Patents
Literature
830 results about "Optical transfer function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
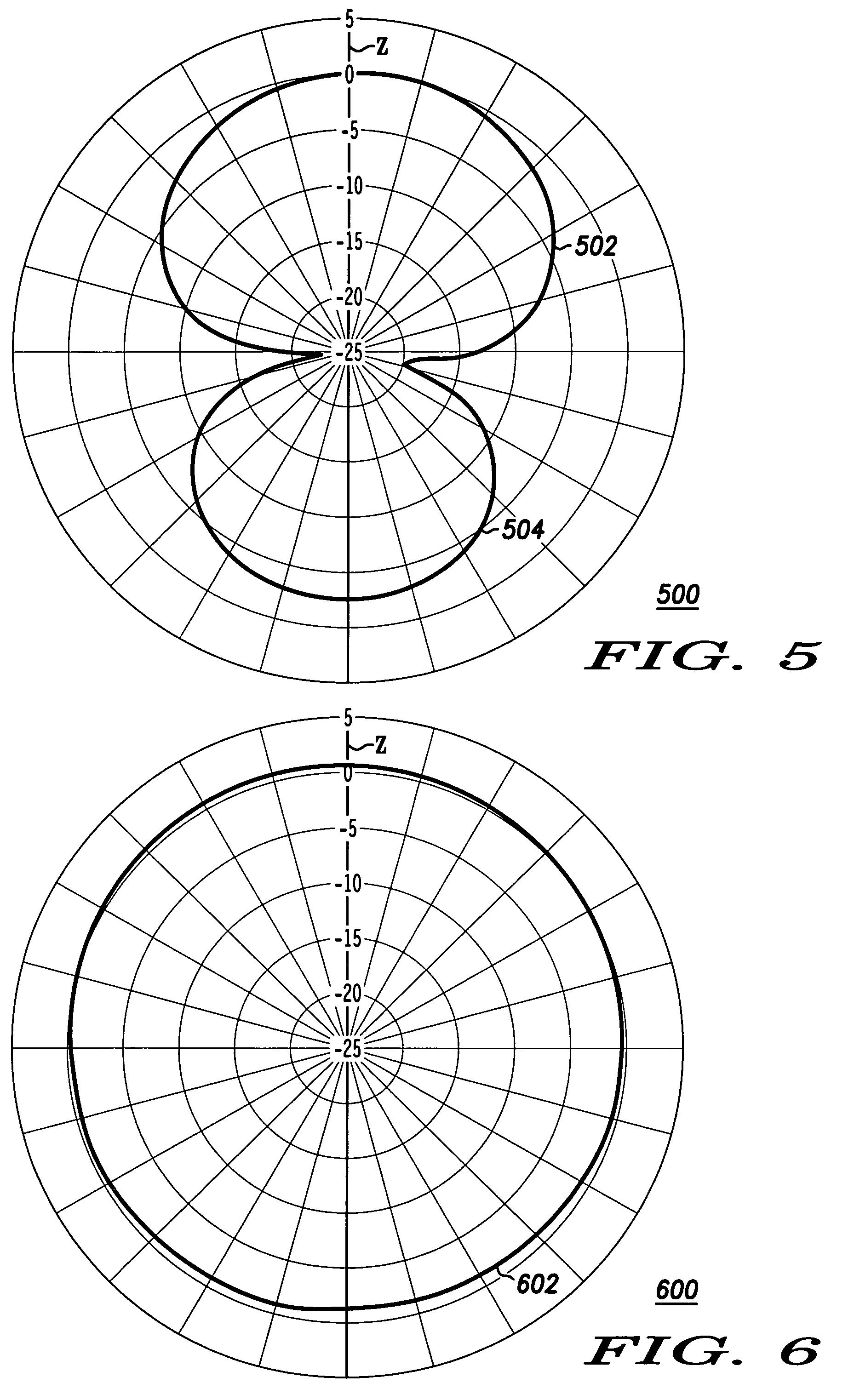
The optical transfer function (OTF) of an optical system such as a camera, microscope, human eye, or projector specifies how different spatial frequencies are handled by the system. It is used by optical engineers to describe how the optics project light from the object or scene onto a photographic film, detector array, retina, screen, or simply the next item in the optical transmission chain. A variant, the modulation transfer function (MTF), neglects phase effects, but is equivalent to the OTF in many situations.
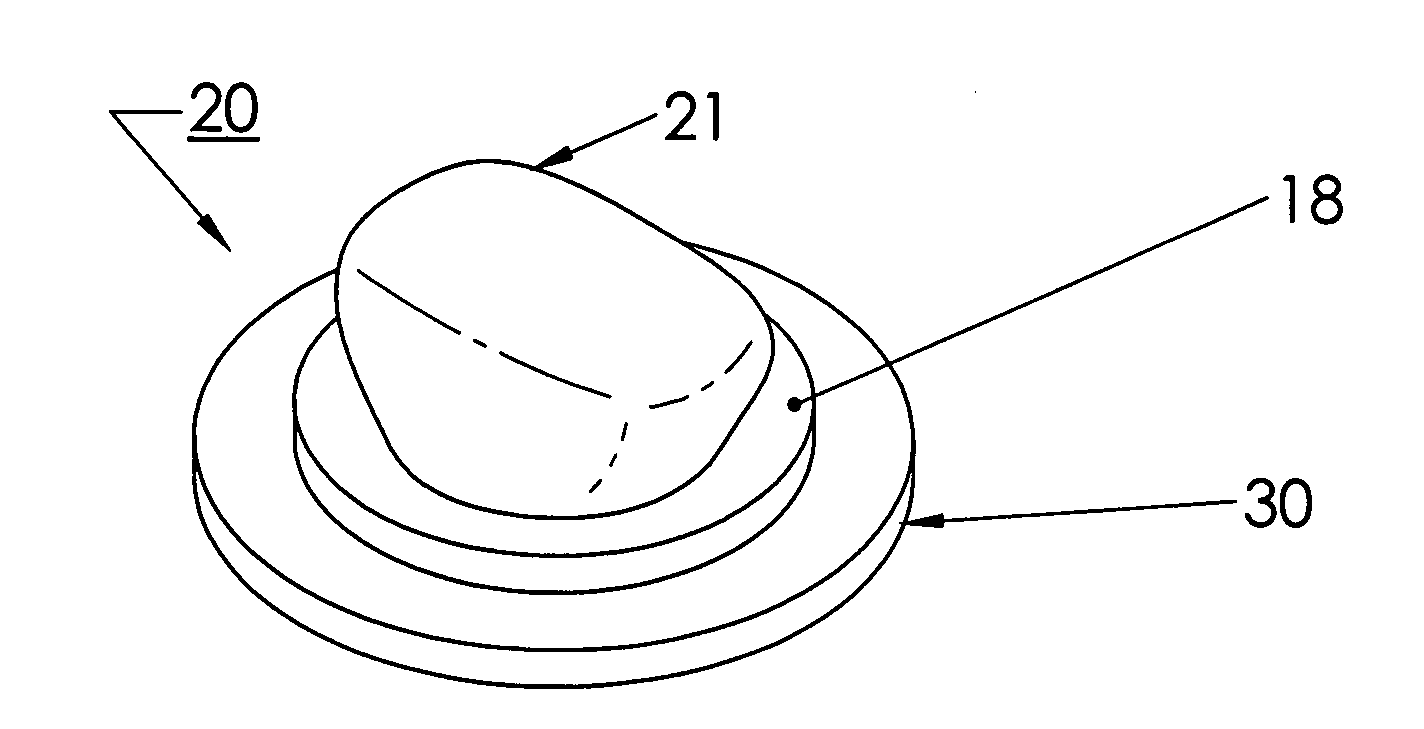
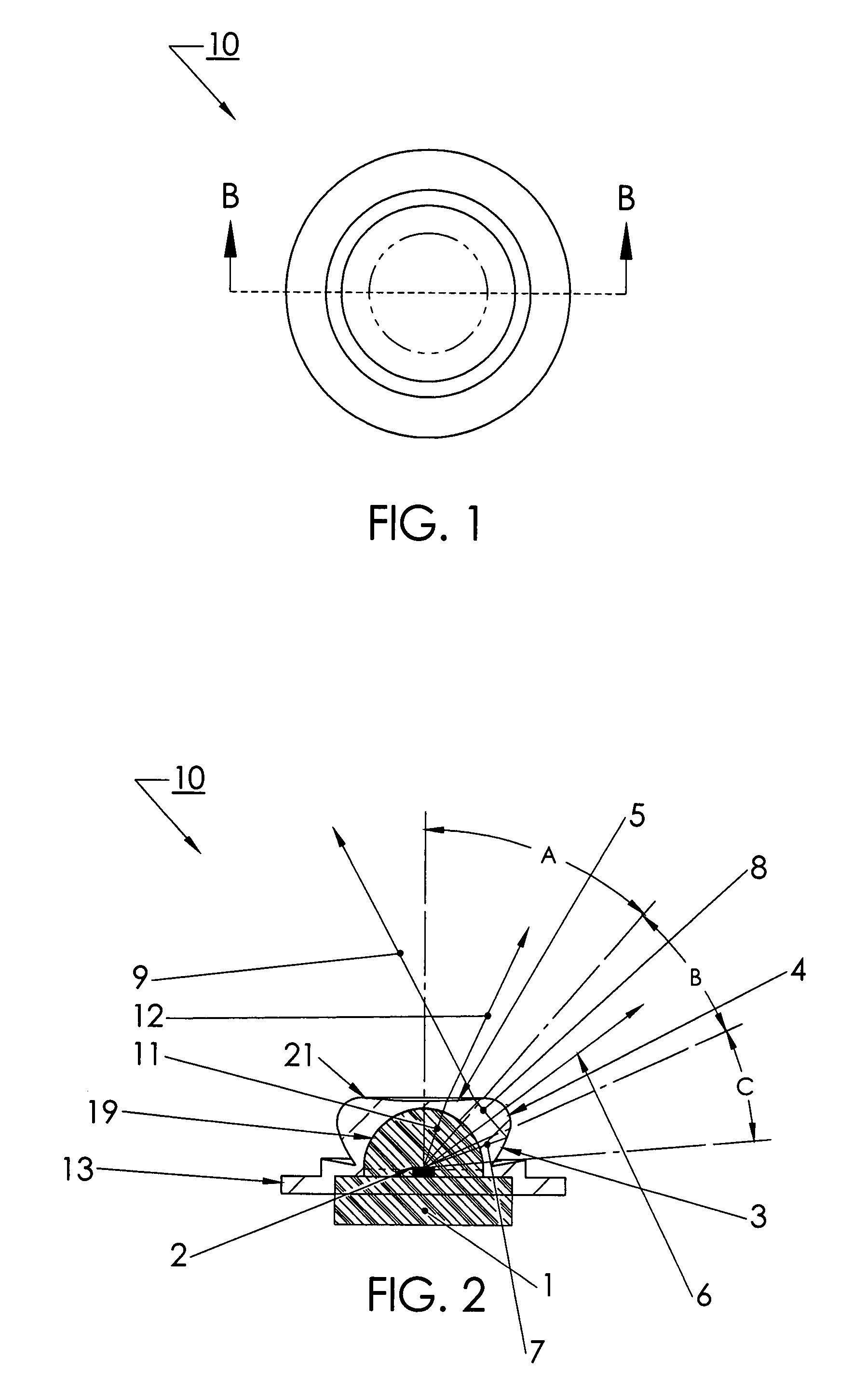
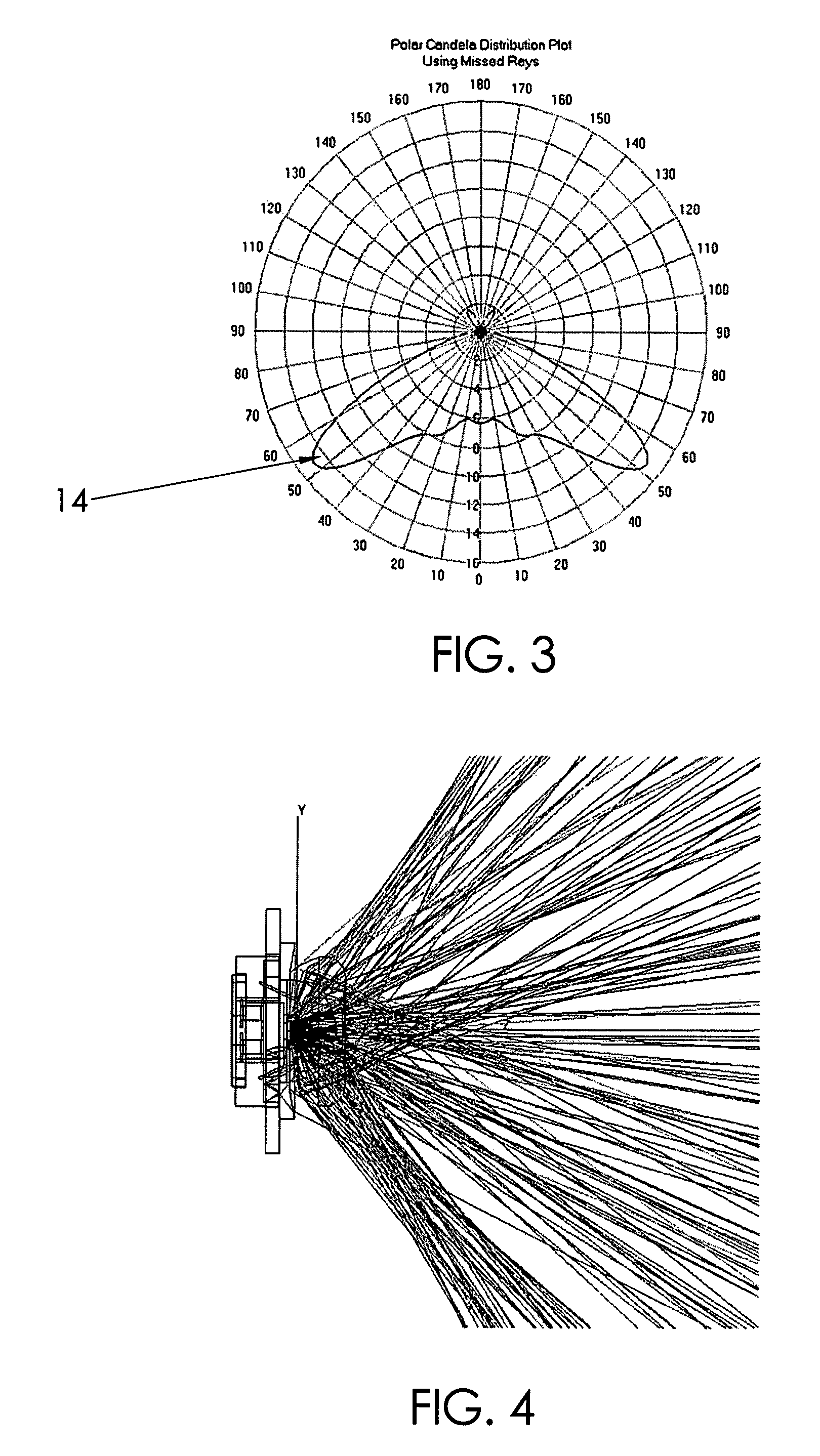
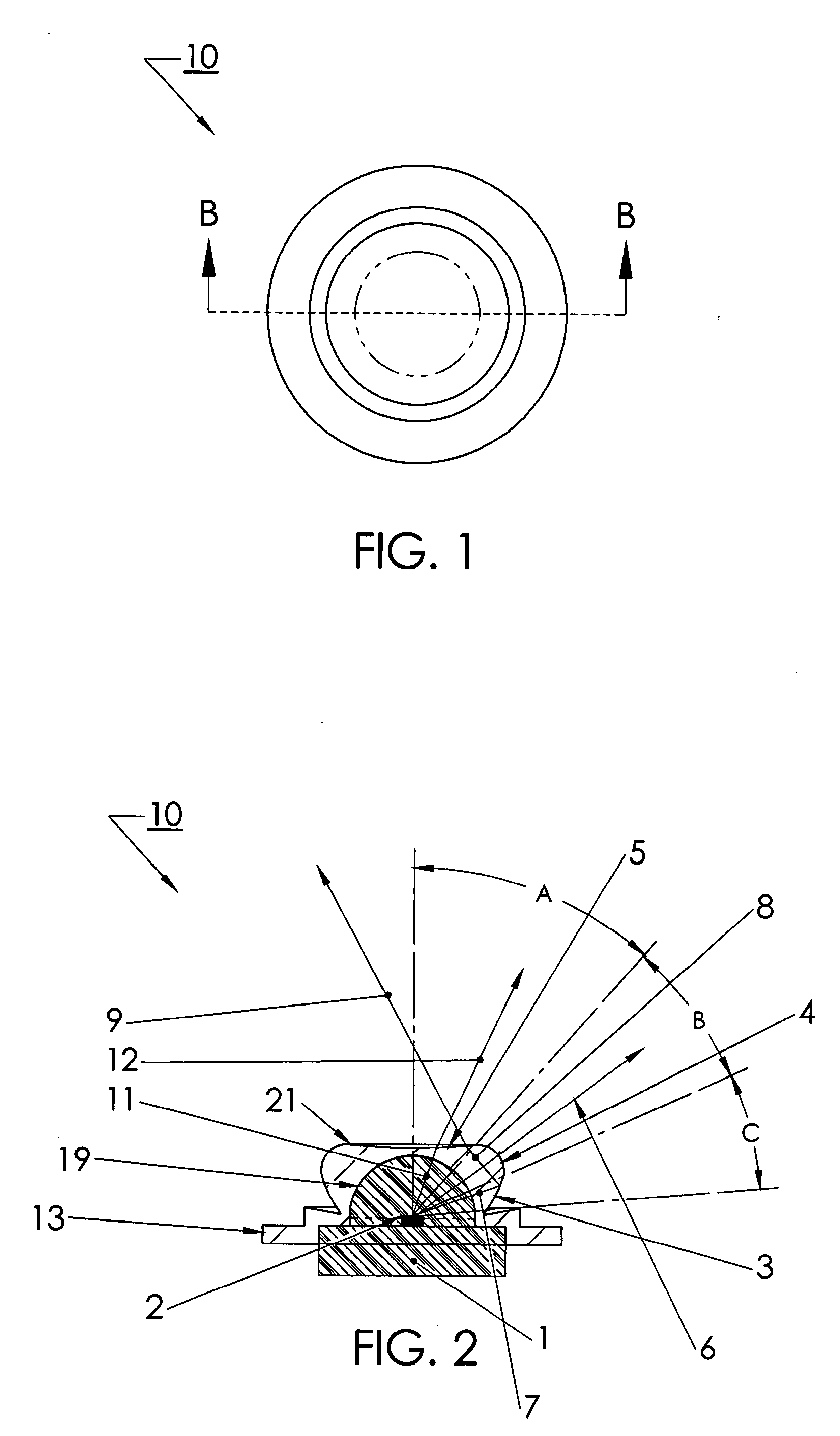
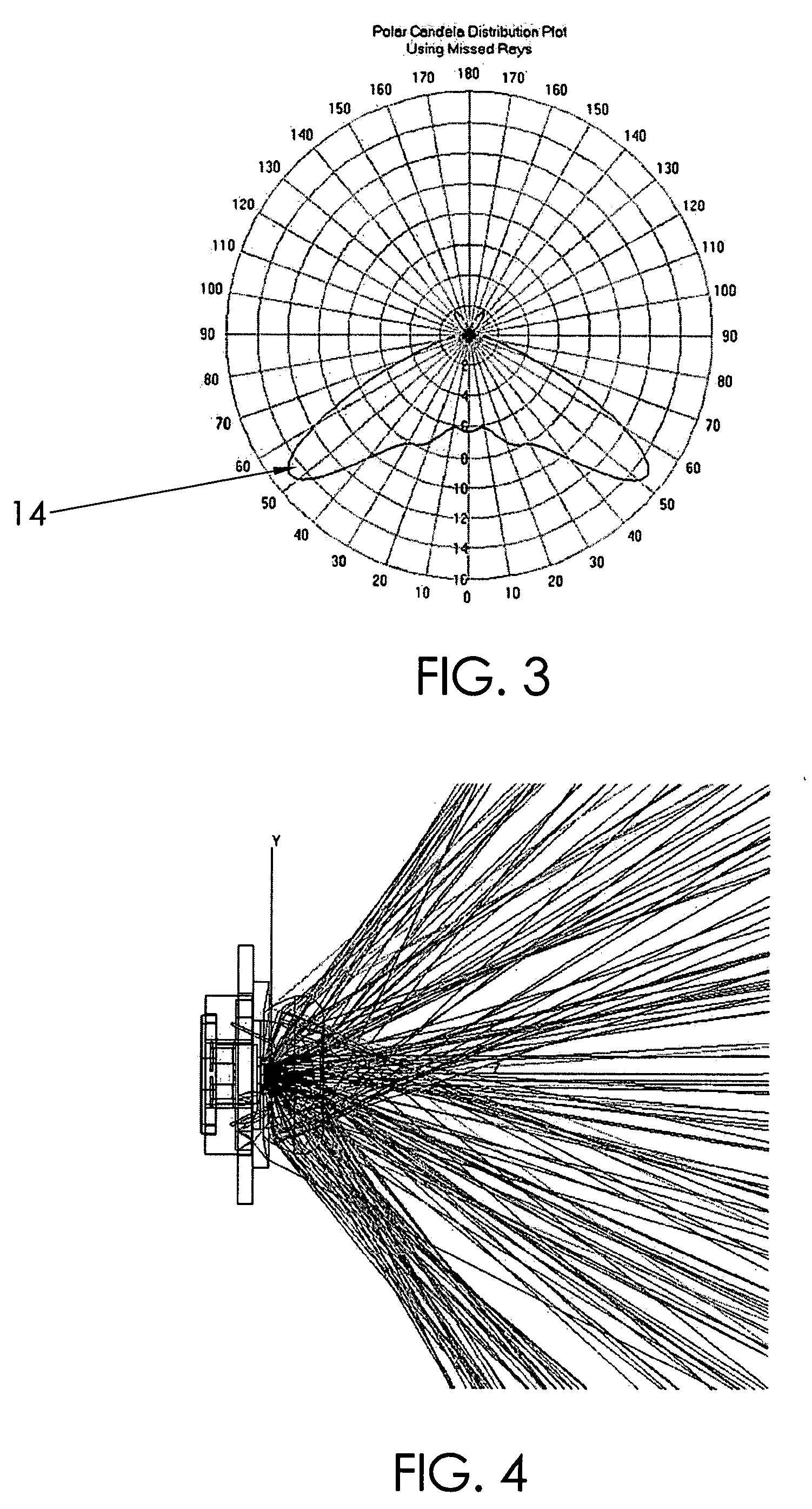
LED device for wide beam generation
ActiveUS7674018B2Easy to combineReduce discontinuityPlanar light sourcesMechanical apparatusSurface patternWide beam
An apparatus and method is characterized by providing an optical transfer function between a predetermined illuminated surface pattern, such as a street light pattern, and a predetermined energy distribution pattern of a light source, such as that from an LED. A lens is formed having a shape defined by the optical transfer function. The optical transfer function is derived by generating an energy distribution pattern using the predetermined energy distribution pattern of the light source. Then the projection of the energy distribution pattern onto the illuminated surface is generated. The projection is then compared to the predetermined illuminated surface pattern to determine if it acceptably matches. The process continues reiteratively until an acceptable match is achieved. Alternatively, the lens shape is numerically or analytically determined by a functional relationship between the shape and the predetermined illuminated surface pattern and predetermined energy distribution pattern of a light source as inputs.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Binaural synthesis, head-related transfer functions, and uses thereof
InactiveUS6118875AReduce the differenceFunction increaseTwo-channel systemsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsTime domainSound sources
PCT No. PCT / DK95 / 00089 Sec. 371 Date Dec. 27, 1996 Sec. 102(e) Date Dec. 27, 1996 PCT Filed Feb. 27, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO95 / 23493 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 31, 1995A method and apparatus for simulating the transmission of sound from sound sources to the ear canals of a listener encompasses novel head-related transfer functions (HTFs), novel methods of measuring and processing HTFs, and novel methods of changing or maintaining the directions of the sound sources as perceived by the listener. The measurement methods enable the measurement and construction of HTFs for which the time domain descriptions are surprisingly short, and for which the differences between listeners are surprisingly small. The novel HTFs can be exploited in any application concerning the simulation of sound transmission, measurement, simulation, or reproduction. The invention is particularly advantageous in the field of binaural synthesis, specifically, the creation, by means of two sound sources, of the perception in the listener of listening to sound generated by a multichannel sound system. It is also particularly useful in the designing of electronic filters used, for example, in virtual reality systems, and in the designing of an "artificial head" having HTFs that approximate the HTFs of the invention as closely as possible in order to make the best possible representation of humans by the artificial head, thereby making artificial head recordings of optimal quality.
Owner:M O SLASHED LLER HENRIK +3
Imaging system and method for providing extended depth of focus, range extraction and super resolved imaging
InactiveUS7646549B2Improving geometrical resolutionIncrease depth of focusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffraction gratingsImaging lensField of view
An imaging system is presented for imaging objects within a field of view of the system. The imaging system comprises an imaging lens arrangement, a light detector unit at a certain distance from the imaging lens arrangement, and a control unit connectable to the output of the detection unit. The imaging lens arrangement comprises an imaging lens and an optical element located in the vicinity of the lens aperture, said optical element introducing aperture coding by an array of regions differently affecting a phase of light incident thereon which are randomly distributed within the lens aperture, thereby generating an axially-dependent randomized phase distribution in the Optical Transfer Function (OTF) of the imaging system resulting in an extended depth of focus of the imaging system. The control unit is configured to decode the sampled output of the detection unit by using the random aperture coding to thereby extract 3D information of the objects in the field of view of the light detector unit.
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
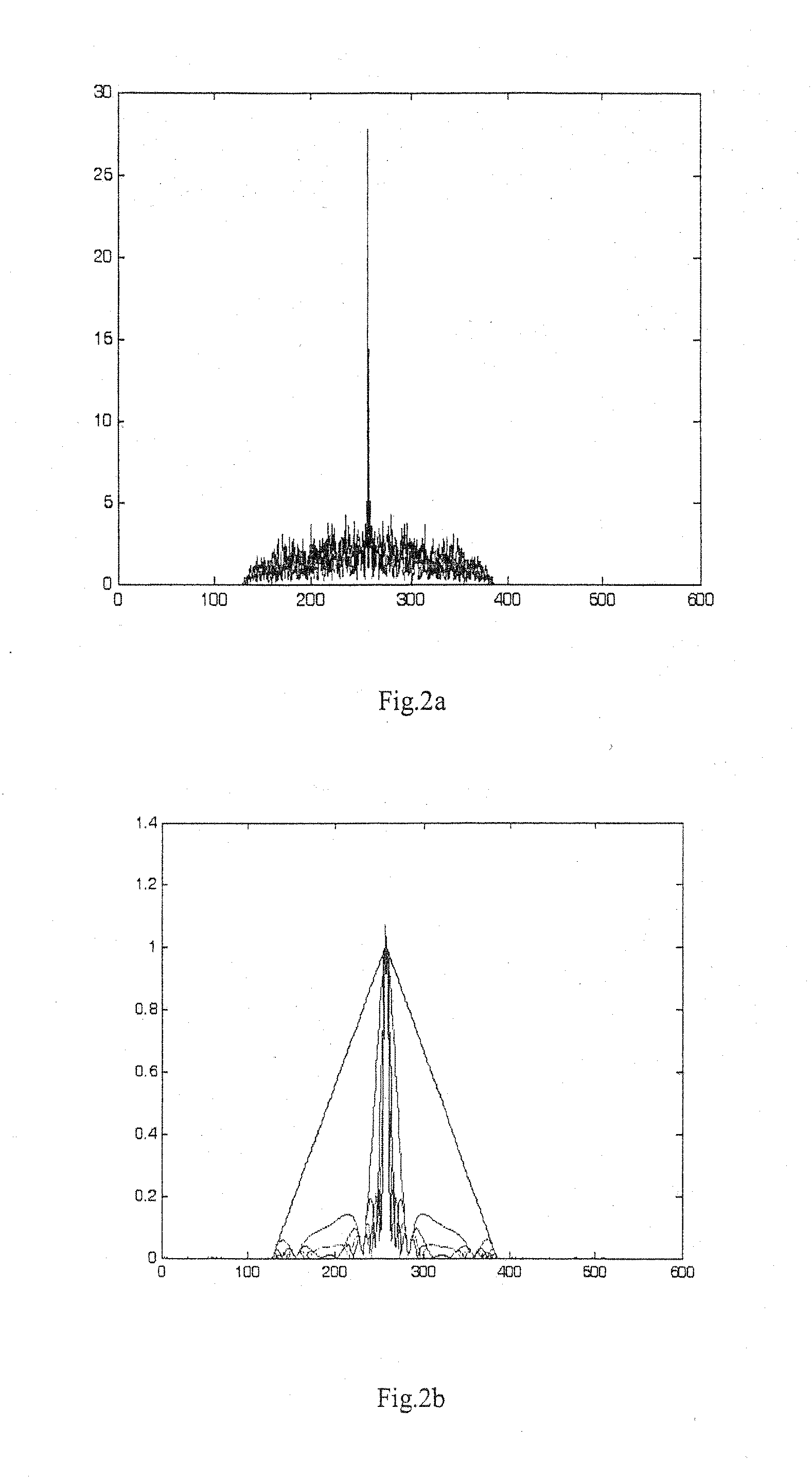
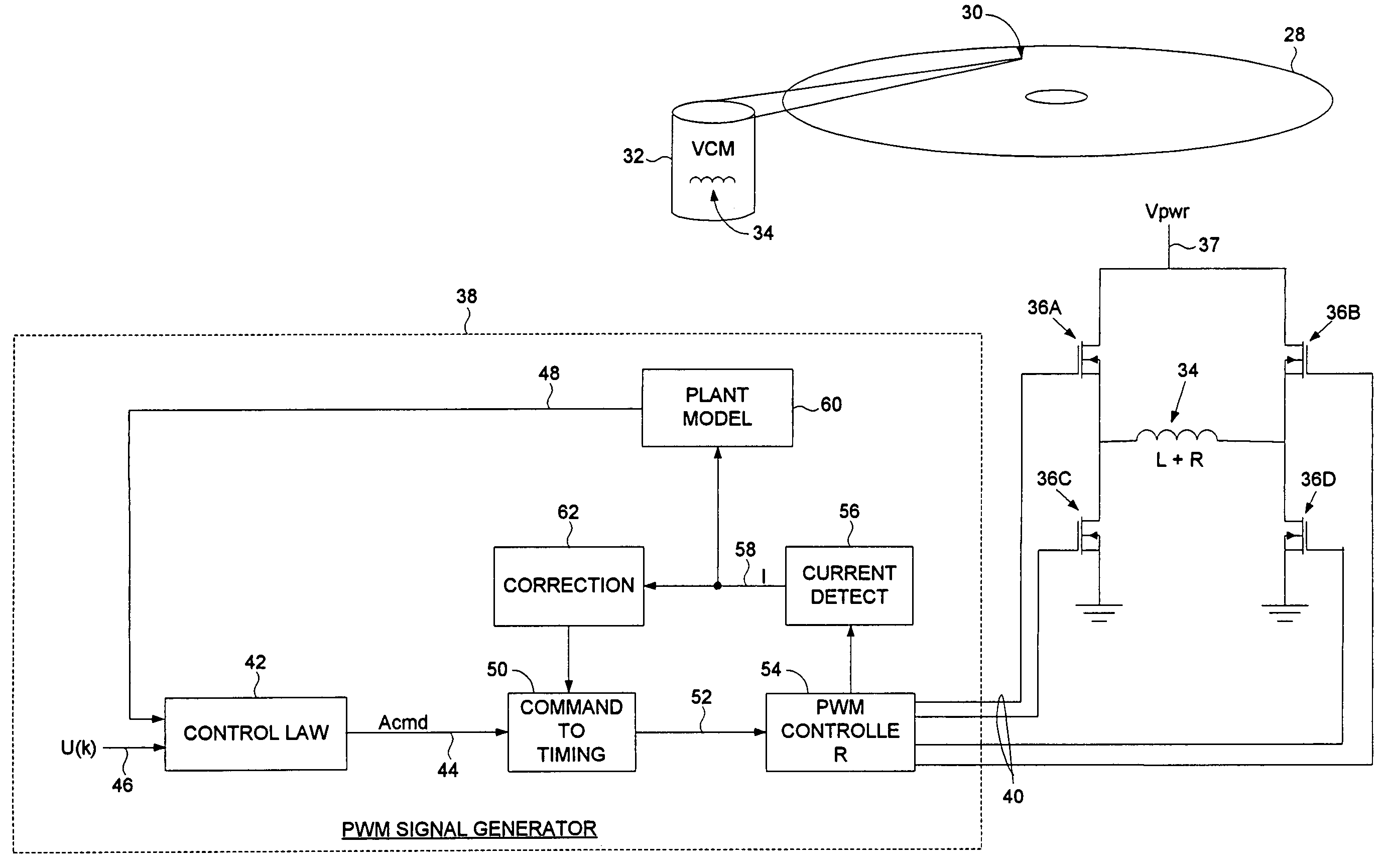
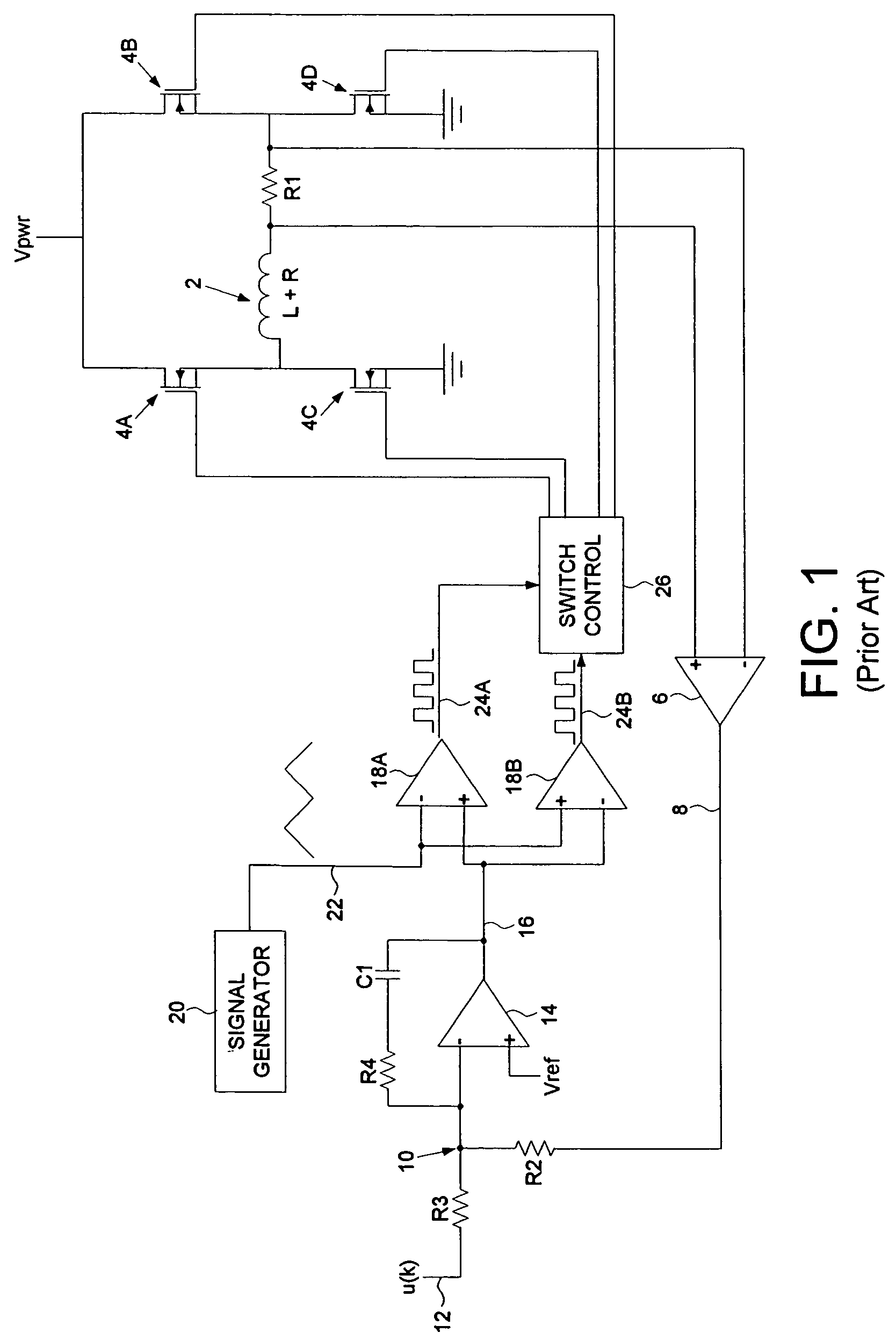
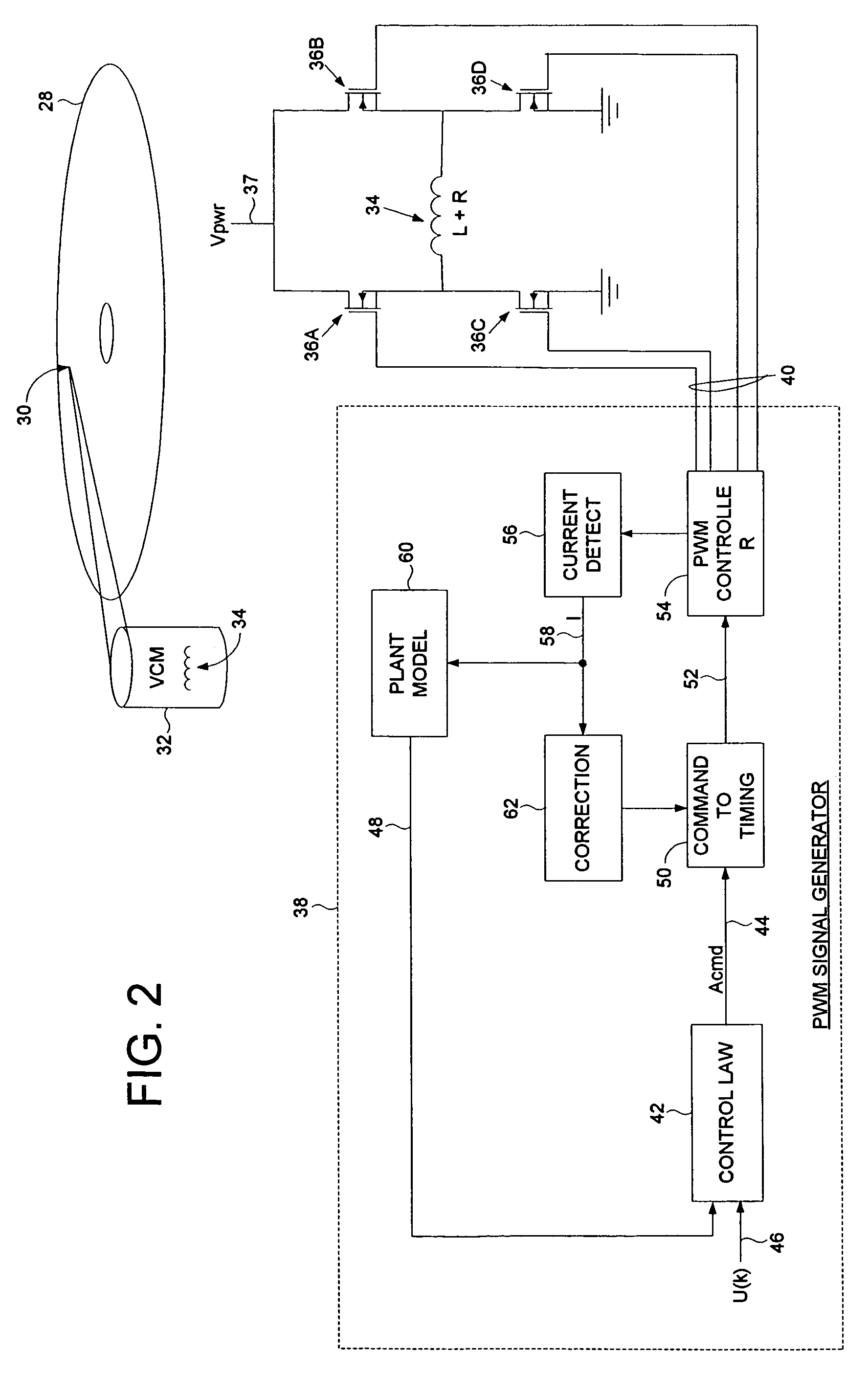
Disk drive pulse width modulating a voice coil motor using model reference current feedback
InactiveUS7209321B1Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksReference currentElectric machine
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a voice coil motor (VCM) driven in a PWM mode using model reference current feedback. The PWM circuitry and VCM form a plant transfer function which varies with changes to the plant characteristics, such as the resistance of the voice coil fluctuating with temperature drift. A plant model having a model transfer function generates an estimated state of the VCM in response to a detected current flowing through the voice coil. A correction block, responsive to the detected current, adjusts PWM timing signals so that the plant transfer function substantially matches the model transfer function.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
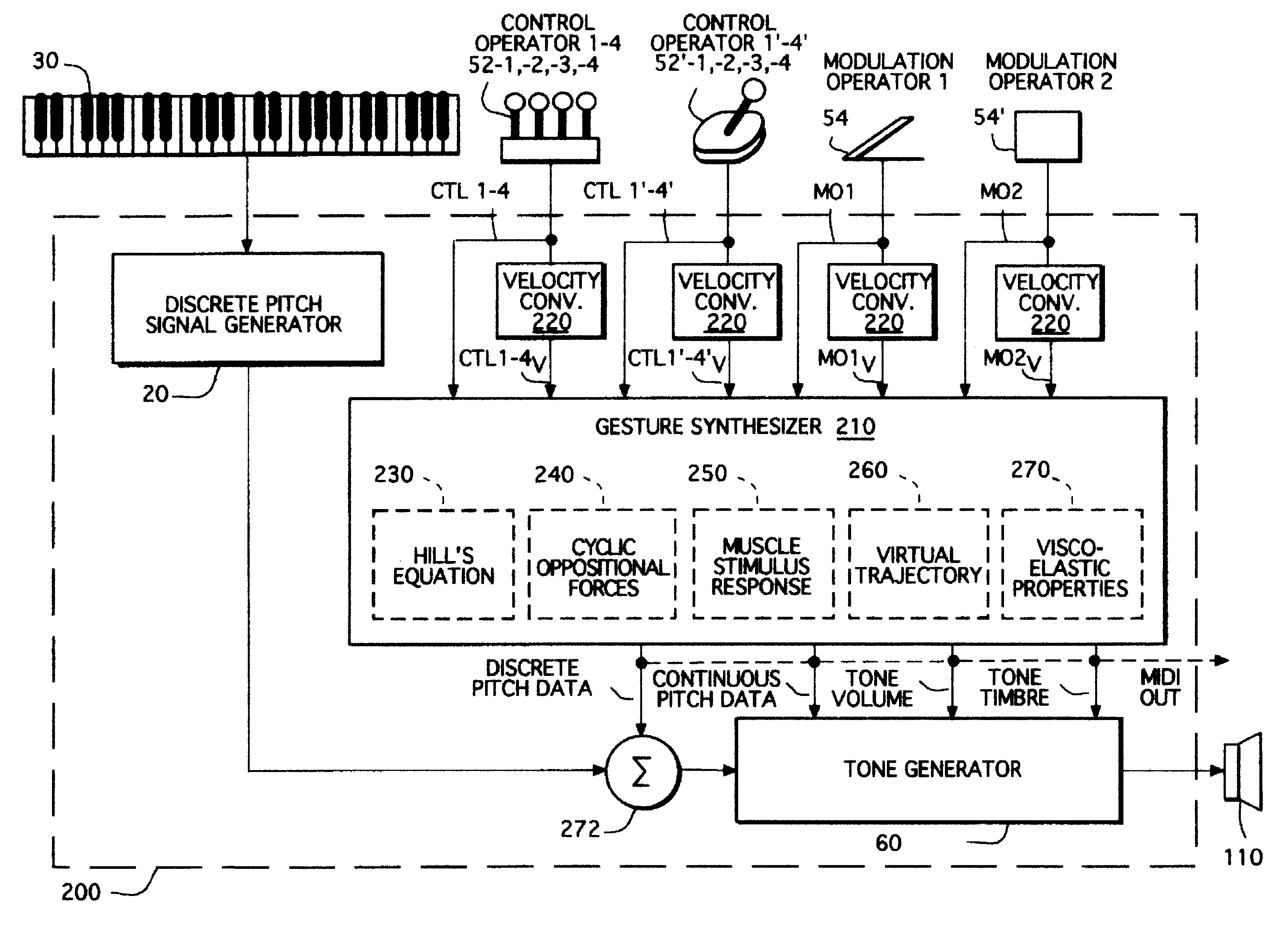
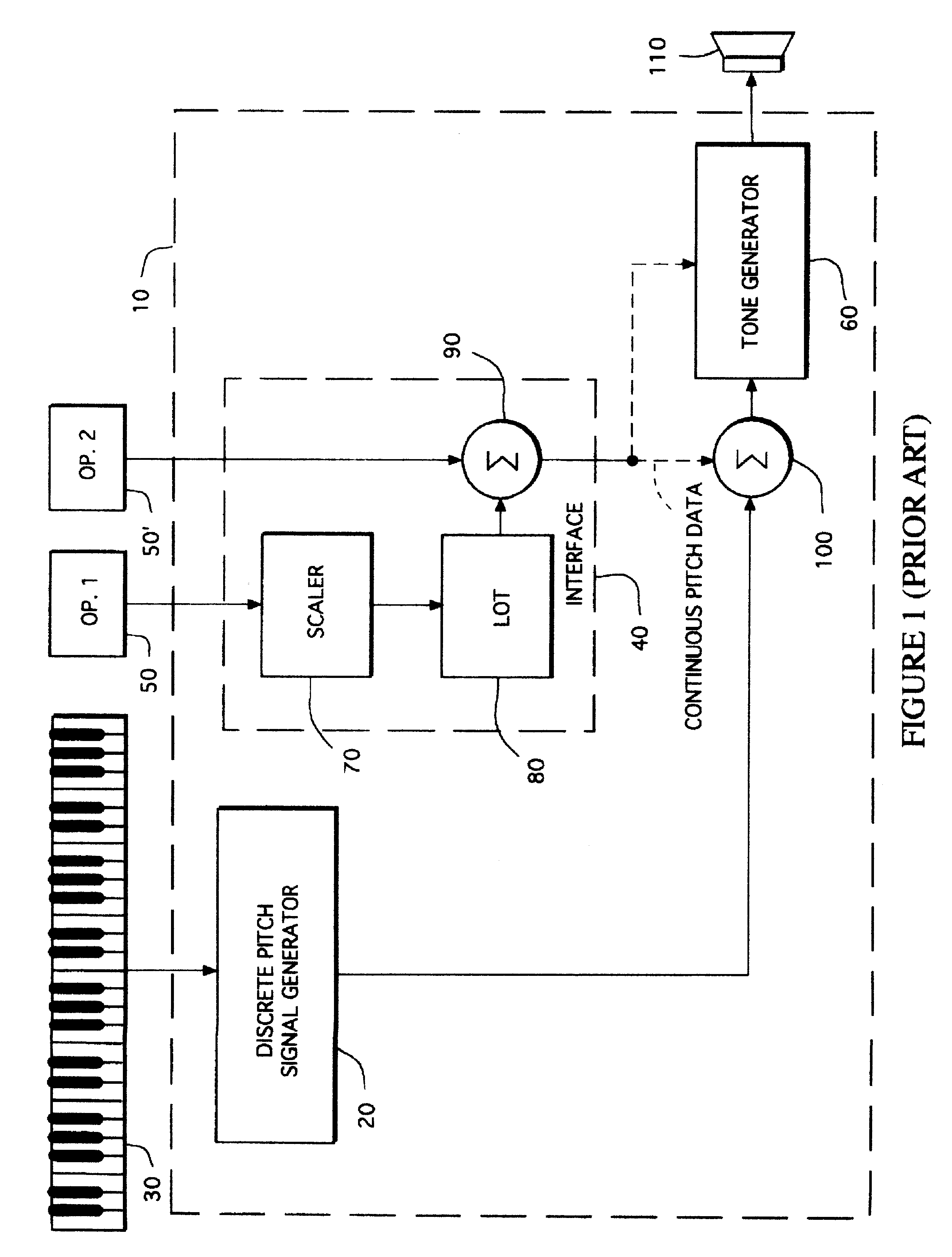
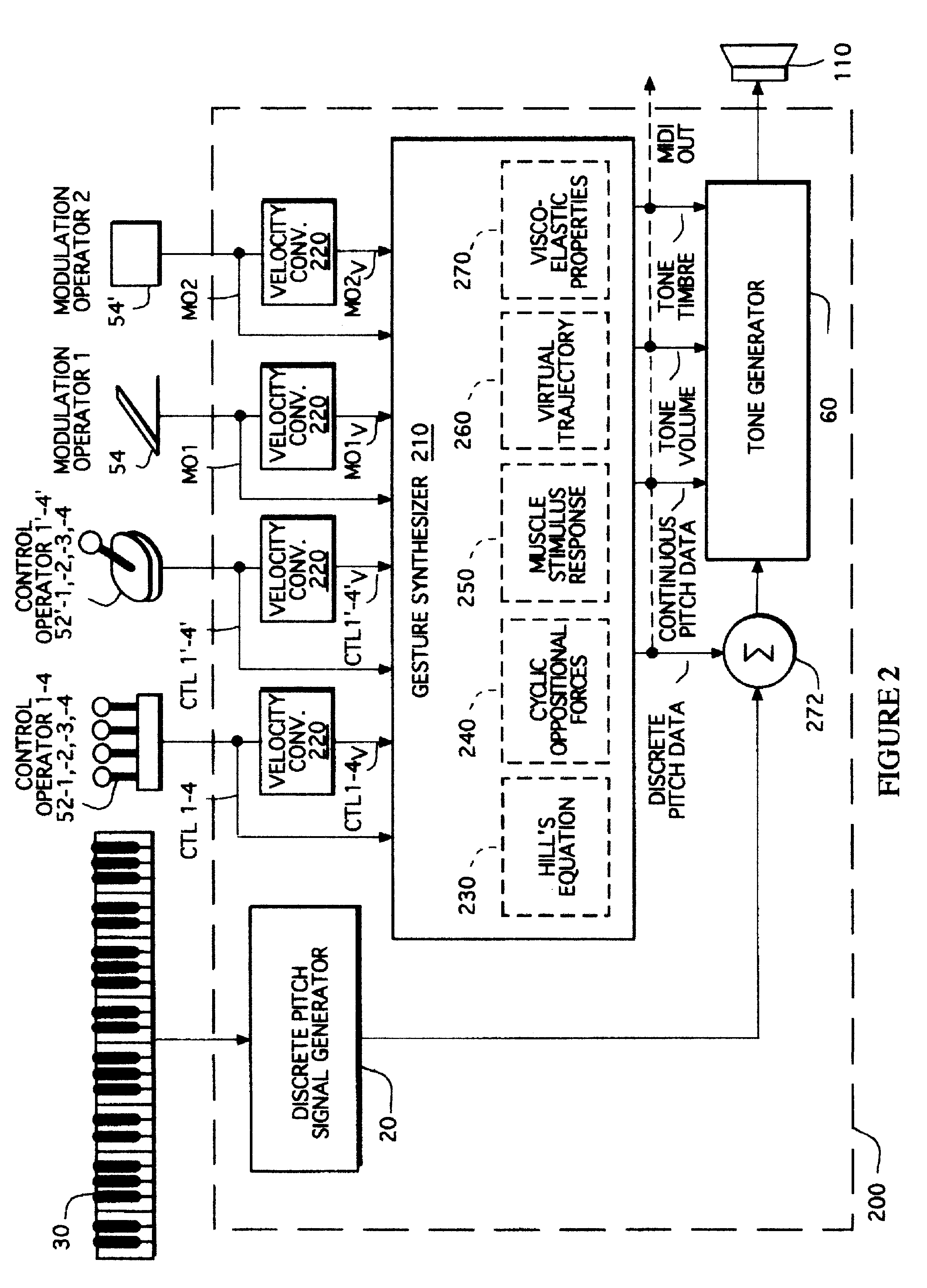
Gesture synthesizer for electronic sound device
InactiveUSRE37654E1Modifies musical gestureElectrophonic musical instrumentsLinear/angular speed measurementMuscle responseElectrical impulse
A MIDI-compatible gesture synthesizer is provided for use with a conventional music synthesizer to create musically realistic<DEL-S DATE="20020416" ID="DEL-S-00001" / >ally<DEL-E ID="DEL-S-00001" / > sounding gestures. The gesture synthesizer is responsive to one or more user controllable input signals, and includes several transfer function models that may be user-selected. One transfer function models properties of muscles using Hill's force-velocity equation to describe the non-linearity of muscle activation. A second transfer function models the cyclic oscillation produced by opposing effects of two force sources representing the cyclic oppositional action of muscle systems. A third transfer function emulates the response of muscles to internal electrical impulses. A fourth transfer function provides a model representing and altering virtual trajectory of gestures. A fifth transfer function models visco-elastic properties of muscle response to simulated loads. The gesture synthesizer outputs <DEL-S DATE="20020416" ID="DEL-S-00002" / >MIDI-compatible<DEL-E ID="DEL-S-00002" / > continuous pitch data, tone volume and tone timbre information. The continuous pitch data is combined with discrete pitch data provided by the discrete pitch generator within the conventional synthesizer, and the combined signal is input to a tone generator, along with the tone volume and tone timbre information. The tone generator outputs tones that are user-controllable in real time during performance of a musical gesture.
Owner:LONGO NICHOLAS
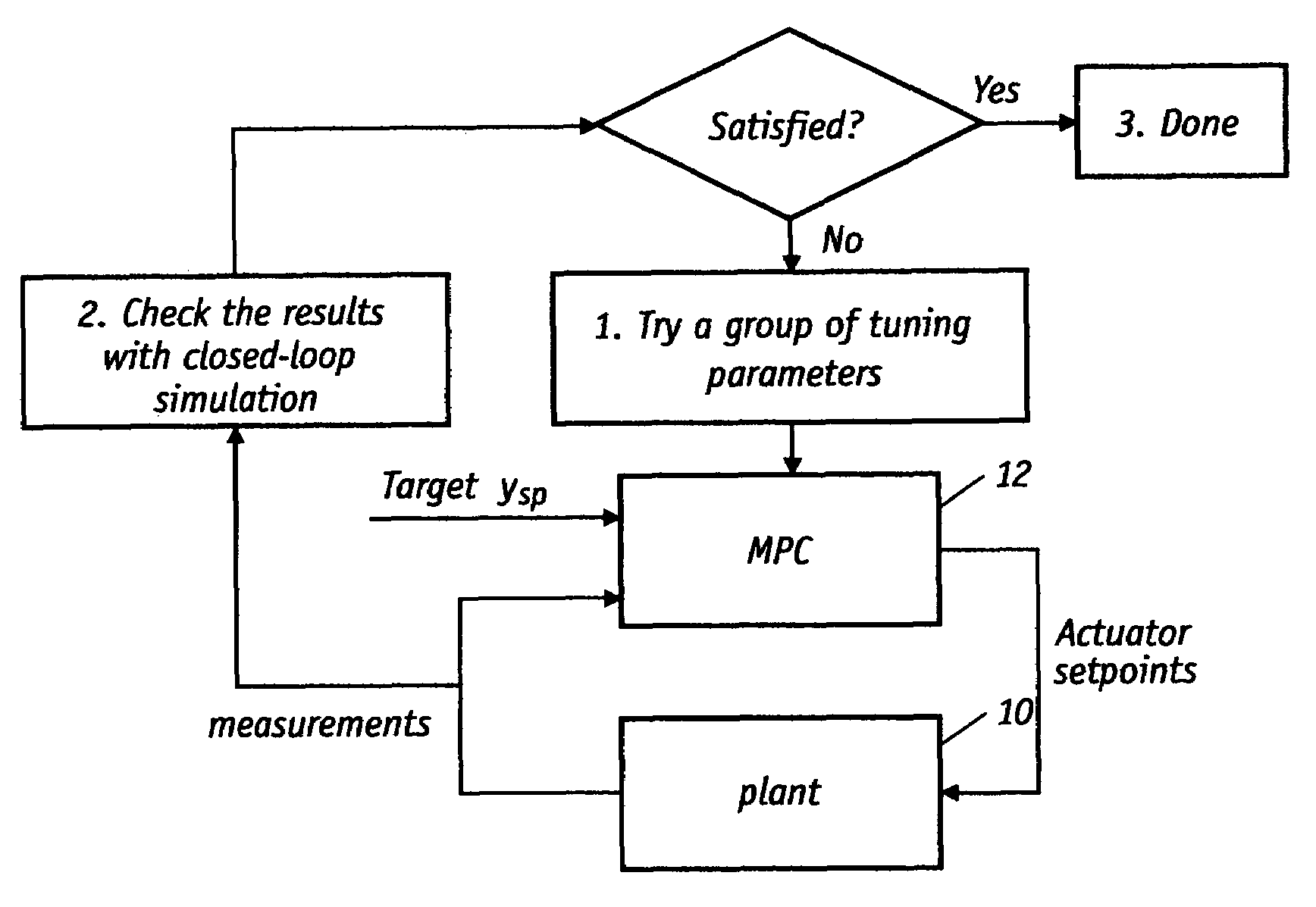
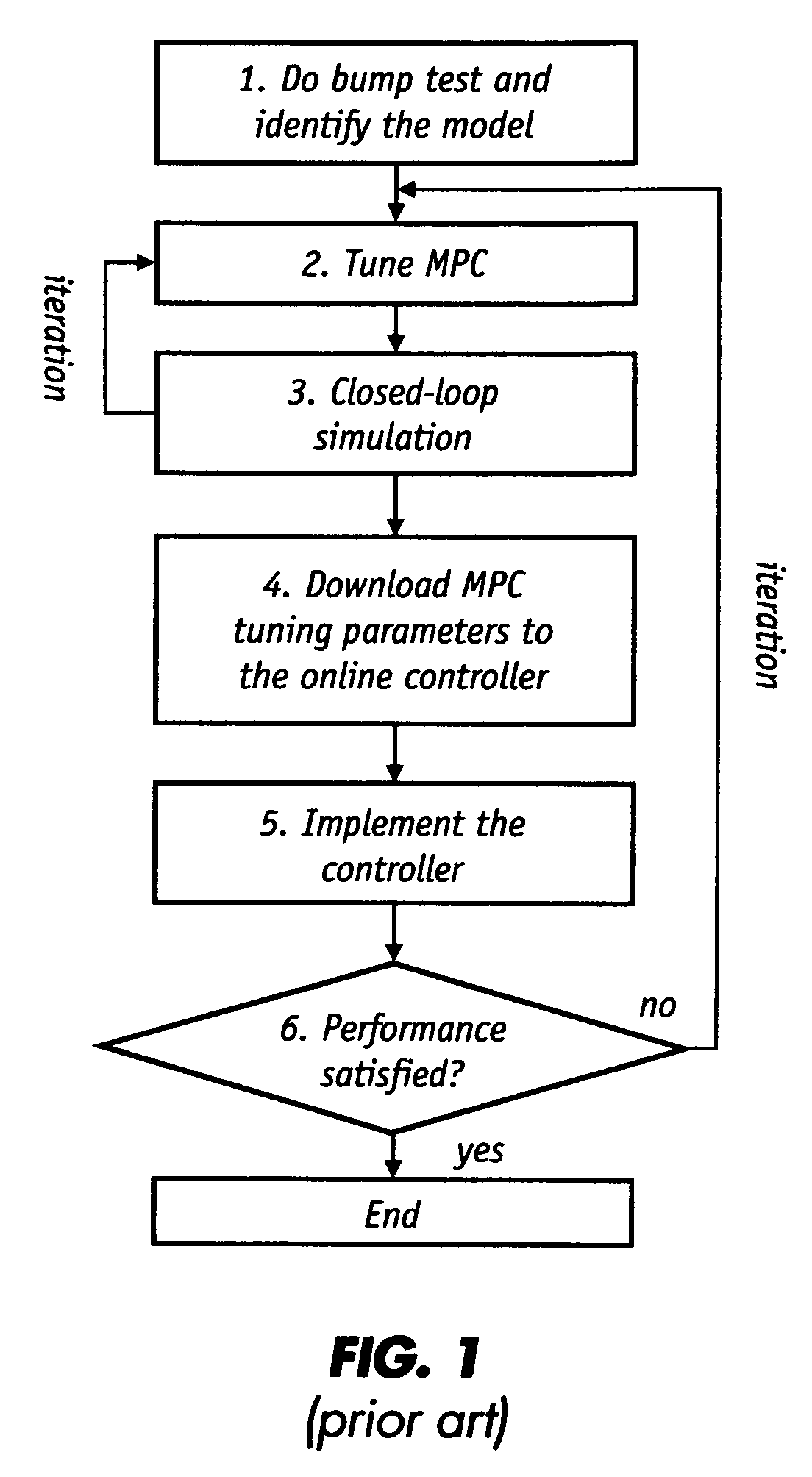
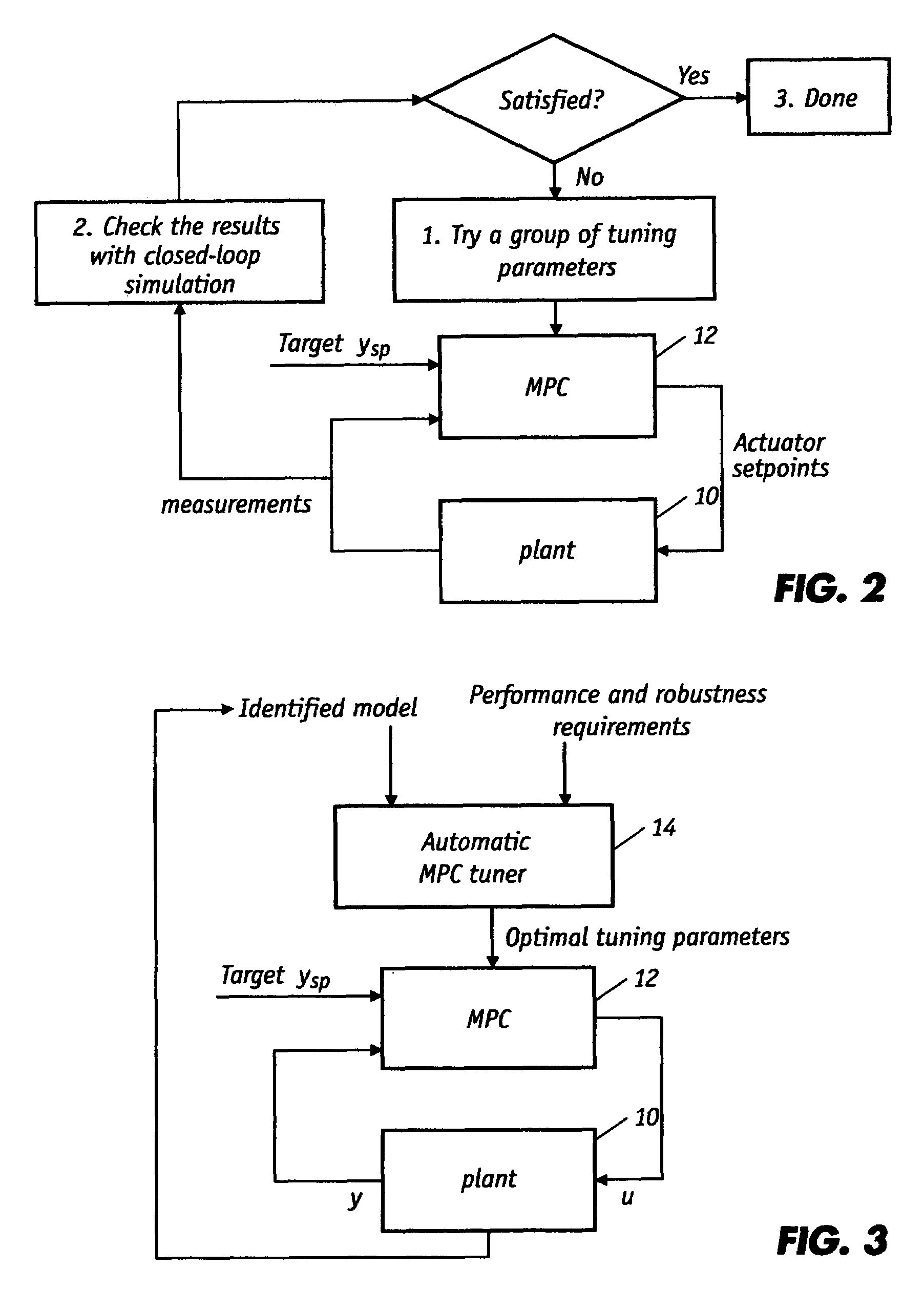
Automatic tuning method for multivariable model predictive controllers
ActiveUS7577483B2Fast and reliableDigital computer detailsElectric controllersRobustificationPredictive controller
A fast and reliable technique for tuning multivariable model predictive controllers (MPCs) that accounts for performance and robustness is provided. Specifically, the technique automatically yields tuning weights for the MPC based on performance and robustness requirements. The tuning weights are parameters of closed-loop transfer functions which are directly linked to performance and robustness requirements. Automatically searching the tuning parameters in their proper ranges assures that the controller is optimal and robust. This technique will deliver the traditional requirements of stability, performance and robustness, while at the same time enabling users to design their closed-loop behavior in terms of the physical domain. The method permits the user to favor one measurement over another, or to use one actuator more than another.
Owner:HONEYWELL ASCA INC
Method for the use of and interaction with business system transfer functions
A method for using and interacting with mathematical or algorithmic business system transfer functions in support of a business information, analysis, decisioning and control system. The method includes developing at least one high-level business system view wherein the transfer function is configured to quantitatively express the business system view; identifying a number of input parameters associated with one or more of the resources used in the business process, identifying at least one output parameter associated with the operation of the business process; collecting operational data that associate the number of input parameters with the at least one output parameter based on an actual operation of the business process. The method also includes a primary display layer that presents a control scenario for a testbed environment for the business information and decisioning control system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
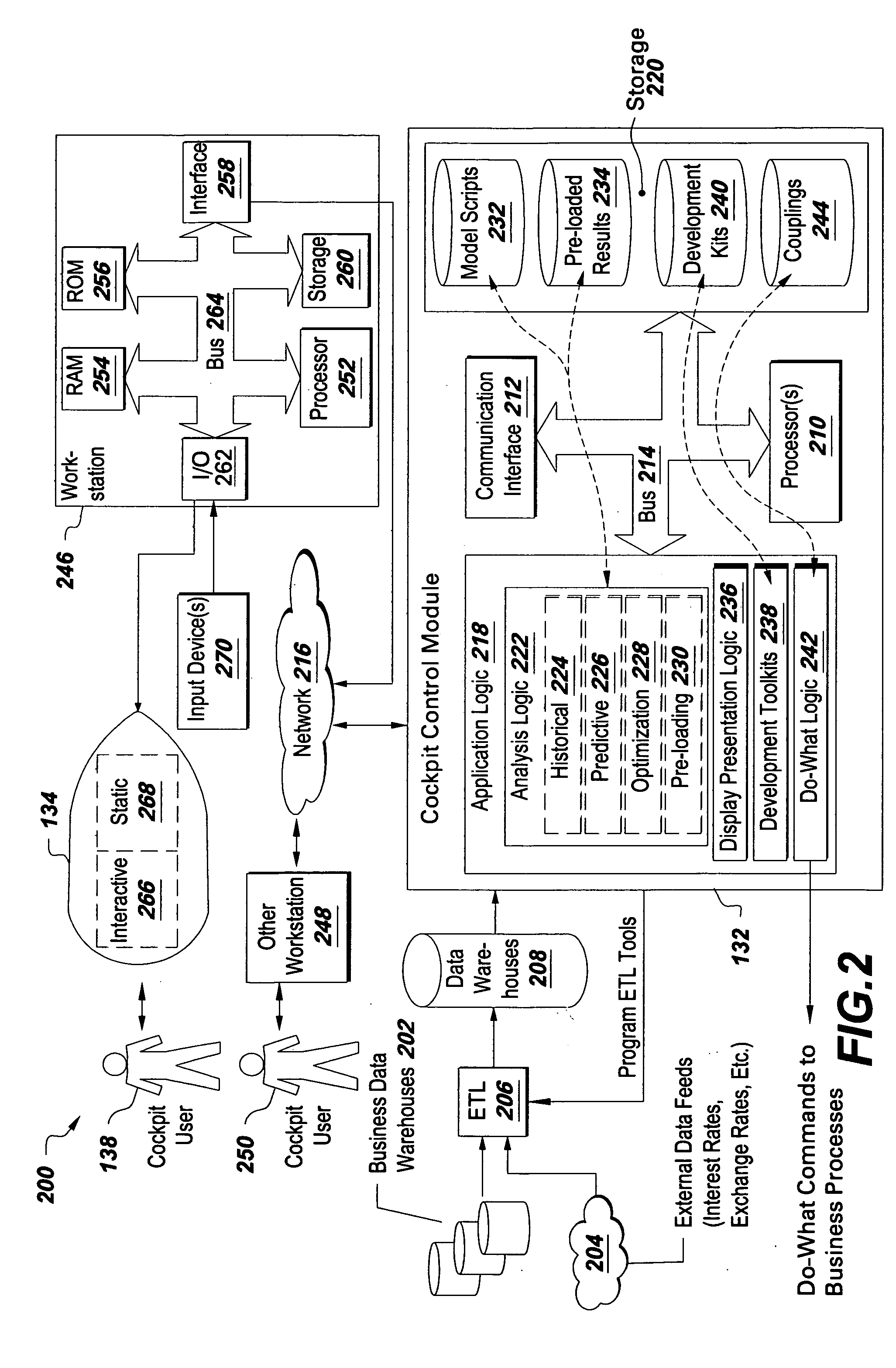
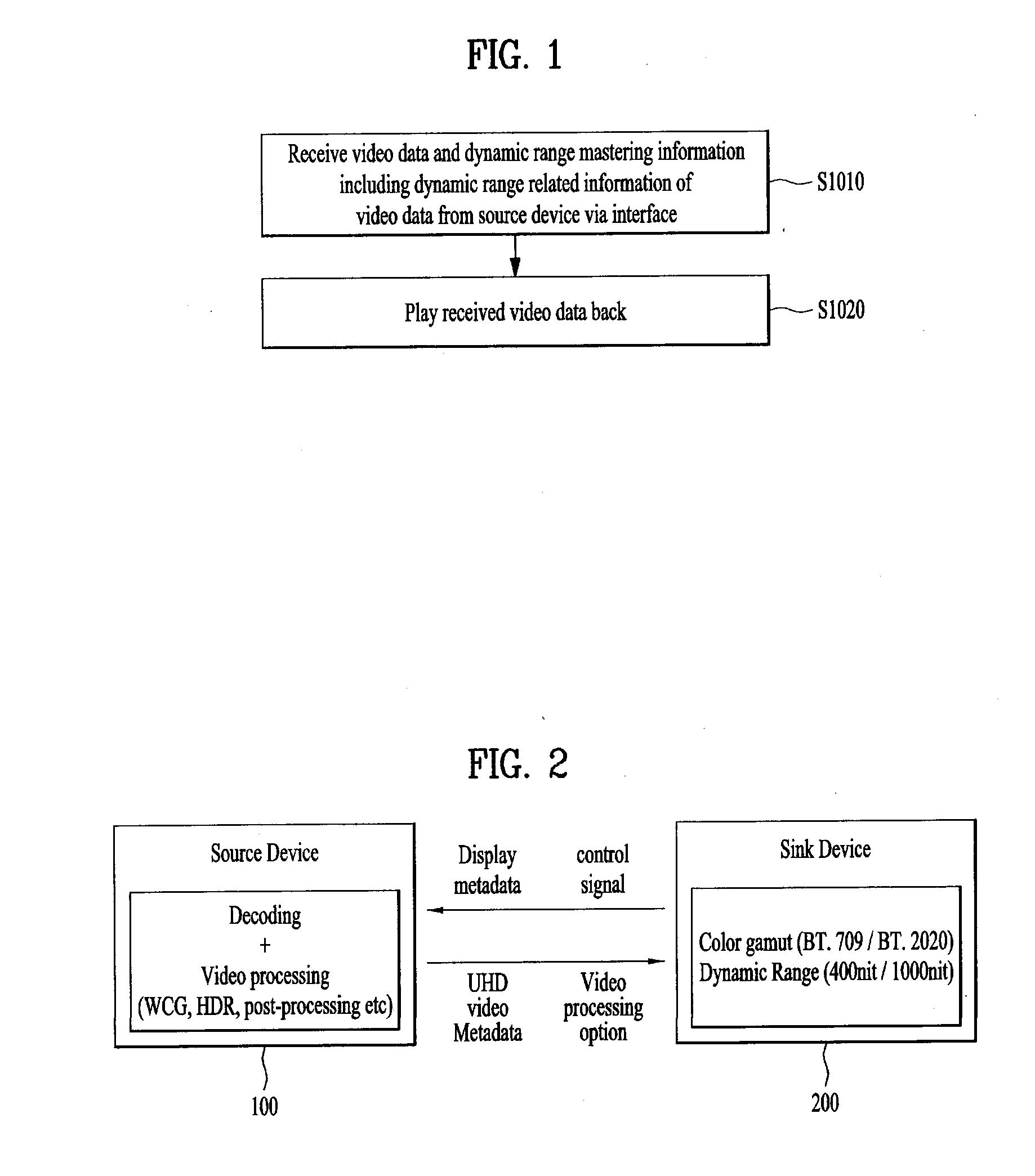
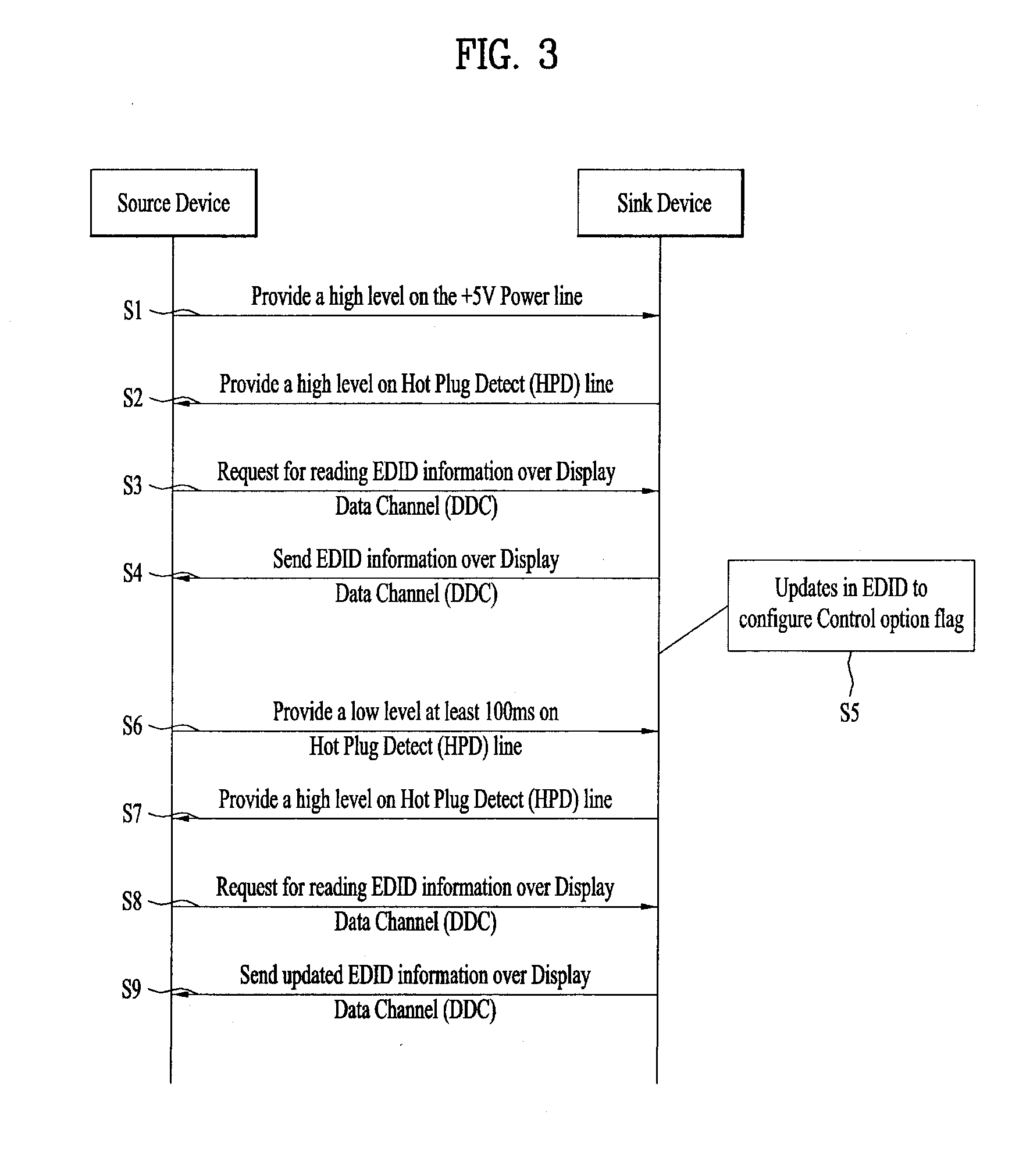
Video data processing method and device for display adaptive video playback
ActiveUS20150341611A1Optimally view contentReduce brightnessTelevision system detailsColor television signals processingComputer graphics (images)Adaptive video
A video data processing method and / device for display adaptive video playback are disclosed. The video data processing method includes receiving video data and dynamic range mastering information including dynamic range related information of the video data from a source device via an interface, and playing the received video data back. The dynamic range mastering information includes electro optical transfer function, EOTF, type information for identifying an EOTF used for the video data.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
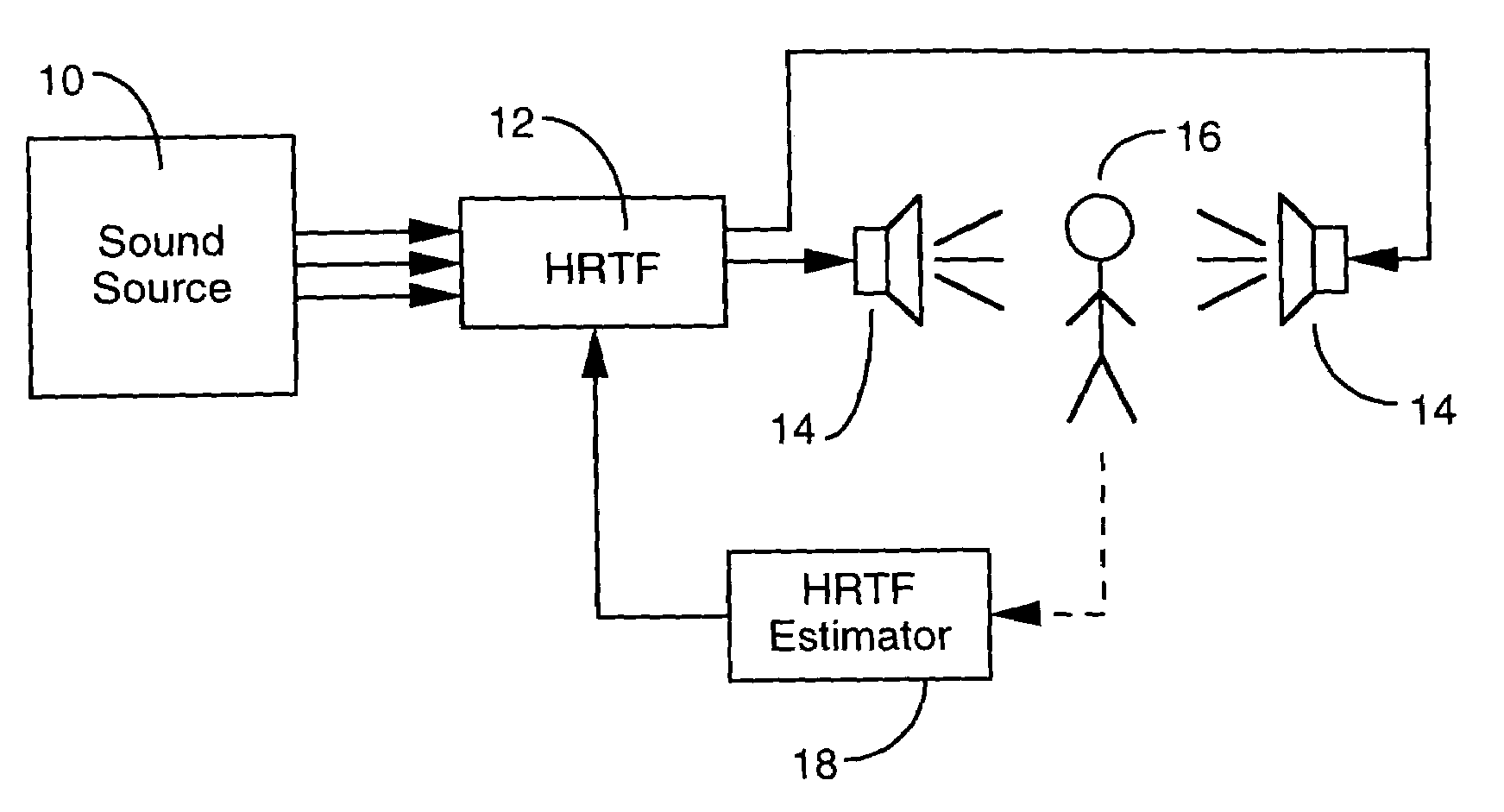
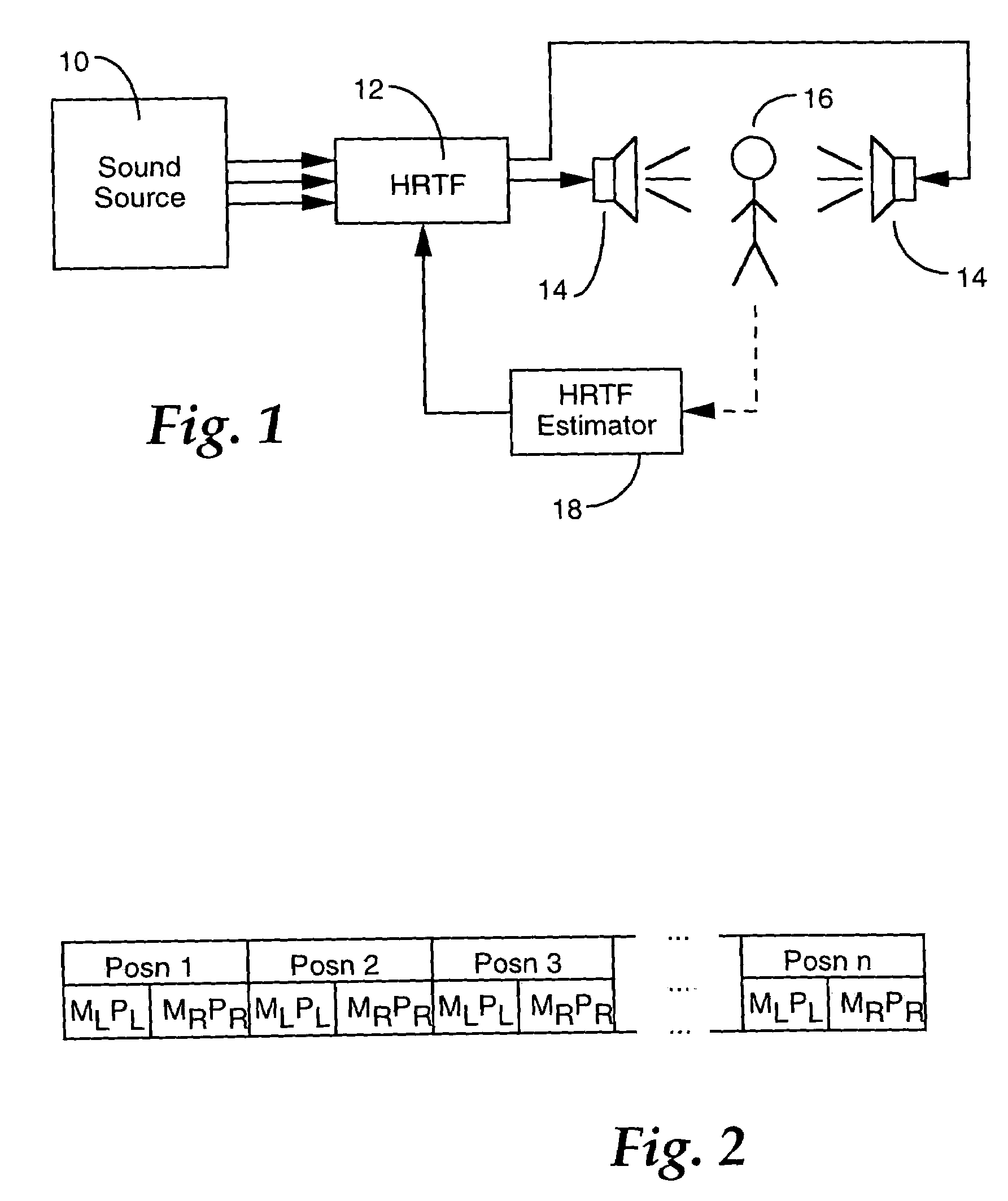
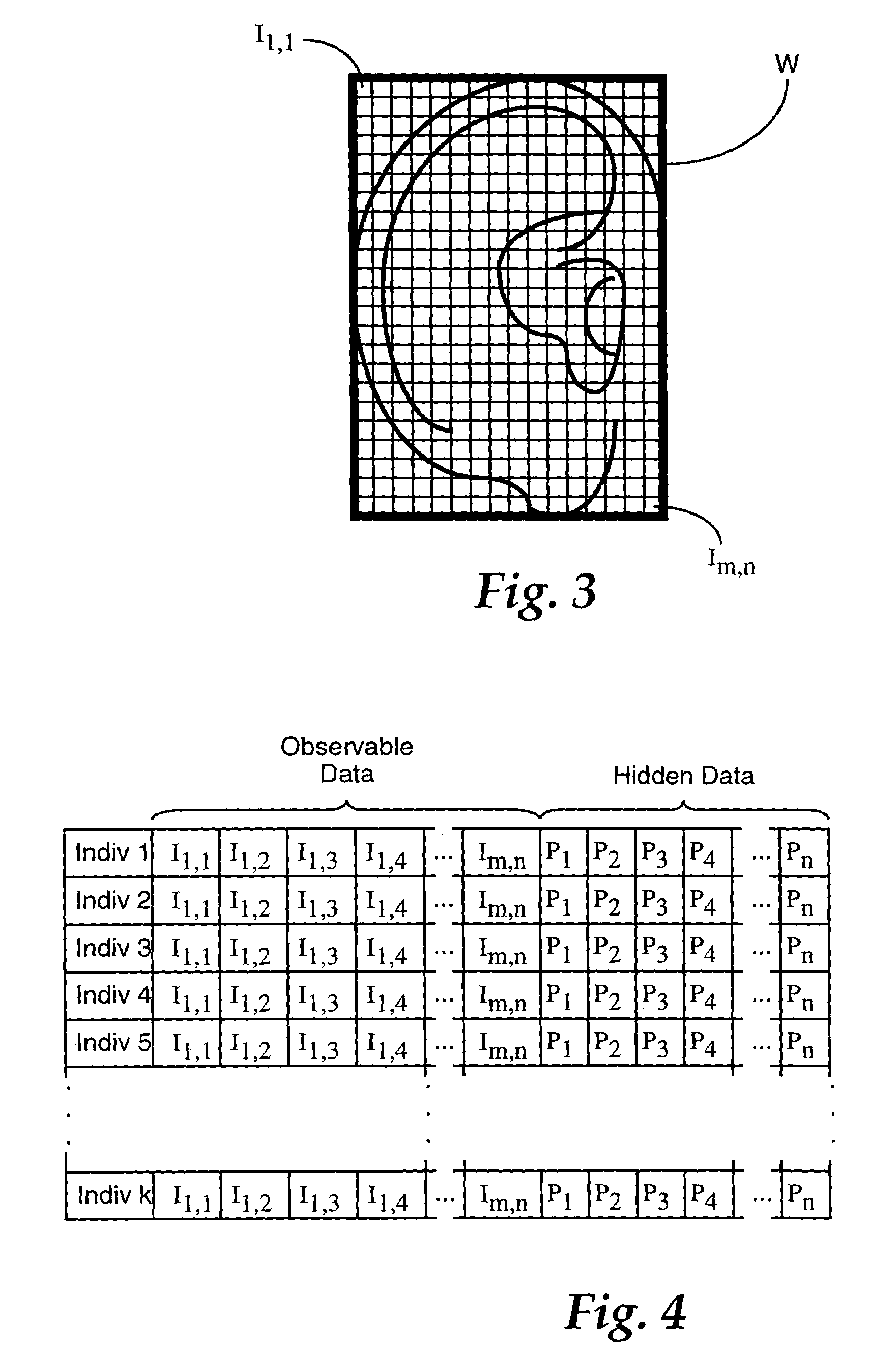
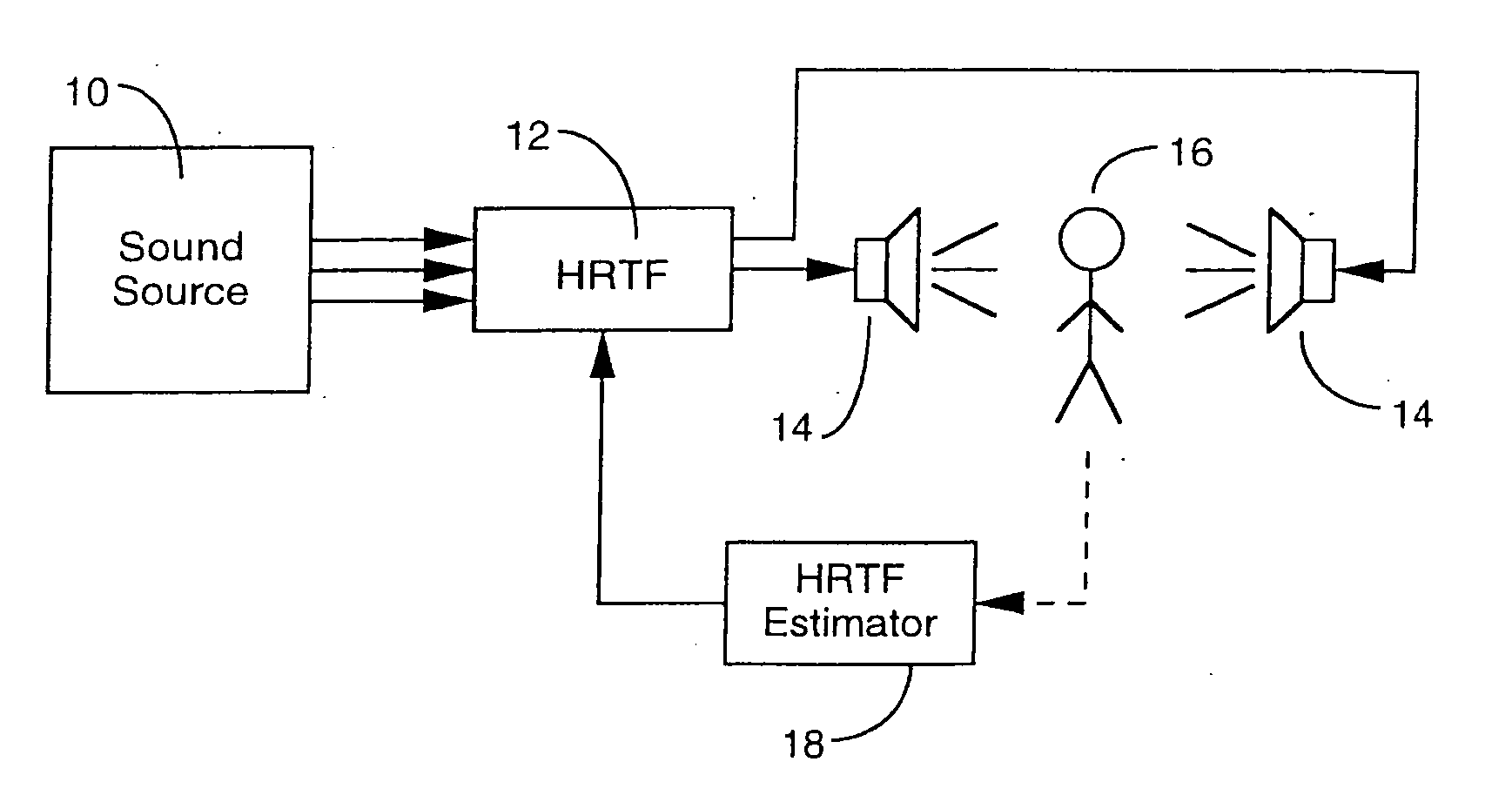
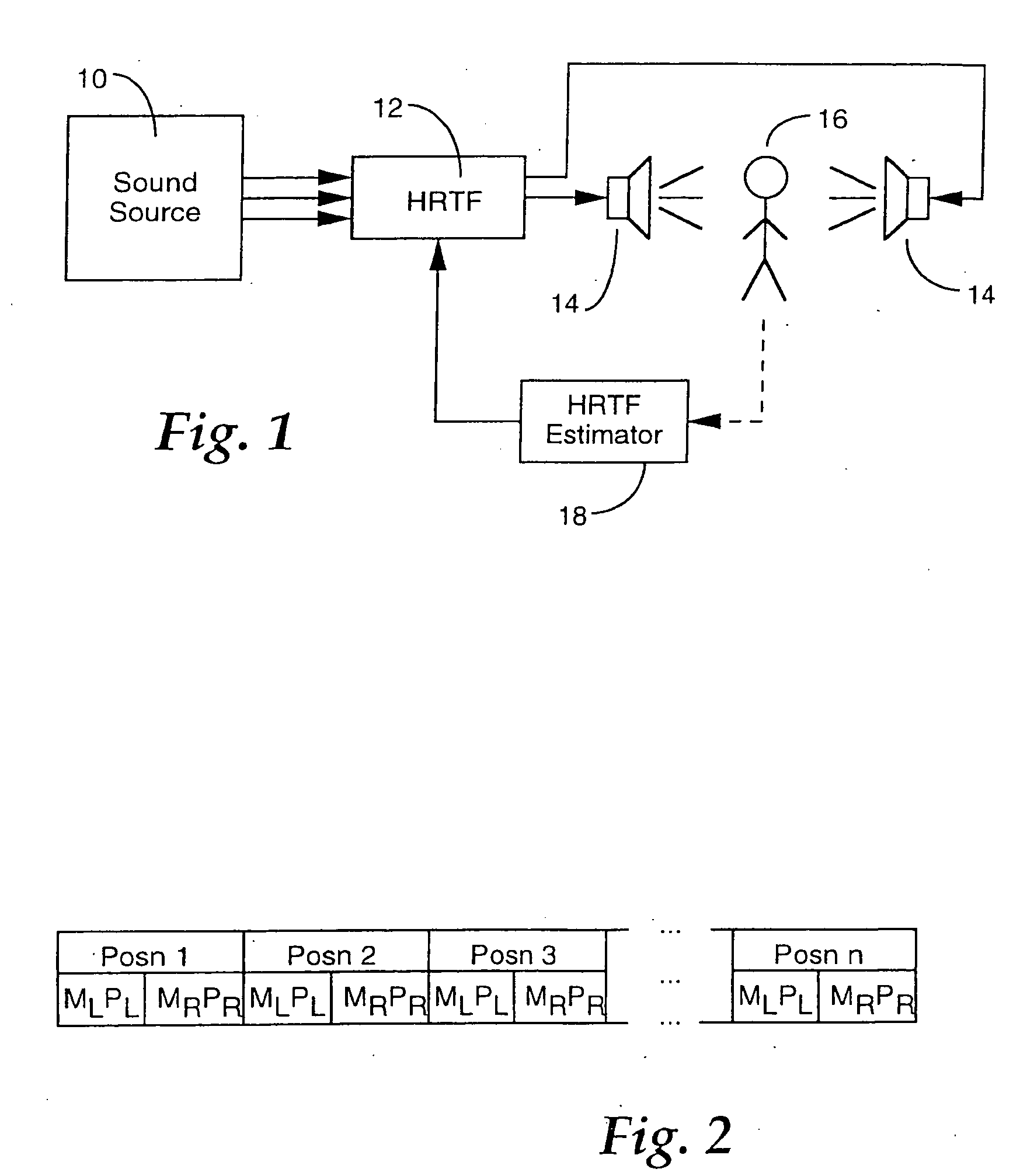
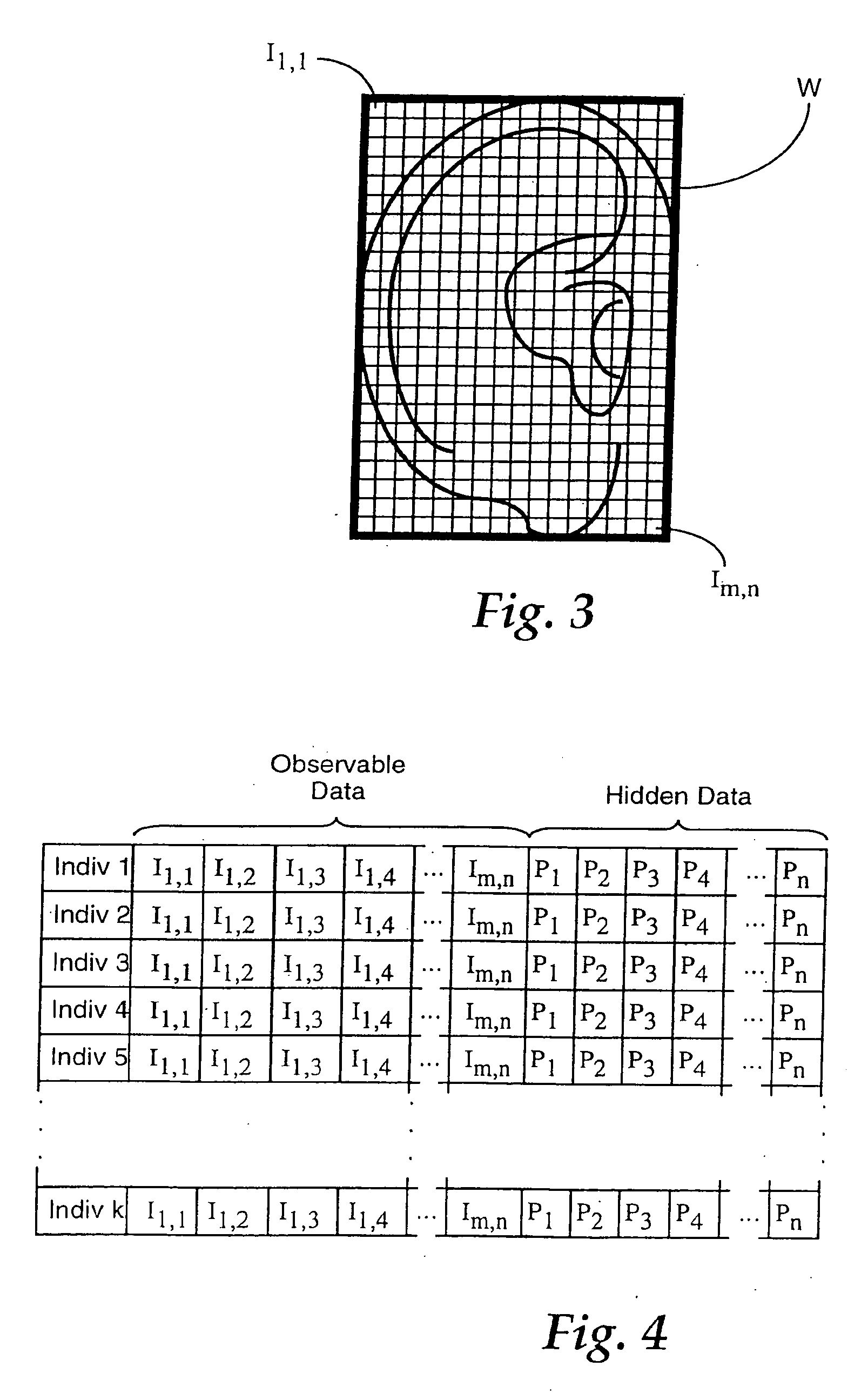
Estimation of head-related transfer functions for spatial sound representative
InactiveUS6996244B1Two-channel systemsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsOptical transfer functionTransfer function
The estimation of an HRTF for a given individual is accomplished by means of a coupled model, which identifies the dependencies between one or more images of readily observable characteristics of an individual, and the HRTF that is applicable to that individual. Since the HRTF is highly influenced by the shape of the listener's outer ear, as well as the shape of the listener's head, images of a listener which provides this type of information are preferably applied as an input to the coupled model. In addition, dimensional measurements of the listener can be applied to the model. In return, the model provides an estimate of the HRTF for the observed characteristics of the listener.
Owner:INTERVAL RESEARCH CORPORATION
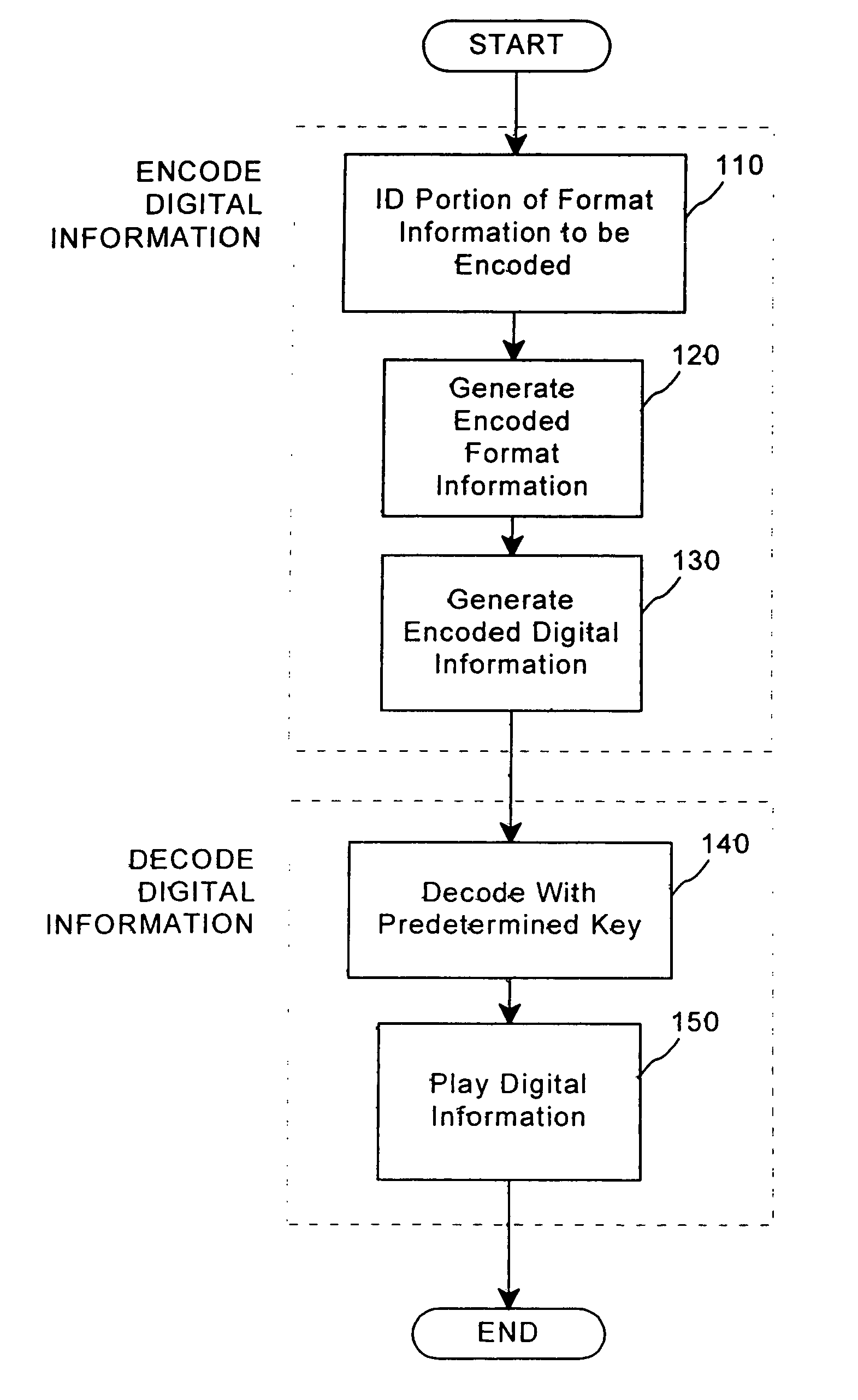
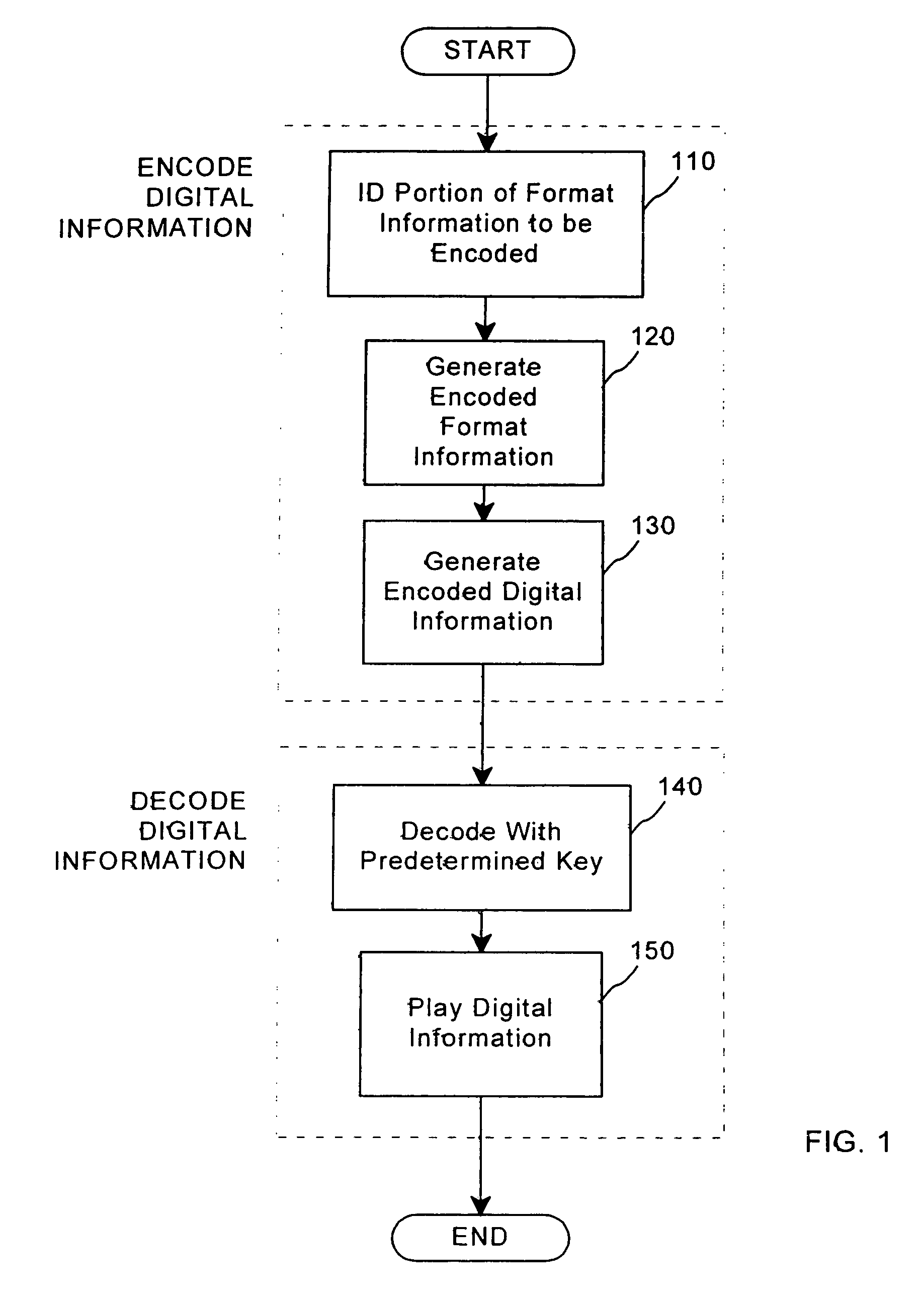
Method for combining transfer functions with predetermined key creation
InactiveUS7664263B2Data stream serial/continuous modificationDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwareGranularity
A method for combining transfer functions with predetermined key creation. In one embodiment, digital information, including a digital sample and format information, is protected by identifying and encoding a portion of the format information. Encoded digital information, including the digital sample and the encoded format information, is generated to protect the original digital information. In another embodiment, a digital signal, including digital samples in a file format having an inherent granularity, is protected by creating a predetermined key. The predetermined key is comprised of a transfer function-based mask set to manipulate data at the inherent granularity of the file format of the underlying digitized samples.
Owner:WISTARIA TRADING INC
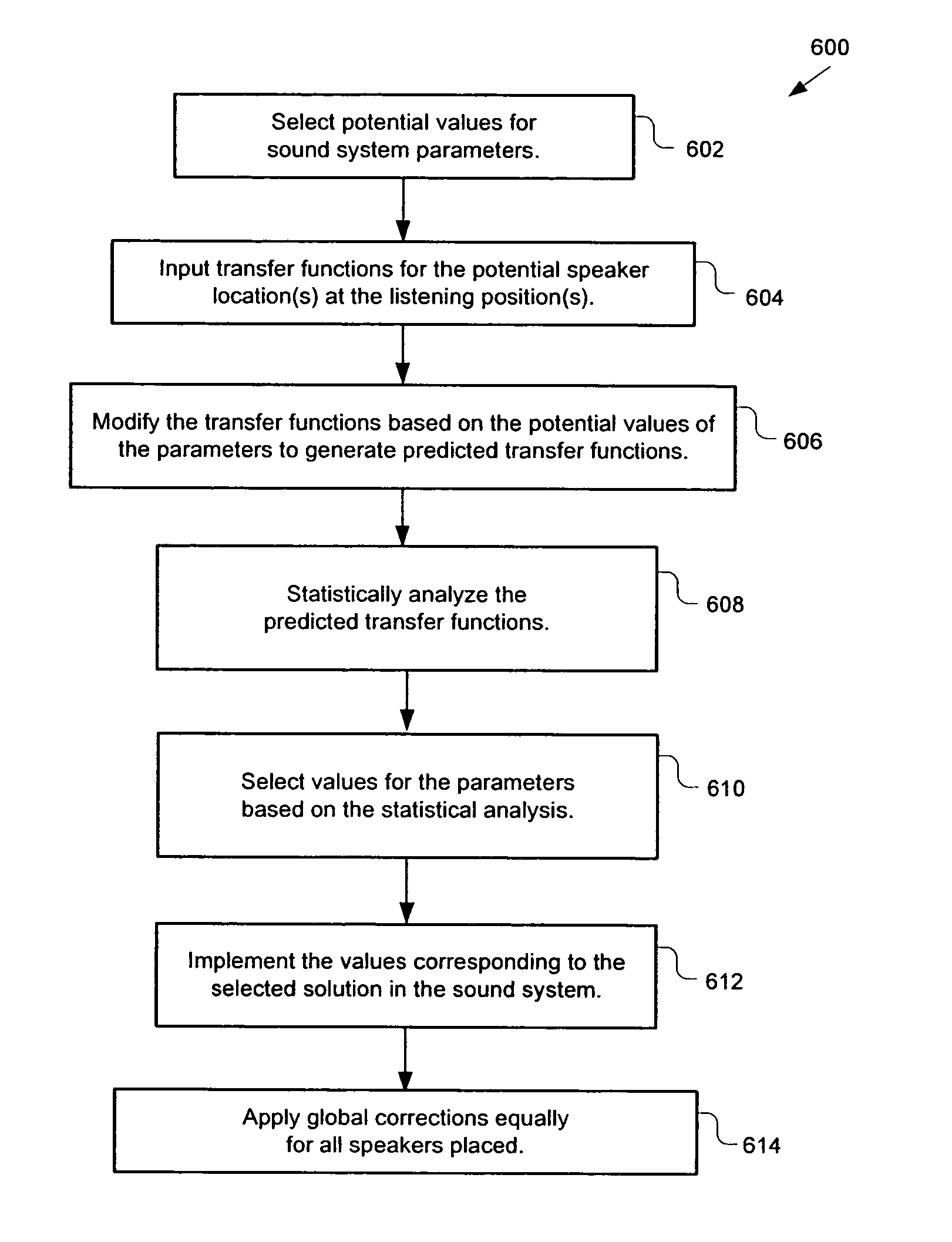
Statistical analysis of potential audio system configurations
ActiveUS20050031135A1Public address systemsStereophonic systemsStatistical analysisSystem configuration
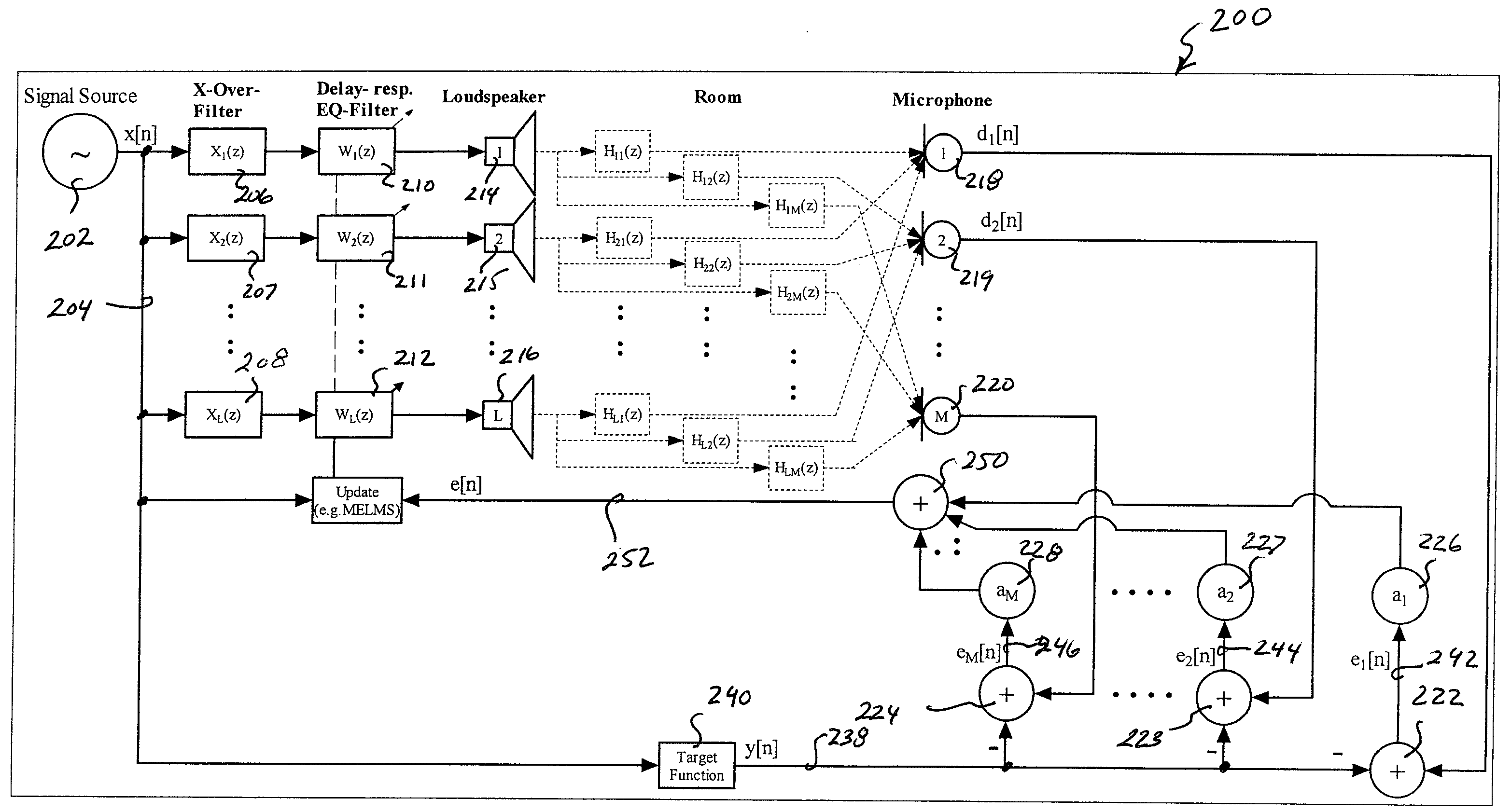
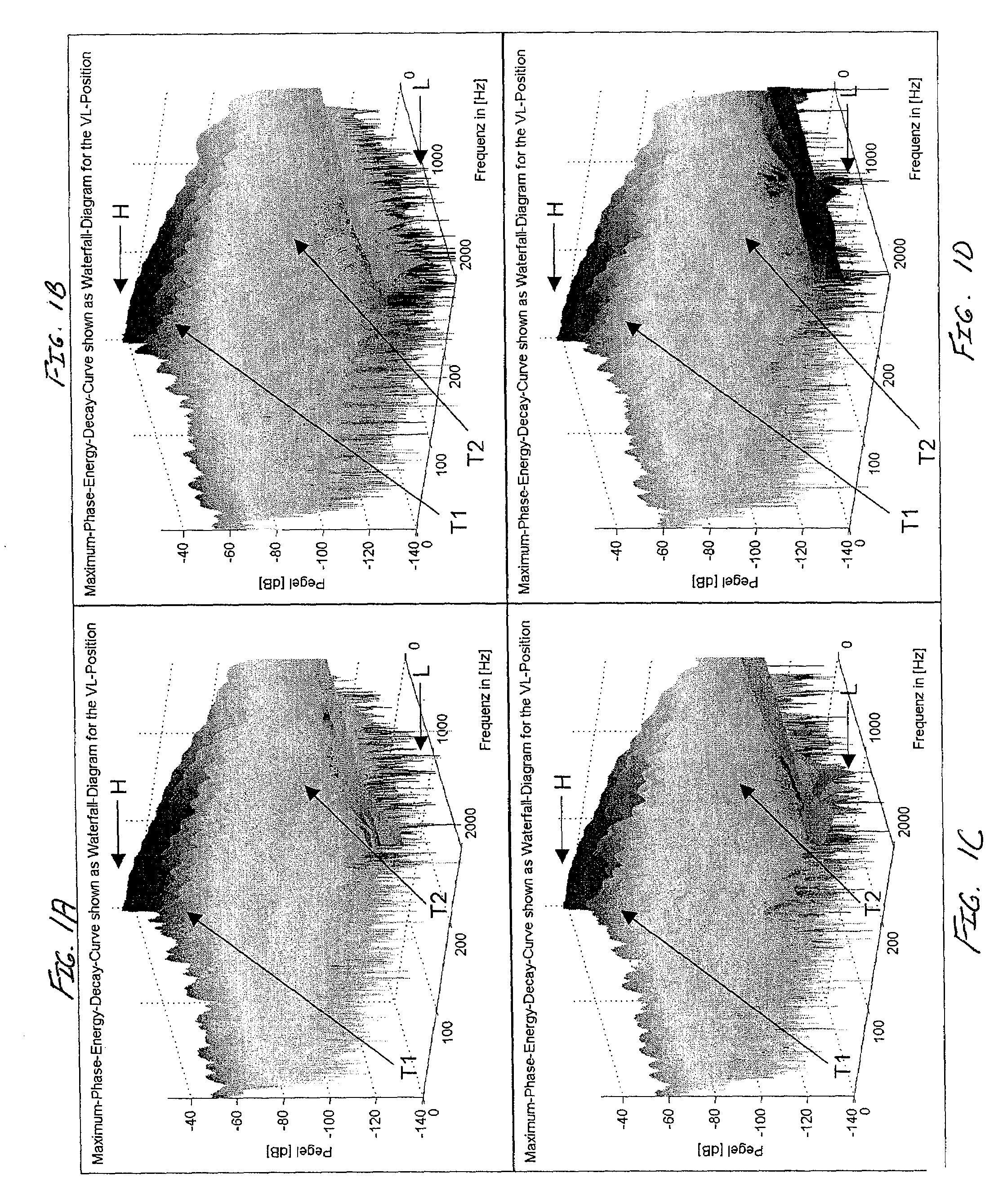
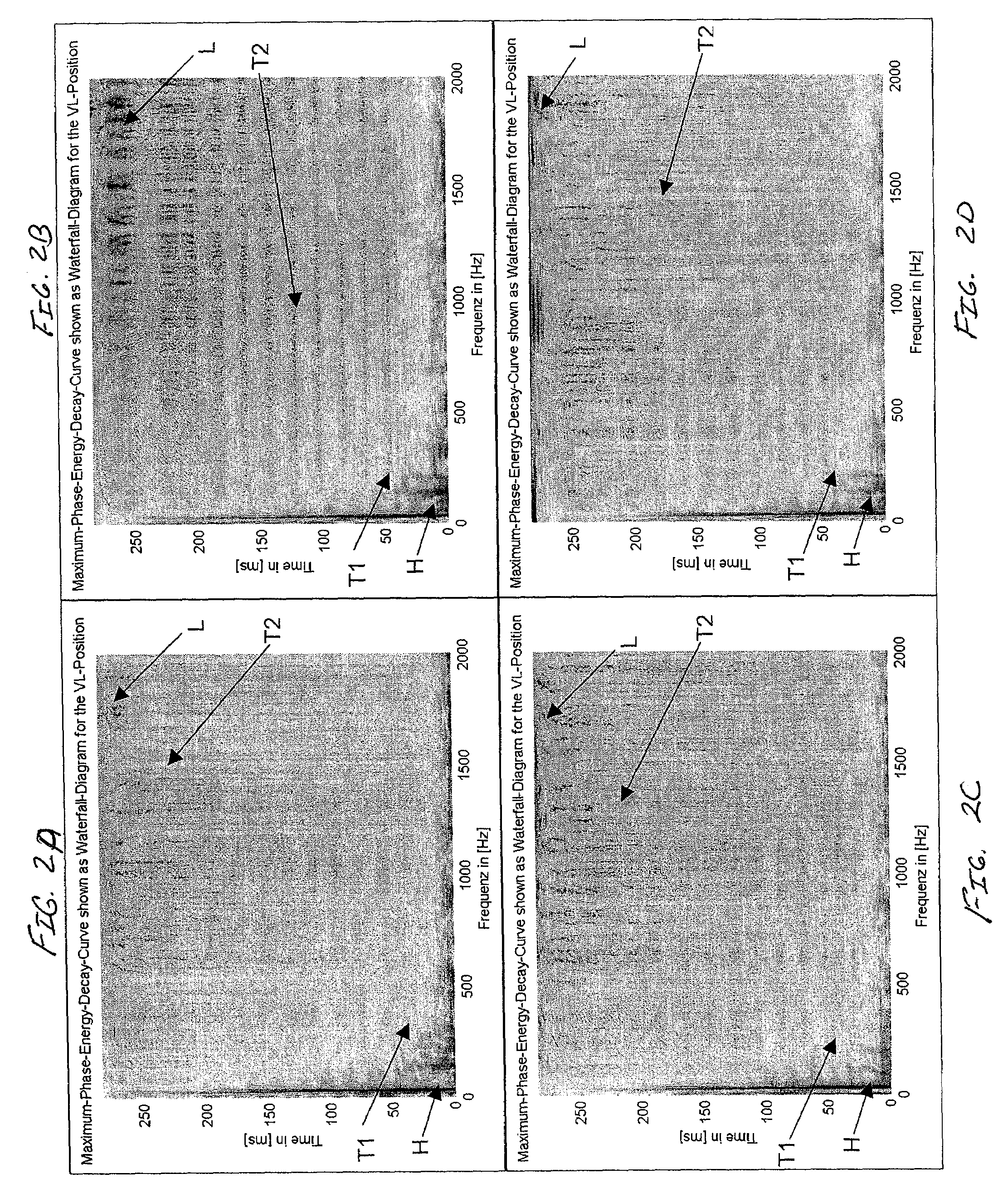
A system is provided for configuring an audio system for a given space. The system may statistically analyze potential configurations of the audio system to configure the audio system. The potential configurations may include positions of the loudspeakers, numbers of loudspeakers, types of loudspeakers, listening positions, correction factors, or any combination thereof. The statistical analysis may indicate at least one metric of the potential configuration including indicating consistency of predicted transfer functions, flatness of the predicted transfer functions, differences in overall sound pressure level from seat to seat for the predicted transfer functions, efficiency of the predicted transfer functions, or the output of predicted transfer functions. The system also provides a methodology for selecting loudspeaker locations, the number of loudspeakers, the types of loudspeakers, correction factors, listening positions, or a combination of these schemes in an audio system that has a single listening position or multiple listening positions.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Extended depth of field optical systems
InactiveUS7218448B1Increase depth of fieldMinimize impactCharacter and pattern recognitionDirection/deviation determining electromagnetic systemsIntermediate imageSignal transfer function
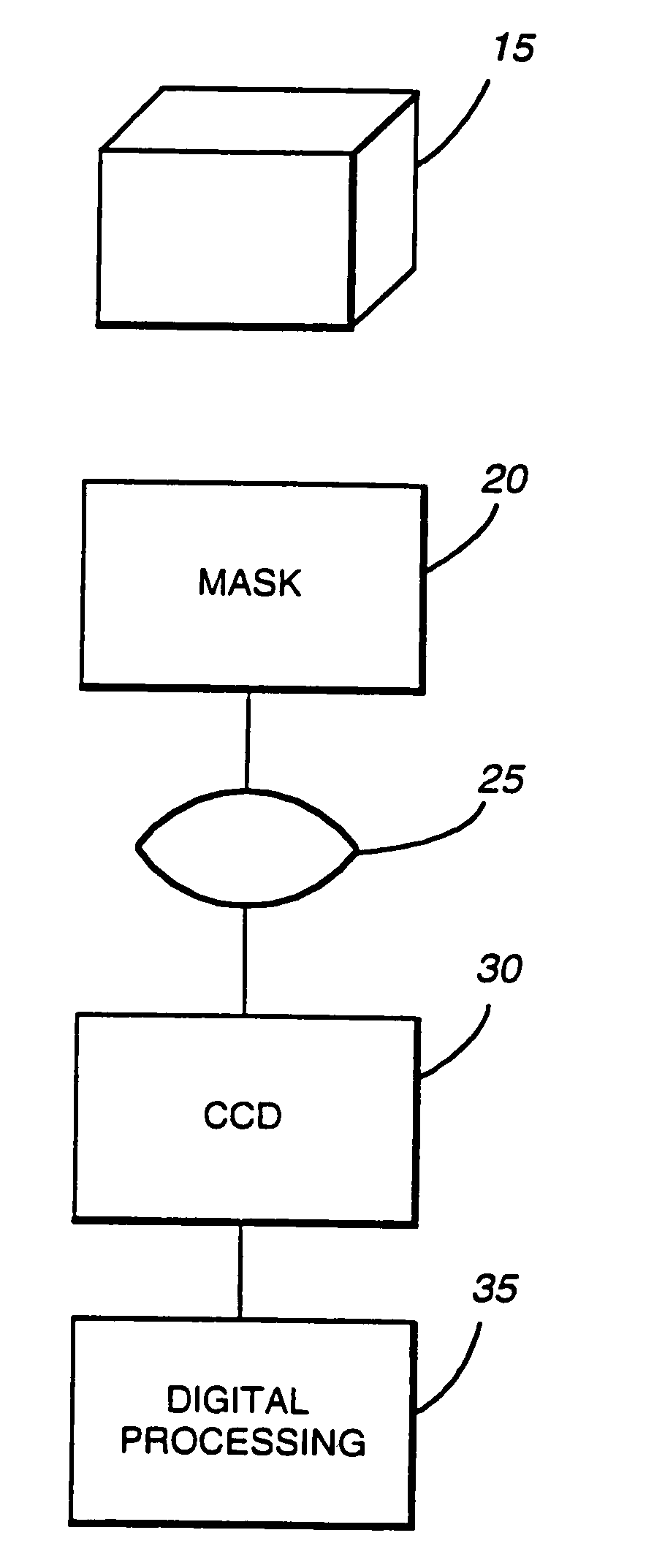
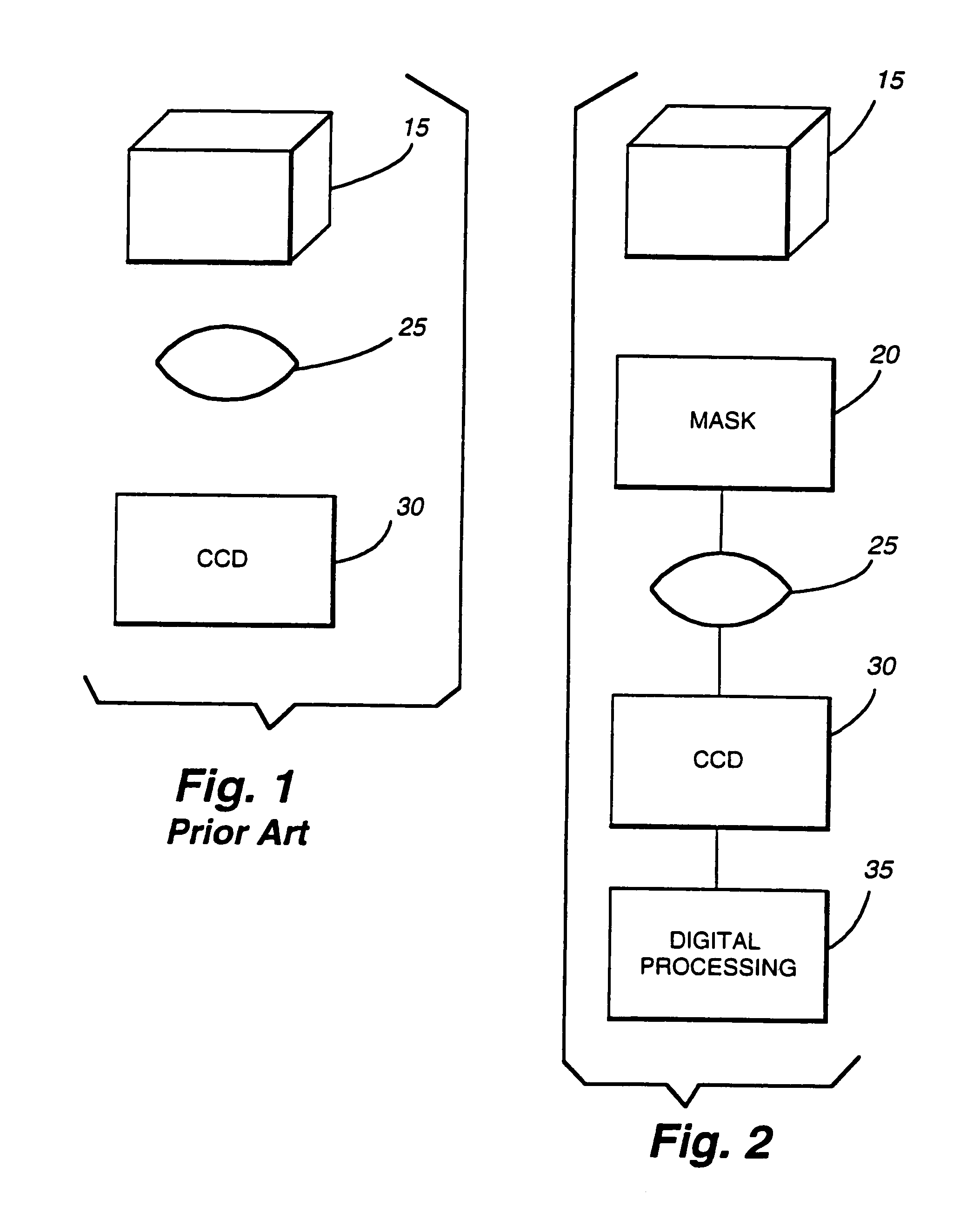
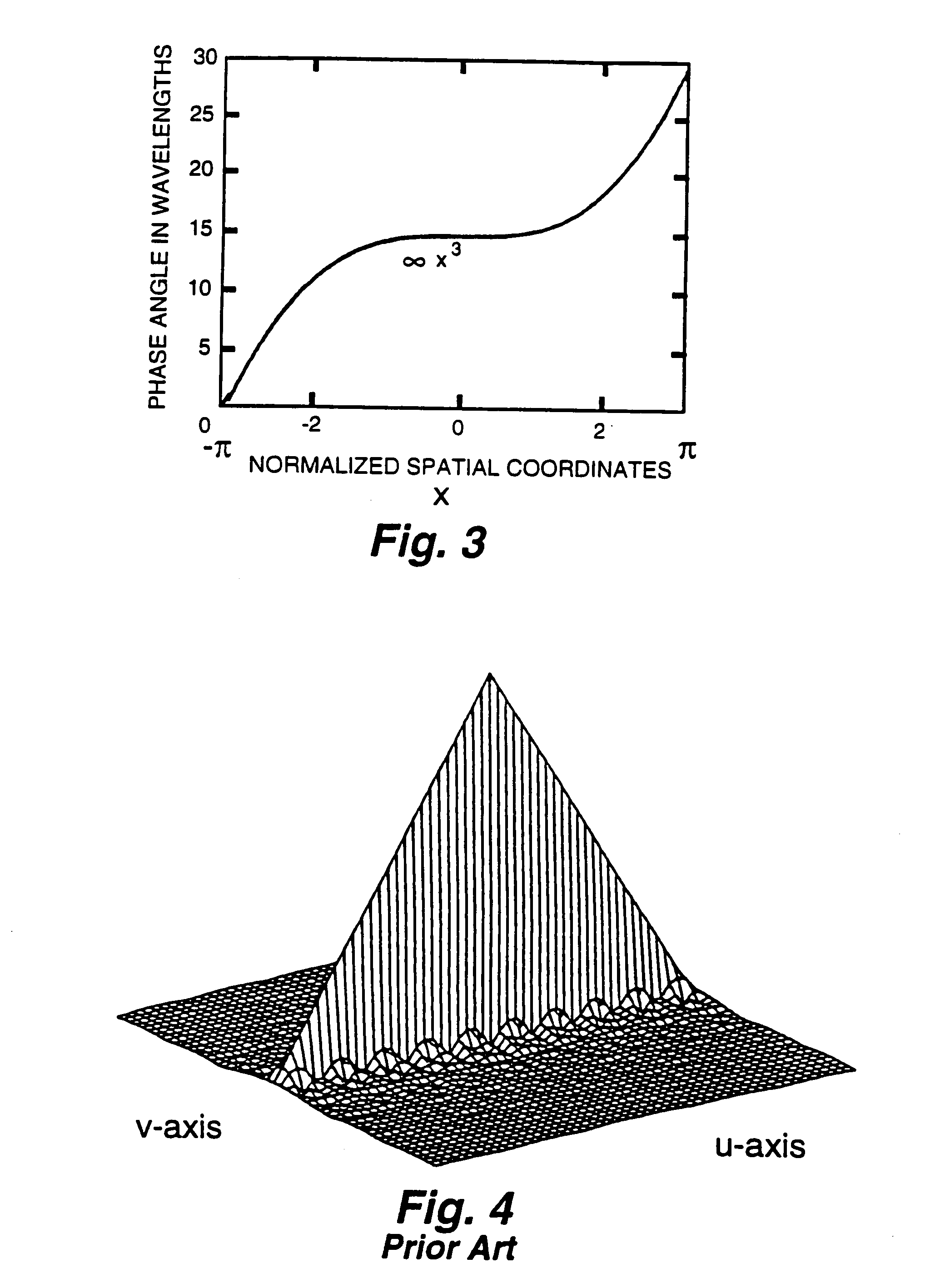
A system for increasing the depth of field and decreasing the wavelength sensitivity of an incoherent optical system incorporates a special purpose optical mask into the incoherent system. The optical mask has been designed to cause the optical transfer function to remain essentially constant within some range from the in-focus position. Signal processing of the resulting intermediate image undoes the optical transfer modifying effects of the mask, resulting in an in-focus image over an increased depth of field. Generally the mask is placed at or near an aperture stop or image of the aperture stop of the optical system. Preferably, the mask modifies only phase and not amplitude of light, though amplitude may be changed by associated filters or the like. The mask may be used to increase the useful range of passive ranging systems.
Owner:UNIV TECH
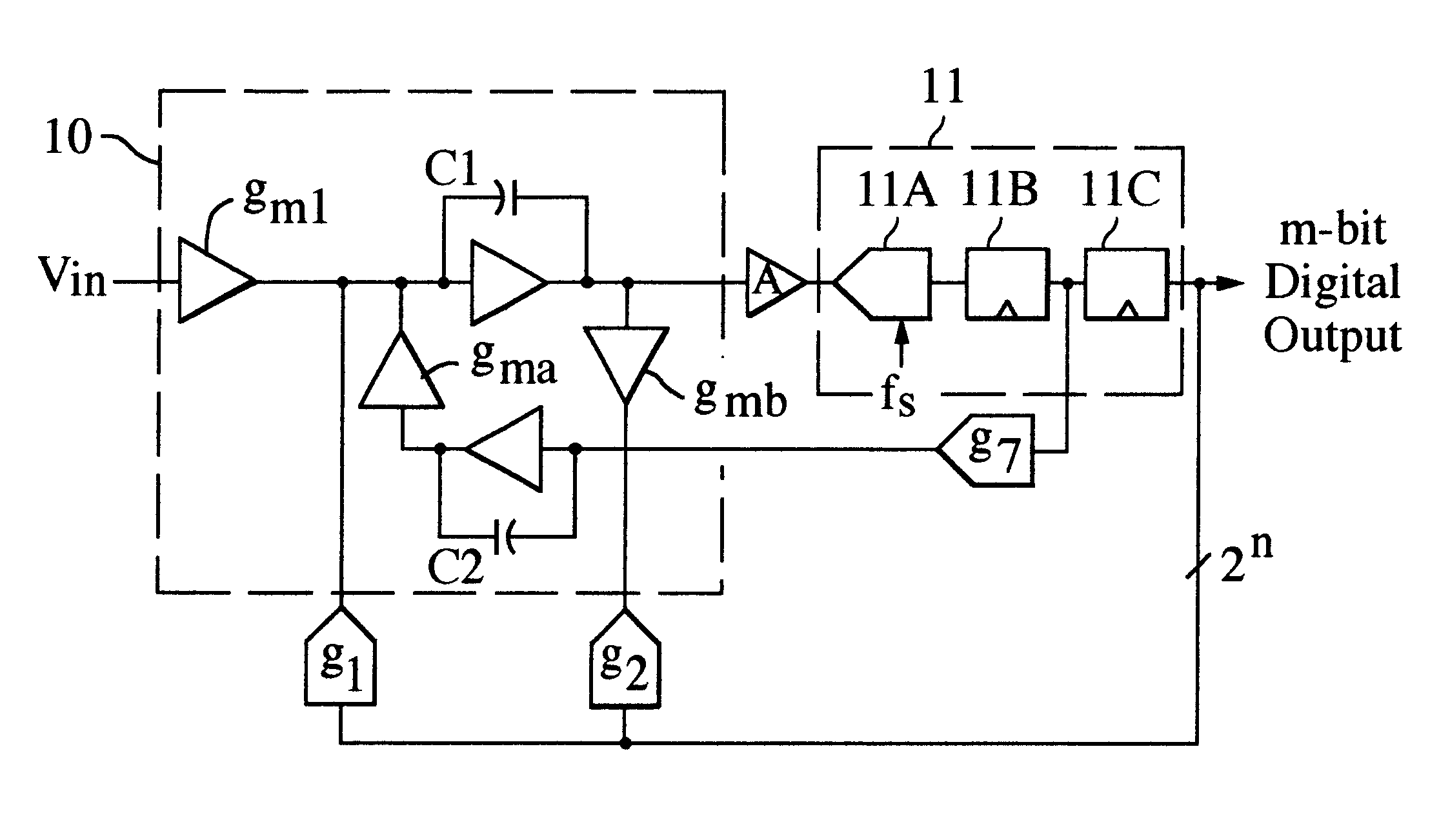
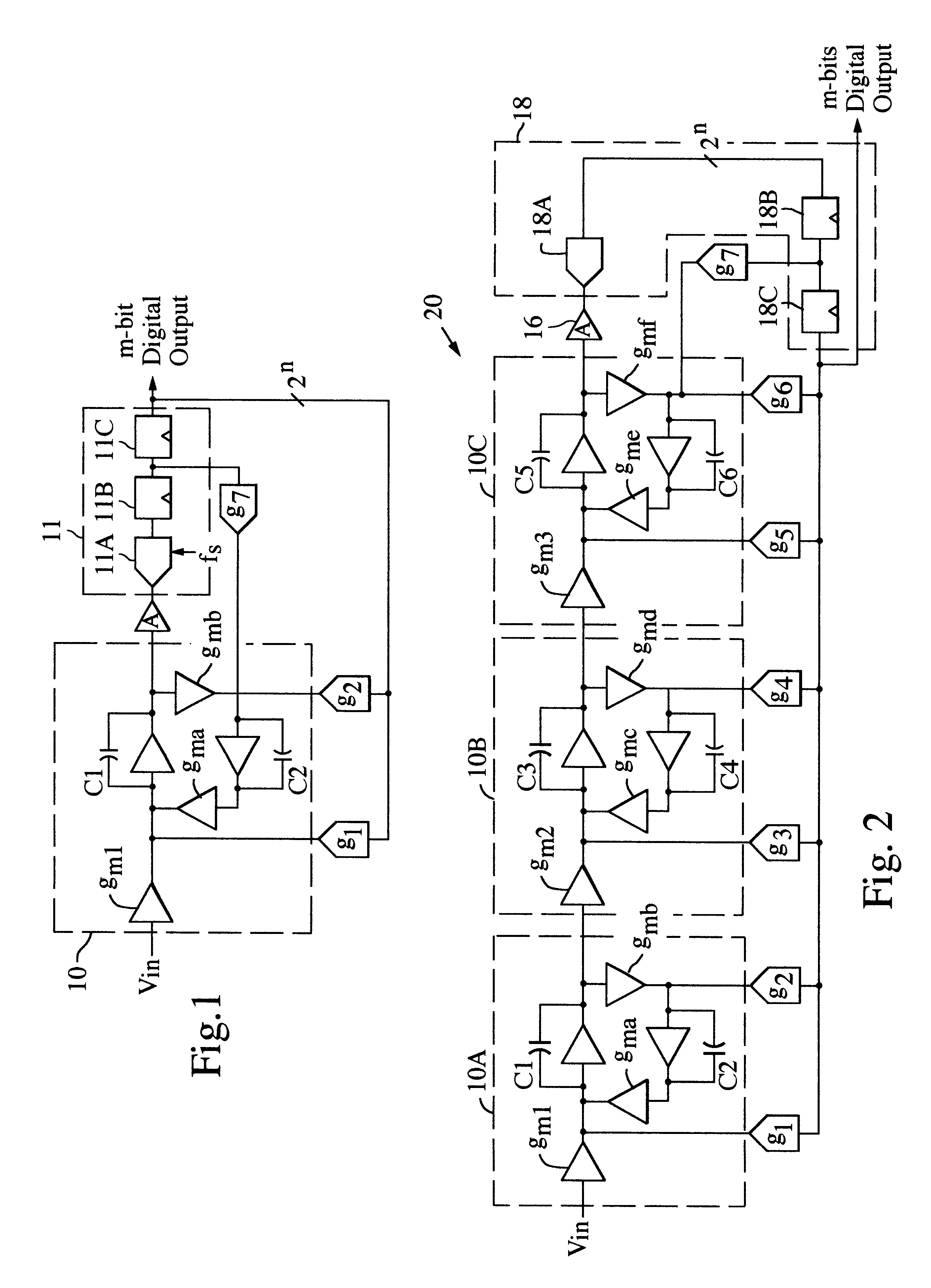
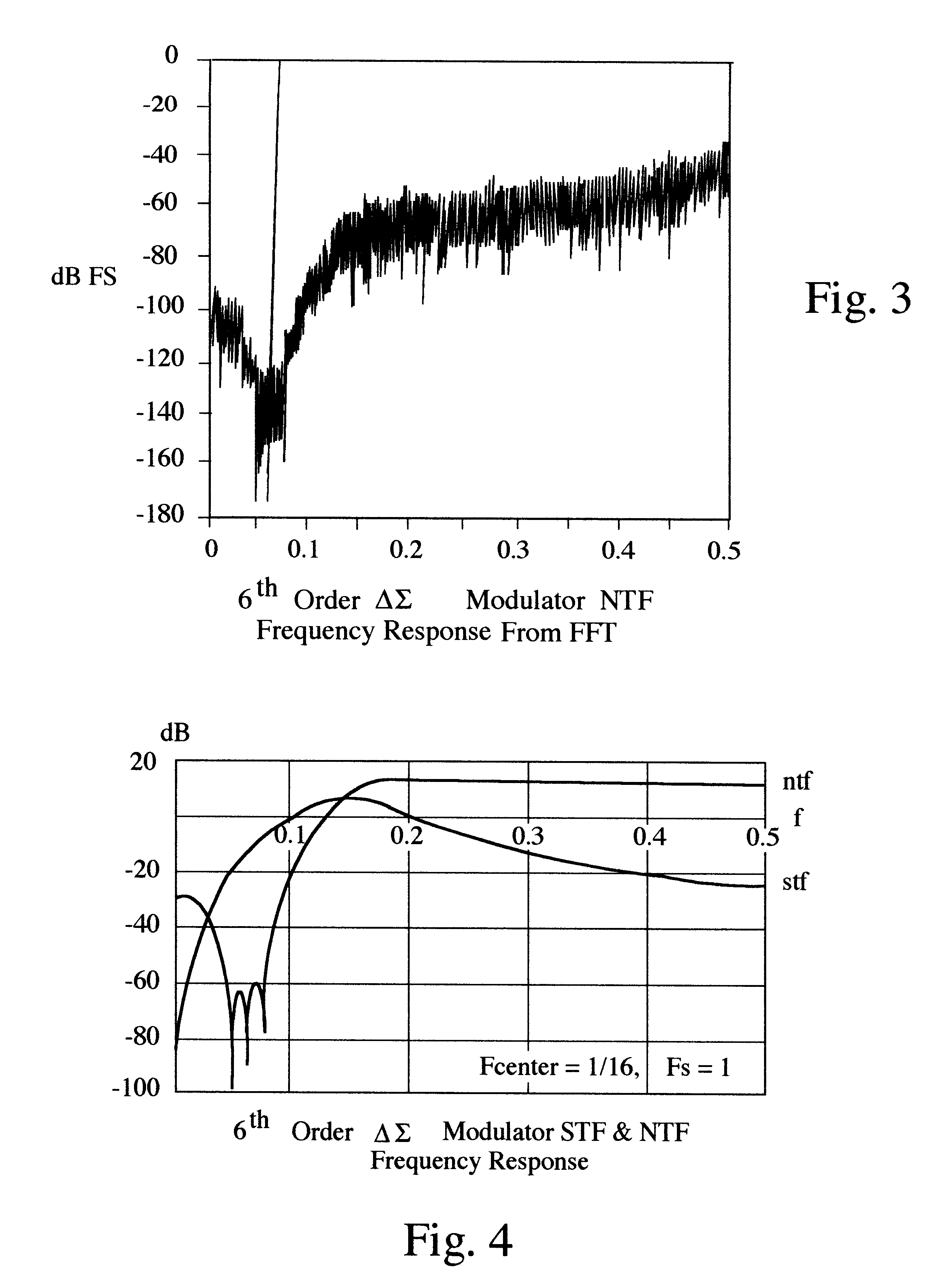
Continuous time bandpass delta sigma modulator ADC architecture with feedforward signal compensation
InactiveUS6396428B1Reduce system complexityInherent errorElectric signal transmission systemsDifferential modulationSignal transfer functionOptical transfer function
A continuous time Bandpass Delta Sigma (DELTASIGMA) Modulator architecture with feedforward and feedback coefficients to completely specify both the signal transfer function (STF) and the noise transfer function (NTF) for a stable modulator ADC system.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
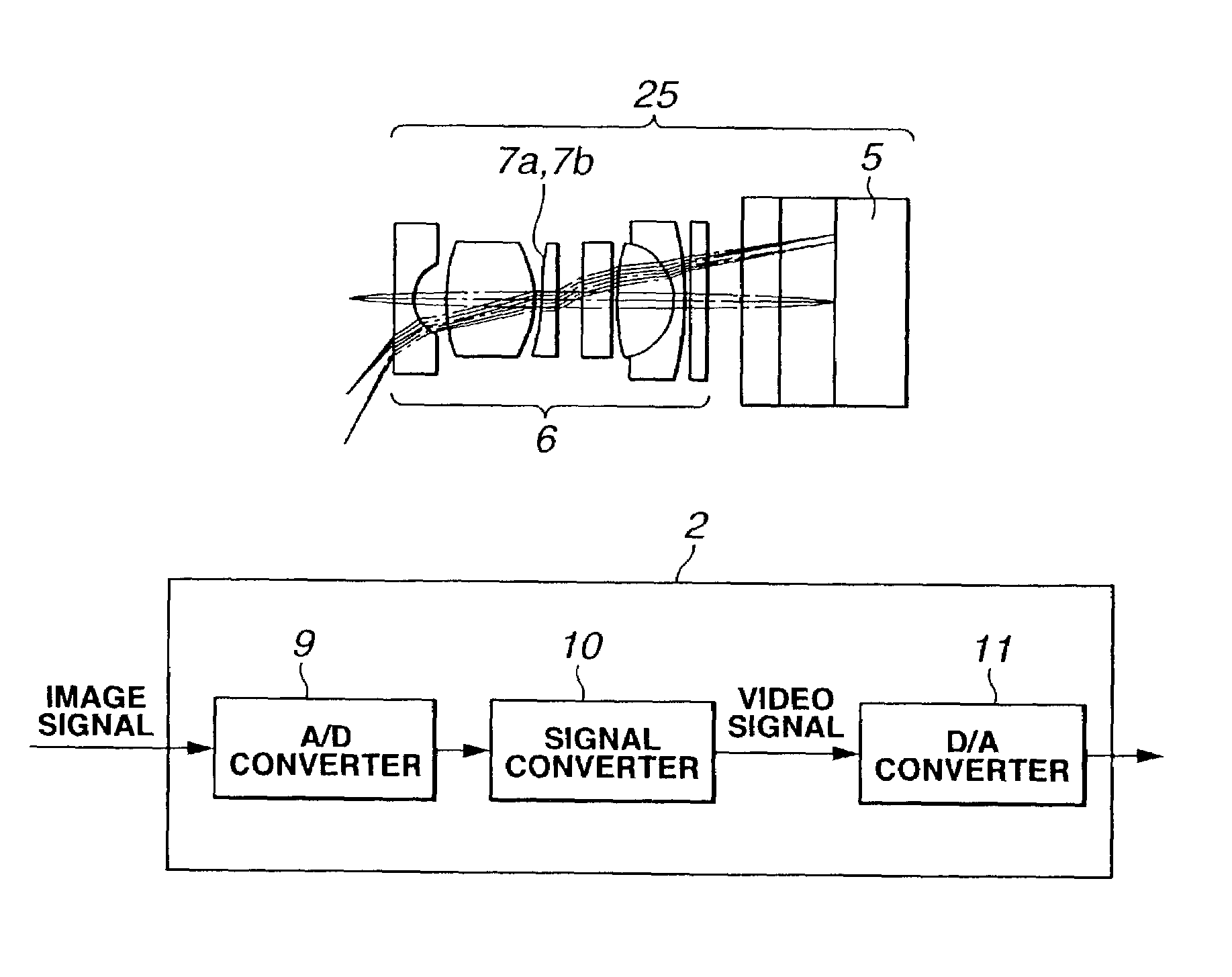
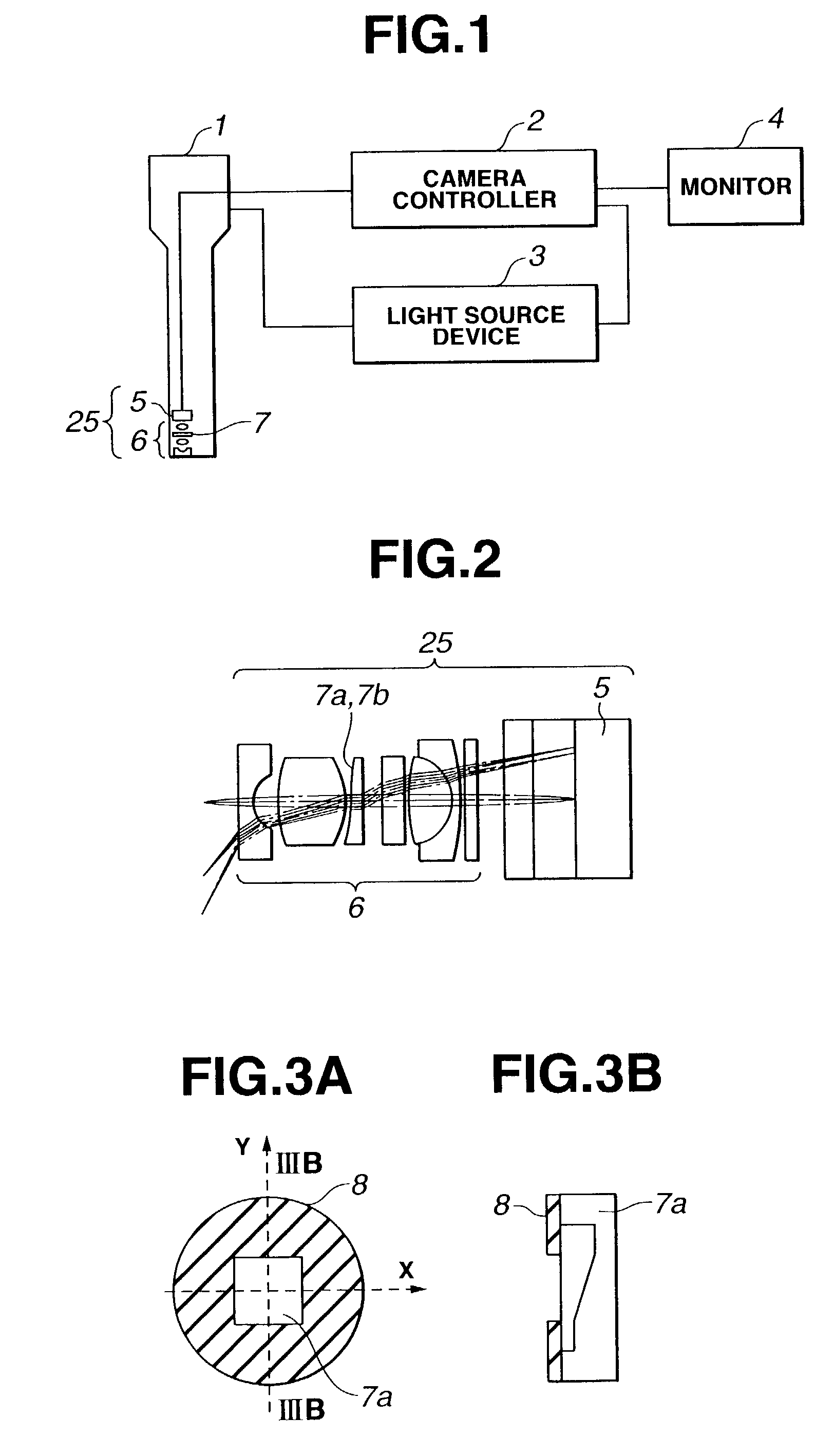
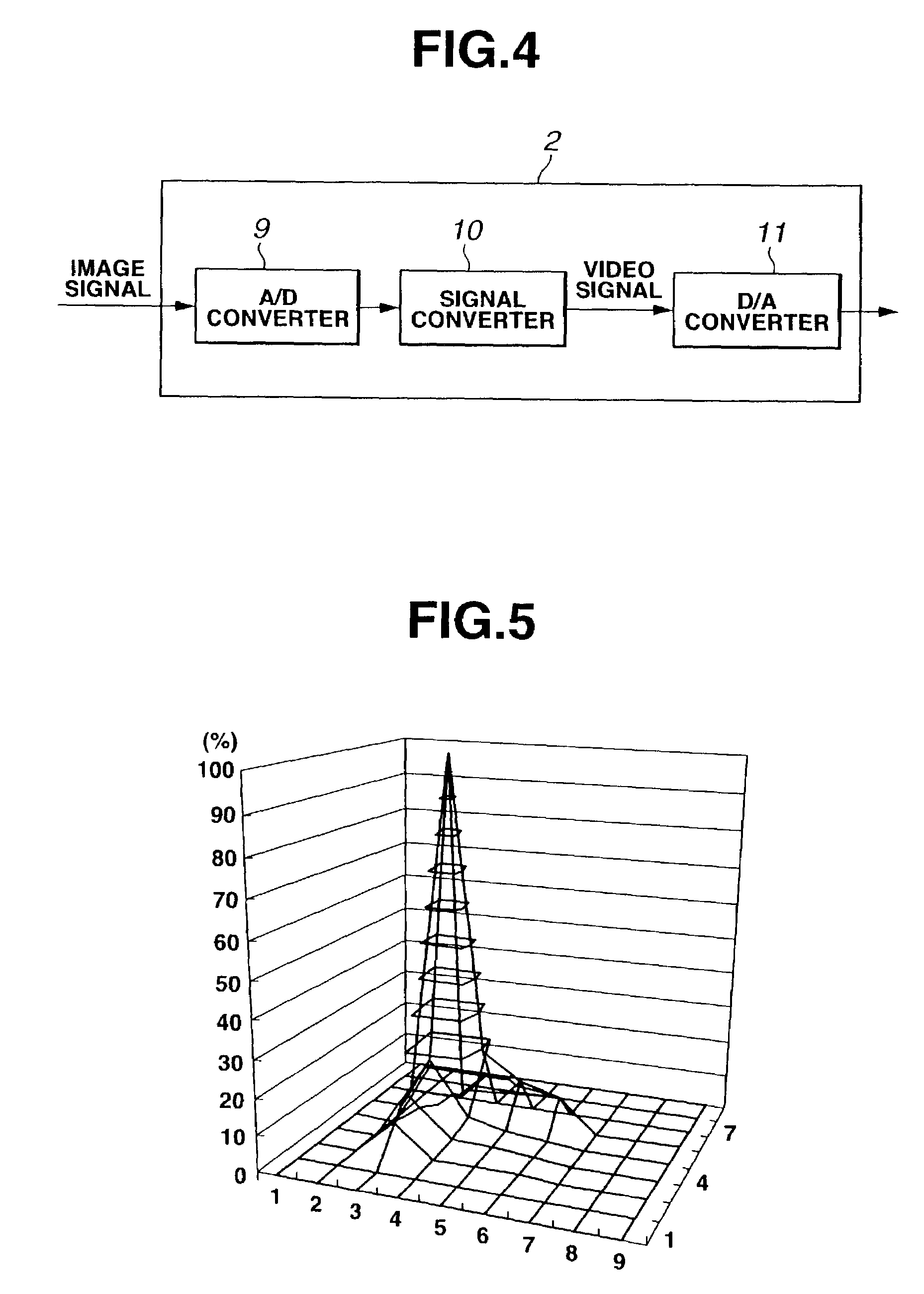
Endoscope and endoscope system with optical phase modulation member
InactiveUS6984206B2Add depthHigh-resolution imageTelevision system detailsSurgeryDepth of fieldImage signal
An endoscope system consists mainly of: an endoscope having a solid-state imaging device and an objective optical system that converges an object image on said solid-state imaging device; and a signal processing unit that processes an image signal produced by the endoscope so as to produce a video signal. The objective optical system includes an optical phase modulation member. The optical phase modulation member exhibits a response of 0.2 or more derived from an optical transfer function relative to a spatial frequency on the solid-state imaging device determined based on the Nyquist theorem, that is, a Nyquist frequency, over a wider range of distances than a depth of field offered by an objective optical system not having the optical phase modulation member.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
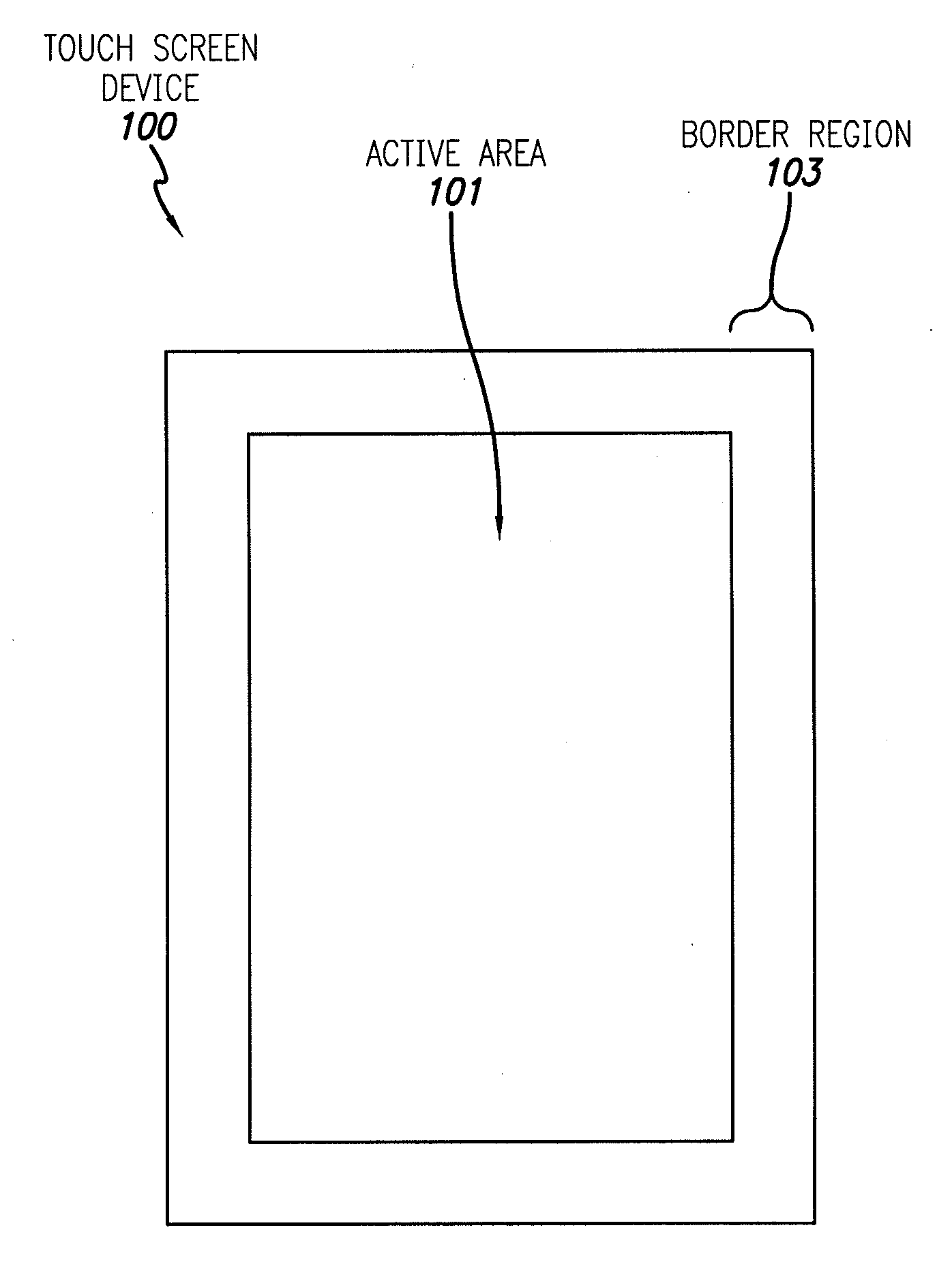
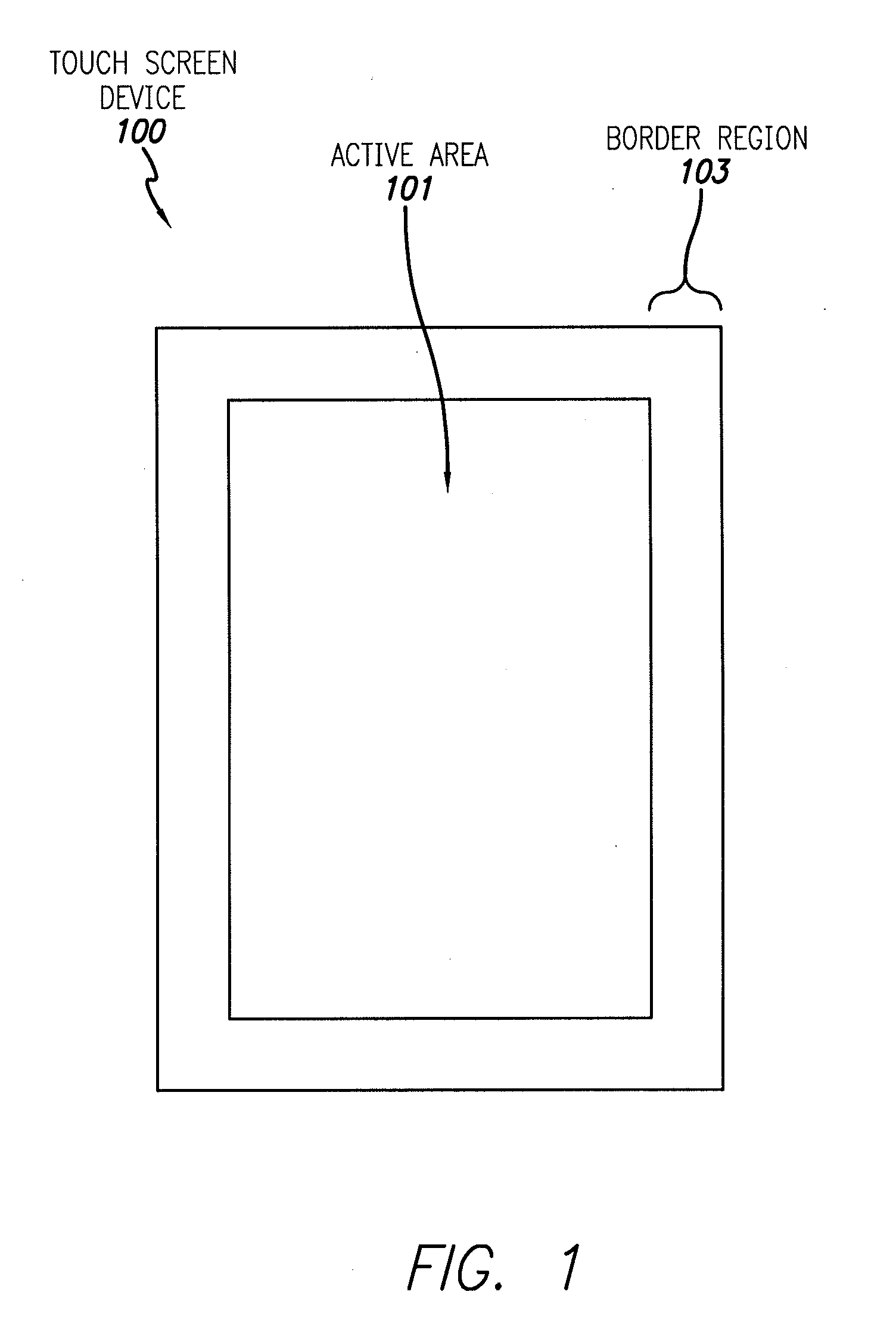
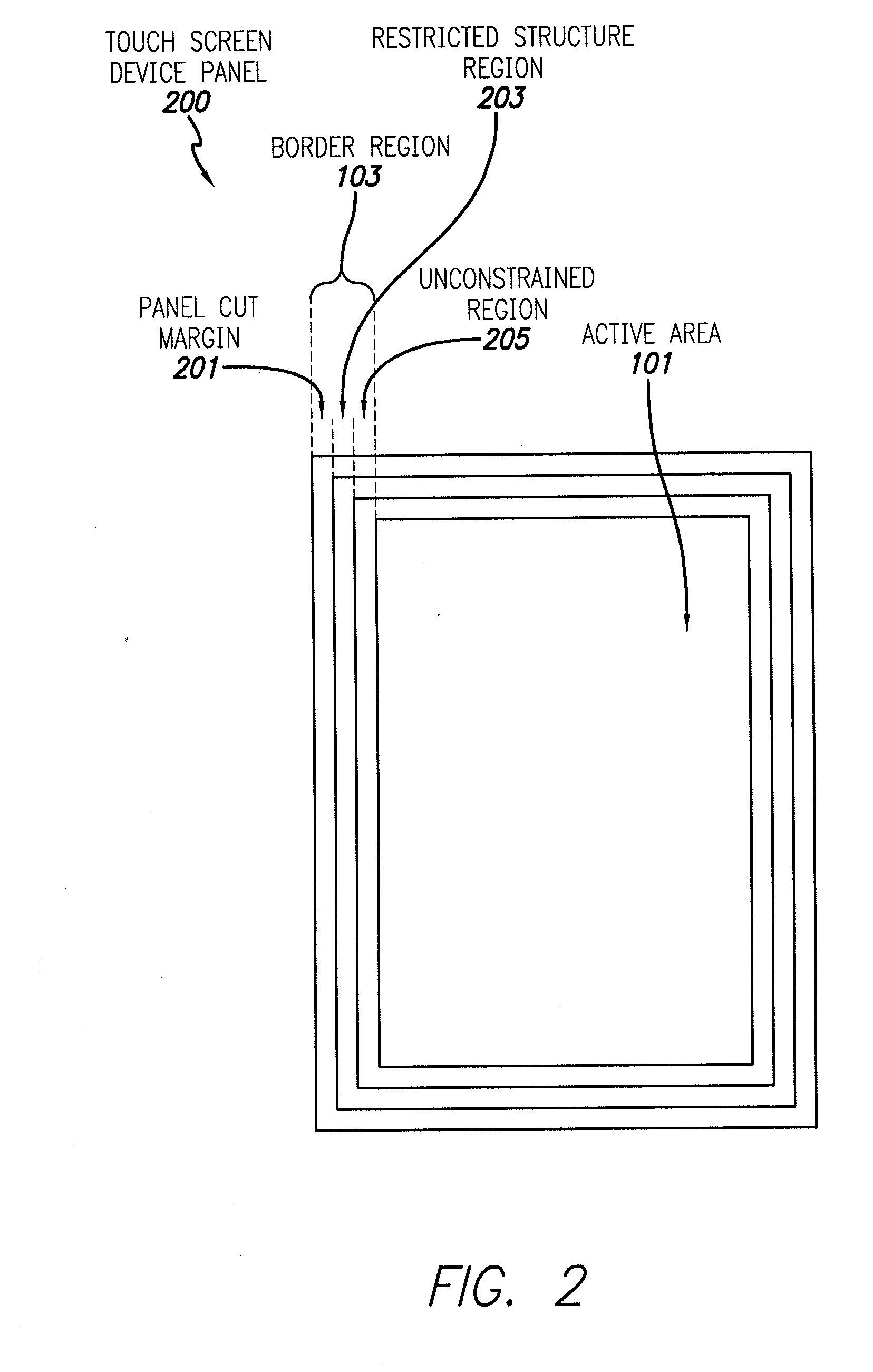
Touch Screen Border Regions
ActiveUS20110074705A1Light weightMany regionStatic indicating devicesDigital data processing detailsTouch SensesTransistor circuits
Touch screens with more compact border regions can include an active area that includes touch sensing circuitry including drive lines, and a border region around the active area. The border region can include an area of sealant deposited on conductive lines, and transistor circuitry, such as gate drivers, between the active area and the sealant. The conductive lines can extend from the sealant to the active area without electrically connecting to the transistor circuitry. The conductive lines can have equal impedances and can connect the drive lines to a touch controller off of the touch screen. A set of drive signal characteristics for the drive lines can be obtained by determining a transfer function associated with each drive line, obtaining an inverse of each transfer function, and applying a set of individual sense signal characteristics to the inverse transfer functions to obtain the corresponding set of drive signal characteristics.
Owner:APPLE INC
Mixed reality spatial audio
ActiveUS20190116448A1Input/output for user-computer interactionHeadphones for stereophonic communicationMixed realitySignal transfer function
A method of presenting an audio signal to a user of a mixed reality environment is disclosed. According to examples of the method, an audio event associated with the mixed reality environment is detected. The audio event is associated with a first audio signal. A location of the user with respect to the mixed reality environment is determined. An acoustic region associated with the location of the user is identified. A first acoustic parameter associated with the first acoustic region is determined. A transfer function is determined using the first acoustic parameter. The transfer function is applied to the first audio signal to produce a second audio signal, which is then presented to the user.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
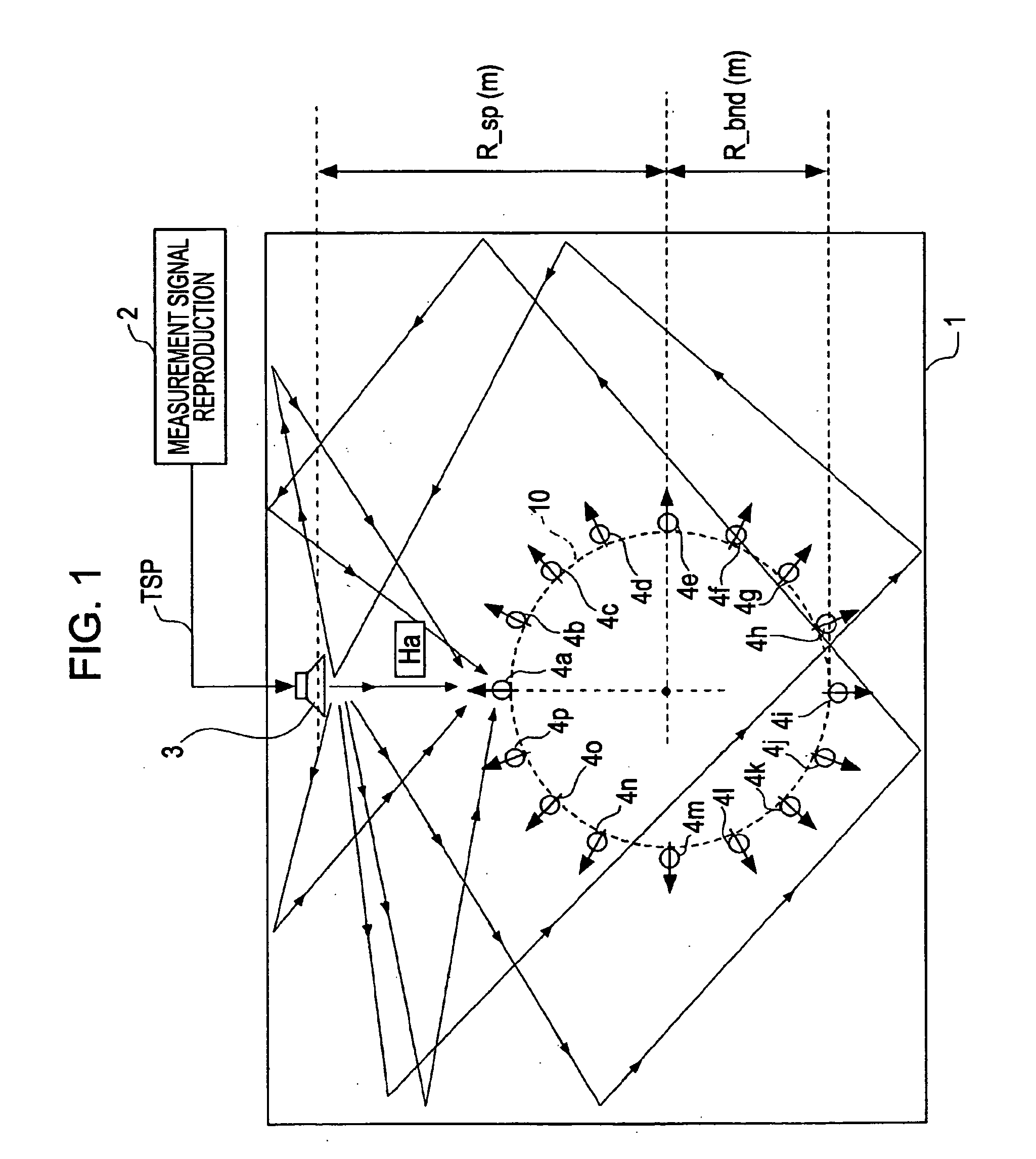
Audio processing method and sound field reproducing system
InactiveUS20070025560A1AdjustAdjust sound quality of soundGain controlSound producing devicesSound imageComposite function
An audio signal processing method comprises the steps of emitting a sound at a virtual sound image location in space on the outer side of a closed surface, generating measurement-based directional transfer functions corresponding to a plurality of positions on the closed surface based on a result of measuring the sound at the plurality of respective positions on the closed surface by using a directional microphone, generating composite transfer functions corresponding to the plurality of respective positions on the closed surface by respectively adding, at a specified ratio, the measurement-based directional transfer functions and auxiliary transfer functions and generating reproduction audio signals corresponding to the plurality of respective positions on the closed surface by performing a calculation process on an input audio signal in accordance with the set of composite functions.
Owner:SONY CORP
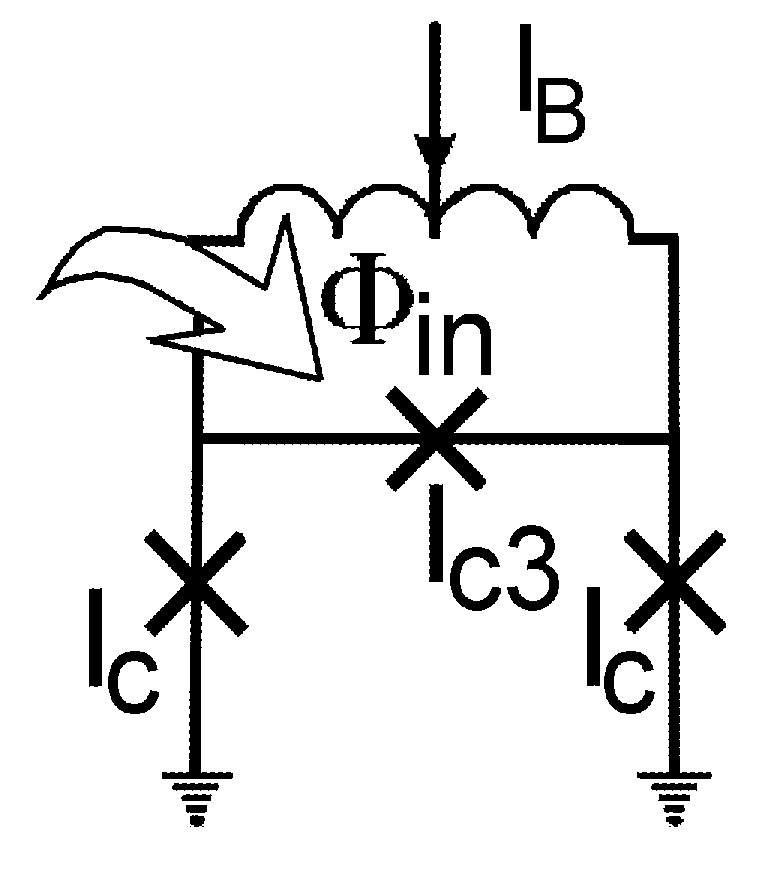
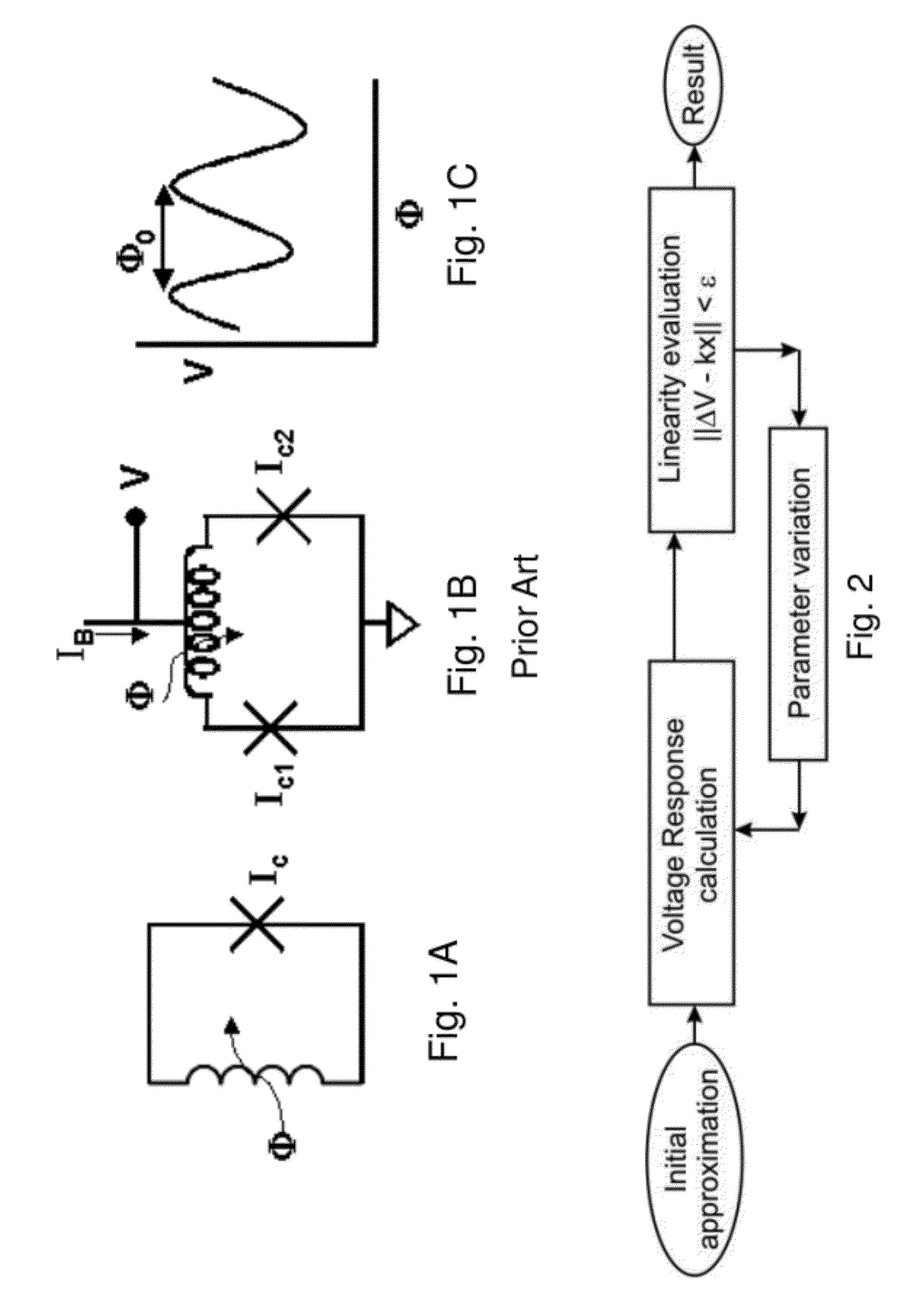
High linearity superconducting radio frequency magnetic field detector
ActiveUS8179133B1Total nonlinearities have been significantly reduced or eliminatedAvoid interferenceSuperconductors/hyperconductorsElectric pulse generatorTotal harmonic distortionRadio frequency
A superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUID) comprises a superconducting inductive loop with at least two Josephson junction, whereby a magnetic flux coupled into the inductive loop produces a modulated response up through radio frequencies. Series and parallel arrays of SQUIDs can increase the dynamic range, output, and linearity, while maintaining bandwidth. Several approaches to achieving a linear triangle-wave transfer function are presented, including harmonic superposition of SQUID cells, differential serial arrays with magnetic frustration, and a novel bi-SQUID cell comprised of a nonlinear Josephson inductance shunting the linear coupling inductance. Total harmonic distortion of less than −120 dB can be achieved in optimum cases.
Owner:SEEQC INC
Transmit diversity wireless communication
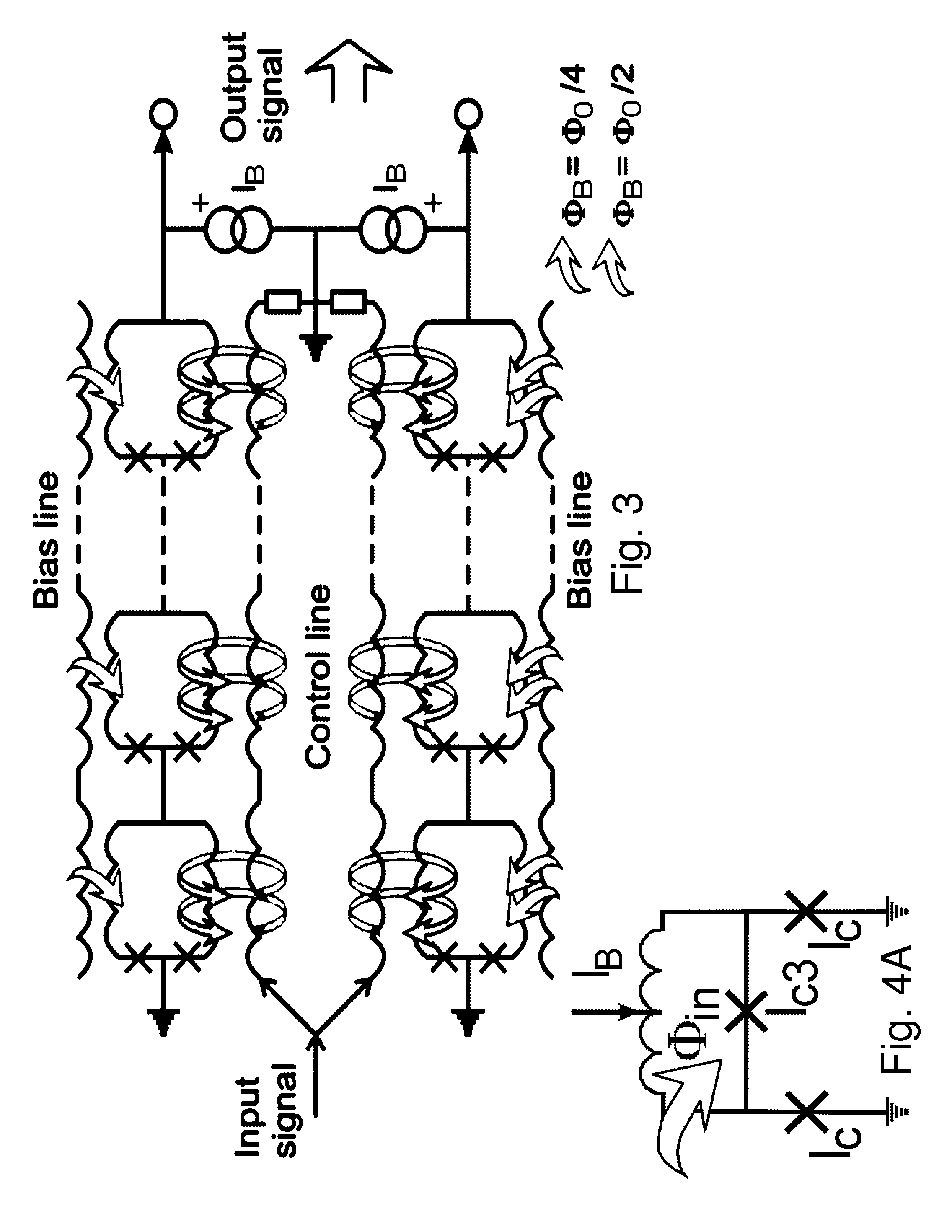
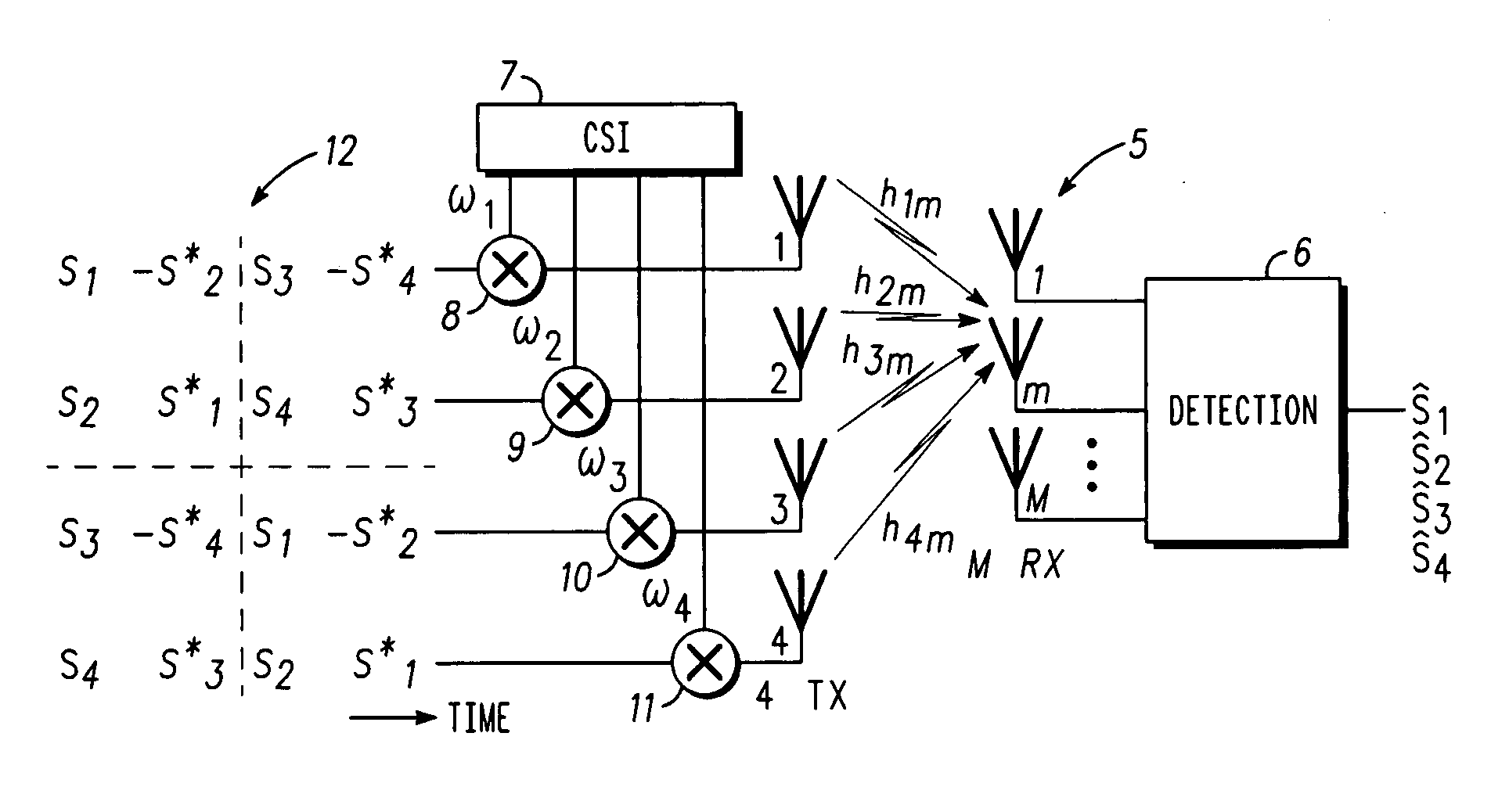
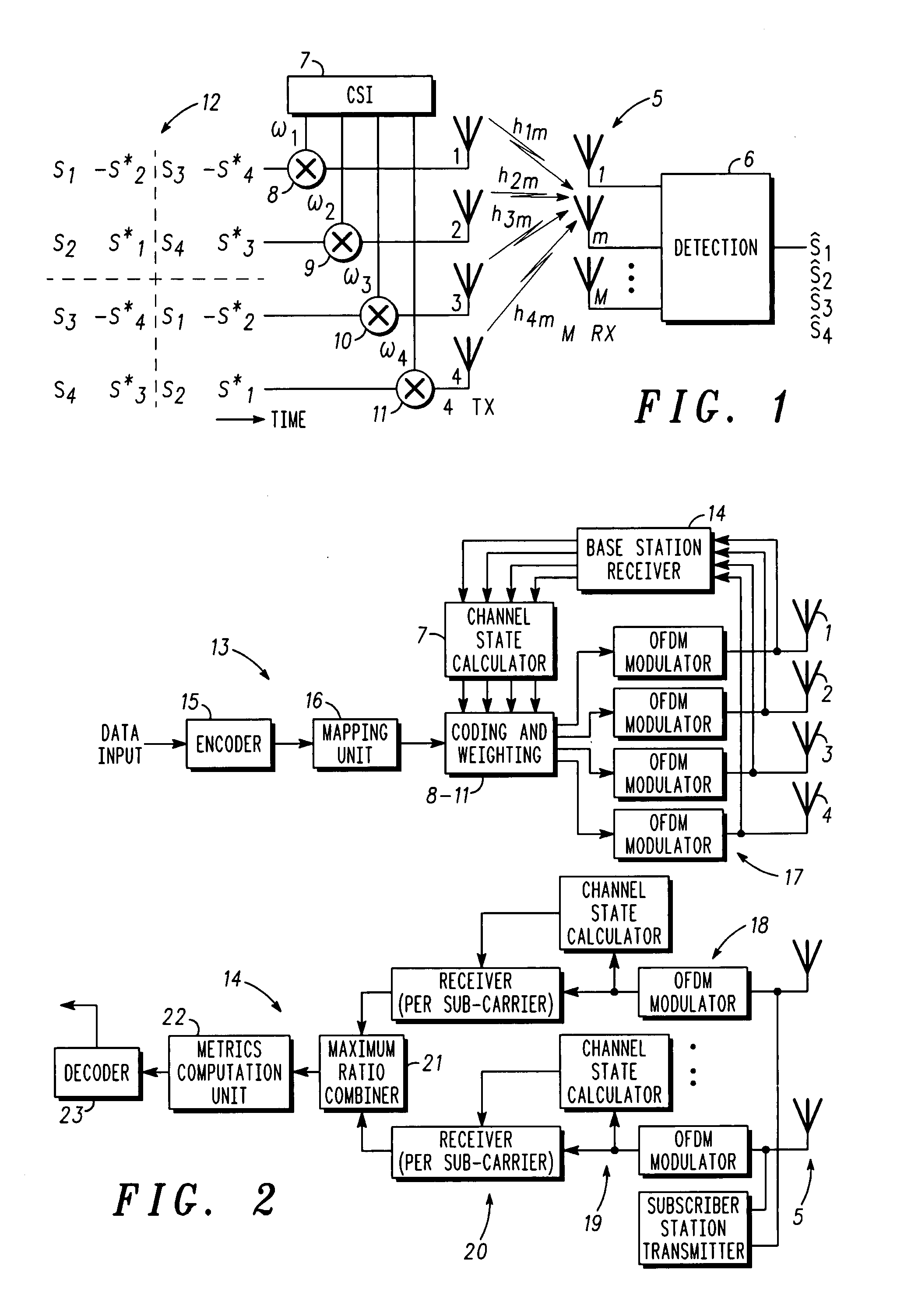
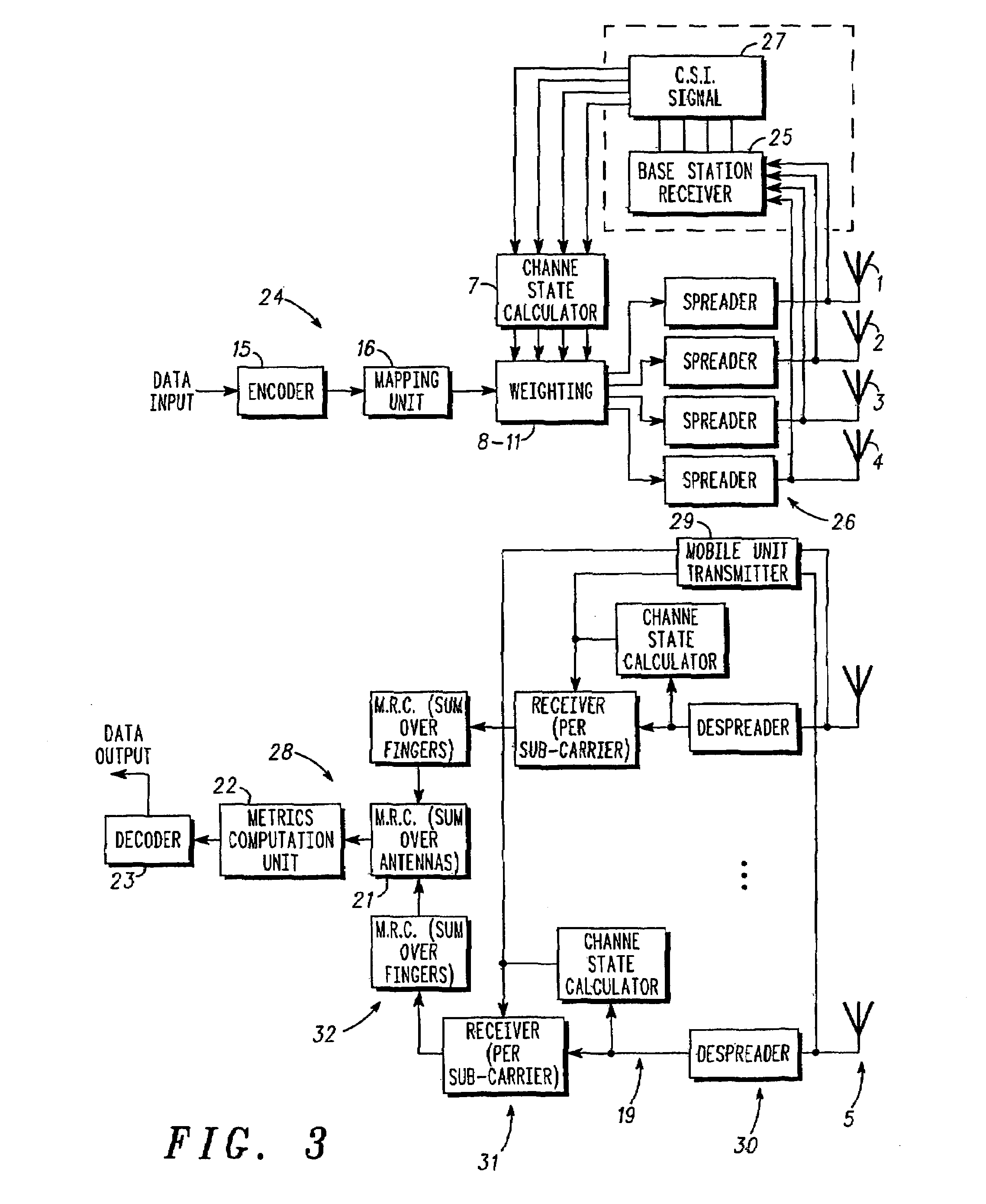
ActiveUS7308035B2Spatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityEngineeringAntenna element
A method of transmitting data from a transmitter (13,24) to a remote receiver (14,28) using transmit diversity wireless communication, the transmitter (13,24) comprising three or more transmit antenna elements (1,2,3,4). The data is encoded in symbol blocks (12), the symbols (s1,s2,s3,s4) of a block (12) being permuted within respective sub-sets of symbols between the transmit antenna elements (1,2,3,4) over time with respective replications and complex conjugations and / or negations. At least one of the sub-sets of said transmit antenna elements (1,2,3,4). The signals transmitted over at least one of the transmit antenna elements (1,2,3,4) are modified as a function of channel information at least approximately related to the channel transfer function (h1,h2,h3 and h4) of the transmitted signals, and the sub-sets of symbols and permuted symbols are permuted over time between said sub-sets of transmit antenna elements, so that the received signal is detectable at the receiver (14,28) using an orthogonal detection matrix scheme.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Estimation of head-related transfer functions for spatial sound representation
InactiveUS20060067548A1Two-channel systemsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsComputer scienceOptical transfer function
The estimation of an HRTF for a given individual is accomplished by means of a coupled model, which identifies the dependencies between one or more images of readily observable characteristics of an individual, and the HRTF that is applicable to that individual. Since the HRTF is highly influenced by the shape of the listener's outer ear, as well as the shape of the listener's head, images of a listener which provides this type of information are preferably applied as an input to the coupled model. In addition, dimensional measurements of the listener can be applied to the model. In return, the model provides an estimate of the HRTF for the observed characteristics of the listener.
Owner:INTERVAL RESEARCH CORPORATION
LED device for wide beam generation
ActiveUS20100172135A1Easy to combineReduce discontinuityMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceSurface patternWide beam
An apparatus and method is characterized by providing an optical transfer function between a predetermined illuminated surface pattern, such as a street light pattern, and a predetermined energy distribution pattern of a light source, such as that from an LED. A lens is formed having a shape defined by the optical transfer function. The optical transfer function is derived by generating an energy distribution pattern using the predetermined energy distribution pattern of the light source. Then the projection of the energy distribution pattern onto the illuminated surface is generated. The projection is then compared to the predetermined illuminated surface pattern to determine if it acceptably matches. The process continues reiteratively until an acceptable match is achieved. Alternatively, the lens shape is numerically or analytically determined by a functional relationship between the shape and the predetermined illuminated surface pattern and predetermined energy distribution pattern of a light source as inputs.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
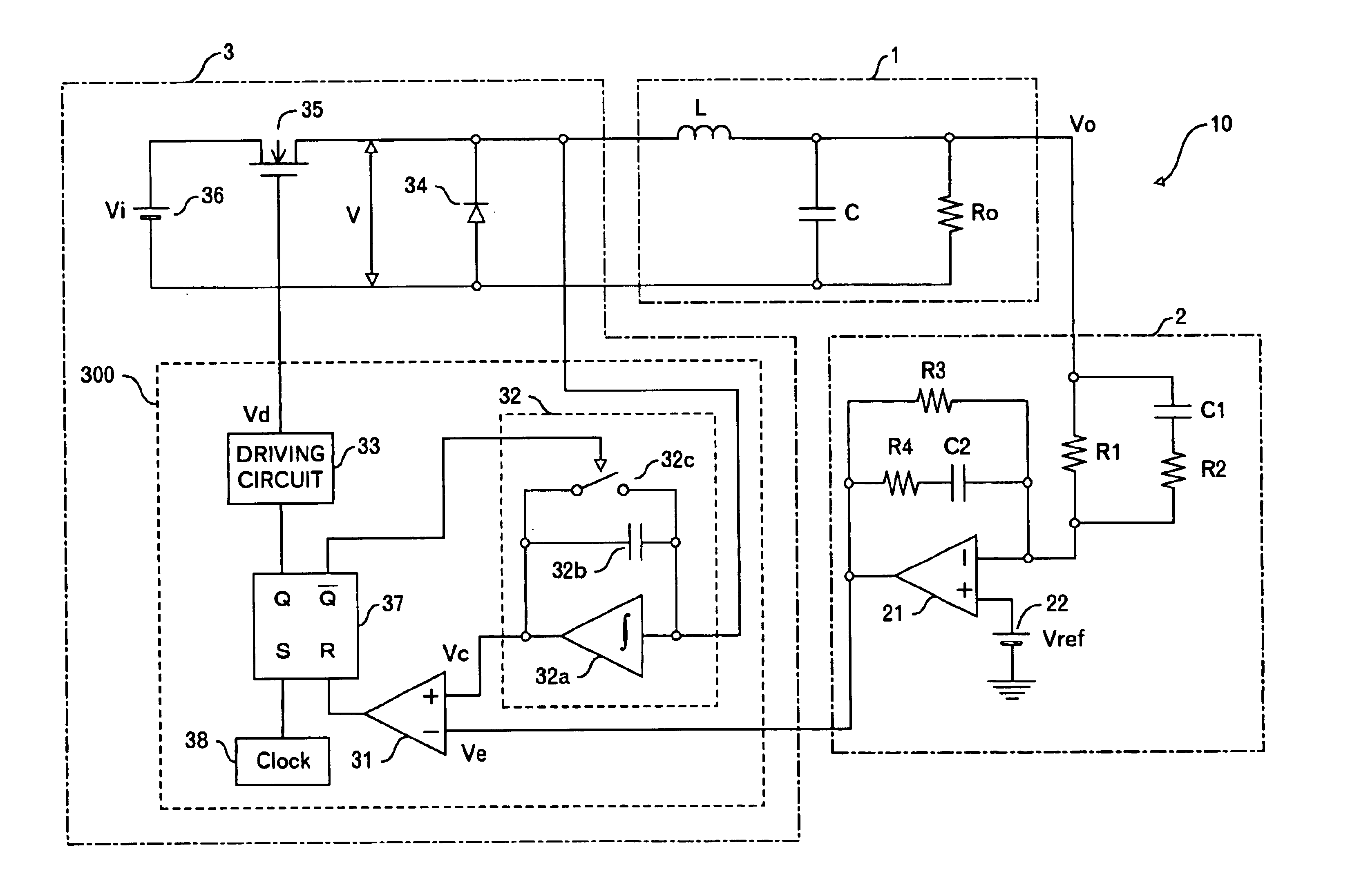
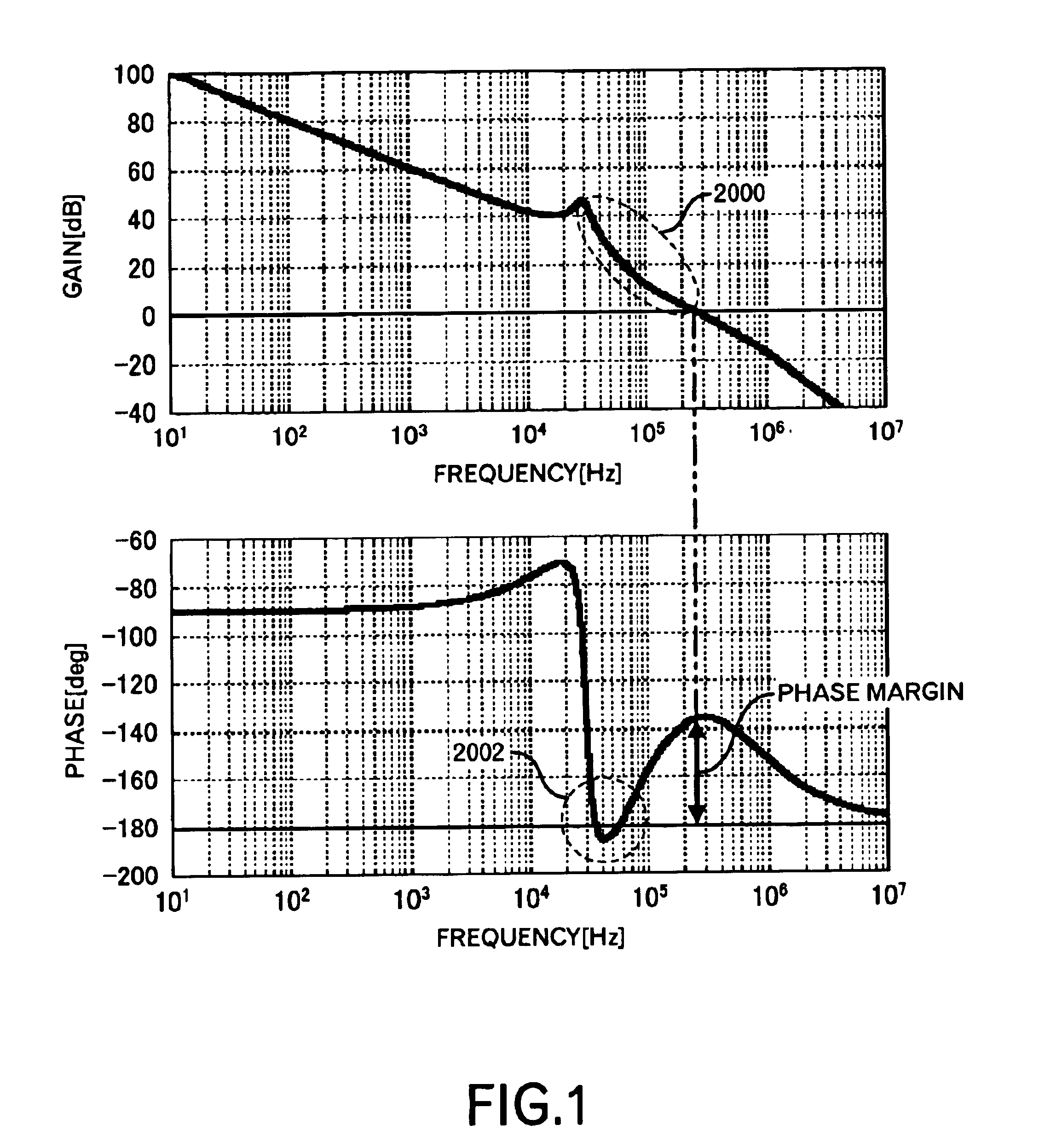
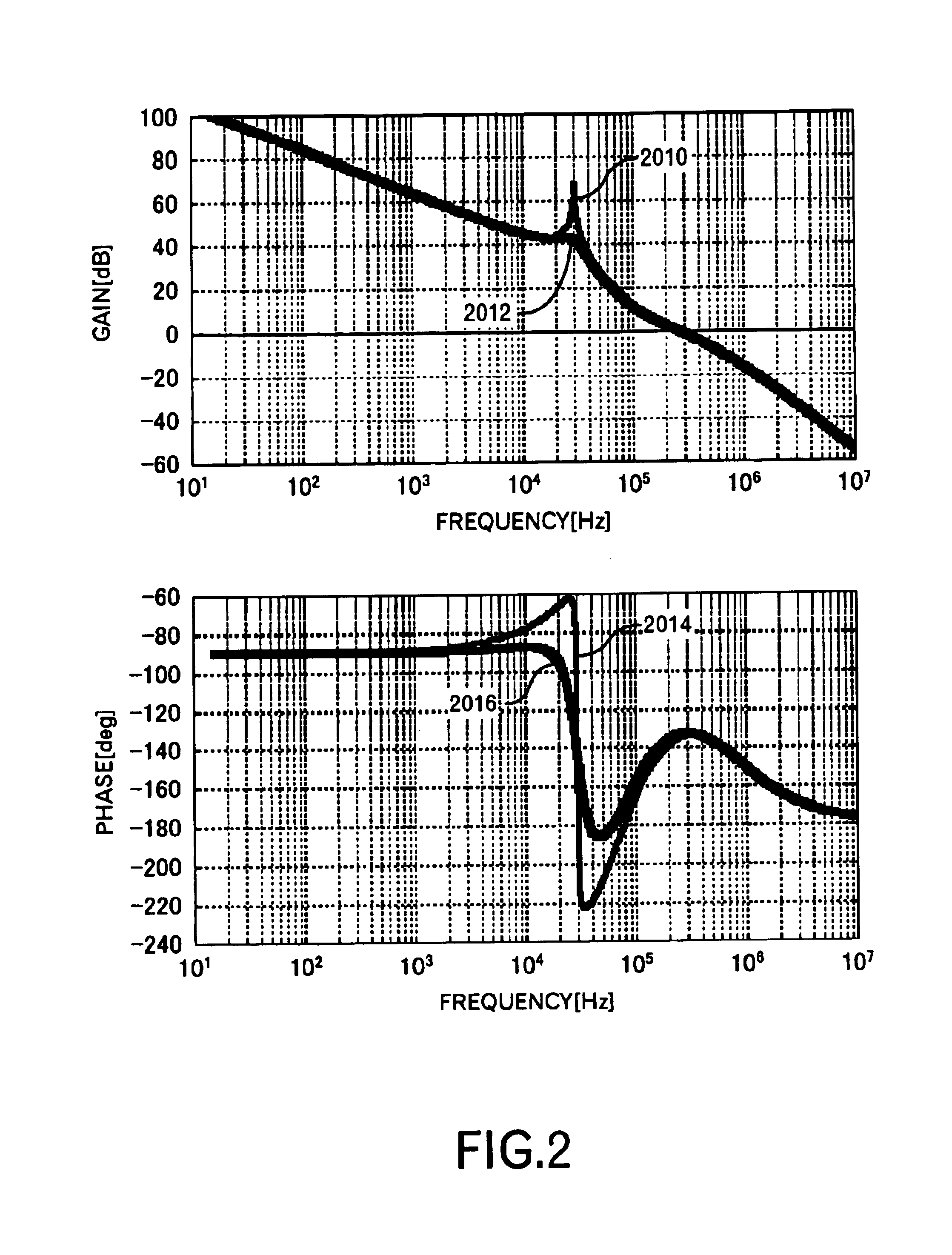
Power supply apparatus
InactiveUS6963190B2High speed responseHighly practicalDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationSignal transfer functionEngineering
An object of this invention is to provide a power supply apparatus, which realizes a frequency characteristic of an open-loop transfer function having a trap point, and can deal with input fluctuation. A controller of the power supply apparatus of the invention is a circuit in which although the form of its transfer function is the same as a conventional one, values of respective coefficients are different, only a phase margin is ensured without ensuring a gain margin, and the transfer function is realized which provides a frequency range (i.e. trap point) in which a decrease in gain is remarkable and a phase is considerably delayed. Besides, in order to ensure the stability against input fluctuation, a power conversion circuit is used which converts an input voltage from an input DC power supply so as to be constant in multiplying voltage by time.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
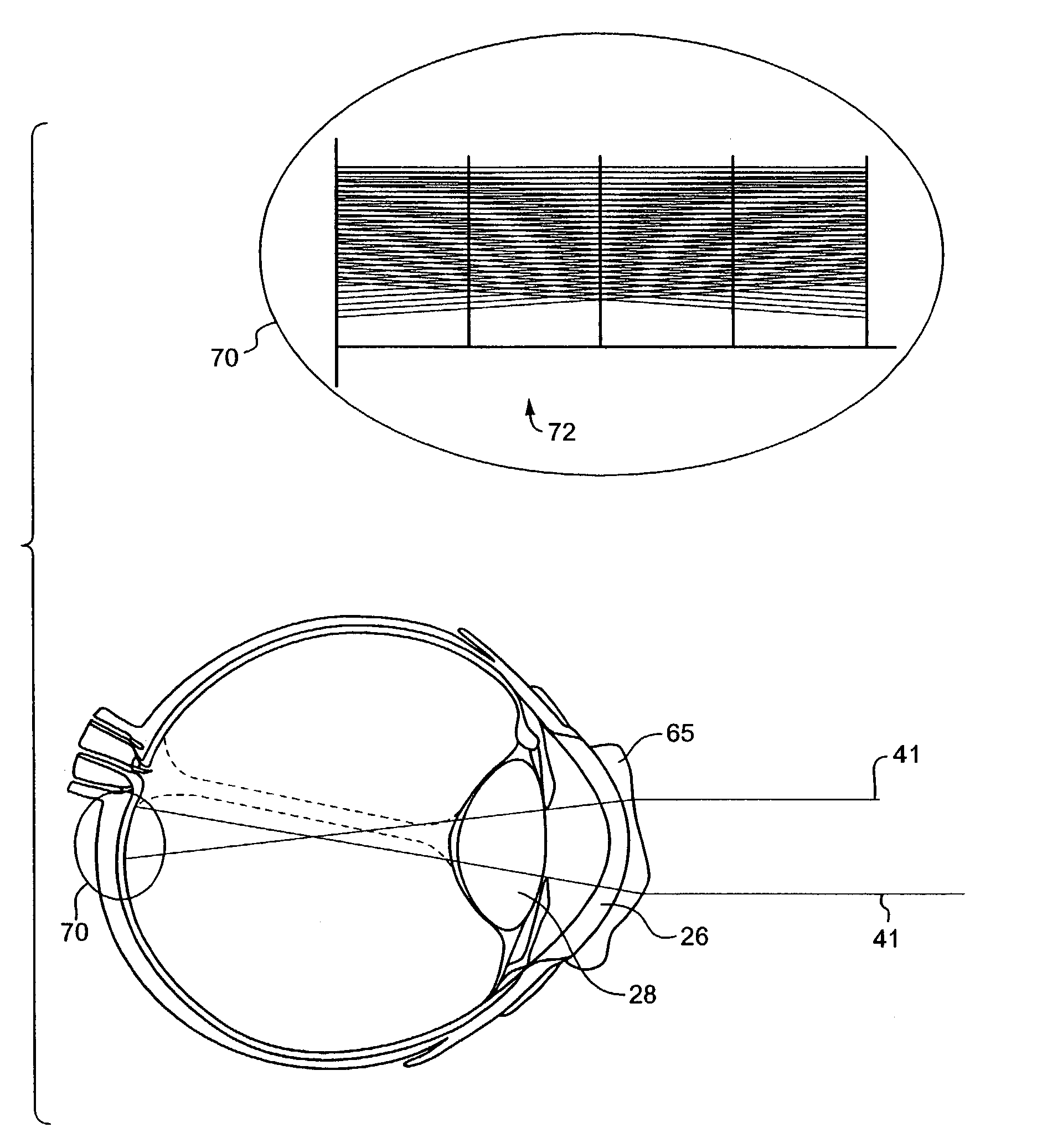
Extended depth of field optics for human vision
The present invention provides extended depth of field to human eyes by modifying contact lenses, intraocular implants, and / or the surface of the eye itself. This may be accomplished by applying selected phase variations to these optical elements (e.g., by varying surface thickness of the cornea of the eye). The phase variations EDF-code the wavefront and cause the optical transfer function to remain essentially constant within a range of distances from the in-focus position. This provides a coded image on the retina. The human brain decodes this coded image, resulting in an in-focus image over an increased depth of field.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Nonlinear filter
InactiveUS6856191B2Digital technique networkOscillations generatorsOptical transfer functionNonlinear filter
A system and method are disclosed for a nonlinear filter having a nonlinear transfer function. The nonlinear filter comprises a plurality of linear filters each having a filter output, a plurality of nonlinear elements each connected to one of the plurality of linear filters, and a combination network connected to the plurality of nonlinear elements. The nonlinear elements are used to produce nonlinear effects and generate a plurality of nonlinear outputs, and the combination network combines the nonlinear outputs.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
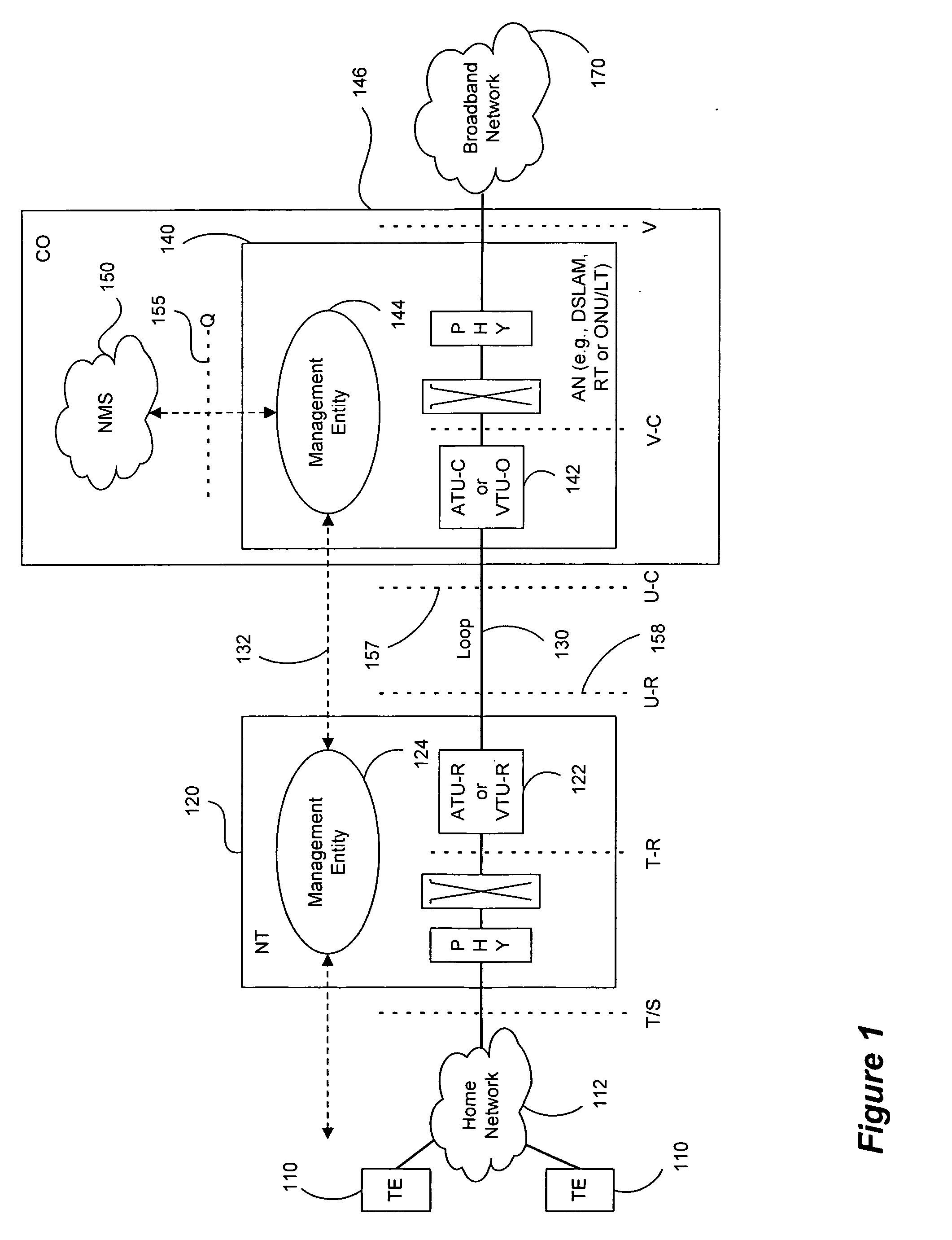
FEXT determination system
ActiveUS20050259725A1Error preventionTelephonic communicationSignal transfer functionTime-invariant system
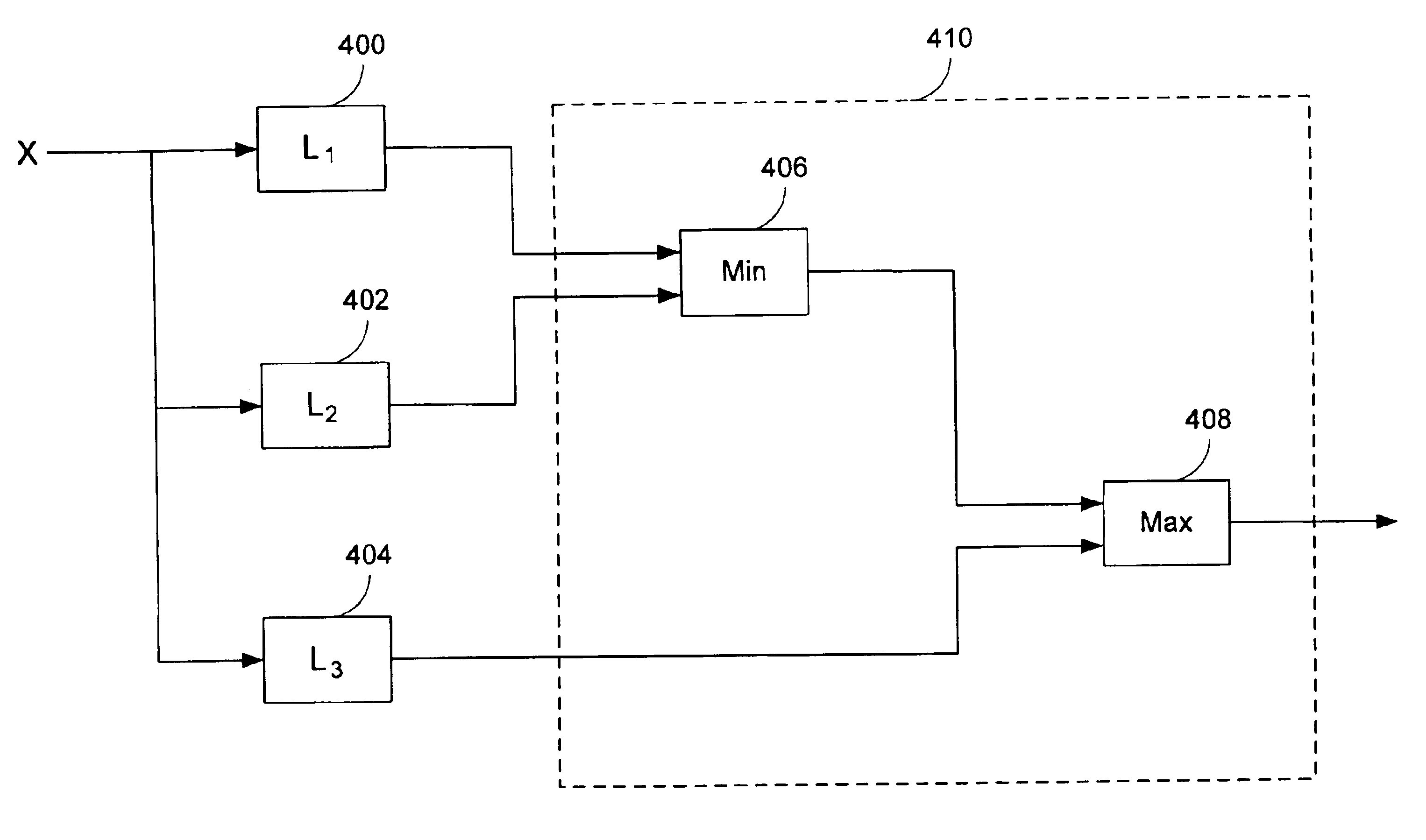
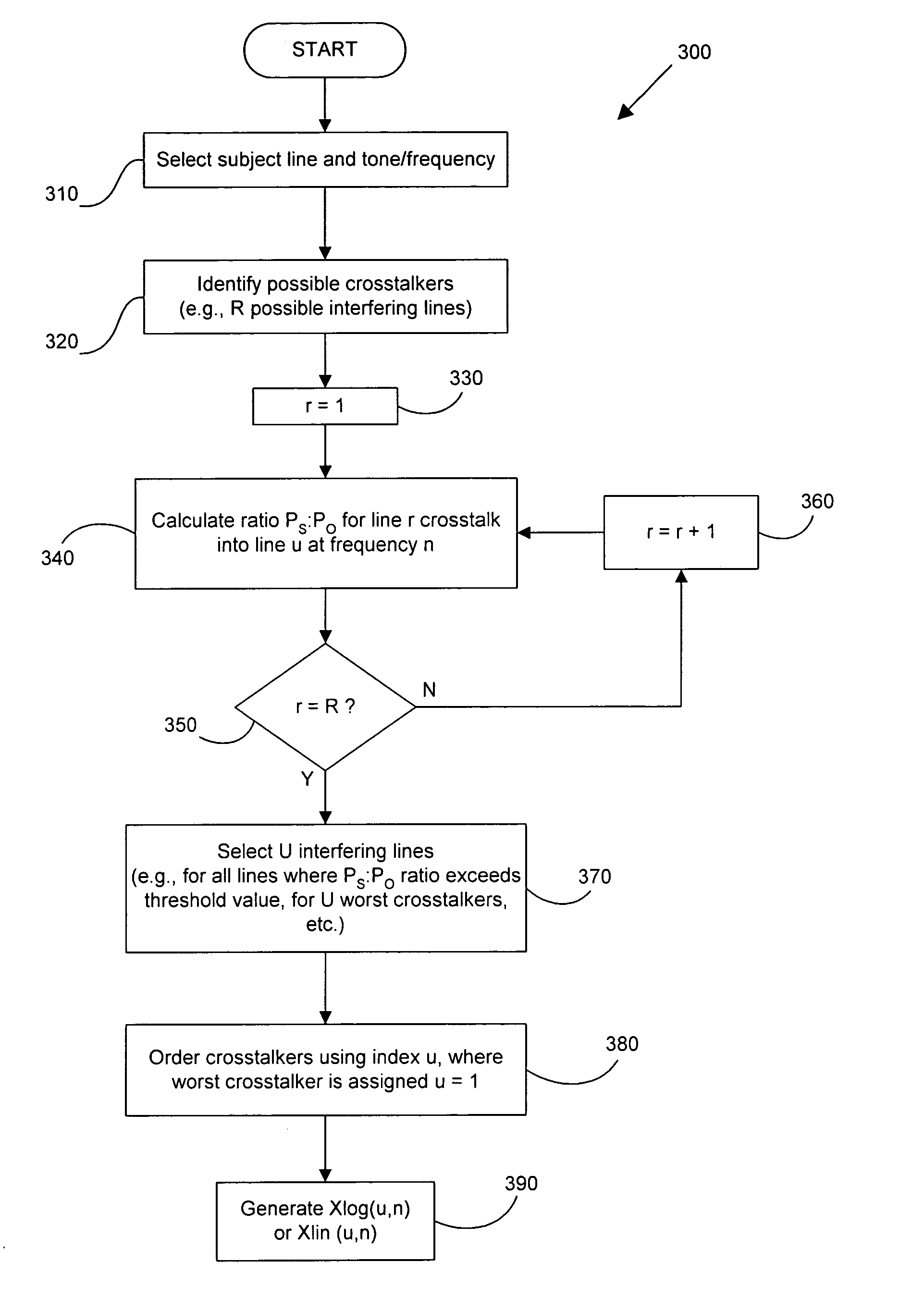
Operational data is utilized to determine the FEXT interference induced by one line into the other DSL line. FEXT interference can be calculated using the NEXT interference measured between the two lines at the upstream ends of the loops and the downstream channel transfer function of one of the loops. Because the NEXT and transfer function constitute a linear time-invariant system, as does the FEXT interference between the lines, the NEXT interference and line transfer function can be multiplied (if in linear format) or added (if in logarithmic format) to approximate the FEXT interference between the lines. The collection of data, calculations and other functions performed in these techniques may be performed by a system controller, such as a DSL optimizer. An Xlog(u,n) quantity is a decibel-magnitude representation of the insertion-loss equivalent of FEXT transfer functions and is defined as the ratio of (1) a line u's source power into a matched load of 100 Ohms when no binder is present to (2) the power at the output of the subject line when line u is excited with the same source and the binder is present. Xlin(u,n) is the linear equivalent of Xlog(u,n). The Xlog(u,n) and Xlin(u,n) quantities may be represented in specific formats that assist in their use in DSL and other systems. When defined as a line's insertion loss, Xlin (or equivalently Xlog) does not include the effect of any transmit filter.
Owner:ASSIA SPE LLC CO THE CORP TRUST CO
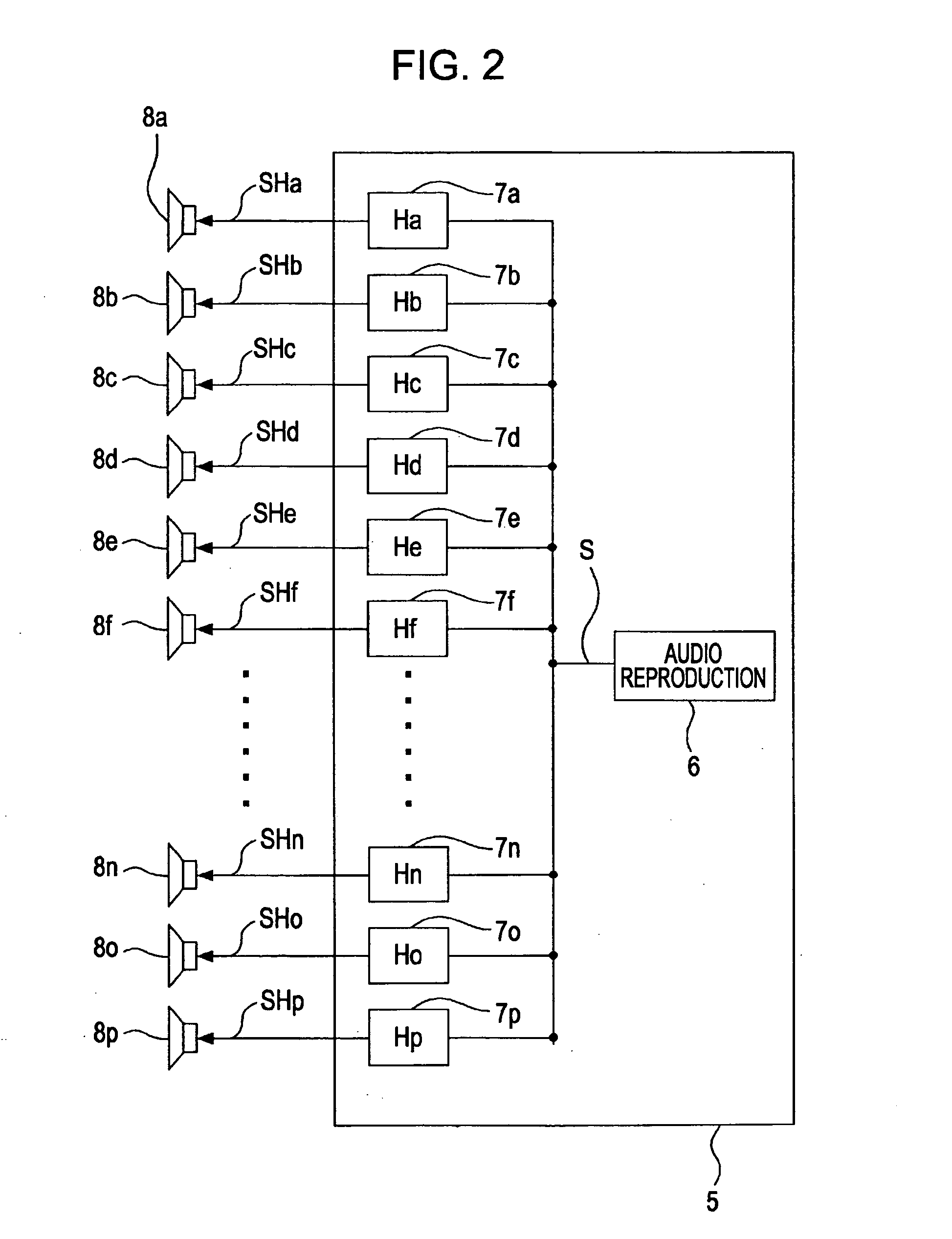
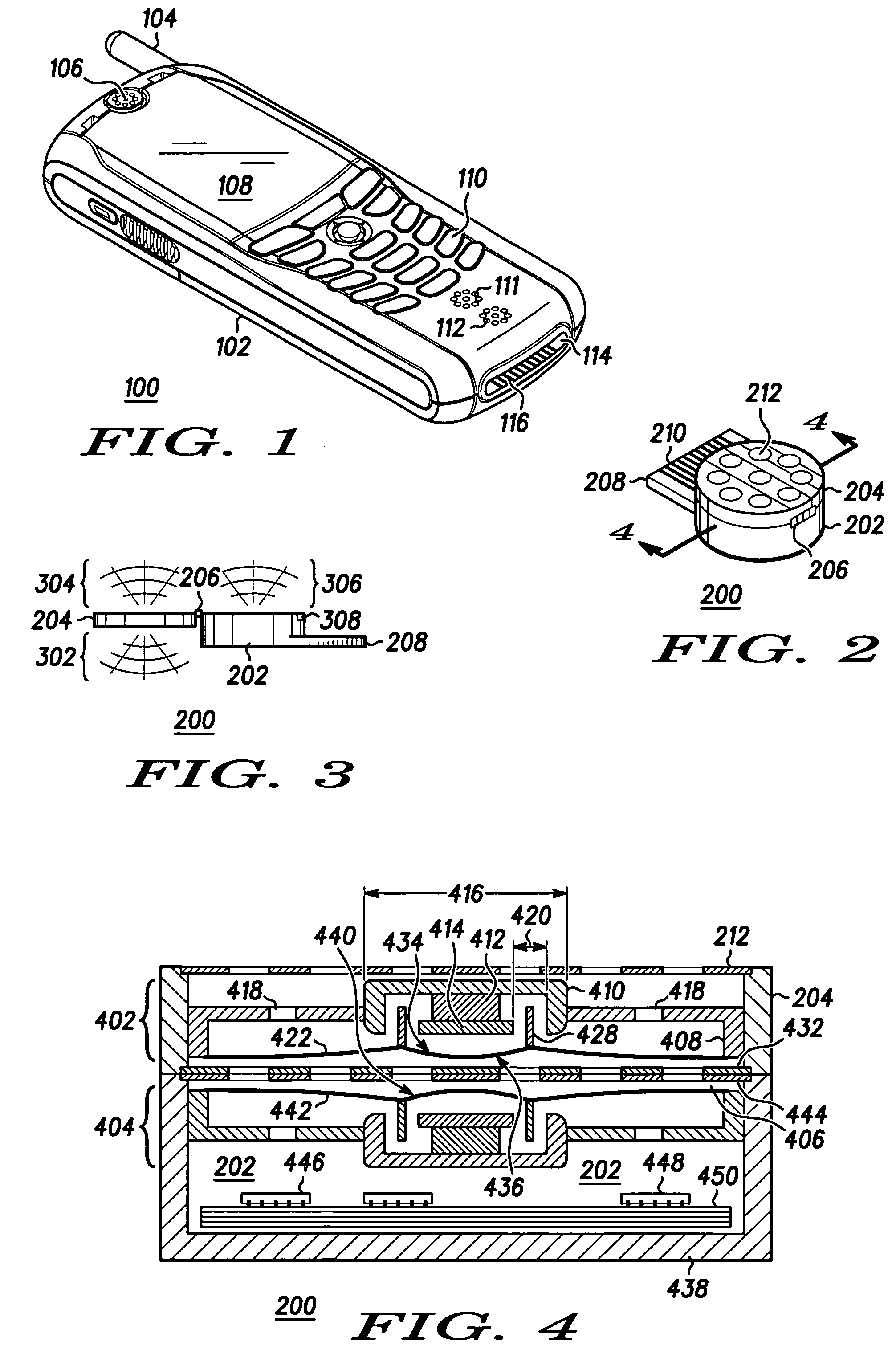
Handheld device loudspeaker system
Loudspeaker systems for handheld devices (2400, 2500) such as cellular telephones (100, 1400, 1600, 1900) are provided. The loudspeaker systems include at least one omnidirectional monopole loudspeaker (404, 1504, 1802, 1918, 1920) and at least one dipole loudspeaker (402, 1502, 1804, 1914, 1916). Filtering is used to compensate for differences between electric-to-acoustic signal transfer functions of the loudspeakers in order to achieve destructive interference of emitted audio in one direction and reinforcement in another direction. Various loudspeaker systems that are reconfigurable from directional mode, to omnidirectional mode are provided. Filtering is also used to add a frequency dependent phase to one signal in order to alter a direction of maximum sound pressure level. Two monopole-dipole pairs can be used to produce a stereo effect. The monopole and dipole loudspeakers can be housed in a detachable loudspeaker accessory (200).
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
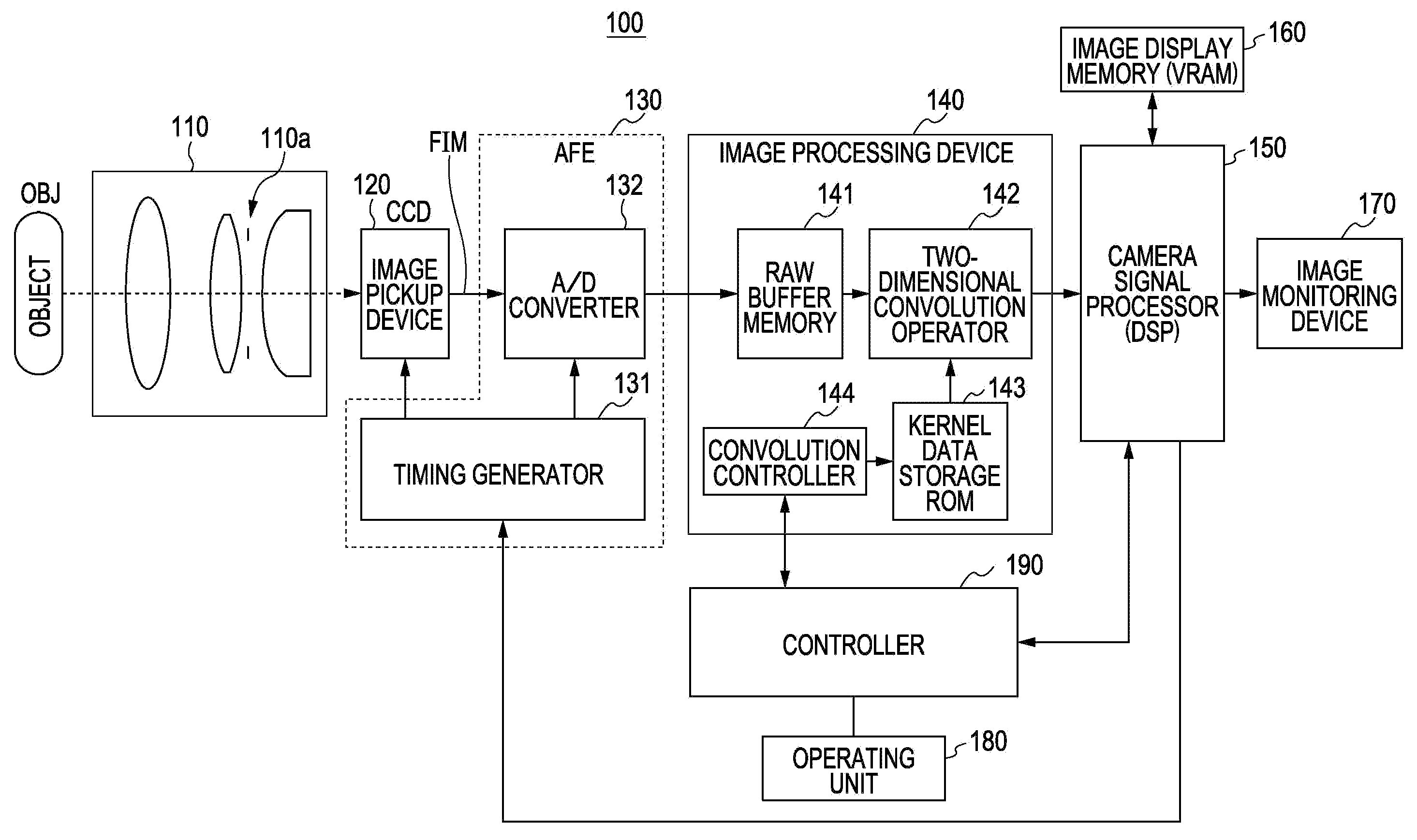
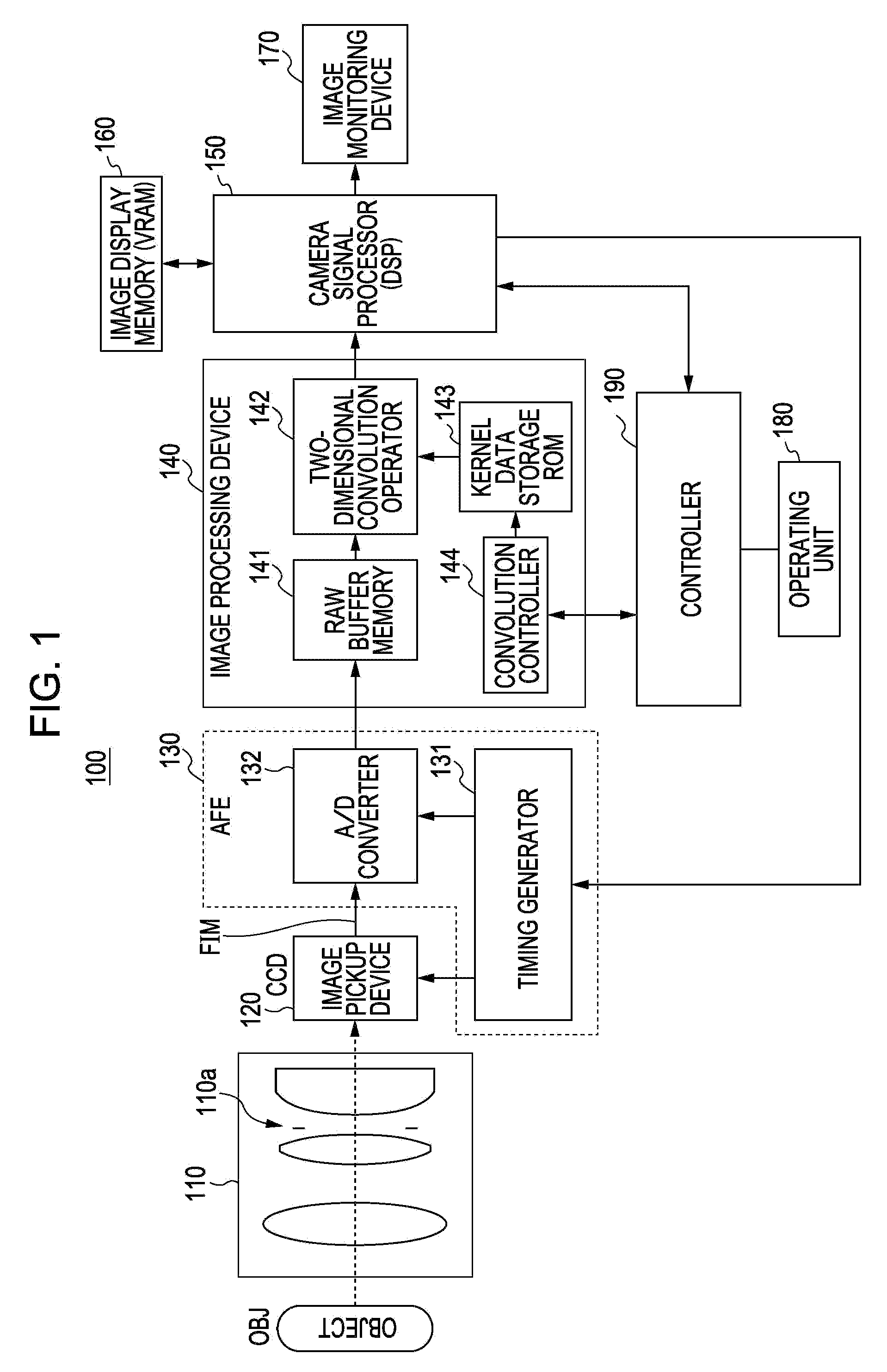
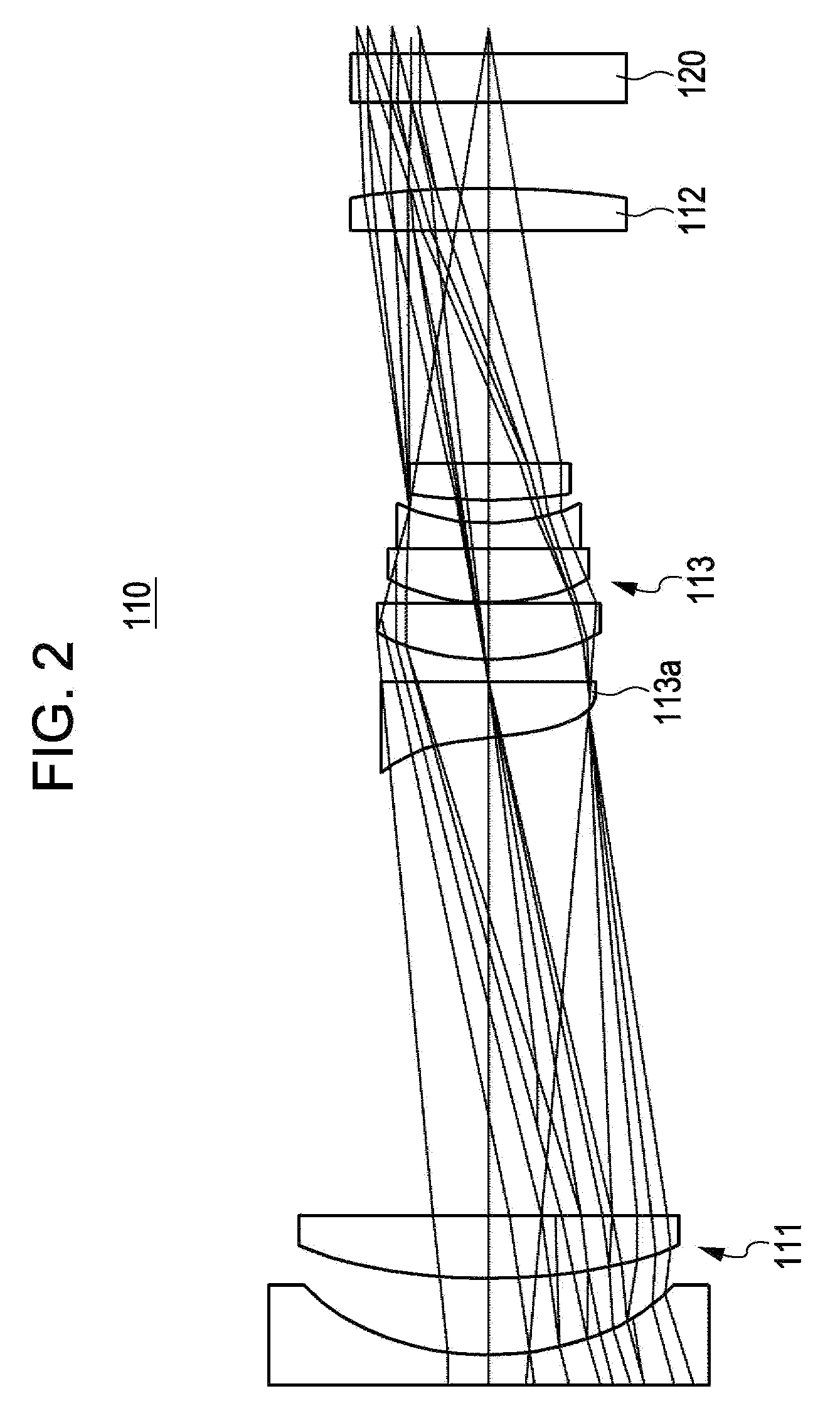
Image pickup apparatus and method and apparatus for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080007797A1Increase contrastLittle blurTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsWavefrontObject based
An image pickup apparatus includes an element-including optical system, a detector, and a converter. The element-including optical system has an optical system and an optical wavefront modulation element which modulates an optical transfer function. The detector picks up an object image that passes through the optical system and the optical wavefront modulation element. The converter generates an image signal with a smaller blur than that of a signal of a blurred object image output from the detector by performing a filtering process of the optical transfer function to improve a contrast. A focal position of the element-including optical system is set by moving the element-including optical system to the focal position which is corresponding to a predetermined object distance using a contrast of the object based on the image signal.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Sound tuning method
The invention relates to a method for automated tuning of a sound system, the sound system comprising delay lines, equalizing filters, and at least two loudspeakers, the method comprising the steps of reproducing a useful sound signal through the loudspeakers, measuring sound pressure values at least one location, providing a target transfer function for tuning the delay lines and the equalizing filters of the sound system, the target transfer function representing a desired transfer characteristics of the sound system, adjusting the delay of the delay lines, and adjusting amplitude responses of the equalizing filters such, that the actual transfer characteristics of the sound system approximates the target function.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Weld surface defect identification method based on image texture
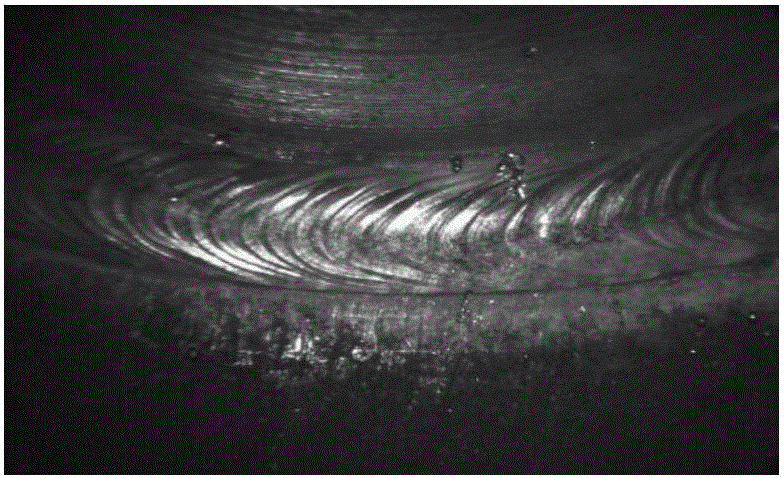
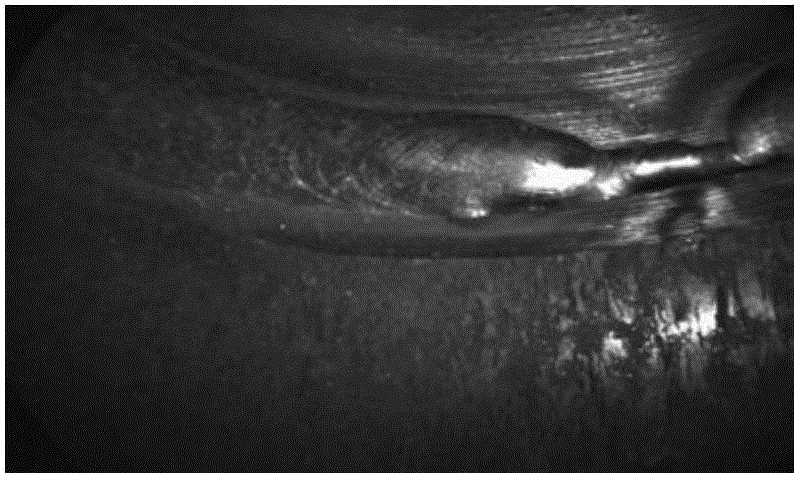
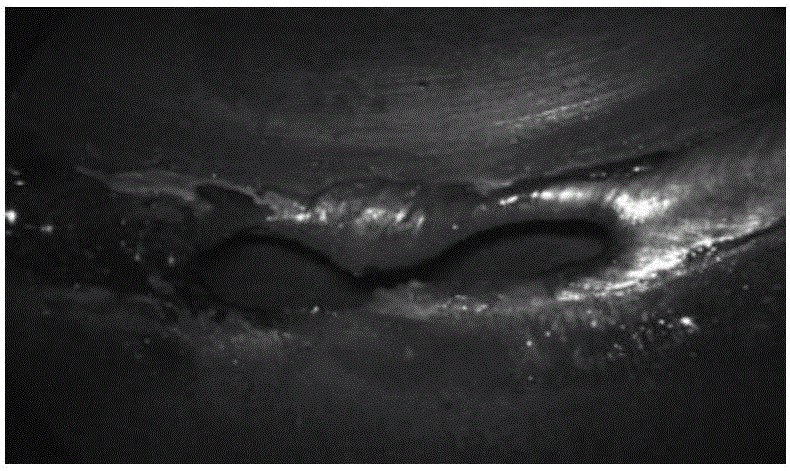
InactiveCN105938563AEffectively distinguish texture featuresRealize classification recognitionCharacter and pattern recognitionOptically investigating flaws/contaminationColor imageSample image
The invention provides a weld surface defect identification method based on image texture. Miniature CCD camera photographing parameters are set according to the acquisition image standard; an acquired true color image is converted into a grey-scale map, and a gray scale co-occurrence matrix is created; 24 characteristic parameters in total, including energy, contrast, correlation, homogeneity, entropy and variance, are respectively extracted in the direction of 0 degree, 45 degrees, 90 degrees and 135 degrees, and normalization processing is performed on the extracted characteristic parameters; a BP neural network is trained by utilizing a training sample image, and the number of neurons of the neural network, a hidden layer transfer function, an output layer transfer function and a training algorithm transfer function are set; test sample characteristic parameters are outputted to the trained BP neural network to perform classification and identification; and the matching degree of the test sample and different types of surface welding quality training samples is calculated so that automatic classification and identification of the test sample surface welding quality can be completed.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Image processing method, image processing apparatus, and image pickup apparatus for correcting degradation component of image
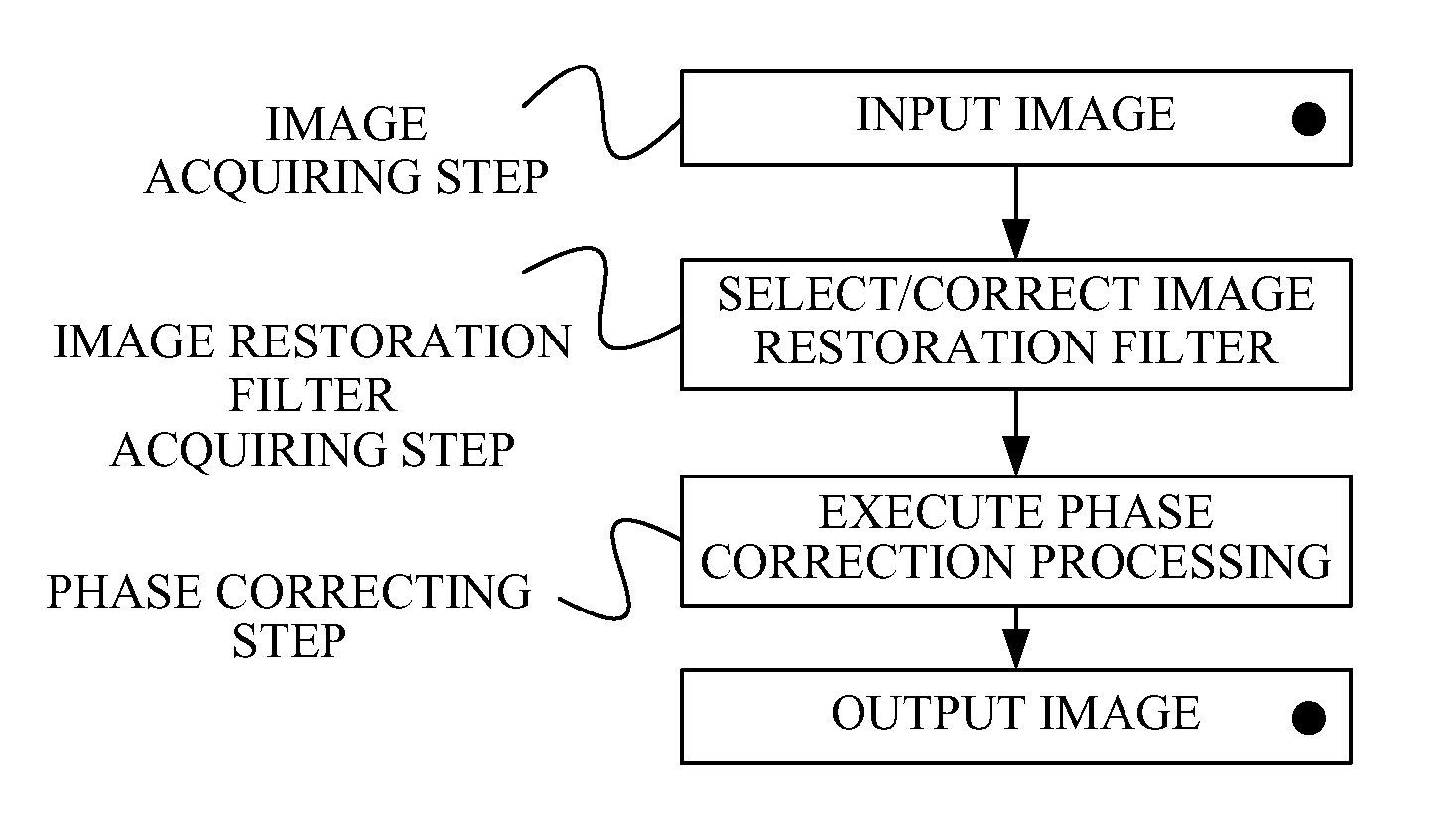
ActiveUS20110135216A1Reduce componentsImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingImage restoration
An image processing method includes the steps of obtaining an image generated by an image pickup system, and performing correction processing for the image by utilizing an image restoration filter generated or selected based on an optical transfer function of the image pickup system. The image restoration filter is a filter configured to reduce a phase degradation component of the image.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com