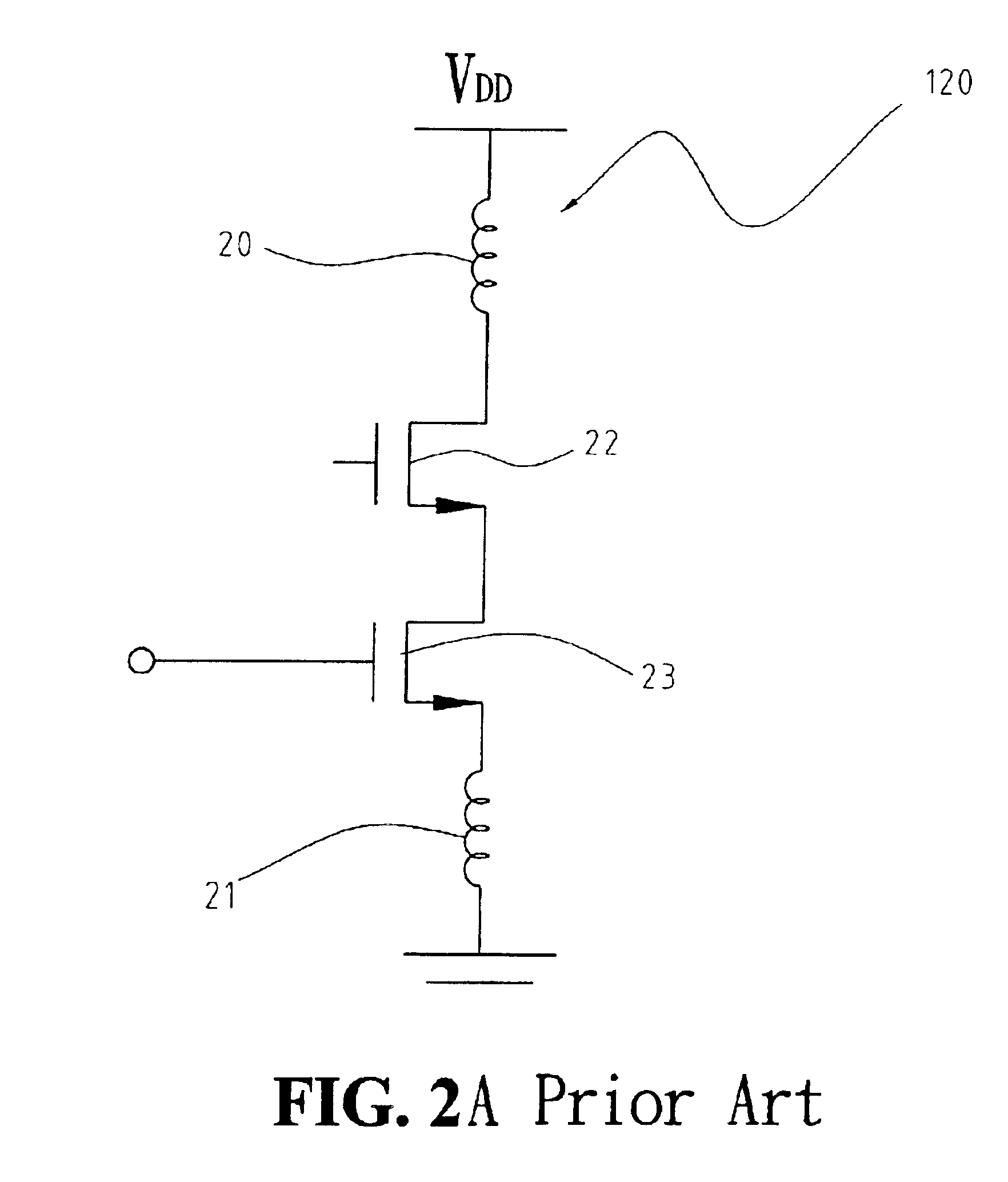
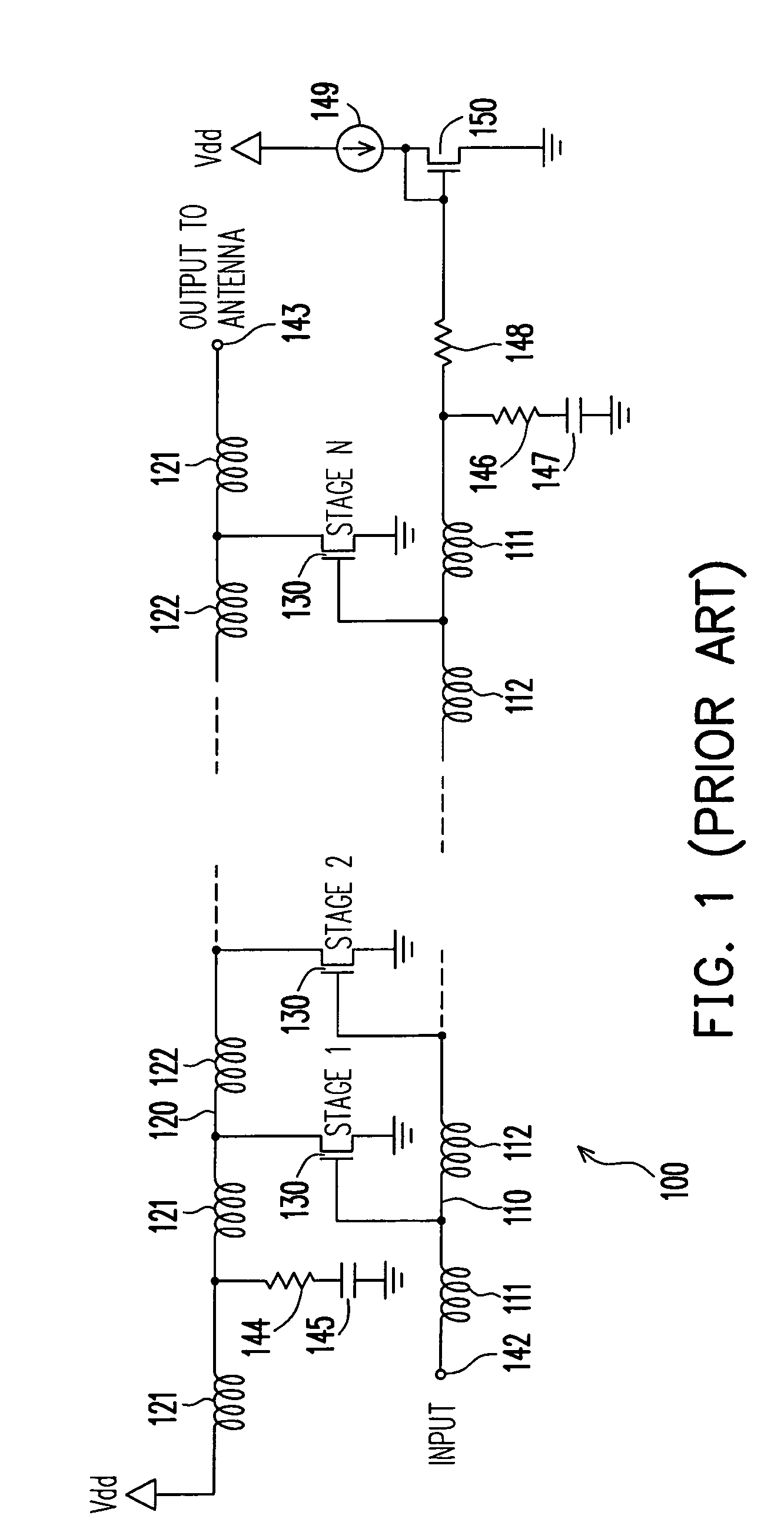
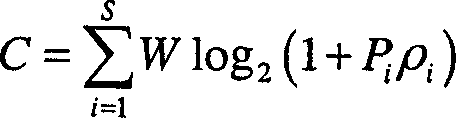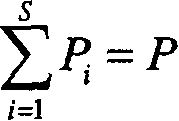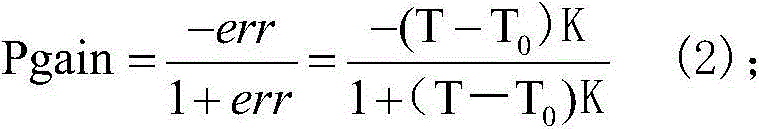Patents
Literature
482 results about "Power gain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The power gain of an electrical network is the ratio of an output power to an input power. Unlike other signal gains, such as voltage and current gain, "power gain" may be ambiguous as the meaning of terms "input power" and "output power" is not always clear. Three important power gains are operating power gain, transducer power gain and available power gain. Note that all these definitions of power gains employ the use of average (as opposed to instantaneous) power quantities and therefore the term "average" is often suppressed, which can be confusing at occasions.
Method of assigning an uplink random access channel in a CDMA mobile communication system
ActiveUS20070274278A1Easy to useMinimize timePower managementSynchronisation arrangementData transmission timeRandom-access channel
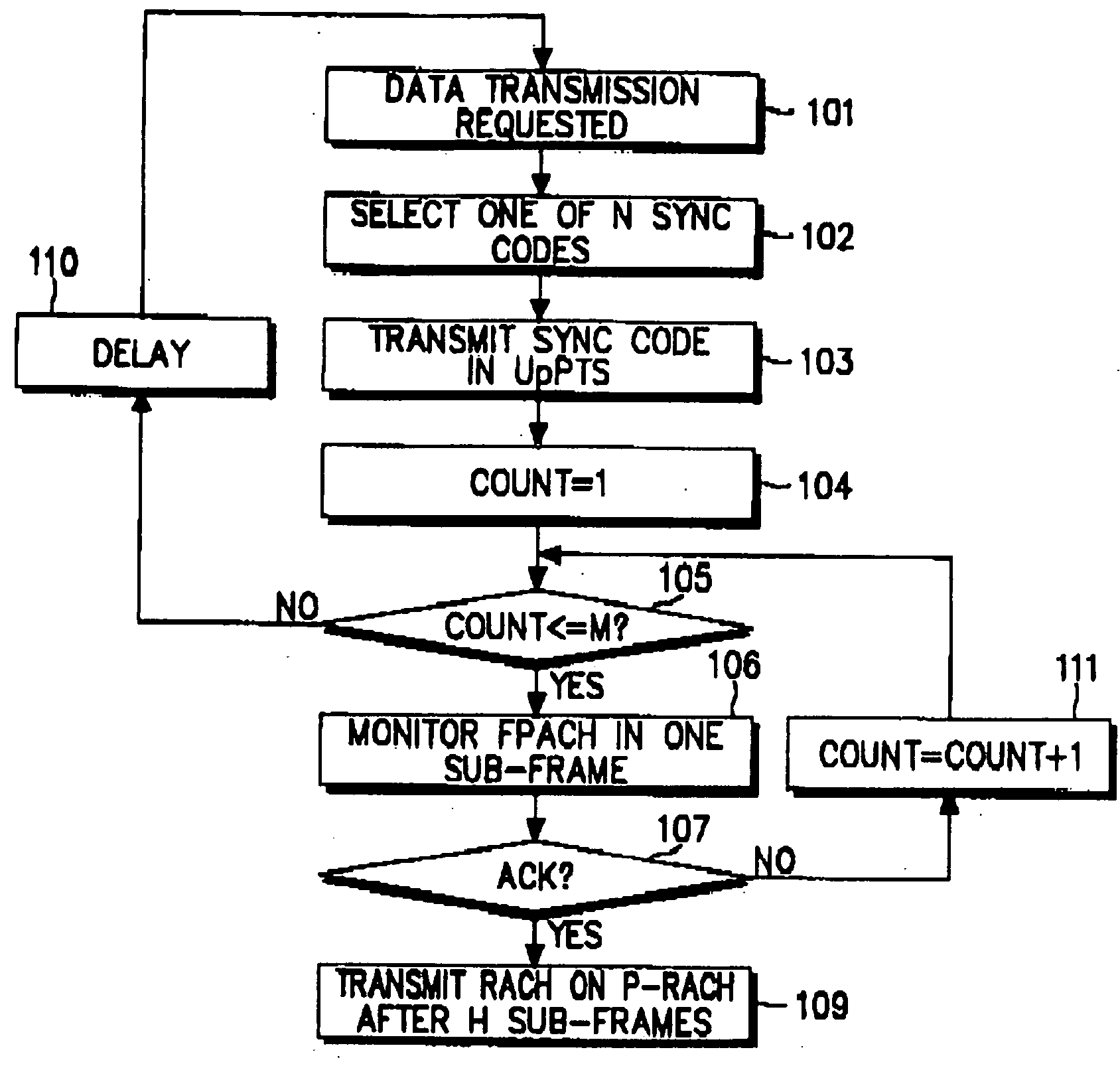
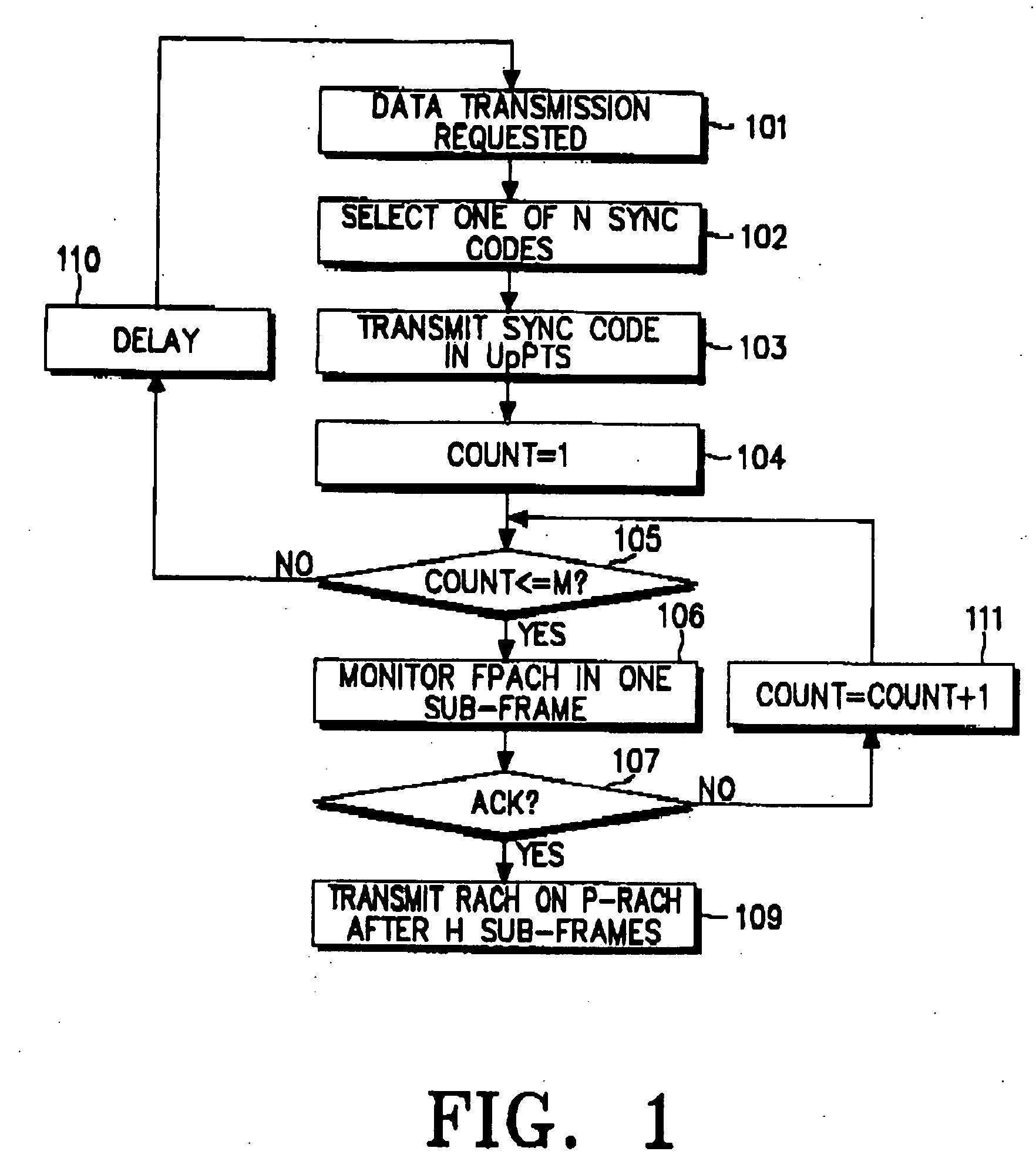
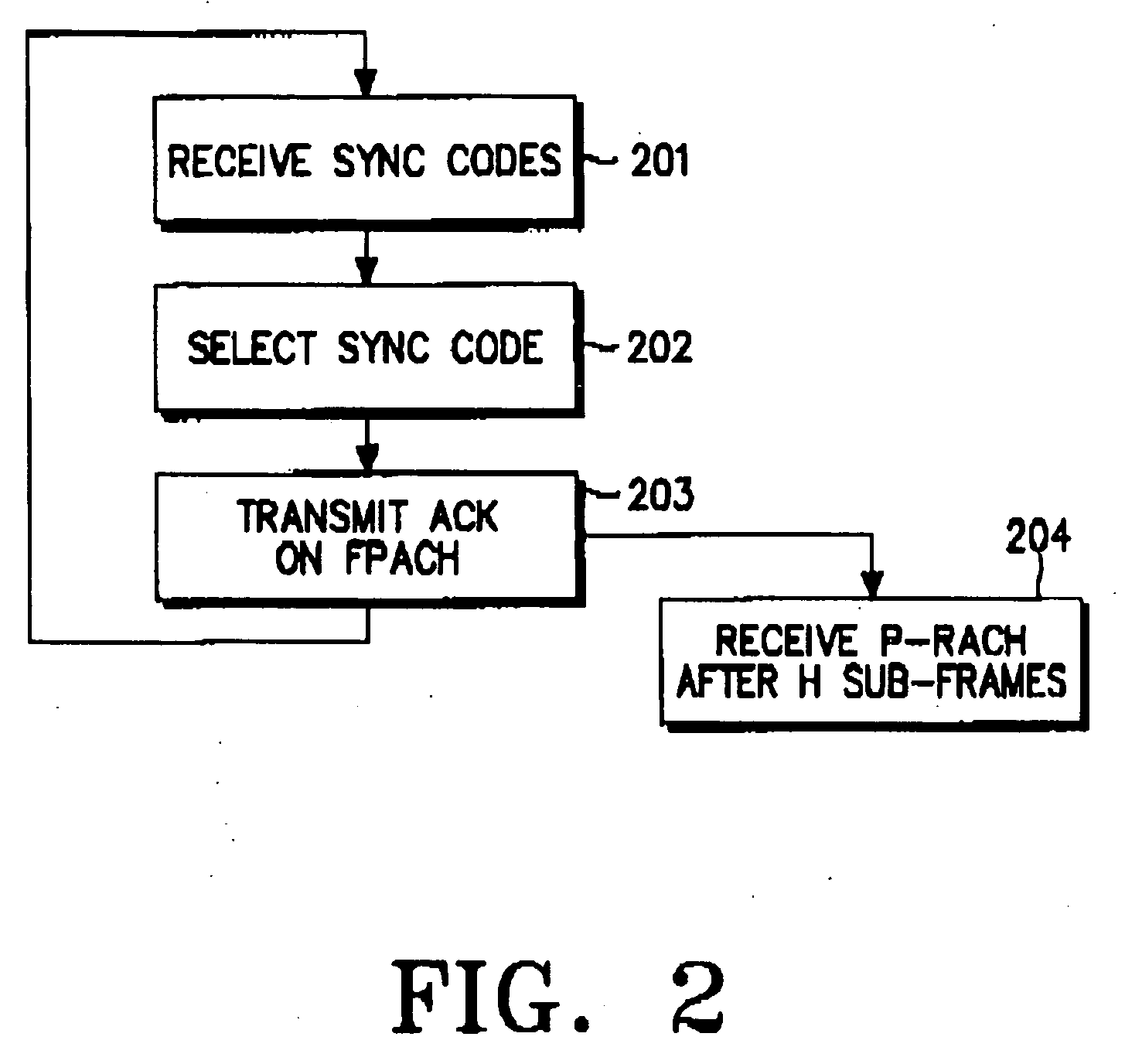
Disclosed is an uplink random access procedure in an NB-TDD (Narrow Band Time Division Duplexing) system. To achieve an acknowledgement for data transmission from a UTRAN (UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network), a UE selects one of a plurality of sync codes by which the UTRAN identifies UEs that request data transmission and transmits the selected sync code in a time slot of a sub-frame to the UTRAN. Then, the UE receives the sync code information, information about the arrival time of the sync code, time update information indicating a variation in the transmission time of data, and power information indicating an adjustment to a power gain in the UE from the UTRAN on an FPACH (Fast Physical Access Channel). The UE transmits the data on a P-RACH (Physical Random Access Channel) mapped from the FPACH according to the time update information and the power information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
FMOD transceivers including continuous and burst operated TDMA, FDMA, spread spectrum CDMA, WCDMA and CSMA
InactiveUS6928101B2Improve performanceLow costAsymmetric modulation circuitsPhase-modulated carrier systemsModem deviceFrequency spectrum
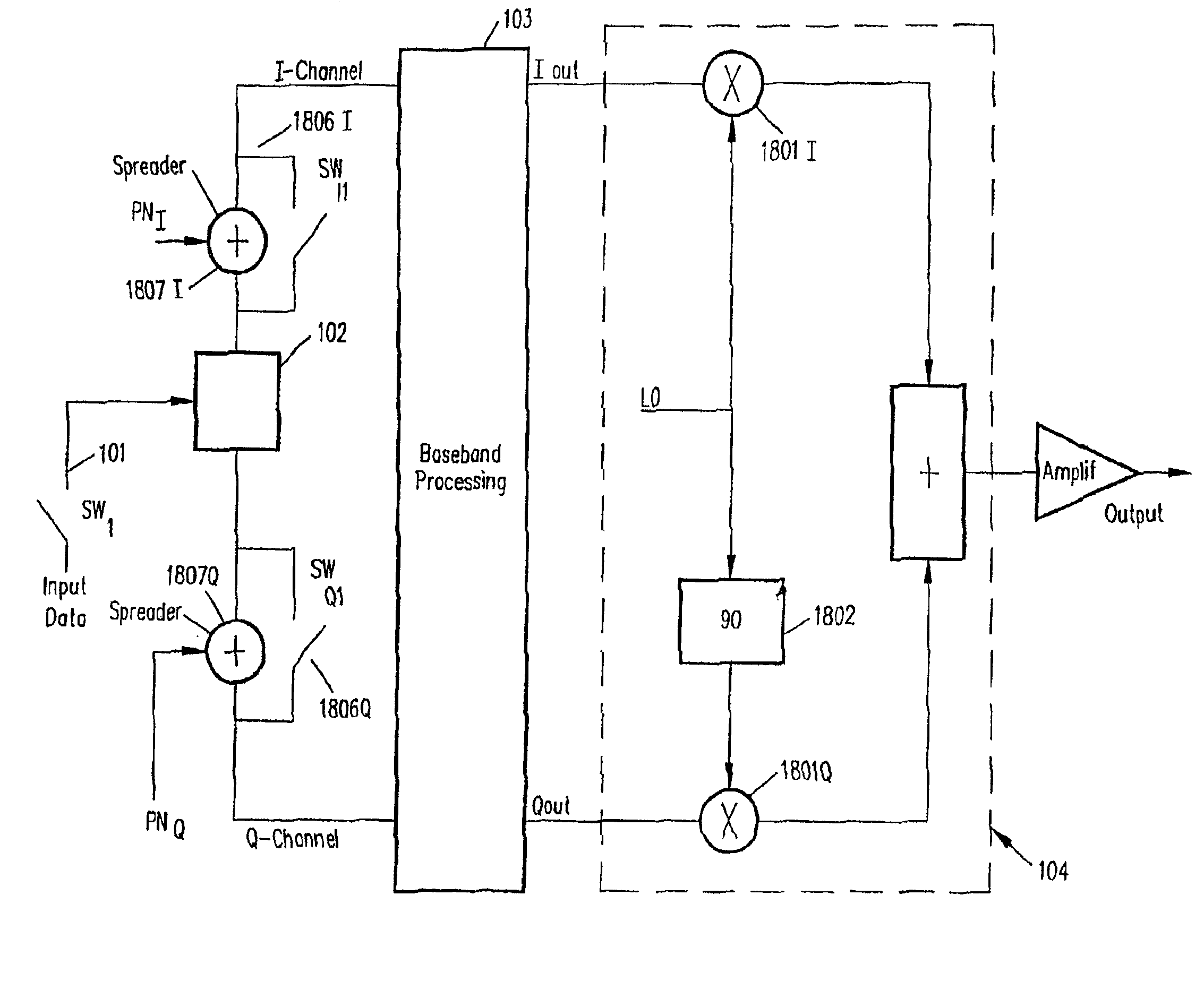
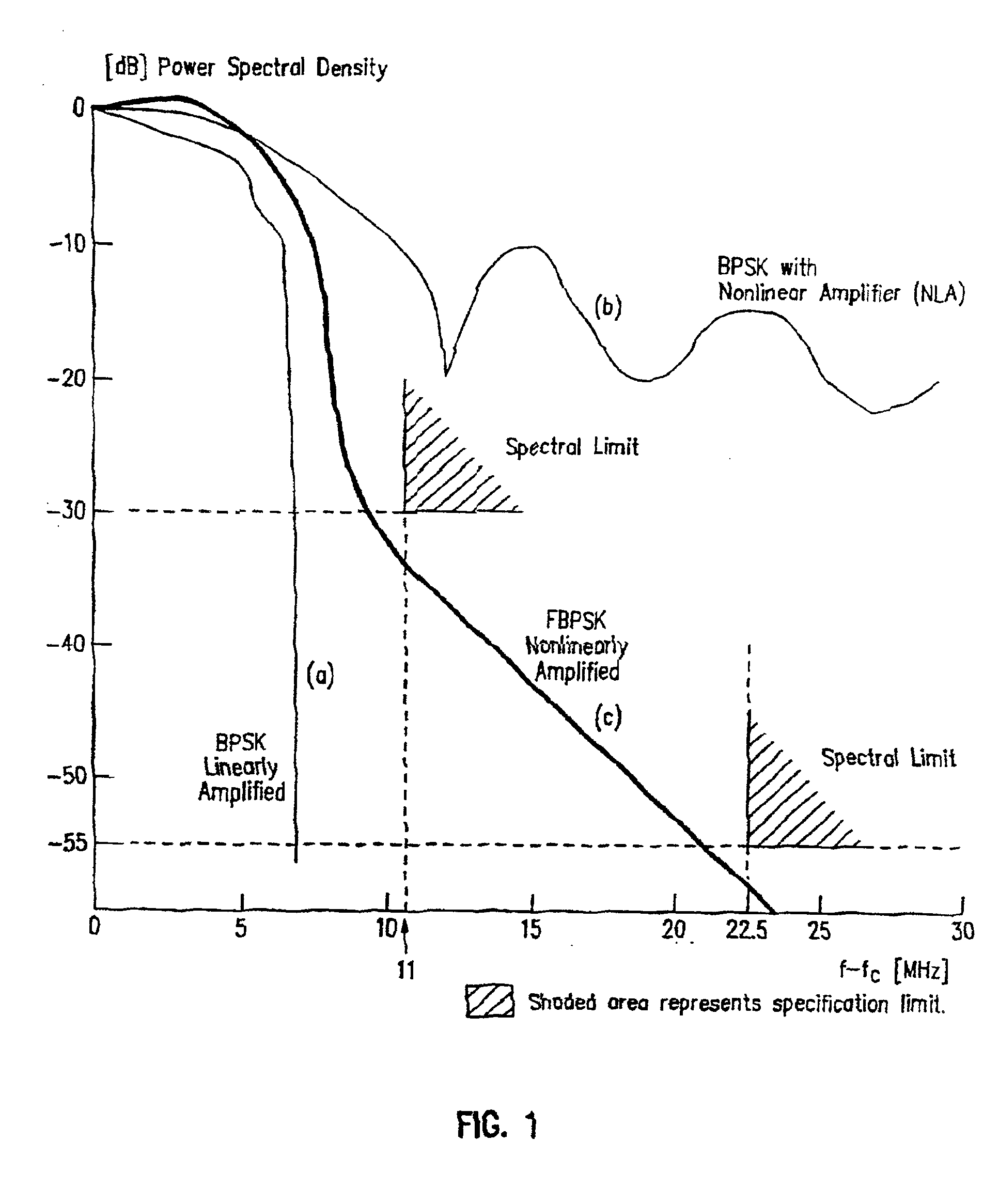
Binary and Quadrature Feher's Modulation (F-Modulation, or FMOD) Transmitter-Receiver systems and circuits exhibit reduced envelope fluctuation and peak radiation, and increased efficiency. A subclass of these systems has a constant envelope. They advantageously provide lower power operation with improved performance including robust BER performance, and compatibility with both linearly and nonlinearly amplified narrow spectrum, and without disadvantages of conventional BPSK, DBPSK QPSK and pi / 4-QPSK. Feher's BPSK (FBPSK) is an improved efficiency transmitter which is compatible with conventional BPSK receivers. FBPSK modems are based on using quadrature structure where Q-channel data is inserted in quadrature with I-channel data for certain applications. The Q-channel data may be “offset” from the I-channel data by an amount selectable between zero and a specified time. Further improvement in the spectrum is attained using correlation between I and Q channels. FBPSK modem is shown to meet the IEEE 802.11 specified spectral direct sequence spread spectrum mask (−30 dB point) for wireless LAN, and leads to an output power gain of 6.5 dB over conventional BPSK modems. The cross-coupled quadrature FMOD structure is also suitable for continuous mode and for burst operated TDMA, FDMA, CDMA, WCDMA and CSMA Frequency Modulation Quadrature AM (QAM), QPSK and offset QPSK, as well as pi / 4-shifted QPSK modems / processors. Reduced modulation index Gaussian FSK (GFSK), multilevel FM and cross-coupled Quadrature Amplitude Modulated (QAM) transmitters and combinations of these modulations and corresponding coherent demodulators are disclosed. Controlled rise and fall time descriptions of burst operated systems are included.
Owner:INTEL CORP
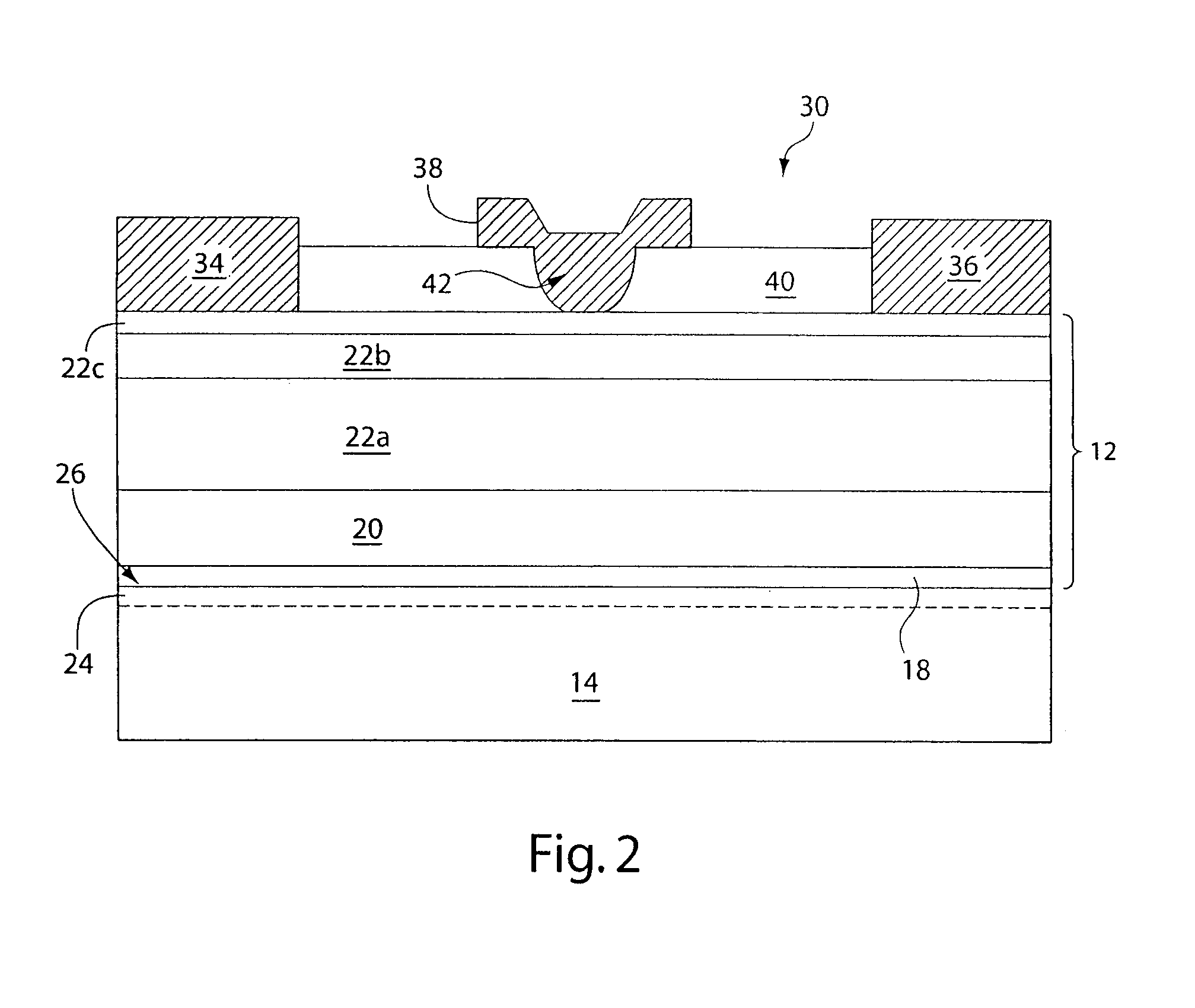
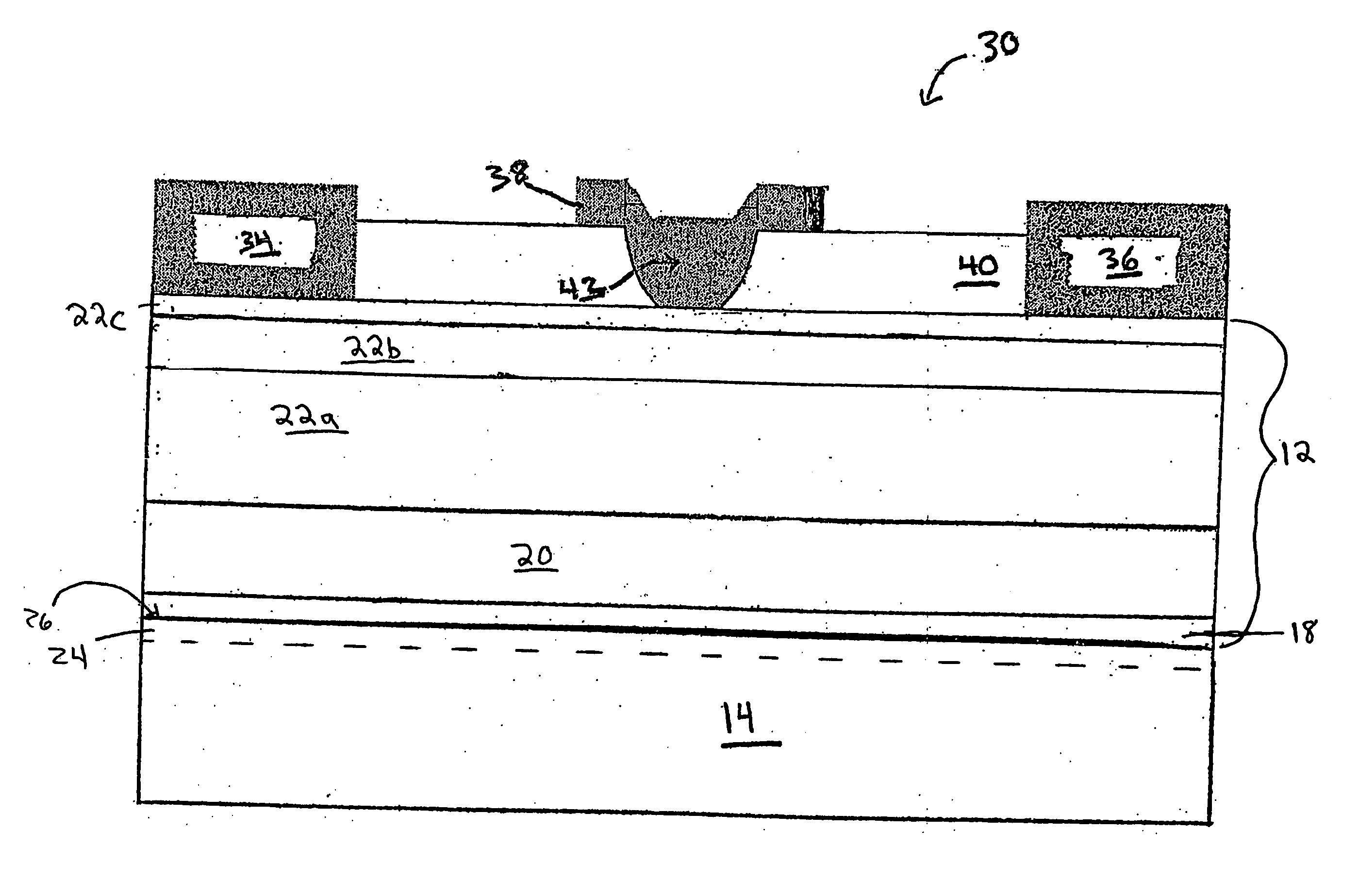
III-nitride material structures including silicon substrates
InactiveUS7247889B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesNitrideSilicon
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
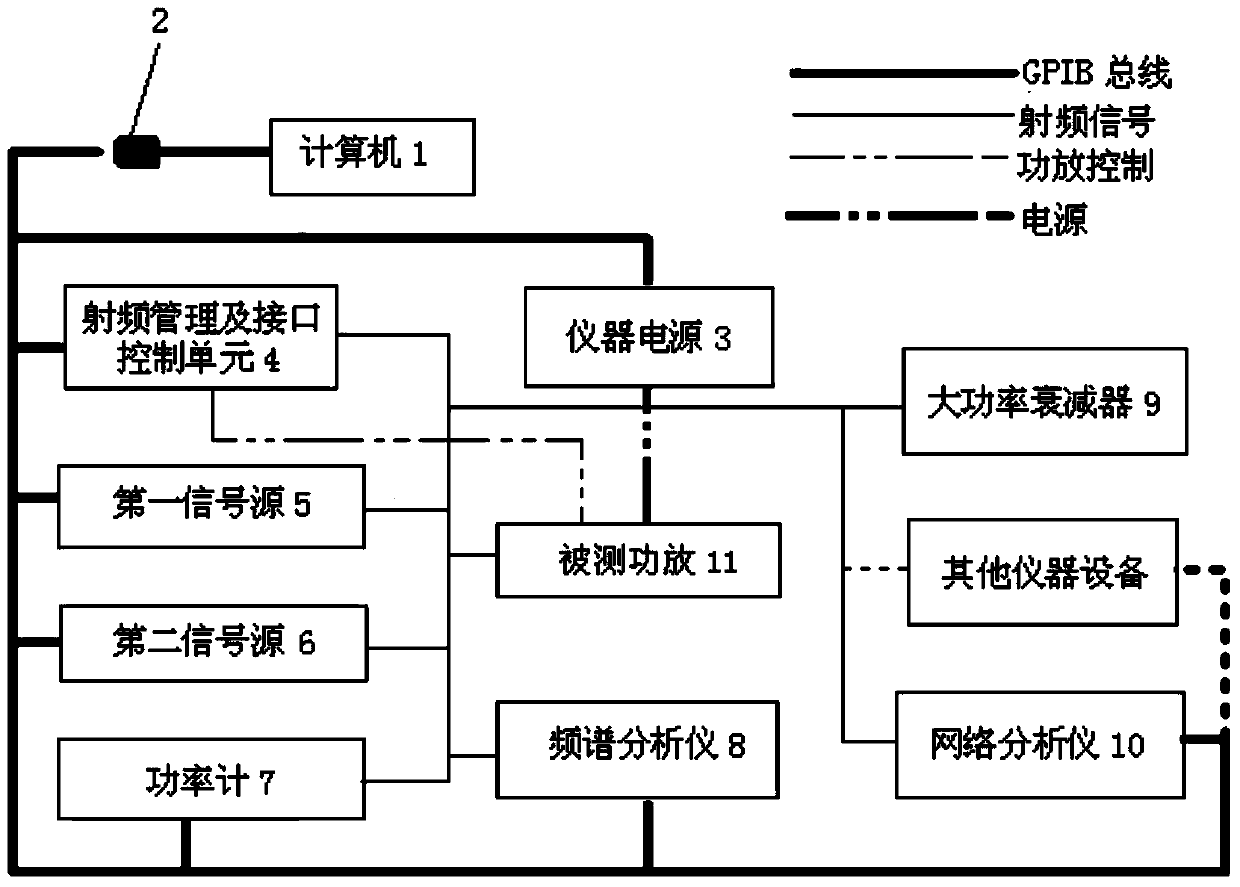
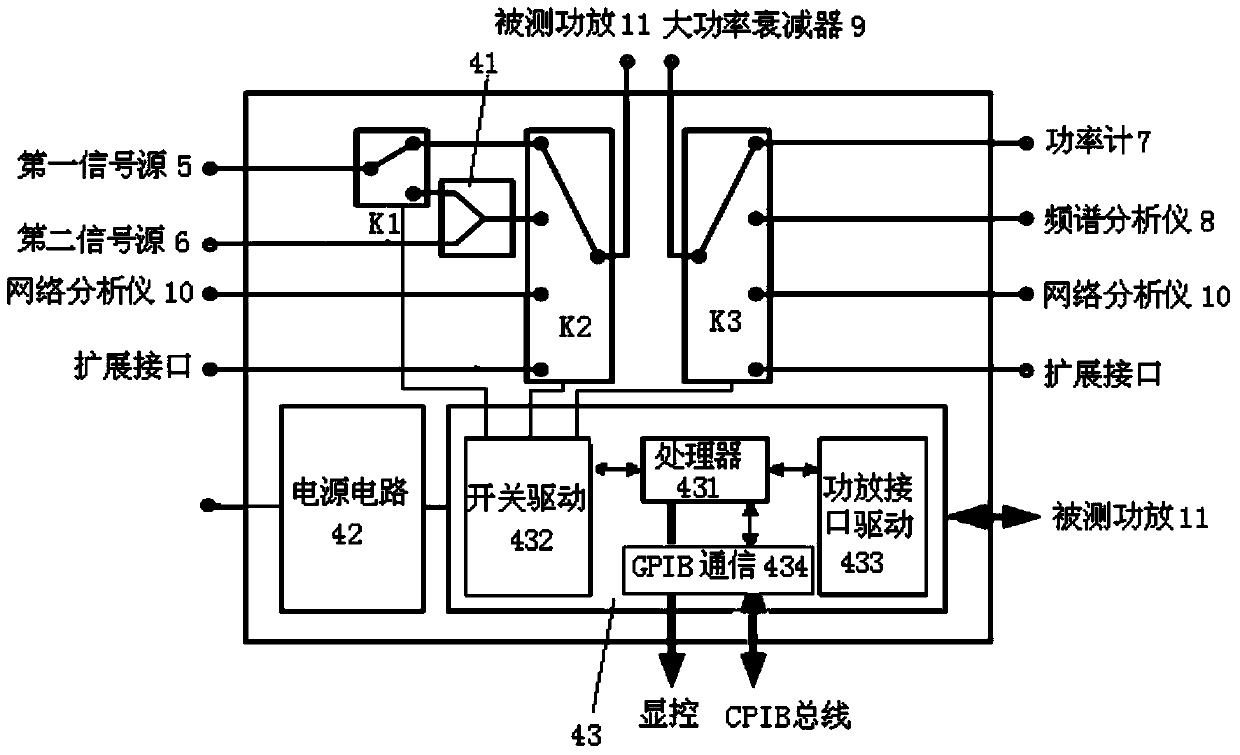
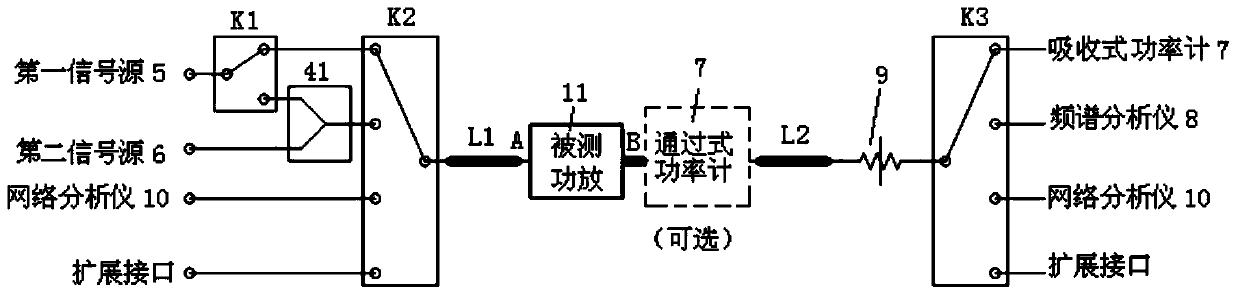
An automatic testing system and an automatic testing method of a continuous wave radio frequency power amplifier
ActiveCN103744010AAchieve calibrationRealize power amplifier transceiverElectronic circuit testingWave bandVIT signals
The invention relates to an automatic testing system and an automatic testing method of a continuous wave radio frequency power amplifier. The method comprises contents 1 that a computer is used for via a communication bus comprehensively managing devices such as an instrument power supply, a signal source, a power meter, a spectrum analyzer, a network analyzer, a radio frequency management and interface control unit, and a power amplifier, and automatically measuring power characteristic, saturation power, gain characteristic, output stationary waves, flatness characteristic, harmonic suppression, spurious suppression, cross modulation characteristic, group delay, and AM / PM characteristics of the radio frequency power amplifier, 2 that calibration of a radio frequency input access and a radio frequency output access is achieved; 3 that the radio frequency management and interface control unit provides all radio frequency accesses, cables are not required to be detached and radio frequency ports are not required to be replaced when indexes are tested, and TTL level, 422 level, relay driving, a serial port, and a LAN bus remote control interface are provided for different power amplifying single machines, and power amplifying transmission and reception, wave band remote control, and state monitoring are achieved; 4 and that system software modular design is achieved.
Owner:36TH RES INST OF CETC
Electrostatic discharge protection device for giga-hertz radio frequency integrated circuits with varactor-LC tanks
InactiveUS6885534B2Solution value is not highHigh ESD levelSolid-state devicesEmergency protective arrangement detailsImpedance matchingEngineering
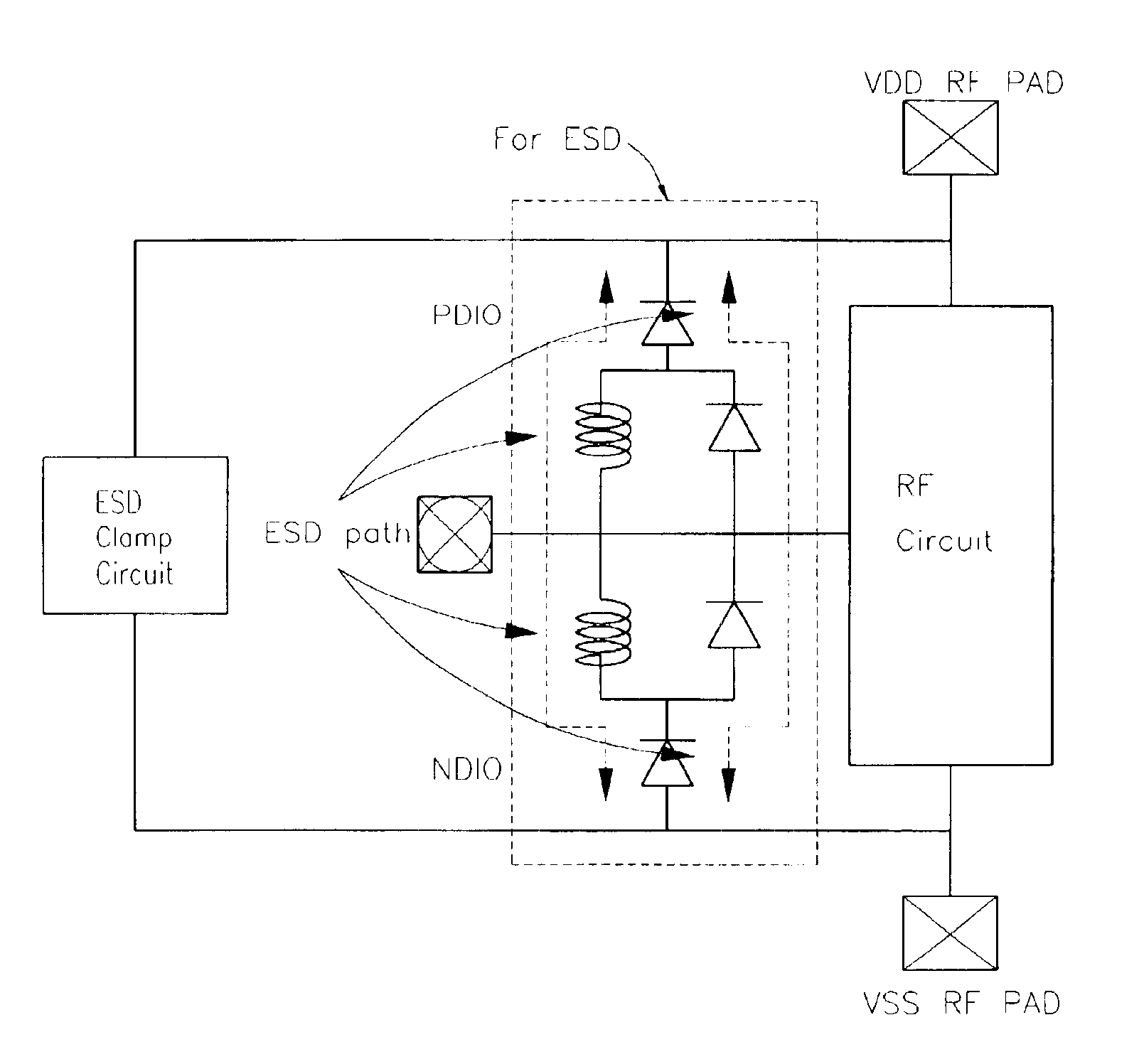
The present invention relates to a device for protecting high frequency RF integrated circuits from ESD damage. The device comprises at least one varactor-LC circuit tank stacked to avoid the power gain loss by the parasitic capacitance of ESD circuit. The varactor-LC tank could be designed to resonate at the RF operating frequency to avoid the power gain loss from the parasitic capacitance of ESD circuit. Multiple LC-tanks could be stacked for further reduction in the power gain loss. A reverse-biased diode is used as the varactor for both purposes of impedance matching and effective ESD current discharging. Because the inductor is made of metal, both the inductor and the varactor can discharge ESD current when ESD condition happens. It has a high enough ESD level to prevent ESD discharge.
Owner:LIBERTY PATENTS LLC
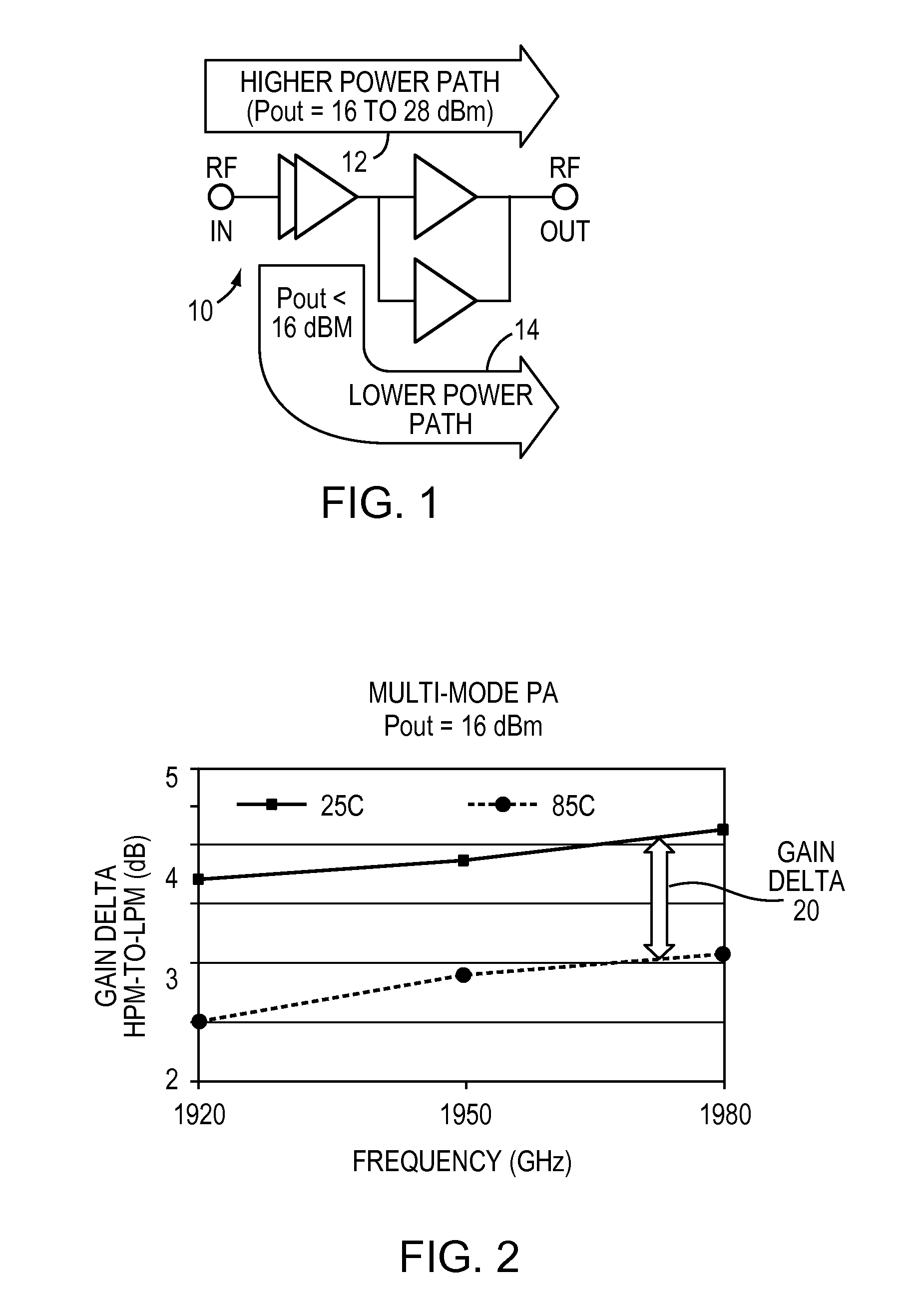
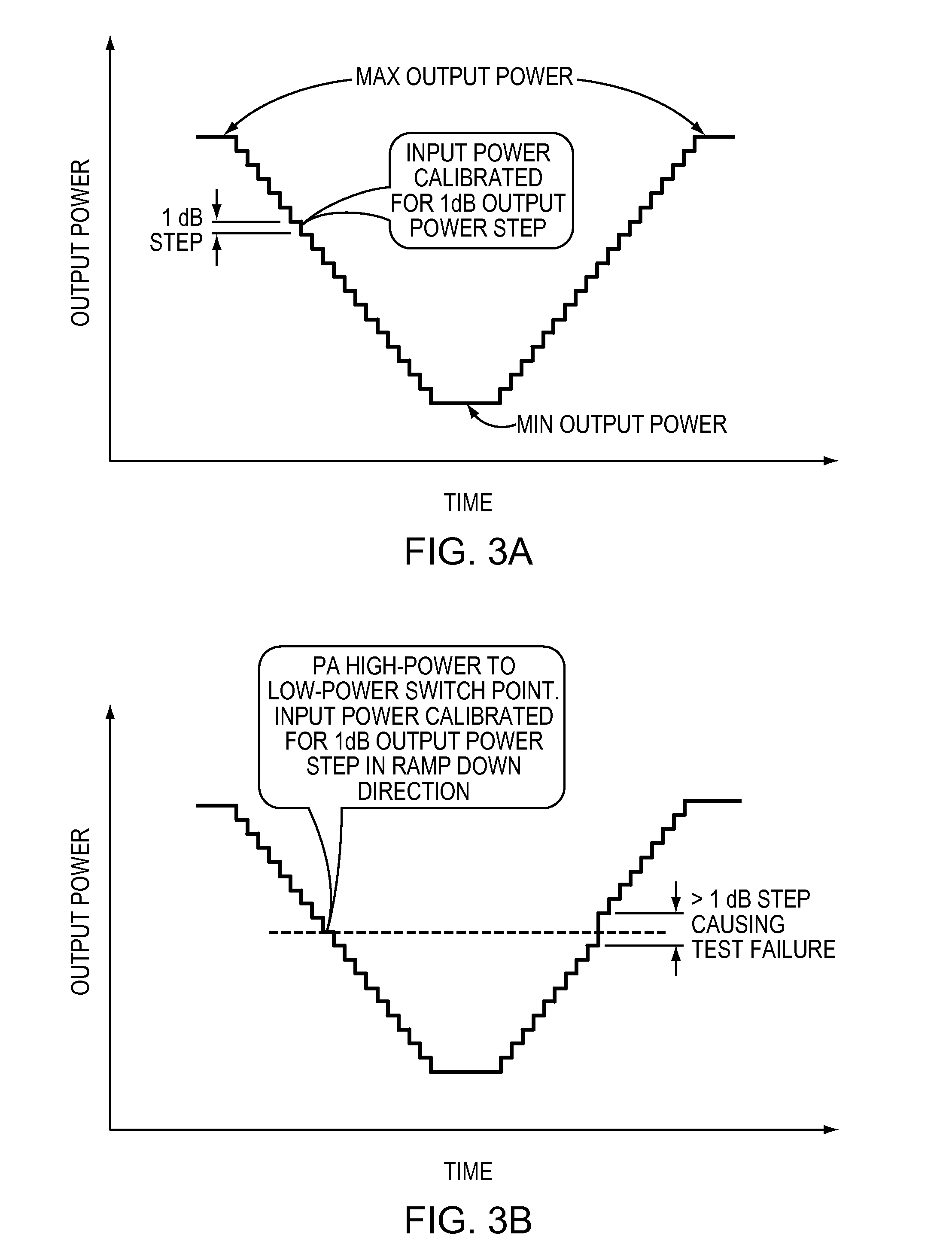
Multi-mode power amplifier with low gain variation over temperature
ActiveUS7554407B2High frequency amplifiersAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationElectricityInner loop
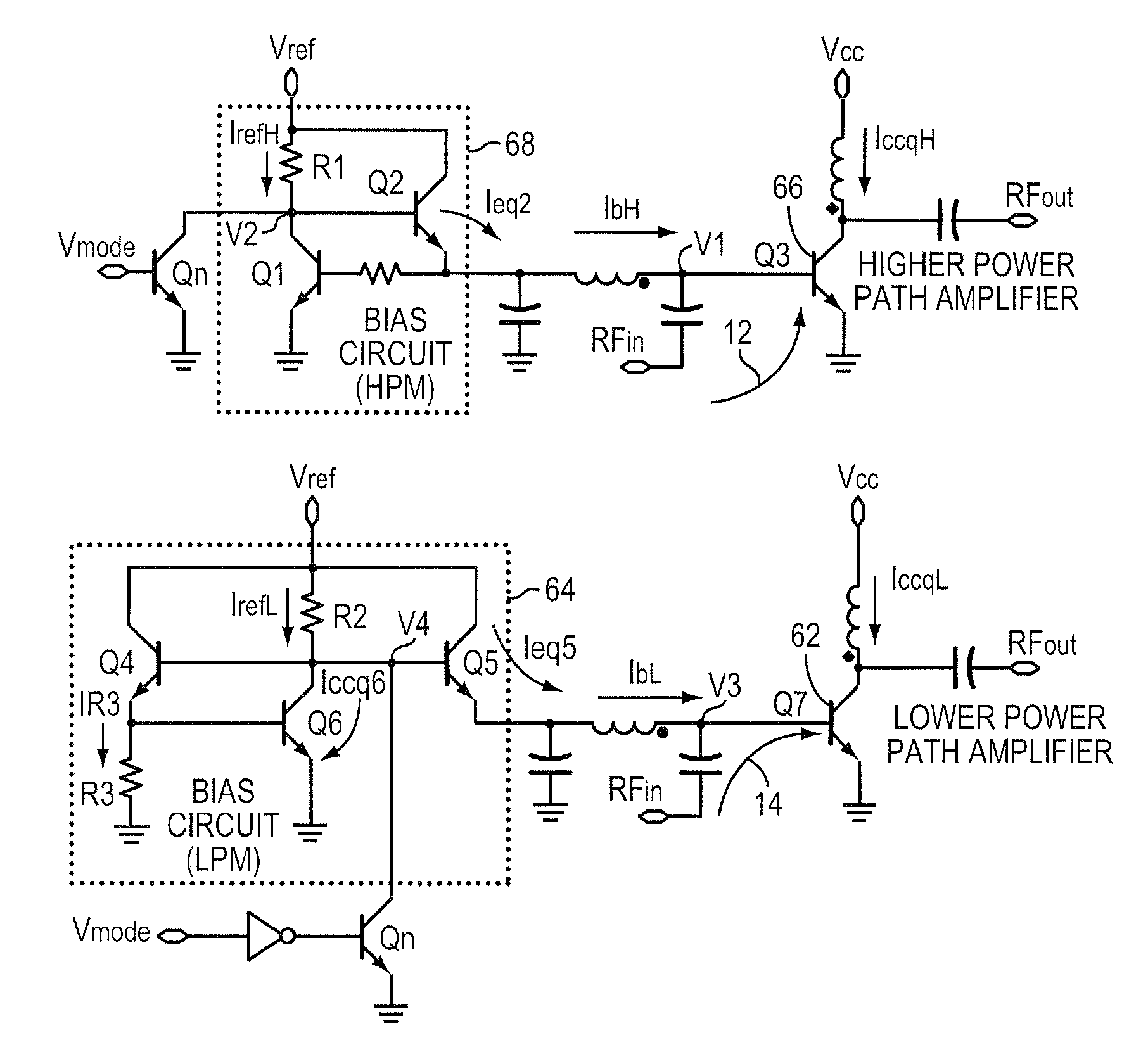
A multi-mode RF amplifier is described having at least a higher and a lower power path coupling an input to an output. At a pre-selected output power level, the higher power path is enabled while the lower power path is disabled when more output power is required. The process is reversed when less power is needed. The present invention matches the power gain variation over temperature characteristic of each path such that, especially at the cross over point, the gain delta (the difference in power gain between the two paths) has minimal variation over temperature. Such power gain characteristic is required for meeting the test requirements, specifically the inner loop power control, for third generation (3G) cellular handsets.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
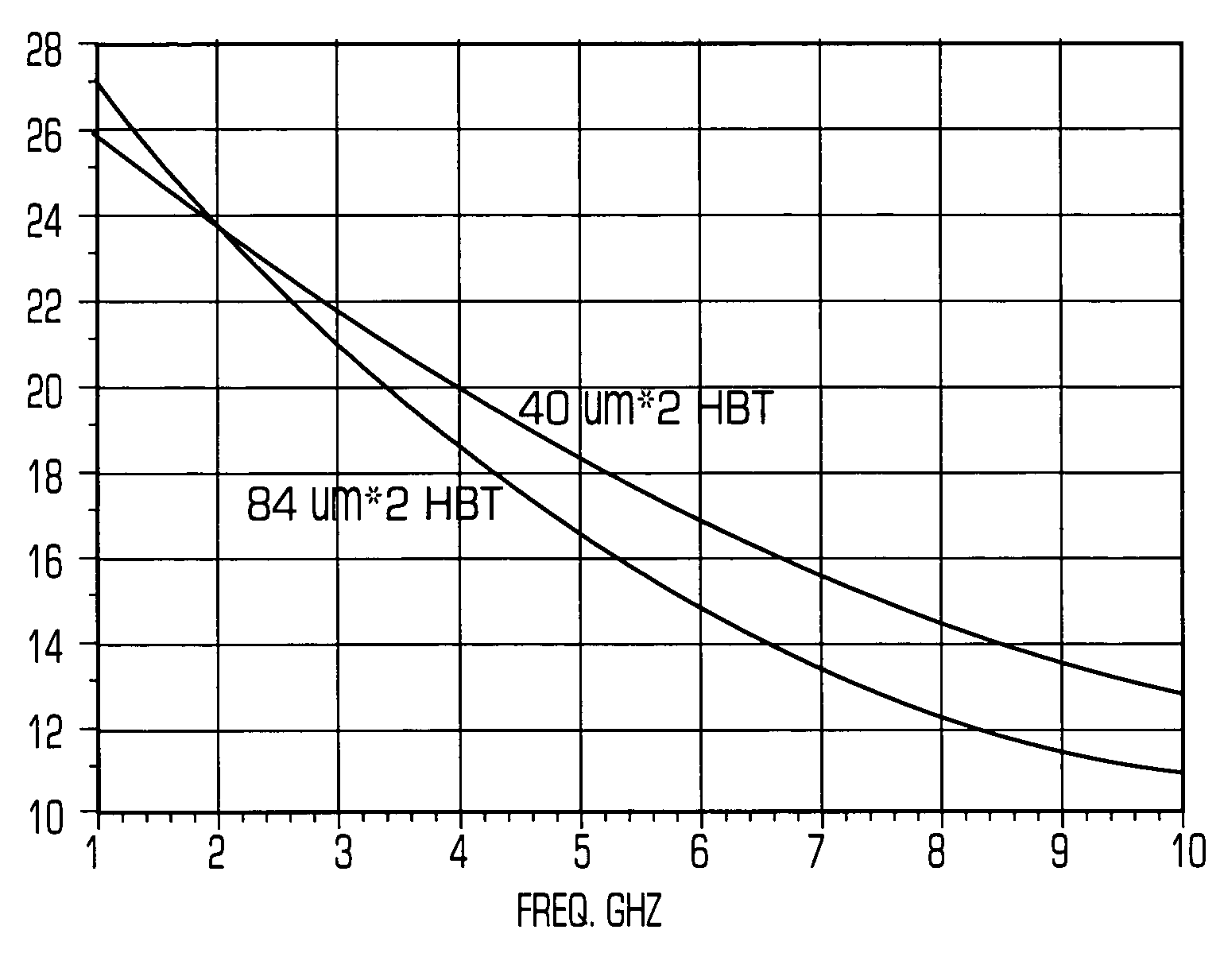
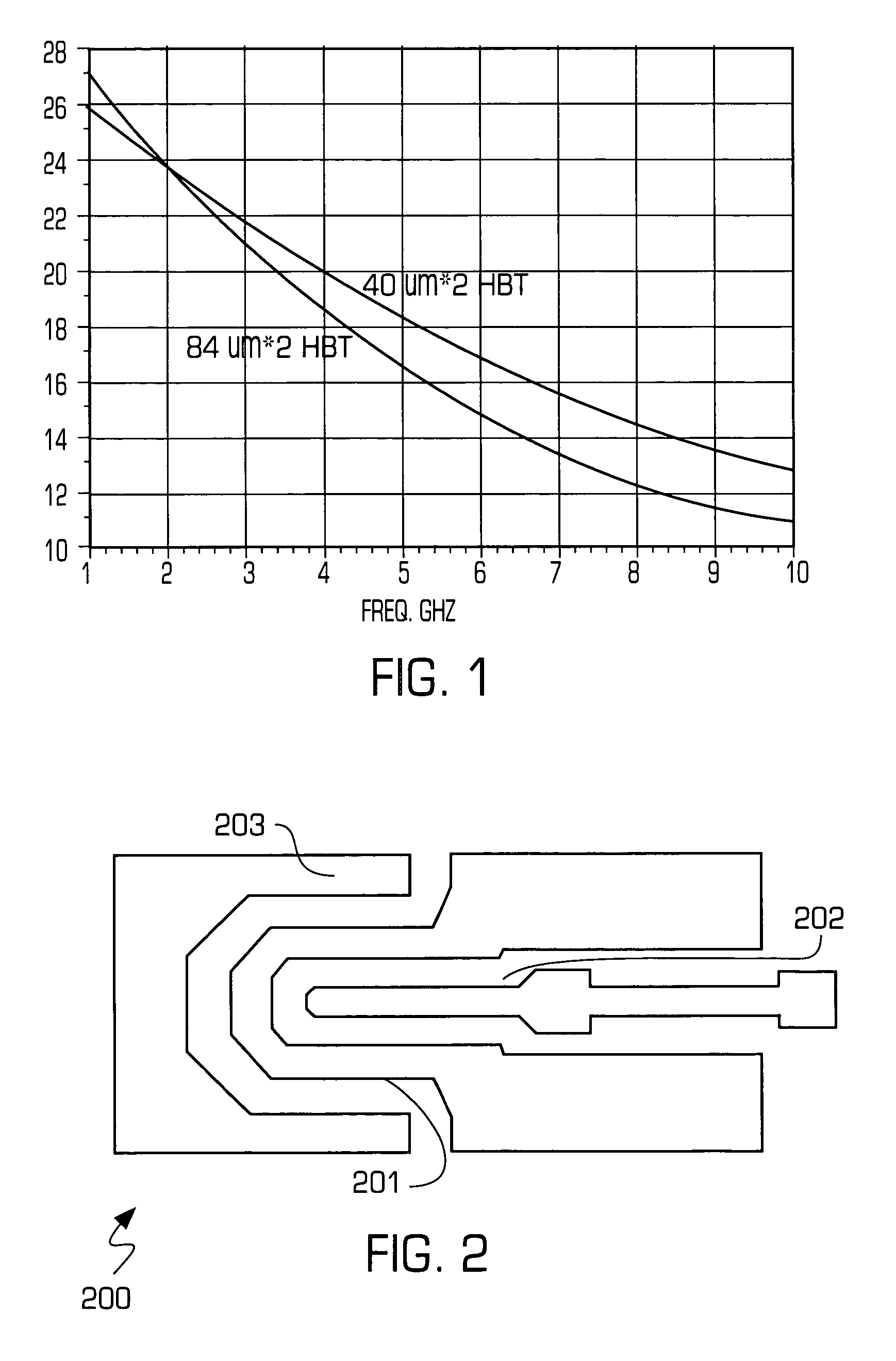
High linearity smart HBT power amplifiers for CDMA/WCDMA application
ActiveUS7026876B1Increase power gainImprove RF efficiencyHigh frequency amplifiersAmplifier combinationsTransistor arrayHbt power amplifier
A power amplifier includes larger size transistors to provide higher power gain at lower frequencies. Transistors of transistor unit cells include a horseshoe-shaped emitter and a strip-shaped base to increase gain. Transistors are combined at a first level to form transistor arrays, which are combined with bonding wires at a second level to an output micro strip transmission line. A Vbe referenced bias circuit may include a smart function to lower quiescent current.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
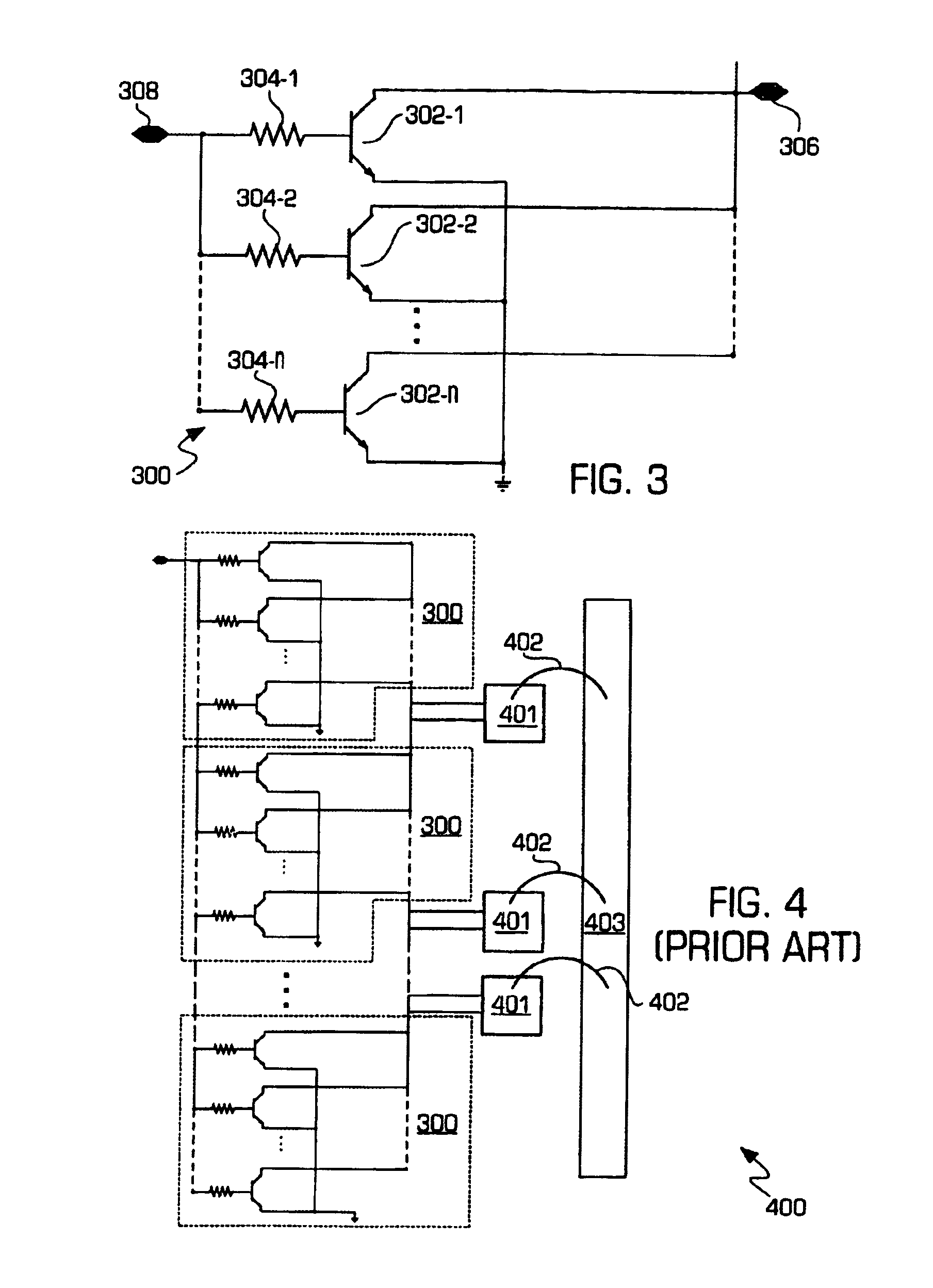
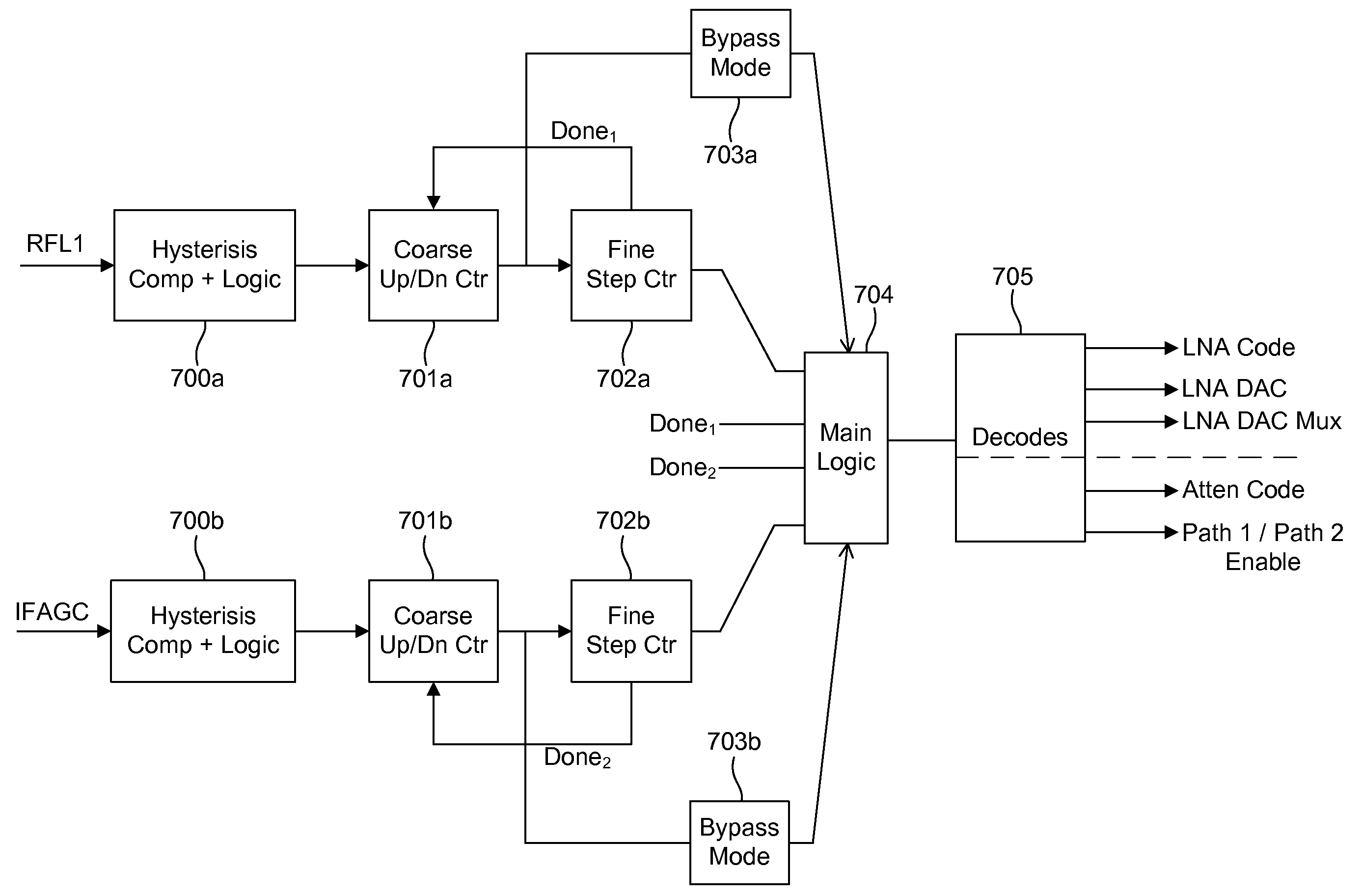
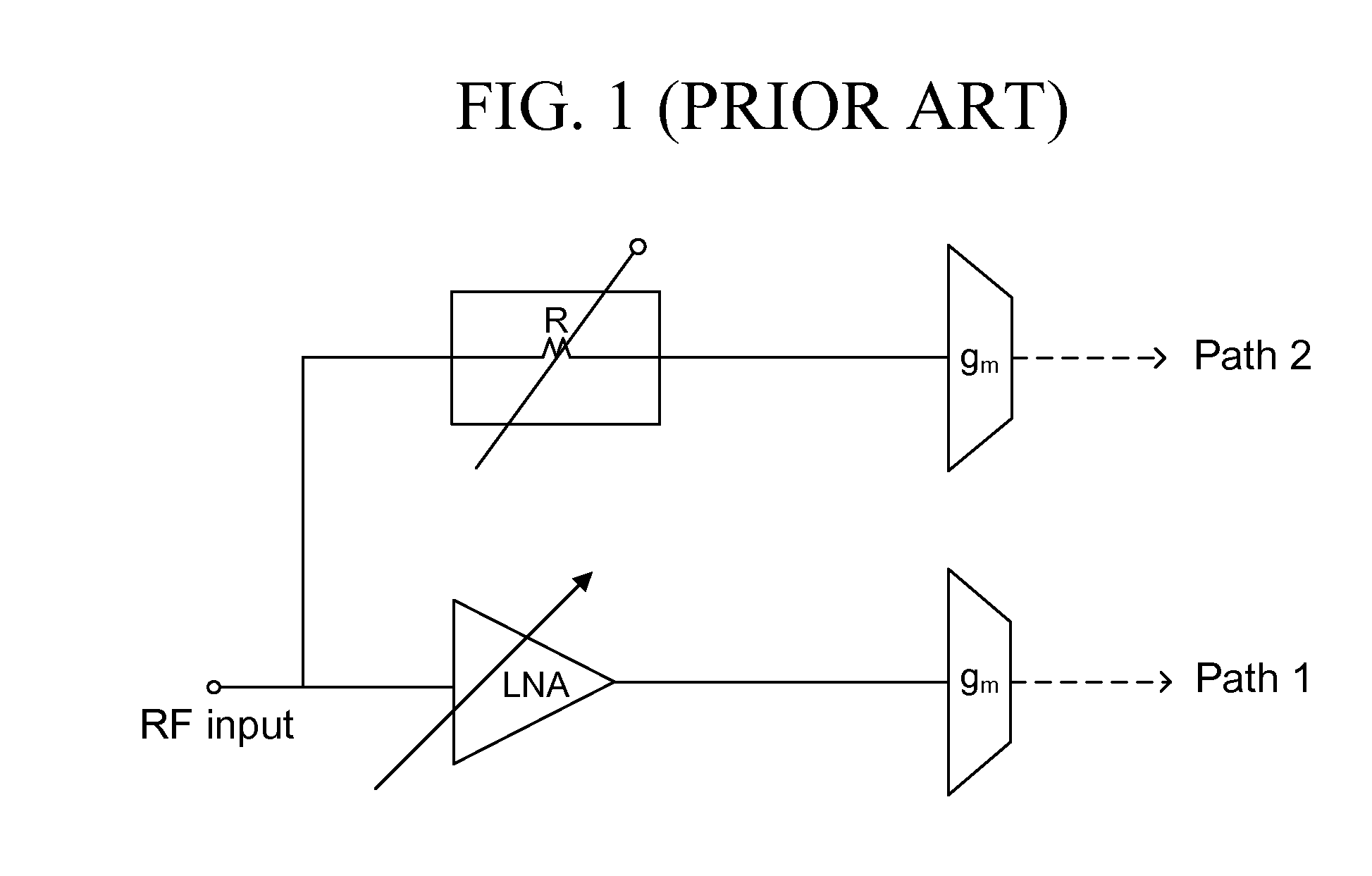
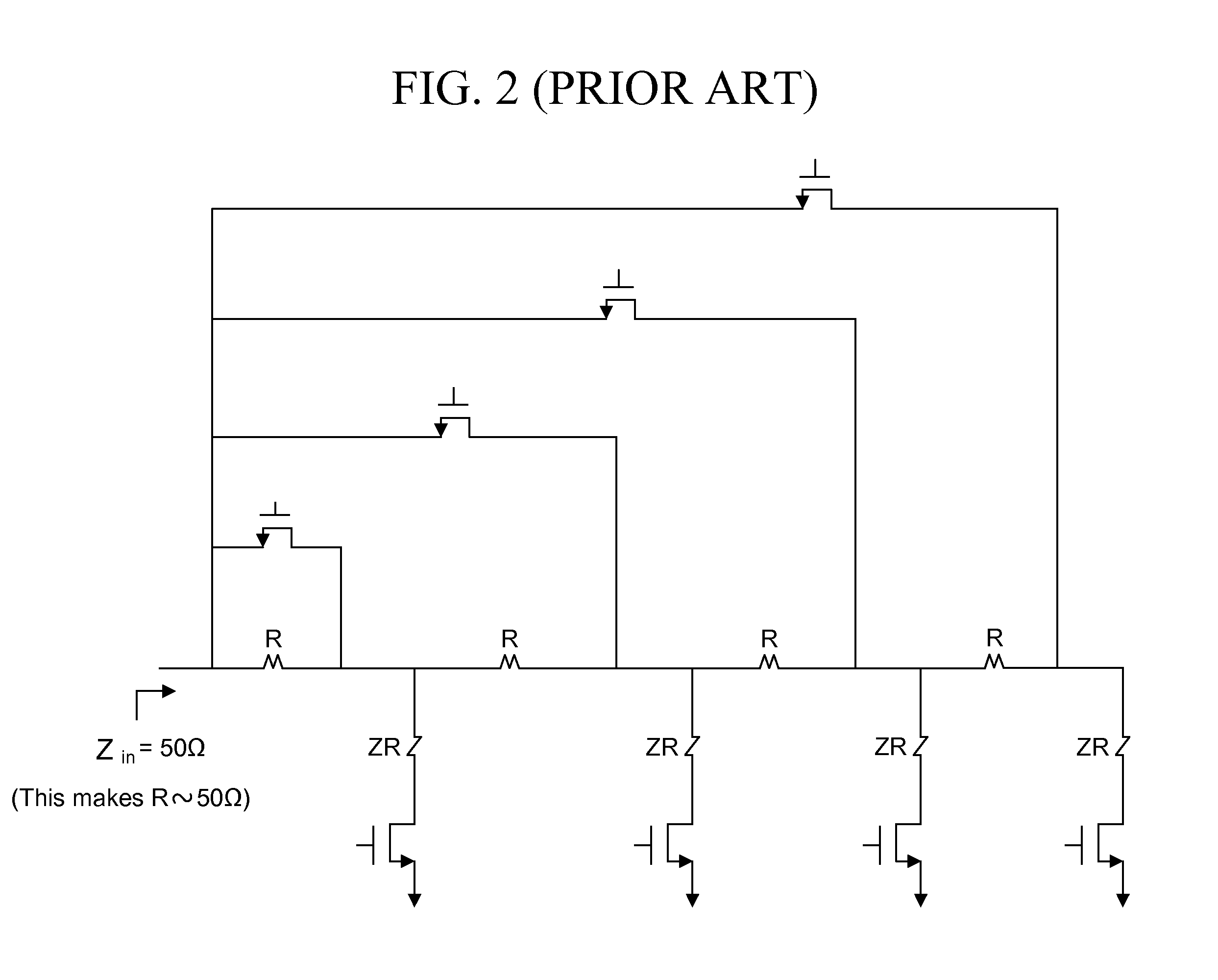
High linearity, low noise figure, front end circuit with fine step gain control
A system, method, and electrical circuit comprises a LNA signal line path comprising a LNA and a first signal mixer operatively connected to the LNA. The circuit further comprises an attenuator signal line path comprising an attenuator and a second signal mixer operatively connected to the attenuator; a radio frequency (RF) power detector operatively connected to an output of each of the LNA and the attenuator, wherein the RF power detector is adapted to vary a front end power gain of the electrical circuit; and logic circuitry operatively connected to the RF power detector, wherein the logic circuitry is adapted to (i) select transmission of a signal through only one of the LNA signal line path or the attenuator signal line path, and (ii) output the selected signal.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
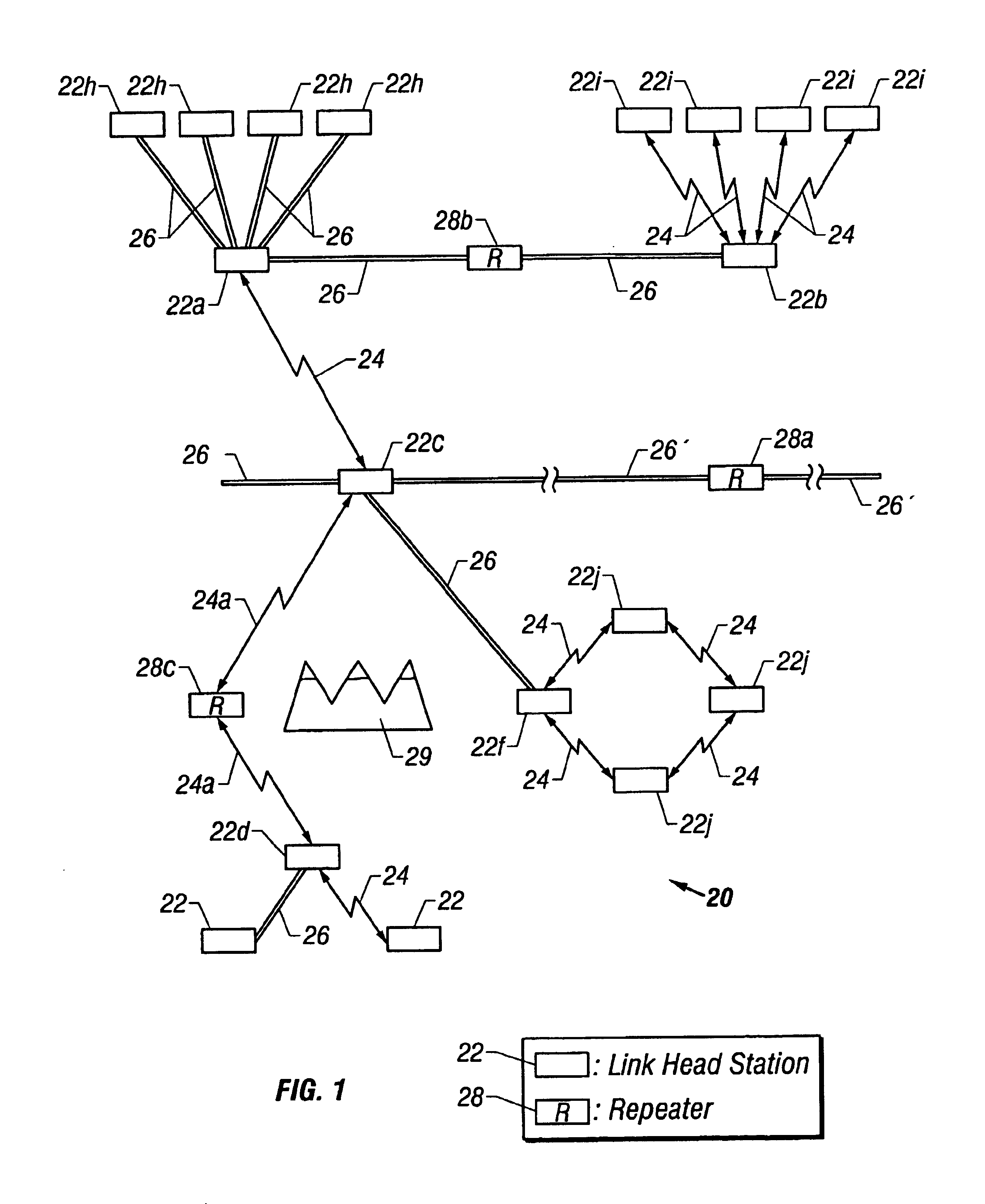
Terrestrial optical communication network of integrated fiber and free-space links which requires no electro-optical conversion between links
InactiveUS6868237B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsUltrasound attenuationLight beam
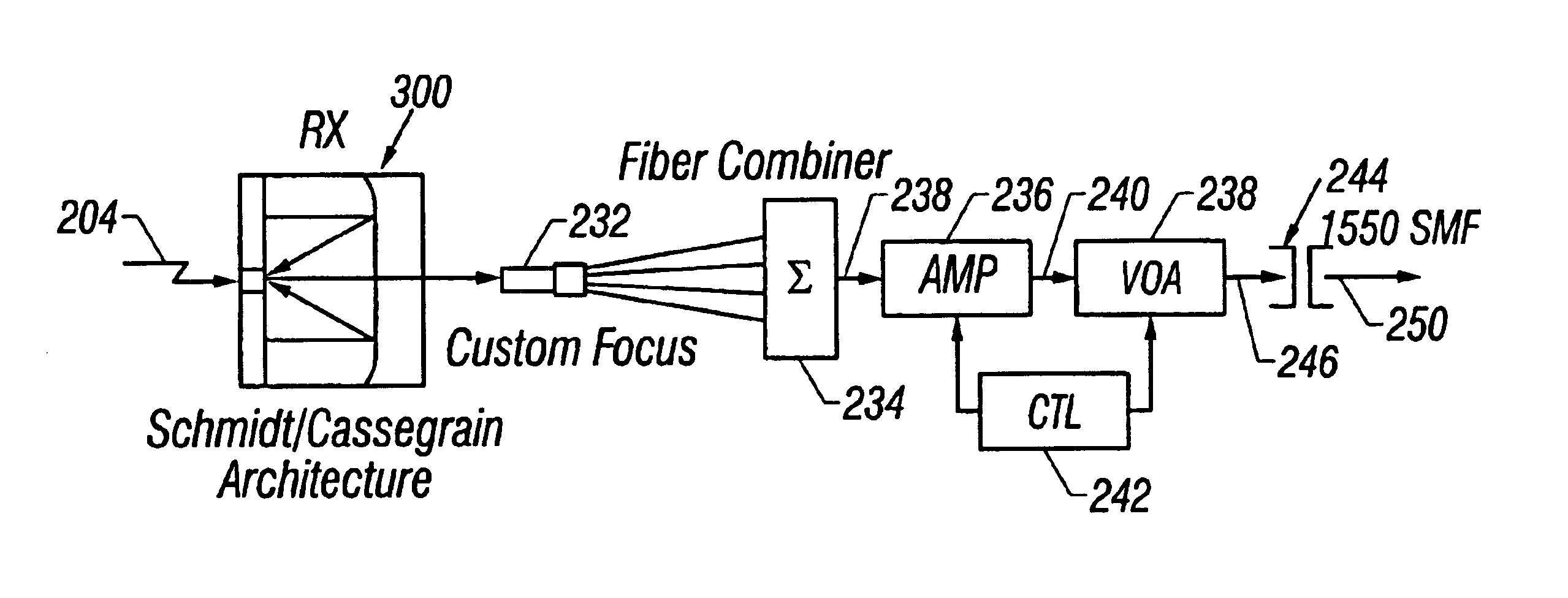
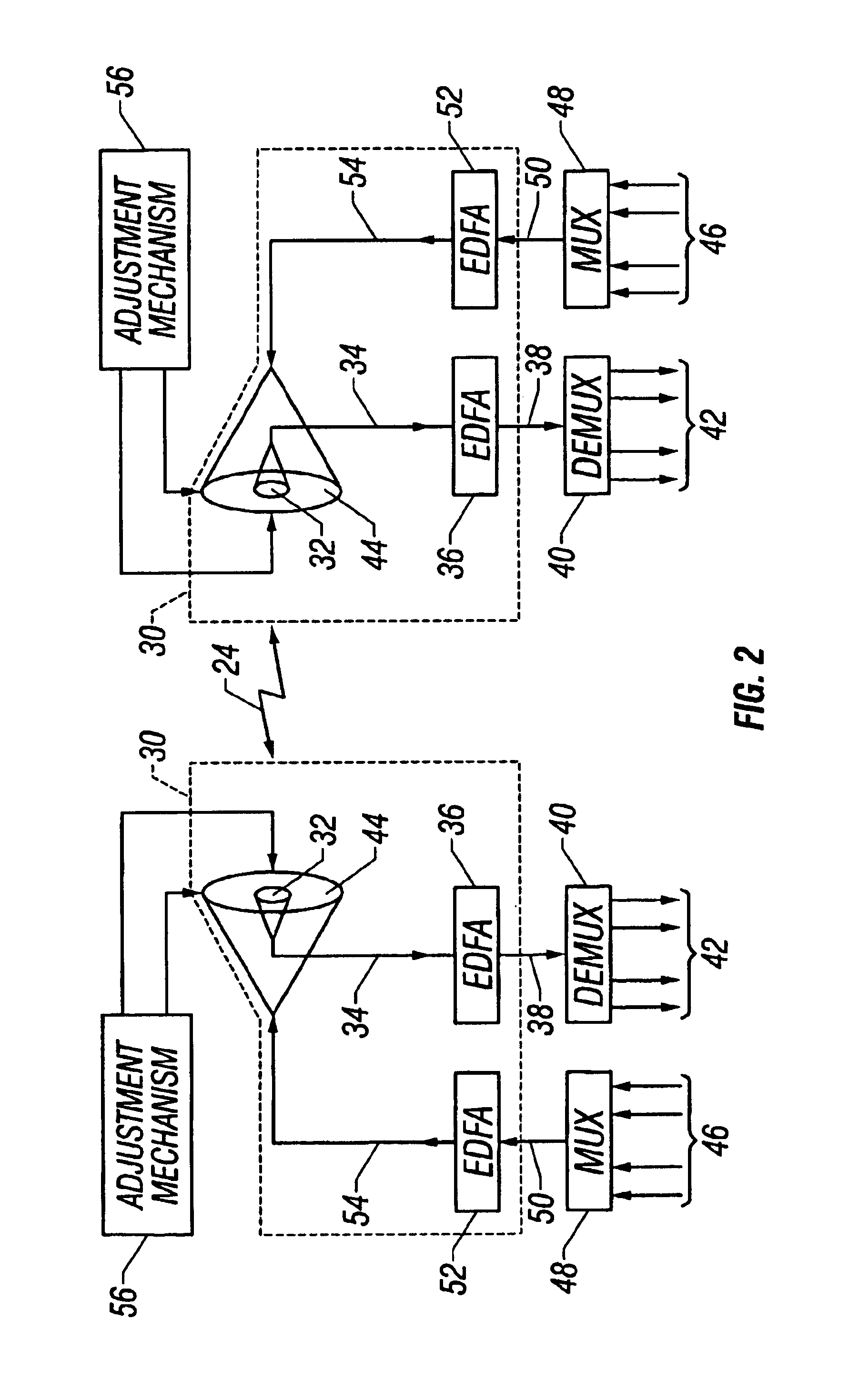
Optical signals are received from a free-space link by directing received light onto a plurality of microlenses and then directing light received through each of the microlenses into a respective single mode optical fiber (SMF). Light beams from the SMFs are combined into a single light beam in one SMF. The single light beam is amplified with a multi-wavelength fiber amplifier and attenuated with a variable optical attenuator. The power gain of the multi-wavelength fiber amplifier and the attenuation of the variable optical attenuator are controlled. The single light beam is directed into a fiber optic communication system that is optically coupled to the variable optical attenuator.
Owner:LIGHTPOINTE COMM
Method and apparatus for controlling uplink transmission power within a satellite communication system
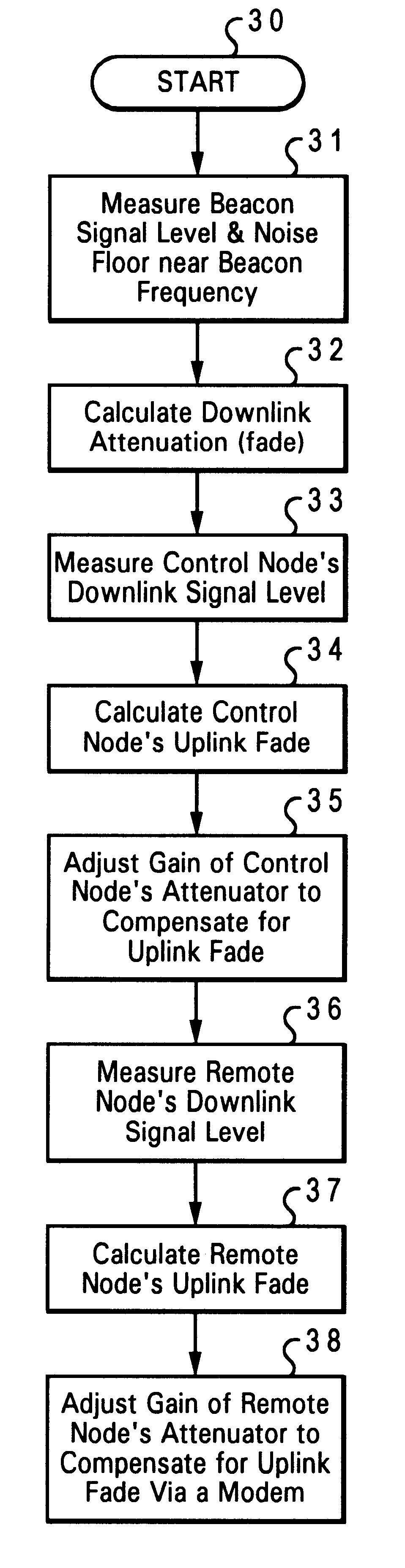
A method and apparatus for controlling uplink transmission power in a satellite communication system is disclosed. The satellite communication system includes a satellite and one or more earth stations, one of which serving as a control station. The satellite can receive uplink signals from any one of the earth stations and retransmits the uplink signals as downlink signals, along with a beacon signal. The control station measures the power of the downlink signals and the beacon signal received from the satellite, and also measures the noise power near the beacon signal. From these measurements, the control station determines an appropriate gain value of the power for uplink transmissions for each of the earth stations.
Owner:SOLA COMM
Low power low noise amplifier
InactiveUS20020084855A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlAudio power amplifierEngineering
The present invention relates to a low power low noise amplifier, more particularly to the low power low noise amplifier composed with low power by sharing the bias current. The present invention is composed of cascode structure which consists of common source transistor and common gate transistor connecting with common source transistor, inverter type structure connecting with common source transistor and structure improving the third-order intermodulation component using the parallel connected common source transistor and common gate transistor. The present invention provides a low noise amplifier gives high power gain without increasing power consumption by sharing the bias current.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Low noise amplifier for wideband tunable matching
ActiveUS7323939B2Improve performanceNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierEngineering
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Low power low noise amplifier
InactiveUS6556085B2Improve linearityIncrease power gainAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlAudio power amplifierEngineering
A low power low noise amplifier achieves a high power gain without increasing power consumption by sharing the bias current. The amplifier is composed of a cascade structure which consists of a parallel connected common source transistor and common gate transistor connected to a common source transistor, an inverter type structure connected to the common source transistor, and structure improving the third-order intermodulation component using the parallel connected common source transistor and common gate transistor.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
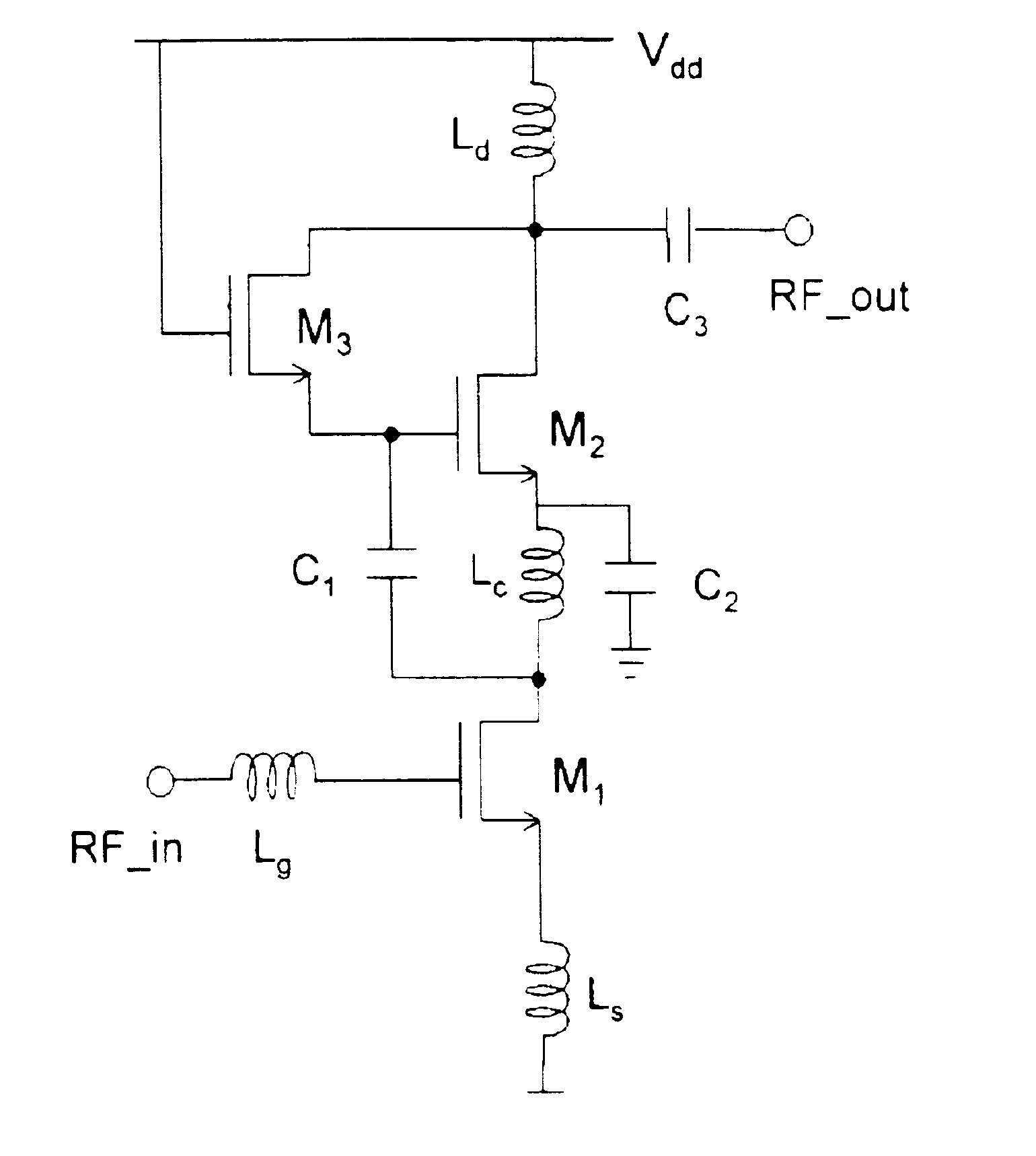
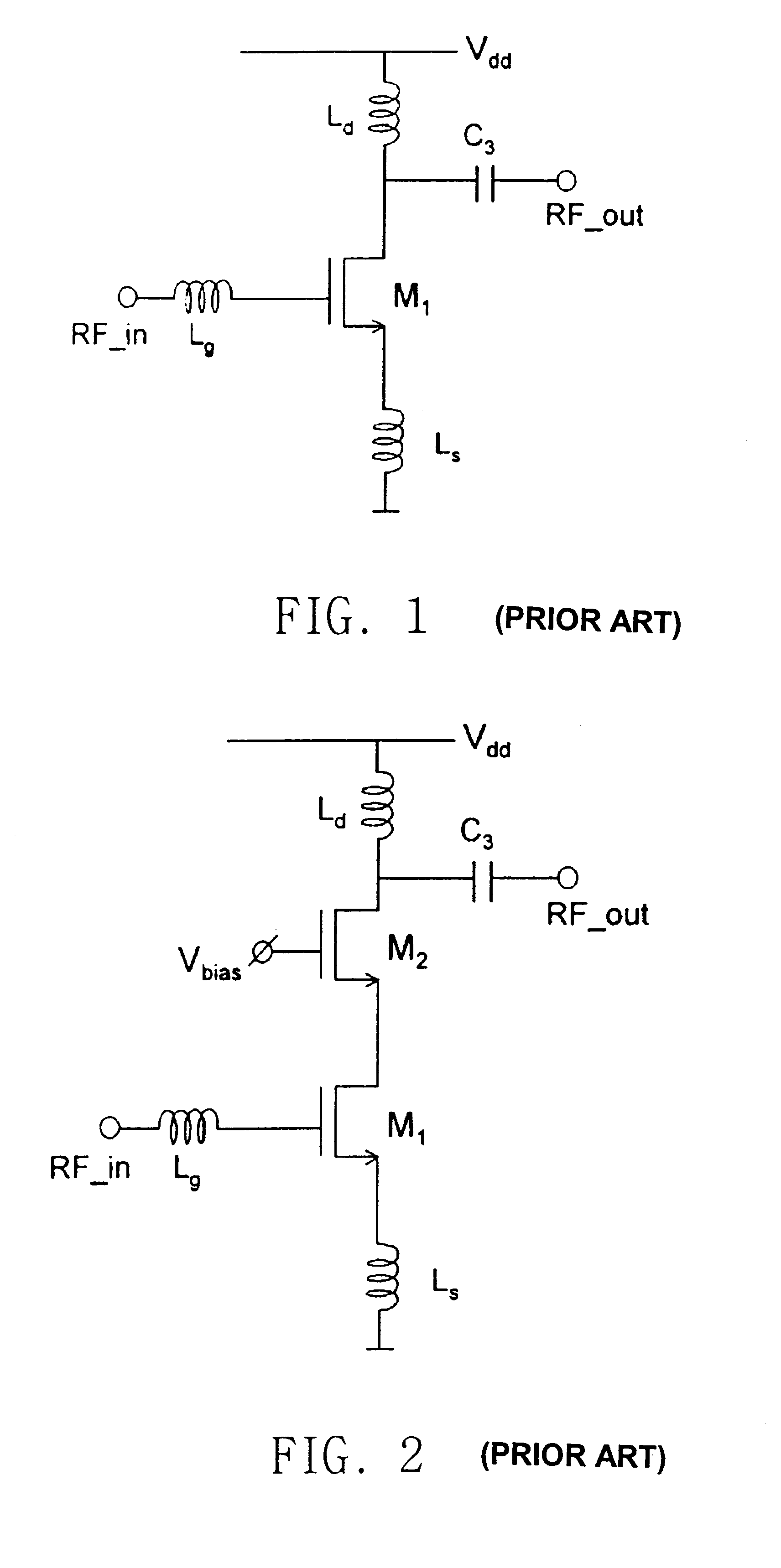
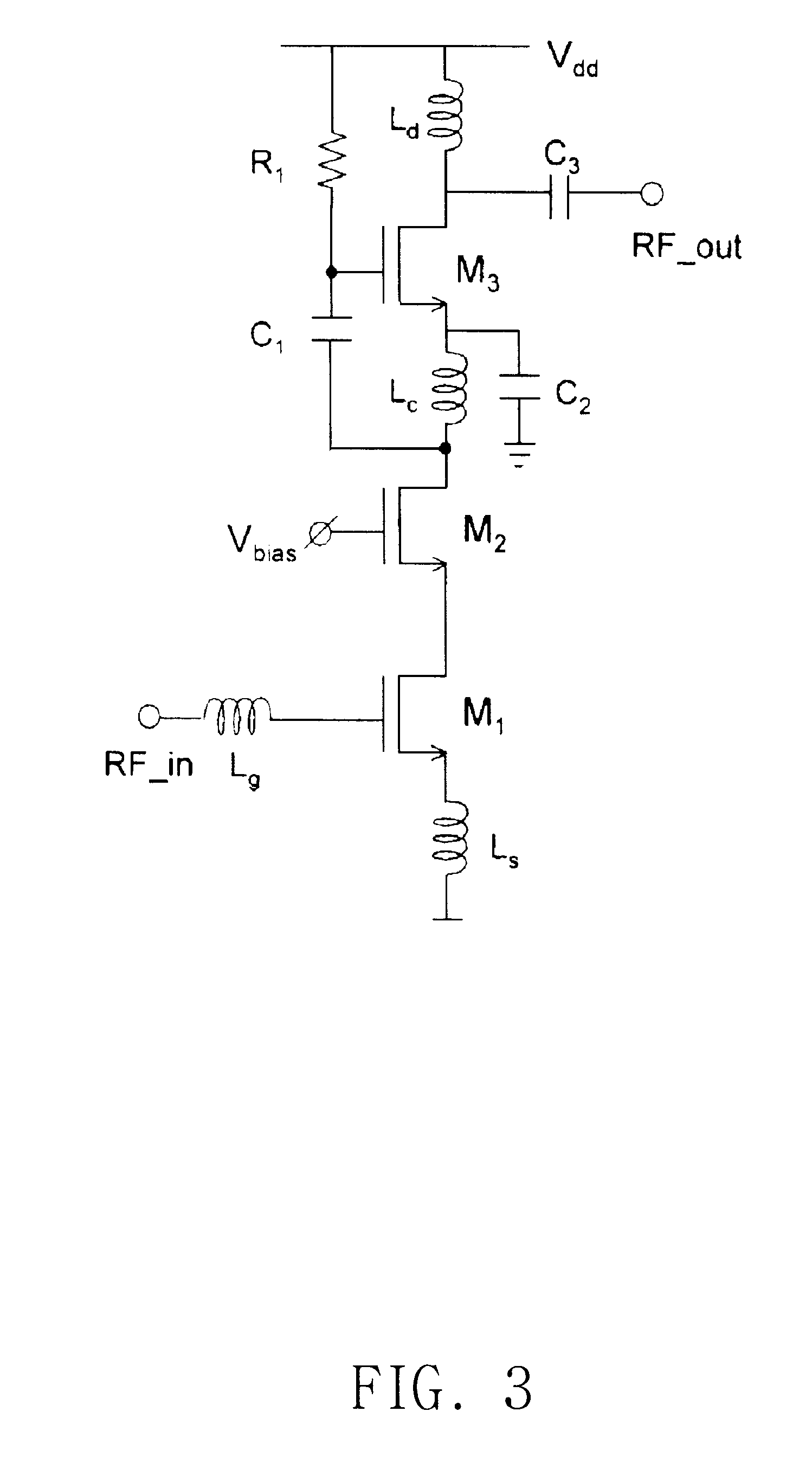
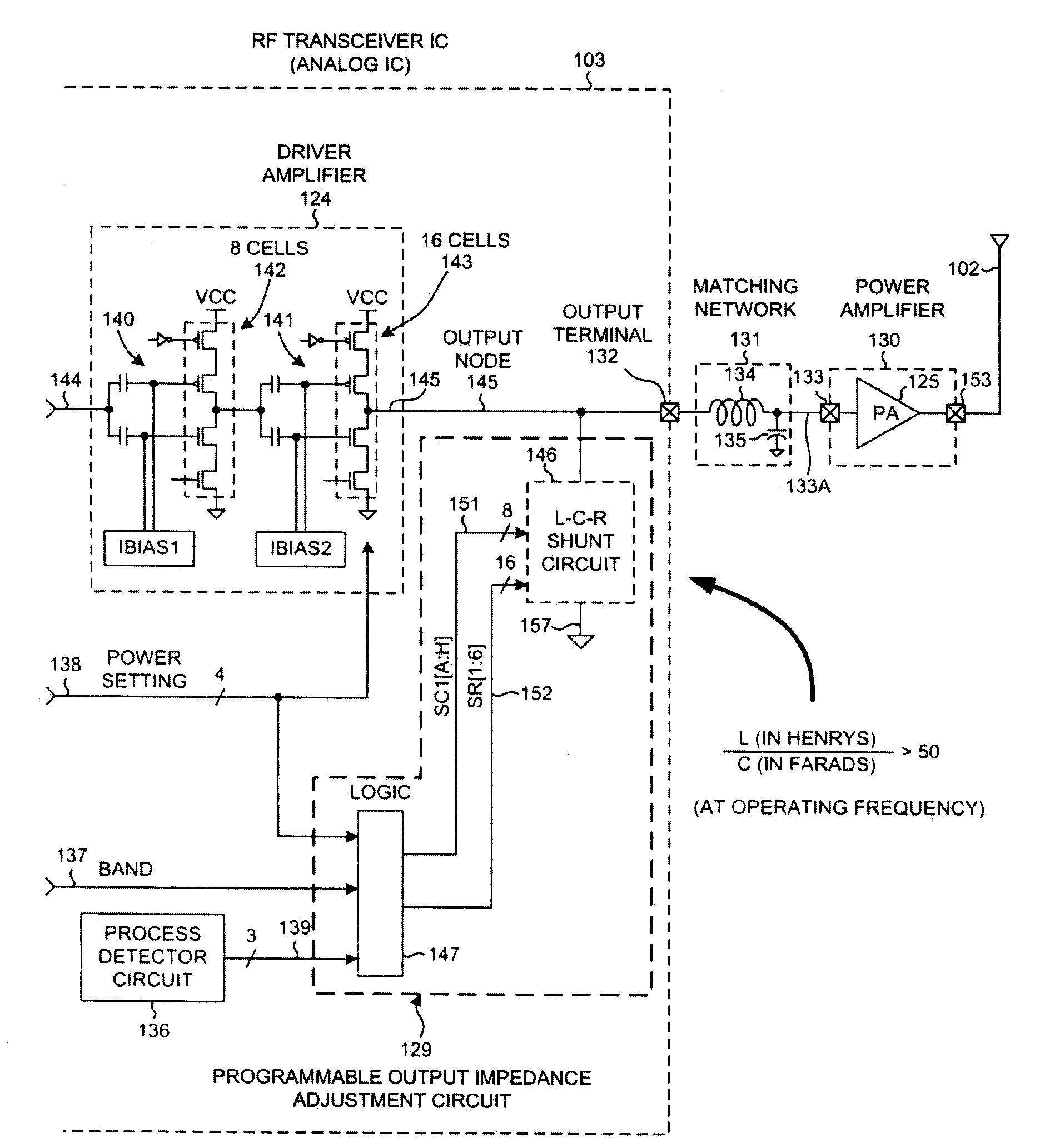
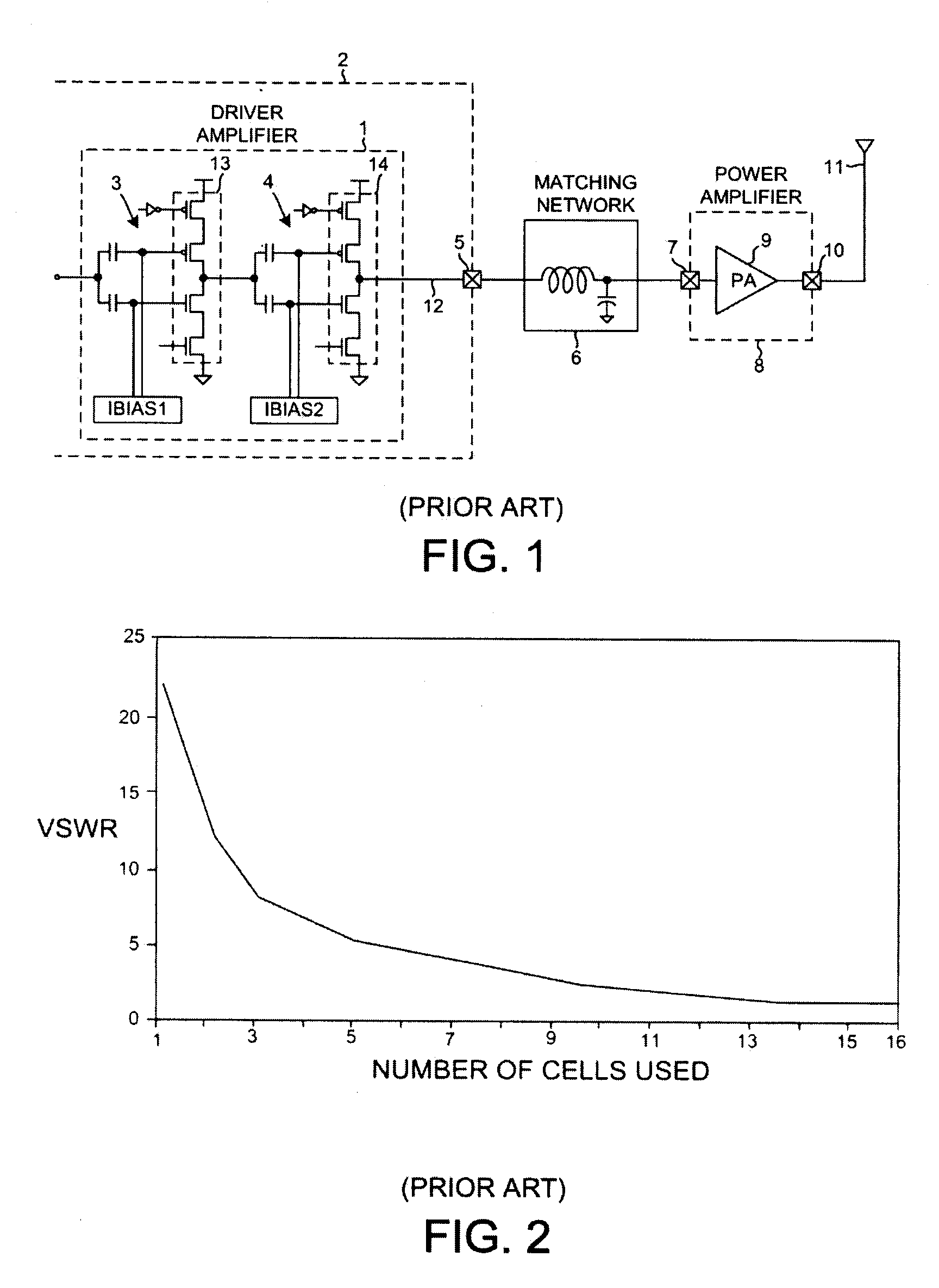
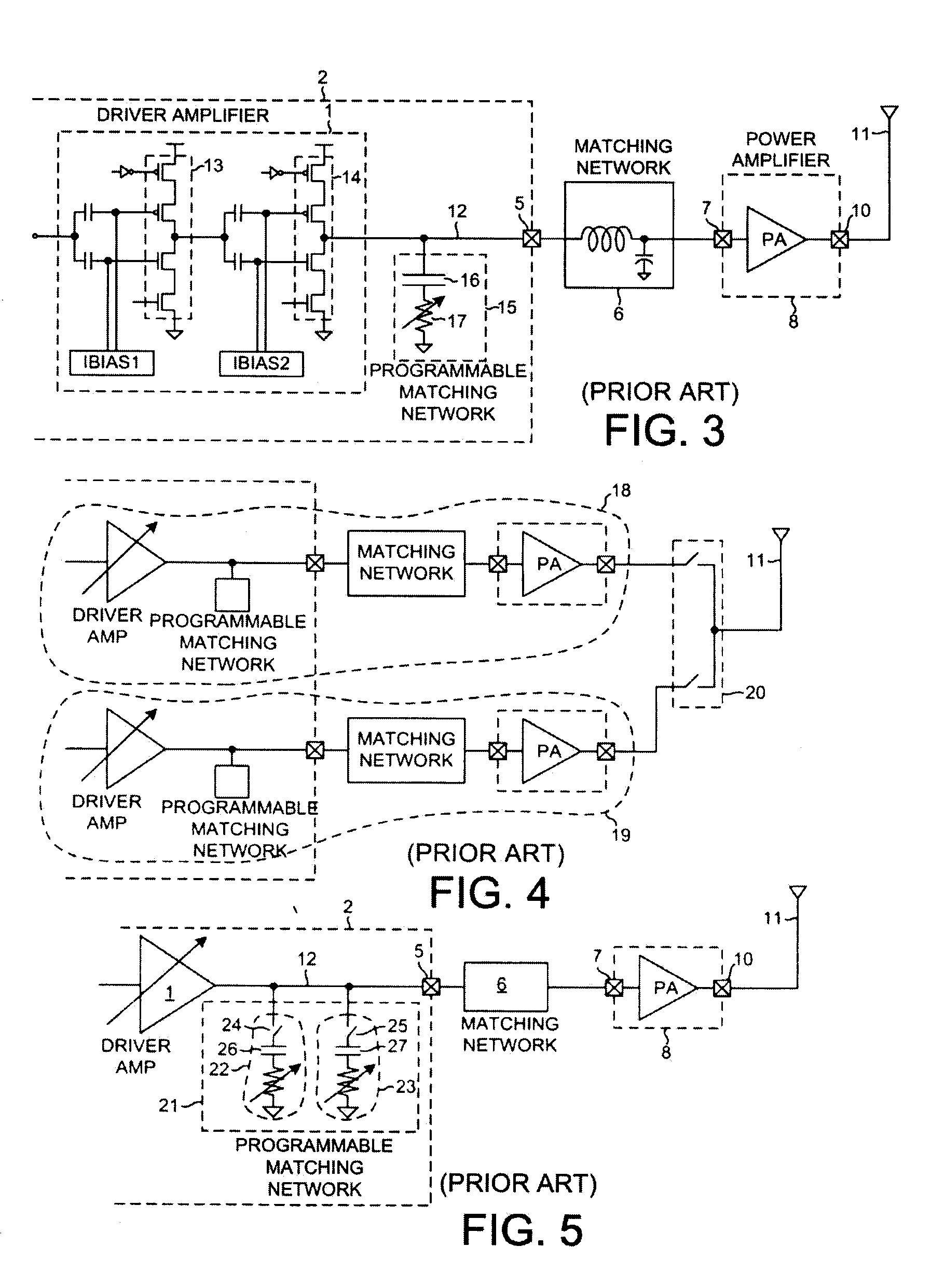
Driver amplifier having a programmable output impedance adjustment circuit
ActiveUS20100026393A1Improving Impedance MatchingReduce the amount requiredModulation with suppressed carrierTransmission monitoringCapacitanceMulti band
A driver amplifier in an integrated circuit is suitable for driving a signal onto an output node and through an output terminal, and through a matching network to a power amplifier. A novel Programmable Output Impedance Adjustment Circuit (POIAC) within the integrated circuit is coupled to the output node and affects an output impedance looking into the output terminal. When the output impedance would otherwise change (for example, due to a driver amplifier power gain change), the POIAC adjusts how it loads the output node such that the output impedance remains substantially constant. The POIAC uses a series-connected inductor and capacitor L-C-R circuit to load the output node, thereby reducing the amount of capacitance and die area required to perform multi-band impedance matching with a power amplifier. Multi-band operation is accomplished by changing an effective capacitance in the L-C-R circuit depending on communication band information received by the POIAC.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
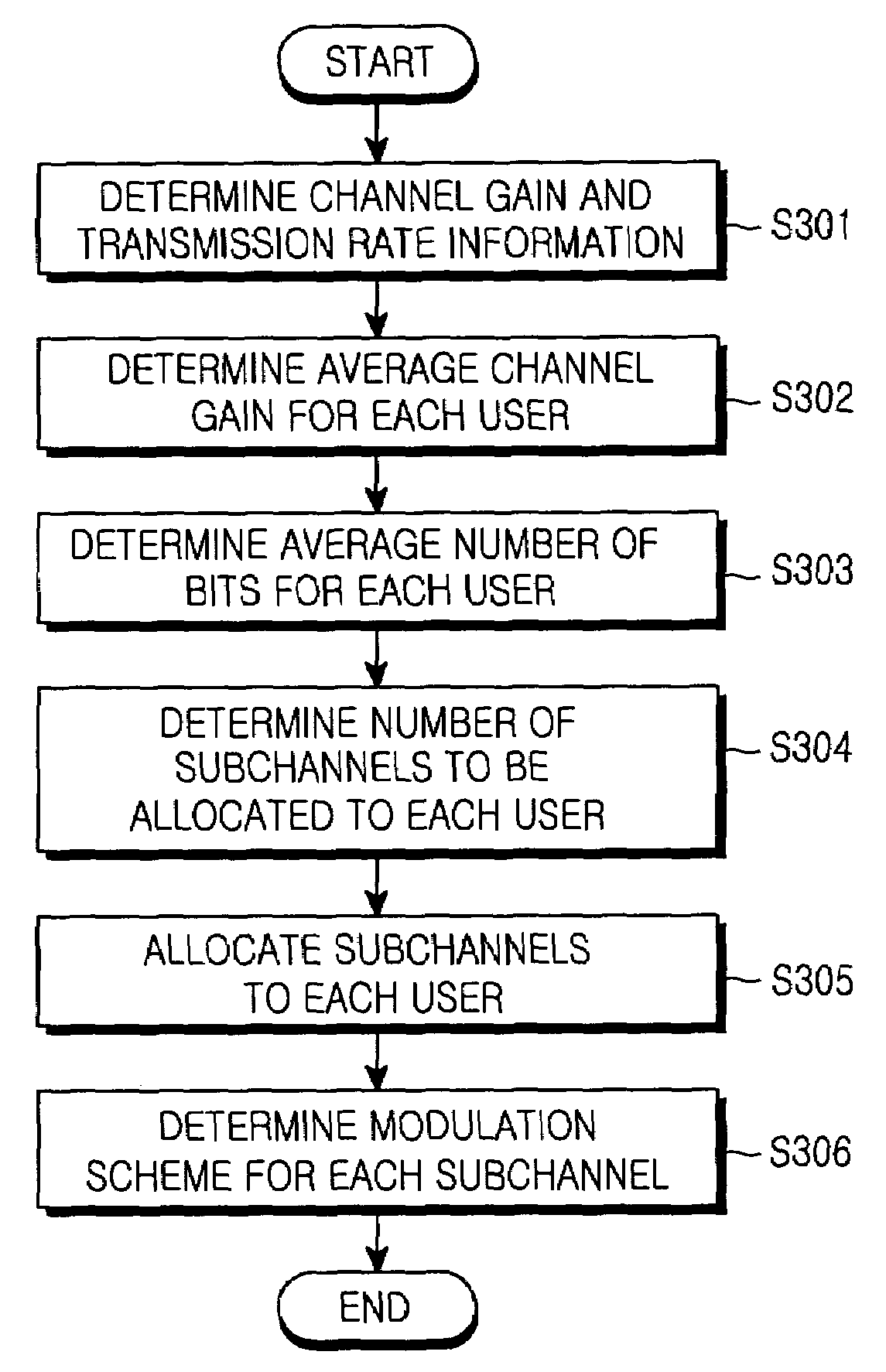
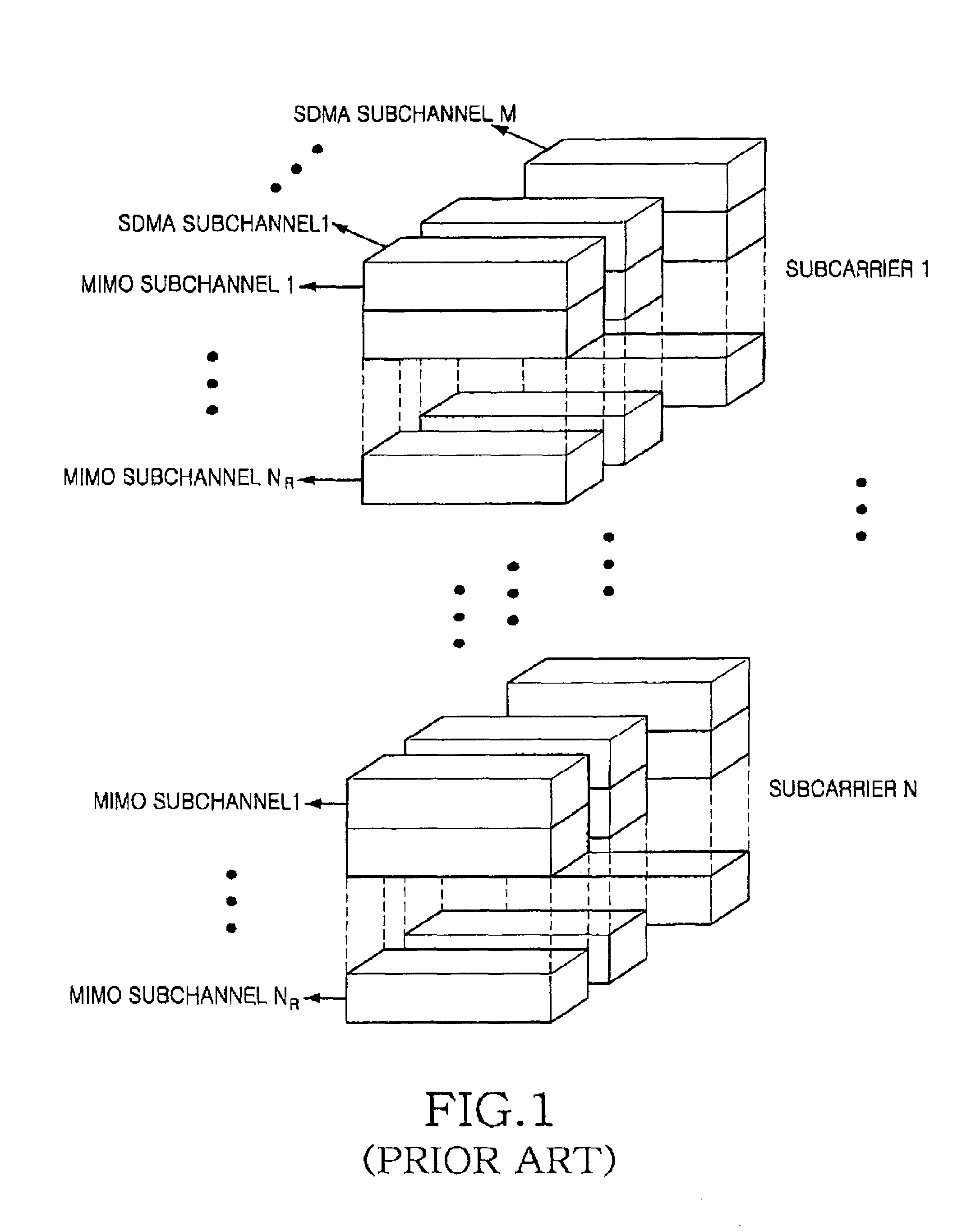
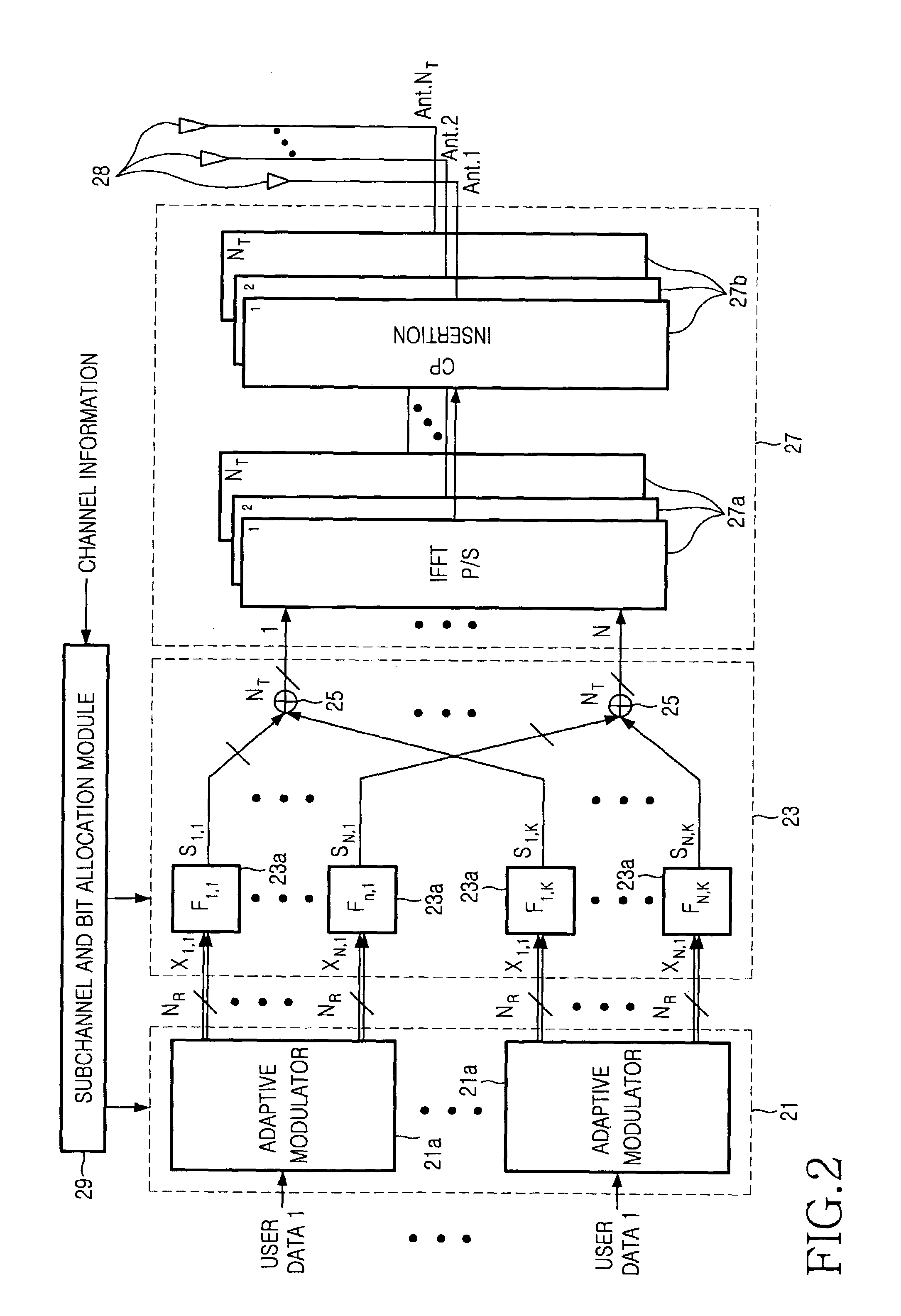
Dynamic subchannel and bit allocation in a multiuser-MIMO/OFDMA system
ActiveUS7372830B2Effective distributionImprove efficiencyPolarisation/directional diversityTransmission path divisionMultiuser systemBit allocation
A resource allocation method in a multiuser-multiple-input multiple-output / orthogonal frequency division multiple access (MIMO / OFDMA) system. In the multiuser-MIMO / OFDMA system feedback information is received from terminals. A channel gain and a transmission rate for each user are determined using the feedback information. An average channel gain for each user is computed according to the channel gain. The average number of bits for each user is determined according to the average channel gain. The number of subchannels for each user is computed according to the average number of bits for each user. At least one subchannel is allocated to each user according to the number of subchannels for each user. A modulation scheme for each of the at least one subchannel is determined. The resource allocation method adaptively allocates subchannels and bits according to channel environment, thereby considerably improving frequency use efficiency as well as a power gain.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Method and apparatus of allocating power in multiple-input multiple-output communication system
InactiveUS7269436B2Low costImprove efficiencyPower managementSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemAntenna element
A method and apparatus for allocating a power in a multiple-input multiple-output communication system is disclosed. A method of allocating power can include estimating a channel condition based on a reference signal received from a receiver, estimating power gains from the estimated channel condition, and determining respective power levels of transmission signals and a number of available antenna elements for the transmission signals by using the power gains.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
III-nitride material structures including silicon substrates
InactiveUS20060118819A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesNitrideCondensed matter physics
III-nitride material structures including silicon substrates, as well as methods associated with the same, are described. Parasitic losses in the structures may be significantly reduced which is reflected in performance improvements. Devices (such as RF devices) formed of structures of the invention may have higher output power, power gain and efficiency, amongst other advantages.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
Low noise amplifier for wideband tunable matching
ActiveUS20060132242A1Improve performanceNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierInductor
Provided is a low noise amplifier with a common source and a source degeneration, which has linearity, power gain, noise factor, and lossless input matching. The low noise amplifier includes: a first inductor having one terminal connected to an input terminal receiving a signal; a second inductor having one terminal connected to a ground; a MOS transistor having a gate connected to the first inductor, a source connected to the other terminal of the second inductor, and a drain transmitting a signal; and a variable capacitor connected between the source and gate of the MOS transistor and varying an input matching frequency at the input terminal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Tunable low noise amplifier and current-reused mixer for a low power RF application
InactiveUS6850753B2Reduce noiseReduce power consumptionModulation transference balanced arrangementsComputations using contact-making devicesEngineeringTransconductance
A radio frequency front-end receiver includes a single stage low noise amplifier connected with a resistor array and a capacitor array, and a Gilbert-type mixer connected with a PMOS transconductance stage, an inductor and a serially connected current source. The resistor array enables the adjustment of the power gain of the low noise amplifier. The capacitor array tunes the low noise amplifier so that the maximum power gain is at the desired operating frequency. The PMOS transconductance stage reduces the power consumption of the mixer. The inductor increases the impedance and the current source improves the common-mode rejection of the mixer.
Owner:MUCH IP
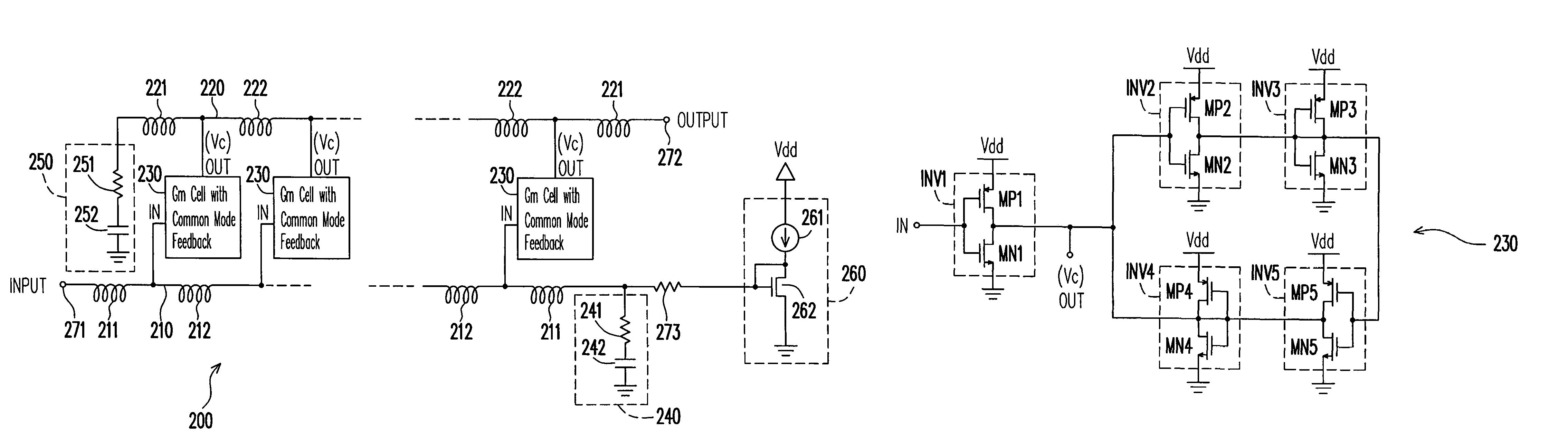
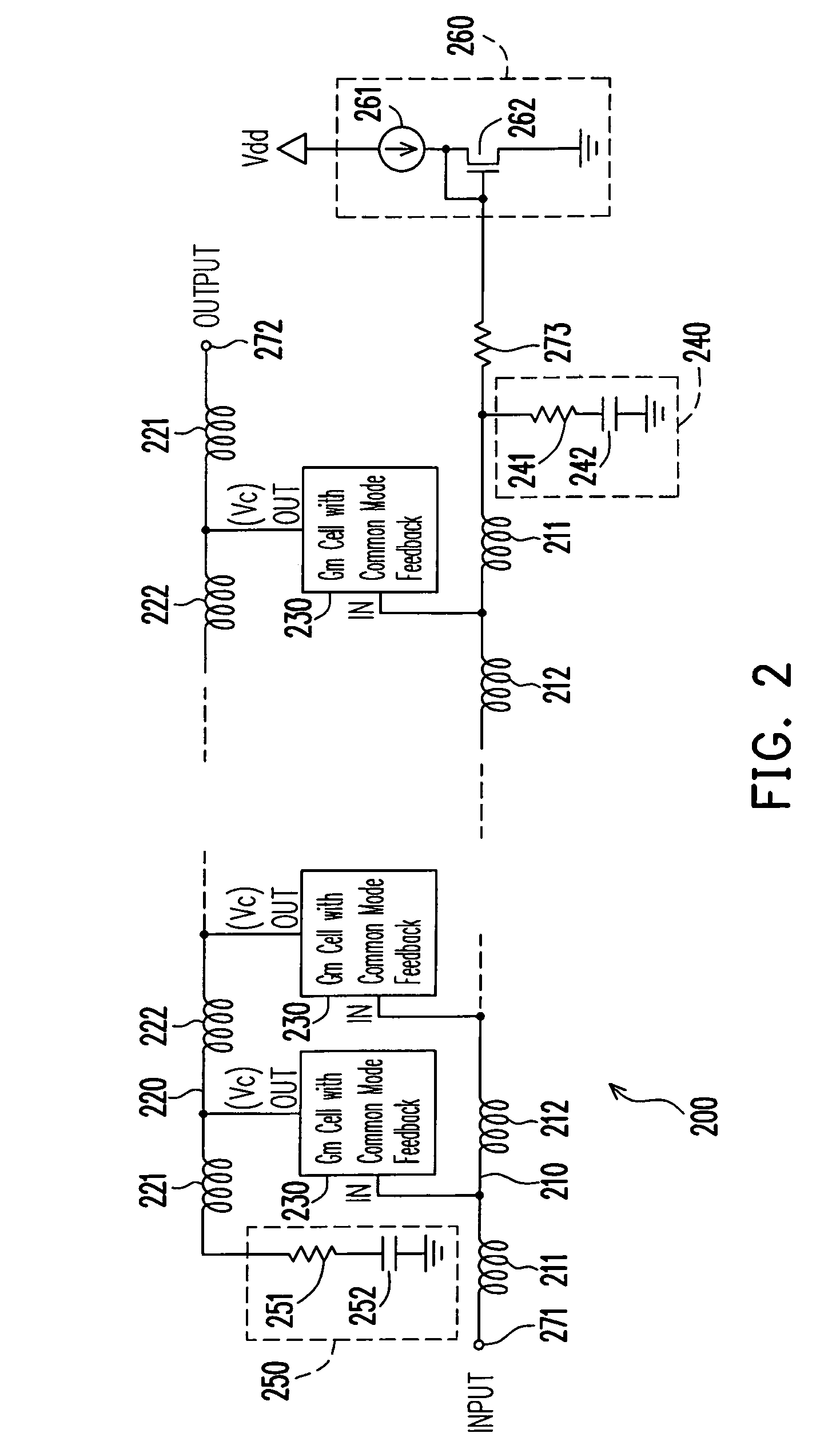
Low power comsumption, low noise and high power gain distributed amplifiers for communication systems
ActiveUS7579913B1Reduce power consumptionIncrease power gainAmplifier combinationsAmplifiers wit coupling networksLow noiseDistributed amplifier
Provided is a distributed amplifier in communication systems, including: an input transmission line; an output transmission line; an input impedance match and an output impedance match, for providing termination of the input transmission line and the output transmission line, respectively and for preventing signal reflection in the input transmission line and the output transmission line, respectively; multi-stage Gm cells with common mode feedback, the input transmission line being coupled to the output transmission line by the transconductance of the Gm cells; and an input gate bias circuit, for providing bias for the multi-stage Gm cells. In at least one of the Gm cells, one inverter performs V / I conversion while other inverters provide negative resistance to control common mode of output voltage and to enhance DC gain of the Gm cell. Due to common mode feedback, no output gate bias is needed.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
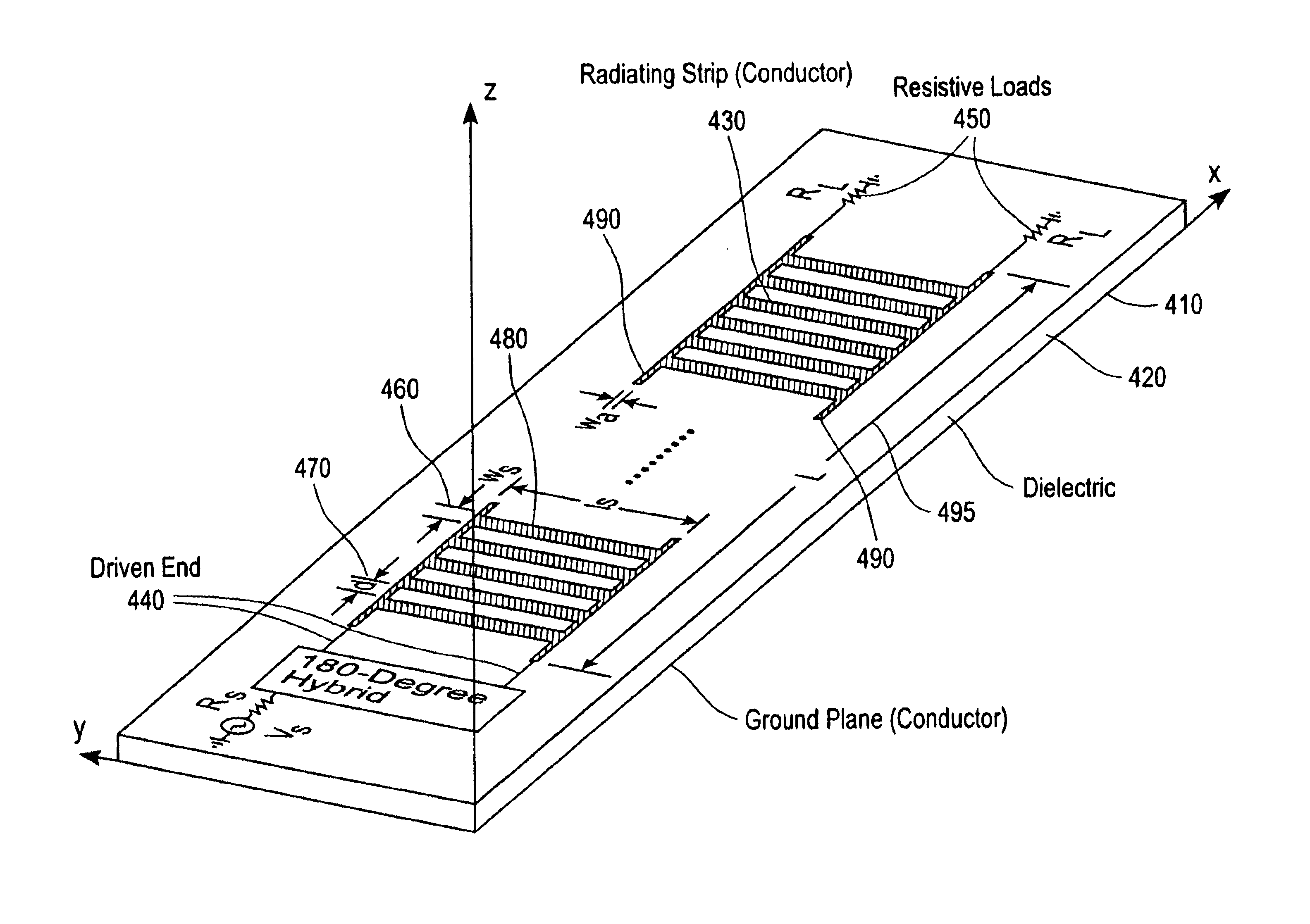
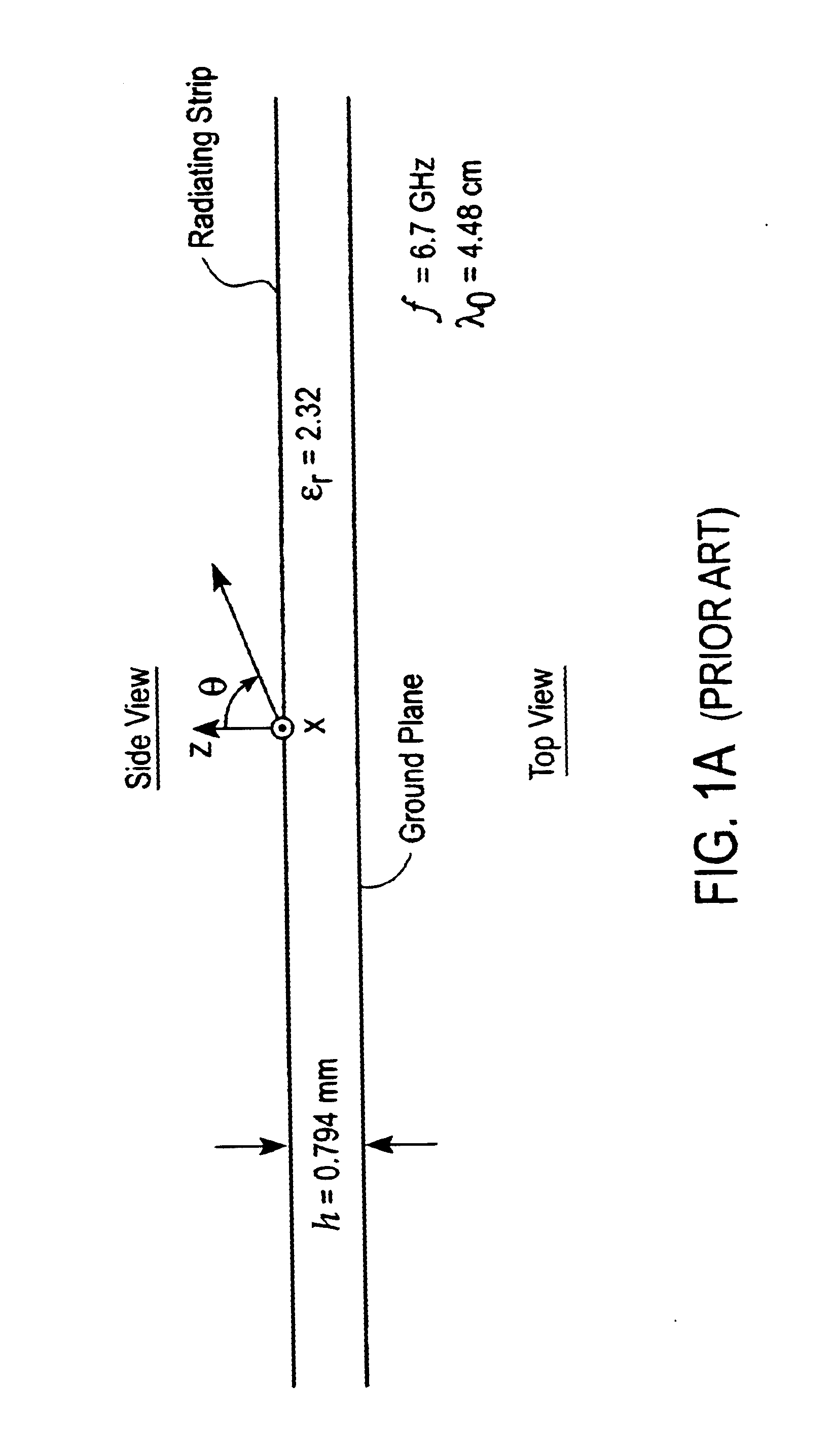
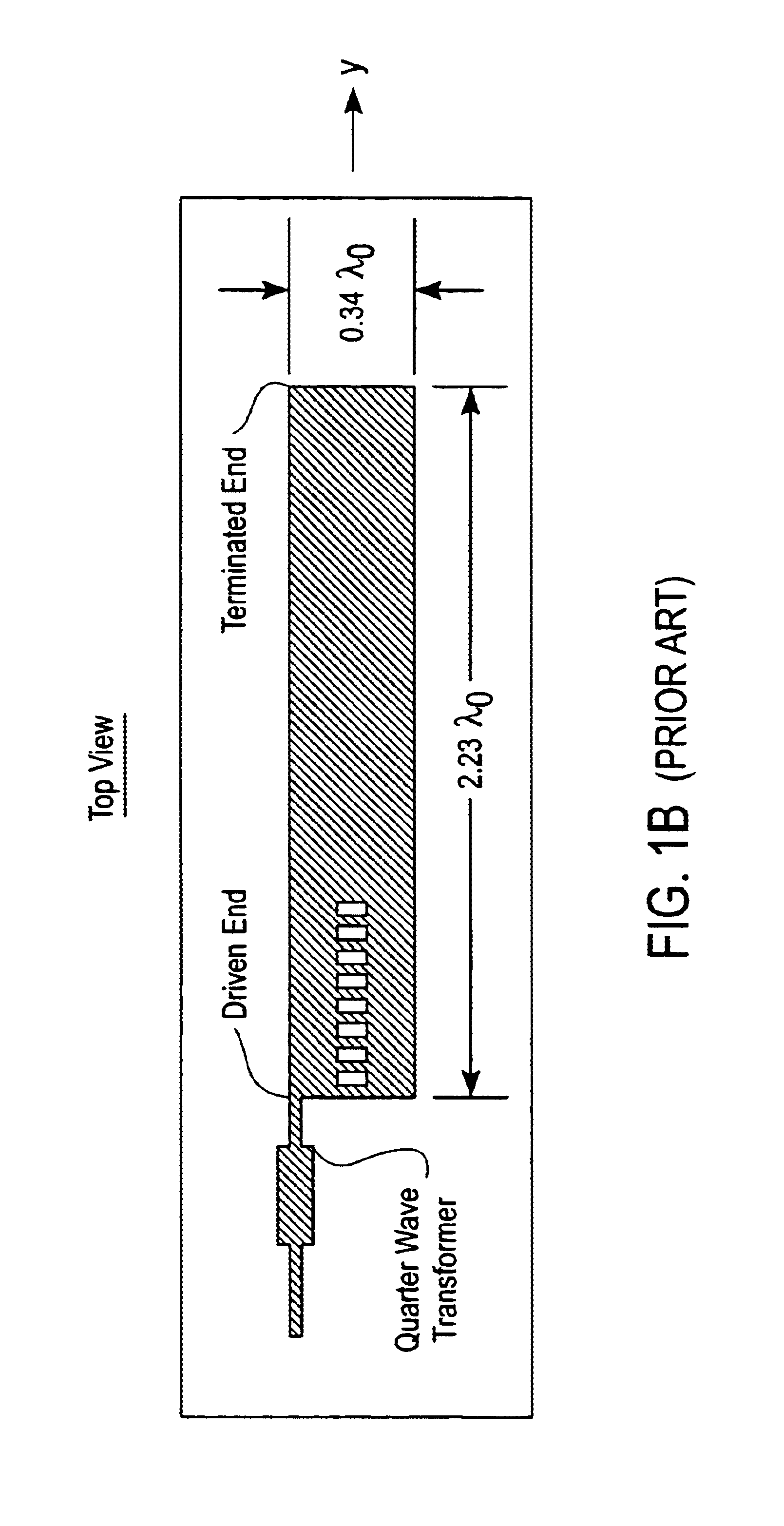
Leaky wave microstrip antenna with a prescribable pattern
InactiveUS6839030B2Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectricElectricity
A system and method for prescribing an amplitude distribution to a leaky-wave microstrip antenna having an array of radiating cells. The leaky-wave microstrip antenna includes a grounded element, a dielectric member coupled to the grounded element and a top conducting strip coupled to the dielectric member, the conducting strip including a first and second non-radiating conducting strip and a plurality of radiating cells. This distribution requires that the microstrip antenna possess a variable leakage-constant profile along its length, and is chosen so as to yield an H-plane power-gain pattern having low sidelobes. The leakage-constant profile is achieved by configuring the width and inter-cell spacing of the antenna radiating cells and keeping the phase constant fixed. The length or loading of the radiating cells may also be manipulated to achieve the desired leakage constant profile. This results in the desired distribution along the antenna's aperture and yields a power-gain pattern with low sidelobes. The antenna is excited by two equal-amplitude and 180° out-of-phase signals. These signals are applied to the feed end of the microstrip at two feeding ports. The microstrip antenna length is chosen such that more than 97% of the input power is radiated by the traveling electromagnetic, wave, while the remaining power is absorbed by the resistively terminated antenna end.
Owner:ANRITSU CORP
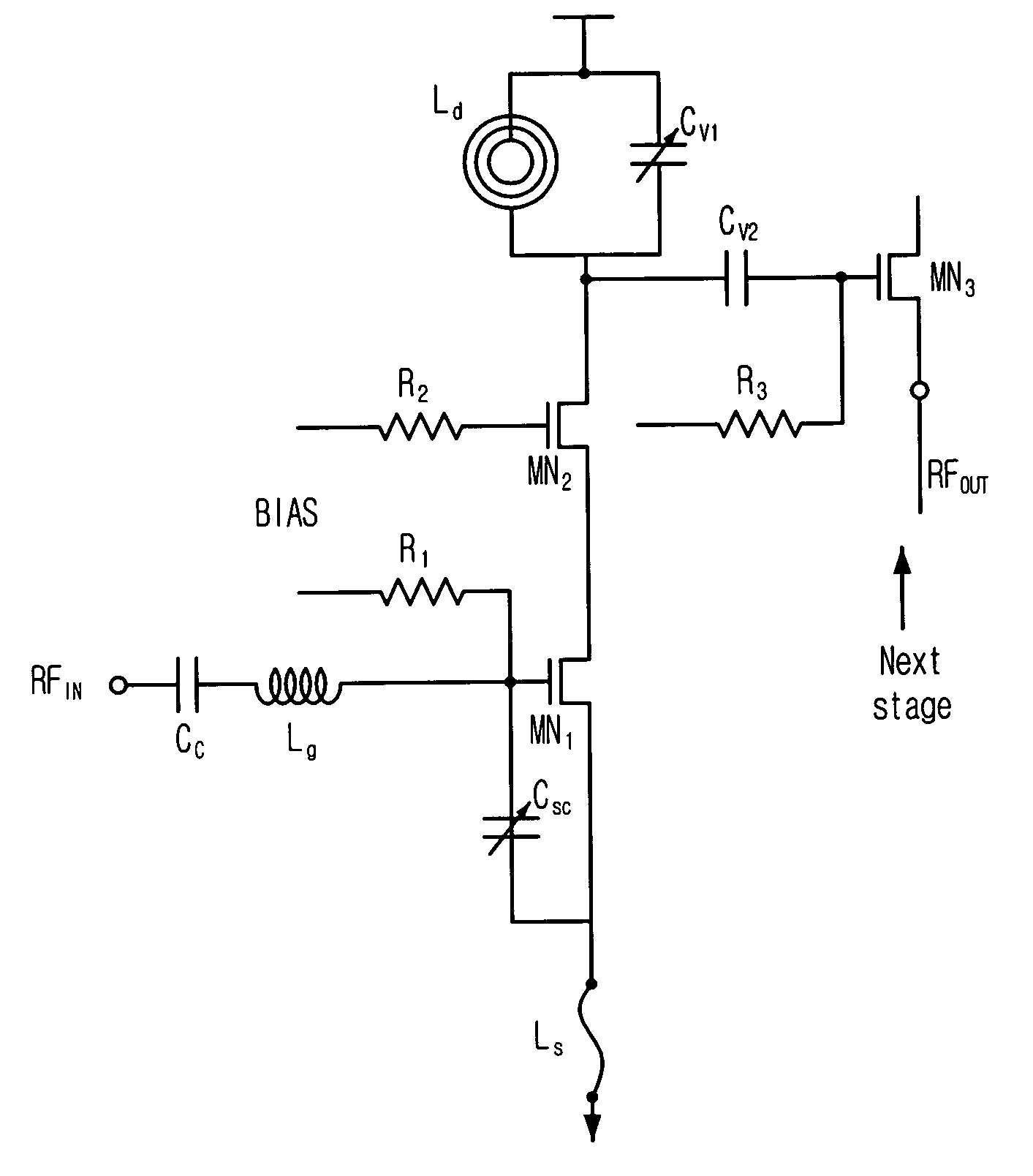
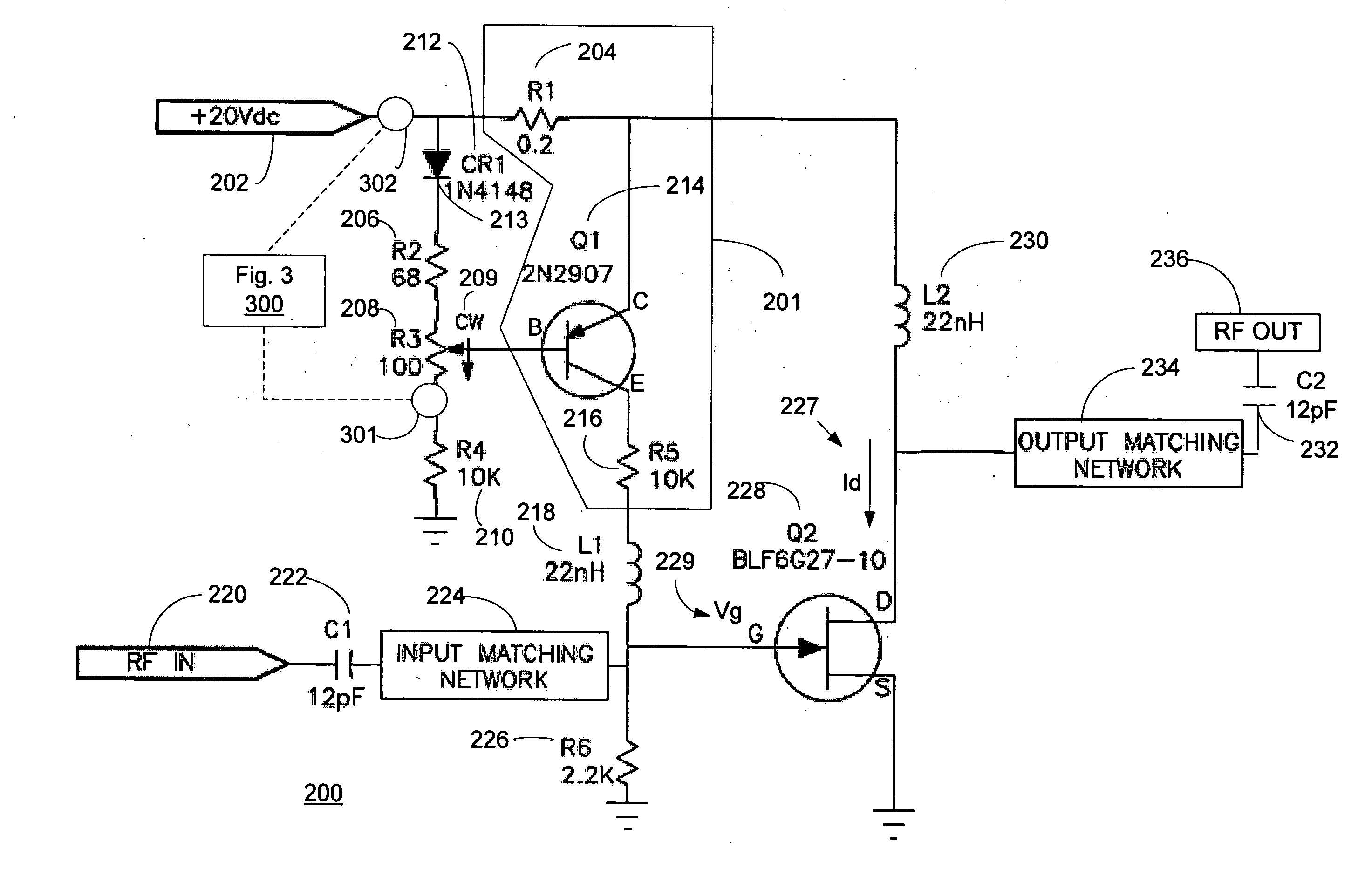
Method and system for providing automatic gate bias for field effect transistors
ActiveUS20110279185A1Low costLight weightHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAuto regulationEngineering
The present invention provides a feedback gate bias circuit for use in radio frequency amplifiers to more effectively control operation of LDFET, GaNFET, GaAsFET, and JFET type transistors used in such circuits. The invention provides a transistor gate bias circuit that senses drain current and automatically adjusts or biases the gate voltage to maintain drain current independently of temperature, time, input drive, frequency, as well as from device to device variations. The invention provides additional circuits to provide temperature compensation, RF power monitoring and drain current control, RF output power leveler, high power gain block, and optional digital control of various functions.
Owner:EMHISER RES
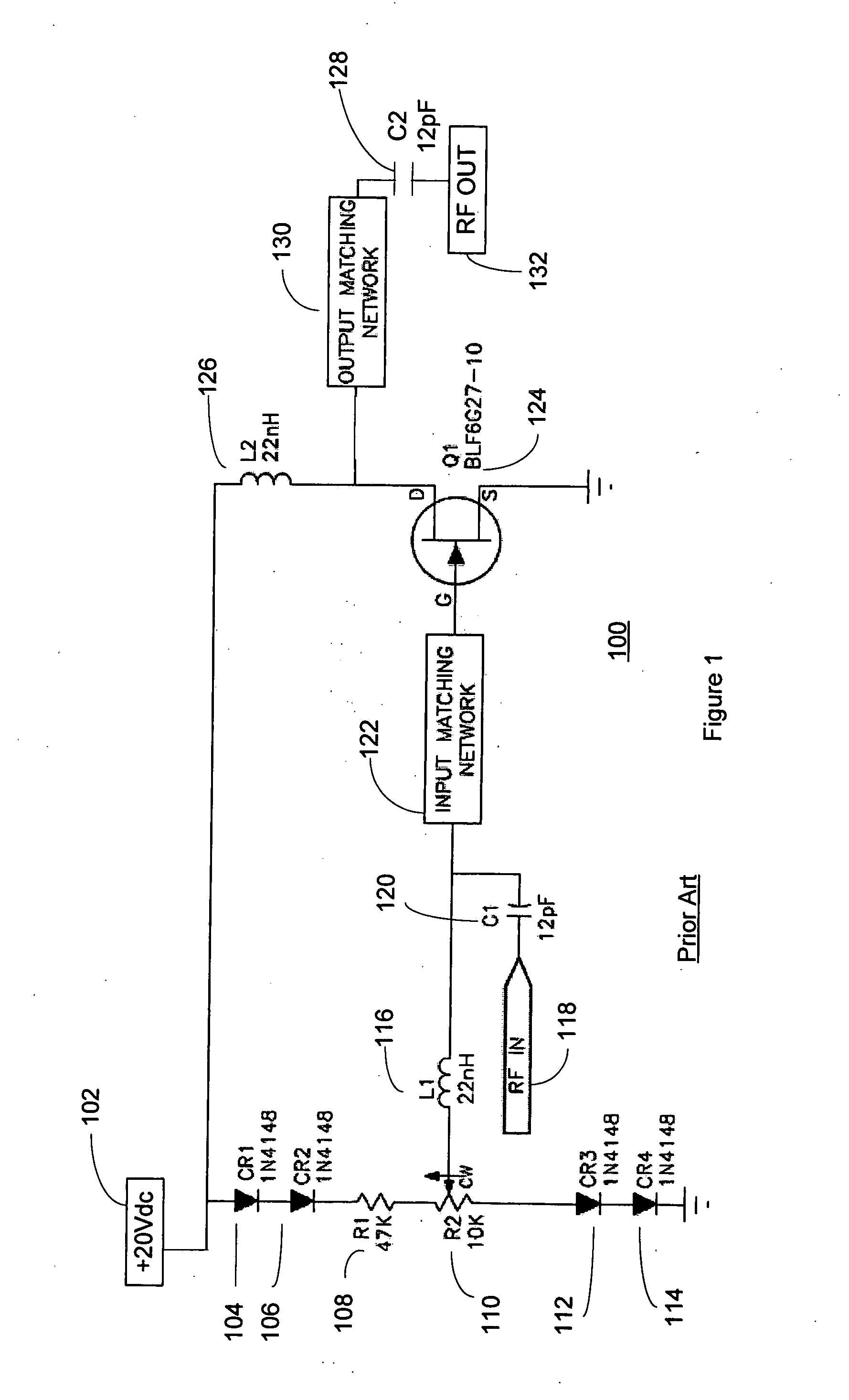
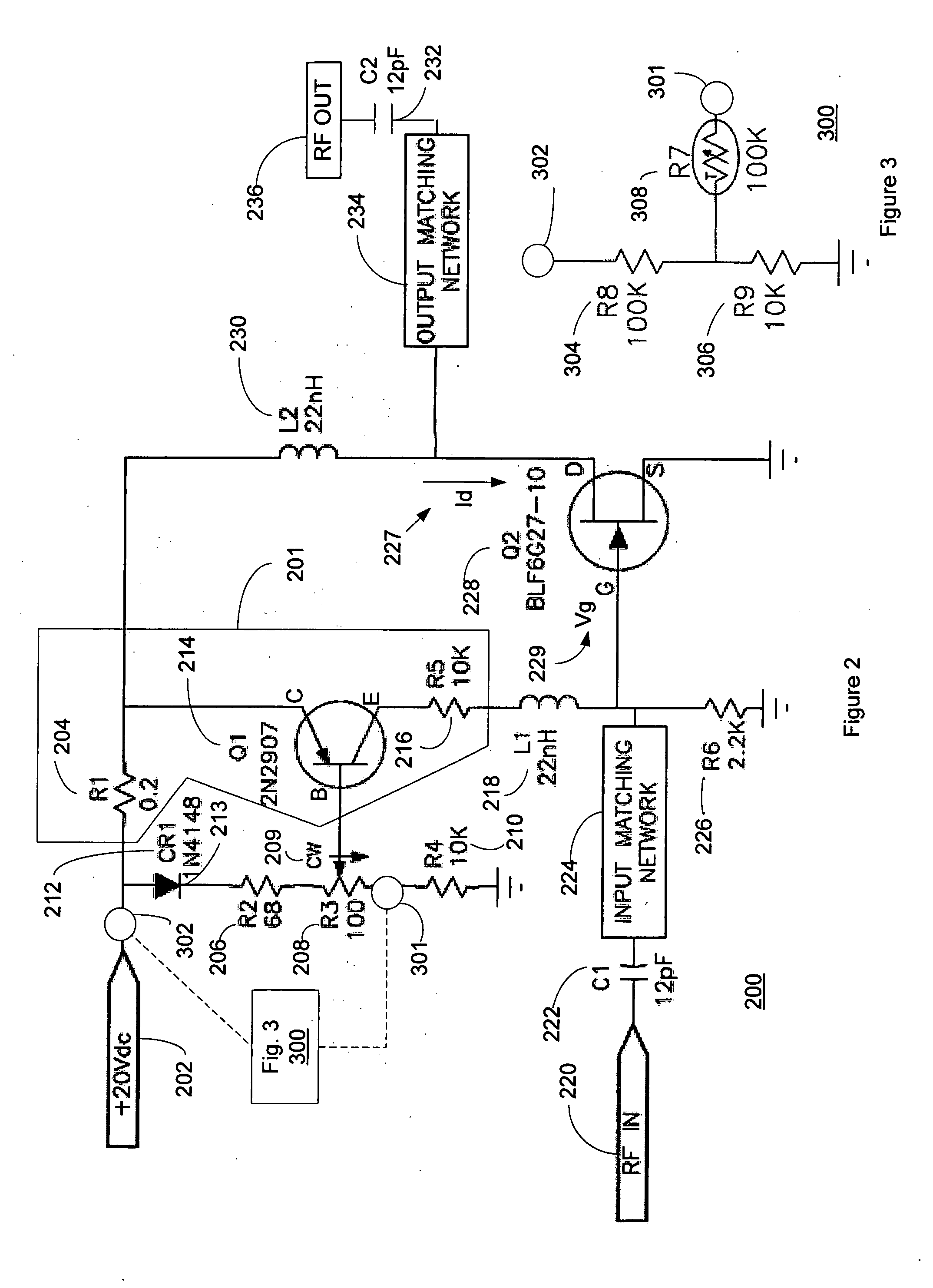
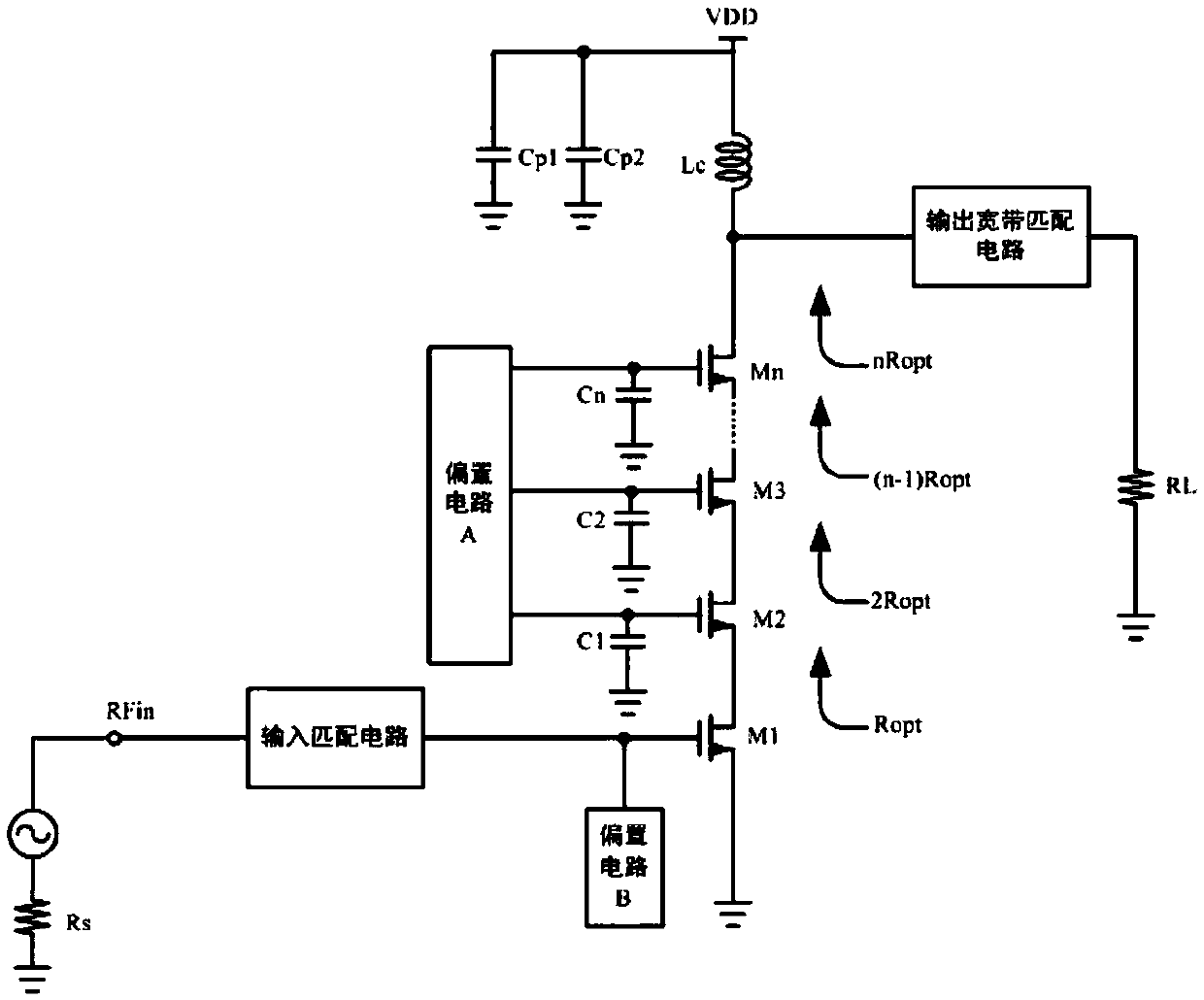
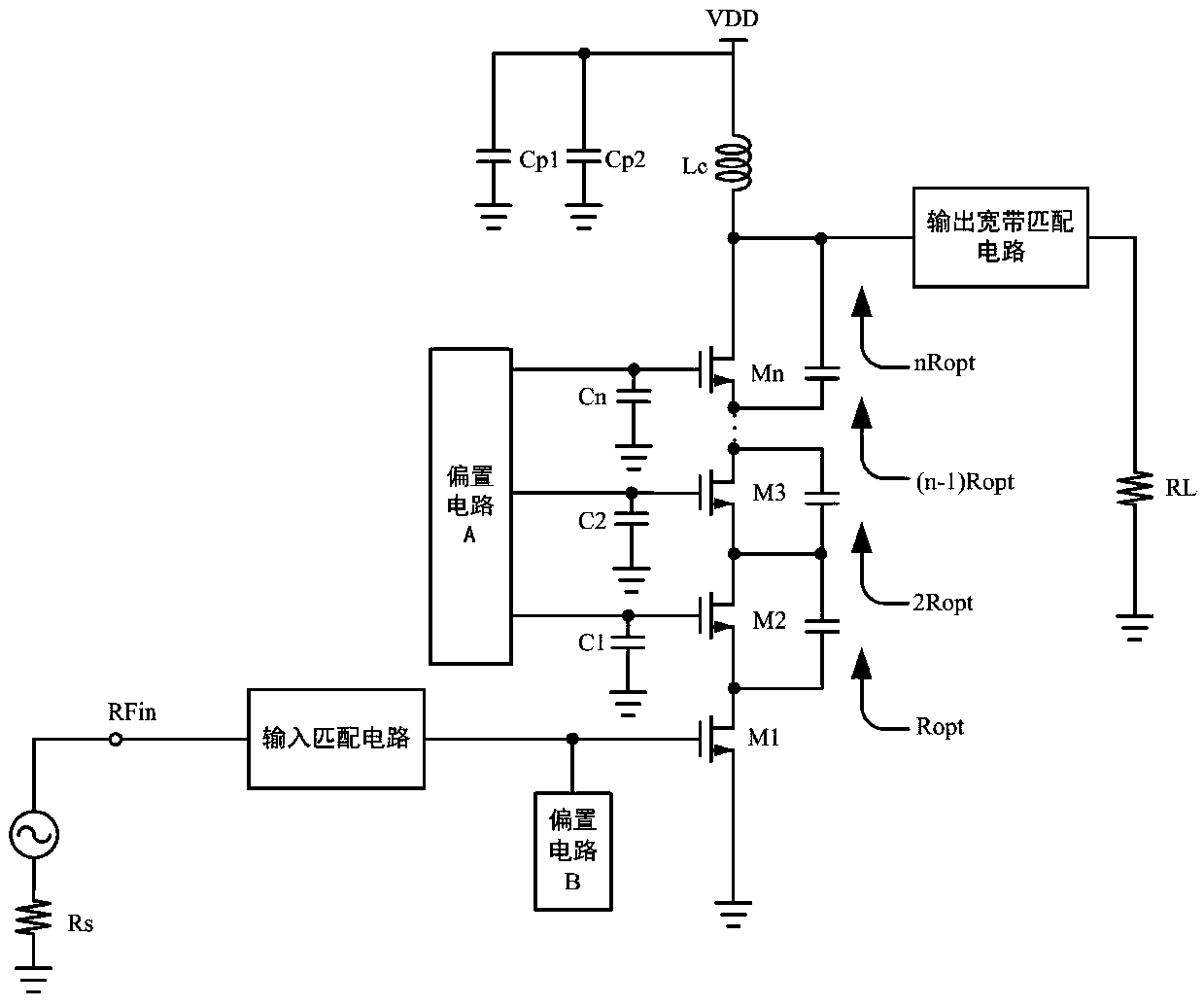
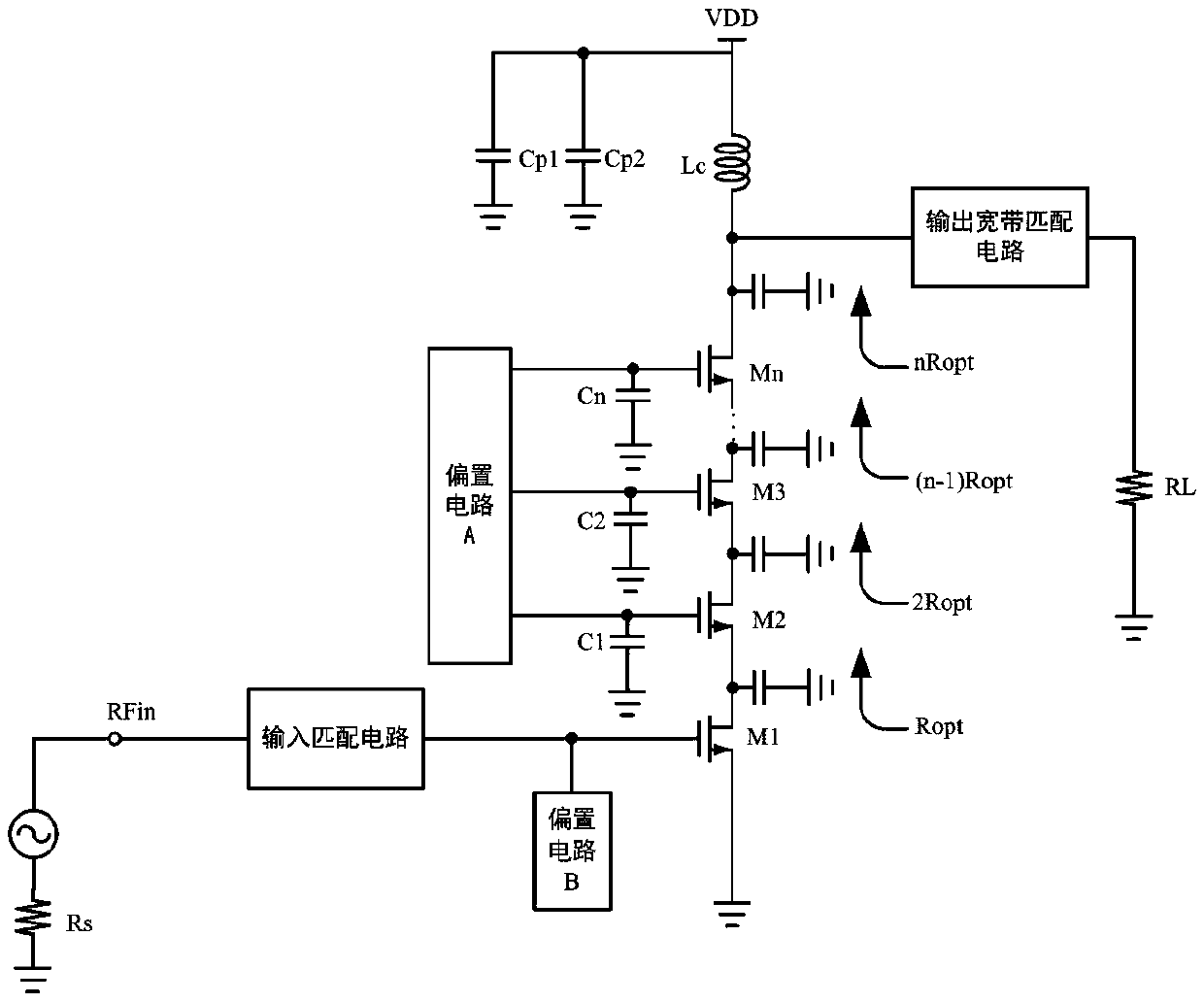
Radio-frequency power amplifier with stack structure
InactiveCN105515542AImprove pressure resistanceIncreased power output capabilityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a radio-frequency power amplifier with a stack structure. The radio-frequency power amplifier comprises an input matching circuit, an output broadband matching circuit, a biasing circuit A, a biasing circuit B and a power amplification circuit, and the power amplification circuit is formed by stacking of at least two transistors with drains and sources connected. A radio-frequency signal source is connected with a grid electrode of the bottom transistor of the power amplification circuit through the input matching circuit, the biasing circuit B is connected with the grid electrode of the bottom transistor, and the source of the bottom transistor is grounded. The drain of the top transistor of the power amplification circuit is connected with a load through the output broadband matching circuit. Integral linearity, output voltage swing, operation bandwidth, power efficiency, power gain and maximum output power of the radio-frequency power amplifier are increased, and excellent second harmonic inhibition effects are achieved.
Owner:臻智微芯(广州)技术有限公司
High-linearity low-noise amplifier
ActiveCN103248324AImprove linearityIncrease the overdrive voltageAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNonlinear distortionLow noise
The invention provides a high-linearity low-noise amplifier of the front end of an ultrahigh-frequency RFID (radio frequency identification) receiver. The amplifier detects two common levels from two differential output ends of a full-differential amplifier through a common-feedback circuit, bias current of the amplifier is adjusted validly and feedback voltage is outputted to a grid of a tail current source, and accordingly, overdrive voltage of the tail current source is increased, input current is increased and linearity is improved. Meanwhile, the problem of non-linear distortion caused by instability of the output common levels is solved. In addition, a coupling capacitor is crossed interstagely to increase power grain, and noise figure is reduced to improve noise performance. The high-linearity low-noise amplifier has the advantages of low noise figure, low power consumption, and high linearity, and solves the problem of carrier leak in ultrahigh-frequency RFID receivers and zero intermediate frequency receivers, and linearity of the low-noise amplifier is improved, so that weak available signals can be amplified linearly and distortionlessly in the process of receiving block signals.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM INST AT NANJING CO LTD
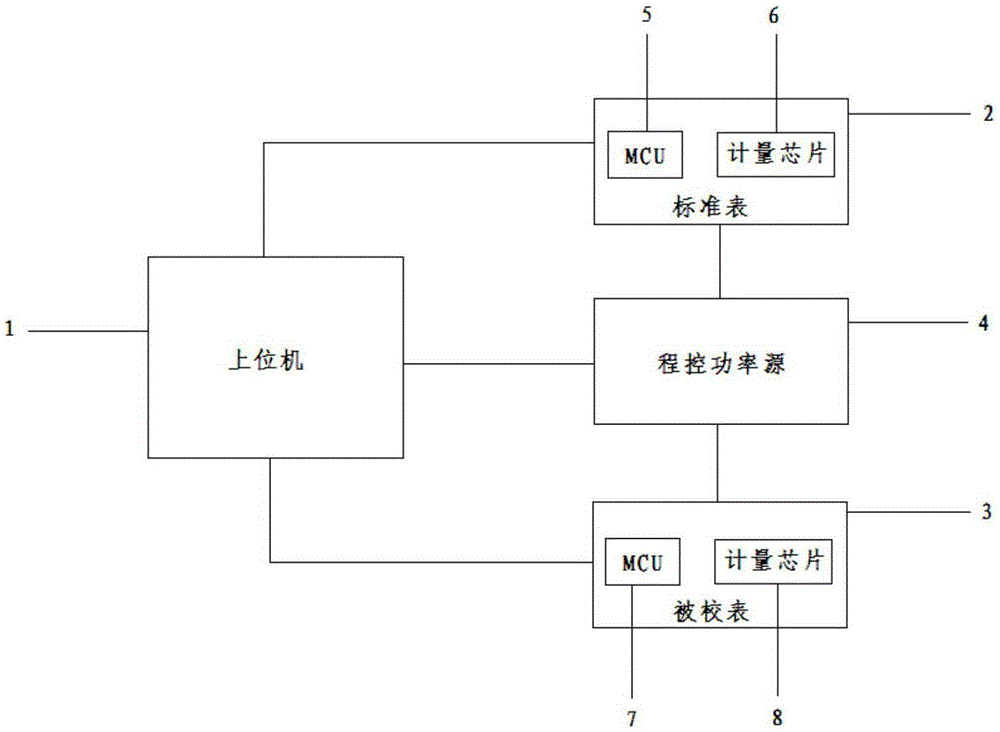
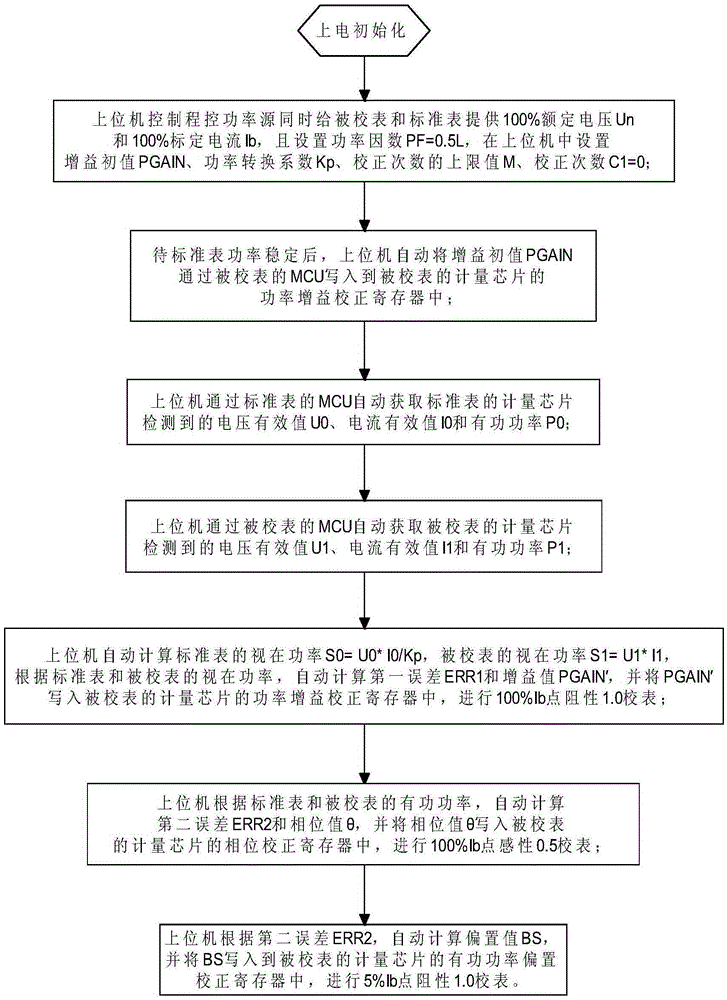
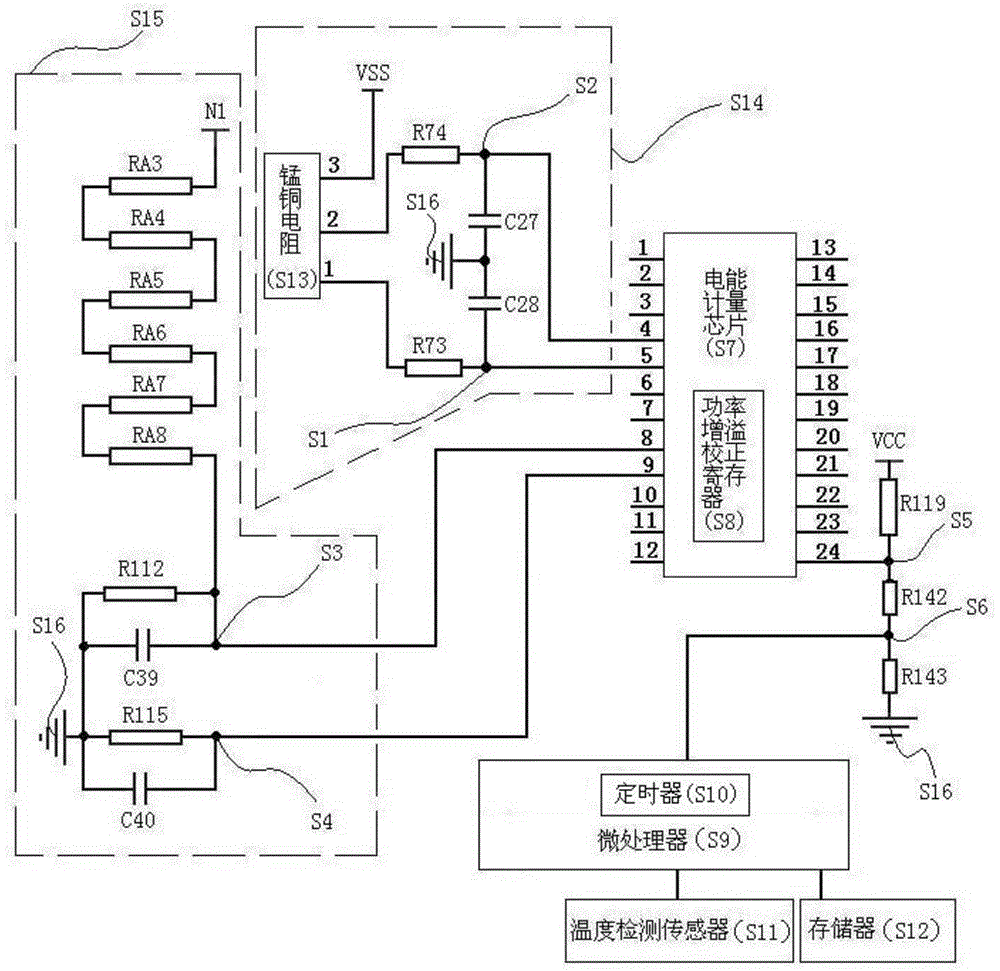
Fast calibration method of single-phase electric energy meter
ActiveCN105242233AFast stabilizationReduce waiting timeElectrical measurementsPhase correctionSignal correction
The invention relates to a fast calibration method of a single-phase electric energy meter. According to the fast calibration method, the gain initial value of a power gain correction register of a metering chip of a calibrated meter is preset so as to be fast positioned to a target error value, only a 100%Ib-point 0.5-induction error point is debugged; apparent power deviation and active power deviation are simultaneously obtained at the error point; 100%Ib-point 1.0-resistance gain correction is performed through utilizing the apparent power deviation; 100%Ib-point 0.5-induction phase correction is performed through utilizing the active power deviation; and a 100%Ib-point 0.5-induction error value which has been obtained through calculation is directly utilized to perform 5%Ib-point 1.0-resistance small signal correction, and therefore, too long debugging time of small signals can be avoided. The fast calibration method has the advantages of fast error target value positioning, high meter calibration efficiency and significantly-improved accuracy.
Owner:NINGBO SANXING MEDICAL & ELECTRIC CO LTD
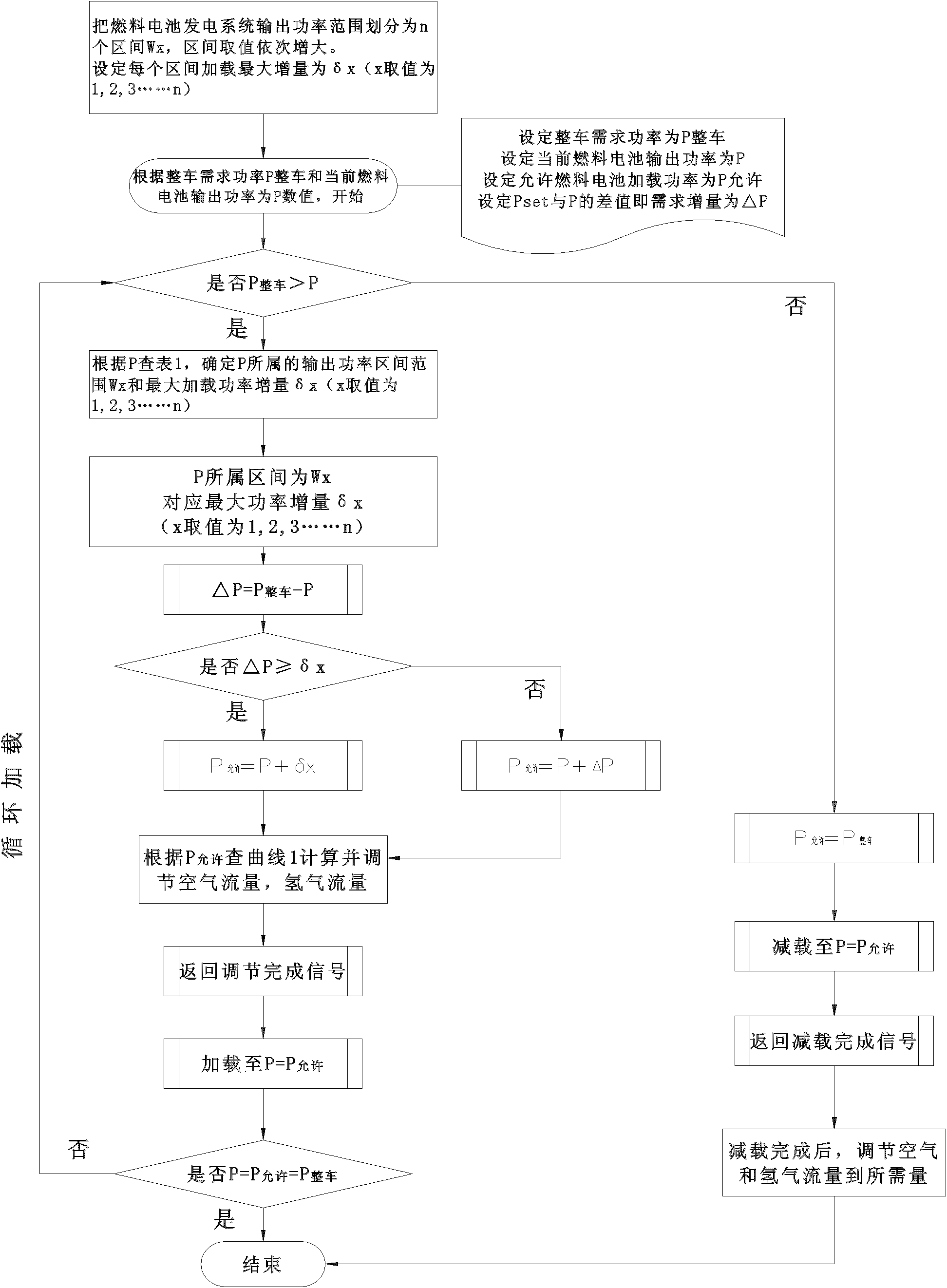
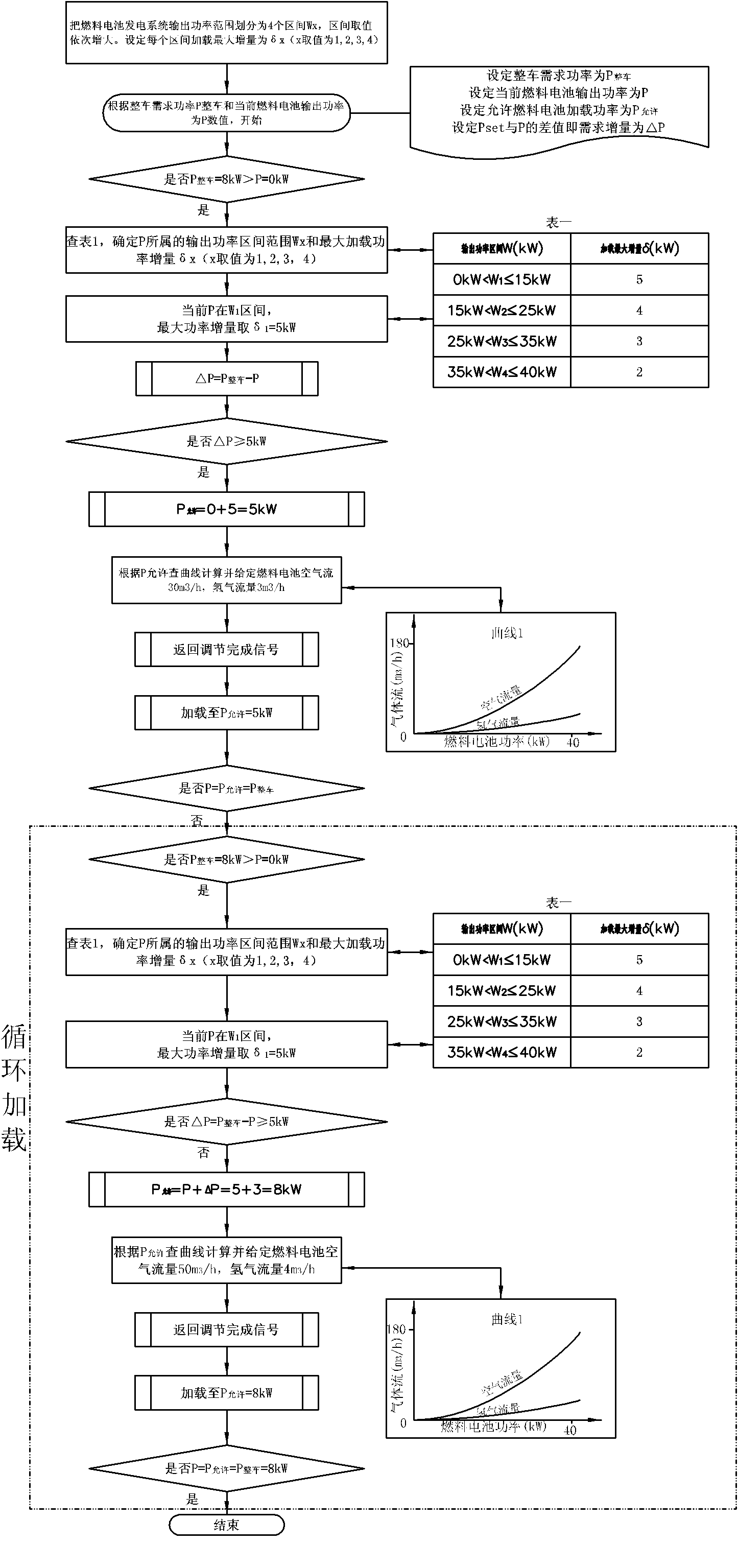
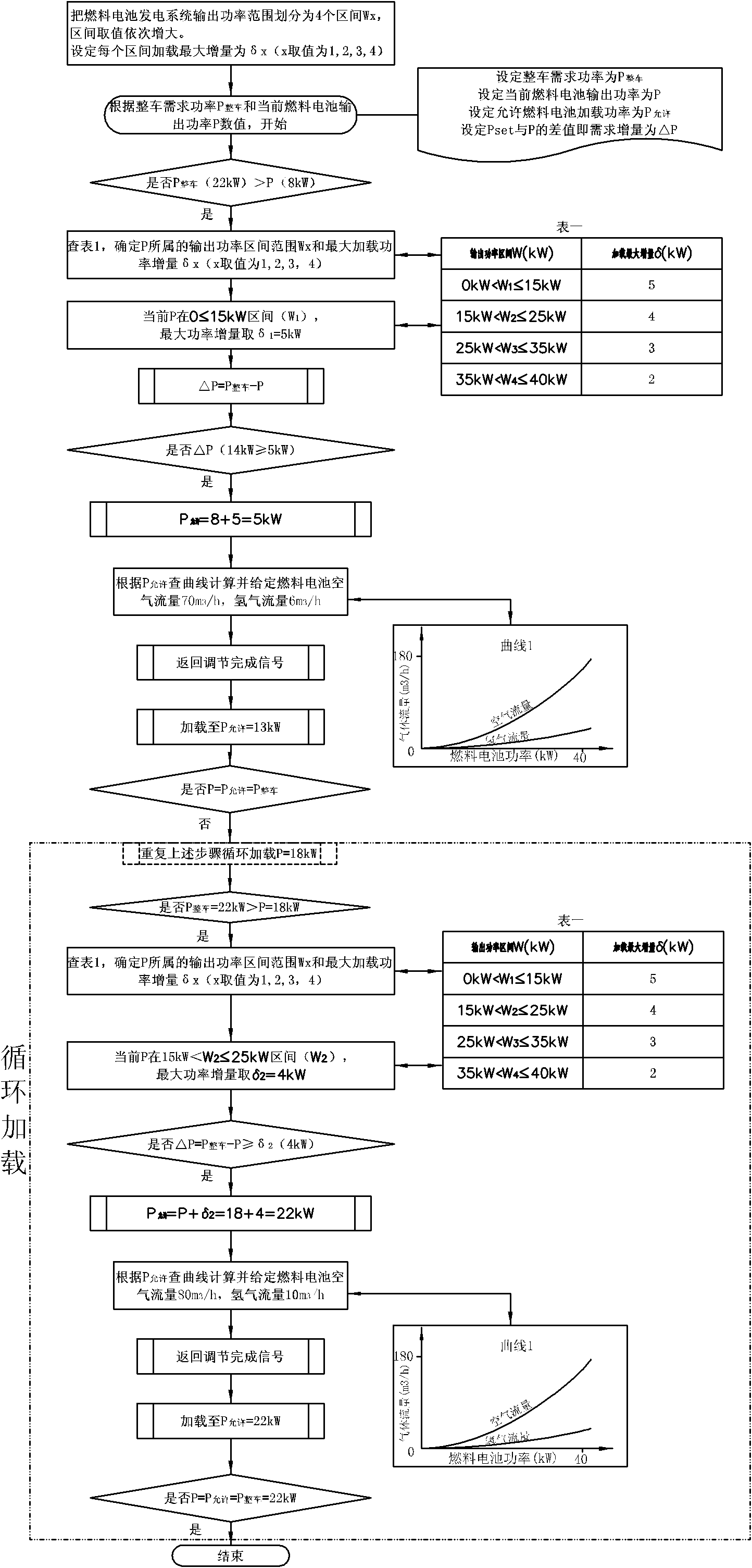
Loading control method for power generation system of automobile fuel cell
ActiveCN102522581AExtended service lifeAvoid polarity reversalFuel cell auxillariesFuel cellsGreek letter sigma
The invention provides a loading and deloading control method for a power generation system of an automobile fuel cell. The method comprises the following steps of: during loading, setting a maximum power gain sigma(x), comparing the maximum power gain sigma(x) with a difference value delta(P) between the power P(whole automobile) required by a whole automobile and the loading power P of the conventional fuel cell to determine a loading amount, and calculating the allowable power P(allowable) to be output by the power generation system of the fuel cell; adjusting corresponding parameters of the power generation system of the fuel cell according to the calculated allowable loading power P(allowable); after the adjustment is finished, returning a finish signal, repeatedly and cyclically loading until the power P(whole automobile) is equal to the power P(allowable), and cyclically loading repeatedly until the power P(allowable) is equal to the power P(whole automobile); during deloading, directly deloading; and after finishing the deloading, adjusting the parameters of the power generation system of the fuel cell. The method has the advantages that: by continuously loading according to low gain, the damage of gas insufficiency, antipole and the like to membrane electrodes, which are caused by low mass transfer because of high-speed large load loading, is reduced; and the service life of the power generation system of the fuel cell is prolonged.
Owner:SUNRISE POWER CO LTD
System resource distribution method and device based on wave beam shaping
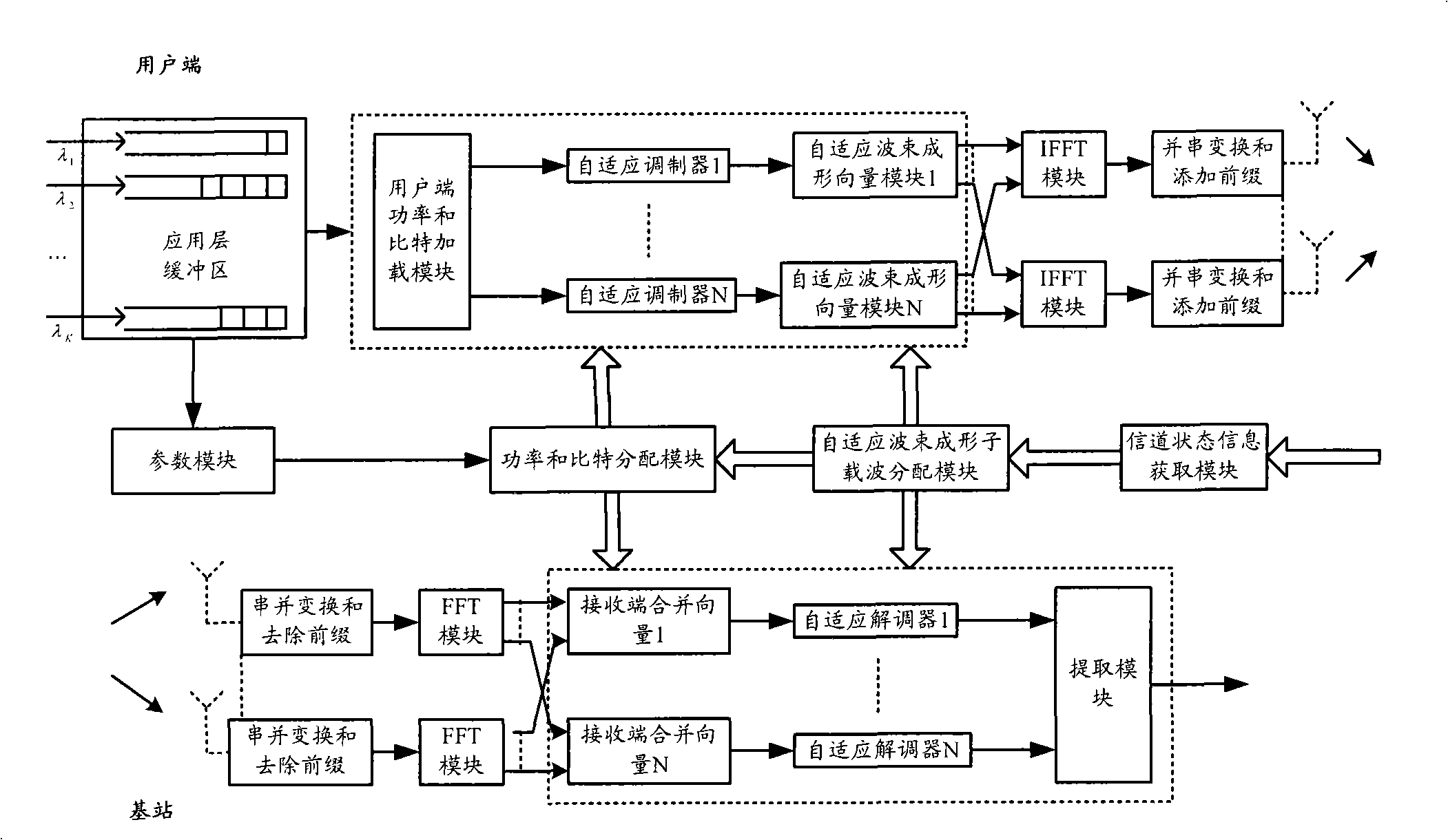
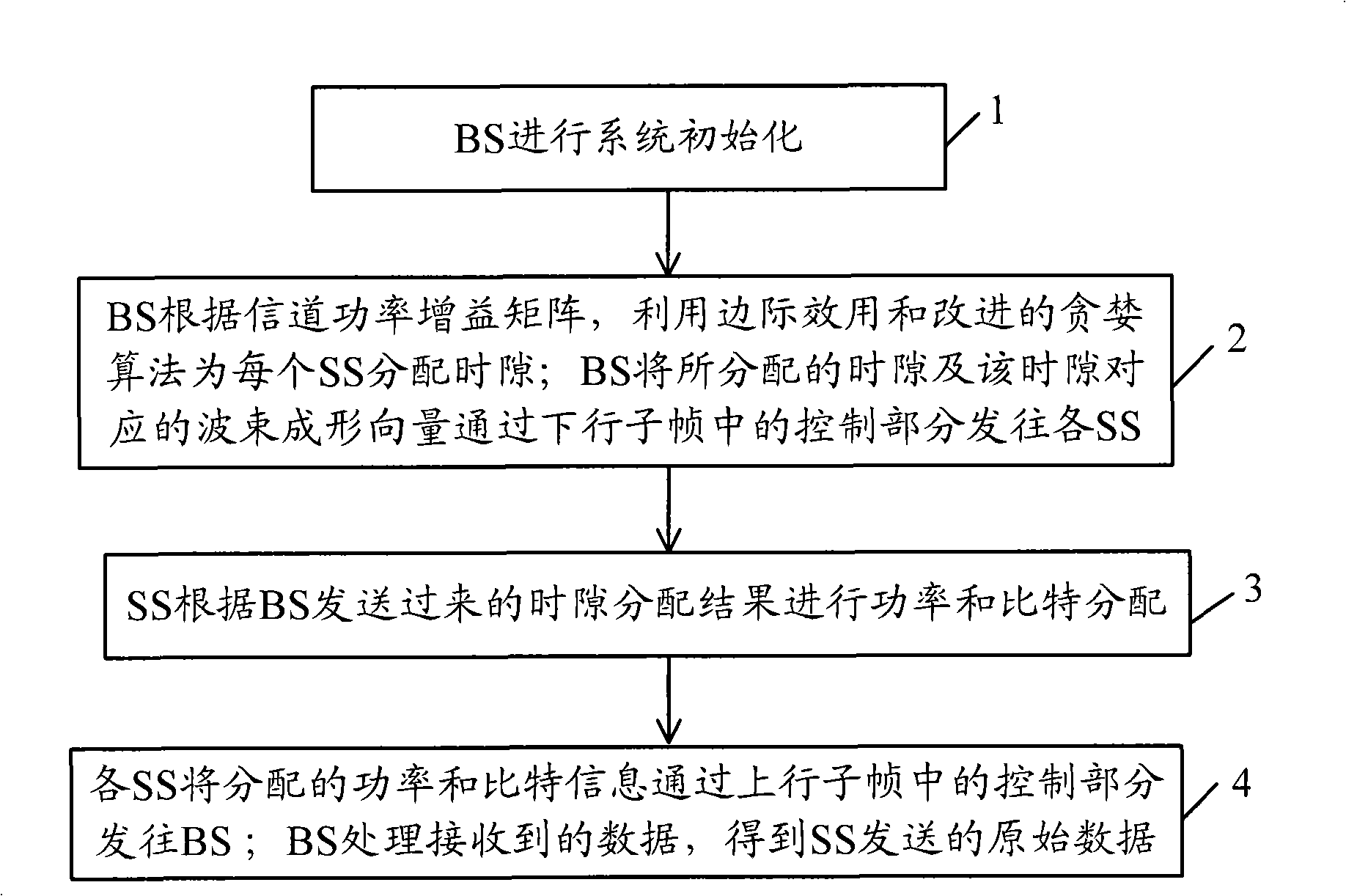
InactiveCN101340223AReduce transmit powerImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityError preventionChannel powerOriginal data
The invention discloses an uplink system resource allocation method based on beam forming; in allocation period, BS can obtain channel state information of each SS uplink in each time slot in a frame by the channel detection technology, and for each SS, the eigenvalue of MIMO channel matrix is decomposed in each time slot. The biggest eigenvalue after decomposition and corresponding eigenvectors form channel power gain matrix of each SS in each time slot; BS utilizes marginal effect and improved greedy algorithm to allocate time slots for each SS; each SS extracts allocated time slot information from a received downlink subframe and allocates power and bit; each SS sends the information of allocated power and bit to BS by a control part of an uplink subframe; BS is used for processing the received data to obtain the original data sent by SS. The invention also discloses a corresponding device, comprising a self-adaptive beam forming, sub-carrier allocation module as well as a power and bit allocation module. The method is of low complexity and good real-time property.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Transmitting method, device and system for multiple input-output comunication system
InactiveCN1832369AImprove decoding performanceIncrease capacitySpatial transmit diversityTransmission control/equalisingCommunications systemSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
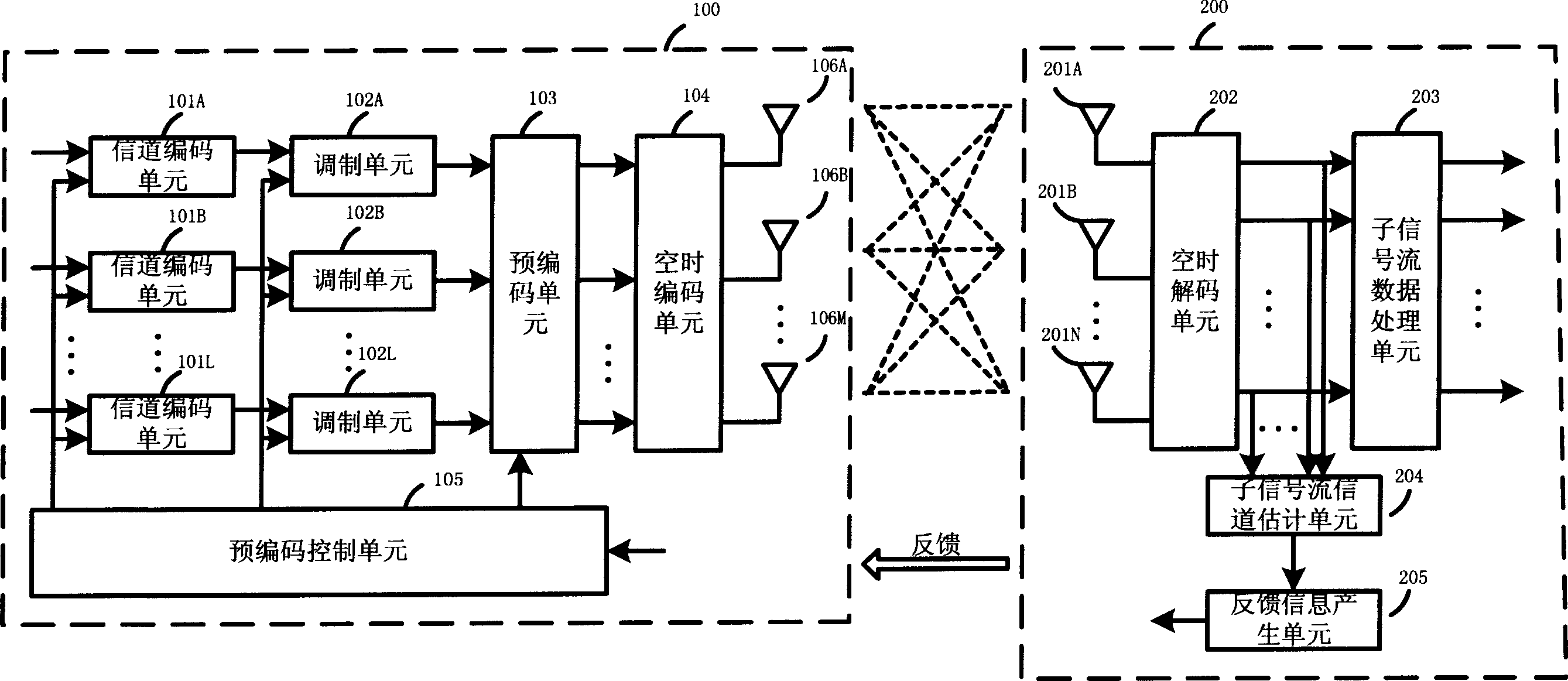
This invention discloses an emission method for an adaptive close loop multi-in multi-out communication system including the following steps: an emitter receives total or partial channel information fed back by a receiver including the S / N ratio of each signal flow to get a pre-coding matrix based on the information fed back by the receiver and distributes the power gain of every sub-signal flow unevenly based on the S / N ratio to adaptively select a modulation code mode for each sub-signal flow to modulate codes, pre-codes the sub-signal flow data and carries out empty time coding. This invention also discloses an emitter for realizing said method and an emitting system.
Owner:吴中武
Signal modulation circuit and signal modulation method
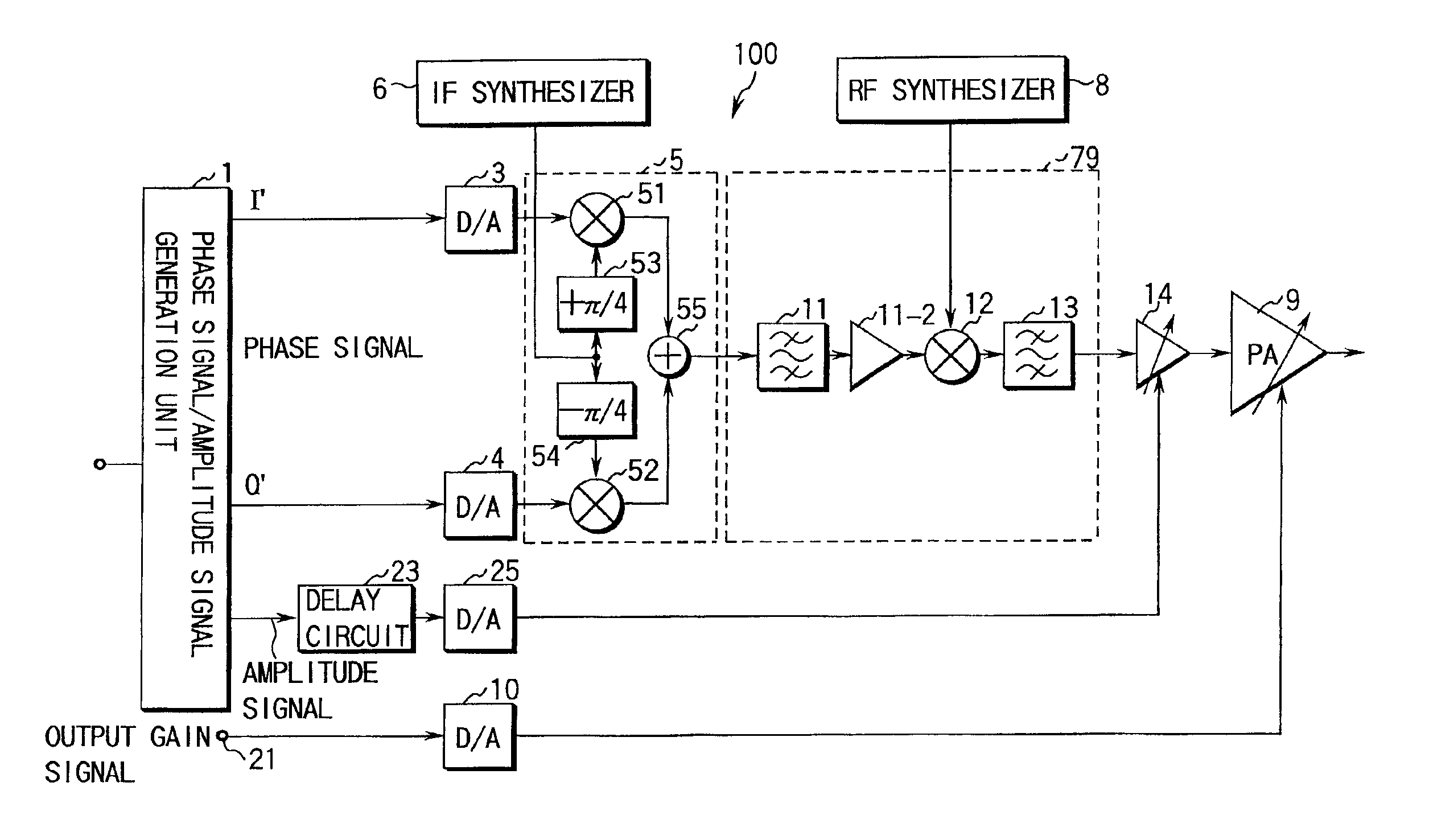
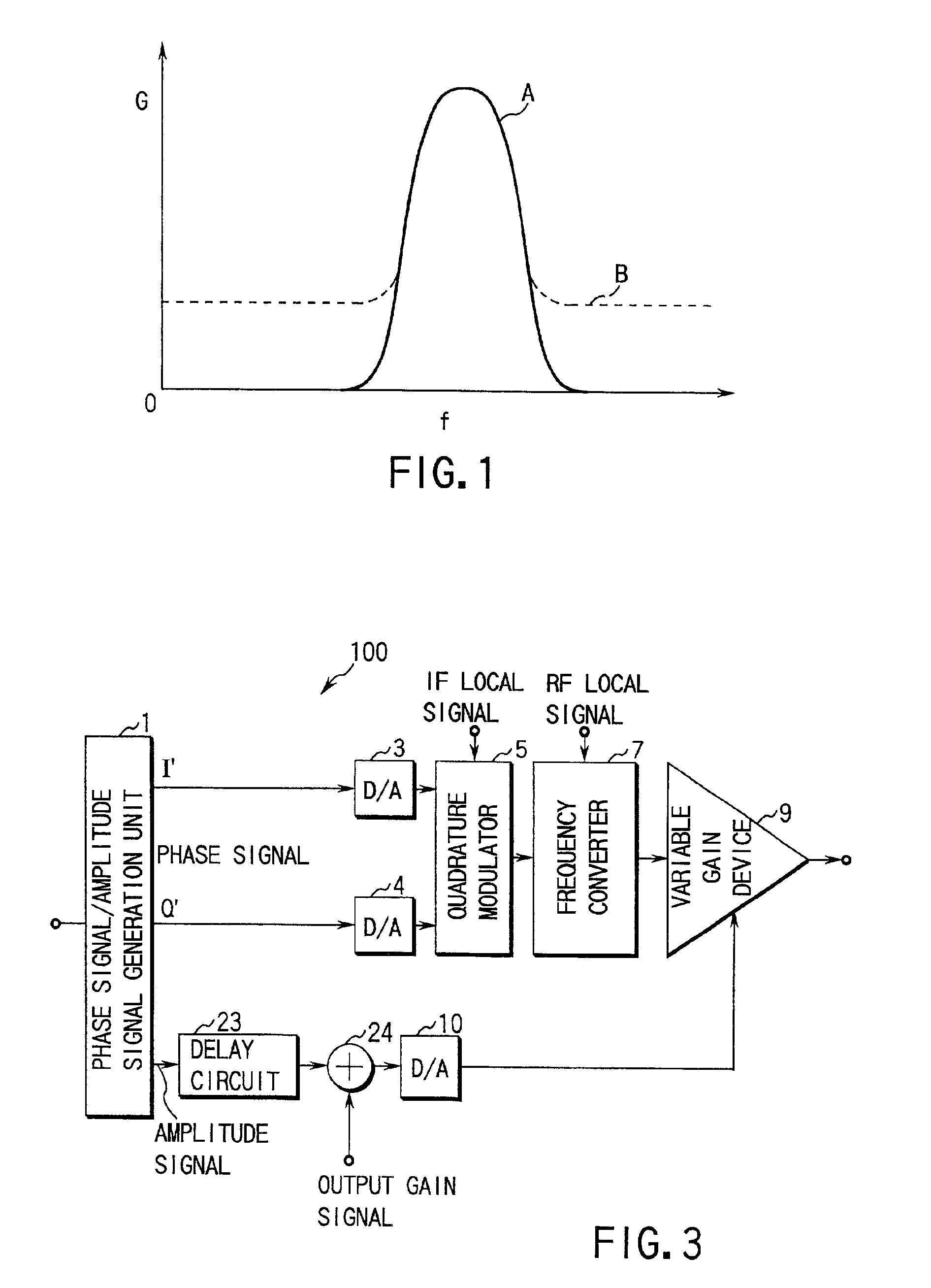
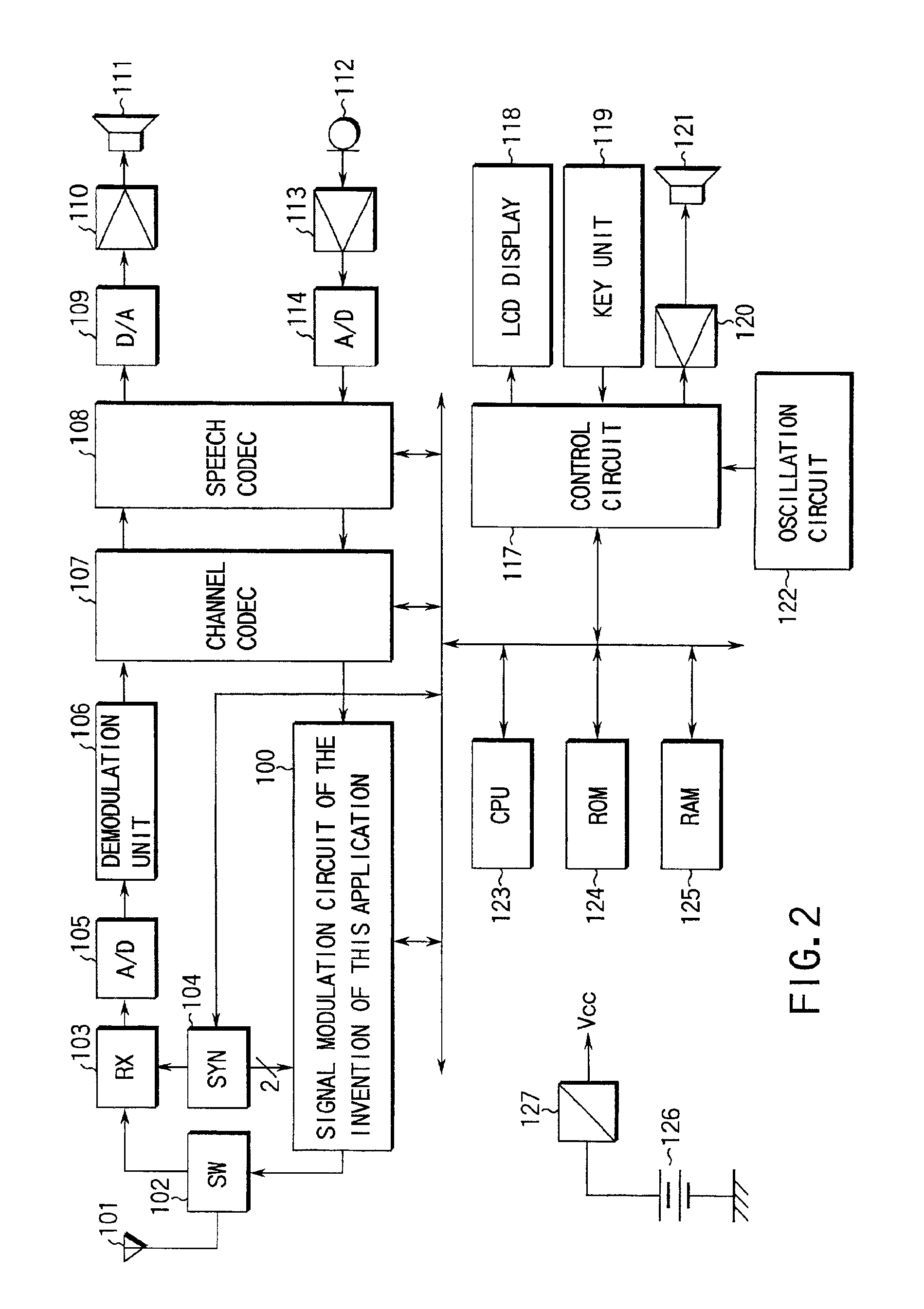
A phase signal is modulated in quadrature modulation by a quadrature modulator, and the frequency of this modulated phase signal is converted into carrier frequency by a frequency converter. An amplitude signal extracted from the modulating signal is delayed by a delay circuit, and an output gain signal designating the output average power gain is supplied to the output signal of the delay circuit. Synchronization of this frequency modulated phase signal and the amplitude signal delayed and added to the output gain signal allows to obtain an RF signal with little out of band undesired component even if the modulating signal contains amplitude variation. Therefore, the RF signal with little out of band undesired component is output even if the modulating signal contains amplitude variation.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Calibration method for automatically compensating electric energy metering error of electric energy meter according to temperature
ActiveCN104965186AConsumption deviation is smallImprove fairnessElectrical measurementsElectricityProcessor register
The invention discloses a calibration method for automatically compensating an electric energy metering error of an electric energy meter according to temperature. The calibration method may timely compute a new power gain correcting register calibration value according to environment temperature and replaces an original power gain correcting register calibration value in a power gain correcting register so as to enable a low difference between the actual electric energy consumption of a user and the electric energy metering of the electric energy meter. A calibration device and a calibration method adaptive to the same are included. The calibration device comprises a temperature detecting sensor, a memory, a current signal sampling circuit, a voltage signal sampling circuit, a microprocessor, and an electric energy metering chip with a built-in power gain correcting register. The electric energy metering chip, the temperature detecting sensor, and the memory are connected with the microprocessor. The current signal sampling circuit and the voltage signal sampling circuit are connected with the electric energy metering chip. The calibration method is mainly used in electric energy meter automatic compensation calibration technology according to temperature variation.
Owner:HANGZHOU XILI INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com