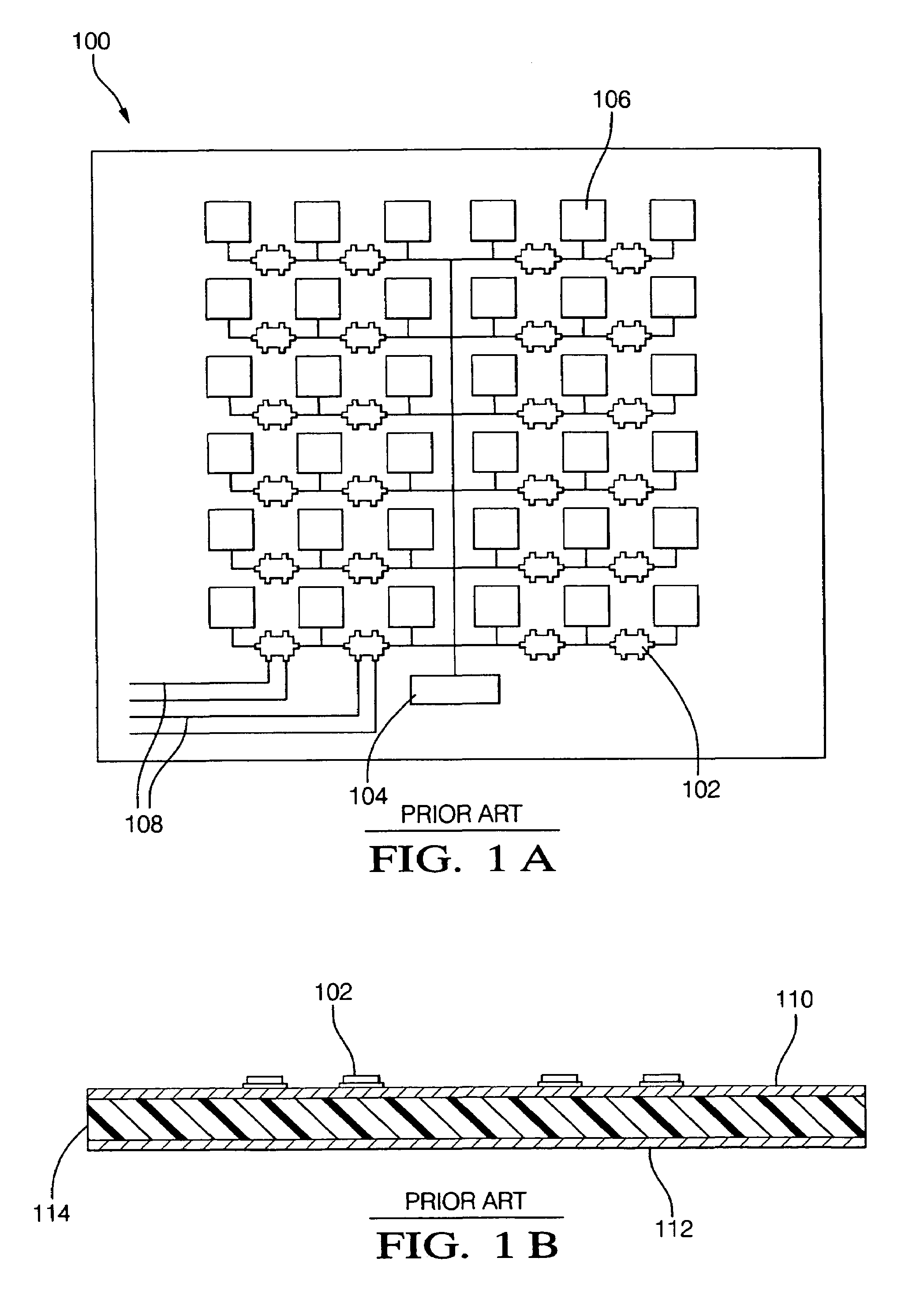
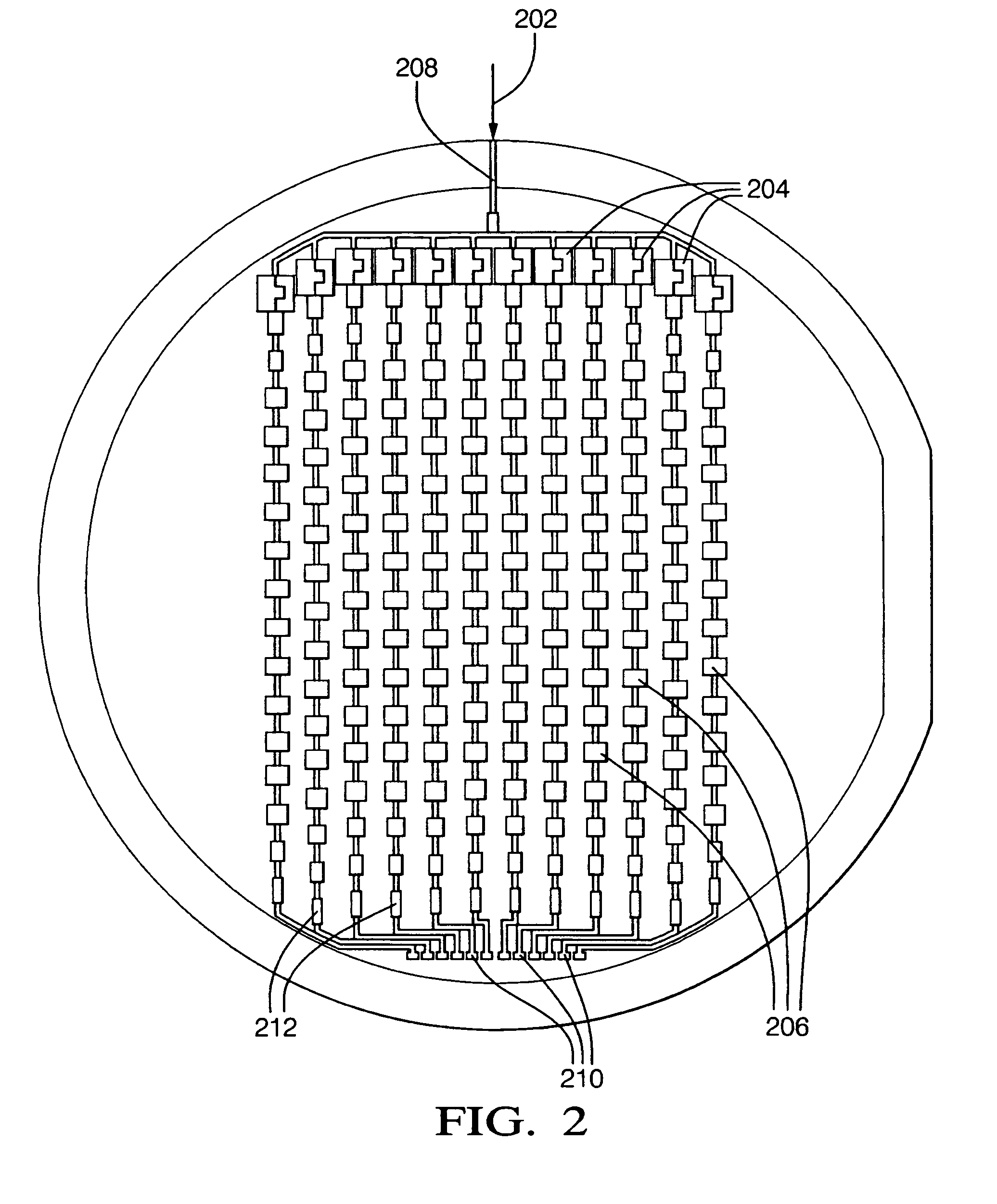
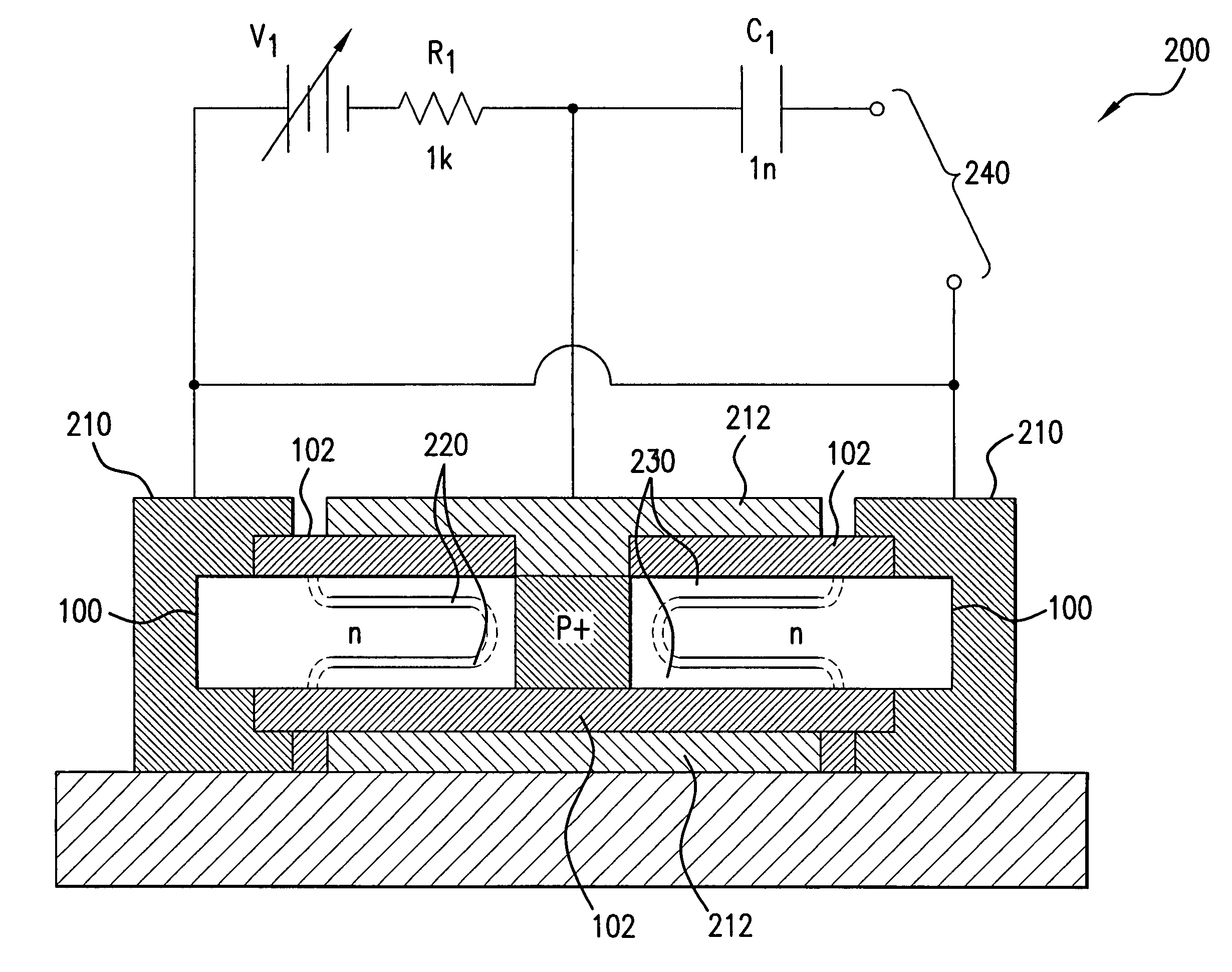
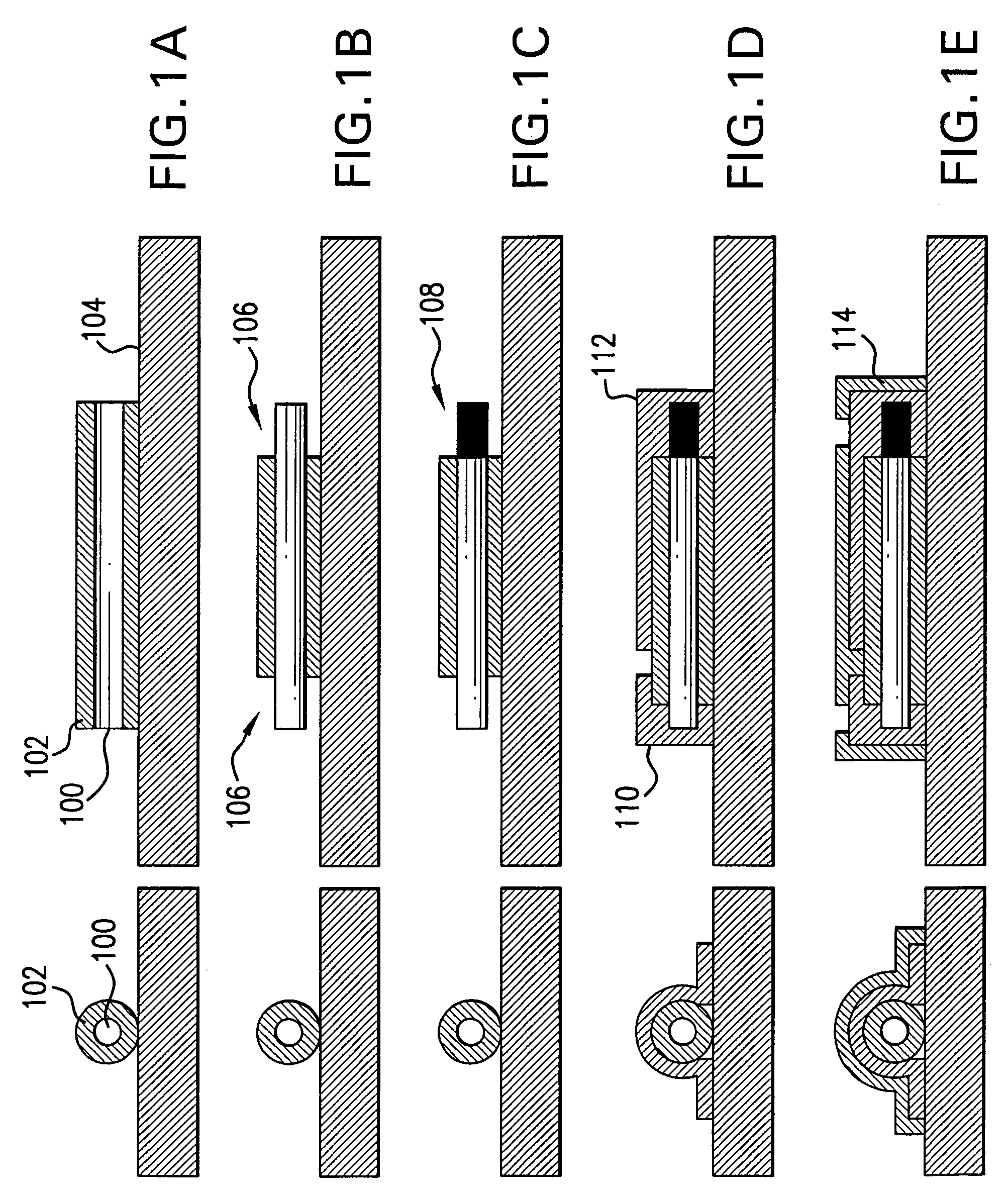
Patents
Literature
1150 results about "Varicap" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
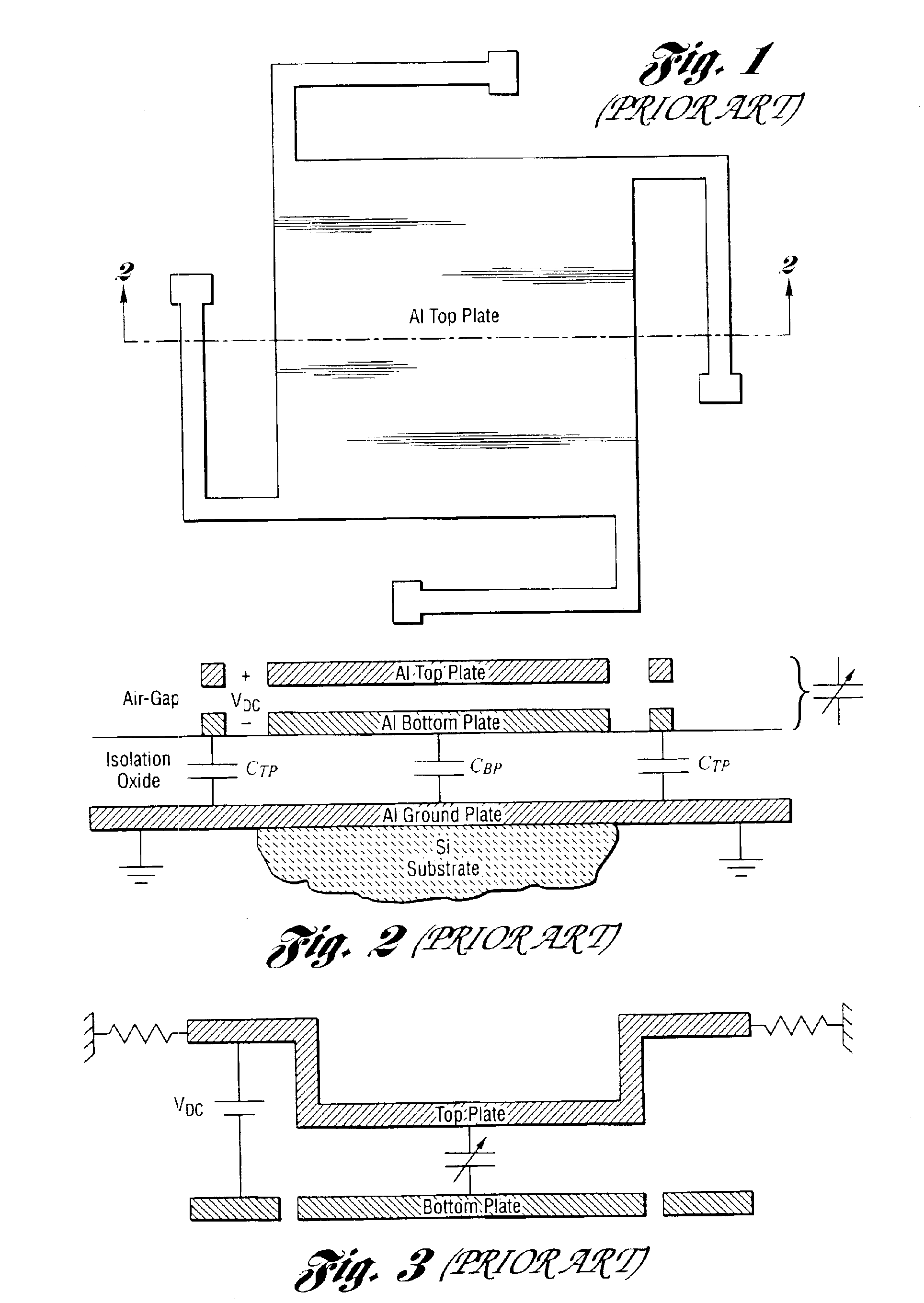
In electronics, a varicap diode, varactor diode, variable capacitance diode, variable reactance diode or tuning diode is a type of diode designed to exploit the voltage-dependent capacitance of a reverse-biased p–n junction.
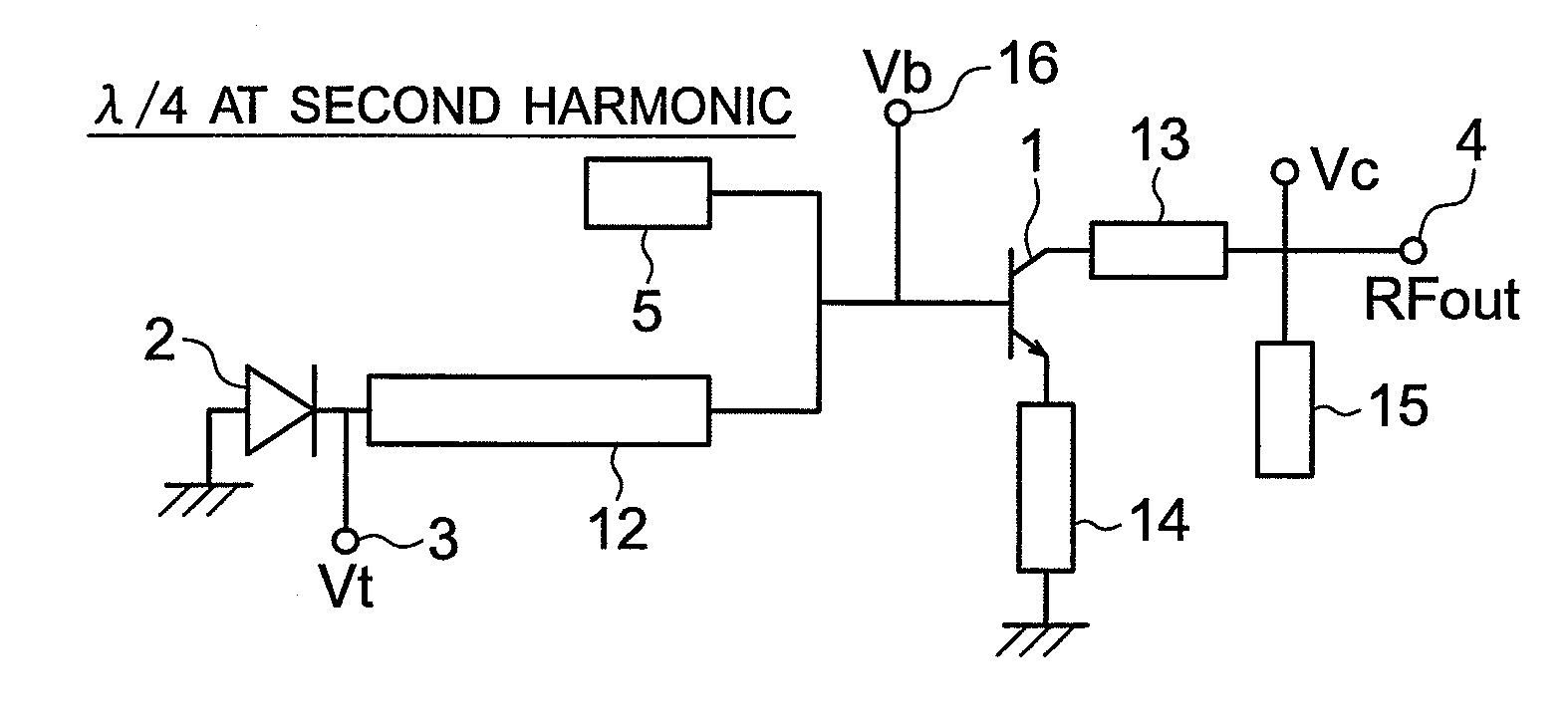
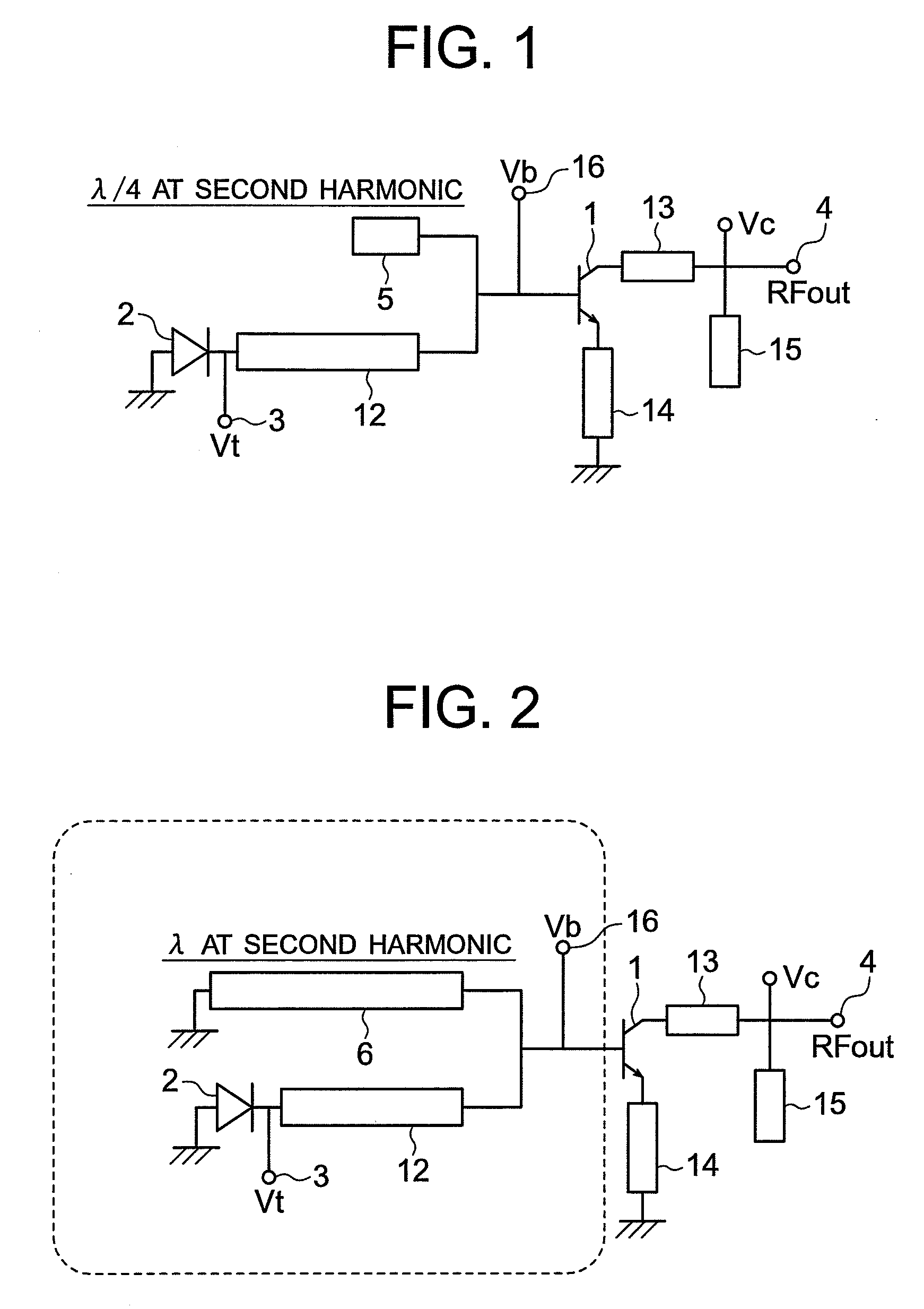
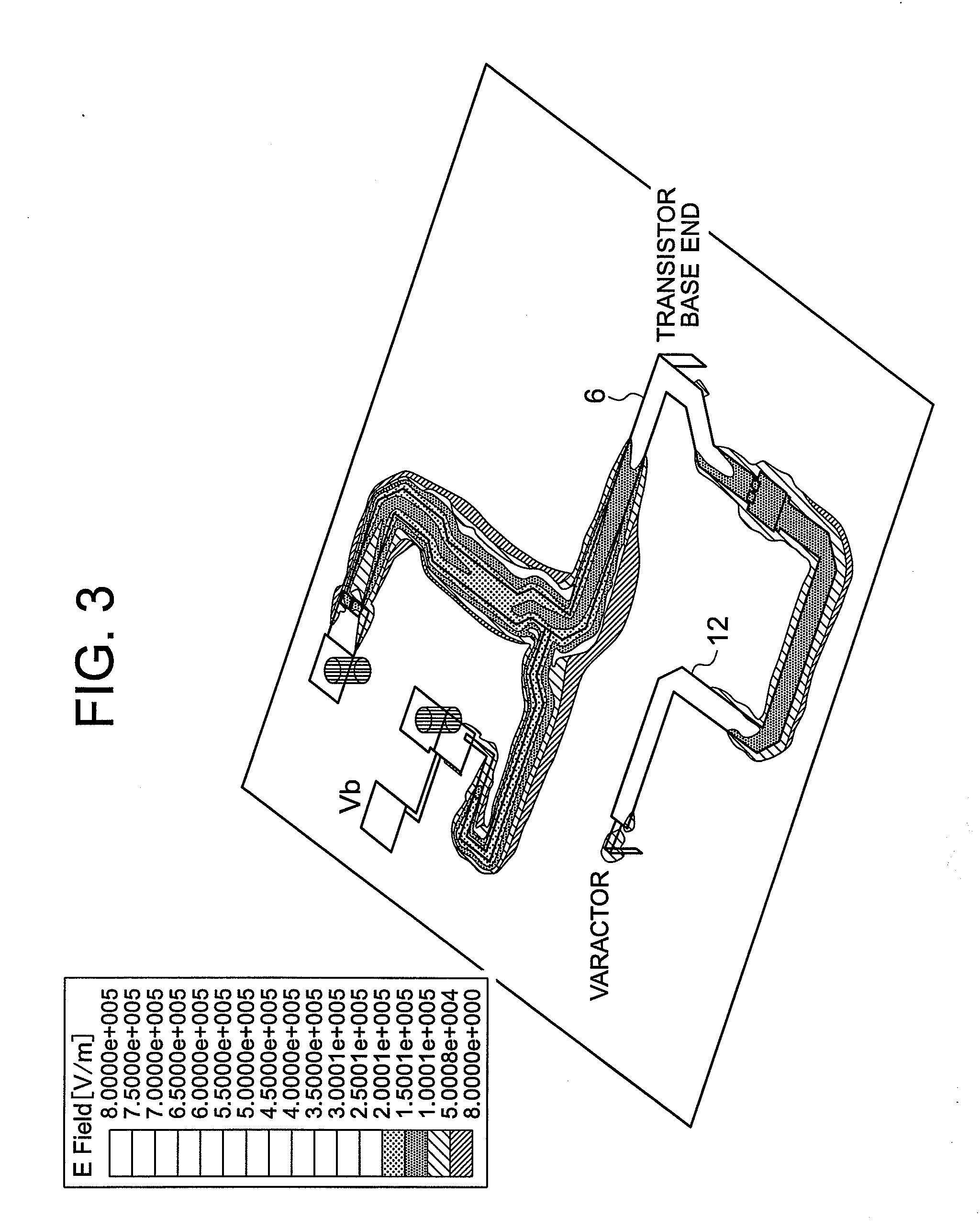
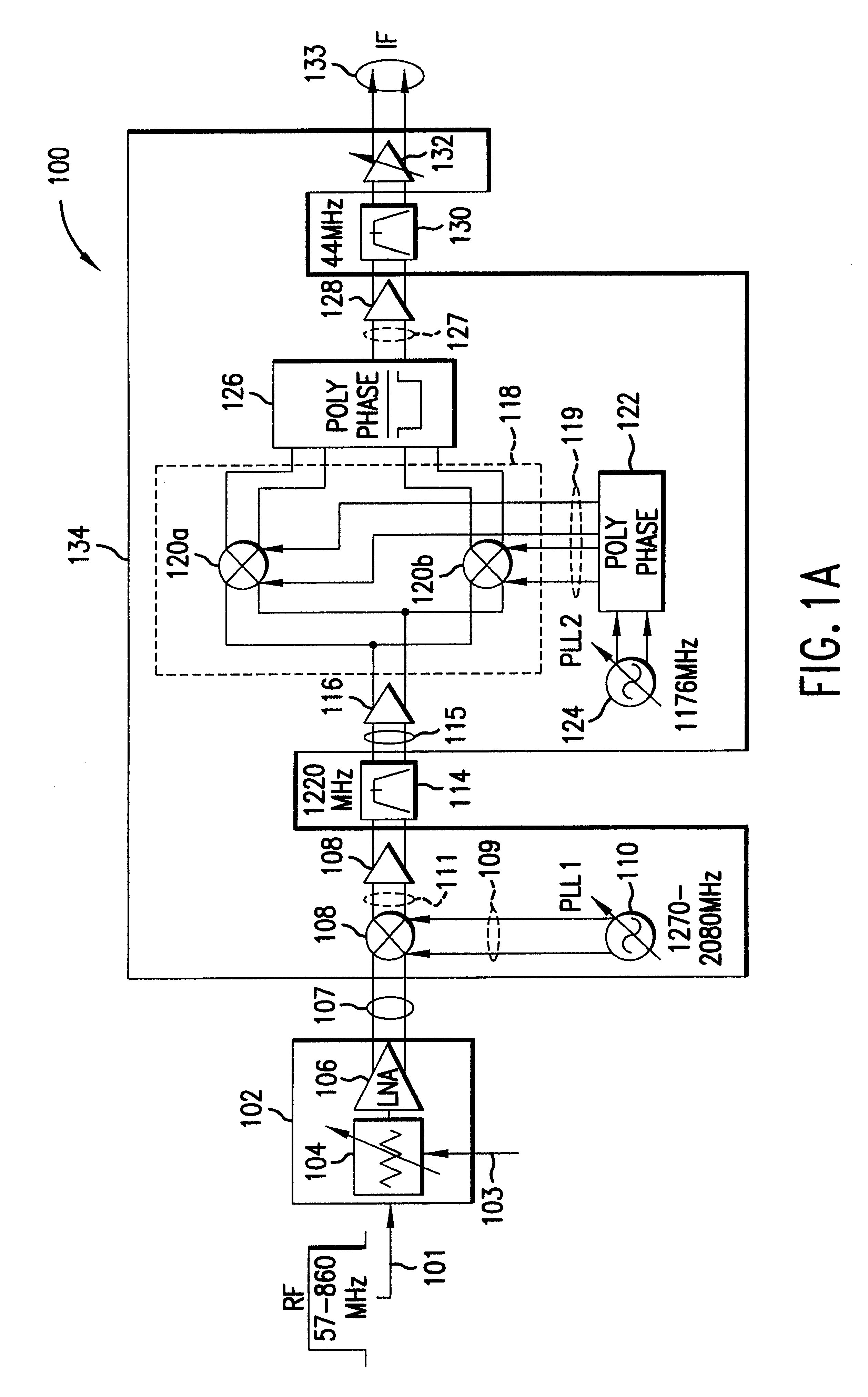
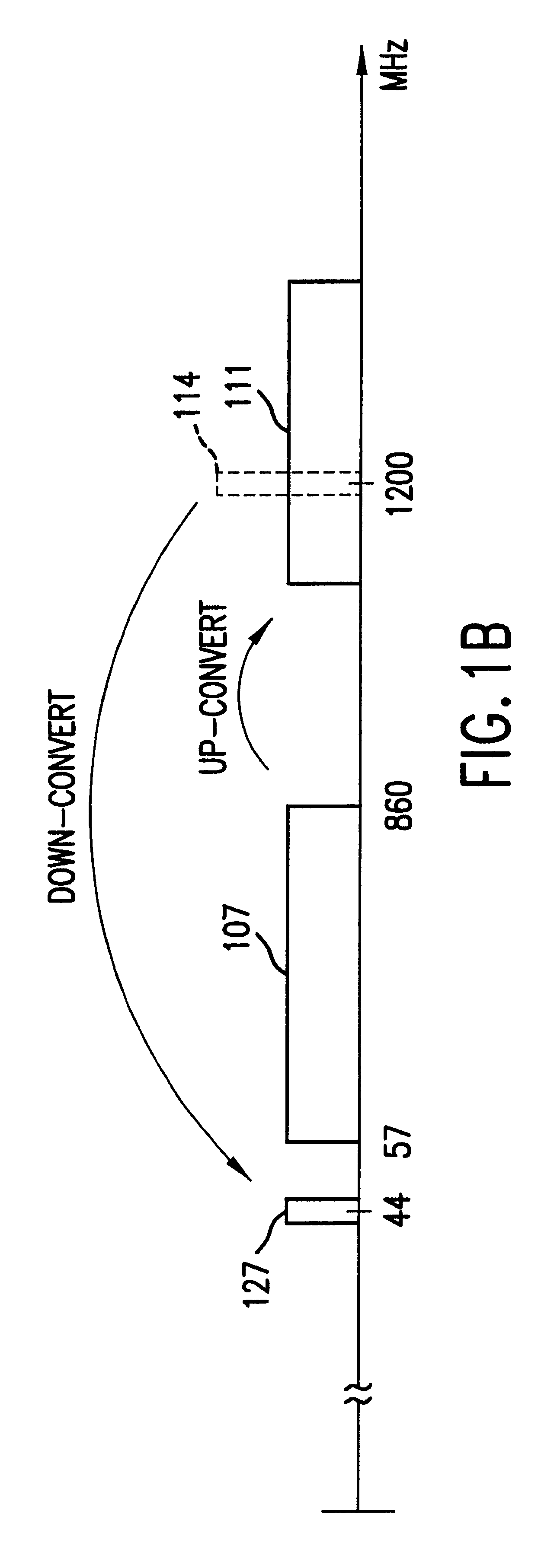
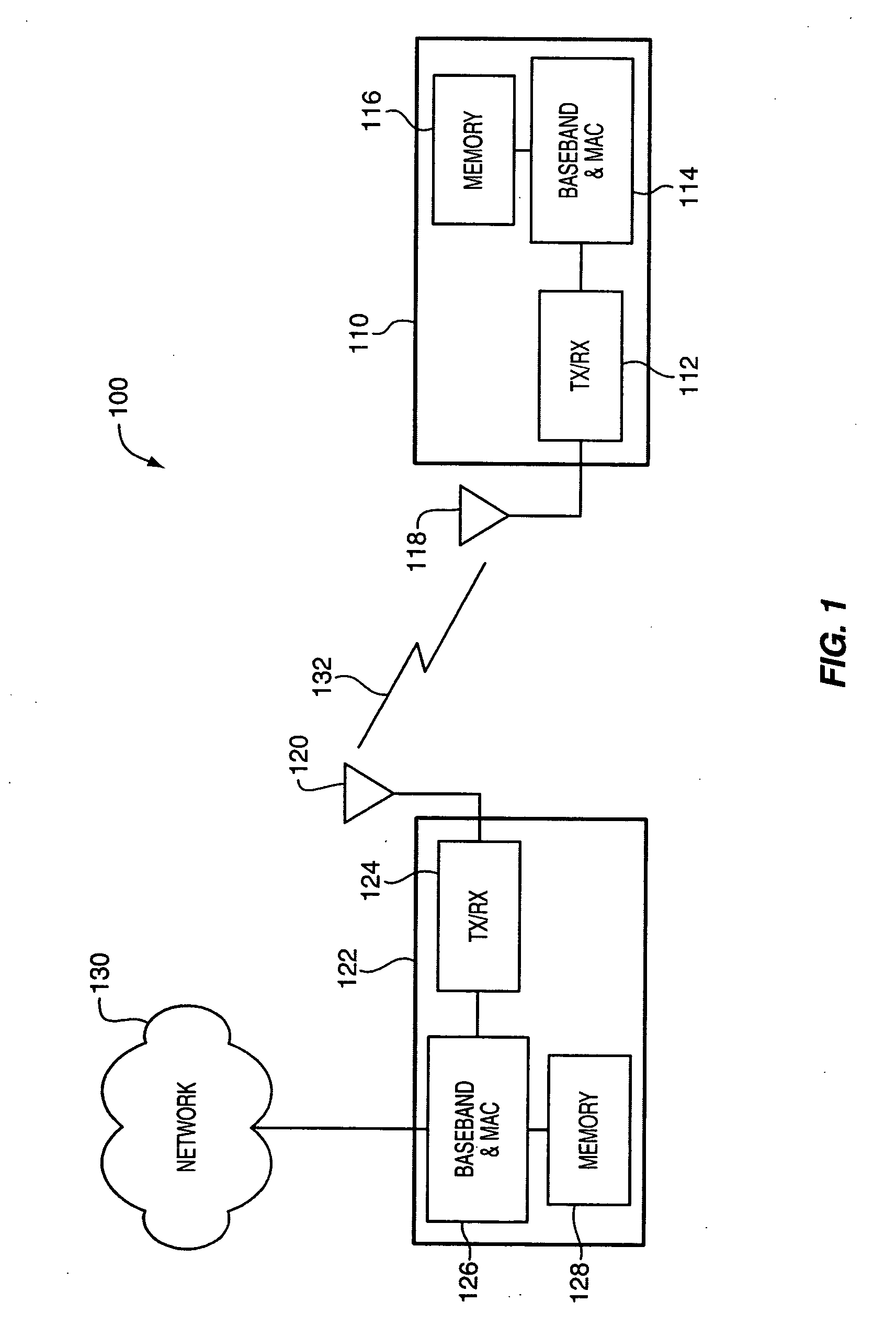
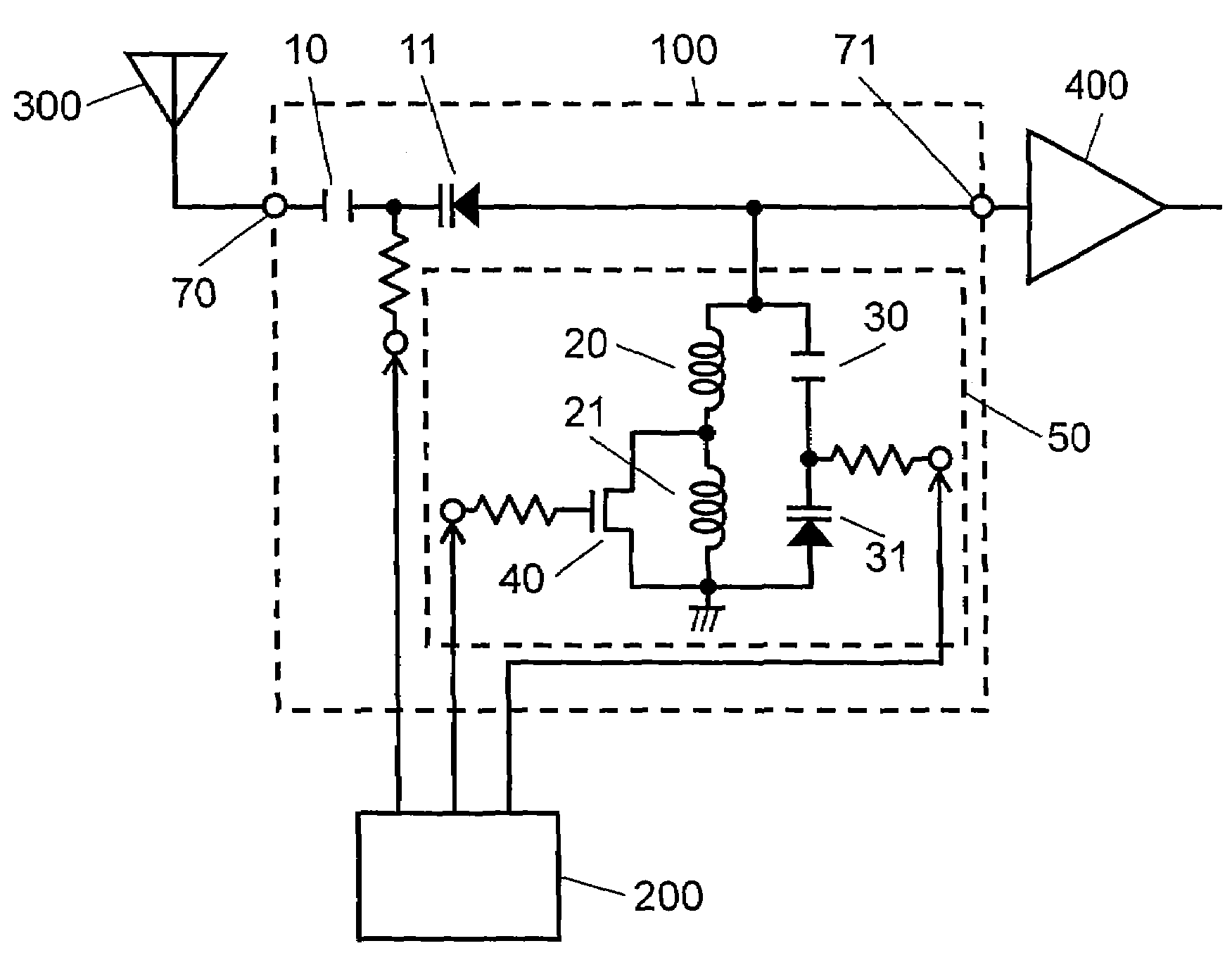
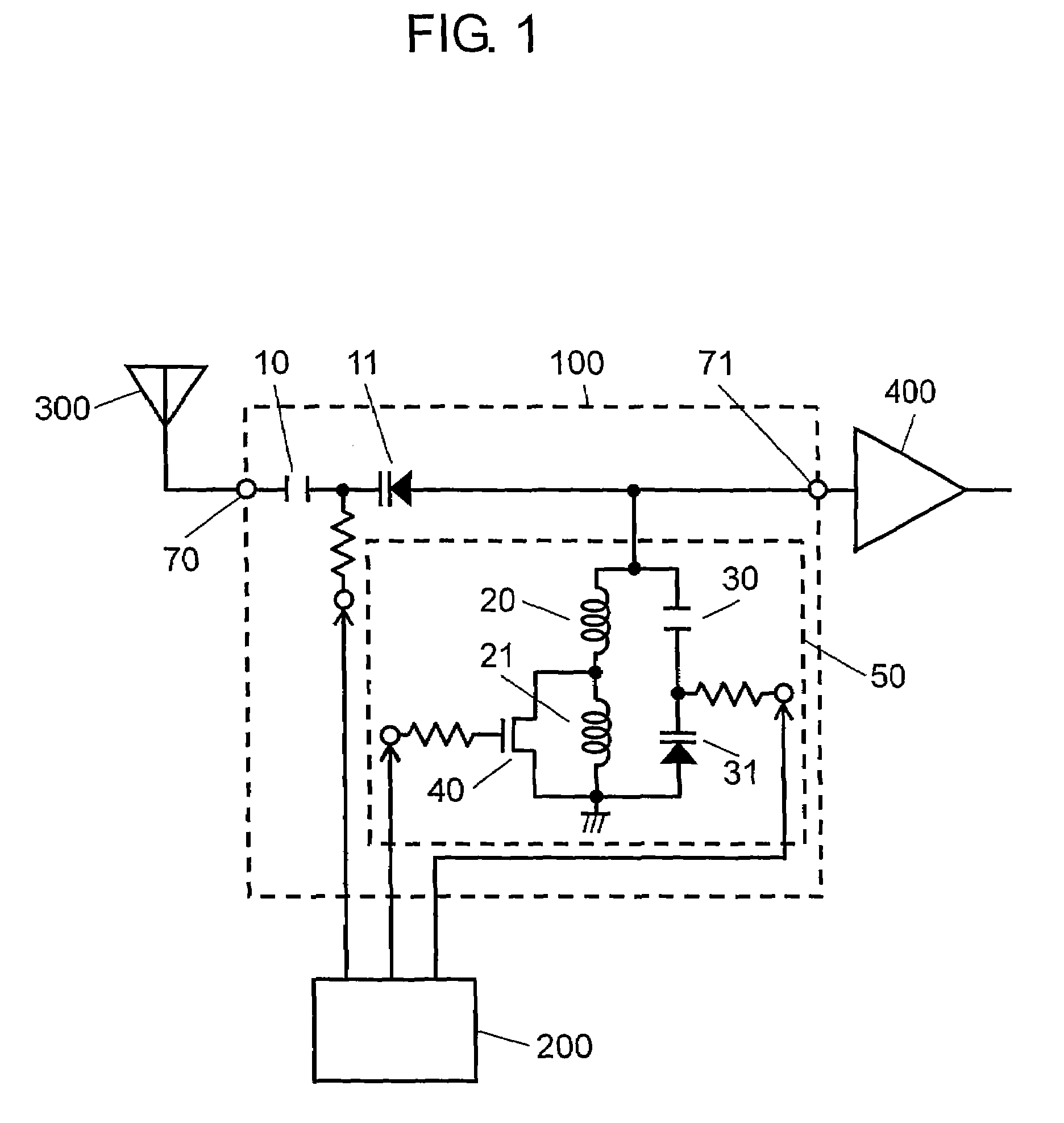
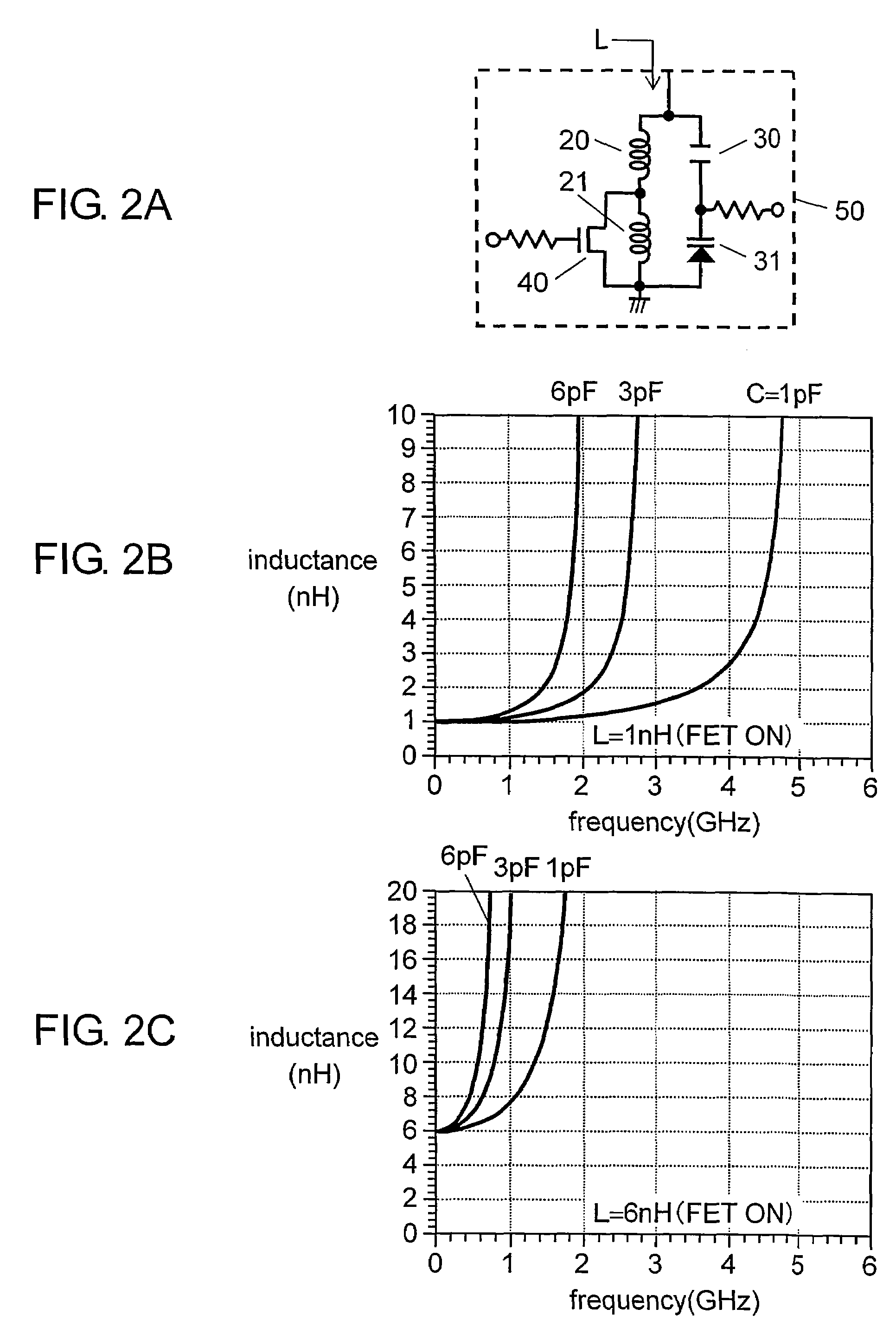
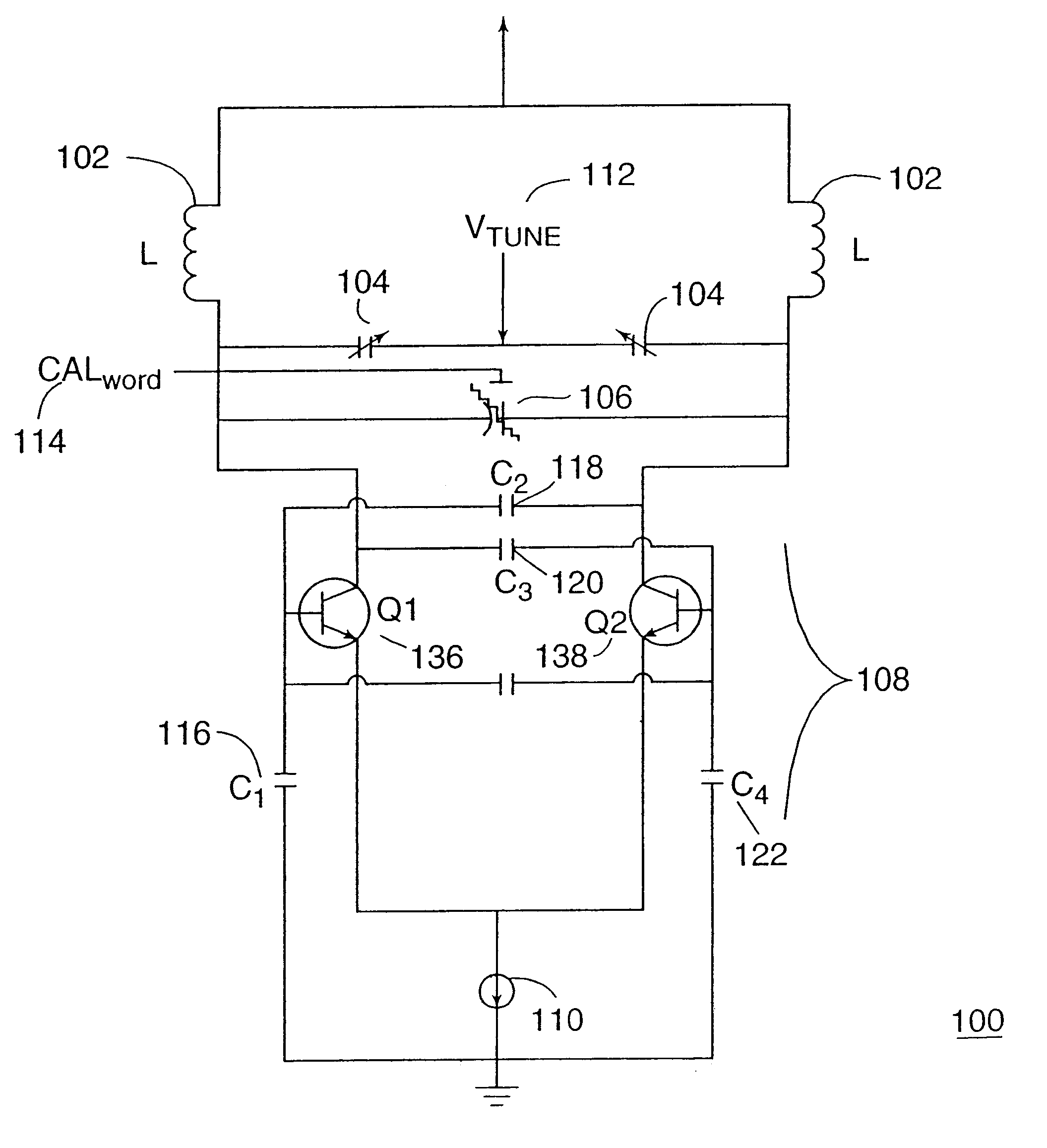
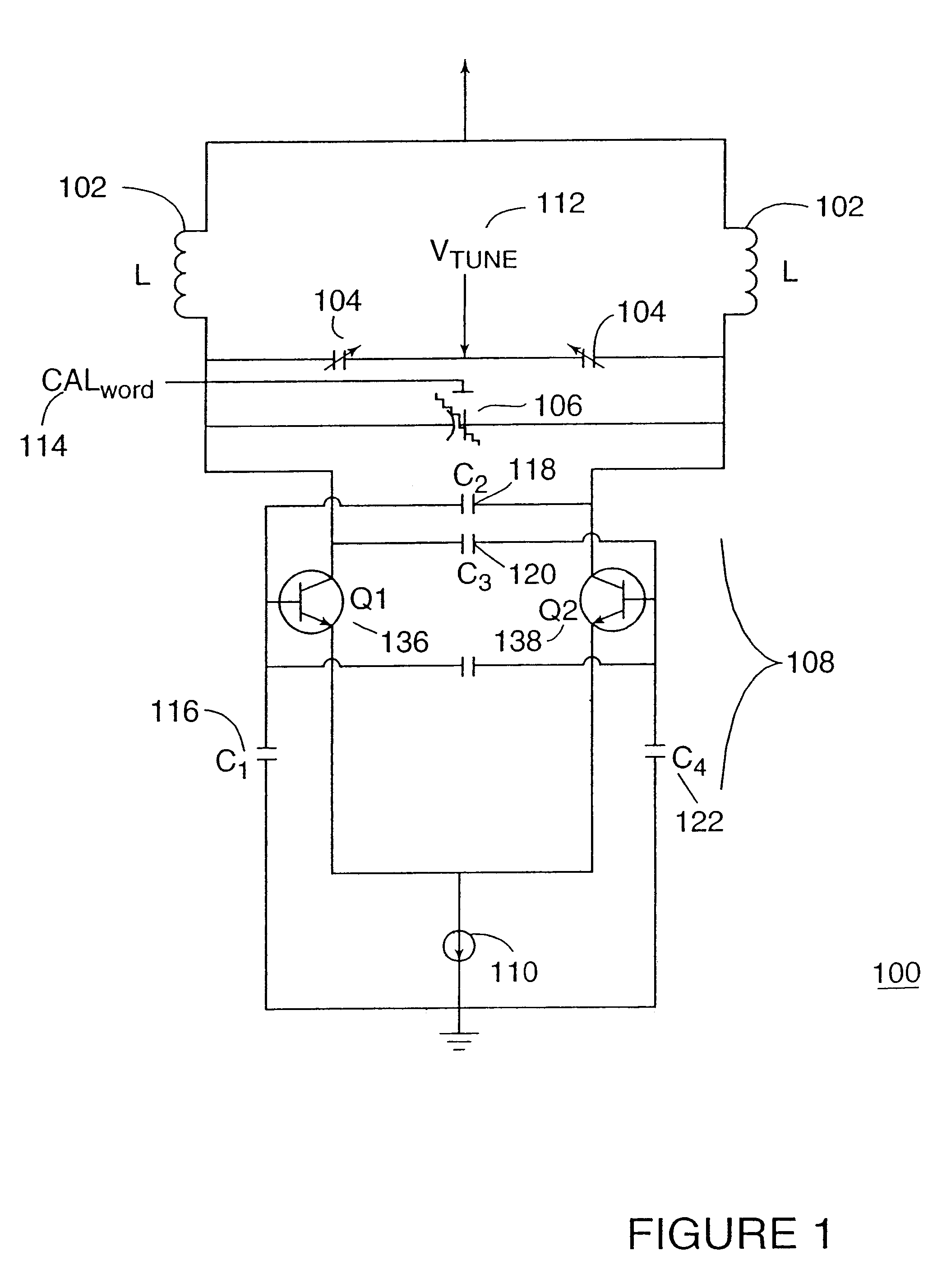
Voltage controlled oscillator, mmic, and high frequency wireless device
InactiveUS20100052799A1Low phase noise characteristicReduce noisePulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsPhase noiseHarmonic
A voltage controlled oscillator having low phase noise and including: a variable resonator including a varactor and a control voltage terminal; and an open-end stub connected in parallel to the variable resonator, the open-end stub having a length shorter than or equal to an odd multiple of one quarter of a wavelength of a harmonic signal plus one sixteenth of the wavelength of the harmonic signal, and longer than or equal to an odd multiple of one quarter of the wavelength of the harmonic signal minus one sixteenth of the wavelength of the harmonic signal. In this structure, a high Q value is realized for a fundamental wave frequency. Fluctuation in a control voltage due to a harmonic signal is controlled.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
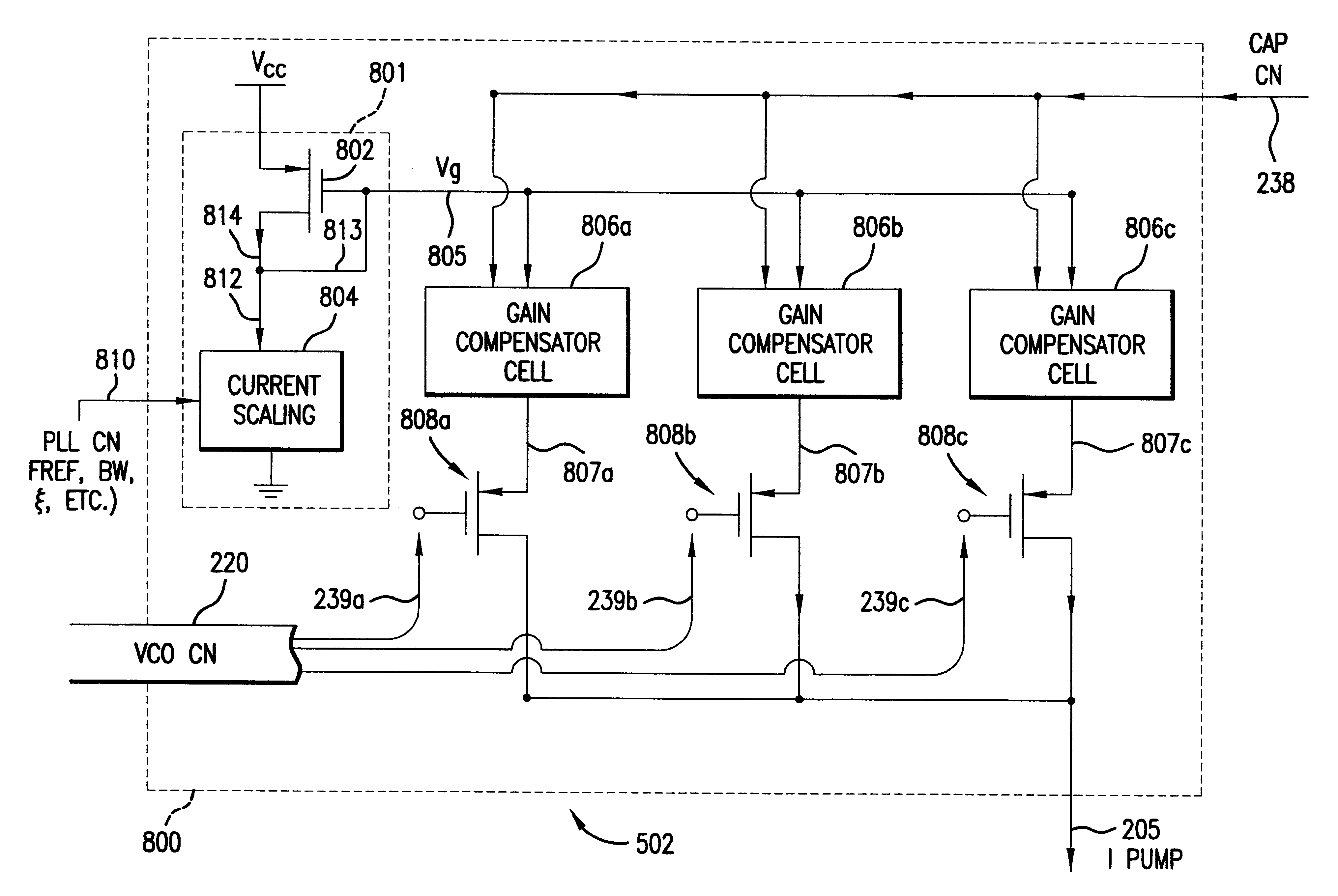
Apparatus and method for phase lock loop gain control using unit current sources
InactiveUS6583675B2Pulse automatic controlDiscontinuous tuning for band selectionFixed capacitorReference current
A gain compensator compensates for the gain variation of a varactor-tuned voltage tuned oscillator (VCO) in a phase lock loop (PLL). The VCO includes a parallel LC circuit having multiple fixed capacitors that can be switched-in or switched-out of the LC circuit according to a capacitor control signal to perform band-select tuning of the VCO. The gain compensator compensates for the variable VCO gain by generating a charge pump reference current that is based on the same capacitor control signal that controls the fixed capacitors in the LC circuit. The gain compensator generates the charge pump reference current by replicating a reference scale current using unit current sources. The number of times the reference scale current is replicated is based on the fixed capacitance that is switched-in to the LC circuit and therefore the frequency band of the PLL. The reference scale current is generated based on a PLL control that specifics certain PLL characteristics such as reference frequency, loop bandwidth, and loop damping. Therefore, the reference pump current can be efficiently optimized for changing PLL operating conditions, in addition to compensating for variable VCO gain.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
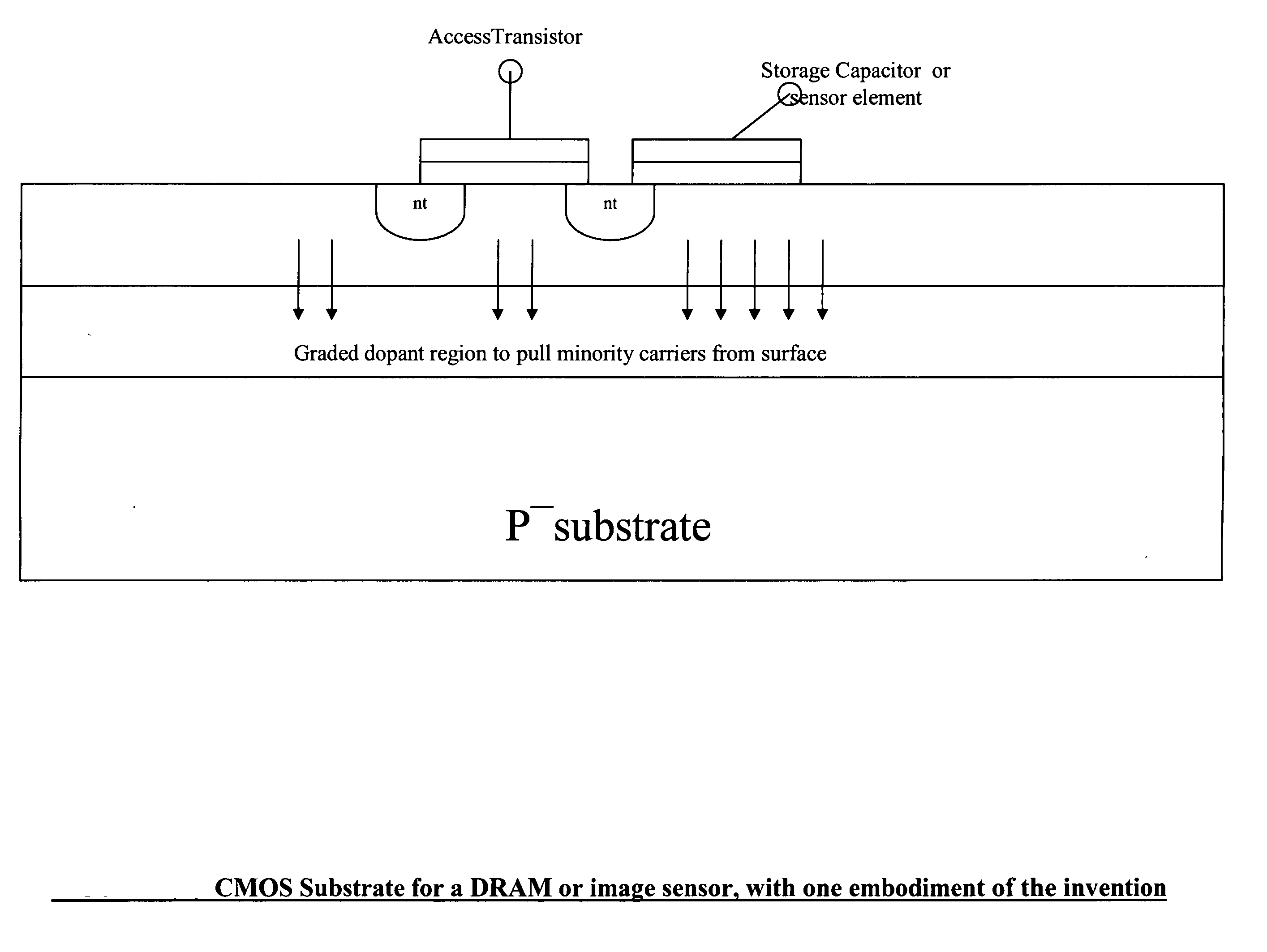
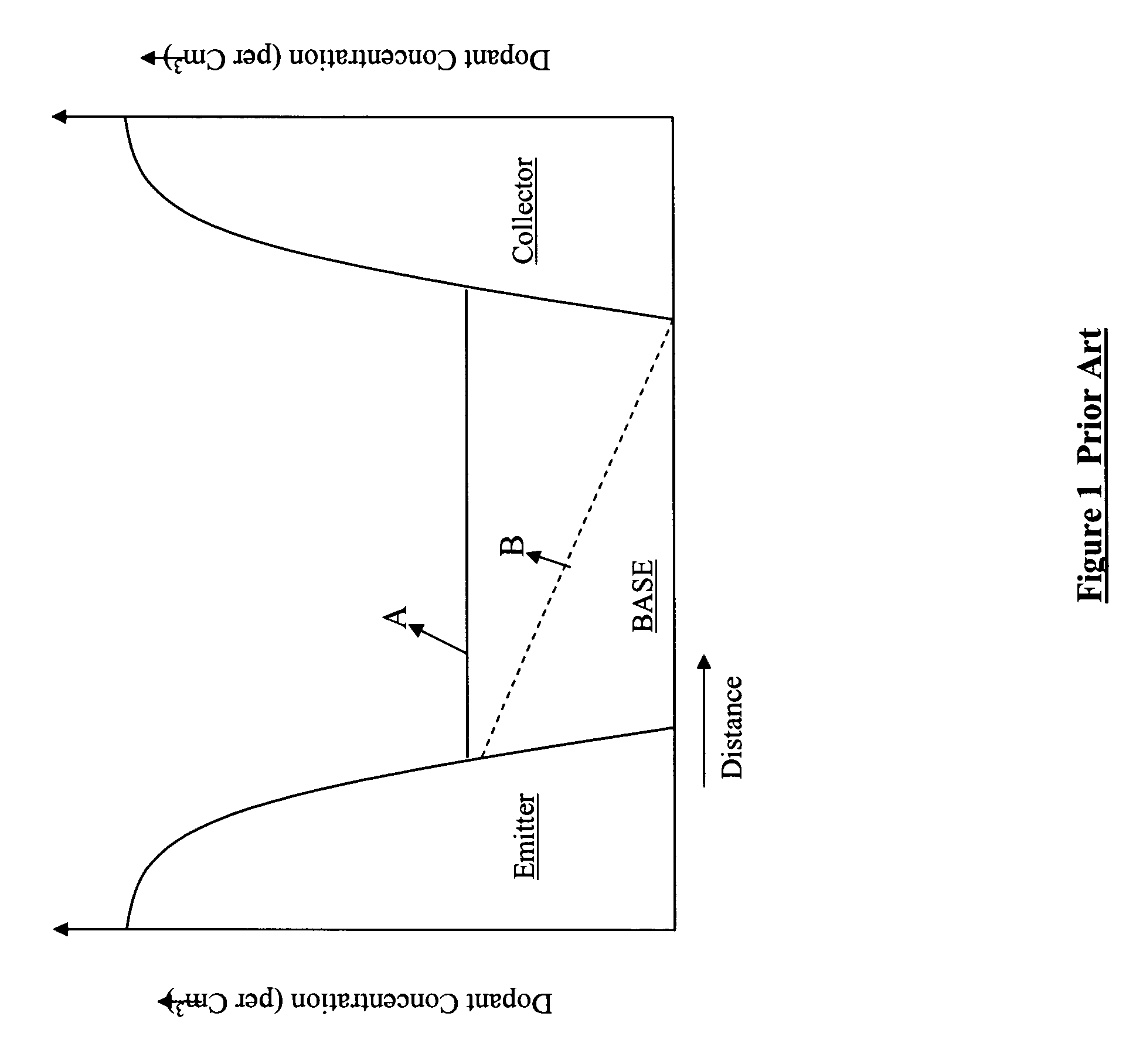
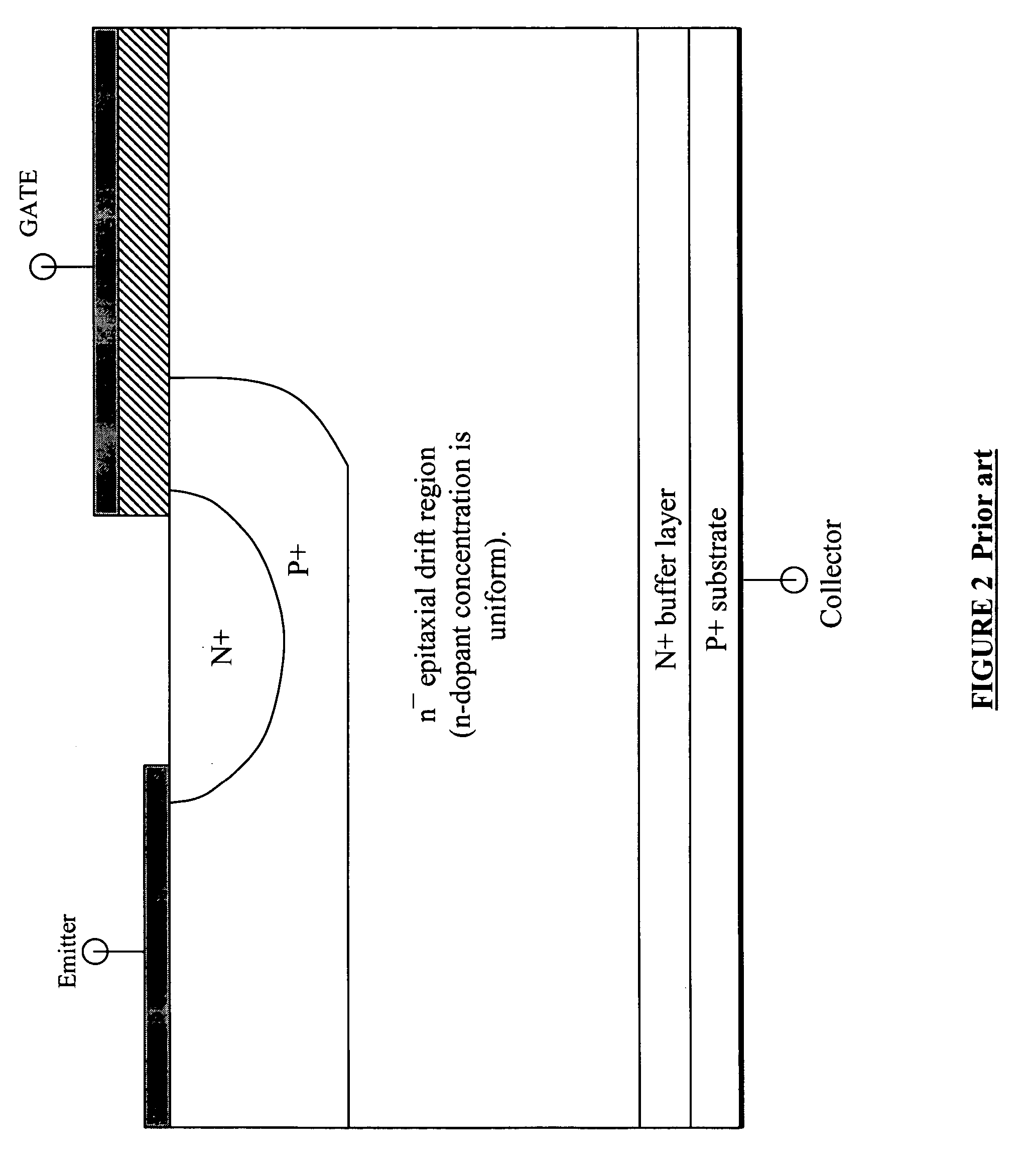
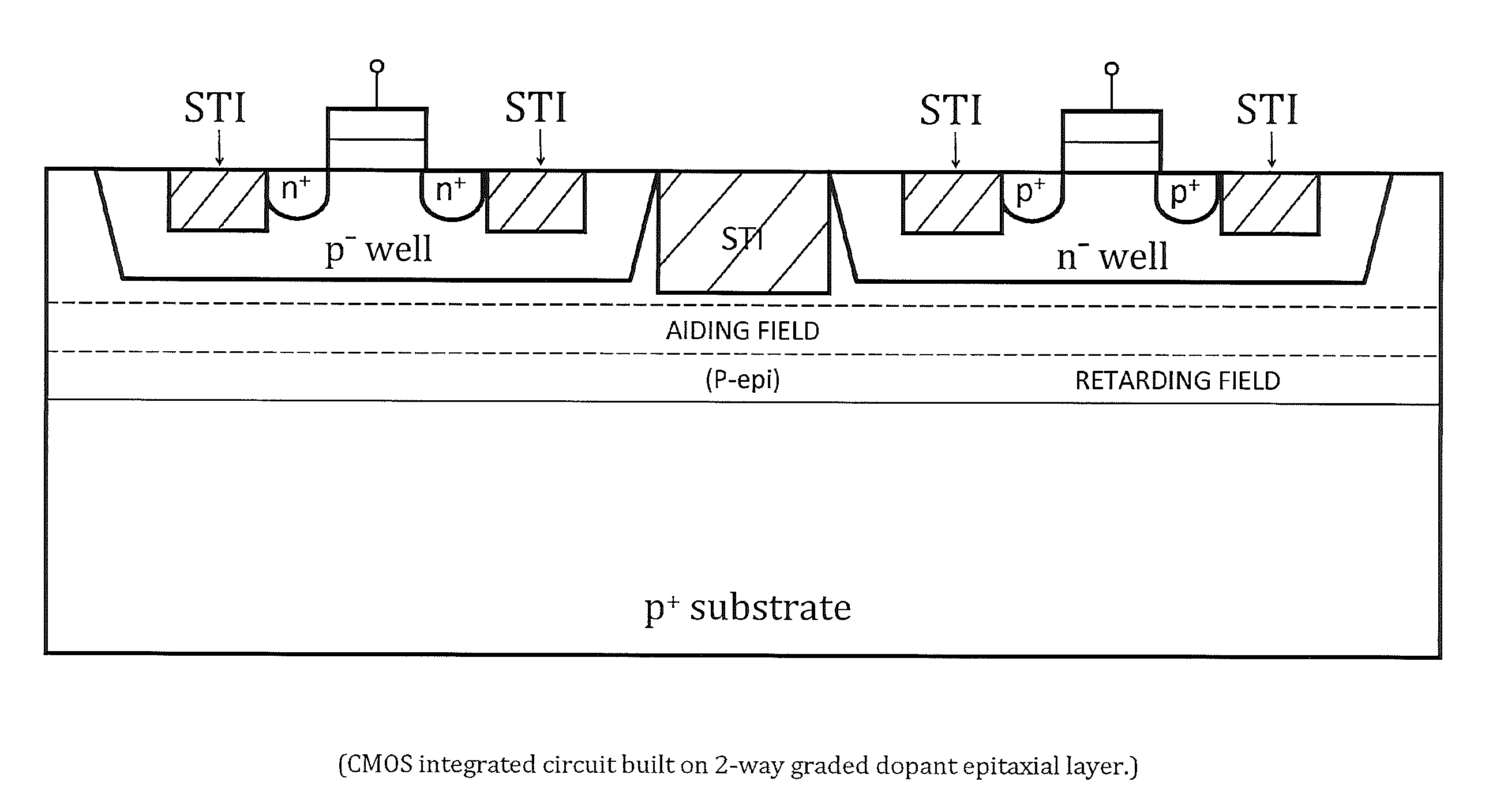
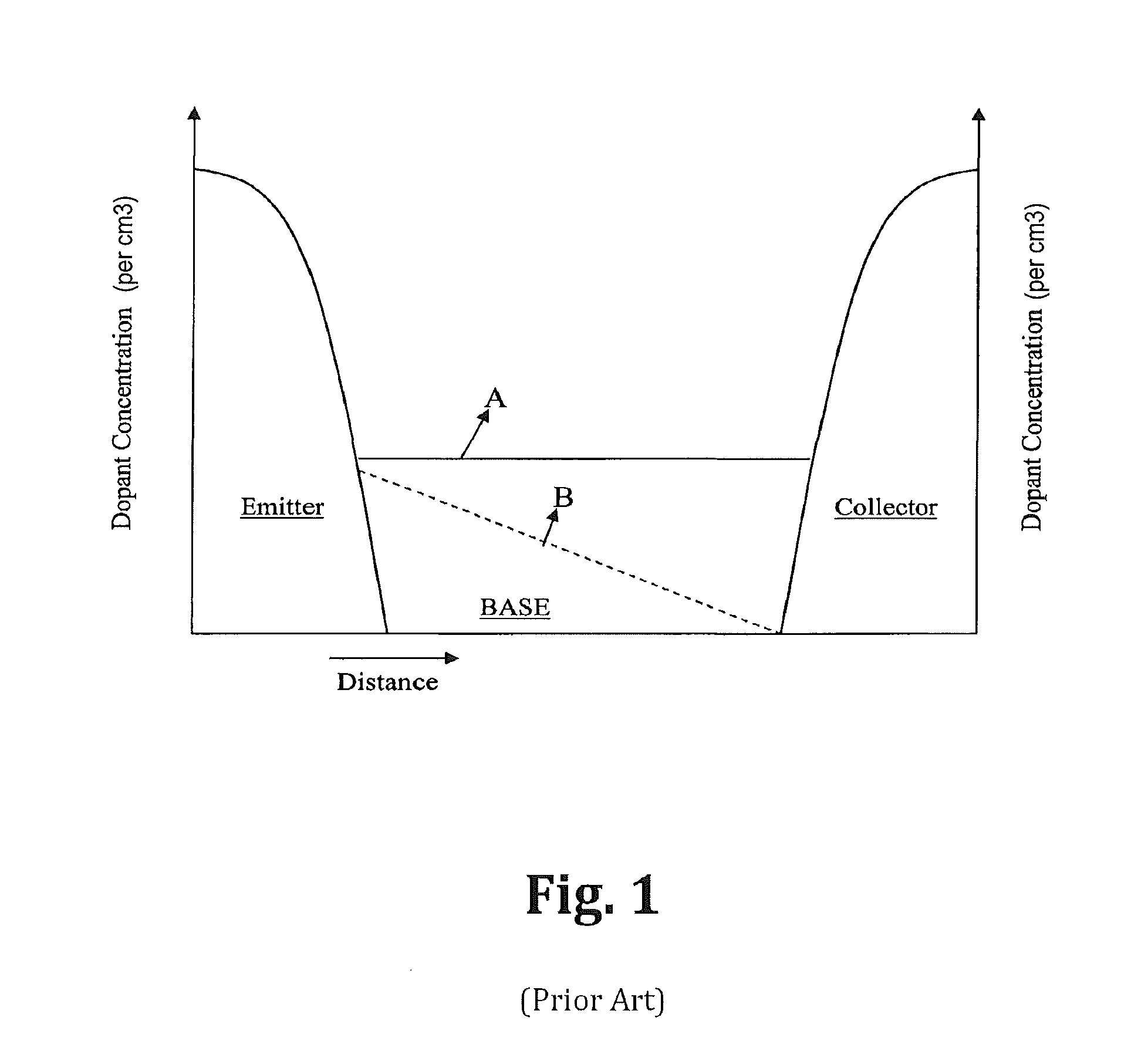
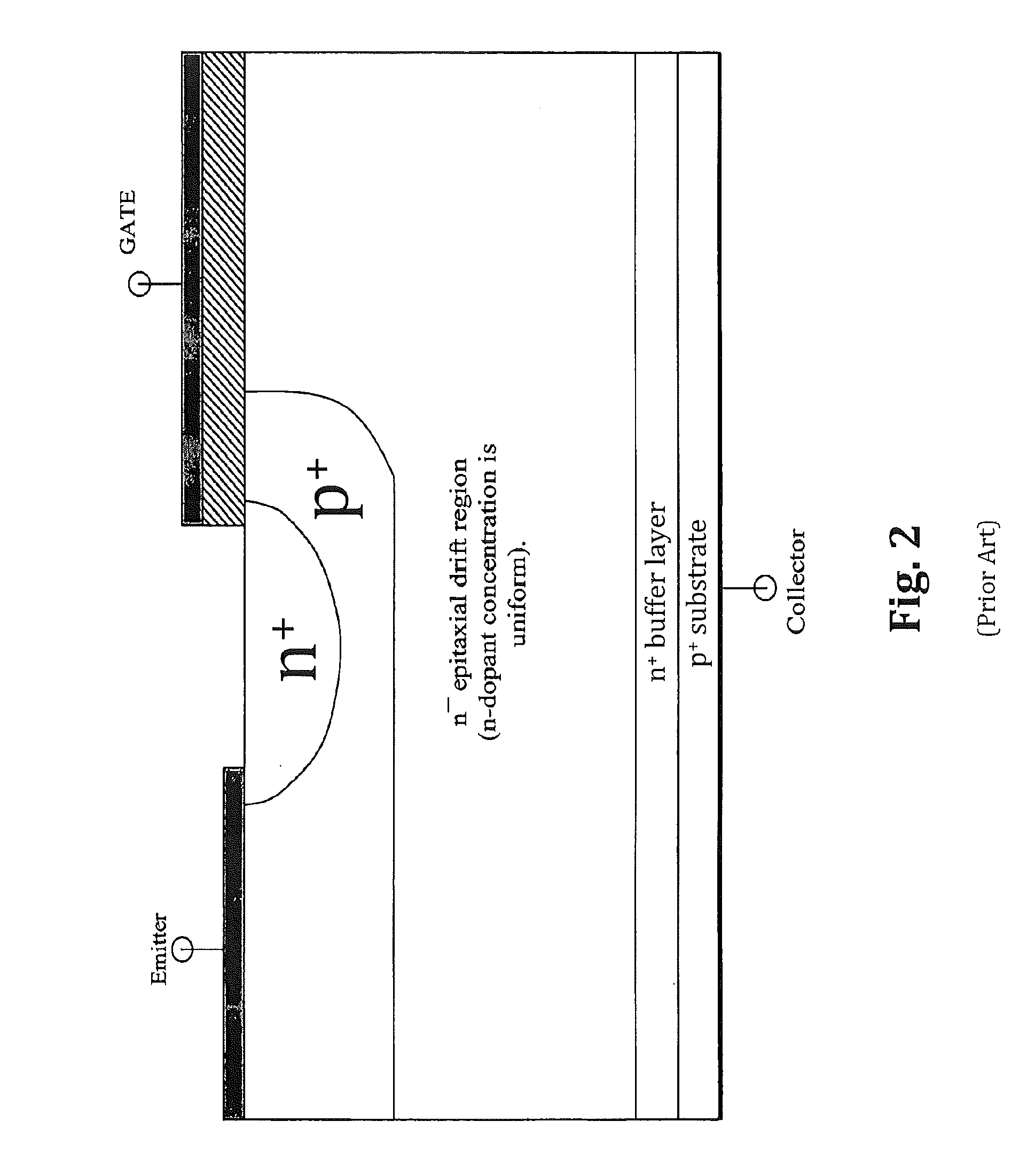
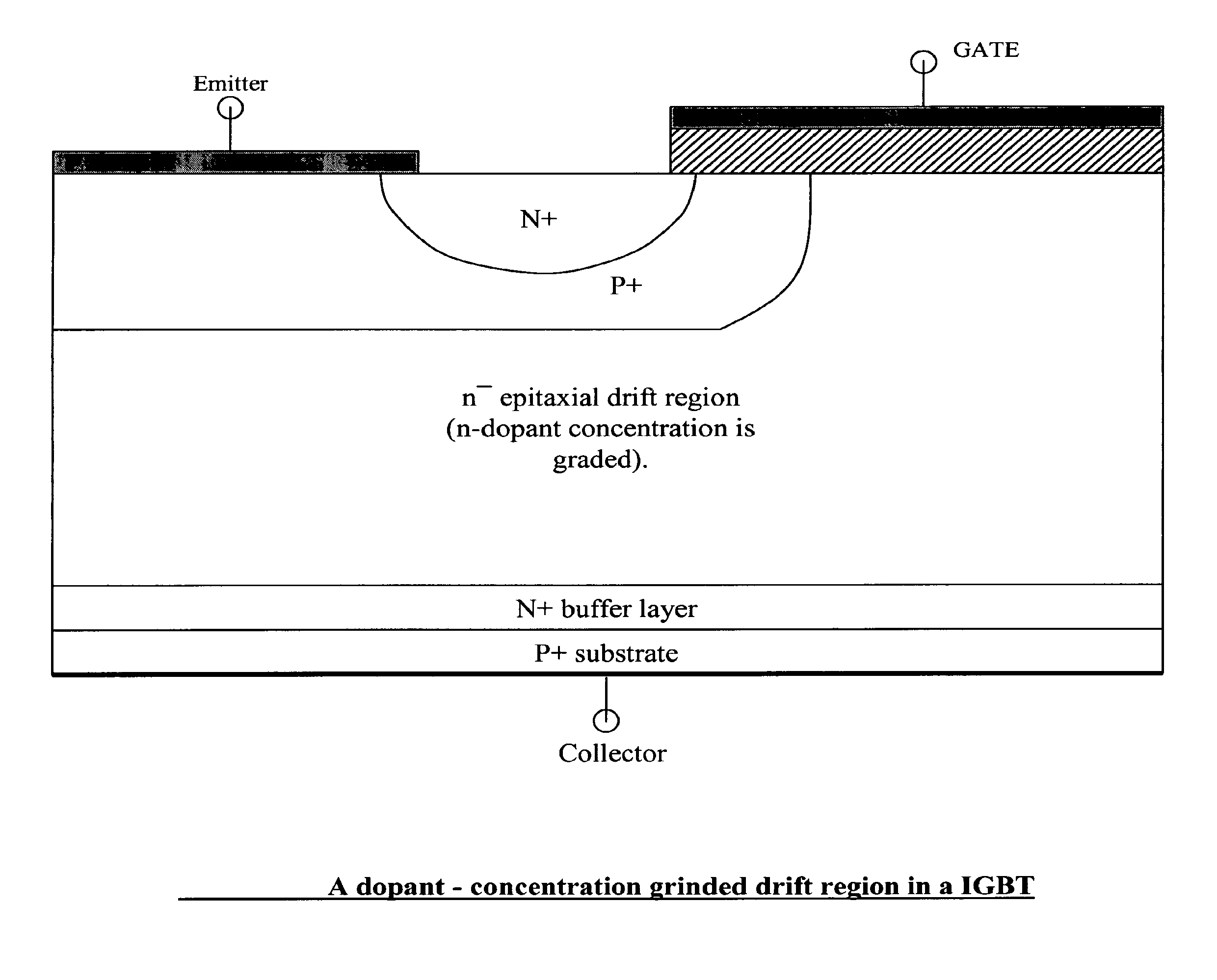
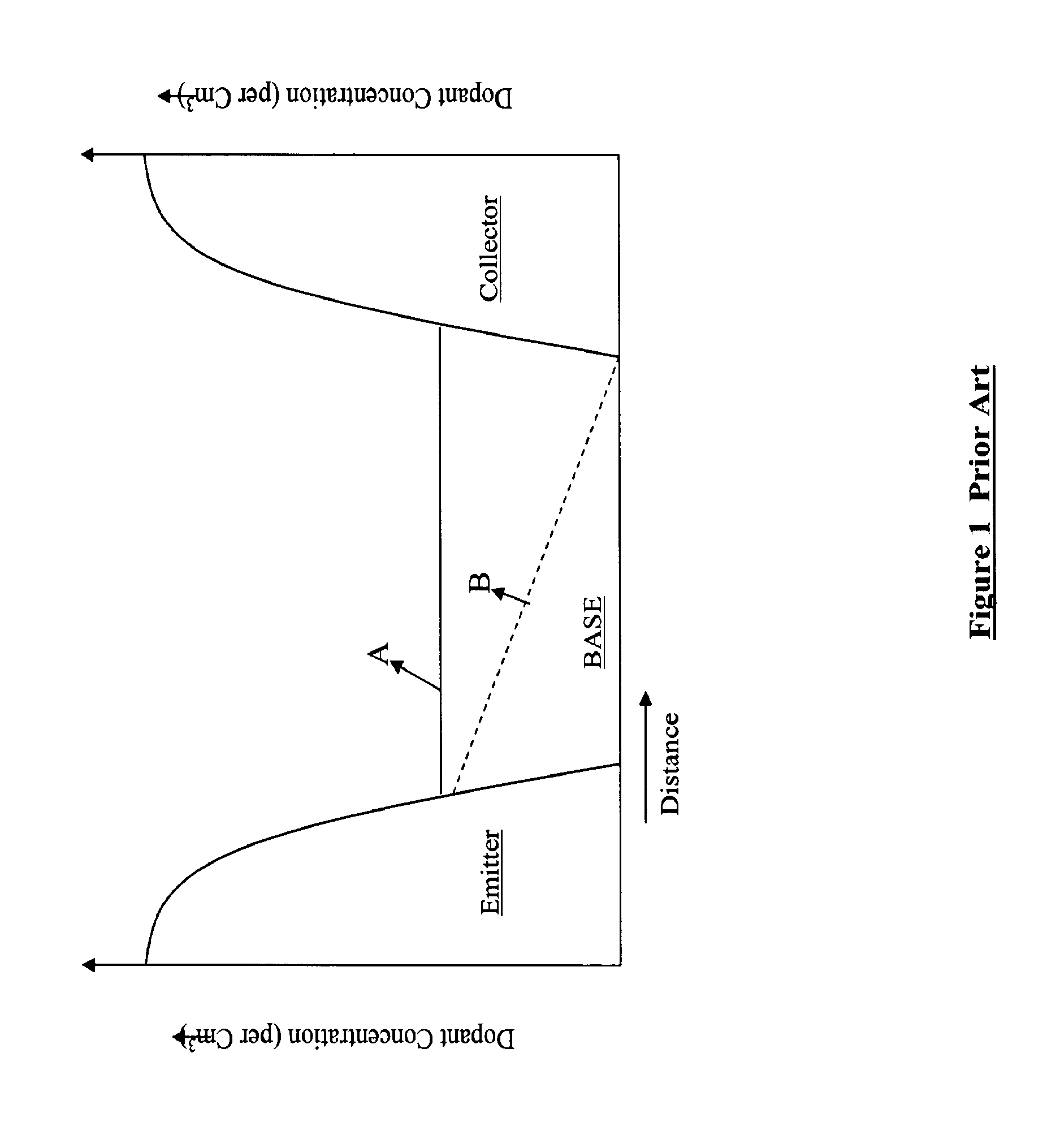
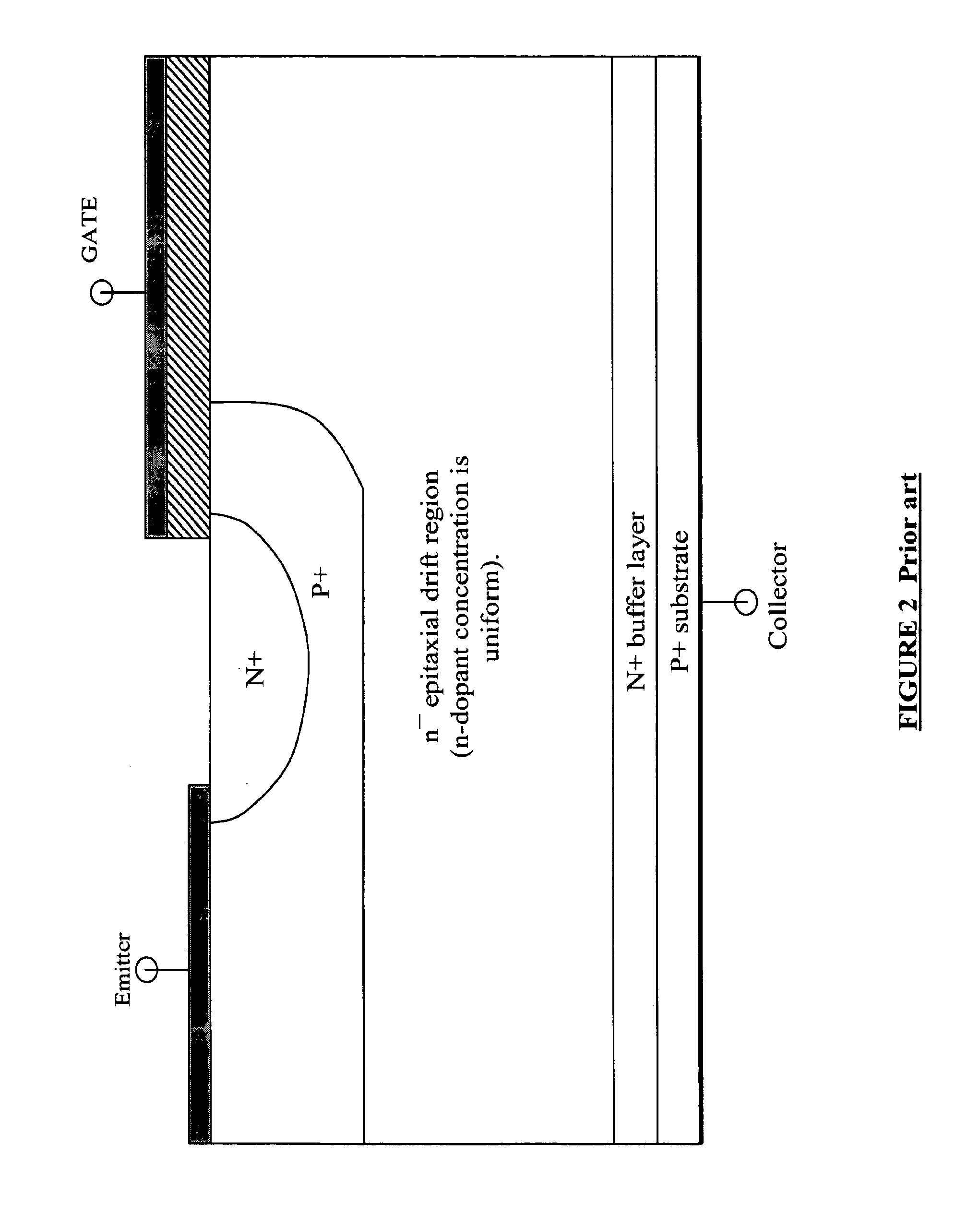
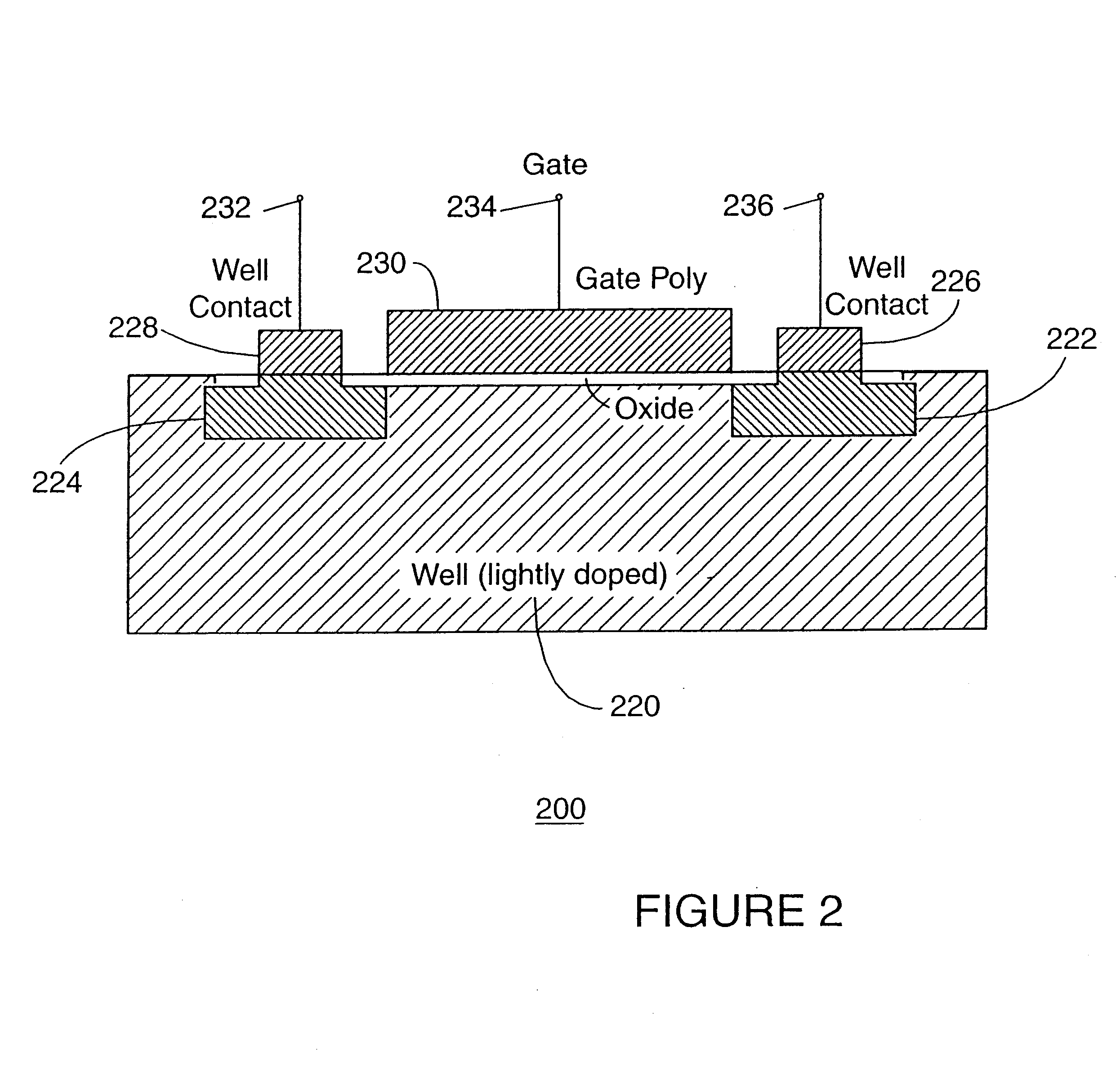
Semiconductor devices with graded dopant regions
Most semiconductor devices manufactured today, have uniform dopant concentration, either in the lateral or vertical device active (and isolation) regions. By grading the dopant concentration, the performance in various semiconductor devices can be significantly improved. Performance improvements can be obtained in application specific areas like increase in frequency of operation for digital logic, various power MOSFET and IGBT ICS, improvement in refresh time for DRAM's, decrease in programming time for nonvolatile memory, better visual quality including pixel resolution and color sensitivity for imaging ICs, better sensitivity for varactors in tunable filters, higher drive capabilities for JFET's, and a host of other applications.
Owner:GREENTHREAD
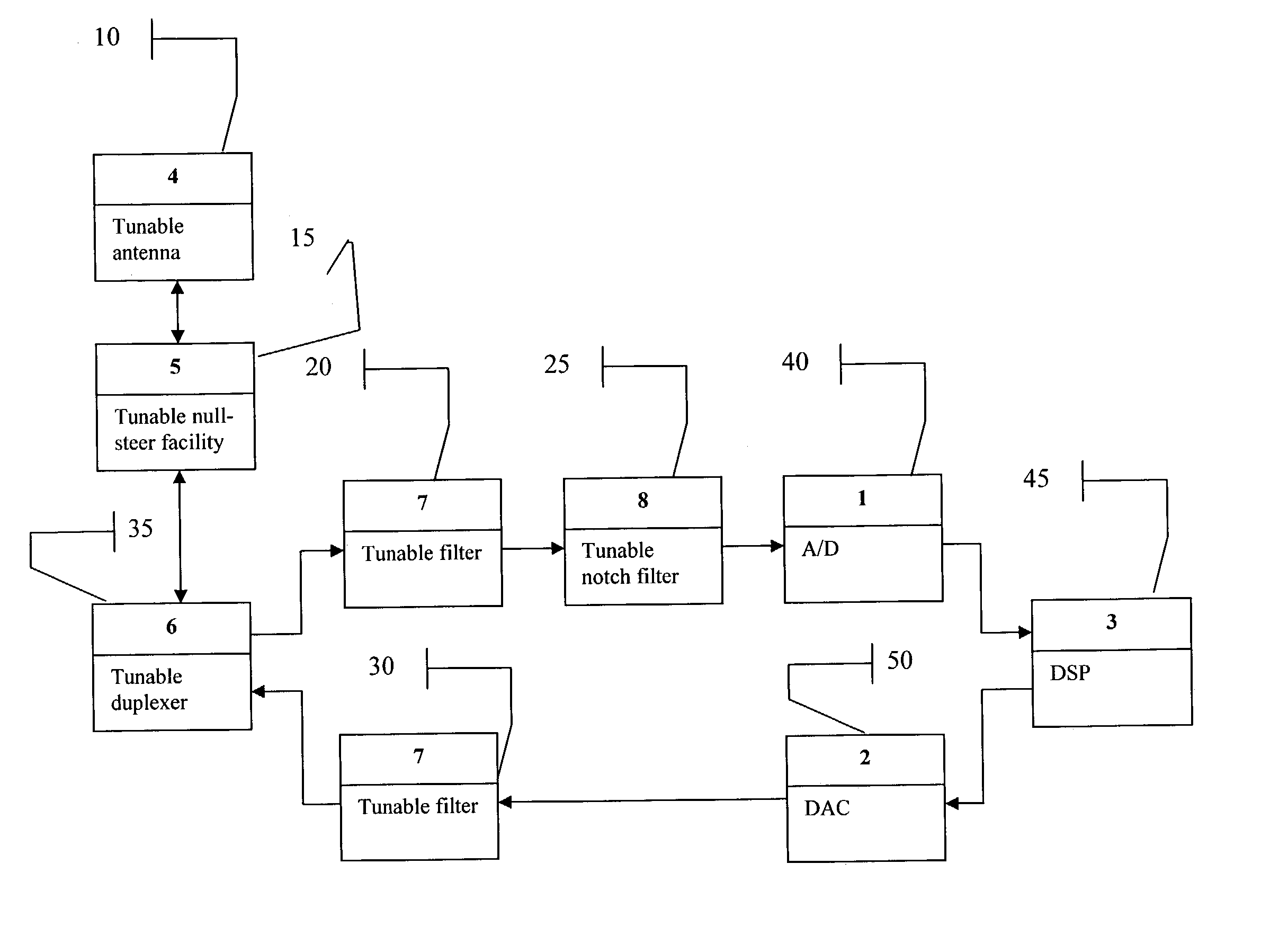
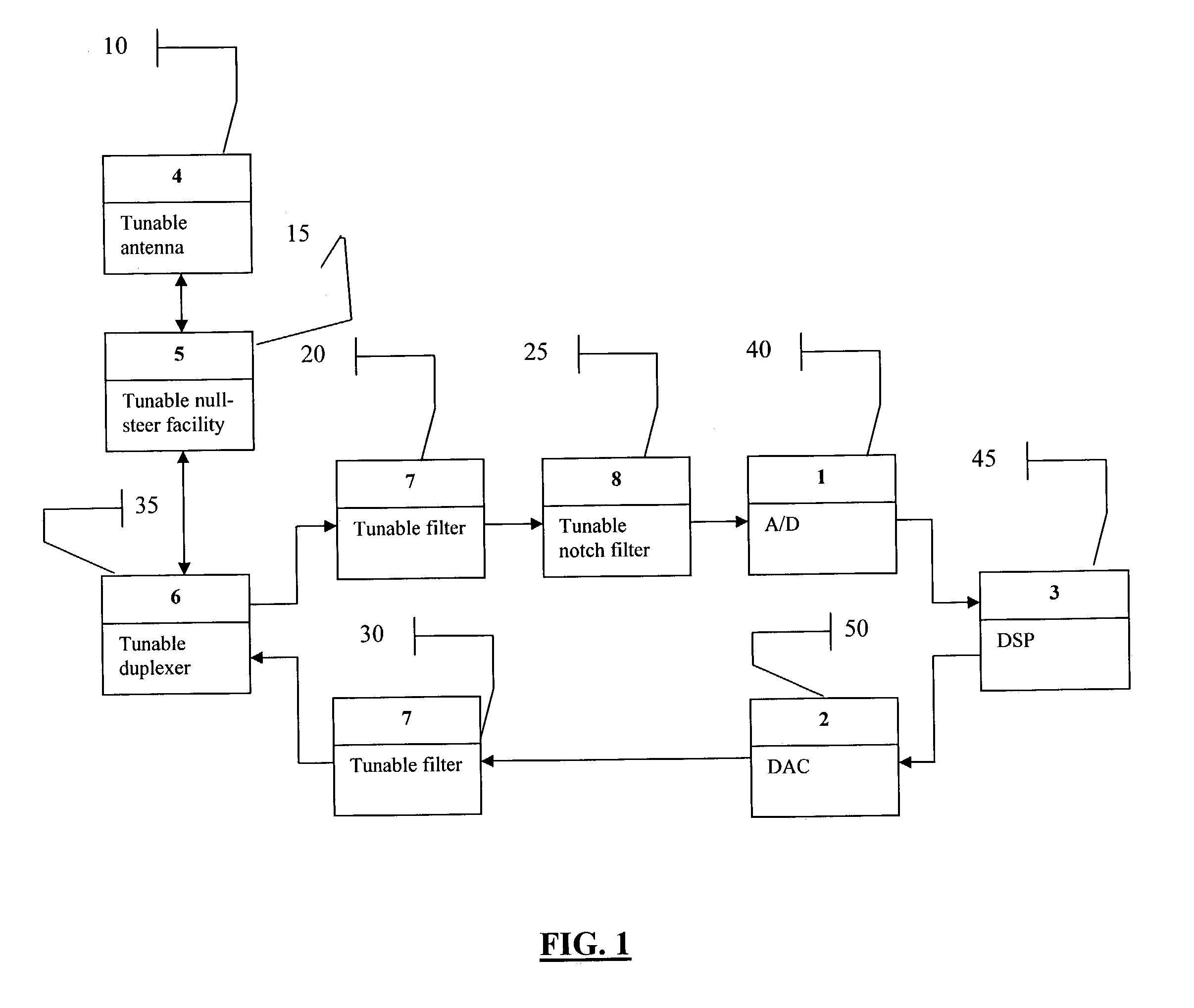
Smart radio incorporating Parascan(R) varactors embodied within an intelligent adaptive RF front end
ActiveUS7107033B2Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionDigital analog converterRF front end
A smart radio incorporating Parascan® varactors embodied within an intelligent adaptive RF front end. More specifically, this is provided for by a smart radio incorporating Parascan® varactors embodied within an intelligent adaptive RF front end that comprises at least one tunable antenna; at least one antenna null steering facility associated with said at least on tunable antenna; at least one tunable duplexer receiving the output from and providing input to said at least one antenna null steering facility; a first tunable RF filter receiving the output from said at least one tunable duplexer and providing the input to an analog to digital converter, said analog to digital converter providing the input to a digital signal processor, the output of which is input for a digital to analog converter; a second tunable RF filter receiving the analog output of said digital to analog converter and providing an input to said at least one tunable duplexer.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Slot antenna having a MEMS varactor for resonance frequency tuning
Briefly, in accordance with one embodiment of the invention, a slot antenna may include a primary slot and one or more secondary slots. The size of the antenna may be reduced by adding one or more of the secondary slots which may add additional inductance to the antenna. Furthermore, the size of the antenna may be reduced by increasing the inductance of the secondary slots via increasing the length of the slots or by changing the shape of the slots. The antenna may include one or more MEMS varactors coupled to one or more of the secondary slots. The resonant frequency of the slot antenna may be tuned to a desired frequency by changing the capacitance value of one or more of the MEMS varactors to a desired capacitance value.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Semiconductor devices with graded dopant regions
ActiveUS8106481B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPower MOSFET
Most semiconductor devices manufactured today, have uniform dopant concentration, either in the lateral or vertical device active (and isolation) regions. By grading the dopant concentration, the performance in various semiconductor devices can be significantly improved. Performance improvements can be obtained in application specific areas like increase in frequency of operation for digital logic, various power MOSFET and IGBT ICS, improvement in refresh time for DRAM's, decrease in programming time for nonvolatile memory, better visual quality including pixel resolution and color sensitivity for imaging ICs, better sensitivity for varactors in tunable filters, higher drive capabilities for JFET's, and a host of other applications.
Owner:GREENTHREAD
Semiconductor devices with graded dopant regions
Most semiconductor devices manufactured today, have uniform dopant concentration, either in the lateral or vertical device active (and isolation) regions. By grading the dopant concentration, the performance in various semiconductor devices can be significantly improved. Performance improvements can be obtained in application specific areas like increase in frequency of operation for digital logic, various power MOSFET and IGBT ICS, improvement in refresh time for DRAM's, decrease in programming time for nonvolatile memory, better visual quality including pixel resolution and color sensitivity for imaging ICs, better sensitivity for varactors in tunable filters, higher drive capabilities for JFET's, and a host of other applications.
Owner:GREENTHREAD
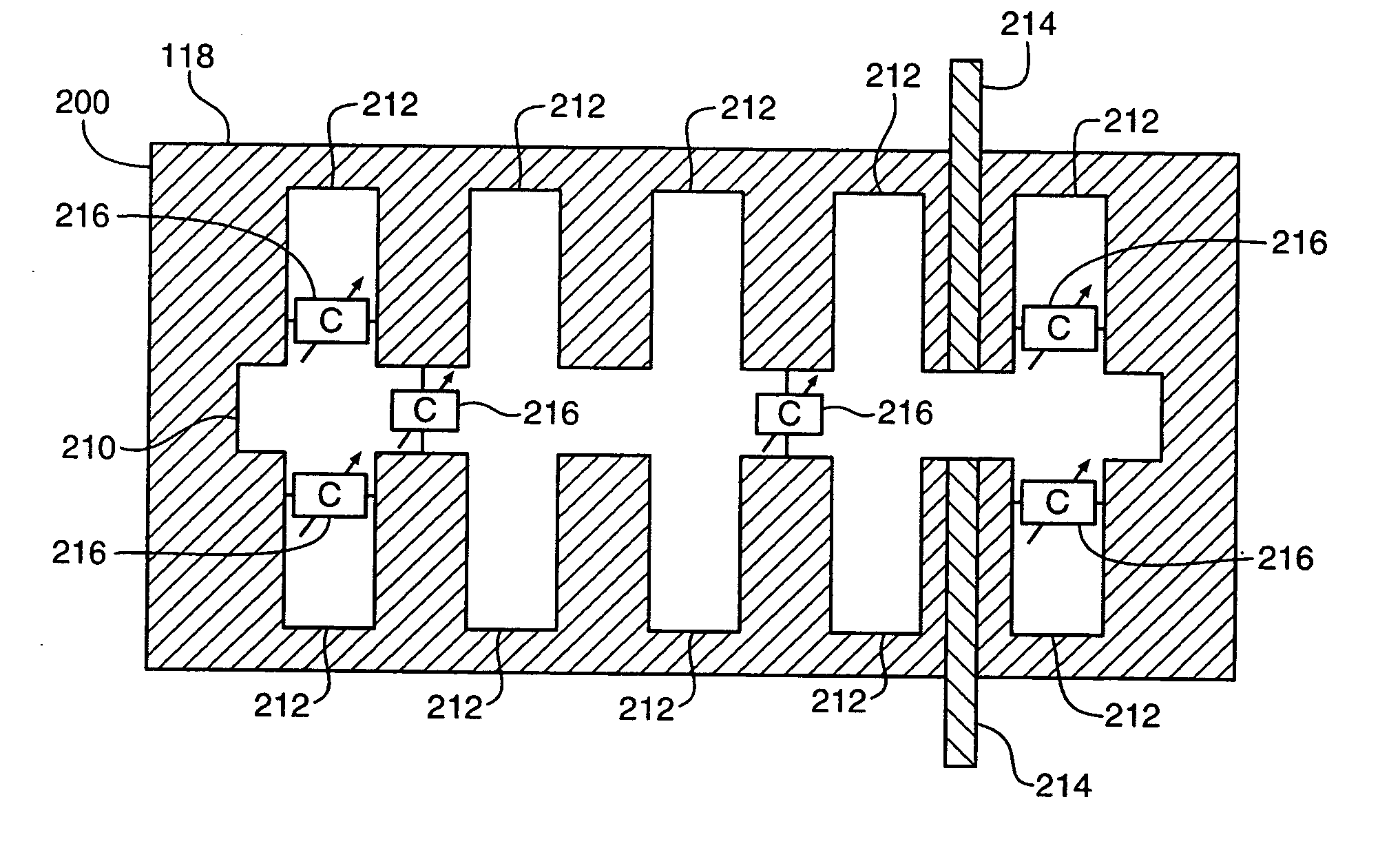
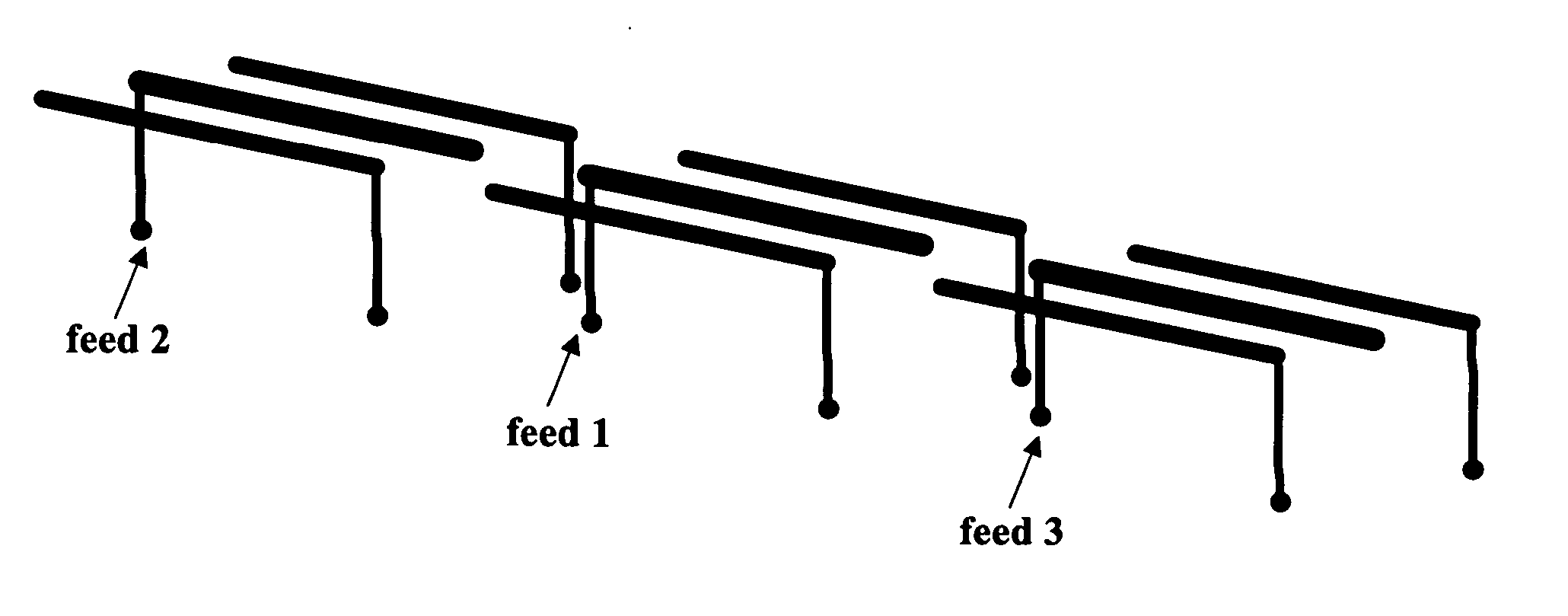
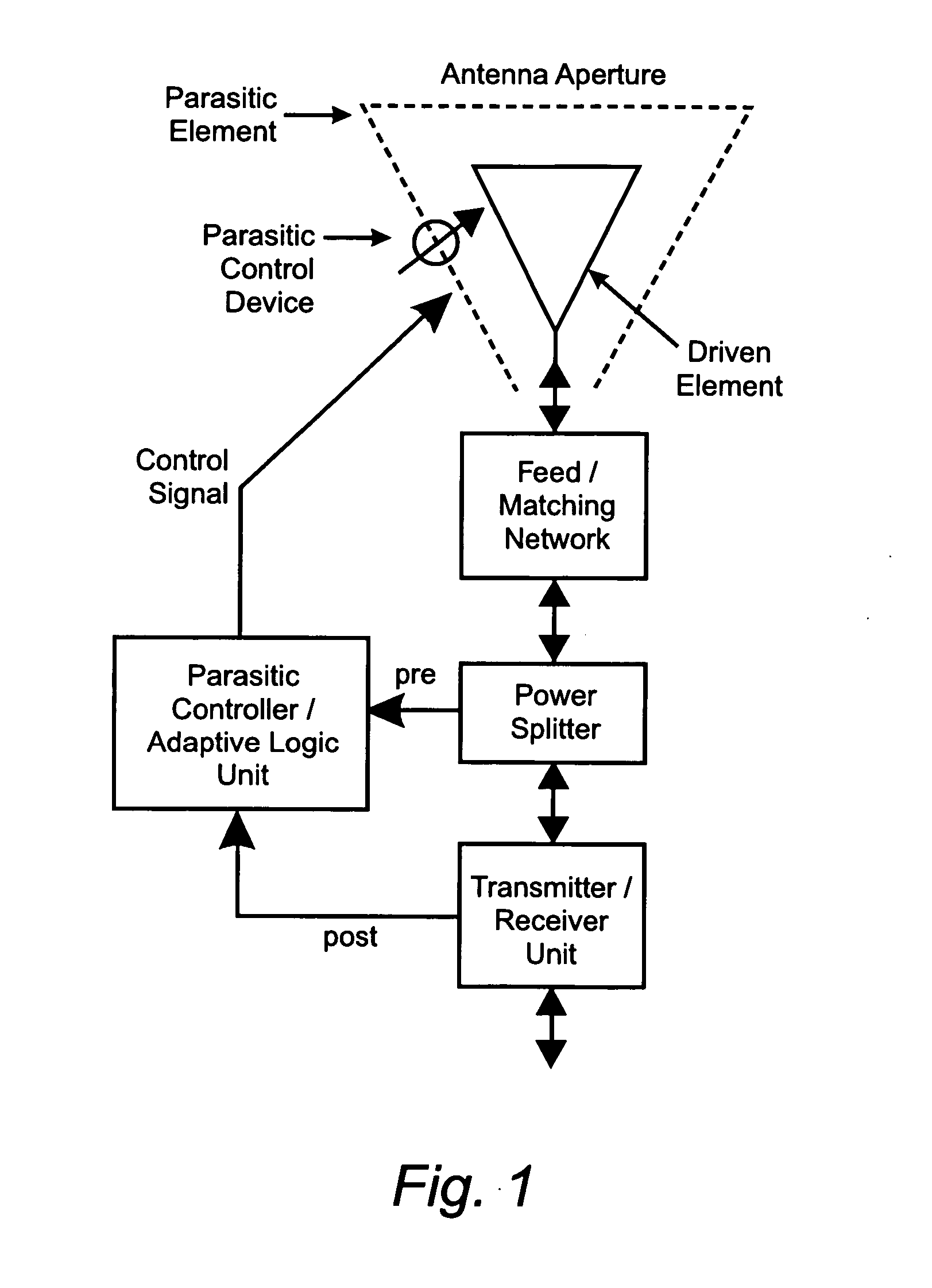
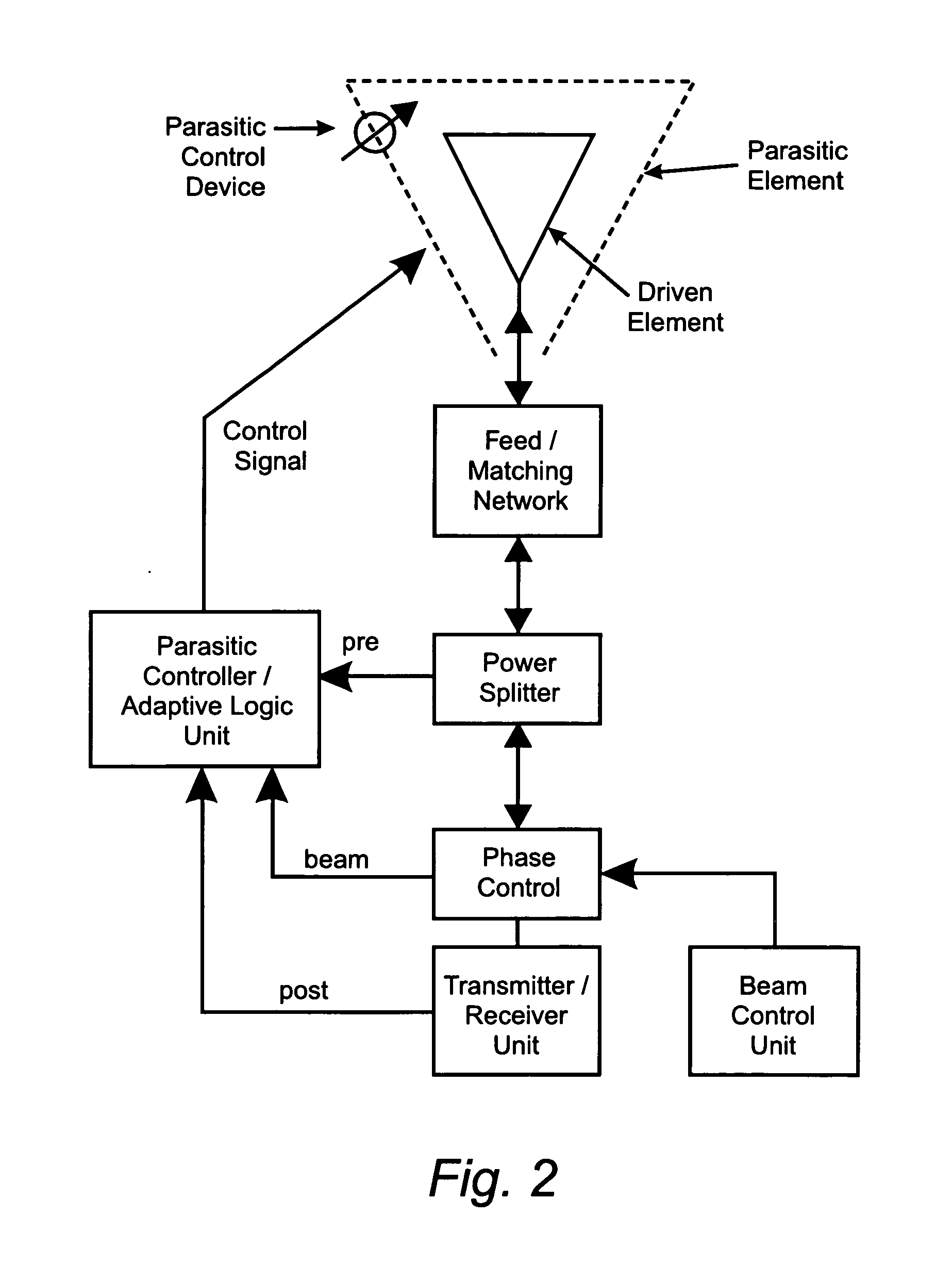
Reconfigurable parasitic control for antenna arrays and subarrays
InactiveUS20050088358A1Reduce decreaseScan angles can be increasedLogperiodic antennasAntenna arraysEngineeringArray element
Reconfiguration of parasitically controlled elements in a phased array is used to expand the range of operational functions. Embedded array elements can be frequency tuned, and bandwidth can be improved by using reconfiguration to broaden the bandwidth of the embedded elements. For high gain arrays, beam squint can be a limiting factor on instantaneous bandwidth. Reconfiguration can alleviate this problem by providing control of the element phase centers. Scan coverage can be improved and scan blindness alleviated by controlling the embedded antenna patterns of the elements as well as by providing control of the active impedance as the beam is scanned. Applying limited phase control to the elements themselves can alleviate some of the complexity of the feed manifold. A presently preferred method of designing reconfigurable antennas is to selectively place controlled parasitic elements in the aperture of each of the antenna elements in the phased array. The parasitic elements can be controlled to change the operational characteristics of the antenna element. The parasitic elements are controlled by either switching load values in and out that are connected to the parasitic elements or are controlled by applying control voltages to variable reactance circuits containing devices such as varactors. The parasitic elements can be controlled by the use of a feedback control subsystem that is part of the antenna system which adjusts the RF properties of the parasitic components based on some observed metric. The controllable characteristics include directivity control, tuning, instantaneous bandwidth, and RCS.
Owner:TOYON RES CORP
Phase shifters deposited en masse for an electronically scanned antenna
ActiveUS7324043B2Increase processing costPatterning of backsideSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectricEngineering
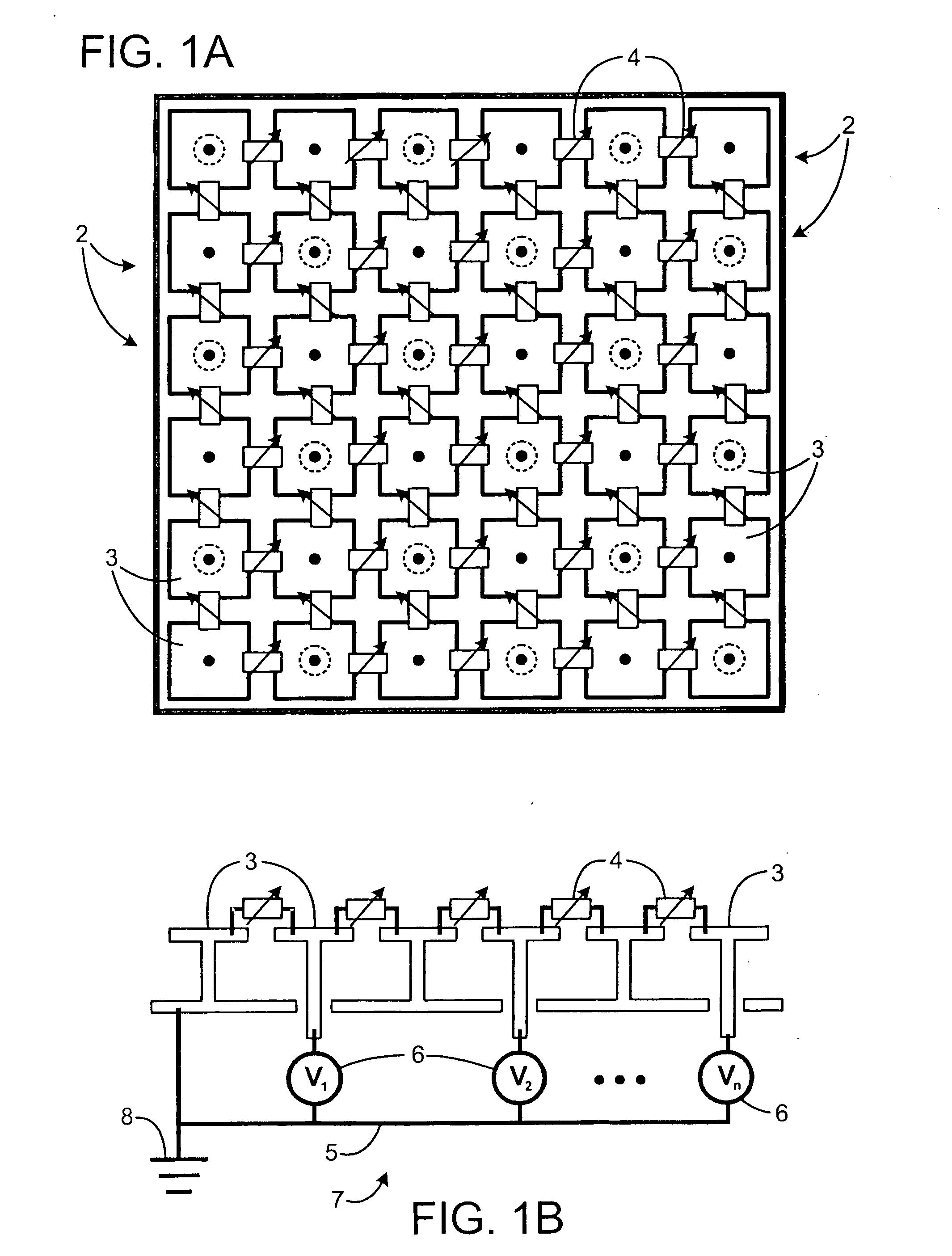
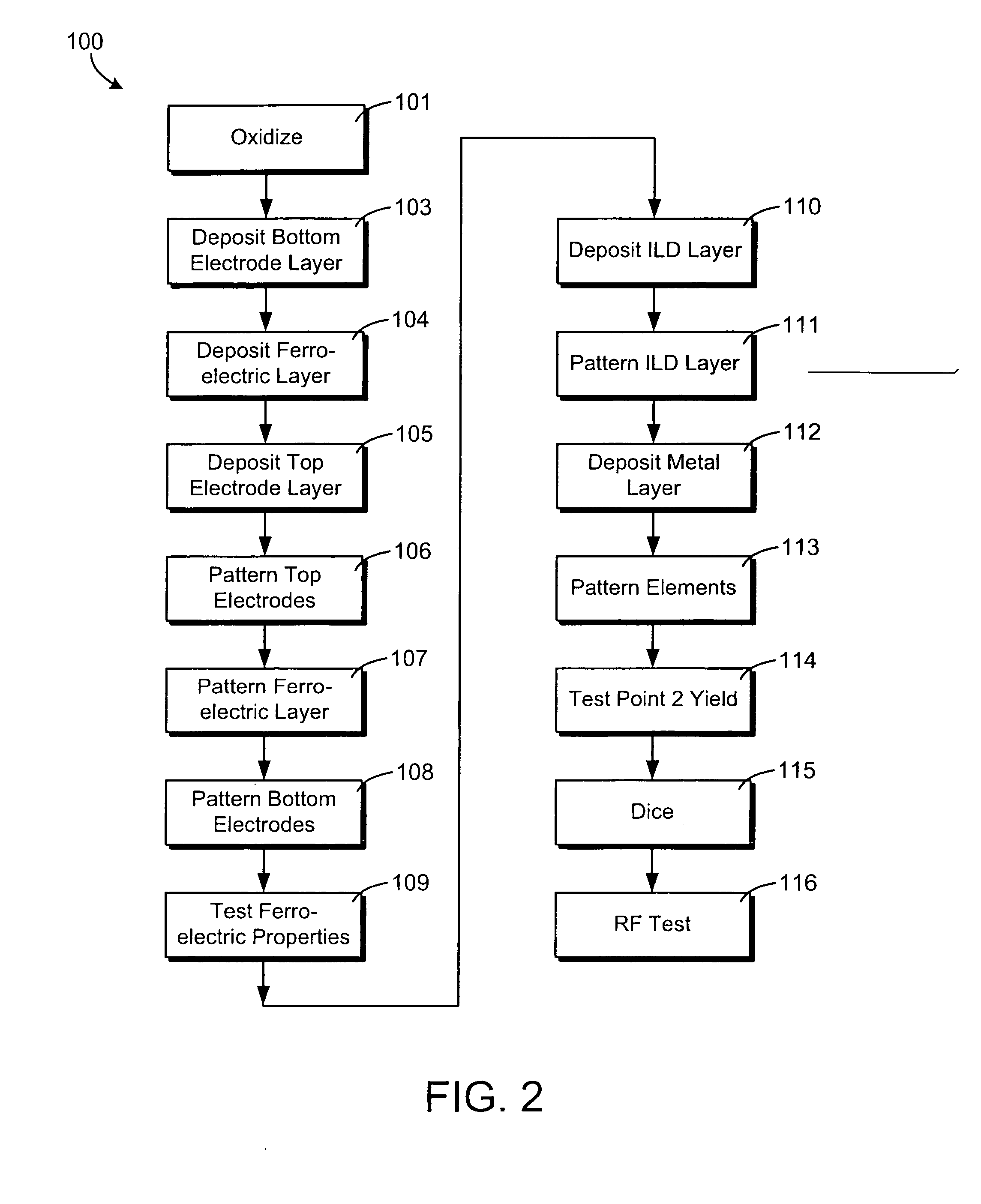
A system and method for an electronically scanned antenna is provided in which phase shifters are deposited en masse along with other electronically scanned antenna components on a wafer scale substrate using a thin film process. Alternative wafer scale sizes may be utilized to furnish a required antenna aperture area. Significant processing costs for radar and communication systems are saved utilizing the present invention as compared with contemporary discrete phase shifters that are individually mounted on an antenna. In an aspect, the phase shifter is made up of a base electrode, a barium strontanate titanate (BST) ferroelectric varactor and a top electrode. The BST ferroelectric material is a voltage variable dielectric, which generates a radiation phase. The radiation phase is regulated by a phase shifter control. The radiation phase generates an electromagnetic field about a radiating element and electromagnetic radio waves are radiated from the radiating element.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Nanowire varactor diode and methods of making same
InactiveUS7115971B2Facilitate conductionNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanowireNon doped
A nanowire varactor diode and methods of making the same are disclosed. The structure comprises a coaxial capacitor running the length of the semiconductor nanowire. In one embodiment, a semiconductor nanowire of a first conductivity type is deposited on a substrate. An insulator is formed on at least a portion of the nanowire's surface. A region of the nanowire is doped with a second conductivity type material. A first electrical contact is formed on at least part of the insulator and the doped region. A second electrical contact is formed on a non-doped potion of the nanowire. During operation, the conductivity type at the surface of the nanowire inverts and a depletion region is formed upon application of a voltage to the first and second electrical contacts. The varactor diode thereby exhibits variable capacitance as a function of the applied voltage.
Owner:NANOSYS INC
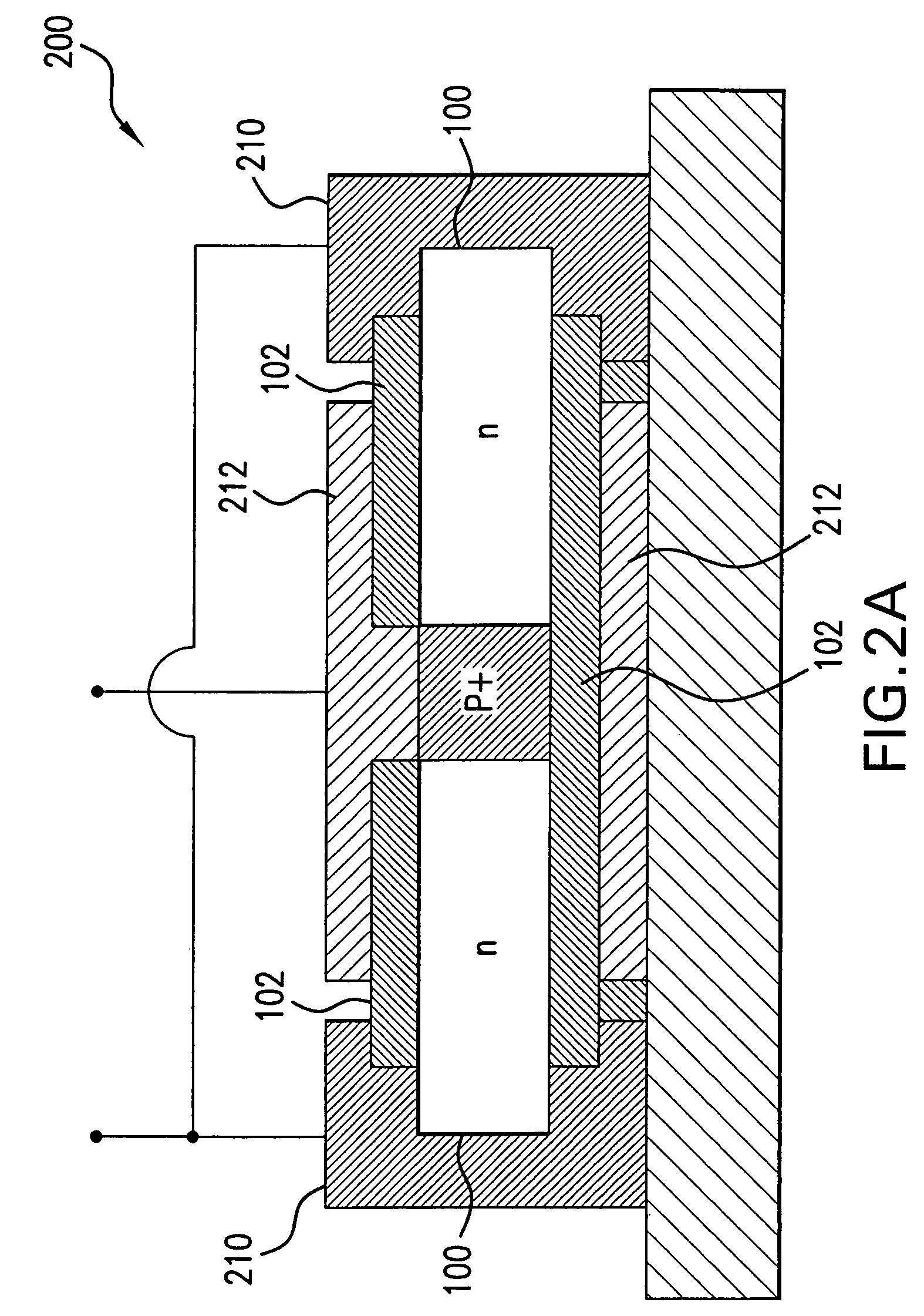
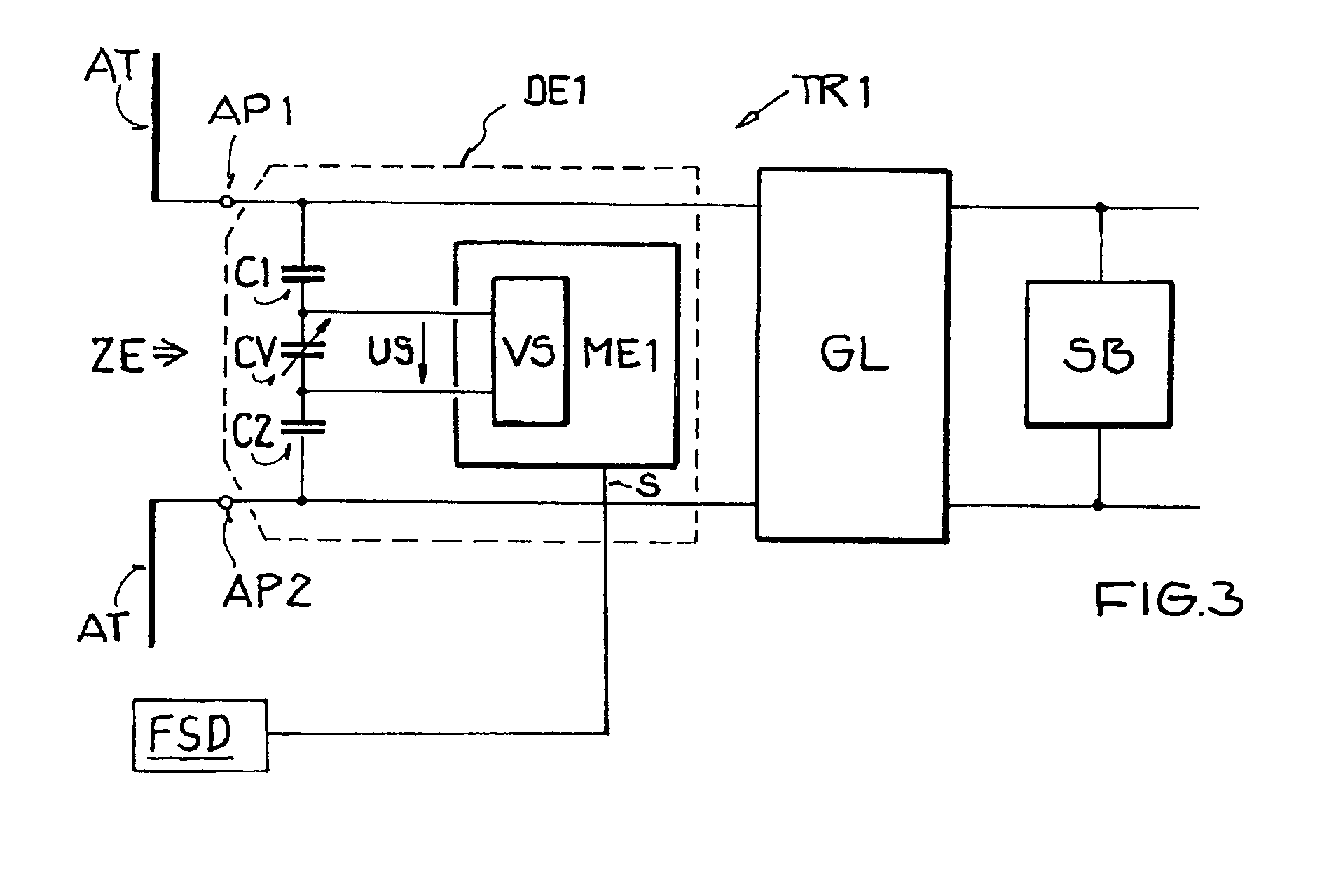
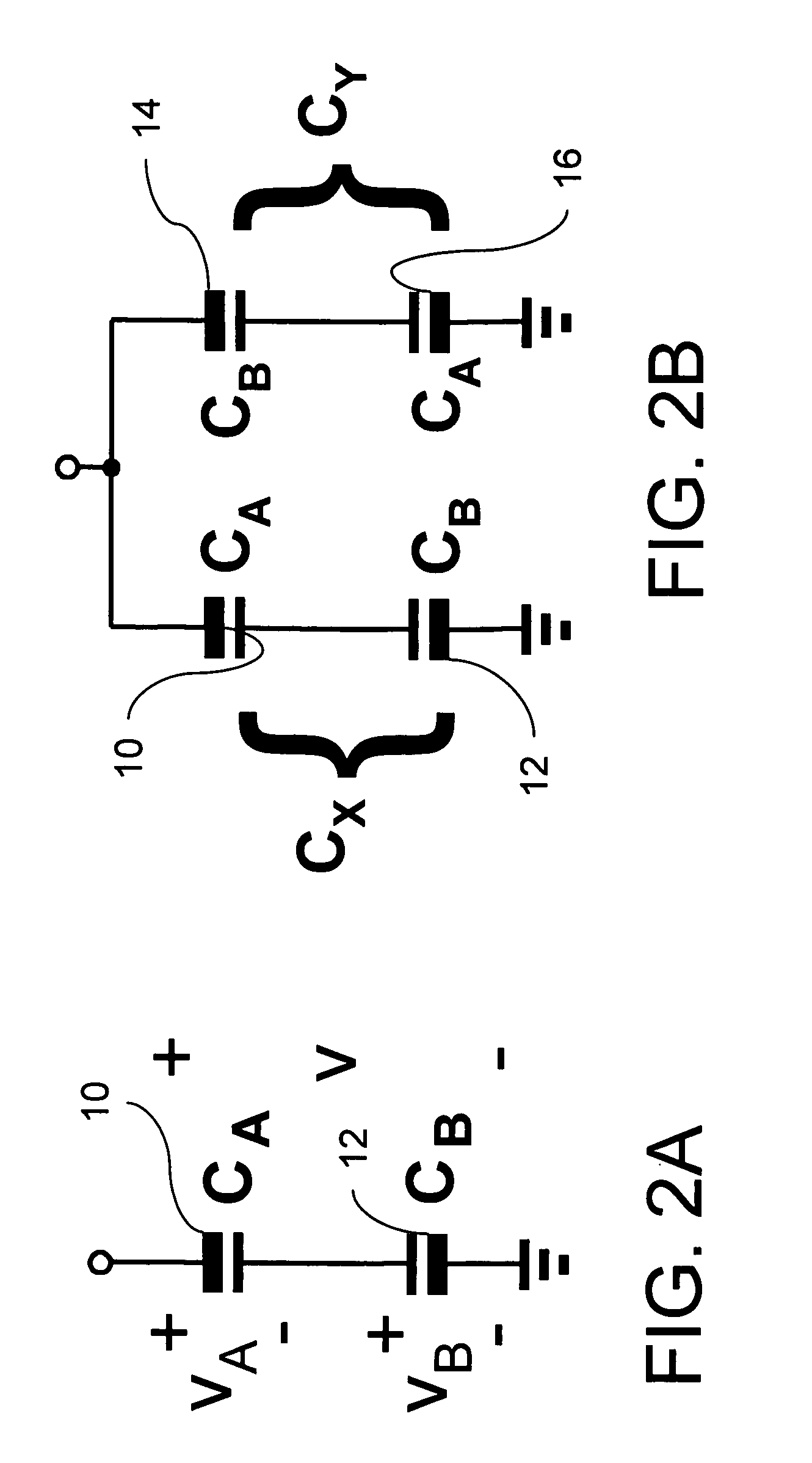
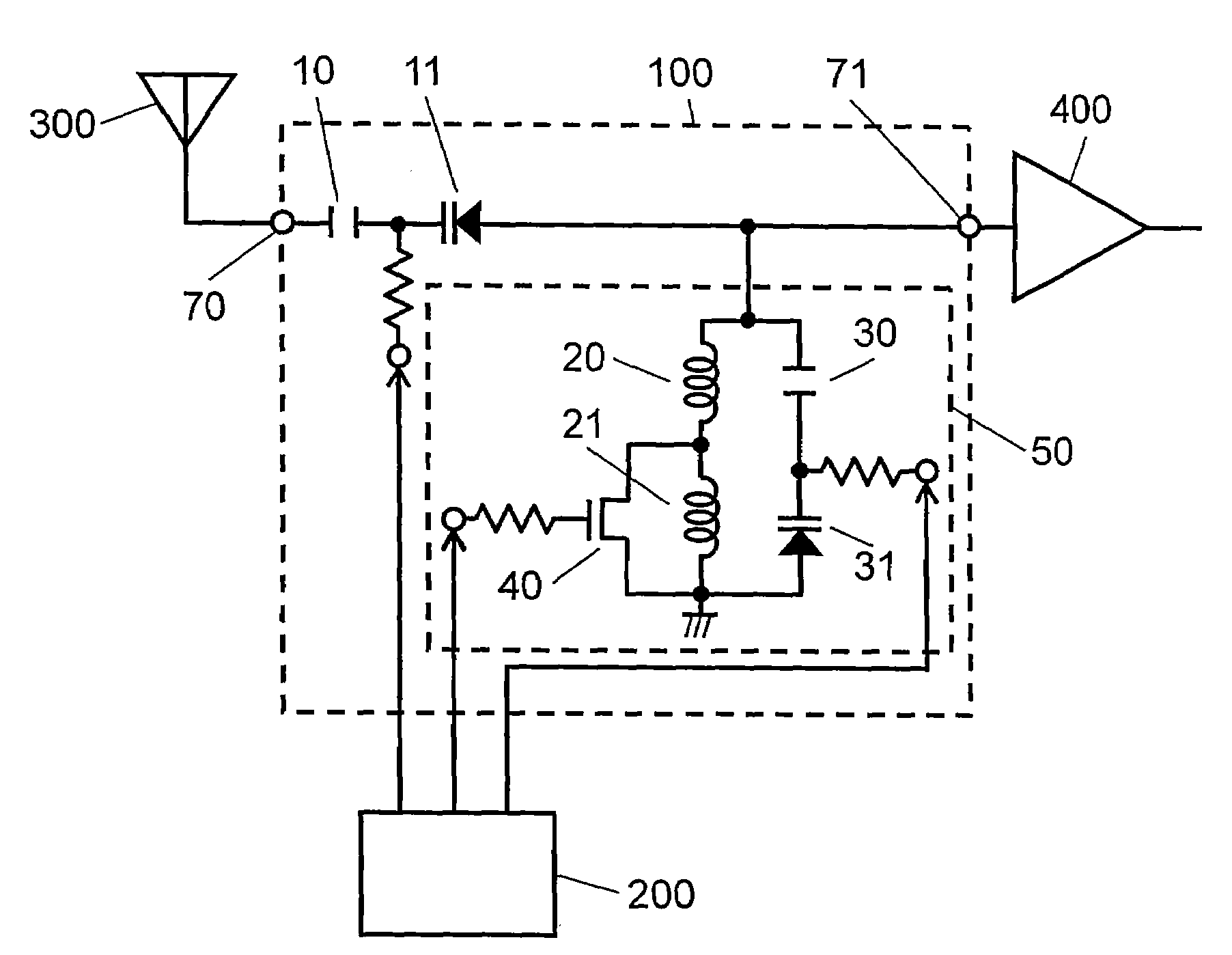
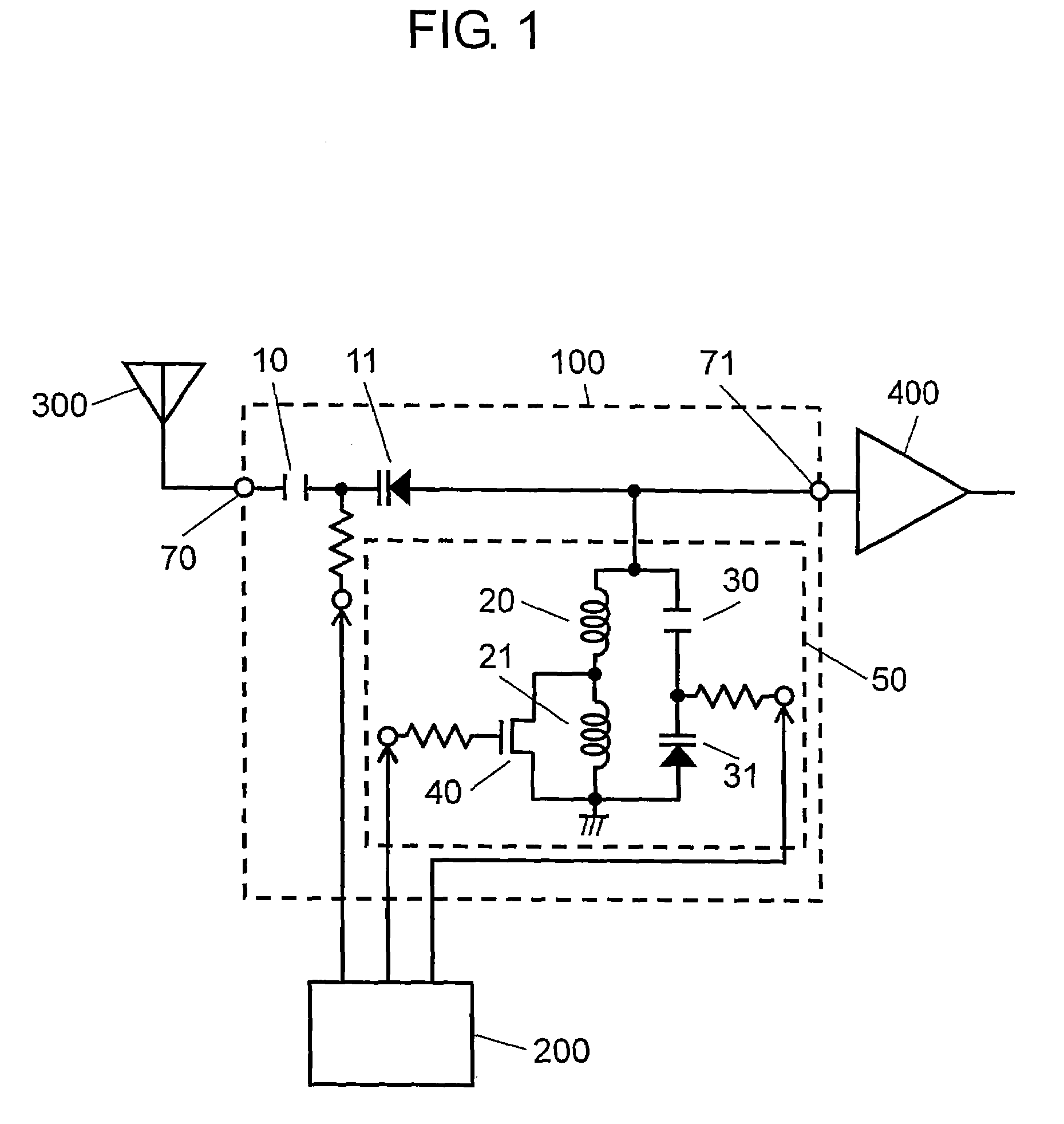
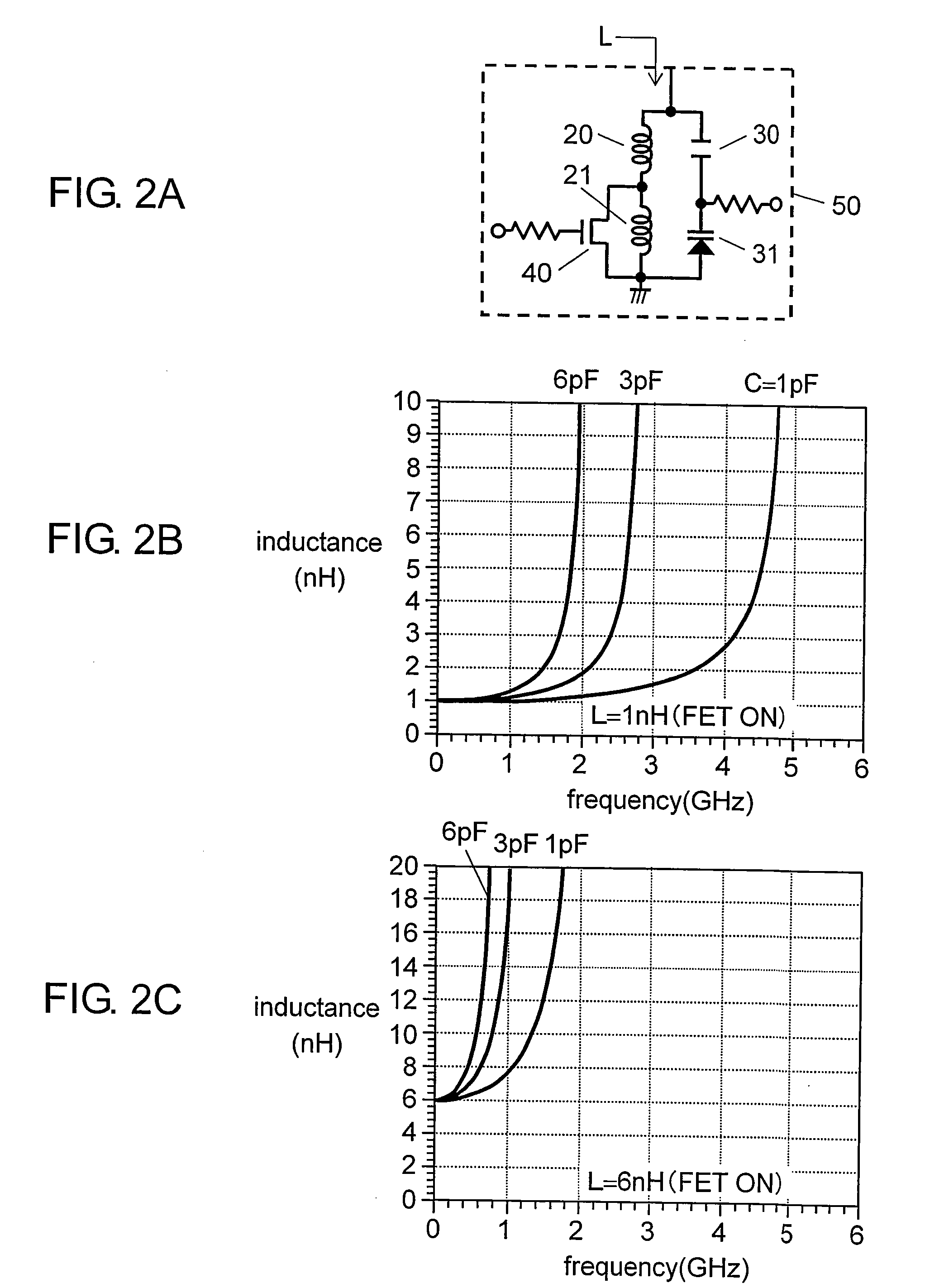
Variable matching circuit
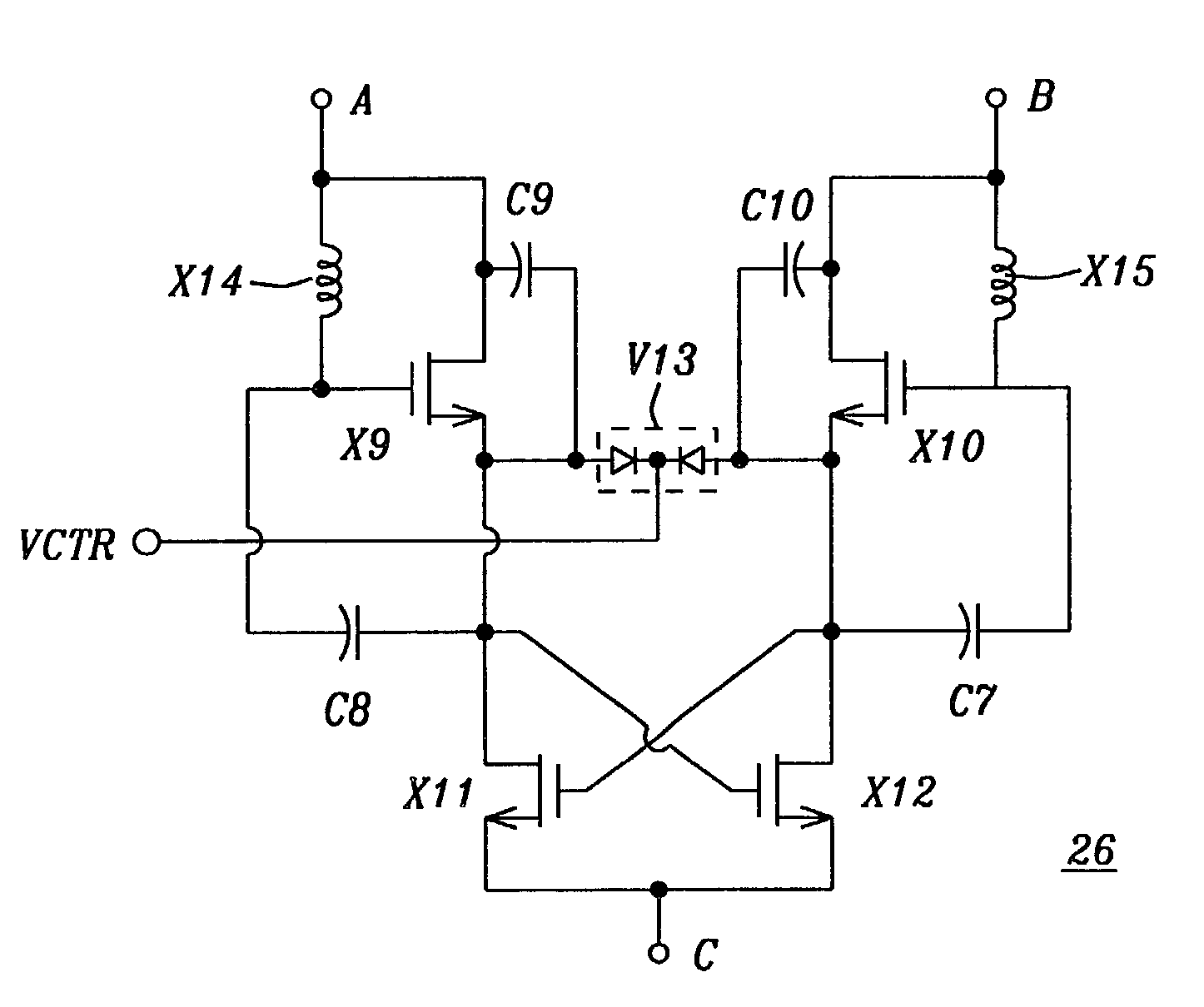
A variable matching circuit includes a variable capacitance circuit formed of a capacitor coupled to varactor diode and provided between terminals, and a resonator-type circuit includes a plurality of inductors and a variable capacitance circuit formed of a capacitor and a varactor diode. The inductors and the variable capacitance circuit are coupled in parallel together. The resonator-type circuit is connected in shunt with the terminal. The foregoing structure forms an L-type matching circuit. The bias of the varactor diodes can be thus varied, and plural values of the inductance of the resonator-type circuit can be switched over with a FET. The variable matching circuit can electrically control an impedance conversion available for wider ranges of frequency bandwidths.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and apparatus for fully integrating a voltage controlled oscillator on an integrated circuit
InactiveUS6268778B1Wide tuning capacitance rangeReduce parasitic capacitanceAngle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlLc resonatorSelf resonance
A method and apparatus for fully integrating a Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) on an integrated circuit. The VCO is implemented using a differential-mode circuit design. The differential-mode implementation of the VCO preferably comprises a differential mode LC-resonator circuit, a digital capacitor, a differential pair amplifier, and a current source. The LC-resonator circuit includes at least one tuning varactor and two high Q inductors. The tuning varactor preferably has a wide tuning capacitance range. The tuning varactor is only used to "fine-tune" the center output frequency f0 of the VCO. The center output frequency f0 is coarsely tuned by the digital capacitor. The VCO high Q inductors comprise high gain, high self-resonance, and low loss IC inductors. The IC VCO is fabricated on a high resistivity substrate material using a trench isolated guard ring. The guard ring isolates the fully integrated VCO, and each of its component parts, from RF signals that may be introduced into the IC substrate by other devices. By virtue of the improved performance characteristics provided by the digital capacitor, the analog tuning varactor, the high Q inductor, and the trench isolated guard ring techniques, the inventive VCO is fully integrated despite process variations in IC fabrication.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
Tunable impedance surface and method for fabricating a tunable impedance surface
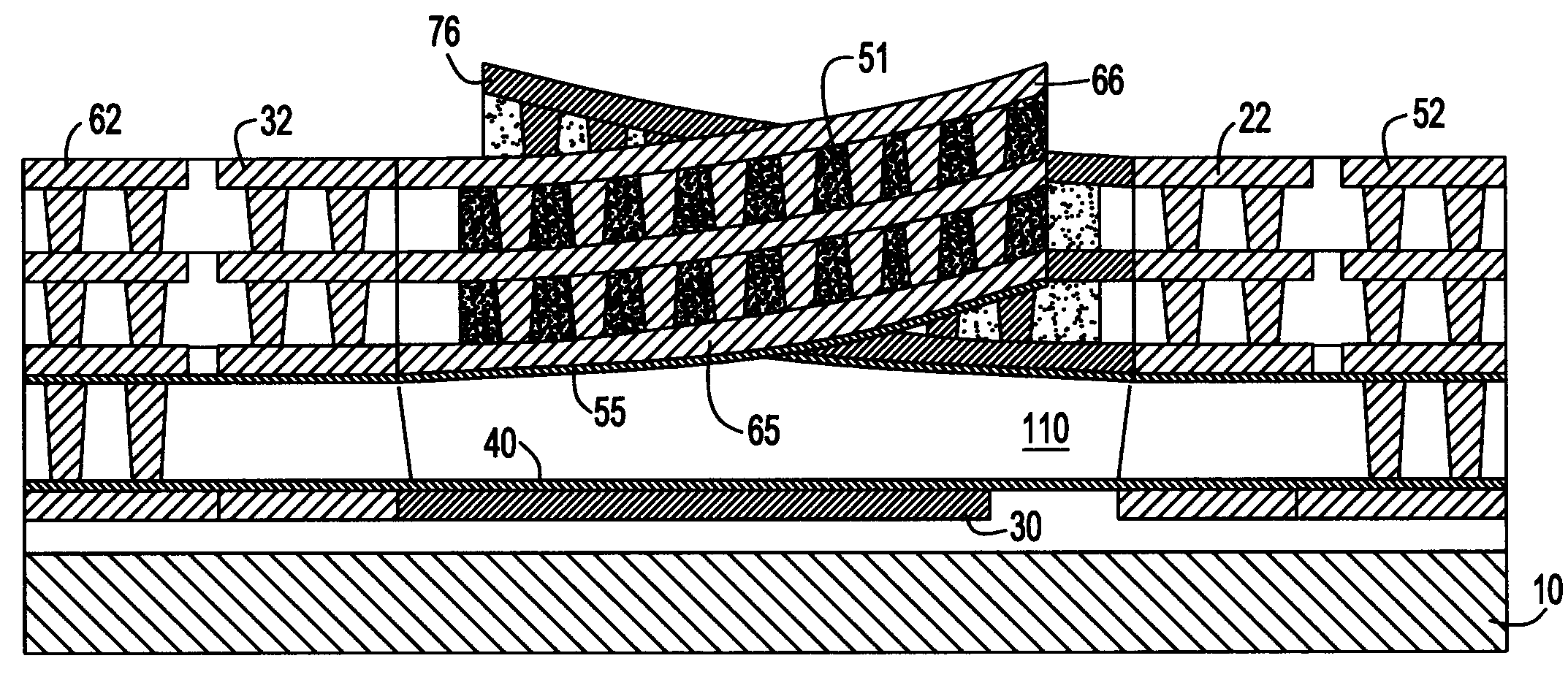
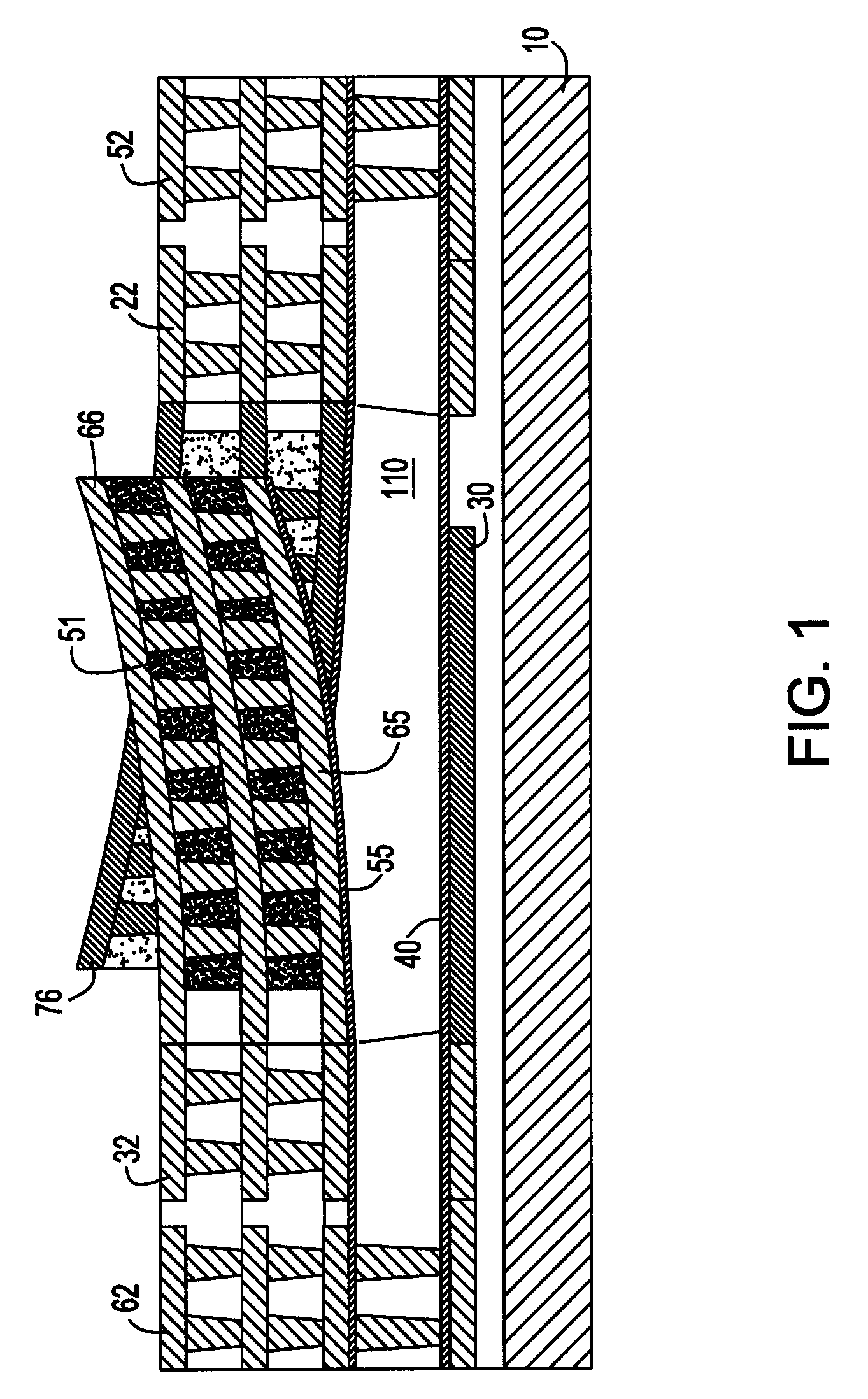
ActiveUS20070182639A1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsVaricapElectrical and Electronics engineering
A tunable impedance surface includes a varactor. The varactor comprises a bottom electrode formed on a surface of a substrate. First and second ferroelectric elements are on top of the bottom electrode and electrically connected to one another through the bottom electrode. A first top electrode is on top of and electrically connected to the first ferroelectric element and a second top electrode is on top of and electrically connected to the second ferroelectric element.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
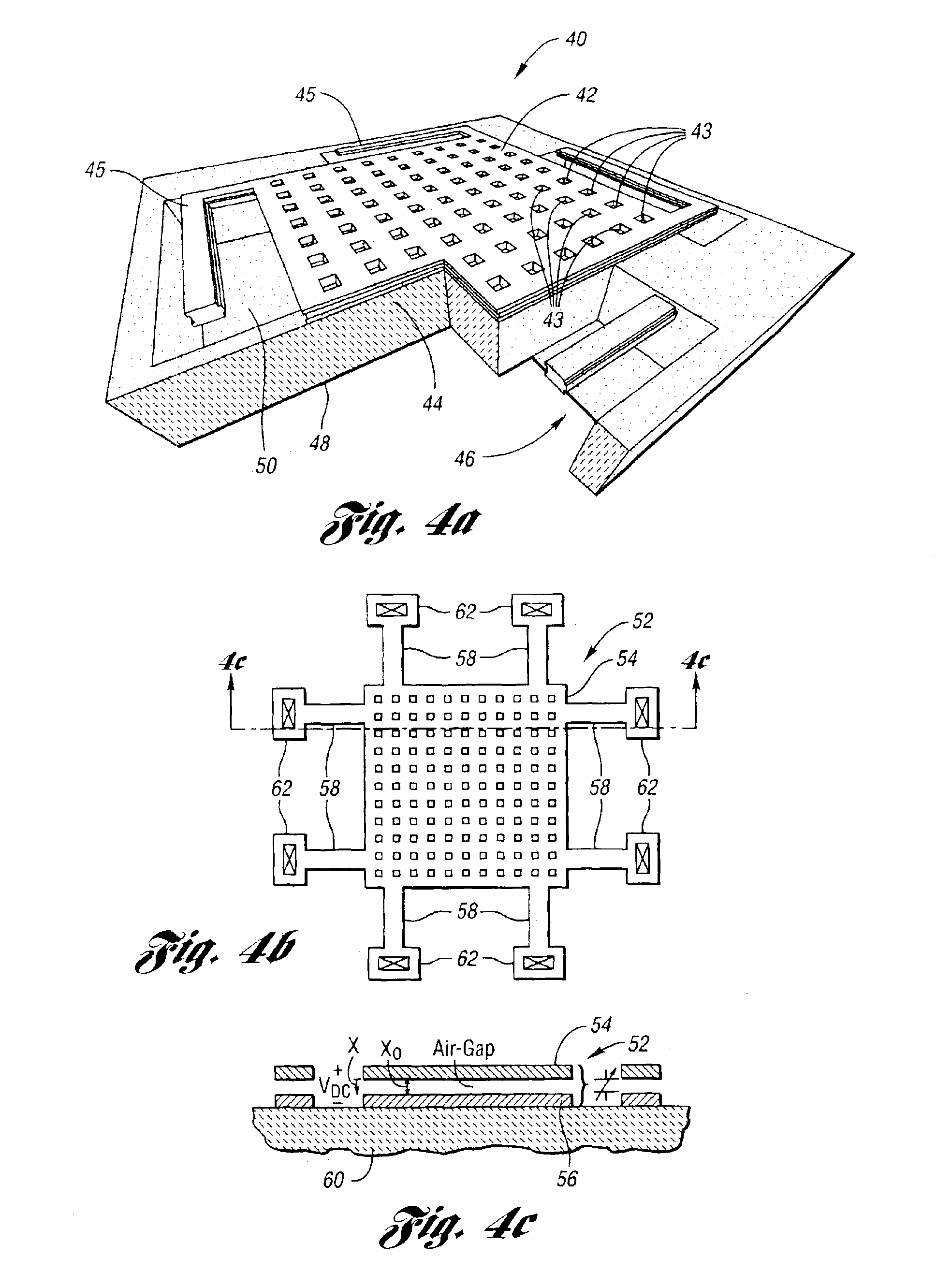
Elastomeric CMOS based micro electromechanical varactor
InactiveUS20060003482A1Increase capacitance densityIncreased side wall areaCapacitor with electrode distance variationMultiple capacitorsElastomerElectrical polarity
A micro electro-mechanical system (MEMS) variable capacitor is described, wherein movable comb electrodes of opposing polarity are fabricated simultaneously on the same substrate and are independently actuated. The electrodes are formed in an interdigitated fashion to maximize capacitance. The MEMS variable capacitor includes CMOS manufacturing steps in combination with elastomeric material selectively used in areas under greatest stress to ensure that the varactor will not fail as a result of stresses that may result in the separation of dielectric material from the conductive elements. The combination of a CMOS process with the conducting elastomeric material between vias increases the overall sidewall area, which provides increased capacitance density.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method for extending tuning range of electro-acoustic film resonators
InactiveUS7030718B1Increase spacingExceeding initial spacingImpedence networksElectric pulse generatorThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorAcoustic wave
A tuning circuit for adjusting an oscillation frequency of an oscillator circuit. The tuning circuit comprises a film bulk acoustic wave resonator (FBAR) having a series resonance frequency and a parallel resonance frequency, and an inductor coupled in series or parallel with the film bulk acoustic wave resonator. The series connection of the inductor and FBAR decreases the series resonance frequency. The parallel connection of the inductor and the FBAR increases the parallel resonance frequency. The tuning circuit further comprises a varactor coupled in series or parallel with the inductor and the FBAR combination. The varactor tunes the oscillation frequency over the increased tuning range.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
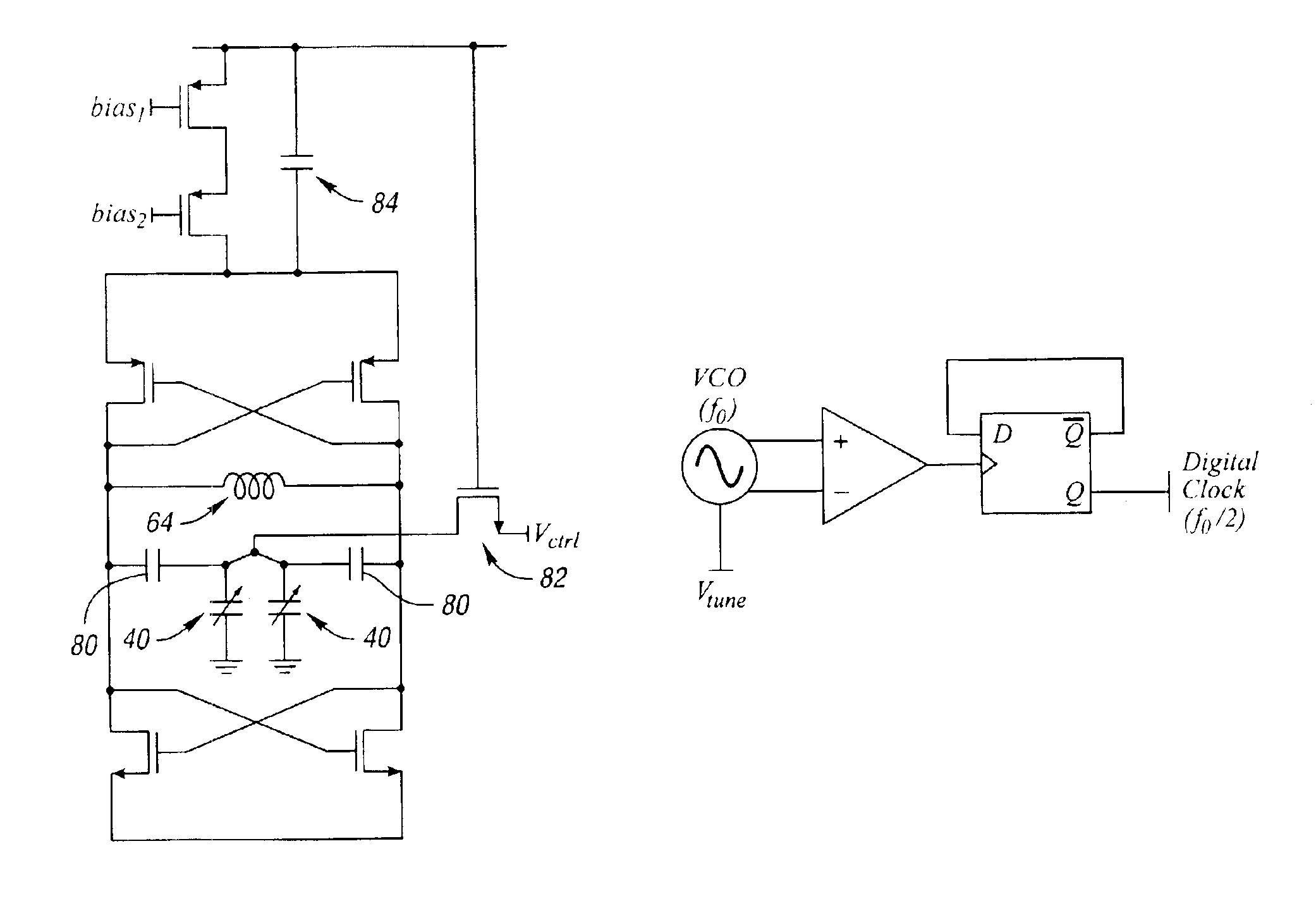
MEMS-based, computer systems, clock generation and oscillator circuits and LC-tank apparatus for use therein
InactiveUS6972635B2Reduce flicker noiseReduce phase noiseAngle modulation by variable impedenceMultiple-port networksEngineeringVaricap
MEMS-based, computer system, clock generation and oscillator circuits and LC-tank apparatus for use therein are provided and which are fabricated using a CMOS-compatible process. A micromachined inductor (L) and a pair of varactors (C) are developed in metal layers on a silicon substrate to realize the high quality factor LC-tank apparatus. This micromachined LC-tank apparatus is incorporated with CMOS transistor circuitry in order to realize a digital, tunable, low phase jitter, and low power clock, or time base, for synchronous integrated circuits. The synthesized clock signal can be divided down with digital circuitry from several GHz to tens of MHz—a systemic approach that substantially improves stability as compared to the state of the art. Advanced circuit design techniques have been utilized to minimize power consumption and mitigate transistor flicker noise upconversion, thus enhancing clock stability.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
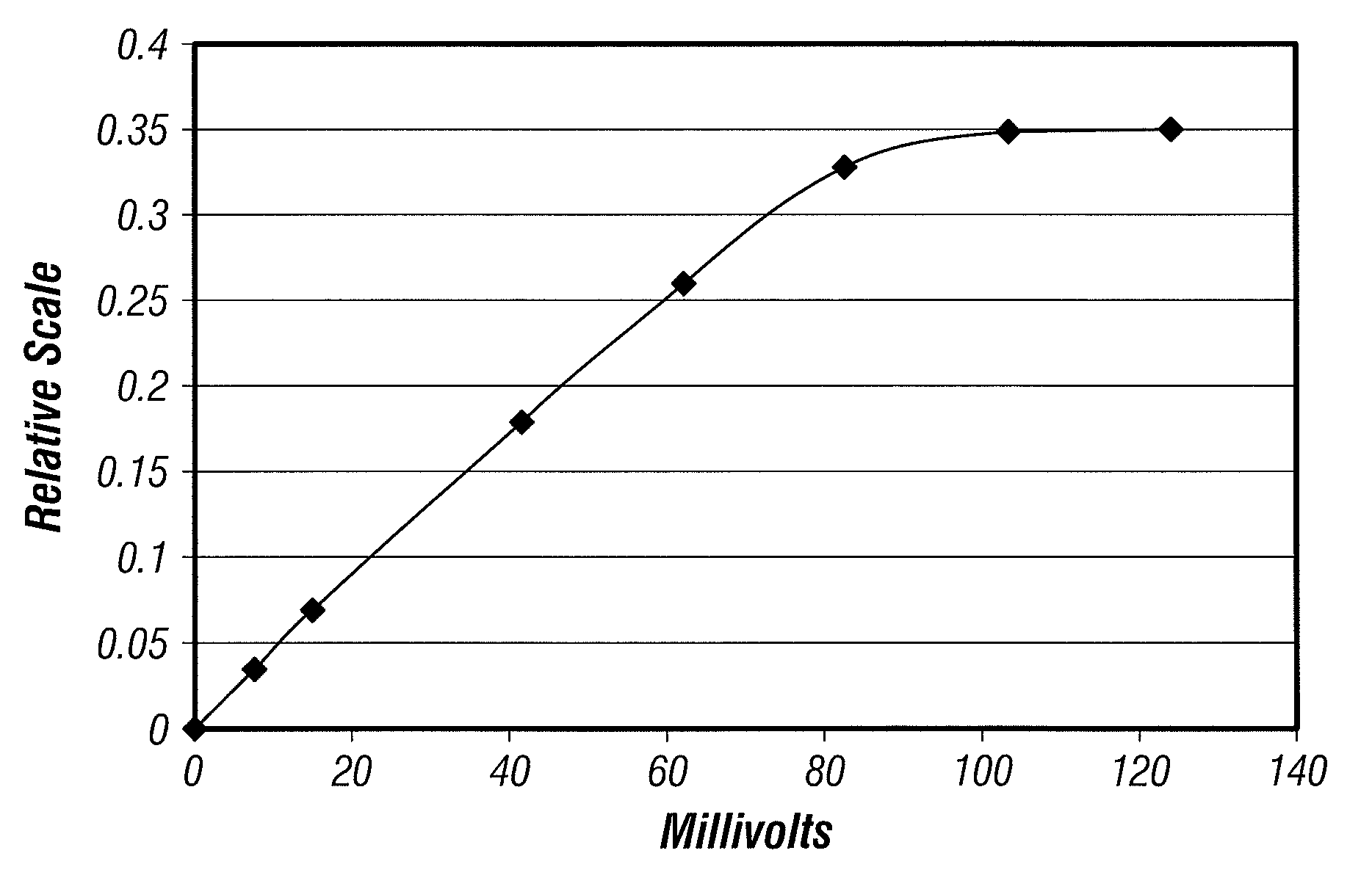
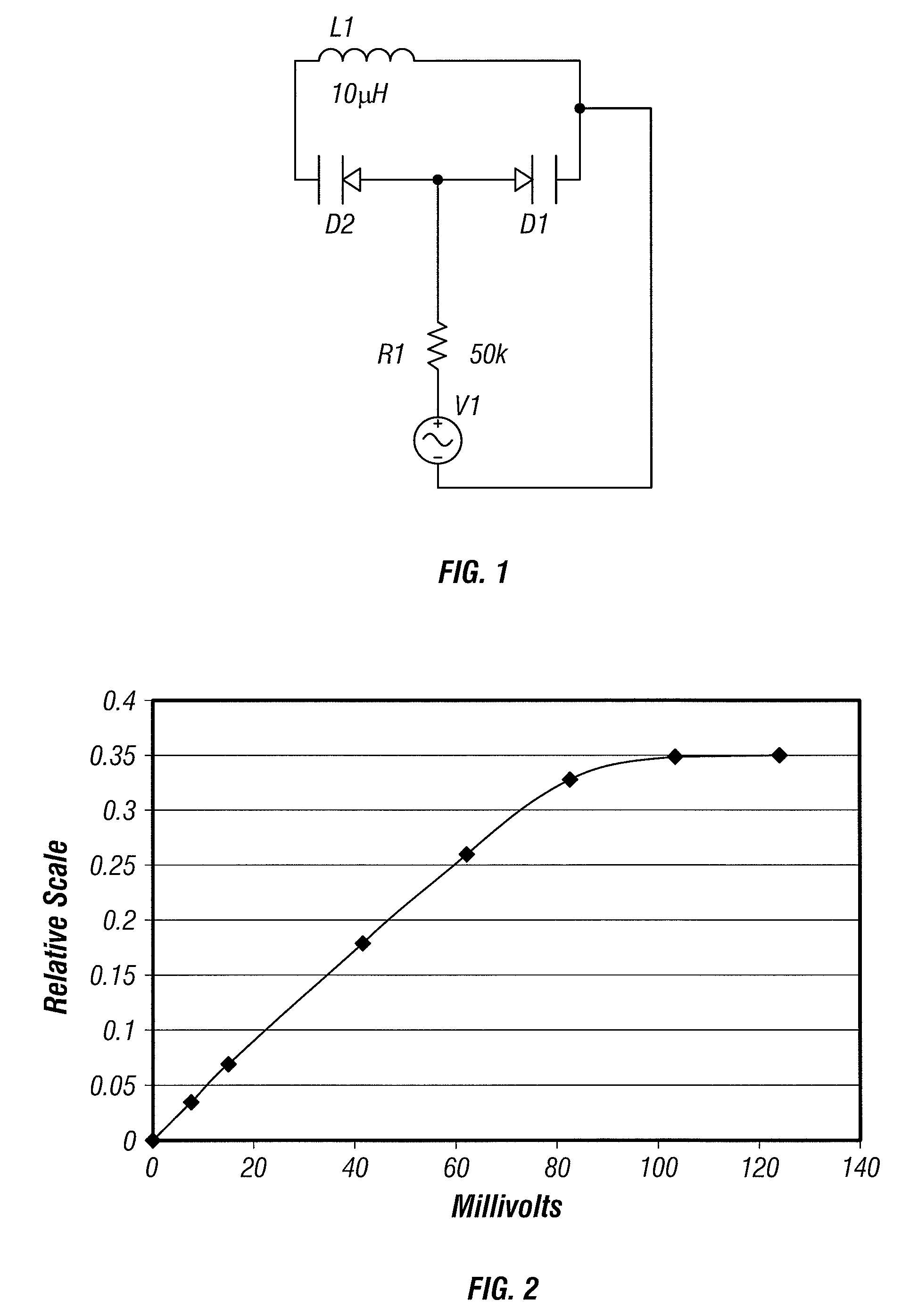
Systems and Methods for Wireless Transmission of Biopotentials
The invention relates to wireless biotelemetry of low level bioelectric and biosensor signals by means of directly modulating the backscatter of a resonant circuit. Low level electrical analog or digital signals are directly applied to a resonant circuit containing a voltage-variable capacitor such as a varactor diode, that proportionally shifts the resonant frequency and so amplitude of radiofrequency backscatter in a way that represents analog bioelectric or biosensor waveform data. By strongly driving the resonant circuit with a radiofrequency source, a voltage variable capacitance can be caused to amplify the bio-signal level by a parametric process and so provide sufficient sensitivity to telemeter for low millivolt and microvolt level signals without additional amplification. A feature of the device is its simplicity and that it accomplishes both modulation and preamplification of low level sensor signals by the same variable capacitance circuit which reduces the device size and power consumption.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
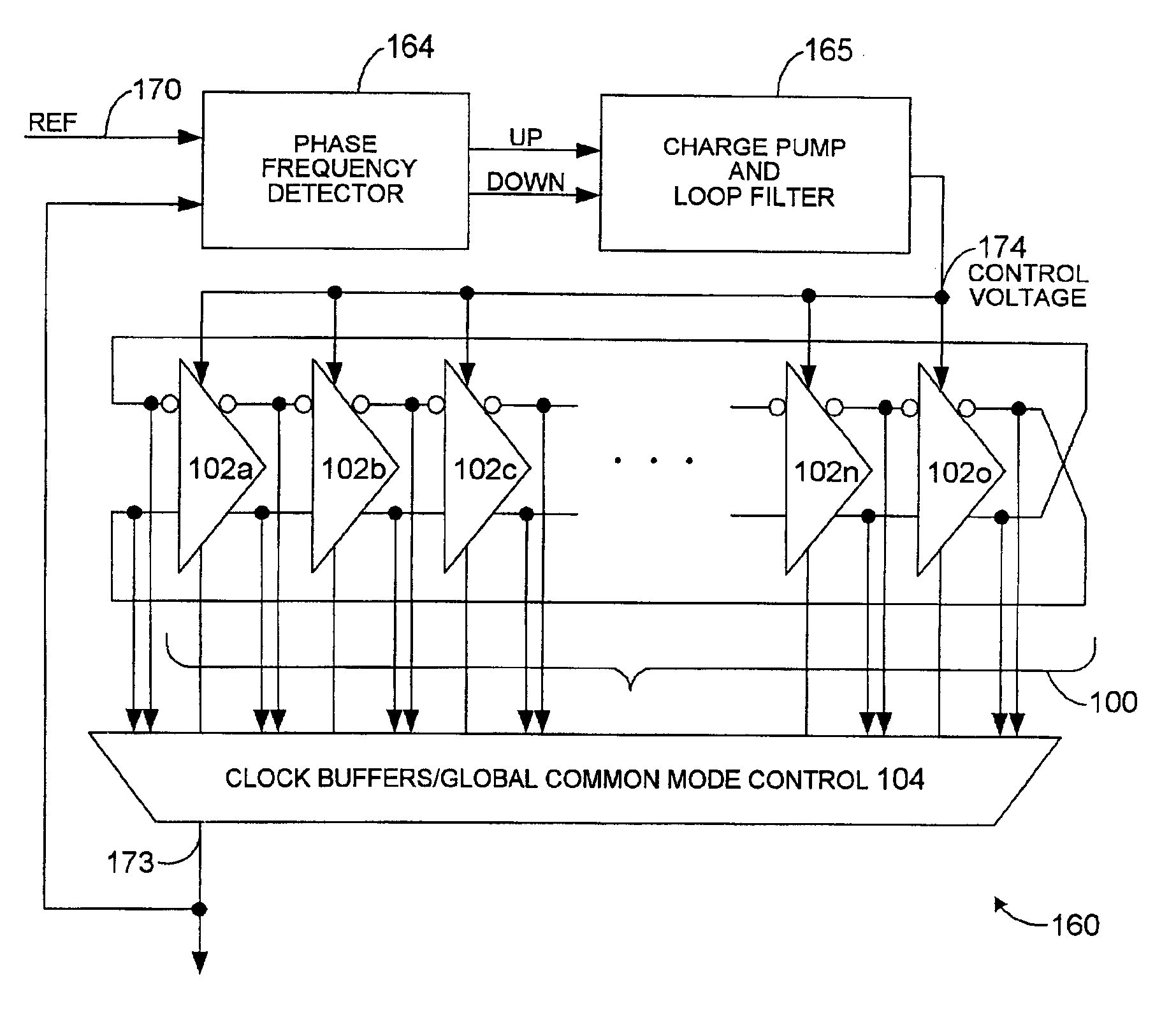
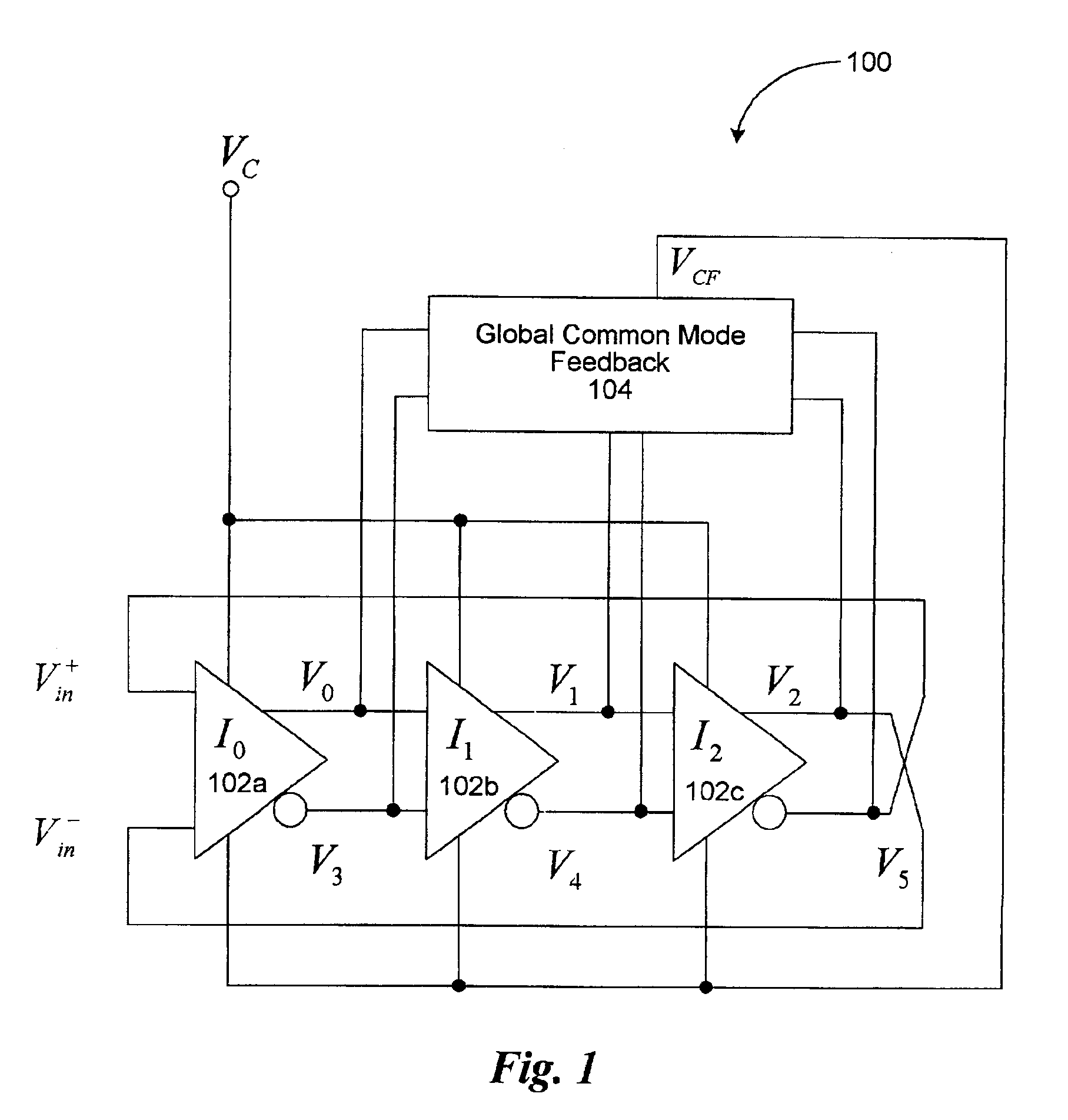
Multi-phase voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) with common mode control
A voltage controlled oscillator ("VCO") circuit capable of generating signals with reduced jitter and / or low-phase noise is provided. One embodiment provides a plurality of cascaded VCO cells, where each VCO cell can include a source coupled differential pair, a bias transistor connected to the differential pair for biasing the differential pair, a resistive load pair connected to the differential pair, and a voltage controlled capacitor pair or varactor pair connected to the differential pair. The varactors provide control over the frequency of the oscillations produced by the VCO circuit in combination with a control voltage. A phase frequency detector combined with a charge pump and loop filter provide the control voltage.
Owner:UNIVERSAL CONNECTIVITY TECH INC
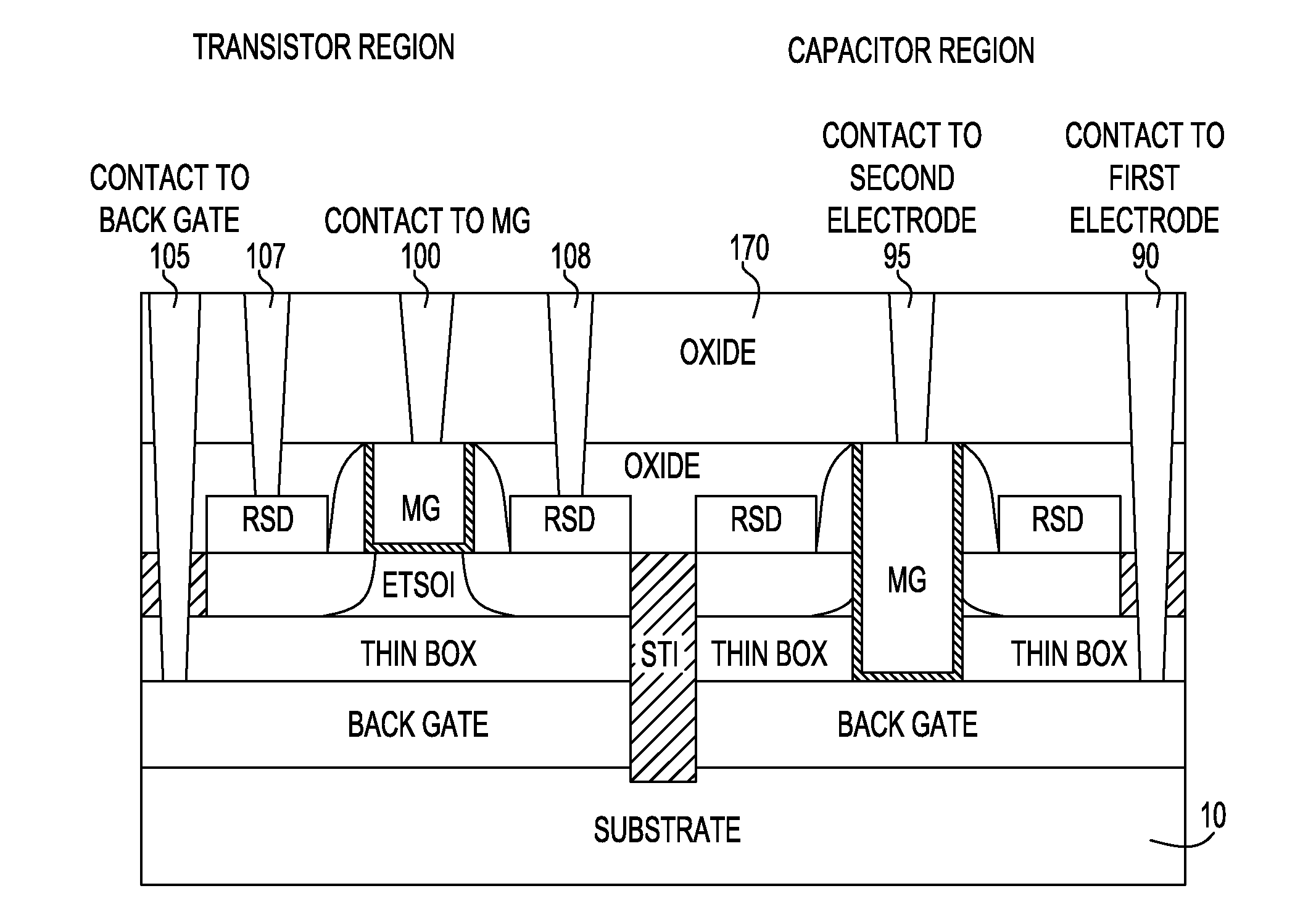
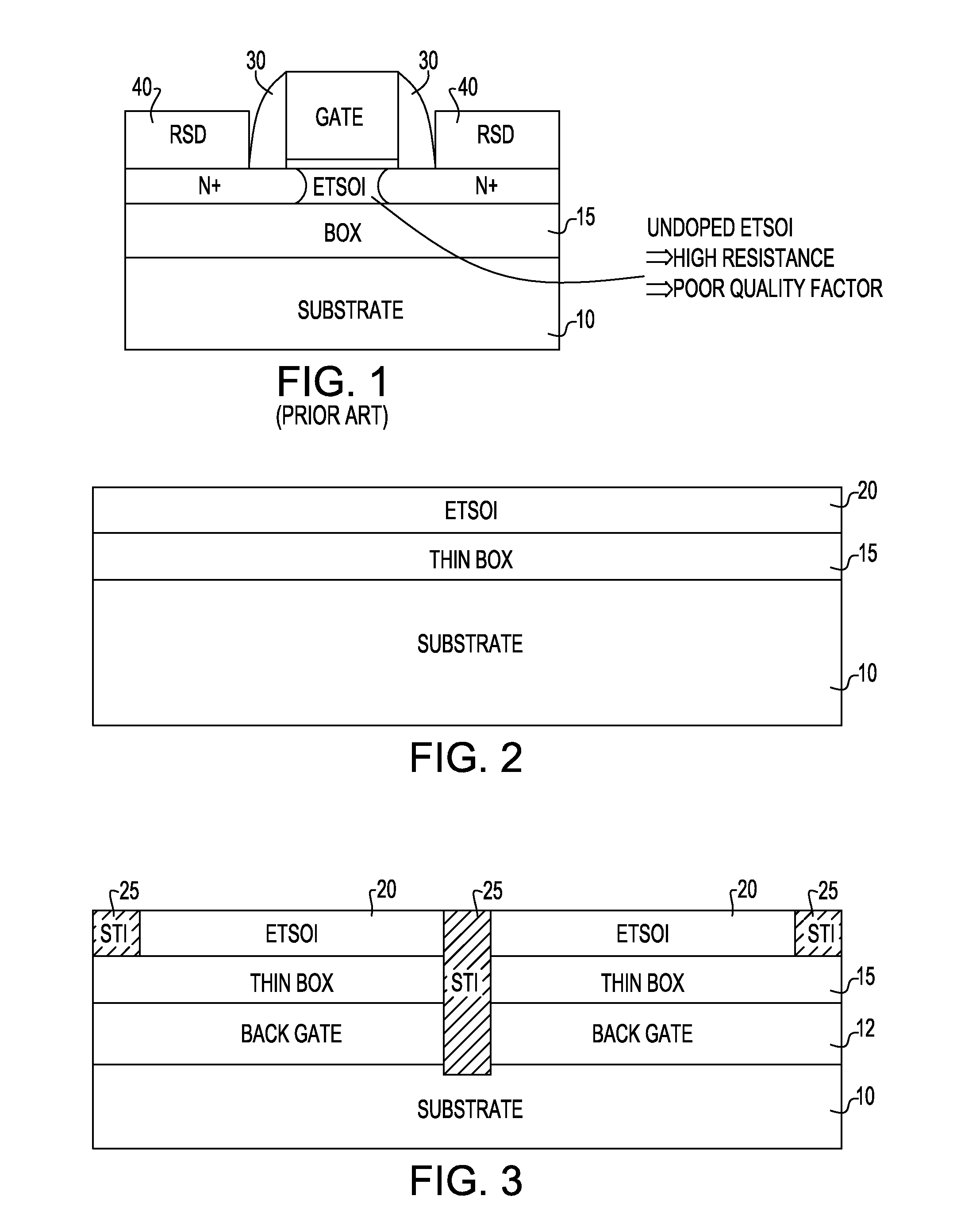
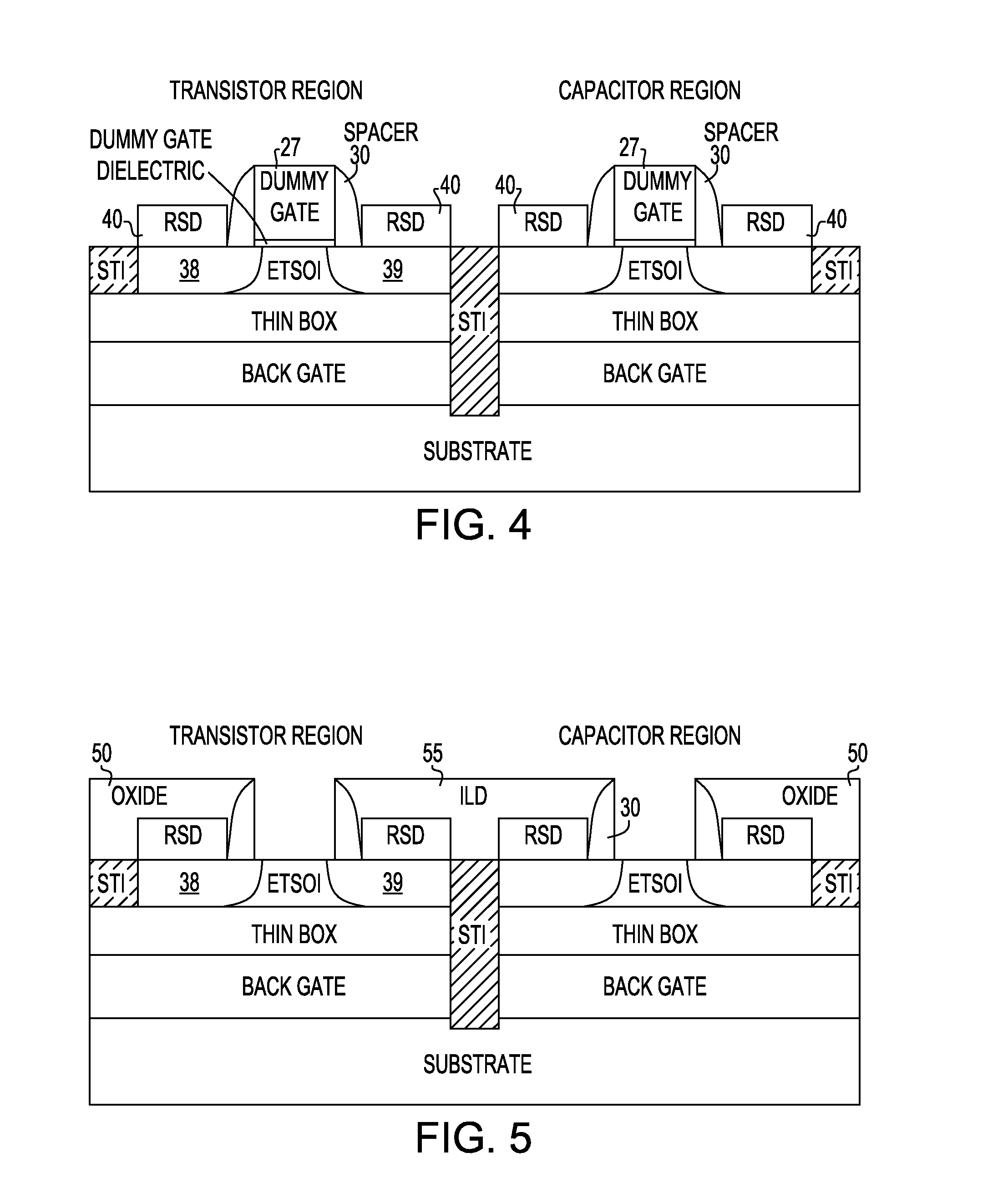
Method and Structure For Forming On-Chip High Quality Capacitors With ETSOI Transistors
ActiveUS20130146959A1Improving capacitorImproving varactor qualityTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSLithographic artist
An ETSOI transistor and a capacitor are formed respectively in a transistor and capacitor region thereof by etching through an ETSOI and thin BOX layers in a replacement gate HK / MG flow. The capacitor formation is compatible with an ETSOI replacement gate CMOS flow. A low resistance capacitor electrode makes it possible to obtain a high quality capacitor or varactor. The lack of topography during dummy gate patterning are achieved by lithography in combination accompanied with appropriate etch.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
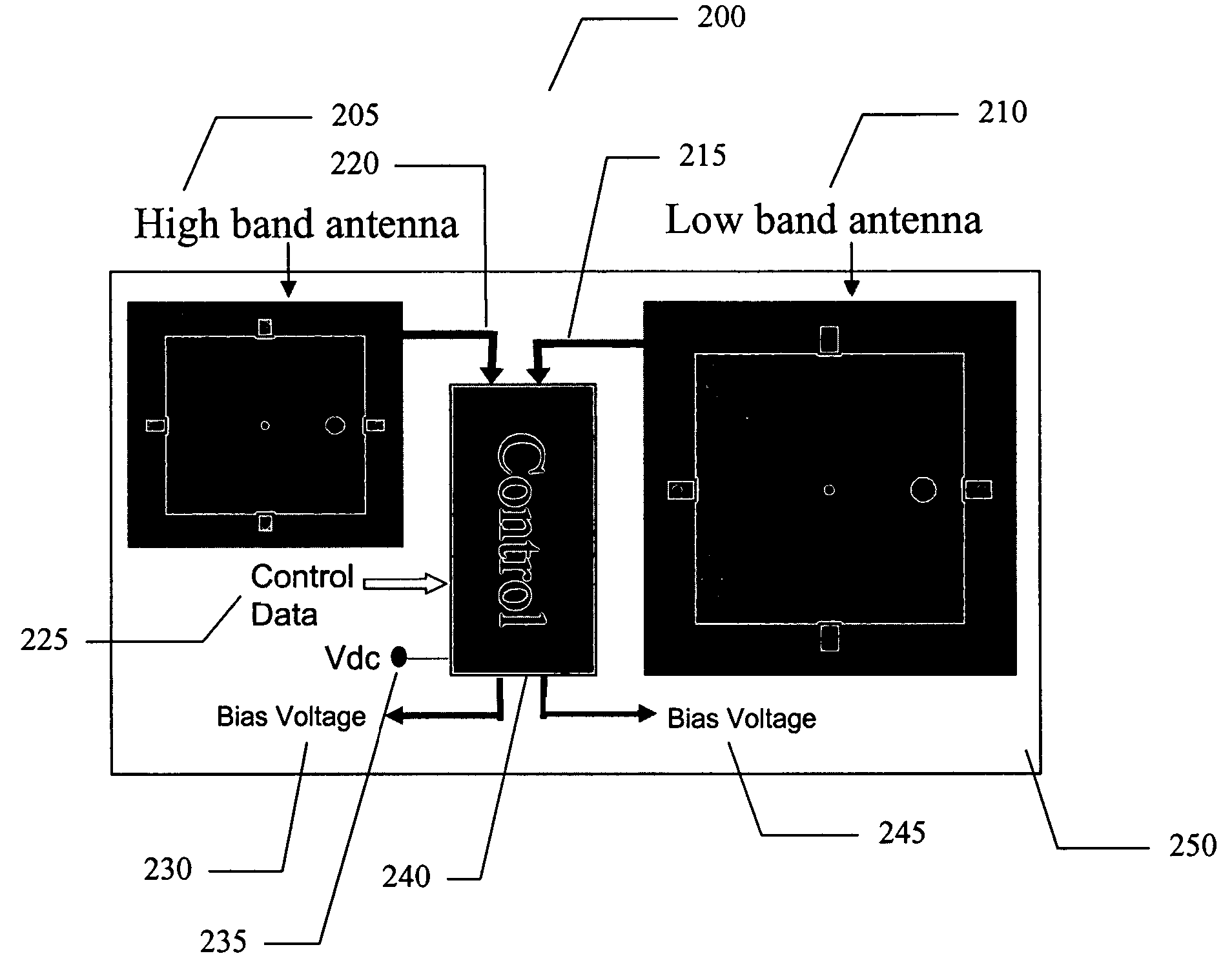
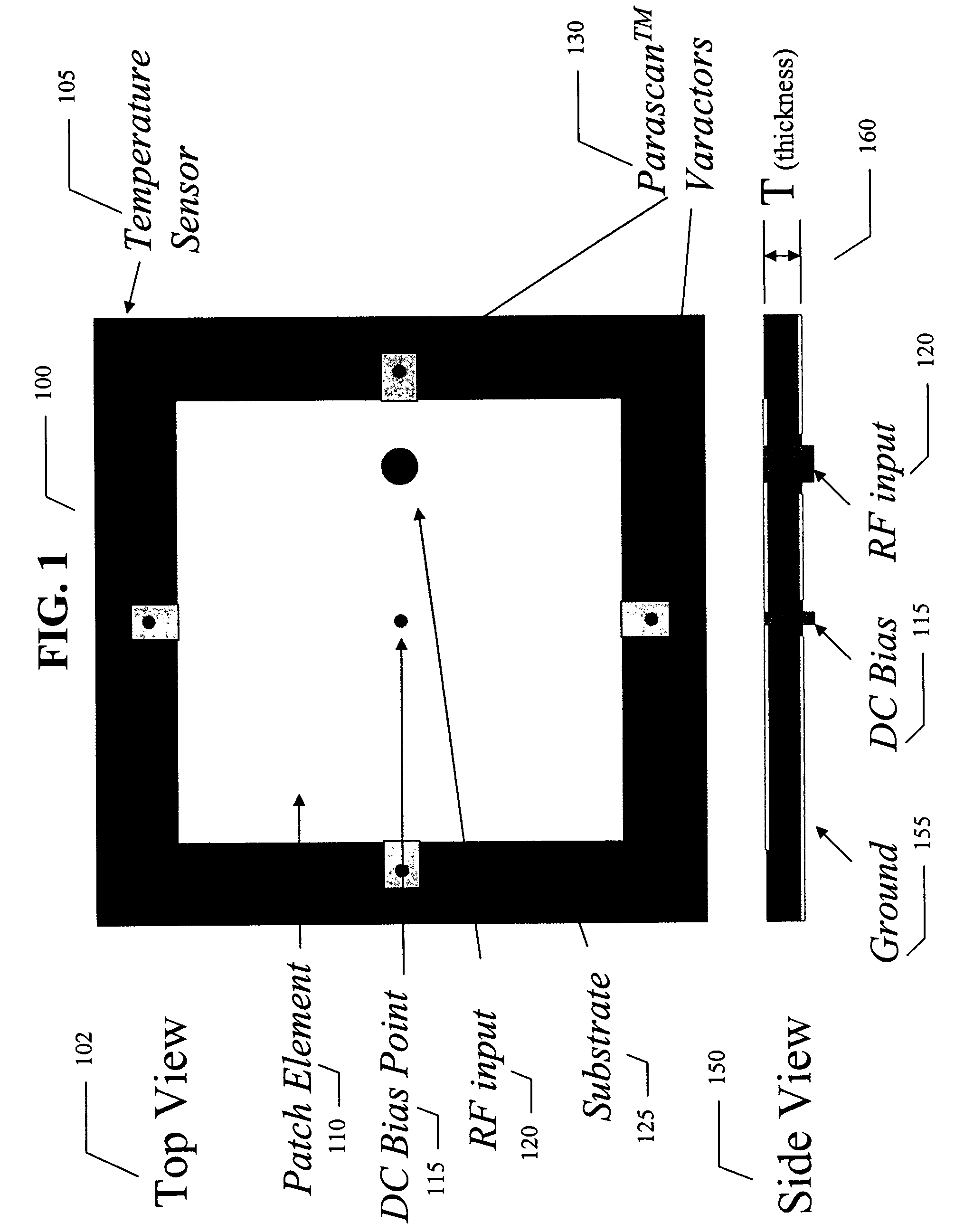
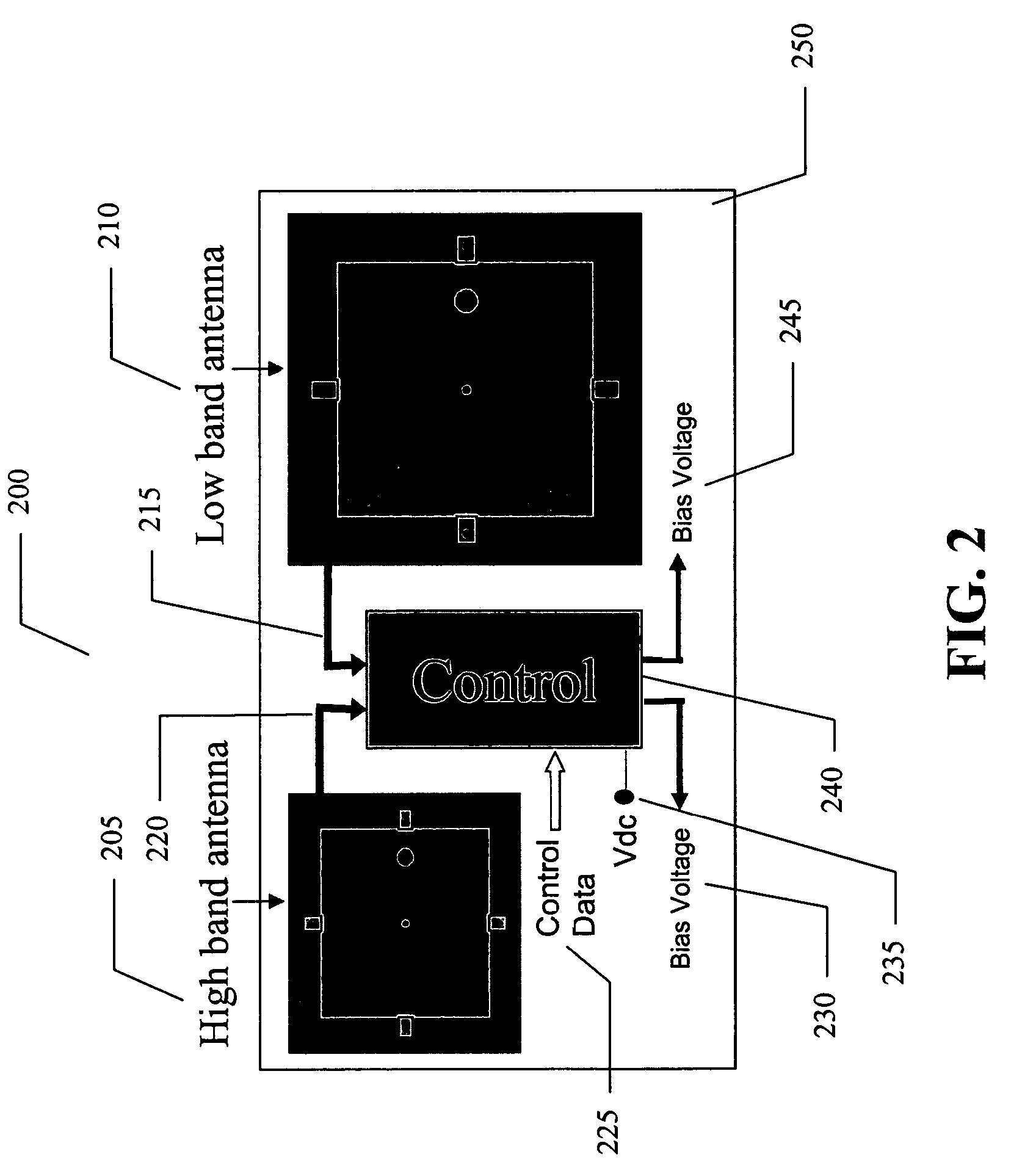
Electronically tunable quad-band antennas for handset applications
An electronically tunable quad-band antenna which includes a tunable high band antenna tuned by at least one tunable varactor associated therewith; the tunable high band antenna further includes a substrate, a patch element on said substrate, at least one voltage tunable varactor associated with the patch element, a DC bias point on the patch element, an RF input on the patch element, and a temperature sensor associated with the high band pass antenna. Also included in a preferred embodiment of the electronically tunable quad-band antenna of the present invention is a tunable low band antenna tuned by at least one tunable varactor associated therewith, the tunable low band antenna further including a substrate, a patch element on said substrate, at least one voltage tunable varactor associated with said patch element, a DC bias point on said patch element, an RF input on said patch element, and a temperature sensor associated with said low band pass antenna.Also included is a controller receiving control data, and receiving output information from said low band antenna and output information from said high band antenna and controlling a first bias voltage for biasing the at least one voltage tunable varactor associated with the high band antenna and a second bias voltage for biasing the at least one voltage tunable varactor associated with the low band antenna. The bias voltages can be provided by a DC to DC converter regulator.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Wideband monolithic tunable high-Q notch filter for image rejection in RF application
InactiveUS6990327B2Good image rejectionWide tunable rangeMultiple-port networksTransmissionEngineeringInductor
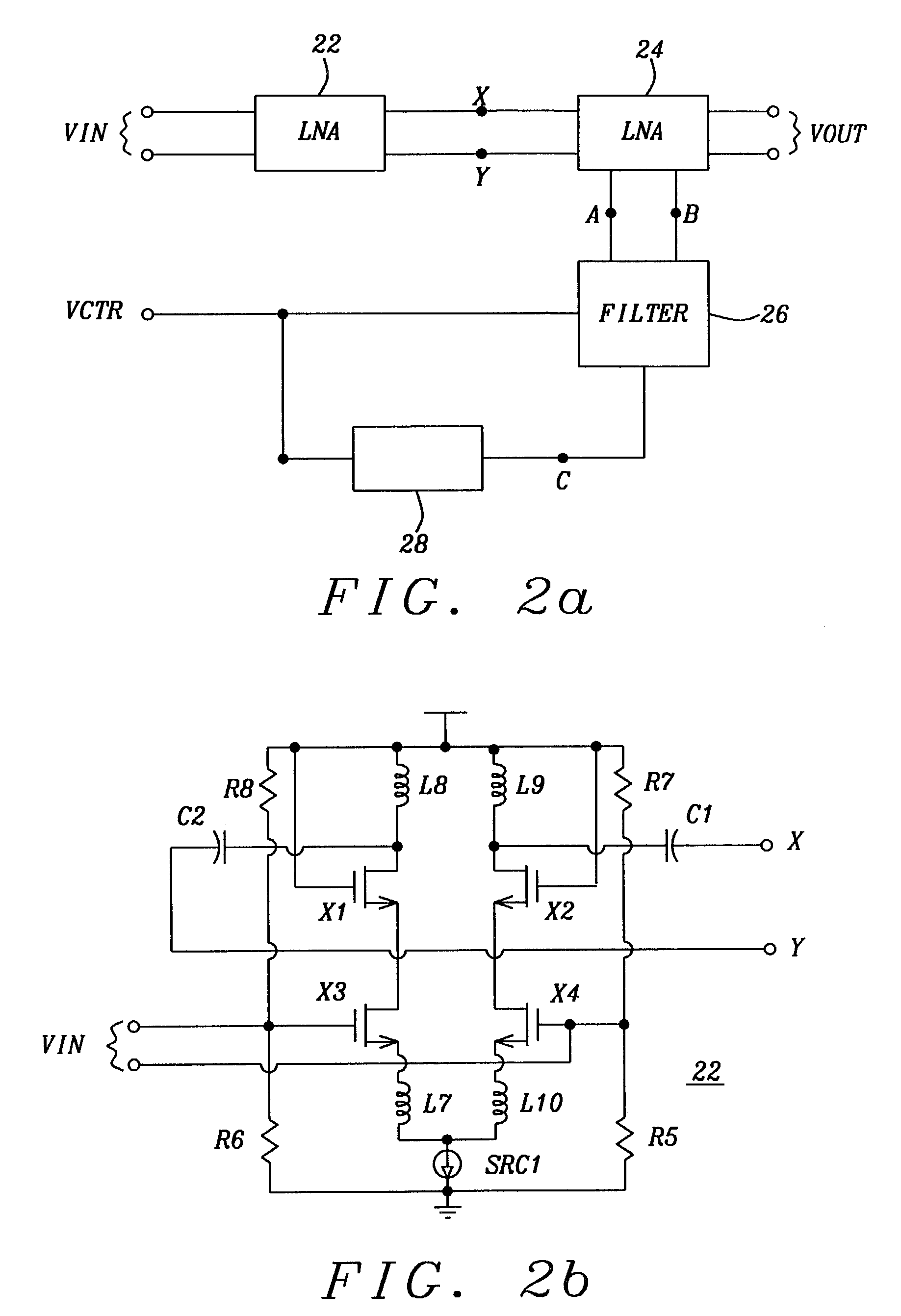
A notch filter with a high Q factor, which is integrated with a first and a second cascoded LNA, is totally contained on an integrated chip. The notch filter, comprising two Q-enhancement circuits, is coupled to the second differential LNA. The two Q-enhancement circuits are combined to generate sufficient negative impedance to compensate for the loss in the on-chip low Q inductors. To improve the image rejection of the notch filter in a wide frequency band, the notch filter uses an automatic current tuning circuit which consists of an analog multiplier and fixed and voltage controlled current sources. Furthermore, by modifying the connection and location of the tunable varactor, another wideband tunable notch filter is implemented. The notch filter can be applied in all current wireless receiver systems.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
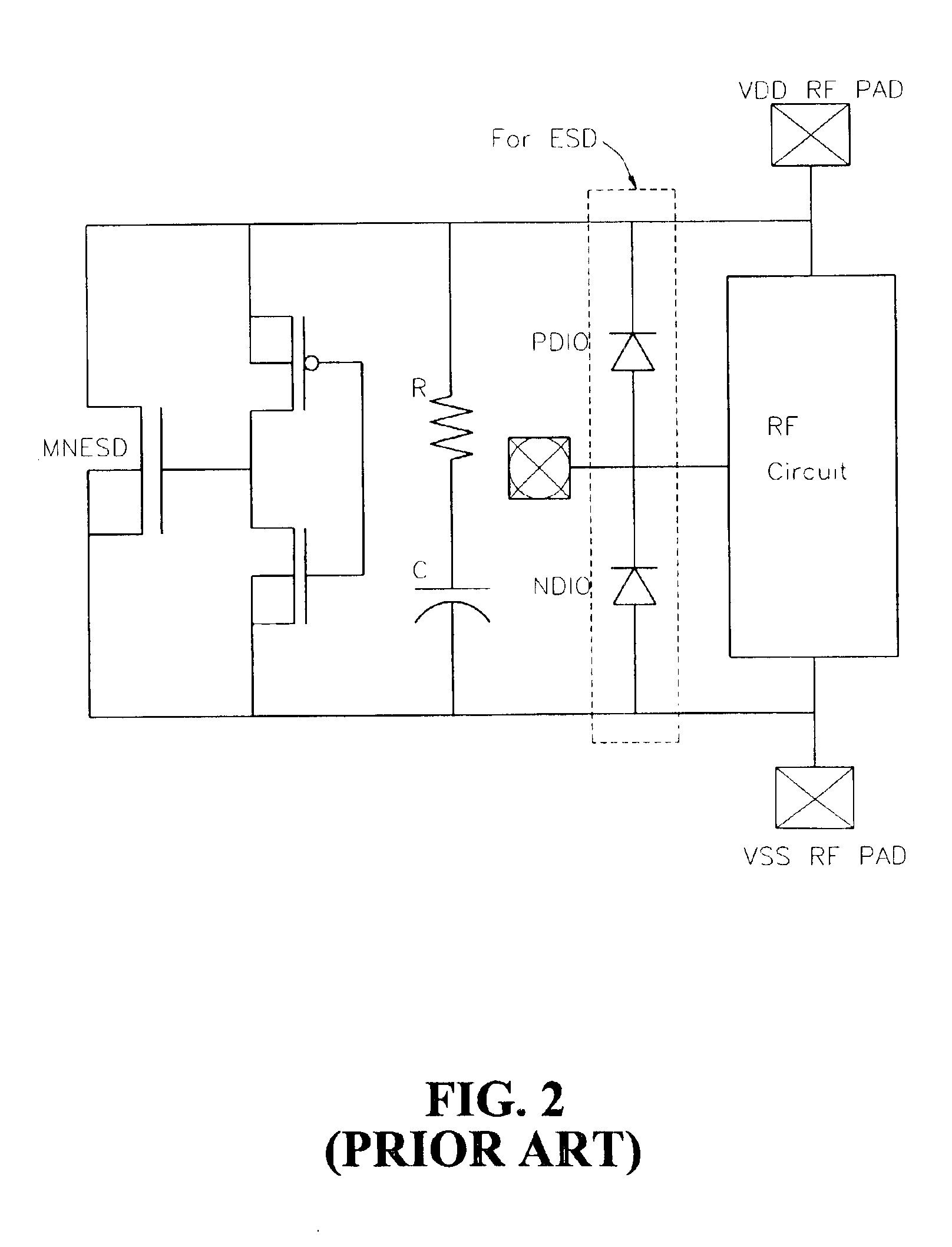
Electrostatic discharge protection device for giga-hertz radio frequency integrated circuits with varactor-LC tanks
InactiveUS6885534B2Solution value is not highHigh ESD levelSolid-state devicesEmergency protective arrangement detailsImpedance matchingEngineering
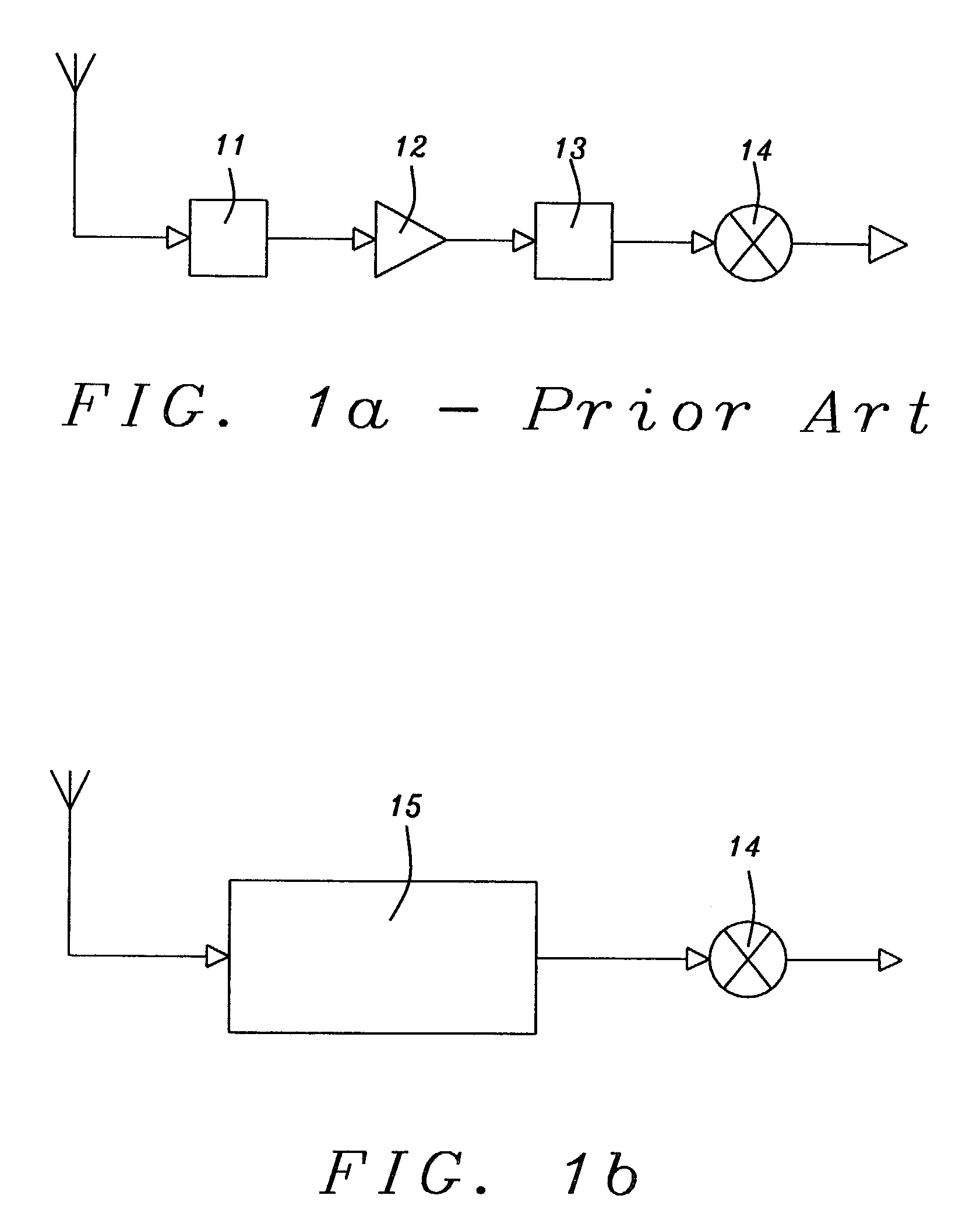
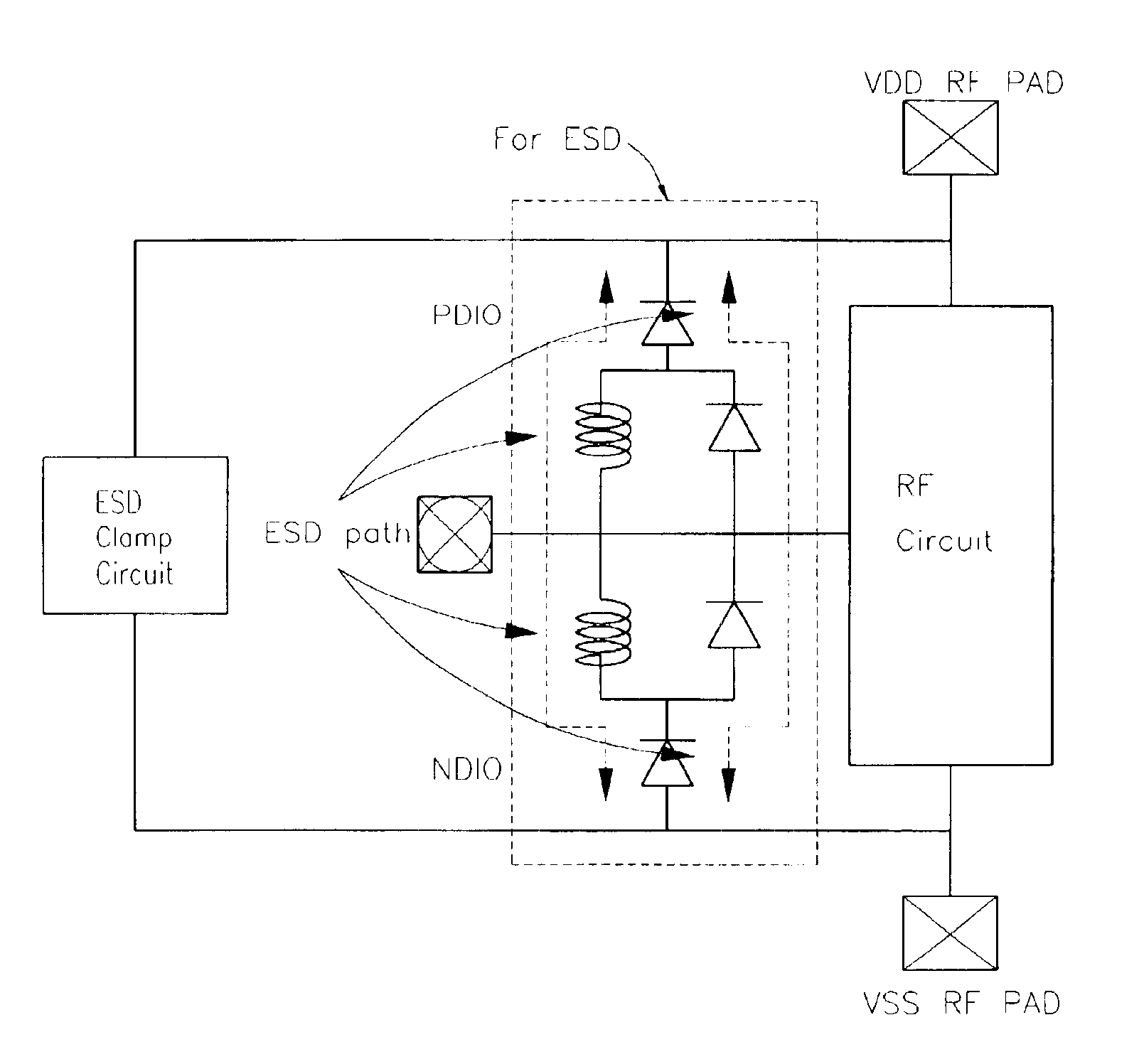
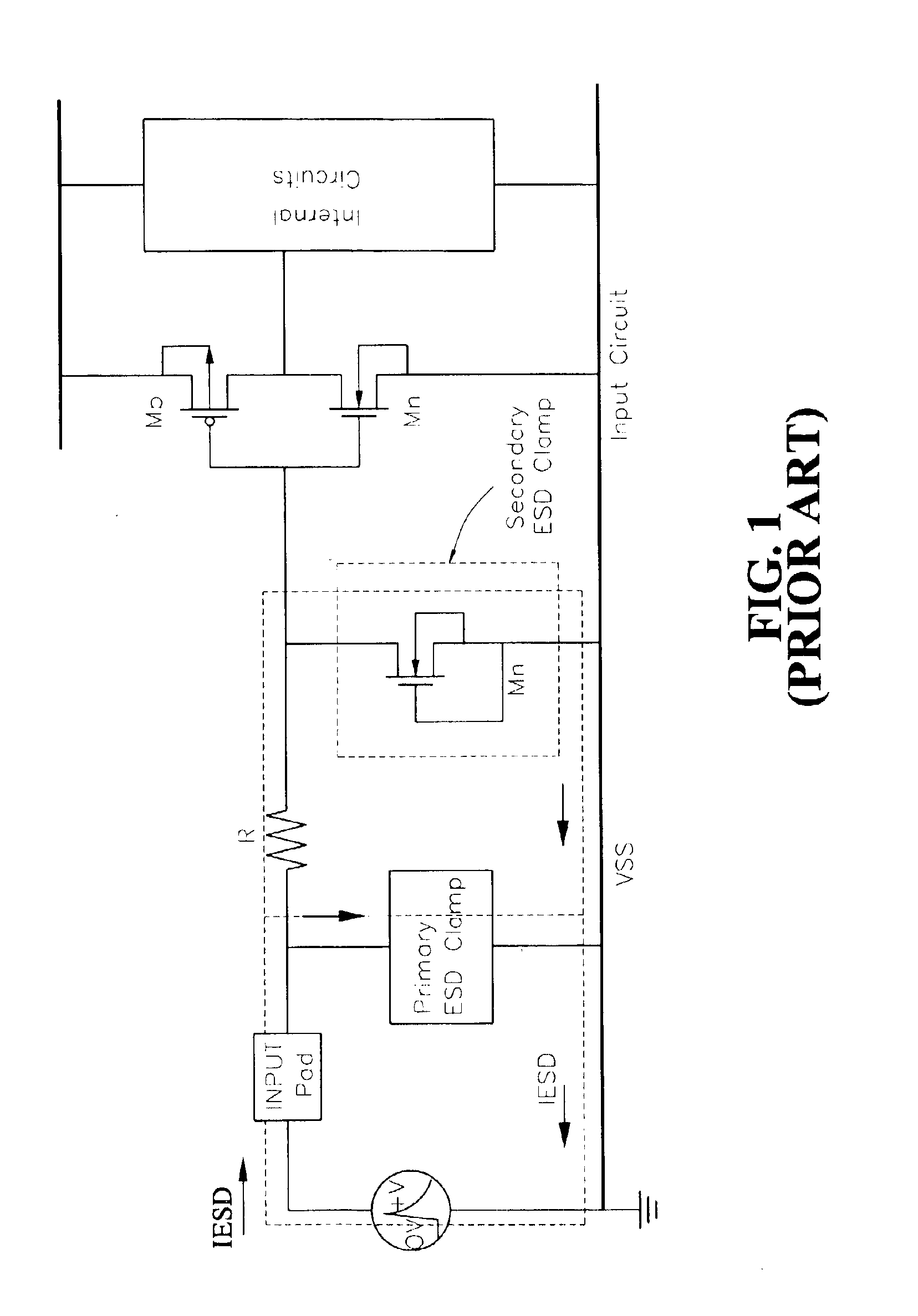
The present invention relates to a device for protecting high frequency RF integrated circuits from ESD damage. The device comprises at least one varactor-LC circuit tank stacked to avoid the power gain loss by the parasitic capacitance of ESD circuit. The varactor-LC tank could be designed to resonate at the RF operating frequency to avoid the power gain loss from the parasitic capacitance of ESD circuit. Multiple LC-tanks could be stacked for further reduction in the power gain loss. A reverse-biased diode is used as the varactor for both purposes of impedance matching and effective ESD current discharging. Because the inductor is made of metal, both the inductor and the varactor can discharge ESD current when ESD condition happens. It has a high enough ESD level to prevent ESD discharge.
Owner:LIBERTY PATENTS LLC
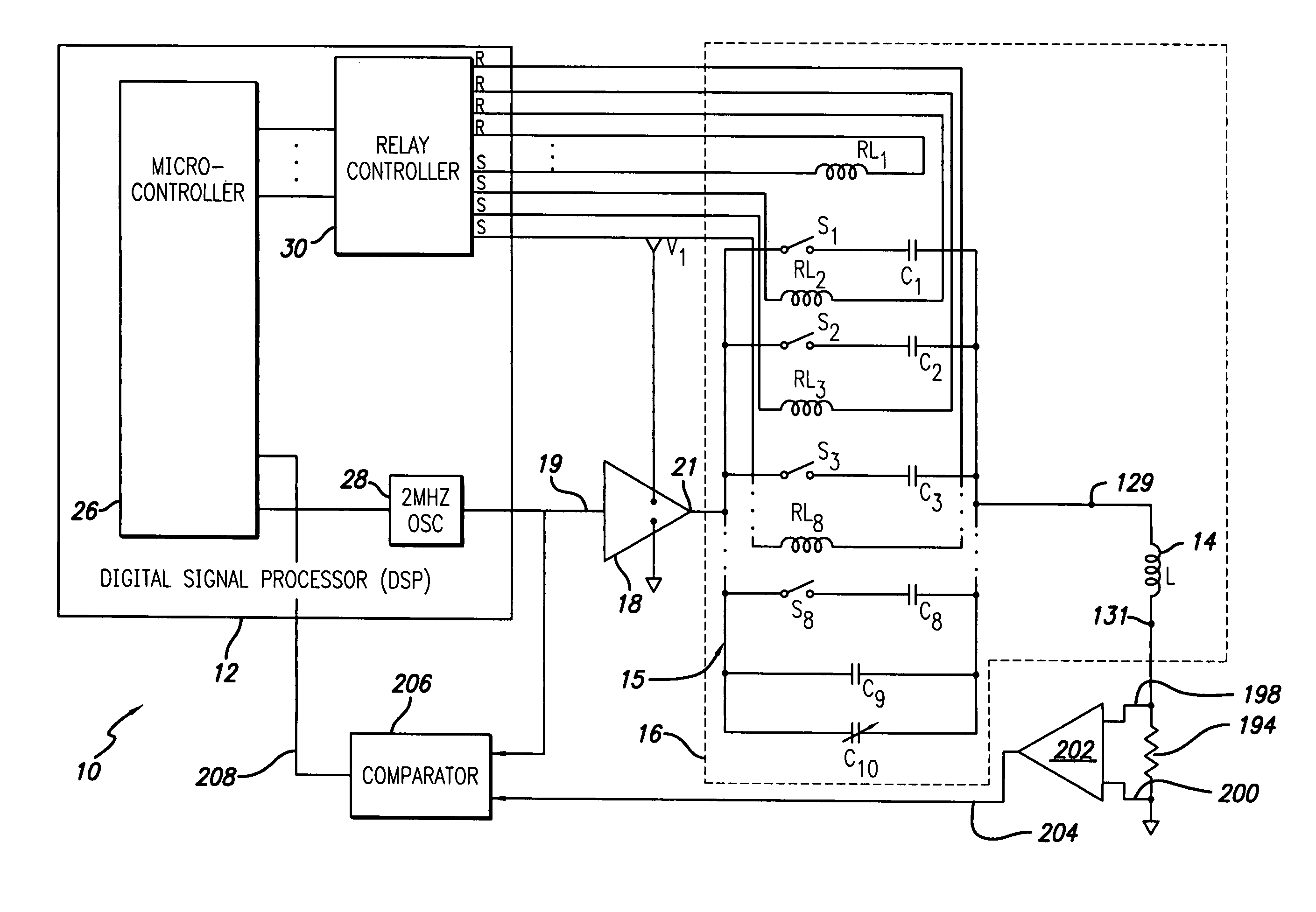
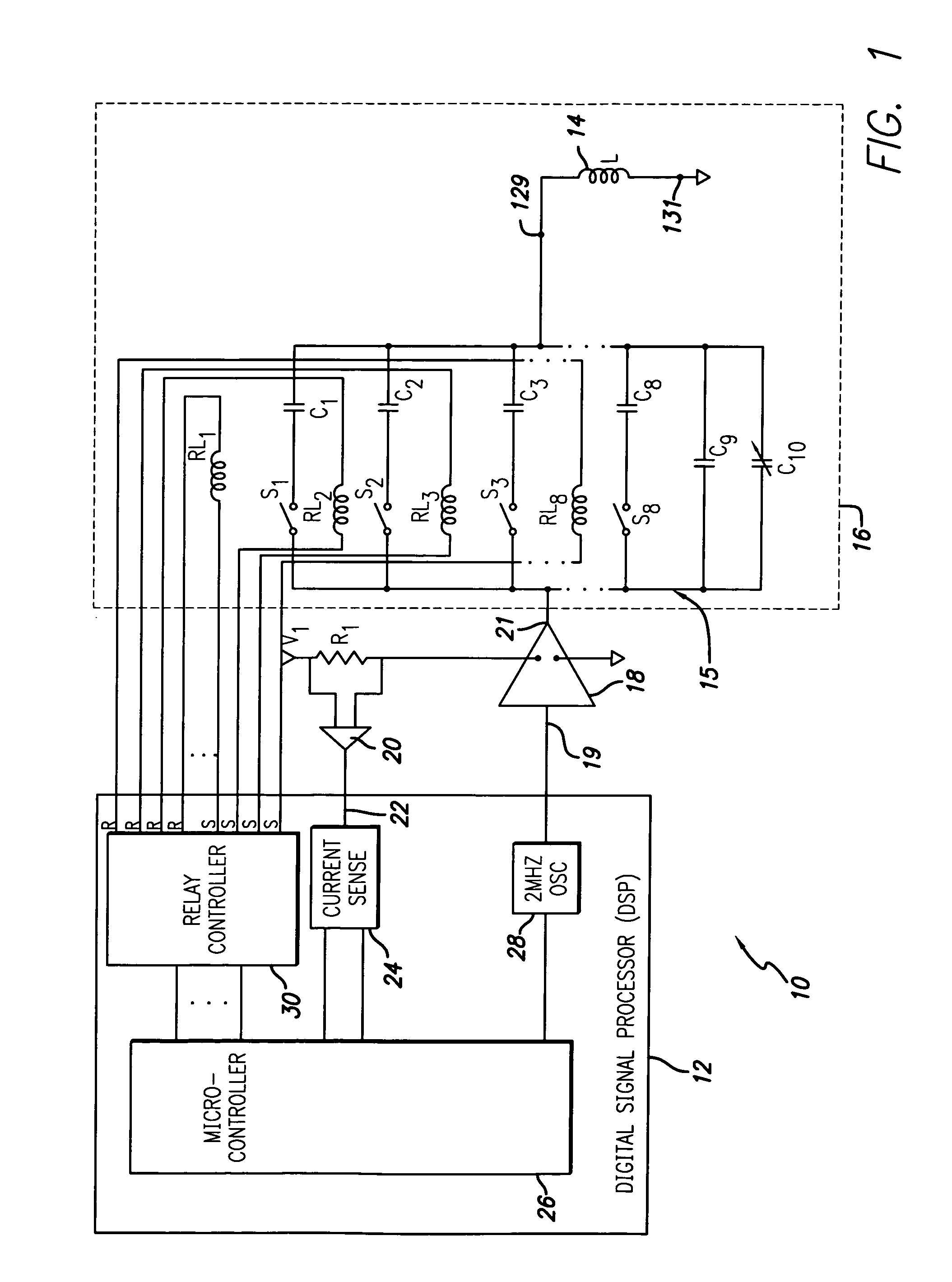
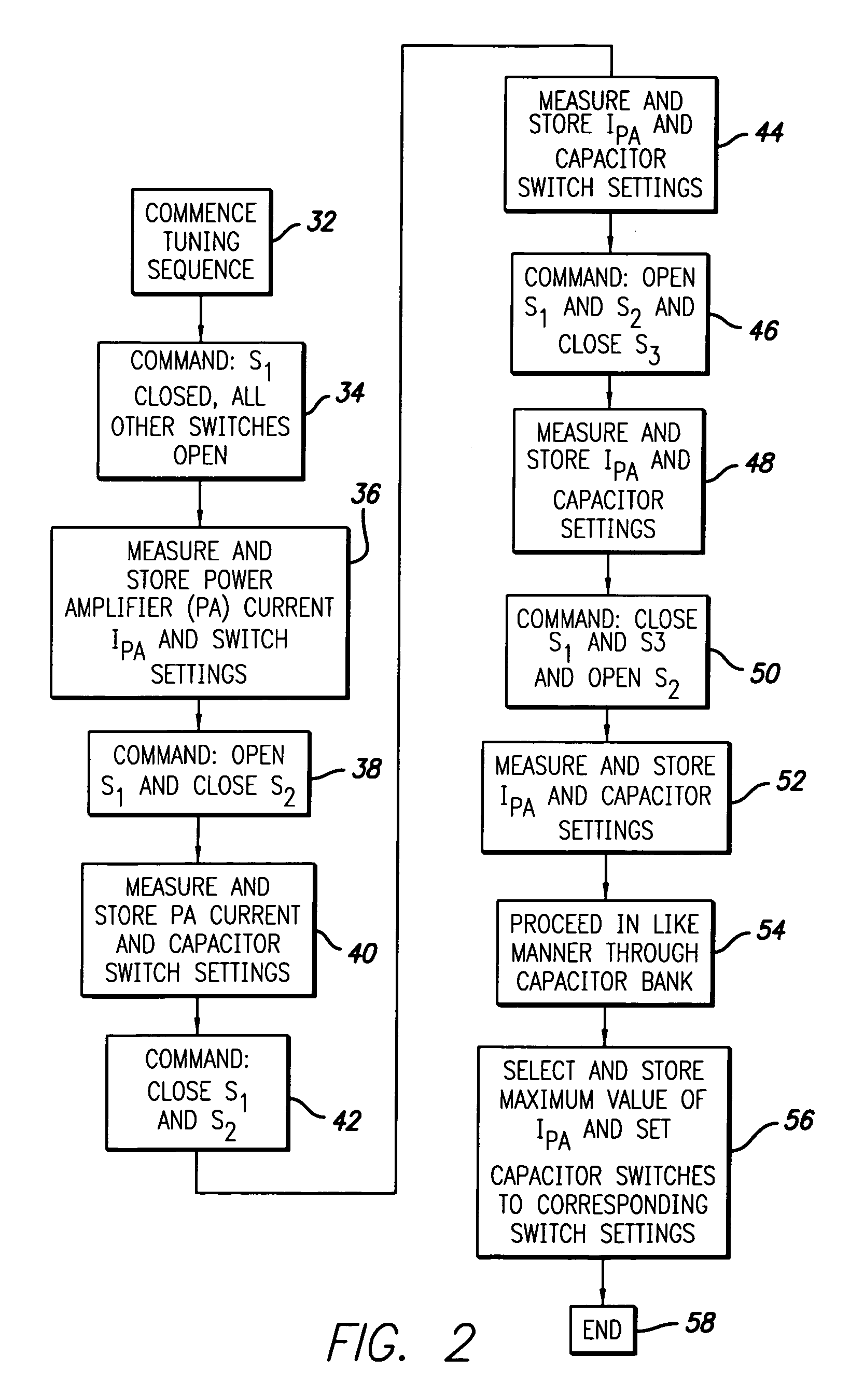
System and method for automatic tuning of a magnetic field generator
ActiveUS7515012B2Power maximizationMaximize power outputElectrotherapyTransmission control/equlisationHemt circuitsEngineering
An automatic tuning system for a magnetic field generating tuned circuit includes a processor configured to maintain the resonant frequency of a tuned circuit equal to a reference frequency. The tuned circuit is driven by a power amplifier whose output provides an amplified signal at the reference frequency. The tuned circuit includes a magnetic field generating inductor and a bank of individually switchable capacitors controlled by the processor capable of adding and removing the respective capacitances to and from the tuned circuit. The inductor includes a Faraday shield to shield the tuned circuit from the influence of electric fields. In an embodiment of the invention, the variable capacitor is in the form of a diode variable capacitor (varicap) in parallel circuit relationship with the tuned circuit capacitor and the inductor. In an alternate embodiment the inductor and a fixed capacitor are in series circuit relationship with the varicap in parallel circuit relationship with the fixed capacitor and the tuning sequence relies on a phase locked loop using the phase of a reference frequency signal and the phase of the inductor voltage as control parameters.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
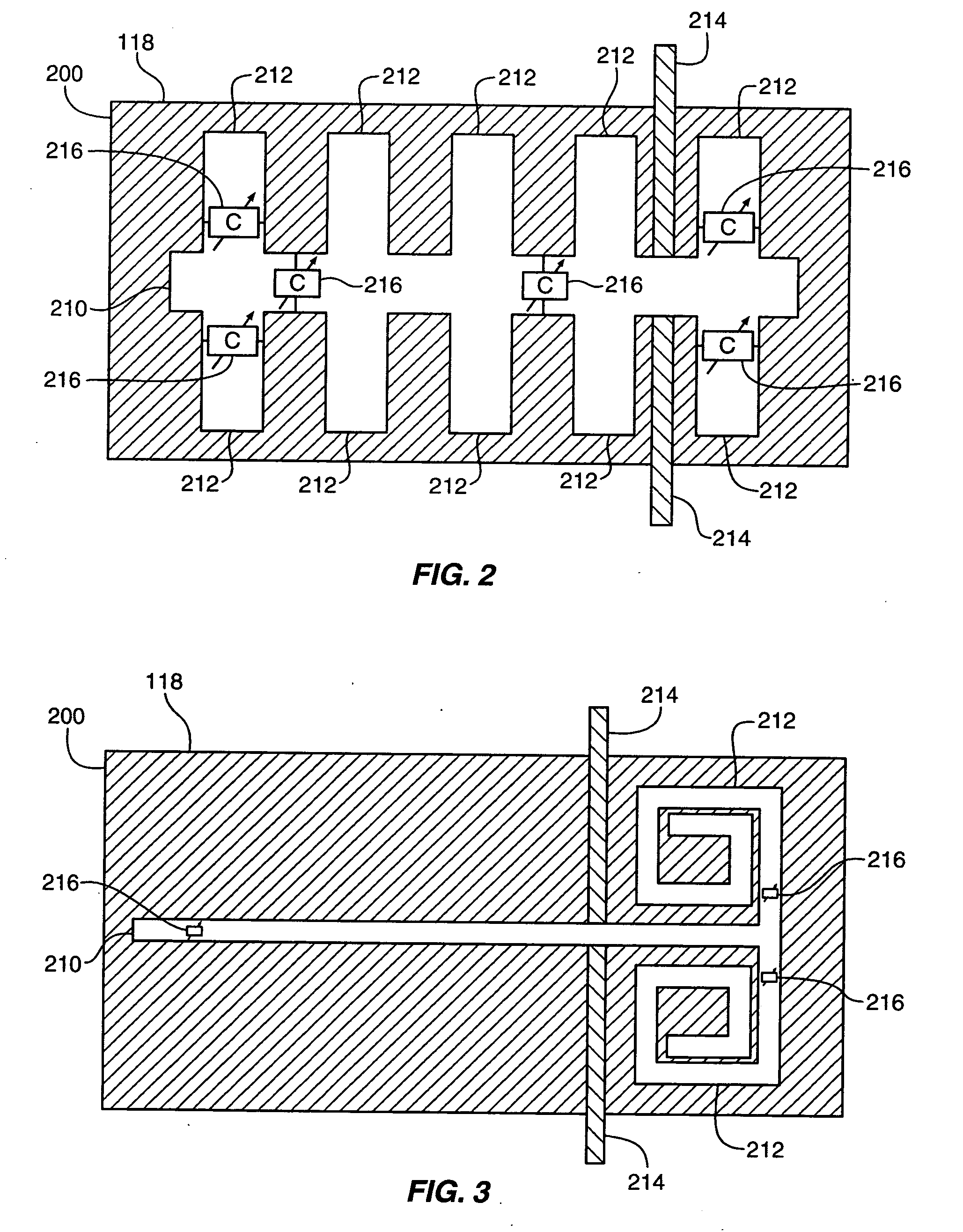
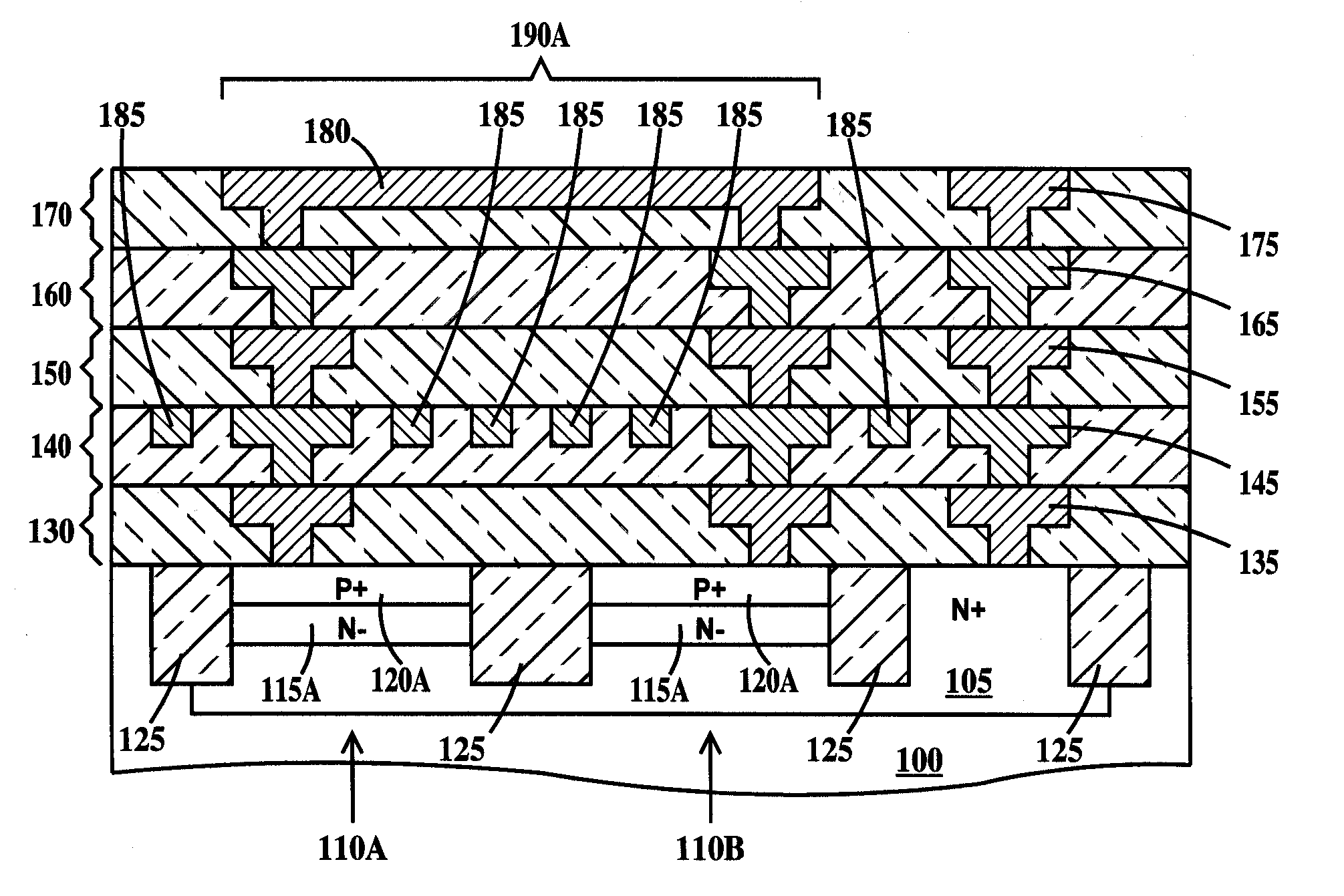
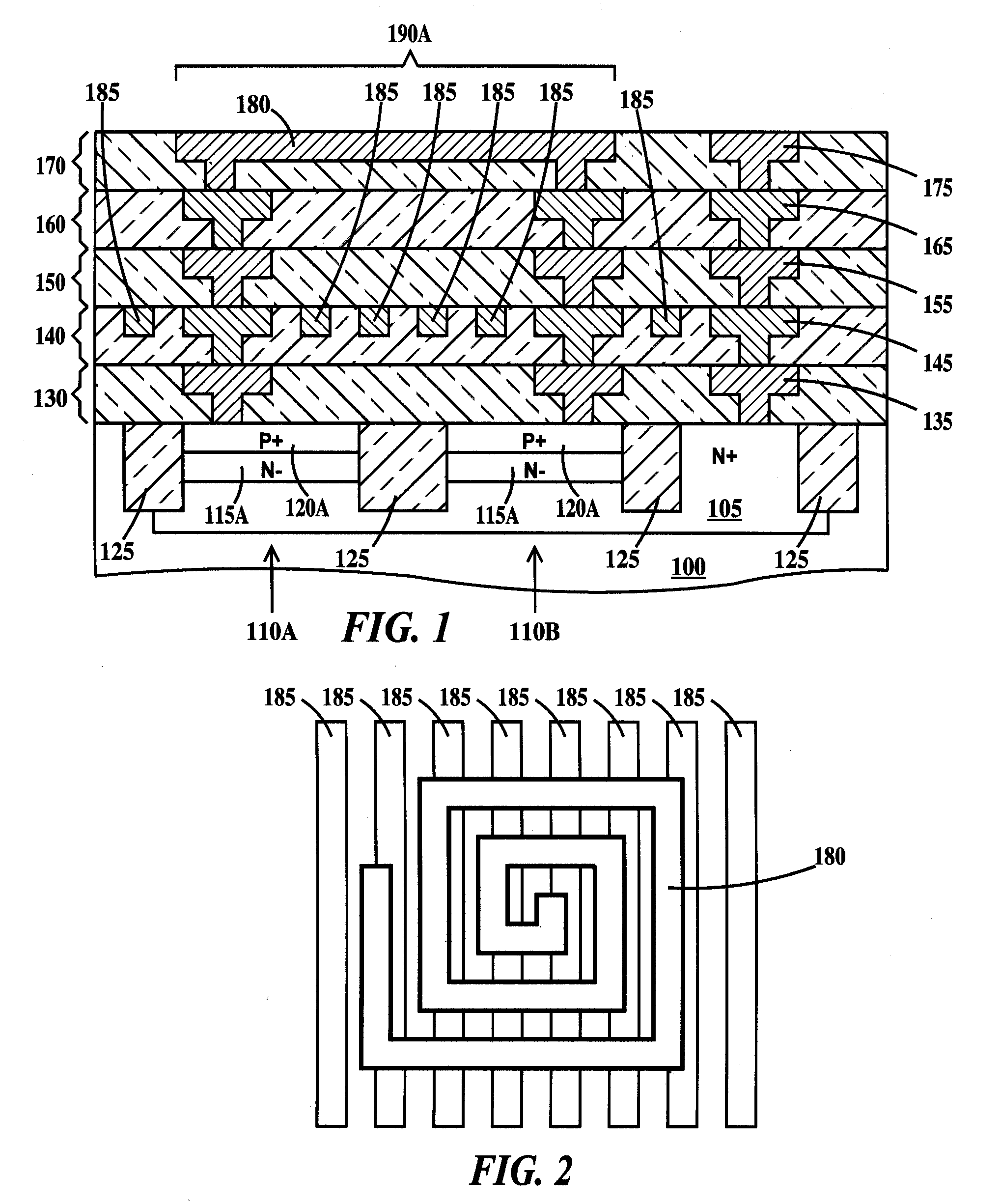
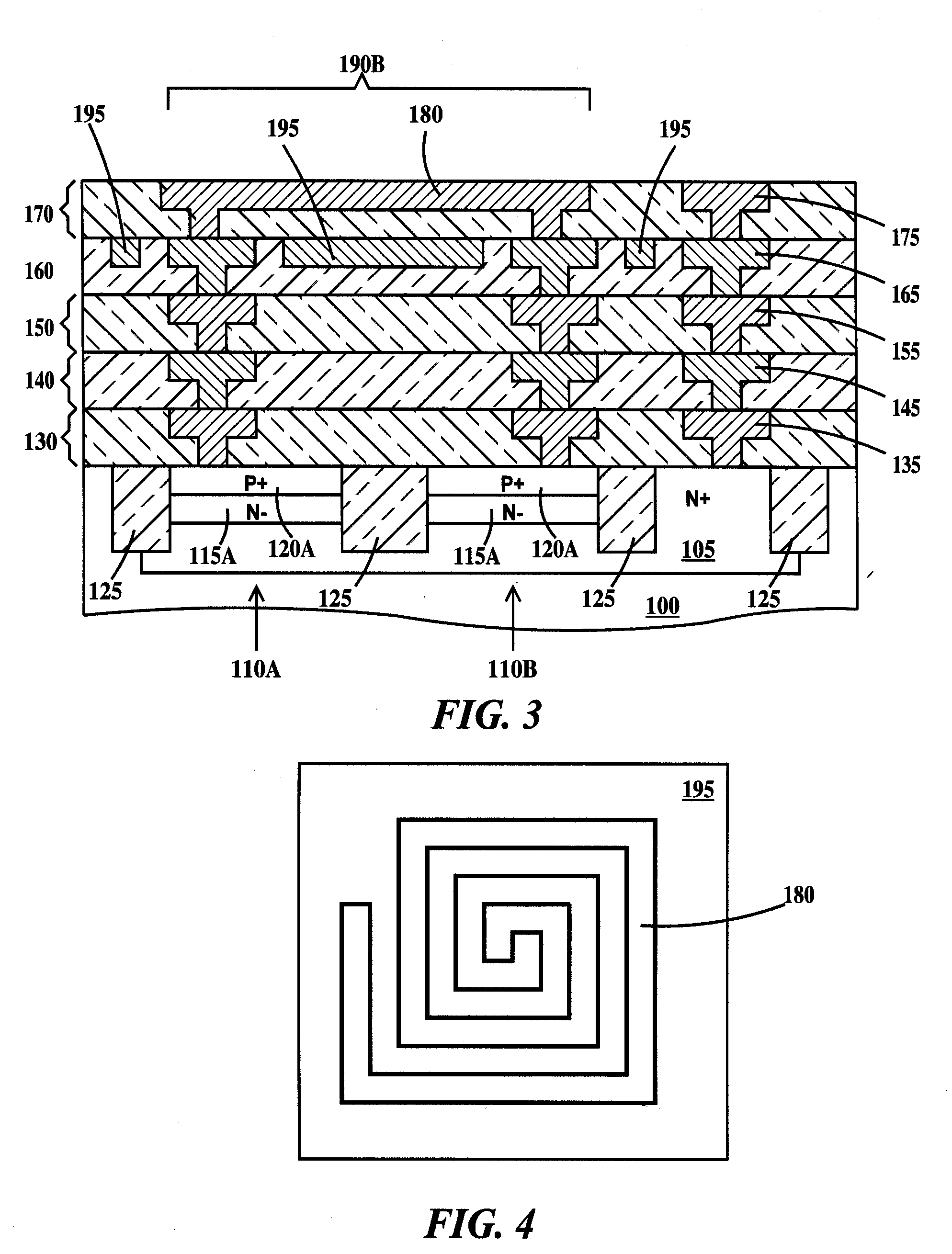
Vertical LC tank device
An LC tank structure. The structure, including a set of wiring levels on top of a semiconductor substrate, the wiring levels stacked on top of each other from a lowest wiring level nearest the substrate to a highest wiring level furthest from the substrate; an inductor in the highest wiring level, the inductor confined within a perimeter of a region of the highest wiring level; and a varactor formed in the substrate, the varactor aligned completely under the perimeter of the region of the highest wiring level. The structure may additionally include an electric shield in a wiring level of the set of wiring levels between the lowest wiring level and the highest wiring level. Alternatively, the inductor includes a magnetic core and alternating electrically non-magnetic conductive metal coils and magnetic coils around the core.
Owner:IBM CORP
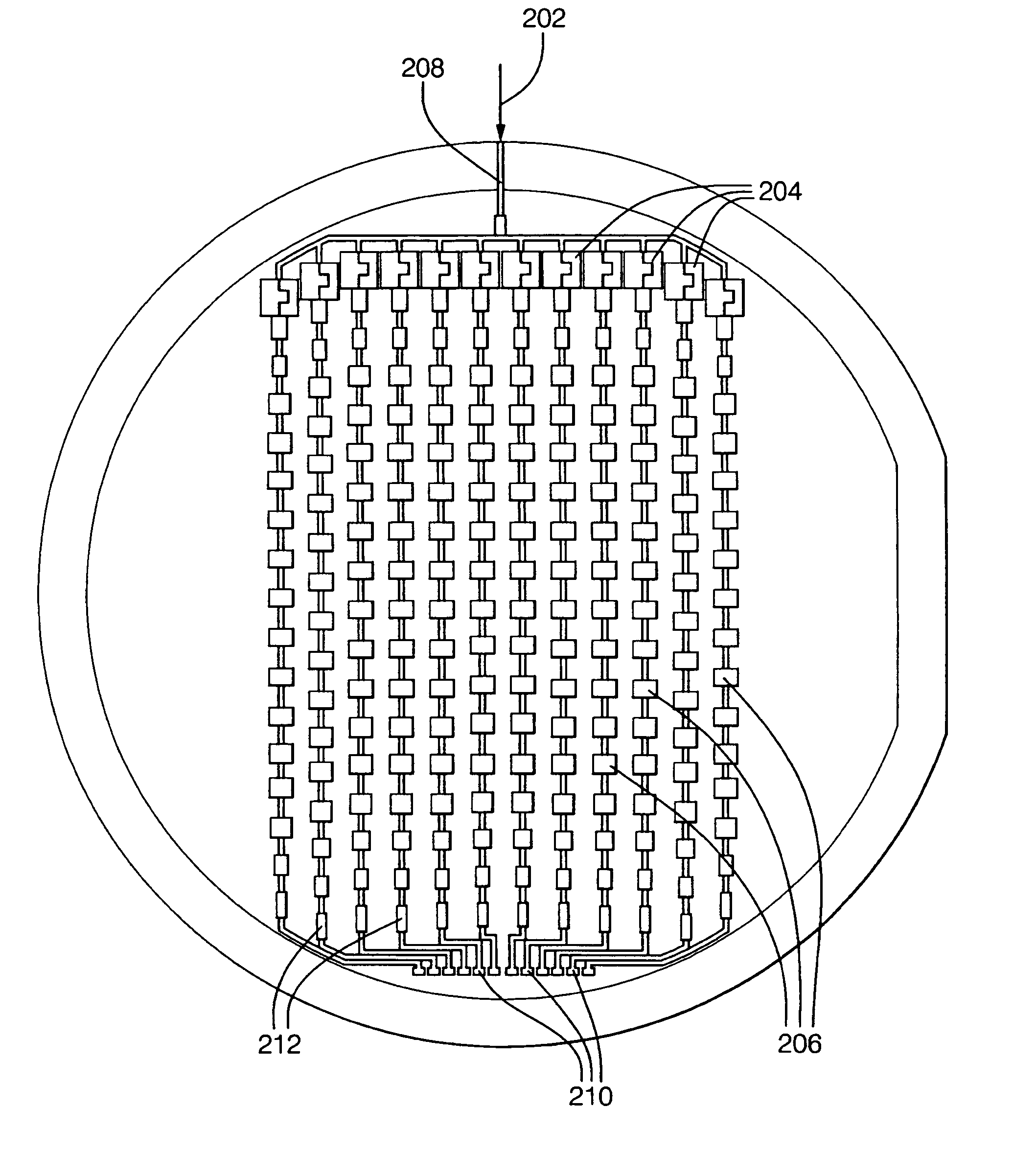
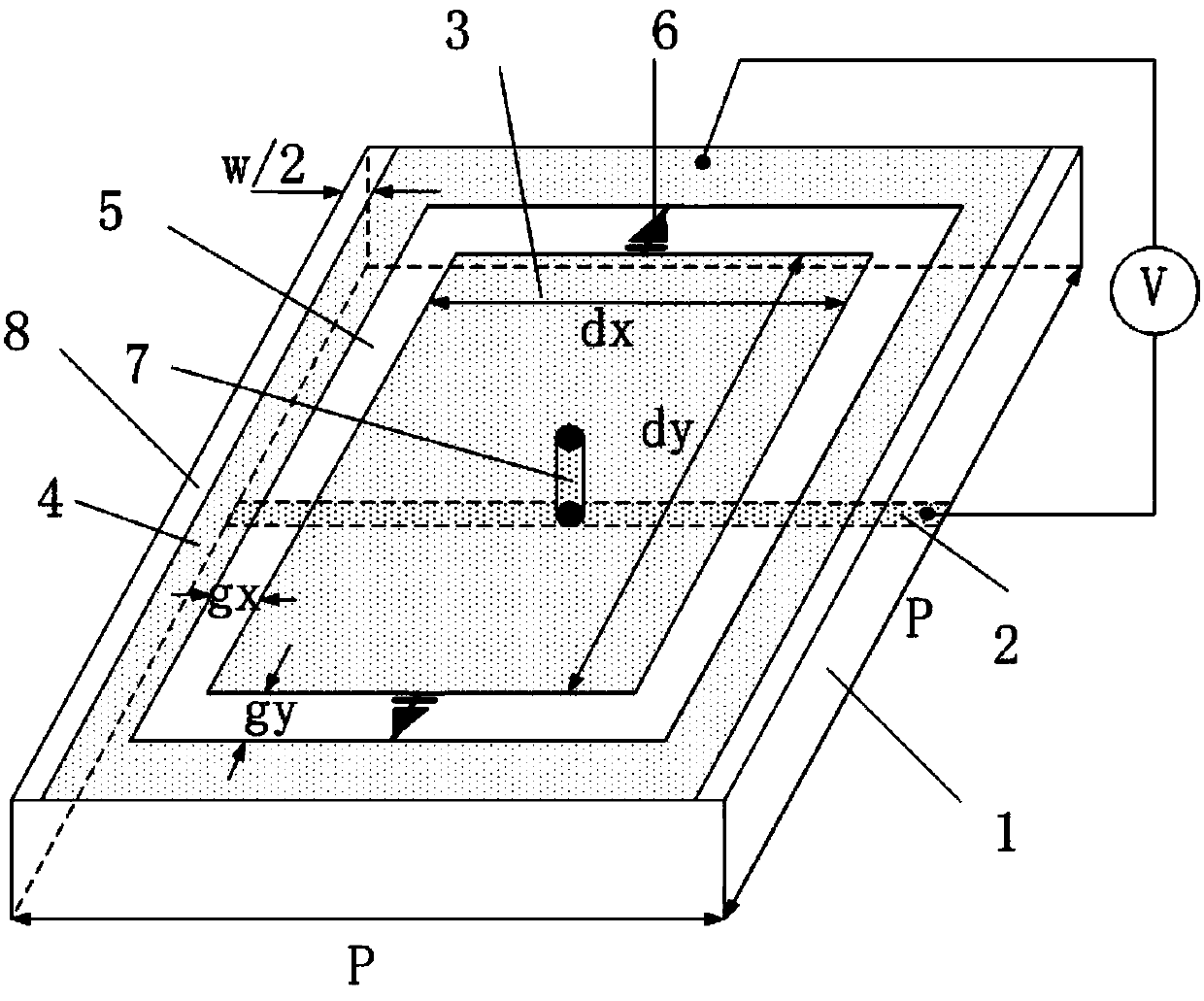
Phased-array antenna based on dynamic-regulating artificial electromagnetic structural materials
ActiveCN103474775ARealize two-dimensional dynamic scanningSimple structureWaveguide hornsEngineeringDielectric slab
The invention provides a phased-array antenna based on dynamic-regulating artificial electromagnetic structural materials. The phased-array antenna comprises a horn feed source and multiple layers of the dynamic-regulating artificial electromagnetic structural materials covering the upper portion of the horn feed source. Each layer of the materials is formed in the modes that metal patches with annular gaps distributed periodically are printed on the front of a dielectric slab, variable capacitance diodes are embedded in vertical centers of the annular gaps, gap lines used for isolating direct currents are etched between the annular gaps in different columns, and metal leads are printed on the back of the dielectric slab and via holes are metallized so that direct-current voltage can be provided for the metal patches in the annular gaps in different rows. Capacitance of the variable capacitance diodes between different rows or different columns is adjusted through controlling of a direct-current voltage source, so that radiation phases of regions in adjacent rows or adjacent columns gradually increase or decrease, the phase different value is dynamically adjusted, and dynamic scanning of antenna beams can be achieved. The phased-array antenna has the advantages of being simple in structure, convenient to power up, low in insertion loss, low in cost and the like and can achieve two-dimensional dynamic scanning of an E face and an H face.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
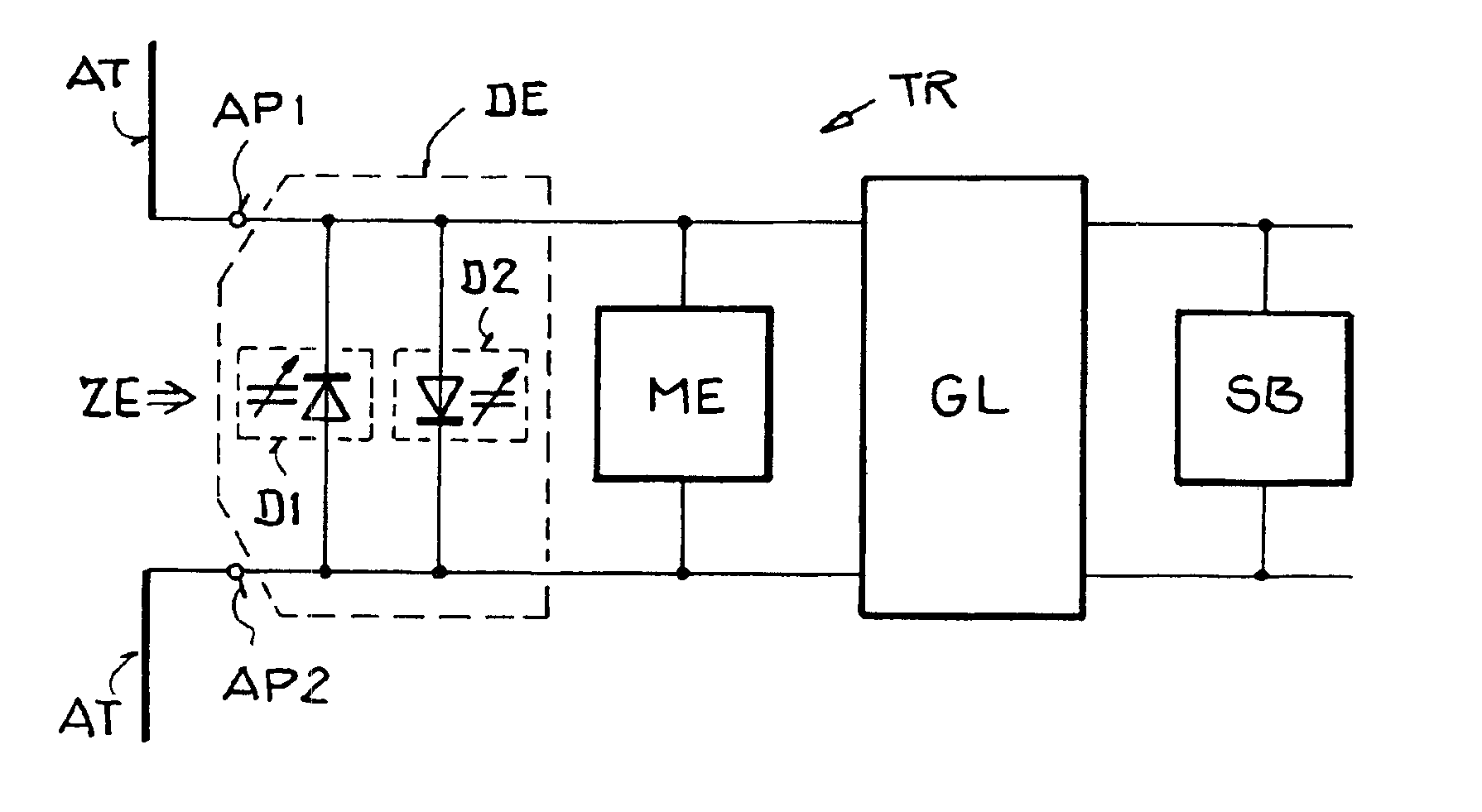
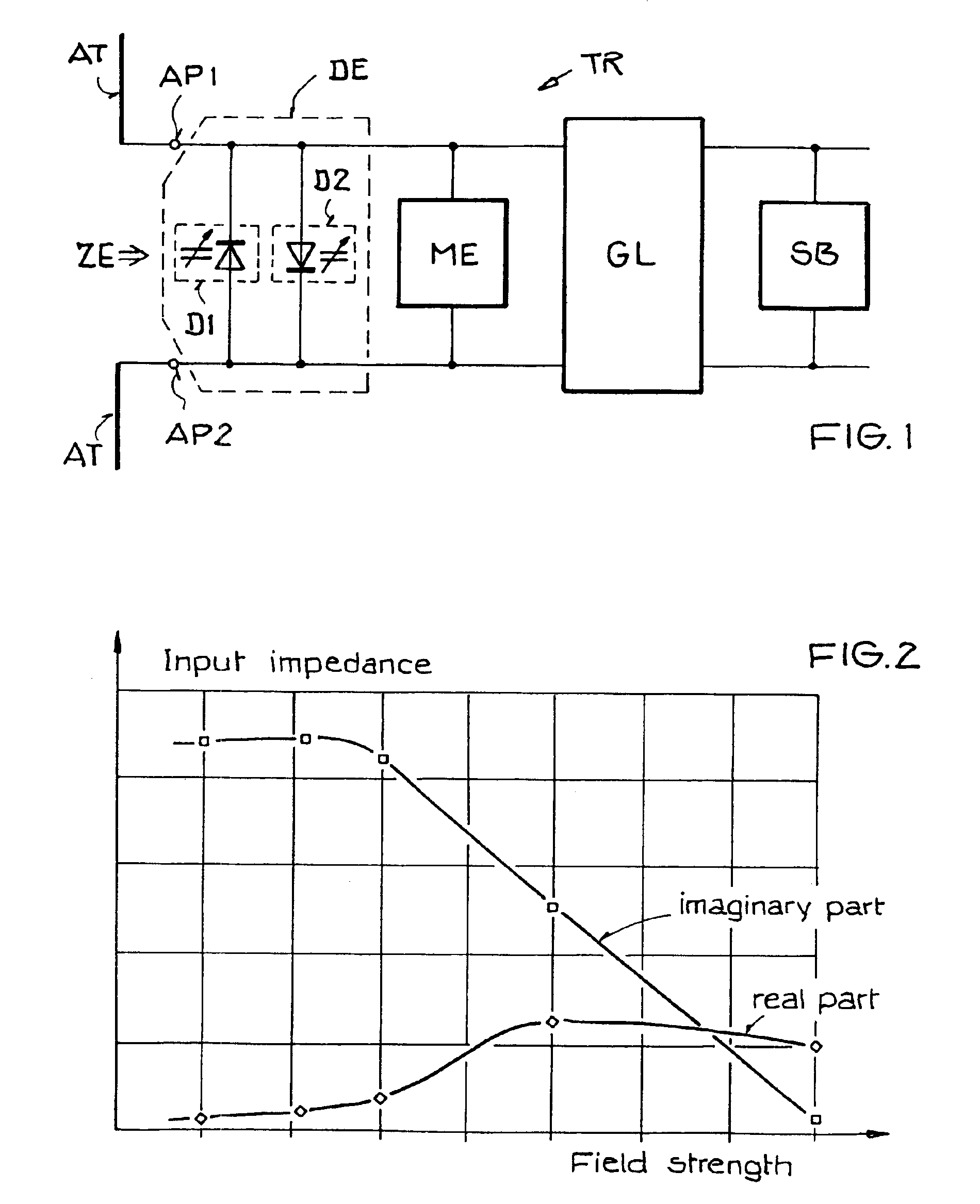
Circuit arrangement and method for deriving electrical power from an electromagnetic field
ActiveUS6940467B2Prevent destruction and damage and failureAvoiding excessive power absorptionNear-field transmissionElectromagnetic wave systemElectric forceImpedance matching
A circuit arrangement for deriving electrical power from a received electromagnetic field to power a transponder includes a detuning unit connected between two antenna terminals for limiting the power absorbed by the antenna. The detuning unit includes a component having an impedance that passively varies or is actively varied dependent on the field strength of the field prevailing at the antenna. One arrangement of the detuning unit includes two varactor diodes connected anti-parallel between the antenna terminals. Another arrangement of the detuning unit includes a varactor arranged in series between two capacitors between the antenna terminals, a field strength detector, and a controllable voltage source connected to apply to the varactor a control voltage that varies depending on the detected field strength. Thereby, the input impedance varies depending on the field strength, to achieve impedance matching for a low field strength, and a mis-matched condition for a high field strength.
Owner:ATMEL GERMANY +1
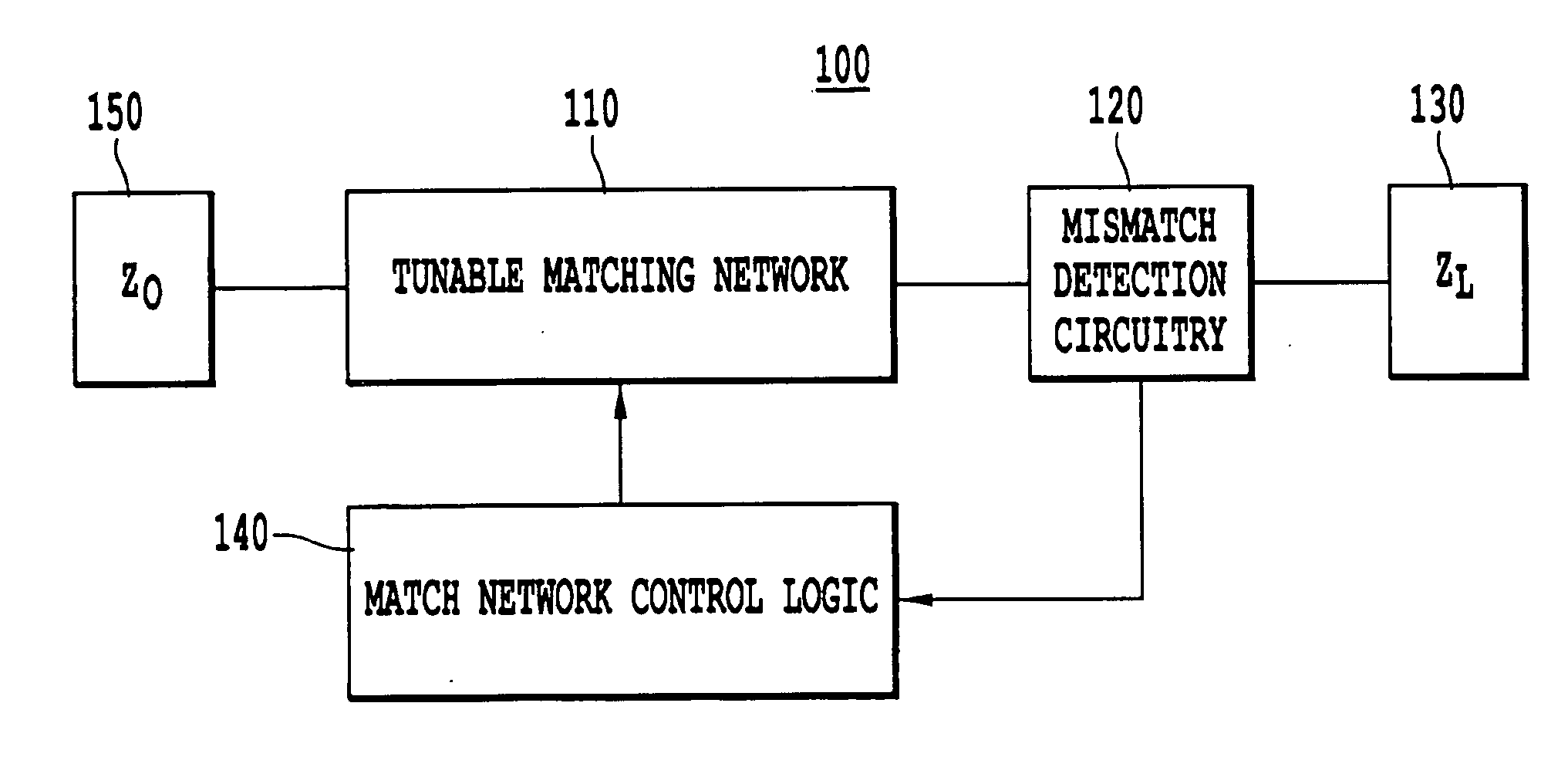
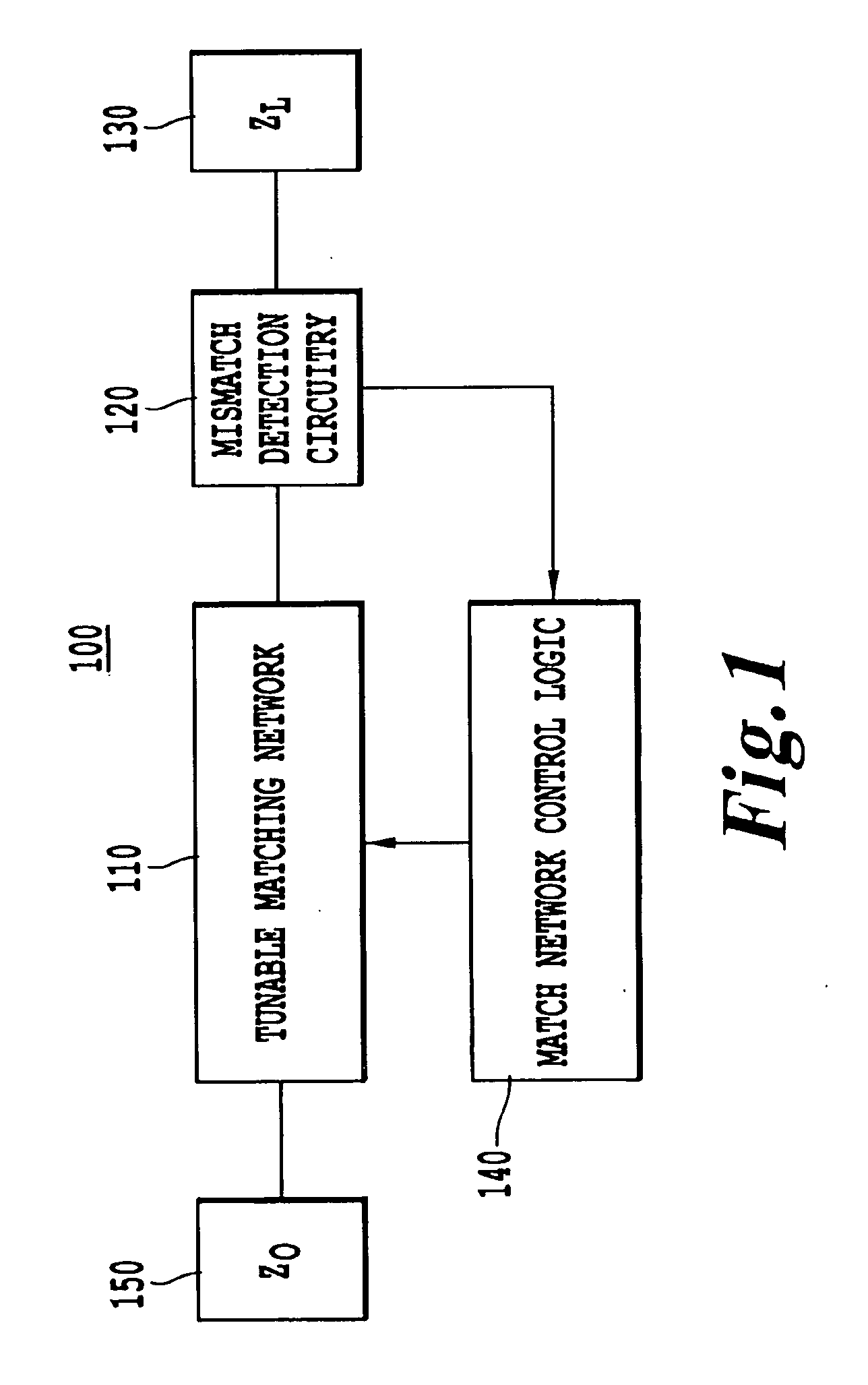
Apparatus and method of selecting components for a reconfigurable impedance match circuit
ActiveUS20090167457A1Eliminate needMultiple-port networksResistance/reactance/impedenceSimulation basedEngineering
A method of selecting component values for an analog circuit includes identifying a cost function that evaluates similarity between an approximate frequency response function and a preferred frequency response function for at least one characteristic of the functions, determining the approximate frequency response function of the analog circuit based on an approximate component value, and changing the approximate component value based on a determined magnitude of similarity between the preferred frequency response function and the approximate frequency response function for the at least one characteristic. An impedance matching apparatus includes a mismatch detection circuit that produces a difference between source and load impedances, a match network controller that produces a control value based on the difference, and a reconfigurable varactor match network including at least one stub mounted varactor having a capacitance controlled by the control value to match the source and load impedances.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Linear variable voltage diode capacitor and adaptive matching networks
InactiveUS20090134960A1Reduce distortion problemsHighly linear voltage variableTransistorMultiple-port networksSize ratioAdaptive matching
An integrated variable voltage diode capacitor topology applied to a circuit providing a variable voltage load for controlling variable capacitance. The topology includes a first pair of anti-series varactor diodes, wherein the diode power-law exponent n for the first pair of anti-series varactor diodes in the circuit is equal or greater than 0.5, and the first pair of anti-series varactor diodes have an unequal size ratio that is set to control third-order distortion. The topology also includes a center tap between the first pair anti-series varactor diodes for application of the variable voltage load. In preferred embodiments, a second pair of anti-series varactor diodes is arranged anti-parallel to the first pair of anti-series varactor diodes so the combination of the first pair of anti-series varactor diodes and the second pair of anti-series varactor diodes control second-order distortion as well.
Owner:TECH UNIV DELFT +1
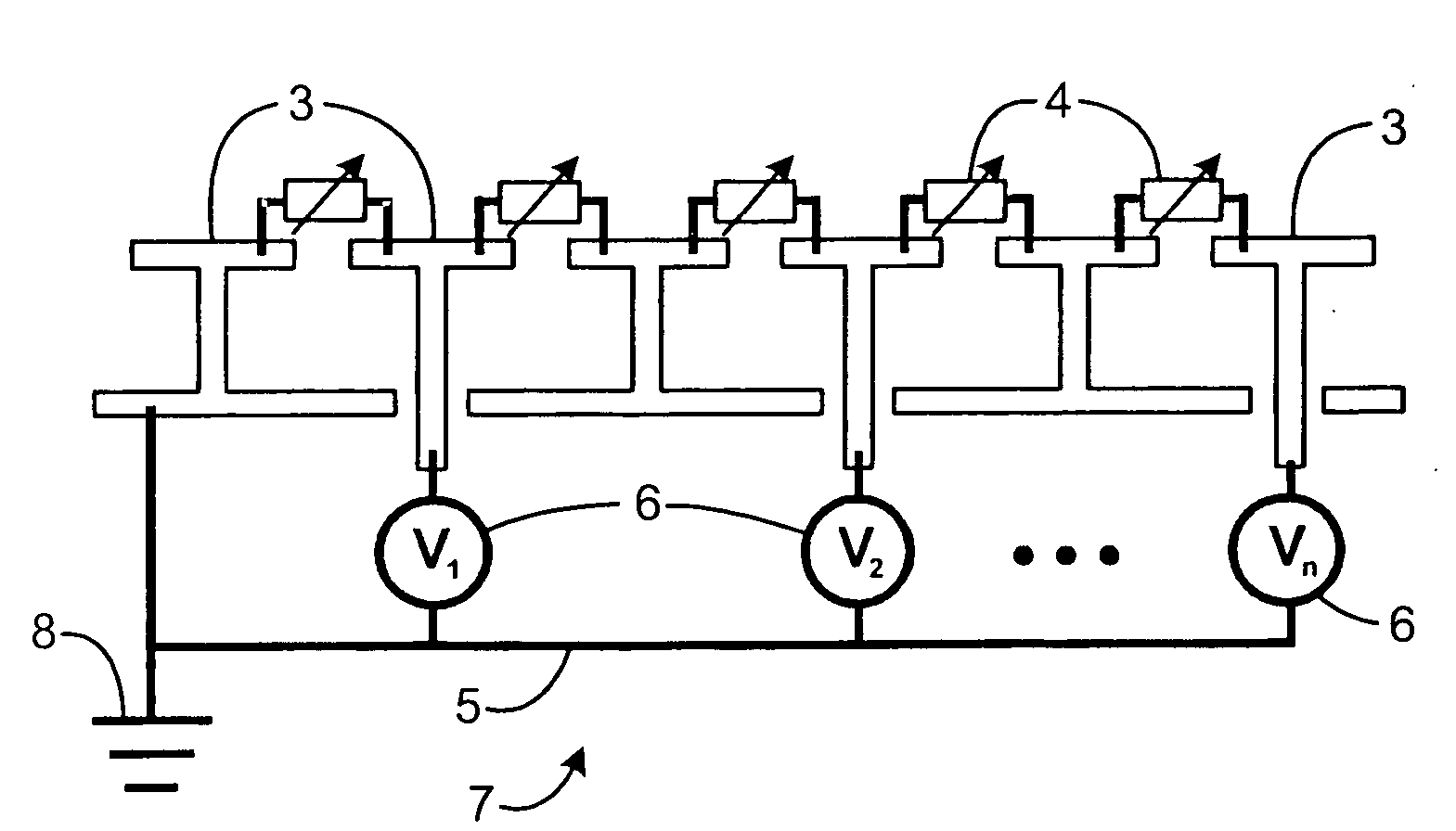
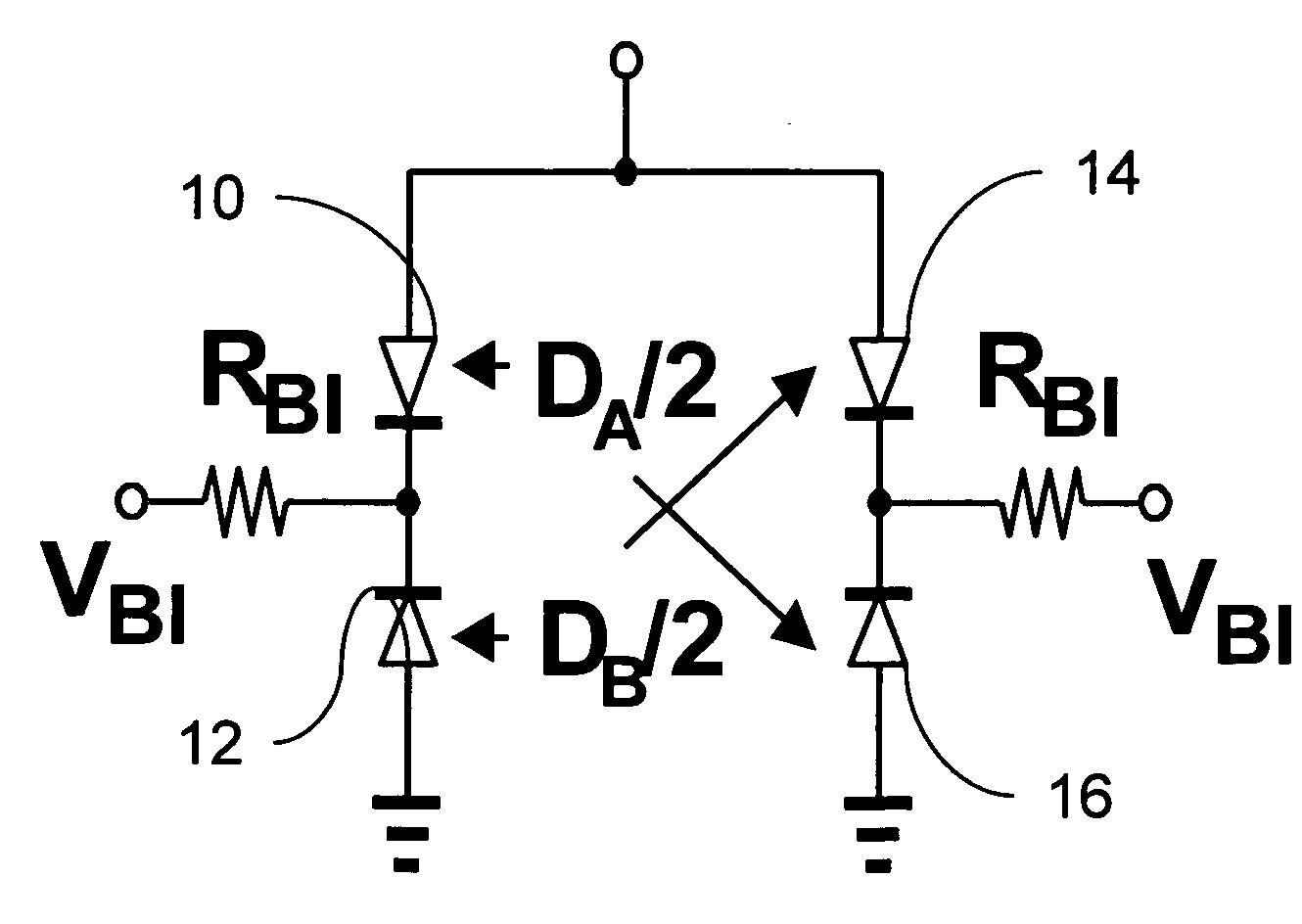
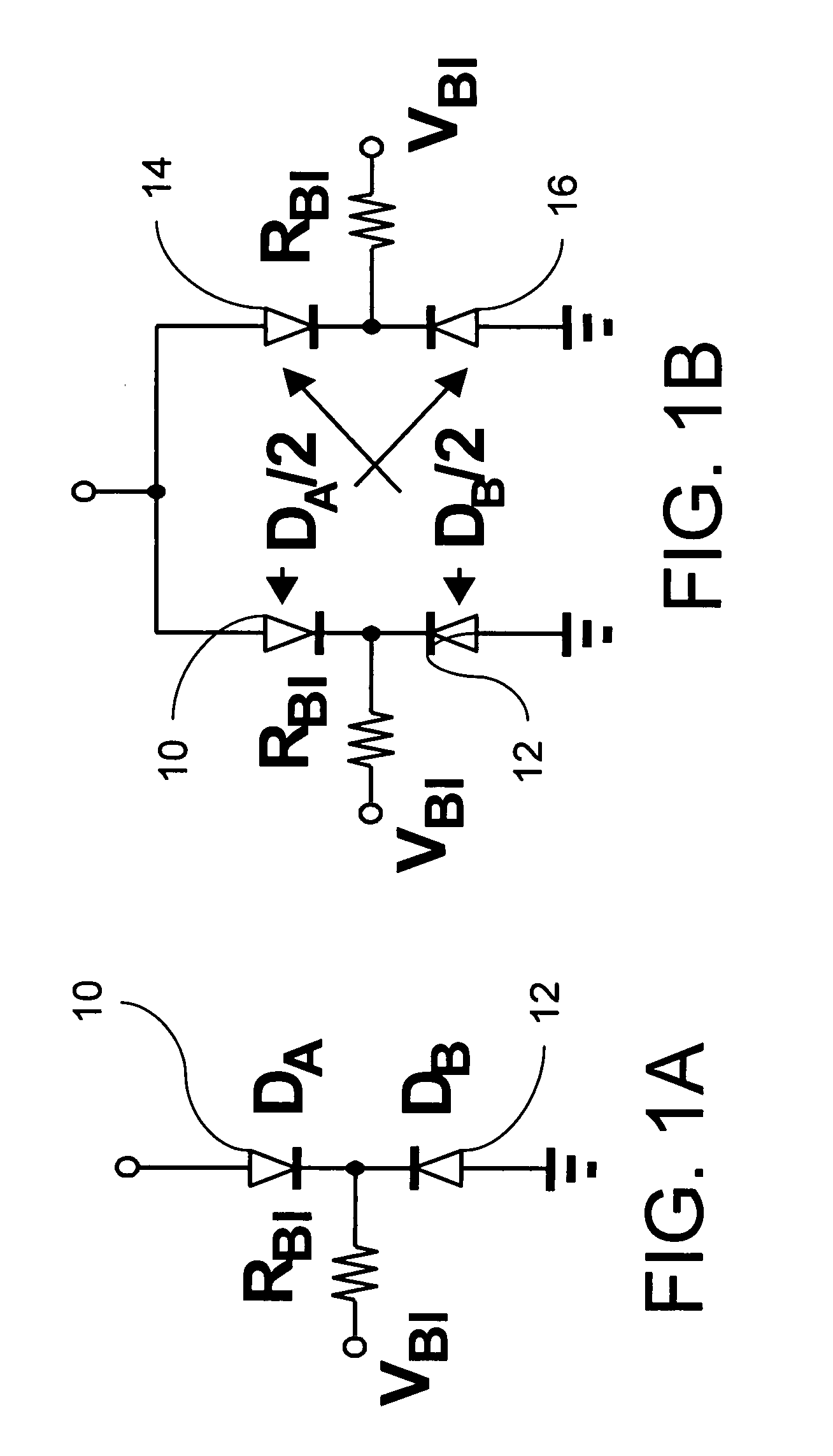
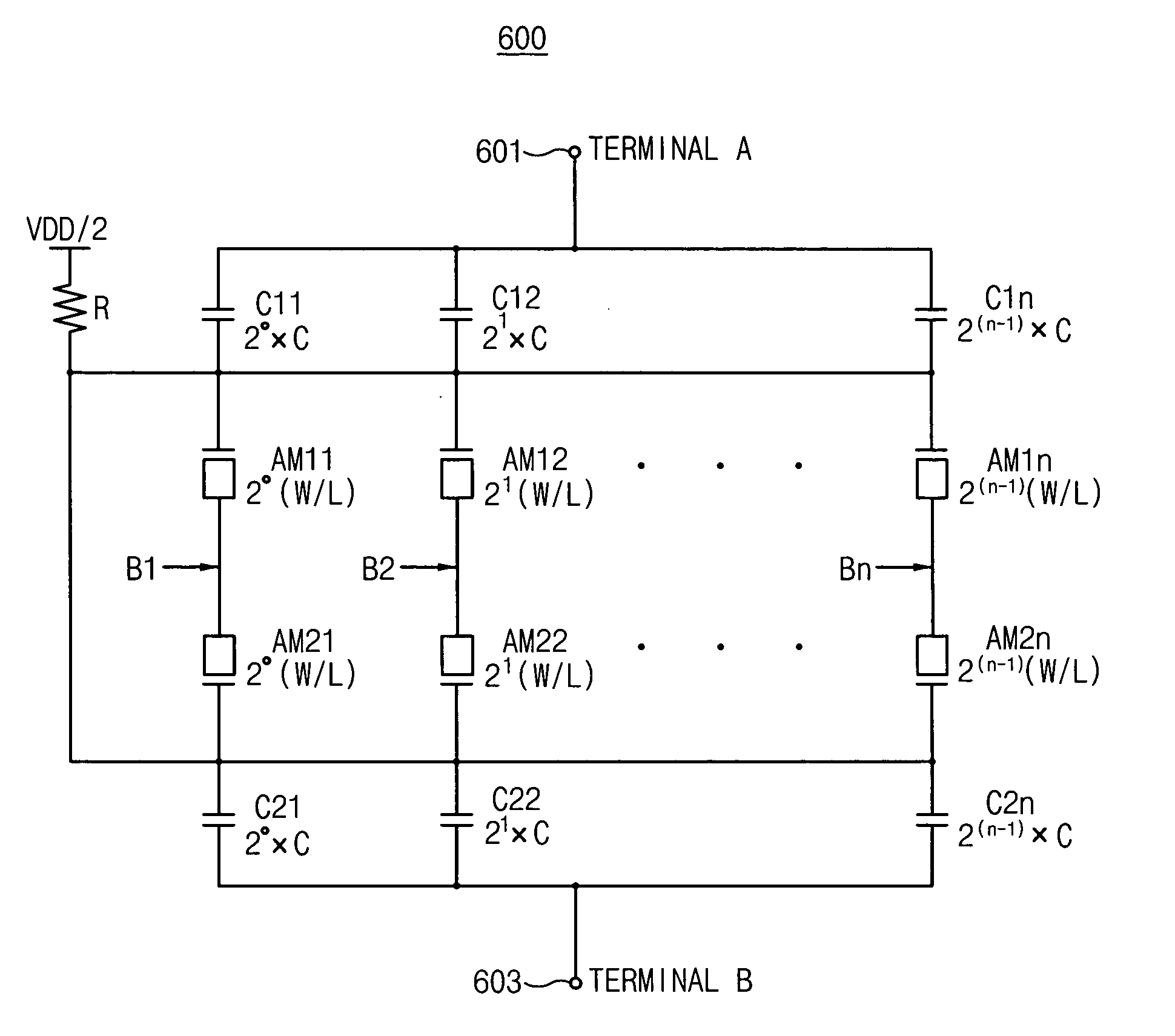
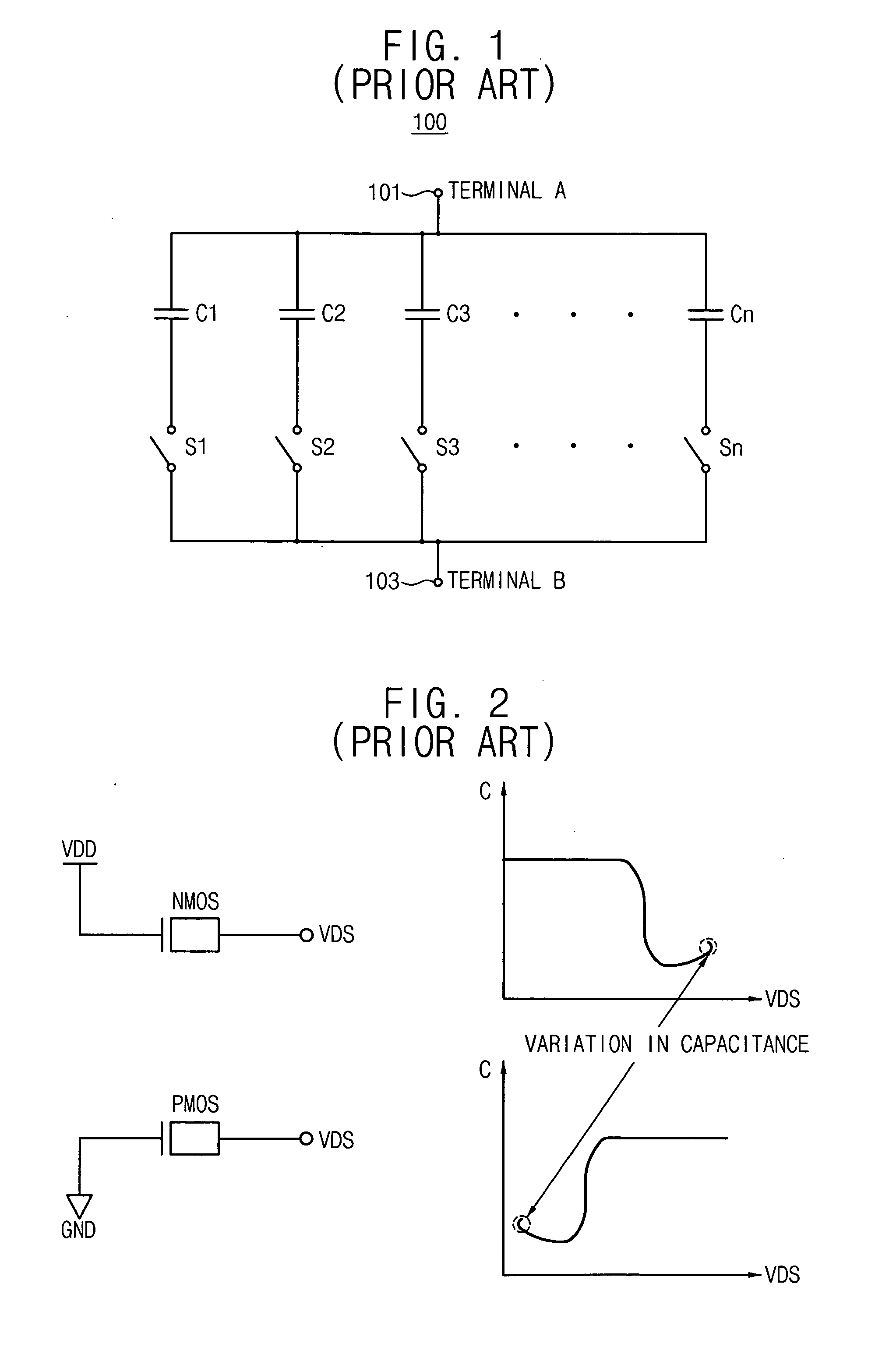
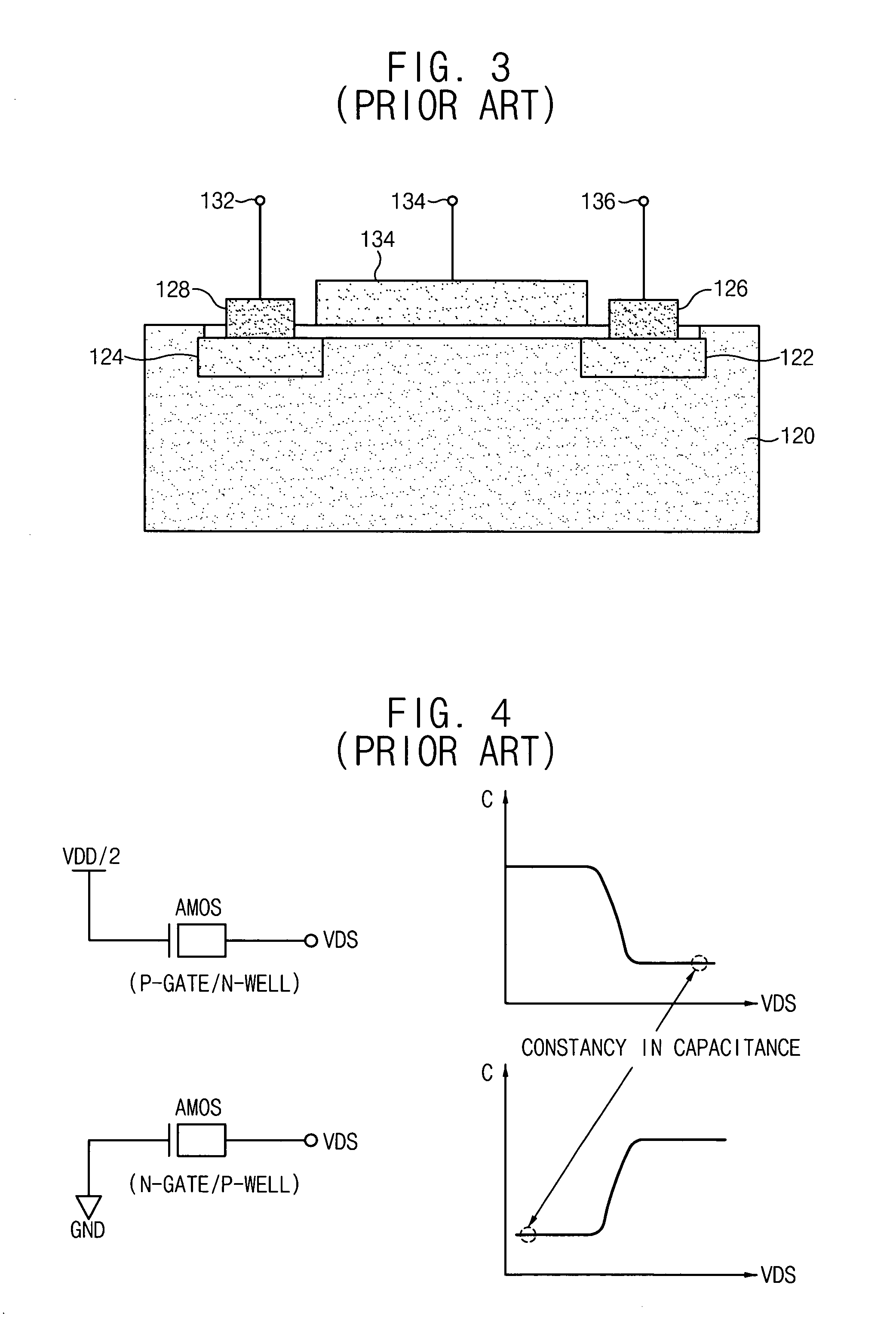
Capacitor bank and voltage controlled oscillator having the same
ActiveUS20050184812A1Prevent phase noise degradationAvoid degradationResonant circuit tuningPulse automatic controlPhase noiseCapacitor
A capacitor bank includes a first node, a second node, first blocking capacitors, N first AMOS varactors, second blocking capacitors and N second AMOS varactors. The first blocking capacitors have first terminals connected to the first node and second terminals where a bias voltage is applied. The N first AMOS varactors have first terminals connected to the second terminals of the first block capacitors. The second blocking capacitors have first terminals connected to the second node and second terminals where the bias voltage is applied. The N second AMOS varactors have first terminals connected to the second terminals of the second blocking capacitors and second terminals connected to second terminals of the first AMOS varactors, respectively, wherein N binary coded signals are applied to the respective second terminals of the first AMOS varactors and the second AMOS varactors. Therefore, phase-noise degradation caused by the FM modulation may be avoided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
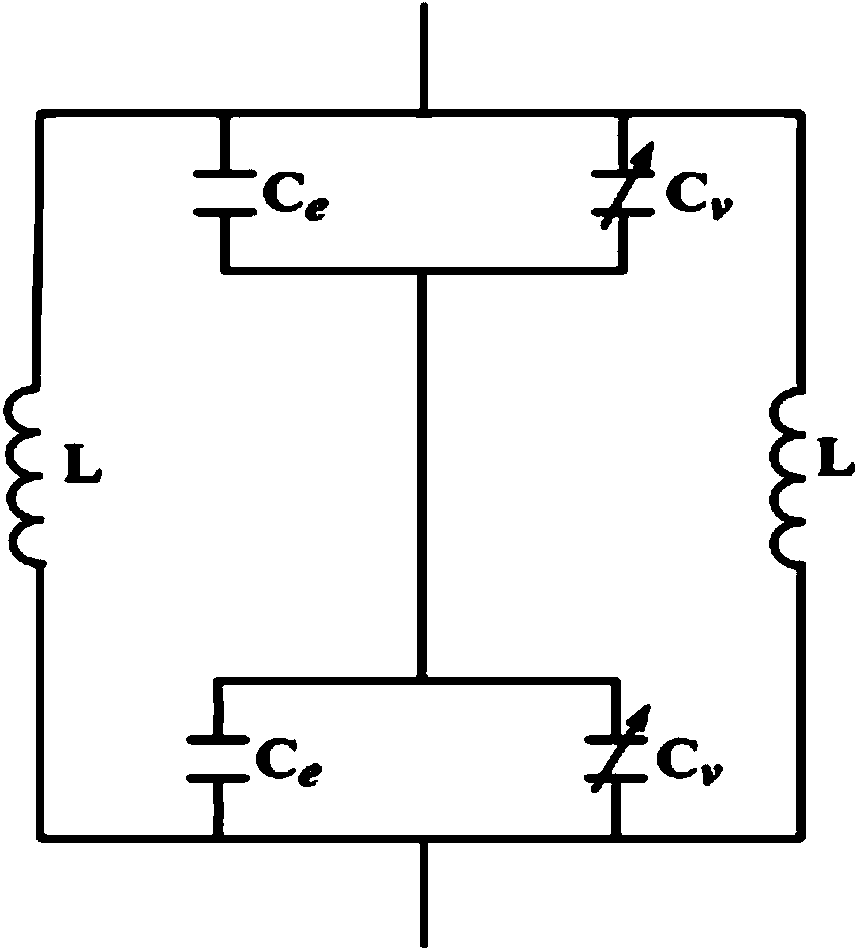
Variable Matching Circuit
A variable matching circuit includes a variable capacitance circuit formed of a capacitor coupled to varactor diode and provided between terminals, and a resonator-type circuit includes a plurality of inductors and a variable capacitance circuit formed of a capacitor and a varactor diode. The inductors and the variable capacitance circuit are coupled in parallel together. The resonator-type circuit is connected in shunt with the terminal. The foregoing structure forms an L-type matching circuit. The bias of the varactor diodes can be thus varied, and plural values of the inductance of the resonator-type circuit can be switched over with a FET. The variable matching circuit can electrically control an impedance conversion available for wider ranges of frequency bandwidths.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com