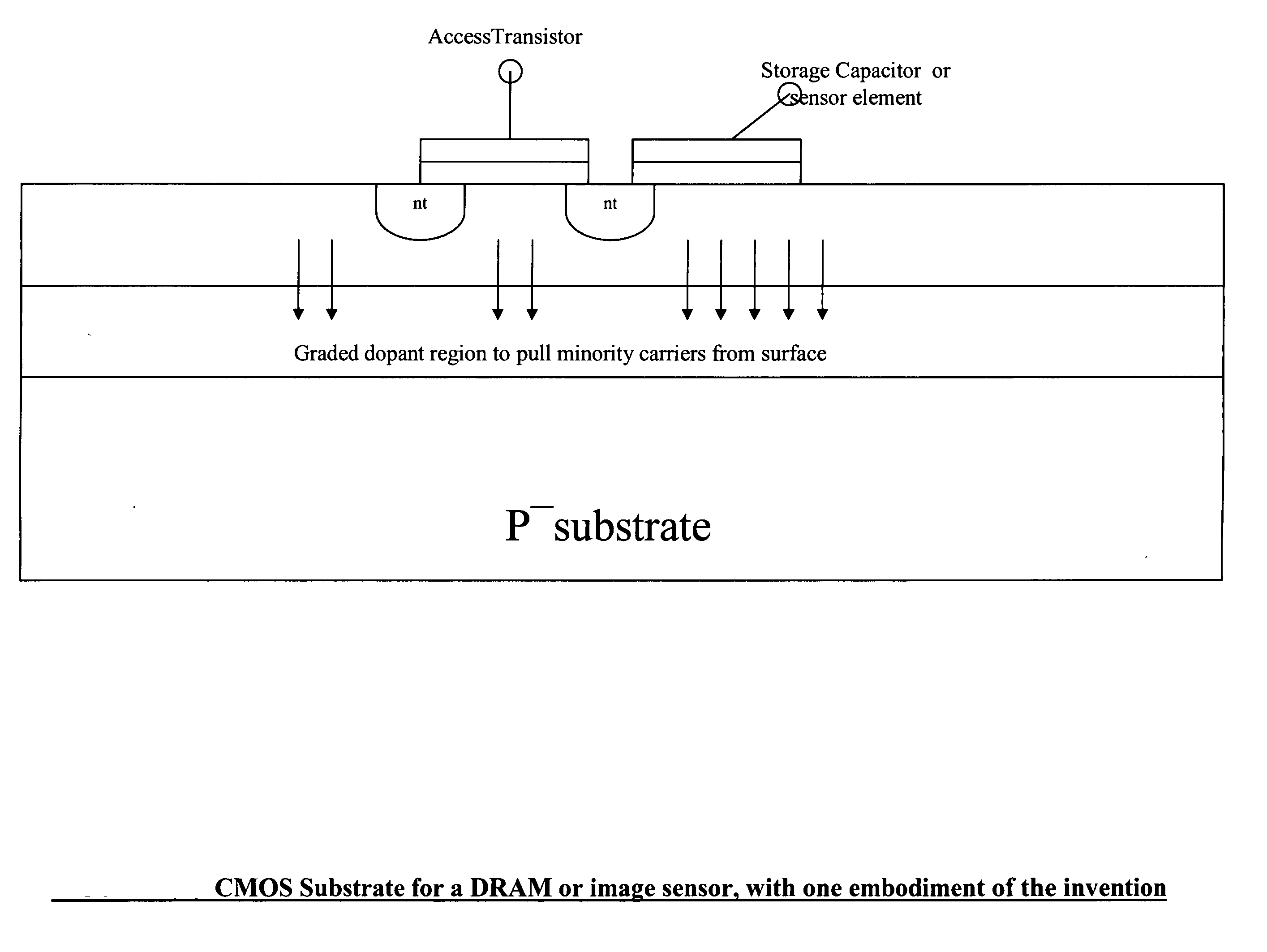
Semiconductor devices with graded dopant regions
a technology of dopant regions and semiconductor devices, applied in semiconductor devices, diodes, transistors, etc., can solve the problems of a small but finite role of majority carriers in modulating
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
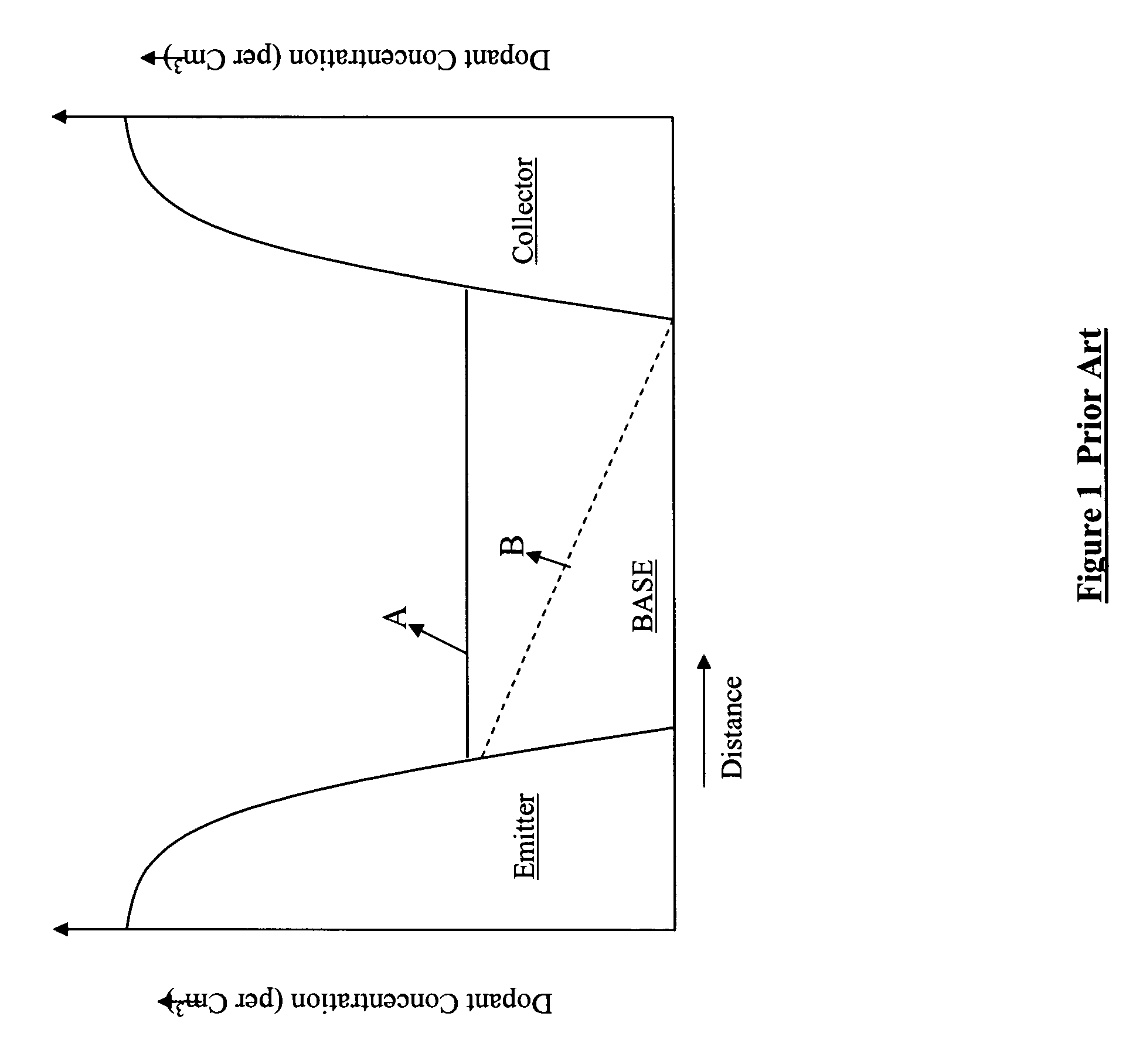
[0011] The relative doping concentrations of emitter and collector regions varies from 1018 to 1020 / cm3, where as the base region is 1014 to 1016 / cm3 depending on the desired characteristics of the BJT. In graded base p-n-p transistors, the donor dopant concentration may be 10 to 100× at the emitter-base junction, relative to the base-collector junction (1×). The gradient can be linear, quasi linear, exponential or complimentary error function. The relative slope of the donor concentration throughout the base, creates a suitable aiding drift electric field, to help the holes (p-n-p transistor) transverse from emitter to collector. Since the aiding drift field helps hole conduction, the current gain at a given frequency is enhanced, relative to a uniformly-doped-(base) BJT. The improvement in cut-off frequency (or, frequency at unity gain, fT) can be as large as 2×-5×. Similar performance improvements are also applicable to n-p-n transistors.
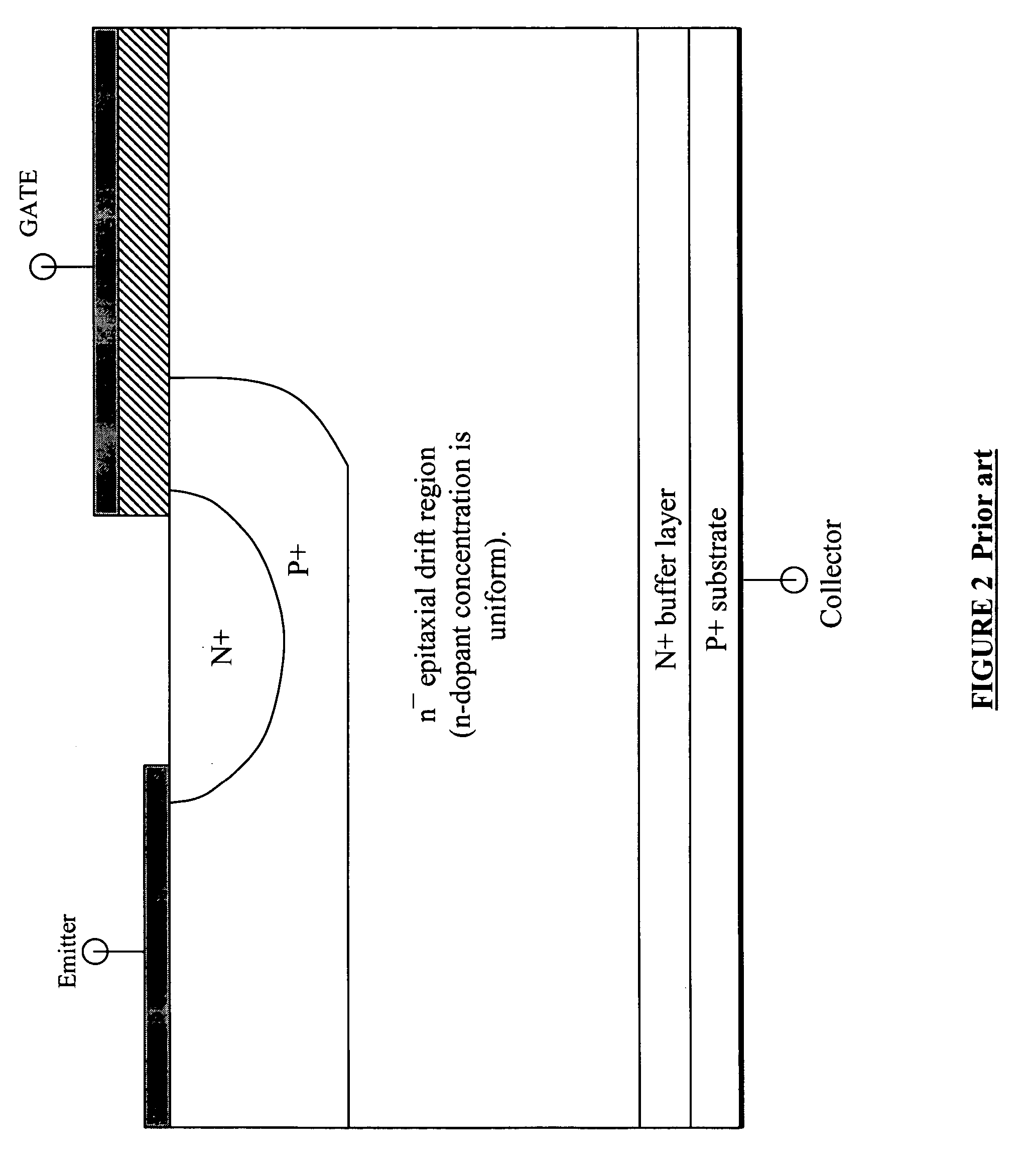
[0012] As illustrated in FIG. 4, in one e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com