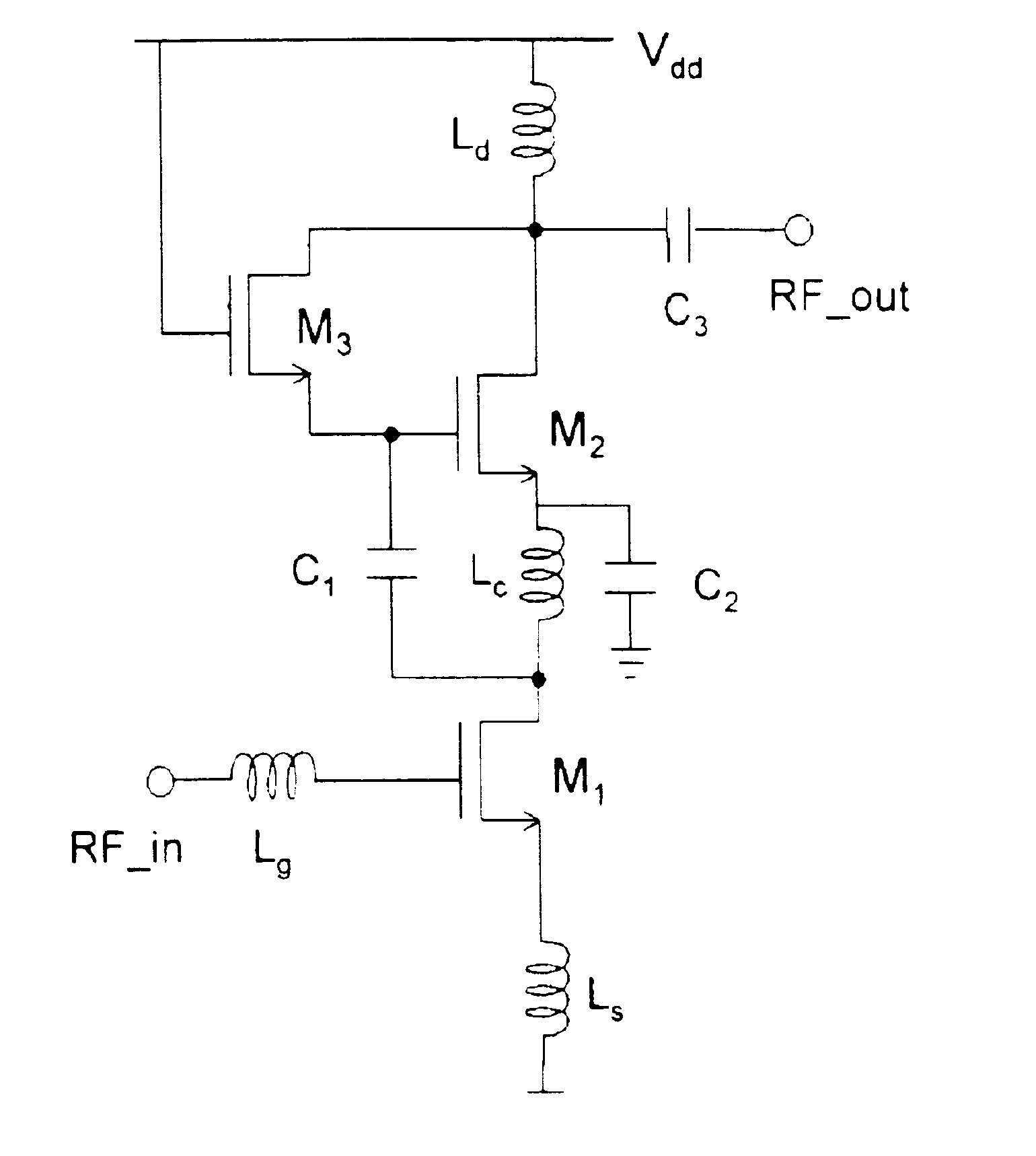
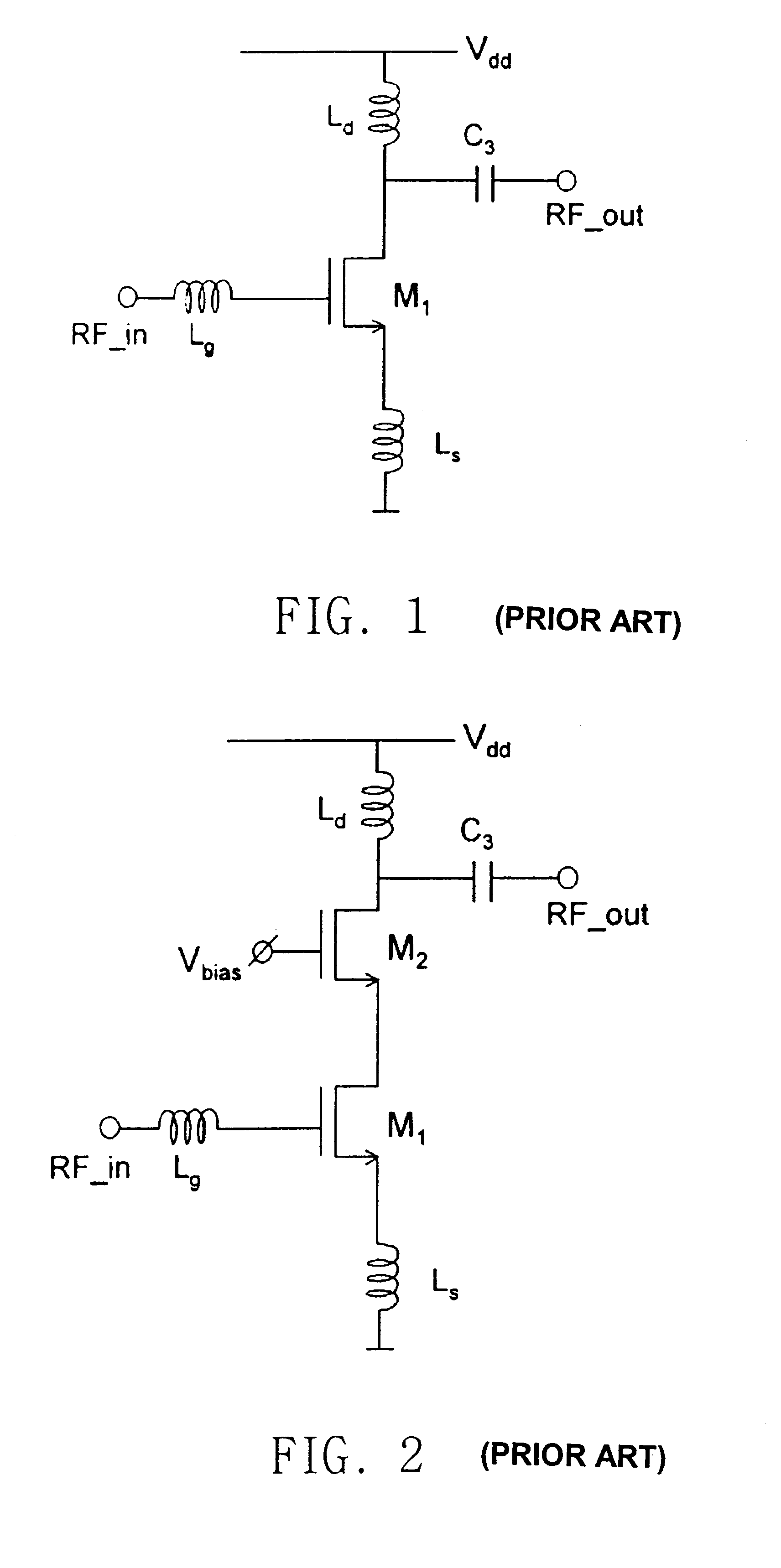
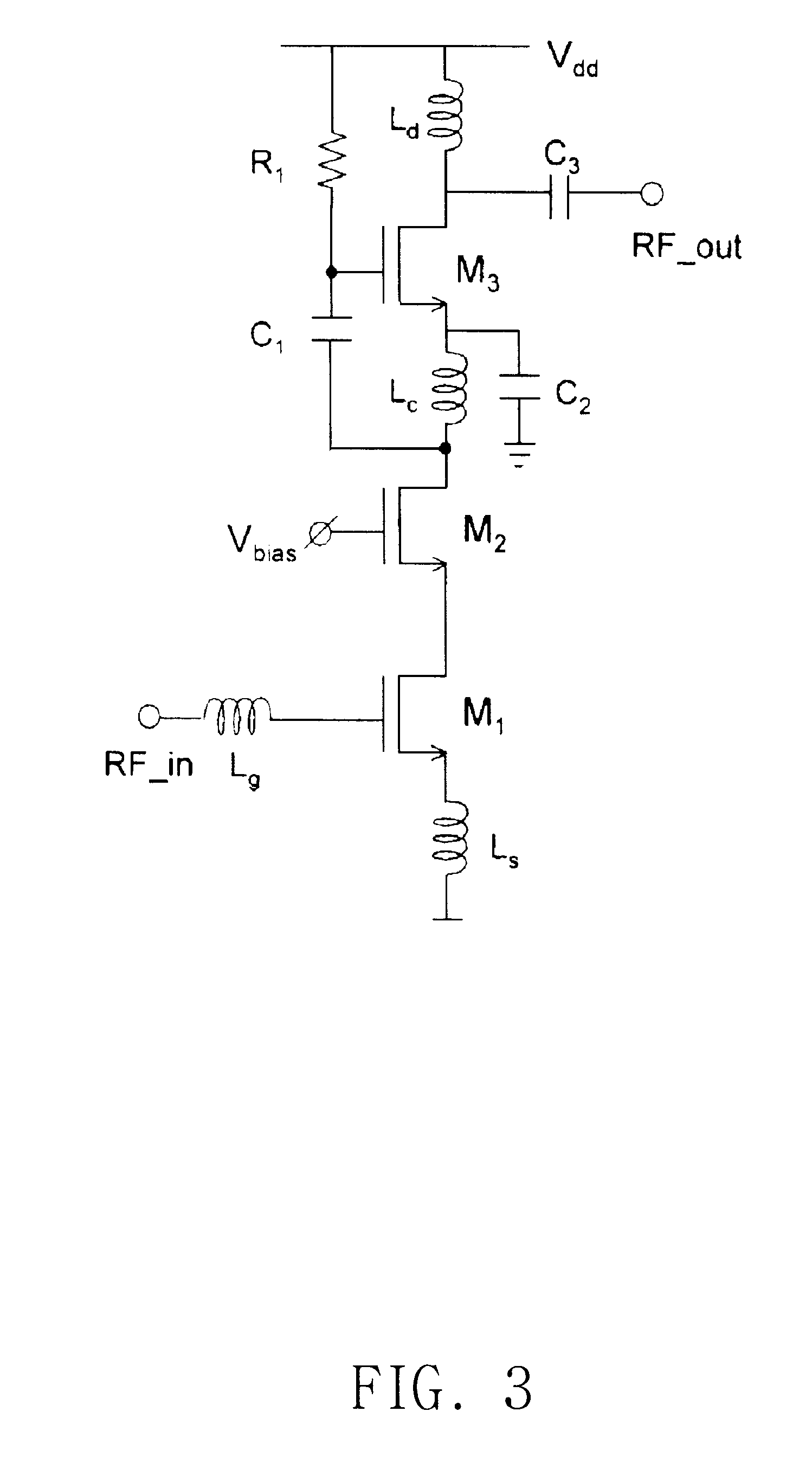
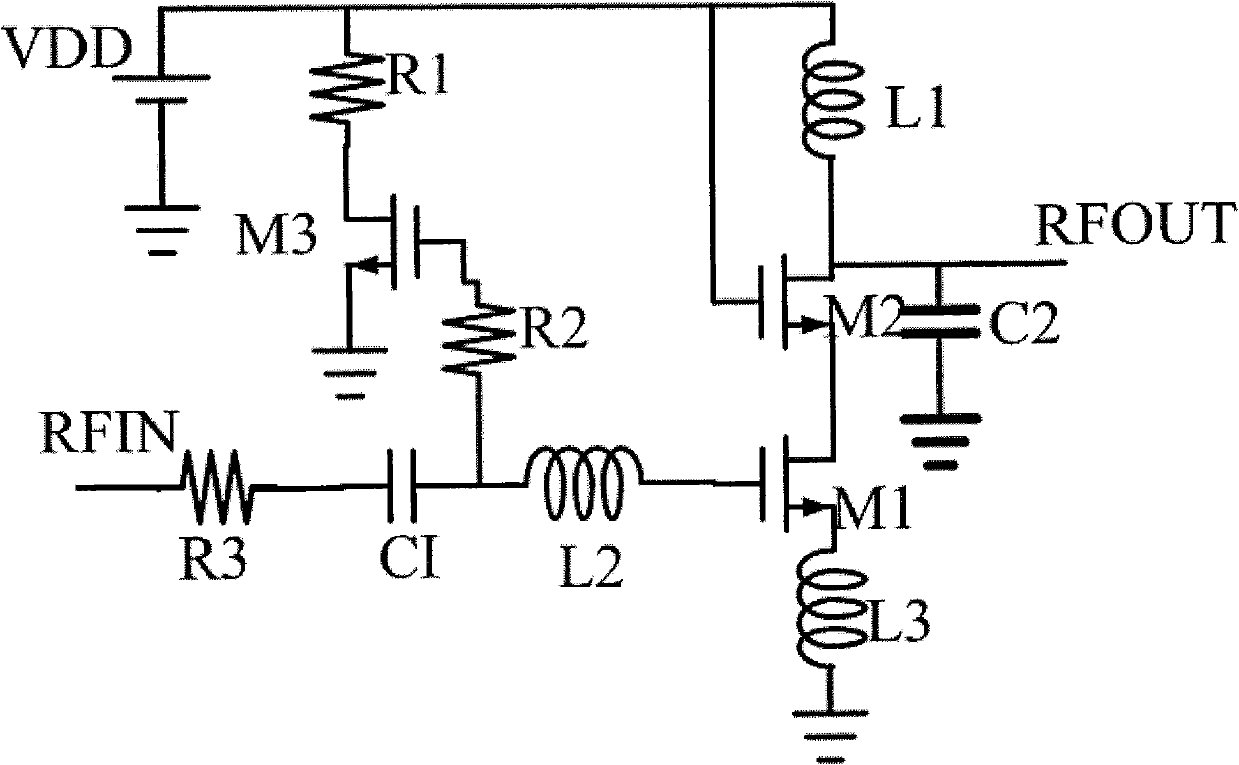
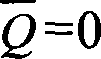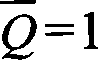Patents
Literature
641 results about "Common gate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
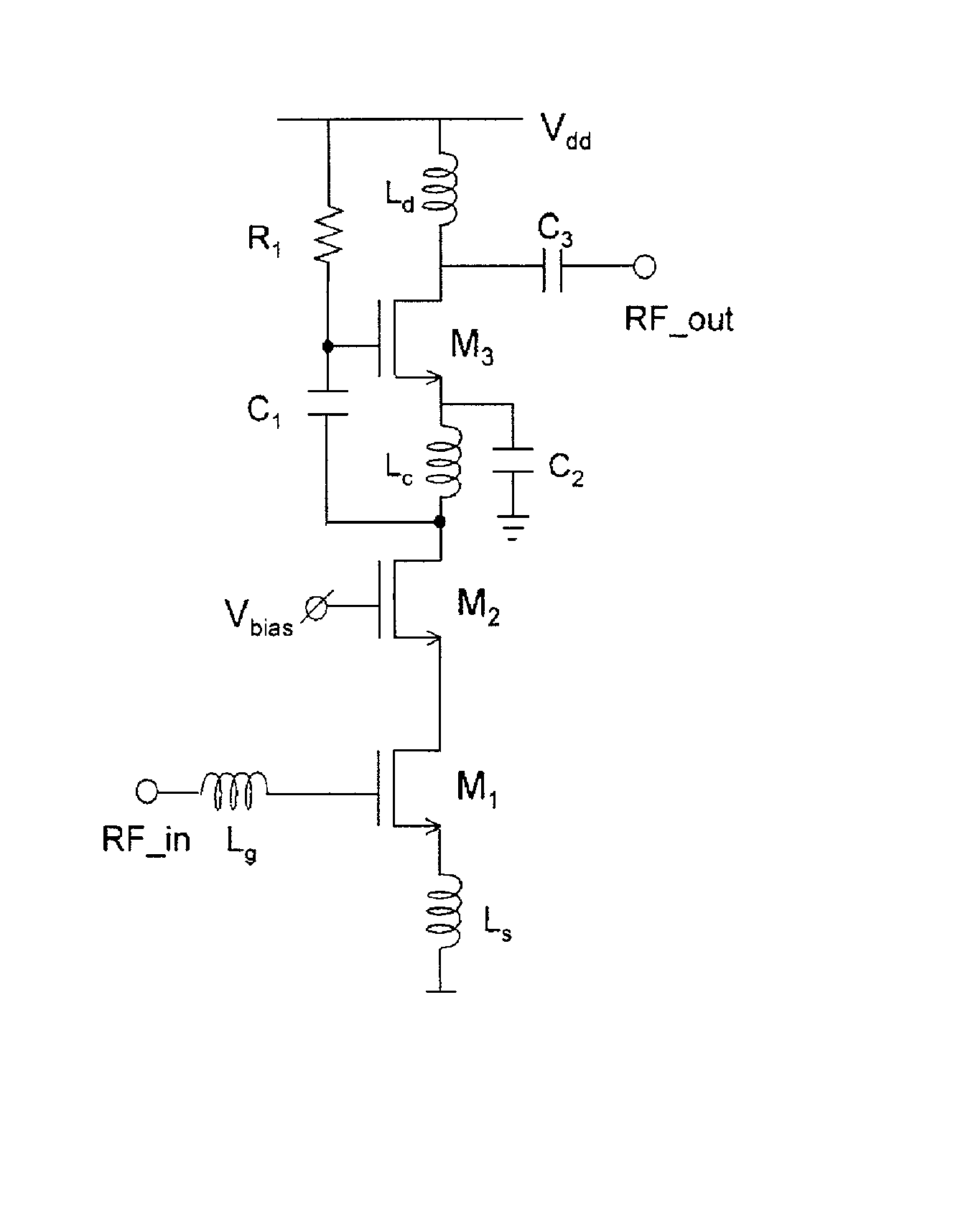
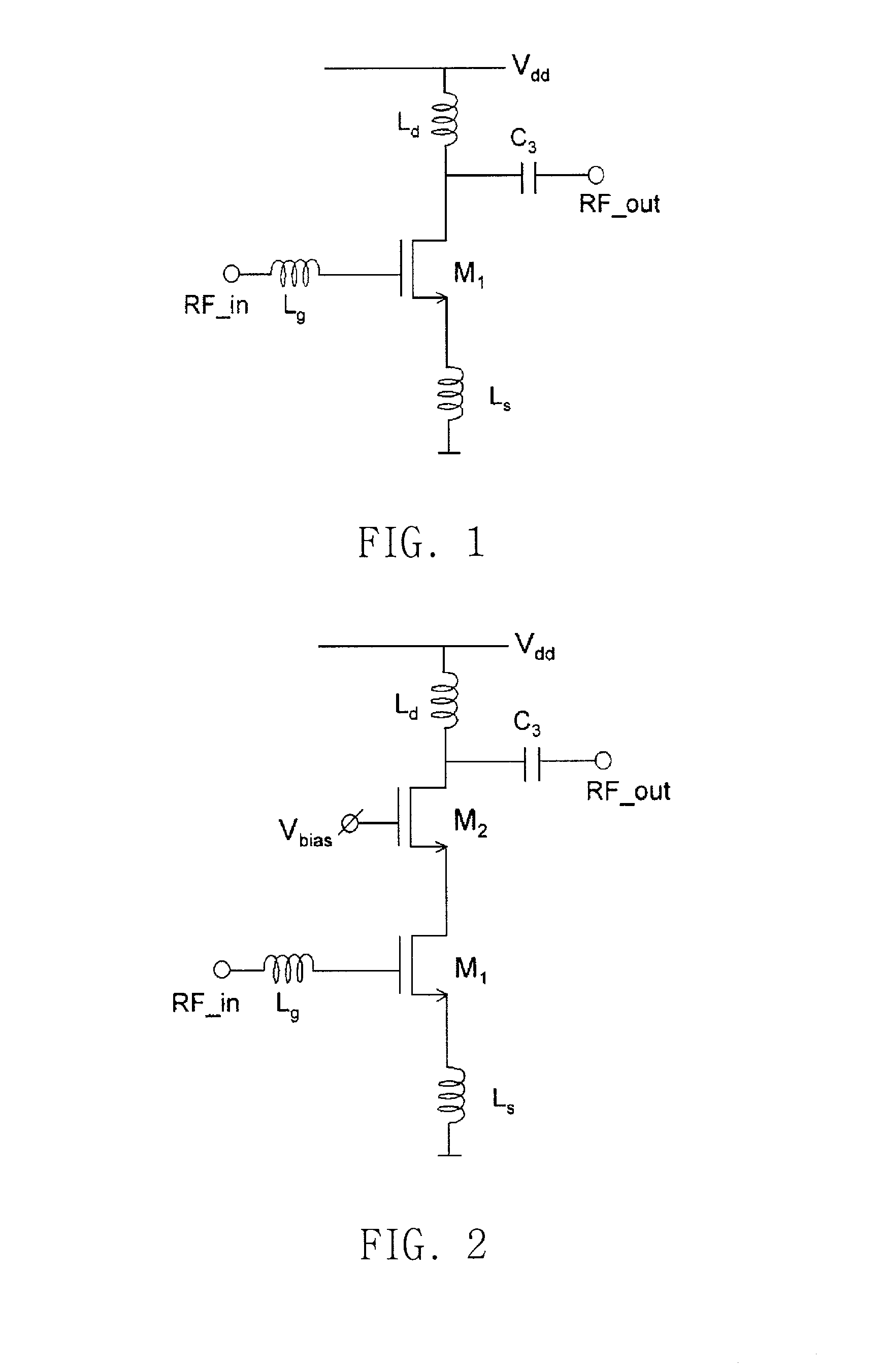
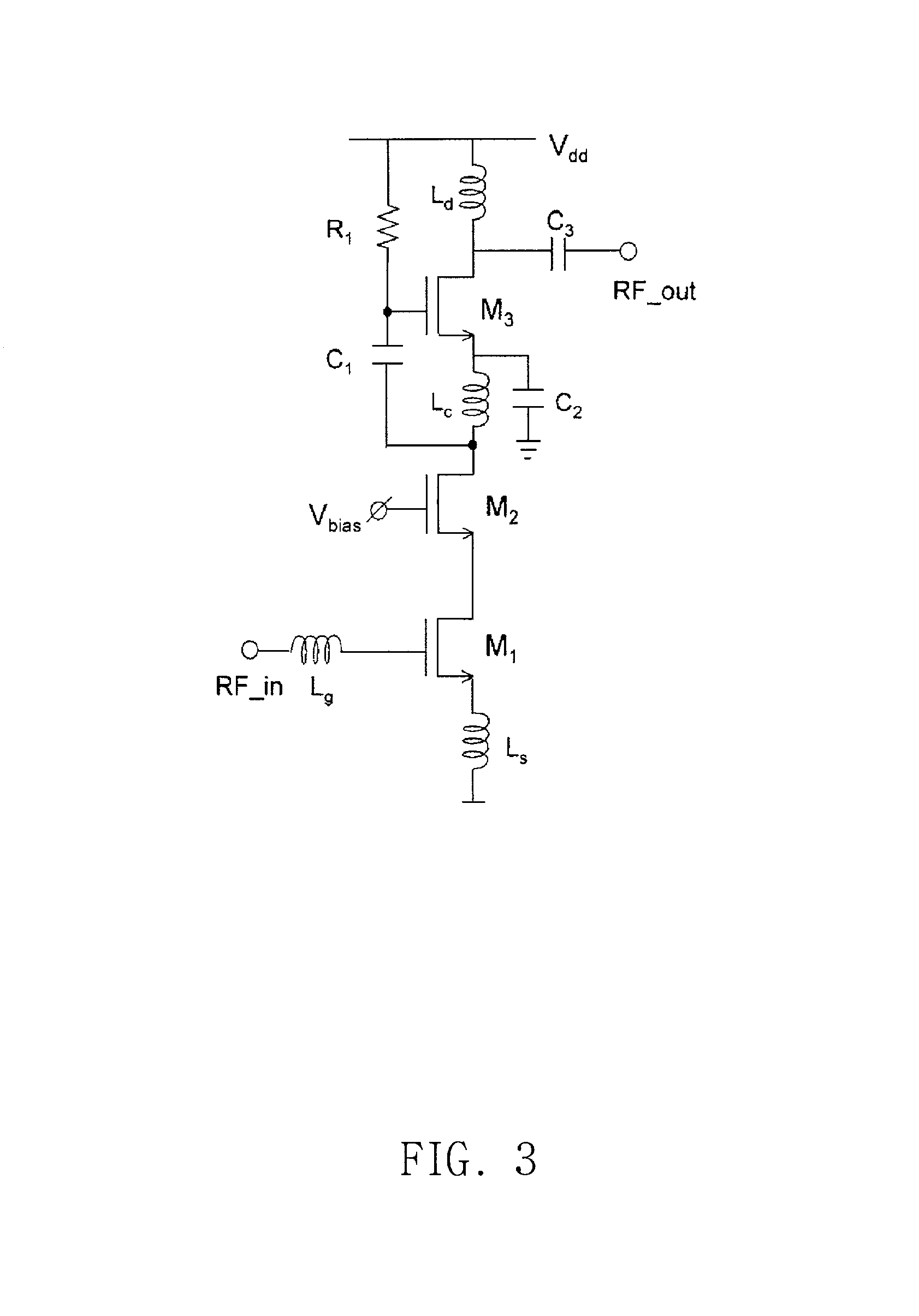
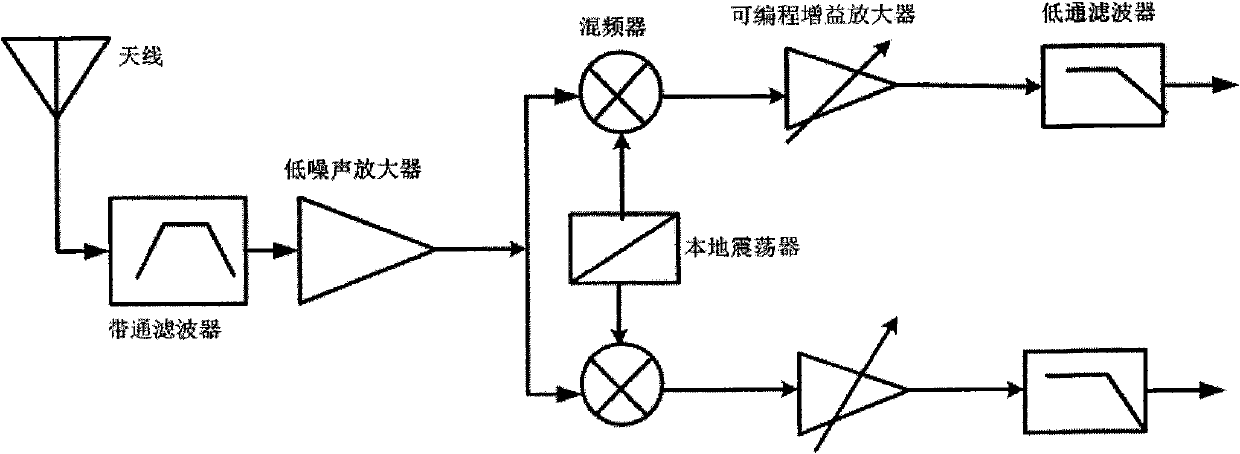
In electronics, a common-gate amplifier is one of three basic single-stage field-effect transistor (FET) amplifier topologies, typically used as a current buffer or voltage amplifier. In this circuit the source terminal of the transistor serves as the input, the drain is the output and the gate is connected to ground, or "common," hence its name. The analogous bipolar junction transistor circuit is the common-base amplifier.
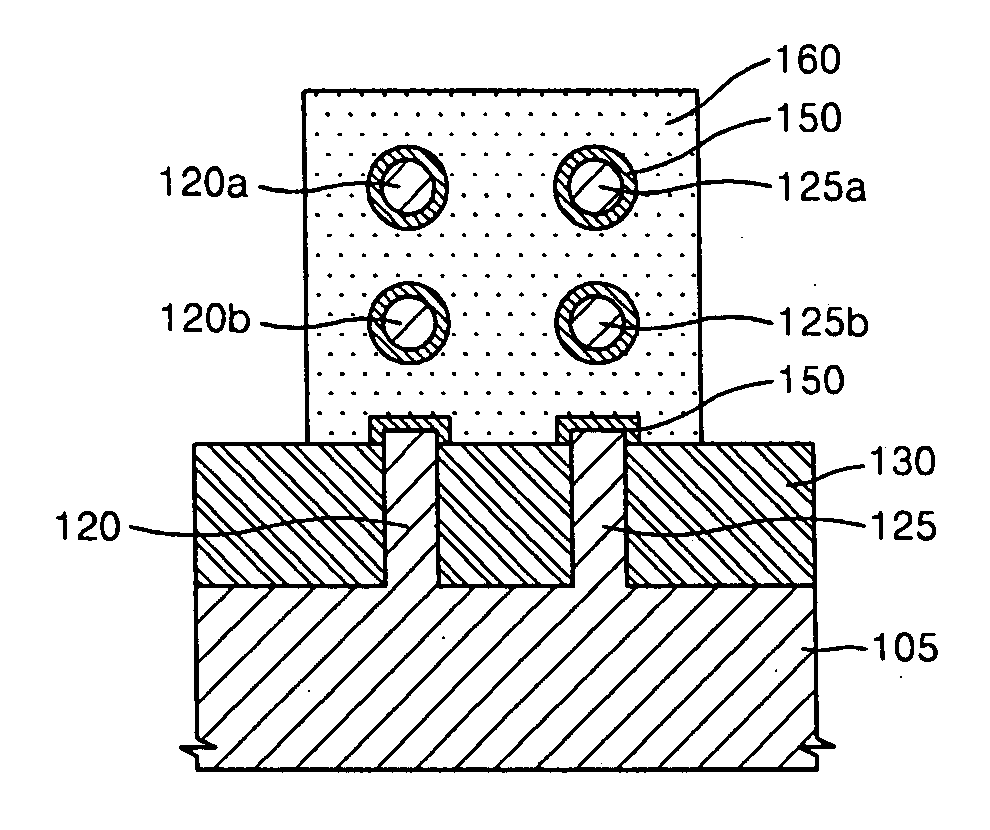
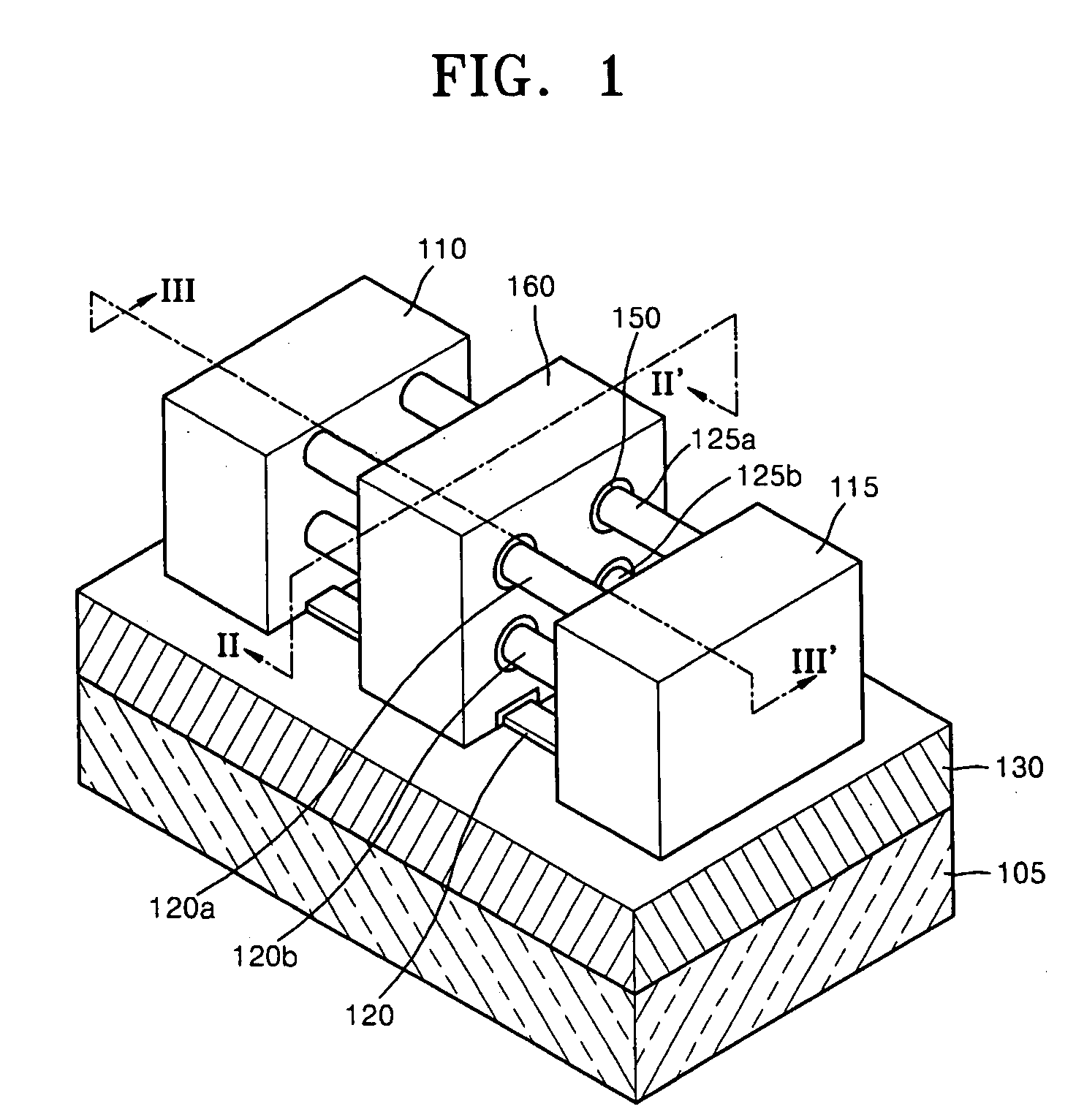
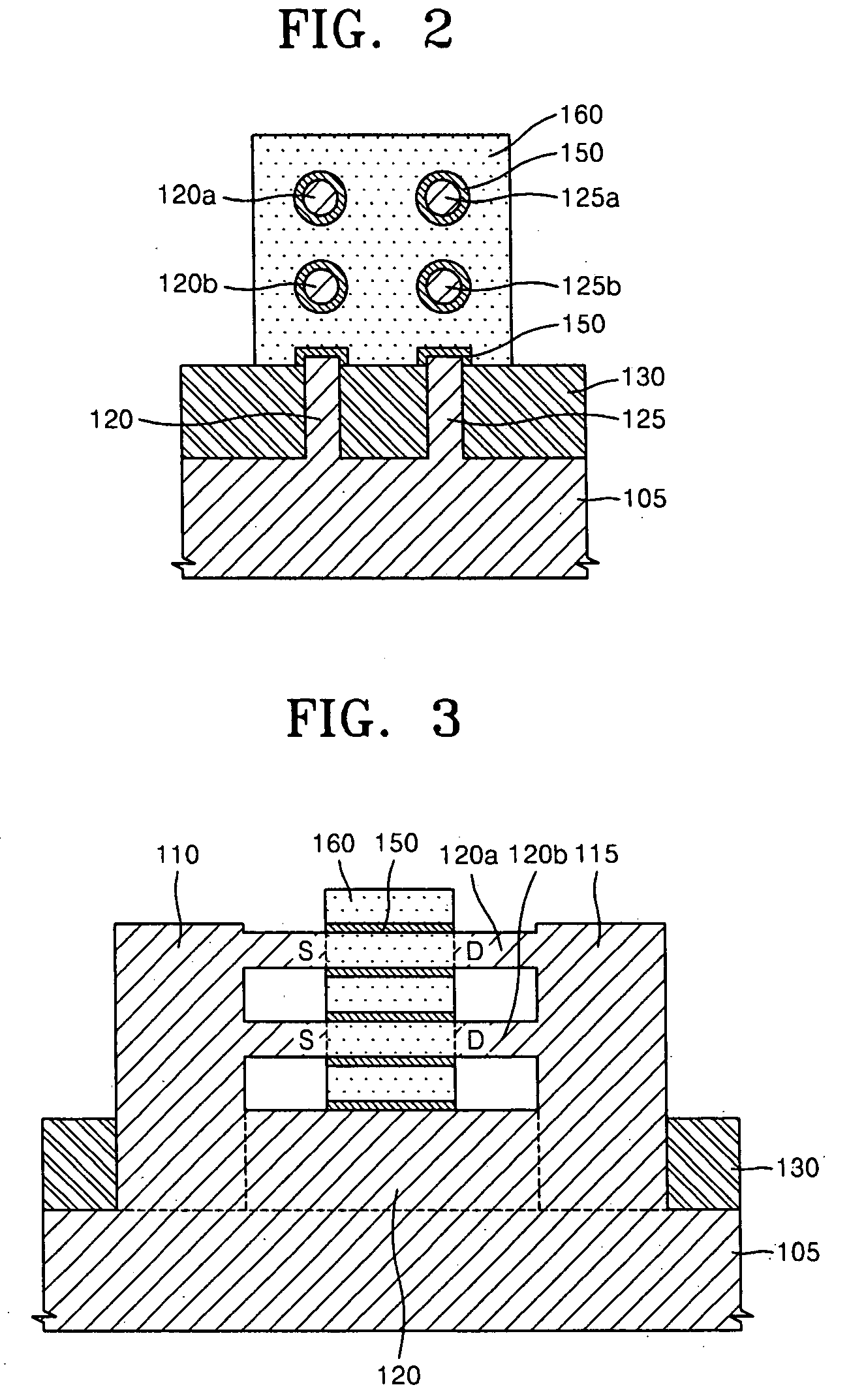
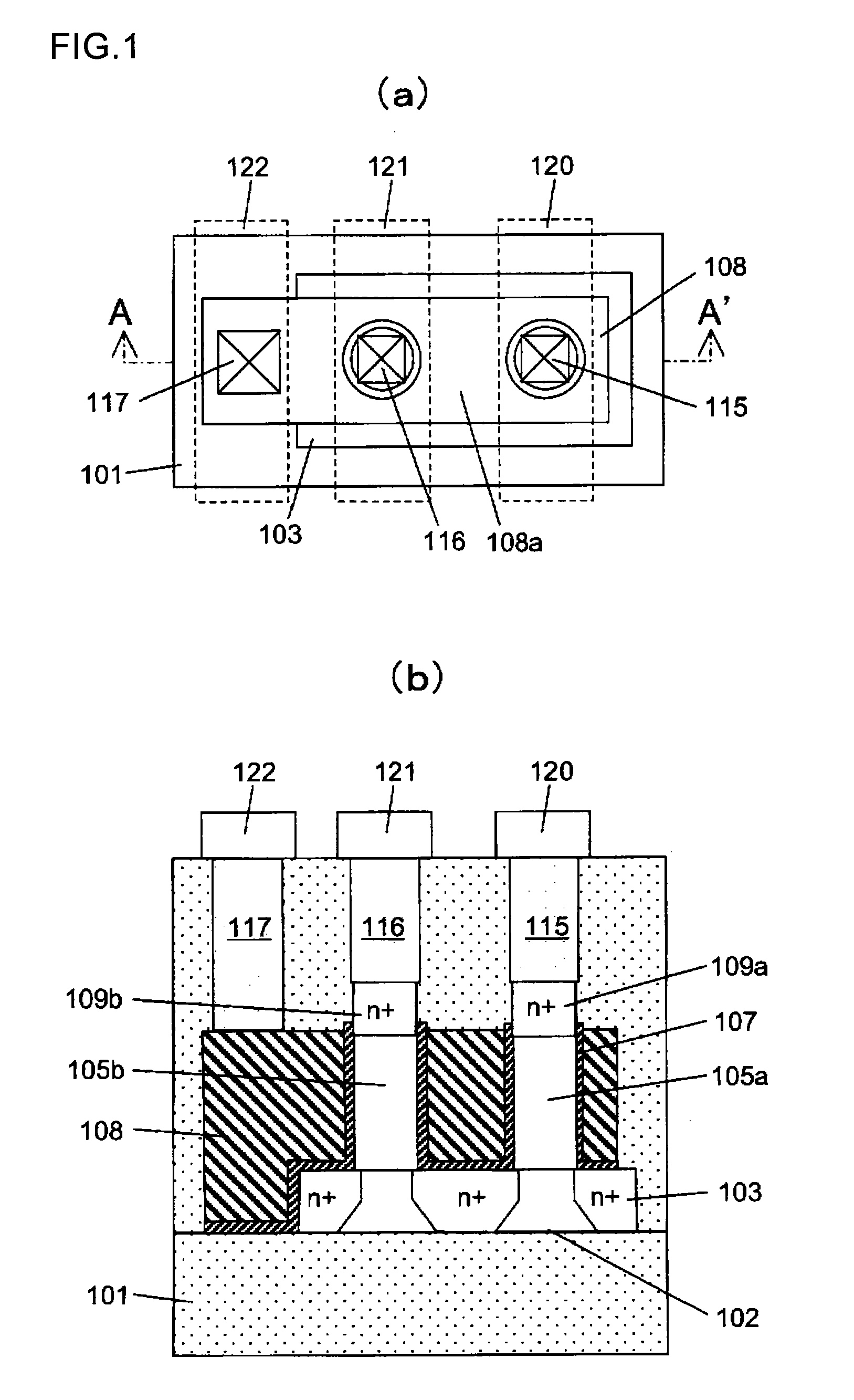
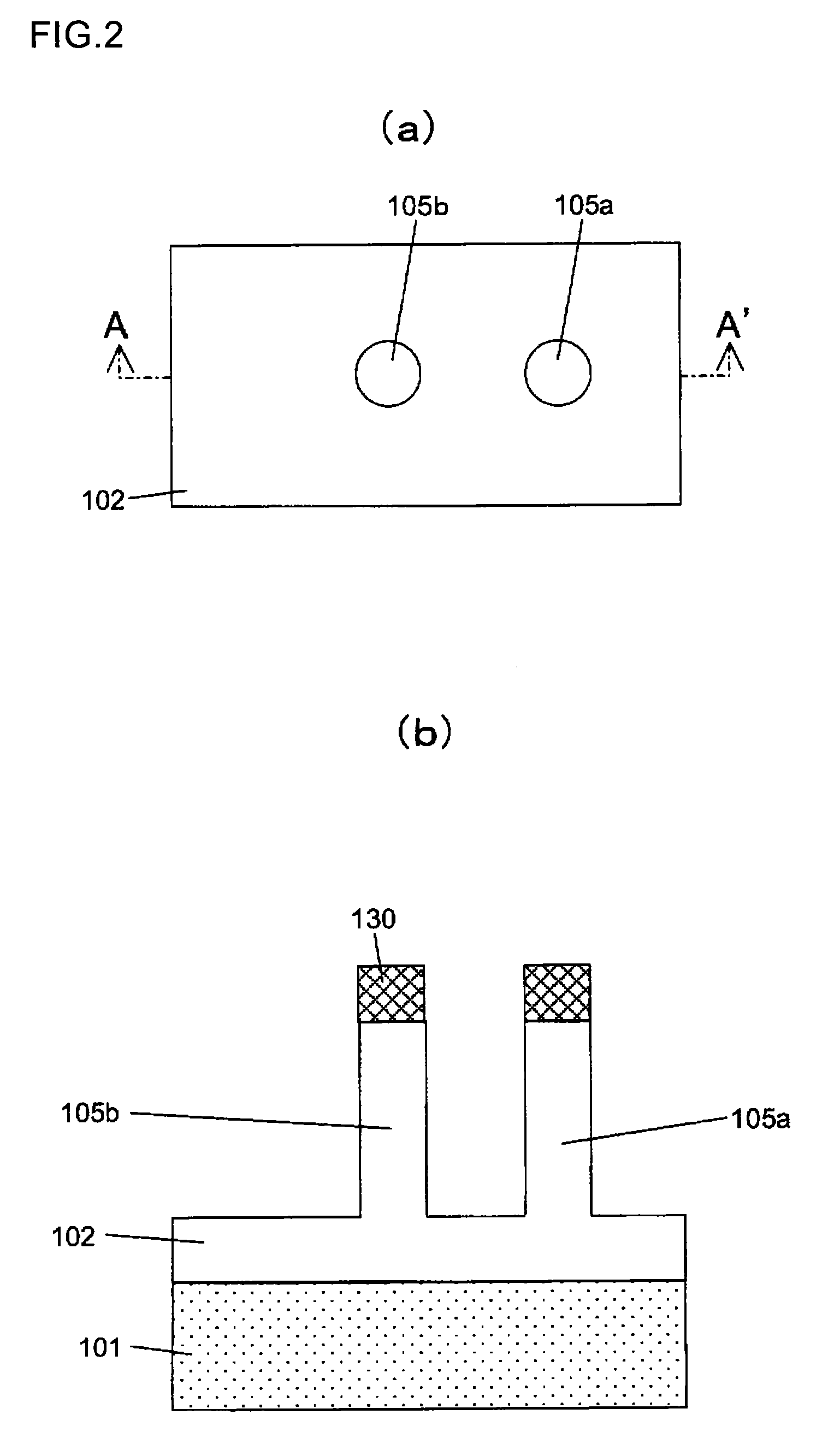
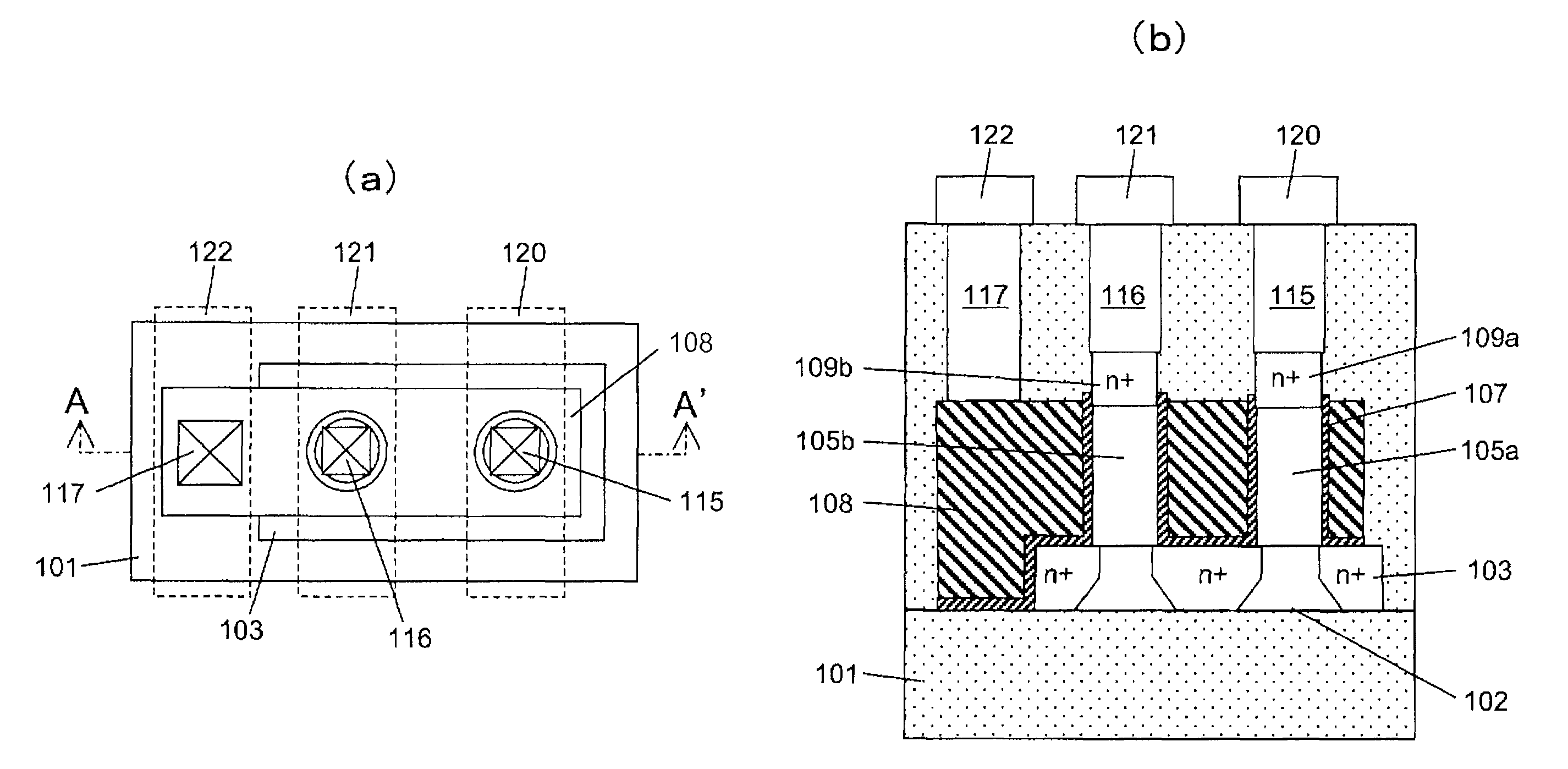
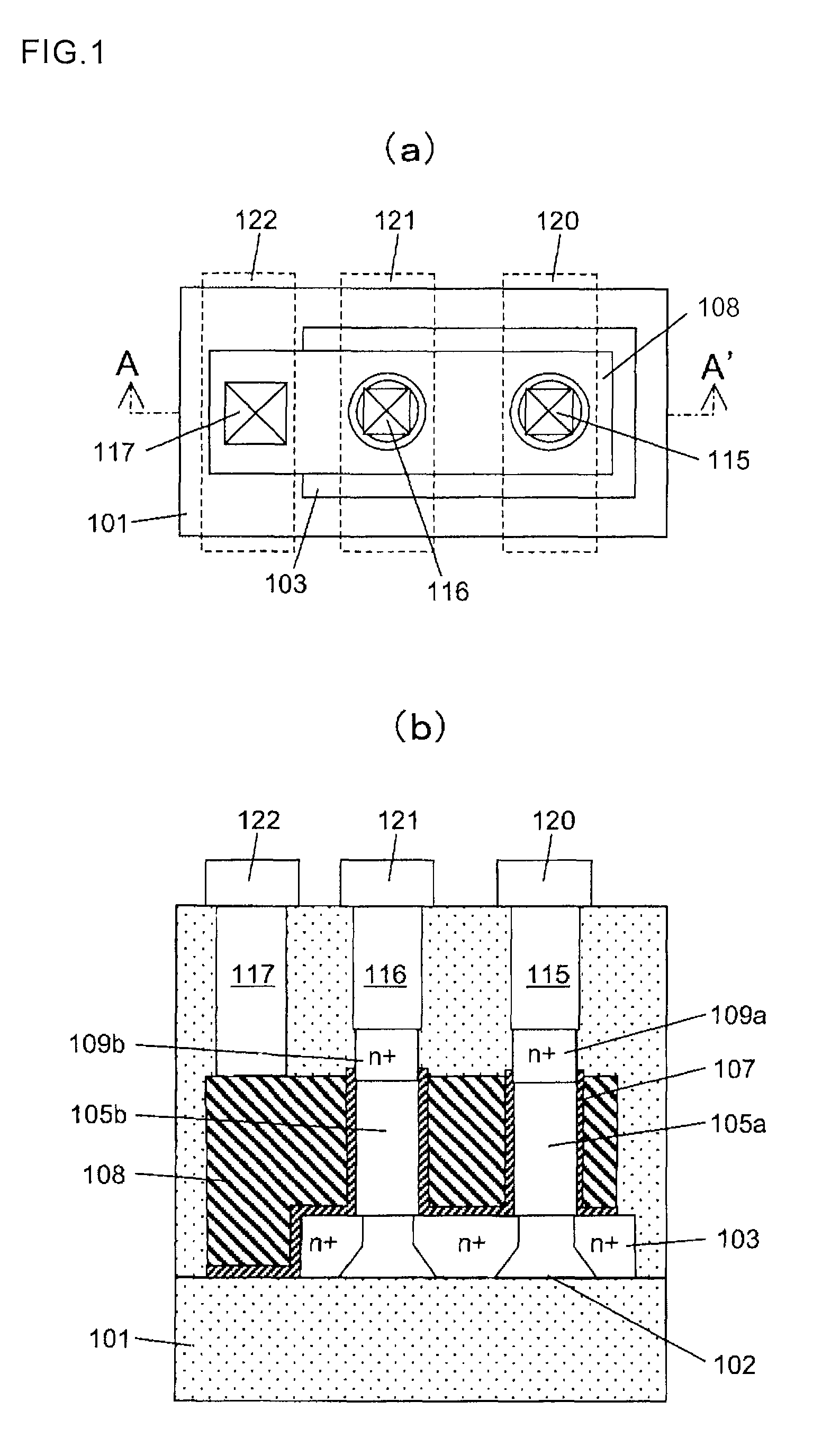
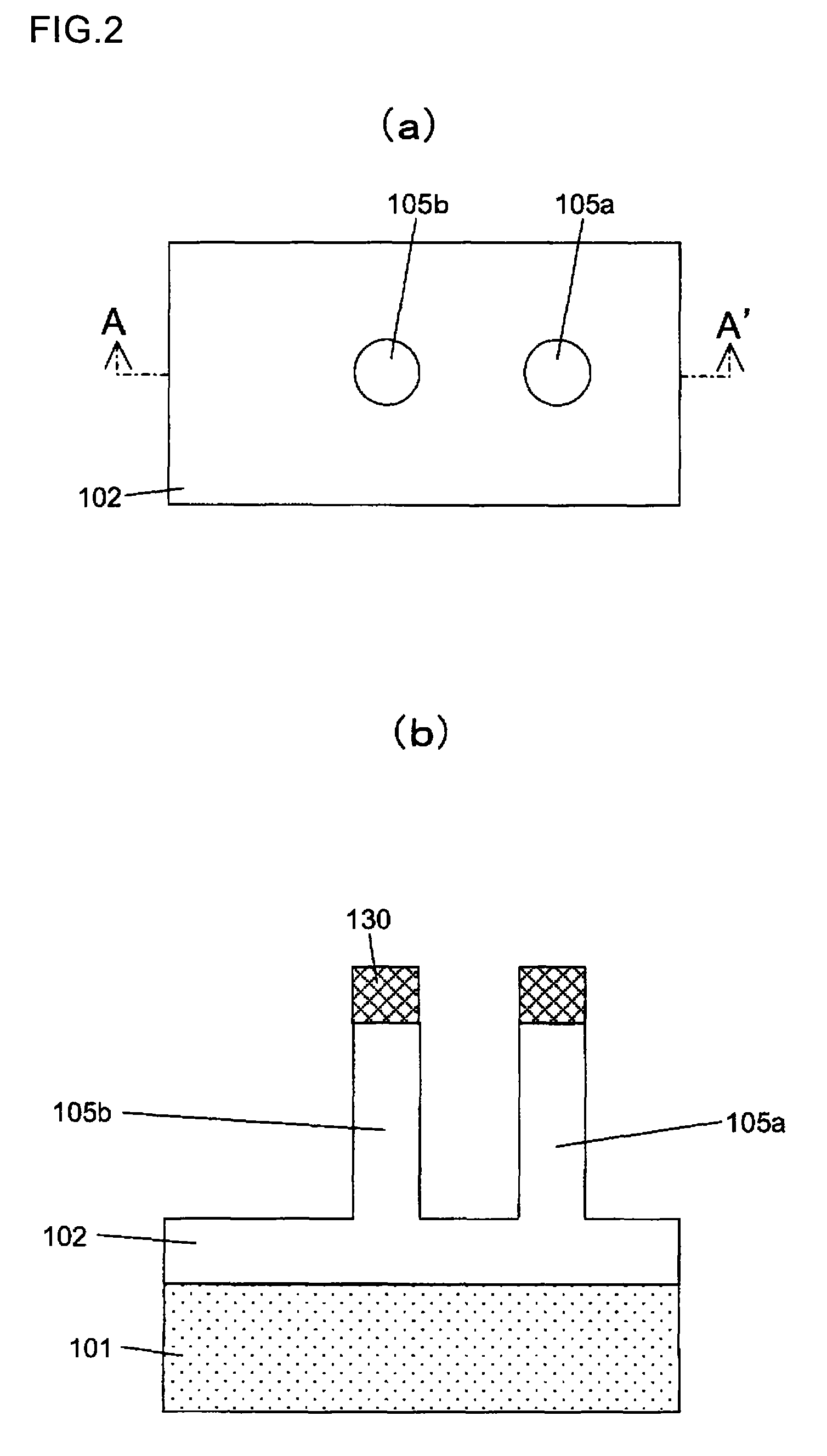
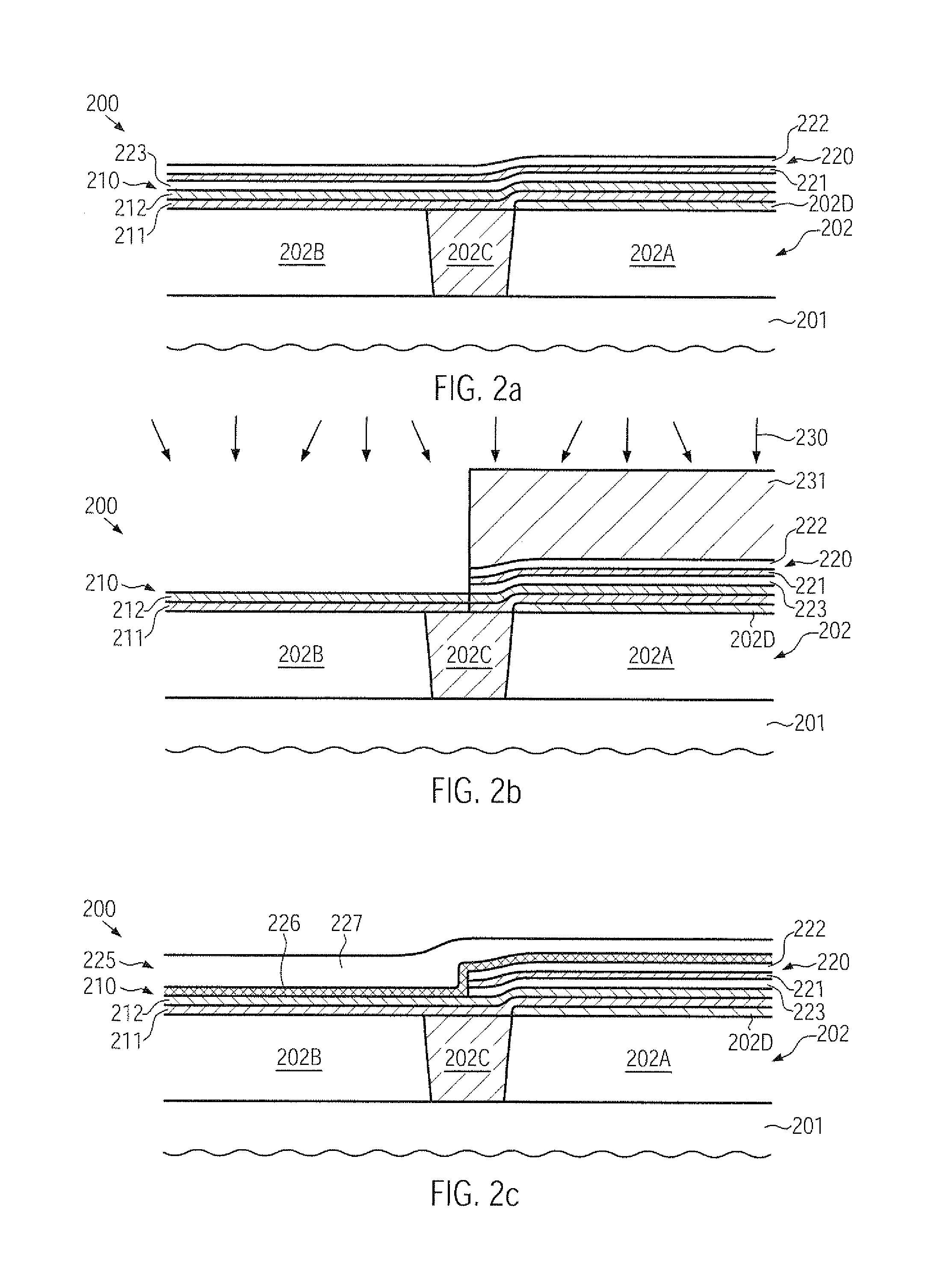
Wire-type semiconductor devices and methods of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20080017934A1Suppression of short channel effectsInexpensive to fabricateTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
Provided are relatively higher-performance wire-type semiconductor devices and relatively economical methods of fabricating the same. A wire-type semiconductor device may include at least one pair of support pillars protruding above a semiconductor substrate, at least one fin protruding above the semiconductor substrate and having ends connected to the at least one pair of support pillars, at least one semiconductor wire having ends connected to the at least one pair of support pillars and being separated from the at least one fin, a common gate electrode surrounding the surface of the at least one semiconductor wire, and a gate insulating layer between the at least one semiconductor wire and the common gate electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of fabricating CMOS devices having a single work function gate electrode by band gap engineering and article made thereby
InactiveUS20070069302A1Lower threshold voltageEasy to manufactureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSWork function
A method utilizing a common gate electrode material with a single work function for both the pMOS and nMOS transistors where the magnitude of the transistor threshold voltages is modified by semiconductor band engineering and article made thereby.
Owner:INTEL CORP
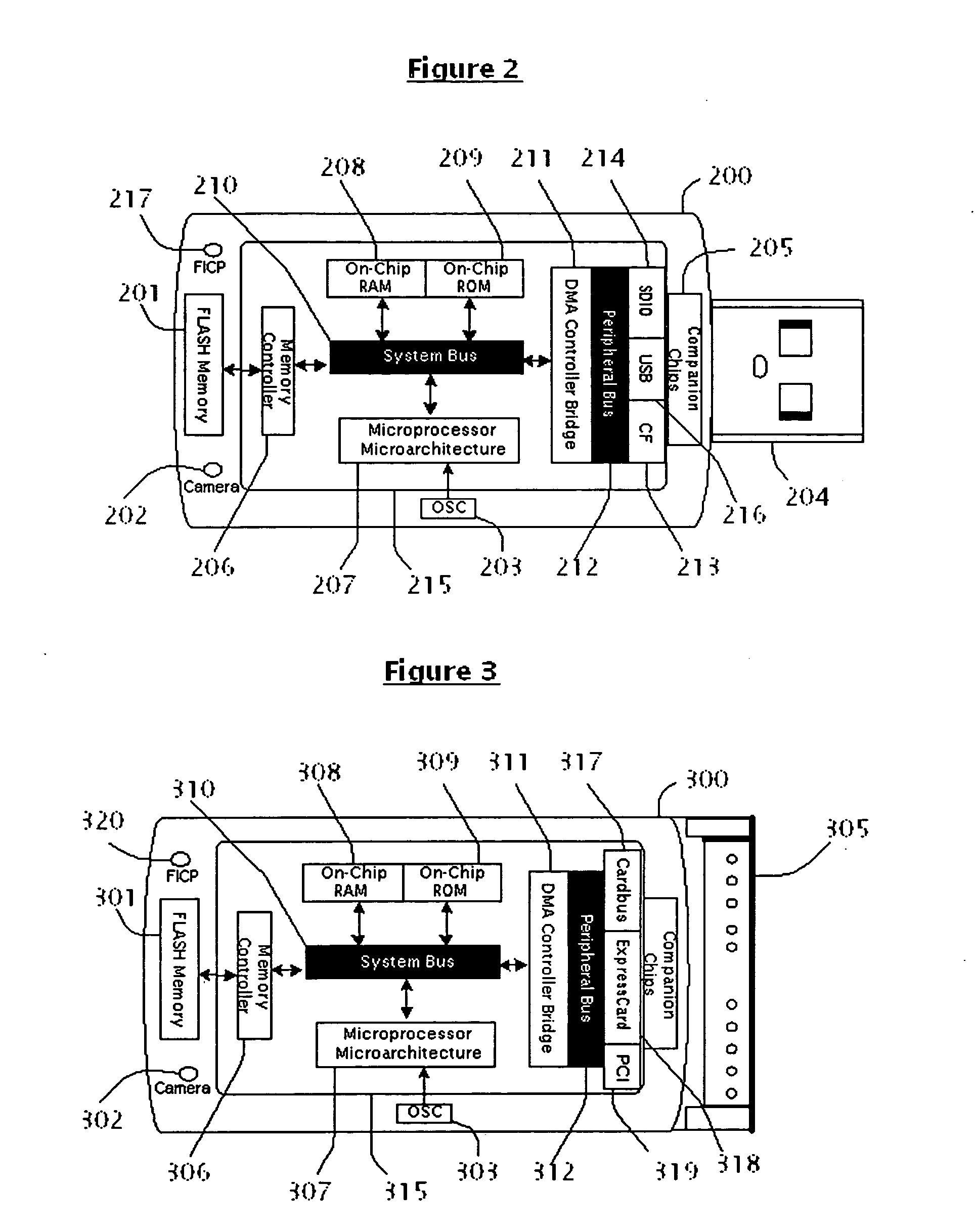
Method and aparatus for plug-and-play webserver
InactiveUS20060075174A1Simplify the development processEasy to adaptComponent plug-in assemblagesProgram loading/initiatingPCI ExpressUSB
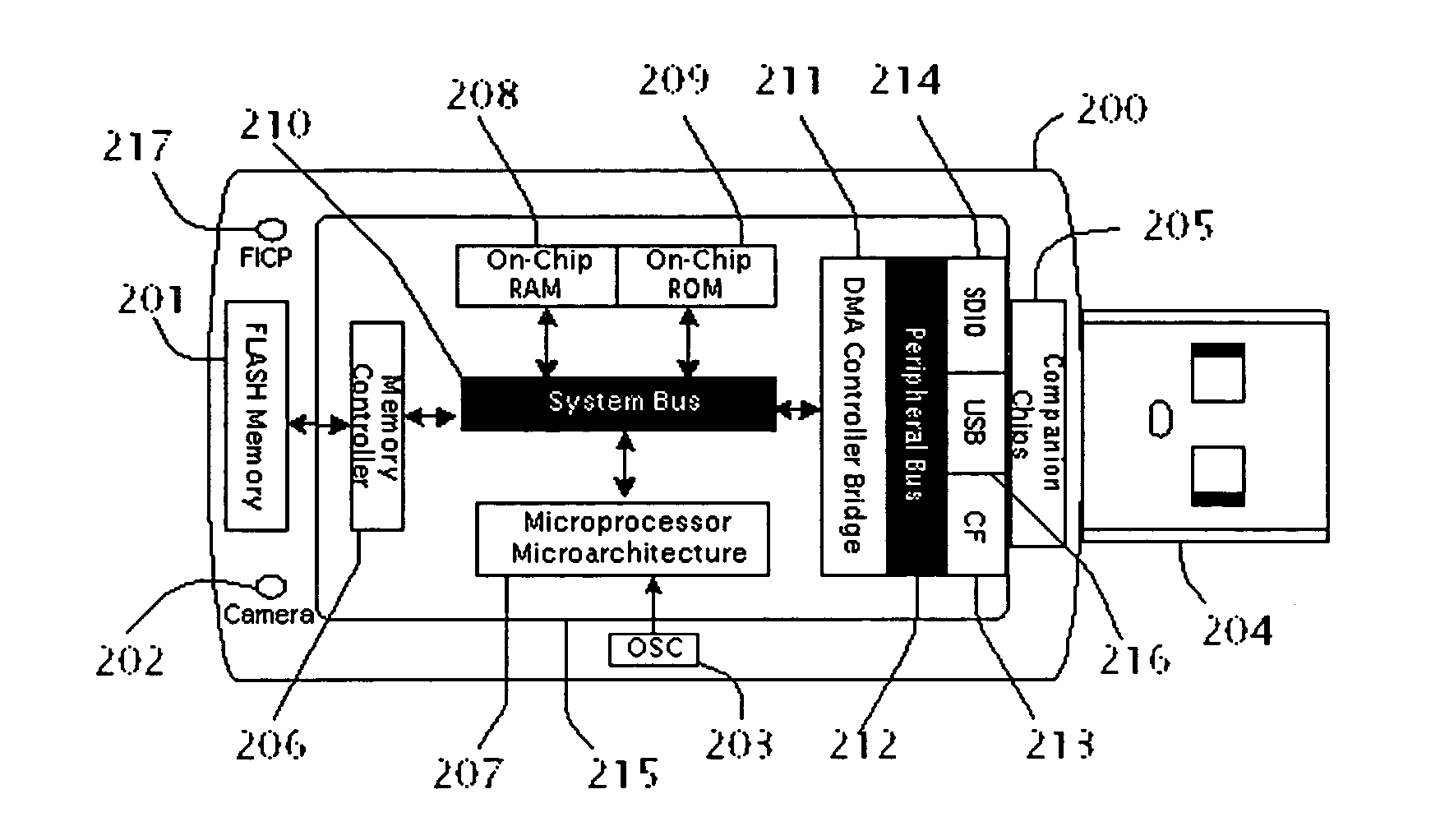
A system, method and computer program for an apparatus is described. An apparatus is a very convenient, plug-and-play, ultra small, smart device that lets the end-users to host their websites at computer peripheral port. When said device is plugged in one of the computer peripheral ports: Universal Serial Bus (USB), Secure Digital Input and Output (SDIO), Compact Flash (CF), Cardbus, Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI), PCI-Express and ExpressCard; it shall function as a dedicated web hosting device powerful and robust enough to handle web hosting functions for Personal Home Page, File Transfer Protocol (FTP) Files Server, Streaming media, Common Gate Interface (CGI) scripts, Active Server Pages, or Game Server.
Owner:MR VUONG CORY THANG
Broad output current scope low pressure difference linear manostat
InactiveCN101339443AIncreased unity-gain bandwidthImprove stabilityLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceCurrent range
A low dropout linear voltage regulator with wide output current range and low pressure difference, comprises an error amplifier in the folding common source and common gate structure, a buffer circuit, a driving element, a feedback circuit, a load capacitance equivalent series resistance compensating circuit and a multistage Miller compensation circuit, wherein the buffer circuit changes the low frequency pole into a medium frequency pole and a high frequency pole; the large load capacitance of the load capacitance equivalent series resistance compensating circuit pushes the main pole to the low frequency, causing the gain crossover point to push inwards, and generating a medium frequency zero point for counteracting the medium frequency pole connected serially with the equivalent series resistance; the stride multilevel Miller compensation circuit generates a medium high frequency pole and a medium high frequency zero point slightly smaller than the medium high frequency pole for advancing the phase margin, thereby not only adding the unity gain bandwidth, but also saving considerable chip area. When the output current has a large change range, the structure provided by the invention generates wider unity gain bandwidth, provides the phase margin of greater than 85 degrees, ensures the stability of the system and advances the low pressure difference linear voltage stabilization performance.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
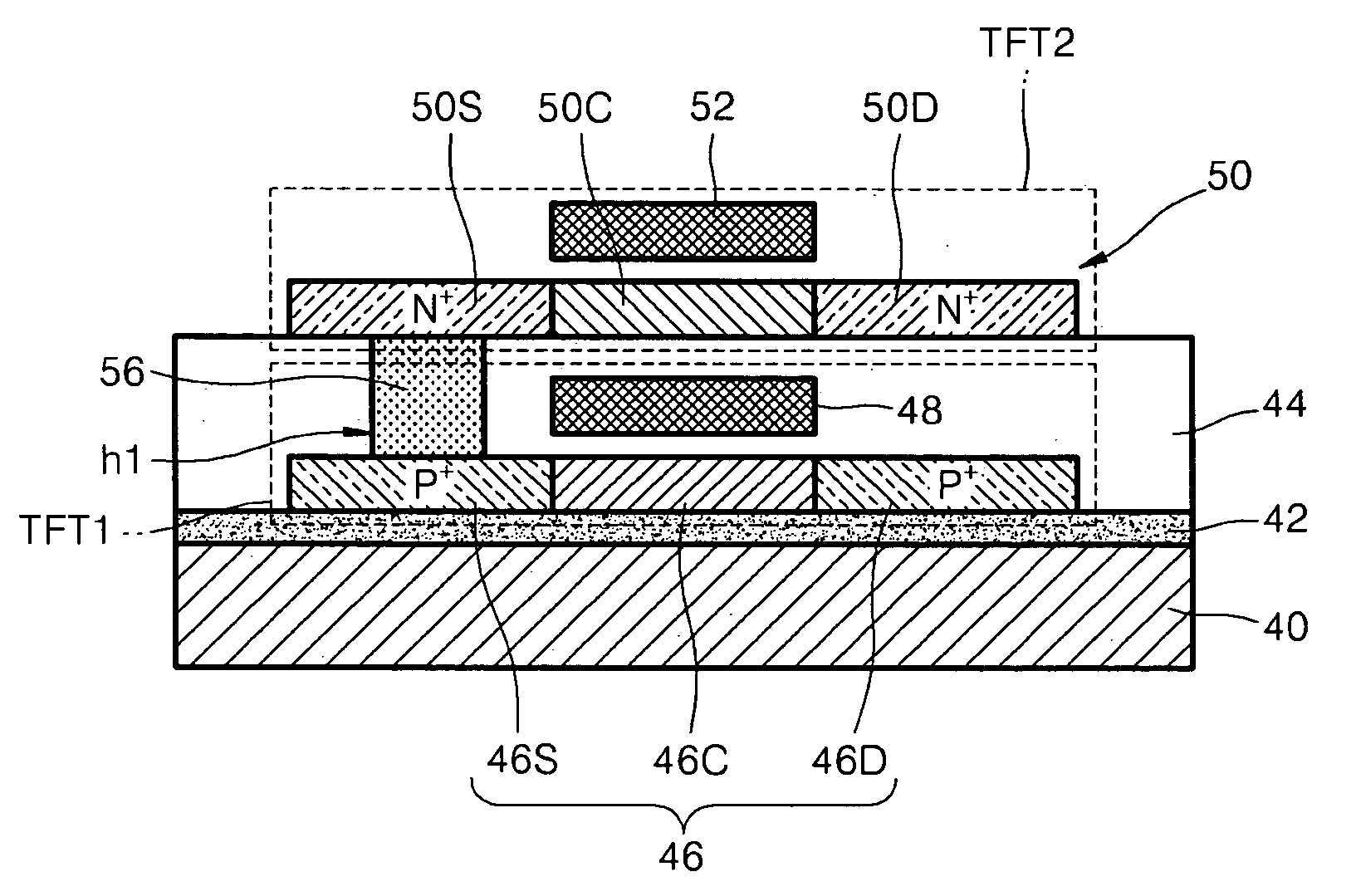
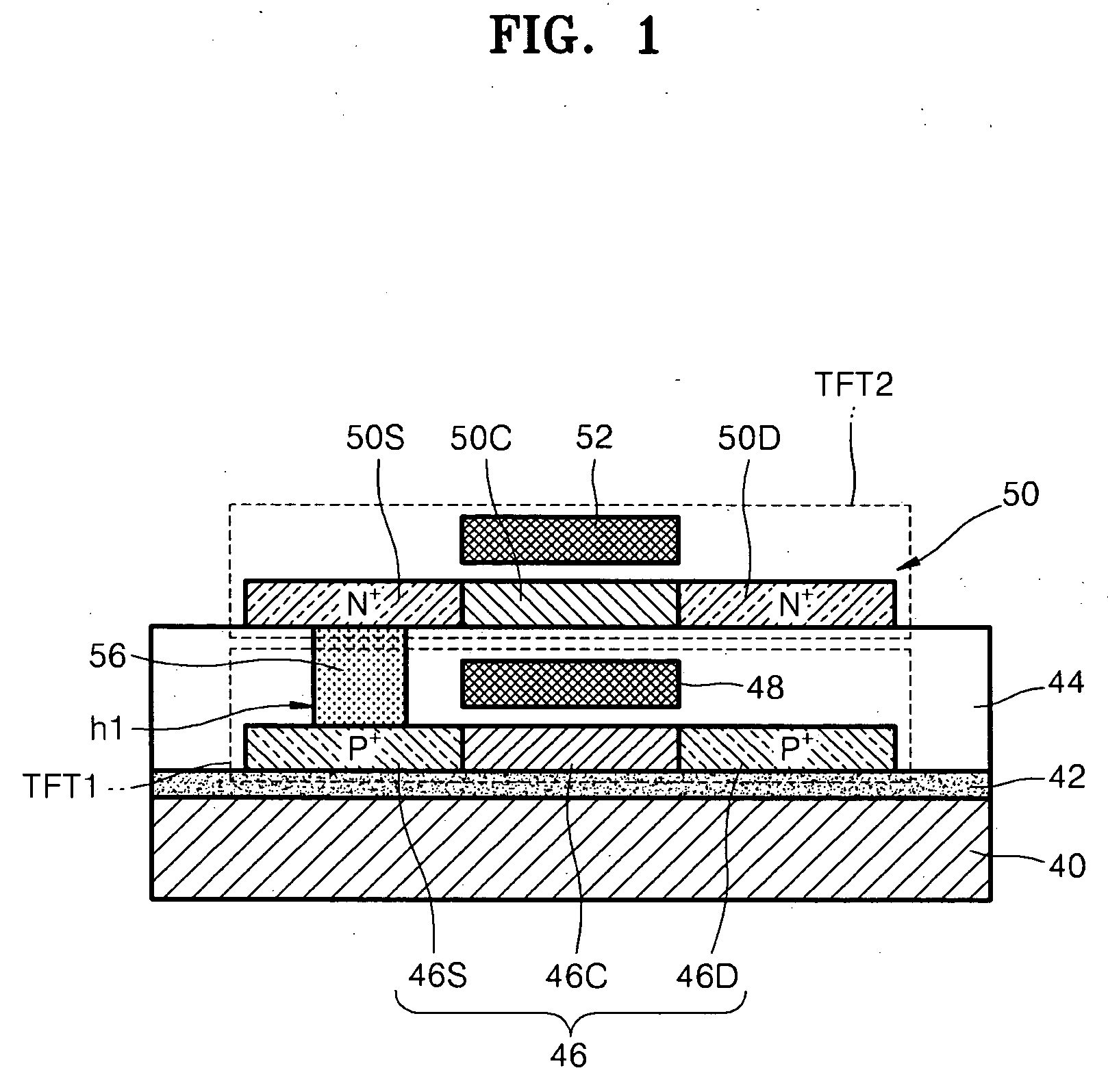
Active device and active device array substrate
InactiveUS20130240886A1Increase the on-currentEffectively improve ON-currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesEngineeringCommon gate
An active device and an active device array substrate are provided, wherein the active device array substrate includes a substrate and a plurality of active devices being located on the substrate, and at least one of the active devices includes a first thin film transistor and a second thin film transistor. The first thin film transistor is located on the substrate and has a first channel layer. The second thin film transistor stacks on the first thin film transistor, wherein the second thin film transistor has a second channel layer. The first thin film transistor and the second thin film transistor share a common gate electrode and the common gate electrode is located between the first channel layer and the second channel layer.
Owner:DONGGUAN MASSTOP LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY +1
Semiconductor device
Owner:UNISANTIS ELECTRONICS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
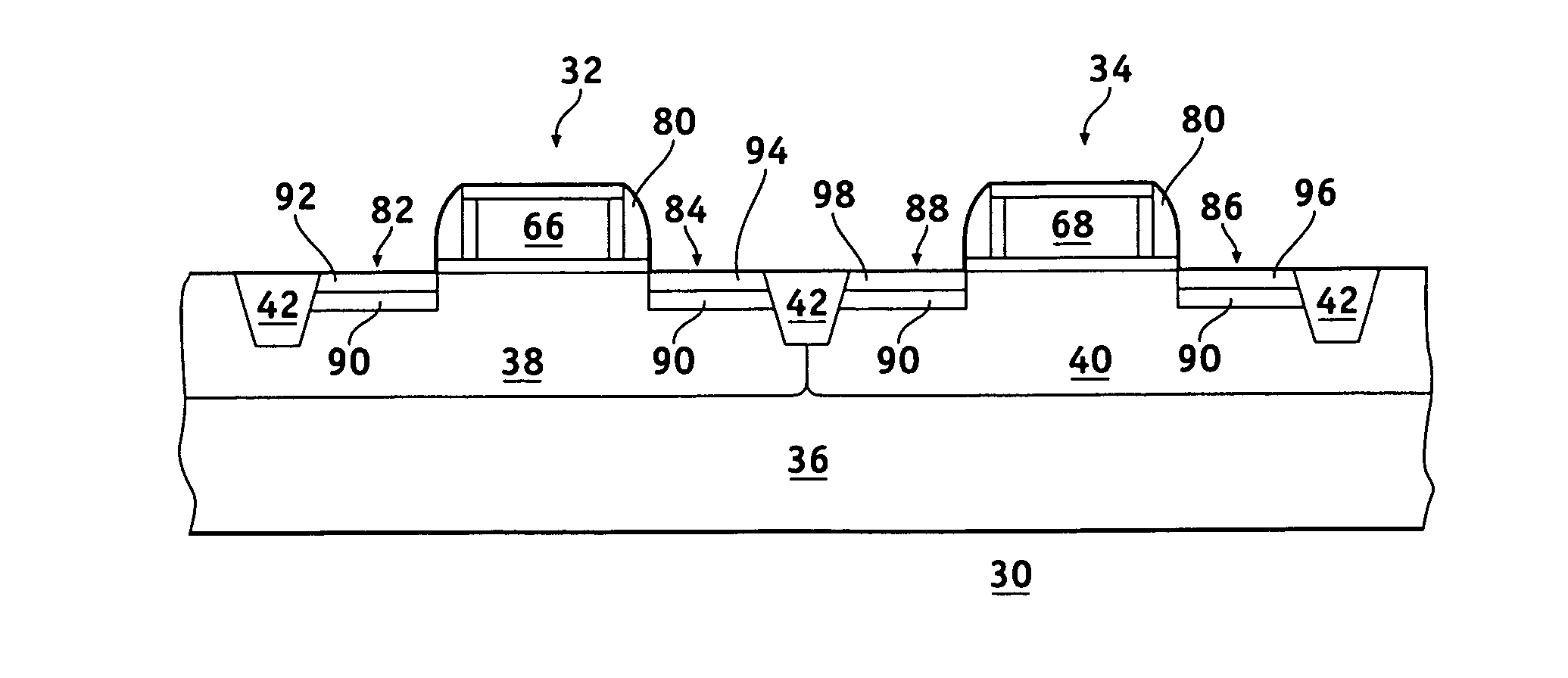
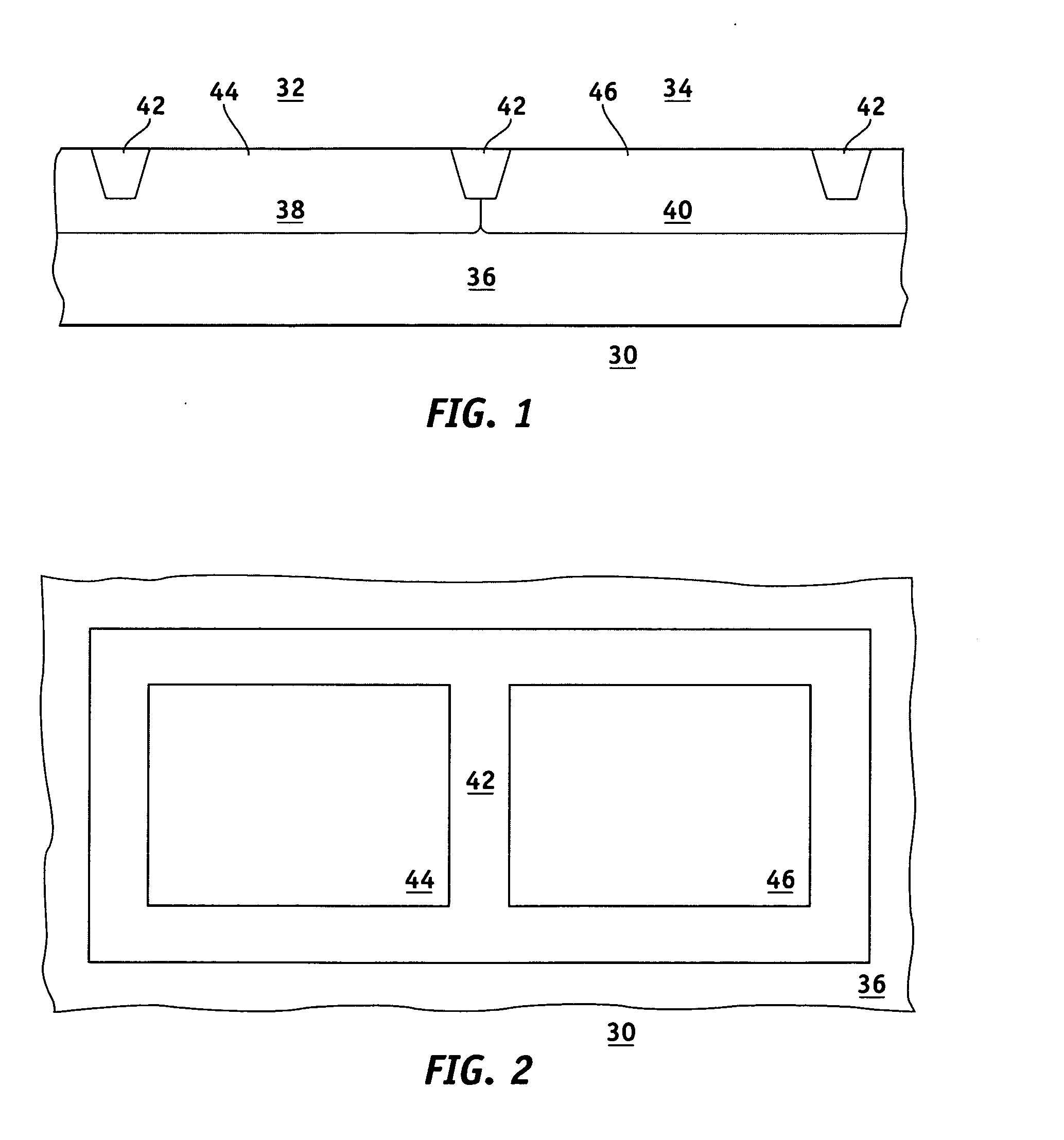
Methods for fabricating a stressed MOS device
InactiveUS20070026599A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesStress inducedSemiconductor materials
Methods are provided for fabricating a stressed MOS device. The method comprises the steps of forming a plurality of parallel MOS transistors in and on a semiconductor substrate. The parallel MOS transistors having a common source region, a common drain region, and a common gate electrode. A first trench is etched into the substrate in the common source region and a second trench is etched into the substrate in the common drain region. A stress inducing semiconductor material that has a crystal lattice mismatched with the semiconductor substrate is selectively grown in the first and second trenches. The growth of the stress inducing material creates both compressive longitudinal and tensile transverse stresses in the MOS device channel that enhance the drive current of P-channel MOS transistors. The decrease in drive current of N-channel MOS transistors caused by the compressive stress component is offset by the tensile stress component.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
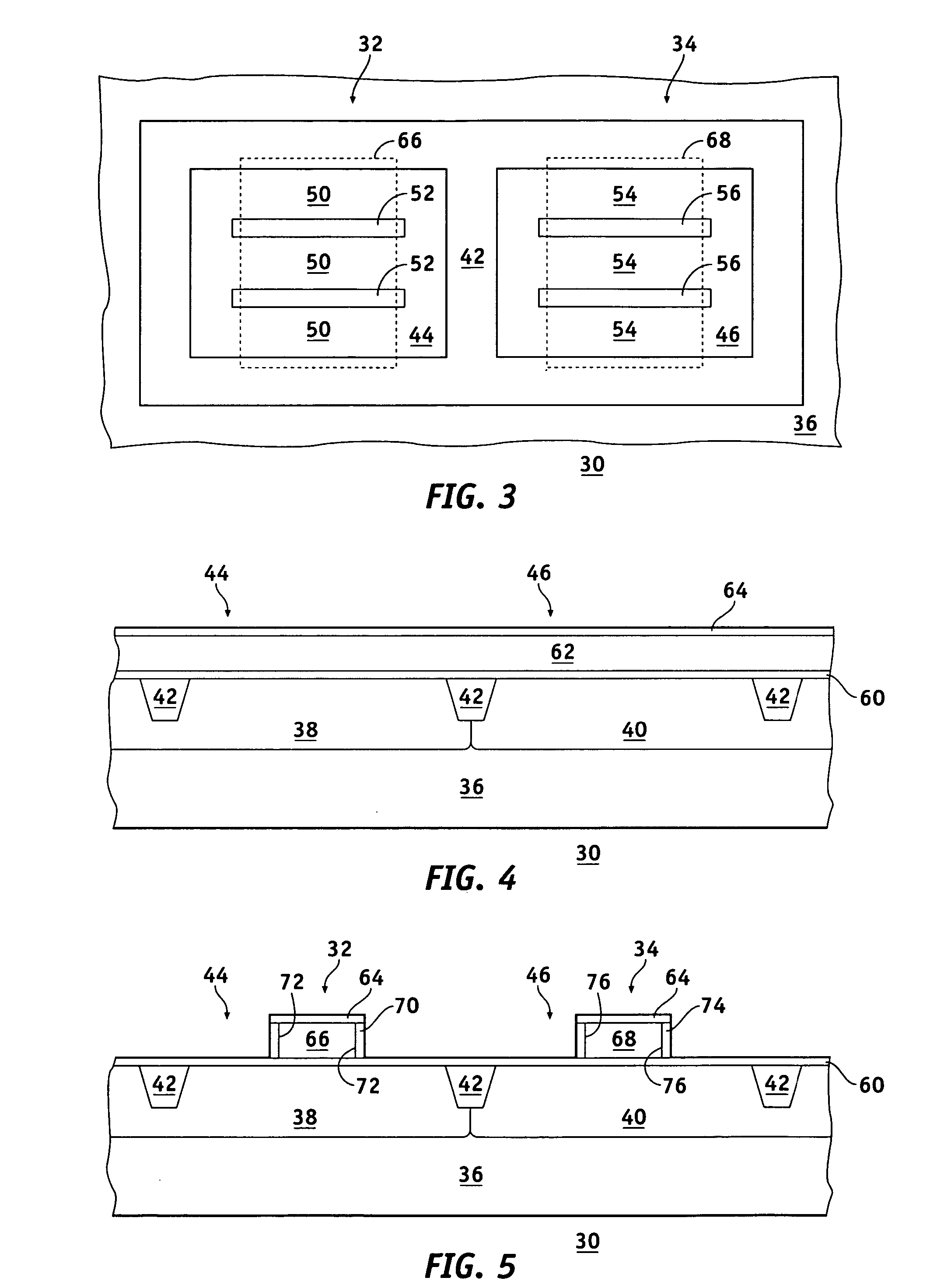
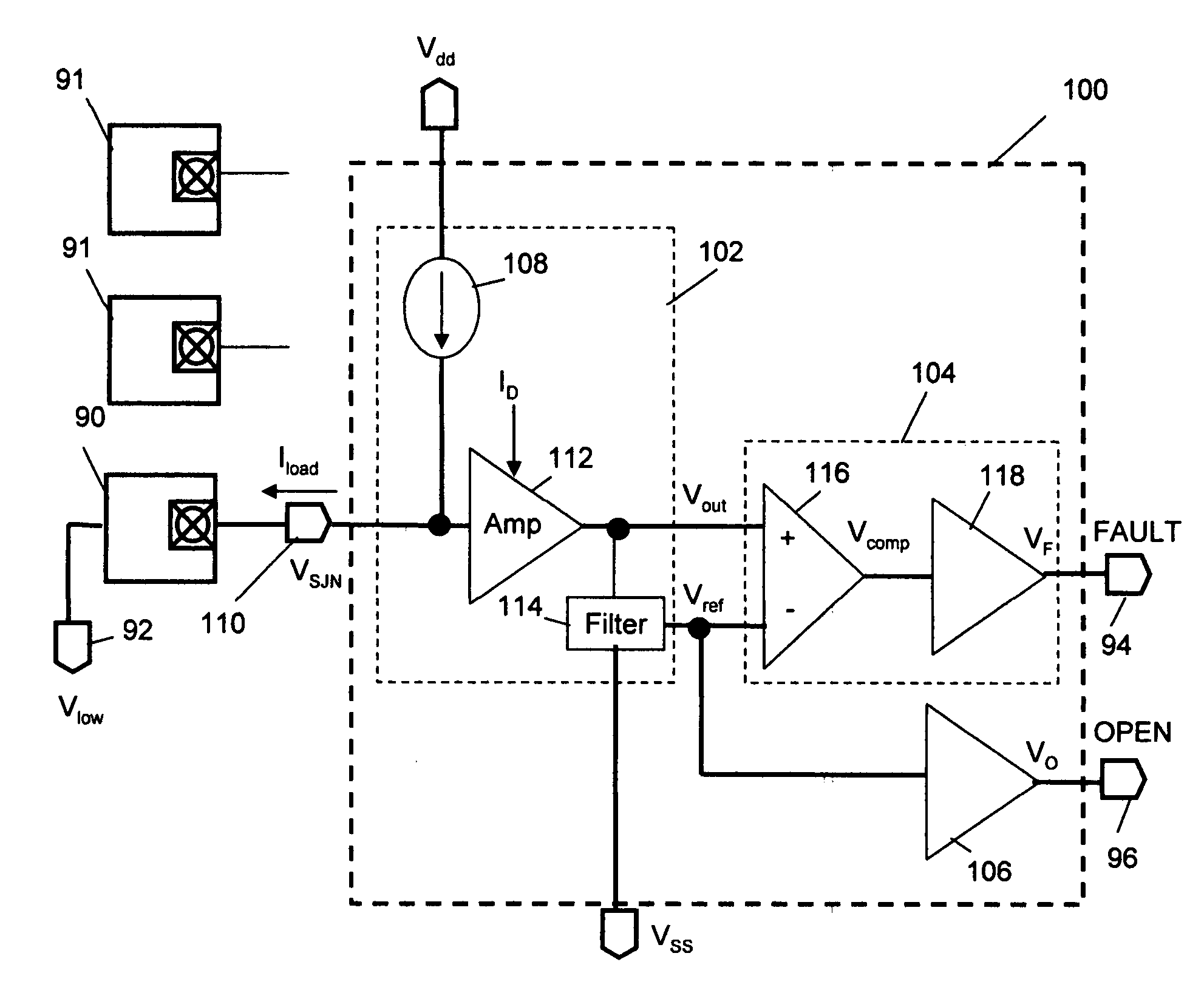
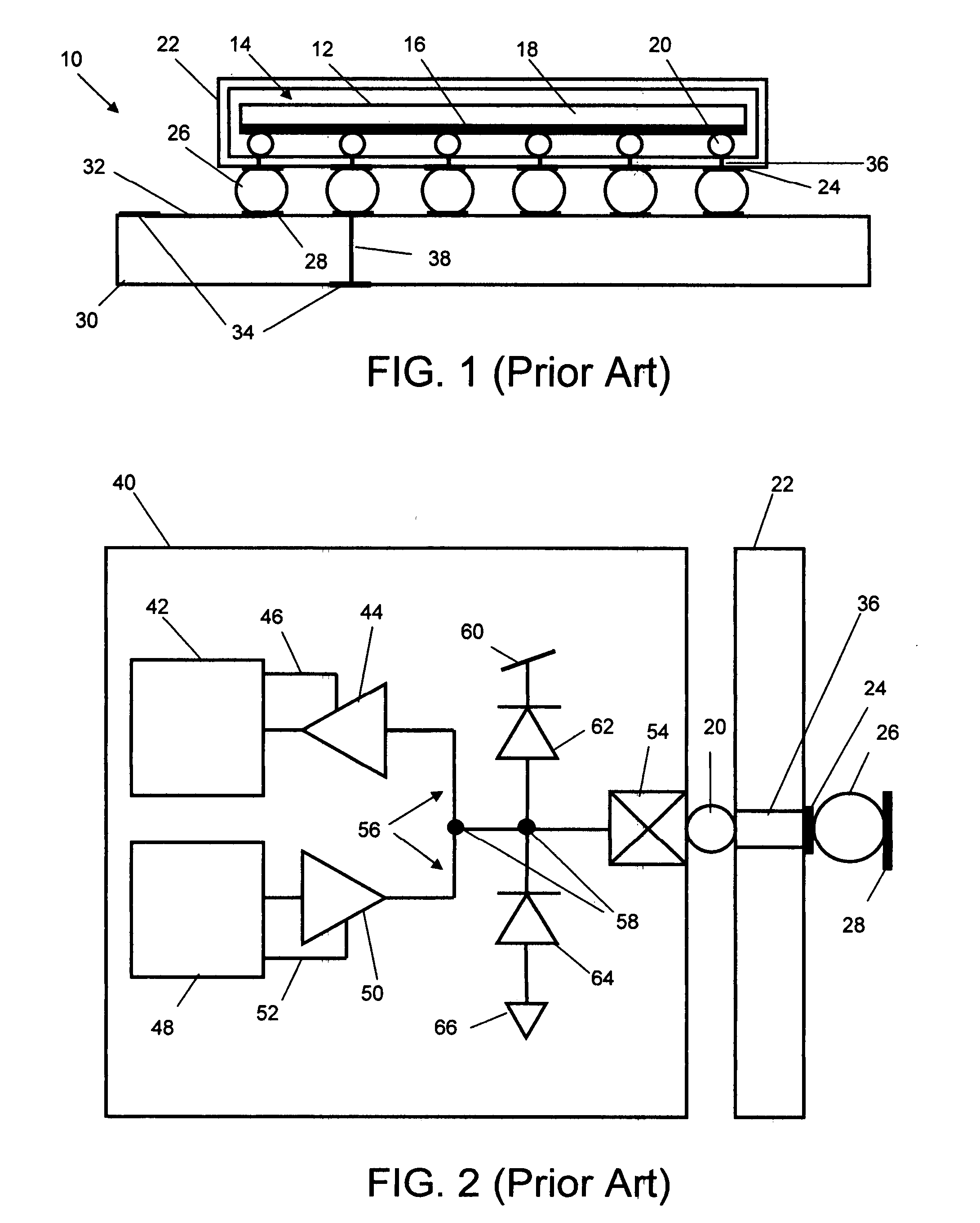
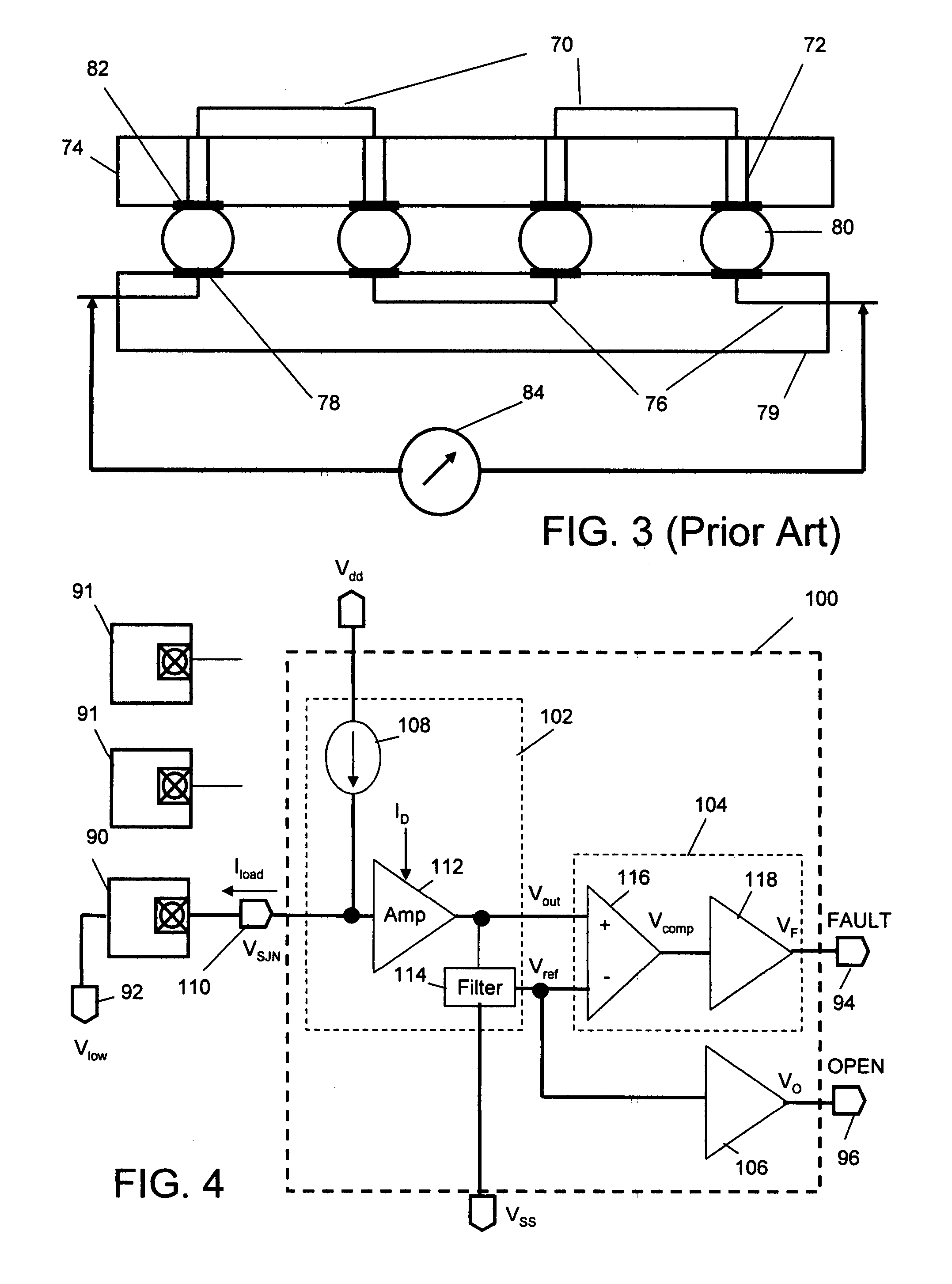
Method and circuit for low-power detection of solder-joint network failures in digital electronic packages
InactiveUS20080144243A1Reliable detectionLow powerElectric connection testingEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentLow voltageVoltage reference
A low power circuit and method for detects in-situ failures or precursors to failures in solder-joint networks on actual operational devices and packages in the field. An amplifying detector such as provided by a common-gate transistor sources current to the network to generate a signal voltage and a reference voltage that is sensitive to the low voltage applied to the other side of the network. Generation of this self-adjusting reference voltage makes the detection circuit insensitive to the network low-voltage. Additional power savings and performance gains can be provided with the addition of a differential amplifier to set a fixed bias point and a level shifter to cancel noise. The detected failure or precursor of a selected monitor solder-joint network(s) is an indicator of the integrity of other operational solder-joint networks in the package, on the PWB or between PWBs.
Owner:RIDGETOP GROUP
Radiation-hardened transistor and integrated circuit
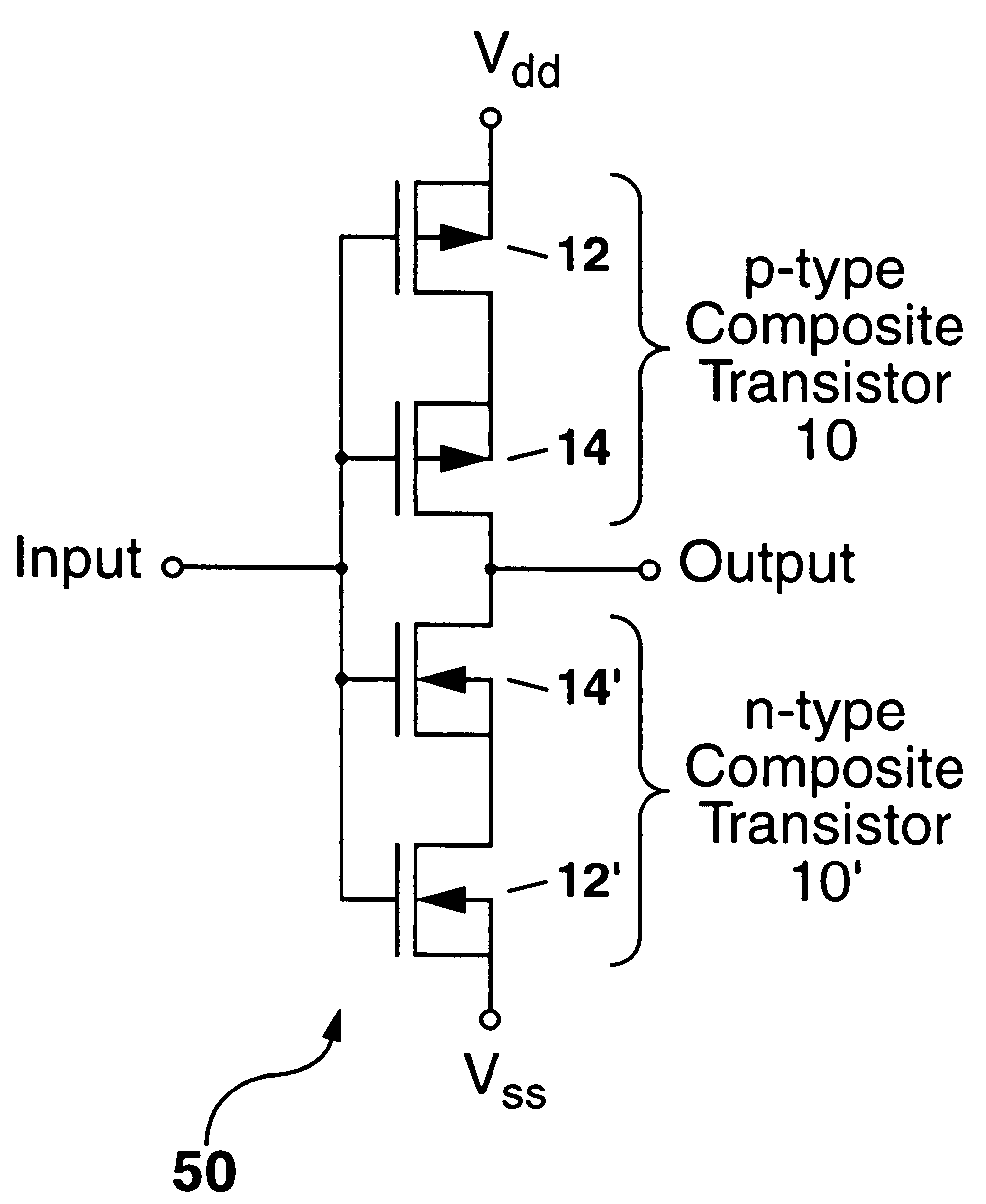
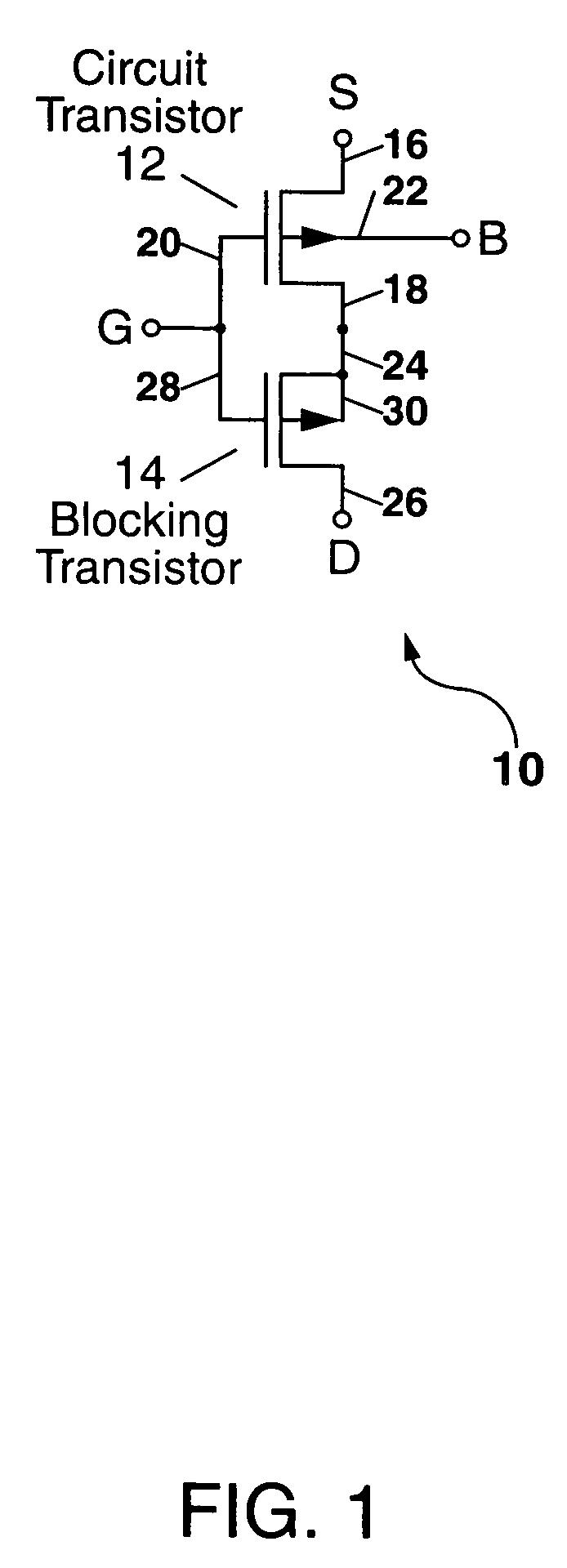
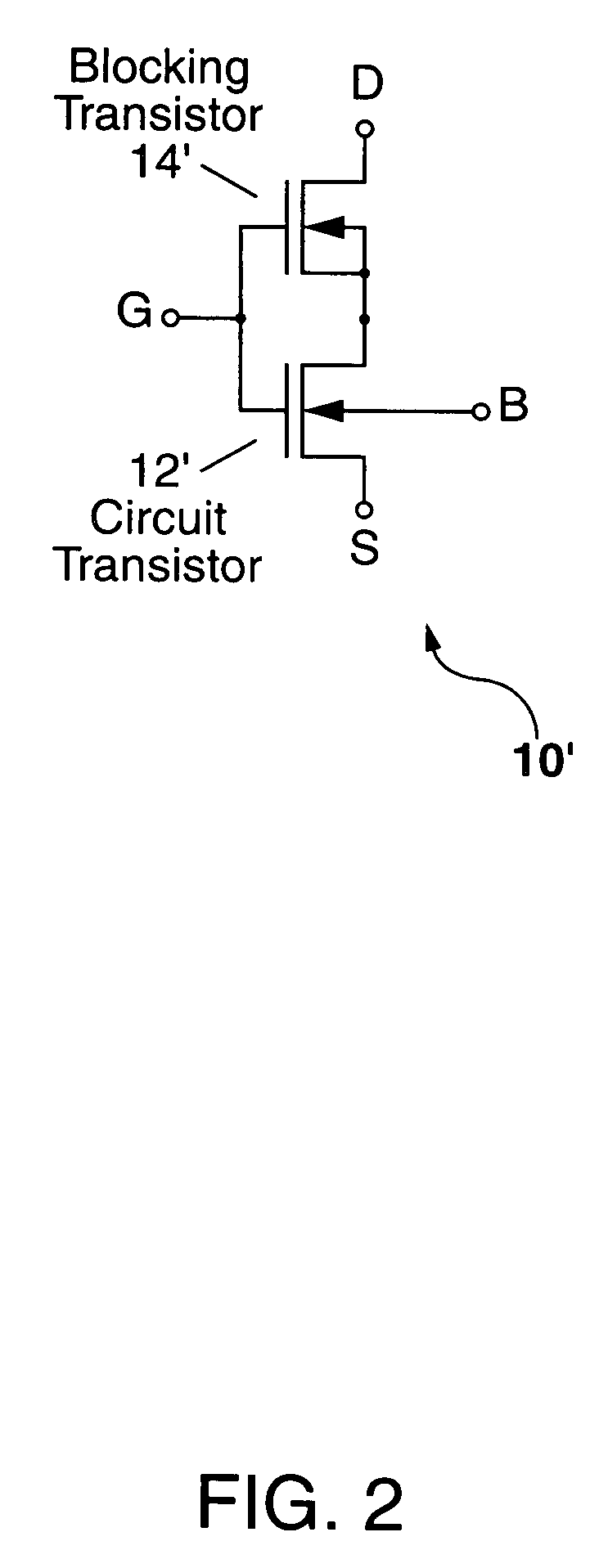
A composite transistor is disclosed for use in radiation hardening a CMOS IC formed on an SOI or bulk semiconductor substrate. The composite transistor has a circuit transistor and a blocking transistor connected in series with a common gate connection. A body terminal of the blocking transistor is connected only to a source terminal thereof, and to no other connection point. The blocking transistor acts to prevent a single-event transient (SET) occurring in the circuit transistor from being coupled outside the composite transistor. Similarly, when a SET occurs in the blocking transistor, the circuit transistor prevents the SET from being coupled outside the composite transistor. N-type and P-type composite transistors can be used for each and every transistor in the CMOS IC to radiation harden the IC, and can be used to form inverters and transmission gates which are the building blocks of CMOS ICs.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
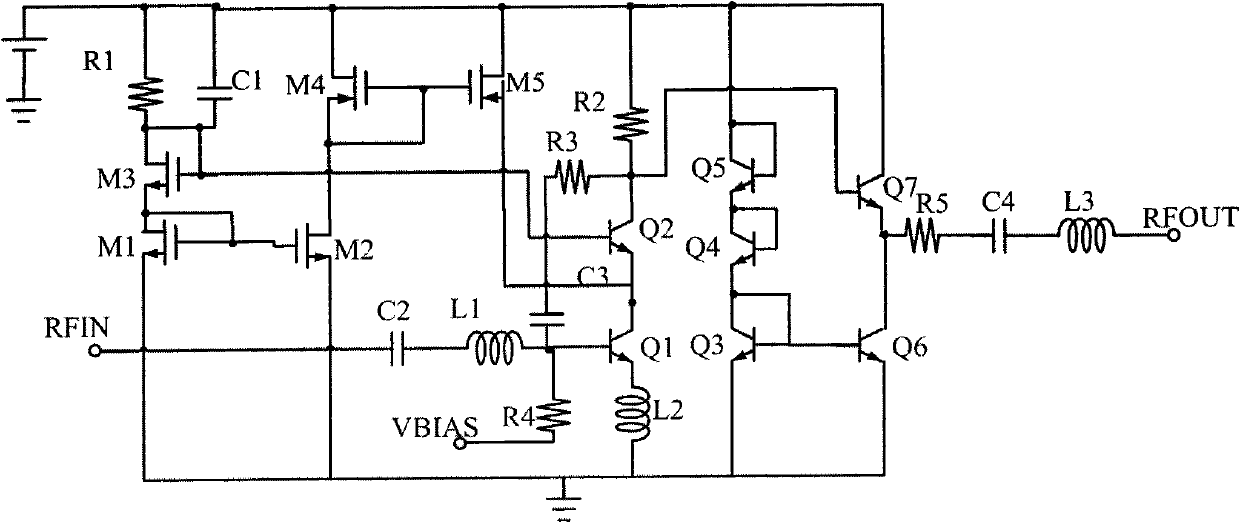
Wide band radio-frequency low noise amplifier with single-ended input and differential output
InactiveCN101777877AHigh voltage gainImprove dynamic rangeEnergy efficient ICTDifferential amplifiersMulti protocolEngineering
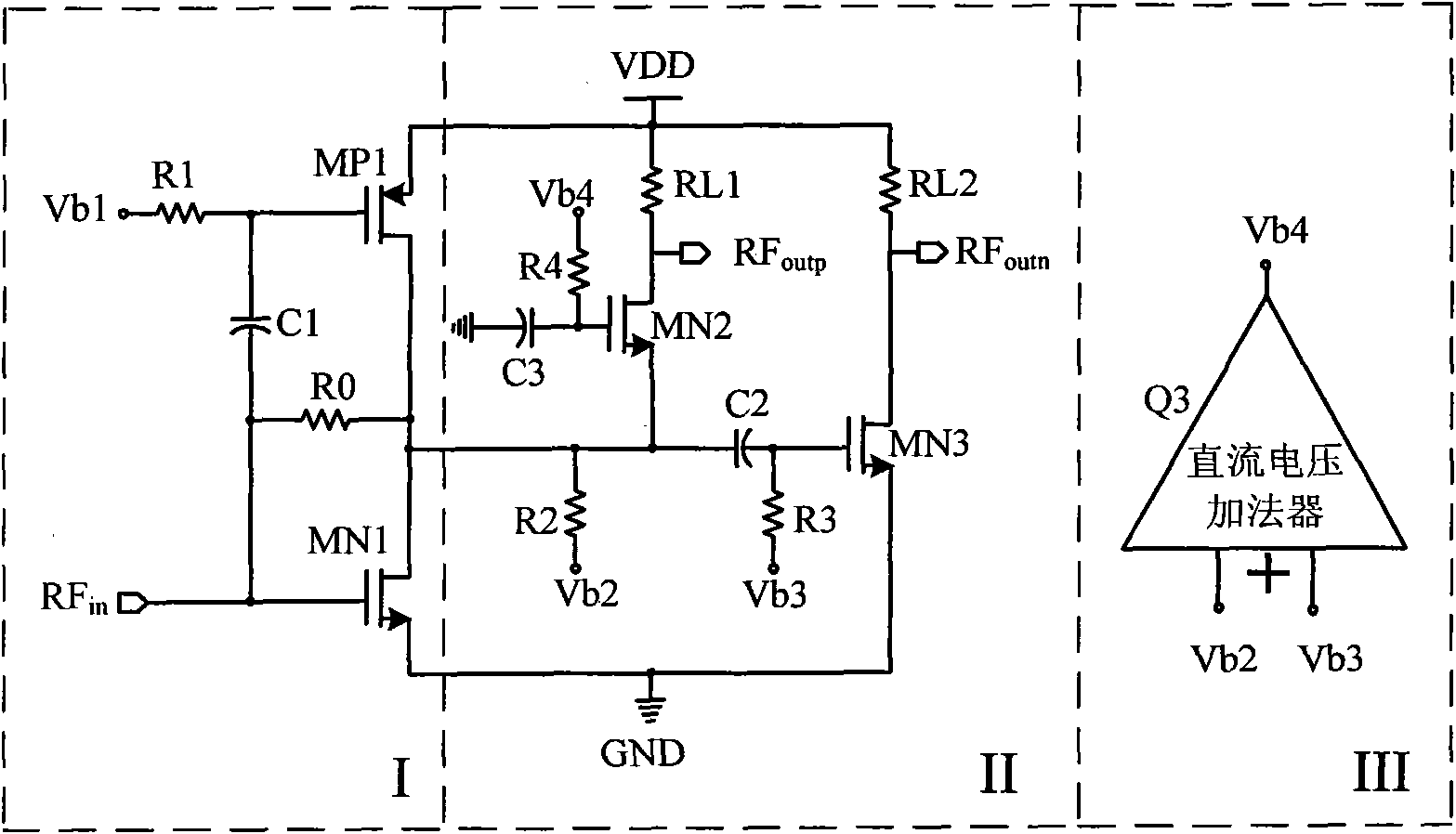
The invention relates to a wide band radio-frequency low noise amplifier with single-ended input and differential output, belonging to the technical field of radio-frequency integrated circuits. The broadband radio-frequency low noise amplifier comprises a main amplifying circuit with the single-ended input, an active balun and an offset control circuit, wherein the active balun is connected with the main amplifying circuit and is converted from being single-ended to be differential; the main amplifying circuit mainly comprises an N-shaped transistor and a P-shaped transistor; and the active balun from being single-ended to be differential comprises a common-gate amplifying circuit and a common-source amplifying circuit. The low noise amplifier has very wide working frequency range, can cover the frequency range of a digital television from 50 MHz to 860 MHz and even wider, is suitable for wide bands and multi-mode multi-protocol communication system integration, and reduces the equipment cost. The invention can reduce the power consumption and the volume of the low noise amplifier, increase the gain, optimize the noise and enhance the linearity, also has simple structure, decreases off-chip elements, eliminates extra system noise generated by an off-chip balun, has extensive application potential in a wireless communication receiving system, and the like.
Owner:南京广嘉微电子有限公司
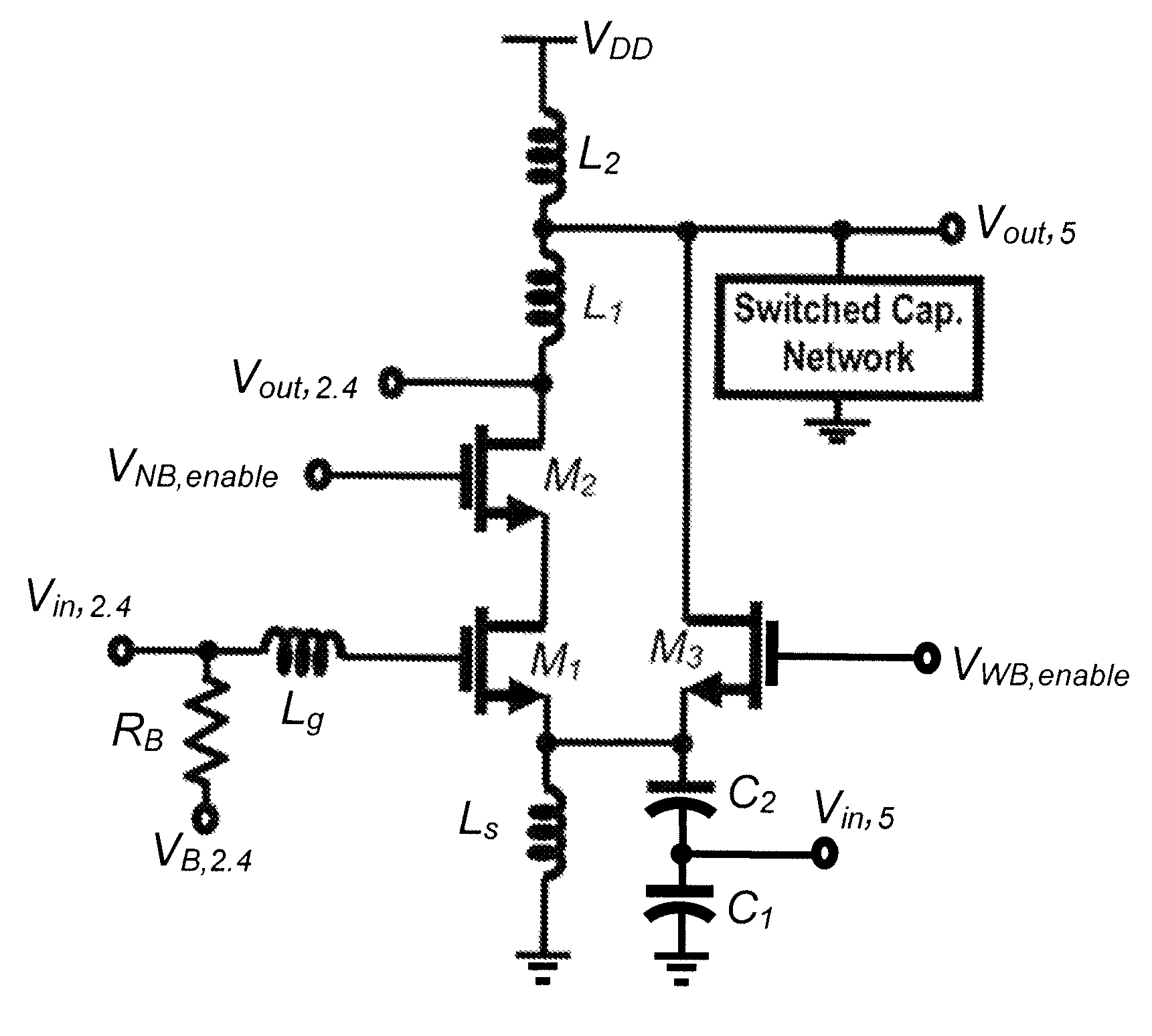
Multi-band, inductor re-use low noise amplifier
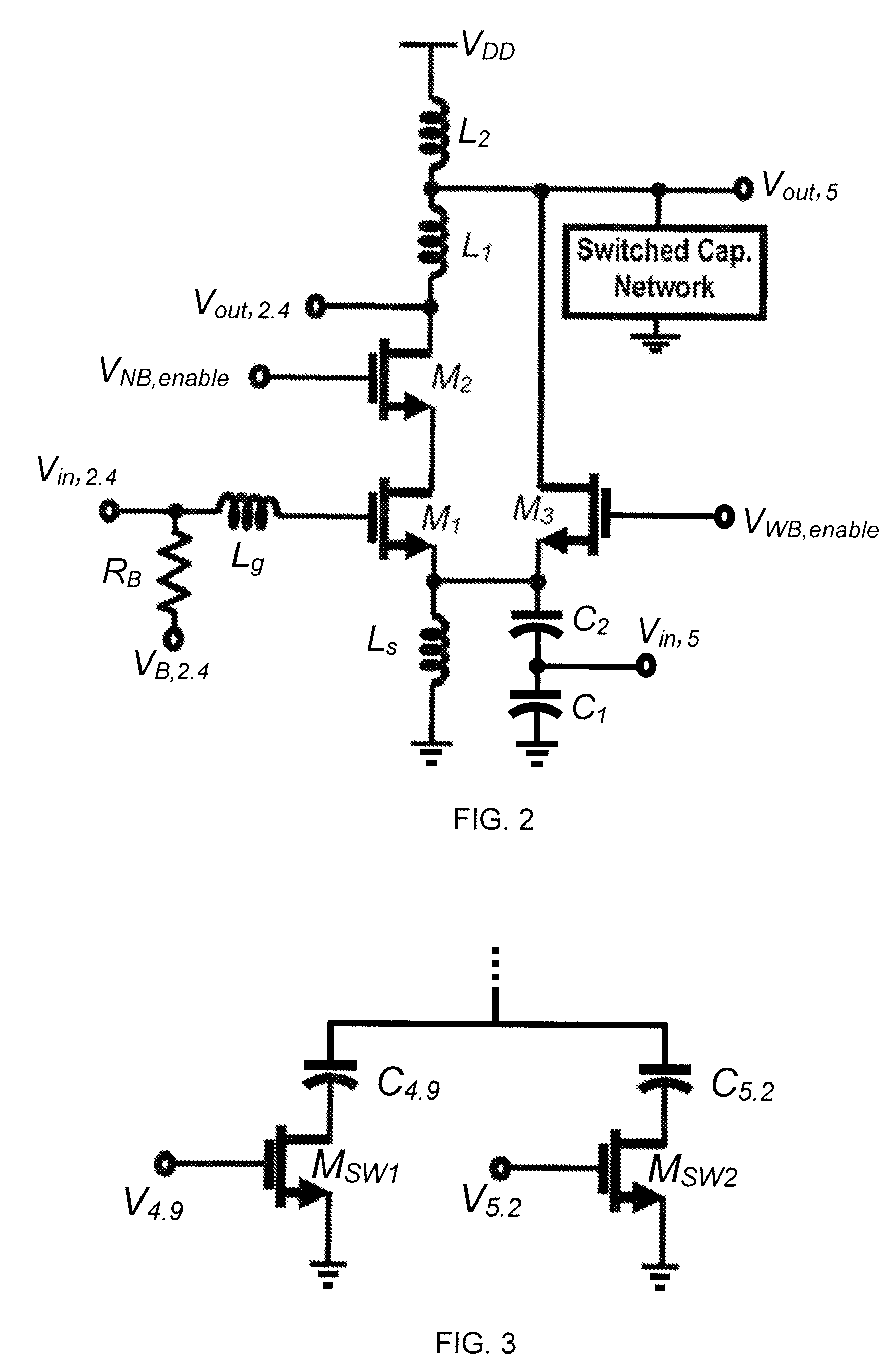
Described herein are multi-band LNAs that reuse inductors for different frequency bands to minimize chip area. In an embodiment, a multi-band LNA is capable of operating in a narrowband (NB) and a wideband (WB) while reusing at least one input impedance matching inductor and at least one load inductor for both bands. The reuse of inductors results in a more efficient use of chip area. In an exemplary embodiment, the LNA comprises a common source transistor and a common gate transistor. In this embodiment, the LNA operates in a common source configuration using the common source transistor to amplify input signals in the NB, and operates in a common gate configuration using the common gate transistor to amplify input signals in the WB. The LNA reuses an input impedance matching inductor and a load inductor in both configurations, and thus both bands.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multi-level DRAM trench store utilizing two capacitors and two plates
InactiveUS6282115B1Efficient storage densityImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesDigital dataSemiconductor materials
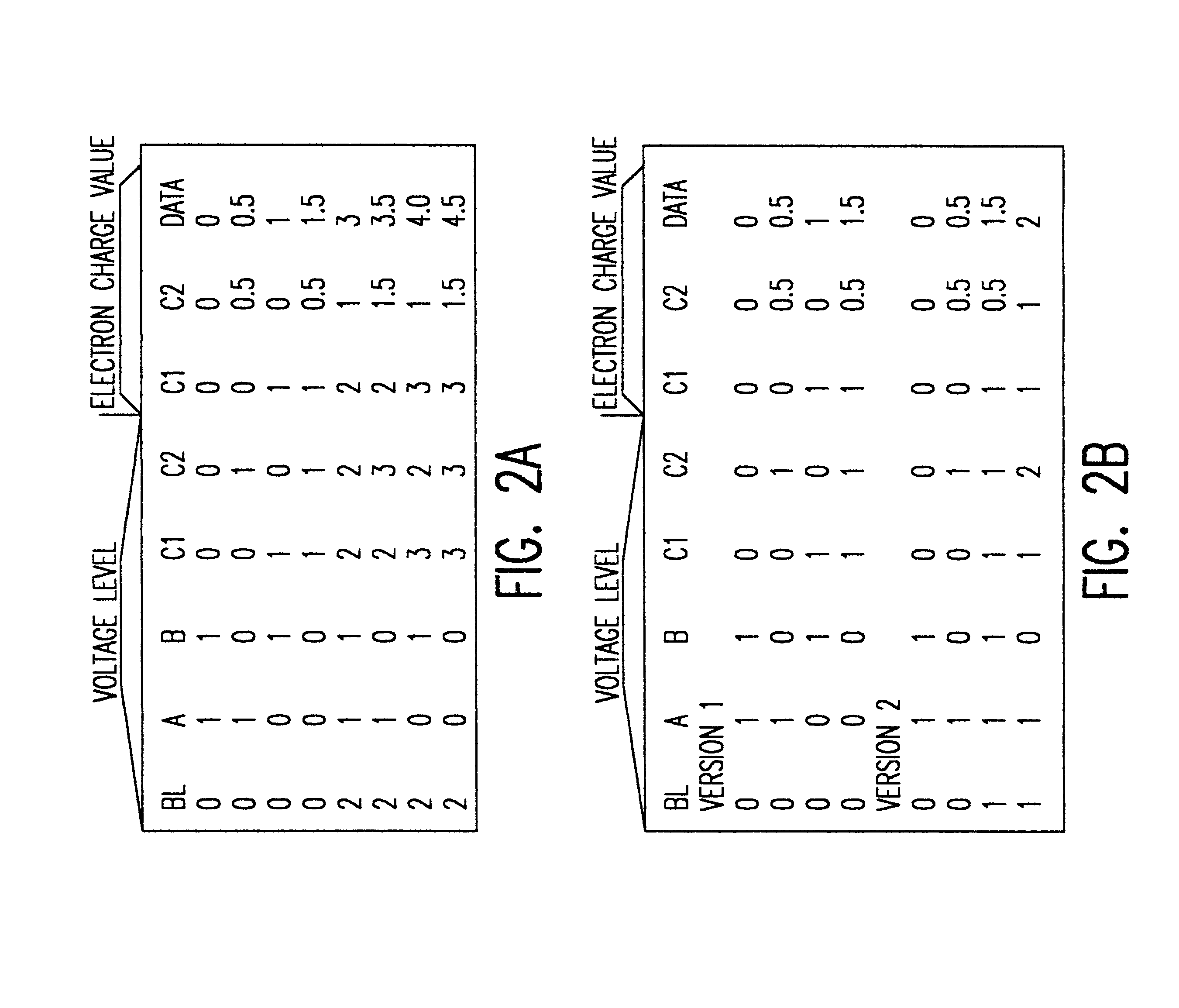
A multi-level memory cell capable of storing two or three bits of digital data occupies only four lithographic squares and requires only one or two logic level voltage sources, respectively. High noise immunity derives from integration of the multi-level signal in the memory cell directly from logic level digital signals applied to two capacitors (as well as the bit line for the eight level mode of operation) by using capacitors having different values in order to avoid digital-to-analog conversion during writing. The capacitors can be simultaneously written and read to reduce memory cycle time. Transistor channels and capacitor connections are formed on adjacent semiconductor pillars using plugs of semiconductor material between pillars as common gate structures and connections. Opposite surfaces of the pillars also serve as storage nodes with common capacitor plates formed by conformal deposition between rows of plugs and pillars.
Owner:IBM CORP
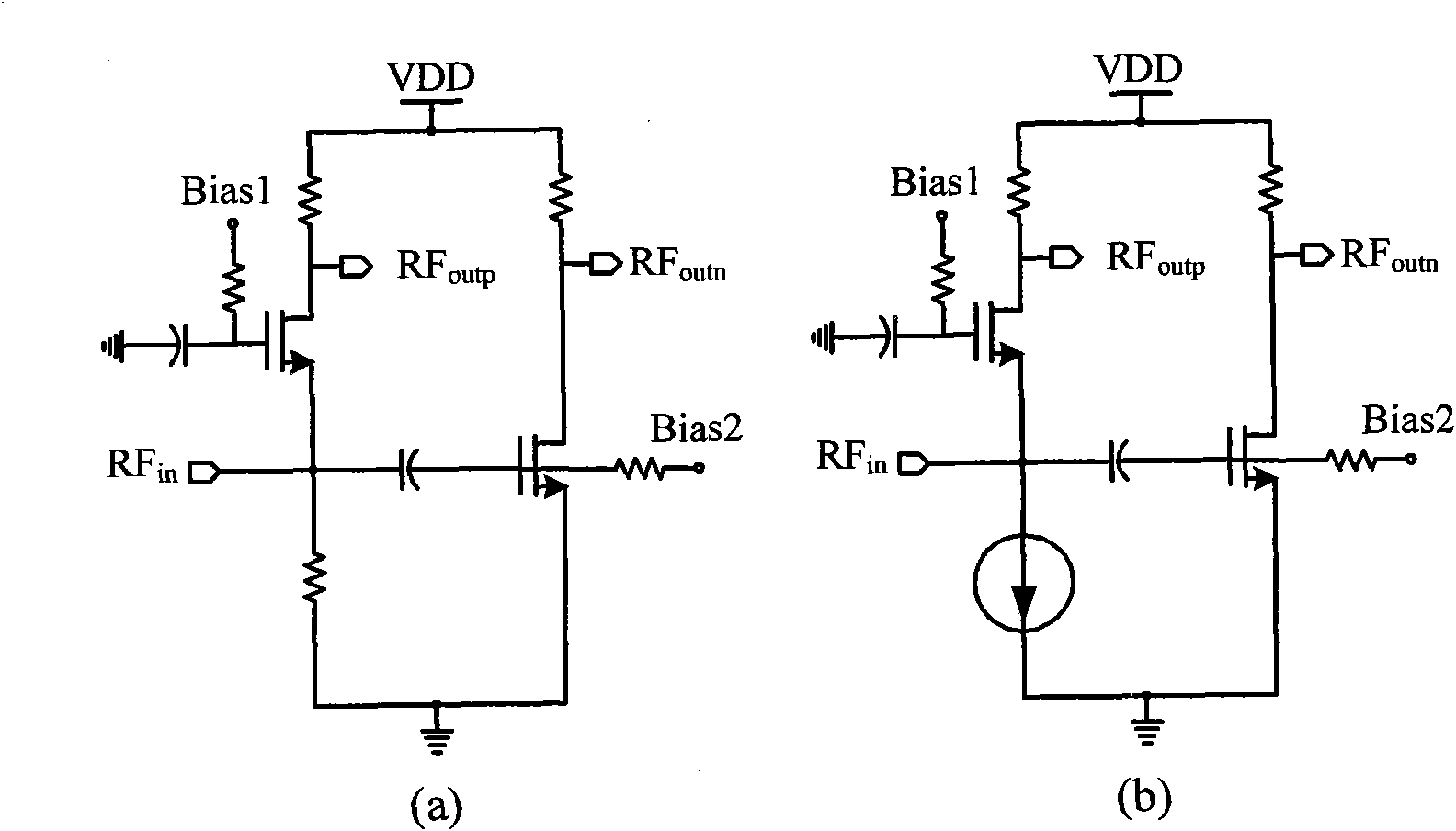
Low power low noise amplifier
InactiveUS20020084855A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlAudio power amplifierEngineering
The present invention relates to a low power low noise amplifier, more particularly to the low power low noise amplifier composed with low power by sharing the bias current. The present invention is composed of cascode structure which consists of common source transistor and common gate transistor connecting with common source transistor, inverter type structure connecting with common source transistor and structure improving the third-order intermodulation component using the parallel connected common source transistor and common gate transistor. The present invention provides a low noise amplifier gives high power gain without increasing power consumption by sharing the bias current.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
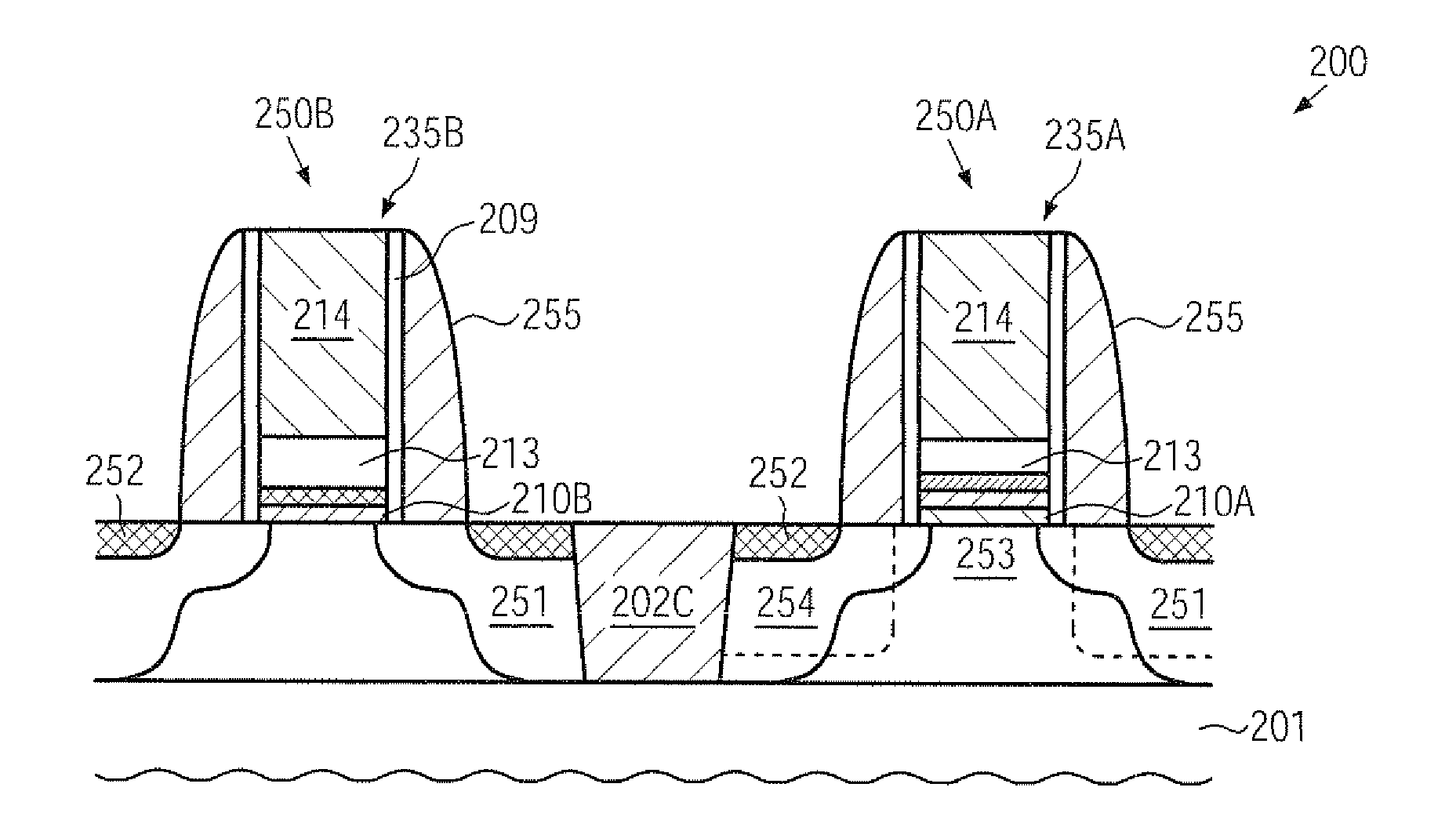
Semiconductor device having increased gate length implemented by surround gate transistor arrangements
In a vertical transistor comprising a pillar-shaped semiconductor layer and a gate electrode formed around the pillar-shaped semiconductor layer, it is difficult to form a transistor having a gate length greater than that of the vertical transistor. The present invention provides a semiconductor device which comprises two vertical transistors comprising first and second pillar-shaped semiconductor layers each formed on a first diffusion layer on a substrate. The vertical transistors have a common gate electrode. A first upper diffusion layer formed on a top of the first pillar-shaped semiconductor layer is connected to a source electrode, and a second upper diffusion layer formed on a top of the second pillar-shaped semiconductor layer is connected to a drain electrode. The vertical transistors are connected in series to operate as a composite transistor having a gate length two times greater than that of each of the vertical transistors.
Owner:UNISANTIS ELECTRONICS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Uniform high-k metal gate stacks by adjusting threshold voltage for sophisticated transistors by diffusing a metal species prior to gate patterning
ActiveUS20100327373A1Reduce complexityDesired degree of flexibility in obtaining the desired work functionsTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricWork function
Sophisticated gate electrode structures for N-channel transistors and P-channel transistors are patterned on the basis of substantially the same configuration while, nevertheless, the work function adjustment may be accomplished in an early manufacturing stage. For this purpose, diffusion layer and cap layer materials are removed after incorporating the desired work function metal species into the high-k dielectric material and subsequently a common gate layer stack is deposited and subsequently patterned.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
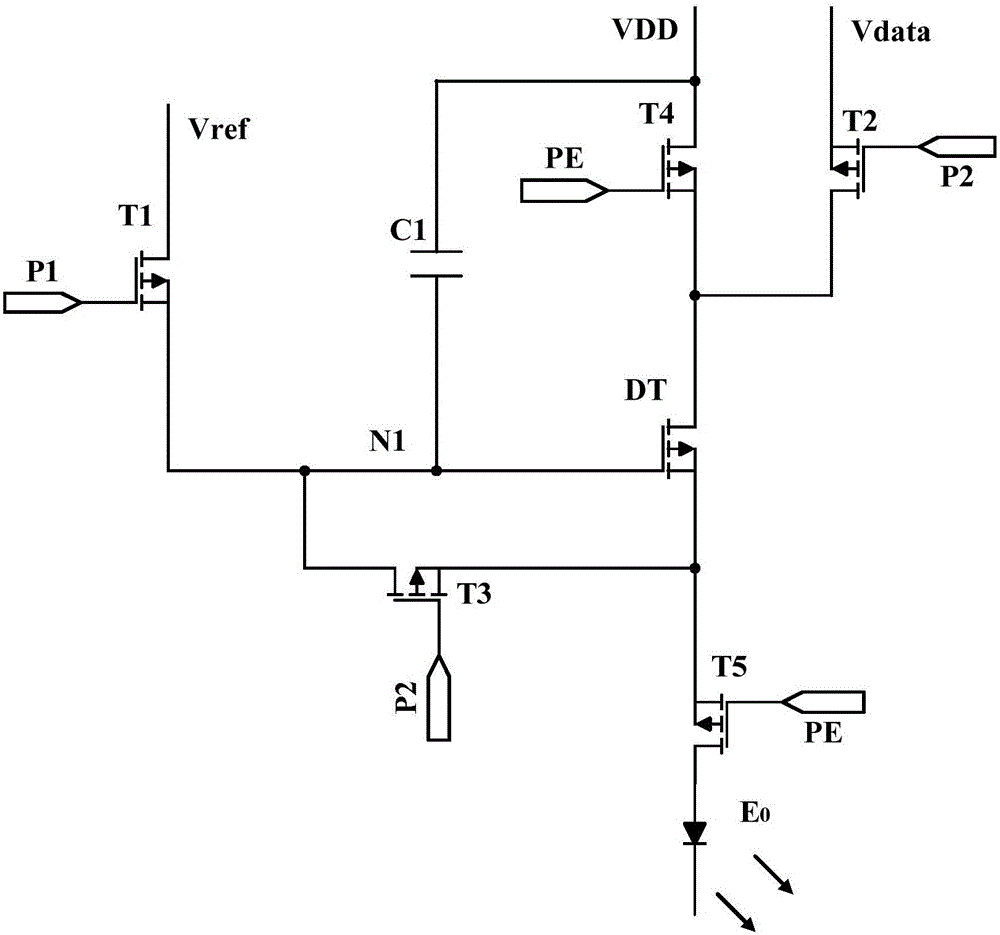
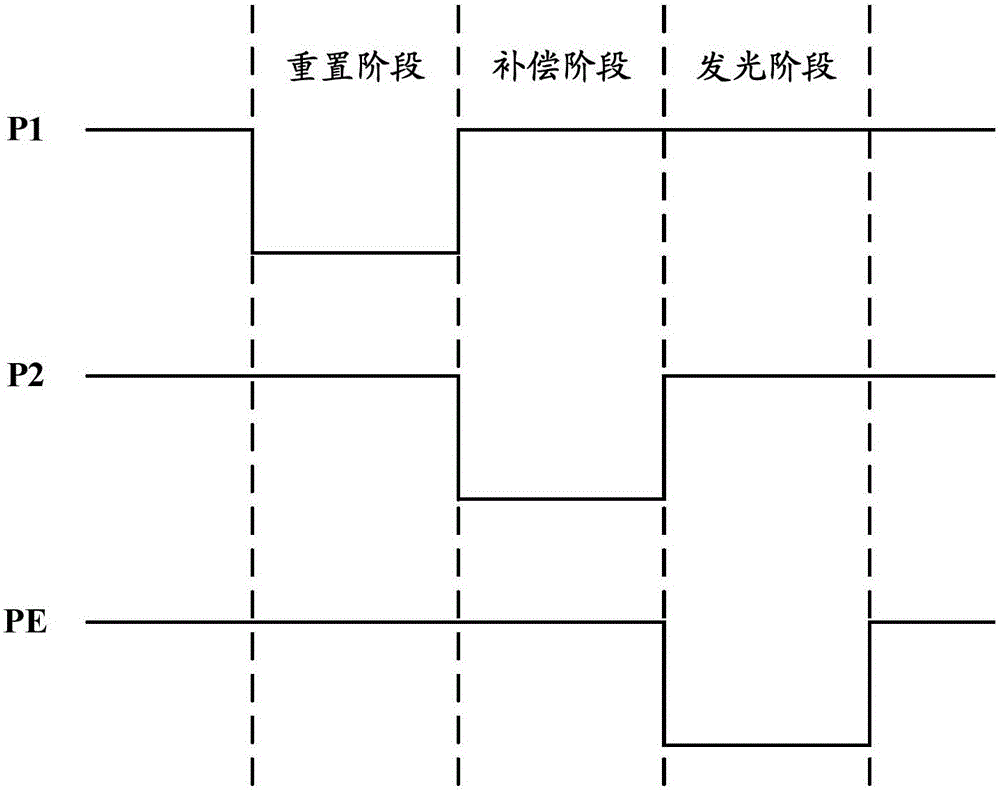
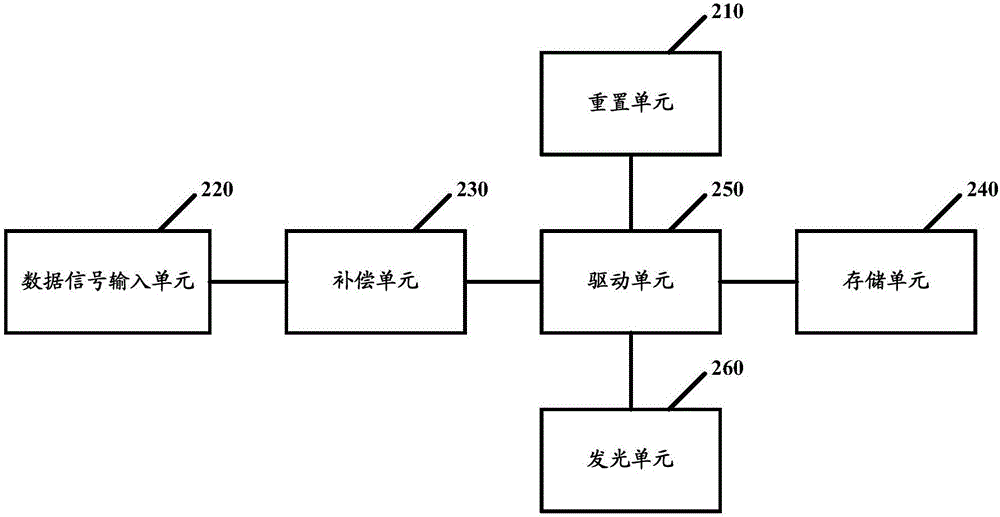
Organic light-emitting pixel driving circuit and driving method thereof
ActiveCN105702210AFast chargingImprove the problem of poor uniformity of light emissionStatic indicating devicesDriver circuitPower flow
The application discloses an organic light-emitting pixel driving circuit and a driving method thereof. The organic light-emitting pixel driving circuit comprises a reset unit, a data signal input unit, a compensation unit, a storage unit, a driving unit and a light-emitting unit. The driving unit generates light emission current based on a data signal and provides light emission current to the light-emitting unit. The driving unit comprises a first driving transistor and a second driving transistor which are connected in series and have a common gate electrode. The first driving transistor is used for storing the data signal to the storage unit in the compensation phase. The first driving transistor and the second driving transistor are used for providing light emission current to a light-emitting diode in the light emission phase. According to the scheme, current of the compensation phase is relatively high so that the data signal is enabled to be rapidly stored to the storage unit.
Owner:SHANGHAI TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Low power low noise amplifier
InactiveUS6556085B2Improve linearityIncrease power gainAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlAudio power amplifierEngineering
A low power low noise amplifier achieves a high power gain without increasing power consumption by sharing the bias current. The amplifier is composed of a cascade structure which consists of a parallel connected common source transistor and common gate transistor connected to a common source transistor, an inverter type structure connected to the common source transistor, and structure improving the third-order intermodulation component using the parallel connected common source transistor and common gate transistor.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Broadband low noise amplifier
InactiveCN101951230AHigh gainImproved Gain FlatnessAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceLow noisePower flow
The invention discloses a broadband low noise amplifier which comprises a primary common source and common gate amplifying circuit, a secondary common source amplifying circuit, an input and output matching circuit for providing a high gain for the circuit, a current extraction circuit for reducing the noise factor of the circuit, an MOS tube current source bias circuit, an HBT bias circuit and a bias network filter circuit for further reducing the noise factor of the circuit, wherein the common source and common gate circuit provides the high gain and simultaneously increases the reverse isolation degree of the circuit, and the common source amplifying circuit further improves the gain of the circuit; the MOS bias circuit and the HBT bias circuit provide stable low noise bias for a common gate tube and a common source tube; and the bias filter circuit filters radio-frequency signals on the bias to stabilize the bias, thereby reducing the noise factor to the minimum. The invention can be widely applied to modern wireless communication standards such as GSM850, GSM900, DCS1800, PCS1900, WCDMA and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
Semiconductor device including single crystal silicon layer and method of manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20060267100A1Great tensile stressImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialSingle crystal
A semiconductor device including a substrate, a P-MOS single crystal TFT formed on the substrate, and an N-MOS single crystal TFT formed on the P-MOS single crystal TFT. The source region of the P-MOS single crystal TFT and the source region of the N-MOS single crystal TFT may be connected to each other. The P-MOS single crystal TFT and the N-MOS single crystal TFT may share a common gate. Also, the P-MOS single crystal TFT may include a single crystal silicon layer with a crystal plane of (100) and a crystal direction of <100>. The N-MOS single crystal TFT may include a single crystal silicon layer having the same crystal direction as the single crystal silicon layer of the P-MOS single crystal TFT and having a tensile stress greater than the single crystal silicon layer of the P-MOS single crystal TFT.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Receiver with colpitts differential oscillator, colpitts quadrature oscillator, and common-gate low noise amplifier
InactiveUS7414481B2Amplifier combinationsAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceCapacitanceSignal on
Embodiments of the present invention include a common-gate amplifier having an input terminal and an output terminal, a transistor having a source, a drain, and a gate, four inductors, and two capacitors, and a negative amplification circuitry. The negative amplification circuitry has an input terminal to receive an RF signal. The negative amplification circuitry applies negative or zero amplification to the RF signal and outputs the negative or zero amplified signal on an output terminal. Alternative embodiments include a Colpitts differential oscillator, which includes two Colpitts single-ended oscillators. Each Colpitts single-ended oscillator includes a transistor. The source of the transistor in one Colpitts single-ended oscillator may be capacitively coupled to the gate of the transistor in the other Colpitts single-ended oscillator.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Liquid crystal display and method for driving same
ActiveUS20060197882A1Increase ratingsExtension of timeStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
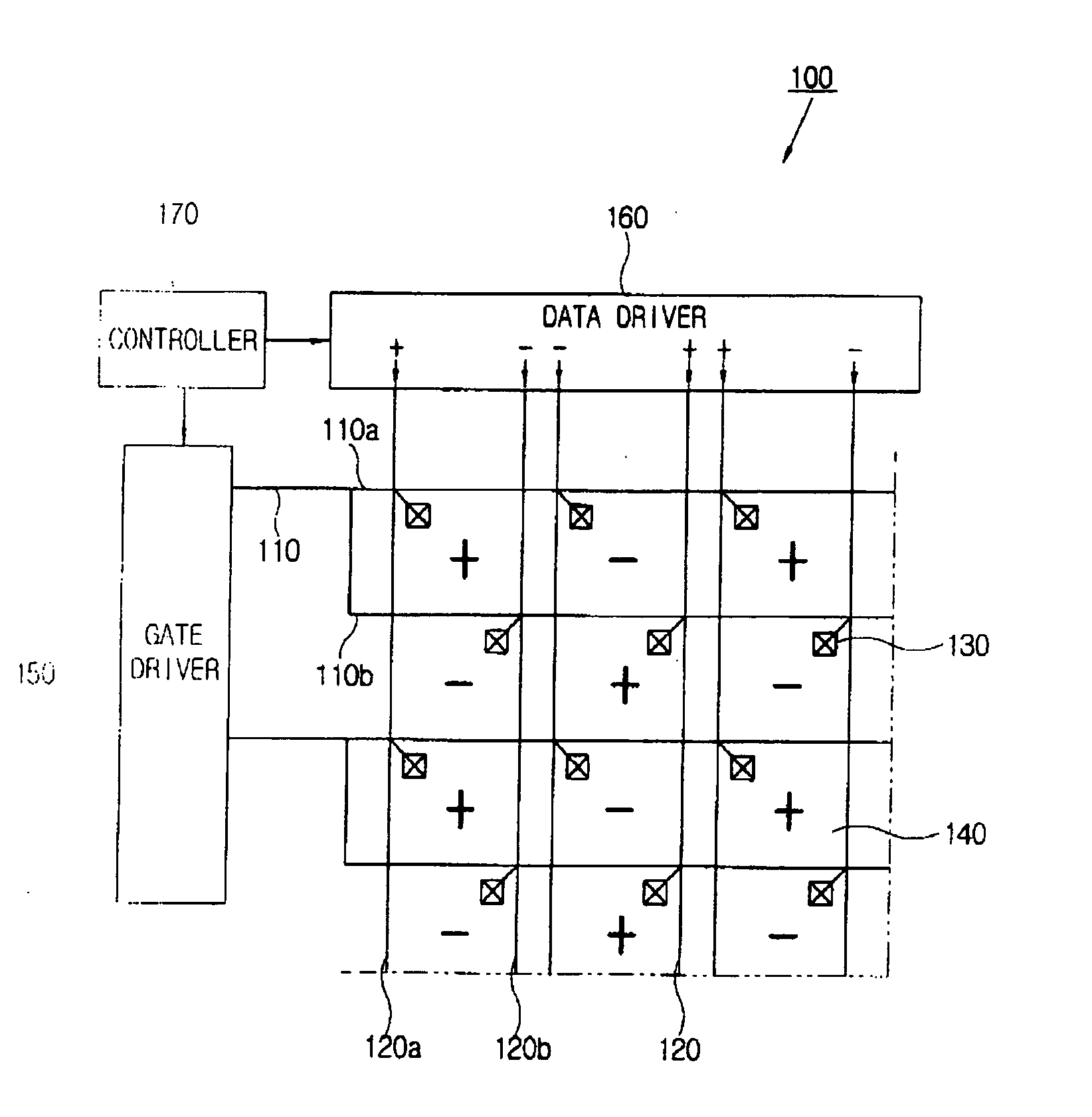
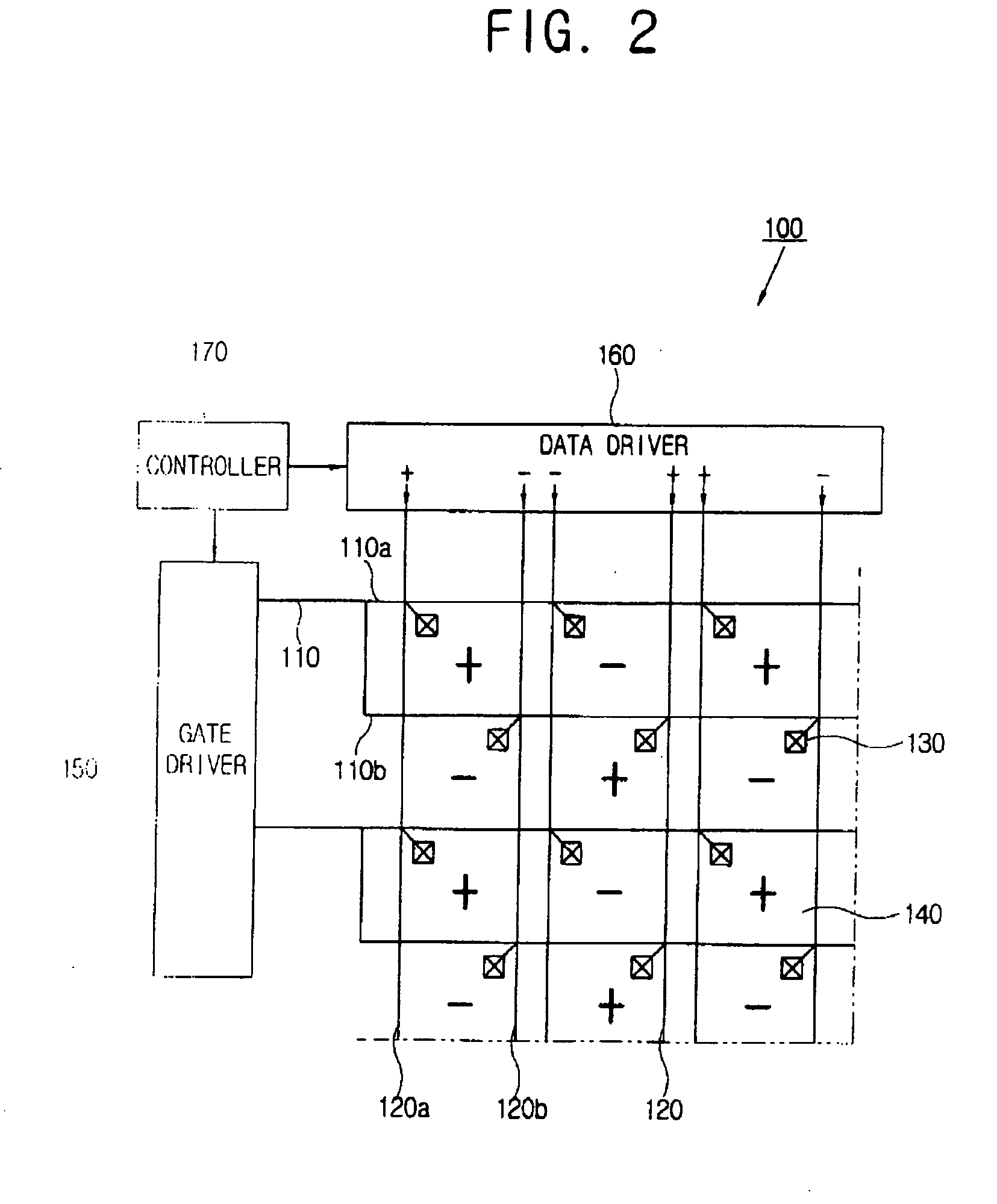
Disclosed is an LCD comprising a plurality of data lines extending in a first direction, a plurality of gate lines extending in a second direction defining with the plurality of data lines a plurality of pixel areas arranged in a matrix configuration and supplying a gate signal to at least two rows of the pixel areas simultaneously. Thin film transistors are connected to the plurality of gate lines and the plurality of data lines. Also disclosed is a driving method for an LCD including a thin film transistor substrate including pixel areas arranged in a matrix form with a gate line extending in a first direction and a data line extending in a second direction, along with a backlight providing the TFT substrate with light of three primary colors. In the method, the three primary colors are sequentially provided in one frame period and at least two rows of pixel areas and simultaneously provided with a common gate signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Integration of a sense fet into a discrete power mosfet
ActiveUS20090250770A1Not affect accuracy of designedAffect the accuracy of designed sense ratioTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringPower MOSFET
A semiconductor device includes a main field effect transistor (FET) and one or more sense FETs, and a common gate pad. The main FET and the one or more sense FETs are formed in a common substrate. The main FET and each of the sense FETs include a source terminal, a gate terminal and a drain terminal. The common gate pad connects the gate terminals of the main FET and the one or more sense FETs. An electrical isolation is disposed between the gate terminals of the main FET and the one or more sense FETs. Embodiments of this invention may be applied to both N-channel and P-channel MOSFET devices.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
Integrated circuit having a low power, gain-enhanced, low noise amplifying circuit
An amplifying circuit includes an n-type transistor having a source, a gate coupled to a first bias voltage, and a drain coupled to a first supply voltage through a first impedance circuit. A p-type transistor of the circuit has a source coupled to the source of the n-type transistor, a gate coupled to a second bias voltage, and a drain coupled to a second supply voltage through a second impedance circuit. A first differential input is coupled to the gate of the n-type transistor through a first capacitor and to the gate of the p-type transistor through a second capacitor. A second differential input is coupled to the sources of the n-type and the p-type transistors. A third capacitor has a first end coupled to the drain of the n-type transistor, and a fourth capacitor has a first end coupled to the drain of the p-type transistor and a second end coupled to a second end of the third capacitor. An output of the amplifier circuit is provided at the second ends of the third and the fourth capacitors. The n-type transistor and the first impedance circuit serve as a common-source amplifier for a signal at the first differential input and as a common-gate amplifier for the signal at the second differential input. Similarly, the p-type transistor and the second impedance circuit serve as a common-source amplifier for the signal at the first differential input and as a common-gate amplifier for the signal at the second differential input.
Owner:CHIPCON +1
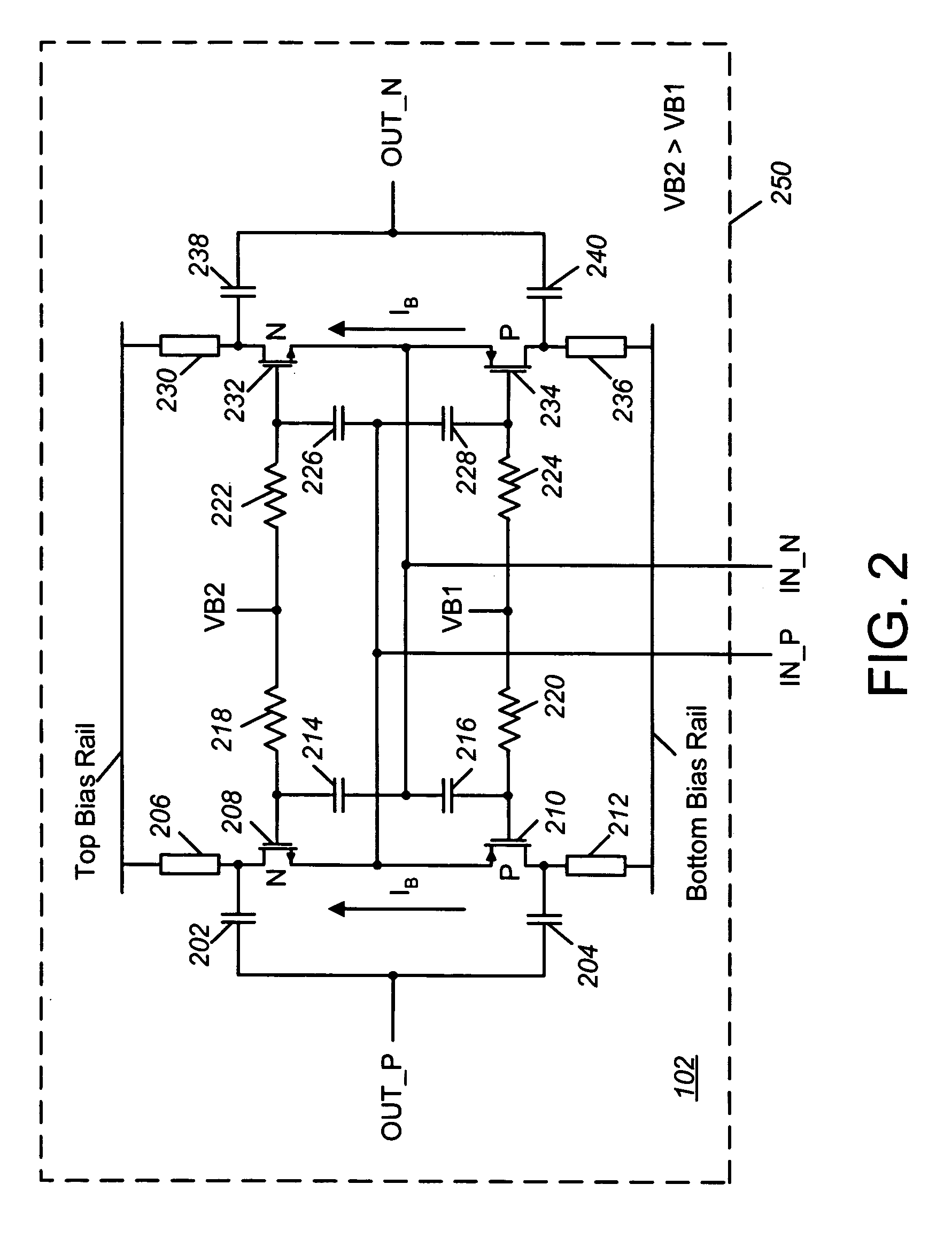
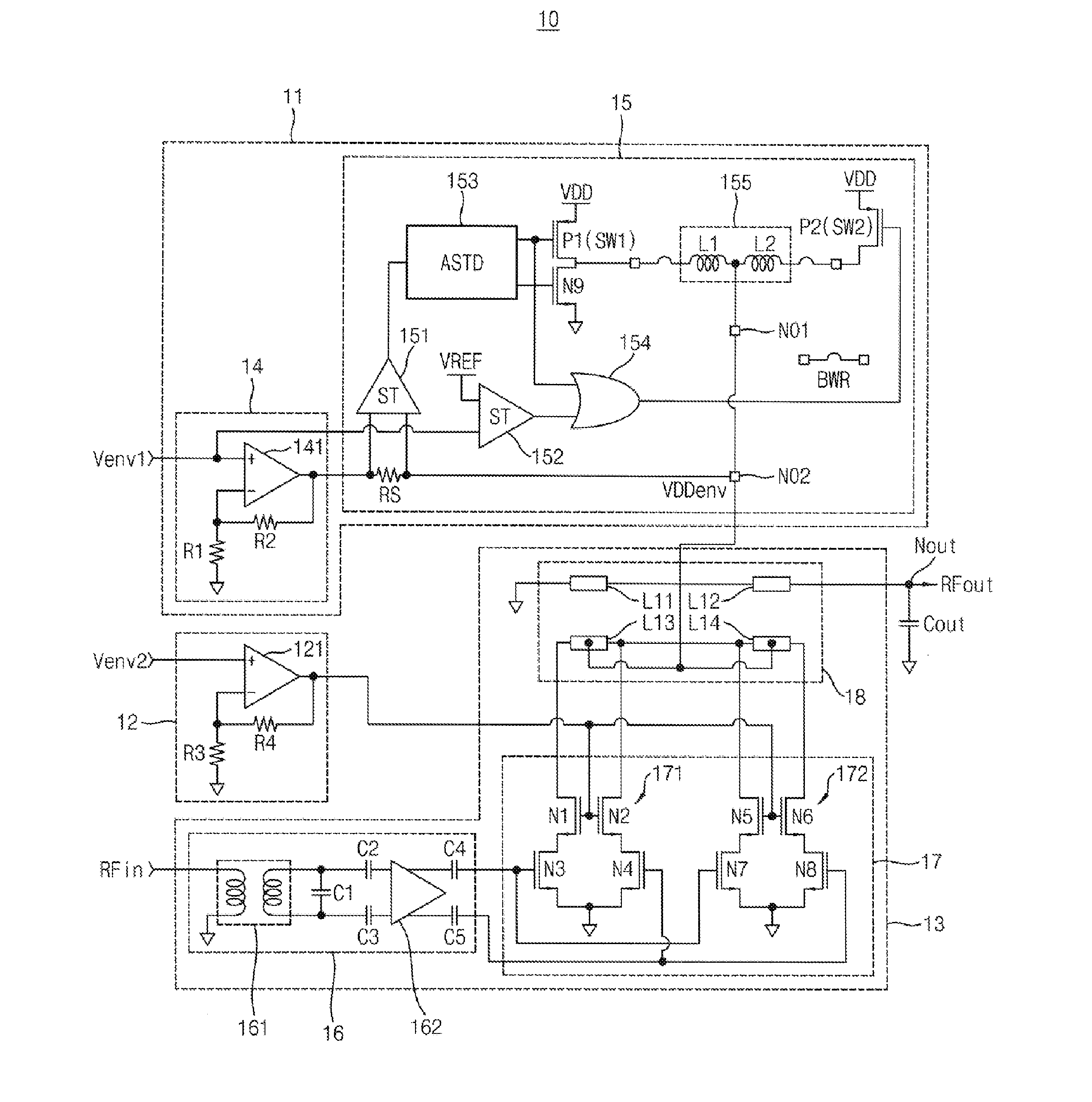
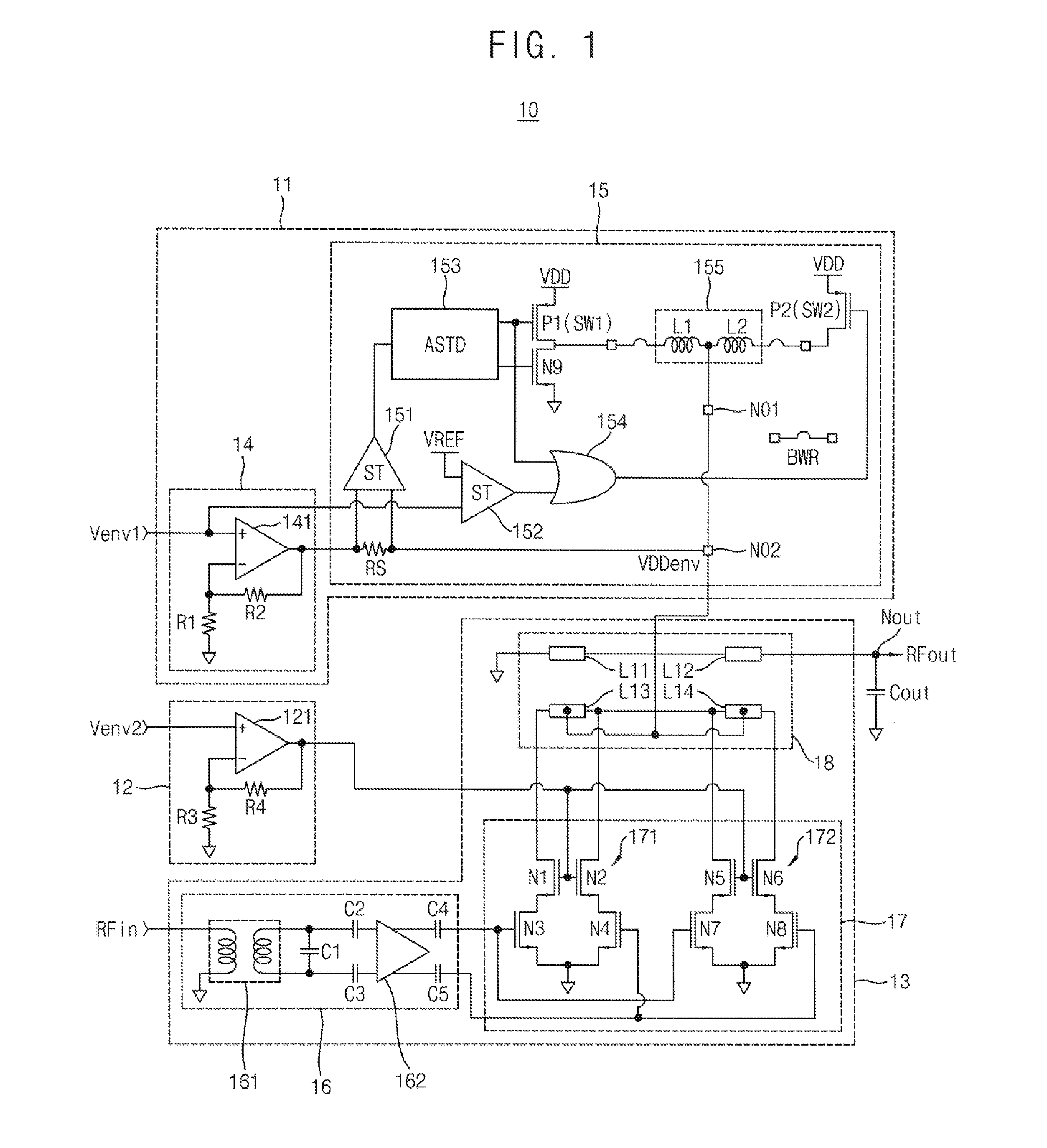
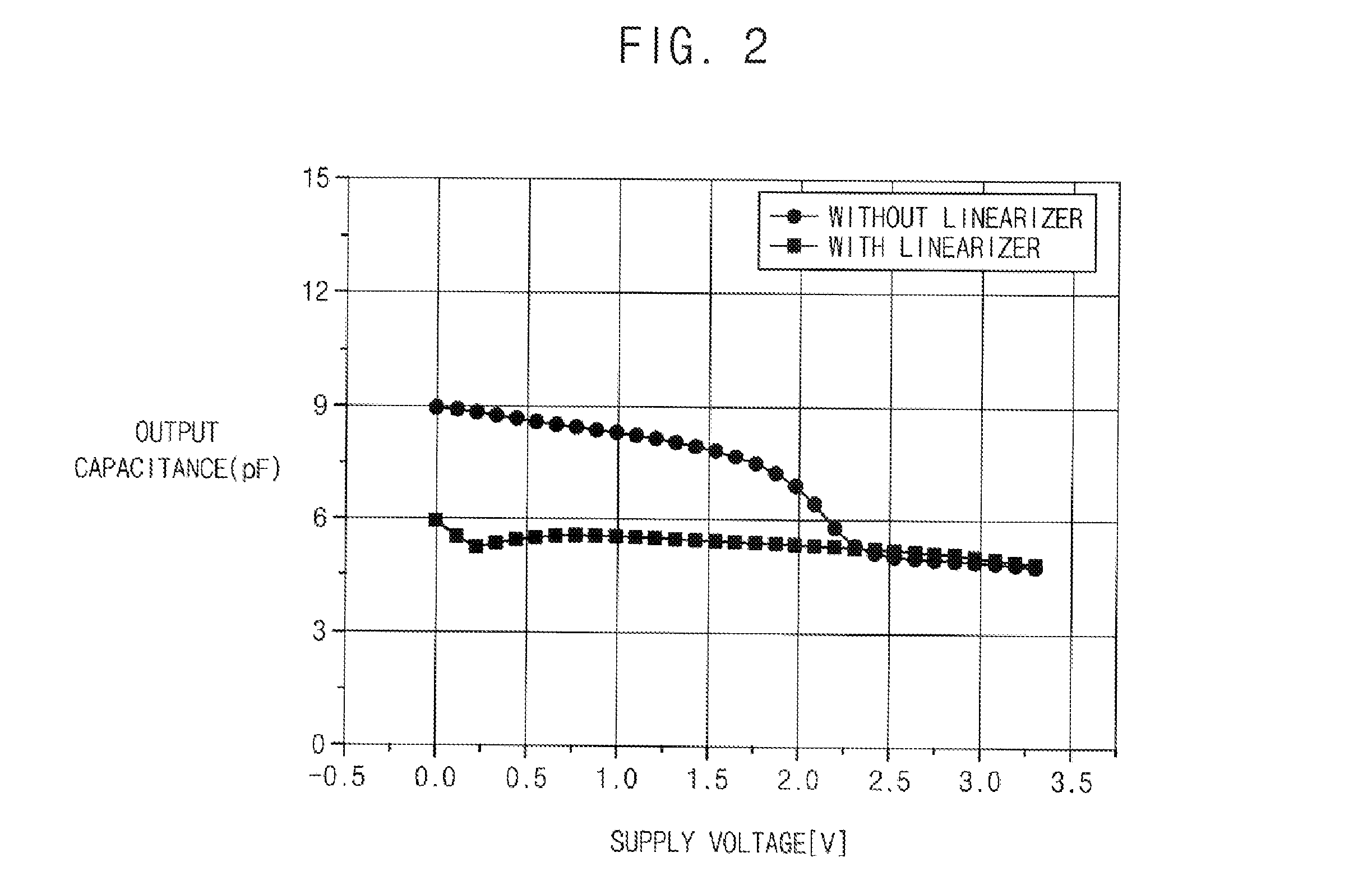
Envelope tracking power transmitter using common-gate voltage modulation linearizer
InactiveUS20150091645A1Maintain output capacitanceImprove featuresAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyCapacitancePower modulation
An envelope tracking power transmitter includes an envelope amplifier, a common-gate power modulation linearizer and a power amplifier. The envelope amplifier may receive a first envelope voltage to generate a power supply voltage that is amplified in proportion to change of the first envelope voltage. The common-gate power modulation linearizer may receive a second envelope voltage to amplify the second envelope voltage according to change of the second envelop voltage. The power amplifier may receive a first output of the envelope amplifier as a power supply voltage and a drain bias voltage, may receive a second output of the common-gate power modulation linearizer as a common gate bias voltage, and may amplify a radio frequency (RF) input signal to provide a RF output signal by maintaining an output capacitance according to an envelope of the RF input signal.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Method and system for amplifying a signal
ActiveUS20060152288A1Improve linearityHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAudio power amplifierDc current
According to one embodiment of the invention, an amplifier includes a gate bias circuit operable to generate a gate bias voltage and a common gate amplifier that includes a transistor having a gate biased by an output of the gate bias circuit and also having a source connected to an inductor for providing a path to ground for direct current flowing through the transistor. According to another embodiment of the invention, a method for amplifying a signal by an amplifier includes generating a gate bias voltage indicative of a difference between a reference voltage and an output voltage of the amplifier, biasing the gate of the common-gate amplifier with the gate bias voltage, and blocking, by a passive device, alternating current signals from flowing from the source of the transistor to ground.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Ultra-wide band low-noise single-ended input and differential output amplifier
InactiveCN102946230ASuppress post-stage noiseReduce noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceOscillations generatorsLow noiseCapacitance
The invention provides an ultra-wide band low-noise single-ended input and differential output amplifier, which is characterized in that the amplifier comprises a common-gage amplification stage (1), a single-ended-to-differential stage (2) and a capacitor cross-coupling output buffer (3), wherein an output end of the common-gate amplification stage (1) is connected with an input end of the single-ended-to-differential stage (2); and an output end of the single-ended-to-differential stage (2) is connected with an input end of the capacitor cross-coupling output buffer (3). According to amplifier, a pre-amplification stage and the single-ended-to-differential stage adopt a current reuse technology, so that one stage of current consumption can generate two stages of amplification; the common-gate amplification stage provides wide band input matching and avoids a no-source matching network; load impedances of the pre-amplification stage and the single-ended-to-differential stage are resonated at different frequencies respectively; functions of signal amplification of the wide band and single-ended-to-differential are realized by gain complementation of the pre-amplification stage and the single-ended-to-differential stage; a capacitor cross-coupling technology is applied in the output buffer additionally; amplitude and phase of an output differential signal are compensated to reach the balance between the amplitude and the phase of the differential signal; and the gain of the output buffer is increased.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
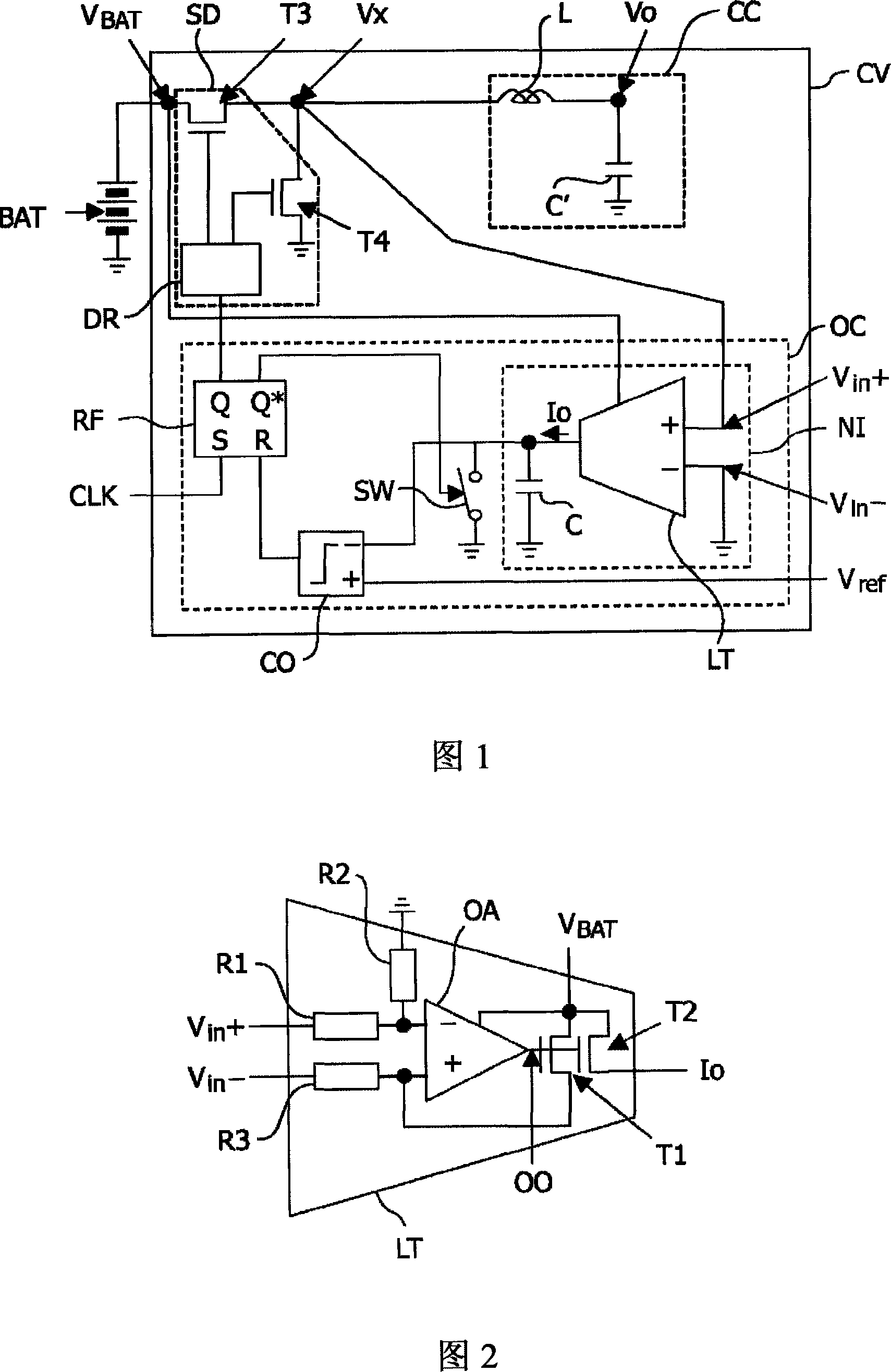
Linear transconductor for a one-cycle controller, notably for a DC-DC switching converter
A linear transconductor (LT), for instance for a one-cycle controller (OC), comprises i) an operational amplifier (OA) having non-inverting (+) and inverting (-) inputs, a power supply input intended to be connected to a DC voltage (VBAT), and an output (OO), ii) a voltage divider means (Rl, R2) comprising a first terminal defining a transconductor non-inverting input (Vin+) and intended to be connected to a first voltage (Vx), and a second terminal connected to the operational amplifier inverting input (-), iii) a resistor (R3) comprising a first terminal defining a transconductor inverting input (Vin-) intended to be connected to a second voltage and a second terminal connected to the operational amplifier non-inverting input (+), iv) first (Tl) and second (T2) matched transistors having respective sources connected together and to the operational amplifier power supply input, respective common gates connected to the operational amplifier output (OO), and respective drains, the drain of the first transistor (Tl) being connected to the operational amplifier non-inverting input (+) and the drain of the second transistor (T2) defining a transconductor output.
Owner:NXP BV
Full differential CMOS multimode low-noise amplifier
InactiveCN101895265ASynchronous input matchingSimultaneously achieve scalabilityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceEngineeringRadio frequency
The invention belongs to the technical field of radio frequency integrated circuits, and in particular relates to a full differential CMOS multimode low-noise amplifier. The low-noise amplifier can be applied to a front end of a multimode receiver with the frequency of between 0.5 and 10.6 GHz. The low-noise amplifier consists of a matching stage, an amplification stage, a feedback stage and a loading stage, wherein the matching stage tunes broadband input impedance by using a feedback inductor; the amplification stage takes a current multiplexing common source NMOS tube and a PMOS tube as an input end and takes a common gate NMOS tube connected with the output of drain terminals of the NMOS tube and the PMOS tube as a current follower; an NMOS tube between a grid of an input NMOS tube and a drain of the NMOS tube of the current follower forms a 'voltage-current' type negative feedback circuit with a resistor; and the loading stage adopts resistive load. The full differential CMOS multimode low-noise amplifier has the advantages of simple structure, small chip occupied area, low power consumption and wide bandwidth coverage.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
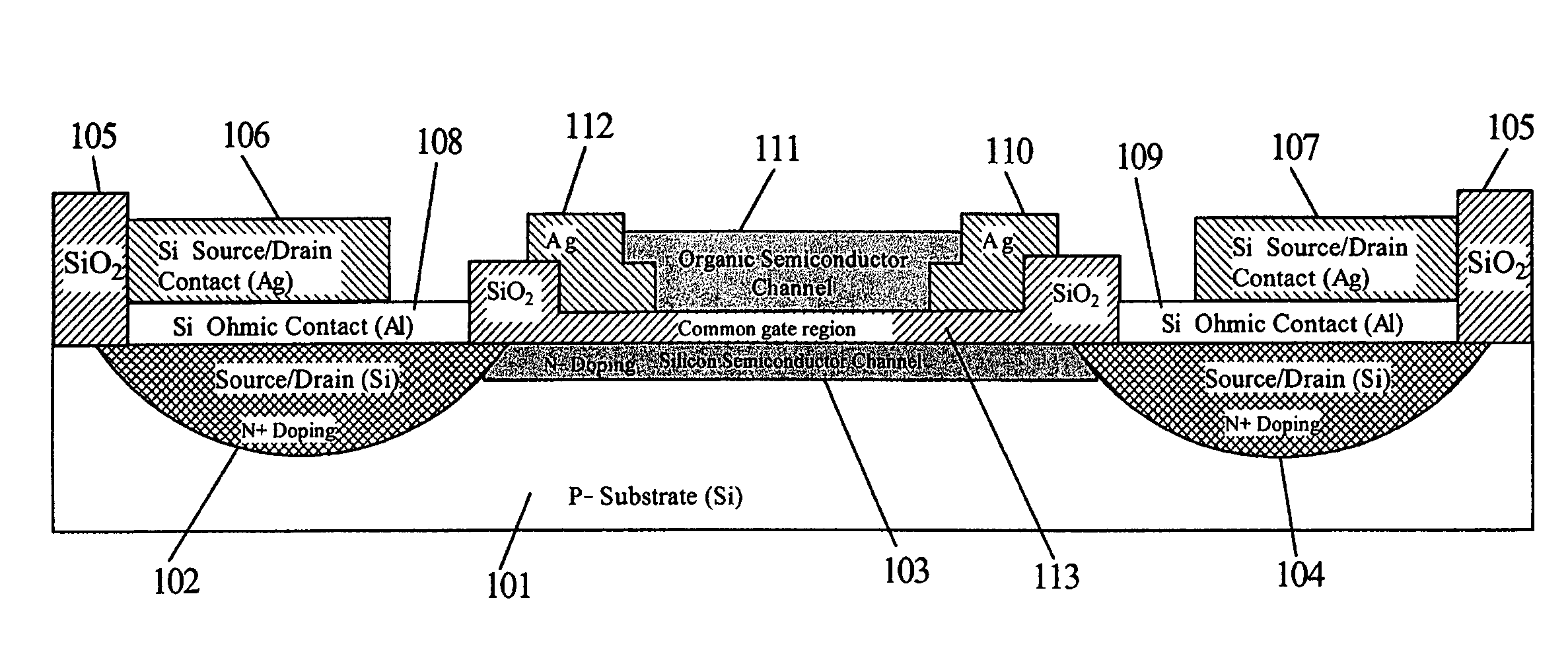
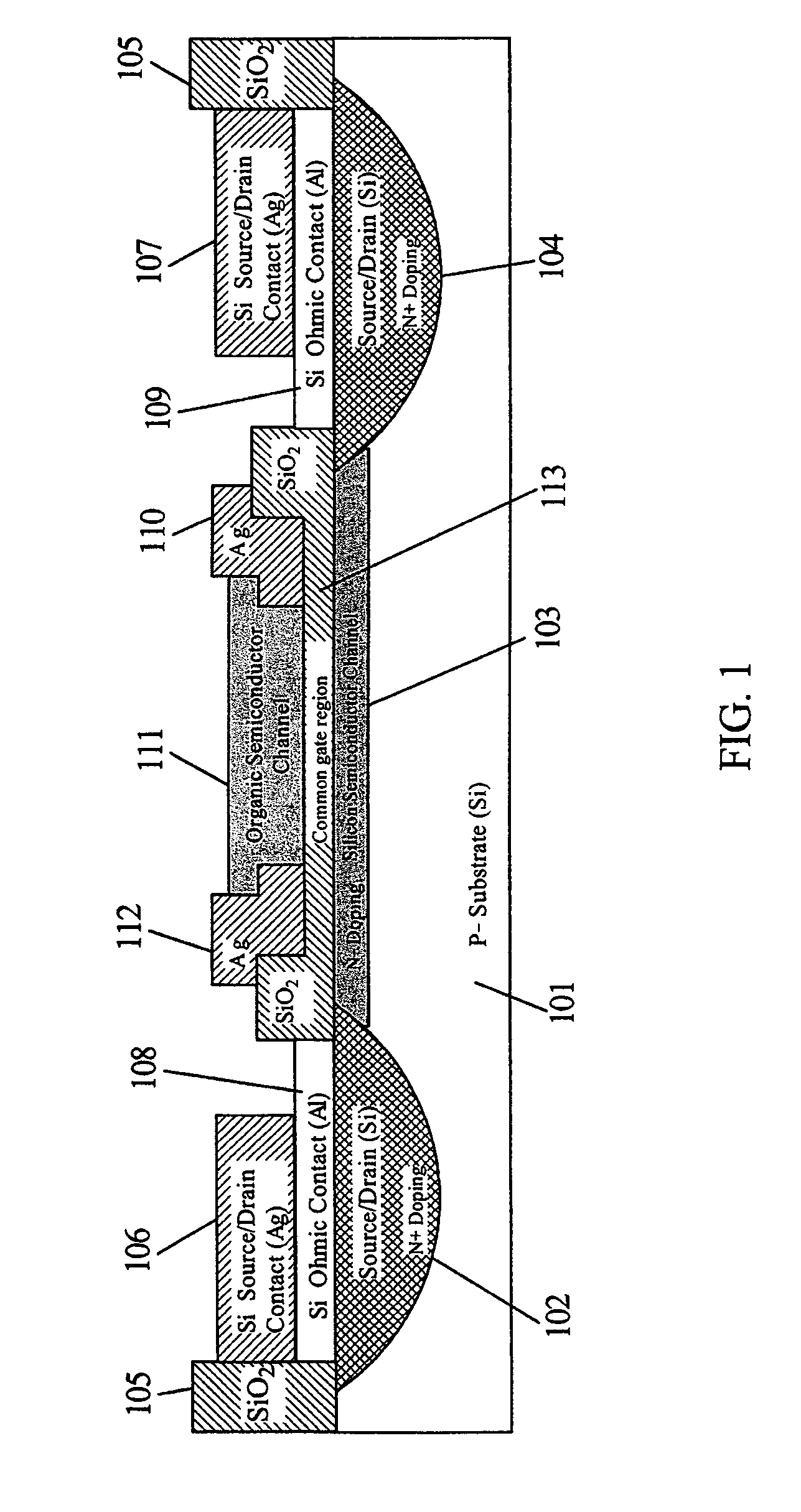
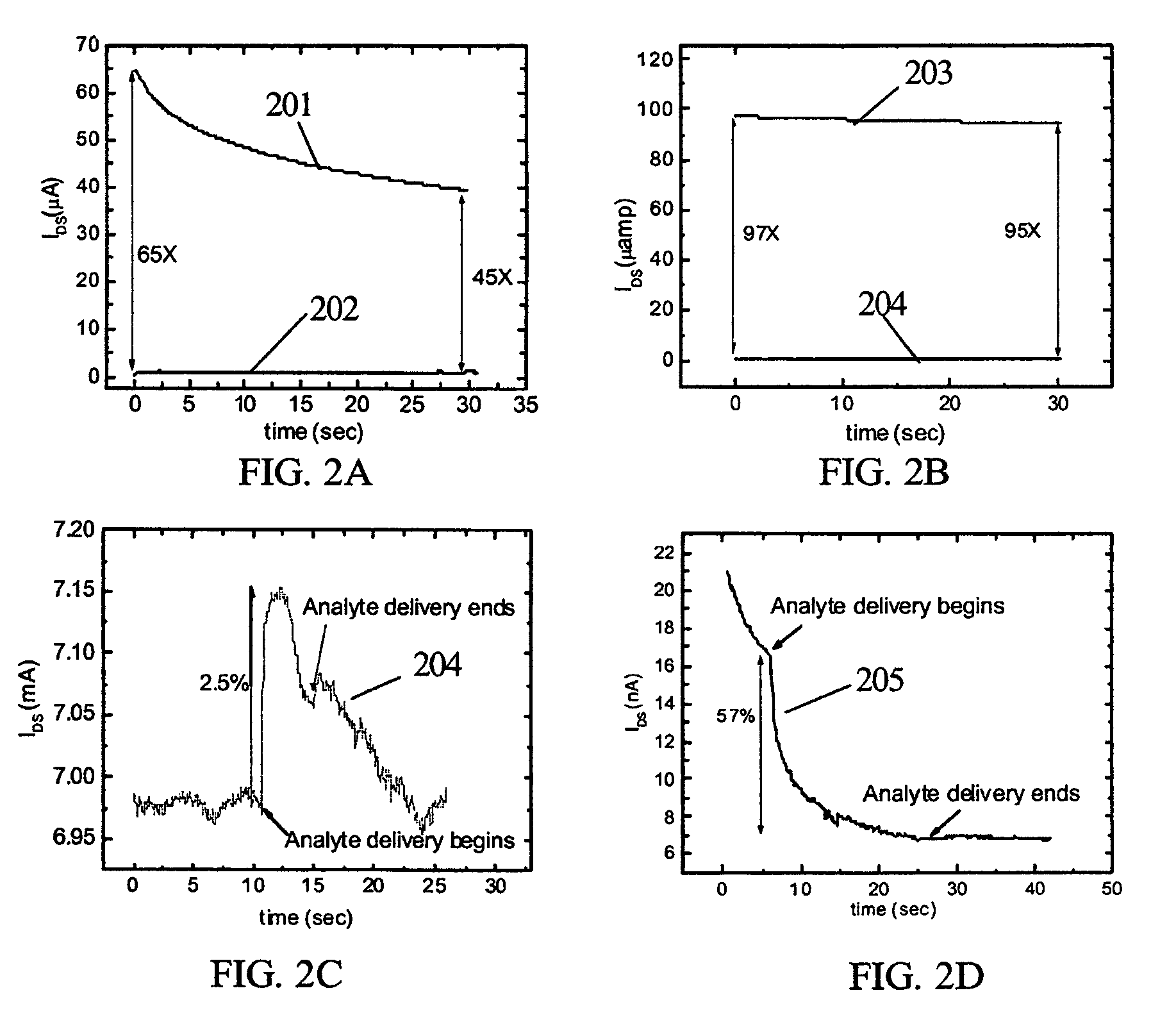
Structure for and method of using a four terminal hybrid silicon/organic field effect sensor device
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
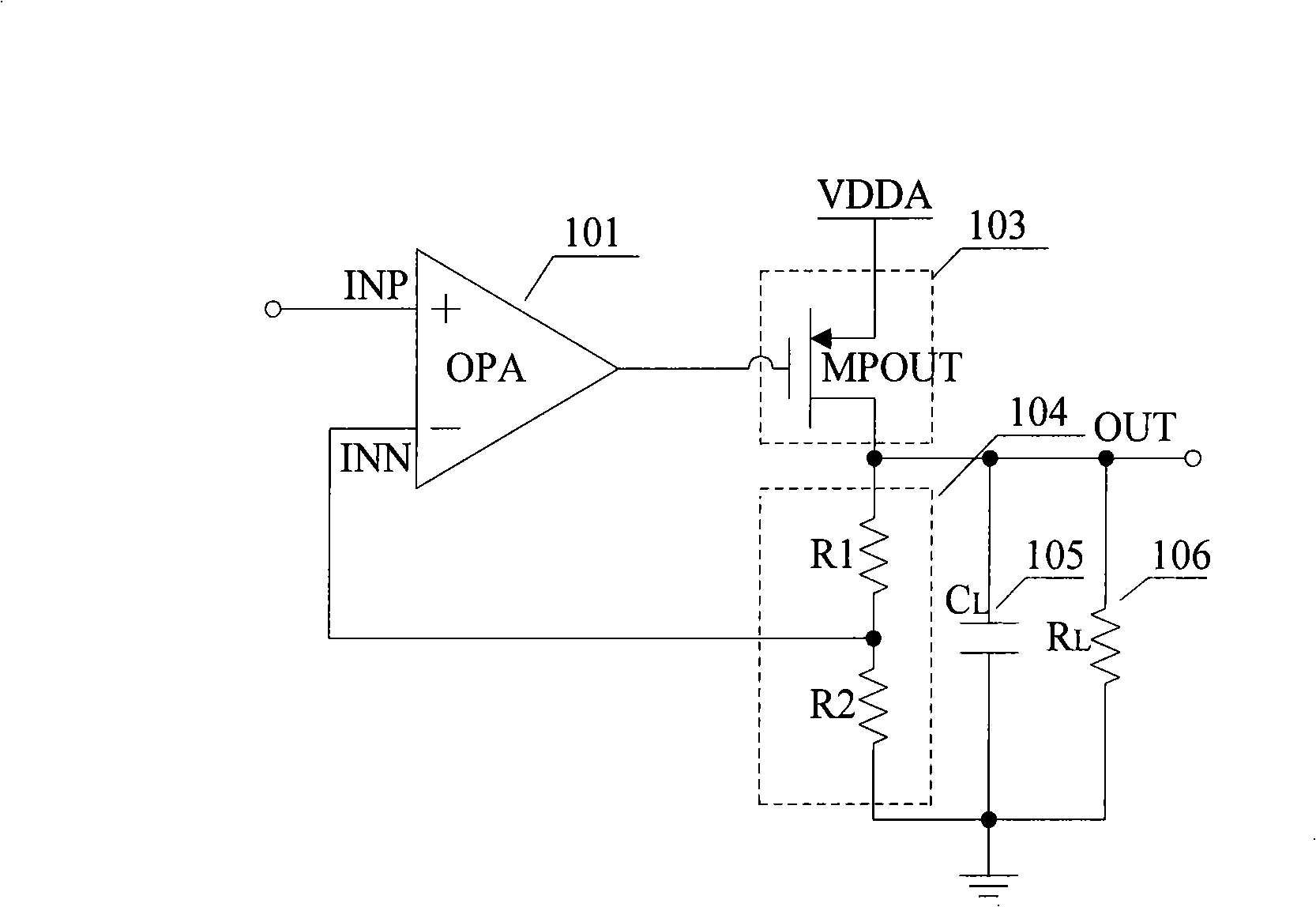
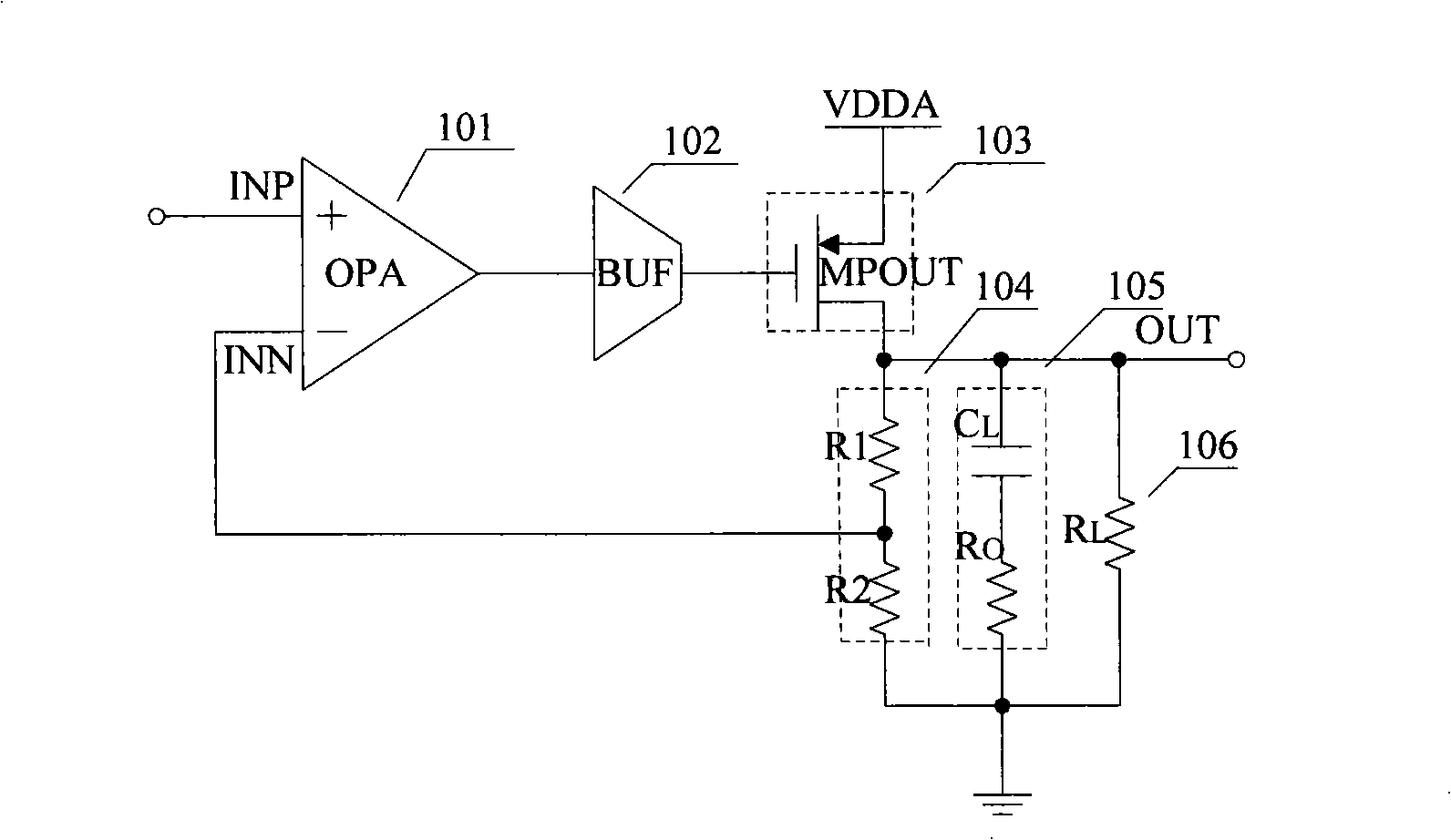
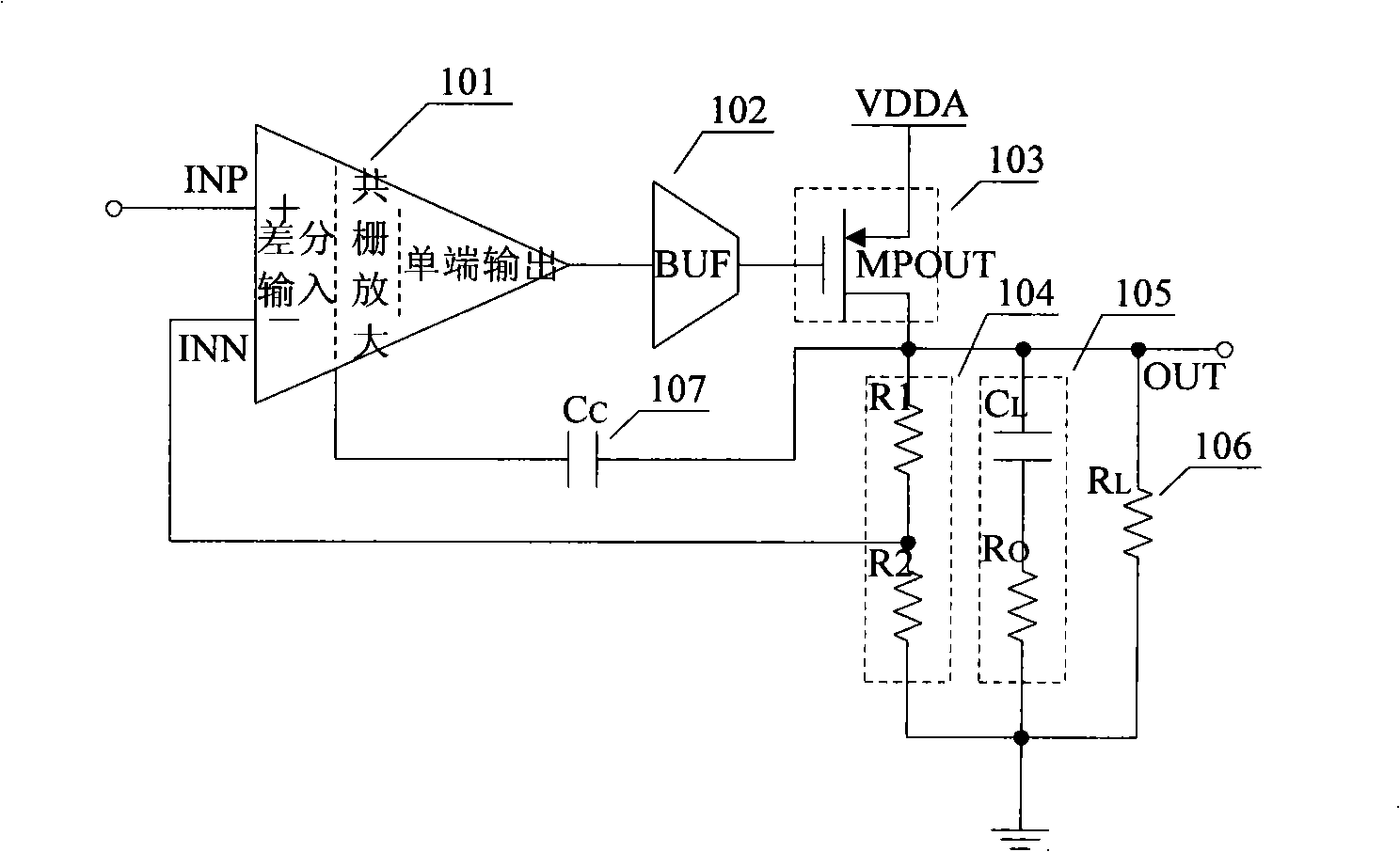
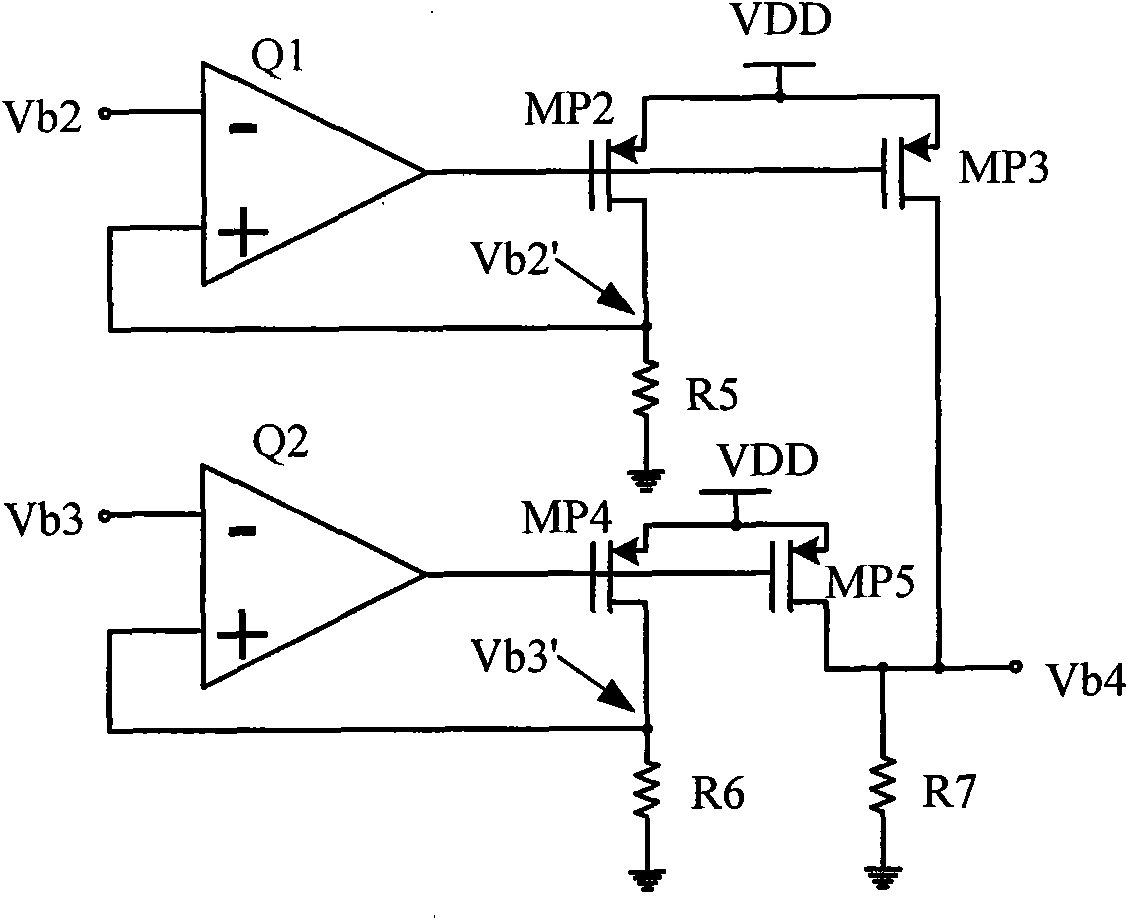
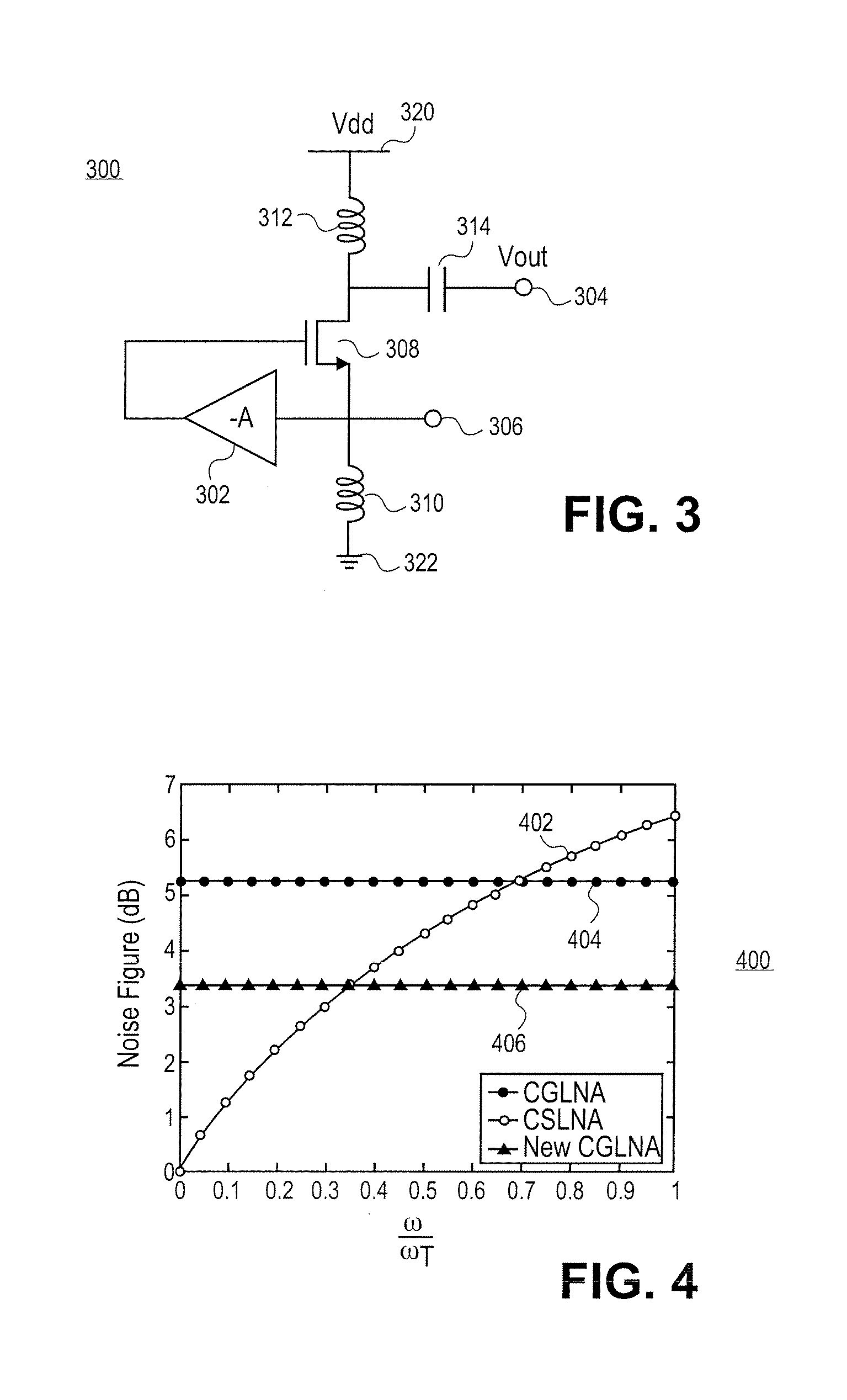
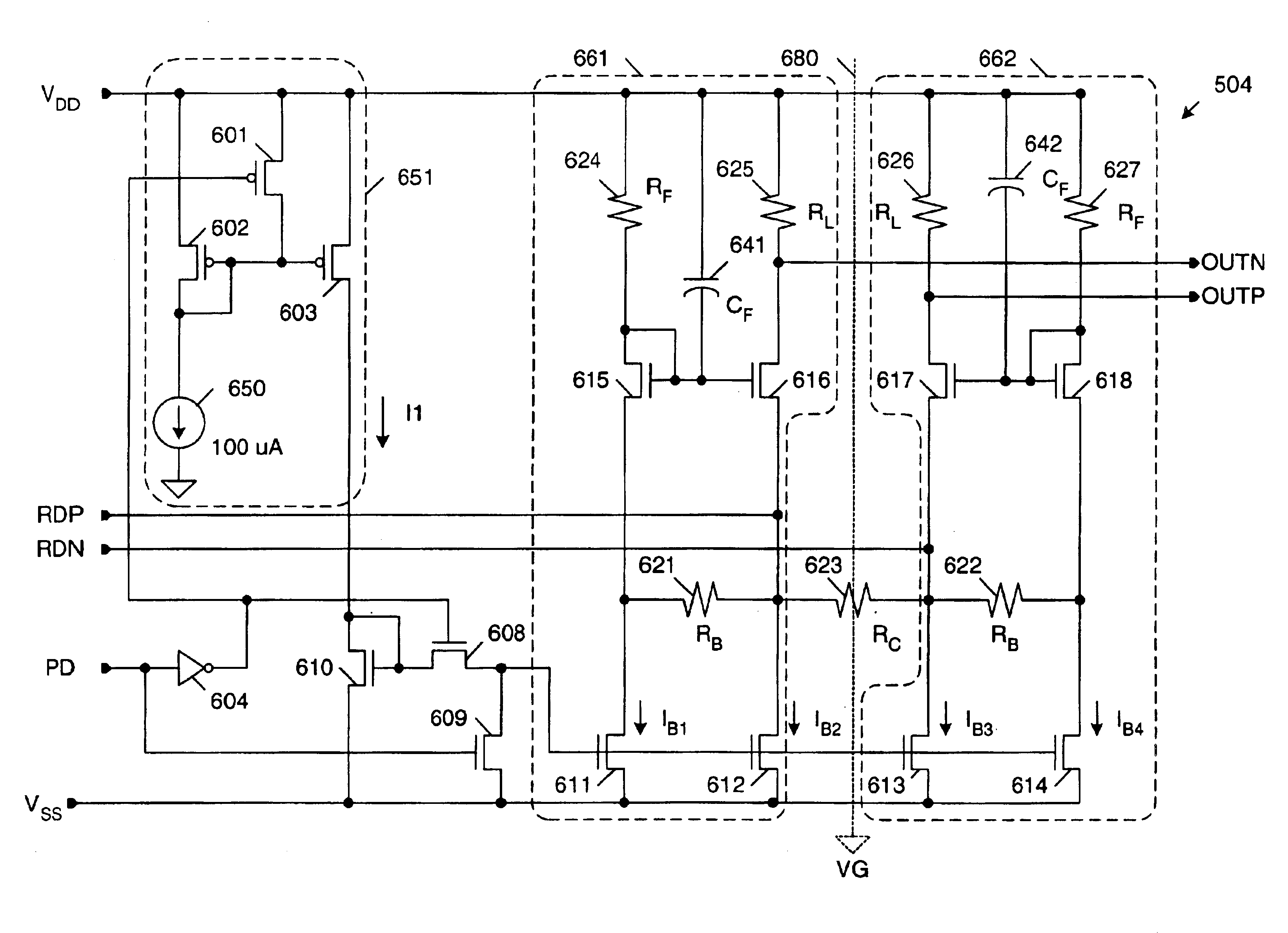
Self-biasing for common gate amplifier
InactiveUS6882224B1Reduce functionHigh transfer functionAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationPulse shapingTransmission channelPeak value
A data receiver having a transfer function that exhibits peaking at high frequencies is provided to compensate an input signal provided on a transmission channel having a low pass transfer function. The data receiver includes first and second differential input terminals, which receive the differential input signal from the transmission channel. The first differential input terminal is coupled to the source of a first common gate transistor in a first self-biased common gate amplifier. The second differential input terminal is coupled to the source of a second common gate transistor in a second self-biased common gate amplifier. A differential output signal is provided from the drain terminals of the first and second common gate transistors. The first and second differential input terminals are not directly connected to any transistor gates in the data receiver, thereby enabling these differential input terminals to be safely connected directly to the transmission channel.
Owner:XILINX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com