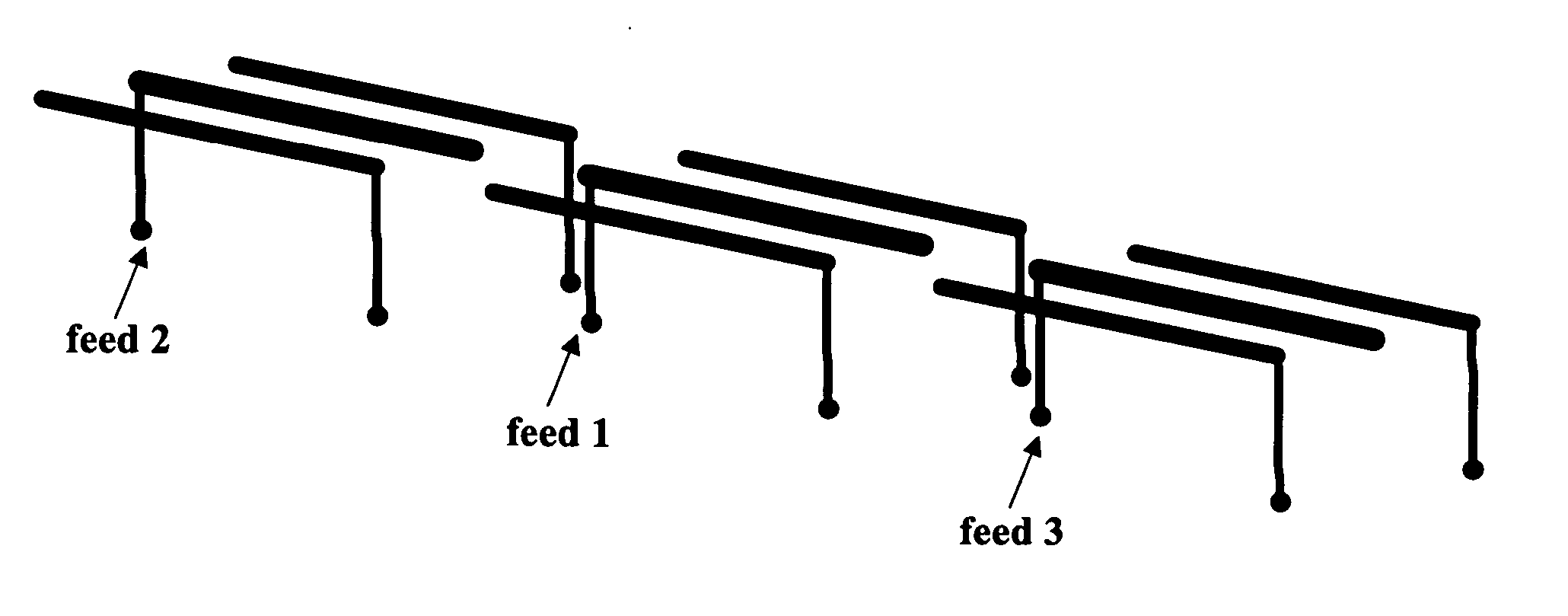
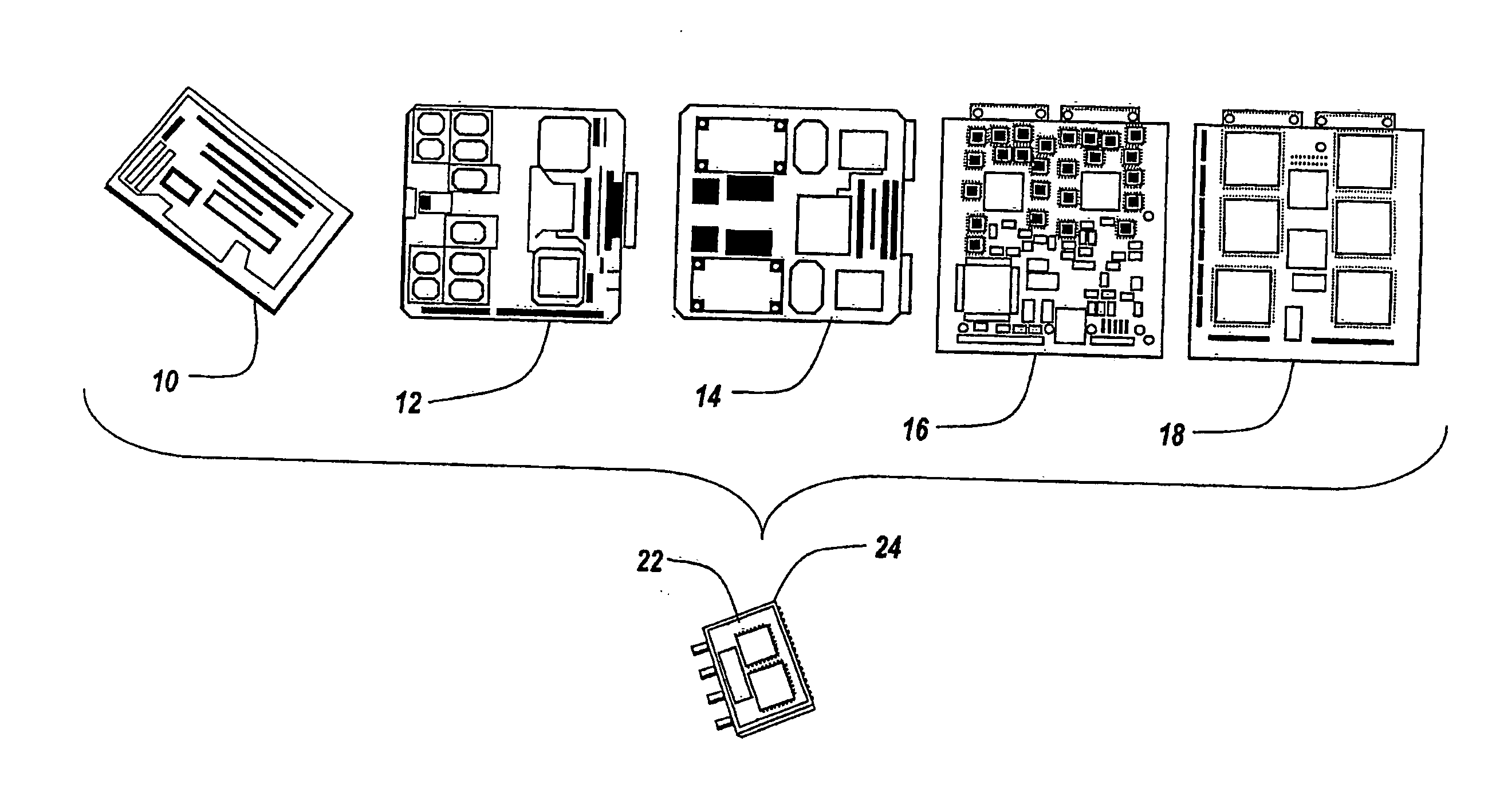
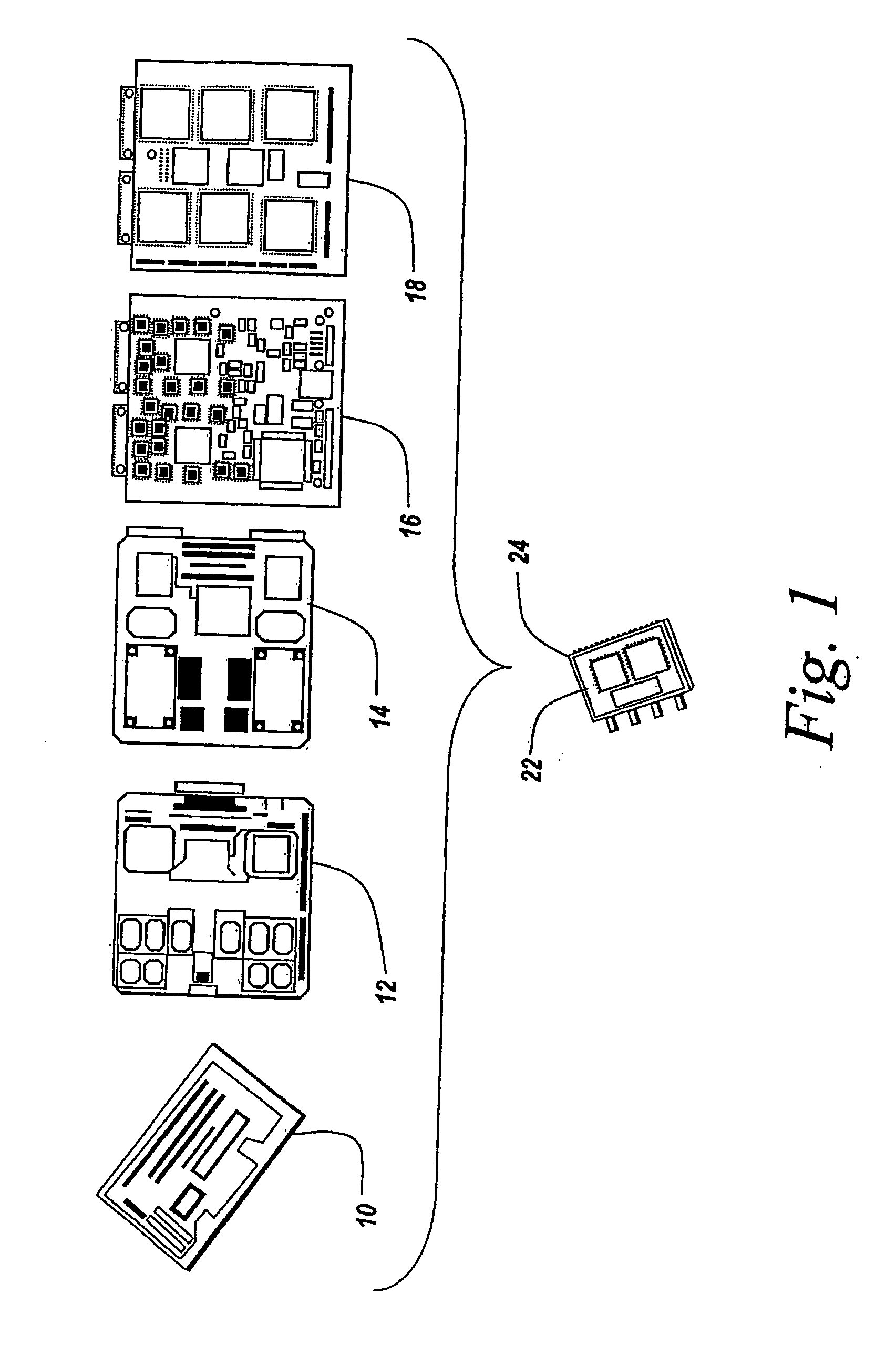
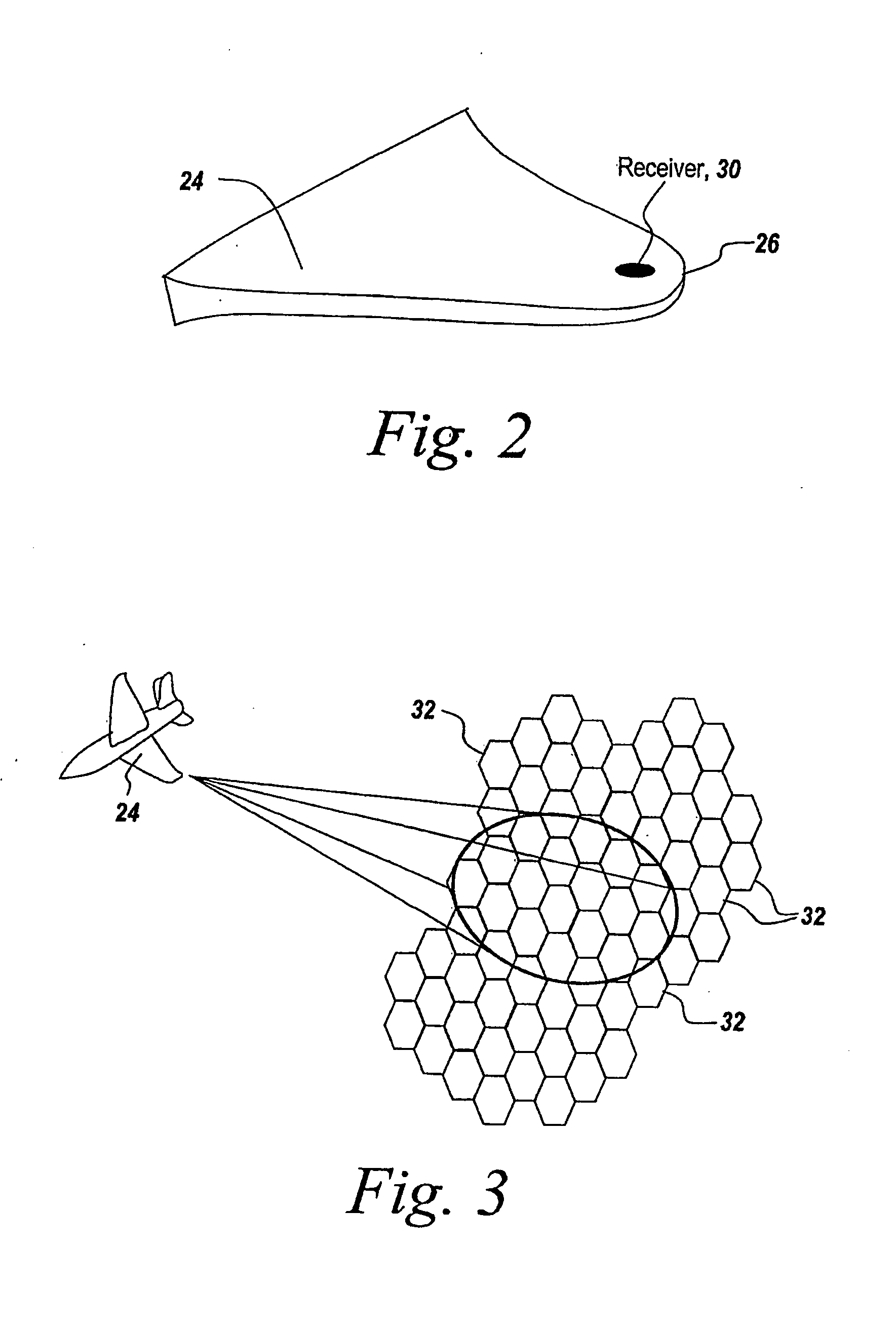
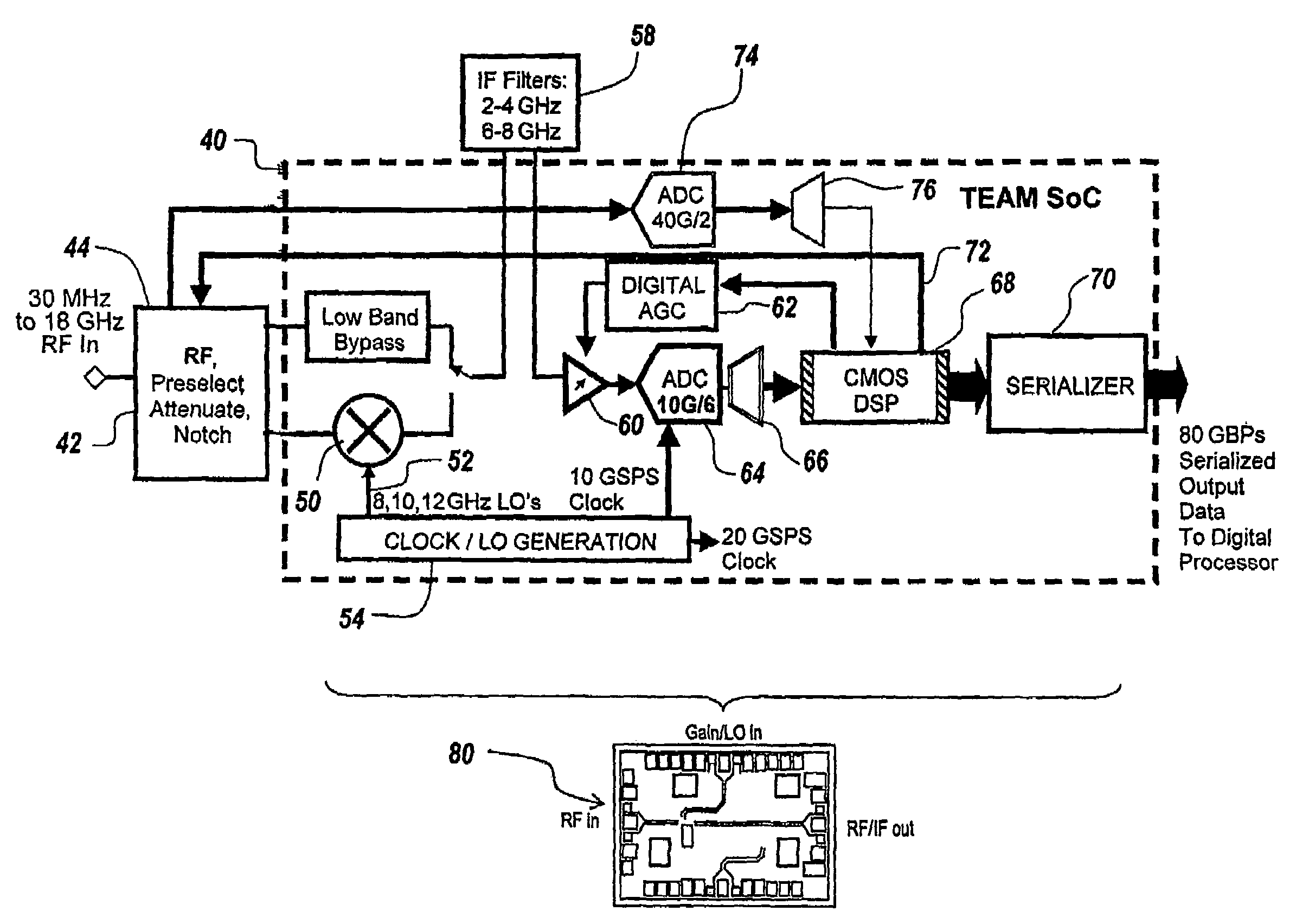
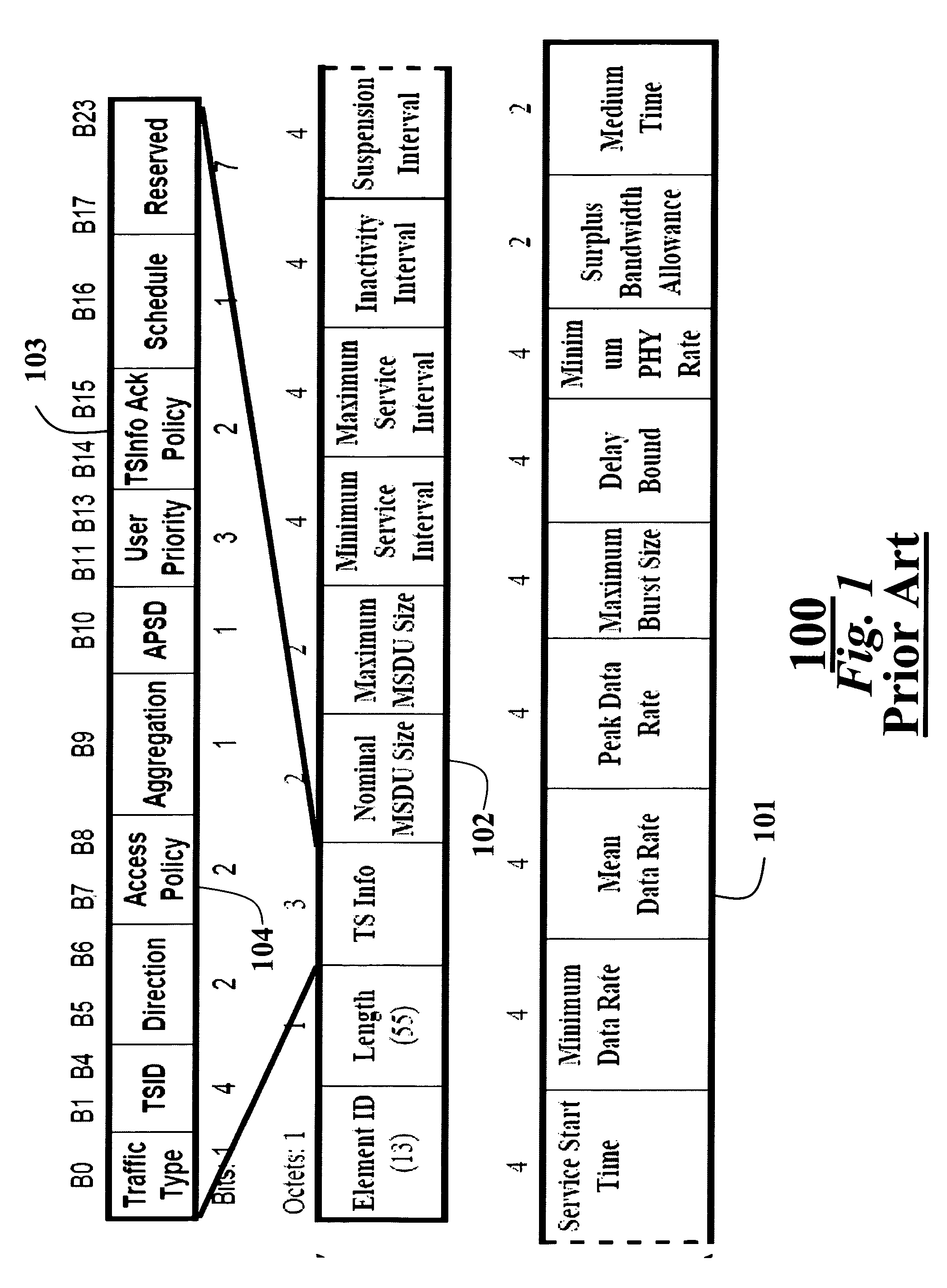
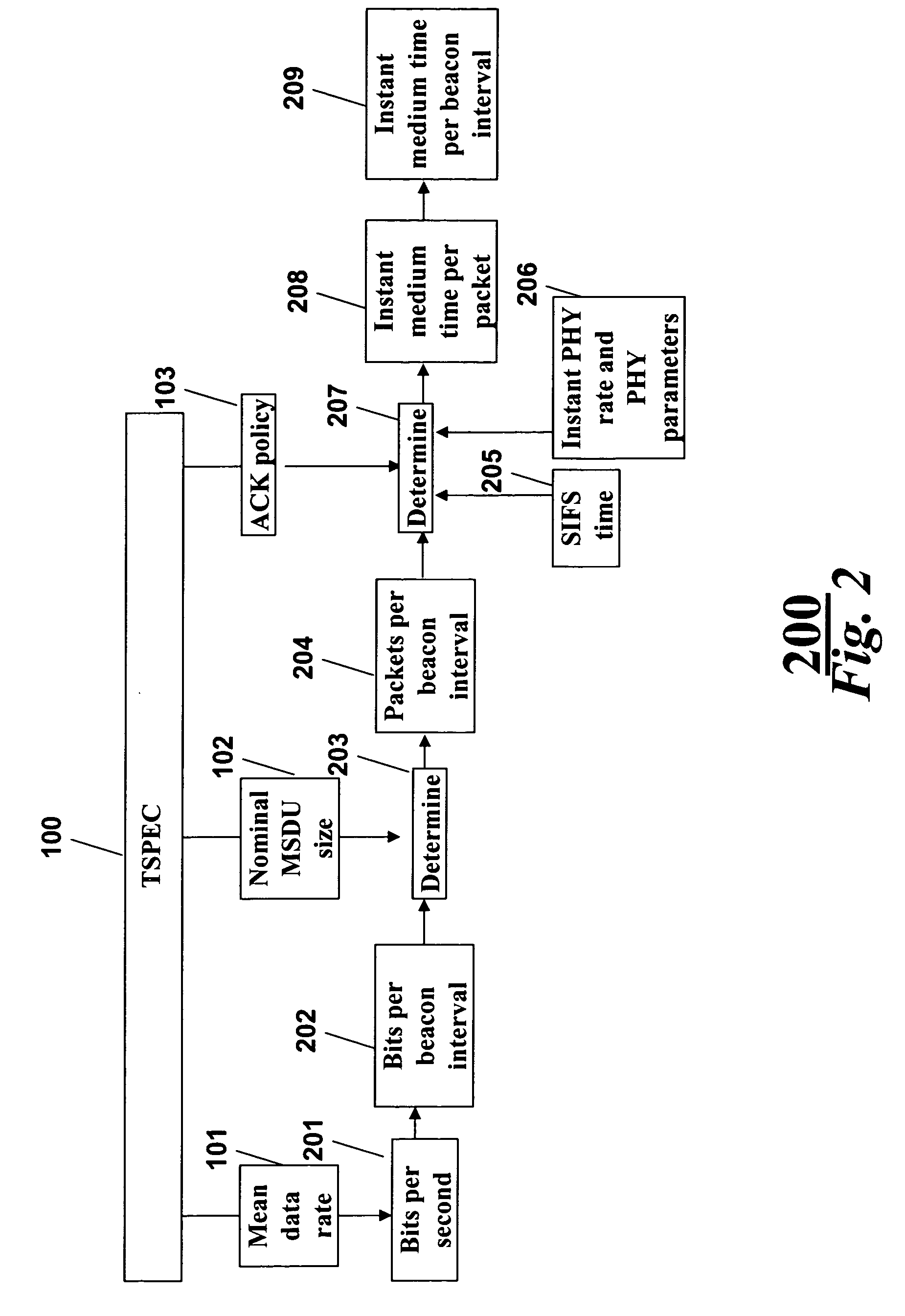
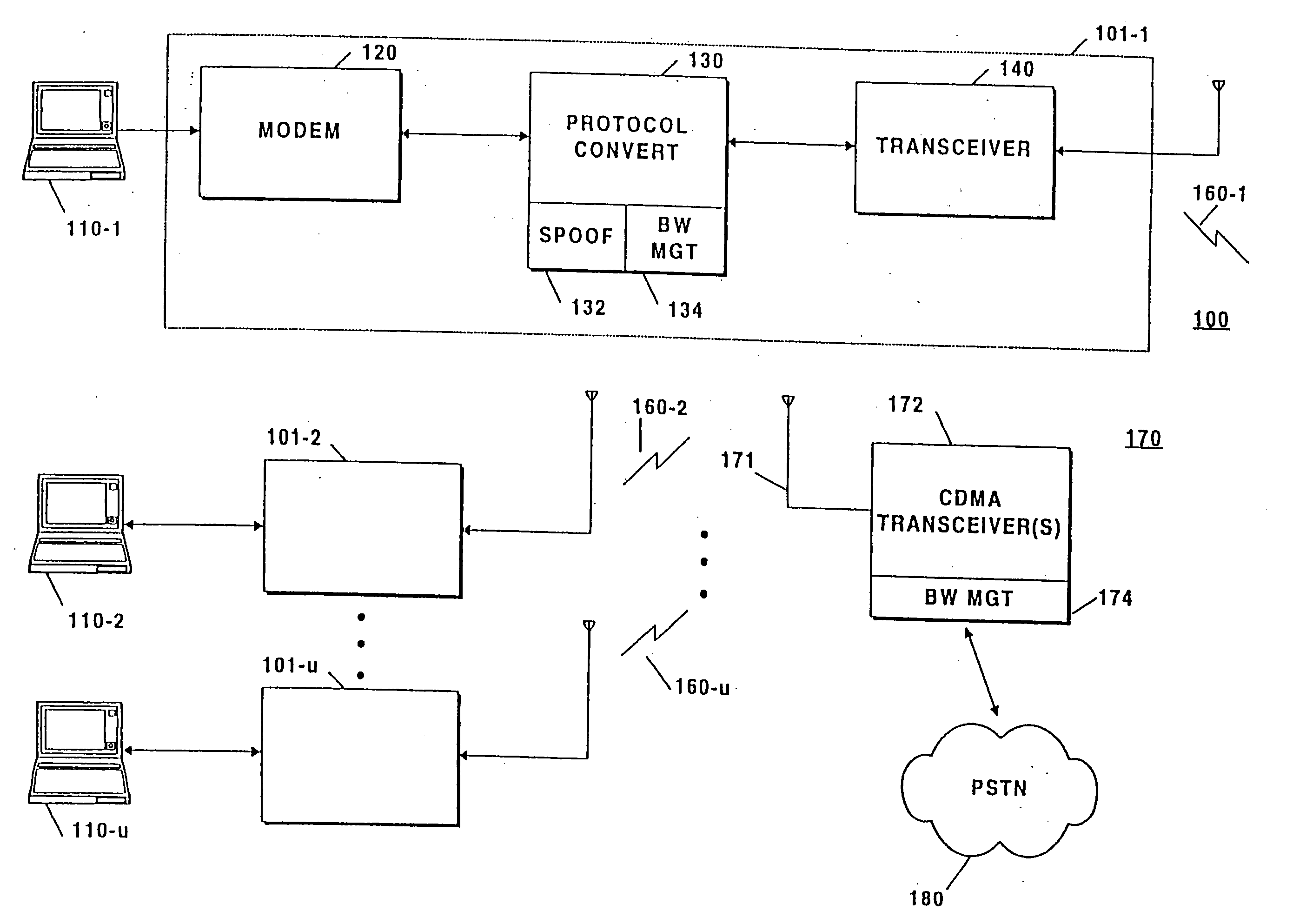
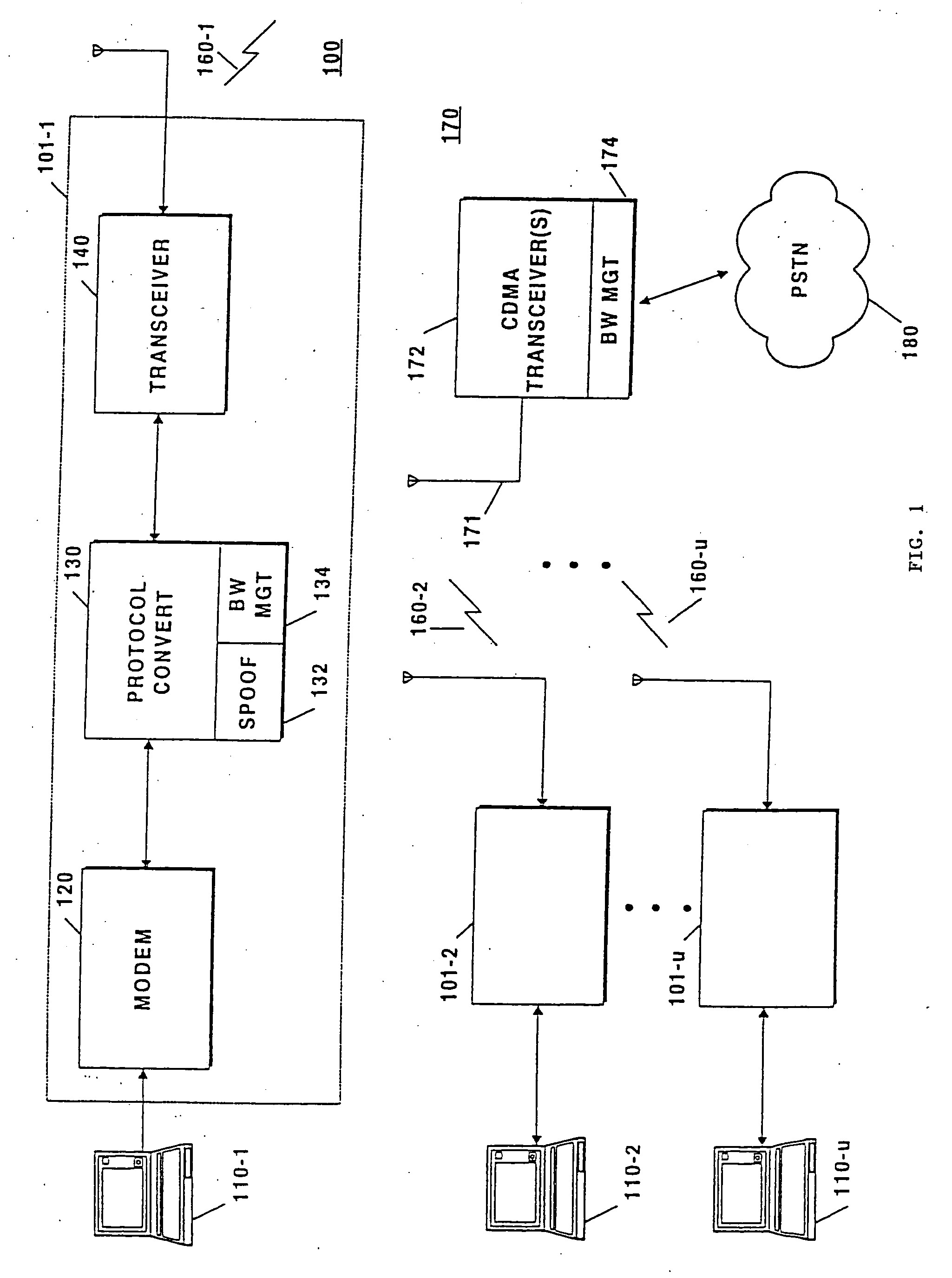
Patents
Literature
116 results about "Instantaneous bandwidth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Instantaneous bandwidth is a statistical measure of the seismic wavelet, but it relates to various physical conditions: Represents seismic data bandwidth sample by sample. It is one of the high-resolution character correlators. Shows overall effects of absorption and seismic character changes.
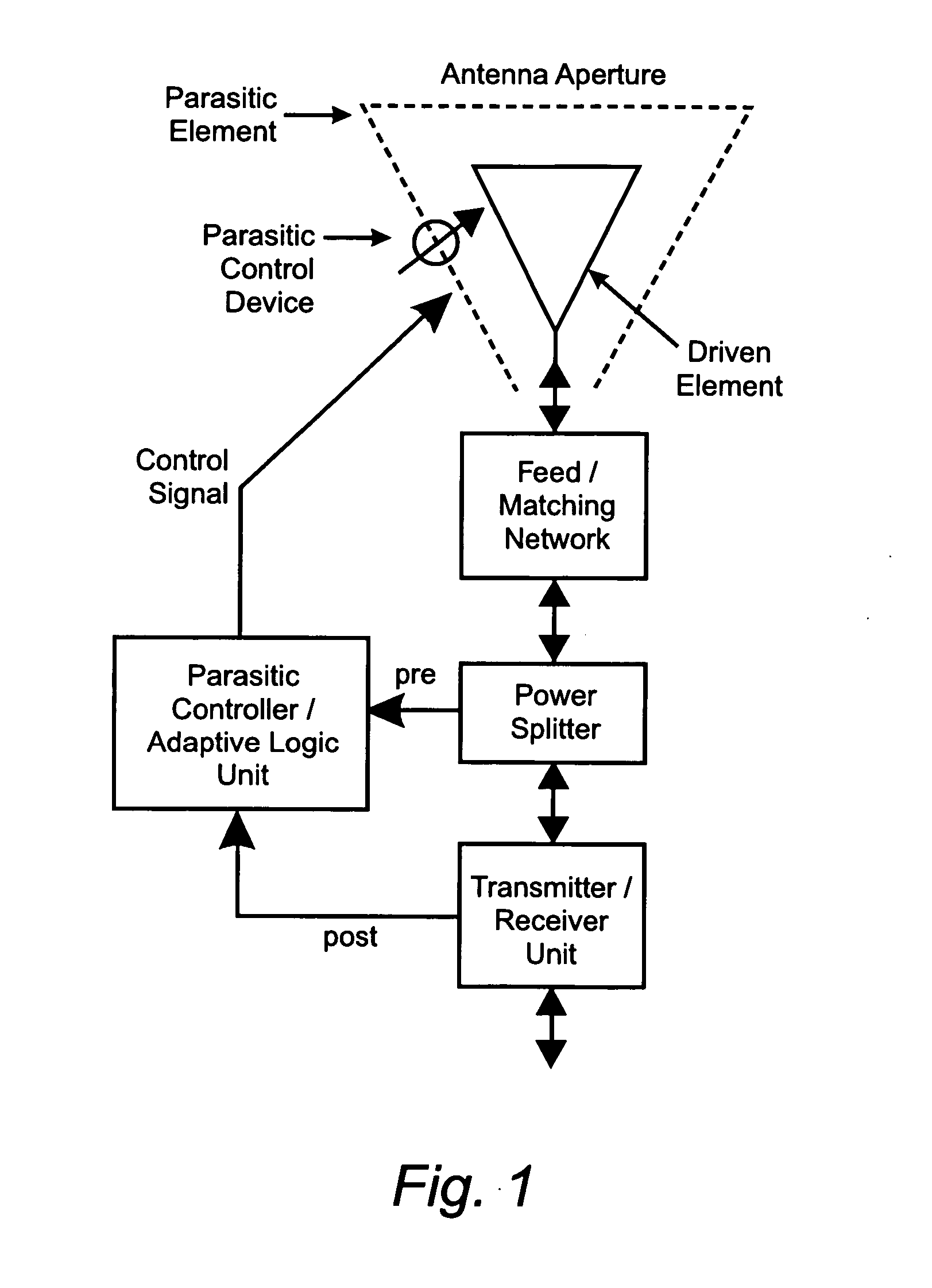
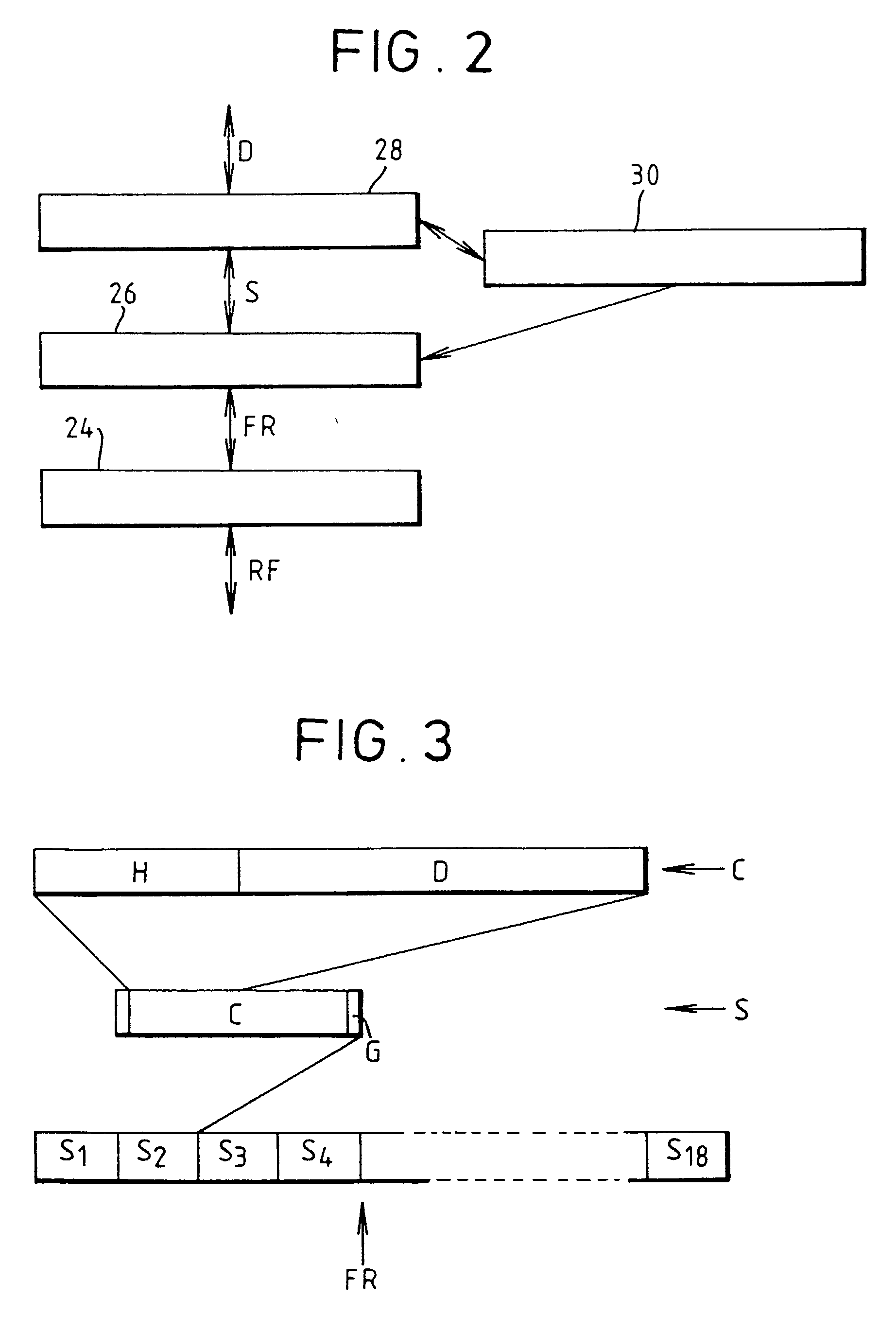
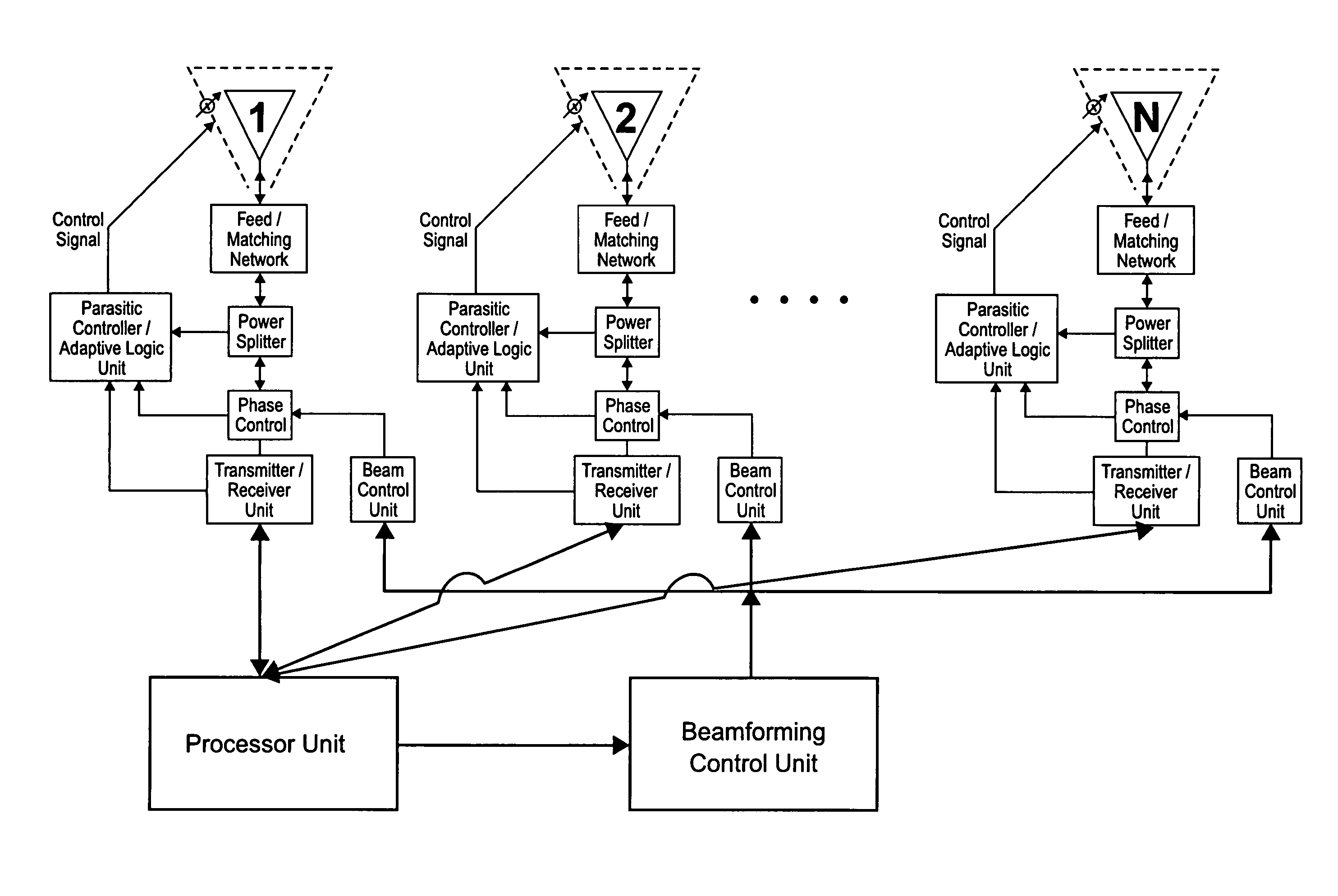
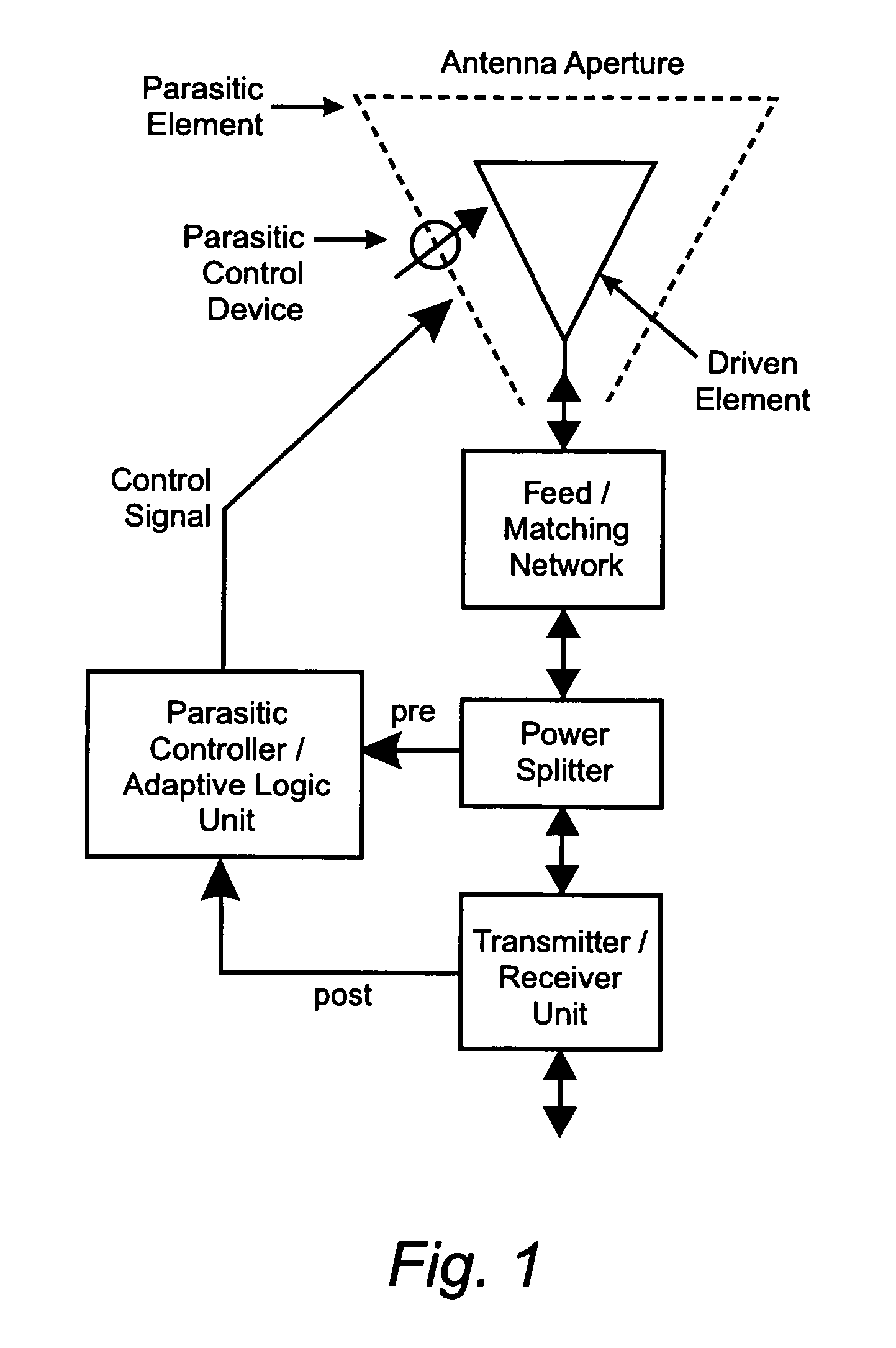
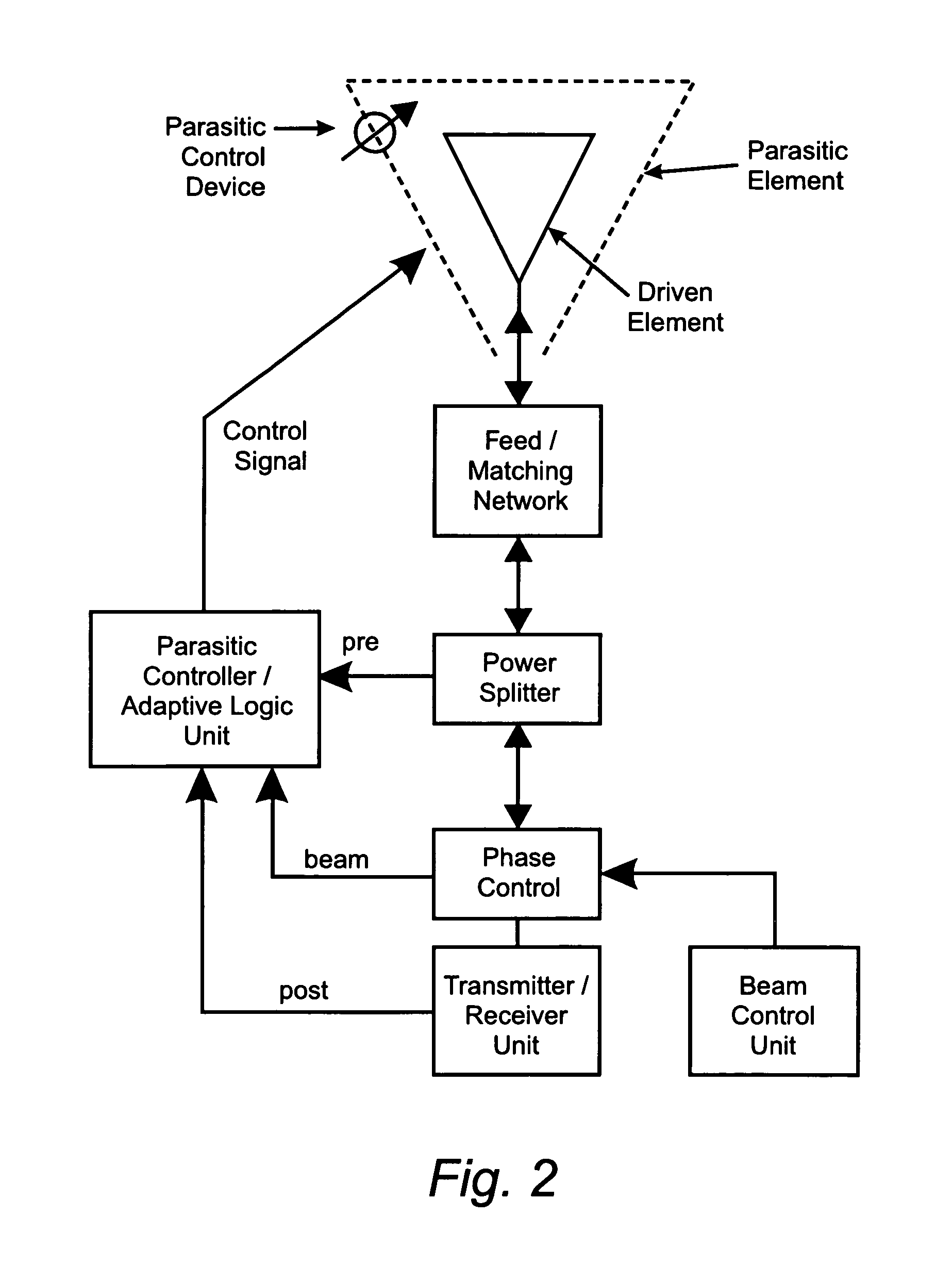
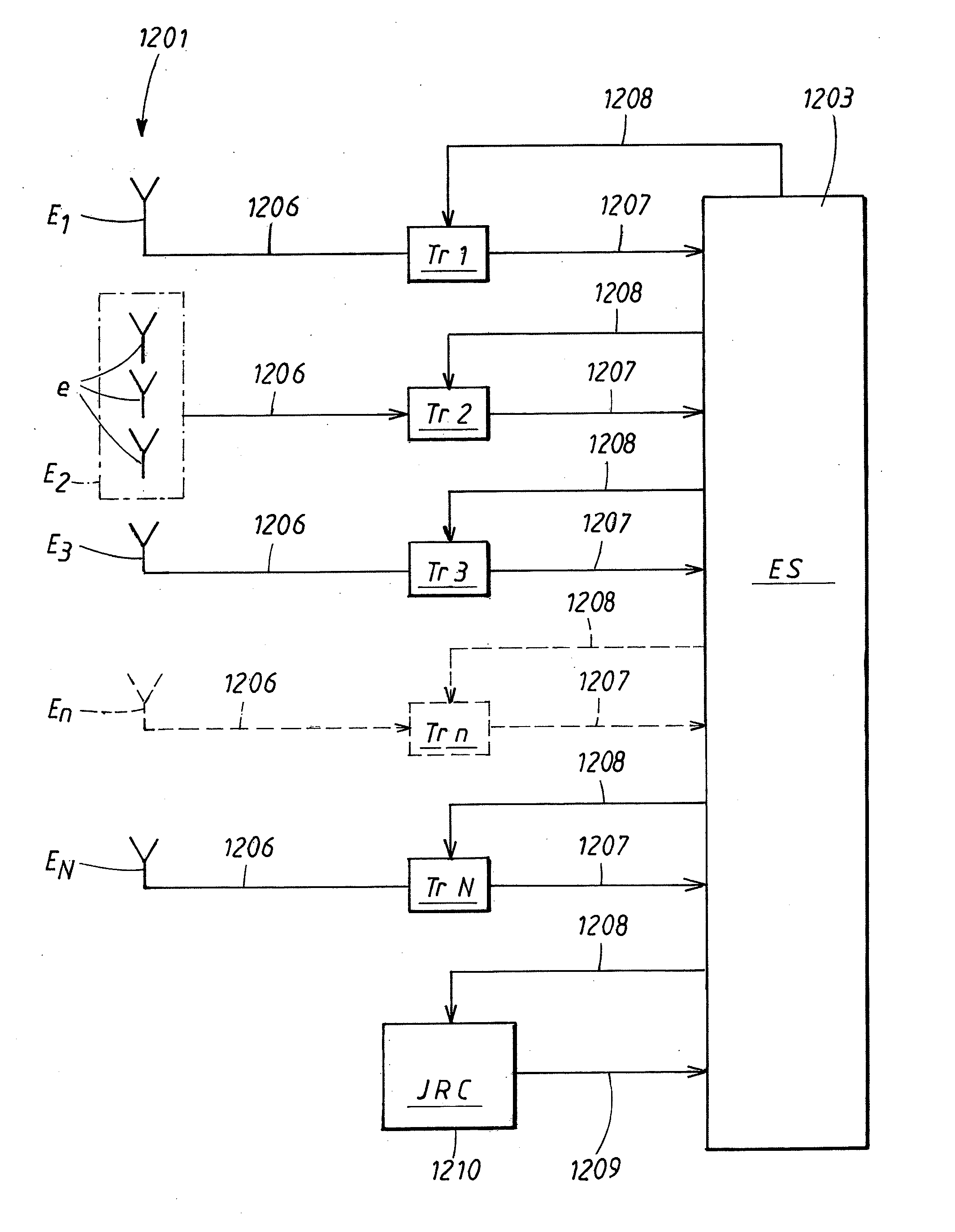
Reconfigurable parasitic control for antenna arrays and subarrays
InactiveUS20050088358A1Reduce decreaseScan angles can be increasedLogperiodic antennasAntenna arraysEngineeringArray element
Reconfiguration of parasitically controlled elements in a phased array is used to expand the range of operational functions. Embedded array elements can be frequency tuned, and bandwidth can be improved by using reconfiguration to broaden the bandwidth of the embedded elements. For high gain arrays, beam squint can be a limiting factor on instantaneous bandwidth. Reconfiguration can alleviate this problem by providing control of the element phase centers. Scan coverage can be improved and scan blindness alleviated by controlling the embedded antenna patterns of the elements as well as by providing control of the active impedance as the beam is scanned. Applying limited phase control to the elements themselves can alleviate some of the complexity of the feed manifold. A presently preferred method of designing reconfigurable antennas is to selectively place controlled parasitic elements in the aperture of each of the antenna elements in the phased array. The parasitic elements can be controlled to change the operational characteristics of the antenna element. The parasitic elements are controlled by either switching load values in and out that are connected to the parasitic elements or are controlled by applying control voltages to variable reactance circuits containing devices such as varactors. The parasitic elements can be controlled by the use of a feedback control subsystem that is part of the antenna system which adjusts the RF properties of the parasitic components based on some observed metric. The controllable characteristics include directivity control, tuning, instantaneous bandwidth, and RCS.
Owner:TOYON RES CORP
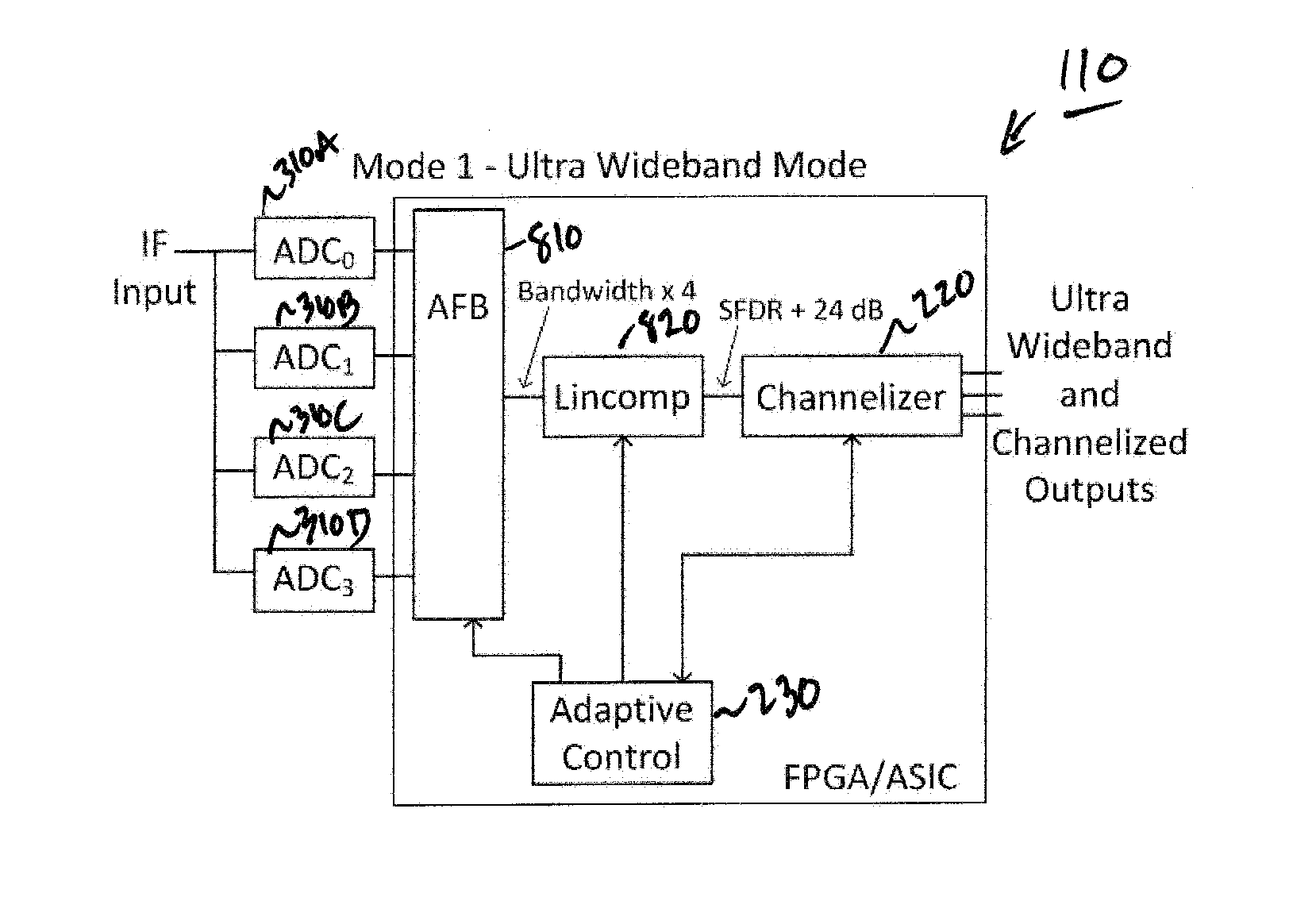
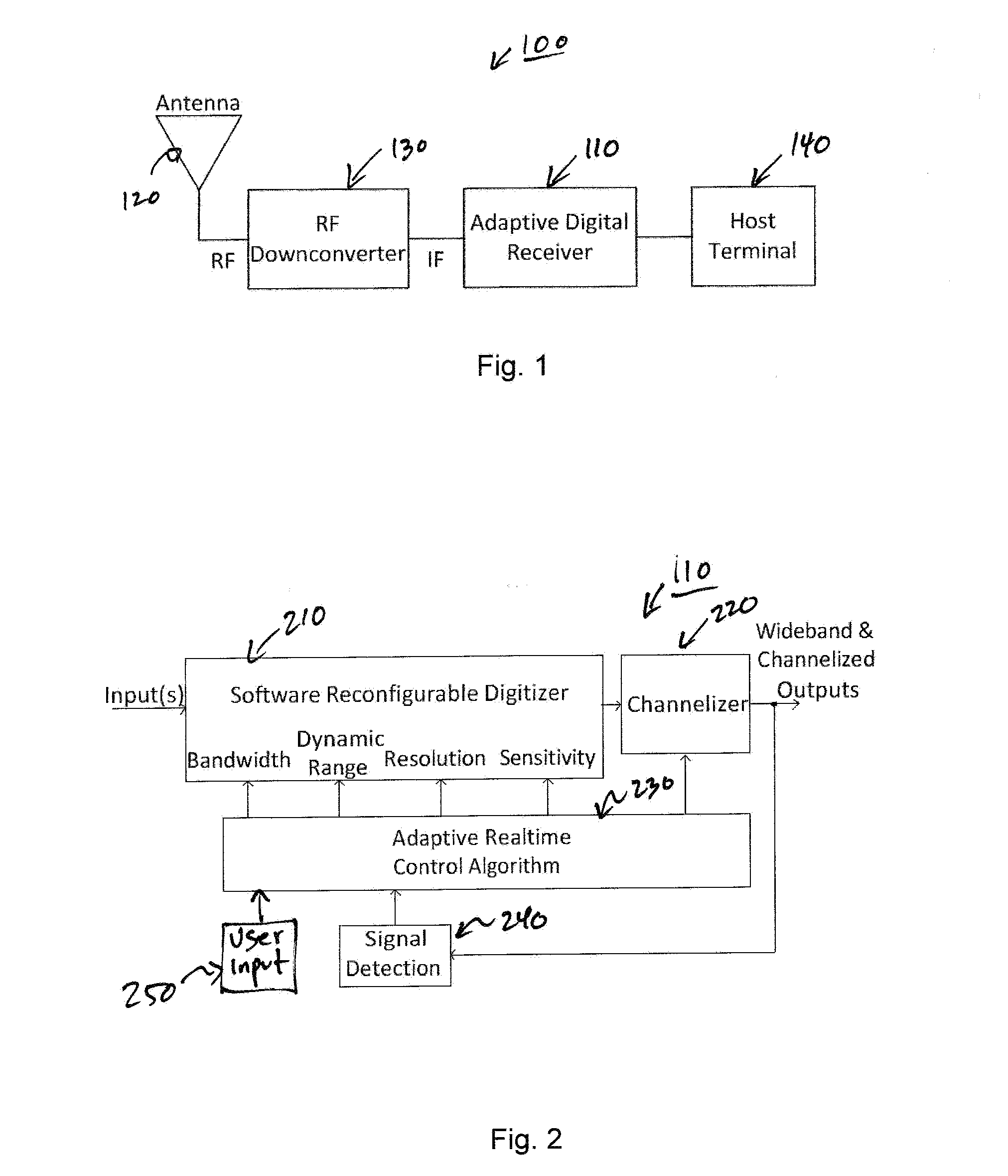
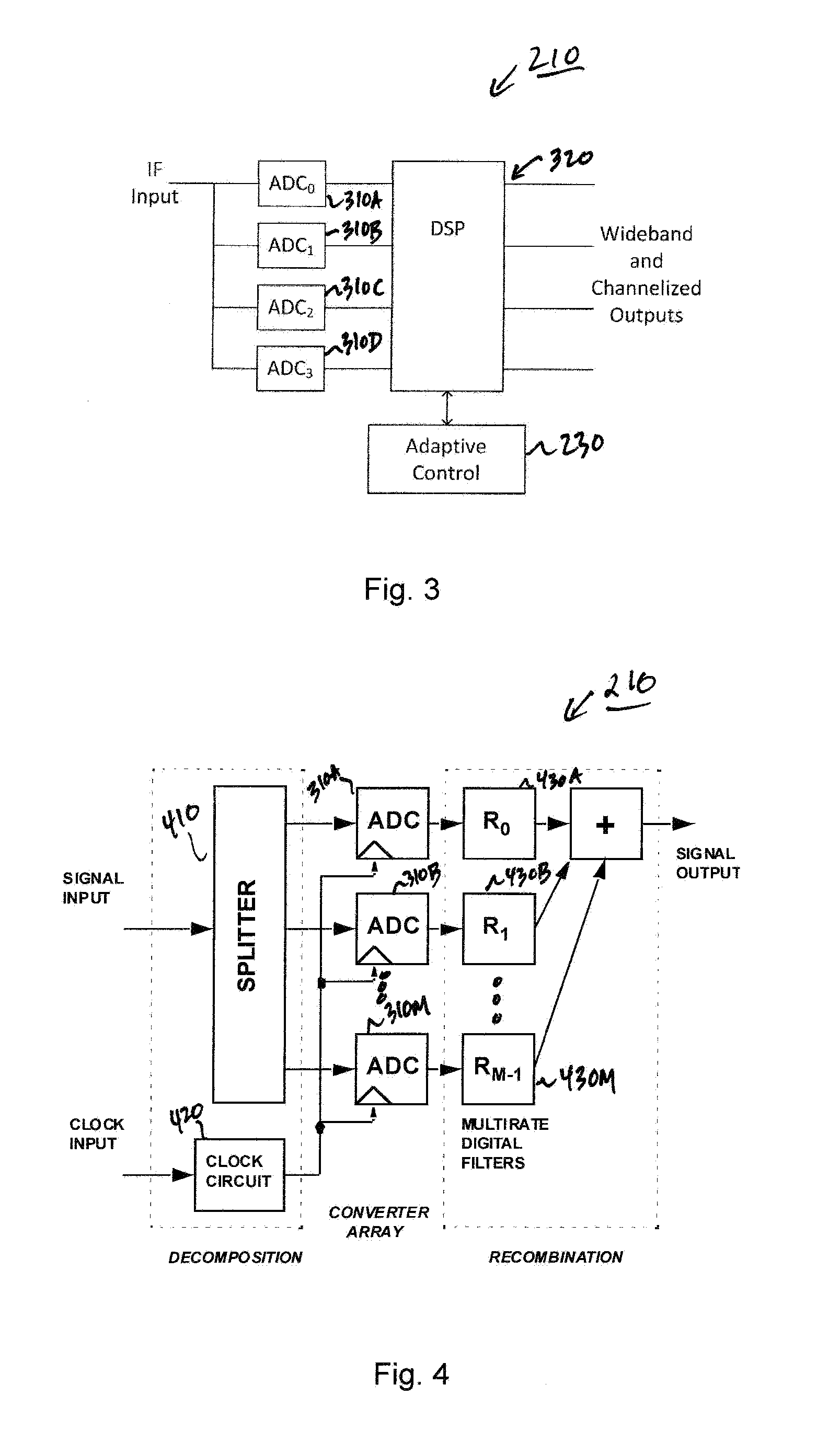
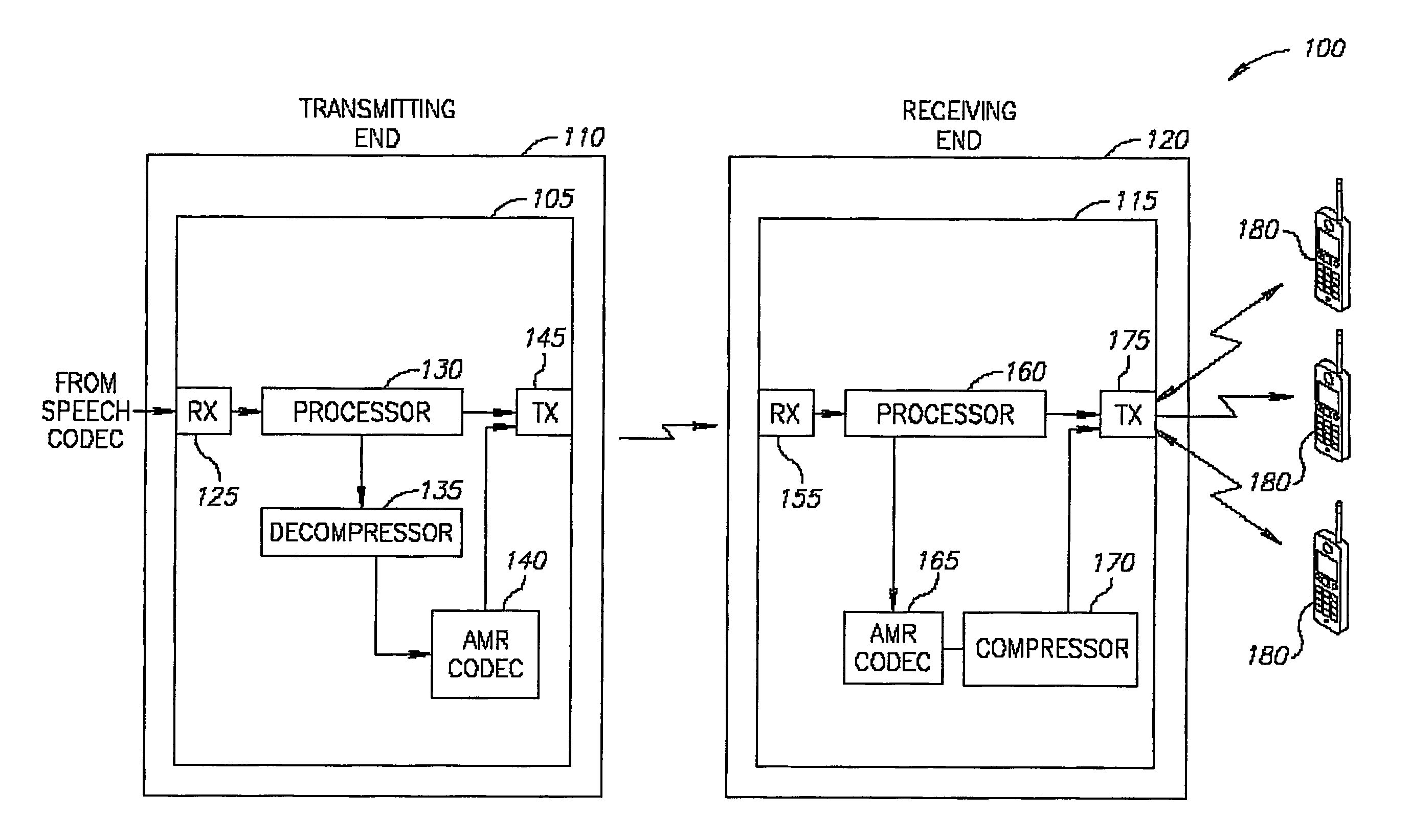
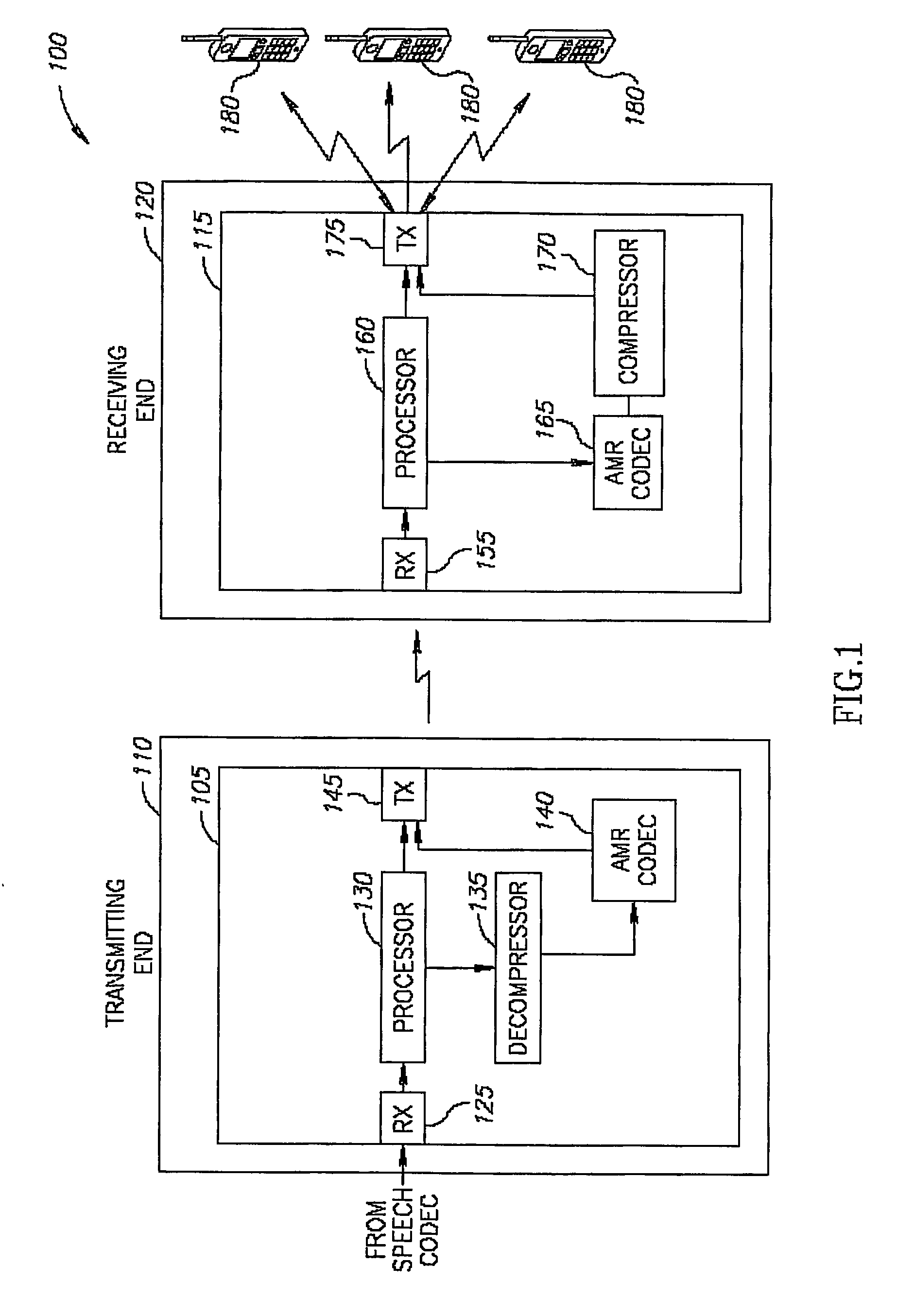
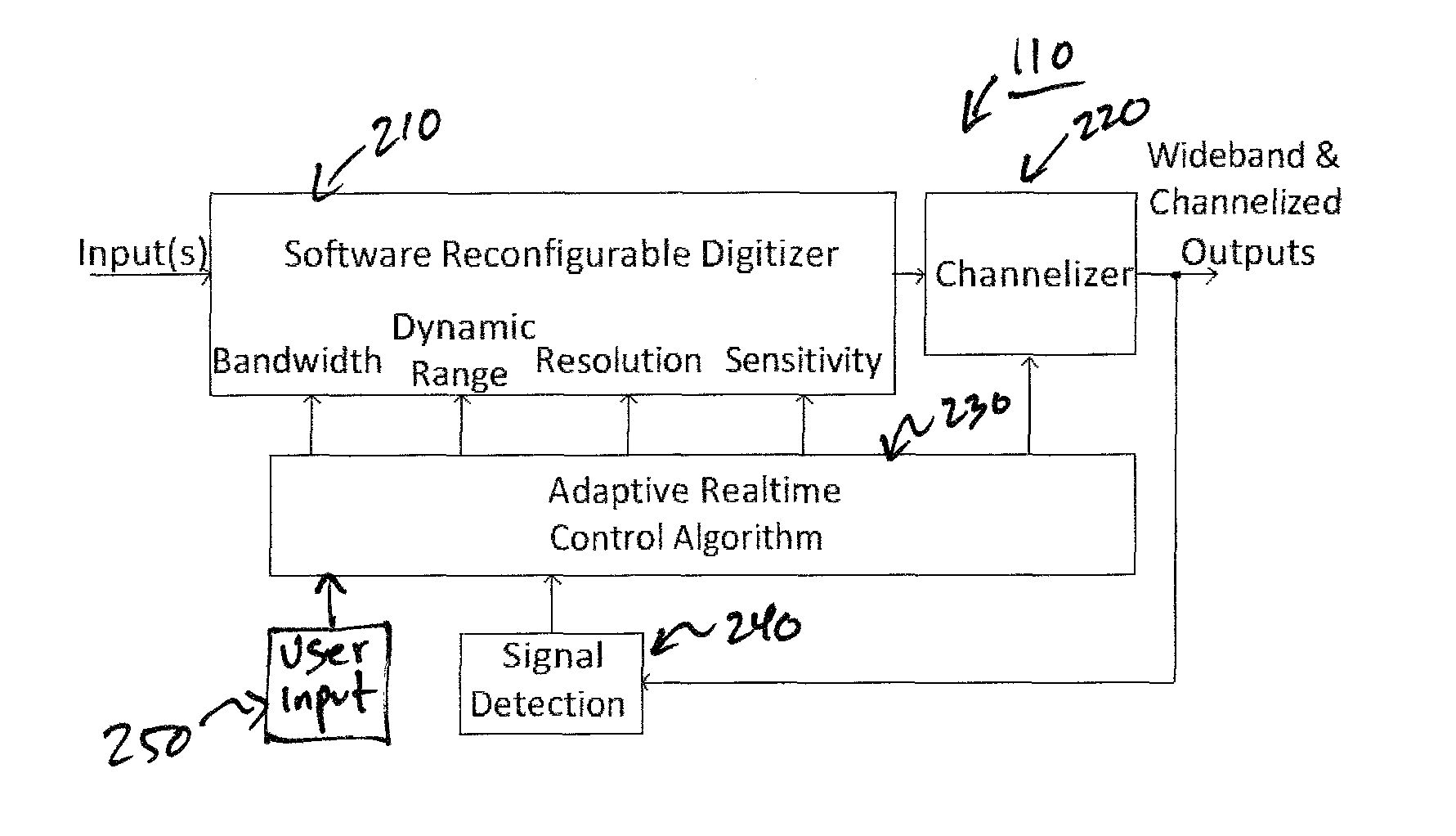
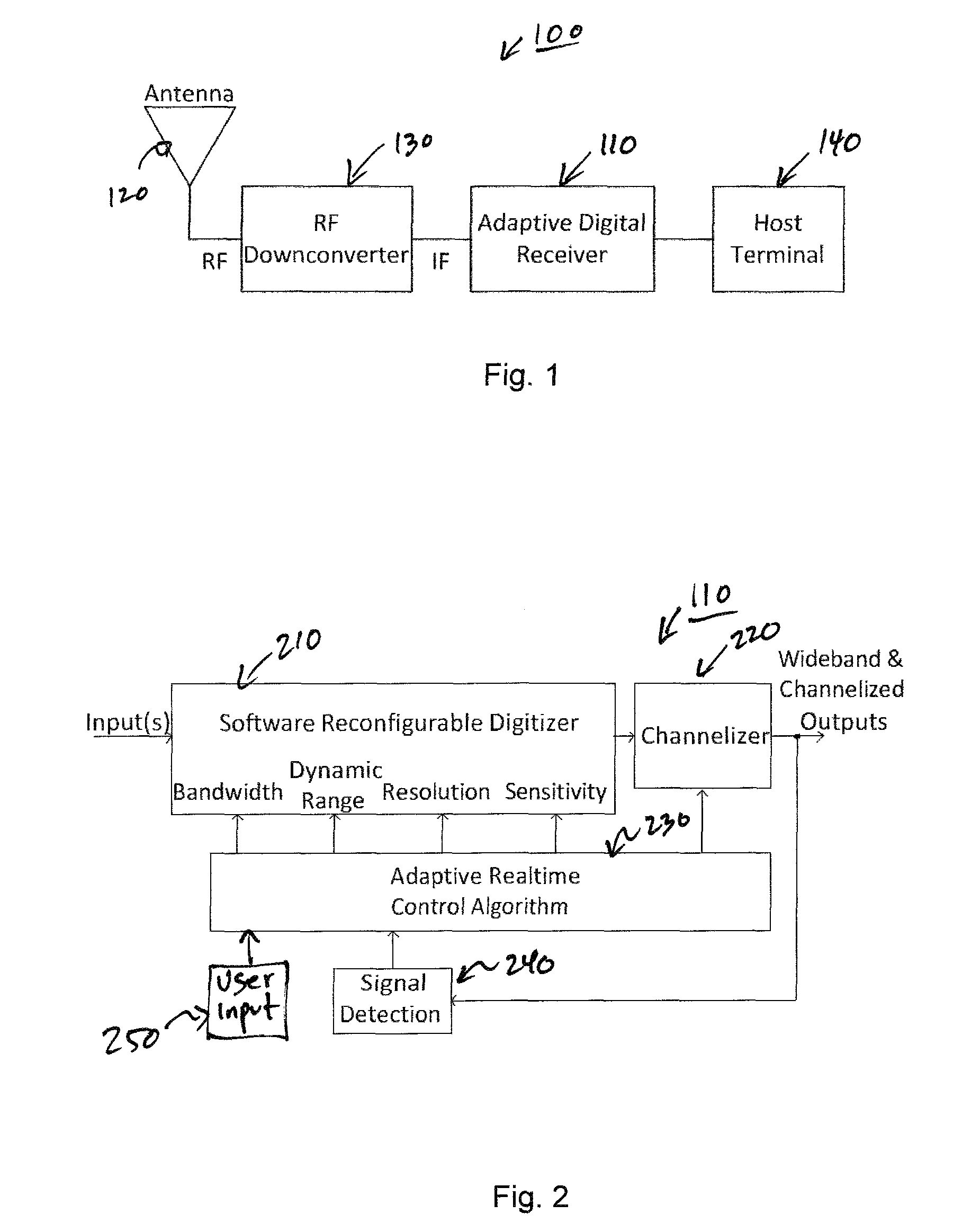
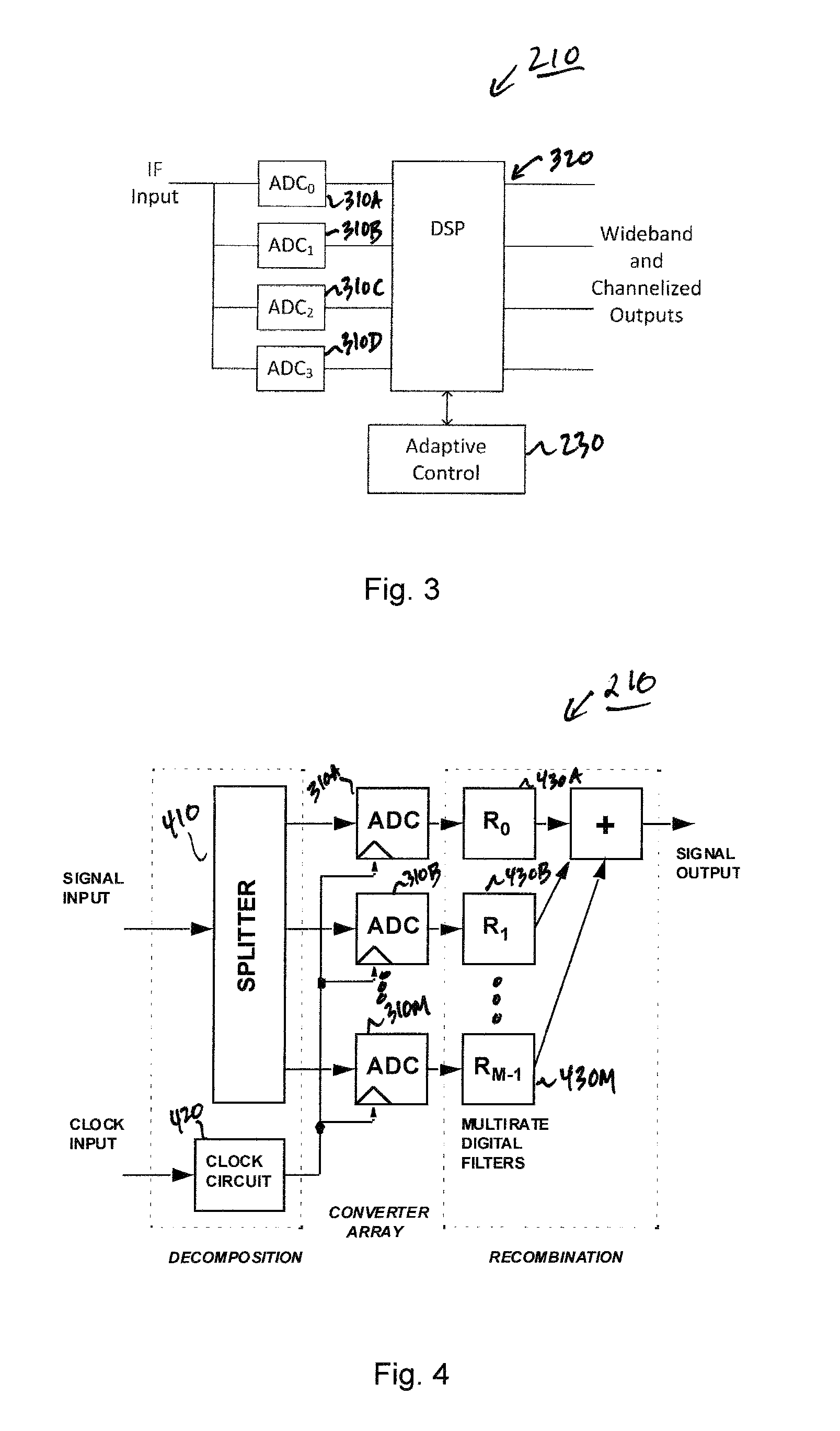
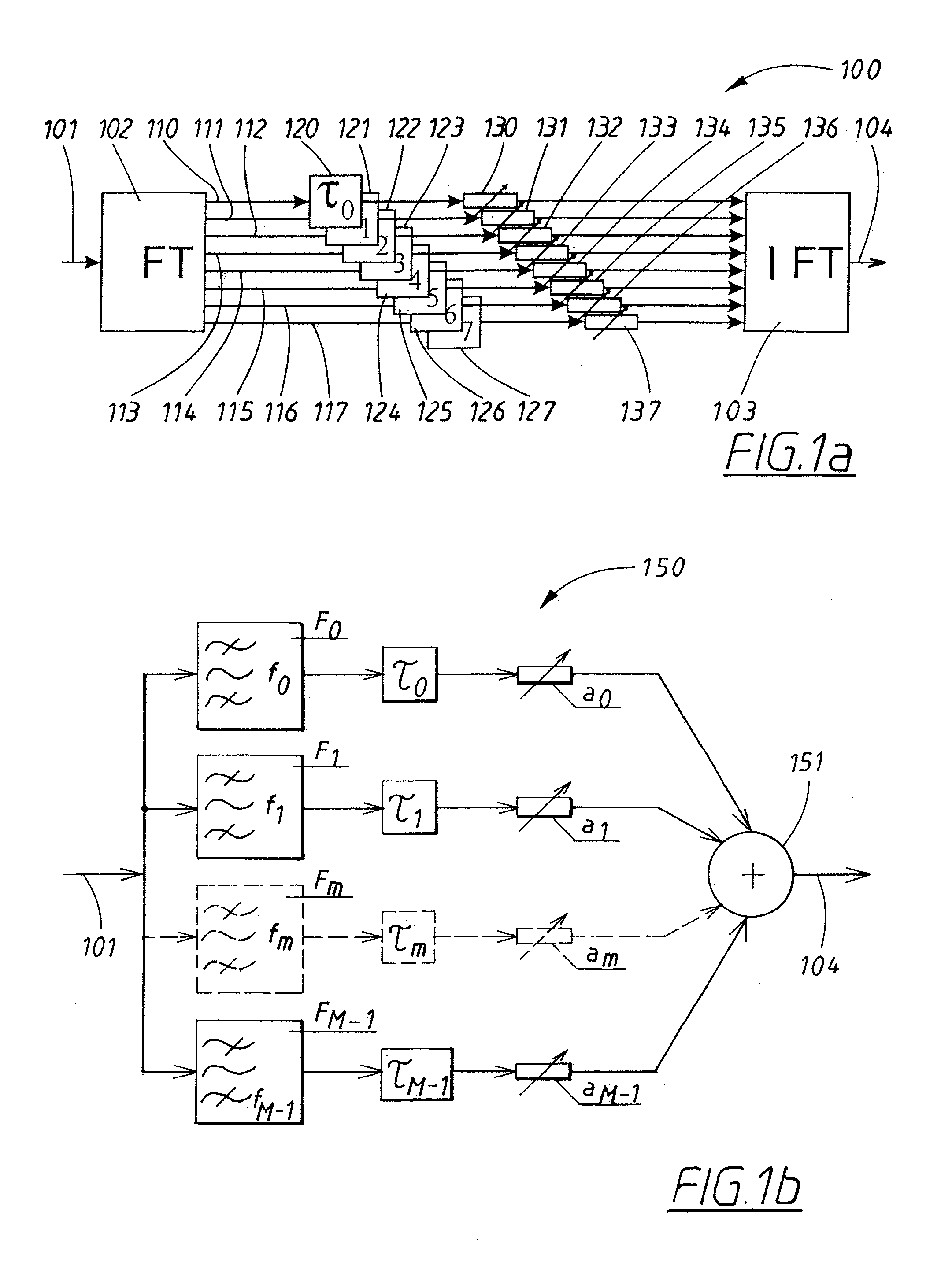
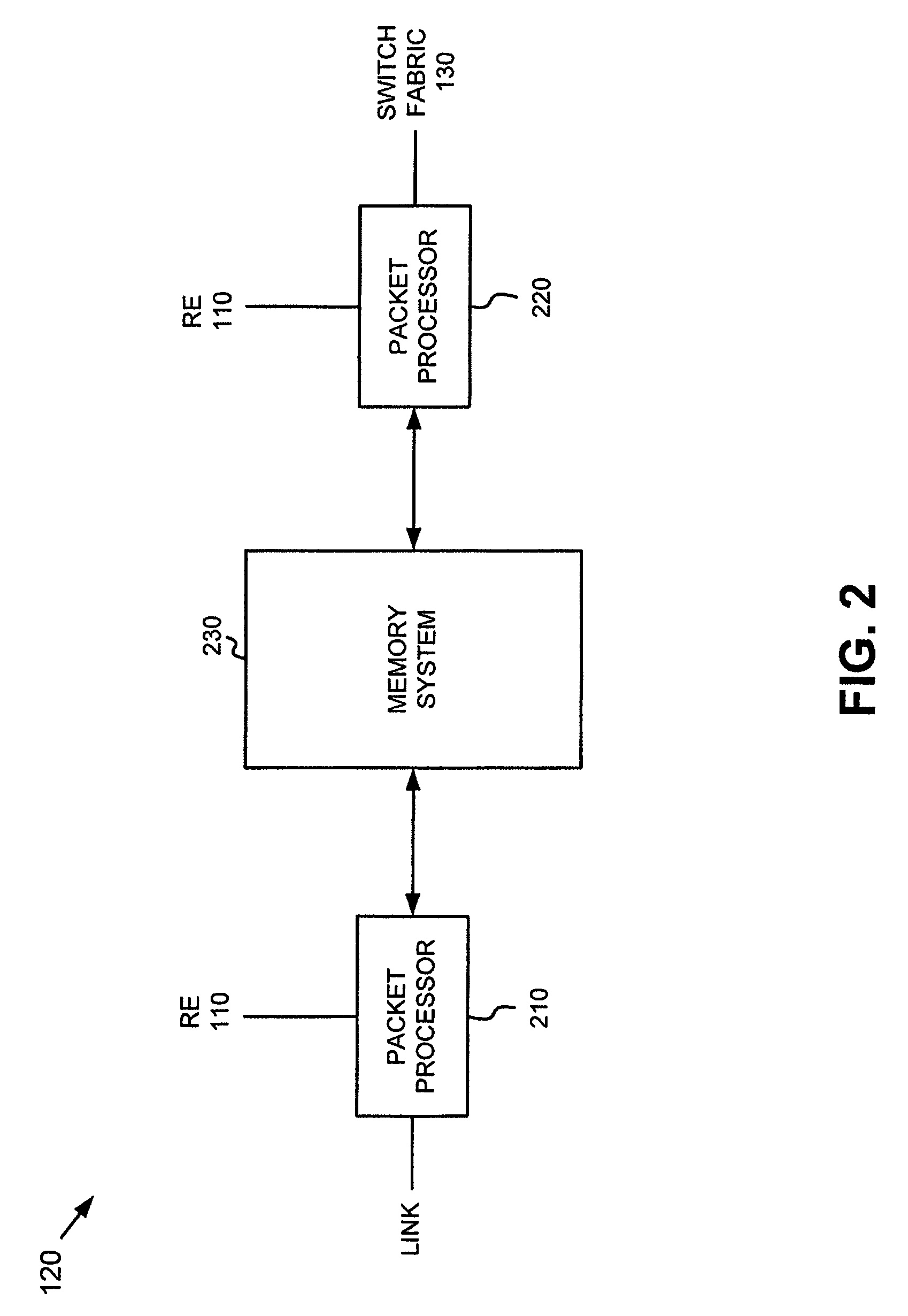
Adaptive digital receiver
ActiveUS20130016798A1Wide bandwidthHigh resolutionElectric signal transmission systemsChannel dividing arrangementsAdaptive optimizationEngineering
The present invention provides a high-performance adaptive digital receiver with adaptive background control that optimizes the performance in rapidly changing signal environments and provides 3.6 GH; instantaneous bandwidth, SFDR>90 dB, SNR=66 dB, with dynamic digital channelization. The receiver takes advantage of several levels of adaptivity that conventional approaches do not offer. In addition to a dynamic digital channelizer that is adaptively tuned based on detected signals, the present invention employs a powerful software reconfigurable digitizer that is adaptively optimized for the current signal environment to control important receiver parameters such as bandwidth, dynamic range, resolution, and sensitivity.
Owner:LINEARITY LLC
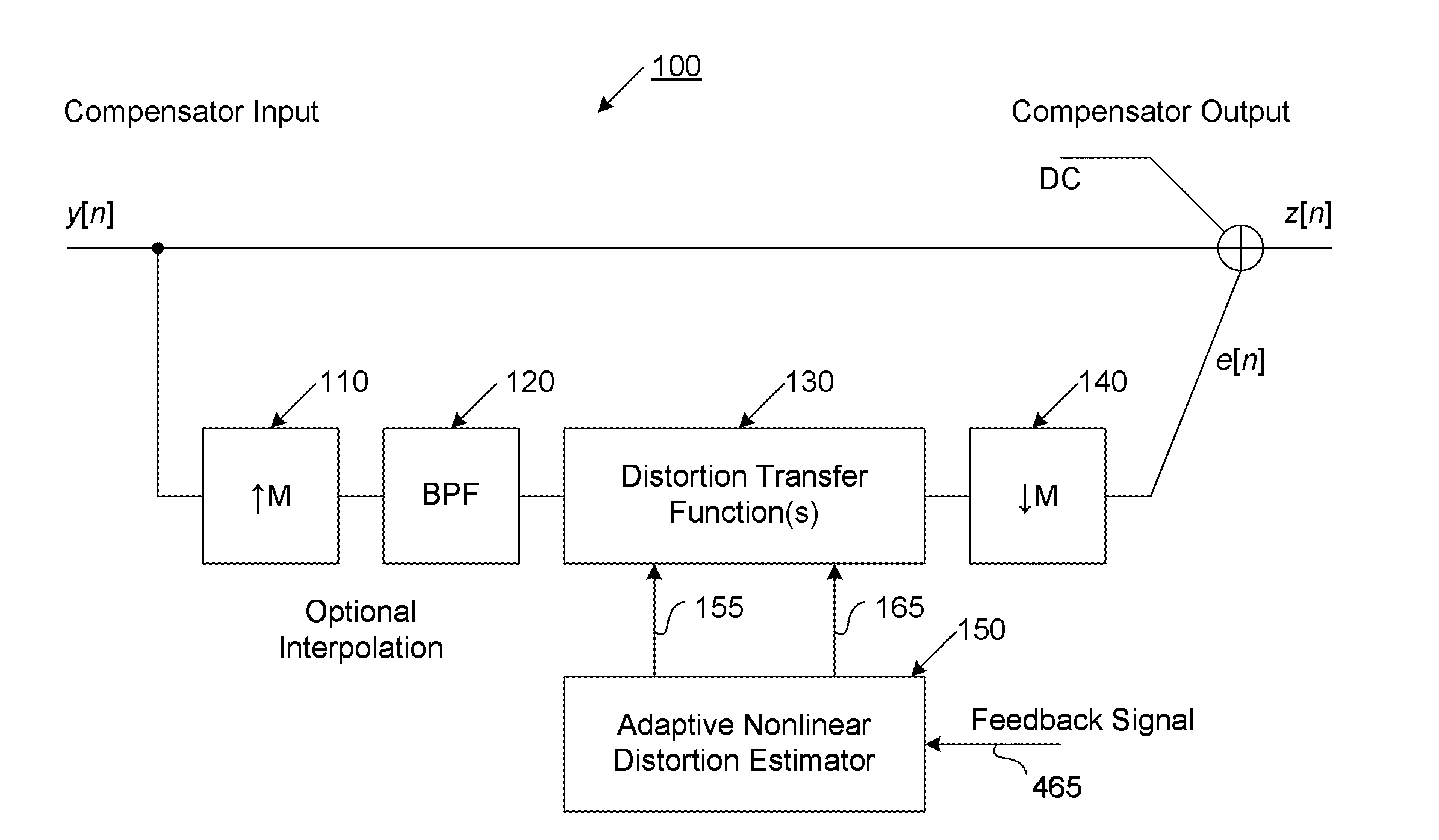
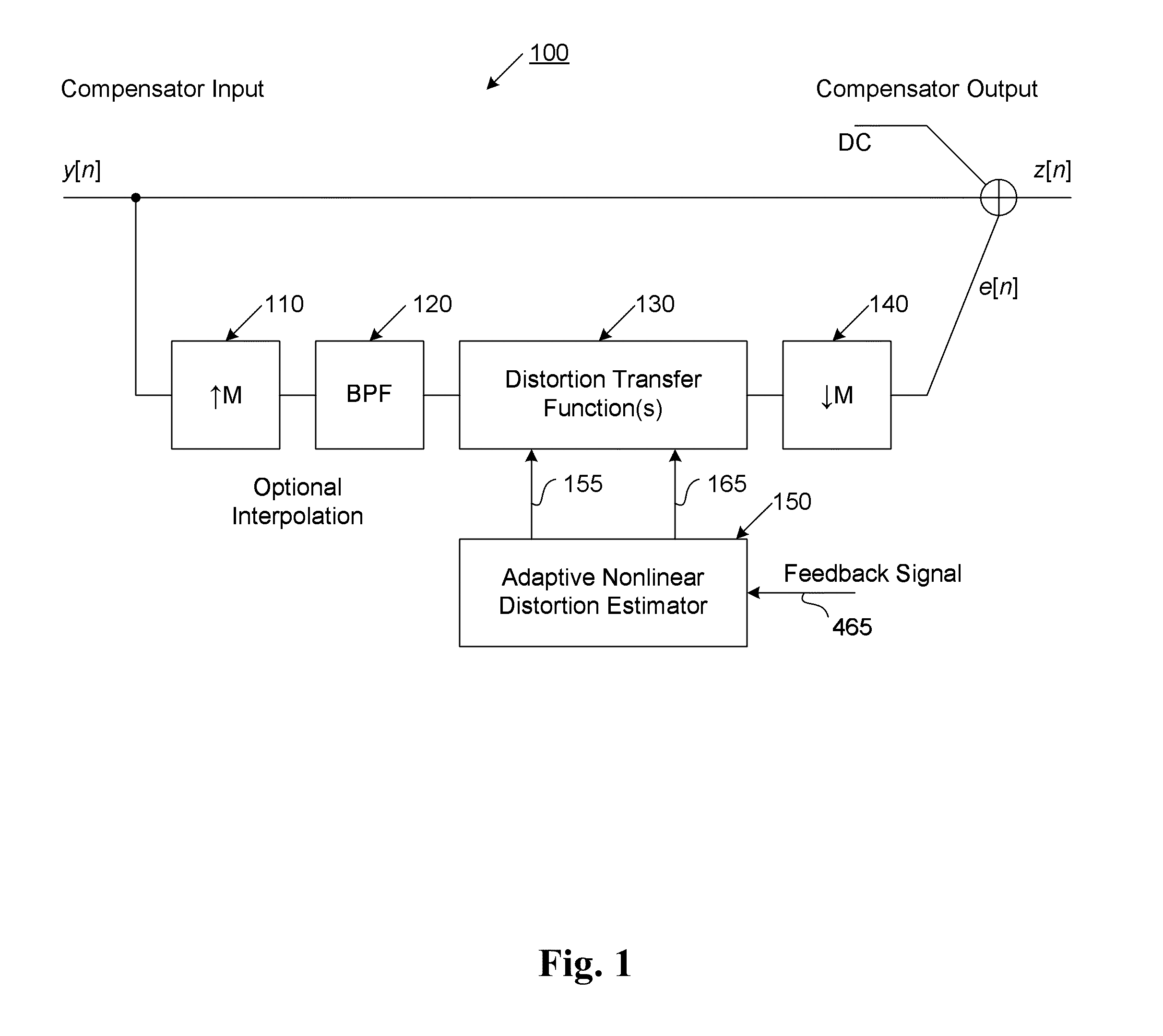
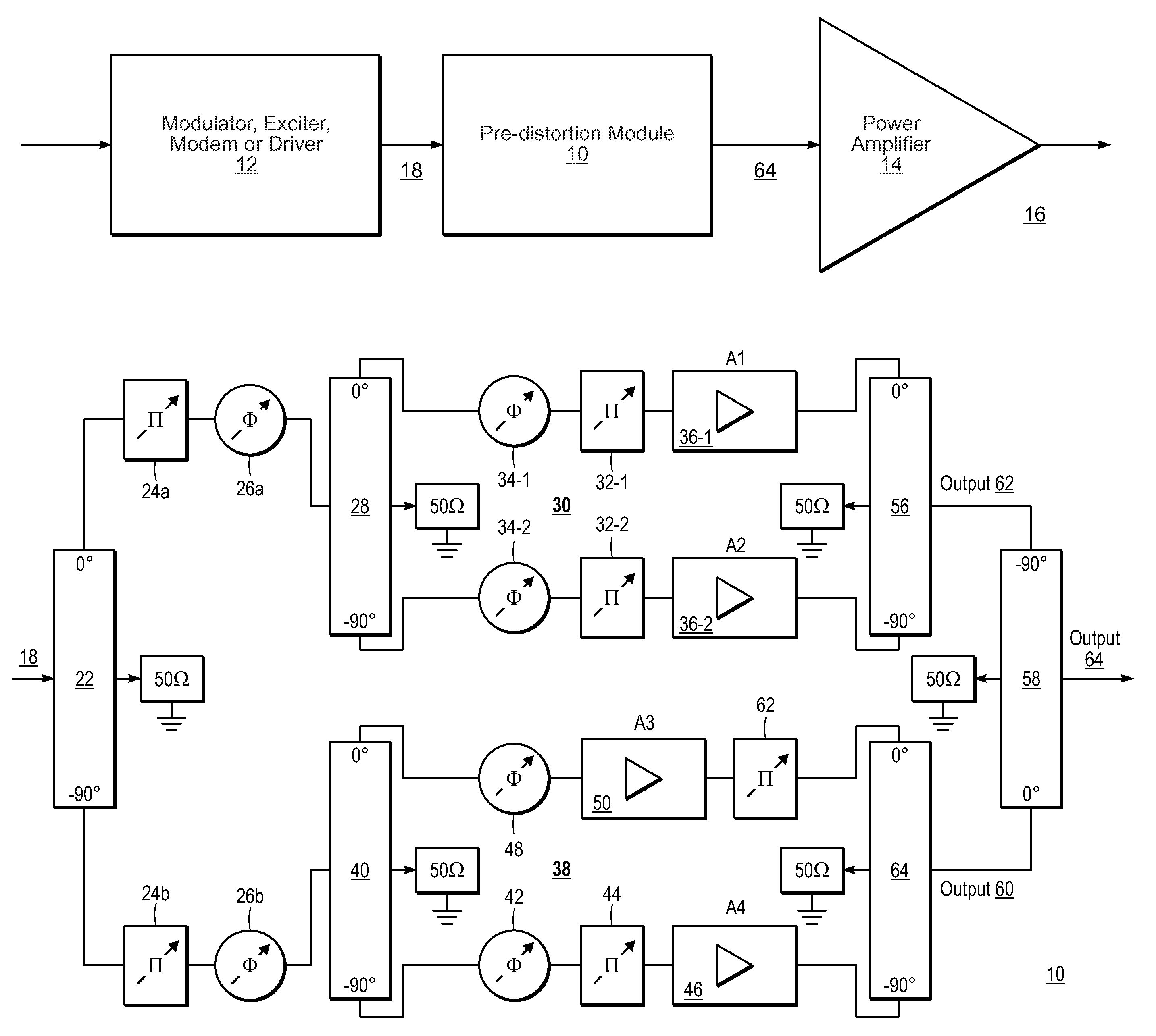
Amplifier linearizer
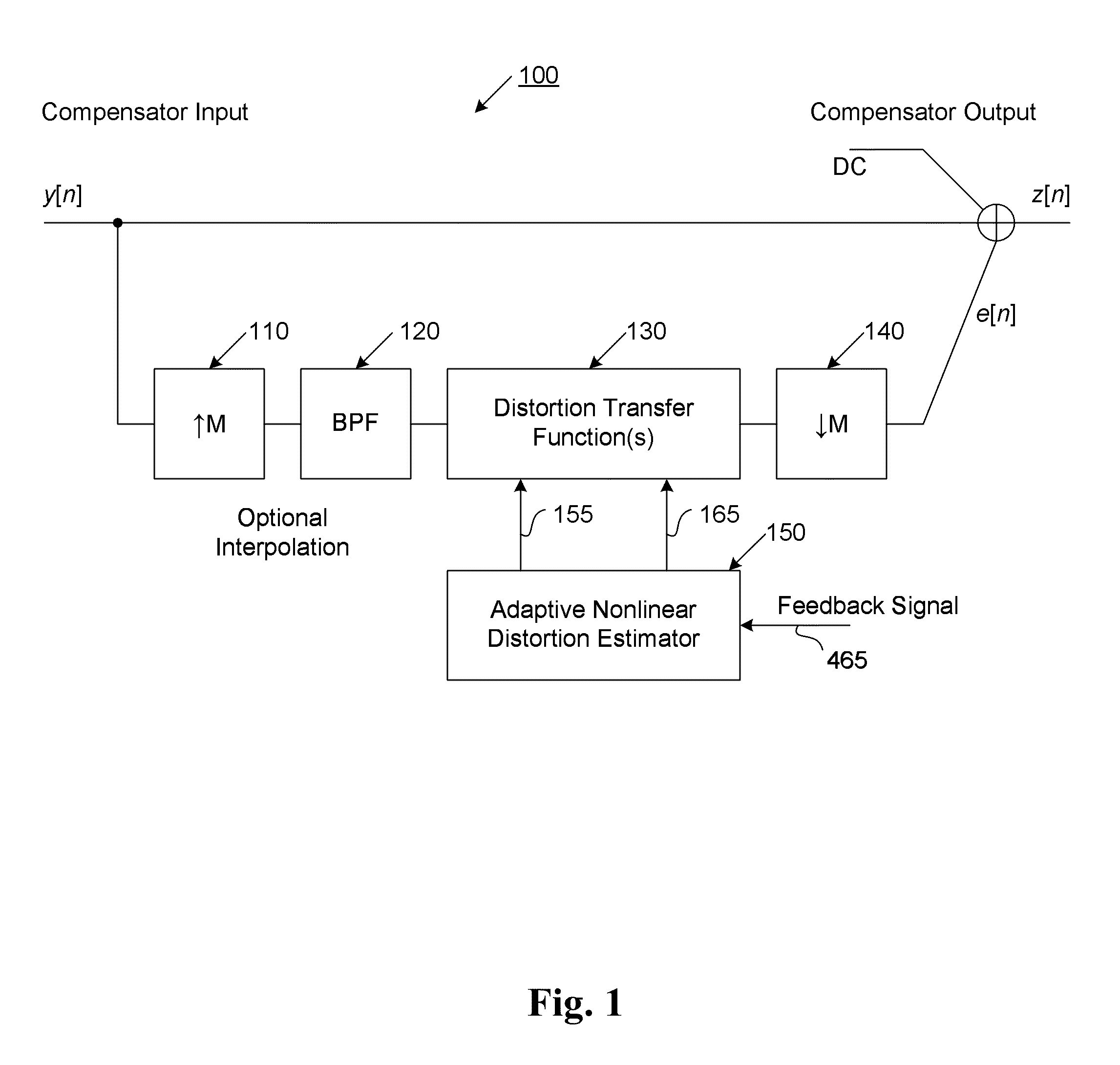
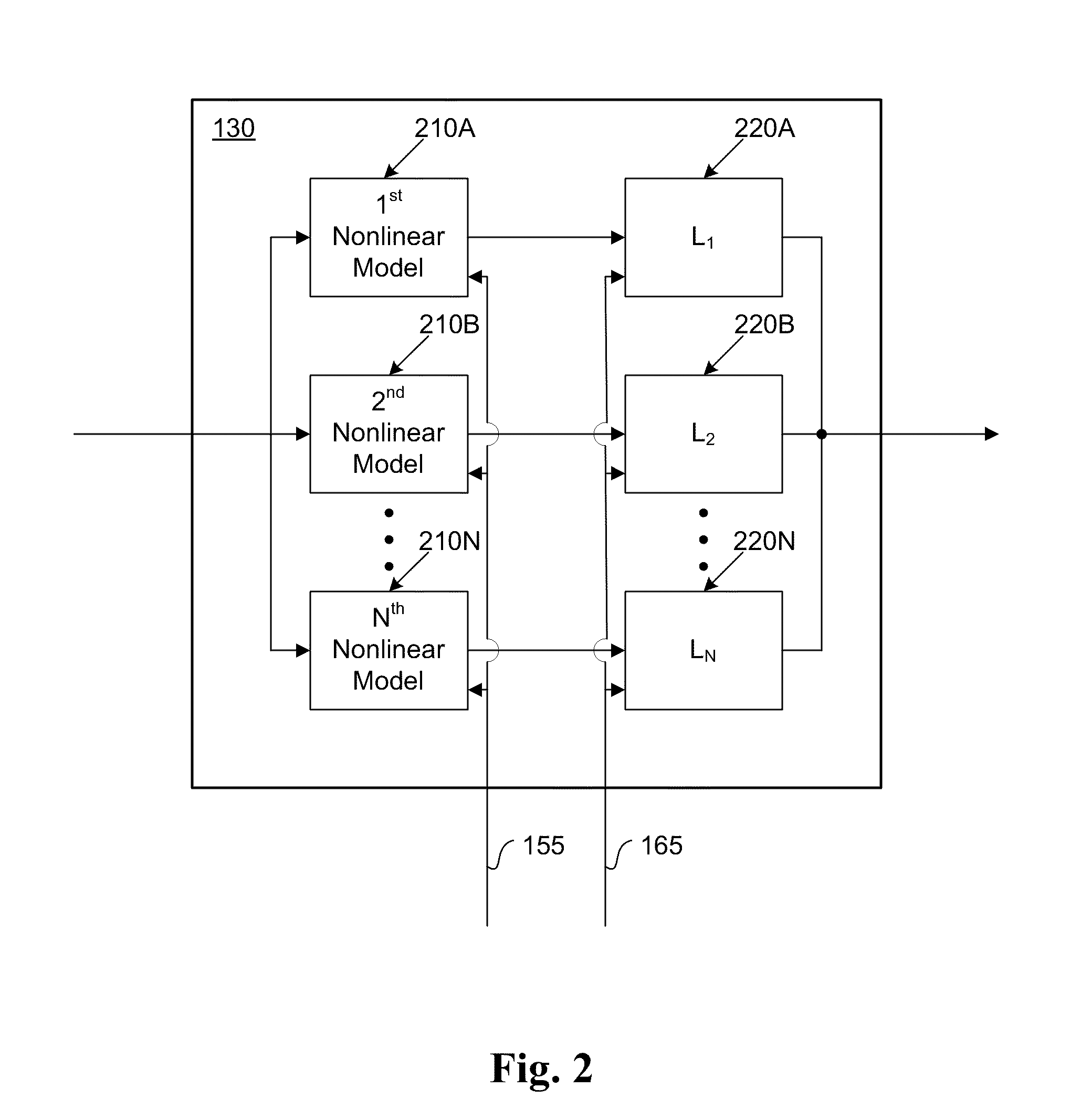
ActiveUS20110095819A1Reduce nonlinear distortionLow powerResonant long antennasElectric signal transmission systemsNonlinear distortionCurve fitting
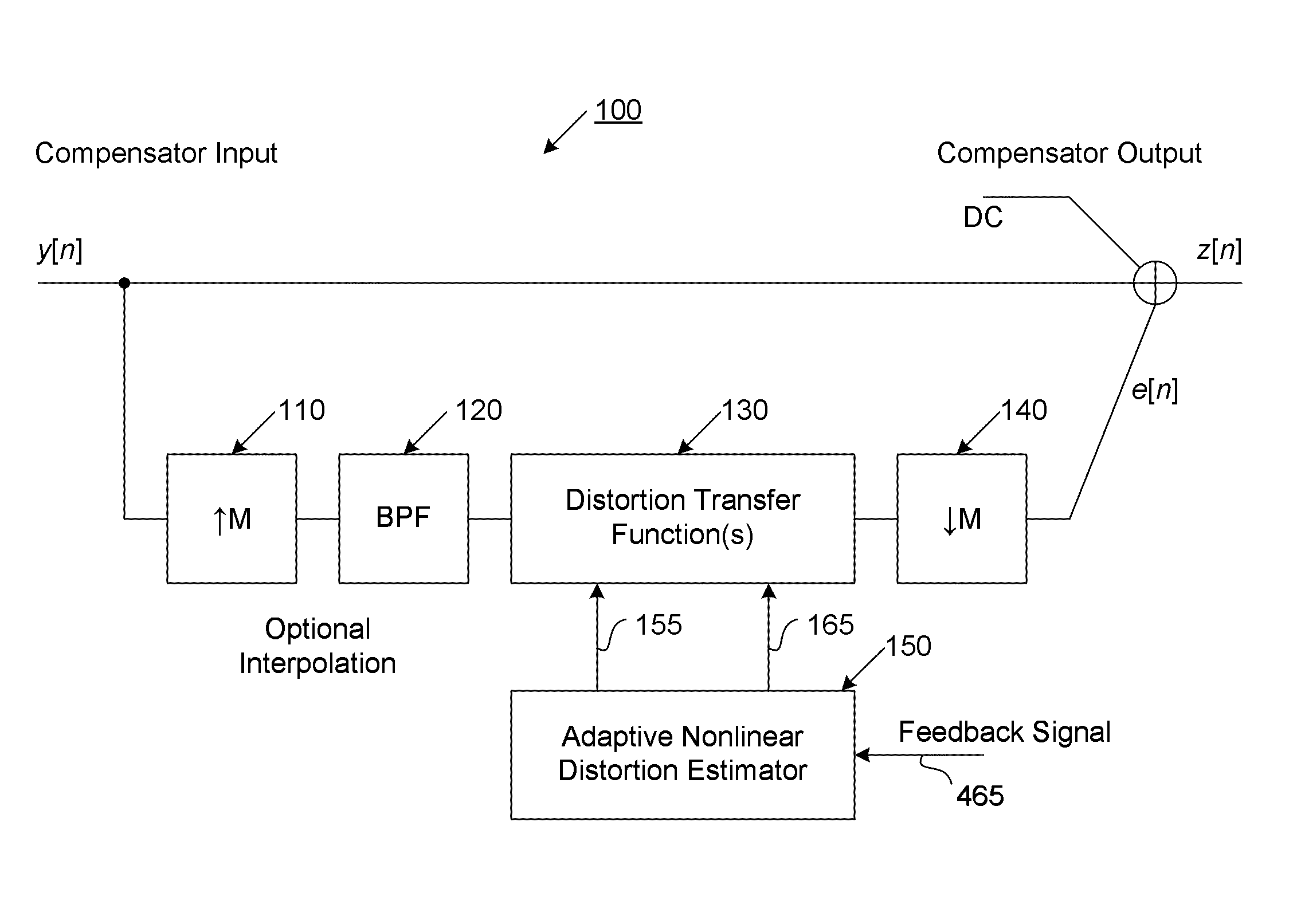
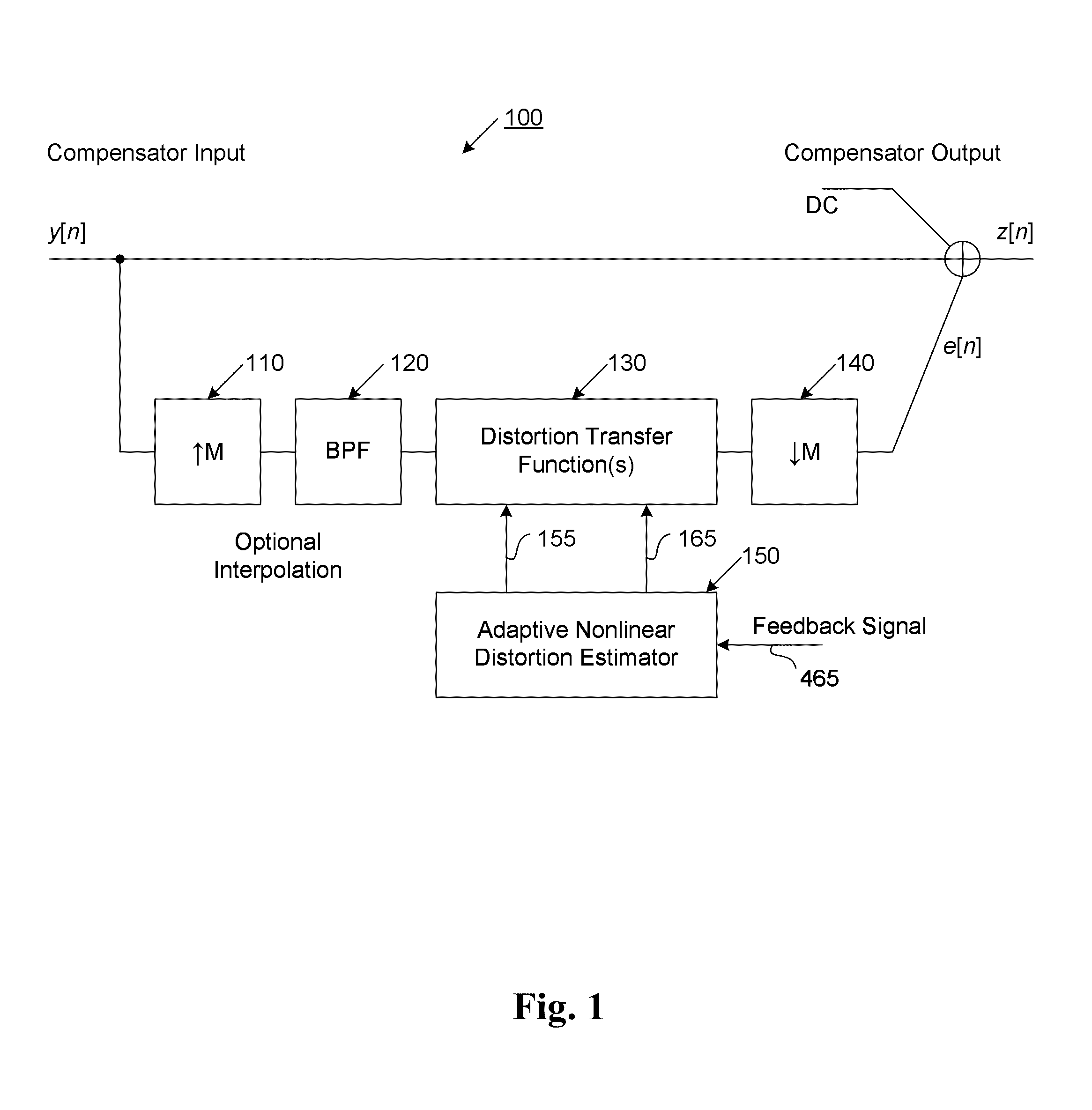
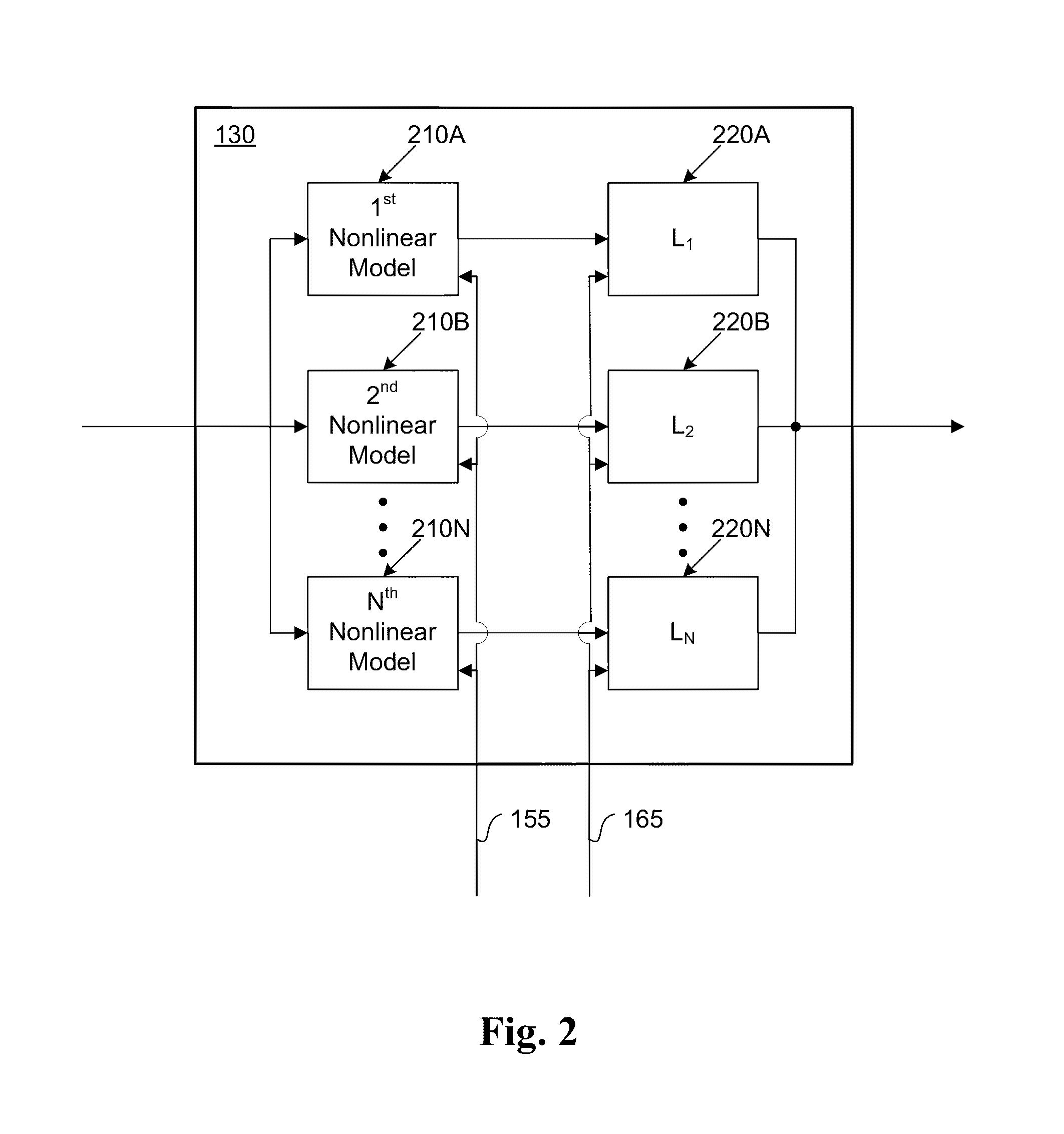
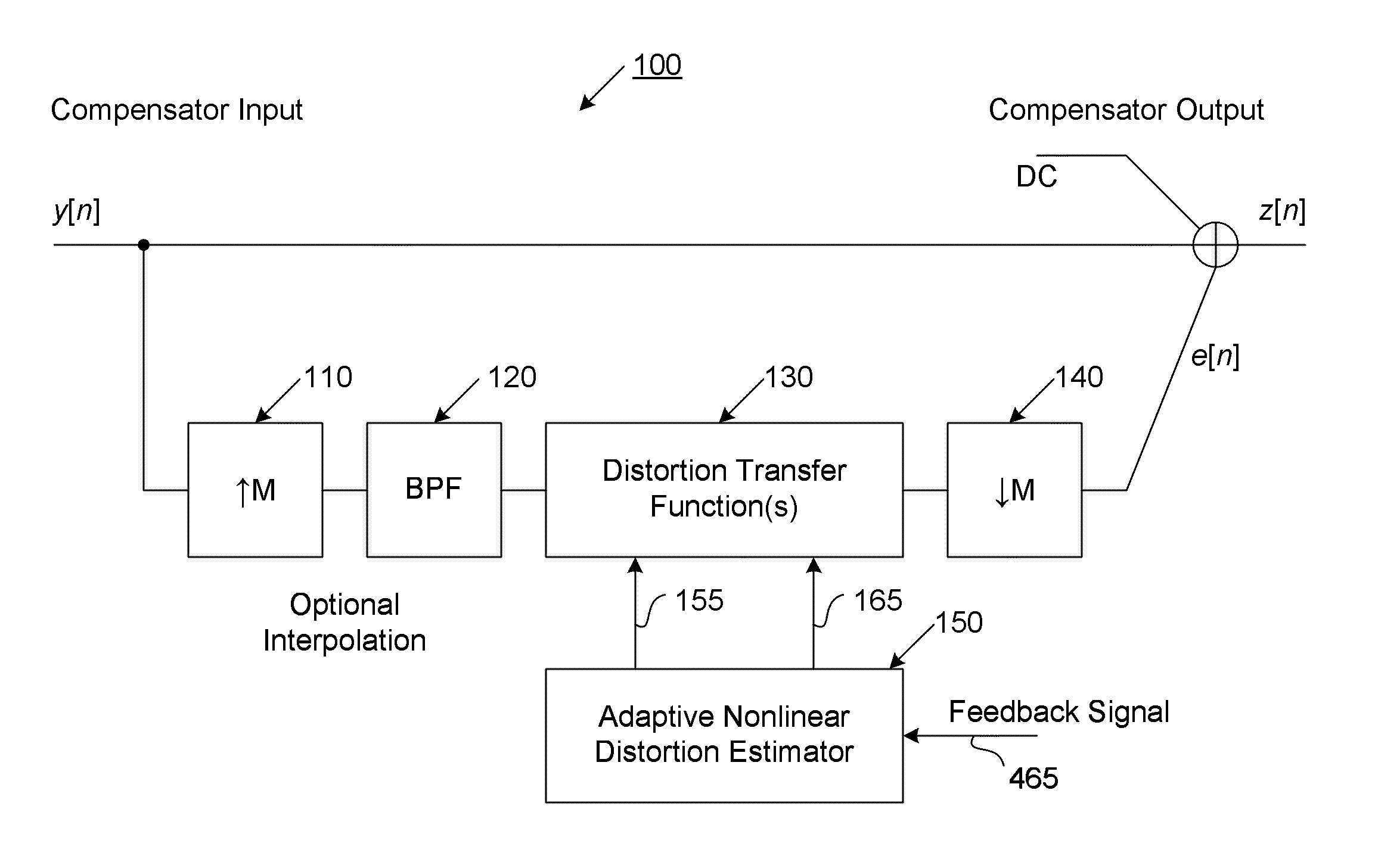
The present invention provides an advanced adaptive predistortion linearization technique to dramatically reduce nonlinear distortion in power amplifiers over a very wide instantaneous bandwidth (up to 2 GHz) and over a wide range of amplifier types, input frequencies, signal types, amplitudes, temperature, and other environmental and signal conditions. In an embodiment of the invention, the predistortion linearization circuitry comprises (1) a higher-order polynomial model of an amplifier's gain and phase characteristics—higher than a third-order polynomial model; (2) an adaptive calibration technique; and (3) a heuristic calibration technique. The higher-order polynomial model is generated by introducing, for example, a plurality of multi-tone test signals with varying center frequency and spacing into the power amplifier. From the power amplifier's corresponding output, the nonlinearities are modeled by employing a higher-order curve fit to capture the irregularities in the nonlinear transfer function. Different distortion transfer functions can be implemented for different operating conditions. The adaptive calibration technique is based on a feedback analysis technique, which updates the applicable distortion transfer function by analyzing the error signal between the introduced input signal and the output signal in real-time. The heuristic calibration technique implements different distortion transfer functions based on historical operating conditions and optimal configurations of the power amplifier.
Owner:TM IP HLDG LLC
Band Stitching Electronic Circuits and Techniques
InactiveUS20140105256A1Reduce signal distortionReduced responseWave based measurement systemsDuplex signal operationTransceiverTime delays
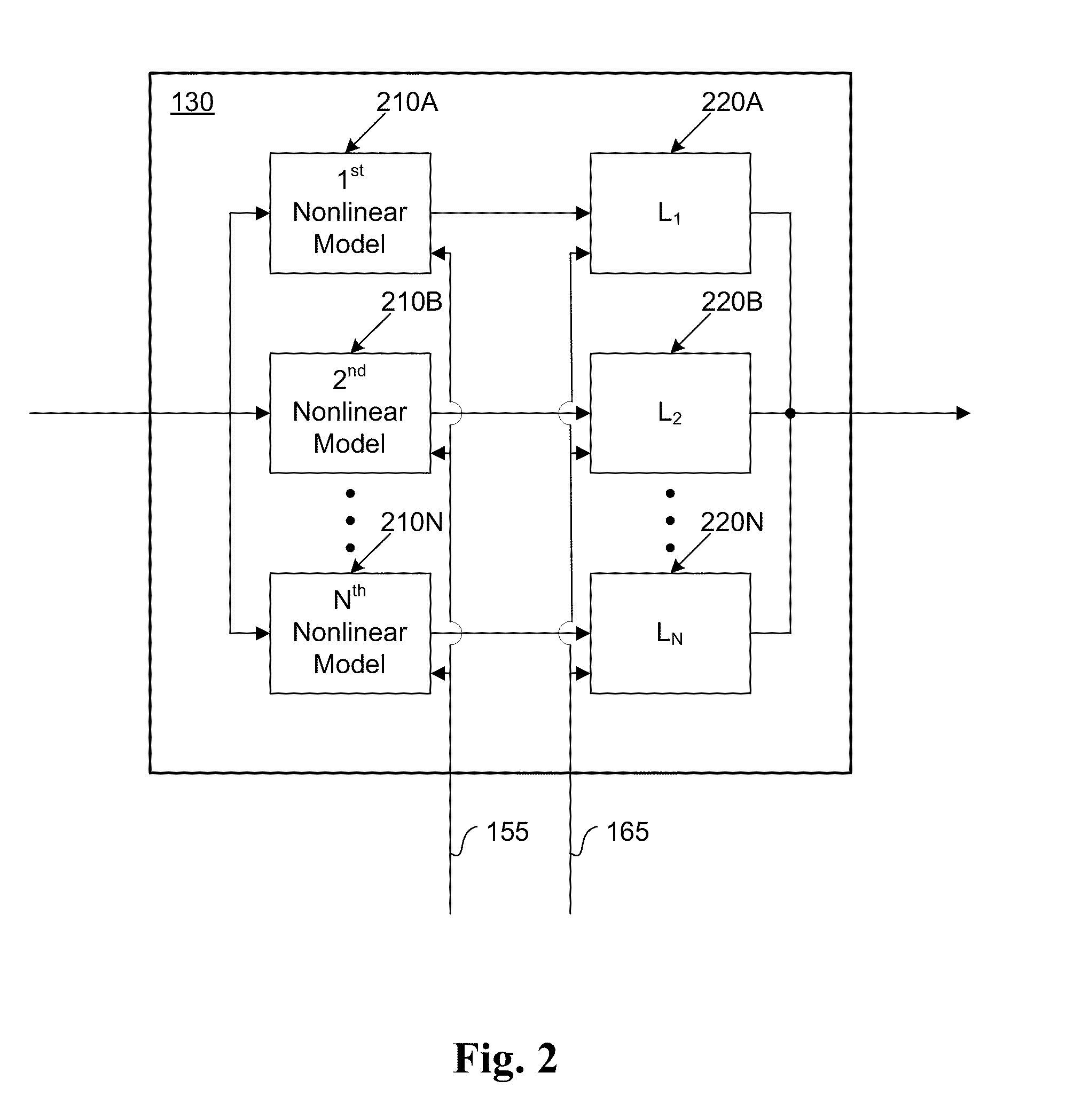
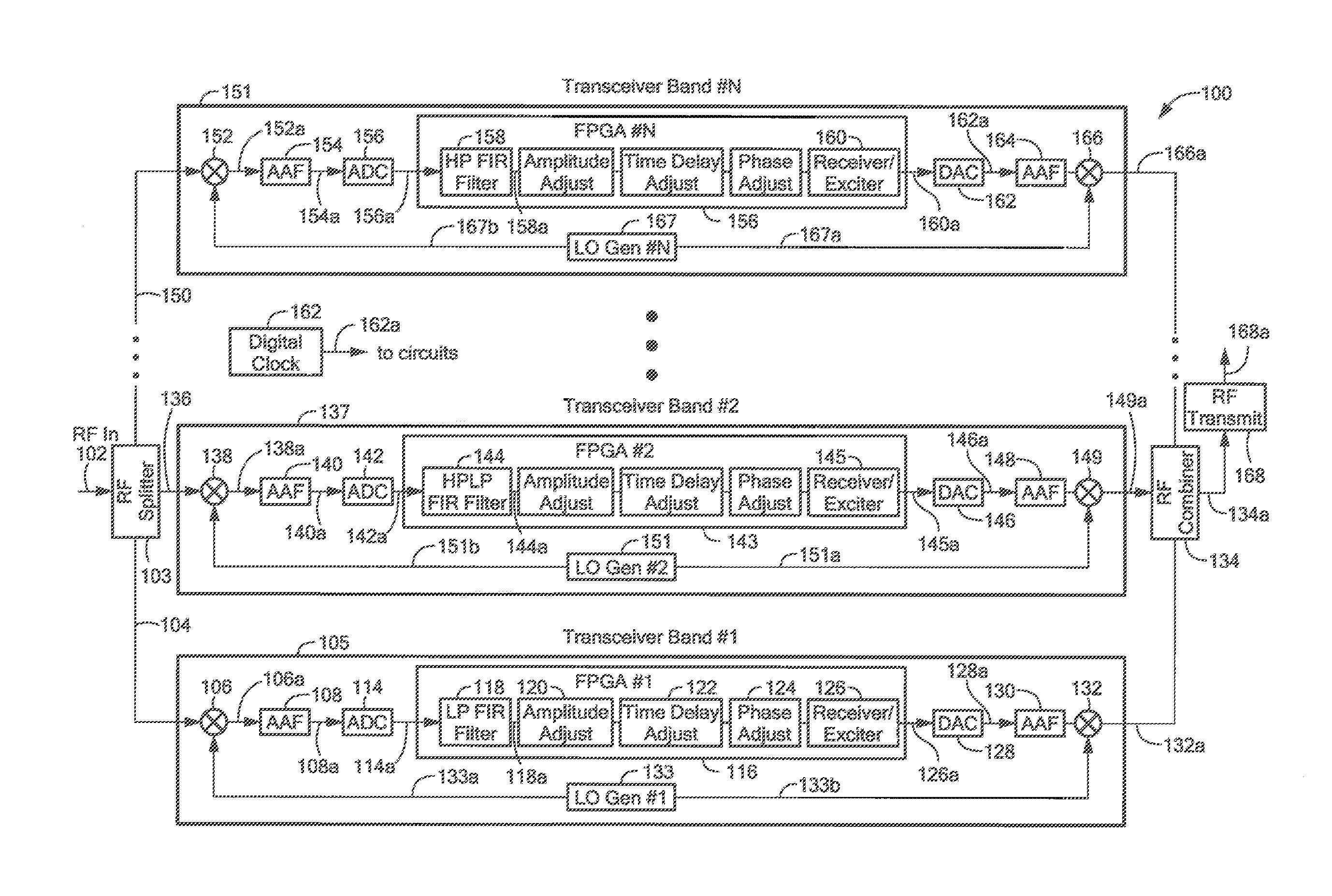
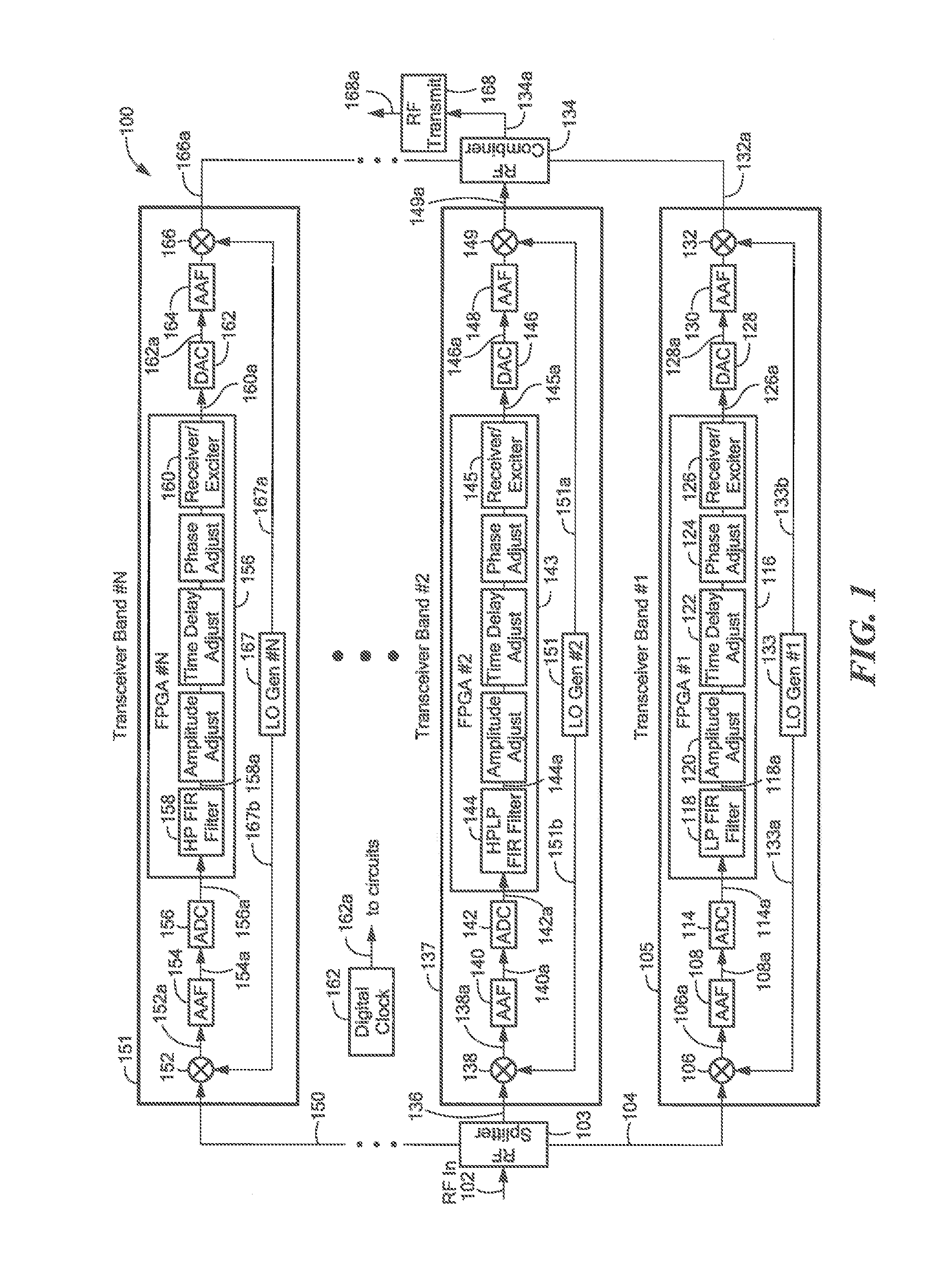
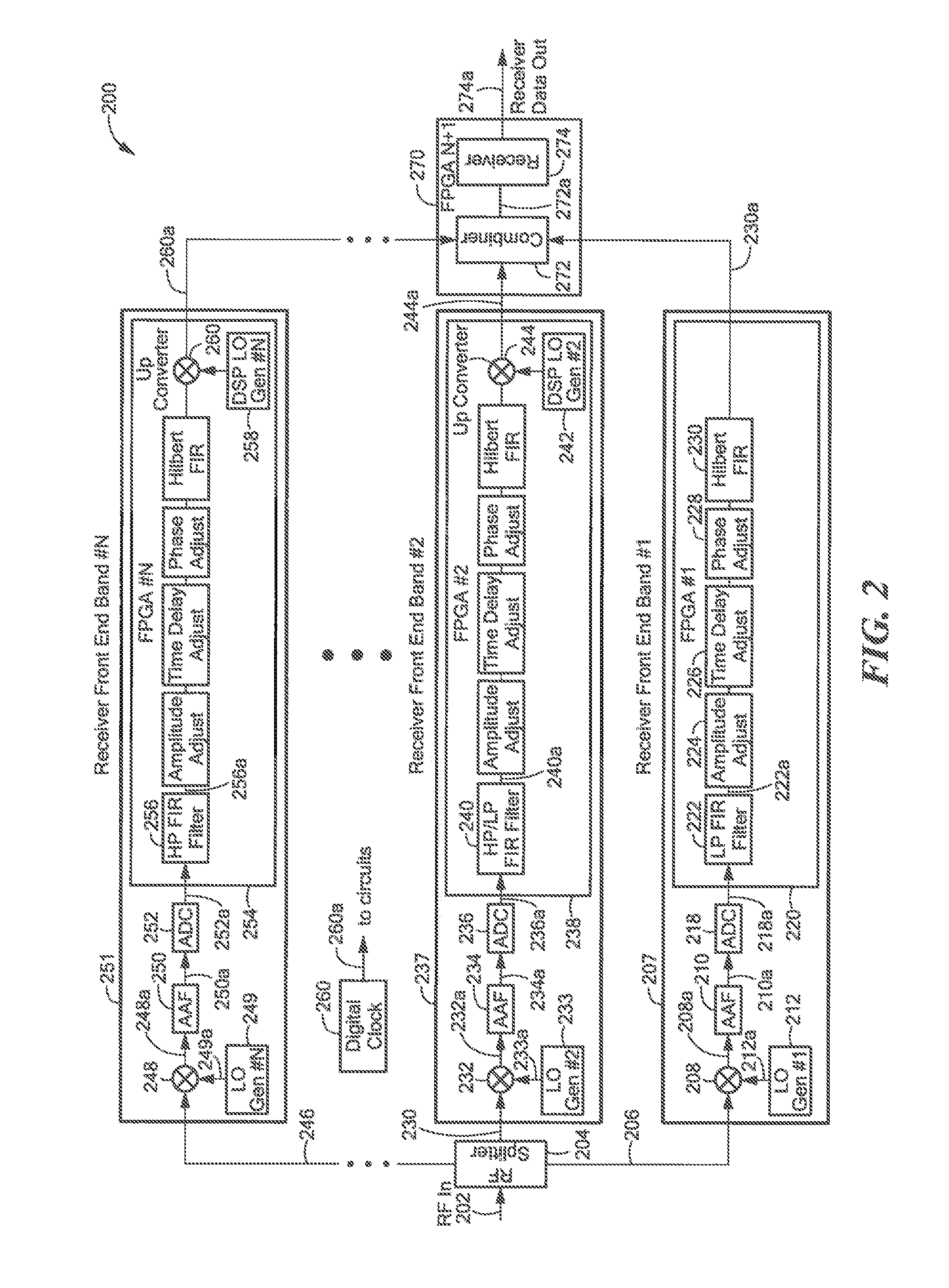
An electronic circuit combines two or more individual wideband RF receivers or transceiver band circuits to produce a usable instantaneous bandwidth that is wider than the bandwidth of the individual band circuits. The electronic circuit overcomes the difficulties of combining bands to provide low signal distortion across the band edges and throughout the combined instantaneous bandwidth of the two or more individual band circuits. This electronic circuit utilizes an amplitude, time delay, and phase adjustment procedure that uses associated adjustable circuitry to eliminate misalignments between the two or more individual band circuits.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Multifunction receiver-on-chip for electronic warfare applications
InactiveUS20060071845A1Increase flexibilityEfficiently digitizedCommunication jammingSpecial data processing applicationsFiberElectronic warfare
What is provided is a receiver-on-a-chip comprising a monolithic integrated circuit that reduces the receiver to a cigarette-pack-sized assembly mountable directly at an antenna element, with a much-increased operational bandwidth and instantaneous bandwidth, increased dynamic range and with a two-order-of-magnitude decrease in size and weight. Moreover, because of the elimination of all of the I / O drivers and attendant circuitry, power consumption is reduced by two-thirds, whereas the mean time before failure is increased to 10,000 hours due to the robustness of the monolithic integrated circuit and use of fiber optics.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Multifunction receiver-on-chip for electronic warfare applications
InactiveUS7542812B2Small sizeTransmission line lossCommunication jammingSpecial data processing applicationsFiberEngineering
What is provided is a receiver-on-a-chip comprising a monolithic integrated circuit that reduces the receiver to a cigarette-pack-sized assembly mountable directly at an antenna element, with a much-increased operational bandwidth and instantaneous bandwidth, increased dynamic range and with a two-order-of-magnitude decrease in size and weight. Moreover, because of the elimination of all of the I / O drivers and attendant circuitry, power consumption is reduced by two-thirds, whereas the mean time before failure is increased to 10,000 hours due to the robustness of the monolithic integrated circuit and use of fiber optics.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
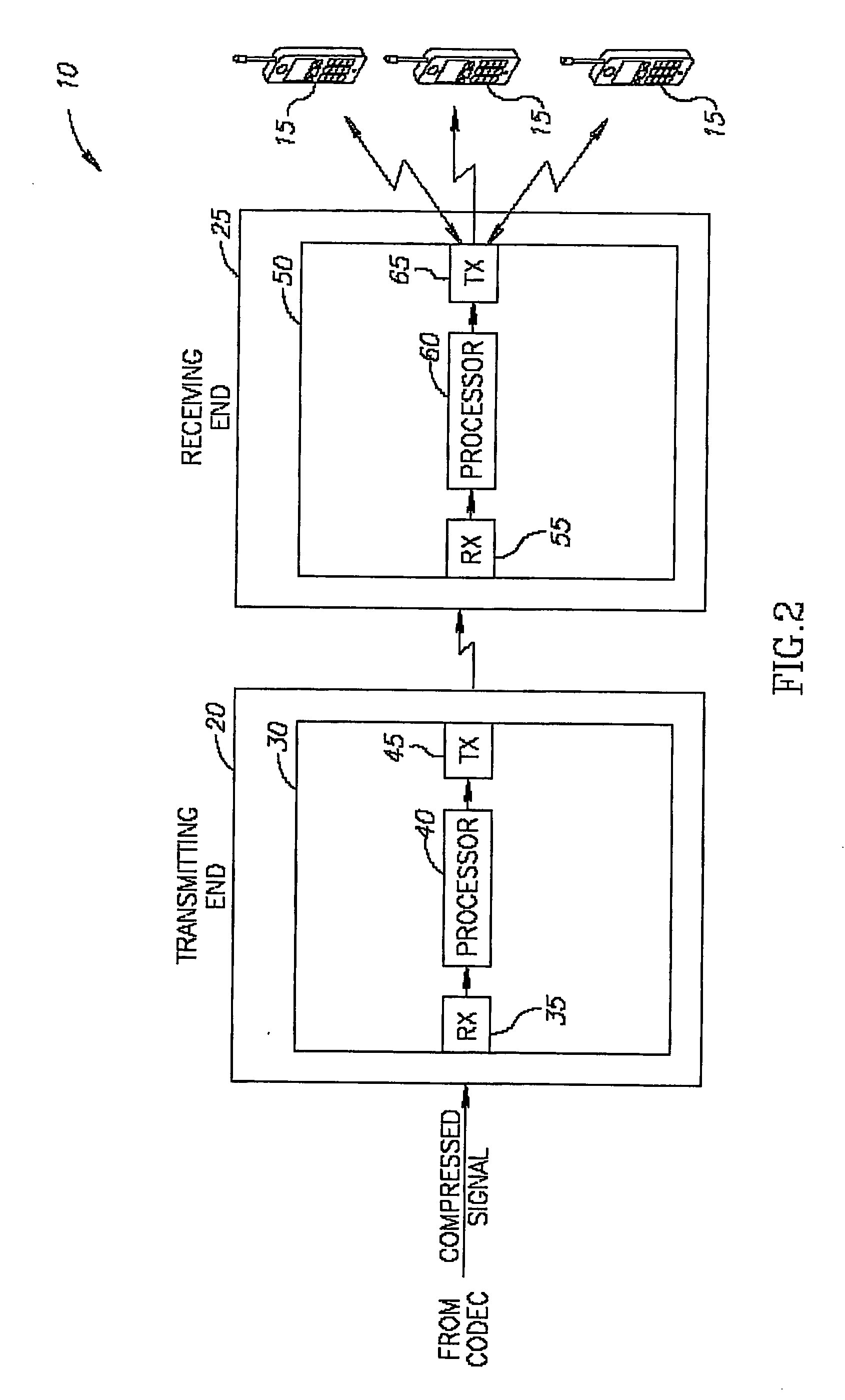
Bandwidth allocation method and apparatus
InactiveUS20030032429A1High bandwidthAttenuation bandwidthNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesCommunications systemThe Internet
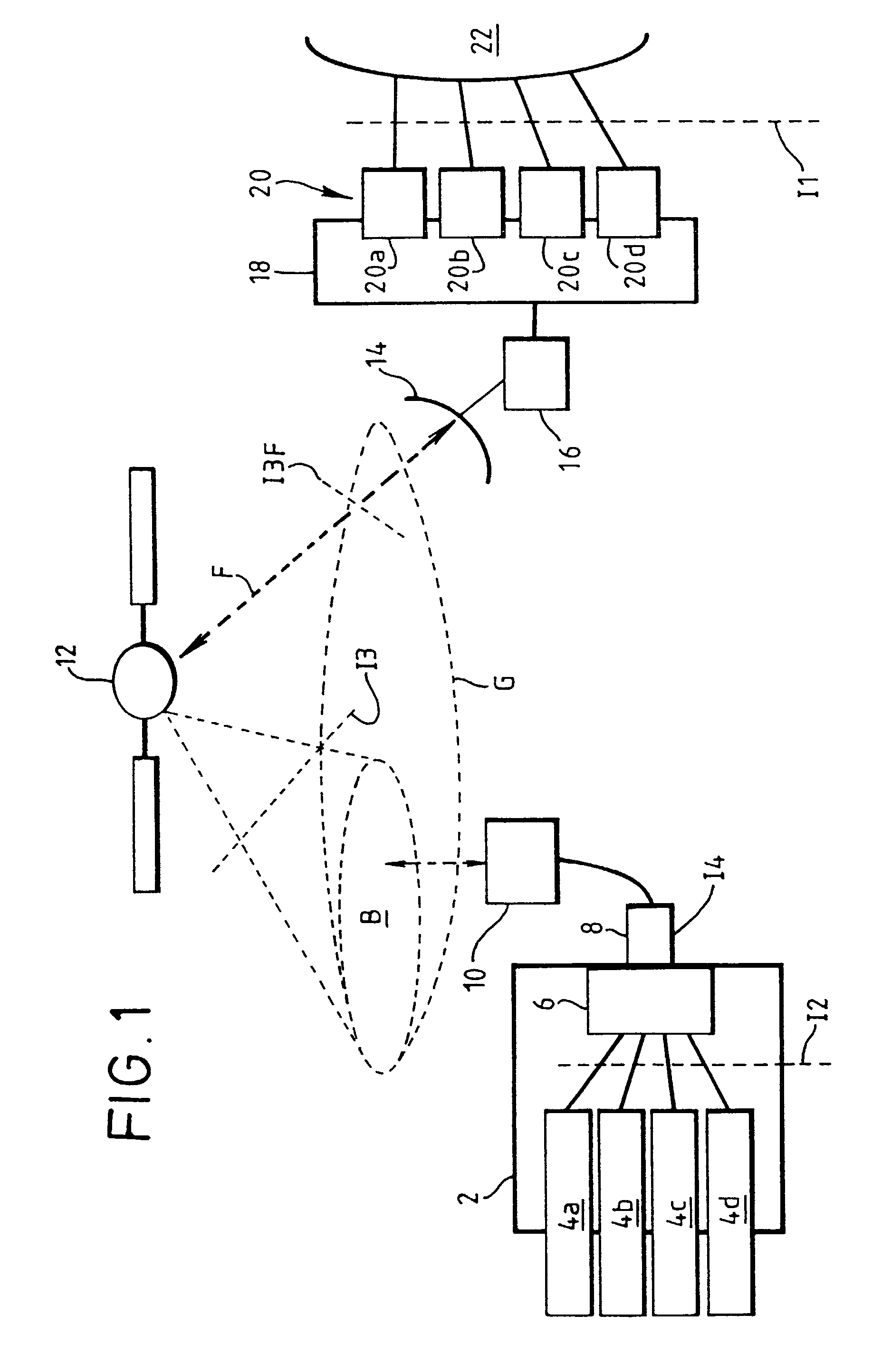
A satellite communications system provides a communications service to a mobile terminal (2) on which different communications applications (4a to 4d) may be run. Calls are set up between any of the applications (4a to 4d) via a satellite (12) to a network management center (18) which provides different service adaptors (20a to 20d) which adapt the calls to different types of service provided over terrestrial networks (22), such as telephony, facsimile, internet or ATM services. The bandwidth allocated to each call over the satellite link may be varied during the call according to demand either from the relevant application (4) or from the network management center (18). Multiple calls may be connected concurrently to or from different applications running on the mobile terminal. A maximum bandwidth is allocated to each call. Efficient use is thereby made of the limited bandwidth available over the satellite (12), according to the instantaneous bandwidth requirements of different applications (4). For real-time calls requiring multiple slots per frame in a TDMA channel, the slots are mutually spaced apart to reduce delay.
Owner:IMMARSAT TWO CO
Method and device for quality management in communication networks
ActiveUS20060245357A1Easy to manageMaximize qualityError preventionTransmission systemsSignal qualityEngineering
A method and apparatus are provide for managing varying traffic loads in a packetized communication network. At a predefined location, the instantaneous demand for bandwidth required for delivering traffic via a plurality of active channels is compared with the available bandwidth. When the available bandwidth at that pre-defined location is less than the bandwidth required to convey the signals carried along all these active channels, a rate adjusting mechanism is applied to at least one of the active channels, while repeating this check periodically. The rate adjusting mechanism is applied on packetized signals arriving along at least one group of active channels so as to ensure that: a substantially equalized signal quality is maintained for signals delivered via all of the active channels belonging to certain one or more groups of active channels, and the instantaneous overall bandwidth required to convey all the signals arriving at the pre-defined location, is not more than the available instantaneous bandwidth.
Owner:DIALOGIC NETWORKS (ISRAEL) LTD
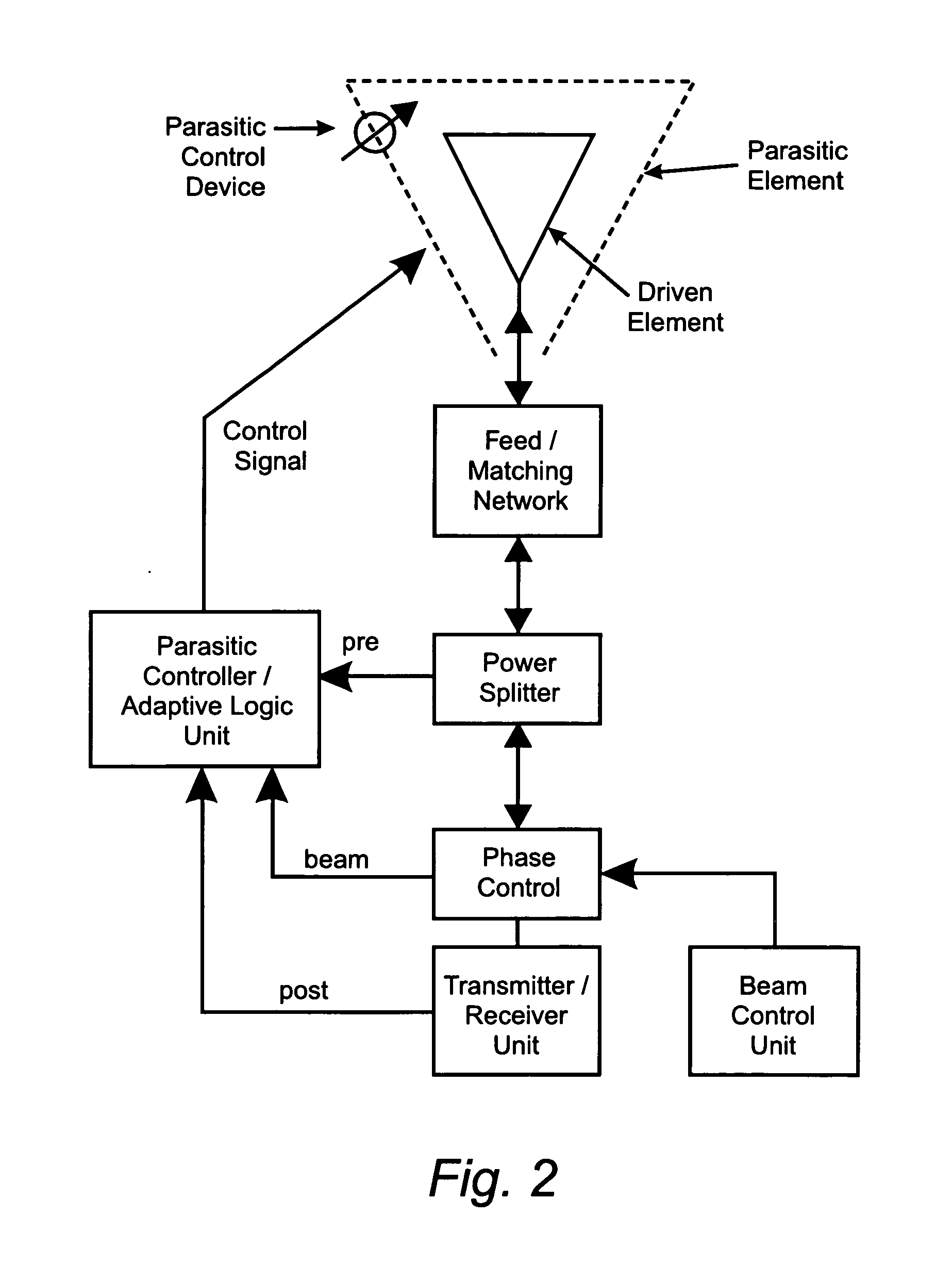
Reconfigurable parasitic control for antenna arrays and subarrays
InactiveUS7453413B2Reduce decreaseFrequency property can be controlledLogperiodic antennasAntenna arraysLight beamArray element
Reconfiguration of parasitically controlled elements in a phased array is used to expand the range of operational functions. Embedded array elements can be frequency tuned, and bandwidth can be improved by using reconfiguration to broaden the bandwidth of the embedded elements. For high gain arrays, beam squint can be a limiting factor on instantaneous bandwidth. Reconfiguration can alleviate this problem by providing control of the element phase centers. Scan coverage can be improved and scan blindness alleviated by controlling the embedded antenna patterns of the elements as well as by providing control of the active impedance as the beam is scanned. Applying limited phase control to the elements themselves can alleviate some of the complexity of the feed manifold. A presently preferred method of designing reconfigurable antennas is to selectively place controlled parasitic elements in the aperture of each of the antenna elements in the phased array. The parasitic elements can be controlled to change the operational characteristics of the antenna element. The parasitic elements are controlled by either switching load values in and out that are connected to the parasitic elements or are controlled by applying control voltages to variable reactance circuits containing devices such as varactors. The parasitic elements can be controlled by the use of a feedback control subsystem that is part of the antenna system which adjusts the RF properties of the parasitic components based on some observed metric. The controllable characteristics include directivity control, tuning, instantaneous bandwidth, and RCS.
Owner:TOYON RES CORP
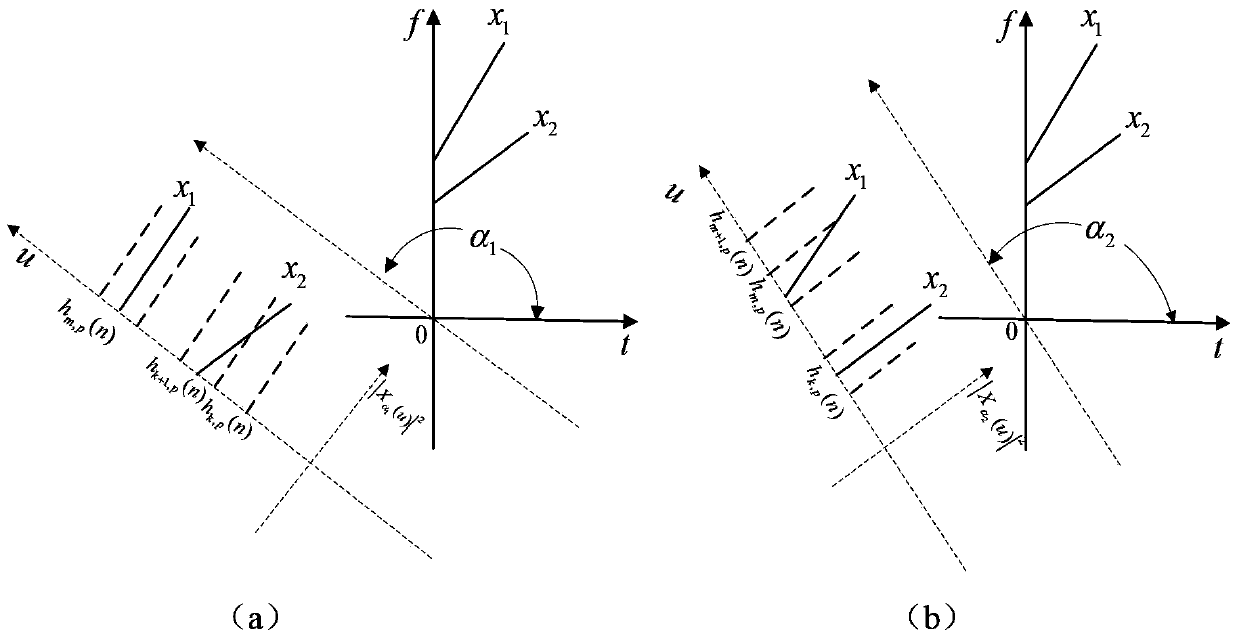
Broadband linear frequency-modulated (LFM) signal multi-decoy interference method based on fractional Fourier domain channelization
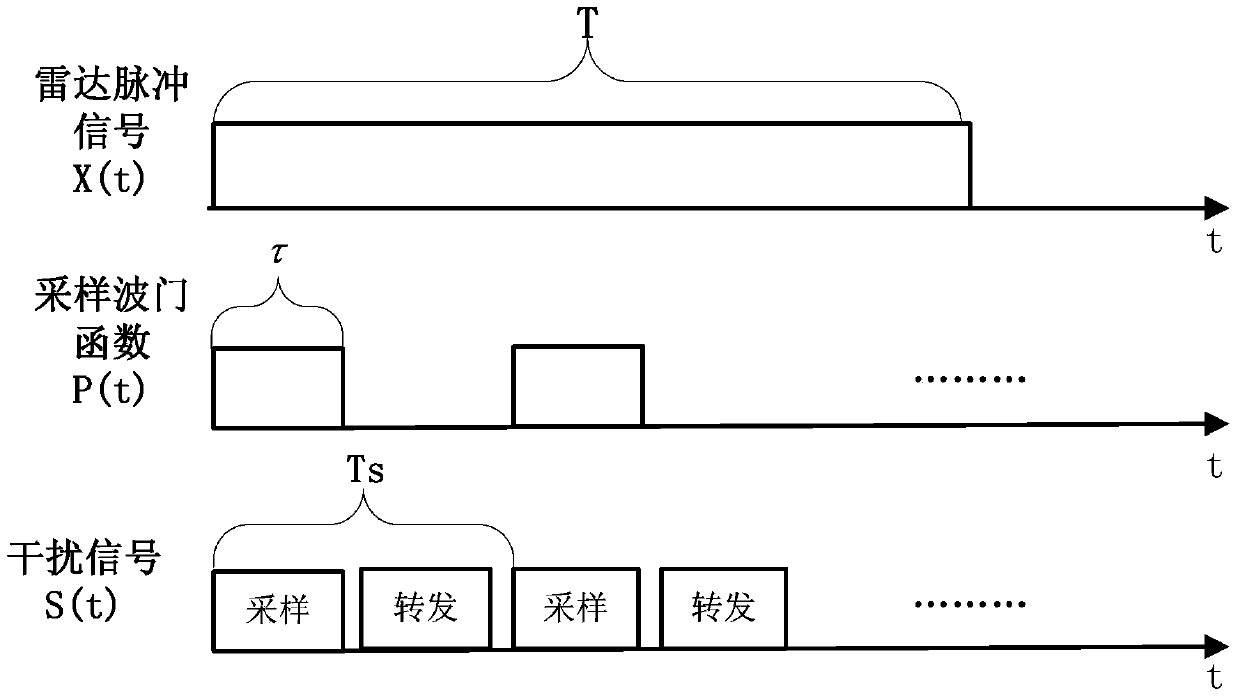
InactiveCN103532656AIntegrity guaranteedReduce instantaneous bandwidth requirementsCommunication jammingBroadbandEngineering
The invention relates to a broadband linear frequency-modulated (LFM) signal multi-decoy interference method based on fractional Fourier domain channelization, in particular to an interference method for performing multi-decoy deception on a broadband LFM signal in a pulse on the basis of fractional Fourier domain channelization, and belongs to the technical field of electronic interference. According to the broadband LFM signal multi-decoy interference method based on fractional Fourier domain channelization, all broadband LFM signals can be focused into one channel for outputting by using the energy focusing property of fractional Fourier transform on instable signals, so that the completeness of the signals is ensured, and the problems of reduction of signal energy and distortion of waveforms since the energy of the broadband LFM signals overflow into two or more channels in the conventional Fourier domain channelization are solved; meanwhile, the requirement on the instant bandwidth of a DRFM (Digital Radio Frequency Memory) system is lowered.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
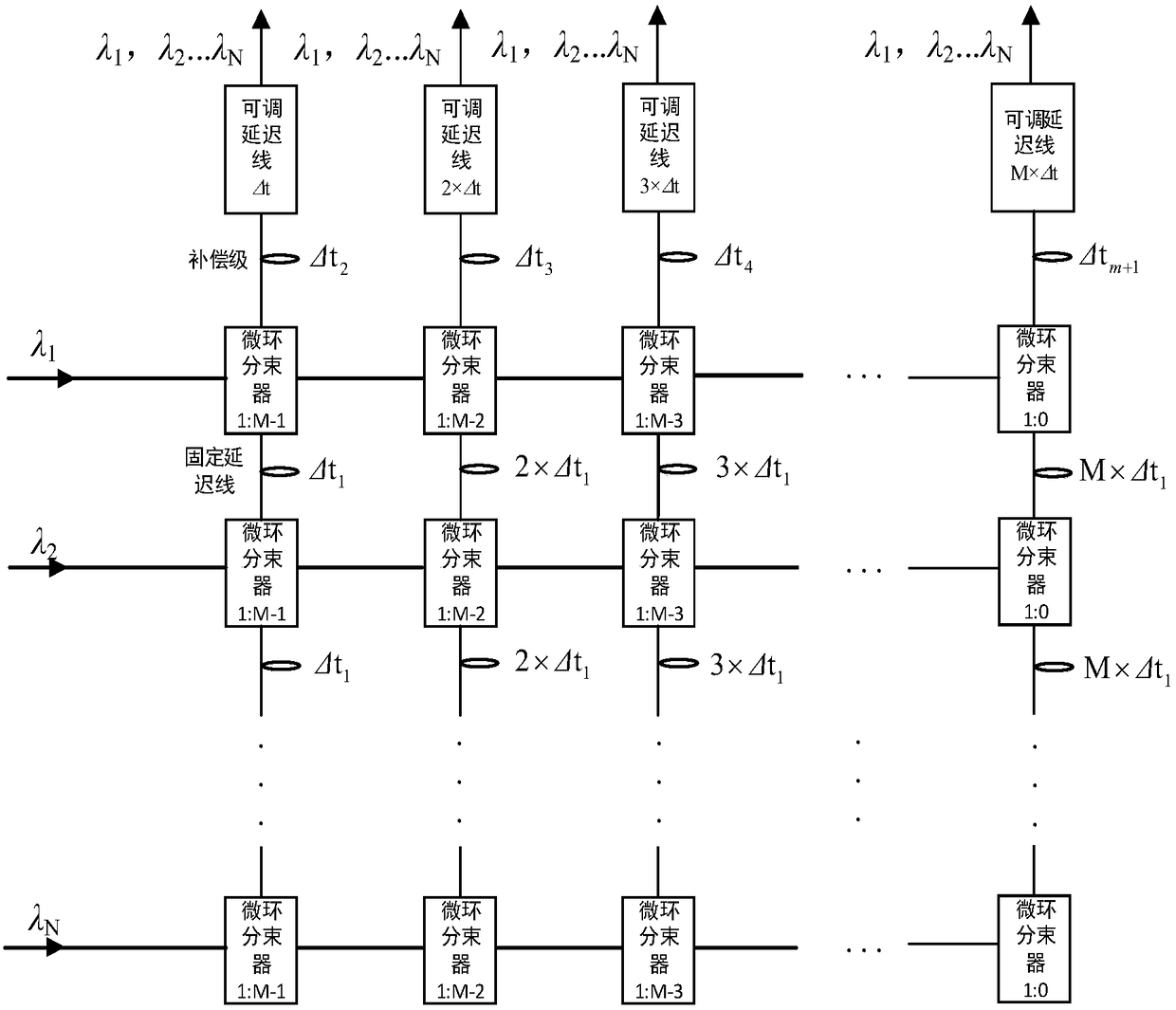
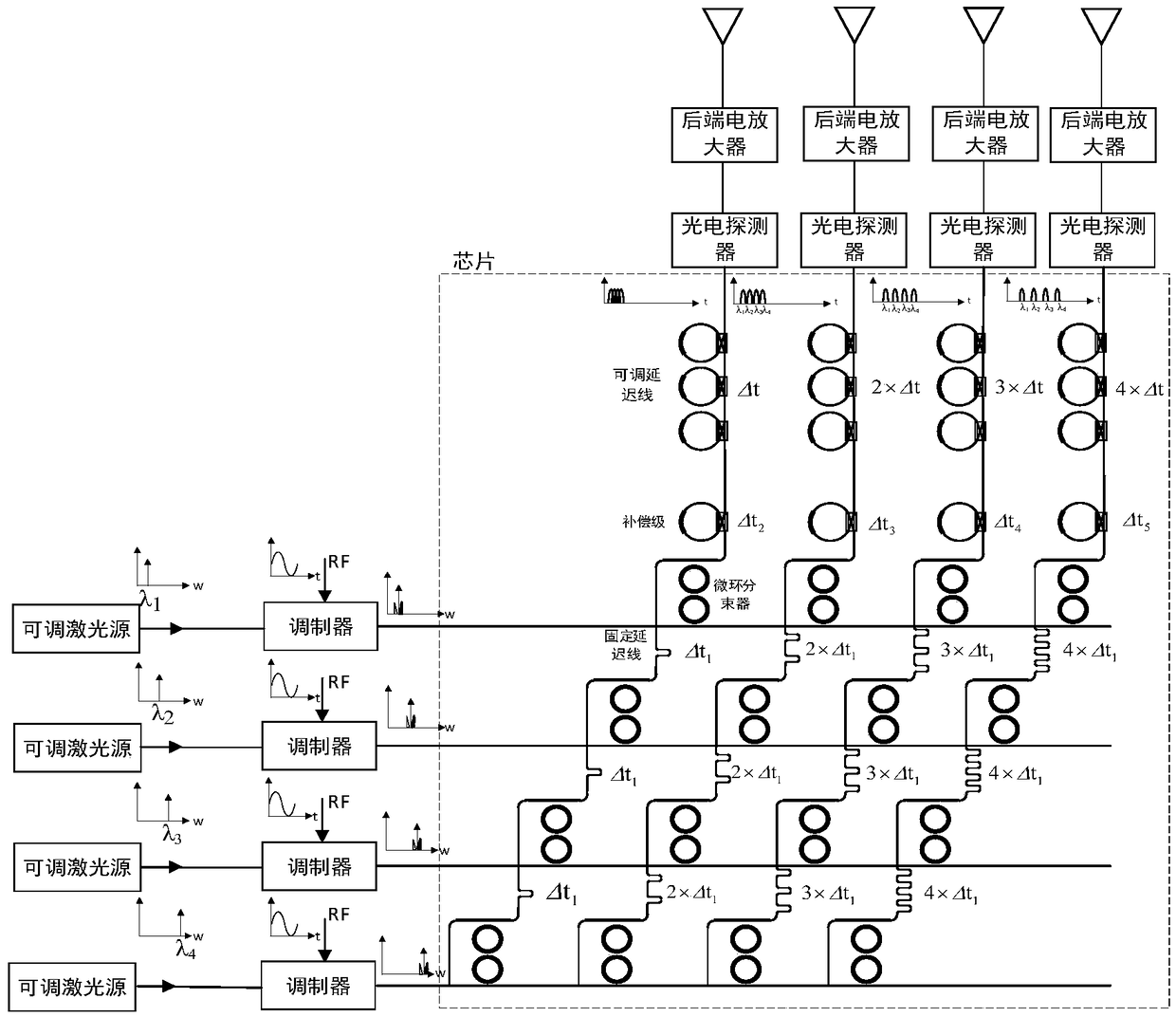
Wavelength division multiplexing based integrated multi-beam optical phased array delay network
ActiveCN108761439AIncrease instantaneous bandwidthHigh resolutionICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBeam splitterArray element
A wavelength division multiplexing based integrated multi-beam optical phased array delay network for a microwave photonic multi-beam phased array radar, consists of N-channel row waveguides, NxM micro-ring beam splitters, an NxM fixed photo-true delay network, M-channel dimmable true delay arrays and M-channel column waveguides; the NxM micro-ring beam splitters are arranged in N rows and M columns; and the NxM fixed photo-true delay network is connected to the NxM micro-ring beam splitters. The invention only needs M adjustable units, and can realize the phased array radar of M array elements and N beams, is simple and flexible in structure control, is high in integration degree, and is large in instantaneous bandwidth and high in resolution.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Amplifier linearizer
ActiveUS7940198B1Reduce nonlinear distortionLow powerResonant long antennasElectric signal transmission systemsNonlinear distortionCurve fitting
The present invention provides an advanced adaptive predistortion linearization technique to dramatically reduce nonlinear distortion in power amplifiers over a very wide instantaneous bandwidth (up to 2 GHz) and over a wide range of amplifier types, input frequencies, signal types, amplitudes, temperature, and other environmental and signal conditions. In an embodiment of the invention, the predistortion linearization circuitry comprises (1) a higher-order polynomial model of an amplifier's gain and phase characteristics—higher than a third-order polynomial model; (2) an adaptive calibration technique; and (3) a heuristic calibration technique. The higher-order polynomial model is generated by introducing, for example, a plurality of multi-tone test signals with varying center frequency and spacing into the power amplifier. From the power amplifier's corresponding output, the nonlinearities are modeled by employing a higher-order curve fit to capture the irregularities in the nonlinear transfer function. Different distortion transfer functions can be implemented for different operating conditions. The adaptive calibration technique is based on a feedback analysis technique, which updates the applicable distortion transfer function by analyzing the error signal between the introduced input signal and the output signal in real-time. The heuristic calibration technique implements different distortion transfer functions based on historical operating conditions and optimal configurations of the power amplifier.
Owner:TM IP HLDG LLC
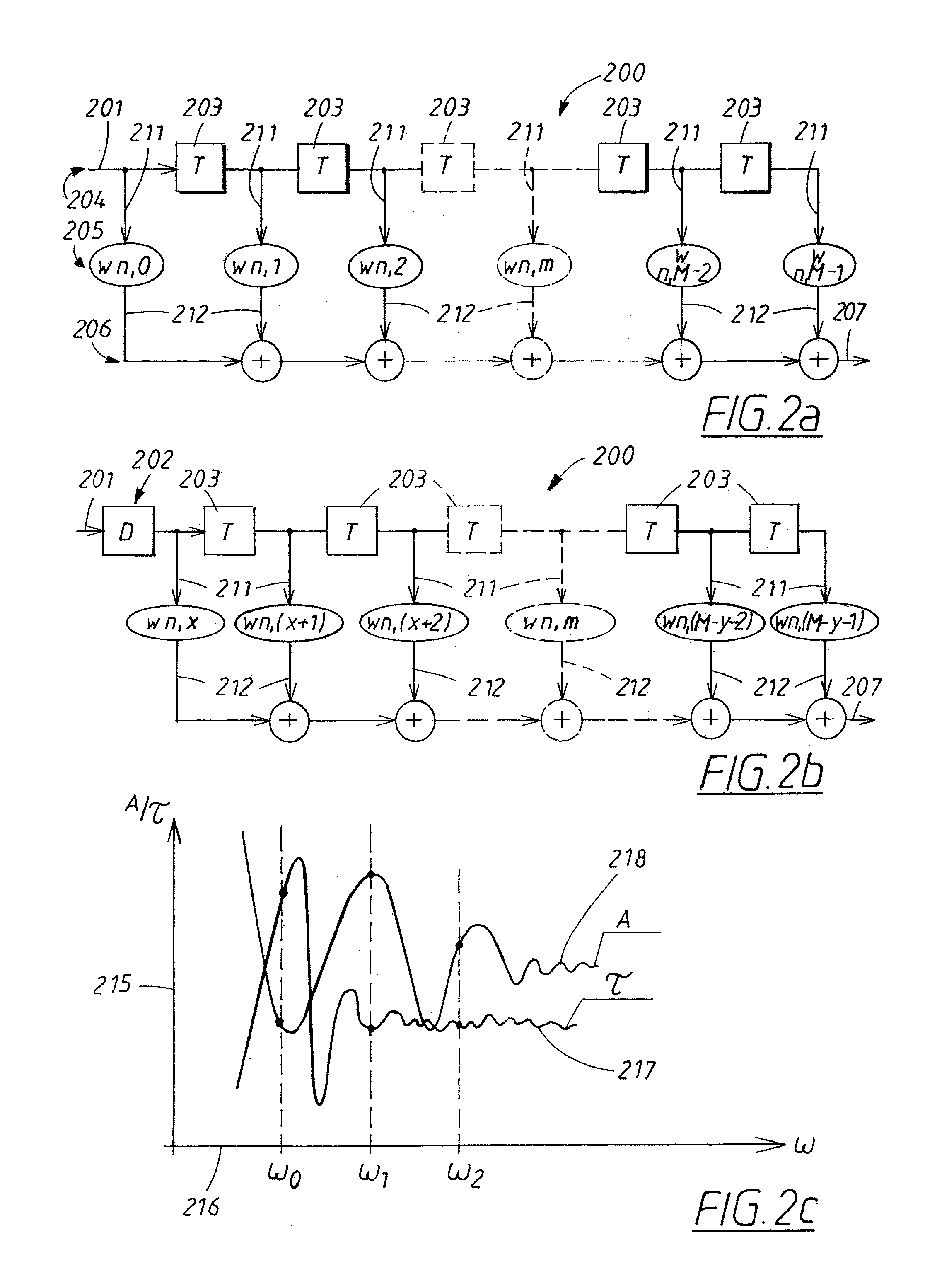
Reconfigurable antenna array and associated method of use
ActiveUS20180102593A1Narrow bandwidthMeet different requirementsSimultaneous aerial operationsPolarisation/directional diversityReconfigurable antennaPolarization diversity
A reconfigurable antenna array capable of utilizing a common antenna aperture which can cover a wide frequency range in a continuous way. With the basic antenna element based on a slot-ring and using a self similar structure approach and RE' switches, the antenna array operates without grating lobes. The antenna array exhibits polarization diversity and single-side radiation capability. When varactors are implemented into the array, the antenna array can cover the frequency range by continuously tuning the center frequency with a relatively narrow instantaneous bandwidth.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
QoS for AV transmission over wireless networks
InactiveUS20070127410A1Reducing bandwidth allocatedIncrease bandwidth allocatedNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsControl channelDynamic management
A method manages dynamically bandwidth for transport streams in a wireless network. An available bandwidth is defined for the network. An instantaneous bandwidth required by transport streams transmitted according to a hybrid coordination function controlled channel access (HCCA) category and an enhanced distributed channel access (EDCA) category is determined. The available bandwidth is compared to the instantaneous bandwidth, and the bandwidth of low priority transport streams is adjusted dynamically if the instantaneous bandwidth is different than the available bandwidth.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
System and method for maintaining wireless channels over a reverse link of a CDMA wireless communication system
InactiveUS20040213176A1Minimize overhead transmissionMinimizing start up delayError prevention/detection by using return channelChannel dividing arrangementsCommunications systemComputer science
A service option overlay for a CDMA wireless communication in which multiple allocatable subchannels are defined on a reverse link by assigning different code phases of a given long pseudonoise (PN) code to each subchannel. The instantaneous bandwidth needs of each on-line subscriber unit are then met by dynamically allocating none, one, or multiple subchannels on an as needed basis for each network layer connection. The system efficiently provides a relatively large number of virtual physical connections between the subscriber units and the base stations on the reverse link for extended idle periods such as when computers connected to the subscriber units are powered on, but not presently actively sending or receiving data. These maintenance subchannels permit the base station and the subscriber units to remain in phase and time synchronism in an idle mode and also request additional channels. This in turn allows fast acquisition of additional subchannels as needed by allocating new code phase subchannels. Preferably, the code phases of the new channels are assigned according to a predetermined code phase relationship with respect to the code phase of the corresponding maintenance subchannel.
Owner:INTEL CORP
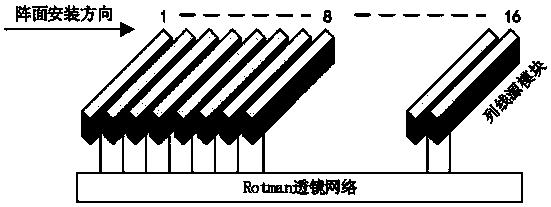
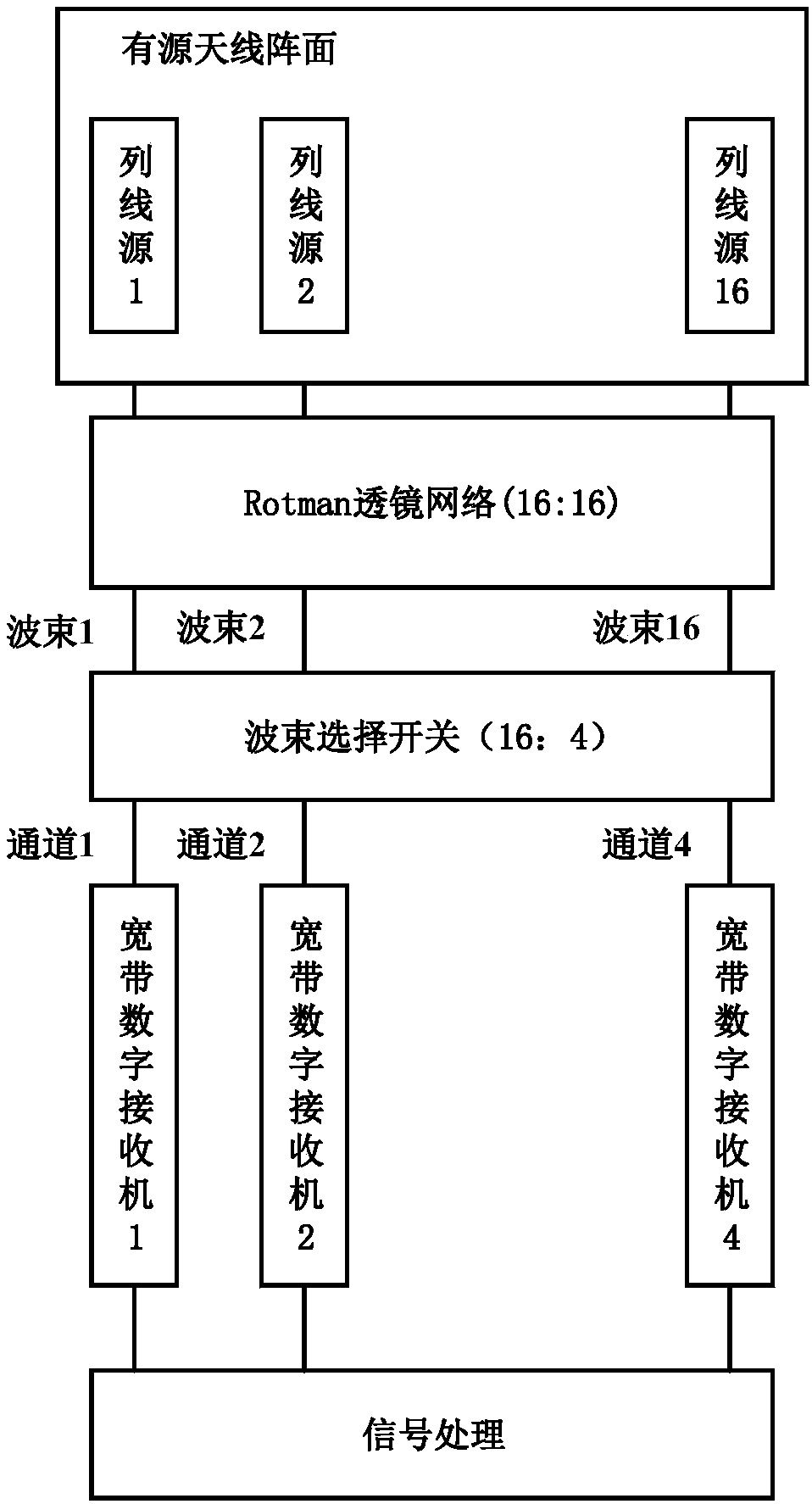
Broadband low-minor-lobe analog multi-beam array reconnaissance system
InactiveCN108562876AAddressing Noise Figure DeteriorationImprove phase errorWave based measurement systemsAntenna arraysElectromagnetic environmentVIT signals
A broadband low-minor-lobe analog multi-beam array reconnaissance system comprises a broadband active antenna array, a Rotman lens network, a beam selection switch, a broadband digital receiver, a signal processing unit. The broadband active antenna array is connected with an analog multi-beam network. The Rotman lens network is configured to form multiple beams simultaneously in a large instantaneous bandwidth. Further, by assigning corresponding amplitude and phase weights to respective amplitude-phase weighting modules of the antenna array, the beam selection switch performs radio frequencyselection in multiple beams according to a control command and sends a selected signal to the broadband digital receiver. The digital receiver processes the data from multiple beams and frequency bands in parallel, and performs parameter measurement on the data to form a radar pulse descriptor and sends the radar pulse descriptor to the signal processing unit. The signal processing unit processesthe signal to form a radar descriptor. The system achieves high sensitivity, wide frequency-domain coverage, wide airspace coverage, flexible beam scheduling and good complex electromagnetic environment adaptability.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
Method for predicting pore pressure
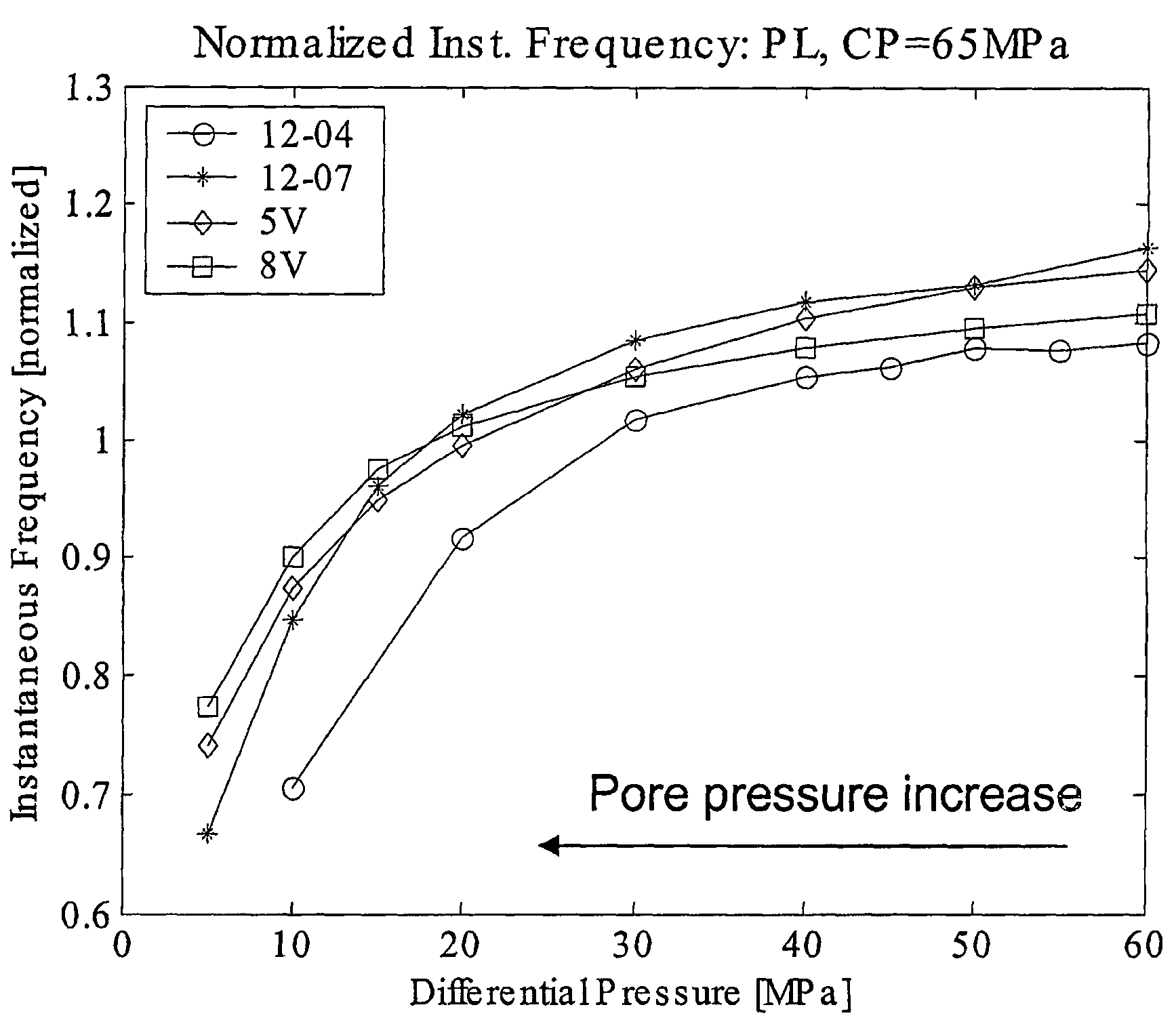
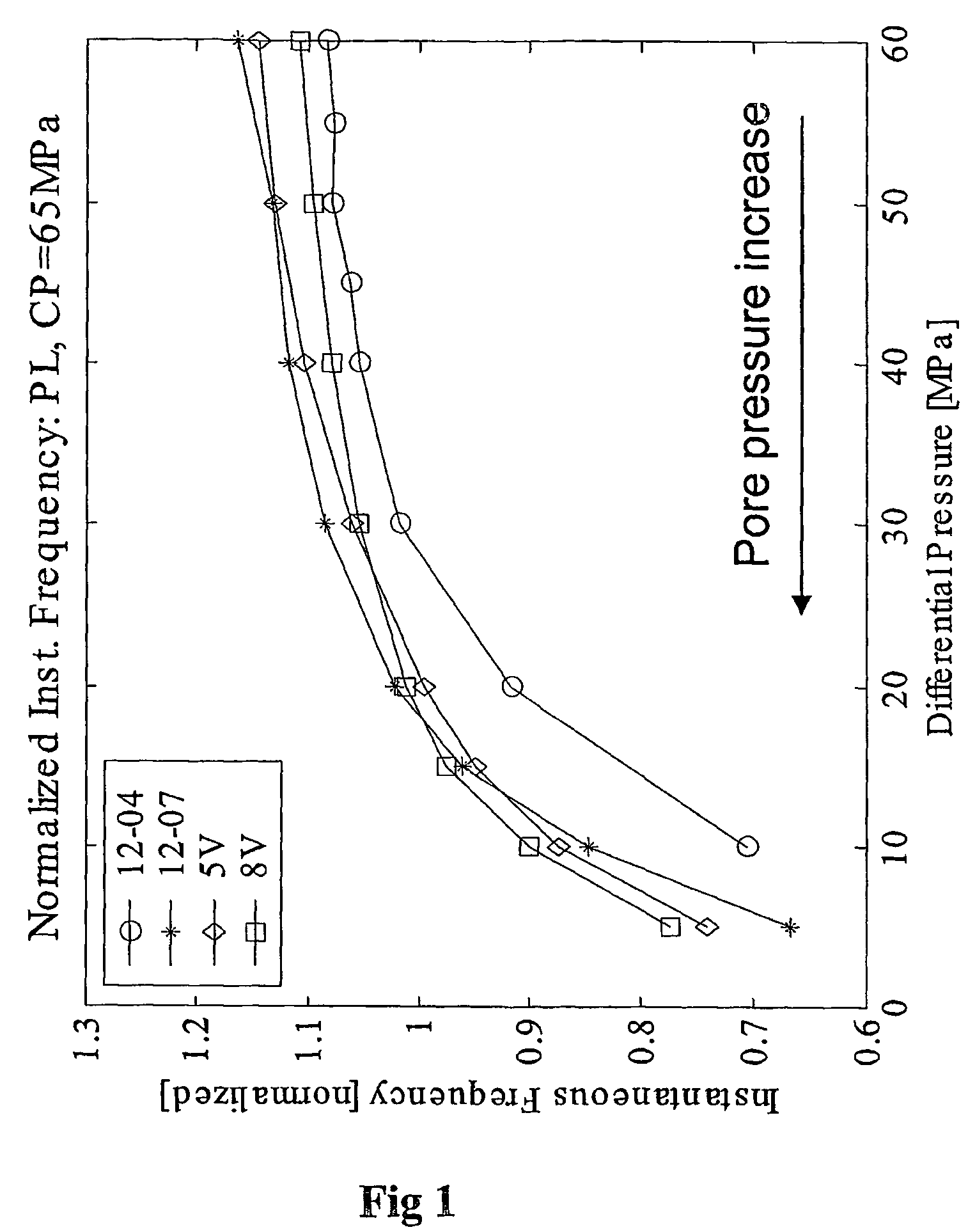
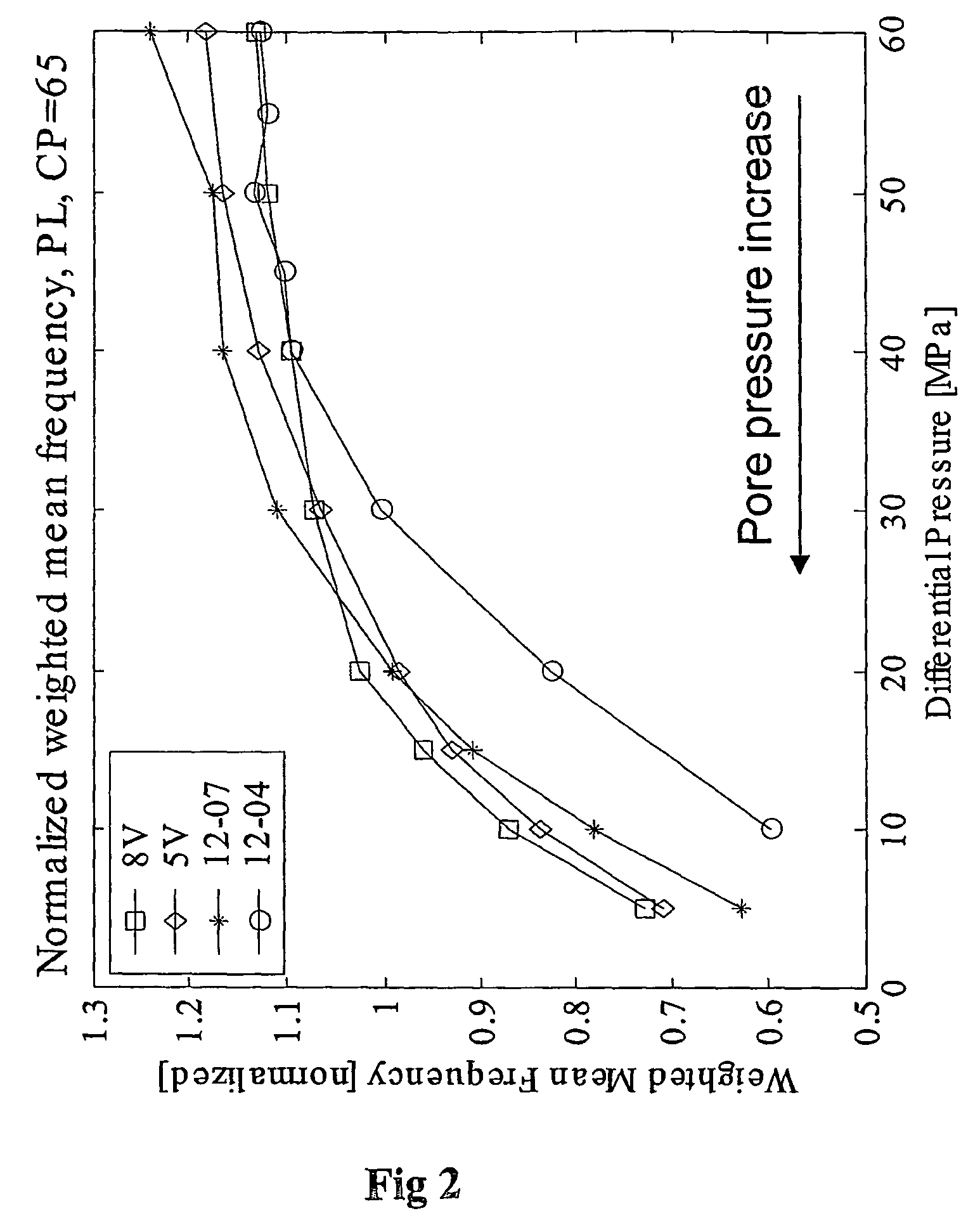
InactiveUS7274992B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingPore water pressureSeismic attribute
A method for predicting pore pressure is described which initially involves obtaining, for one point in a volume of Earth, a value of pore pressure and one or more seismic attributes. A relationship is determined between the value of pore pressure and the seismic attribute, for example by use of a neural network. Seismic data is then obtained for the volume of earth and the same attributes as selected above when determining relationship are extracted from the seismic data for another point in the volume. The extracted seismic attributes are then used as inputs to the previously determined relationship to produce as an output, a prediction of pore pressure at the other point. The seismic attributes are frequency related seismic attributes and include for example instantaneous frequency, weighted mean frequency, instantaneous pseudo-quality factor, instantaneous dominant frequency, instantaneous bandwidth, instantaneous phase, effective bandwidth, peak frequency, envelope and energy half time.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Amplifier Linearizer
ActiveUS20110175678A1Reduce nonlinear distortionLow powerMultiple-port networksElectric signal transmission systemsNonlinear distortionReal time analysis
The present invention provides an advanced adaptive predistortion linearization technique to dramatically reduce nonlinear distortion in power amplifiers over a very wide instantaneous bandwidth (up to 2 GHz) and over a wide range of amplifier types, input frequencies, signal types, amplitudes, temperature, and other environmental and signal conditions. In an embodiment of the invention, the predistortion linearization circuitry comprises (1) a higher-order polynomial model of an amplifier's gain and phase characteristics—higher than a third-order polynomial model; (2) an adaptive calibration technique; and (3) a heuristic calibration technique. The higher-order polynomial model is generated by introducing, for example, a plurality of multi-tone test signals with varying center frequency and spacing into the power amplifier. From the power amplifier's corresponding output, the nonlinearities are modeled by employing a higher-order curve fit to capture the irregularities in the nonlinear transfer function. Different distortion transfer functions can be implemented for different operating conditions. The adaptive calibration technique is based on a feedback analysis technique, which updates the applicable distortion transfer function by analyzing the error signal between the introduced input signal and the output signal in real-time. The heuristic calibration technique implements different distortion transfer functions based on historical operating conditions and optimal configurations of the power amplifier.
Owner:TM IP HLDG LLC
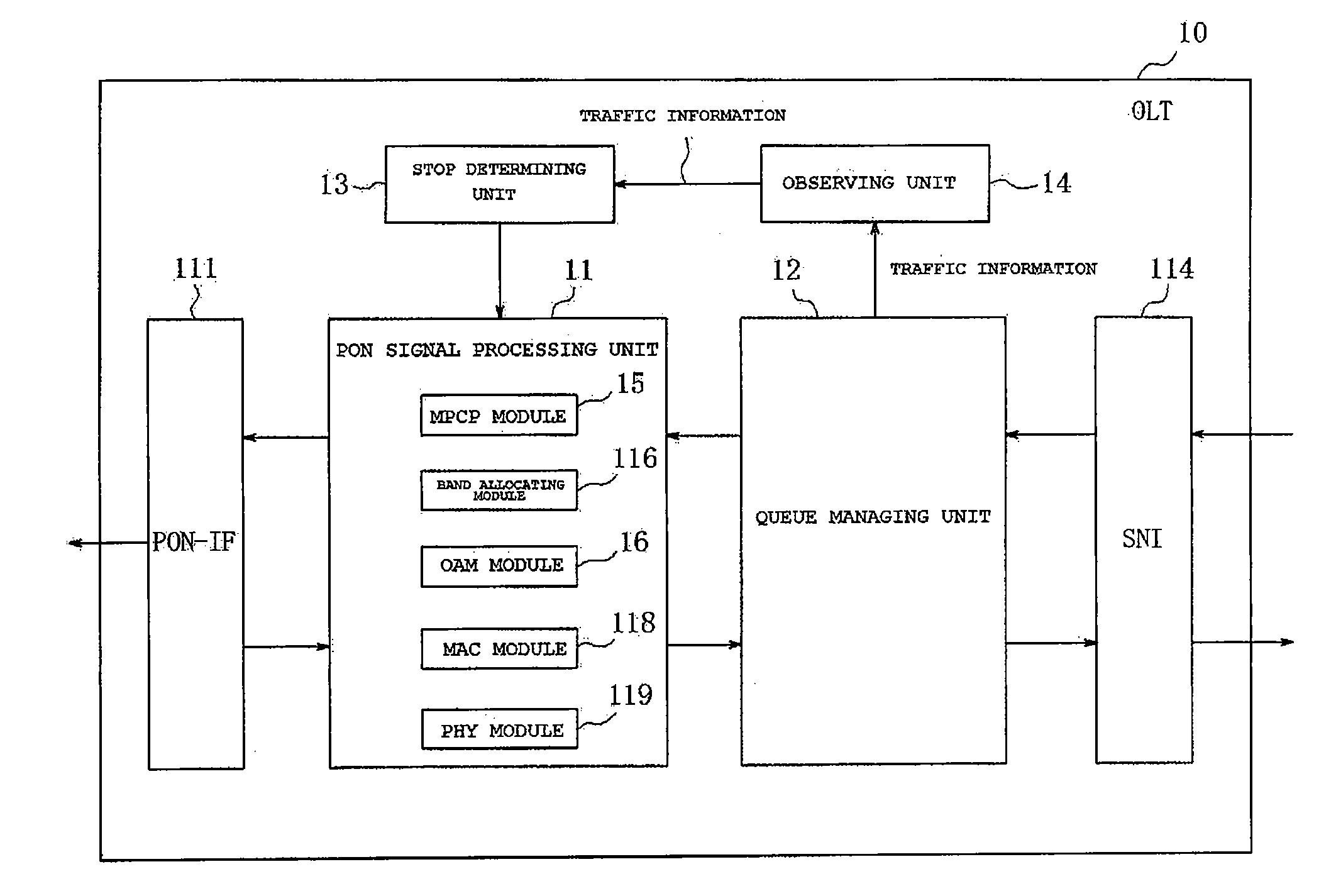
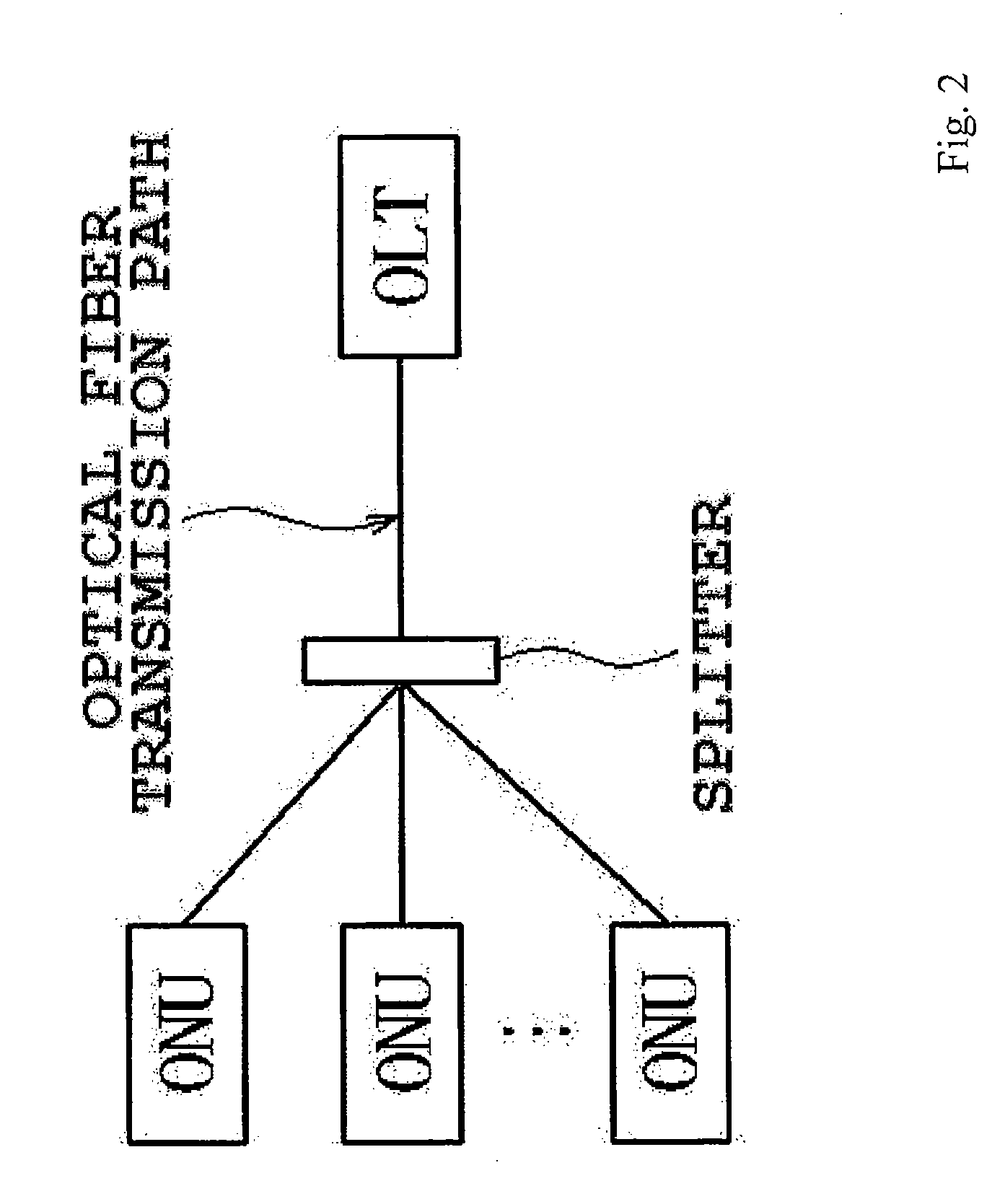
Optical line terminal and optical network unit
ActiveUS20110318008A1Increase in consumption powerIncrease powerMultiplex system selection arrangementsEnergy efficient ICTSleep timeSleep state
An optical line terminal which includes an observing unit that observes information of any one or all of an arrival interval of frames, an instantaneous bandwidth under use of a flow, a queue length of a queue temporarily storing the frames, and a traffic type, and a stop determining unit that dynamically determines a sleep time to be a period in which a sleep state where partial functions of the ONU are stopped is maintained, on the basis of the information obtained by the observing unit. The ONU is entered into a sleep state, immediately after communication ends, after a predetermined waiting time passes from when the communication ends, or after a waiting time determined on the basis of the information passes from when the communication ends.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
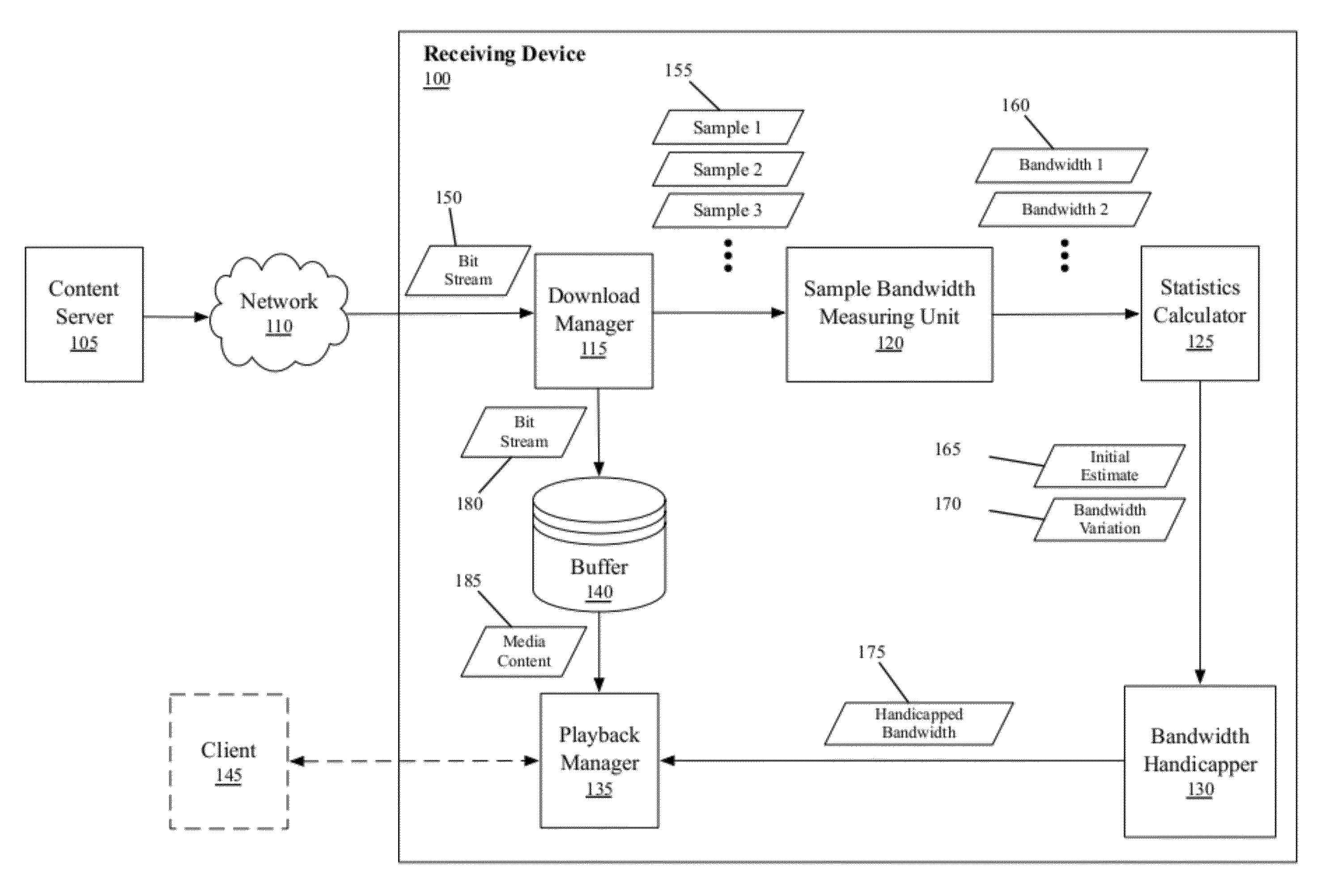
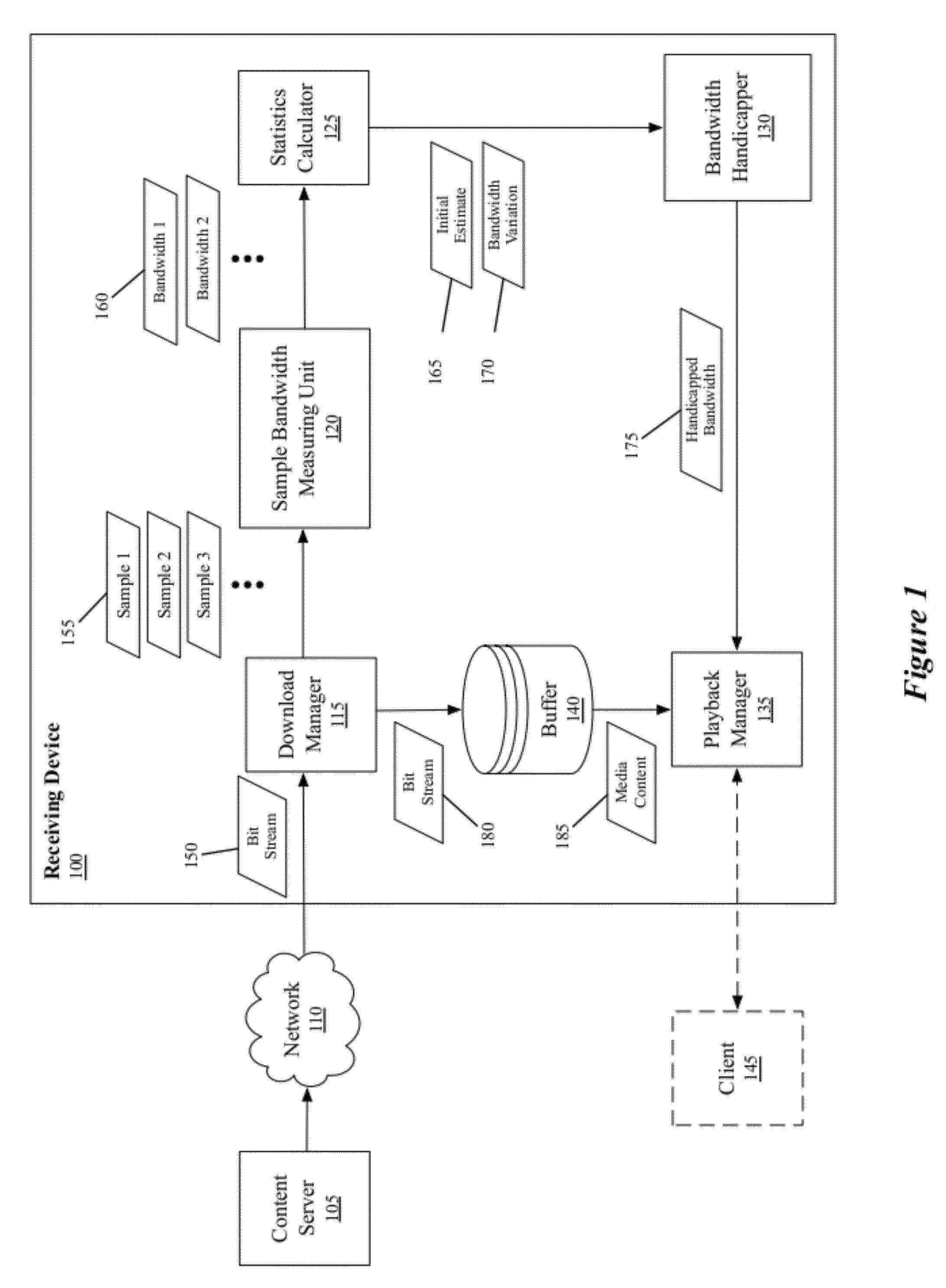
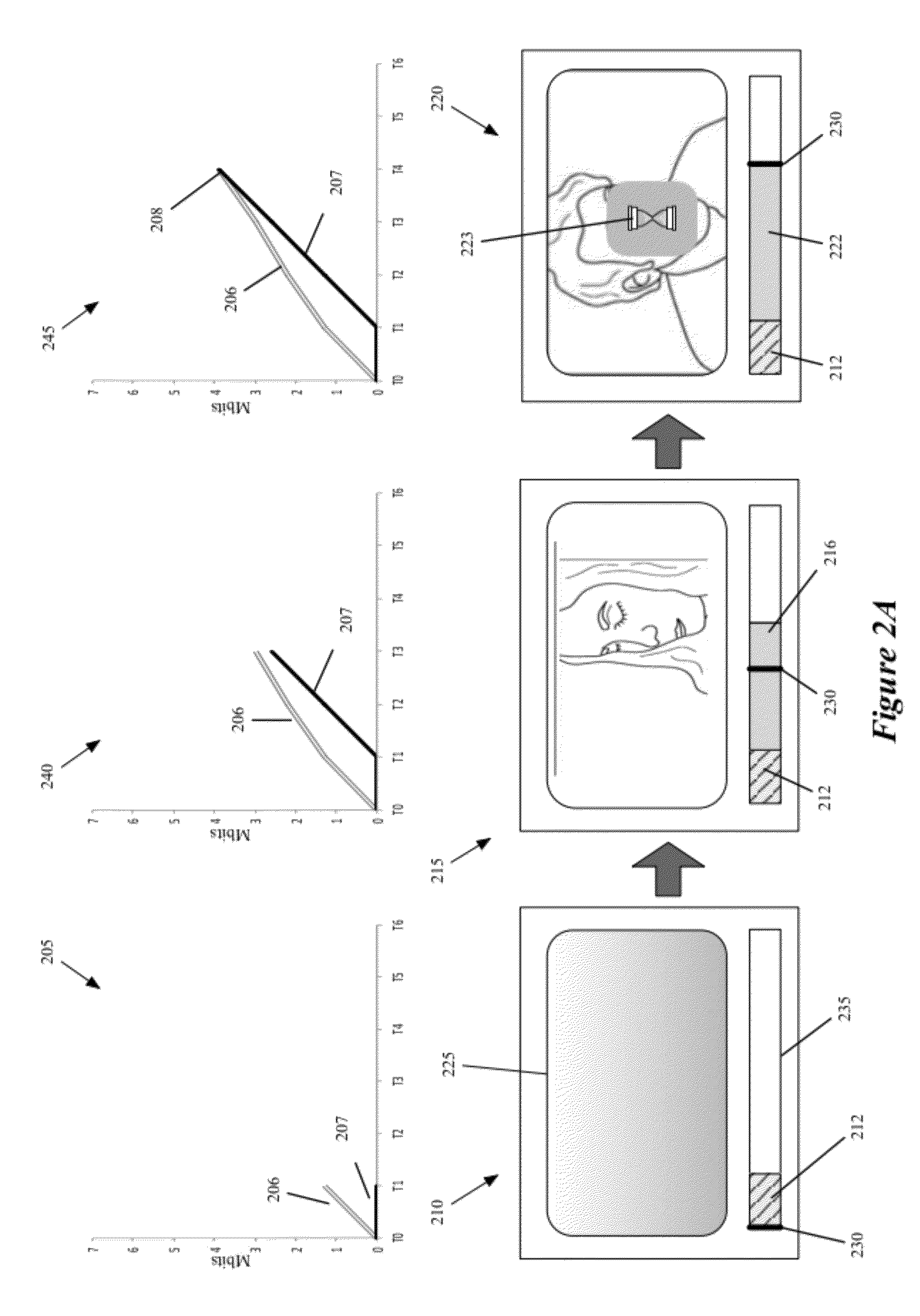
Bandwidth Estimation Based on Statistical Measures
Some embodiments provide a method for estimating bandwidth estimate based on a set of statistical measurements that quantifies bandwidth variation. The method receives a piece of media content at a receiving device and computes several instantaneous bandwidth measurements based on sample data blocks or media content received at the receiving device. The method computes the set of statistical measures that quantifies variation between the computed instantaneous bandwidth measurements. Based on the set of statistical measures, the method computes a revised bandwidth estimate for receiving media content at the receiving device. In some embodiments, the method uses the revised bandwidth estimate to determine an amount of media content data to buffer in order to provide an uninterrupted playback.
Owner:APPLE INC
Adaptive digital receiver
ActiveUS8582694B2High resolutionWide bandwidthElectric signal transmission systemsChannel dividing arrangementsImage resolutionAdaptive optimization
The present invention provides a high-performance adaptive digital receiver with adaptive background control that optimizes the performance in rapidly changing signal environments and provides 3.6 GH; instantaneous bandwidth, SFDR>90 dB, SNR=66 dB, with dynamic digital channelization. The receiver takes advantage of several levels of adaptivity that conventional approaches do not offer. In addition to a dynamic digital channelizer that is adaptively tuned based on detected signals, the present invention employs a powerful software reconfigurable digitizer that is adaptively optimized for the current signal environment to control important receiver parameters such as bandwidth, dynamic range, resolution, and sensitivity.
Owner:LINEARITY LLC
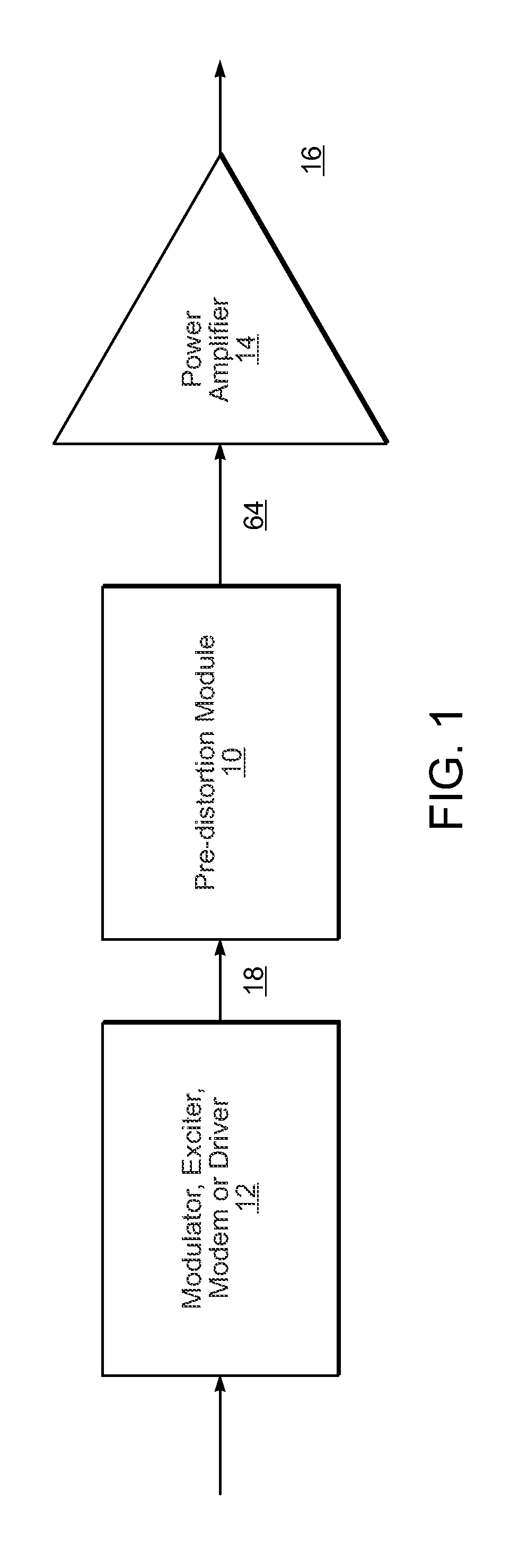
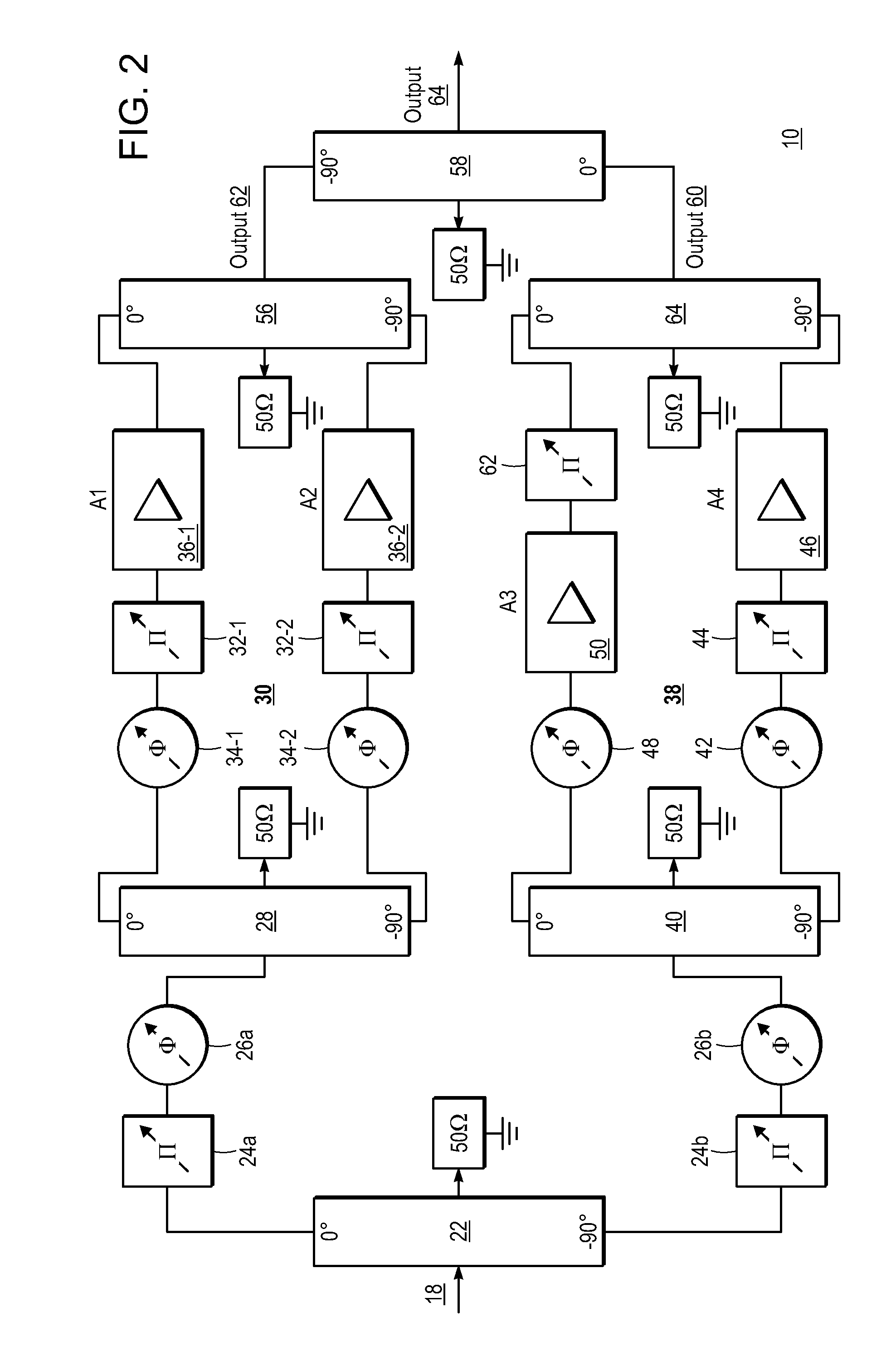
Broadband linearization module and method
ActiveUS8736365B2Amplifiers with memory effect compensationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierCommunications system
A system including a power amplifier and a pre-distortion module coupled to the power amplifier. The pre-distortion module includes one or more smaller versions of the power amplifier to generate a pre-distortion signal that compensates for any memory-effect or inertia present in the power amplifier with application on frequency hopping and larger (up to 1 octave) instantaneous bandwidth communication systems.
Owner:EMPOWER RF SYST
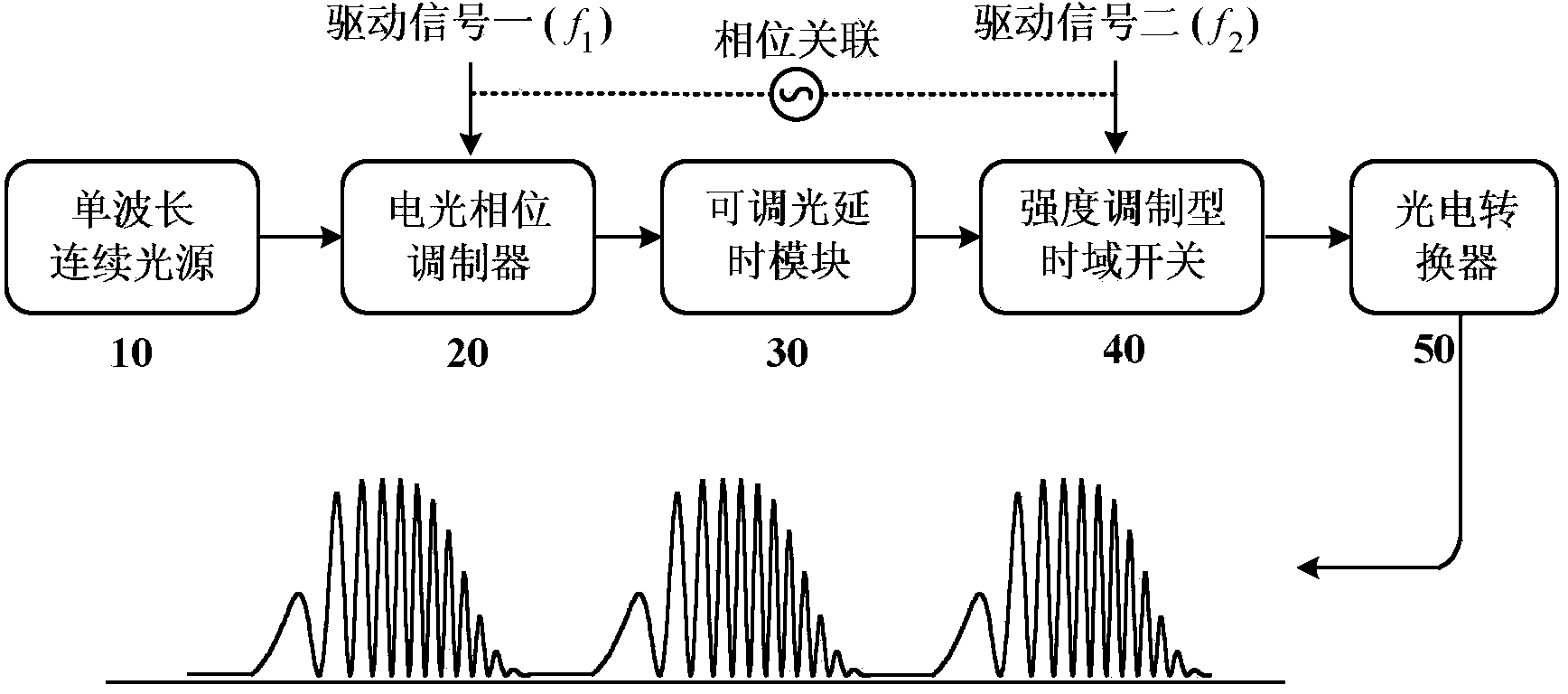
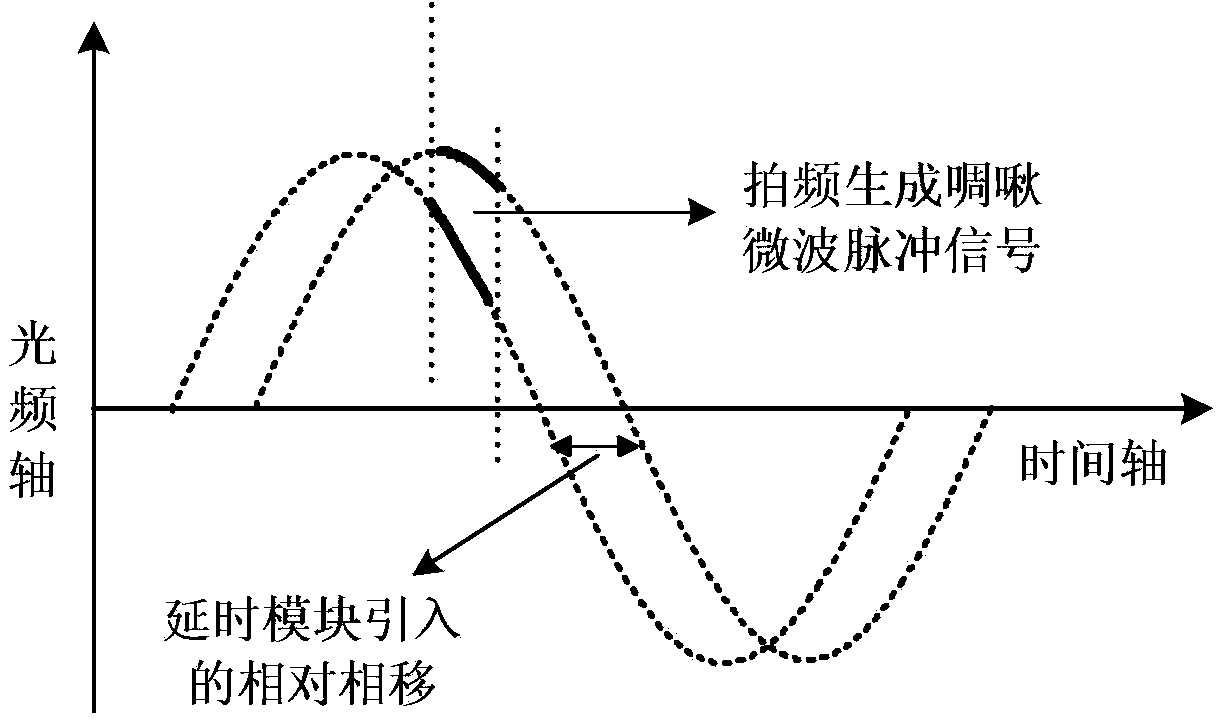
Chirp microwave pulse signal generation method and device based on electro-optic external modulation nonlinear effect
The invention discloses a chirp microwave pulse signal generation method and device based on an electro-optic external modulation nonlinear effect. Under a large signal modulation mode, single-wave-length-light carrier waves are subjected to phase modulation with a large modulation depth in an electro-optic modulator; relative phase shift or malposition are introduced into phase modulation signals through a dimmable delaying module, after nonlinear frequency chirp zone selecting is achieved through a time domain switch, the signals are input to an photoelectric converter for beat frequency, and microwave pulse signals with adjustable pulse speed, pulse and center carrier frequency are obtained. The method and device have the photonics advantages of being high in frequency, large in instant bandwidth and the like, and have the advantages of being high in signal parameter accuracy, easy to tune, relatively simple in structure, wide in application prospect and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
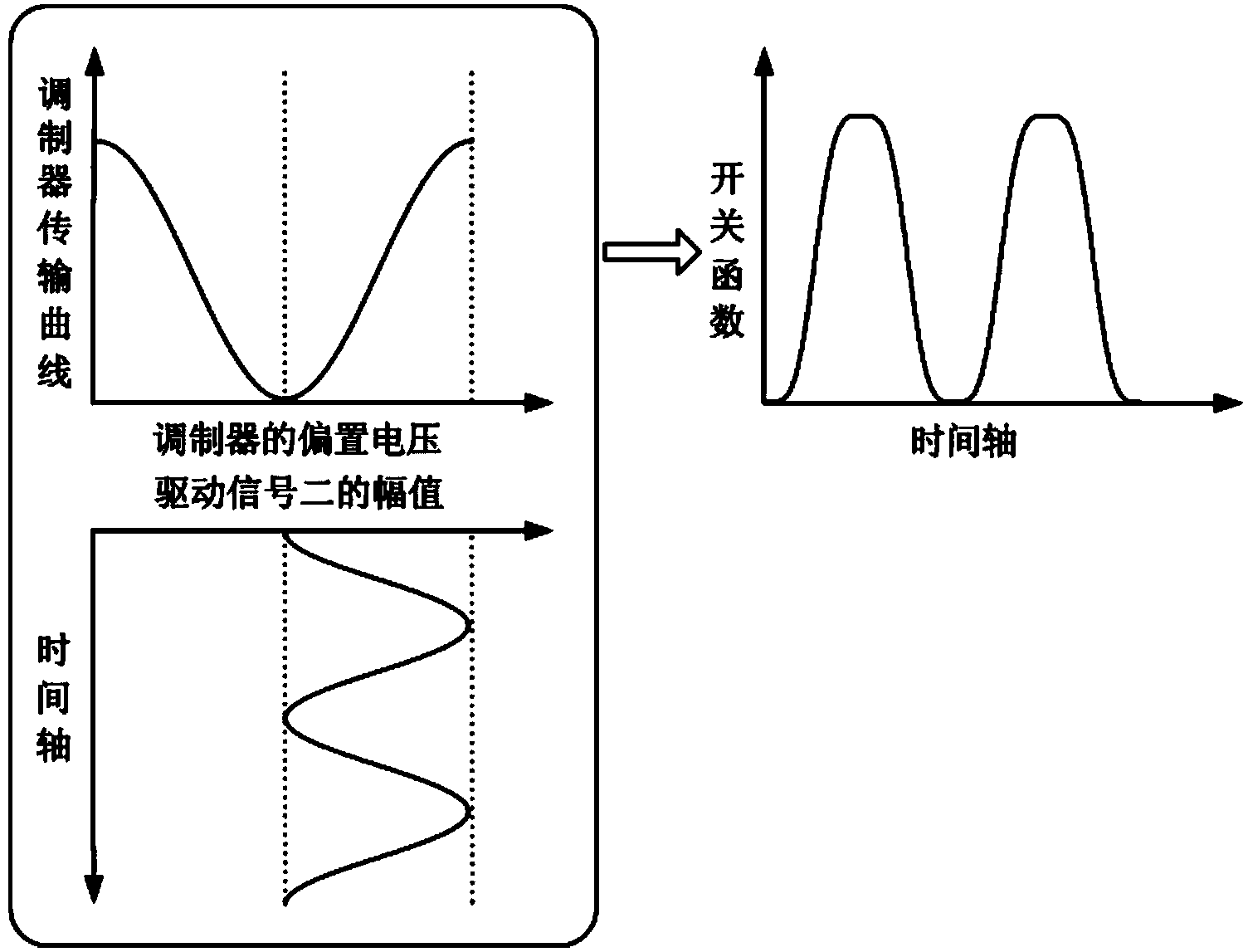
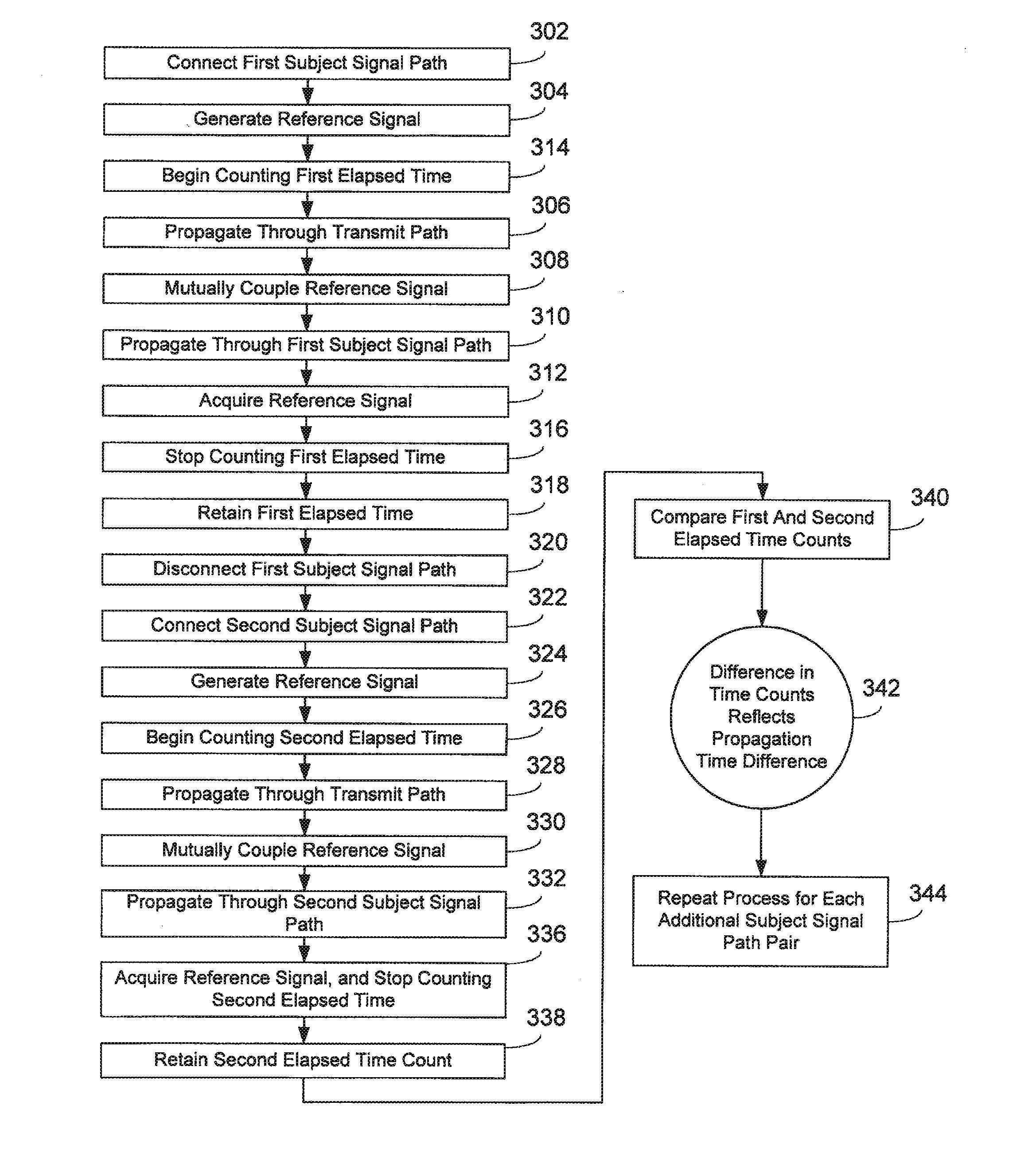
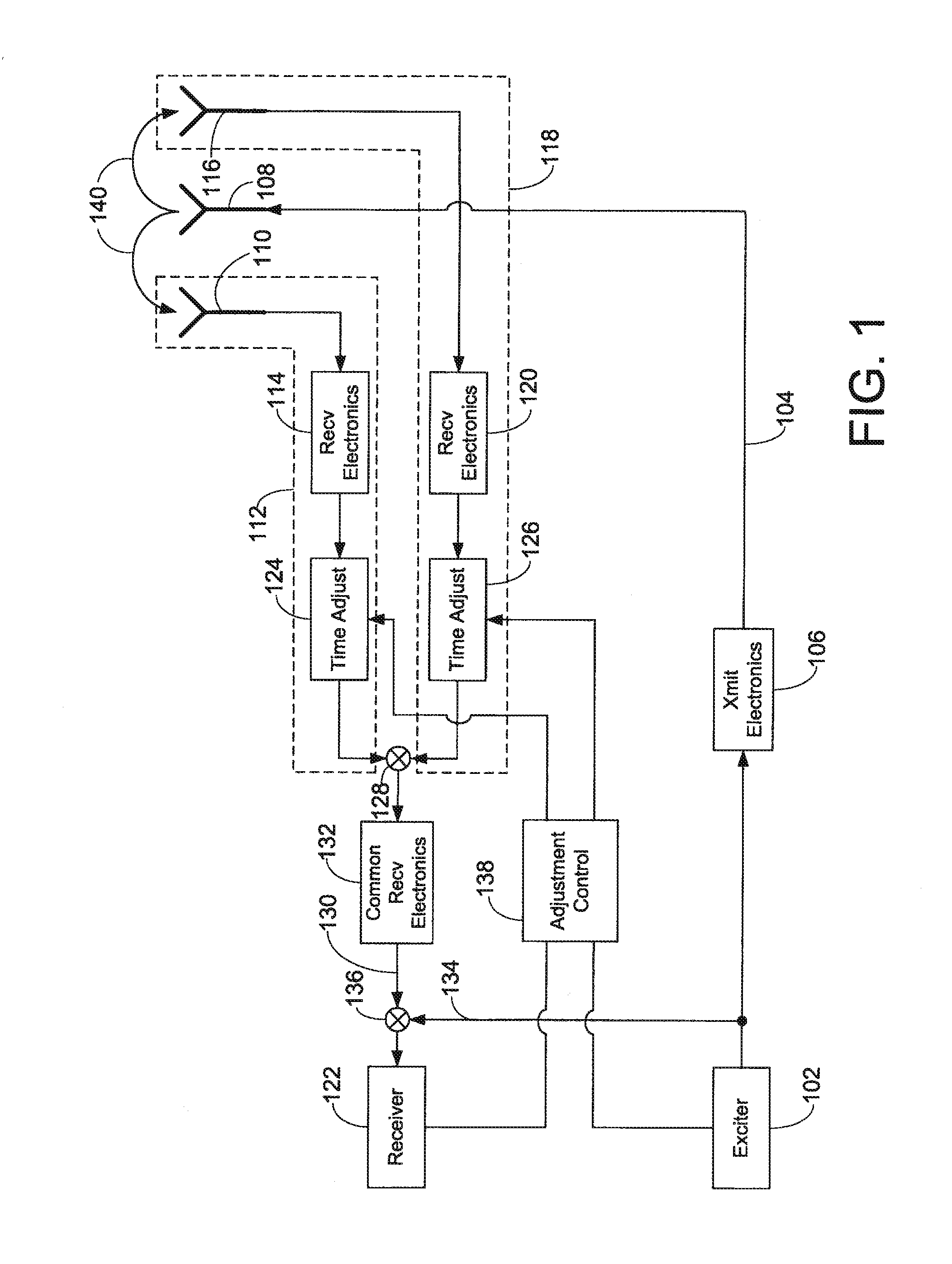
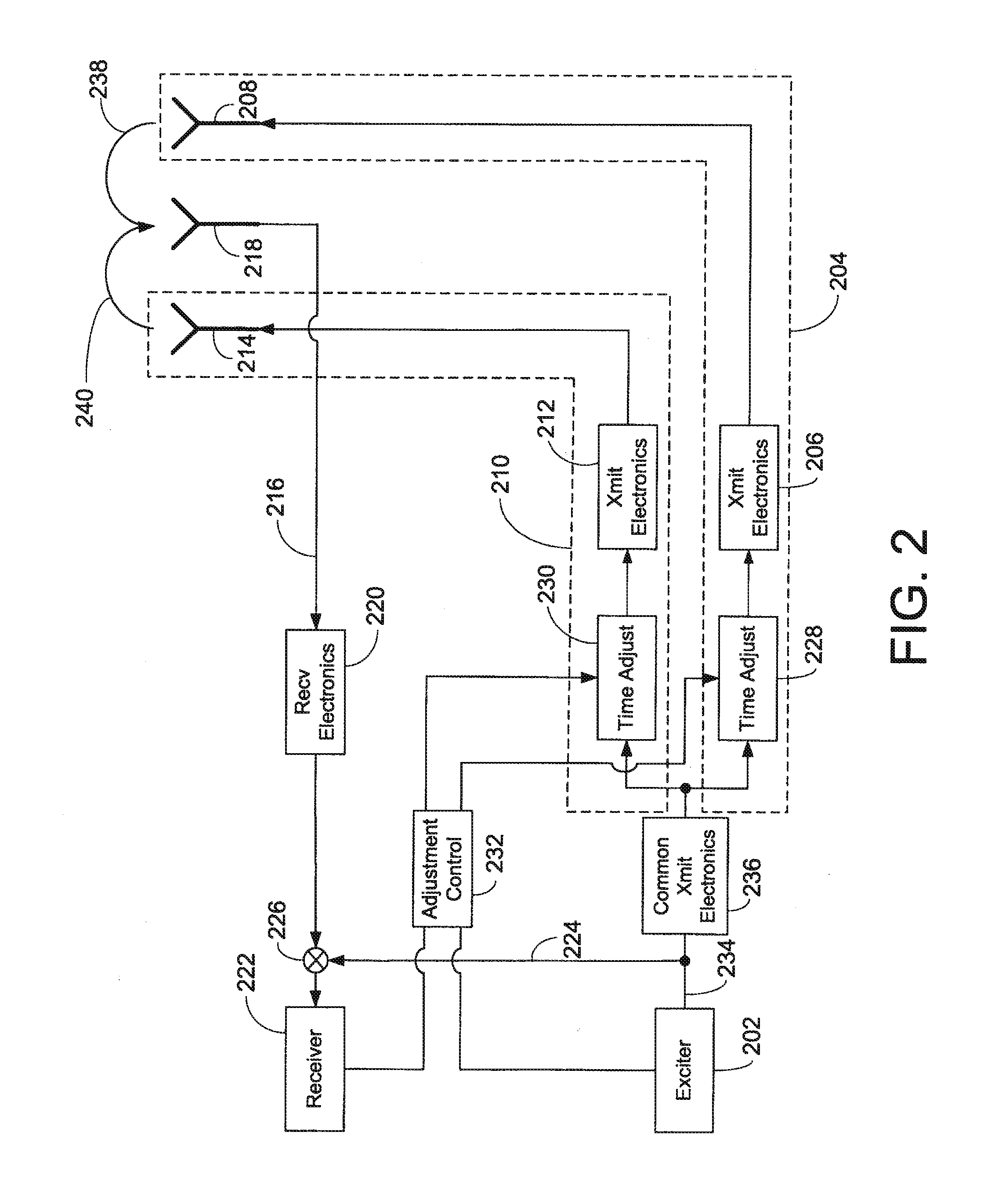
Method and system for propagation time measurement and calibration using mutual coupling in a radio frequency transmit/receive system
InactiveUS20110319034A1Improve bandwidth performanceMaximum energy transferWave based measurement systemsTransmission monitoringPropagation timeCoupling
A method and system use the mutual coupling property of multiple antenna elements for measuring differences in propagation time among various signal paths involving antenna elements in a radio frequency transmit / receive system. The method and system alleviate the need for external test equipment by using the same hardware used in standard operation of the transmit / receive system for performing propagation time measurement through the generation, mutual coupling, and acquisition of a specially selected reference signal. In an embodiment involving calibration of various signal paths to realize matched propagation times, the signal energy returned through these various paths during standard system operation arrives for acquisition more closely coincident in time, increasing the instantaneous bandwidth of the system.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method and wideband antenna system to minimise the influence of interference sources
ActiveUS20120115429A1Maximizing processing gainModulated-carrier systemsPolarisation/directional diversitySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Interference ratio
A method to minimize influence of interference sources by control of a signal to noise / interference ratio of a wideband antenna system connected to an electronic system. The wideband antenna system includes at least one array of at least two antenna elements / sub arrays. The signal to noise / interference ratio control includes establishing of cancellation directions for interfering frequencies in the antenna pattern in the direction of interference sources. The wideband antenna system is operational over a system bandwidth and operates with an instantaneous bandwidth. Estimation of interference source parameters is performed in an evaluation process. A wideband antenna system implementing the method.
Owner:SAAB AB
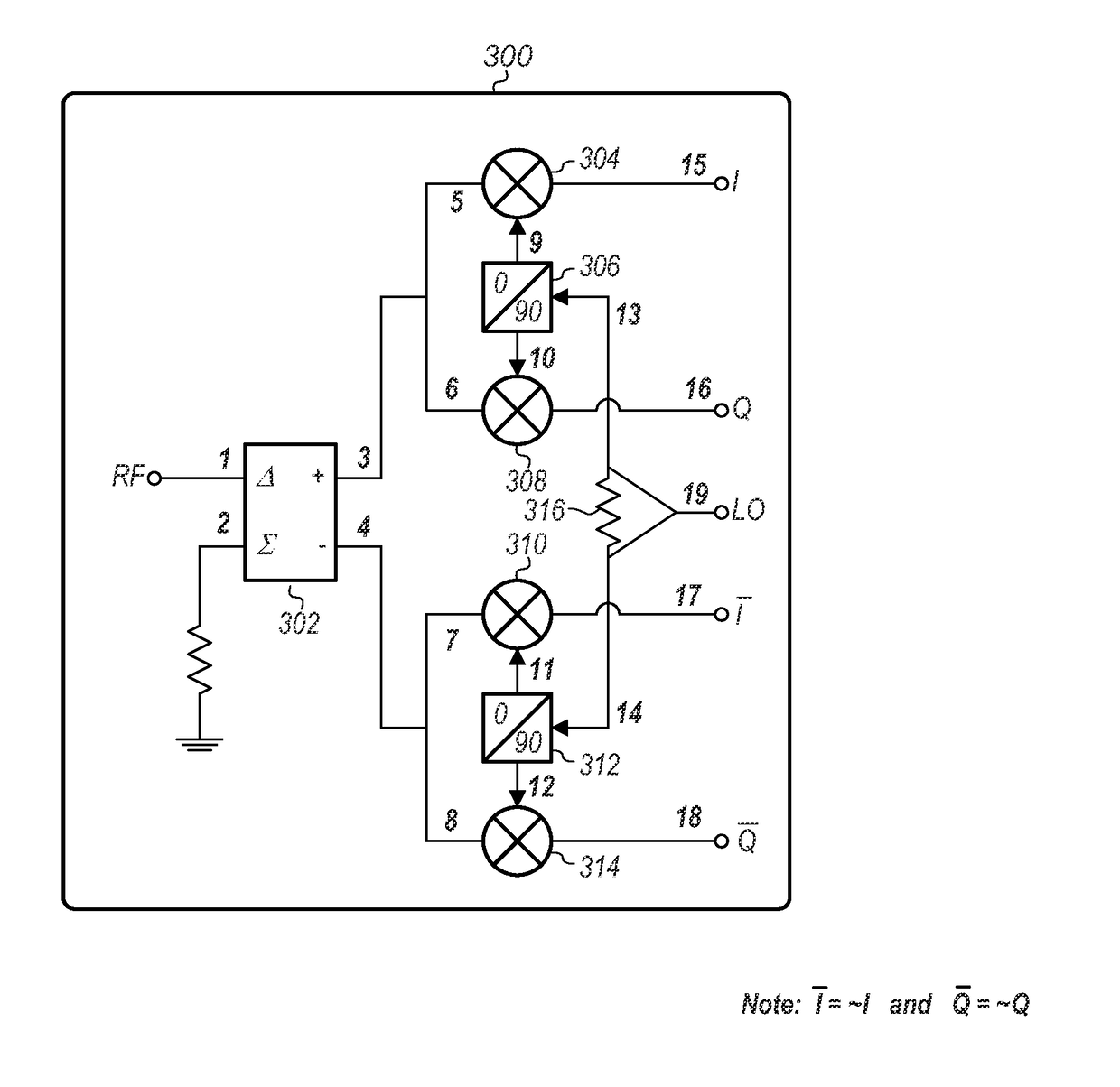
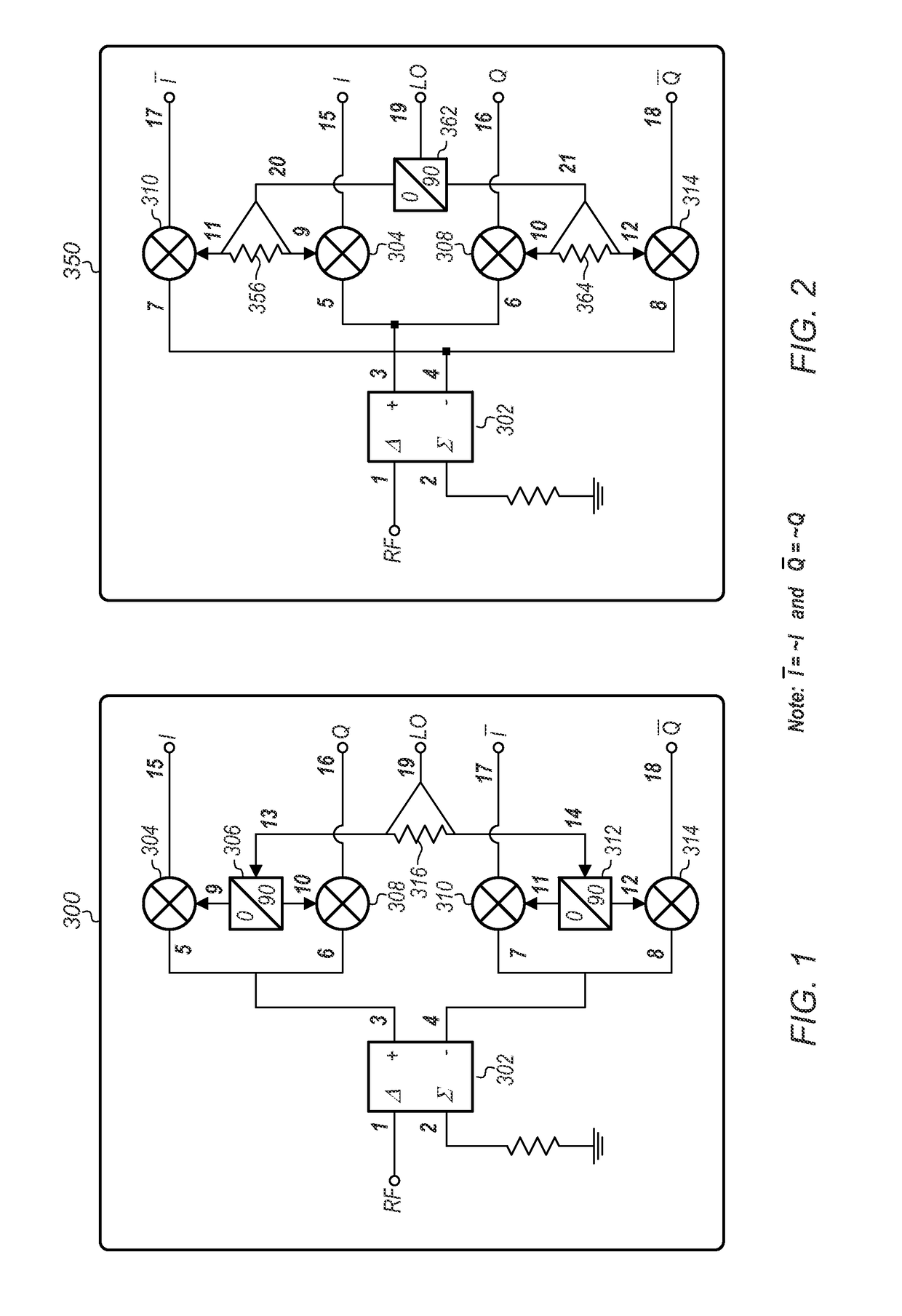
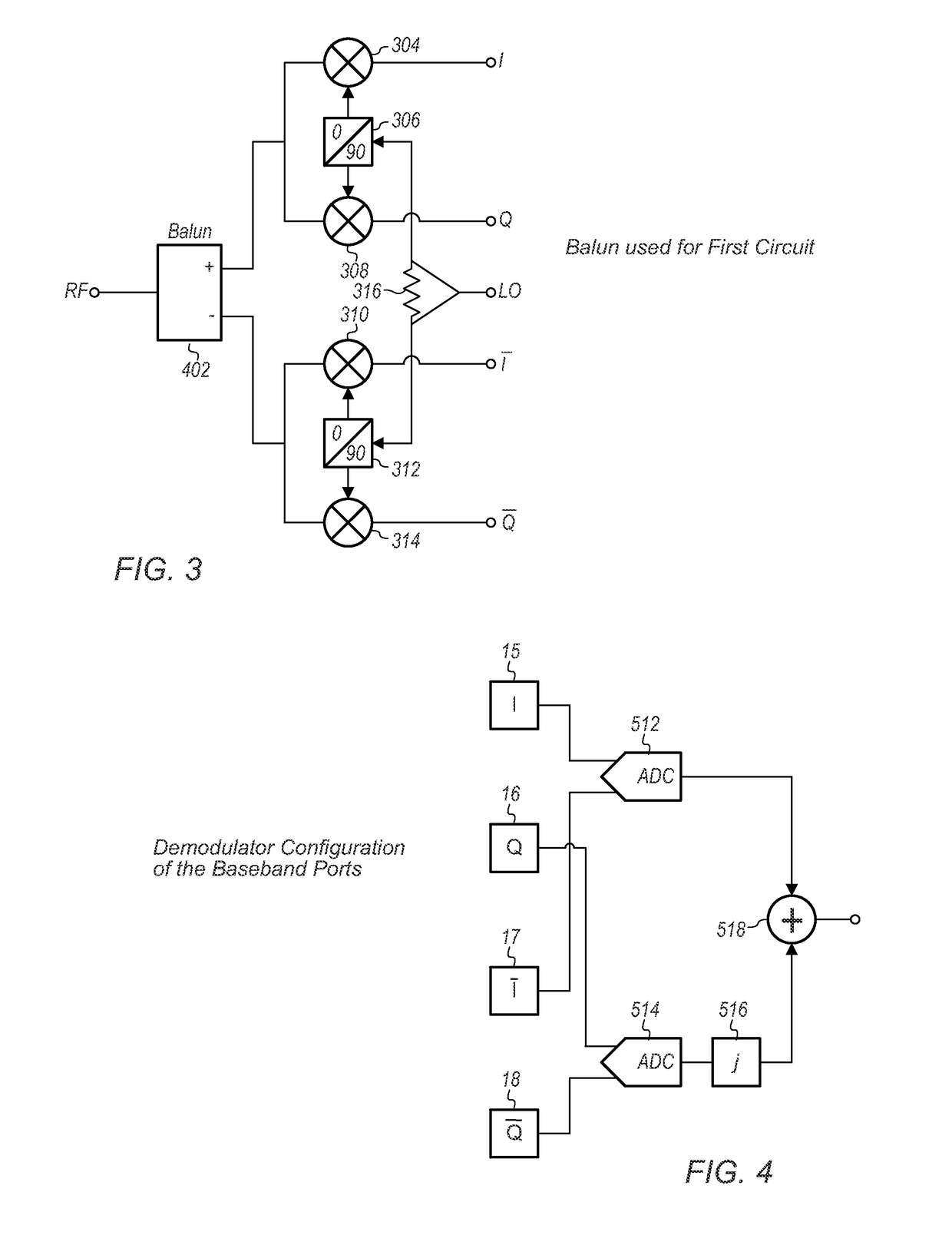
I/Q modulator and demodulator with wide instantaneous bandwidth and high local-oscillator-port-to-radio-frequency-port isolation
ActiveUS9621387B1Wide instantaneous bandwidthFirmly connectedModulation transferencePhase-modulated carrier systemsFrequency changerQuadrature modulator
An improved quadrature modulator / demodulator (IQMD) may use two-phase quadrature local oscillator (LO) signal generation for generating 0° and 90° LO signals, and an anti-phase combiner / divider (at 0° and 180°) on the RF (radio frequency) port. The IQMD may include mixers (which may be double-balanced passive mixers) that function as downconverters when a signal is incident at their radio frequency (RF) ports, and function as upconverters when signals are incident on their intermediate frequency (IF) ports. Accordingly, the IQMD may function as an I / Q modulator by connecting digital-to-analog converters (DAC) to the differential I and Q ports, and / or it may also function as an I / Q demodulator by connecting analog-to-digital converters (ADC) to the differential I and Q ports.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
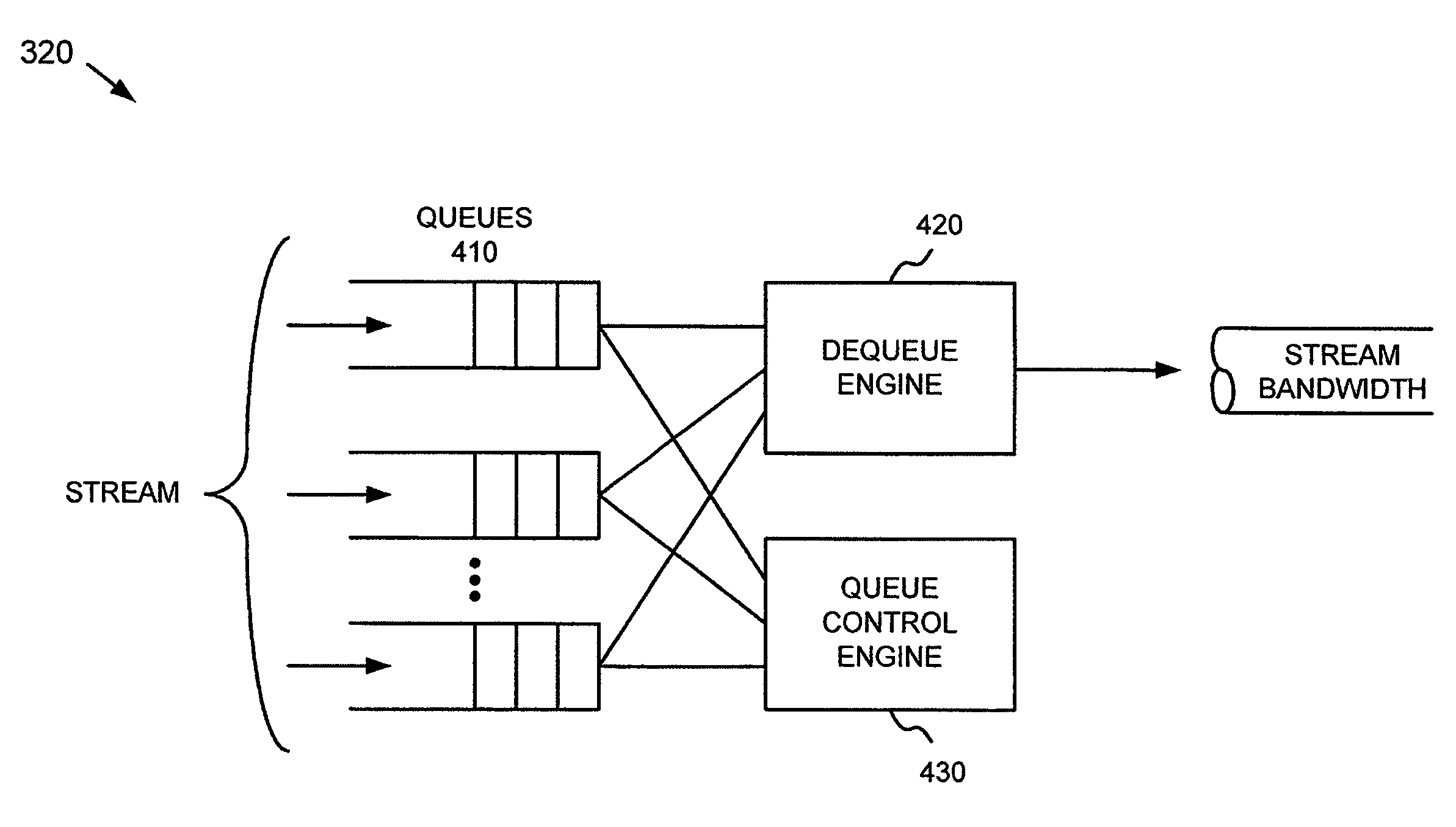
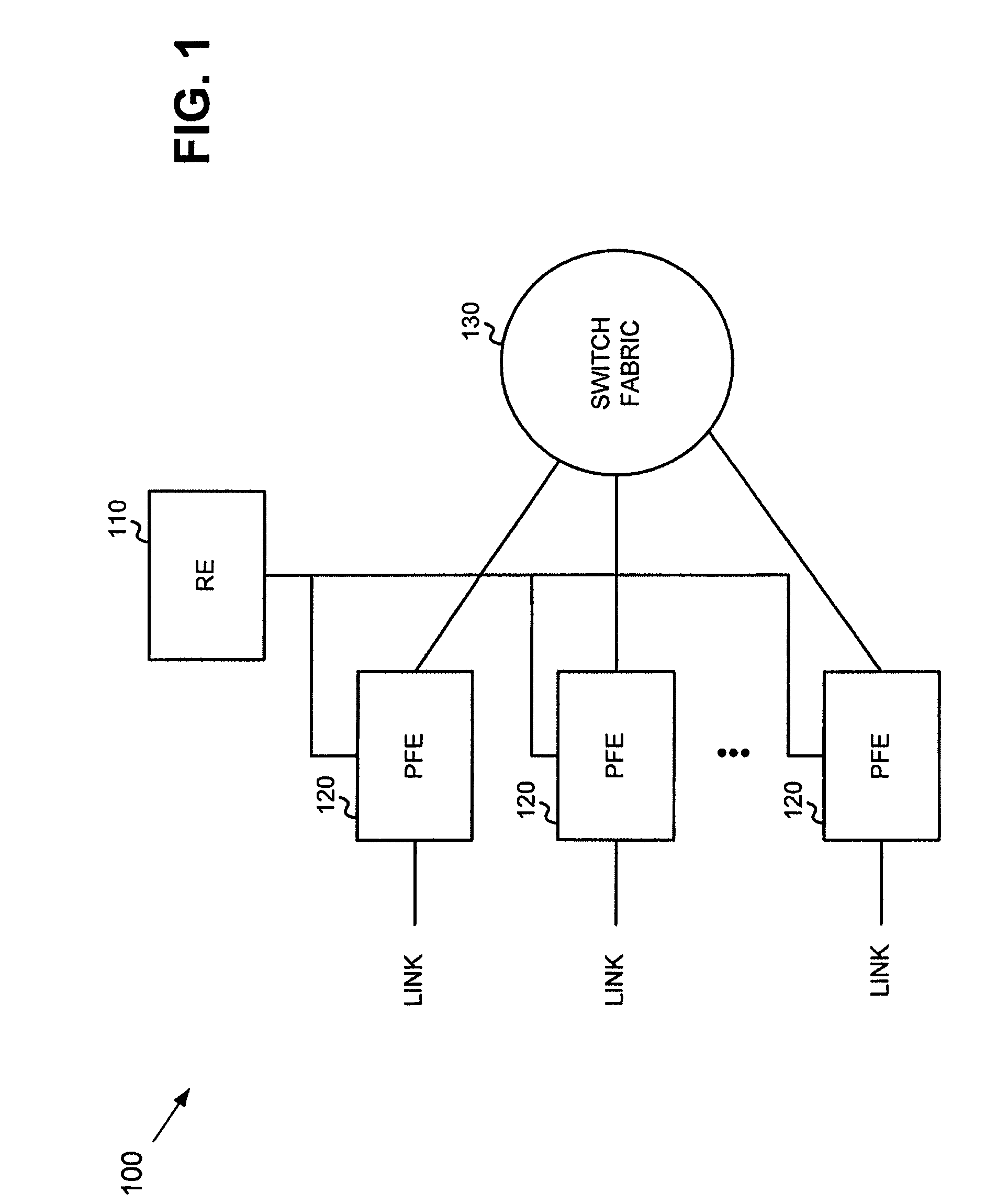
Systems and methods for determining the bandwidth used by a queue
InactiveUS7711005B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDistributed computingInstantaneous bandwidth
A system determines bandwidth use by queues in a network device. To do this, the system determines an instantaneous amount of bandwidth used by each of the queues and an average amount of bandwidth used by each of the queues. The system then identifies bandwidth use by each of the queues based on the instantaneous bandwidth used and the average bandwidth used by each of the queues.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
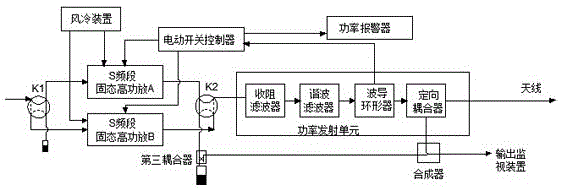
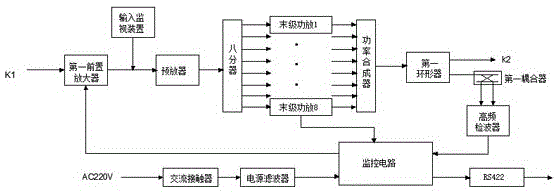
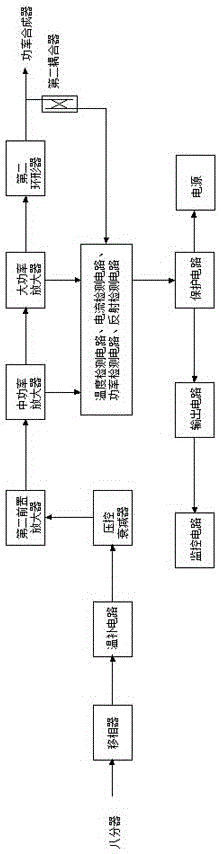
S-band continuous-wave solid-state high power amplification device
ActiveCN105119576AImprove accuracyImprove Phase ConsistencyAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationPower amplifiersFailure rateHigh power amplifier
The invention provides an S-band continuous-wave solid-state high power amplification device. The S-band continuous-wave solid-state high power amplification device consists of an S-band solid-state high power amplifier A, an S-band solid-state high power amplifier B, a switching unit and a power transmitting unit, wherein the switching unit comprises a coaxial electric switch, a waveguide electric switch and an electric switch controller; the input ends of the S-band solid-state high power amplifier A and the S-band solid-state high power amplifier B are connected with the coaxial electric switch respectively; the output ends of the S-band solid-state high power amplifier A and the S-band solid-state high power amplifier B are connected with one end of the waveguide electric switch respectively; the other end of the waveguide electric switch is connected with the power transmitting unit; the input end of the electric switch controller is connected with the output end of the power transmitting unit; and the output end of the electric switch controller is connected with the S-band solid-state high power amplifier A and the S-band solid-state high power amplifier B respectively. The S-band continuous-wave solid-state high power amplification device has the advantages of large instantaneous bandwidth, no tuning requirements, high efficiency, high reliability, easiness in operation, long service lifetime, low failure rate and the like.
Owner:河南方达空间信息技术有限公司
Method and device for quality management in communication networks
ActiveUS7489631B2Easy to manageMaximize qualityError preventionTransmission systemsSignal qualityEngineering
A method and apparatus are provided for managing varying traffic loads in a packetized communication network. At a predefined location, the instantaneous demand for bandwidth required for delivering traffic via a plurality of active channels is compared with the available bandwidth. When the available bandwidth at that pre-defined location is less than the bandwidth required to convey the signals carried along all these active channels, a rate adjusting mechanism is applied to at least one of the active channels, while repeating this check periodically. The rate adjusting mechanism is applied on packetized signals arriving along at least one group of active channels so as to ensure that: a substantially equalized signal quality is maintained for signals delivered via all of the active channels belonging to certain one or more groups of active channels, and the instantaneous overall bandwidth required to convey all the signals arriving at the pre-defined location, is not more than the available instantaneous bandwidth.
Owner:DIALOGIC NETWORKS (ISRAEL) LTD
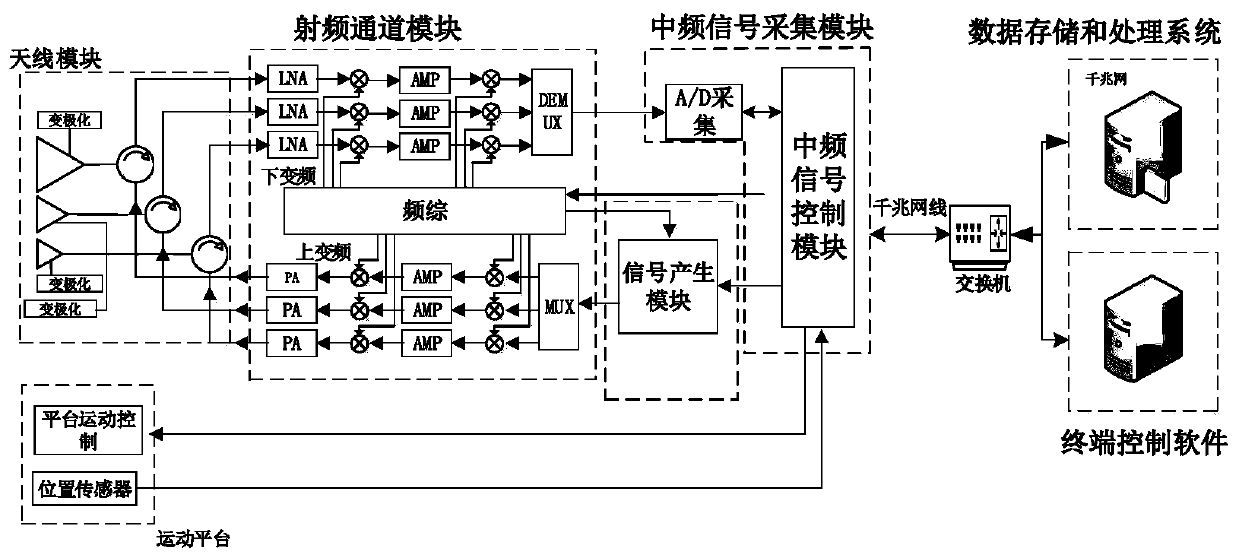
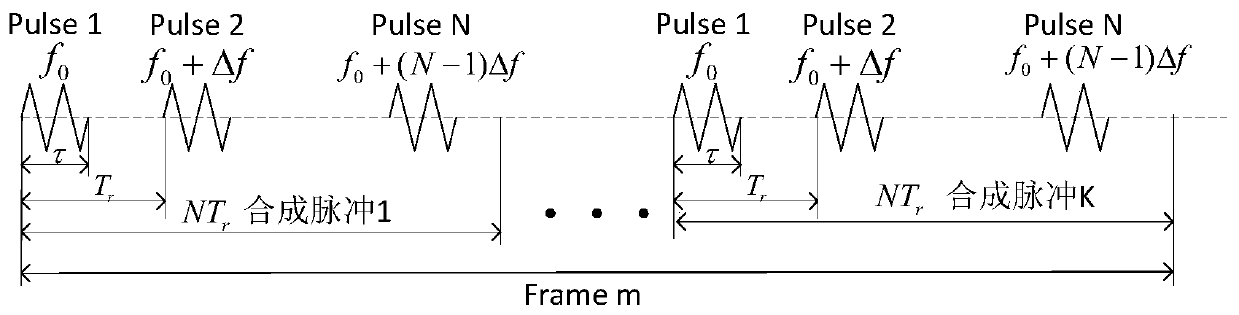
Stepping frequency synthetic aperture radar-based near-distance RCS measurement electronic system
ActiveCN110133650AReduce design requirementsReduce design costRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingRadar systems
The invention discloses a stepping frequency synthetic aperture radar-based near-distance RCS measurement electronic system, and relates to a frequency stepping technology, an SAR image processing andan FPGA digital signal processing. Compared with a traditional method such as far-field measurement and compact-field measurement, the radar RCS near-field imaging method has the advantages that theacquired information quantity is greatly increased, and richer target scattering characteristic distribution can be obtained with regard to near-distance measurement of a target relative to a radar system. Aiming at defect of a background technology, the radar system employs a stepping frequency narrow pulse signal to transmit and receive a shared antenna, the distance blind region is small, the measurable range is large, and the problem of isolation of a continuous wave mechanism is prevented; the stepping frequency signal belongs to one of pulse signals; in the radar employing the frequencystepping signal, large bandwidth at an arbitrary frequency can be flexibly acquired by carrier frequency jump of each pulse in a coherent pulse string, and an effect of high distance resolution is obtained by IDFT processing on pulse echo; and meanwhile, the index requirements of instantaneous bandwidth processing of a digital signal and digital processing hardware of an echo signal of a receivingare reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com