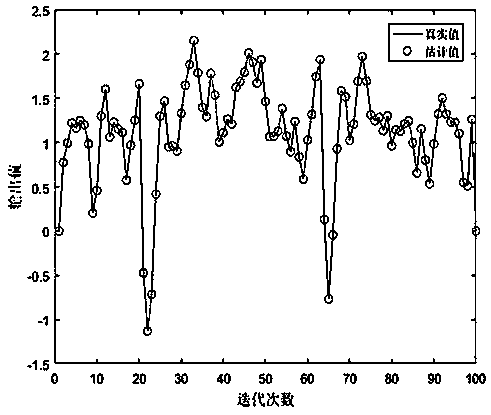
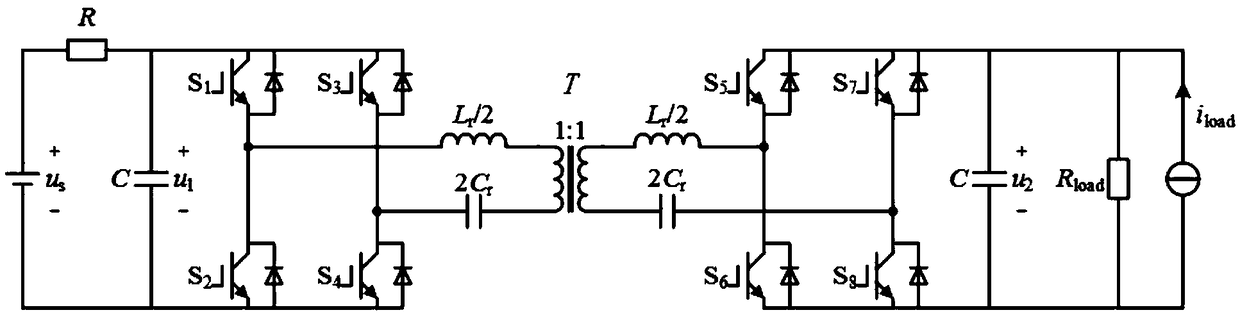
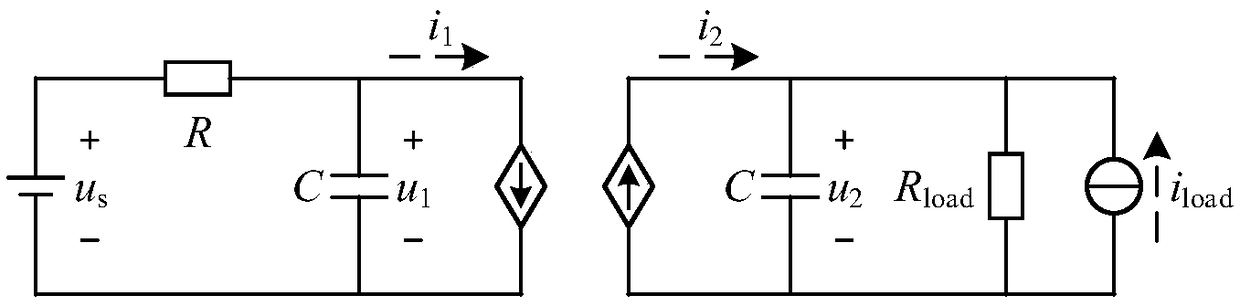
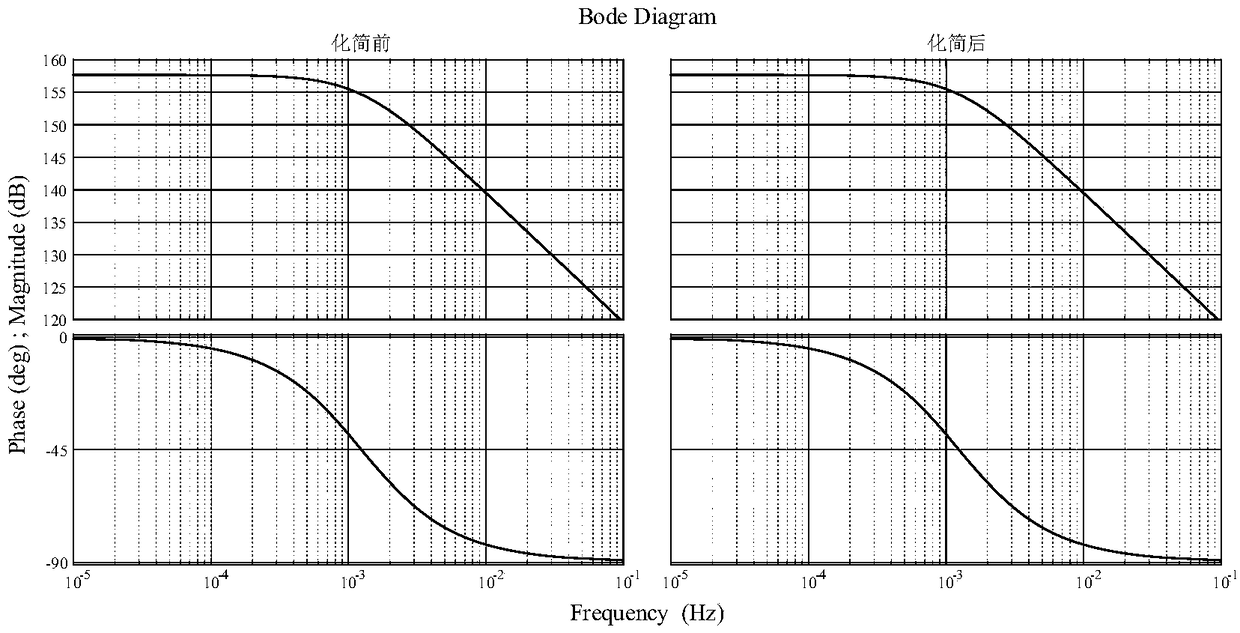
Patents
Literature
62 results about "Nonlinear transfer function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
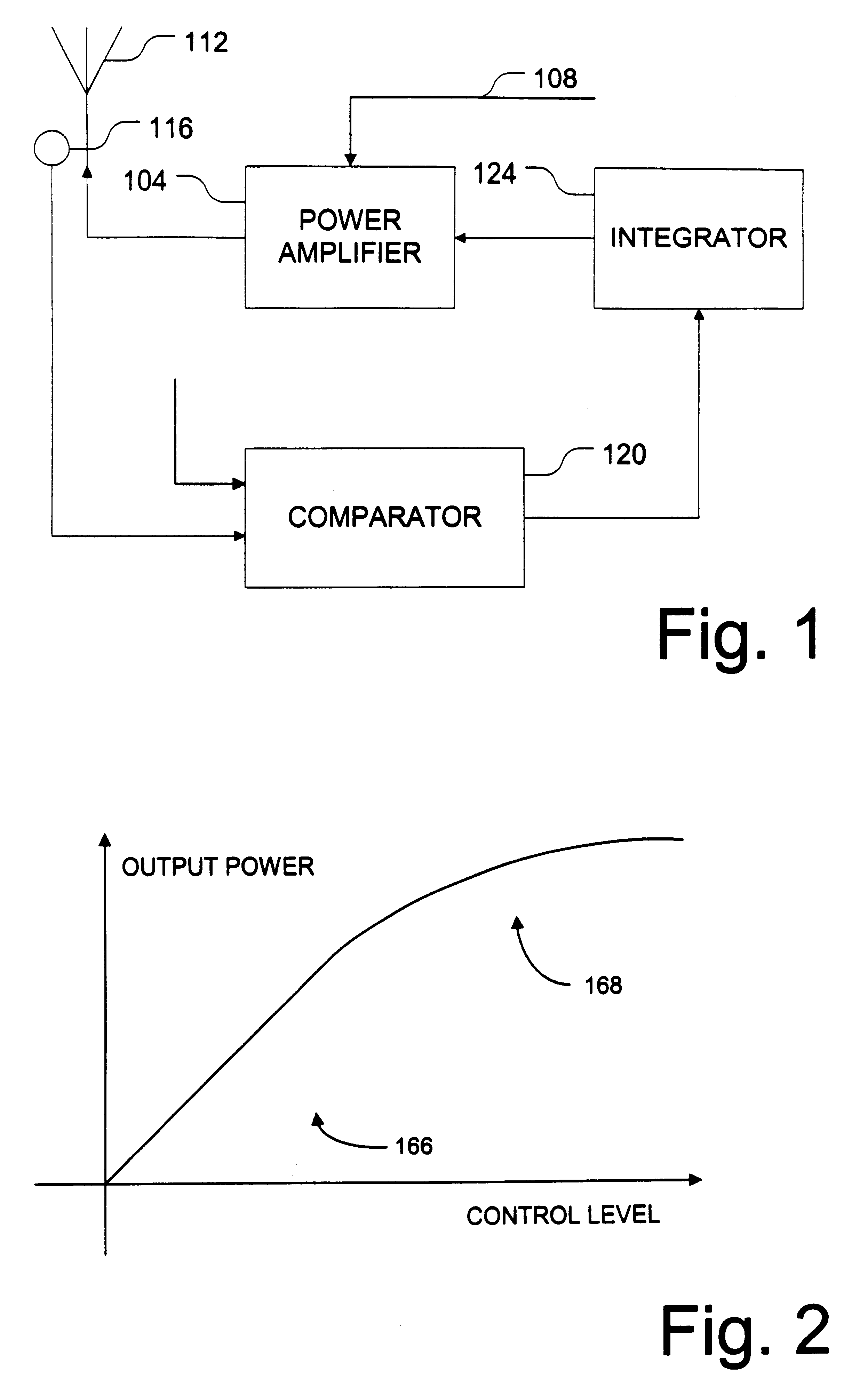
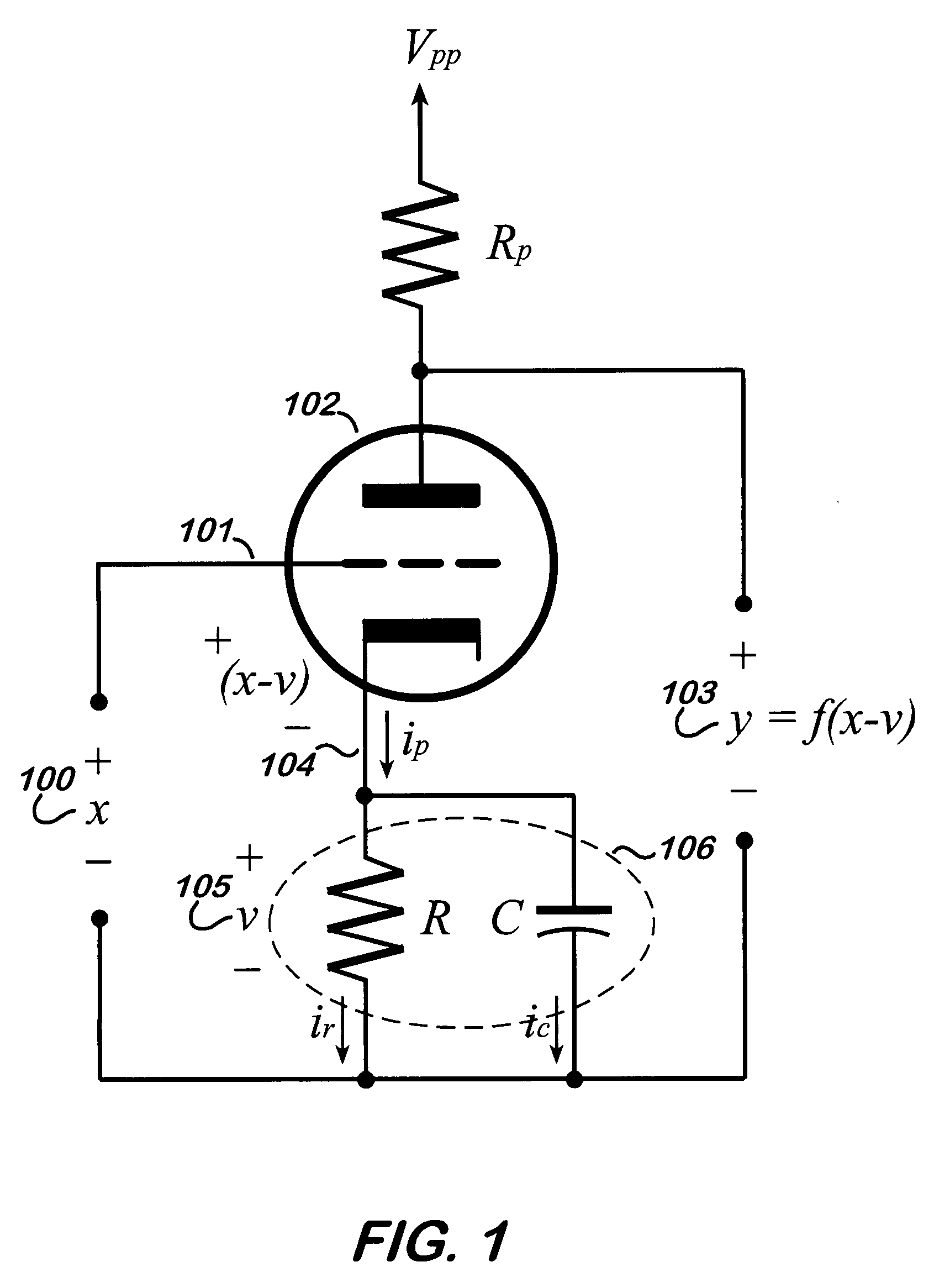
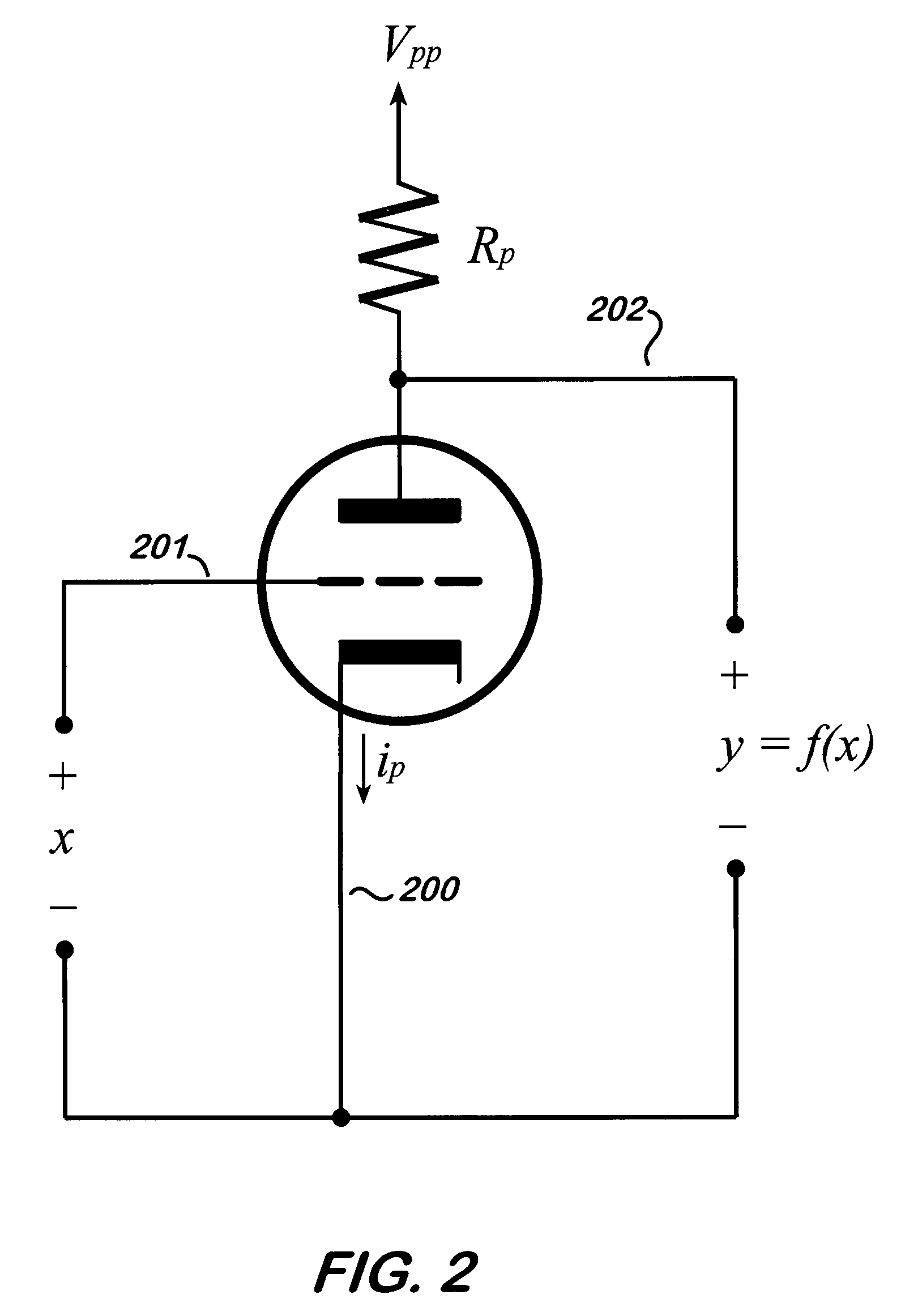
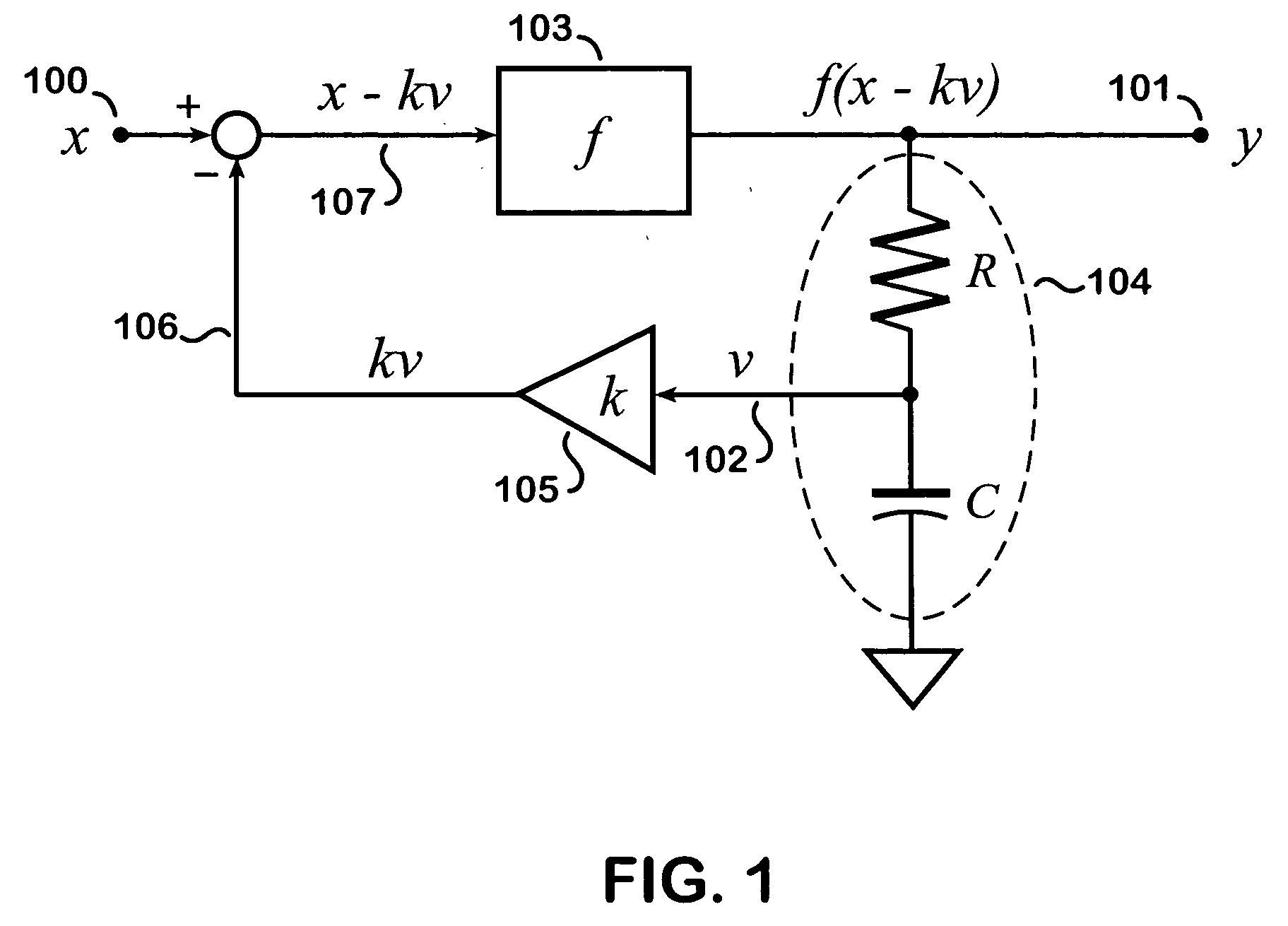
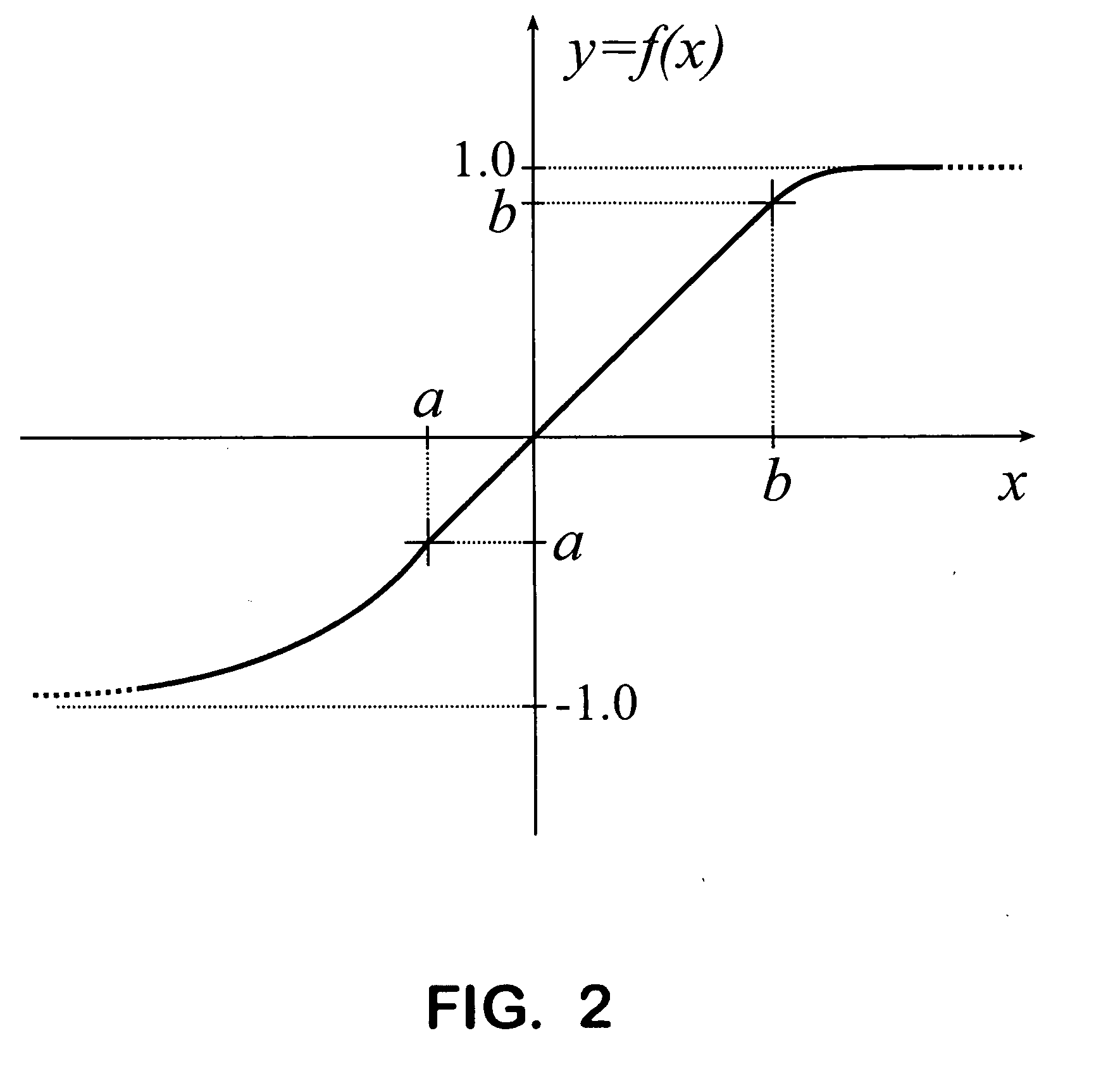
RE: Derive Non-Linear Transfer Function. A transfer function (in the continuous-time domain) is the ratio of the output of a linear time-invariant system to the input of the system, in the s-domain, when all initial conditions are zero.
Amplifier linearizer
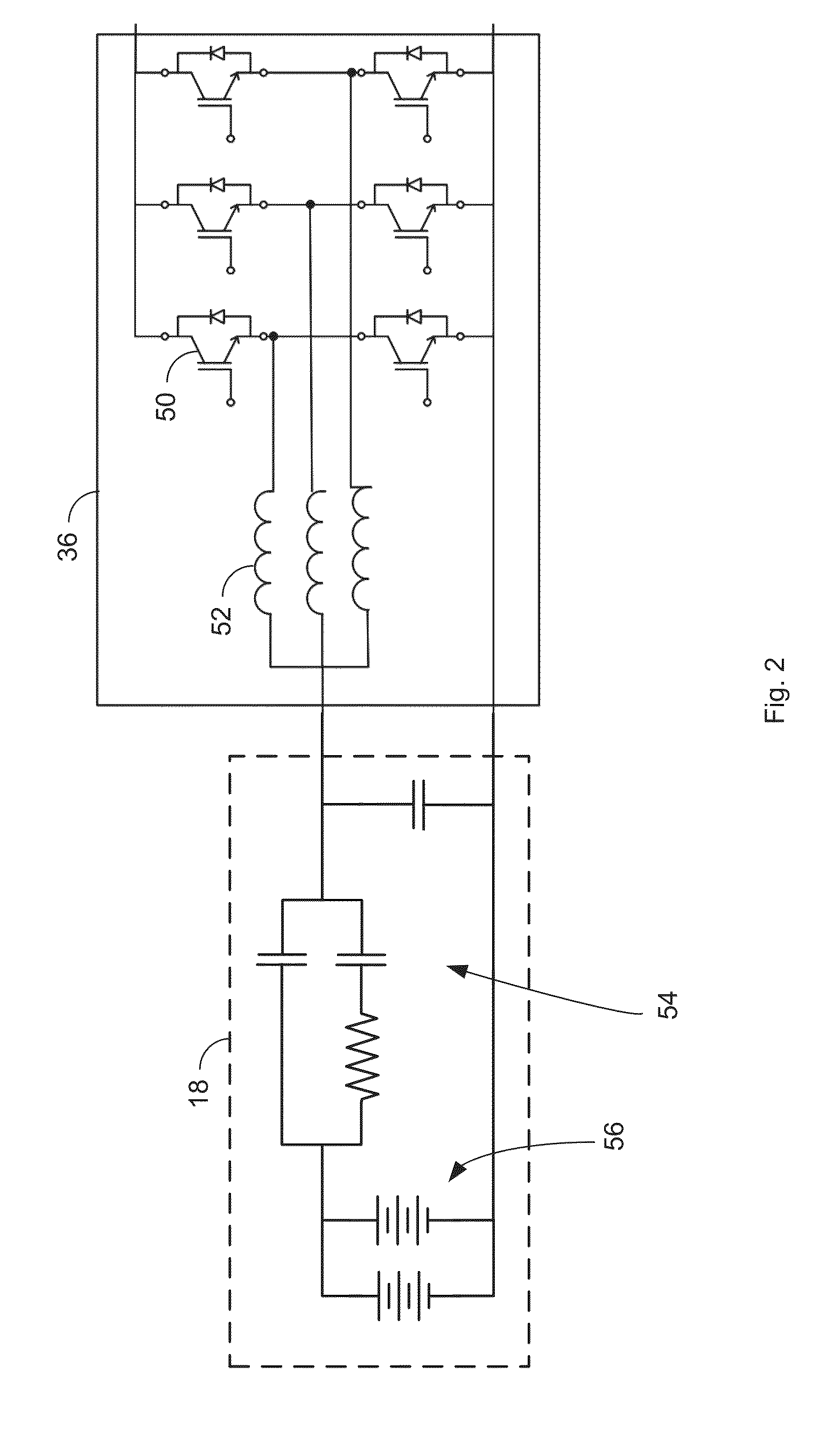
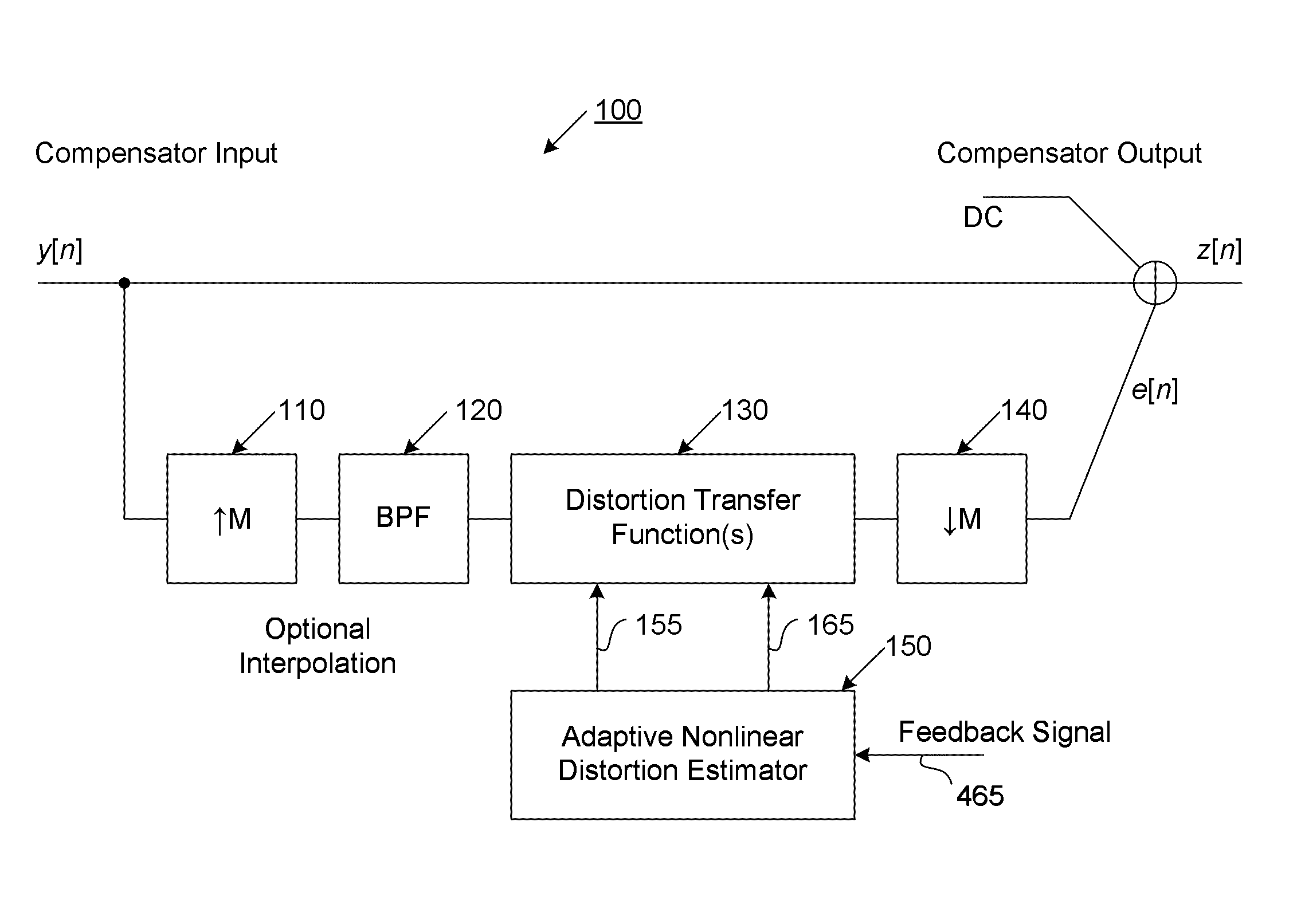
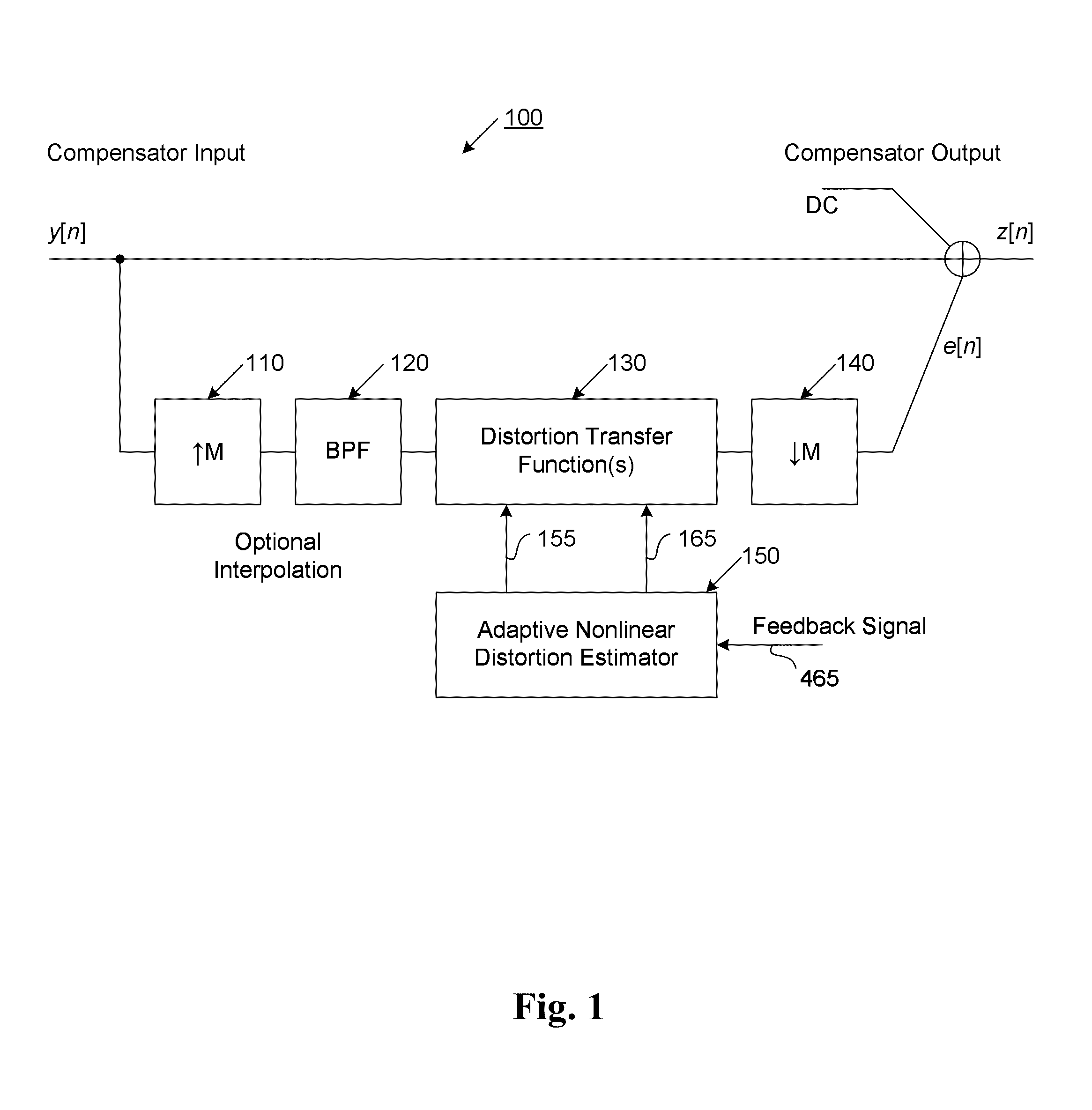
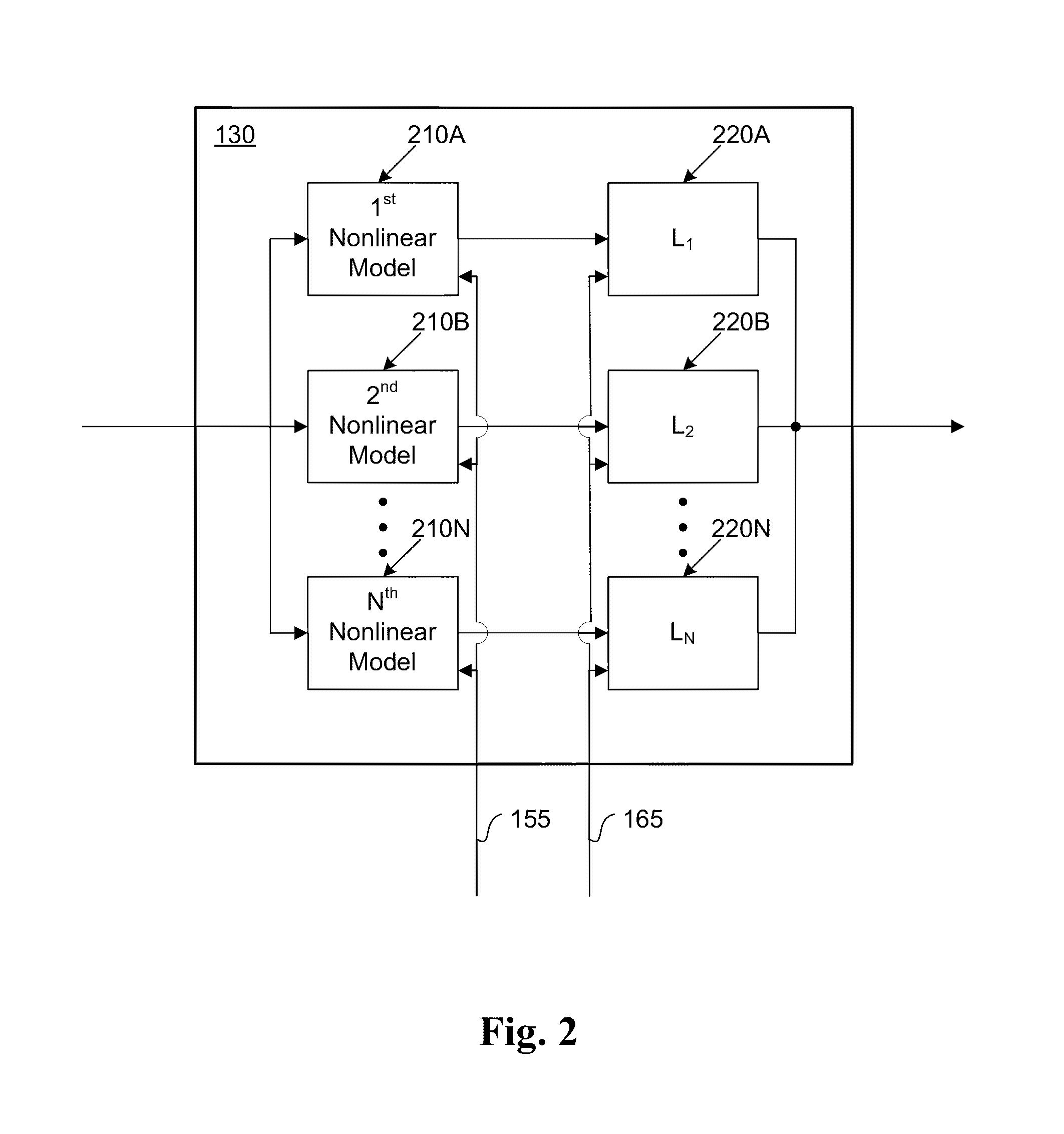
ActiveUS20110095819A1Reduce nonlinear distortionLow powerResonant long antennasElectric signal transmission systemsNonlinear distortionCurve fitting
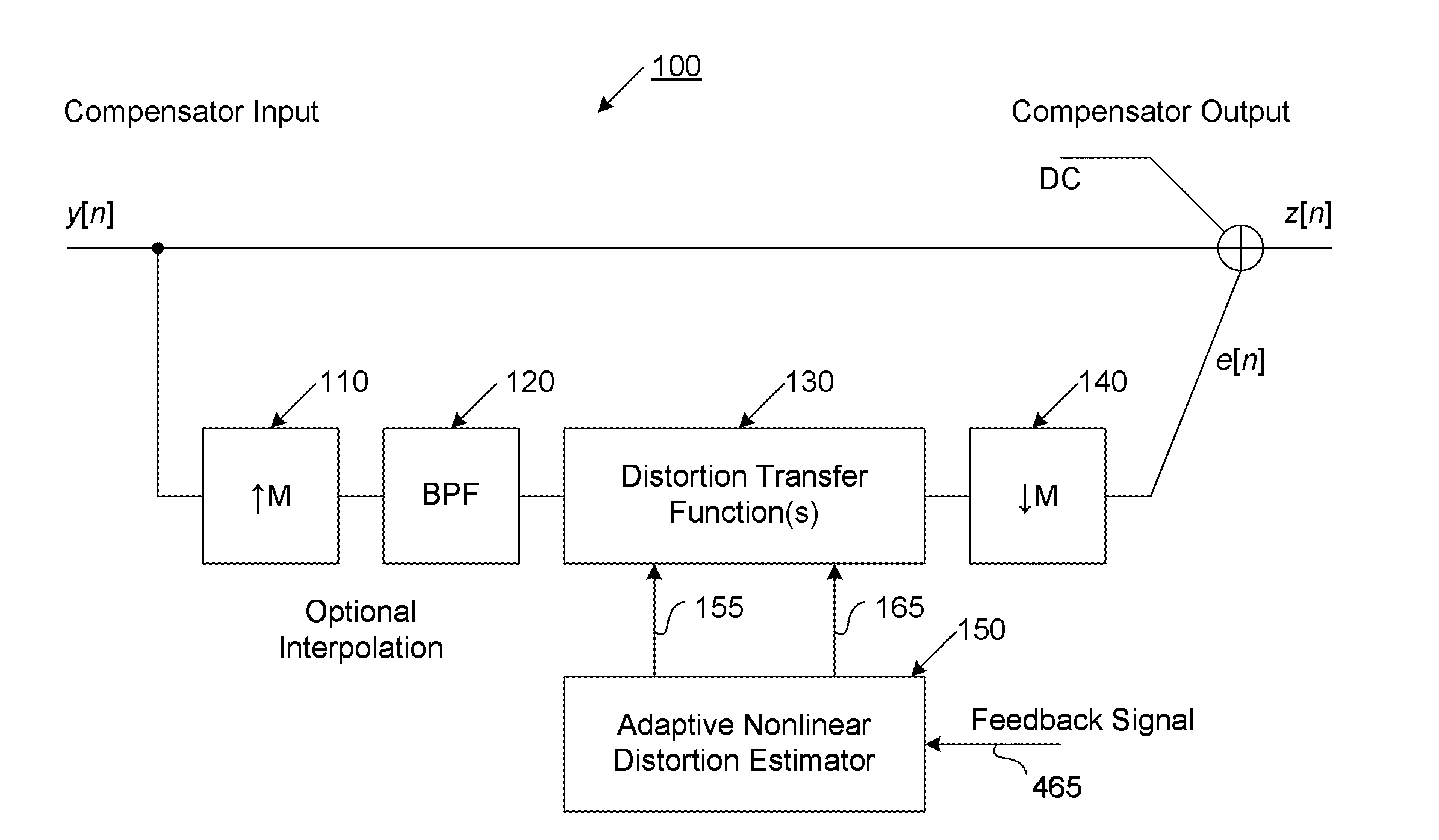
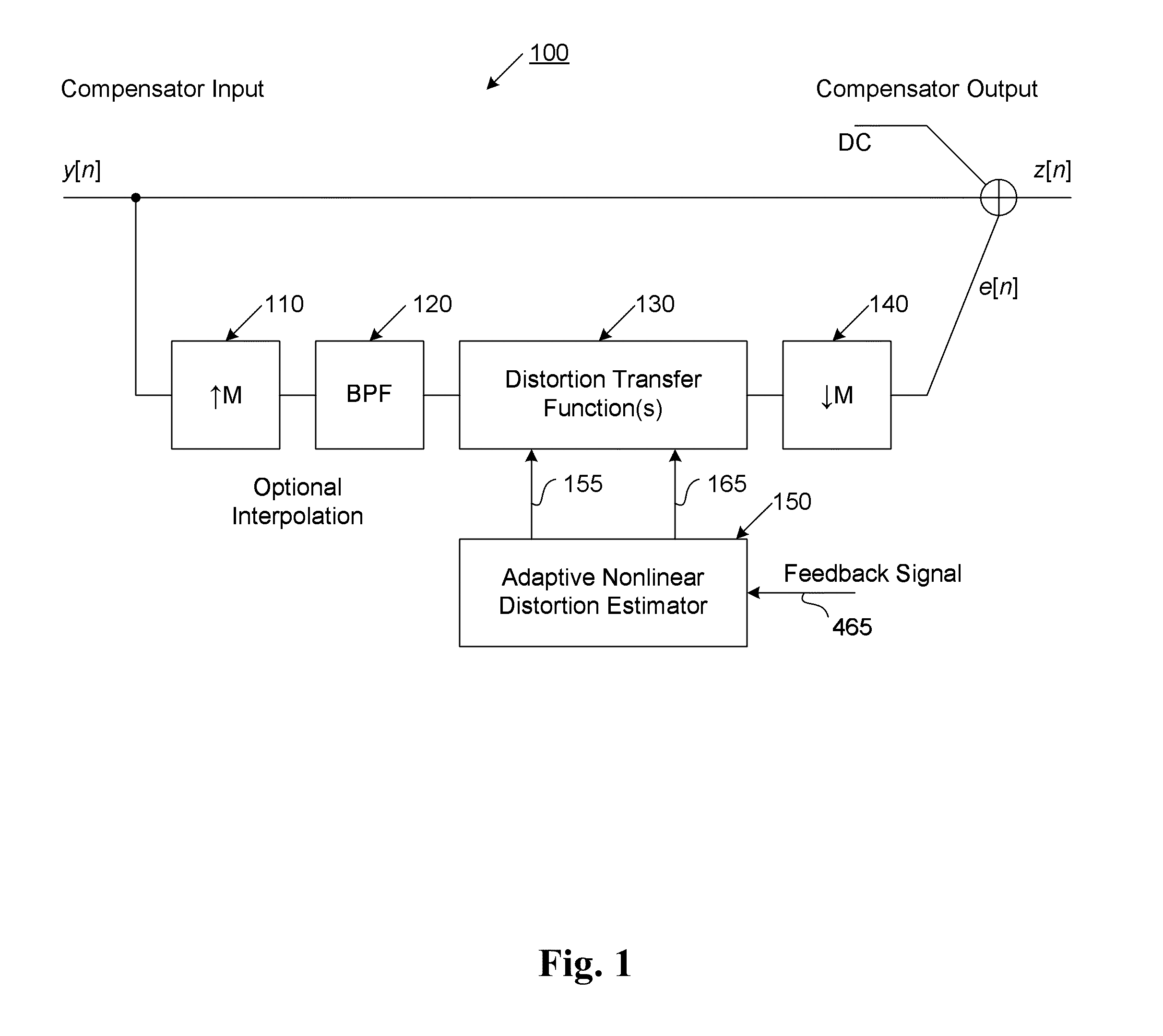
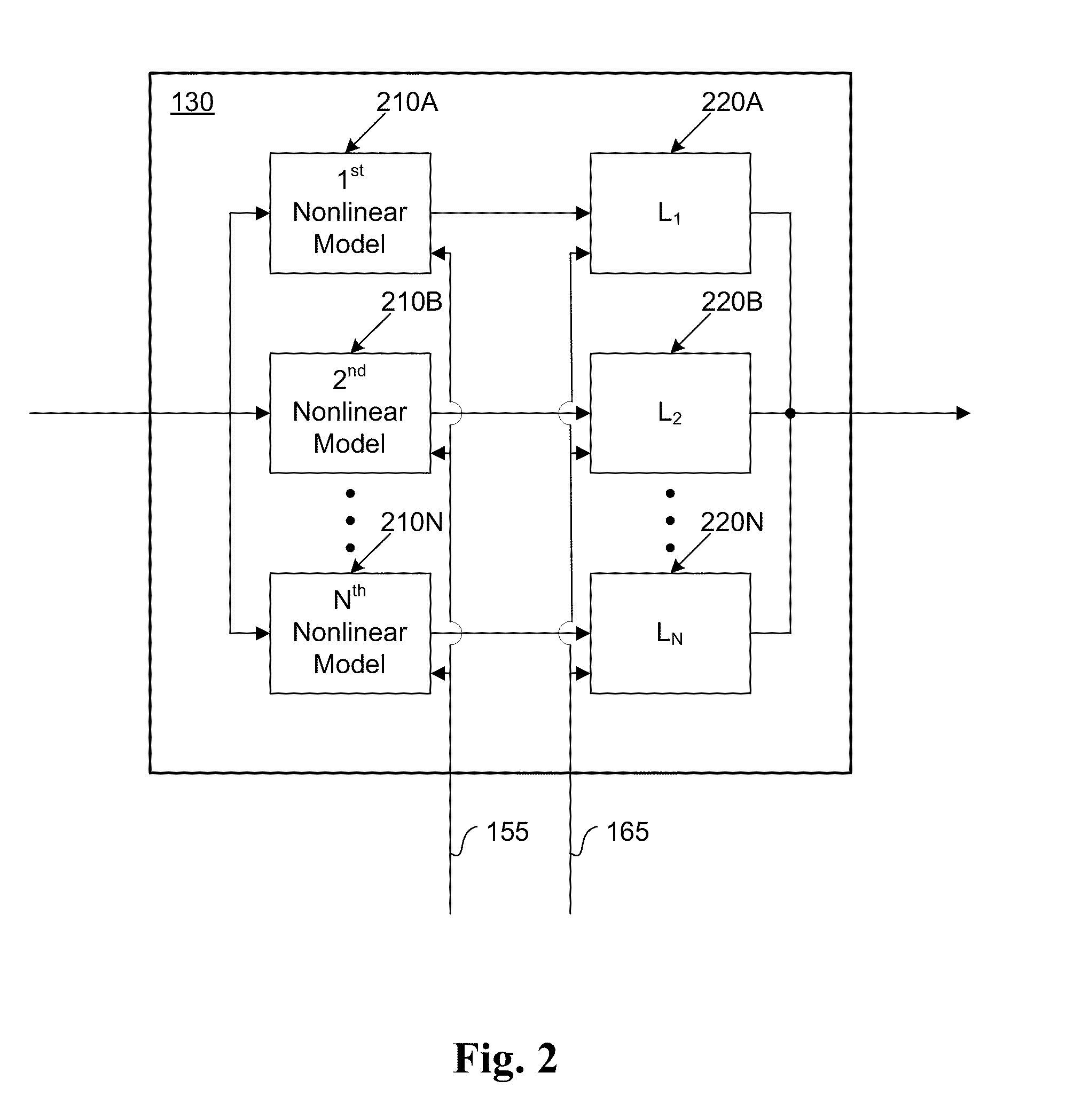
The present invention provides an advanced adaptive predistortion linearization technique to dramatically reduce nonlinear distortion in power amplifiers over a very wide instantaneous bandwidth (up to 2 GHz) and over a wide range of amplifier types, input frequencies, signal types, amplitudes, temperature, and other environmental and signal conditions. In an embodiment of the invention, the predistortion linearization circuitry comprises (1) a higher-order polynomial model of an amplifier's gain and phase characteristics—higher than a third-order polynomial model; (2) an adaptive calibration technique; and (3) a heuristic calibration technique. The higher-order polynomial model is generated by introducing, for example, a plurality of multi-tone test signals with varying center frequency and spacing into the power amplifier. From the power amplifier's corresponding output, the nonlinearities are modeled by employing a higher-order curve fit to capture the irregularities in the nonlinear transfer function. Different distortion transfer functions can be implemented for different operating conditions. The adaptive calibration technique is based on a feedback analysis technique, which updates the applicable distortion transfer function by analyzing the error signal between the introduced input signal and the output signal in real-time. The heuristic calibration technique implements different distortion transfer functions based on historical operating conditions and optimal configurations of the power amplifier.
Owner:TM IP HLDG LLC
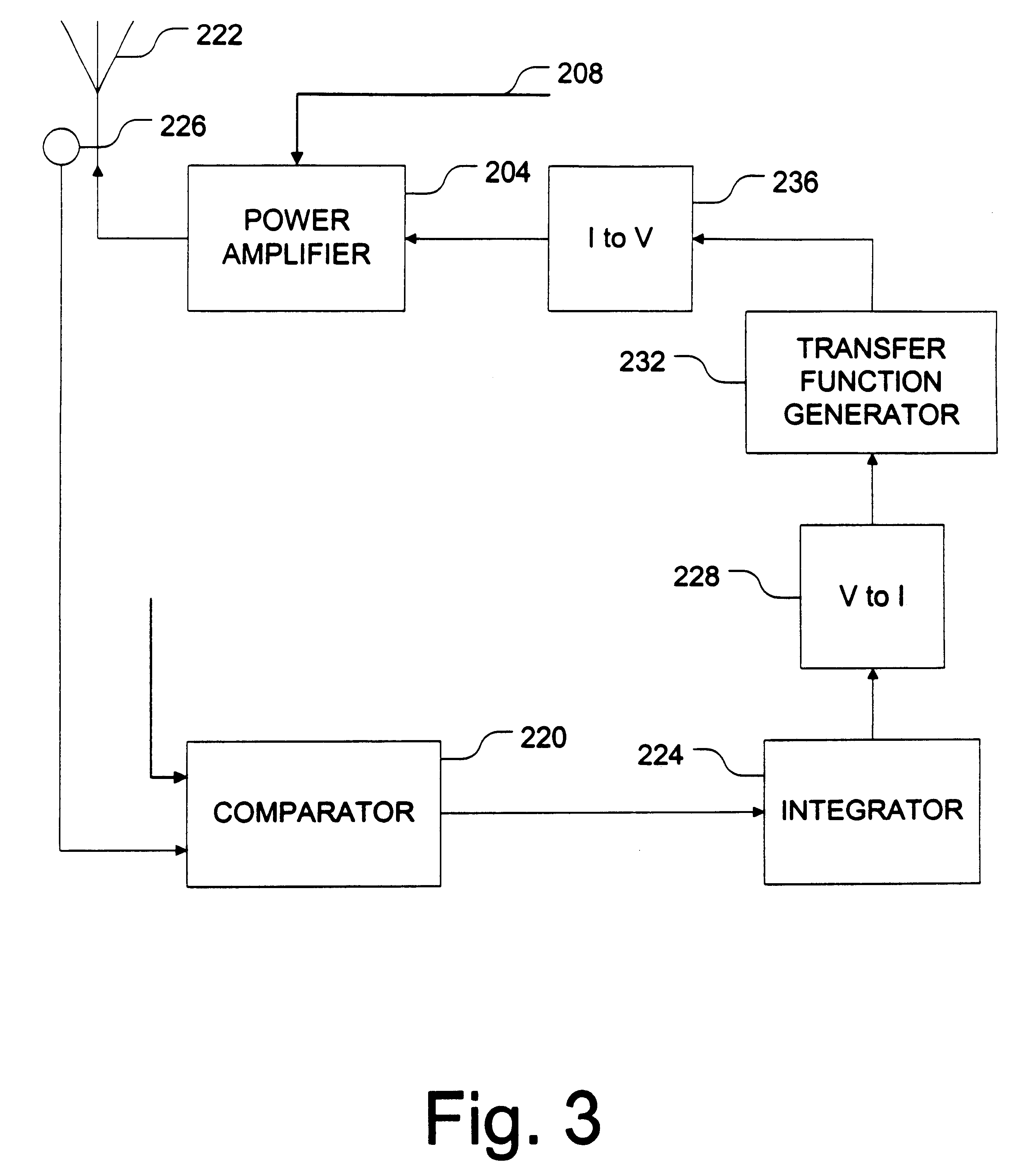
Distortion control feedback loop utilizing a non-linear transfer function generator to compensate for non-linearities in a transmitter circuit
InactiveUS6321072B1Adjustable outputLimiting output levelAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasFunction generatorTransmitter
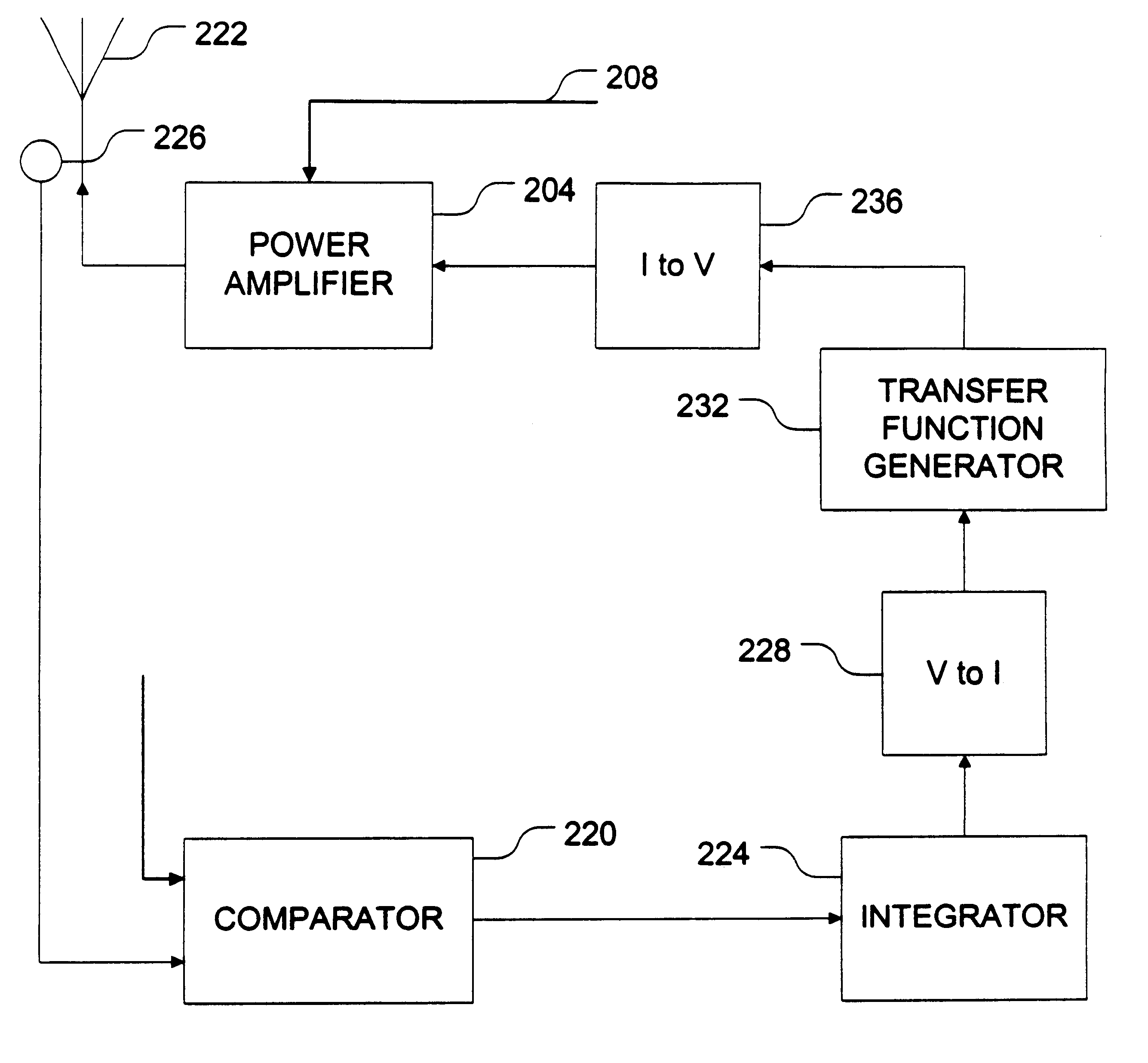
A transfer function generator provides the ability to provide a non-linear response in a feedback loop to compensate for non-linearities introduced elsewhere in the system. The transfer function generator includes a non-linear function generator configured to provide an output current that is a non-linear function of an input signal representing an error to be corrected. The transfer function generator can also include a linear function generator configure to provide a linear output current as a function of an input current representing the error corrected. Tuning devices can be provided to adjust the turn-on level of the non-linear function generator and the output level of the linear function generator to allow the transfer function generator flexibility in implementation.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
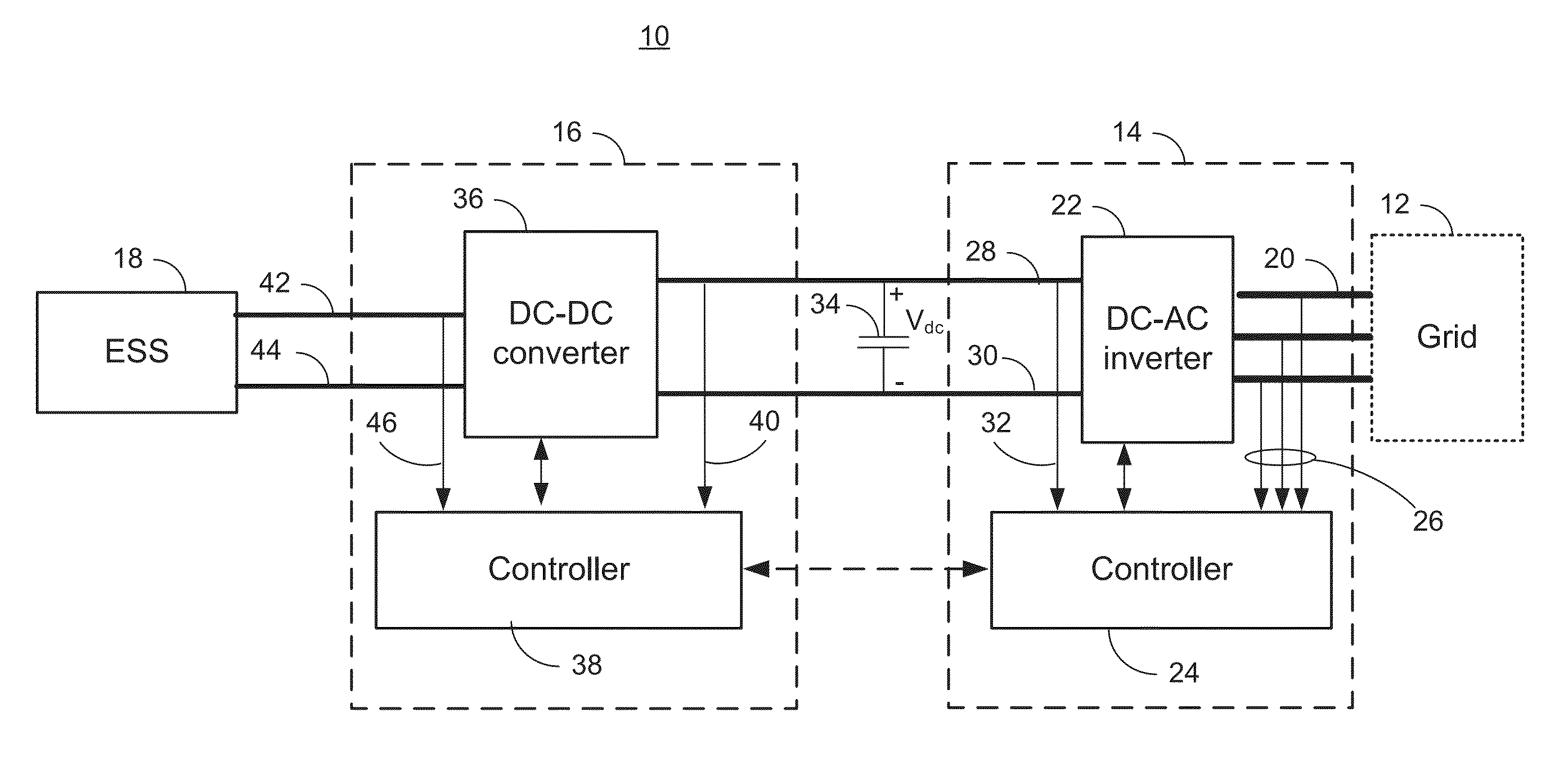
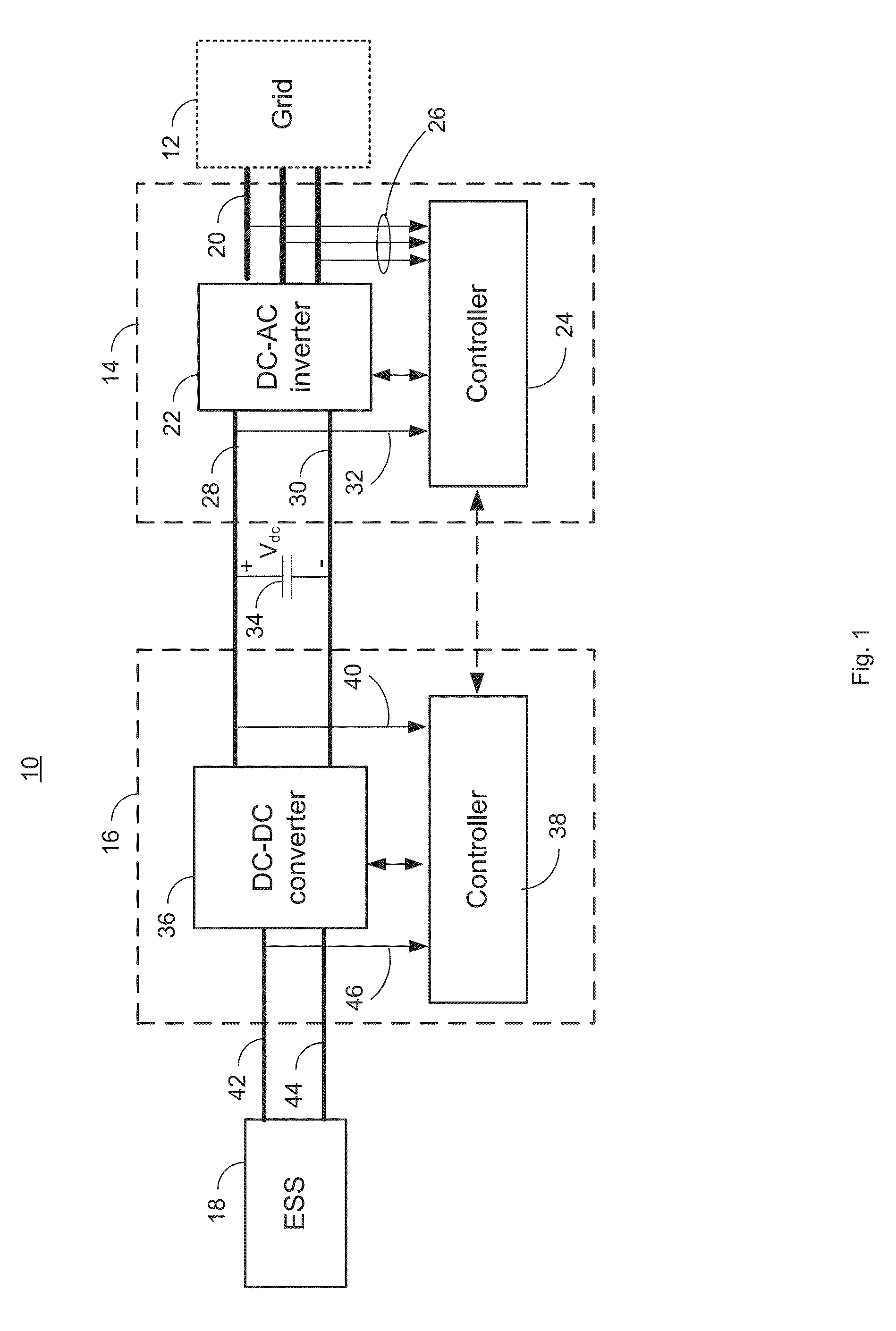
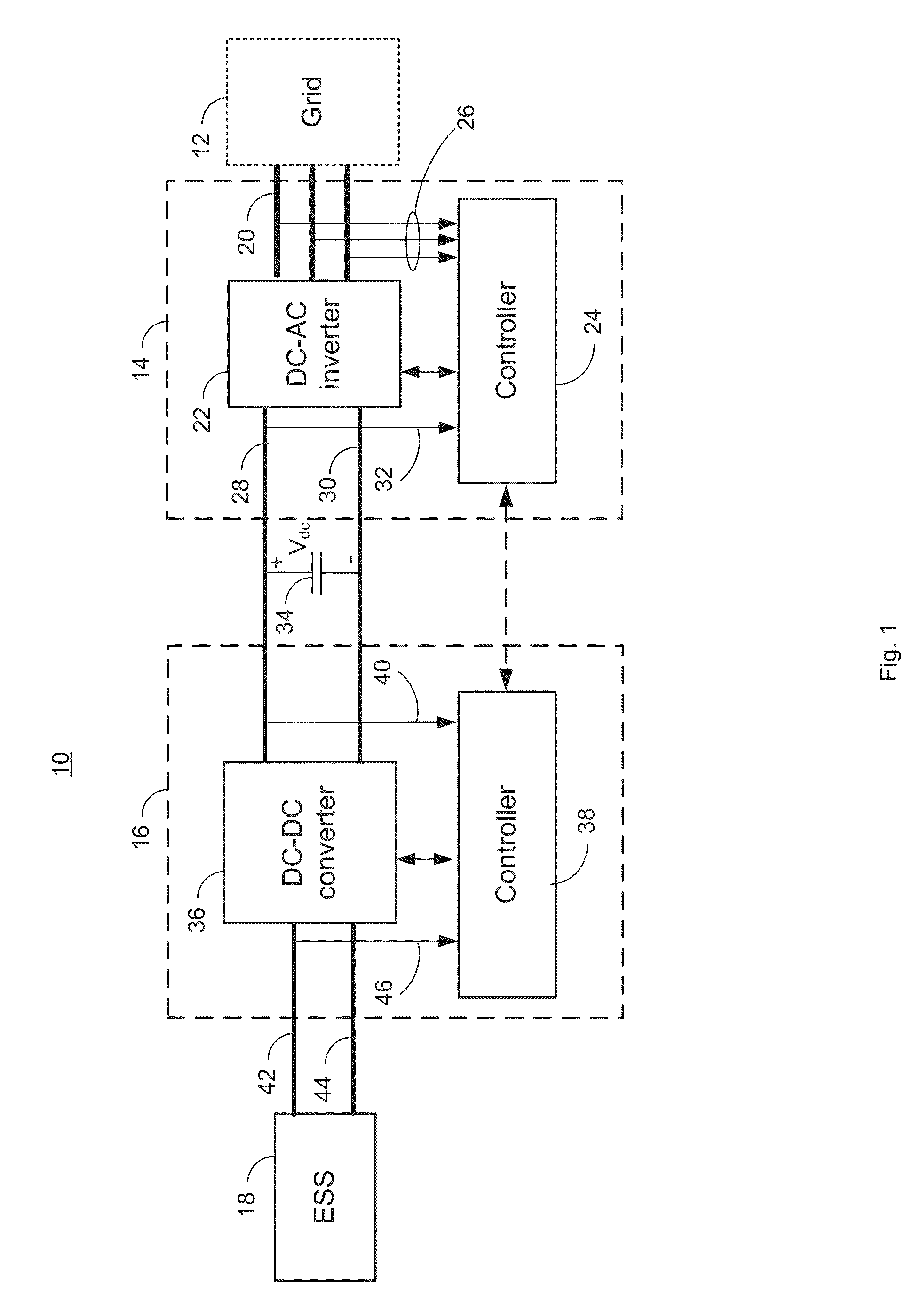
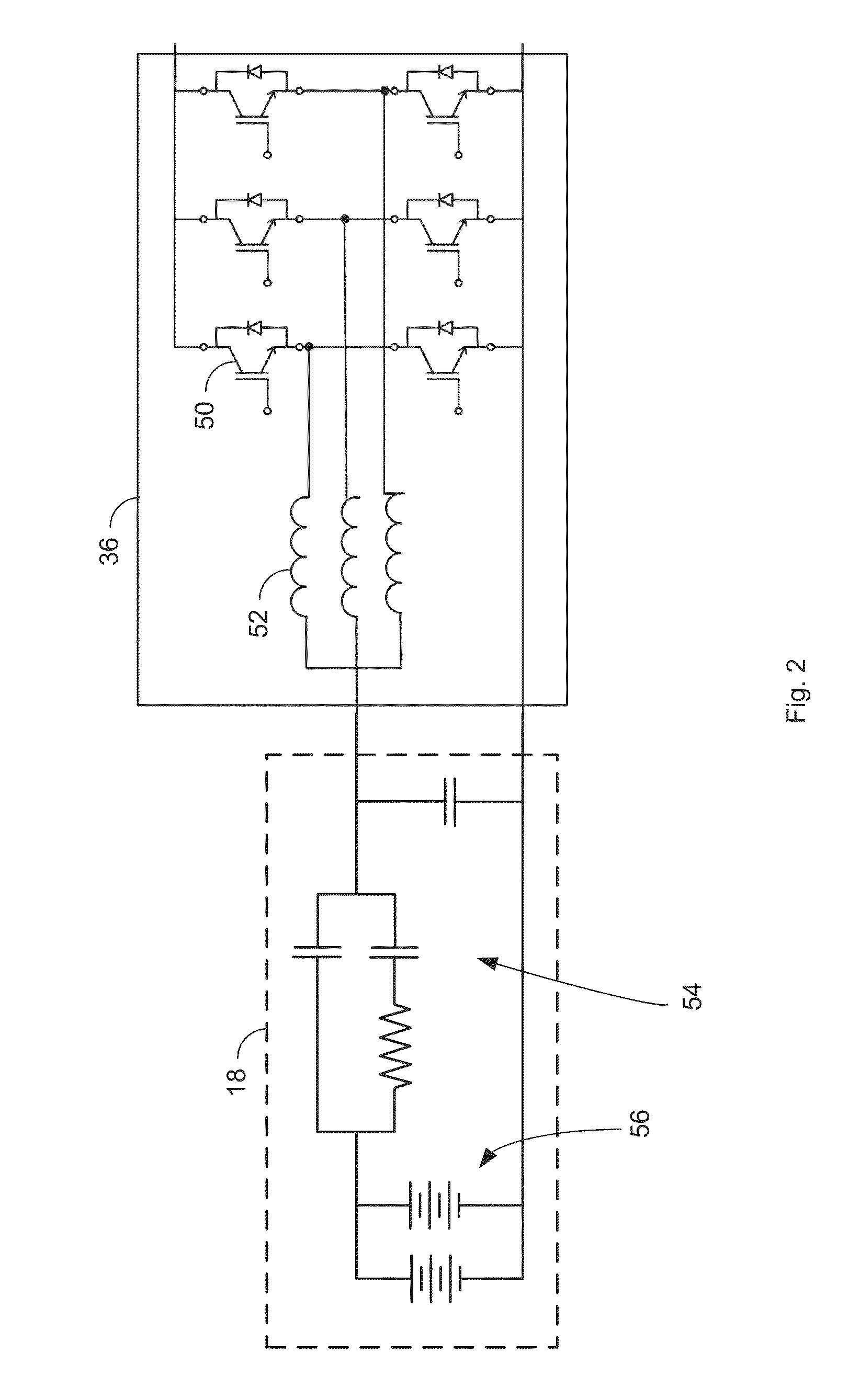
Control of Energy Storage System Inverter System in a Microgrid Application
ActiveUS20140218985A1Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionElectric power transmissionFast charging
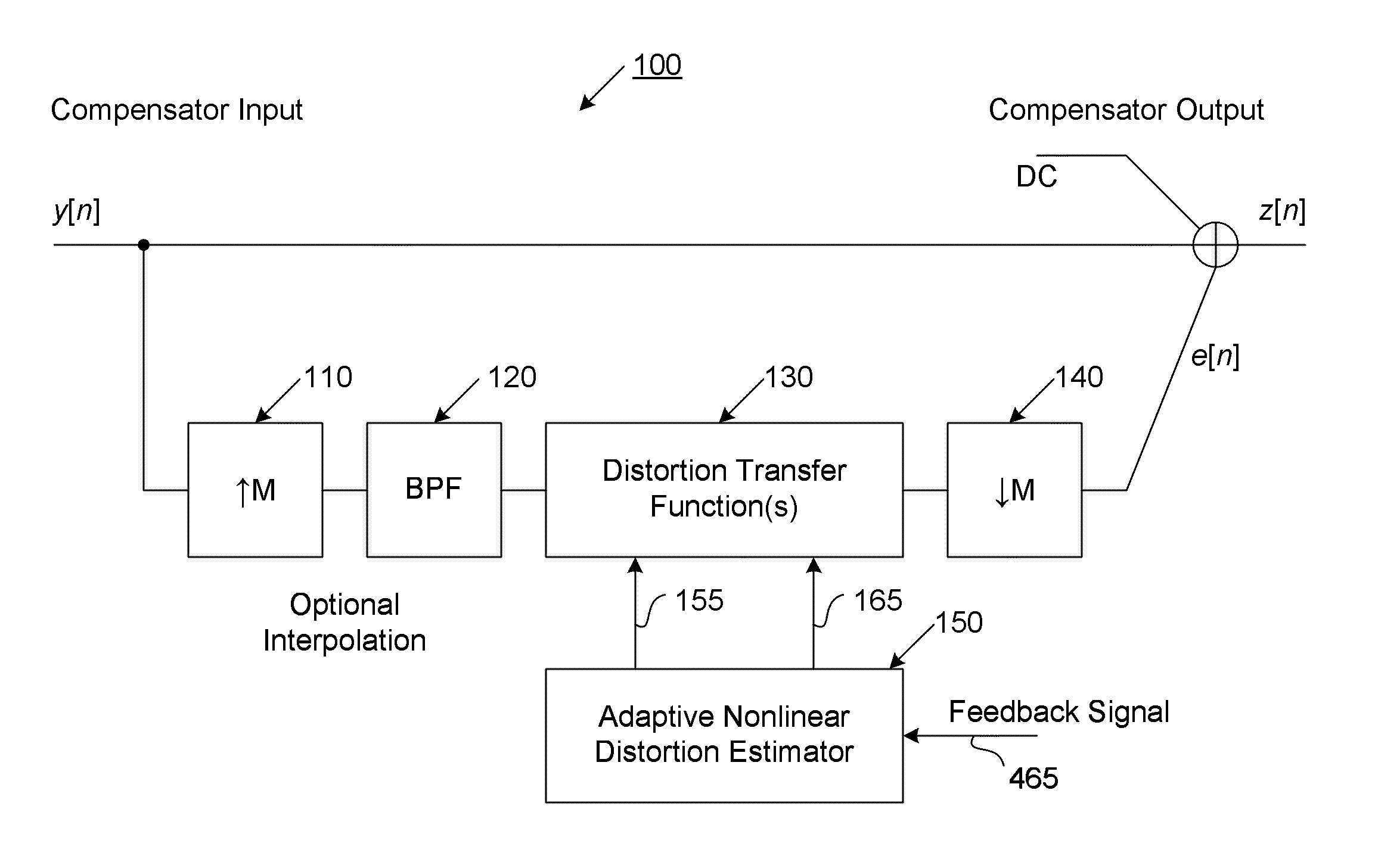
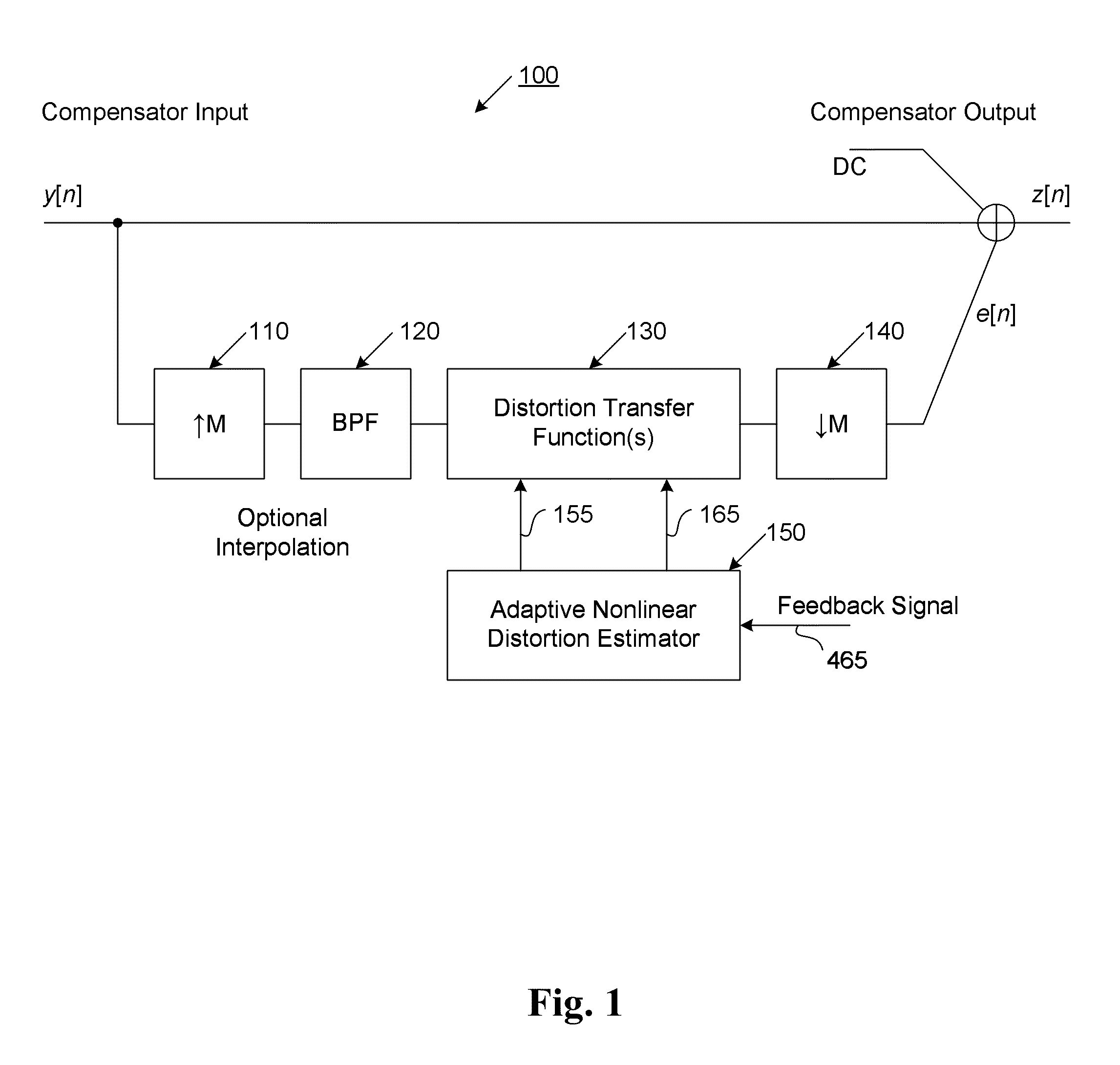
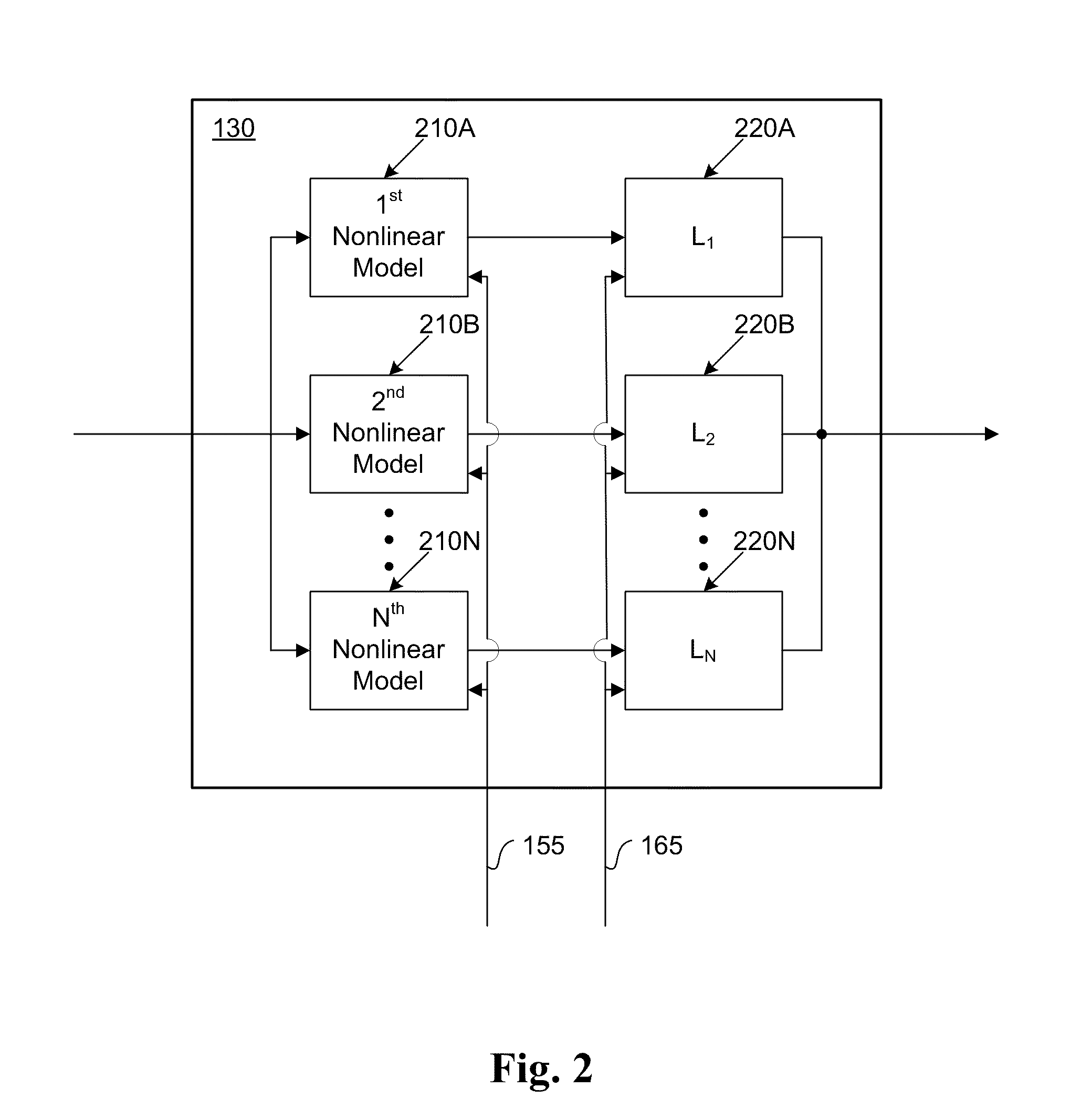
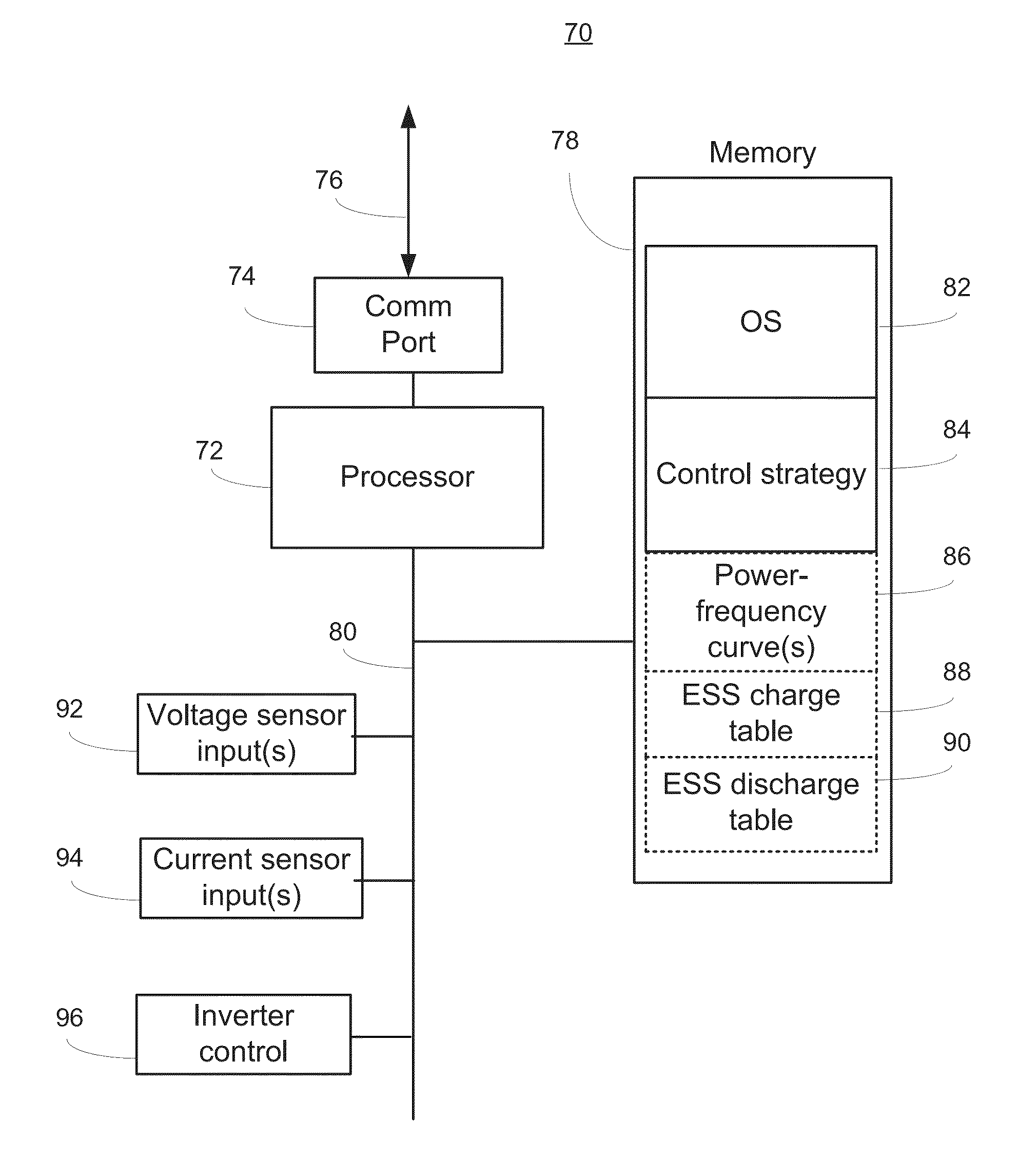
A system that manages a supplemental energy source connected to a power grid uses a two stage control strategy to manage power transfers in and out of the power grid as well as in and out of an energy storage system, such as a battery bank. One stage uses a non-linear transfer function to control an output frequency of a DC-to-AC inverter to limit undesired effects of power transients that occur on the grid. A second stage uses control strategy for transferring energy between the energy storage system and an internal DC link based on a relationship between a voltage on a DC link connecting the first and second stages and a DC link reference voltage, the voltage on the DC link, and a voltage at the energy storage system. The control strategy includes rapid charging, over-charging protection, and grid transient stabilization.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Amplifier linearizer
ActiveUS7940198B1Reduce nonlinear distortionLow powerResonant long antennasElectric signal transmission systemsNonlinear distortionCurve fitting
The present invention provides an advanced adaptive predistortion linearization technique to dramatically reduce nonlinear distortion in power amplifiers over a very wide instantaneous bandwidth (up to 2 GHz) and over a wide range of amplifier types, input frequencies, signal types, amplitudes, temperature, and other environmental and signal conditions. In an embodiment of the invention, the predistortion linearization circuitry comprises (1) a higher-order polynomial model of an amplifier's gain and phase characteristics—higher than a third-order polynomial model; (2) an adaptive calibration technique; and (3) a heuristic calibration technique. The higher-order polynomial model is generated by introducing, for example, a plurality of multi-tone test signals with varying center frequency and spacing into the power amplifier. From the power amplifier's corresponding output, the nonlinearities are modeled by employing a higher-order curve fit to capture the irregularities in the nonlinear transfer function. Different distortion transfer functions can be implemented for different operating conditions. The adaptive calibration technique is based on a feedback analysis technique, which updates the applicable distortion transfer function by analyzing the error signal between the introduced input signal and the output signal in real-time. The heuristic calibration technique implements different distortion transfer functions based on historical operating conditions and optimal configurations of the power amplifier.
Owner:TM IP HLDG LLC
Amplifier Linearizer
ActiveUS20110175678A1Reduce nonlinear distortionLow powerMultiple-port networksElectric signal transmission systemsNonlinear distortionReal time analysis
The present invention provides an advanced adaptive predistortion linearization technique to dramatically reduce nonlinear distortion in power amplifiers over a very wide instantaneous bandwidth (up to 2 GHz) and over a wide range of amplifier types, input frequencies, signal types, amplitudes, temperature, and other environmental and signal conditions. In an embodiment of the invention, the predistortion linearization circuitry comprises (1) a higher-order polynomial model of an amplifier's gain and phase characteristics—higher than a third-order polynomial model; (2) an adaptive calibration technique; and (3) a heuristic calibration technique. The higher-order polynomial model is generated by introducing, for example, a plurality of multi-tone test signals with varying center frequency and spacing into the power amplifier. From the power amplifier's corresponding output, the nonlinearities are modeled by employing a higher-order curve fit to capture the irregularities in the nonlinear transfer function. Different distortion transfer functions can be implemented for different operating conditions. The adaptive calibration technique is based on a feedback analysis technique, which updates the applicable distortion transfer function by analyzing the error signal between the introduced input signal and the output signal in real-time. The heuristic calibration technique implements different distortion transfer functions based on historical operating conditions and optimal configurations of the power amplifier.
Owner:TM IP HLDG LLC
Control of energy storage system inverter system in a microgrid application
ActiveUS9042141B2Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionElectric power transmissionMicrogrid
A system that manages a supplemental energy source connected to a power grid uses a two stage control strategy to manage power transfers in and out of the power grid as well as in and out of an energy storage system, such as a battery bank. One stage uses a non-linear transfer function to control an output frequency of a DC-to-AC inverter to limit undesired effects of power transients that occur on the grid. A second stage uses control strategy for transferring energy between the energy storage system and an internal DC link based on a relationship between a voltage on a DC link connecting the first and second stages and a DC link reference voltage, the voltage on the DC link, and a voltage at the energy storage system. The control strategy includes rapid charging, over-charging protection, and grid transient stabilization.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
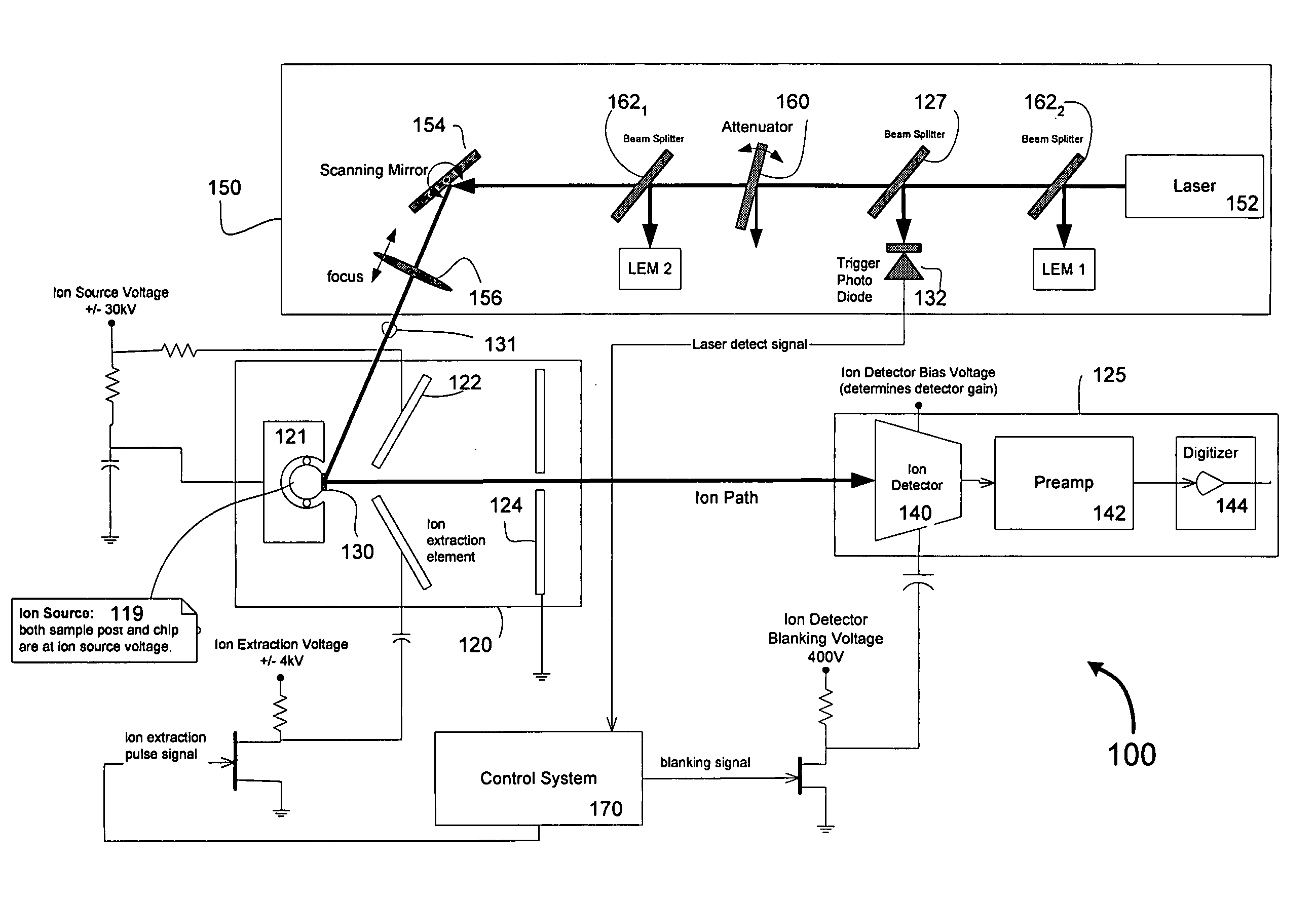
Non-linear signal amplifiers and uses thereof in a mass spectrometer device
InactiveUS20060000982A1Accurately approximatedIncrease speedSpectrometer detectorsTime-of-flight spectrometersAudio power amplifierHigh bandwidth
Signal amplifiers having a non-linear transfer function. A high speed (high bandwidth) circuit with a non-linear transfer function over a limited range of input signal is provided. By appropriate choice of components, the non-linear transfer function can be used to accurately approximate any monotonic function such as a square root transfer function. In another aspect, a piecewise non-linear circuit arrangement using a set of non-linear sub-circuits is provided to accurately generate a desired non-linear transfer function over an extended dynamic range of input signal. In one implementation of such a circuit, each of the sub-circuits approximates the desired non-linear function over a portion of the input range.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
RBF dual neural network adaptive sliding mode control method for active power filter
ActiveCN107147120AEnsure real-time trackingImplement trackingActive power filteringAc network to reduce harmonics/ripplesFractional-order controlMathematical model
The invention discloses an RBF dual neural network adaptive sliding mode control method for an active power filter. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: step (1), establishing a mathematical model of the active power filter; (2) designing an adaptive RBF dual neural network based on a fractional order sliding mode surface, and separately approximating the nonlinear function and the upper bound of interference of the system by using the two RBF neural networks; and step (3) controlling the active power filter according to a fractional order RBF dual neural network sliding mode controller. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the characteristics that the fractional order can get rid of the dependence of system functions and improve the control response of the system are adopted; on this basis, the nonlinear function and the upper bound of interference values of the system can be approximated by adopting the characteristic that the RBF neural networks do not relay on the model of the system; and moreover, the stability of a system controller can be proved by designing the Lyapunov function, the real-time tracking compensation can be performed for the instruction current, and high reliability, high robustness to parameter variation and high stability can be achieved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Image enhancement method under ambient light
ActiveCN105825479AIncrease brightnessEnhance detailsImage enhancementImage analysisVisibilityImaging processing
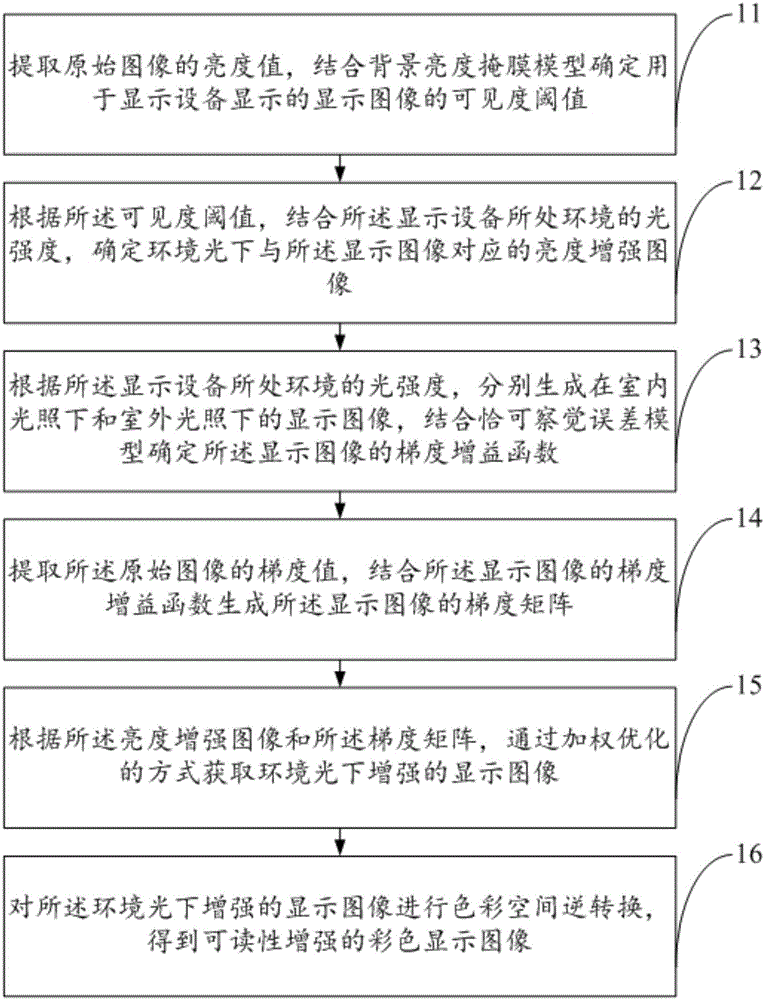
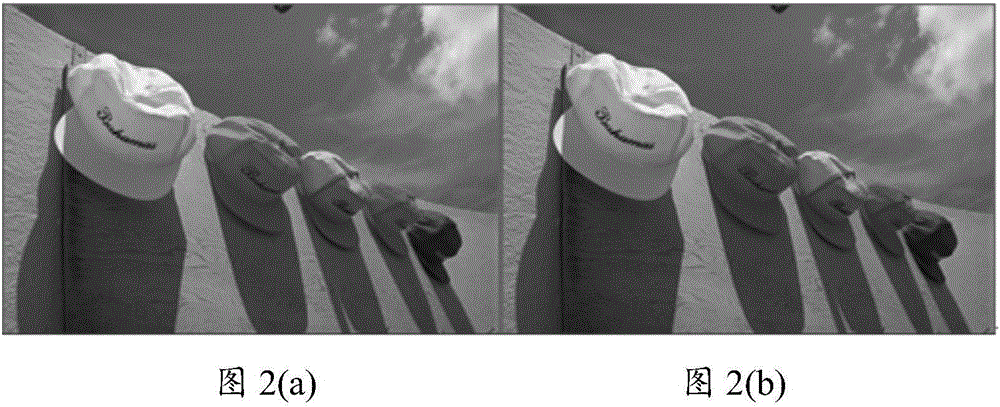
The invention discloses an image enhancement method under ambient light, and belongs to the field of image processing. The image enhancement method comprises the steps that the brightness value of an original image is extracted, a visibility threshold is determined, and a brightness enhanced image is determined through combination of light intensity of the environment in which display equipment is arranged. The gradient gain function of a display image is determined through combination of a just-noticeable-distortion model according to the light intensity of the environment in which the display equipment is arranged so that the enhanced display image under ambient light is acquired through a weighed optimization mode. A readability enhanced color display image is obtained through color spatial conversion. The brightness and the details of the display image are enhanced through a gradient domain optimization framework based on weighting so that readability of the display image under ambient light can be enhanced, the brightness of the display image is enhanced by using a nonlinear transfer function under ambient light, gradient loss caused by ambient light can be compensated by adopting the just-noticeable-distortion model, and finally readability of the image on the display equipment can be enhanced.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
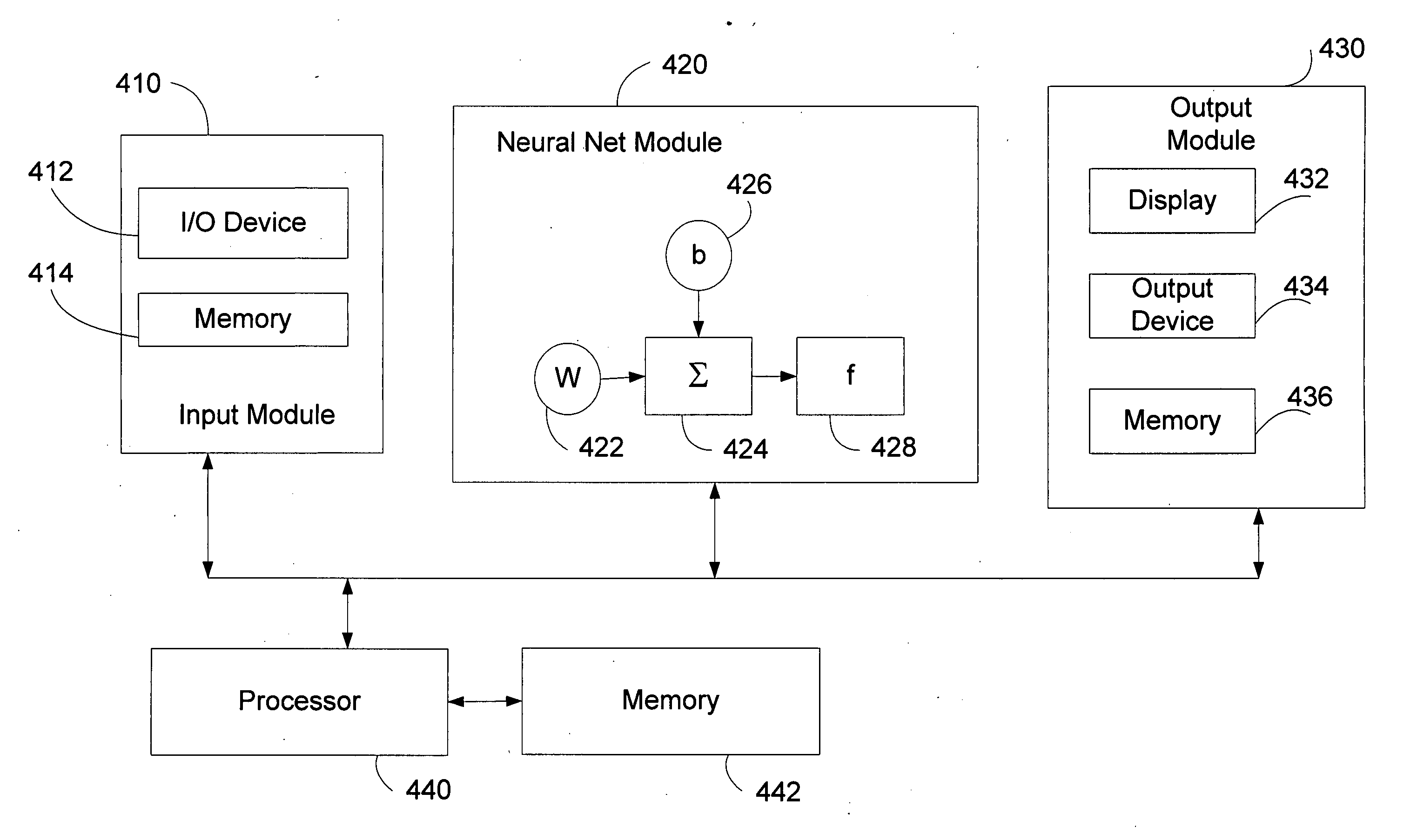
Neural network for aeroelastic analysis
ActiveUS7617166B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsElement modelNerve network
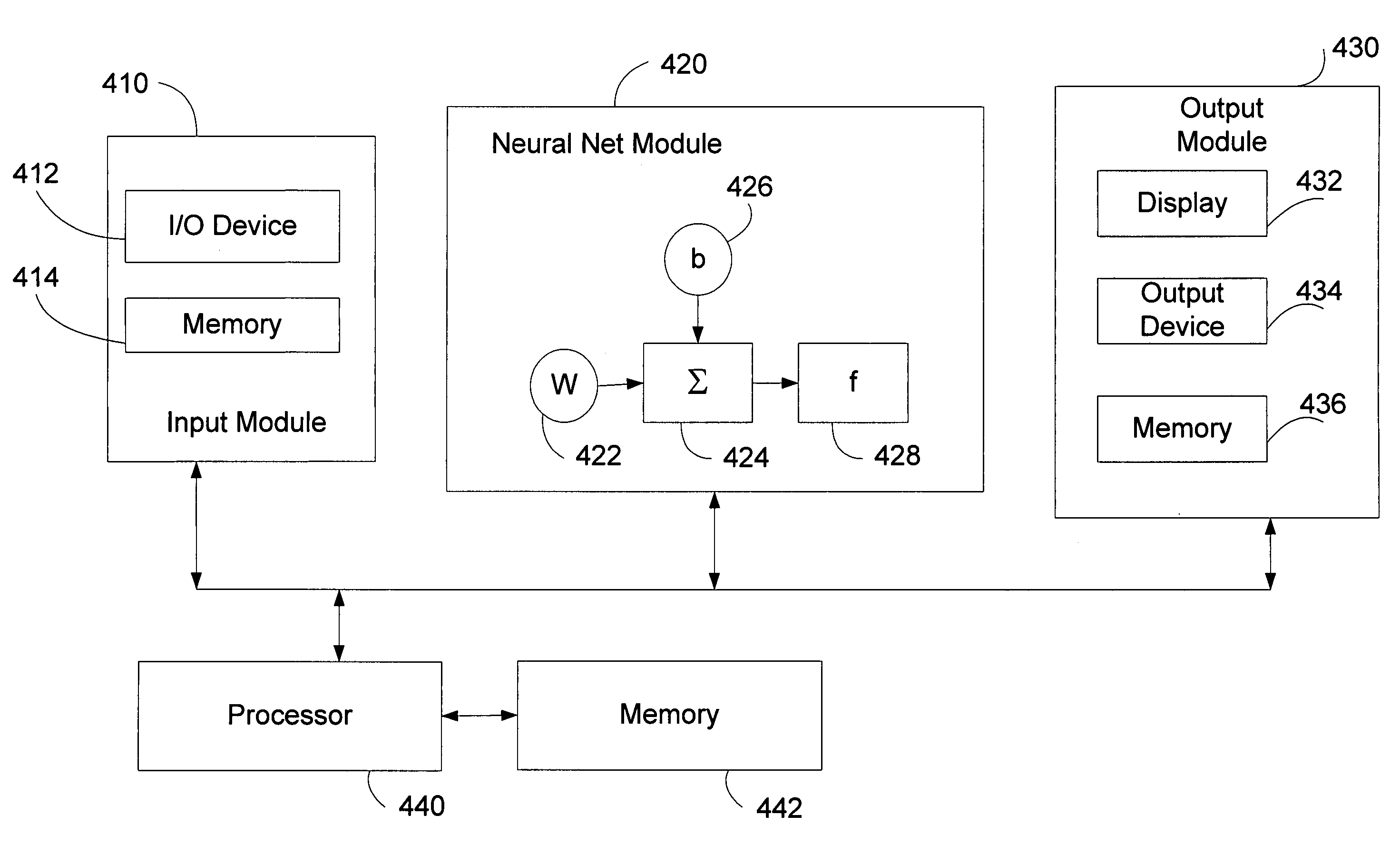
A system and method of performing aeroelastic analysis using a neural network. Input parameters, such as mass and location, contributing to aeroelastic characterization are determined and constrained. A model of a structure to be analyzed can be constructed. The model can include a number of locations where the input parameters can be varied. The aeroelastic characteristic of the structure can be analyzed using a finite element model to determine a number of output characteristics, each of which can correspond to at least one of a plurality of input samples. A neural network can be generated for determining the aeroelastic characteristic based on input parameters. The input sample / output characteristic pairs can be used to train the neural network. The weights and bias values from the trained neural network can be used to generate a non-linear transfer function that generates the aeroelastic characteristic in response to input parameters.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method and system for digital equalization of non-linear distortion
ActiveUS7263144B2Remove distortionOverall approximated linear system performanceMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsNonlinear distortionEqualization
A method is provided for equalization of nonlinear distortion in a distorted signal comprising the steps of: digitizing the distorted signal and passing the digitized distorted signal through an inverse non-linear transfer function to equalize the nonlinear distortion. Other systems and methods are disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
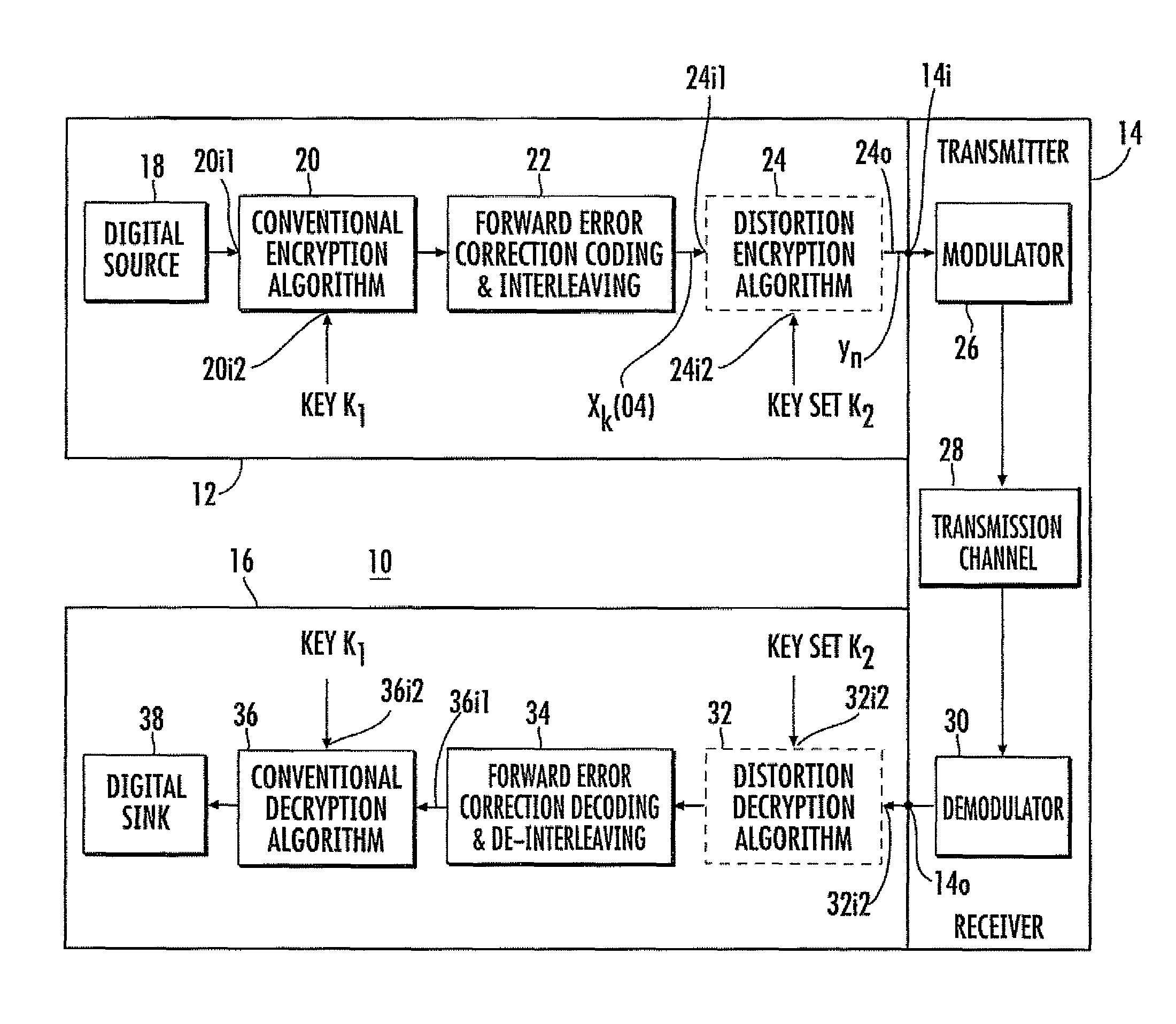
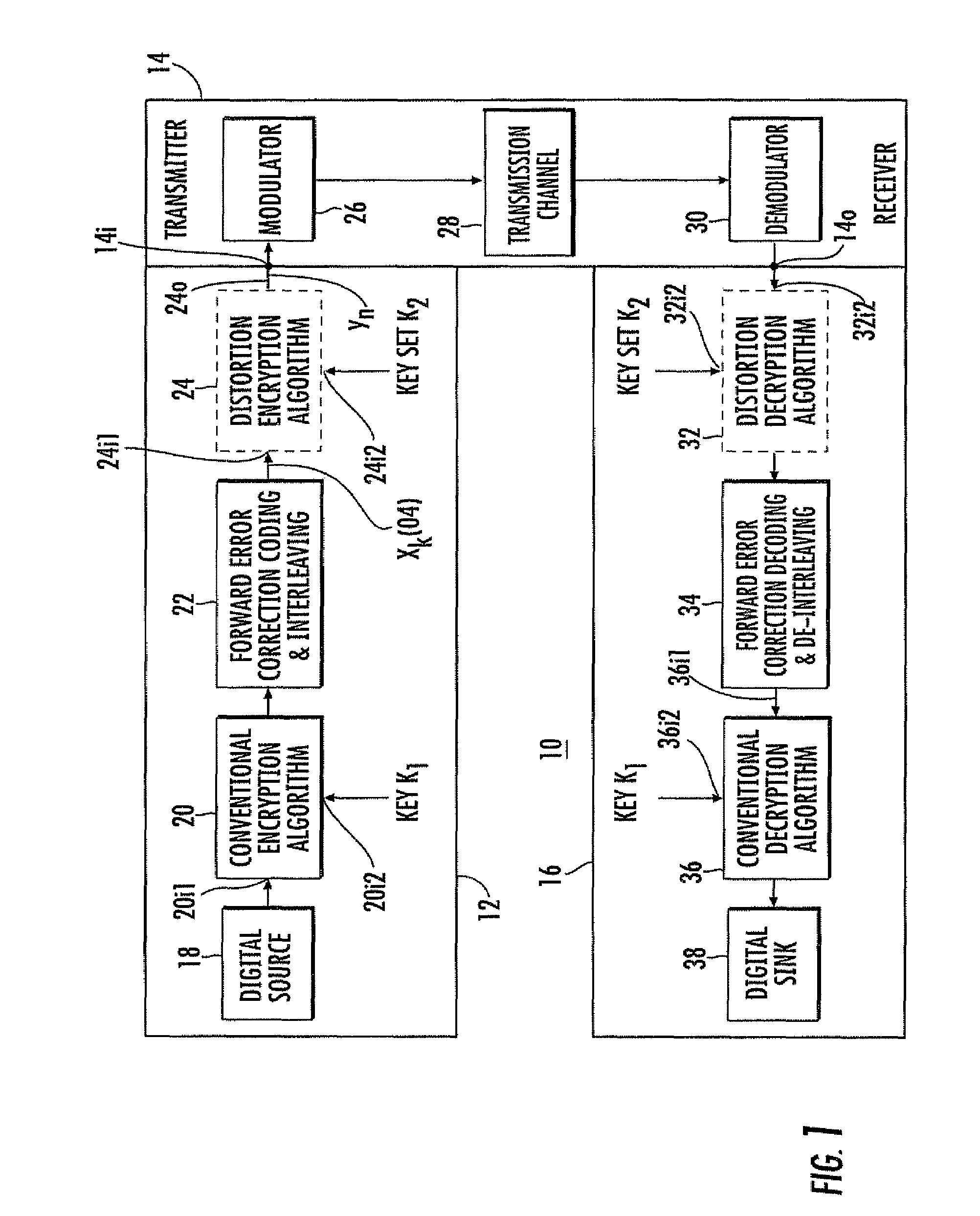
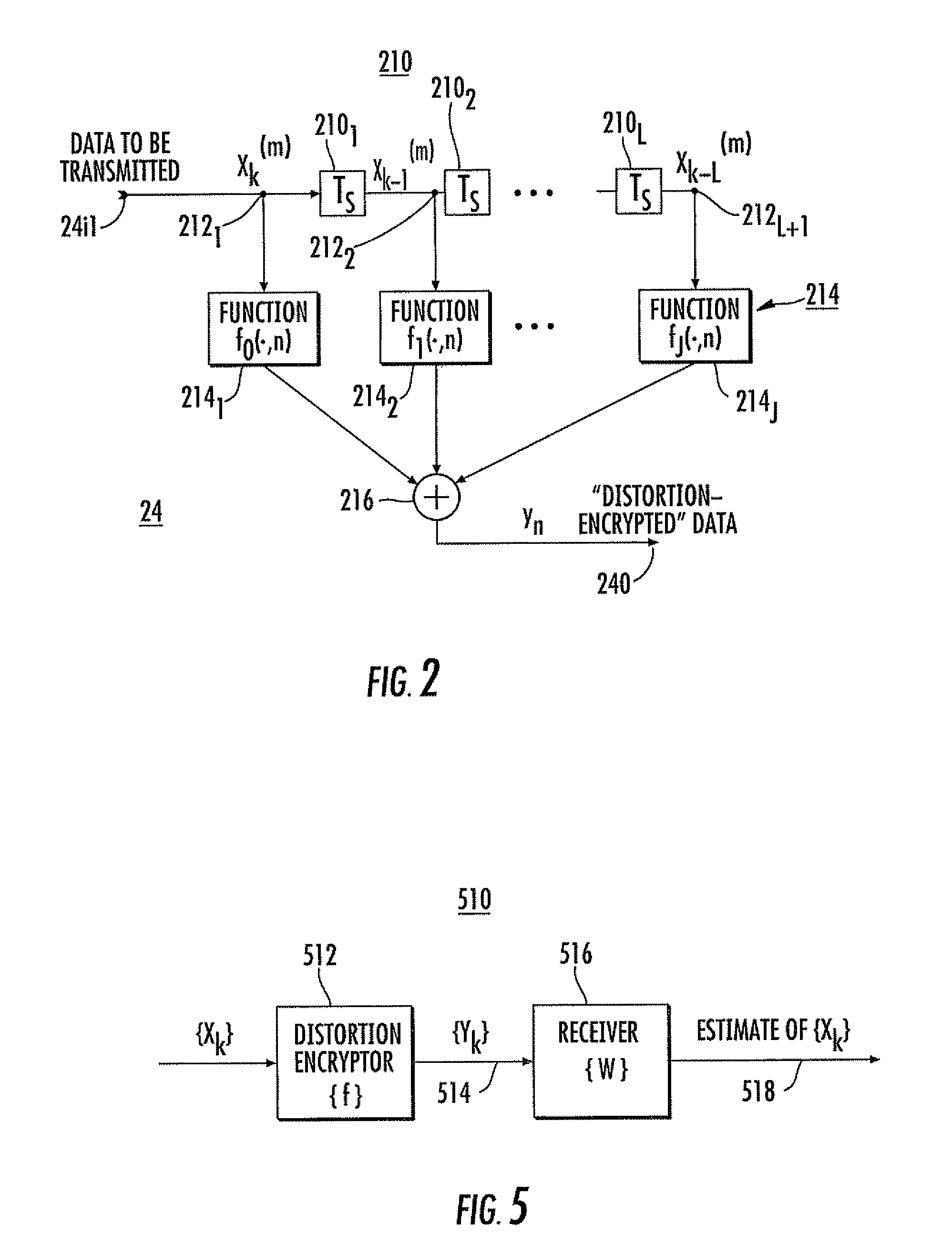
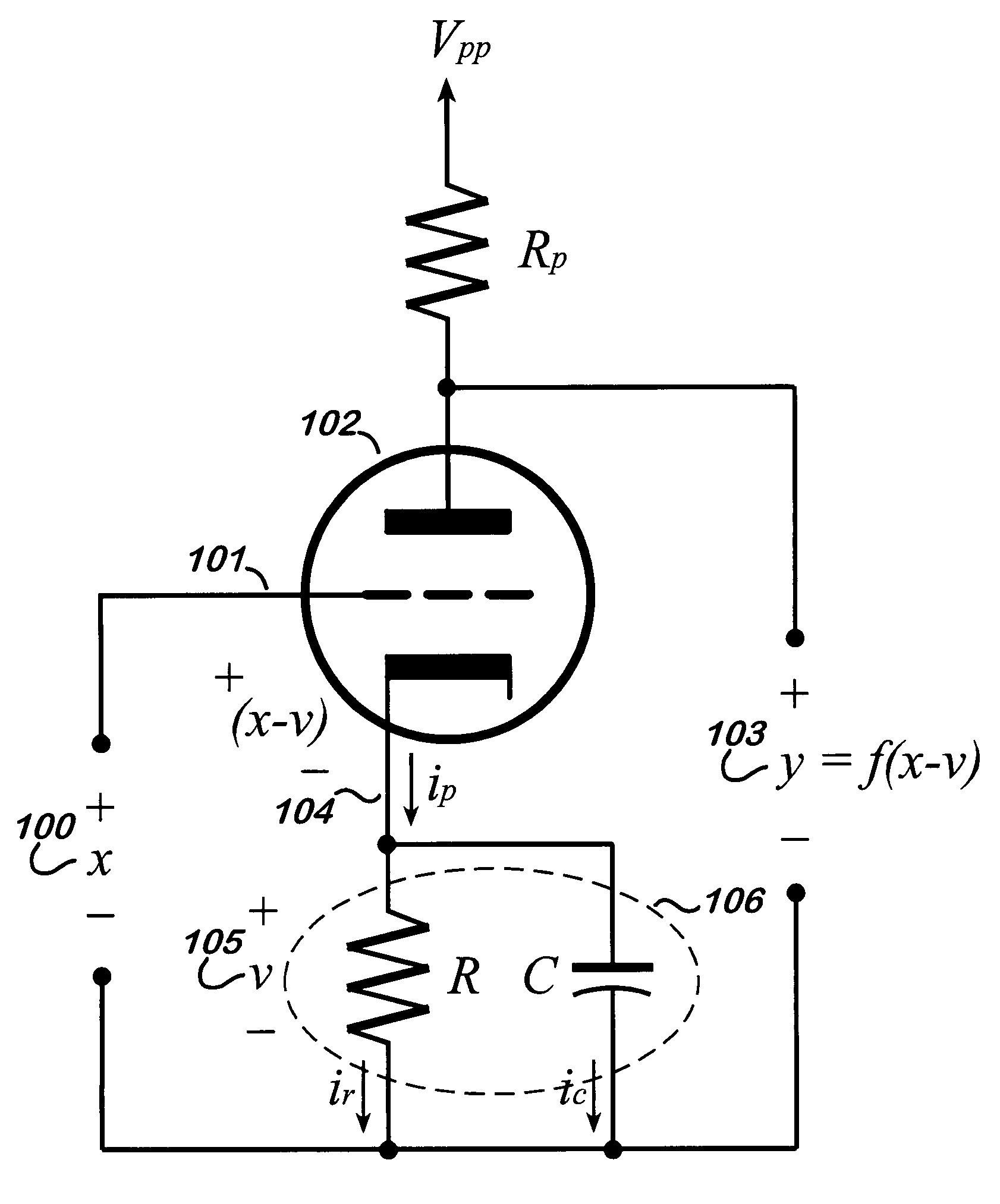
Data encryption by nonlinear transfer function
InactiveUS7672453B1Multiple keys/algorithms usageEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwareCommunications system
A communication system includes an encryptor and a decryptor. For improved encryption security, the encryptor includes a multitap delay line to produce mutually delayed samples of the signal to be encrypted. Each sample is operated on by a key or function to produce modified signal samples, and the modified signal samples are summed or combined to produce the encrypted signal. According to one aspect of the invention, at least one of the keys or functions includes a nonlinear function. In some embodiments, the functions are time-variant for improved security. Decryption is accomplished in some embodiments by an equalizer. The preferred equalizer is the maximum-likelihood-sequence estimators matched to the encryption functions. A Viterbi algorithm makes it easy to implement the matched equalizer.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
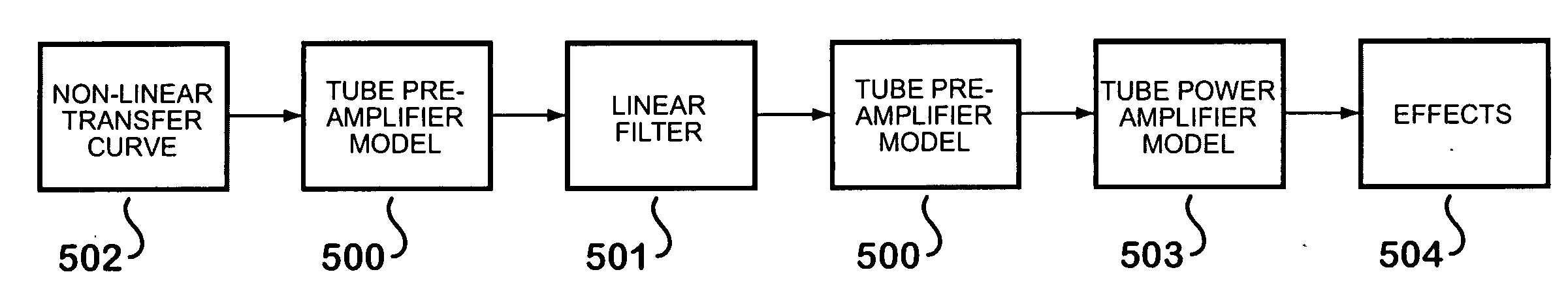
Method and apparatus for distortion of audio signals and emulation of vacuum tube amplifiers
InactiveUS20080218259A1Reduce artifactsReduce noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectrophonic musical instrumentsDigital signal processingNonlinear filter
Owner:GALLO MARC NICHOLAS
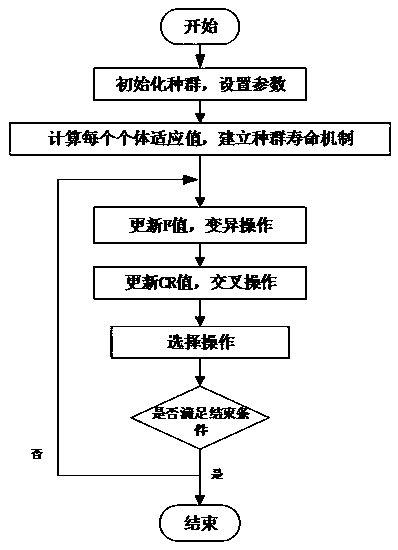
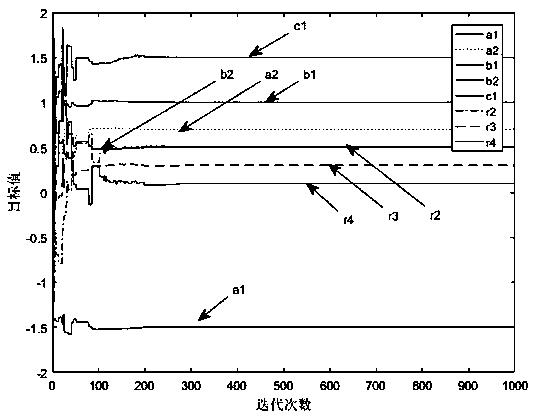
Parameter identification of nonlinear system based on improved differential evolution algorithm
PendingCN109284579AThe principle is simpleFew controlled parametersArtificial lifeDesign optimisation/simulationNonlinear modelAlgorithm convergence
Aiming at the difficulty and inaccuracy of parameter identification of nonlinear model, this invention proposes an identification algorithm based on improved differential evolution algorithm. By establishing a lifetime mechanism, the scaling factor and crossover rate can be adjusted dynamically according to the lifetime value, so as to avoid premature convergence at the beginning of the algorithmand retain high-quality solution at the later stage, so as to accelerate the convergence rate. In order to verify the performance and practicability of the improved algorithm, the typical test functions are used to compare and test, and the nonlinear transfer function model and Hammerstein model are identified. The experimental results show that the improved algorithm has fast convergence speed and high identification accuracy, and it is effective and feasible for parameter identification of nonlinear system.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Dual-active-bridge resonant convert modeling, ord reduction, design method, device and system
ActiveCN109271698AThe principle is simpleOverall claritySpecial data processing applicationsSmall-signal modelControl system
The invention discloses a dual-active-bridge resonant convert modeling, ord reduction, design method, device and system. Under the condition of controlling the output voltage of resonant double activebridge converter by single phase-shifting control method, by using the transmission power formula of resonant double active bridge converter, the order of resonant elements in resonant double activebridge converter is reduced, and the average value equivalent model is established. Based on the average mode equivalence, the small signal model of the resonant double active bridge converter is established by using small signal method, and the transfer function is obtained according to the control quantity and the control object. the zero-pole distribution of the transfer function is analyzed and the order of the transfer function is reduced; Aiming at the reduced-order transfer function, the controller parameter design method is used to design the typical type II system. The invention has the advantages of simple principle and clear organization, provides the theoretical basis for the analysis of the resonant double active bridge converter, reduces the difficulty of analysis and design,and is easy to adopt the traditional control system parameter design scheme to design the controller.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +5
Neural network for aeroelastic analysis
ActiveUS20050234839A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsElement modelNerve network
A system and method of performing aeroelastic analysis using a neural network. Input parameters, such as mass and location, contributing to aeroelastic characterization are determined and constrained. A model of a structure to be analyzed can be constructed. The model can include a number of locations where the input parameters can be varied. The aeroelastic characteristic of the structure can be analyzed using a finite element model to determine a number of output characteristics, each of which can correspond to at least one of a plurality of input samples. A neural network can be generated for determining the aeroelastic characteristic based on input parameters. The input sample / output characteristic pairs can be used to train the neural network. The weights and bias values from the trained neural network can be used to generate a non-linear transfer function that generates the aeroelastic characteristic in response to input parameters.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
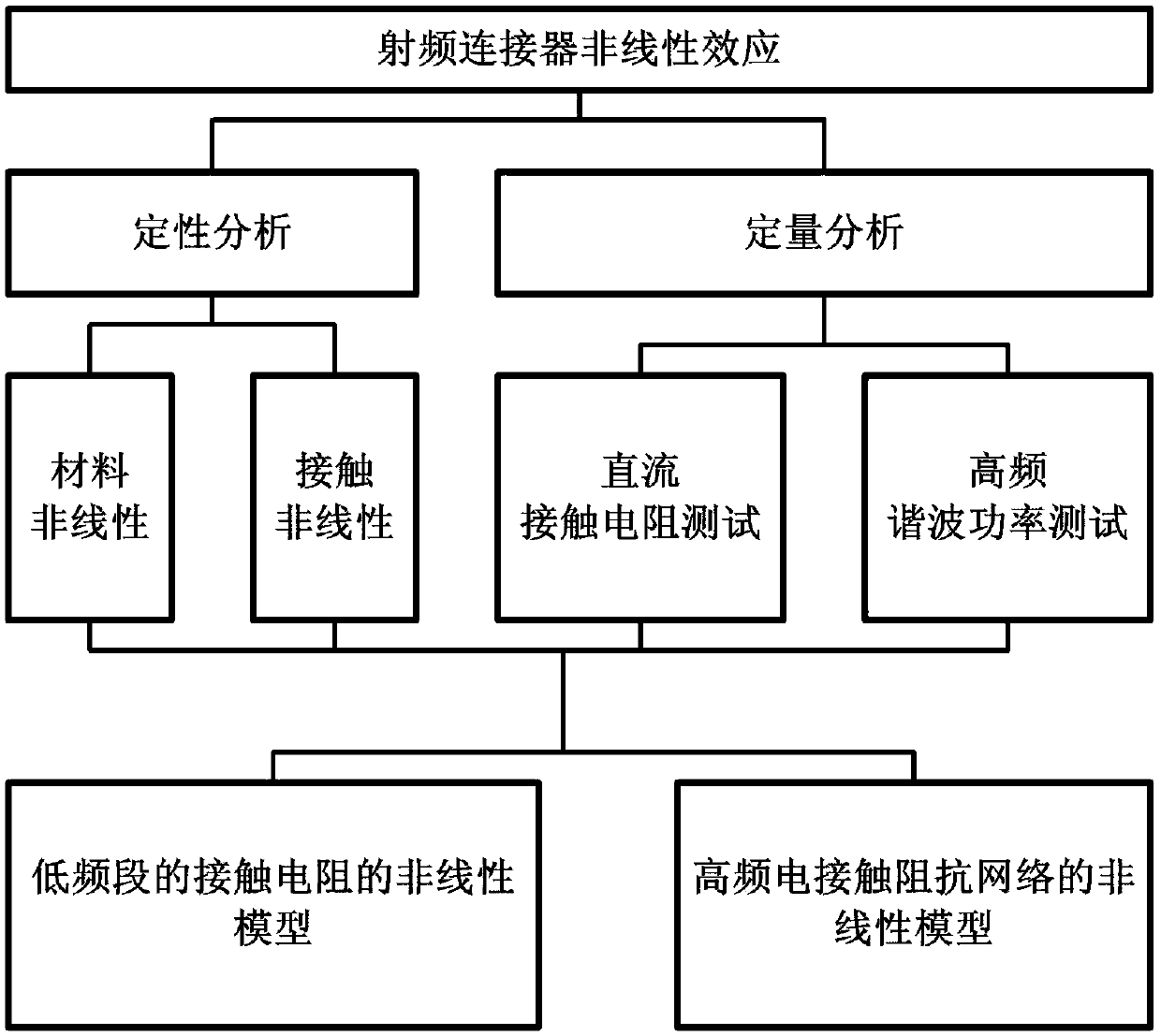
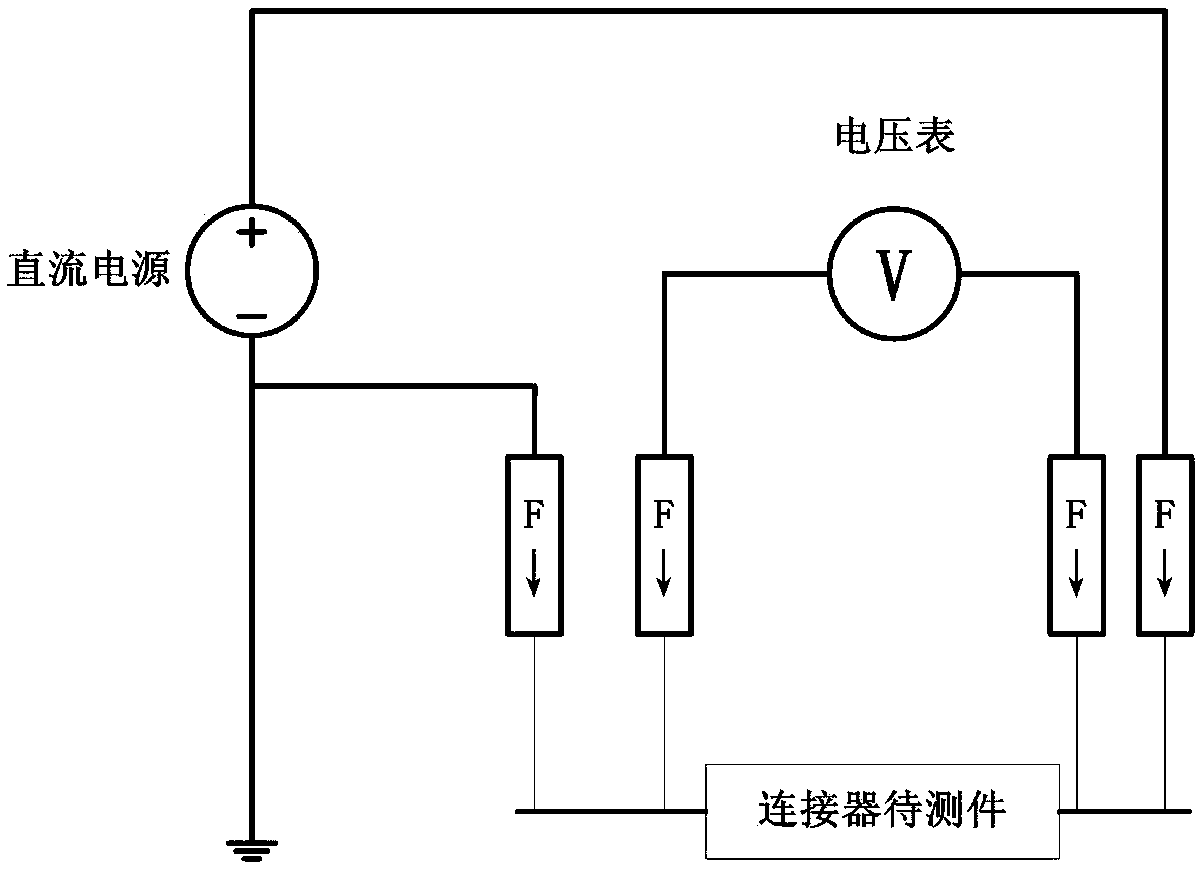
Nonlinear effect modeling method for radio frequency coaxial connector
ActiveCN108761241AAvoid unnecessary errorsImprove theoretical supportElectrical testingSpecial data processing applicationsNon-linear effectsEnergy spectrum
The invention discloses a nonlinear effect modeling method for a radio frequency coaxial connector. The method comprises: a structure and material characteristics of a connector are determined by electron microscope scanning and an energy spectrum analysis method, so that a qualitative analysis of a nonlinear effect is realized; voltage-current curve testing is carried out by using a microhm microvoltmeter to realize a quantitative test analysis of a nonlinear effect under the direct current of the connector; with a passive intermodulation tester, a third-order intermodulation power is testedso as to realize a quantitative test analysis of the nonlinear effect under the high frequency of the connector; and on the basis of a tunnel effect, a skin effect, and a high-frequency electrical contact theory, a nonlinear contact resistor model, a high-frequency equivalent circuit model and a nonlinear transfer function are established to realize the theoretical analysis of the nonlinear effectof the connector. According to the invention, on the basis of combination of experimental testing and theoretical modeling, the nonlinear effect of the connector is analyzed comprehensively from thequalitative and quantitative perspectives. The method is suitable for the nonlinear effect analyses of coaxial connectors in all communication systems.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
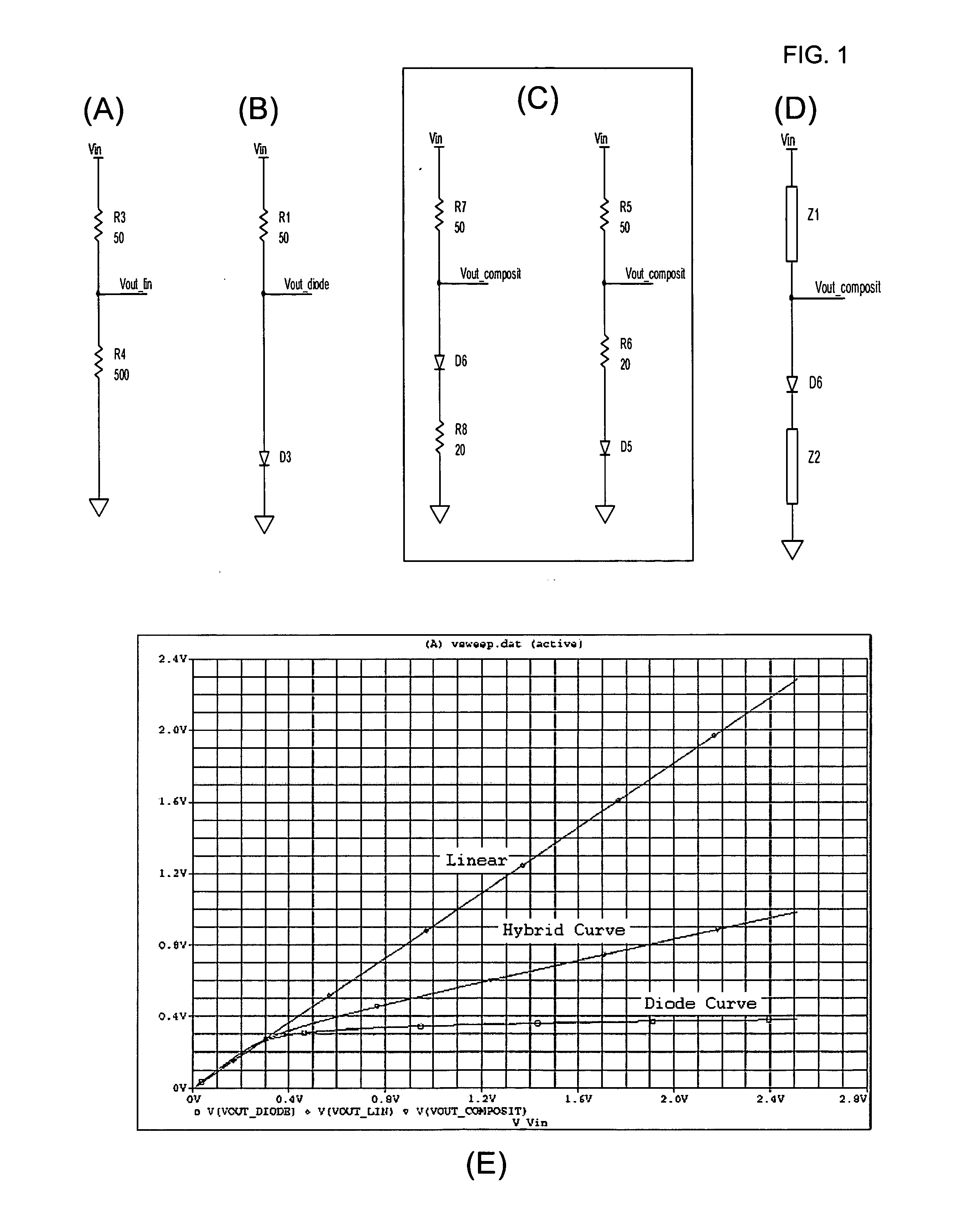
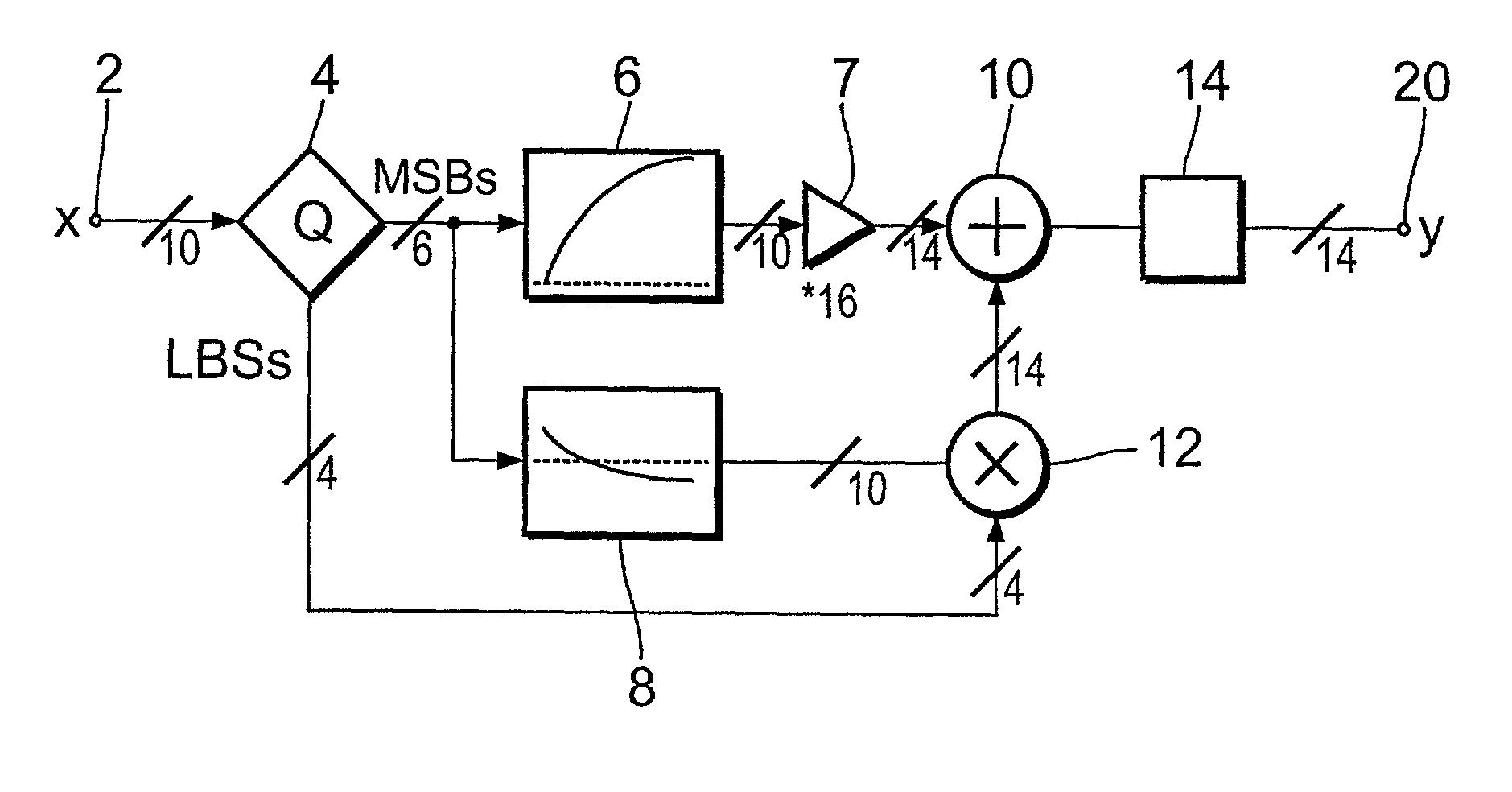
Gamma correction circuit
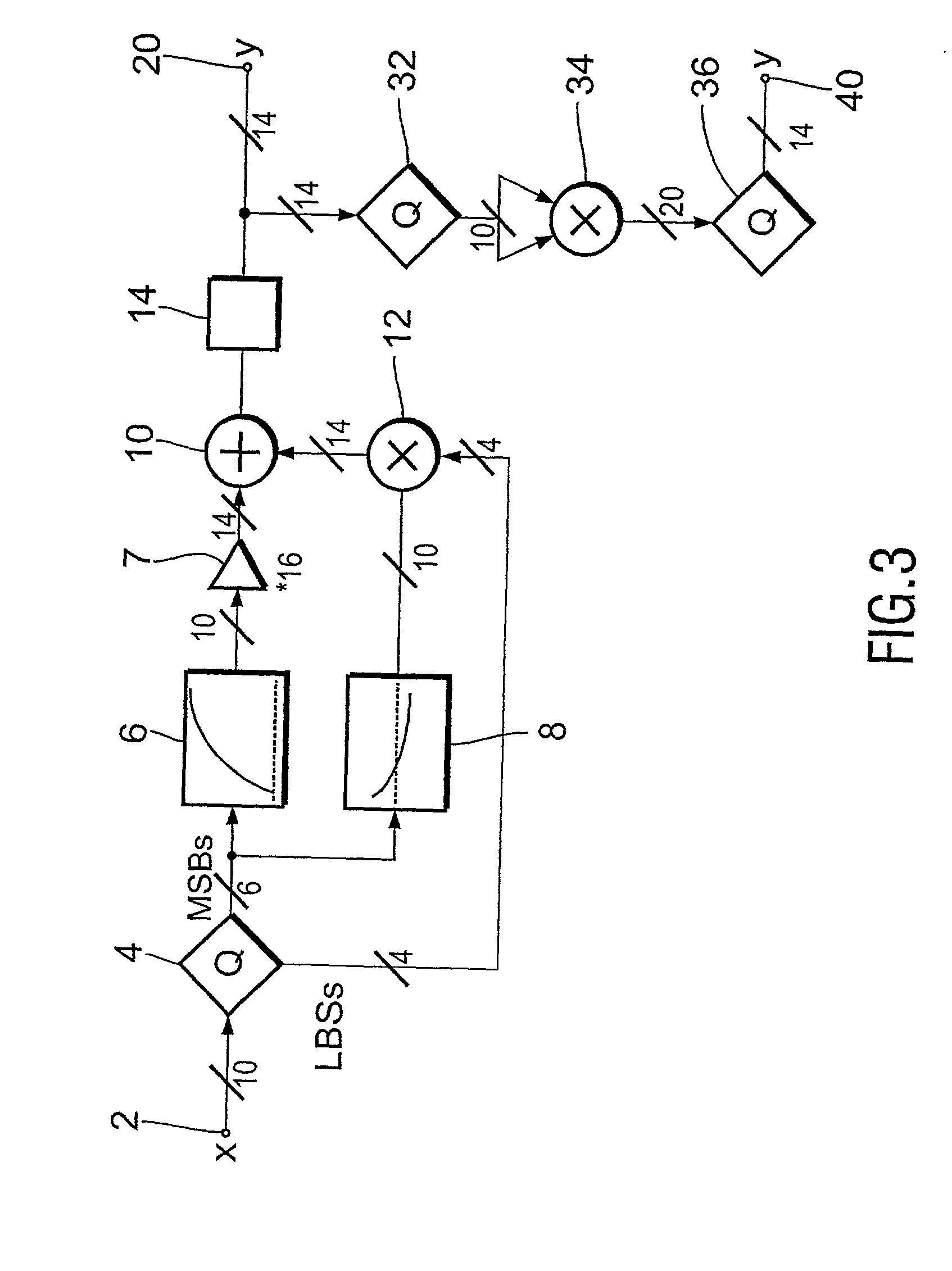
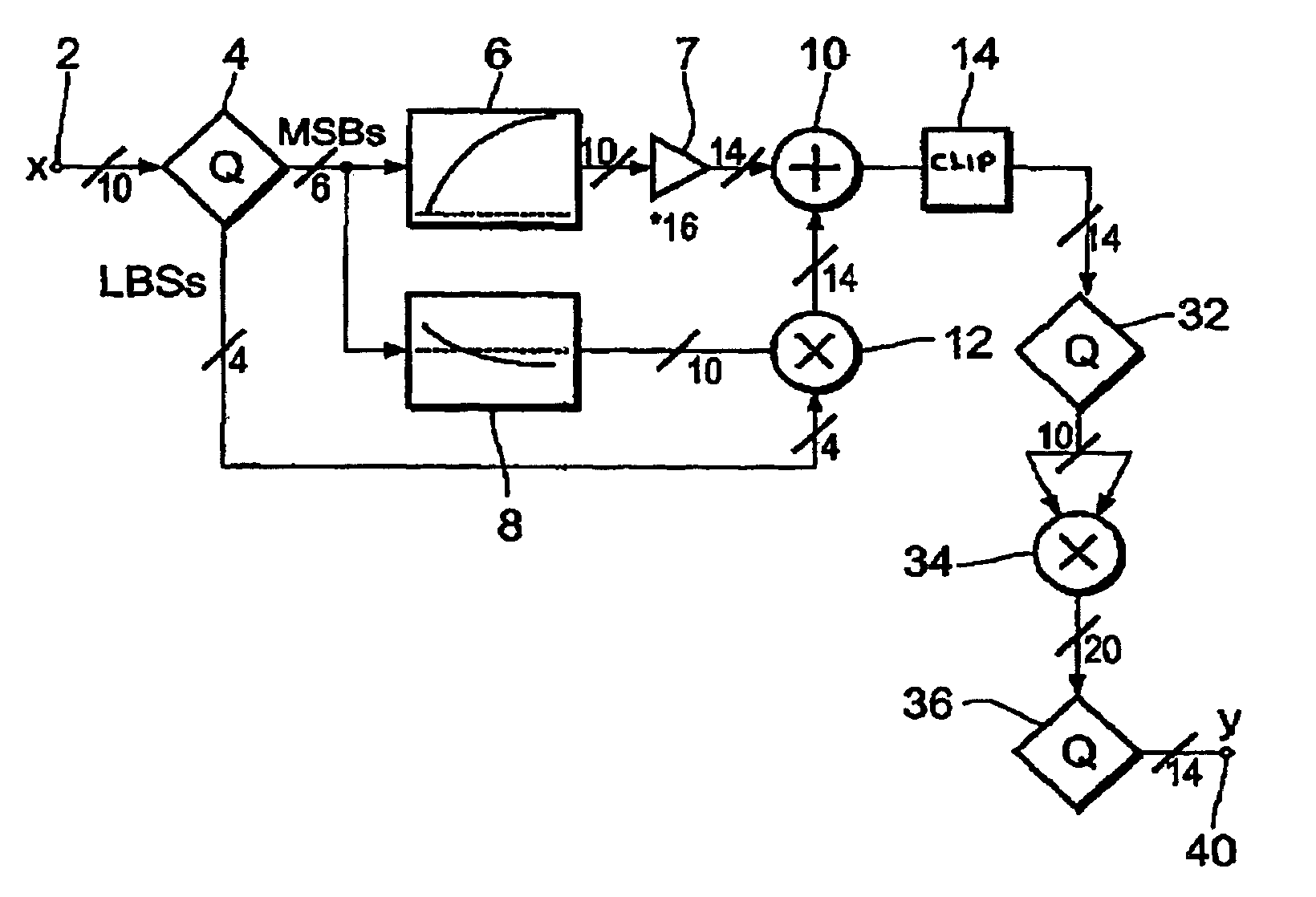
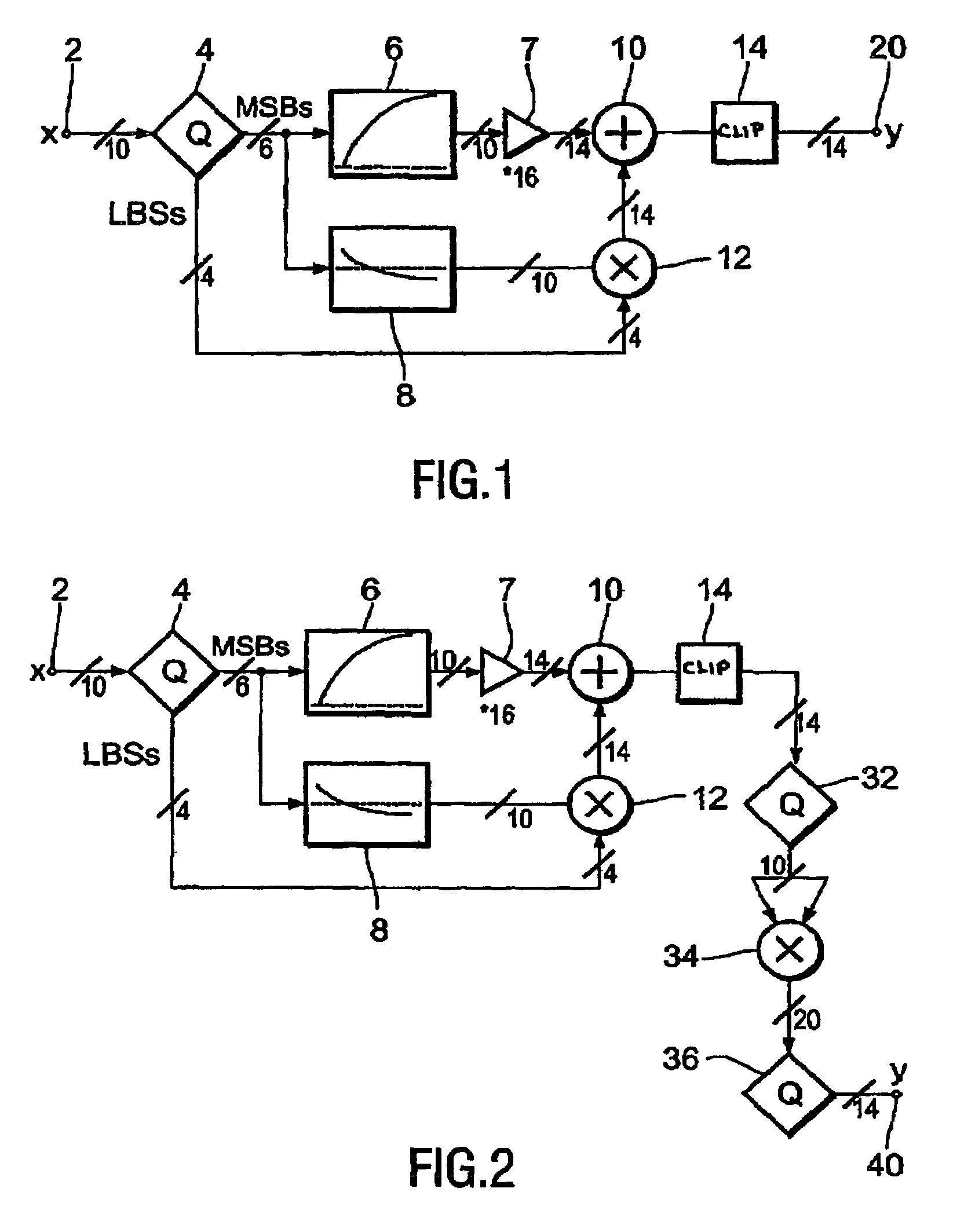
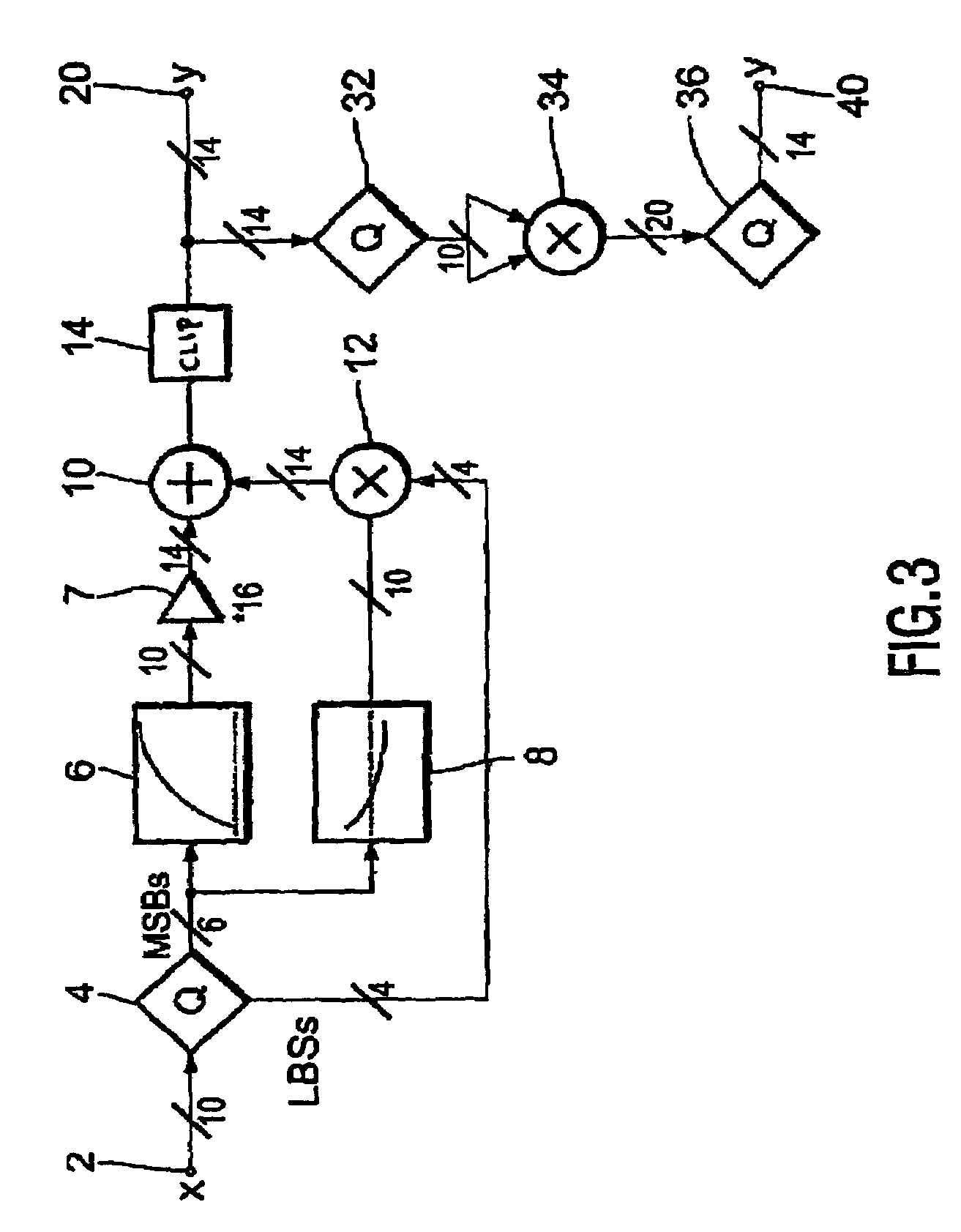
InactiveUS20030156226A1Improve visibilityLow component requirementsTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital videoLeast significant bit
A gamma correction circuit for correcting a digital video signal, the circuit comprising first (6) and second (8) lookup tables for storing discrete output intensity data and the associated slope data of a non-linear transfer function, respectively, for each of the discrete input video signal intensities, an adder (10) having a first input connected to the output of the first lookup table, a multiplier (12) having a first input connected to the output of the second look-up table (8), characterized by a quantizer (4) for providing the most significant bits of the incoming video signal to address the first (6) and second (8) lookup tables and to transfer the corresponding output intensity data to the adder (10) and the associated slope data to the multiplier (12), the quantizer (4) transmitting the remaining least significant bits of the input video signal to the second input of the multiplier (12), the multiplier (12) multiplying the slope data with the remaining least significant bits and feeding the multiplication result to the second input of the adder (10), the adder (10) adding the output intensity data and the multiplication result to generate a corrected video signal.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Method and Apparatus for Distortion of Audio Signals and Emulation of Vacuum Tube Amplifiers
InactiveUS20110033057A1Increase signal gainElectrophonic musical instrumentsGain controlDigital signal processingNonlinear filter
Owner:GALLO MARC NICHOLAS
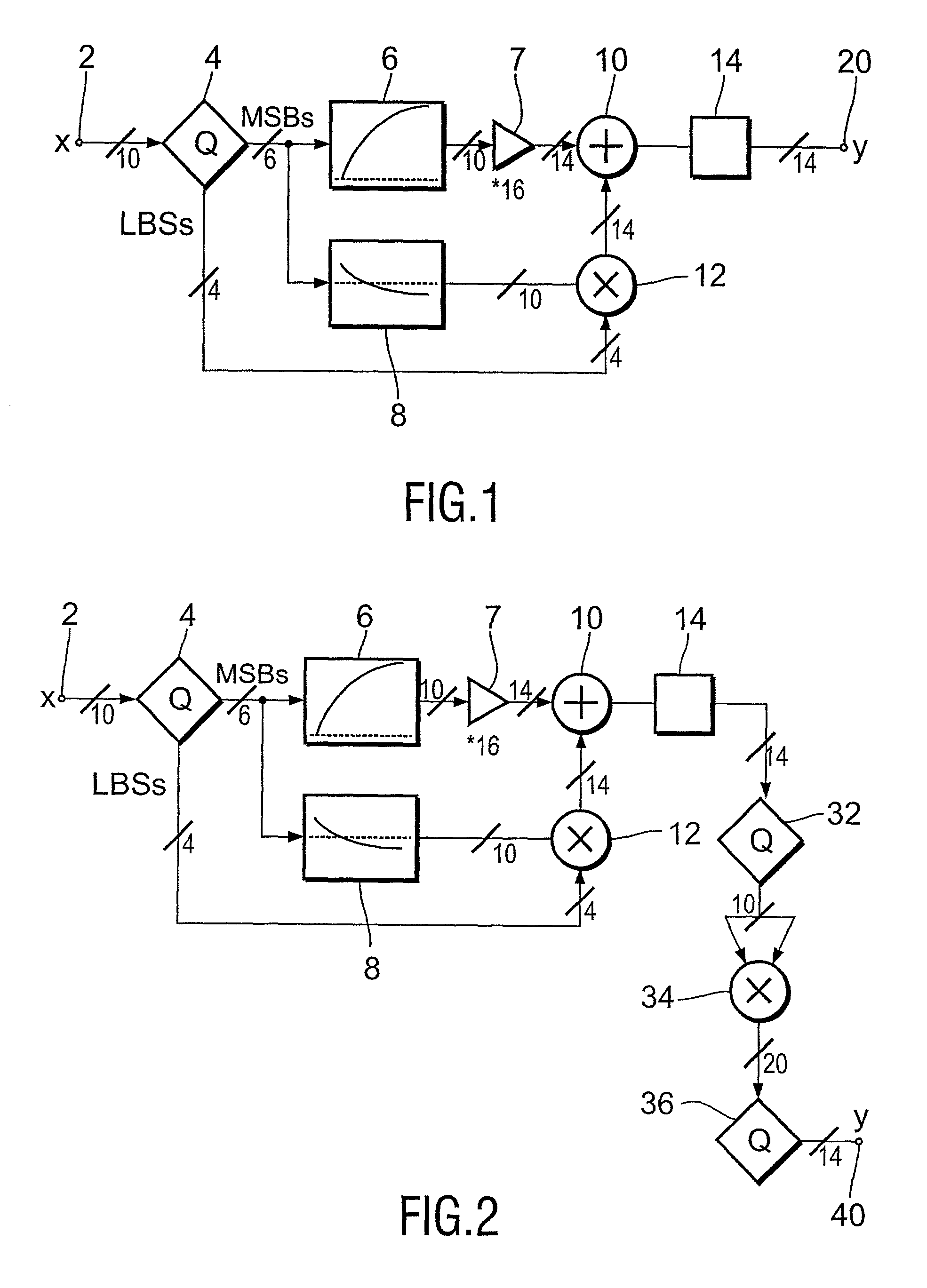
Gamma correction circuit
InactiveUS7038721B2Reduces the hardware costs of the circuit without losing accuracy of the approximationReduce quantization errorTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital videoLeast significant bit
A gamma correction circuit for correcting a digital video signal, the circuit comprising first (6) and second (8) lookup tables for storing discrete output intensity data and the associated slope data of a non-linear transfer function, respectively, for each of the discrete input video signal intensities, an adder (10) having a first input connected to the output of the first lookup table, a multiplier (12) having a first input connected to the output of the second look-up table (8), characterized by a quantizer (4) for providing the most significant bits of the incoming video signal to address the first (6) and second (8) lookup tables and to transfer the corresponding output intensity data to the adder (10) and the associated slope data to the multiplier (12), the quantizer (4) transmitting the remaining least significant bits of the input video signal to the second input of the multiplier (12), the multiplier (12) multiplying the slope data with the remaining least significant bits and feeding the multiplication result to the second input of the adder (10), the adder (10) adding the output intensity data and the multiplication result to generate a corrected video signal.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
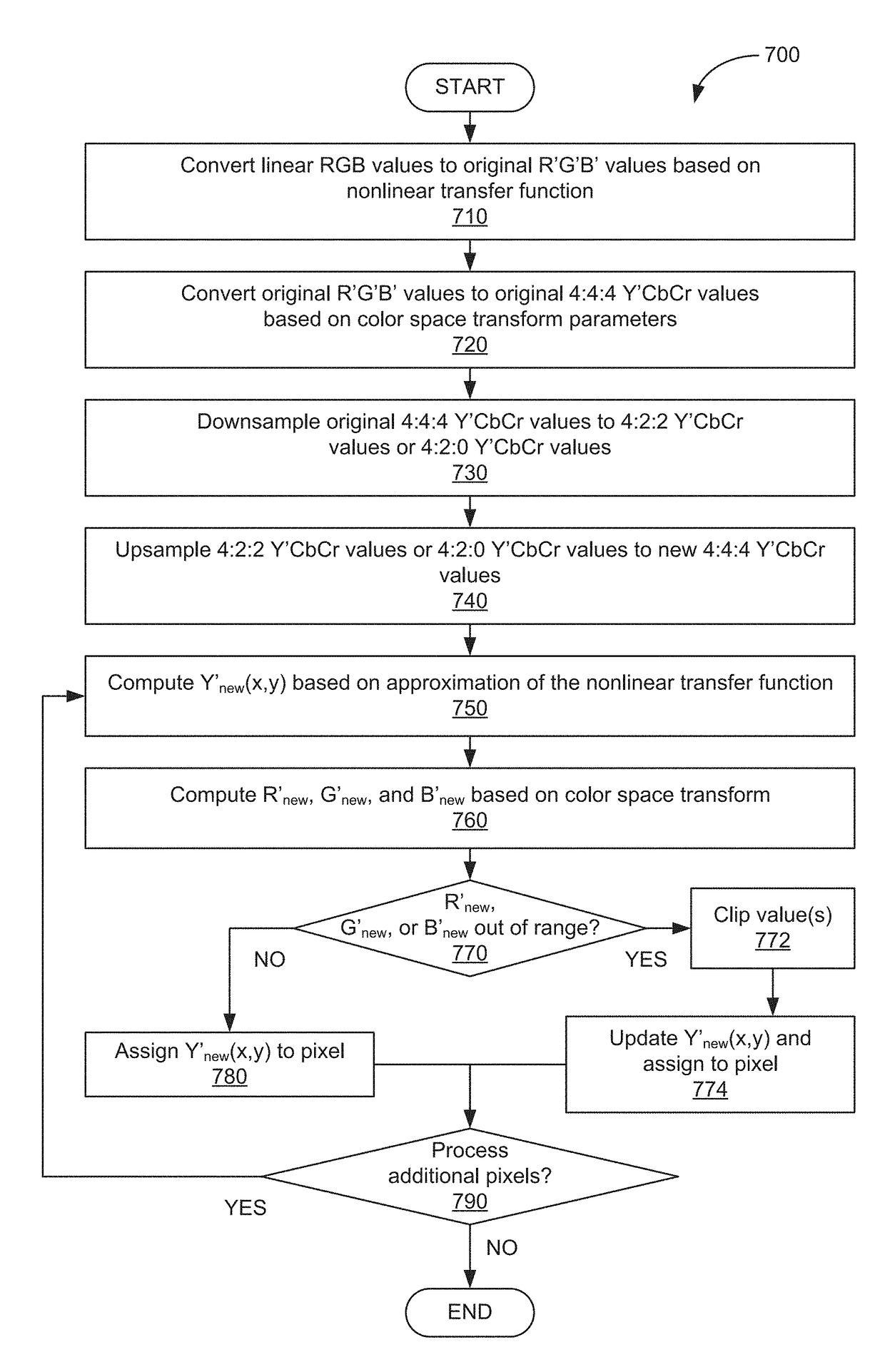
High dynamic range color conversion correction
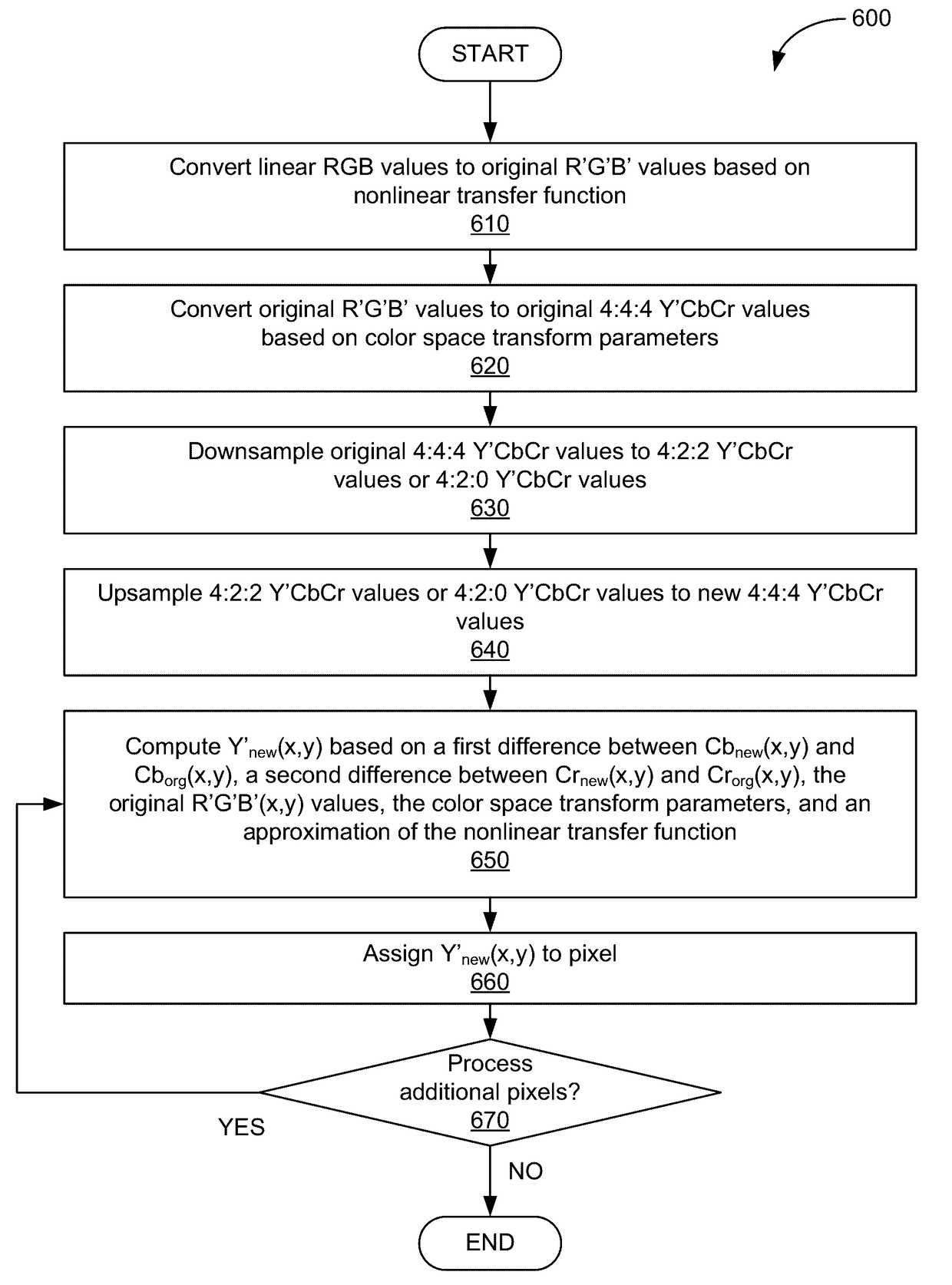
ActiveUS20170134703A1Low technical requirementsReduce complexityColor signal processing circuitsBrightness and chrominance signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionOptical transfer function
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for correcting color values. The technique includes downsampling first color space values to generate downsampled color space values and upsampling the downsampled color space values to generate second color space values. The technique further includes modifying at least one component value included in the downsampled color space values based on a first component value included in the first color space values, a second component value included in the second color space values, and an approximation of a nonlinear transfer function.
Owner:NETFLIX
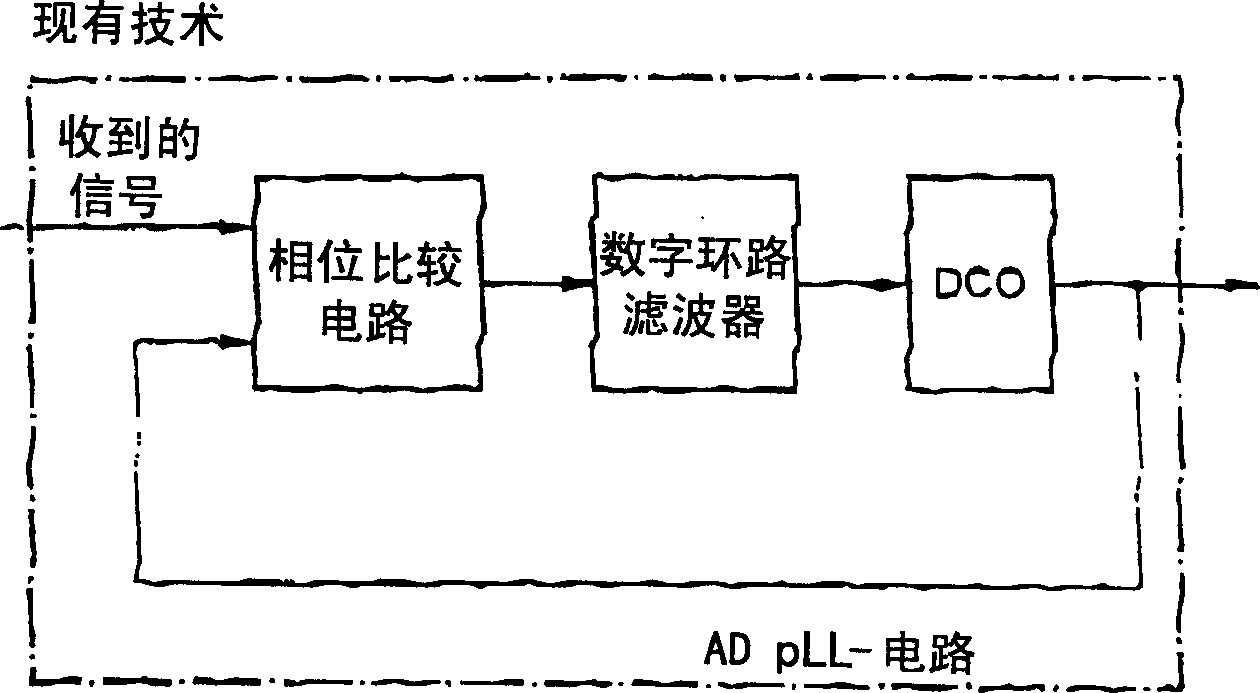
Phase-locked loop circuit of eliminating self-shaking in signals received by control circuit
InactiveCN1455513AEliminate self-jitterEliminate control self-bouncingPulse automatic controlSynchronising arrangementLoop filterPhase locked loop circuit
PLL circuit for eliminating self-jitter in a signal which is received by a control circuit, having a phase comparison circuit for producing a phase difference signal, which indicates the phase difference between the received signal and a fed-back output signal from the PLL circuit; having a loop filter for filtering the phase difference signal which is produced; having an oscillator, which is controlled by the filtered phase difference signal, for producing the output signal from the PLL circuit; with the loop filter having a nonlinear transfer function.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for reduced power consumption ADC conversion
ActiveUS7432838B2Electric signal transmission systemsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesNormal densityNon linear functions
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
System and Method for Chromatic Dispersion Tolerant Direct Optical Detection
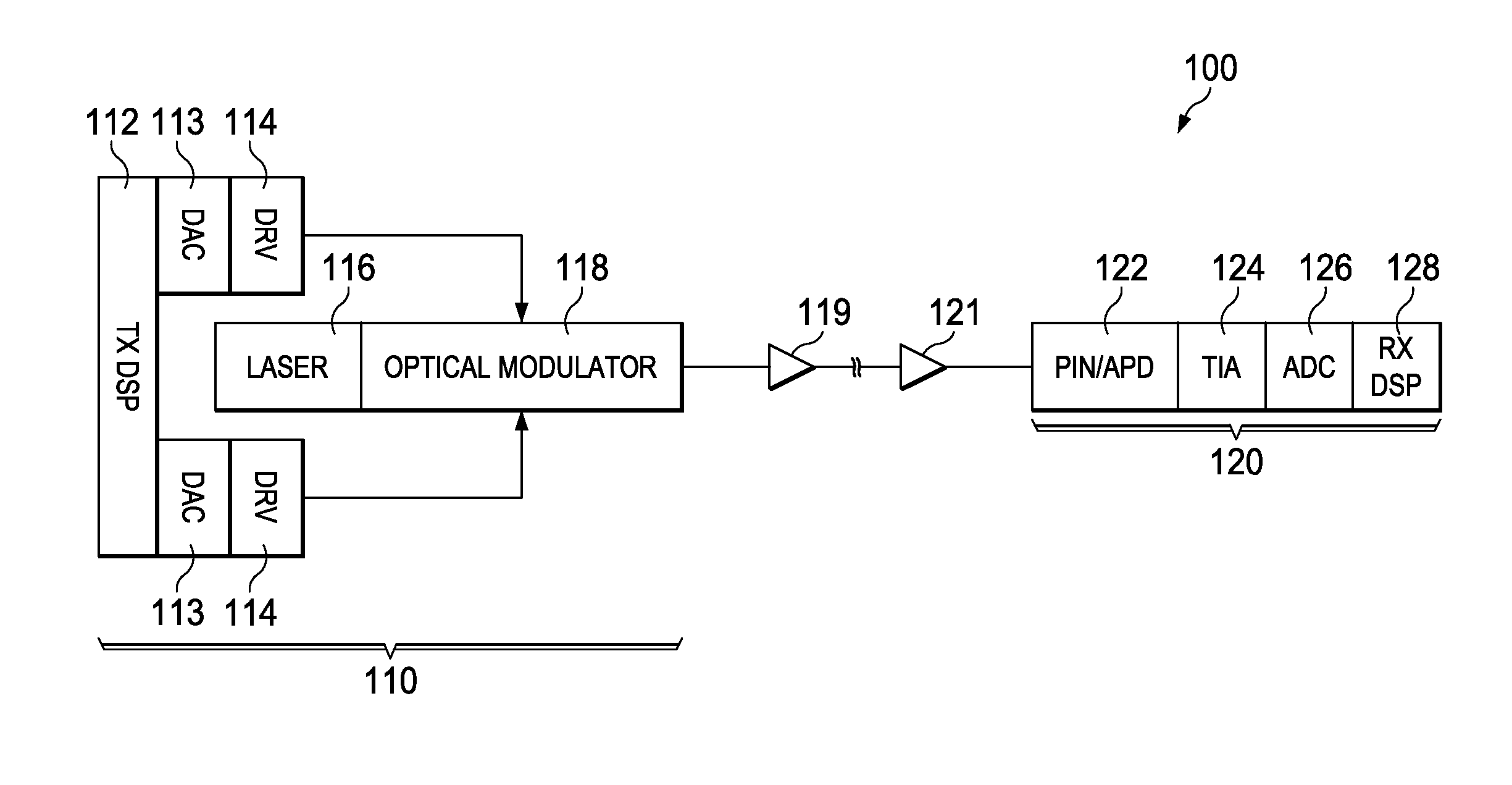
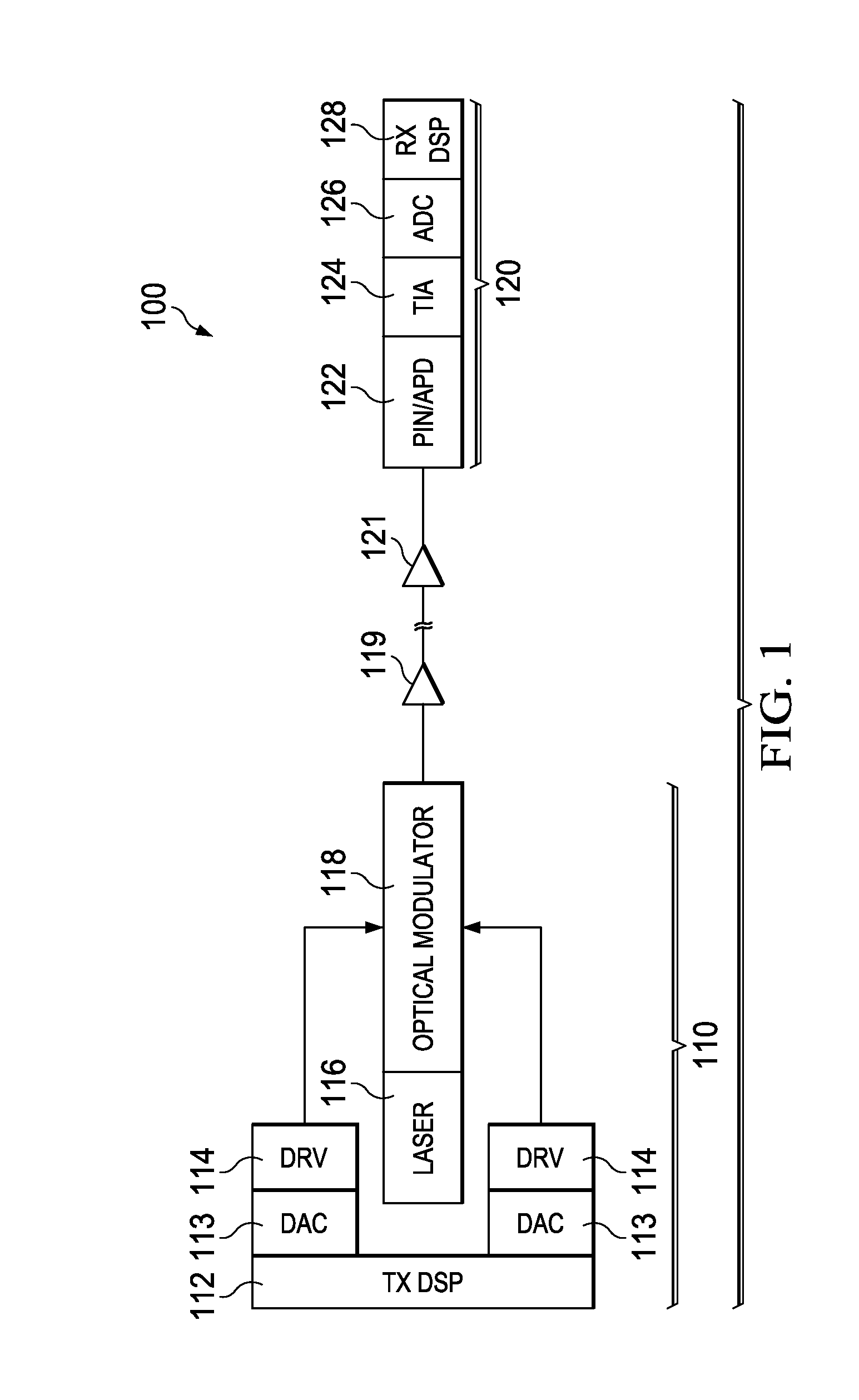
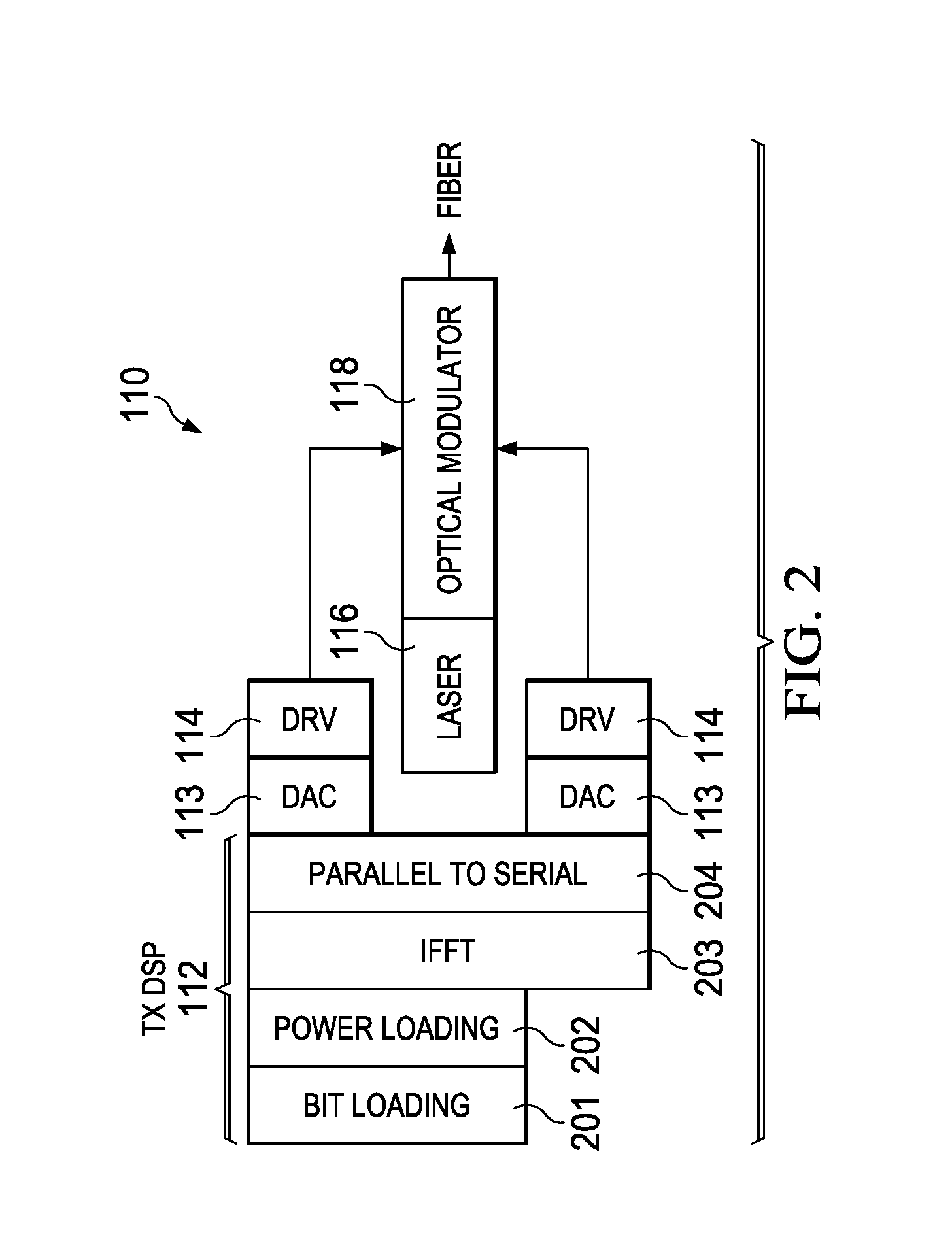
Embodiments are provided to improve direct detection for optical transmissions. In an embodiment, a method by a transmitter includes adjusting, using a nonlinear equalizer (NLE), a drive voltage for an optical modulator in accordance with a mapping between the drive voltage and an output of the optical modulator. The mapping is an inverse function of a nonlinear transfer function at the optical modulator between the output and to the drive voltage. The method further includes driving, using the adjusted drive voltage, the output of the optical modulator. The output is a single-side band (SSB) signal and is sufficiently linear with respect to the drive voltage for allowing direct detection at a receiver.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Pixel pre-processing and encoding
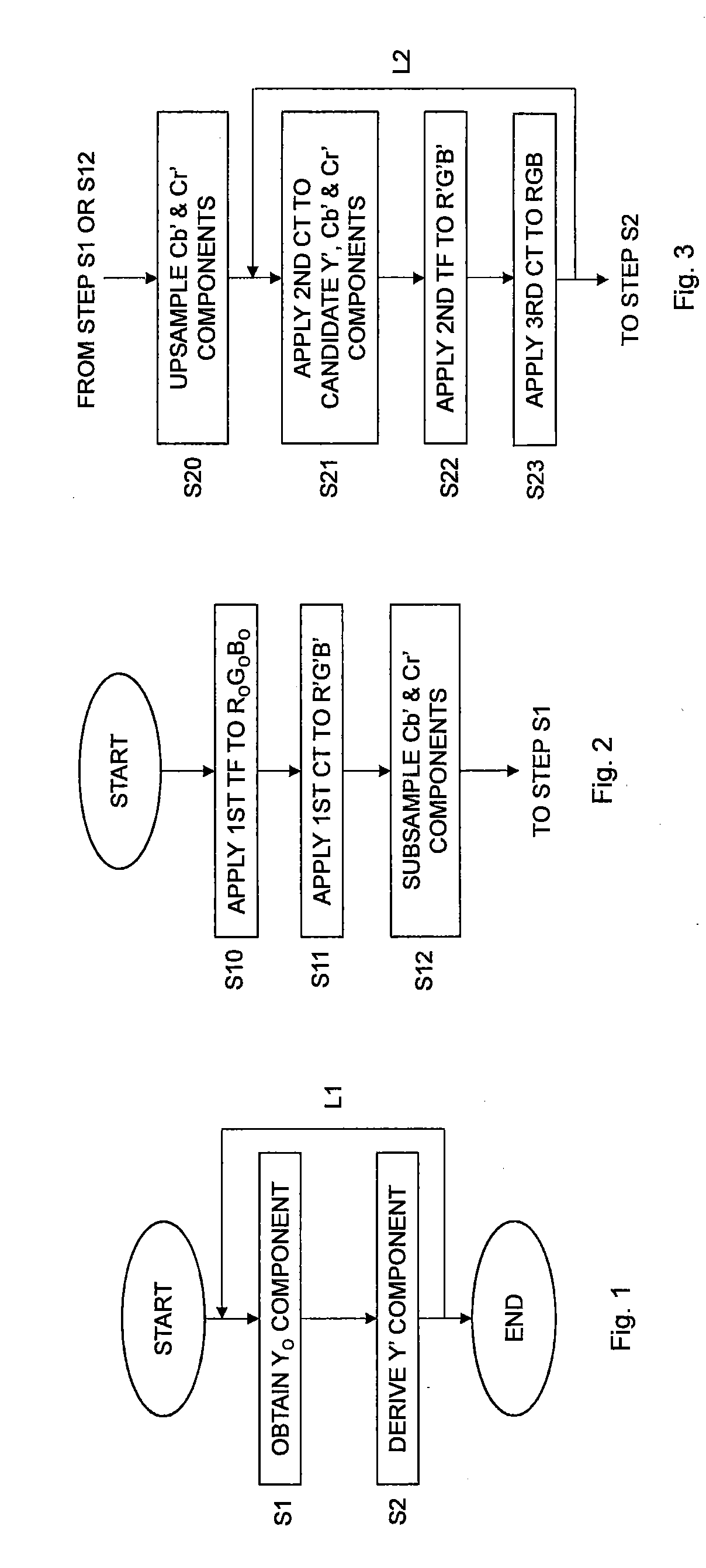
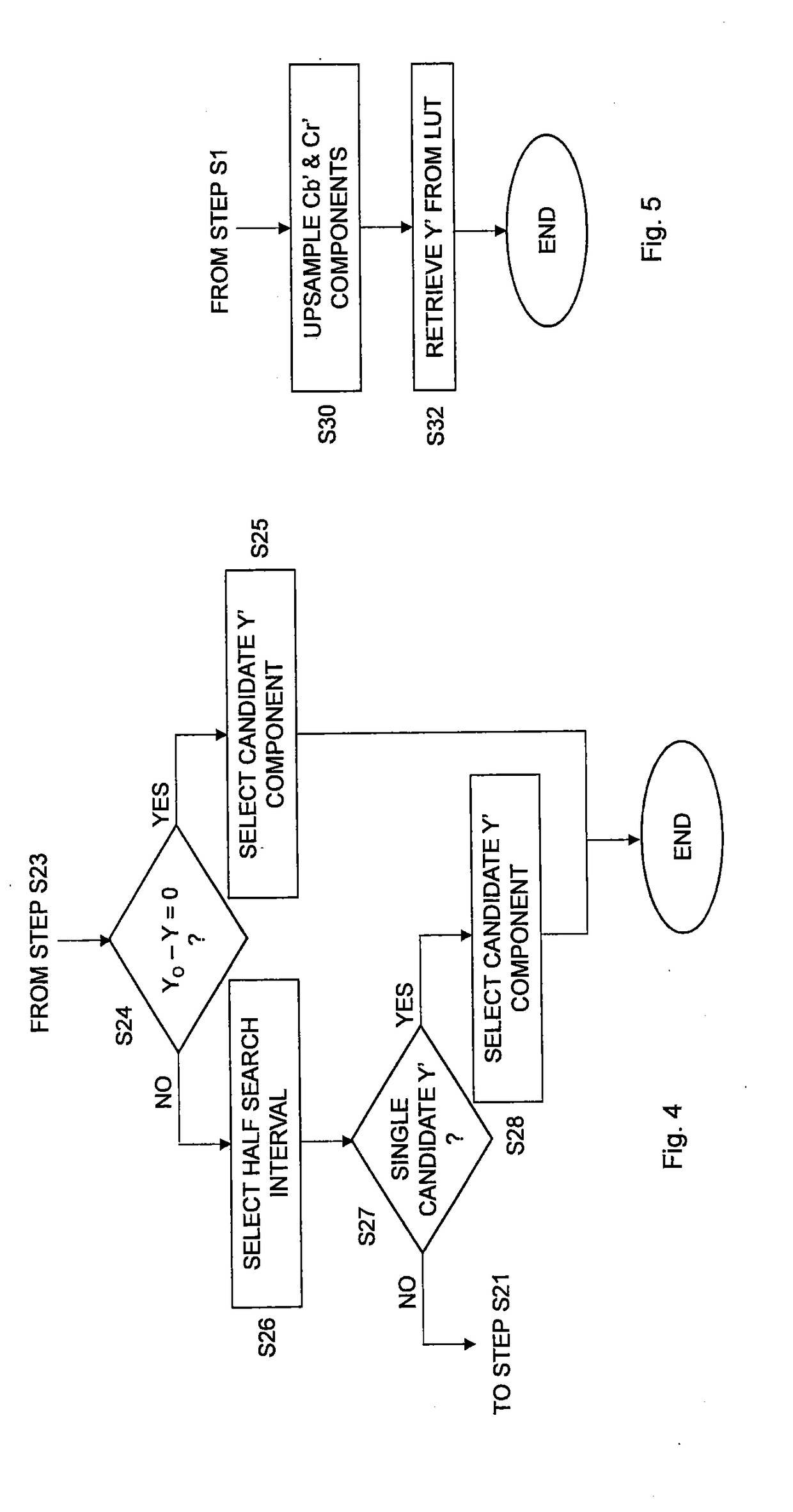
ActiveUS20170208310A1Increase brightnessColor signal processing circuitsGeometric image transformationChroma subsamplingPixel based
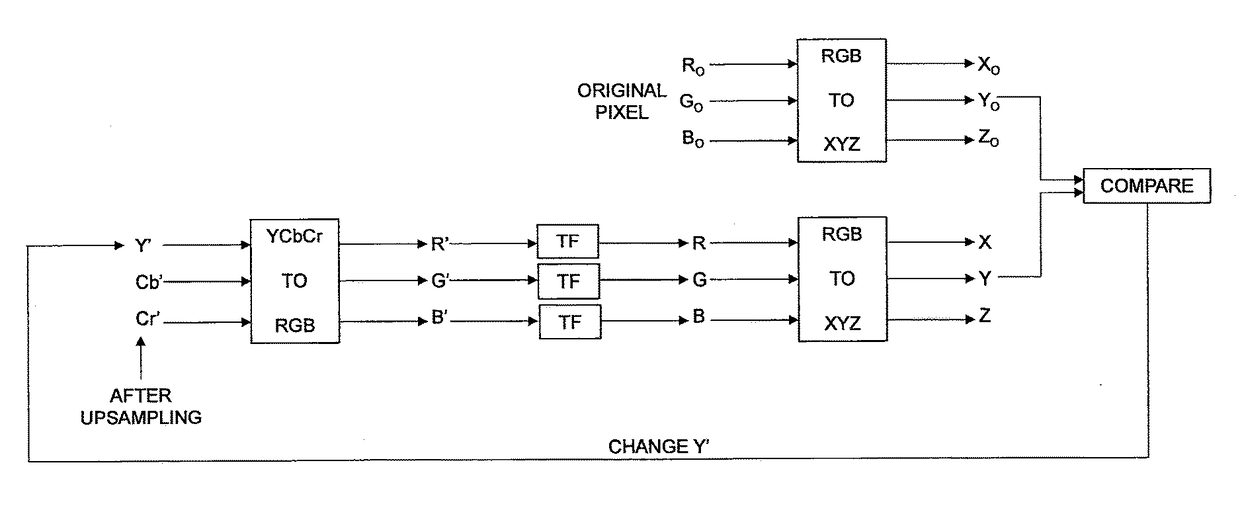
A pixel pre-processing comprises obtaining an original linear luminance component value of a pixel in a picture in a third color space determined based on a linear color of the pixel in a first color space. A non-linear luma component value in a second color space is derived for the pixel based on a first non-linear chroma component value in the second color space, a second non-linear chroma component value in the second color space and the original linear luminance component value in the third color space. The pre-processing reduces luminance artifacts that otherwise may occur when chroma subsampling is used in combination with a non-linear transfer function.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
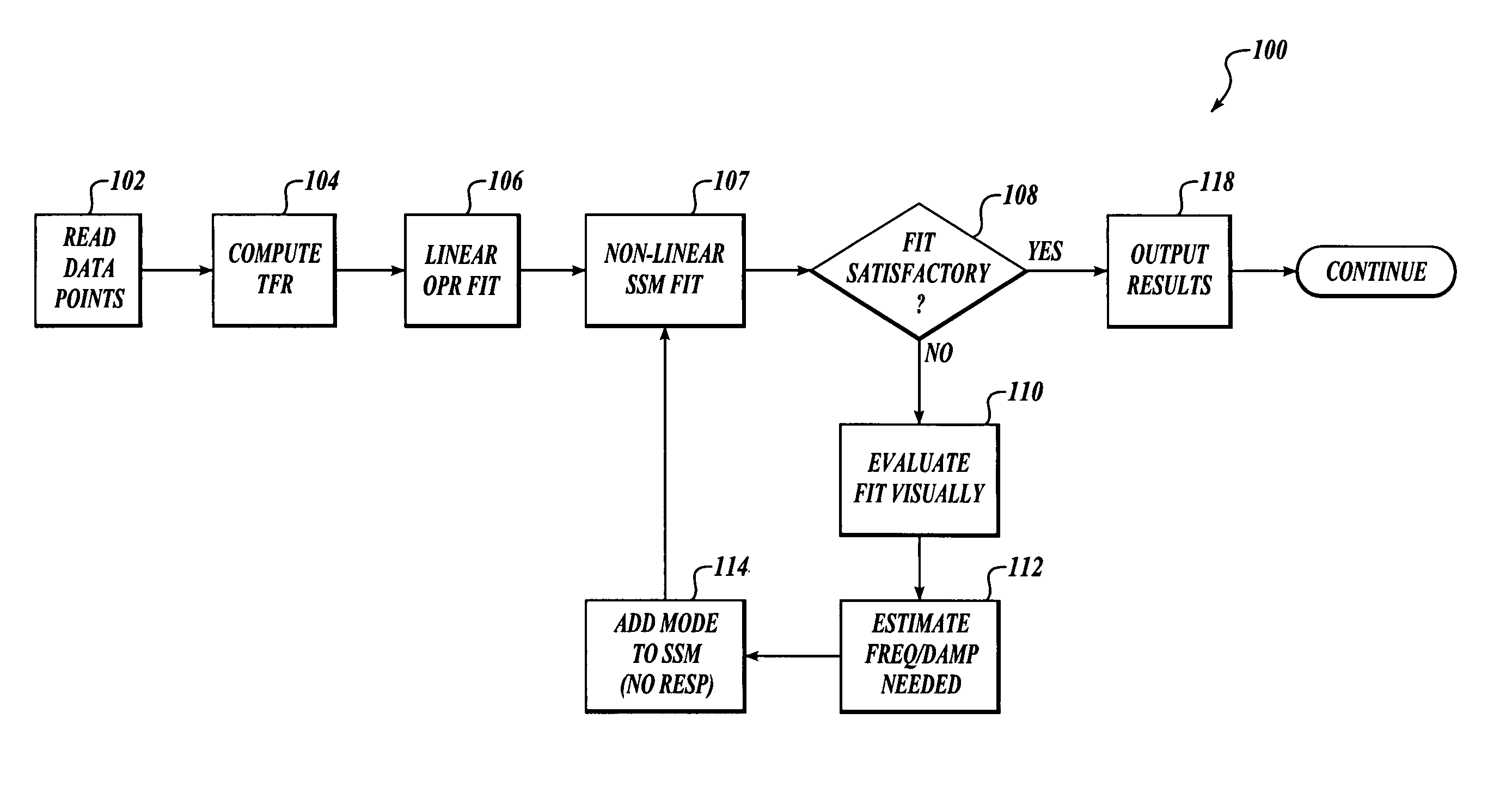
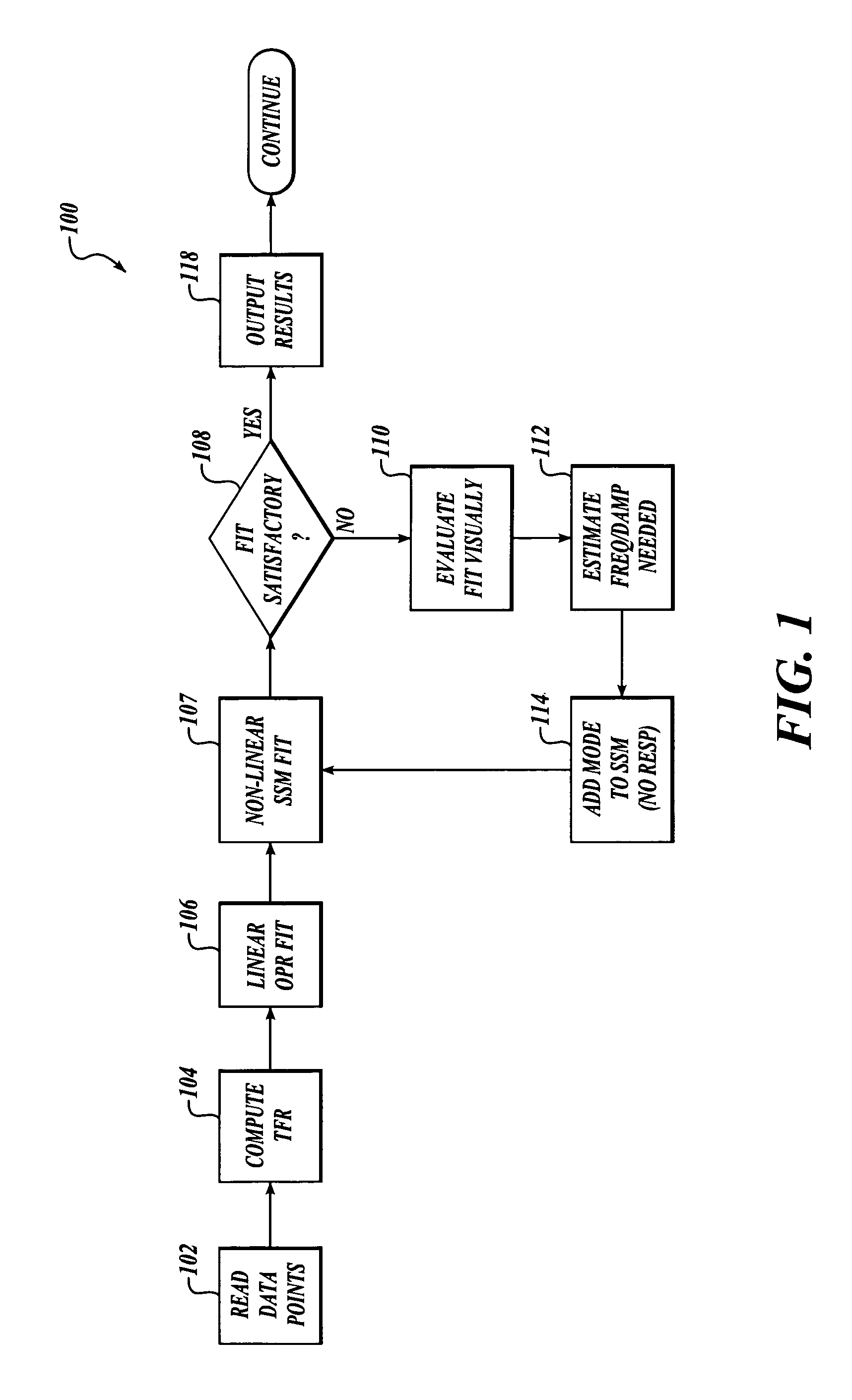
Methods and systems for analyzing flutter test data using non-linear transfer function frequency response fitting
InactiveUS7054785B2Well representedLow costAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNuclear monitoringComputer scienceFrequency response
Methods and systems for analyzing flutter test data using non-linear transfer function frequency response fitting are provided. In one embodiment, a plurality of data points are read, with each data point representing a motion of an aeroelastic structure (e.g. an aircraft surface) at a different location. A closed form fit to the plurality of data points is performed to obtain an initial curve fit condition. At least one non-linear transfer function frequency response curve fit is then performed to the plurality of data points.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Dynamic characterisation of amplifier using multiple envelope shaping functions
InactiveUS20150088445A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic circuit testingAudio power amplifierSignal envelope
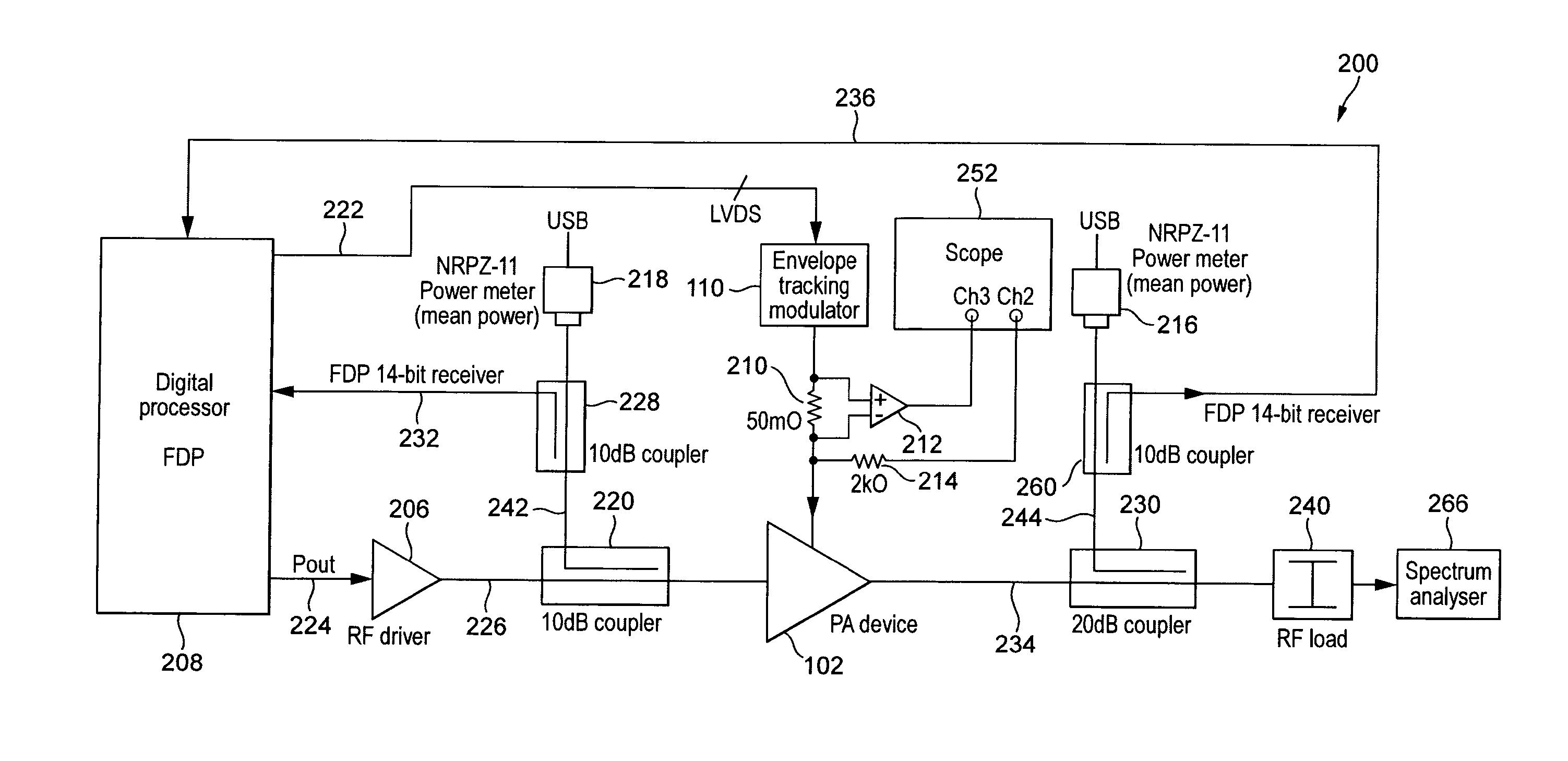
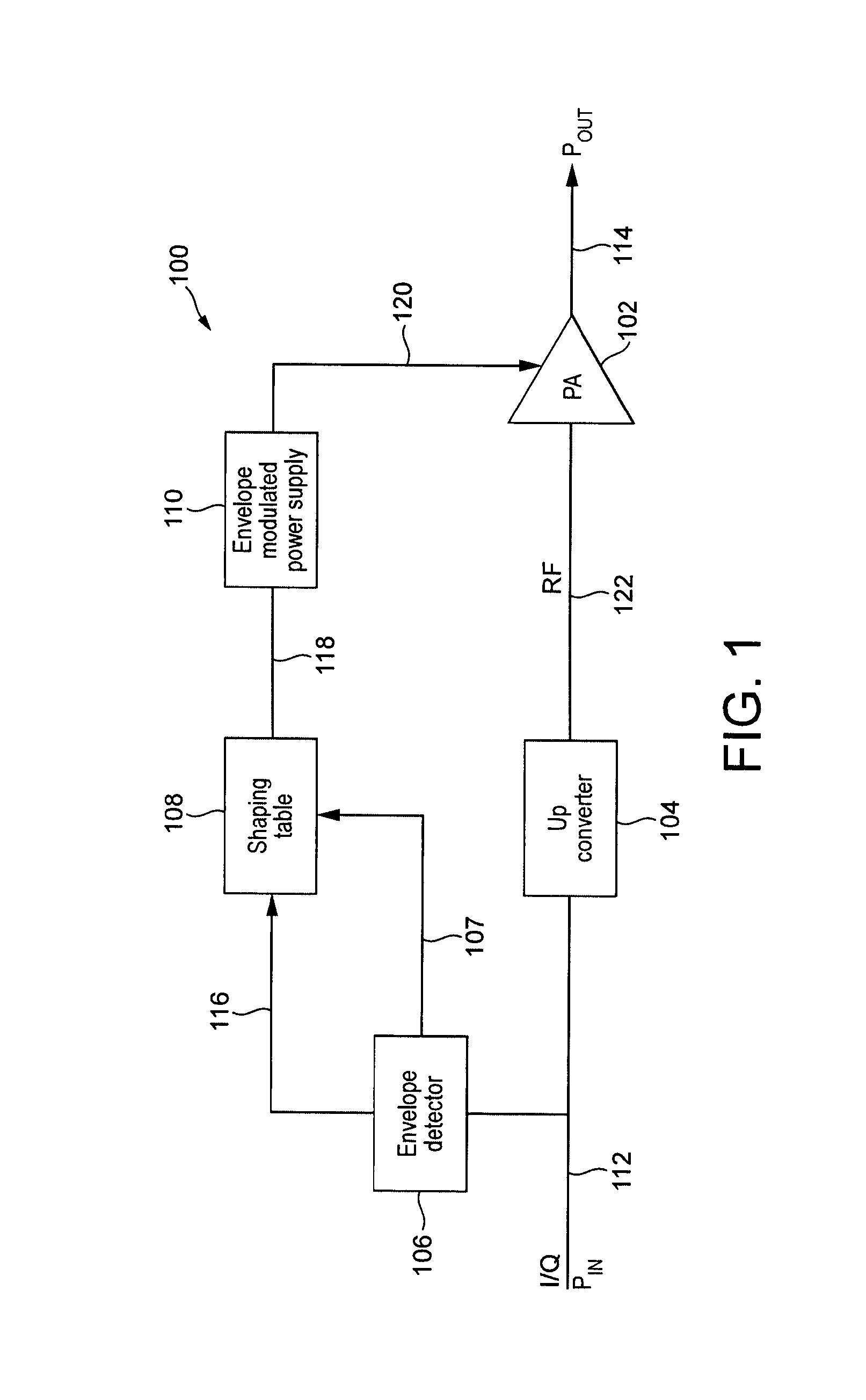
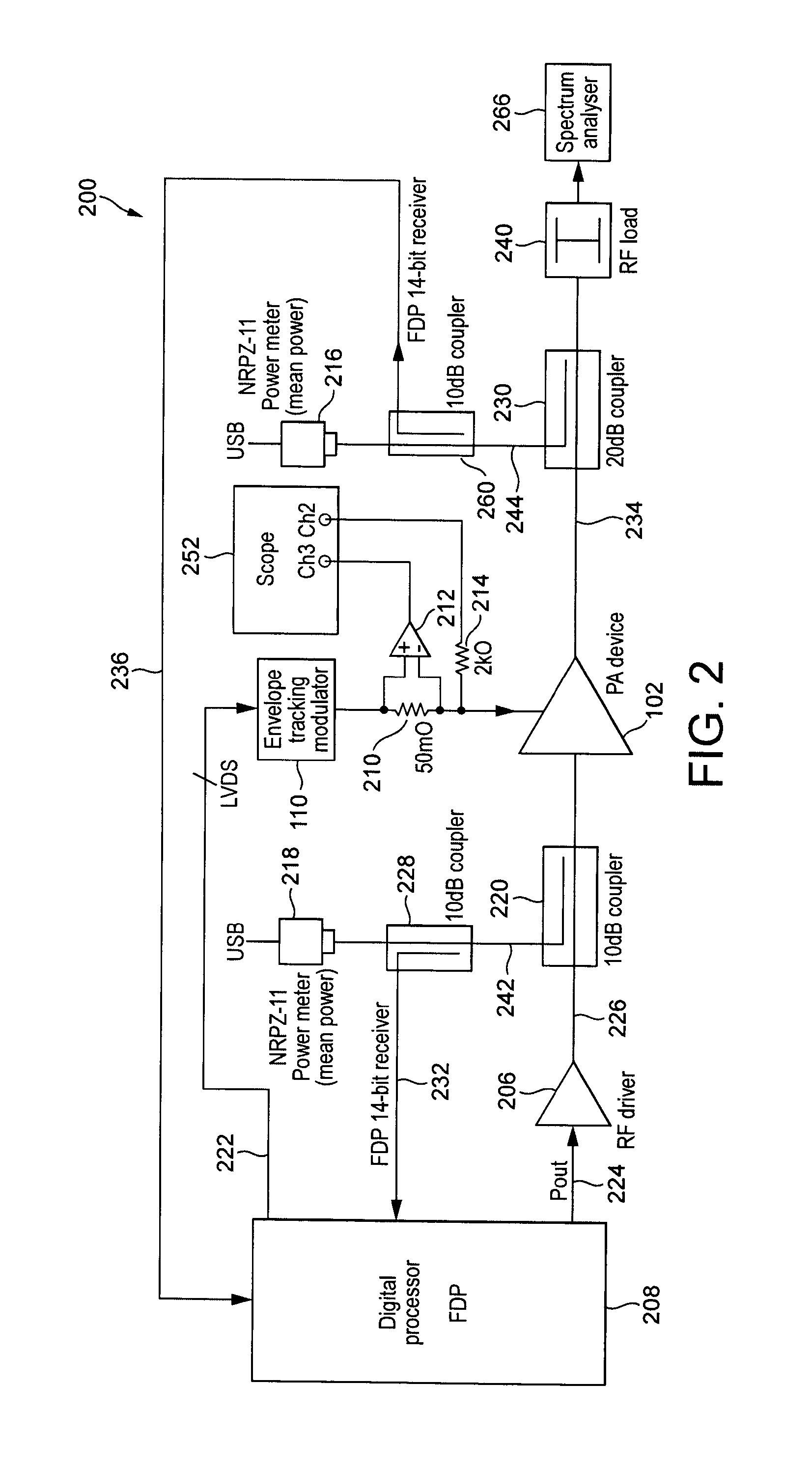
A method of characterizing an envelope tracking amplification stage, the method comprising: generating an input test waveform which is representative of an input waveform under normal operating conditions of the amplification stage; applying a respective one of a plurality of different shaping functions, each comprising a non-linear transfer function, to the input signal envelope in each of a plurality of test periods during the period in which the input test waveform is applied as the input signal to generate the input to the envelope tracking modulated supply voltage; measuring parameters of the amplification stage during the period in which the input test waveform is applied in order to allow determination of the gain, phase and efficiency characteristics of the amplifier; and for each of the gain, phase and efficiency characteristics, generating a three dimensional plot of the characteristic with respect to input power and supply voltage applied to the amplifier.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
High dynamic range color conversion correction
ActiveUS20180048892A1Low technical requirementsReduce complexityTelevision system detailsImage enhancementPattern recognitionVideo bitstream
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for correcting color values. The technique includes downsampling first color space values to generate downsampled color space values and upsampling the downsampled color space values via a first upsampling filter type to generate second color space values. The technique further includes modifying at least one component value included in the downsampled color space values based on a first component value included in the first color space values, a second component value included in the second color space values, and an approximation of a nonlinear transfer function. The technique further includes at least one of (i) storing an indication of the first upsampling filter type in conjunction with a video bitstream associated with the at least one component value, and (ii) transmitting the indication of the first upsampling filter type to a receiving device in conjunction with the video bitstream.
Owner:NETFLIX
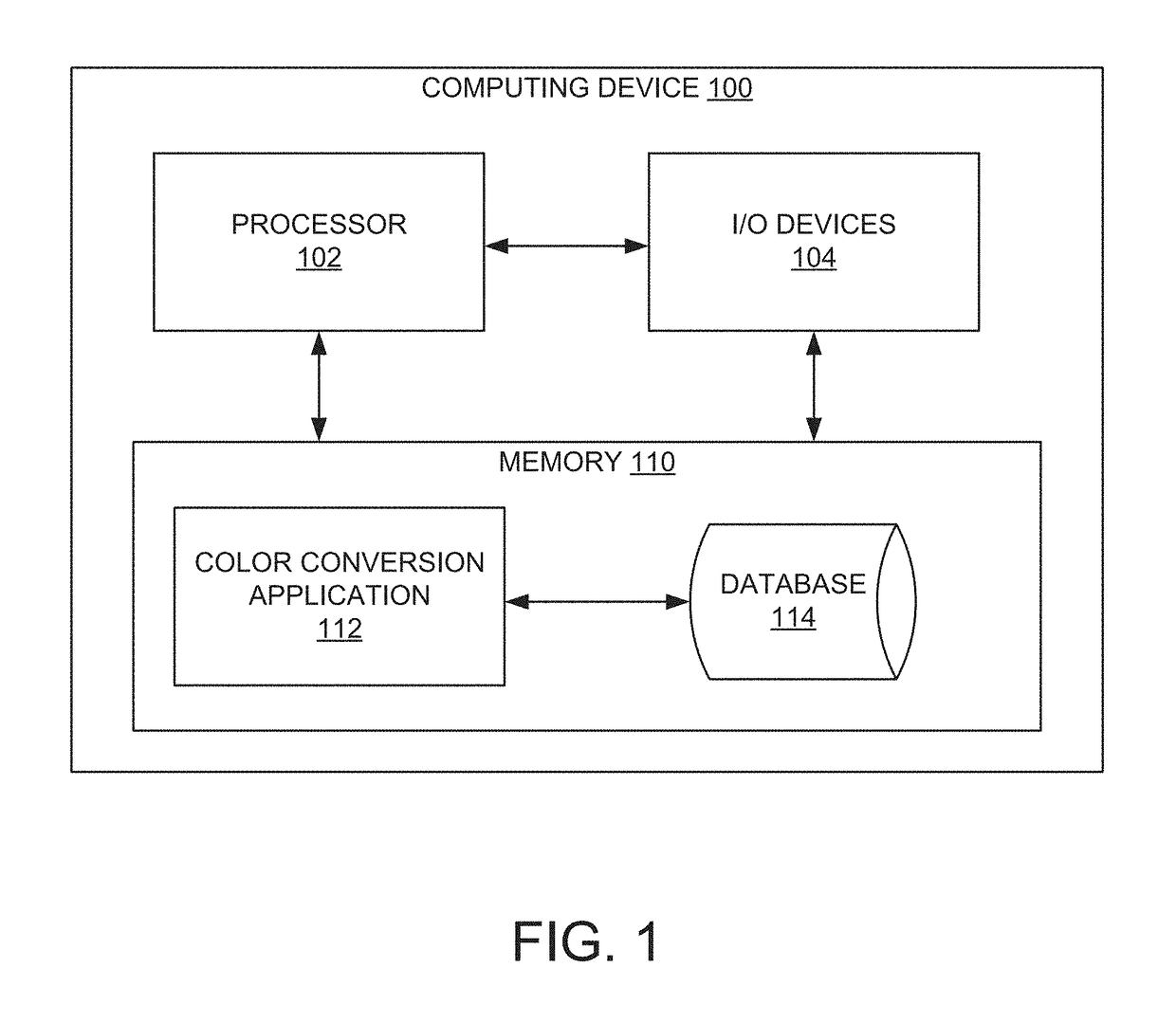
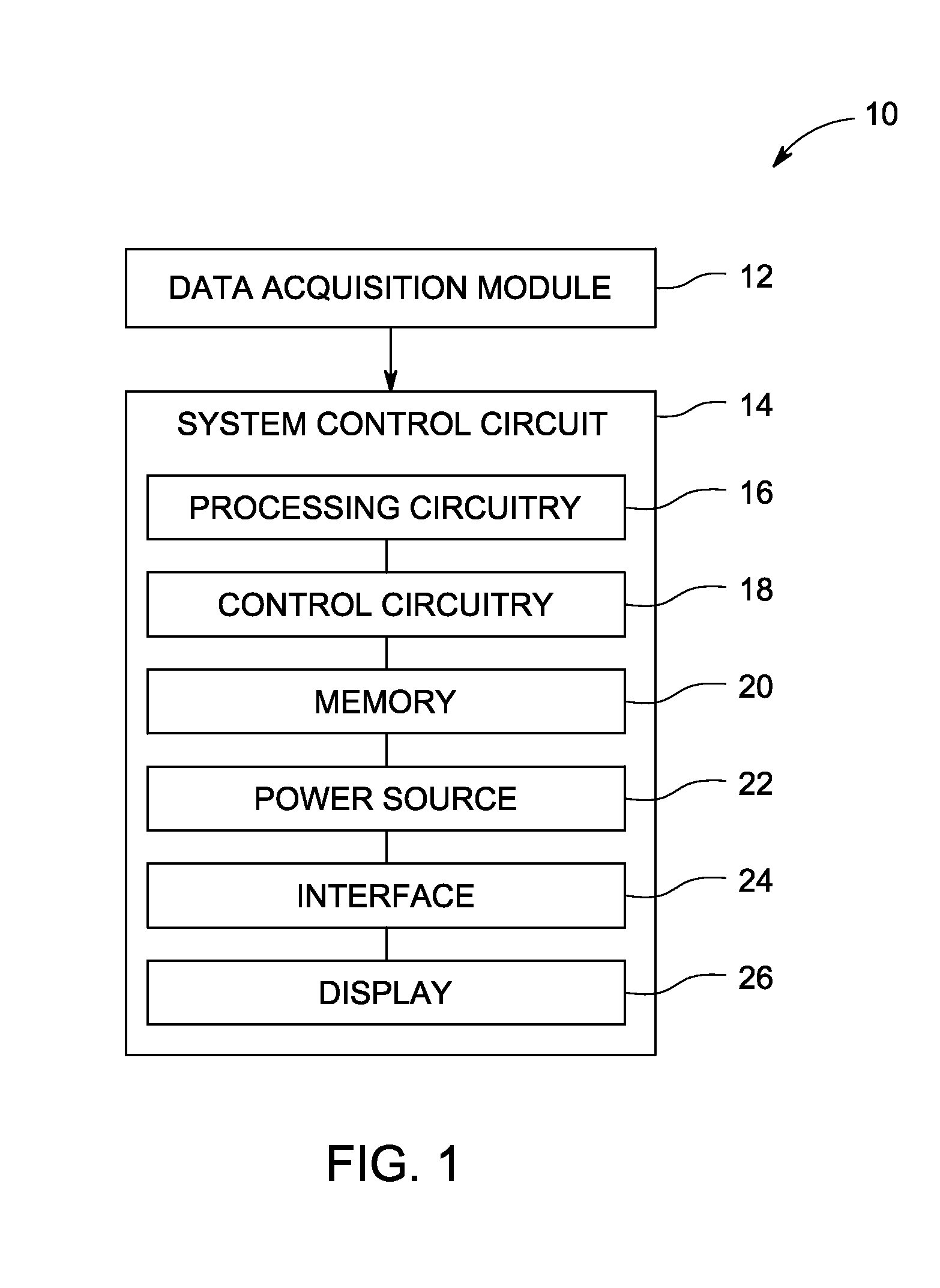
Systems and methods for nonlinear elastography
ActiveUS20140180058A1Delayed slopeMagnetic measurementsOrgan movement/changes detectionData acquisitionImaging equipment
Nonlinear elastography systems and methods are provided. The elastography system includes a data acquisition module, such as an imaging device, and associated system control circuitry. The data acquisition module is configured to acquire various data, such as displacement and / or force data, from a material. A nonlinear transfer function is applied to the acquired data to generate information about the material's stiffness. In one implementation, a map representative of the material's stiffness is generated.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
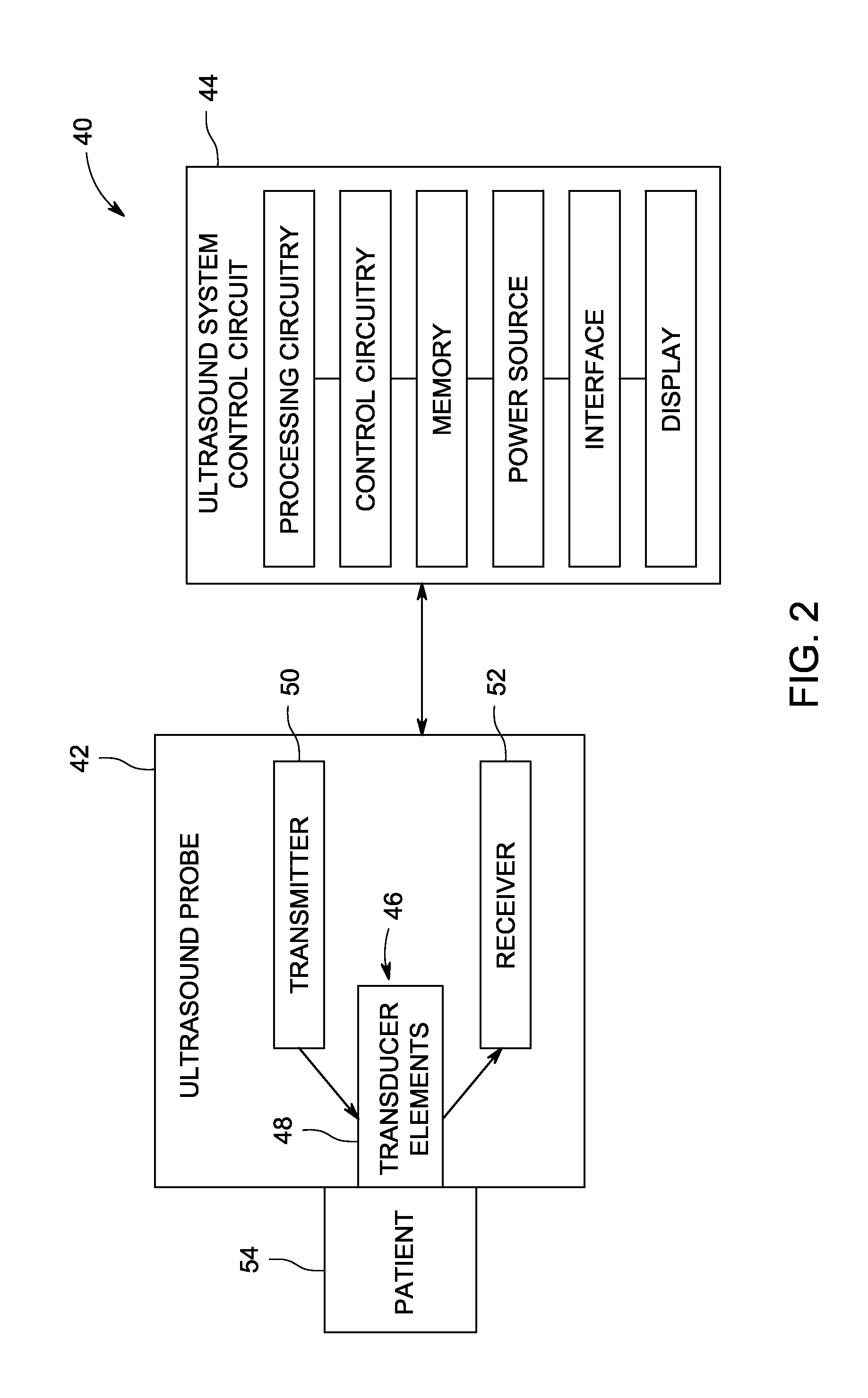
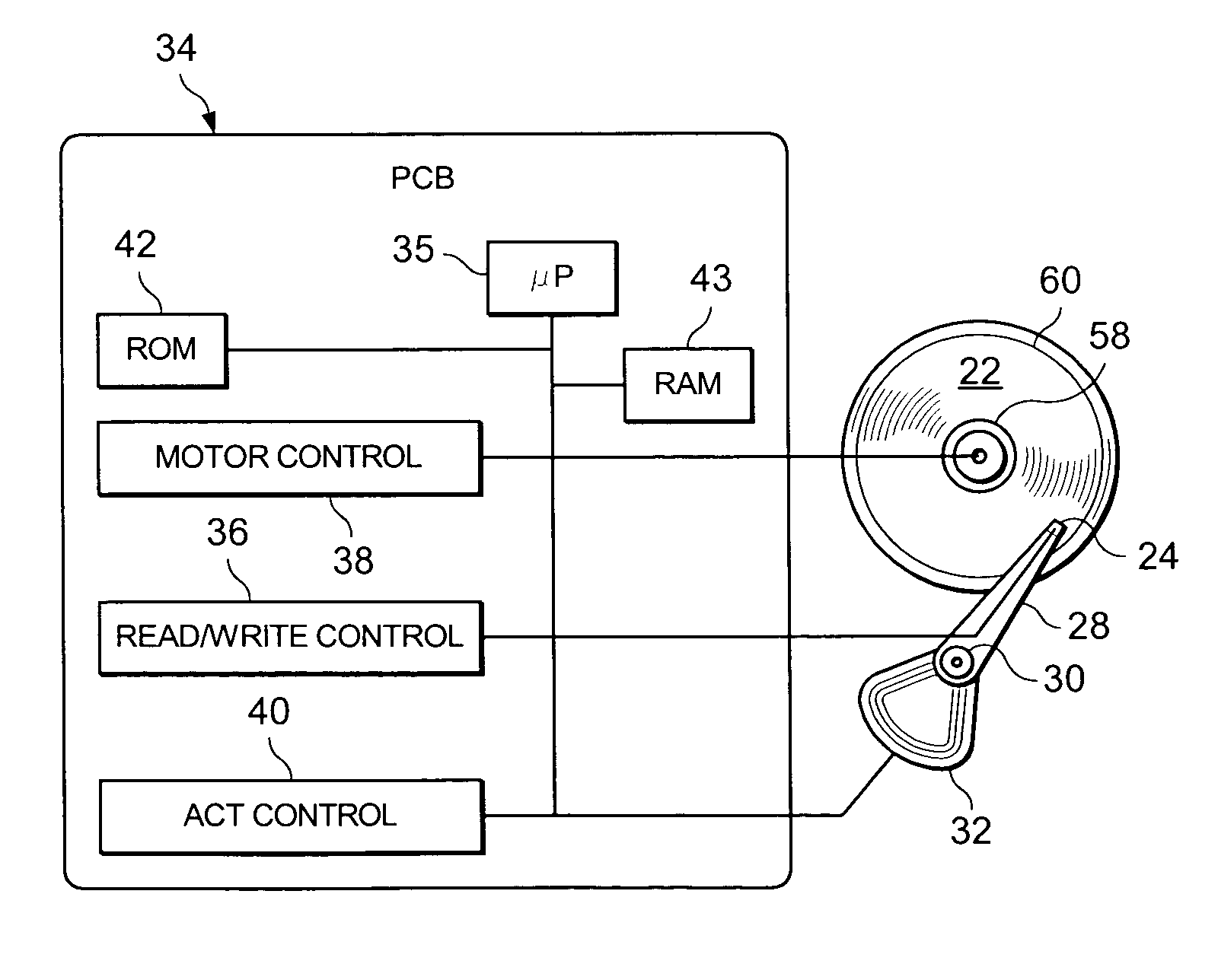
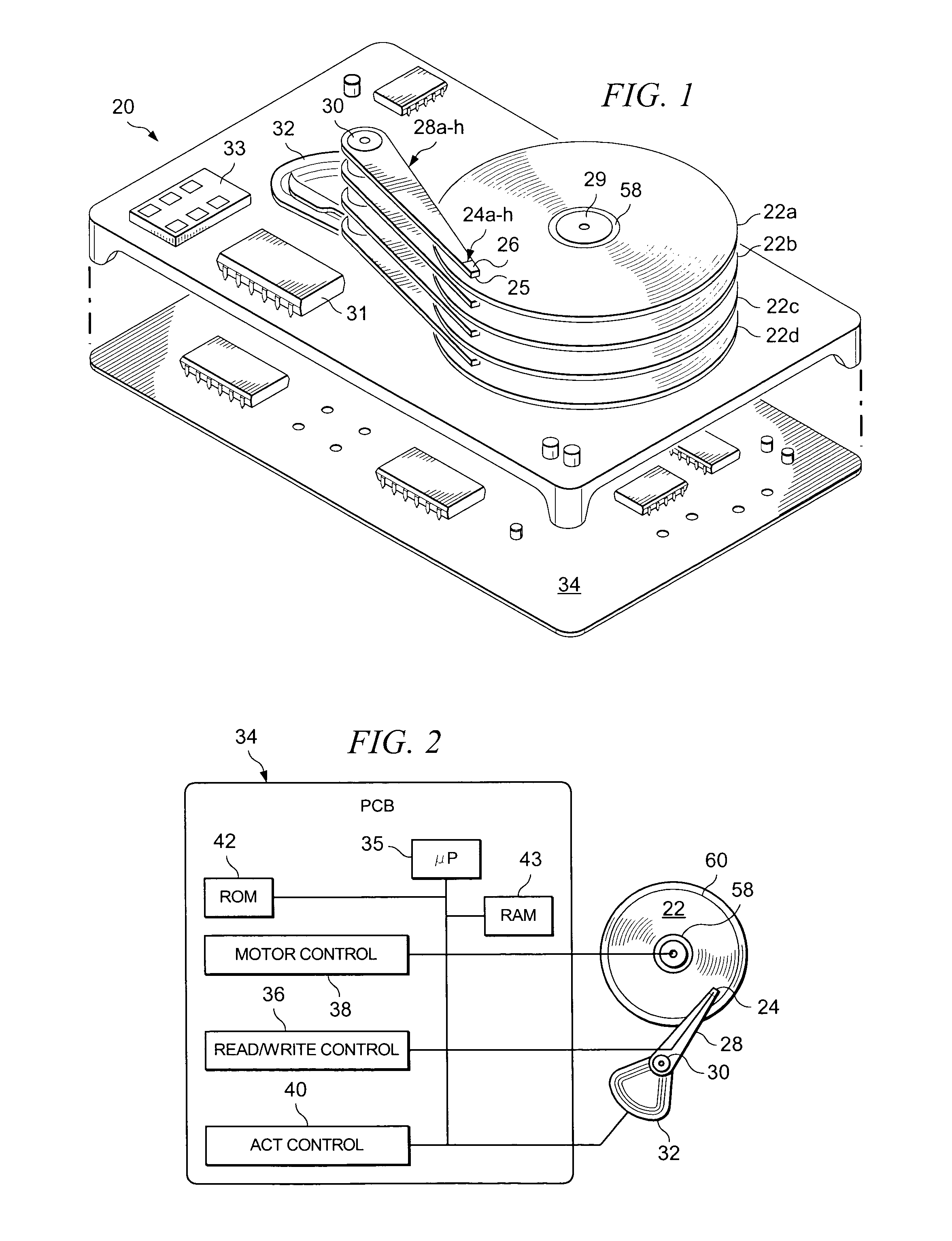
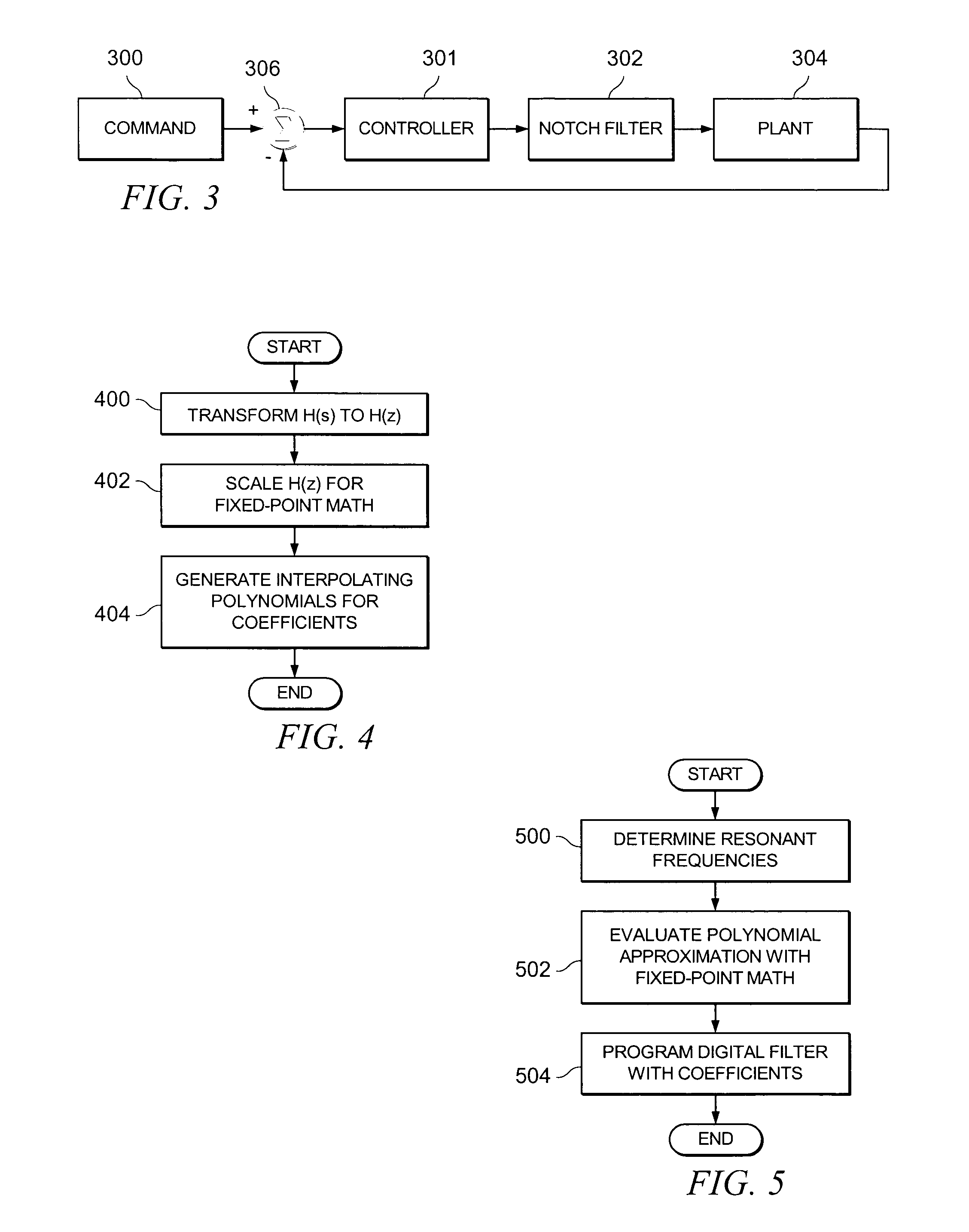
Efficient notch coefficient computation for a disc drive control system using fixed point math
InactiveUS7023646B2Effective calculationTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageBilinear transformControl system
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com