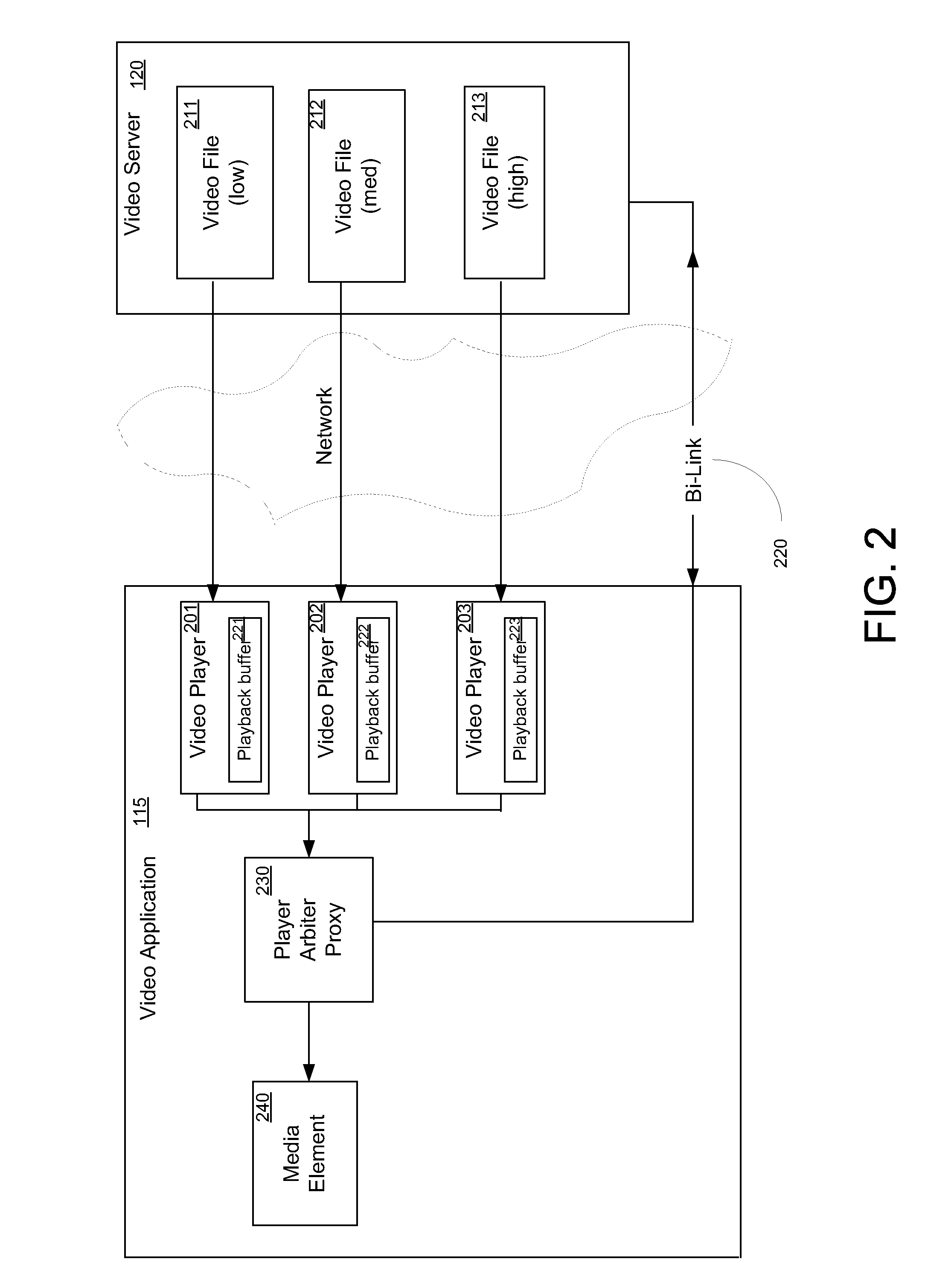
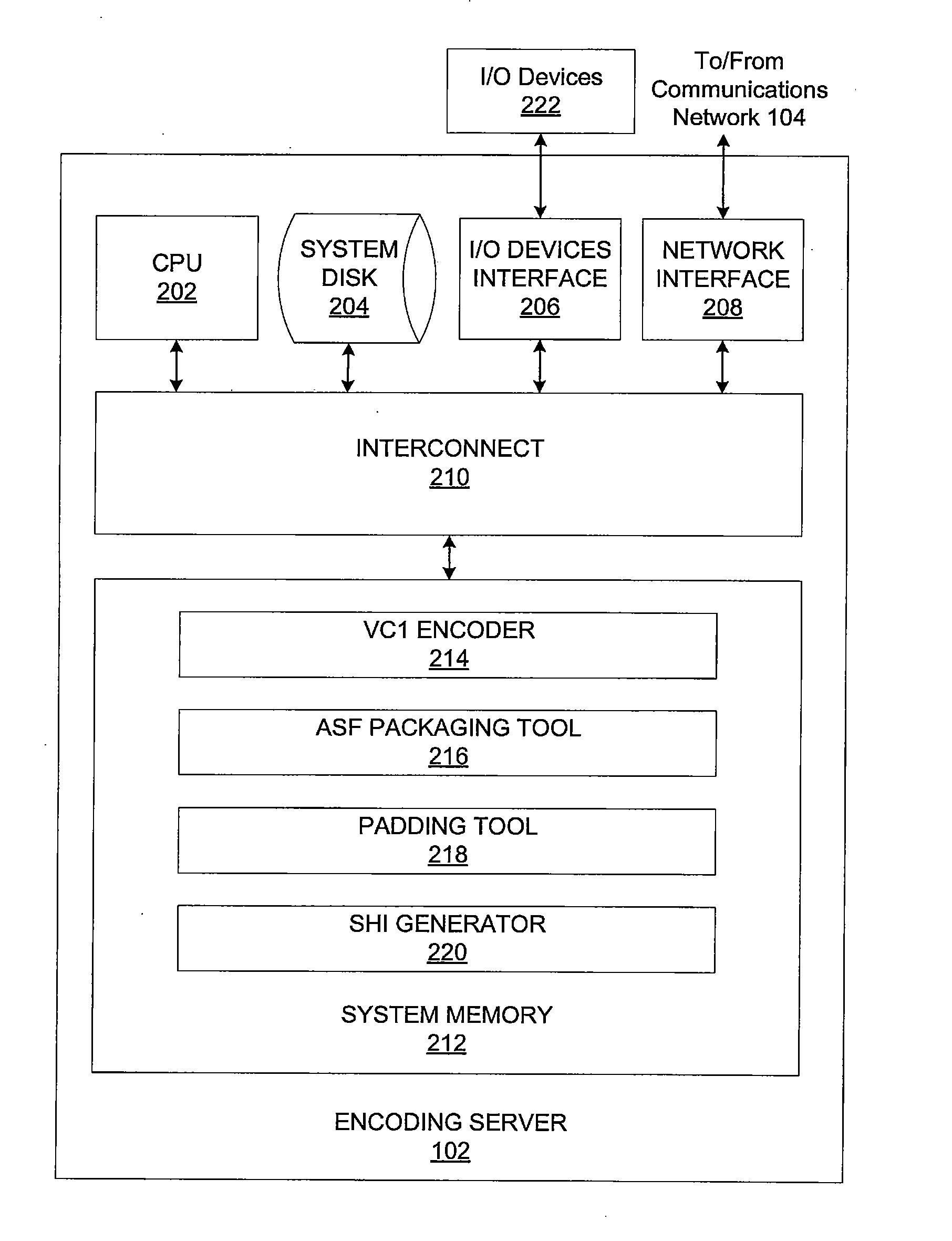
Encoding video streams for adaptive video streaming
ActiveUS20110268178A1Efficient switchingColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareNetwork packet
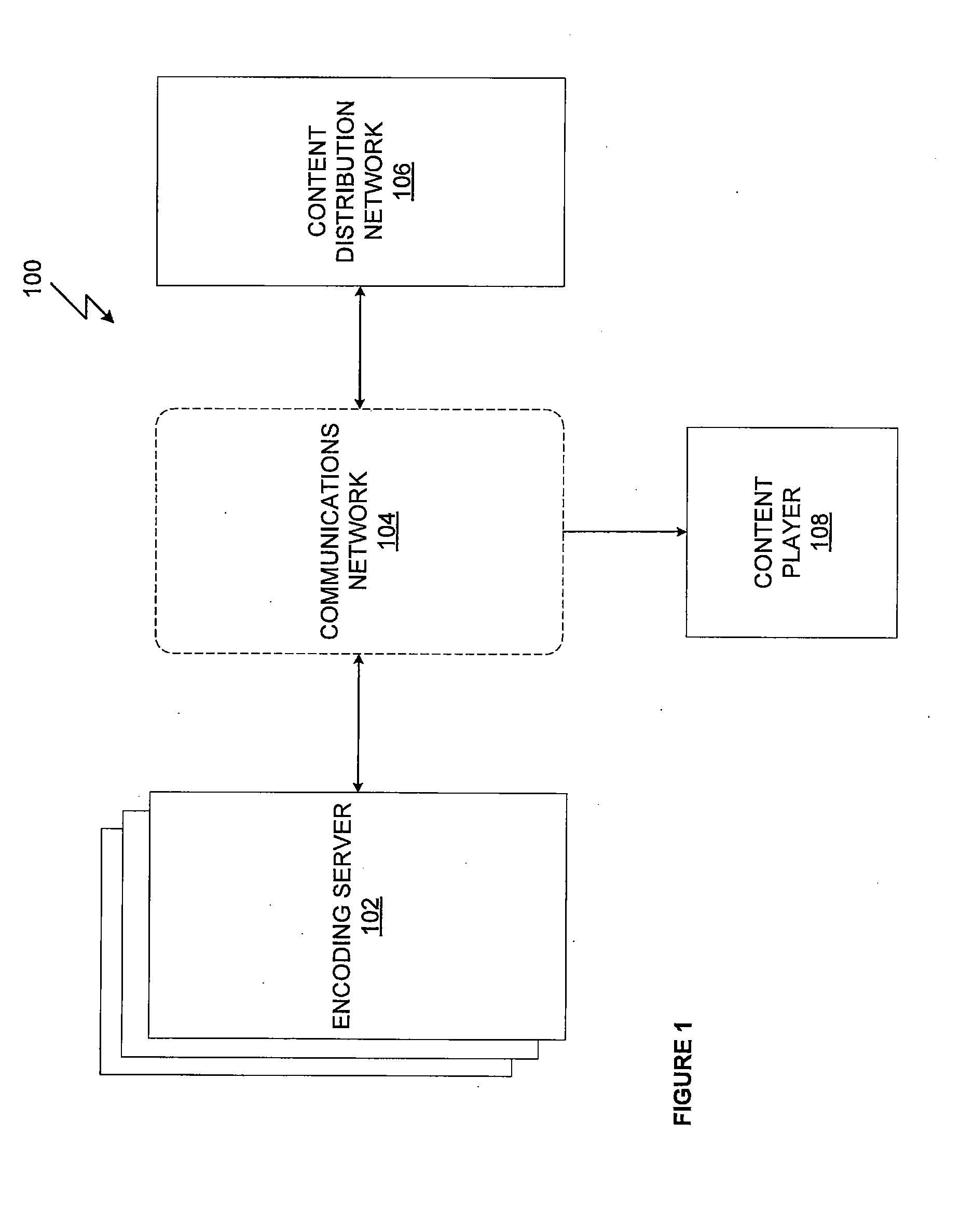
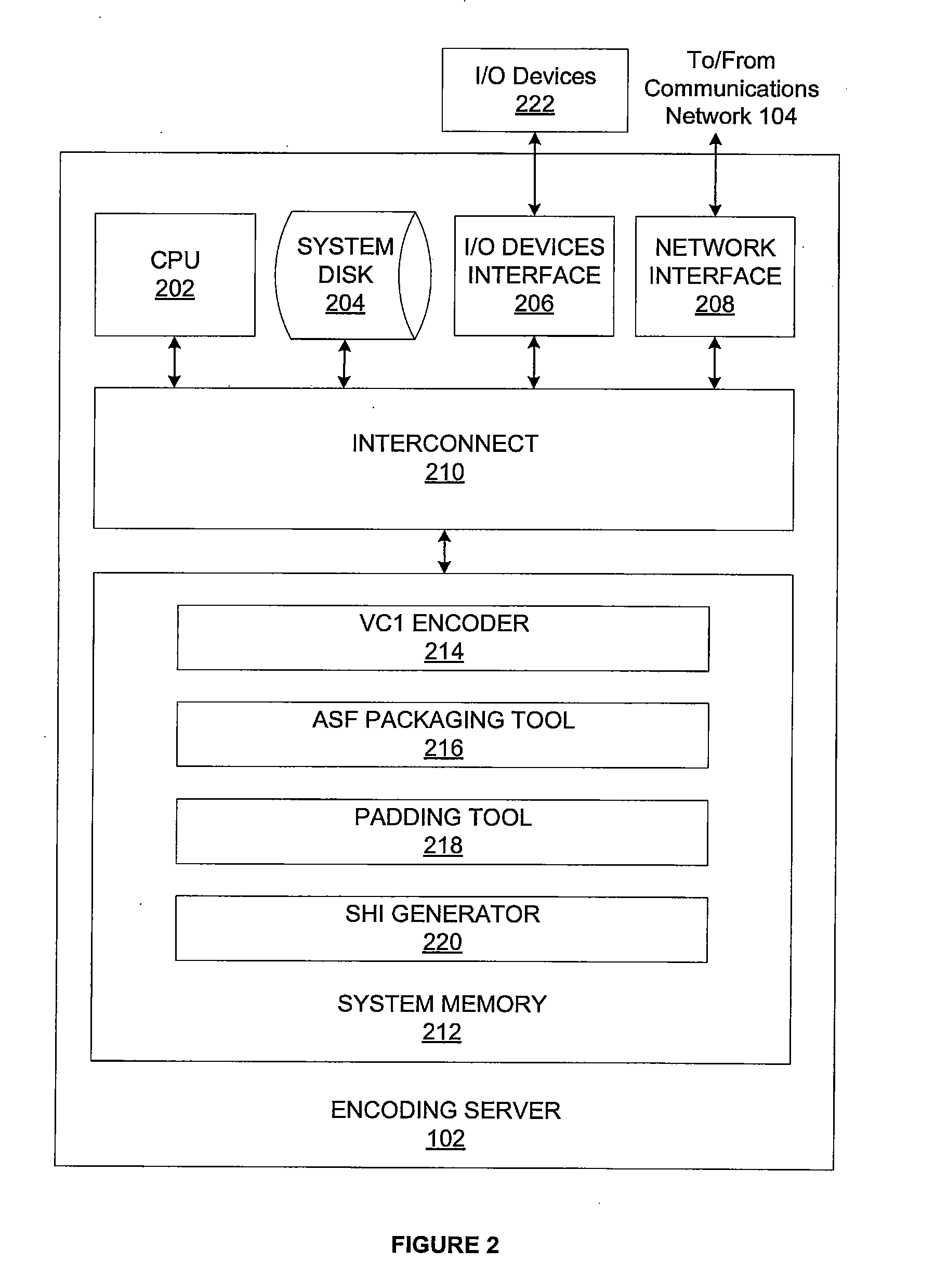
One embodiment of the invention sets forth an encoding server including components configured to encode a video stream associated with a content title for adaptive streaming. The video stream is first processed by a VC1 encoder to generate an encoded video stream comprising a multiple GOPs, each GOP including a key frame and having a different playback offset. The encoded video stream is then packaged such that the GOPs are stored in data packets of the packaged encoded stream. An SHI generator generates an SHI associated with the packaged encoded stream that includes a switch point associated with each GOP. Each switch point includes the playback offset associated with the corresponding GOP and the data packet storing the key frame of the corresponding GOP. The SHI associated with multiple packaged encoded video streams associated with the same content title and encoded to different playback bit rates have corresponding switch points.
Owner:NETFLIX
Adaptive video on-demand system and method using tempo-differential file transfer
InactiveUS20020129375A1Cost effectiveTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDistribution systemAdaptive video
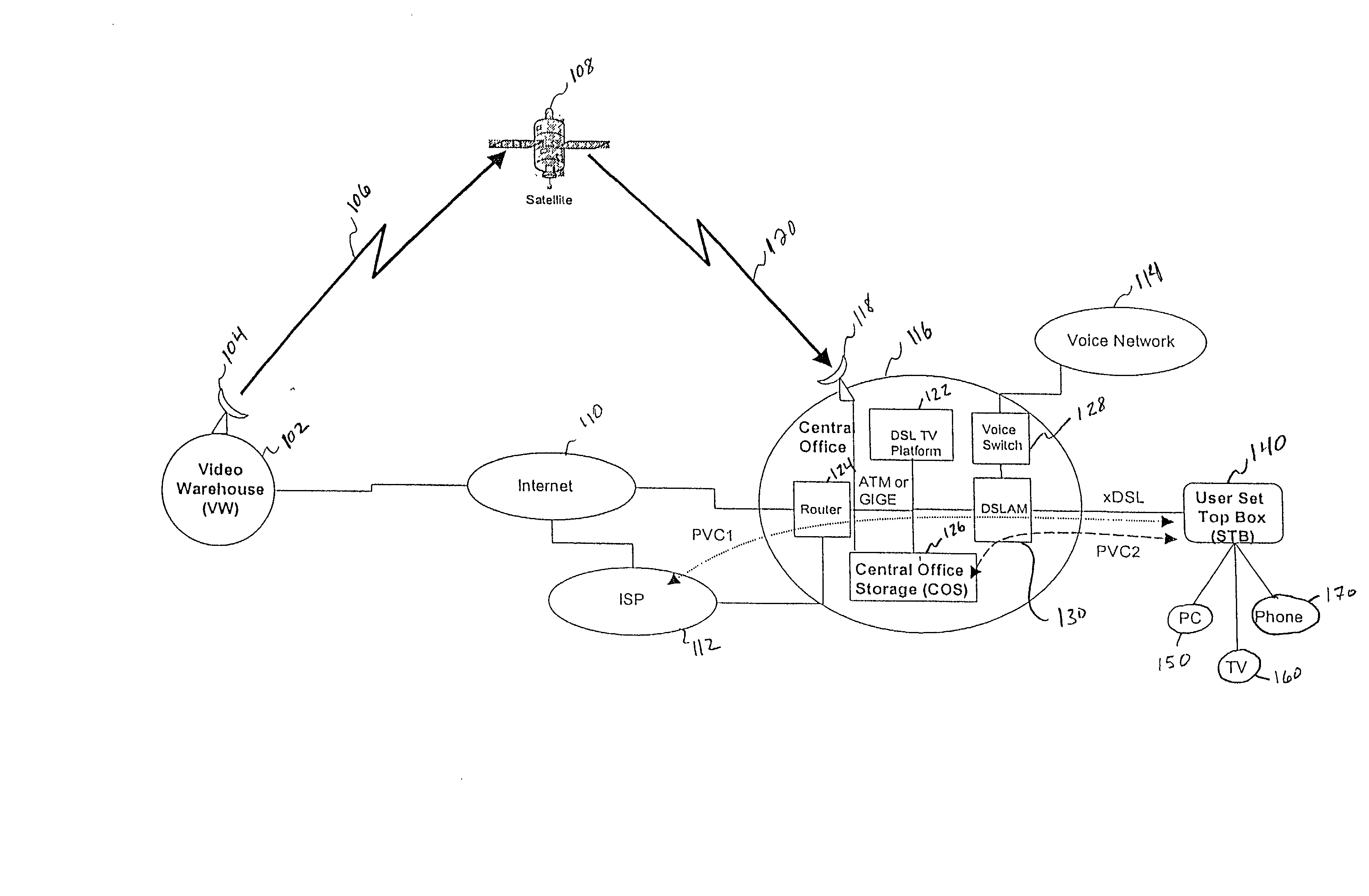
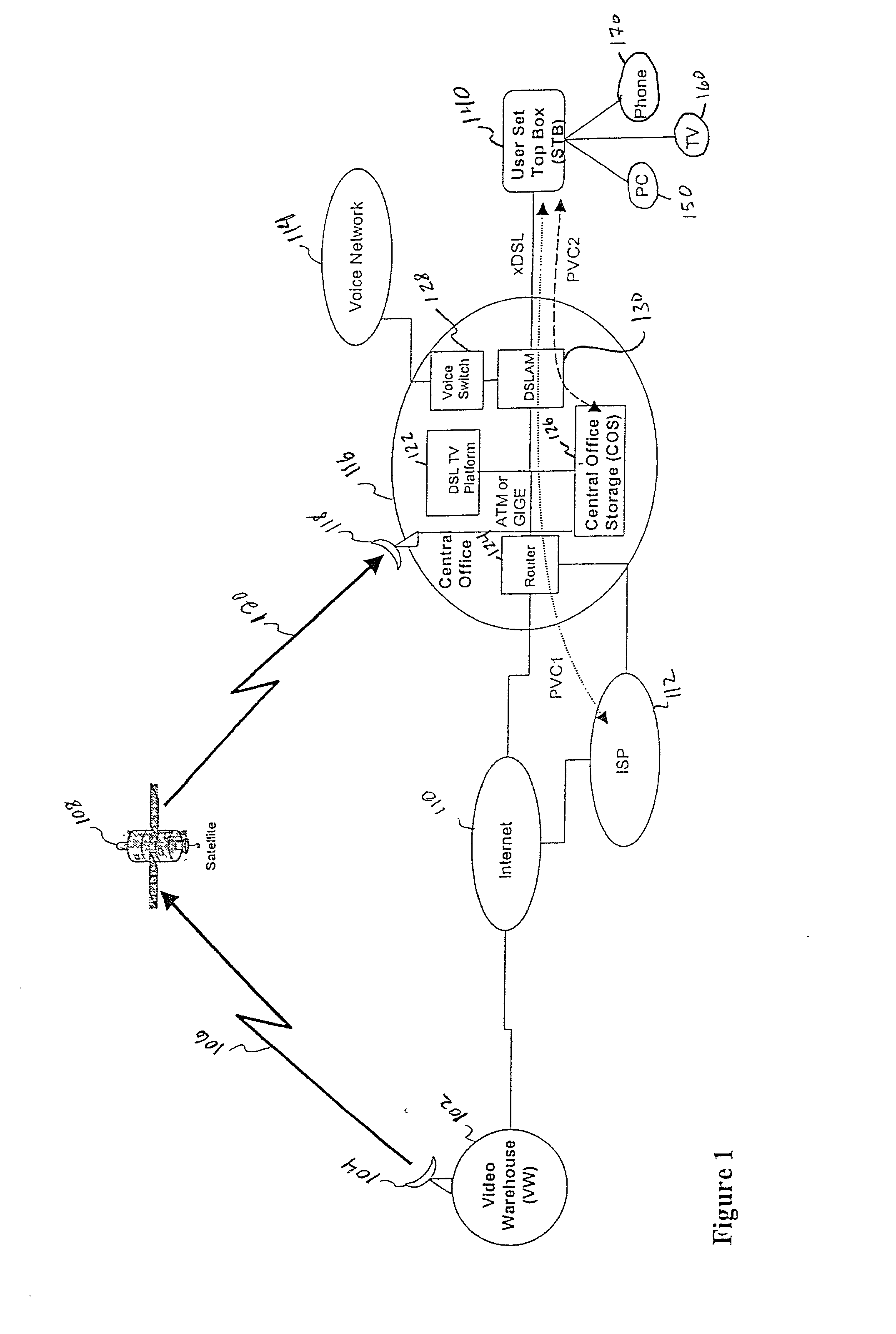
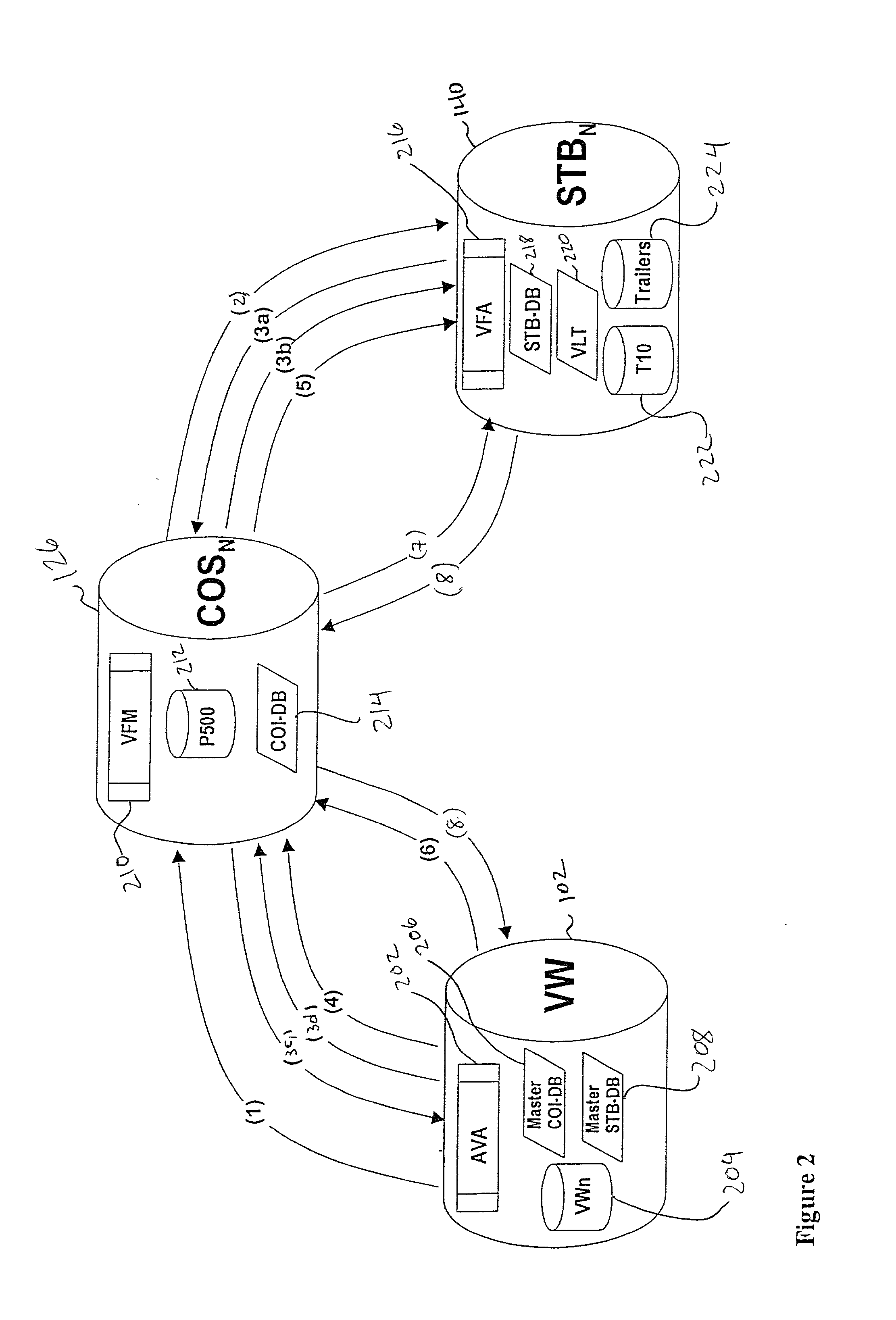
A video-on-demand (VOD) system is disclosed and method for providing a real-time VOD experience using Tempo-Differential file transfer with various buffering techniques and an adaptive file distribution system. The system is configured to populate users' Set-Top-Boxes (STBs) with a set of videos which correspond to the individual user's preferences, and populates a Central Office Storage (COS) server with a larger set of videos based on an analysis of all of the users' preferences. The system thus provides a real time VOD service by either correctly predicting the videos that a user will request and preloading them onto that user's STB, or by delivering the requested video from the COS to the STB using a Tempo-Differential file transfer which delays the playing of the requested video while video trailers or other information is displayed on the video screen. When using a DSL connection to the COS, only a portion of the requested video needs to be buffered on the STB before the requested video begins playing. Accordingly, by predicting which videos a user will request and by using the Temp-Differential file transfer, a real time VOD experience is achieved.
Owner:ARTISTA COMM
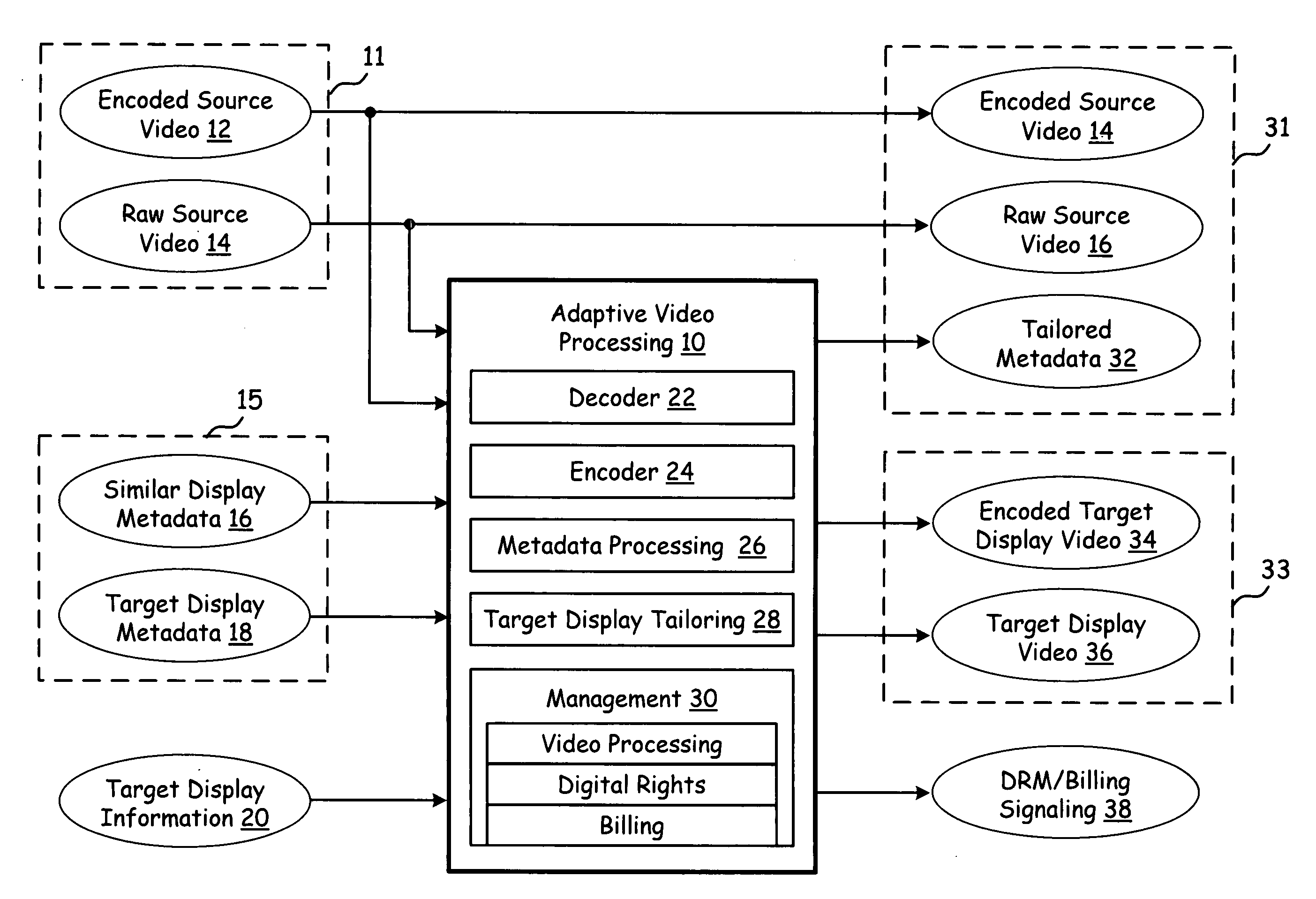
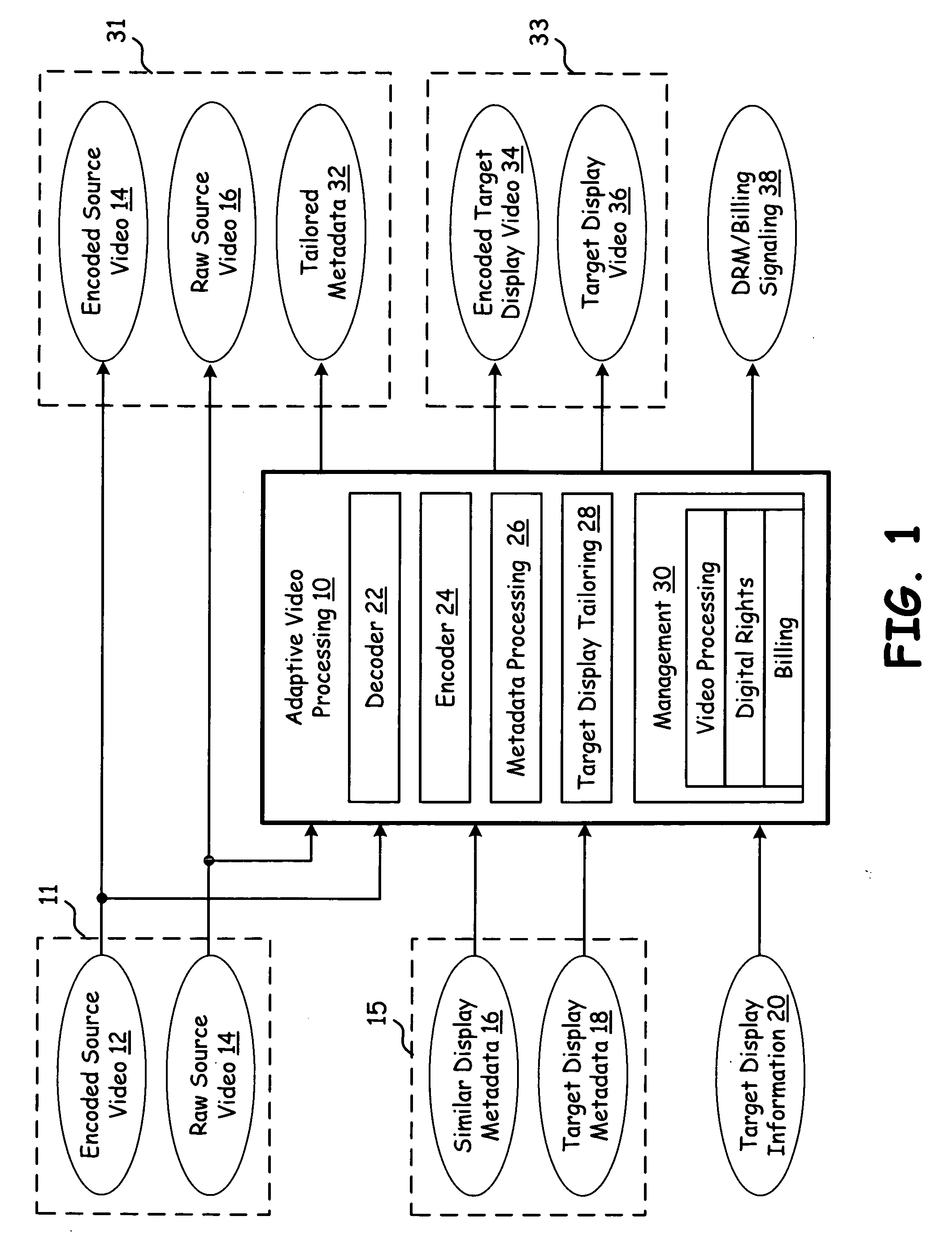
Adaptive video processing circuitry & player using sub-frame metadata
ActiveUS20080018785A1Television system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationVideo playerComputer graphics (images)
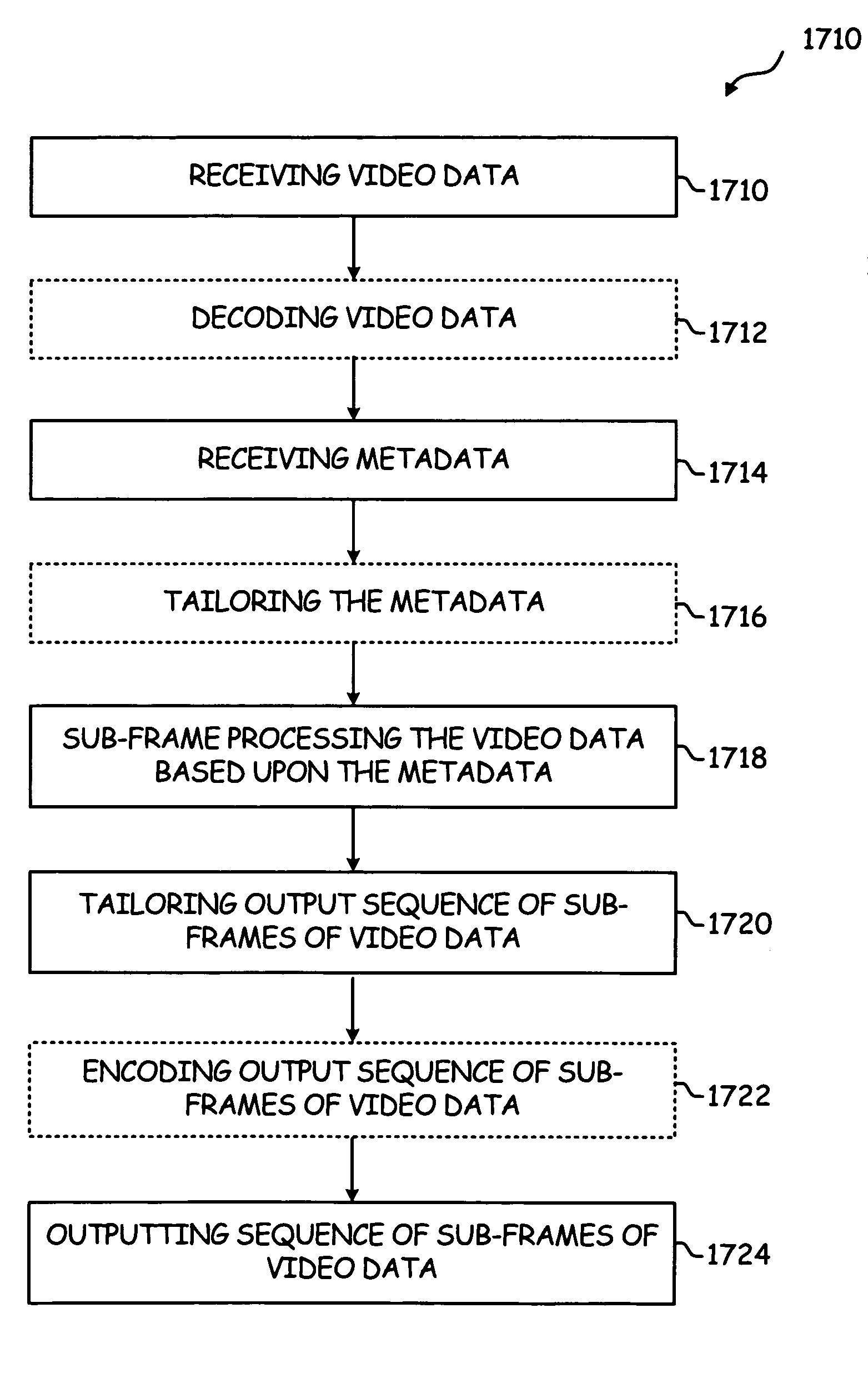
Video player circuitry used with encoded source video and a display. Decoder circuitry receives encoded source video and decodes the encoded source video to produce a sequence of full frames of video data. Pre-processing circuitry, pursuant to sub-frame information, generates a plurality of sequences of sub-frames of video data from the sequence of full frames of video data, a first sequence of the plurality of sequences of sub-frames of video data having a different center point within the sequence of full frames of video data than that of a second sequence of the plurality of sequences of sub-frames of video data. Post-processing circuitry, pursuant to supplemental information, modifies the plurality of sequences of sub-frames of video data to produce an output. Interface circuitry that delivers the output for subsequent presentation on the display.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Adaptive video processing using sub-frame metadata
InactiveUS20080007649A1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer graphics (images)Video processing
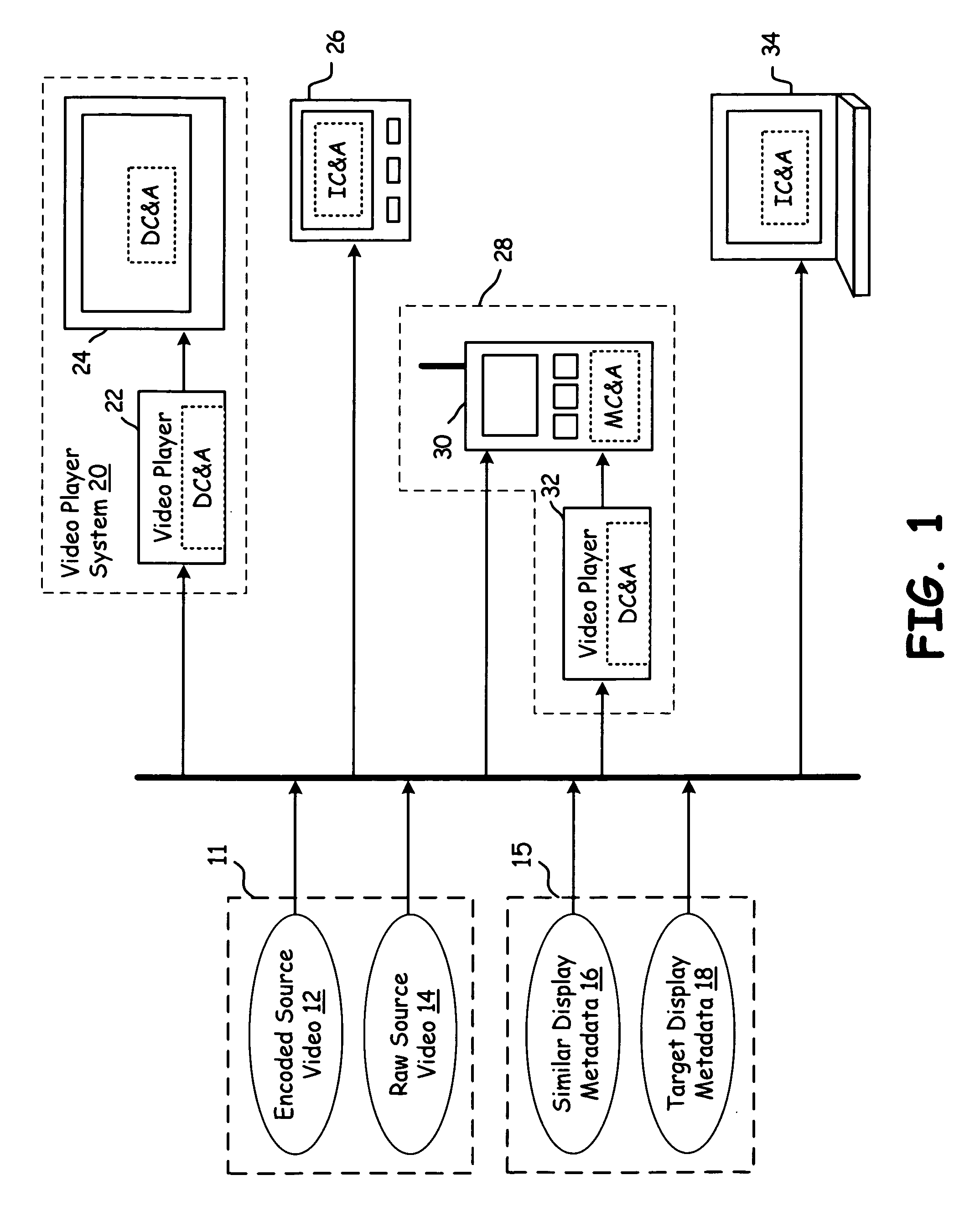
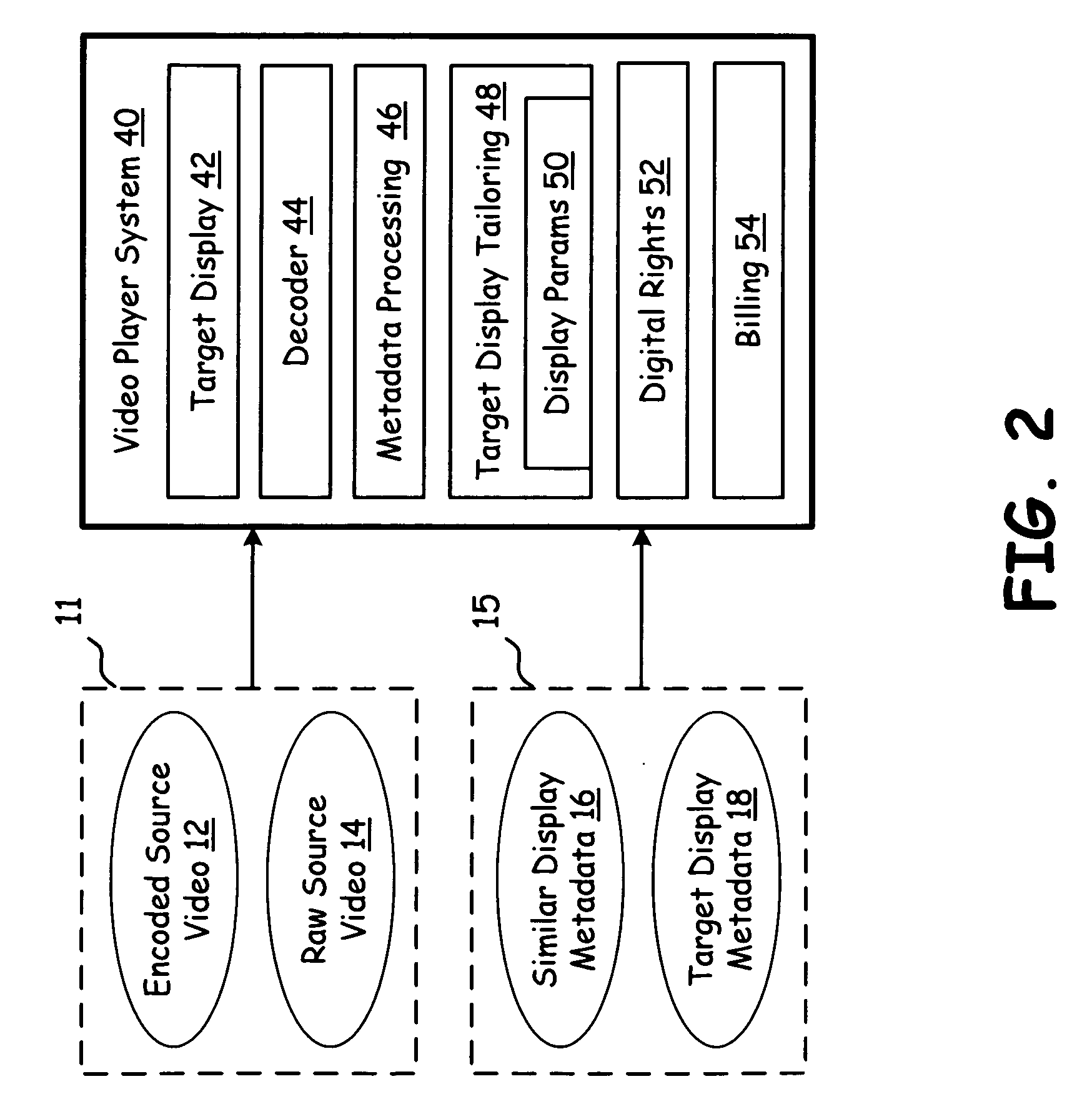
A video processing system applies sub-frame processing to video data to generate both a first sequence of sub-frames of video data and a second sequence of sub-frames of video data. The first sequence of sub-frames of video data and the second sequence of sub-frames of video data are defined by metadata. The processing circuitry generates a third sequence of sub-frames of video data by combining the first sequence of sub-frames of video data with the second sequence of sub-frames of video data. Adaptive video processing circuitry receives encoded source video data, raw source video data, similar display metadata, target display metadata, and / or target display information. The adaptive video processing circuitry processes its input information to produce one or more outputs that include tailored metadata, encoded target display video data, target display video data, and DRM / Billing Signaling.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
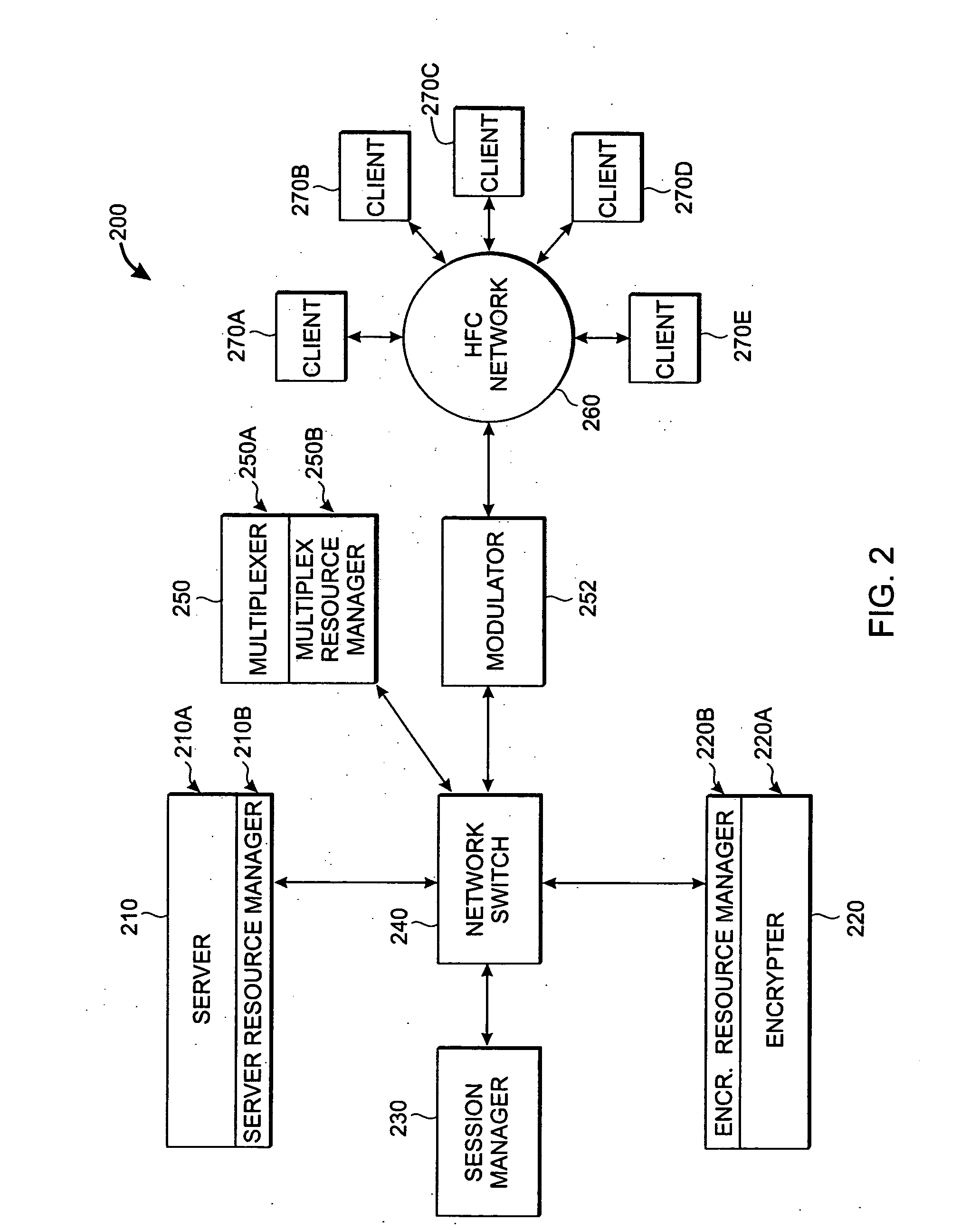
Advanced, adaptive video multiplexer system
ActiveUS20050198686A1Facilitates auto-discoveryReduce correlation and clippingPulse modulation television signal transmissionGHz frequency transmissionMultiplexerForward error correction
An advanced multiplexer designed and optimized for next generation on-demand video distribution is described. Features and capabilities include auto-discovery, channel-staggering and compatibility with static Virtual Channel Tables (VCTs). The multiplexer system facilitates auto-discovery by inserting identifiers into MPTSs (Multi-Program Transport Streams). These identifiers are echoed back to the multiplexer by the client set-top thereby indicating correspondence between modulators, service groups, and clients. When modulating multiple channels, FEC frames (Forward Error Correction frames) are staggered across channels to reduce correlation and clipping in the IFFT processor.
Owner:IMAGINE COMM
System and Method for Adaptive Videos
InactiveUS20120030029A1Efficient integrationReduce designTelevision system detailsMarket predictionsAdaptive videoSelf adaptive
A system and method for computer-implemented adaptive videos selects and arranges video elements in media instances in accordance with inferred preferences based, at least in part, on usage behaviors. Variations of the system and method include automatically selecting and / or arranging the video elements in accordance with the contents of the video elements, physical location, and physiological responses. Soundtracks may be selected in accordance with selected video elements. Information as to why video elements were selected for inclusion in media instances may be provided to media instance recipients.
Owner:MANYWORLDS CONSULTING
Redundancy elimination in a content-adaptive video preview system
InactiveUS20050200762A1Reducing visual redundancyEfficiently contentTelevision system detailsDrawing from basic elementsAdaptive videoSelf adaptive
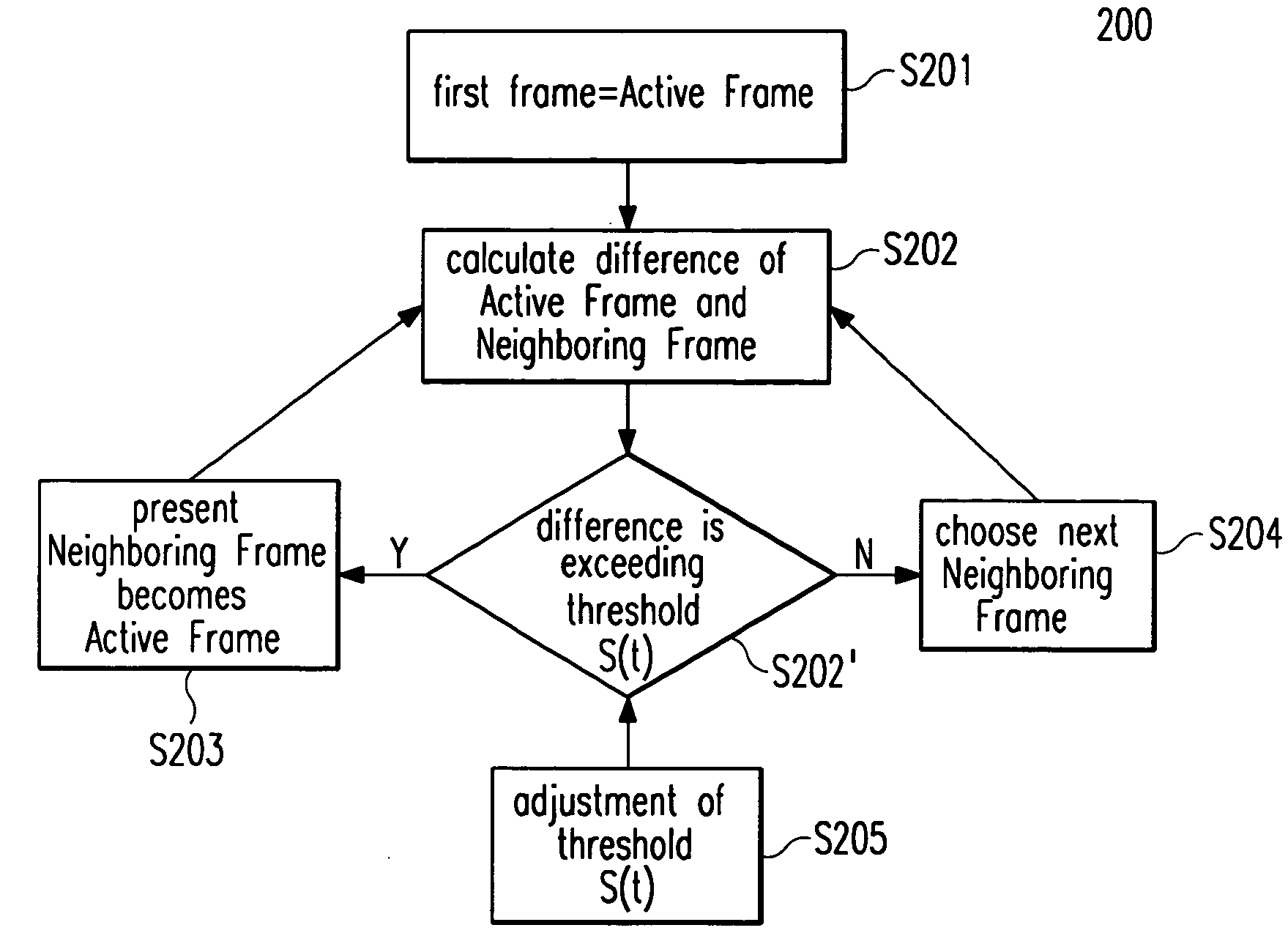
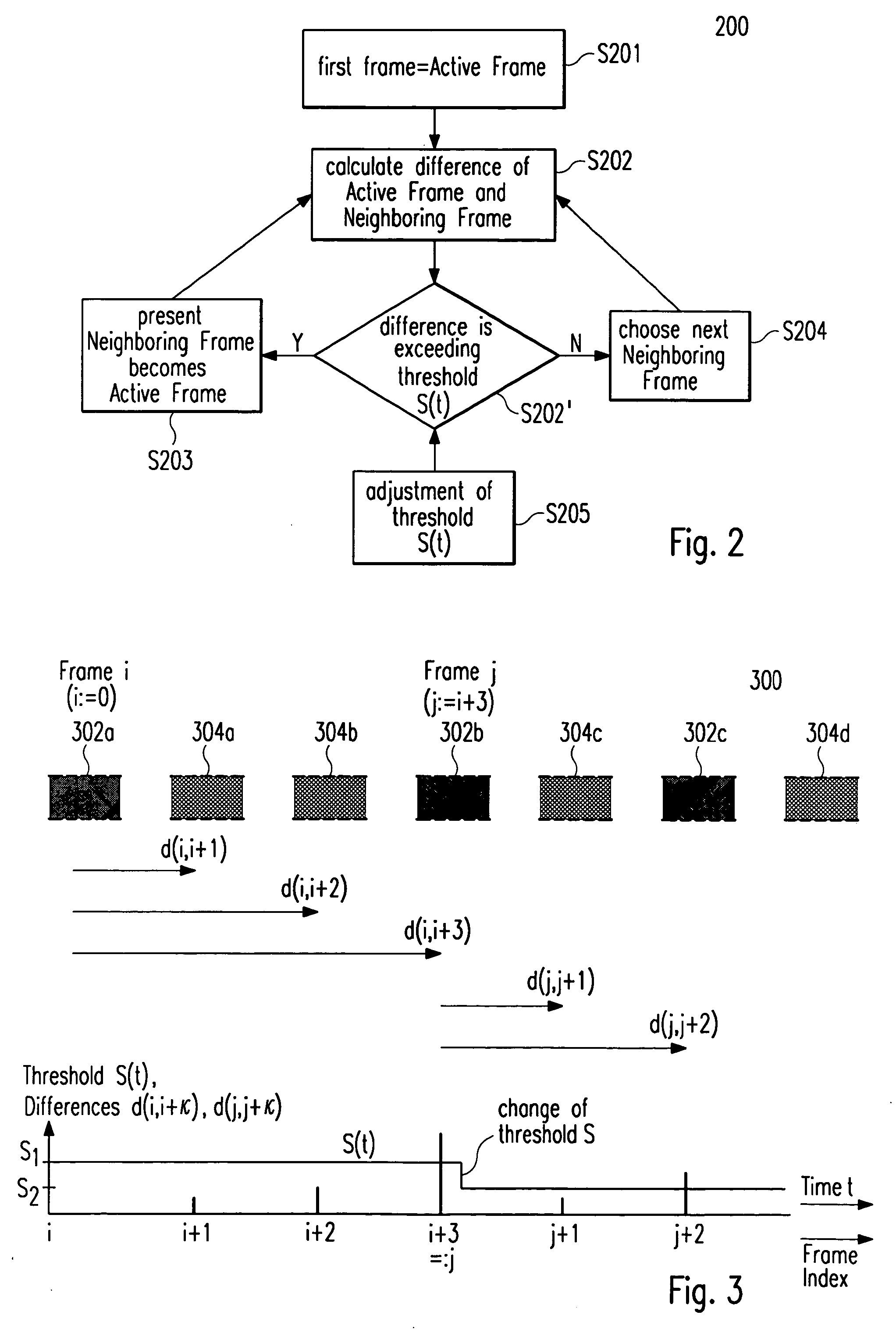
A content-adaptive video preview system (100) allows to go faster through a video than existing video skimming techniques. Thereby, a user can interactively adapt (S1) the speed of browsing and / or the abstraction level of presentation. According to one embodiment of the invention, this adaptation procedure (S1) is realized by the following steps: First, differences between precalculated spatial color histograms associated with chronologically subsequent pairs of video frames said video file is composed of are calculated (S1a). Then, these differences and / or a cumulative difference value representing the sum of these differences are compared (S1b) to a predefined redundancy threshold (S(t)). In case differences in the color histograms of particular video frames (302a-c) and / or said cumulative difference value exceed this redundancy threshold (S(t)), these video frames are selected (S1c) for the preview. Intermediate video frames (304a-d) are removed and / or inserted (S1d) between each pair of selected chronologically subsequent video frames depending on the selected abstraction level of presentation. Thereby, said redundancy threshold value (S(t)) can be adapted (S1b′) for changing the speed of browsing and / or the abstraction level of presentation.
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
Wireless integrated security controller
InactiveUS20080288986A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsColor television detailsDigital videoMulti camera
A system and method are disclosed for improved video transmission, particularly in security settings. An improved security controller combines the interfaces and functionality for high quality video delivery over often less-than-perfect wireless networks, multi-camera analog / digital video controllers and encoders, multi-frequency wireless camera support, connectivity for serial controllers, network switching, and distributed digital video recording with optional object and motion detection. The video transmission is enhanced using wireless adaptive video encoding, mobile viewing optimization, and wireless bandwidth improvement.
Owner:REEDY CO TRUSTEE OF ARMIDA TECH LIQUIDATING TRUST MATTHEW C +1
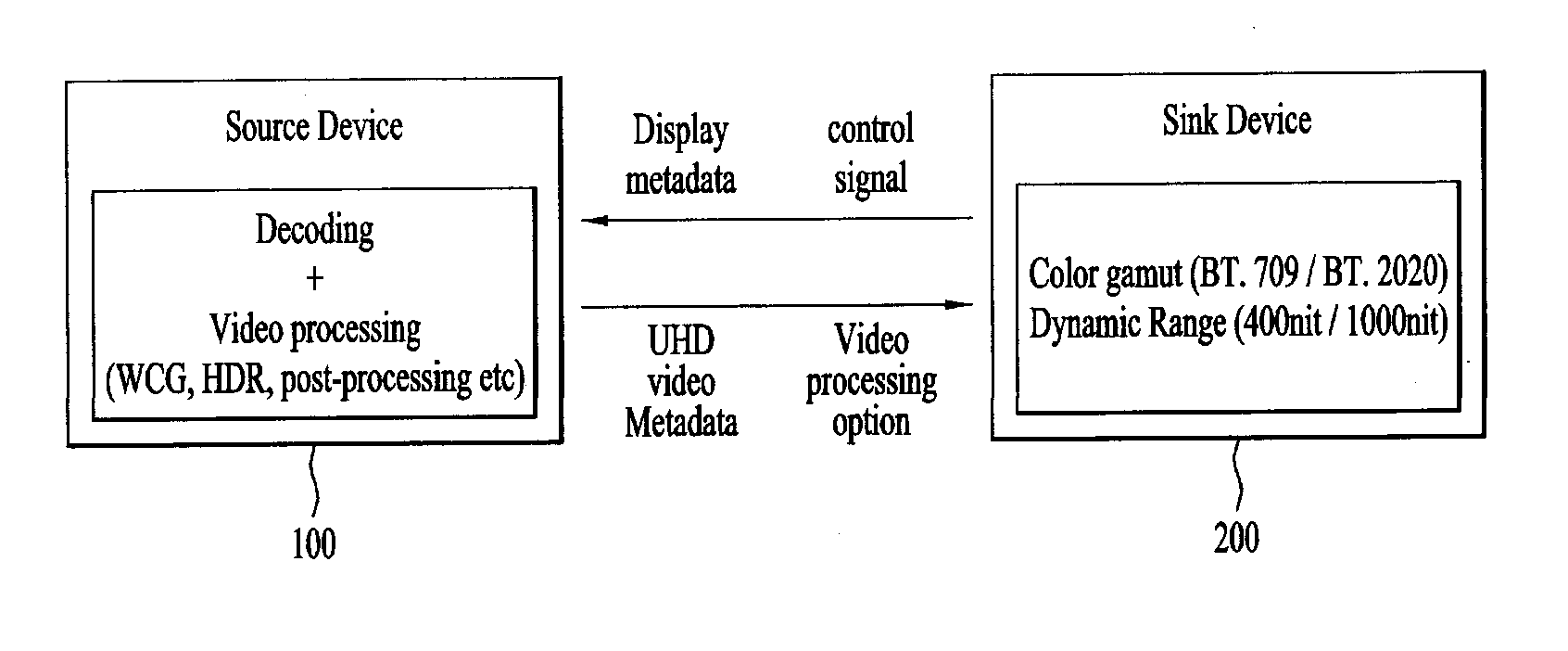
Video data processing method and device for display adaptive video playback
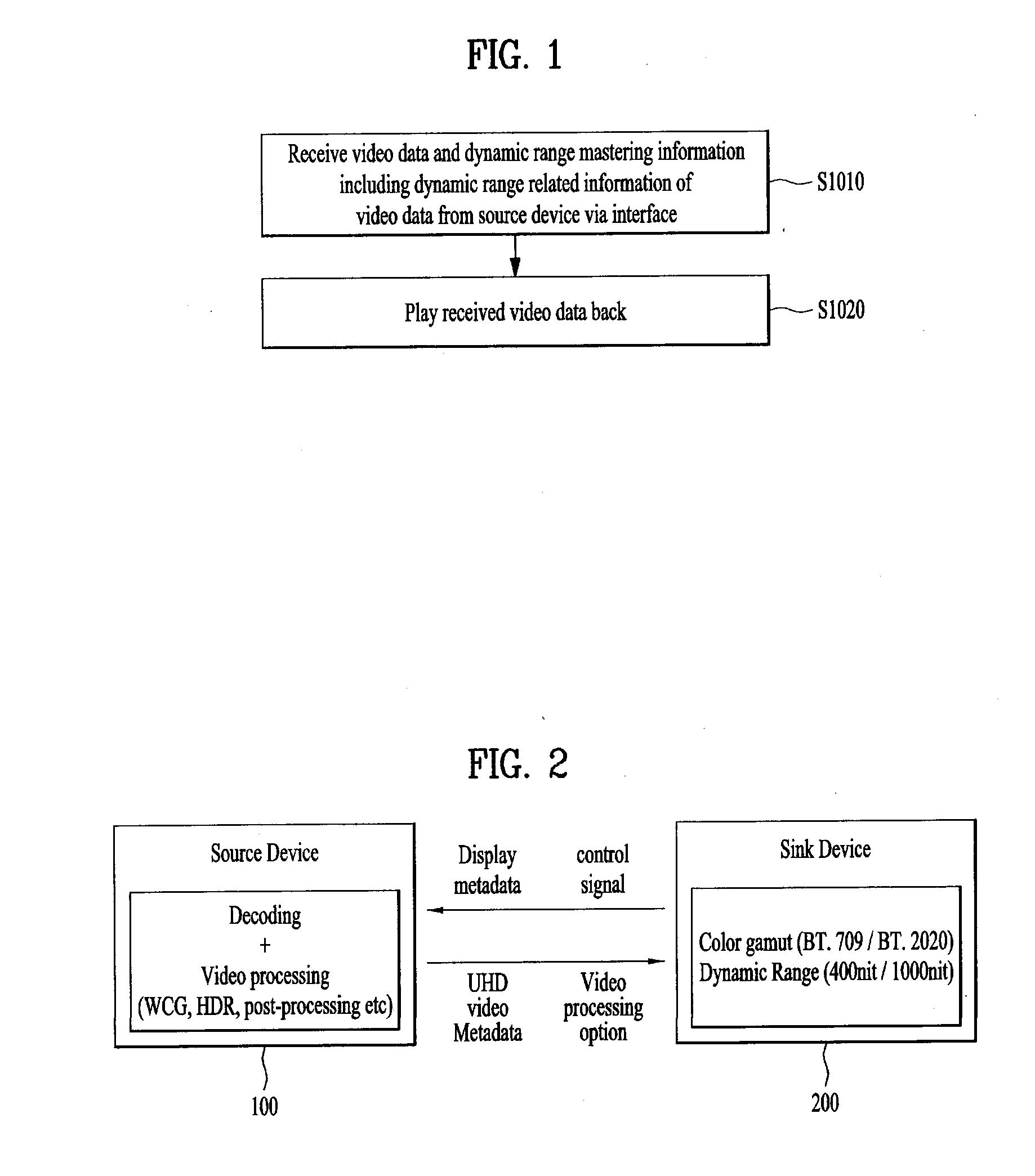
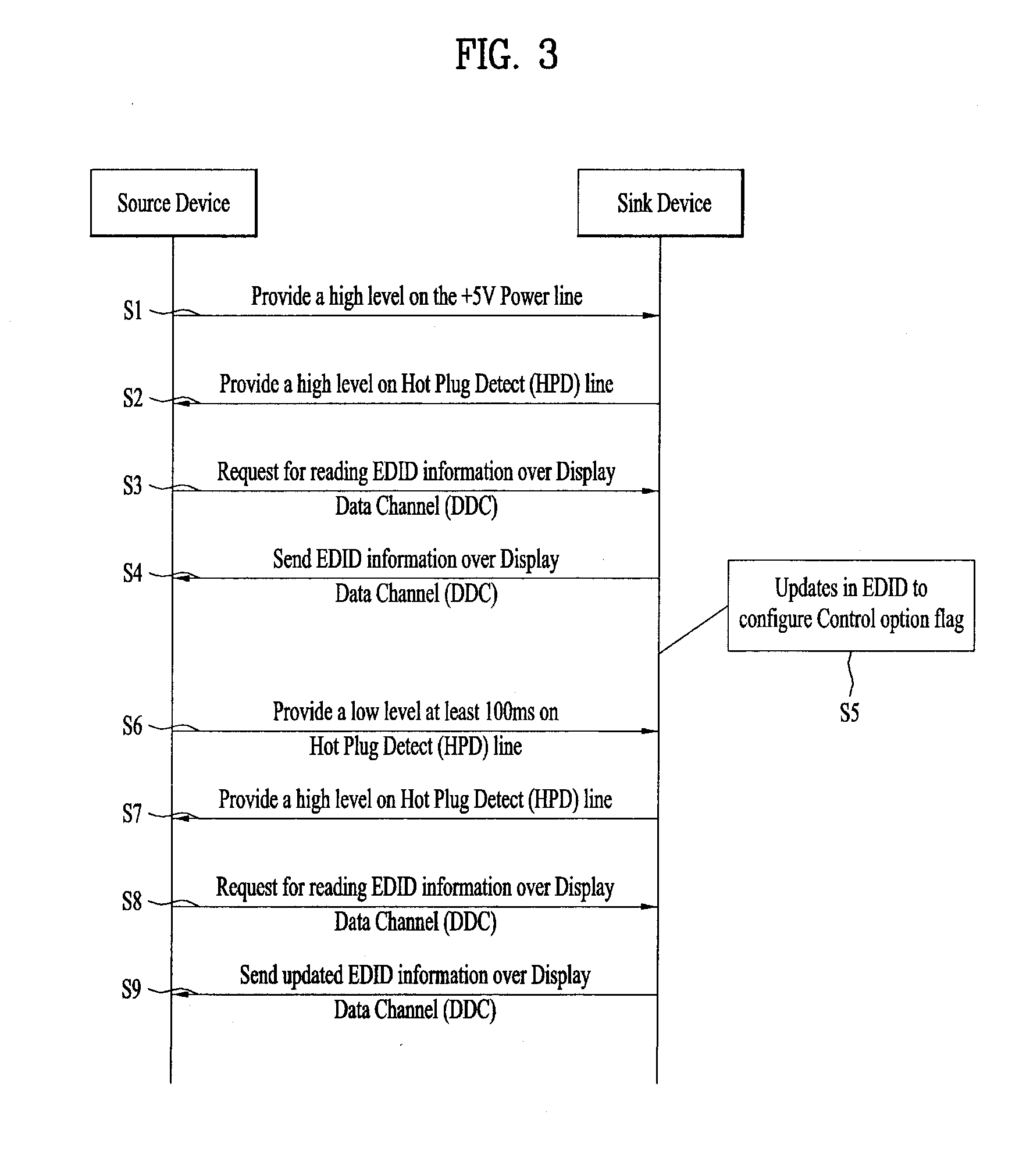
ActiveUS20150341611A1Optimally view contentReduce brightnessTelevision system detailsColor television signals processingComputer graphics (images)Adaptive video
A video data processing method and / device for display adaptive video playback are disclosed. The video data processing method includes receiving video data and dynamic range mastering information including dynamic range related information of the video data from a source device via an interface, and playing the received video data back. The dynamic range mastering information includes electro optical transfer function, EOTF, type information for identifying an EOTF used for the video data.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
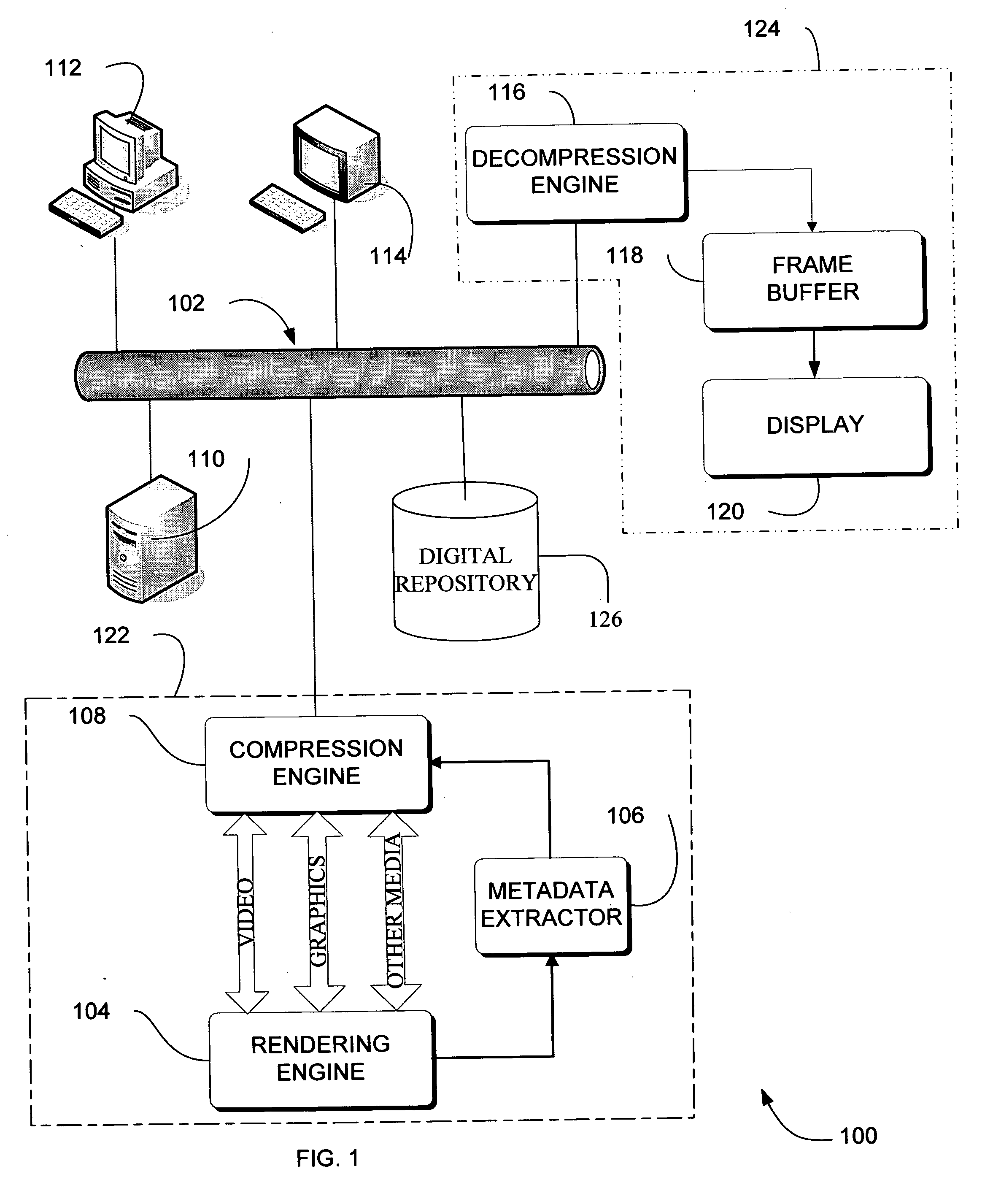
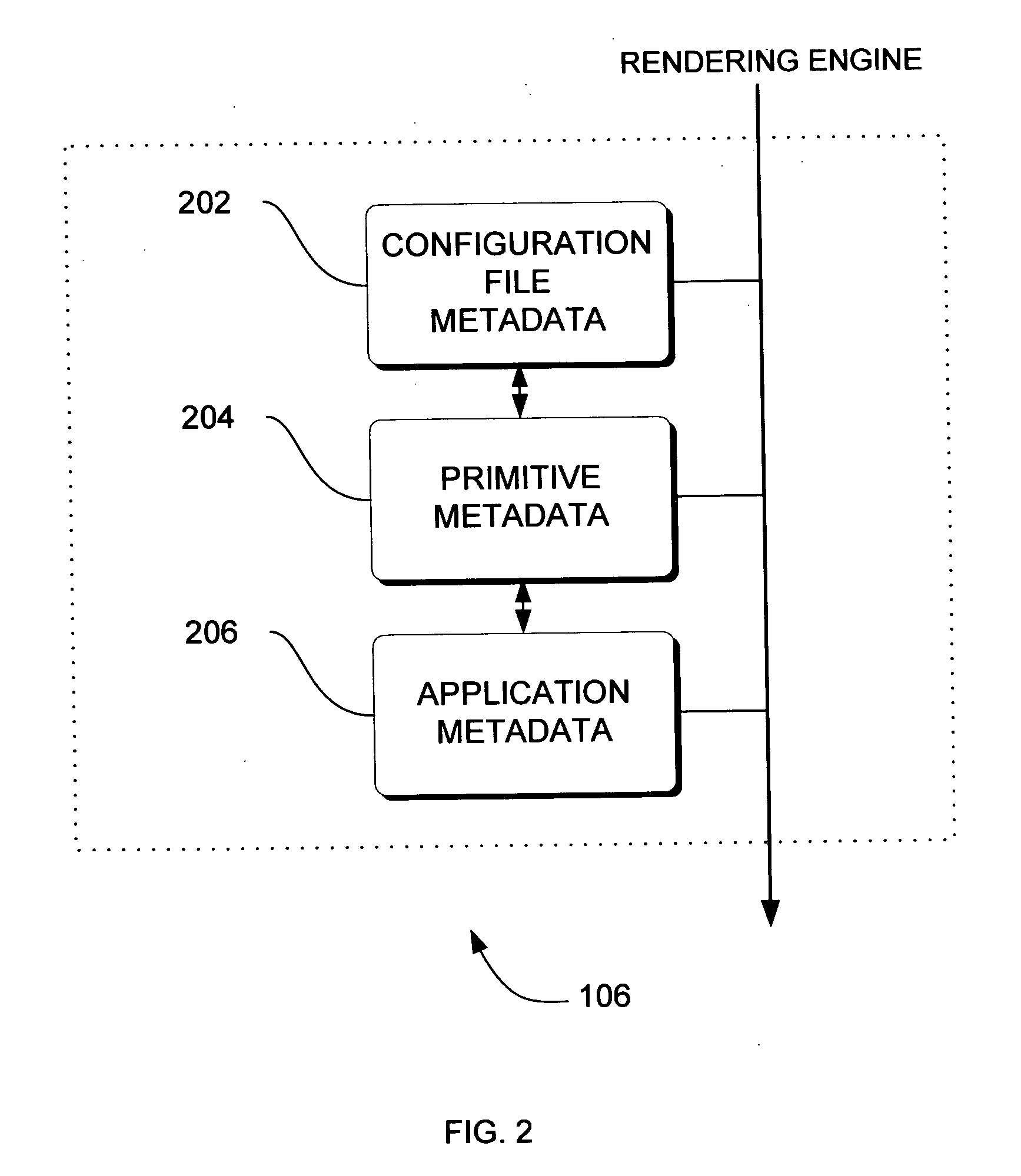
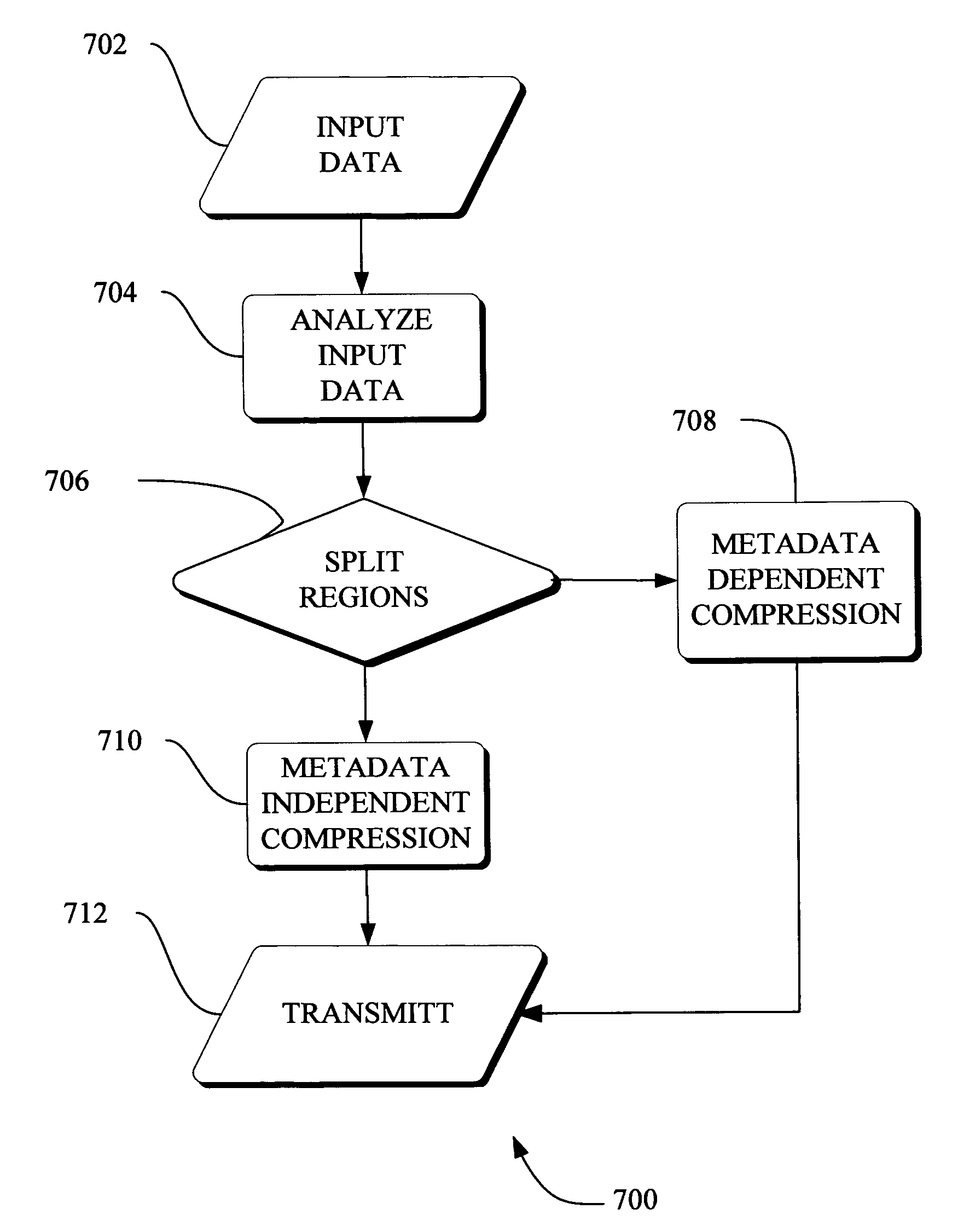
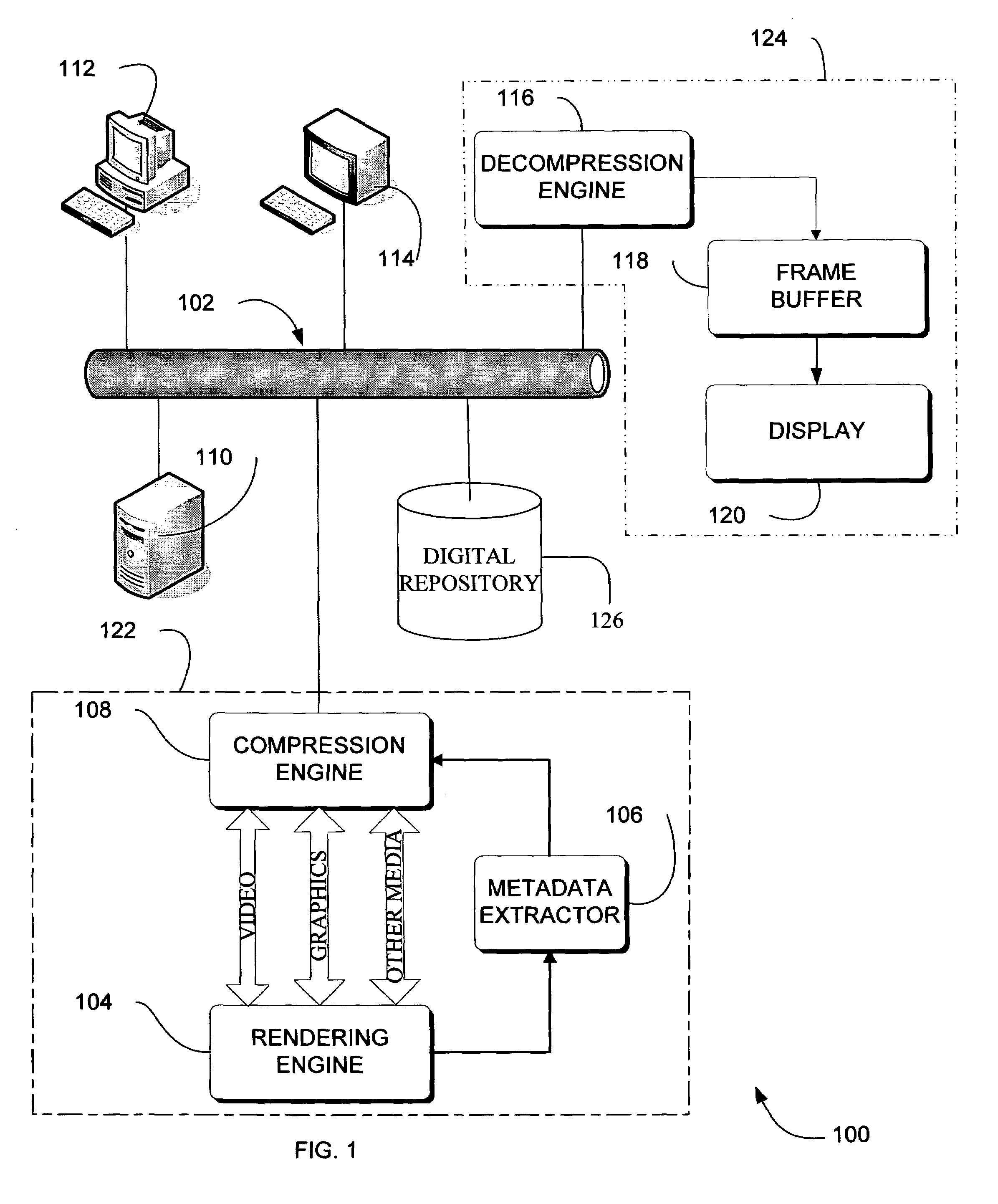
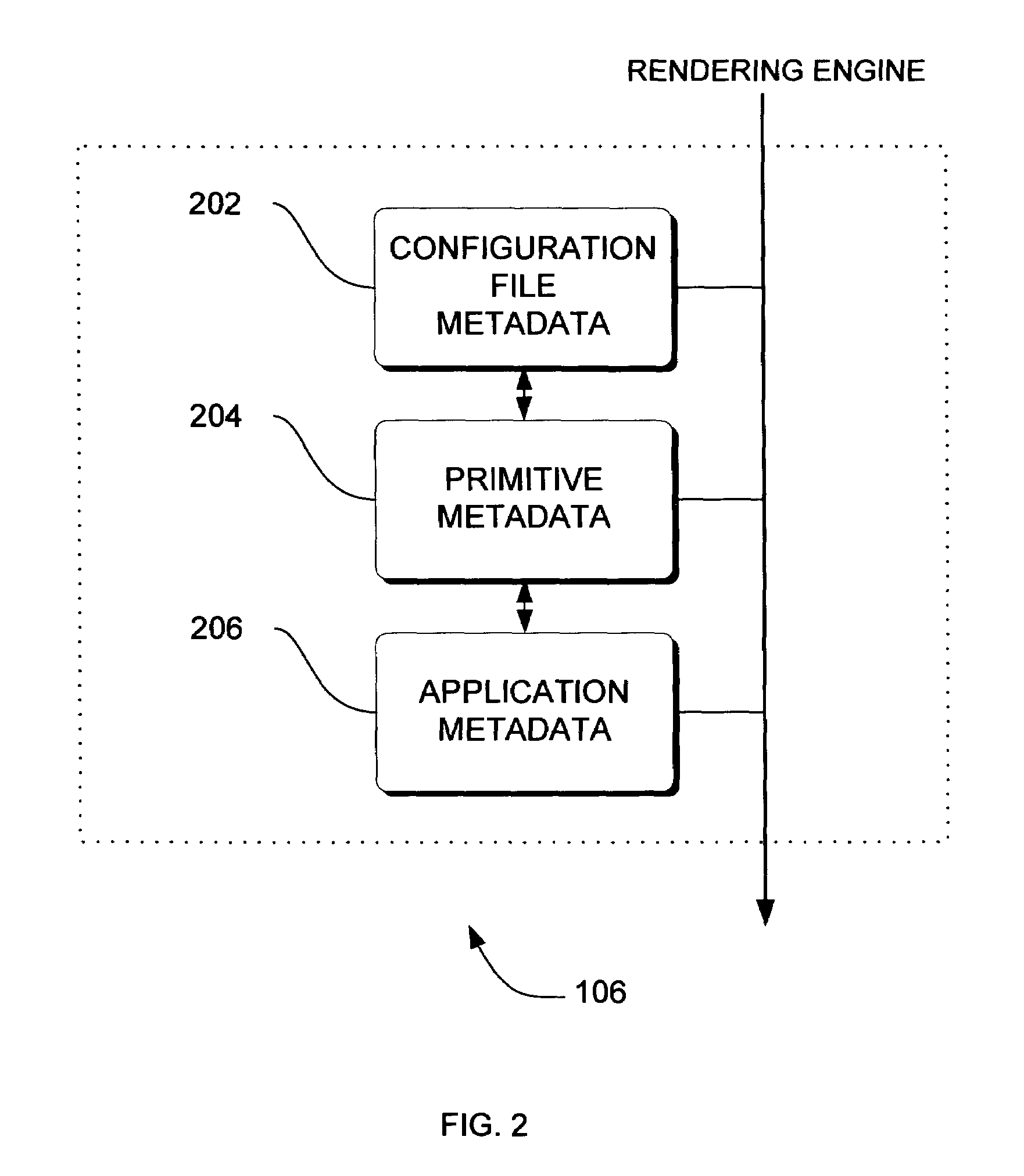
Adaptive video compression of graphical user interfaces using application metadata
InactiveUS20060294125A1Digital data processing detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionData streamDisplay device
Systems, methods and computer accessible medium are provided through which an input data stream consisting one or more media regions before entering a network to be rendered by a display coupled a remote video frame buffer is compressed on the basis of one or more configuration file metadata, source primitive metadata, and application high-level metadata of identified media regions. The input data stream is compressed by using one or more MPEG compression, JPEG compression, vector graphics compression, Huffman coding, or user defined compression scheme.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
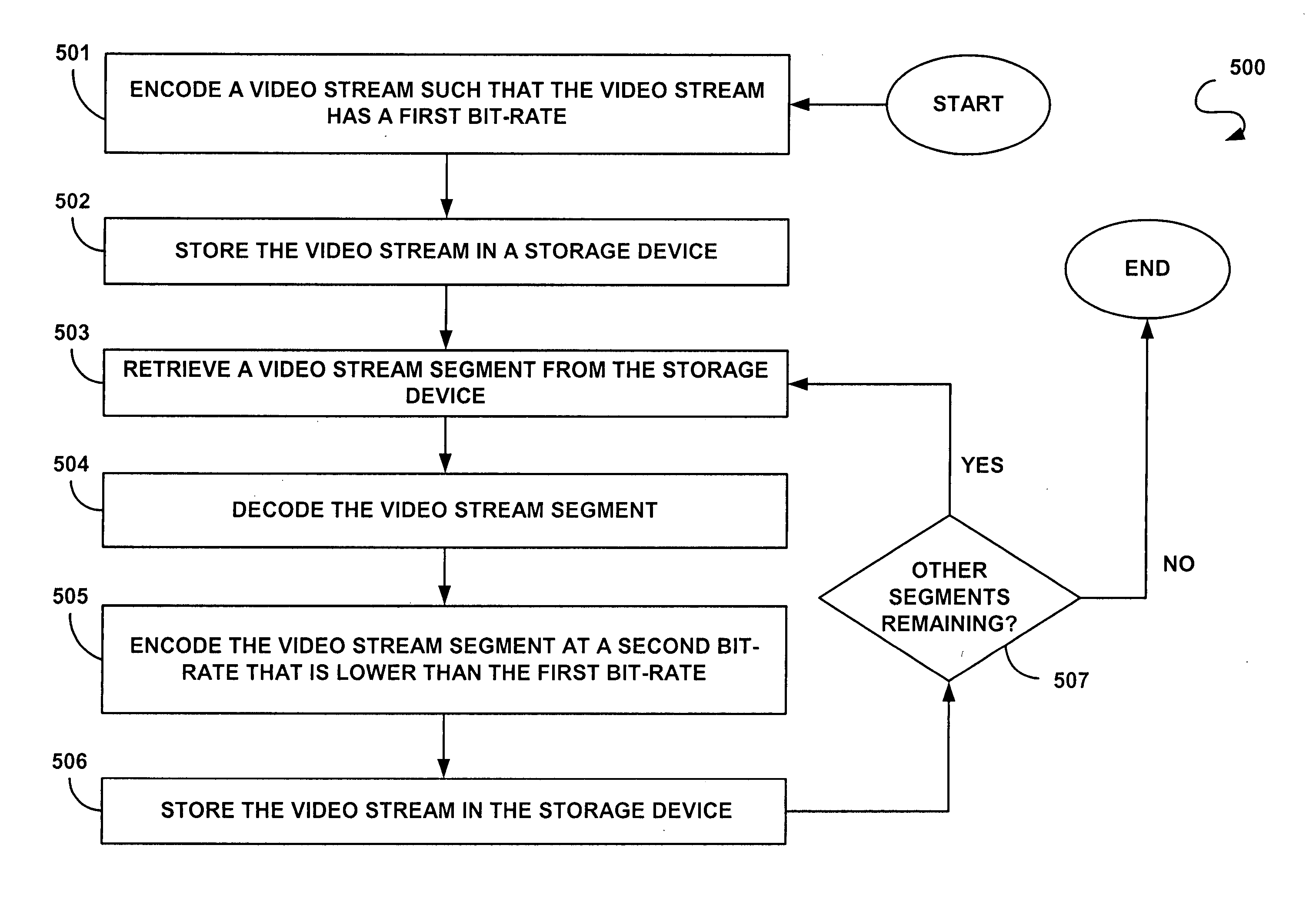
Resource-adaptive management of video storage
InactiveUS20050074063A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningVideo storageComputer graphics (images)
A method for providing adaptive video compression includes encoding a video stream in a first compressed format, storing the video stream in a storage device, retrieving the video stream from the storage device, decoding the video stream, encoding the video stream in a second compressed format, and storing the video stream in the storage device. Systems and other methods for providing adaptive video compression are also disclosed.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
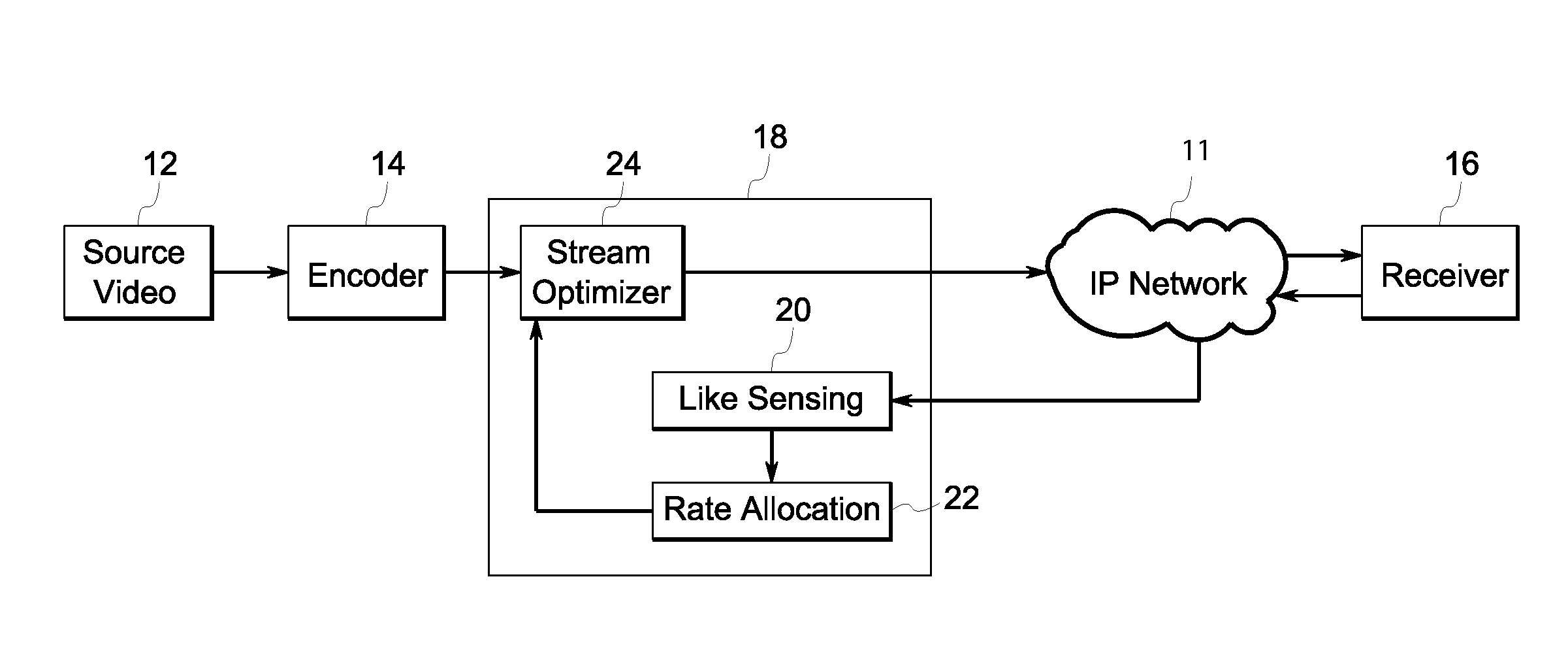
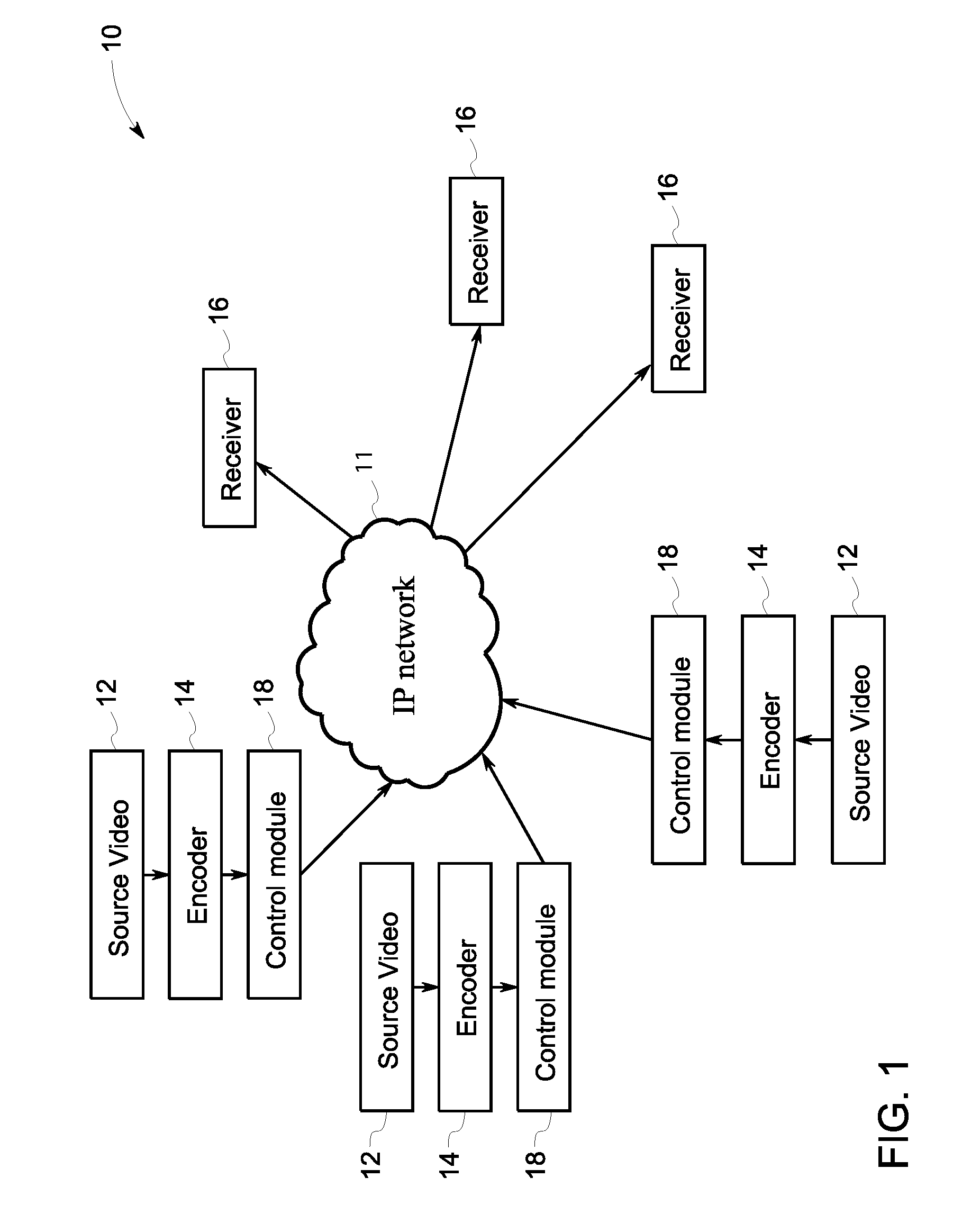
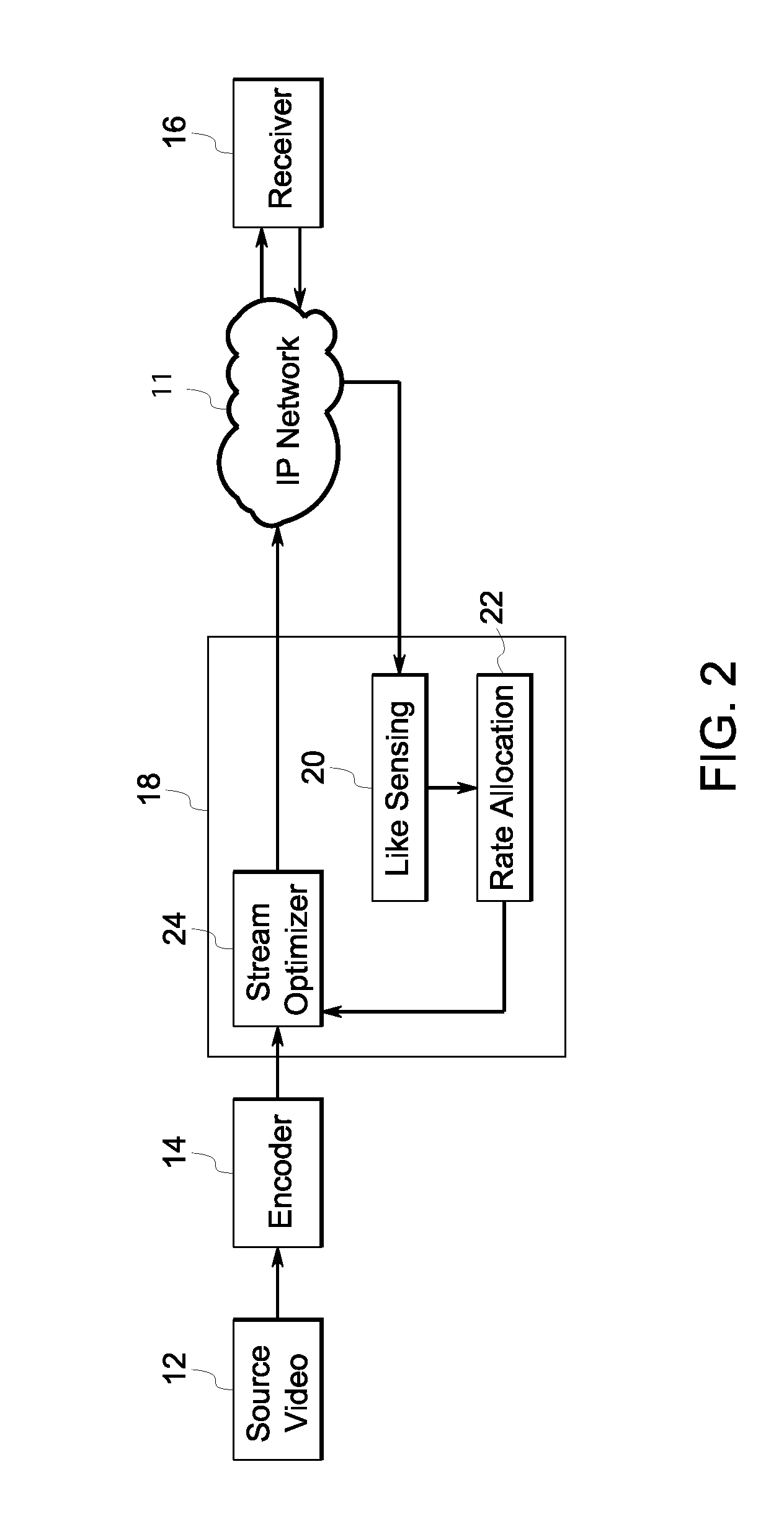
Adaptive video streaming system and method
ActiveUS20100074324A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningAdaptive videoSelf adaptive
A method of transmitting a video stream over an IP network. The method includes encoding a source video into a plurality of packets. The method also includes measuring a real-time transmission status of a current set of the plurality of packets. The method also includes mapping a utility curve for the video which reflects utilities of the video at corresponding sending rates. The method also includes calculating a target sending rate for a next set of the plurality of packets according to the real-time transmission status of the current set of the plurality of packets and the utility curve. The method also includes determining a proper strategy to meet the target sending rate for the next set of the plurality of packets.
Owner:UTC FIRE & SECURITY AMERICAS CORPORATION INC
Network-aware adaptive video compression for variable bit rate transmission
InactiveUS20050002453A1Improve video qualityQuality improvementColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionTraffic capacityData stream
In a method of transmitting video data over a packet network, an input video stream is fed to a compressor that generates a compressed output stream. The compressor determines a target bit rate for the output stream based on desired picture quality. A traffic management unit a determines the available bit rate for the compressed data stream based on network condition. The output is adjusted if the target bit rate exceeds the granted bit rate.
Owner:CHANG LEIGH +1
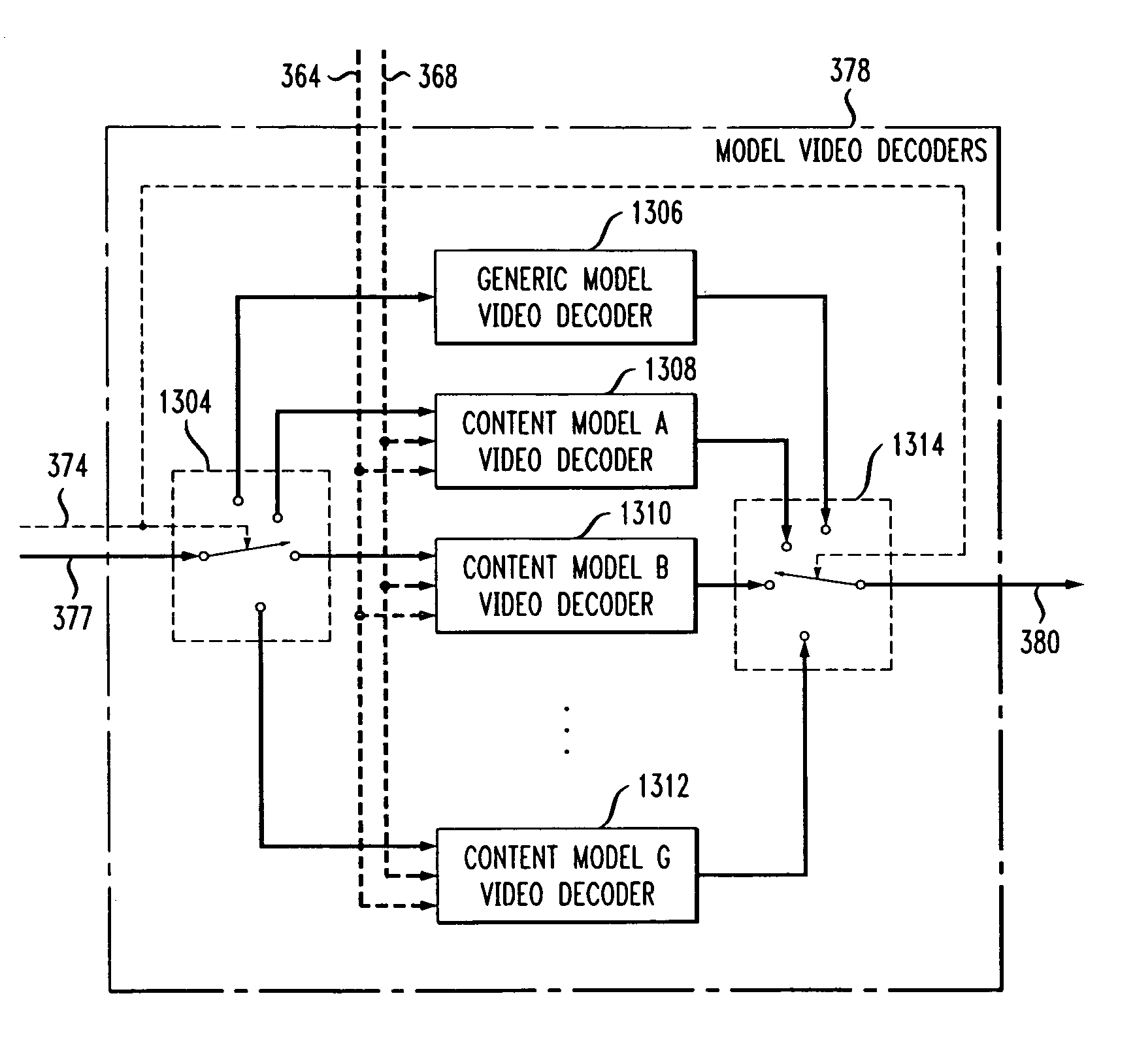
Method of content adaptive video decoding
InactiveUS6968006B1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionSubject matter
The invention relates to a method of receiving an encoded bitstream wherein video content is segmented into portions based on predefined classifications or models. Based on the segment classifications, each segment or portion is encoded with a different encoder chosen from a plurality of encoders, each encoder being associated with a model. The chosen encoder is particularly suited to encoding the unique subject matter of the segment. The coded bit-stream for each segment includes information regarding which encoder was used to encode that segment. A matching decoder of a plurality of decoders is chosen using the information in the coded bitstream to decode each segment using a decoder suited for the classification or model of the segment. If scenes exist which do not fall in a predefined classification, or where classification is more difficult based on the scene content, these scenes are segmented, coded and decoded using a generic coder and decoder.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Adaptive video compression of graphical user interfaces using application metadata
InactiveUS7548657B2Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationData streamDisplay device
Systems, methods and computer accessible medium are provided through which an input data stream consisting one or more media regions before entering a network to be rendered by a display coupled a remote video frame buffer is compressed on the basis of one or more configuration file metadata, source primitive metadata, and application high-level metadata of identified media regions. The input data stream is compressed by using one or more MPEG compression, JPEG compression, vector graphics compression, Huffman coding, or user defined compression scheme.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
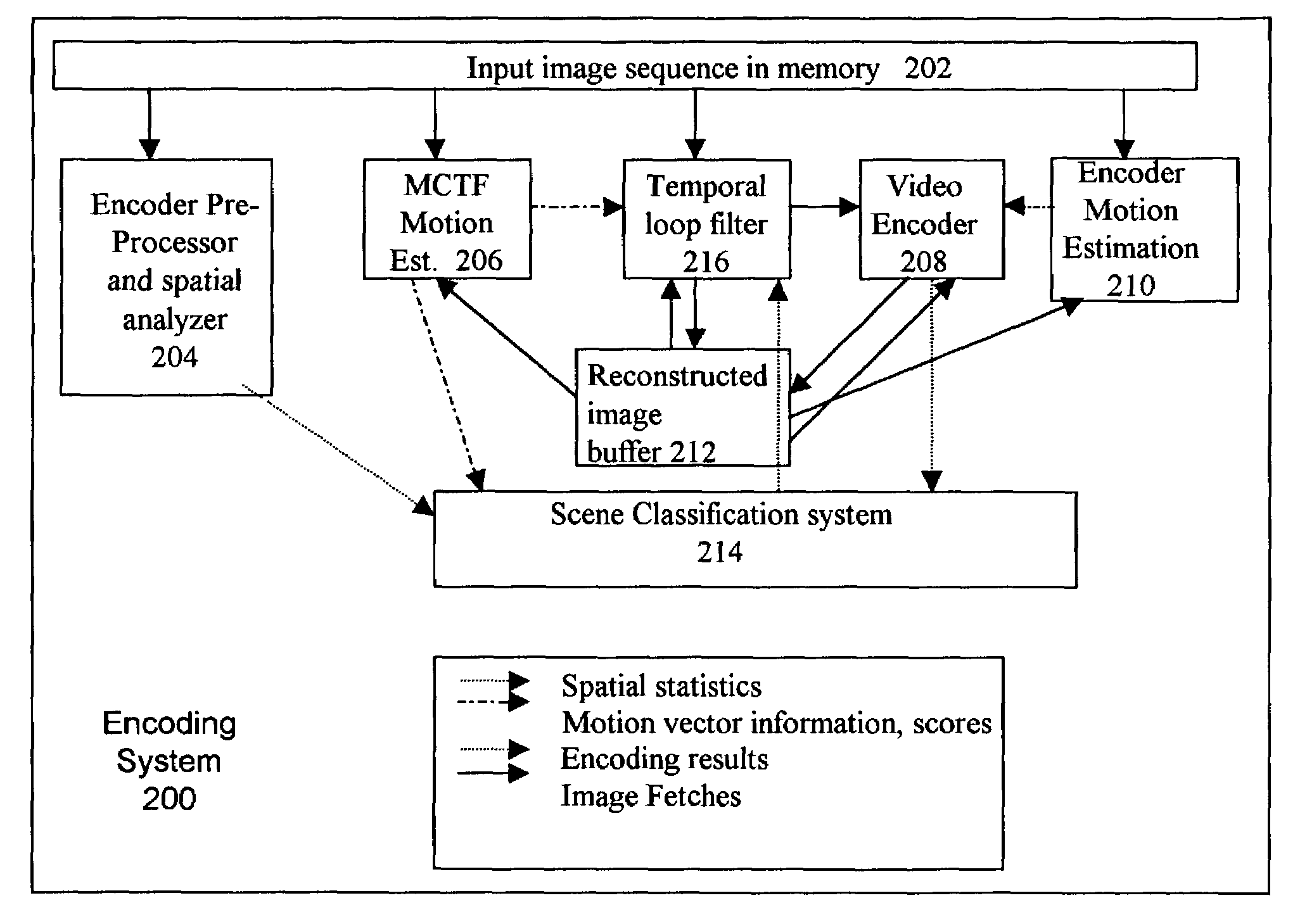
Content adaptive video processor using motion compensation
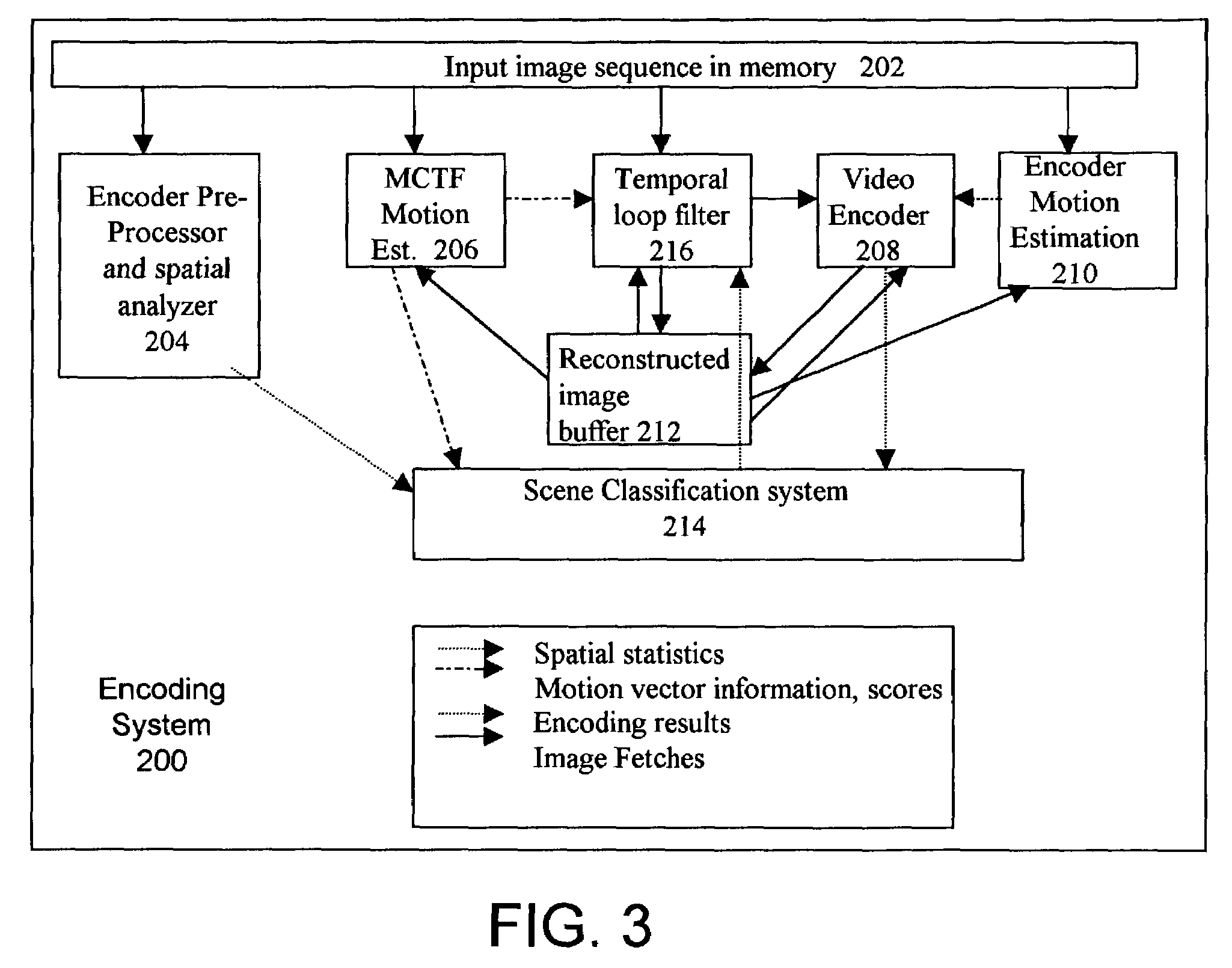
InactiveUS7068722B2Effectively reducing artifactImage enhancementTelevision system detailsVideo sequenceAdaptive video
A system and method for providing a method for reducing artifacts in a video sequence of image frames is disclosed. The method and system include classifying scenes in the sequence of image frames, analyzing the content of the image frames and performing temporal filtering on the image frames. The method and system further include applying a set of rules to results of the classification and the content analysis to adapt characteristics of the temporal filtering for the scene.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Adaptive video image enhancing method based on lightness detection
InactiveCN101340511AAvoid mergingImprove visual effectsImage enhancementTelevision system detailsIlluminanceLimit value
The invention provides a self-adaptive video image enhancement method on the basis of brightness detection. The method of the invention detects the images under different illumination conditions and enhances the low-illumination images according to the detection result. When the images are detected, average values of brightness values of all sampling points of YUV-format images in a RGB colour space are taken as the brightness value of current frame of image. For each frame of image to be processed, if the brightness value of the frame of image is less than the prearranged brightness limit value of image under normal illumination, piecewise linearity is transformed for the value of Y-component of each pixel point in the area to be processed of the frame of image so as to improve the visible effect of the low-illumination image. In order to quicken the operation speed, the brightness values of all sampling points of the image in the RGB colour space are gained and the linear transform on the Y-component of the image under low illumination is operated in a form of table lookup. The method of the invention has small calculated quantities, meets the requirement of real-time performance and can be used for the processing of video images in video communication of mobile phones and televisions.
Owner:ZTE CORP
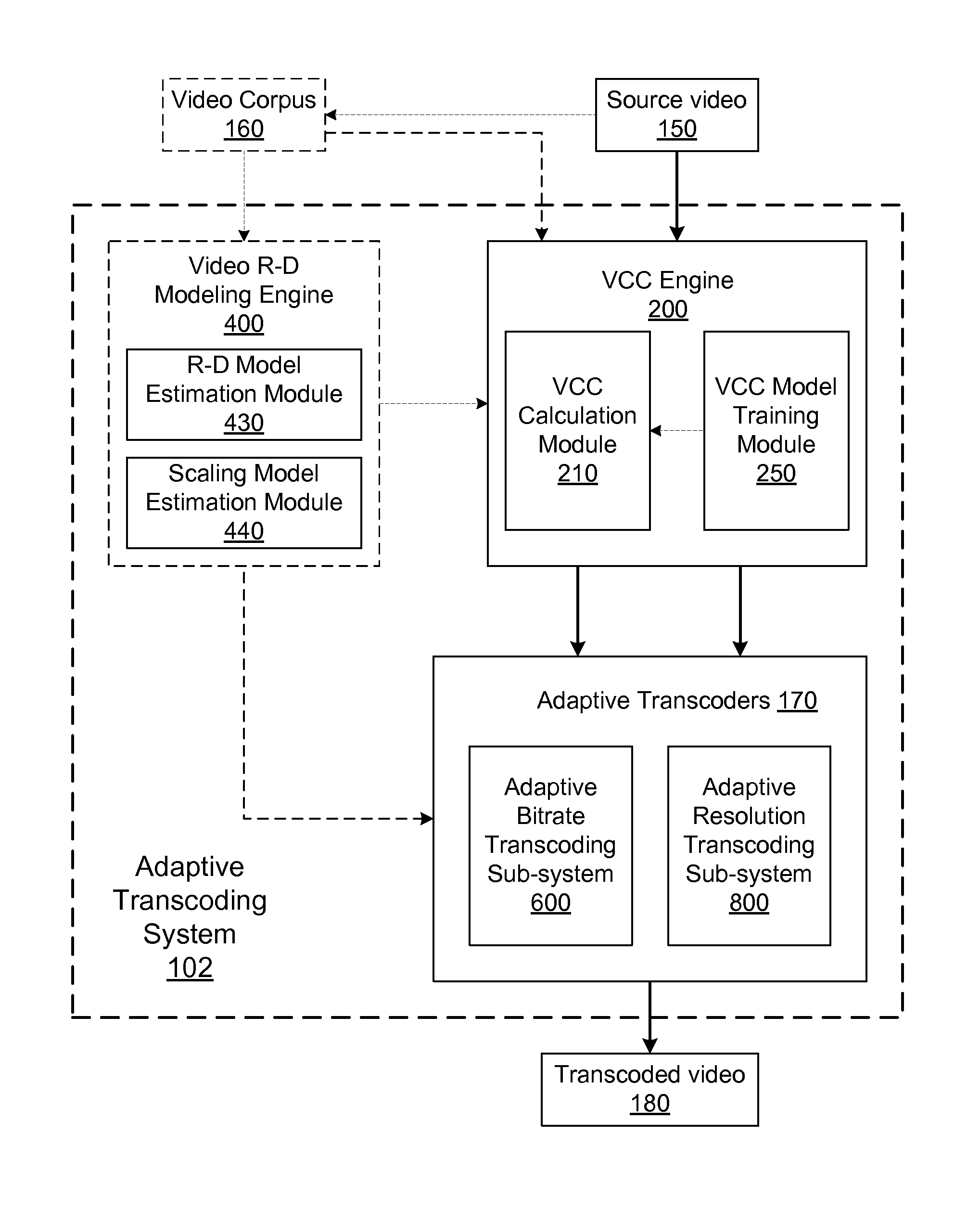
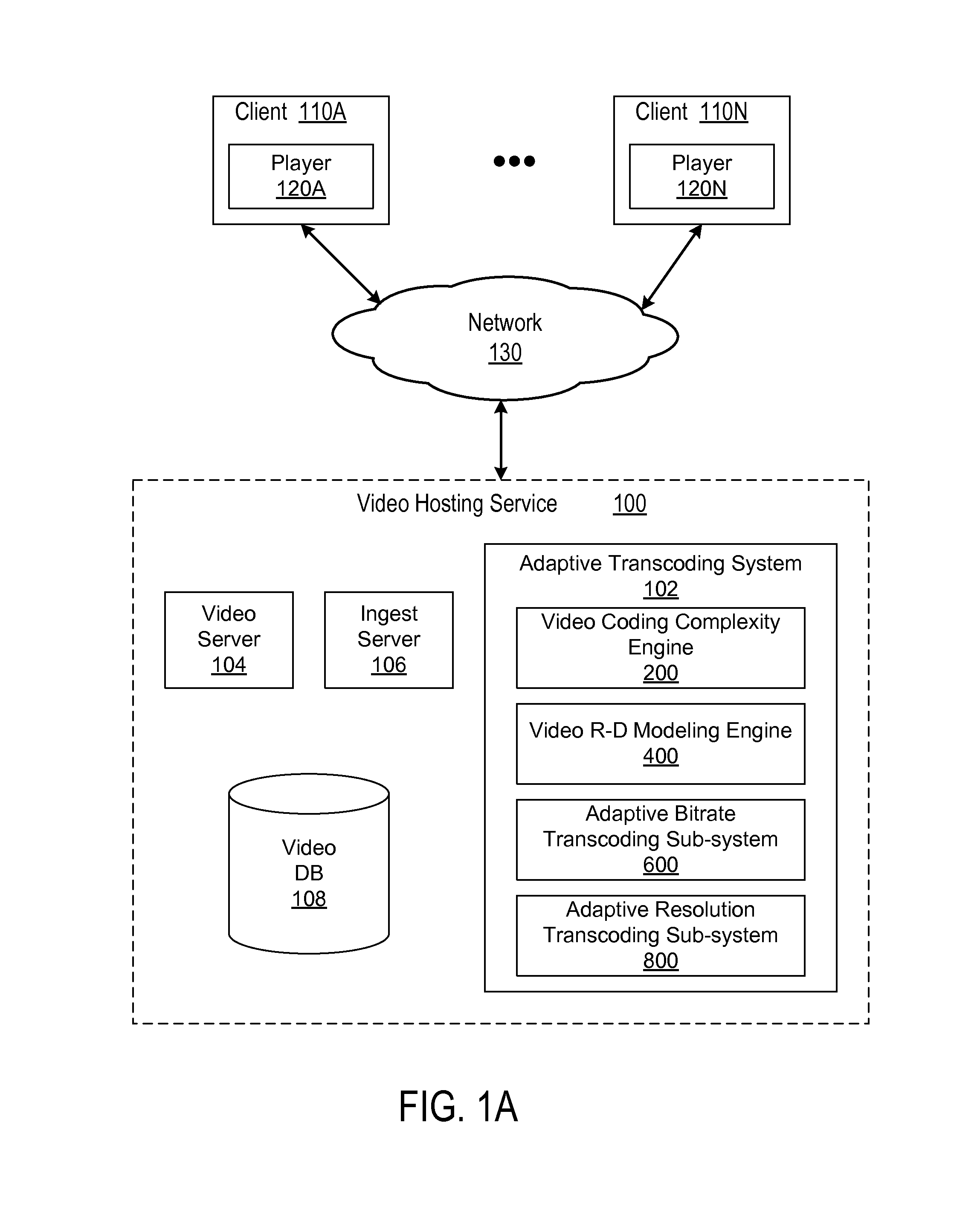
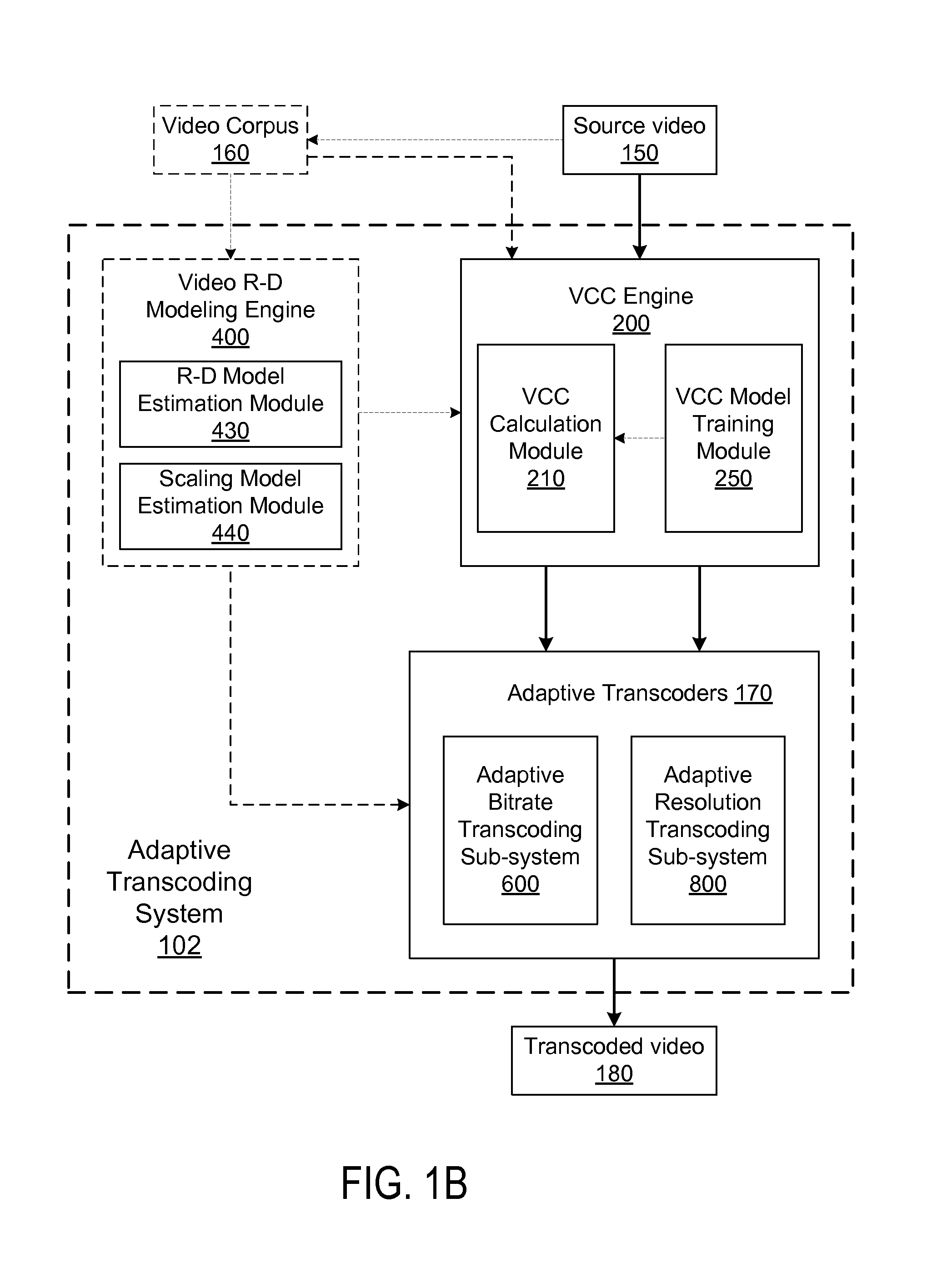
Content-based adaptive video transcoding framework
ActiveUS8767825B1Optimized resolutionImprove visual qualityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern recognitionVideo rate
A system and method provide a video coding system for adaptively transcoding videos based on video coding complexity (VCC). A VCC engine of the system is configured to generate a measure of how difficult to encode a source video based on a trained VCC model. A video rate-distortion modeling engine of the system is configured to estimate a rate-distortion model and a scaling model. The VCC model, rate-distortion model and the scaling model are trained on a video corpus of the system. The trained VCC model, rate-distortion model and the scaling model are used by an adaptive bitrate transcoding sub-system to transcode a source video with an optimized bitrate and visual quality. The trained VCC model, rate-distortion model and the scaling model are further used by an adaptive resolution transcoding sub-system to transcode a source video with an optimized resolution and visual quality.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
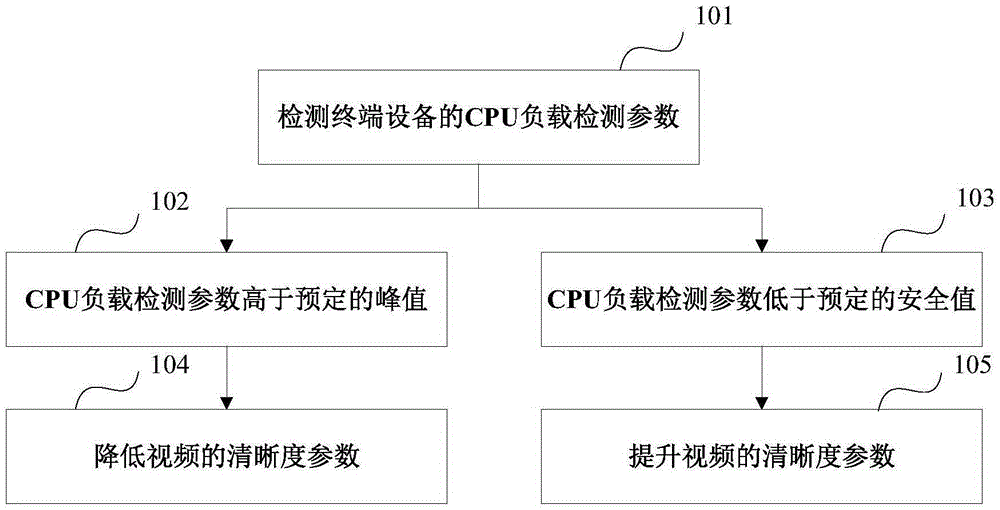
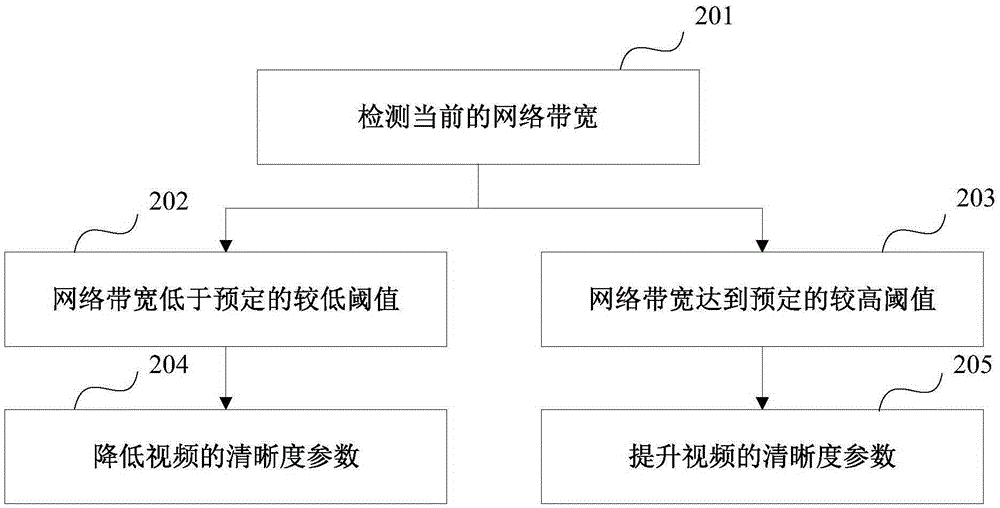
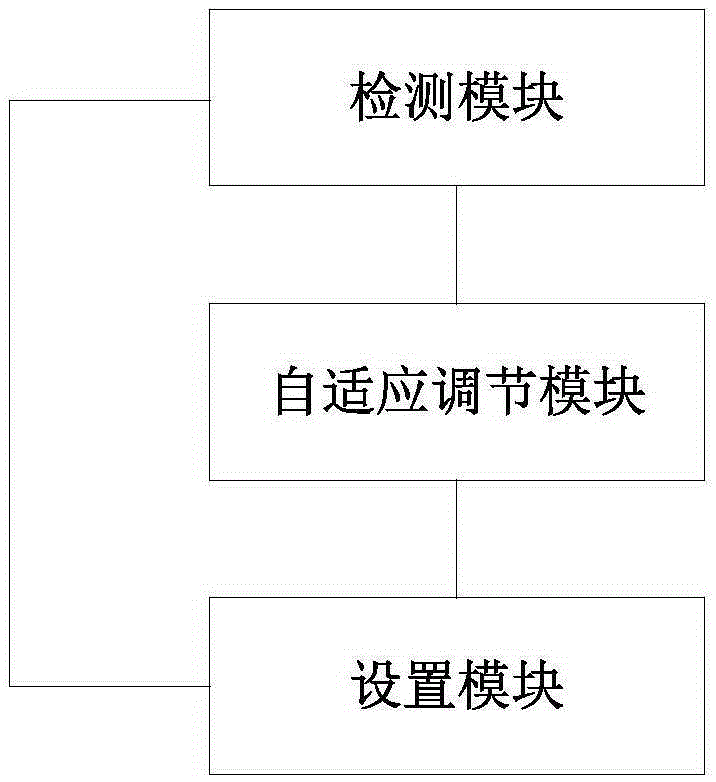
Adaptive video definition adjusting method, apparatus and terminal
InactiveCN105657321AGuaranteed uptimeImprove fluencySupplementary picture signal insertionTwo-way working systemsImage resolutionTerminal equipment
The invention provides an adaptive video definition adjusting method, apparatus and terminal. The adaptive video definition adjusting method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: detecting a current CPU load detection parameter of a terminal device participating in a video call in a video call process; judging whether the current CPU load detection parameter reaches a preset peak value, and if judging that the current CPU load detection parameter reaches the preset peak value, reducing the definition parameter of the video according to a predetermined adjustment strategy, wherein the definition parameter of the video comprises resolution, a code rate and / or a frame rate of the video. According to the adaptive video definition adjusting method provided by the invention, the definition parameter of the video is dynamically and adaptively adjusted via CPU load detection and network bandwidth detection and the like, so as to guarantee the normal operation of the video call and guarantee better smoothness as well.
Owner:LE SHI ZHI ZIN ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY (TIANJIN) LTD
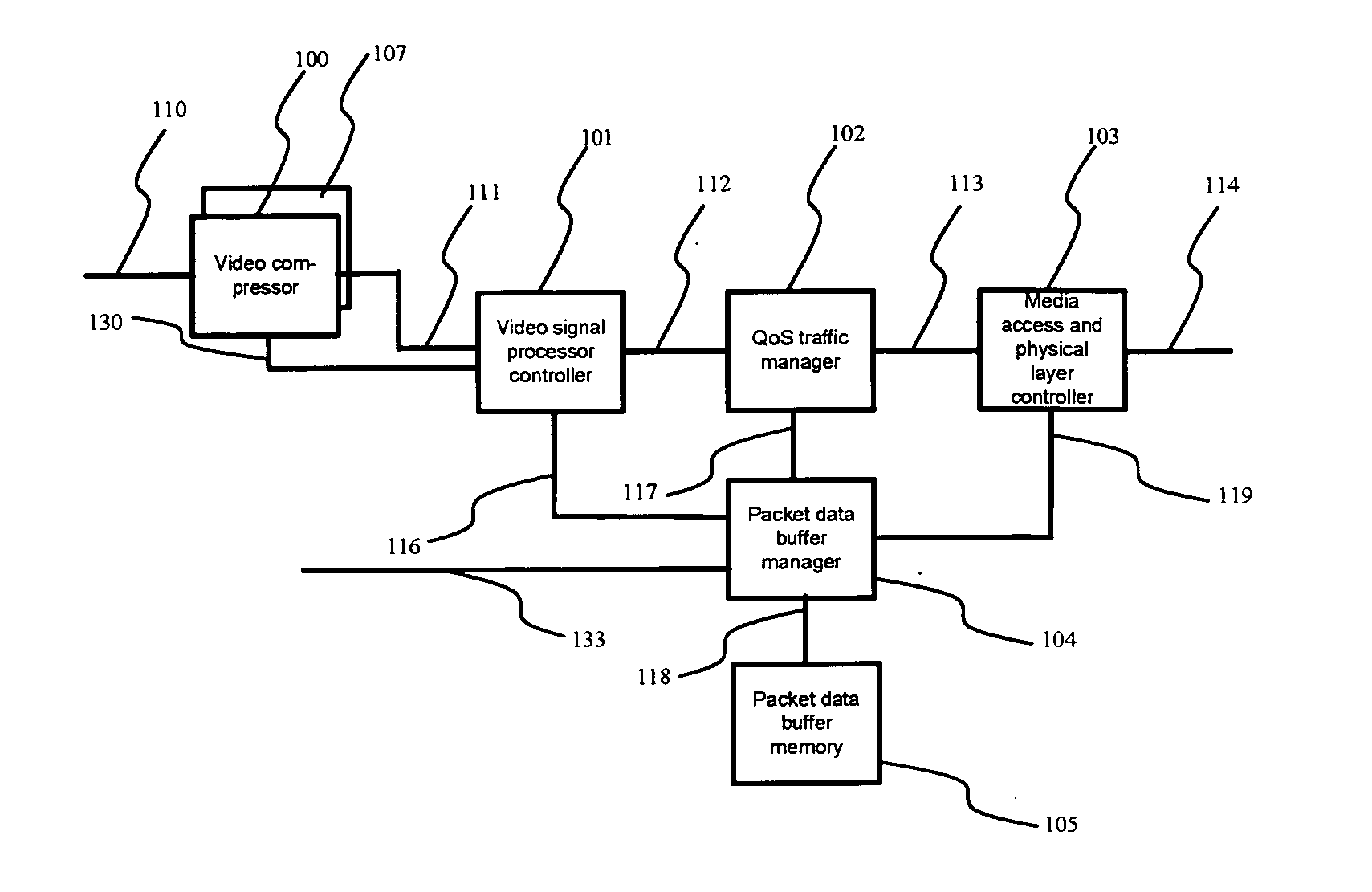
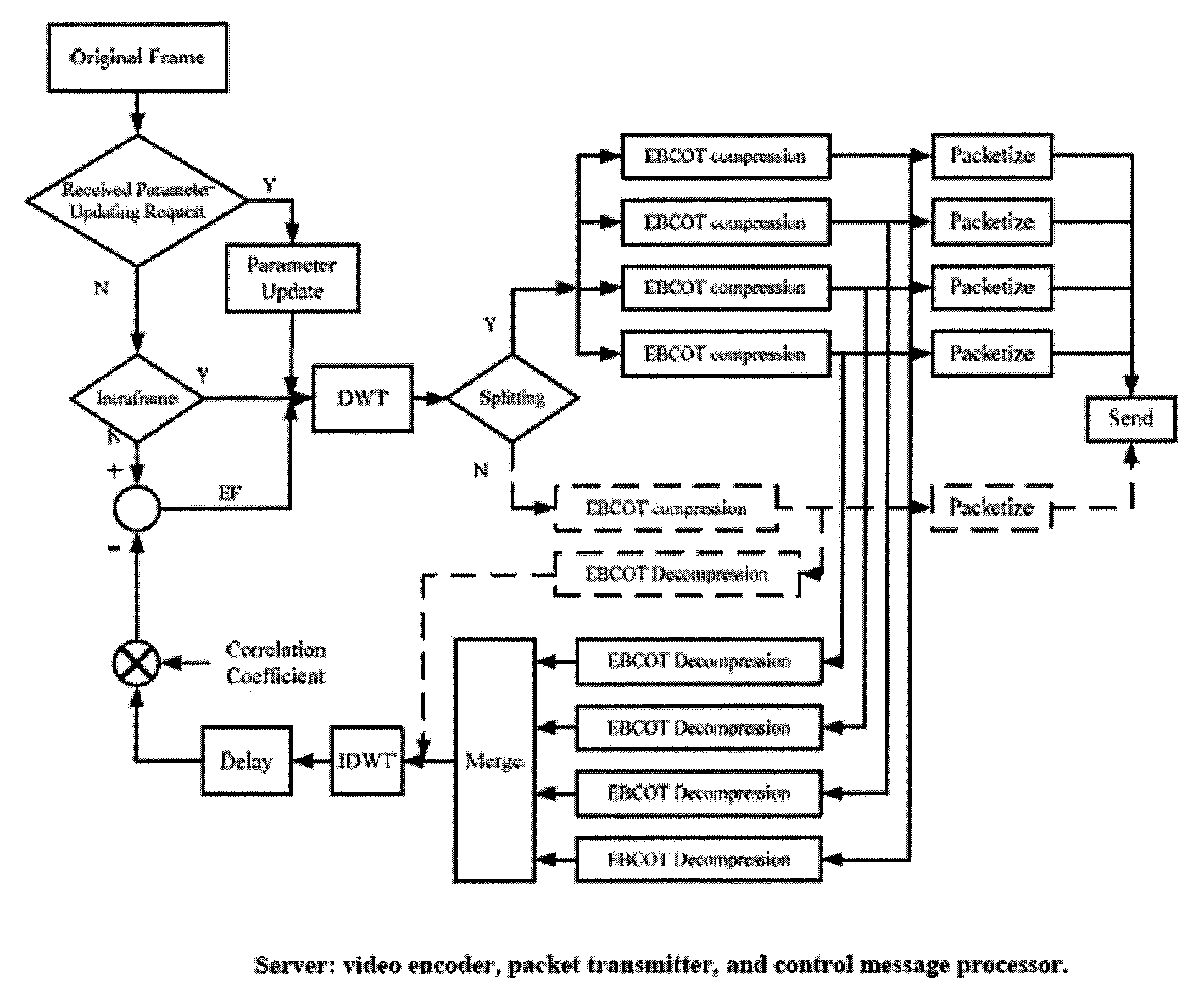
Method and apparatus for network-adaptive video coding
InactiveUS20080259796A1Realize automatic adjustmentError preventionTransmission systemsRate limitingAdaptive coding
Methods and devices for a media processing is provided. In one respect, the methods can provide initiating a bandwidth throttle or a frame rate throttle when resources of a network exceed resources of client device. The methods of the present disclosure may also provide techniques for handling lost packets during transmission using wavelet coefficients.
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS C4 SYSTEMS +1
User interface for adaptive video fast forward
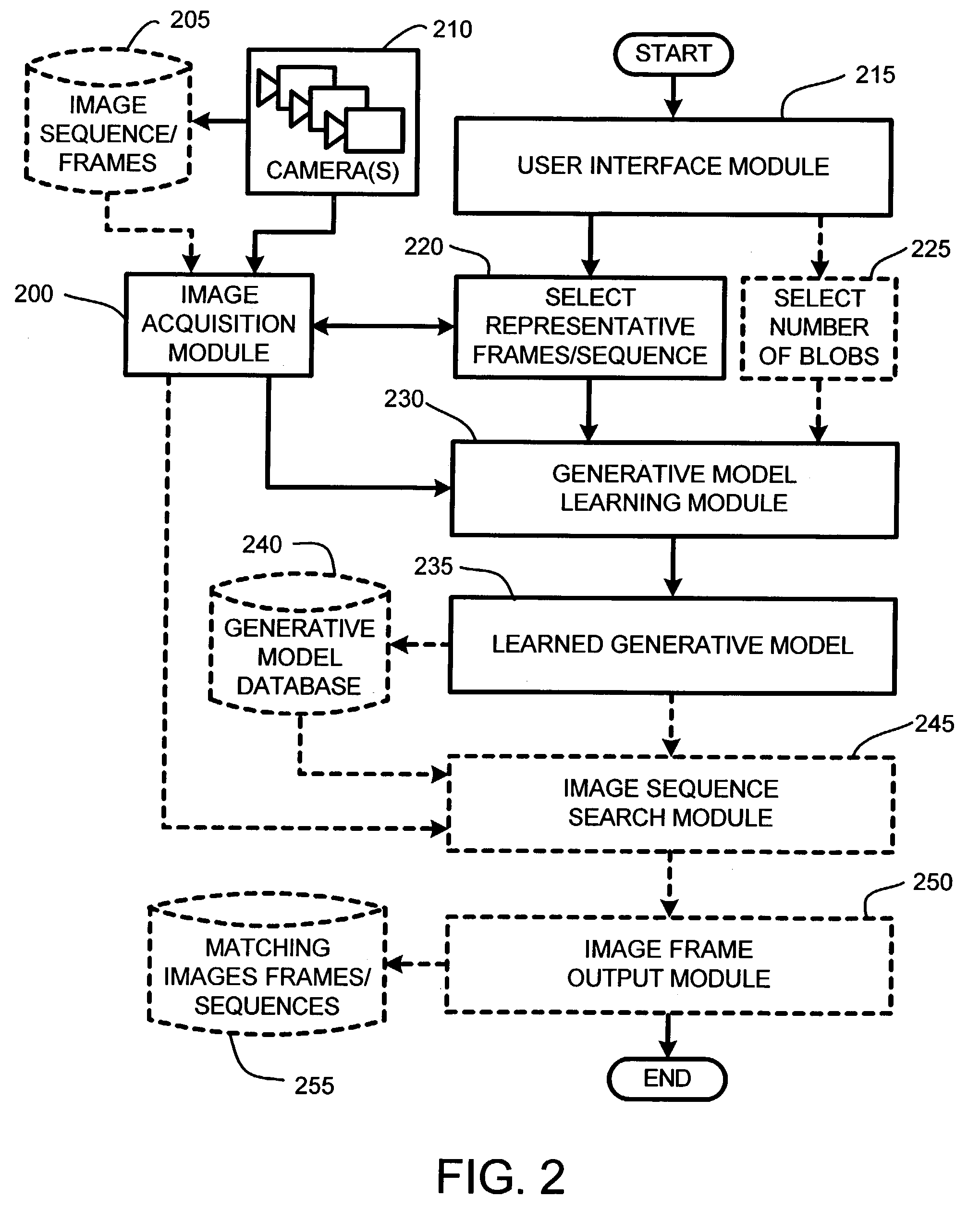
InactiveUS7152209B2Low similarityQuick ViewTelevision system detailsData processing applicationsAdaptive videoSelf adaptive
A user interface (UI) for adaptive video fast forward provides a novel fully adaptive content-based UI for allowing user interaction with an image sequence or video relative to a user identified query sample. This query sample is drawn either from an image sequence being searched or from another image sequence entirely. The user interaction offered by the UI includes providing a user with computationally efficient searching, browsing and retrieval of one or more objects, frames or sequences of interest in video or image sequences, as well as automatic content-based variable-speed playback based on a computed similarity to the query sample. In addition, the UI also provides the capability to search for image frames or sequences that are dissimilar to the query sample, thereby allowing the user to quickly locate unusual or different activity within an image sequence.
Owner:SZ DJI TECH CO LTD
Performance adaptive video encoding with concurrent decoding
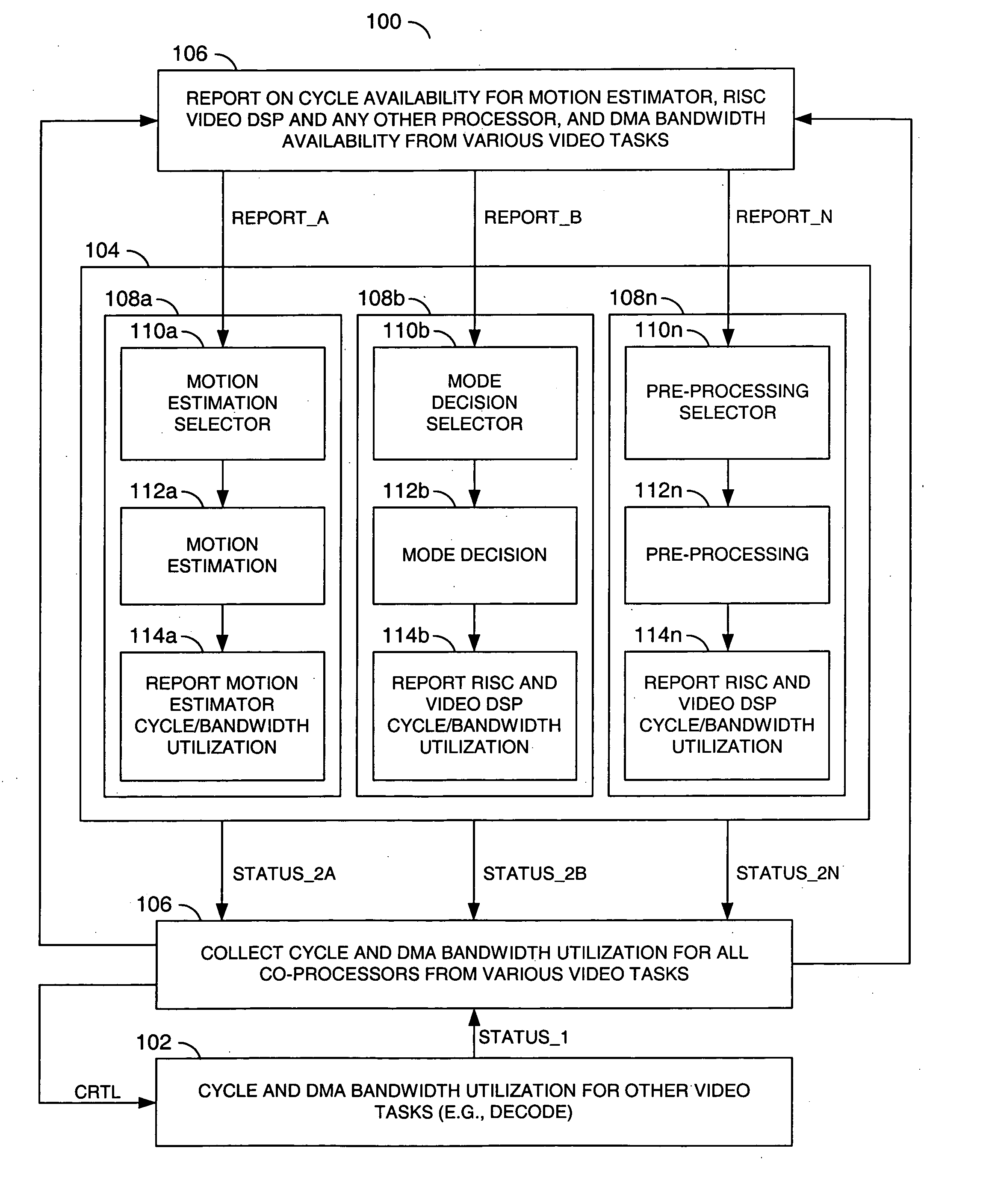
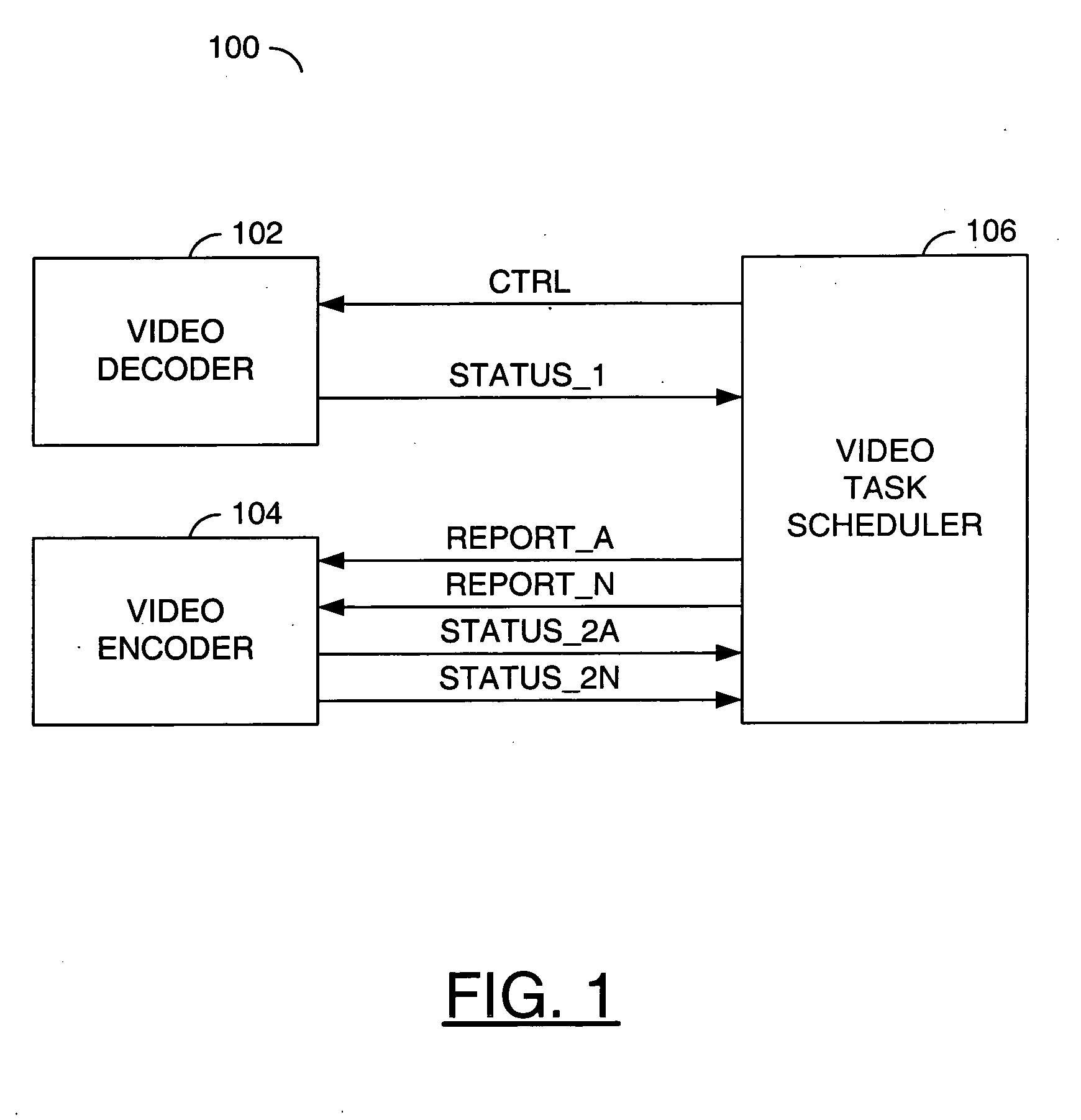
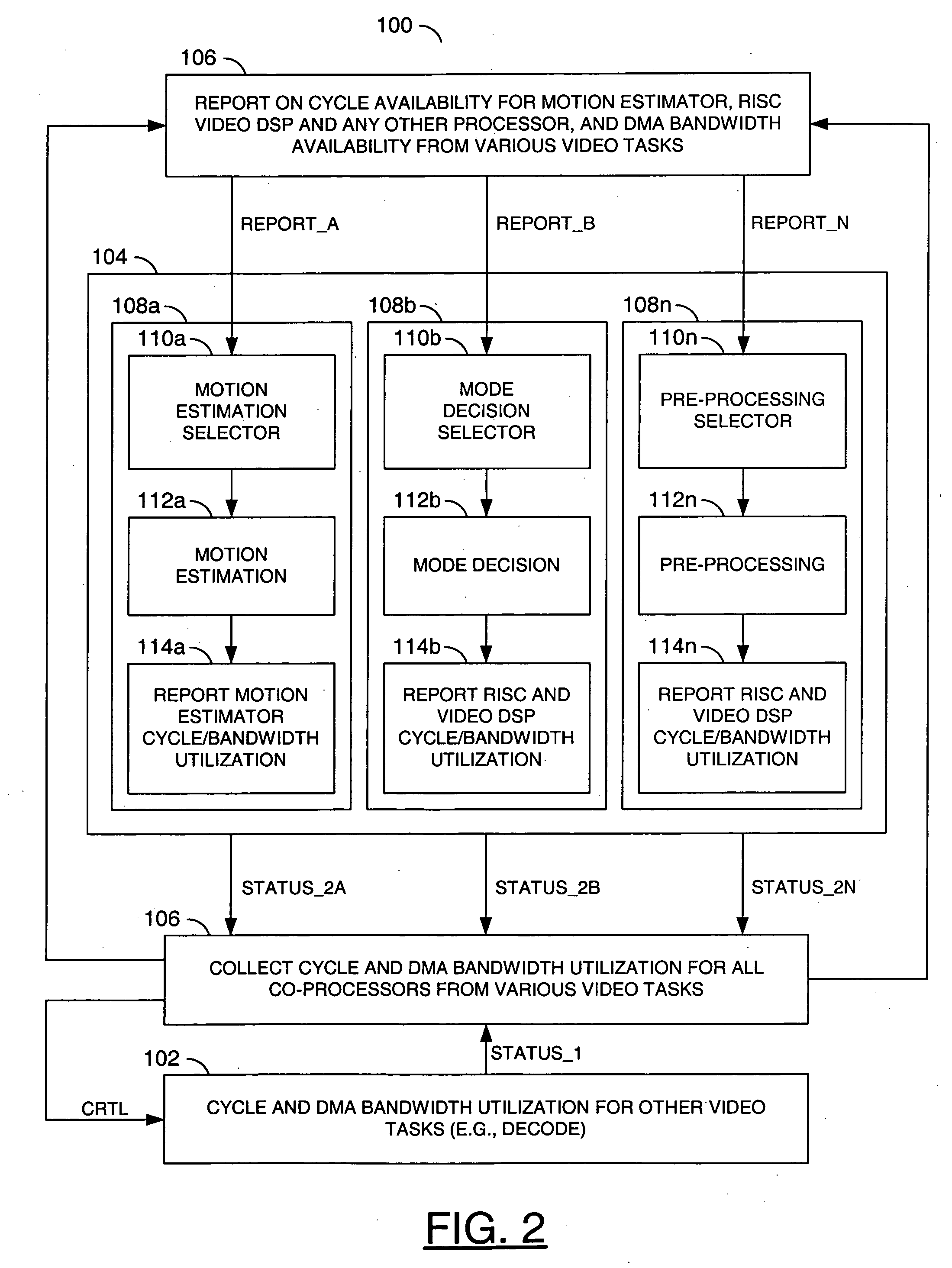
ActiveUS20070030898A1Improve video qualityImprove codec efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureControl signal
An encoder circuit, a task scheduler circuit and a decoder circuit. The encoder circuit may be configured to (i) generate one or more first status signals in response to one or more report signals and (ii) perform video encoding tasks based on available central processing unit (CPU) cycles and memory bandwidth. The task scheduler circuit may be configured to (i) generate a control signal and the one or more report signals in response to the one or more first status signals. The decoder circuit may be configured to (i) generate one or more second status signals and (ii) perform concurrent decoding while the encoder circuit perform adaptive video encoding tasks in response to the control signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Multiple network transport sessions to provide context adaptive video streaming
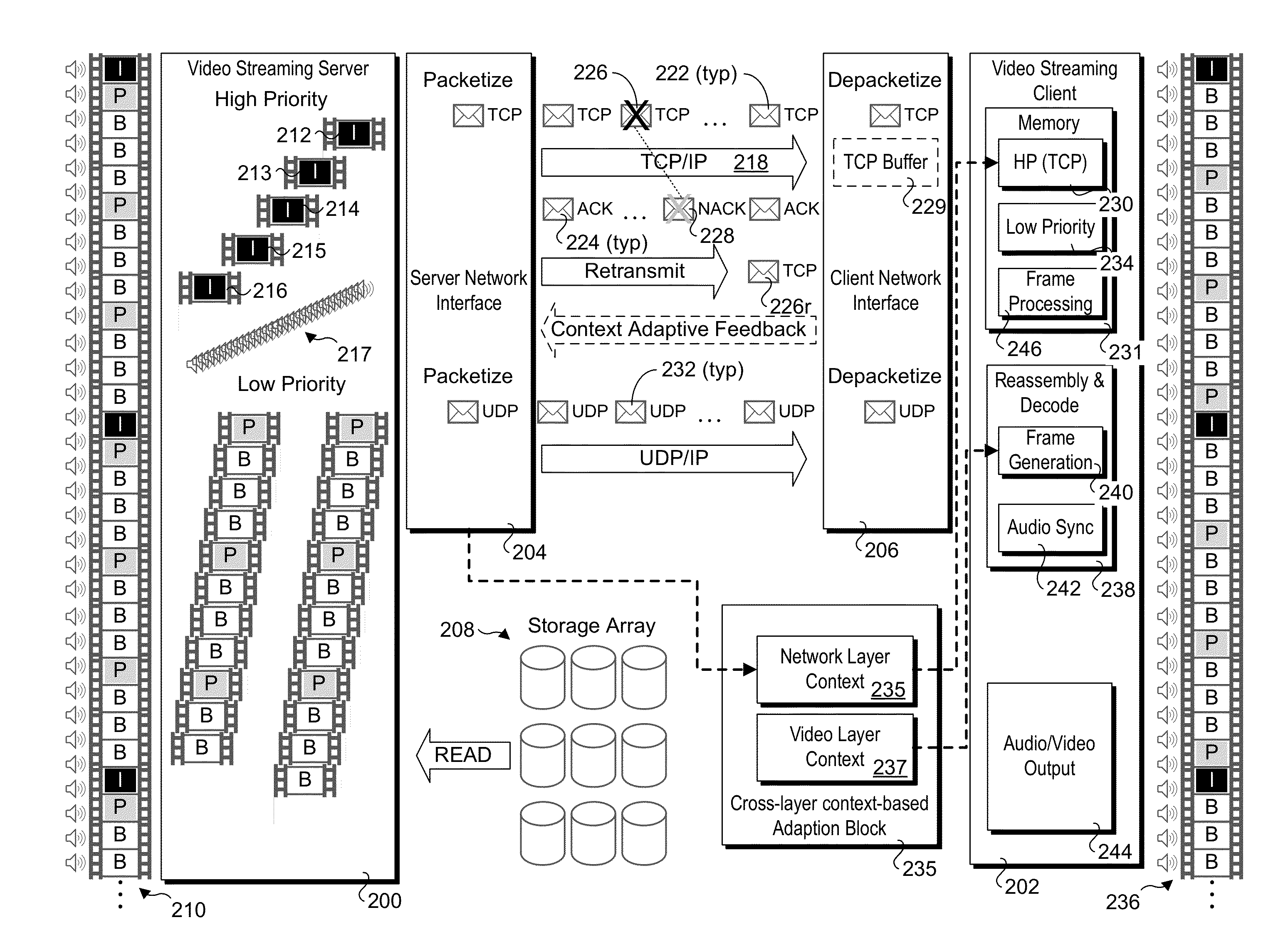
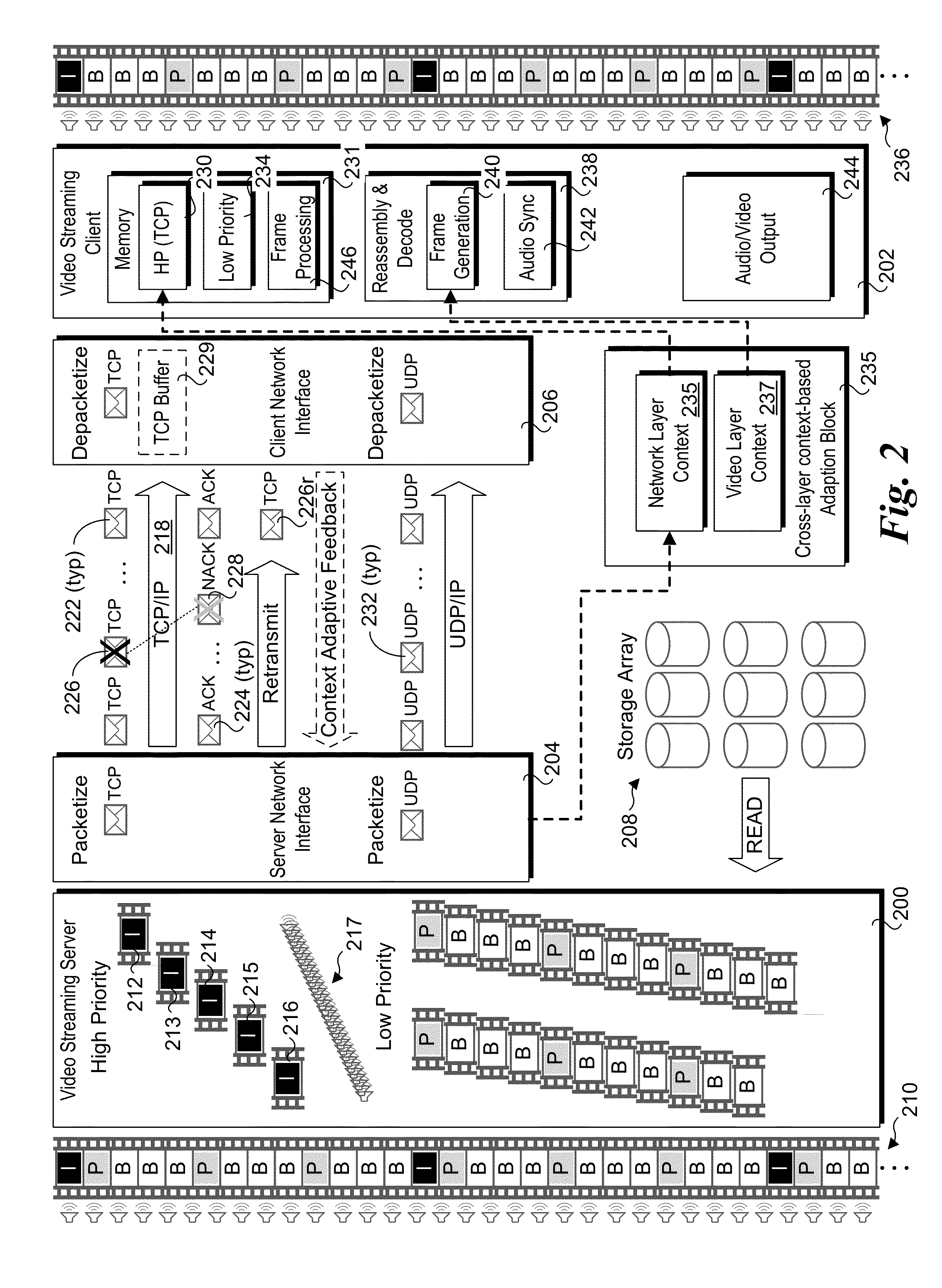
Methods, apparatus, systems, and software for implementing context adaptive video streaming using multiple streaming connections. Original video content is split into multiple bitstreams at a video streaming server and streamed to a video streaming client. Higher-importance video content, such as I-frames and the base layer for scalable video coder (SVC) content are streamed over a high-priority streaming connection, while lower-importance video content is streamed over a low-priority streaming connection. The high-priority streaming connection may employ a reliable connection protocol such as TCP protocol, while the lower-priority connection may employ UDP or a modified TCP protocol under which some portions of the bitstream may be dropped. Cross-layer context adaptive streaming may be implemented under which context data such as network context and video application context information may be considered to adjust parameters associated with implement one or more streaming connections.
Owner:INTEL CORP
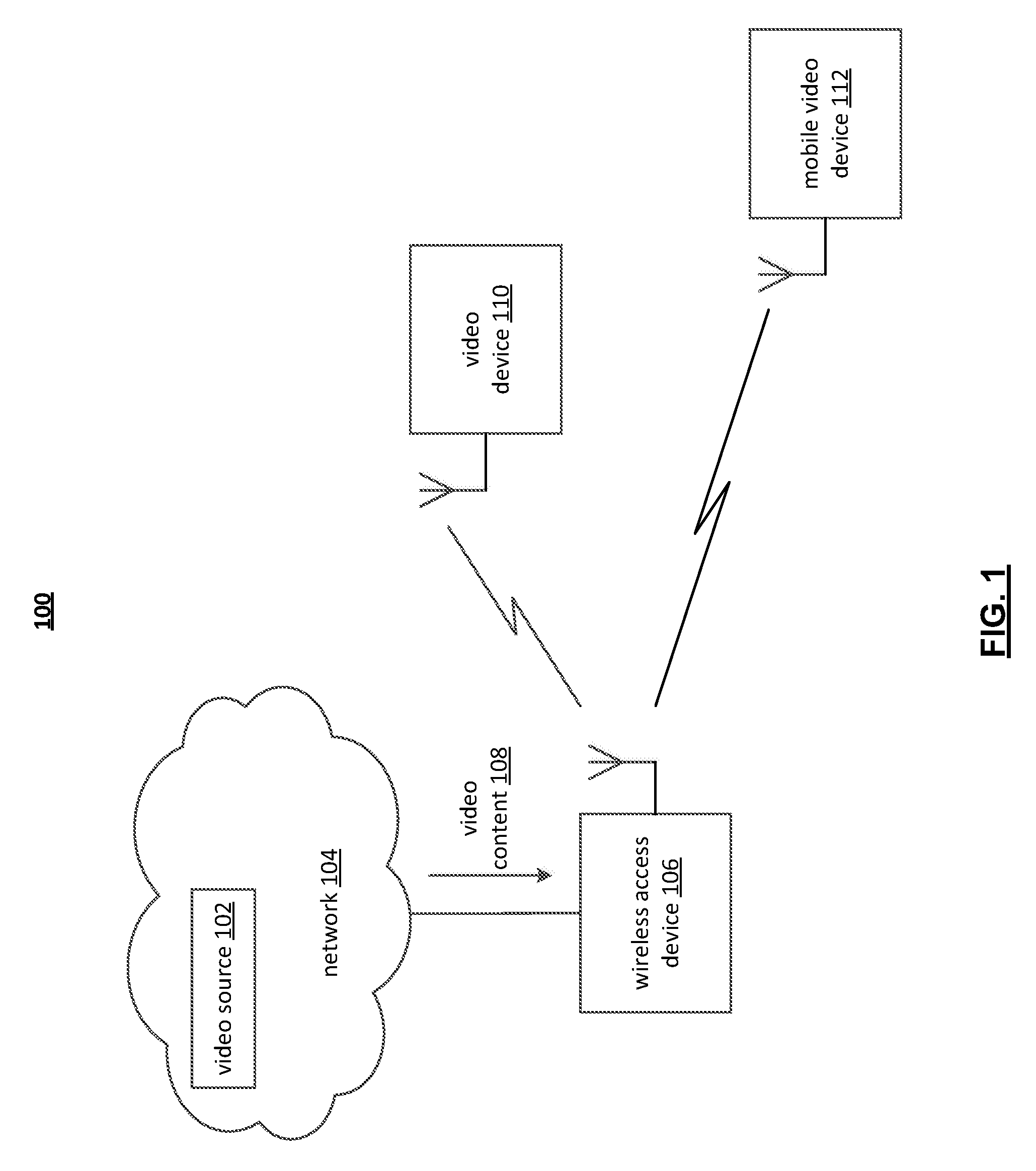
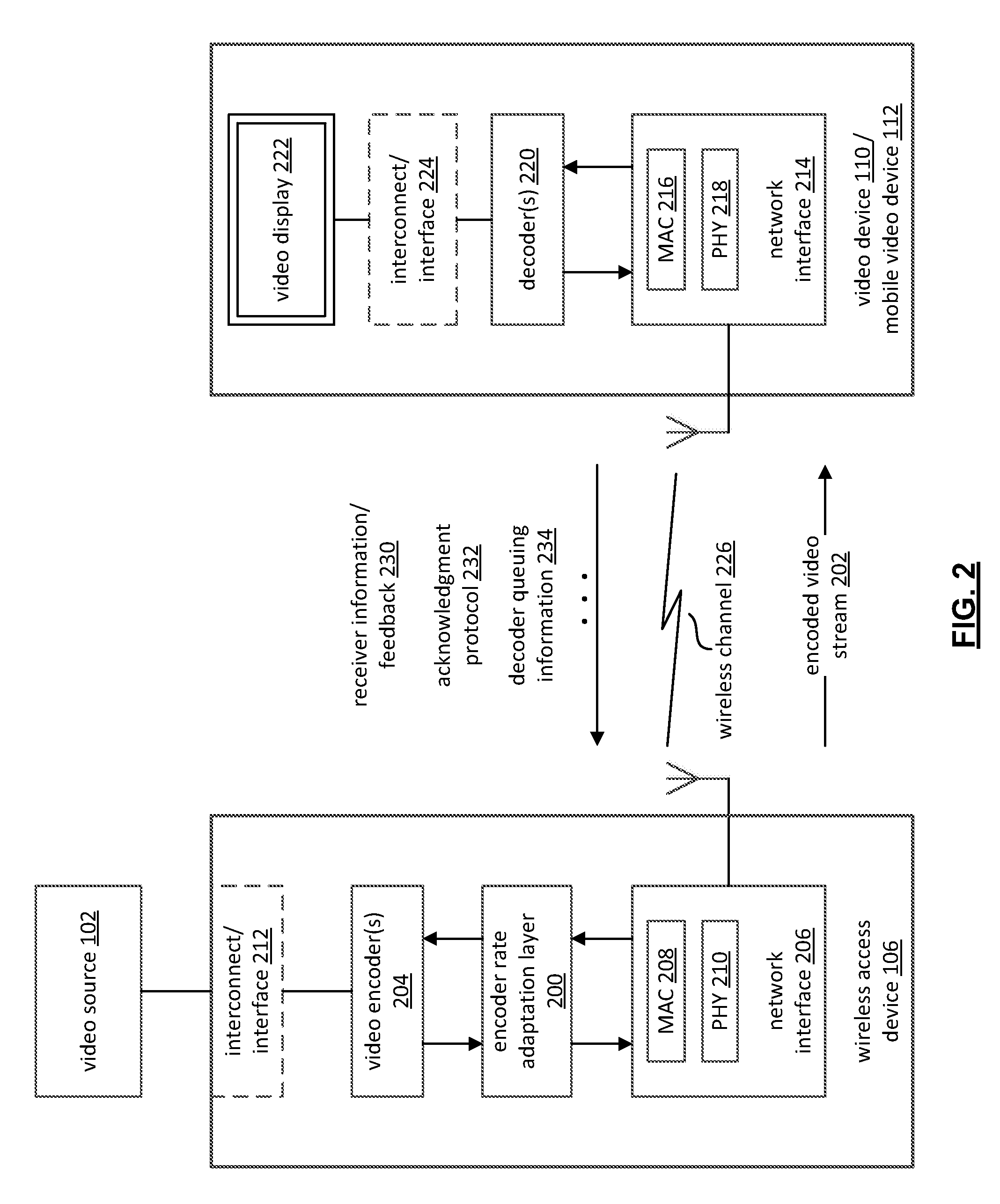
Adaptive Video Encoding Based on Predicted Wireless Channel Conditions
InactiveUS20120307886A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningRate adaptationVideo delivery
Adaptive video encoding based on predicted wireless channel conditions. Based on at least one of a number of transmitter side indications of the available throughput of a wireless channel for video delivery, an encoder rate adaptation mechanism generates an estimate of the supportable throughput of the wireless channel under different operating conditions. An encoding parameter, such as encoder bit rate, is subsequently altered based on the estimated throughput value. In one instance, transmitter side throughput indicia is used to generate target encoder bit rates for multiple potential PHY data rates / channel MCS selections that may be used in video delivery. In anticipation of or immediately following a transition to one such PHY data rate / MCS selection, the encoder bit rate is altered in accordance with an associated target bit rate. In another mode, average transmit queue latency information is used to further regulate the encoder bit rate.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
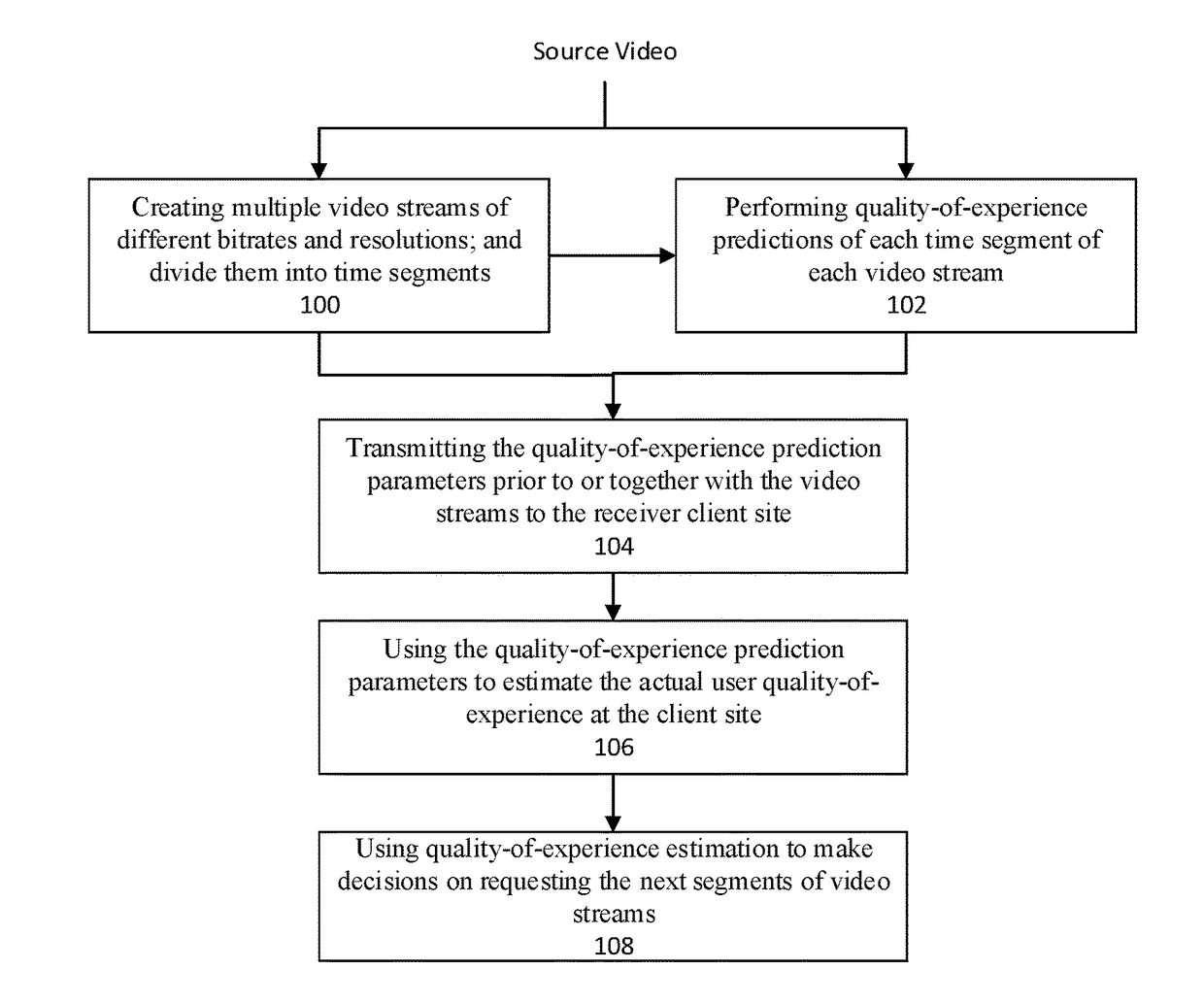
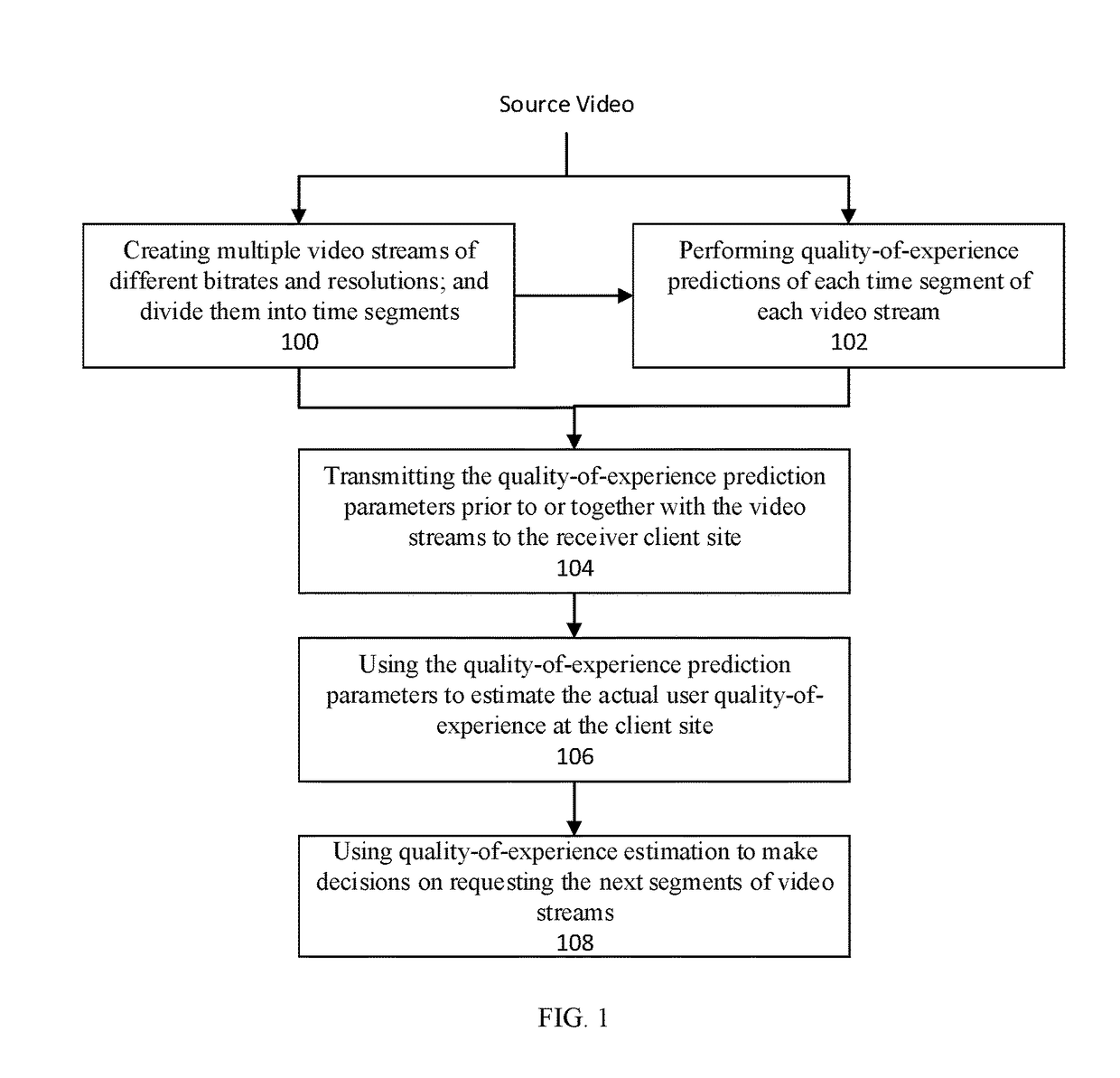
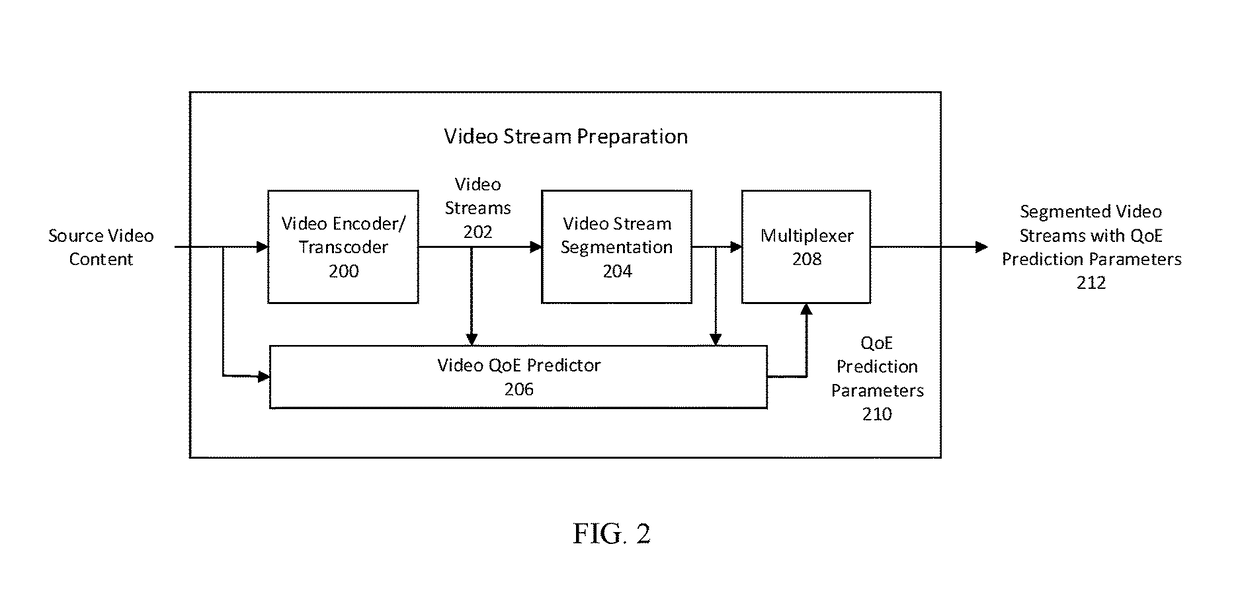
Method and system for smart adaptive video streaming driven by perceptual quality-of-experience estimations
ActiveUS20180041788A1Save bandwidthReduce probabilityDigital video signal modificationTransmissionCache serverVideo delivery
The present invention is a system or method that facilitates smart decision makings at the client side for adaptive video streaming over a video delivery network by making use of perceptual video quality-of-experience predictions performed during the video preparation stage, at the video hosting or cache server side, or inside the video delivery network, and then transmitted to the client. Compared with prior art approaches of adaptive bitrate video streaming, the present invention can result in one or more of the following benefits: 1) save the overall bandwidth for the delivery of the video content without scarifying the client users' quality-of-experience; 2) create better overall visual quality-of-experience of the client users; 3) create smoother visual quality-of-experience of the client users; and 4) reduce the probability of rebuffering or stalling events at the client user side.
Owner:SSIMWAVE INC
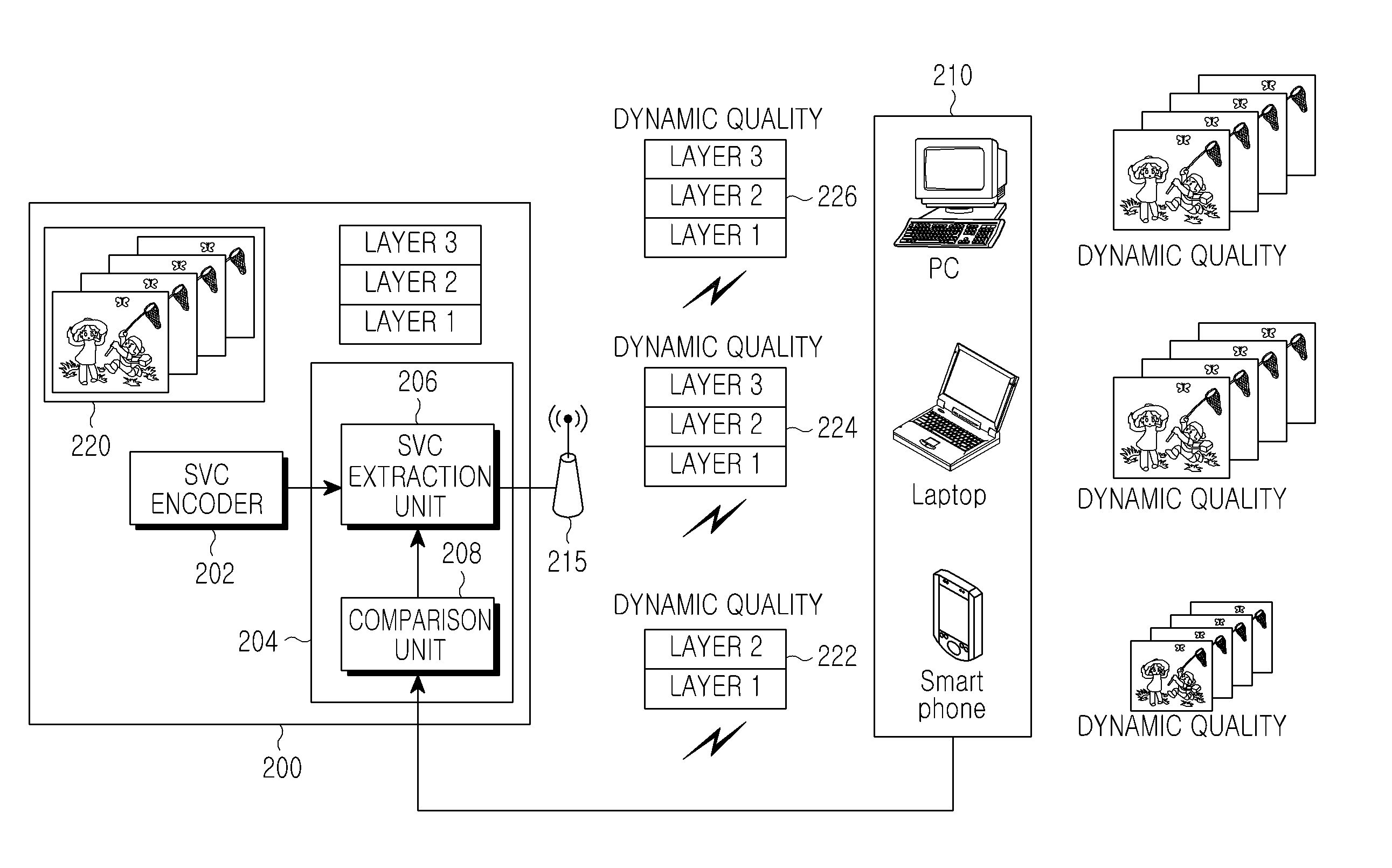
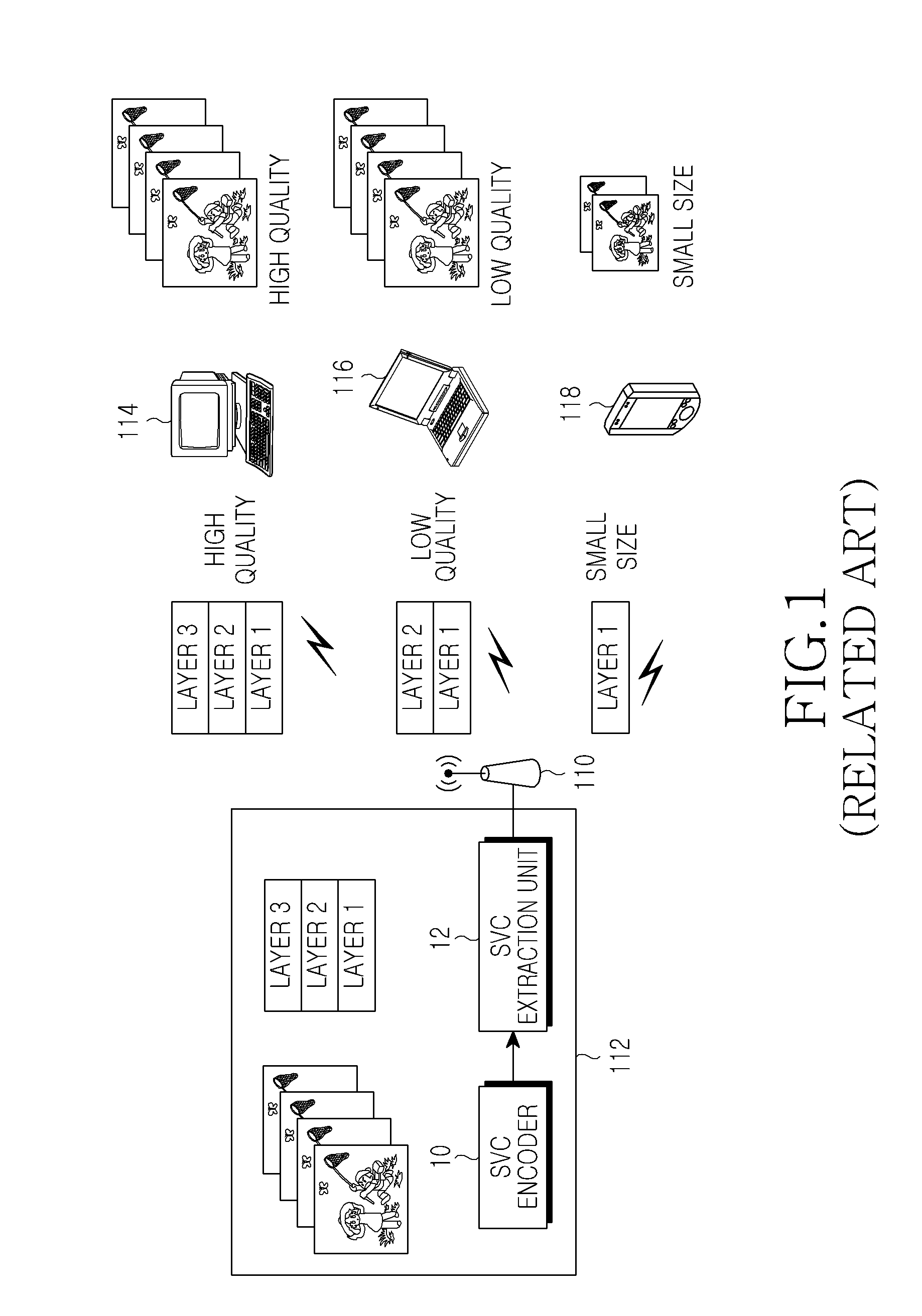
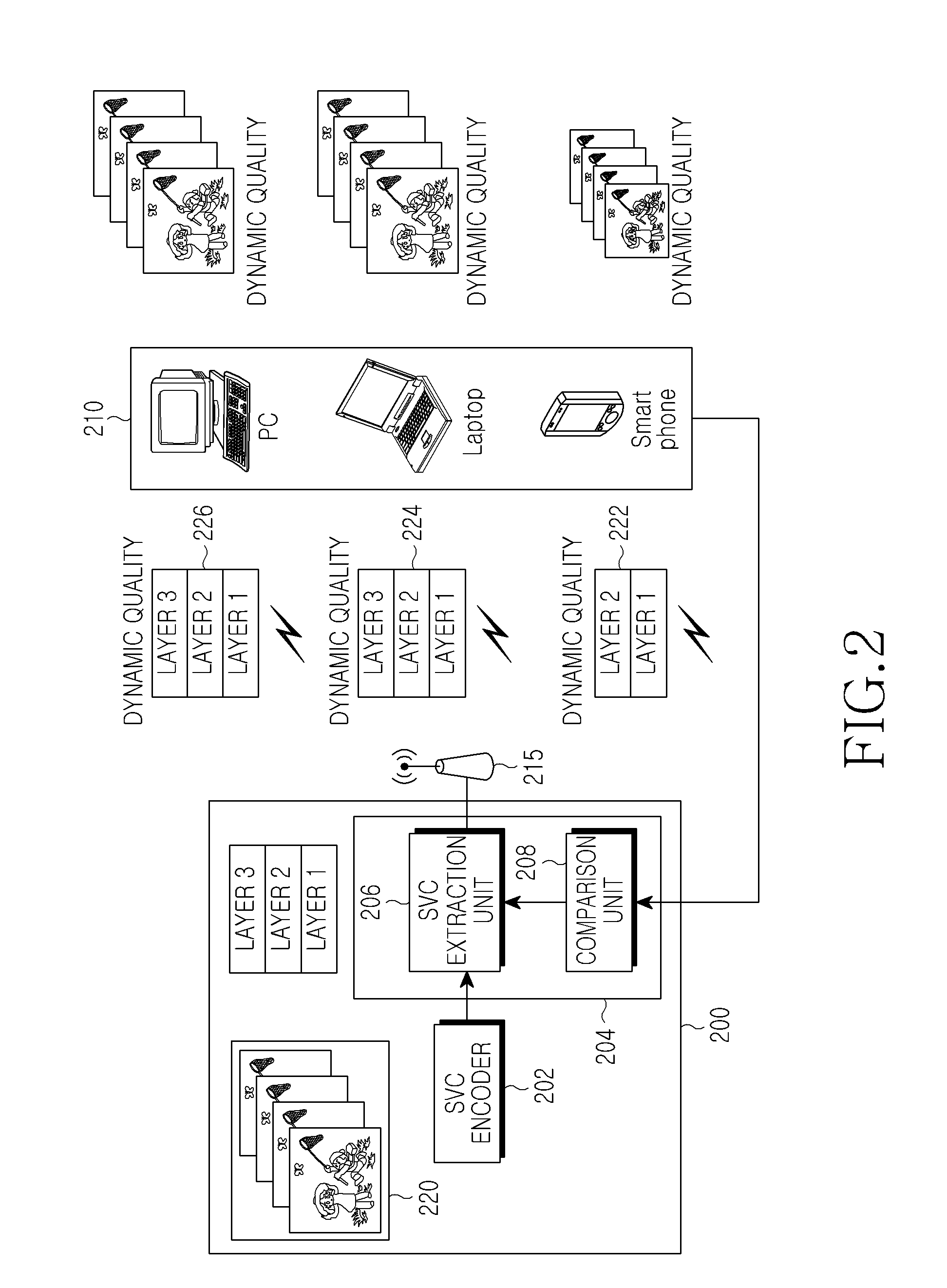
Channel adaptive video transmission method, apparatus using the same, and system providing the same
ActiveUS20100262712A1Multiple digital computer combinationsDigital video signal modificationComputer hardwareVideo transmission
A video transmission method is provided, which includes receiving state information from at least one mobile terminal that intends to perform a video stream service through a wireless network, determining a size of an image by selecting a specified spatial layer bit stream on the basis of the state information of the mobile terminal from a plurality of spatial layer bit streams generated at different bit rates during encoding of the bit stream, selecting a specified time and an SNR layer bit stream by increasing or decreasing time of the image and a layer position of the SNR layer bit stream on the basis of network parameters included in the state information of the mobile terminal, and transmitting the bit stream generated by extracting the specified layer bit stream of the selected layer to the mobile terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com